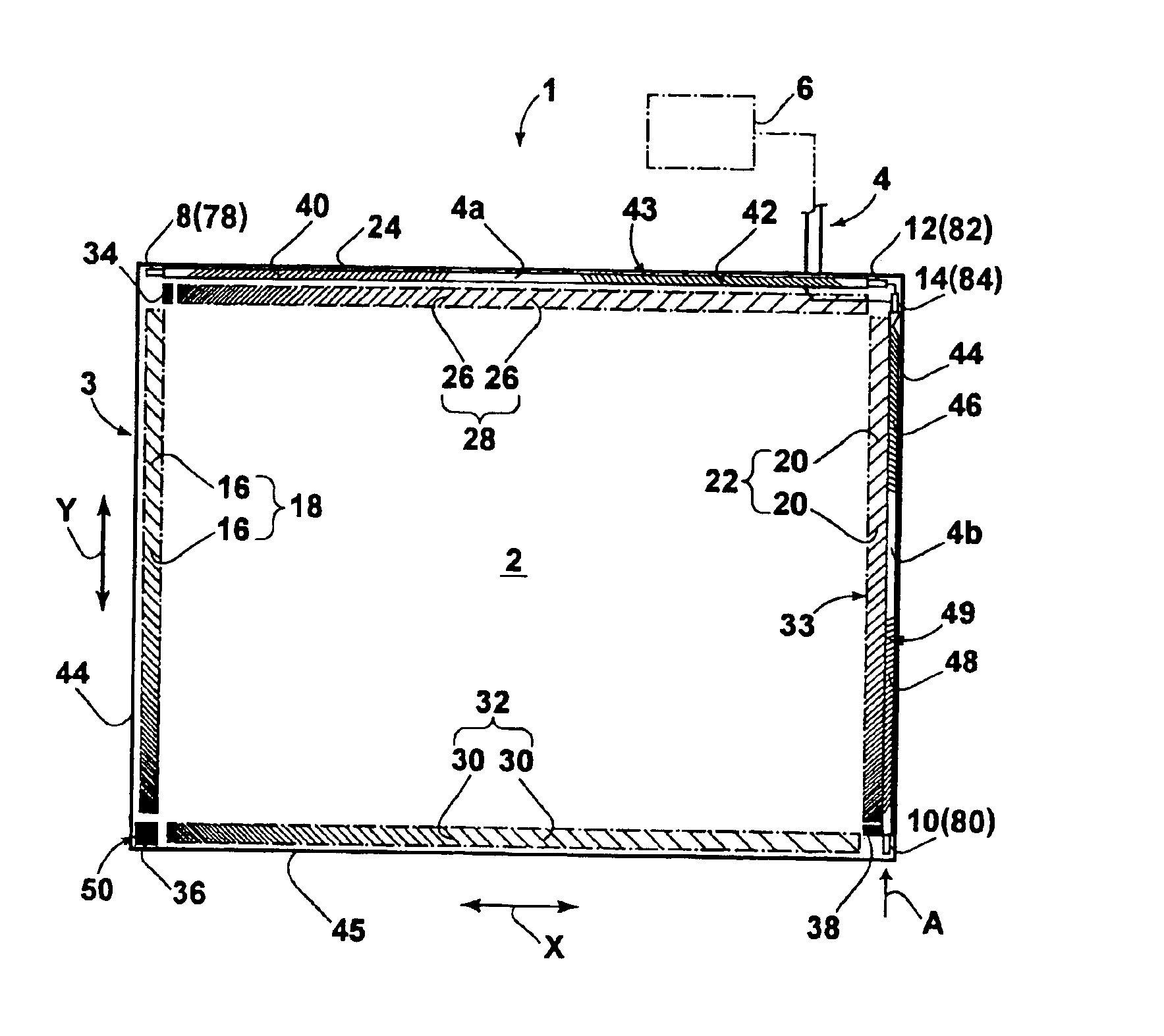
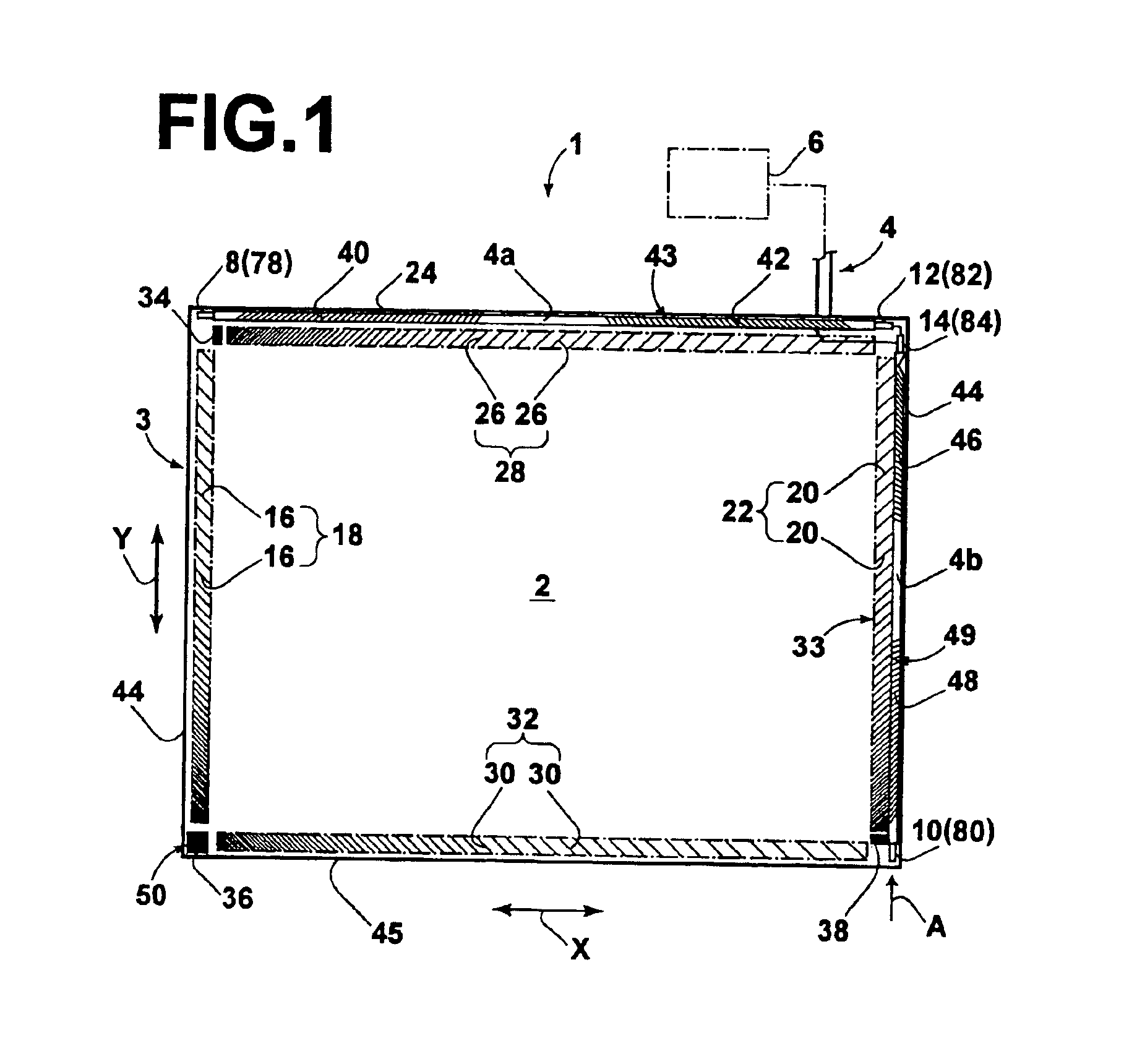
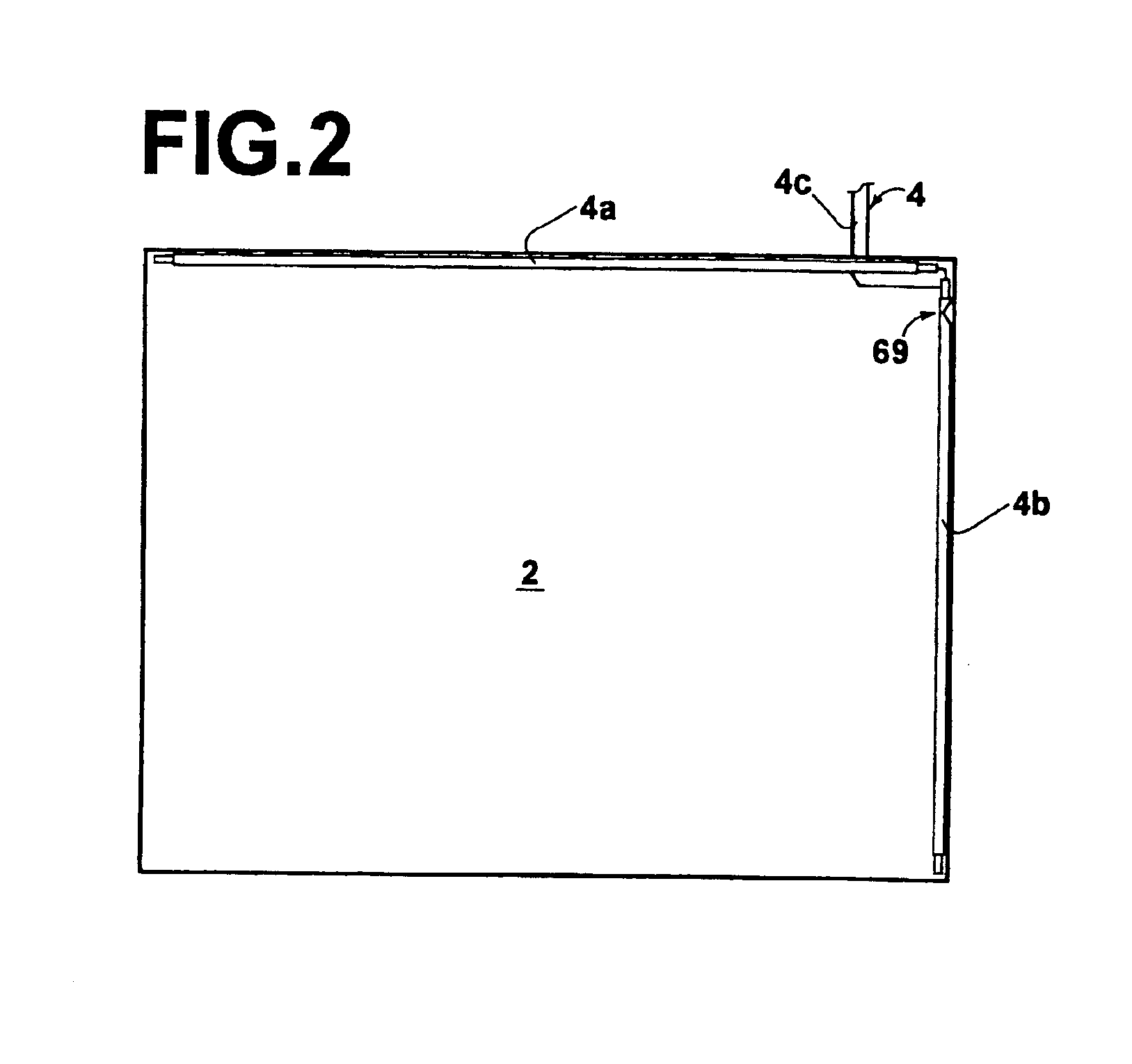
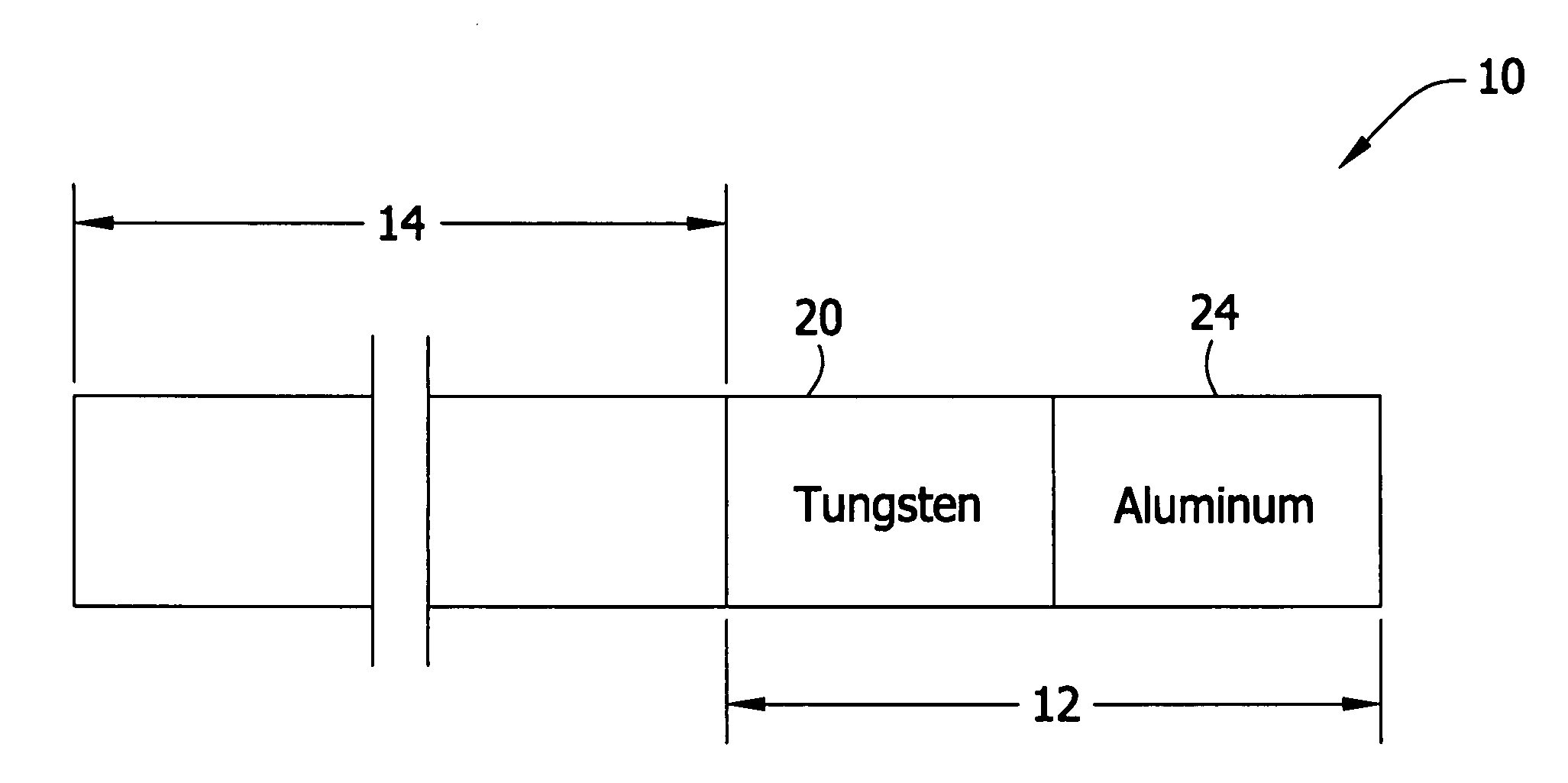
Patents
Literature
4192results about "Using subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
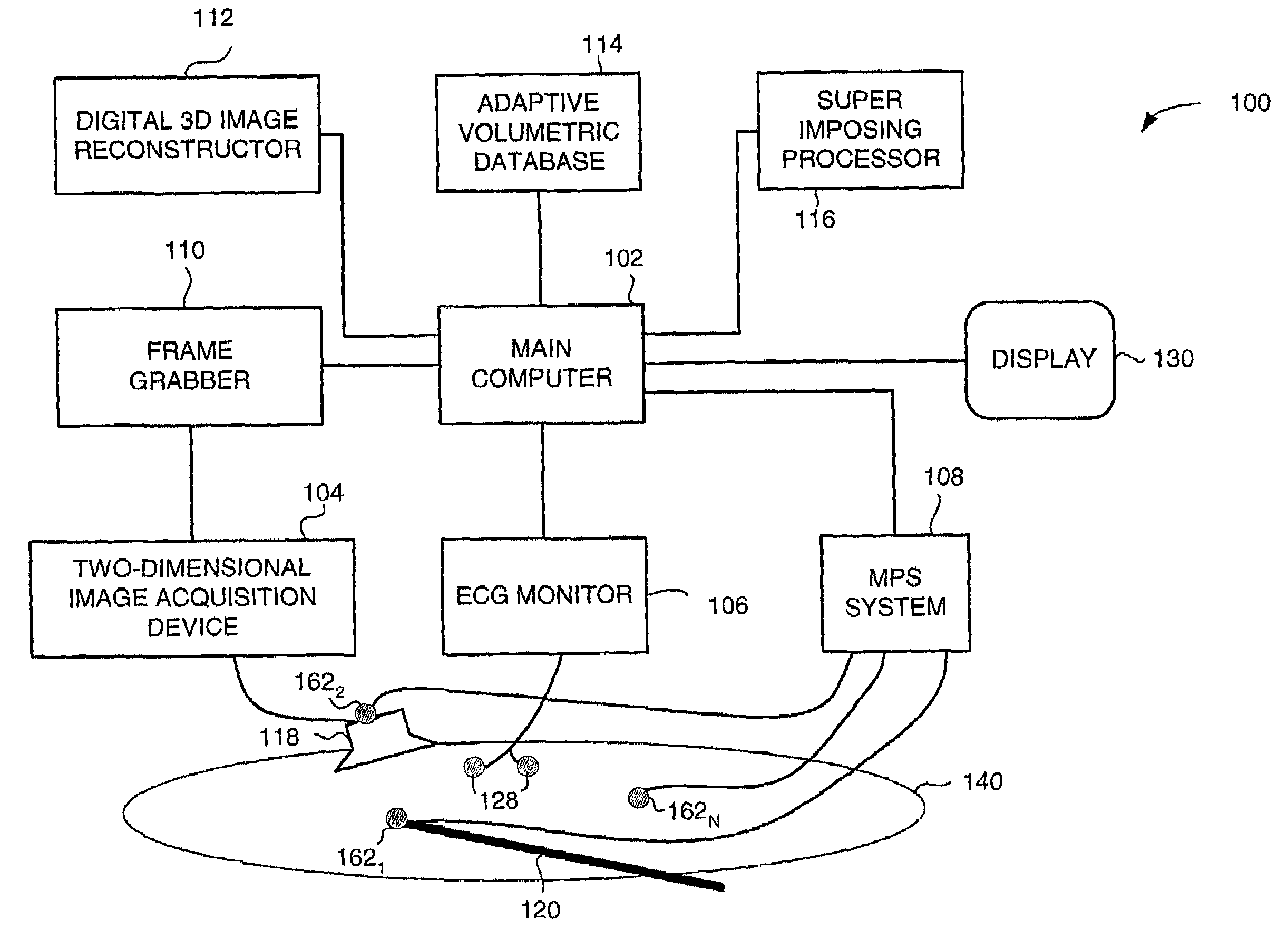
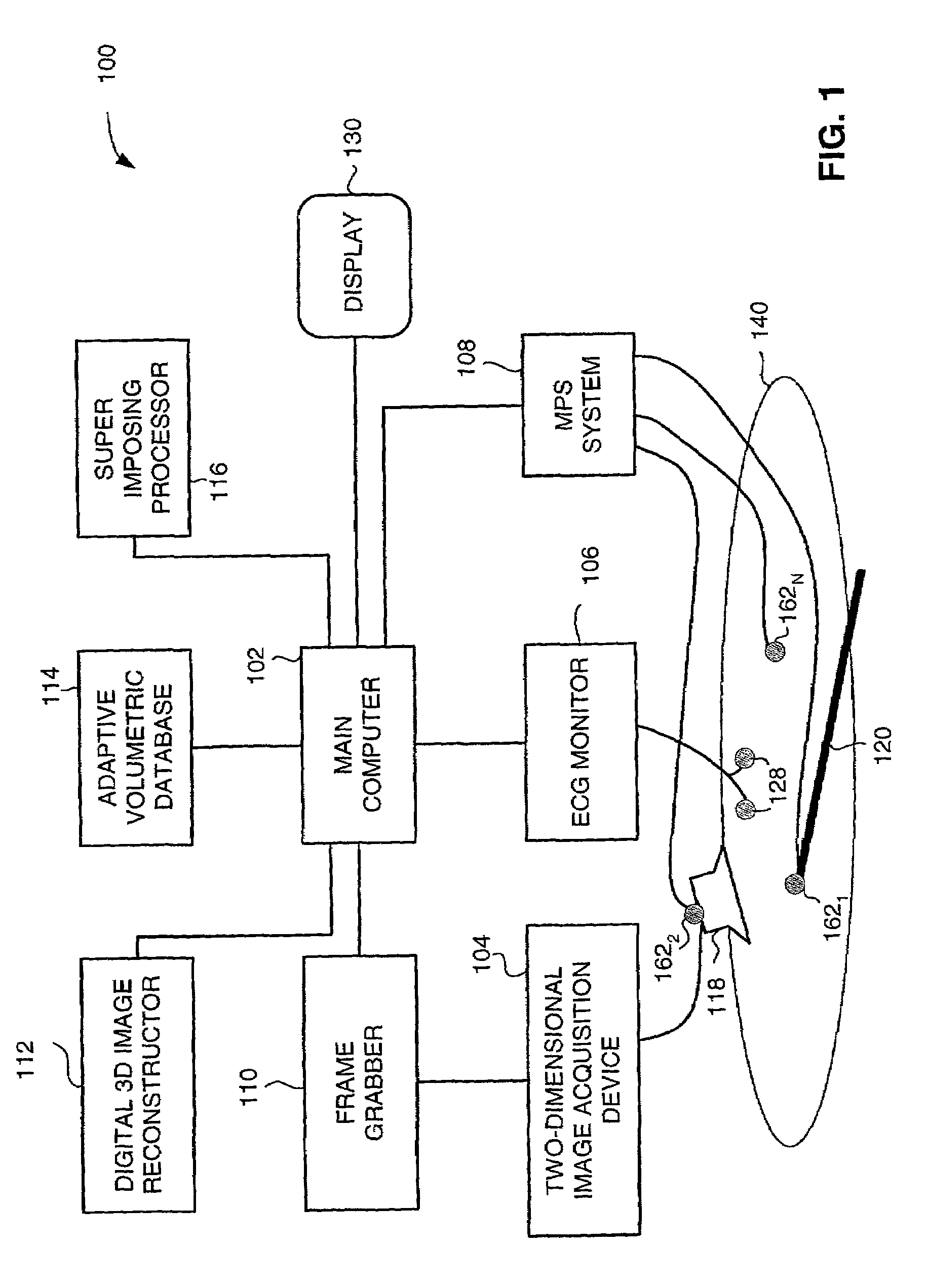
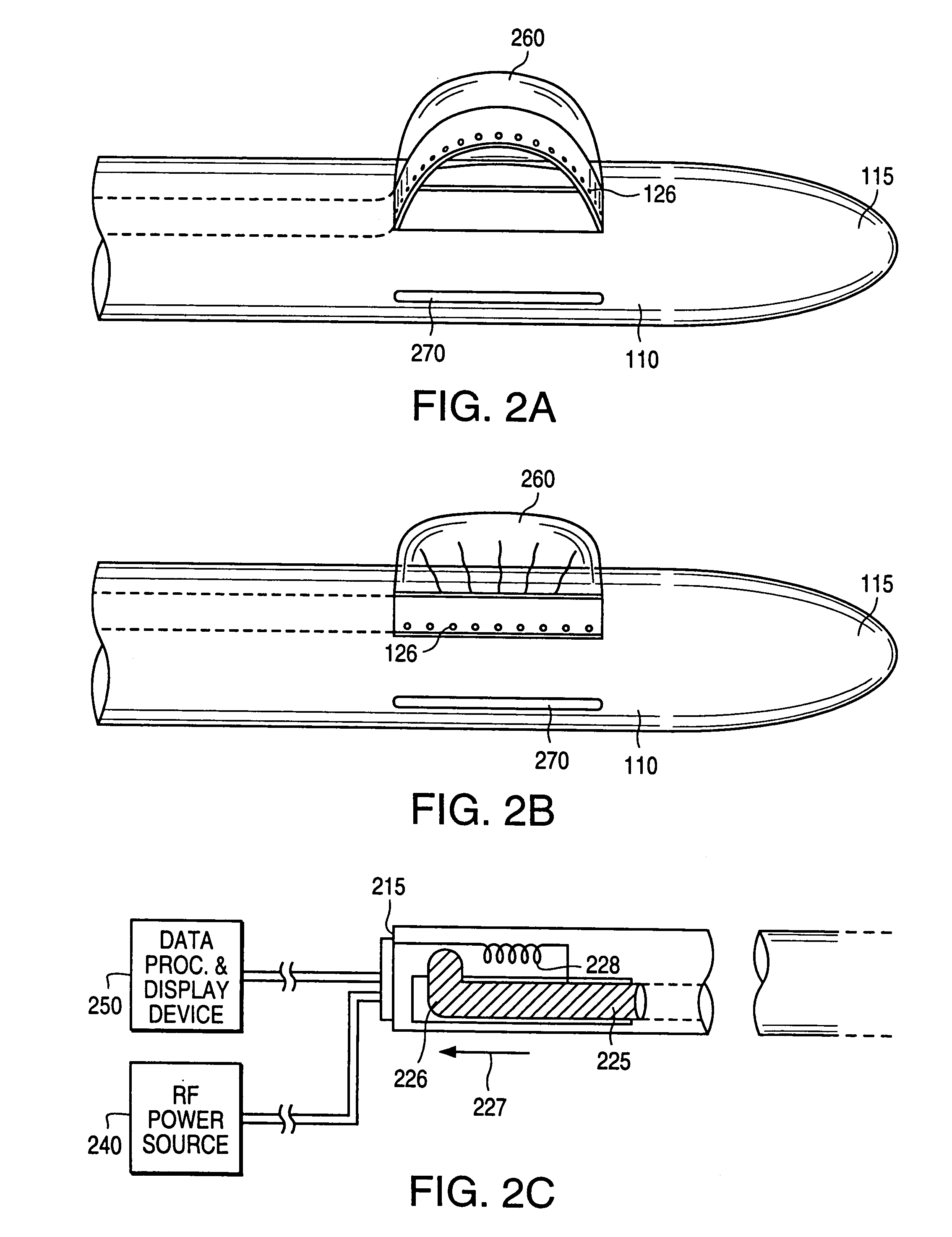
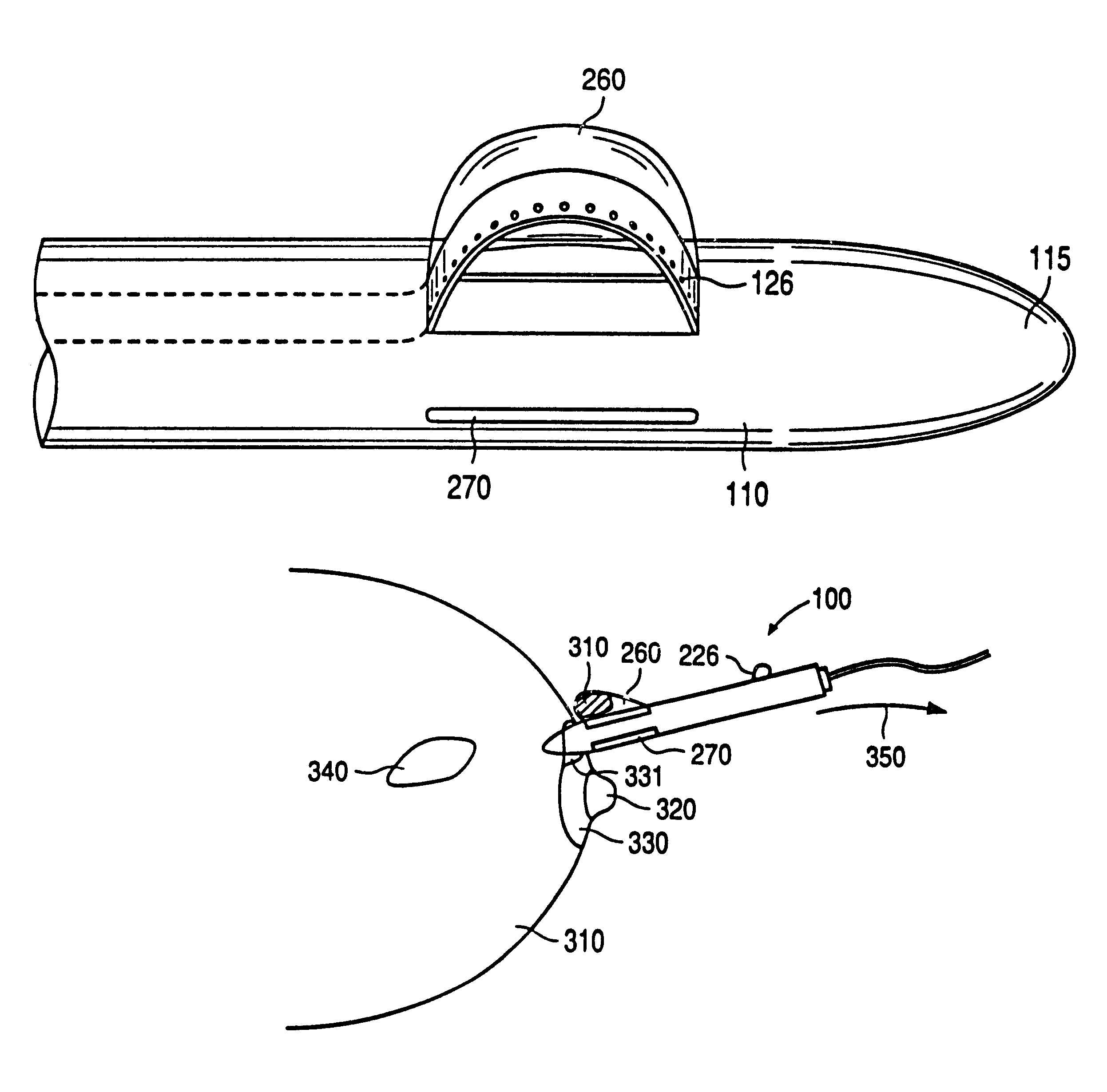
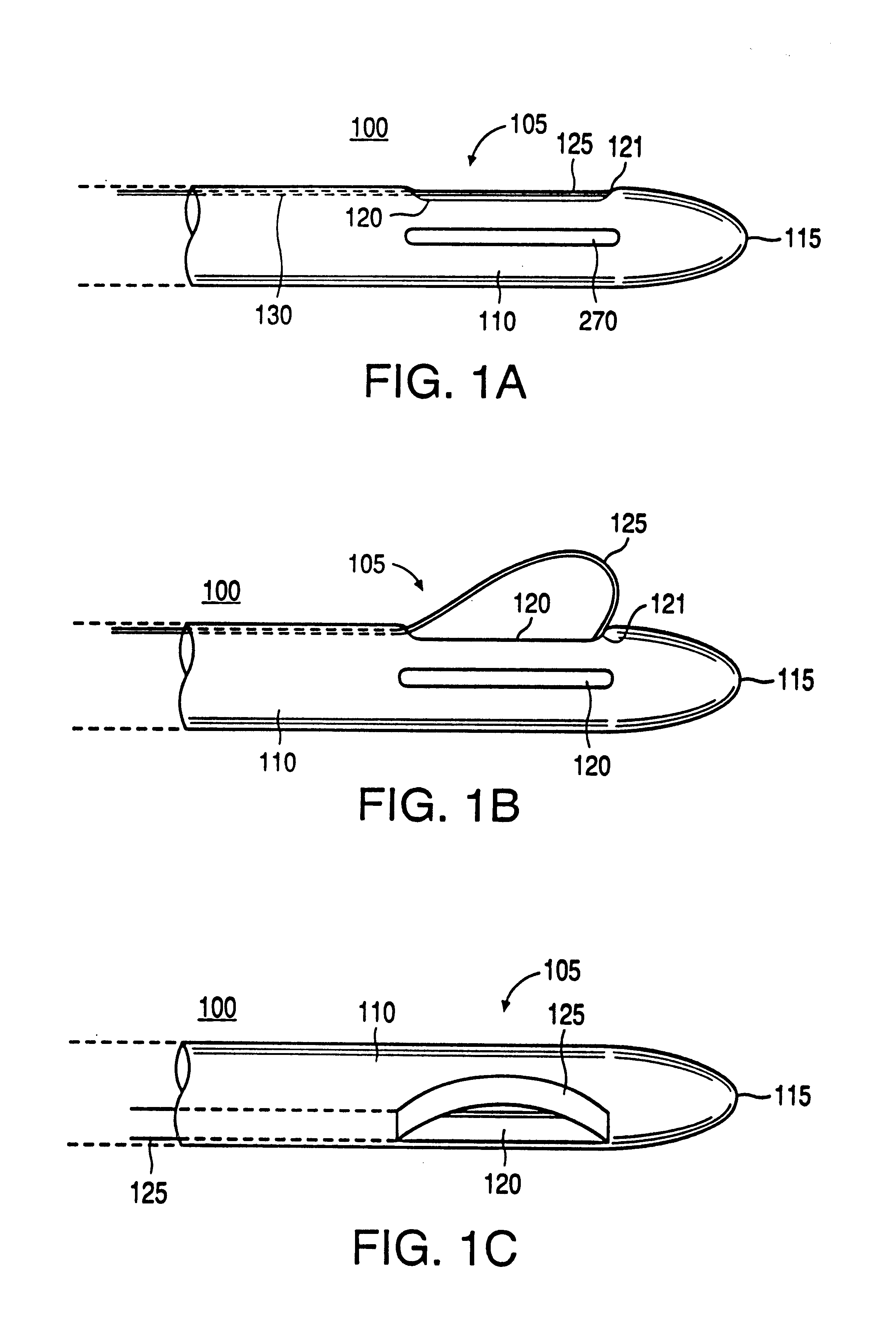
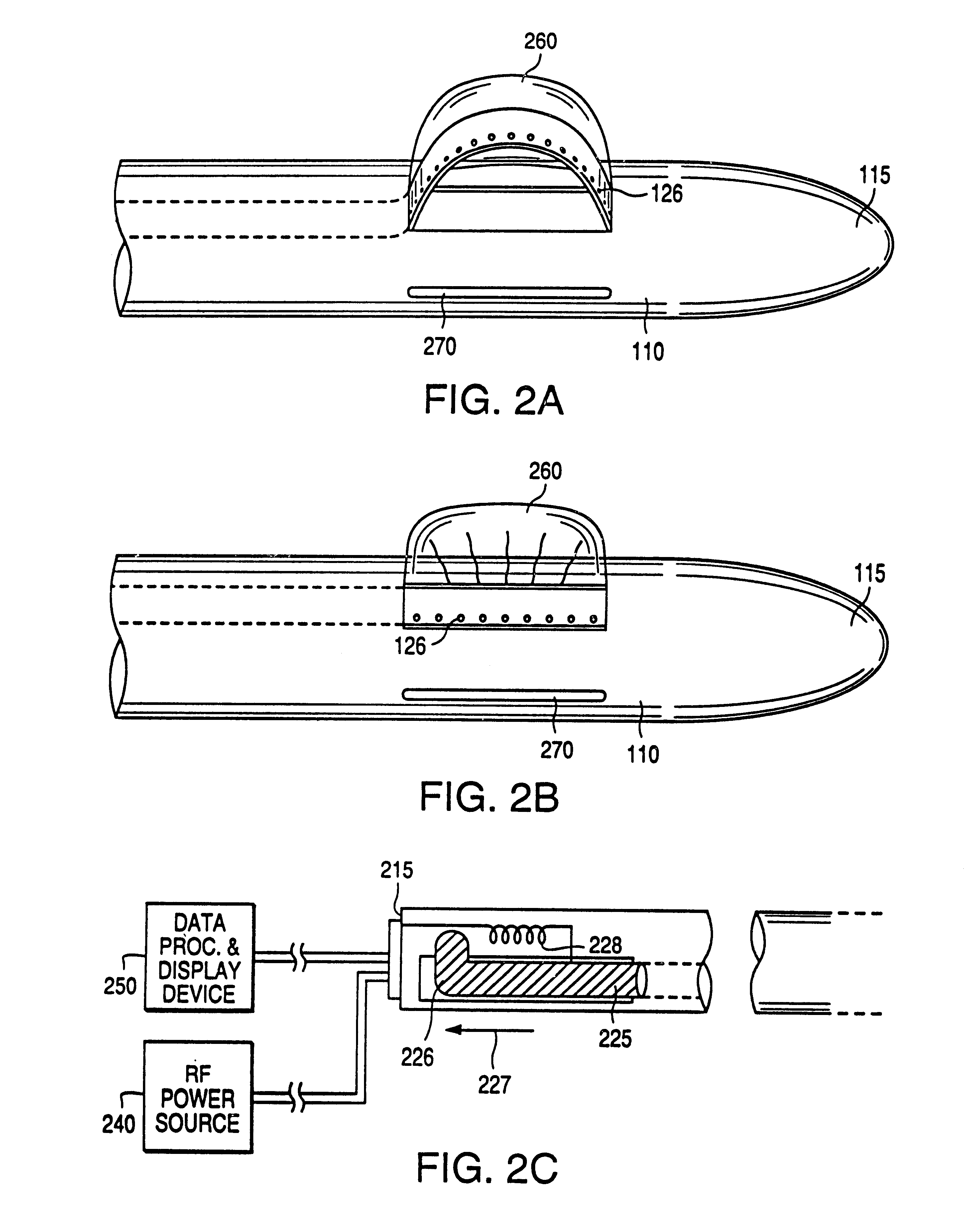
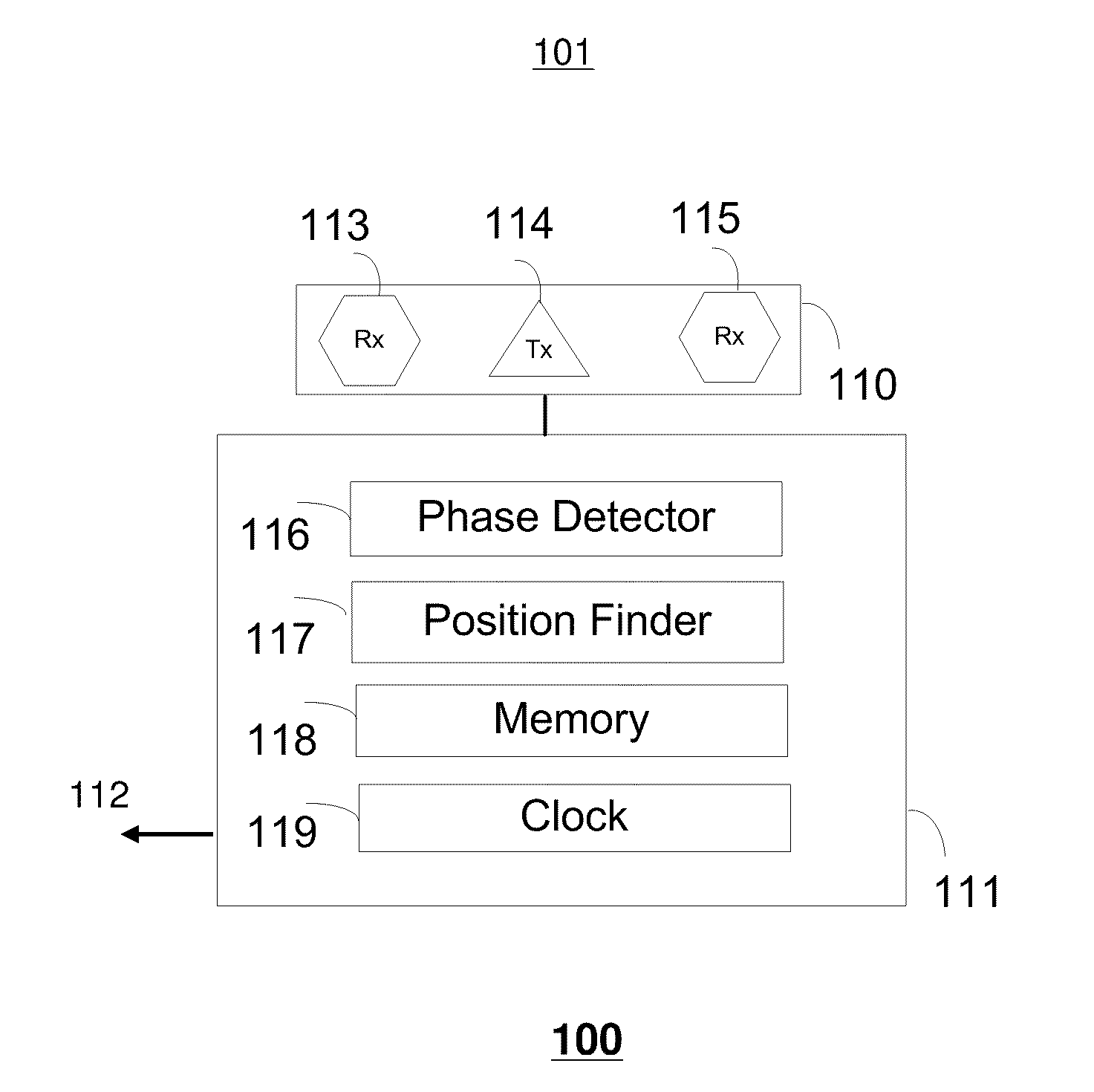
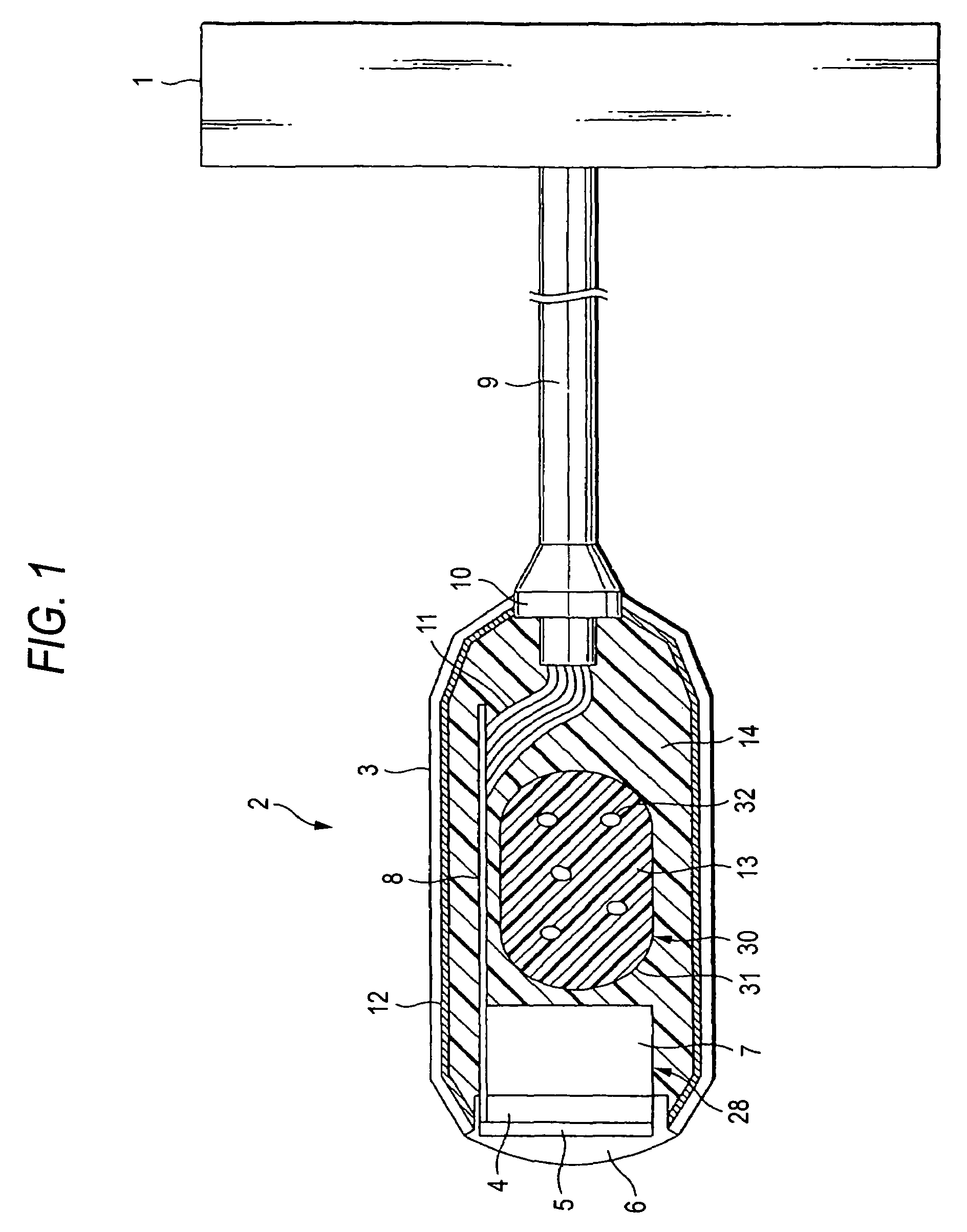
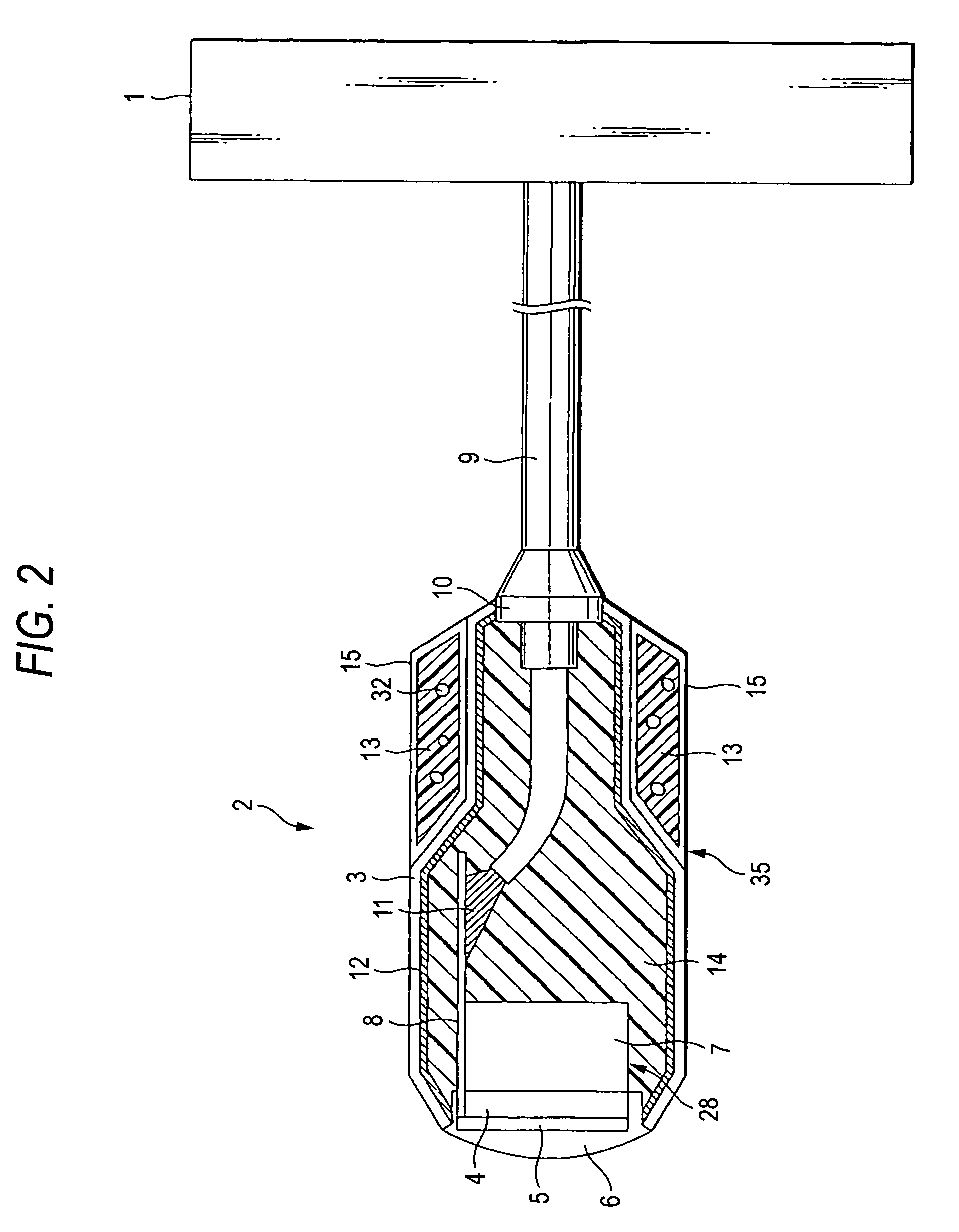
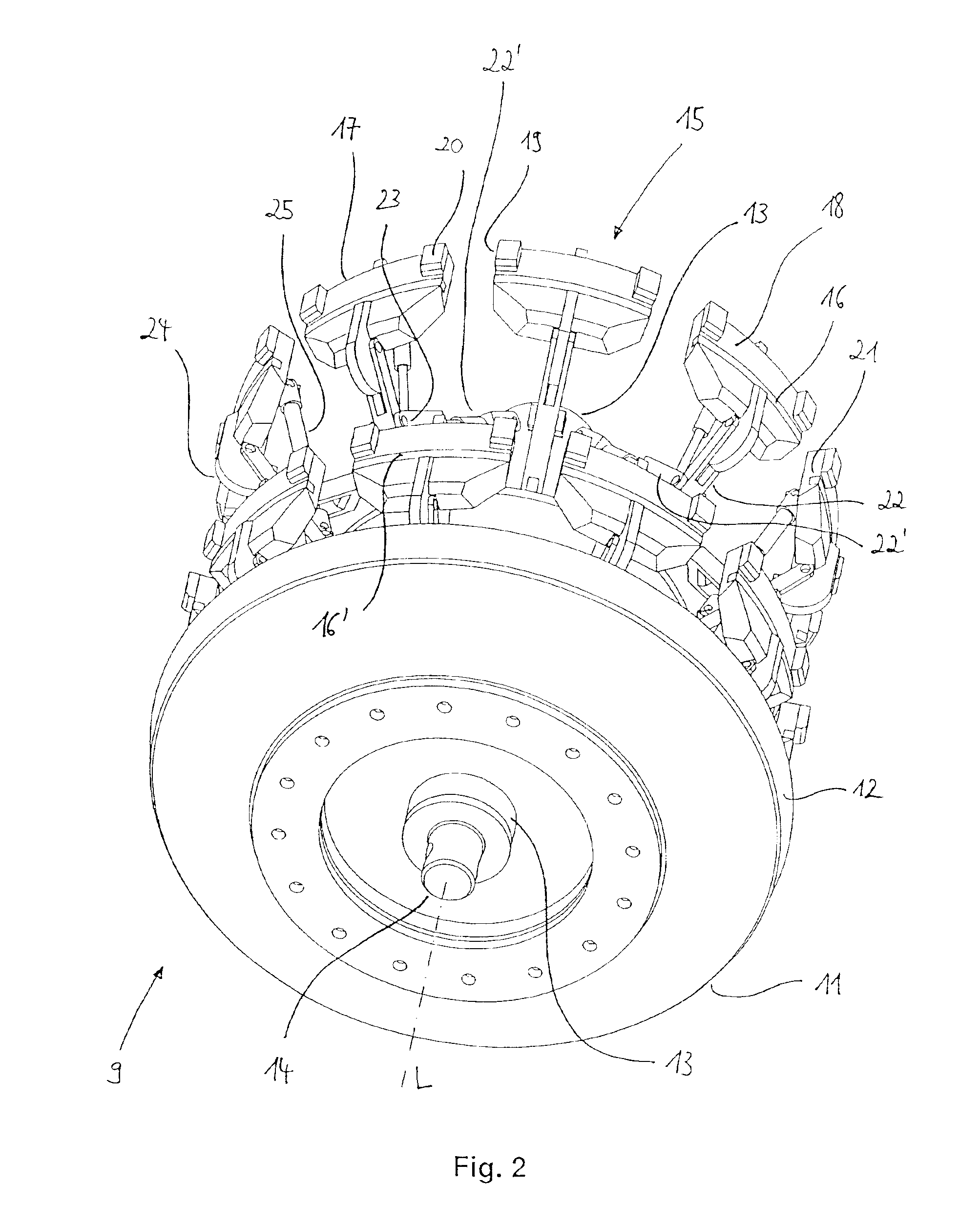
Method and apparatus for real time quantitative three-dimensional image reconstruction of a moving organ and intra-body navigation
InactiveUS7343195B2Operating tablesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansImage detectionMedical imaging
Medical imaging and navigation system including a processor, a medical positioning system (MPS), a two-dimensional imaging system and an inspected organ monitor interface, the MPS including an imaging MPS sensor, the two-dimensional imaging system including an image detector, the processor being coupled to a display unit and to a database, the MPS being coupled to the processor, the imaging MPS sensor being firmly attached to the image detector, the two-dimensional imaging system being coupled to the processor, the image detector being firmly attached to an imaging catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
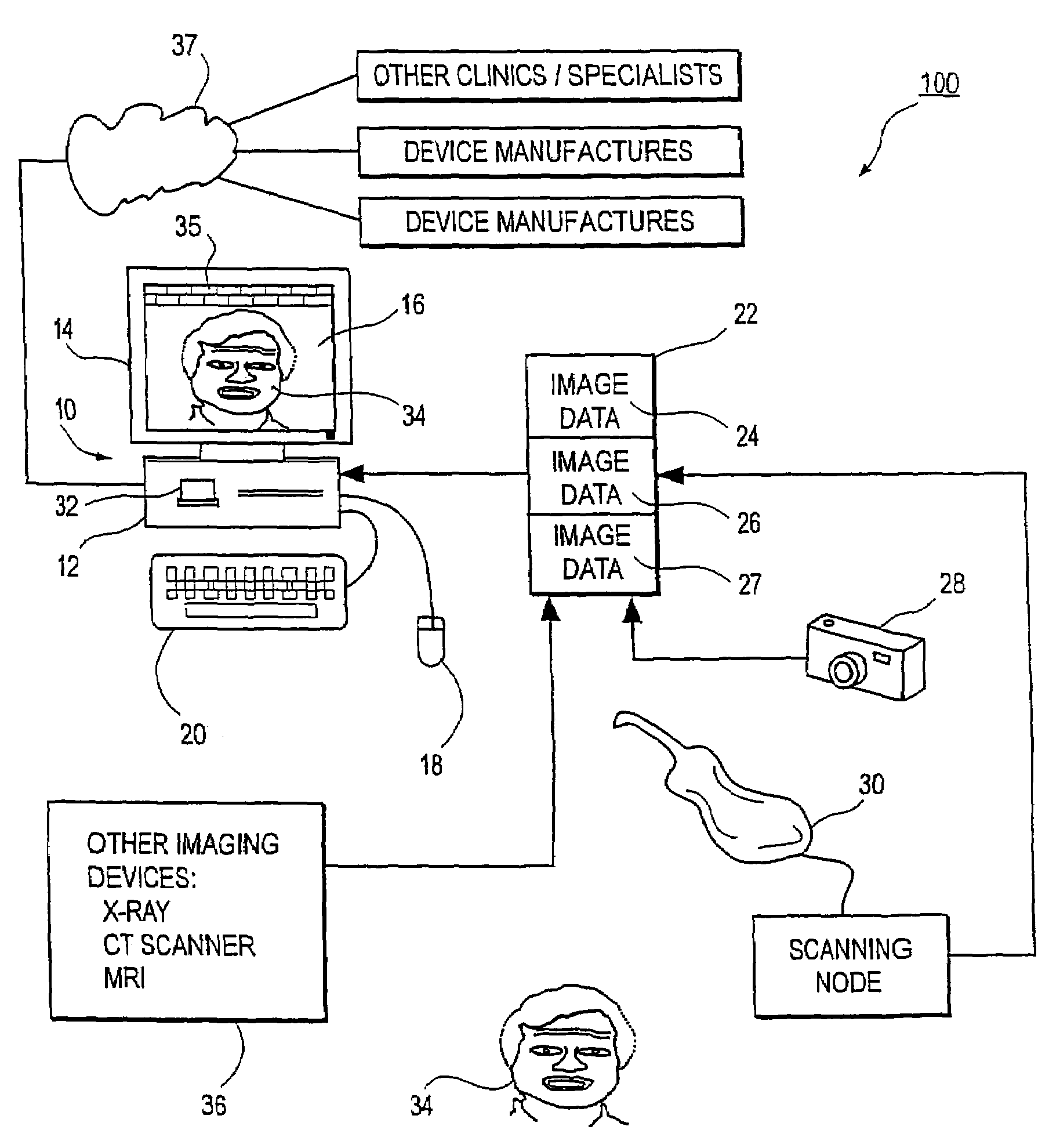
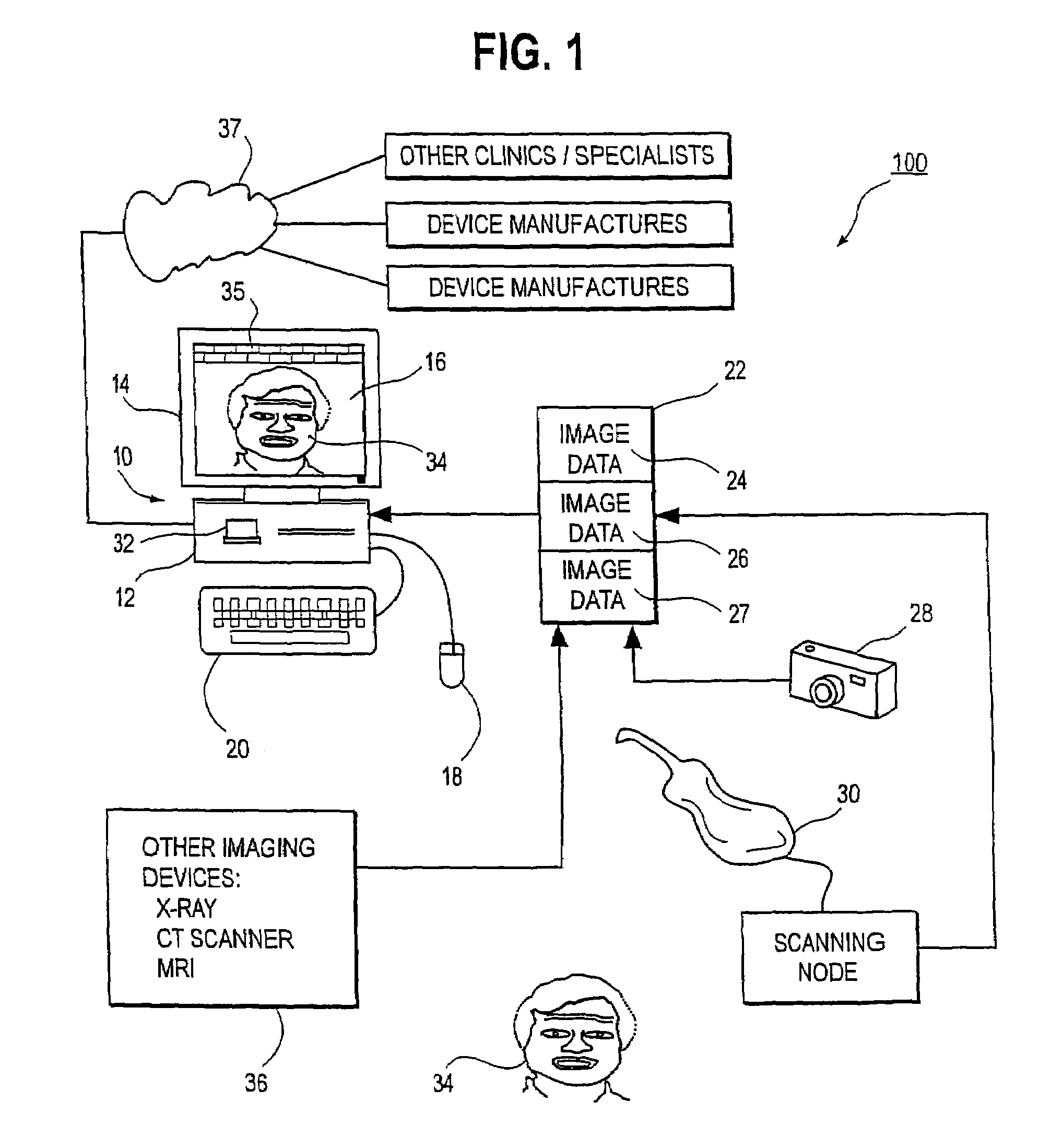
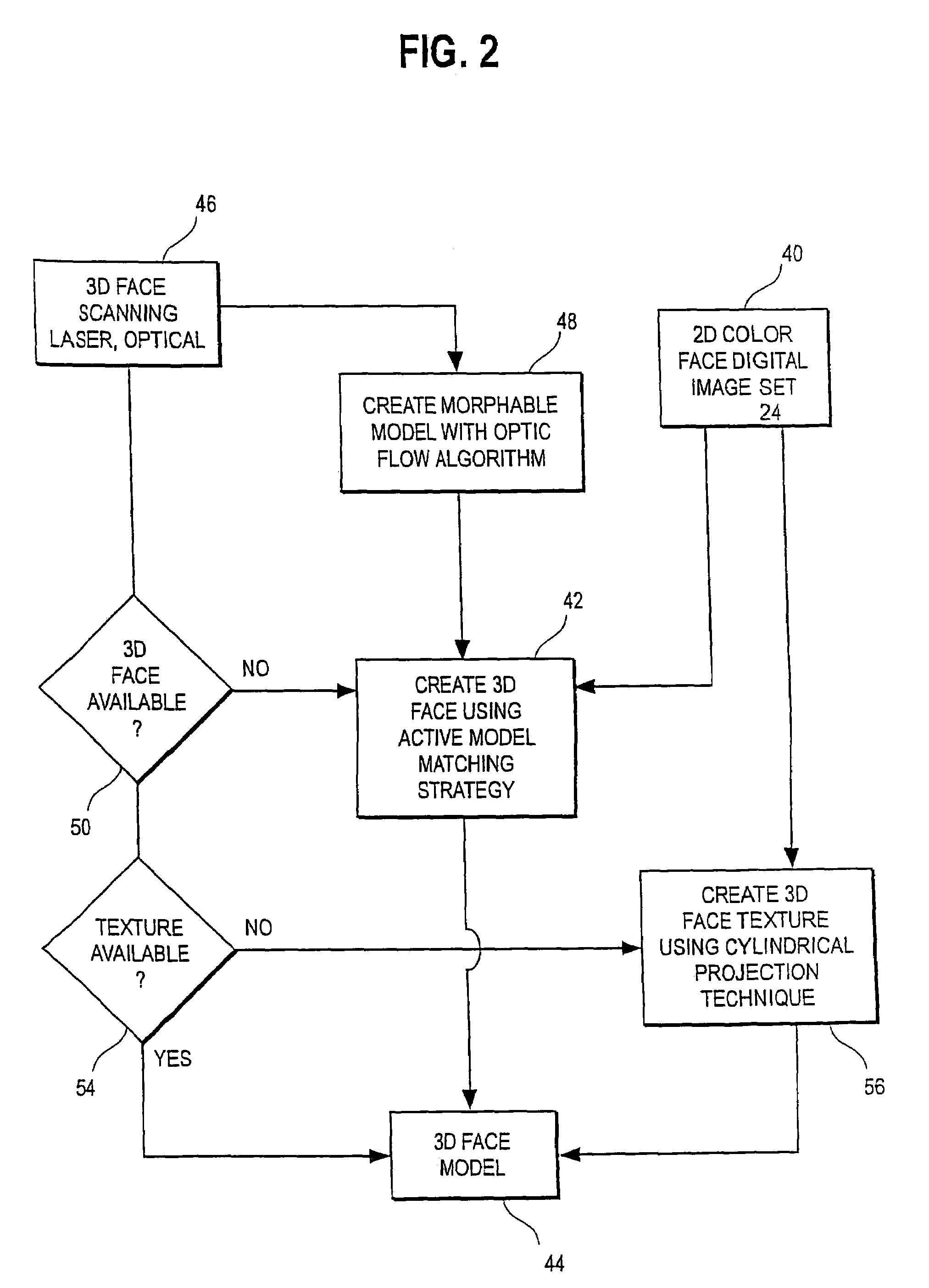
Unified workstation for virtual craniofacial diagnosis, treatment planning and therapeutics
InactiveUS7234937B2Quick analysisPowerful toolDental implantsImpression capsPlan treatmentPatient model
An integrated system is described in which digital image data of a patient, obtained from a variety of image sources, including CT scanner, X-Ray, 2D or 3D scanners and color photographs, are combined into a common coordinate system to create a virtual three-dimensional patient model. Software tools are provided for manipulating the virtual patient model to simulation changes in position or orientation of craniofacial structures (e.g., jaw or teeth) and simulate their affect on the appearance of the patient. The simulation (which may be pure simulations or may be so-called “morphing” type simulations) enables a comprehensive approach to planning treatment for the patient. In one embodiment, the treatment may encompass orthodontic treatment. Similarly, surgical treatment plans can be created. Data is extracted from the virtual patient model or simulations thereof for purposes of manufacture of customized therapeutic devices for any component of the craniofacial structures, e.g., orthodontic appliances.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
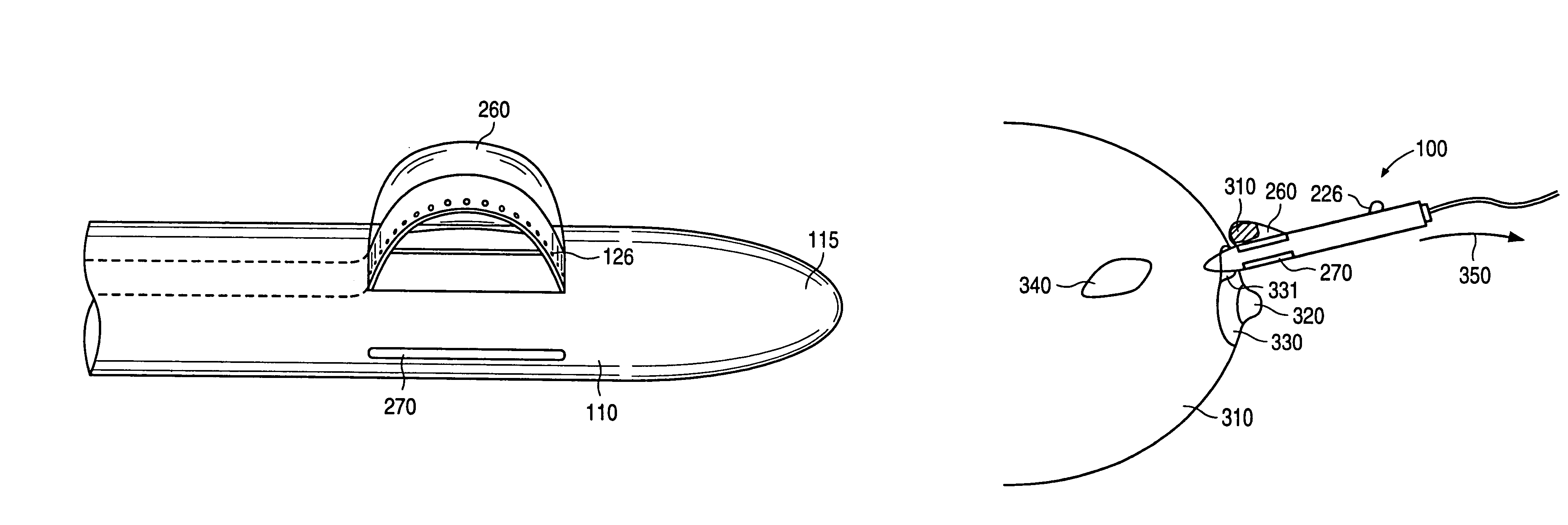
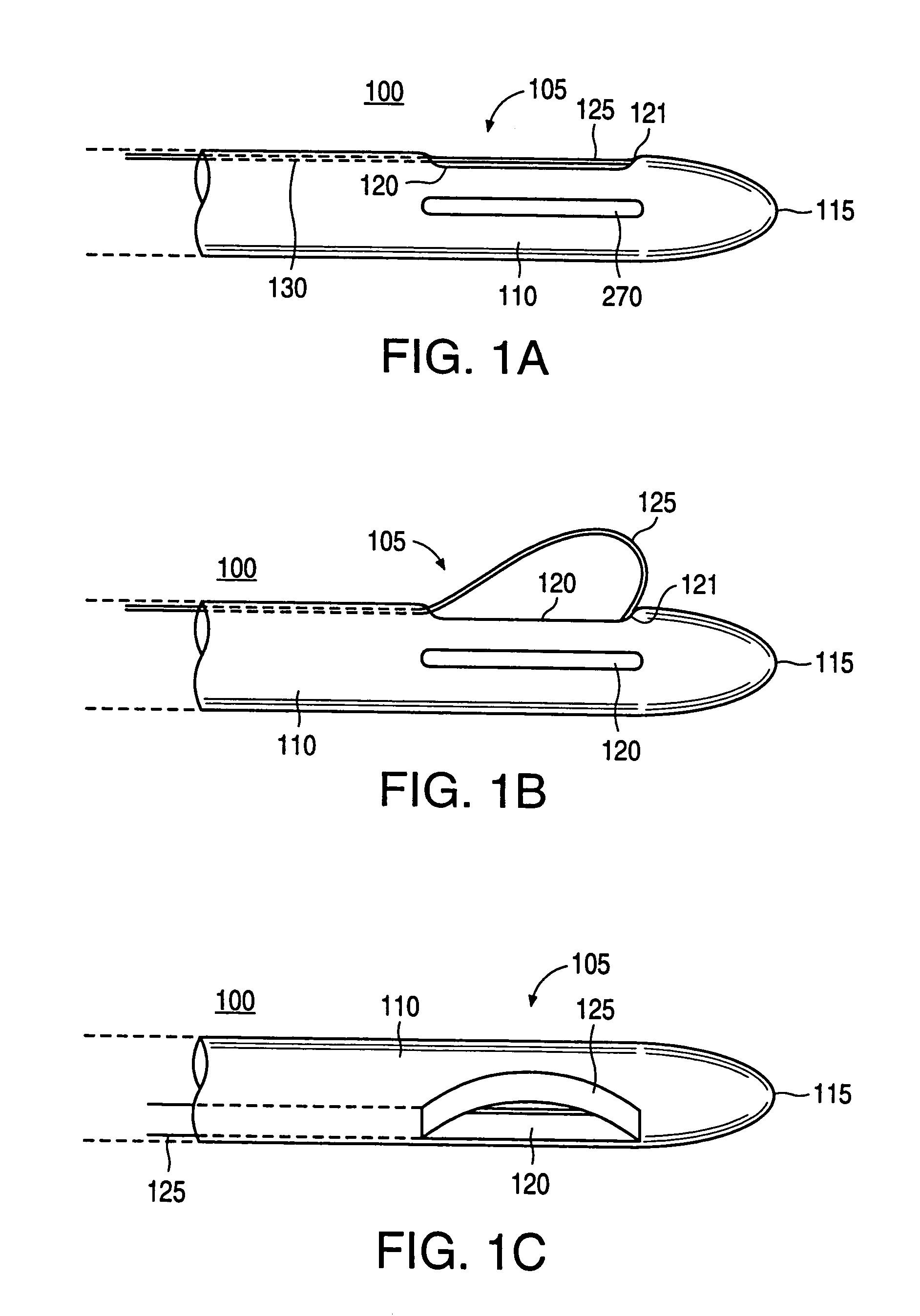
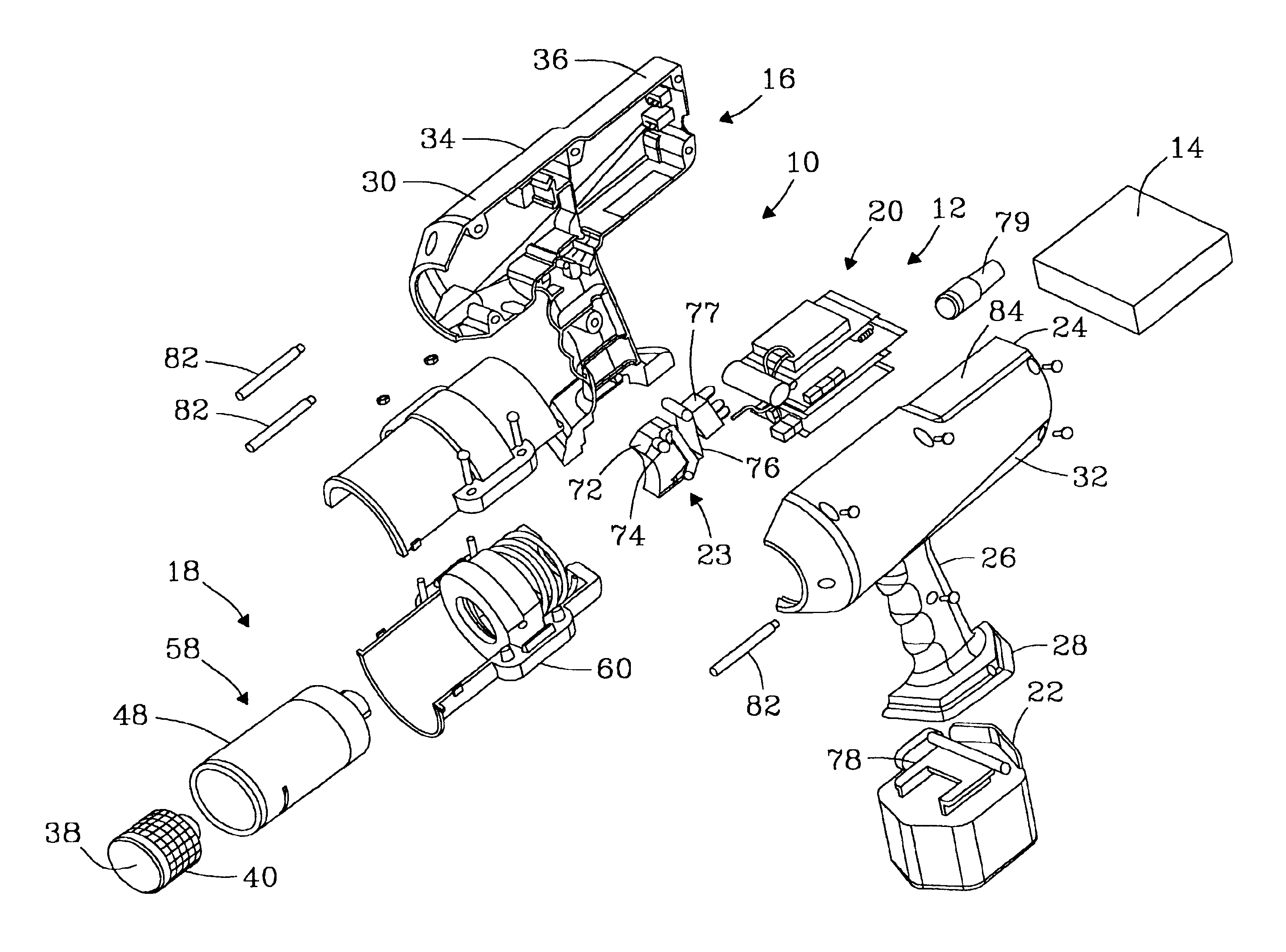
Excisional biopsy devices and methods
InactiveUS7303531B2Efficiently and safely exciseMinimized in sizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasBiopsy methodsTissue Collection
An excisional biopsy device includes a tubular member having a window near a distal tip thereof; a cutting tool, a distal end of the cutting tool being attached near the distal tip of the tubular member, at least a distal portion of the cutting tool being configured to selectively bow out of the window and to retract within the window; and a tissue collection device externally attached at least to the tubular member, the tissue collection device collecting tissue excised by the cutting tool as the biopsy device is rotated and the cutting tool is bowed. An excision al biopsy method for soft tissue includes the steps of inserting a generally tubular member into the tissue, the tubular member including a cutting tool adapted to selectively bow away from the tubular member and an external tissue collection device near a distal tip of the tubular member; rotating the tubular member; selectively varying a degree of bowing of the cutting tool; collecting tissue severed by the cutting tool in the tissue collection device; and retracting the tubular member from the soft tissue. The tubular member may include an imaging transducer and the method may include the step of displaying information received from the transducer on a display device and the step of varying the degree of bowing of the cutting tool based upon the displayed information from the imaging transducer. Alternatively, the imaging transducer may be disposed within a removable transducer core adapted to fit within the tubular member.
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
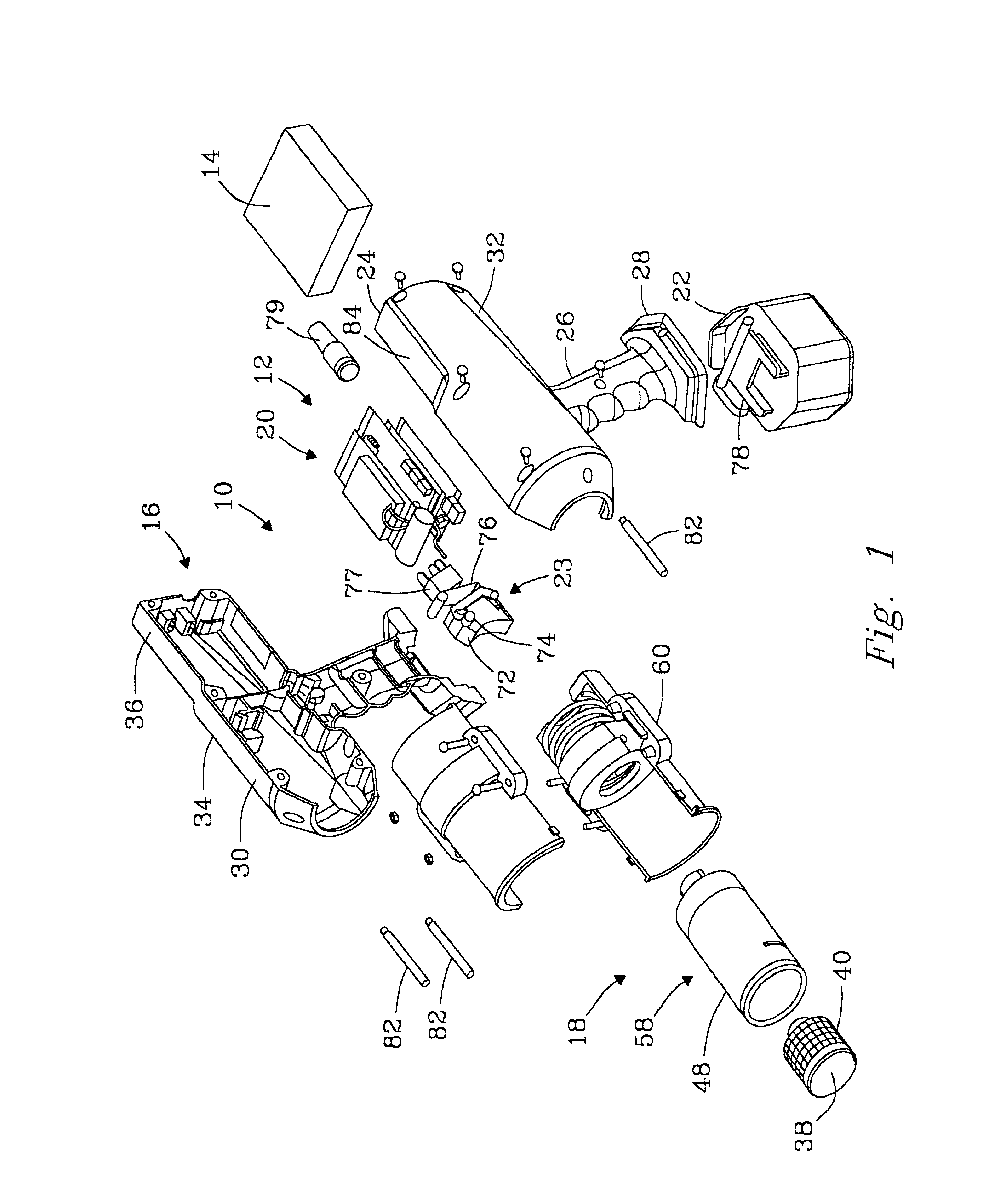
Excisional biopsy device and methods
InactiveUS6849080B2Efficiently and safely exciseMinimize complicationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasBiopsy methodsDistal portion
An excisional biopsy device includes a tubular member having a window near a distal tip thereof; a cutting tool, a distal end of the cutting tool being attached near the distal tip of the tubular member, at least a distal portion of the cutting tool being configured to selectively bow out of the window and to retract within the window; and a tissue collection device externally attached at least to the tubular member, the tissue collection device collecting tissue excised by the cutting tool as the biopsy device is rotated and the cutting tool is bowed. An excisional biopsy method for soft tissue includes the steps of inserting a generally tubular member into the tissue, the tubular member including a cutting tool adapted to selectively bow away from the tubular member and an external tissue collection device near a distal tip of the tubular member; rotating the tubular member; selectively varying a degree of bowing of the cutting tool; collecting tissue severed by the cutting tool in the tissue collection device; and retracting the tubular member from the soft tissue. The tubular member may include an imaging transducer and the method may include the step of displaying information received from the transducer on a display device and the step of varying the degree of bowing of the cutting tool based upon the displayed information from the imaging transducer. Alternatively, the imaging transducer may be disposed within a removable transducer core adapted to fit within the tubular member.
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
Acoustic wave touch detecting apparatus
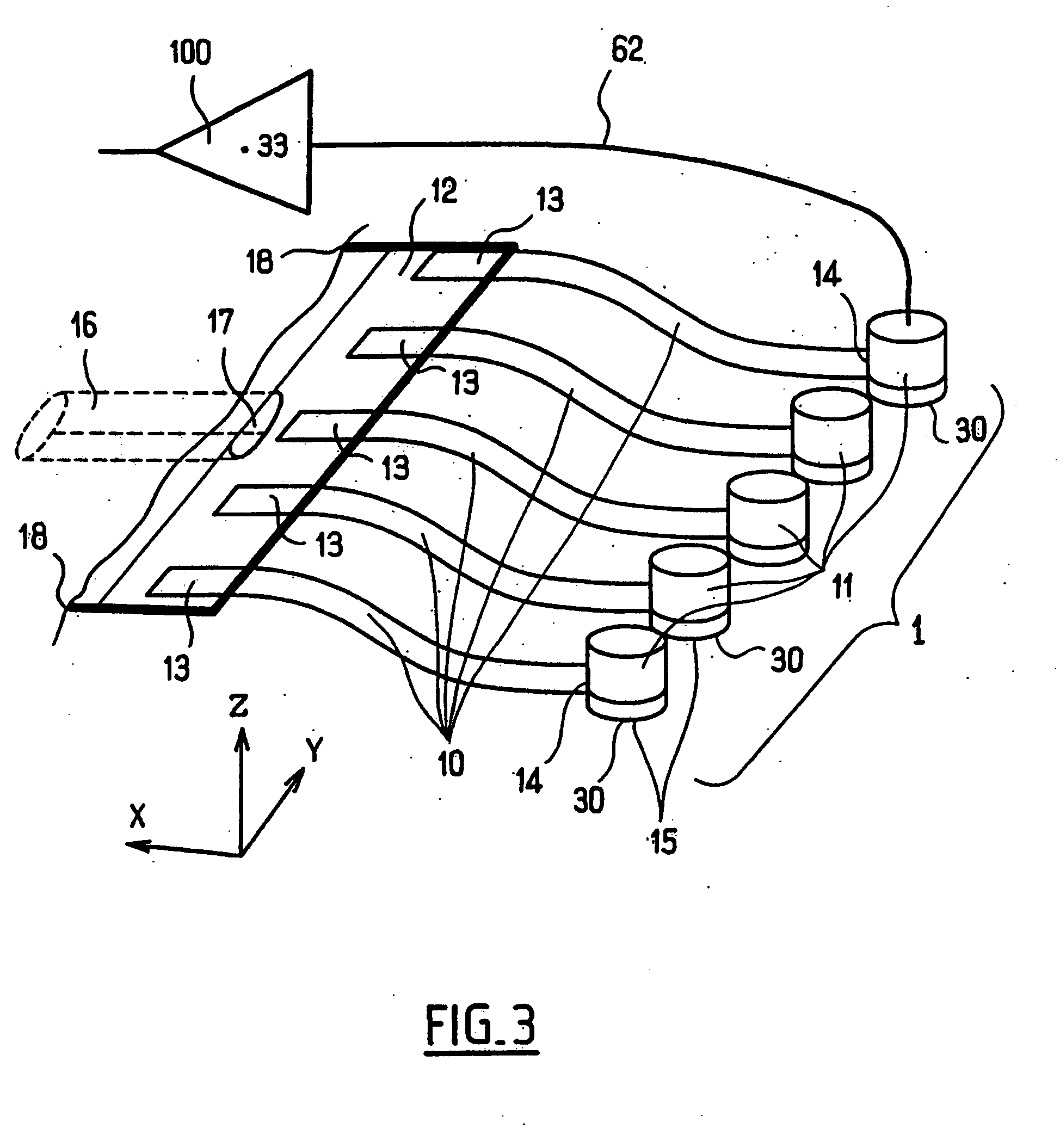
InactiveUS6948371B2Superior in anti-Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) propertiesLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesEngineeringAcoustic wave
An FPC is constructed of two FPC branches, and a connection line that connects to a controller. Printed wiring of the connection line includes ten printed wires. The central four printed wires are signal reception wires, which are connected to two converters (sensors). Grounding wires are provided on both sides of the four signal reception wires. Two outer signal wires are provided adjacent to the grounding wires, respectively toward the outsides thereof. Further, two more grounding wires are provided adjacent to the outer signal wires, respectively on the outsides thereof. This construction results in shielding of all of the signal wires. This relationship is maintained in the FPC branches as well.
Owner:ELO TOUCH SOLUTIONS INC
Amplifying ultrasonic waveguides
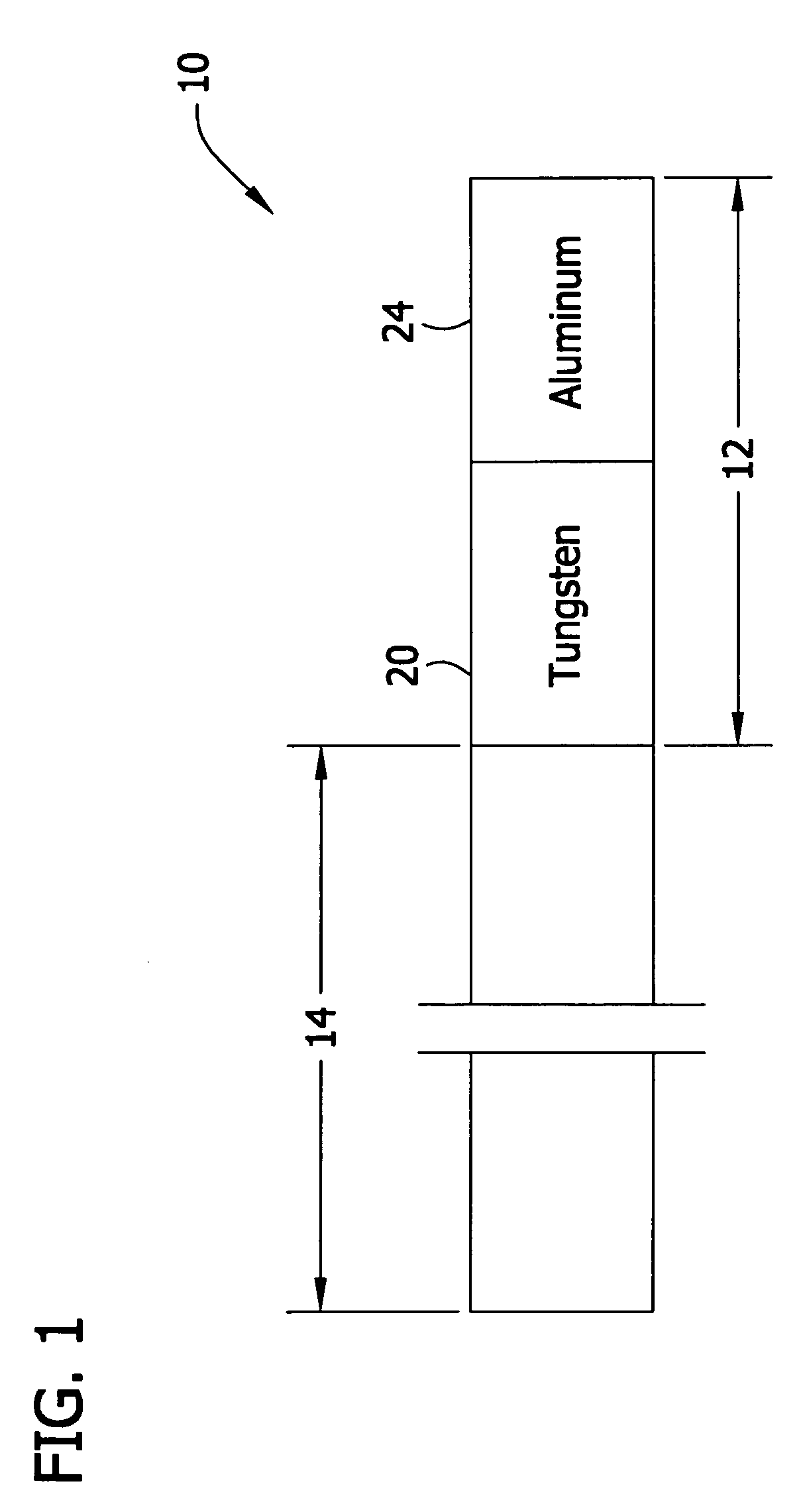
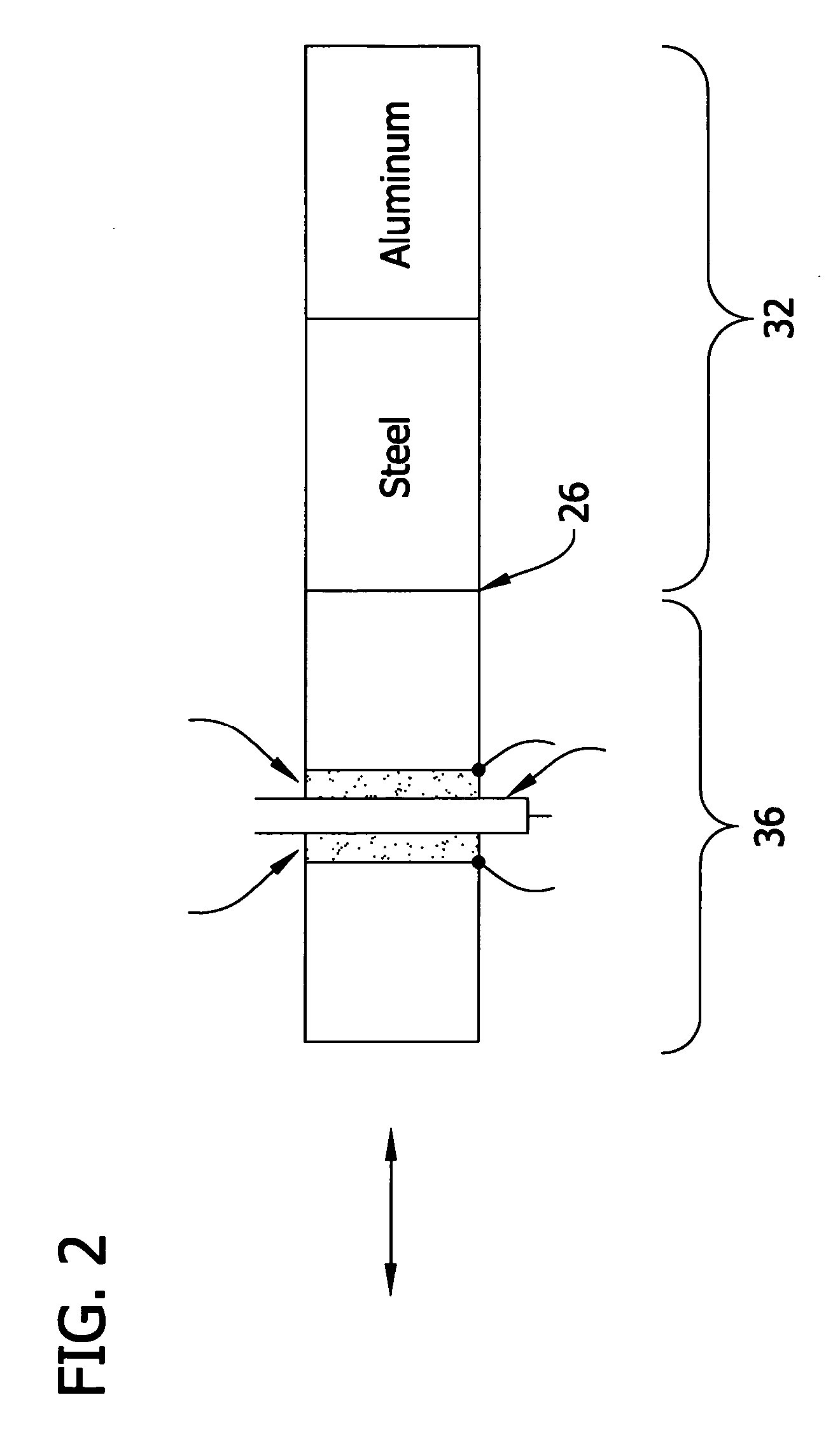
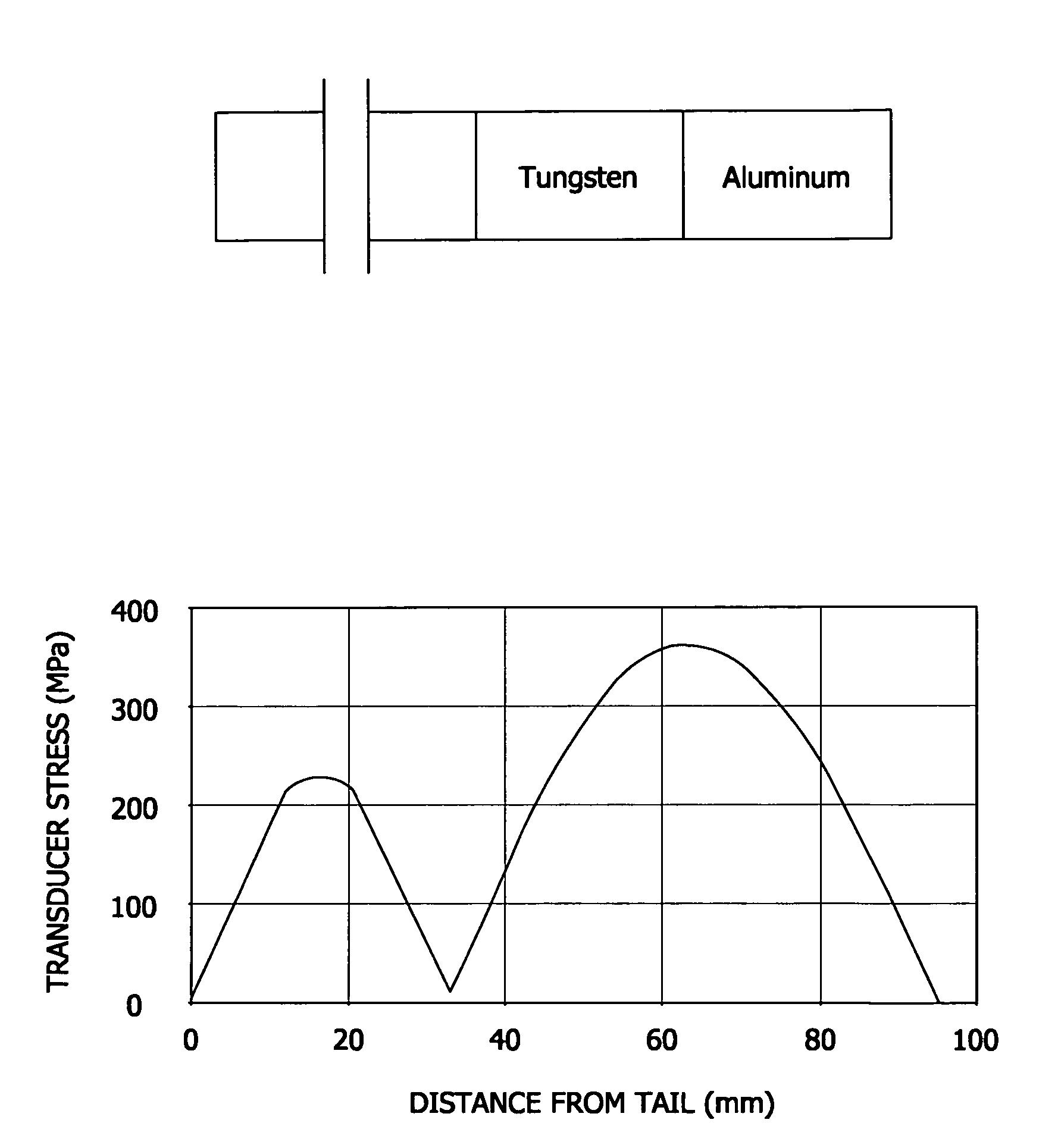
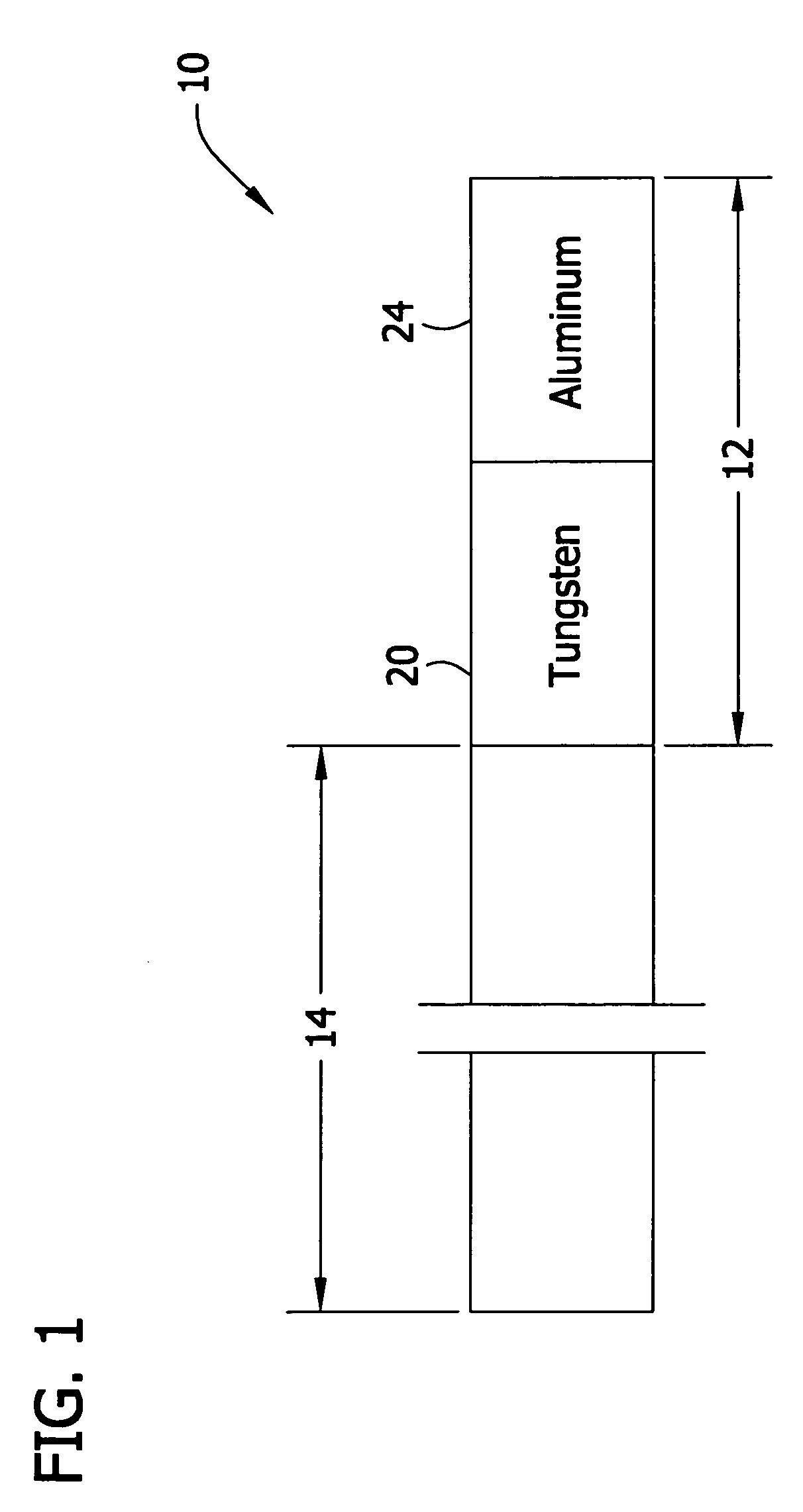
ActiveUS20070131034A1High magnificationReduce stressUltrasound therapyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWaveguideAcoustic impedance
Ultrasonic waveguides having improved velocity gain are disclosed for use in ultrasonic medical devices. Specifically, the ultrasonic waveguides comprises a first material having a higher acoustic impedance and a second material having a lower acoustic impedance.
Owner:PIEZOINNOVATIONS +1
Amplifying ultrasonic waveguides
InactiveUS8033173B2High magnificationReduce riskUltrasound therapyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcousticsWaveguide
Ultrasonic waveguides having improved velocity gain are disclosed for use in ultrasonic medical devices. Specifically, the ultrasonic waveguides comprises a first material having a higher acoustic impedance and a second material having a lower acoustic impedance.
Owner:PIEZOINNOVATIONS +1
Optical metrology optimization for repetitive structures
InactiveUS20050209816A1Feeler-pin gaugesMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsComputational physicsOptical metrology
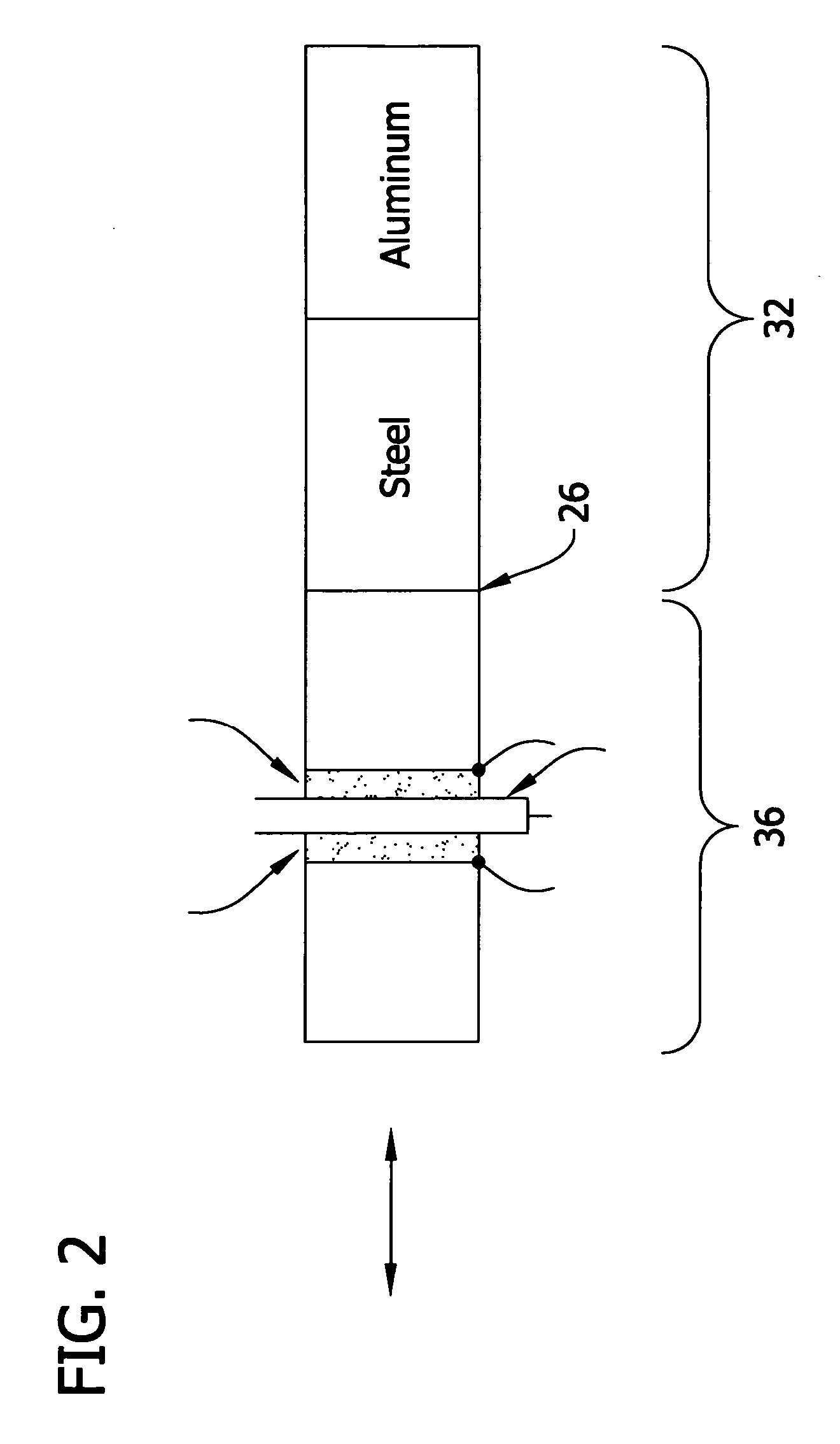
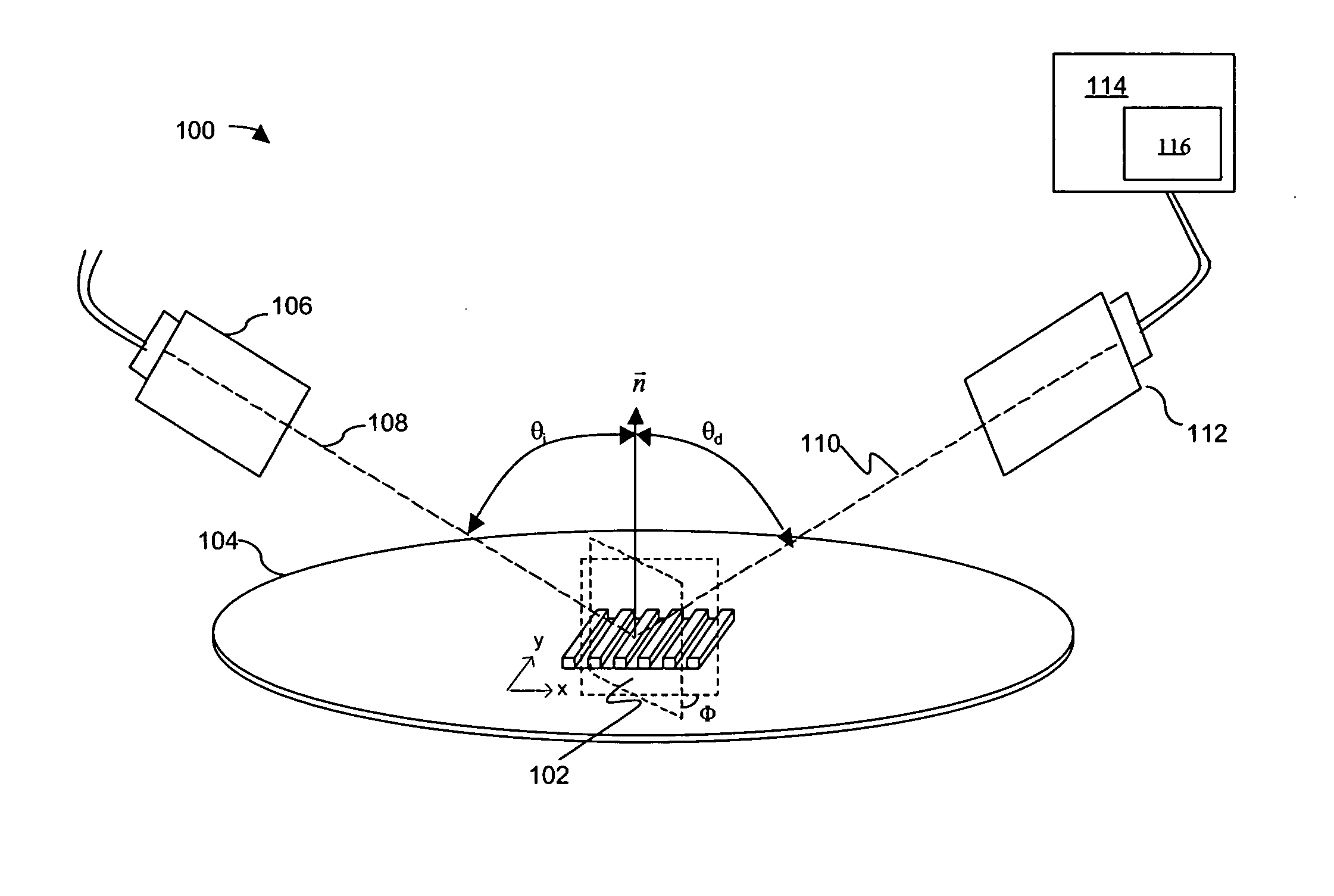
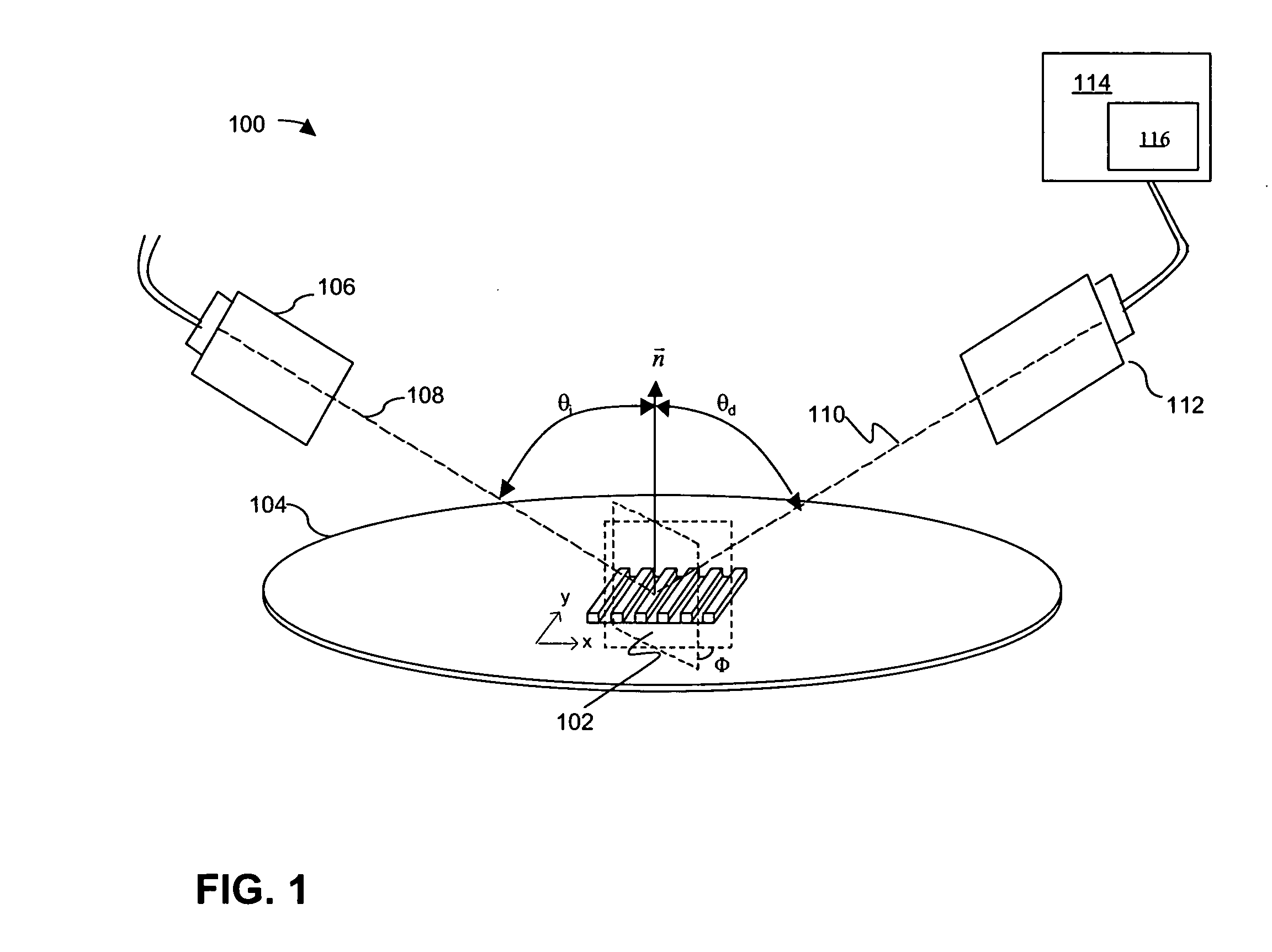
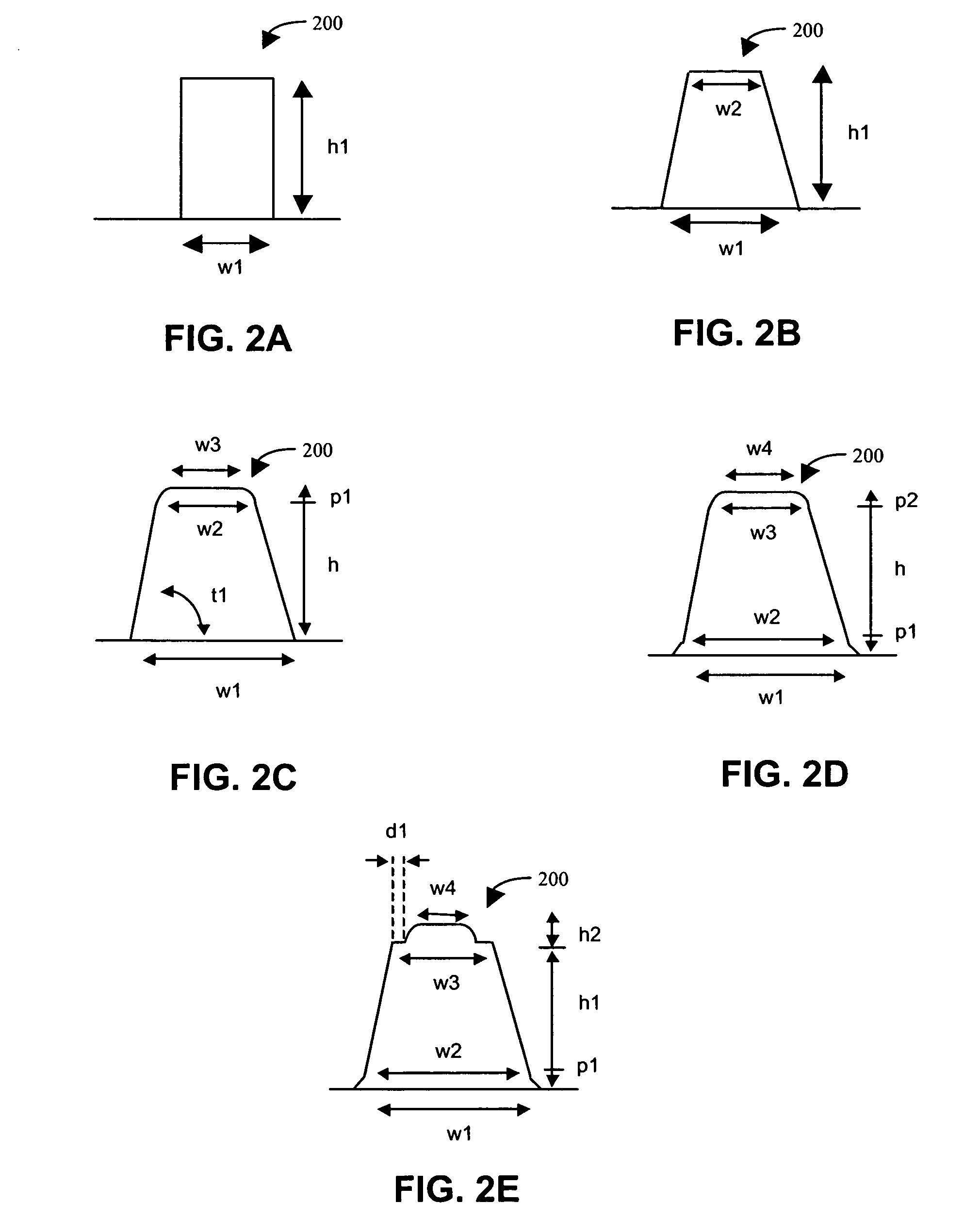
The top-view profiles of repeating structures in a wafer are characterized and parameters to represent variations in the top-view profile of the repeating structures are selected. An optical metrology model is developed that includes the selected top-view profile parameters of the repeating structures. The optimized optical metrology model is used to generate simulated diffraction signals that are compared to measured diffraction signals.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
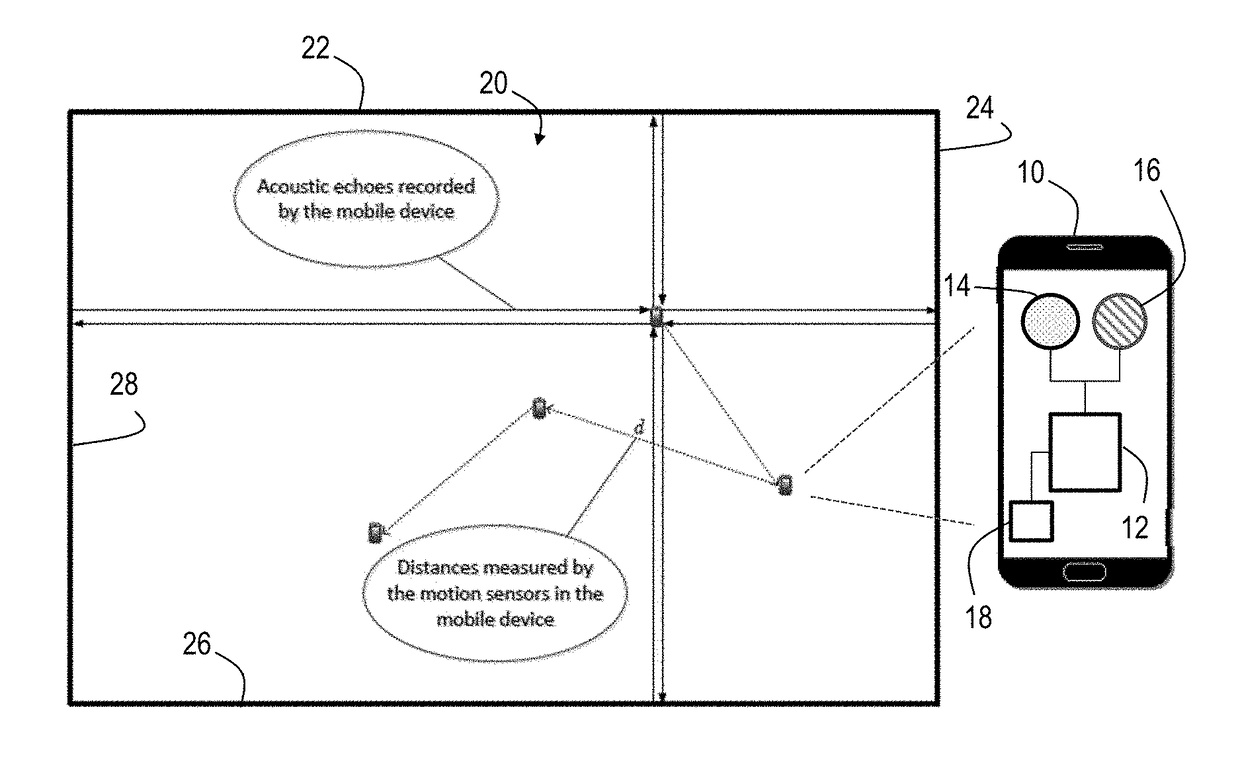
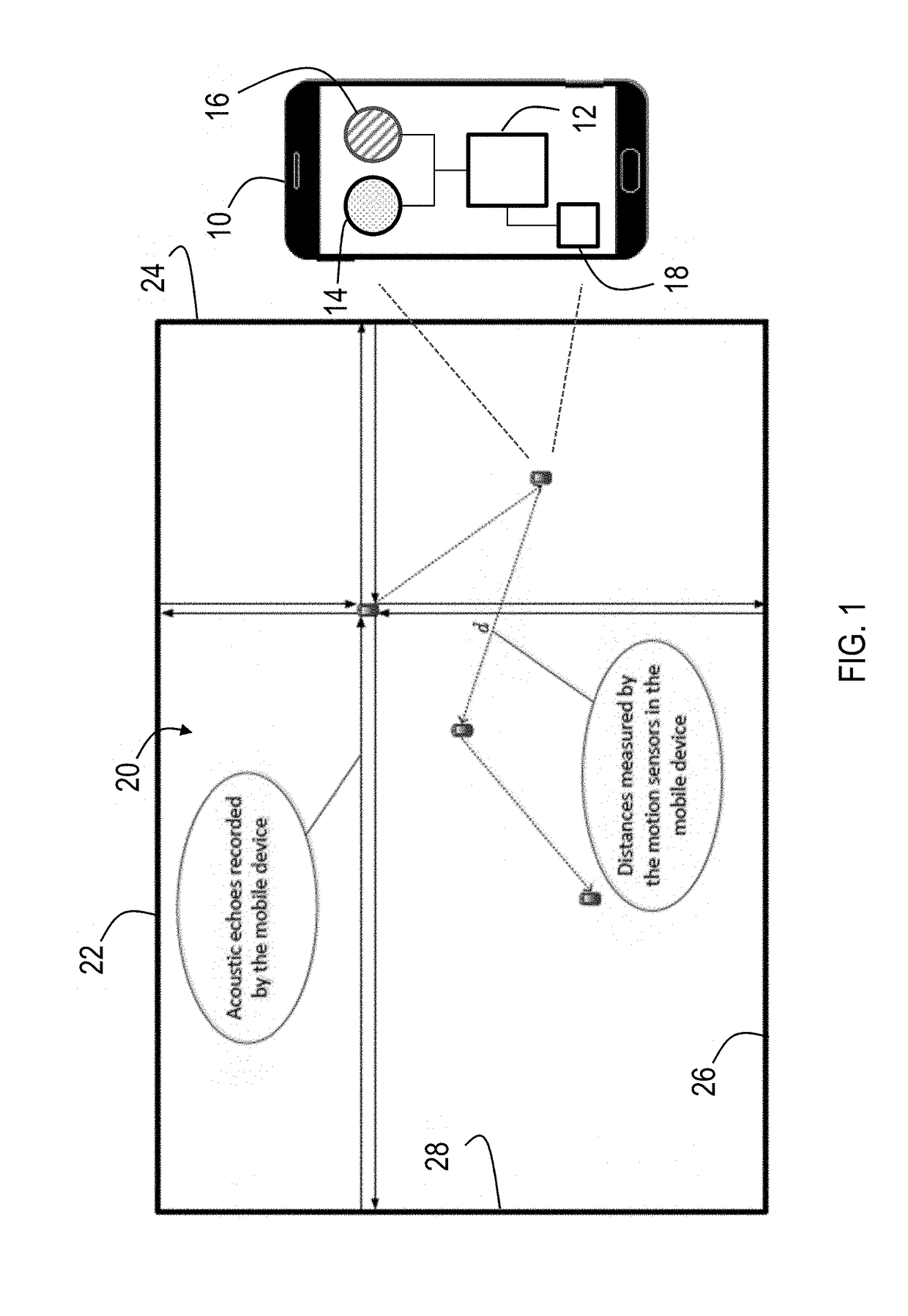
Motion sensor assisted room shape reconstruction and self-localization using first-order acoustic echoes
ActiveUS20170370710A1Improve performanceUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansAcoustic wave reradiationPractical algorithmContinuous measurement
Simultaneous 2-D room shape reconstruction and self-localization is accomplished using no pre-established infrastructure. A mobile device with co-located microphone and loudspeaker is used to collect echoes reflected by the walls. The system uniquely recovers arbitrary 2-D convex room shape as well as the position of mobile device 10 by collecting and processing distances between three consecutive measurement points as well as acoustic echoes from the device. A practical algorithm for room shape reconstruction and self-localization in the presence of noise and higher order echoes is proposed. Experimental results are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
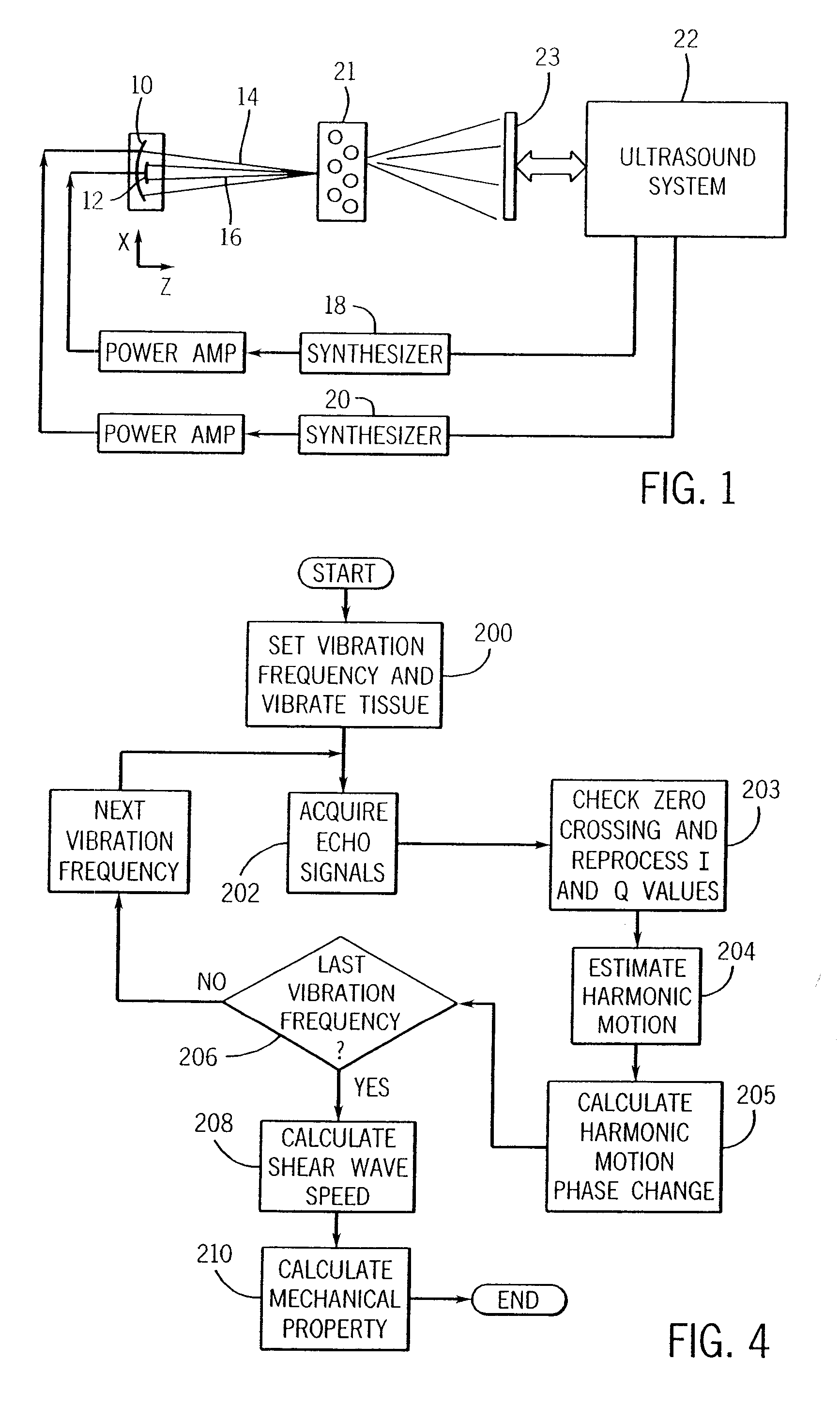
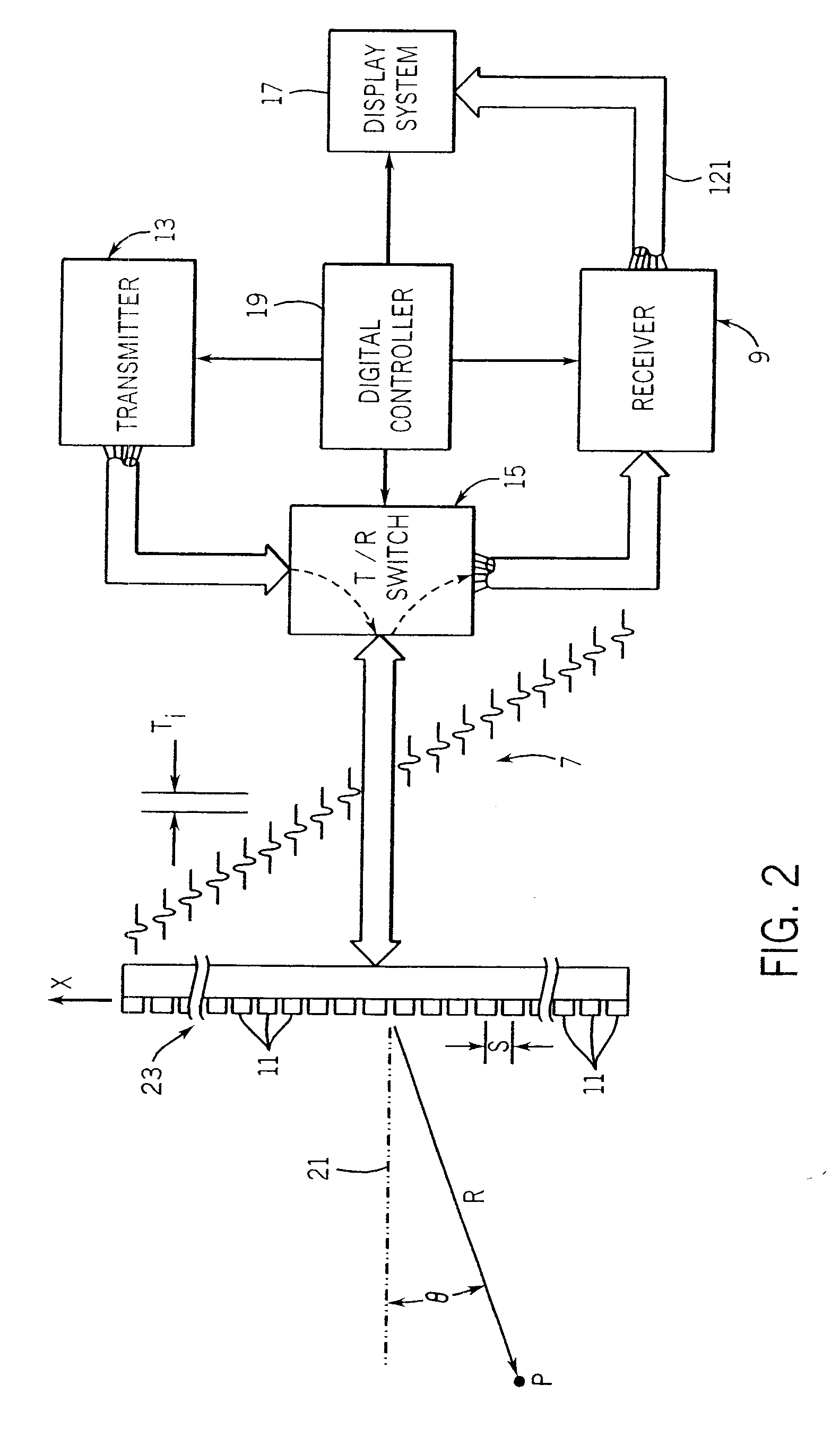
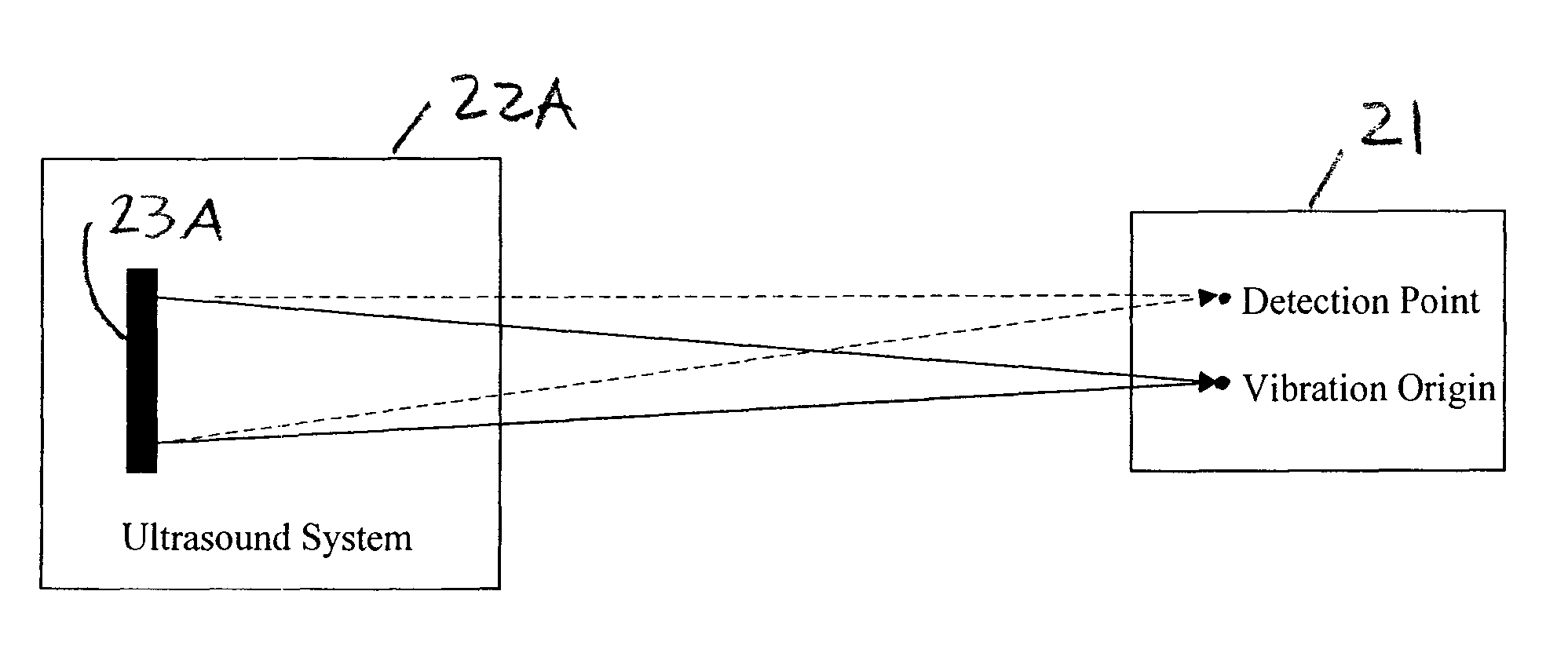
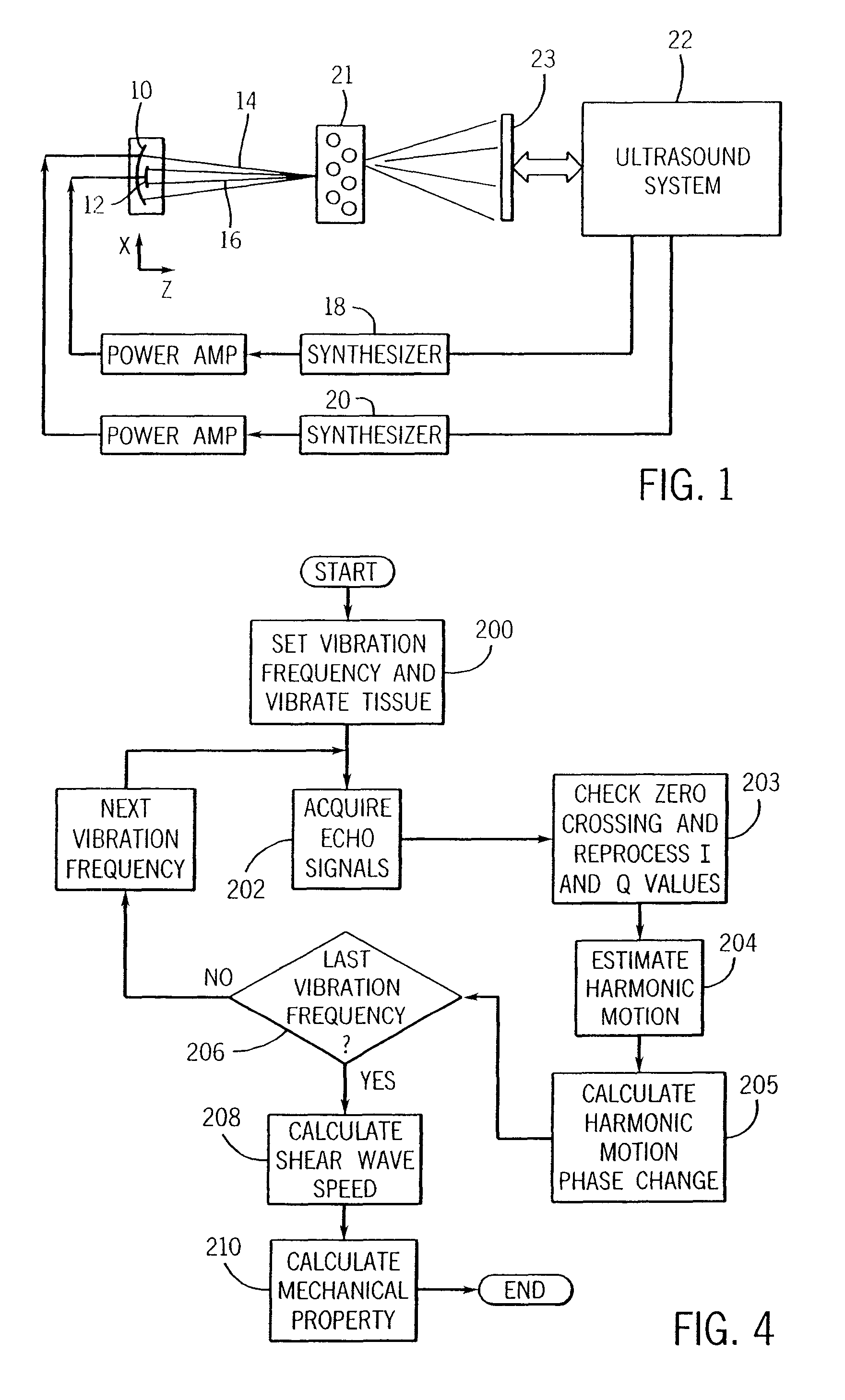
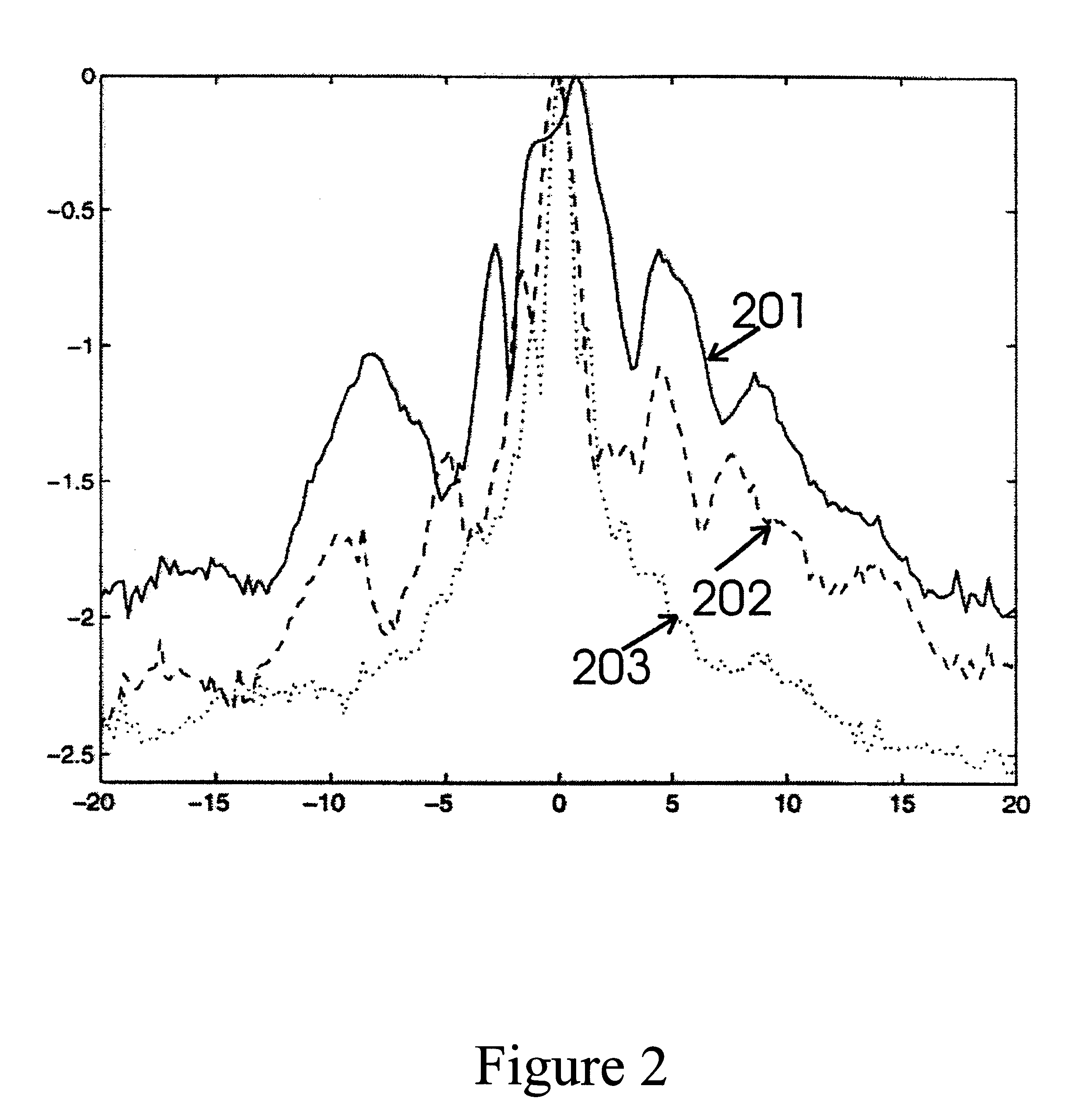
Ultrasound vibrometry
ActiveUS20070038095A1Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSonificationMechanical property
A method for measuring a mechanical property of a subject includes using an ultrasonic transducer to apply ultrasonic vibration pulses to a vibration origin in the subject in an on-off time sequence in order to impart a harmonic motion at a prescribed frequency to the subject, and when the vibration pulses are off, using the same transducer to apply ultrasonic detection pulses to a motion detection point and to receive echo signals therefrom in order to sense the harmonic motion on the subject at the motion detection point. From the harmonic signal information, a harmonic signal is detected and a characteristic such as amplitude or phase of the detected harmonic signal is measured. The mechanical property is calculated using the measured characteristic using for example a wave speed dispersion method.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
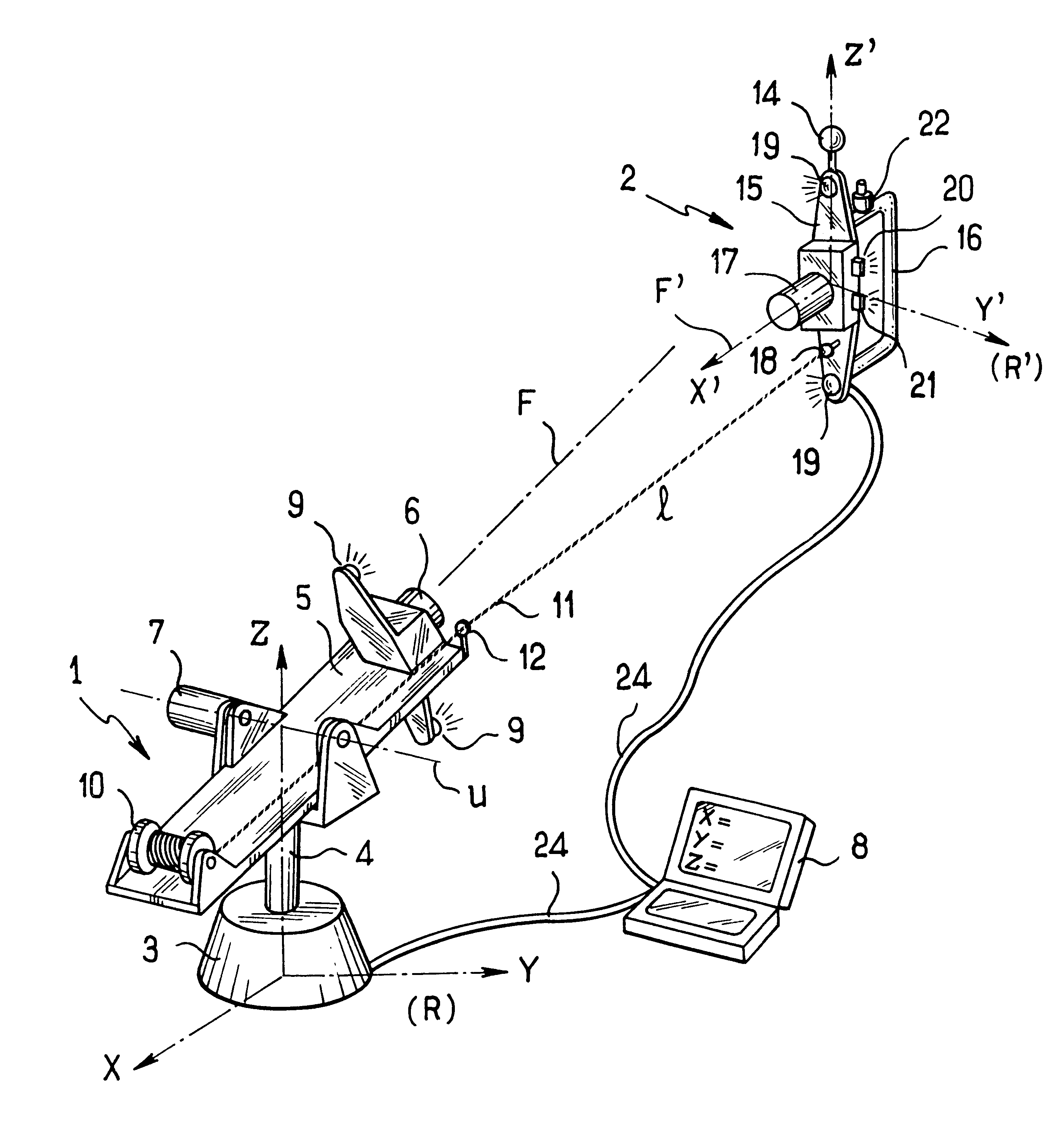
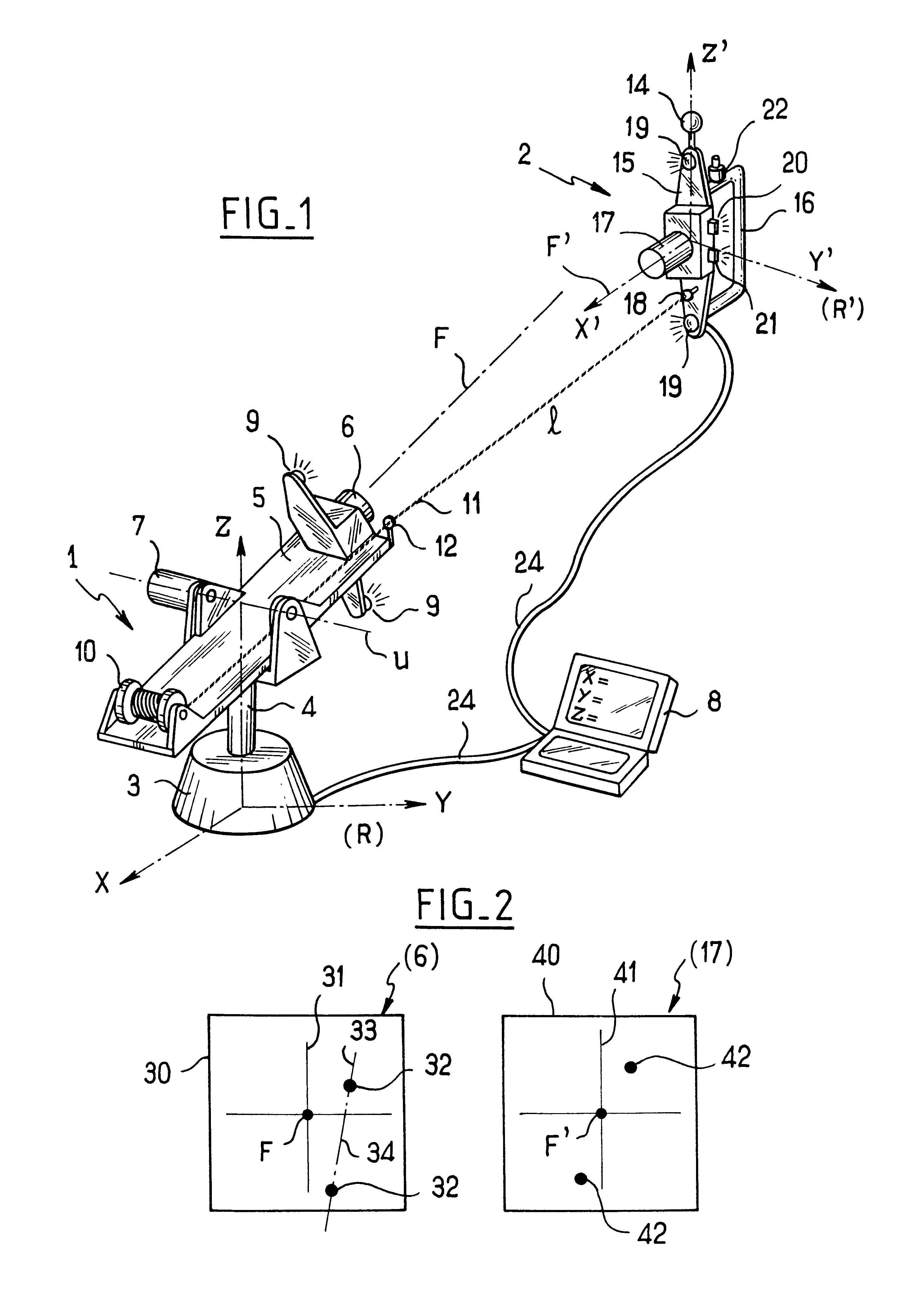
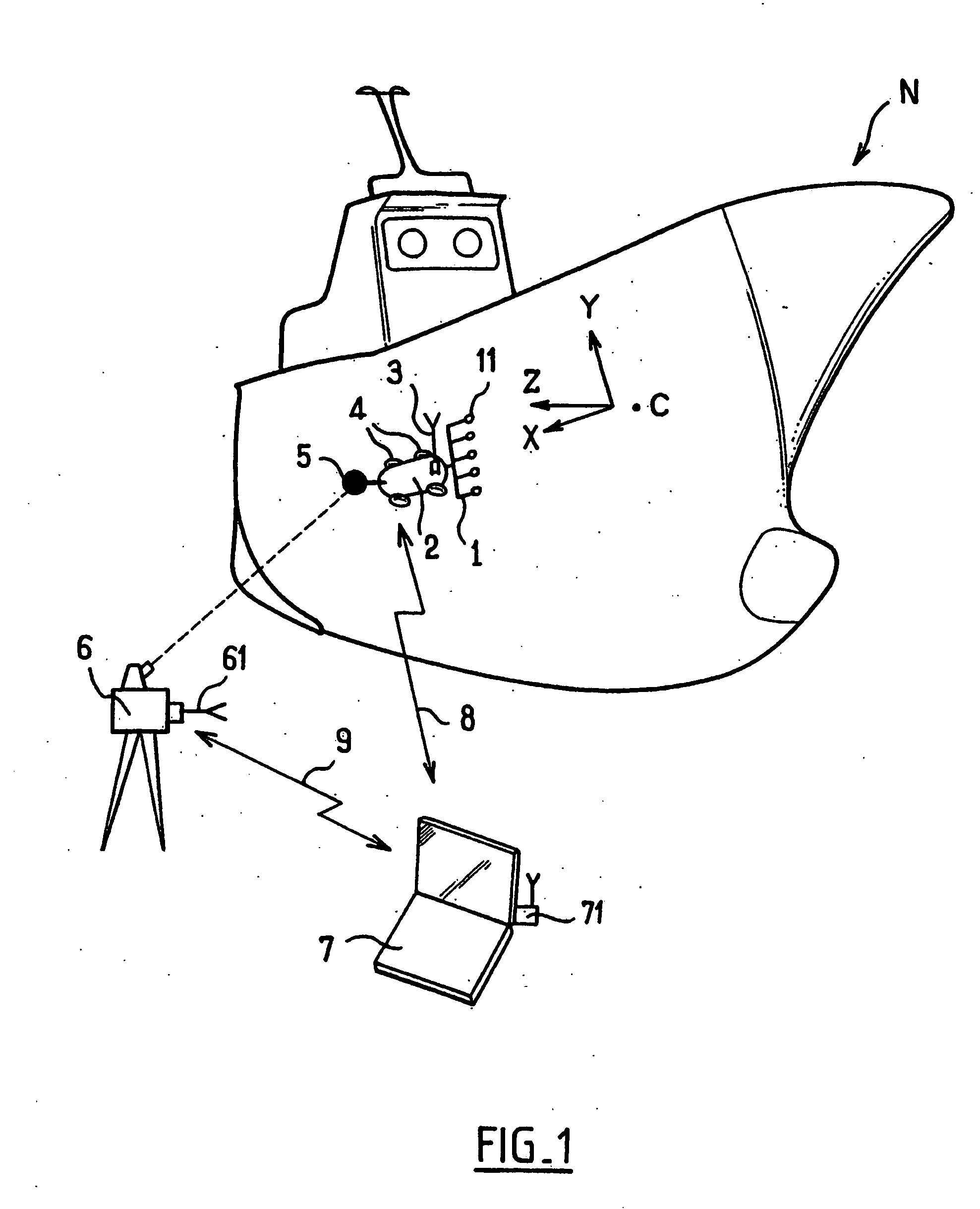
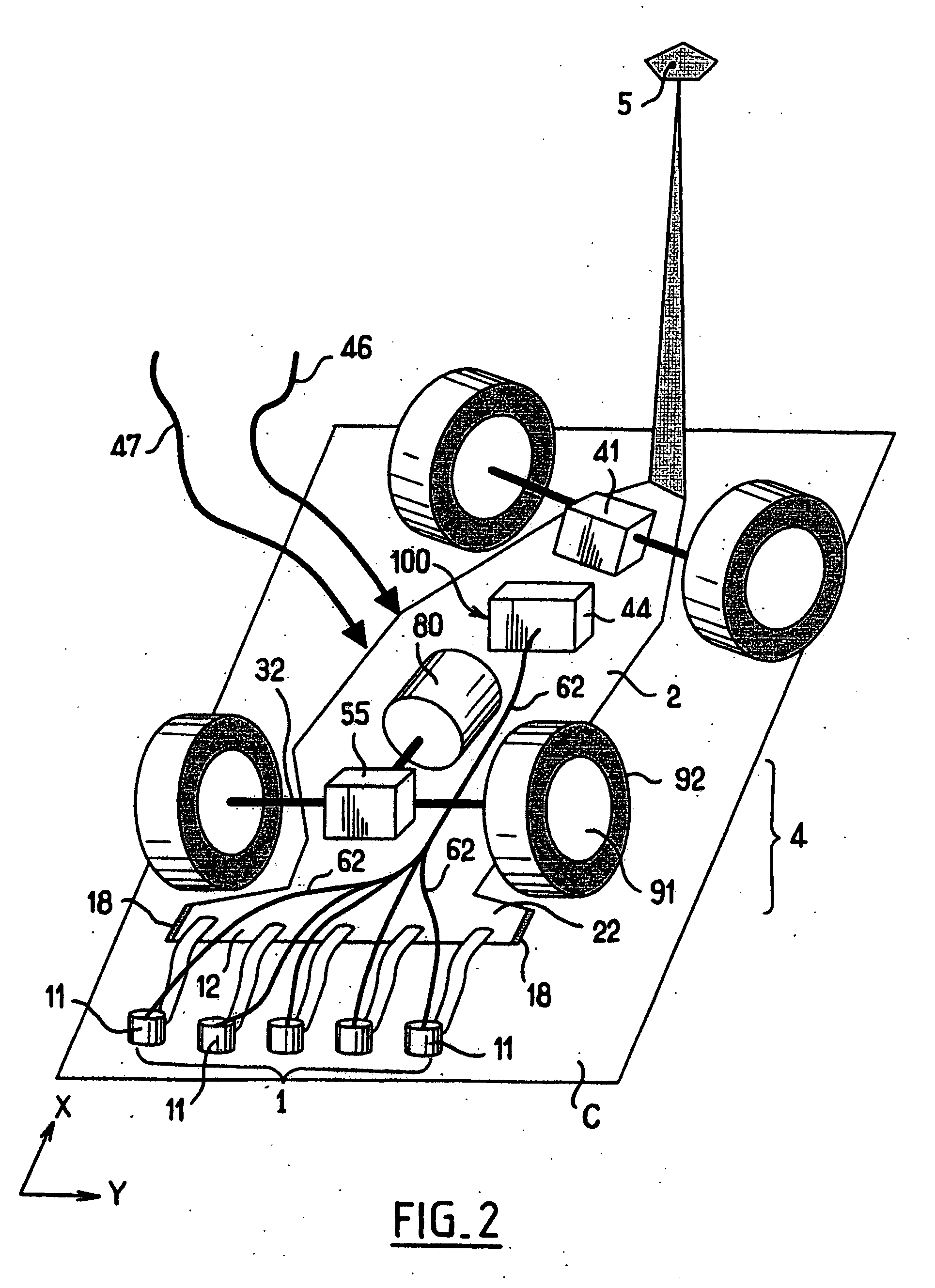
Measuring method for determining the position and the orientation of a moving assembly, and apparatus for implementing said method
InactiveUS6639659B2Easy to transportOptical rangefindersFeeler-pin gaugesMeasurement deviceFrame of reference
Owner:HEXAGON TECH CENT GMBH
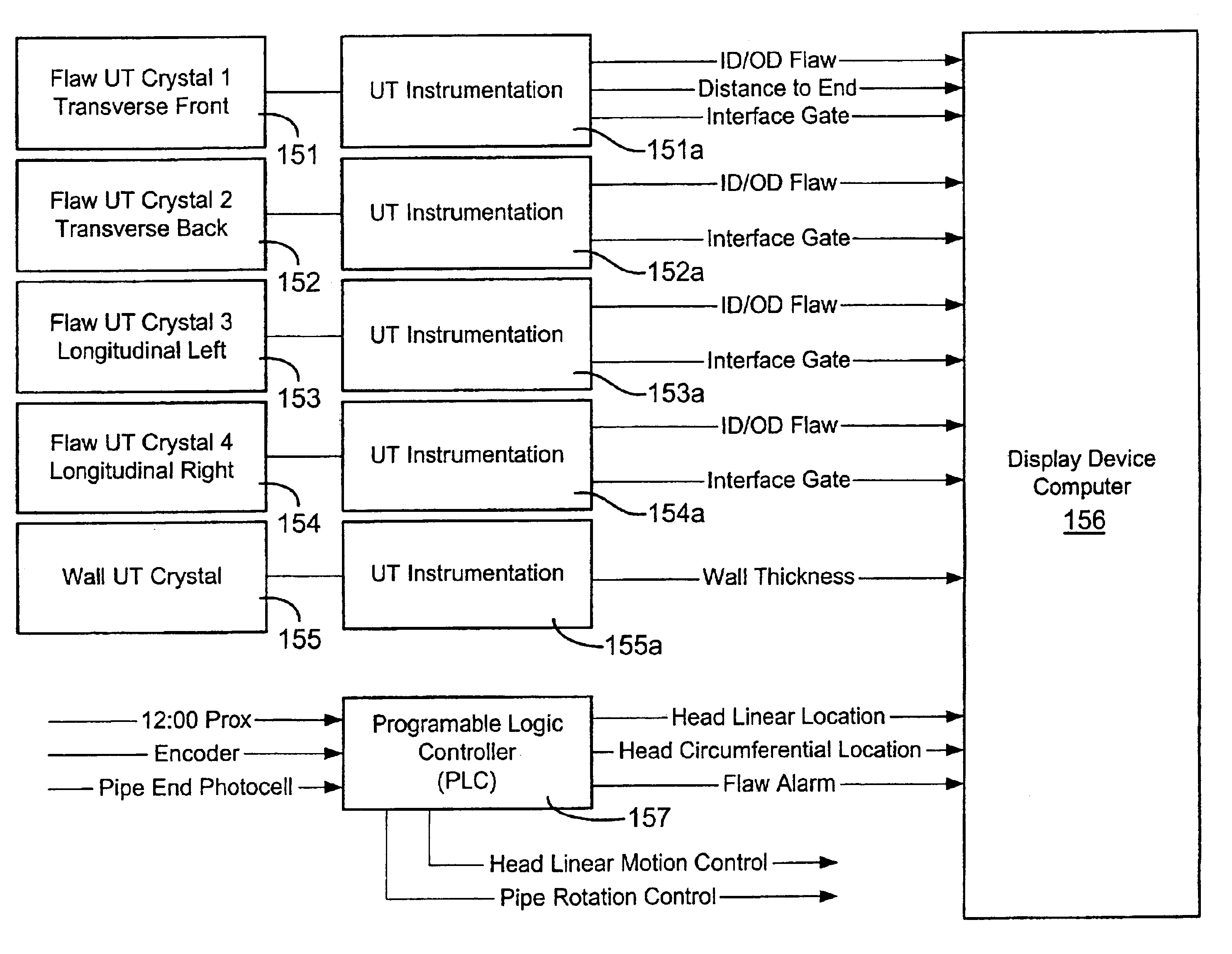
Ultrasonic detection of flaws in tubular members
InactiveUS6578422B2Efficient and effective inspectionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionTransducerEngineering
Owner:VARCO I P INC
Method and system for positional measurement using ultrasonic sensing
InactiveUS20100204955A1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementDiagnosticsRelative displacementSonification
A method for determining position and alignment is provided. The method includes monitoring a first and second sequence of ultrasonic signals transmitted from the first device to a second device, estimating a location of the first device from Time of Flight measurements of the ultrasonic signals at respective microphones on the second device, calculating a set of phase differences, weighting a difference of an expected location and estimated location of the first device with the set of phase differences to produce a relative displacement, and reporting a position of the first device based on the relative displacement.
Owner:ORTHOSENSOR
Ultrasonic probe
InactiveUS7308828B2Inhibit temperature riseAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave based measurement systemsElectricityTransducer
An ultrasonic probe has a probe proper, a connector and a cable for electrically connecting between the probe proper and the connector. The probe proper includes a transducer that converts between ultrasonic wave and electricity, and a phase change member having a property to cause a phase change of from solid to liquid at a particular temperature reached in an operation time period of the transducer and a phase change of from liquid to solid at lower than the particular temperature.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
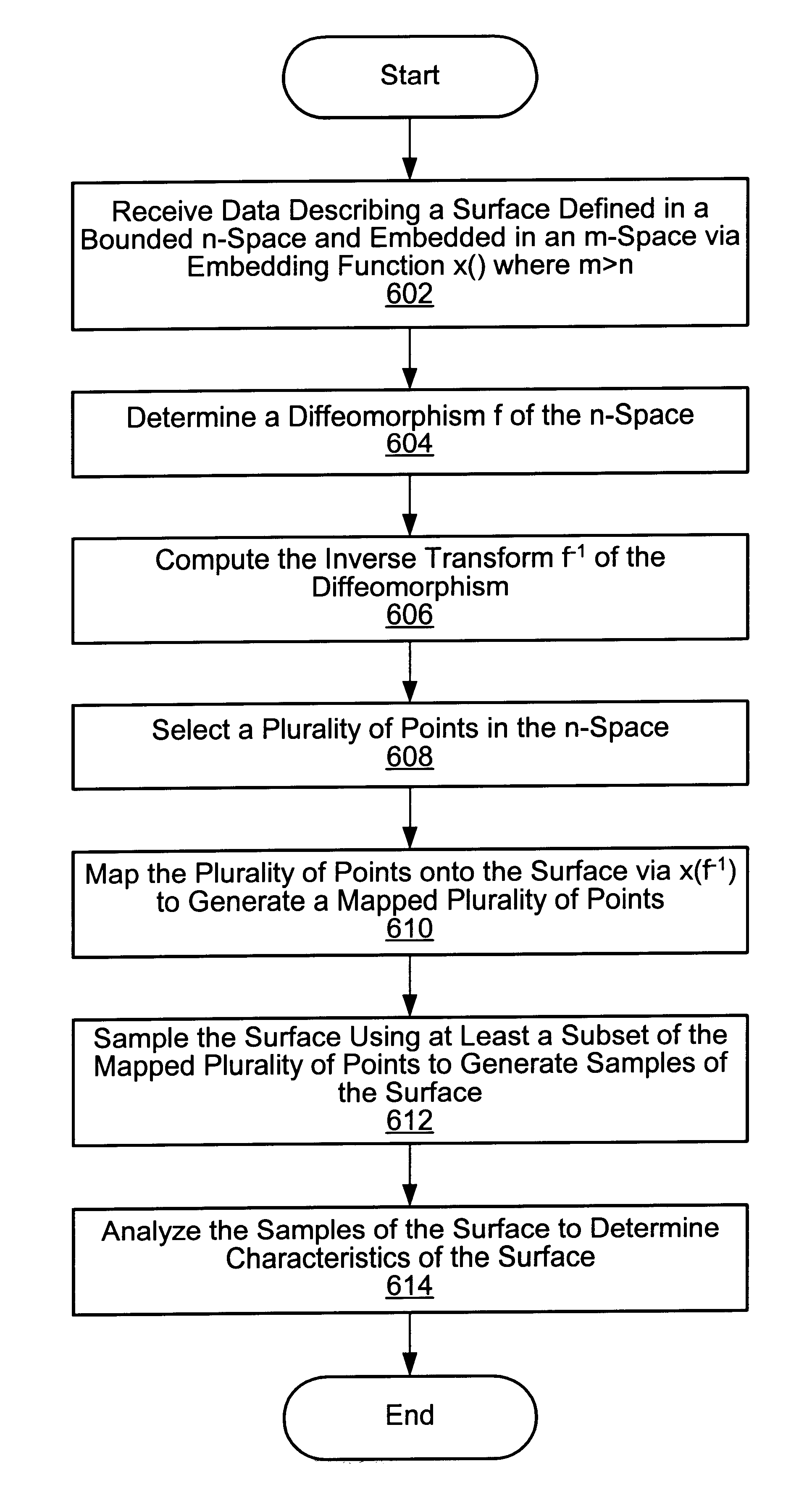
System and method for analyzing a surface by mapping sample points onto the surface and sampling the surface at the mapped points
A system and method for analyzing a surface. The system includes a computer including a CPU and a memory medium operable to store programs executable by the CPU to perform the method. The method may include: 1) receiving data describing an n-dimensional surface defined in a bounded n-dimensional space, where the surface is embedded in an m-dimensional real space via embedding function x( ), and where m>n; 2) determining a diffeomorphism f of the n-dimensional space; 3) computing the inverse transform f-1 of the diffeomorphism f; 4) selecting points, e.g., a Low Discrepancy Sequence, in the n-dimensional space; 5) mapping the points onto the surface using x(f-1), thereby generating mapped points on the surface; 6) sampling the surface using at least a subset of the mapped points to generate samples of the surface; and 7) analyzing the samples of the surface to determine characteristics of the surface.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
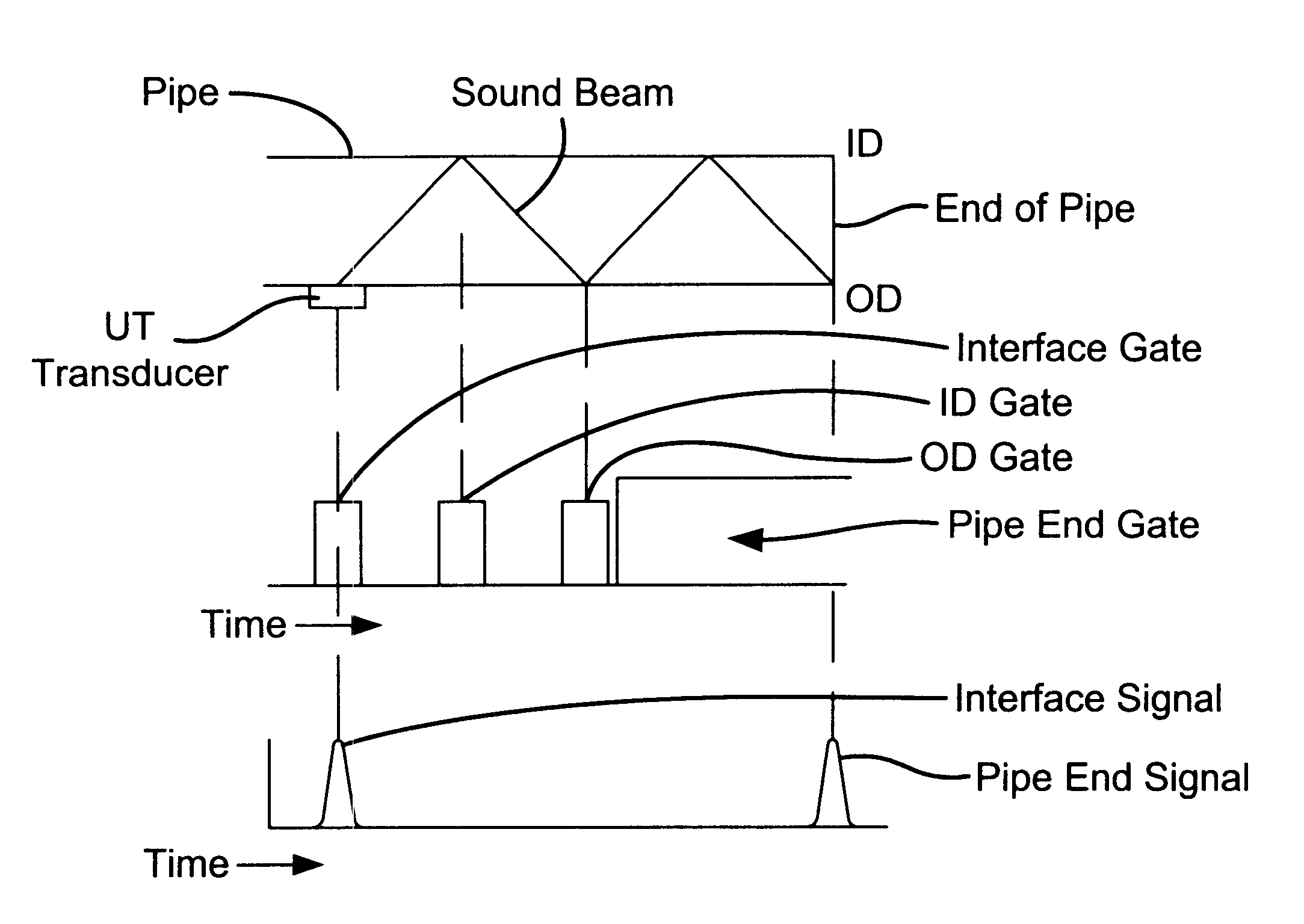
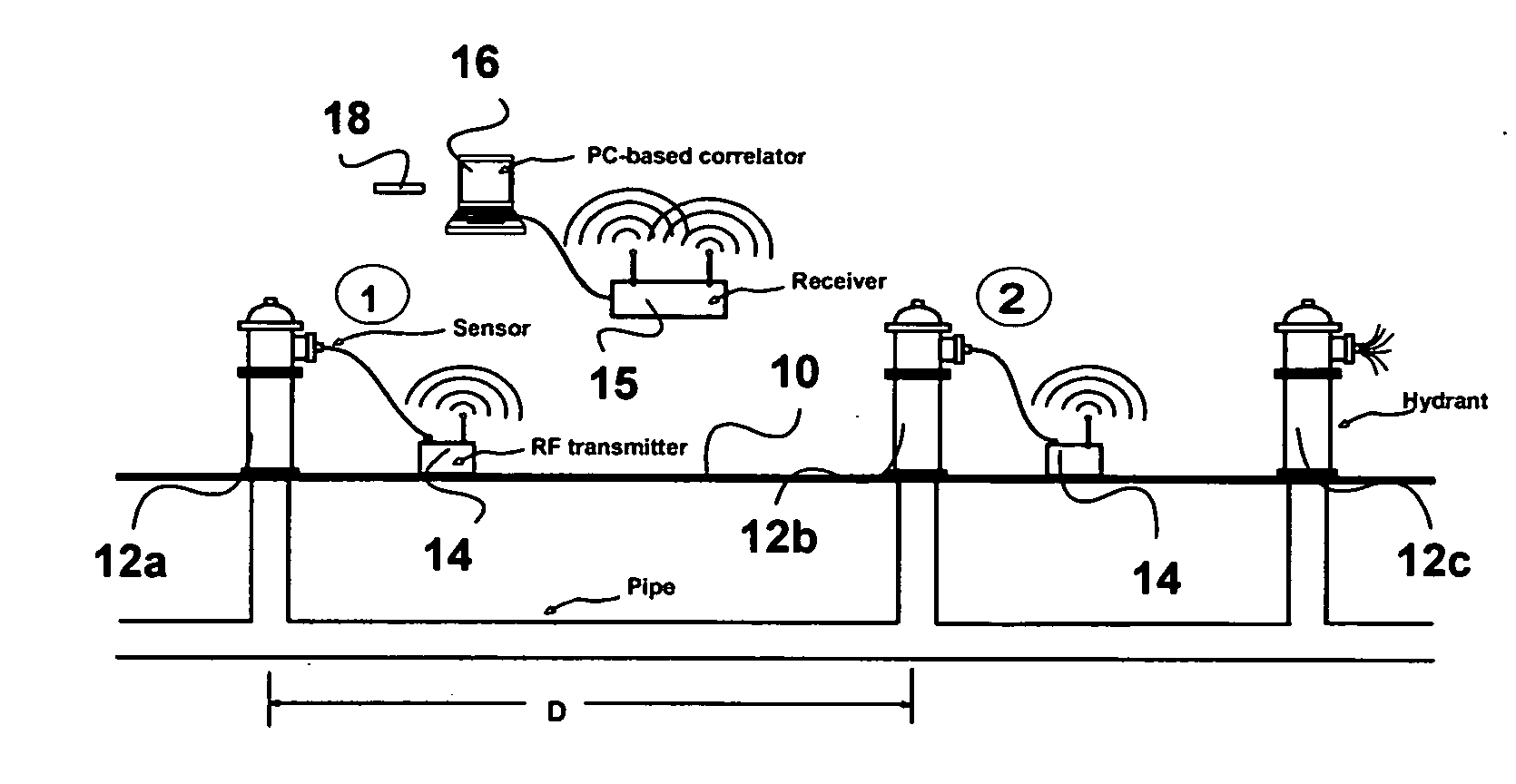
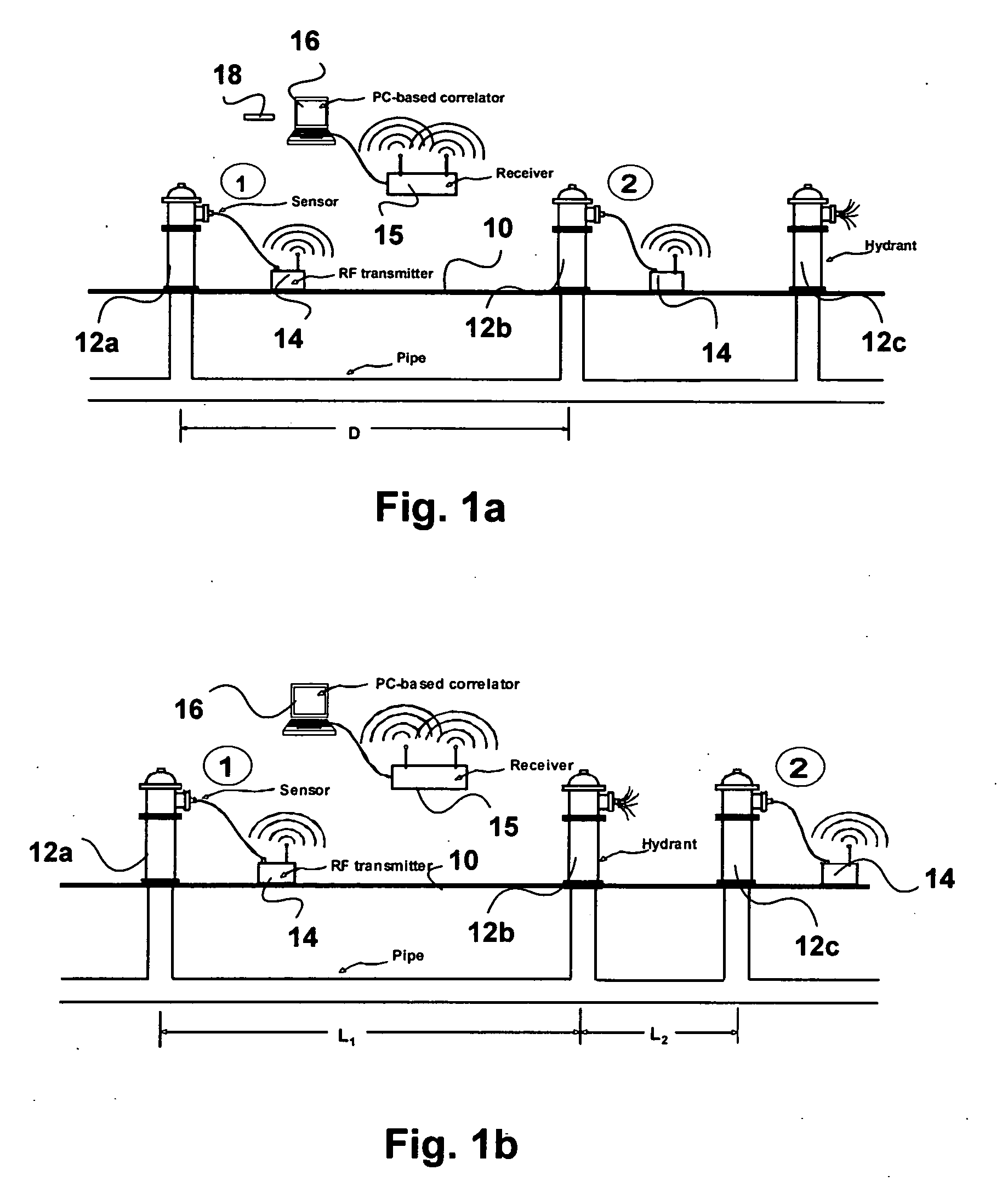
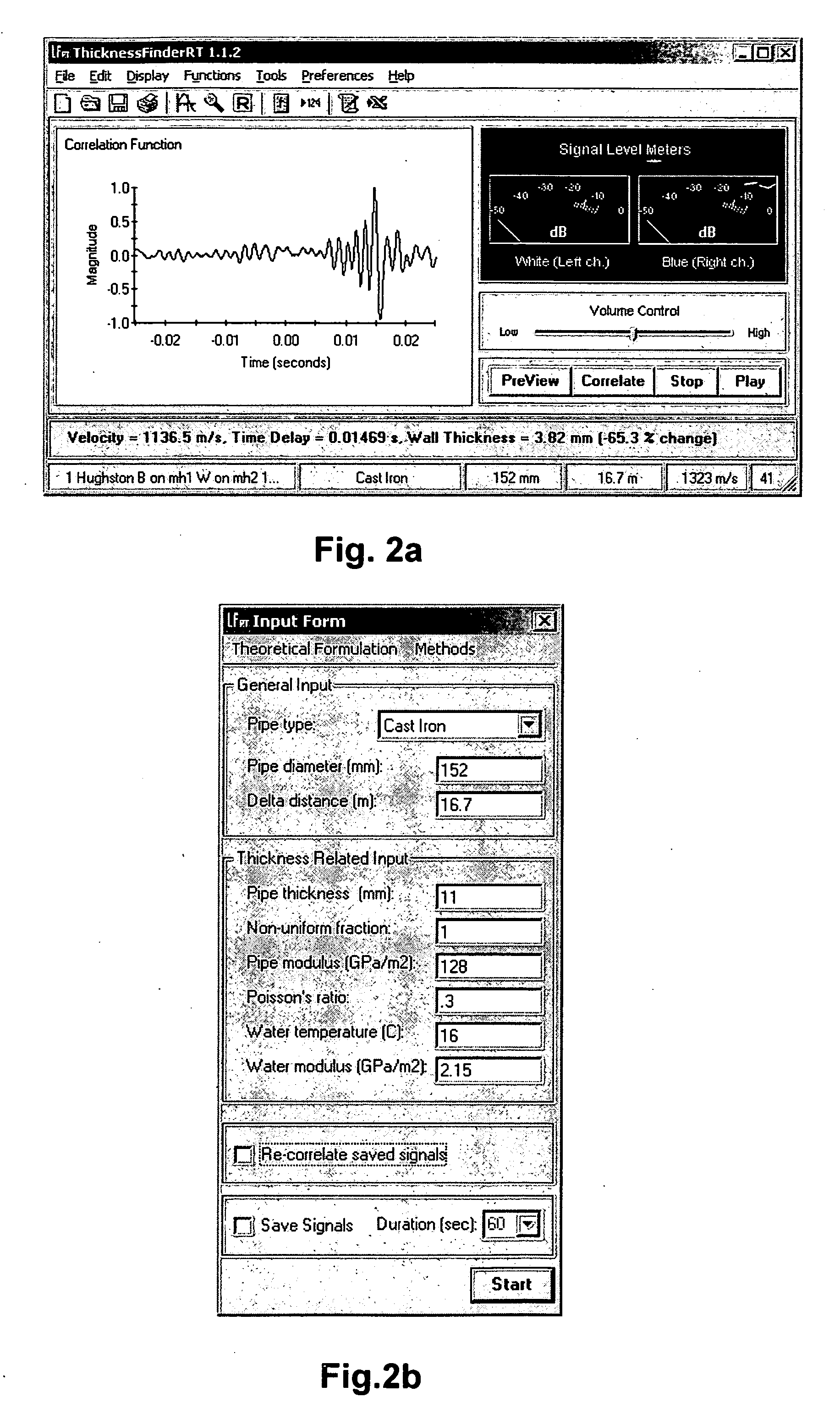
Non-destructive testing of pipes
ActiveUS20060283251A1Easy to measureEasy to calculateAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveEngineering
To perform a non-destructive condition assessment of a pipe carrying a fluid, an actual value representative of the propagation velocity of an acoustic disturbance propagating between two longitudinally separated points on the pipe is determined. A corresponding predicted value for the propagation velocity is computed as a function of at least one wall thickness parameter of the pipe by using a theoretical model for the propagation of acoustic waves in the pipe that assumes said pipe has a finite wall thickness with a predetermined circumferential thickness profile. The wall thickness parameter is then computed by matching the actual value with the predicted value, for example, by substituting the actual value in a formula predicting the theoretical value.
Owner:MUELLER INT LLC
Tool, Sensor, and Device for a Wall Non-Distructive Control
InactiveUS20090301203A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansNon destructiveBiomedical engineering
Owner:ROBOPLANET
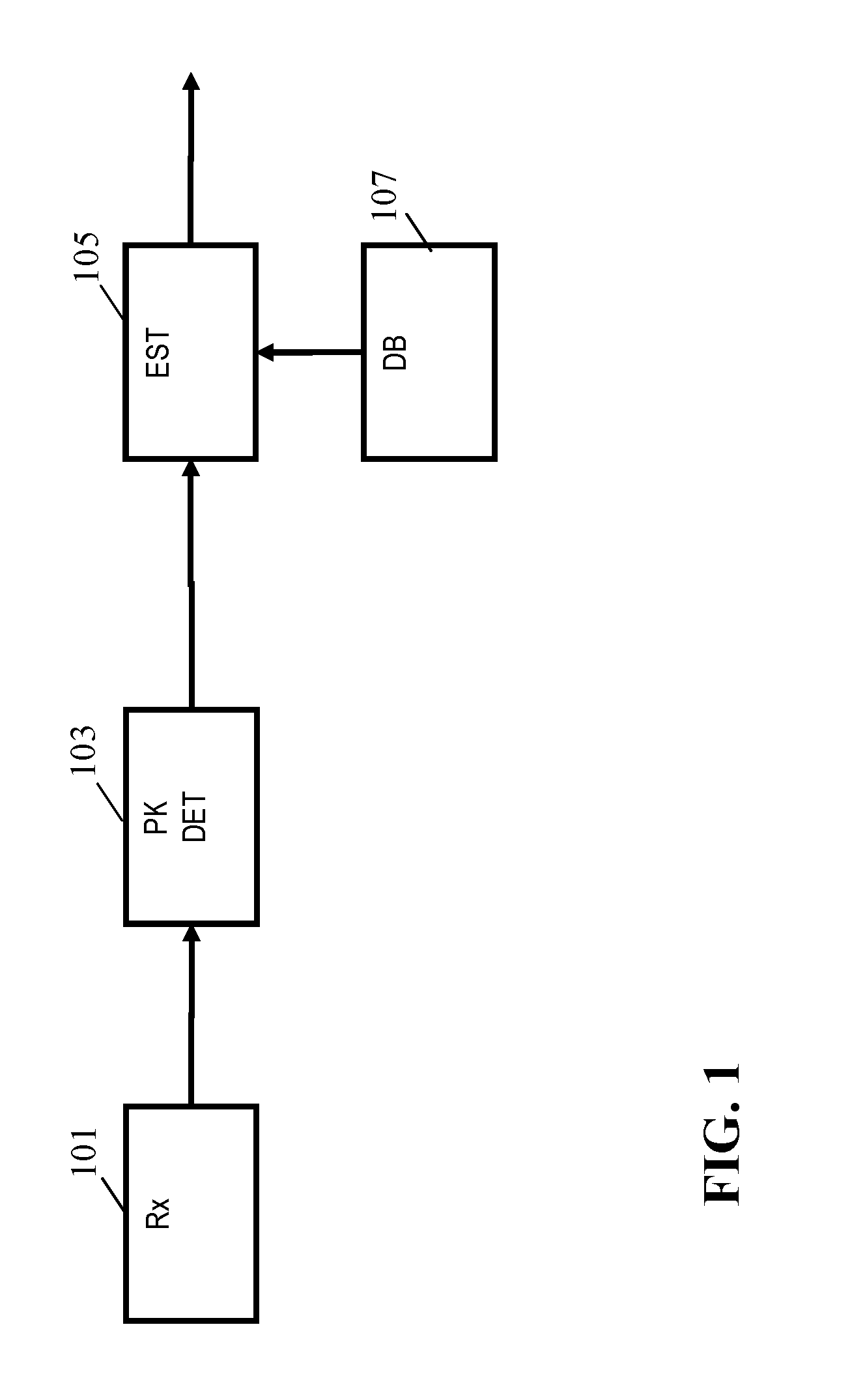
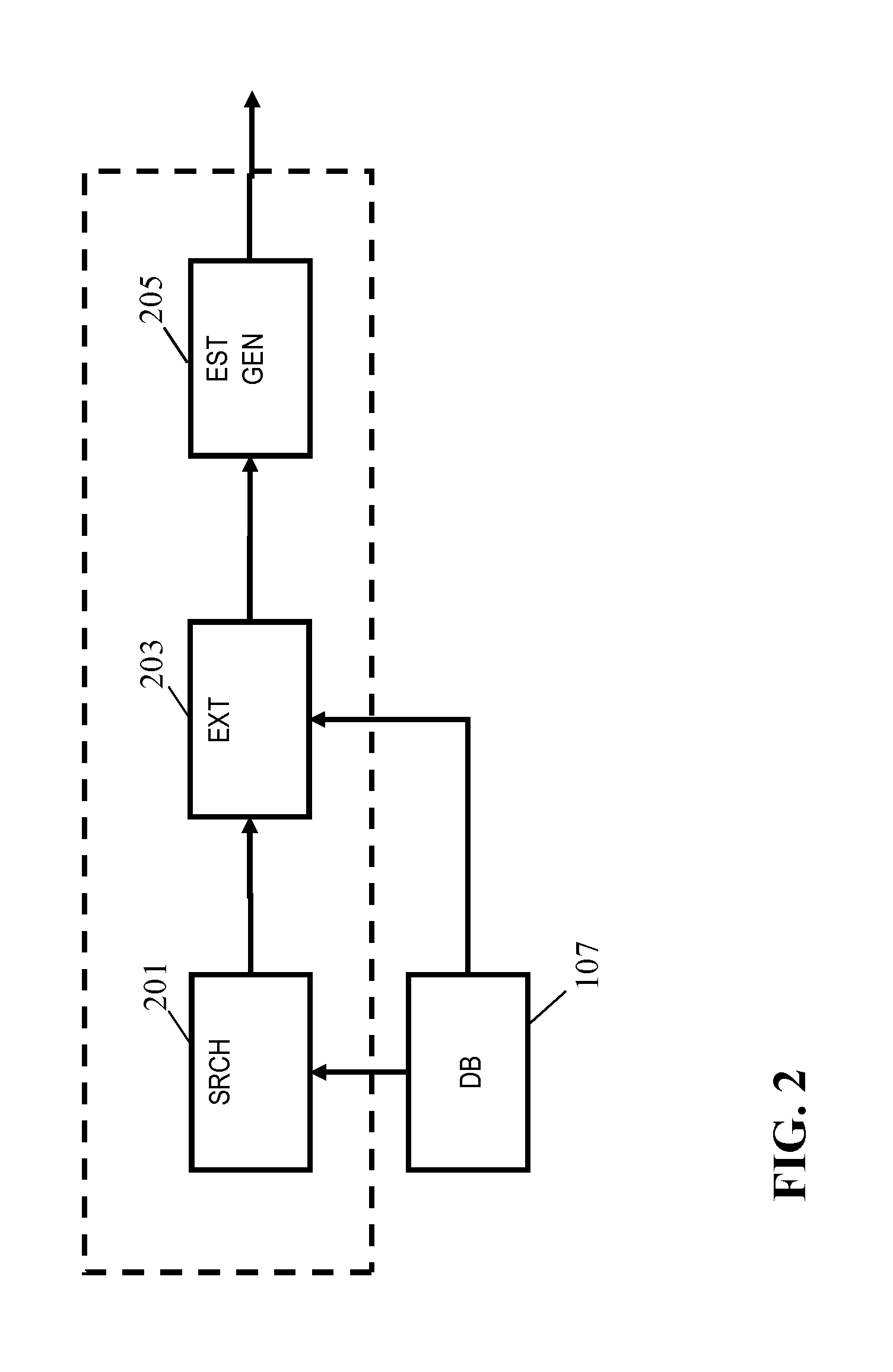
Determination of a room dimension estimate
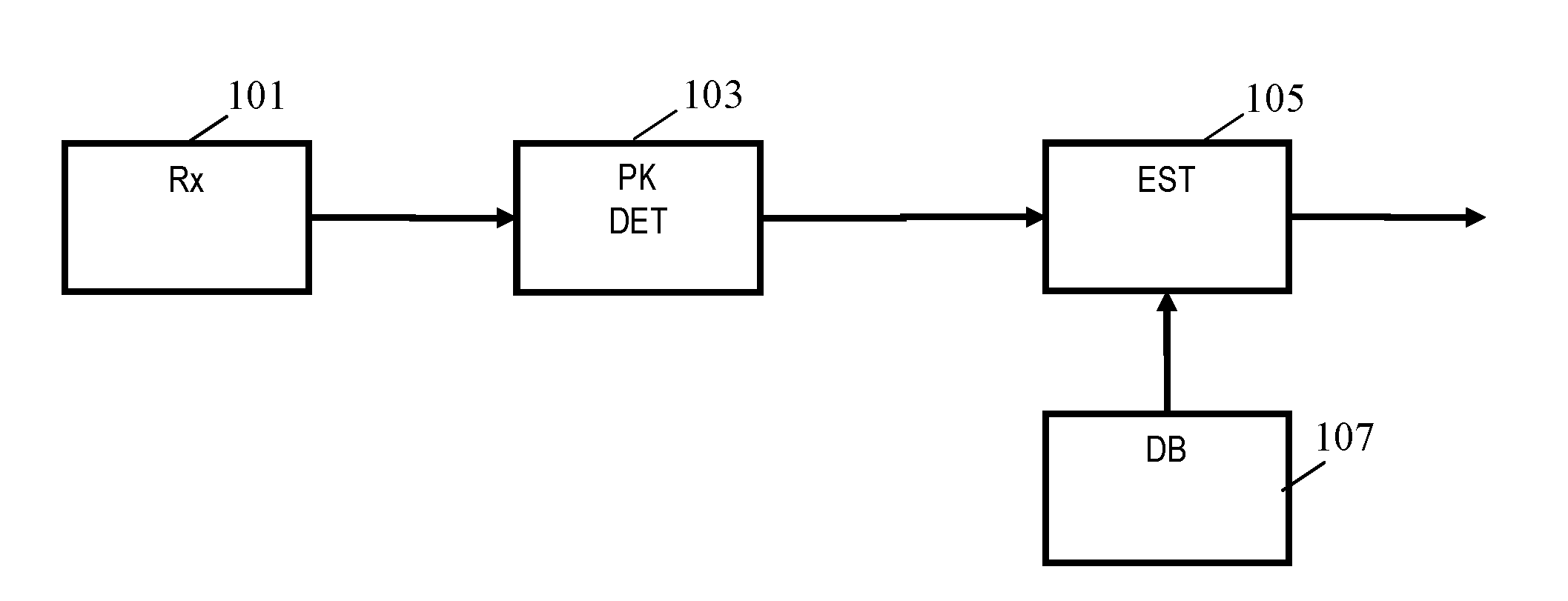
ActiveUS20160061597A1Improved and facilitated determinationWell representedDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansPeak valuePeak oil
An apparatus for determining a room dimension estimate comprises a receiver (101) providing an acoustic room response e.g. generated from acoustic measurements. A peak detector (103) detects a set of peaks in the acoustic room response in a frequency interval having an upper frequency of no more than 400 Hz. A store (107) comprises a set of peak profiles with associated room dimension data, and an estimator (105) determines the room dimension estimate from the associated room dimension data and a comparison of the set of peaks to the peak profiles. The estimator may perform the steps of first finding a matching peak profile for the set of peaks from the set of peak profiles; extracting first room dimension data associated with the matching peak profile(s) from the store; and determining the room dimension estimate in response to the first room dimension data. The peak profiles may represent calculated Eigenfrequencies.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and device for inspecting pipelines
InactiveUS6848313B2Avoid bouncingImprove resilientAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationEngineeringBoundary region
The invention concerns a method and a device for inspecting pipelines, in particular for detecting defects in pipelines by means of ultrasound. Towards this end, measuring sensors transmit ultrasound signals during passage through a pipeline. The signals reflected on boundary regions of a pipeline wall, e.g. surfaces or defects, are then measured and evaluated. The invention is characterized in that partial regions of the measuring sensors (virtual sensors) formed of a plurality of neighboring sensor elements irradiate ultrasound signals into the pipe wall at at least one radiation angle which is inclined with respect to the normal to the pipe wall and the signals reflected at boundary regions of the pipe wall are received by same and / or other partial regions of the respective measuring sensors, wherein defects in the pipe wall are determined by evaluation of the acoustical signals reflected by different boundary regions.
Owner:PII PIPETRONIX
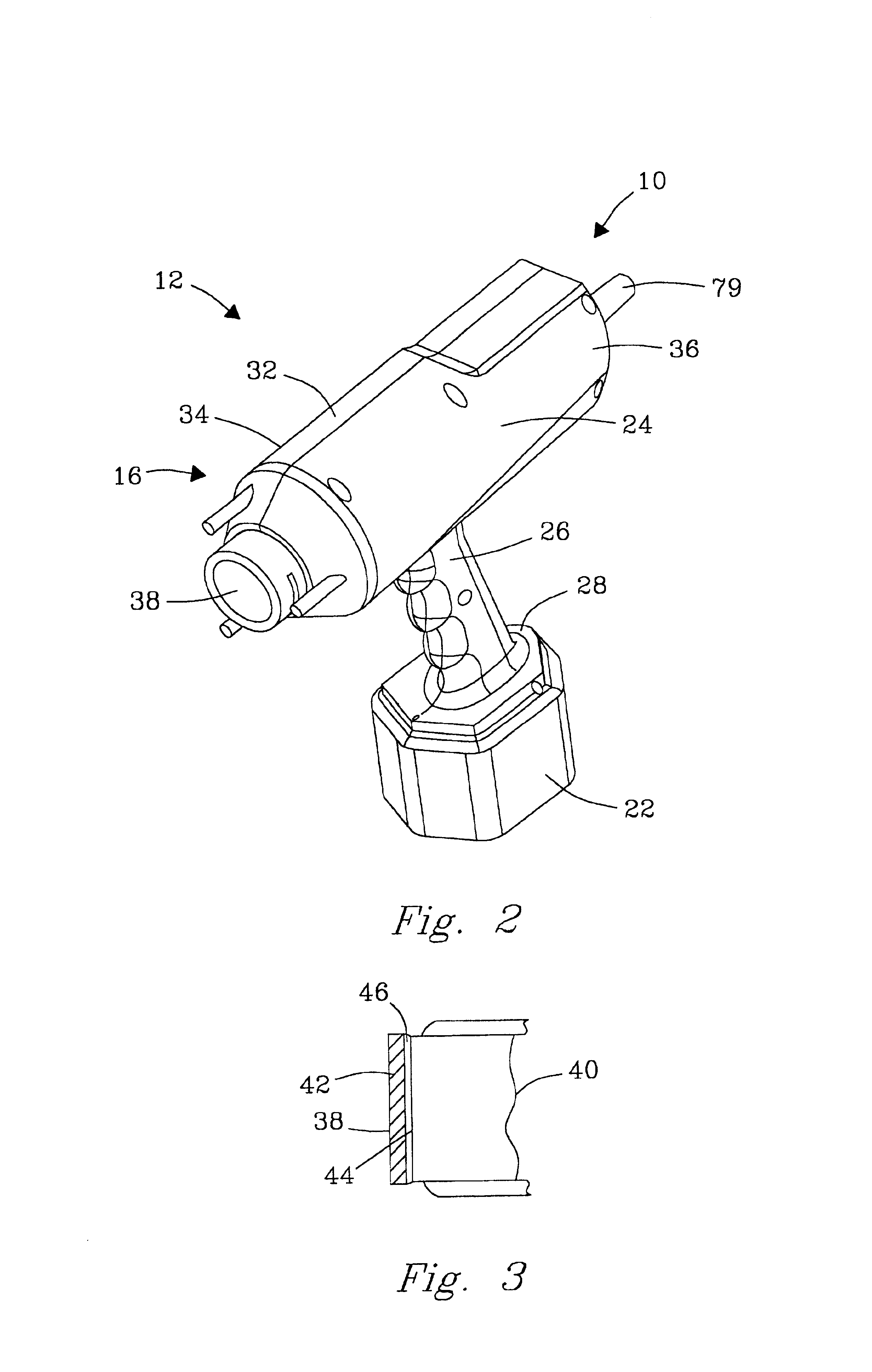
Acoustic inspection device
InactiveUS6938488B2Minimal noise figureRapid determinationUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansMagnetic property measurementsUltrasound sonographyTransducer
An ultrasound inspection apparatus particularly adapted to examine containers (sealed or unsealed) containing a liquid or solid bulk material. The apparatus has an overall configuration of a hand held pistol with a front transducer contact surface that is positioned against a front wall of the container. An ultrasound pulse is transmitted from the apparatus to be reflected from a back wall of a container being investigated. The received echo pulse is converted to a digital waveform. The waveform is analyzed relative to temperature, travel distance of the pulse(s), and time of travel to ascertain characteristics of the liquid or other materials and to provide identification of the same.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Ultrasound vibrometry
ActiveUS7753847B2Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSonificationHarmonic
A method for measuring a mechanical property of a subject includes using an ultrasonic transducer to apply ultrasonic vibration pulses to a vibration origin in the subject in an on-off time sequence in order to impart a harmonic motion at a prescribed frequency to the subject, and when the vibration pulses are off, using the same transducer to apply ultrasonic detection pulses to a motion detection point and to receive echo signals therefrom in order to sense the harmonic motion on the subject at the motion detection point. From the harmonic signal information, a harmonic signal is detected and a characteristic such as amplitude or phase of the detected harmonic signal is measured. The mechanical property is calculated using the measured characteristic using for example a wave speed dispersion method.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
System and method for identifying road features
ActiveUS7516041B2Instruments for road network navigationFeeler-pin gaugesComputer scienceGraph database
A system and method identifies road features that may not appear on a map database, such as paths not described as roads on the map database, and whether all the roads at a crossing cross at the same grade level. The system and method may thus be used to identify points of departure from, or points of merging onto, a road described by the map database or a path identified as described herein, but not described by the map database.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
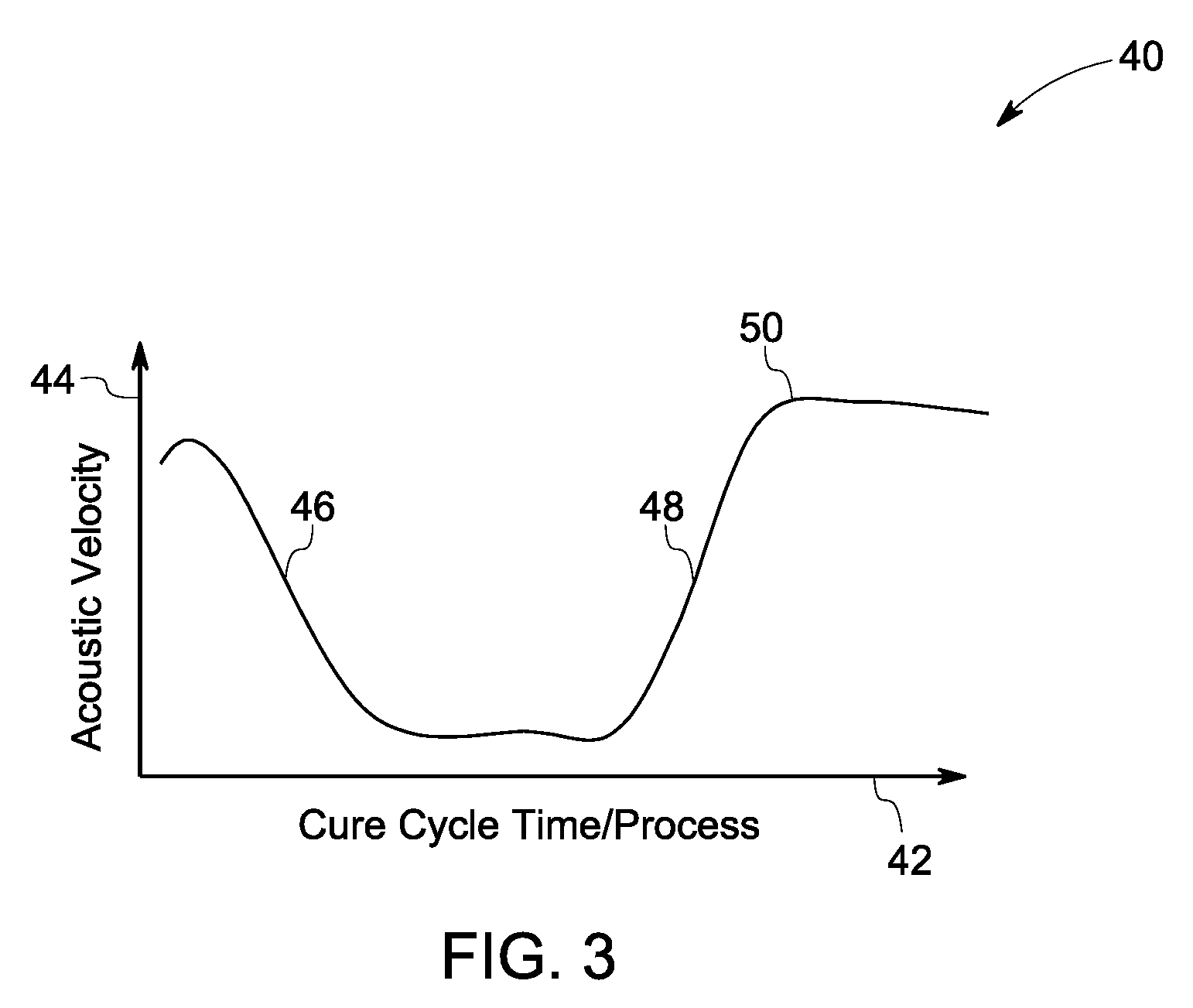
Systems and methods for monitoring a composite cure cycle
InactiveUS20080315462A1Using subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansAuxillary shaping apparatusFiberEngineering
A system for monitoring at least one of a resin infusion process and a composite cure cycle of a composite article is provided. The system includes an ultrasonic transmitter configured to deliver an acoustic wave to a resin-infused fiber preform and an ultrasonic receiver configured to receive the acoustic wave propagated through the resin-infused fiber preform. The system also includes a processor configured to estimate at least one parameter using the received acoustic wave and to use the at least one parameter to determine an extent to which at least one resin has infused into the resin-infused fiber preform.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
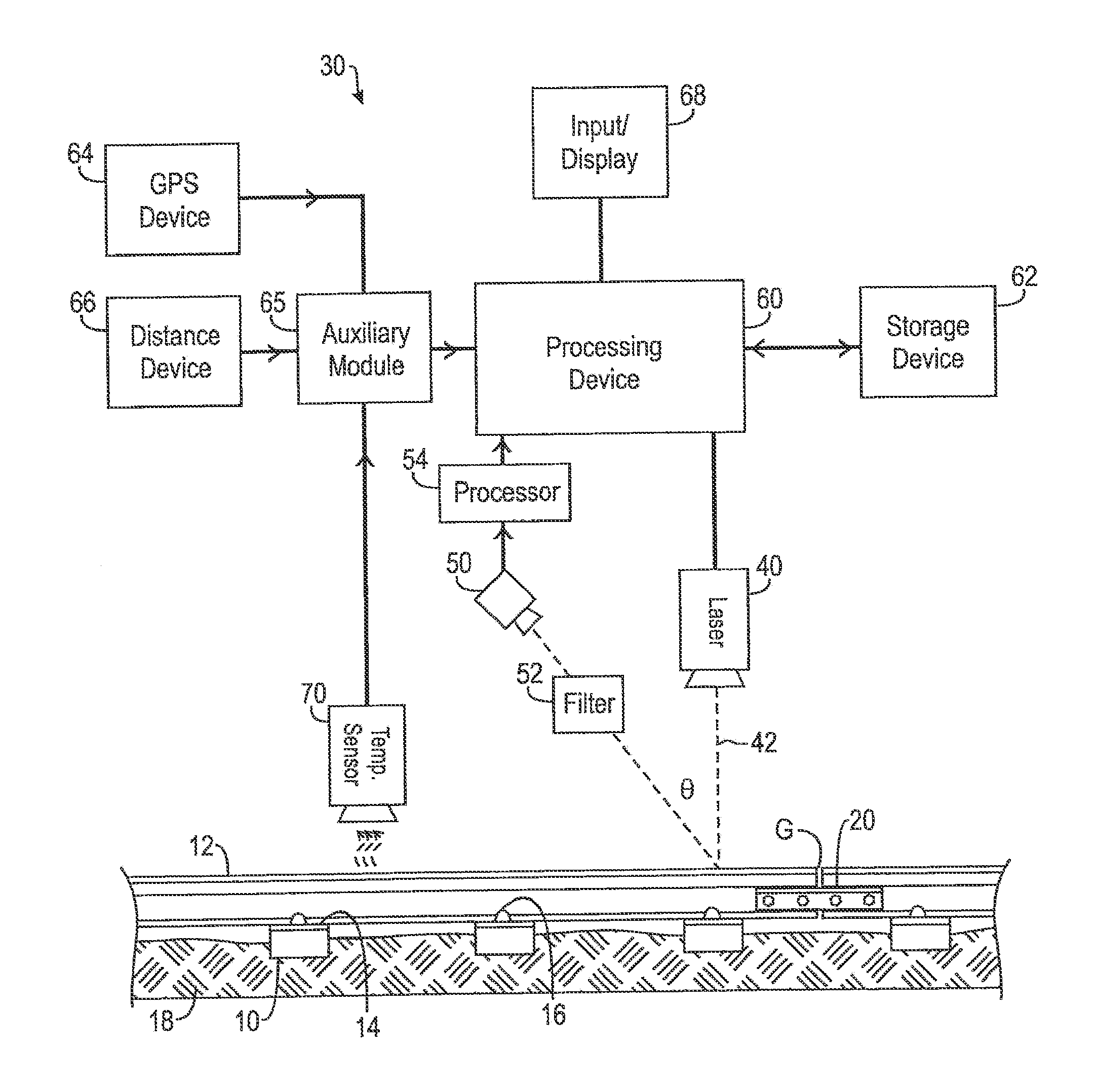
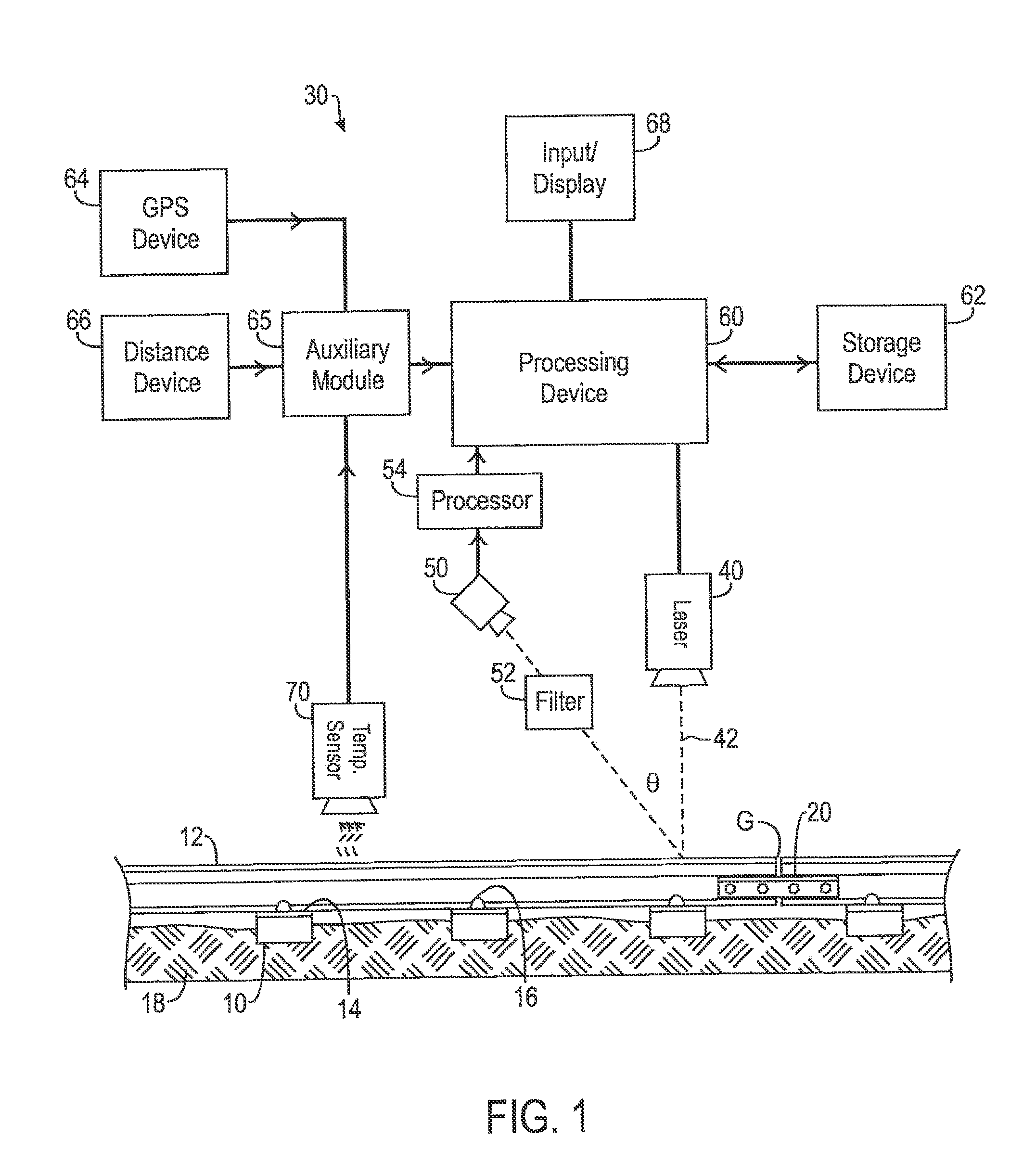
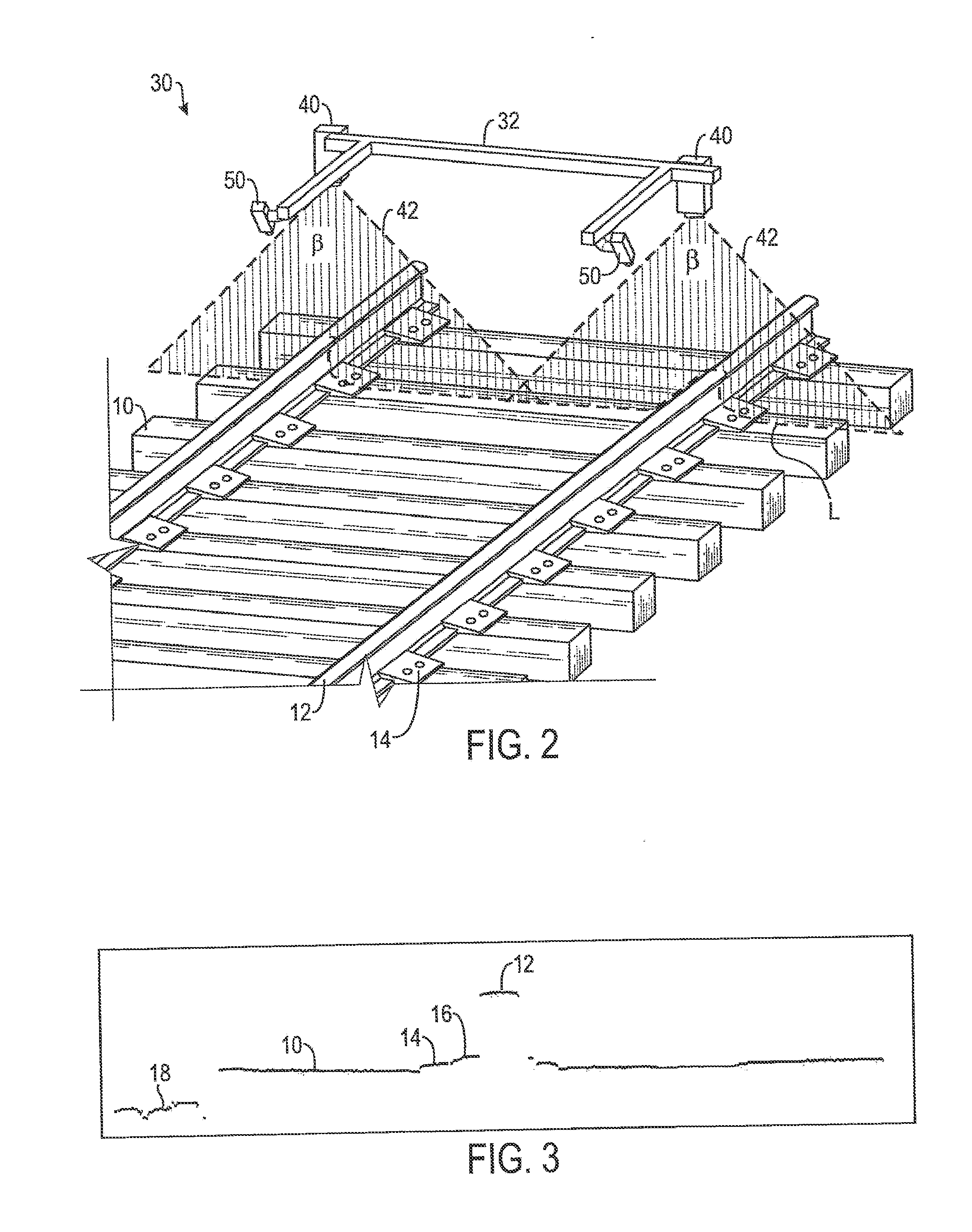
System and method for inspecting railroad ties
A system for inspecting railroad ties in a railroad track includes a light generator, an optical receiver and a processor. The light generator is oriented to project a beam of light across the railroad track while moving along the railroad track in a travel direction. The optical receiver is oriented to receive at least a portion of the beam of light reflected from the railroad track and configured to generate image data representative of a profile of at least a portion of the railroad track. The processor is configured to analyze the image data by applying one or more algorithms configured to find boundaries of a railroad tie and determine one or more condition metrics associated with the railroad tie.
Owner:LORAM TECH INC
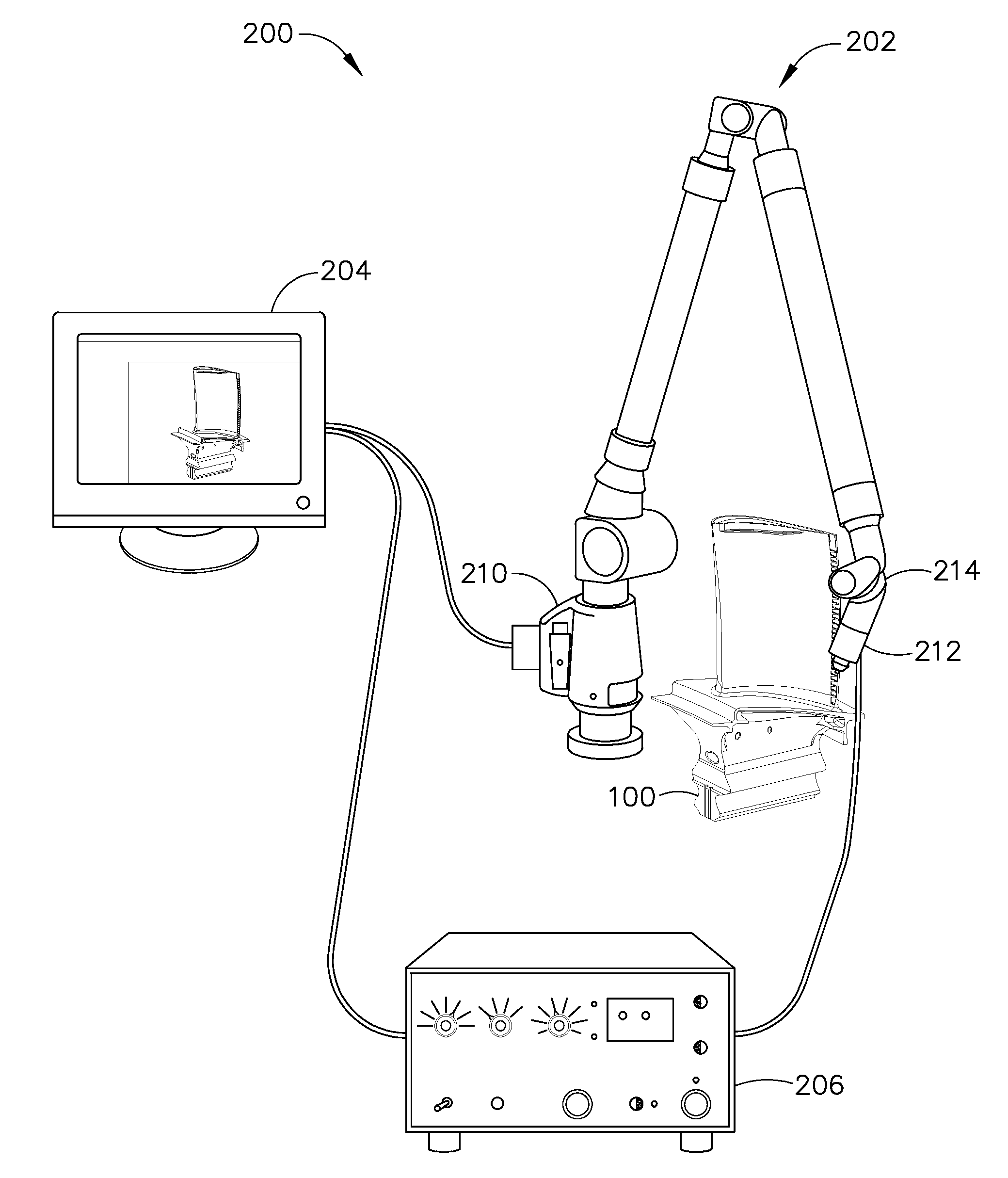
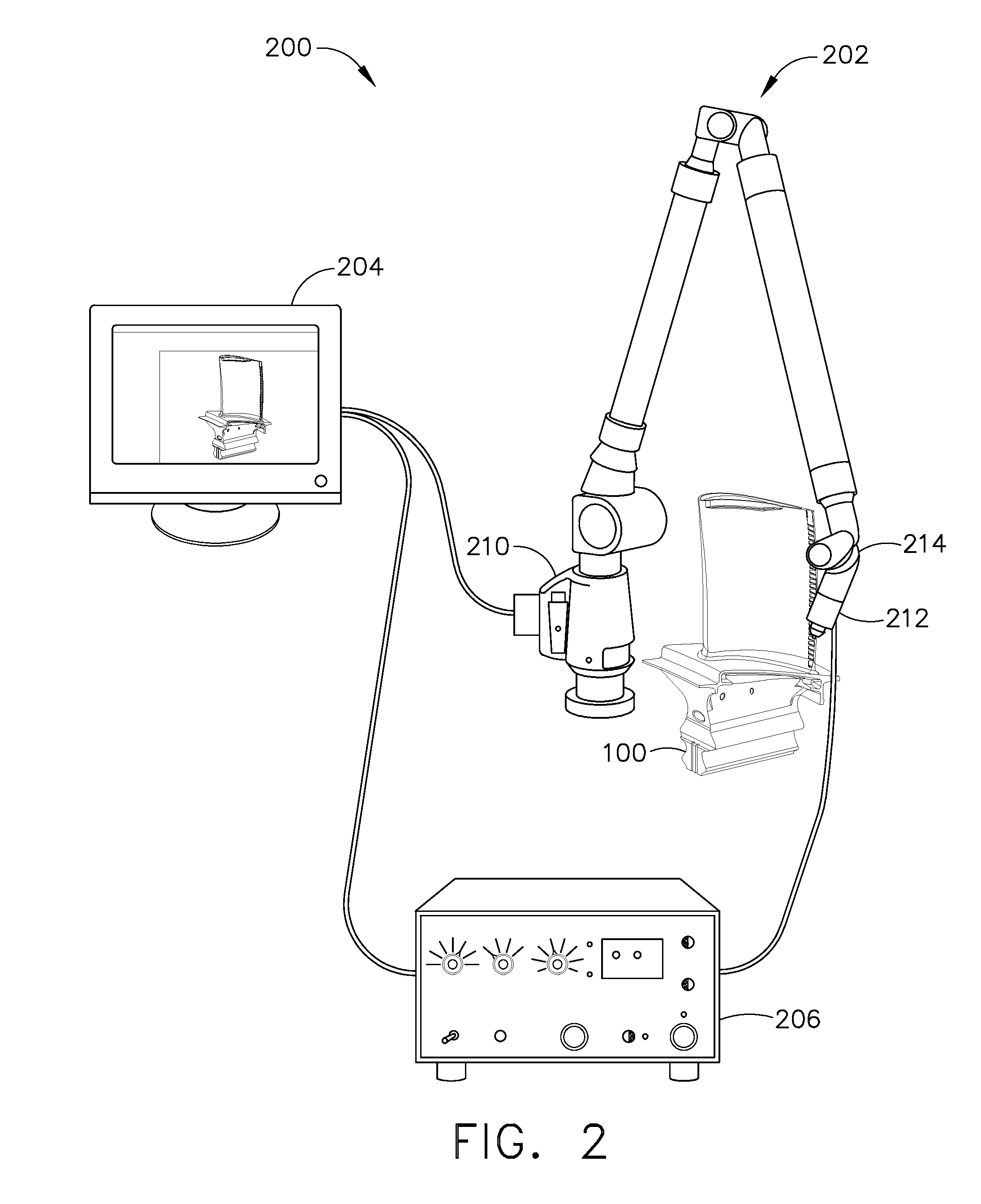
Method and system for integrating ultrasound inspection (UT) with a coordinate measuring machine (CMM)
InactiveUS20090165317A1Easy to measureAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFeeler-pin gaugesMeasurement deviceCoordinate-measuring machine
A method is provided for assembling a measurement device for use in measuring a machine component. The method includes providing a coordinate measuring machine (CMM). The method also includes combining ultrasonic inspection (UT) capabilities and CMM capabilities to form an inspection probe. The inspection probe is installed on the CMM so that the inspection probe measures external boundaries of the machine component with the CMM capabilities and substantially simultaneously measures internal boundaries of the machine component with the UT capabilities.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
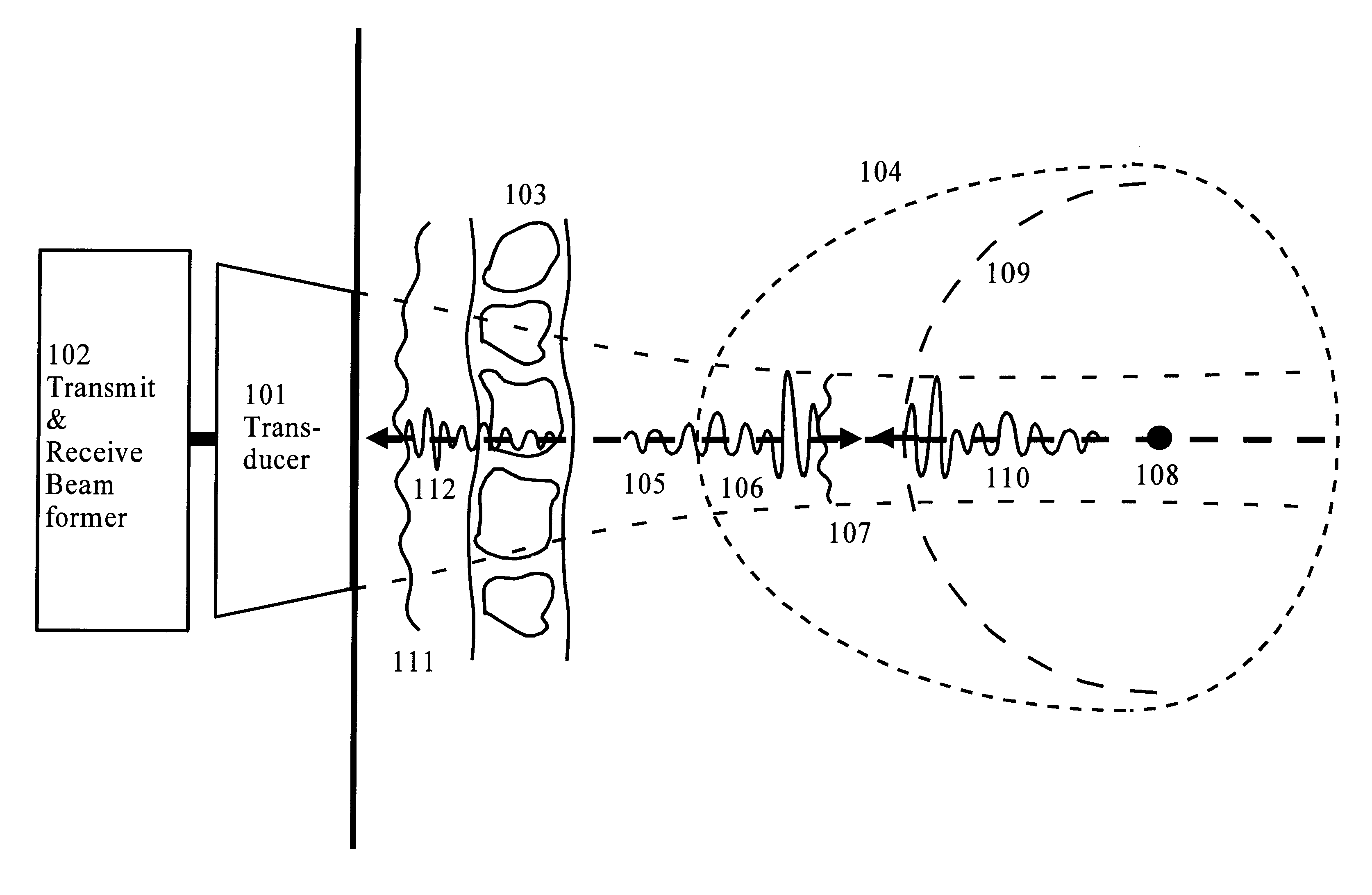
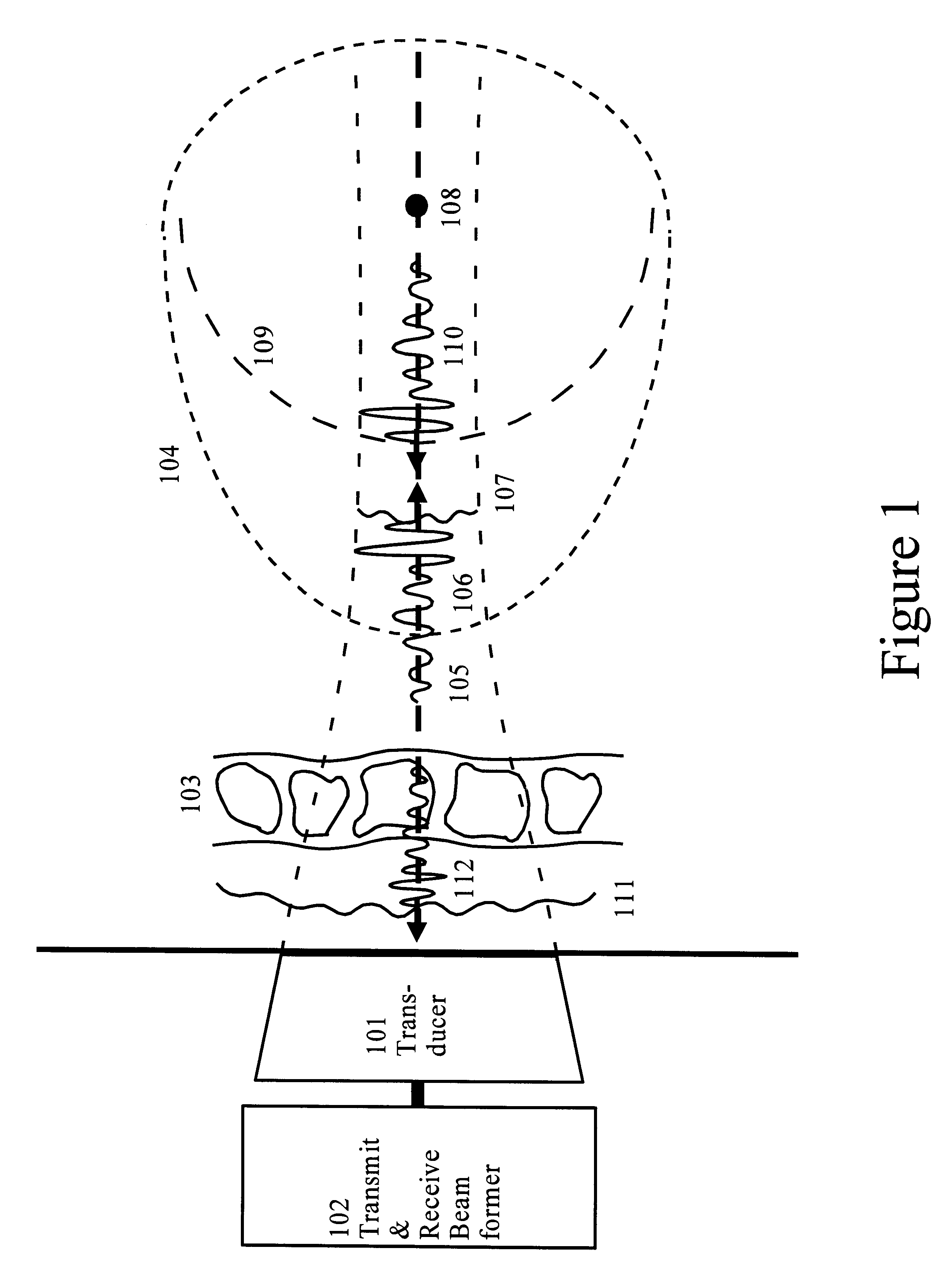
Correction of phasefront aberrations and pulse reverberations in medical ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS6485423B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingUltrasonography
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
Method for the automatic simultaneous synchronization, calibration and qualification of a non-contact probe
The present invention relates to an improved method for the simultaneous calibration and qualification of a non-contact probe on a localizer using a single artifact, in which non-contact probe readings and localizer readings are synchronised using parameters determined simultaneously with calibration and qualification. The invention also relates to a non-contact probe and other devices, and a computer program for performing the invention.
Owner:METRIS +1
Ultrasound matrix inspection
ActiveUS20140238136A1Maximize continuityMaximize lengthAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidData connectionSonification
A device and method for performing ultrasound scanning of a substantially cylindrical object, the device comprising a cuff adapted to fit around a circumference of the object, a carrier mounted slidably on the cuff and adapted to traverse the circumference of the object, an ultrasound probe mounted on the carrier and positioned to scan the circumference of the object as the carrier traverses the circumference of the object, a carrier motor mounted on the cuff or the carrier and used to drive the movement of the carrier about the circumference of the object, and one or more data connections providing control information for the carrier motor and the ultrasound probe and receiving scanning data from the ultrasound probe.
Owner:ONTARIO POWER GENERATION INC
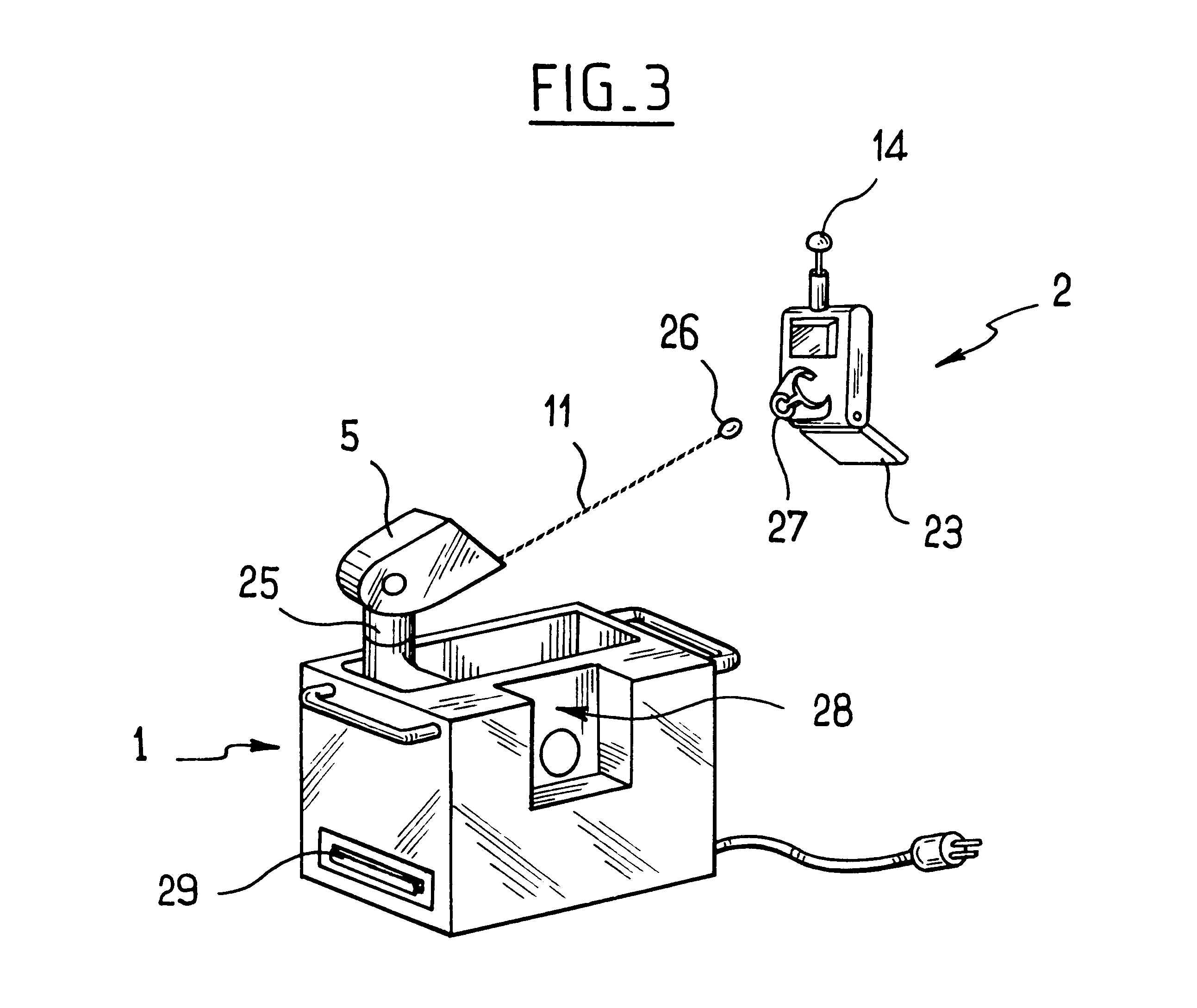
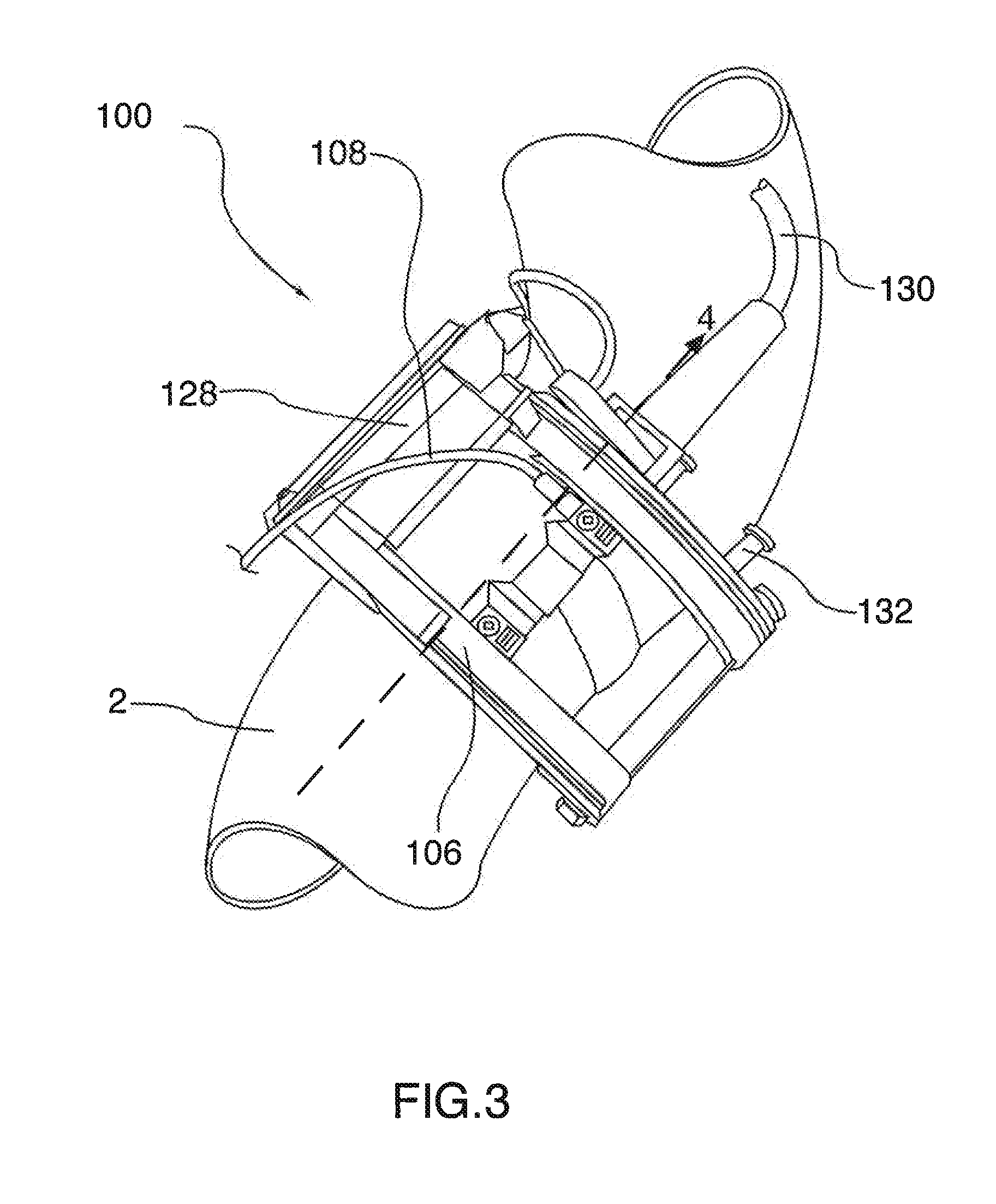
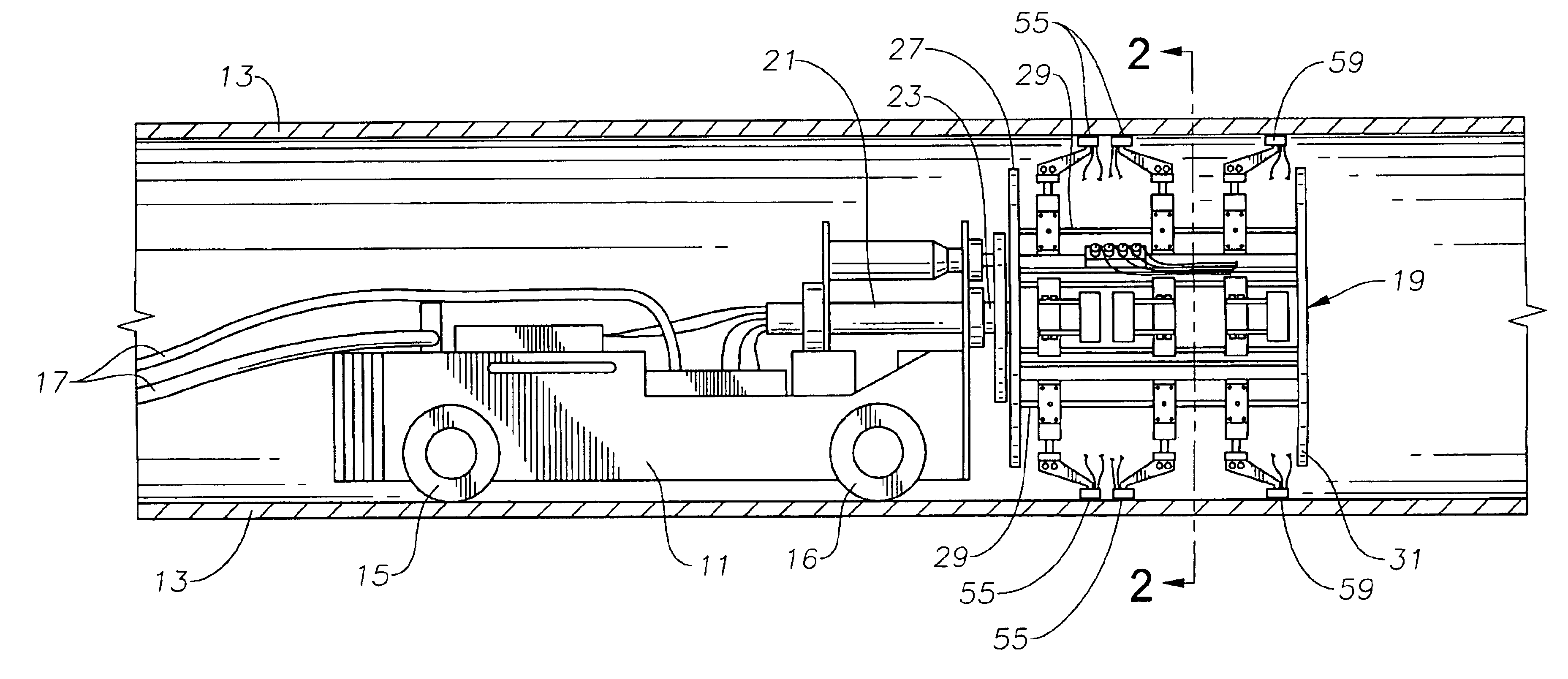
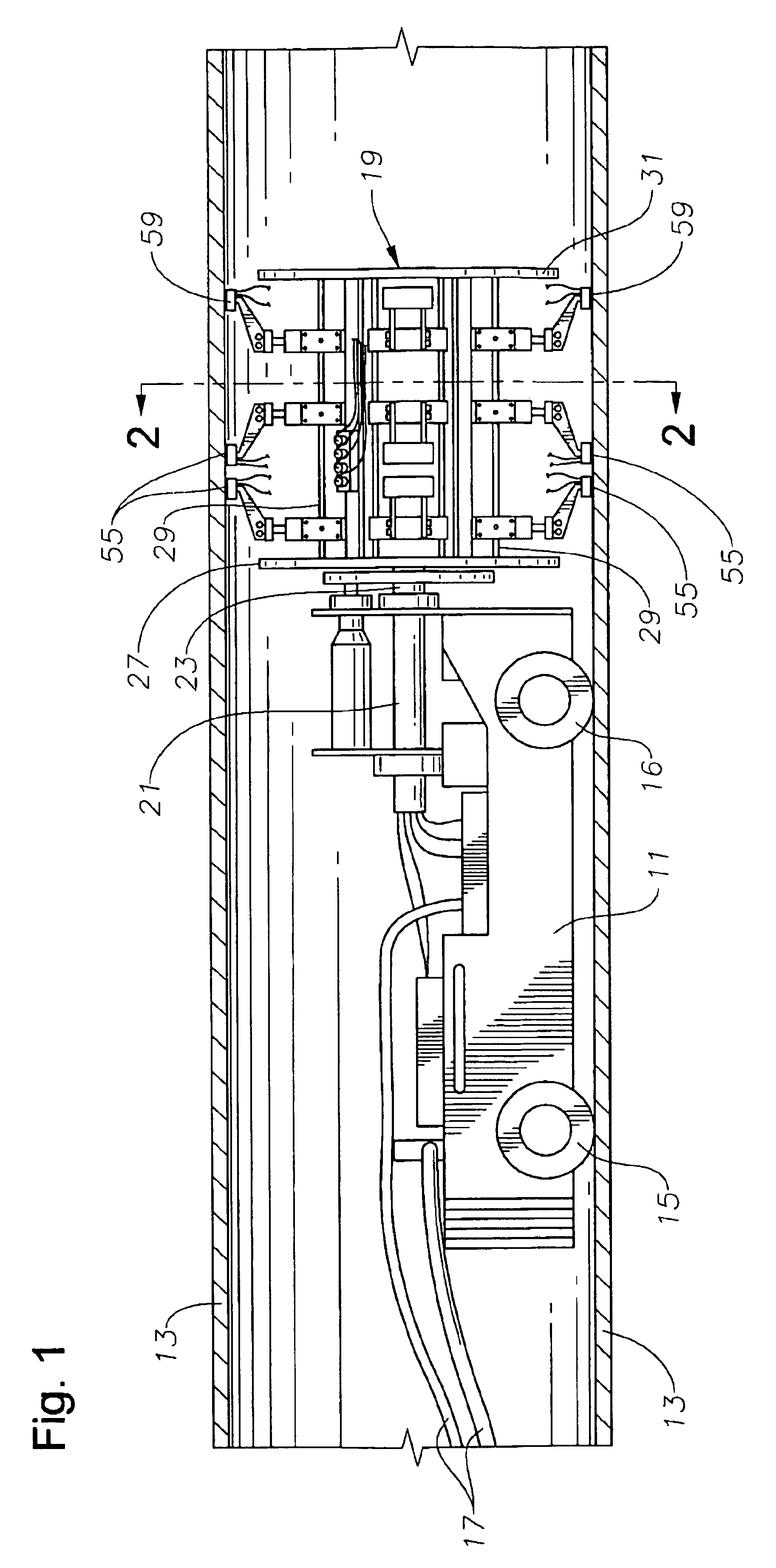
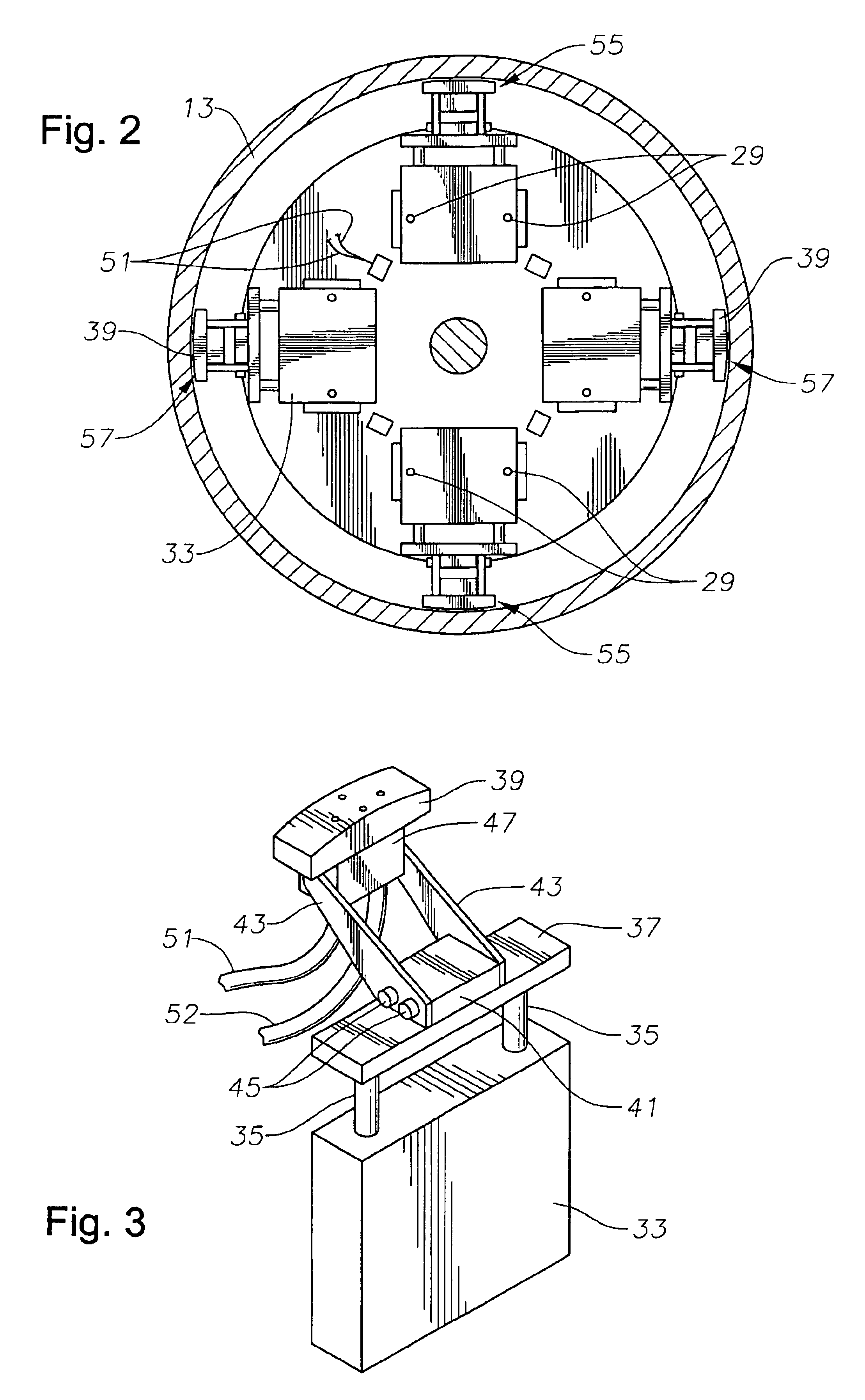
Internal riser inspection device
InactiveUS6904818B2Small diameterAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansUltrasonic sensorTransducer
An internal inspection unit for pipe has ultrasonic transducers that inspect weld volume, weld root, and wall thickness. The ultrasonic transducers are mounted to a portion of the inspection unit that is rotatable, but no more than one full revolution. One of the units has independently movable shoes for each separate transducer. The shoes are moved between retracted and extended positions by pneumatic cylinders. The other unit has shoes that support more than one transducer, the shoes being biased outwardly by springs.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Flaw detection in tubular members
InactiveUS6748808B2Efficient and effective inspectionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionTransducerEngineering
Owner:VARCO I P INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com