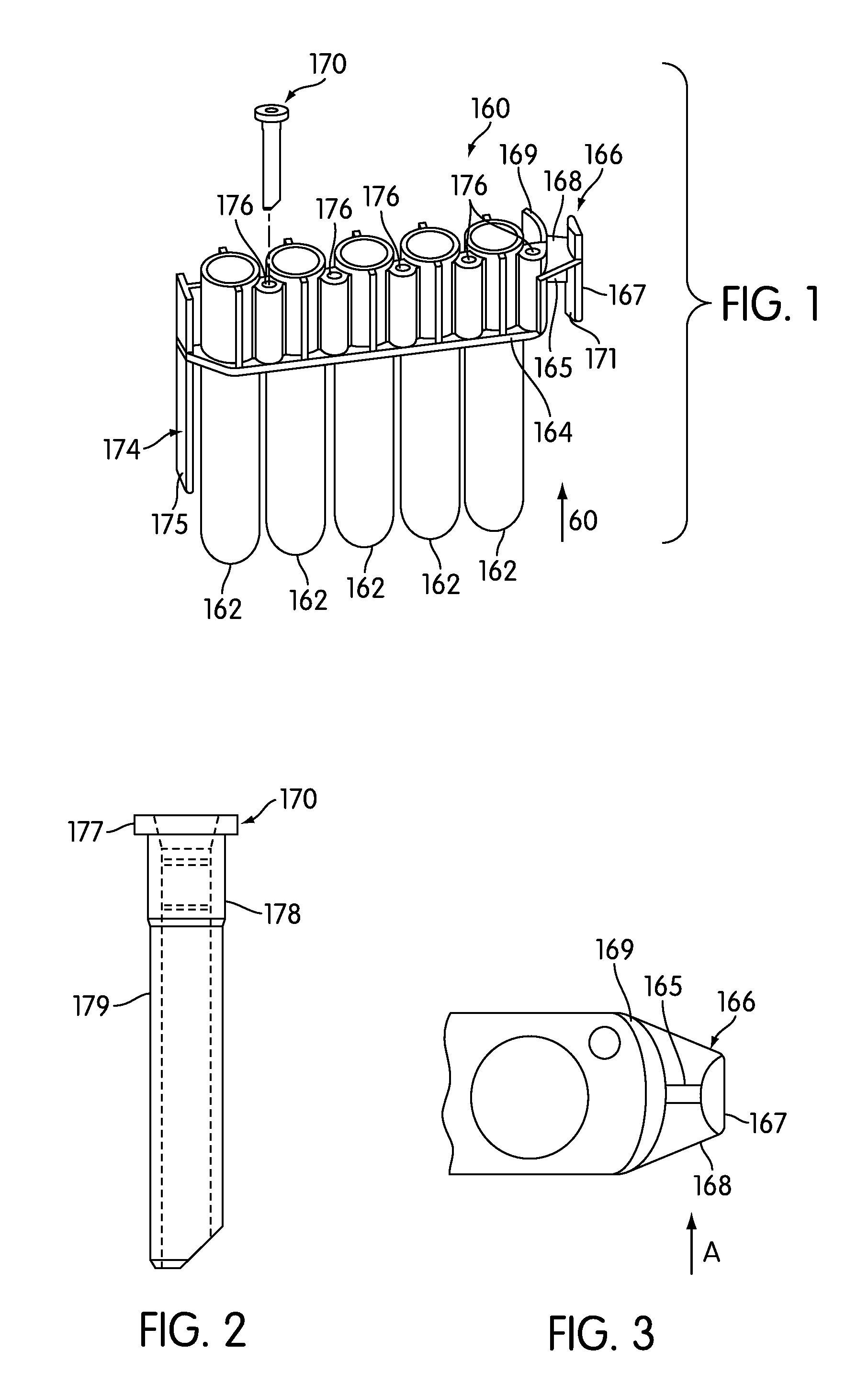
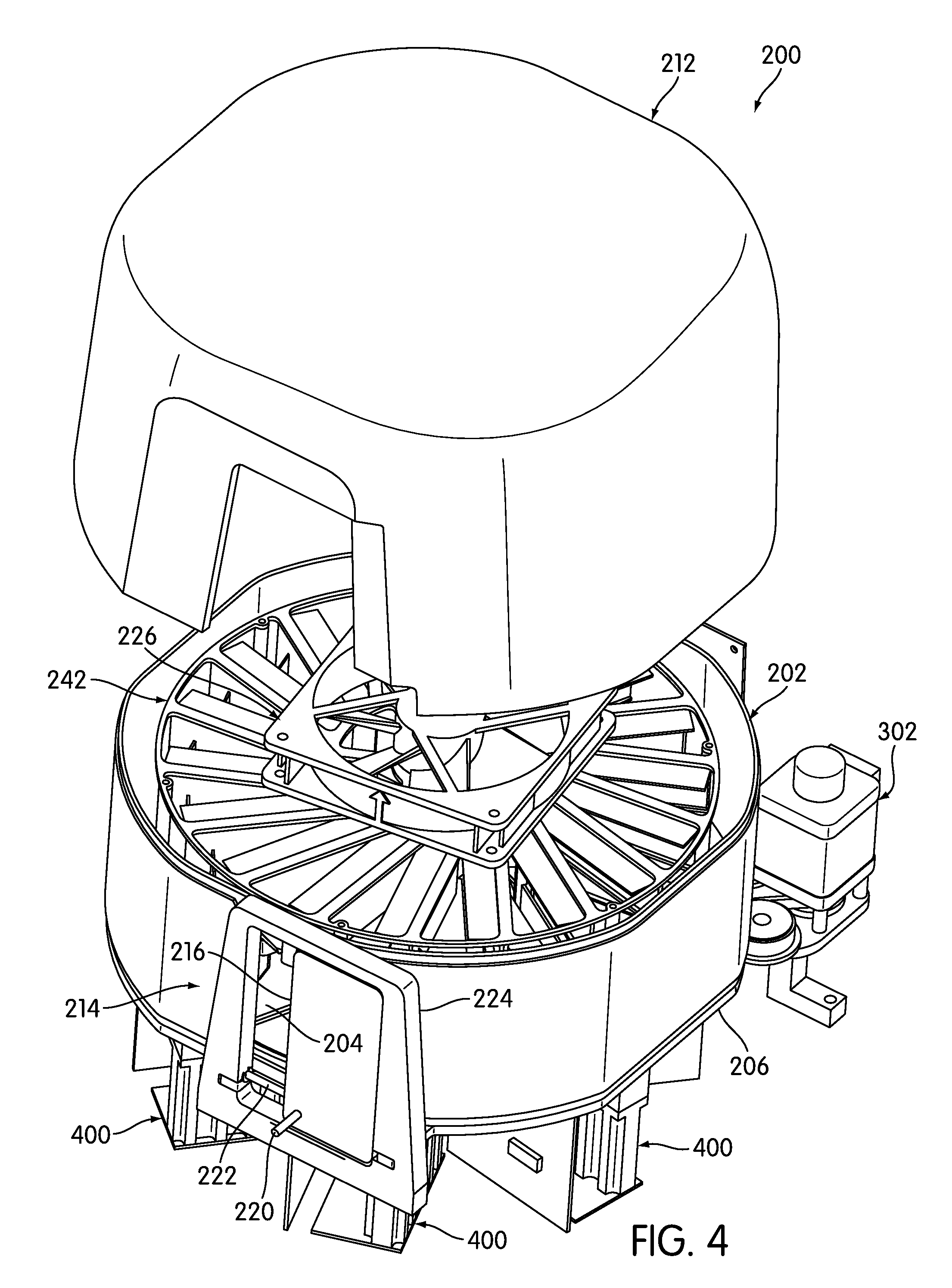
Patents
Literature
196 results about "Optical noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
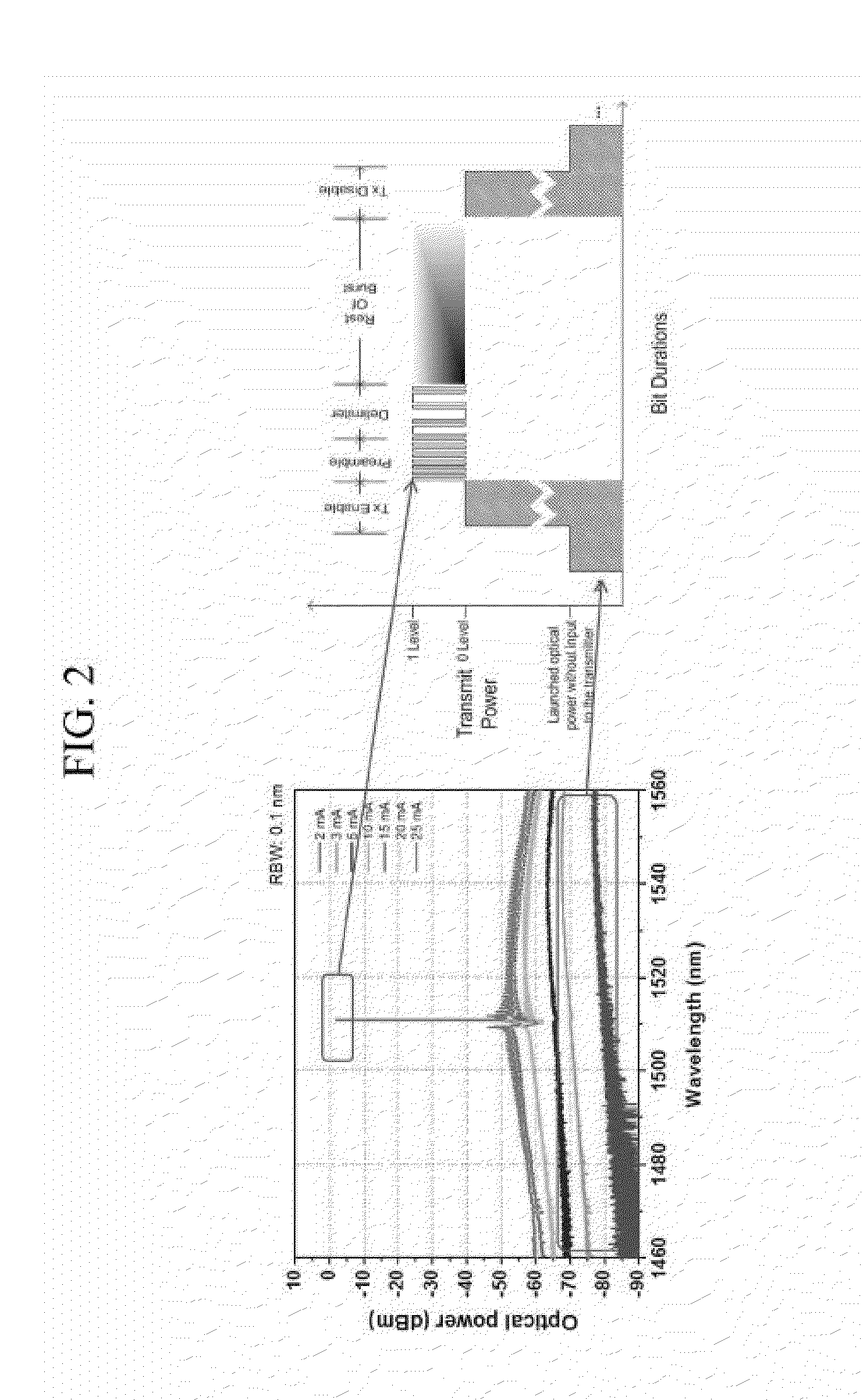
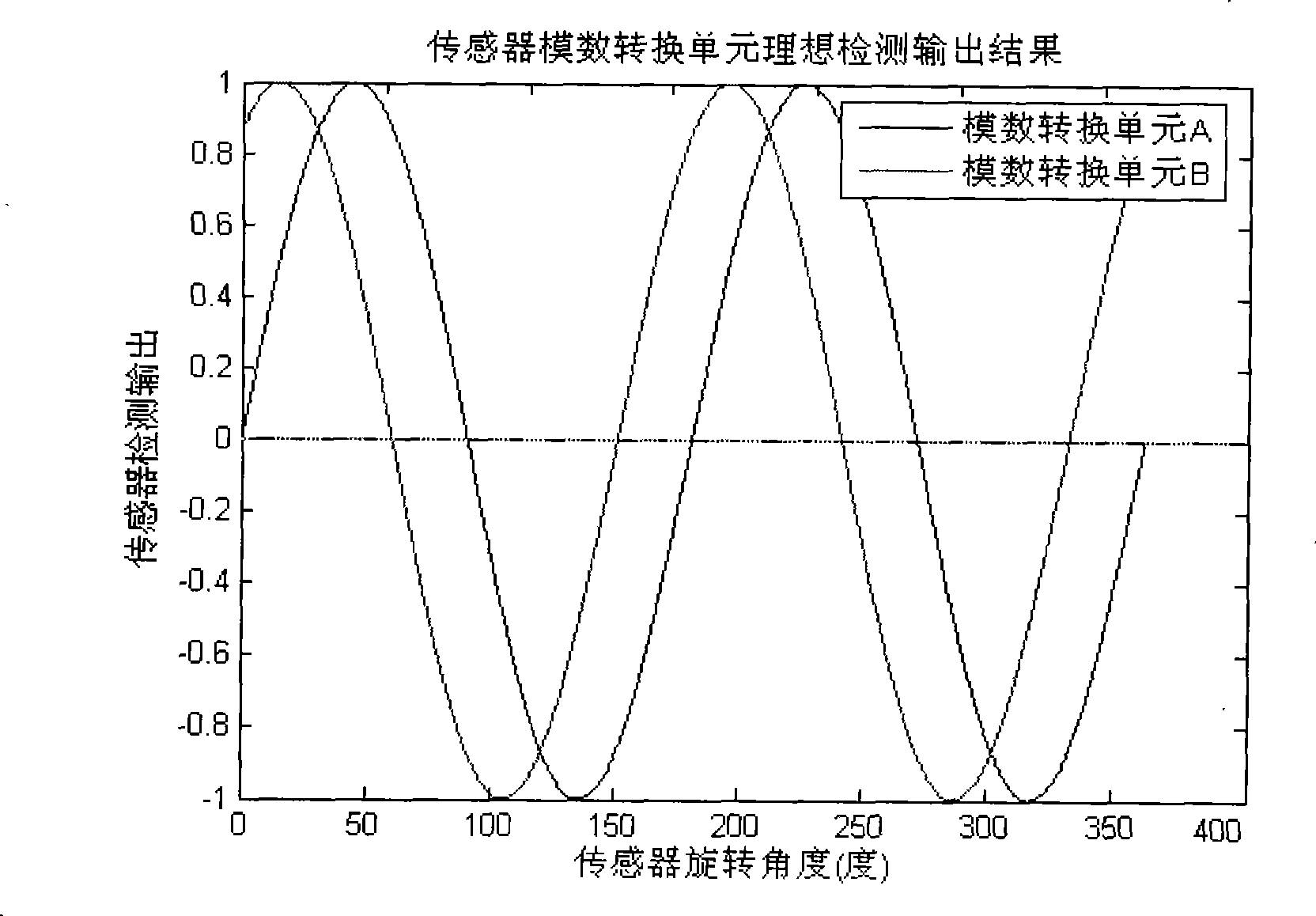
Noise is defined as the deviation from an ideal signal, and is usually associated with random processes. By definition it corrupts t he information content and fidelity of the signal, particularly at low levels. In our case, we will be dealing with voltage noise, current noise, and optical intensity noise.
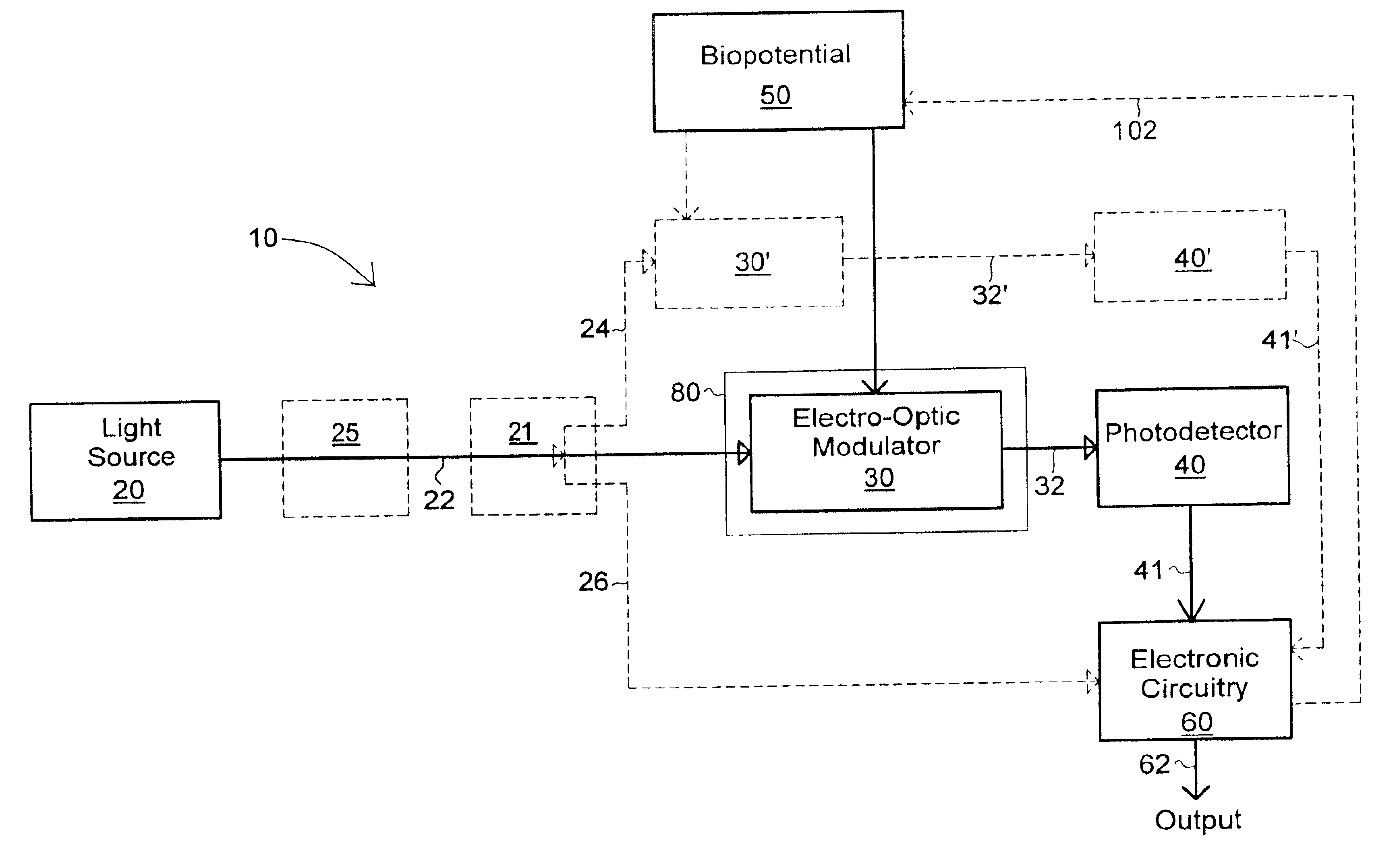
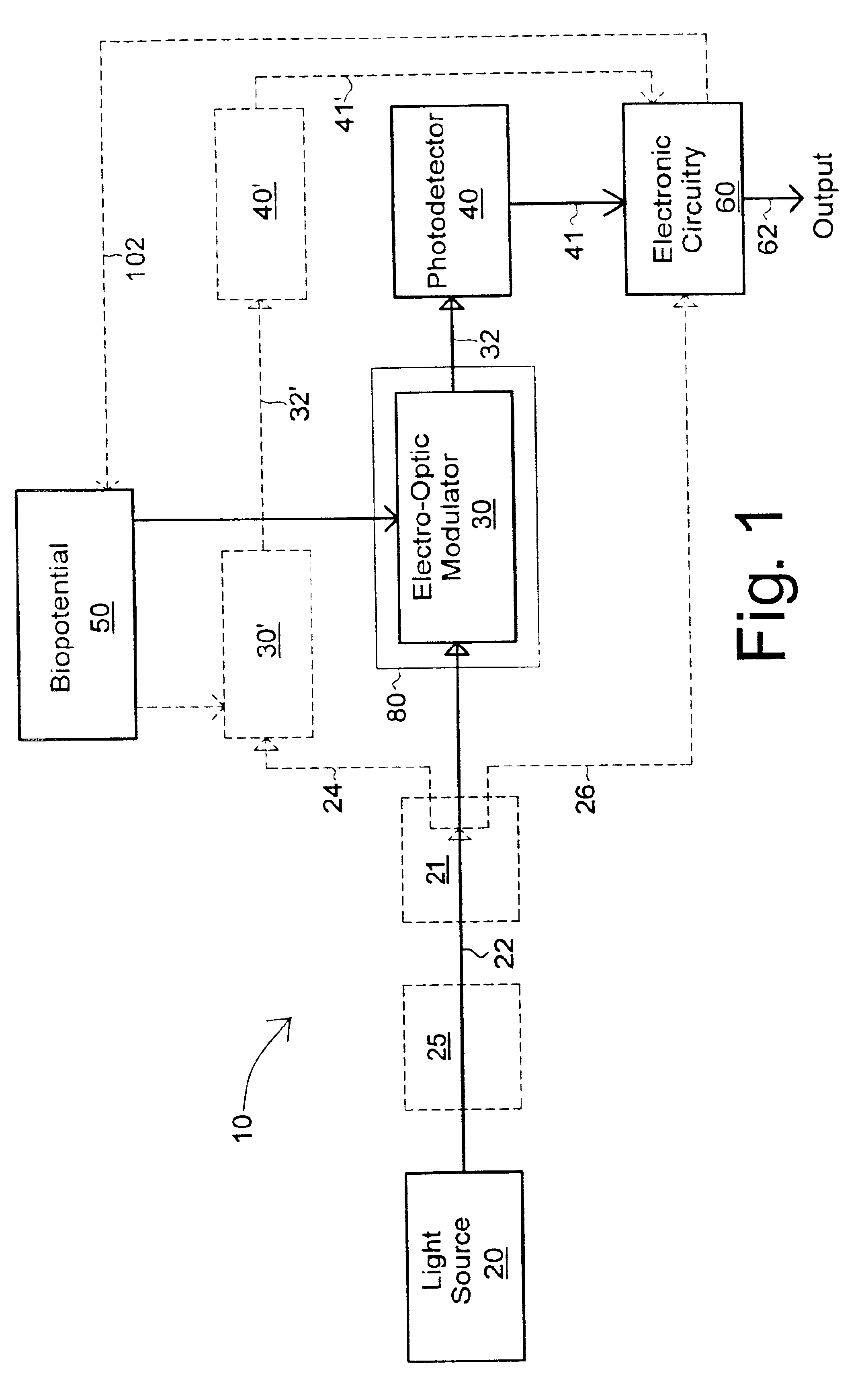
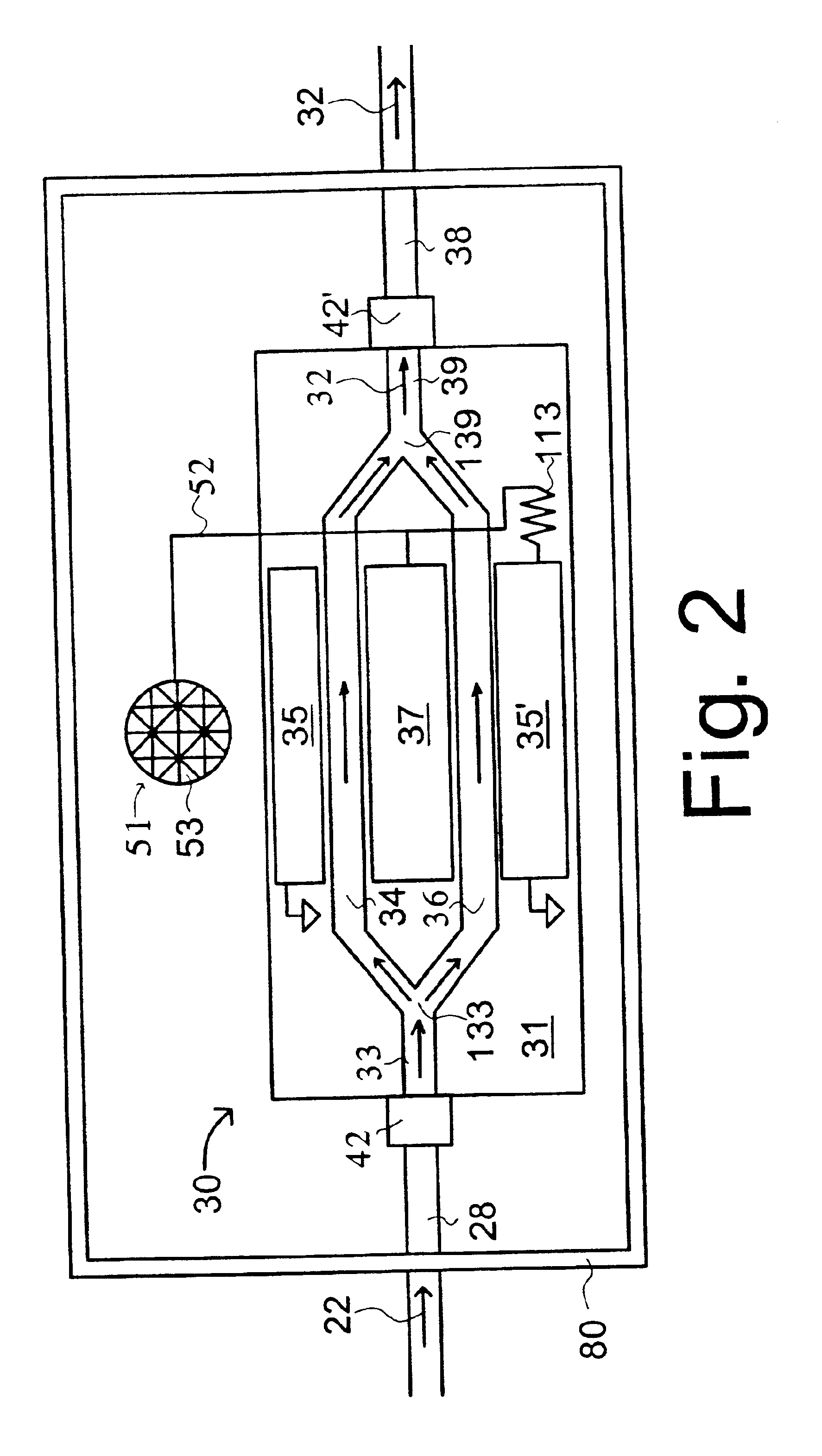
High-impedance optical electrode
InactiveUS6871084B1Prevent removalHigh impedanceElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyPhase shiftedOptoelectronics
High-impedance optical electrodes modulate light in response to a life-form bio-potential and then converts the modulated light to an electrical signal that provides traditional EEG and EEC type output. Light splitters are used to provide multiple electrodes and an electronic reference source. A pilot tone is used to achieve high sensitivity and synchronize multiple units while an optical phase-shift modulator is used to reduce optical noise.
Owner:SRICO
Optical touchpad with three-dimensional position determination
InactiveUS20080007542A1Easy to controlIncrease frame rateCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingTouchpadFrame rate
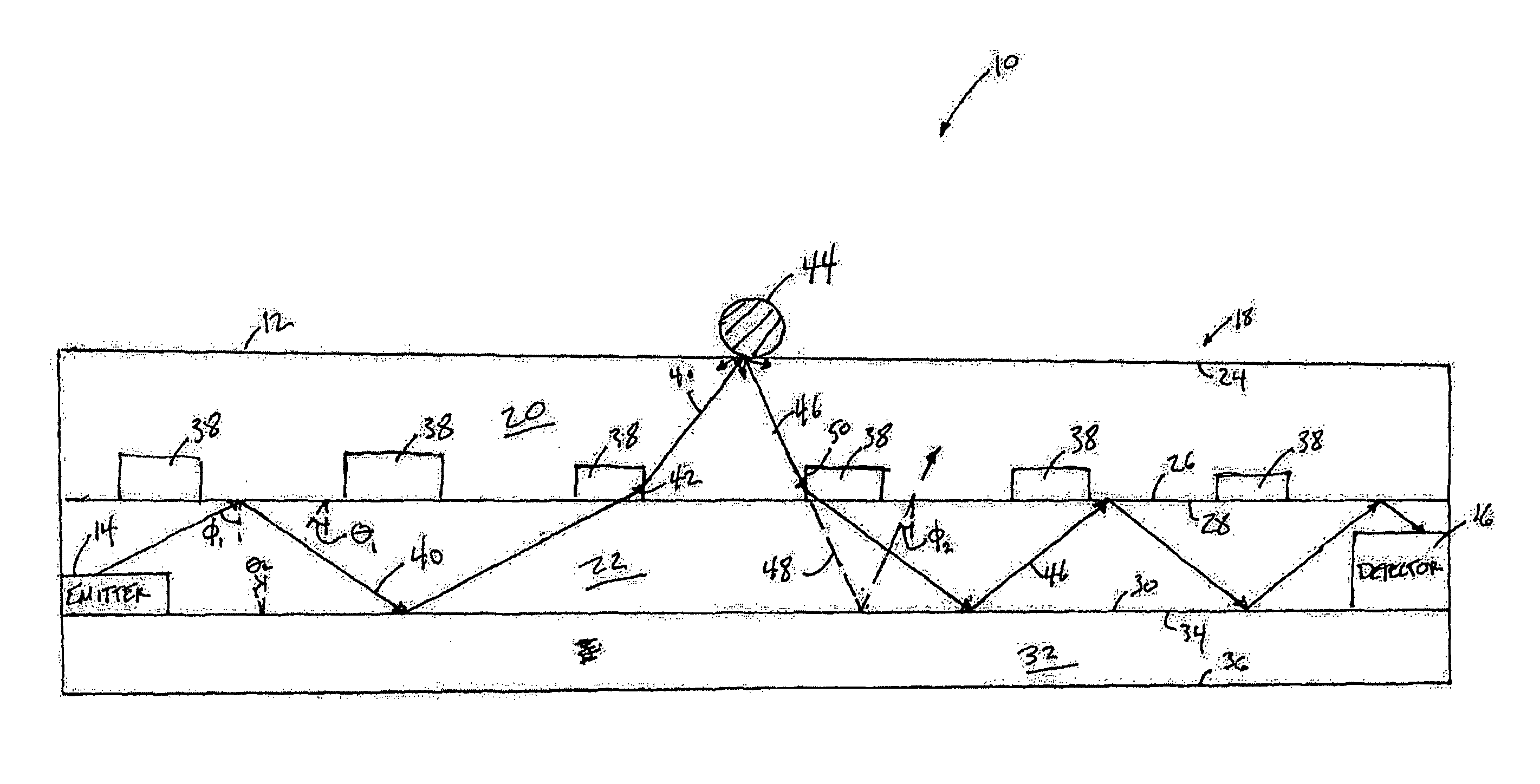
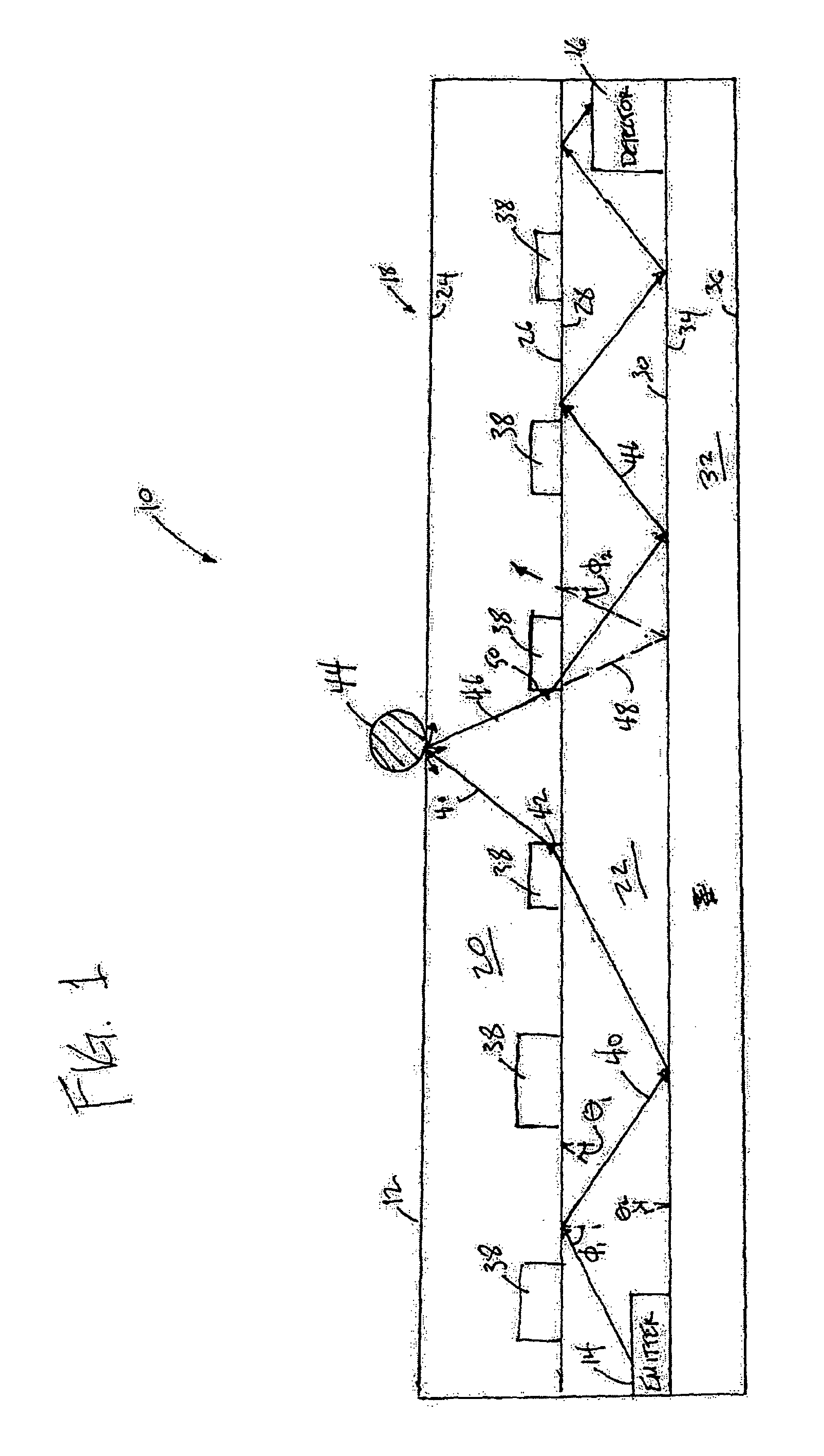
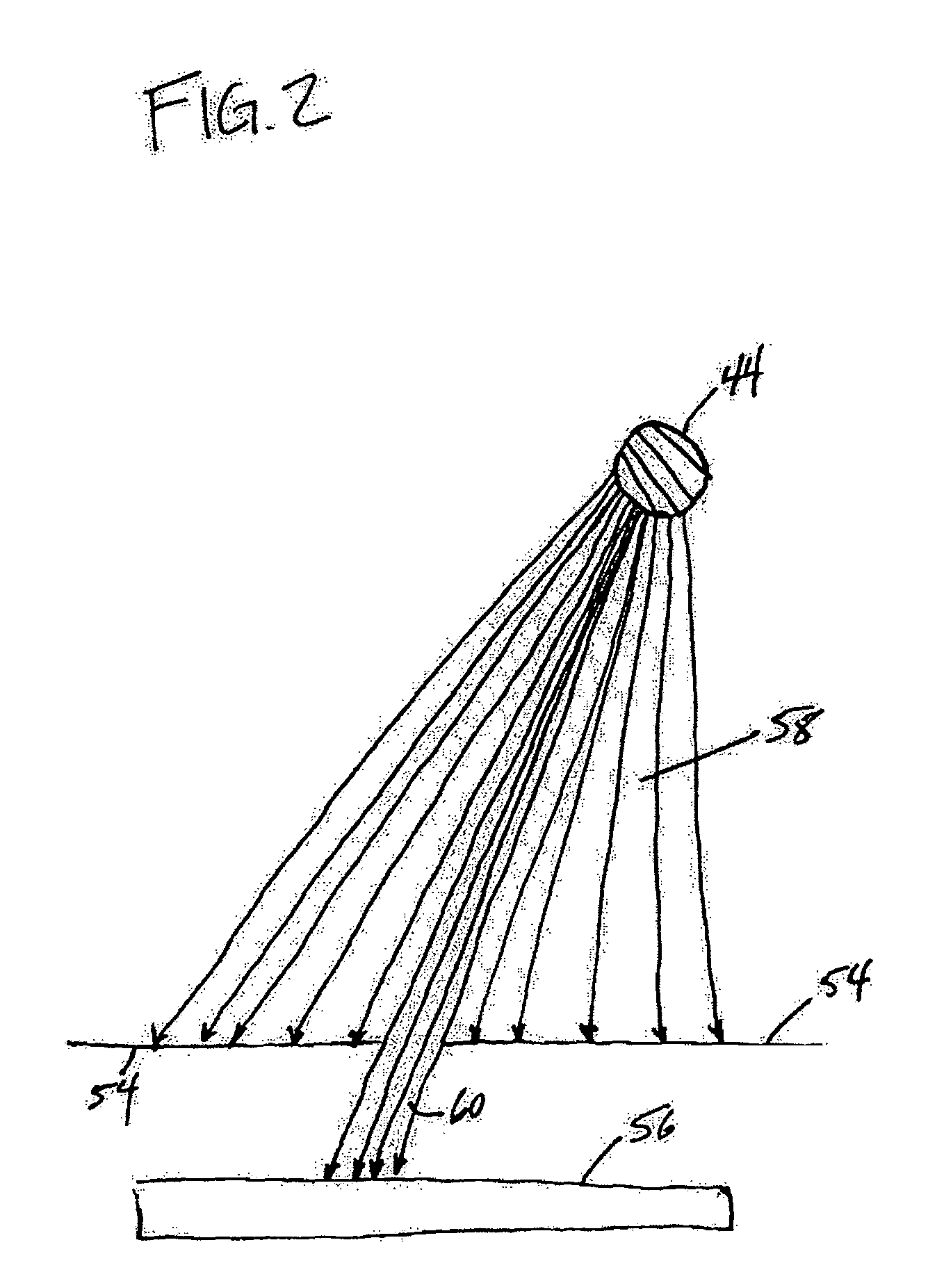
An optical touchpad that may be able to provide accurate, reliable information about the position of an object in three-dimensions. The optical touchpad may enable a determination as to whether the object is engaged with the touchpad or hovering just above the touchpad. When the object is in contact with the optical touchpad, the optical touchpad may enable a determination of the force applied by the object to the optical touchpad. The optical touchpad may enable a determination of an object type of the object. These and other determinations of information related to the object may enhance the control provided by the touchpad system to the user as an electronic interface. The operation of the optical touchpad may further enable an enhanced frame rate, reduced optical noise in the optical signal(s) guided to the one or more sensors, augment the ruggedness of the optical touchpad, an enhanced form factor (e.g., thinner), and / or provide other advantages.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Ultra-high multiplex analytical systems and methods
ActiveUS8247216B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsLiquid surface applicatorsDirect illuminationSequence determination
Apparatus, systems and methods for use in analyzing discrete reactions at ultra high multiplex with reduced optical noise, and increased system flexibility. Apparatus include substrates having integrated optical components that increase multiplex capability by one or more of increasing density of reaction regions, improving transmission of light to or collection of light from discrete reactions regions. Integrated optical components include reflective optical elements which re-direct illumination light and light emitted from the discrete regions to more efficiently collect emitted light. Particularly preferred applications include single molecule reaction analysis, such as polymerase mediated template dependent nucleic acid synthesis and sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Reducing light leakage and improving contrast ratio performance in FTIR display devices
InactiveUS20070047887A1Tolerant of errorReduce noiseOptical waveguide light guideThin layerRefractive index
An optical noise reduction mechanism for reducing undesired frustration of total internal reflected light. Such optical noise may stem from defects in waveguide construction. Such optical noise may also stem from the difference in refractive index between any cladding layers disposed onto the planar waveguide and the refractive index of the medium (e.g., air) between the light sources and the light insertion surface of the planar waveguide. By interposing a material of appropriate refractive index, either as a thin layer onto the light insertion surface of the waveguide or filling the space between the waveguide and the light source, the planar waveguide becomes more tolerant of geometry errors and cladding layer properties because a safe operating area is established between the unadjusted critical angle of the system and the actual range of ray angles allowed admittance into the waveguide.
Owner:RAMBUS DELAWARE
Wavelength and Intensity Stabilized Laser Diode and Application of Same to Pumping Solid-State Lasers
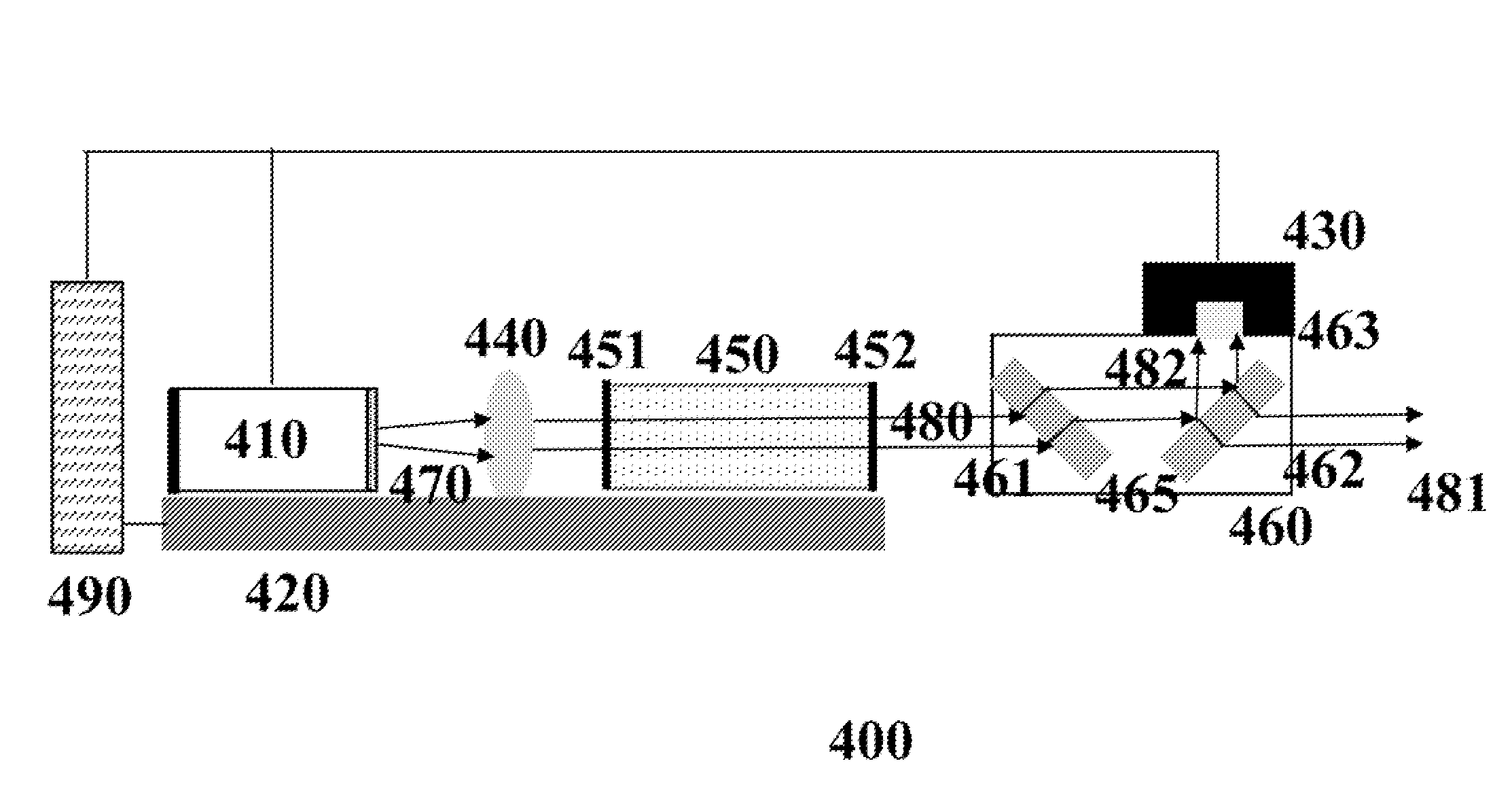
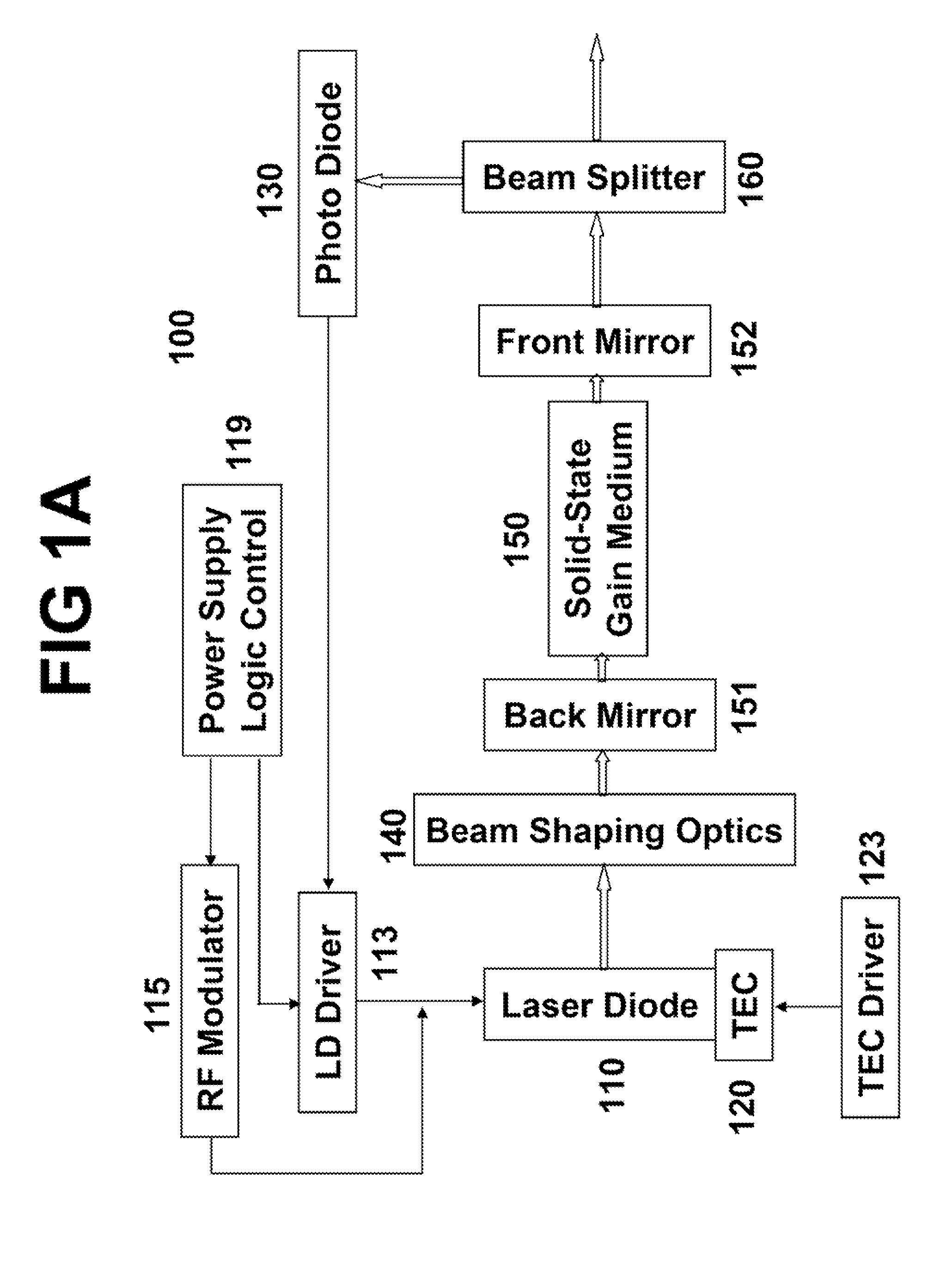
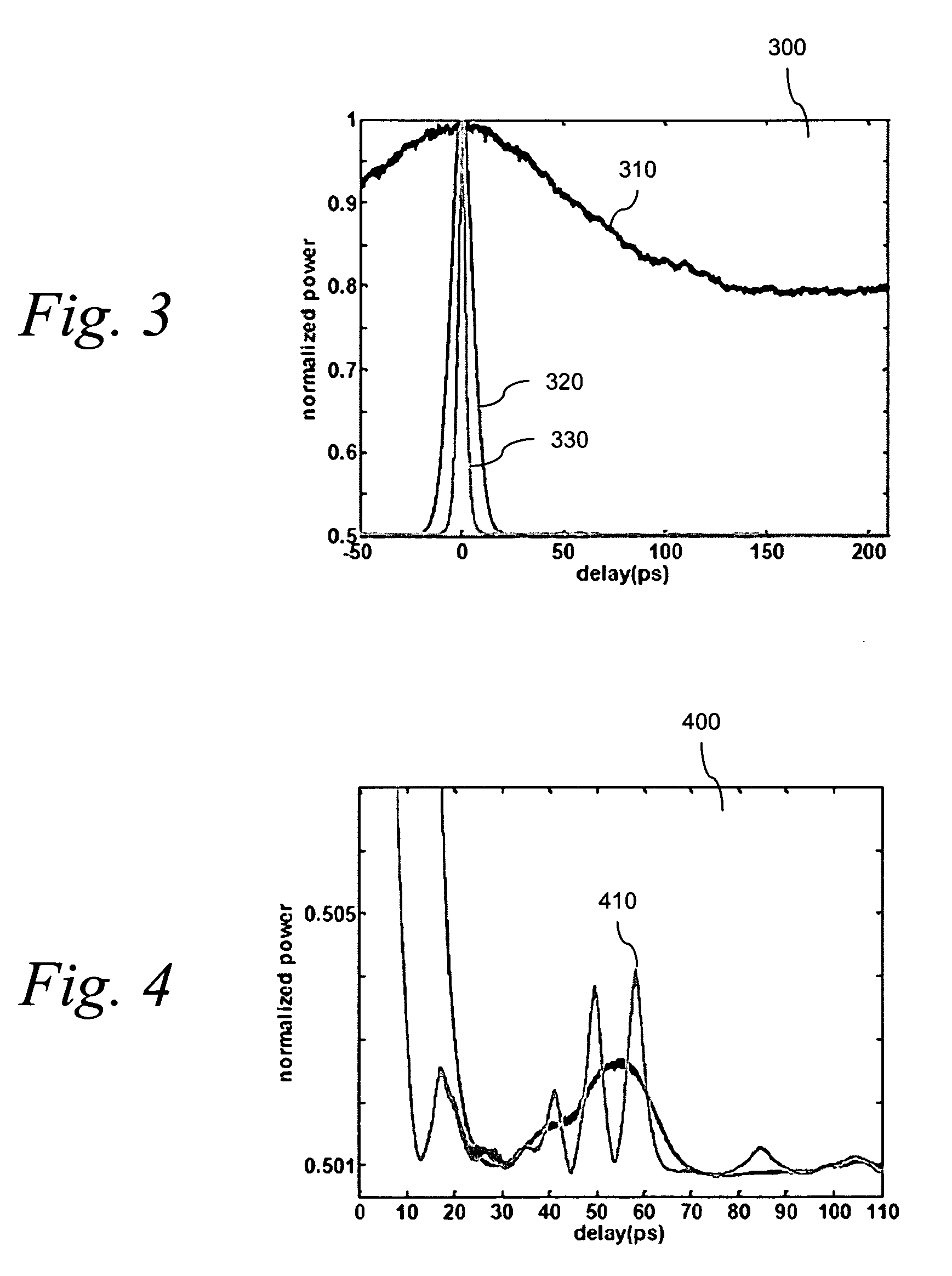
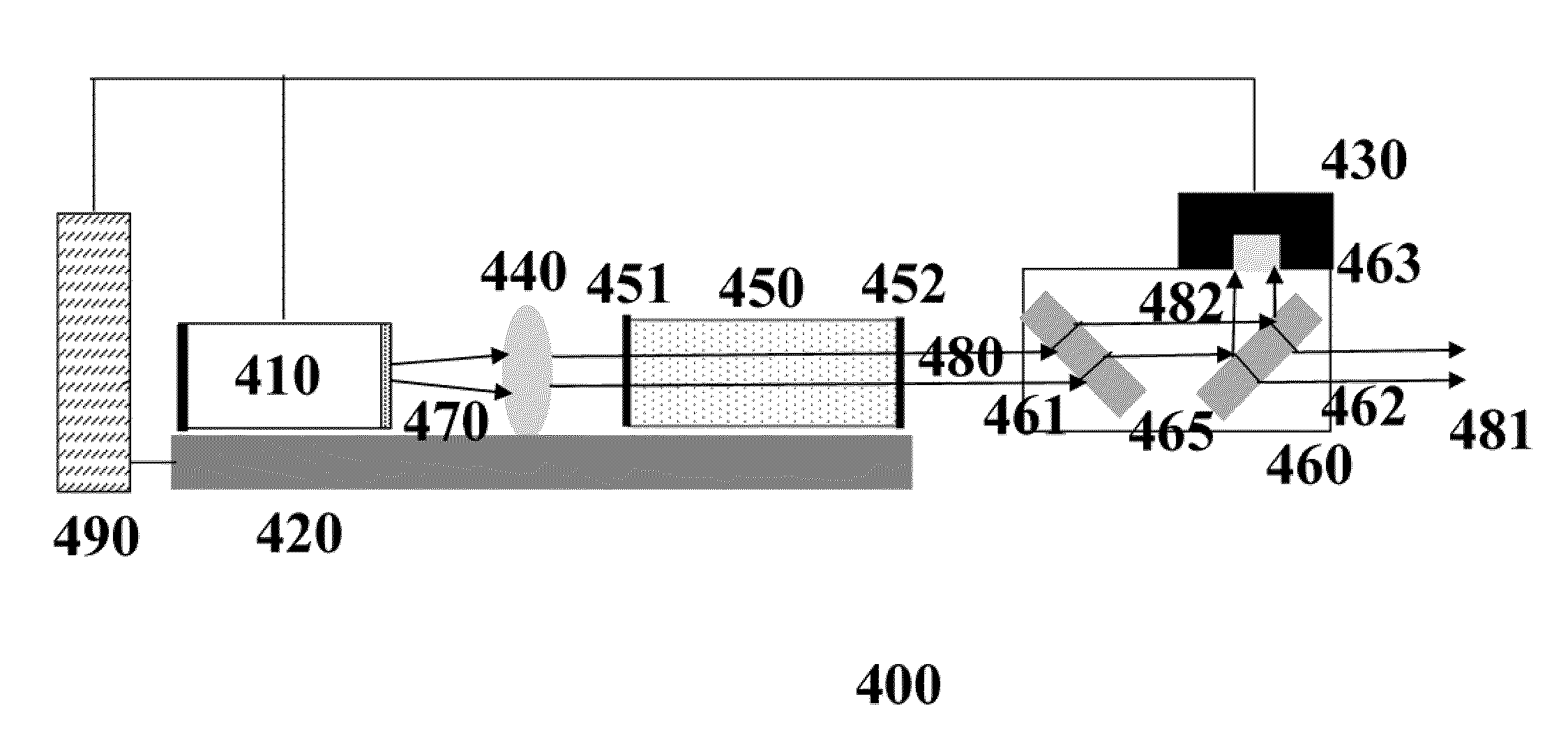
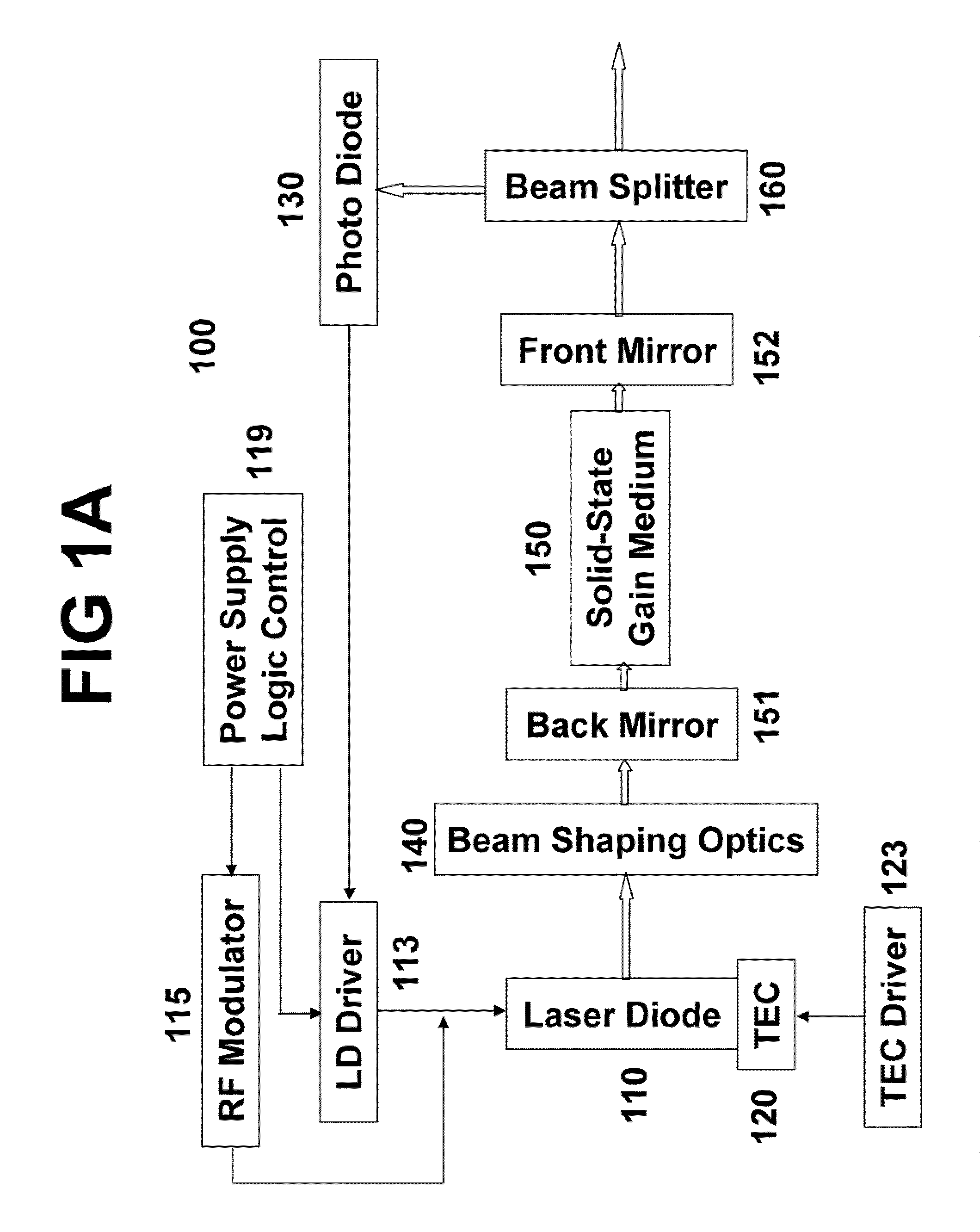
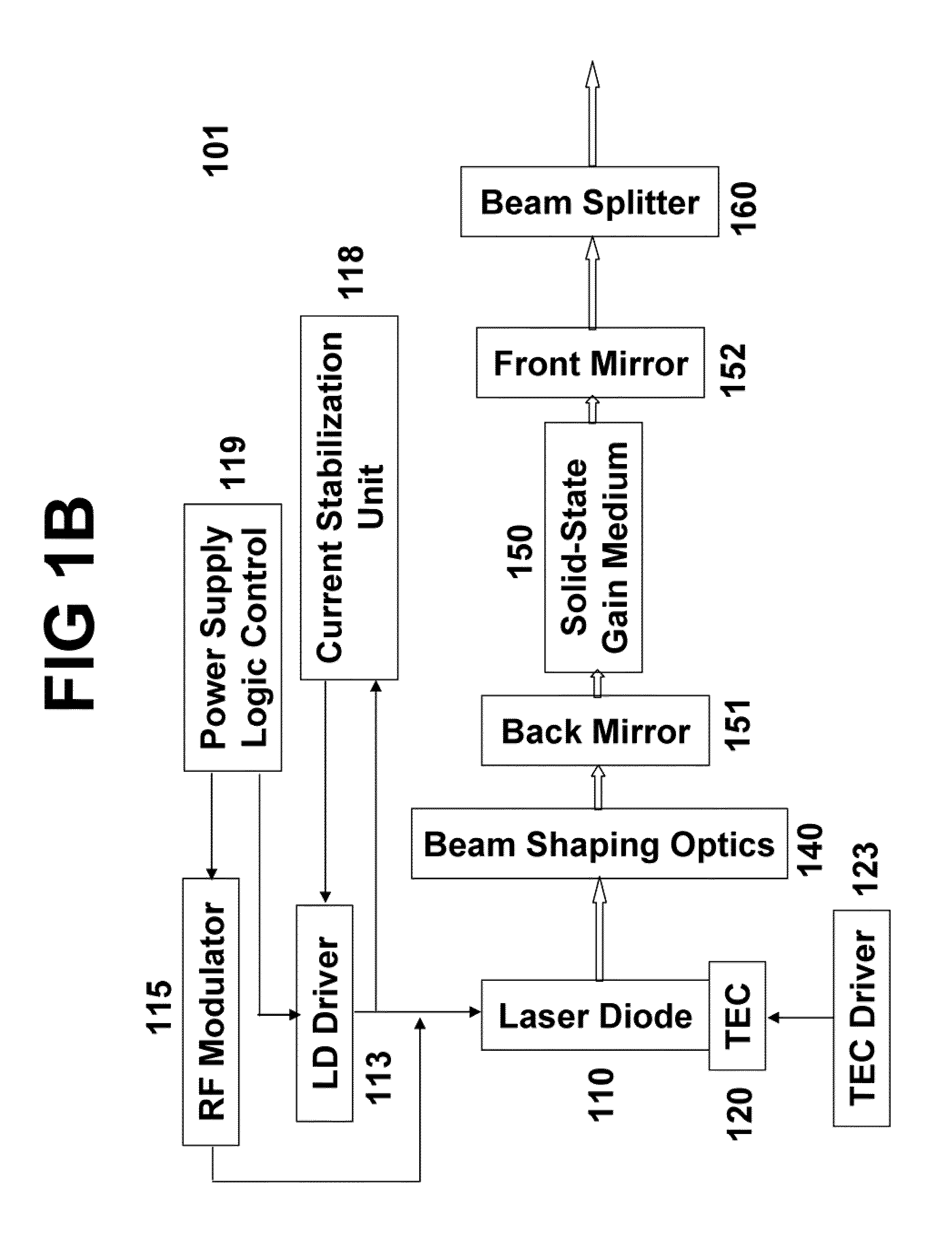
ActiveUS20090097507A1Avoid excessive perturbationLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionLow noisePeak value
An efficient and low-noise solid-state laser is optically pumped by one or more laser diode(s) driven by RF modulated current. The solid-state laser operation is stabilized by the pump source stable in both spectrum and intensity, in conjunction with automatic power control wherein the feedback loop accurately reflects the true drift in the output power. Moreover, the pump efficiency is optimized and the optical noise is minimized by adjusting the diode operation temperature such that the pump wavelength coincides with the absorption peak of the gain medium. By internally or externally modulating the amplitude of the drive current, the pump diode(s) operate in pulsed mode with controllable shape, width, repetition rate, and pulse-to-pulse intervals, which enables essentially constant optical energy produced from each pulse of the solid-state laser in high repetition rates with variable pulse-to-pulse intervals.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Systems and methods for distinguishing optical signals of different modulation frequencies in an optical signal detector
ActiveUS20120221252A1Limiting and avoiding crosstalkAccelerated programMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingSignal detectorExcitation signal
Systems and method for detecting optical signals, and for discriminating optical signals emitted by an emission moiety that is excited by an associated excitation signal from background signals and other optical noise, employing digital techniques for determining the portion of a detected optical signal having a modulation frequency corresponding to a modulation of the associated excitation signal.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
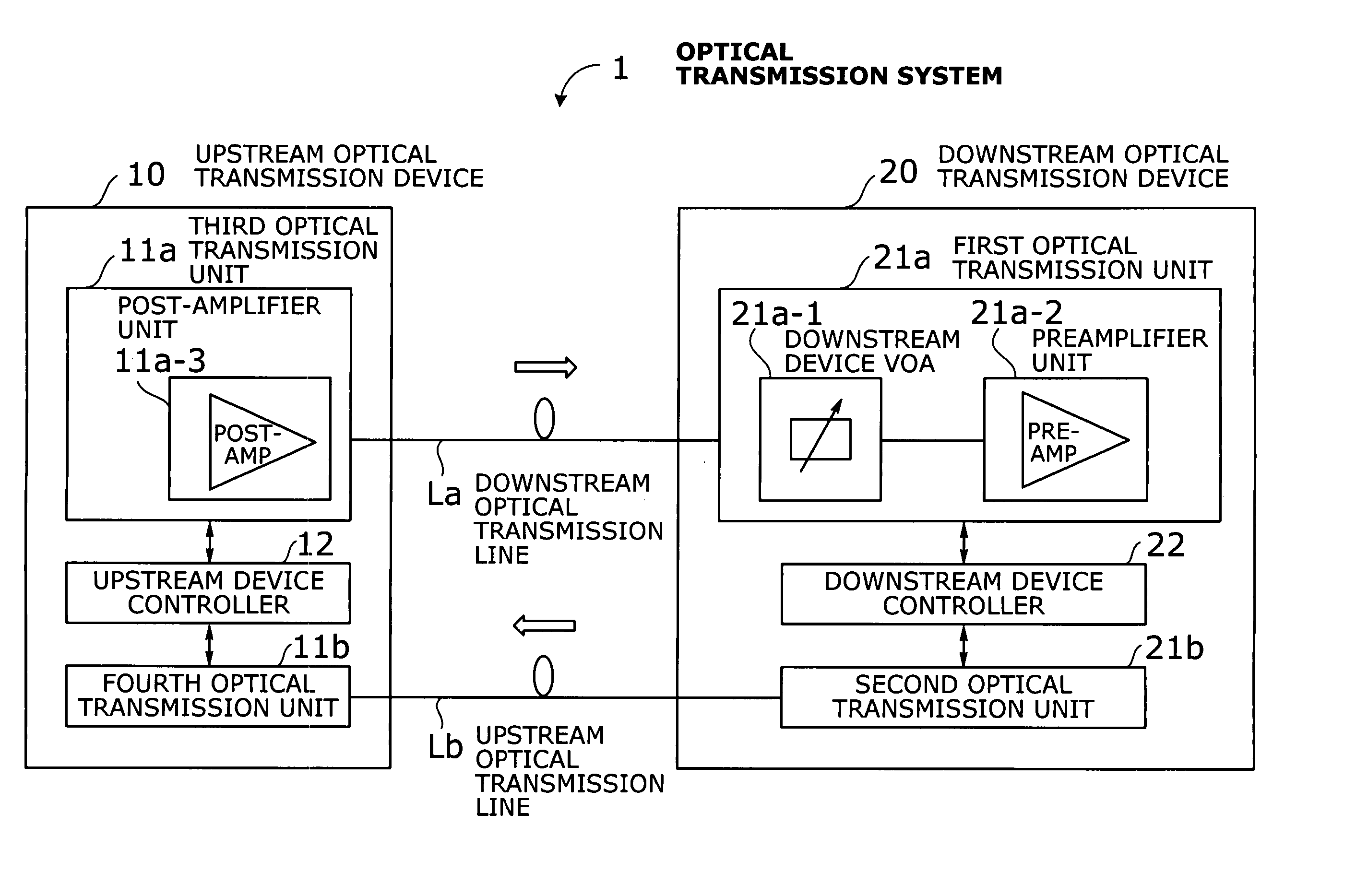
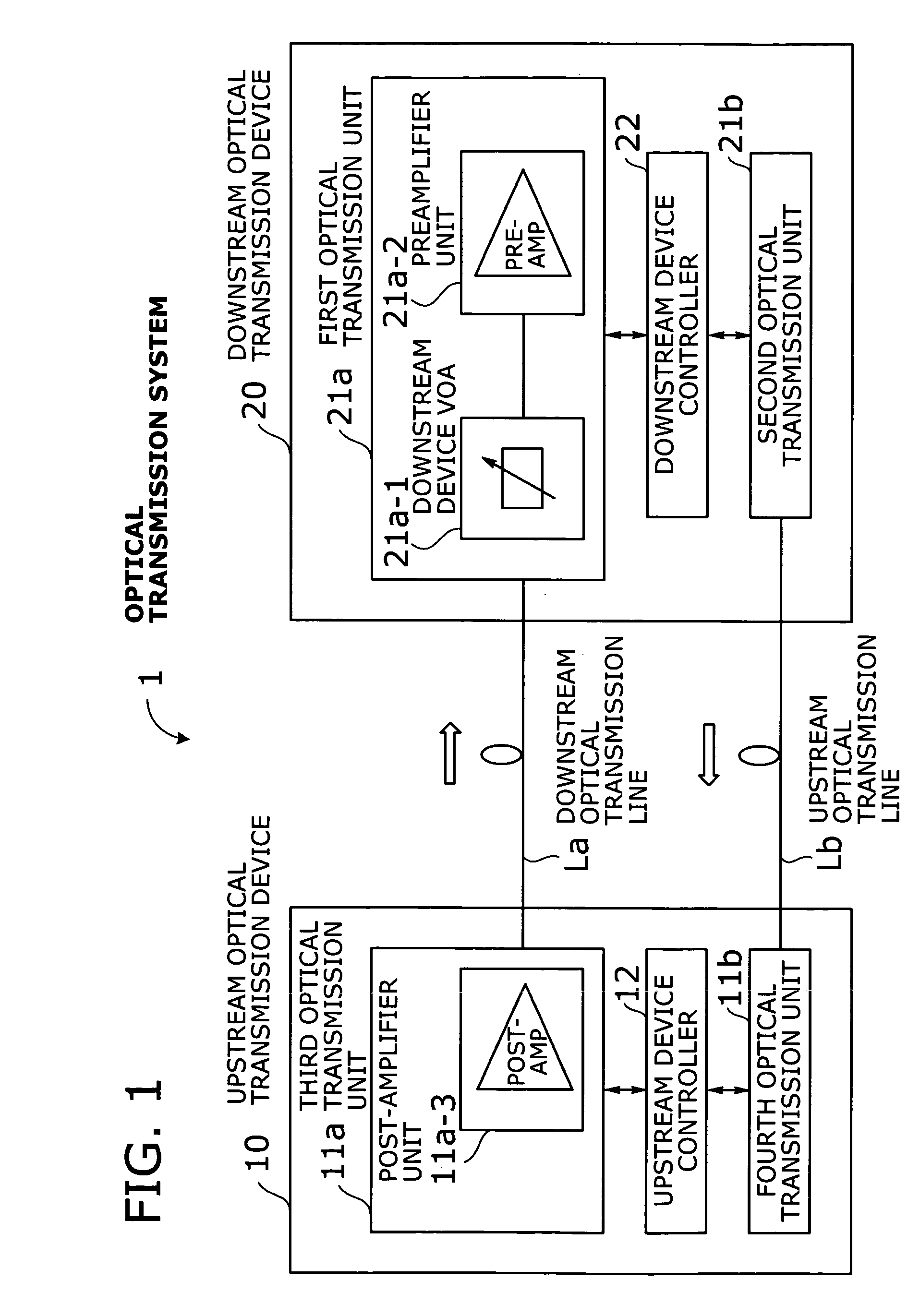
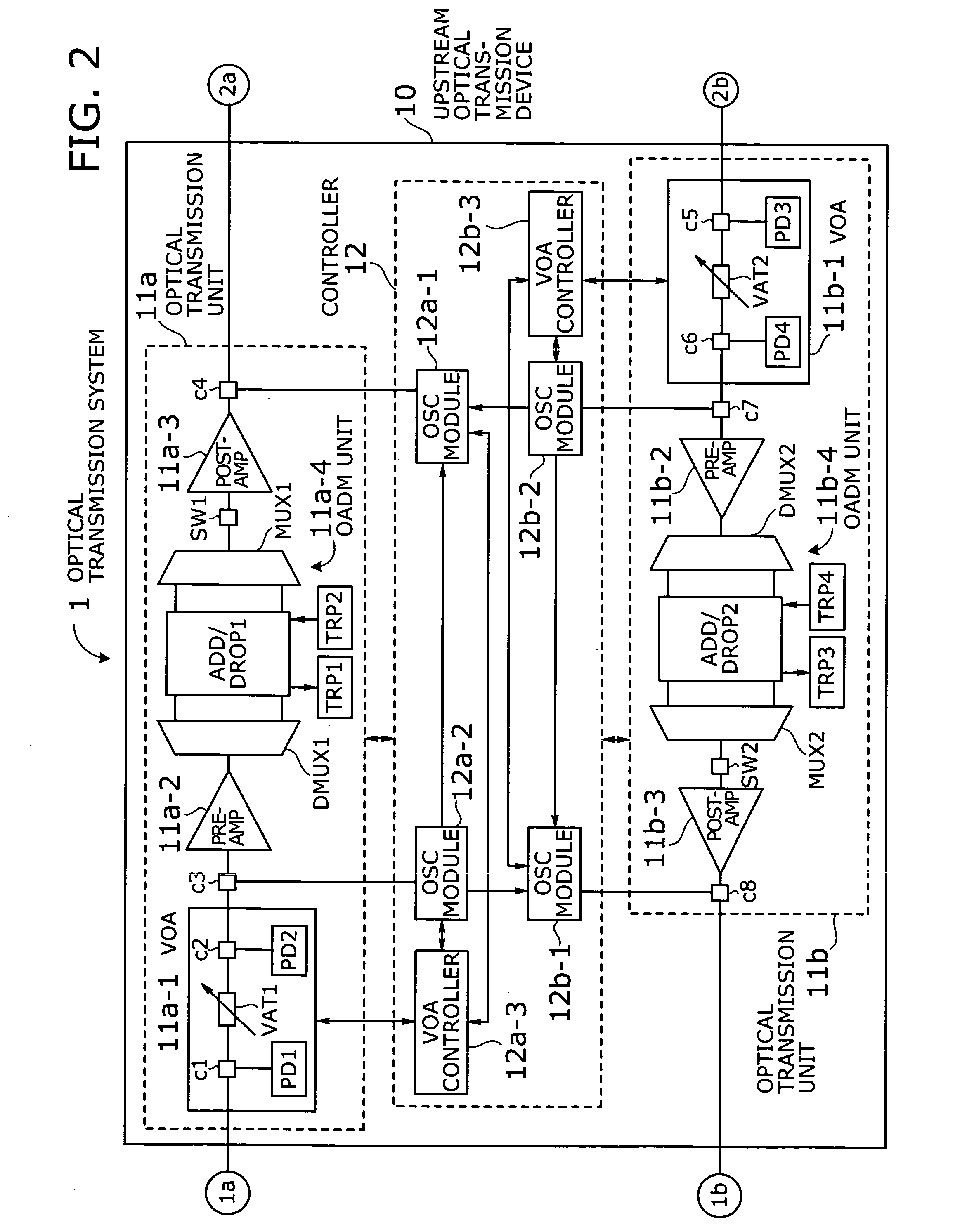
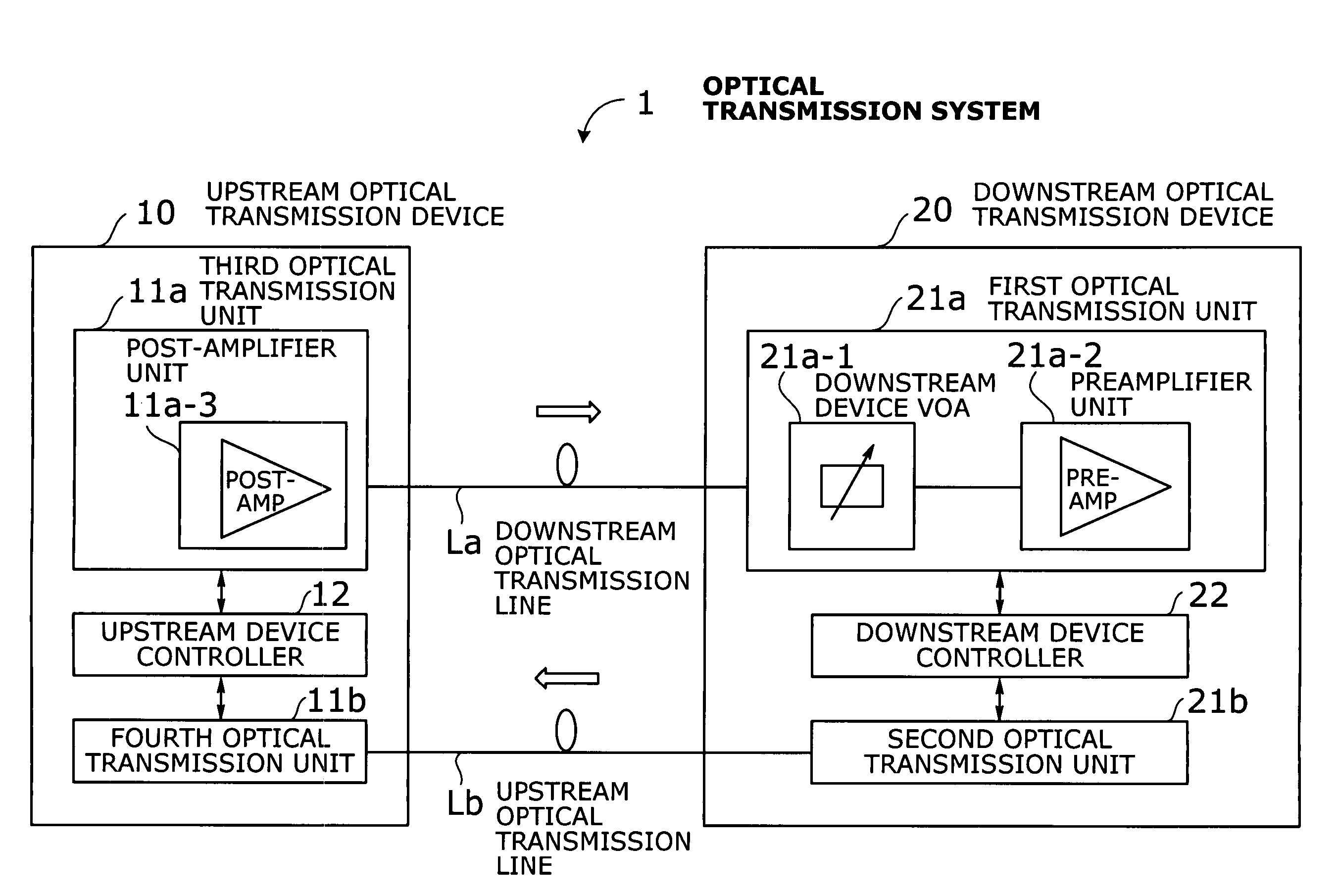
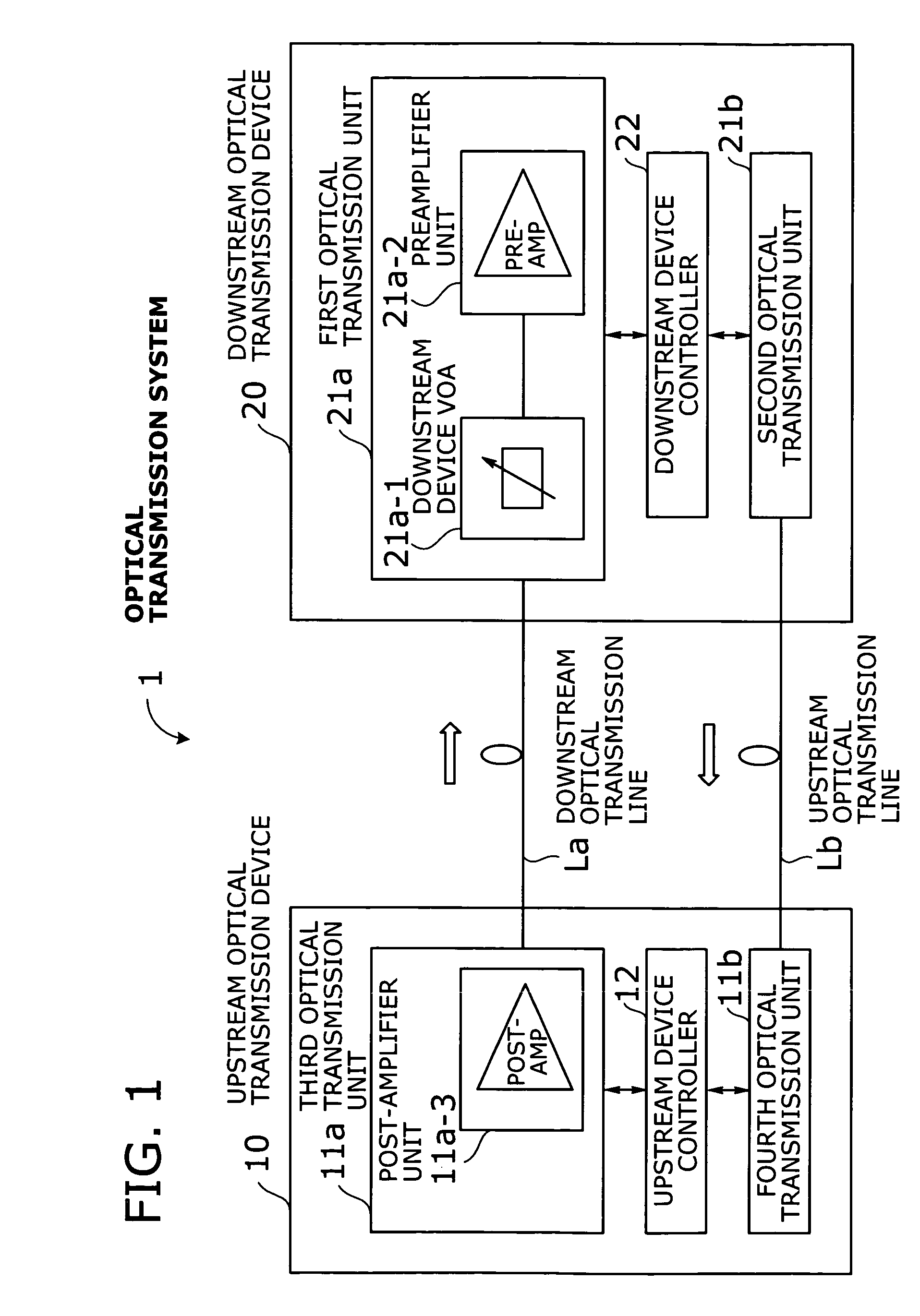
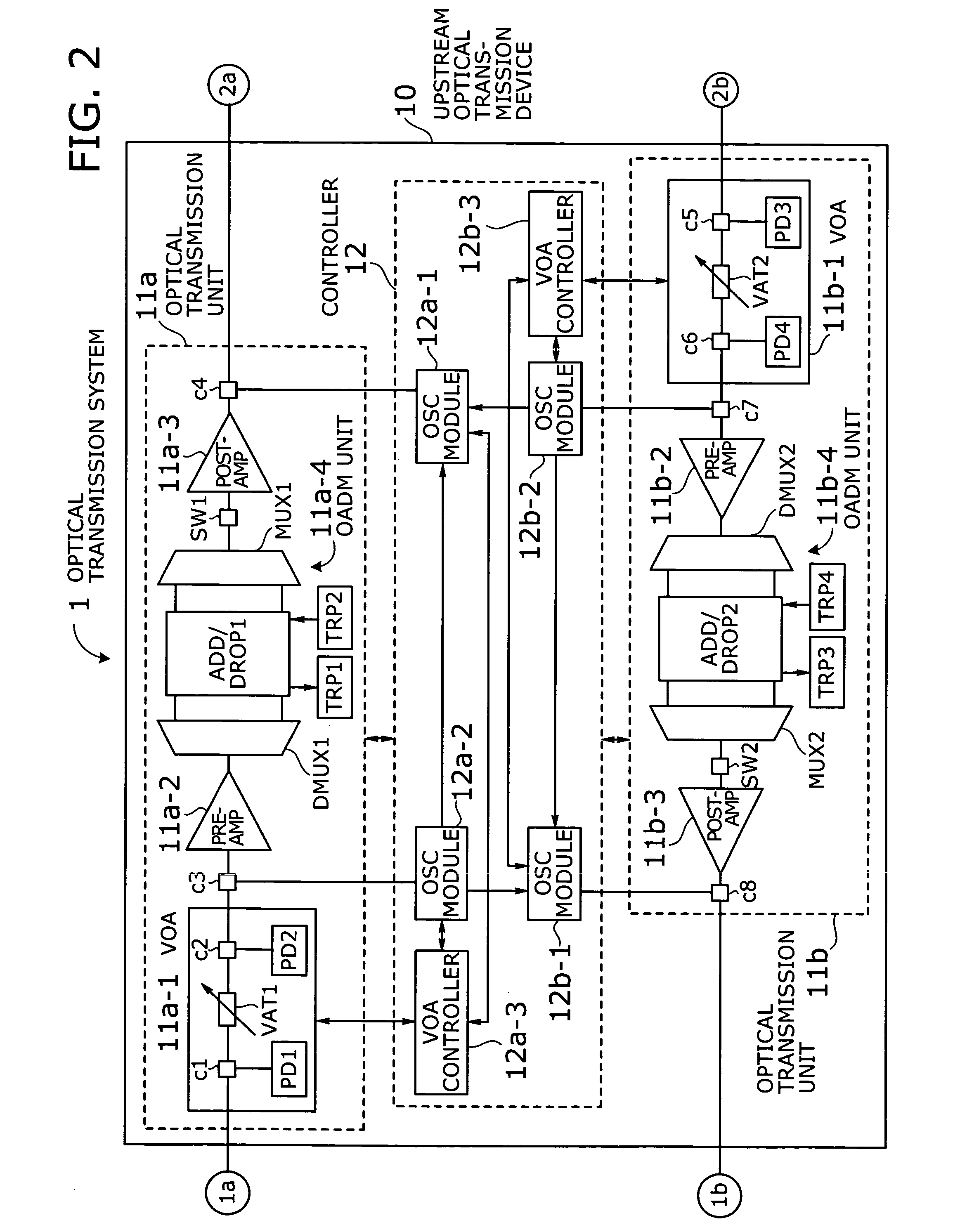
Optical transmission system with automatic signal level adjustment and startup functions
ActiveUS20050158057A1Easy maintenanceEasy to operateWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsEngineeringOperation mode
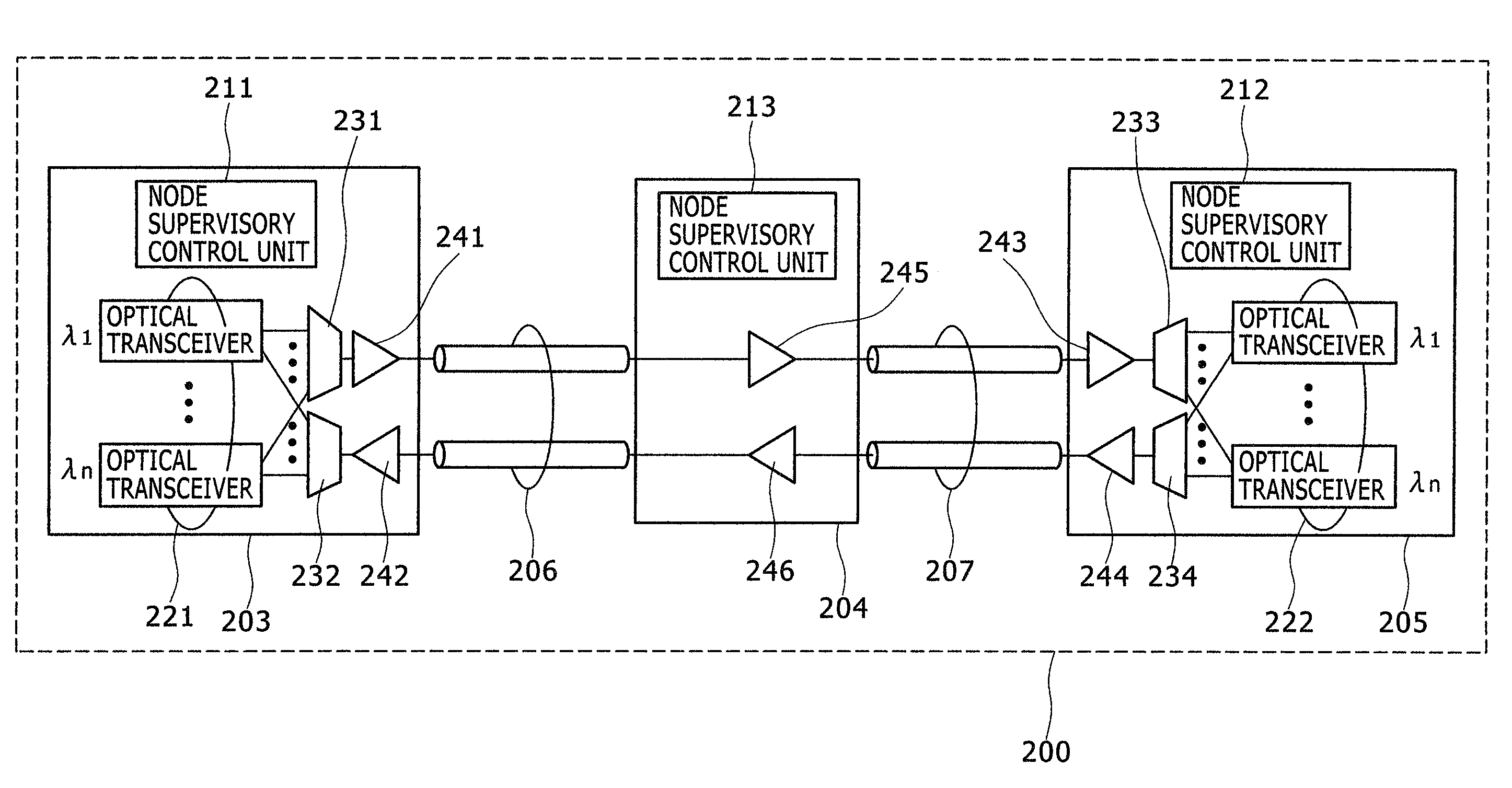
An optical transmission system with automatic startup functions to optimize the power level of optical signals entering each optical amplifier and operate those amplifiers in appropriate mode. In the process of starting up an optical transmission system, upstream and downstream optical transmission devices set up themselves under the coordination of their internal controllers. The downstream device controller adjusts its local variable optical attenuator by utilizing optical noise emission from a post-amplifier in the upstream optical transmission device, and it selects and sets a preamplifier unit to work in appropriate operating mode. The upstream device controller, on the other hand, selects and sets operating mode of its local post-amplifier unit. During this process, the upstream and downstream device controllers exchange messages over supervisory control channels to achieve the purpose.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical touchpad with three-dimensional position determination
InactiveUS8094136B2Easy to controlReduce Optical NoiseTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInformation opticsOphthalmology
An optical touchpad that may be able to provide accurate, reliable information about the position of an object in three-dimensions. The optical touchpad may enable a determination as to whether the object is engaged with the touchpad or hovering just above the touchpad. When the object is in contact with the optical touchpad, the optical touchpad may enable a determination of the force applied by the object to the optical touchpad. The optical touchpad may enable a determination of an object type of the object. These and other determinations of information related to the object may enhance the control provided by the touchpad system to the user as an electronic interface. The operation of the optical touchpad may further enable an enhanced frame rate, reduced optical noise in the optical signal(s) guided to the one or more sensors, augment the ruggedness of the optical touchpad, an enhanced form factor (e.g., thinner), and / or provide other advantages.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
In-band OSNR measurement on polarization-multiplexed signals
ActiveUS20150110486A1Low costReducing thermal dissipationPolarisation multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringPolarization multiplexedSymbol rate
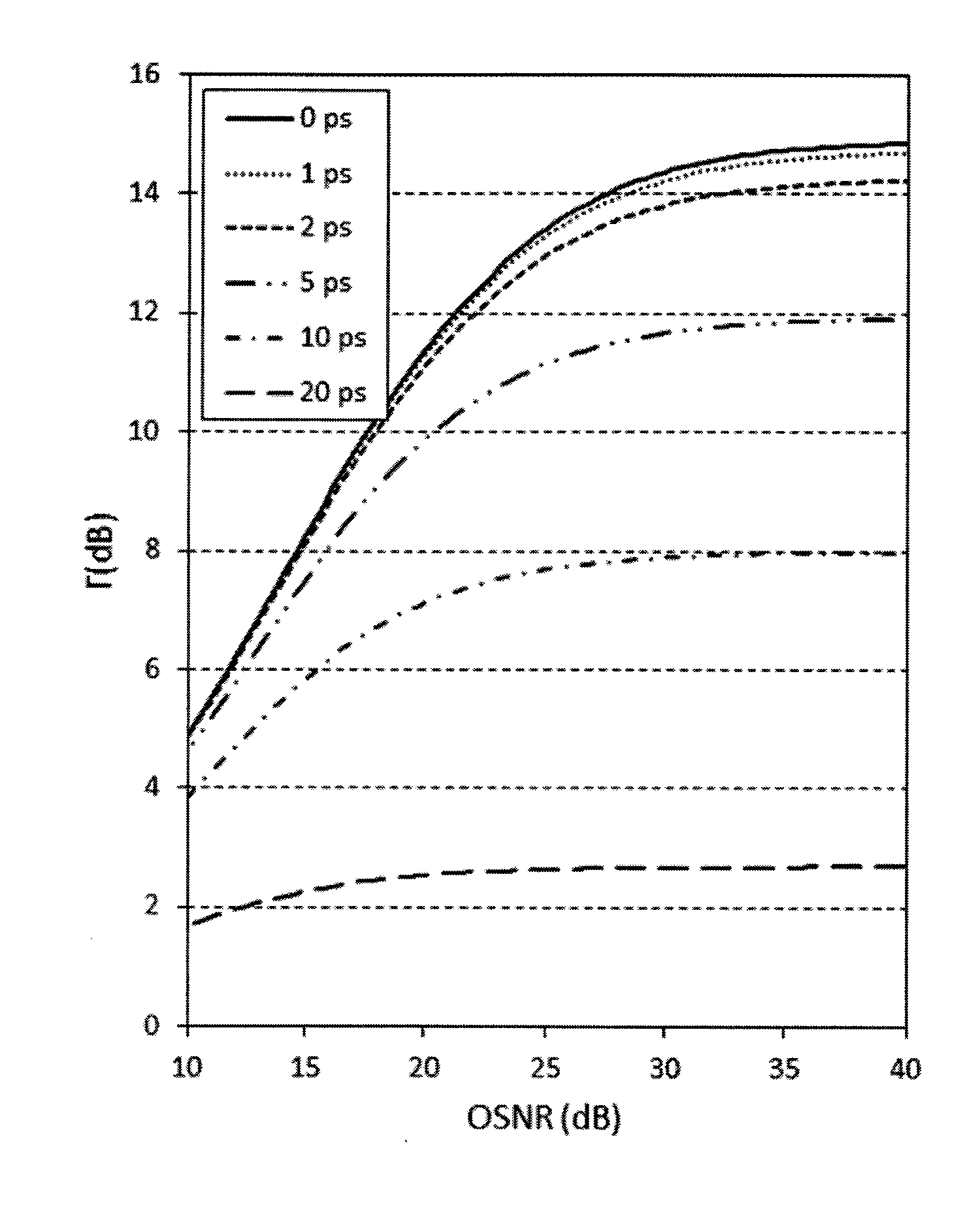
There is provided a system and a method for determining an in-band noise parameter representative of the optical noise contribution (such as OSNR) on a polarization-multiplexed optical Signal-Under-Test (SUT) comprising two polarized phase-modulated data-carrying contributions and an optical noise contribution. For each of a multiplicity of distinct polarization-analyzer conditions, the SUT is analyzed to provide at least one polarization-analyzed component of the SUT and the polarization-analyzed component is detected with an electronic bandwidth at least ten times smaller than the symbol rate of the SUT to obtain a corresponding acquired electrical signal; for each acquired electrical signal, a value of a statistical parameter is determined from the ac component of the acquired electrical signal, thereby providing a set of statistical-parameter values corresponding to the multiplicity of distinct polarization-analyzer conditions; and, from the set of statistical-parameter values, the in-band noise parameter is mathematically determined.
Owner:EXFO
Optical Signal Transmission Apparatus
InactiveUS20090238563A1Ring-type electromagnetic networksBus-type electromagnetic networksSignal qualityEngineering
There is provided an optical signal transmission apparatus having a stable dispersion compensation function without unnecessarily controlling a compensation value even when a main signal quality is deteriorated due to a factor other than dispersion or in the case of a transmission failure. When it is determined that a signal quality is deteriorated due to dispersion of a fiber by determining a control mode of a variable dispersion compensator by means of optical noise information and received power information in addition to bit error information of a received signal, a compensation value of the variable dispersion compensator is varied and a compensation value other than the dispersion of the optical fiber is held to an existing set value.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
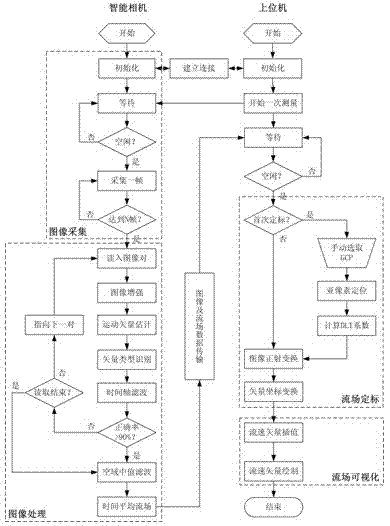
Non-contact river surface flow field imaging measuring method
ActiveCN102866260AIncrease Brightness ContrastImprove accuracyFluid speed measurementMotion vectorFlow tracer
The invention discloses a non-contact river surface flow field imaging measuring method and belongs to the technical field of open channel flow measurement. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, mounting a near-infrared light filter in front of an image sensor to realize near-infrared imaging, and enhancing the brightness contrast between a flow tracer and the water surface background; secondly, carrying out airspace high-pass filtering on an image, and restraining optical noises of the water surface; thirdly, carrying out motion vector estimation by a fast Fourier cross-correlation algorithm to obtain displacement vectors of each analyzed area; fourthly, reestablishing a time average flow field by a method based on space-time federal filtering; and fifthly, carrying out normal incidence correction on flow rate vectors by a direct linear transformation method to realize the calibration and the visualization of the flow field. The non-contact river surface flow field imaging measuring method can be stably and reliably applied to river surface flow field measuring under complex water surface optical environments.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Under-screen fingerprint module, electronic device and fingerprint image processing method
PendingCN109284742AReduce distractionsImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionPolarizerComputer science
The embodiment of the application discloses an under-screen fingerprint module, an electronic device and a fingerprint image processing method. The electronic device comprises a screen and an under-screen fingerprint module arranged in a preset area relative to the screen. The screen is provided with a first polarizer, the fingerprint module under the screen is provided with a second polarizer, and the polarizing directions of the first polarizer and the second polarizer are identical; the first polarizer and the second polarizer are used for filtering the first optical noise, the first optical noise is reflected light, the reflected light is light reflected by the first light through the screen, and the first light is light irradiated in the Z-axis of the screen; the second polarizer is used for filtering the second optical noise, the second optical noise is a direct light ray, and the direct light ray is a second light ray emitted from the emitted light ray, which is reversely irradiated along the Z-axis of the screen. Embodiments of the present application are advantageous in reducing optical noise of fingerprints and improving accuracy and efficiency of fingerprint acquisitionby electronic devices.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Optical error simulation system
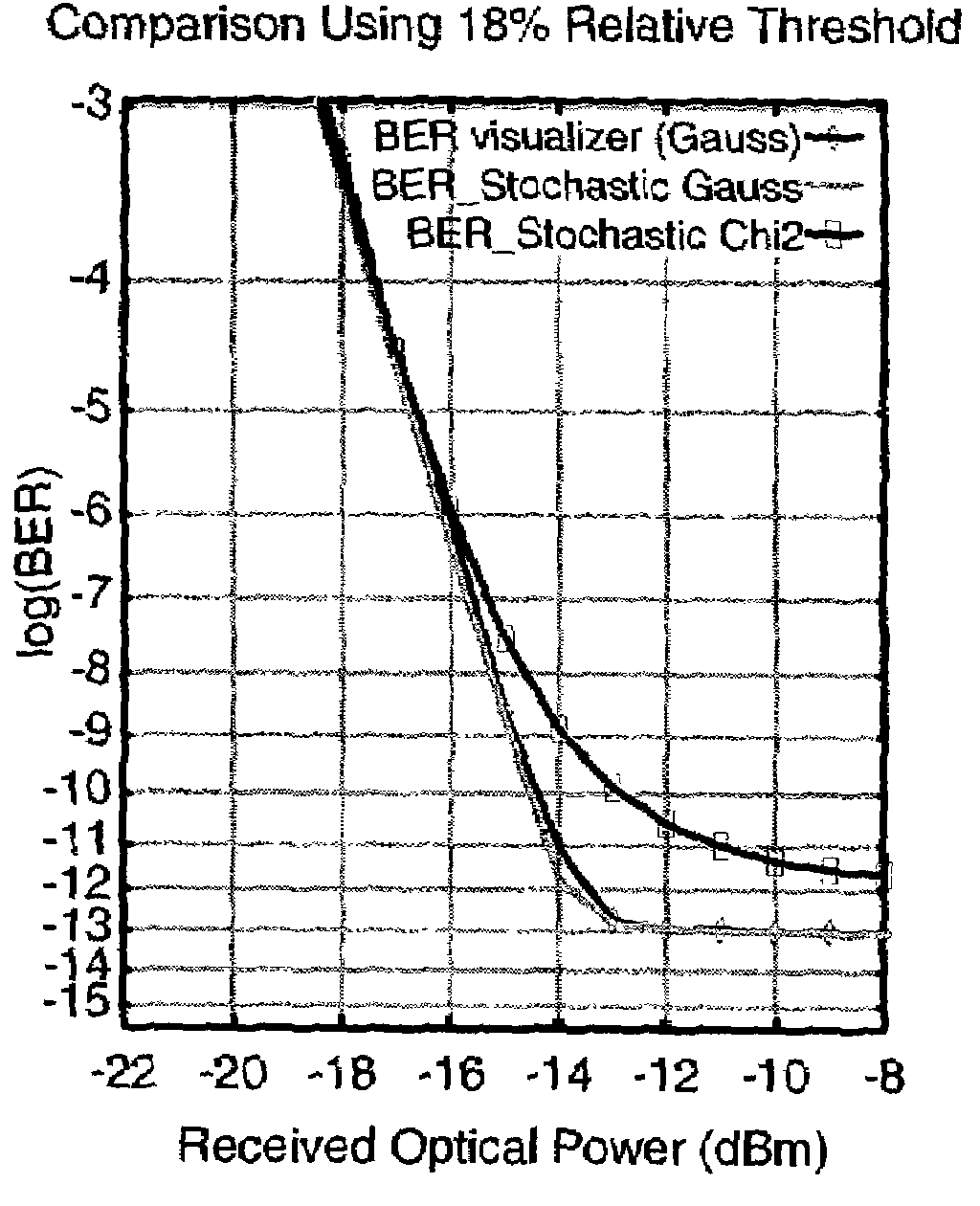
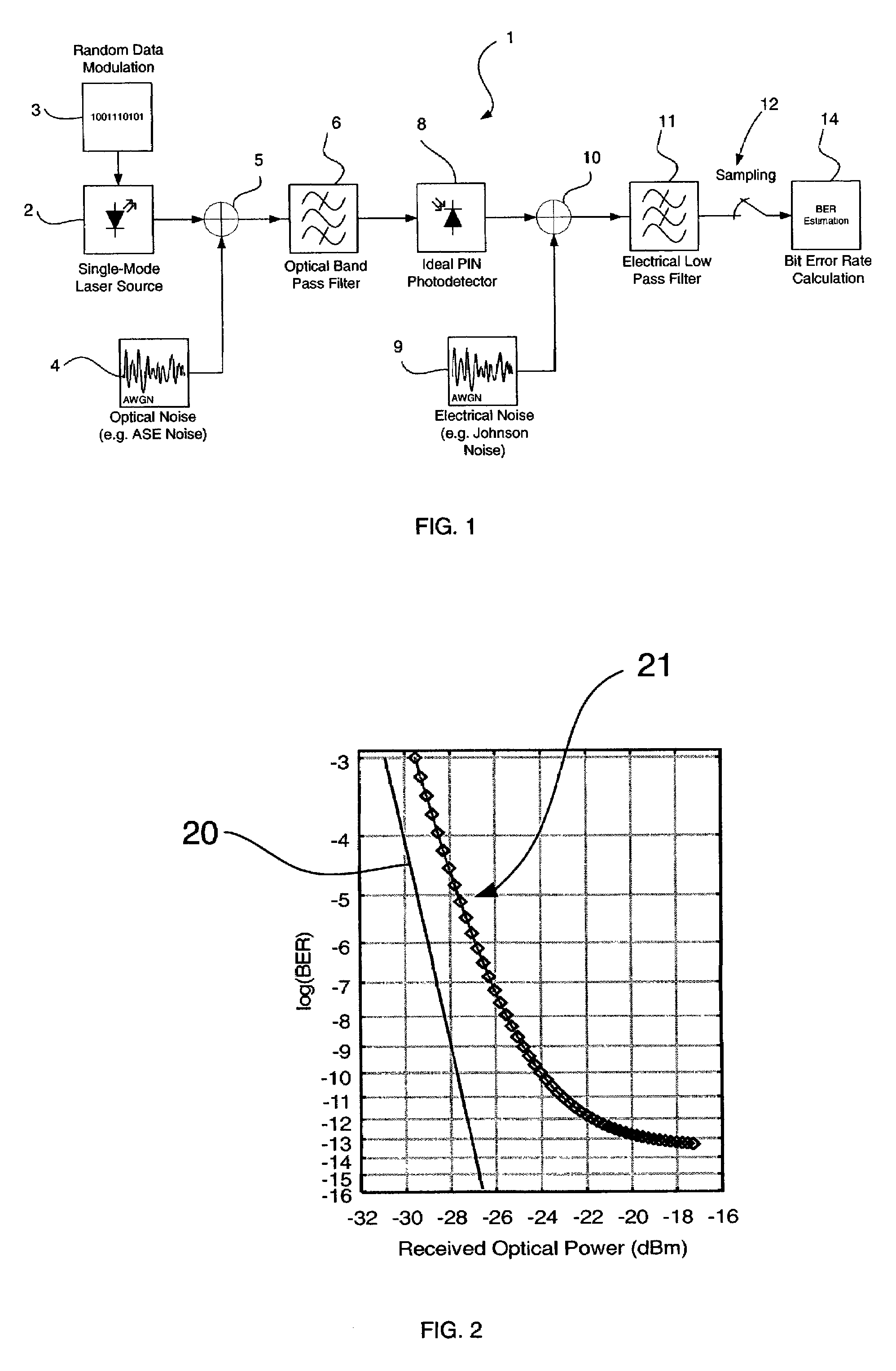
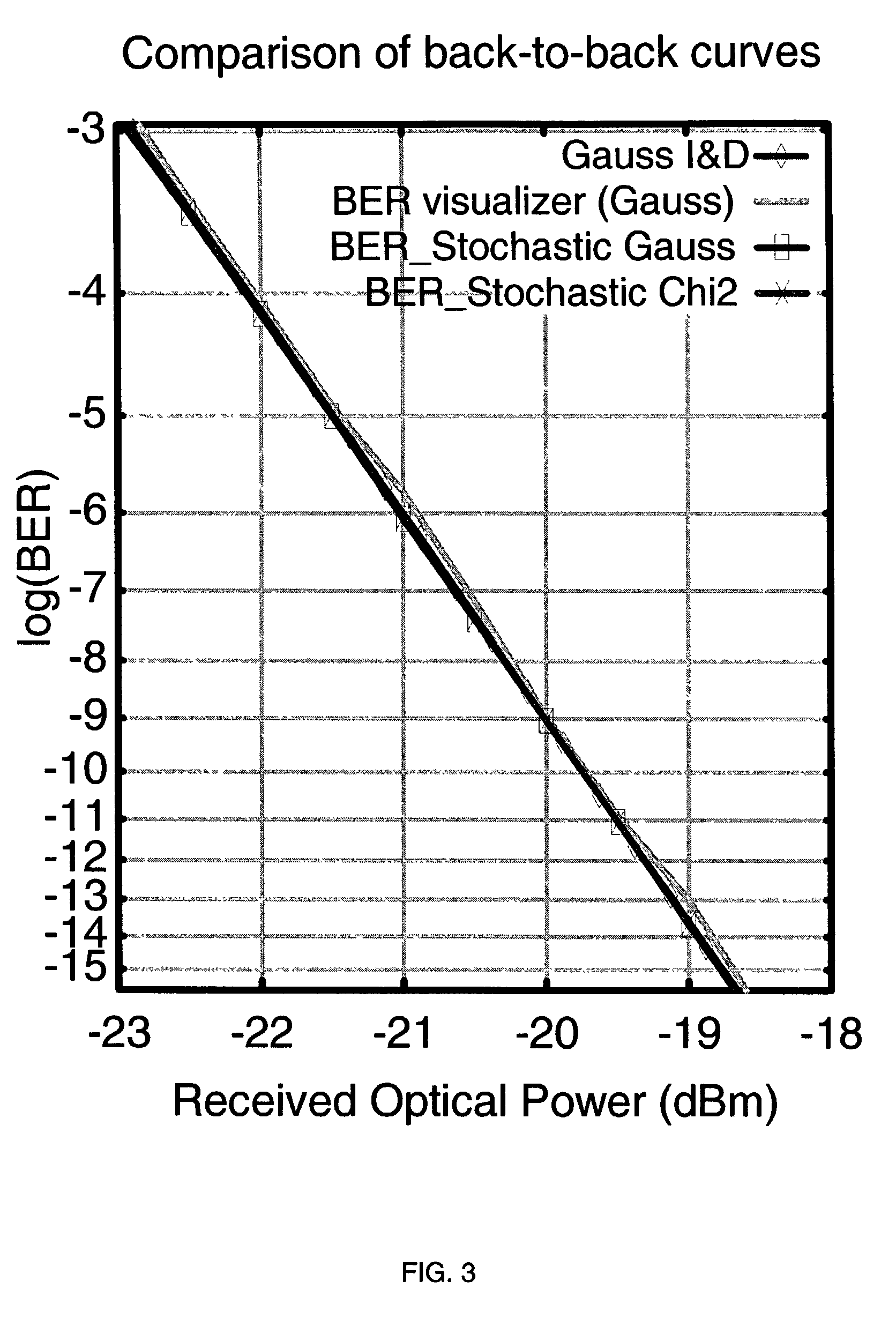
ActiveUS7233962B2Accurate estimateShorten the construction periodTransmission monitoringPicture interpretationCommunications systemOptical communication
There is disclosed a method and computer program product for estimating a measure of the quality of the received signal in a computer simulation of an optical transmission system, wherein the simulation includes additive optical noise generated by components within the transmission system. The method and product are able to account for non-Gaussian statistics of noise fluctuations observed in the receivers of optical communications systems, in order to provide for the more accurate simulation of system performance than may be the case using prior art methods based on Gaussian approximation.
Owner:ASTORIA CONSULTANCY LTD
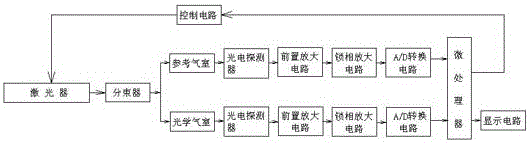
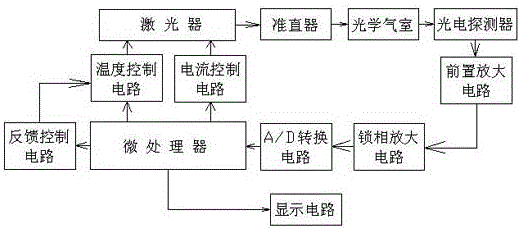
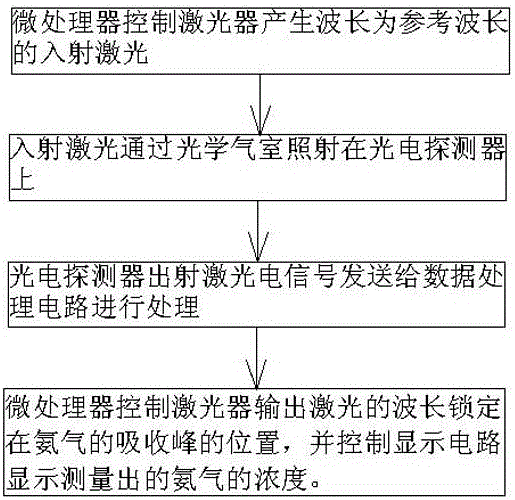
TDLAS based escaped ammonia concentration detection device and method
ActiveCN105806806AQuick lockReduce development costsColor/spectral properties measurementsFeedback controlMicroprocessor
The invention discloses a TDLAS based escaped ammonia concentration detection device and method. The device comprises a microprocessor, a current control circuit, a temperature control circuit, a feedback control circuit, a laser, a collimator, an optical gas chamber, a photoelectric detector, a data processing circuit and a display circuit, wherein the output ends of the current control circuit and the temperature control circuit are connected with the input end of the laser, the output end of the photoelectric detector is connected with the output end of a pre-amplification circuit, and the output end of the microprocessor is connected with the input ends of the current control circuit, the temperature control circuit and the feedback control circuit. According to the invention, the absorption peak position of ammonia gas can be locked accurately and quickly without a reference gas chamber, so that the development cost of an escaped ammonia monitoring device is saved, optical noise generated when light rays pass through an optical fiber splitter can be avoided, the signal to noise ratio of a system is improved, and the accuracy of an escaped ammonia concentration detection result can be improved greatly.
Owner:HENAN RELATIONS
Interferometric method and apparatus for measuring optical signal quality in optical communications system
Differences in the interferometric patterns of modulated telecommunication signals and broadband optical noise sources are identified and are exploited in measuring the optical signal-to-noise measurements in reconfigurable photonic networks. A light output power from said interferometer corresponding to a specified delay setting in the interferometer is measured, and a coherent optical signal is distinguished from the incoherent optical noise based on the light output power measurement.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Wavelength and intensity stabilized laser diode and application of same to pumping solid-state lasers
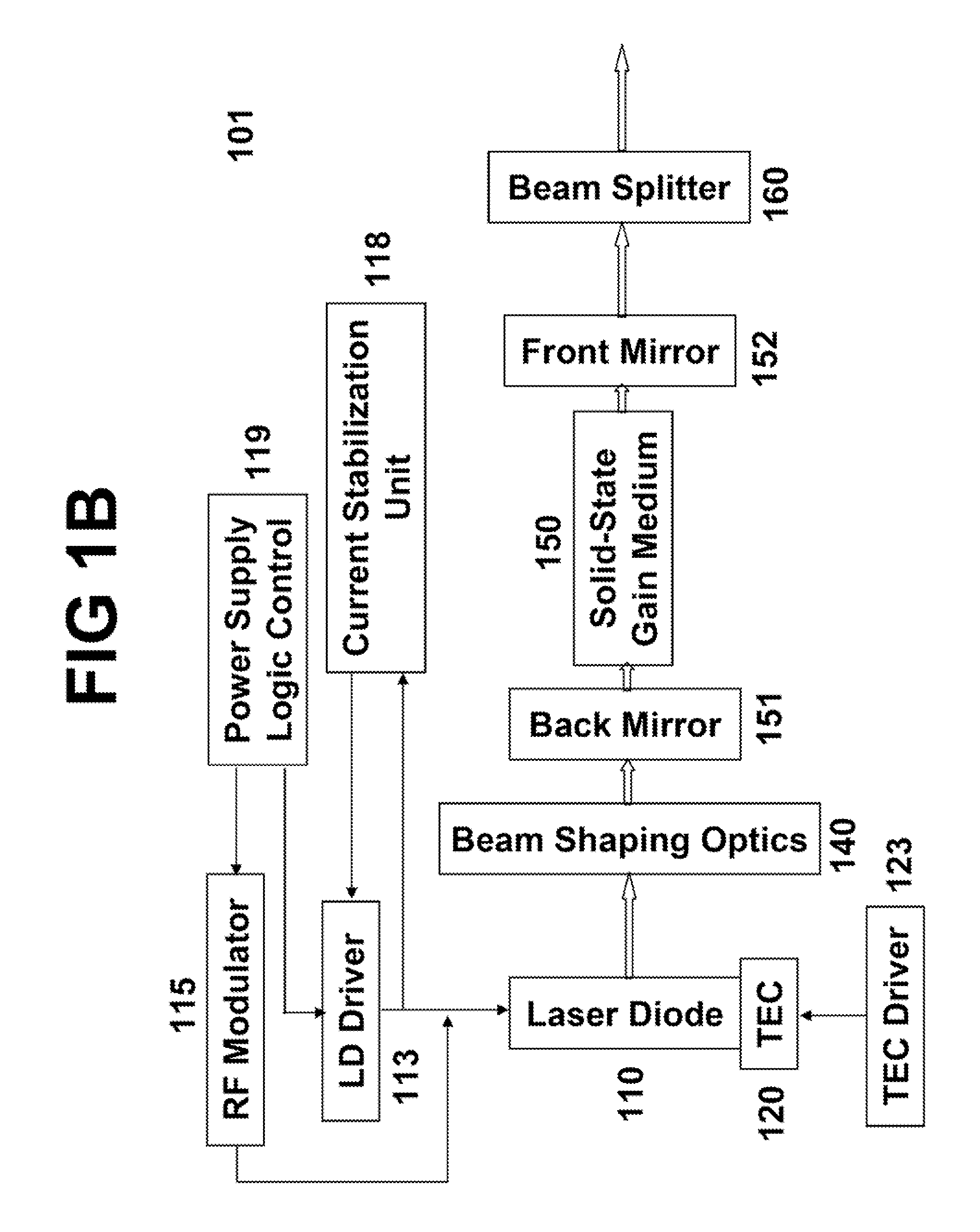
ActiveUS7606273B2Easy to controlImprove modulationLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor lasersLow noiseFrequency spectrum
An efficient and low-noise solid-state laser is optically pumped by one or more laser diode(s) driven by RF modulated current. The solid-state laser operation is stabilized by the pump source stable in both spectrum and intensity, in conjunction with automatic power control wherein the feedback loop accurately reflects the true drift in the output power. Moreover, the pump efficiency is optimized and the optical noise is minimized by adjusting the diode operation temperature such that the pump wavelength coincides with the absorption peak of the gain medium. By internally or externally modulating the amplitude of the drive current, the pump diode(s) operate in pulsed mode with controllable shape, width, repetition rate, and pulse-to-pulse intervals, which enables essentially constant optical energy produced from each pulse of the solid-state laser in high repetition rates with variable pulse-to-pulse intervals.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Laser detection method based on dense pulses
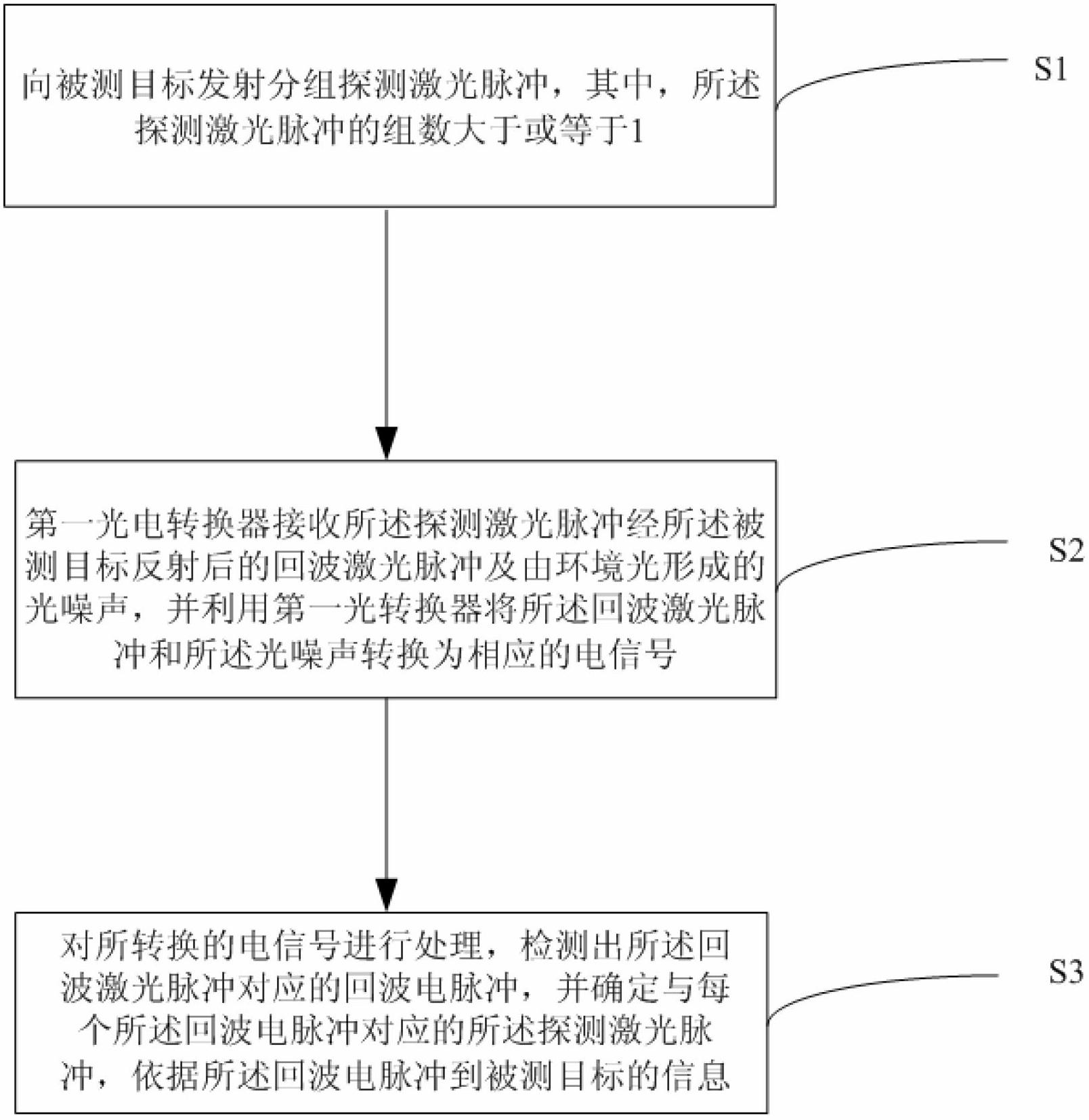
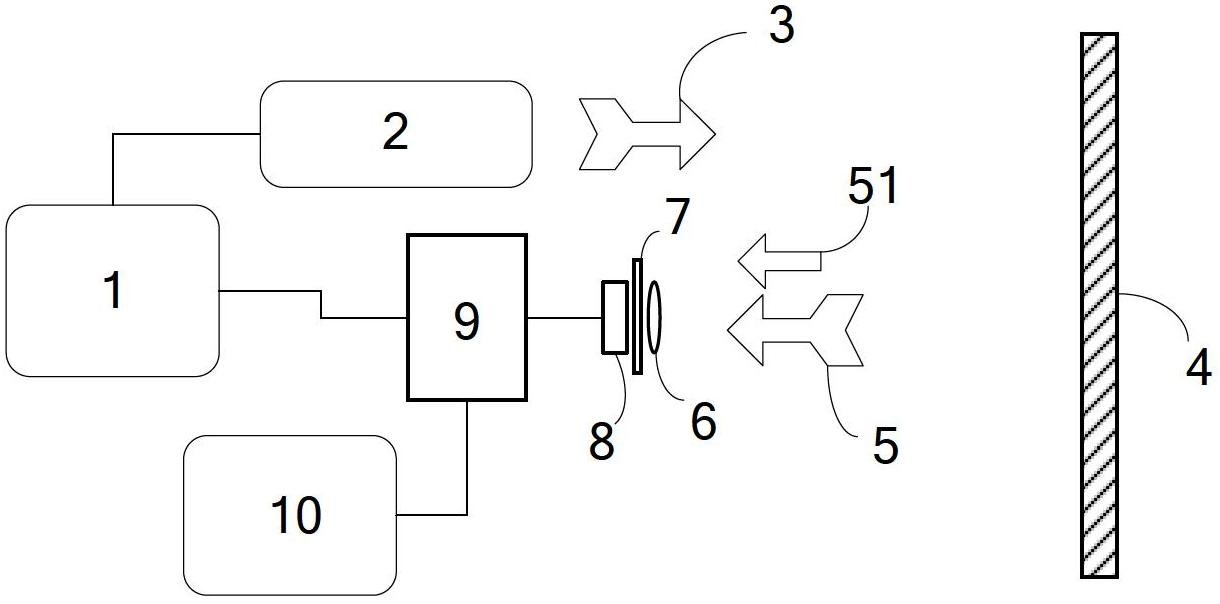
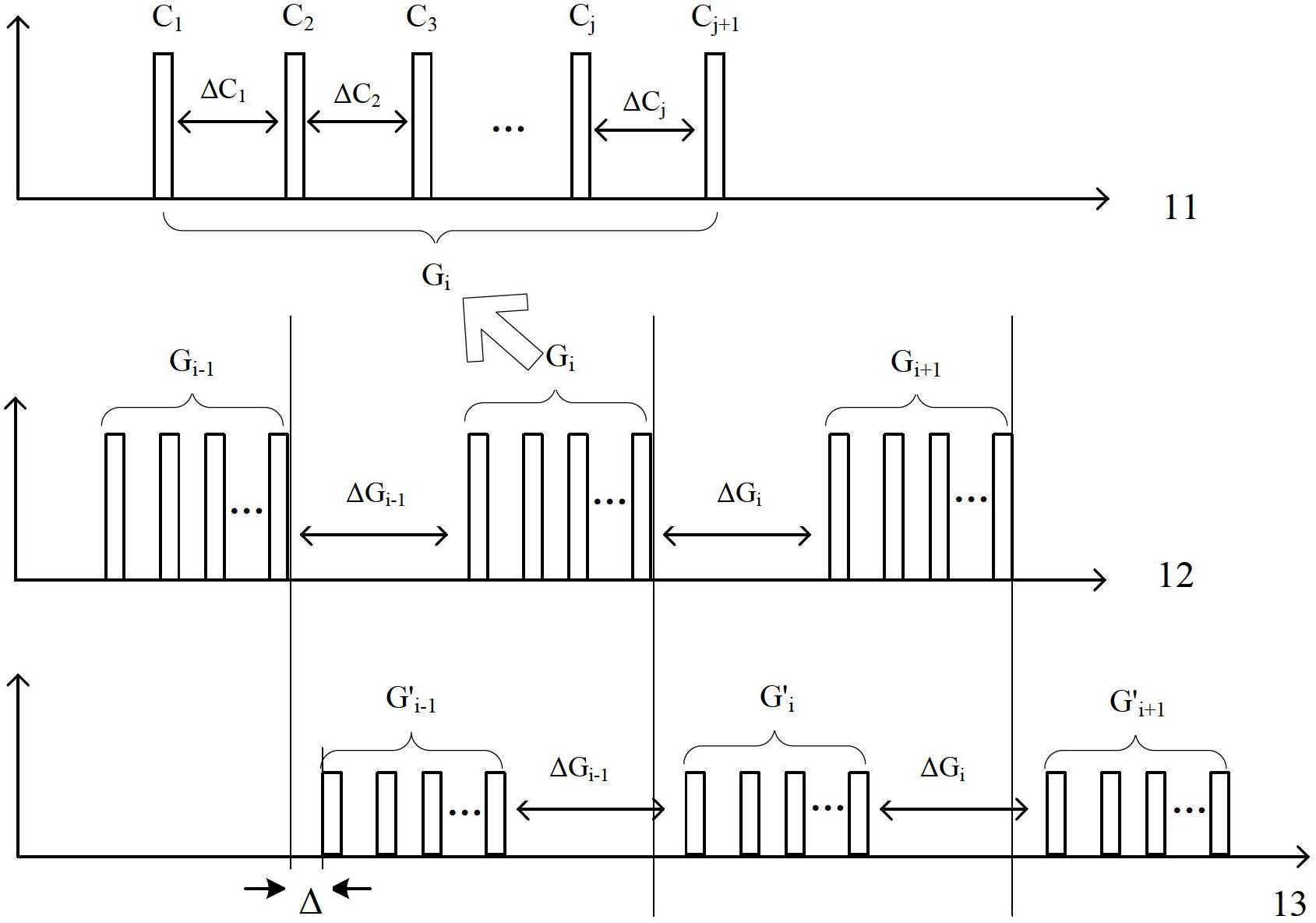
InactiveCN102692622AShorten detection timeIncrease flexibilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Optical power
The invention relates to the field of laser detection, and discloses a laser detection method based on dense pulses. The laser detection method includes steps that a laser emits grouping detection laser pulses to detected targets, wherein the number of the grouping detection laser pulses is larger than or equal to one, and each group of detection laser pulses includes multiple dense pulses; a first photoelectric converter receives echo laser pulses of the detection laser pulses reflected by the detected targets and surrounding environment optical noises, converts the echo laser pulses and the optical noises into corresponding electric signals, wherein the echo laser pulses include information of the detected targets; a signal processor is used for processing the electric signals converted by a detection unit, highlighting the electric signals corresponding to the echo laser pulses according to the time interval among the dense pulses, suppressing electric noises generated by the electric signals corresponding to the optical noises and circuits, and finally acquiring information of the detected target according to the electric signals corresponding to the echo laser pulses. The laser detection method based on the dense pulses can suppress noises, highlight signals, increase signal to noise ratio and reduce the minimum detectable optical power.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fluorescence microscope and observation method using the same
ActiveUS7297961B2Easy to getReduce Optical NoisePhotometryPhase-affecting property measurementsMicroscopic observationRefractive index
The present invention relates, in general, to a fluorescence microscope and method of observing samples using the microscope and, more particularly, to a fluorescence microscope and method of observing samples using the microscope, which can reduce optical noise and obtain images with higher sensitivity, thus obtaining precise information about the density, quantity, location, etc. of a fluorophore, and which can simultaneously process separate images even when a plurality of fluorophores having different excitation and fluorescent wavelength ranges is distributed, thus easily obtaining information about the fluorophores. The fluorescence microscope of the present invention includes an objective lens, and first and third medium units. The first medium unit has a refractive index of n1 to accommodate one or more micro-objects including fluorophores and provide a path of excitation light to excite the fluorophores. The third medium unit has a refractive index of n3, and is placed between the first medium unit and the objective lens to totally reflect the excitation light incident through the first medium unit at an interface of the third medium unit coming into contact with the first medium unit. The refractive indices of the third and first medium units satisfy a relationship of n1>n3.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Laser gas analyzer for multicomponent multiplexing measurement
InactiveCN102654455AImprove accuracyAvoid optical noiseColor/spectral properties measurementsMultiplexingLaser light
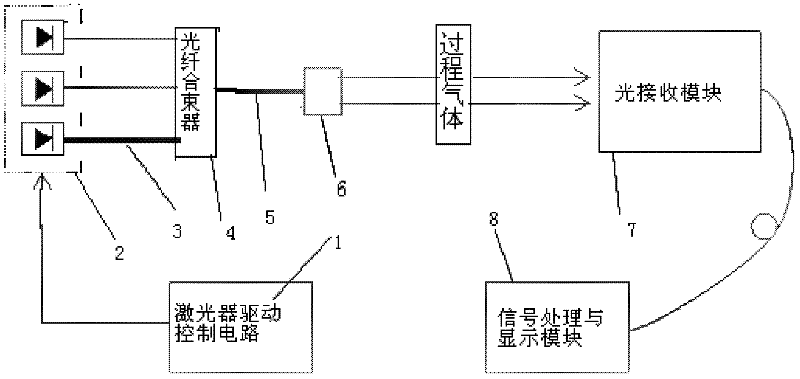
The invention discloses a laser gas analyzer for multicomponent multiplexing measurement, comprising a laser driving control circuit, three packaged lasers, an optical fiber beam combiner, a collimating lens, an optical receiving module and a signal processing and display module, wherein the laser driving control circuit modulates and drives the three packaged lasers to emit different laser light rays needing to be modulated in wavelength; the laser light emitted by each packaged laser is transmitted through a single-mode optical fiber; the single-mode optical fibers are combined into an optical fiber beam through the optical fiber beam combiner; the laser light is emitted from the tail part of the optical fiber beam, and enters into the optical receiving module for collection and light-splitting detection after collimation in the collimating lens; and a signal obtained after light-splitting detection is transmitted to the signal processing and display module for processing so that real-time concentrations of a plurality of gases needing to be detected can be obtained. According to the invention, multiplexing detection is carried out on the laser lights with various wavelengths in an optical fiber beam mode; and such a method is capable of effectively avoiding optical noise aroused by the processing of a wavelength division multiplexing device, improving the accuracy of the analyzer measuring concentrations and reducing the cost.
Owner:ANHUI WAYEE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for distinguishing optical signals of different modulation frequencies in an optical signal detector
ActiveUS8718948B2Limiting and avoiding crosstalkMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingSignal detectorExcitation signal
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Laser diode structure with reduced interference signals
ActiveUS8199786B2High resolutionReducing or completely eliminating the etalons and/or the self-mixingMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor laser optical deviceTemperature controlElectrical connection
A laser diode structure for generating a collimated or divergent laser beam, preferably for application in gas detection, with a laser diode arranged in a closed housing, with the housing comprising a housing bottom, an exit window, electrical connections, a temperature control device for the laser diode, and an optical element for influencing the laser beam. The temperature control device carrying the laser diode is arranged on the housing bottom and the optical element is positioned at a distance from the laser diode. The invention proposes an electrically controllable power device for the cyclic alteration of the position and / or alignment of the optical element in relation to the laser diode so that the optical path length for the laser beam in the housing changes periodically. The oscillating motion of the optical element has the effect of time-averaging the etalon and / or self-mixing effects caused by the back-reflections of the laser beam in the housing, thereby reducing the optical noise of the laser diode structure.
Owner:AXETRIS AG
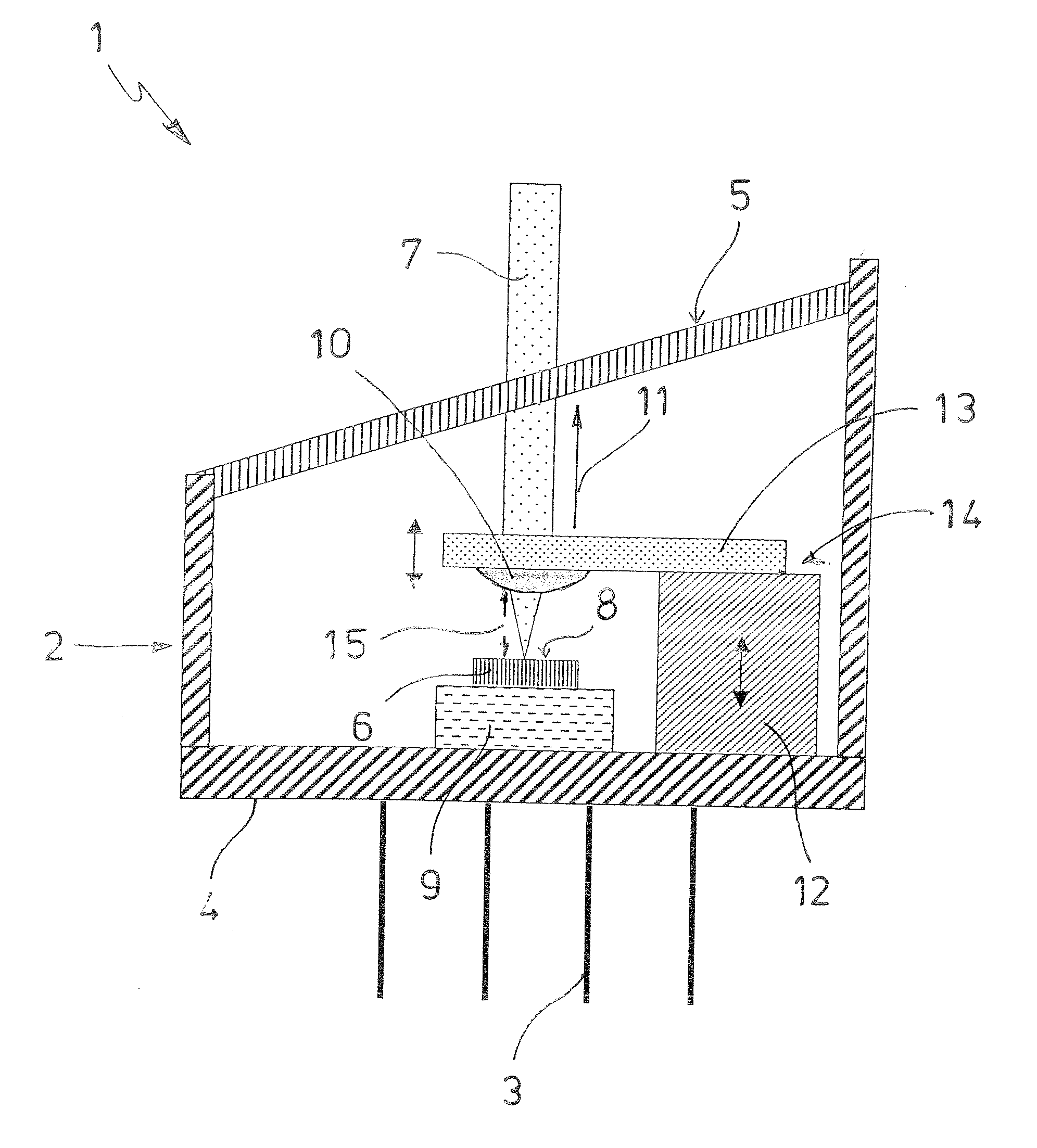
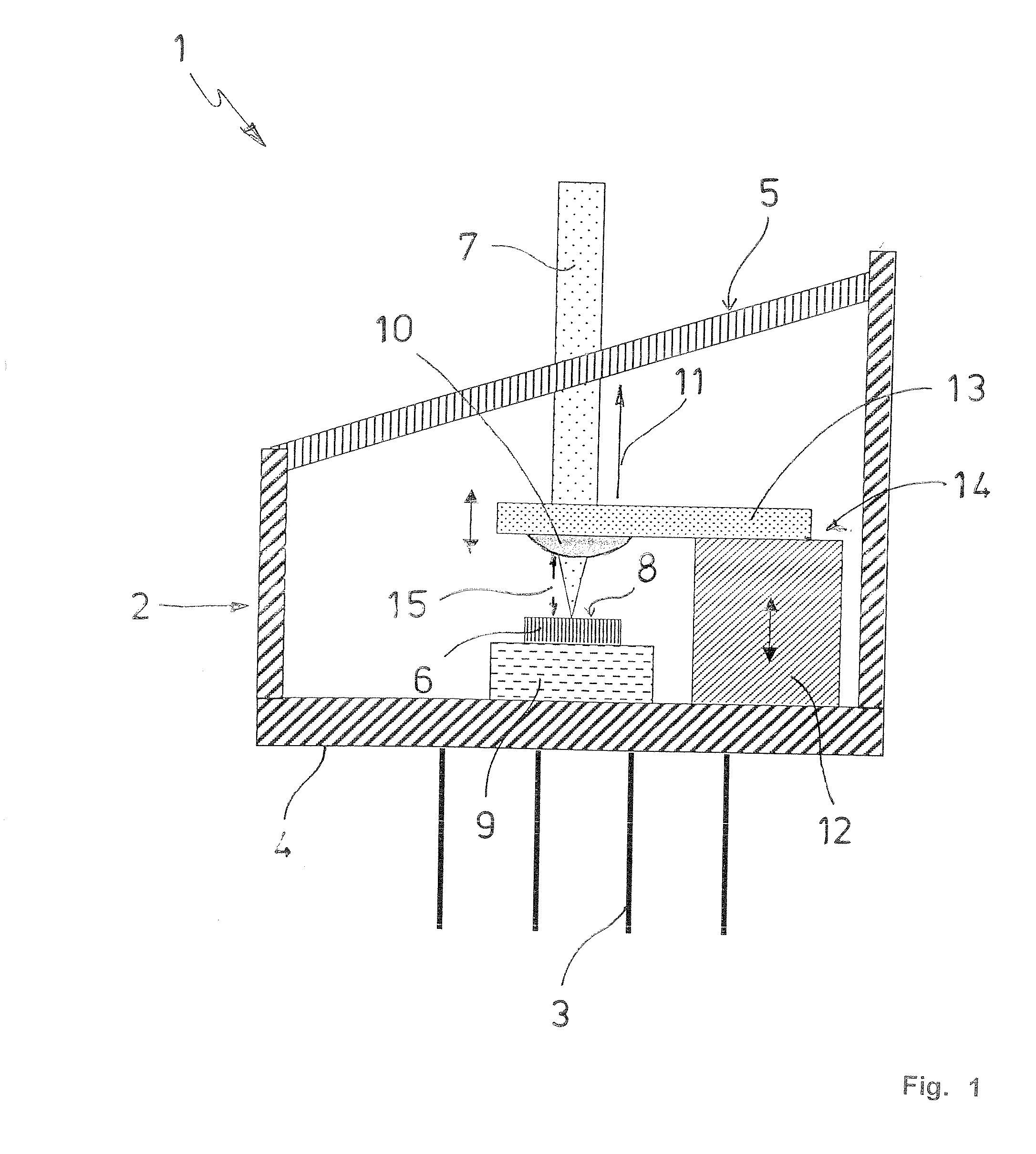
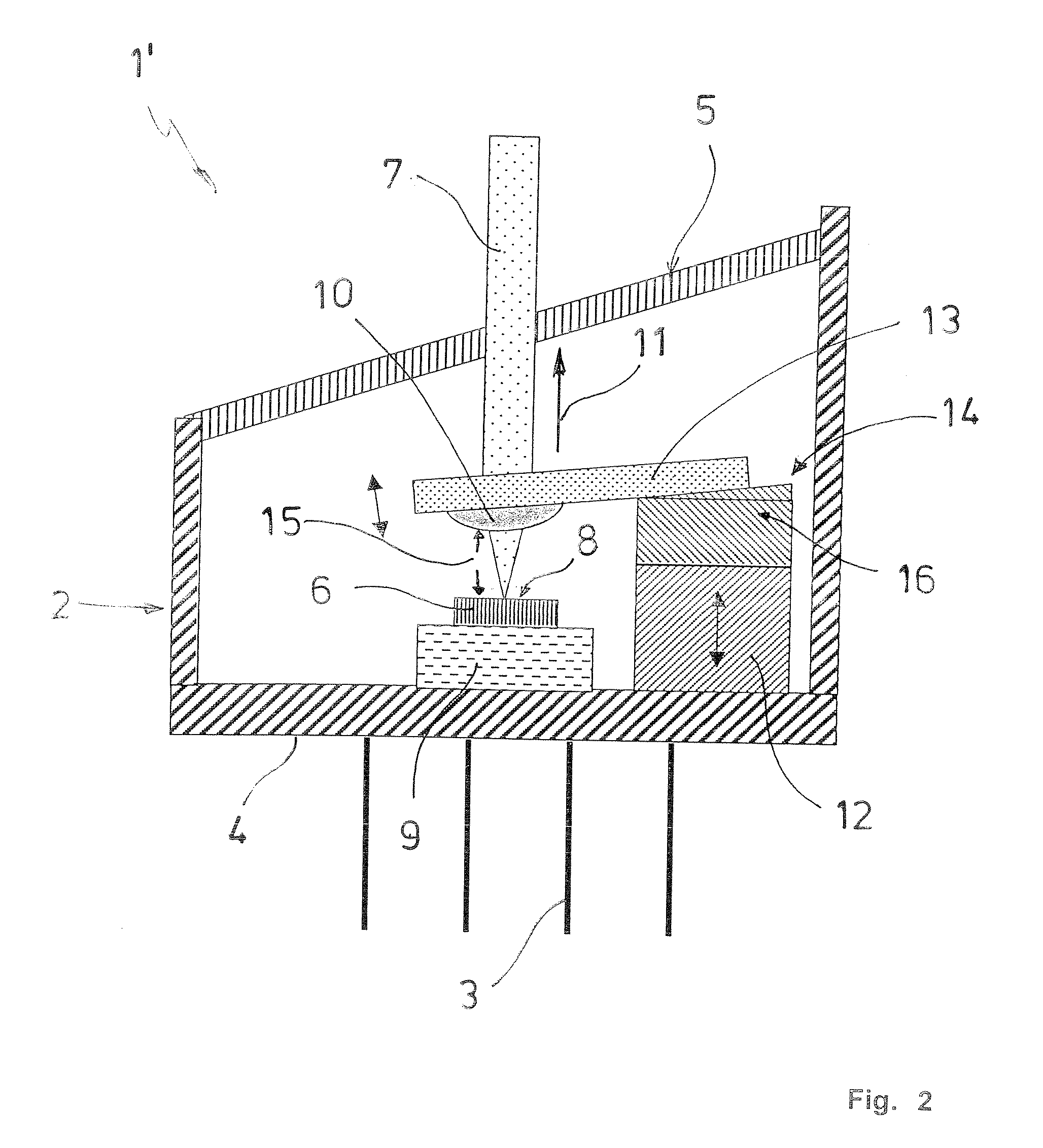
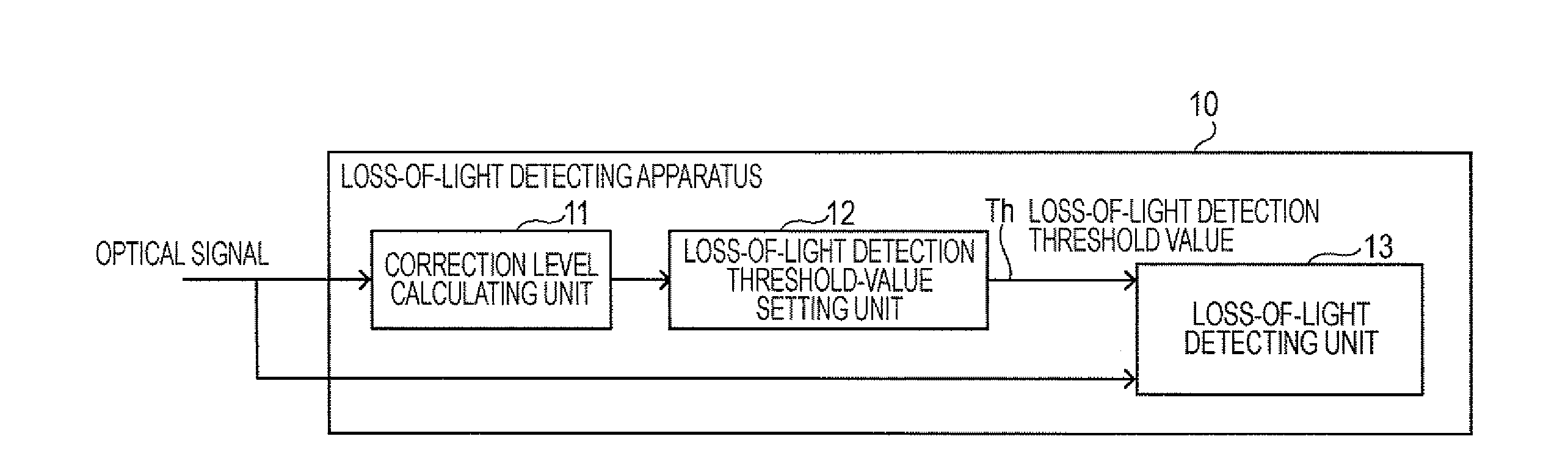
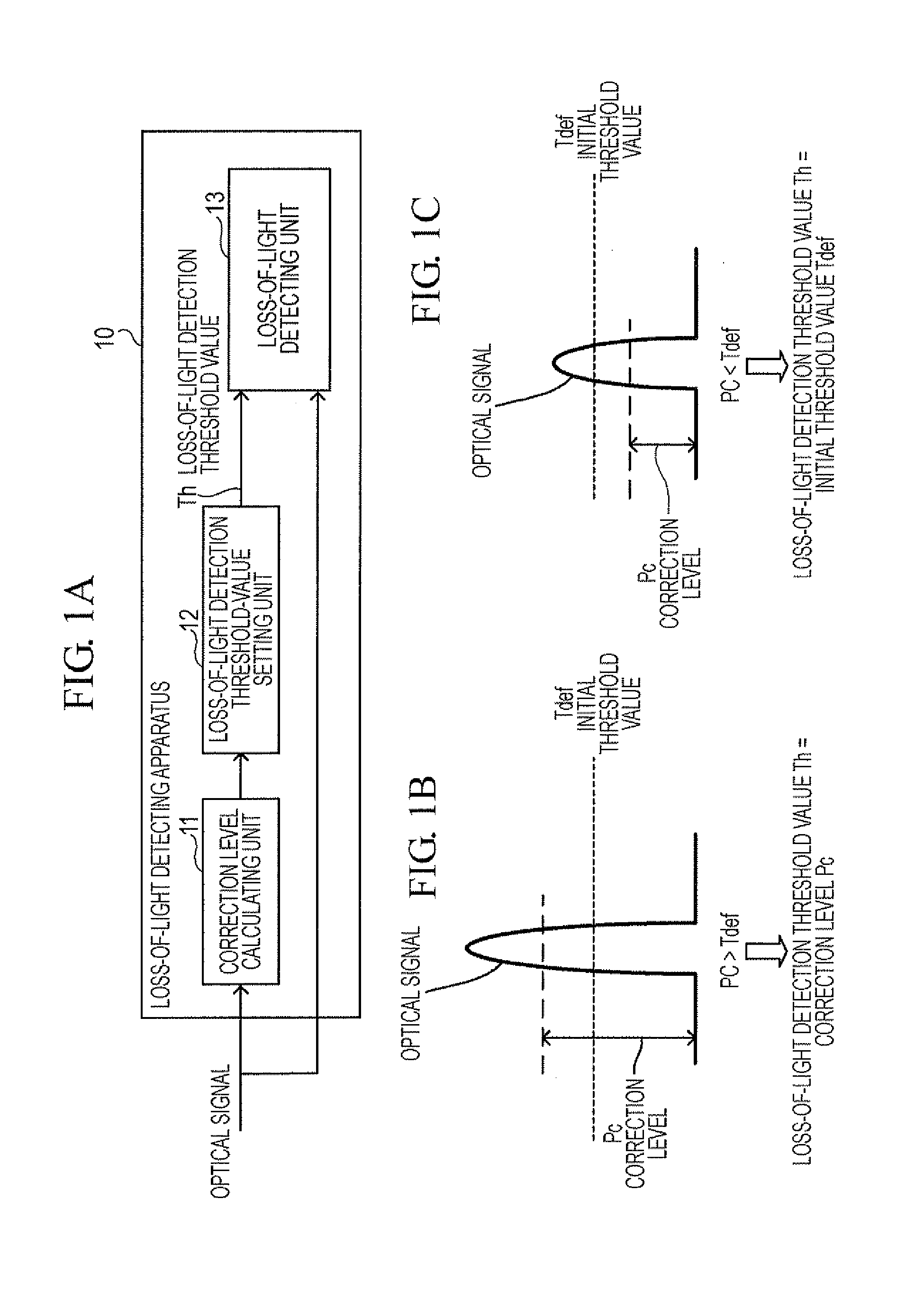
Loss-of-light detecting apparatus
InactiveUS20080232798A1Transmission monitoringElectromagnetic transmittersSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Maximum level
According to an aspect of an embodiment, an apparatus comprises: a correction level calculating unit that calculates a correction level, which is the input light level necessary to meet an optical signal-to-noise ratio at the maximum level of an optical noise signal; a loss-of-light detection threshold-value setting unit that compares the correction level with an initial threshold value to set a loss-of-light detection threshold value used in detection of any loss of light on the basis of the comparison result; and a loss-of-light detecting unit that compares the level of an input optical signal with the loss-of-light detection threshold value to determine that any loss of light is caused if the level of the input optical signal is lower than the loss-of-light detection threshold value.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Passive optical network system using time division multiplexing
InactiveUS20150055956A1Avoid quality lossPerformance deteriorationTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical time division multiplexingEngineering
Disclosed is a passive optical network system using a time division multiplexing scheme. According to one exemplary embodiment, the passive optical network system includes a plurality of optical network units (ONUs); an optical line terminal (OLT) to be connected to the plurality of ONUs for communication and to transmit and receive an optical signal to and from the plurality of ONUs using a time division multiplexing (TDM) scheme, wherein each of the plurality of ONUs includes a light source that generates an optical signal with a predetermined intensity even in burst-off state; and an optical filter disposed on a receiving path of an optical receiver of the OLT to filter out an optical noise signal received from an ONU in burst-off state among the plurality of ONUs.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
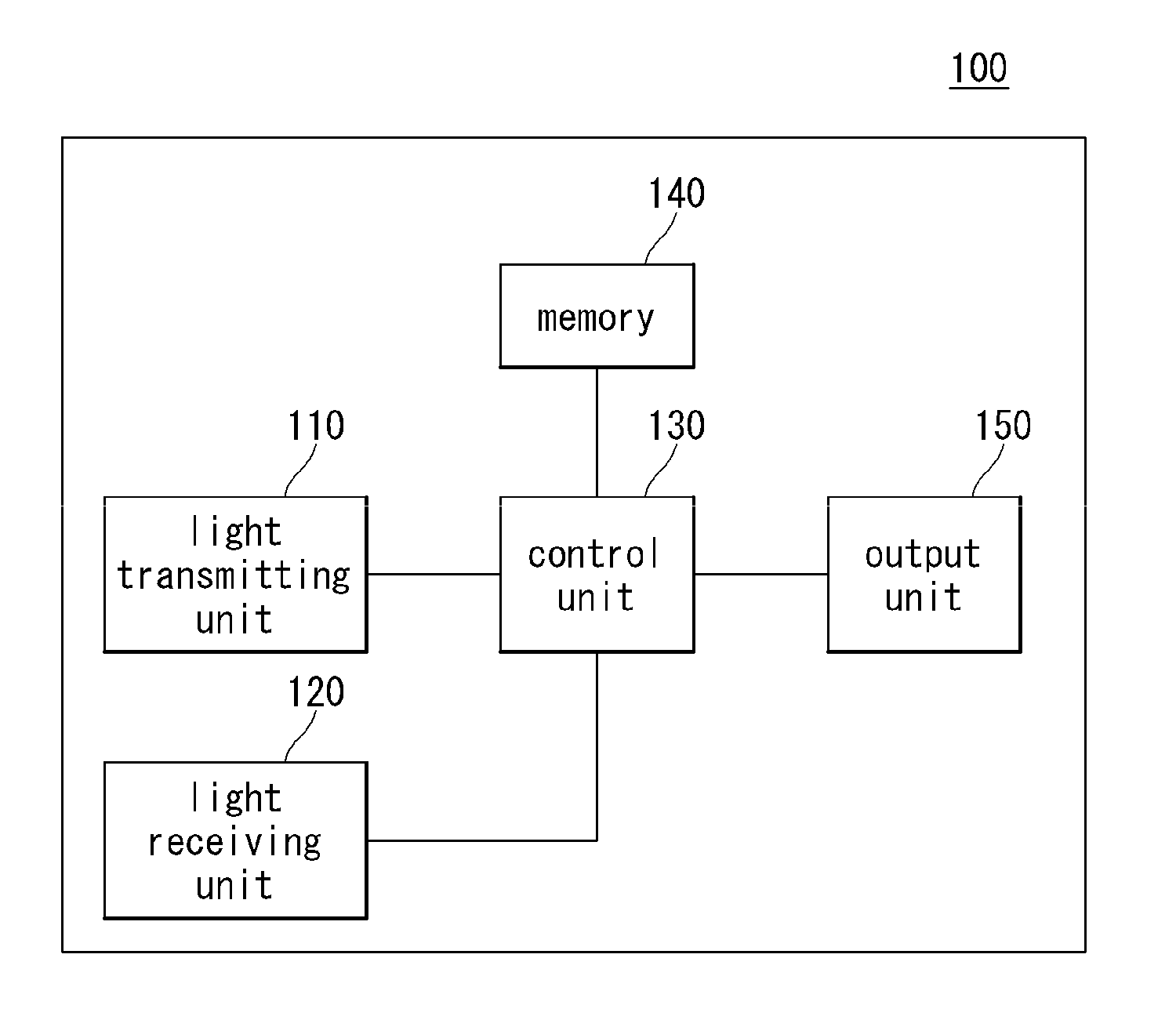
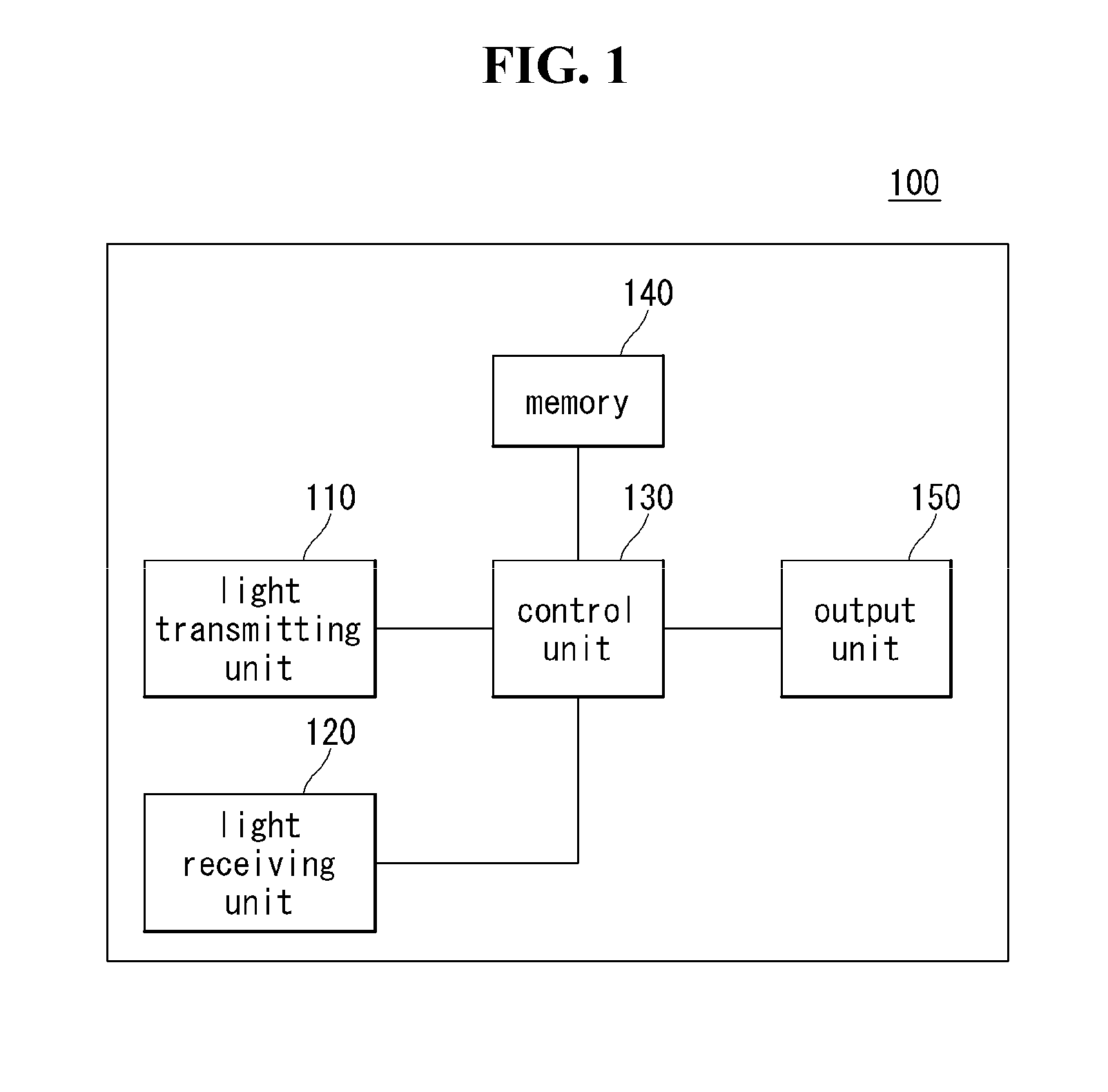
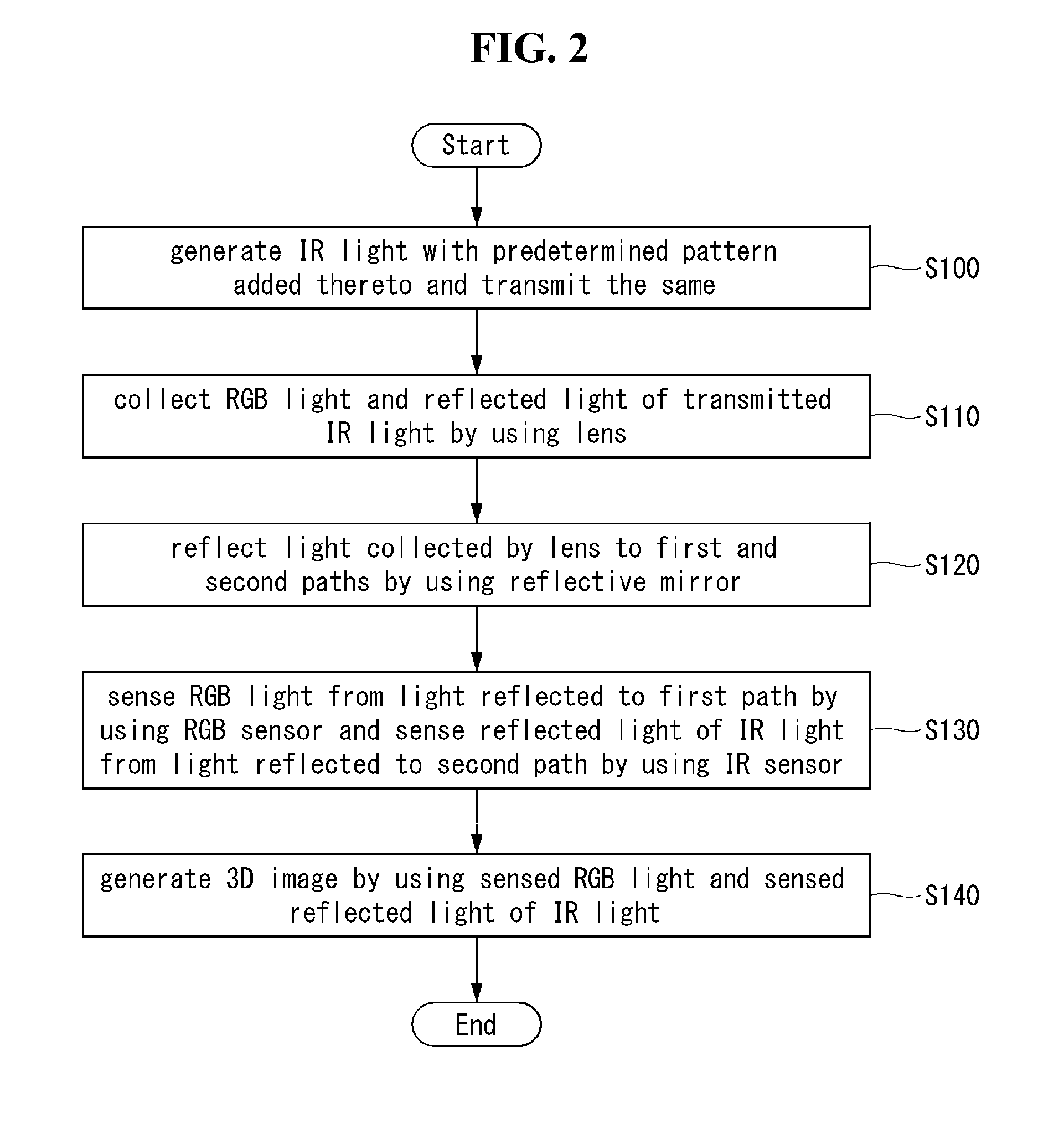
3 dimensional camera and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20150156477A1Efficient disposalOptical noise can be more preventedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptoelectronicsOptical noise
A three-dimensional (3D) camera and a method for controlling the same are provided. In sensing RGB light and infrared (IR) light, the RGB light and the IR light are prevented from acting as optical noise to each other.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Optical transmission system with automatic signal level adjustment and startup functions
ActiveUS7343102B2Easy maintenanceEasy to operateWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsTransport systemEngineering
An optical transmission system with automatic startup functions to optimize the power level of optical signals entering each optical amplifier and operate those amplifiers in appropriate mode. In the process of starting up an optical transmission system, upstream and downstream optical transmission devices set up themselves under the coordination of their internal controllers. The downstream device controller adjusts its local variable optical attenuator by utilizing optical noise emission from a post-amplifier in the upstream optical transmission device, and it selects and sets a preamplifier unit to work in appropriate operating mode. The upstream device controller, on the other hand, selects and sets operating mode of its local post-amplifier unit. During this process, the upstream and downstream device controllers exchange messages over supervisory control channels to achieve the purpose.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Self-reference interference alignment system for photoetching equipment
ActiveCN103365122AQuality improvementEliminate alignment errorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical ModuleLight beam
The invention discloses a self-reference interference alignment system for photoetching equipment. The system comprises a laser light source module, an optical module, a signal acquisition module and a processing module, wherein the laser light source module is used for providing illumination beams; the optical module is used for marking the illumination beams to form a diffraction optical signal; the signal acquisition module is used for processing the optical signal to acquire a light intensity signal; the processing module is used for processing the light intensity signal to acquire an alignment position by combining position data of a workpiece table; the optical module comprises a first optical channel and a second optical channel; an optical signal in the second optical channel is processed to be used for eliminating optical noises in the first optical channel.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
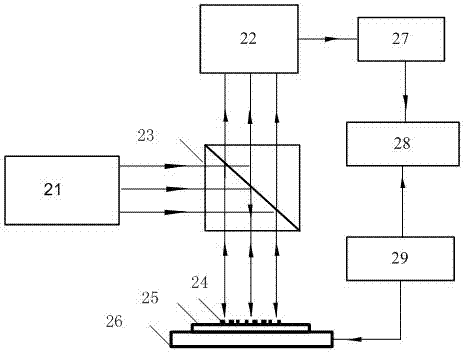
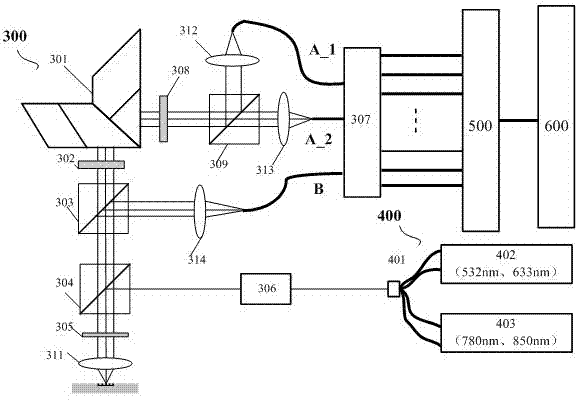
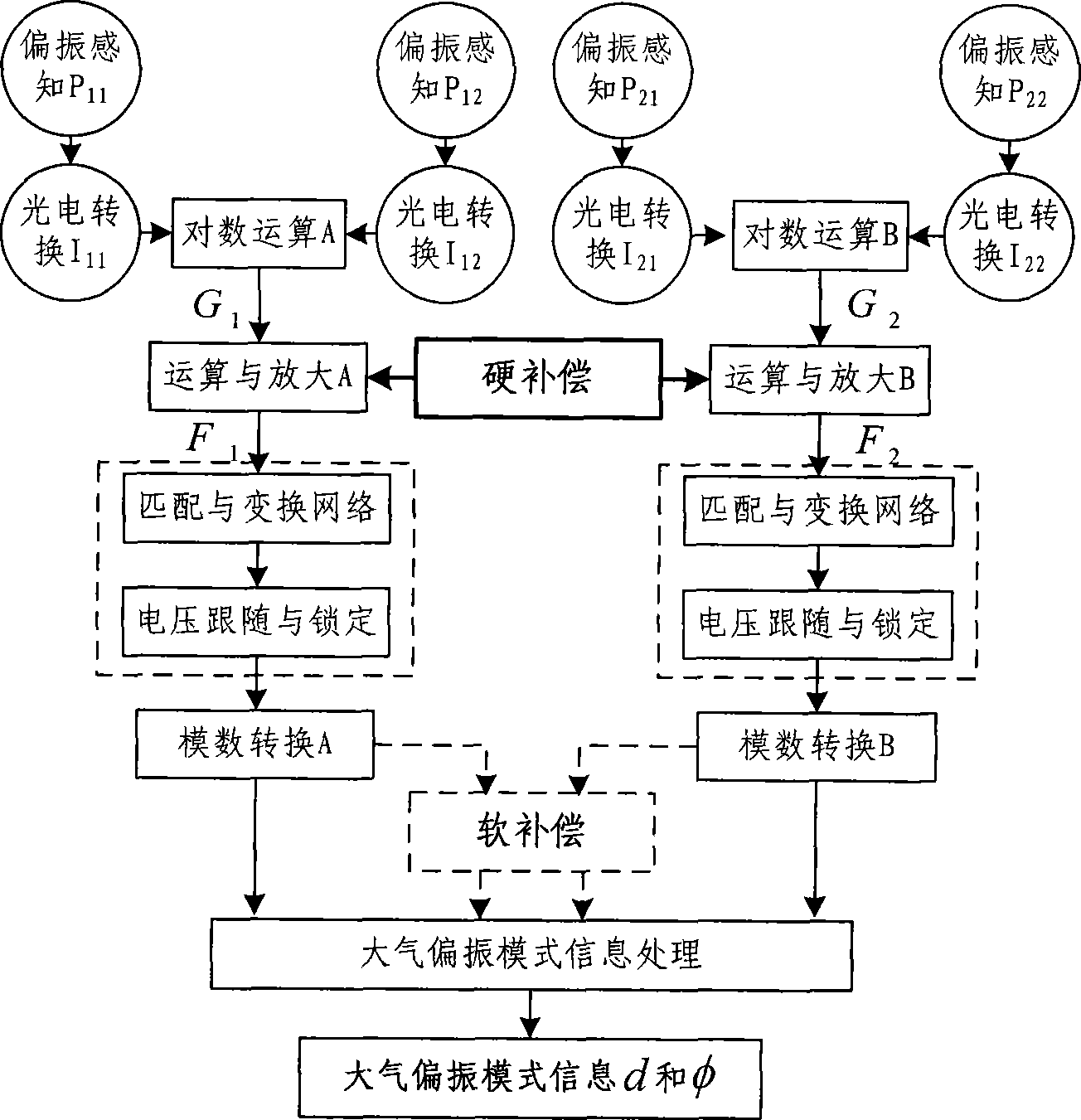
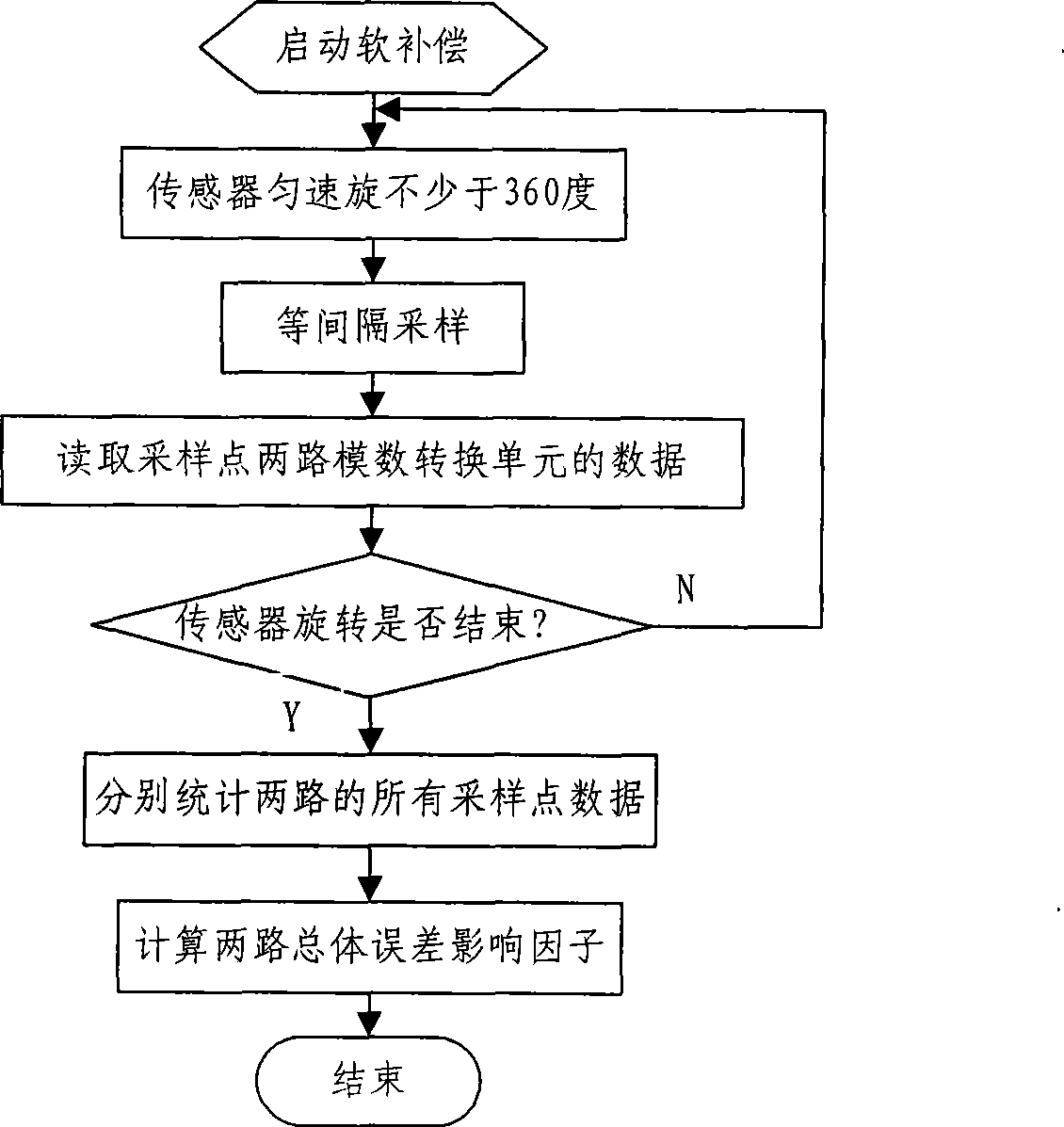
Signal processing and compensating method of four-channel atmosphere polarization information detection sensor
InactiveCN101441171AImprove detection accuracyImprove detection reliabilityPolarisation-affecting propertiesInformation processingRandom noise
A four-channel atmospheric polarization information testing sensor signal processing and compensating method, characterized in utilizing a method of step by-step signal processing, comprises: performing step by-step processing to real-time dynamic testing data from the four-channel atmospheric polarization information testing sensor, in the step by-step processing process, through two classifying compensation method of hard compensation and soft compensation, performing signal compensation and matching to error and noise of sensor step by-step signal, so as to obtain effective coherence compensation and suspension to drift error component and amplitude error of each channel signal of the sensor caused by different signal response and transmission characteristics of each channel step by-step physical device, and the random noise caused by the physical noise and environment optical noise of the sensor, therefore effective sensor output is obtained. Through performing atmospheric polarization mode information processing to the obtained digital electric signal, therefore the accurate, reliable atmospheric polarization mode information is obtained.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Fluorescence microscope and observation method using the same
ActiveUS20050092934A1Efficiently blocking unnecessary fluorescenceReduce working spacePhotometryPhase-affecting property measurementsMicroscopic observationRefractive index
The present invention relates, in general, to a fluorescence microscope and method of observing samples using the microscope and, more particularly, to a fluorescence microscope and method of observing samples using the microscope, which can reduce optical noise and obtain images with higher sensitivity, thus obtaining precise information about the density, quantity, location, etc. of a fluorophore, and which can simultaneously process separate images even when a plurality of fluorophores having different excitation and fluorescent wavelength ranges is distributed, thus easily obtaining information about the fluorophores. The fluorescence microscope of the present invention includes an objective lens, and first and third medium units. The first medium unit has a refractive index of n1 to accommodate one or more micro-objects including fluorophores and provide a path of excitation light to excite the fluorophores. The third medium unit has a refractive index of n3, and is placed between the first medium unit and the objective lens to totally reflect the excitation light incident through the first medium unit at an interface of the third medium unit coming into contact with the first medium unit. The refractive indices of the third and first medium units satisfy a relationship of n1>n3.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for optical noise cancellation
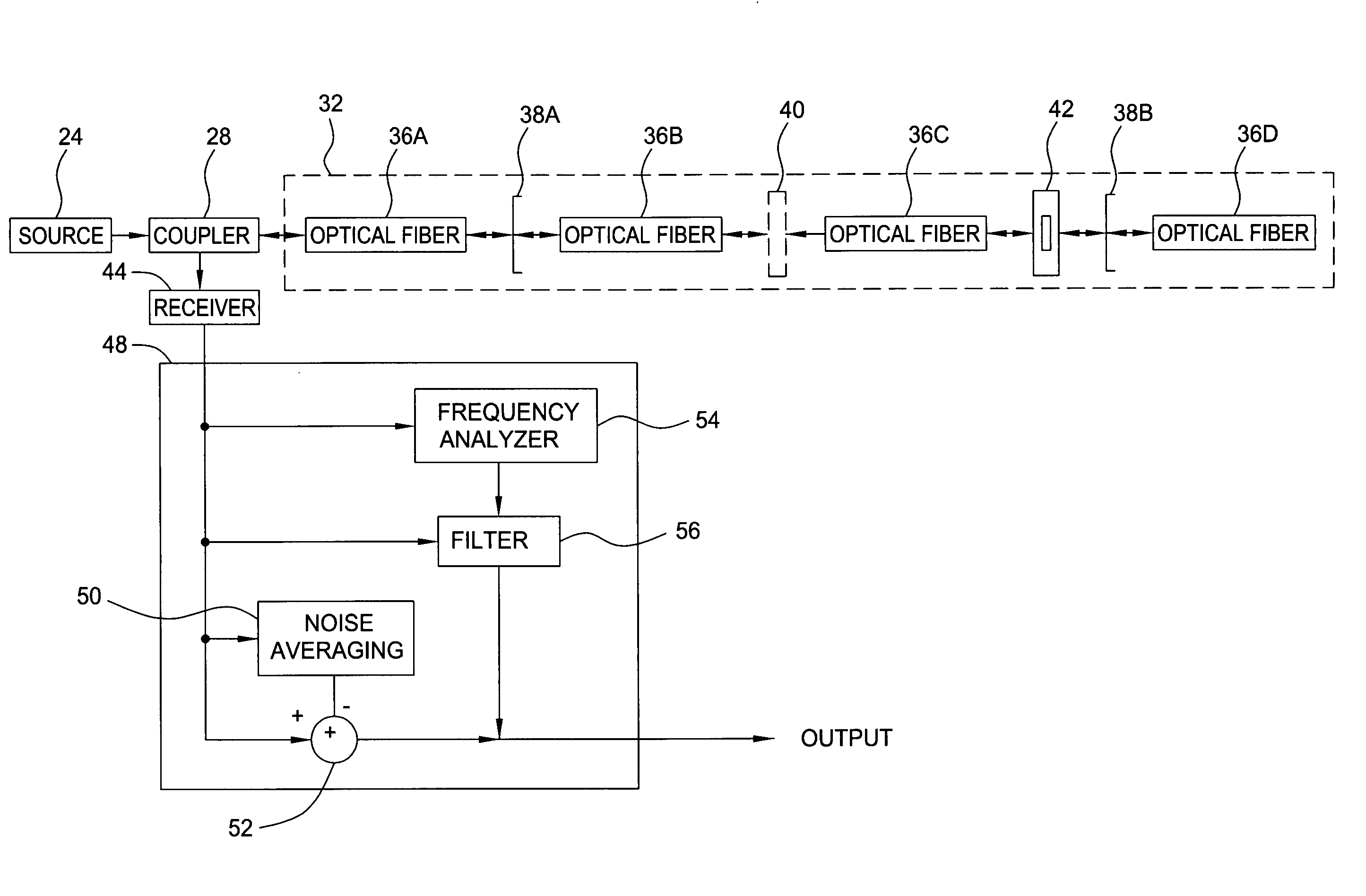
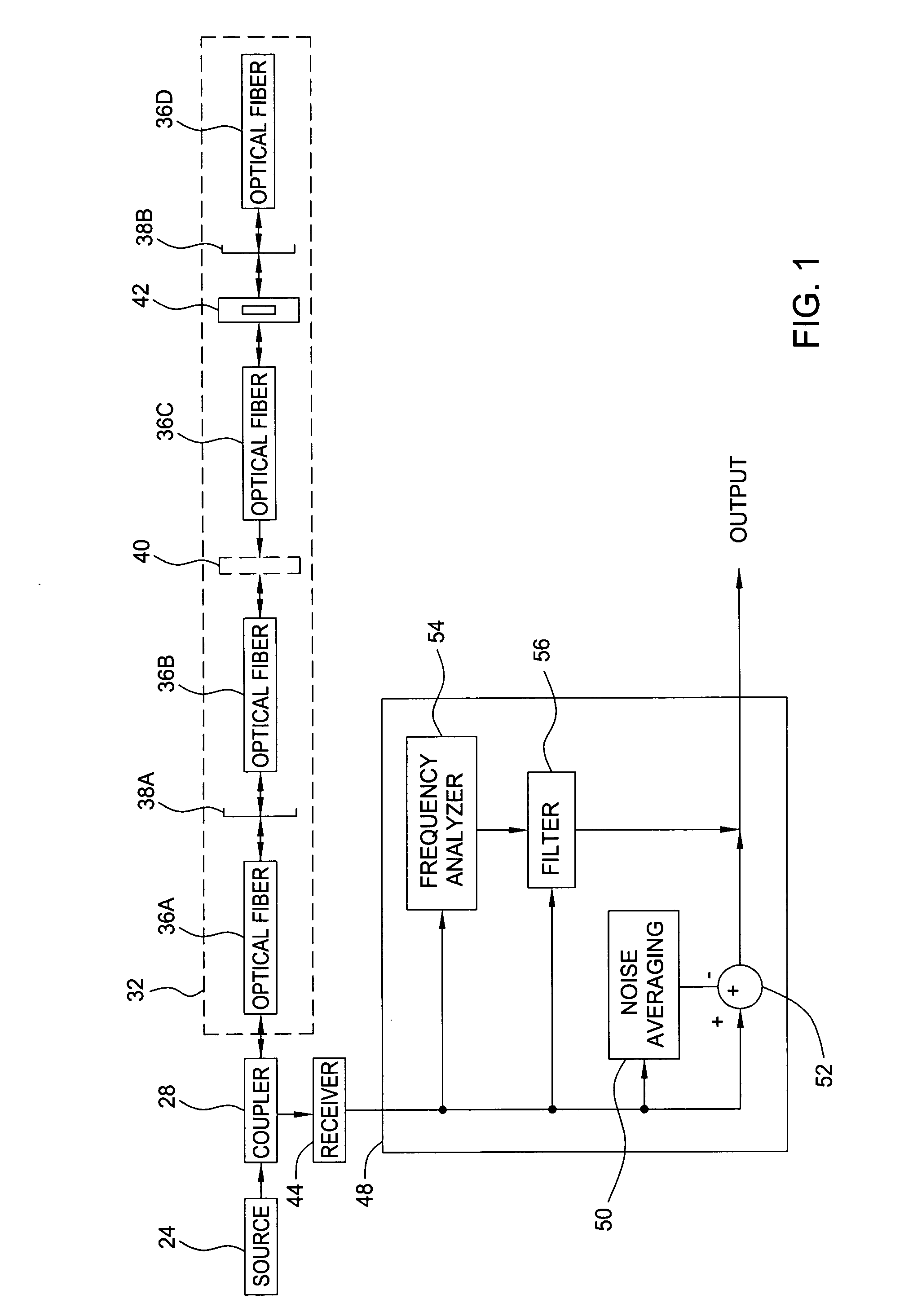
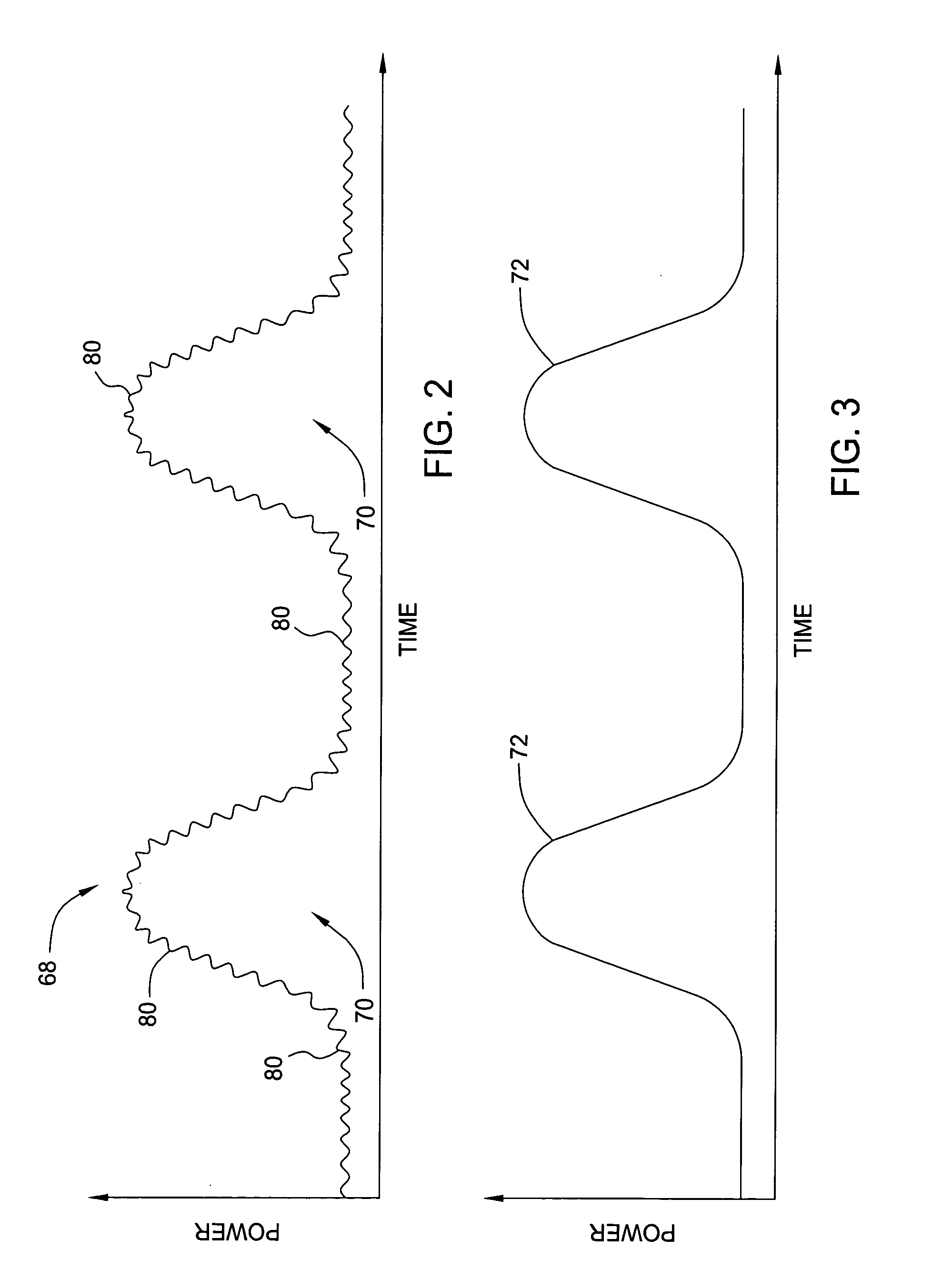
InactiveUS20050058457A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioDistortion/dispersion eliminationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Broadband
A method and apparatus for removing optical noise from an optical system. A light source produces optical signals applied to a remote optical element that produces reflected optical signals and is subject to optical background noise such as reflections from splices and optical connections. Part of the reflected optical signals and at least some of the background noise is applied to a receiver. The receiver output is analyzed to determine either the amount of noise (if broadband) or the frequency components of the noise. If broadband, the noise is subtracted from the composite signal, thus increasing the signal to noise ratio. If periodic, the frequency components of the noise are gated out of the receiver output.
Owner:WEATHERFORDLAMB
Optical device, optical device apparatus, camera module, and optical device manufacturing method
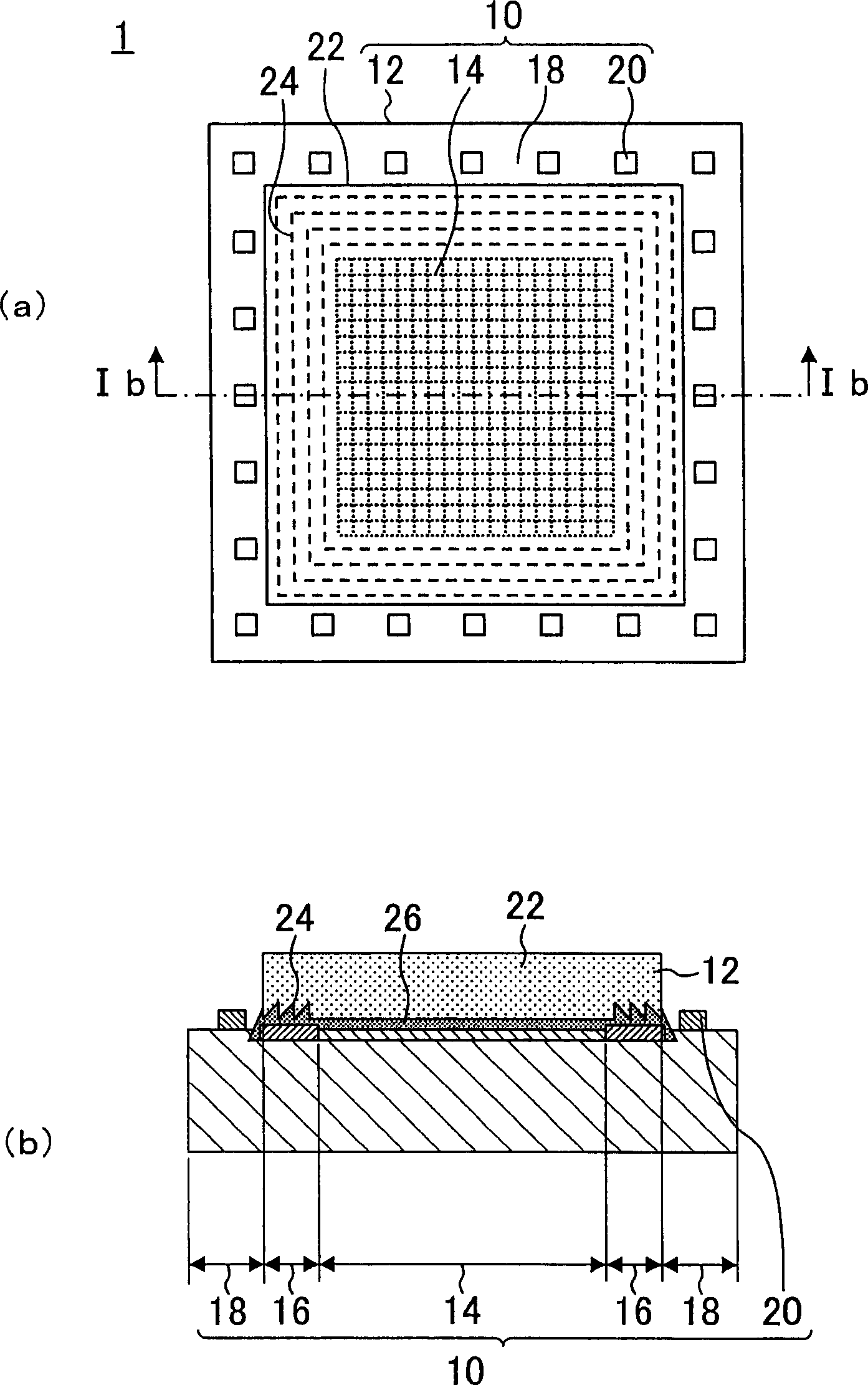
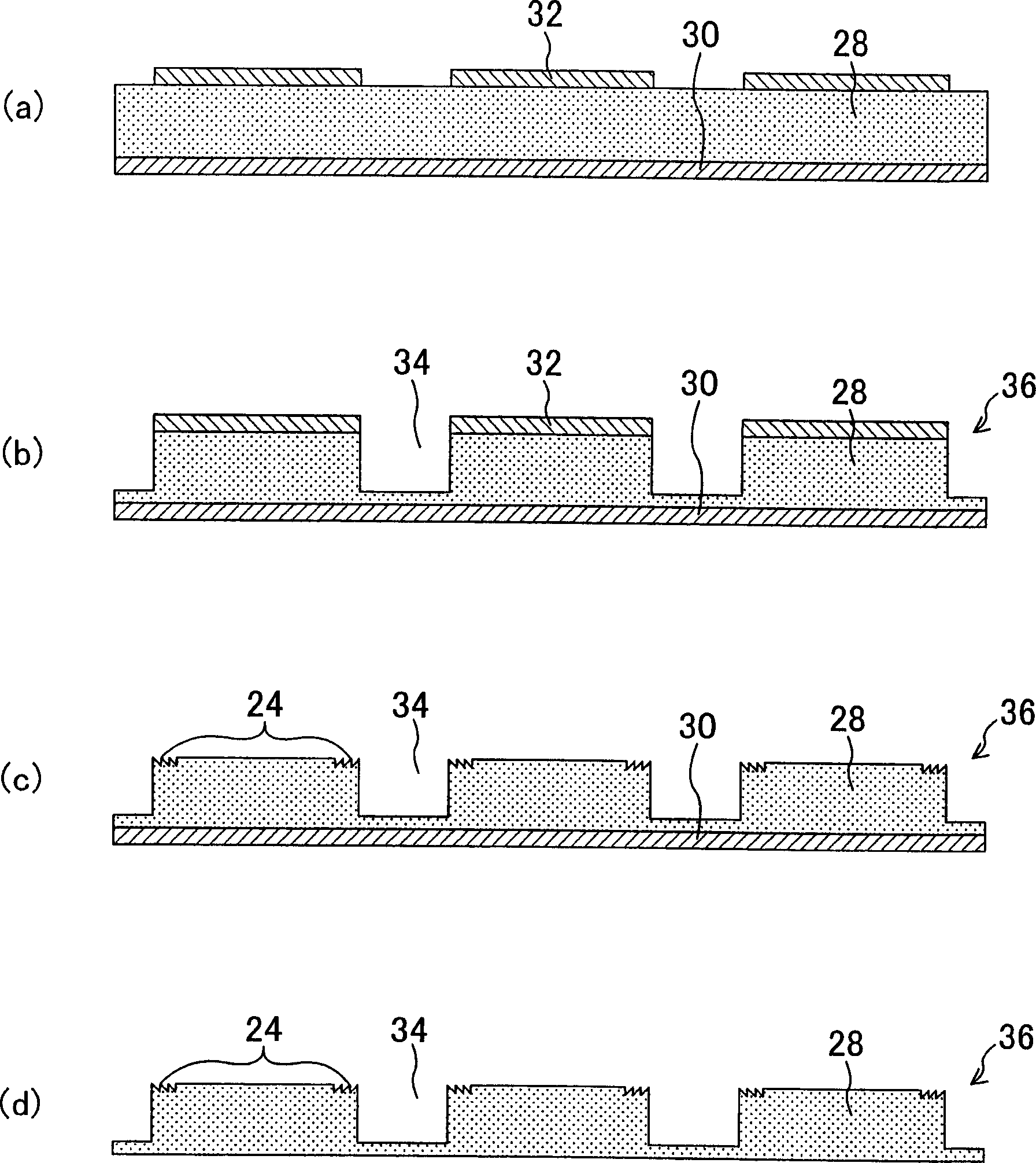
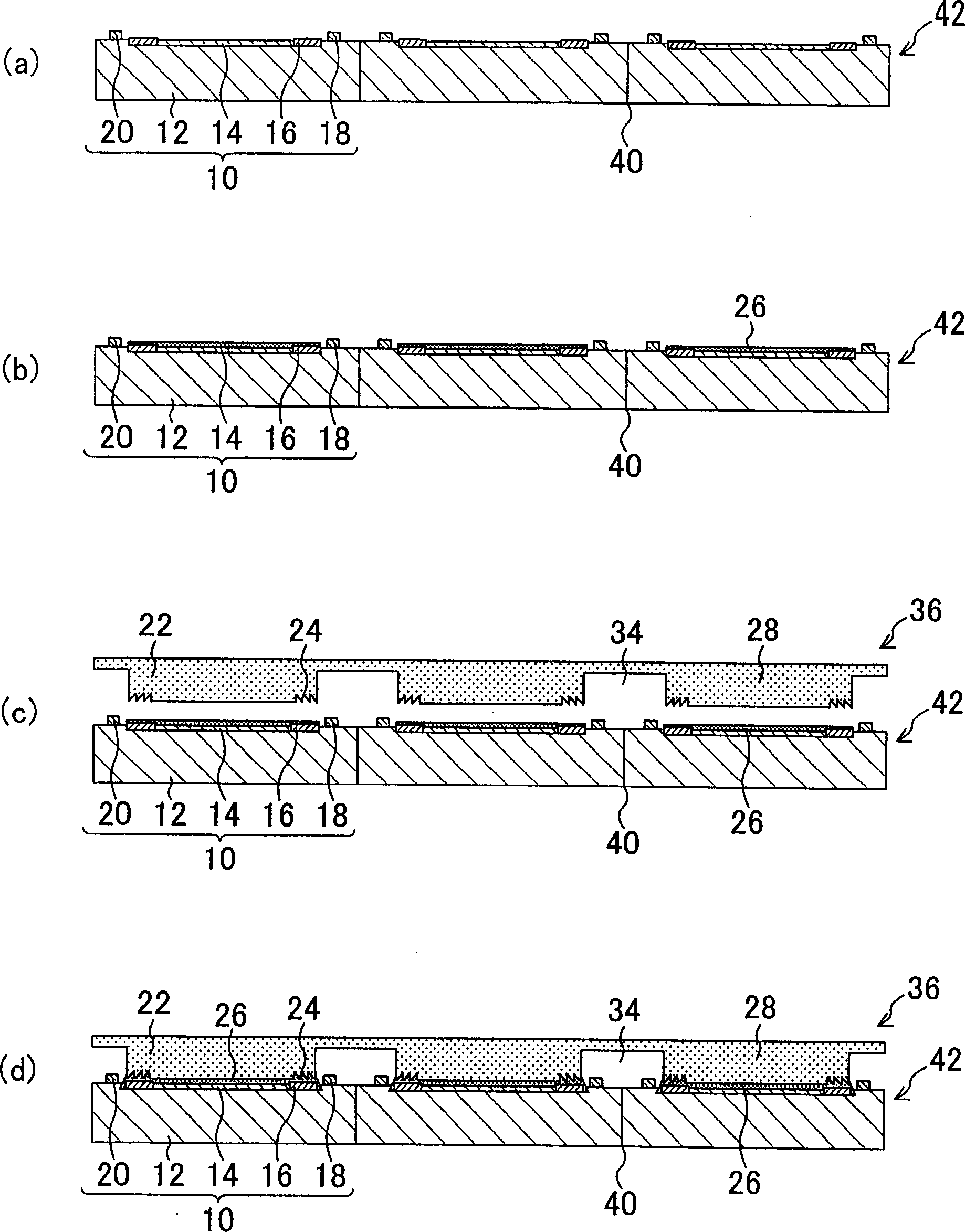
InactiveCN1901212AAchieve thinningMiniaturizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical junctionCamera module
To provide a compact and thin optical device that can simplify a manufacturing process, and suppresses optical noise, and to provide a method of manufacturing the optical device. The optical device comprises a light detection region 14; a peripheral circuit region 16 formed at the outer-periphery section of the light detection region 14; an electrode region 18 formed at the outer periphery of the peripheral circuit region 16; an optical element 10 having a plurality of microlenses in the light detection region 14; a transparent member 22 arranged on the optical element 10; and a transparent resin adhesive 26 for adhering and fixing the transparent member 22 onto the circuit formation surface of the optical element 10. A roughening region 24 having a sawtooth-like cross section is formed on an adhesive surface with the optical element 10 at a portion overlapping with the outer-periphery region of the light detection region 14 flatly in a plane view in the transparent member 22.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com