Patents
Literature
72 results about "Wdm transmission systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
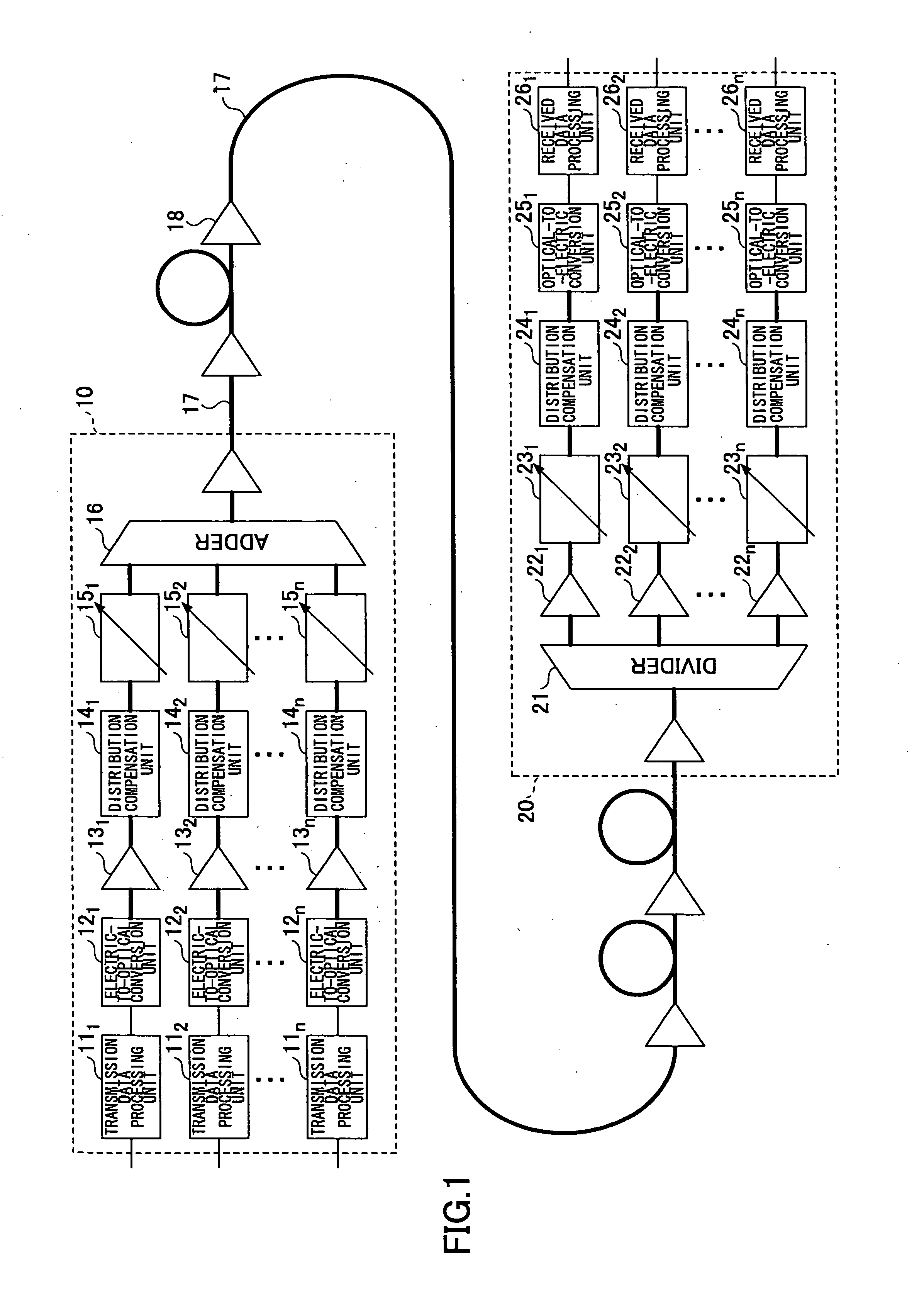
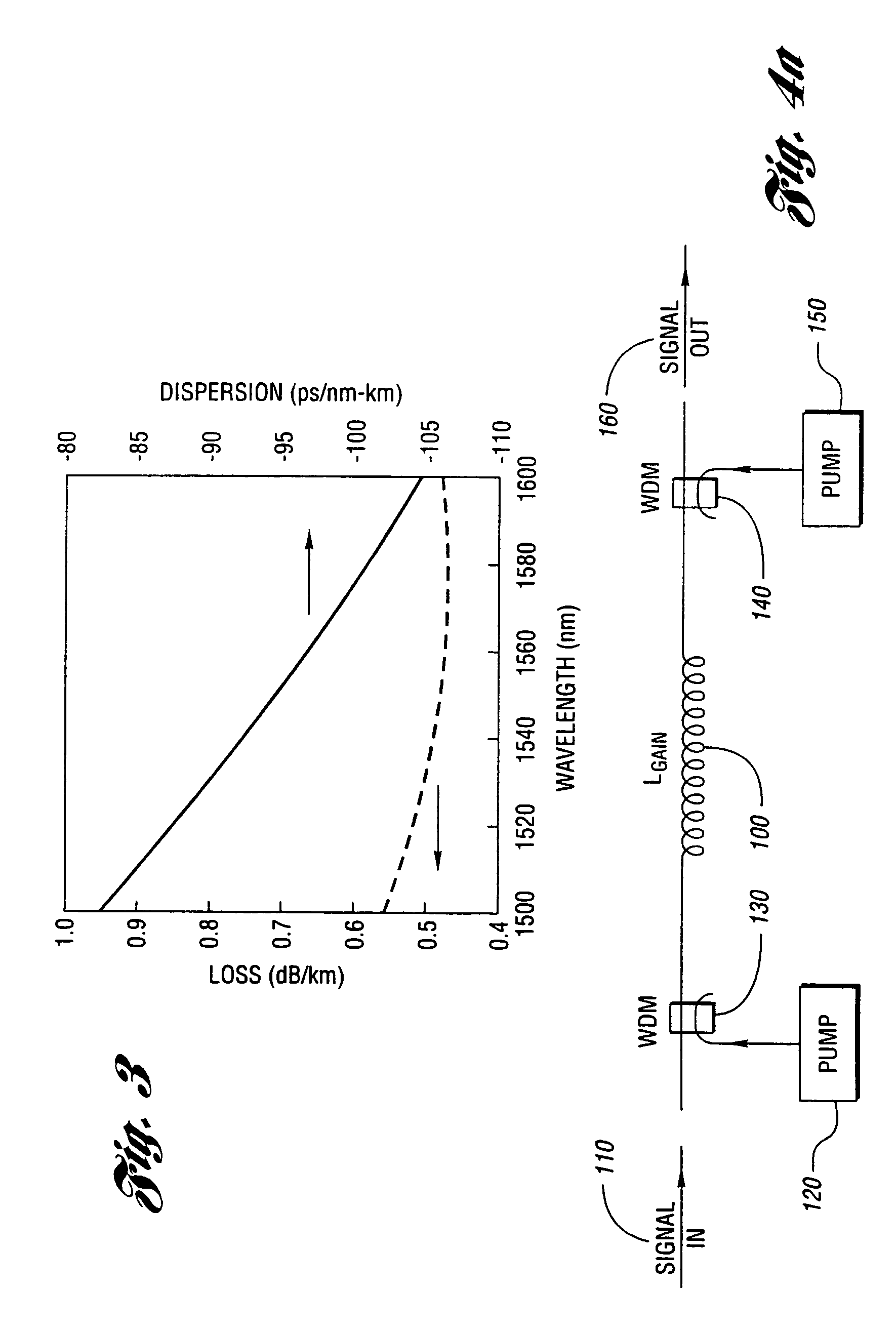
Line fiber for WDM optical fiber transmission systems
InactiveUS6396987B1Increasing channel data rateLow costOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWdm transmission systemsTransport system
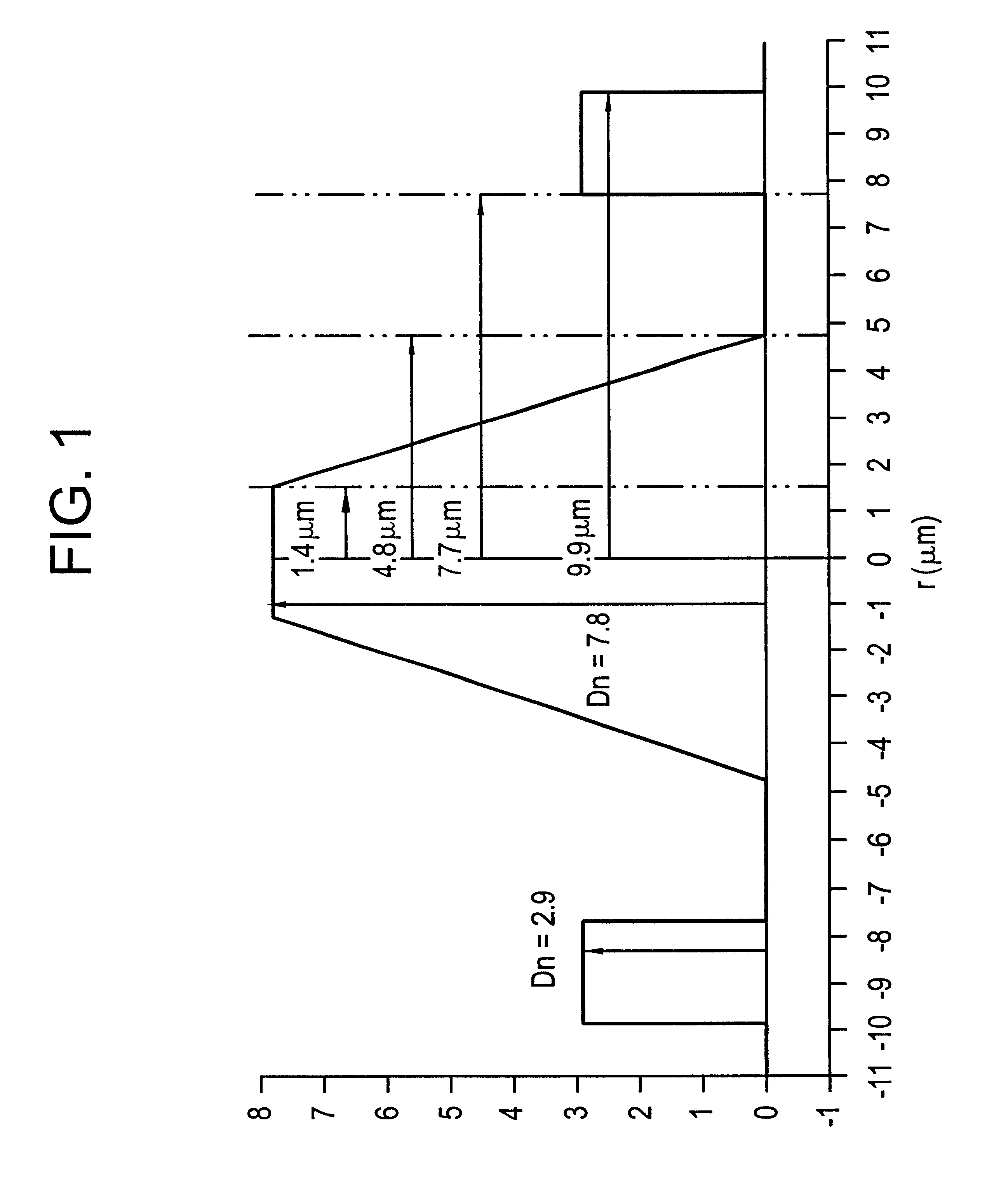
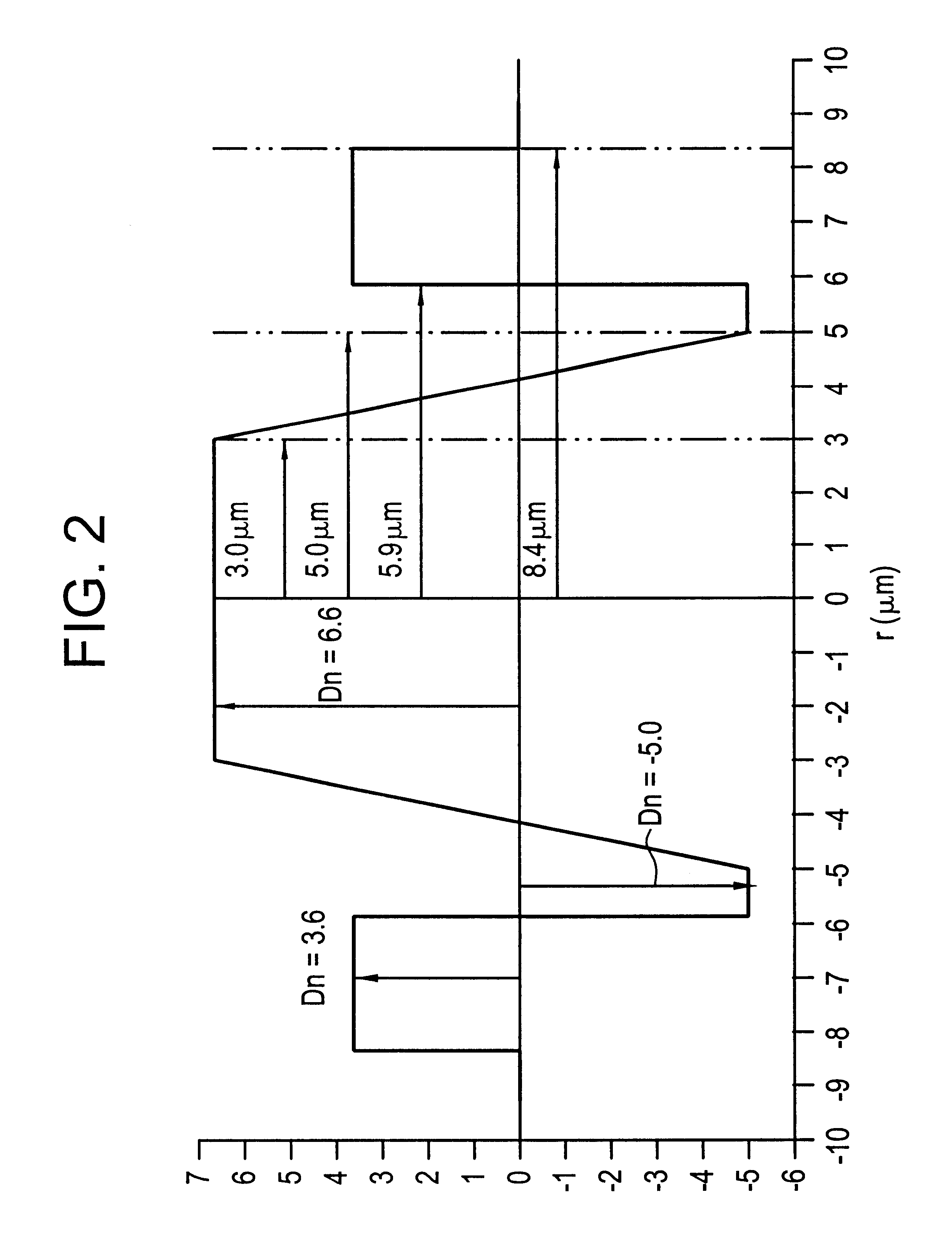
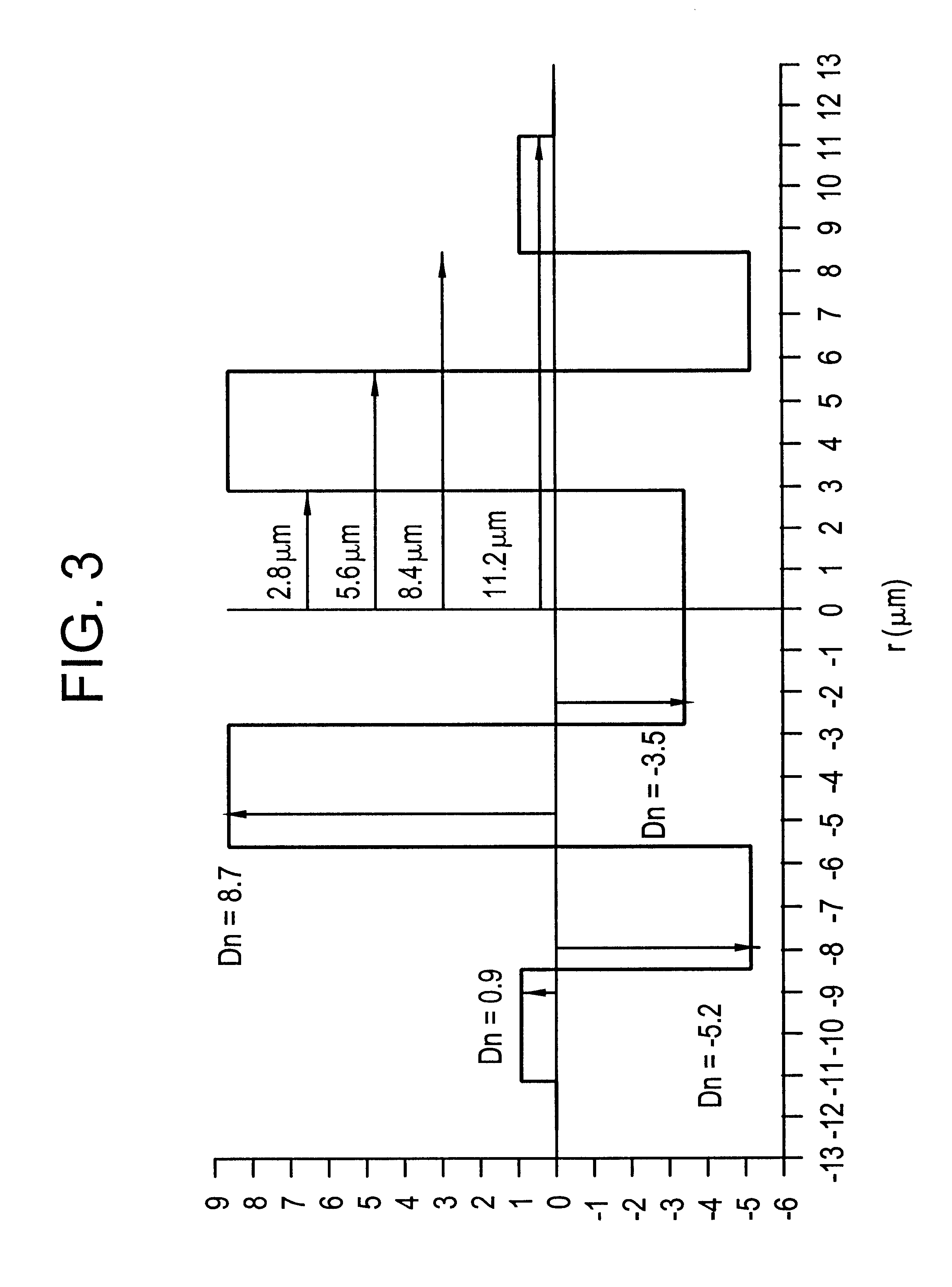
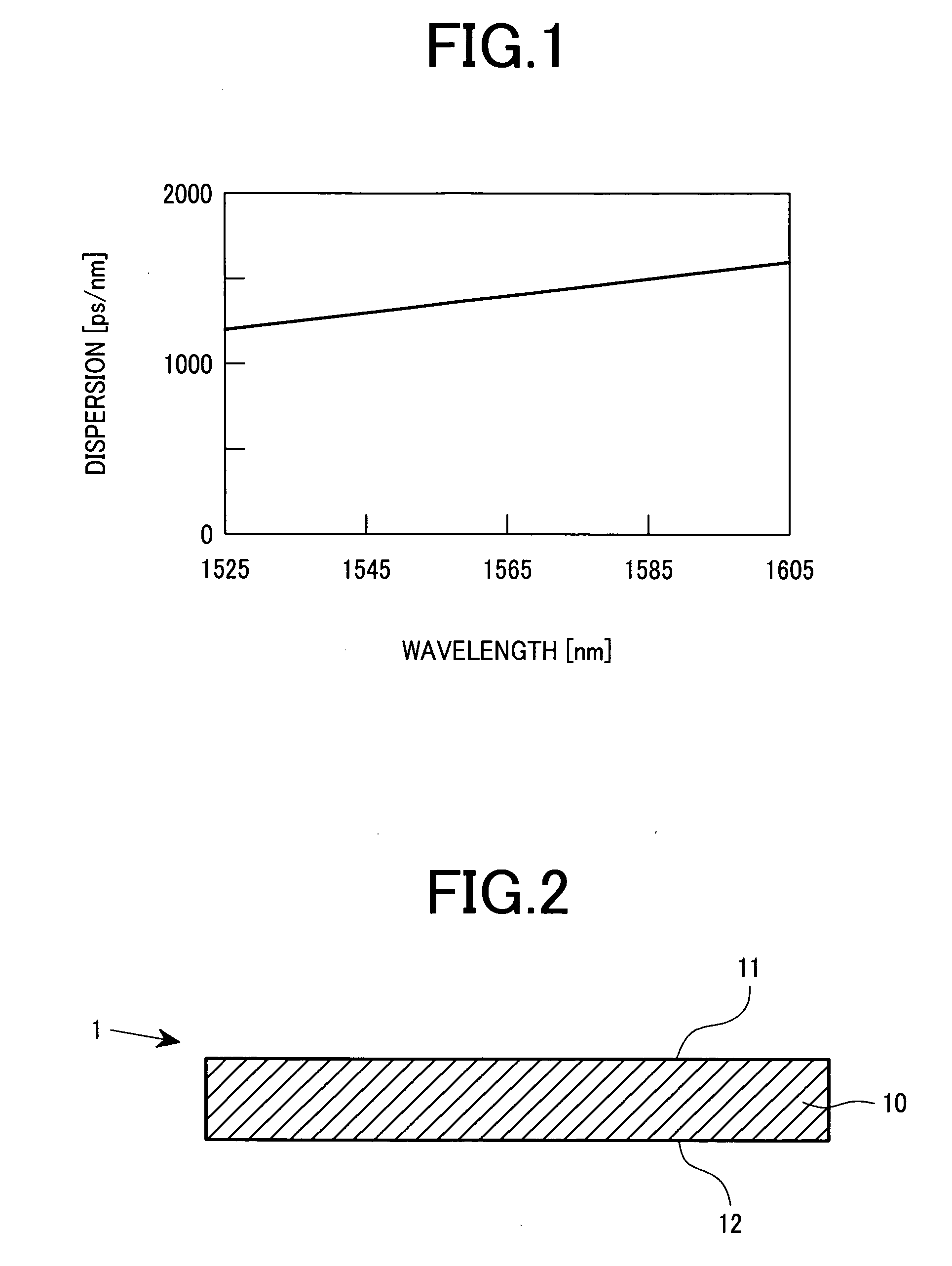
The invention provides a monomode optical fiber having, at a wavelength of 1550 nm: an effective section area greater than or equal to 60 mum2; chromatic dispersion close to 8 ps / (nm.km); a chromatic dispersion slope of absolute value less than 0.07 ps / (nm2.km). In the range of wavelengths used in a WDM transmission system, typically 1530 nm to 1620 nm, the fiber has chromatic dispersions greater than 7 ps / (nm.km), thereby making it possible to limit non-linear effects. The invention also provides a WDM optical fiber transmission system using such a fiber as a line fiber. The small slope of its chromatic dispersion is an advantage in such a system.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
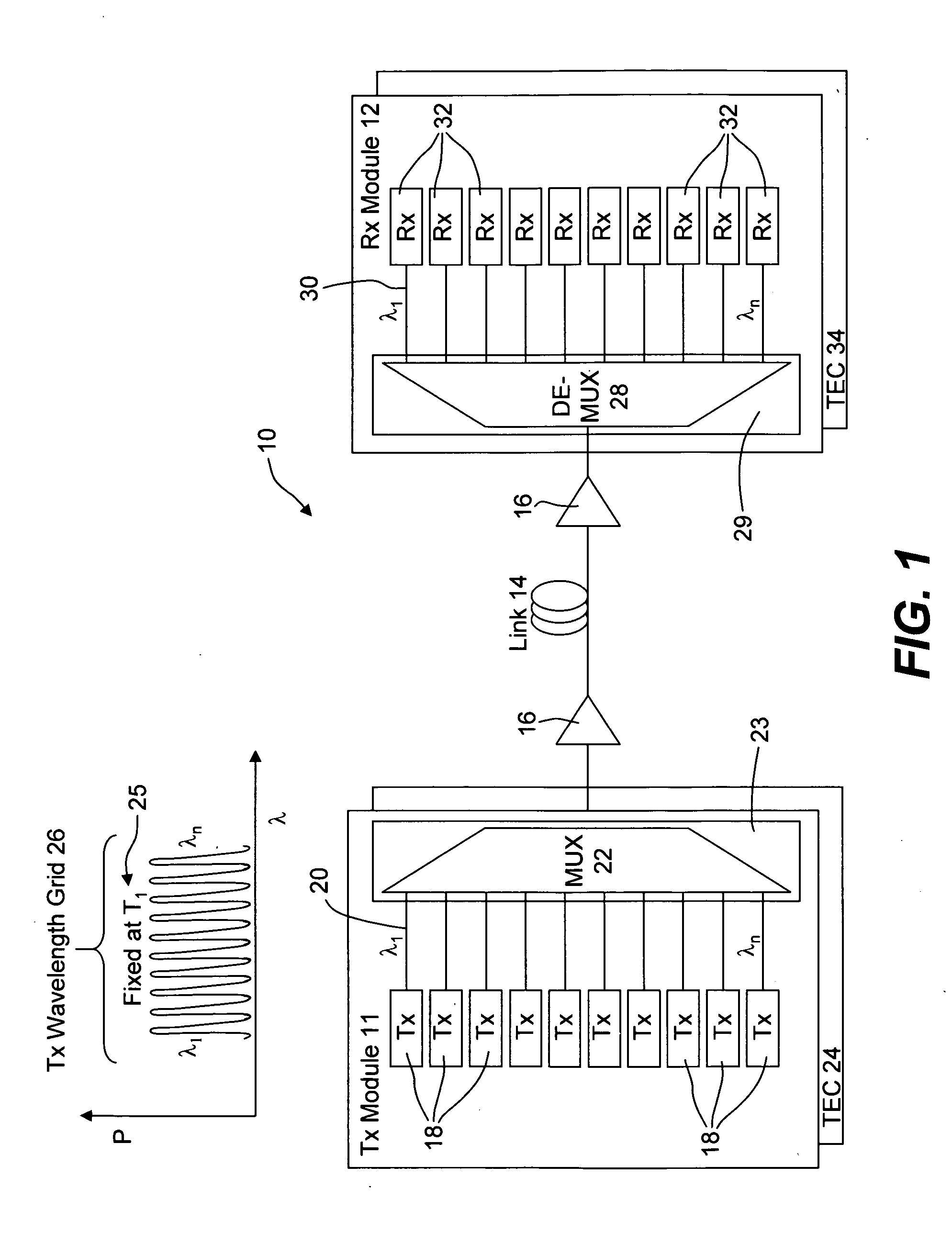
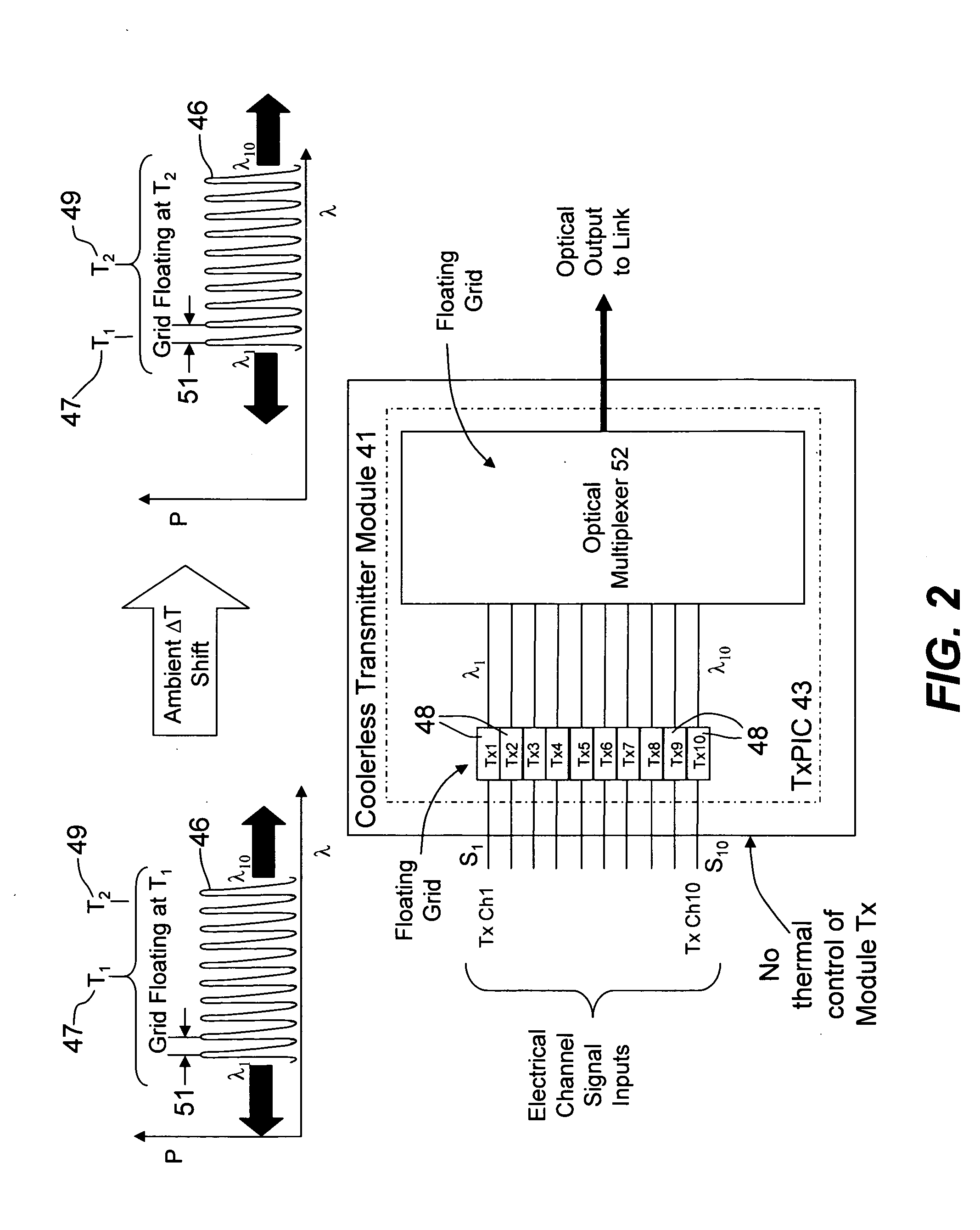
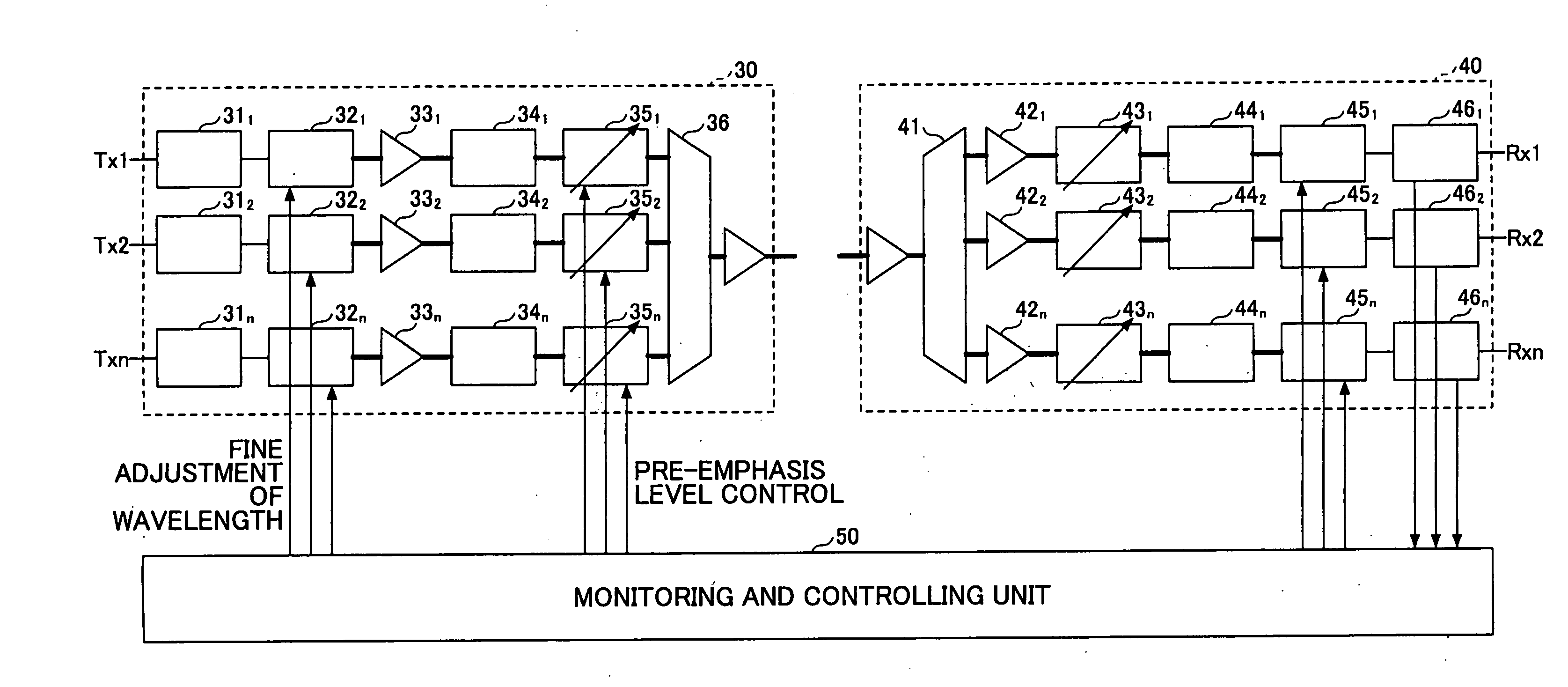
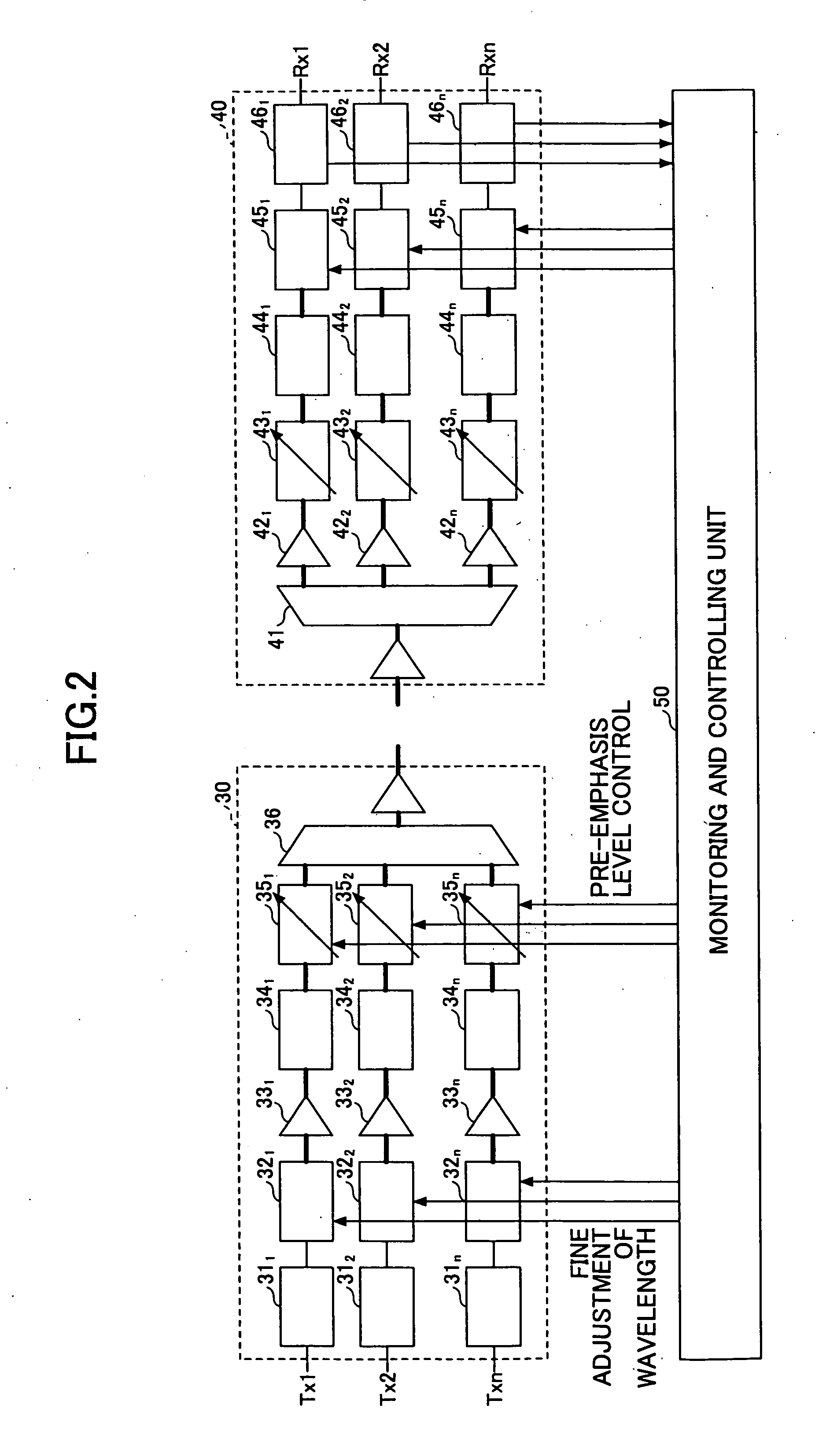
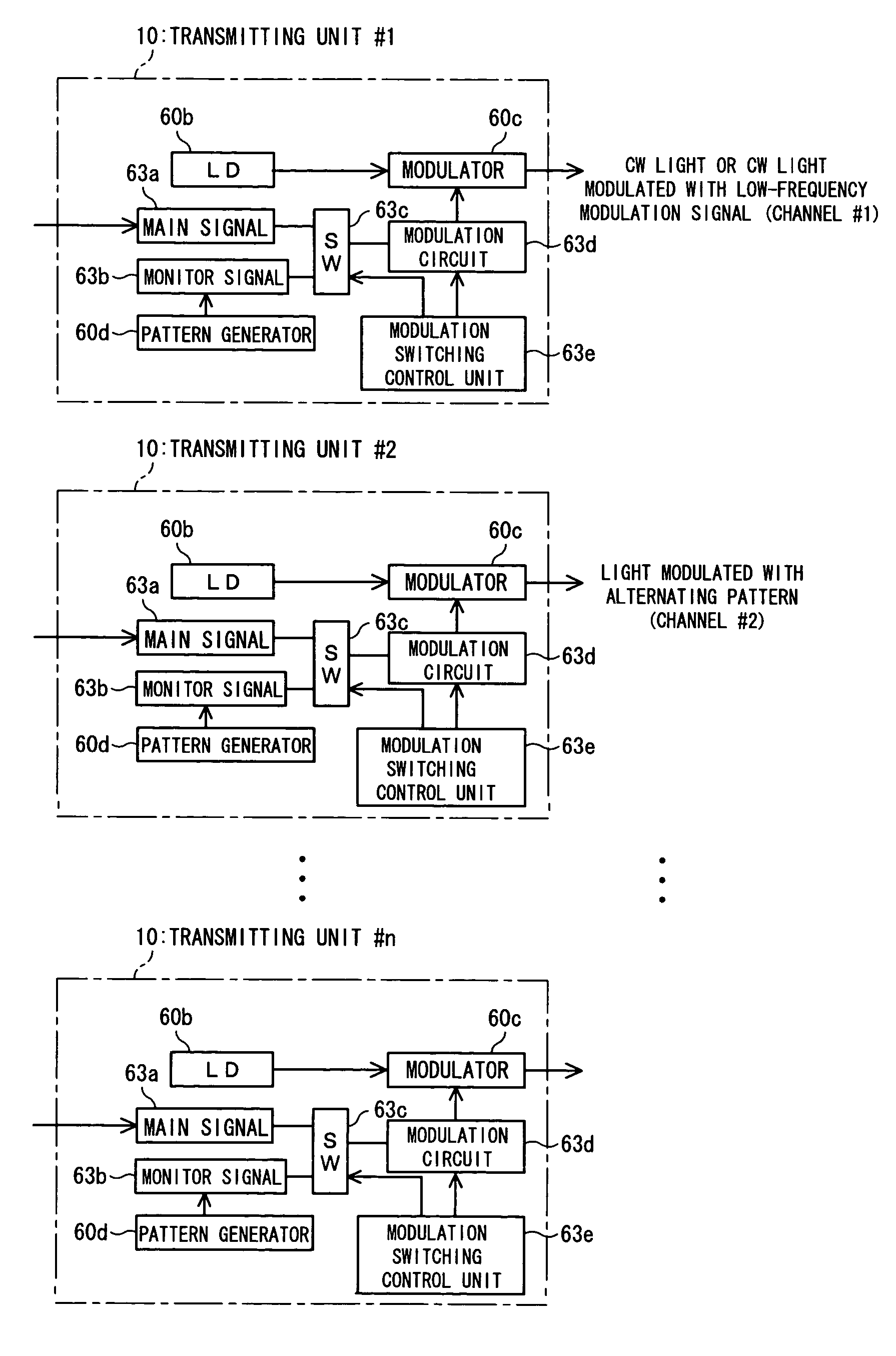
Thermally-floating transmitter wavelength grid of signal channels in a WDM transmission system
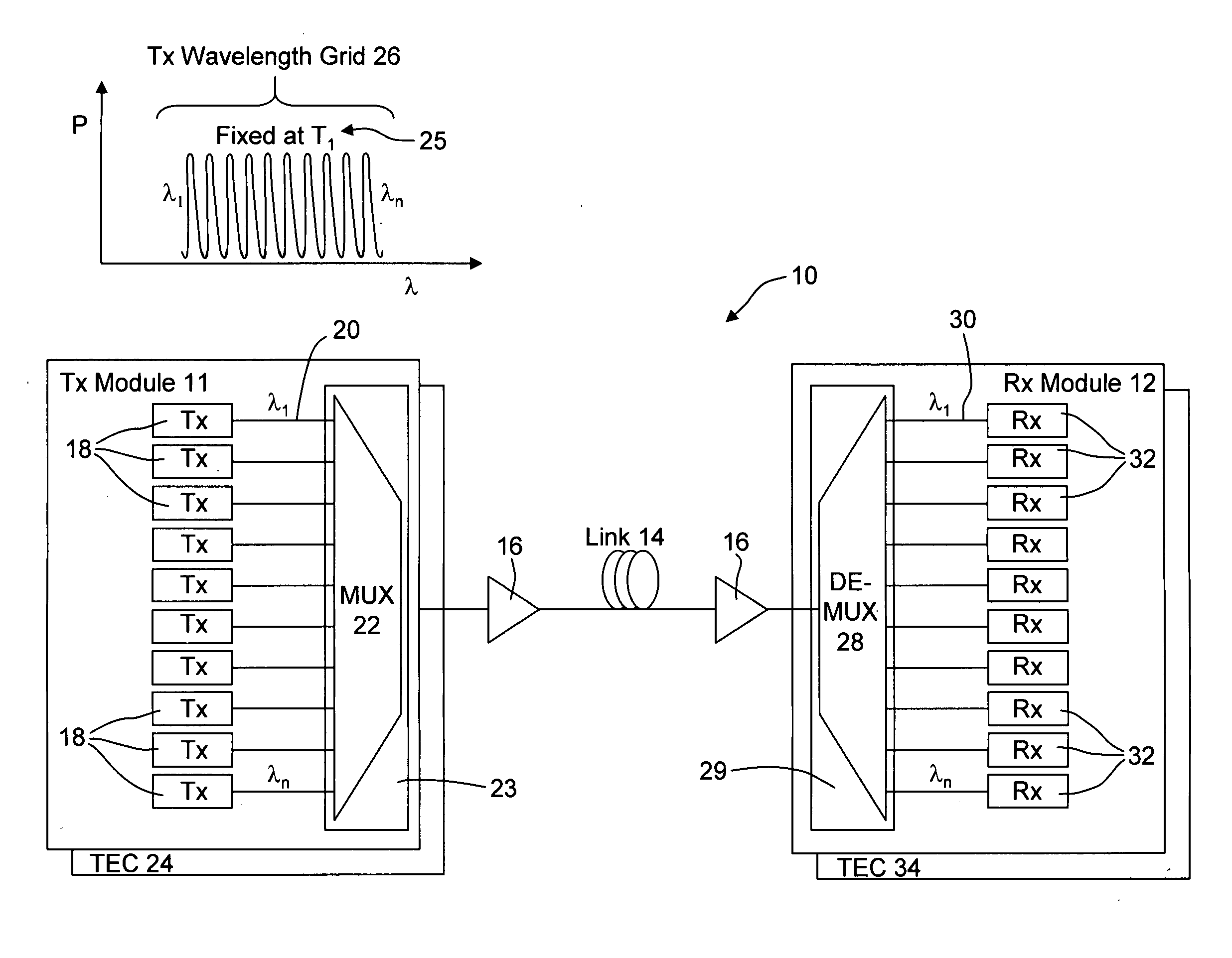
ActiveUS20060088319A1Fixed spacingControl eliminatedWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionWdm transmission systemsEngineering
A method and apparatus is provided for tracking a thermally floating wavelength signal channel grid generated at an optical transmitter (Tx) in an optical transmission system or optical network where the wavelengths of the individual Tx signal channels may move in wavelength due to, for example, changes in ambient temperature at the optical transmitter but the channel spacing between Tx signal channels along the thermally floating Tx wavelength grid remains constant. An optical receiver (Rx) is provided that has a demultiplexed signal channel grid that may have a different channel spacing from that of the floating Tx wavelength grid, that is either larger, the same as, or smaller Rx grid spacing compared to the Tx grid spacing, and includes a number of demultiplexed channel signal outputs along an Rx channel grid in excess of the number of Tx signal channels on the Tx channel grid so that the optical receiver is capable of detecting the floating Tx channel grid and providing electrical output signals representative of the Tx channel signals transported over the optical network.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
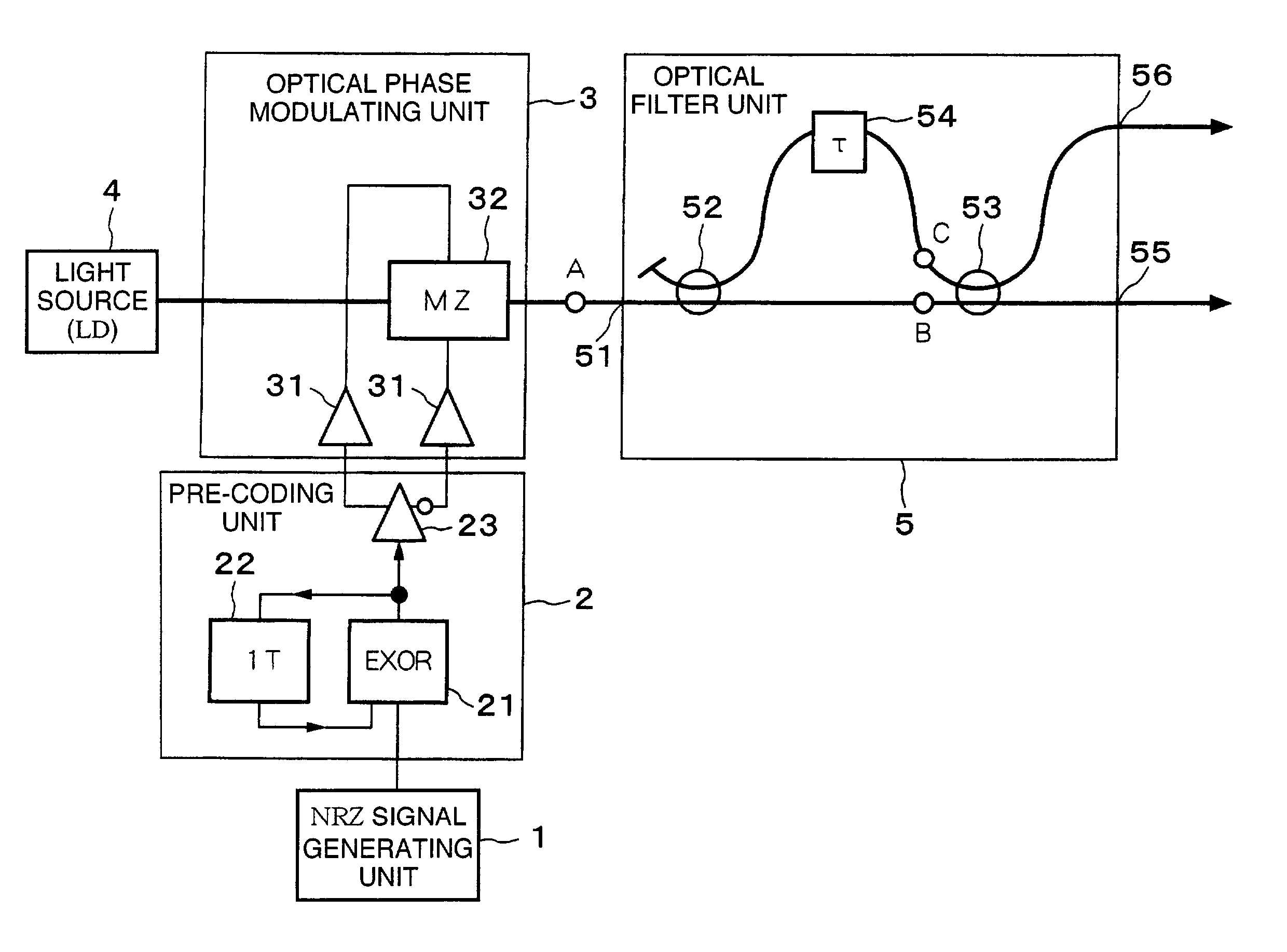
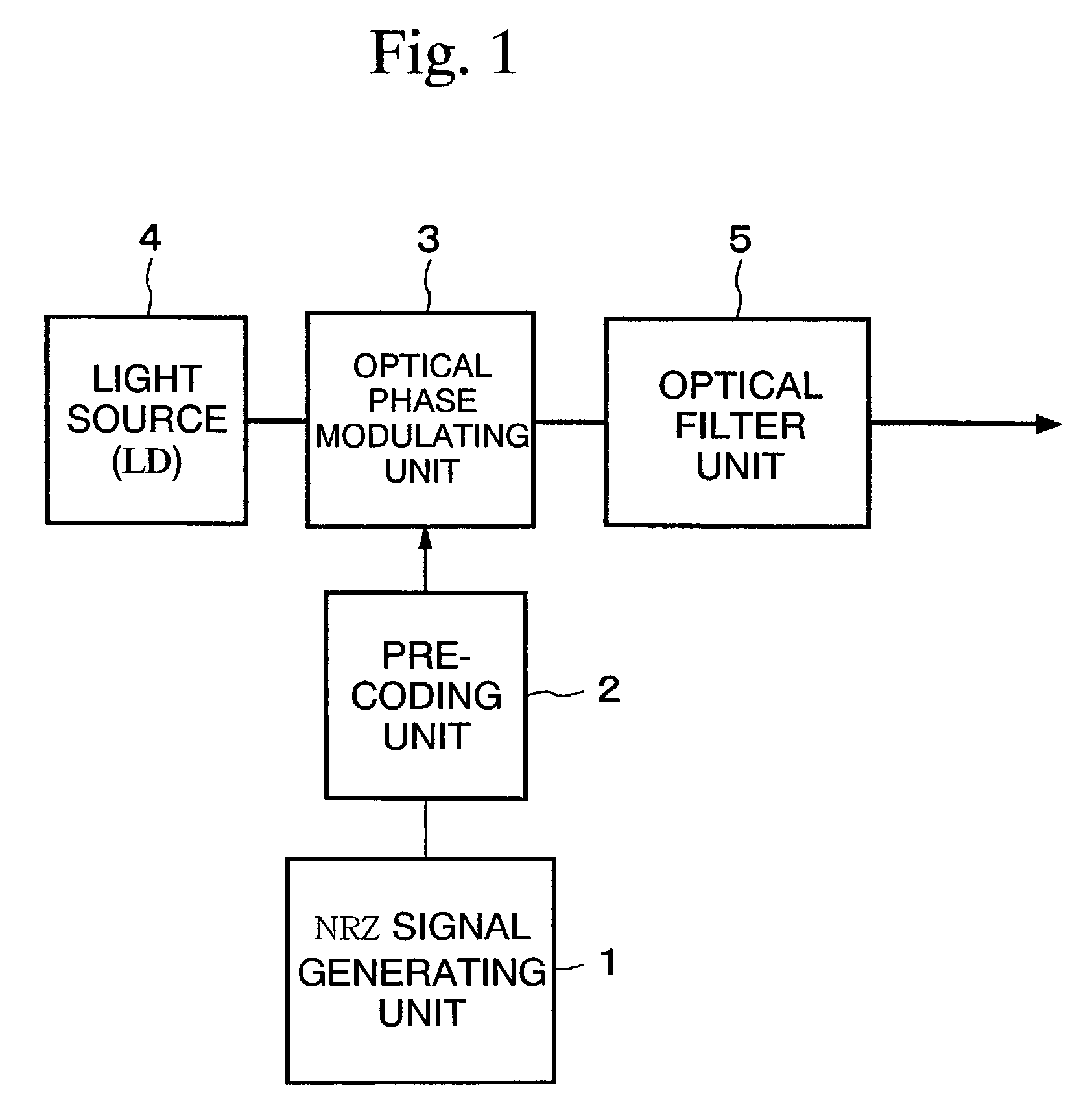
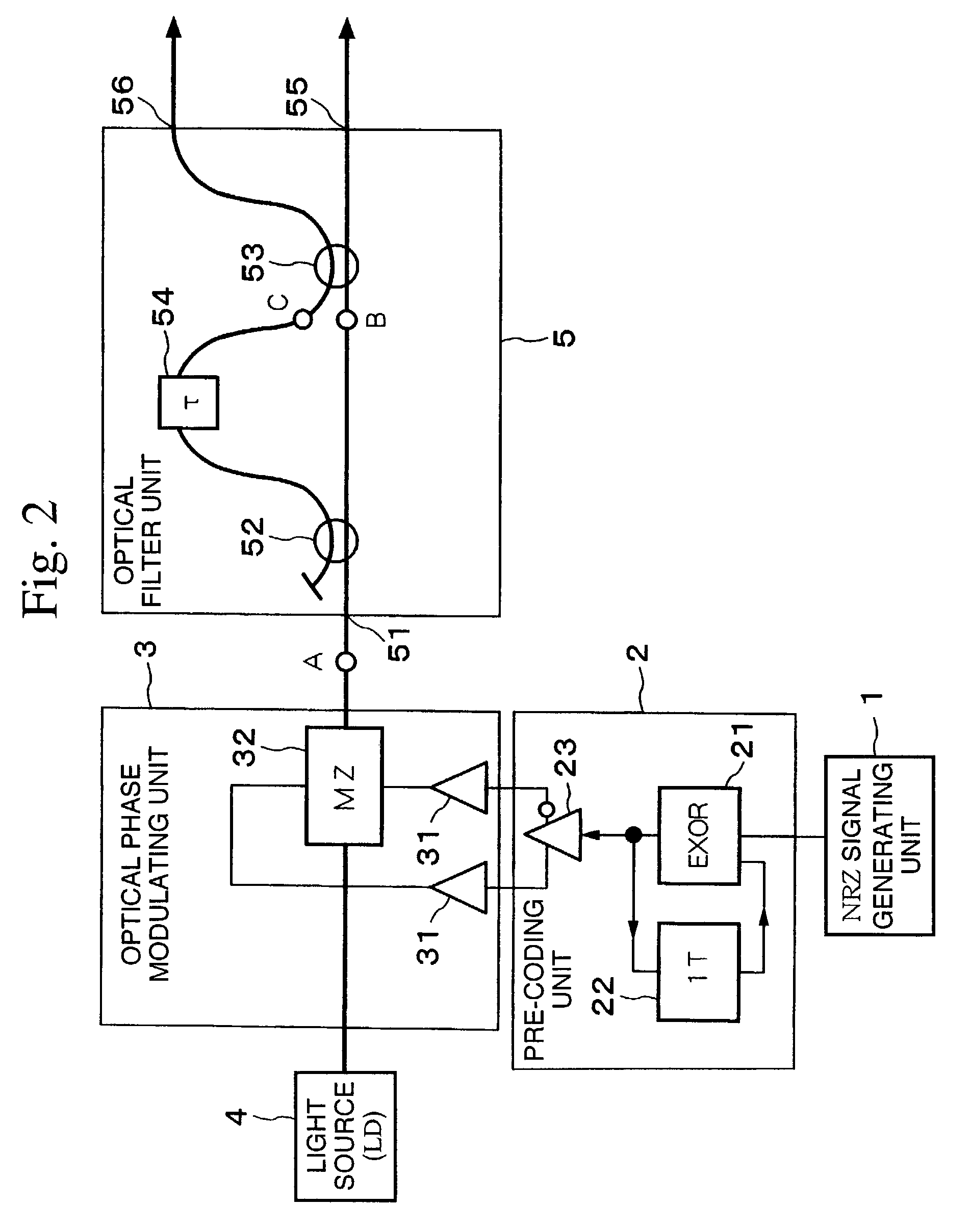
Optical transmitter and optical transmission system
ActiveUS7116917B2Line rate can be increasedEasy to operateDistortion/dispersion eliminationOptical multiplexEngineeringTransmission quality
The present invention suppresses to a minimum the degradation of the transmission quality caused by chromatic dispersion characteristic of an optical transmission medium, and the interplay between the chromatic dispersion and non-linear optical effects in dense WDM transport systems. A baseband input data signal is pre-coded in advance by a pre-coding unit, phase modulation is carried out using a pre-coded signal by the optical phase modulating unit, and the phase modulated optical signal is converted to an RZ intensity modulated signal by the optical filter unit that performs phase-shift-keying to amplitude-shift-keying conversion. For example, an optical phase modulating unit generates an encoded DPSK phase modulated signal using a differential phase shirt keying (DPSK) format, and a phase modulated signal is converted to an RZ intensity modulated signal by the optical filter unit disposed downstream of the optical phase modulating unit.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
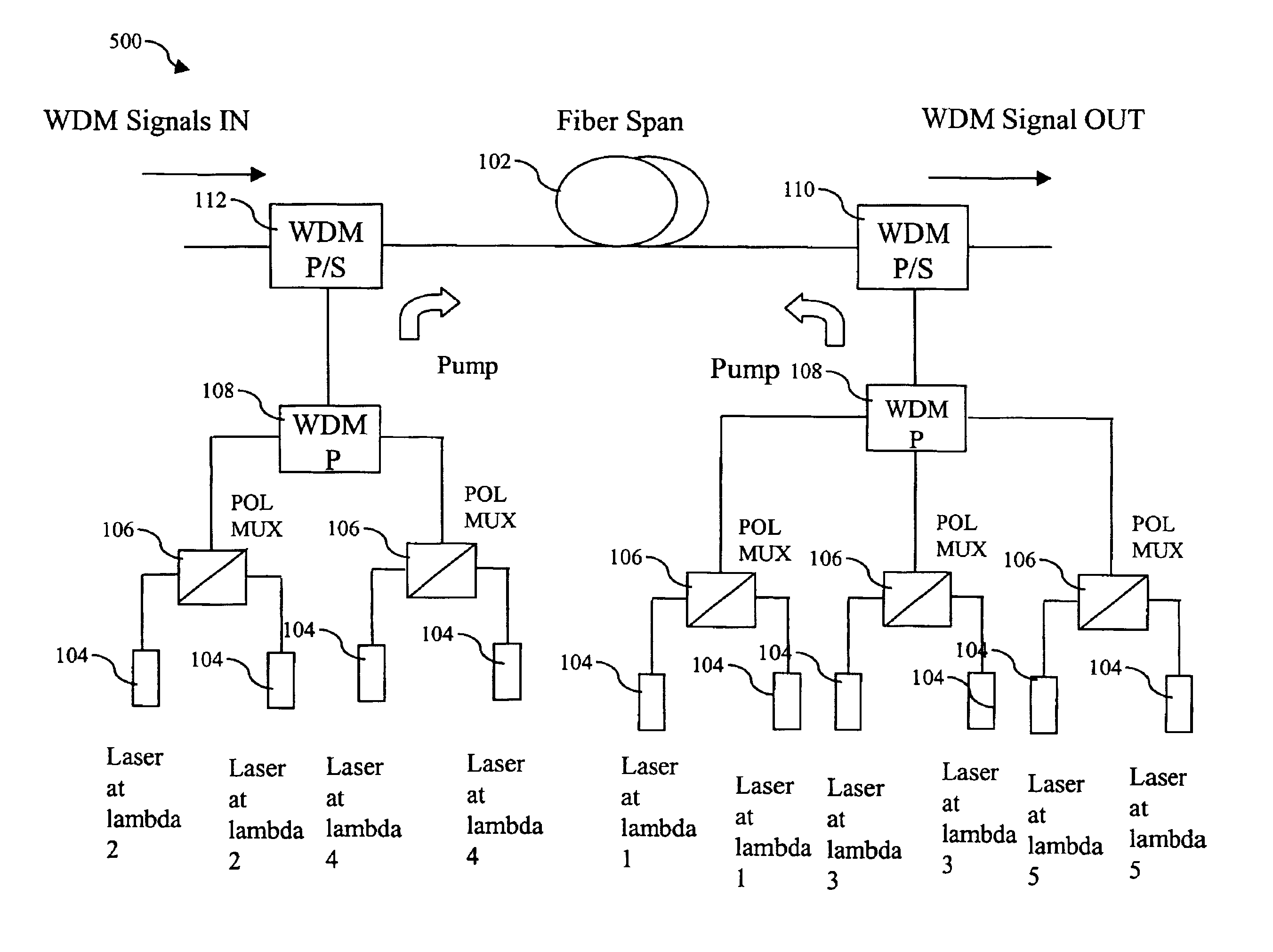
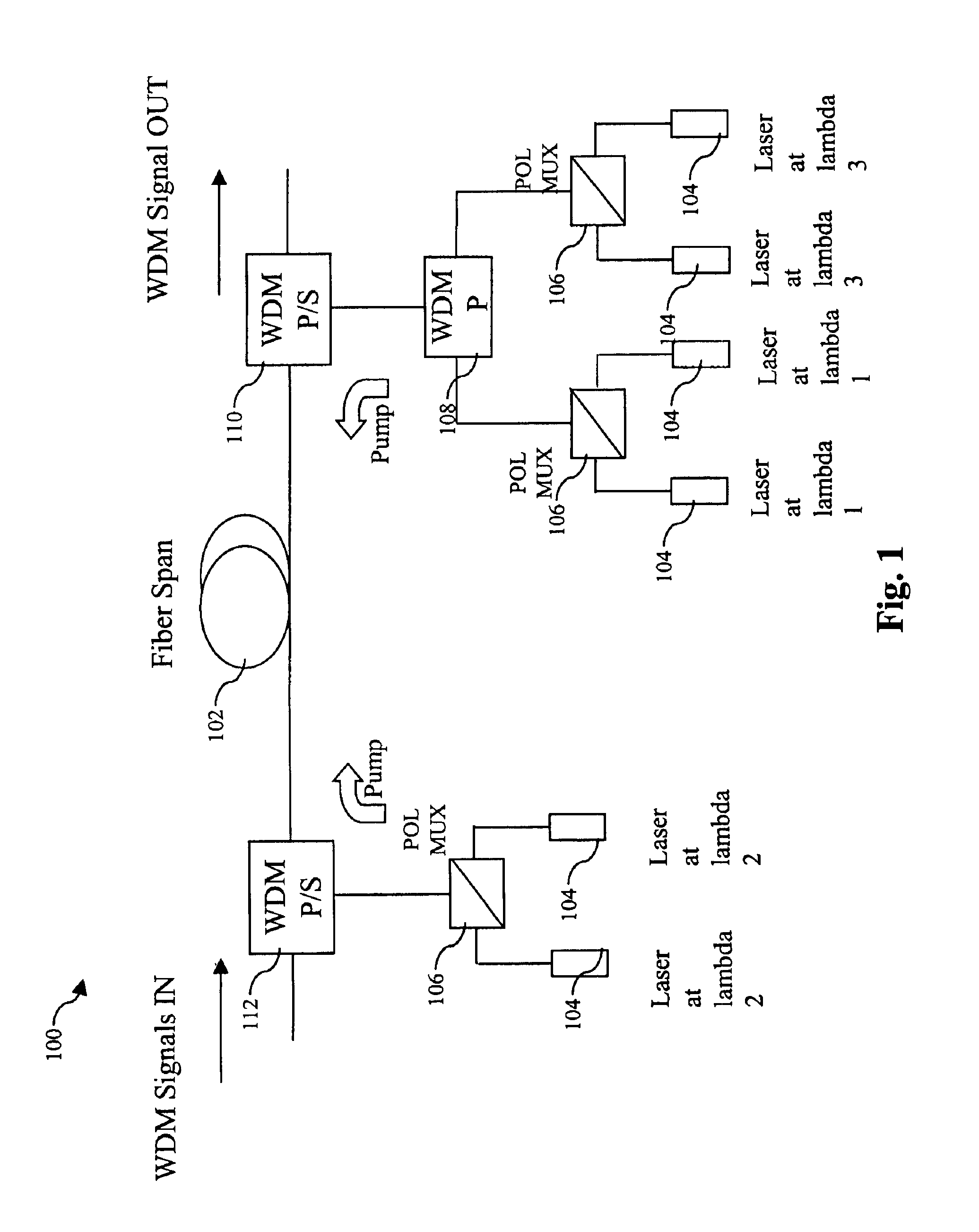
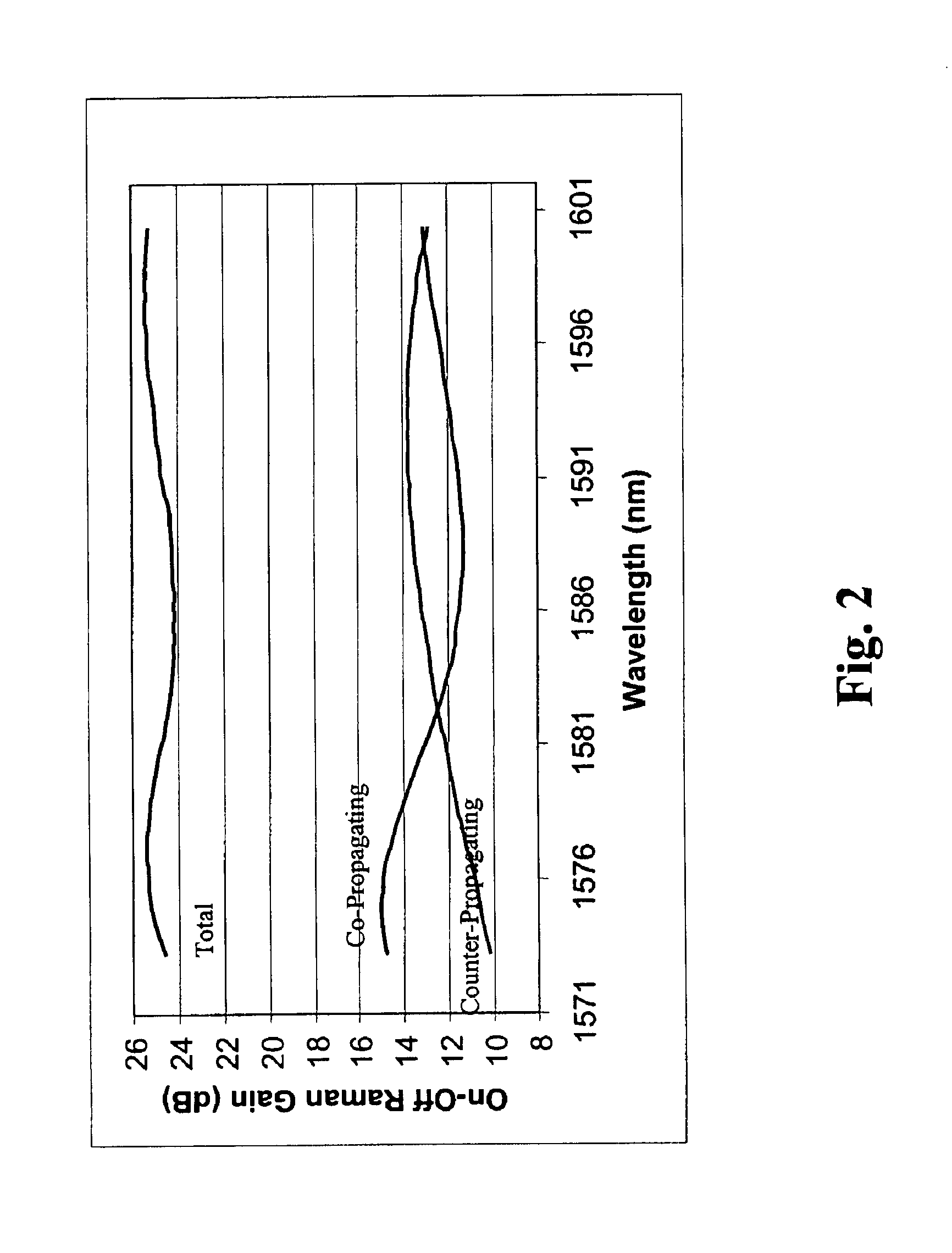
Gain flattened bi-directionally pumped Raman amplifier for WDM transmission systems
InactiveUS6903863B1Improved Gain FlatnessRelatively large bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsElectromagnetic transmissionWdm transmission systemsFiber
Raman amplification of a WDM signal with excellent gain flatness across a very large bandwidth is achieved. Co-propagating and counter-propagating Raman pumping are combined in the same fiber. Multiple pumping wavelengths are employed. Wavelengths employed for co-propagating pumping and wavelengths employed for counter-propagating pumping alternate in order of wavelength. In one embodiment, N co-propagating pump wavelengths and N+1 counter-propagating pump wavelengths are used. Alternatively, one may use N+1 co-propagating pump wavelengths and N counter-propagating pump wavelengths.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
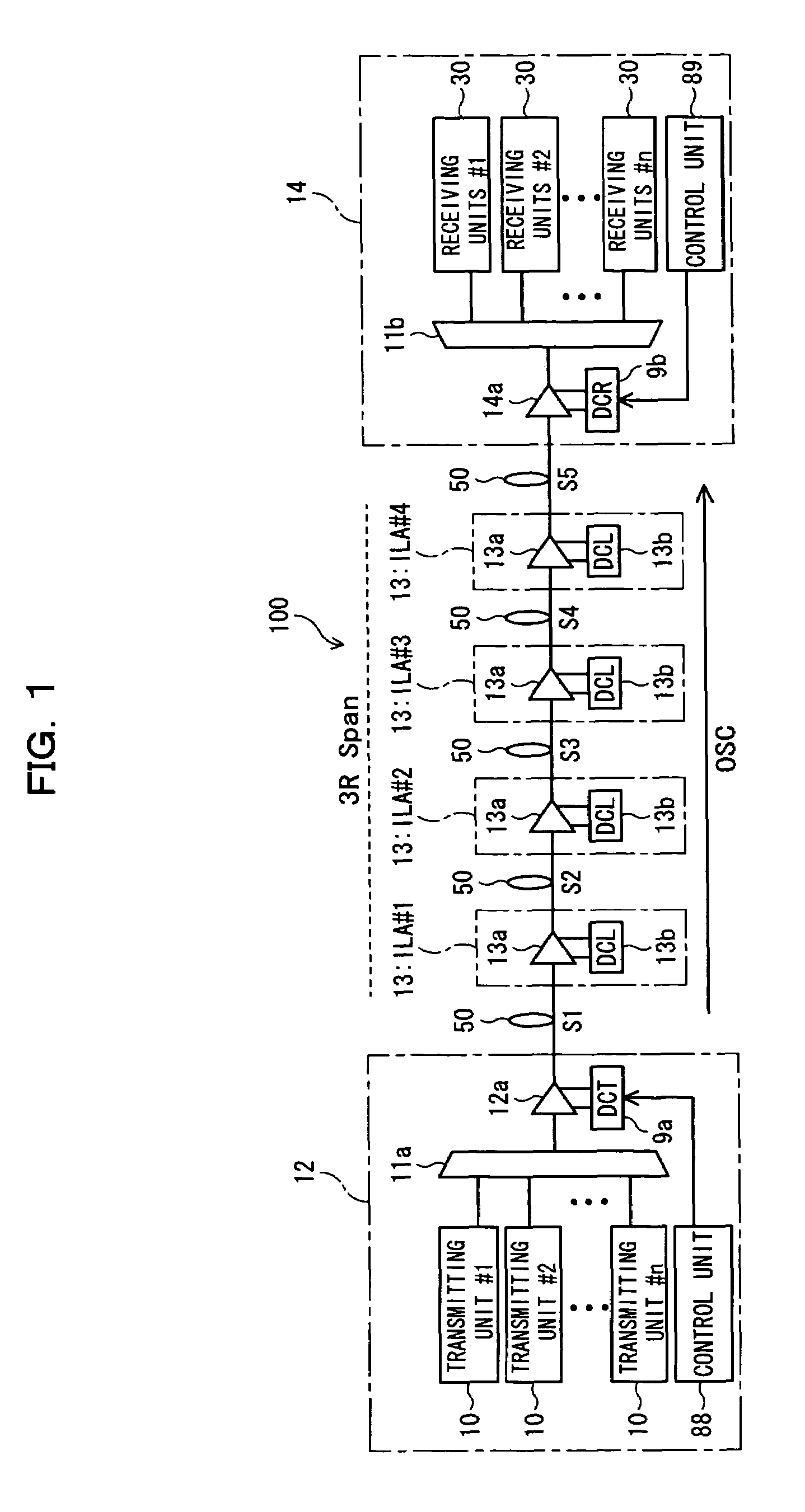
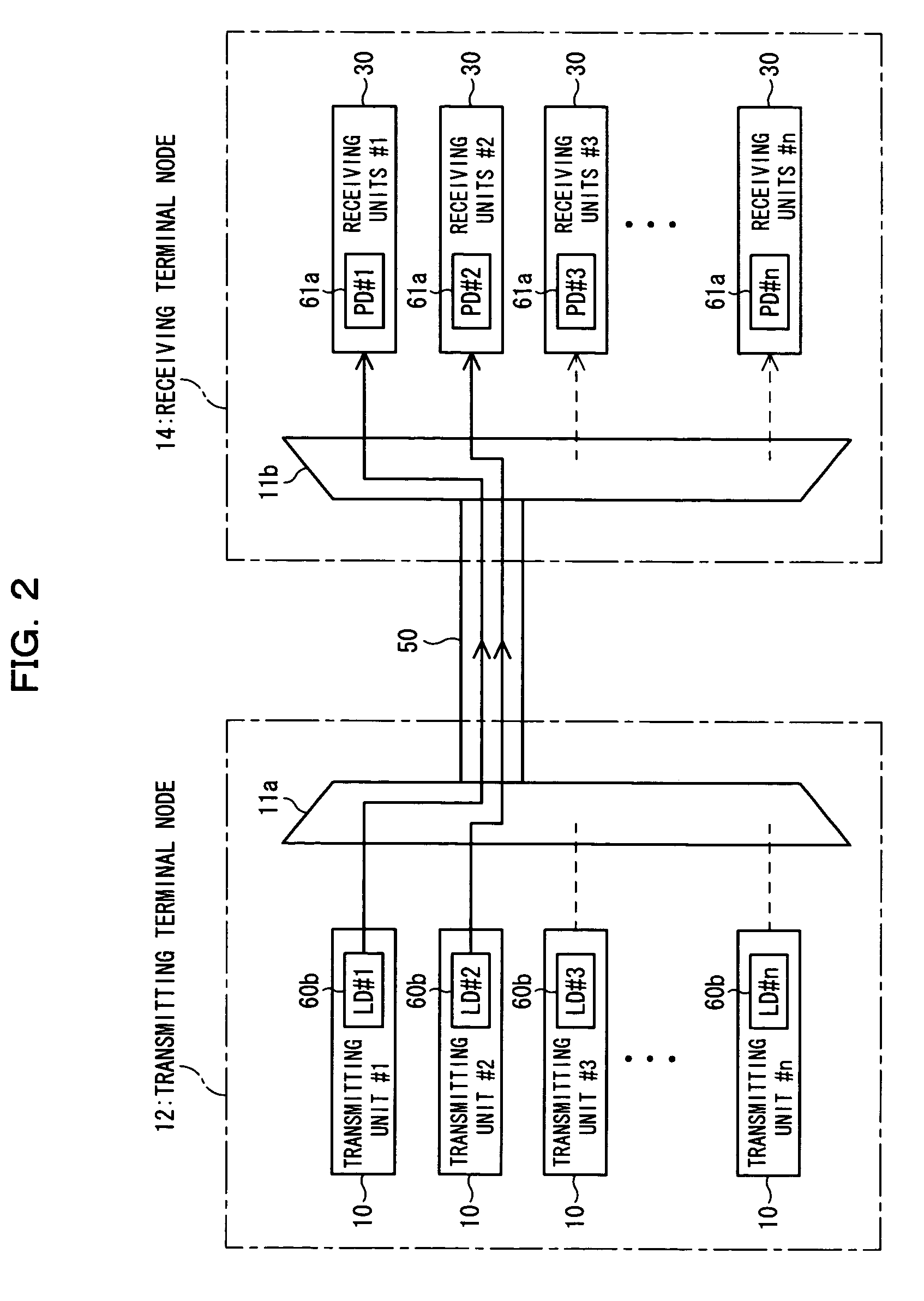
Dispersion compensation quantity setting method, receiving terminal station, and wavelength-multiplexing optical transmission system
InactiveUS20050238362A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationWdm transmission systemsTransport system
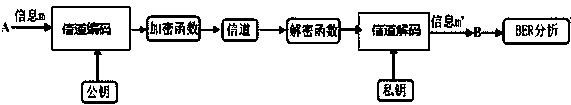
In a dispersion compensation quantity setting technique for use in a WDM transmission system, a transmitting terminal node transmits CW light and modulated light obtained by modulation using a modulation pattern signal, while a receiving terminal node detects a physical quantity stemming from cross phase modulation occurring between the transmitting terminal node and the receiving terminal node on the basis of a variation of an intensity of the transmitted CW light and sets a dispersion compensation quantity on the basis of a variation of the detected physical quantity. Moreover, this optimizes the crosstalk, suppresses the output power of transmitted light, eliminates the nonlinear optical effect of the transmitted light, and carries out dispersion compensation superior in cost performance.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
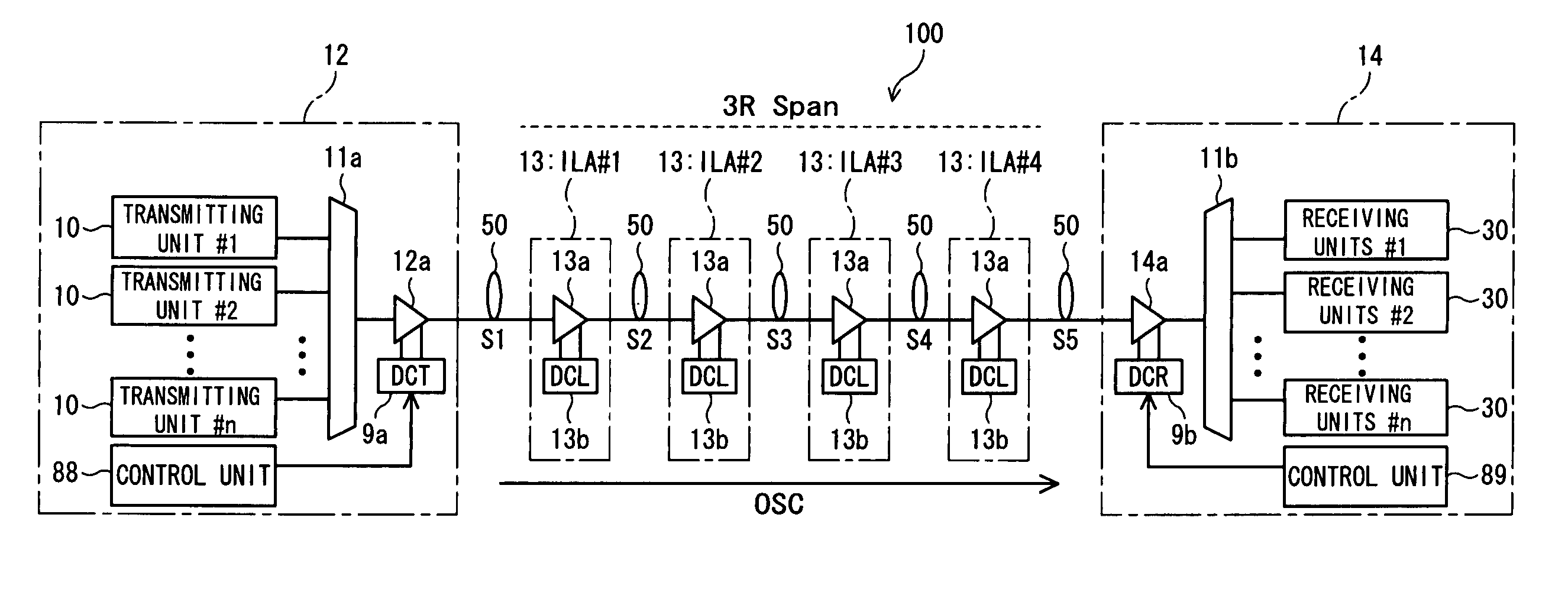
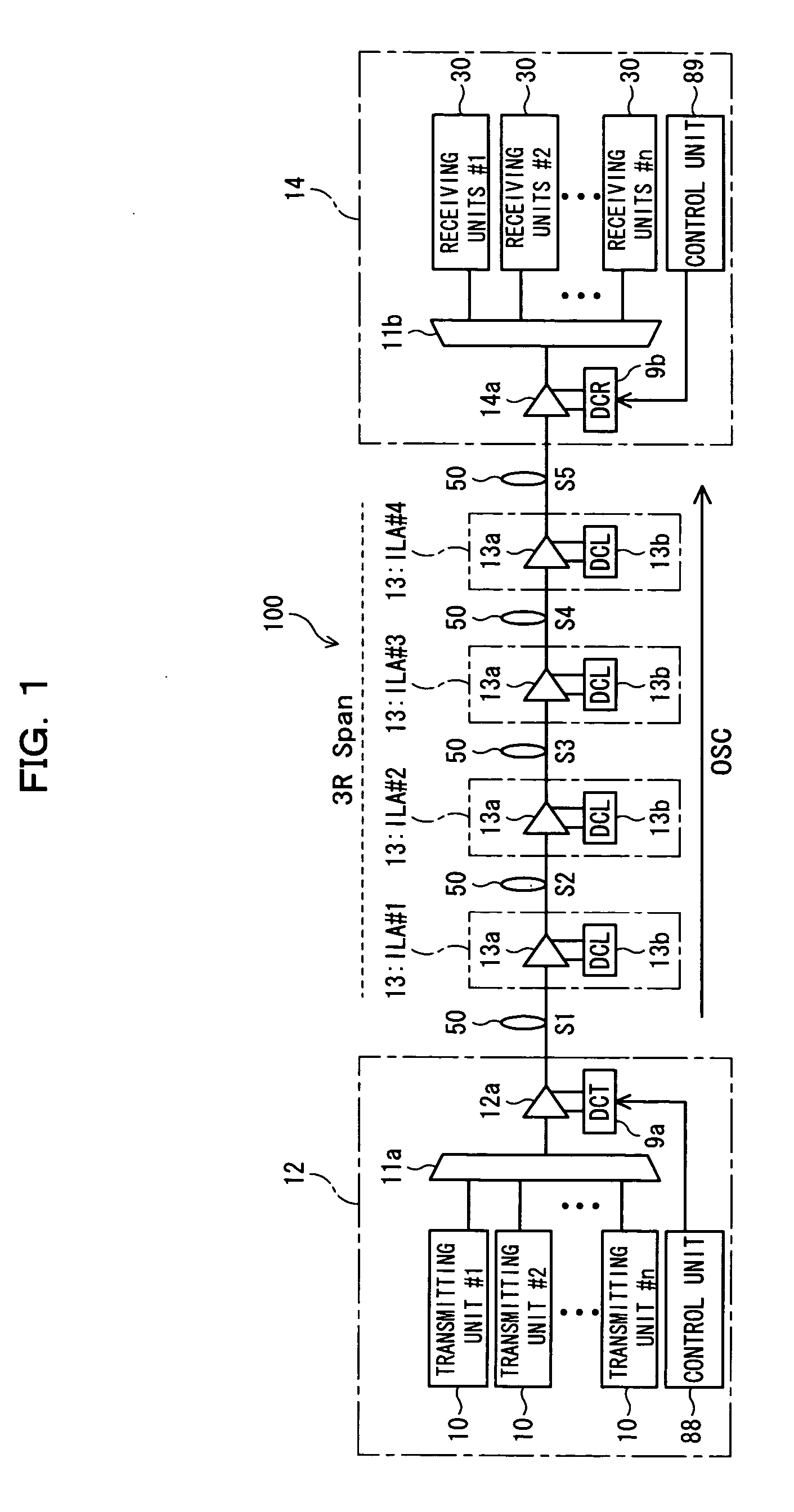
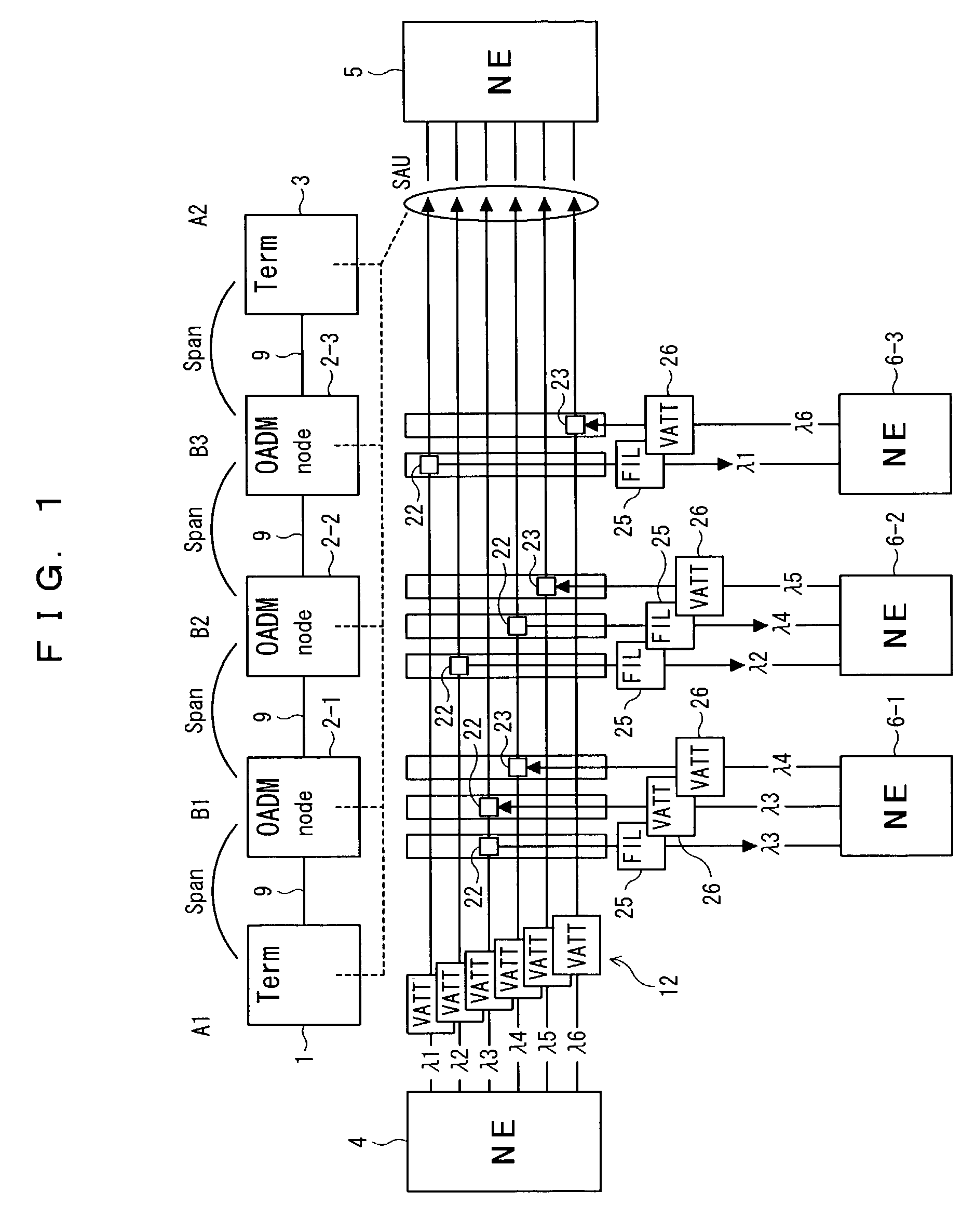
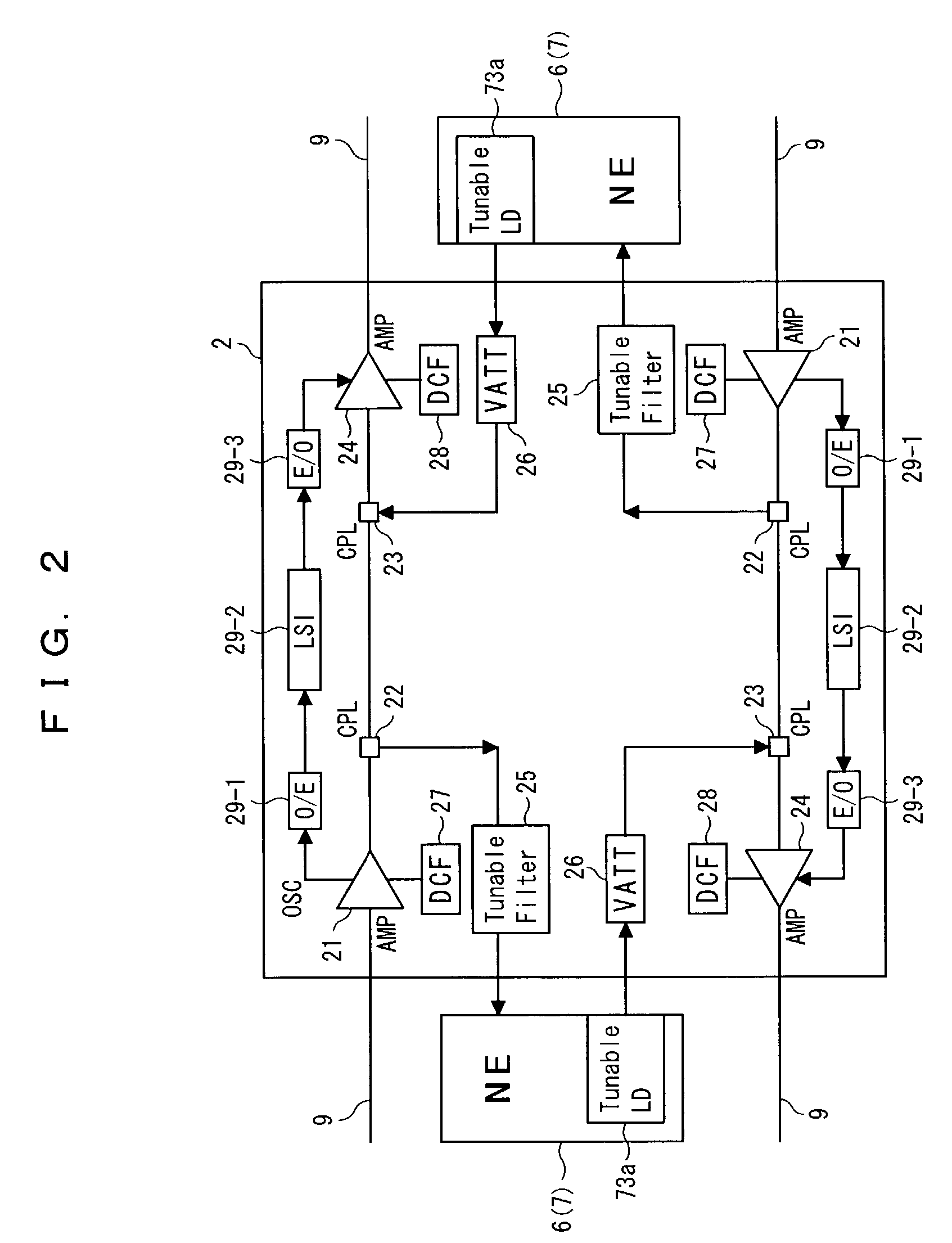
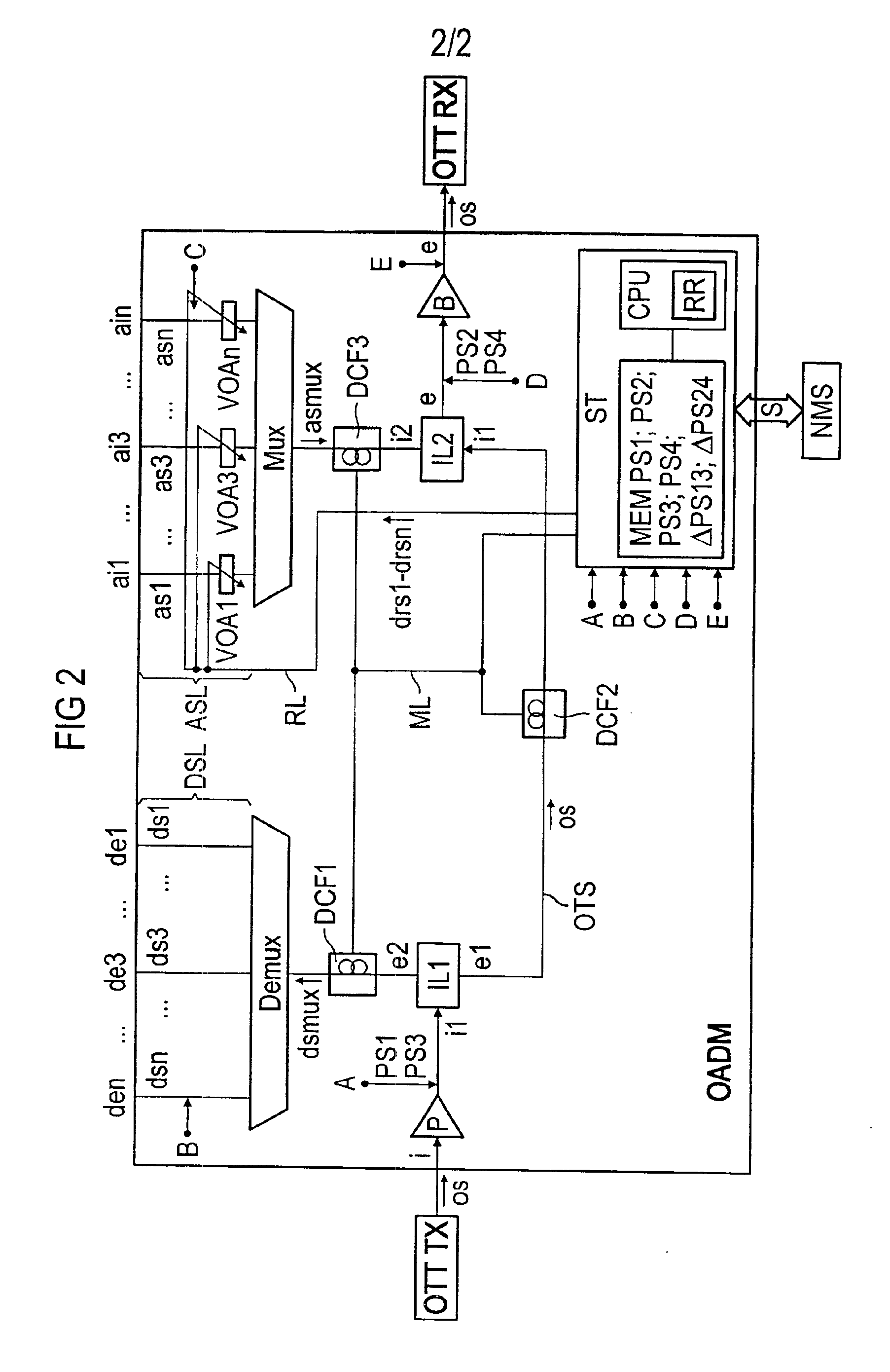
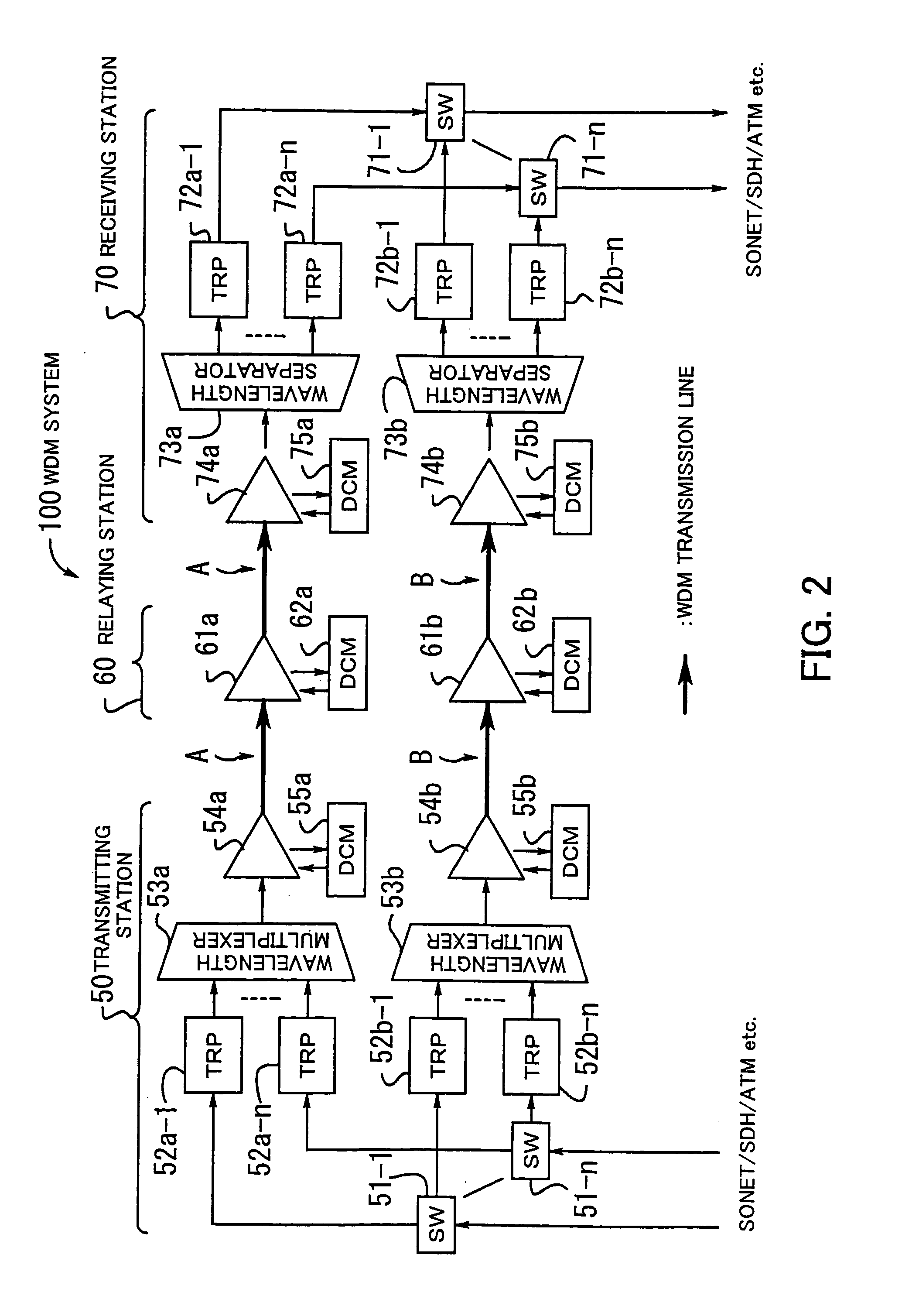
Signal transmission method in WDM transmission system, and WDM terminal, optical add-drop multiplexer node, and network element used in the same system
InactiveUS7139484B2Low costImprove system performanceLaser detailsBus-type electromagnetic networksWdm transmission systemsTransport system
Disclosed herein is a signal transmission method in a wavelength-division-multiplex (WDM) transmission system. The WDM transmission system comprises a first WDM terminal for transmitting a WDM signal, a second WDM terminal for receiving the WDM signal, and an optical add-drop multiplexer (OADM) node for transmitting to a network element an optical signal of a specific wavelength of the WDM signal which is transmitted between the first and second WDM terminals. The WDM signal is transmitted from the first WDM terminal to the second WDM terminal regardless of whether an optical signal is added or dropped at the OADM node. The network element employs an optical signal of an idle wavelength of the WDM signal that has no transmission data, to transmit another transmission data that is transmitted by the network element.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
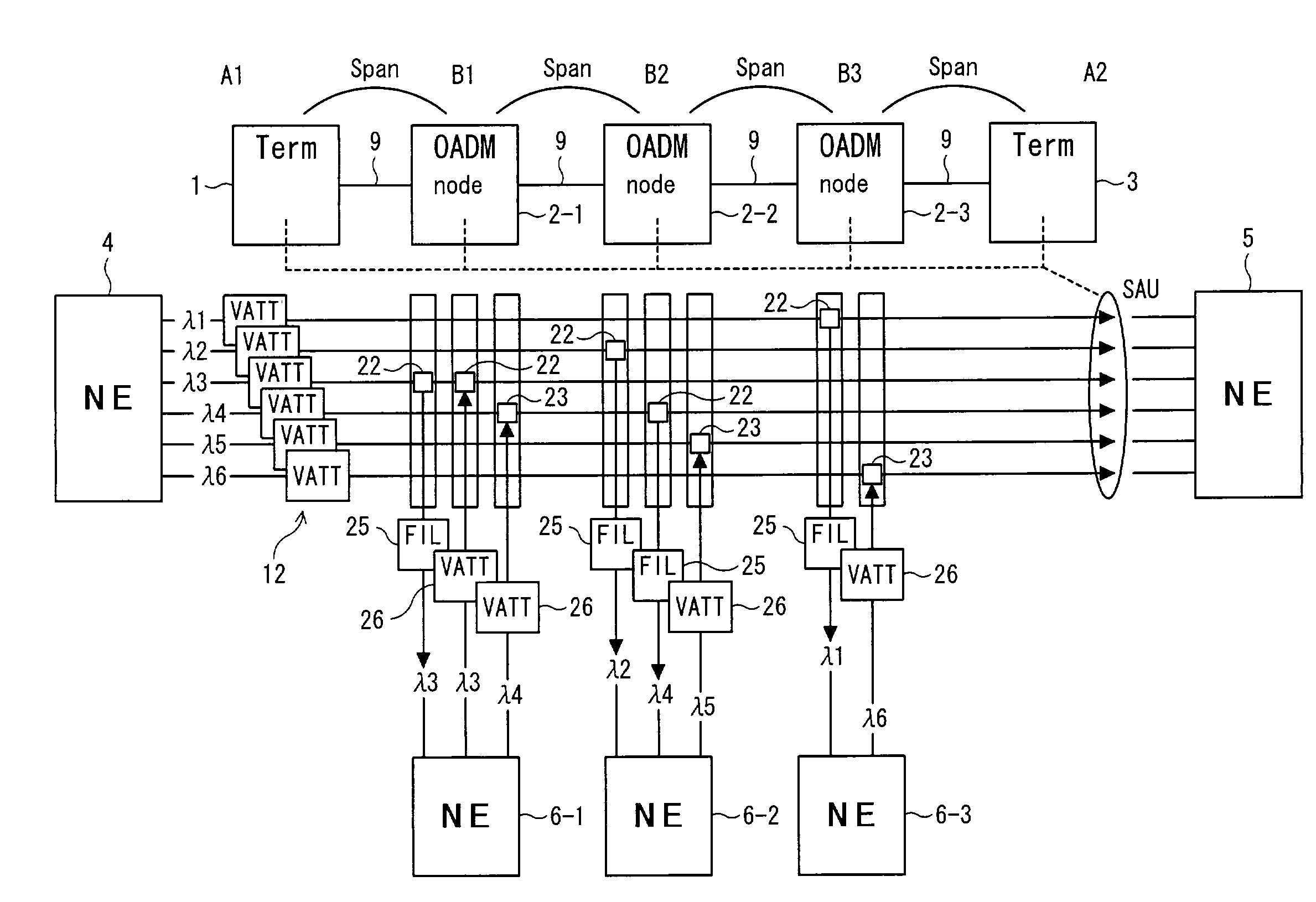
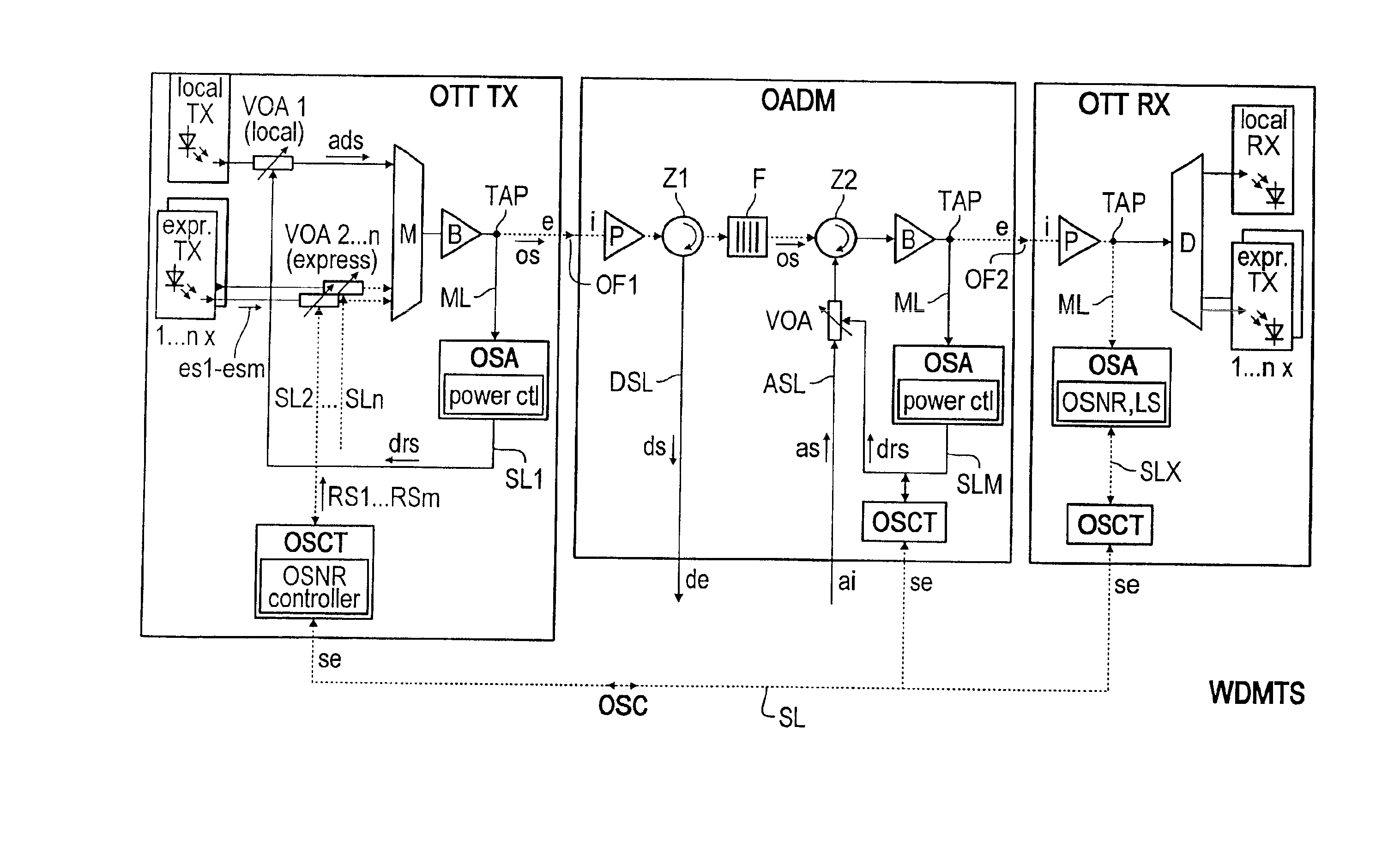
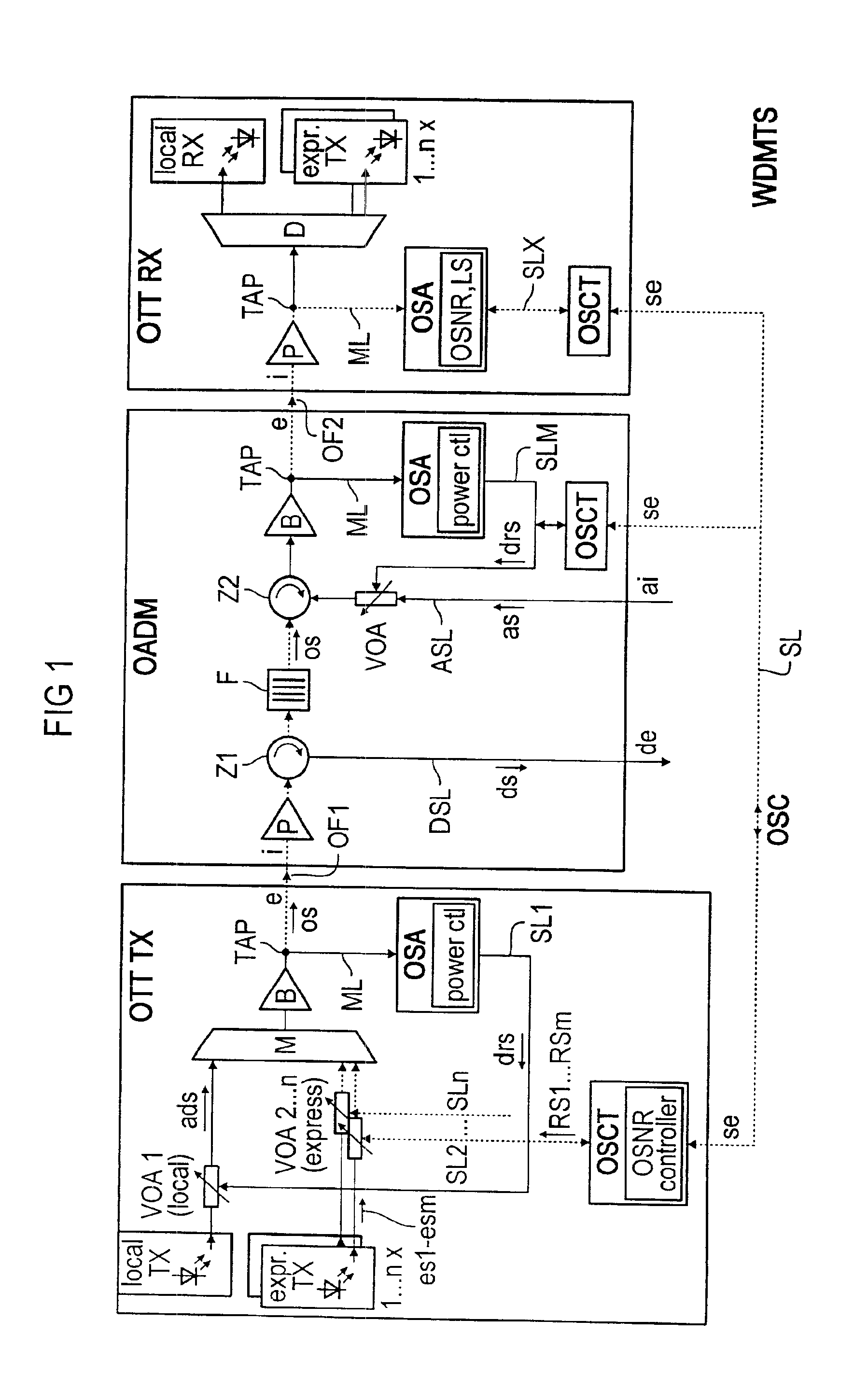
Method for controlling the signal/noise ratio of optical add/drop signals
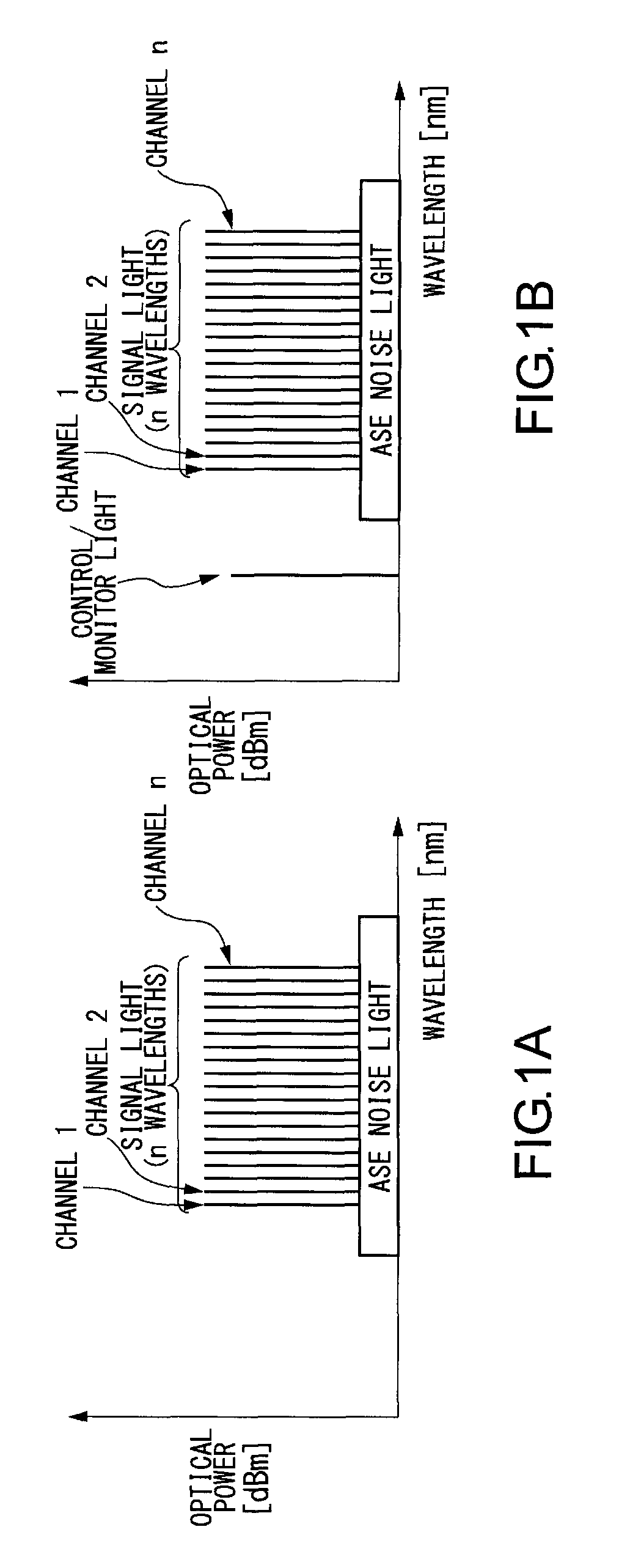
InactiveUS6885820B2Raise the ratioExpand the transmission rangeWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringWdm transmission systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method and apparatus for controlling the signal / noise ratio of optical add / drop signals in an optical WDM transmission system having a transmitter unit, a receiver unit and at least one optical add / drop multiplexer for transmitting optical express signals and at least one optical add / drop signal wherein the power spectrum of the pre-emphasized express signals is determined, and the signal level of the at least one optical add / drop signal is adapted to the power spectrum determined for the express signals.
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
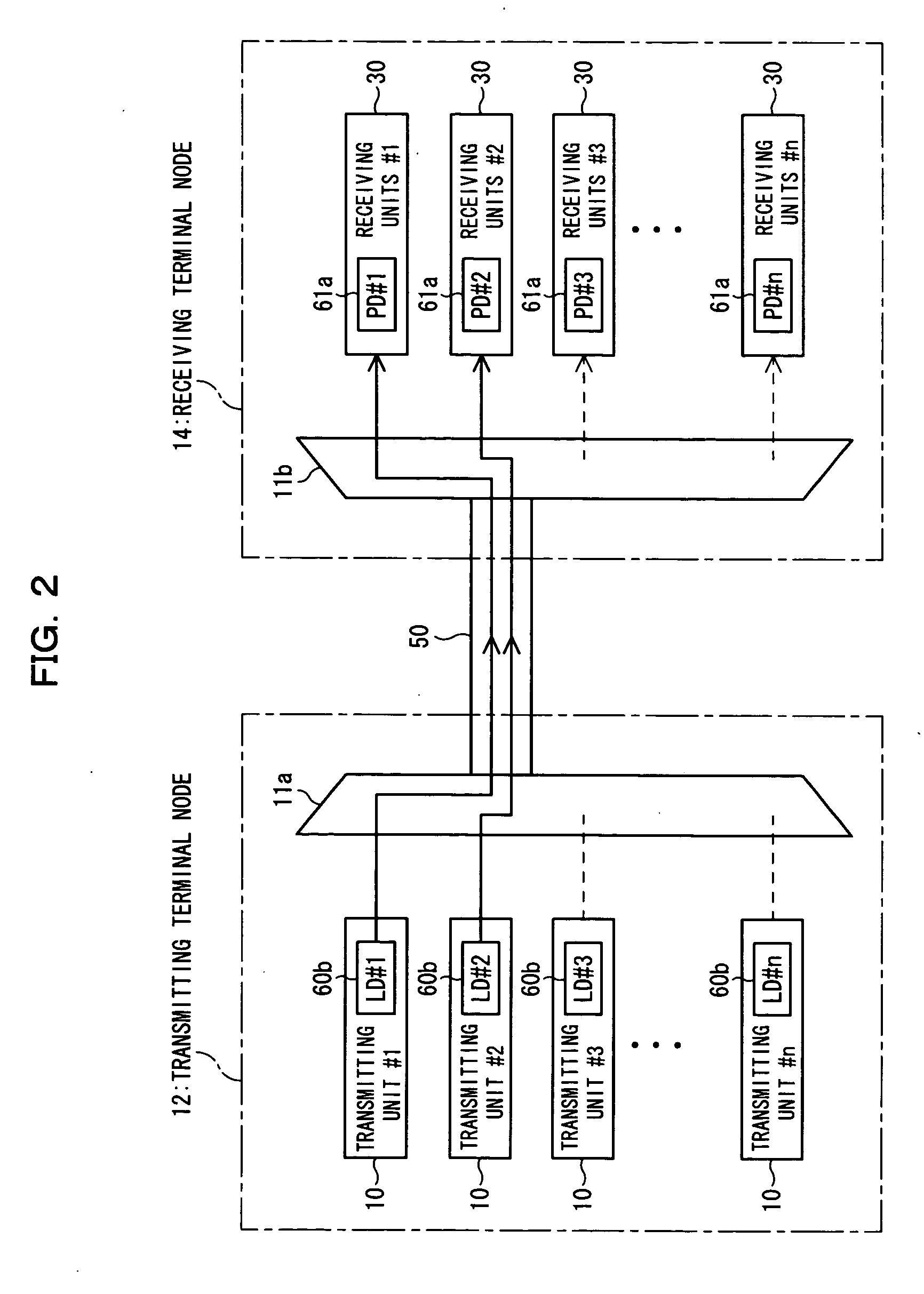
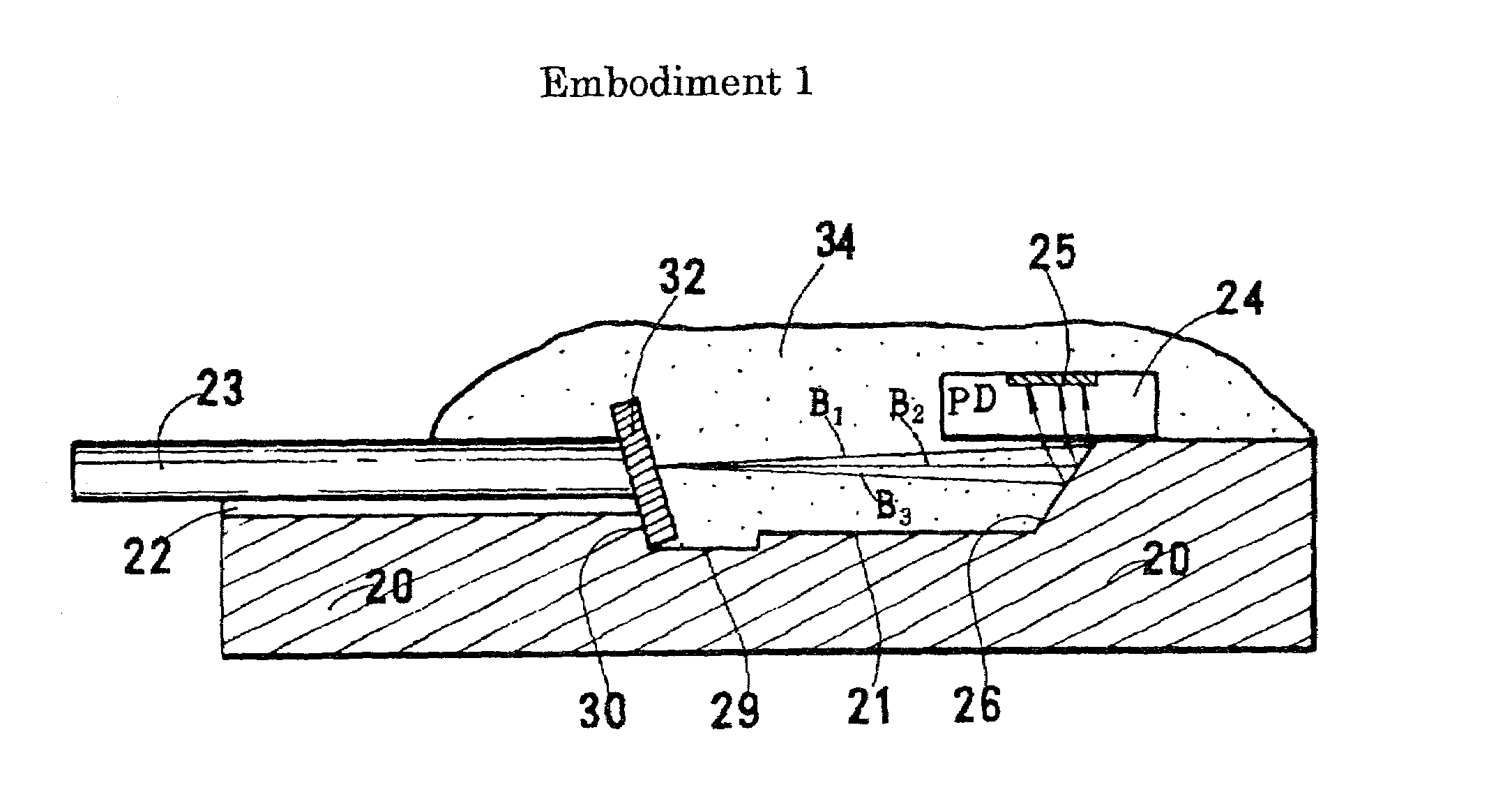
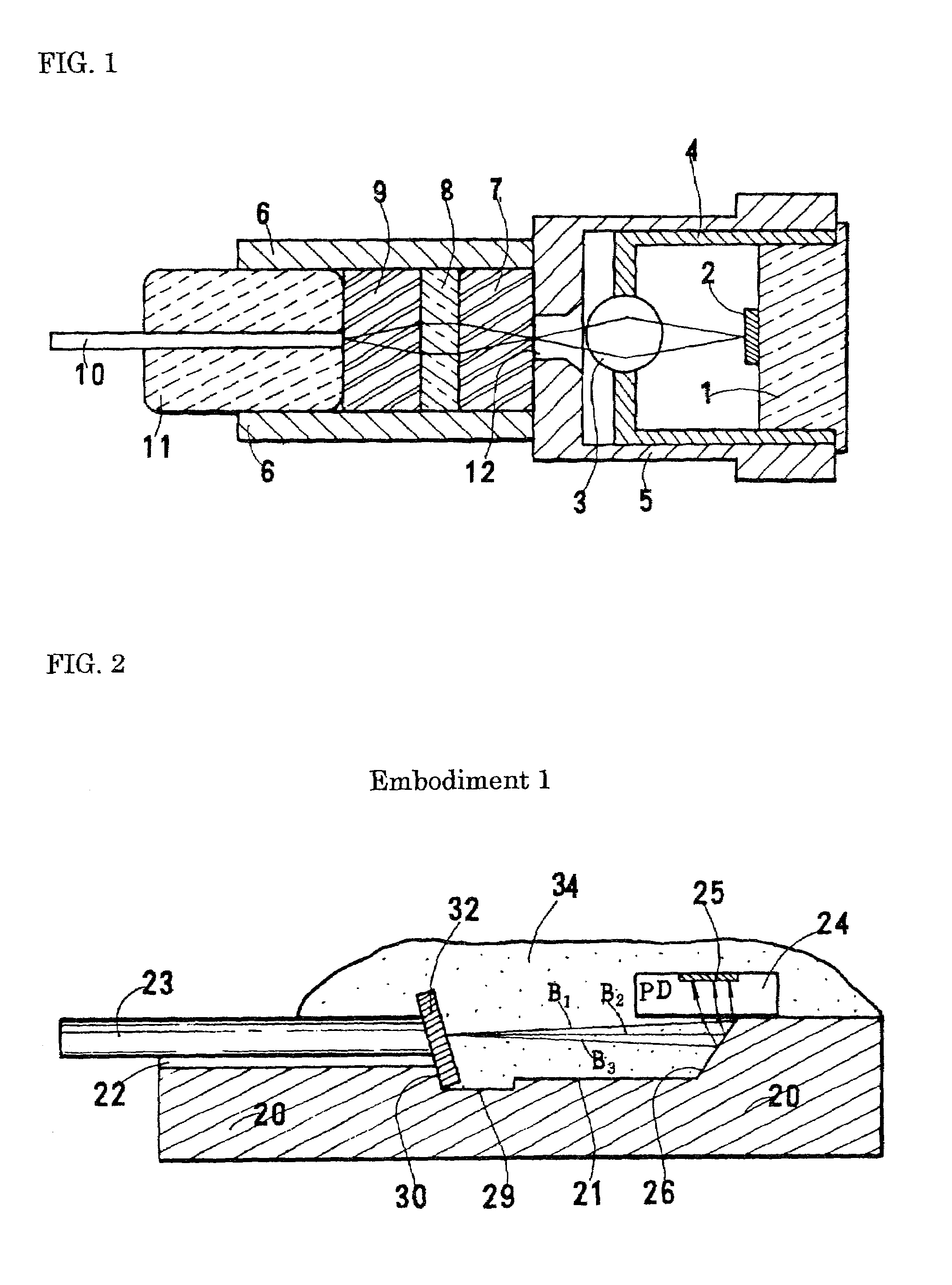
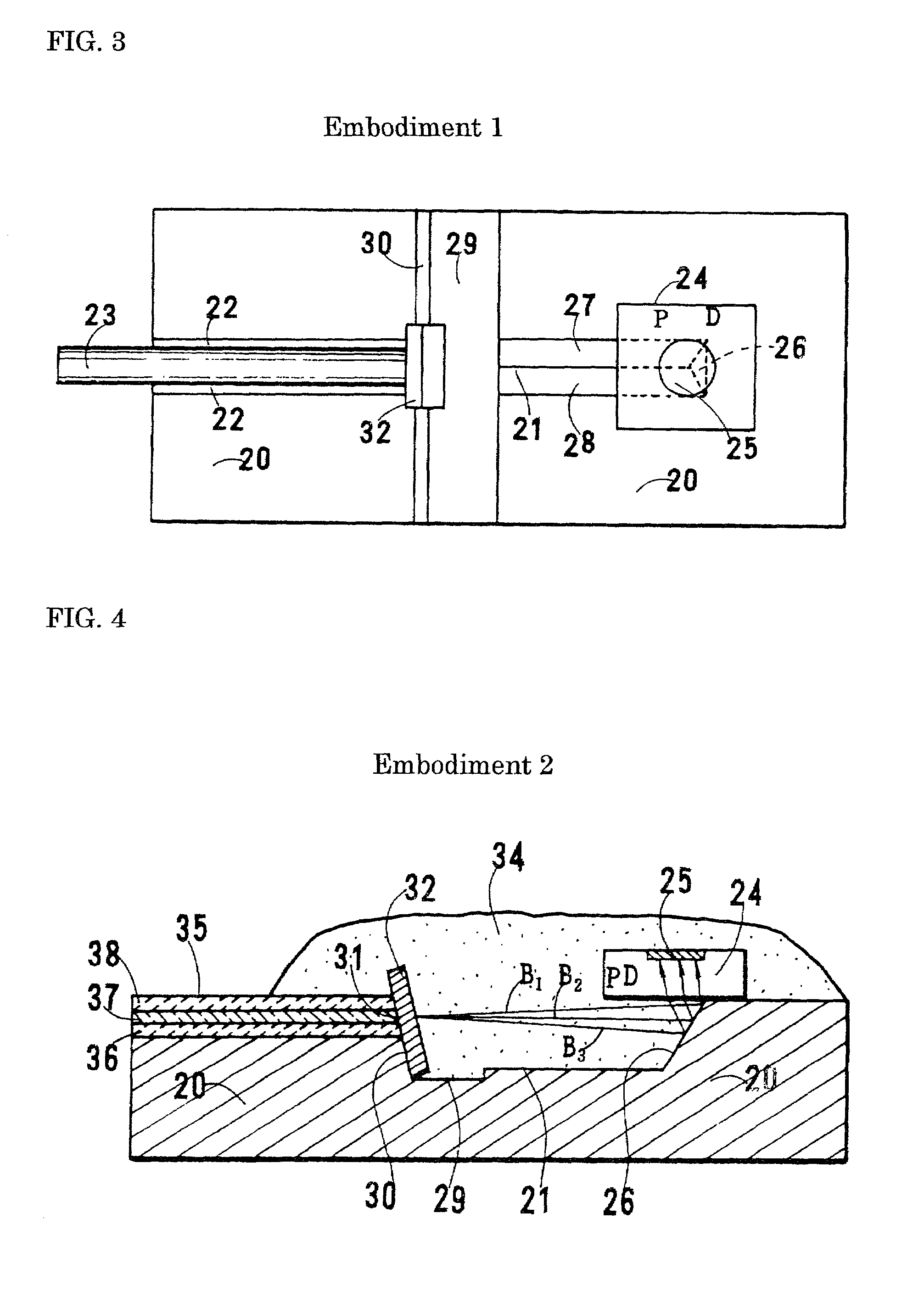
Optical receiver
ActiveUS7106980B2Improve performanceSmall sizePhotometrySolid-state devicesFiberWdm transmission systems
An optical receiver, small and inexpensive, is used for a WDM transmission system in place of a wavelength demultiplexer. In the receiver, a light-transmitting medium and a photodiode (PD) are placed on the same substrate, a wavelength-selecting filter is attached perpendicularly or obliquely to the end face of or to a cut section at the midpoint of the medium, the filter transmits only the assigned wavelength included in the incident light having multiplexed wavelengths, and the PD detects only the assigned wavelength. With an optical fiber, the fiber can be housed in a ferrule. In this case, the filter is inserted into a filter-supporting hole provided at a midpoint of the ferrule, the ferrule is fixed in a groove formed on the substrate, and an optical pathway-changing groove formed on the substrate reflects light having emerged from the optical fiber to introduce it into the PD.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
WDM system having chromatic dispersion precompensation
ActiveUS7400835B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionWdm transmission systemsMultiplexer
Chromatic dispersion in a high speed CS-RZ WDM transmission system is reduced by providing tailored “precompensation” for individual and / or groups of optical signals. Such precompensation is achieved by passing the optical signals through a dispersion compensating elements, such as dispersion compensating fiber, within an optical multiplexer, i.e., prior to multiplexing the signals onto a single optical fiber. Additional dispersion compensation can be performed in optical amplifiers and within an optical demultiplexer downstream from the optical multiplexer.
Owner:CIENA
Optical amplifier, passing-wavelength characteristic control method in optical amplifier, and optical transmission system
InactiveUS20040136053A1Laser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm transmission systemsOptical power
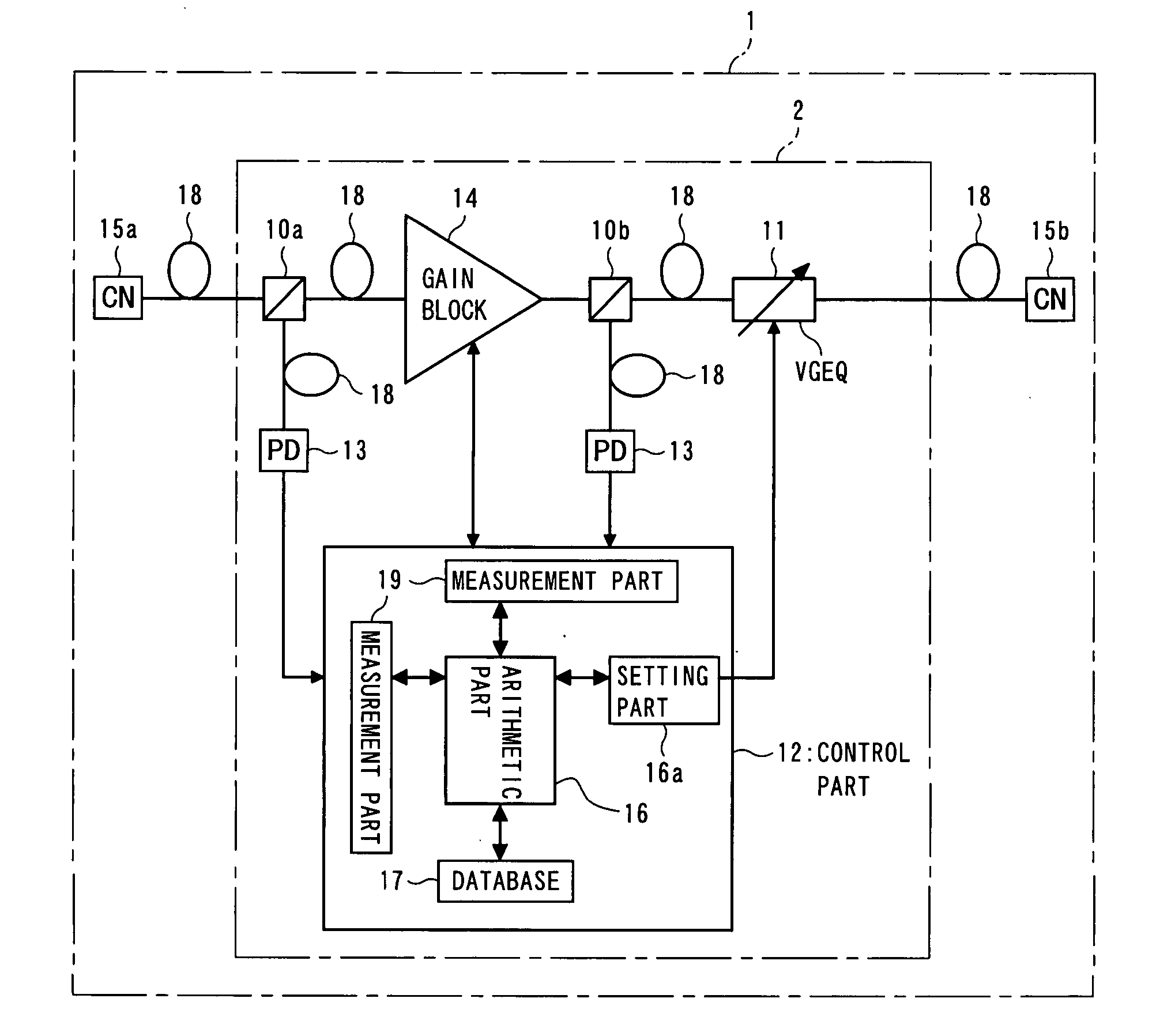
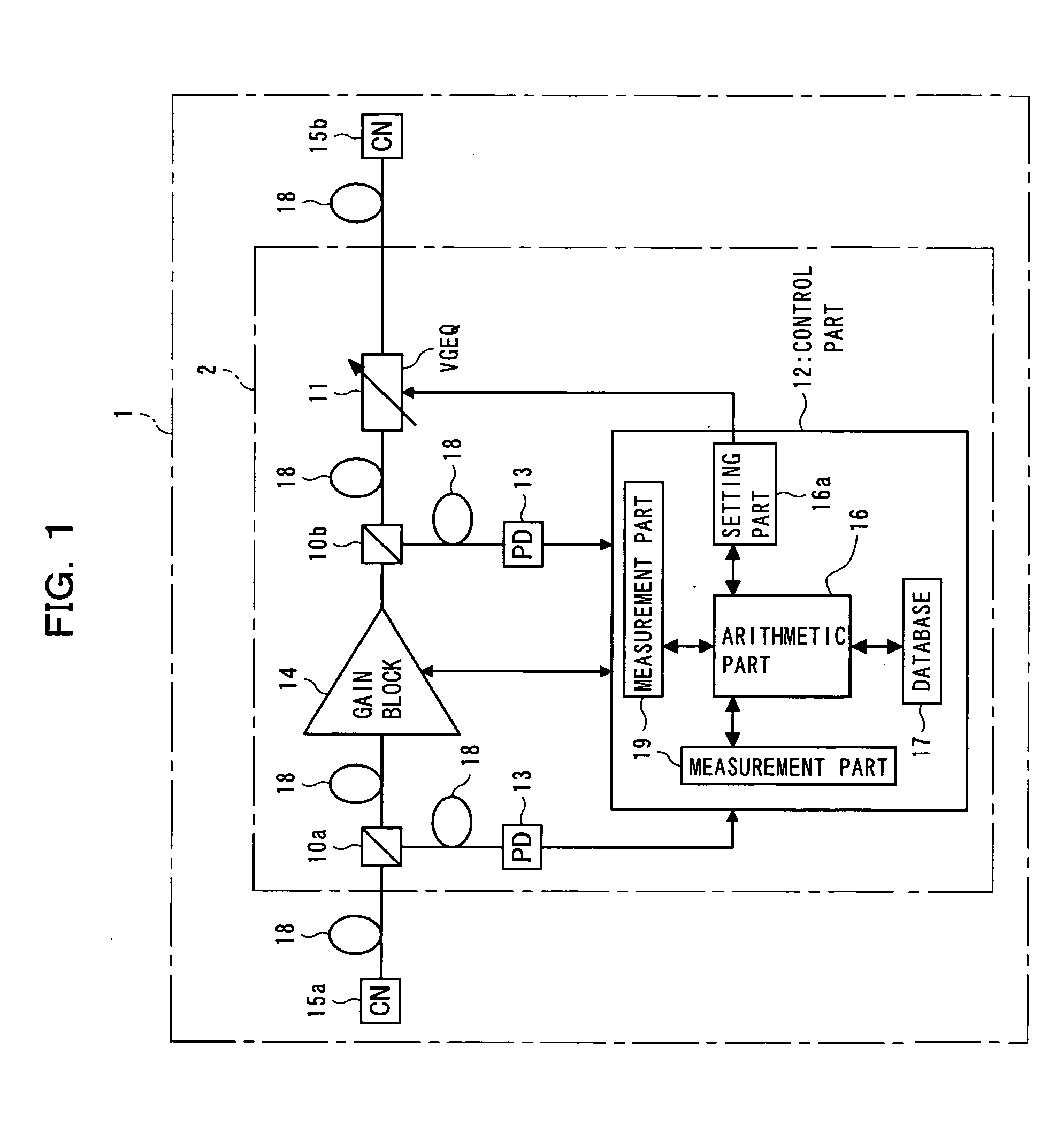
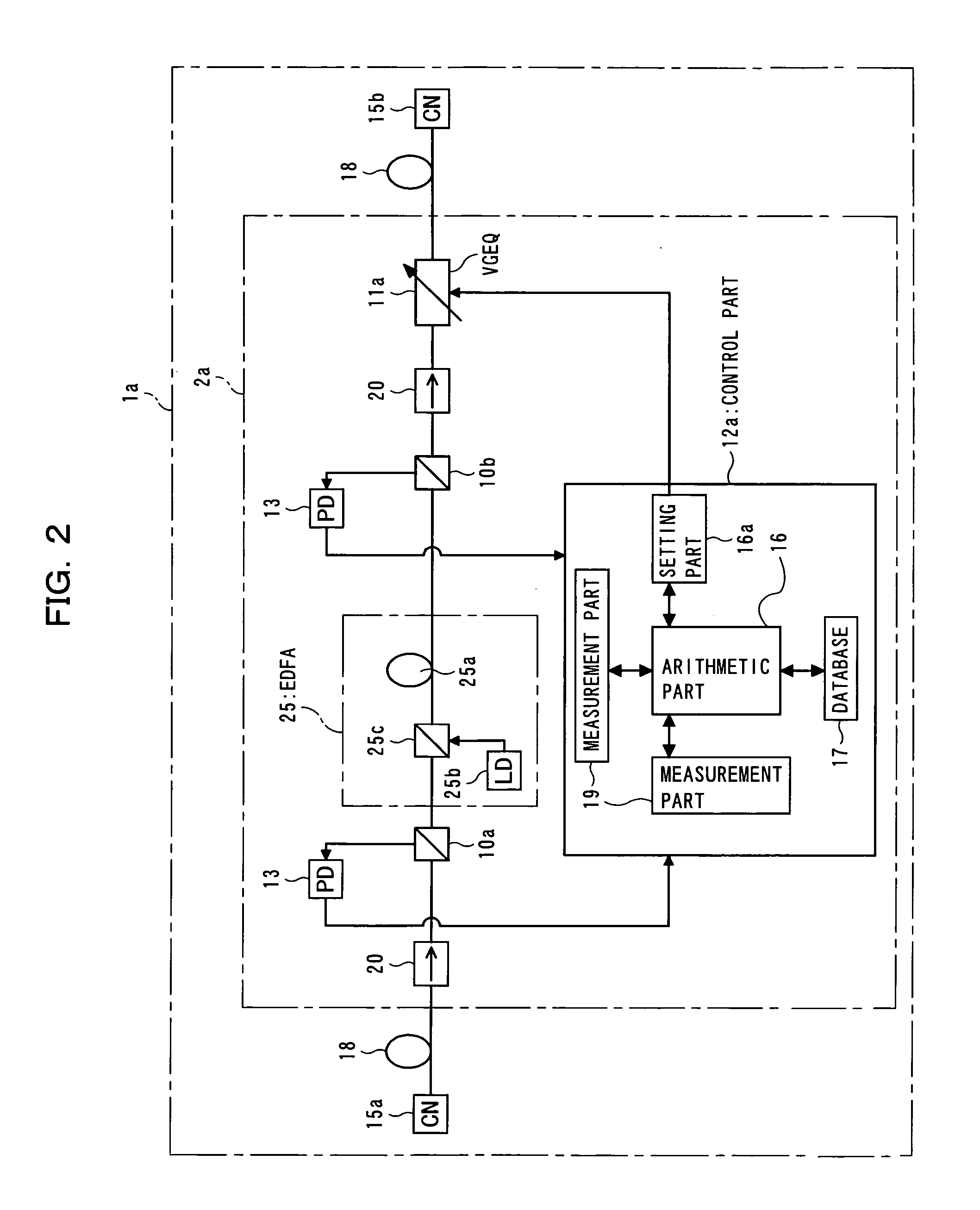
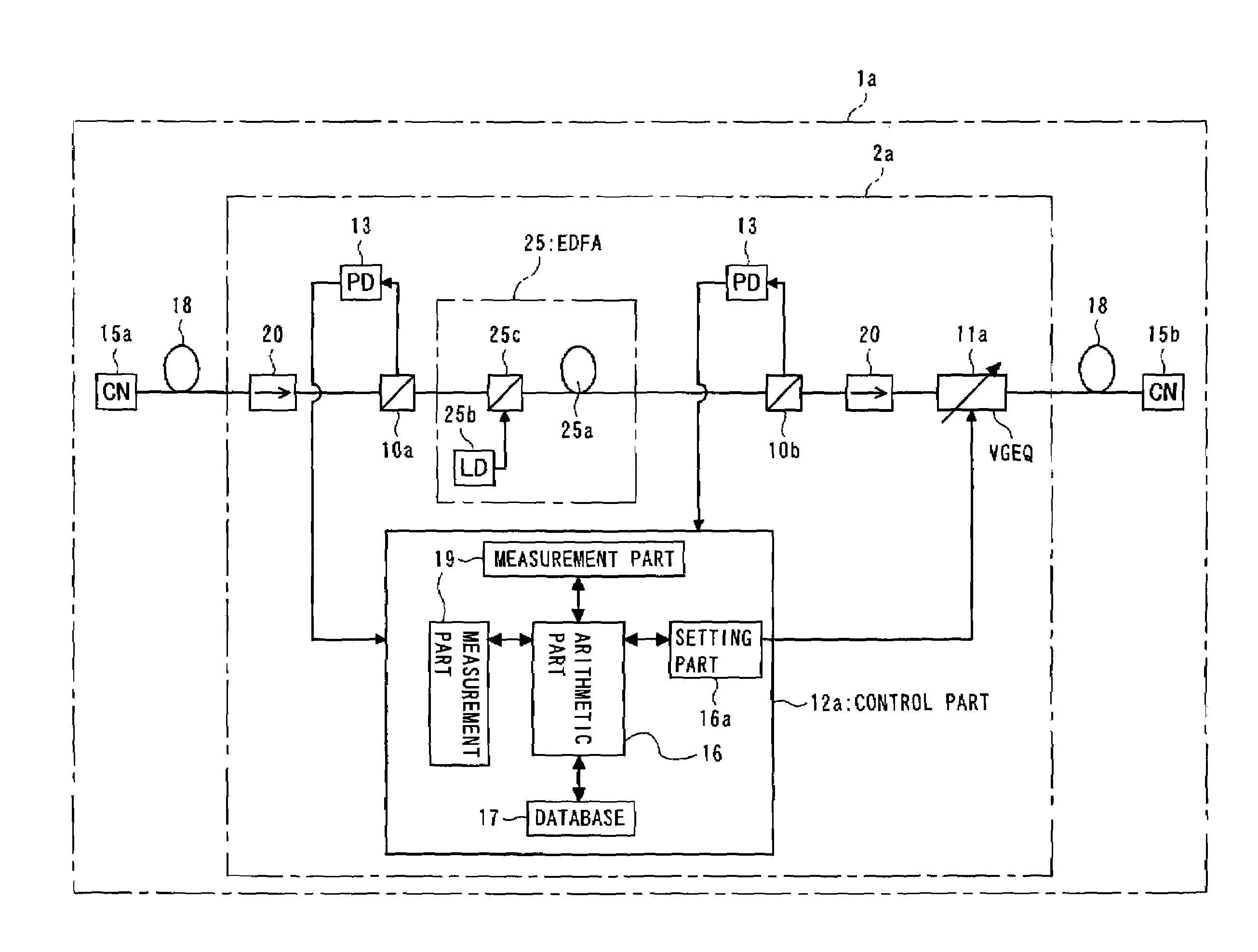
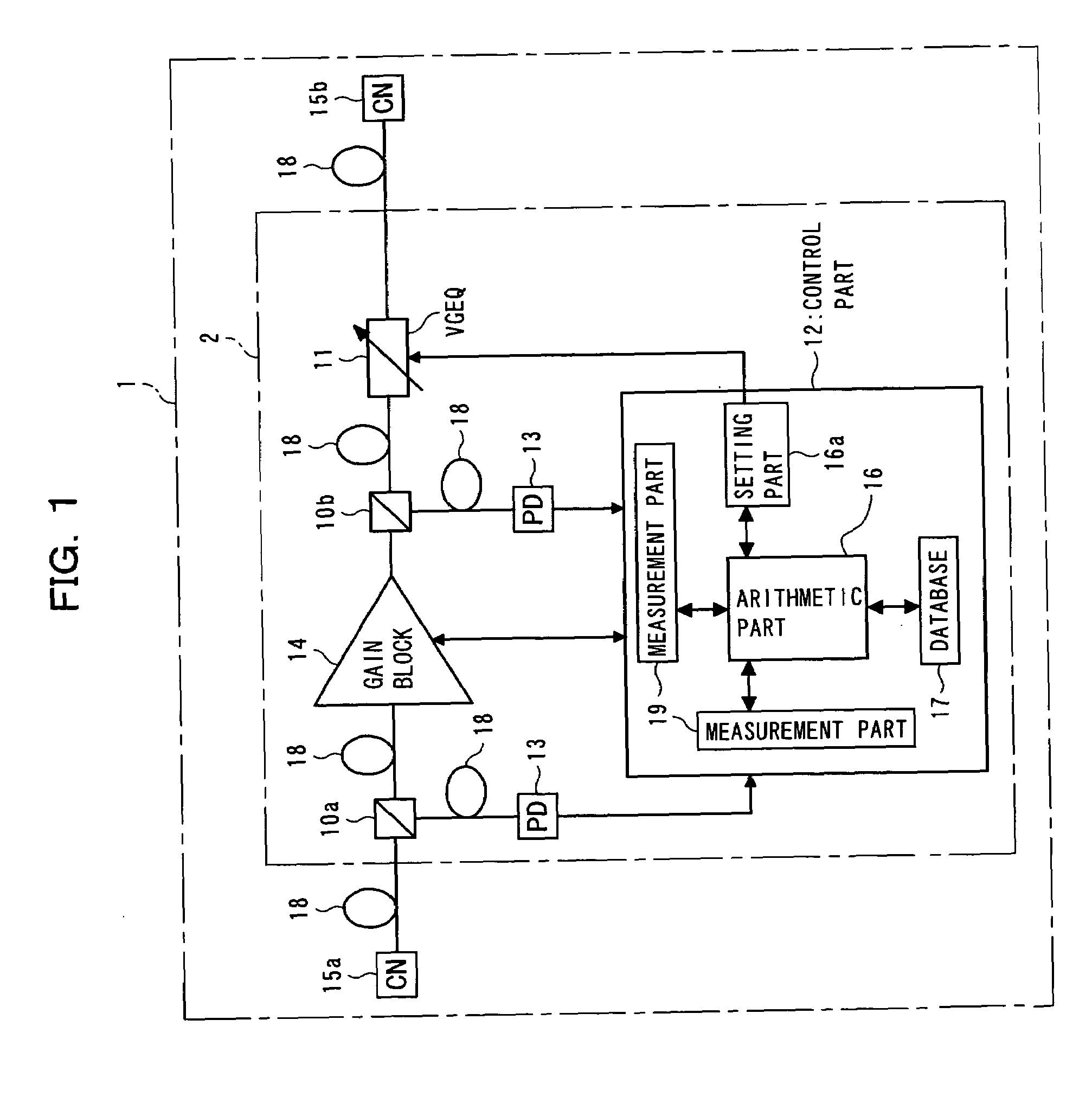
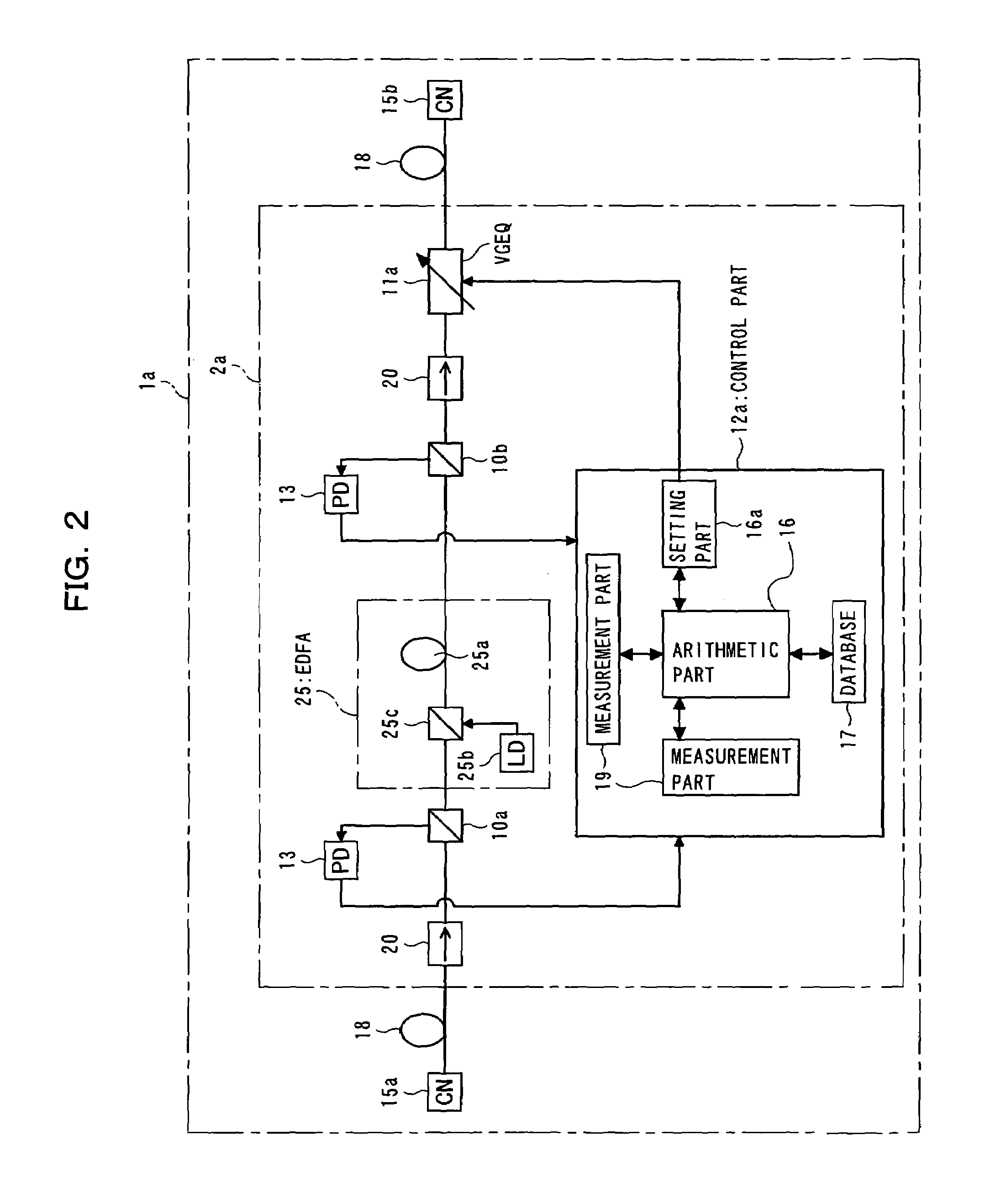
An optical amplifier, provided in a WDM transmission system, contains an amplification medium for amplifying WDM light, a measurement part for measuring at least one input optical power of the WDM light on both input and output sides of the amplification medium, a variable gain equalizer for variably setting a passing-wavelength characteristic, a database for holding data representing wavelength characteristics that respectively correspond to transmission line types, an arithmetic part for computing an inverted passing-wavelength characteristic resulting from a passing-wavelength, based on an acquired transmission line type, the optical power measured by the measurement part, and the data held in the database, and a setting part for setting a passing-wavelength characteristic of the variable gain equalizer, based on the inverted passing-wavelength characteristic computed by the arithmetic part, and with this, capable of controlling optical filters more quickly and amplifying optical signals more efficiently in WDM systems.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
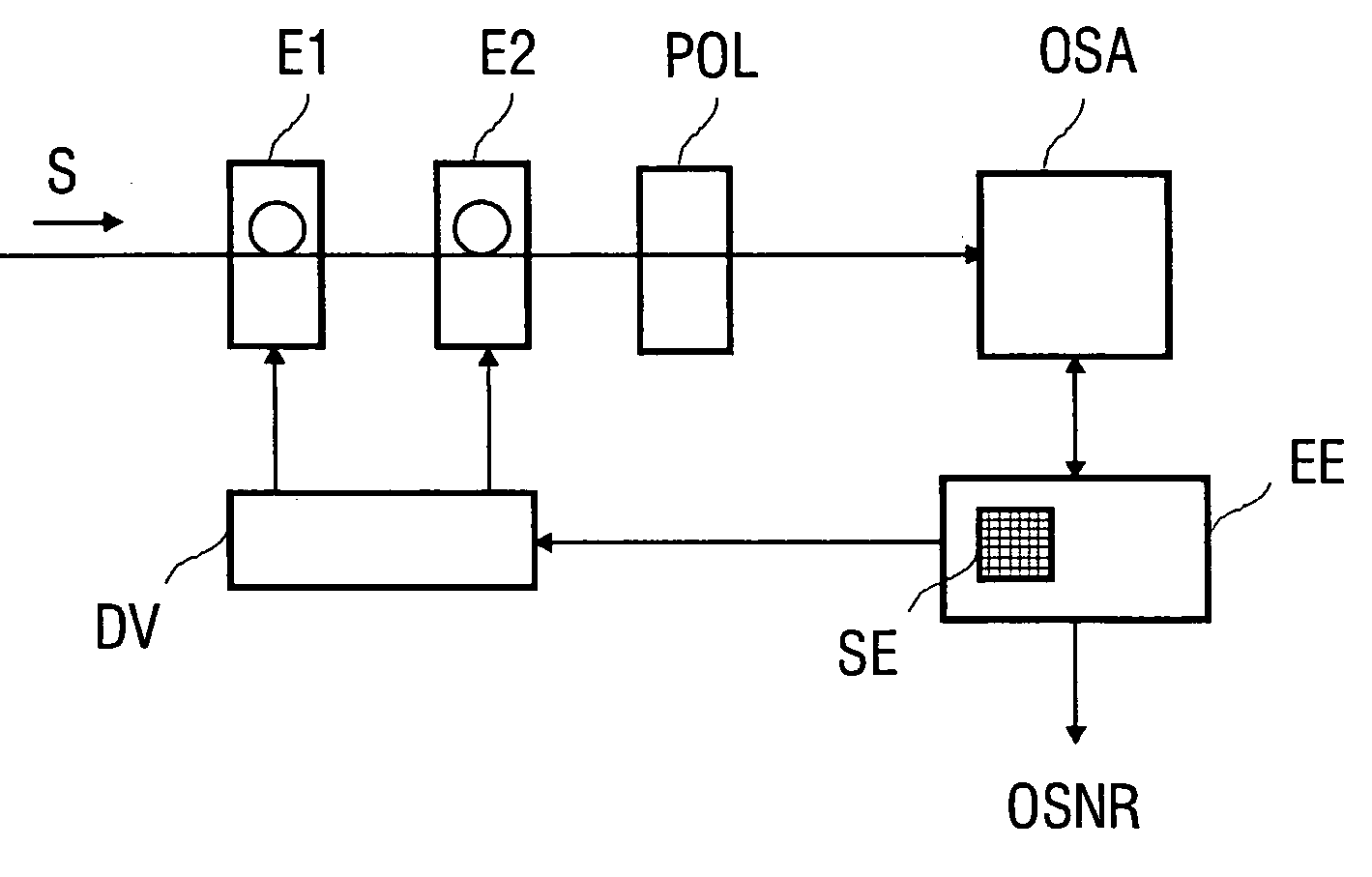
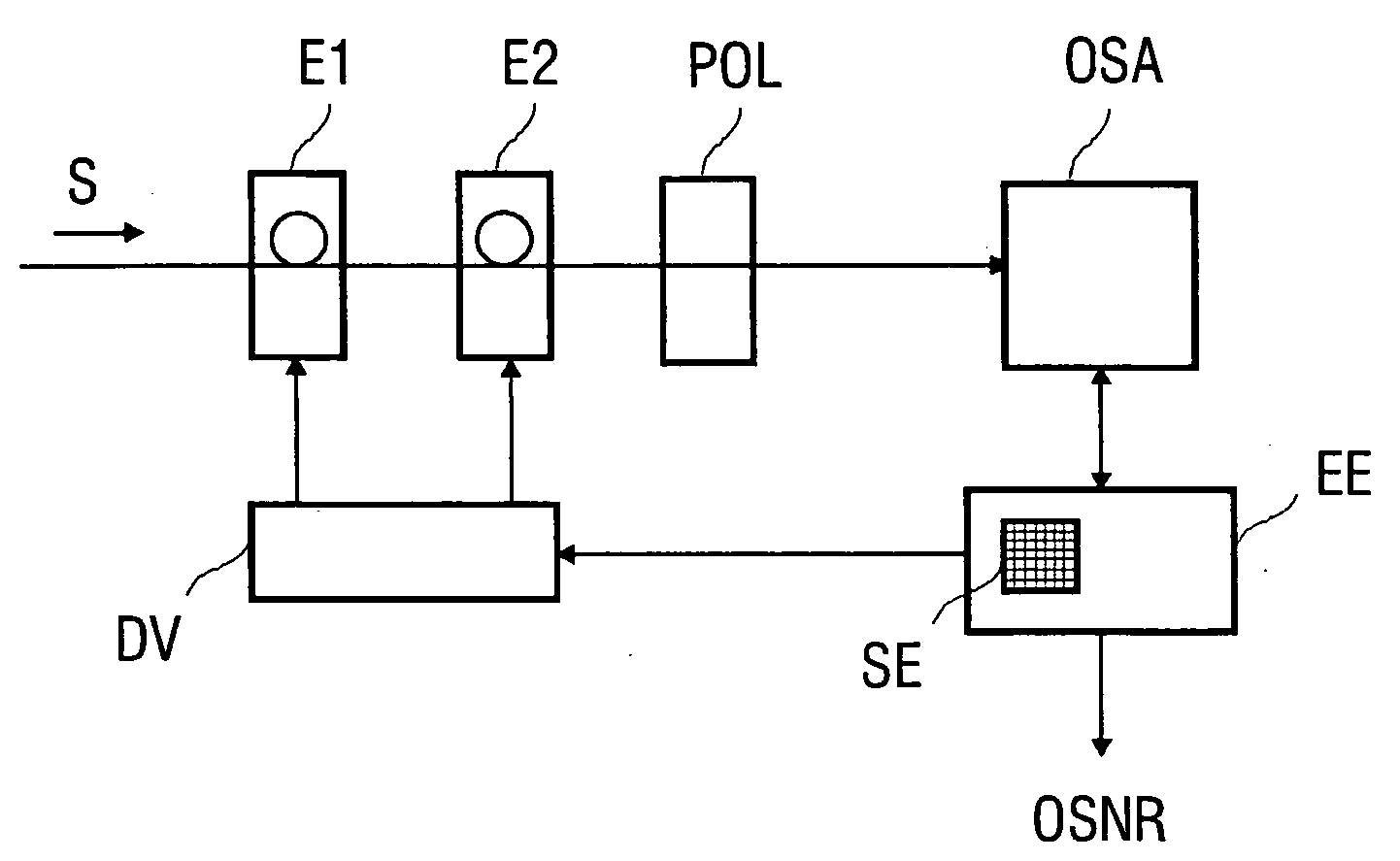
Method for determining the signal-to-noise ratio of an optical signal
InactiveUS20060051087A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsWdm transmission systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method for determining signal-to-noise ratios and noise levels in an optical signal is disclosed, the first polarisation state of which is converted into a second polarisation state by means of number of tunings of a polarisation regulator. Defined changes to the second polarisation state are adjusted on the Poincare sphere by means of the polarisation regulator, whereby power values for the optical signal are determined after selection of a component of the electrical field. Some of the determined power values for the optical signal are stored and serve for the calculation of the signal-to-noise ratio of optical signals. Said method is rapid, requires little complicated equipment and is particularly suitable for a WDM transmission system in which many channels in a WDM signal are transmitted with small channel separations.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Optical wavelength controlling method and a system thereof
InactiveUS20070077066A1Improve accuracyWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringMultiplexingWdm transmission systems
An optical wavelength controlling method and a system thereof for an optical wavelength division multiplexing transmission system, wherein a plurality of wavelengths of channels are multiplexed and transmitted by an optical transmitting unit, and the multiplexed wavelengths are divided into the wavelengths of the channels by an optical receiving unit, are disclosed. The optical wavelength controlling method includes: a step of reducing optical power of the wavelength of a target channel, and transmitting the wavelengths; a step of evaluating channel crosstalk based on a code error rate of a channel adjacent to the target channel, and detecting a shift of the wavelength of the target channel; and a step of compensating for the shift of the wavelength of the target channel.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
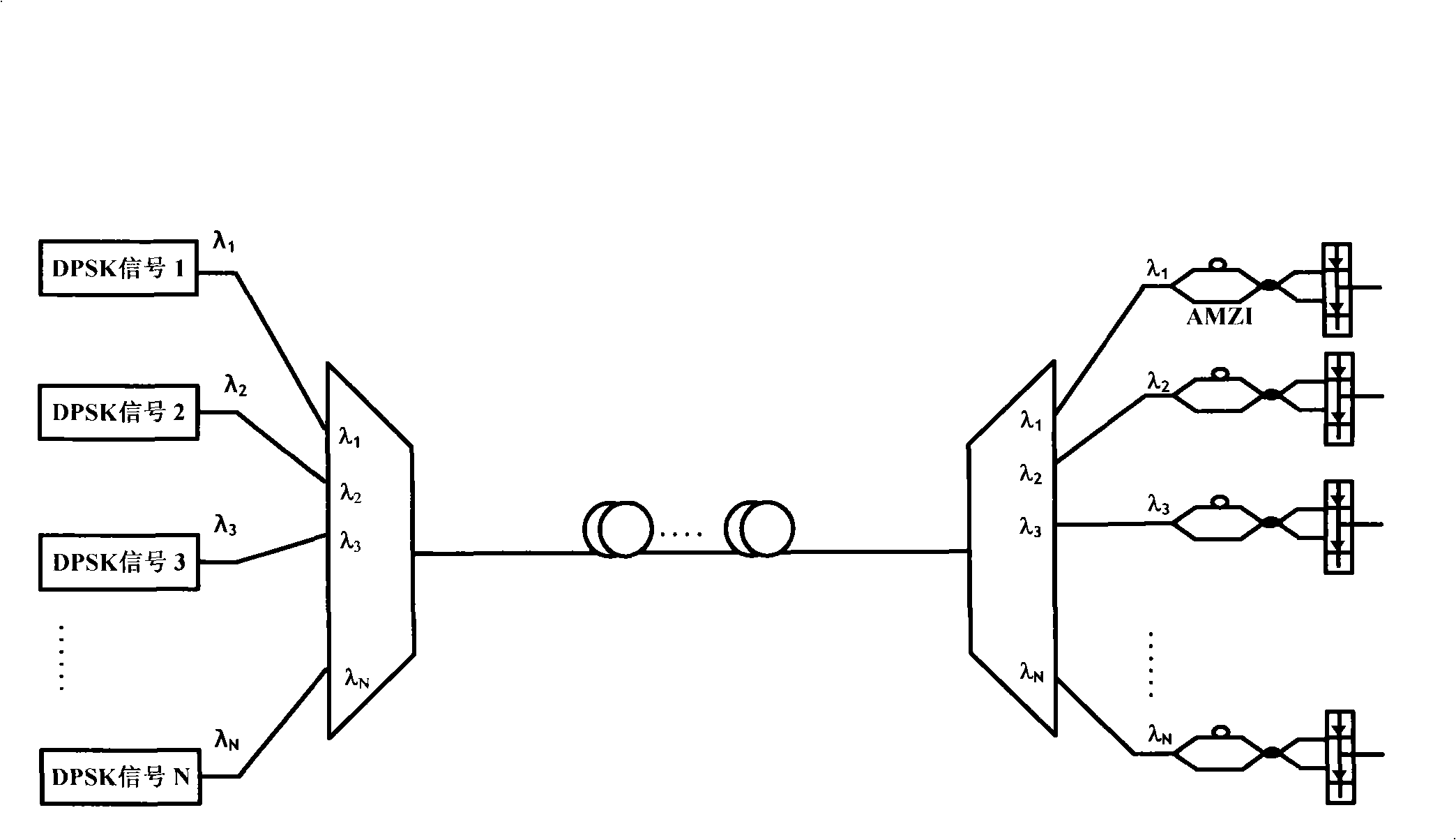
Transmission control method of wavelength division multiplexing system
InactiveCN101272214AApplicable transmissionIncrease flexibilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingWdm transmission systems
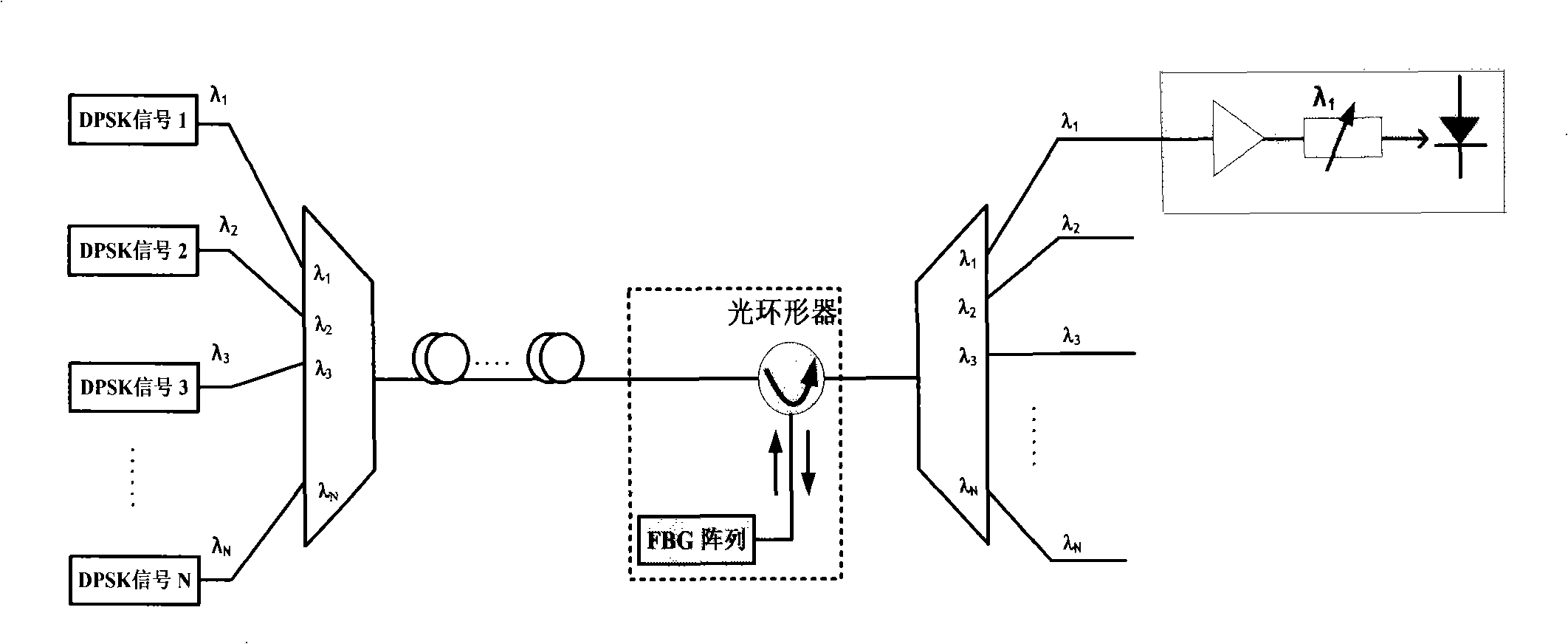
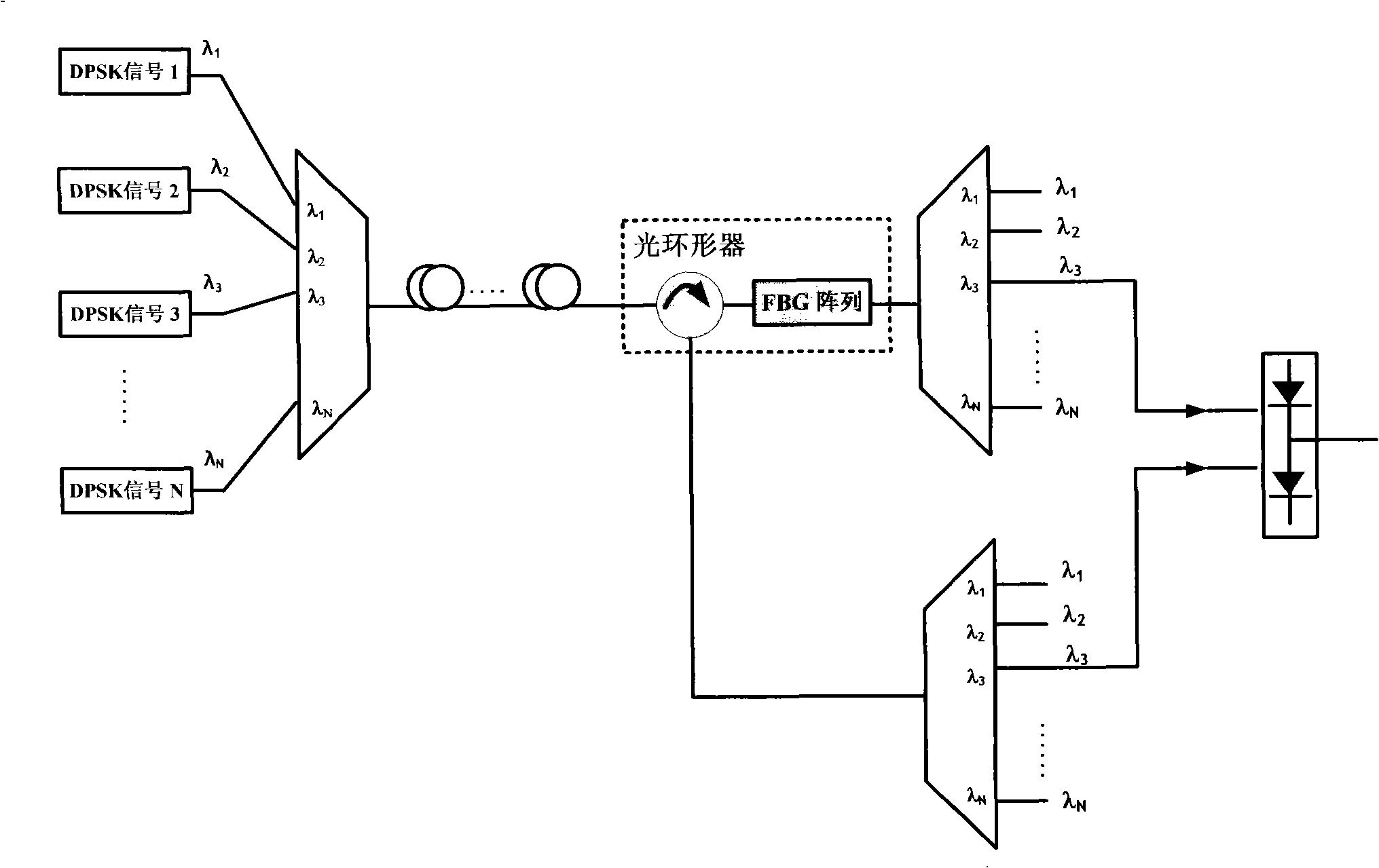
The invention relates to the transmission control of a wavelength division multiplexing system (WDM) in a fiber optic transmission system and proposes a transmission control method of a WDM transmission system. A channel is selected on an array wave-guide grating (AWG) at the transmitting end at intervals to carry out multi-channel signal transmission under the situation of not changing the current WDM system; the interval amount is an integer parameter m which is larger than zero, but less than one second of the amount of the channels; the channel of a receiving end AWG corresponding to the channel of the transmitting end AWG transmission signal receives the original signal transmitted by the AWG channel of the transmitting end, downloads and carries out transferring or continuously transmitting; the demodulating signal of the original signal is received in the neighboring channel of a receiving channel and the information is selected by filter or directly picked up. The transmission control method of a WDM system provided by the invention can simultaneously realize the demodulating and de-multiplexing of a nonreturn-to-zero phase position demodulating mode in the wavelength division multiplexing system without needing to carry out any alternation on the original system or adding any apparatus and is suitable for transmitting a nonreturn-to-zero (NRZ) signal and a nonreturn-to-zero differential phase shift keying(NRZ-DPSK) signal with different speeds.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
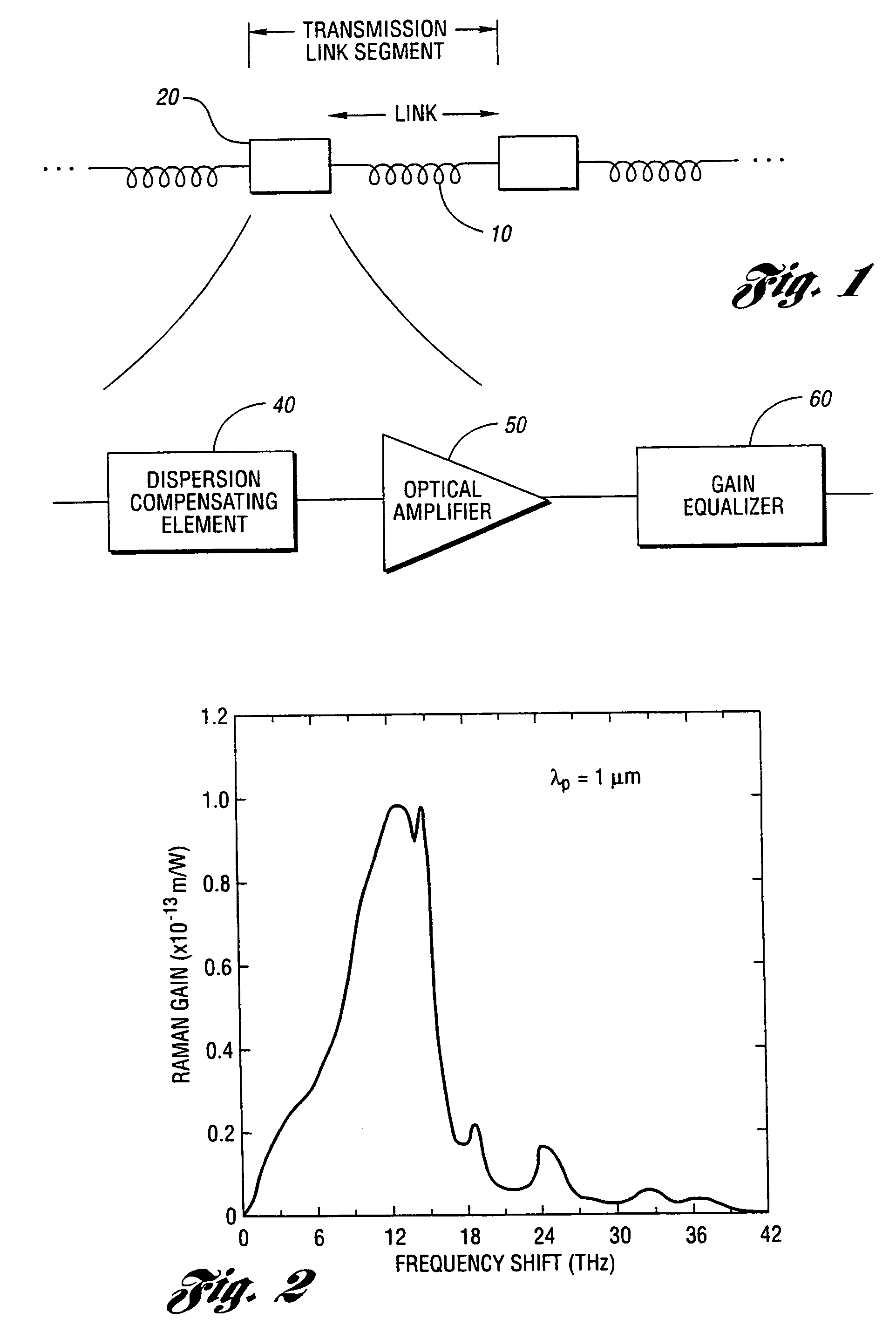
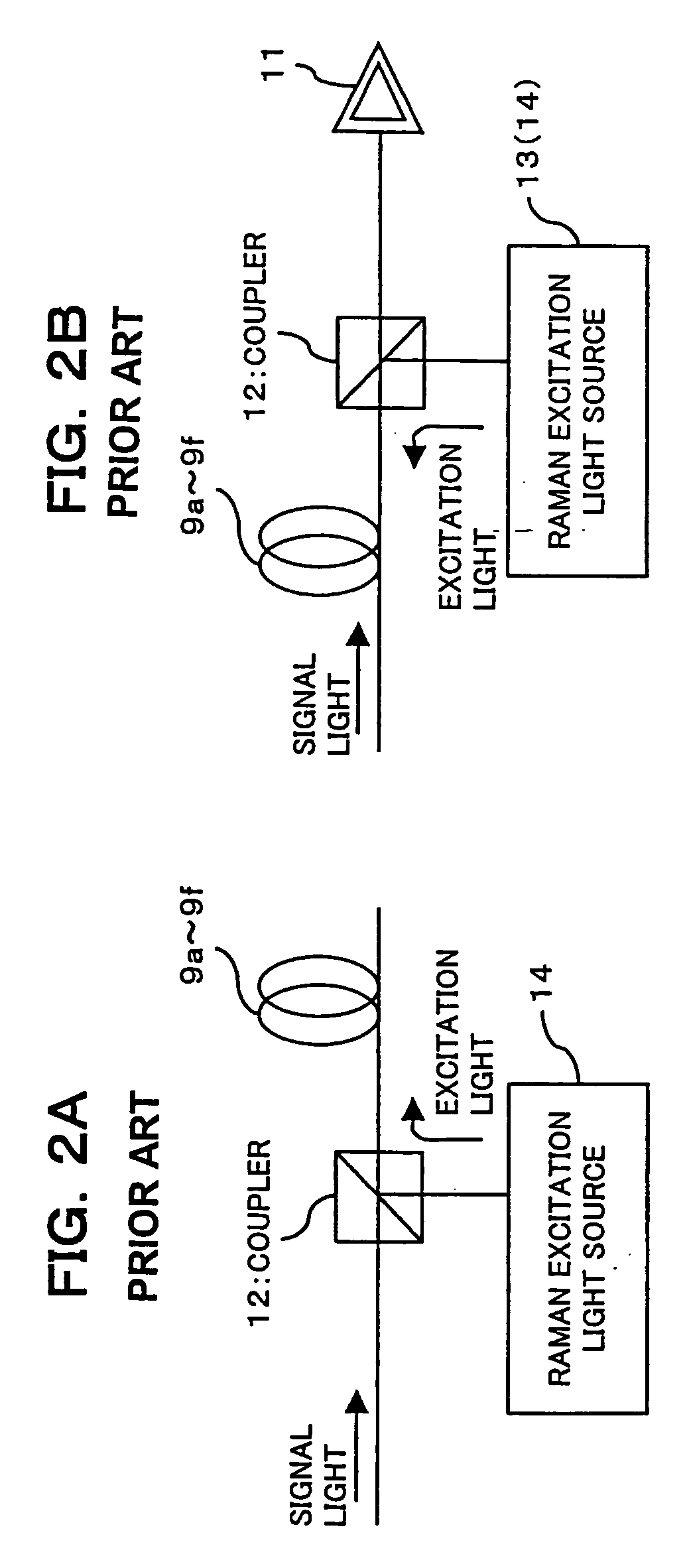
Fiber-optic compensation for dispersion, gain tilt, and band pump nonlinearity
InactiveUS6985283B1Simple system implementationCost-effectiveLaser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesErbium dopingInstability
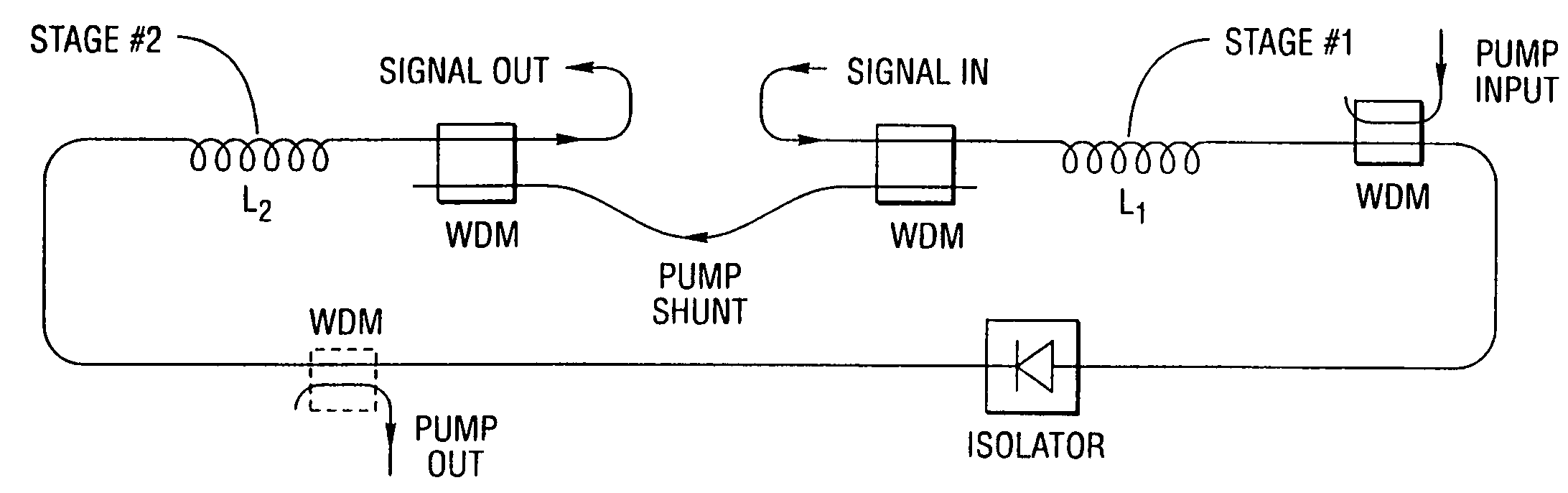
An apparatus and method are described for combining optical amplification and dispersion compensation in a Raman amplifier. A Dispersion-Managing Raman Amplifier (DMRA) combines Raman amplification with dispersion compensation by selecting the length and dispersion of the gain fiber to balance the dispersion of the link. This gain fiber is also single-mode at the signal and pump wavelengths. The pumping level is adjusted to balance the losses from the gain fiber and transmission link, while the pumping configuration is selected to remain within the 3 dB loss length for the pumping light. When the amplifier is split into two segments, the two segments may be joined by an isolator, a gain equalization element, and / or an optical add / drop multiplexer. For WDM transmission systems based on dispersion-shifted fiber (DSF), operation in the “violet band” between 1430–1530 nm is based on Raman amplification. By using a DMRA, a dispersion and nonlinearity managed system can be implemented. In particular, 4WM does not phase match in such a system, and modulation instability is absent in the transmission link. Furthermore, gain equalization can be added to the DMRA by cascading one or two Mach-Zehnder frequency filters. The invention also includes a method for symmetrically adding channels below and above the C-band, the gain tilt within the C-band can be minimized. Therefore, a roughly equal number of channels should be placed in the short-wavelength S-band and the long-wavelength L-band to minimize the Raman energy exchange in the C-band. Also, whereas C- and L-bands can be amplified using erbium-doped fiber amplifiers, the S-band can use either discrete or distributed Raman amplifiers. To minimize the interaction between pumps for different bands, alternate band pumps can be spatially dispersed and / or cross-polarized. The distributed Raman amplification can be achieved by pumping the transmission line with discrete laser diodes or by a Raman oscillator.
Owner:NEPTUNE SUBSEA IP LTD +1
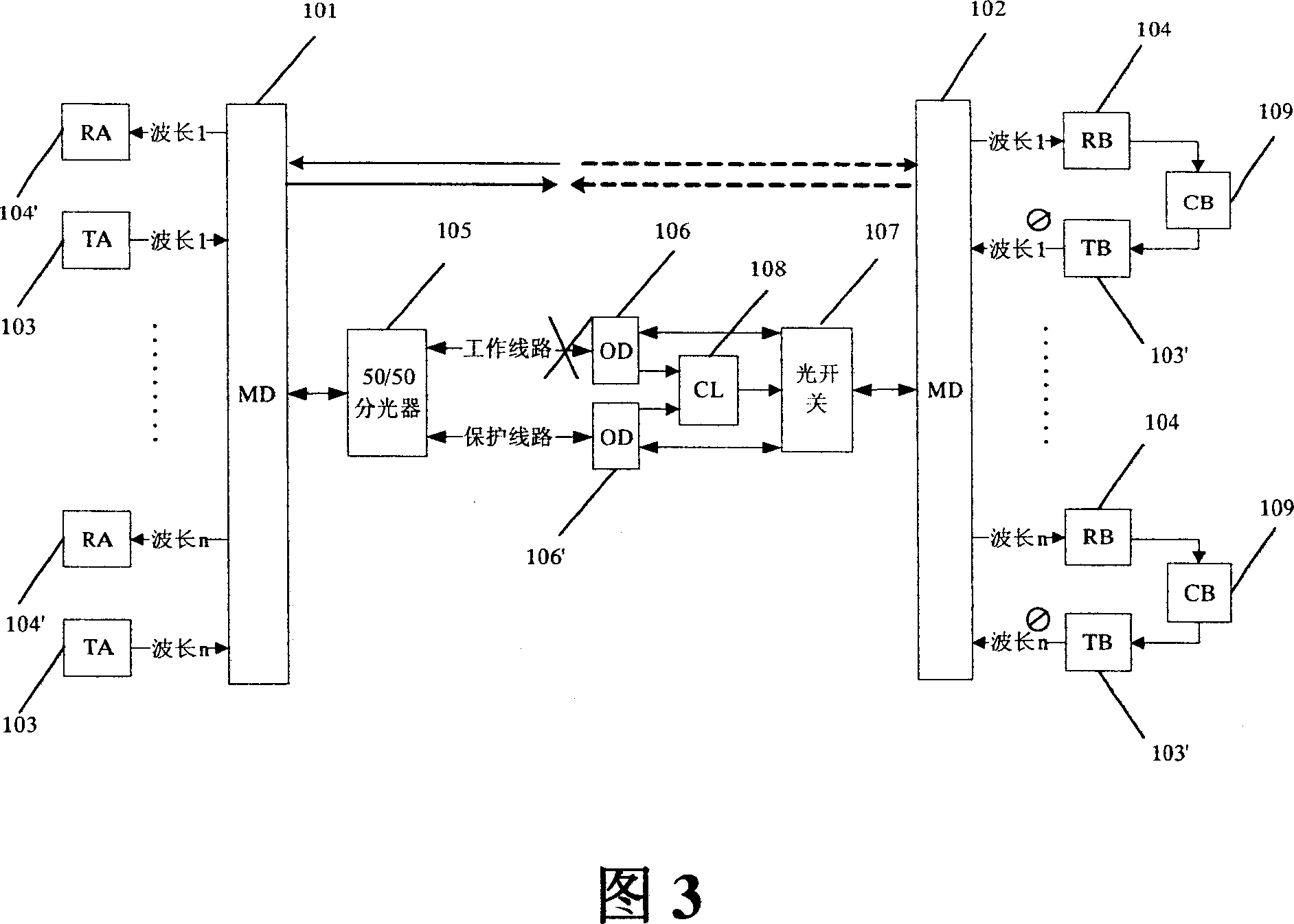
WDM transmission system protection method and apparatus
ActiveCN1968141AReduce network construction costsWavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching networksAccess networkWdm transmission systems
The invention relates to a WDM (wavelength division multiplex) transmission system applied in local network access network, and relative device, wherein the light modulation method comprises that: 1, terminal node checks condition of descending service; 2, when the descending service has accidence, the terminal node marks the accident descending path and generates descending path accidence information; 3, transmitting the accident information to the central node via ascending path; 4, central node switches descending service from work path into protective path. The invention inactivates the distributing node to reduce network cost.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Wavelength division multiplex (WDM) transmission system
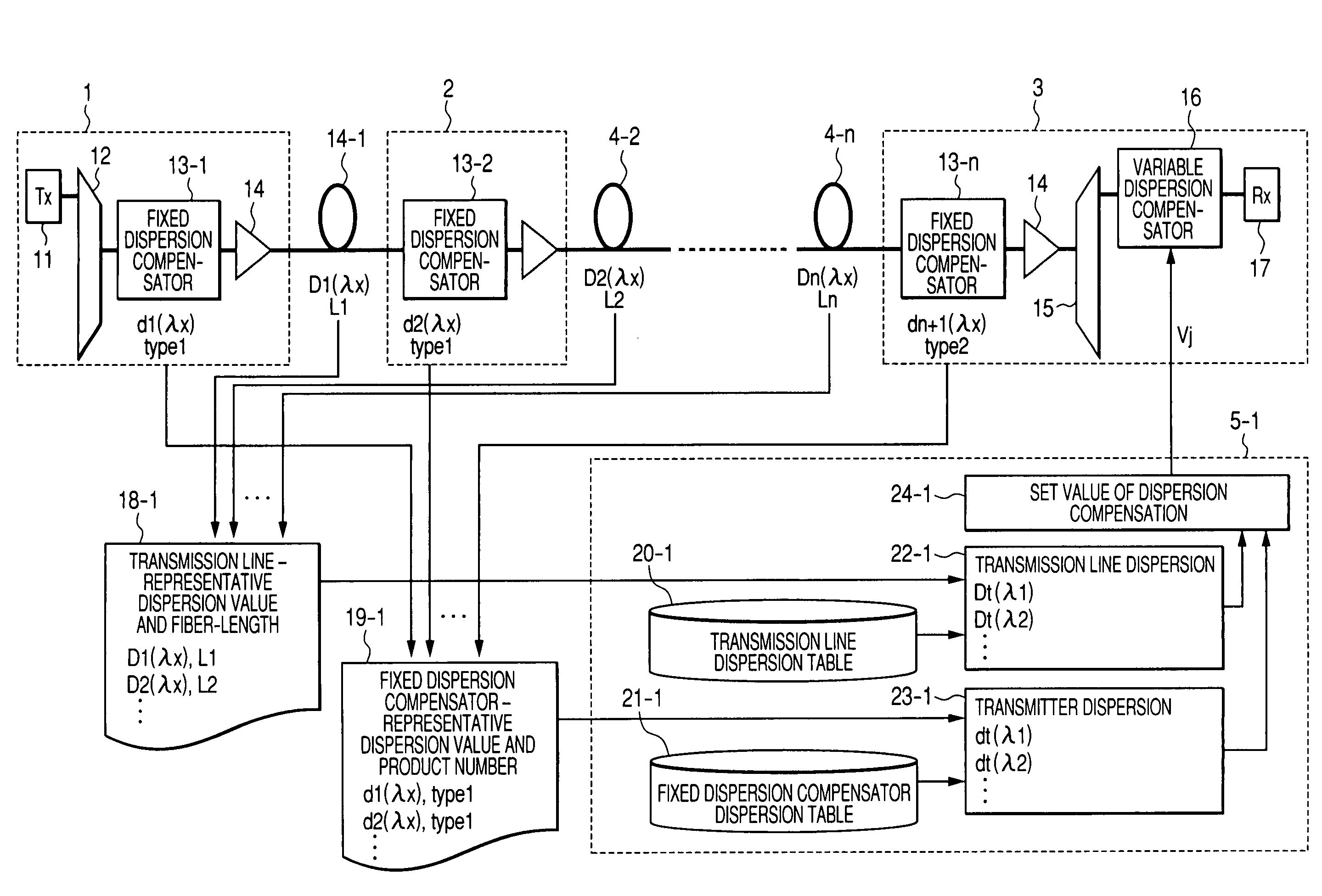
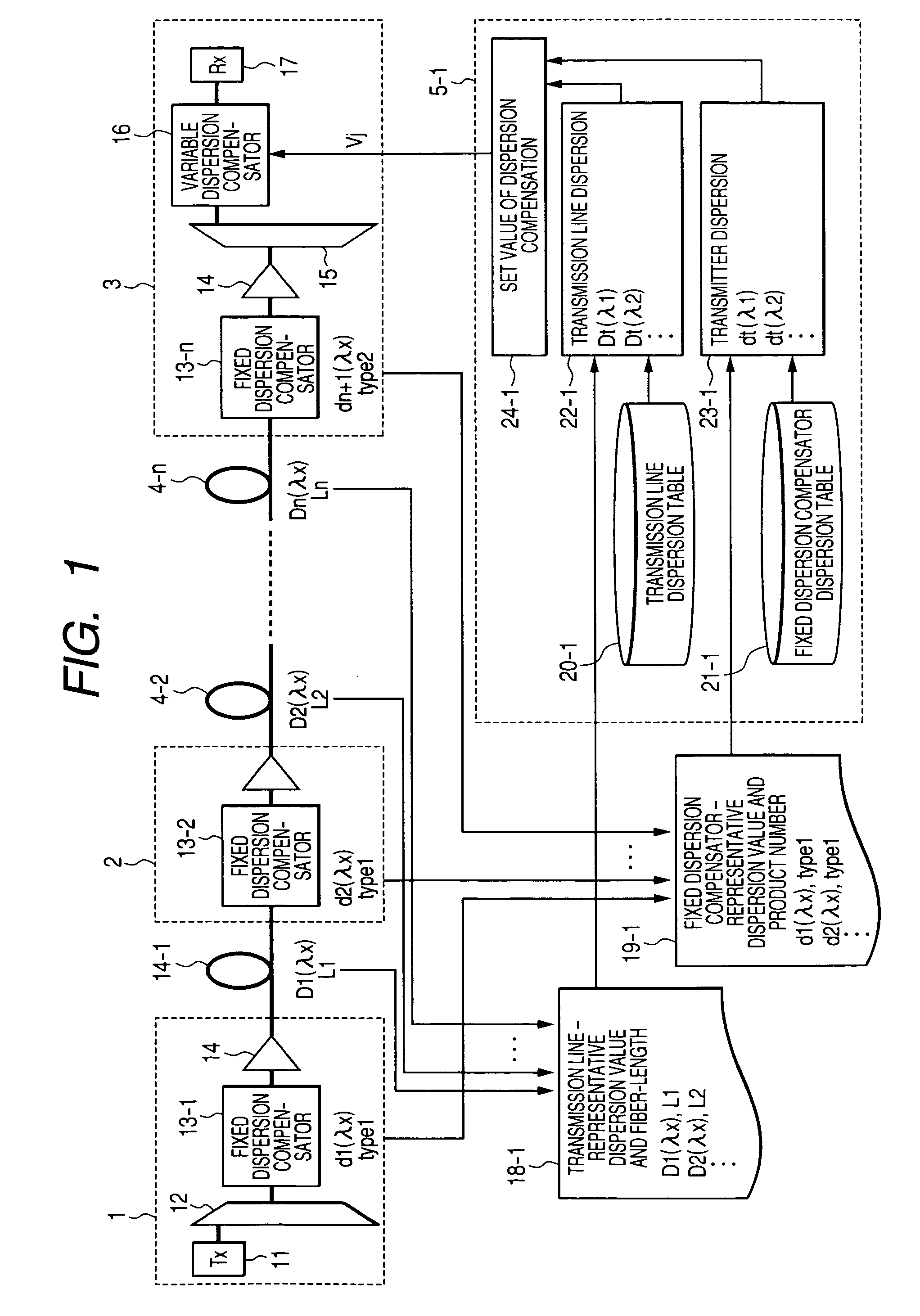
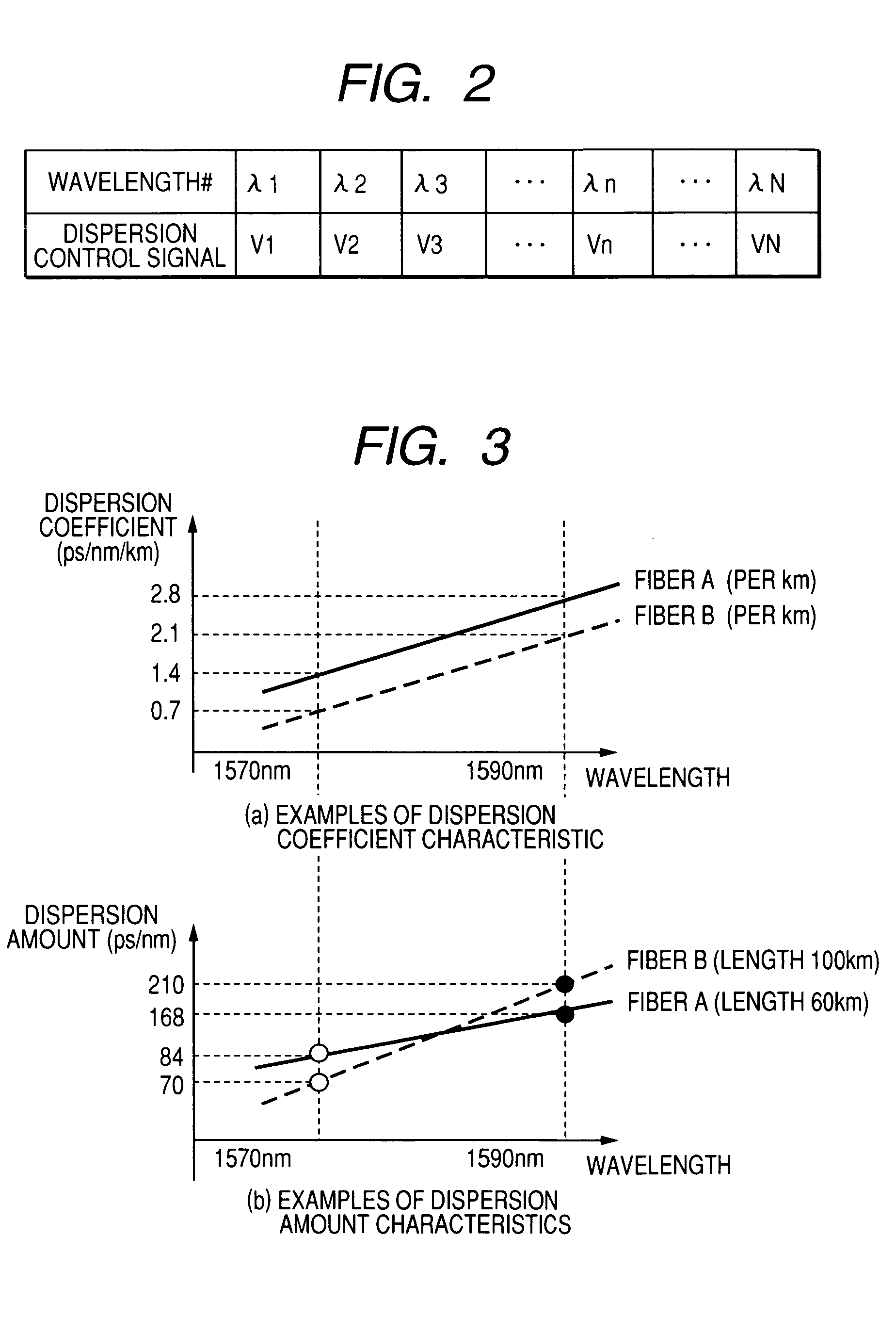
InactiveUS20070177877A1Low-cost configurationIncrease speedCladded optical fibreWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm transmission systemsClassical mechanics
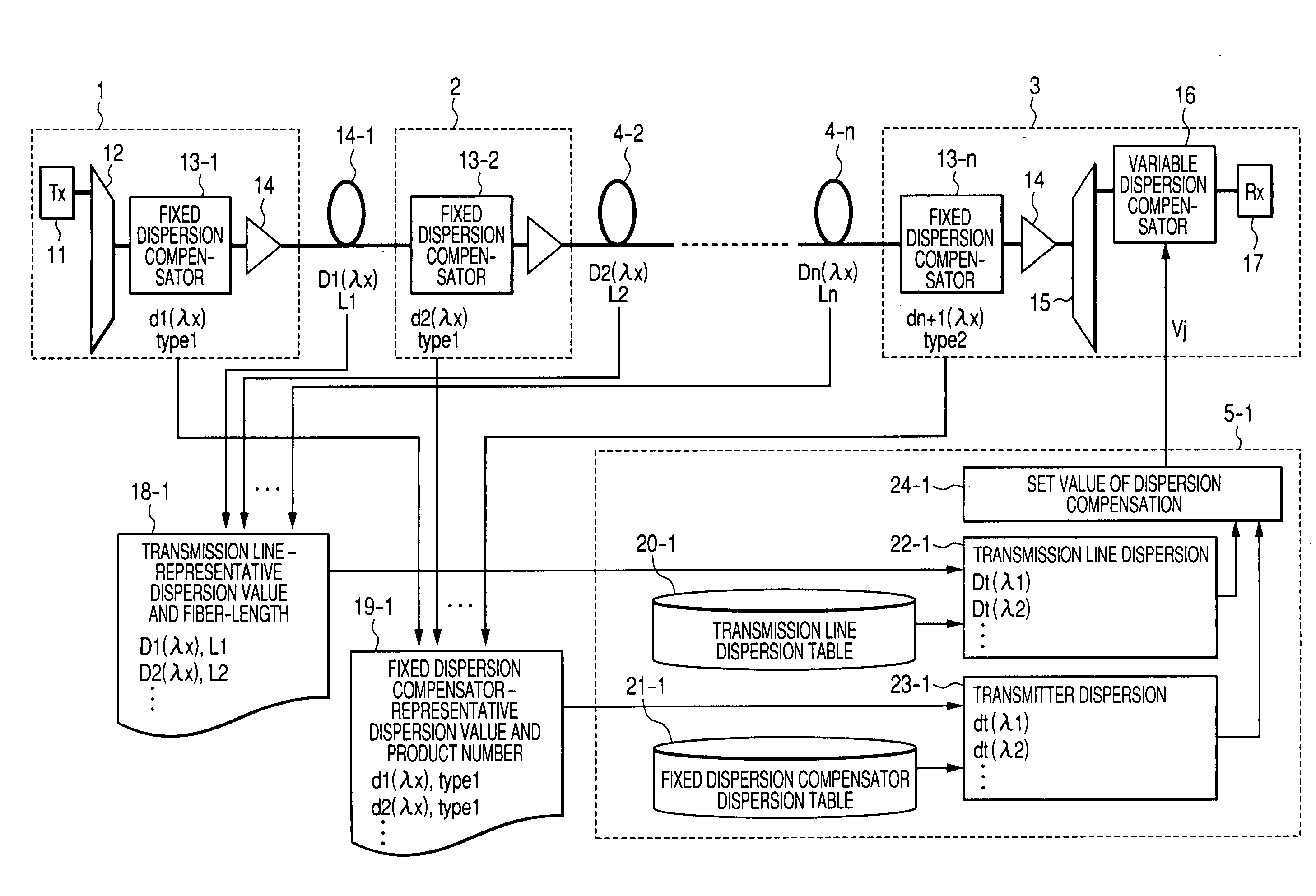
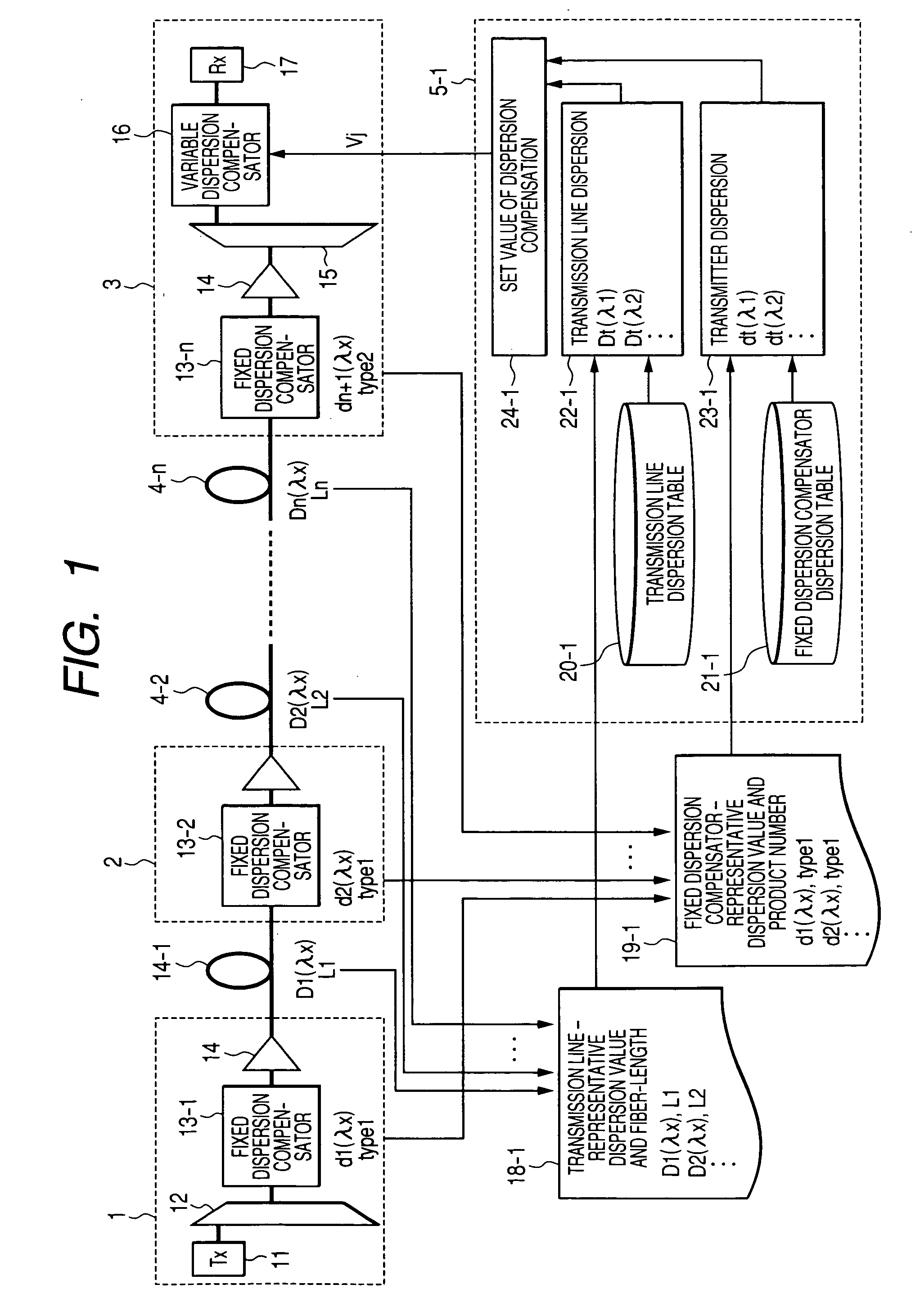
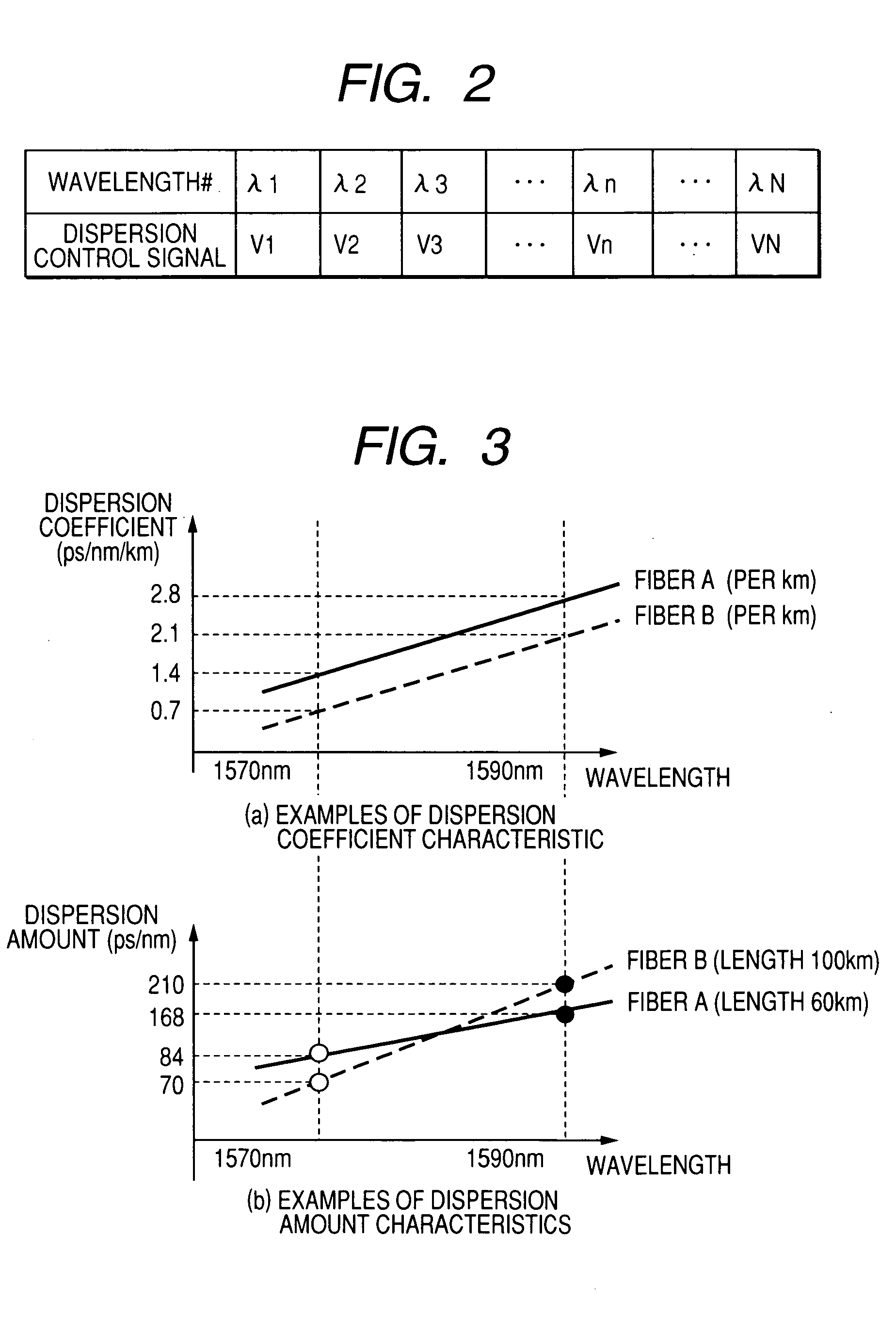
A low-cost configuration of, and at the same time to control the variable dispersion compensator at a high speed in a variable dispersion compensator for compensating the wavelength dependent accumulated dispersion resulting from the wavelength dependency of the transmission fiber and fixed dispersion compensator in a long-distance high-speed WDM transmission system. In order to achieve the object mentioned above, the wavelength dependent representative characteristic of the transmission fibers 4-1 . . . n, and the wavelength dependent representative characteristic of the DCFs 13-1 . . . n are recorded and maintained in advance in the dispersion control circuit 5-1 . . . n of the variable dispersion compensator 16, and based on the input of dispersion amount at the representative length of the transmission fiber and the fiber length, the dispersion amount at the representative wavelength of the DCF, the accumulated dispersion amount is computed from the wavelength dependent representative characteristic recorded and maintained in advance, and the dispersion amount of the variable dispersion compensator 16 is determined by taking this as the reference.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Wavelength division multiplexing transmission system
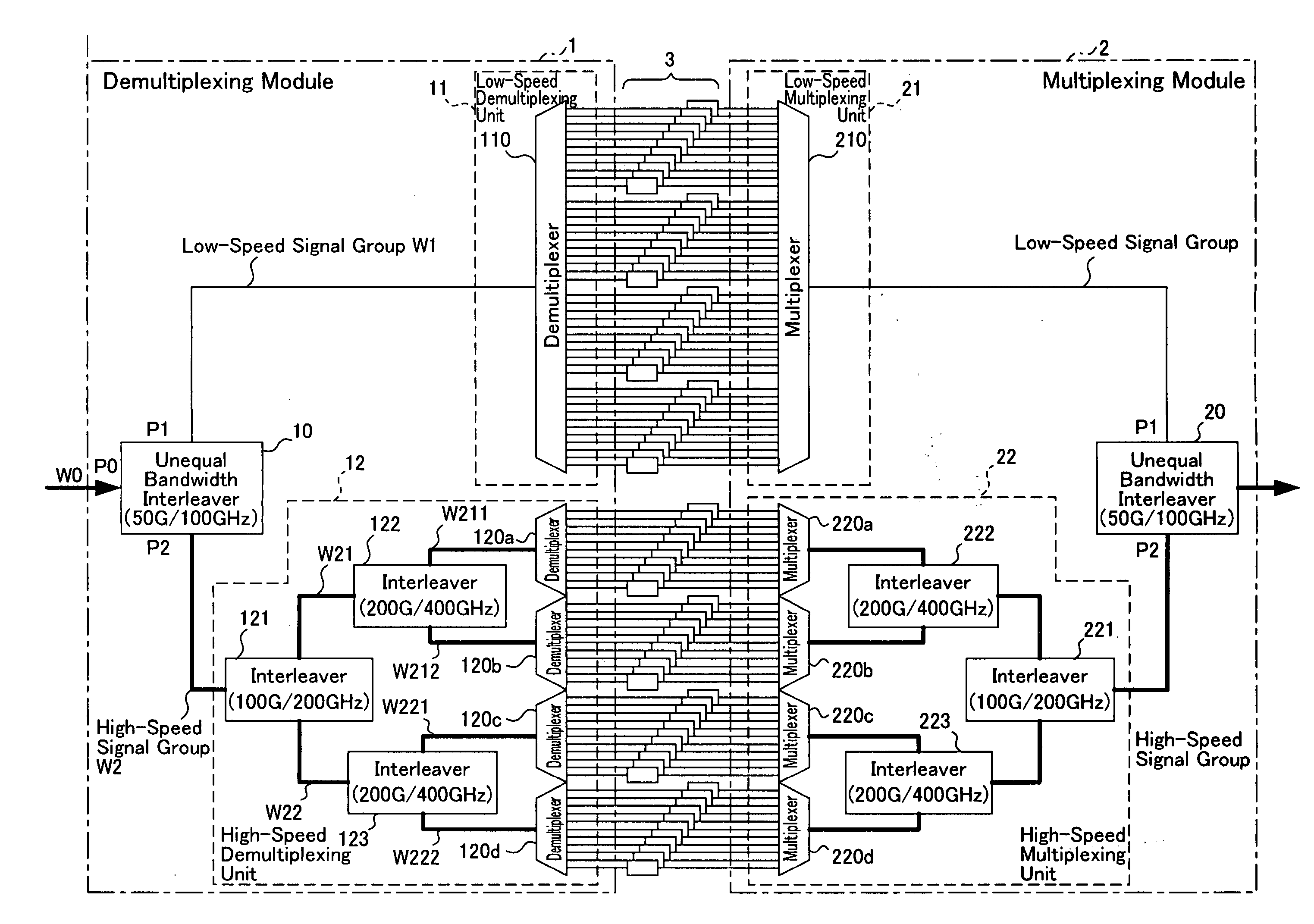
InactiveUS20050041975A1Improve performanceFunctionalWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationWdm transmission systemsLow speed
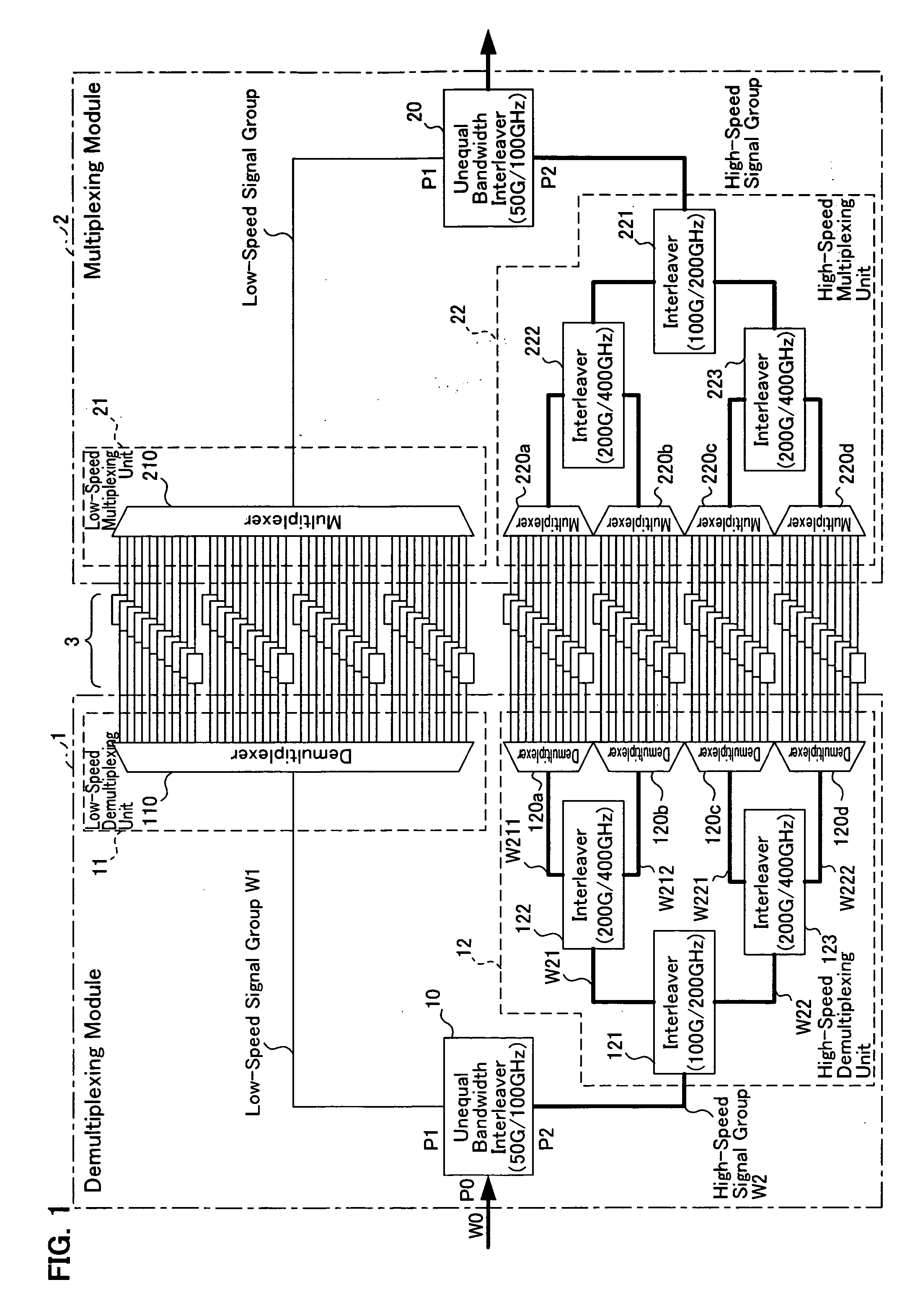
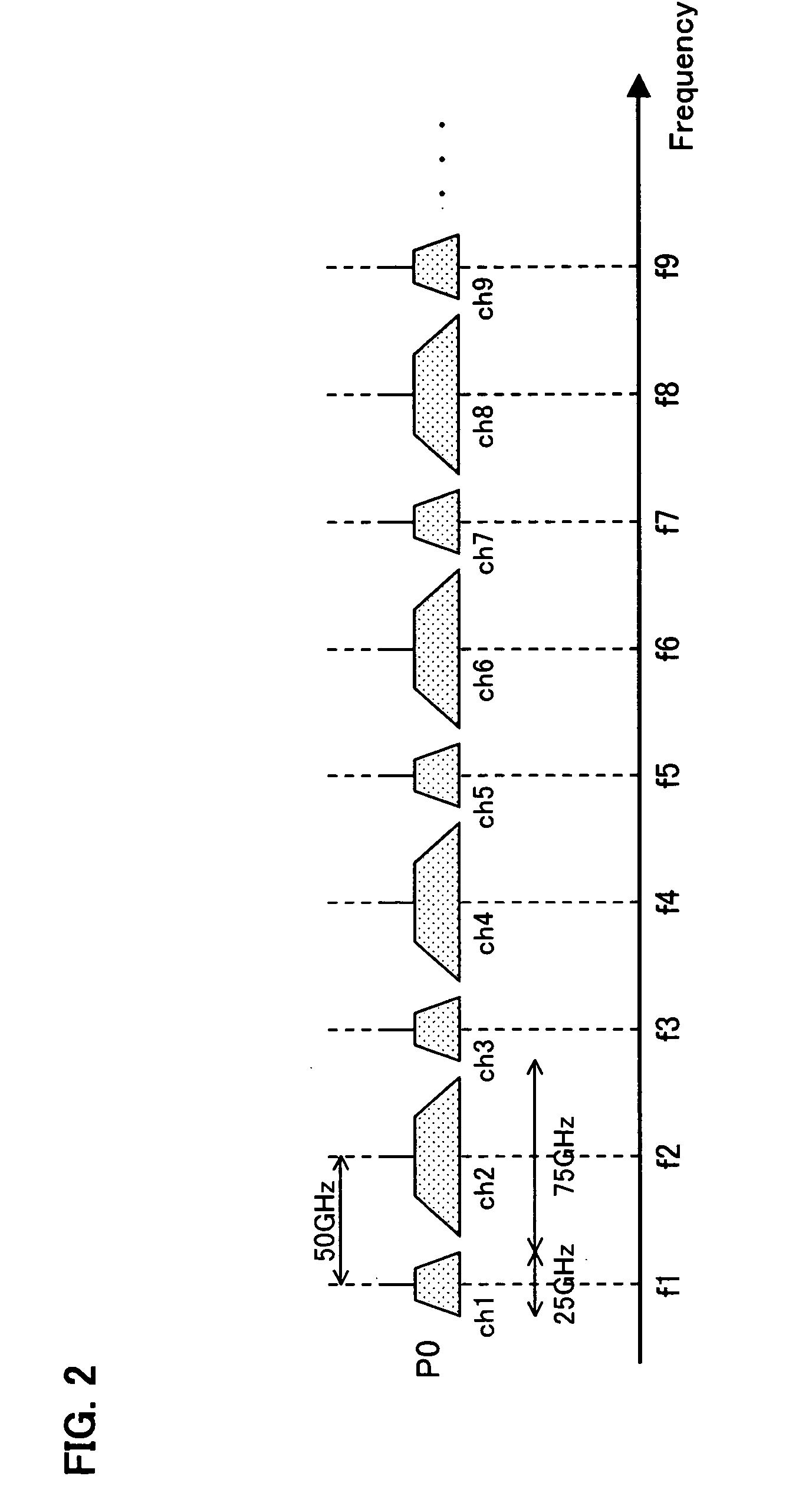
The present invention provides a wavelength division multiplexing transmission system for separating wavelength division multiplexing signals, where signal lights with different bit rates are wavelength division multiplexed, according to the bit rate, and processing the separated signals individually. The wavelength division multiplexed signals, where a low-speed bit rate signal is disposed in an odd channel group and a high-speed bit rate signal is disposed in an even channel group, are demultiplexed into a low-speed signal group and a high-speed signal group by an unequal bandwidth interleaver. The low-speed signal group is processed (e.g. demultiplexing, dispersion compensation) by an optical device appropriate for the low-speed signals, and the high-speed signal group is processed by an optical device appropriate for the high-speed signals. By this, a relatively expensive and high function optical device can be applied only for the high-speed signal side, so an increase in the device cost can be kept down. Also a device with specifications appropriate for each signal can be used.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Redundant WDM transmission system optical receiver with reduced variable optical attenuators and/or variable dispersion compensation modules
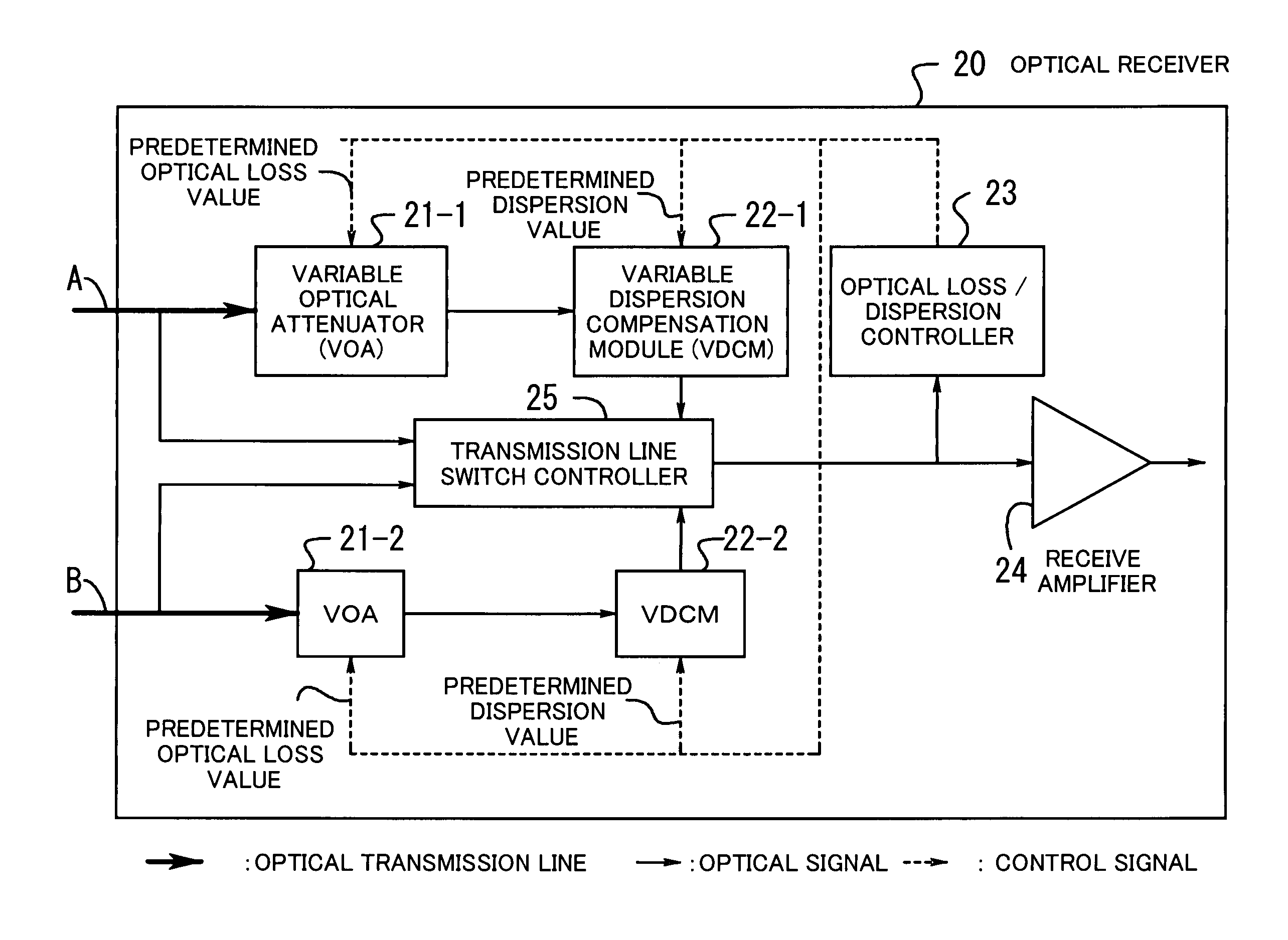
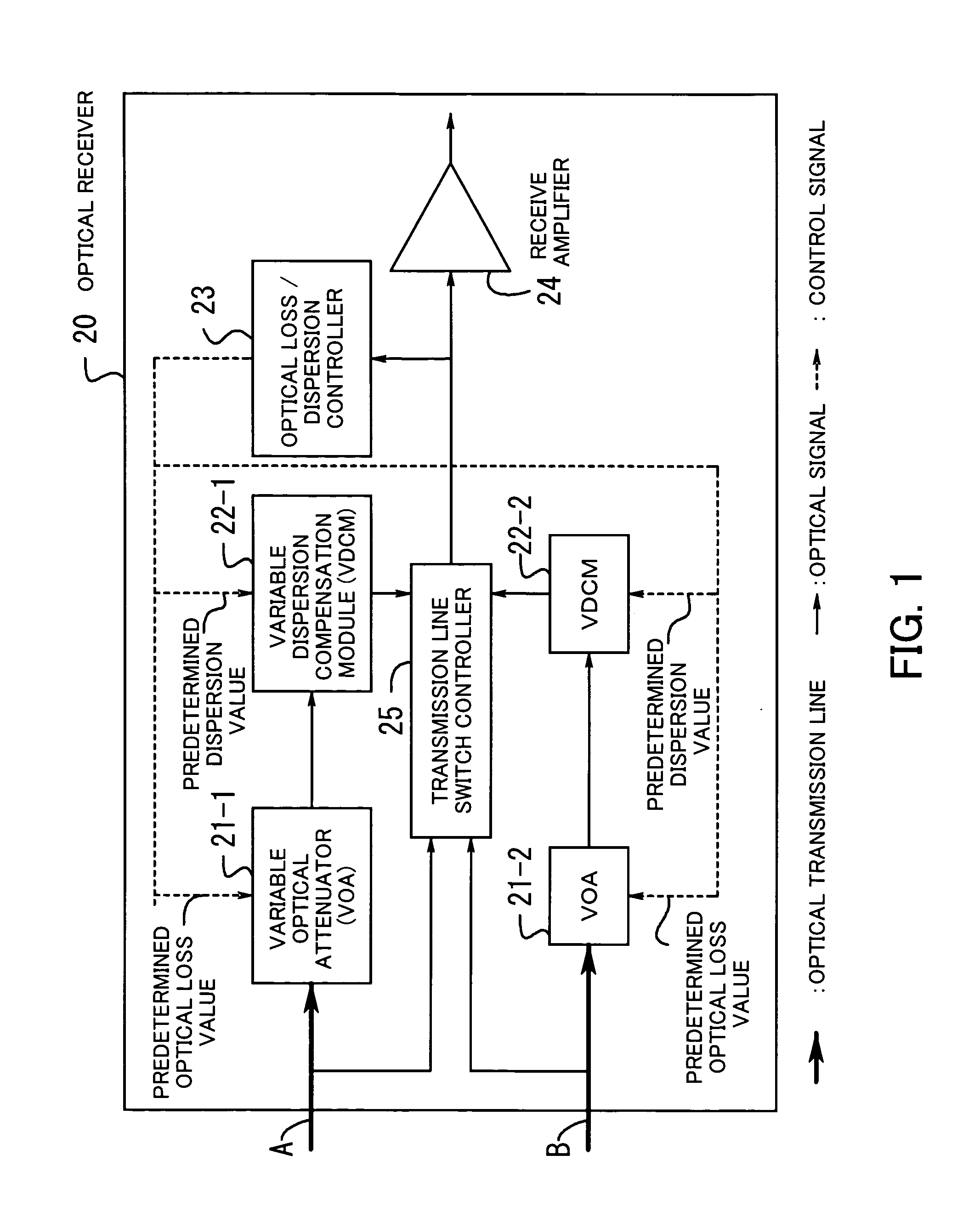
InactiveUS7113709B2Quality improvementSuppress transmissionLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm transmission systemsAudio power amplifier
An optical receiver including a variable optical attenuator for controlling an optical loss value for each optical transmission line based on a predetermined optical loss value; a variable dispersion compensation module for controlling a wavelength dispersion value for each optical transmission line based on a predetermined dispersion value; an optical loss / dispersion controller for measuring the optical loss value and the wavelength dispersion value of every optical transmission line, outputting these values so that they are equal in all the optical transmission lines, and controlling the attenuator and the module based on the outputted predetermined values; a receive amplifier for receiving the optical signal whose light level is kept constant and amplifying the signal; and, a transmission line switch control module is provided for switching a working transmission line into a protection line if the optical signal level of the working line is lower than a threshold value.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
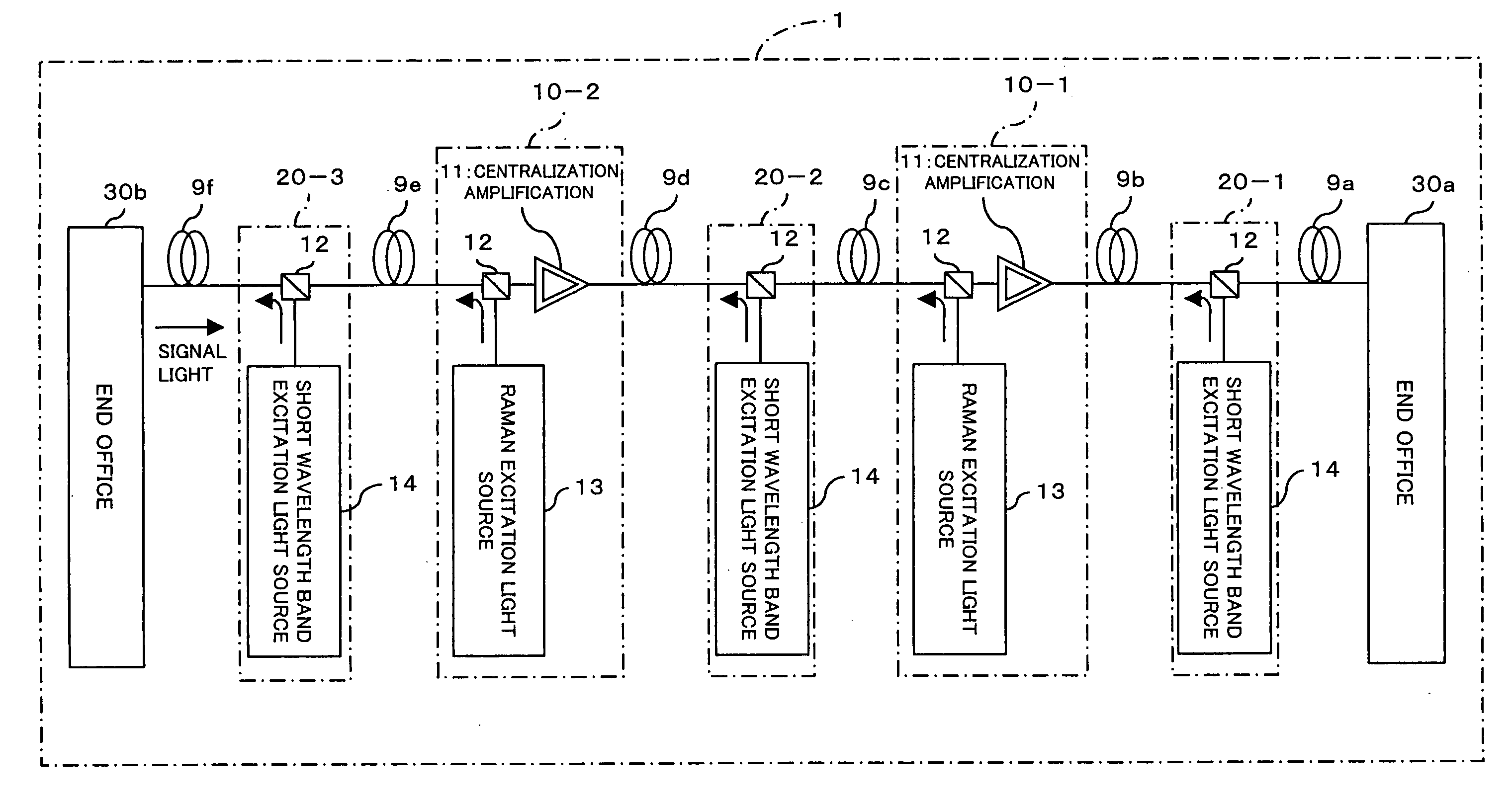
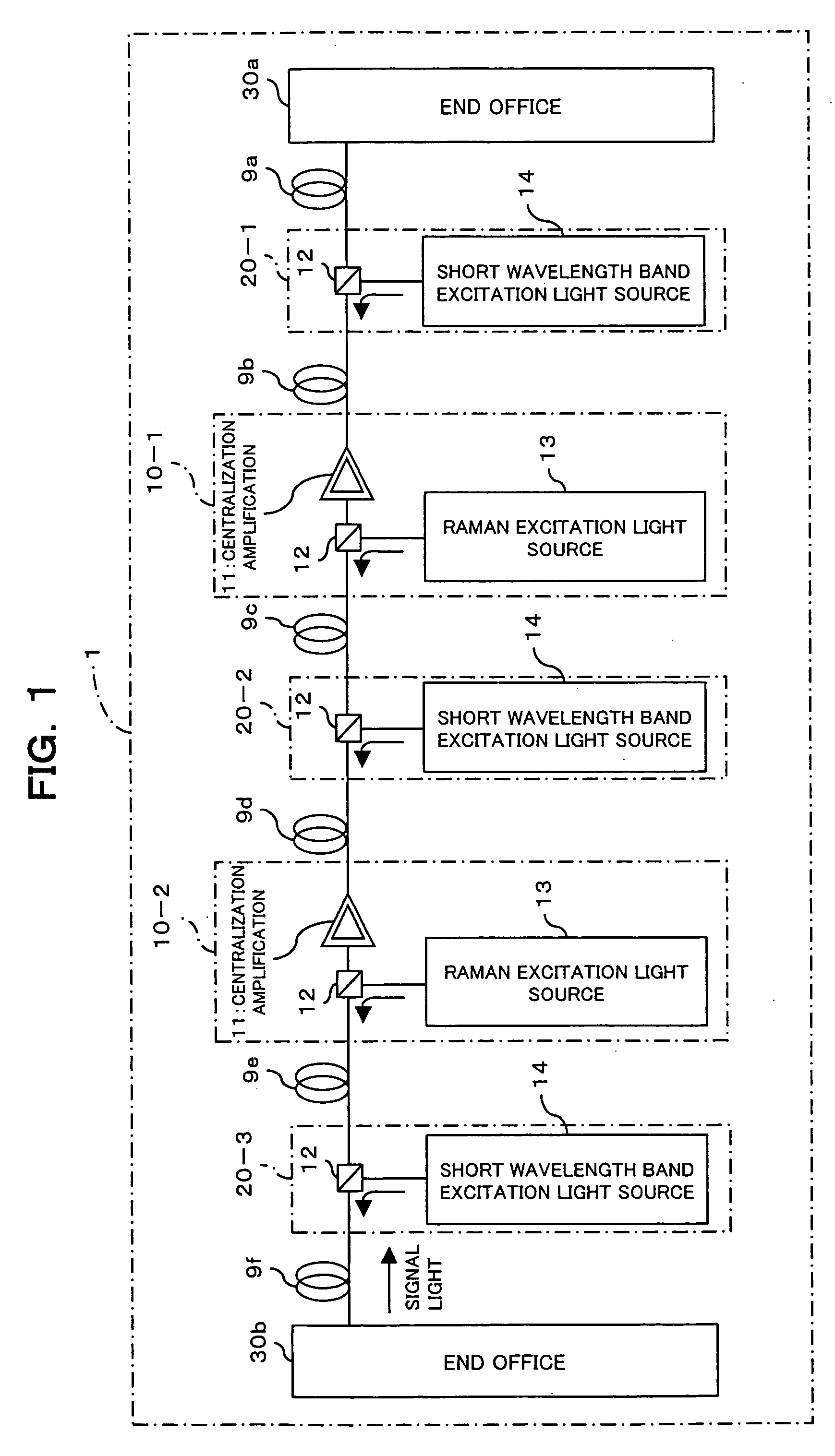
Optical transmission system, optical repeater, and optical transmission method
InactiveUS20060176545A1Raise the ratioPrevent degradationLaser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingUltrasound attenuation
In a WDM transmission system employing a plurality of short wavelength bands having great attenuation due to optical fiber transmission, an optical repeater is constructed of a first multiplexing section and a second multiplexing section. The first multiplexing section is used for wavelength-multiplexing both the excitation light from a first Raman excitation light source, which distributively amplifies an S+ band included in light propagating through an optical fiber, and the light propagating through the optical fiber. The second multiplexing section is used for wavelength-multiplexing both the excitation light from a second Raman excitation light source, which distributively amplifies an S+ band included in light propagating through an optical fiber, and the light propagating through the optical fiber. The first and second multiplexing sections are provided between the optical fibers disposed between end offices. Thus an equal and satisfactory optical SN ratio even at any band are obtained.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
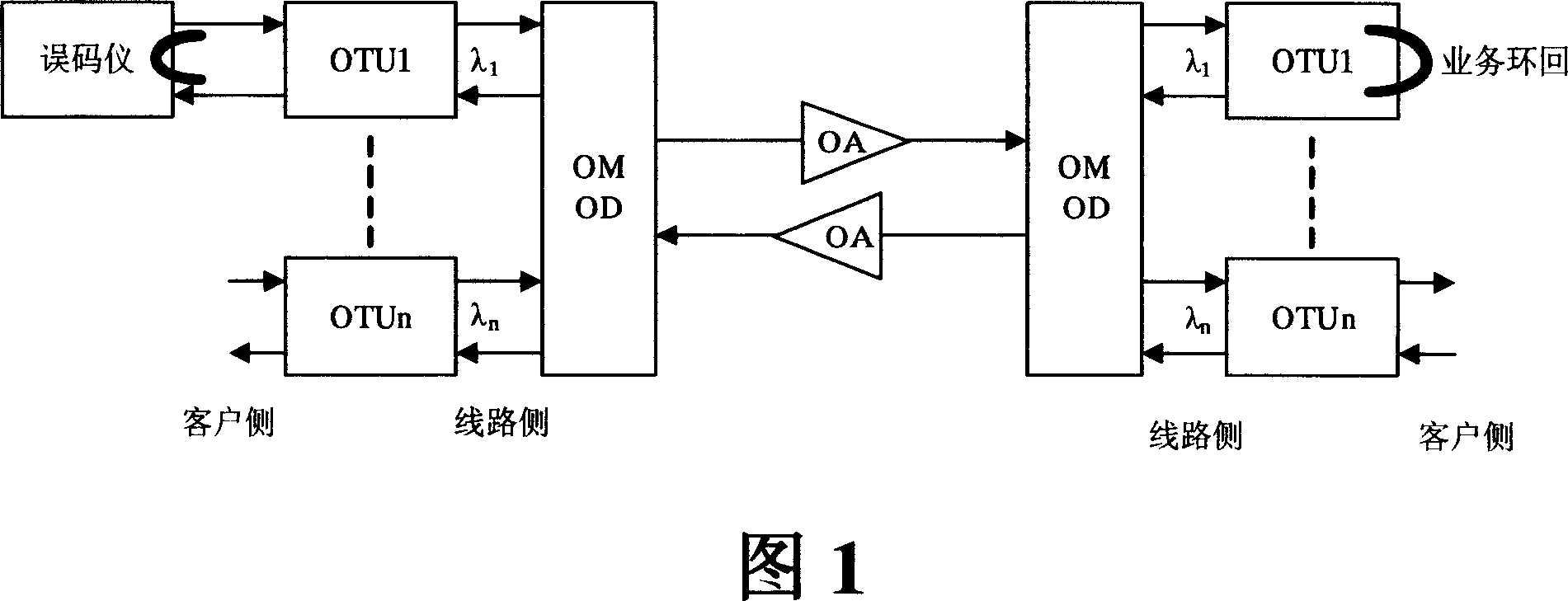
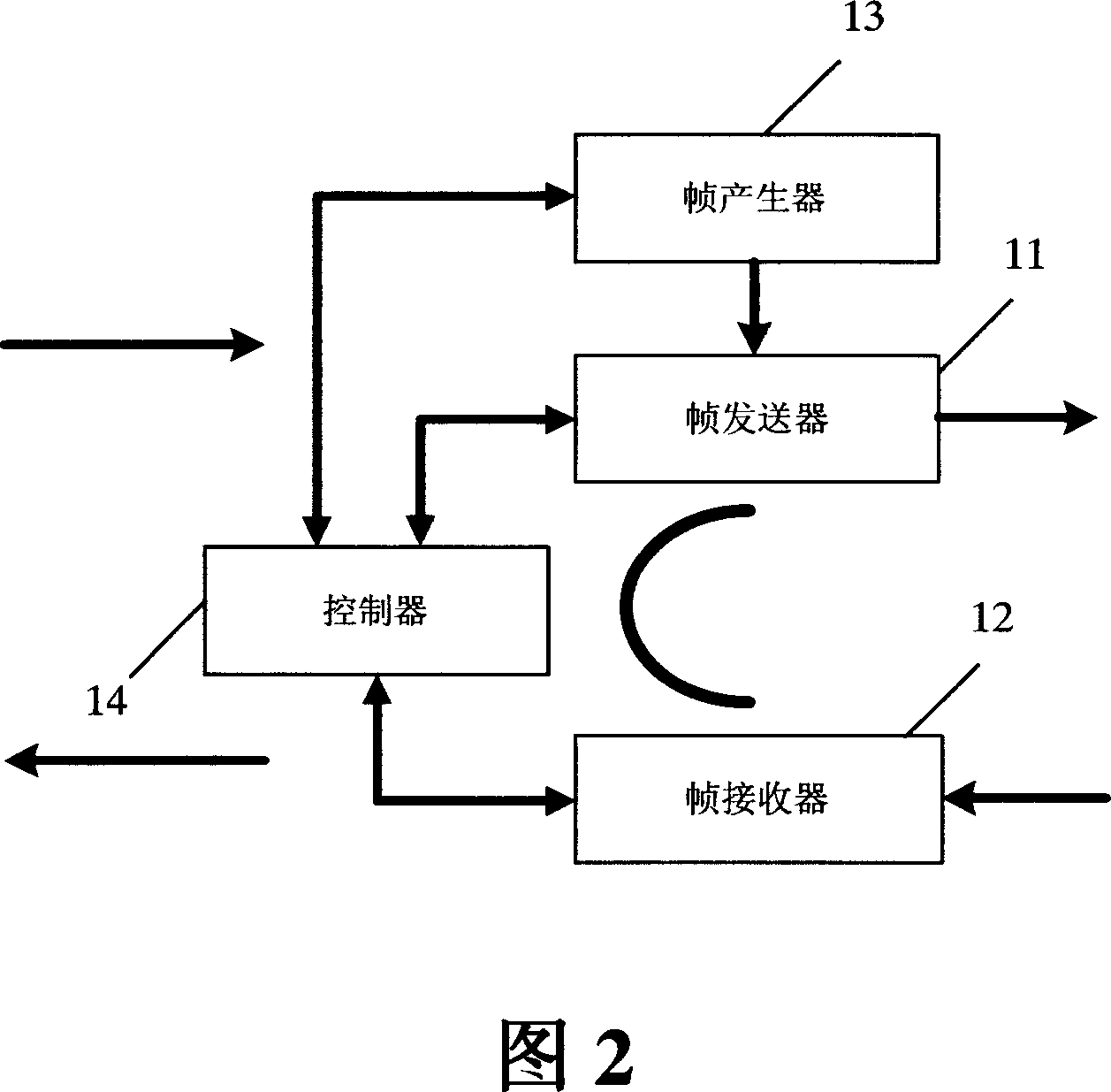
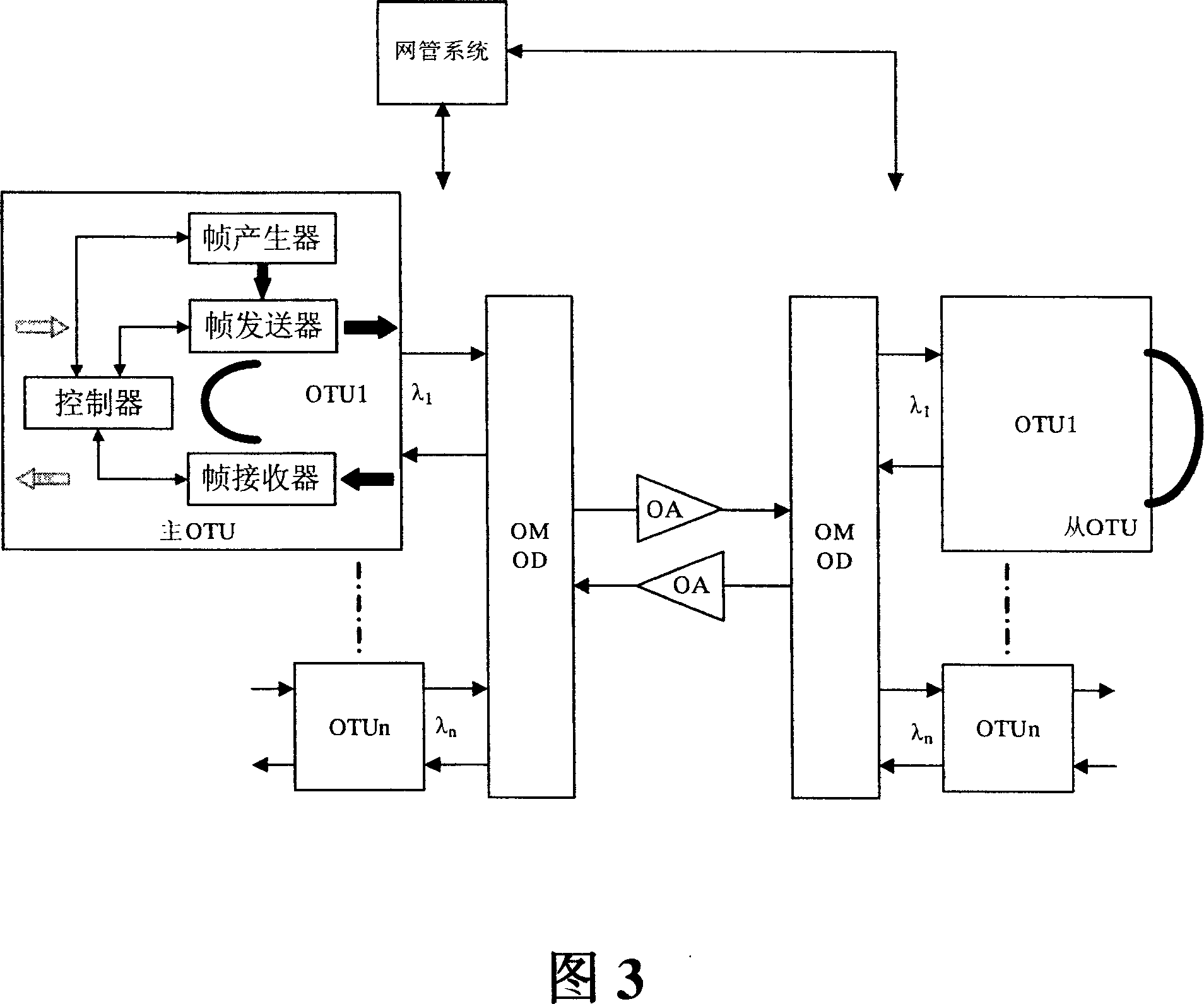
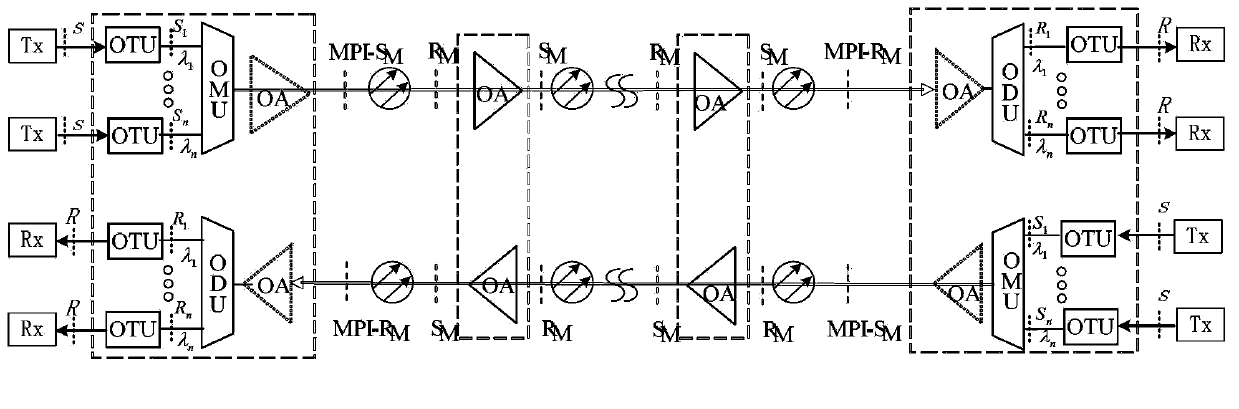
Optical convering unit, transmission system for wavelength division multiplexing and error-code testing method
ActiveCN101030891AAchieve the effect of online bit error testSave operating costsWavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching networksTest frameEngineering
The optical repeater unit (ORU) comprises: a frame transmitter, a frame receiver, a controller and a frame generator. The frame generator is used for sending the error-code testing frame to the frame transmitter according to the instruction of the controller; the frame transmitter is used for relaying the test frame; the frame receiver is used to checking the frame and reporting the error-indication to the controller; the controller is used for reporting the checking result and the error-indication. By invention adds a frame generator into the ORU to generate the error-code testing frame which is used to make error-code testing.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Monitoring device and method for optical wavelength division multiplexing transmission system
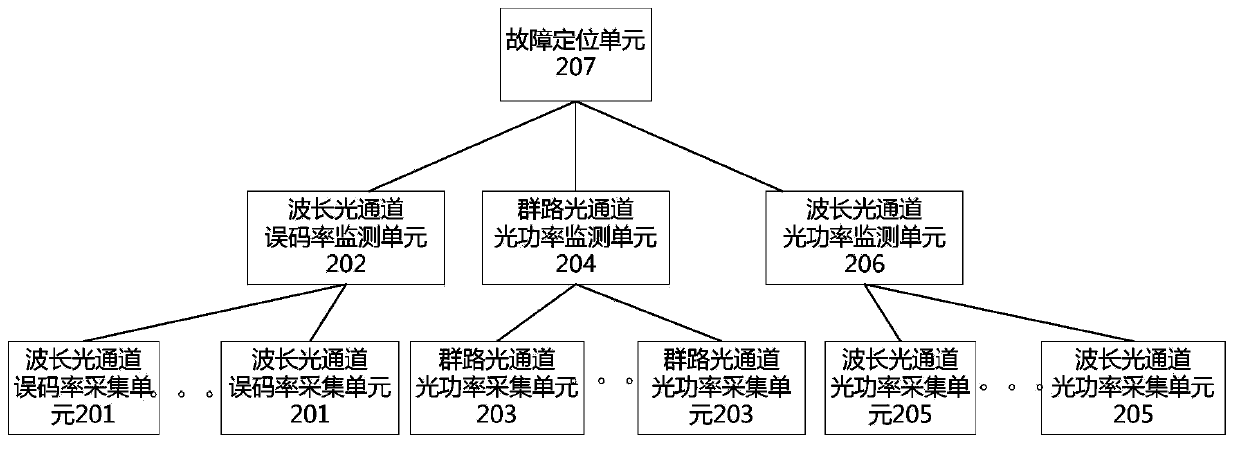
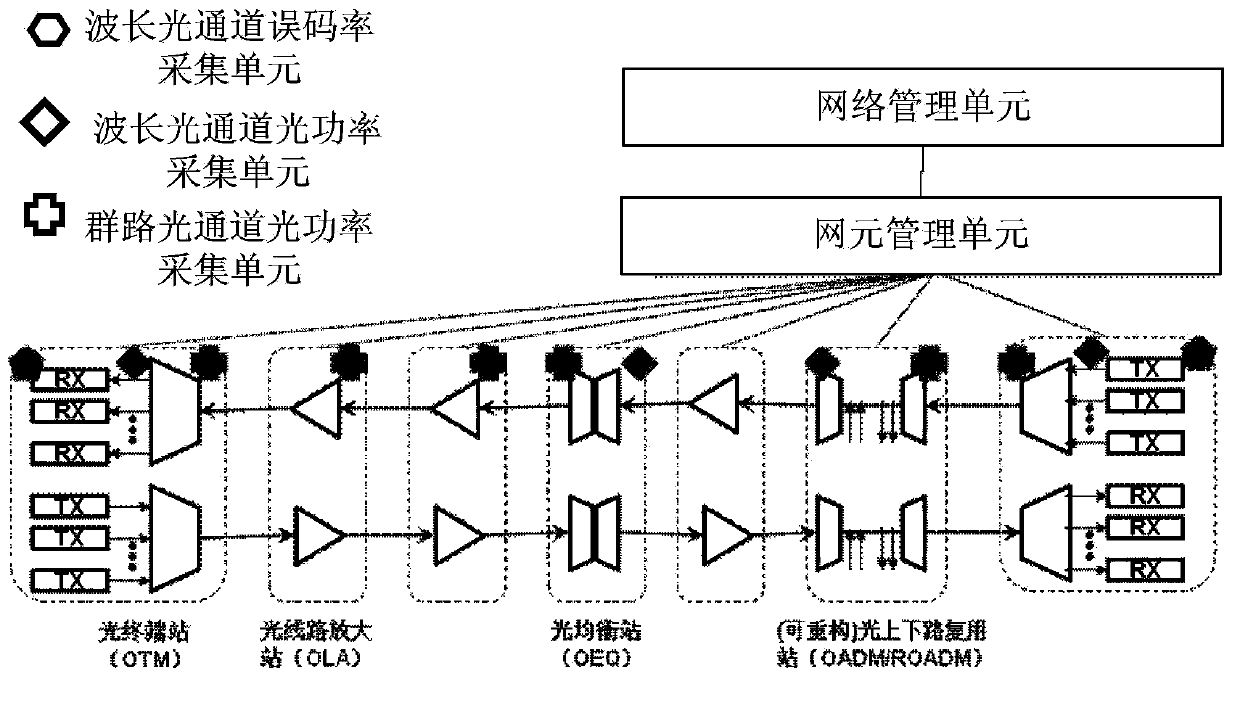
ActiveCN104184518ARealize whole-process and whole-network monitoringError preventionWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm transmission systemsMultiplexing
The invention discloses a monitoring device and method for an optical wavelength division multiplexing transmission system. The monitoring device includes a wavelength optical channel error rate acquisition unit used for acquiring error rates of n wavelength optical channel routes; a group optical channel optical power acquisition unit used for acquiring group optical channel optical powers of group optical channel routes; a wavelength optical channel optical power acquisition unit used for acquiring wavelength optical channel optical powers of the wavelength optical channel routes; a wavelength optical channel error rate monitoring unit used for sending alarm information of a wavelength optical channel error rate when the error rate exceeds a preset error rate threshold; and a group optical channel optical power motoring unit and a wavelength optical channel optical power monitoring unit respectively used for monitoring the group optical channel optical powers and the wavelength optical channel optical powers. The monitoring device and method for the optical wavelength division multiplexing transmission system provide whole-course whole-network monitoring of optical channel performance of the optical wavelength division multiplexing transmission system.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Optical amplifier with variable gain equalization
InactiveUS7139120B2Quick controlAmplifying optical signals more efficientlyLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm transmission systemsOptical power
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Single-span long distance WDM line fiber transmission system
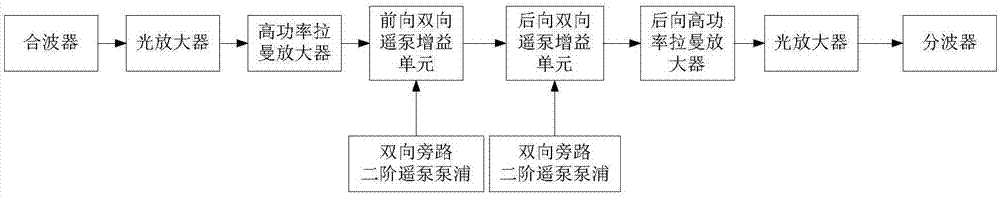
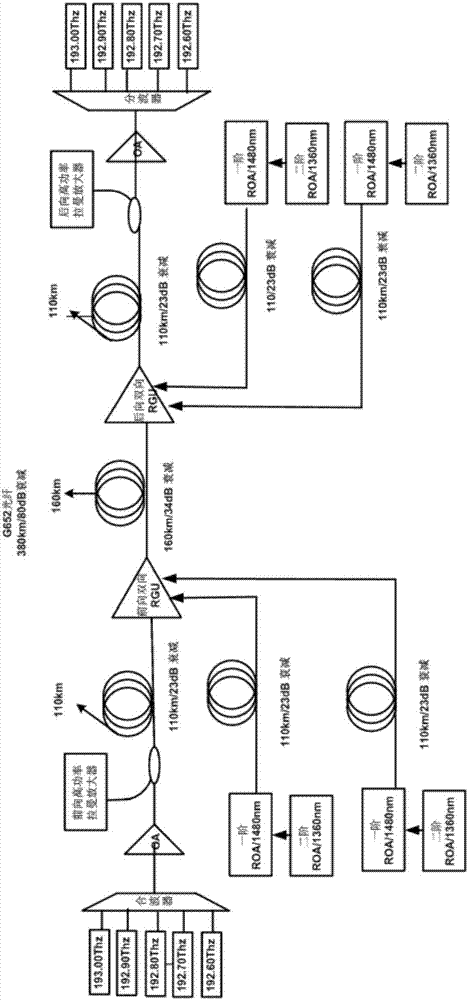
ActiveCN107294604ALower noise figureLong transmission distanceFibre transmissionWdm transmission systemsInformation transmission
The invention discloses a single-span long distance WDM line fiber transmission system, and relates to the optical information transmission technical field; the single-span long distance WDM line fiber transmission system comprises the following units from an optical signal sending end to a receiving end: a forward high rating raman amplifier, a forward bidirectional remote pump gain unit, a backward high rating raman amplifier, and a backward bidirectional remote pump gain unit; the single-span long distance WDM line fiber transmission system also comprises two bidirectional bypass second order remote pump pumping, wherein one bidirectional bypass second order remote pump pumping outputs pumping lights to the forward bidirectional remote pump gain unit, and the other bidirectional bypass second order remote pump pumping outputs pumping lights to the backward bidirectional remote pump gain unit. The WDM line fiber transmission system OSNR performance can be improved, and the WDM system is suitable for line super long single-span distance optical information transmission.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Wavelength division multiplex (WDM) transmission system
InactiveUS7653310B2High speed controlLow costCladded optical fibreWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm transmission systemsClassical mechanics
A low-cost configuration of, and at the same time to control the variable dispersion compensator at a high speed in a variable dispersion compensator for compensating the wavelength dependent accumulated dispersion resulting from the wavelength dependency of the transmission fiber and fixed dispersion compensator in a long-distance high-speed WDM transmission system. In order to achieve the object mentioned above, the wavelength dependent representative characteristic of the transmission fibers 4-1 . . . n, and the wavelength dependent representative characteristic of the DCFs 13-1 . . . n are recorded and maintained in advance in the dispersion control circuit 5-1 . . . n of the variable dispersion compensator 16, and based on the input of dispersion amount at the representative length of the transmission fiber and the fiber length, the dispersion amount at the representative wavelength of the DCF, the accumulated dispersion amount is computed from the wavelength dependent representative characteristic recorded and maintained in advance, and the dispersion amount of the variable dispersion compensator 16 is determined by taking this as the reference.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
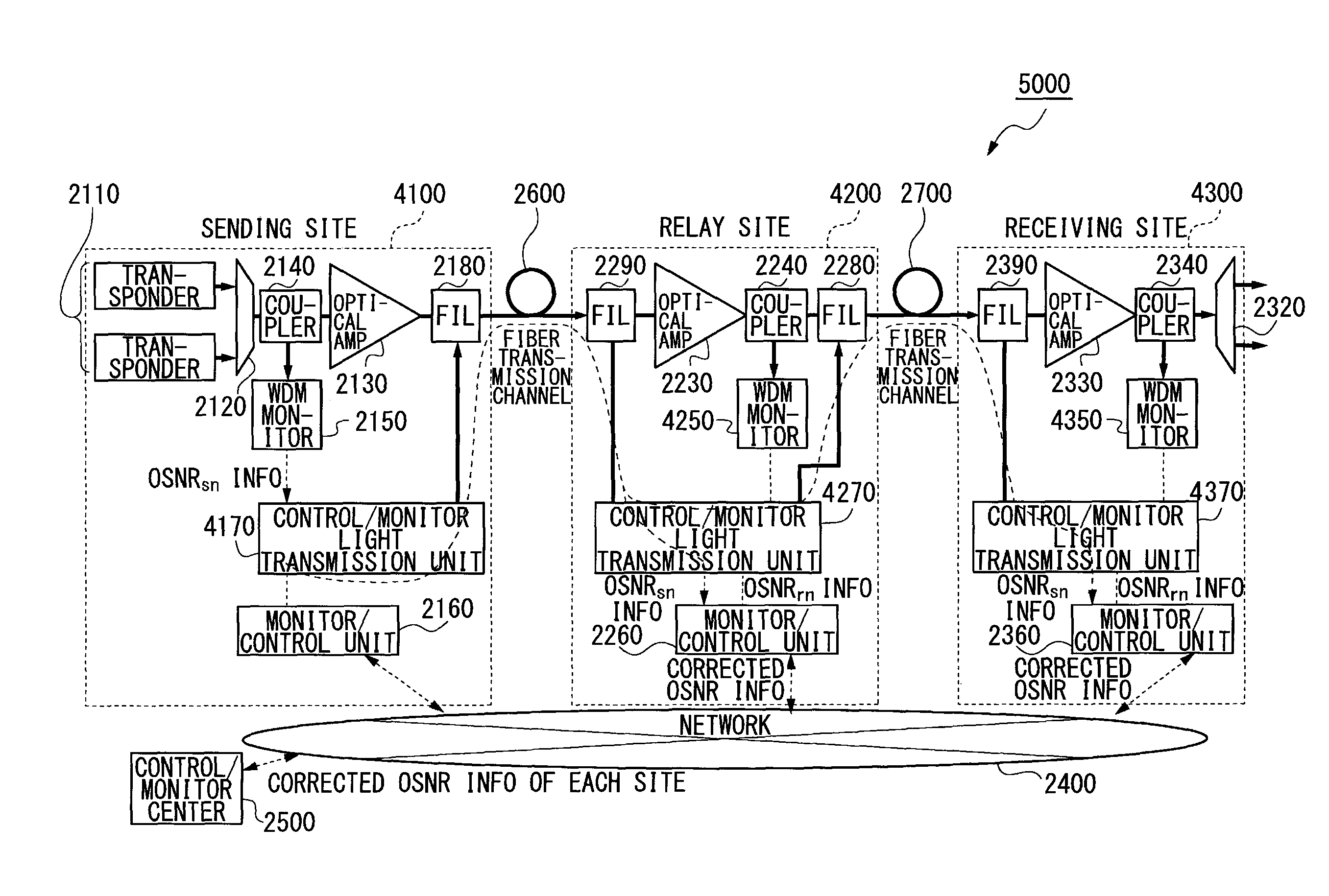
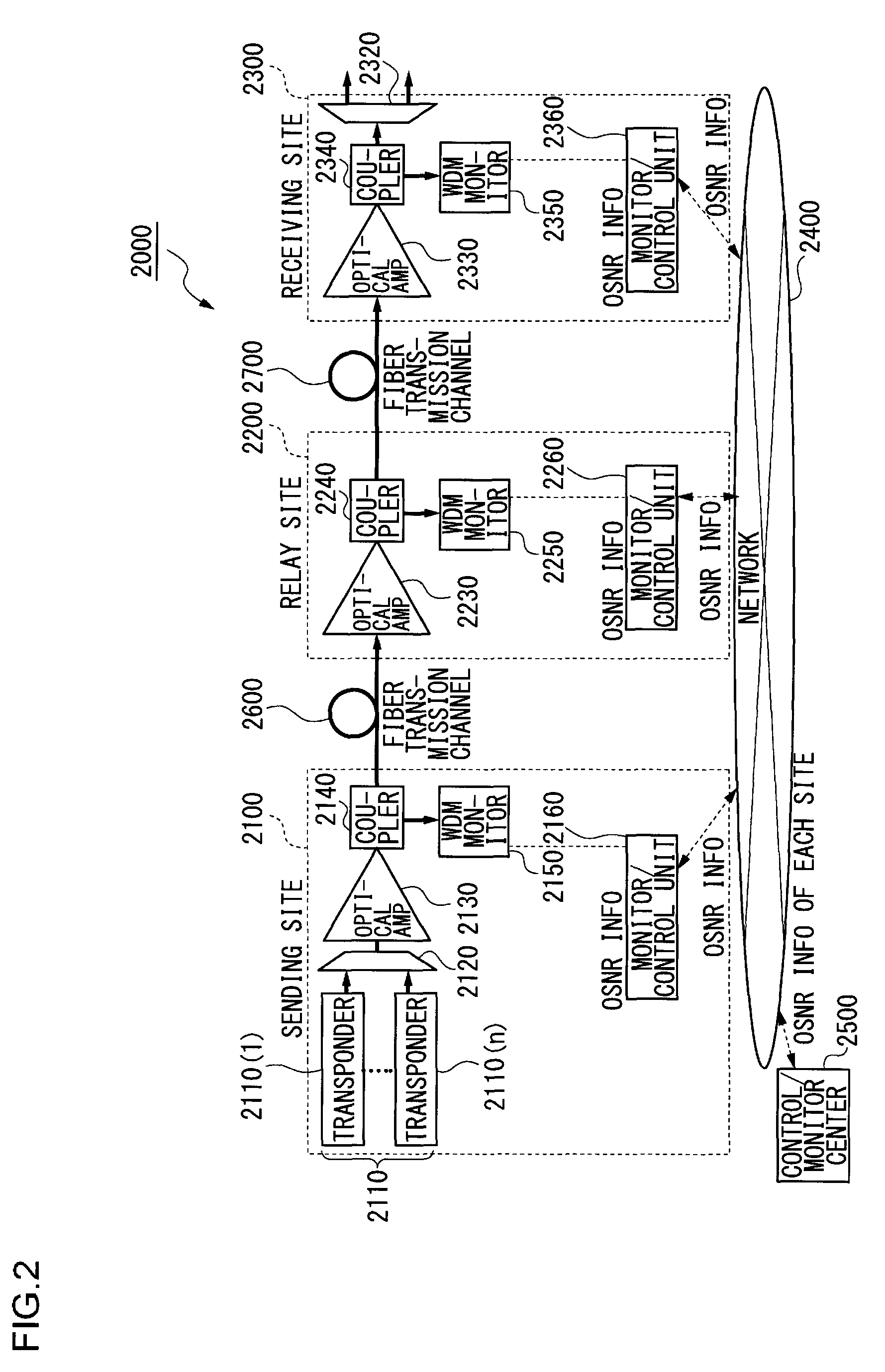
Wavelength division multiplexing transmission system and apparatus and optical signal noise ratio calculation method
InactiveUS8588609B2Accurate measurementReduce impactWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringWdm transmission systemsTransfer system
A wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) transmission system for transmitting a wavelength division multiplexed signal light from a sender transmission apparatus to a receiver transmission apparatus is provided. The system comprises a computing unit that subtracts from a first optical signal noise ratio (OSNR) of the signal light measured by the receiver transmission apparatus a second OSNR ascribed to a sideband of the signal light measured by the sender transmission apparatus so as to compute a corrected OSNR of an amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) noise light with a reduction of an effect of the sideband.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Efficient and reliable physical layer encryption high speed optical communication system
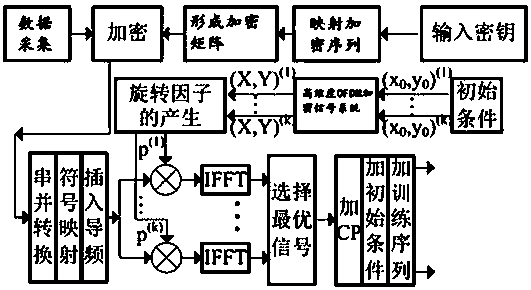
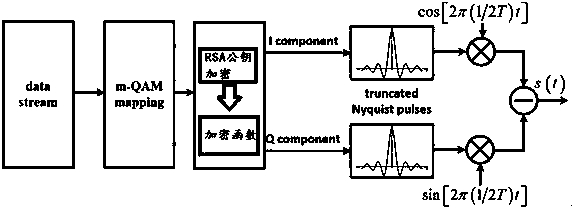
InactiveCN108494544ADensely spacedReduce complexityBaseband system detailsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesFiberComputer hardware
The invention discloses an efficient and reliable physical layer encryption high speed optical communication system, which comprises an optical OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) encryption system and a high spectral efficiency transmission system, wherein the optical OFDM encryption system configures a character inside a high-dimension OFDM encryption signal system according to aninitial condition, then receives data, maps an encryption sequence and forms an encryption matrix through an input key in sequence, and encrypts the acquired data; and the acquired data are subjectedto serial and parallel conversion, character mapping and interpolation piloting. According to the physical layer encryption-based CO (Coherent Optical)-OFDM and Nyquist-WDM transmission system disclosed by the invention, the system makes a systematic research from a research on a physical layer encryption algorithm, synchronization of an OFDM signal and a Nyquist signal and secure transmission ofoptical signals of big data, and has the characteristics of high security, high spectral utilization rate, high access capacity and the like in combination with fiber access.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF HUMANITIES SCI & TECH +1
Dispersion compensation quantity setting method, receiving terminal station, and wavelength-multiplexing optical transmission system
InactiveUS7394993B2Quality improvementImprove reliabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationTransport systemEngineering
In a dispersion compensation quantity setting technique for use in a WDM transmission system, a transmitting terminal node transmits CW light and modulated light obtained by modulation using a modulation pattern signal, while a receiving terminal node detects a physical quantity stemming from cross phase modulation occurring between the transmitting terminal node and the receiving terminal node on the basis of a variation of an intensity of the transmitted CW light and sets a dispersion compensation quantity on the basis of a variation of the detected physical quantity. Moreover, this optimizes the crosstalk, suppresses the output power of transmitted light, eliminates the nonlinear optical effect of the transmitted light, and carries out dispersion compensation superior in cost performance.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for determining the gain spectrum of a raman amplifier in a wdm-transmission system
InactiveUS20050270634A1Easy to adjustAvoid switchingLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionWdm transmission systemsAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a method and device for determining the gain spectrum of a Raman amplifier having an optical amplifier, which is connected in incoming circuit thereto, in a section of a WDM transmission system. A number of spectra are recorded at the output of the Raman amplifier during which the optical amplifier or the Raman amplifier is switched on and off and a high amplified spontaneous emission is generated at the input of the Raman amplifier. Afterwards, the gain spectrum is determined on the basis of the recorded spectra.
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
System for transmitting single-fiber-optic two-way wavelength division multiplexing and its protection
InactiveCN101030879AEfficient switchingEliminate the effects ofWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionMultiplexingSingle fiber
The system comprises: laser; receiver; wave combiner and separator; multiplexing segment protection unit; and laser controller connected to one or more first receiver in the first laser and receiver for use in closing the first laser when the working line fibers or protection line fibers in the multiplexing segment protection unit are broken; the beam from the first laser will be reflected to t he beam detector when the working line fibers and protection fibers are broken.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Variable dispersion compensator
InactiveUS20070147840A1Band widthLow group-delay rippleWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesWdm transmission systemsLight beam
The present invention provides: (1) a compensator that compensates a wide range of amount of dispersion of light in a wide bandwidth band; and (2) a variable dispersion slope compensator applicable to the case where a transmission path suitable for a wavelength division multiplexing transmission system produces a wavelength dispersion slope. The present invention realizes: (1) a variable dispersion compensator that compensates a wide range of amount of dispersion of light in a wide bandwidth band; and (2) a variable dispersion slope compensator suitable for a wavelength division multiplexing transmission system. To realize the above, a dispersion compensating unit is provided with a structure in which a mirror is disposed in parallel to or with a slight angle relative to an etalon to reflect a light beam emitted from a collimator on the etalon multiple times and then emit the light beam into another collimator.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com