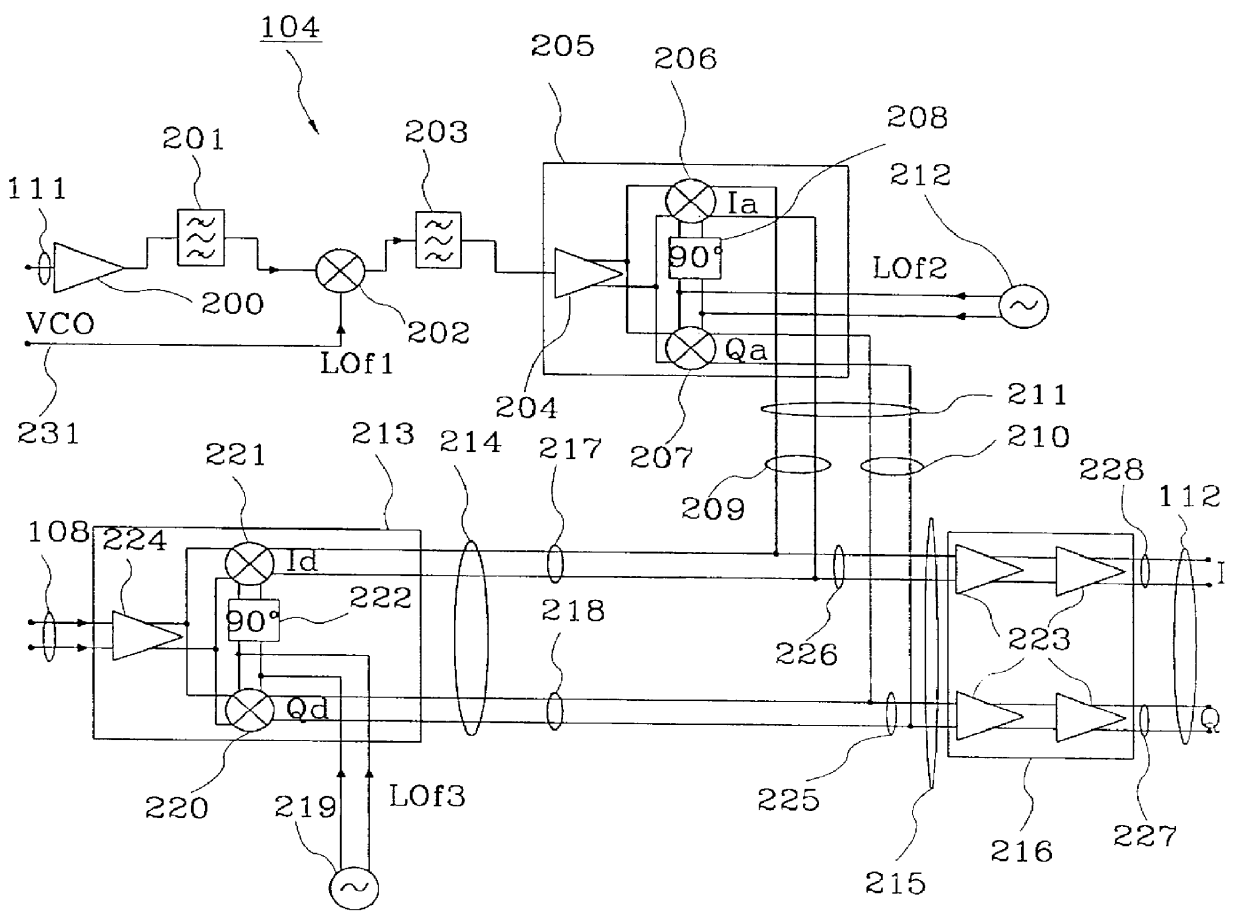
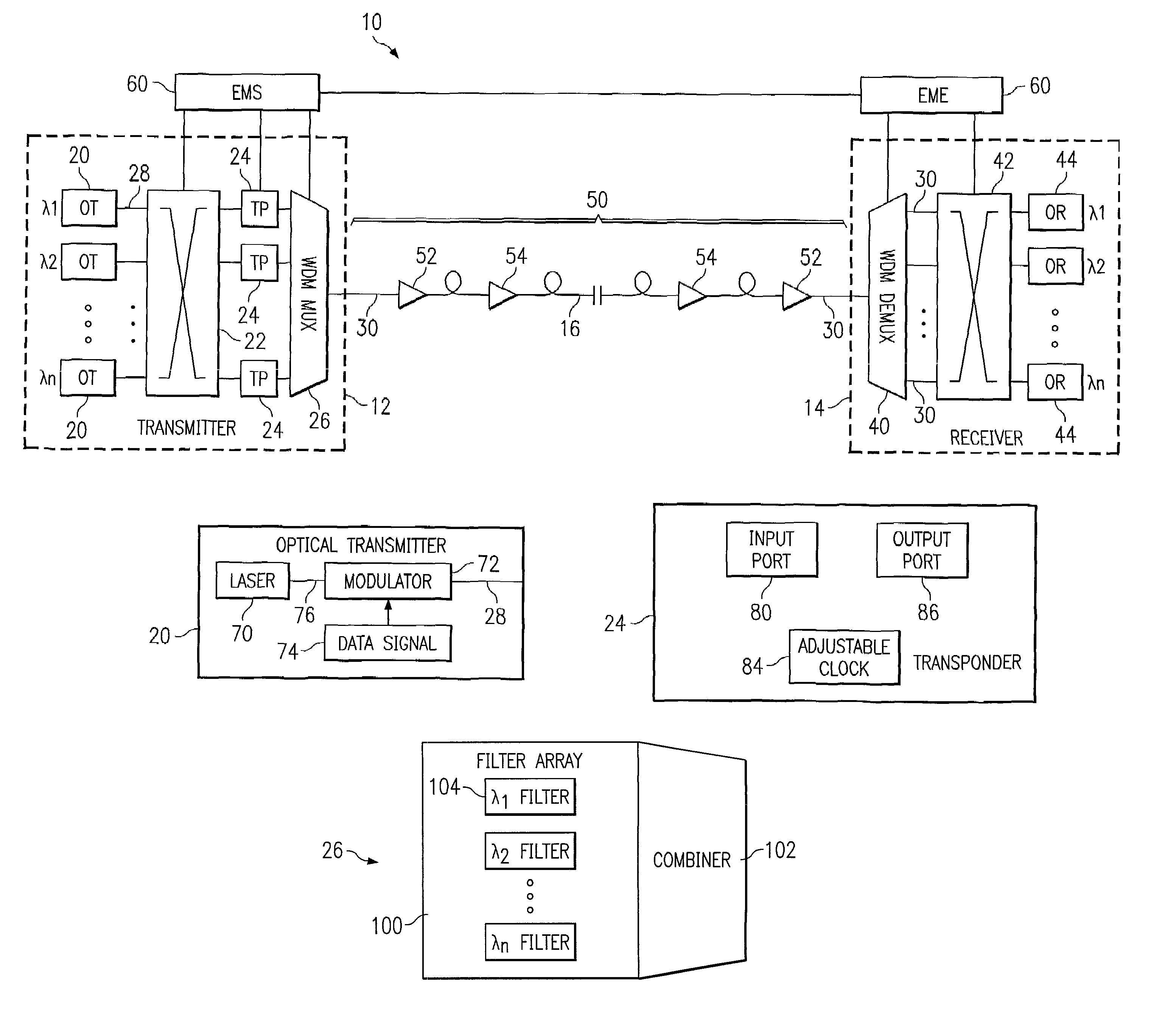
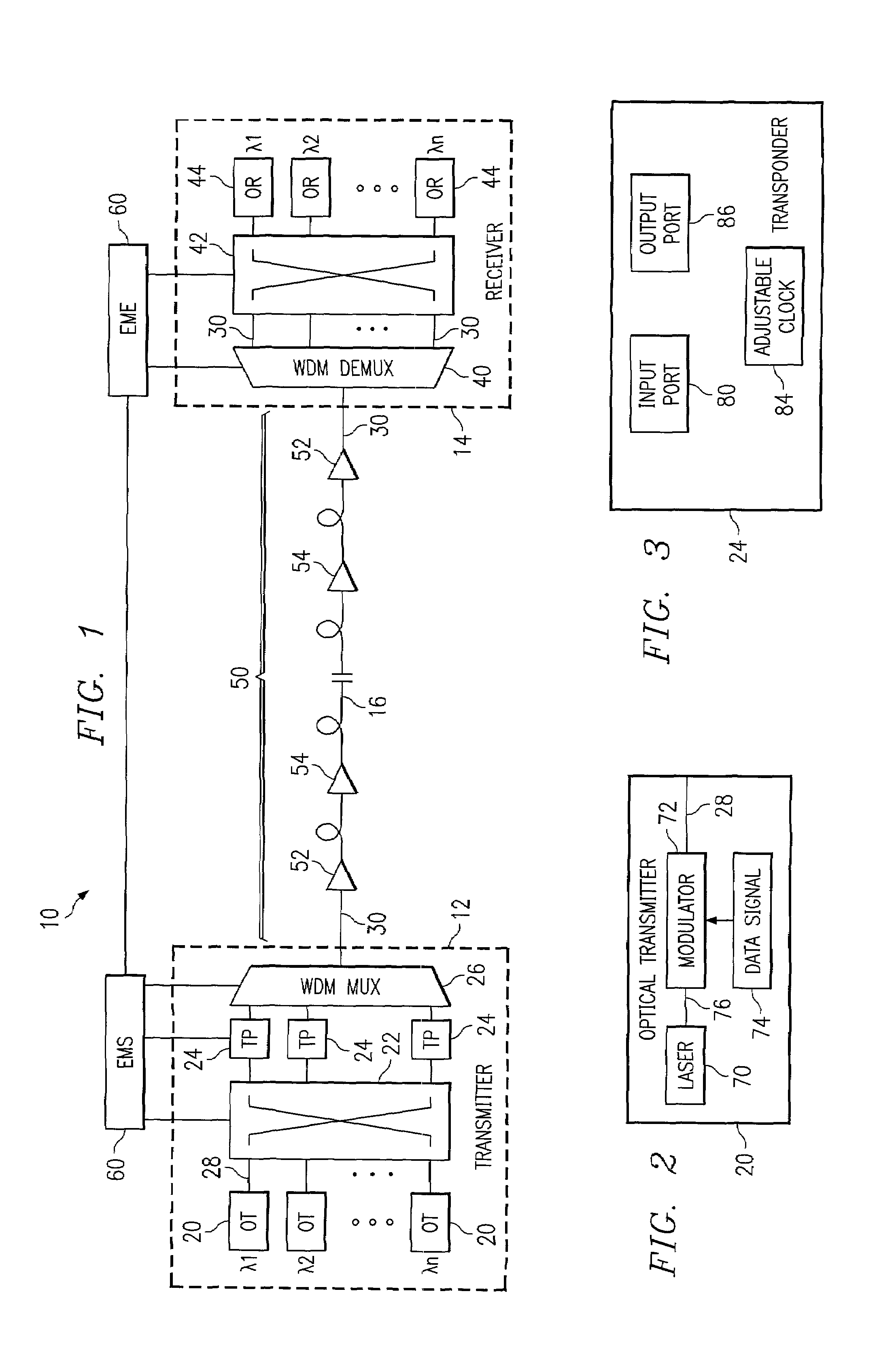
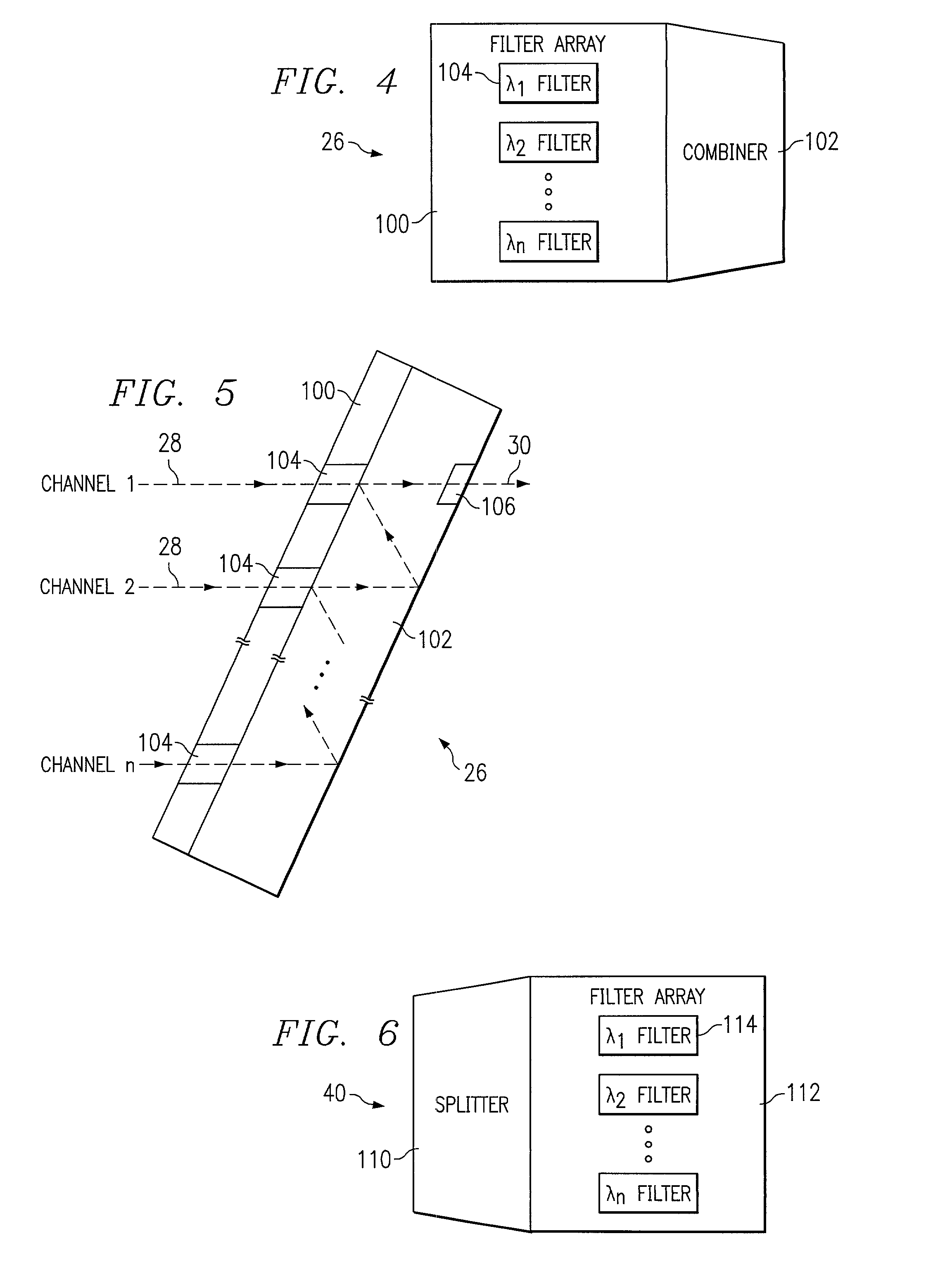
Patents
Literature
259 results about "Channel spacing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
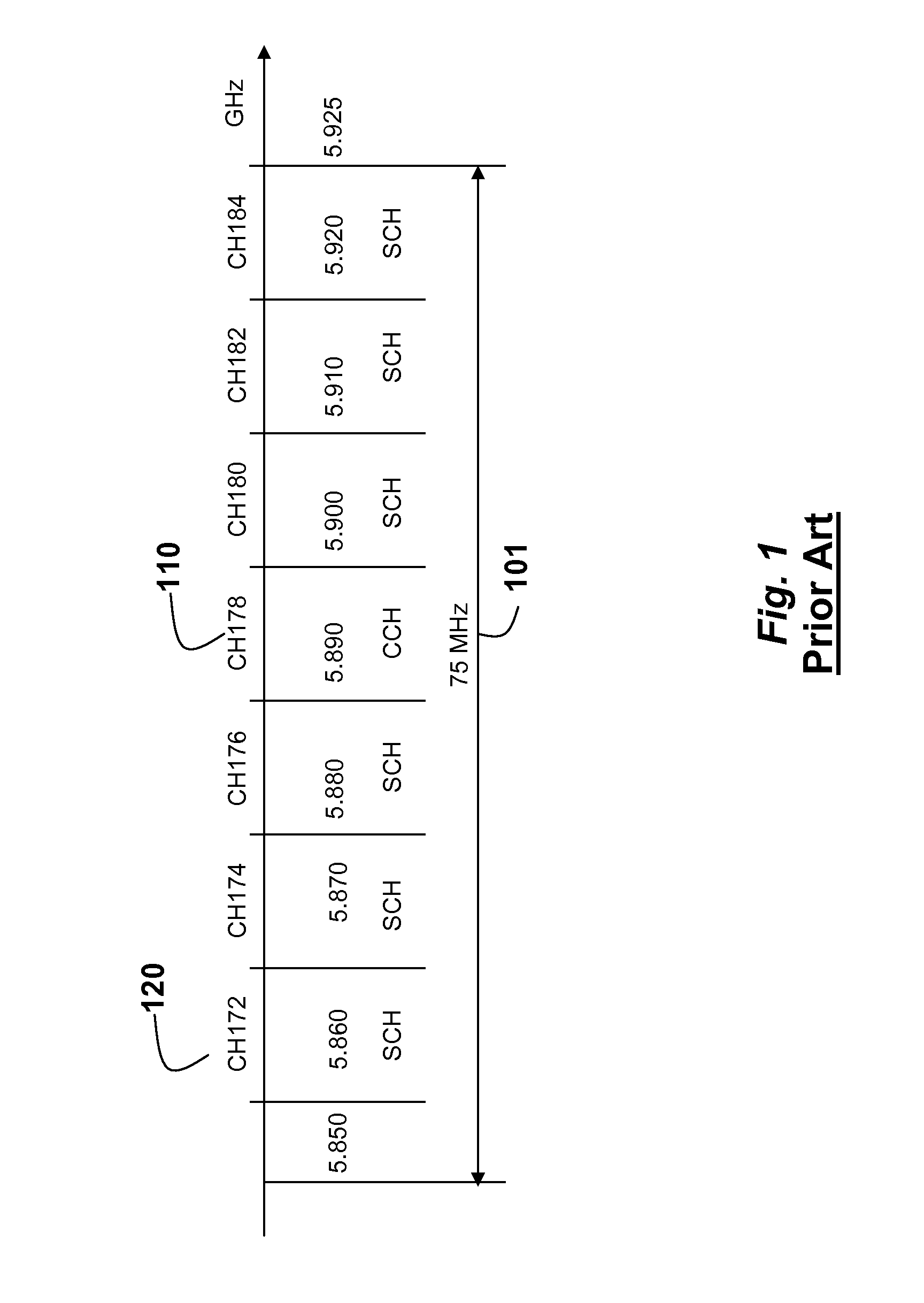
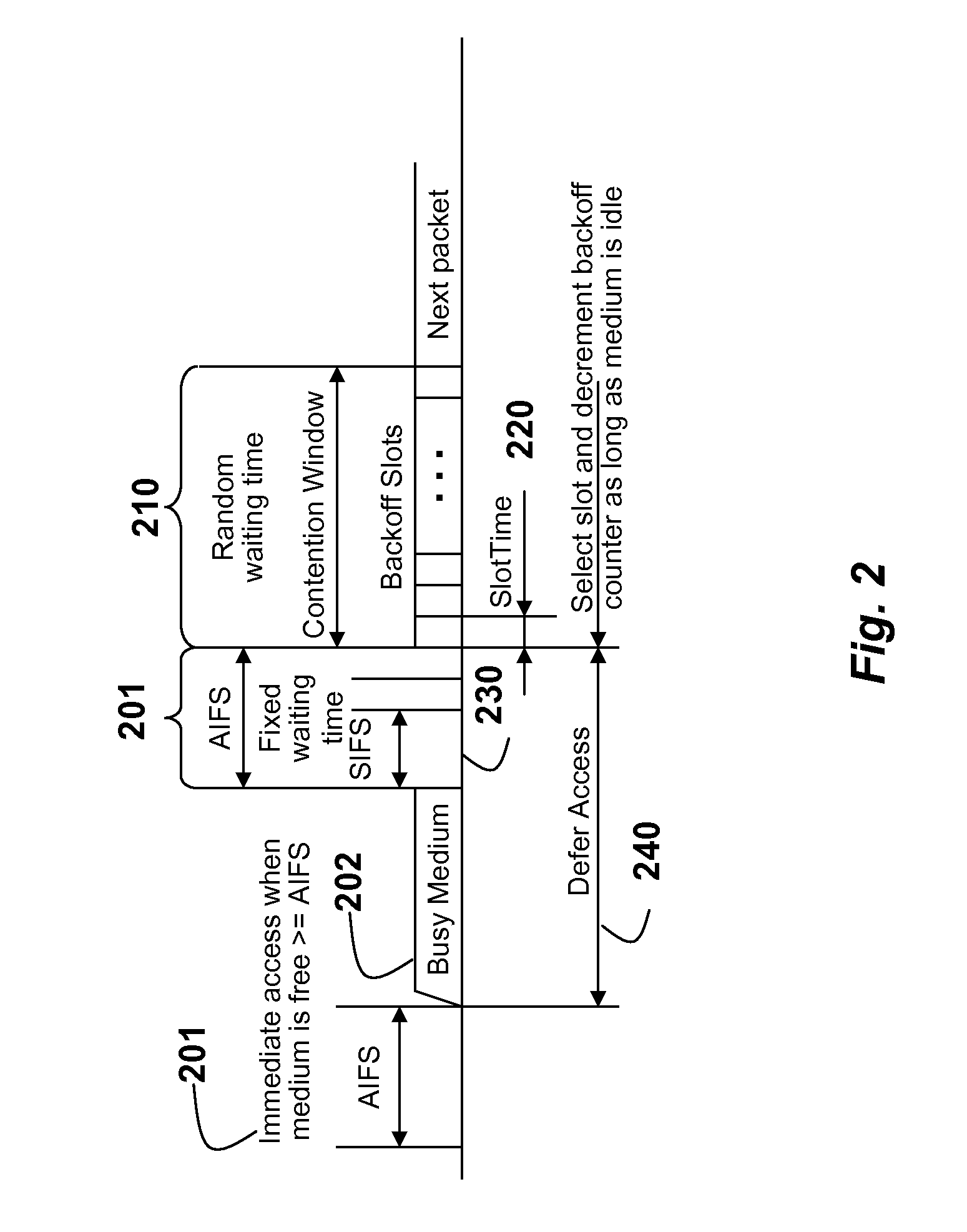
Channel spacing, also known as bandwidth, is a term used in radio frequency planning. It describes the frequency difference between adjacent allocations in a frequency plan. Channels for mediumwave radio stations, for example are allocated in internationally agreed steps of 9 or 10 kHz: 10 kHz in ITU Region 2 (the Americas) and 9 kHz elsewhere in the world.
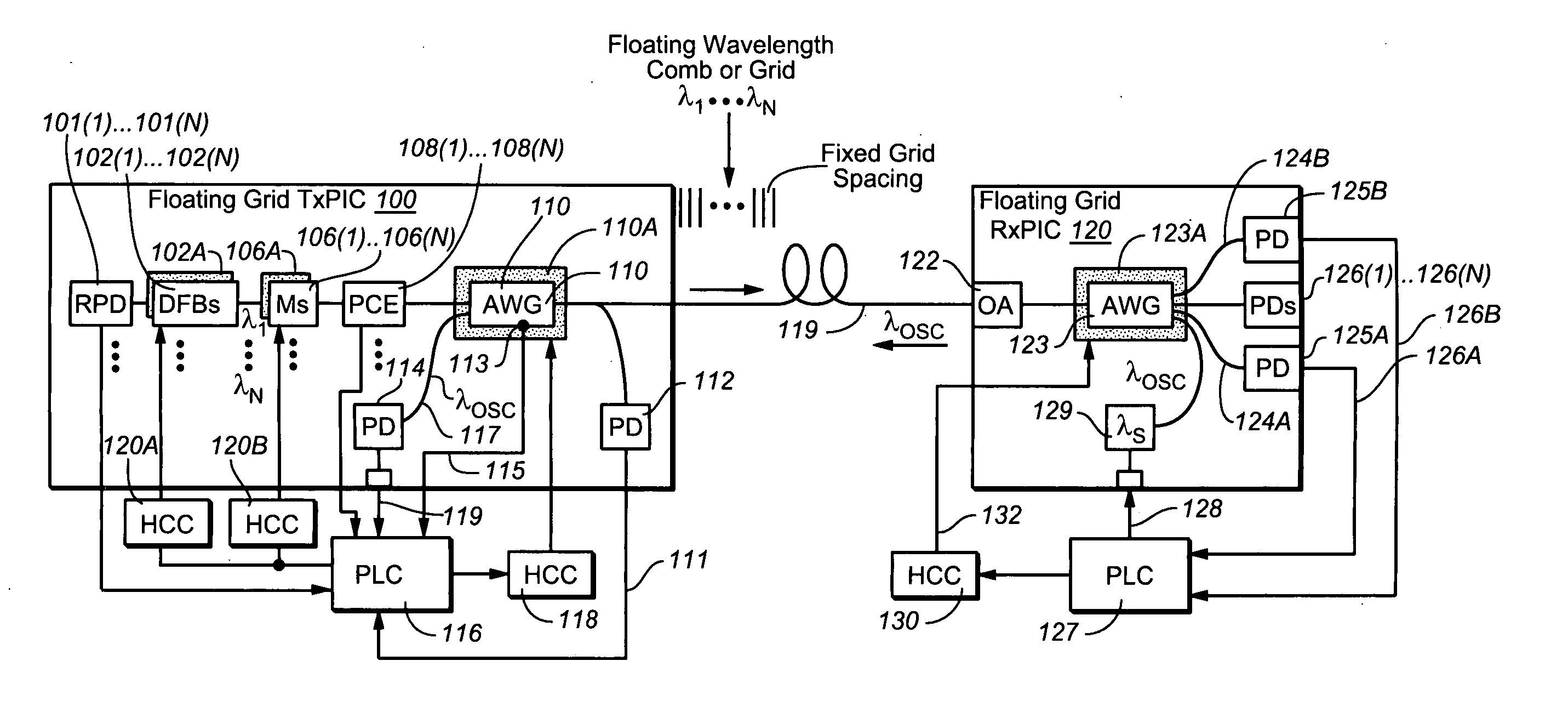
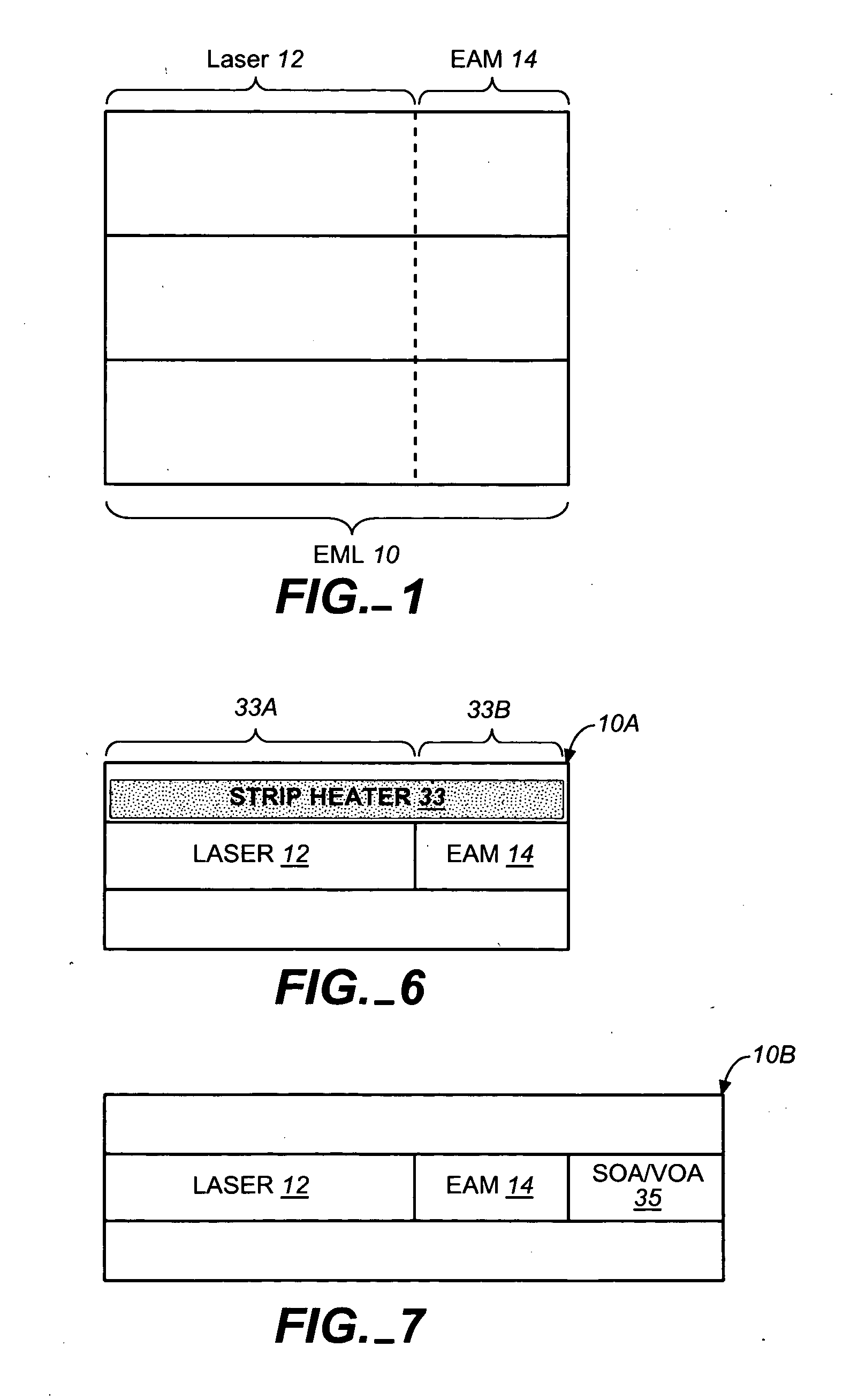
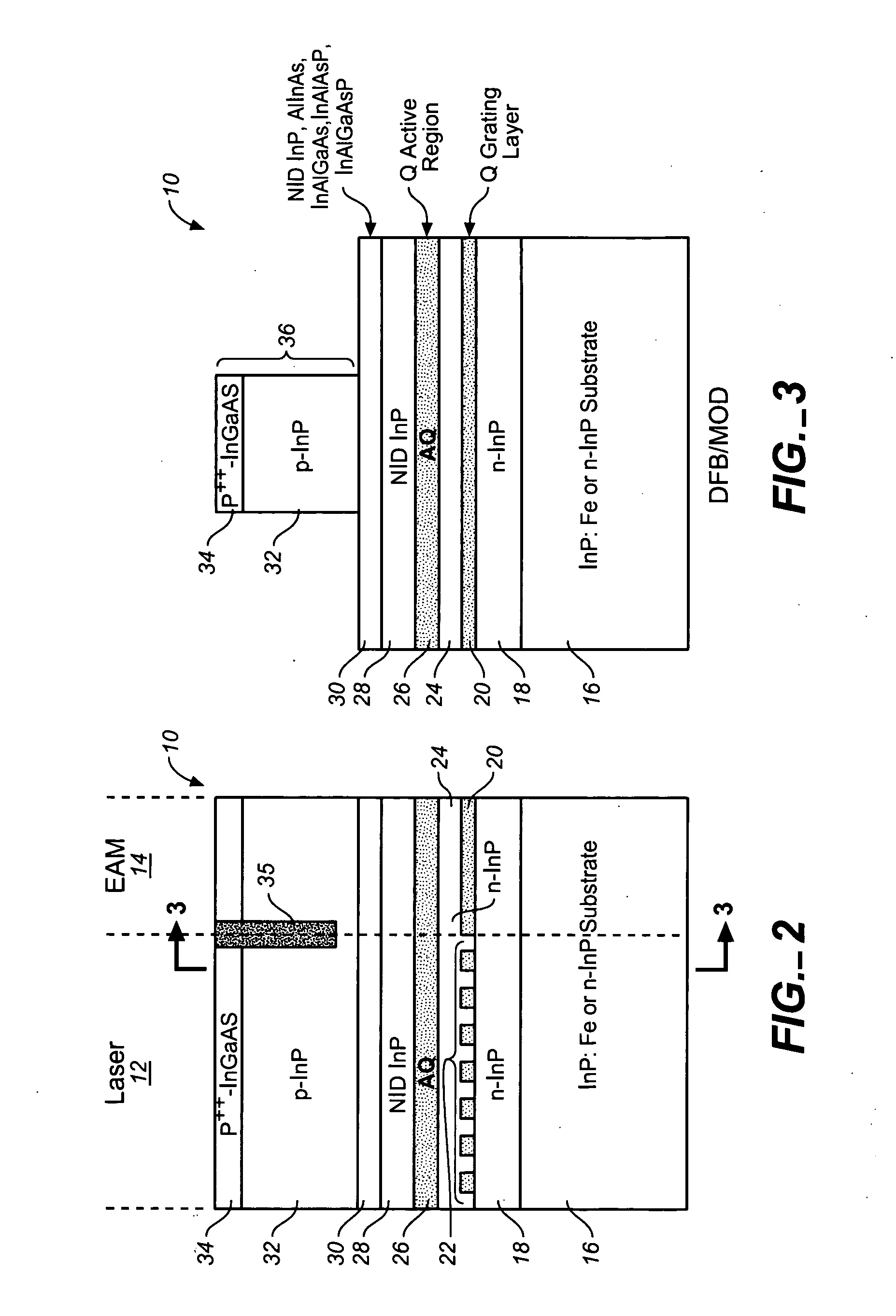
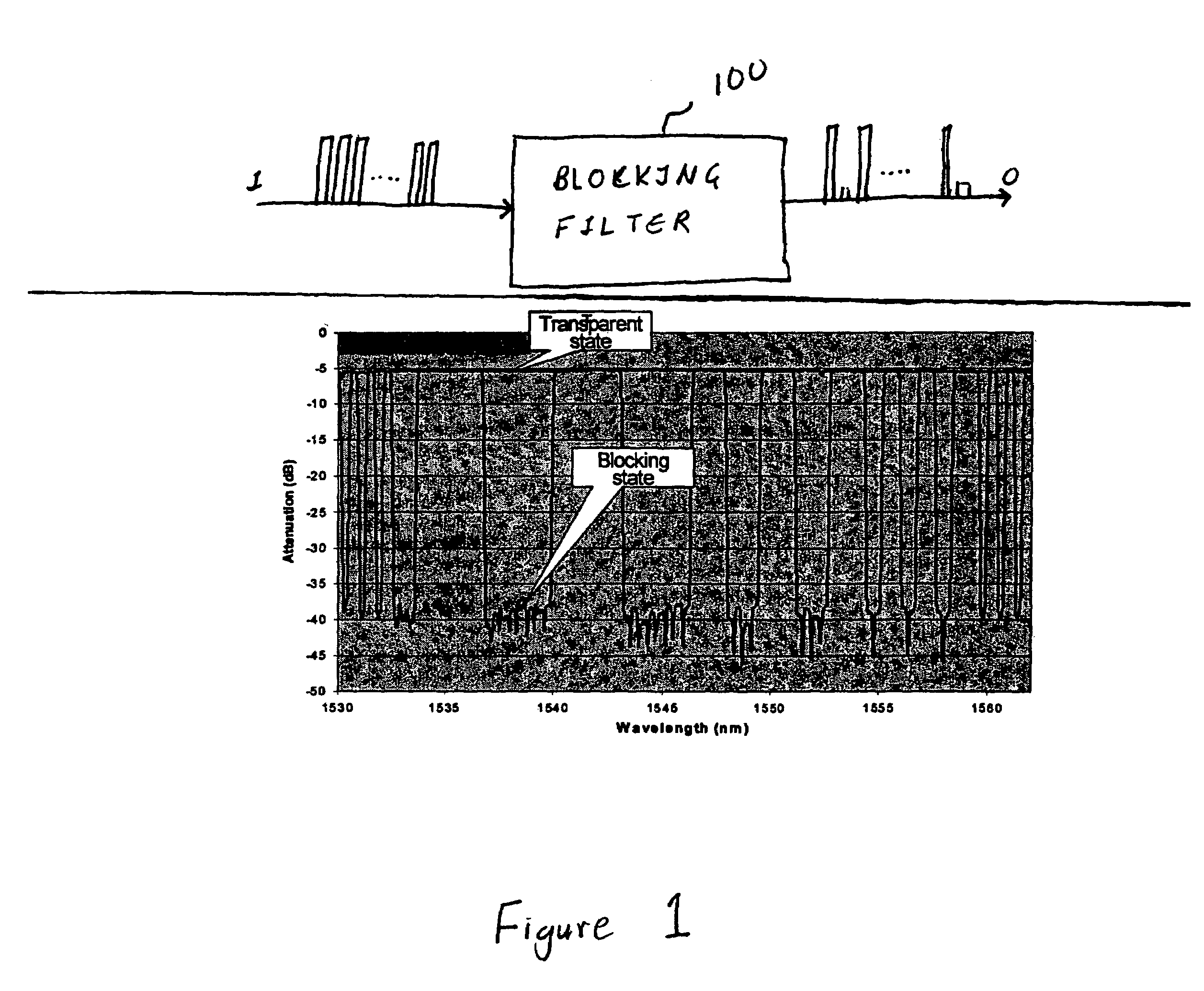
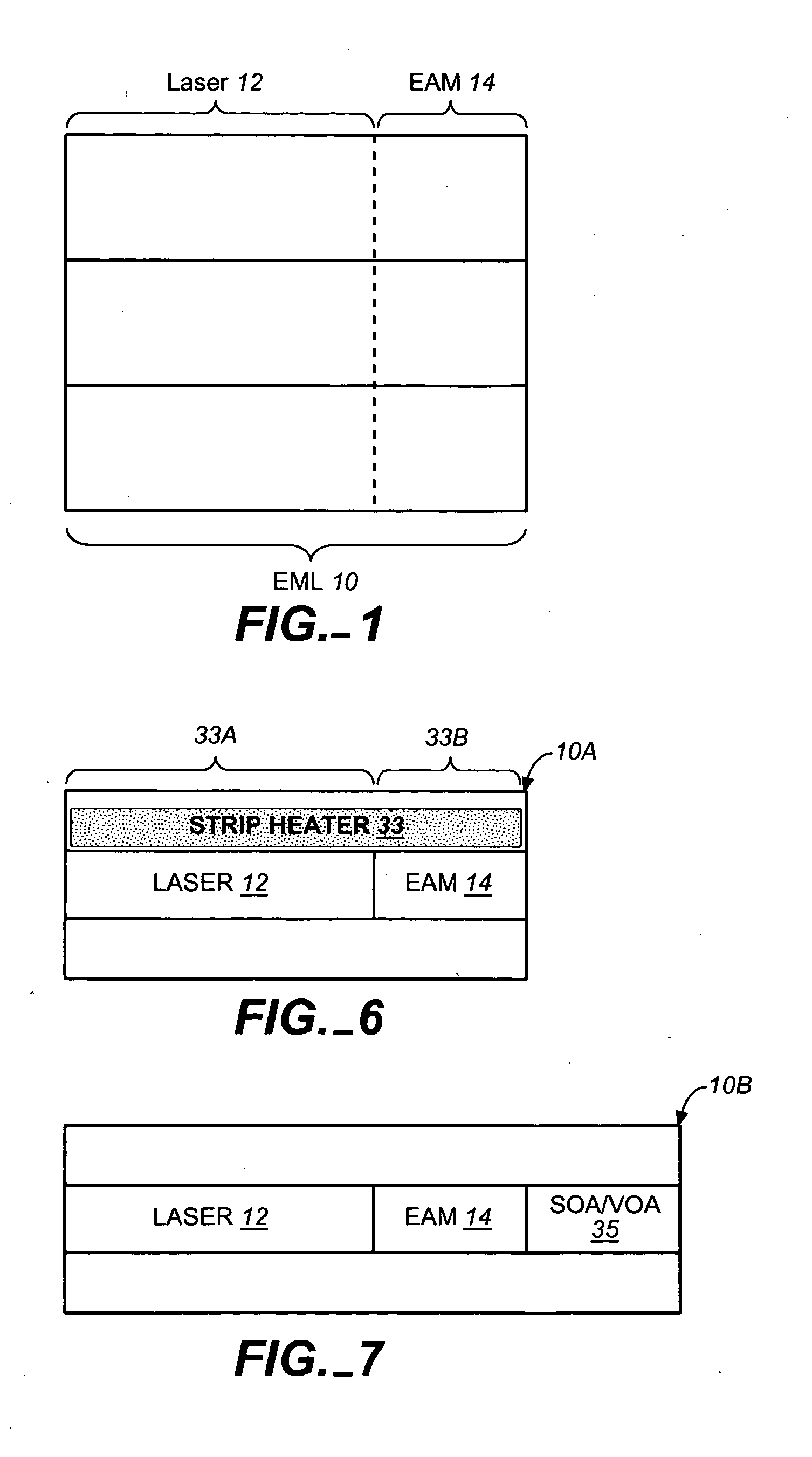
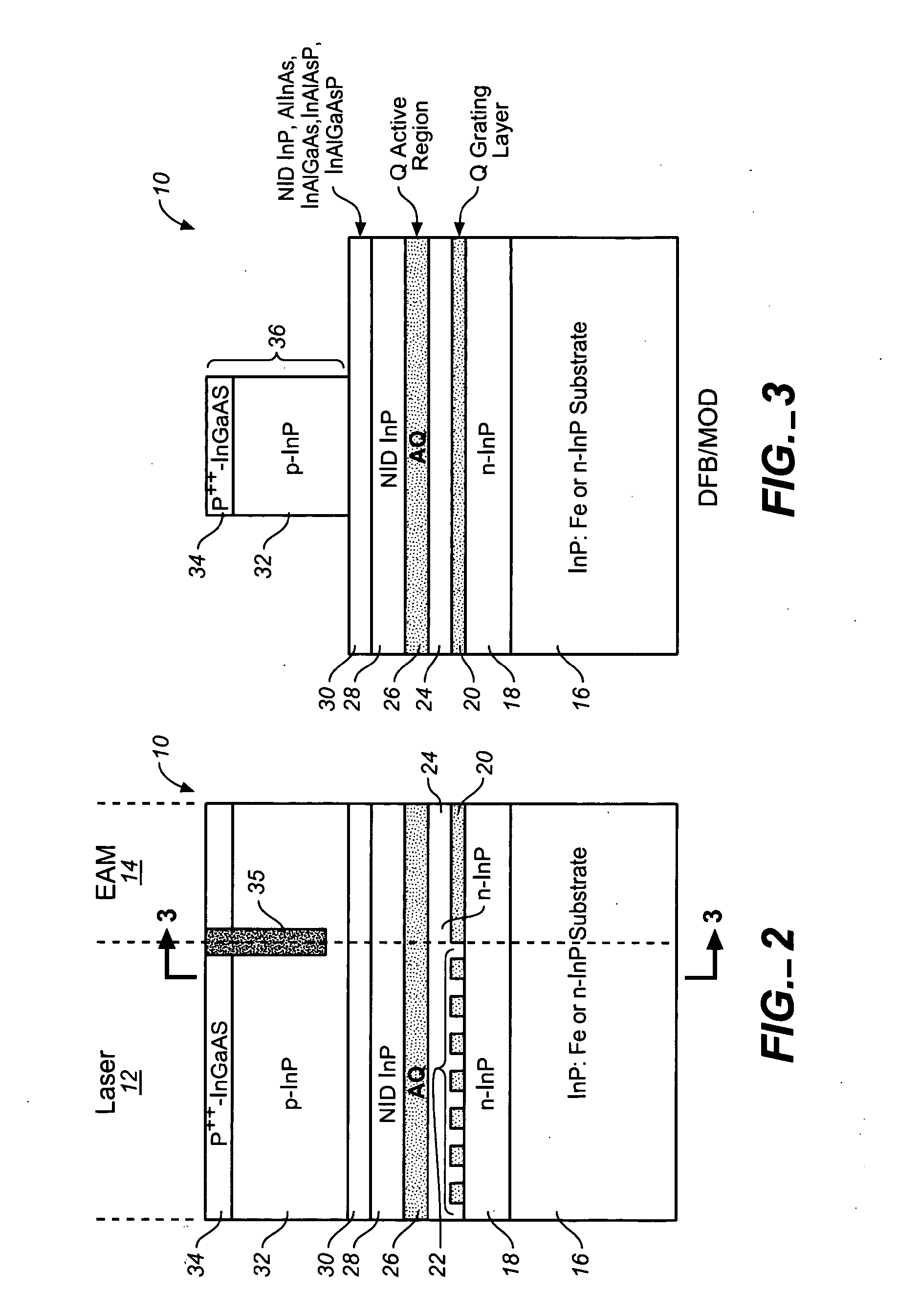
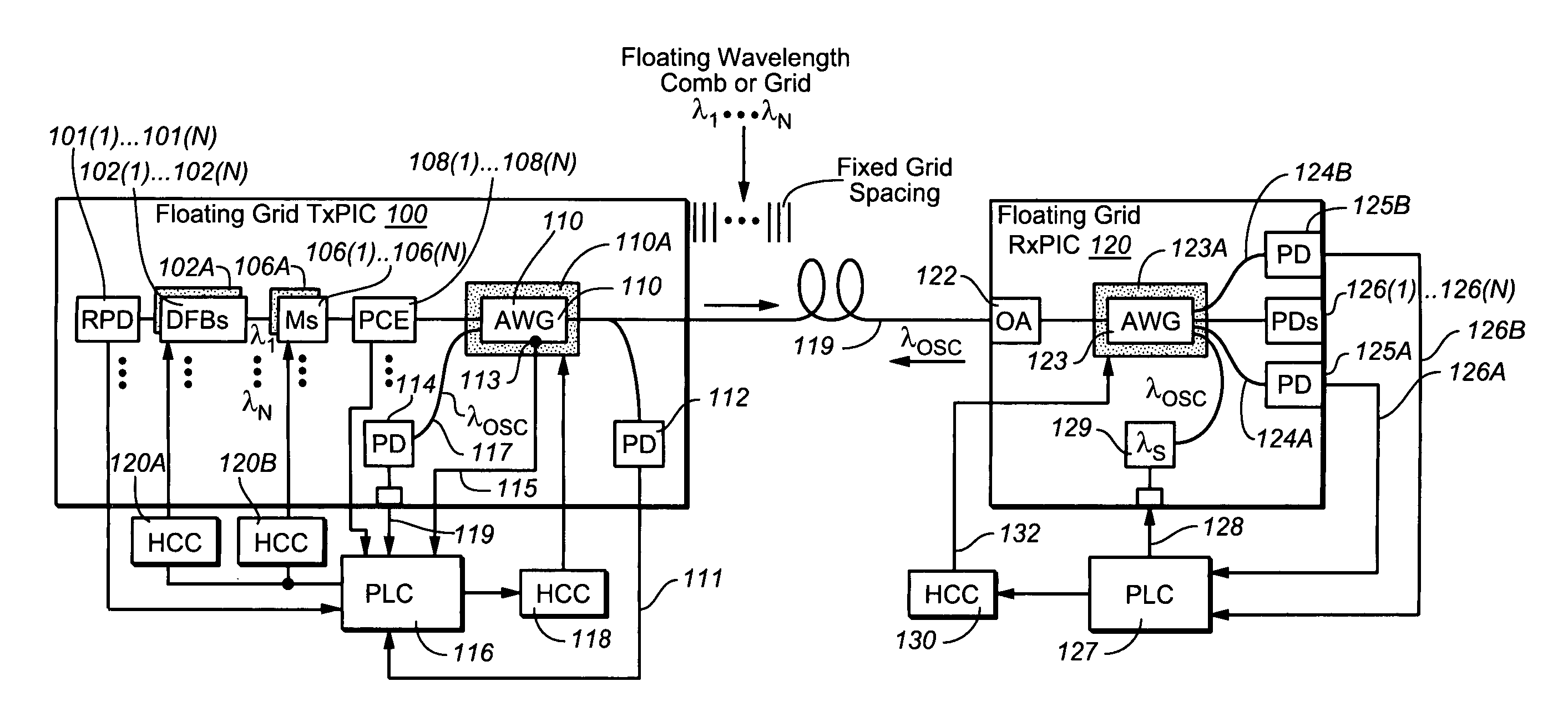
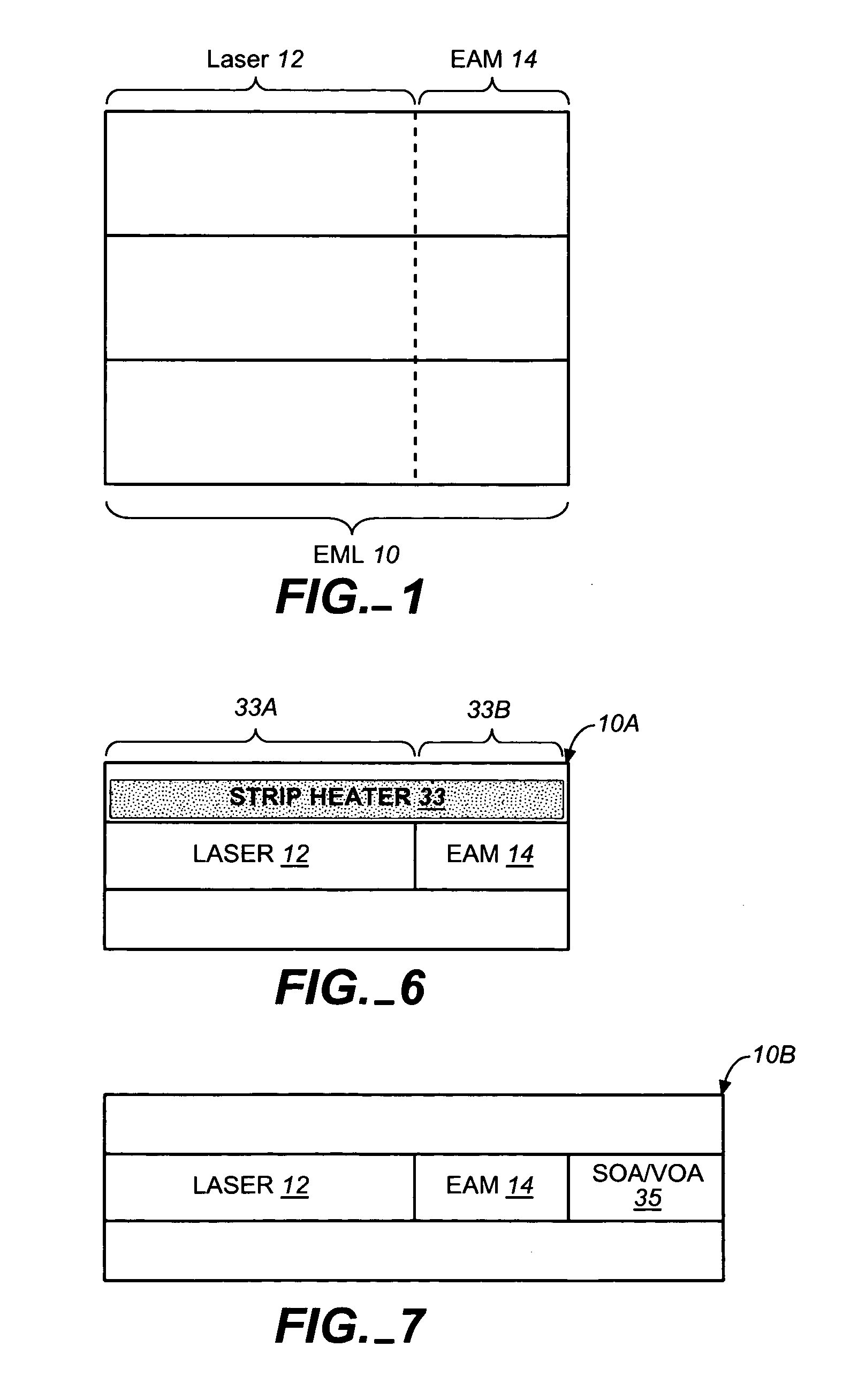
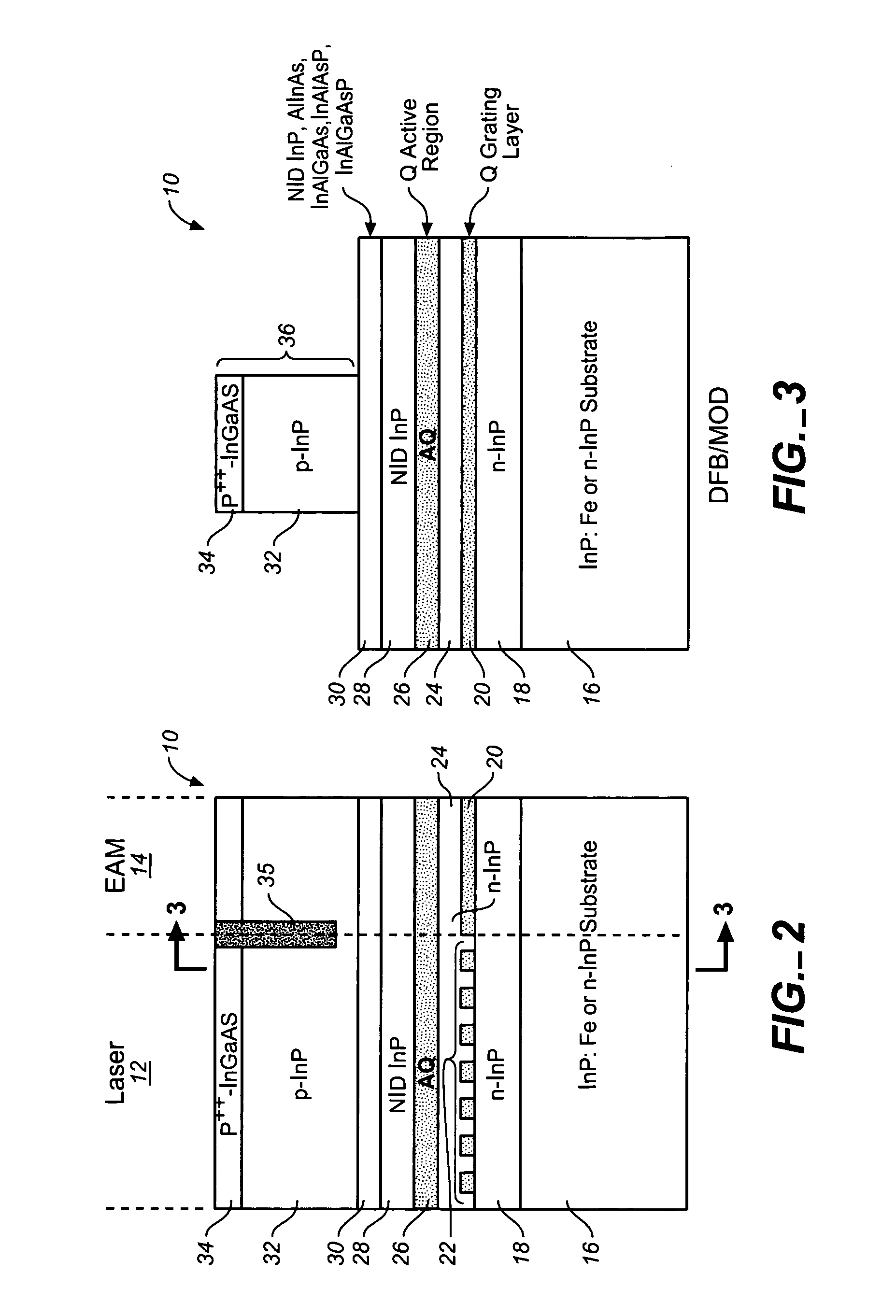
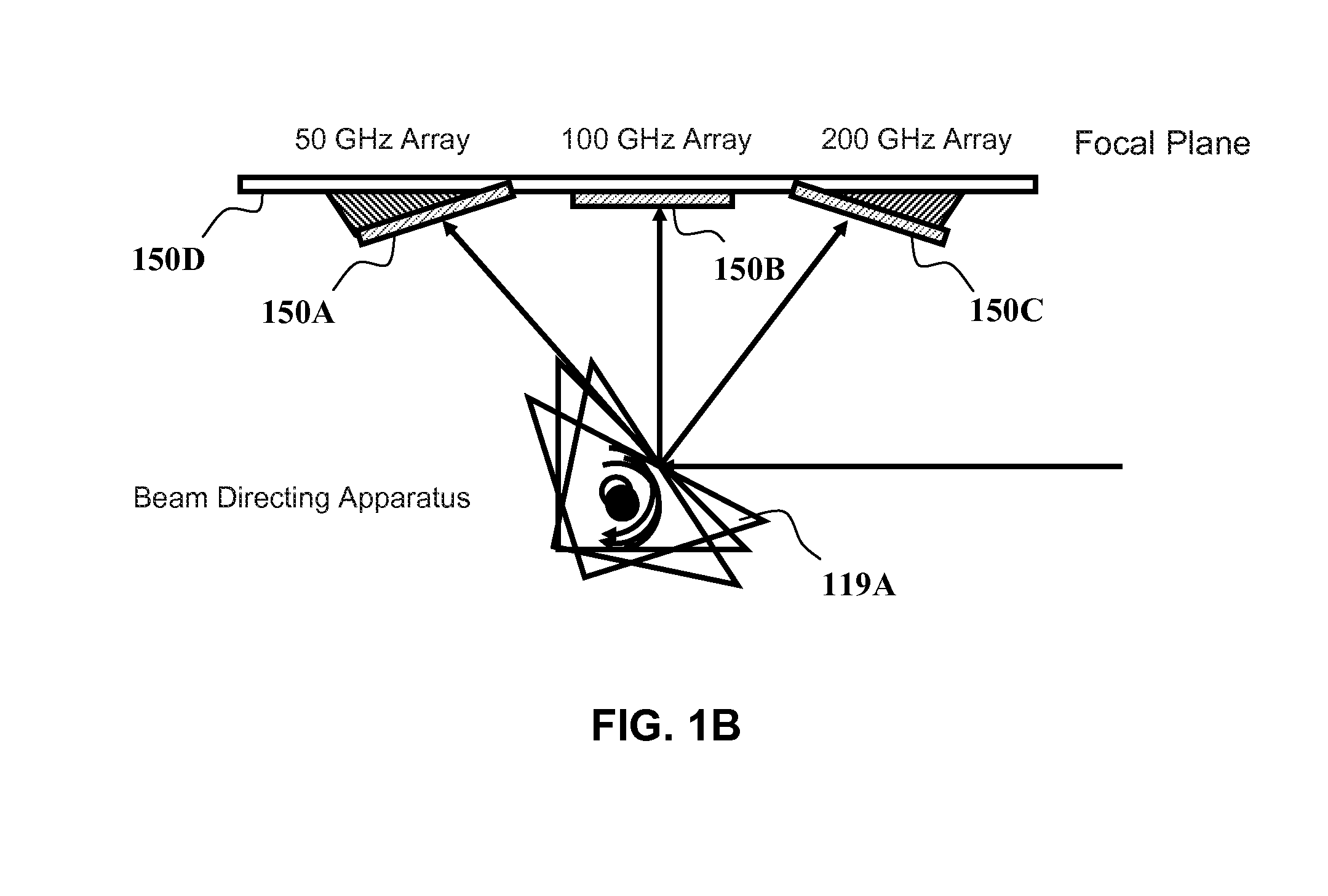
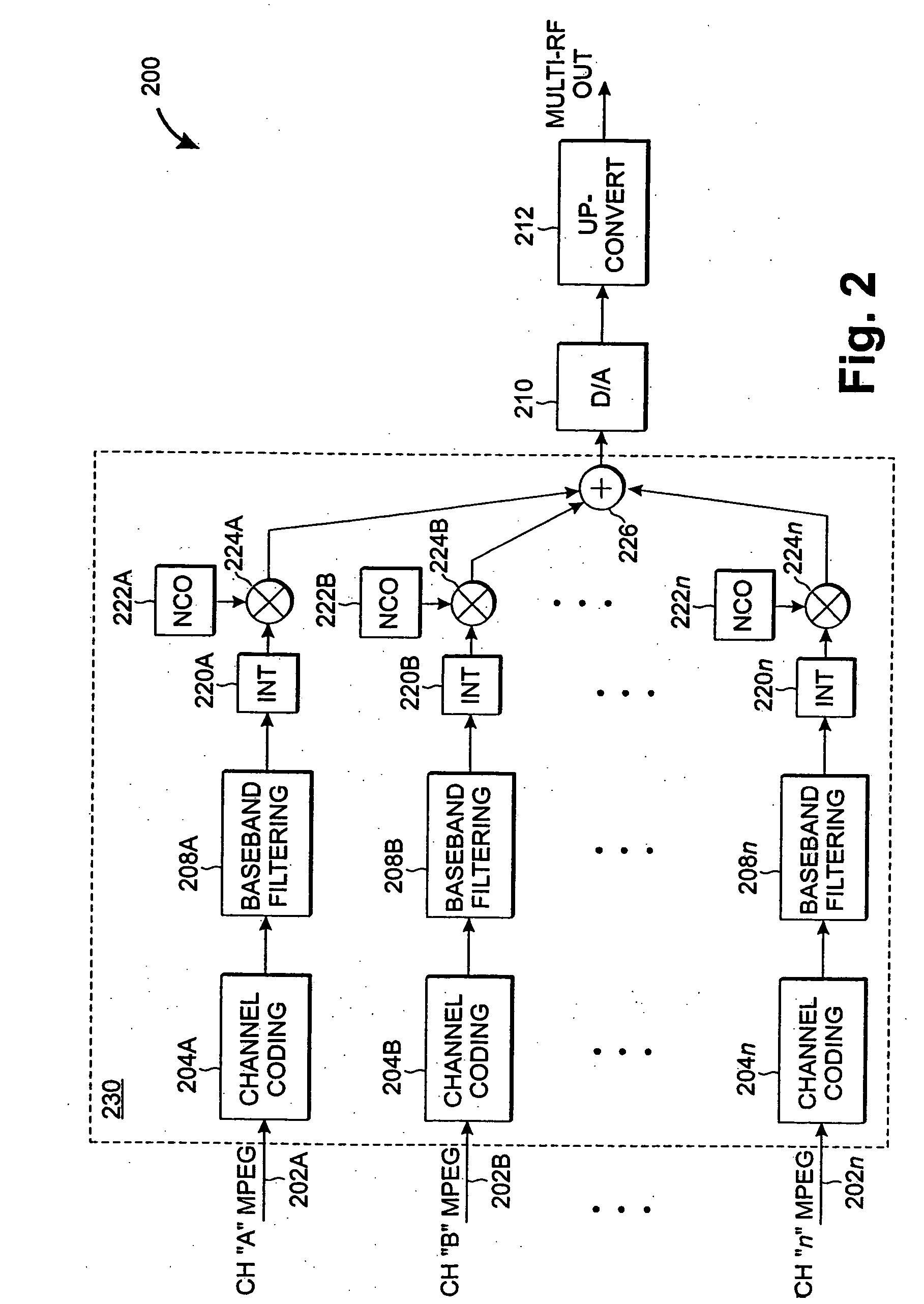
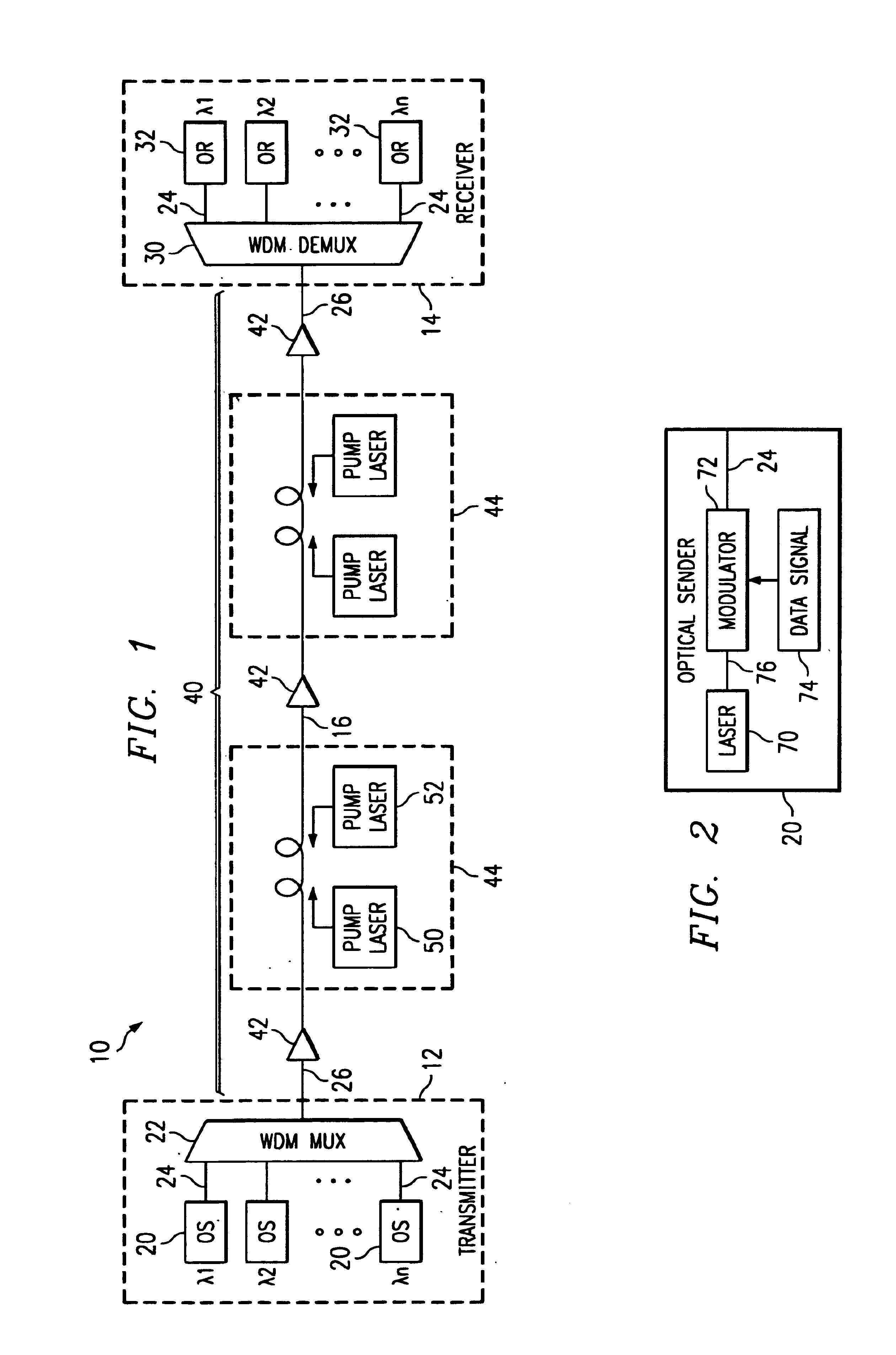
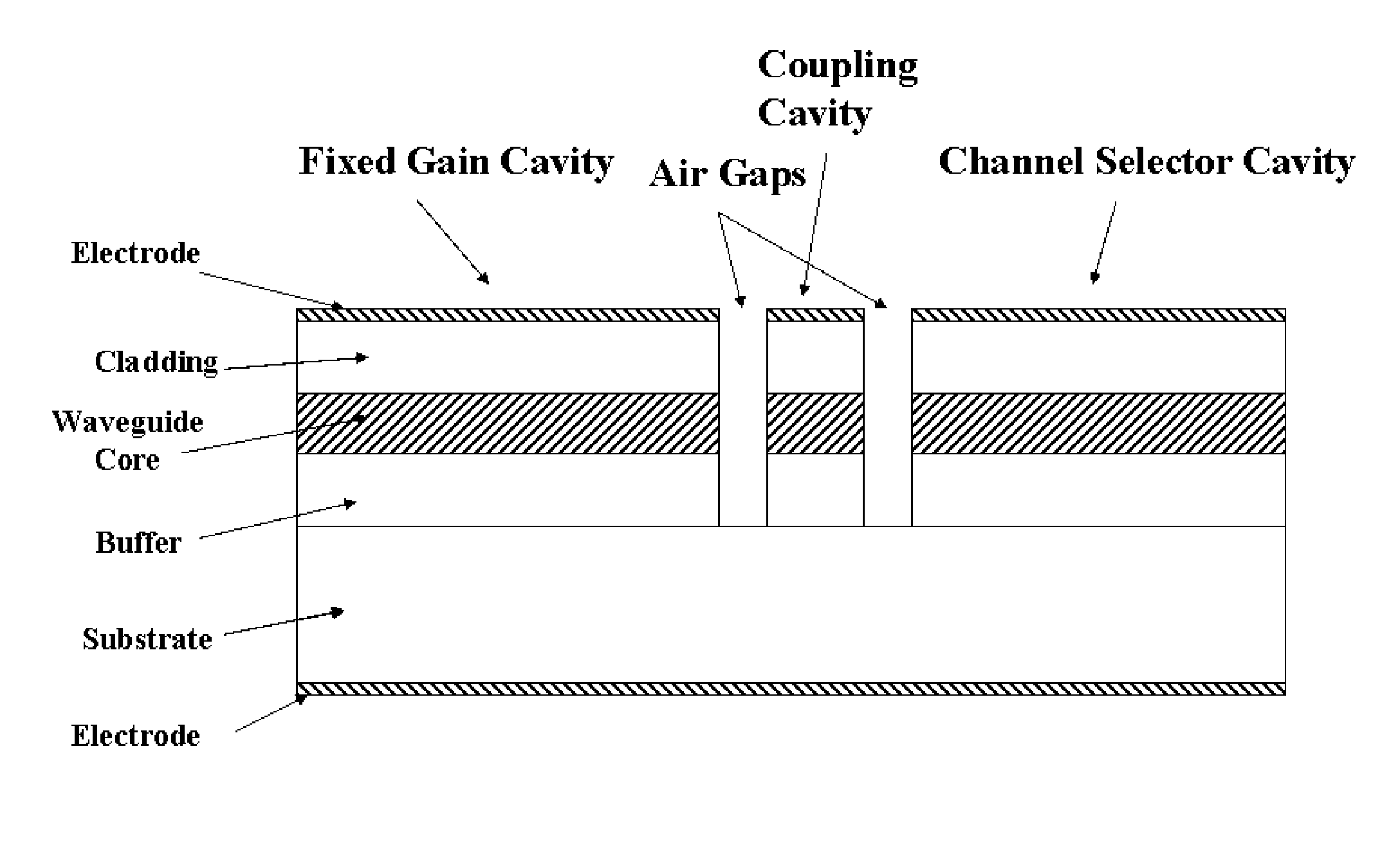
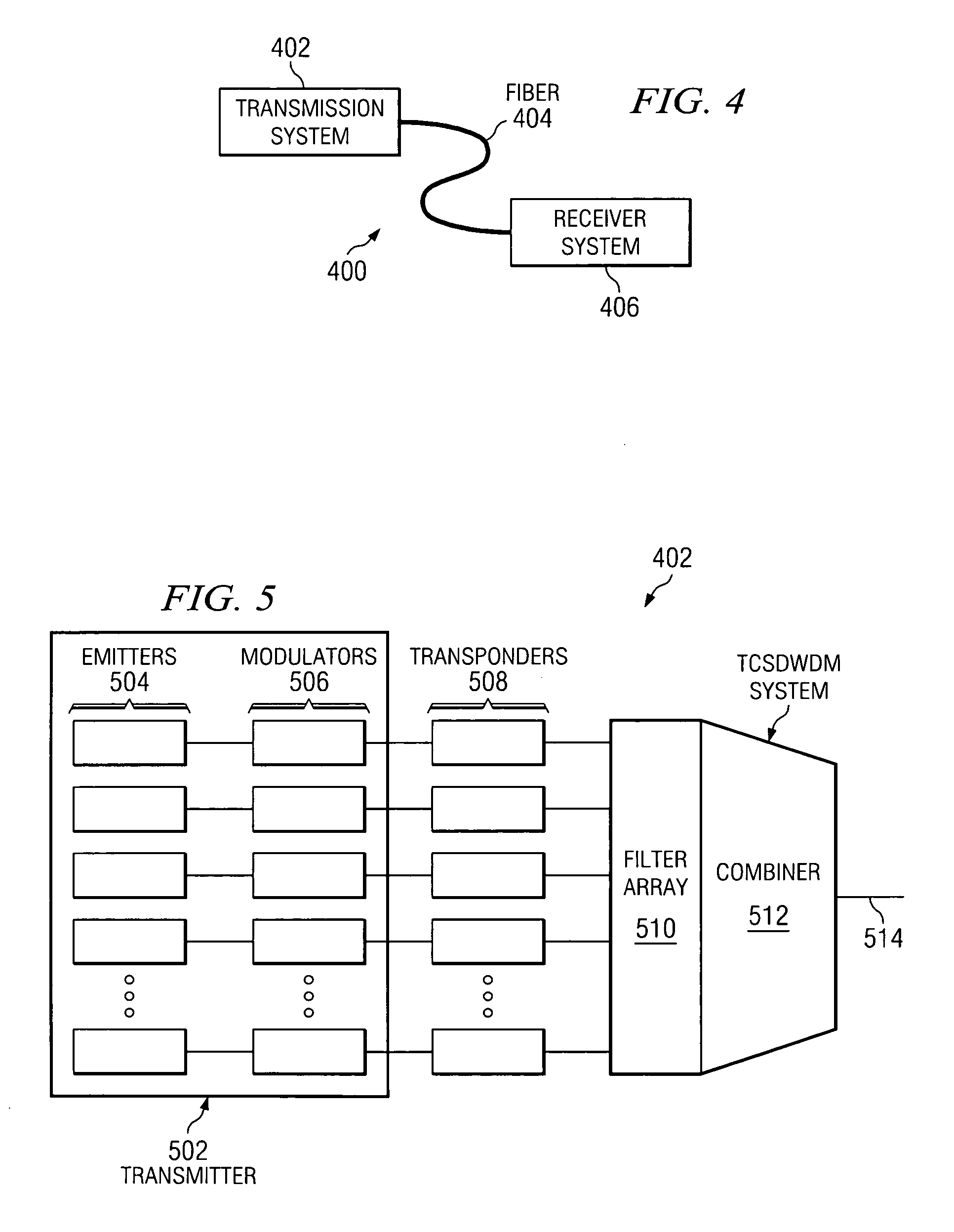
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
ActiveUS20050249509A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedEasy to controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorHermetic packaging
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
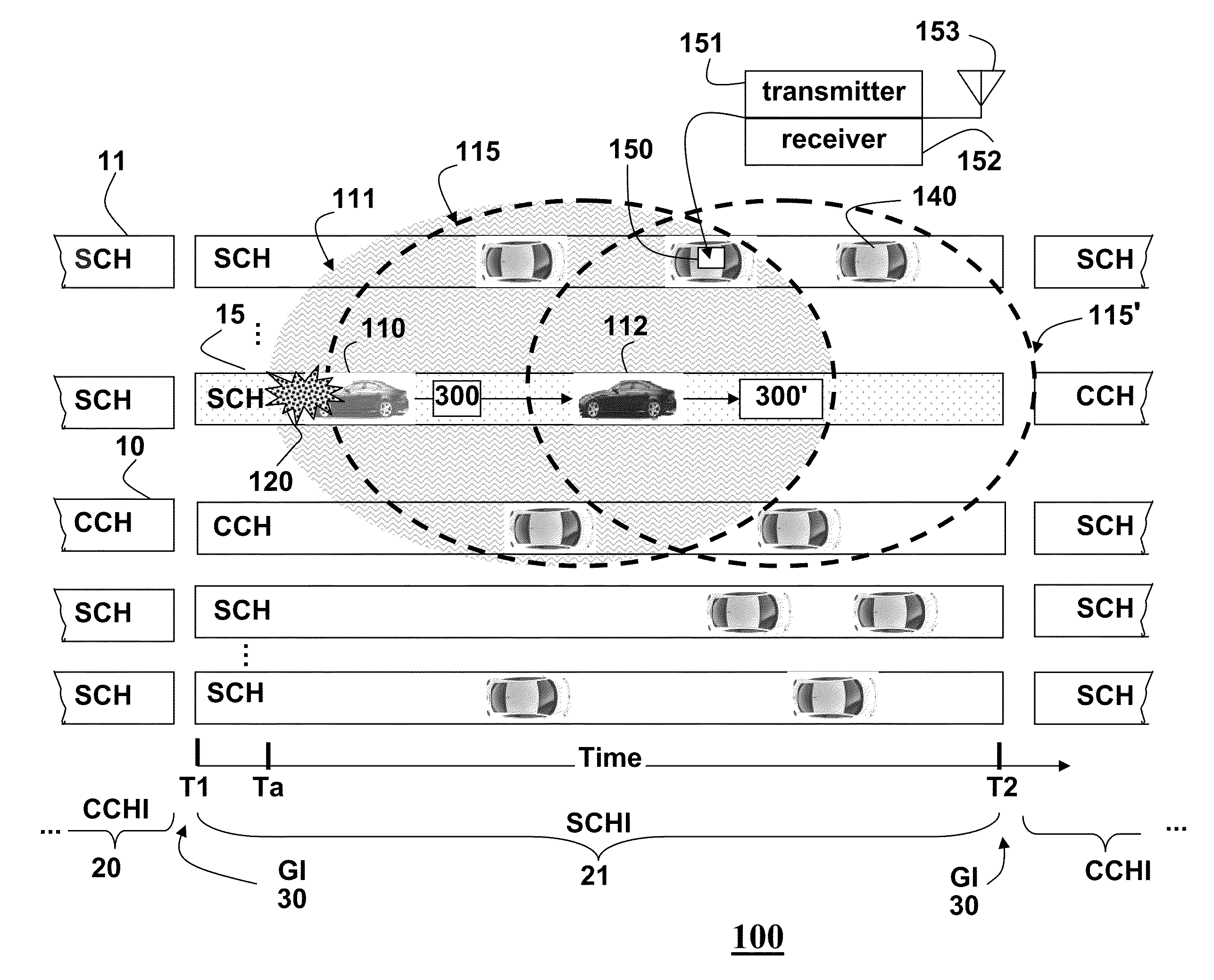
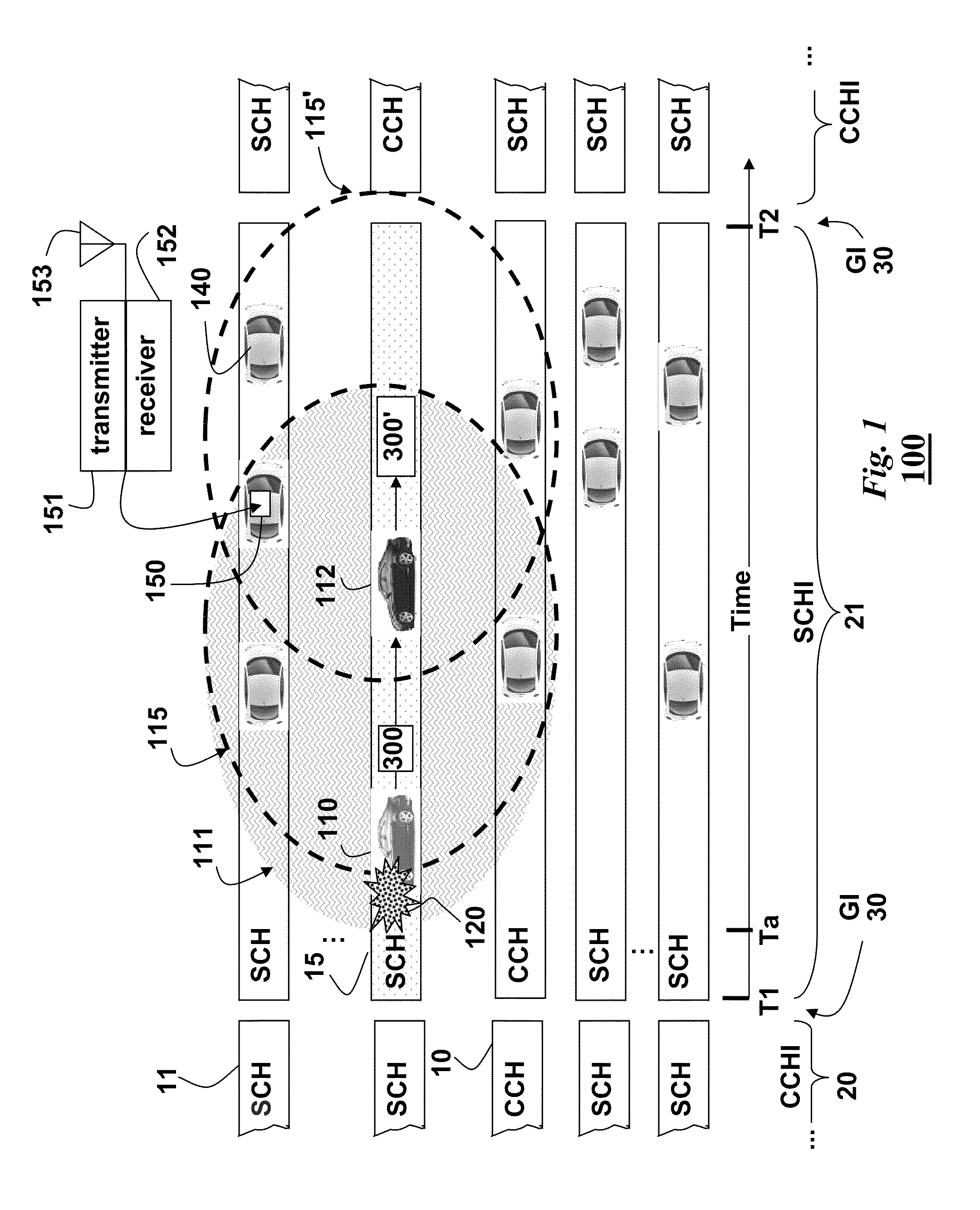
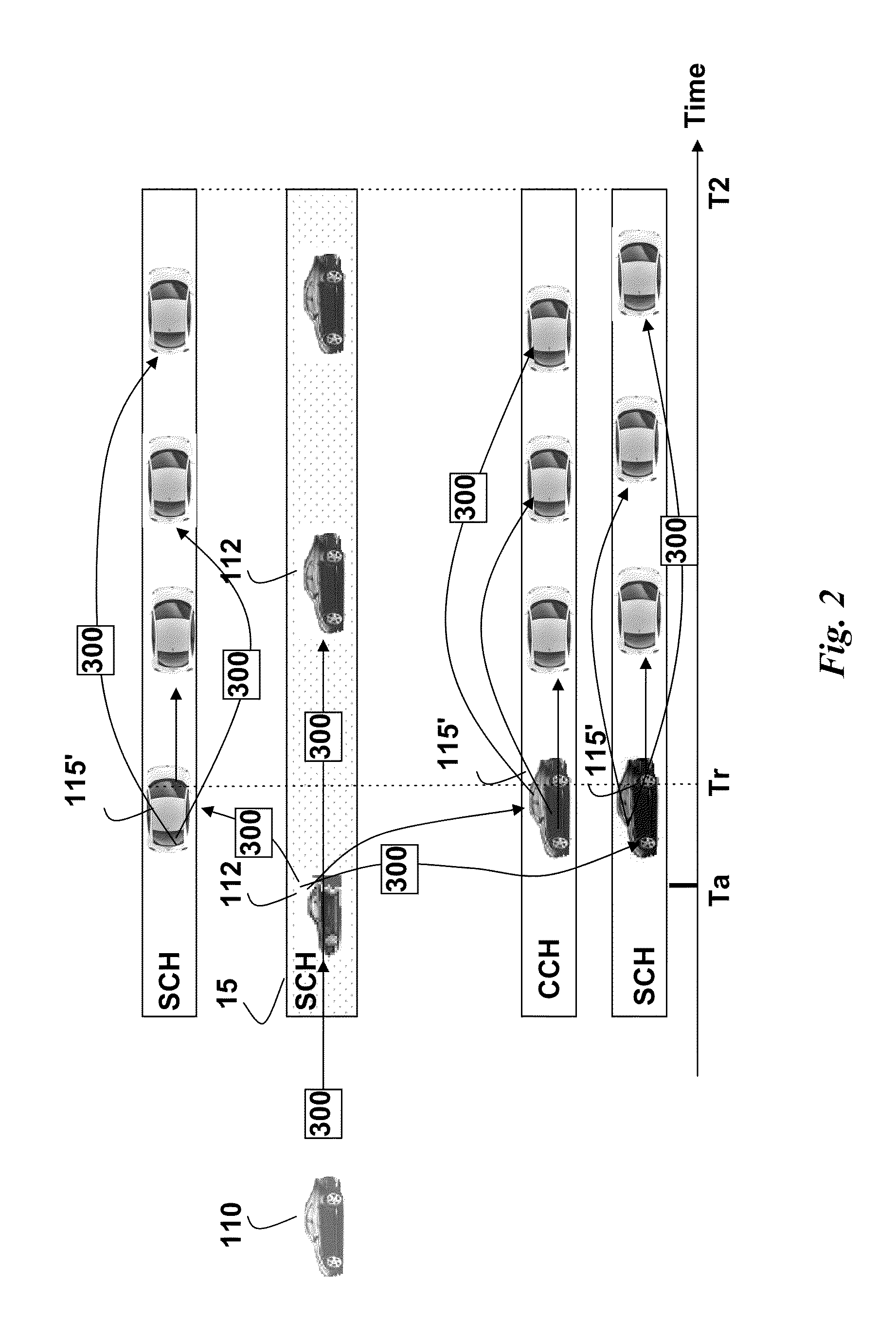
Broadcasting Messages in Multi-Channel Vehicular Networks
ActiveUS20110128902A1Expand coverageLower latencyRoad vehicles traffic controlBroadcast-related systemsTransceiverCurrent channel
Message are broadcast in a vehicular environment using a network of nodes, wherein each node includes a transceiver and a processor arranged in a vehicle, and a bandwidth of the network is partitioned into a control channel (CCH) and multiple service channel (SCH). Time is partitioned into alternating control channel intervals (CCHI) and service channel intervals (SCHI). A source node detects an event and broadcasts a message related to the event. The message specifies current channels and next channels used by the source node to broadcast the message. The message is received in a set of relay nodes. Then, each relay node that receives the message rebroadcasts the message during the SCHI on the CCH or any other channels not specified in the message.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
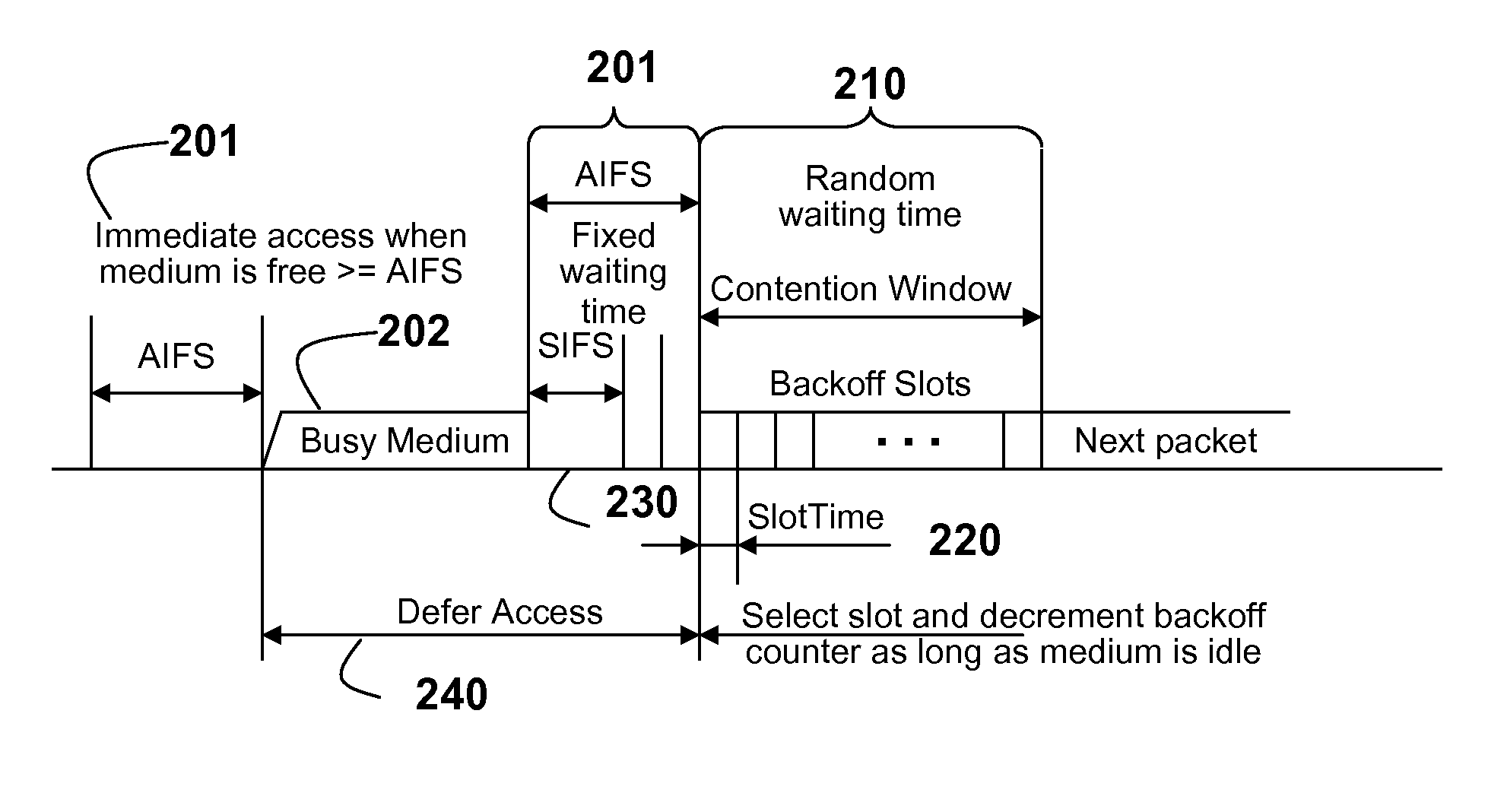
Signaling for Safety Message Transmission in Vehicular Communication Networks
InactiveUS20110128849A1Lower latencyImprove reliabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransceiverSecure transmission
Messages are broadcast in a vehicular environment using a network of nodes. Each node includes a transceiver and a processor arranged in a vehicle. A bandwidth of the network is partitioned into a set of channels including a control channel (CCH) and multiple service channel (SCH). Time is partitioned into alternating control channel intervals (CCHI) and service channel intervals (SCHI). A particular node transmits an attention signal indicating intent to access a particular channel to transmit a high priority safety message, wherein the network is designed according to a standard for a vehicular environment. The node then waits a random length backoff time and transmits the high priority safety message related to the vehicular environment after the random length backoff time.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
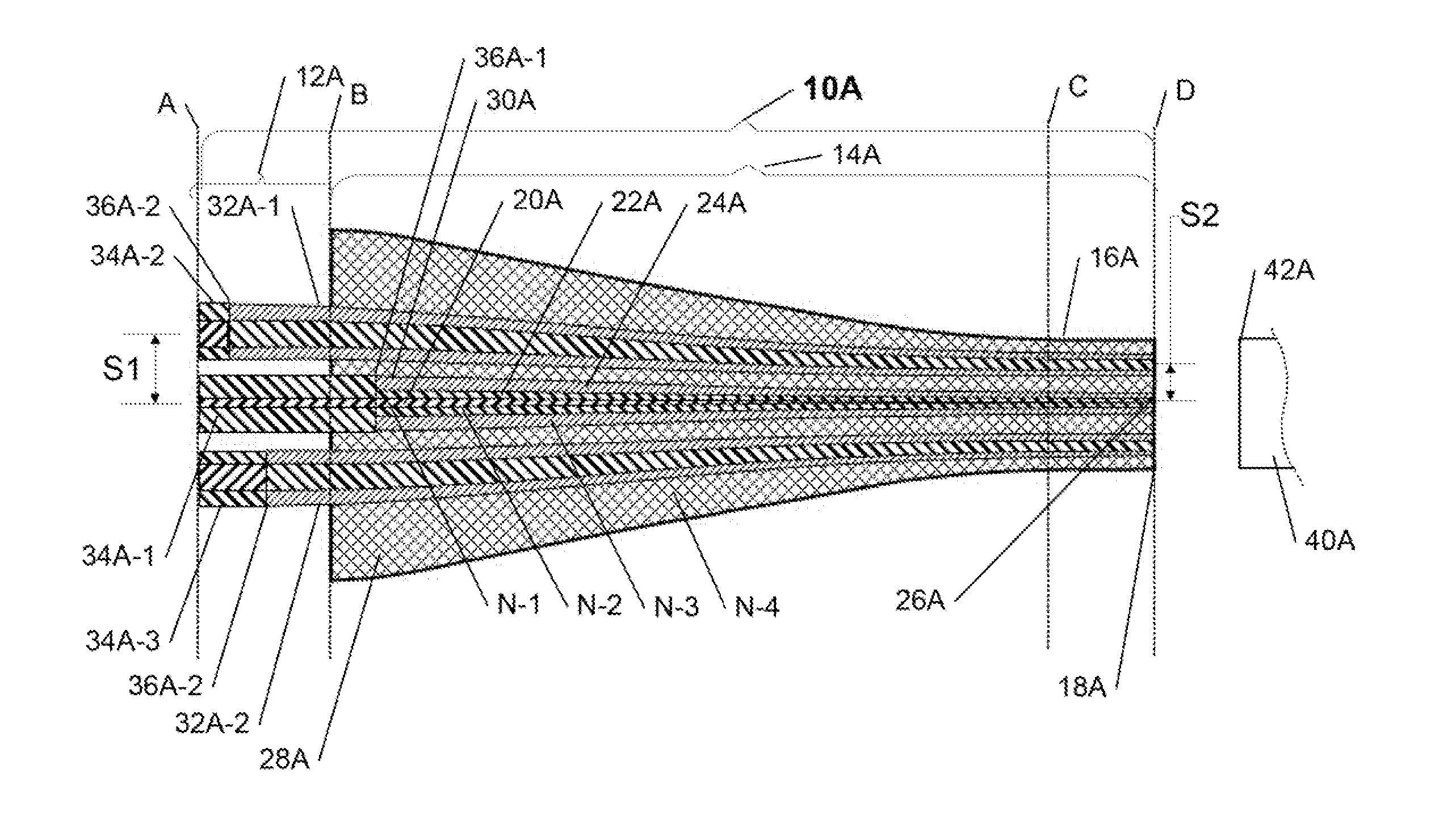
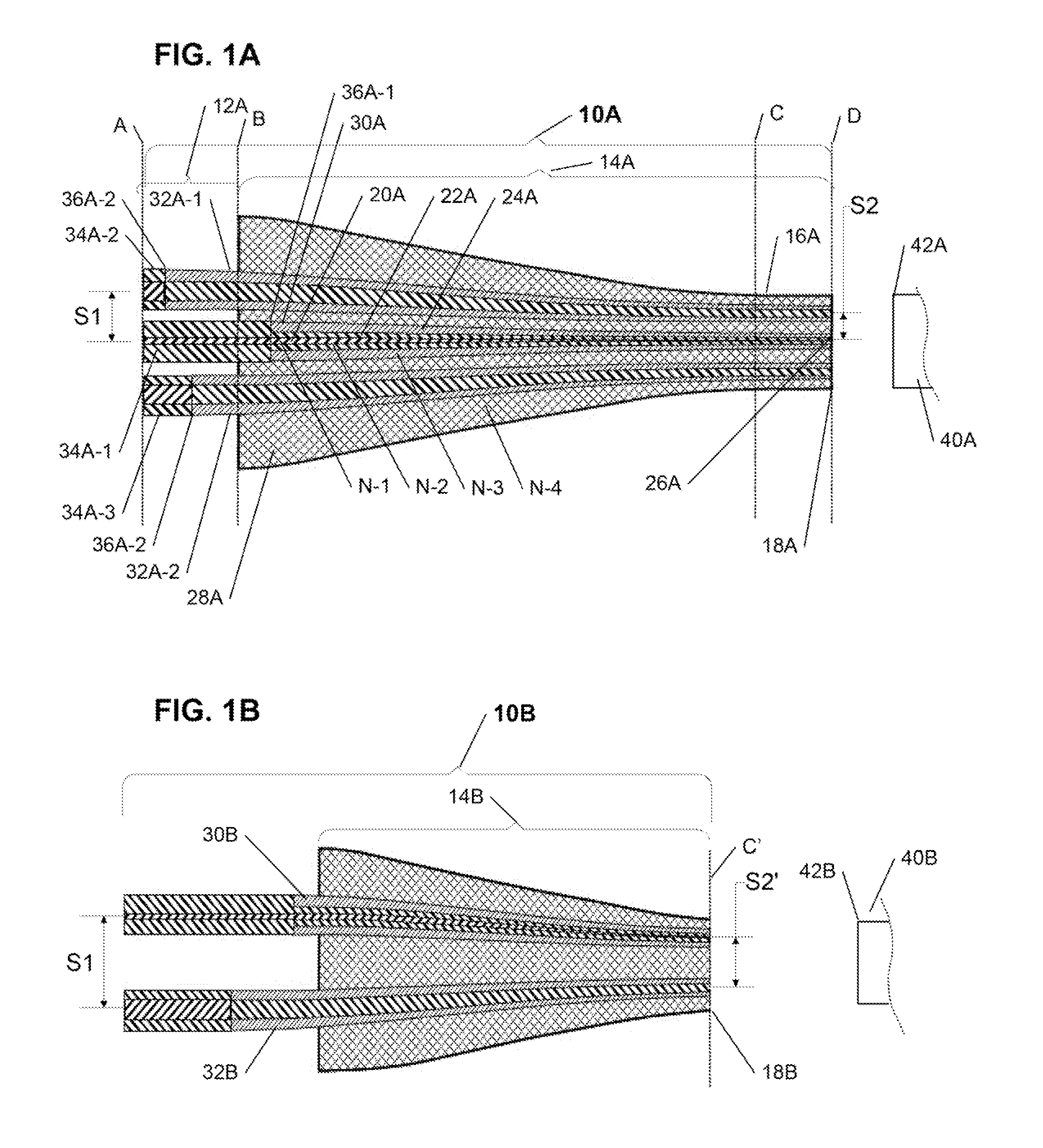
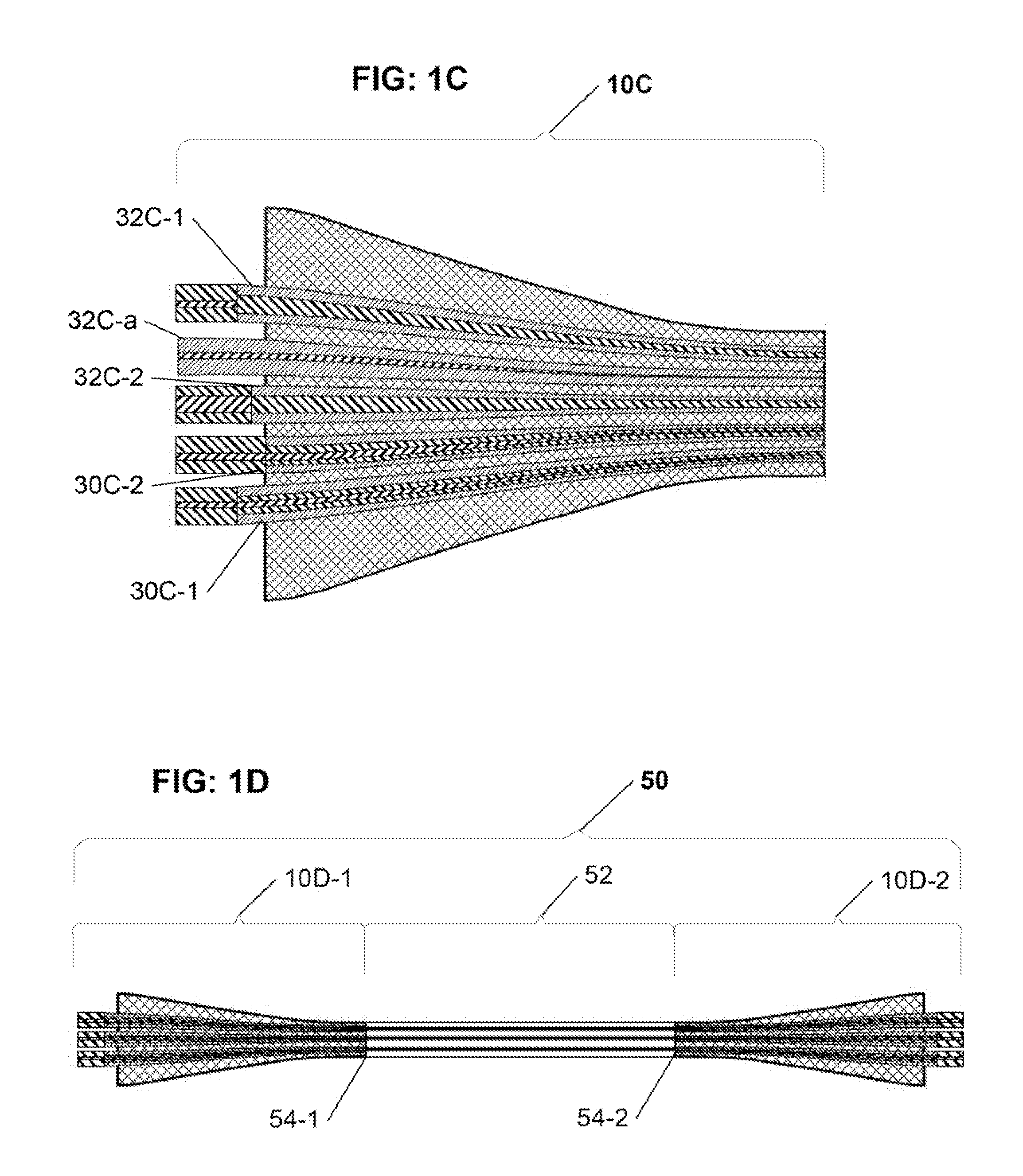
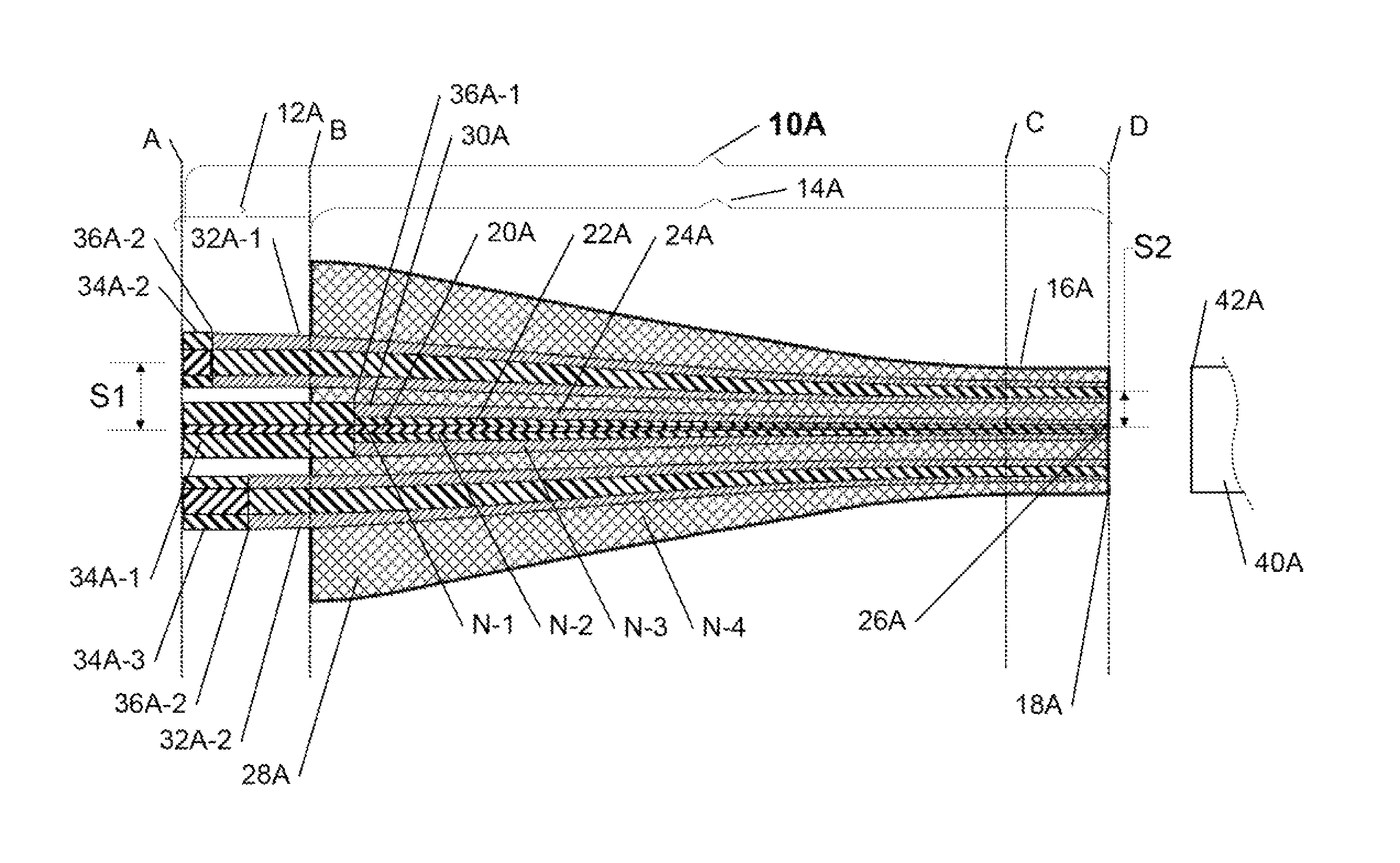
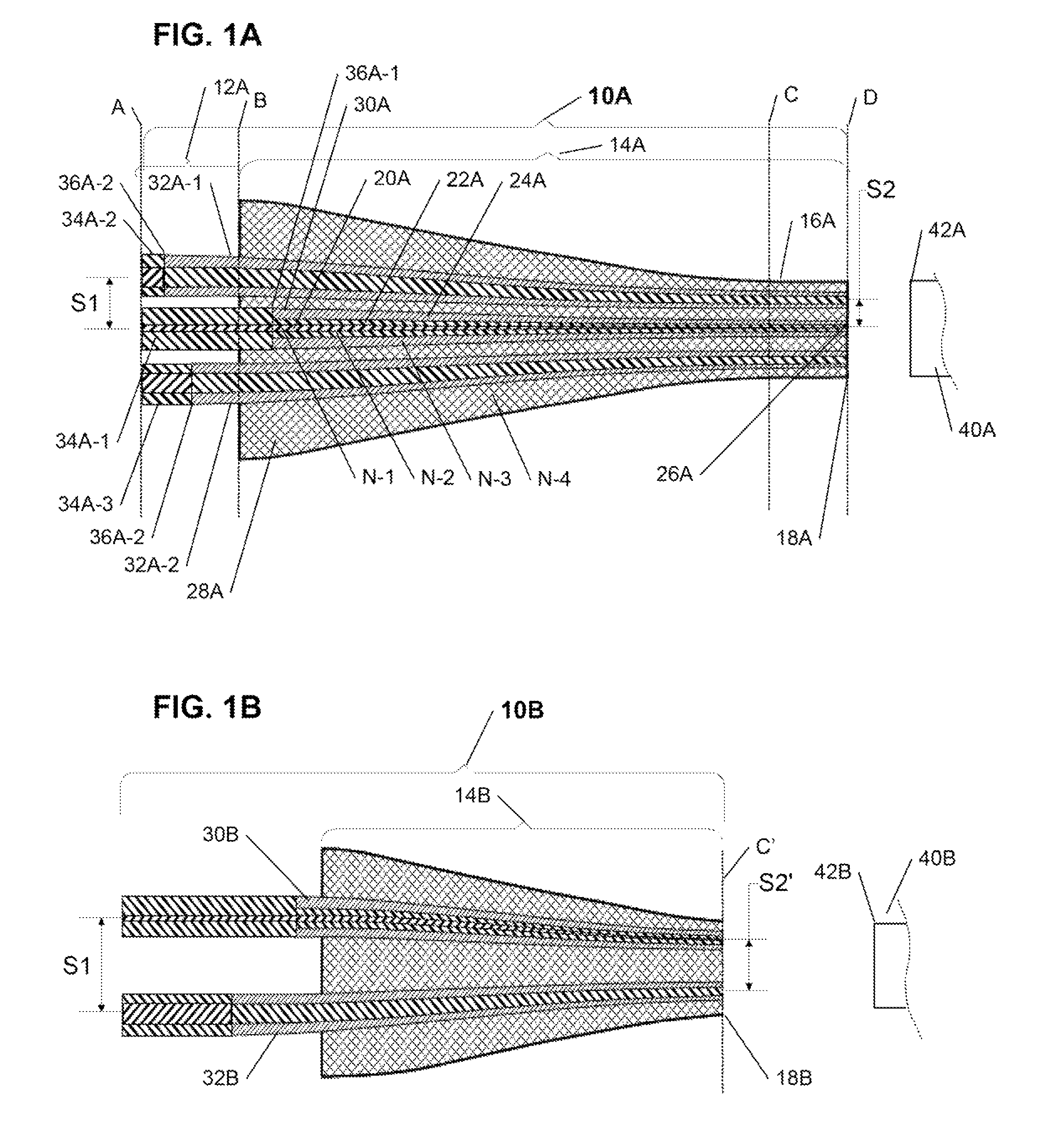
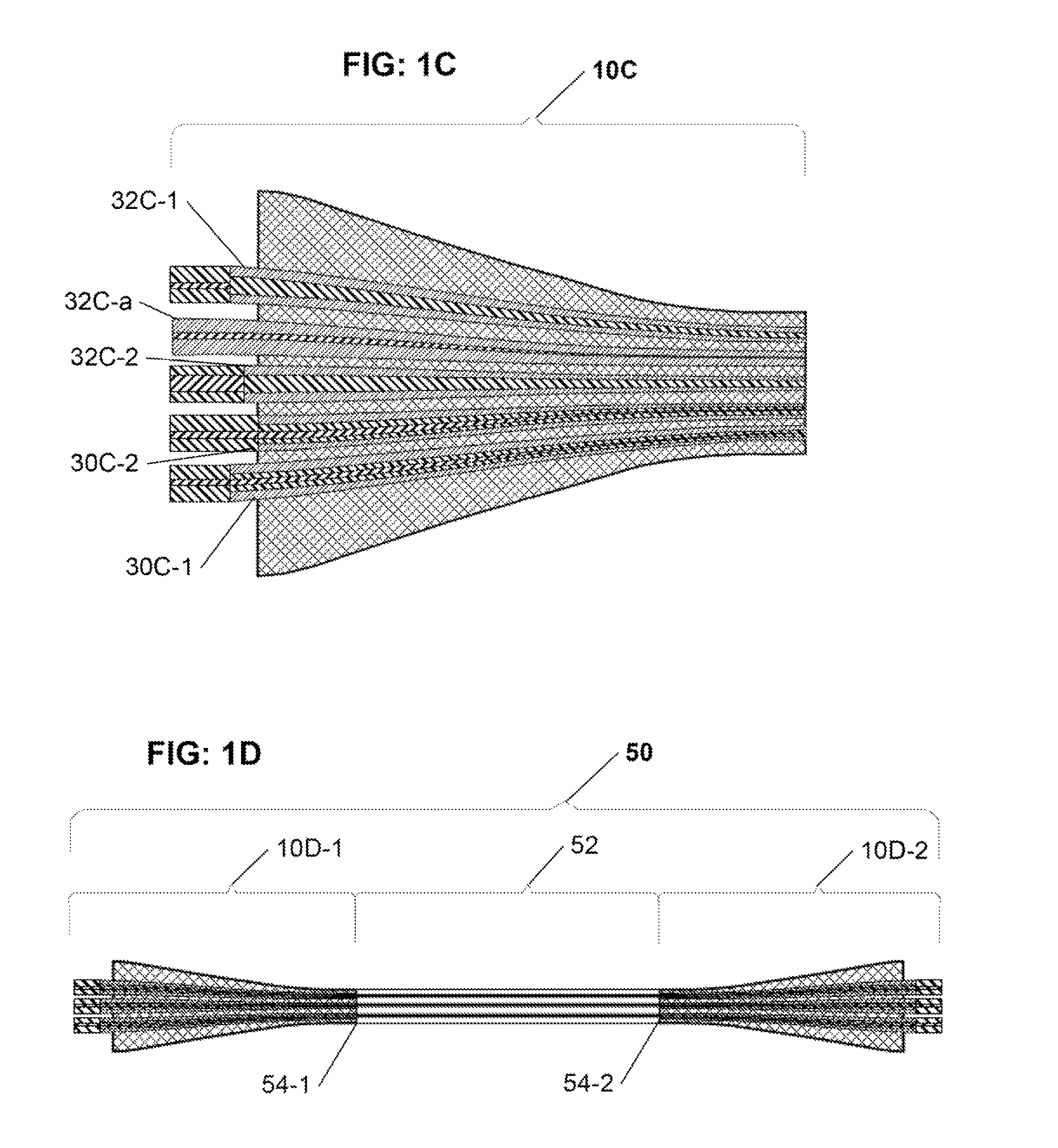
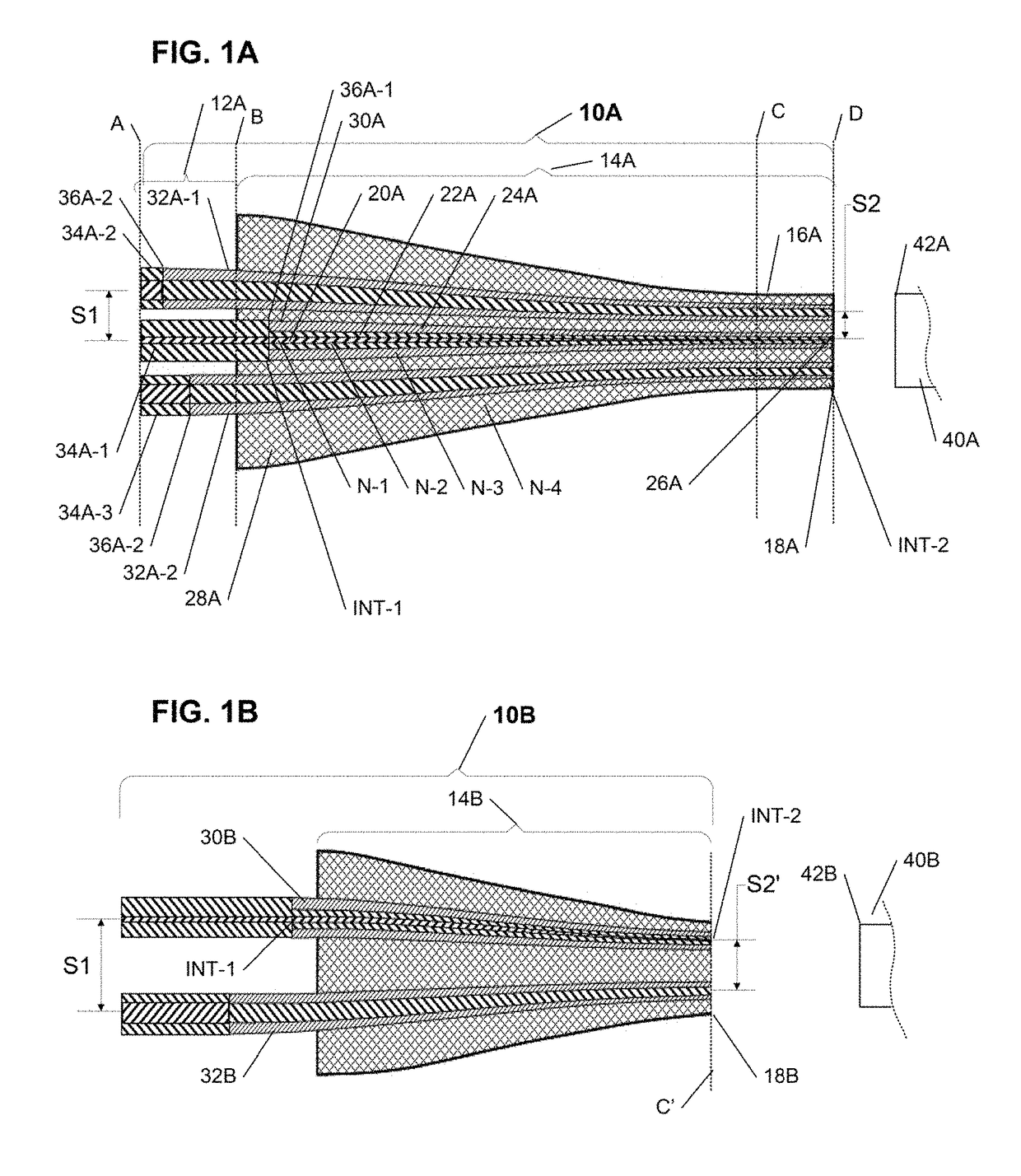
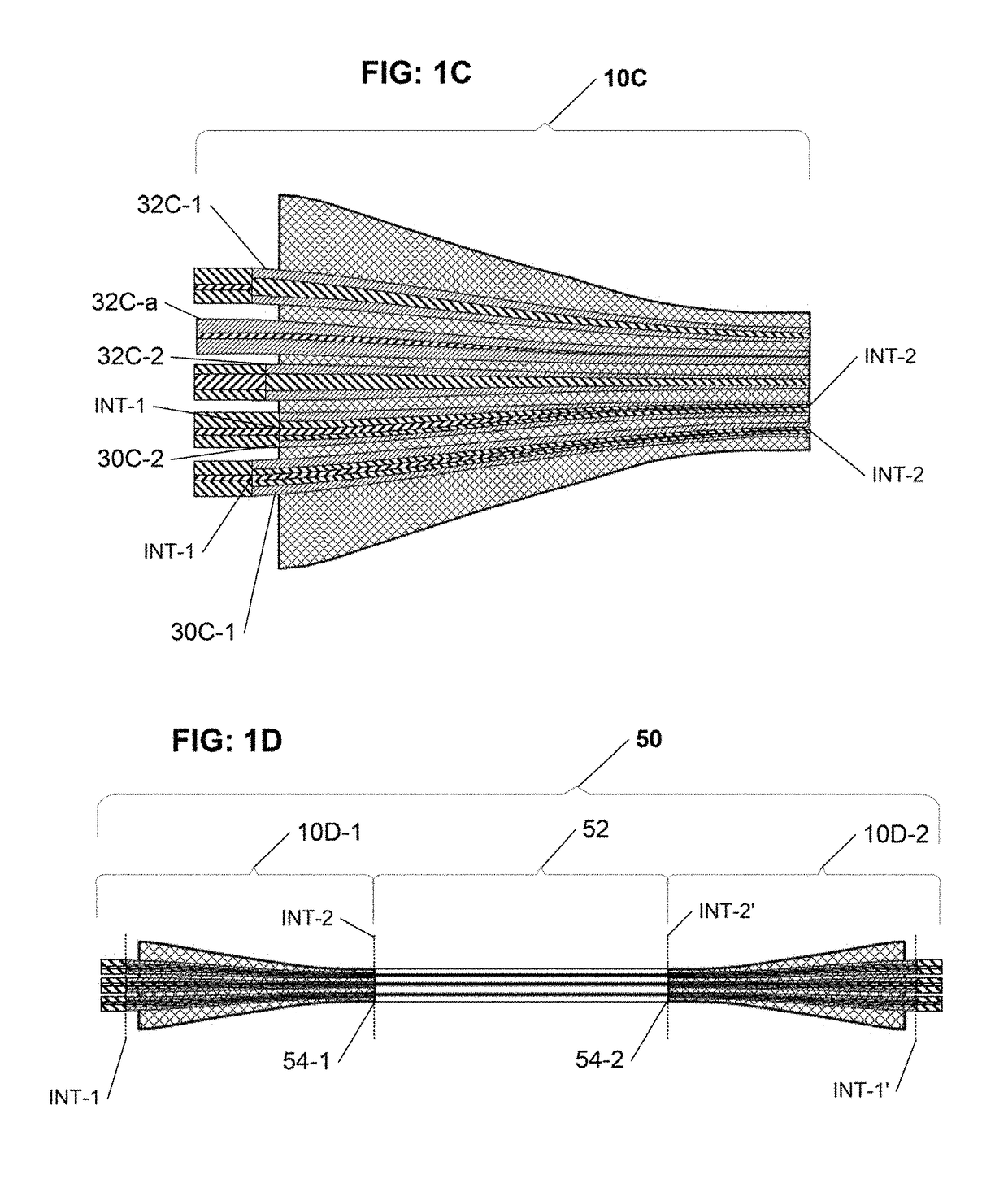
Configurable pitch reducing optical fiber array
InactiveUS20130216184A1Coupling light guidesBundled fibre light guideErbium lasersOptical fiber coupler
The inventive optical fiber coupler array is capable of providing a low loss, high-coupling coefficient interface with high accuracy and easy alignment between a plurality of optical fibers (or other optical devices) with a first channel-to-channel spacing, and an optical device having a plurality of closely-spaced waveguide interfaces with a second channel-to-channel spacing, where each end of the optical fiber coupler array is configurable to have different channel-to-channel spacing, each matched to a corresponding one of the first and second channel-to-channel spacing. The novel optical coupler array includes a plurality of waveguides (at least one of which may optionally be polarization maintaining), that comprises at least one gradually reduced vanishing core fiber, at least in part embedded within a common housing structure. Alternatively, the novel coupler array may be configured for utilization with at least one of an optical fiber amplifier and an optical fiber laser.
Owner:KOPP VICTOR ILICH +4
Flexible wavelength selective switch fabric with arbitrary add and drop capability
ActiveUS7231107B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesLength waveWavelength selectivity
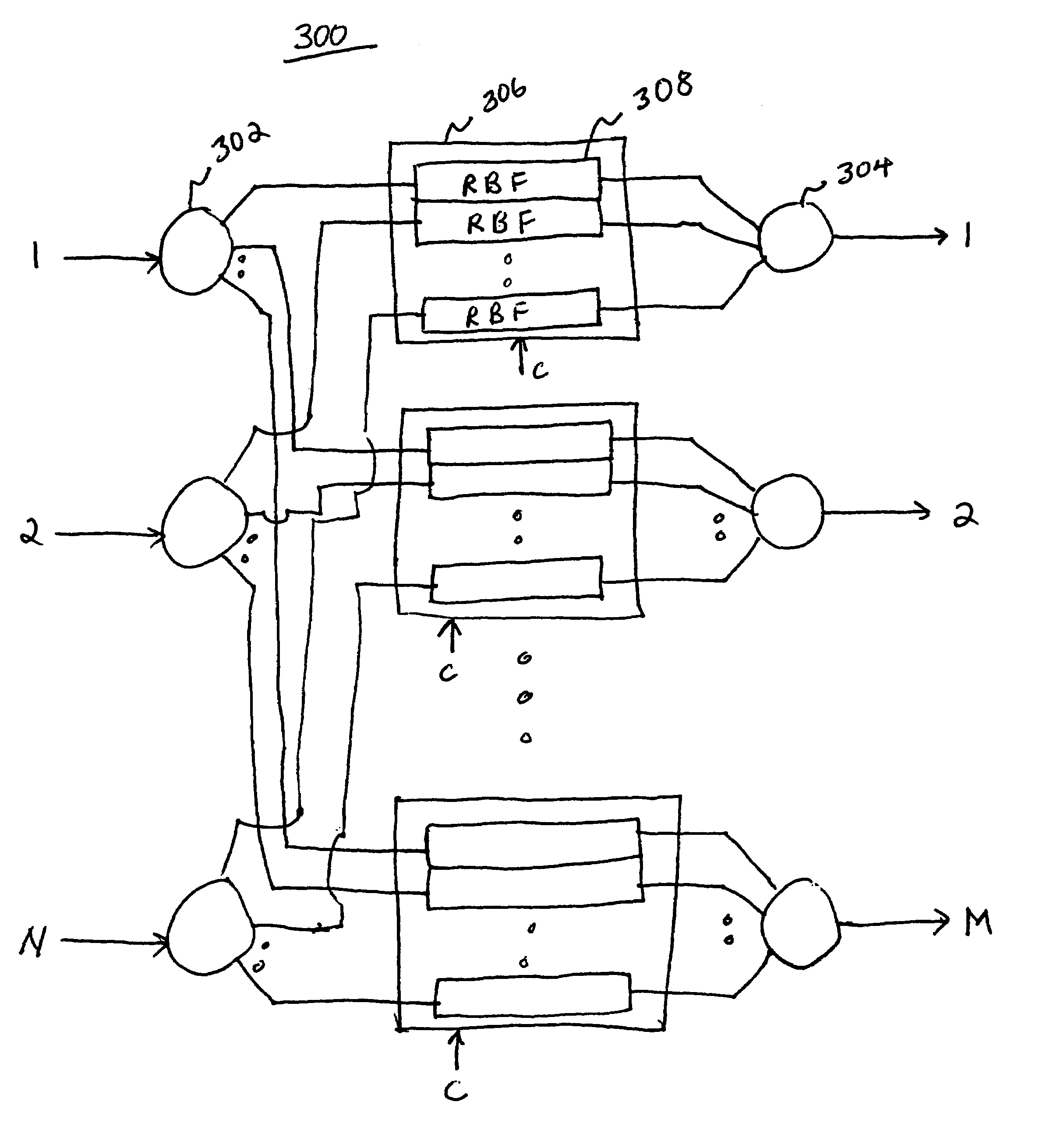
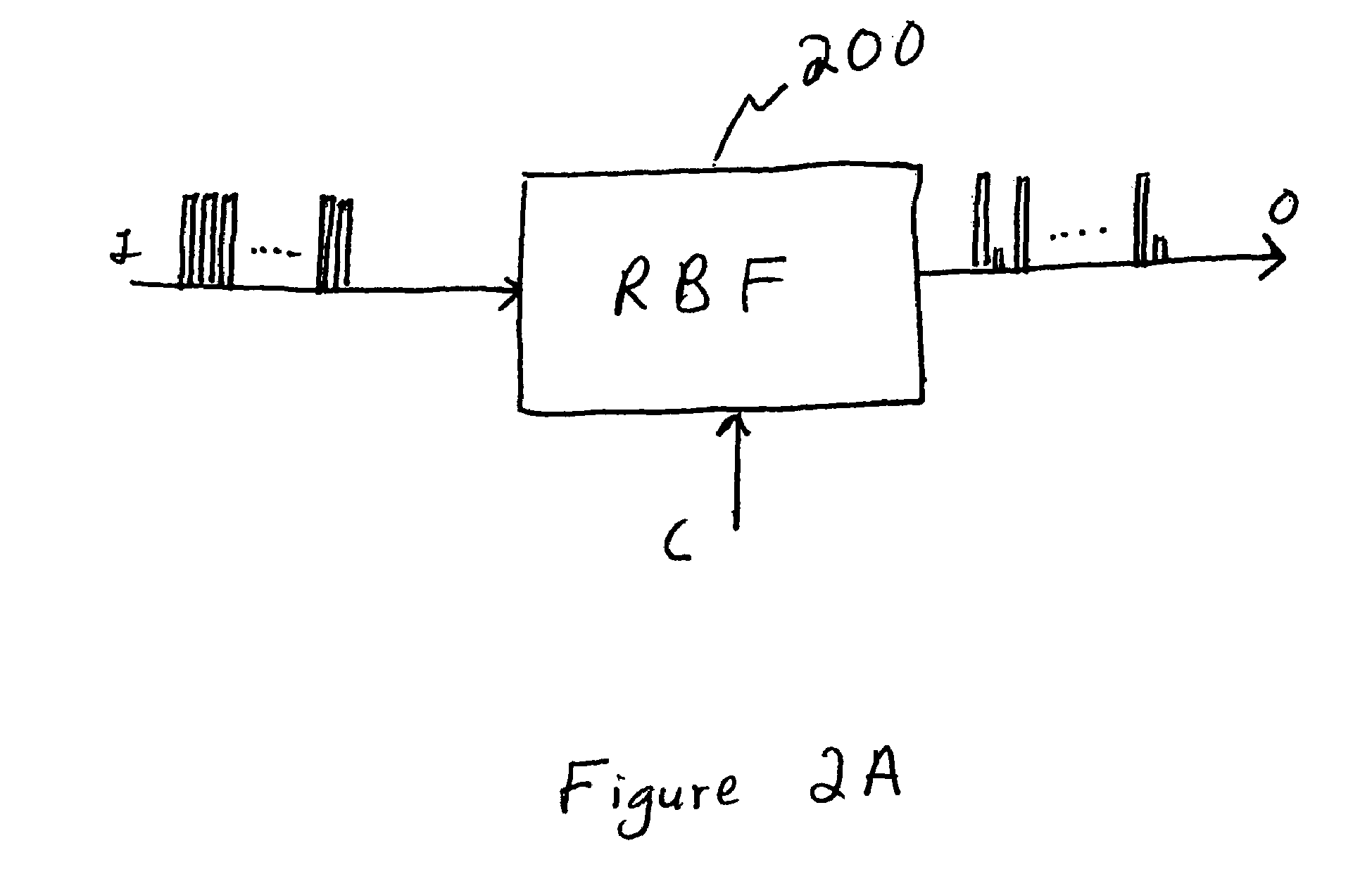
A flexible wavelength switch fabric may be implemented with multiple groups of reconfigurable blocking filters or with multiple multi-in, single out wavelength selective switches. The behaviors of reconfigurable blocking filters are individually settable, such as channel blocking, channel spacing, transmission rate, and default blocking state. Add and drop taps may be added to provide arbitrary add / drop capability. Optical splitters / combiners used may be tunable so that insertion losses may be minimized for the overall network.
Owner:CIENA
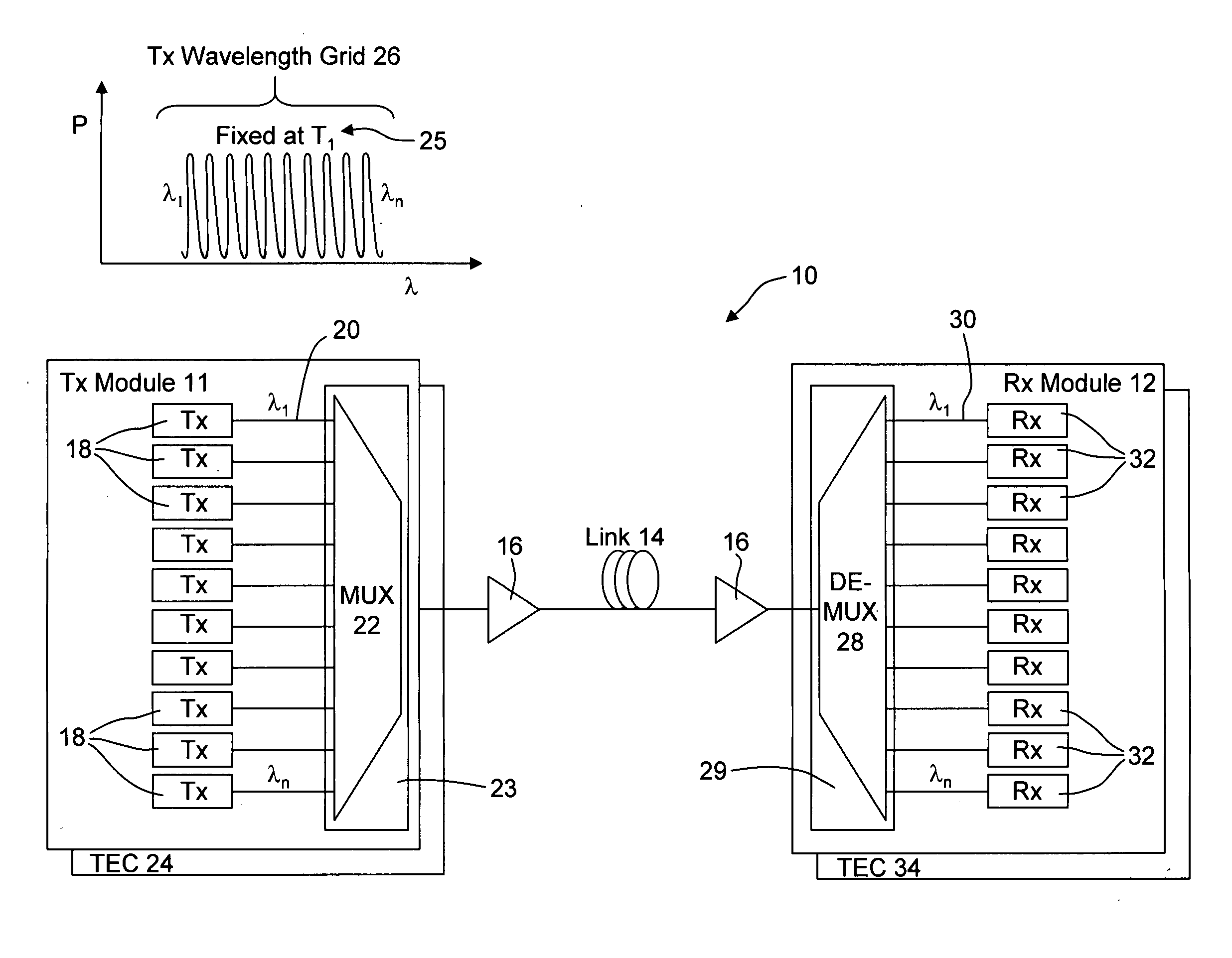
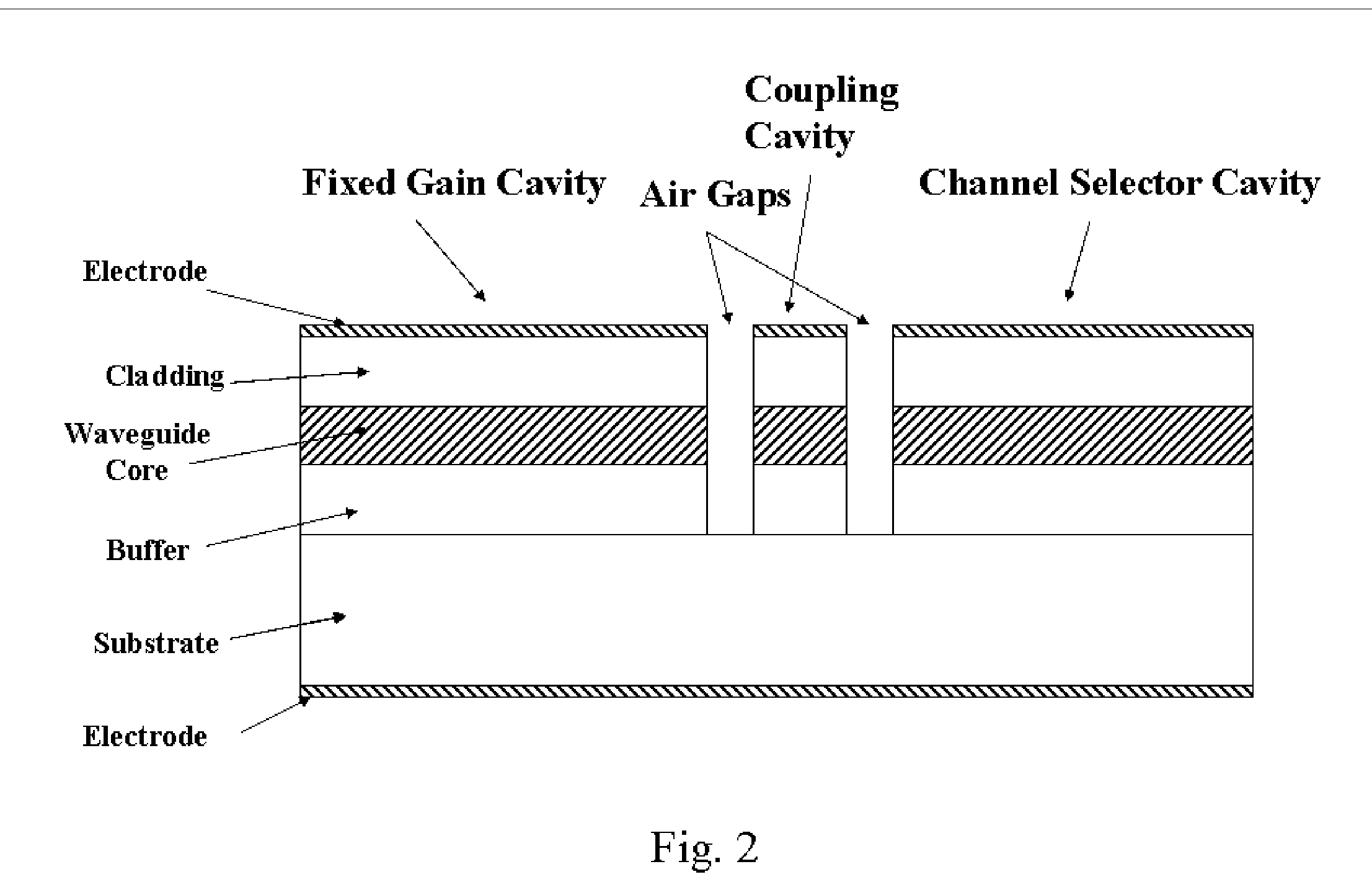
COOLERLESS PHOTONIC INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (PICs) FOR WDM TRANSMISSION NETWORKS AND PICs OPERABLE WITH A FLOATING SIGNAL CHANNEL GRID CHANGING WITH TEMPERATURE BUT WITH FIXED CHANNEL SPACING IN THE FLOATING GRID
ActiveUS20100166424A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorPeak value
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
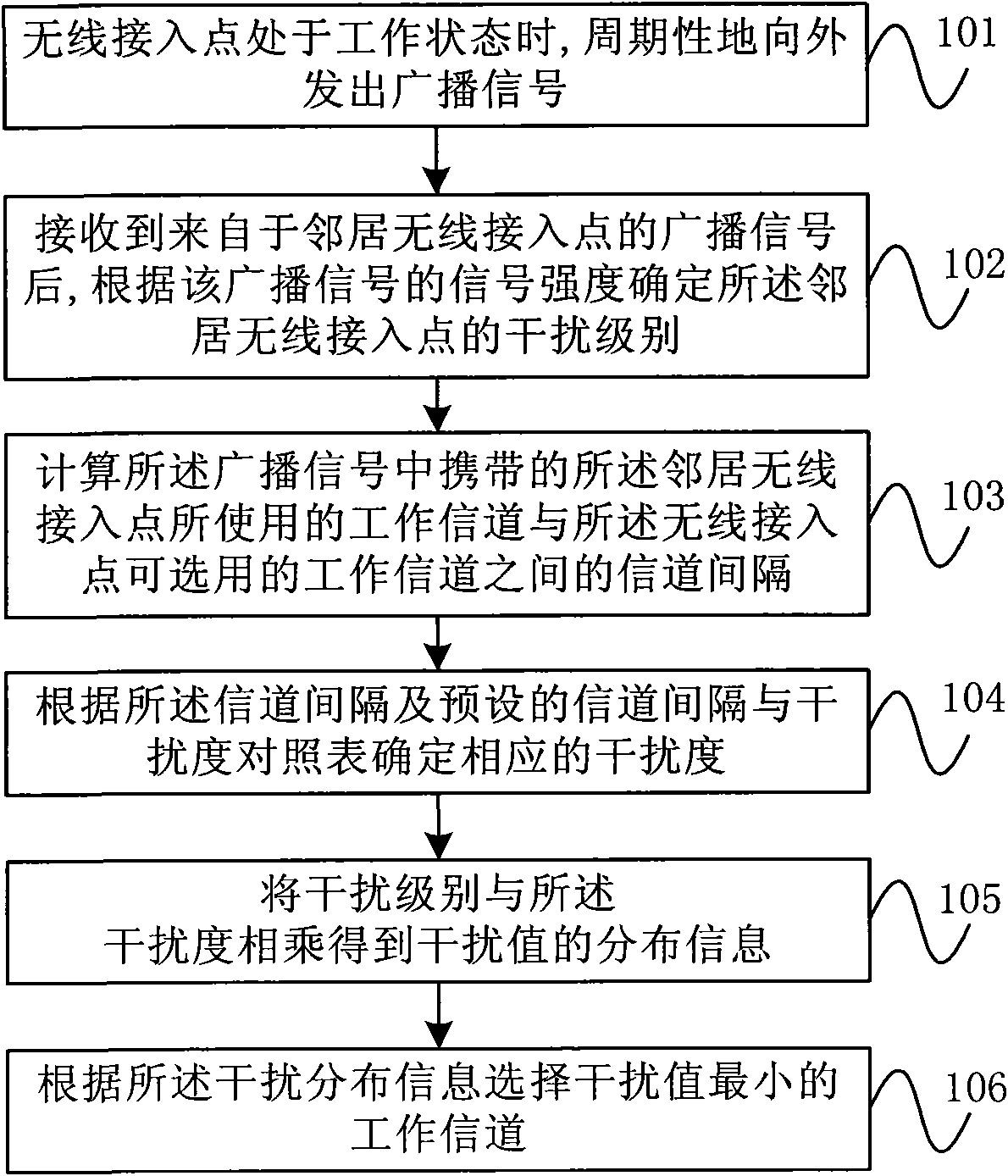
Wireless access point working channel selecting method and device
InactiveCN101835243AReduce distractionsNo need to occupyAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesSystem capacityTelecommunications
The invention provides a wireless access point working channel selecting method and a wireless access point working channel selecting device. The wireless access point working channel selecting method comprises the following steps of: periodically transmitting broadcast signals outwards from an AP which is positioned in a working state; determining the interference level of an adjacent AP according to the signal strength by the AP receiving the broadcast signals; calculating the channel spacing between the working channel used by the adjacent AP and the working channel used by the AP; determining the corresponding interference degree according to the channel spacing and the preset channel spacing and an interference degree comparison table; multiplying the interference level by the interference degree to obtain the distribution information of the interference value; and selecting the working channel with the minimum interference value according to the interference distribution information. The wireless access point working channel selecting method and the wireless access point working channel selecting device can reduce the channel interference and improve the system capacity, does not need to occupy a common channel, avoids the resource waste, can be applied to the common fat AP framework and thin AP framework in the wireless local area network simultaneously, and has wide applicability.
Owner:BEIJING XINWANG RUIJIE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
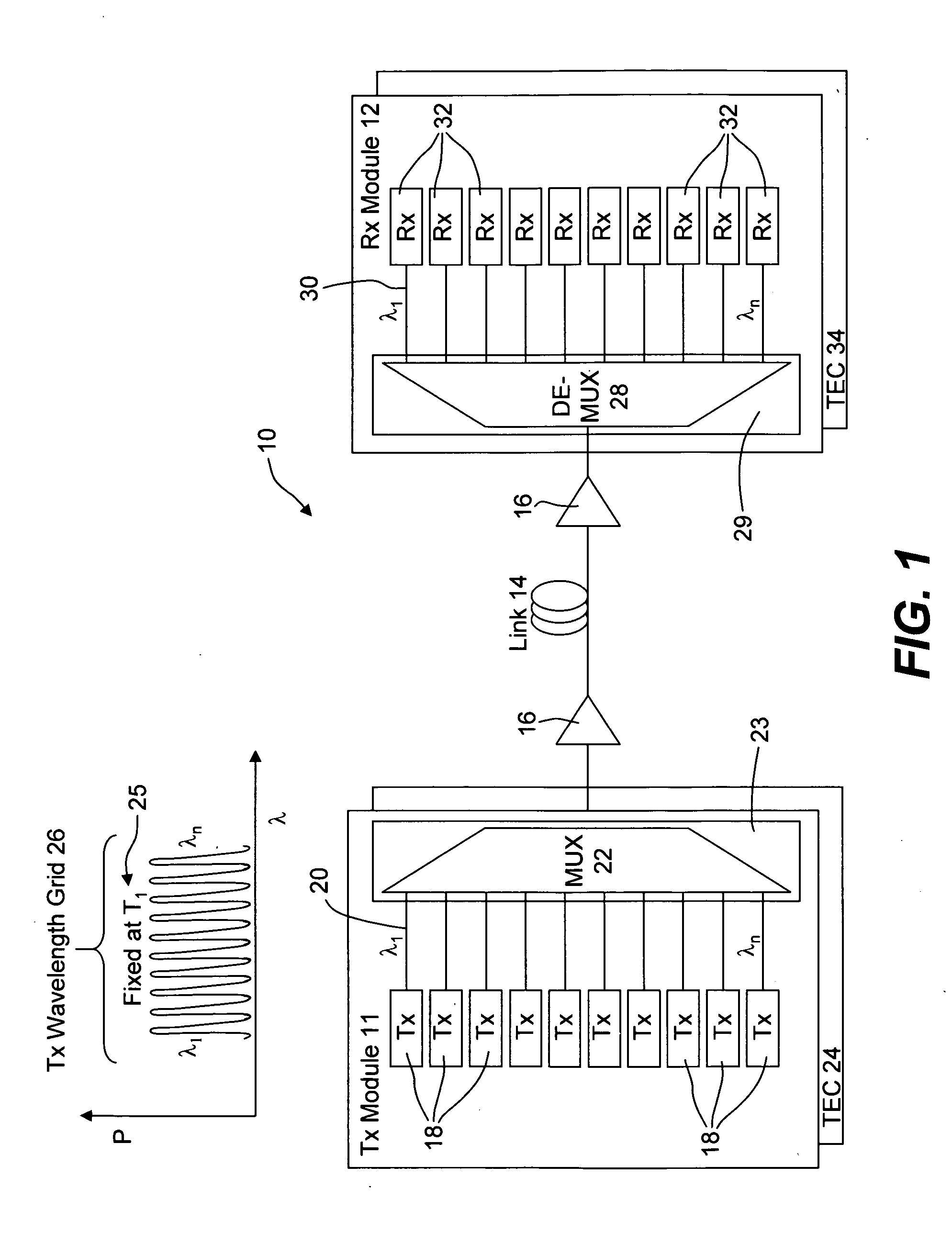
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
ActiveUS7636522B2Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorPeak value
Owner:INFINERA CORP
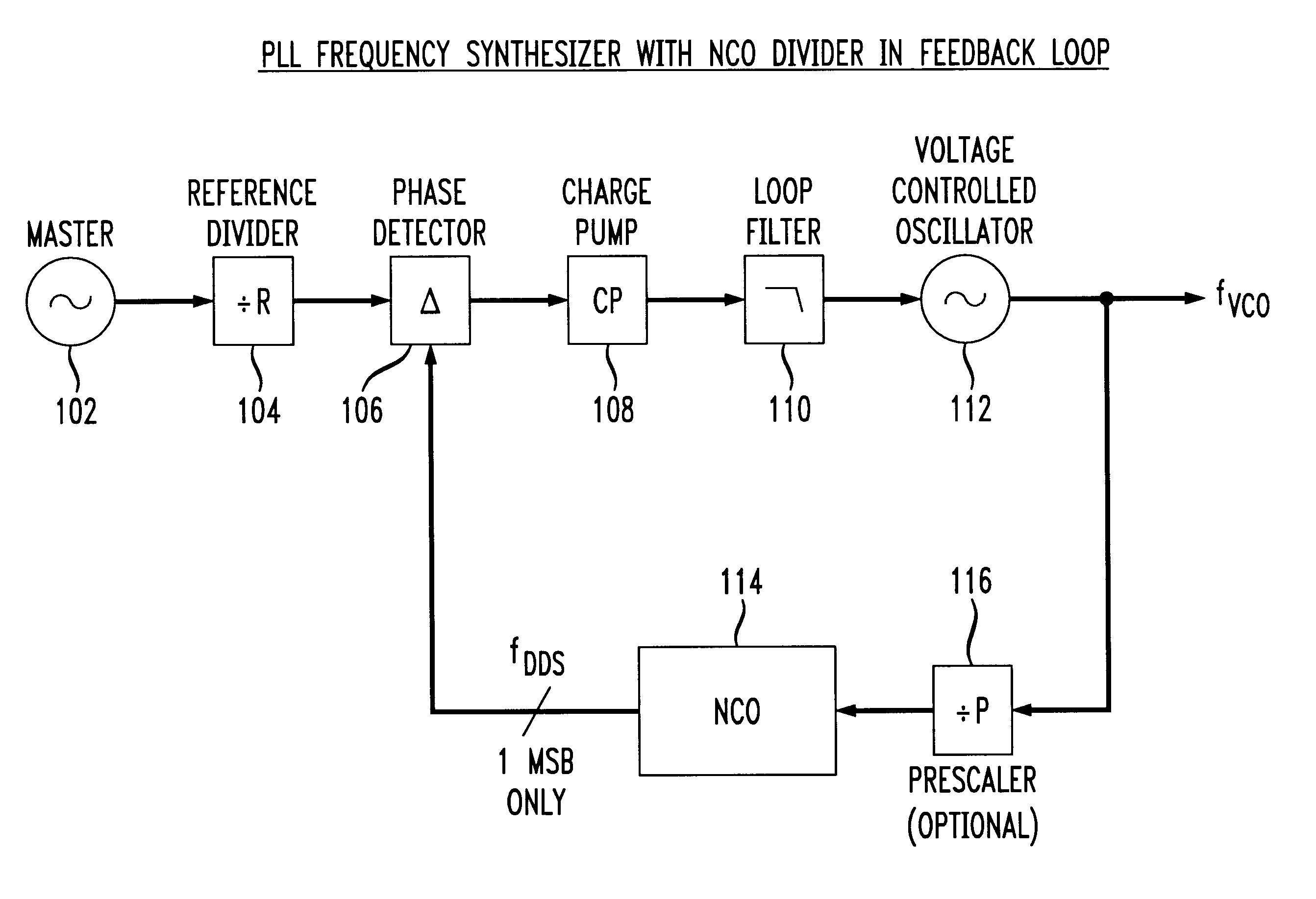
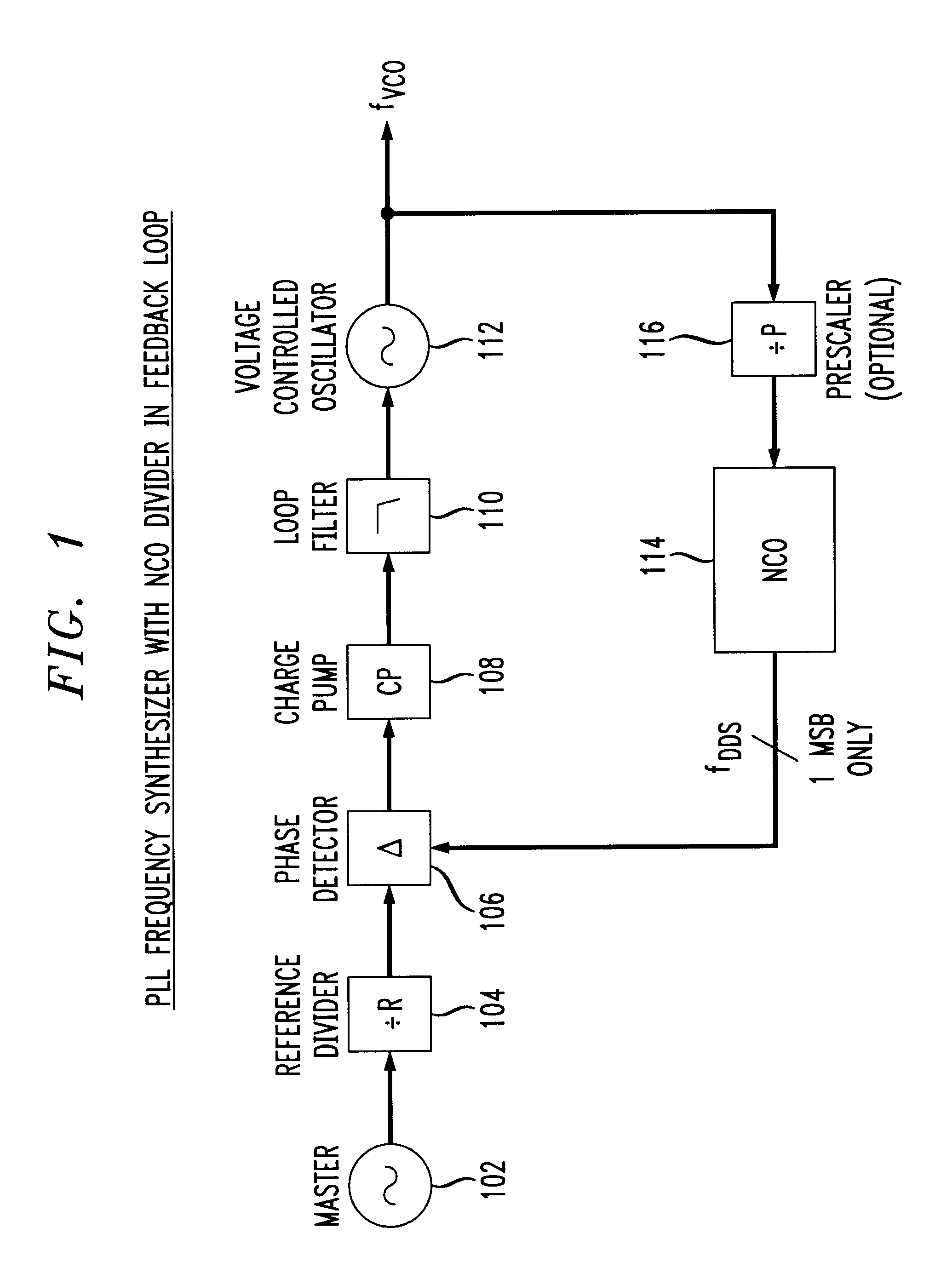
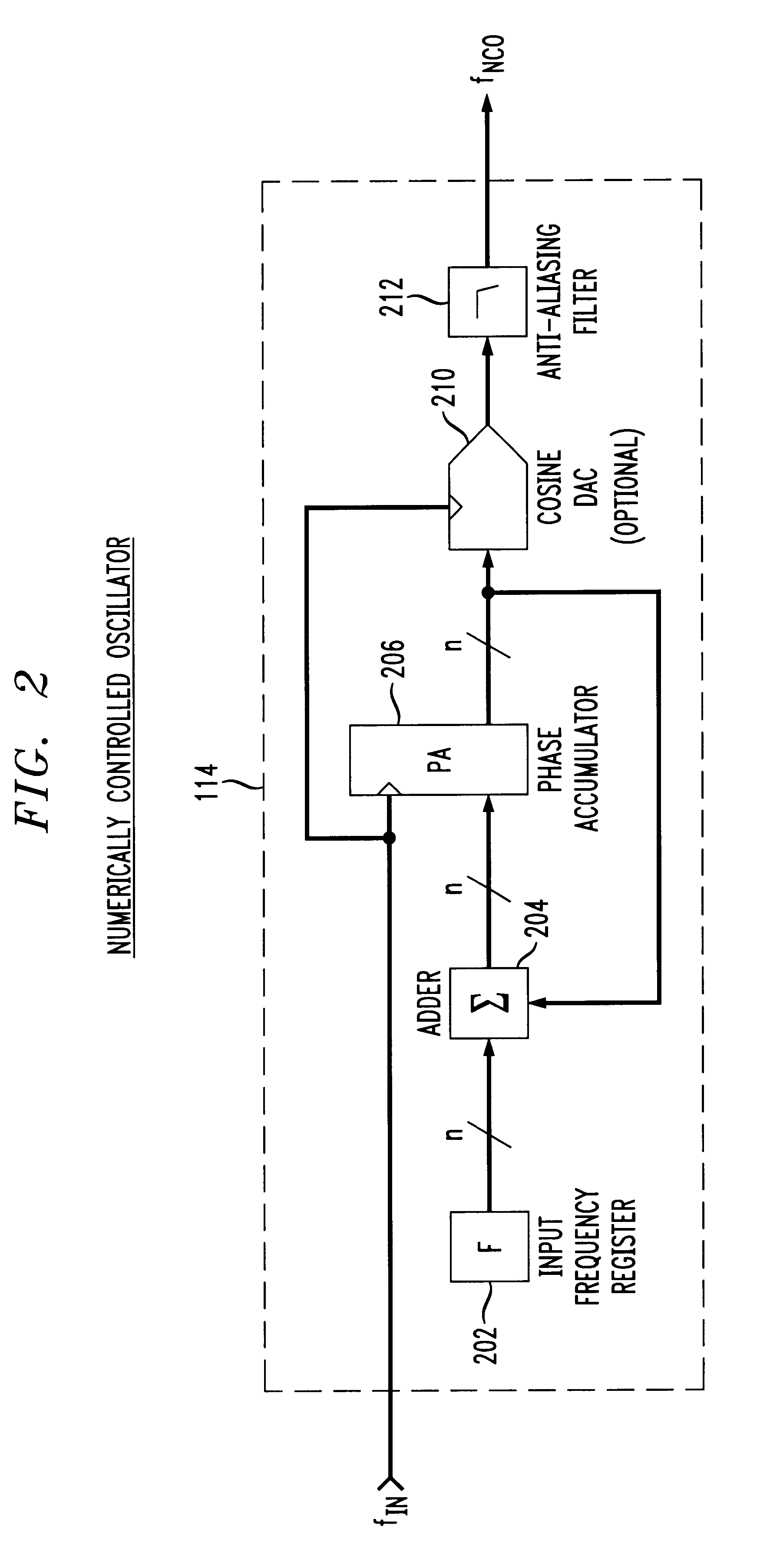
Phase locked loop with numerically controlled oscillator divider in feedback loop
A digital phase locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer includes a 1-bit numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) to negate the requirement that a VCO frequency be an integer multiple of its reference frequency. Thus, in accordance with the principles of the present invention, a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) or numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) is used to form a frequency divider in a feedback path of a PLL. Thus, a synthesizer with fine frequency control and very fast settling time is disclosed. The conventional integer-ratio relationship between the reference frequency fREF and the synthesized output frequency signal fVCO is overcome by replacement of a conventional VCO divider in a feedback path of a digital PLL with a 1-bit NCO. This allows the reference frequency fREF to be greater than the channel spacing, i.e., the channel spacing can be smaller than the reference frequency fREF. Thus, a much quicker settling time and improved VCO phase noise are provided, either of which results in a significant improvement in the performance of virtually any communications system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
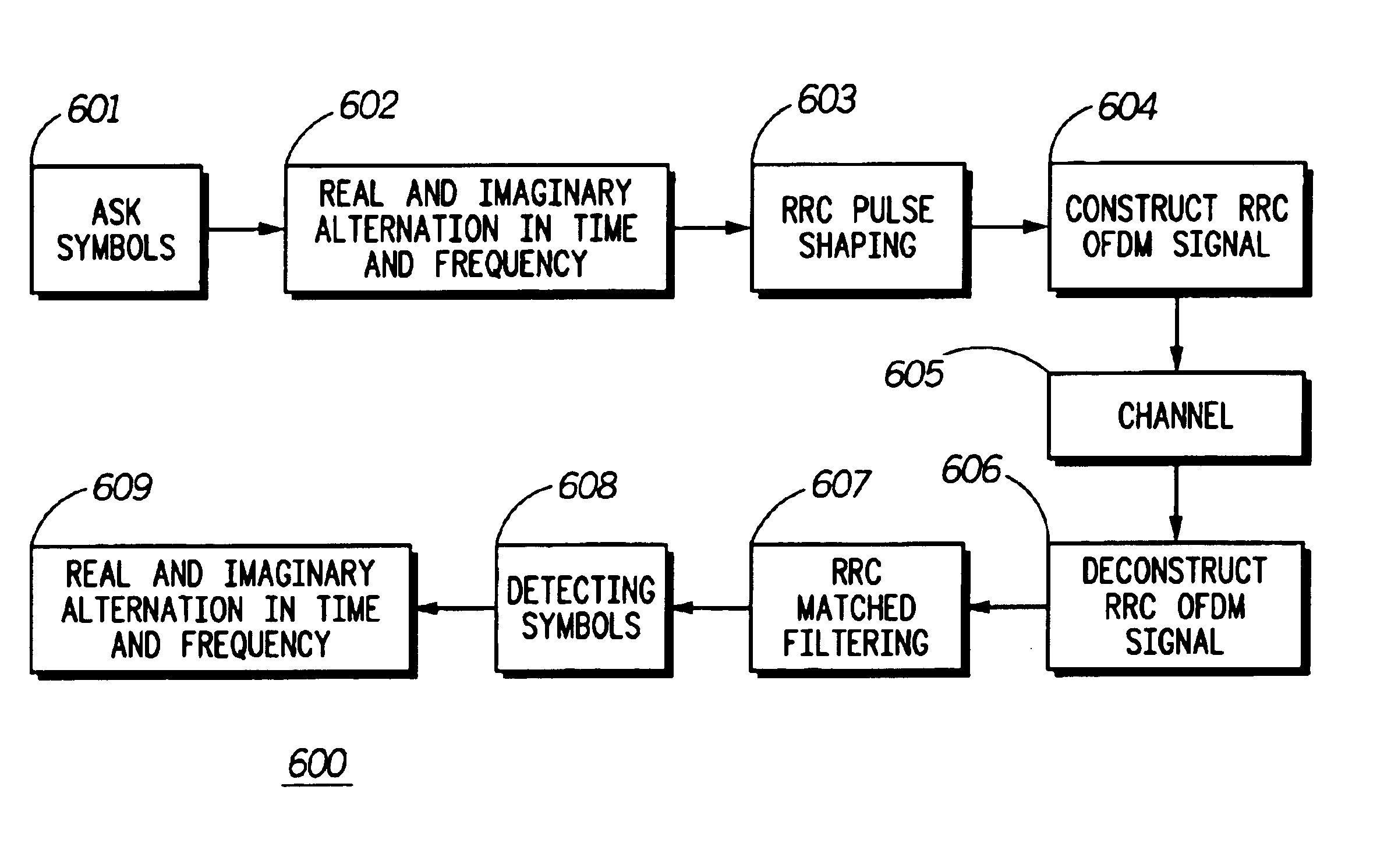
System and method for reducing adjacent channel interference (ACI) in a multicarrier modulation system
InactiveUS6934246B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyReasonable power sensitivity lossError preventionTime-division multiplexAdjacent-channel interferenceFrequency spectrum
An improved multicarrier modulation system and method, which has the advantages of both isotropic orthogonal transfer algorithm orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (IOTA OFDM) and scalable advanced modulation (SAM), is introduced. The invention is root raised cosine (RRC) OFDM using the most spectrally efficient RRC filter without sacrificing the compact subchannel spacing of OFDM. The invention further provides an adjacent channel interference (ACI) suppression scheme and a modified RRC for better suppressing ACI of RRC OFDM. The ACI suppression scheme can also be applied to SAM with the modified RRC and to IOTA OFDM with a modified IOTA. The invention greatly improves a major problem of conventional OFDM namely ACI due to the use of a wide subchannel filter. Thus, the invention allows OFDM to meet even the strictest ACI requirements, which was not possible by using a conventional raised cosine windowing method.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Flex spectrum wss
ActiveUS20090028503A1Eliminate the effects ofEffective and flexible and highly methodCoupling light guidesFrequency spectrumLight beam
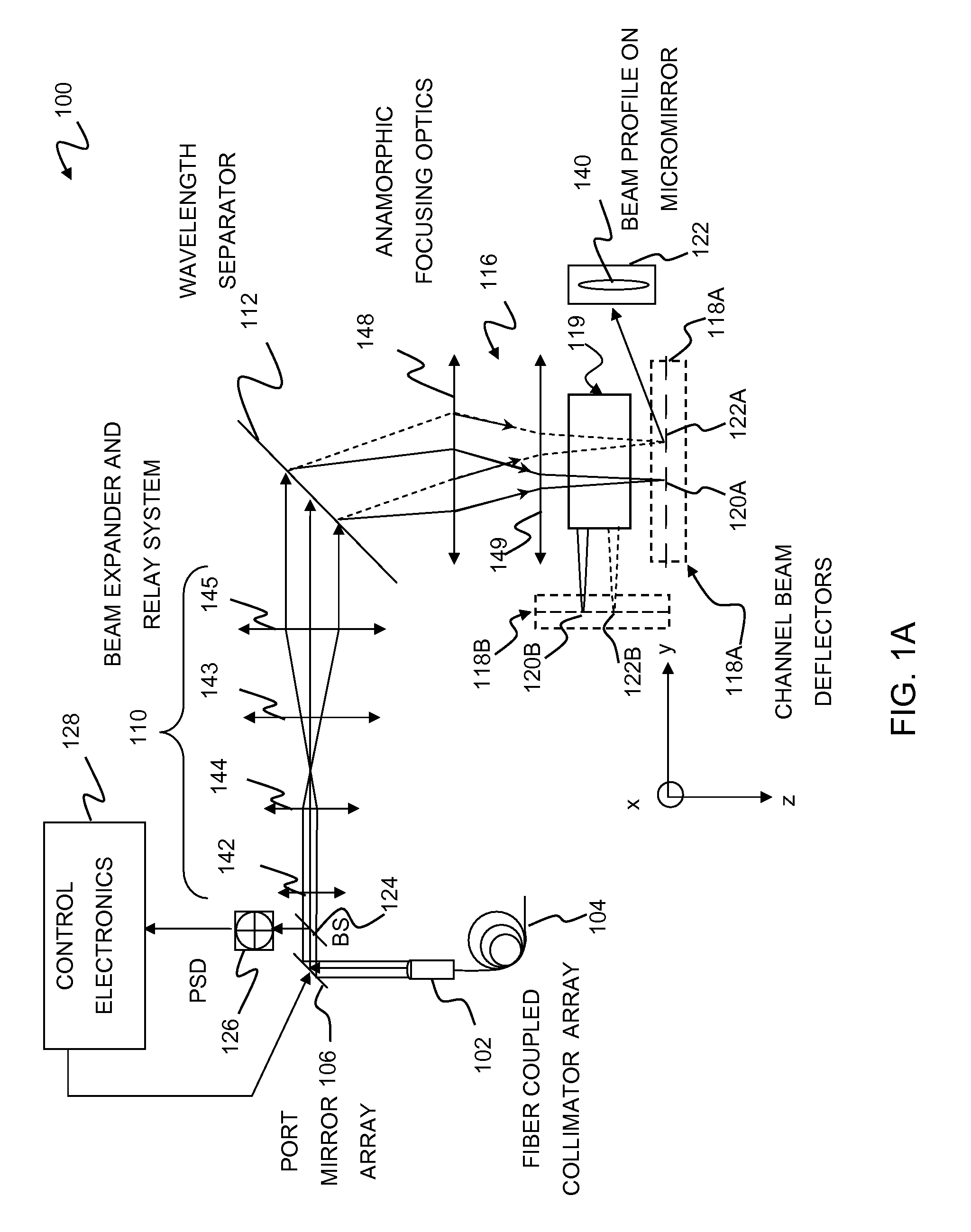
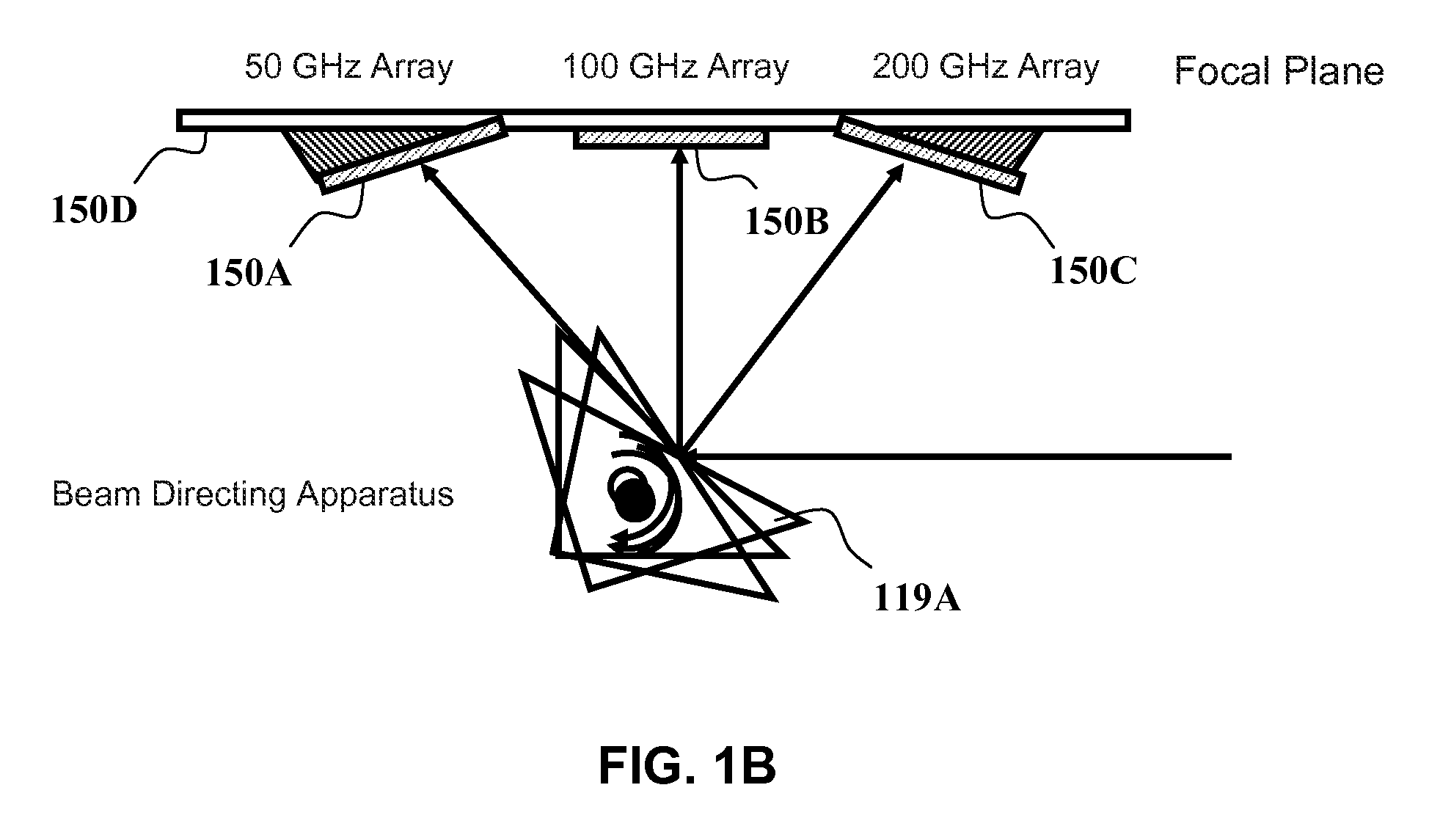
Switching optical signals containing a plurality of spectral channels characterized by a predetermined channel spacing is described. A selected beam deflector array may be selected from among a plurality of available beam deflector arrays configured to accommodate spectral channels of different channel spacings. The selected beam deflector array is configured to accommodate spectral channels of the predetermined channel spacing. The spectral channels are selectively optically coupled to the selected beam deflector array, which selectively optically couples the spectral channels between one or more input ports and one or more output ports.
Owner:CAPELLA PHOTONICS INC
Configurable pitch reducing optical fiber array
The inventive optical fiber coupler array is capable of providing a low loss, high-coupling coefficient interface with high accuracy and easy alignment between a plurality of optical fibers (or other optical devices) with a first channel-to-channel spacing, and an optical device having a plurality of closely-spaced waveguide interfaces with a second channel-to-channel spacing, where each end of the optical fiber coupler array is configurable to have different channel-to-channel spacing, each matched to a corresponding one of the first and second channel-to-channel spacing. The novel optical coupler array includes a plurality of waveguides (at least one of which may optionally be polarization maintaining), that comprises at least one gradually reduced vanishing core fiber, at least in part embedded within a common housing structure. Alternatively, the novel coupler array may be configured for utilization with at least one of an optical fiber amplifier and an optical fiber laser.
Owner:CHIRAL PHOTONICS
Simplified high frequency tuner and tuning method
InactiveUS7116963B2Reduce frequencyLow processing rateFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationTransmission noise suppressionLocal oscillator signalFrequency spectrum
A disclosed method tunes a signal from a channelized spectrum having a predetermined channel spacing. A signal of interest having a predetermined maximum bandwidth is mixed with a local oscillator signal, which has a frequency that is an integer multiple of the channel spacing or one-half of a channel spacing displaced from an integer multiple of the channel spacing. The local oscillator signal is selected to frequency translate the signal of interest to within a near-baseband passband whose lower edge is spaced from DC by at least about the maximum bandwidth of the signal of interest. Problems associated with 1 / f noise, DC offsets, and self-mixing products are avoided or substantially diminished. Other methods and systems are also disclosed.
Owner:WASHINGTON RES FOUND
Nanotechnology-enabled optoelectronics
Nanomaterials for use in optoelectronic applications, and particularly nanocomposite optical amplifiers. nanocomposite optical amplifiers (NOAs), e.g., provided on integrated optical chips, for cost-effective broadband amplification across the entire clear-window of optical fiber. It is expected that such systems could provide a 15× increase in bandwidth over existing technology, while remaining compatible with all future advances in bit-rate and channel spacing.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Cost-effective multi-channel quadrature amplitude modulation
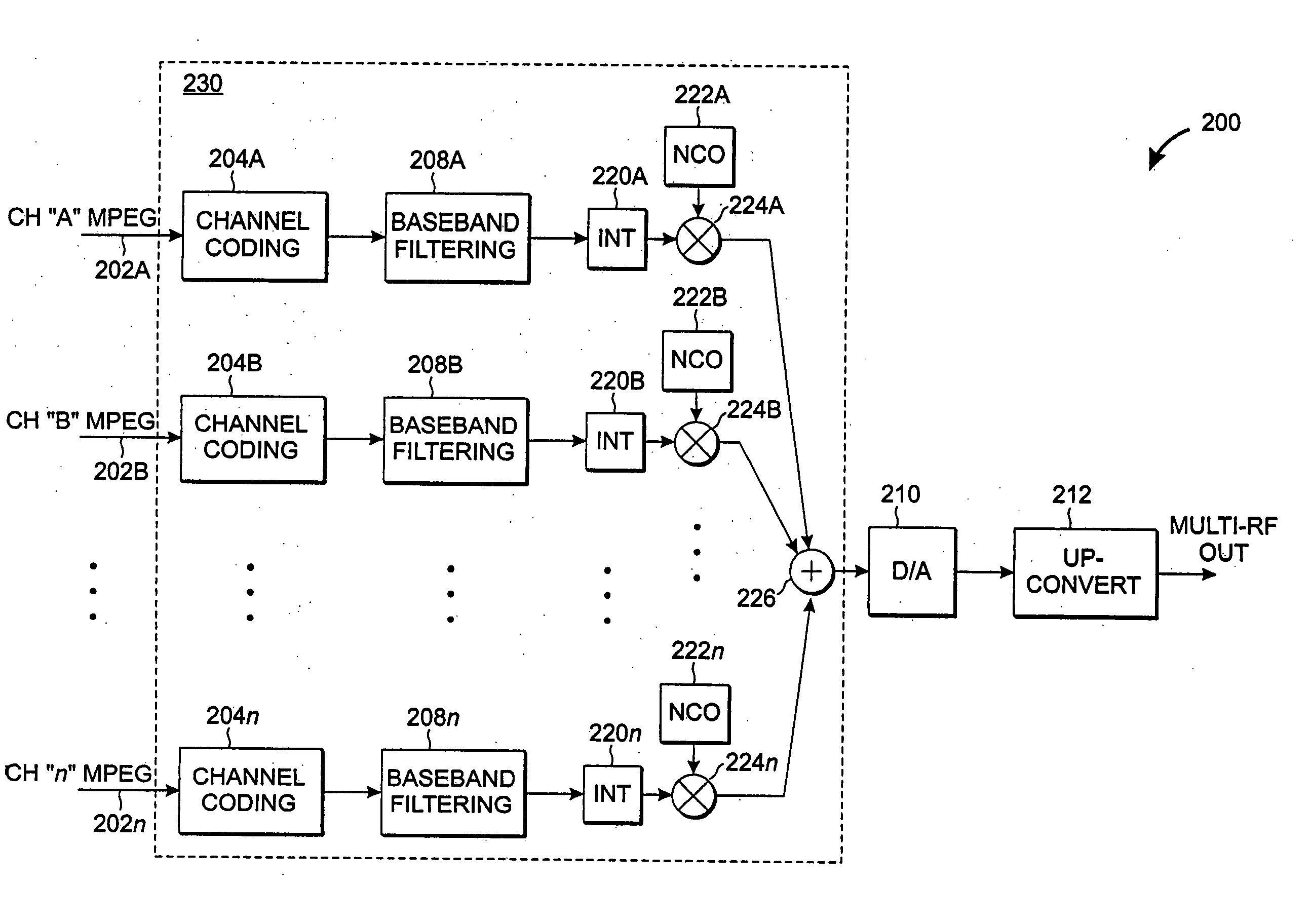
A highly-efficient, cost-effective technique for multi-channel QAM modulation is described. The technique employs an inverse fast-Fourier transform (IFFT) as a multi-channel modulator. QAM encoding expresses QAM symbols as constellation points in the complex plane such that each QAM symbol represents a specific phase and amplitude of a carrier frequency to which it is applied. In multi-channel systems, the carrier frequencies are generally uniformly spaced at a channel-spacing frequency (6 MHz, for digital cable systems in the United States). The IFFT accepts a set of complex frequency inputs, each representing the complex frequency specification (i.e., phase and amplitude) of a particular frequency. The inputs are all uniformly spaced, so assuming that the IFFT is sampled at a rate to provide the appropriate frequency spacing between its frequency-domain inputs, the IFFT will produce a time domain representation of QAM symbols applied to its various inputs modulated onto carriers with the desired channel separation. Since the channel spacing and the symbol rate are different due to excess channel bandwidth, interpolation is used to rectify the difference. An efficient scheme for combining this interpolation with baseband filtering and anti-imaging filtering is described.
Owner:RGB NETWORKS
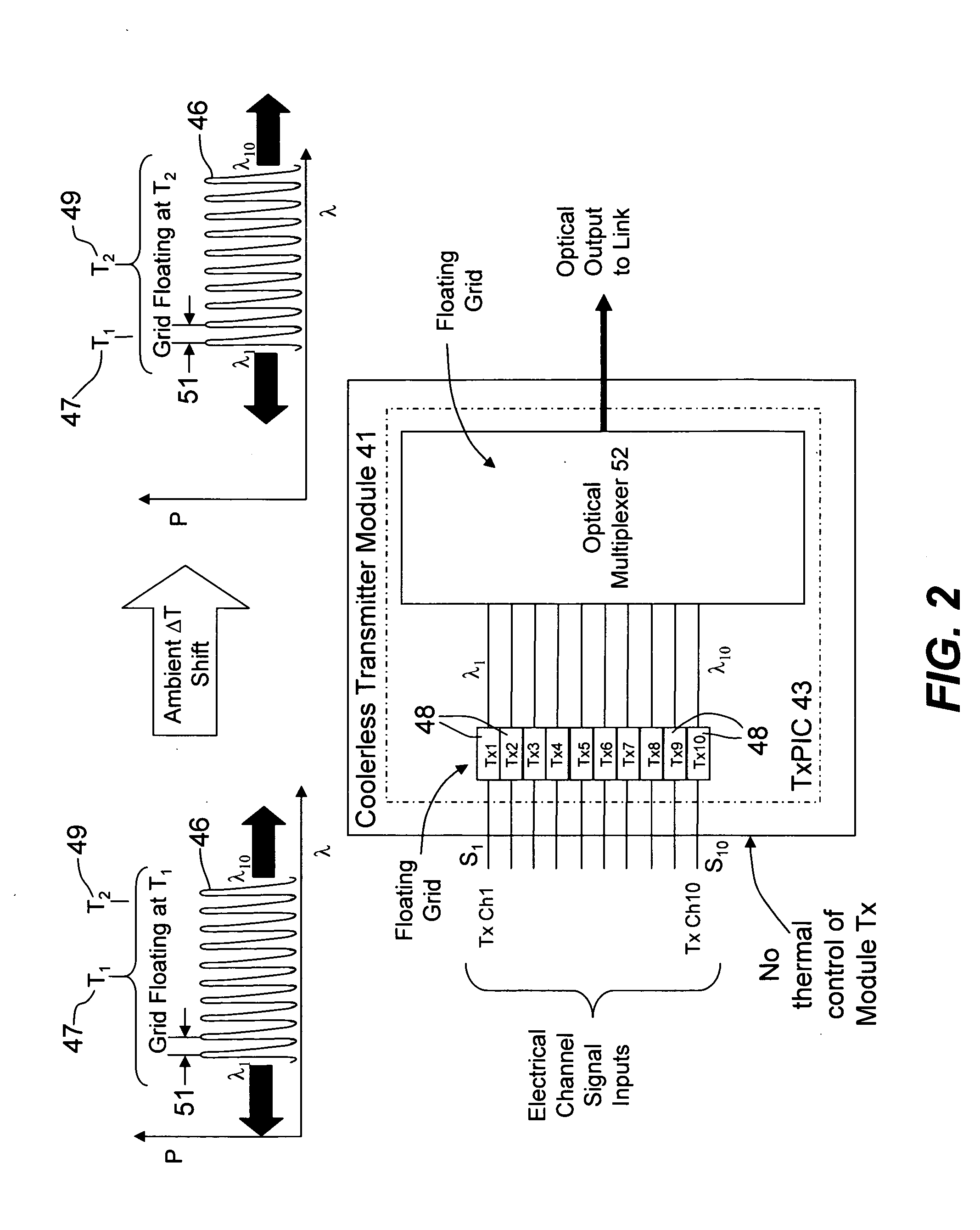
Thermally-floating transmitter wavelength grid of signal channels in a WDM transmission system
ActiveUS20060088319A1Fixed spacingControl eliminatedWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionWdm transmission systemsEngineering
A method and apparatus is provided for tracking a thermally floating wavelength signal channel grid generated at an optical transmitter (Tx) in an optical transmission system or optical network where the wavelengths of the individual Tx signal channels may move in wavelength due to, for example, changes in ambient temperature at the optical transmitter but the channel spacing between Tx signal channels along the thermally floating Tx wavelength grid remains constant. An optical receiver (Rx) is provided that has a demultiplexed signal channel grid that may have a different channel spacing from that of the floating Tx wavelength grid, that is either larger, the same as, or smaller Rx grid spacing compared to the Tx grid spacing, and includes a number of demultiplexed channel signal outputs along an Rx channel grid in excess of the number of Tx signal channels on the Tx channel grid so that the optical receiver is capable of detecting the floating Tx channel grid and providing electrical output signals representative of the Tx channel signals transported over the optical network.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Receiver and method for a multichannel optical communication system
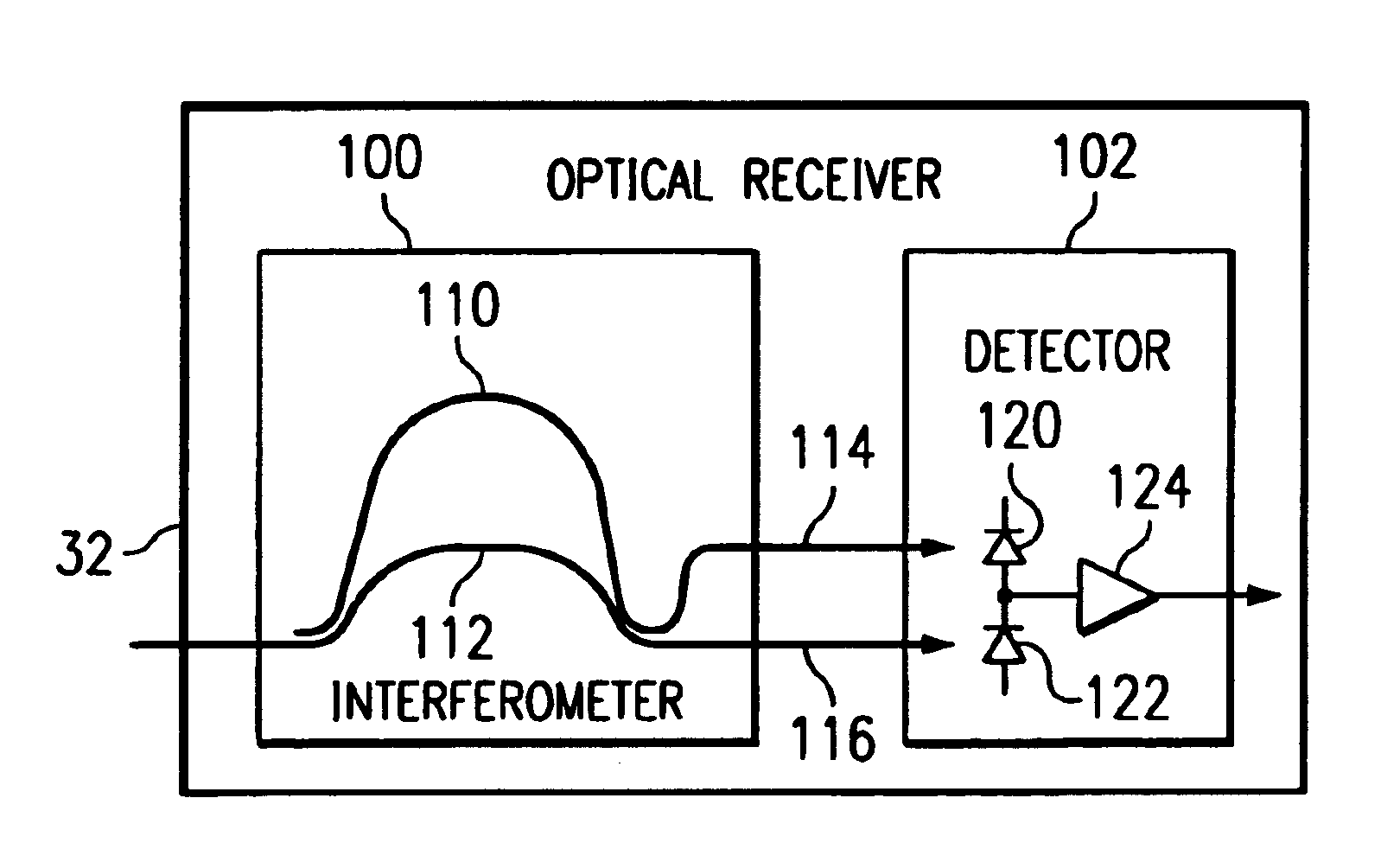
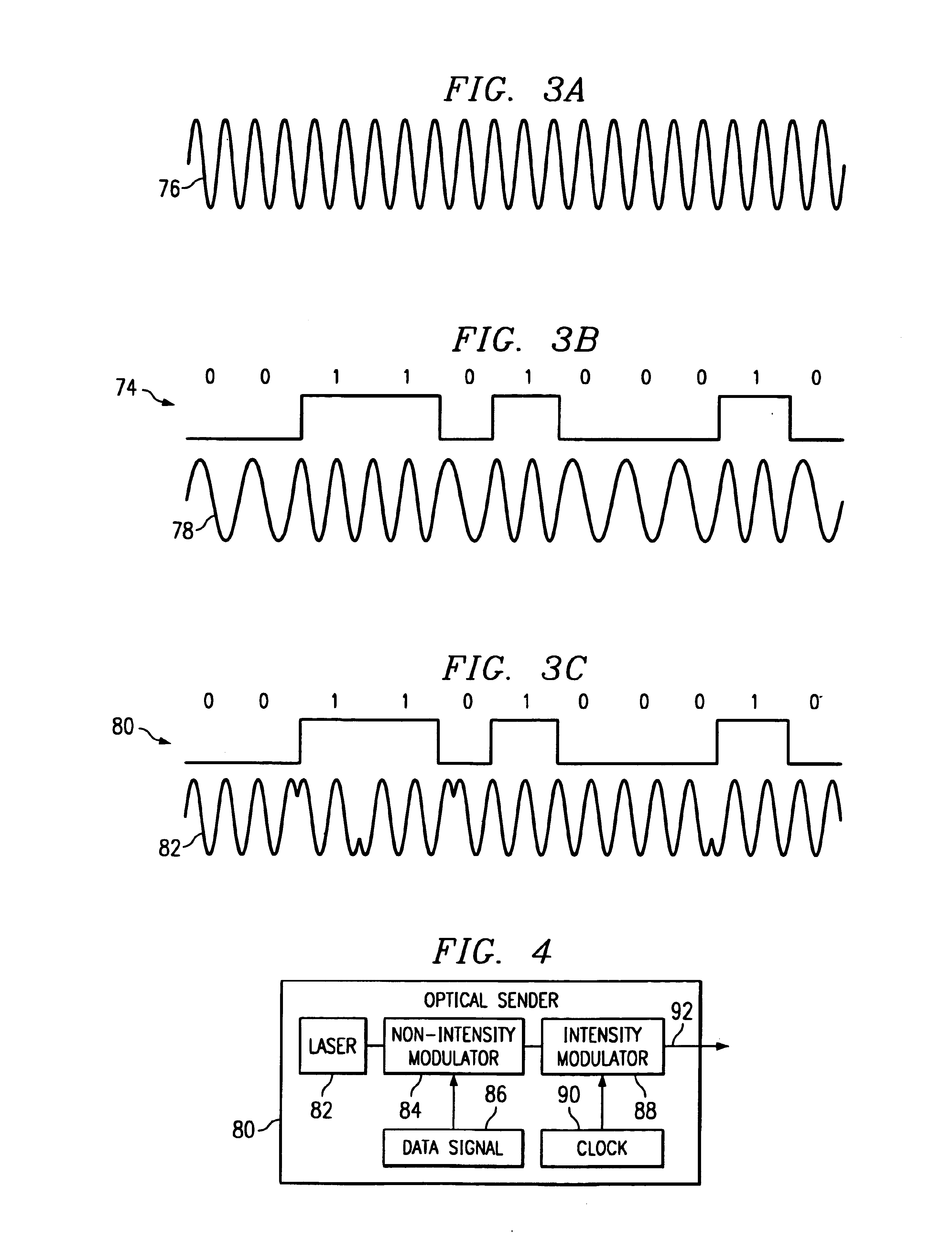
InactiveUS7200344B1Reduce and eliminate and disadvantageReduce and eliminate problemWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersCommunications systemData signal
A method and system for transmitting information in a wavelength division multiplex (WDM) or other suitable multichannel optical communication system includes receiving a multichannel signal having a symbol rate and comprising a plurality of non-intensity modulated optical information signals. The non-intensity modulated optical information signals have a minimum channel spacing comprising a multiple of the symbol rate within 0.4 to 0.6 of an integer. The non-intensity modulated optical information signals are separated from the multichannel signal and each converted into an intensity modulated optical information signal using an asymmetric interferometer. A data signal is recovered from the intensity modulated optical information signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Multi-frequency band receiver for RF signal
The present invention relates to a receiver device comprising a receiver (104) adapted to receive radio signals in two frequency bands (FB1, FB2). The radio signals in one of the frequency bands (FB1) constitute communication signals for a radio system (AMPS, NMT) having a certain channel spacing, whereas the radio signals of the second frequency band (FB2) constitutes communication signals for a second radio system (PCS1900, DCS1800, GSM) having a second certain channel spacing. The receiver (104) comprises two inputs (108, 11) each intended for a radio system having different frequency bands and channel spacing. For radio signals occurring on one input (108), mixing is performed from the RF range directly to the baseband frequency range. For radio signals occurring on the second input (108) the mixing from the radio frequency range to the baseband frequency range is carried out through an intermediate frequency range. Further the receiver (104) comprises an output (112) intended to deliver baseband signals for both radio systems. The output (112) is connected to a baseband unit which is common to the radio systems. In the baseband unit, among other things, lowpass filtering, detection and neighbouring channel suppression are performed on the received radio signal that has been mixed down to the baseband frequency range.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
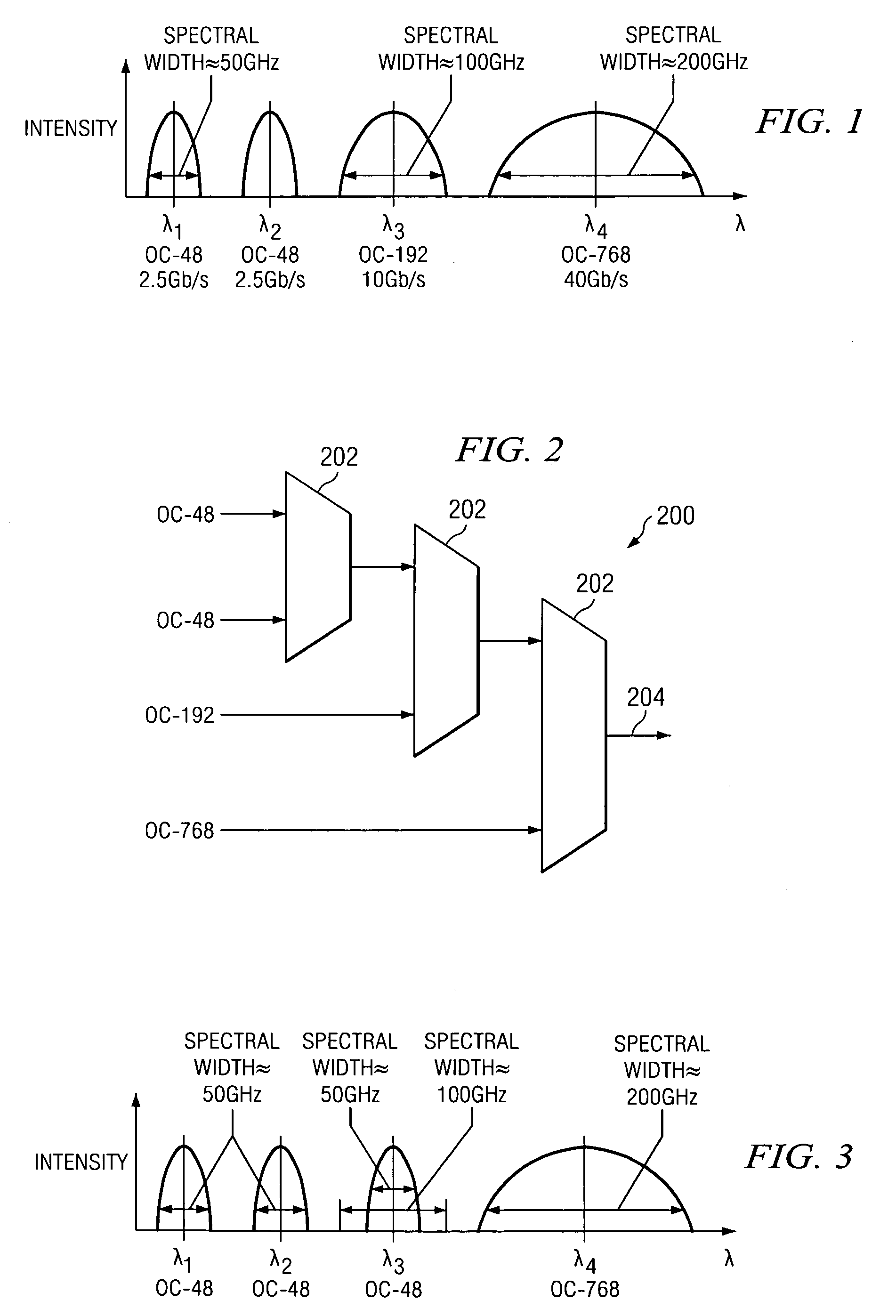
Tunable channel spacing for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) transport system
InactiveUS7092642B2Efficient use ofEasy to transportWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
A method and system for tuning channel spacing for a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) transport system includes determining a spectrum width for a channel. A bandwidth of a group of base channels covering the spectrum width for the channel is allocated to the channel. A passband of a channel filter at a center frequency of the group is adjusted to correspond to the spectrum width of the channel.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
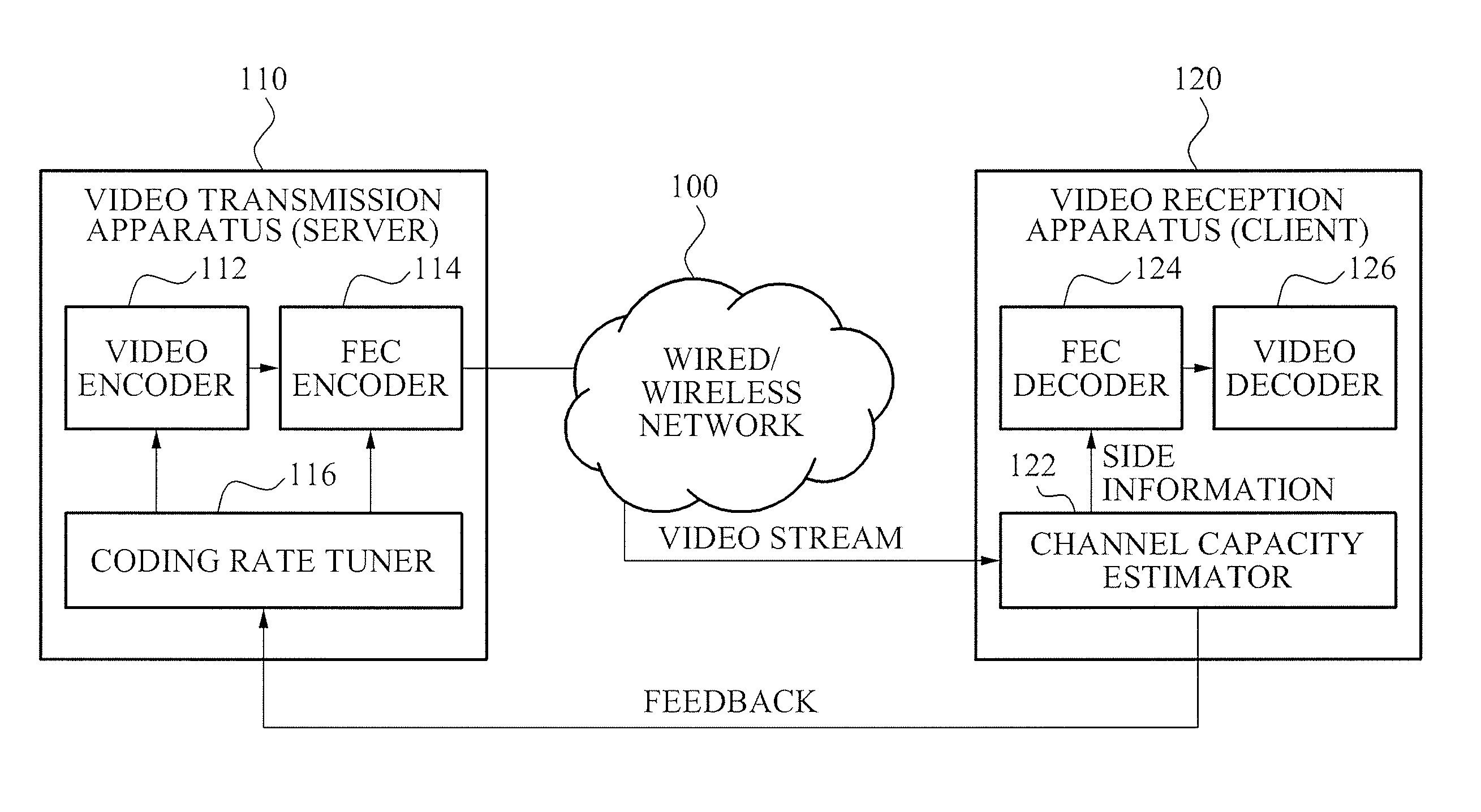
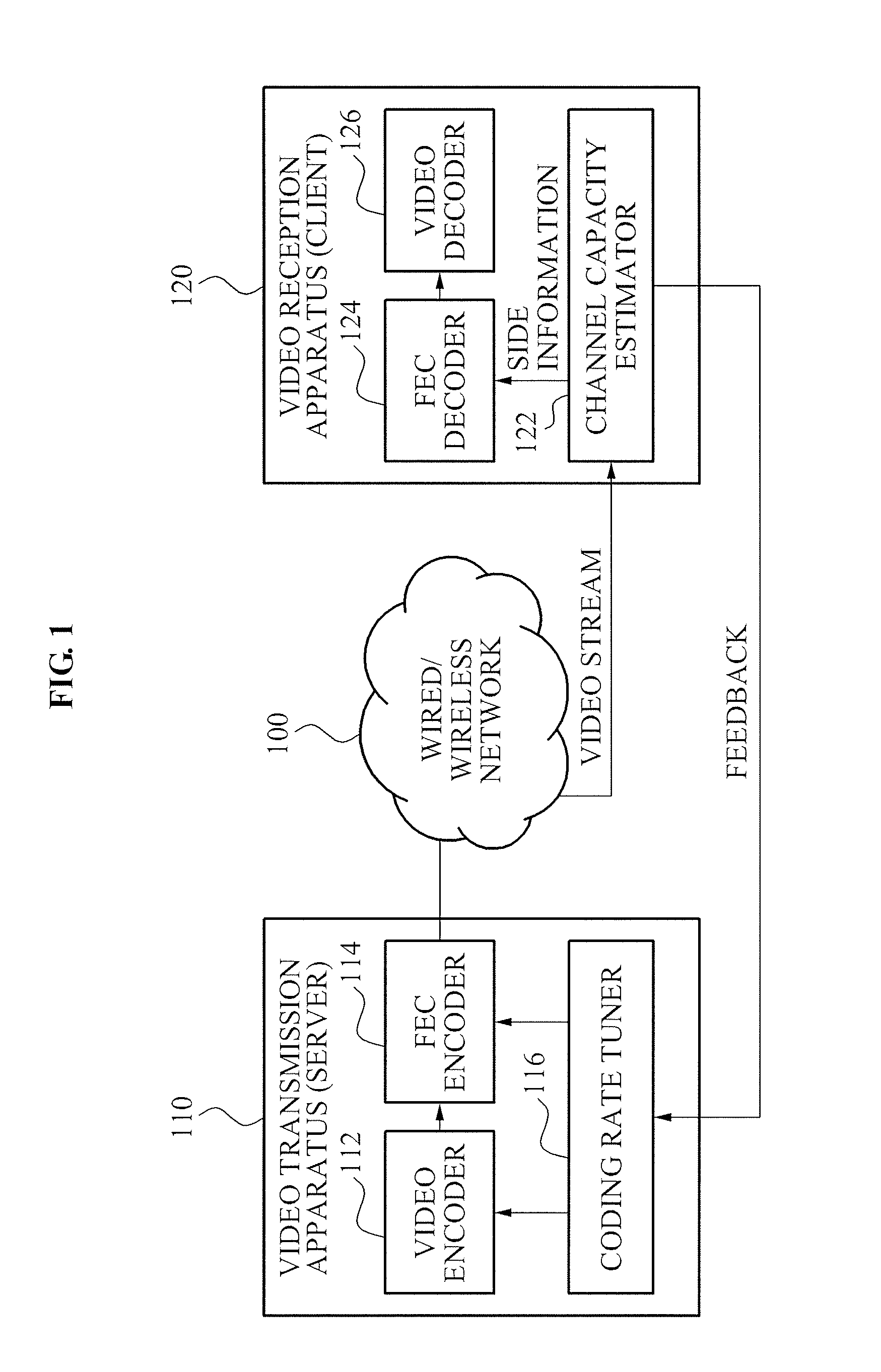
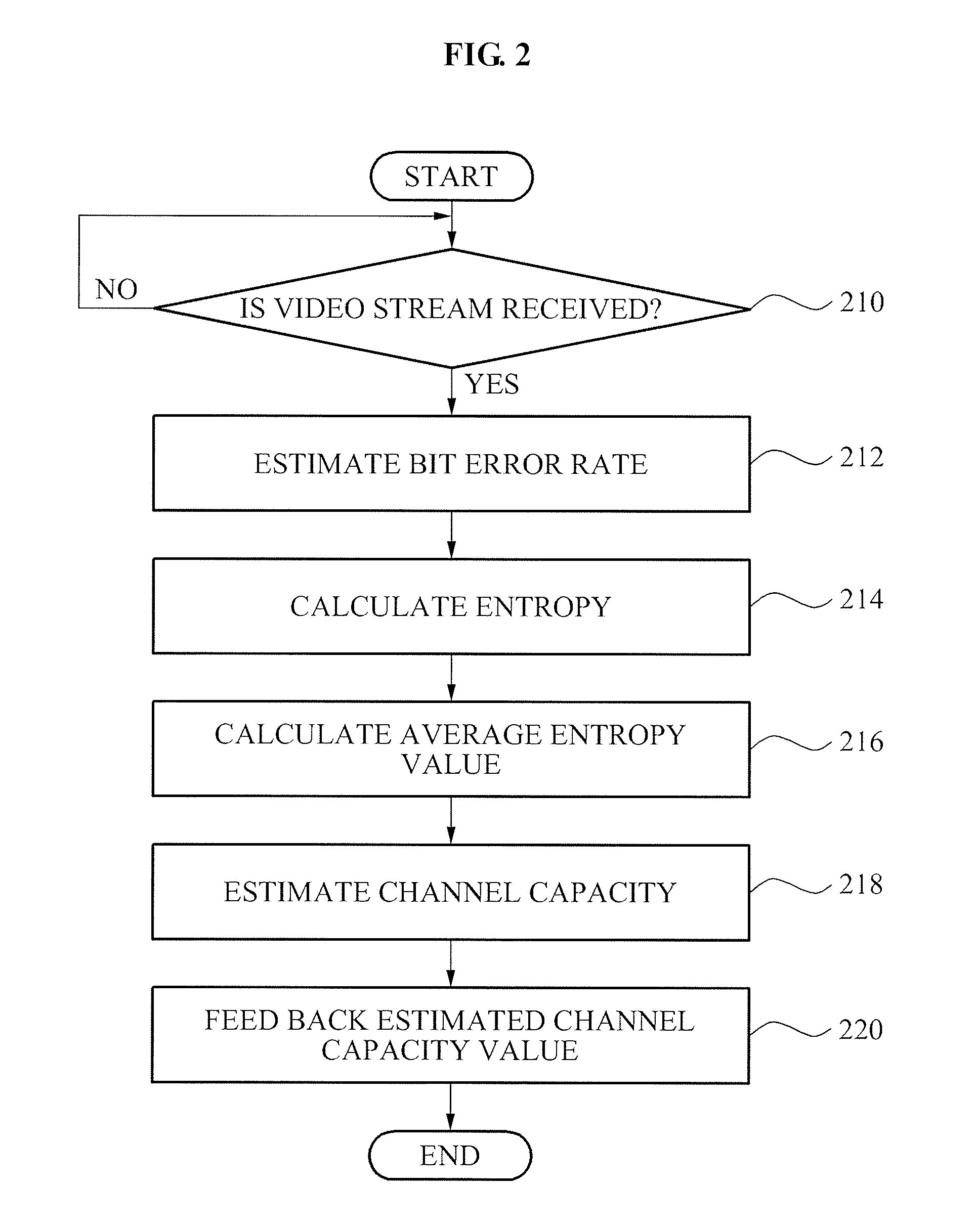
Method for tuning coding rate and applying unequal error protection for adaptive video transmission, and video transmission/reception apparatus using the method
InactiveUS20100171882A1Increase success rateEasy to tuneTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationComputer hardwareVideo transmission
Provided are a method of tuning a coding rate and applying an unequal error protection for an adaptive video transmission, and a video transmission / reception apparatus using the method. The video transmission apparatus may include: a coding rate tuner to predict, as a channel capacity of a subsequent channel interval, an estimated channel capacity value fed back from the video reception apparatus, and to tune video and channel coding rates within the predicted channel capacity; a video encoder to perform video encoding of video frames at the tuned video coding rate, and to generate a video packet; and a forward error correction (FEC) encoder to apply the unequal error protection based on a length of the video packet and a type of the video frames included in the video packet, and to perform channel encoding of the video packet at the tuned channel coding rate to generate a bitstream.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
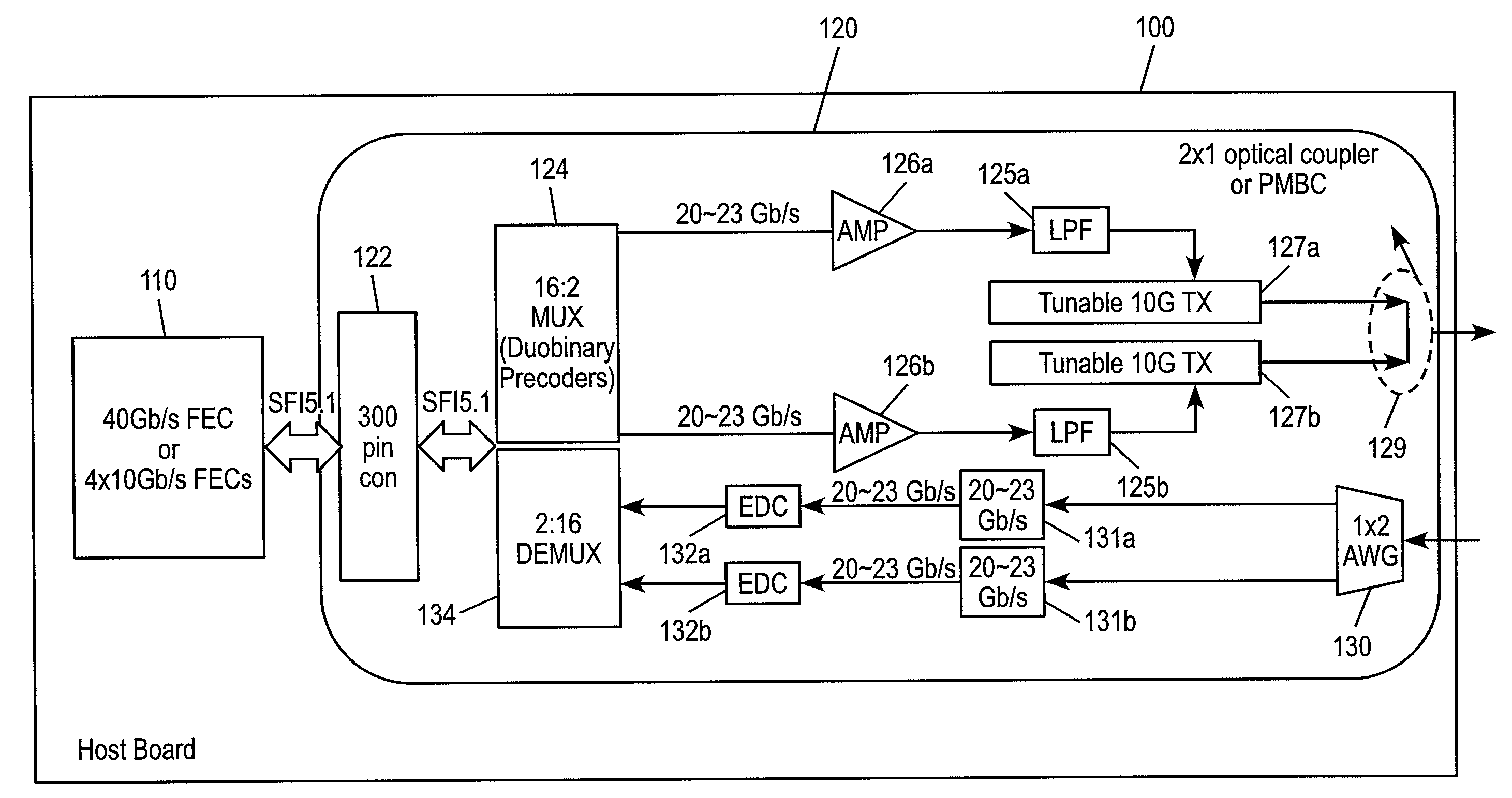
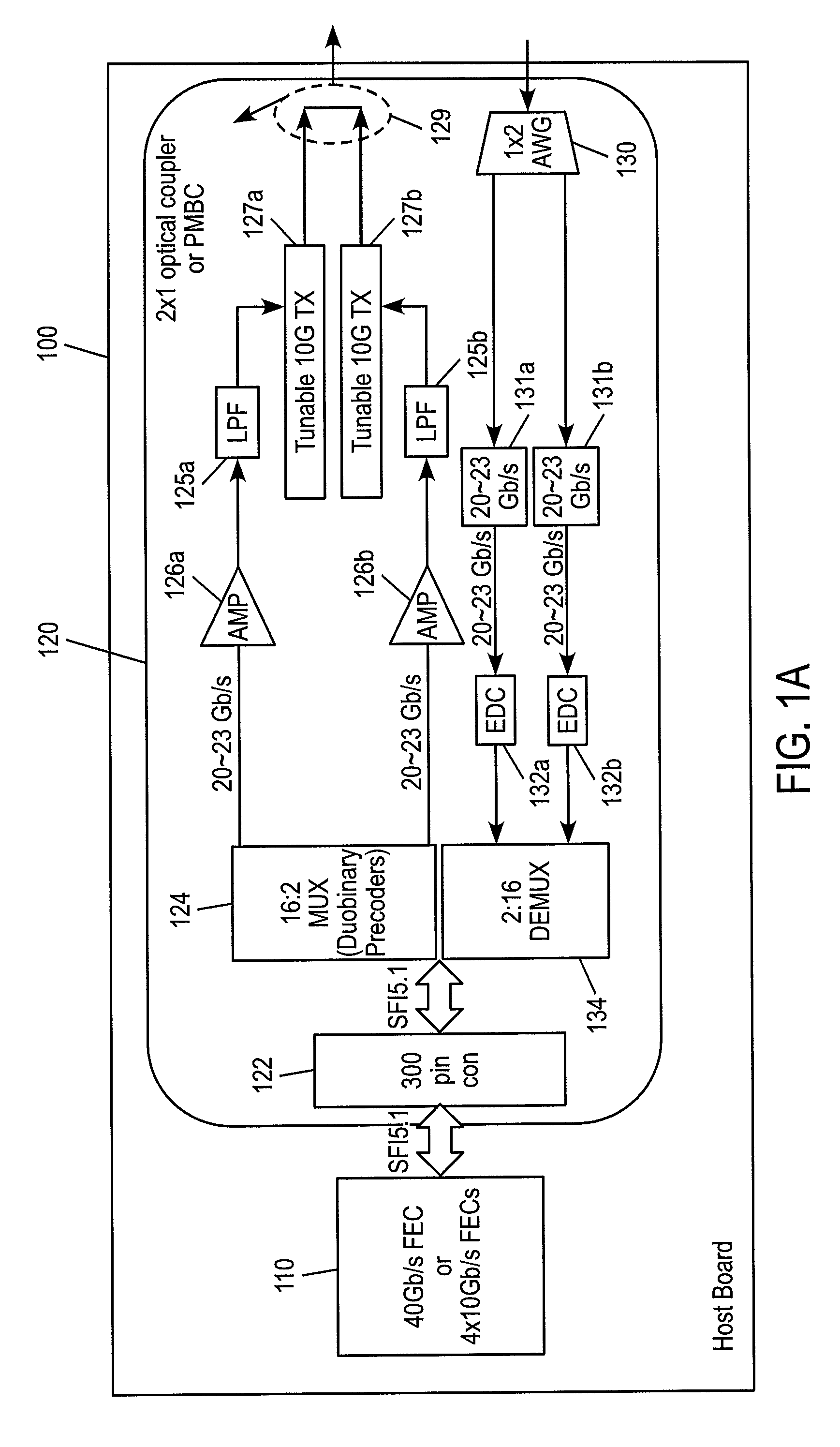
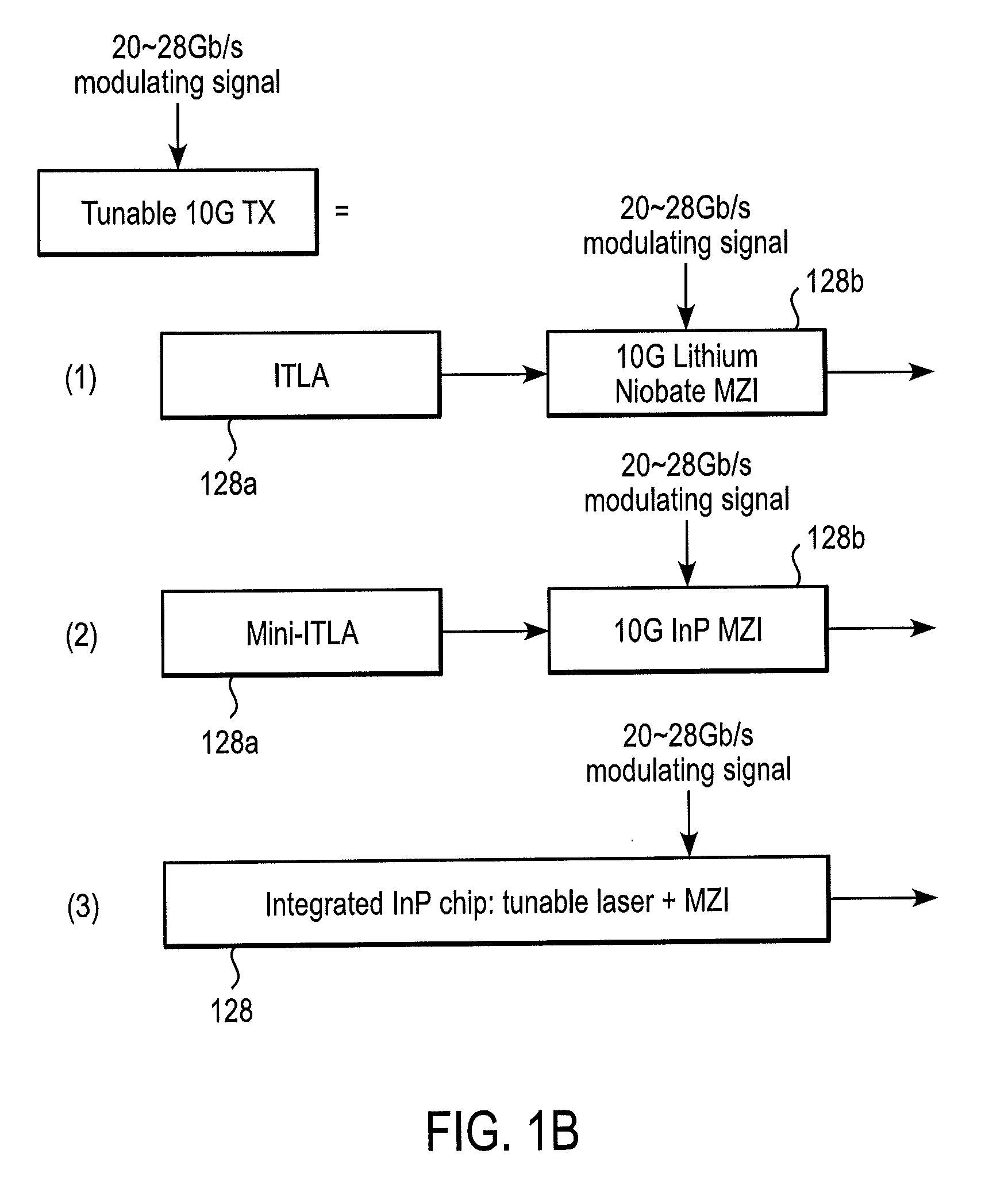
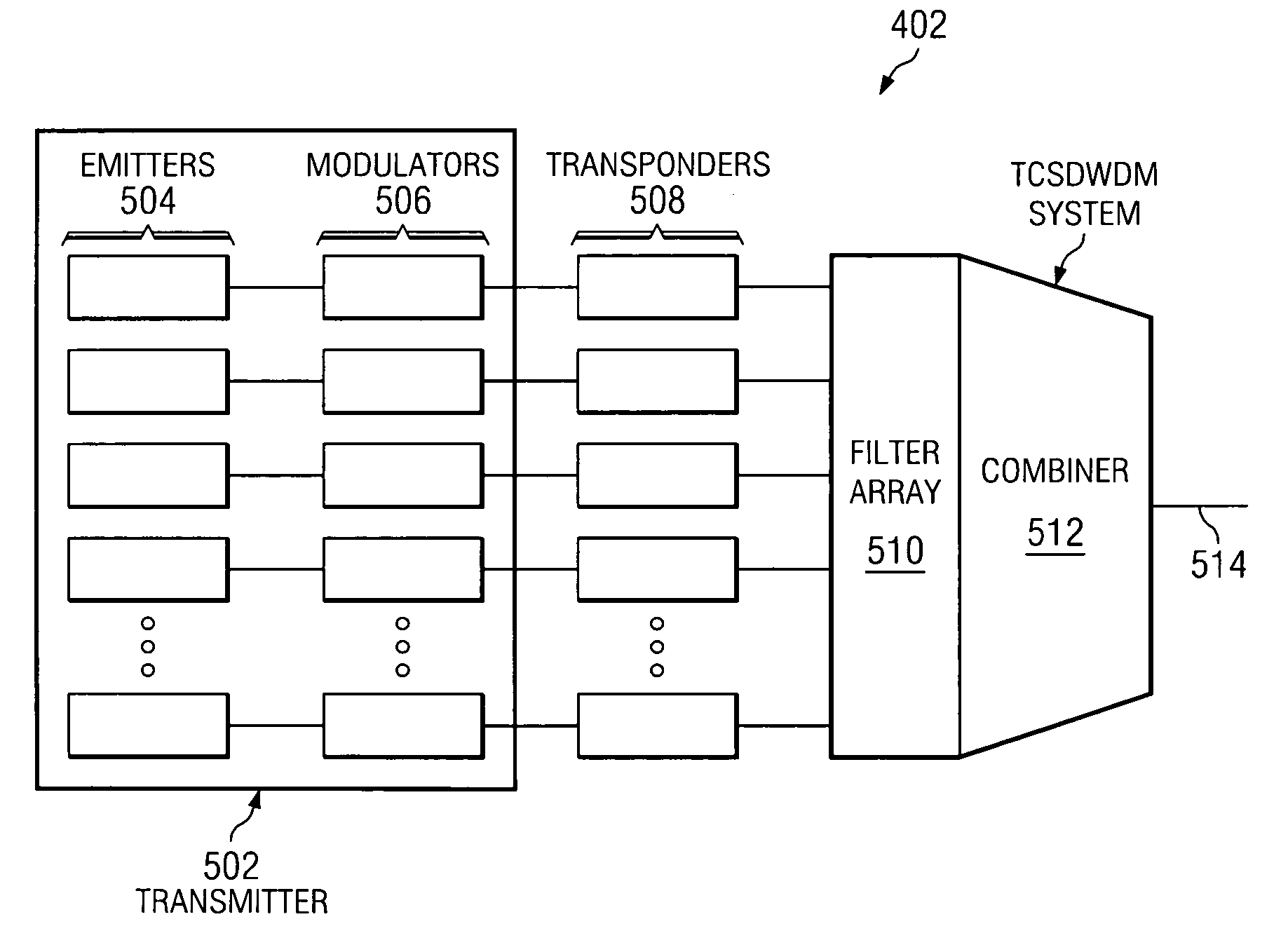
40, 50 and 100 GB/S OPTICAL TRANSCEIVERS/TRANSPONDERS IN 300PIN AND CFP MSA MODULES
ActiveUS20100322632A1Low costFast traffic recoveryWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversTransceiverHardware architecture
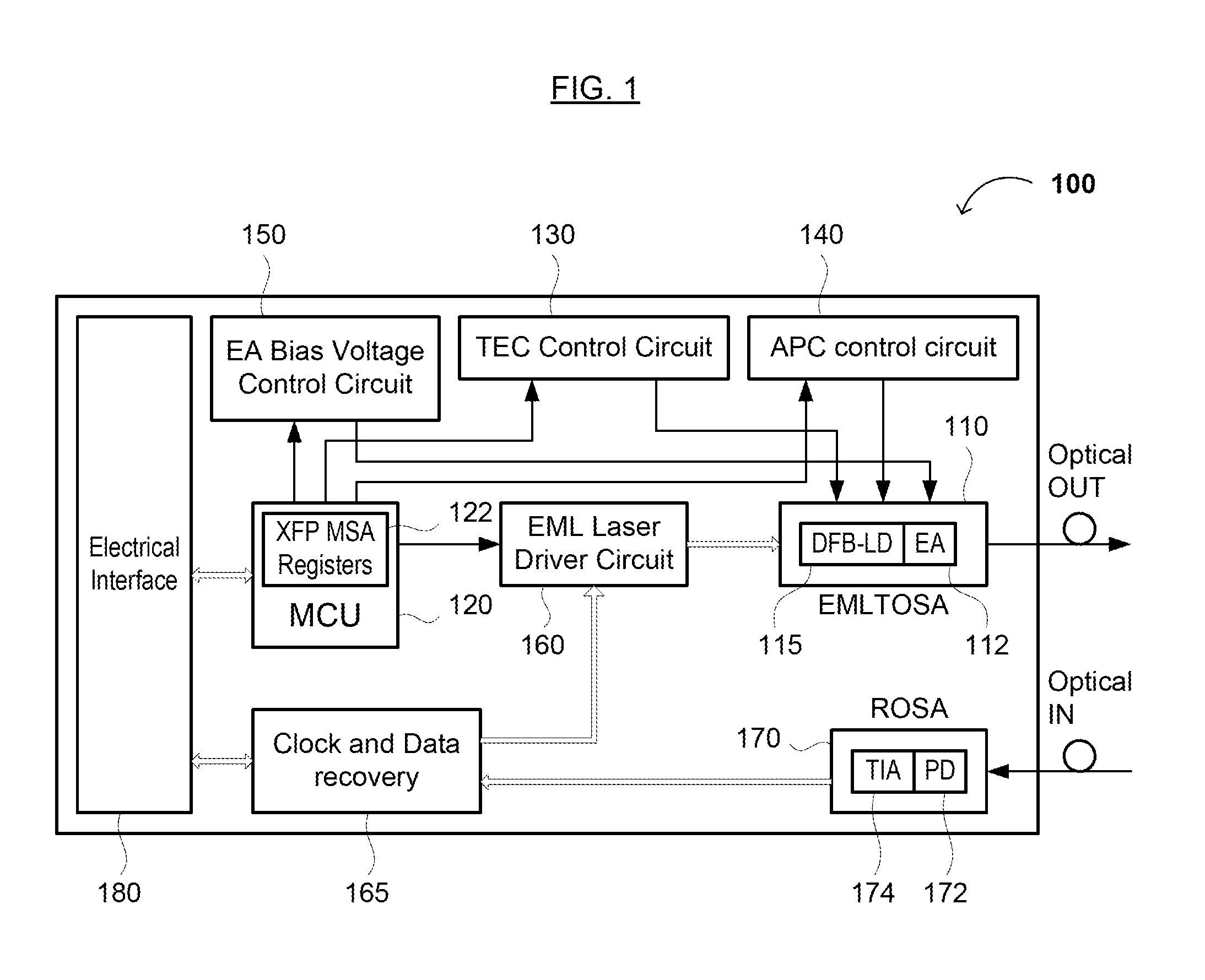
Disclosed by way of exemplary embodiments, a 40 / 50 / 10 Gb / s Optical Transceivers / transponders which use opto-electronic components at data rates collectively that are lower than or equal to half the data rate , using two optical duobinary carriers. More specifically, the exemplary embodiments of the disclosed optical transceivers / transponders relate to a 43 Gb / s 300 pin MSA and a 43˜56 Gb / s CFP MSA module, both include a two-carrier optical transceiver and the appropriate hardware architecture and MSA standard interfaces. The two-carrier optical transceiver is composed of a pair of 10 Gb / s optical transmitters, each using band-limited duobinary modulation at 20˜28 Gb / s. The wavelength channel spacing can be as little as 19˜25 GHz. The same principle is applied to a 100 Gb / s CFP module, which is composed of four tunable 10 Gb / s optical transmitters, with the channel spacing between optical carriers up to a few nanometers.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
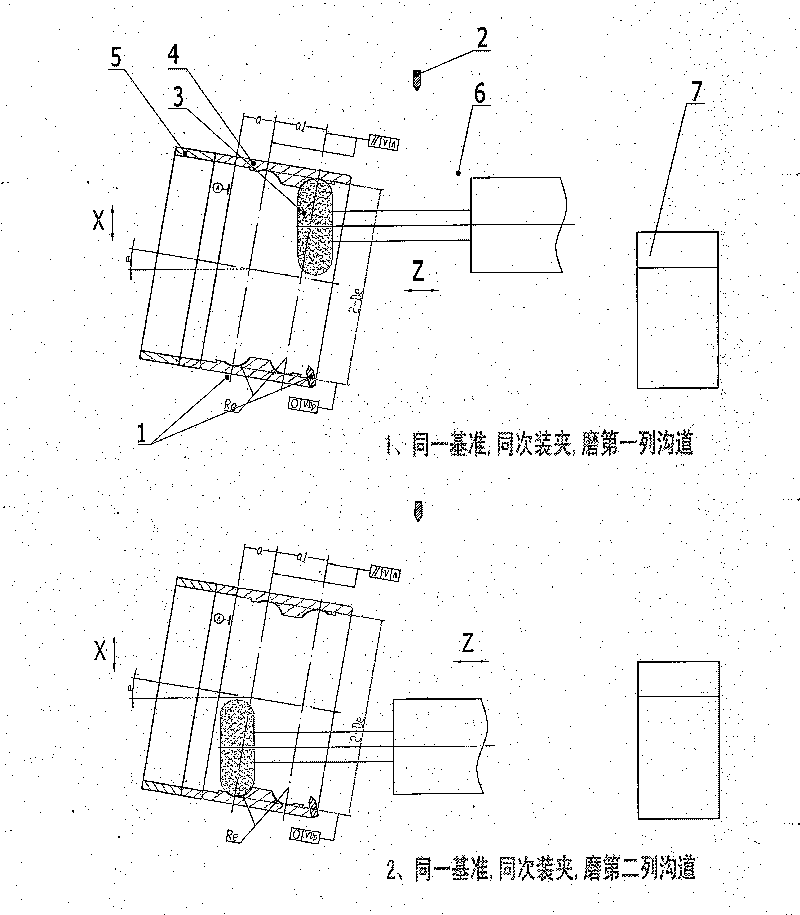
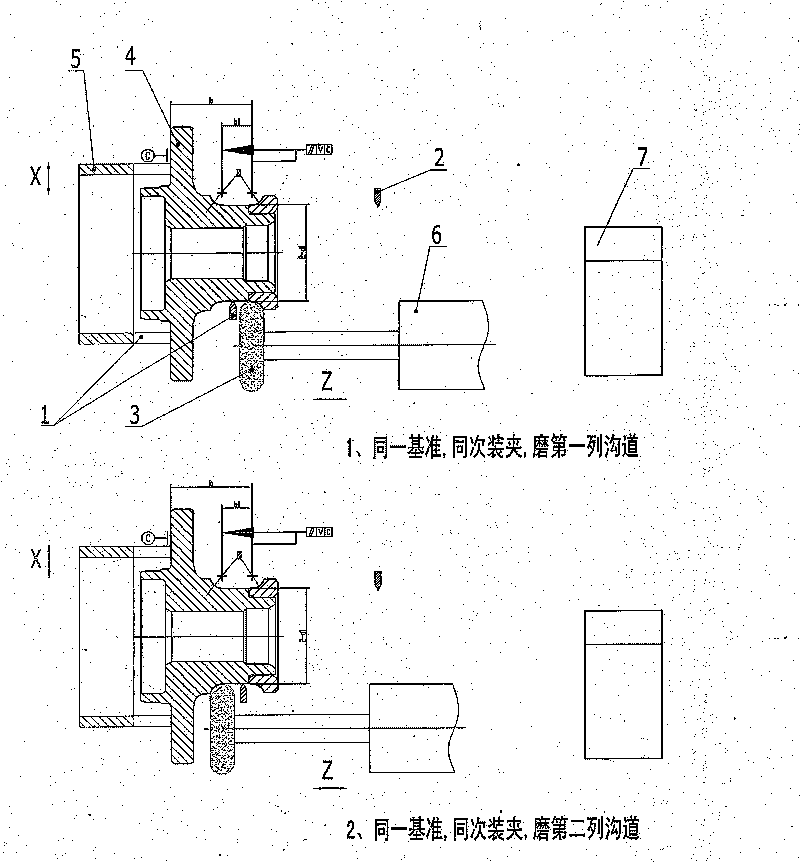
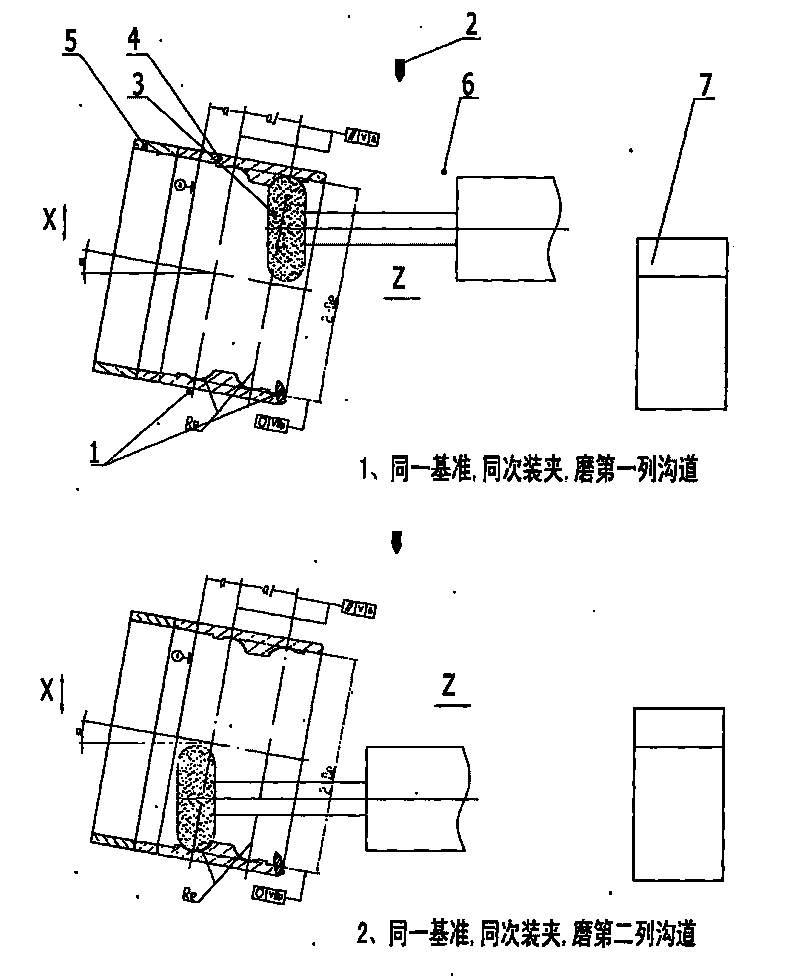
Double-channel grinding method of double-row ball bearing
The invention relates to a double-channel grinding method of a double-row ball bearing. The method is characterized in that a centerless clamp is adjusted, wherein an axial positioning support of the centerless clamp is ground by using an equipment self-grinding mode, and the end face runout of the axial positioning support is controlled within 2 micrometers; the angle alpha of an equipment workpiece frame is adjusted according to the requirements of the sizes of a ground loop, comprising the diameters of channels De / di, the positions of the channels a / b, the channel spacing a1 / b1 and the curvature radiuses of the channels Re / Ri, and the angle adjustment range is between 0 degrees and 25 degrees; a control cabinet of a CNC digital control system is used for controlling the shape of a single-point trimming grinding wheel of an arc trimmer; the positioning surface of the ground loop is fixed on the centerless clamp, and the control cabinet of the CNC digital control system is adopted to control the feed travels of an equipment workpiece X axis and a grinding wheel grinding frame Z axis meanwhile; after locking, a rotating type electric main shaft and a rotating equipment workpiece main shaft drive the ground loop so as to ensure that the grinding wheel enters a first row of channels to be ground; and after the grinding of the first row of channels is finished, the grinding wheel is fed into the second row of channels through the CNC digital control system and locked to grind the second row of channels.
Owner:HANGZHOU RADICAL ENERGY SAVING TECH
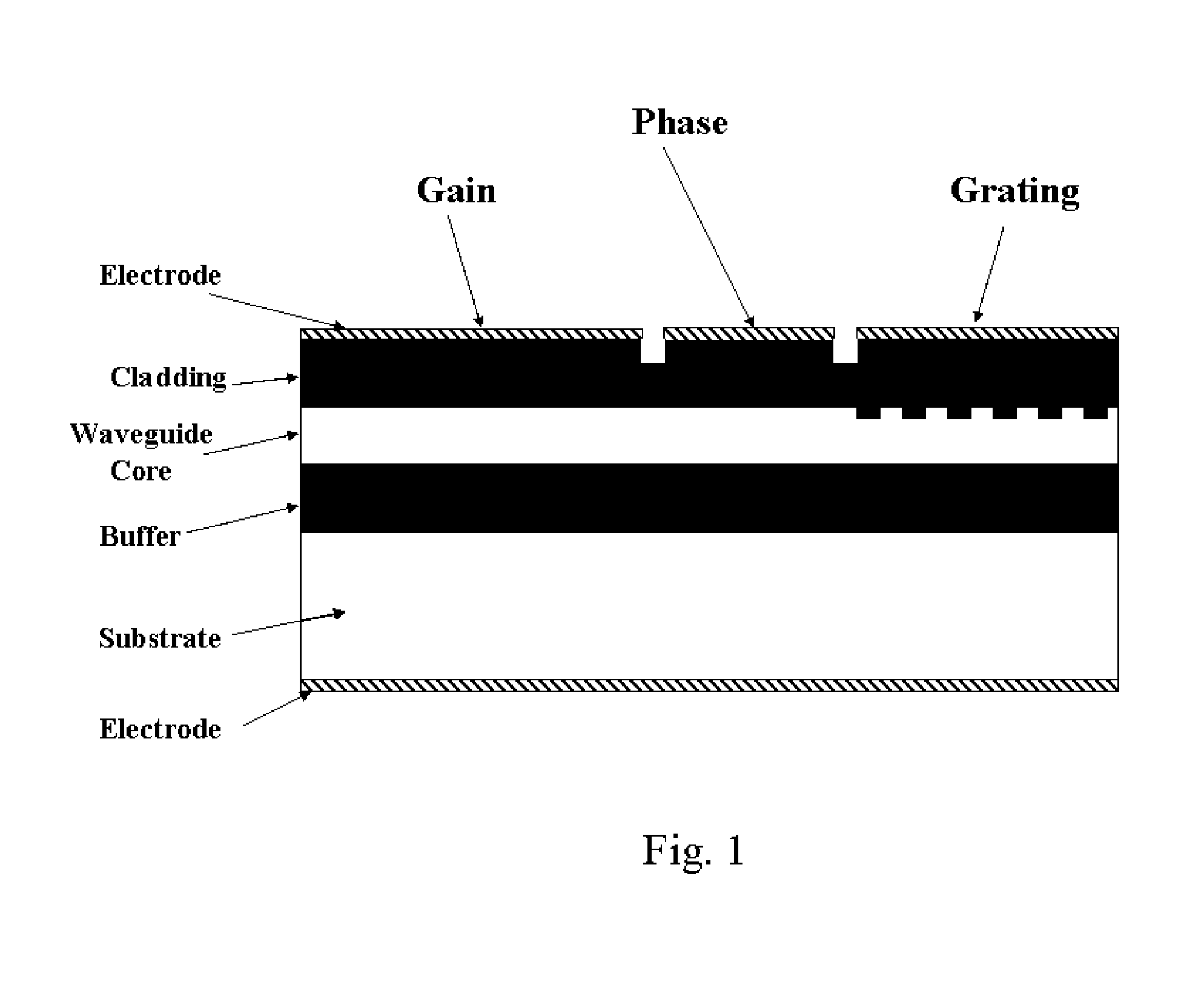
Wavelength switchable semiconductor laser
A monolithically integrated wavelength switchable laser comprises three coupled Fabry-Perot cavities. The length and consequently the free spectral range of the first cavity are designed such that the resonant peaks correspond substantially to a set of discrete operating wavelengths separated by a constant channel spacing. The second cavity has a slightly different length so that only one resonant peak coincides with one of the resonant peaks of the first cavity over the spectral window of the material gain. The lasing action occurs at the common resonant wavelength. The two cavities are coupled through a third short cavity that produces a certain coupling loss and phase relationship between the first and the second cavities in order to achieve an optimal mode selectivity of the combined cavity laser. In operation, both the first and the second cavities are forward biased to provide optical gains for the laser action. The second cavity is tuned by varying the refractive index of at least a portion of the waveguide within the cavity through an electrical means, resulting in wavelength switching of the laser among the set of discrete operating wavelengths as determined by the first cavity.
Owner:LIGHTIP TECH
Method and system for sensing discontiguous channels in a wireless network
ActiveUS20080293410A1Reduce system overheadRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionComputer scienceProcess information
A method for sensing channel availability in a wireless network includes receiving a measurement request message which includes a channel interval list. A first channel interval in the list includes information associated with a first starting channel number, a first number of channels, and first linkage information of the channel interval list. The method includes processing information associated with the message, generating a first list of contiguous channels, and performing at least first channel measurement to determine a first channel availability for each of the first list of contiguous channels. The method also includes determining whether the channel interval list further includes a second channel interval that needs to be processed based on at least first linkage information, and if needed, generating a second list of contiguous channels and performing at least second channel measurement to determine a second channel availability for each of the second list of contiguous channels.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
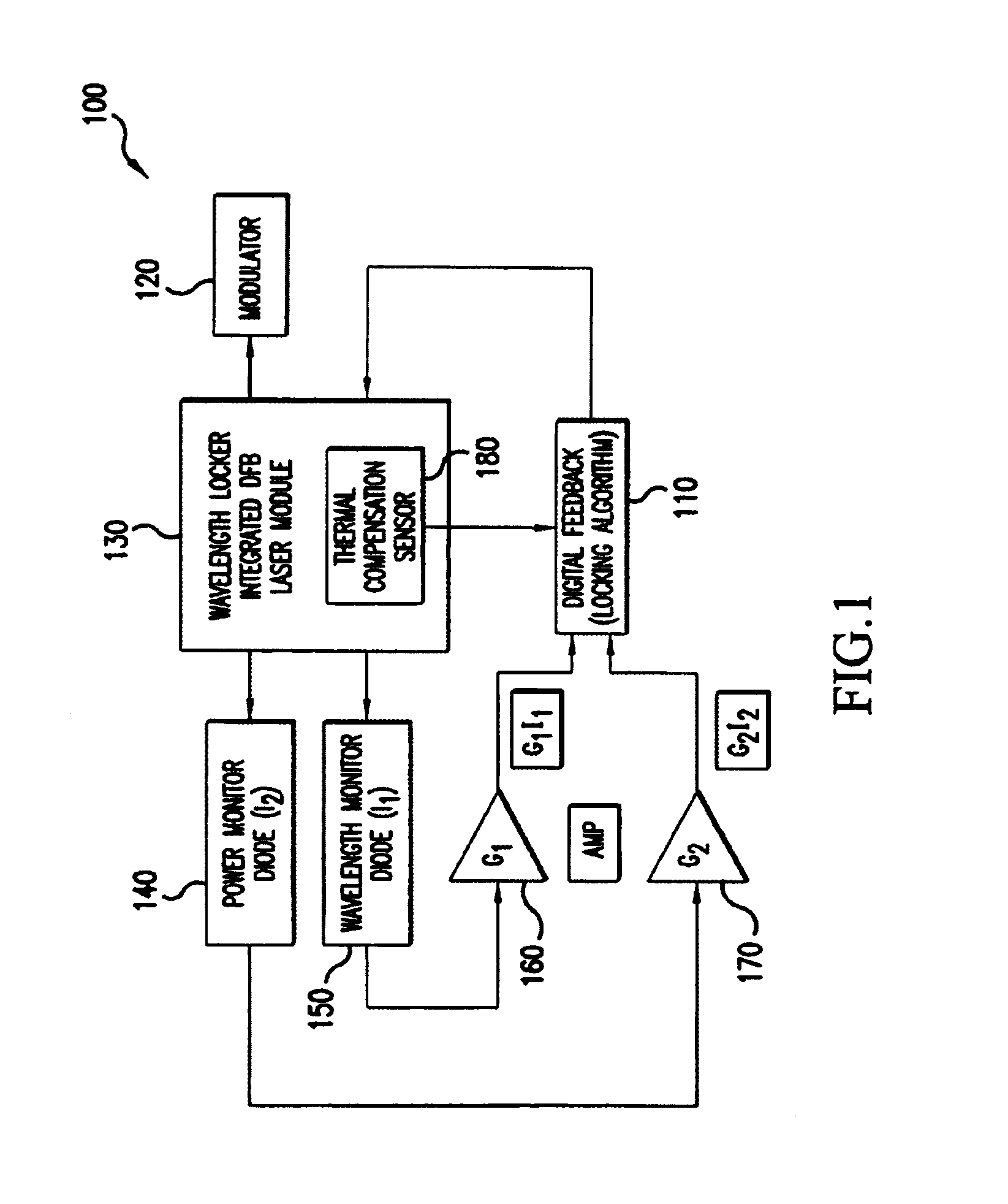
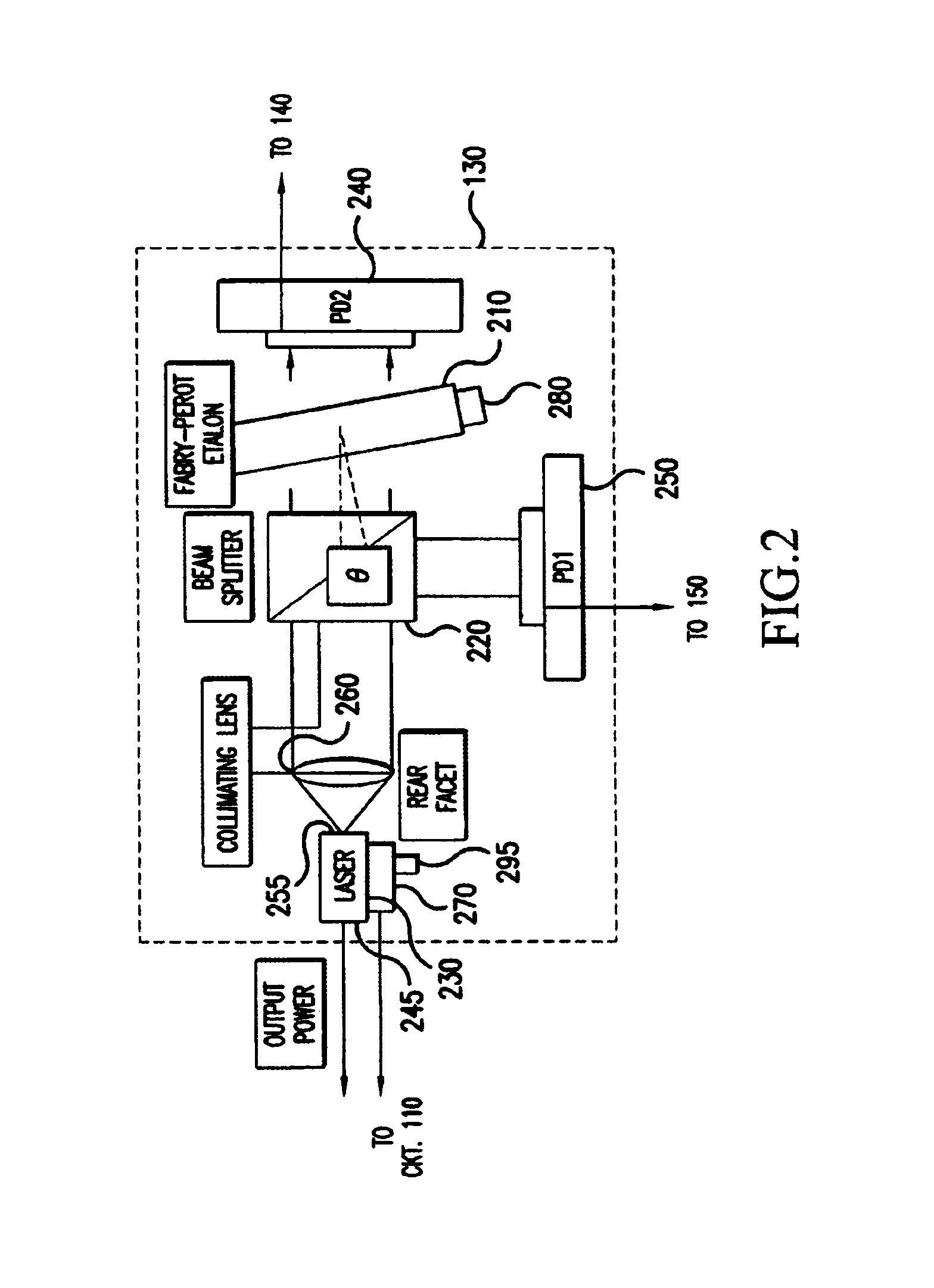
Wavelength locking scheme and algorithm for ultra-high density WDM system
ActiveUS6965622B1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The present invention is directed toward a laser wavelength locking scheme suitable for incorporation into WDM systems having channel spacings of 25 GHz or less. In a preferred embodiment, light output from the laser is supplied to a filtering element, such as an in-fiber Bragg grating or an etalon, and photodetectors are used to sense light transmitted through and either reflected by the filtering element or input to the filtering element. A measured ratio corresponding to a quotient of the photocurrents generated by the photodetectors is calculated and compared to a desired ratio corresponding to a measured temperature of the filtering element when the filtering element transmits the desired wavelength to be locked. Based on the comparison of the desired and measured ratios, a temperature error value is calculated which is used to adjust the laser temperature, as well as the laser wavelength. Accordingly, the temperature of the filtering element, for example, influences the laser temperature, so that wavelength variations stemming from temperature induced changes in the filtering element and other components in the laser package can be compensated, and the output wavelength can remain substantially fixed.
Owner:CIENA
Transport system with tunable channel spacing DWDM
InactiveUS6944406B1Increasing data transmission speed and capacityWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersFiberTransport system
An optical transport system that uses tunable filters to vary the central wavelengths and spectrum widths of channels within the system to more efficiently use the bandwidth of the fiber. Higher bit rate channels may be divided into multiple lower bit rate channels, and lower bit rate channels may be combined to form higher bit rate channels.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Untappable secure optical fiber link component
The inventive configurable optical fiber polarization mode coupler is capable of providing a low-loss, high-coupling coefficient interface with high accuracy and easy alignment between a plurality of optical fibers (or other optical devices) with a first channel-to-channel spacing, and an optical device having a plurality of closely-spaced waveguide interfaces with a second channel-to-channel spacing, where each end of the optical fiber coupler array is configurable to have different channel-to-channel spacing, each matched to a corresponding one of the first and second channel-to-channel spacing, and that are preferably optimized for use with photonic integrated circuits, such as coupling to dense optical input / output interfaces, wafer-level testing, etc. The novel optical coupler array includes a plurality of waveguides (at least one of which may optionally be polarization maintaining), that comprises at least one gradually reduced vanishing core fiber, at least in part embedded within a common housing structure. Advantageously, at least one embodiment of the present invention comprises a physically untappable secure optical fiber link component comprising at least one optical fiber polarization mode coupler configured as a pitch reducing optical fiber array (PROFA) interconnect.
Owner:CHIRAL PHOTONICS
Multi-wavelength light source apparatus and method for generating accurate wavelength interval and high flatness
InactiveCN101321019AImprove flatnessElectromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumEngineering
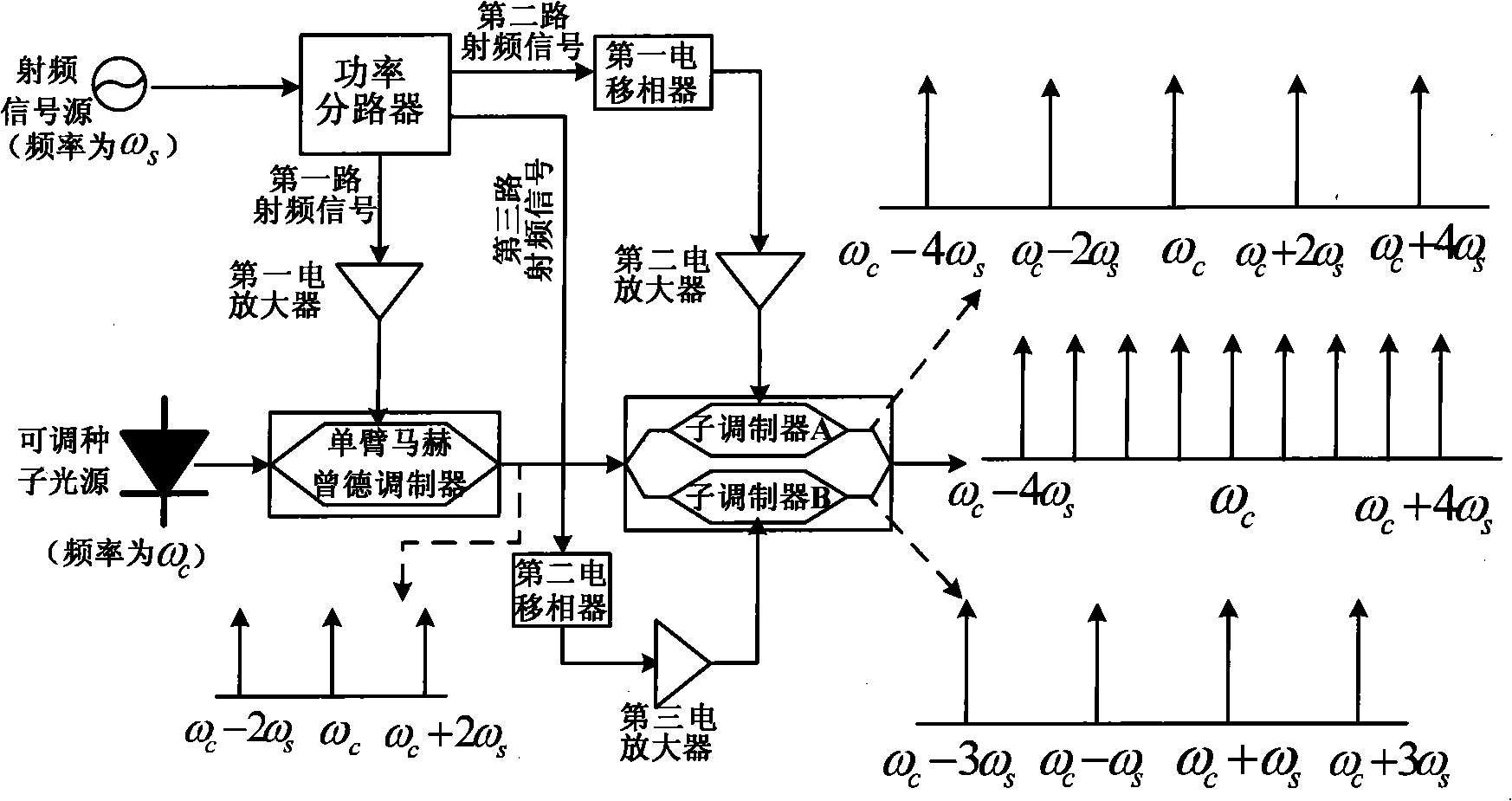
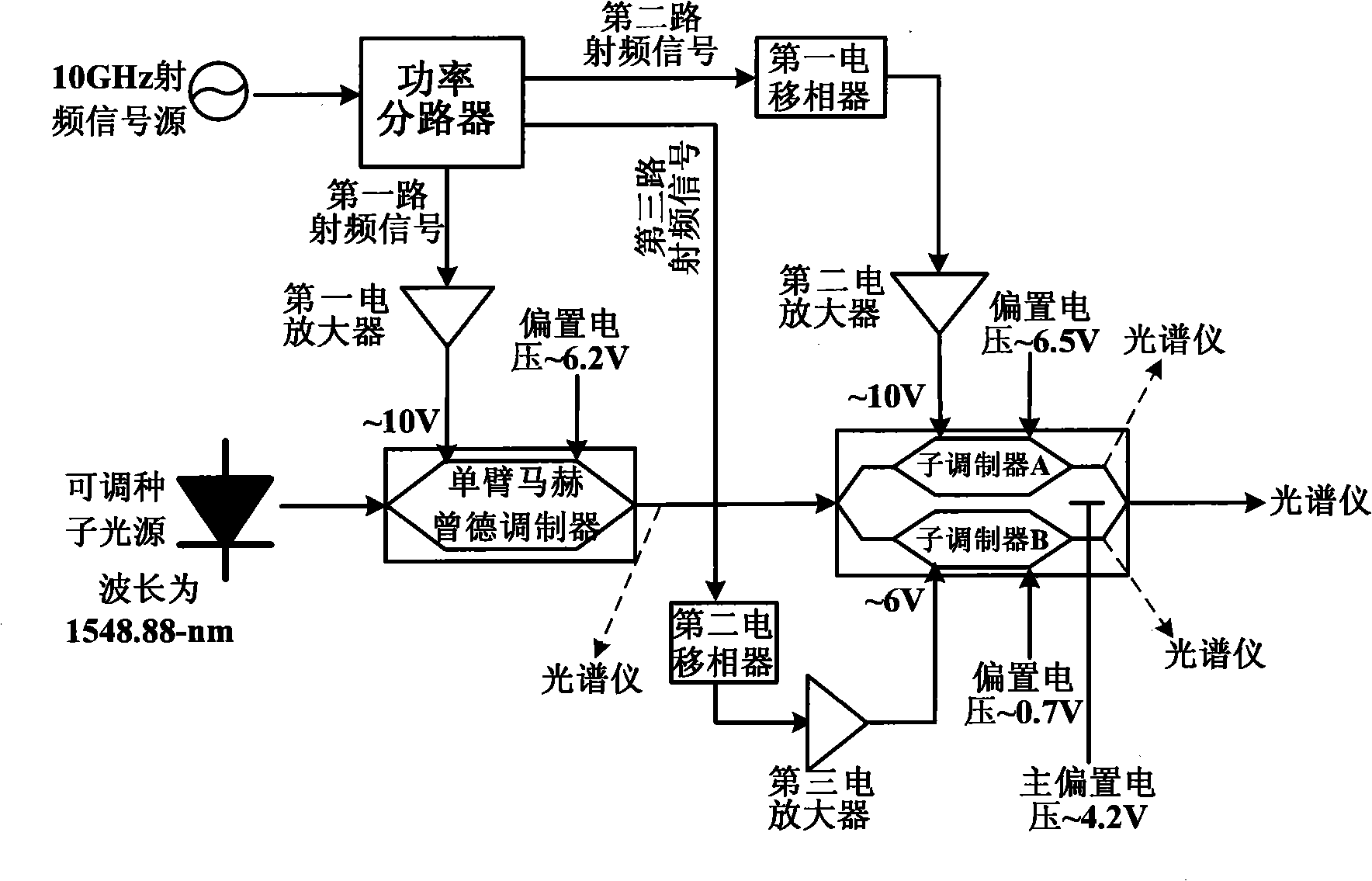
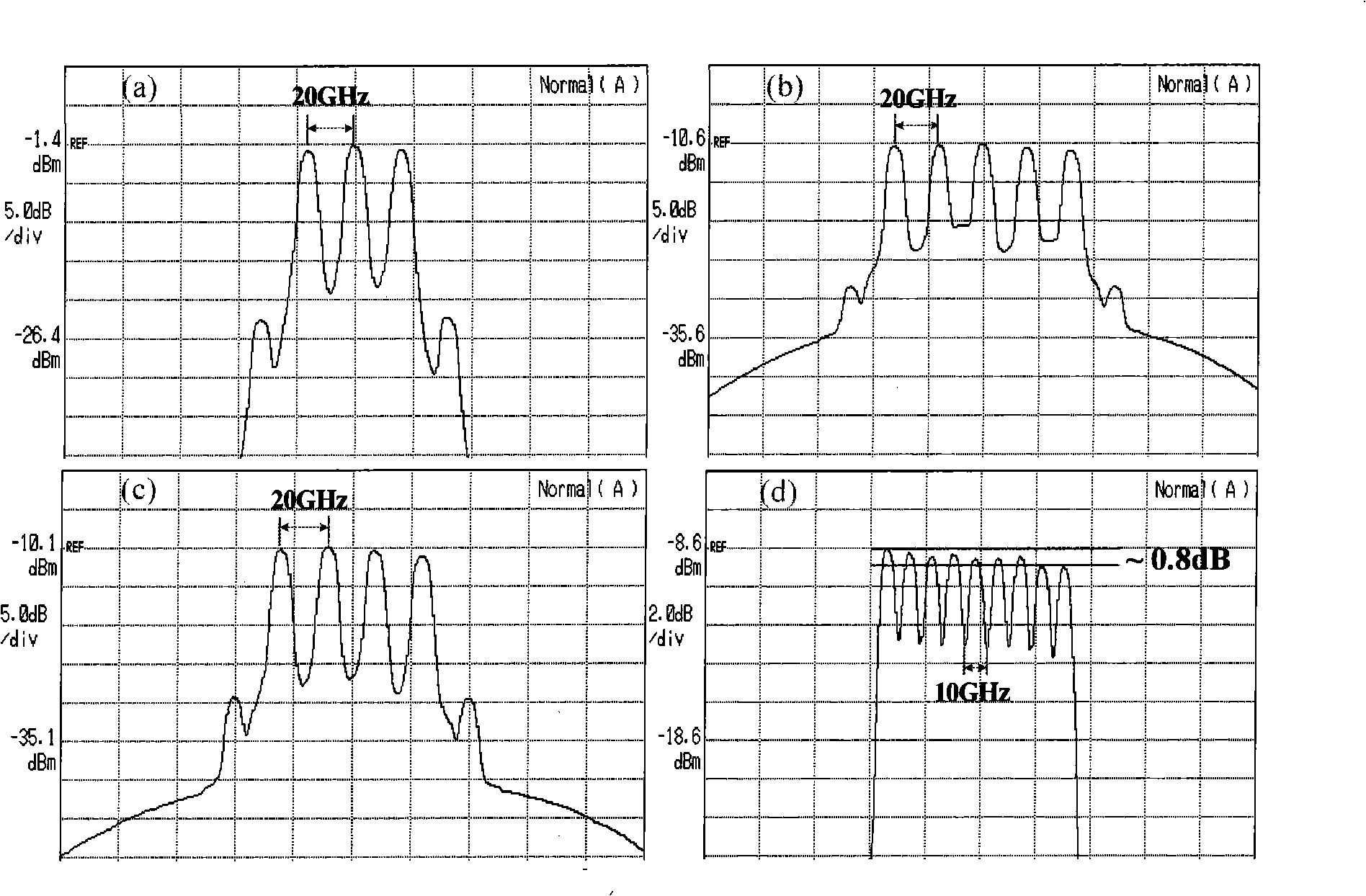
Disclosed is a device with precise channel spacing and multiple wavelength light source with high flatness and a method, belonging to the technical field of the optical communication, comprising an adjustable seed light source, a radio frequency signal source, a single arm mach tsend modulator, a double parallel mach tsend modulator, a power spliter, three electrical amplifiers and two electrical phase shifters. The method comprises: cascading the single arm mach tsend modulator and the double parallel mach tsend modulator, respectively driven by a low speed radio frequency signal, through selecting the bias points of the two modulators respectively as the highest point and the lowest point of the transmission curve, and simply control the amplitude and the phase of the radio frequency signal of the modulator, obtaining the wavelength light source including nine wavelengthes with the frequency interval equal to the frequency of the radio frequency signal. The wavelength light source of the invention has good spectral purity and phase coherence, high flatness, without expensive high power high frequency amplifier, thereby greatly reducing the arrangement cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Flex spectrum WSS
ActiveUS7756368B2Eliminate the effects ofEffective and flexible and highly methodCoupling light guidesFrequency spectrumLight beam
Switching optical signals containing a plurality of spectral channels characterized by a predetermined channel spacing is described. A selected beam deflector array may be selected from among a plurality of available beam deflector arrays configured to accommodate spectral channels of different channel spacings. The selected beam deflector array is configured to accommodate spectral channels of the predetermined channel spacing. The spectral channels are selectively optically coupled to the selected beam deflector array, which selectively optically couples the spectral channels between one or more input ports and one or more output ports.
Owner:CAPELLA PHOTONICS INC
Tunable Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Transceiver, Circuits and Devices Therefor, and Methods for Making and Using Such Transceivers, Circuits and Devices
ActiveUS20110229129A1Overcomes shortcomingMaintain stabilityTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsMicrocontrollerTemperature control
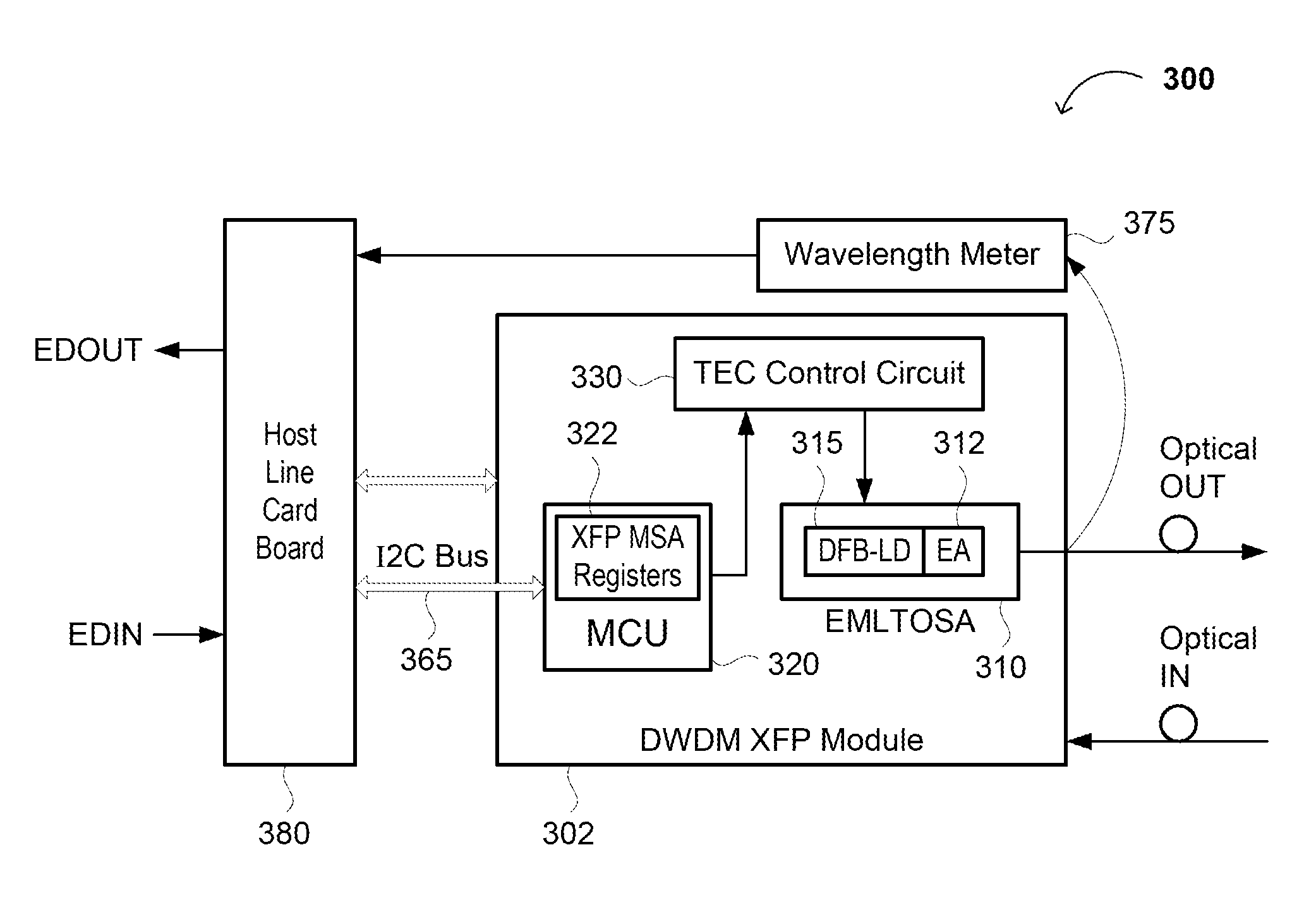
The disclosure relates to a tunable 50 GHz and 100 GHz channel spacing DWDM transceiver, and methods of making and using the same. The transceiver comprises an electro-absorption modulation laser (EML), a system board configured to compare a preset wavelength with an actual emission wavelength of the EML, a microcontroller and one or more associated registers configured to communicate with the system board, a temperature controlling circuit configured to stabilize the actual emission wavelength of the EML; and a wavelength meter connected to the output of the EML and having an output connected to the system board. The system board may be configured to provide a feedback loop from the EML to the microcontroller. The transceiver, suitable for 50 GHz channel spacing standards, can be made from existing standard transceivers and can switch between 50 GHz and 100 GHz channel spacing modes.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com