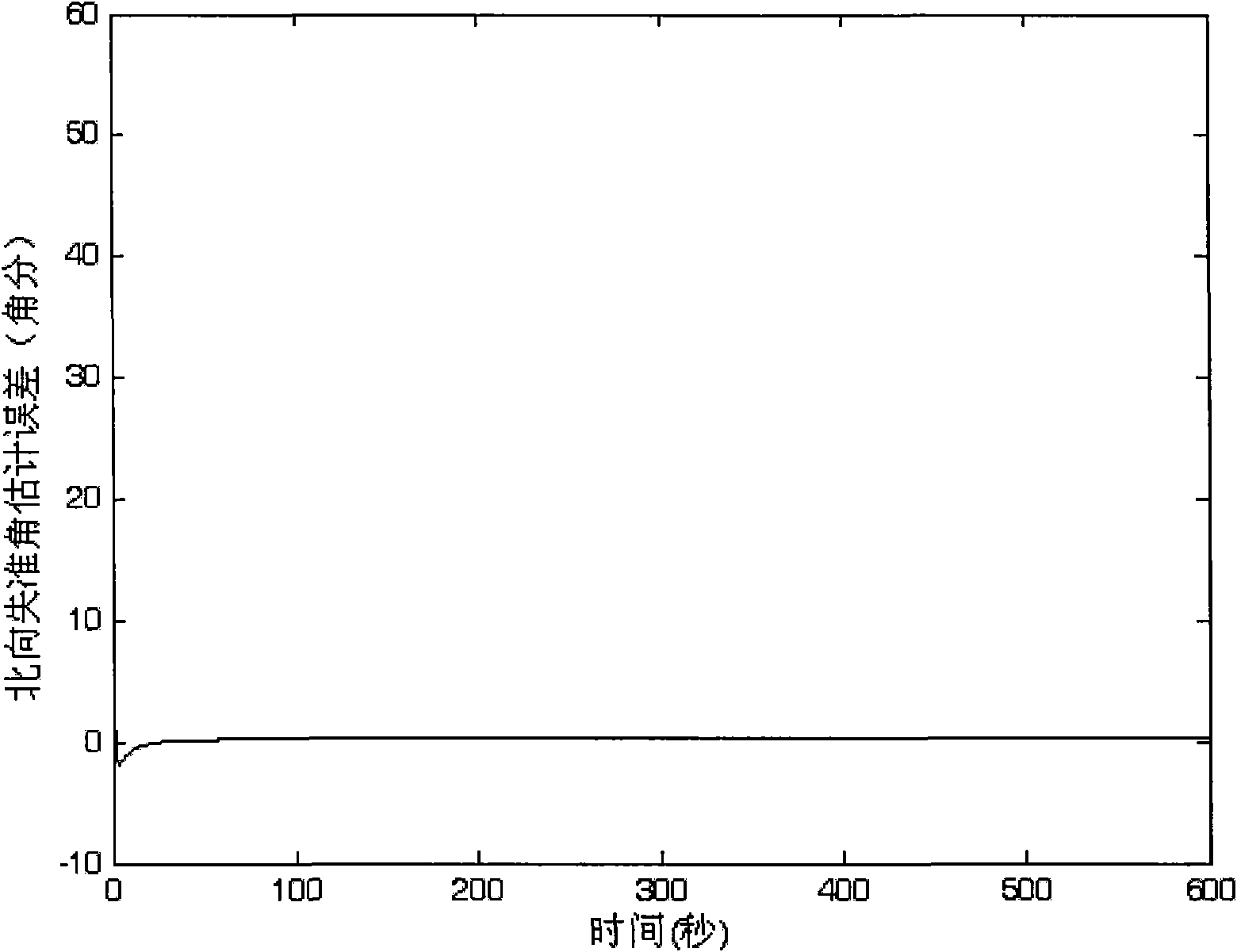
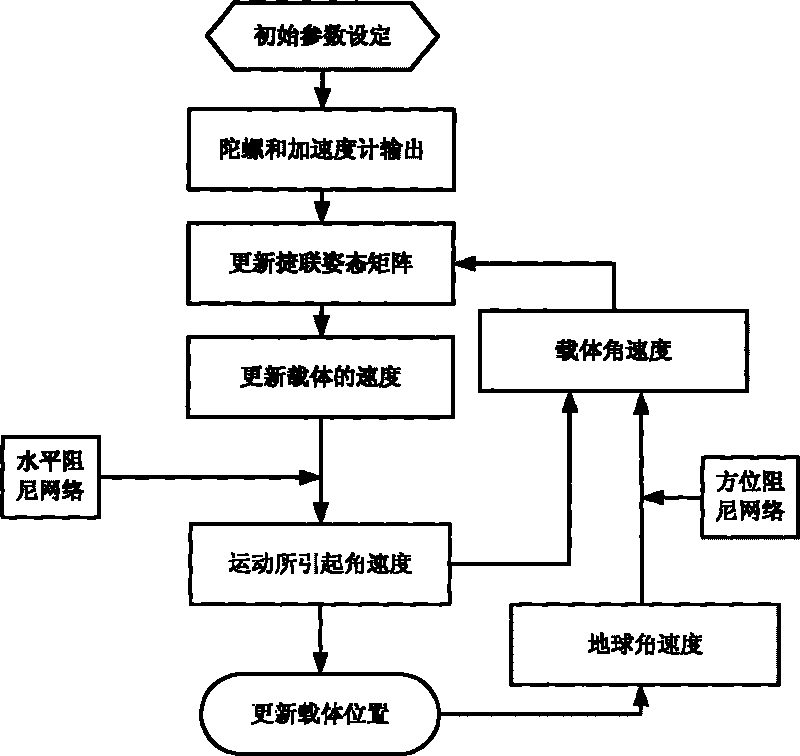
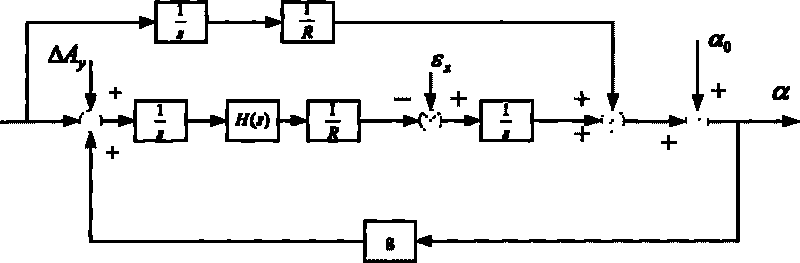
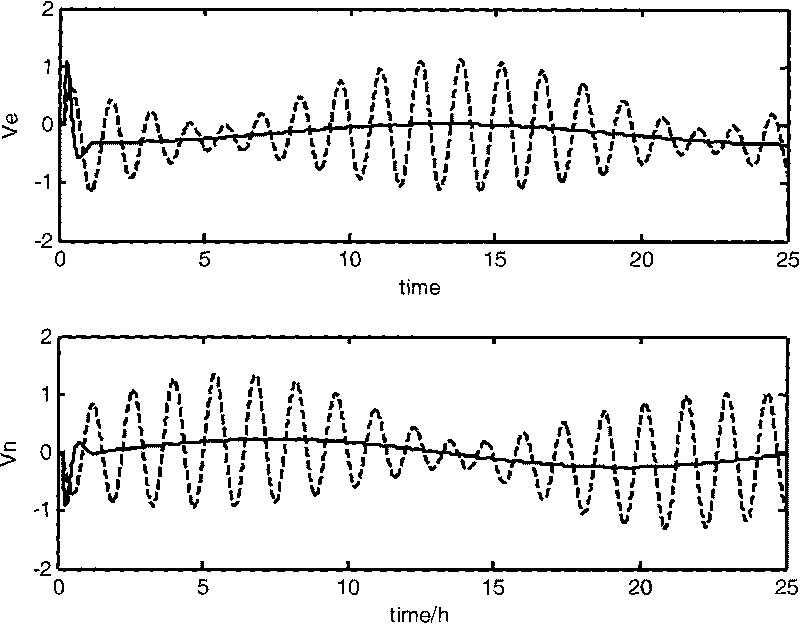
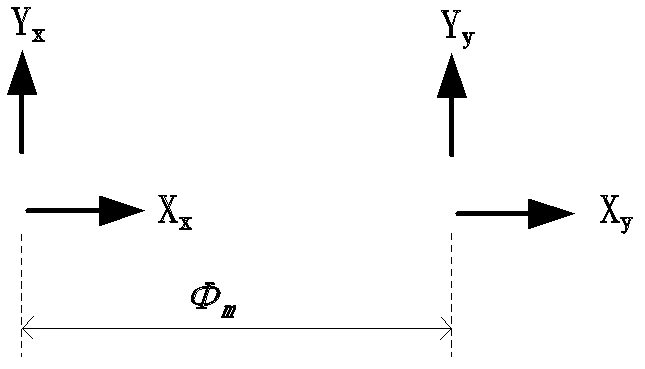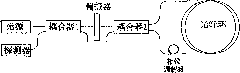Patents
Literature
428 results about "Fibre optic gyroscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
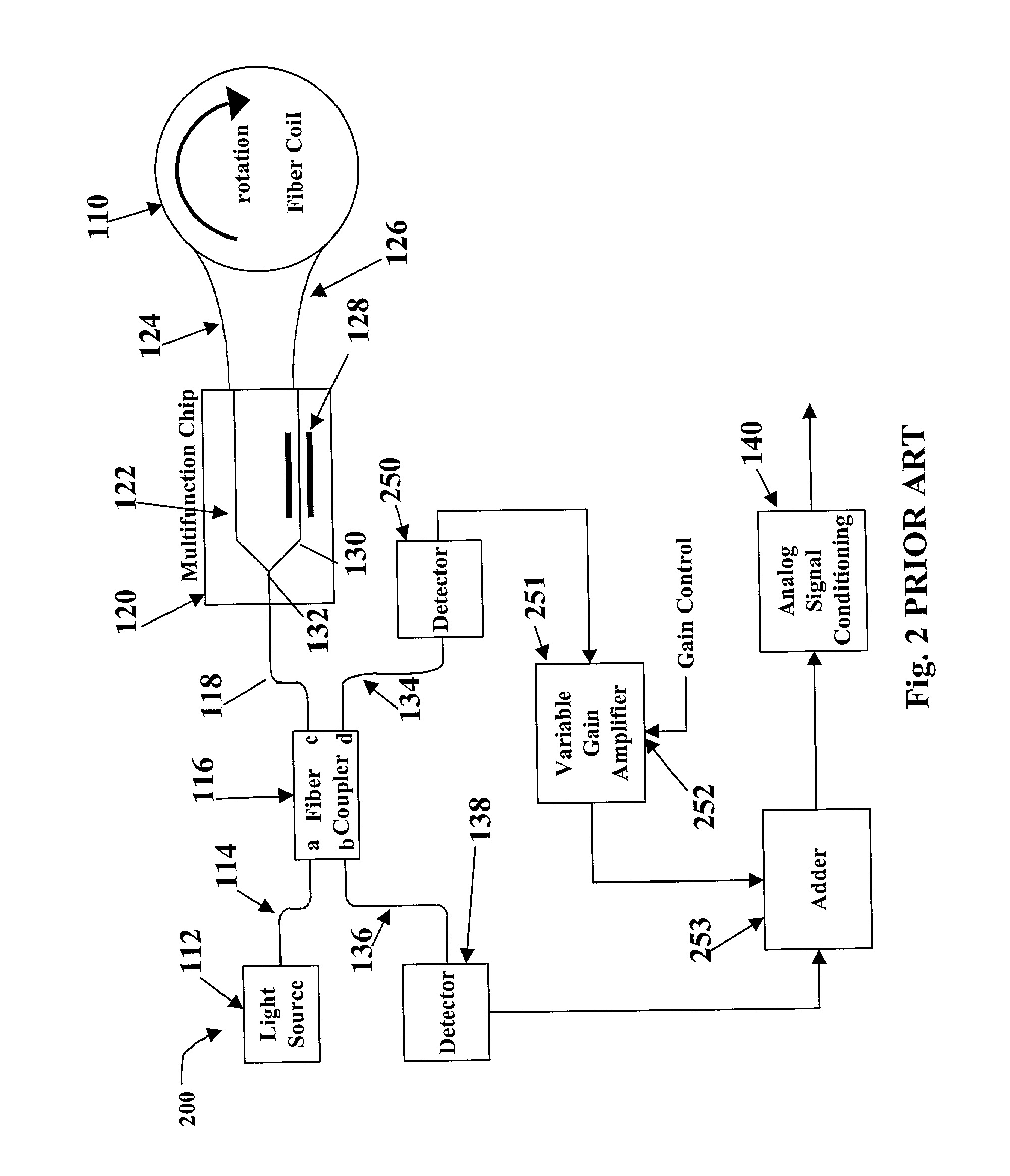
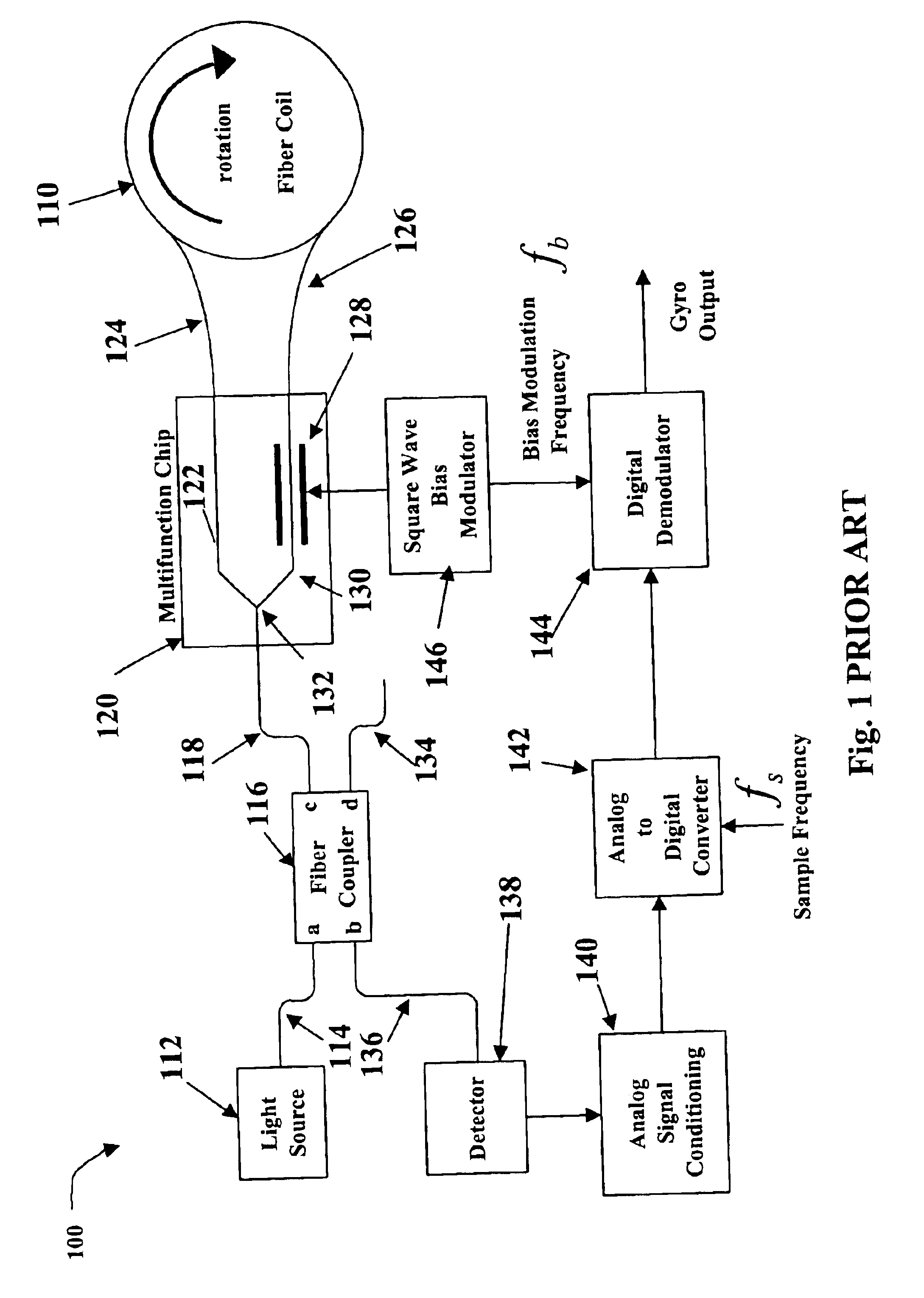
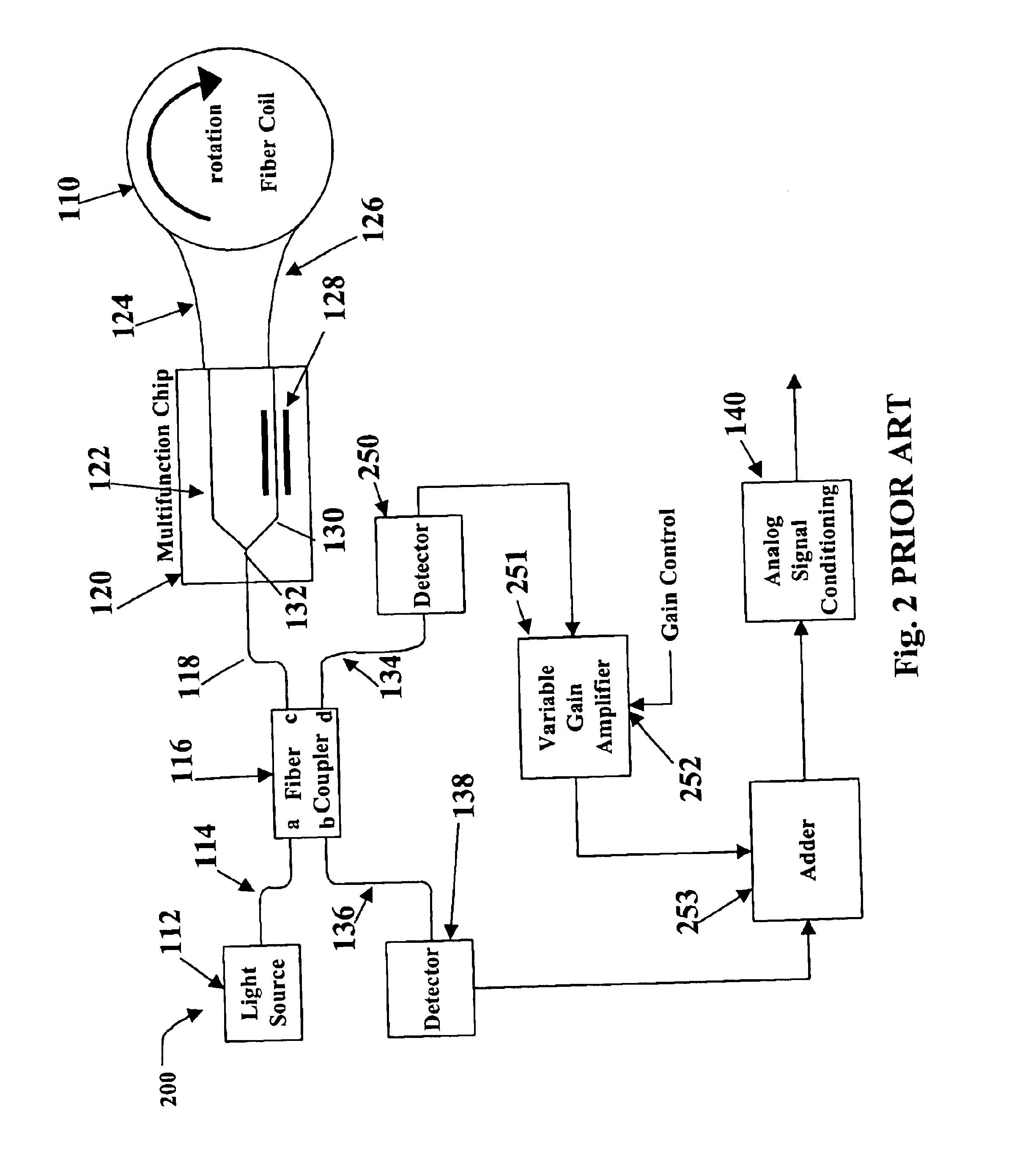
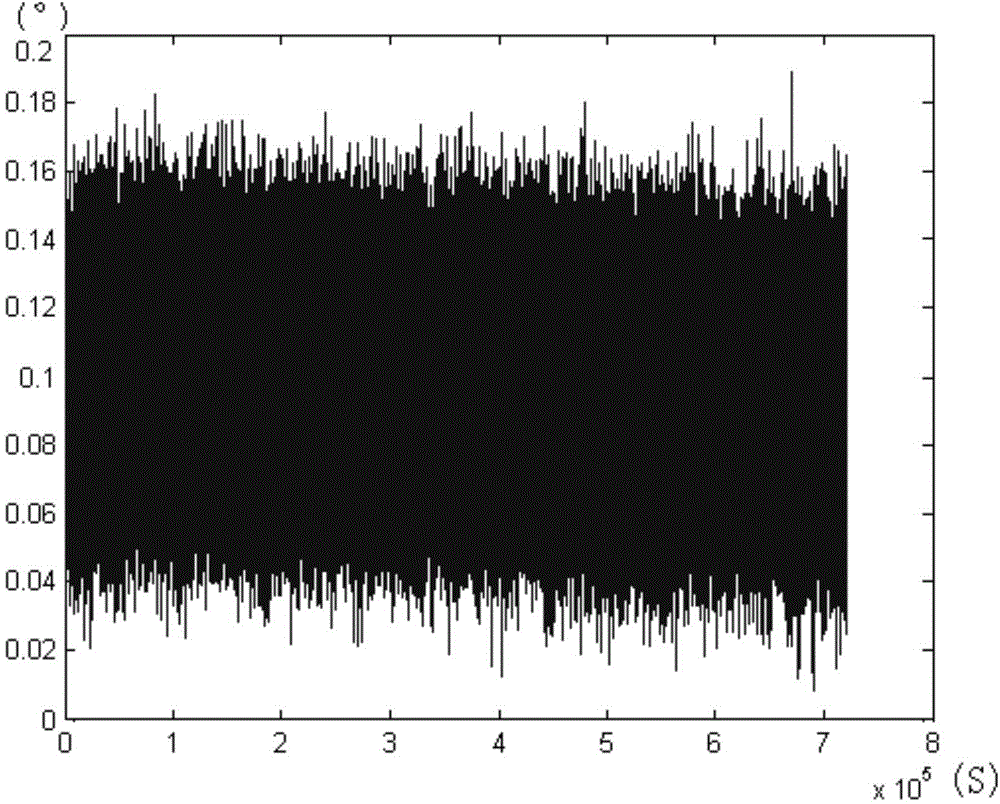
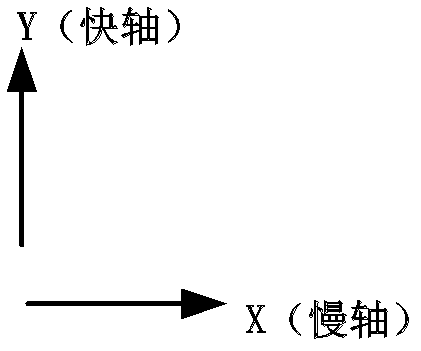
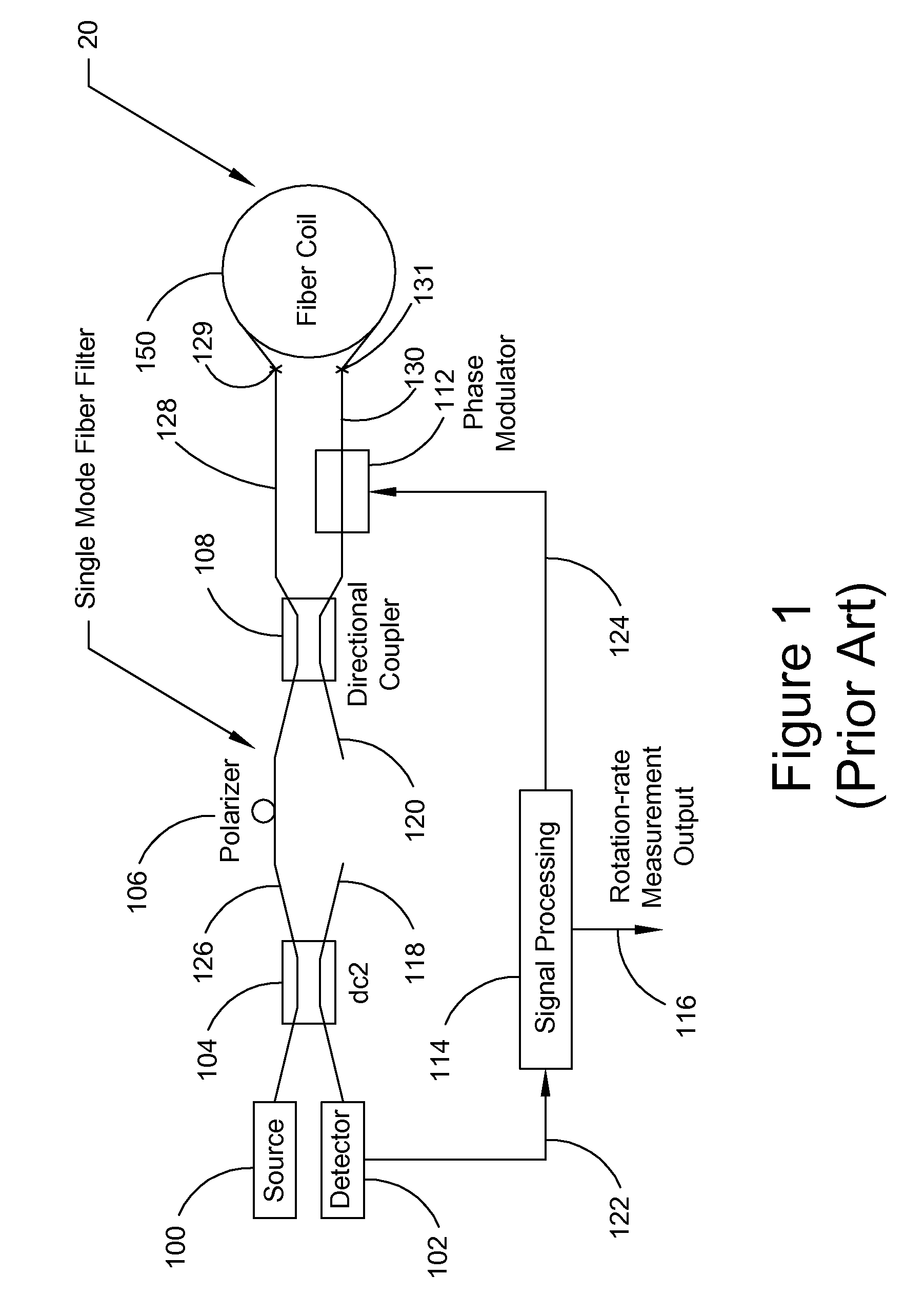
A fibre-optic gyroscope (FOG) senses changes in orientation using the Sagnac effect, thus performing the function of a mechanical gyroscope. However its principle of operation is instead based on the interference of light which has passed through a coil of optical fibre, which can be as long as 5 km.
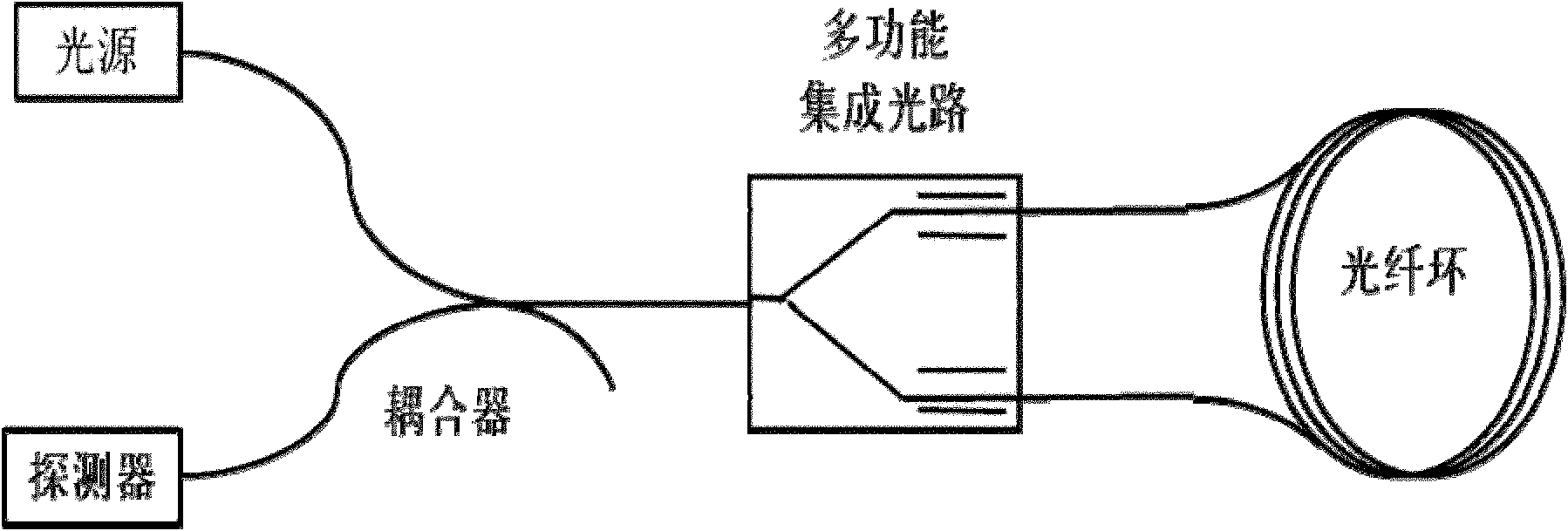
Integrated optical circuit
InactiveUS6163632ASagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberPhase shifted
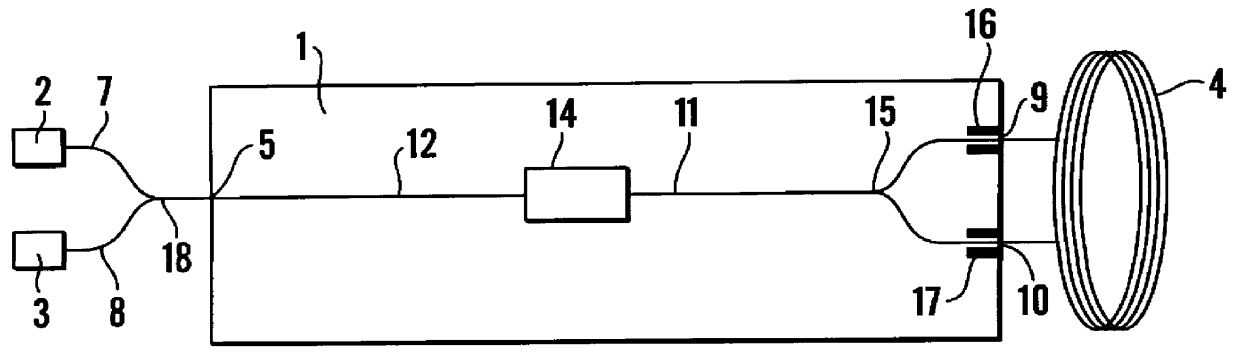
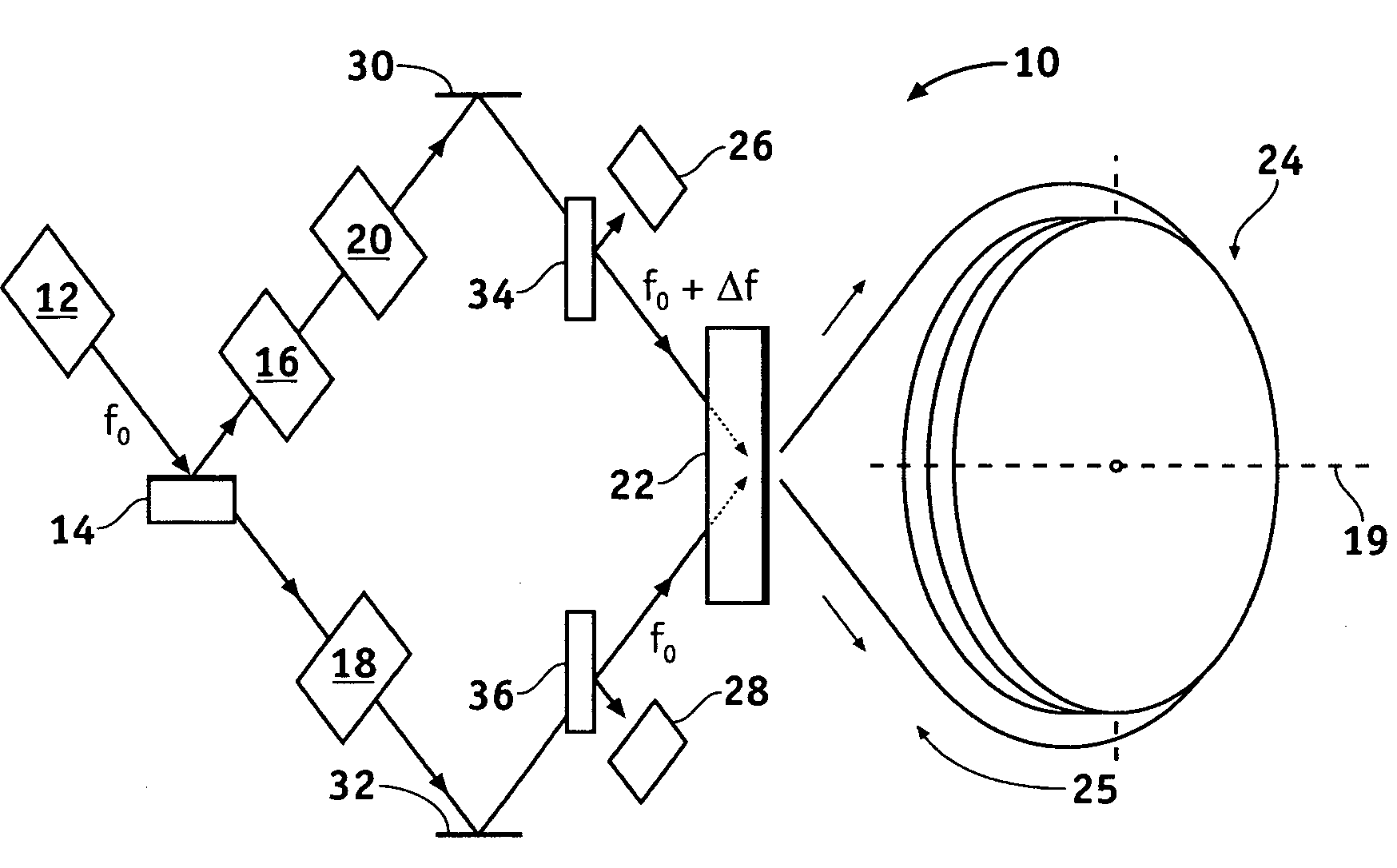
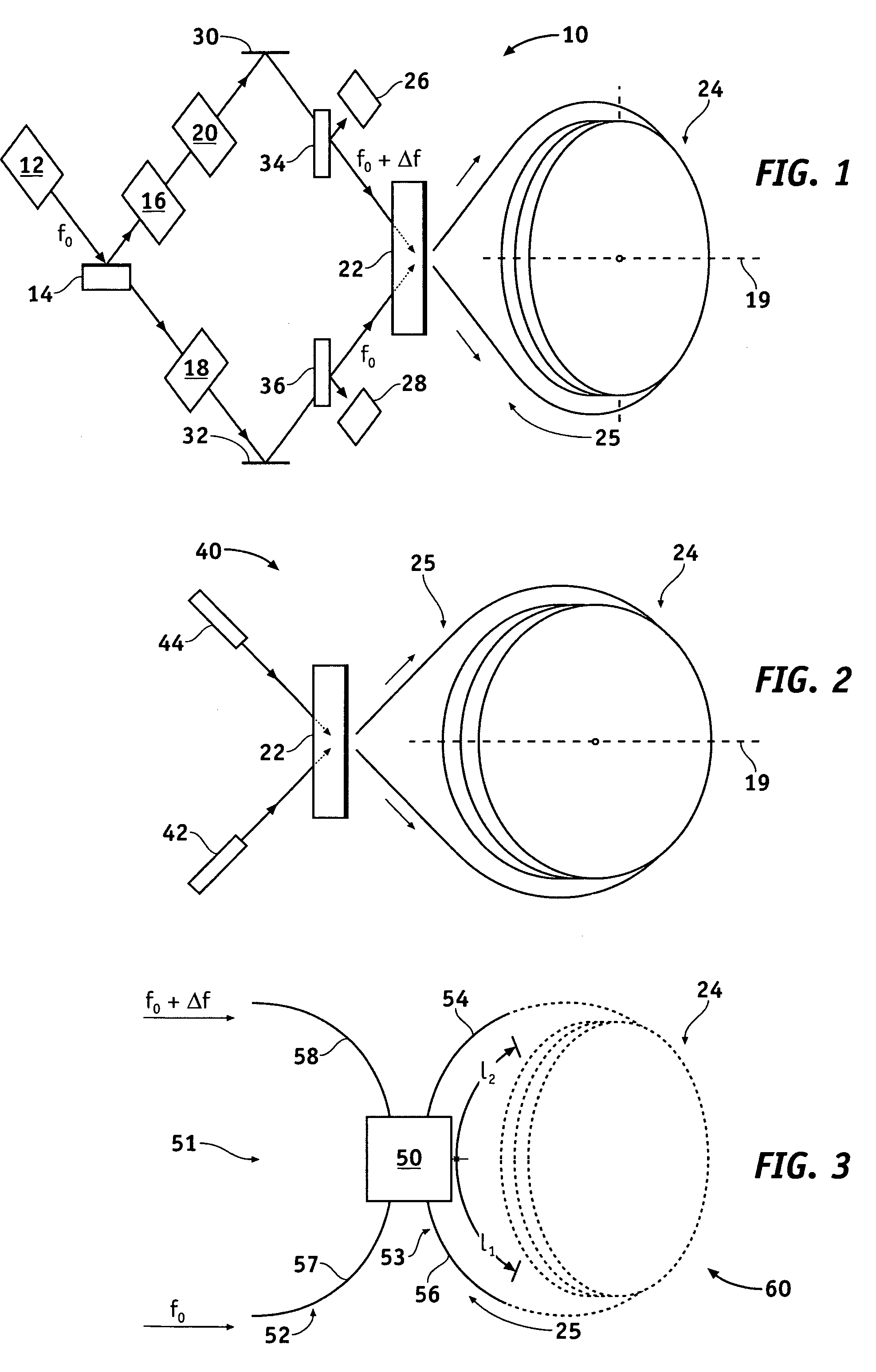
An integrated optical circuit for use in a fibre optic gyroscope which senses rotation rates by determining a phase shift due to the Sagnac Effect between light beams travelling around an optical fibre sensing loop (4) in opposite directions, the circuit being provided on a silicon-on-insulator chip comprising a layer of silicon separated from a substrate by an insulating layer, the circuit comprising: rib waveguides (11) formed in the silicon layer for receiving light from a light source (2) and transmitting light to a light detector (3), fibre optic connectors (9) in the form of grooves etched in the silicon layer for receiving the respective ends of the optical fibre sensing loop (4); rib waveguides (11) formed in the silicon layer for transmitting light to and from said fibre optic connectors (9) so as to direct light beams in opposite directions around the sensing loop (4) and receive light beams returning therefrom, phase determining means and (13,17,31) integrated in silicon layer for determining a phase shift between the light beams returning from the sensing loop (4).
Owner:BOOKHAM TECH
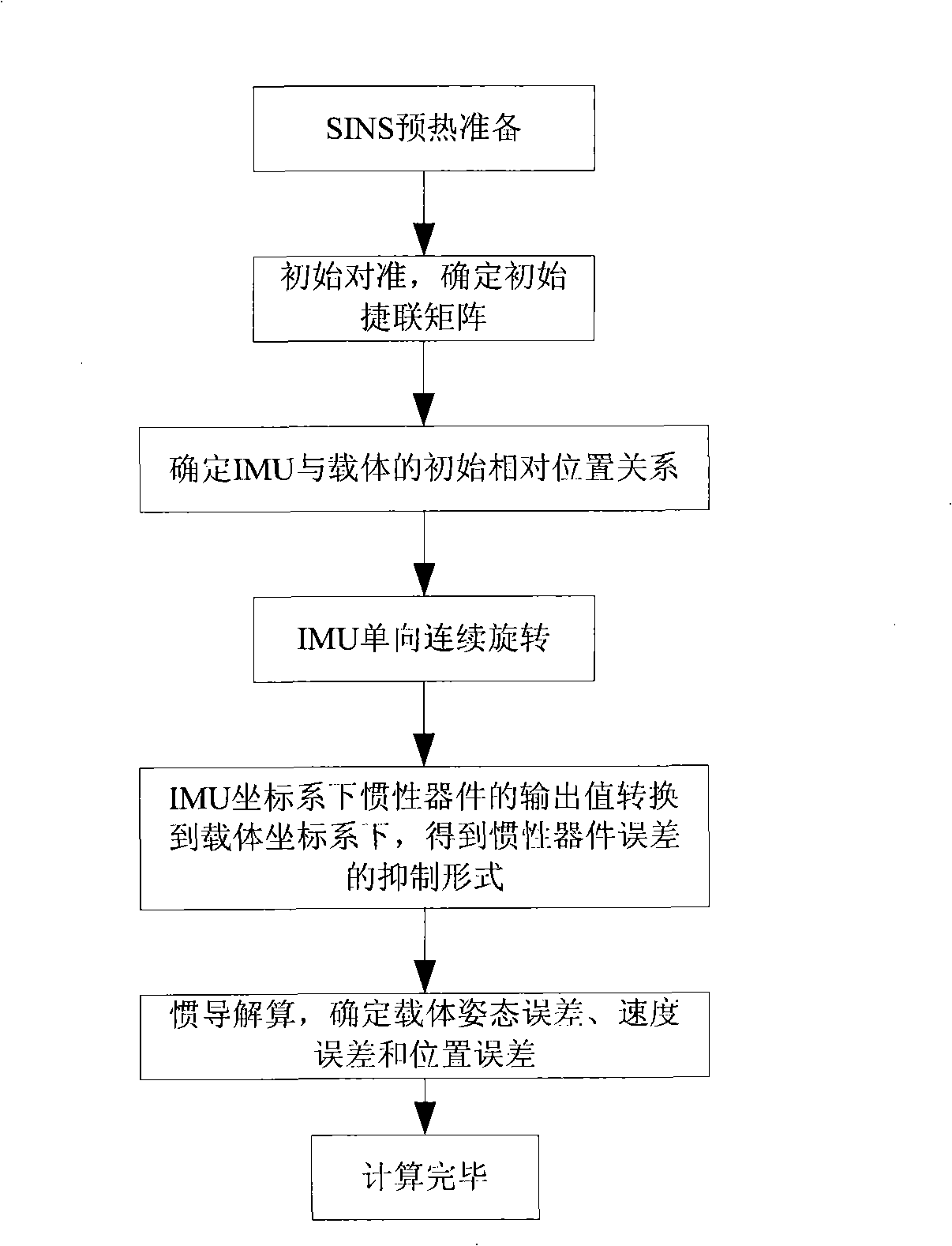
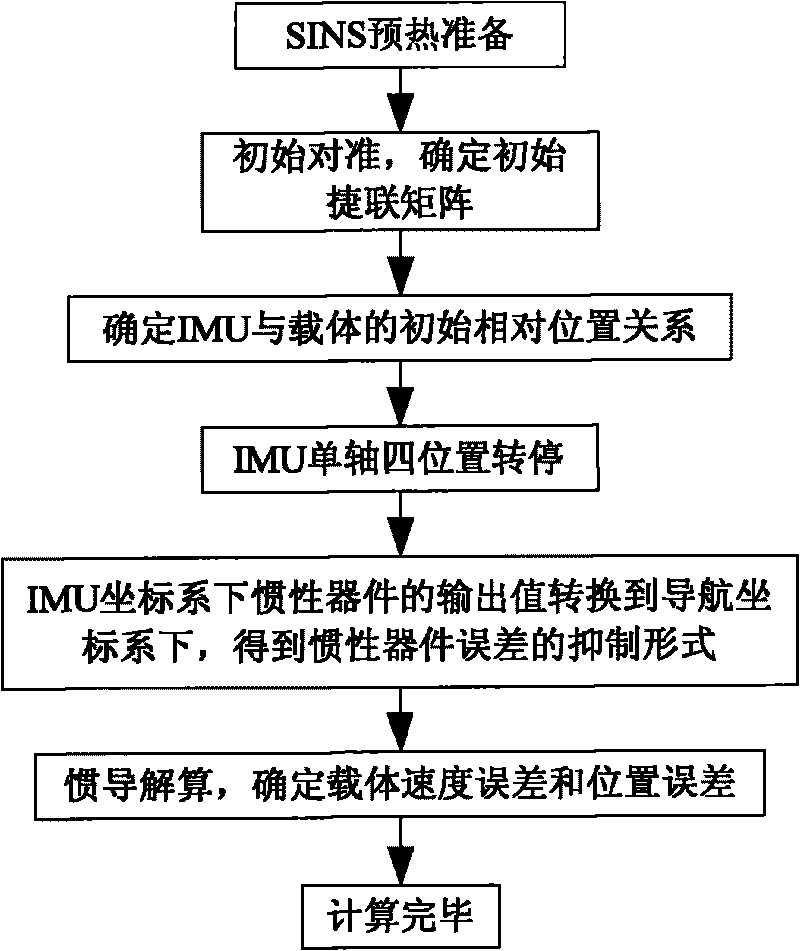
Optical fibre gyro strapdown inertial navigation system error inhibiting method based on single-shaft rotation
InactiveCN101514899AImprove navigation and positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerEarth's rotation
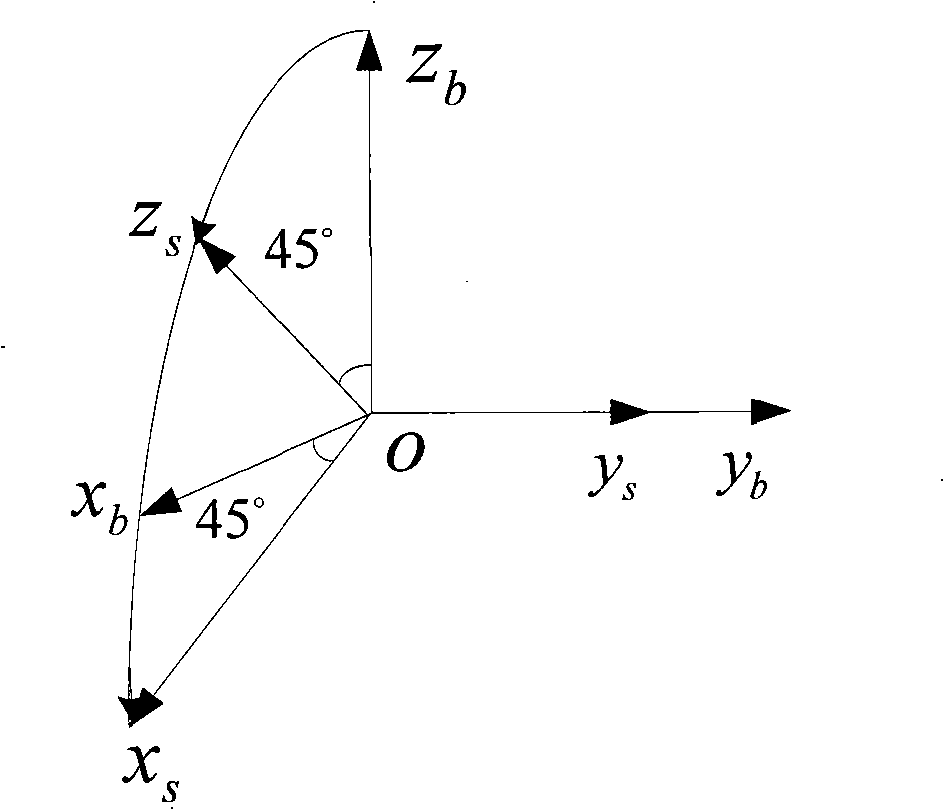
The invention provides an optical fibre gyro strapdown inertial navigation system error inhibiting method based on single-shaft rotation. The initial position parameters of a carrier are confirmed; the data outputted by an optical fibre gyroscope and a quartz accelerometer are collected; the pose information of the carrier is confirmed by the relation between the output of the accelerometer and an acceleration of gravity as well as the relation between the output of the gyroscope and the earth rotation rate; and the initial aligning of the system is finished; an inertial measuring unit coordinate system rotates by 45 degrees along the front direction of the shaft oyb of a carrier coordinate system and the initial opposite position between the two coordinate systems is confirmed; IMU continuously rotates along the front direction of the orientation shaft ozb of the carrier coordinate system by an angular velocity that Omega is equal to 6 degrees / s. The data generated by the optical fibre gyroscope and the quartz accelerometer after the rotation of the IMU is converted under the carrier coordinate system to obtain the modulating form of the constant deviation of an inertial apparatus. The output vale Omega ib of the optical fibre gyroscope is used to update a strapdown matrix Tb; the speed and the position of the carrier after the IMU is rotated and modulated are calculated. The invention modulates the constant deviation of the inertial device on the directions of three shafts to improve the navigation and location precisions.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Optic fiber gyroscope strapdown inertial navigation system two-position initial alignment method based on filtering
ActiveCN101246022AHigh precisionSolve the problem of low accuracy of azimuth misalignment angleNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFiberAccelerometer
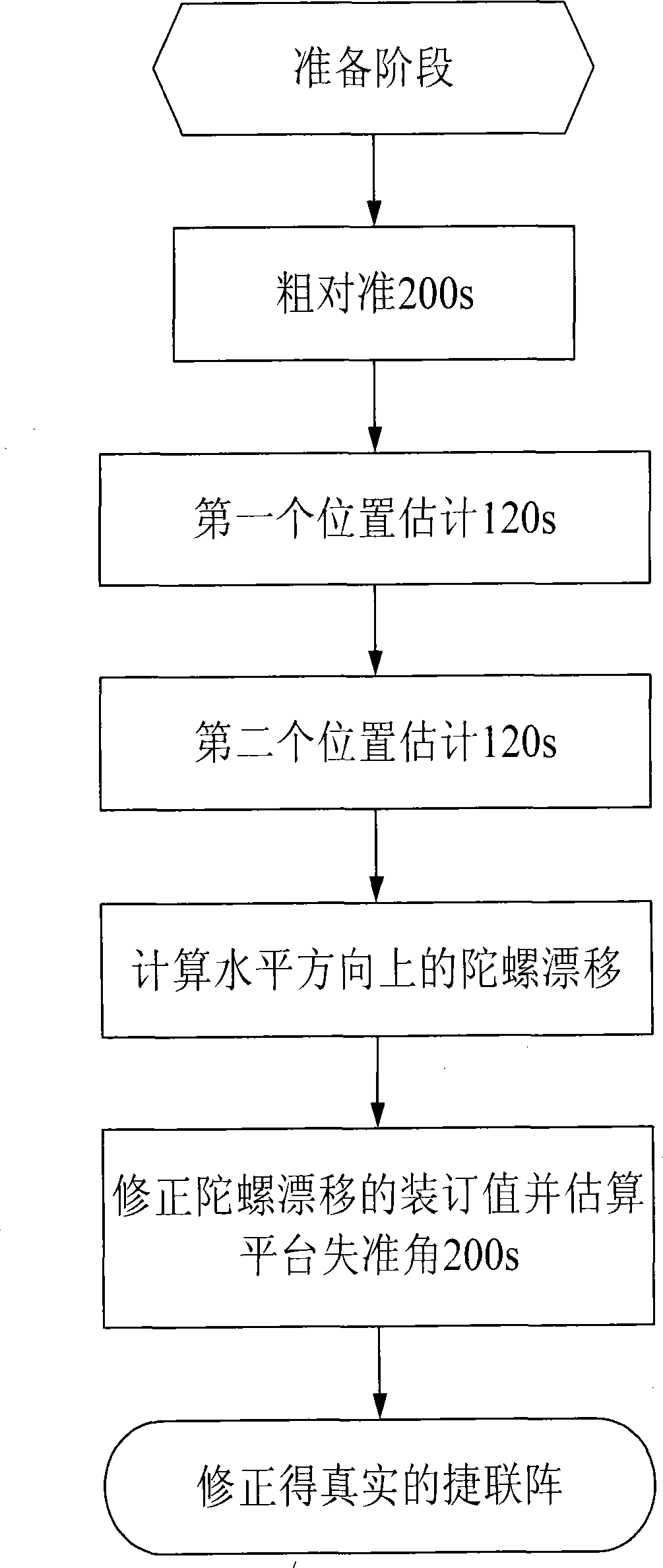
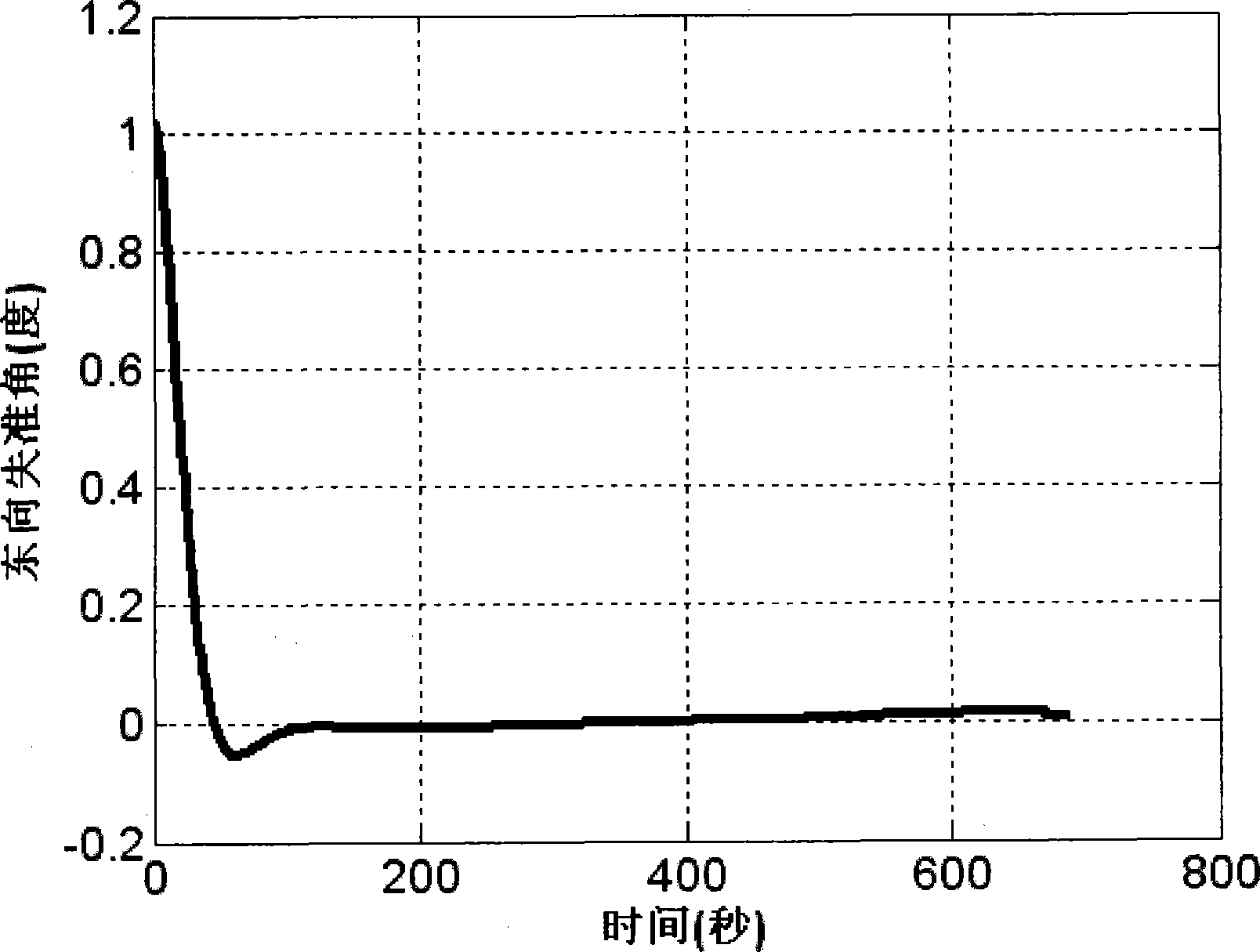
The invention provides an initial alignment method of two positions of a strapdown inertial navigation system of an optical fiber gyro which is based on filtering and comprises the following steps: initial position parameters of a carrier is determined by external equipment; data output by the optical fiber gyro and a quartz accelerometer is collected; the collected data of the optical fiber gyro and the quartz accelerometer is processed; a course angle K1 of the carrier, optical fiber gyro drift Xix1 in the east direction on the b system of a carrier coordinate system, and optical fiber gyro drift Xiy1 in the north direction on the carrier coordinate system are estimated; the carrier is rotated from a first position to a second position around an azimuth axis; a course angle K2 of the carrier, optical fiber gyro drift Xiy1 in the east direction on the b system of the carrier coordinate system, and optical fiber gyro drift Xiy2 in the north direction on the carrier coordinate system are estimated; gyro drift Xix and Xiy of the optical fiber gyro on the carrier coordinate system are computed; successive starting error of the gyro is calibrated; a platform alignment falloff angle is estimated. The initial alignment method of two positions of the strapdown inertial navigation system of the optical fiber gyro can overcome the influence of the equivalent gyro drift in a geographical coordinate system on the estimation precision of the azimuth alignment falloff angle and improve the alignment precision.
Owner:哈尔滨哈船导航技术有限公司
Non-linear alignment method of strapdown inertial navigation system
ActiveCN102519460AEnsure safetyGuaranteed confidentialityNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerComputation complexity
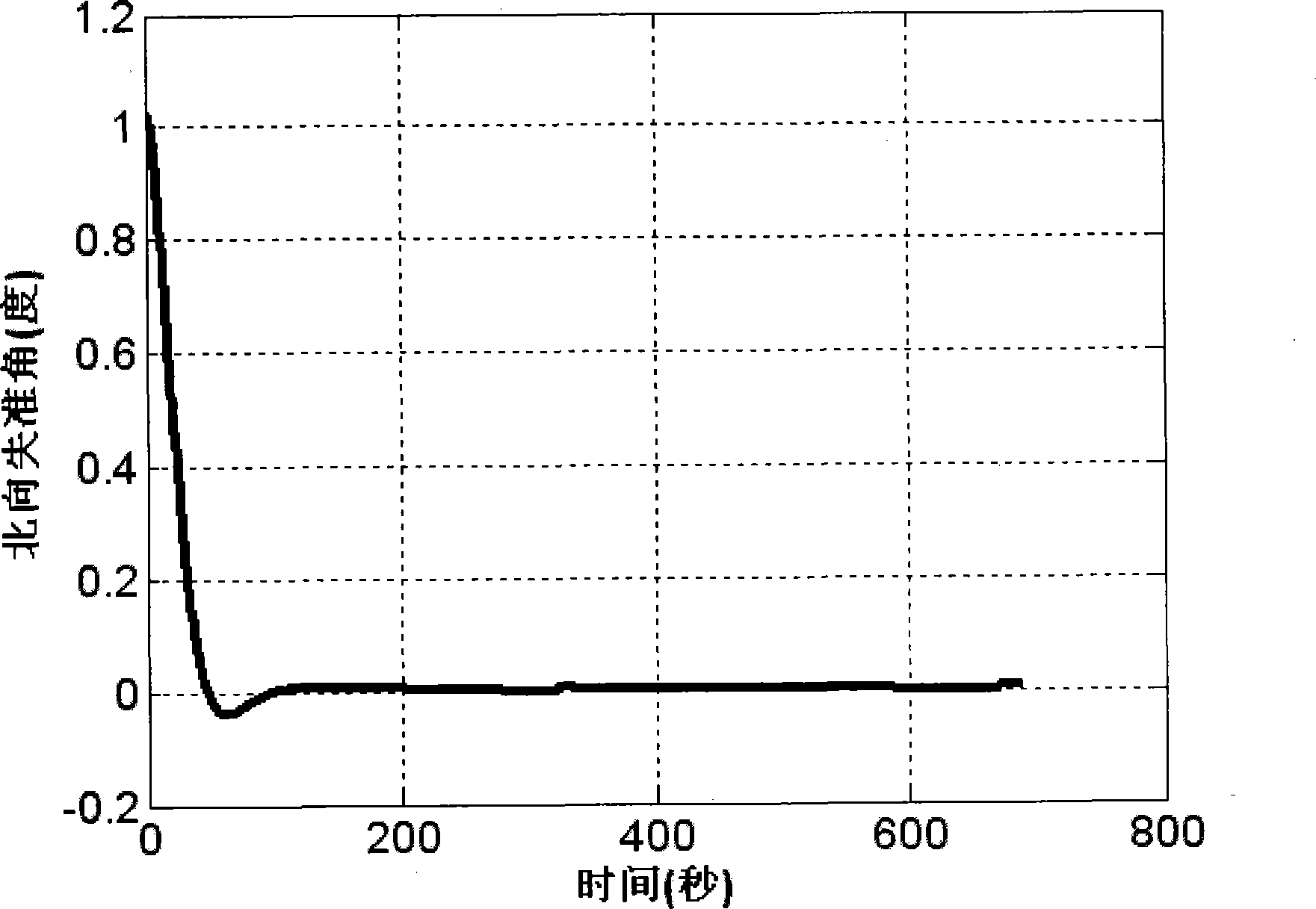
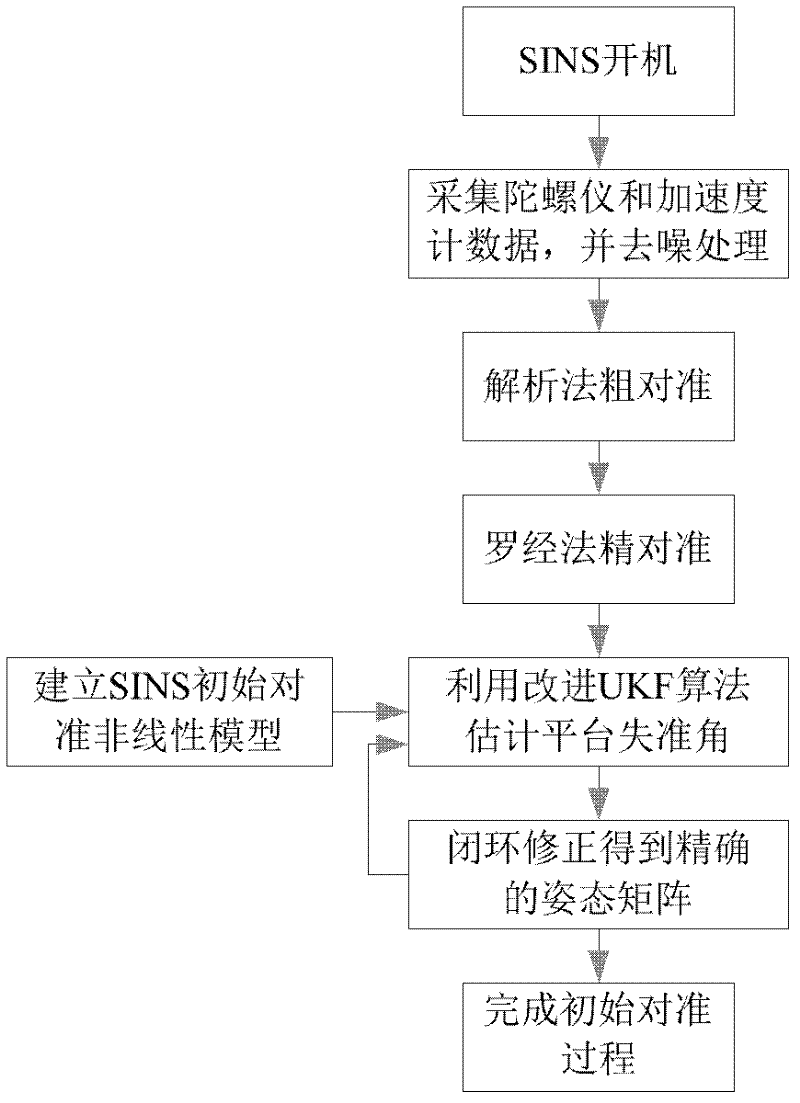
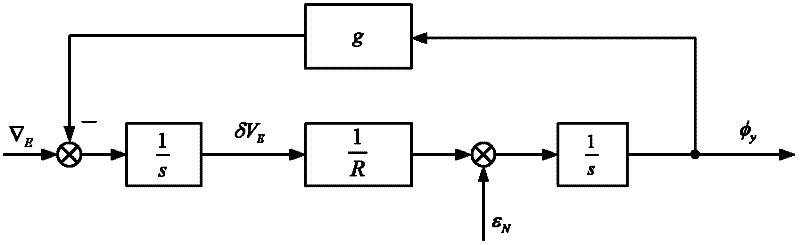
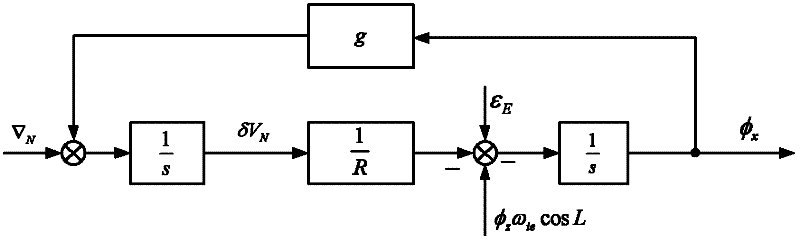
A non-linear alignment method of a strapdown inertial navigation system comprises the following steps of: acquiring data of an accelerometer and a fiber gyroscope of the fiber strapdown inertial navigation system and carrying out denoise processing, realizing coarse alignment and fine alignment processes by the utilization of an analysis method and a compass method, establishing a quaternion-based strapdown inertial navigation system non-linear error model under the condition that attitude angle and azimuth angle are both large misalignment angles, establishing an observation model with speed as observed quantity, carrying out iterative and filter estimation by the use of an improved UKF algorithm on the basis of the model so as to obtain the misaligned angle of the platform, continuously carrying out closed-loop feedback and correcting attitude matrix of the strapdown inertia system in the previous period, so as to accurately complete the initial alignment process. The method can be used to guarantee safety and confidentiality of the initial alignment without the utilization of other sensor information. By the introduction of the quaternion error based non-linear system error model, linearization is not required to guarantee the precision of the model. Computational complexity is reduced, and filtering is carried out on the established non-linear system so as to complete fine alignment.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
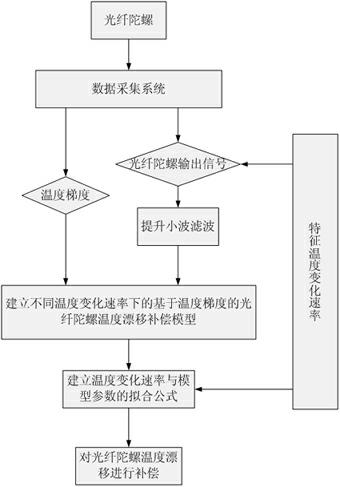
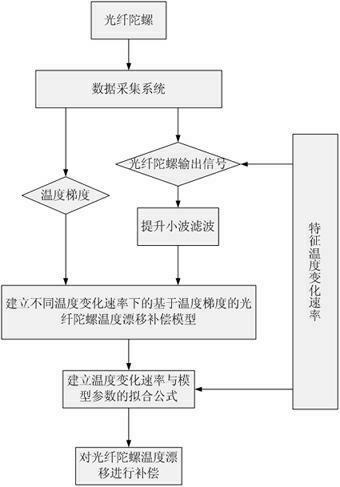
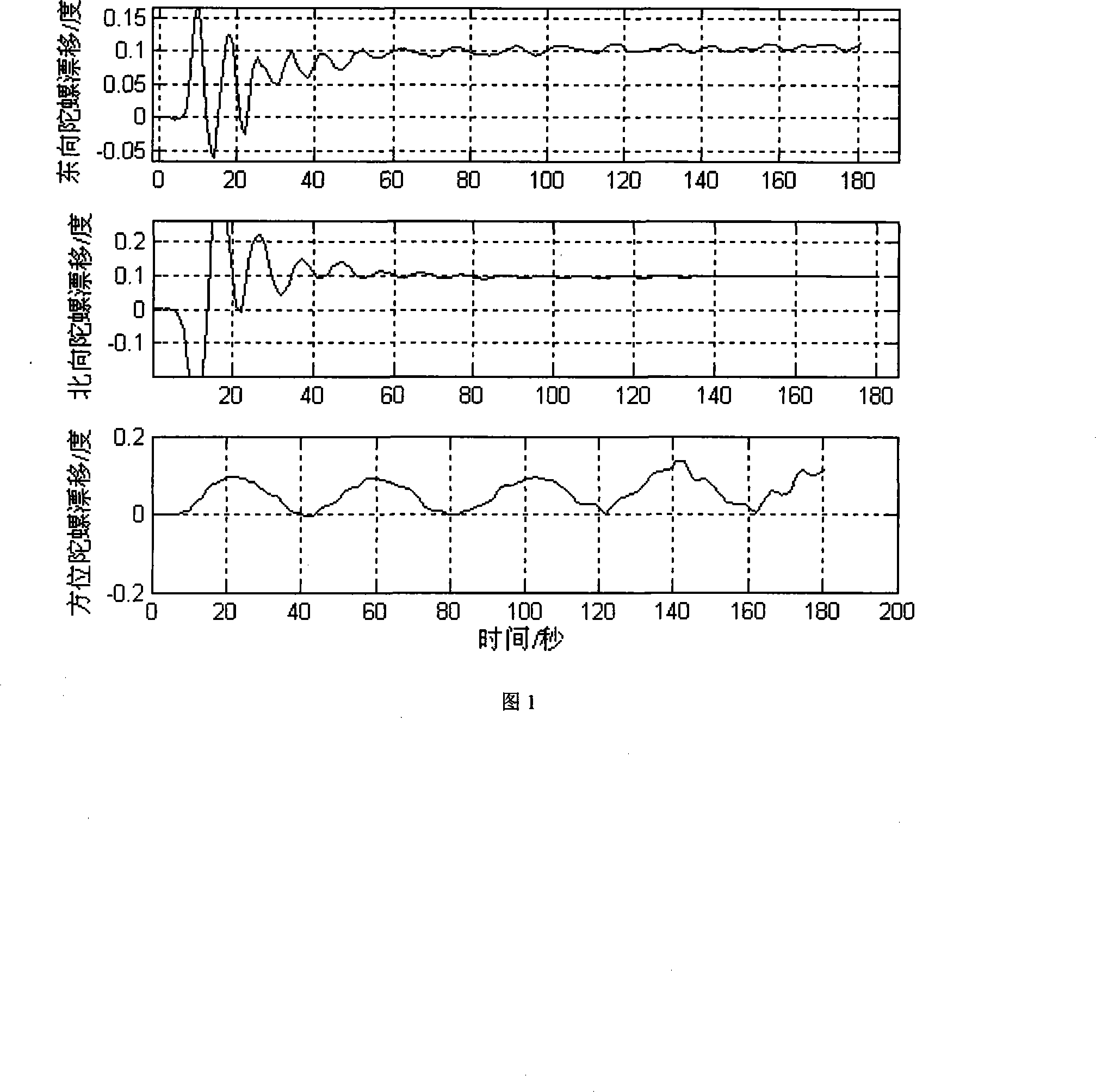
Method for modeling and error compensation of temperature drift of fiber optic gyroscope
ActiveCN102095419AComprehensive analysis to study the effects of temperature driftAnalyzing the effects of temperature driftSagnac effect gyrometersThermodynamicsFibre optic gyroscope
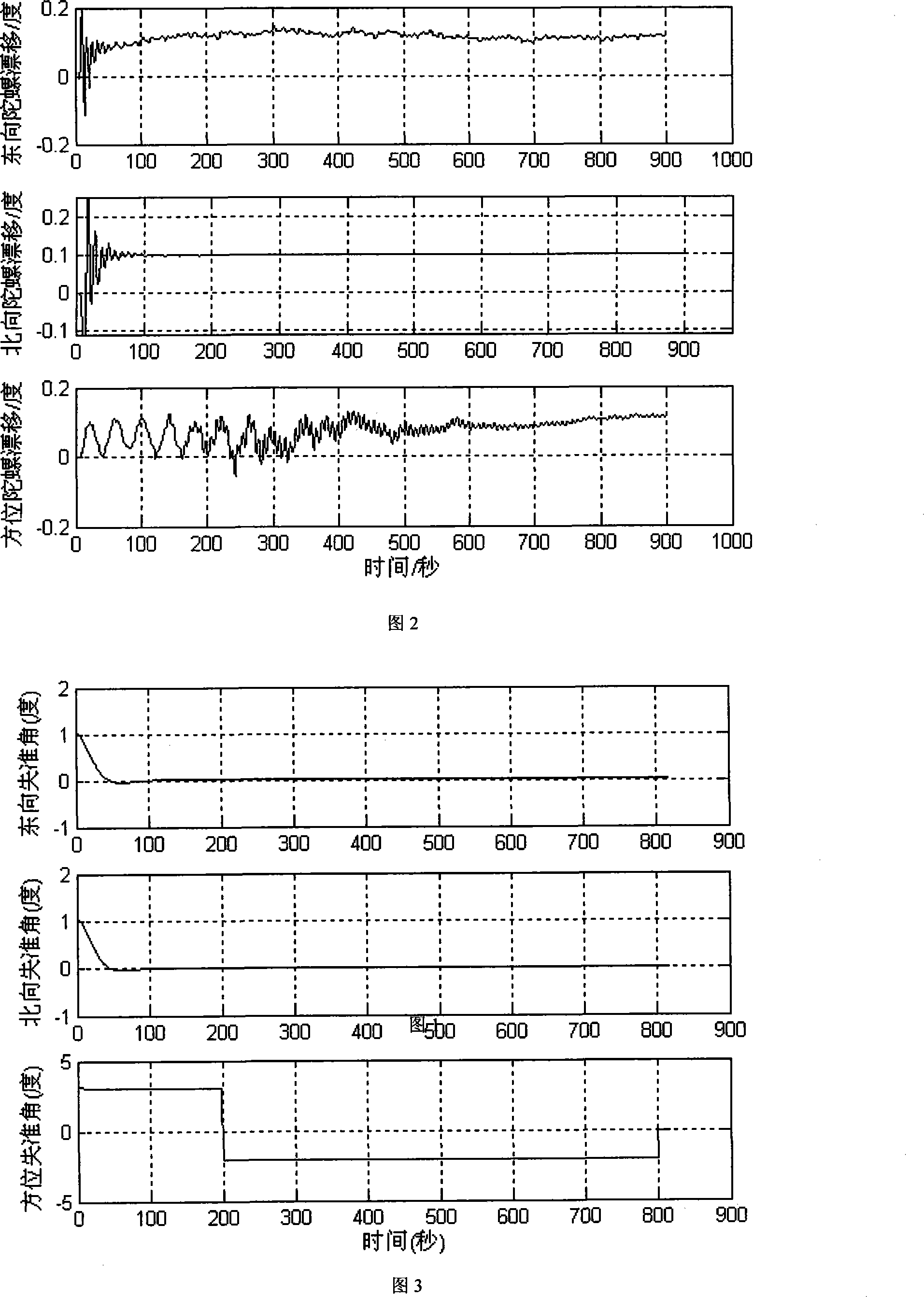
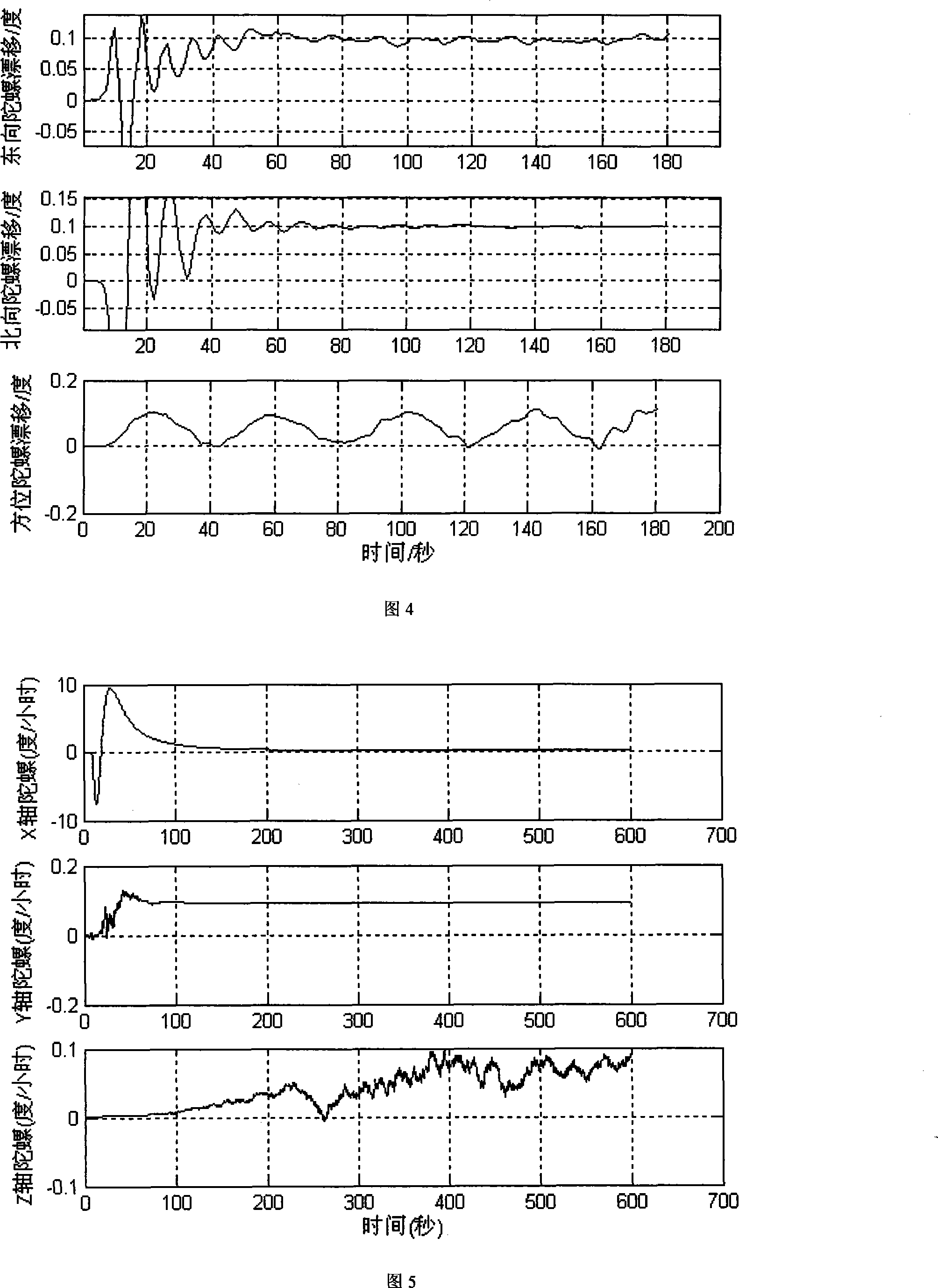
The invention discloses a method for modeling and error compensation of temperature drift of a fiber optic gyroscope, which comprises the following steps of: obtaining a learning sample and denoising the learning sample; establishing a fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation model based on temperature gradient; establishing a parameter formula based on a temperature change rate so as to determine the relations between the temperature change rate and various parameters of the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation model; and subtracting a temperature drift compensation value, obtained by the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation model, from the real-time output data of the fiber optic gyroscope to realize temperature compensation to the fiber optic gyroscope. The invention not only realizes modeling for the temperature drift of the fiber optic gyroscope in mechanism, but also simultaneously and greatly improves the convenience and accuracy of modeling, and has important significance to performance research and improvement of the fiber optic gyroscope in constantly variable temperature environments.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Optical fiber gyroscope strap-down inertial navigation system initial posture determination method
InactiveCN101187567AReduce divergenceReduce system dimensionalityDigital technique networkNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerFiltering theory
The invention discloses a determined method for an initial gesture on the basis of Doppler optical fiber gyro strapdown inertial navigation system, which comprises continuously collecting data which is output by an optical fiber gyro and a quartz flexible accelerometer after being preheated, processing the data of the gyroscope and the accelerometer which are collected, finishing a rough alignment of the strapdown inertial navigation system, entering into an extractive alignment after the rough alignment is finished, establishing a dynamic base error equation of a marine strapdown inertial navigation system, employing an optimal control filtering theory to design an electric filter, and doing a filtering estimation, extracting information of ship hull gesture misalignment angle to correct the ship hull gesture when a combined extractive alignment is finished, finishing extractive initial alignment, simultaneously obtaining shift estimated value of the gyroscope, and realizing a drift course of the initial alignment. The method of the invention can realize accurate estimation to a zero drift of the optical fiber gyro when the requirement of accuracy and rapidity is guaranteed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
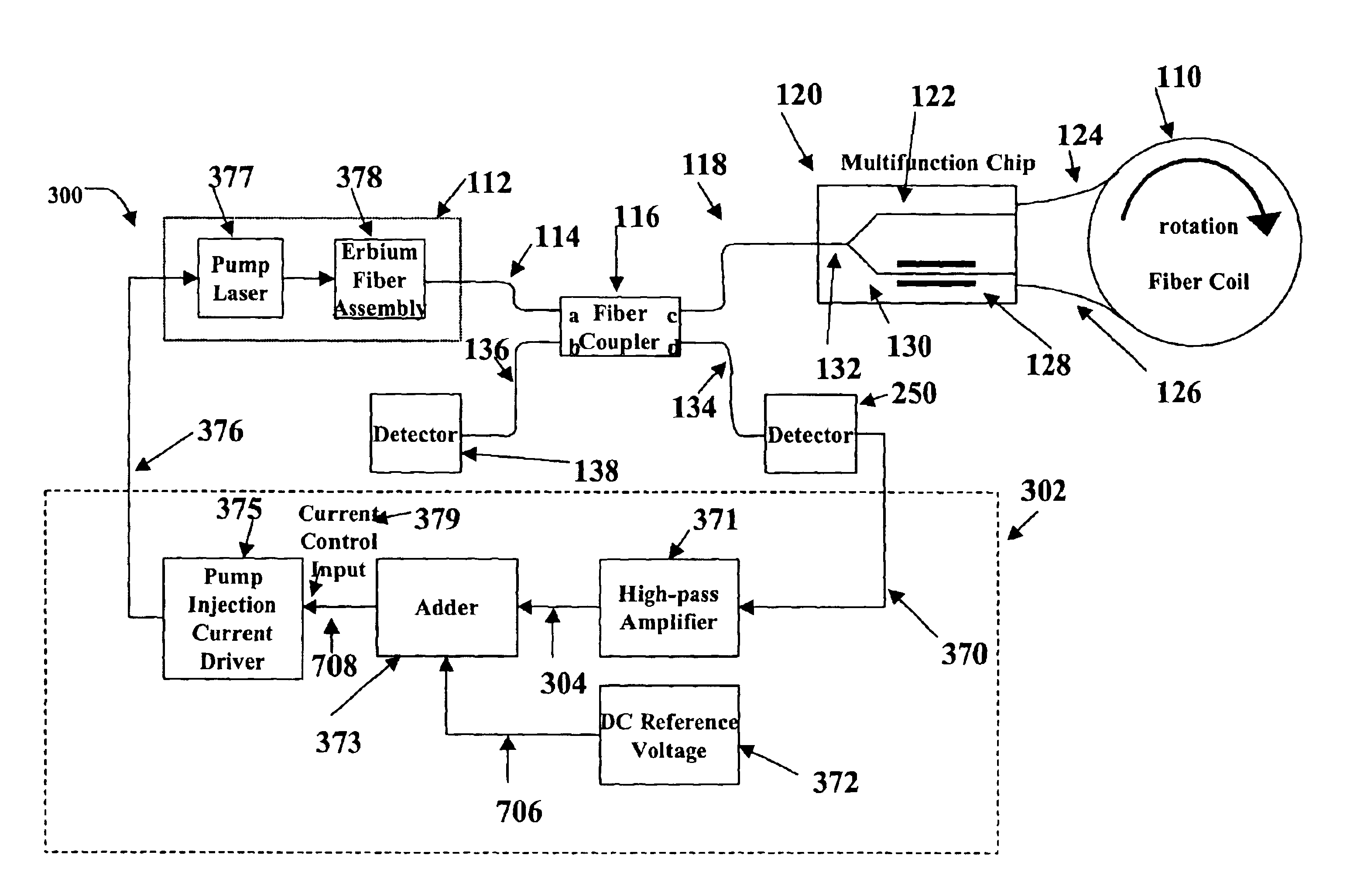
Relative intensity noise controller for fiber light sources
InactiveUS20030128365A1Sagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberOctave
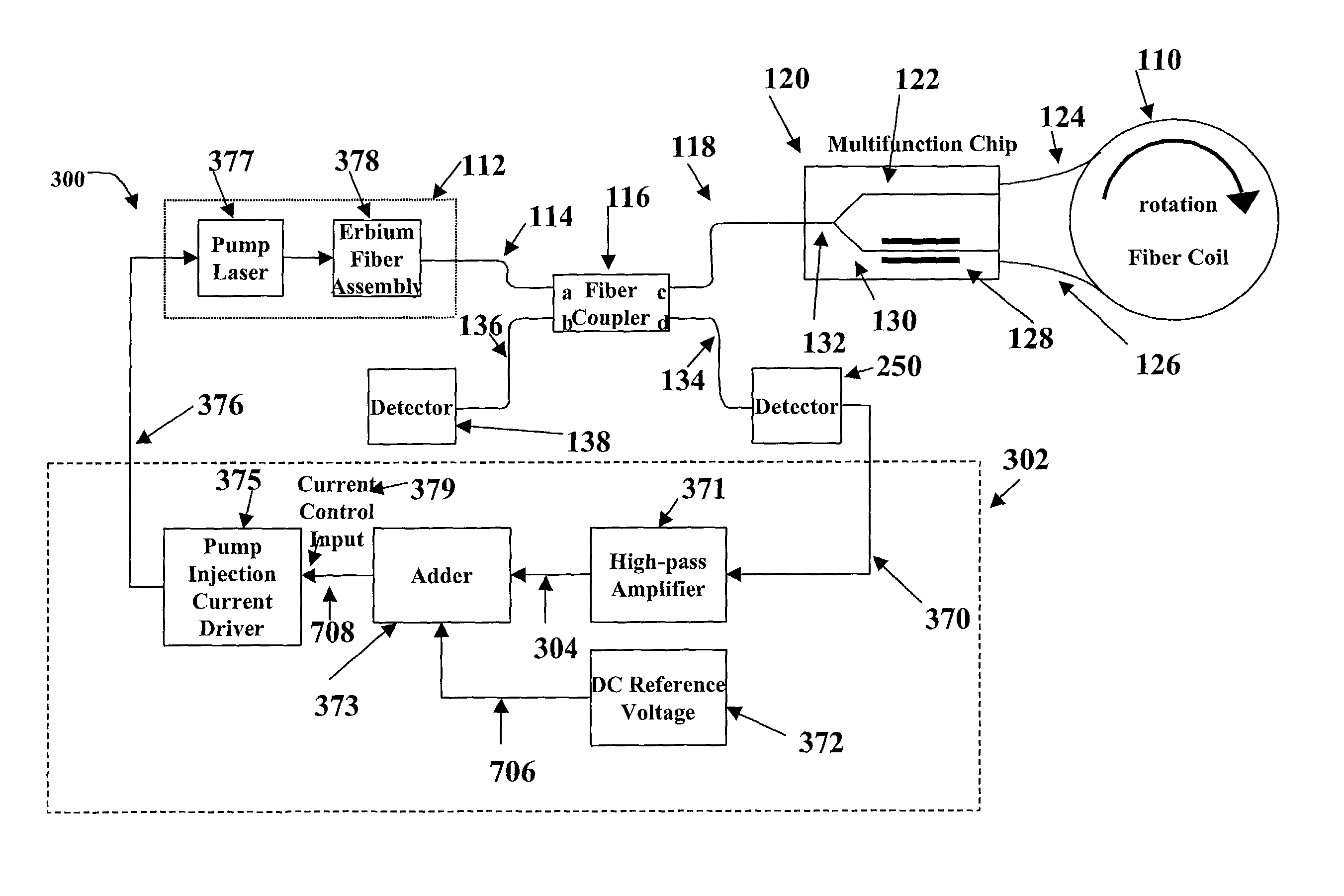
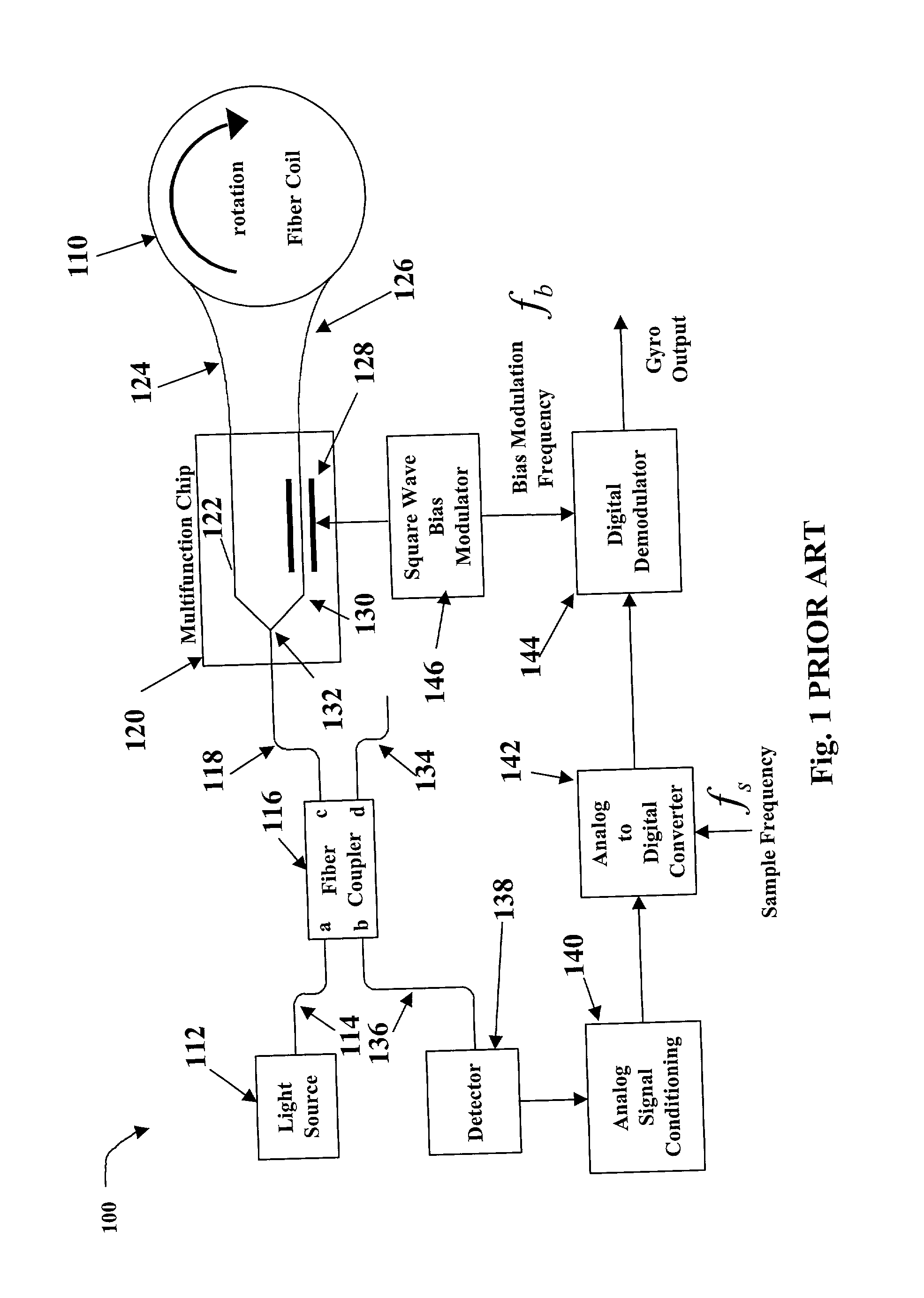
A system and method is provided which suppresses relative intensity noise in a fiber optic gyroscope by taking advantage of the frequency response of erbium fiber. In operation, the gain provided by the erbium fiber is added to the gain of the other components in the feedback loop to provide for stable loop performance up to about 250 kHz. The frequency response of the erbium fiber of about 3 kHz also provides a 6 db per octave roll-off, which, when used in a negative feedback control loop for controlling the current flowing to the gyroscope light source, allows for a relative intensity noise control loop with a bandwidth much greater than 3 kHz; this may be used in high performance gyroscope applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Relative intensity noise controller with maximum gain at frequencies at or above the bias modulation frequency or with second order feedback for fiber light sources
InactiveUS6765678B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberNegative feedback
A system and method is provided which suppresses relative intensity noise in a fiber optic gyroscope by taking advantage of the frequency response of erbium fiber. In operation, the gain provided by the erbium fiber is added to the gain of the other components in the feedback loop to provide for stable loop performance up to about 250 kHz. The frequency response of the erbium fiber of about 3 kHz also provides a 6 db per octave roll-off, which, when used in a negative feedback control loop for controlling the current flowing to the gyroscope light source, allows for a relative intensity noise control loop with a bandwidth much greater than 3 kHz; this may be used in high performance gyroscope applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
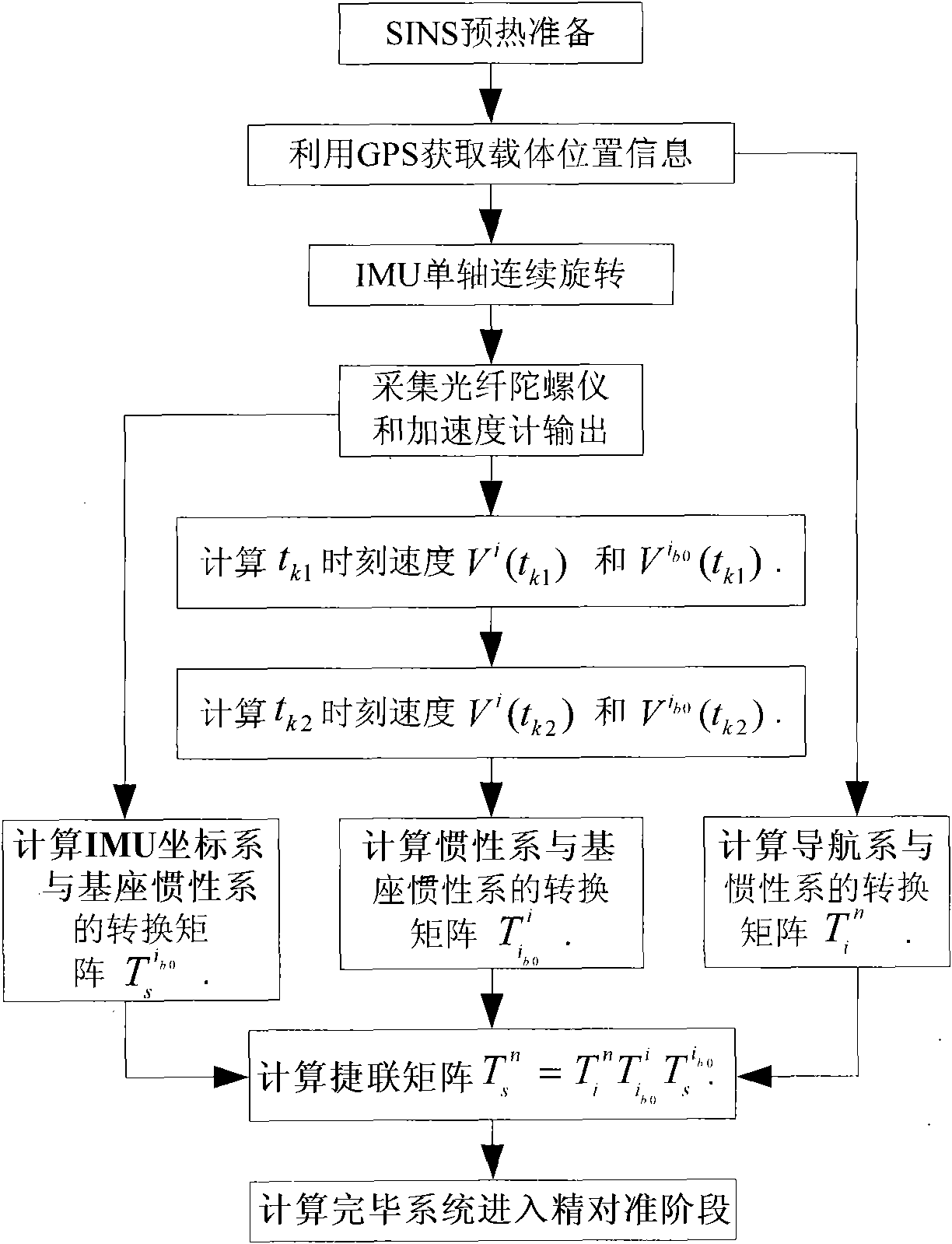
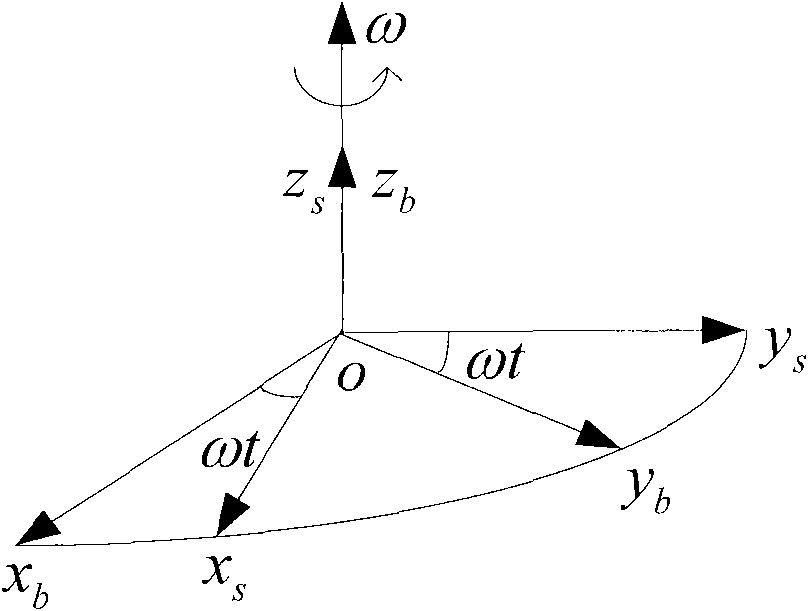
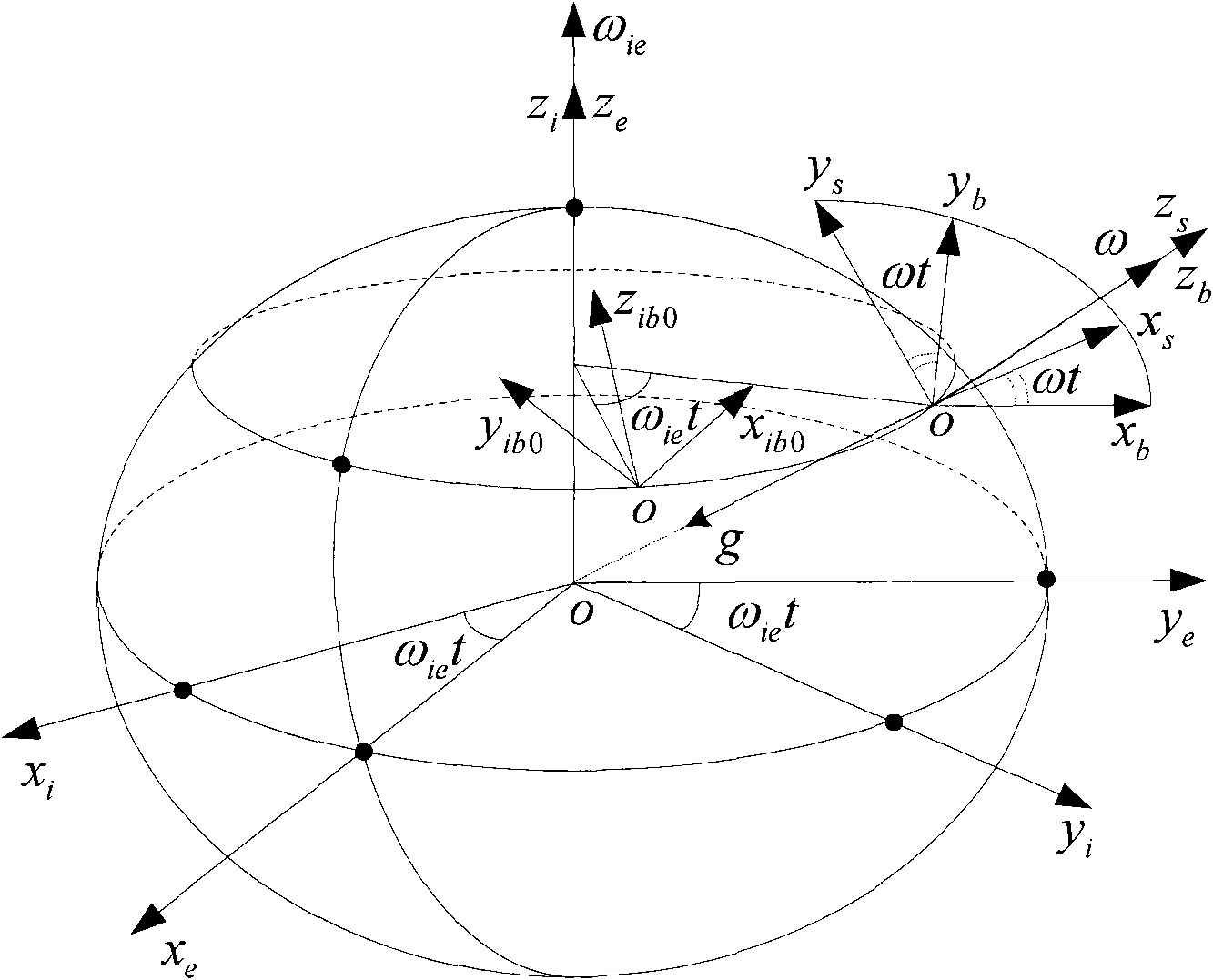
Coarse alignment method for fiber optic gyro strapdown inertial navigation system based on single axis rotation
InactiveCN101629826AImproved Coarse Alignment AccuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFiberAccelerometer
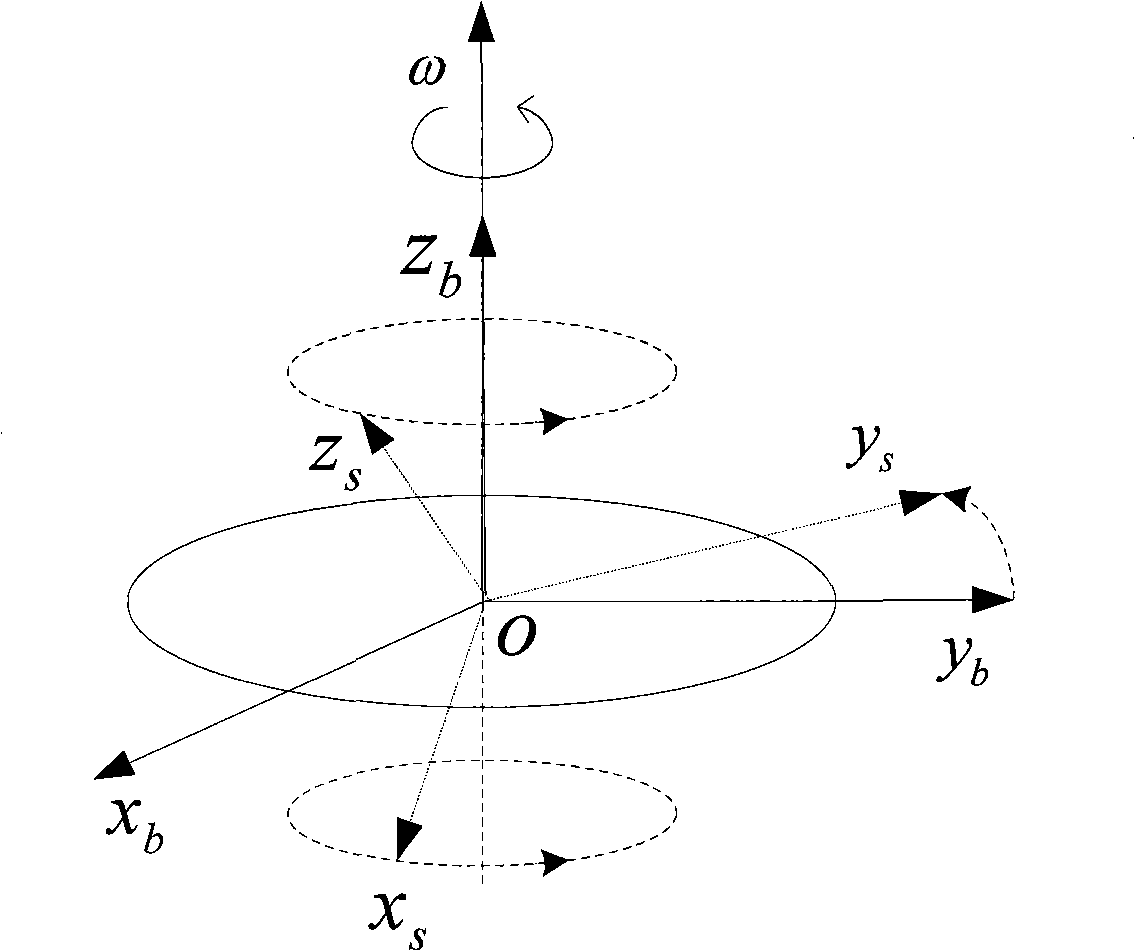
The invention provides a coarse alignment method for a fiber optic gyro strapdown inertial navigation system based on single axis rotation. The coarse alignment method comprises the following steps: (1) determining initial position parameters of a carrier by a GPS; (2) collecting the data output by a fiber optic gyroscope and a quartz accelerometer and processing the data; (3) determining a transfer matrix Ti<n> of a navigation coordinate system and an inertial coordinate system according to the mutual position relation of the coordinate systems; (4) allowing a single axis of an inertial measurement unit to continuously rotate, setting superposition of an initial time IMU coordinate system s and a carrier coordinates b, then allowing the inertial measurement unit to continuously rotate around a positive direction of an azimuth axis ozb of the carrier coordinate system with an angular velocity Omega=6 degrees / s; (5) determining the relative position relation of the inertial coordinate system and a base inertial coordinate system; and (6) determining an expression of a strapdown matrix after coarse alignment is over according to the calculated relative conversion relation of the coordinate systems calculated in step (3), (4) and (5). The coarse alignment method can help obtain higher coarse alignment precision under a swinging interference condition.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
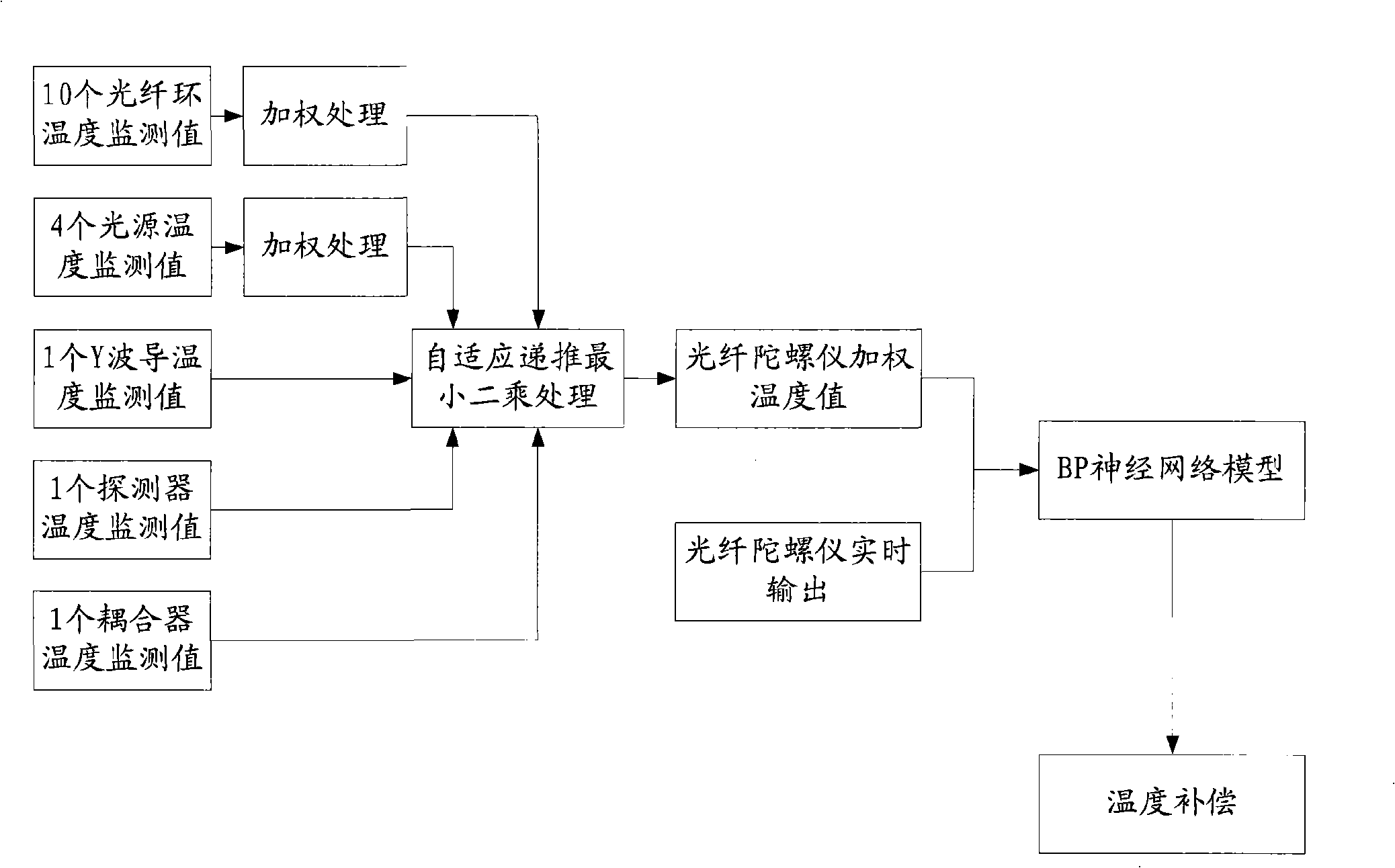
Distributed layer-dividing grade temperature error compensating method of optical fiber gyroscope
ActiveCN101408427AHigh precisionMake sure it's trueThermometers using physical/chemical changesSagnac effect gyrometersFiberThermodynamics
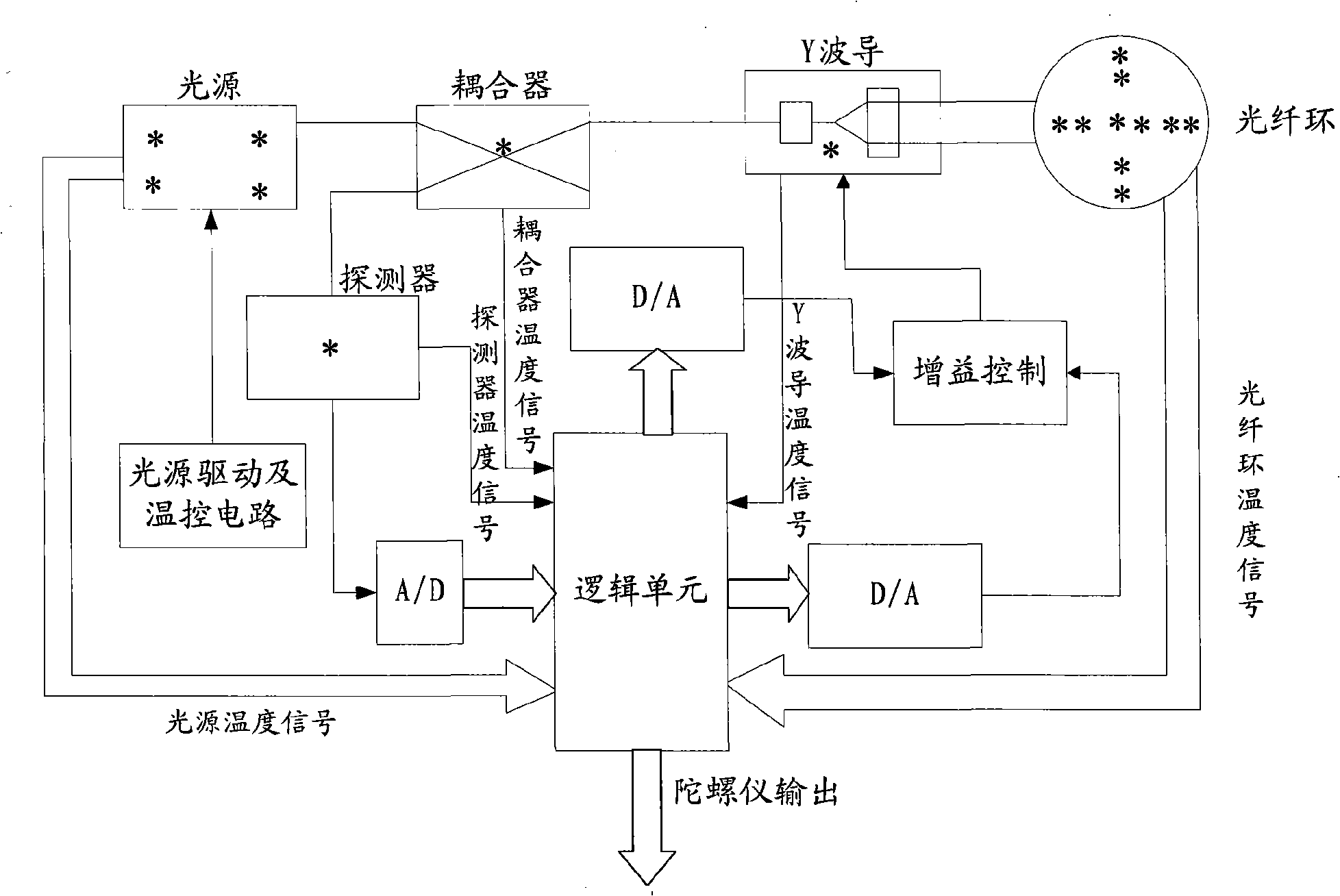
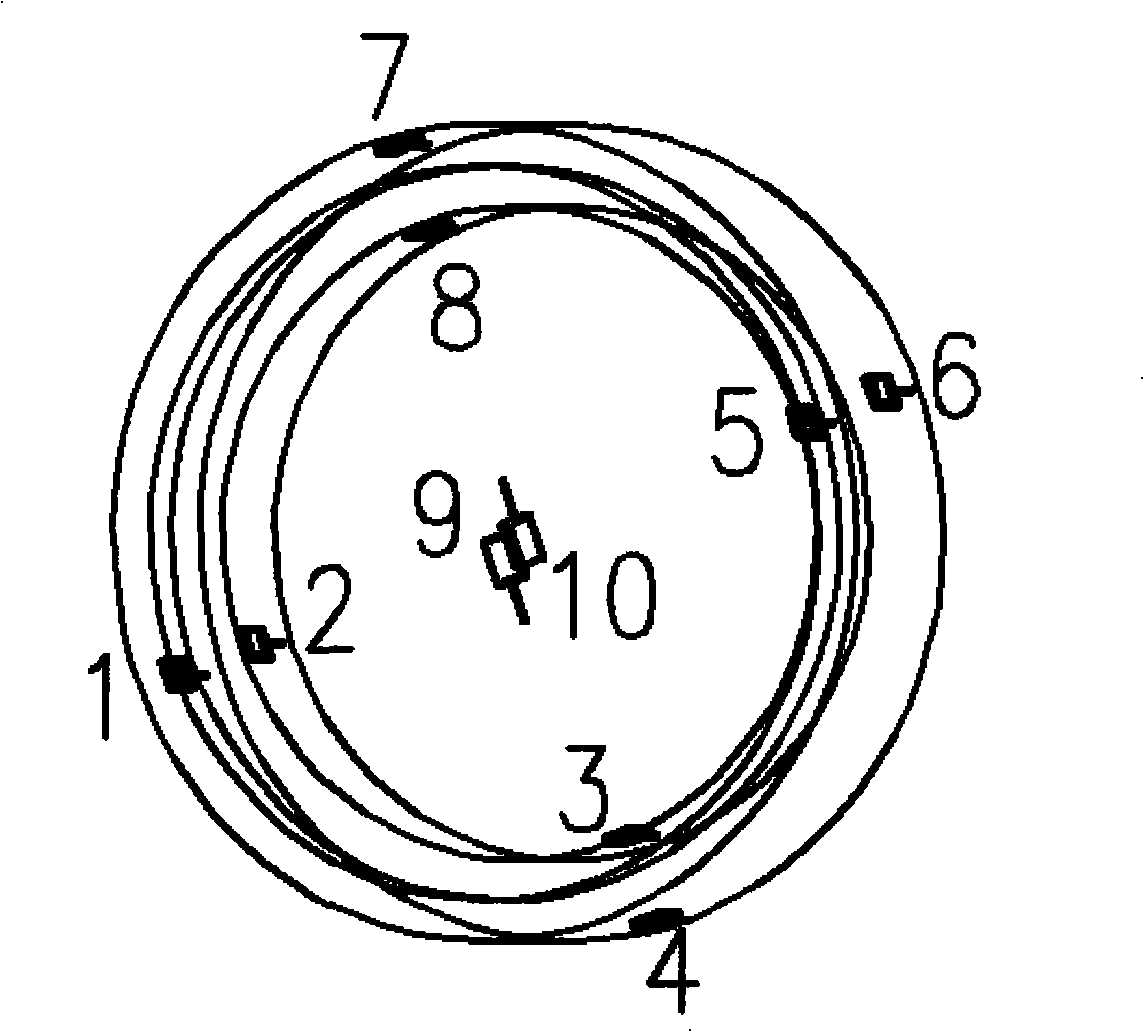
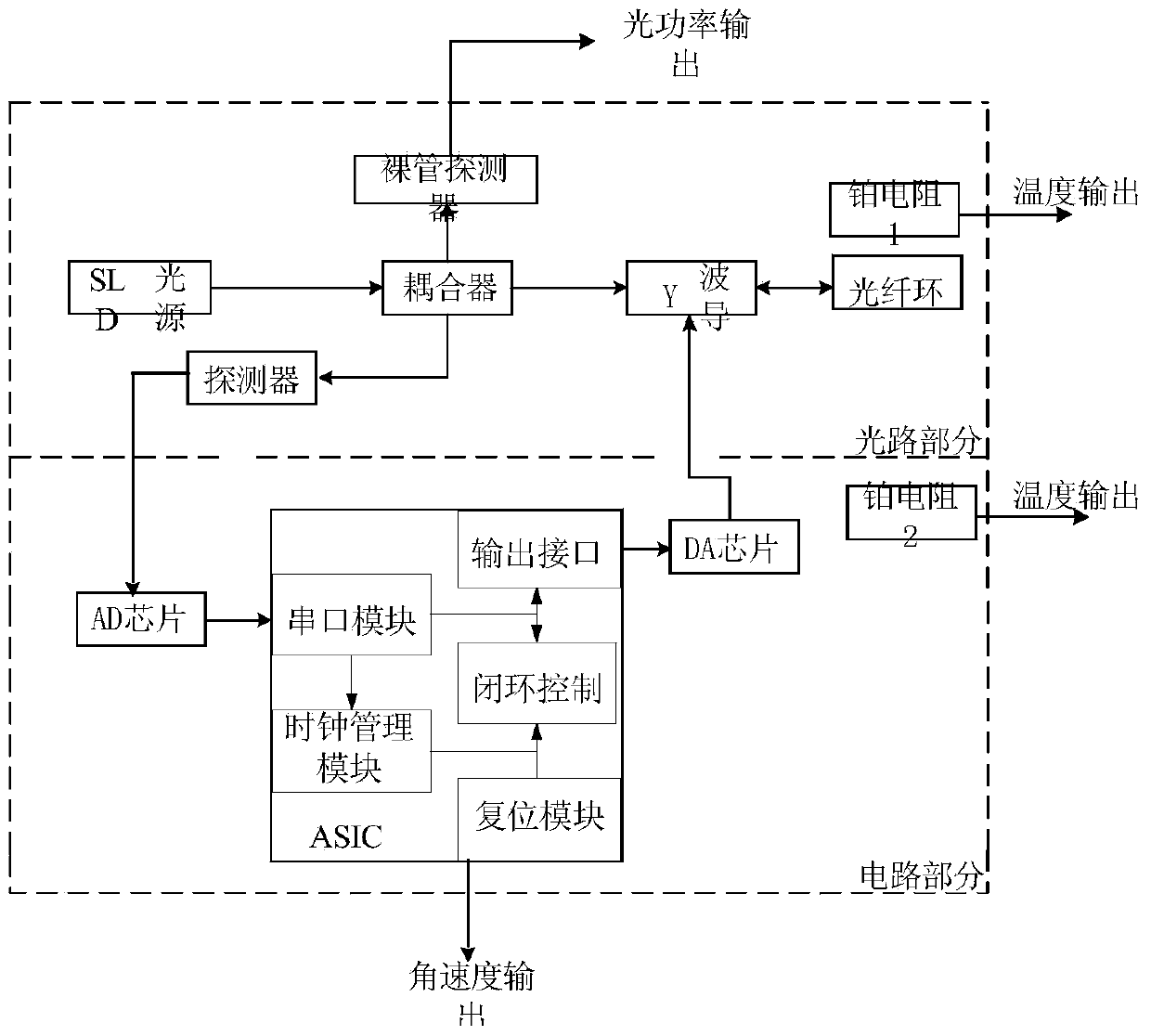
An optical fibre gyroscope distributed layered temperature error compensation method comprises the following steps: (1) five optical components of a fiber-optic ring, a light source, a Y wave guide, a detector and a coupler are taken as temperature monitoring objects for determining the number of the temperature monitoring points of each optical component and the distributing form; (2) self-adapting recurrence and least squares treatment are carried out on monitoring value of each temperature monitoring point for obtaining temperature output value of the optical fibre gyroscope; (3) a neural network model is built for obtaining temperature drift compensation value by utilizing the temperature output value and the real time outputting data of the optical fibre gyroscope; (4) the real time outputting data of the optical fibre gyroscope minus the temperature drift compensation value means temperature compensation of the optical fibre gyroscope. The method can overcome the disadvantages of the prior art and reflect the temperature field inside the optical fibre gyroscope systematically and in an all-round way, and has significance in the performance research and improvement under the condition of the temperature environment of the optical fibre gyroscope.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TIMES OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH
Interference optical fiber gyroscope for measuring multidimensional vector
InactiveCN102128621AEliminate driftCancel noiseNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSagnac effect gyrometersOptical pathFibre optic gyroscope
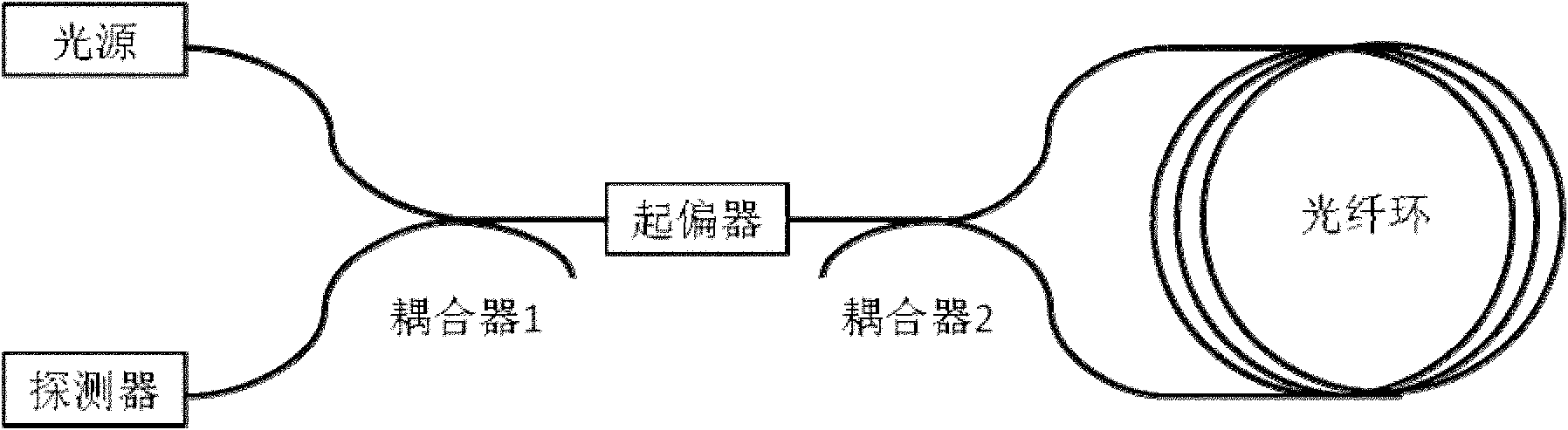
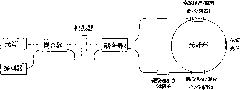
The invention provides an interference optical fiber gyroscope. The interference optical fiber gyroscope comprises a light source, a coupler, two signal detection optical paths, a linearly polarized light generation optical path and a polarization maintaining optical fiber ring, wherein the light source is connected with the coupler through an optical fiber; the two output ends of the coupler are connected with one signal detection optical path in the two signal detection optical paths through an optical fiber respectively; and the two signal detection optical paths are connected with the polarization maintaining optical fiber ring by optical fibers through the linearly polarized light generation optical path.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Apparatus for measuring inertia of fiber gyro composite unit and its calibration method
ActiveCN102735232AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove the accuracy of useSagnac effect gyrometersFiberEngineering
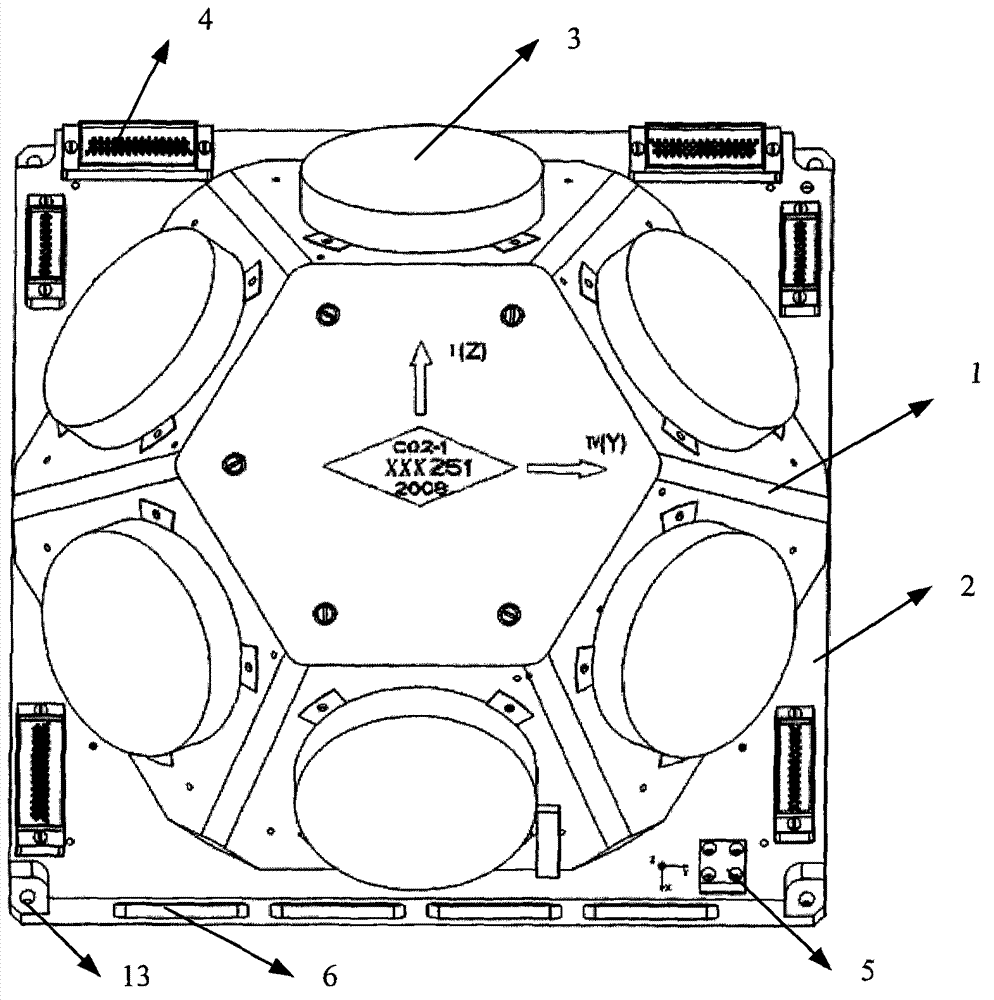
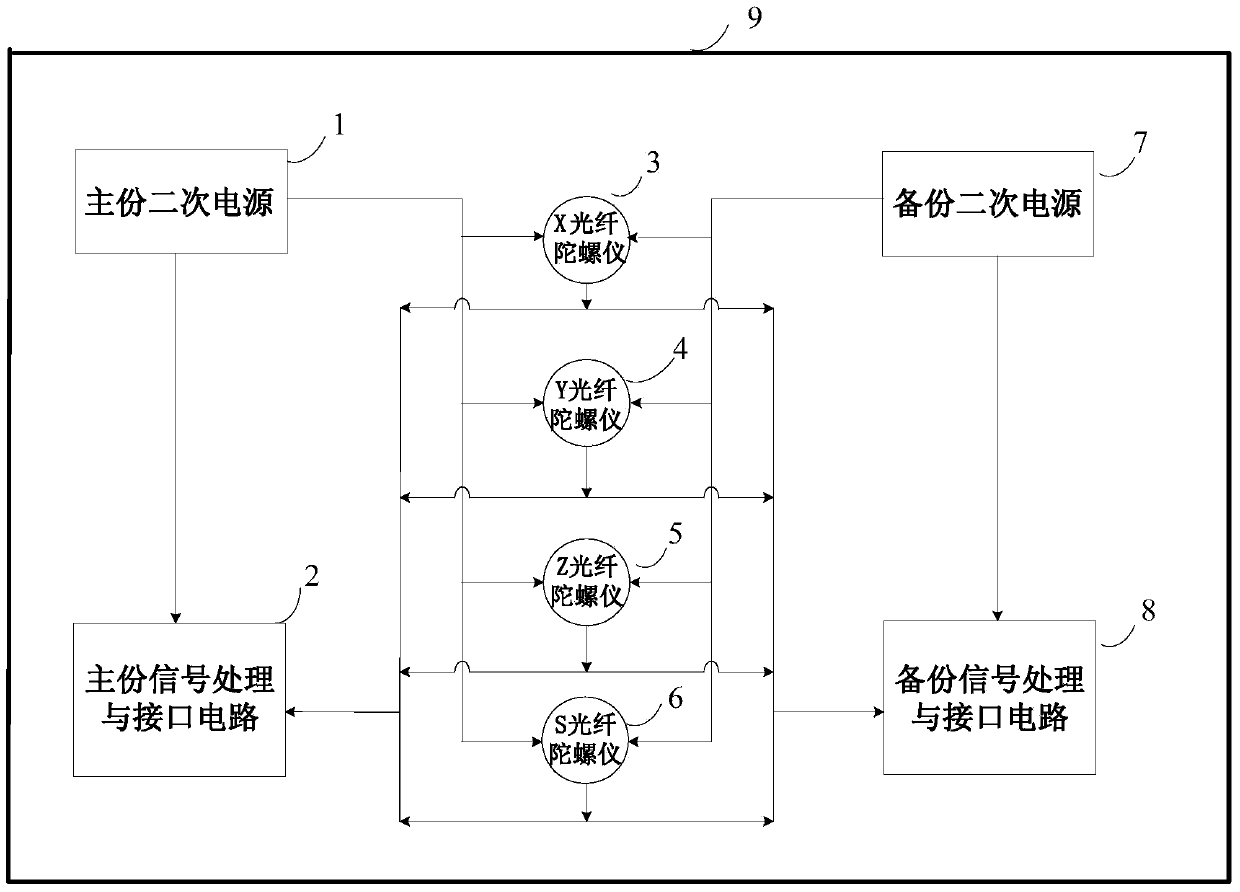
The invention relates to an apparatus for measuring inertia of a fiber gyro composite unit and its calibration method, and especially relates to the apparatus for measuring the inertia of the fiber gyro composite unit with miniaturization, high reliability and redundant multi-tables used for navigation, guidance and control of spacecrafts, which belongs to the inertia measurement technical field. The apparatus comprises a hexangular pyramid and a pedestal; six fiber gyroscopes are uniformly distributed on six side surfaces of the hexangular pyramid, six signal processing and interface circuits and six secondary power sources are arranged in the pedestal. According to the invention, the gravity center is positioned at a geometric center as possible, and the anti-mechanical capacity is good; the six fiber gyroscopes are redundant backup with each other; the reliability is high; in the process of in-orbit operation, a triaxial attitude angle speed can be still provided even the fault is generated by no more than three shafts at will, and the fault detection and the isolation can be realized. The calibration method can accurately calibrate zero position, scale factor and installation error, and can effectively enhance the in-orbit usage precision.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TIMES OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH
System and a method of three-dimensional modeling and restitution of an object
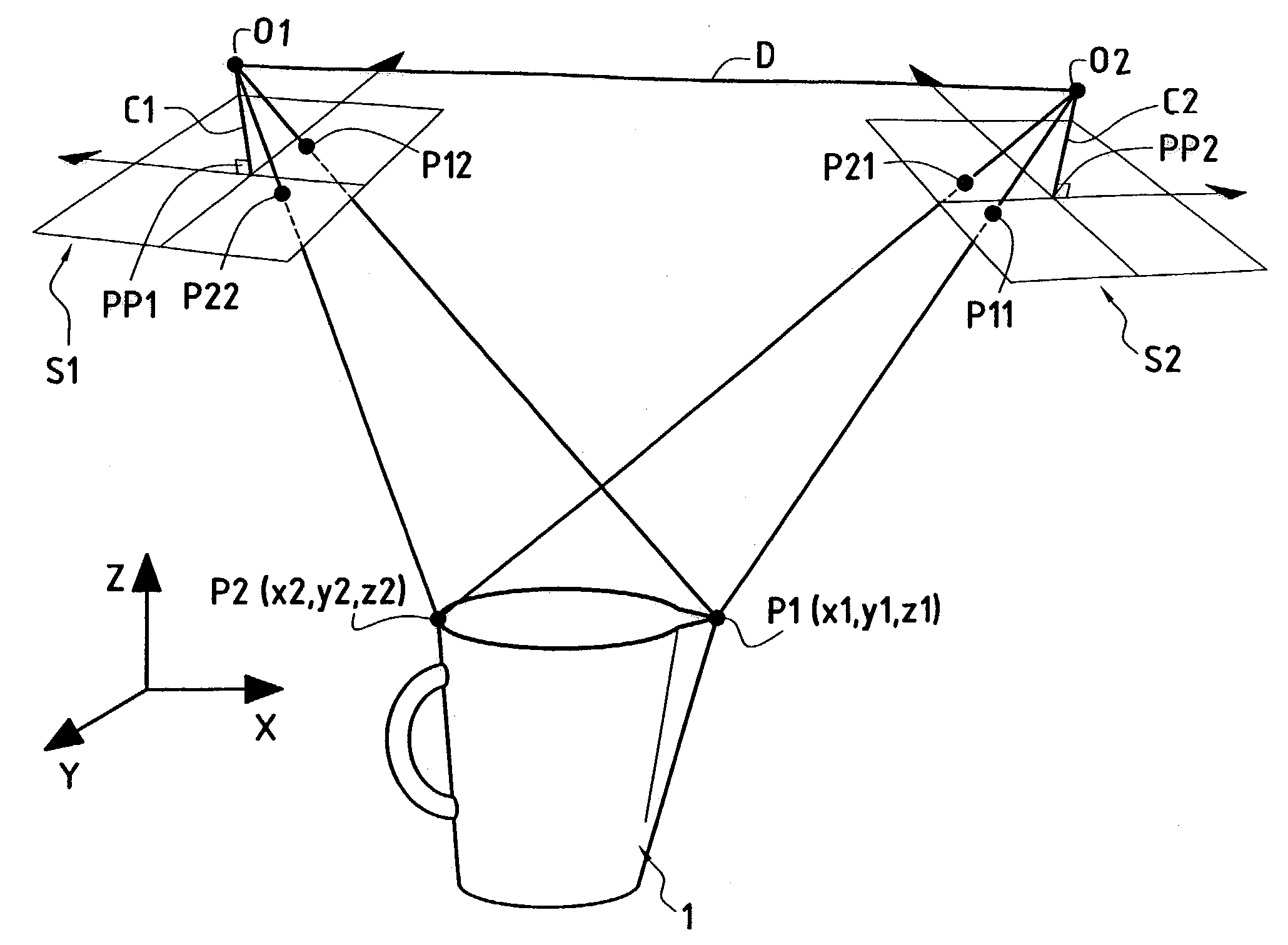
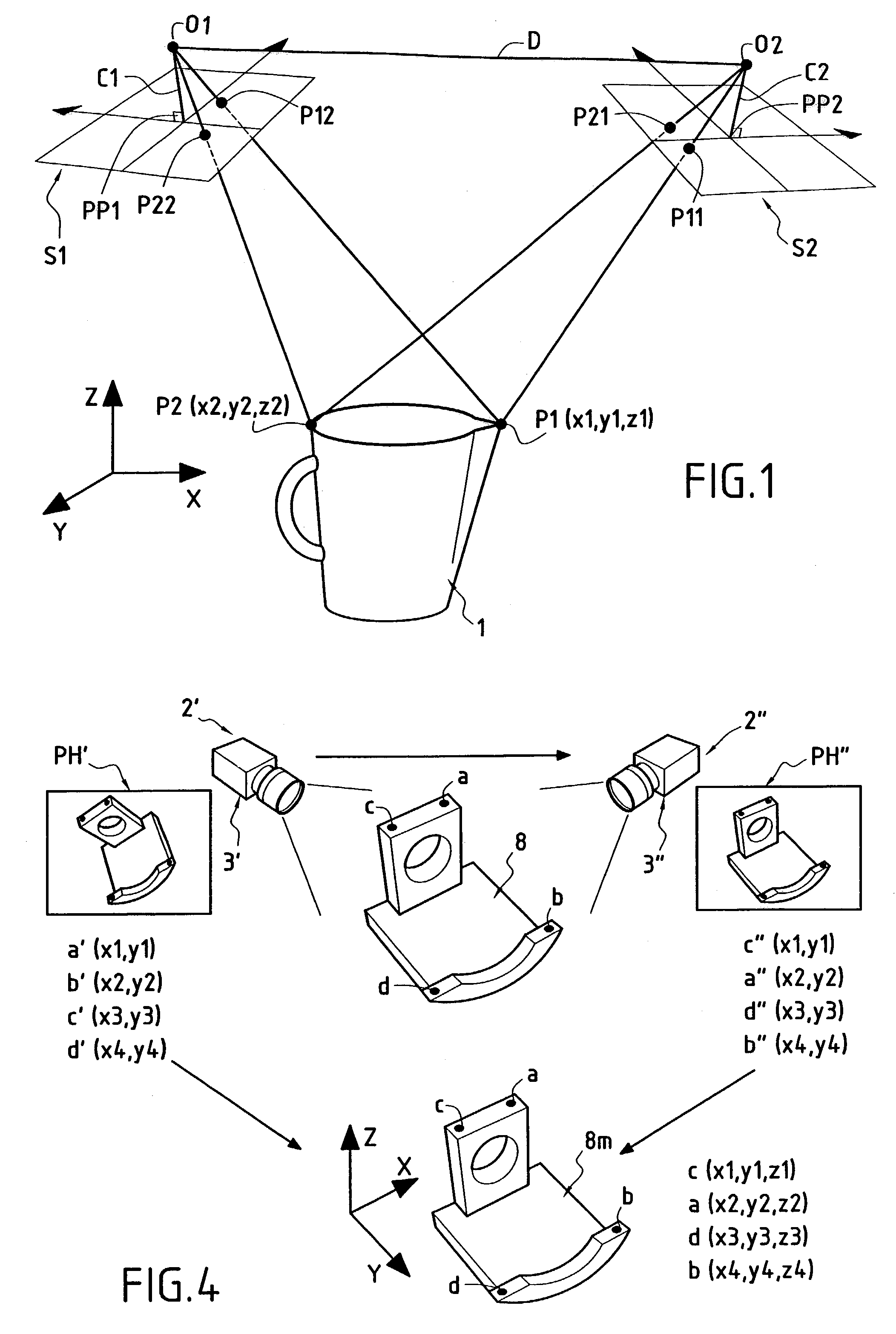
ActiveUS7187401B2Easy to operateEasy to handleNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPicture interpretationDigital videoAccelerometer
Owner:YODEA +1
Fiber optic gyroscope using a low-polarization and polarization-maintaining hybrid light path
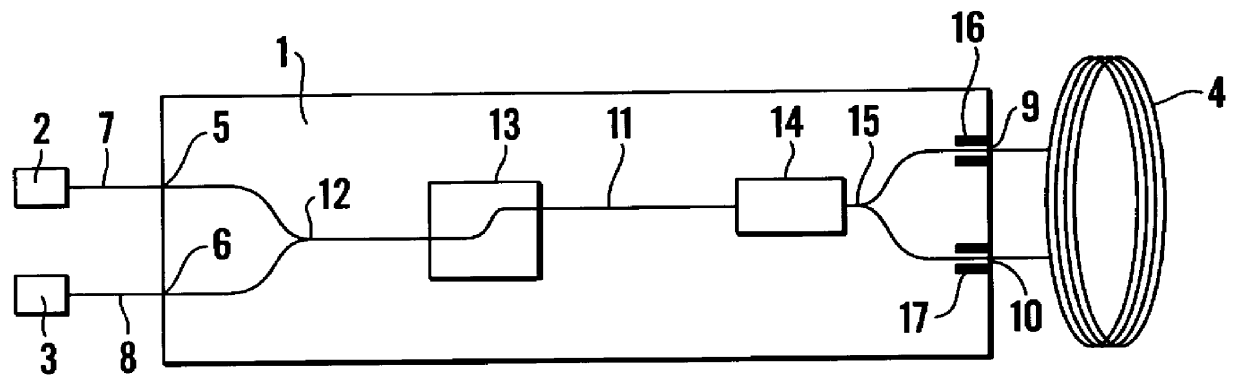
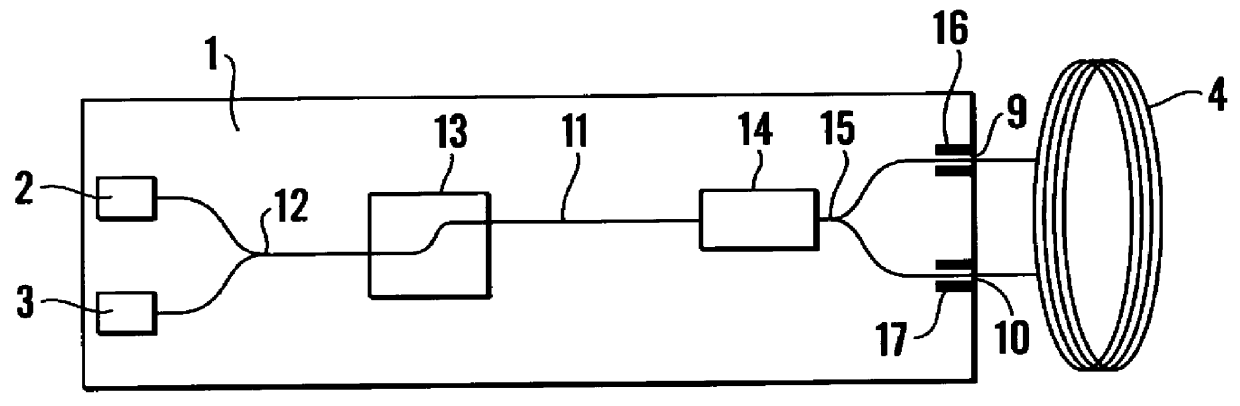
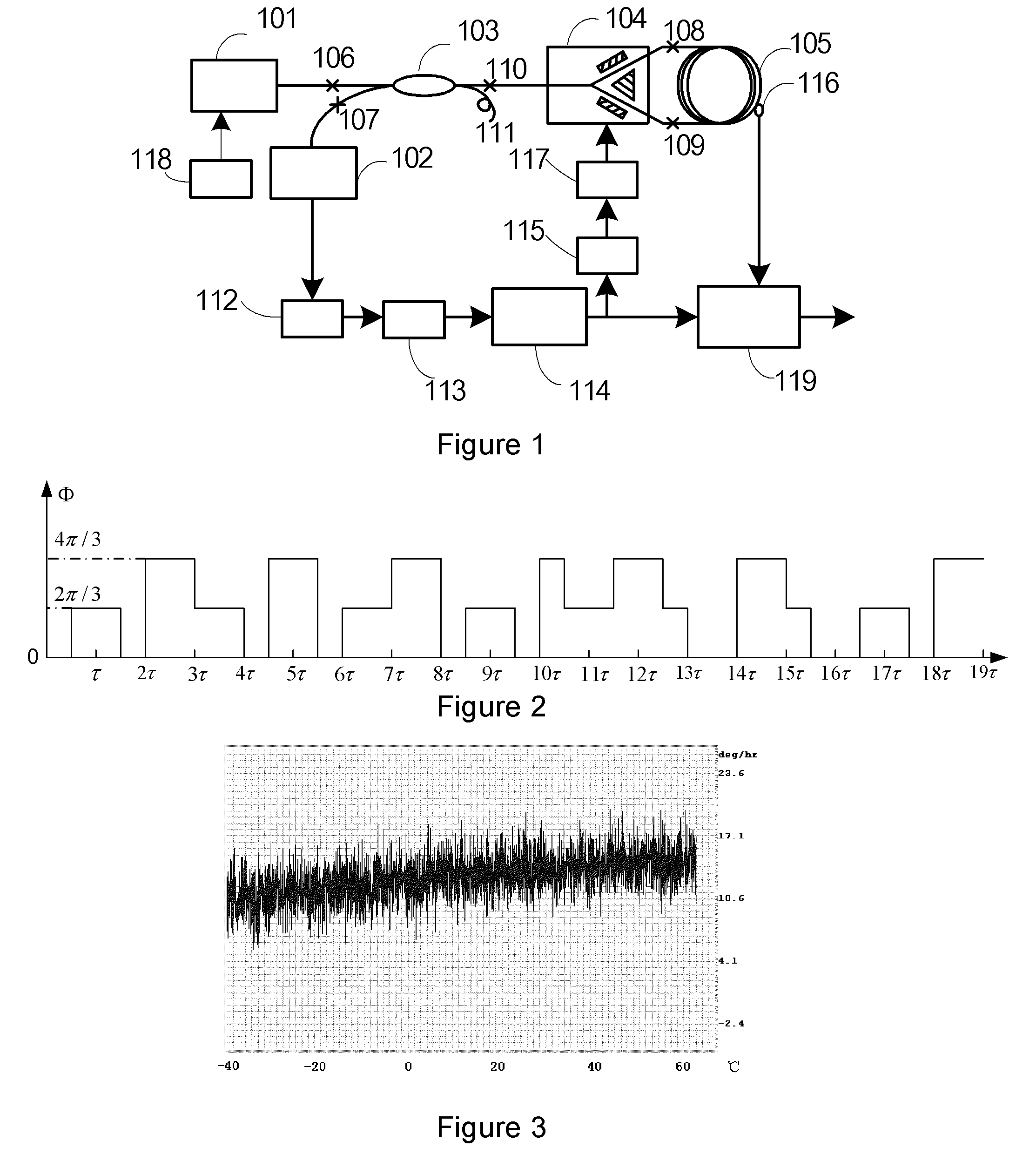
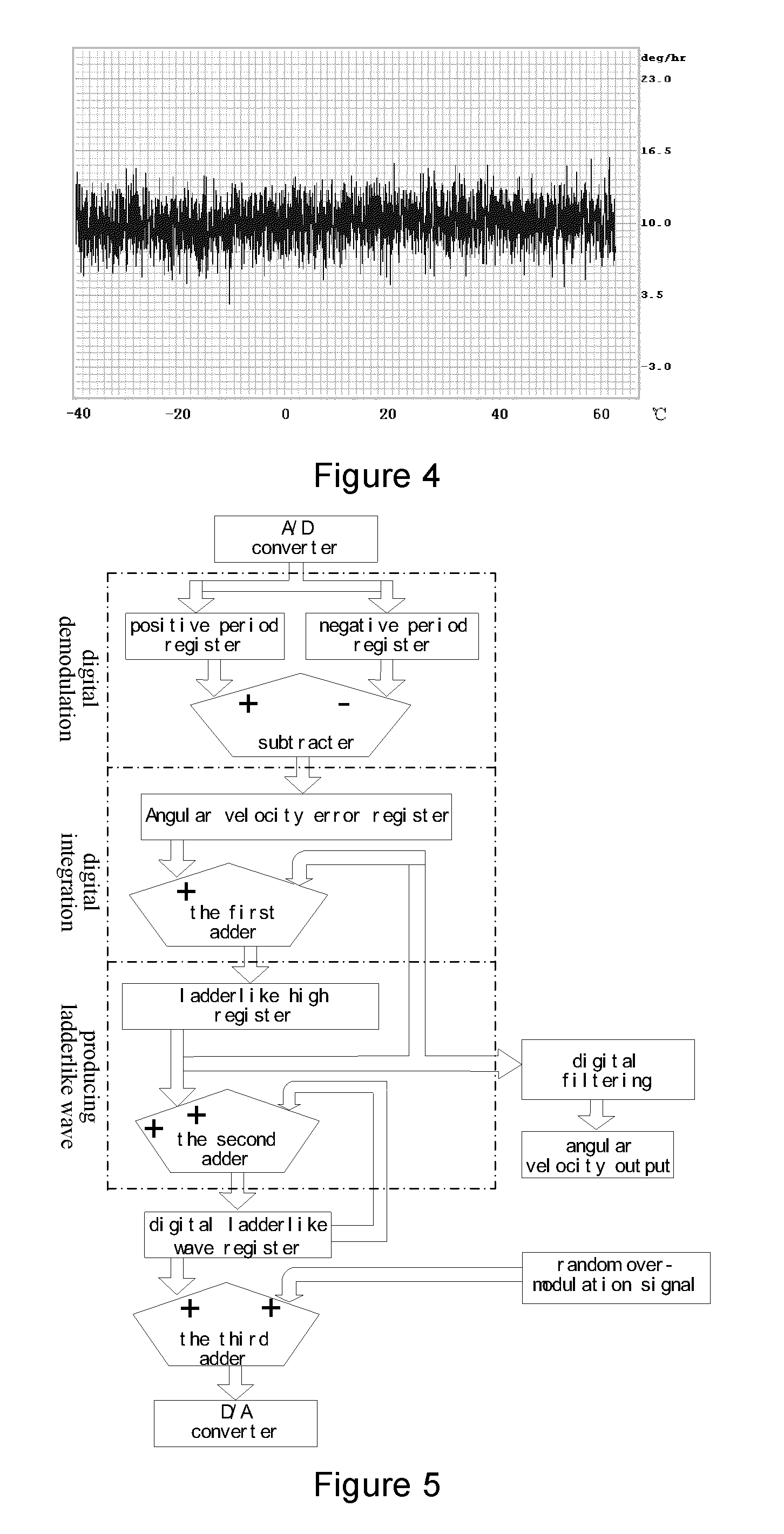
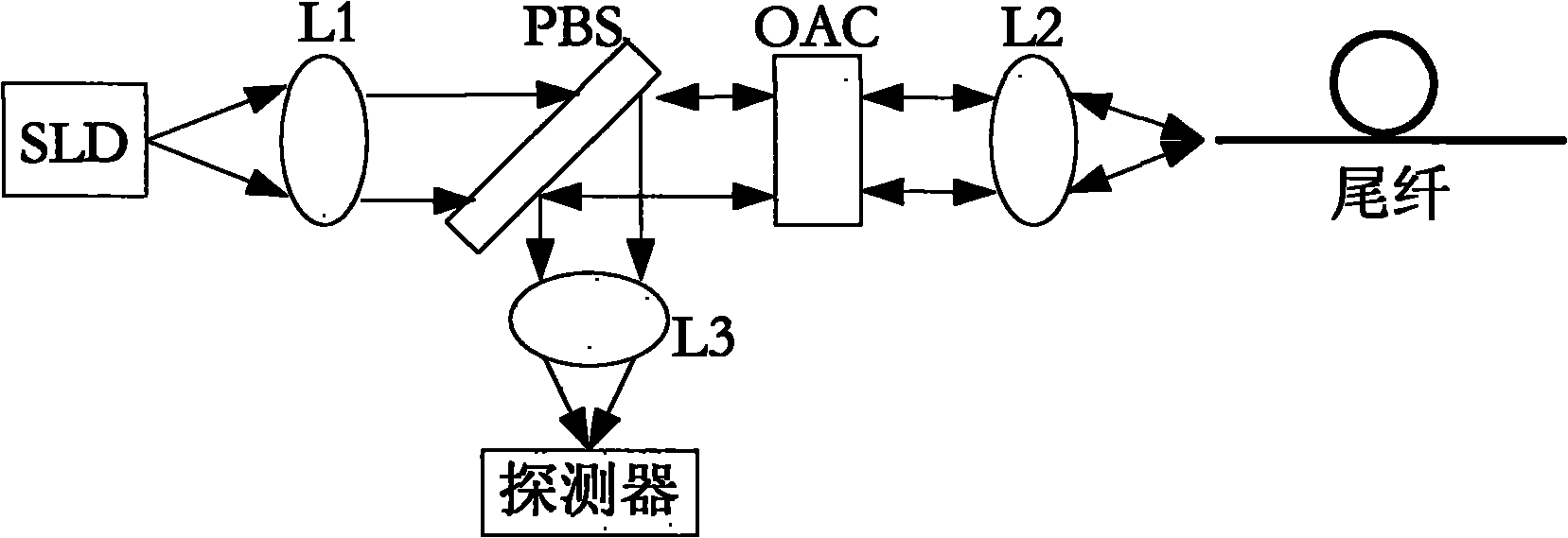
ActiveUS20100238450A1Reduce impactLow costSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersLow noiseFiber coupler
A fiber optic gyroscope using a low-polarization and polarization-maintaining hybrid light path comprises an optical meter head and a circuit signal processing part, The optical meter head comprises: a light source, a multi-functional integrated optic chip, a detector, a coupler and a fiber coil, wherein the light source is a low polarization light source and single mode fiber pigtail coupling; the input terminal of multi-functional integrated optic chip uses a single mode fiber, and the output terminal of multi-functional integrated optic chip adopts a polarization-maintaining fiber; the input fiber pigtail of the said detector is a single mode fiber; the coupler is a 2×2 polarization independence single mode fiber coupler; the fiber coil is a polarization-maintaining fiber. By adopting the scheme of the low-polarization and polarization-maintaining hybrid light path and the signal processing methods such as all-digital closed loop control and random overmodulation etc., the present invention can reduce the effect of light path polarization crosstalk, simplify the assembling technology, enable large scale production and guarantee the good scale factor linearity performance and the lower noise level. Furthermore, by temperature modeling and compensating, the invention enables the bias of the fiber optic gyroscope to drift more slightly within the all-temperature range, and therefore the fiber optic gyroscope with good performance and engineering application can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TIMES OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH
Inertial navigation system combining fibre-optic gyroscope with micromechanical gyroscope and navigation method
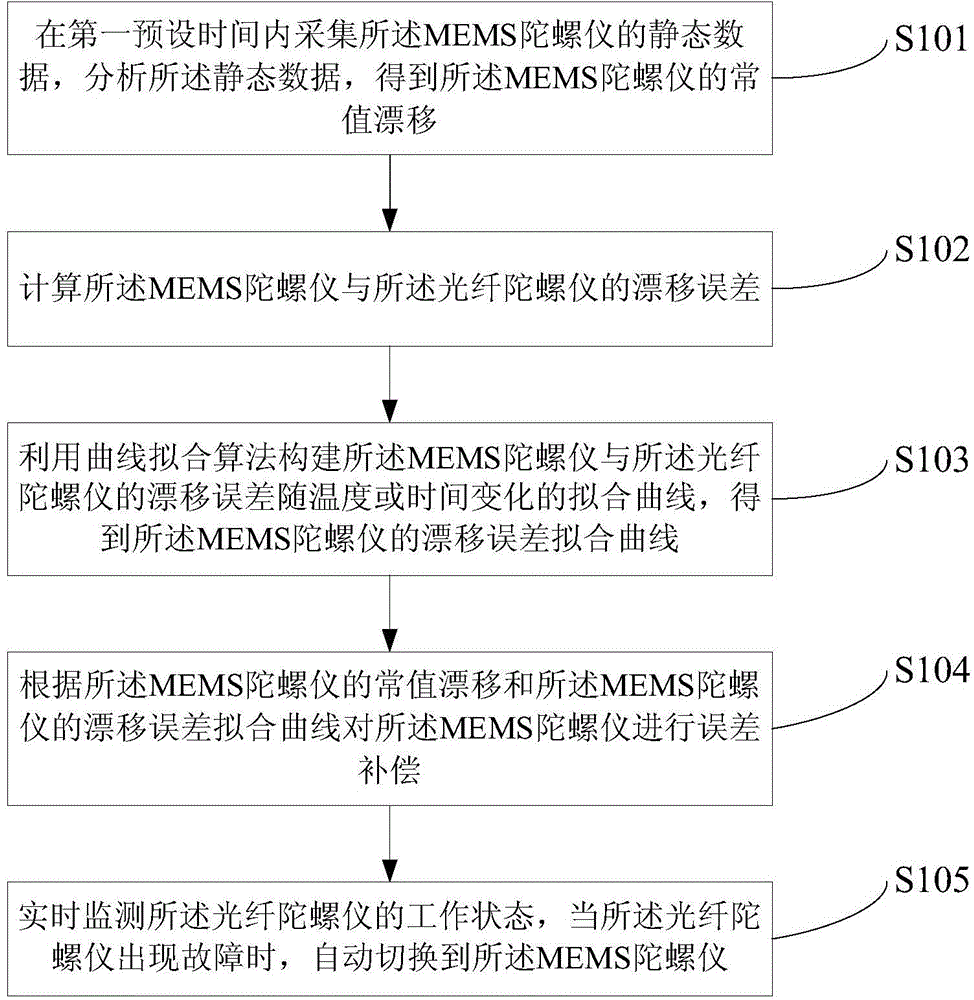
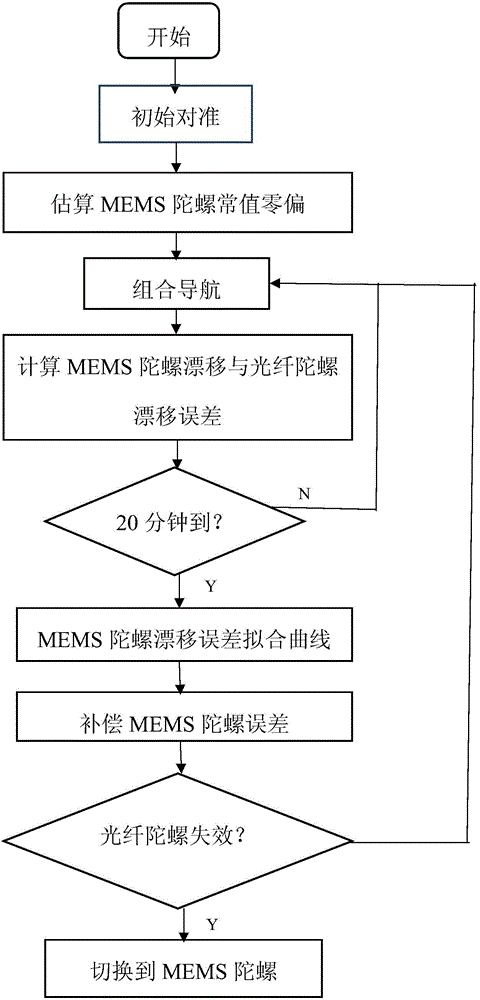
ActiveCN104596513AImprove performanceGuaranteed accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFiberAccelerometer
The invention provides an inertial navigation system combining a fibre-optic gyroscope with a micromechanical gyroscope and a navigation method. The system comprises the fibre-optic gyroscope and an MEMS gyroscope which are arranged in the form of mutual redundancy; in a normal state, the fibre-optic gyroscope measures an angular velocity in an azimuth axis, and is automatically switched to the MEMS gyroscope while being failed. A navigation method of the inertial navigation system combining the fibre-optic gyroscope with the micromechanical gyroscope provided by the invention provides an online calibration and compensation function, that is, after the inertial system finishes rough error calibration, error estimation and compensation for the drifting of the gyroscopes and the zero offset of an accelerometer are realized in a set motion mode, so that the requirements of the system on equipment are reduced, the cost is greatly reduced, and the performance of the inertial system is also improved in real time.
Owner:AKD COMM TECH
Hollow core fiber optical gyro
Apparatus is provided for a fiber optic gyro. The fiber optic gyro includes a ring resonator having first and second counter-propagating directions. The ring resonator includes a coil having an axis and an optical fiber having a hollow core. The ring resonator is configured to produce a first resonance frequency when a first light beam circulates through the hollow core in the first counter-propagating direction and produce a second resonance frequency when a second light beam circulates through the hollow core in the second counter-propagating direction. A difference between the resonance frequencies indicates a rotation rate of the fiber optic gyro about the axis.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
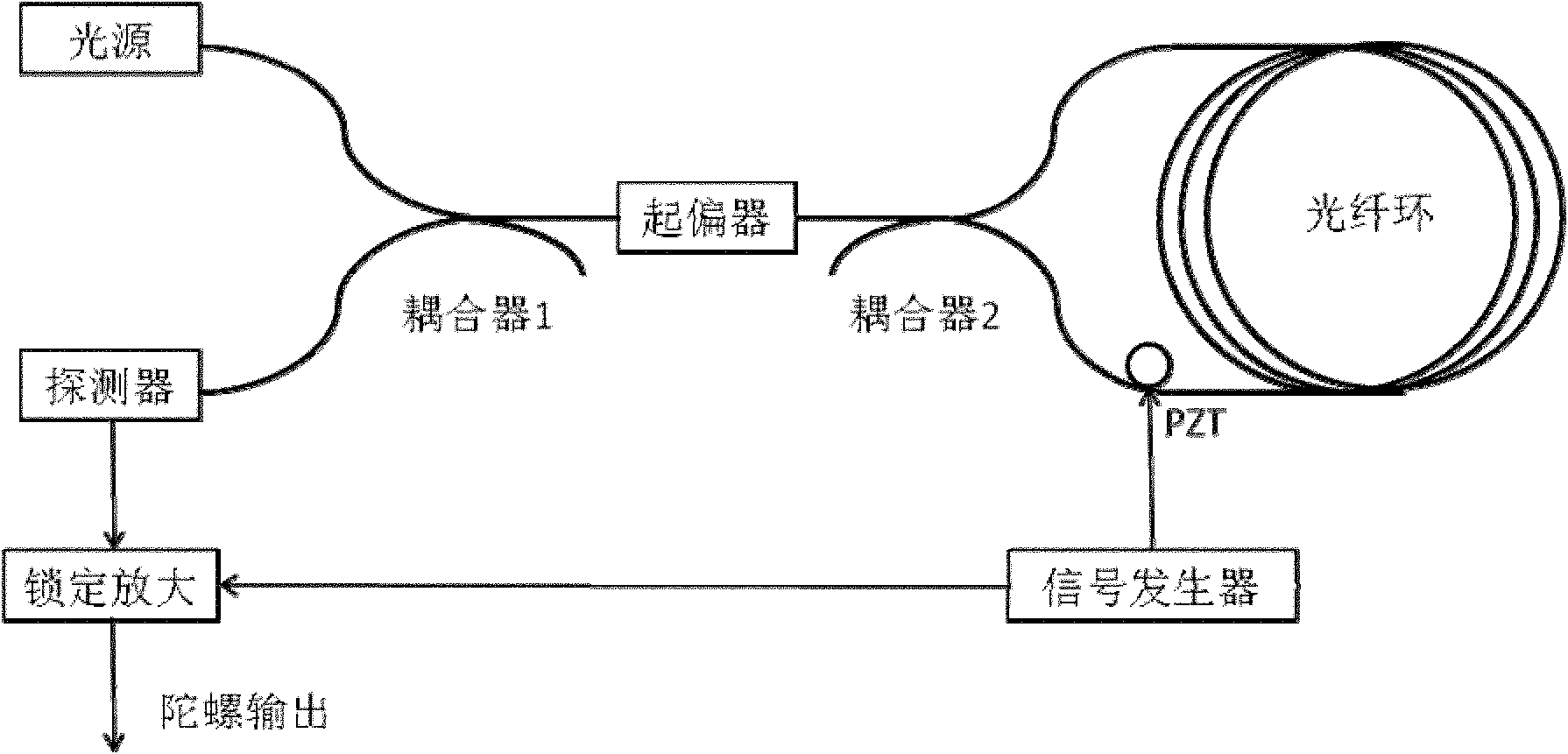
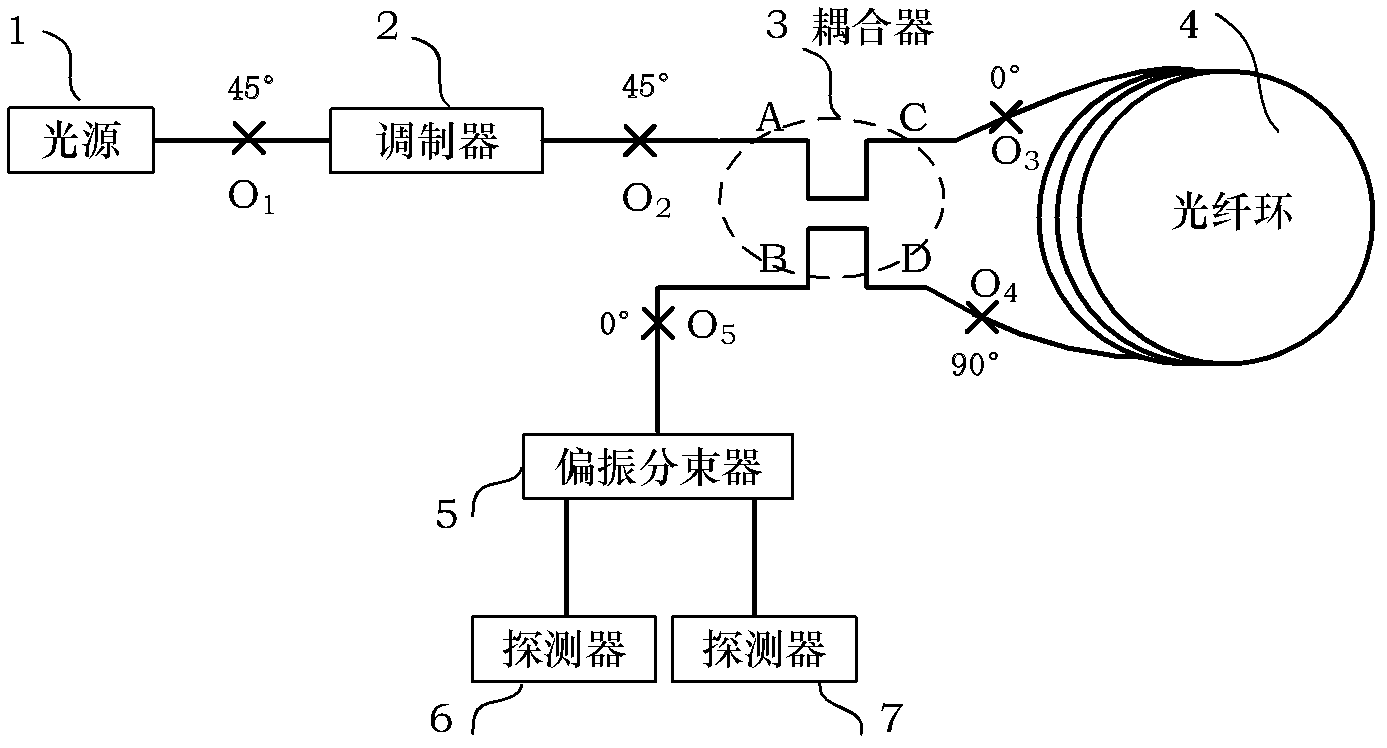
Difference double-interference type optical fiber gyroscope based on birefringence modulation
ActiveCN102494681ARealize closed-loop controlAvoid loud noiseSagnac effect gyrometersClosed loopPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention discloses a difference double-interference type optical fiber gyroscope based on birefringence modulation. The optical fiber gyroscope comprises a light source, a modulator, a coupler, an optical fiber ring, a polarization beam splitter, a first detector and a second detector, wherein the light source and the modulator are welded at a melting point O1 with an angle of 45 DEG; the modulator and a port A of the coupler are welded at a melting point O2 with an angle of 45 DEG; an end C of the coupler and one end of a polarization-maintaining optical fiber ring are welded at a melting point O3 with an angle of 0 DEG; an end D of the coupler and the other end of the optical fiber ring are welded at a melting point O4 with an angle of 90 DEG; an end B of the coupler and an input end of the polarization beam splitter are welded at a melting point O5 with an angle of 0 DEG; and two output ends of the polarization beam splitter are respectively welded to the first detector and the second detector. According to the invention, closed-loop control of the difference double-interference type optical fiber gyroscope is realized; and a wide-spectrum light source with very weak coherent characteristics is adopted, thereby avoiding strong noise brought by various stray wave interferences which are caused by strong coherent characteristics of a laser light source.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
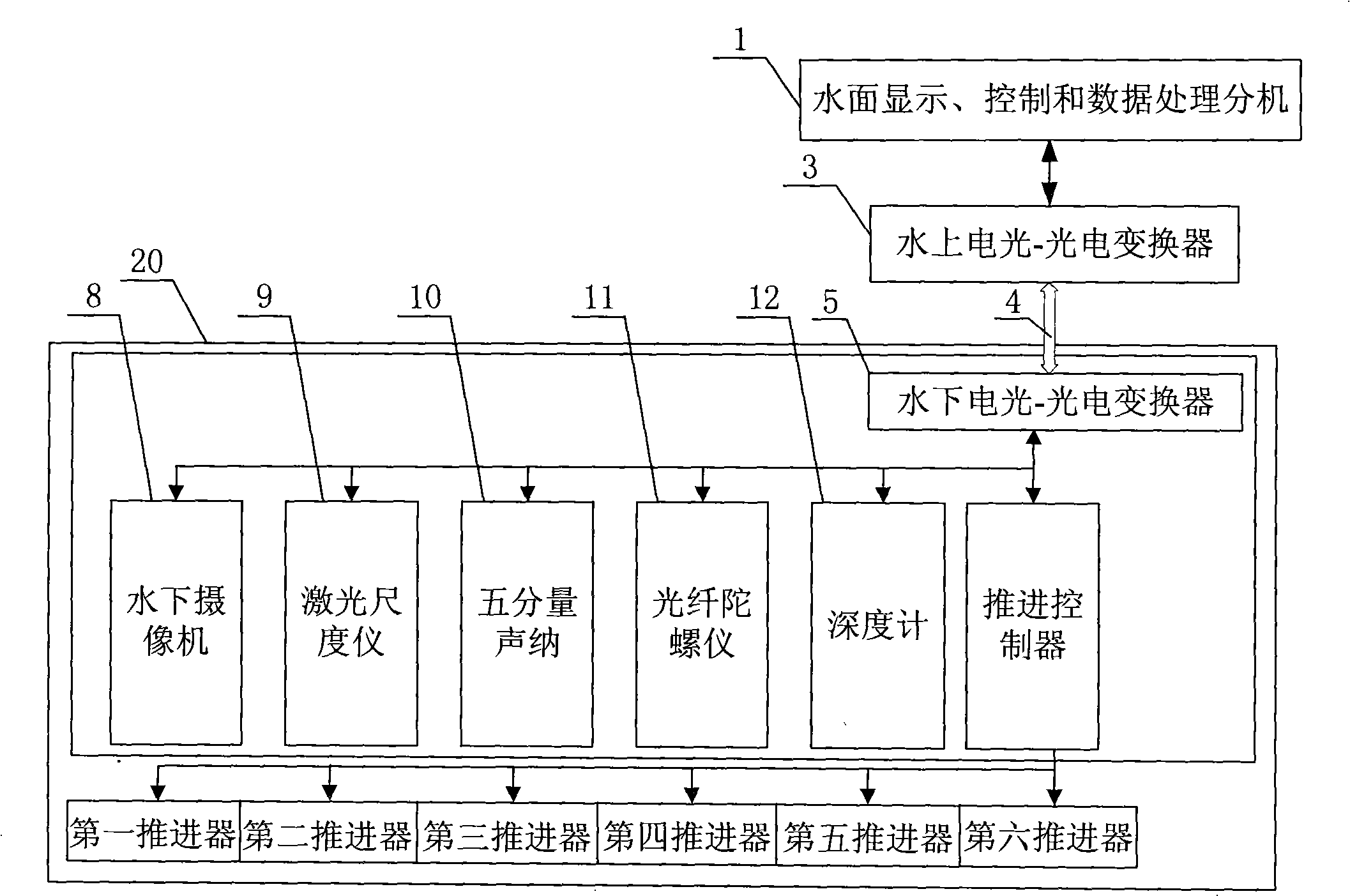
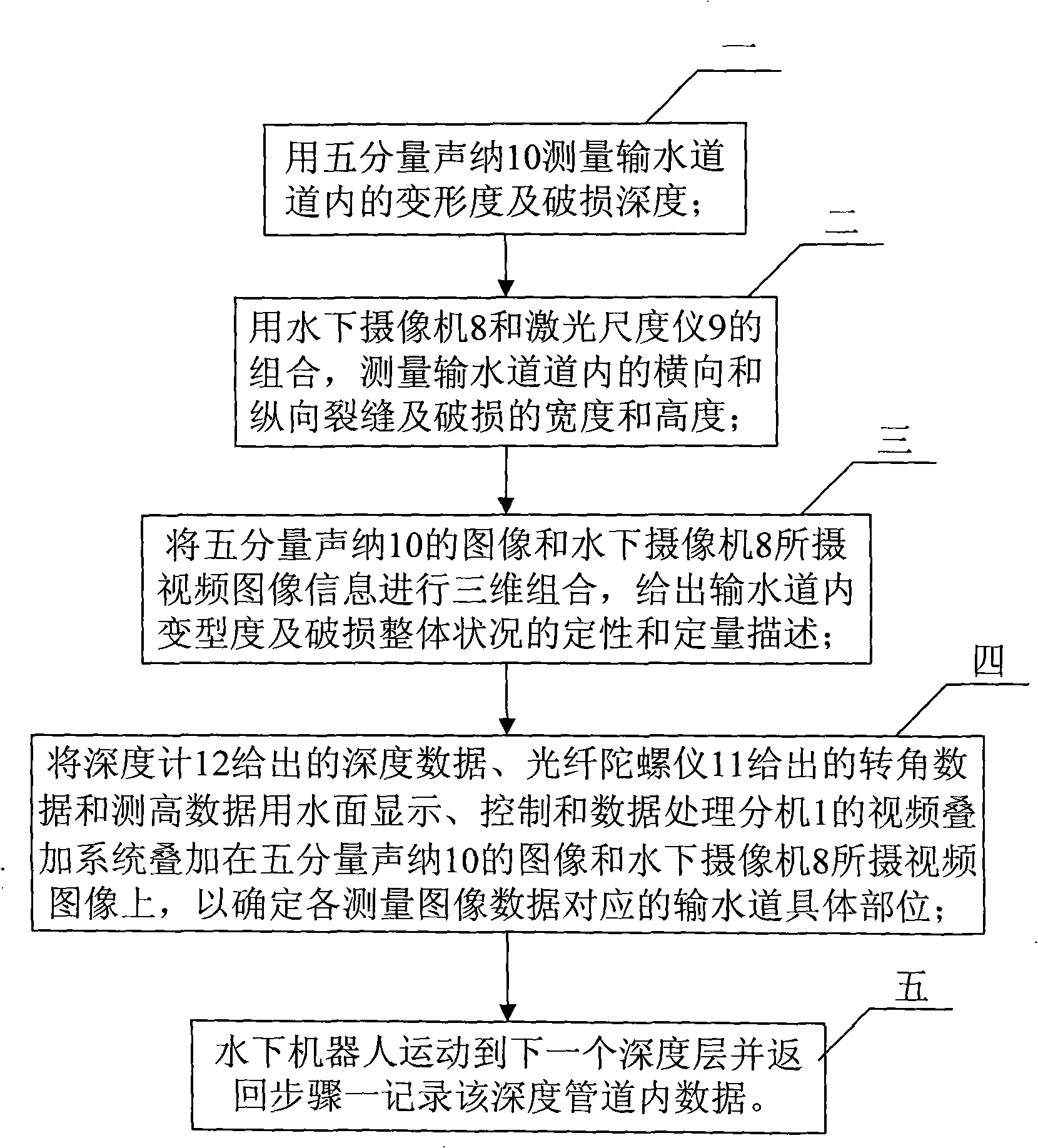
Method for detecting aqueduct well by underwater robot
ActiveCN101294917AImprove visualizationUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansMaterial analysis by optical meansSonarFibre optic gyroscope
The invention discloses a method for detecting the inside of a waterway well by adopting an underwater robot and relates to a method of detecting the inside of a waterway well. The method solves the problems of the prior method, including too much interference, great difficulty and low accuracy. The method comprises the following steps: (1) measuring the degree of deformation and the depth of breakage by using a five-component sonar; (2) measuring the width and the height of crack and breakage in the transversal and the longitudinal directions by using an underwater camera and a laser scale instrument; (3) combining the images measured by the five-component sonar and the underwater camera, and giving the qualitative and the quantitative description of the degree of deformation and the whole state of breakage; (4) superposing the data given by a depth gauge and a optical fiber gyroscope on the images to determine the specific waterway position corresponding to each measured image data; (5) moving the underwater robot to the next depth and returning to step (1) to record the data of the inside of the waterway in the depth. The underwater robot can detect inclined-well and straight-well waterways within 1000 meter.
Owner:HUADONG TIANHUANGPING PUMPED STORAGE +1
Modulation and demodulation circuit of fiber option gyroscope (FOG) open-loop signal
InactiveCN101696882AFind the error reduction of arctangent operationSagnac effect gyrometersFiberSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a modulation and demodulation circuit of fiber option gyroscope (FOG) open-loop signals. The circuit adopts a monolithic LVDT integrated circuit (IC) for modulating and demodulating an FOG open-loop signal, generating a sinusoidal signal, synchronously detecting and dividing one odd harmonic amplitude and one even harmonic amplitude and acquiring the tangent value of a mobile signal phase by low-pass filtration. The invention uses the monolithic LVDT IC to realize the four functions, i.e., sinusoidal signal generation of a drive phase modulator, synchronous detection, the elimination of light-source light-intensity fluctuation influence and low-pass filtration and greatly simplify a signal-processing circuit; the monolithic LVDT IC outputs the tangent value of a mobile signal phase so that when the phase increases and trends to pi / 2, the tangent value bends upwards, does not trend to saturation and reduces the error of a complementary tangent operation; and a division operation is internally realized by the monolithic LVDT IC so that a digital signal processor at a high price can be replaced by a monolithic computer at a low price for non-linear corrosion.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Light transceiving integrated device applied to fiber sensing
ActiveCN101852613AImprove reciprocityImprove stabilitySagnac effect gyrometersOptical elementsBeam splitterPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The embodiment of the invention provides a light transceiving integrated device applied to fiber sensing. The light transceiving integrated device comprises a light source, a photoelectric detector, a polarizing beam splitter, a half-wave plate, a Faraday rotator, a reflector and a lens, wherein the polarization state of emergent light emitted by the light source is regulated through the half-wave plate and the Faraday rotator so that the emergent light is changed between parallel transmission light and vertical reflected light; and the emergent light after the polarizing regulation enters tail fibers of polarization maintaining fibers through the polarizing beam splitter, the reflector and the lens, and the emergent light is received through the photoelectric detector and returned from an interferometer sensor. The structure and the light path process can realize integration and encapsulation of discrete components in a single module, reduce the fiber welding point number in a fiber gyro system, eliminate the 6db inherent loss in the conventional system, and improve the reciprocity and stability of a fiber gyro.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
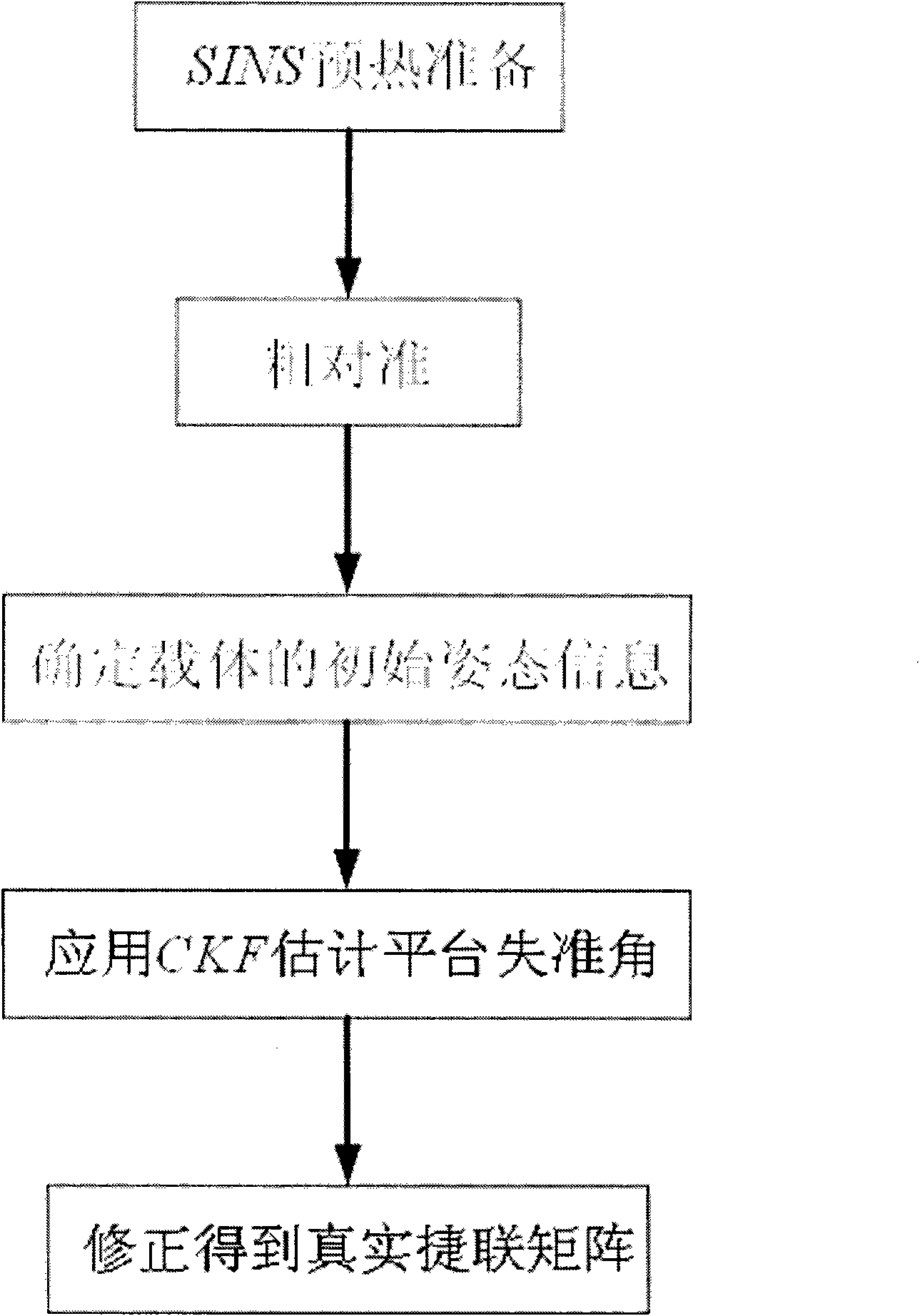
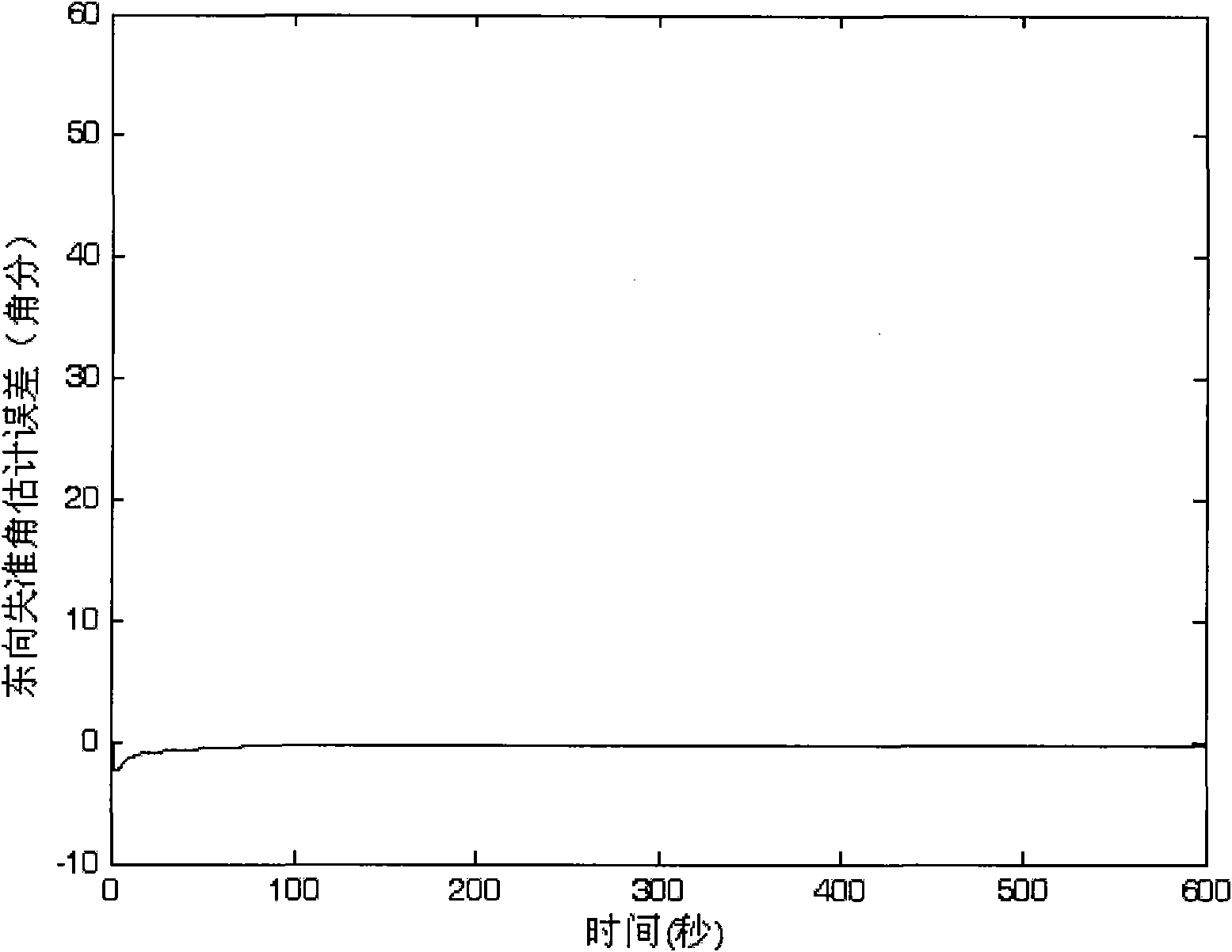
Novel CKF(Crankshaft Fluctuation Sensor)-based SINS (Ship Inertial Navigation System) large misalignment angle initially-aligning method
InactiveCN101915579AAccurate Error Propagation CharacteristicsAccurately reflect the error propagation characteristicsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerNonlinear model
The invention aims at providing a novel CKF(Crankshaft Fluctuation Sensor)-based SINS (Ship Inertial Navigation System) large misalignment angle initially-aligning method comprising the following steps of: determining an initial position parameter of a carrier by using a GPS (Global Position System); acquiring data output by an optical fiber gyroscope and a quartz accelerometer; finishing the coarse alignment of the system by using an analysis method; preliminarily determining the posture information of the carrier; establishing an initial aligning nonlinear model of a strapdown inertial navigation system; establishing a CKF filtering state equation by taking the speed error as the state variable and a measuring equation by taking the speed error as the measurement quantity under a static base; carrying out filtering estimation by using a CKF filtering method to estimate the misalignment angle of the platform; and obtaining an accurate strapdown initial posture matrix by using a strapdown initial posture matrix of a platform misalignment angle correcting system, thereby finishing the accurate initial alignment. The invention can greatly improve the aligning precision of the strapdown inertial navigation system at the large misalignment angle and provide the accurate strapdown initial posture matrix for the navigation process.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Damping method of fiber option gyroscope (FOG) strap-down inertial navigation system
InactiveCN101696883AHigh precisionElimination of Shula cycle oscillationsNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFiberCurrent velocity
The invention provides a damping method of a fiber option gyroscope (FOG) strap-down inertial navigation system, mainly comprising the following steps: acquiring the initial attitude of a carrier by initial alignment; measuring angular velocity input and acceleration input on a carrier coordinate system; calculating an initial attitude matrix; converting carrier-system acceleration output into platform-system acceleration; acquiring all current velocity and angular velocity values; conducting horizontal damping on velocity information; calculating the attitude angular velocity of the carrier to a mathematics platform system; updating the current attitude matrix with quaternion numbers; outputting a carrier attitude angel; and entering the next time cycle. The invention adds suitable horizontal damping in a velocity information position of a horizontal loop of the system to eliminate the Shura periodic oscillation and the Foucault periodic oscillation of the system and adds a suitable directional damping network in an earth angular velocity input information position to eliminate the earth 24-hour periodic oscillation of the system, thereby improving the accuracy of a ship strap-down inertial navigation system.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
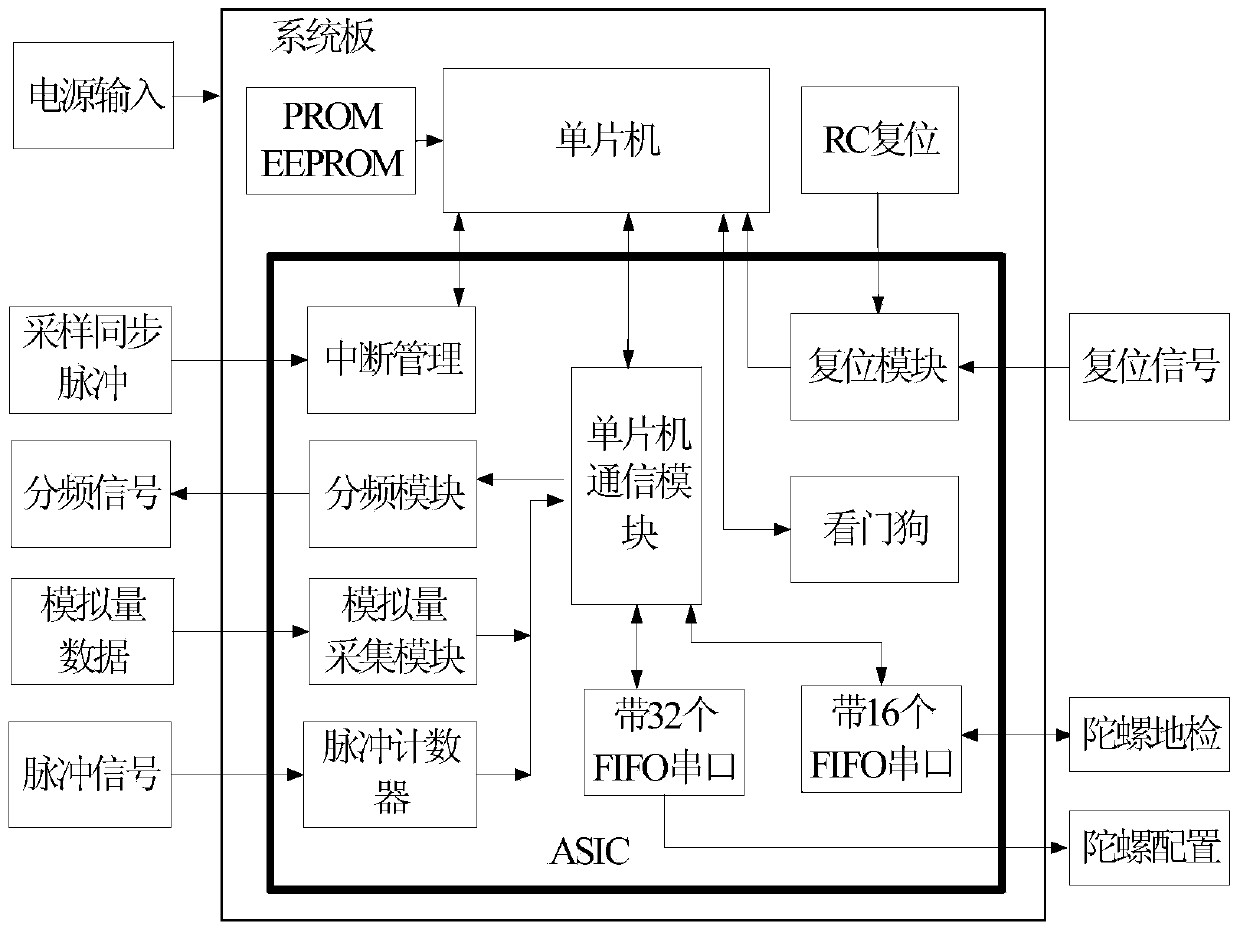
High-reliability redundant four-shaft optical fiber gyroscope inertia measurement device
ActiveCN103697881ADoes not affect functionGuaranteed functionSagnac effect gyrometersMeasurement deviceAngular velocity
The invention relates to a high-reliability redundant four-shaft optical fiber gyroscope inertia measurement device, in particular to a long-life high-reliability redundant inertia measurement device for spacecraft navigation, guidance and control, and belongs to the technical field of inertia measurement. The device comprises a body structure with three orthogonal shafts and one oblique shaft, wherein four optical fiber gyroscopes, two signal processing and interface circuits and two secondary power circuits are arranged in the body. According to the device, the two signal processing and interface circuits are mutually redundant; the two secondary power circuits are mutually redundant; the reliability is high; when the device is used on a track and any one shaft or channel has a fault, the three-shaft attitude angular velocity still can be provided, the redundant configuration can be achieved, and normal product functions can be guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TIMES OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH
Ship's inertial navigation and astronomical positioning method based on attitude measurement
InactiveCN101881619AHigh positioning accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerInertial coordinate system
The invention provides a ship's inertial navigation and astronomical positioning method based on attitude measurement, comprising the following steps of: (1) collecting the output data of an optical fiber gyroscope and a quartz flexible accelerometer after the initial alignment of an inertial navigation system is finished; (2) collecting the output of a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) star sensor, namely the attitude information of the coordinate system of the CCD star sensor relative to an inertial coordinate system i; (3) collecting the attitude matrixes continuously output by the inertial navigation system; (4) resolving the conversion matrix of an earth based coordinate system e relative to the system i; and (5) calculating out the position matrix through the information in steps (1), (2), (3) and (4), and calculating out the position information according to the position matrix. The method is an accumulation-free navigation positioning algorithm and has high positioning precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Reentrant interference optical fiber gyroscope
InactiveCN101825465ALow costIncrease phase shiftSagnac effect gyrometersBeam splittingPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention discloses a reentrant interference optical fiber gyroscope, belonging to the field of optical fiber communication. The reentrant interference optical fiber gyroscope comprises a broadband source, a 2X2 coupler, a polarizer, a detector, a 2X2 polarization-maintaining coupler, a phase modulator, two polarization-maintaining / rotary beam combining / splitting devices and a polarization-maintaining optical fiber ring, wherein one port of the 2X2 polarization-maintaining coupler is connected with a beam splitting port of one polarization-maintaining / rotary beam combining / splitting device, and the other port of the 2X2 polarization-maintaining coupler is connected with the beam splitting port of the other polarization-maintaining / rotary beam combining / splitting device through the phase modulator; the beam combining ports of the two polarization-maintaining / rotary beam combining / splitting devices are respectively connected with the two ports of the polarization-maintaining optical fiber ring; a polarization-maintaining optical fiber segment is connected in the polarization optical fiber ring, and a set angle is arranged between the fast and slow axis of the polarization-maintaining optical fiber segment and the fast and slow axis of the polarization-maintaining optical fiber; and the other beam splitting ports of the two polarization-maintaining / rotary beam combining / splitting devices are connected through optical fibers. The invention reduces the cost of the optical fiber gyroscope and improves the measurement precision of the speed of the angle of rotation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
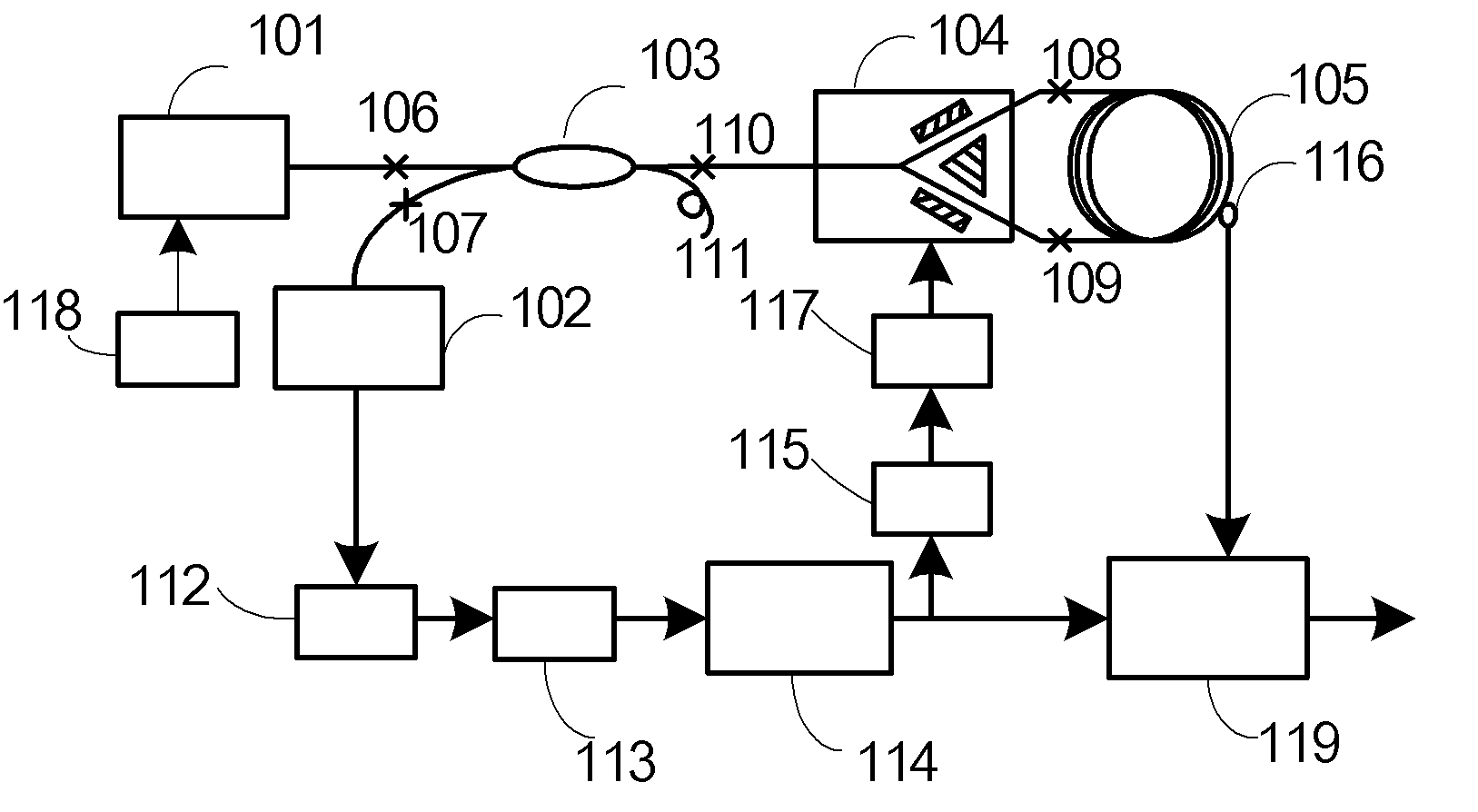
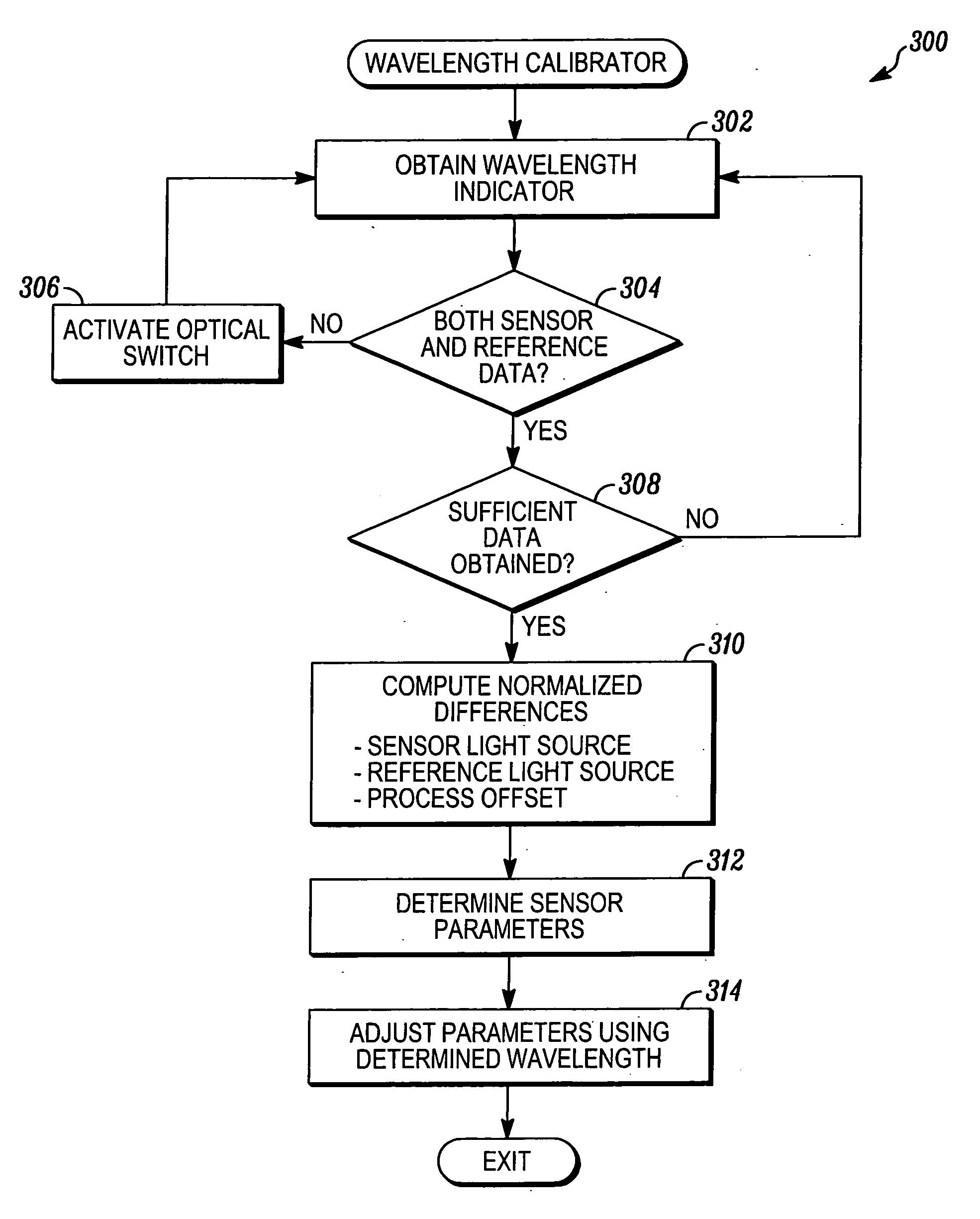
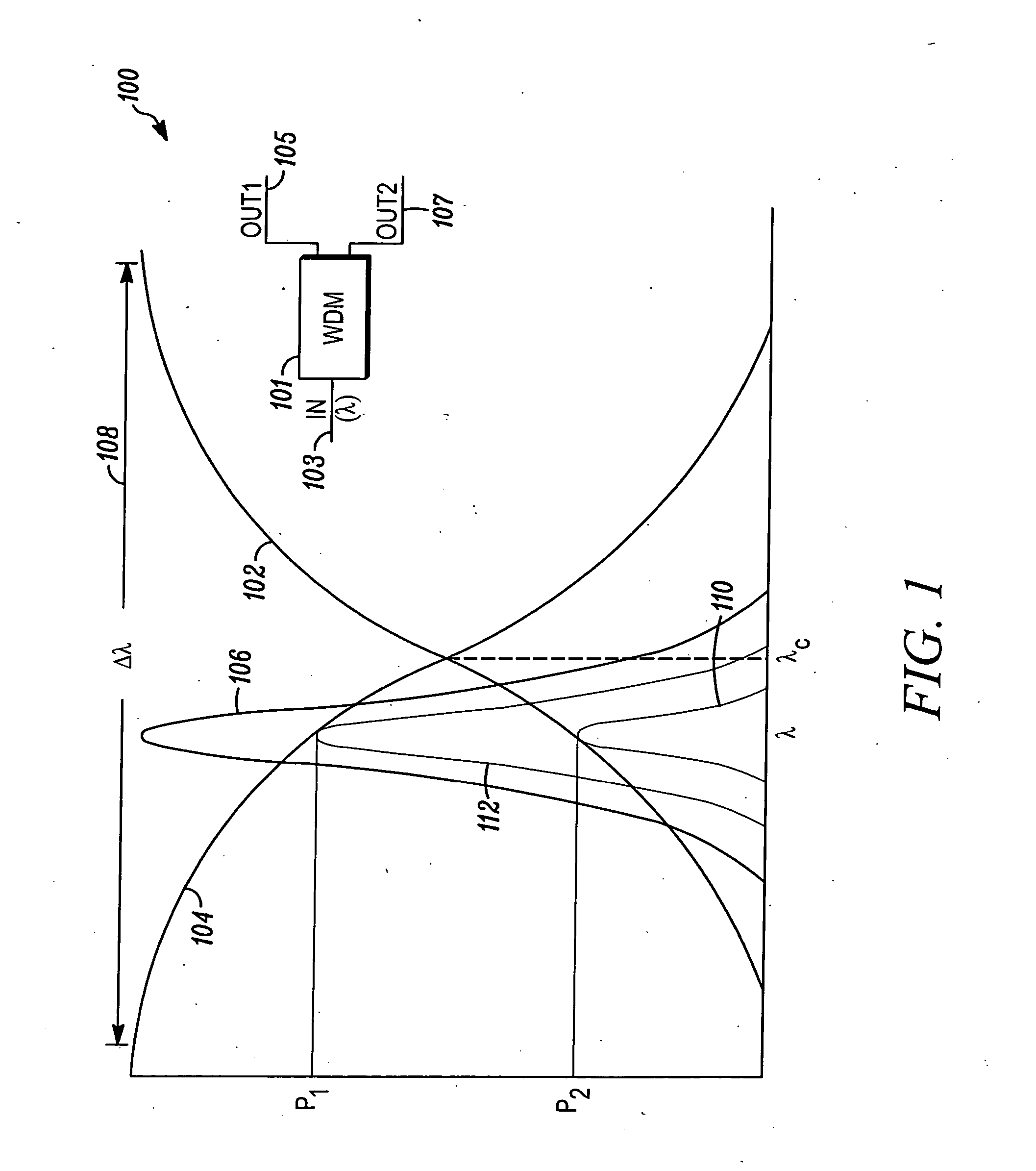
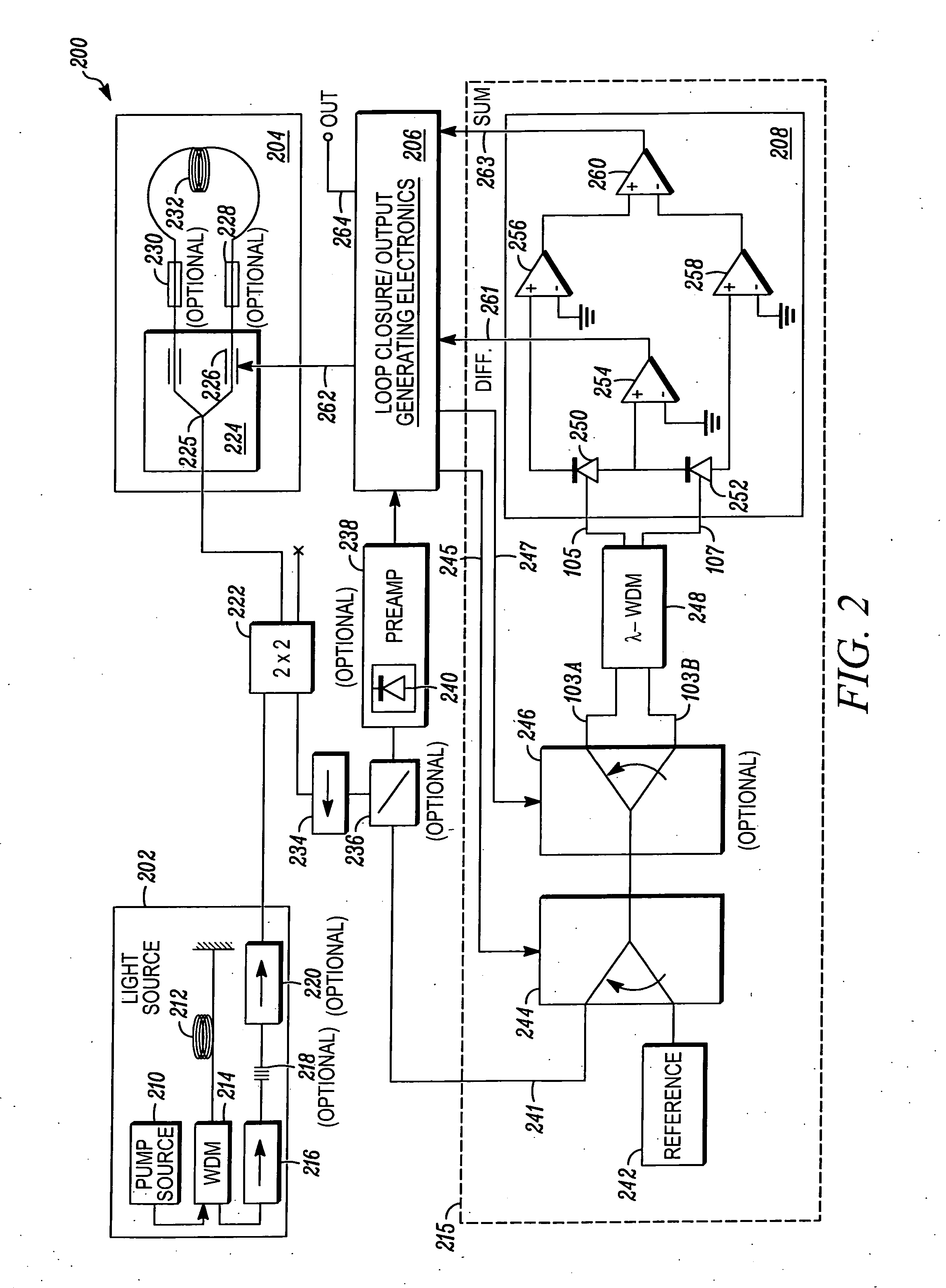
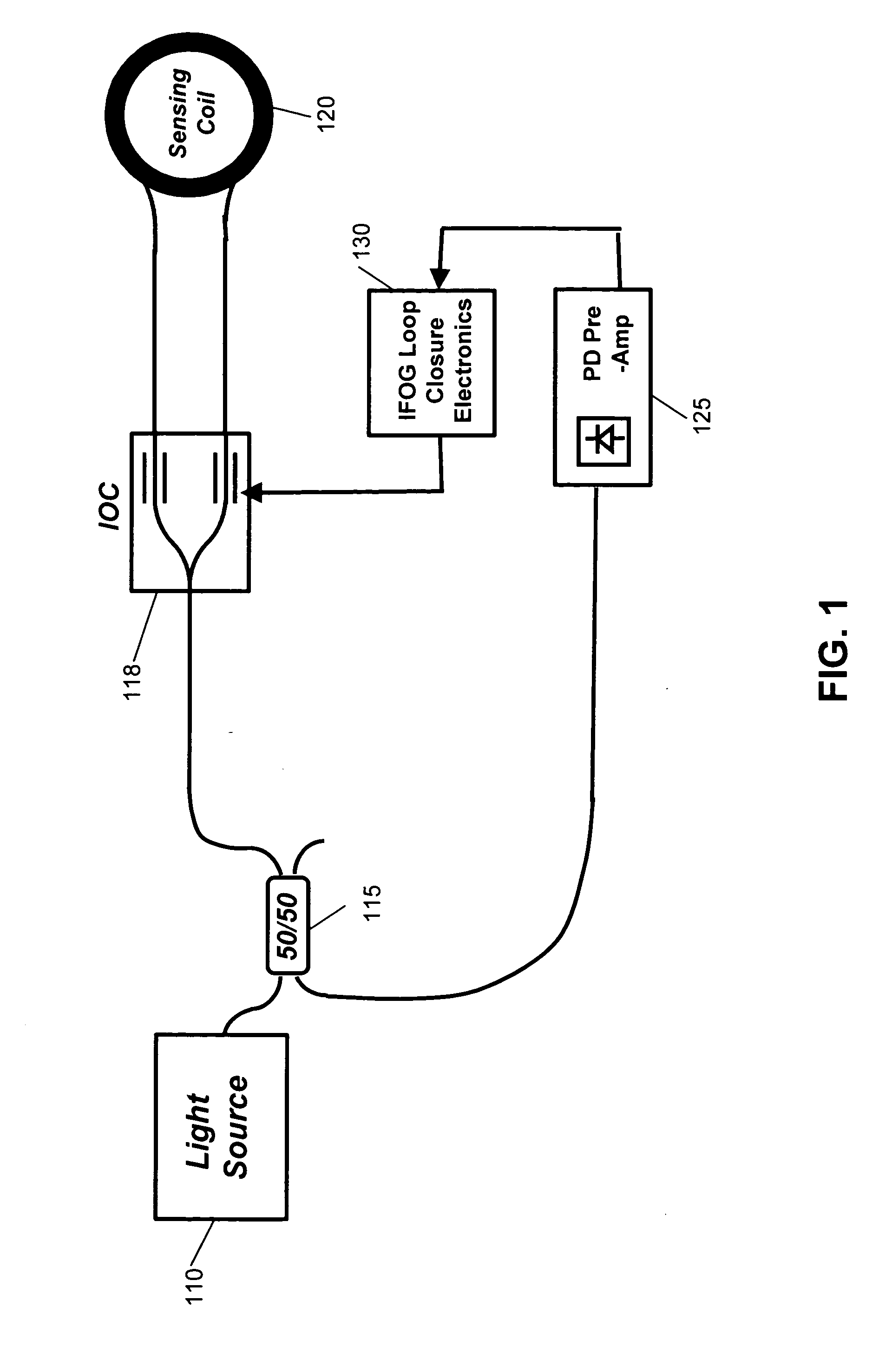
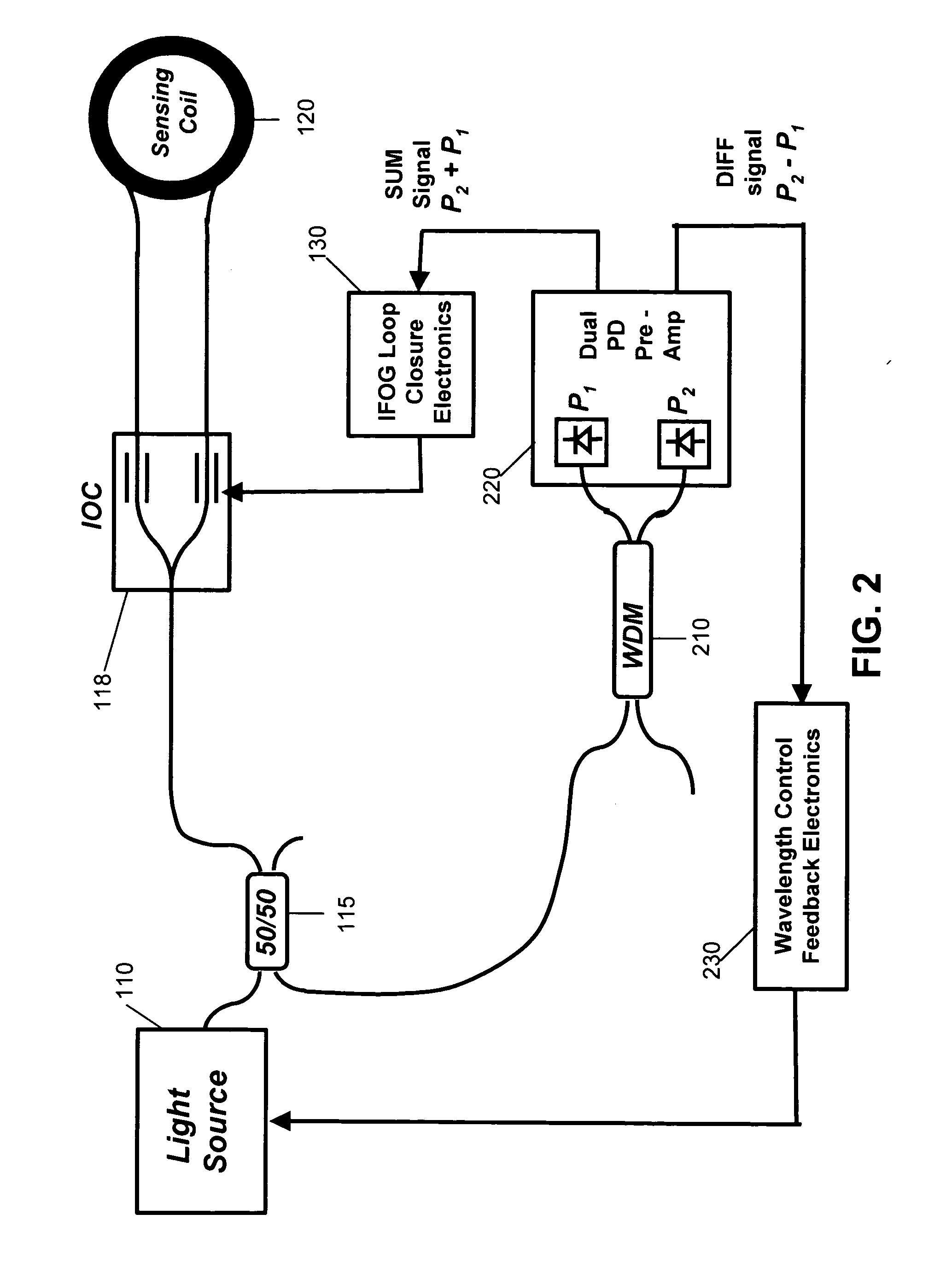
Wavelength calibration in a fiber optic gyroscope
ActiveUS20070229838A1Accurate measurementOptimize operating parametersRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFiberMultiplexer
Methods and apparatus are provided for calibrating a fiber optic gyroscope (FOG) to compensate for wavelength fluctuations. The wavelength of the light propagating in the gyroscope is accurately determined by obtaining wavelength indicia for light originally produced by the sensor light source and for light produced by a reference light source. The wavelength indicia may include normalized power values, such as sum and difference indicia, obtained from two outputs of a wavelength division multiplexer. Such information can be used to determine the wavelength of light produced by the sensor light source, and to adjust a scale factor or other operating parameter of the gyroscope as a function of the determined wavelength. This adjustment, in turn, can be used to compensate the output of the sensor to account for wavelength variations.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
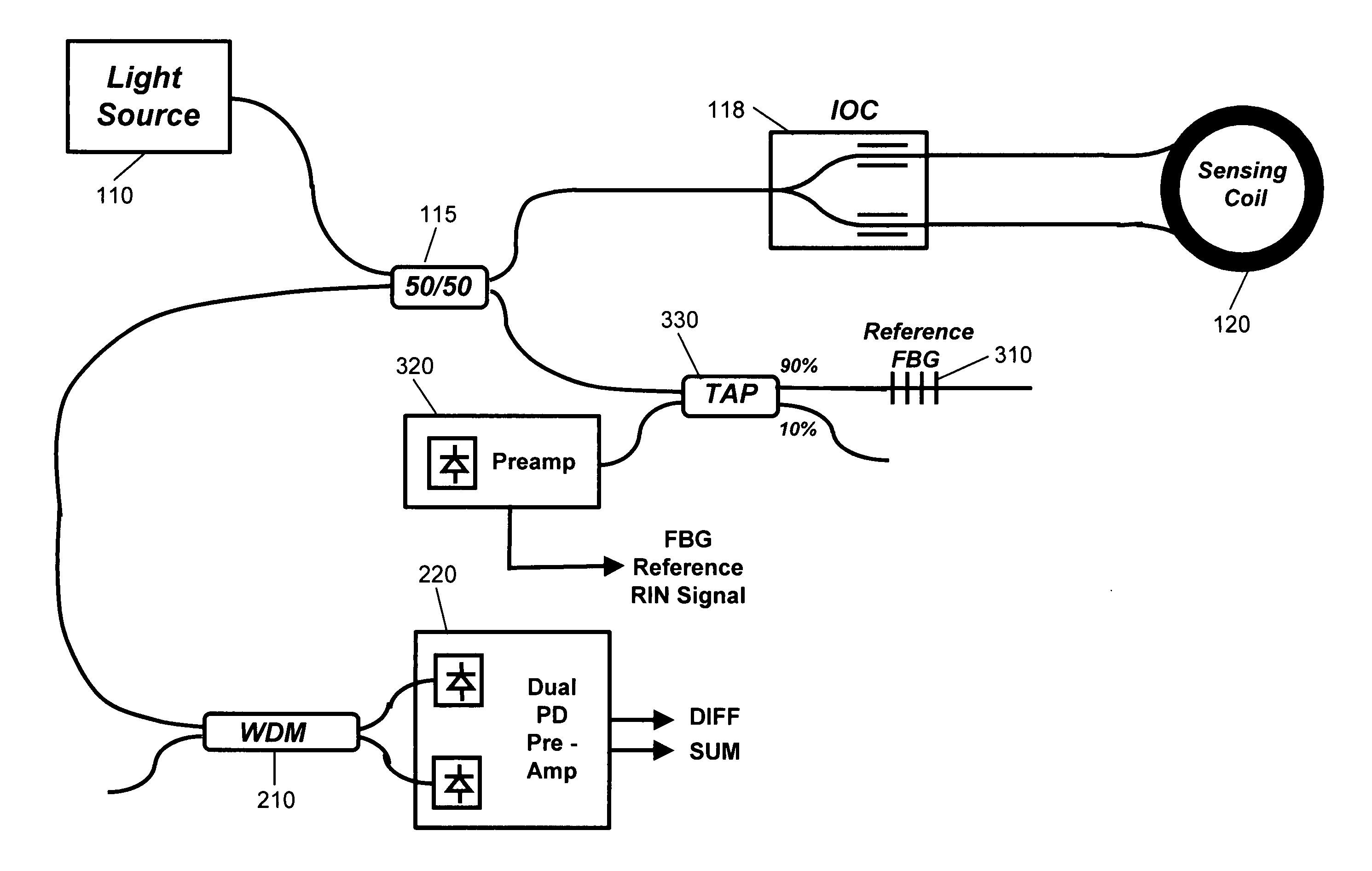
Fiber optic gyroscope using a narrowband FBG filter as a wavelength reference
ActiveUS20050191008A1Improved wavelength stabilityScale factor performanceSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberFiber Bragg grating
Fiber optic gyroscope architectures that incorporate both (i) a WDM-based wavelength control and (ii) a wavelength reference based on a narrowband fiber Bragg grating (FBG), with the latter component providing significant improvement in the stability of the wavelength reference by calibrating out wavelength errors associated with a WDM-based wavelength control scheme.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
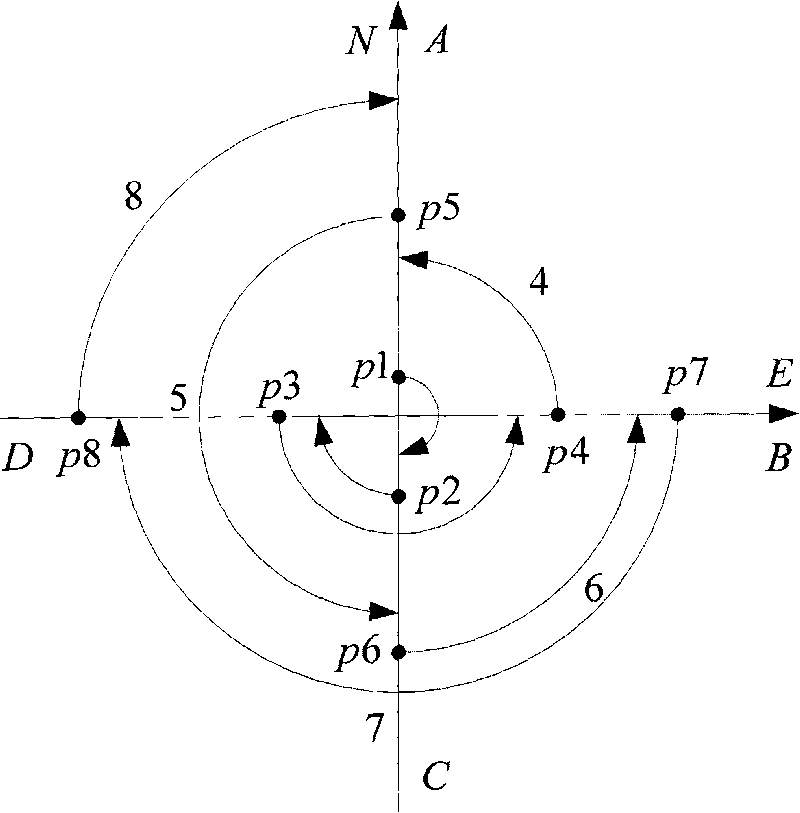
Strapdown system error inhibition method based on uniaxial four-position rotation and stop scheme
InactiveCN101718560AImprove navigation and positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEngineeringOmega
The invention provides a strapdown system error inhibition method based on a uniaxial four-position rotation and stop scheme, which comprises the steps of: (1) determining an initial position parameter of a carrier through a GPS; (2) acquiring data output by an optical fiber gyroscope and output by an acceleration meter and processing the data; (3) positively and negatively rotating and stopping an inertia measuring unit (IMU) around four positions fixed by an azimuth axis of the carrier; (4) converting the data generated by the optical fiber gyroscope and the acceleration meter after rotating the IMU into a navigation coordinate system to obtain a demodulation mode of a constant offset of an inertia device; (5) updating a strapdown matrix Tsn by using an output value Omega iss of the optical fiber gyroscope; and (6) computing the speed and the position of the carrier after rotating and demodulating the IMU.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
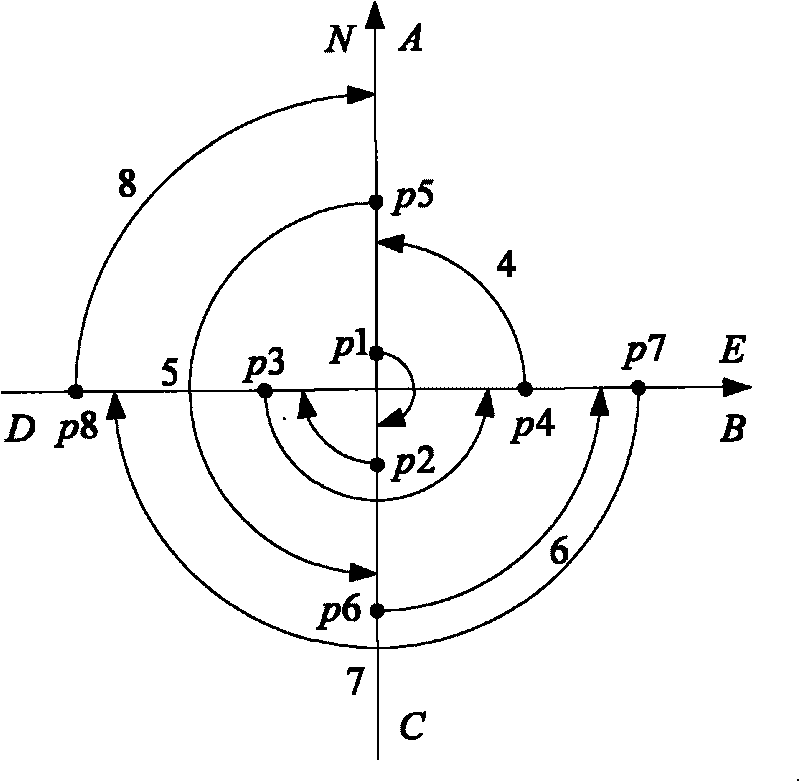
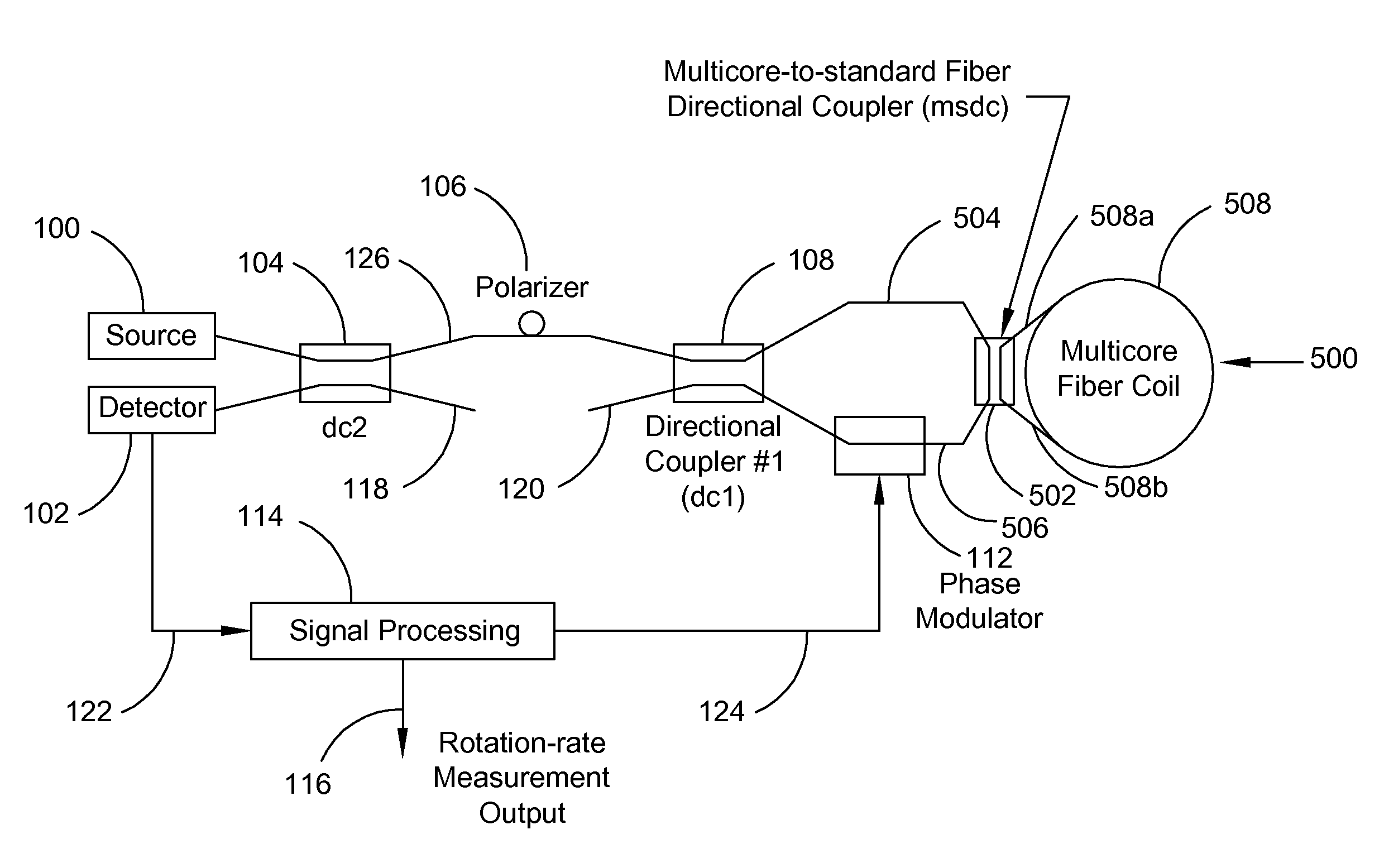
Interferometer employing a multi-waveguide optical loop path and fiber optic rotation rate sensor employing same
ActiveUS20110037972A1Increase the differenceShorten physical lengthMaterial analysis by optical meansSagnac effect gyrometersFiberWaveguide
An interferometer employed, in part, as a Sagnac interferometer or fiber optic gyro (FOG) includes a light source (100) that provides a source light wave that is split into first and second light waves that are directed to traverse a defined optical loop path (508, 500) in opposite directions. The defined optical loop path (508, 500) in accordance with the present invention is provided by multiple waveguides wound into a coil such that the opposite traveling first and second light waves serially travel through all of the waveguides in opposite directions around the optical loop path.
Owner:BERGH RALPH A
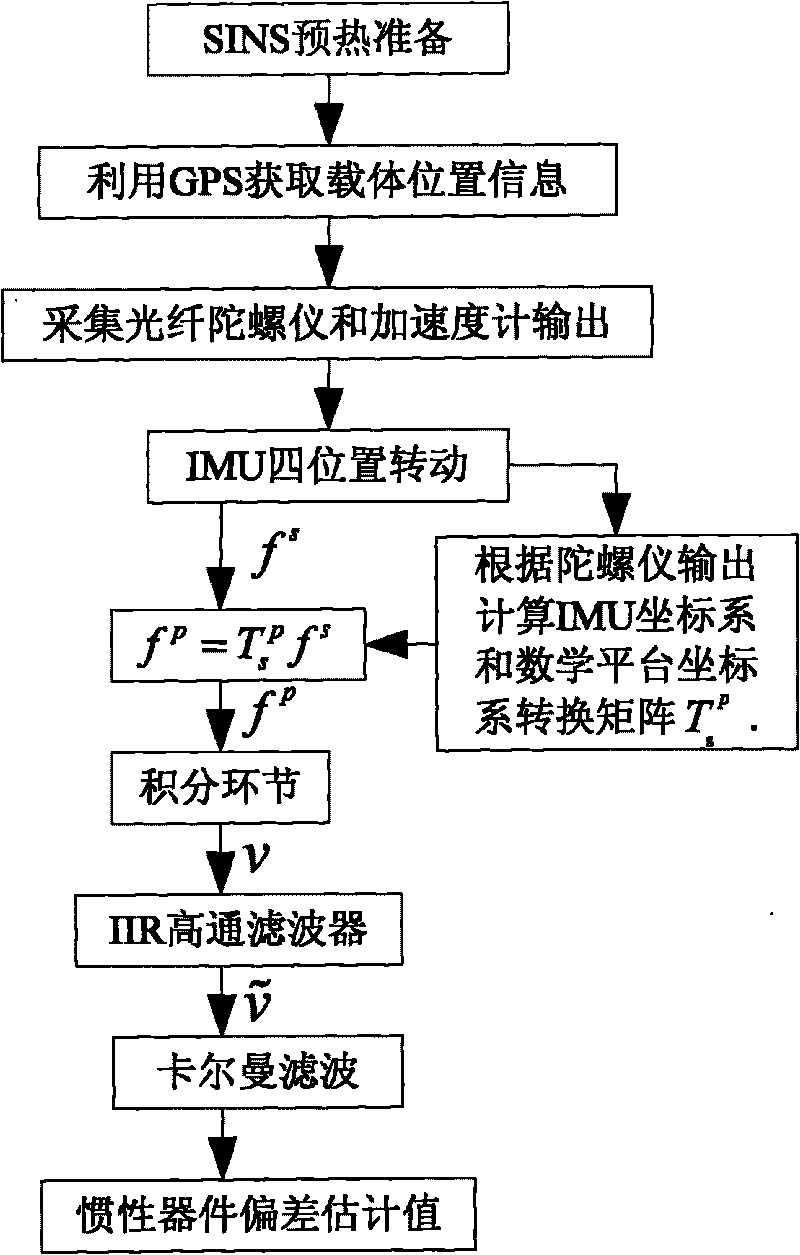
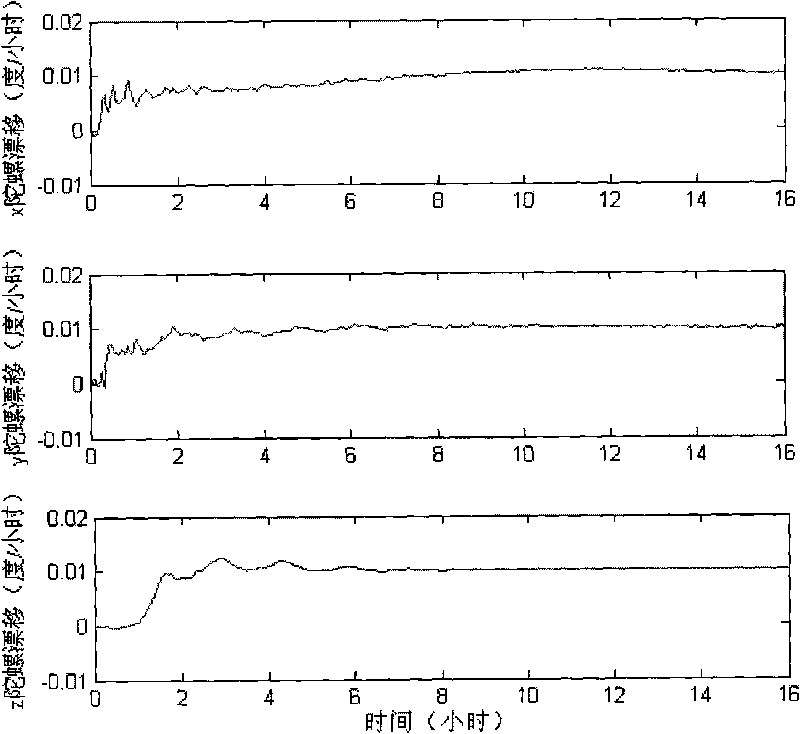
Rotating strapdown system on-site proving method based on digital high-passing filtering
InactiveCN101706287AImprove ObservabilityImprove alignment accuracyMeasurement devicesEngineeringDigital filter
The invention provides a rotating strapdown system on-site proving method based on digital high-passing filtering, which comprises the steps: (1) determining an initial position parameter of a carrier by a GPS; (2) collecting data output by an optical fiber gyroscope and an acceleration meter, and processing the data; (3) rotating and stopping at four positions of a single axis of an inertia measurement unit; (4) analyzing biased observability degree of an inertia device by using a spectral condition number method; (5) filtering the Schuler period contained in velocity information of a navigation system by adopting an IIR high-passing digital filter; and (6) taking filtered velocity information as observed quantity, and estimating the deviation of the inertia device by adopting a Kalman filtering technique. When the carrier is in anchoring state, the adoption of the method can obtain higher on-site proving precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com