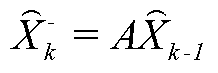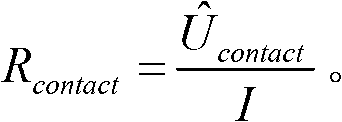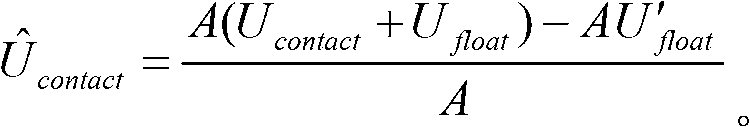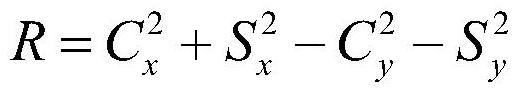Patents
Literature
281 results about "Drift error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Drift Errors. Drift errors are caused by deviations in the performance of the measuring instrument (measurement system) that occur after calibration. Major causes are the thermal expansion of connecting cables and thermal drift of the frequency converter within the measuring instrument.
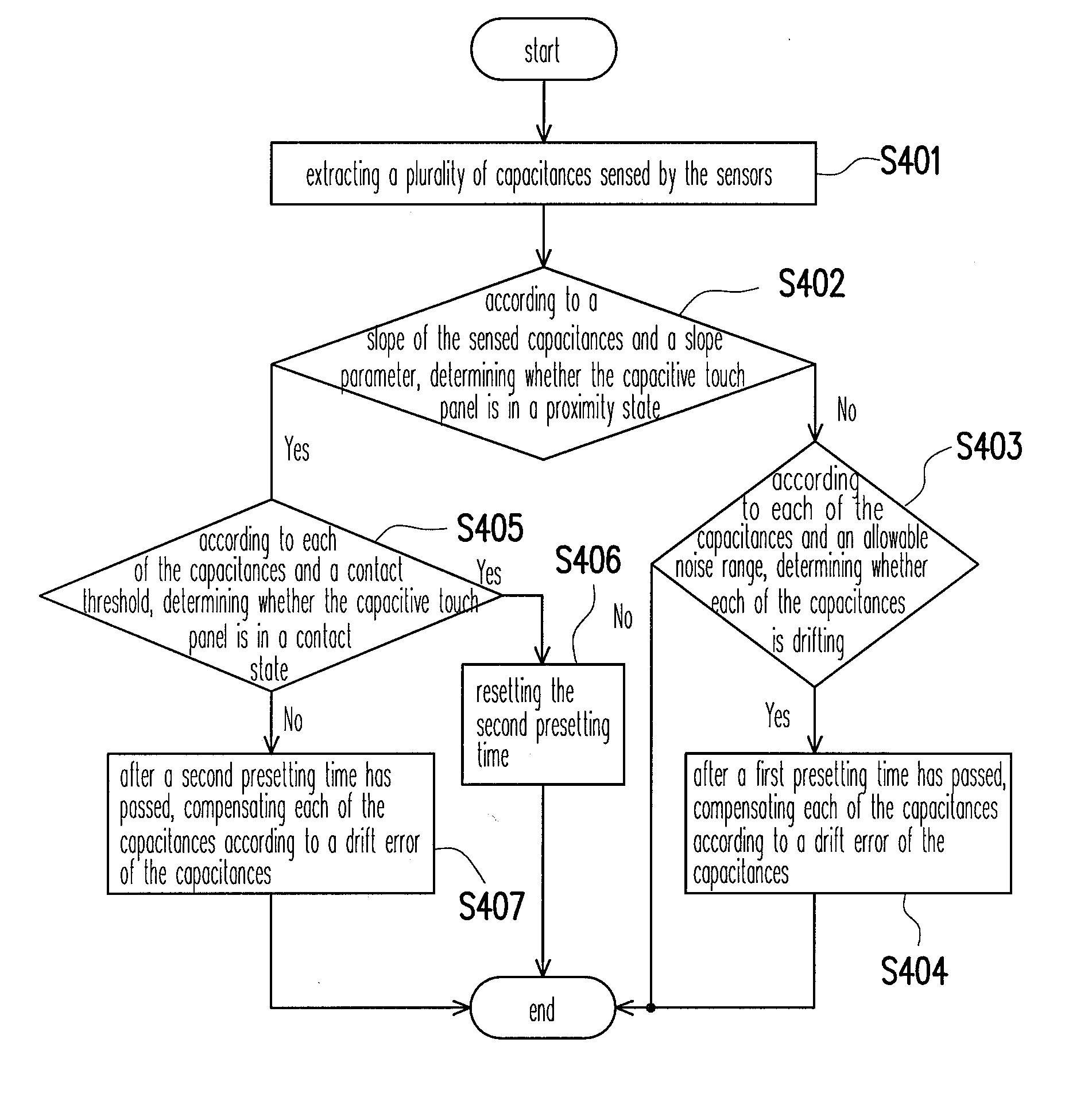
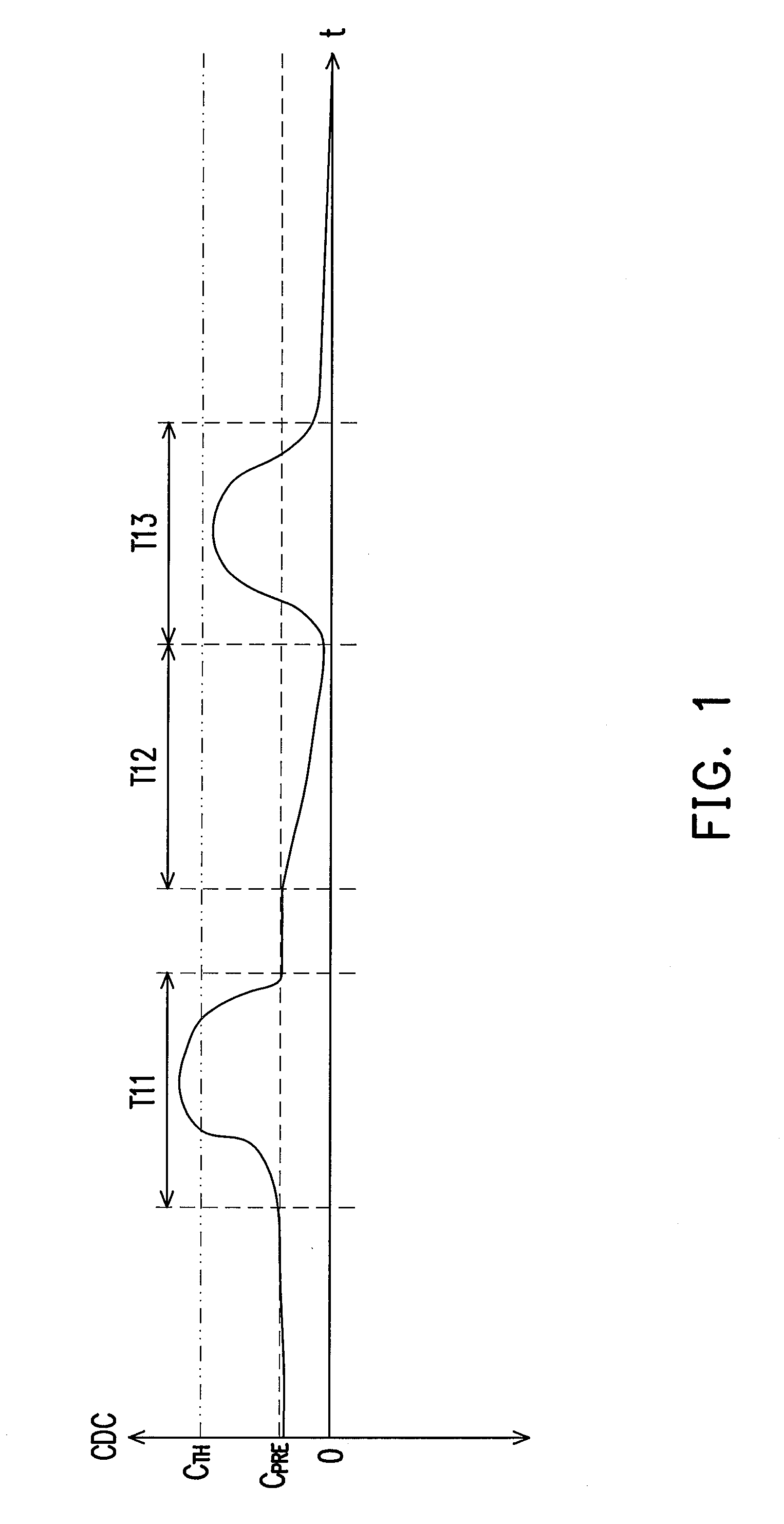
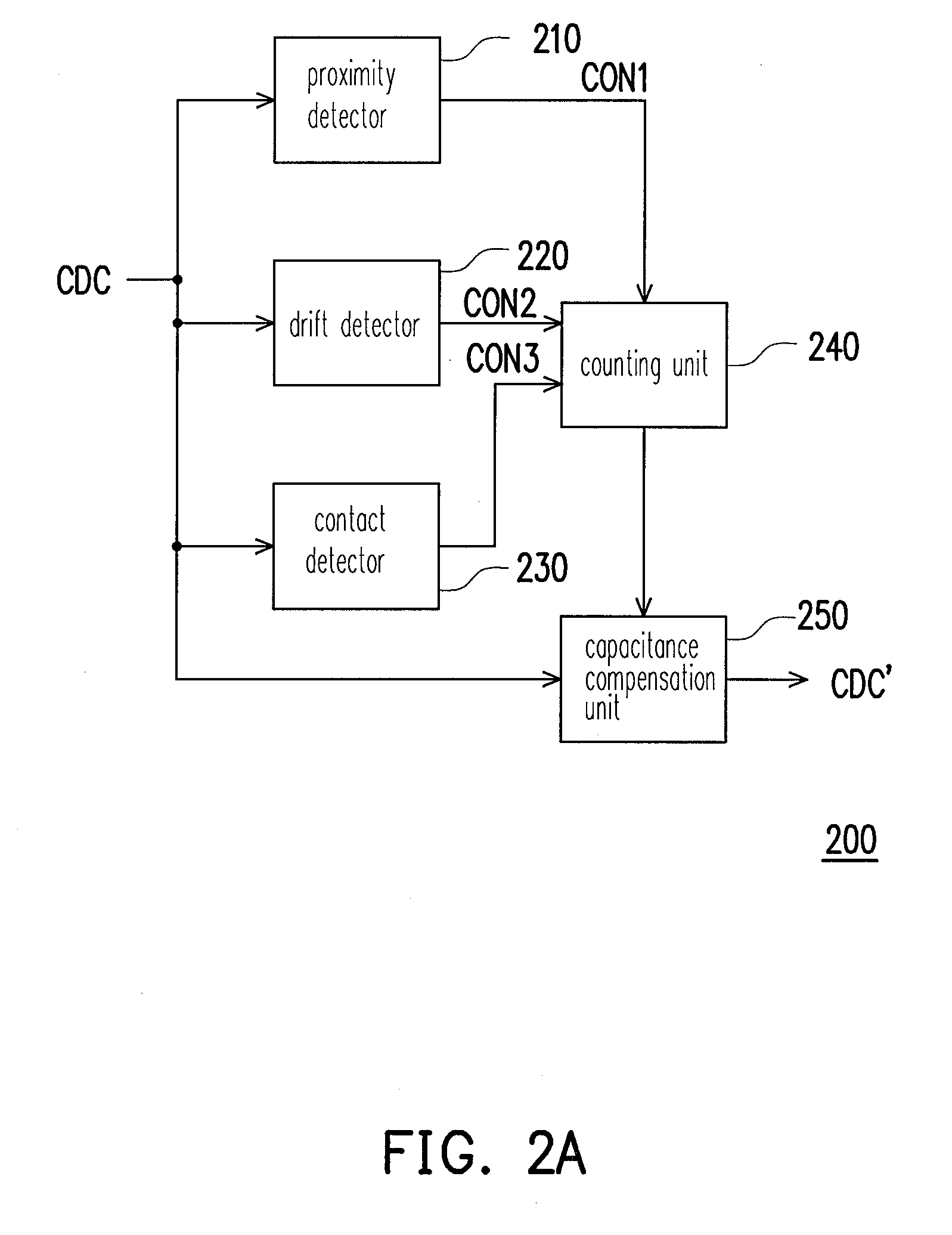
Drift compensation apparatus of capacitive touch panel and drift compensation method thereof
InactiveUS20100214253A1High sensitivityEasy to implementInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceTouchpad
A method and an apparatus adapted to a capacitive touch panel for drift compensation are provided, wherein the touch panel includes a plurality of sensors. In the method for drift compensation, a plurality of capacitances respectively sensed by each of the sensors are extracted. Whether the touch panel is in a proximity state is determined upon a slope of the sensed capacitances and a slope parameter. Whether each of the capacitances is drifted is determined upon the capacitance and an allowable noise range. When the touch panel is not in the proximity state and each of the capacitances is drifted, each of the capacitances is compensated according to a drift error of each of the capacitances after a first presetting time has passed.
Owner:ITE TECH INC
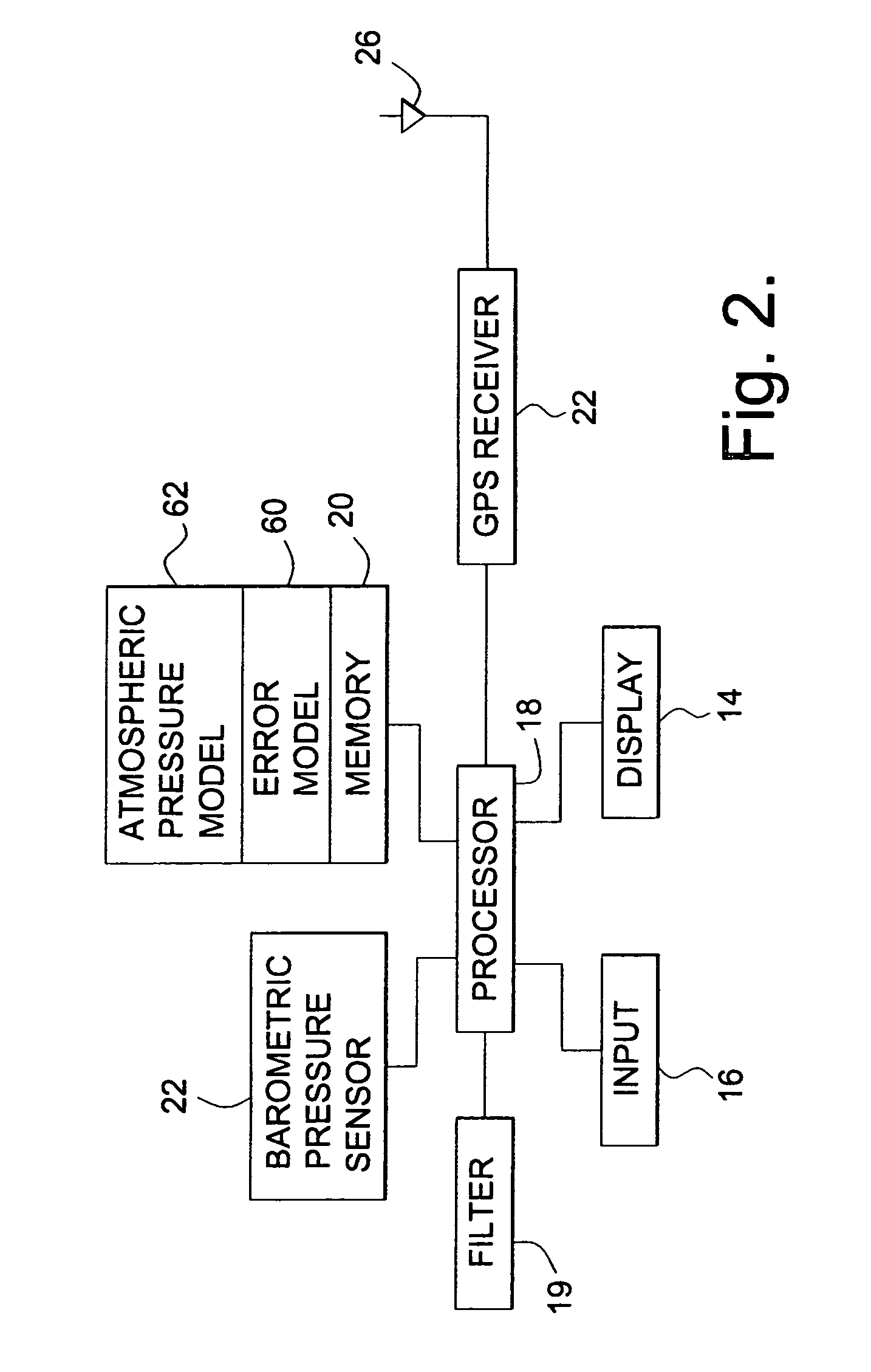
Method and apparatus for calculating altitude based on barometric and GPS measurements
A navigation device and a method of calibrating the same are provided. The device includes a barometric pressure sensor and a GPS receiver. A processor calculates barometric and GPS derived altitudes and, based on a difference therebetween, corrects barometer altitude readings that would otherwise include drift errors. The processor uses a filter, such as a state feedback loop, to determine correction factors. The state feedback loop is adjustable to operate with different time constants. An error drift model is empirically determined and used to set the time constant. The time constant may be adjusted during operation based on a relation between the barometer correction quantity and an uncertainty in the vertical component of the GPS derived altitude. The method includes updating and recalibrating an atmospheric pressure model used to derive altitudes from the output of the barometric pressure sensor.
Owner:GARMIN
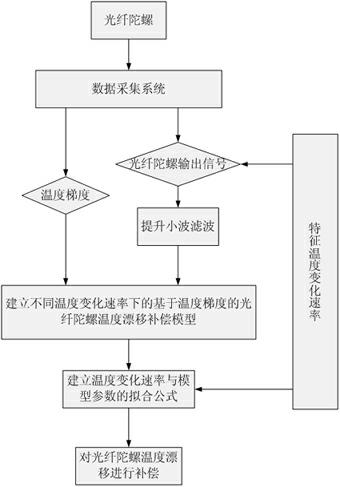
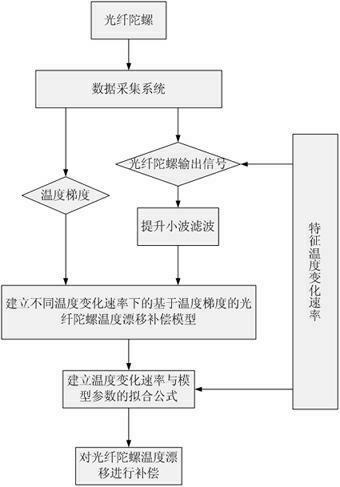
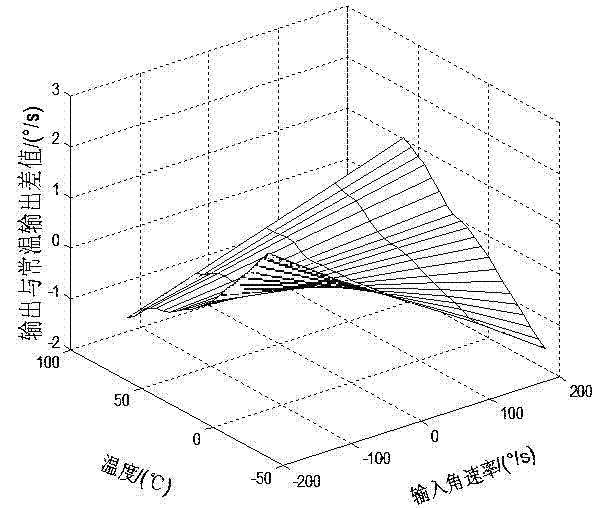
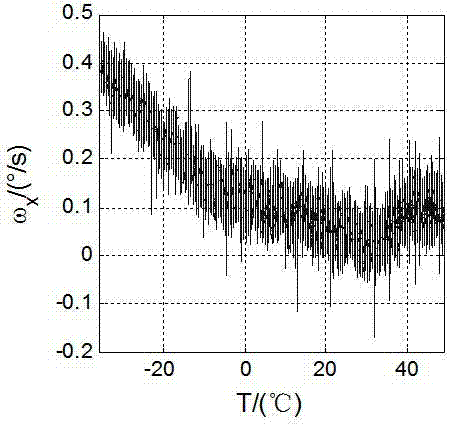
Method for modeling and error compensation of temperature drift of fiber optic gyroscope
ActiveCN102095419AComprehensive analysis to study the effects of temperature driftAnalyzing the effects of temperature driftSagnac effect gyrometersThermodynamicsFibre optic gyroscope
The invention discloses a method for modeling and error compensation of temperature drift of a fiber optic gyroscope, which comprises the following steps of: obtaining a learning sample and denoising the learning sample; establishing a fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation model based on temperature gradient; establishing a parameter formula based on a temperature change rate so as to determine the relations between the temperature change rate and various parameters of the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation model; and subtracting a temperature drift compensation value, obtained by the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation model, from the real-time output data of the fiber optic gyroscope to realize temperature compensation to the fiber optic gyroscope. The invention not only realizes modeling for the temperature drift of the fiber optic gyroscope in mechanism, but also simultaneously and greatly improves the convenience and accuracy of modeling, and has important significance to performance research and improvement of the fiber optic gyroscope in constantly variable temperature environments.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
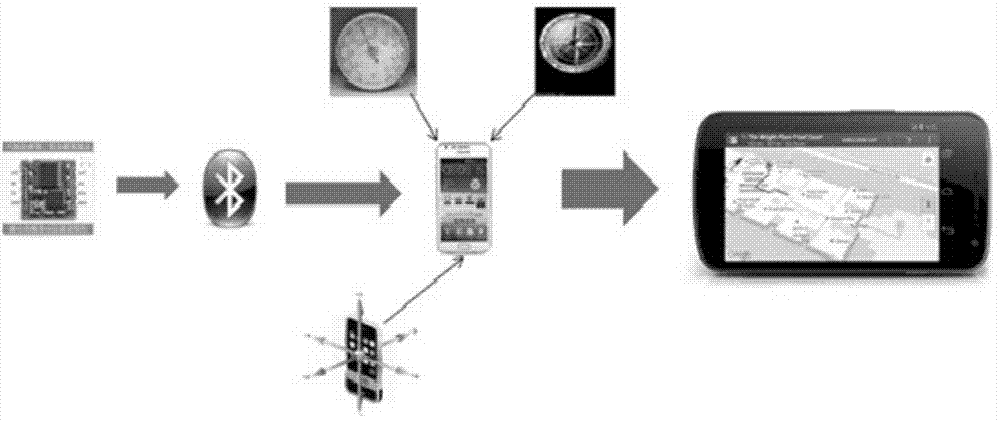
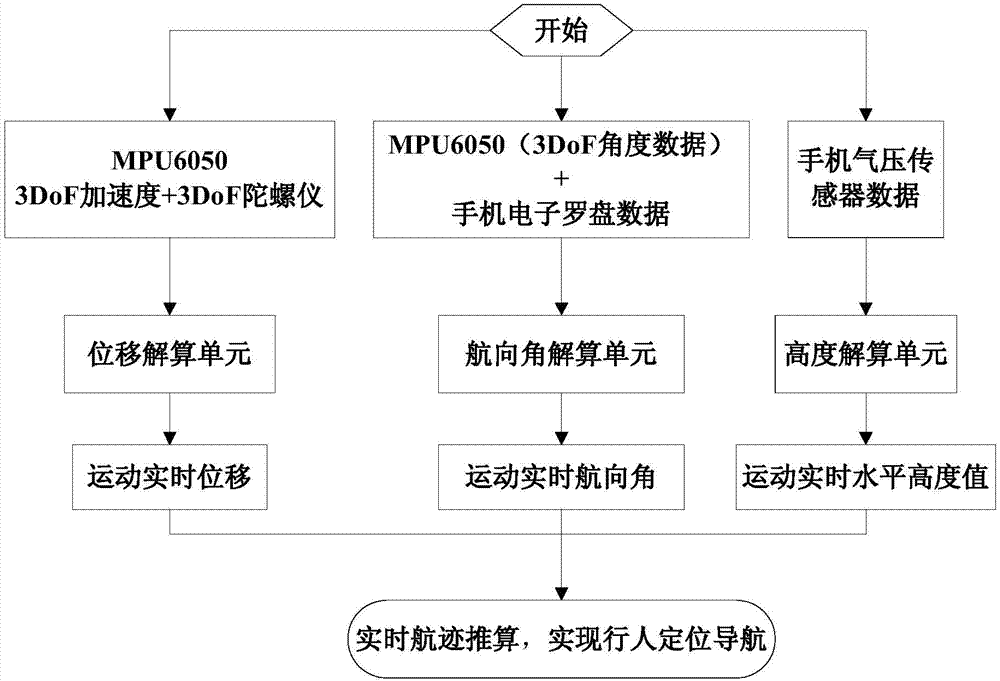
Indoor positioning method based on MEMS insert device and android smart mobile phone fusion
InactiveCN104713554AEliminate cumulative errorsImprove indoor positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeComputer terminal
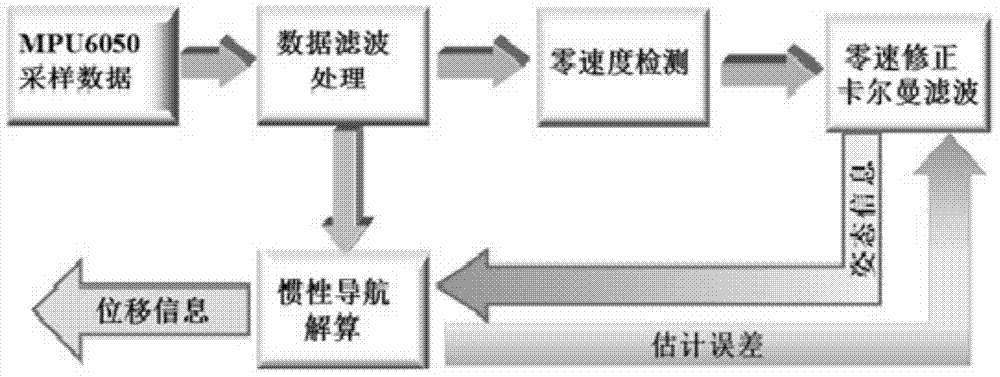
The invention discloses an indoor positioning method based on MEMS insert device and android smart mobile phone fusion, and belongs to the field of data processing and mobile terminal application. The method is characterized in that a Kalman filtering-based zero speed correction accumulative error elimination algorithm is adopted based on the motion characteristics of indoor positioning pedestrians and the drift error of an MEMS inert device on the premise of MEMS insert device and android smart mobile phone fusion; and different data sampling modes are designed based on the advantages and disadvantages of a gyroscope and an electron compass and the motion characteristics of the pedestrians in the pedestrian motion course angle determination process, and are fused with a particle filtering course angle determination algorithm in order to further increase the pedestrian course precision. The method can reduce the accumulative error in the inertial navigation resolving process, and allows accurate pedestrian displacement information and course angle information to be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
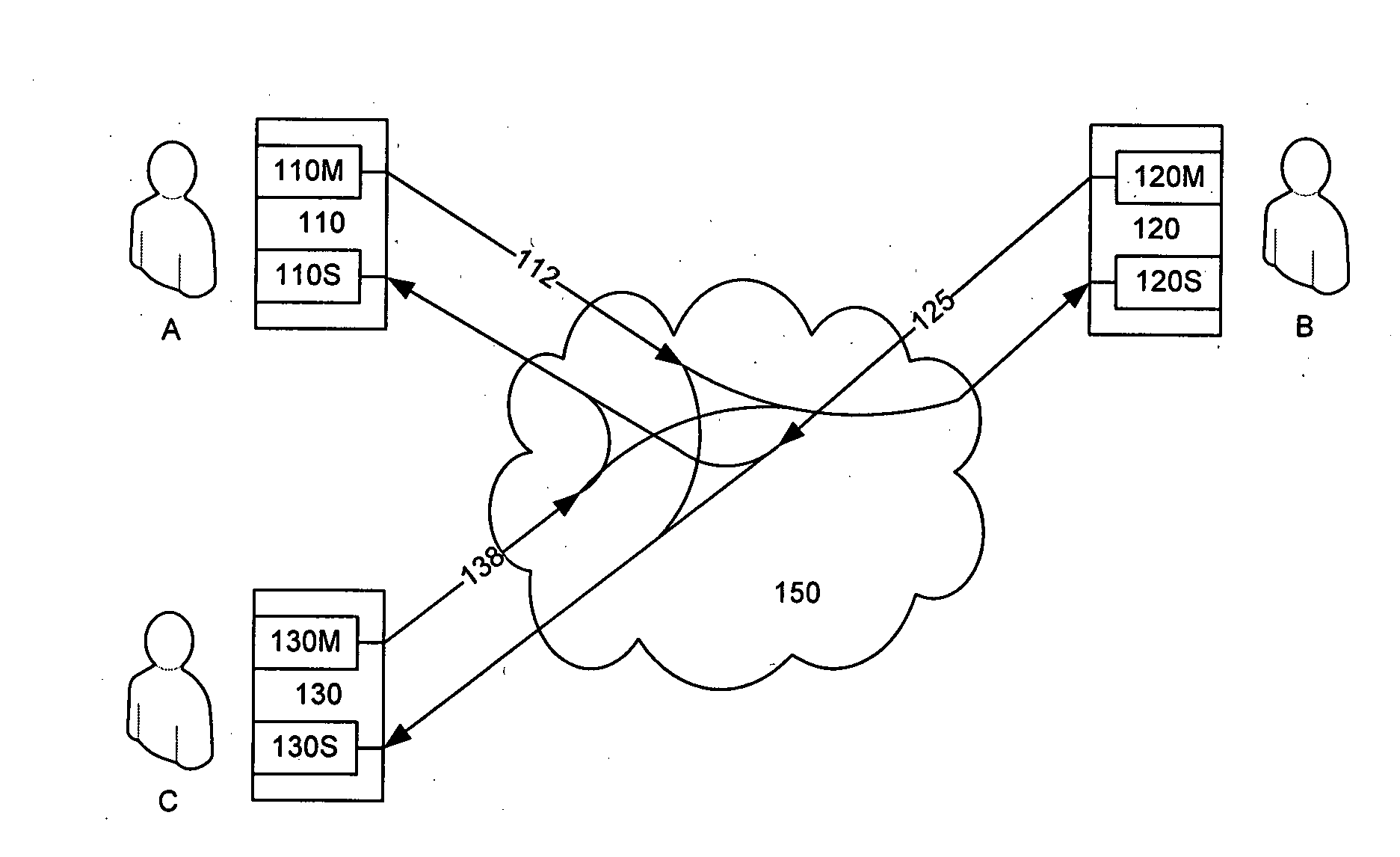
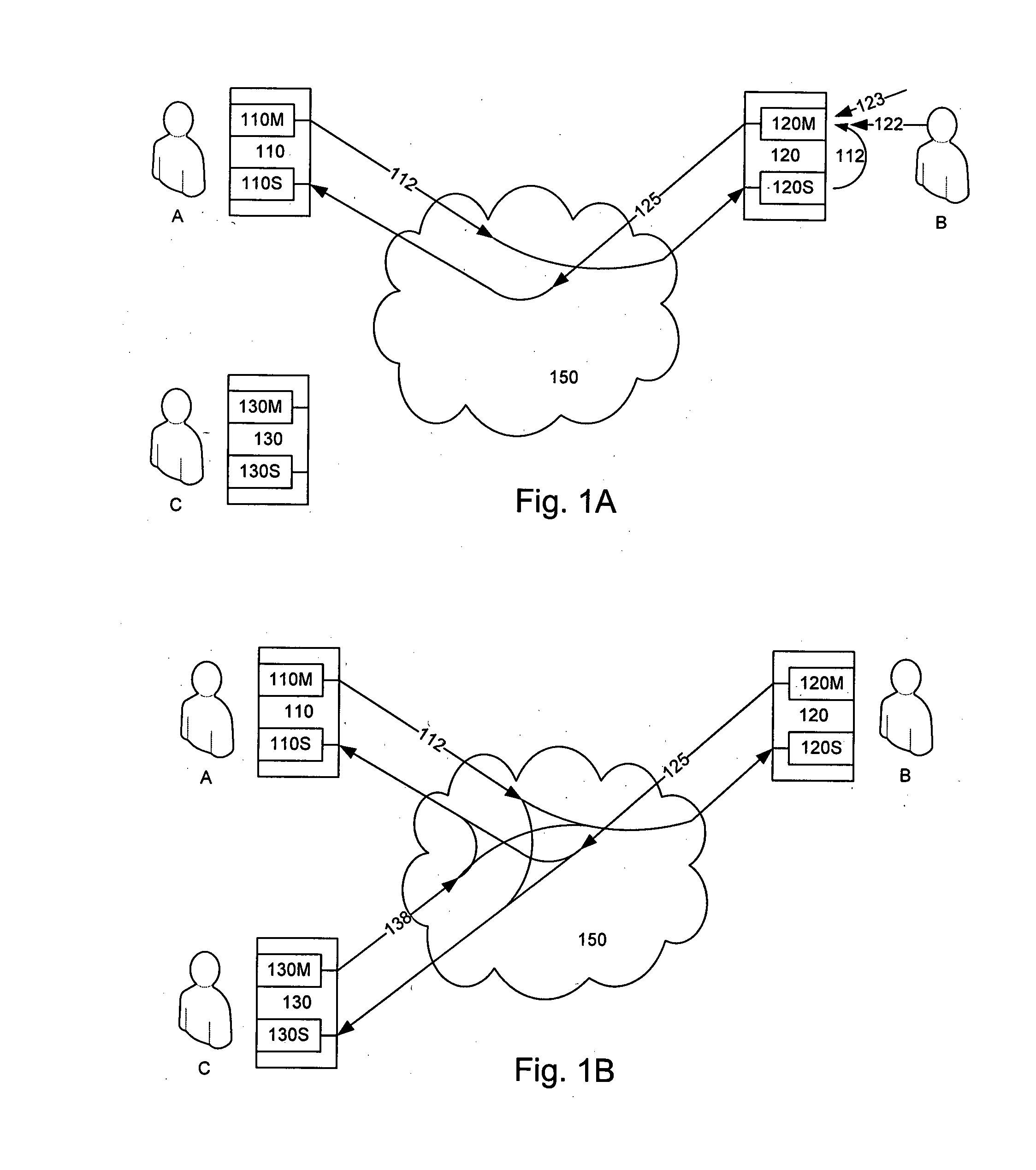
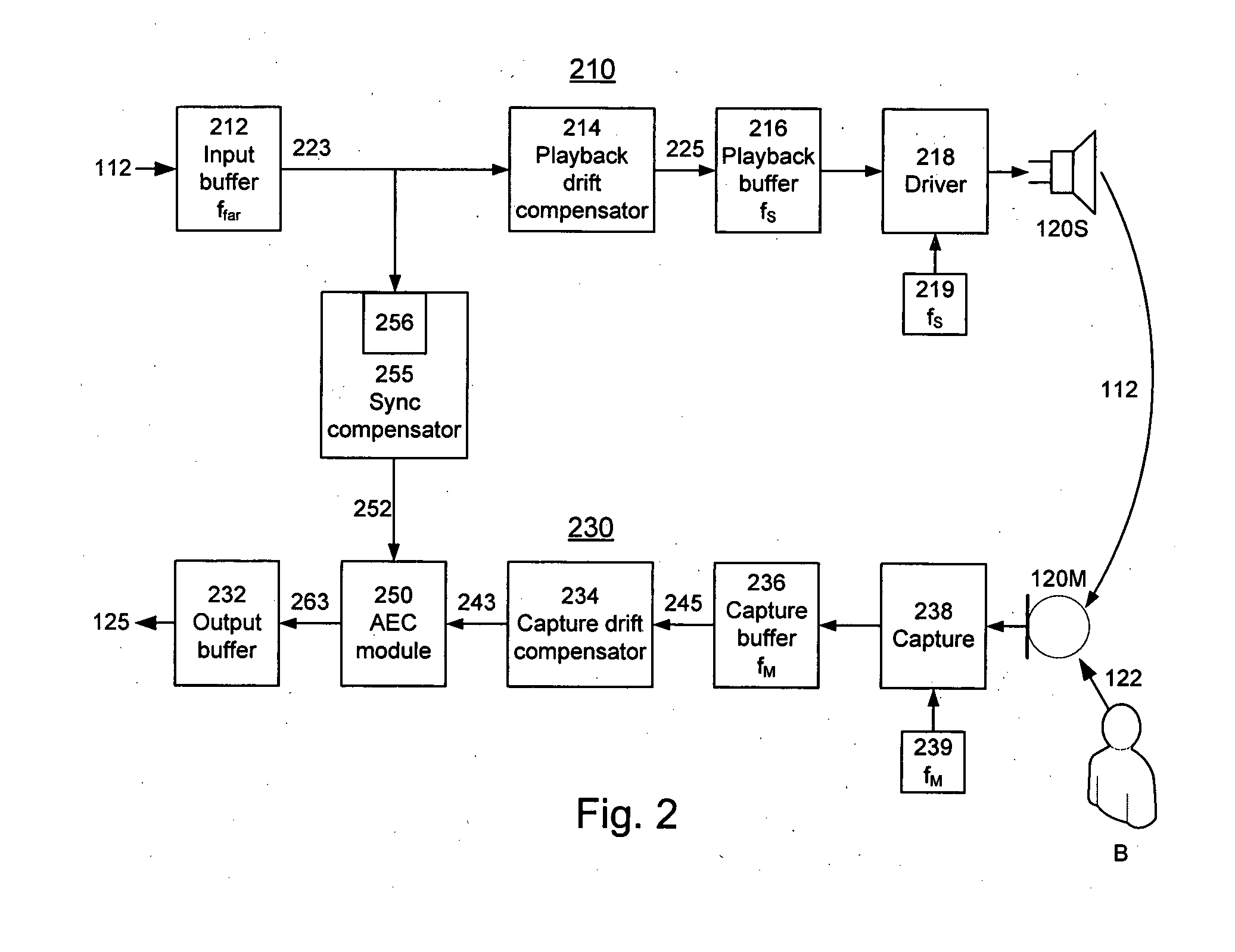
Audio Acoustic Echo Cancellation for Video Conferencing
ActiveUS20130002797A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsTelevision conference systemsProximal pointBuffer overflow
A new audio echo cancellation (AEC) approach is disclosed. To facilitate echo cancellation, the method adjusts for errors (called drift) in sampling rates for both capturing audio and playing audio. This ensures that the AEC module receives both the signals at precisely the same sampling frequency. Furthermore, the far-end signal and near-end mixed signal are time aligned to ensure that the alignment is suitable for application of AEC techniques. An additional enhancement to reduce errors utilizes a concept of native frequency. A by-product of drift compensation allows for excellent buffer control for capture / playback and buffer overflow / underflow errors from drift errors are eliminated.
Owner:RED HAT
Compensation method for error calibration of MEMS gyroscope in MIMU
InactiveCN103196462AGet rid of restrictionsHigh engineering utilization valueMeasurement devicesGyroscopeThermostat
The invention discloses a compensation method for error calibration of an MEMS gyroscope in an MIMU. The method uses a novel error model of the MEMS gyroscope. The method can complete calibration for non-orthogonal errors and temperature errors of the MEMS gyroscope in cases of existing devices: a rotary table with a thermostat and a single shaft being capable of rotating in 360 DEG, and a rotary table without a thermostat and with dual shafts being capable of rotating in 360 DEG; and does not introduce secondary mounting errors, thereby ensuring a calibration precision, overcoming restrictions of calibration devices, and well compensating non-orthogonal errors and temperature drift errors. According to the invention, in a full temperature range, a maximum output error of the MEMS gyroscope is only 0.2 DEG / s, and triaxial errors are also consistent.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
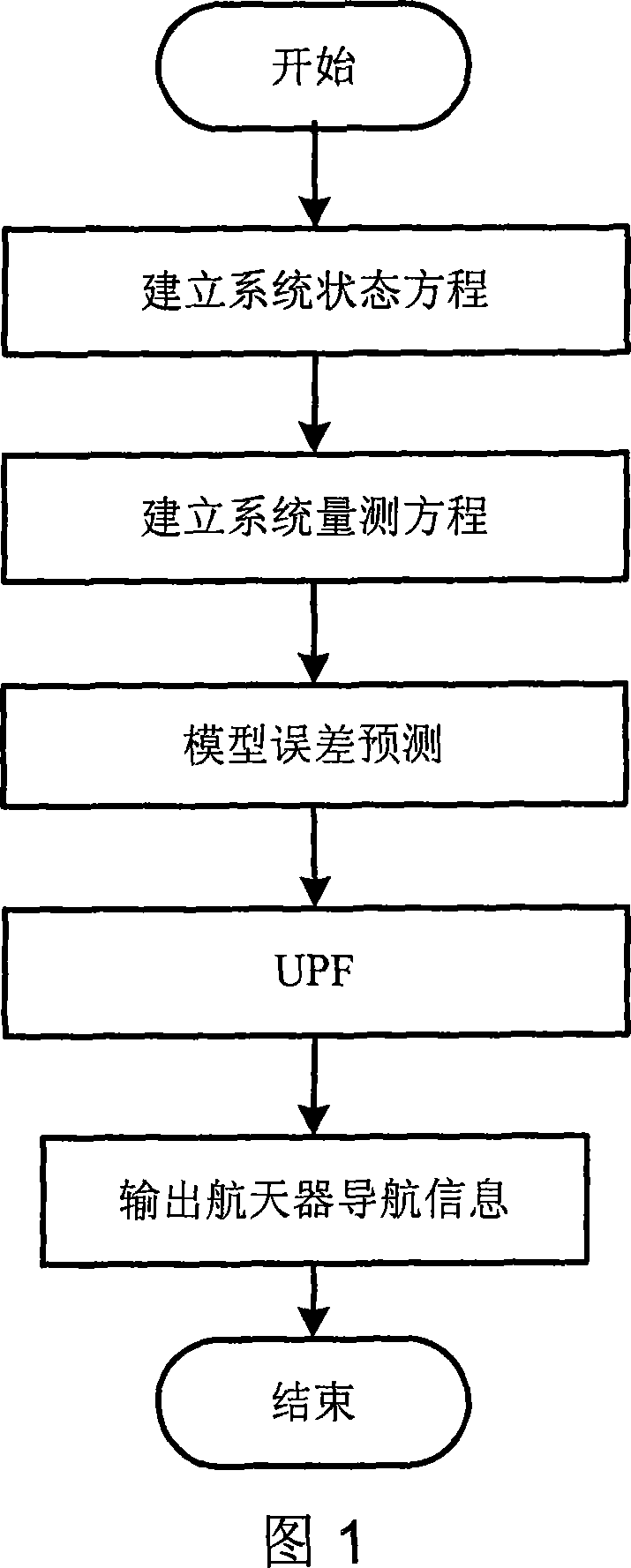
Self boundary marking method based on forecast filtering and UPF spacecraft shading device
ActiveCN101082494AOvercoming inaccuracyImprove filtering accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansSpaceflightInformation integration
There are a sort of predictive filtering and the self-demarcation of the UPF spaceflight, it relates to the spaceflight airmanship field. It applies to the self-demarcation of the spaceflight peg-top, especially it relates to a sort of spaceflight self-demarcation method of the inertia / starlight which bases the predictive filtering and the UPF (Unscented Particle Filter) information coalescence, thereby it applies to the navigation determining gesture of the spaceflight. First it establishes the self-demarcation state equations of the spaceflight, and then it makes the gesture information which is observed by the star sensing device to become the measuring equations, finally it adopts the self-demarcation arithmetic which bases the predictive filtering and the UPF spaceflight to estimate and amend the drift error of the peg-top, thereby it obtain the high exact gesture of the spaceflight.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
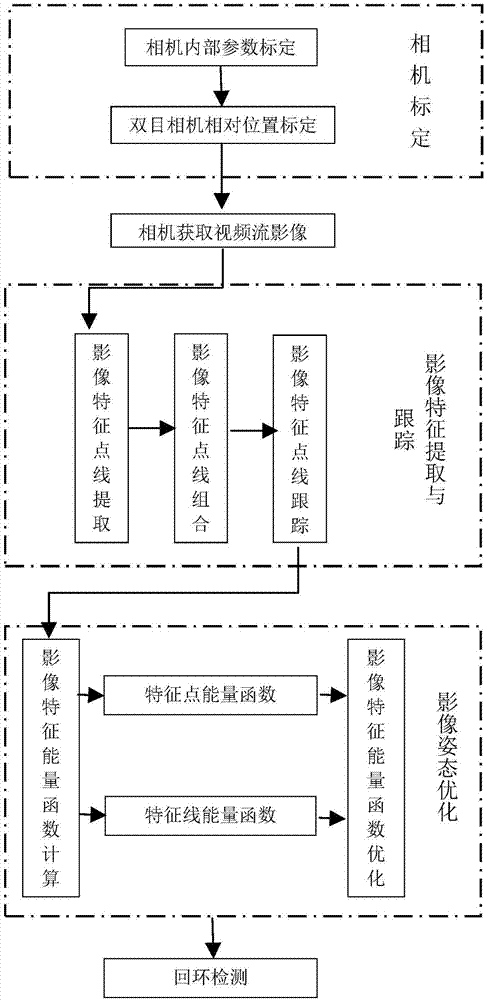
Indoor feature point and structural line combination-based indoor SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) method
ActiveCN107392964AEasy to moveReal-timeImage analysisPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimultaneous localization and mappingClosed loop
The present invention relates to an indoor feature point and structural line combination-based indoor SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) method. The method includes the following steps that: S1, camera internal parameter calibration is performed; S2, feature points and structural lines are extracted from video frame image data acquired by a camera; S3, feature points and structural lines are tracked according to the obtained feature points and structural lines, and key frames are selected; S4, on the basis of the tracking information of the obtained feature points and structural lines, the space points and space lines of a surrounding environment are charted, and the positioning of a platform is optimized; S5, whether the motion trajectory of the platform forms a closed loop is judged, correct closed-loop key frames are obtained, and a global image pose and a map are optimized globally; and S6, a result is outputted. The method of the invention has the advantages of real-time performance and high efficiency. According to the method of the invention, matched feature points and structural lines are utilized to chart the pose of an image and the surrounding environment; loopback detection processing is performed; and therefore, when the structural lines are fully utilized to reduce drift errors, the good positioning result of the mobile robot platform and the structural features of the surrounding environment can be obtained with the loopback detection adopted.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
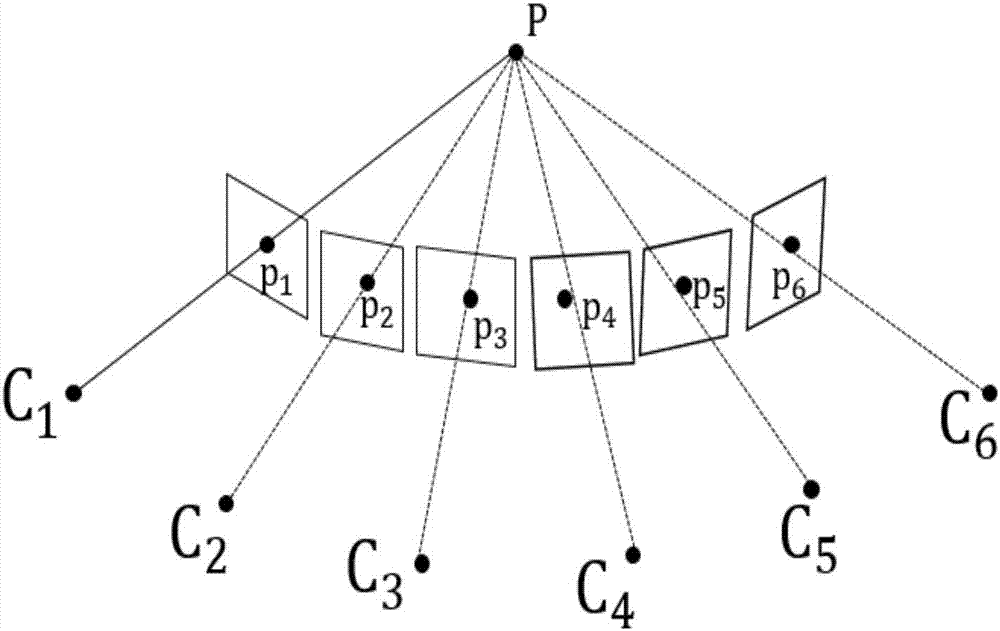
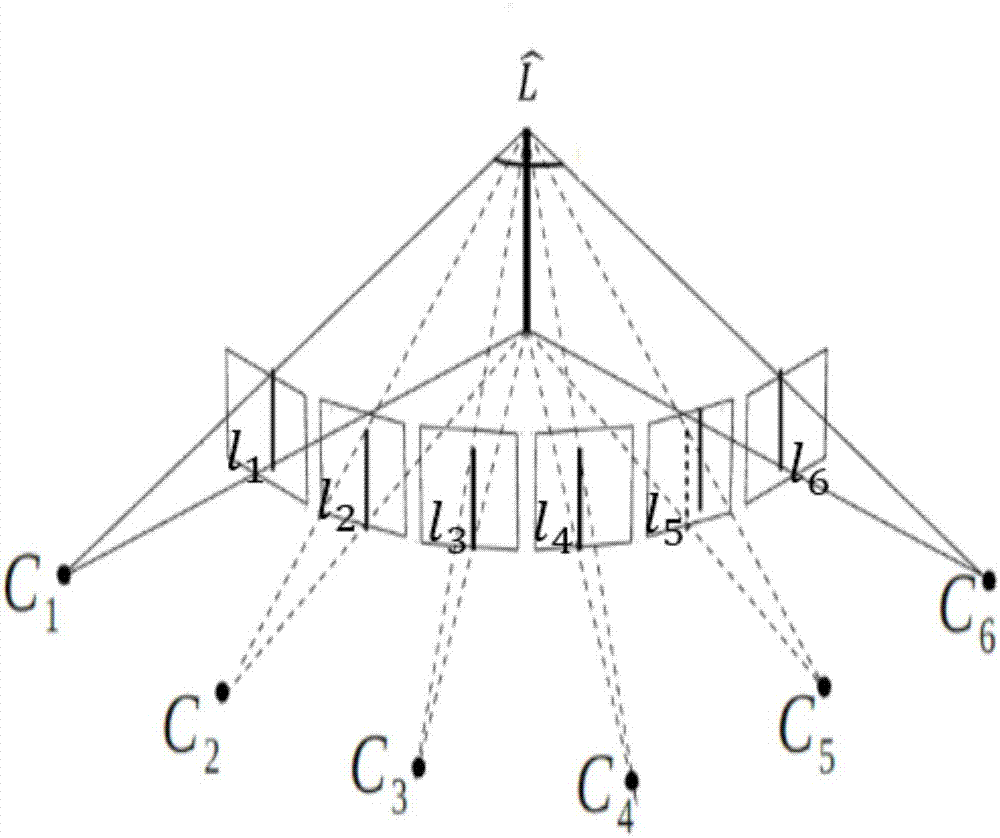
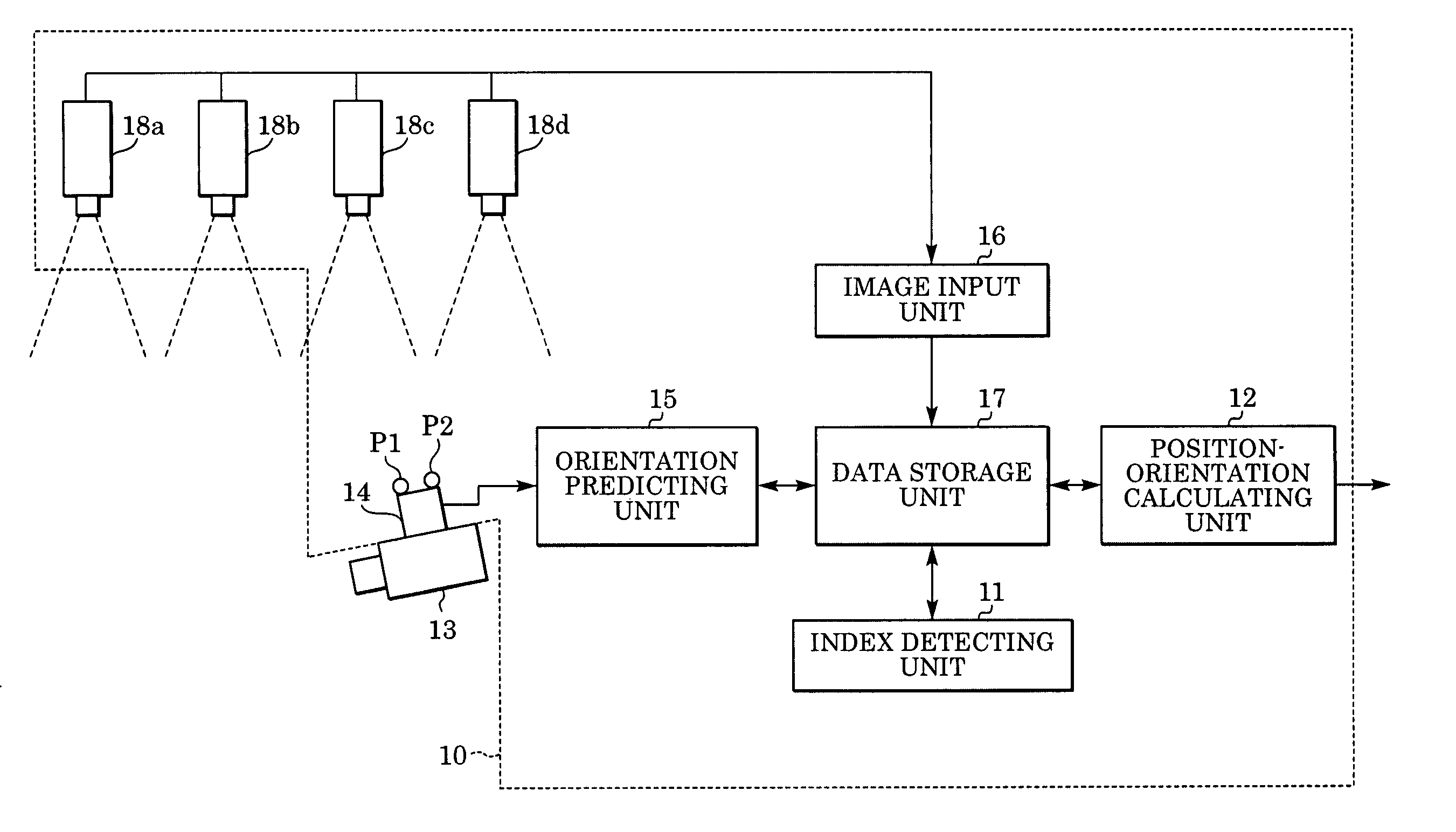
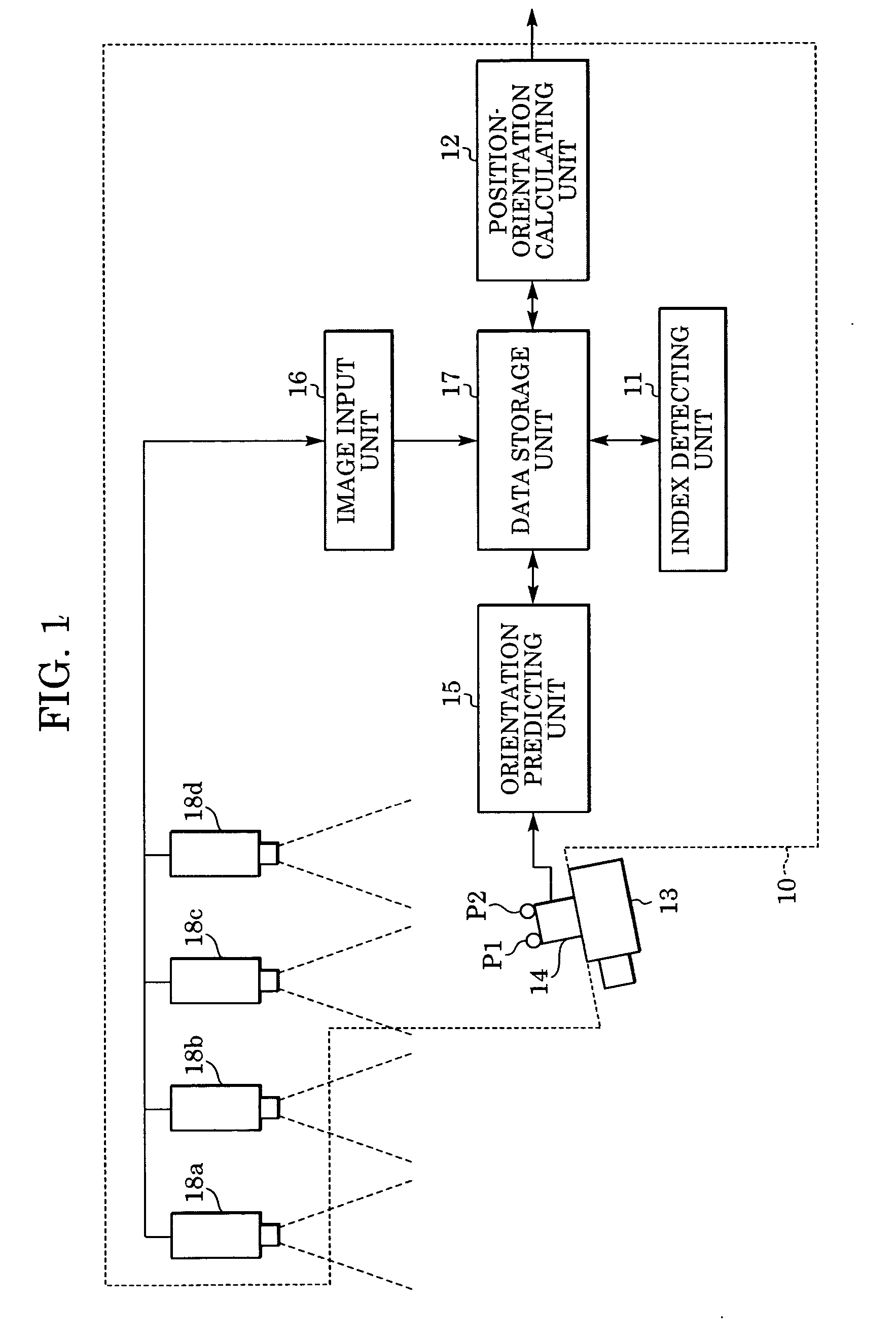
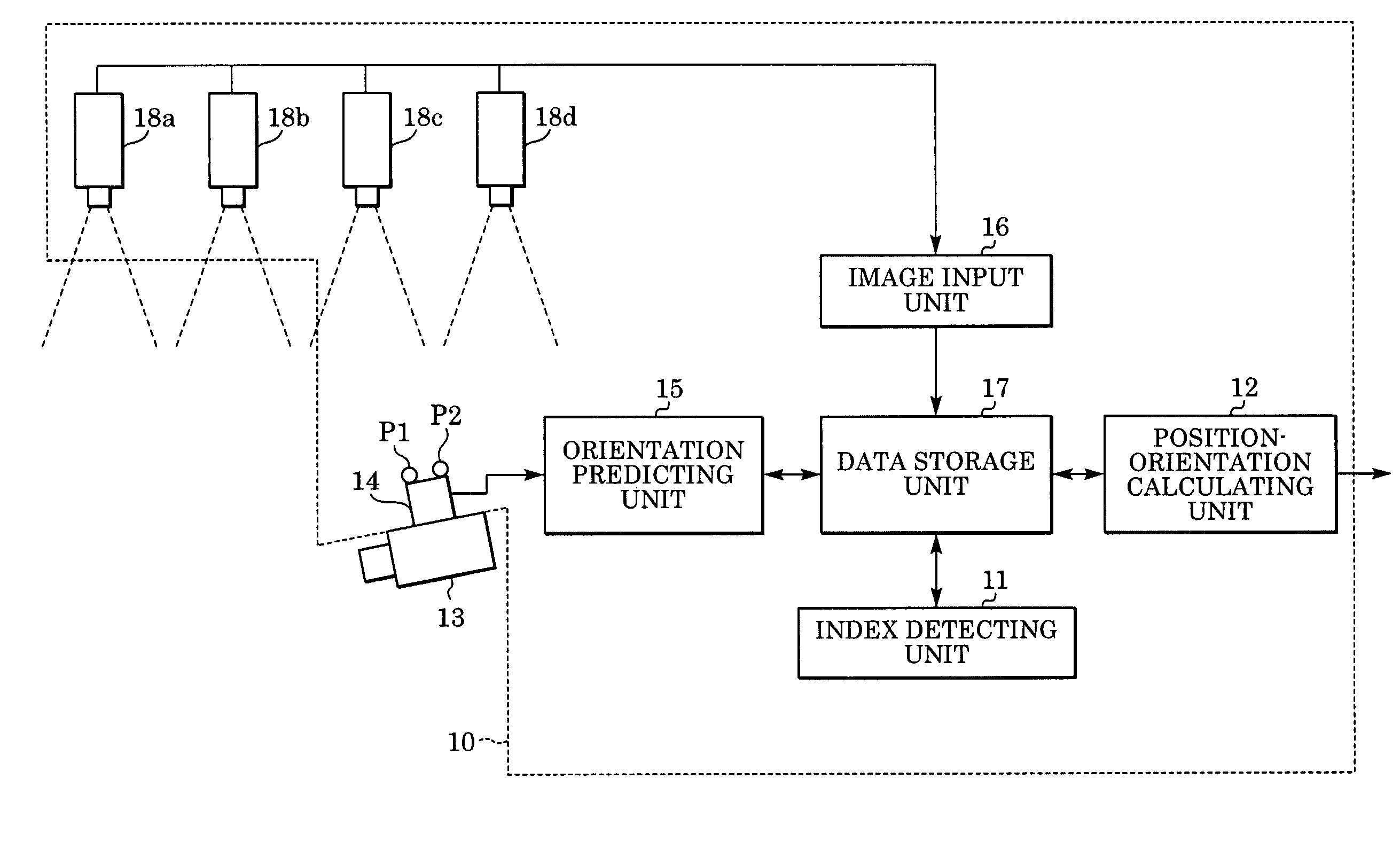
Information processing method and apparatus for finding position and orientation of targeted object
In an information processing method, an orientation sensor is mounted on a targeted object to be measured, and bird's-eye view cameras for capturing images of the targeted object are fixedly installed. From the images captured by the bird's-eye view cameras, an index detecting unit detects indices mounted on the orientation sensor. A measured orientation value from the orientation sensor is input to an orientation predicting unit, and the orientation predicting unit predicts the present orientation of the targeted object based on an azimuth-drift-error correction value. A position-orientation calculating unit uses the image coordinates of the detected indices to calculate the position of the imaging device and an update value of the azimuth-drift-error correction value, which are unknown parameters. From the obtained parameters, the position-orientation calculating unit finds and outputs the position and orientation of the targeted object.
Owner:CANON KK
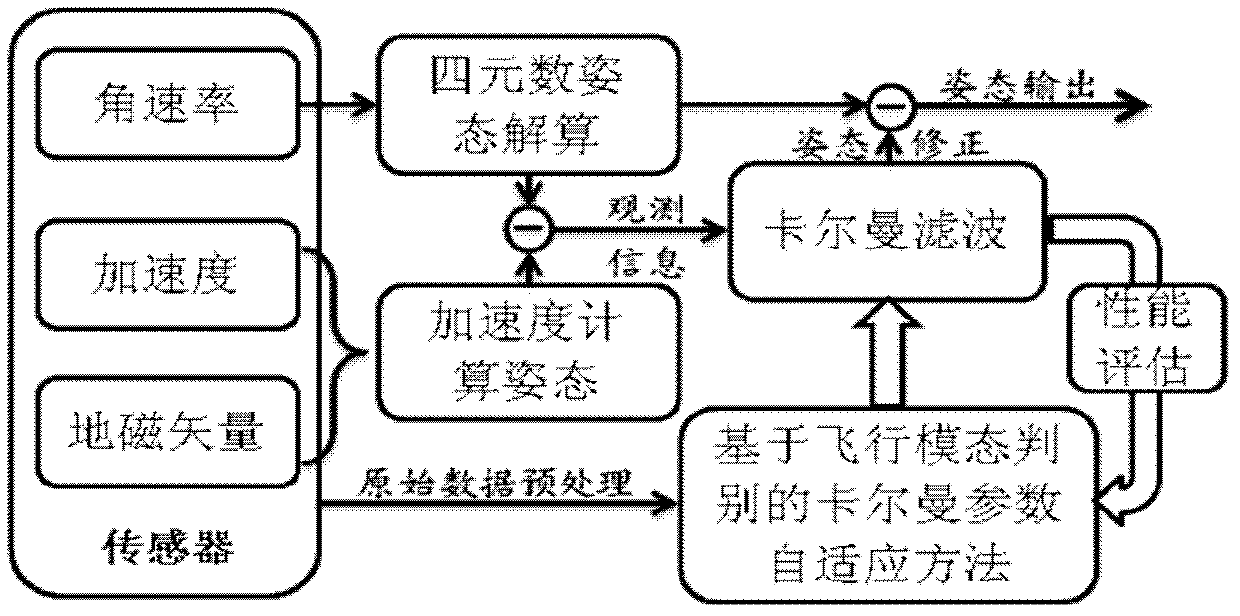
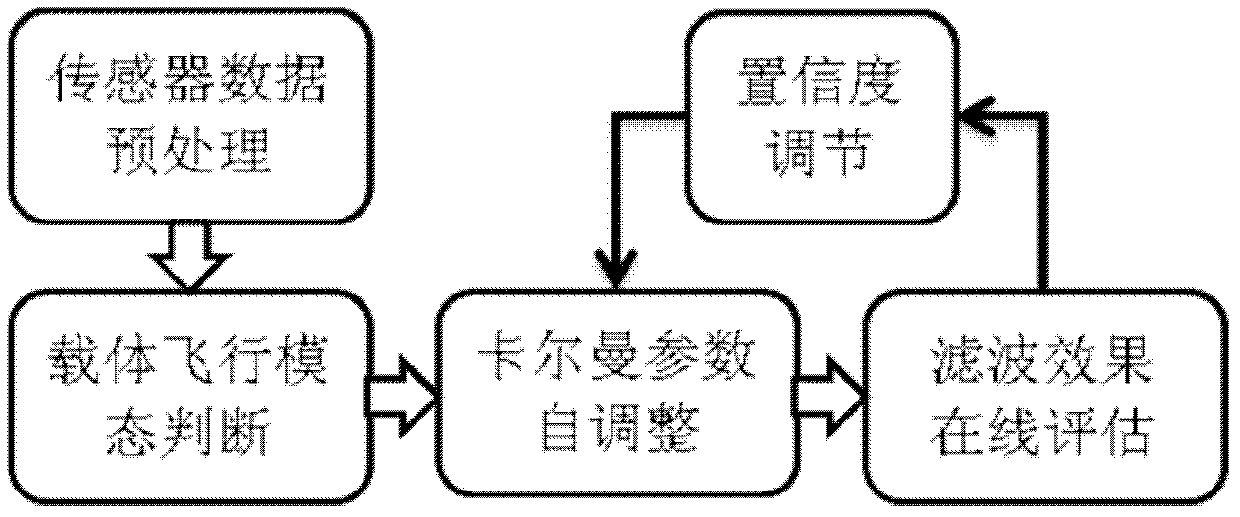
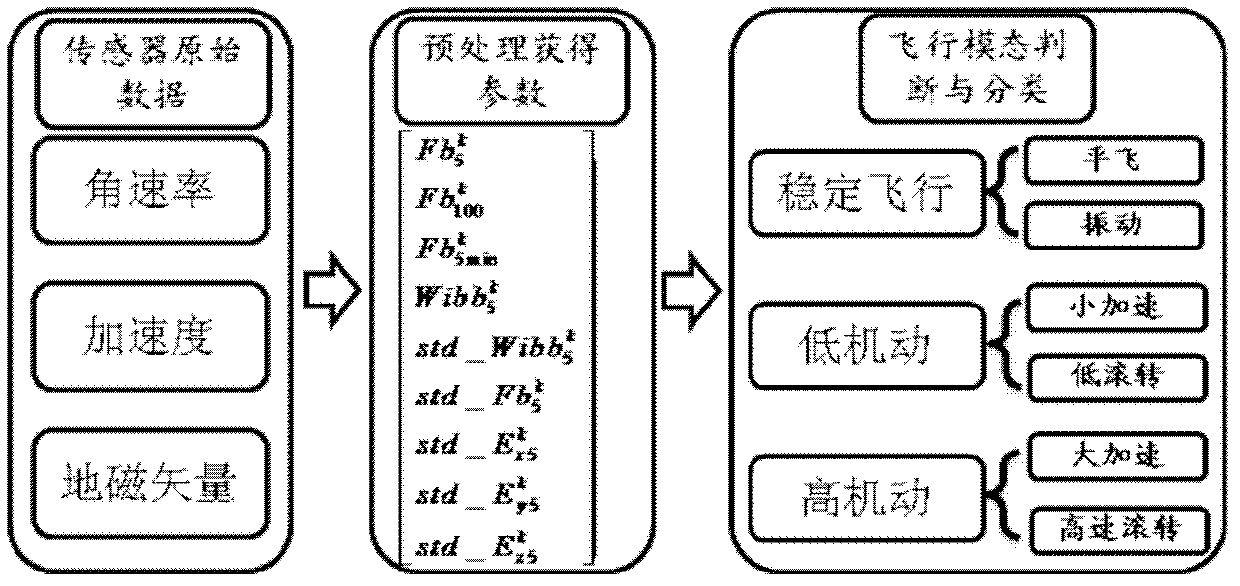
Micro inertial parameter adaptive attitude determination method based on carrier flight mode judgment
InactiveCN102607562ASimplify the acquisition processHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsKaiman filterClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a micro inertial parameter adaptive attitude determination method based on carrier flight mode judgment. The method comprises the following steps of outputting data by a sensor; calculating a long-period characteristic parameter and a short-period characteristic parameter of the sensor; judging a motion mode of a carrier according to the variation and range of the parameters; designing an adaptive adjustment strategy of a kalman filtering parameter according to the error variation characteristics of a micro attitude reference system of the carrier in different motion modes; observing the variation of residual sequence quadratic sum according to the attitude in a kalman filter; and carrying out online difference evaluation for the quality of filter effect of the current parameter, and feeding back the evaluation result in a form of parameter confidence to adjust a filter parameter of the kalman filter. According to the method, selection and setting operations of a judgment threshold in the conventional micro inertial attitude determination method are simplified, the influence of the flying height of the carrier and drifting error of the sensor on a judgment condition is avoided, dynamic and static running characteristics of the micro attitude reference system are considered comprehensively, and the dynamic adaptability and the static stability of the micro attitude reference system are improved effectively.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
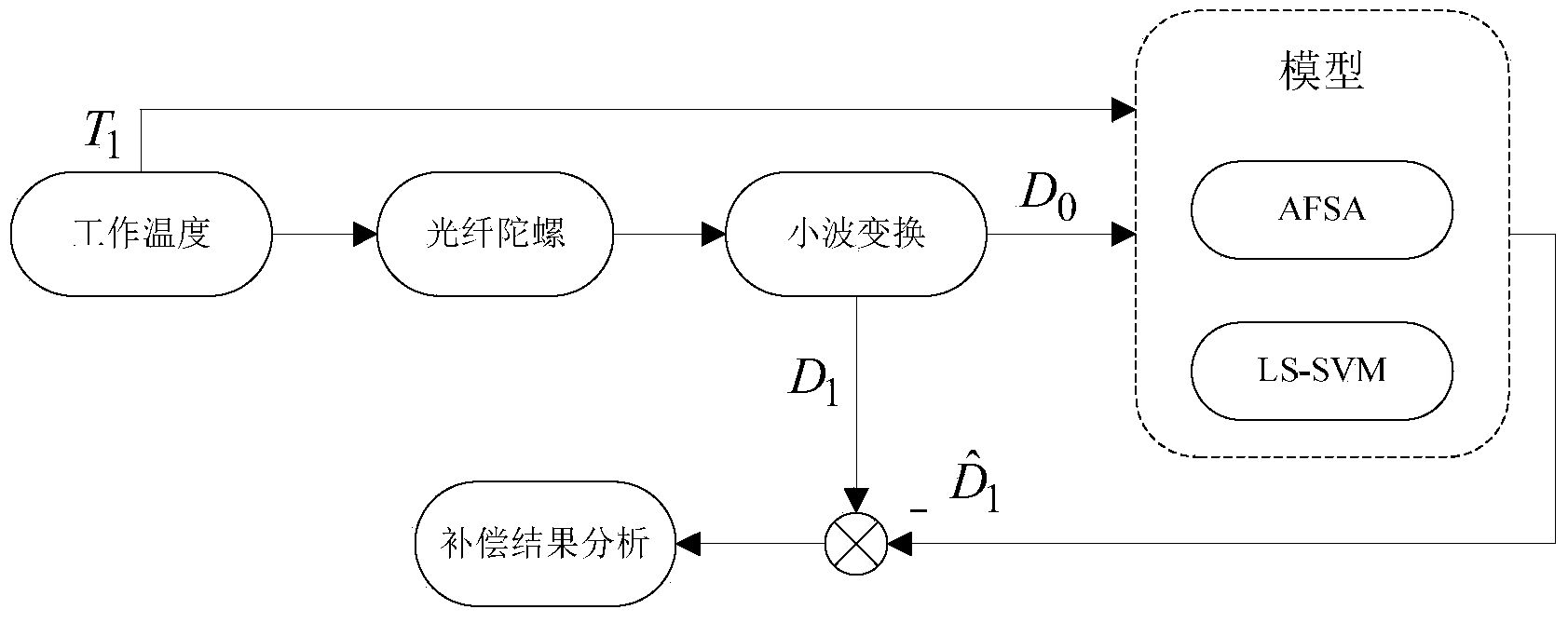
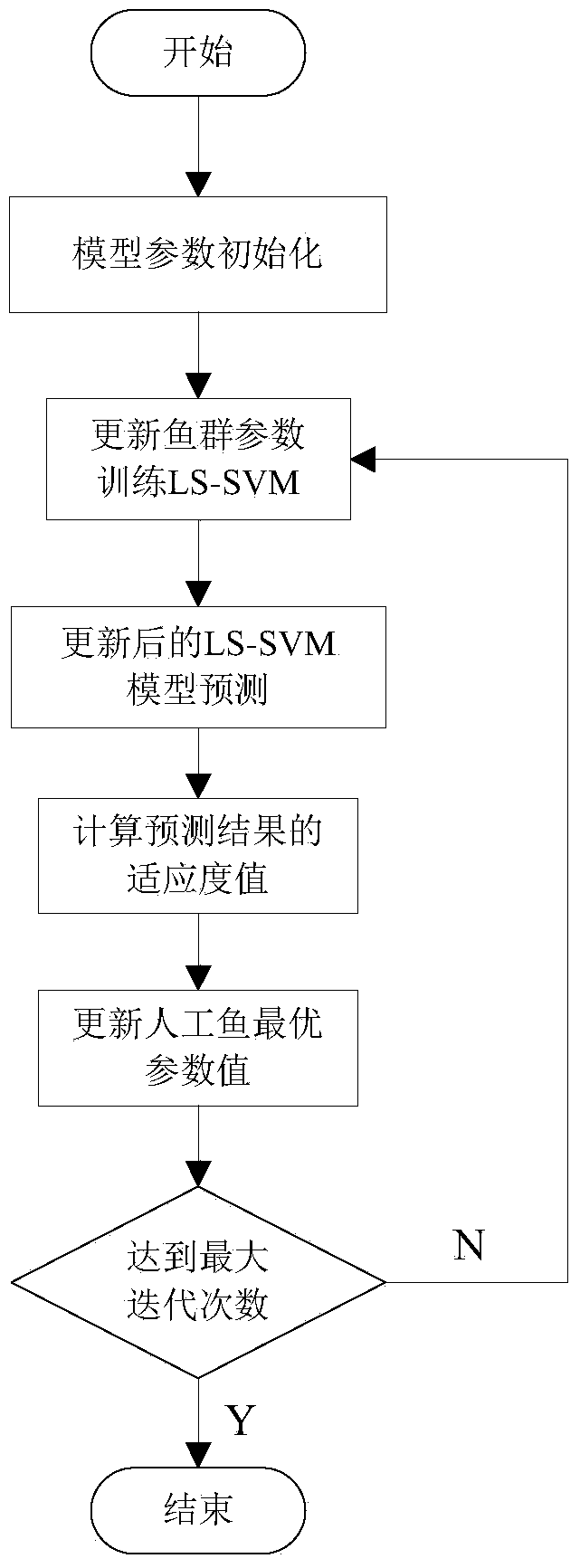
Fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation method based on optimized least square-support vector machine (LS-SVM)
InactiveCN103954300AImprove forecast accuracyImprove generalization abilitySagnac effect gyrometersFiberLocal optimum
The invention discloses a fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation method based on an optimized least square-support vector machine (LS-SVM). The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) initializing an artificial fish swarm algorithm (AFSA) optimization algorithm and LS-SVM model parameters; (2) determining sample data for model training and testing according to fiber optic gyroscope output data, and preprocessing the model input data; (3) training a LS-SVM model by using the training data, and continuously iterating the optimized model parameters through the AFSA algorithm; (4) predicting output of the fiber optic gyroscope according to the trained model, and performing temperature drift error compensation. According to the method, the optimized parameters under set conditions can be acquired according to the training sample by adopting the AFSA algorithm with high global optimization capacity, the condition that local optimization is possibly caused in the optimization process is avoided, and the prediction accuracy of the model can be improved to a certain degree.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Target posture tracking method based on inertia and geomagnetic sensor
InactiveCN104764451AHigh precisionSimple methodNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by terrestrial meansGyroscopeAccelerometer
The invention discloses a target posture tracking method based on inertia and a geomagnetic sensor. According to the target posture tracking method, posture tracking can be realized without any reference marker and a specific tracking environment, and the method is simple and feasible; a gyroscope, an accelerometer and the geomagnetic sensor are used for respectively acquiring components of angular speeds, accelerated speeds and magnetic intensity data corresponding to a current posture of a target in three sensitive axes; a posture tracking result of the gyroscope is corrected by using the accelerometer and the geomagnetic sensor and drift errors are eliminated so that the precision of a tracking result is improved; and the target posture tracking method utilizes an efficient offline operated Kalman filtering algorithm and fuses a multi-sensor tracking result, so that the real-time online posture tracking is realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
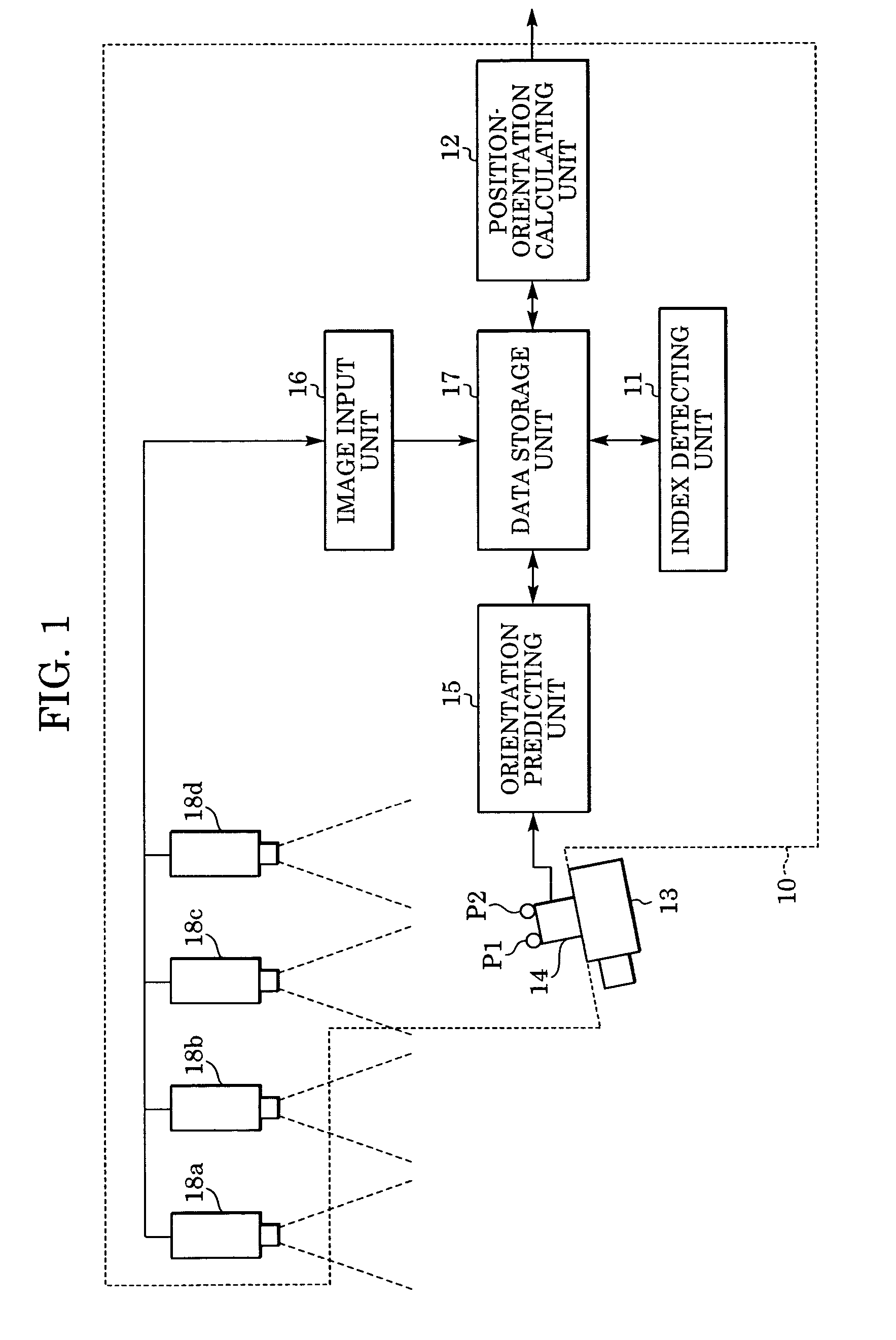
Information processing method and apparatus for finding position and orientation of targeted object
In an information processing method, an orientation sensor is mounted on a targeted object to be measured, and bird's-eye view cameras for capturing images of the targeted object are fixedly installed. From the images captured by the bird's-eye view cameras, an index detecting unit detects indices mounted on the orientation sensor. A measured orientation value from the orientation sensor is input to an orientation predicting unit, and the orientation predicting unit predicts the present orientation of the targeted object based on an azimuth-drift-error correction value. A position-orientation calculating unit uses the image coordinates of the detected indices to calculate the position of the imaging device and an update value of the azimuth-drift-error correction value, which are unknown parameters. From the obtained parameters, the position-orientation calculating unit finds and outputs the position and orientation of the targeted object.
Owner:CANON KK
Indoor positioning method adopting visible light and inert composition
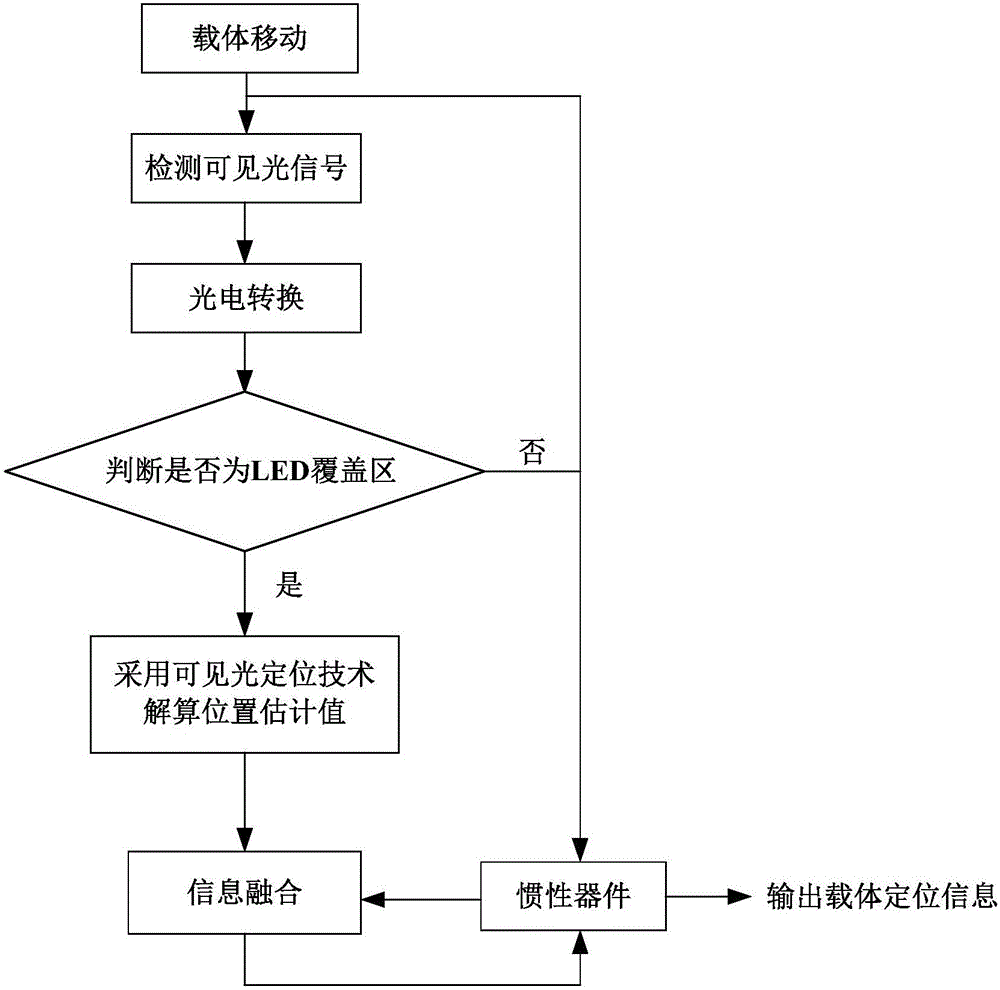
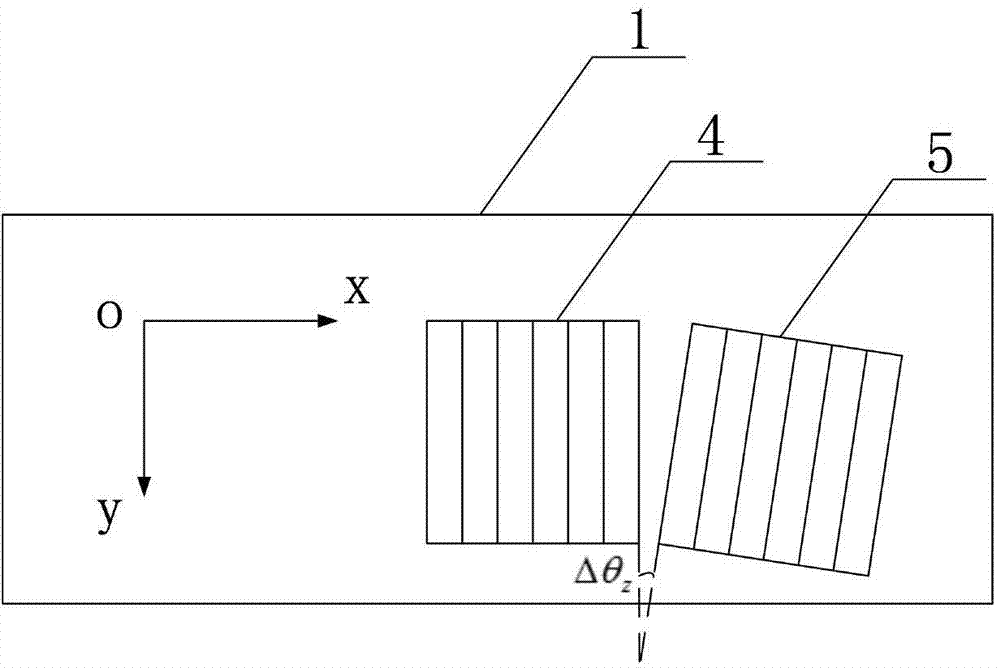
InactiveCN105674986ACommunication Bit Error Rate GuaranteeGuarantee positioning qualityNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLight signalVisible light positioning
The invention provides an indoor positioning method adopting visible light and inert composition. A mobile carrier can detect a visible light signal in a process of moving in a room. The indoor positioning method comprises the following steps: judging whether the mobile carrier is positioned in a visible light strong coverage region according to a light intensity threshold value; if a light intensity value is less than the light intensity threshold value, directly taking a position estimation value acquired by an inert device as carrier positioning information; if the light intensity value is greater than or equal o the light intensity threshold value, calculating the position estimation value according to the visible light signal, subtracting the position estimation value acquired by the inert device from the position estimation value calculated according to the visible light signal, and performing Kalman filtering on an obtained difference value to obtain a drift error of the inert device, wherein the drift error is used for correcting the inert device, and the corrected position estimation value of the inert device is used as the carrier positioning information. According to the indoor positioning method, the influence caused by a cover blind area and a shadow in a visible light positioning process can be effectively avoided, and the shortcoming that the error of the inert device is accumulated along the time is overcome; continuous automatic high-precision indoor positioning is realized.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Copying and splicing method of large-size plane diffraction grating
ActiveCN104749673AEasy to engineerGuaranteed long-term preservationDiffraction gratingsTime momentLarge size
The invention discloses a copying and splicing method of a large-size plane diffraction grating, relates to the technical field of diffraction grating manufacturing and solves the problem that an existing grating splicing method needs to repeatedly and continuously adopt high-accuracy control adjusting technology and is high in requirement on stability of a support and the problem of drift error existing between an adjusting system and a locking system when an exposure method is adopted. The copying and splicing method includes: utilizing a grating mother set to copy in an area adjacent to a grating blank for two times at different time moments; copying a first grating in a left-side area of the grating blank; copying a second grating in a right-side area adjacent to the left-side area of the grating blank; detecting splicing errors of the second copying grating and the first copying grating by a splicing error detection system; detecting two-dimensional splicing errors by an error detection system when the second copying grating is spliced. When the grating is in use, a multi-dimensional mechanical adjusting frame is not needed to adjust posture of the grating in realtime, and the grating can be stored for a long time; only two-dimensional splicing errors need to be detected in the process of splicing, so that difficulty in detection and adjustment is lowered.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
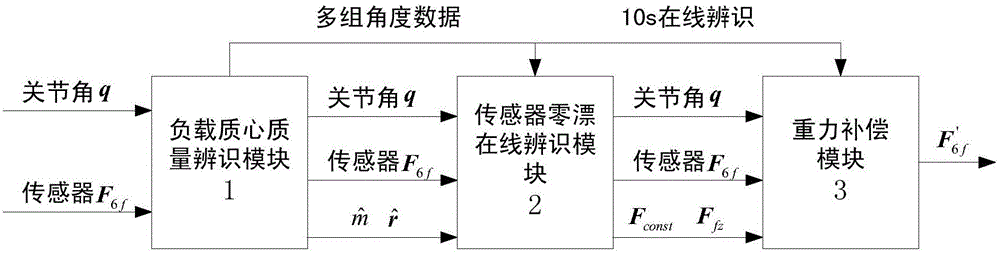
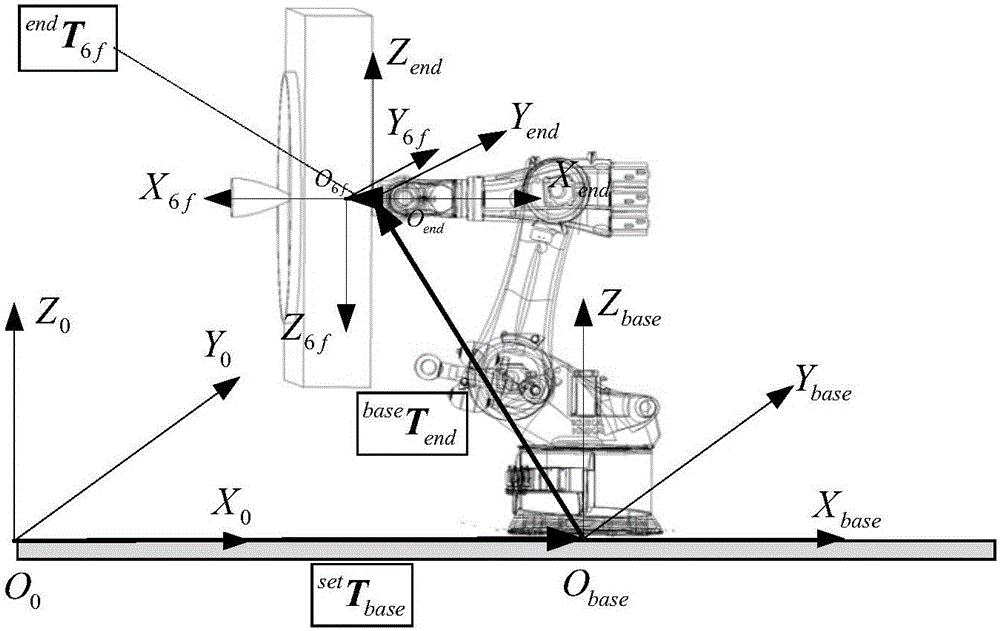
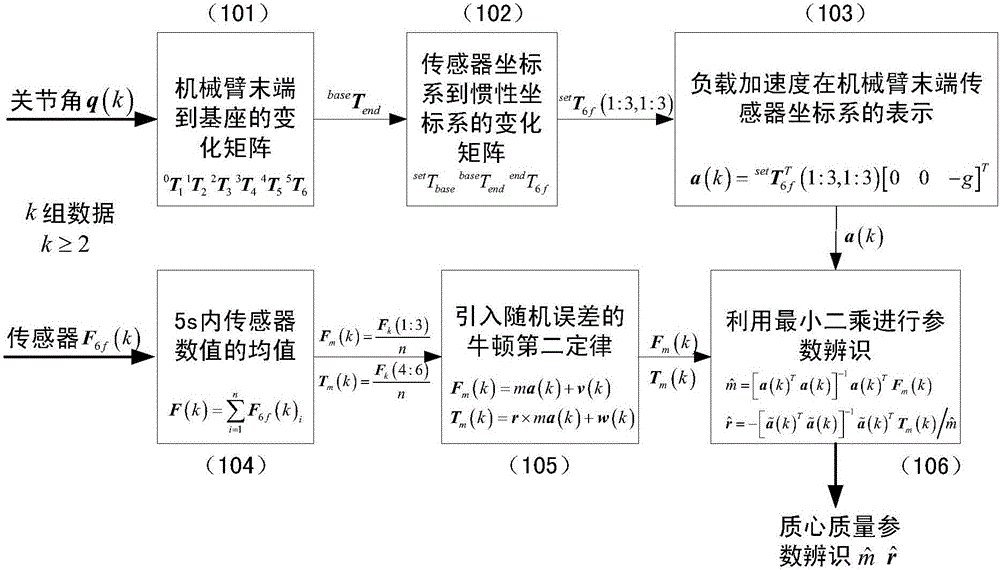
Gravity compensation method for mechanical arm load mass and sensor null drift online recognition
ActiveCN107433590AFunction increaseRealize online identificationProgramme-controlled manipulatorGravitational forceEngineering
The invention provides a gravity compensation method for mechanical arm load mass and sensor null drift online recognition. The gravity compensation method comprises the steps that S1, a load mass center and mass recognition module is adopted for obtaining and recognizing the mass center and mass of loads at the tail end of a mechanical arm, and the recognized mass center and the recognized mass of the loads are obtained; S2, a sensor null drift recognition module is adopted for reading the numerical value of a sensor, calculation is performed according to the recognized mass center and the recognized mass, and sensor null drift is obtained; and S3, a gravity compensation module is adopted for performing gravity compensation on the numerical value of the sensor according to the sensor null drift. By means of the method, the problem that due to the additional force and torque introduced by the loads of the tail end of the mechanical arm to the tail-end six-dimensional force sensor by the gravity effect and the presence of sensor null drift errors, the numerical value of the sensor is inaccurate and the final force control effect is affected can be solved, and uncertainty of the sensor null drift determines the necessity of online recognition of the sensor null drift.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
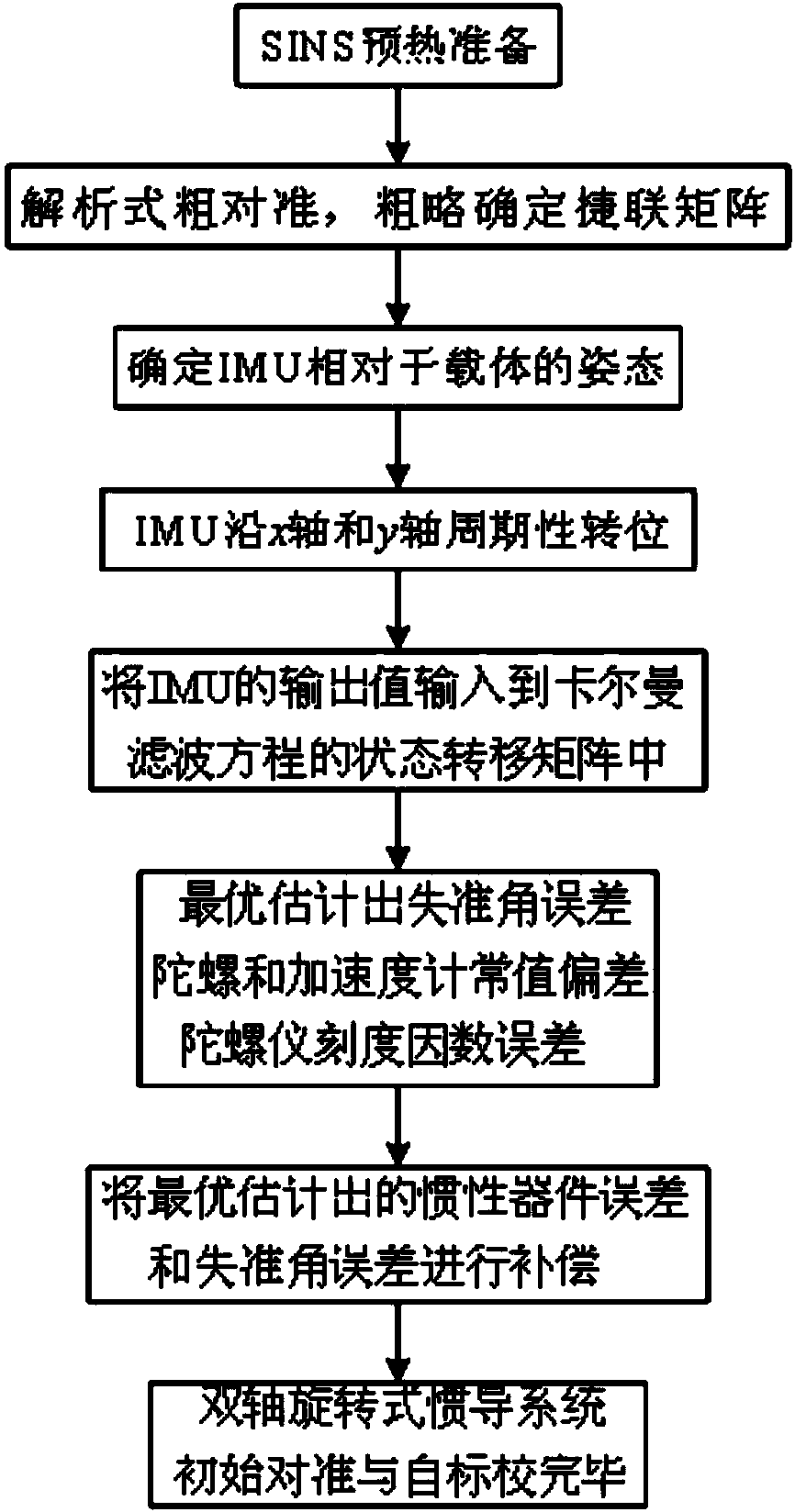
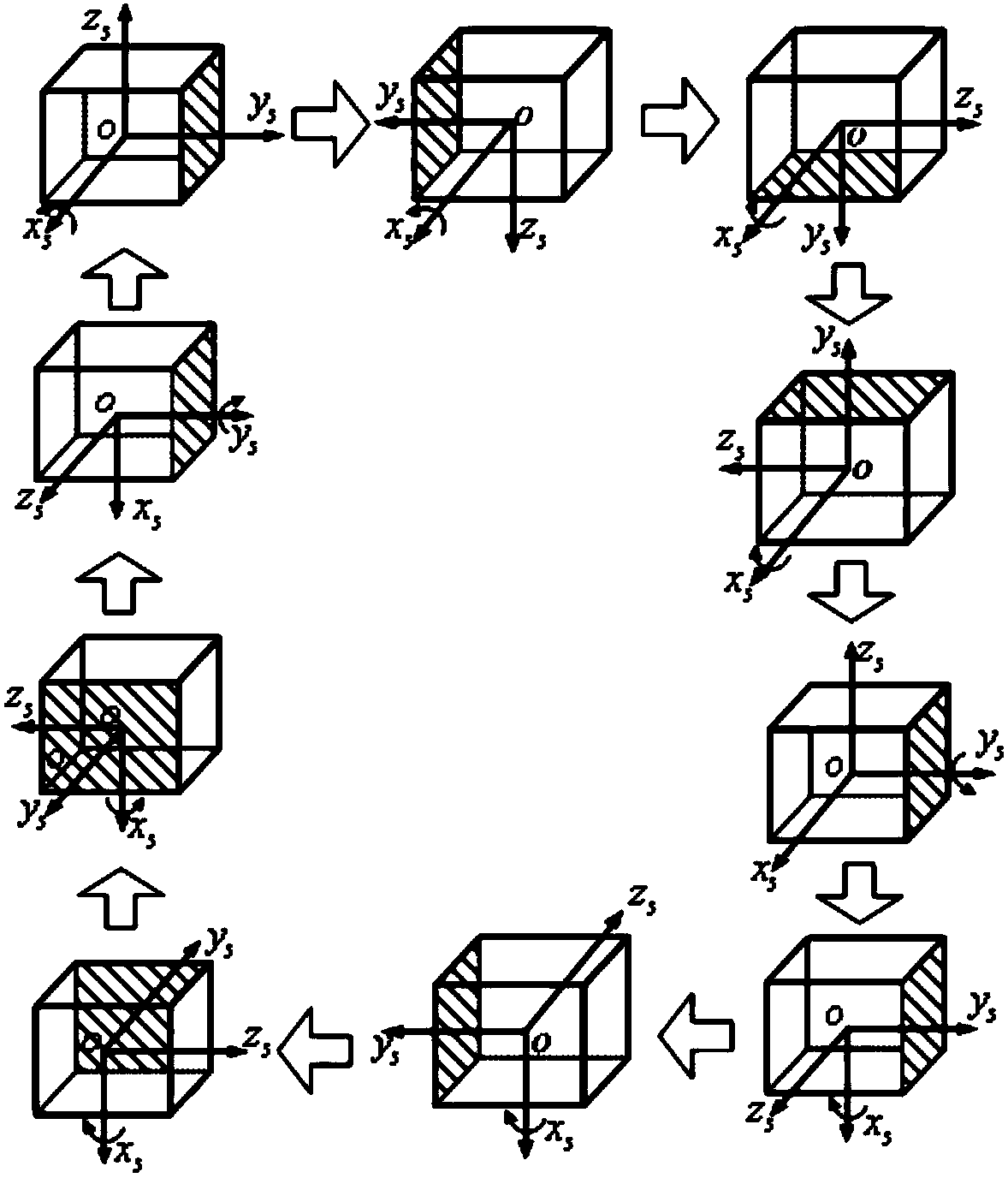
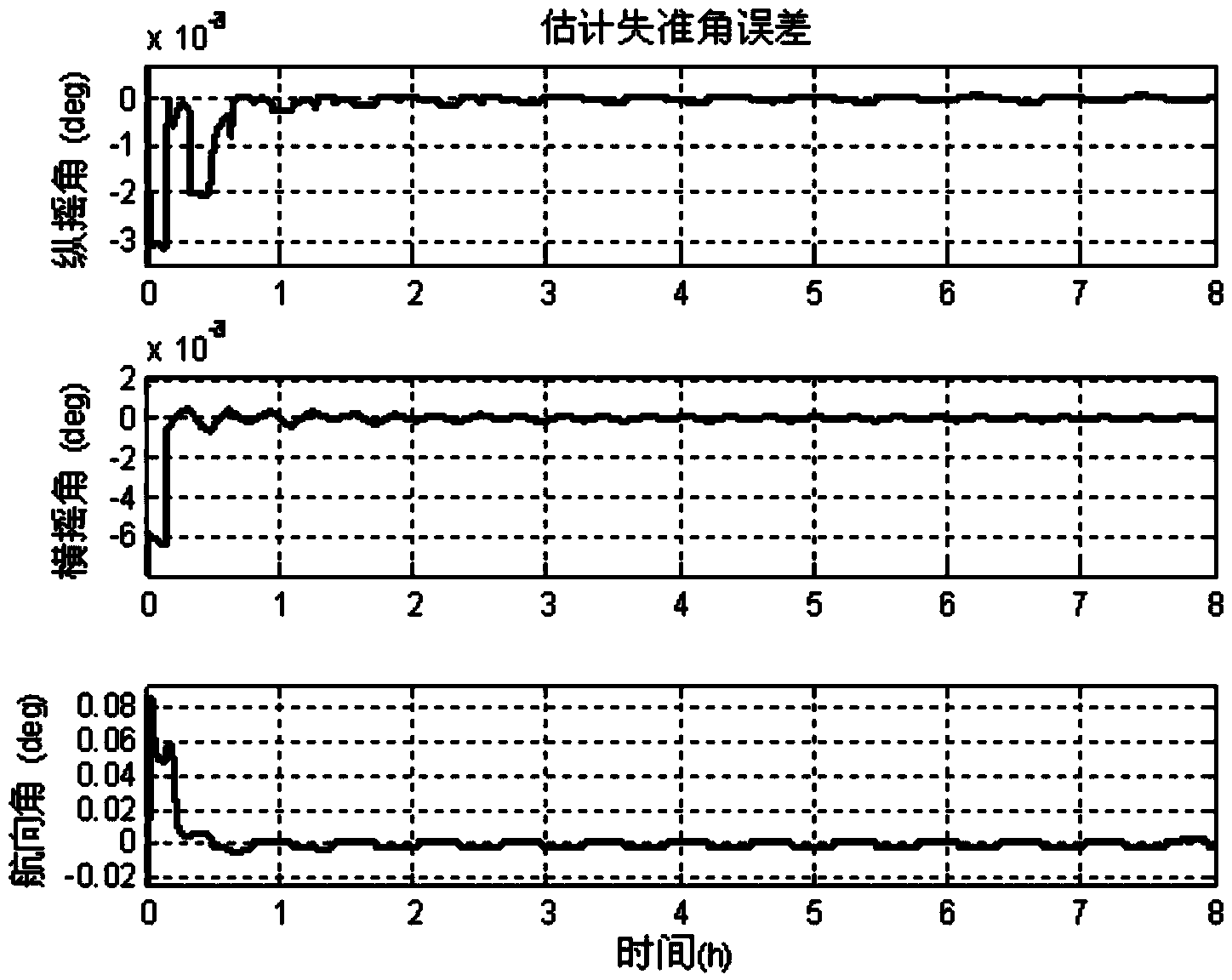
Initial alignment and self-calibration method of double-shaft rotation type strapdown inertial navigation system
InactiveCN103453917AEliminate the effects ofHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComputer scienceMarine navigation
The invention discloses an initial alignment and self-calibration method of a double-shaft rotation type strapdown inertial navigation system. For an inertial navigation system, inertial device errors and misalignment angles are main factors capable of influencing the positioning accuracy of the system; for meeting requirements of long navigation time and high accuracy, the inertial device errors and the misalignment angles can be calibrated so as to guarantee the positioning accuracy of the system. According to a transposition scheme disclosed by the invention, the observable degree of the inertial navigation system can be maximally improved without external auxiliary information, not only can the misalignment angles be rapidly and accurately calibrated, but also the main inertial device errors including constant gyroscopic drift errors, accelerometer zero errors, gyroscope scale factor errors and the like can be calibrated, and the positioning accuracy of the strapdown inertial navigation system can be greatly improved after the errors are compensated.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
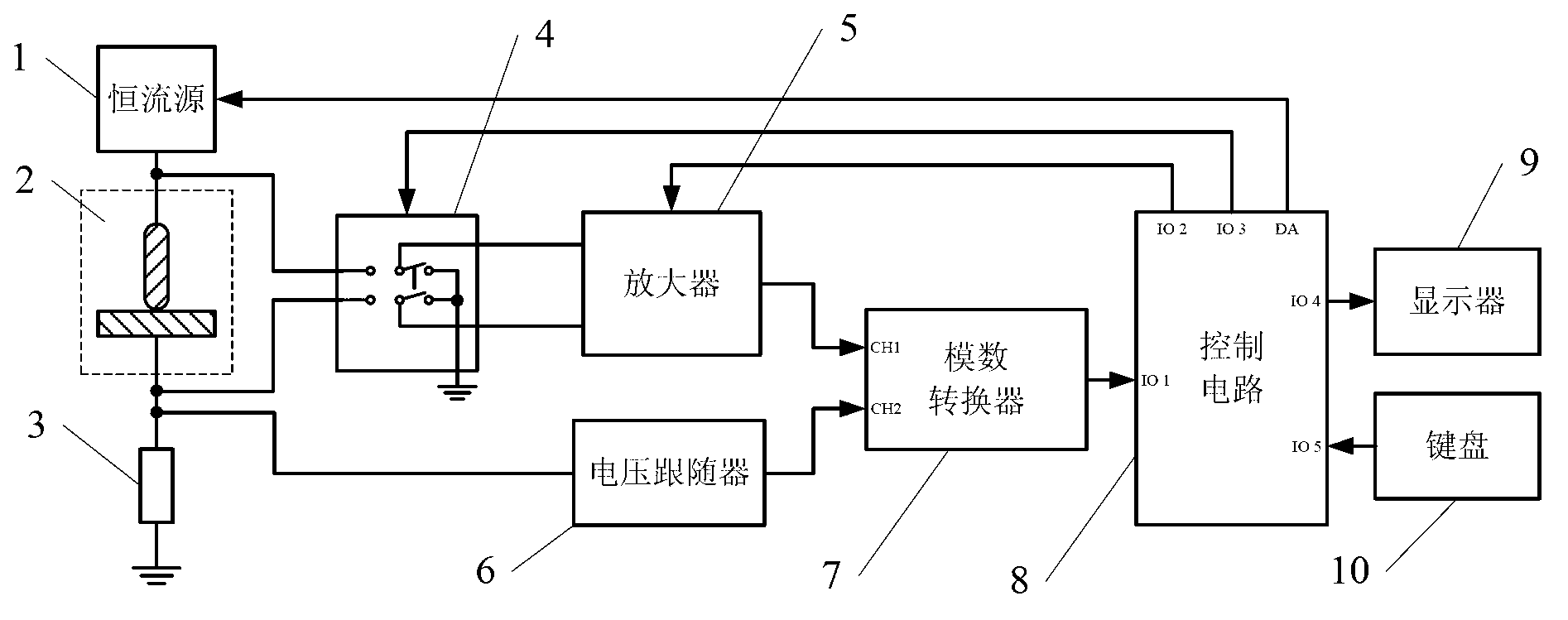
DC microresistivity measuring system
ActiveCN102841260AEasy to getReliable working principleResistance/reactance/impedenceTerminal voltageContact resistance
The invention discloses a DC microresistivity measuring system, relating to a DC microresistivity measuring system, belonging to the technical field of measurement and solving the problem that the measuring precision is influenced by measuring range and temperature drift errors of an amplifier in the traditional DC, AC and pulse methods for measuring contact resistance. According to the DC microresistivity measuring system, a constant current source provides excitation current for serially-connected contact pairs to be measured and a standard current sensing resistor; the standard current sensing resistor is used for acquiring a voltage signal to the ground through a voltage follower; and a terminal voltage measuring module for measuring the terminal voltage of the contact pairs to be measured, a current measuring module for acquiring a current value according to the voltage of the standard current sensing resistor and a resistance calculating module for calculating the contact resistance of the measured contact pairs are embedded into a control circuit. The DC microresistivity measuring system has the advantages of realizing measurement of resistance by a mode of combining software and hardware and effectively avoiding the influence of the measuring range, namely the temperature drift, of the amplifier on the measuring precision and can be widely applied to the technical field of measurement of microresistivity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
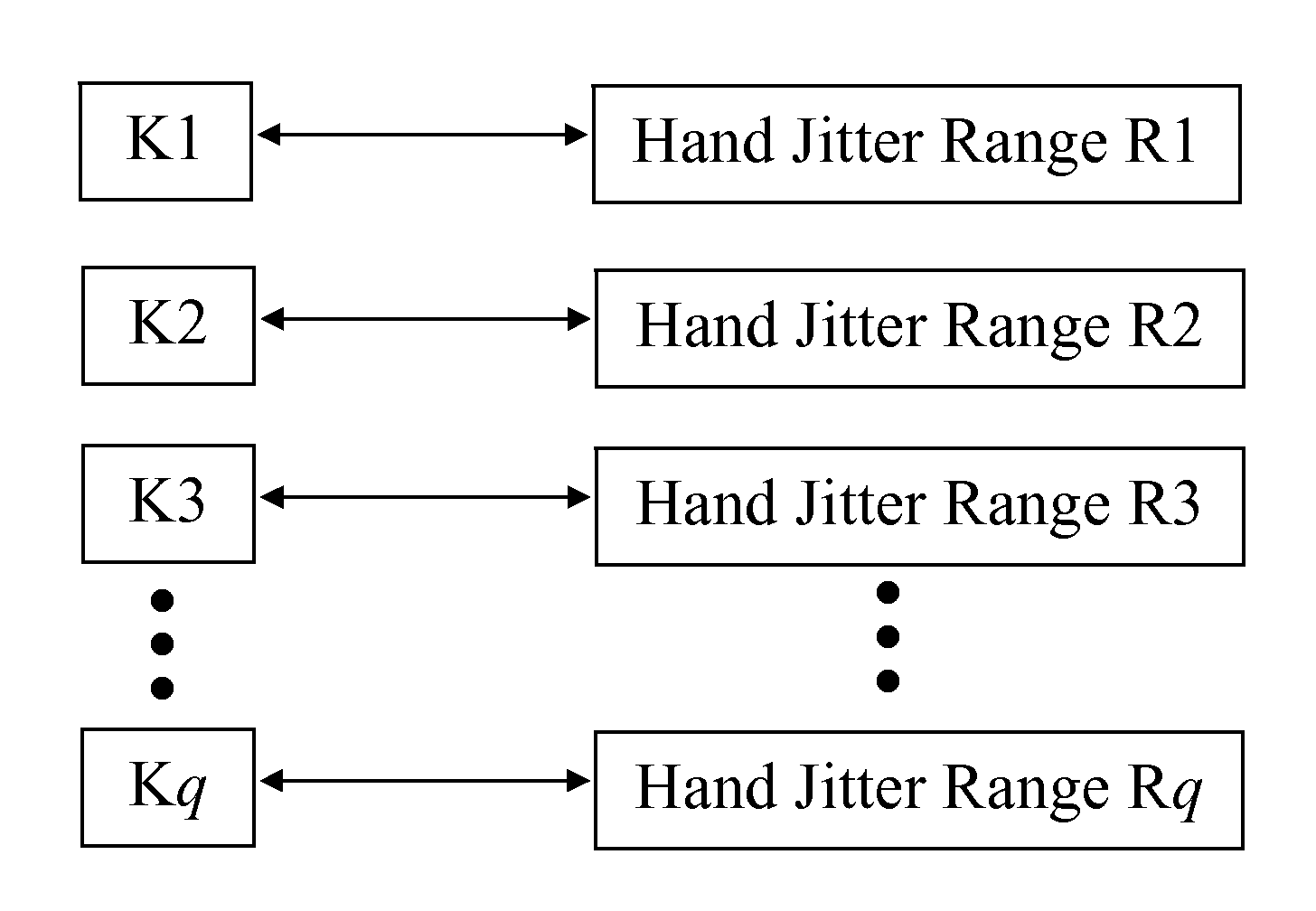
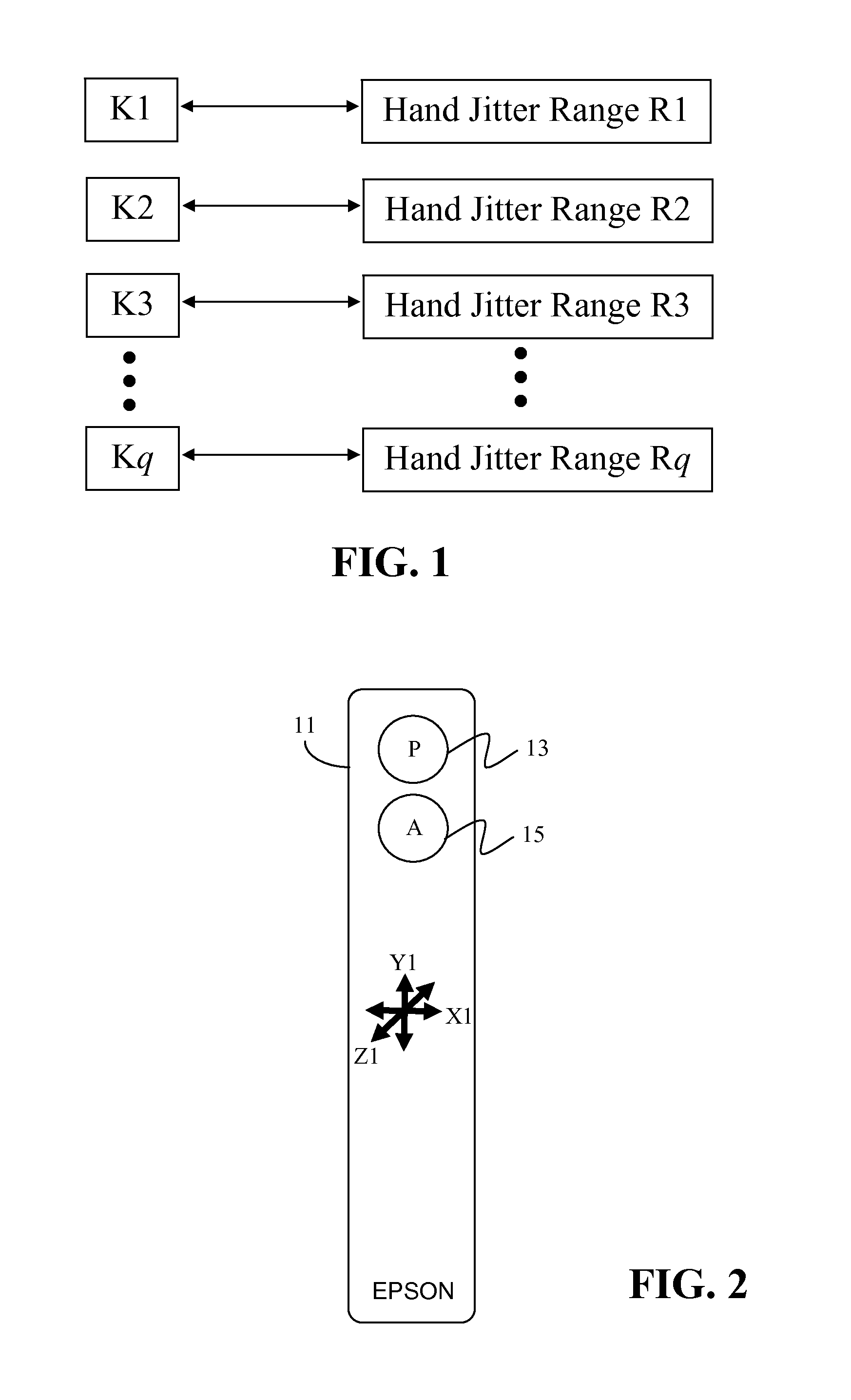
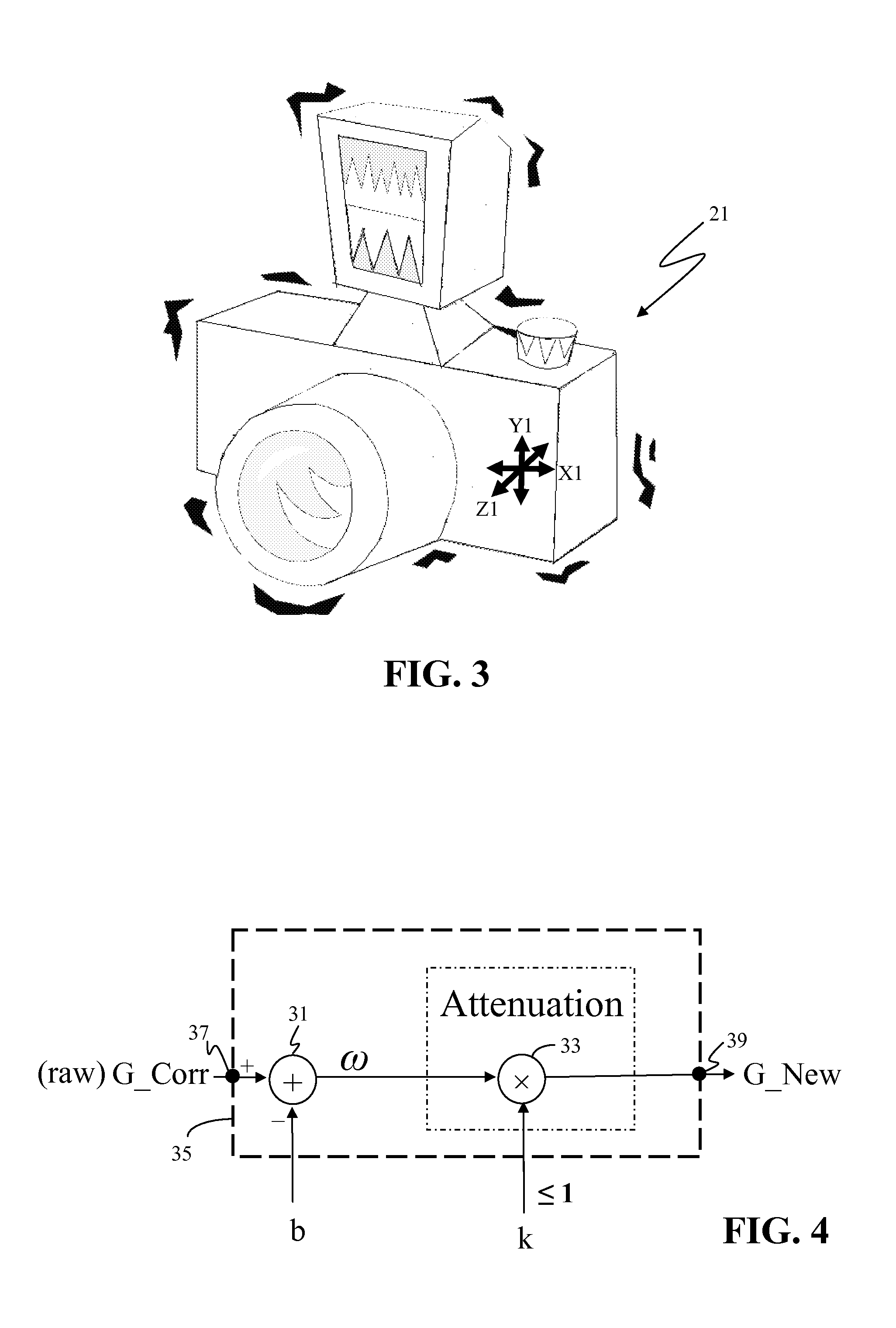
Gyro Mouse De-Drift and Hand Jitter Reduction
ActiveUS20120229385A1High precisionQuick responseTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGyroscopeErrors and residuals
A gyroscope-based device uses a probability model to assign probability of the device being in an intended static state to each received sample of gyroscope data. A new drift error compensation offset and new hand jitter factor are computed for each sample of gyroscope data based on the assigned probability. In this manner, the magnitude of the hand jitter factor varies with the probability of the device being in an intended static state.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Compensation control method and system for damping non-uniformity of all-angle hemispherical resonator gyroscope
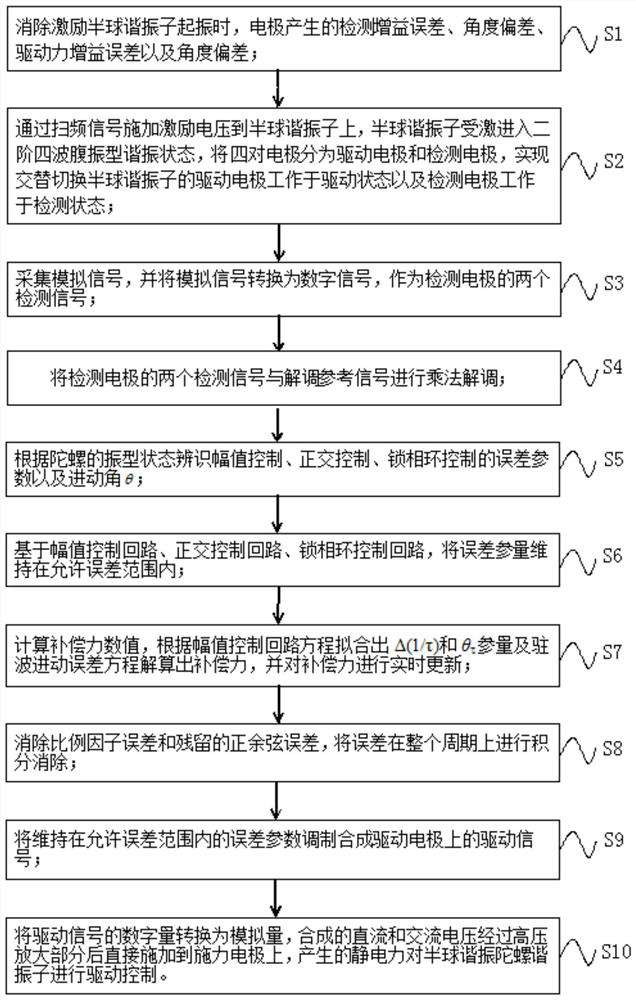
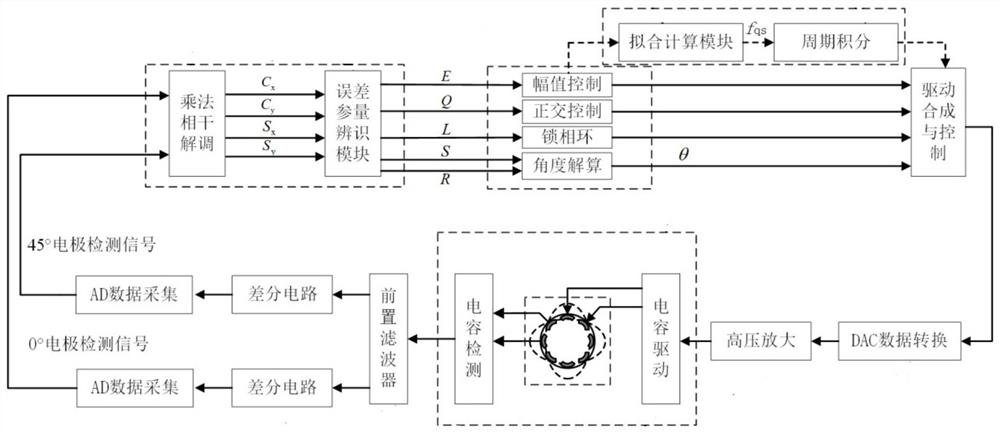
ActiveCN113587954AHigh control precisionSuppression of drift errorsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTurn-sensitive devicesCapacitanceAngle dependence
The invention provides a compensation control method and system for the damping non-uniformity of an all-angle hemispherical resonator gyroscope. According to the method, through fitting calculation and real-time compensation, drift errors caused by damping non-uniformity can be effectively inhibited, and through the period integration technology, scale factor errors and residual sine and cosine errors existing in a loop after fitting compensation can be fundamentally eliminated, and the problem of strong angle dependence caused by a damping non-uniform error is solved, so that the control precision of the gyroscope can be improved. The system comprises a capacitor driving and detection module, an AD data acquisition module, a multiplication coherent demodulation module, an error parameter identification module, an amplitude phase control loop module, a fitting calculation module, a period integration module, a driving synthesis and control module and a DAC digital-to-analog conversion module. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the technical problem of drift error caused by non-uniform damping of the full-angle hemispherical resonator gyroscope is solved.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Modeling and compensation method of radial thermal drift error of spindle of horizontal numerically-controlled machine tool
ActiveCN107942934ASolve the problem of radial thermal error compensationImproved accuracy and stabilityProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlThermal deformation
The invention, which belongs to the field of error compensation of a numerically-controlled machine tool, provides a modeling and compensation method of a radial thermal drift error of a spindle of ahorizontal numerically-controlled machine tool. Two thermal drift errors along the radial direction of a spindle of a umerically-controlled machine tool and corresponding key point temperatures are tested; on the basis of a thermal tilt deformation mechanism of the spindle, a thermal inclination angle of the spindle is obtained and the correlation between the thermal inclination angle and the temperature difference between the left side and the right side of a spindle box is analyzed; according to the positive or negative situation of the thermal drift errors of the tested two points and stretching or contraction situations of the left side and right side of the spindle box, a thermal deformation situation of the spindle is classified and thermal drift error models under various thermal deformation attitudes are established; the influence on the model prediction result by the structural dimension of the machine tool is analyzed; and during real-time compensation, the thermal deformation attitude of the spindle is automatically determined based on the temperatures of the key points and the spindle is compensated by selecting a corresponding thermal drift error model automatically. Therefore, the determination of the thermal deformation attitude of the spindle of the numerically-controlled machine tool is realized during the processing process; and on the basis of the thermal deformation mechanism, the radial thermal drift error of the spindle is predicted.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
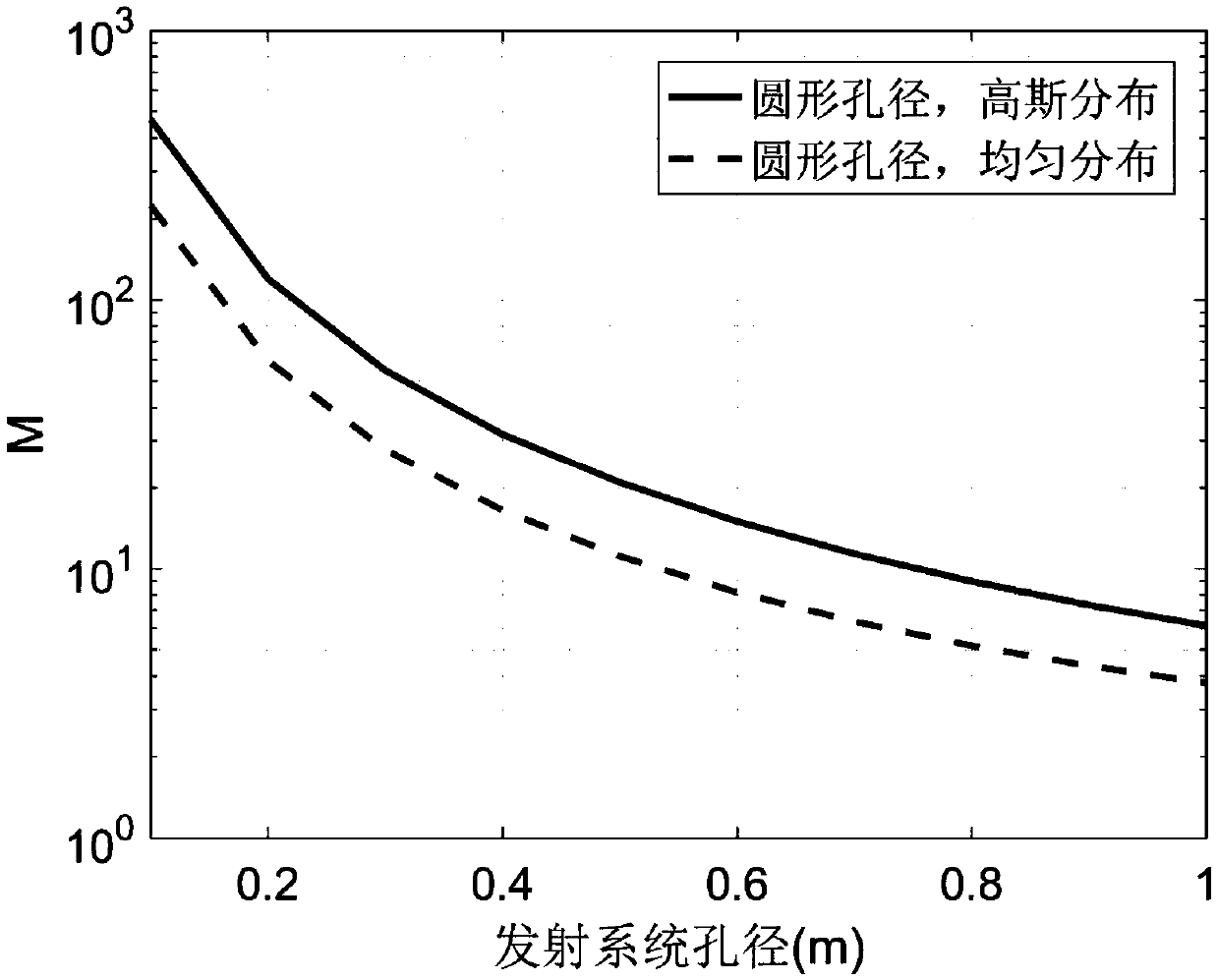
Method for evaluating influence of speckle coherence on ranging accuracy of single-photon laser radar
ActiveCN109541619AImprove compatibilityImprove the detection rateElectromagnetic wave reradiationIntensity normalizationRadar systems
The invention provides a method for evaluating the influence of speckle coherence on the ranging accuracy of a single-photon laser radar. The method comprises the steps of setting the parameters of the single-photon laser radar system, calculating the autocorrelation function of a receiving aperture of the single-photon laser radar system and the normalized covariance function on the intensity ofthe receiving aperture to calculate the speckle degree of freedom M; calculating the average signal photon number Ns according to the laser radar equation, and calculating the total noise rate Nn of the laser radar system; differentiating time through the detection probability based on the root mean square pulse width [Sigma]s of the laser pulse to obtain the detection probability density functionfs(t) of the echo signal with respect to time t, and obtaining the mean value shown in the description and the variance Var of the time when the detector detects the target point; and obtaining the influence of the speckle coherence on the ranging accuracy of the single-photon laser radar according to the drift error Ra and the random error Rp. The invention has good compatibility, can provide guidance for the system parameter design of the laser radar, improve the detection probability and reduce the ranging error as much as possible under the restraint of satisfying the false alarm probability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
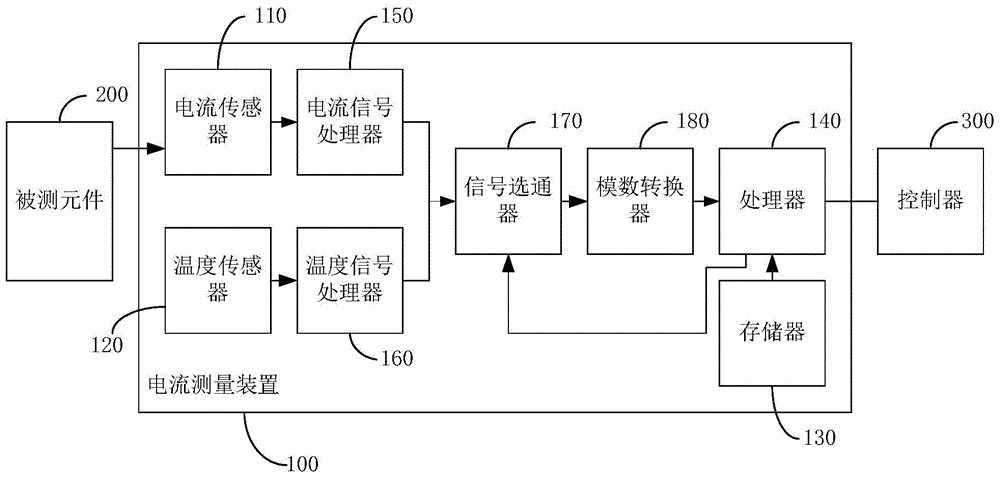
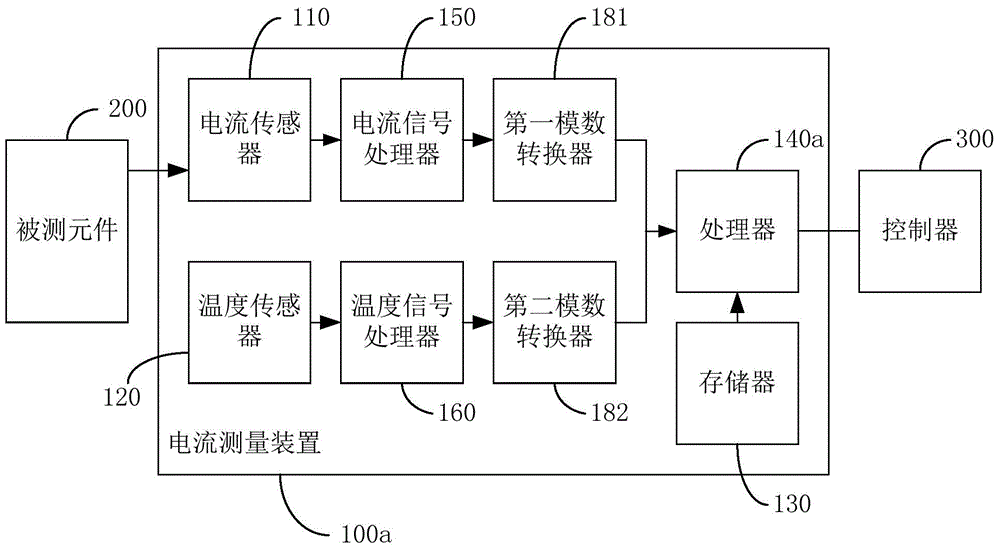
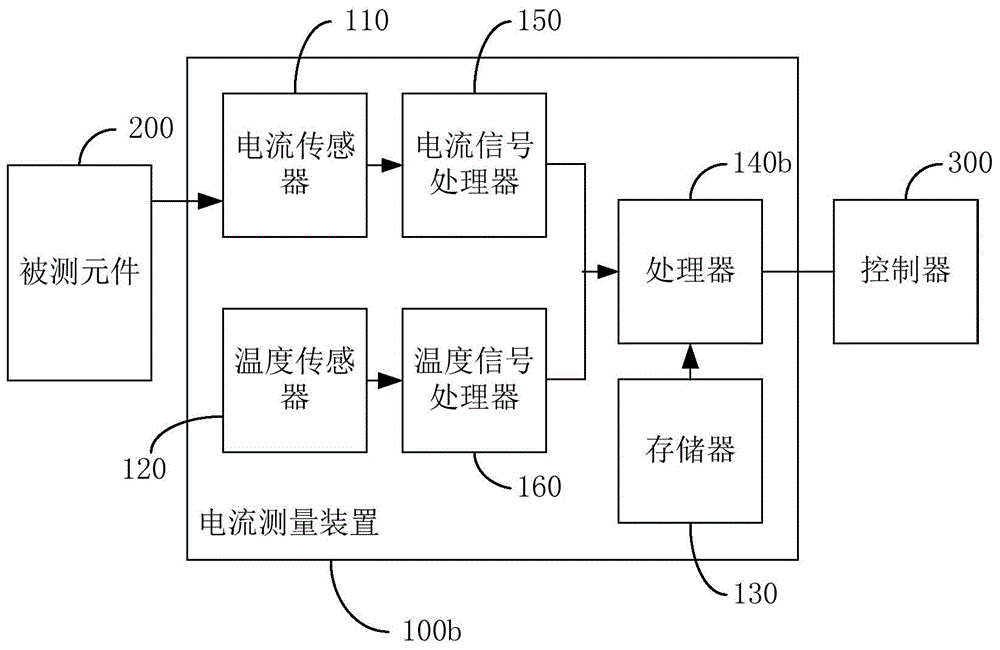
Current measurement device
The invention discloses a current measurement device, and the device comprises a current sensor, a temperature sensor, a storage unit, and a processor. The current sensor is connected with a measured part, and is used for measuring the current of a measured part and obtaining the current value. The temperature sensor is used for measuring the temperature of the device and obtaining the temperature value. The storage unit stores a sensor compensation parameter and a temperature compensation parameter. The processor is used for calibrating the current value according to a calibration formula: Y=K[T](kX-b)-B[T], wherein X is the current measurement value, Y is the calibrated current value, k and b are the sensor compensation parameters and are constants, T is a constant, K[] and B[] are temperature compensation parameters, are arrays and change along with T, and K[T] and B[T] represent two values of K[] and B[] corresponding to T. According to the embodiment of the invention, the device eliminates a zero point error, a gain error, and a temperature drift error, thereby improving the measurement accuracy.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Fiber grating demodulating system with real-time reference
InactiveCN102928003ADrift when solvingSolve temperature driftConverting sensor output opticallyFiberHysteresis
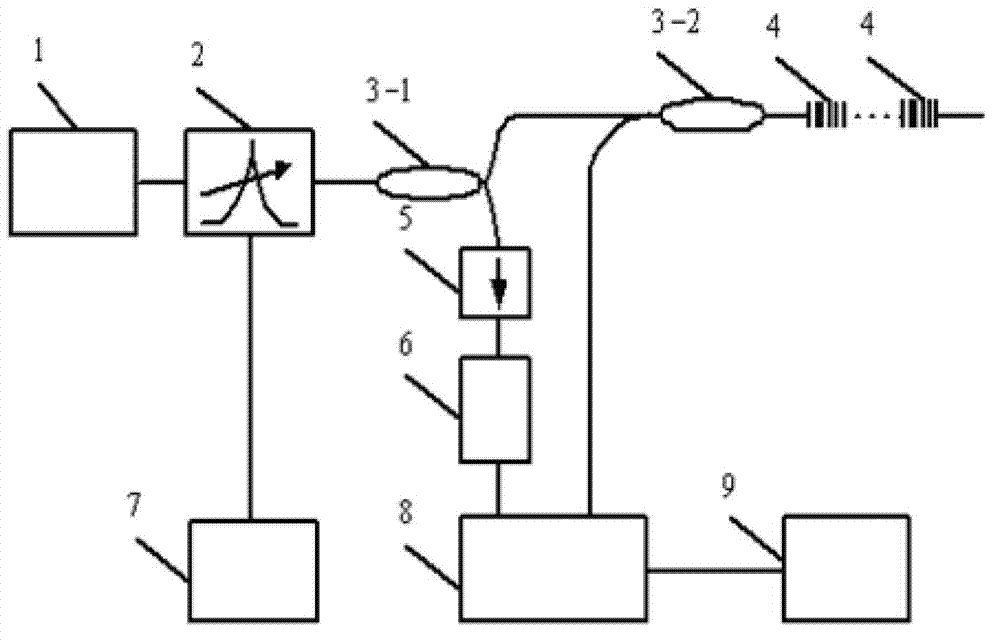
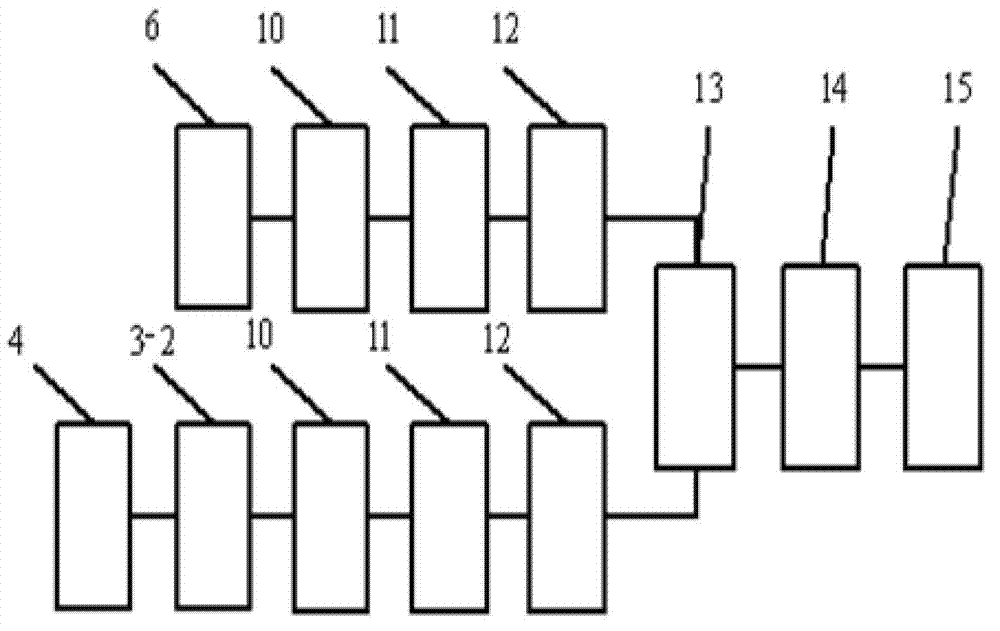
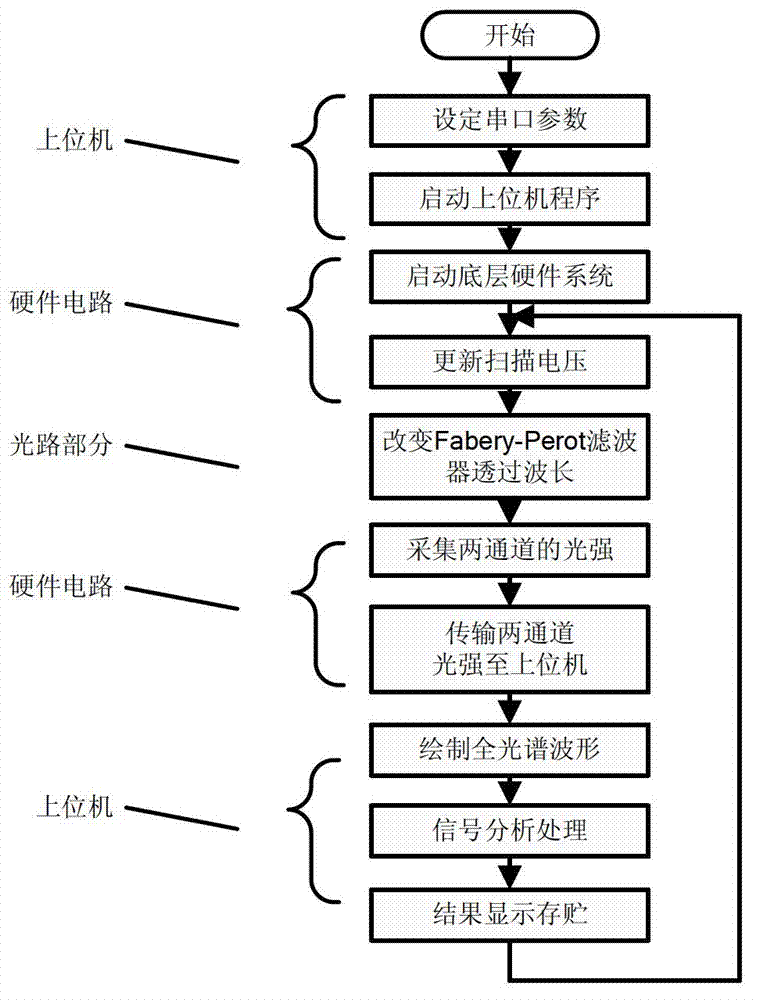
The invention discloses a fiber grating demodulating system with real-time reference, which comprises a light path part, a circuit part, an upper computer and a software program. A reference light path with a precise Fabry-Perot cavity is in parallel connected through a coupler and an isolator on the basis of an original demodulating system based on a Fabry-Perot tunable filter demodulation method, and the measurement result of a measured light path can be corrected in real time through the measurement value of the reference light path, so that demodulation accuracy can be enhanced; two photoelectric signals are acquired and encoded by an underlying hardware circuit and then transmitted to the upper computer, a peak value position is extracted by adopting a Gaussian fitting algorithm on the upper computer, and real-time reference is carried out on the measured light path by utilizing the standard value of the reference light path. The method disclosed by the invention effectively solves the problem of demodulating accuracy degradation caused by the principle errors, namely a time-drift error, a temperature drift error, a hysteresis error, and the like, of a Fabry-Perot tunable filter, thereby providing a new exploring direction for the construction of the fiber grating demodulating system disclosed by the invention.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
High precision on-line error compensation method for drift error of gyro with suspension rotor
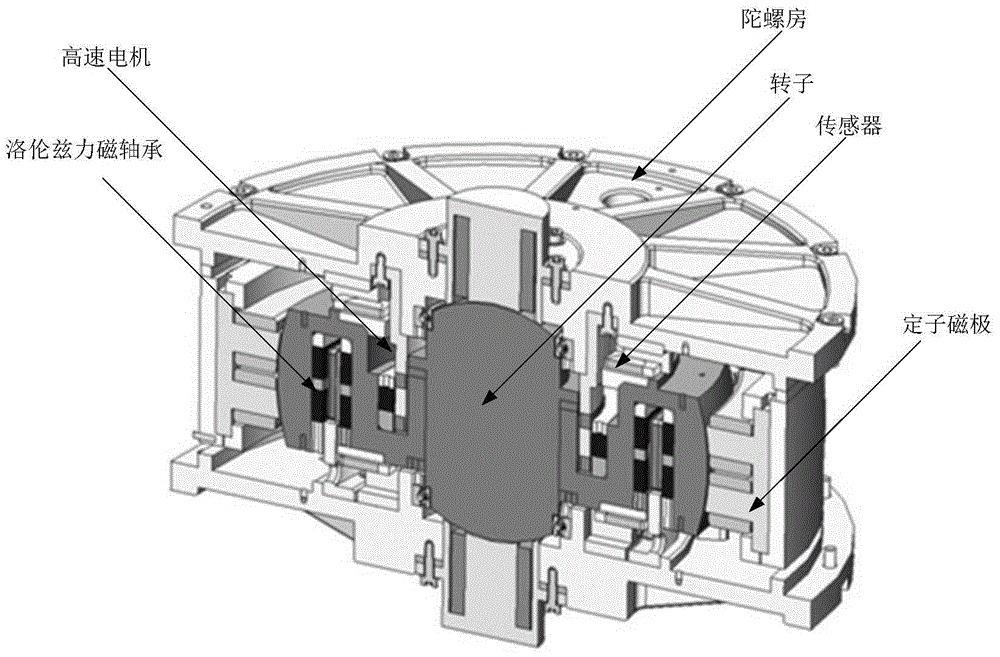
ActiveCN105136170ARealize high-precision real-time compensationRotary gyroscopesMagnetic bearingExcitation current
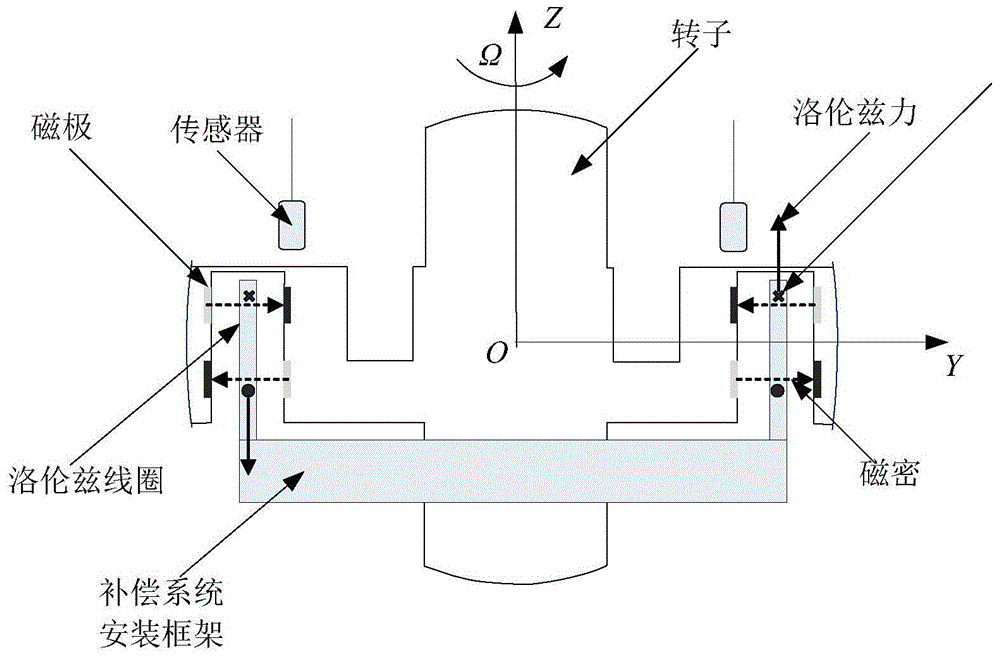
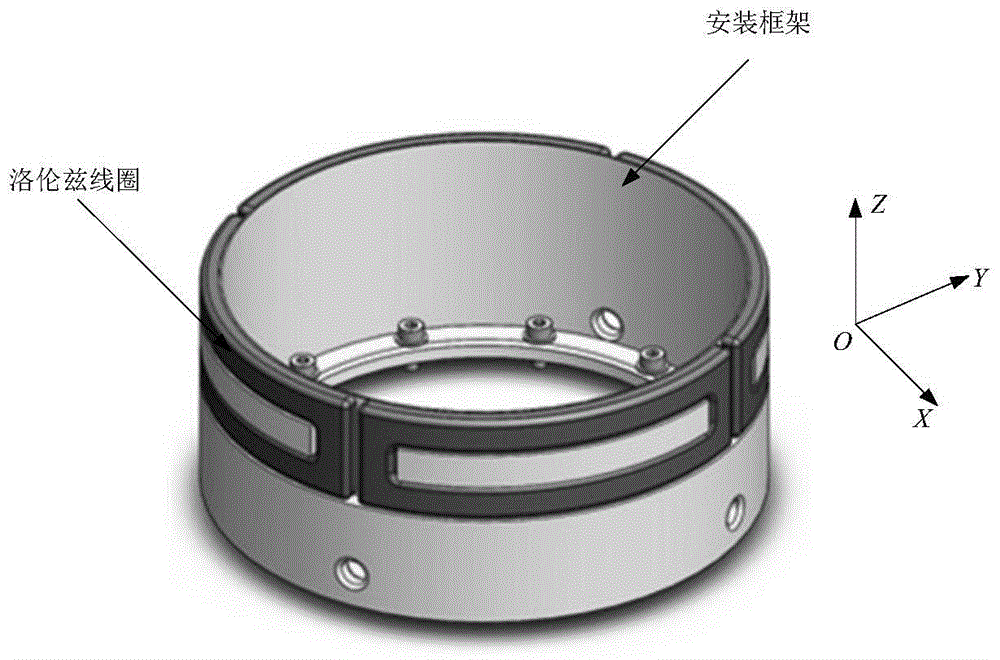
The invention relates to a high precision on-line error compensation method for drift error of gyro with suspension rotor. Based on the rigid body dynamics basic principle, a gyro disturbed torque model is established; based on an axial direction Lorentz force magnetic bearing, a high precision analytical expression of compensating torque is established; real time on-line measurements of gyro rotor corner and Lorentzen coil excitation current by displacement and current sensors are combined, thereby realizing high precision real time on-line compensation of the compensating torque to the disturbed torque. The invention belongs to the field of aerospace measurement and control technology, and is applied to high precision satellite attitude measurement and optimization design, measurement and calibration of the ground gyro.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Signal demodulating method for inhibiting vibration error of fiber optic gyro
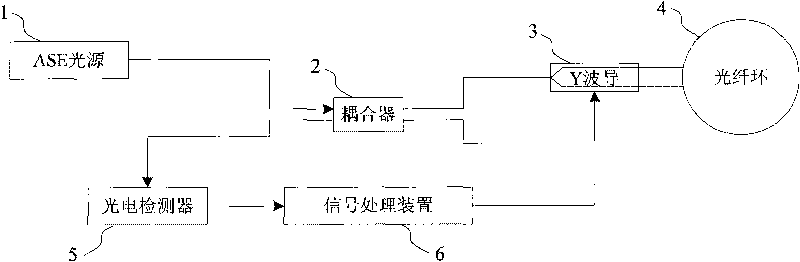
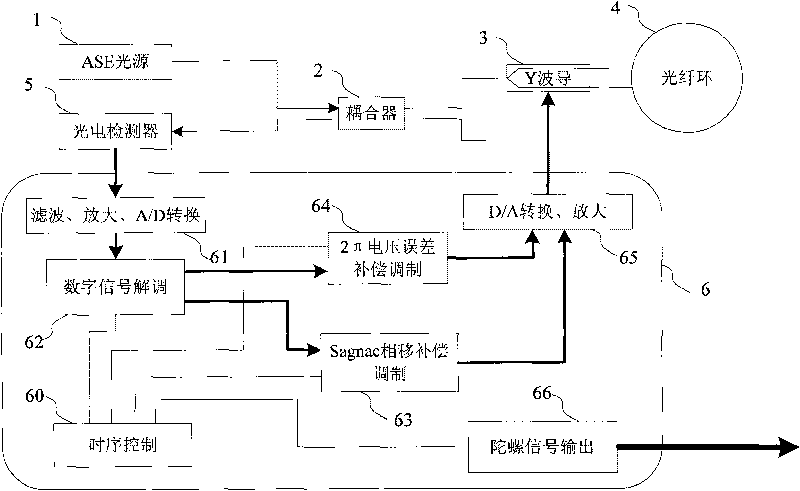
InactiveCN101709971AEliminate errorsHigh measurement accuracySagnac effect gyrometersElectricityFiber
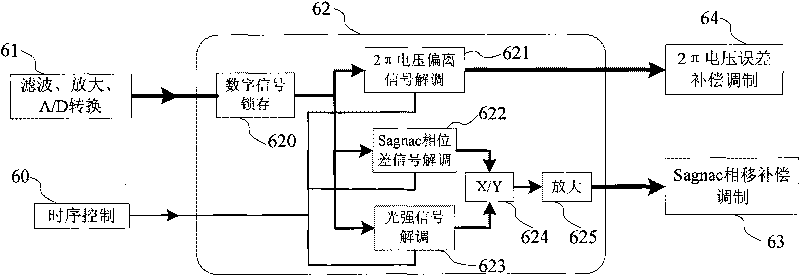
The invention provides a signal demodulating method for inhibiting a vibration error of a fiber optic gyro. After a system is powered on, light power signals detected by a photoelectric detector in real time are subjected to filtration, amplification and an A / D converter to form digital signals; the digital signals are latched by a digital latch module; and the latched light power digital singles are demodulated to form Sagnac phase difference signals, 2pi voltage deviation signals and light power signals; the demodulated Sagnac phase difference signals are divided by the light power signals to obtain new demodulated signals which are amplified and output to a Sagnac phase deviation compensation modulation module; the demodulated 2pi voltage deviation signals are output to a 2pi voltage error compensation modulation module; and then the modulated signals of Sagnac phase deviation compensation signals and 2pi voltage error compensation modulation signals are fed back to a gyro closed loop. In the method, a constant drift error of the gyro and partial additional noise error caused by vibration are eliminated, and the measuring accuracy of the gyro in vibration environment is improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Attitude estimation method based on iteration volume Kalman filter
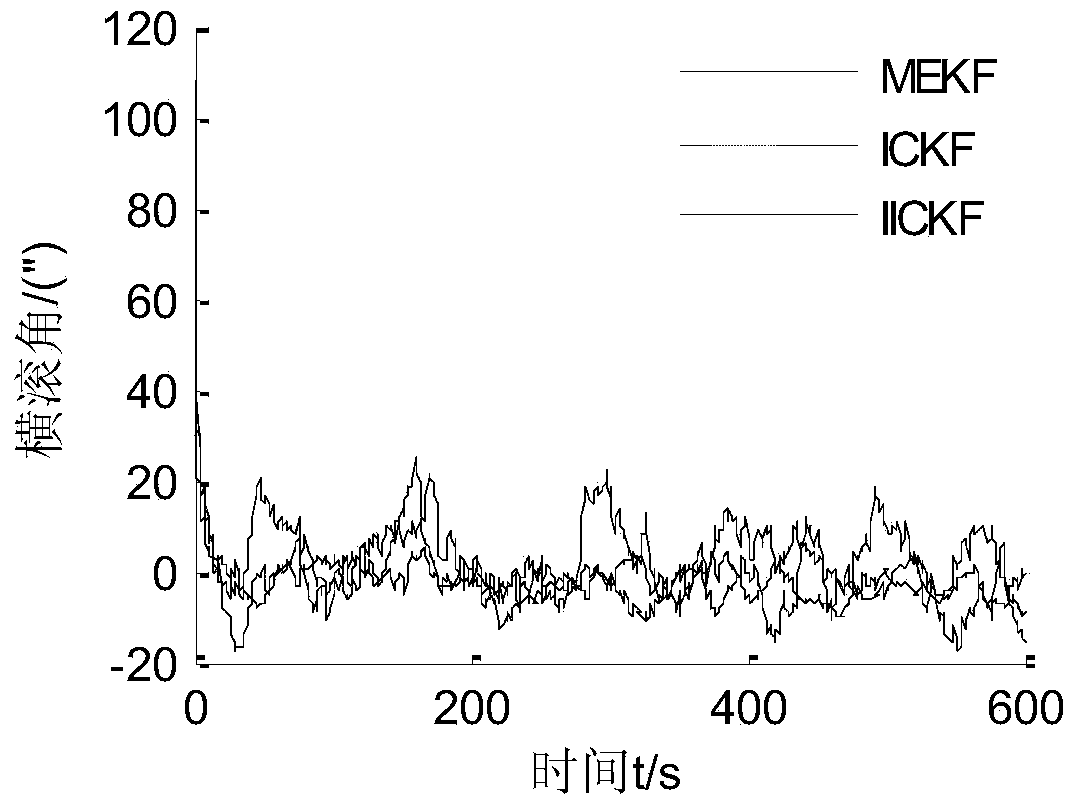
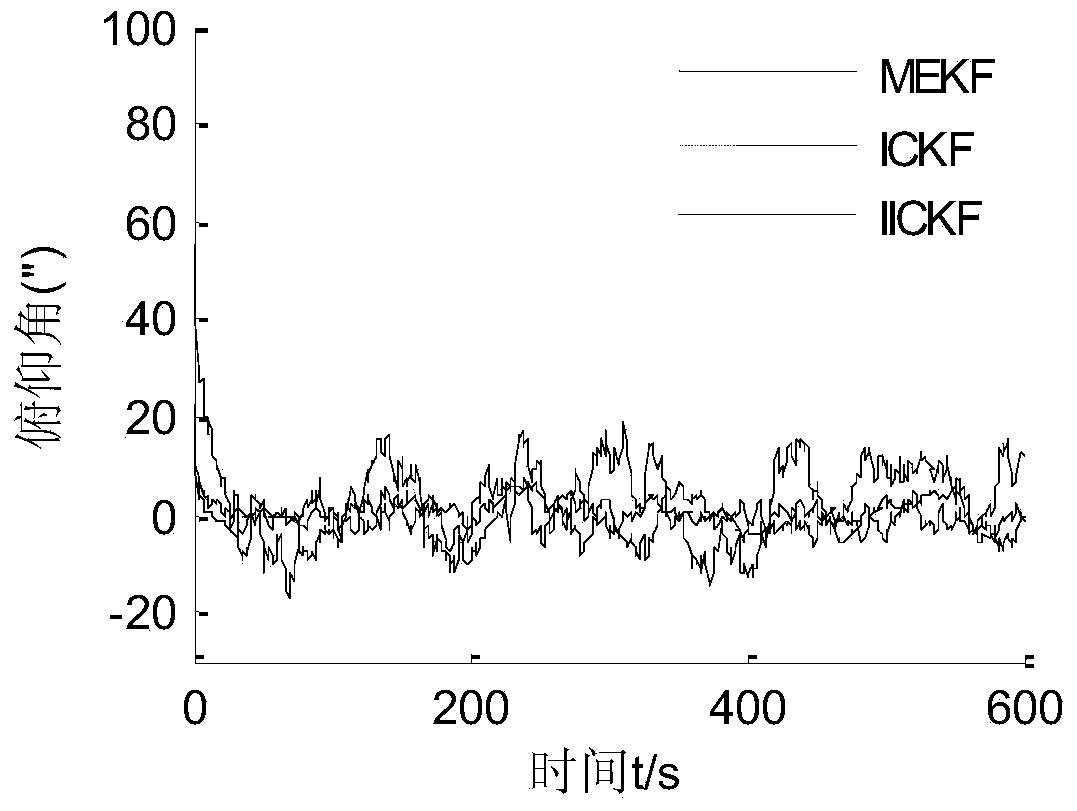
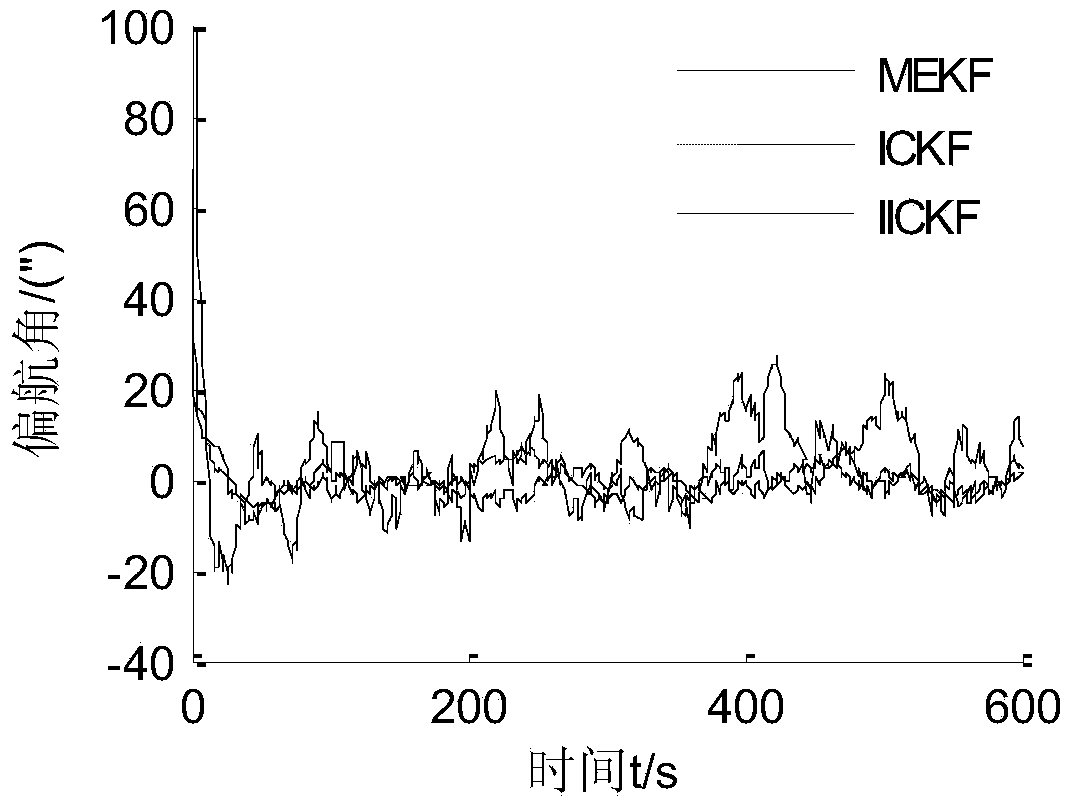
ActiveCN103900574AAvoid calculationImprove estimation accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsGyroscopeAlgorithm
The invention discloses an attitude estimation method based on iteration volume Kalman filter. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring output data of a gyroscope and a star sensor as measurement amount; 2, confirming a state vector quantity and a measurement vector quantity; 3, estimating an error quaternion vector part and a gyroscope drift error at k moment by using the iteration volume Kalman filter at k-1 moment; 4, calculating quaternion estimation and gyroscope drift estimation for the estimation as shown in the specification at the k moment, and correcting the attitude and gyroscope drift, so as to obtain the modified attitude and the gyroscope drift at the k moment; and 5, in the attitude estimation, if the operation time of a non-linear discrete system is M and k is equal to M, outputting the result of the attitude and the gyroscope drift, and if k is smaller than M, repeating the steps 3 and 4 till the attitude estimation system operation is accomplished. The method has the advantages of high estimation precision and small calculation amount.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Indoor localization method based on foot inertia sensor
InactiveCN104197938ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsCurrent velocityDirection information
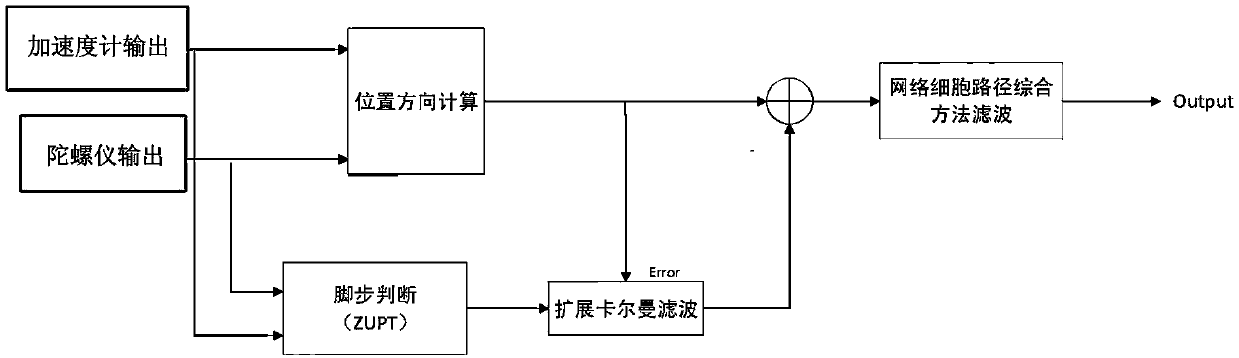
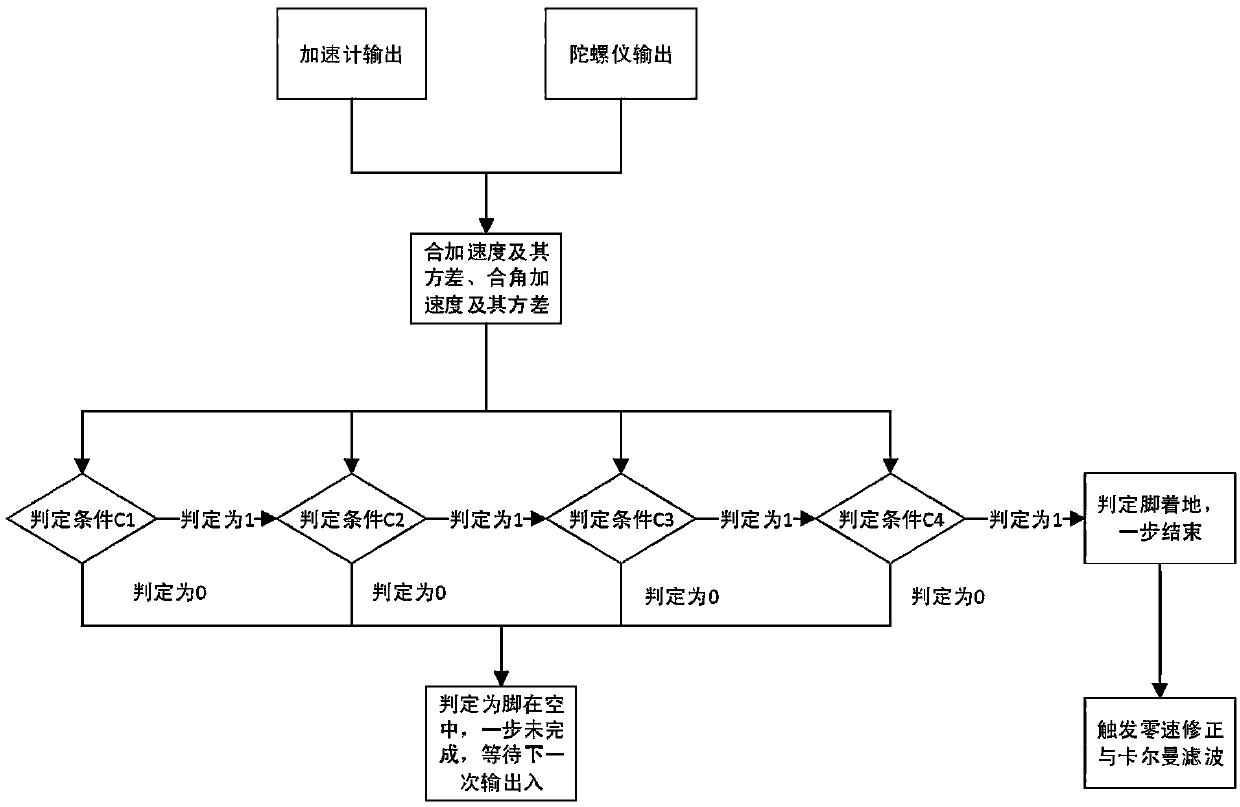
The invention discloses an indoor localization method based on a foot inertia sensor. According to the indoor localization method, a framework of a grid cell path integrating method integrated and simulated on the basis of extended Kalman filter estimation is used; the information of localization positions and directions is obtained by calculating data of the inertia sensor; a plurality of condition judging criteria are used by zero-velocity correction for judging whether the feet touch the ground or not; the current velocity is adjusted to zero and the Kalman filter estimation is triggered when the conditions are met; the calculated nonlinear error increase of the velocity and the position information are corrected; then the velocity information is used as input and a grid cell path integration method is used for further eliminating drift error of the position information.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
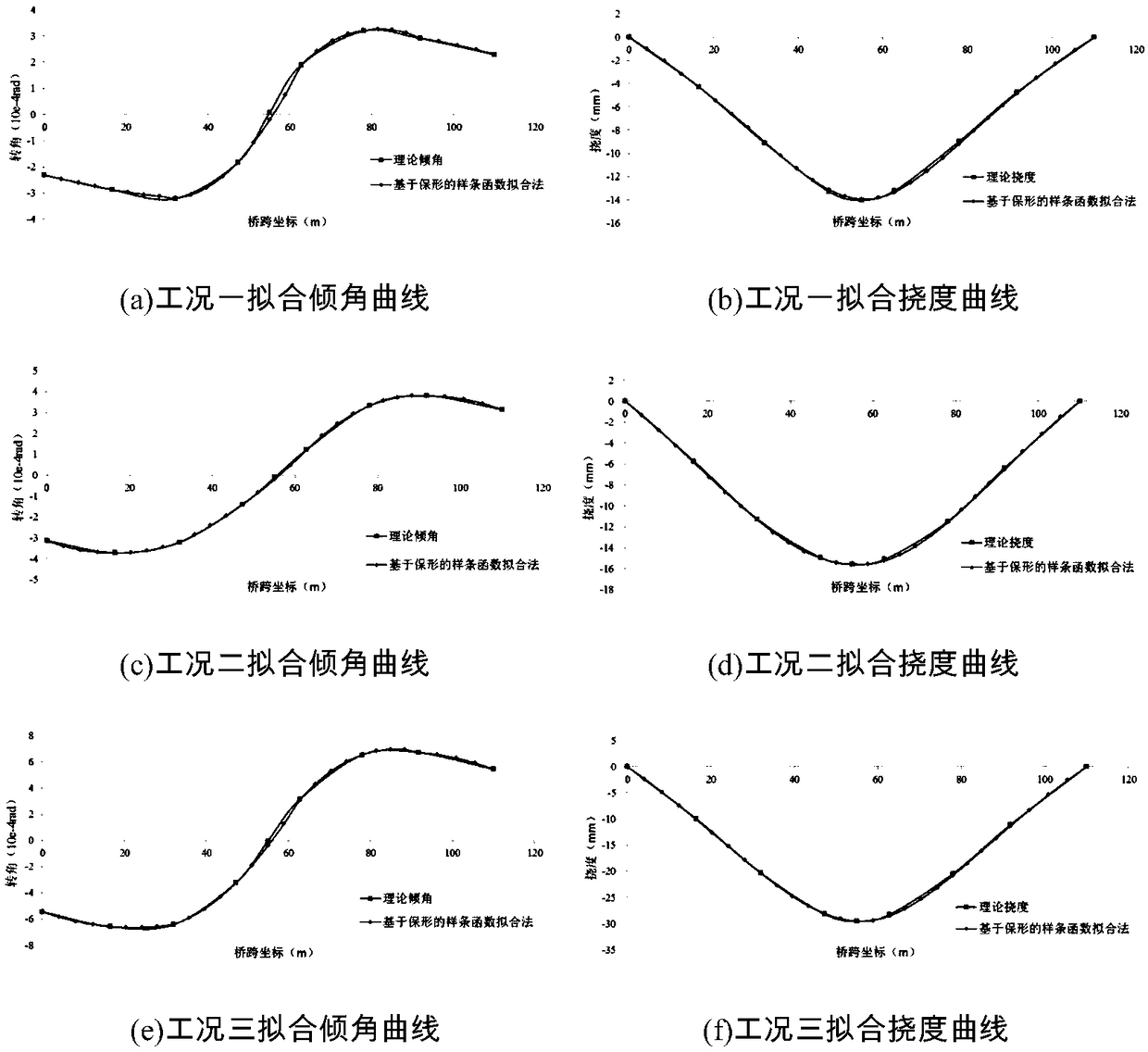
Method for improving bridge deflection testing precision based on inclinometer
ActiveCN109029882AImprove calculation accuracyImprove deflection test accuracyElasticity measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Band-pass filter
The invention discloses a method for improving bridge deflection testing precision based on an inclinometer. The method is mainly used for improving the bridge deflection testing precision by three aspects of temperature error compensation, improvement of signal-to-noise ratio through band-pass filtering, and improvement of a deflection calculation method based on a dip angle value. The method comprises the following steps of a, carrying out temperature calibration on a to-be-used inclinometer in a one-to-one manner, b, acquiring inclination angles corresponding to a plurality of designated positions on the bridge, c, carrying out temperature drift error correction on the obtained inclination angle values by adopting respective pre-calibrated inclinometer temperature error compensation formulas, d, adopting a band-pass filtering algorithm for preprocessing the dip angle values, and eliminating noise influence, and e, adopting an improved conformal spline function fitting method to calculate the bridge deflection. According to the method, on one hand, the inclinometer measuring point arrangement is free of any restriction, and on the other hand, the calculation precision of an original test method is greatly improved, and the dynamic deflection of the bridge can be monitored in real time.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL COMM PLANNING & DESIGN INST +1
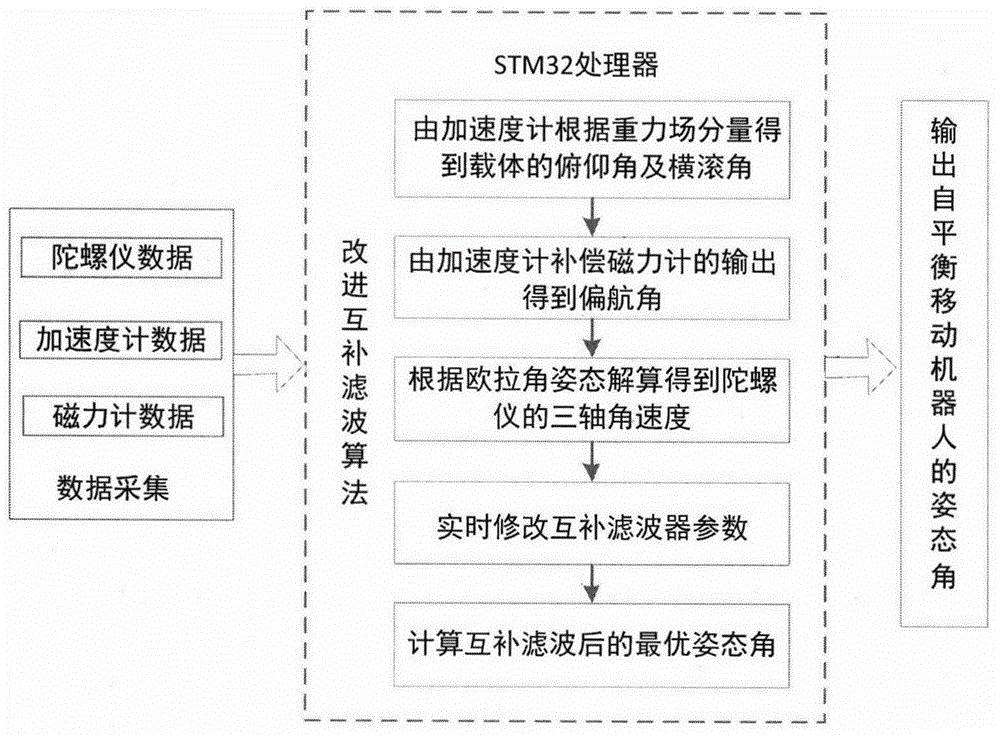
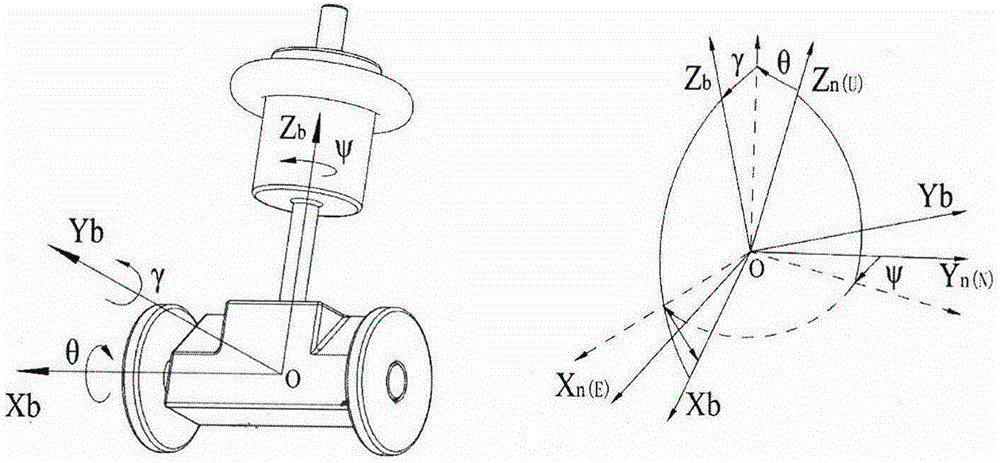
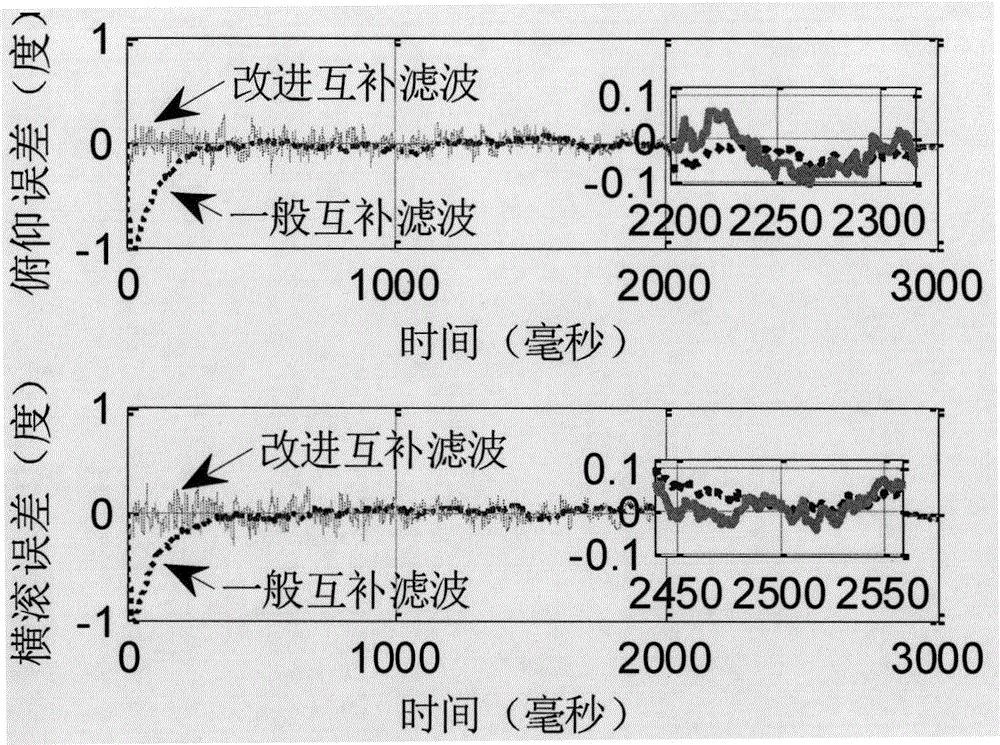
Rapid convergence method based on improved complementary filter for attitude of self-balance mobile robot
The invention provides a rapid convergence method based on an improved complementary filter for an attitude of a self-balance mobile robot, and belongs to the technical field of motion control and multi-sensor data fusion. The method is mainly used at an initial motion stage of the mobile robot and enables the mobile robot to be fast stably started. An attitude detection module mainly comprises an MEMS inertial sensor, such as a micro-controller, a gyroscope, an accelerometer, and a magnetometer. According to the method, an angle of inclination estimated by a component of a gravitational field of the accelerometer is taken as auxiliary information; a yaw angle calculated by the magnetometer is obtained through compensation of the angle of inclination; and angular rate information of the gyroscope at three axes is obtained through an euler angle attitude algorithm. Data of the gyroscope and an auxiliary sensor is fused through a complementary filter with parameters flexibly adjusted, and an optimum attitude angle is calculated in time. According to the method, the attitude detection module can quickly respond to an initial attitude angle; noise and drift error can be obviously suppressed; the mobile robot can be quickly stably started; and the stability of the mobile robot is enhanced.
Owner:苏州力碳新能源发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com