Distributed layer-dividing grade temperature error compensating method of optical fiber gyroscope
A fiber optic gyroscope, temperature error technology, applied in Sagnac effect gyroscopes, thermometers, thermometers with physical/chemical changes, etc., can solve poor model accuracy, temperature field analysis of fiber optic gyroscopes, and ignore other important Links and other issues to achieve the effect of ensuring truthfulness and comprehensiveness and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The method of the present invention will be described in detail below in combination with specific embodiments.
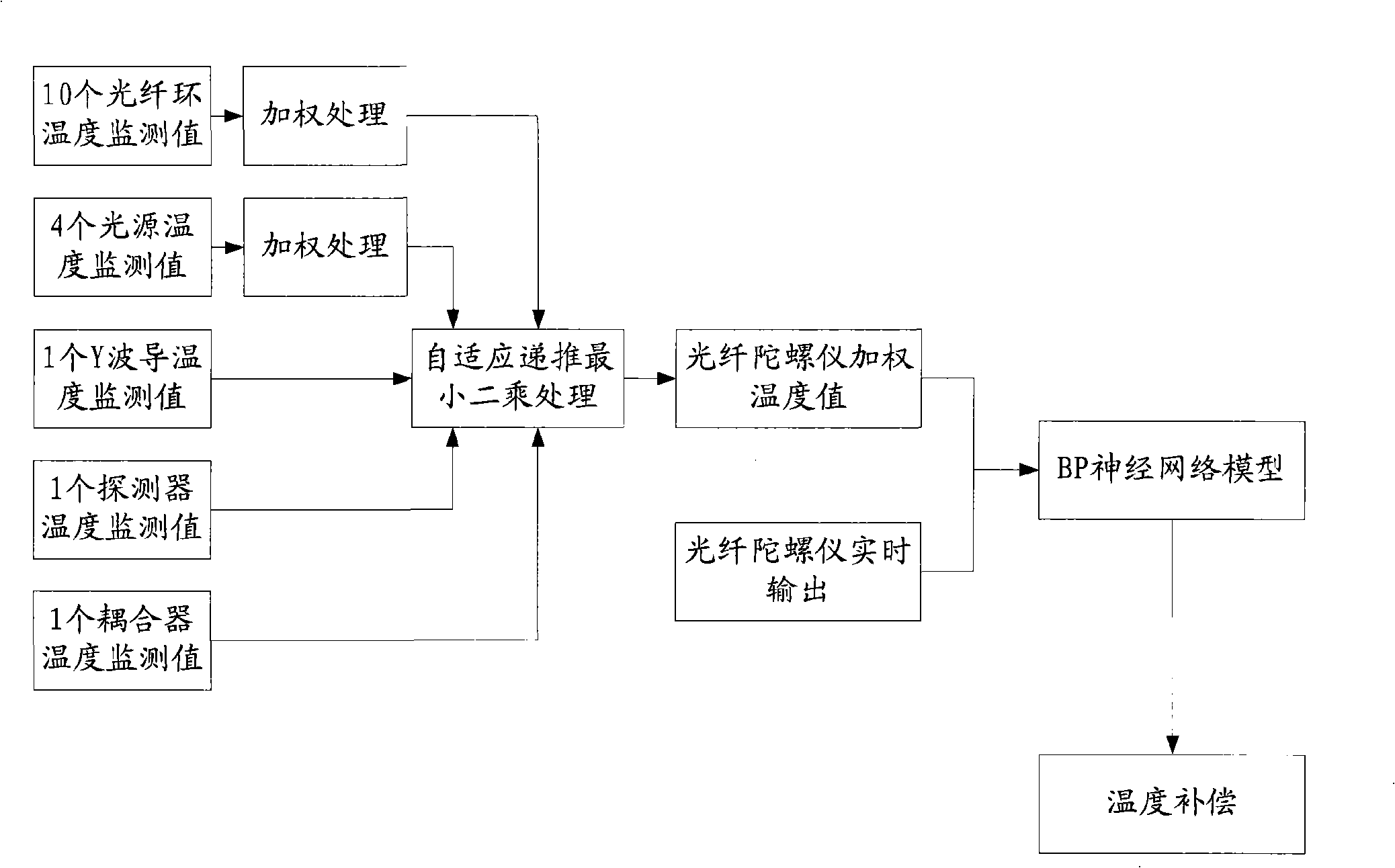
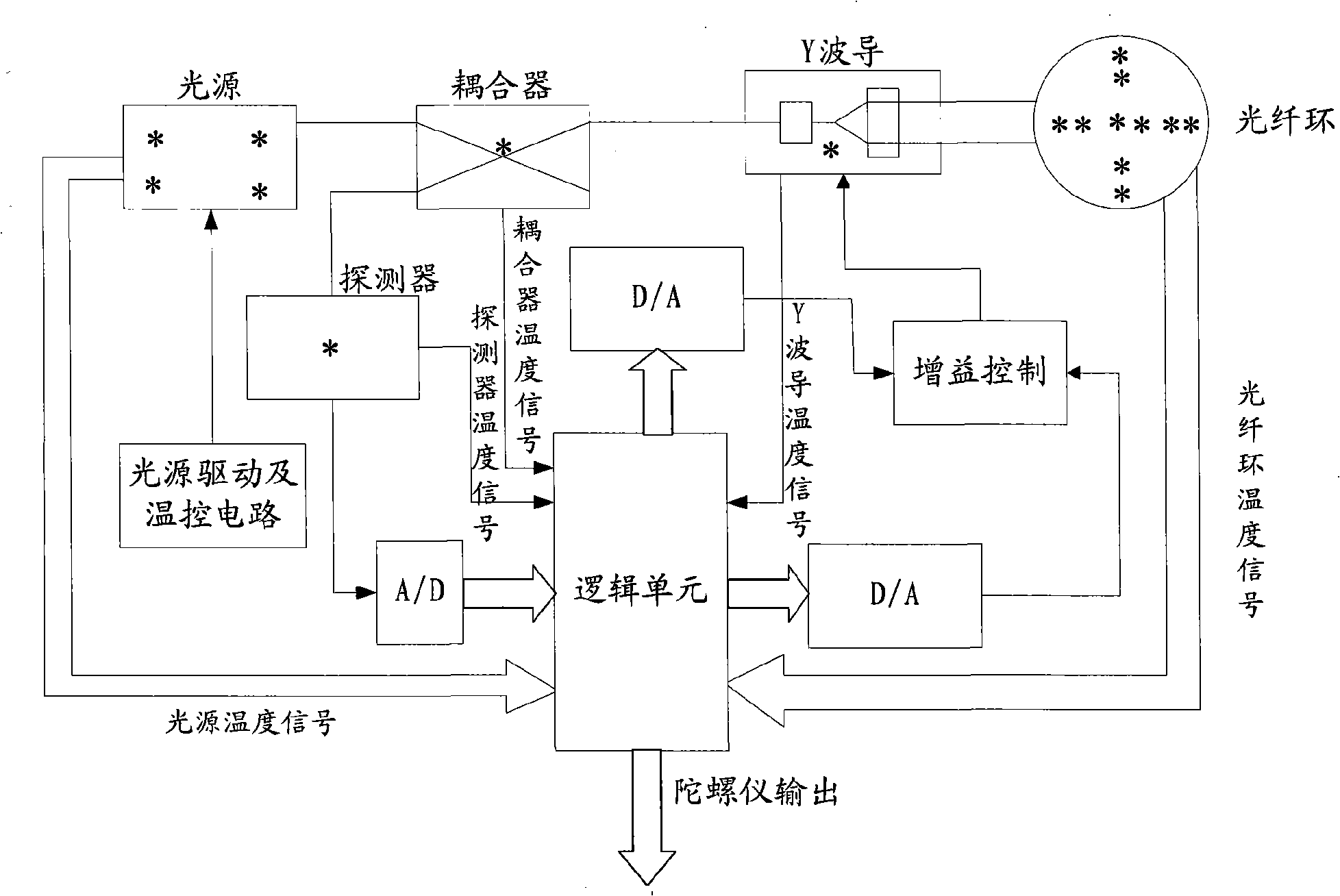
[0047] Such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, the steps of a distributed hierarchical temperature error compensation method for an optical fiber gyroscope in the present invention are as follows:
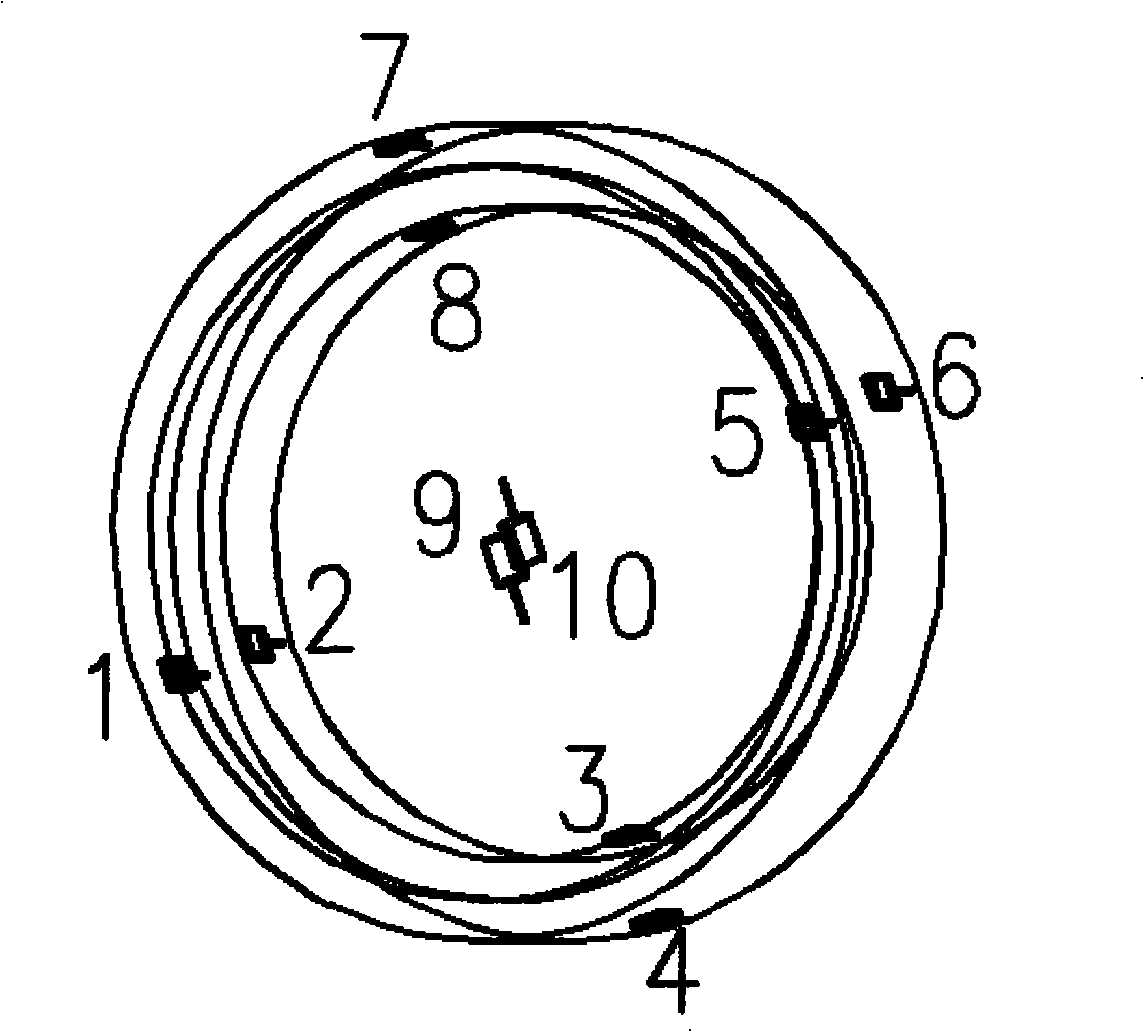
[0048] (1) Take the five optical components of optical fiber ring, light source, Y waveguide, detector and coupler as temperature monitoring objects, and determine the number and distribution of temperature monitoring points for each optical component;
[0049] The number of temperature monitoring points required by the fiber optic ring can be obtained by using formula (1):
[0050] n = Δ · ( L · D · ( λ α ) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com