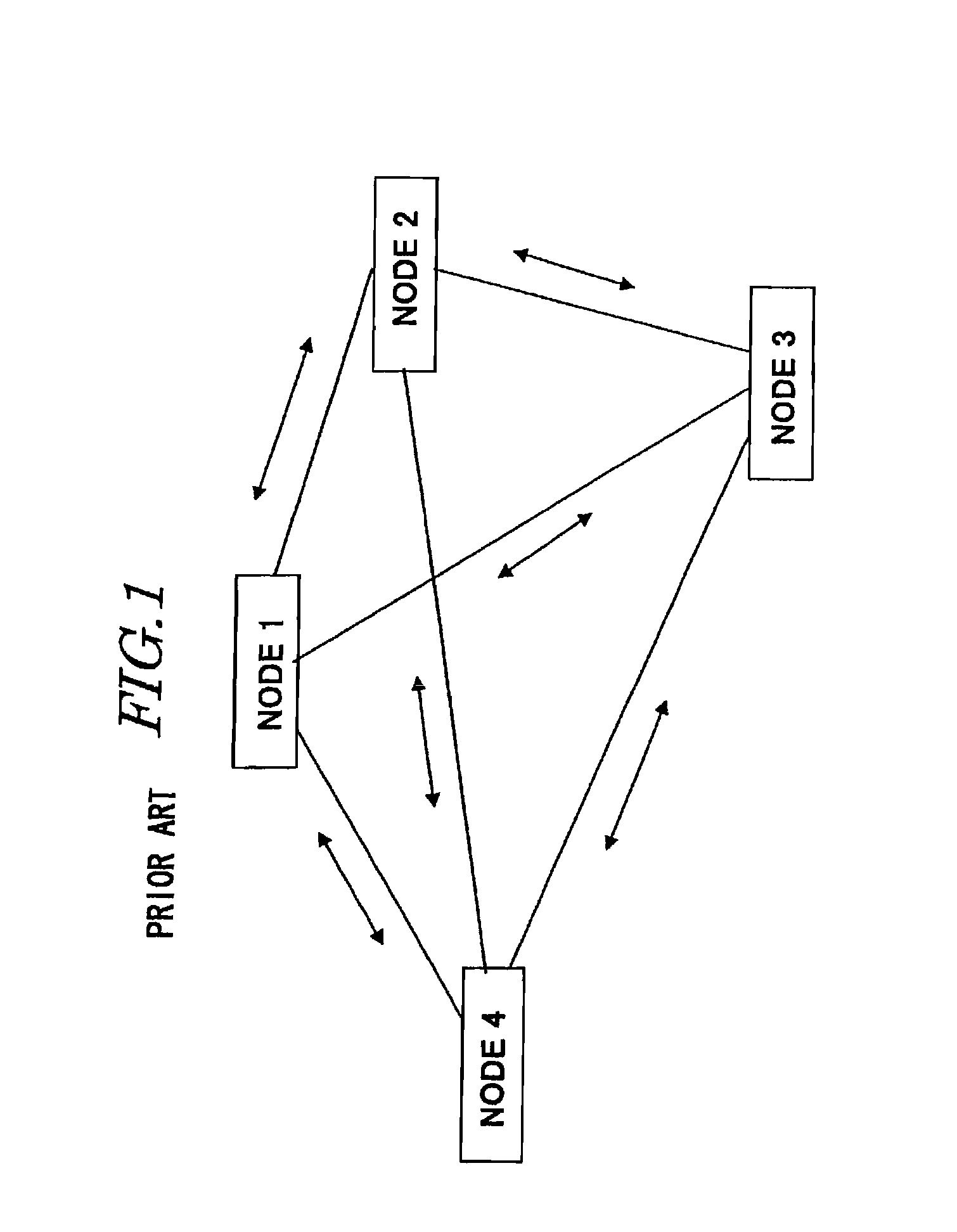
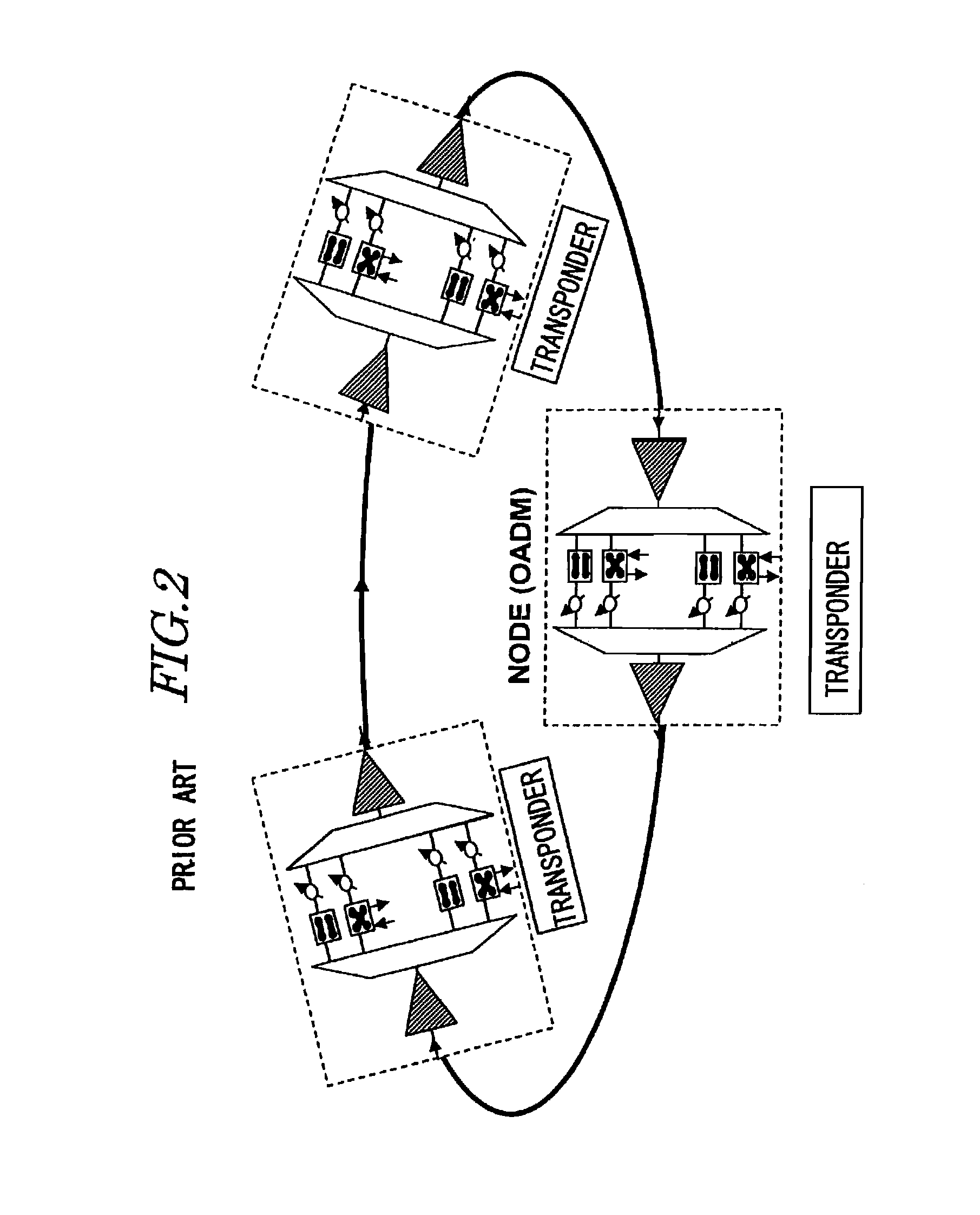
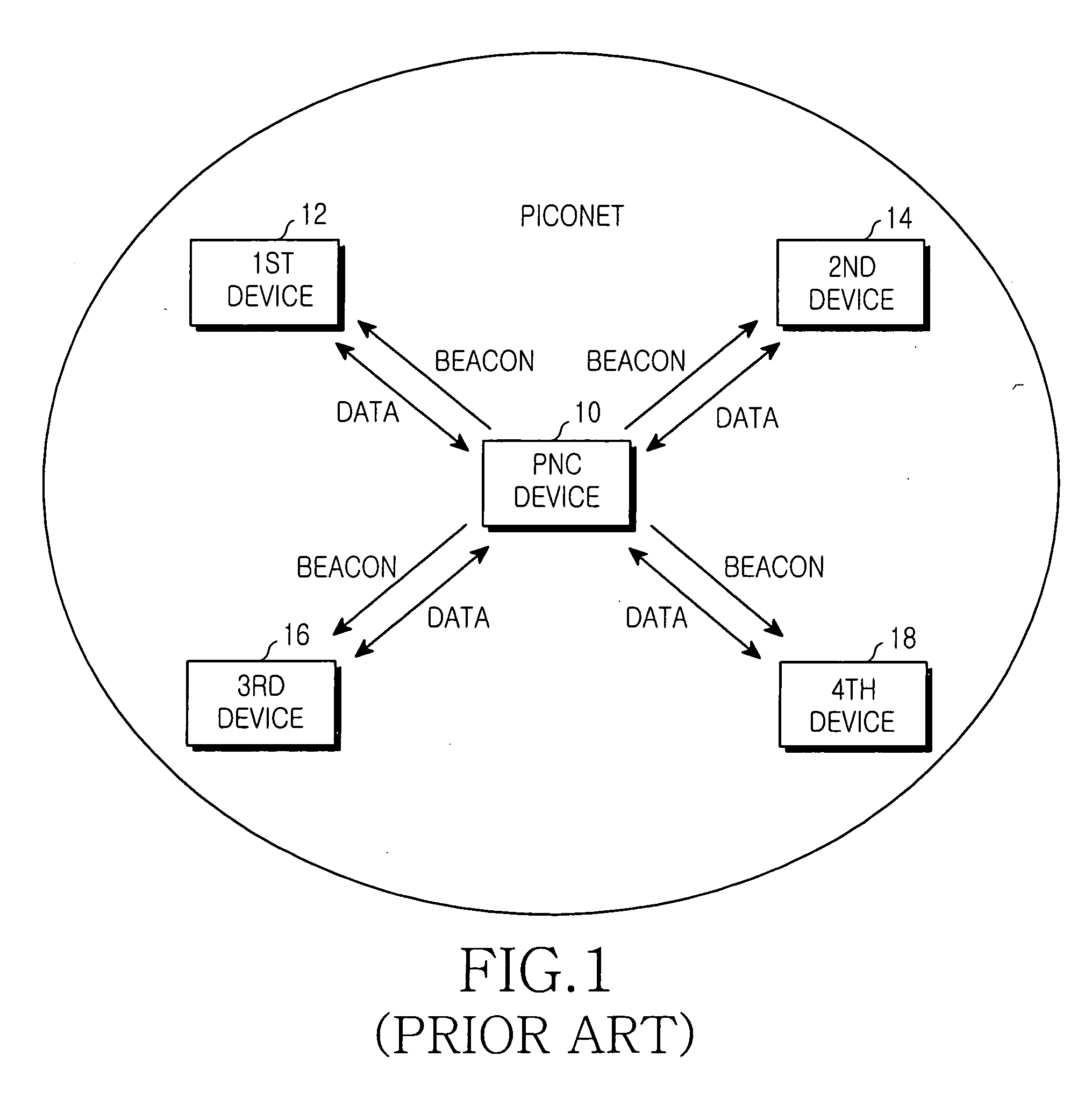
Patents
Literature
208results about "Bus-type electromagnetic networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
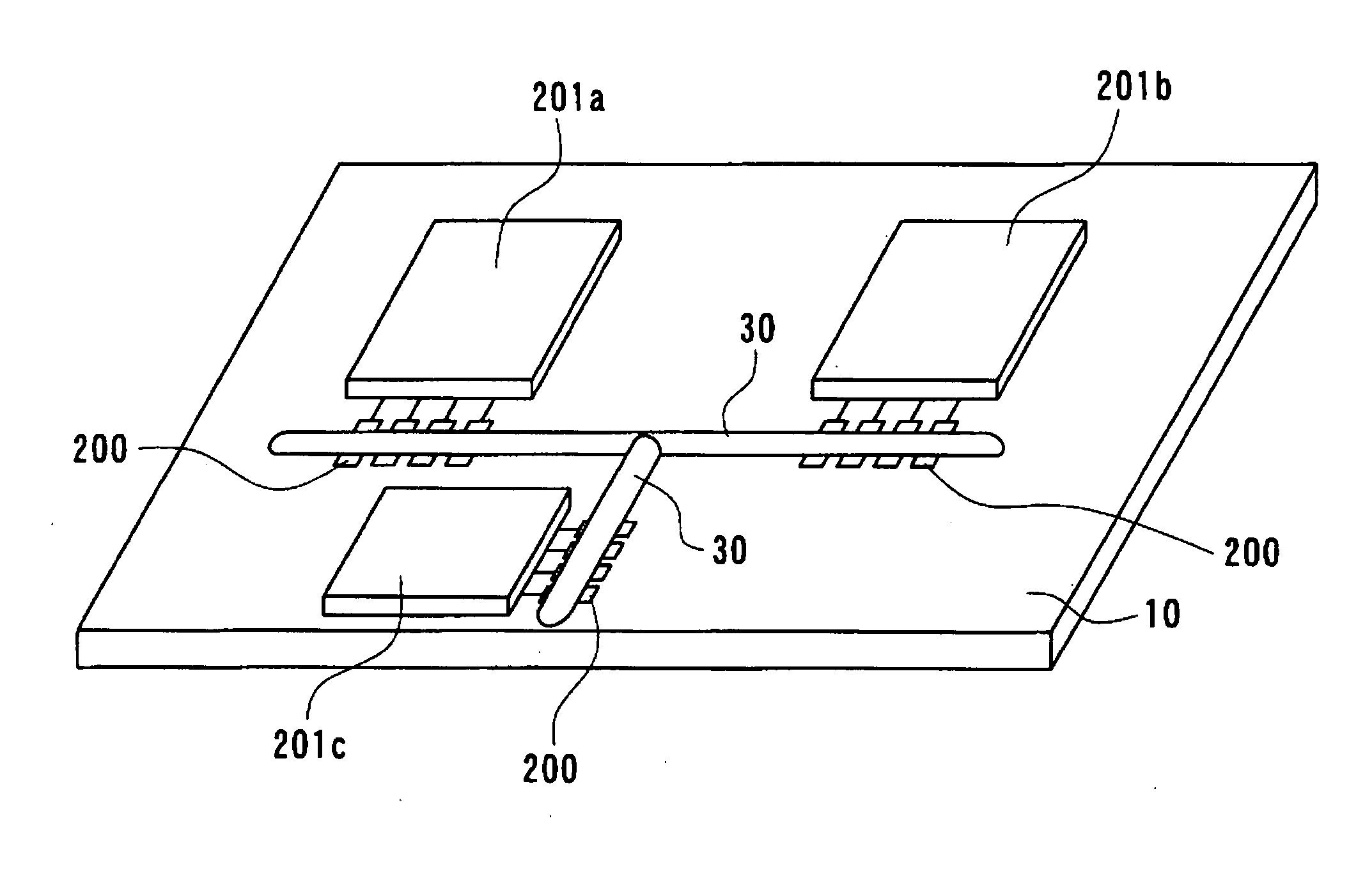
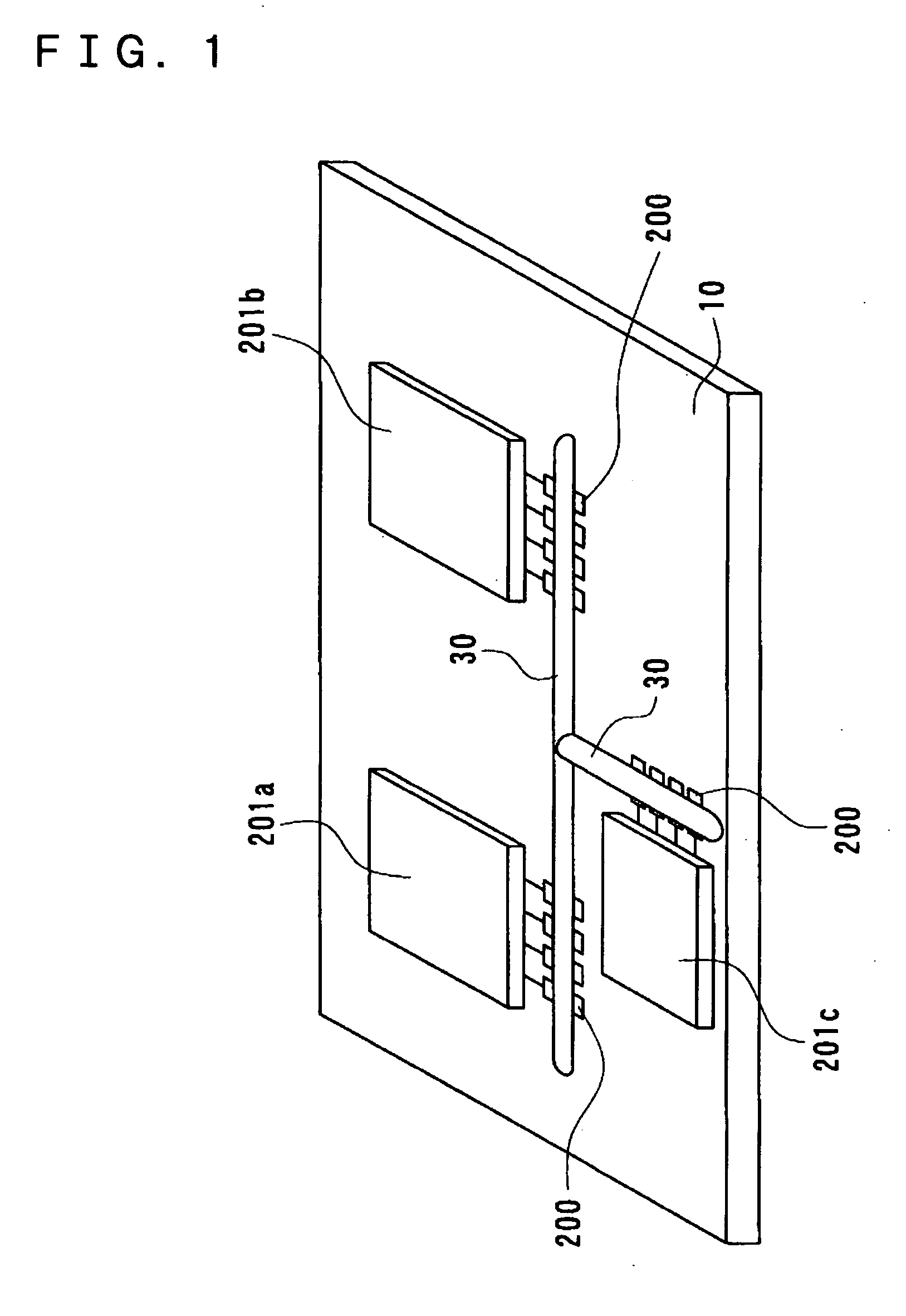
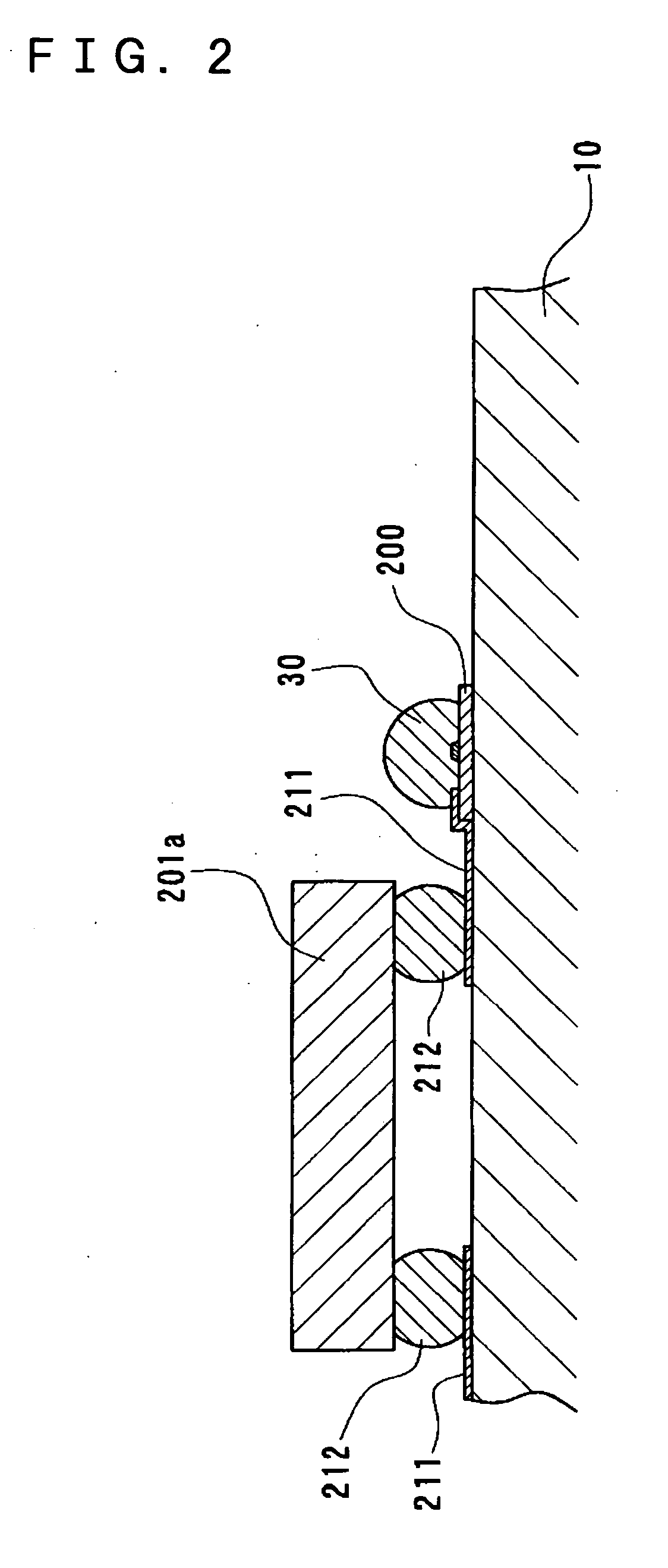
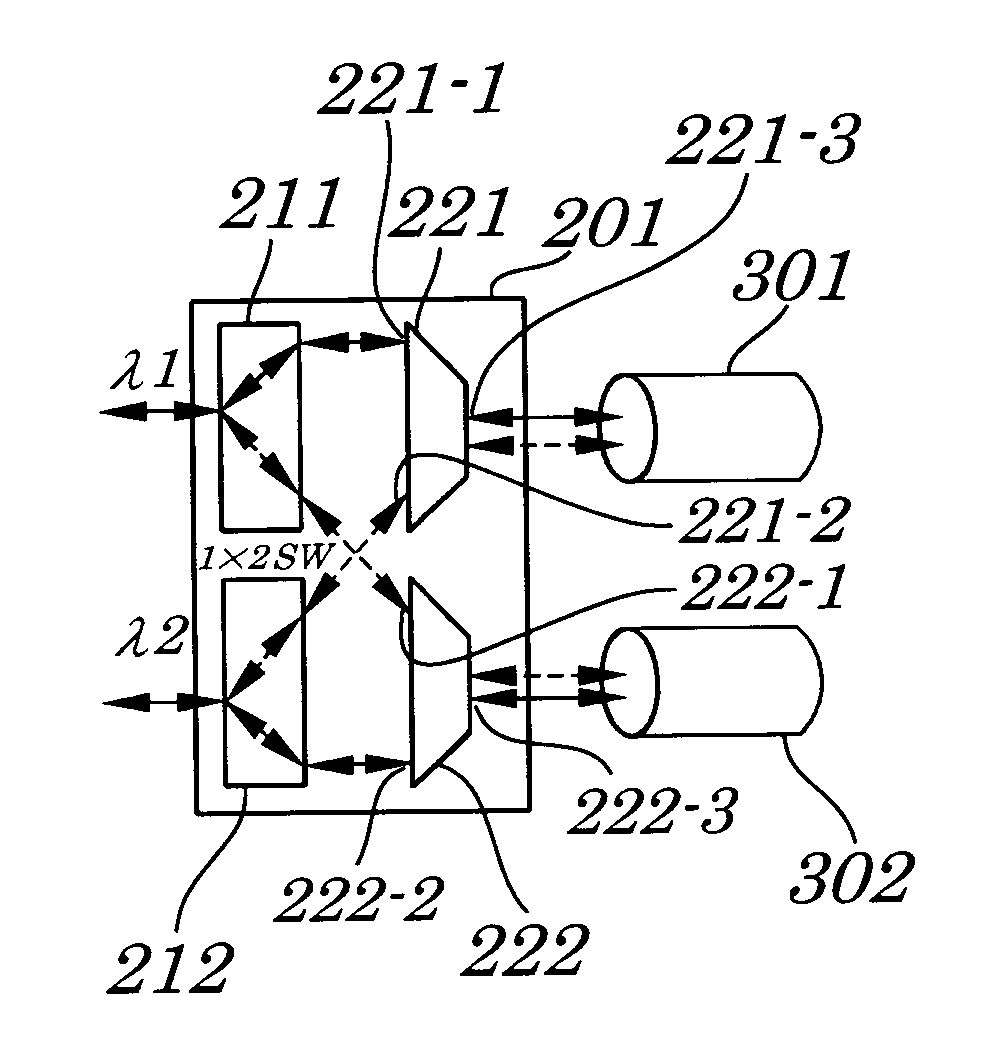
Optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20040264867A1Easy to makeThe transmission is compactRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsMultiplexingLength wave
To provide an optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, capable of increasing signal transmission speed and of being easily made minute thereby being simply and easily fabricated, an electro-optical device, and an electronic apparatus, an optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, which is disposed on a substrate, includes micro-tile shaped elements having a light emitting function or a light receiving function with wavelength selectivity.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
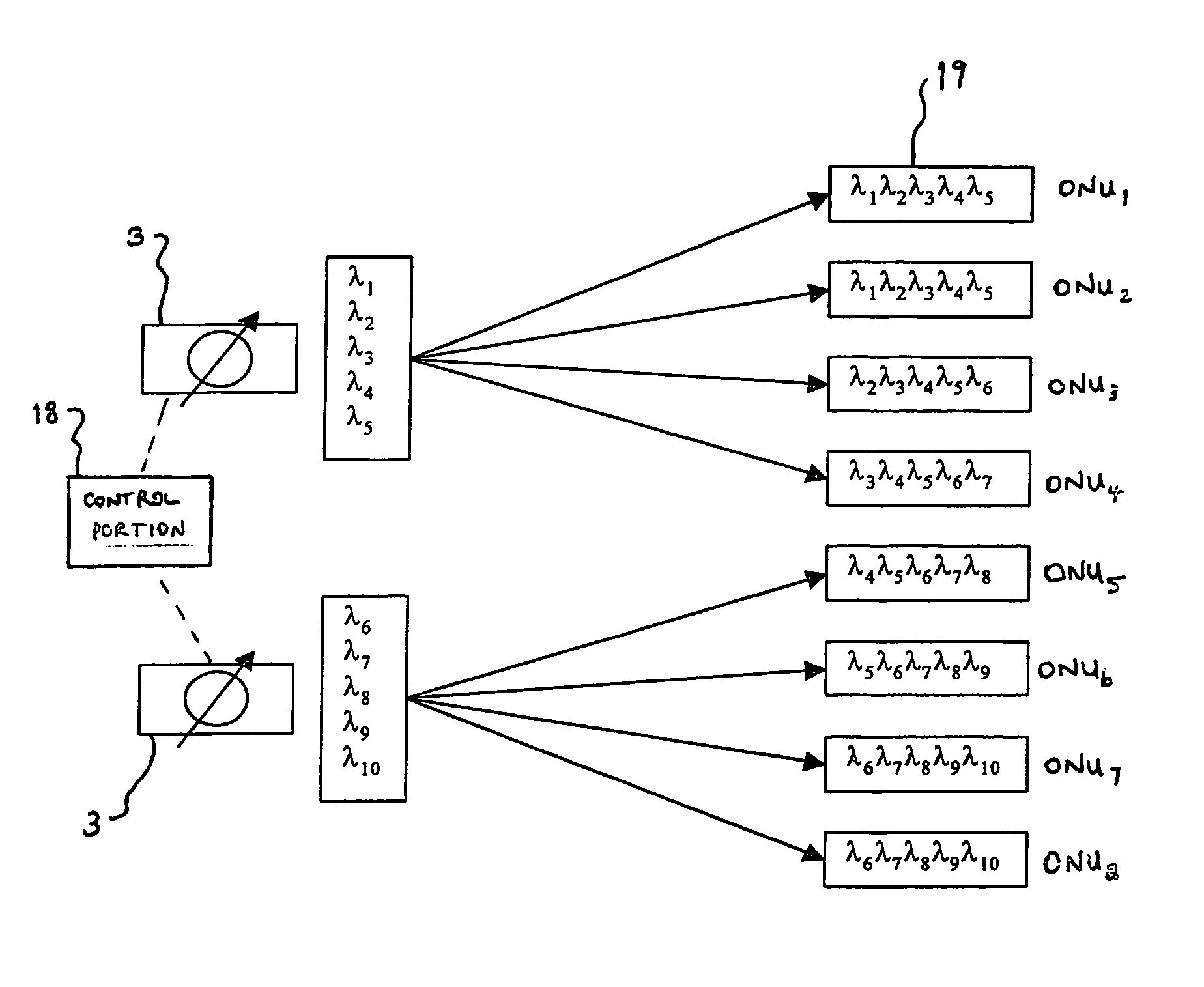
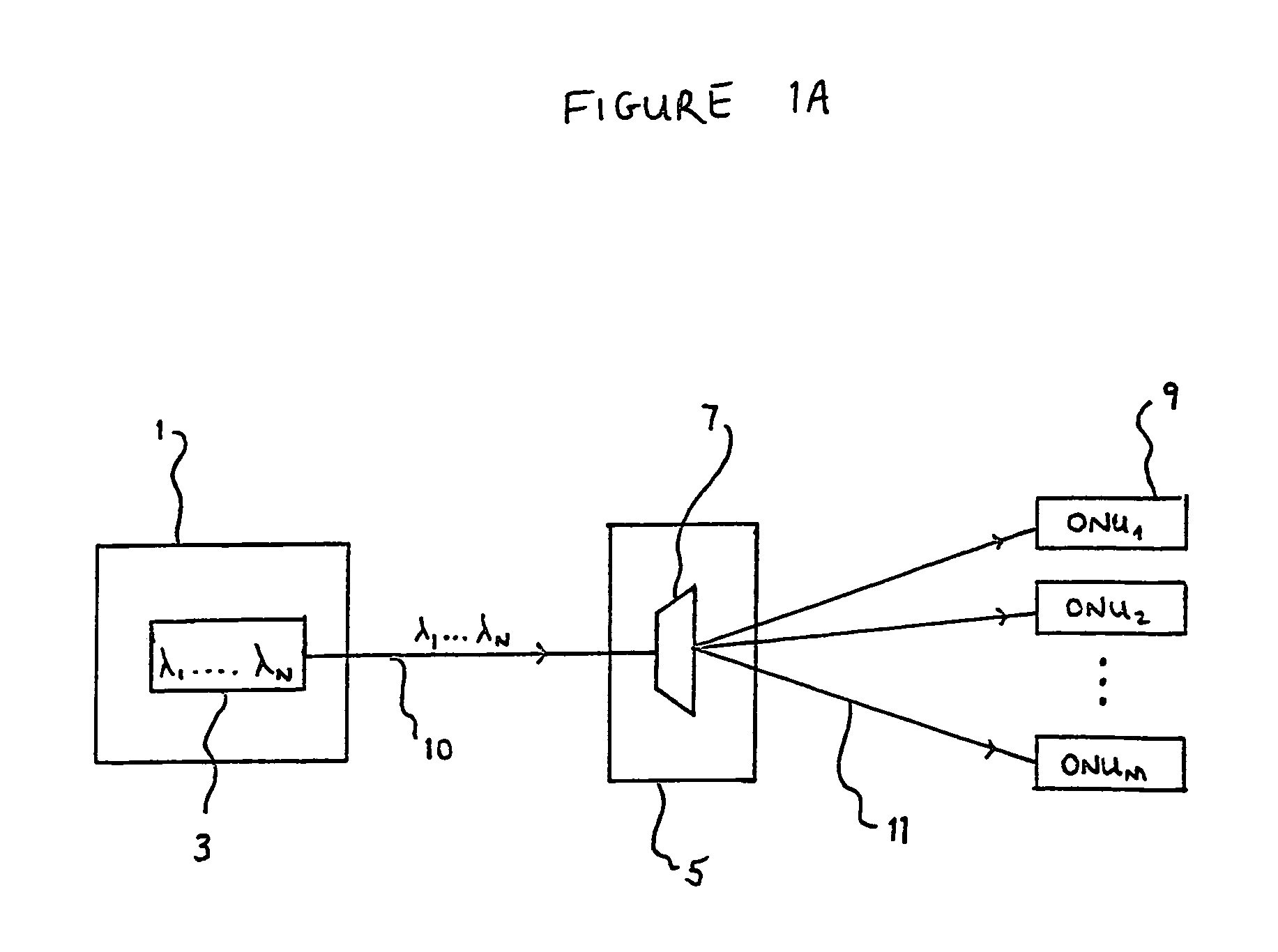
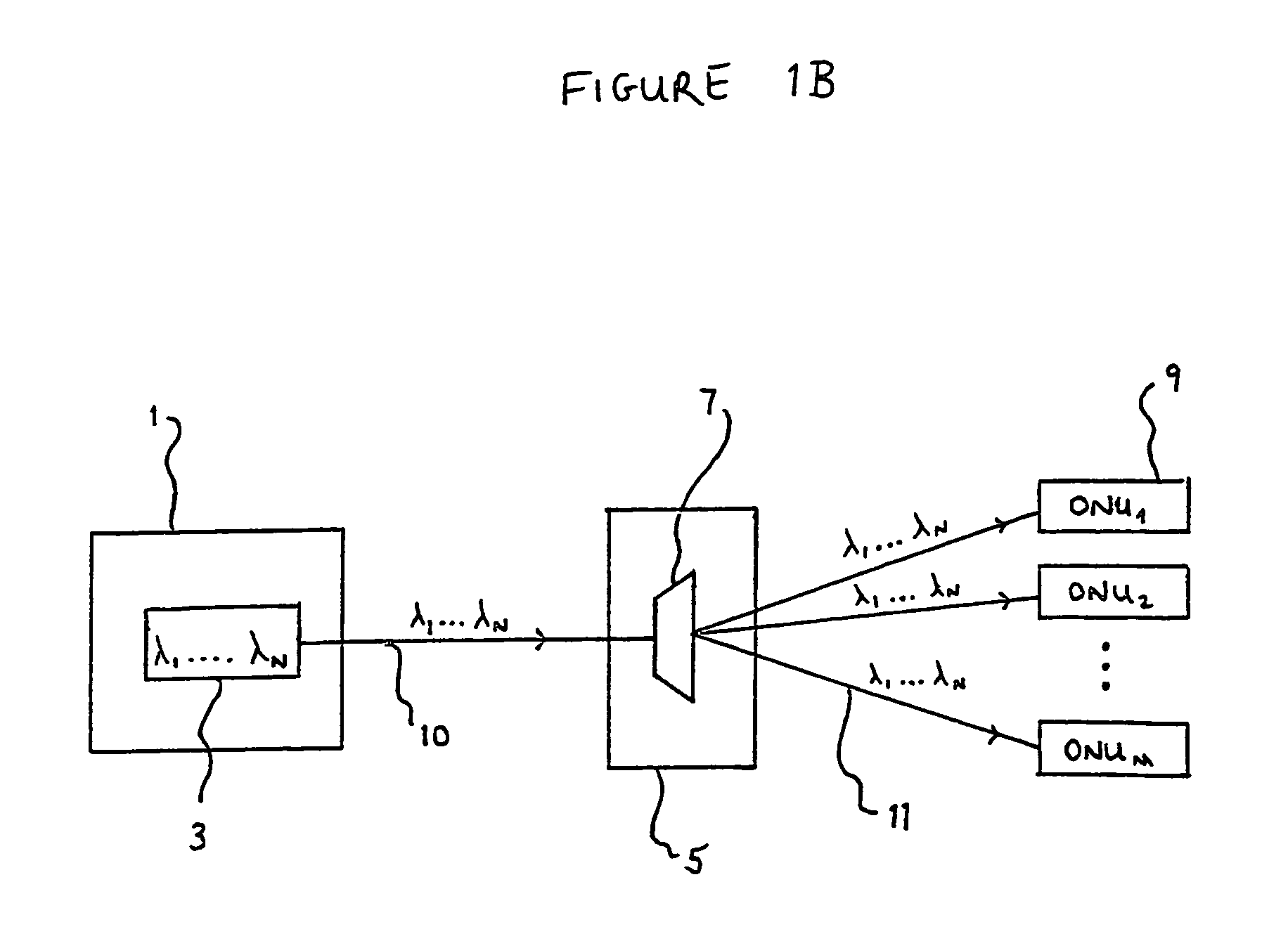
Optical network units preconfigured to accept predetermined subsets of wavelengths
InactiveUS7016608B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksLength waveOptical network unit
An optical network is provided which comprises a plurality of optical network units (19) and optical source means (3) connected and arranged to transmit light signals to each of the plurality of optical network units (19). The optical source means (3) are capable of transmitting light signals at one or more of a plurality of different wavelengths and at least one optical network unit (19) is operable to accept more than one of the said wavelengths. Further, each wavelength of the plurality is accepted by at least one of the optical network units (19) such that each such wavelength is accepted by a different subset of optical network units (19). The optical network further comprises control means (18) operable to cause the optical source means (3) to transmit light signals at one or more selected such wavelengths corresponding to respective desired subsets of the optical network units (19).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High-speed optical fiber bus and realization method for redundance topological structure thereof
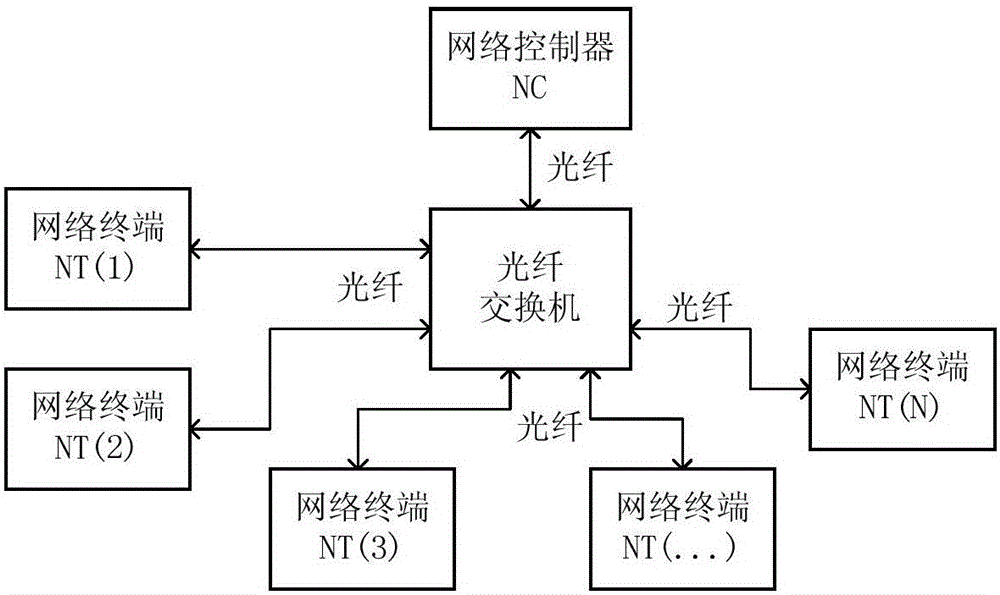
ActiveCN102075247AImprove reliabilityMeet the needs of high-speed busesBus-type electromagnetic networksBus networksNetwork terminationNetwork control
The invention discloses a high-speed optical fiber bus based on a command response type high-speed optical fiber bus protocol. The structure comprises an optical fiber bus, a network controller, a plurality of network terminals and a plurality of remote terminals, wherein the network controller is connected to the optical fiber bus, the network terminals are hooked on the optical fiber bus through a plurality of optical fiber couplers, and the remote terminals are connected to the optical fiber couplers through bridging equipment. The invention also discloses a realization method for a redundance topological structure of the high-speed optical fiber bus, which comprises the following steps of: closing an optical link, and detecting the connectivity of the optical link in real time; mutually serving as a backup by reverse double loops, and selecting the other link when one link fails; and utilizing a network monitor as redundance equipment of the network controller. By adopting the invention, the optical fiber bus can meet the requirement of various application environments, such as aerospace and the like for high speed, real time and high reliability, easily isolate single-point failures and support various topological structures, the communication rate can reach 2.5Gbps, wires are convenient to lay, the equipment used by a system is simple, and the reliability is high.
Owner:BEIJING TASSON SCI & TECH CO LTD
Optical network and arrangement and method in such network
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00374 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 29, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 29, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 26, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 31964 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 10, 1996An optical network which is arranged to ensure communication between nodes in a lower-order loop and a higher-order loop when there is an interruption in the lower-order loop or in the event of hub failure. Each lower-order loop consists of a bus network with hubs and one or a plurality of nodes. Two optical fibers connect the nodes in each bus network and are used for communication in opposite directions between the nodes. Each bus network comprises precisely two hubs of which the first closes the bus network end at the first end thereof and the second closes the bus network at the other end. The hubs connect the bus networks in a lower-order loop and join this loop to a higher-order loop. Each node in the bus network is arranged to communicate with each hub. Channel allocation can be carried out so that channels received in one node are re-used for transmission on the same fiber from the same node.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
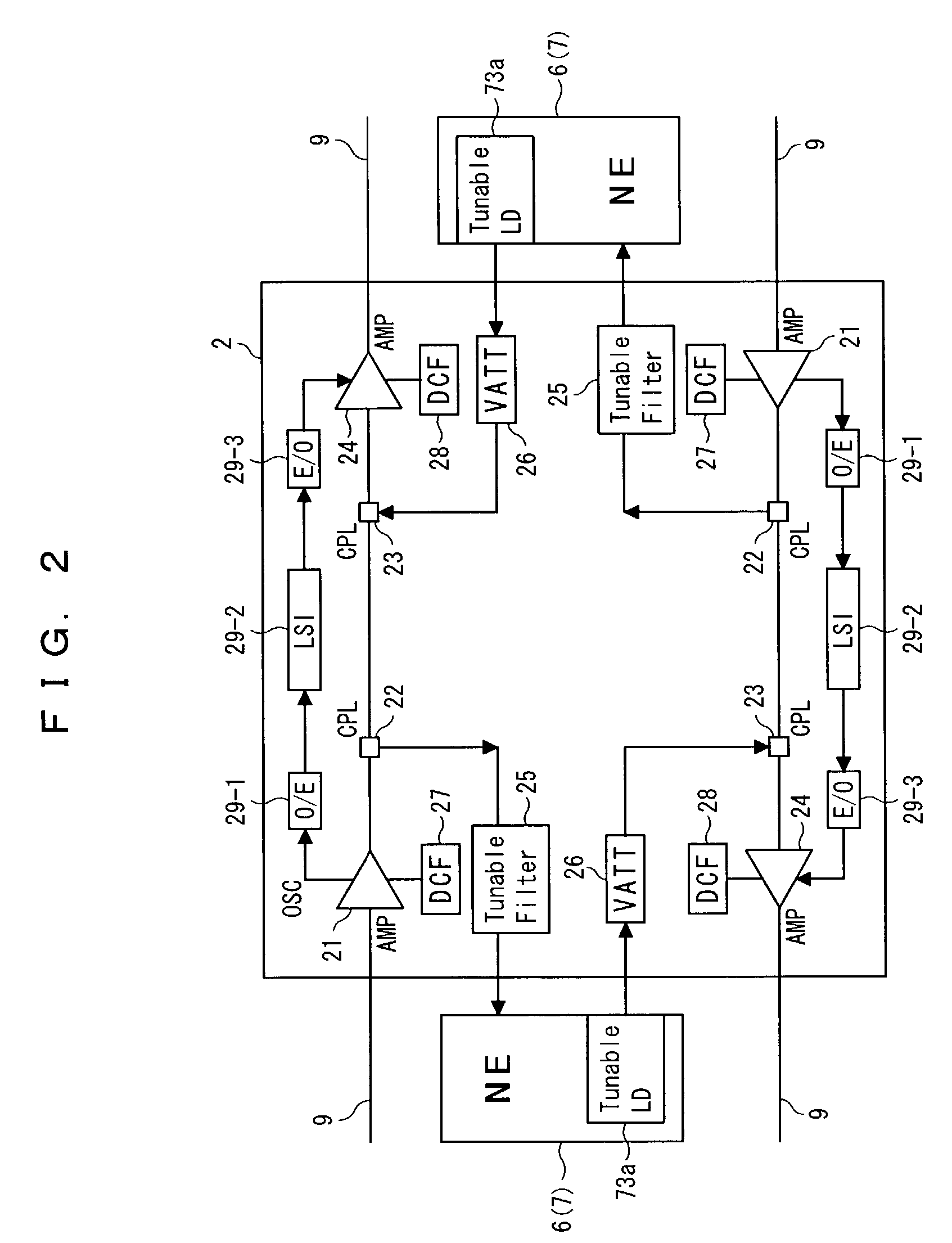
Optical communication apparatus, optical communication system and method for transmitting optical signal
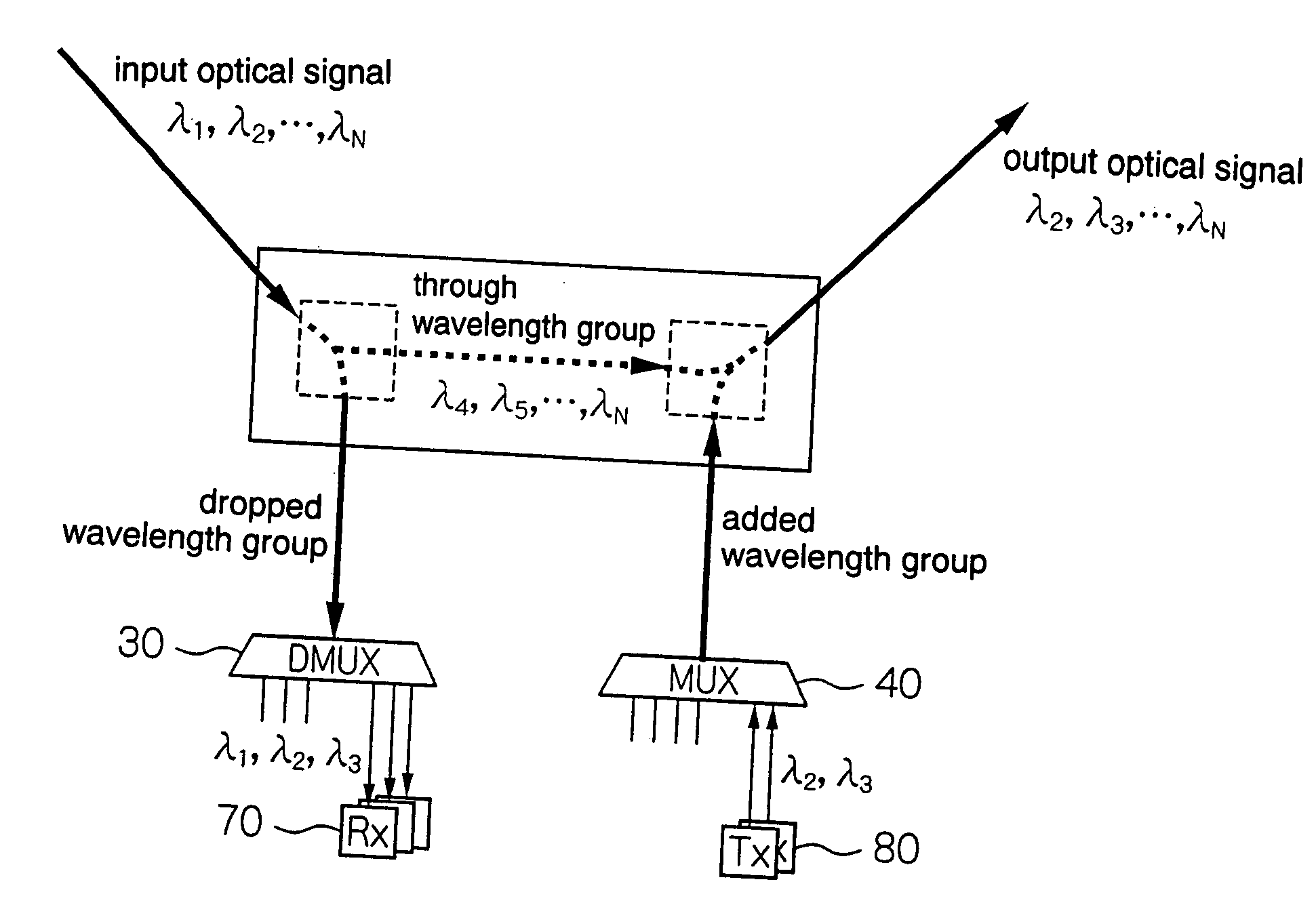
InactiveUS20060045532A1Improve signal transmission performanceProvide requiredBus-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemMultiplexer
The present invention relates to optical communication apparatuses such as OADM node, or OXC node. A receiving dispersion compensating module adjusts the accumulated dispersion of a wavelength-division-multiplexed optical signal such that the accumulated dispersion has an optimum value at a receiver for receiving optical signals in respective wavelength channels which are dropped from the wavelength-division-multiplexed optical signal. An auxiliary dispersion compensating module is provided in a path for an added wavelength group. The auxiliary dispersion compensating module applies the same value of dispersion as the accumulated dispersion adjusted by the receiving dispersion compensating module, to a wavelength-division-multiplexed optical signal in the added wavelength group. Therefore, the accumulated dispersion of a dropped wavelength group has an optimum value, and the accumulated dispersion of a through wavelength group and the accumulated dispersion of the added wavelength group are equalized to each other in a multiplexer.
Owner:NEC CORP
Network for distributing signals to a plurality of user equipment
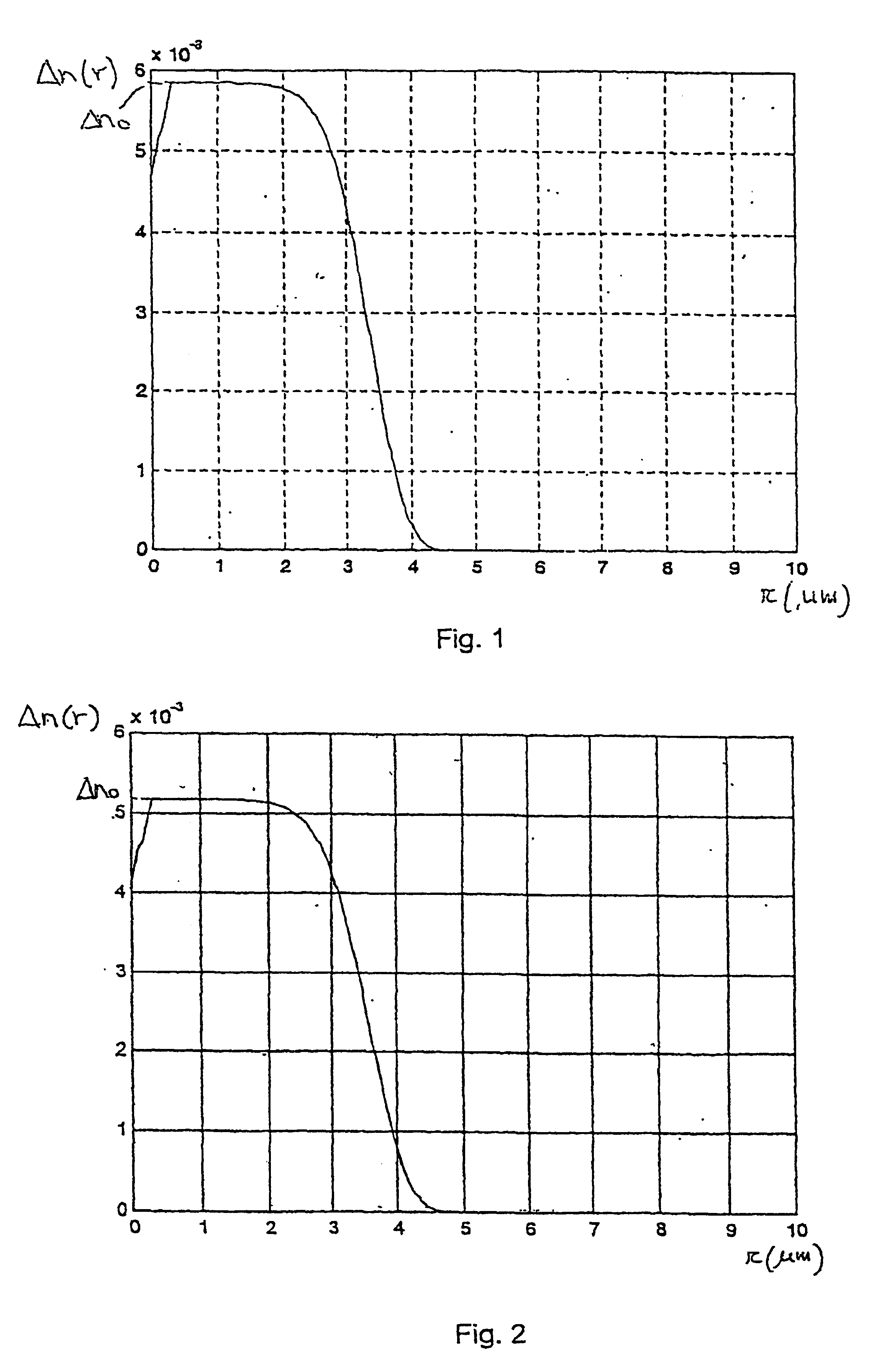
InactiveUS6885802B2Simple refractive index profileEasy to manufactureBus-type electromagnetic networksOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingEngineeringLength wave
A network for distributing signals to a plurality of user having a distribution unit and a plurality of optical cables adapted to make the distribution unit communicate with the plurality of user equipment. In turn, each optical cable has an optical fibre having a core, a cladding and a predetermined simple refractive index profile Δn(r). Each optical fibre is adapted to guarantee a single-mode propagation at higher wavelengths than about 1260 nm and a few-mode propagation at about 850 nm, and each optical fibre has such refractive index profile Δn(r) as to guarantee macro-bending losses at 1550 nm that are less than about 0.5 dB and an intermodal delay Δτ at 850 nm that is less than or equal to, about 1 ns / Km.
Owner:PRYSMIAN CAVI E SISTEMI ENERGIA
Signal transmission method in WDM transmission system, and WDM terminal, optical add-drop multiplexer node, and network element used in the same system
InactiveUS7139484B2Low costImprove system performanceLaser detailsBus-type electromagnetic networksWdm transmission systemsTransport system
Disclosed herein is a signal transmission method in a wavelength-division-multiplex (WDM) transmission system. The WDM transmission system comprises a first WDM terminal for transmitting a WDM signal, a second WDM terminal for receiving the WDM signal, and an optical add-drop multiplexer (OADM) node for transmitting to a network element an optical signal of a specific wavelength of the WDM signal which is transmitted between the first and second WDM terminals. The WDM signal is transmitted from the first WDM terminal to the second WDM terminal regardless of whether an optical signal is added or dropped at the OADM node. The network element employs an optical signal of an idle wavelength of the WDM signal that has no transmission data, to transmit another transmission data that is transmitted by the network element.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
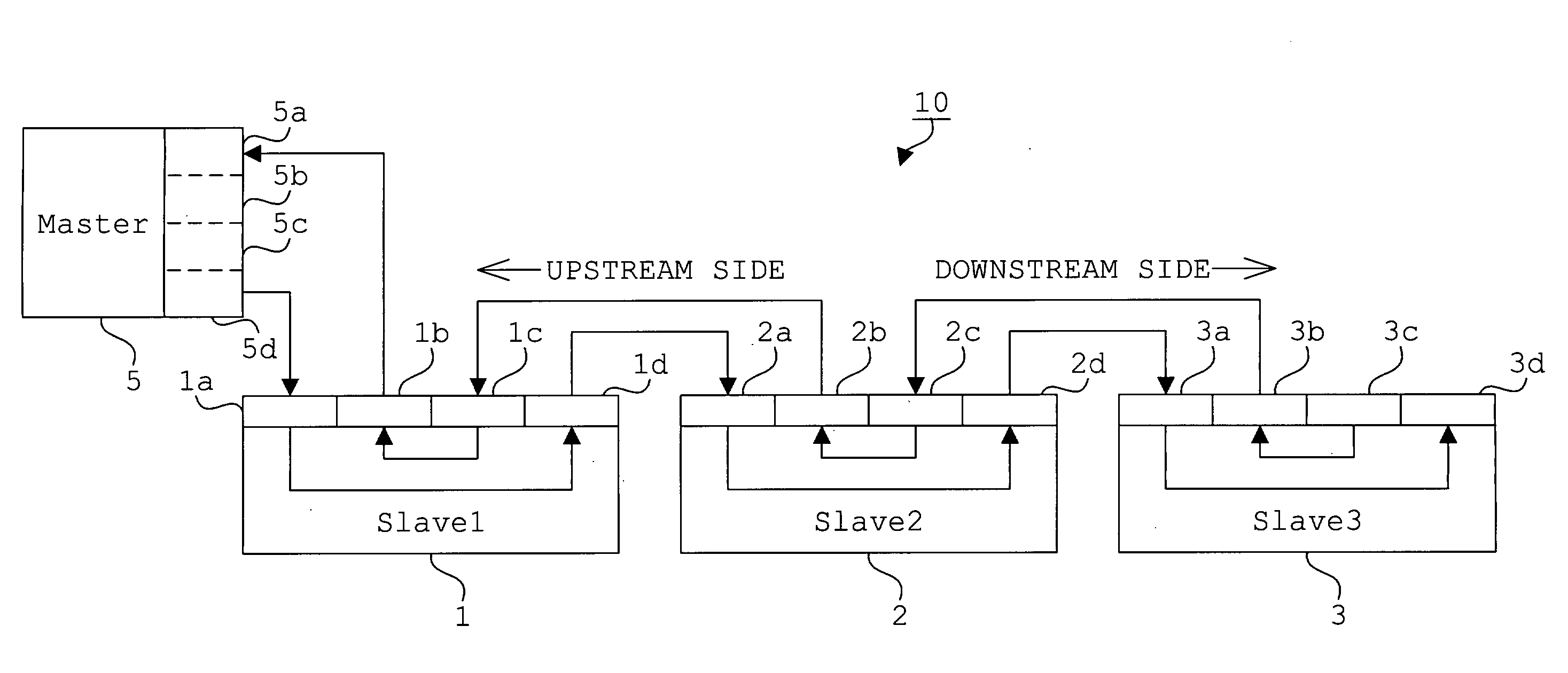
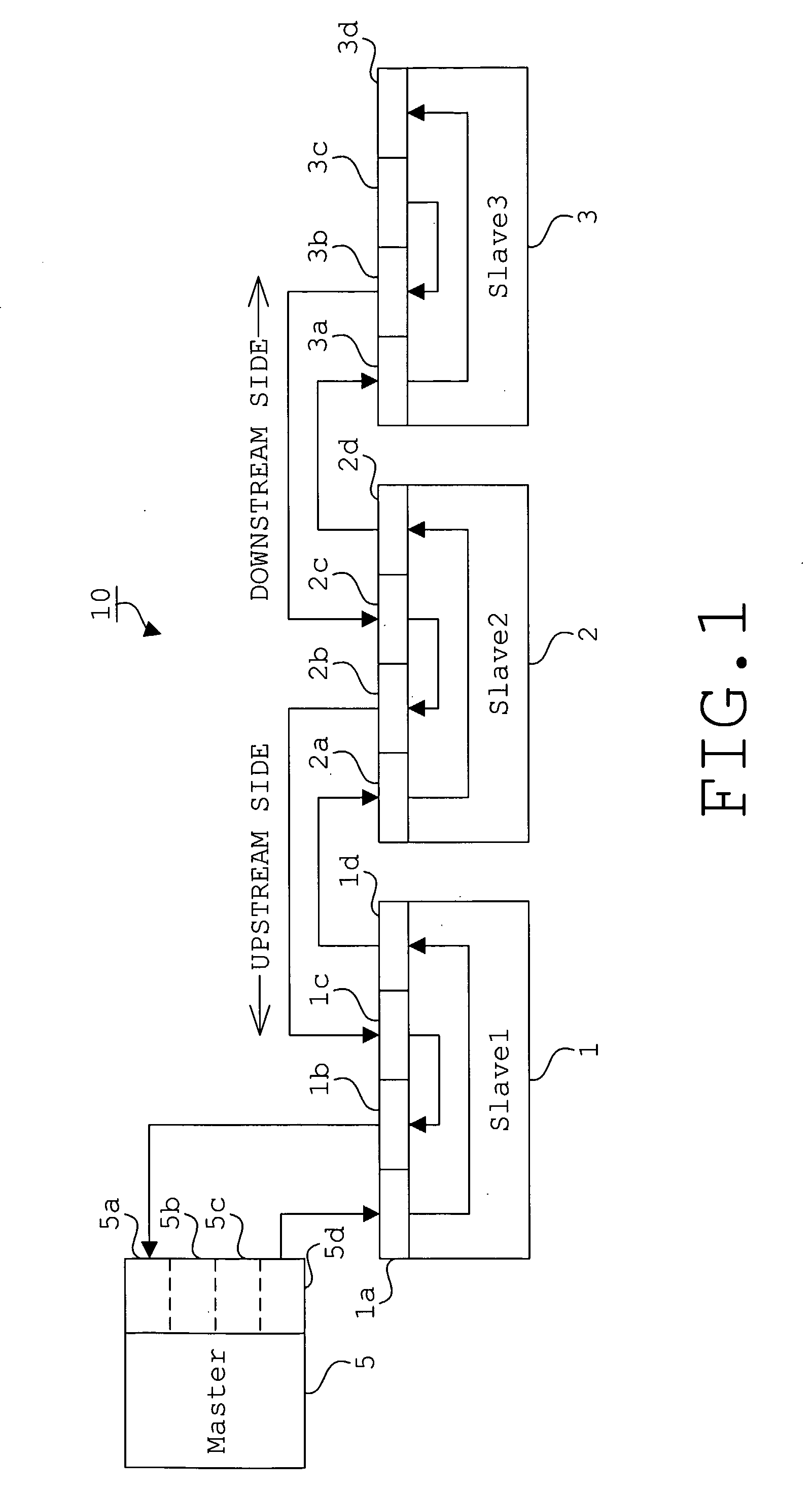
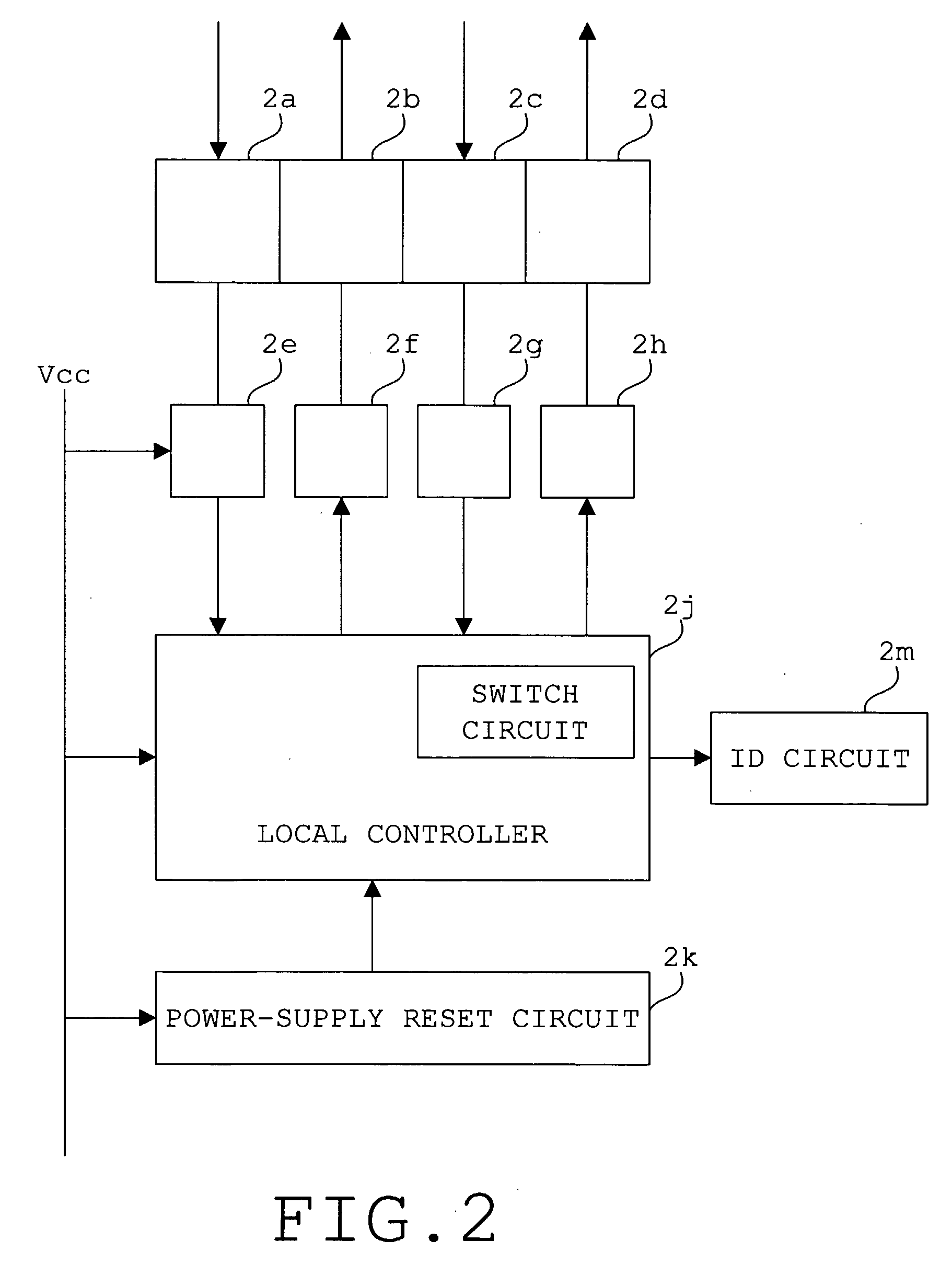
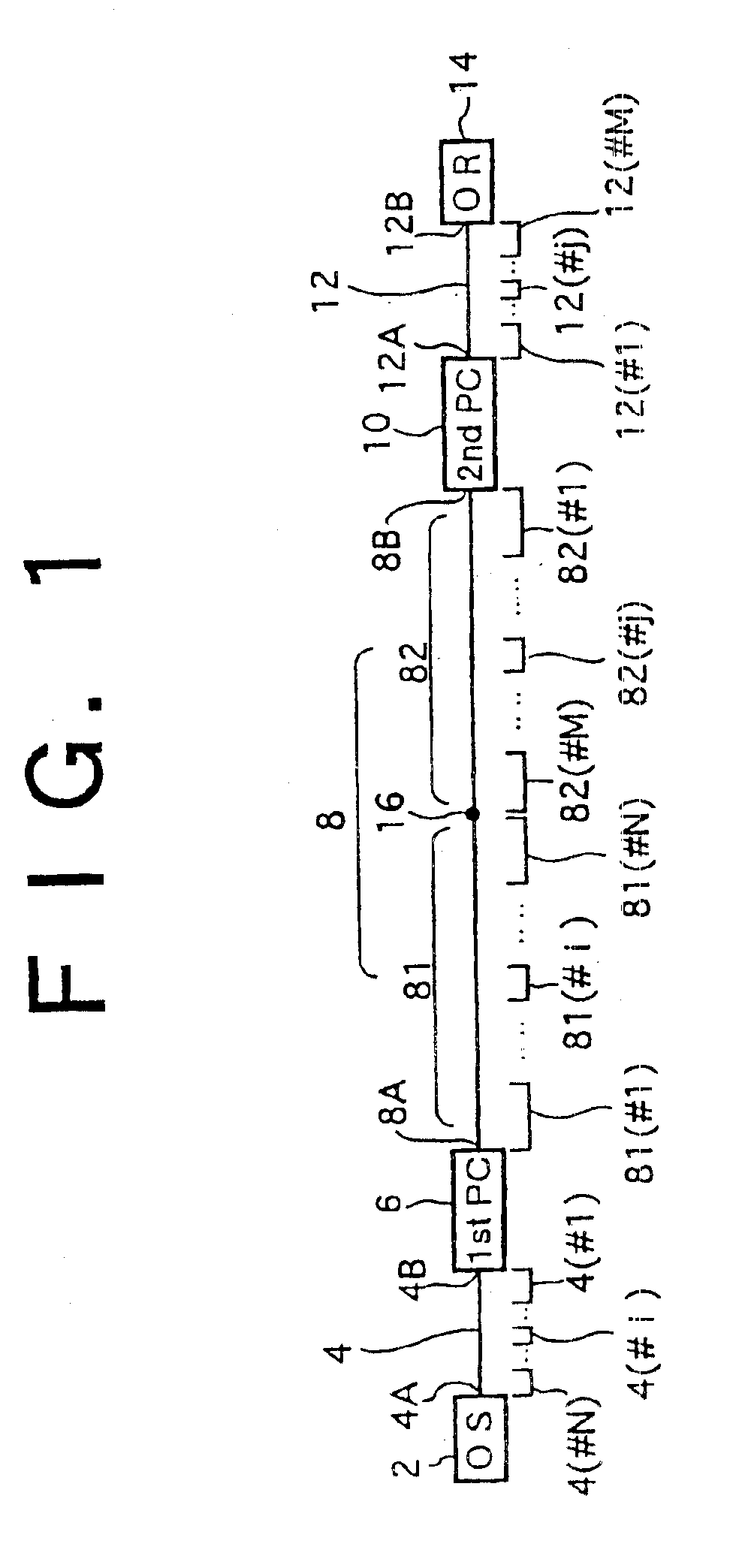
Network System, Master Device, Slave Device, and Start-Up Control Method for Network System
InactiveUS20080091862A1Avoid failureMultiplex system selection arrangementsBus-type electromagnetic networksNetworked systemOptical communication
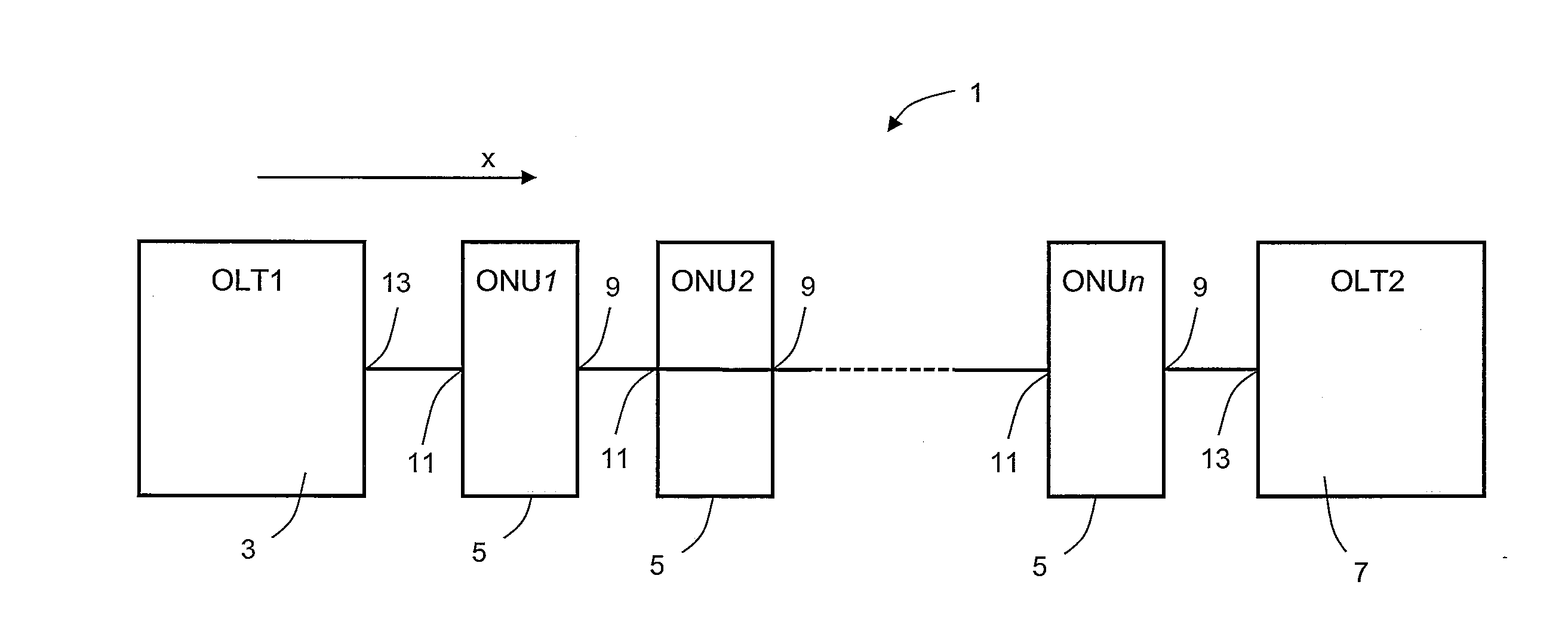
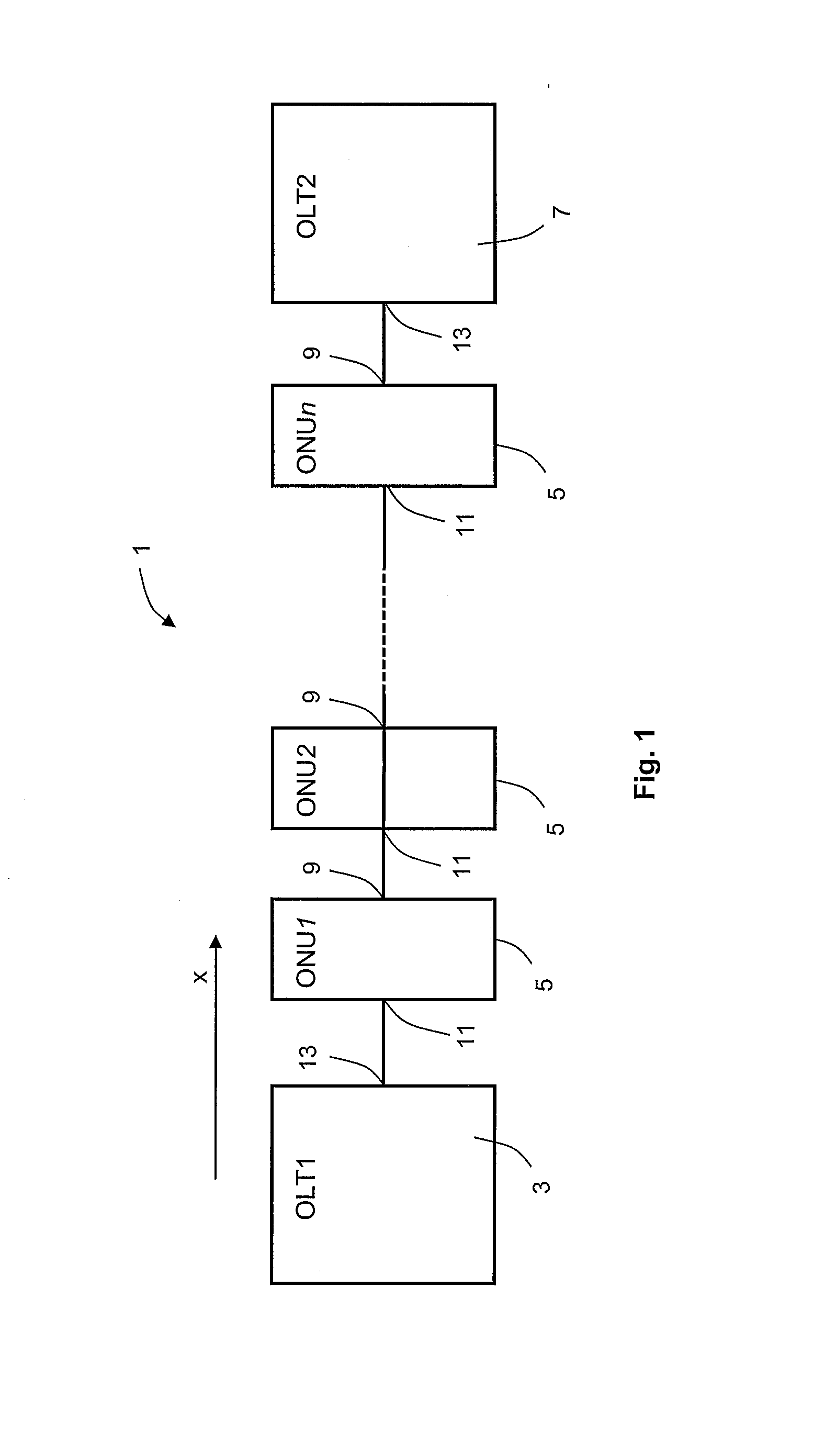
A network system (10) comprises a master device (5) and a plurality of slave devices (1, 2, 3), and those devices are serially connected to one another in such a way that the master device (5) comes to the most upstream side, thereby configuring an optical multidrop network which ensures data transmission and reception by optical communications among contiguous devices. Each of the slave devices (1, 2, 3) self-controls so as to be in such a state as not to receive data from any slave device on the downstream side when starting an operation, and the master device (5) controls the individual slave devices (1, 2, 3) sequentially from the upstream side to the downstream side in such a way that each slave device is capable of receiving data from a downstream side slave device.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON DEVICE
Optical Signal Transmission Apparatus
InactiveUS20090238563A1Ring-type electromagnetic networksBus-type electromagnetic networksSignal qualityEngineering
There is provided an optical signal transmission apparatus having a stable dispersion compensation function without unnecessarily controlling a compensation value even when a main signal quality is deteriorated due to a factor other than dispersion or in the case of a transmission failure. When it is determined that a signal quality is deteriorated due to dispersion of a fiber by determining a control mode of a variable dispersion compensator by means of optical noise information and received power information in addition to bit error information of a received signal, a compensation value of the variable dispersion compensator is varied and a compensation value other than the dispersion of the optical fiber is held to an existing set value.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
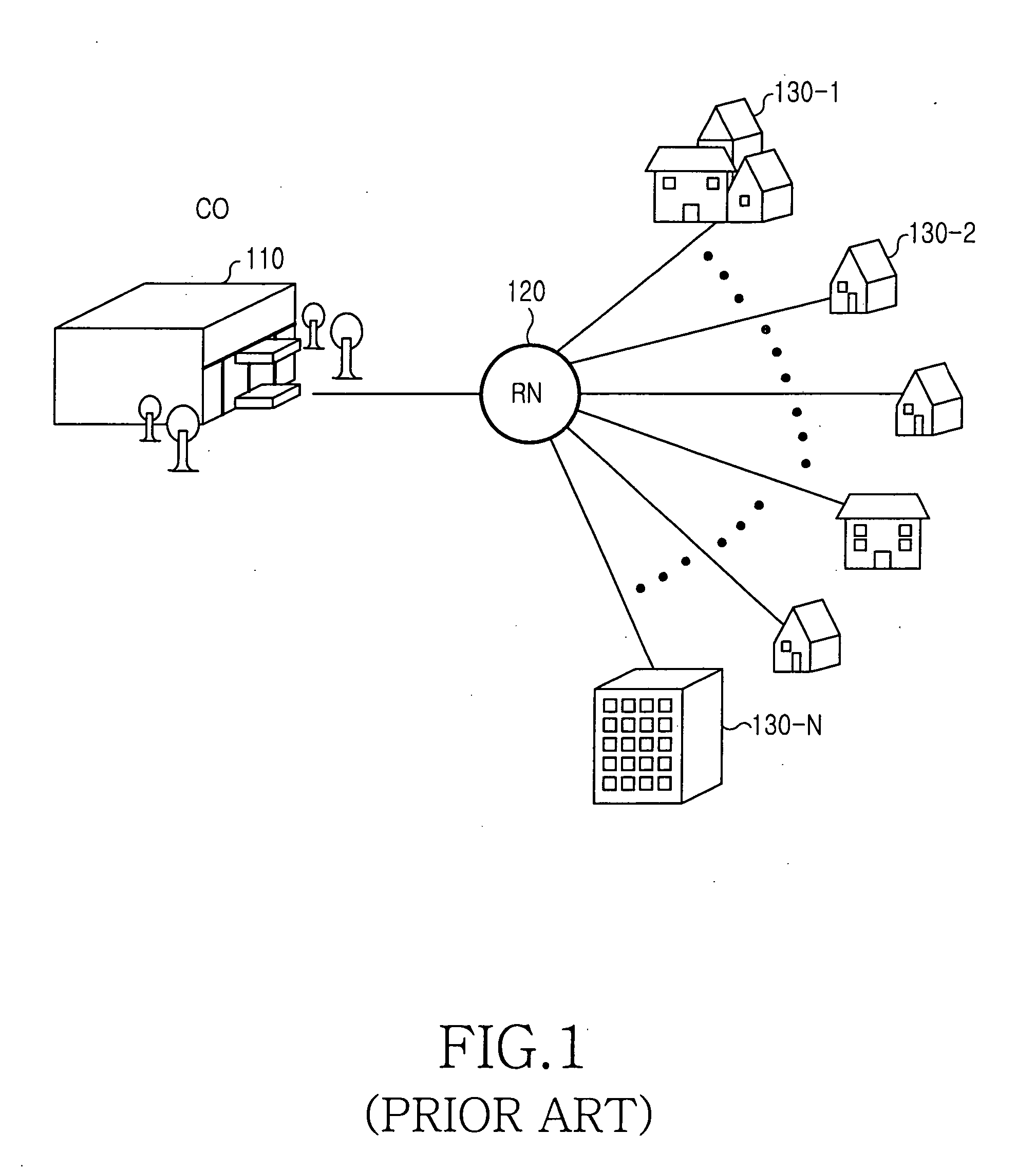
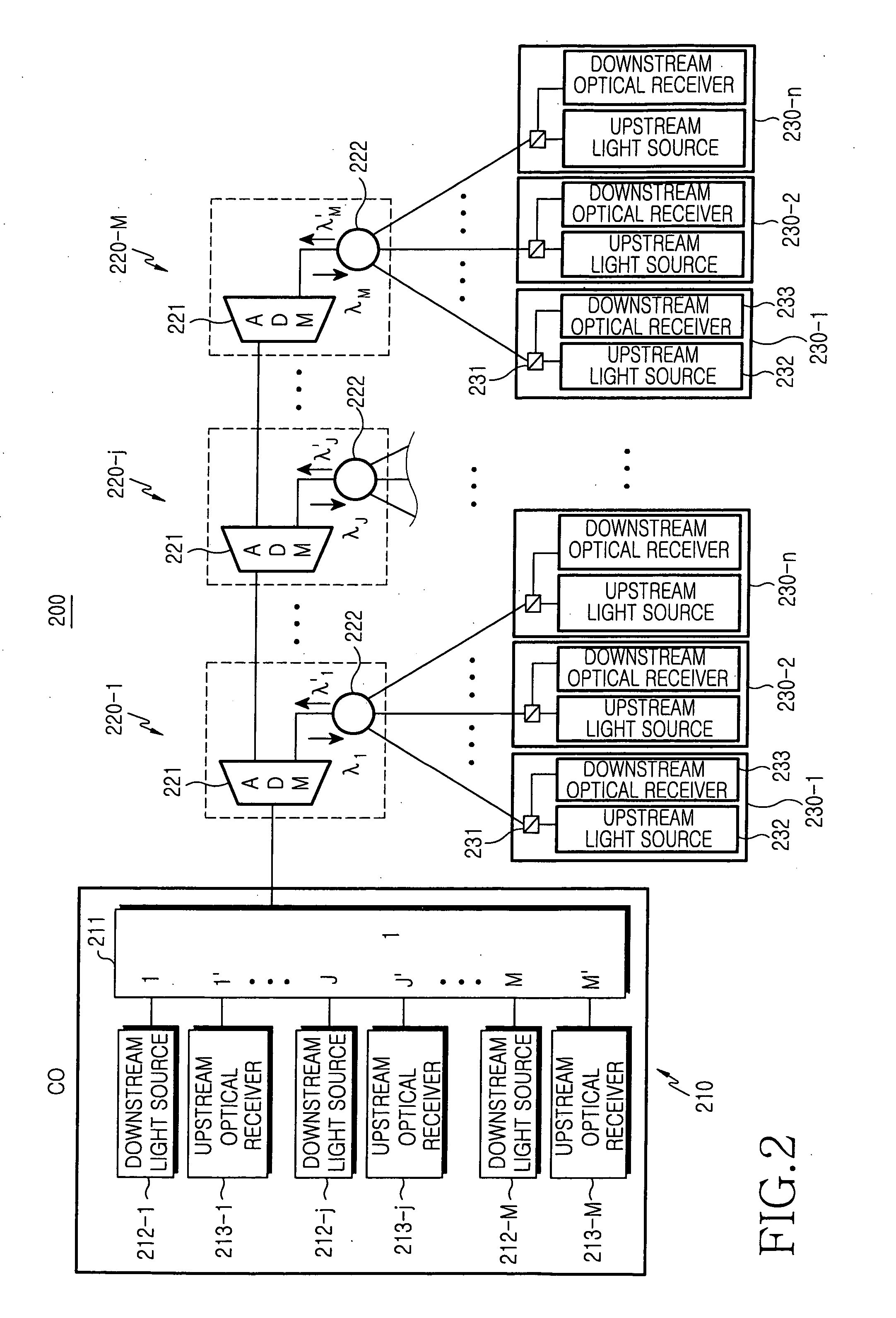
Passive optical network of bus structure
InactiveUS20060067692A1Providing serviceReduce population densityBus-type electromagnetic networksTime-division optical multiplex systemsEngineeringLength wave
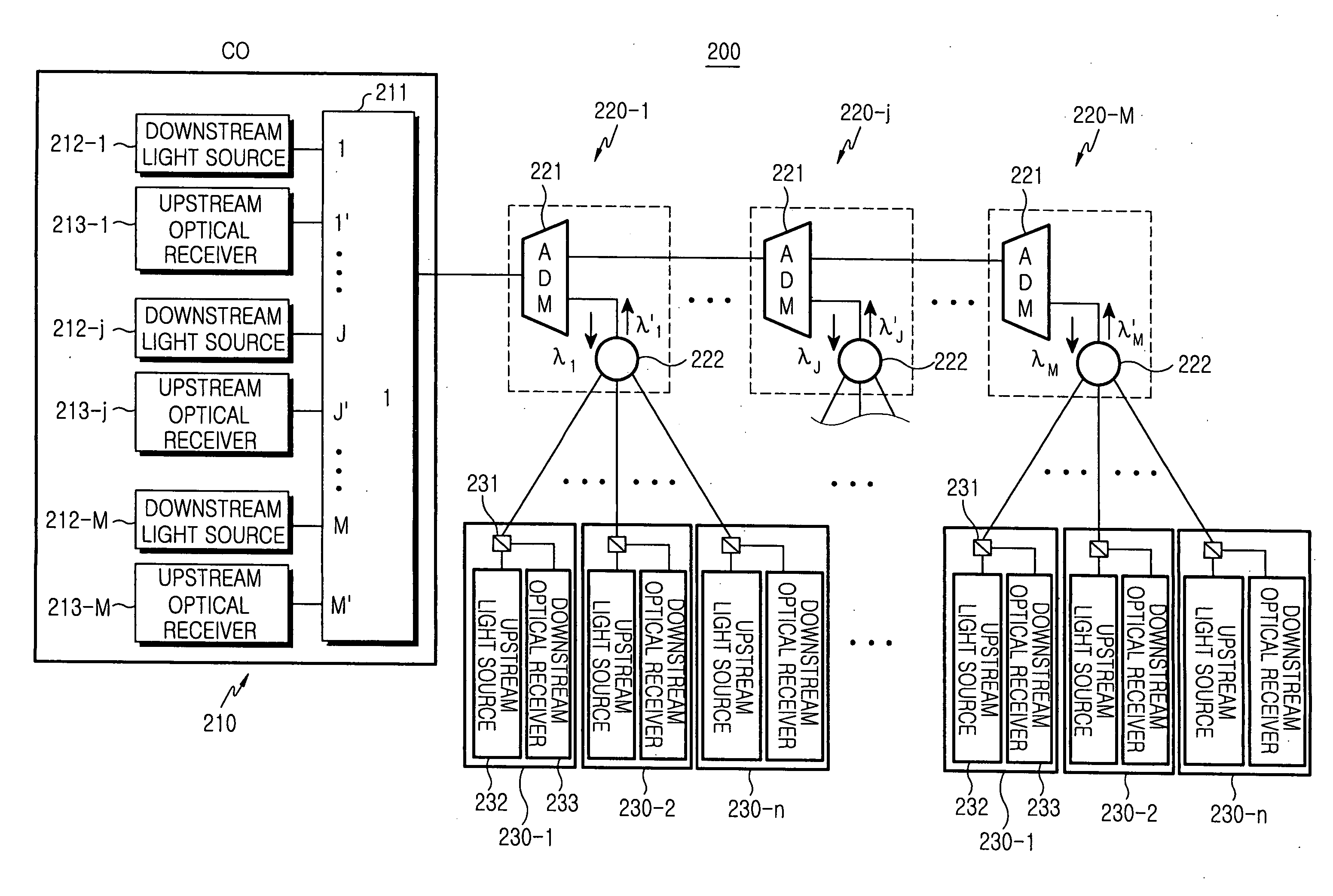
Disclosed is a passive optical network of a bus structure. The passive optical network comprises a central office for wavelength-division multiplexing a plurality of time-division multiplexed downstream optical signals with mutually different wavelengths and receiving upstream optical signals, a plurality of remote nodes positioned in series on an optical path linked to the central office, and a plurality of optical network units for detecting a corresponding downstream channel and being linked with a corresponding remote node in order to transmit each upstream channel to the corresponding remote node, wherein each remote node splits a corresponding downstream optical signal into a plurality of downstream channels and transmits upstream channels to the central office by time-division multiplexing the upstream channels to an upstream optical signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
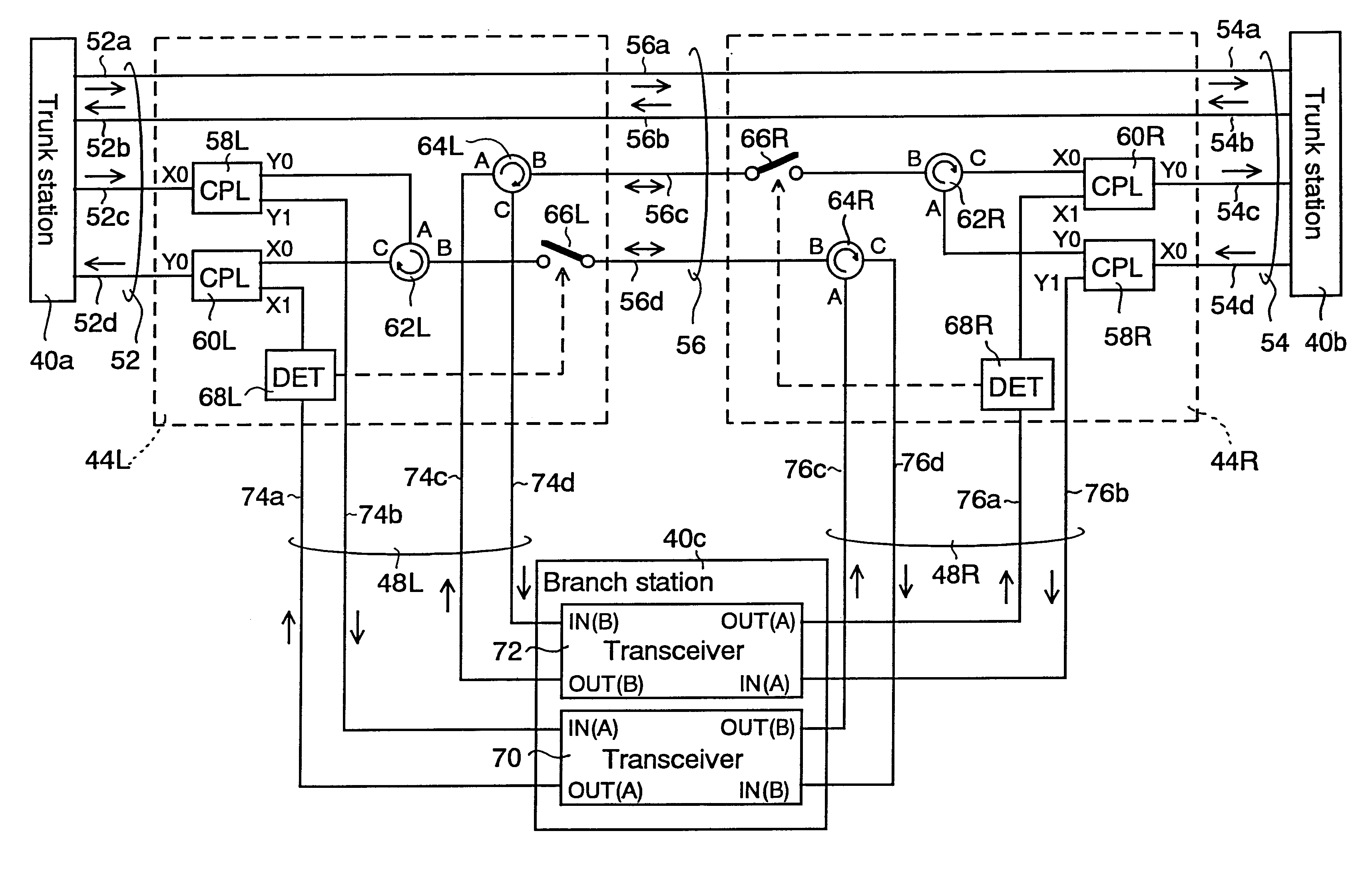
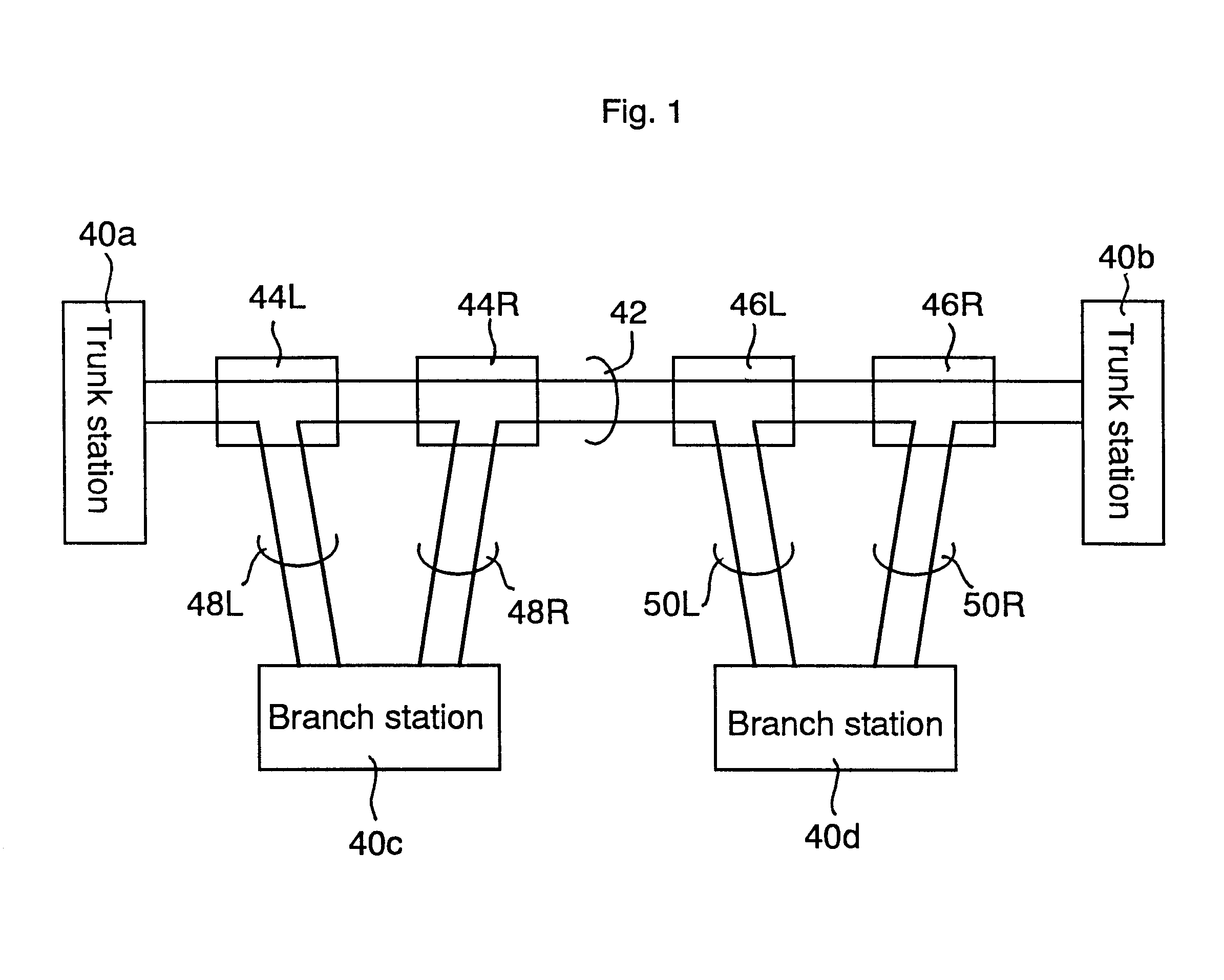
Optical transmission system
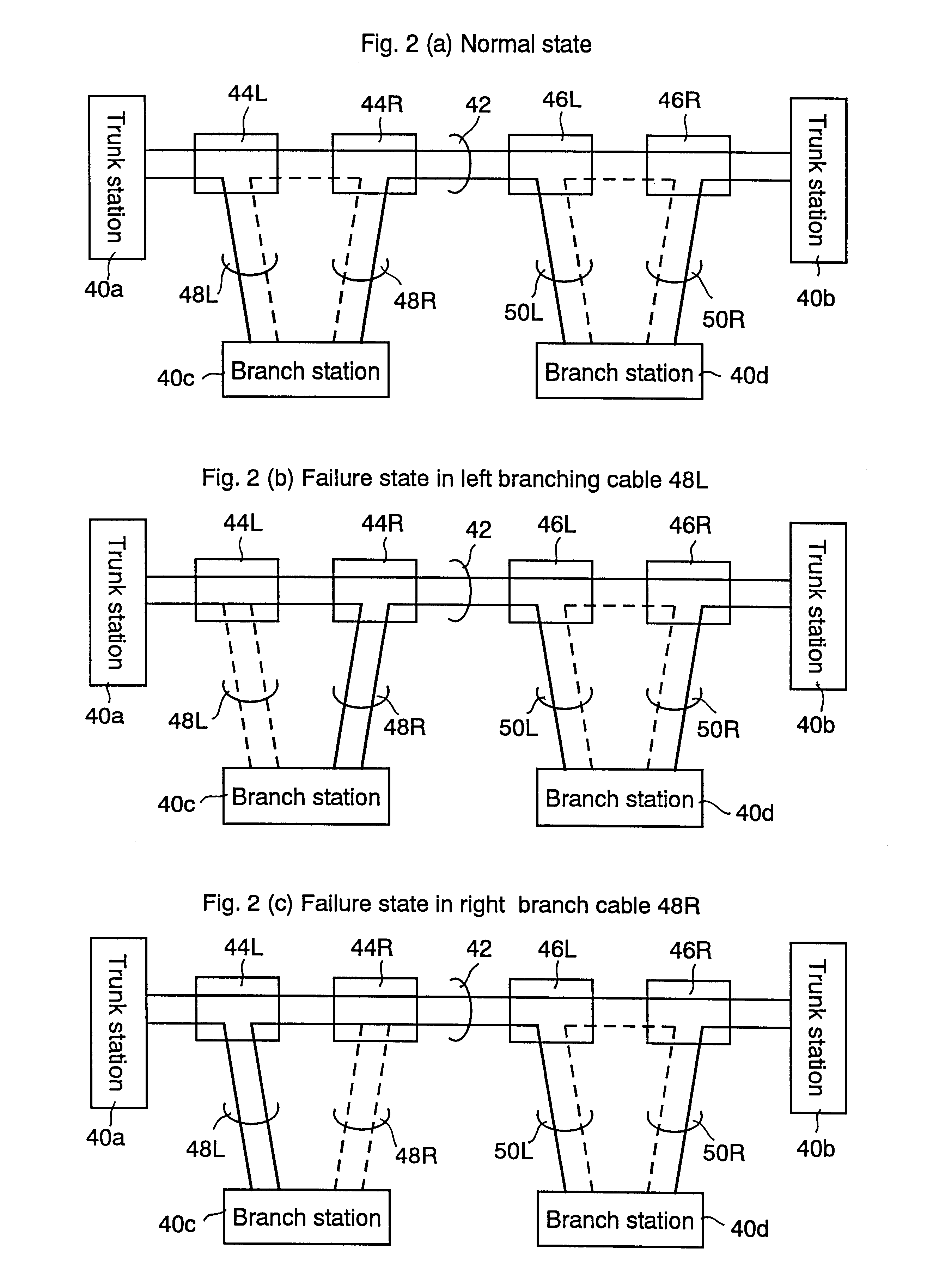
InactiveUS6377373B1Reliably madeReduce harmBus-type electromagnetic networksTime-division optical multiplex systemsFiberOptical fiber cable
In an optical transmission, system, a trunk cable having two pairs of optical fibers is provided between first and second trunk stations to use one of the two pairs of the optical fibers for communication between the first and second trunk stations and the other for communication with first and second branch stations. Two branching units of first and second, and third and forth, are respectively provided for the first and second branch stations, and connected to each of the associated first and second branch stations, by first and second or third and forth branching cables. The first branch station connects to the first branching unit via the first branching cable having two pairs of optical fibers, and connects to the second branching unit via the second branching cable having two pairs of optical fibers. One of the two pairs of the optical fibers of the first branching cable and one of the two pairs of the optical fibers of the second branching cable are normally used, and the others are reserved as spare fibers. Alternatively, the first branching cable is normally used, and the second branching cable is reserved as a spare cable.
Owner:KDDI CORP
Optical transmission apparatus
An optical transmission apparatus includes a reception part for receiving a wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) signal reached via optical amplifiers; a measuring part for measuring an optical power level of each wavelength of the WDM signal received by the reception part; a determination part for determining whether an amount of tilt of the WDM signal calculated based on measurement results of the measuring part is suitable or not; an operation part for calculating the tilt correction amount to be applied to tilt correction processing performed by the optical amplifiers if the amount of tilt of the WDM signal is not suitable; and a notification part for notifying the optical amplifiers of the tilt correction amount.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
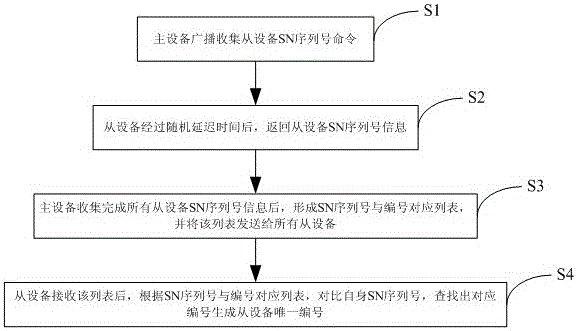
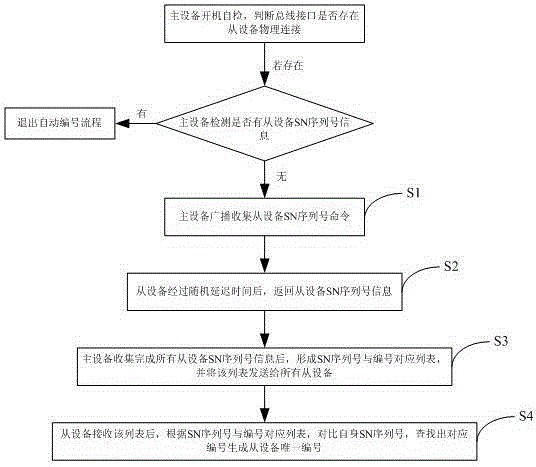
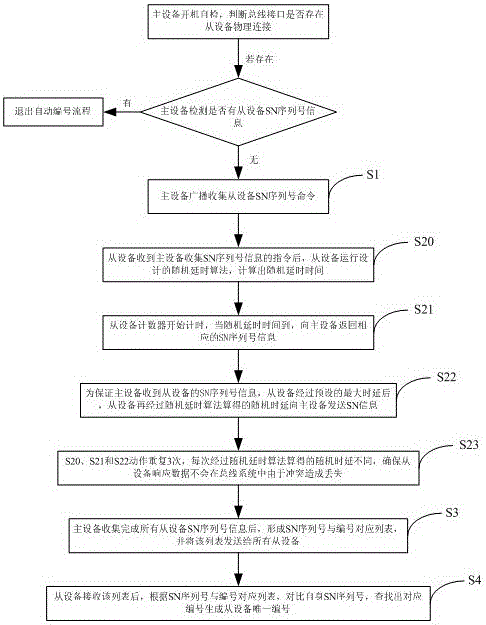
Method and system for master device to automatically number slave devices
InactiveCN105099562APrecise managementAvoid the problem of data conflict lossBus-type electromagnetic networksDevice formGeolocation
The invention discloses a method and a system for a master device to automatically number slave devices, belonging to the technical field of an optical fiber distribution system. The method comprises the following steps that: S1: the master device broadcasts an order of collecting SN sequence numbers of the slave devices; S2: the slave devices return back own SN sequence number information after random delay time; S3: after collecting the SN sequence number information of all the slave devices, the master device forms a SN sequence number and serial number corresponding list, and sends the list to all the slave devices; S4: after receiving the list, the slave devices respectively contrast own SN sequence numbers according to the SN sequence number and serial number corresponding list, find out corresponding serial numbers and generate own unique serial numbers. By automatically and uniquely numbering the slave devices, a problem of collision caused by reporting communication data by multiple slave devices can be avoided, moreover, the SN sequence number, the specific geographical position and the device serial number information of each slave device are maintained at the master device side, thus, state of multiple slave devices can be monitored accurately, project opening efficiency is improved, and later maintenance of the devices is facilitated.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
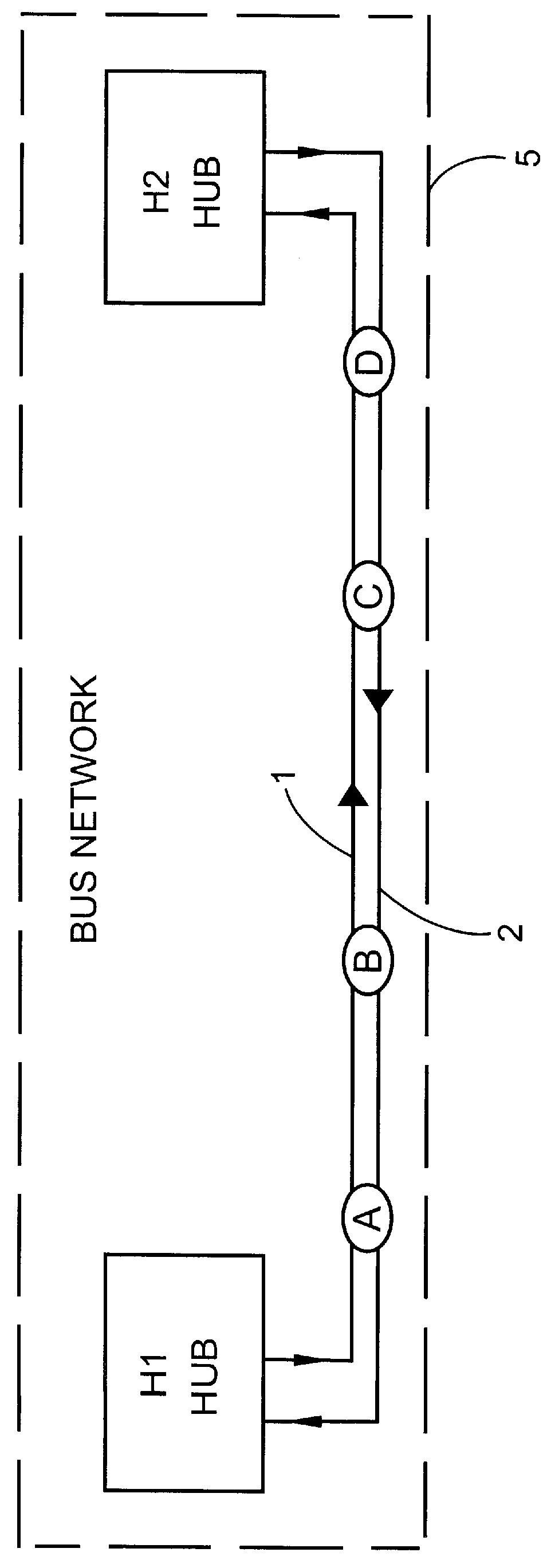
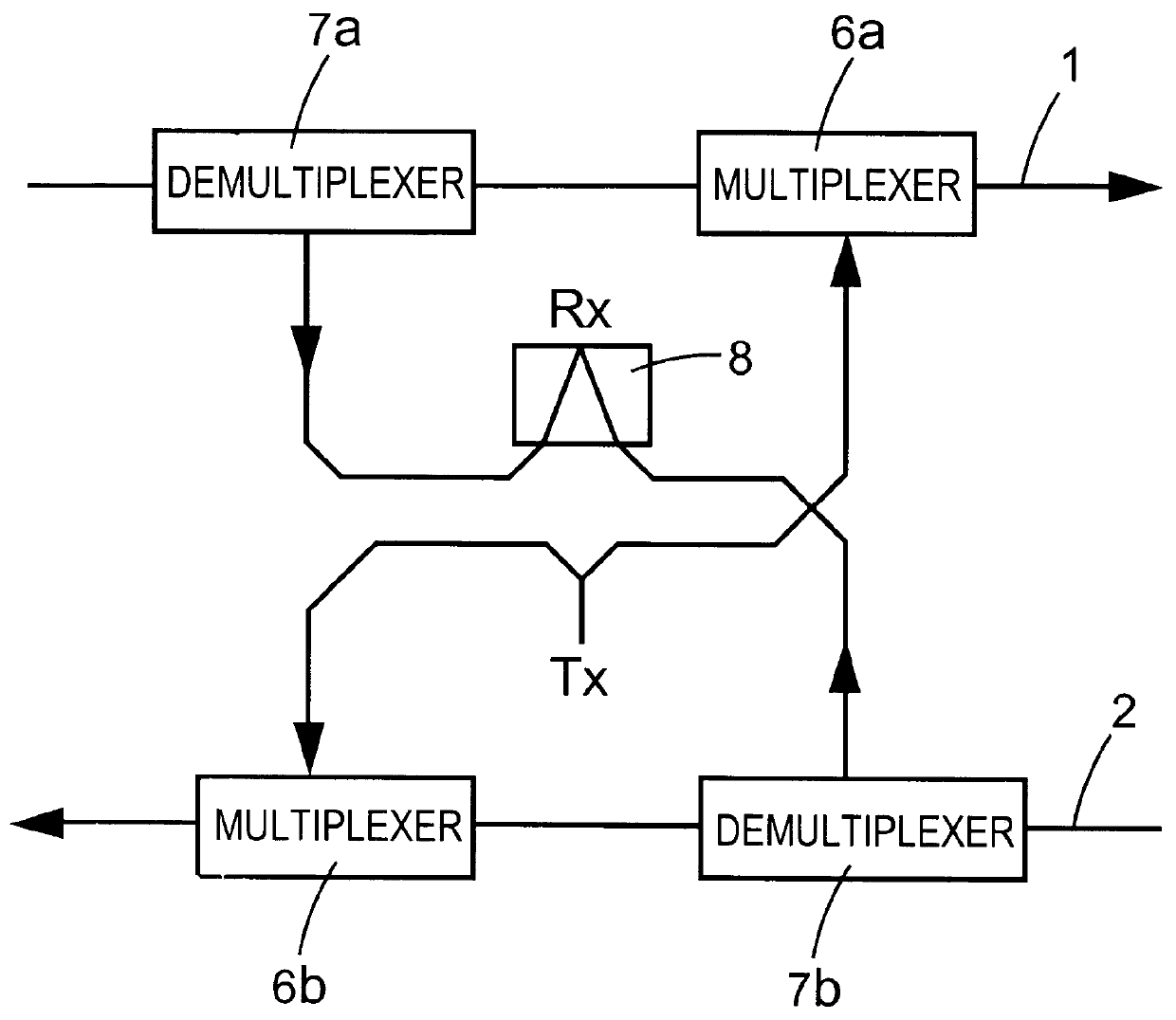
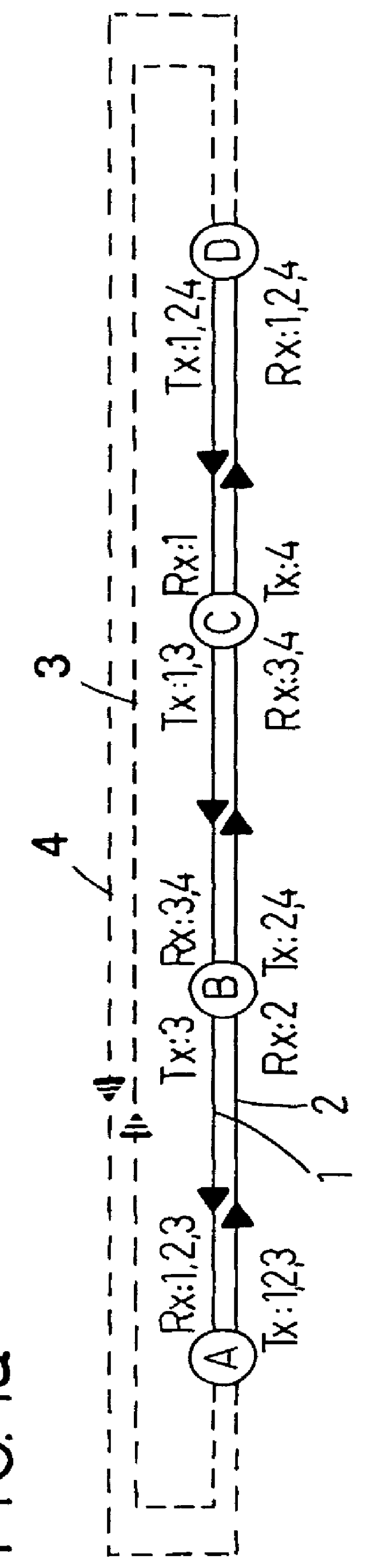
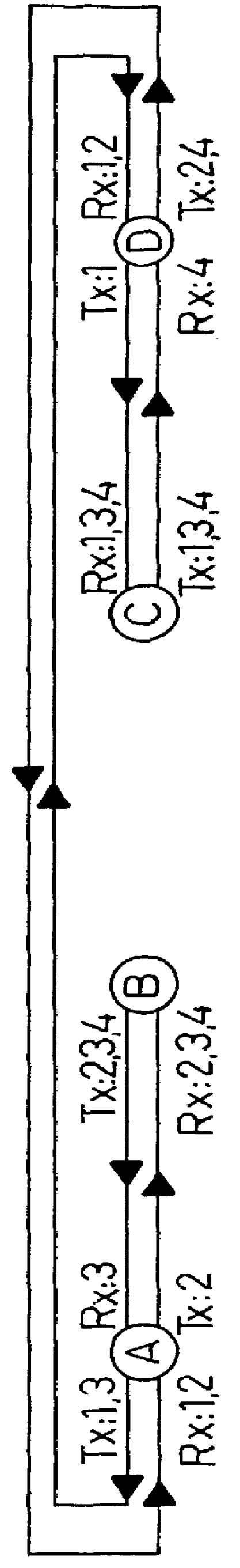
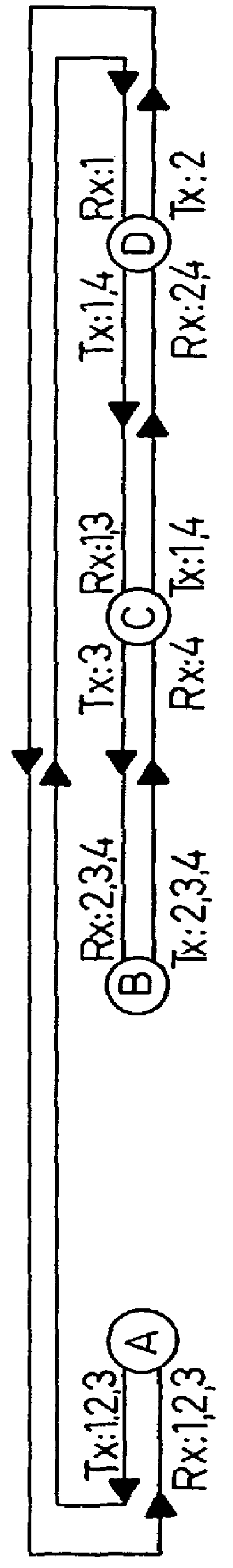
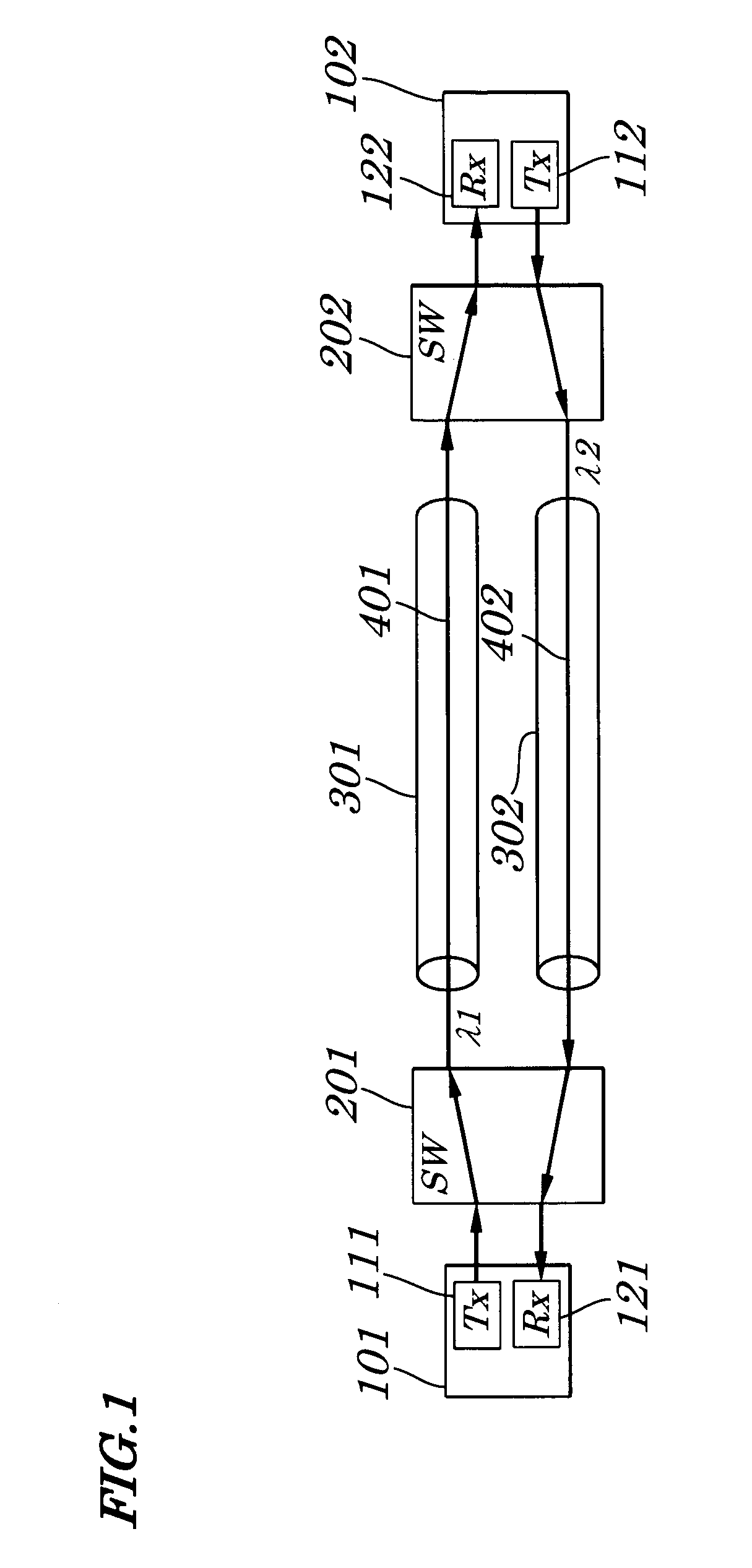
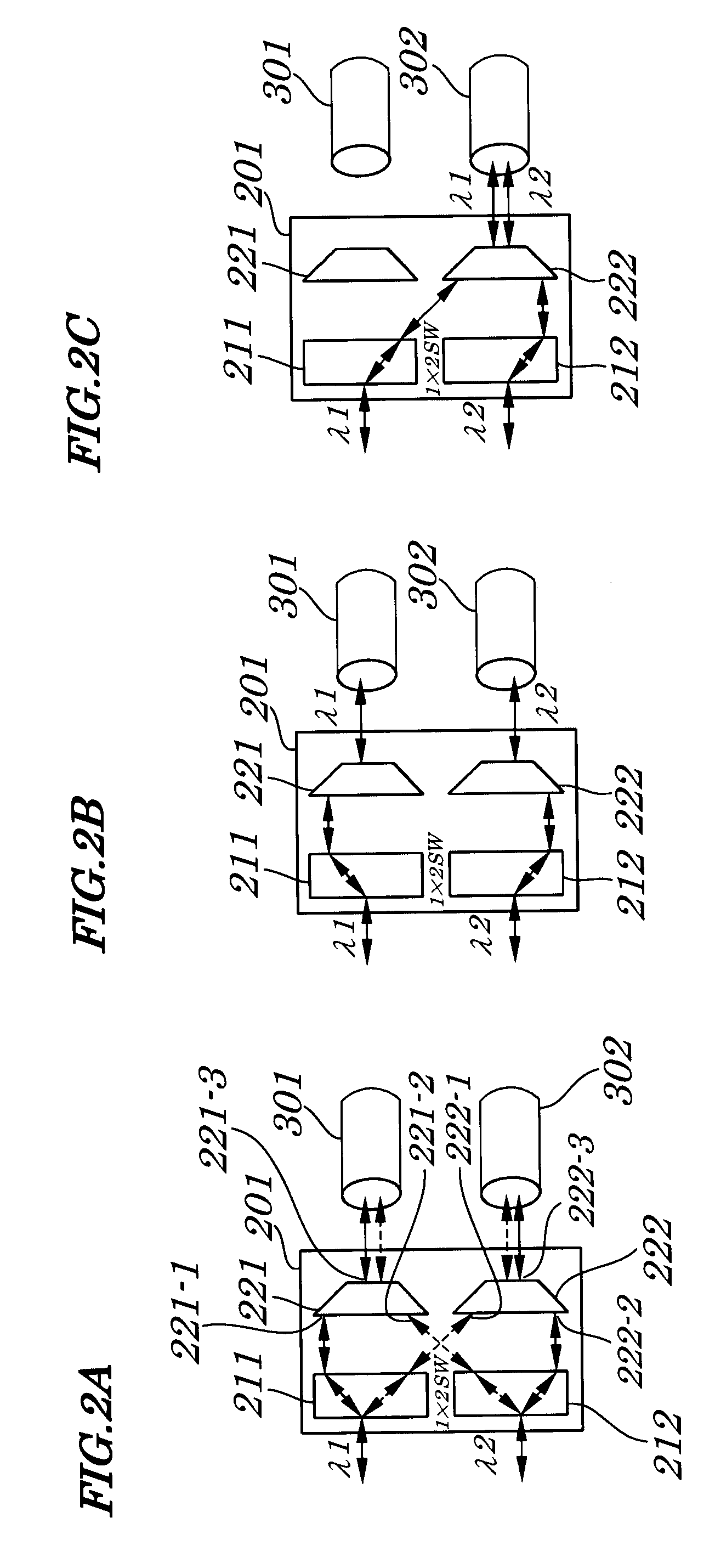
Optical node in an optical bus network
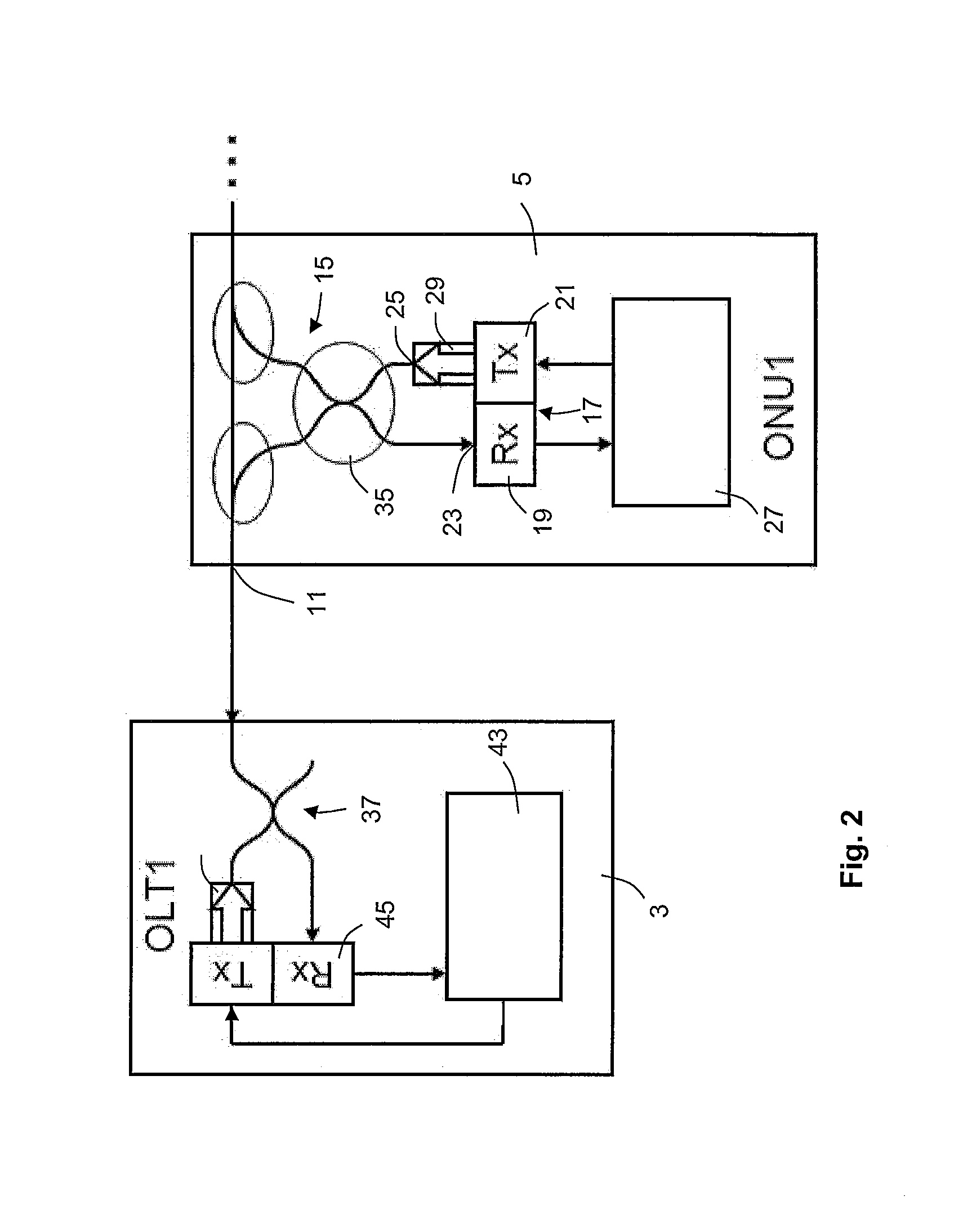
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00323 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 20, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 20, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 13, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 31025 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 3, 1996An optical node in an optical network includes transmitters (Tx:1-3) and receivers (Rx:1-3) adapted to particular wavelength channels and arranged to communicate via the optical bus network, with receivers and transmitters for corresponding wavelength channels in other nodes. The node includes optical safety switching devices (S1-S5) in connection with the transmitters (Tx:1-3) and receivers (Rx:1-3) of the node, so that the transmitters (Tx:1-3) and receivers (Rx:1-3) can be switched from a first optical fiber (1,2) to a second optical fiber (1,2).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
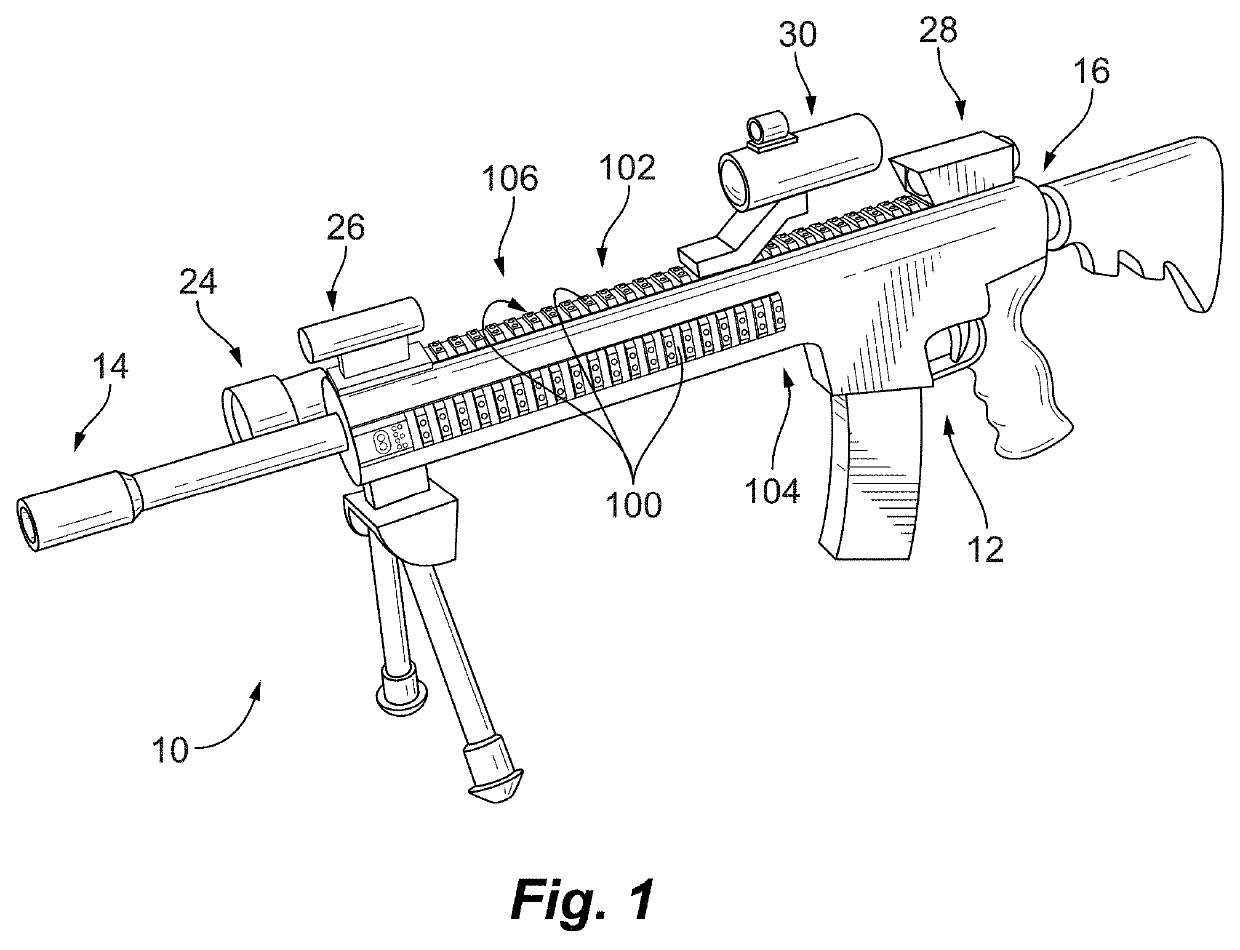
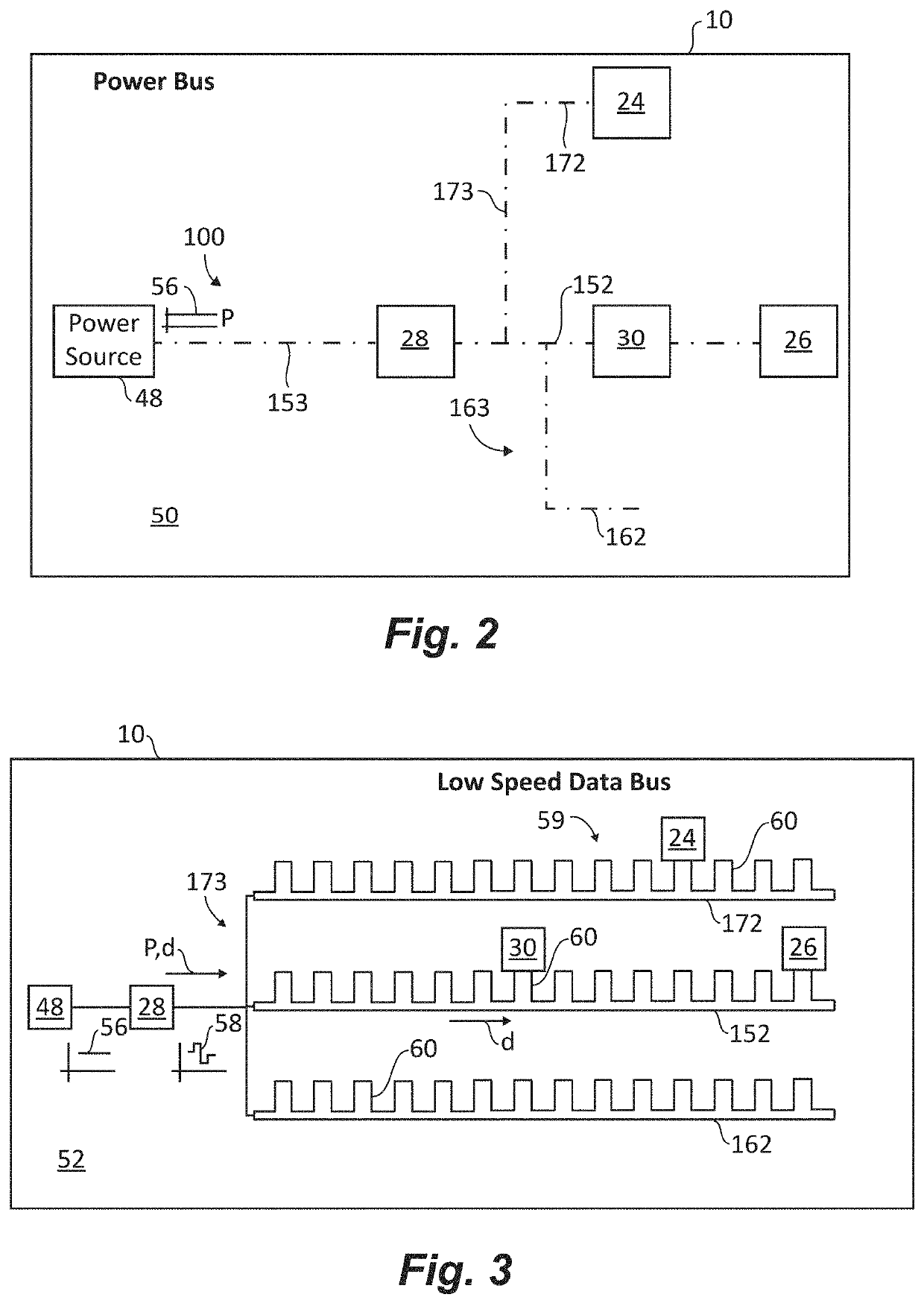
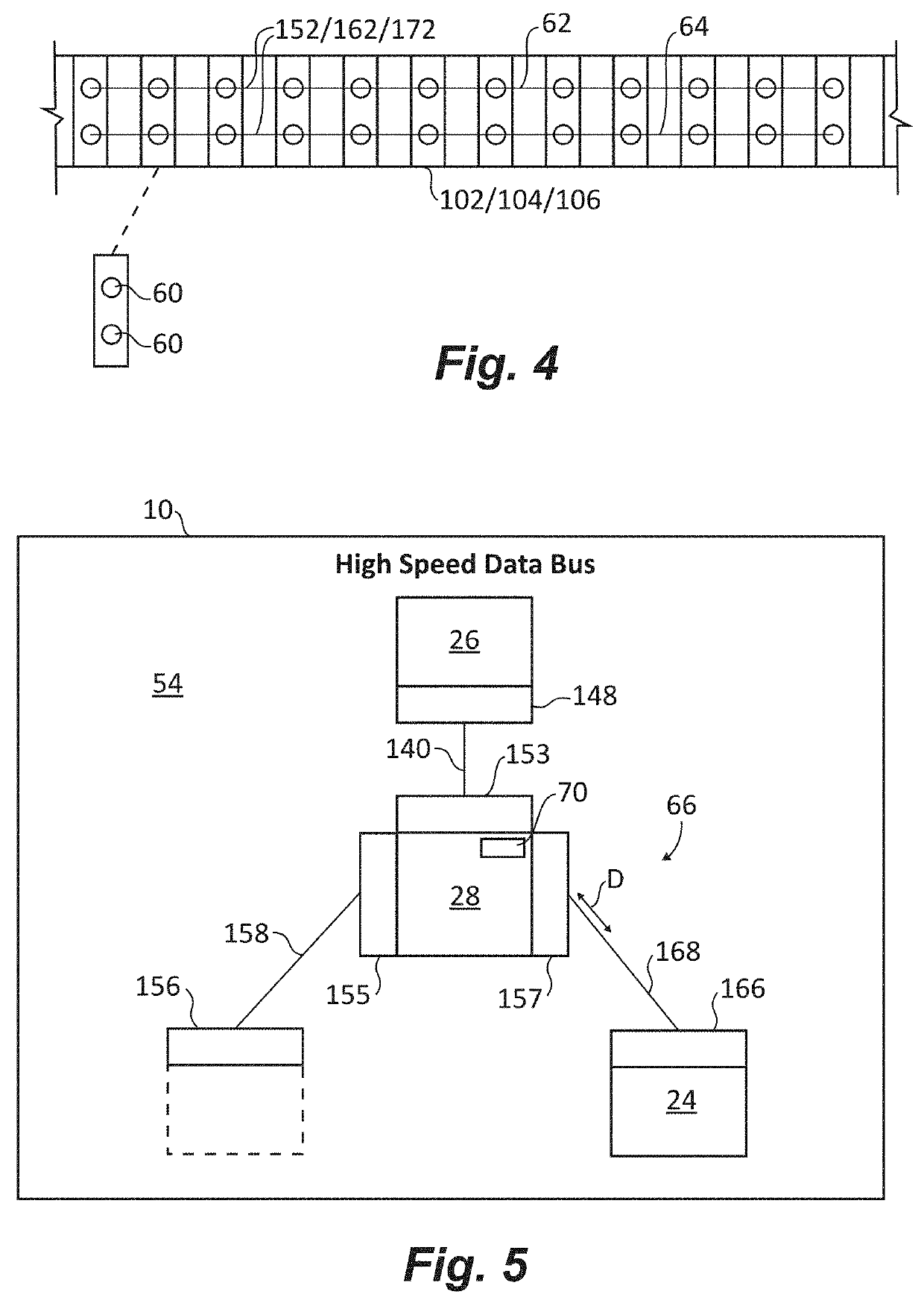
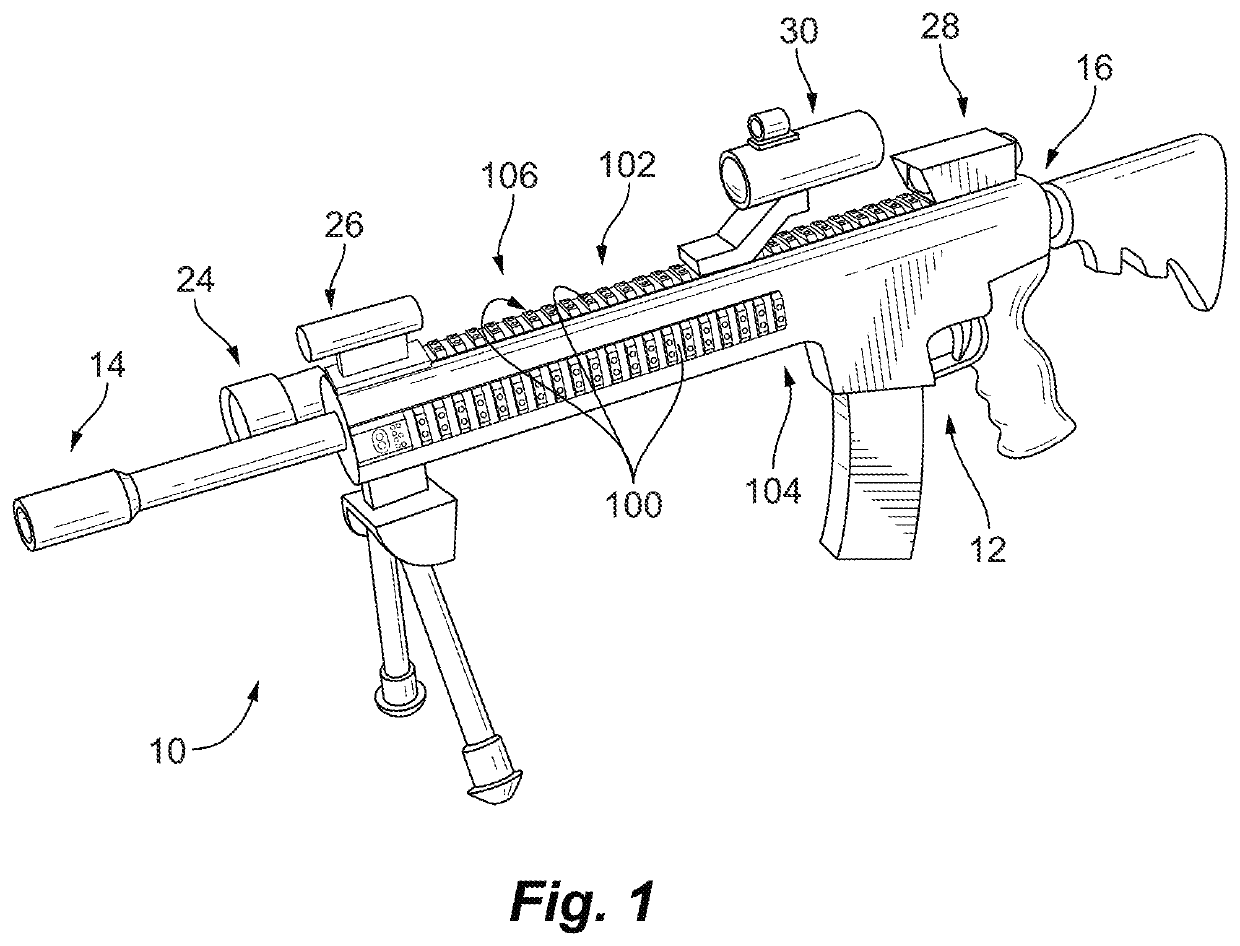
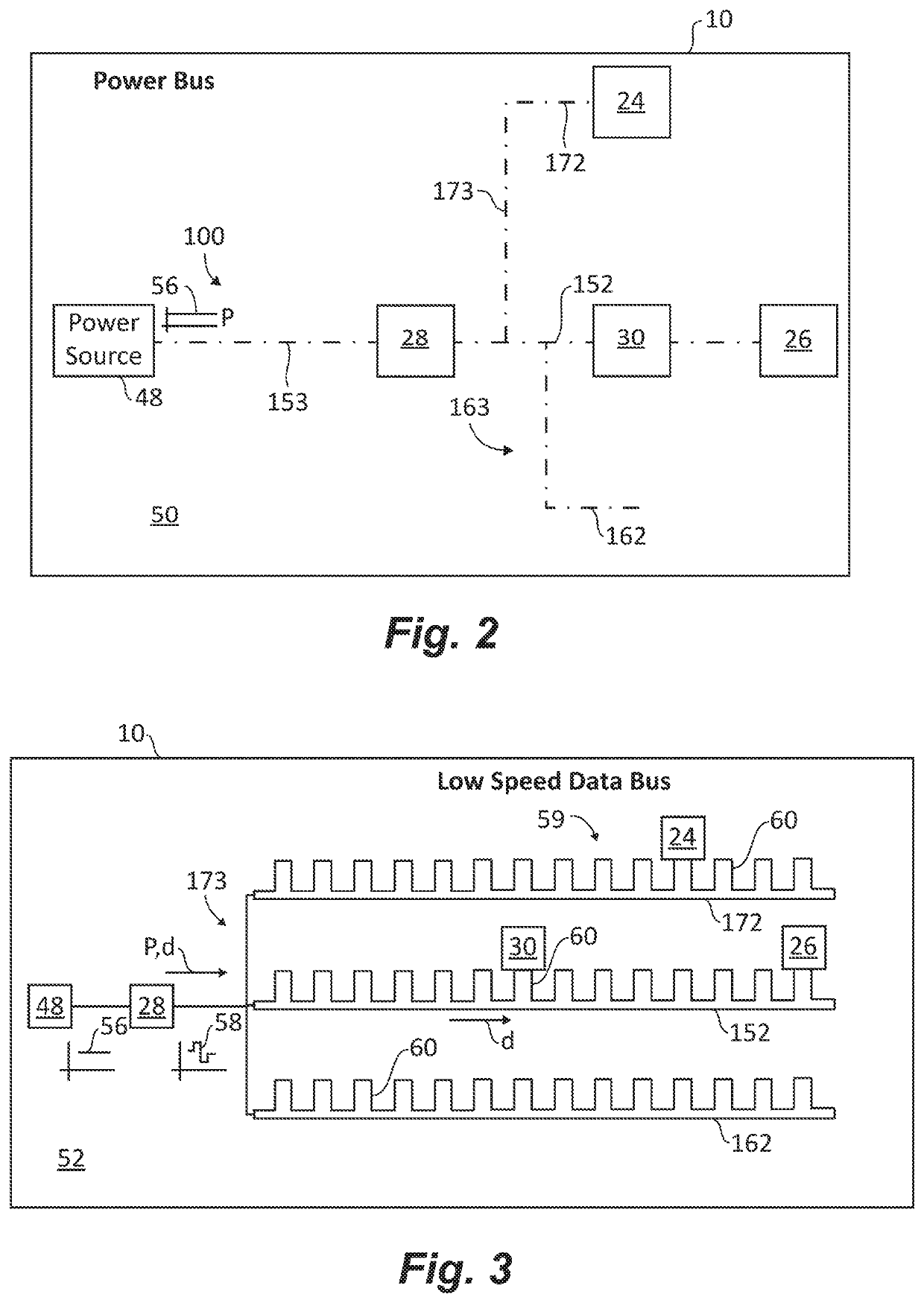
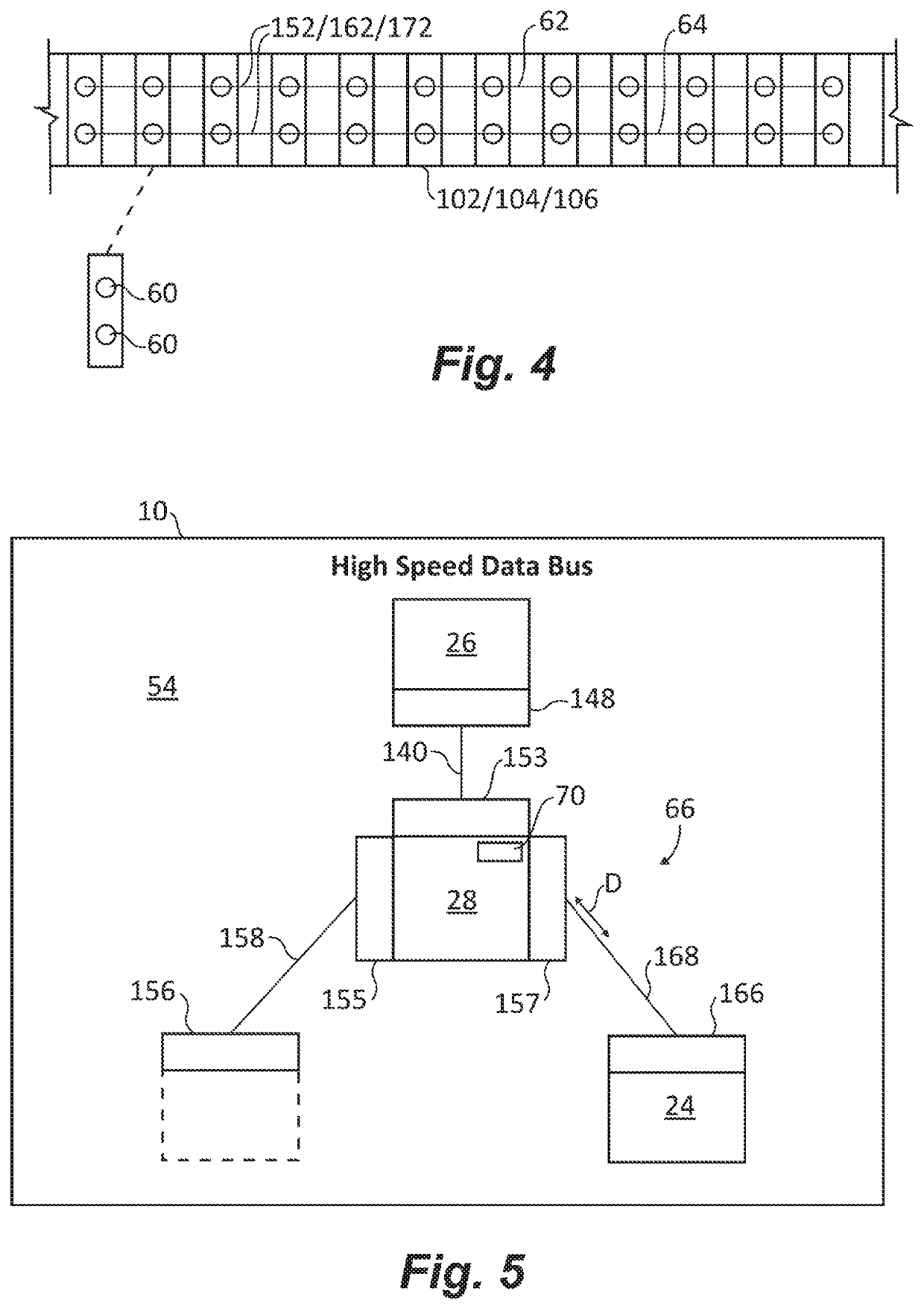
Hybrid tactical rails with slow speed and high speed data buses
InactiveUS20190353461A1Bus-type electromagnetic networksCoupling contact membersLow speedEngineering
A tactical rail for a firearm includes a rail body having a receiver end and a muzzle end and a non-contact optical connection arranged at an end of the rail body and configured to interface with a corresponding non-contact optical interface. A low speed data bus segment extends between the receiver end and the muzzle end of the rail body. A high speed data spoke is connected to the non-contact optical connection for high speed data communication with a high speed data accessory through the non-contact optical connection and the corresponding non-contact optical interface. Tactical rail systems and firearm assemblies having tactical rails are also described.
Owner:SENSORS UNLTD +1
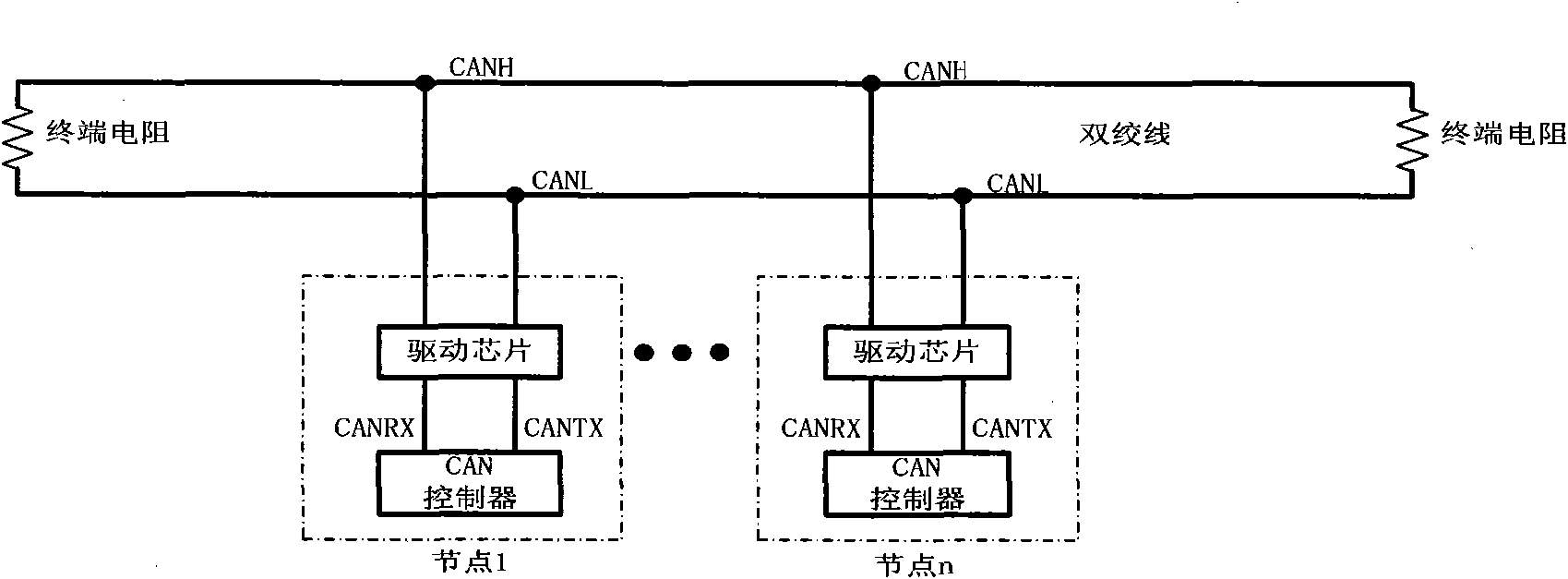
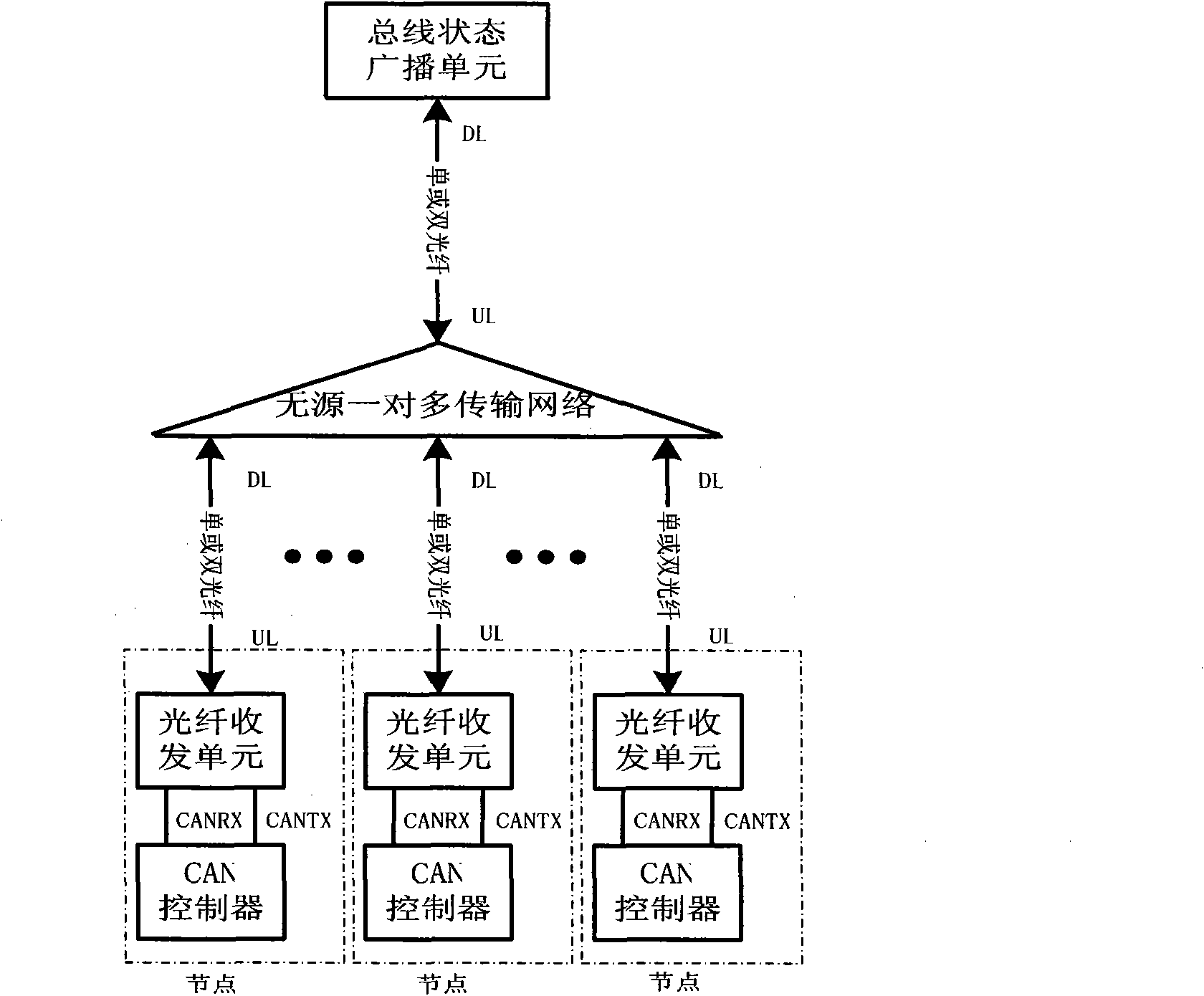
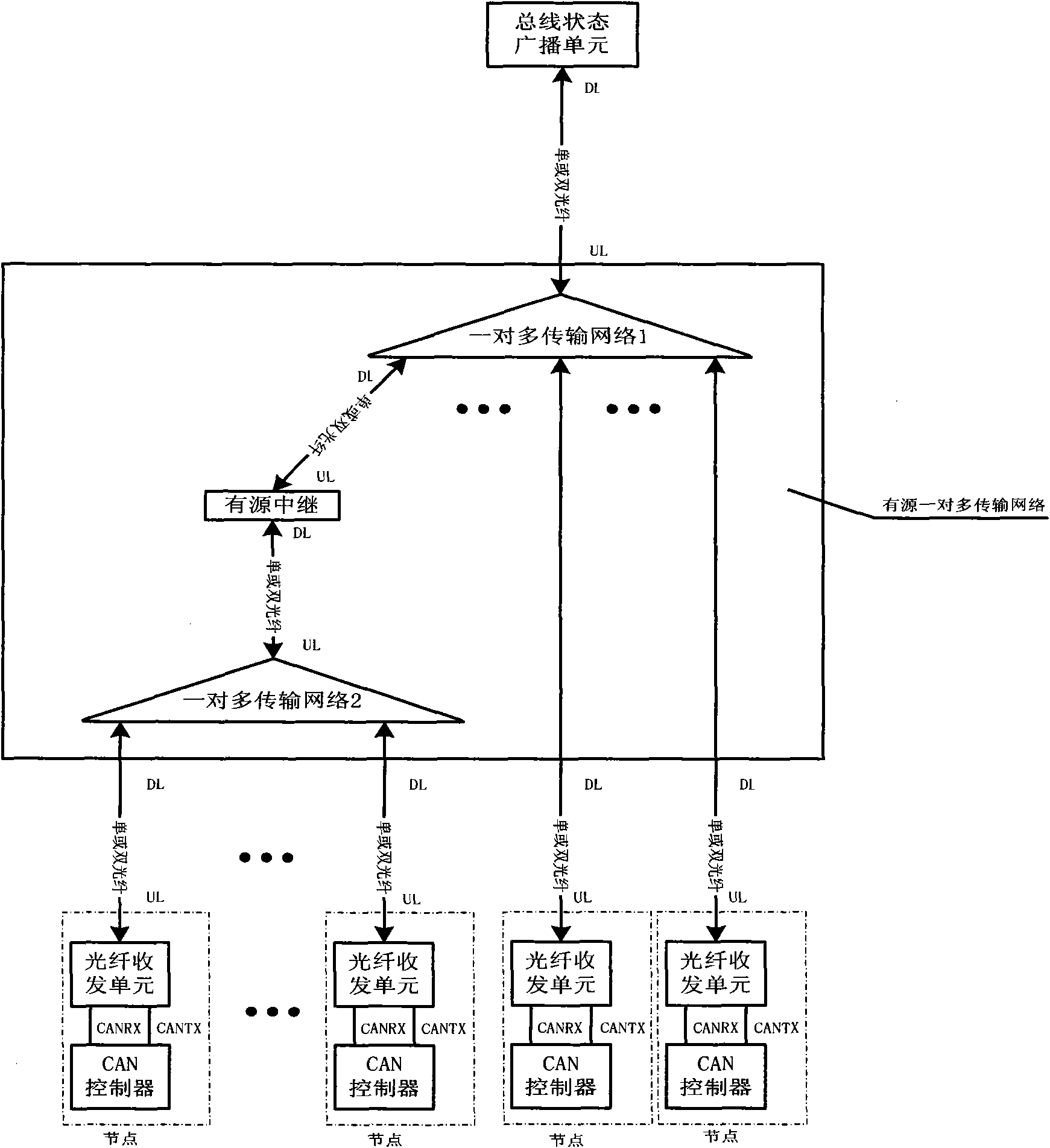
CAN bus physical layer structure based on 1XN passive optical splitter (POS)
InactiveCN101582723AWide network geographical distributionGood anti-electromagnetic interference characteristicsBus-type electromagnetic networksElectromagnetic interferencePhysical layer
The invention discloses a CAN bus physical layer structure based on a 1XN passive optical splitter (POS), comprising a bus state broadcasting unit, a pair of multi-transport networks and a plurality of CAN nodes, which are sequentially connected by optical fibers; the bus state broadcasting unit comprises a lower connective light port and is used for reproducing uplink signals in the CAN bus into downlink signals; a pair of multi-transport networks comprise single or cascaded 1XN POS and are used for transporting the uplink signals and downlink signals; the CAN node comprises a CAN controller and an optical fiber transceiving unit. The CAN bus physical layer structure has excellent anti-electromagnetic interference characteristic and wider network area distribution, and simultaneously improves transmission rate greatly.
Owner:蒋涵民
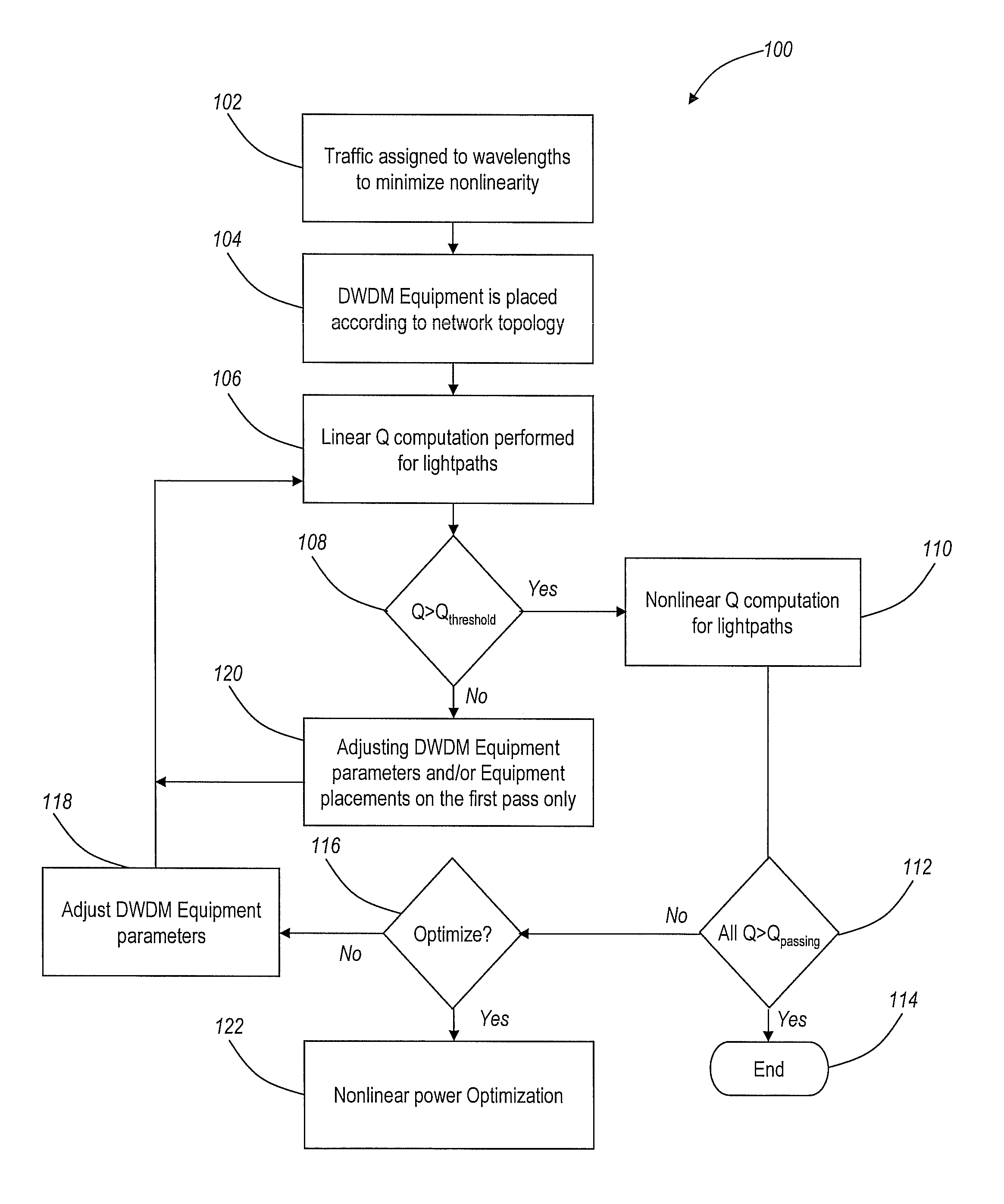
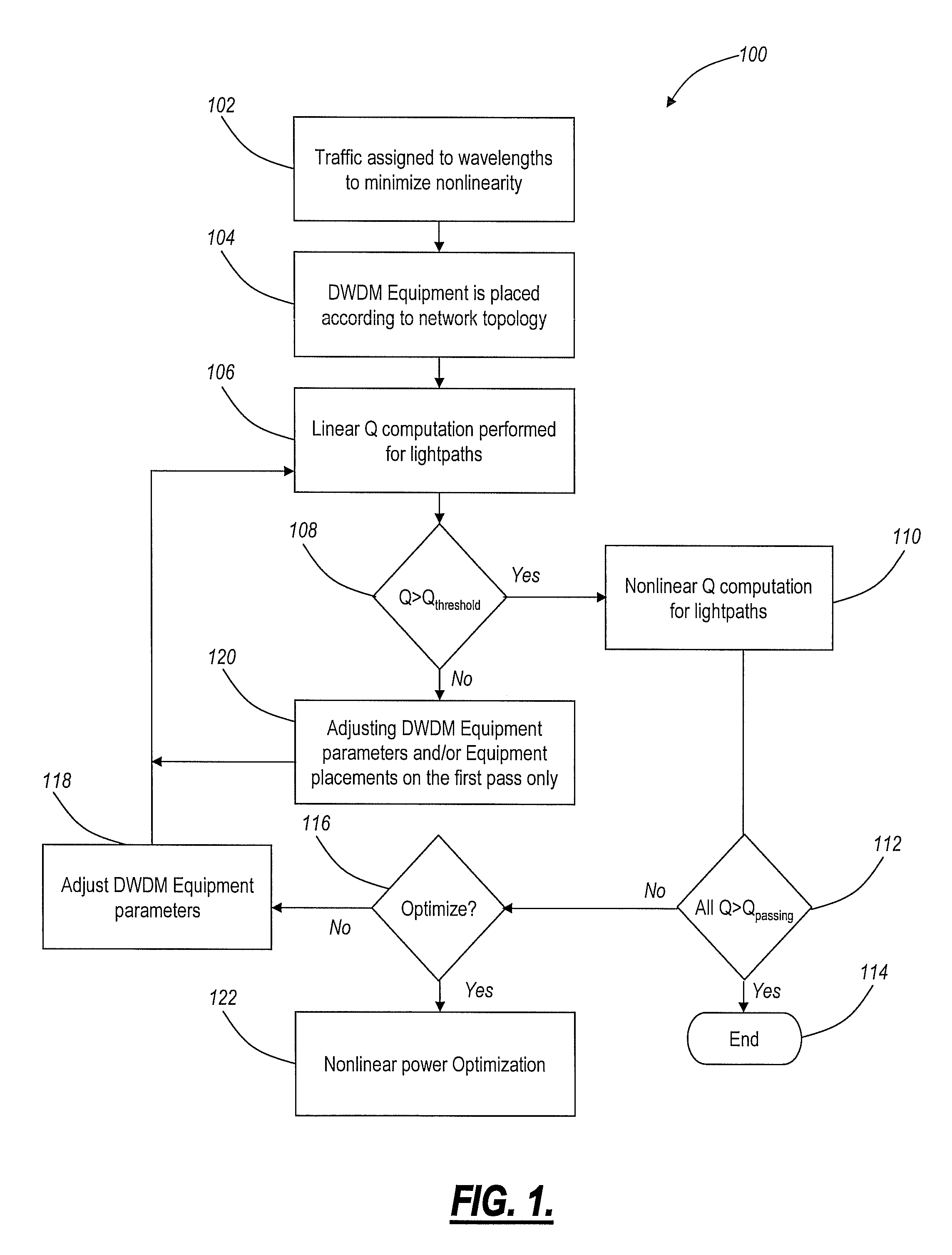
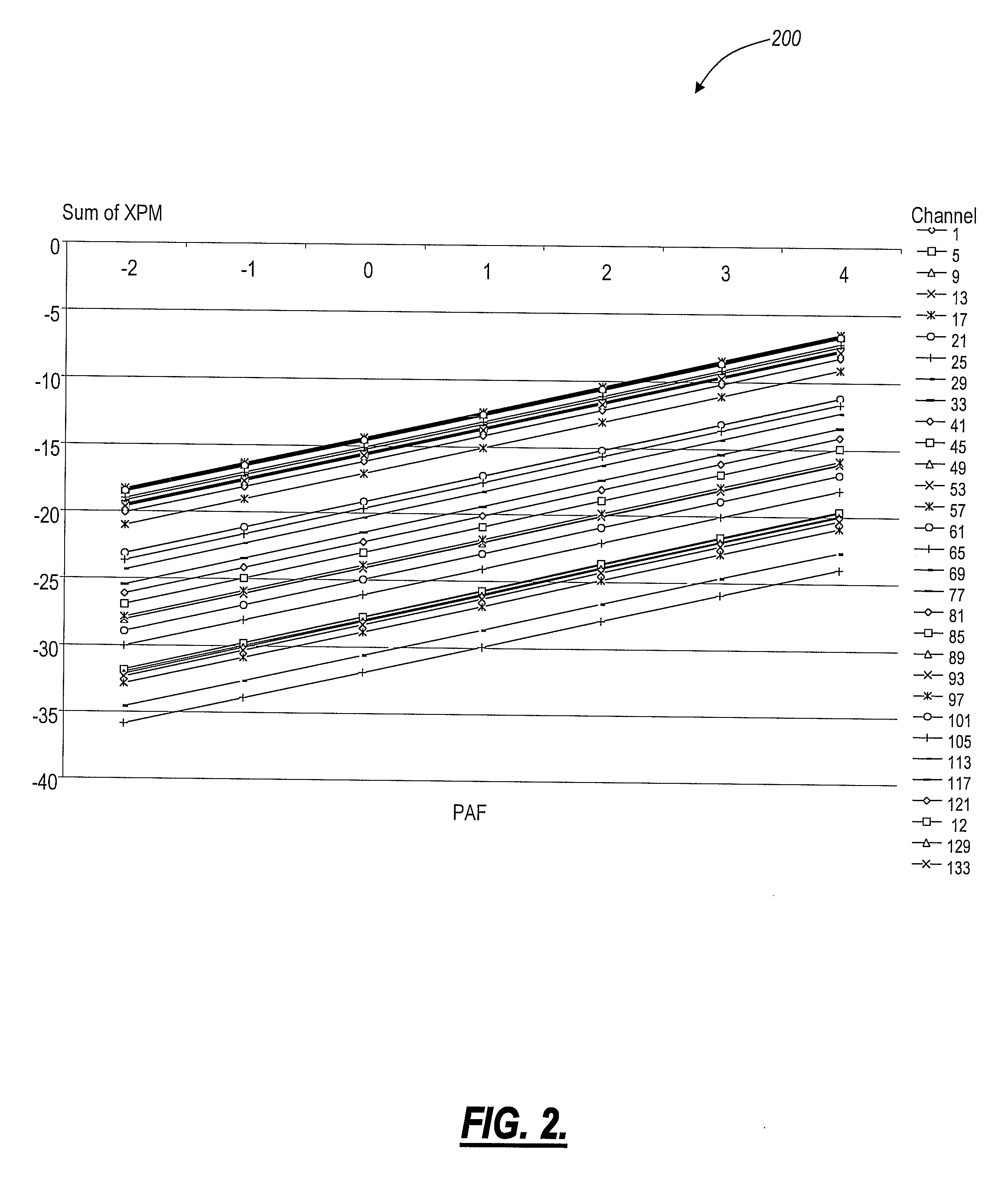
Methods and systems for optimal launch power computation in meshed optical networks
ActiveUS20110052188A1Computationally efficientImprove computing efficiencyBus-type electromagnetic networksTransmission monitoringEngineeringLength wave
The present invention provides methods and systems for efficiently computing optimal optical launch powers for meshed optical networks. The present invention can be utilized to find optimal launch powers for multiple wavelengths in a meshed dense-wave division multiplexed (DWDM) system. Generally, the present invention ensures Q exceeds a threshold for OSNR, and then the launch powers are optimized based on nonlinear penalties. If Q is below the threshold, DWDM equipment changes / additions are incorporated to provide adequate OSNR. The present invention provides a computationally efficient mechanism to optimize launch powers in 10 Gb / s, 40 Gb / s, 100 Gb / s, etc. highly-meshed optical networks.
Owner:CIENA
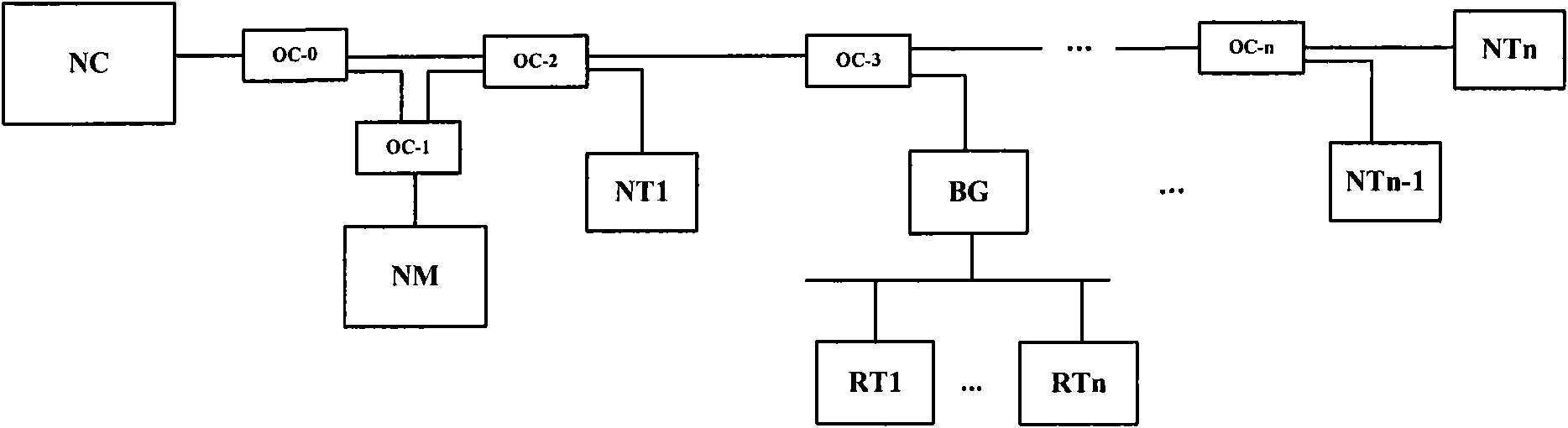
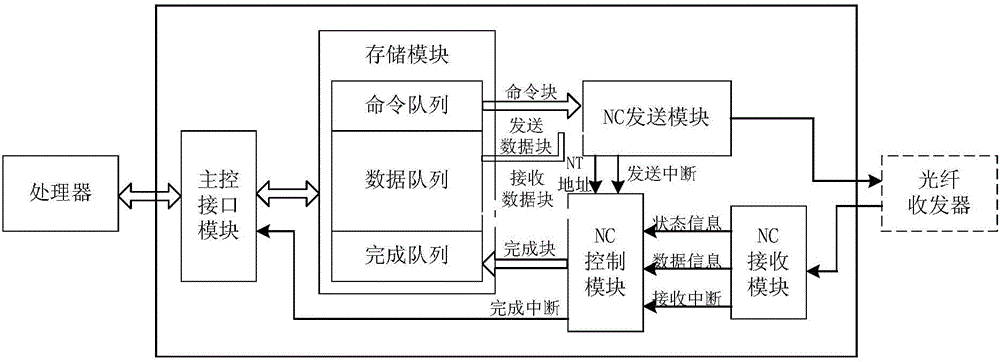
System for improving transmission efficiency of FC-AE-1553 bus
ActiveCN106533872AReduce intervalImprove transmission efficiencyBus-type electromagnetic networksFibre transmissionEmbedded systemBandwidth utilization
The invention relates to a system for improving the transmission efficiency of FC-AE-1553 bus, and belongs the technical field of computer communication. On the basis of an original communication mode, a network controller NC can make network exchange with multiple network terminals NT in an alternative access manner, full duplex is realized, the transmission interval of a sequence in the bus is reduced, the bandwidth utilization rate is improved, and the transmission efficiency of FC-AE-1553 bus is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG COMP TECH RES INST
Tactical rails, tactical rail systems, and firearm assemblies having tactical rails
ActiveUS20190353462A1Bus-type electromagnetic networksData switching current supplyEngineeringOptical connectors
A tactical rail for a firearm includes a rail body having a receiver end and a muzzle end, a non-contact optical connection, and a high speed data spoke. The non-contact optical connection is arranged at an end of the rail body and is configured to interface with a corresponding non-contact optical interface. The high speed data spoke is connected to the non-contact optical connection for high speed data communication through the non-contact optical connection and the corresponding non-contact optical interface. Tactical rail arrangements and firearm with tactical rails and tactical rail arrangements are also described.
Owner:SENSORS UNLTD
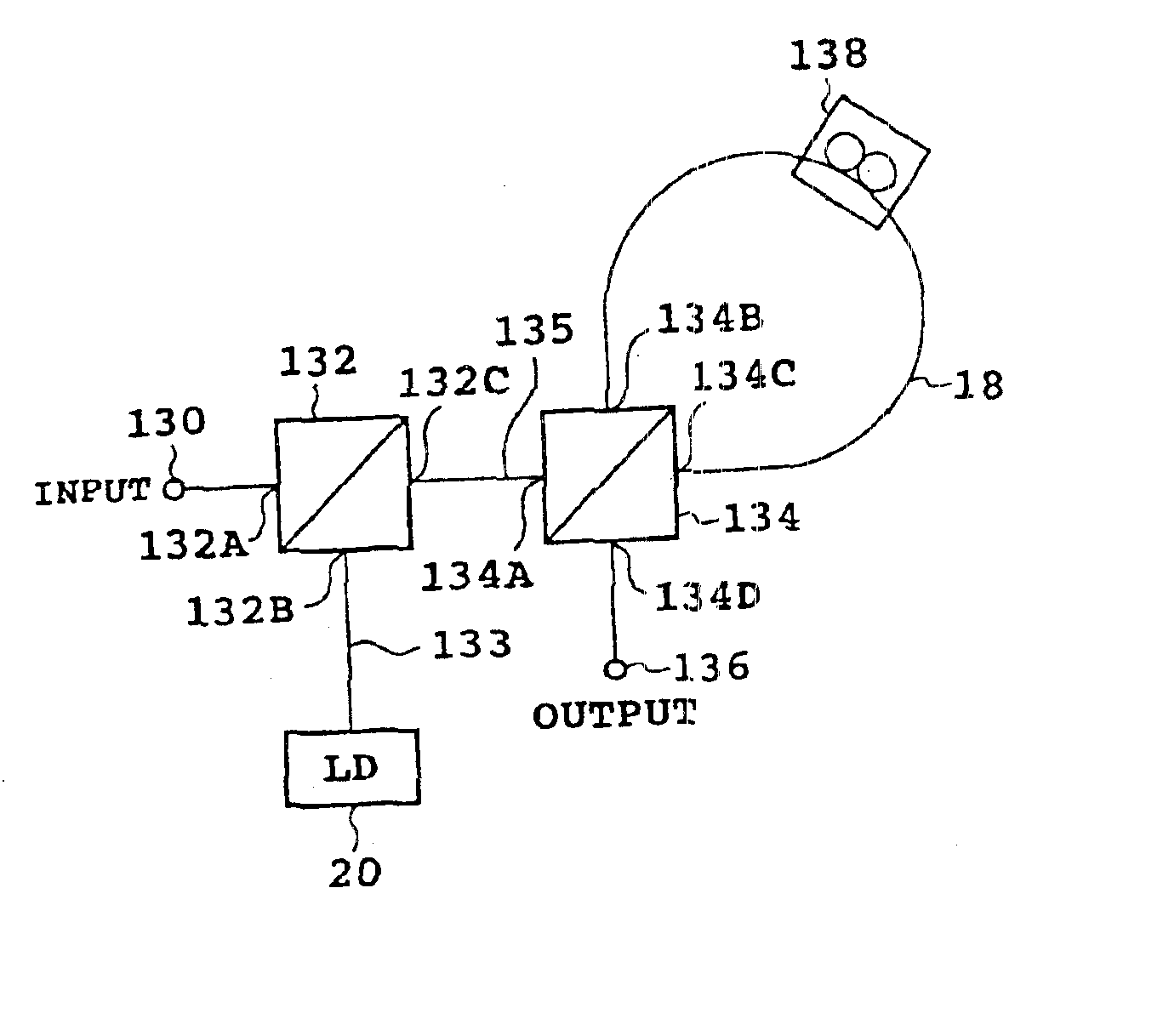
Optical fiber communication system using optical phase conjugation as well as apparatus applicable to the system and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6870974B2Effective compensationCompensation effectRing-type electromagnetic networksBus-type electromagnetic networksOptical phase conjugationSignal beam
An optical fiber communication system according to the present invention has, for example, first and second phase conjugators. The first phase conjugator converts a signal beam from a first optical fiber into a first phase conjugate beam. The first phase conjugate beam is supplied to the second phase conjugator by a second optical fiber. The second phase conjugator converts the first phase conjugate beam into a second phase conjugate beam. The second phase conjugate beam is transmitted by a third optical fiber. The second optical fiber is composed of a first portion located between the first phase conjugator and a system midpoint and a second portion located between the system midpoint and the second phase conjugator. The total dispersion of the first optical fiber substantially coincides with the total dispersion of the first portion, and the total dispersion of the second portion substantially coincides with the total dispersion of the third optical fiber. By the construction, waveform distortion by chromatic dispersion or nonlinearity is compensated for.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
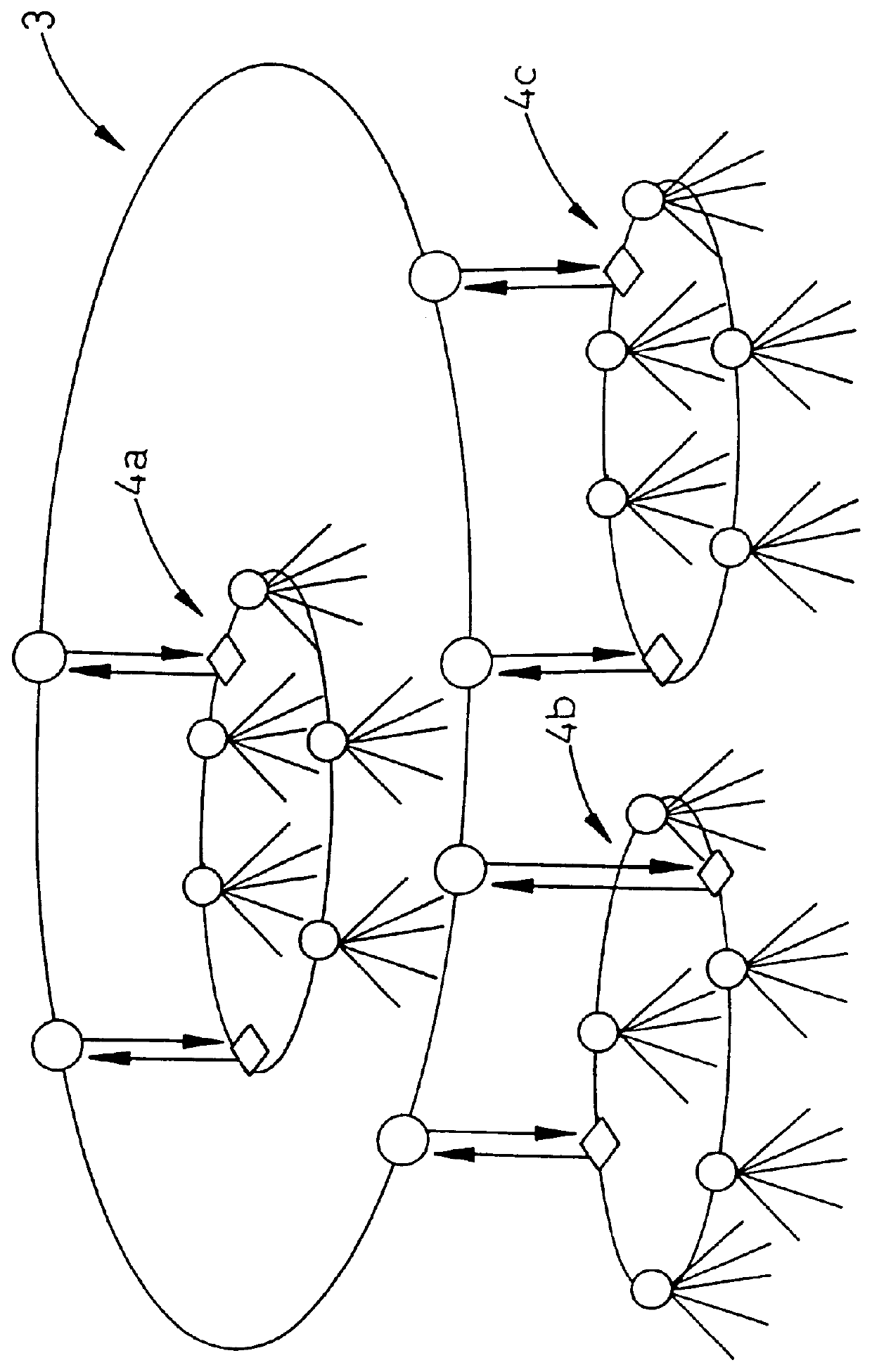
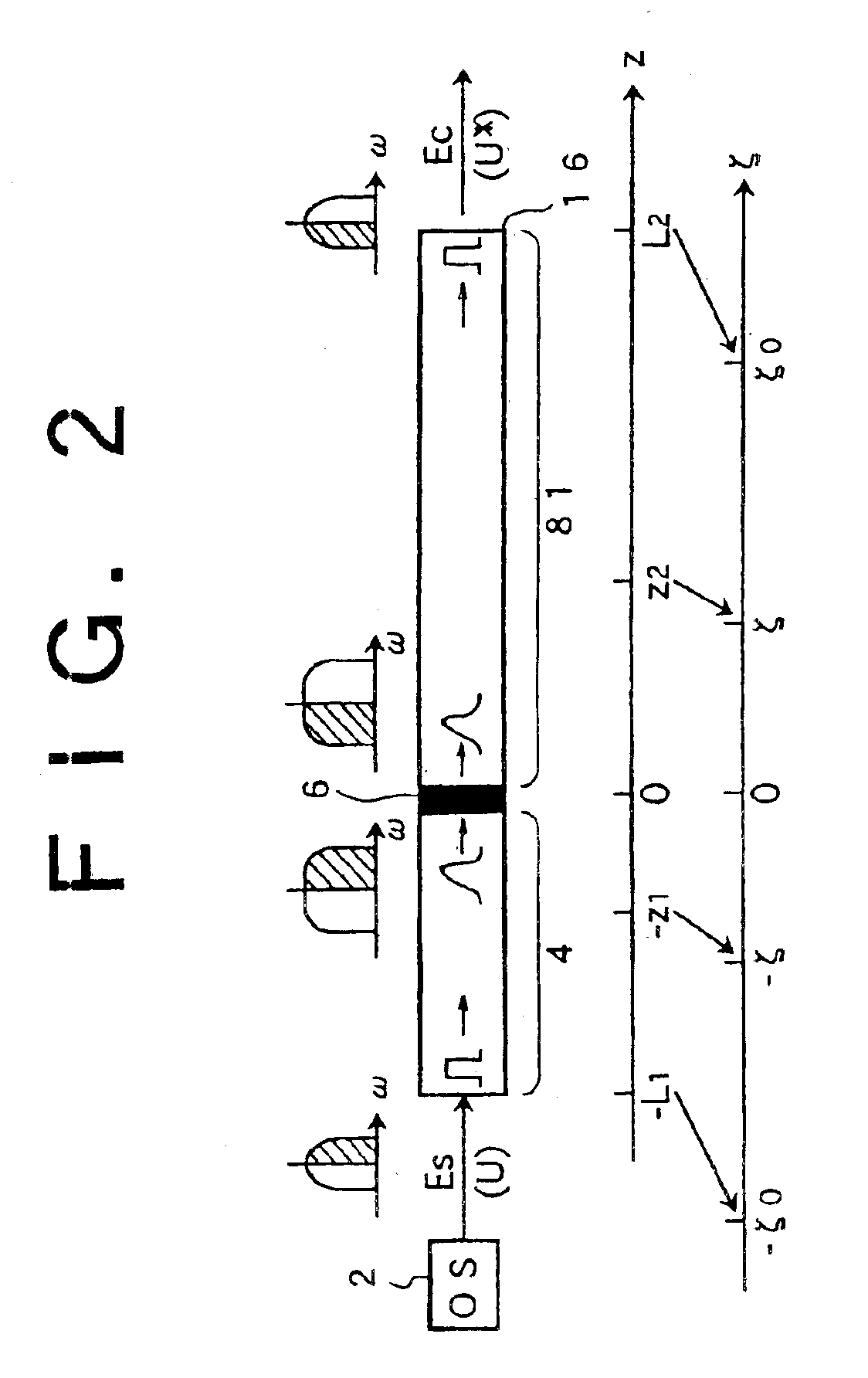
Remote Node and Network Architecture and Data Transmission Method for a Fiber-Optic Network, Especially for Low Bit-Rate Data Transmission
ActiveUS20120328293A1Low bandwidthRing-type electromagnetic networksBus-type electromagnetic networksNetwork architectureData transmission
The invention relates to a remote node architecture for a fiber-optic network, especially for low bit-rate data transmission, the fiber-optic network comprising a central node and a plurality of remote nodes serially connected to each other or to the central node, respectively, the central node and the remote node being capable of communicating by means of digital optical signals created by the central node or a respective remote node, each digital optical signal comprising a data frame.
Owner:ADVA OPTICAL NETWORKING SE
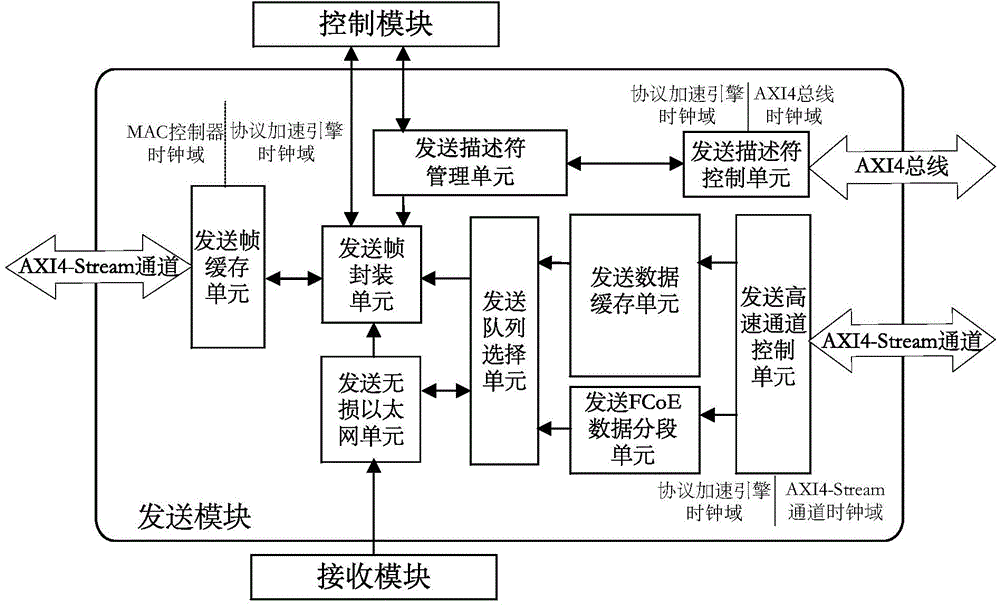
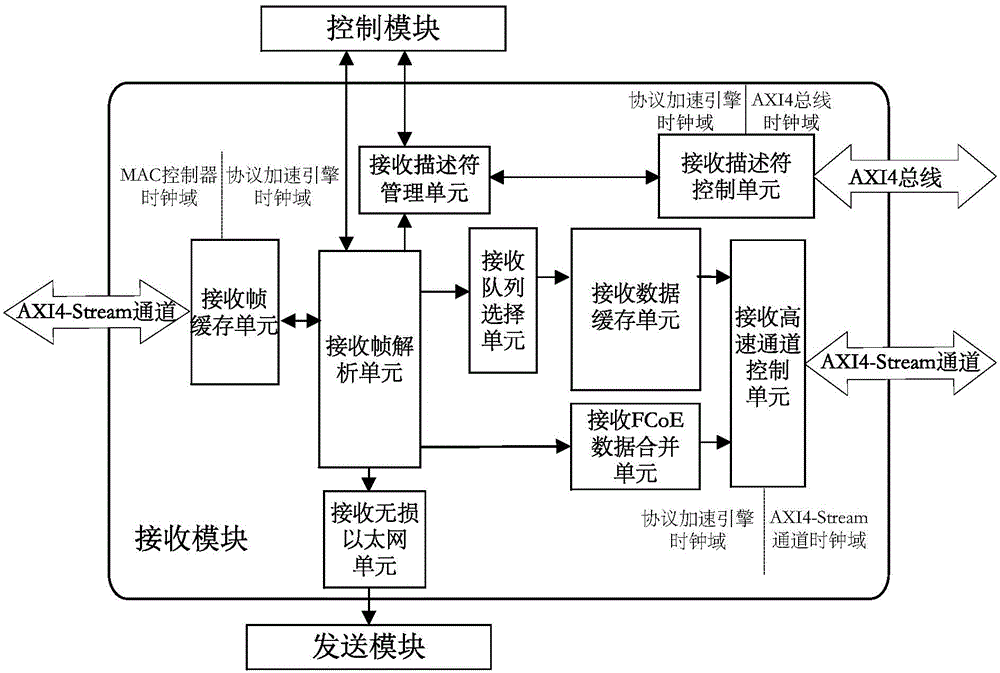
FCoE protocol acceleration engine IP core based on AXI4 bus formwork
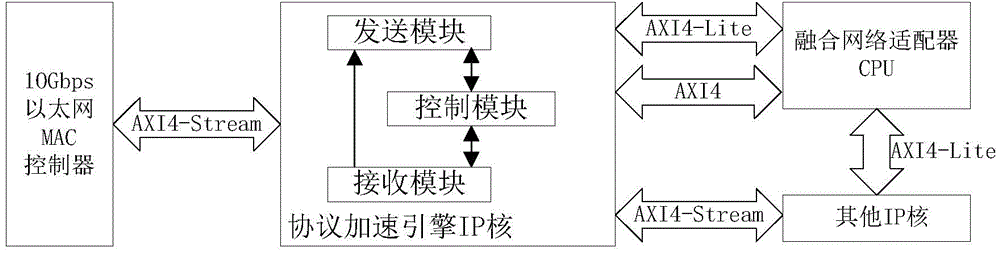
ActiveCN104378161AReduce the burden onImprove compatibilityBus-type electromagnetic networksFibre transmissionFiberVirtualization
The invention discloses an FCoE protocol acceleration engine IP core based on an AXI4 bus formwork, and belongs to the field of Ethernet fiber channels. The FCoE protocol acceleration engine IP core based on the AXI4 bus formwork is applied to an FCoE fusion network adapter and comprises a transmitting module, a receiving module and a control module. The FCoE protocol acceleration engine IP core is based on the AXI4 bus formwork, a register is configured for the IP core through an AXI4-Lite bus, an AXI4 bus is used for reading and writing a transmitting / receiving descriptor, and an AXI4-Stream high-speed channel is used for transmitting sent / received data. The FCoE protocol acceleration engine IP core can be controlled by a CPU of the FCoE fusion network adapter, the IP core is specially used for meeting the need of FCoE data frame hardware processing in the field of Ethernet fiber channels, a full duplex operating mode is adopted, real-time performance and high efficiency are achieved in operation, the data throughout is large, the transmission rate is high, and lossless transmission can be achieved. The FCoE protocol acceleration engine IP core based on the AXI4 bus formwork can support FCoE data segmenting / merging processing and cannot damage the function of the Ethernet and simple root virtualization.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS6983092B2Easy to makeThe transmission is compactRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsMultiplexingLength wave
To provide an optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, capable of increasing signal transmission speed and of being easily made minute thereby being simply and easily fabricated, an electro-optical device, and an electronic apparatus, an optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, which is disposed on a substrate, includes micro-tile shaped elements having a light emitting function or a light receiving function with wavelength selectivity.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
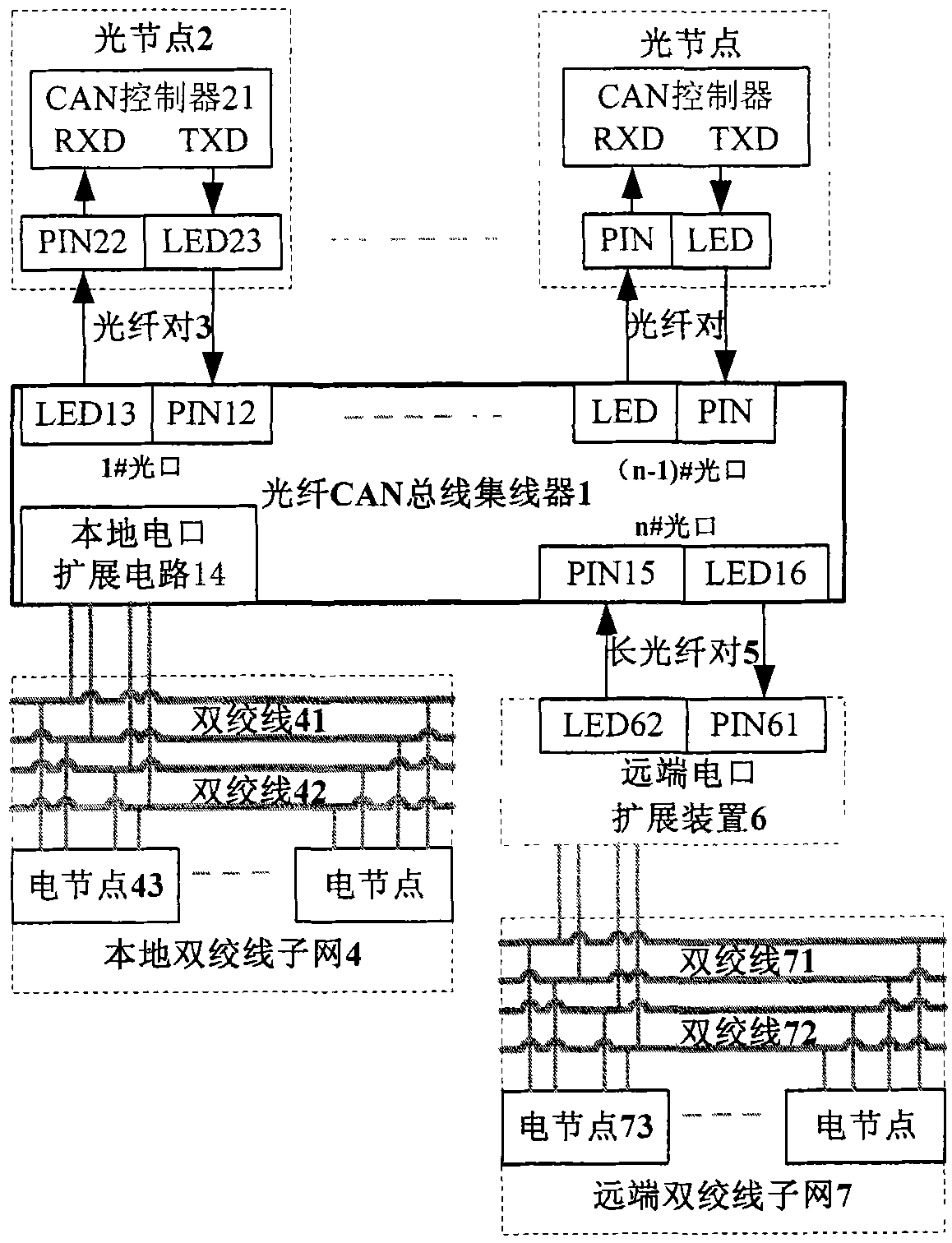
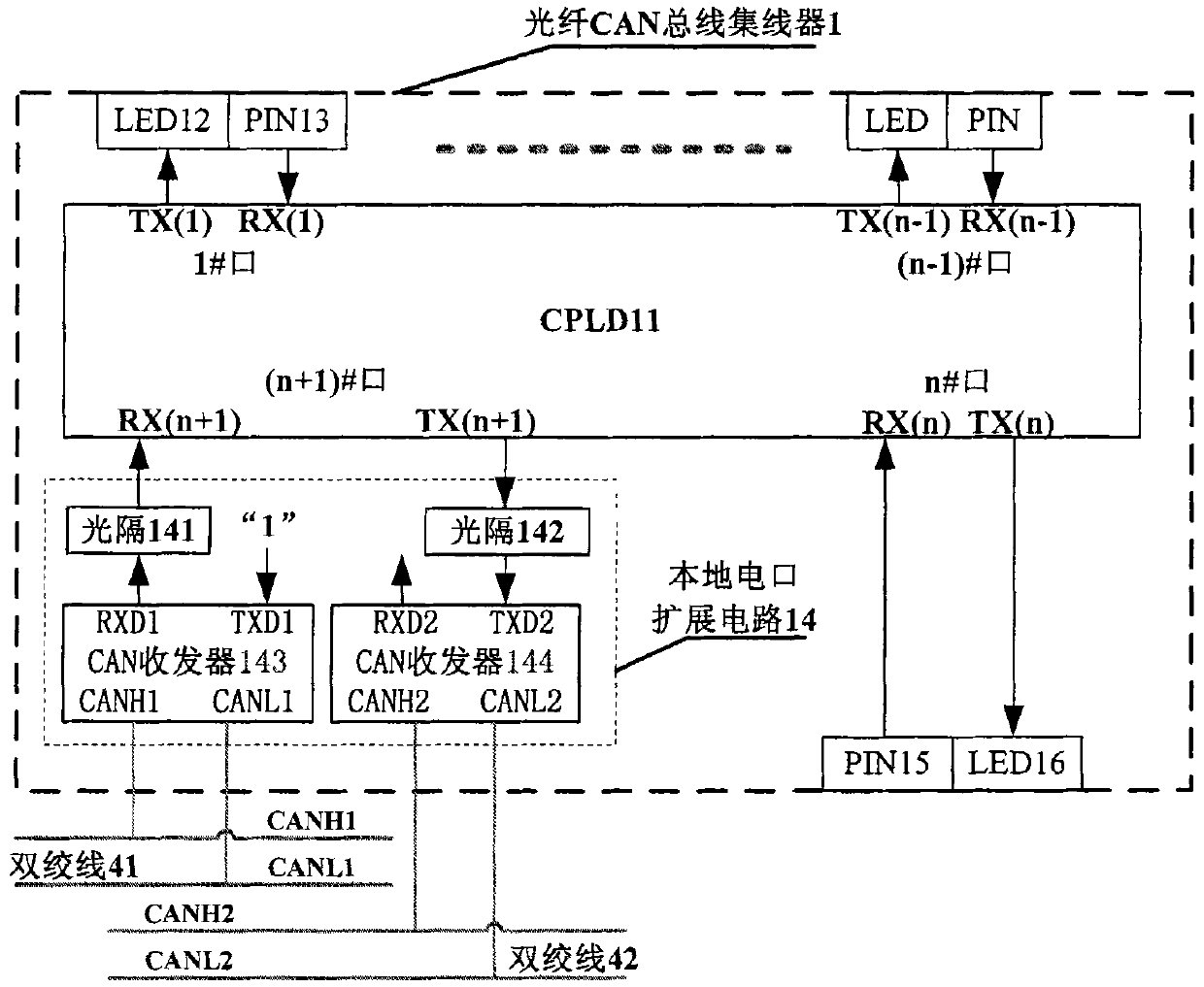
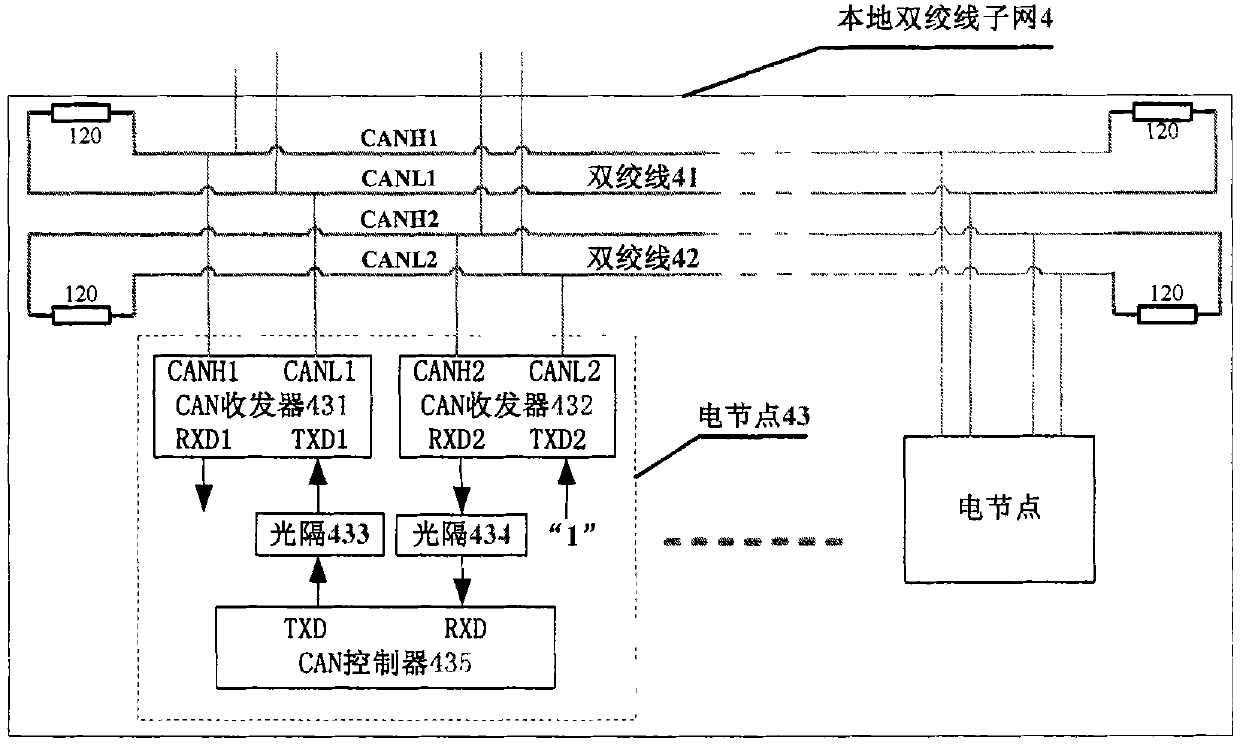
Optical fiber CAN bus hub and networking method thereof
InactiveCN102026050AMultiplex system selection arrangementsBus-type electromagnetic networksTransceiverComplex programmable logic device
The invention discloses a networking method of an optical fiber control area network (CAN) bus hub. A main hub of an optical fiber CAN bus with n optical fiber interfaces and a local twisted pair electrical interface extension circuit and n twisted pair CAN sub-networks for connecting the main hub with n optical nodes, n secondary hubs or n remote electric interface extension devices are connected with a local twisted pair CAN sub-network to form a network; signals are transmitted, received and separated by using the optical fiber CAN bus hub which realizes a wired and function through a complex programmable logic device (CPLD) and is provided with a plurality of optical interfaces and a twisted pair electric interface extension circuit, double CAN transceivers and two twisted pairs, so self-excitation blocking communication caused by a signal transmission loop is avoided; and the optical nodes, the local twisted pair CAN bus sub-network and the remote twisted pair CAN bus sub-network are connected by using the optical fiber CAN bus hub, the optical fiber pair and the remote electric interface extension device to form a high-network-speed wide area networking scheme.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
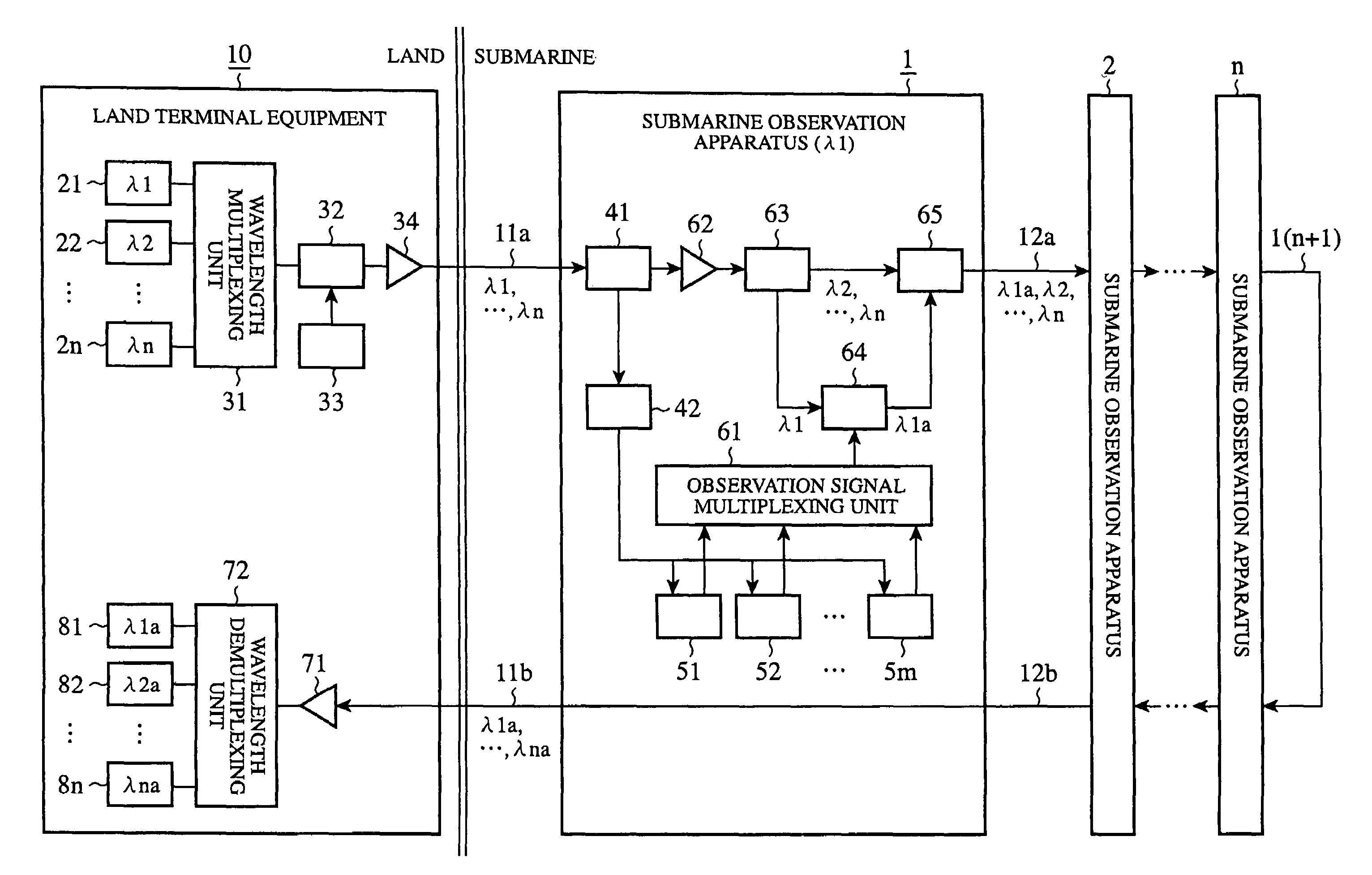
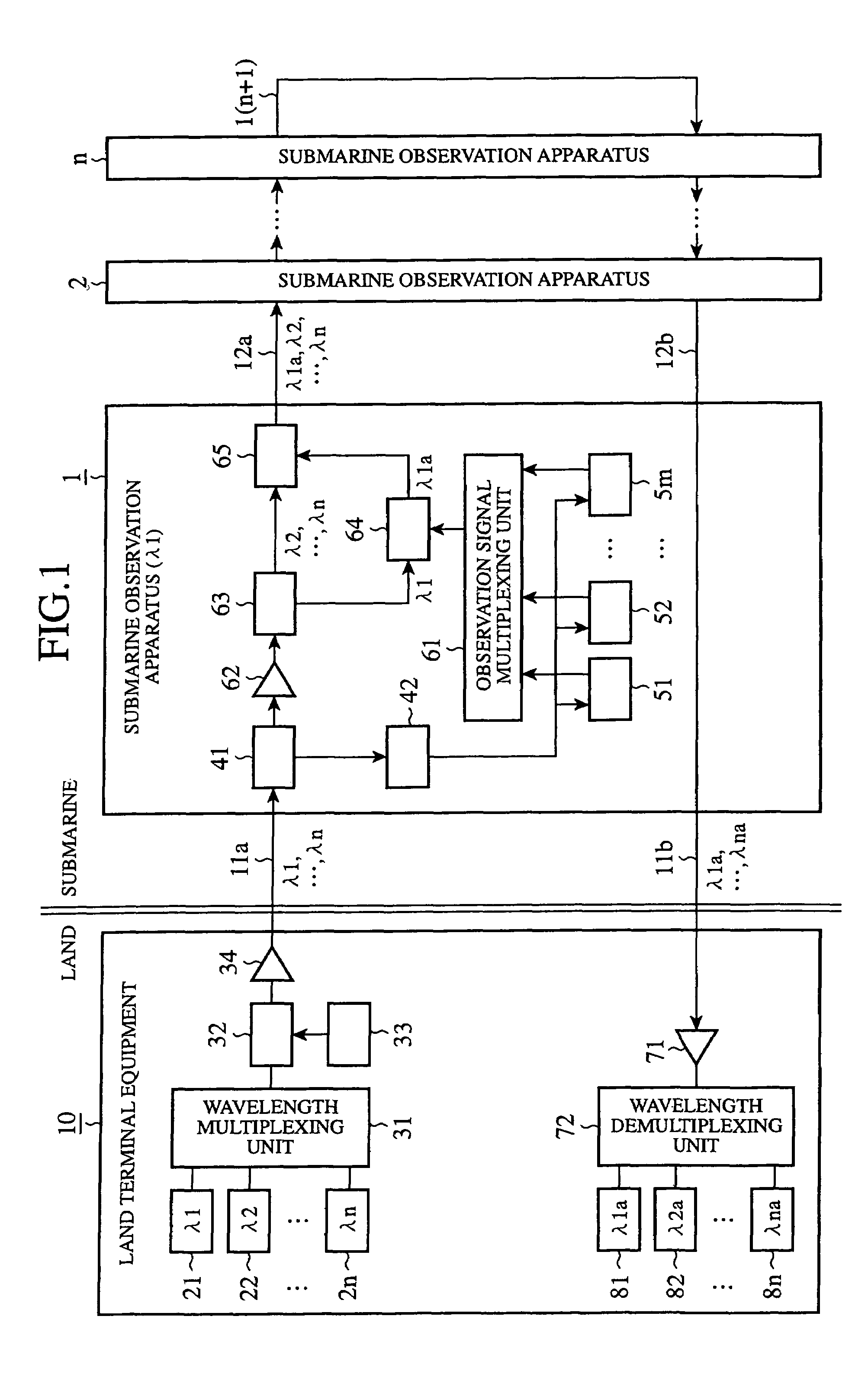
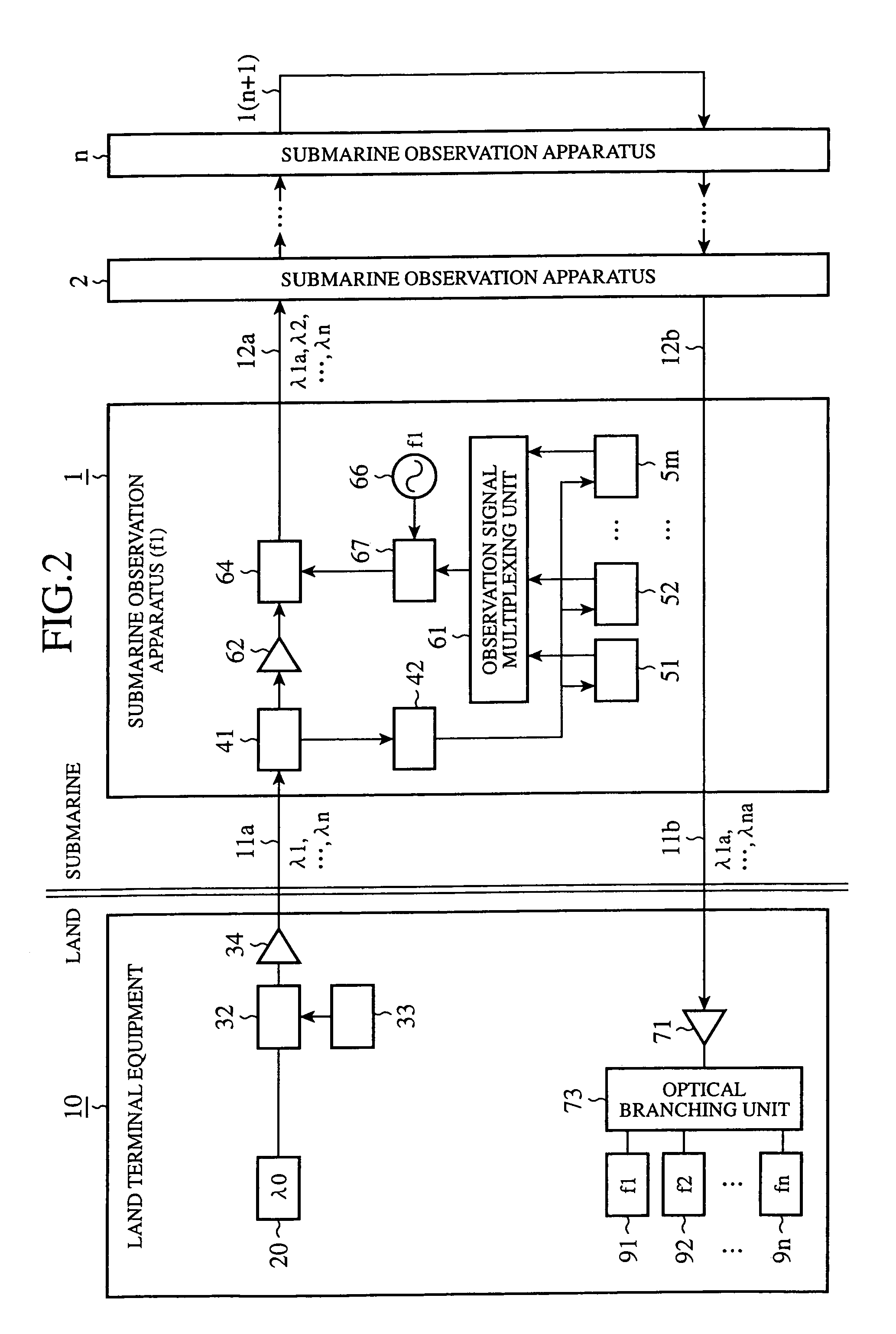
Submarine observation apparatus and submarine observation system
InactiveUS7437070B2Improve scaleIncrease scale and cost can be suppressedRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsLength waveLight signal
Owner:JAPAN AGENCY FOR MARINE-EARTH SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
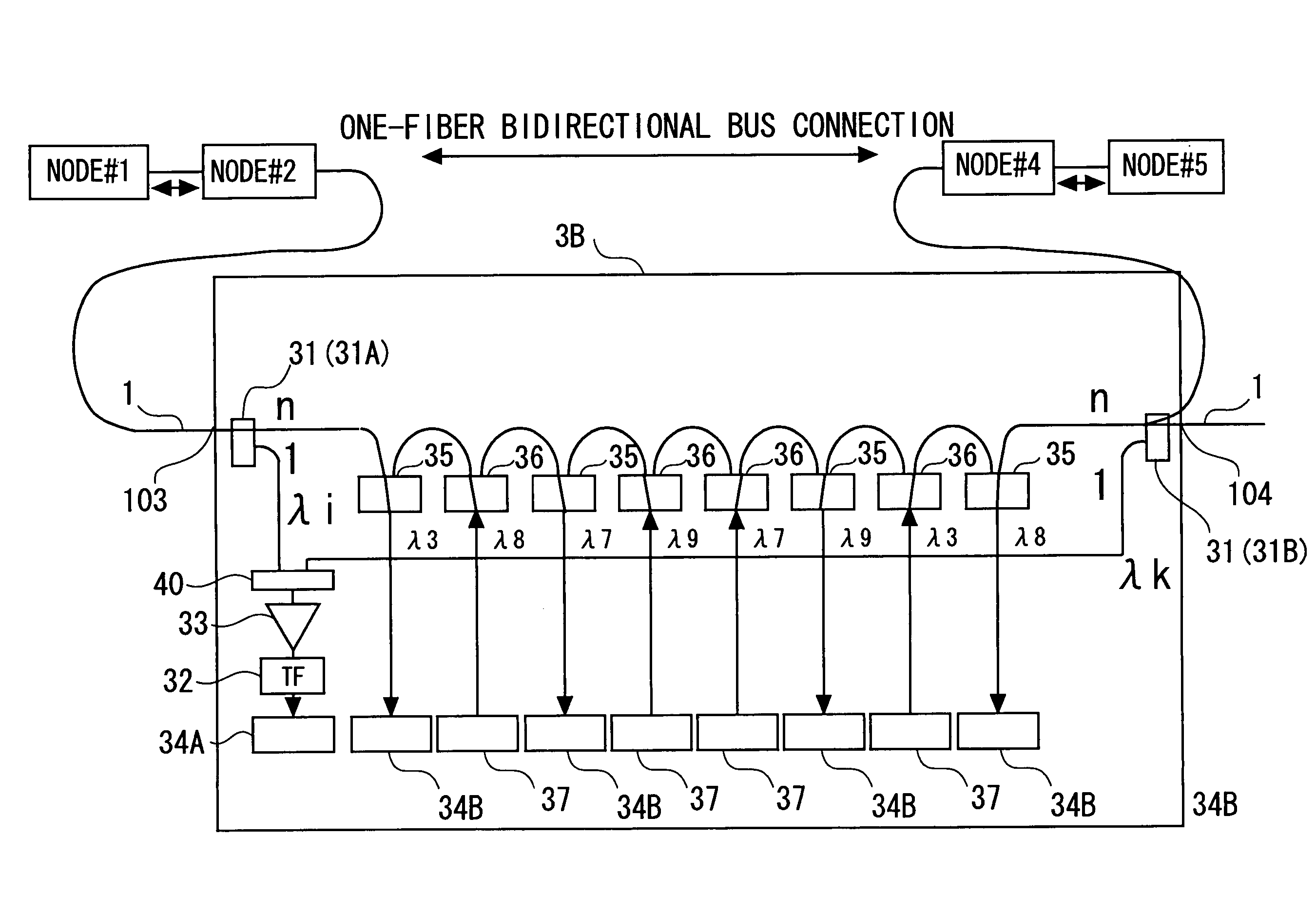
Optical network and optical add/drop apparatus
ActiveUS7433601B2Low costSimple configurationRing-type electromagnetic networksBus-type electromagnetic networksMultiplexingLength wave
Provided are a plurality of fixed wavelength drop filters 35 demultiplexing optical signals having a plurality of different fixed wavelengths, a plurality of fixed wavelength add filters 36 provided corresponding respectively to the fixed wavelength drop filters 35 and adding the optical signals having the fixed wavelengths wavelength division multiplexed light flowing along a transmission path 1, a first optical branching unit 31 branching part of the wavelength division multiplexed light flowing along the transmission path 1, and a variable wavelength drop filter 32 demultiplexing the optical signal having the wavelength corresponding to a specified value from the wavelength division multiplexed light branched by the first optical branching unit 31.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High-speed wireless personal area network system for extending service area
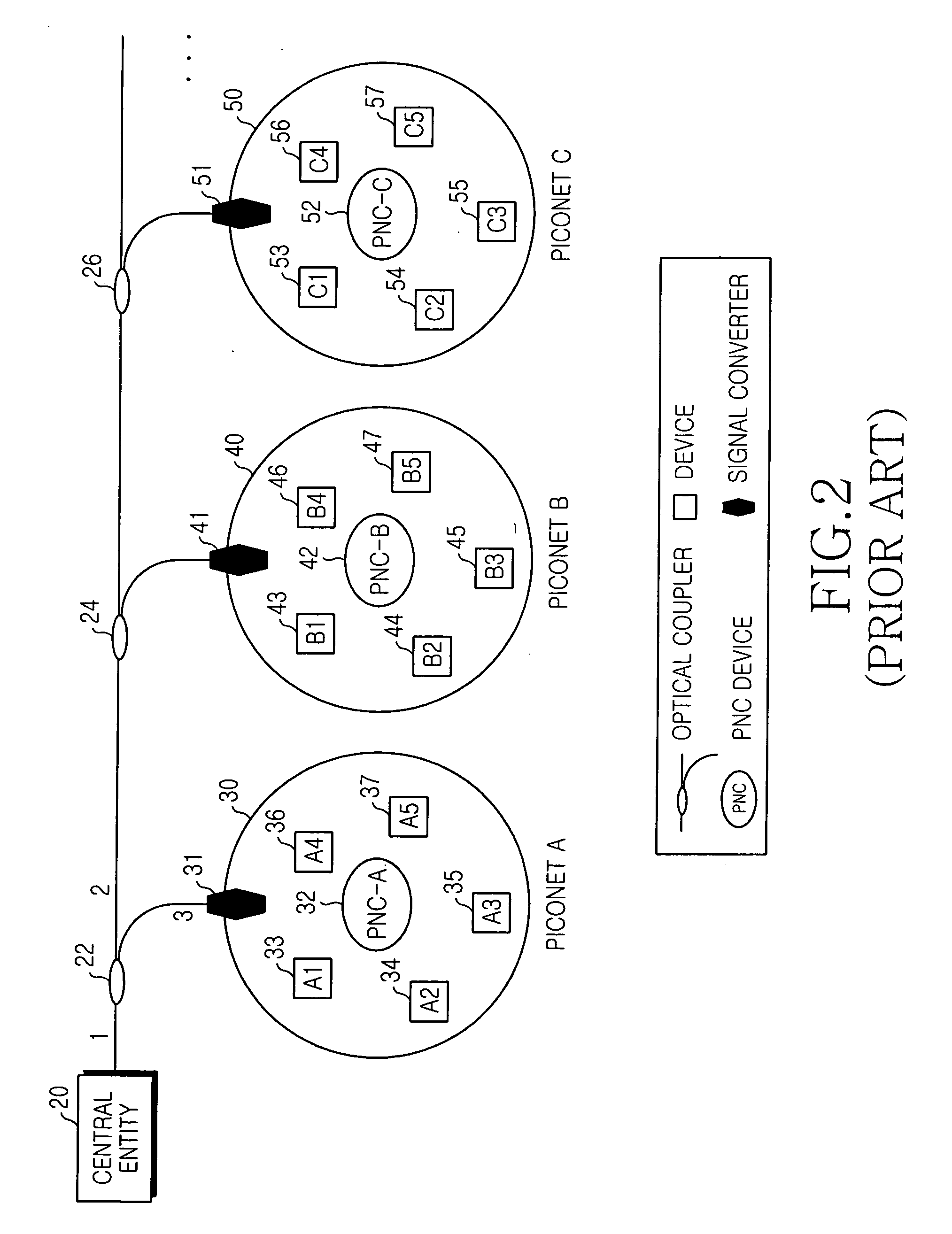
InactiveUS20050025487A1Simply and quickly transmittingSimply and quickly transmitting dataBus-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsNetworked systemEngineering
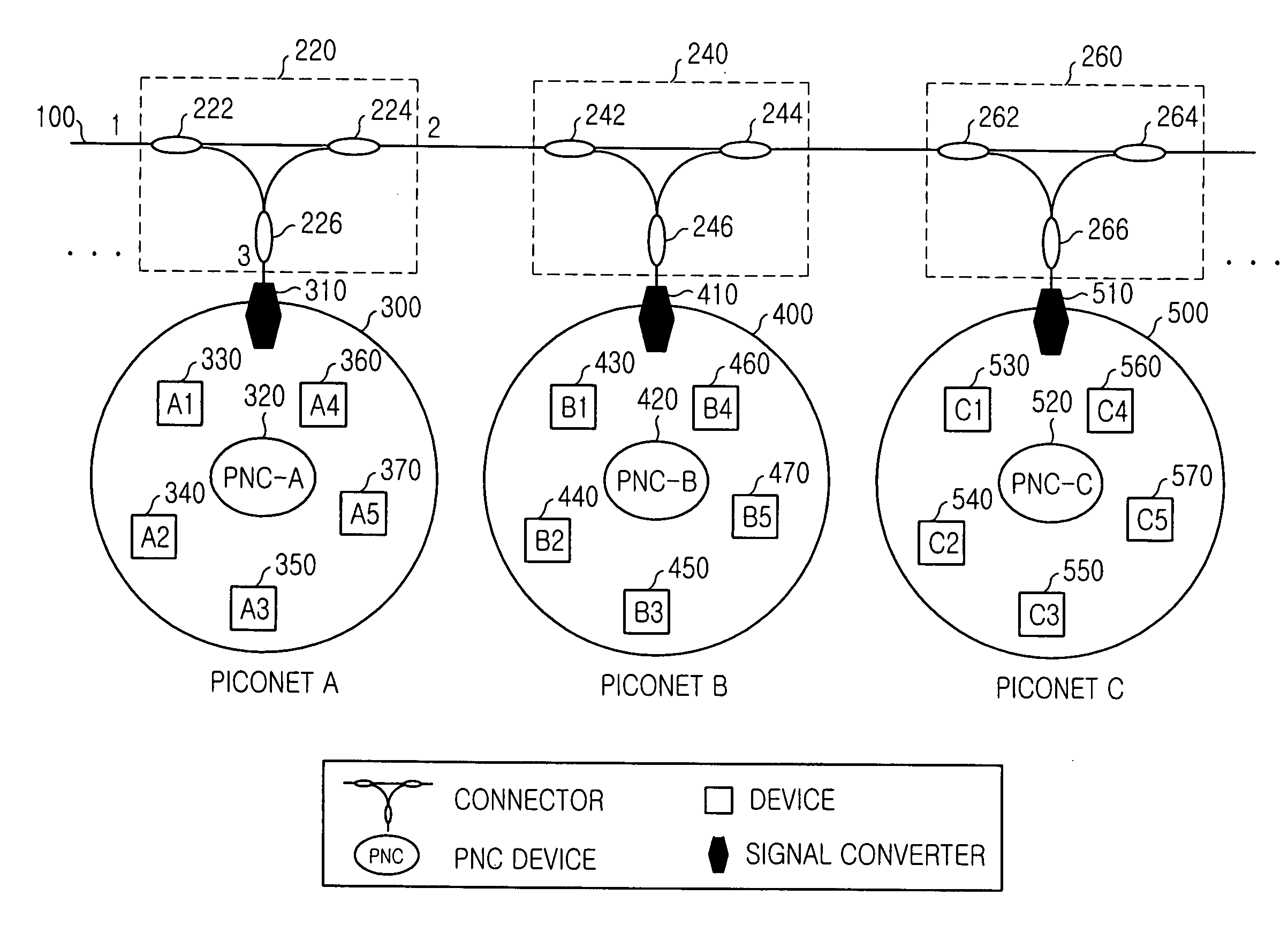
A high-speed WPAN (Wireless Personal Area Network) system for extending a service area includes an optical fiber serving as a medium for transmitting data; a plurality of pico-nets each including a plurality of devices and a PNC (Pico-Net Coordinator) device for managing the devices; a plurality of two-way signal converters corresponding to the pico-nets, each of the signal converters adapted for converting an optical signal received from the optical fiber into an electrical signal to transmit the electrical signal to the pico-nets, and for converting an electrical signal received from each of the pico-nets into an optical signal to transmit the optical signal to the optical fiber. A plurality of connectors are attached to the optical fiber and the signal converters for transmitting signals input from the optical fiber and the signal converters bidirectionally. One of the PNC devices provided in the pico-nets allocates and manages timeslots for all the devices located in the plurality of pico-nets, and the plurality of pico-nets may be operated as a single logical unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical transmission system and optical node
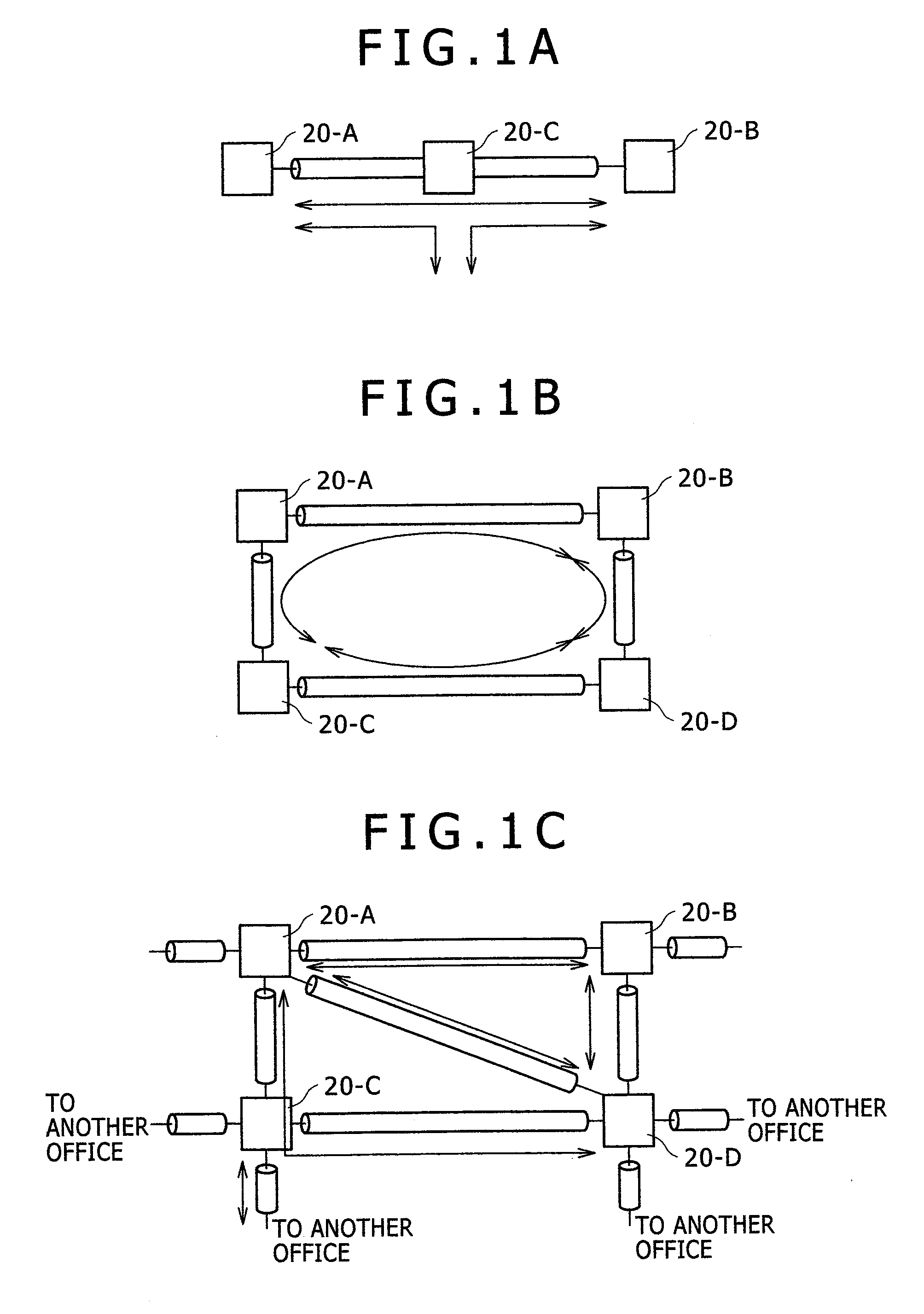
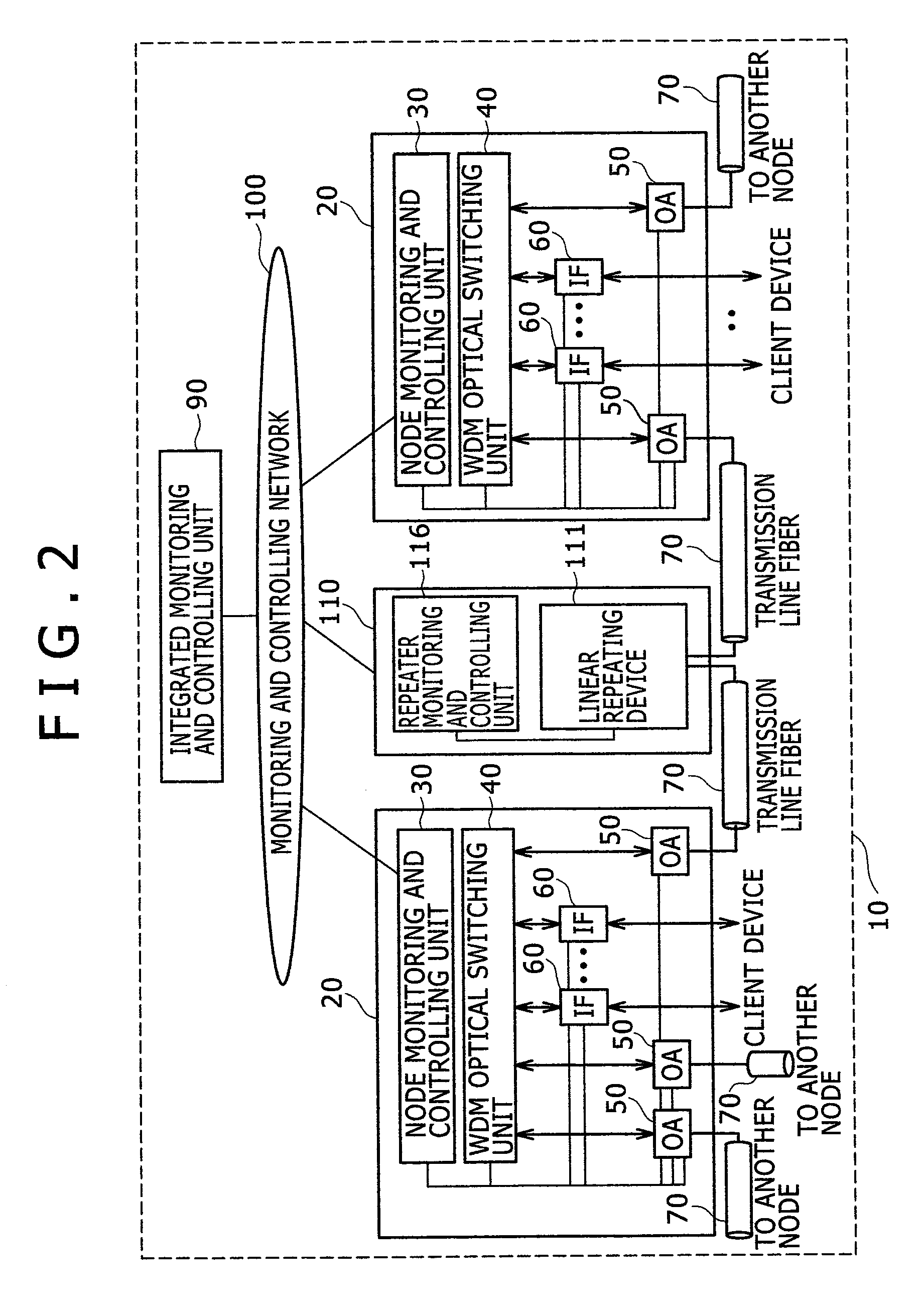
InactiveCN101442376AEasy access managementBus-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsIntegrated monitoringTransceiver
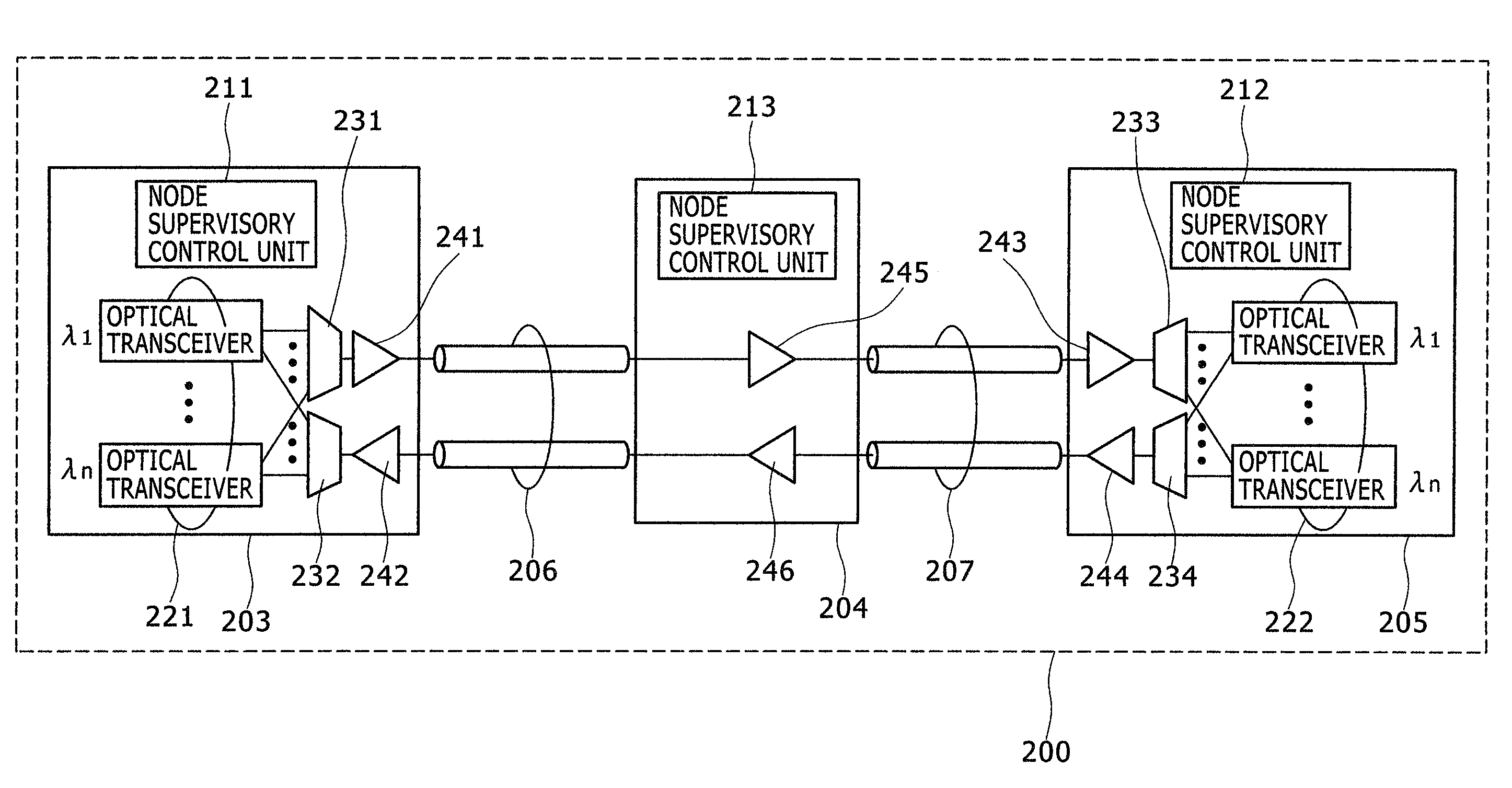
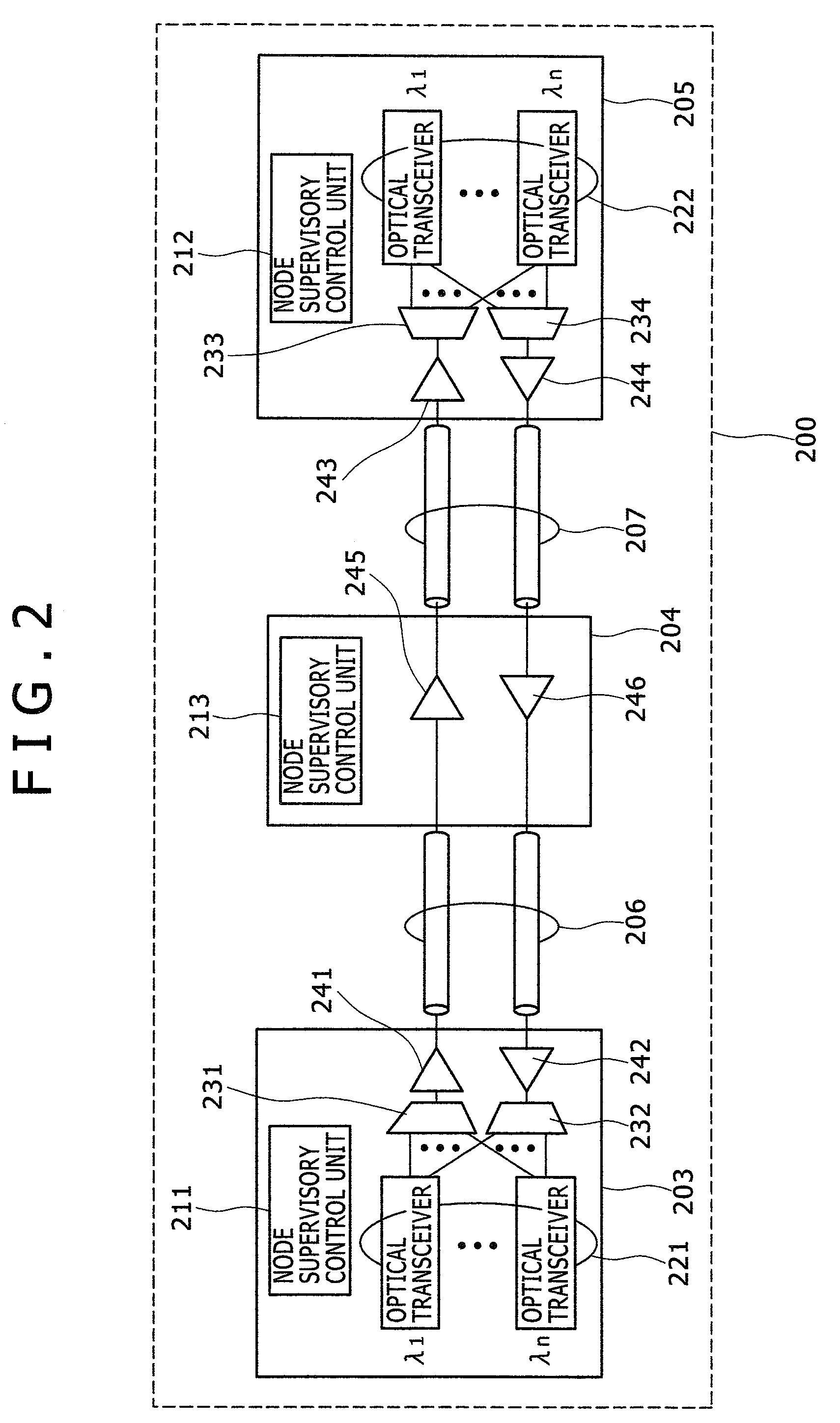
The invention provides an optical transmission system and optical node. On condition of a pair of 1 type gateways and a pair of N type gateways which are mixed, unexpected alarms will not be produced, and gateway management can be carried out as now. The optical transmission system comprises an integrated monitoring and controlling unit which is to control an optical add-drop unit so as to cause transmit signals from the optical transceiver of a first optical node to be received by the optical transceivers of plural different optical nodes, the purpose can be achieved by an optical transmission system provided with an alarm inhibiting device that can inhibit the optical transceiver, which is a source of transmission, from issuing any unexpected alarm.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical signal switching device for use in an optical protection network
ActiveUS7613391B2Improve reliabilityLow costRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsTransceiverNetworked system
An optical network system is provided which has a signal protection function and is able to be constructed of communication nodes manufactured at low costs. An optical signal transceiver has at least one optical signal transmitting device and at least one optical signal receiving device to transmit and receive an optical signal between nodes facing each other. A switching device, when no failure has occurred in the optical signal transmitting communication line and optical signal receiving communication line, transmits an optical signal from the optical signal transmitting device to an optical signal transmitting communication line and an optical signal having been received from the optical signal receiving communication line to an optical signal receiving device. The switching device, when a failure has occurred in the optical signal receiving communication line, does switching so as to be able to receive the optical signal, to be transmitted to the optical signal receiving device, from the optical signal transmitting communication line.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical transmission system and optical node
InactiveUS20090136233A1Easy to manageEfficient deliveryBus-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransceiverIntegrated monitoring
Where an integrated monitoring and controlling unit is to control an optical add-drop unit so as to cause transmit signals from the optical transceiver of a first optical node to be received by the optical transceivers of plural different optical nodes, this purpose can be achieved by an optical transmission system provided with an alarm inhibiting device that can inhibit the optical transceiver, which is a source of transmission, from issuing any unexpected alarm.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com