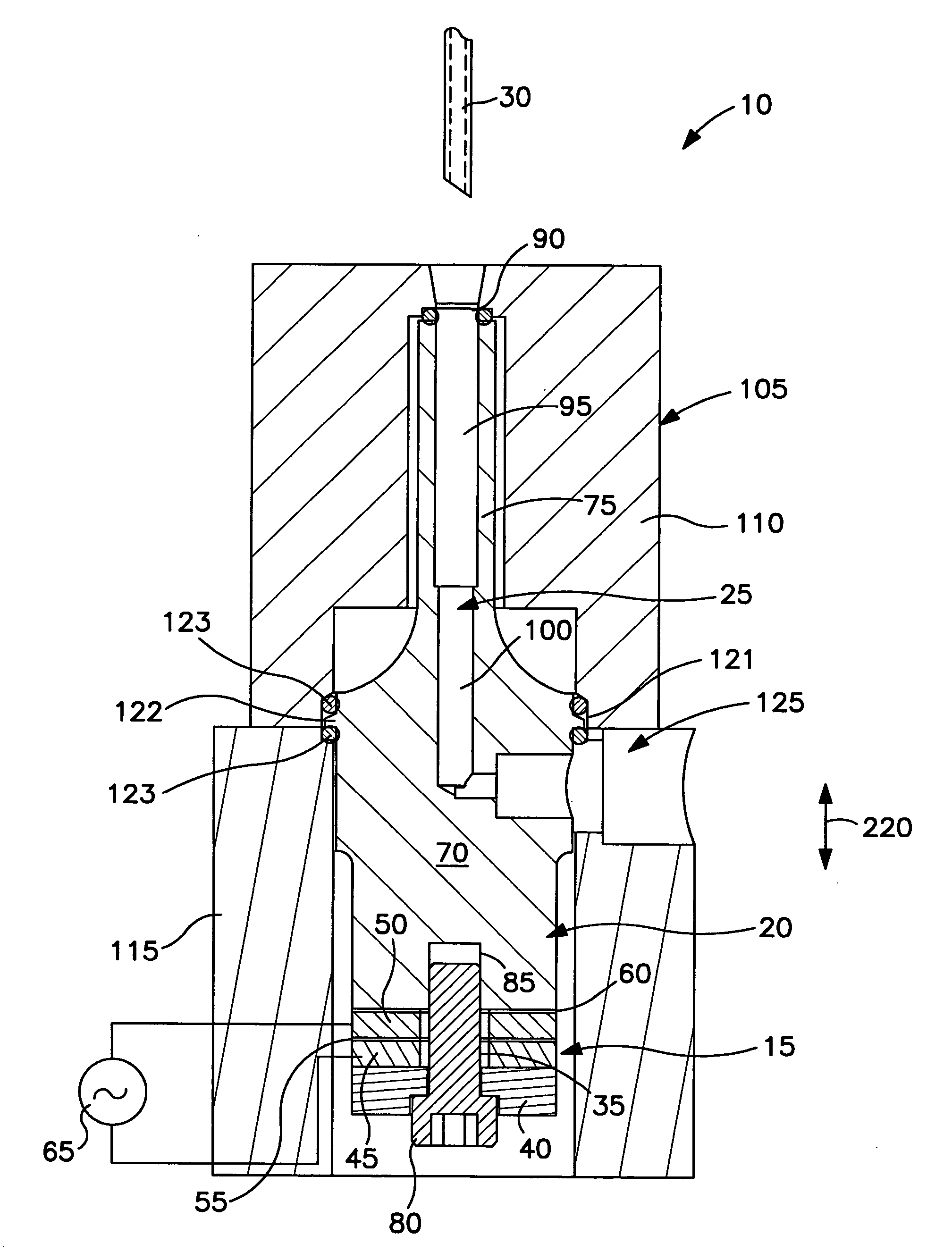
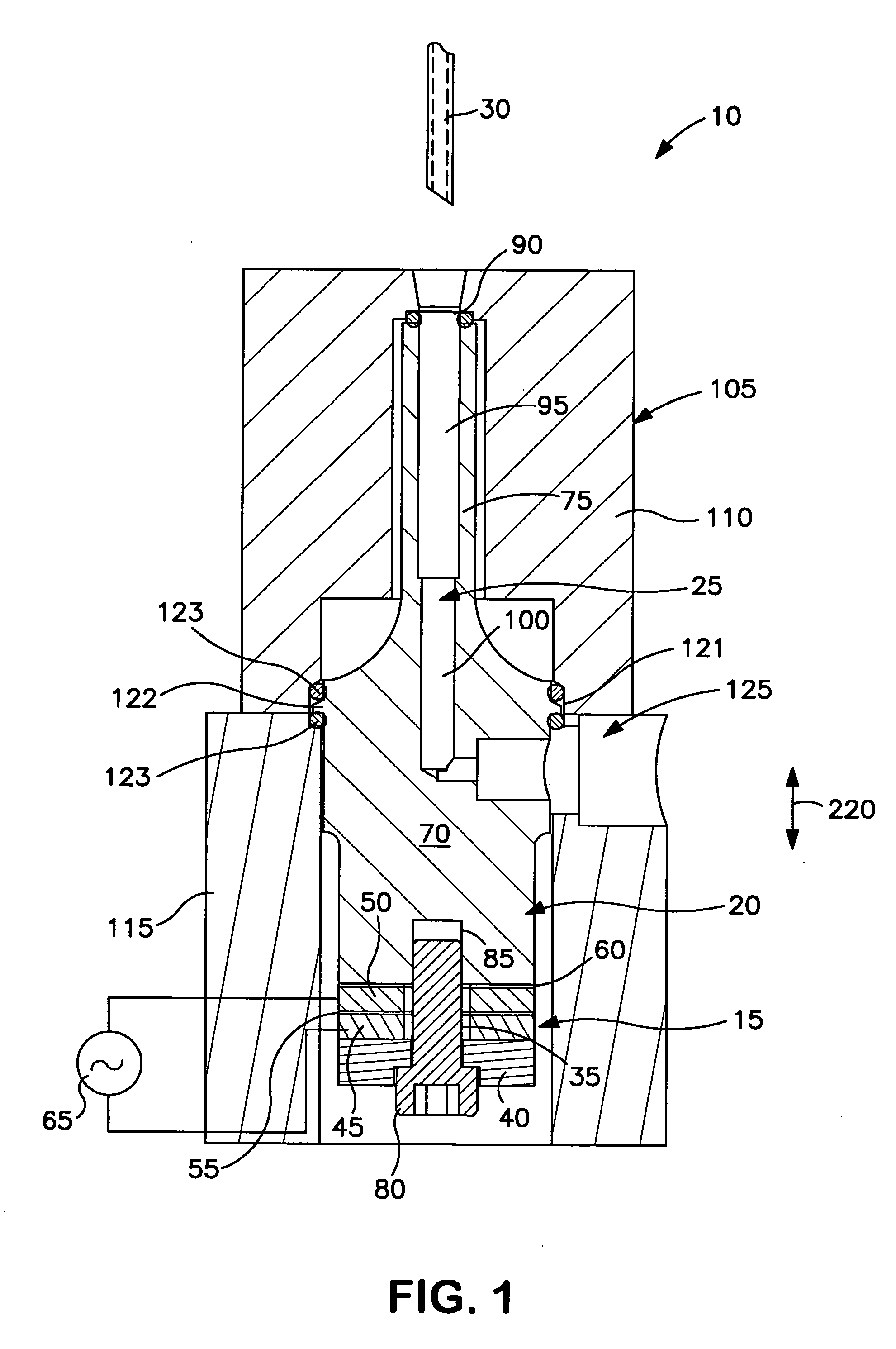
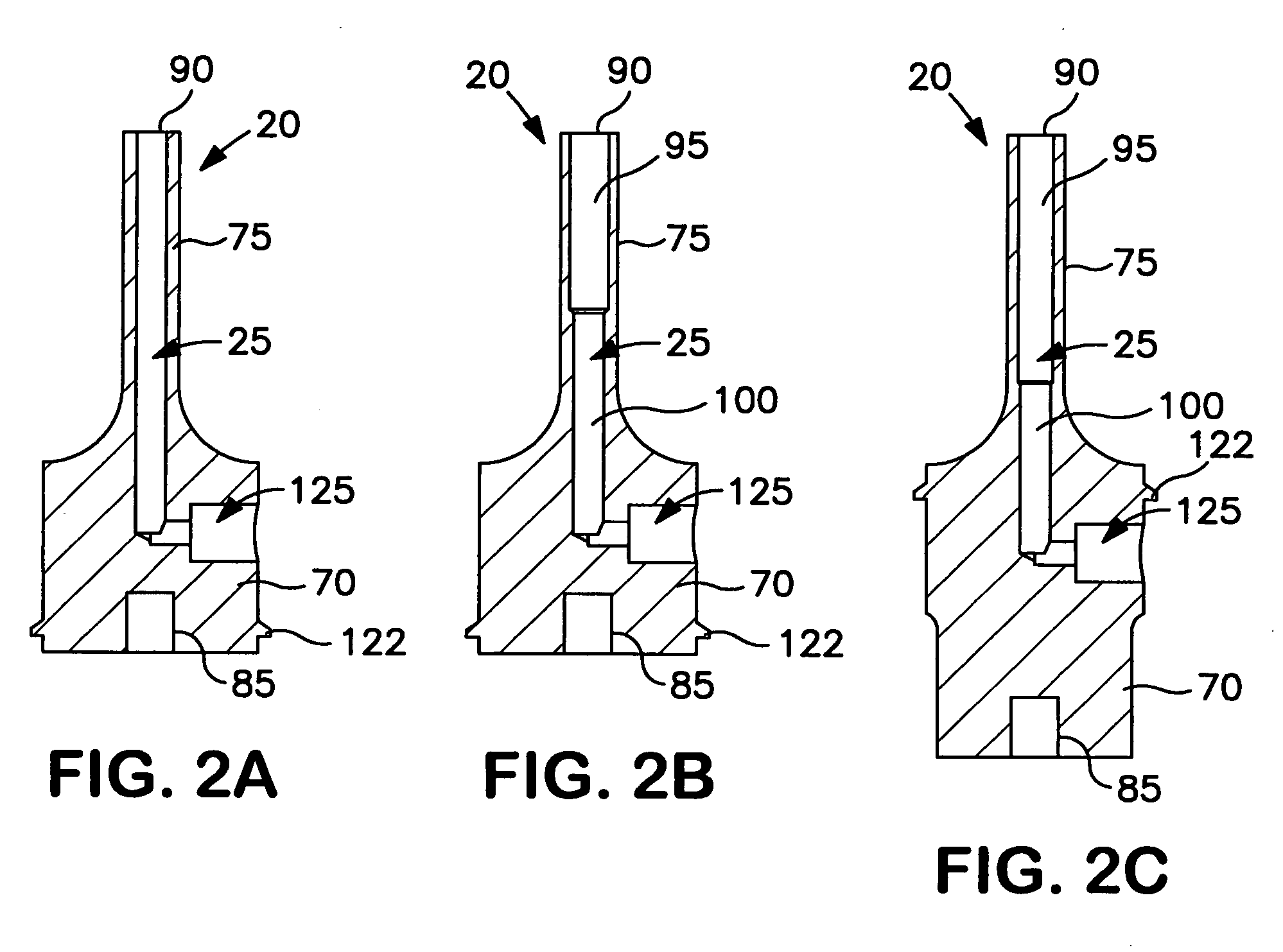
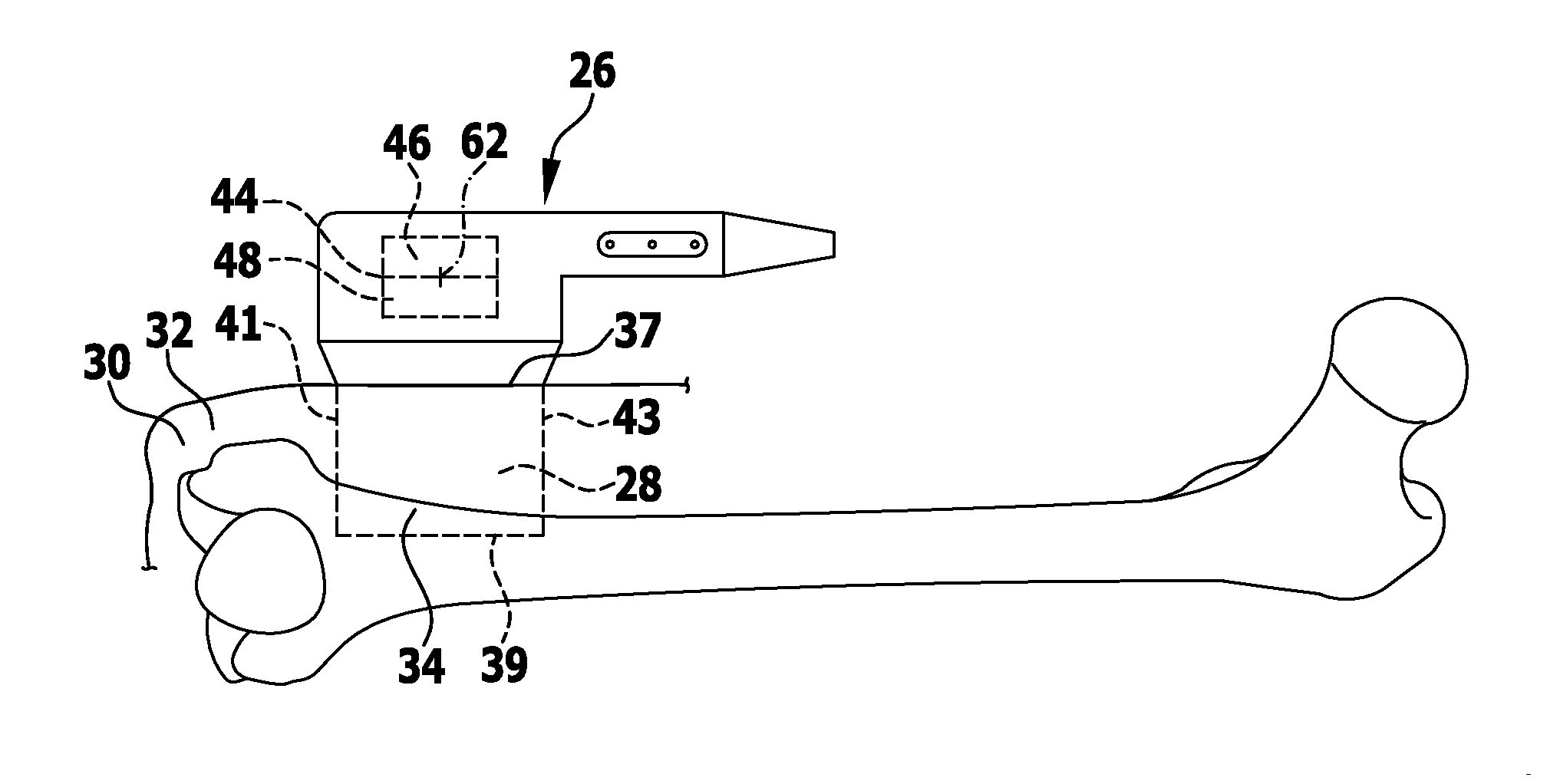
Patents
Literature
284 results about "Ultrasound sonography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sonography is a medical field in which ultrasound devices are used. You may work as a sonographer, using ultrasound equipment to create images of internal body structures for medical analysis.
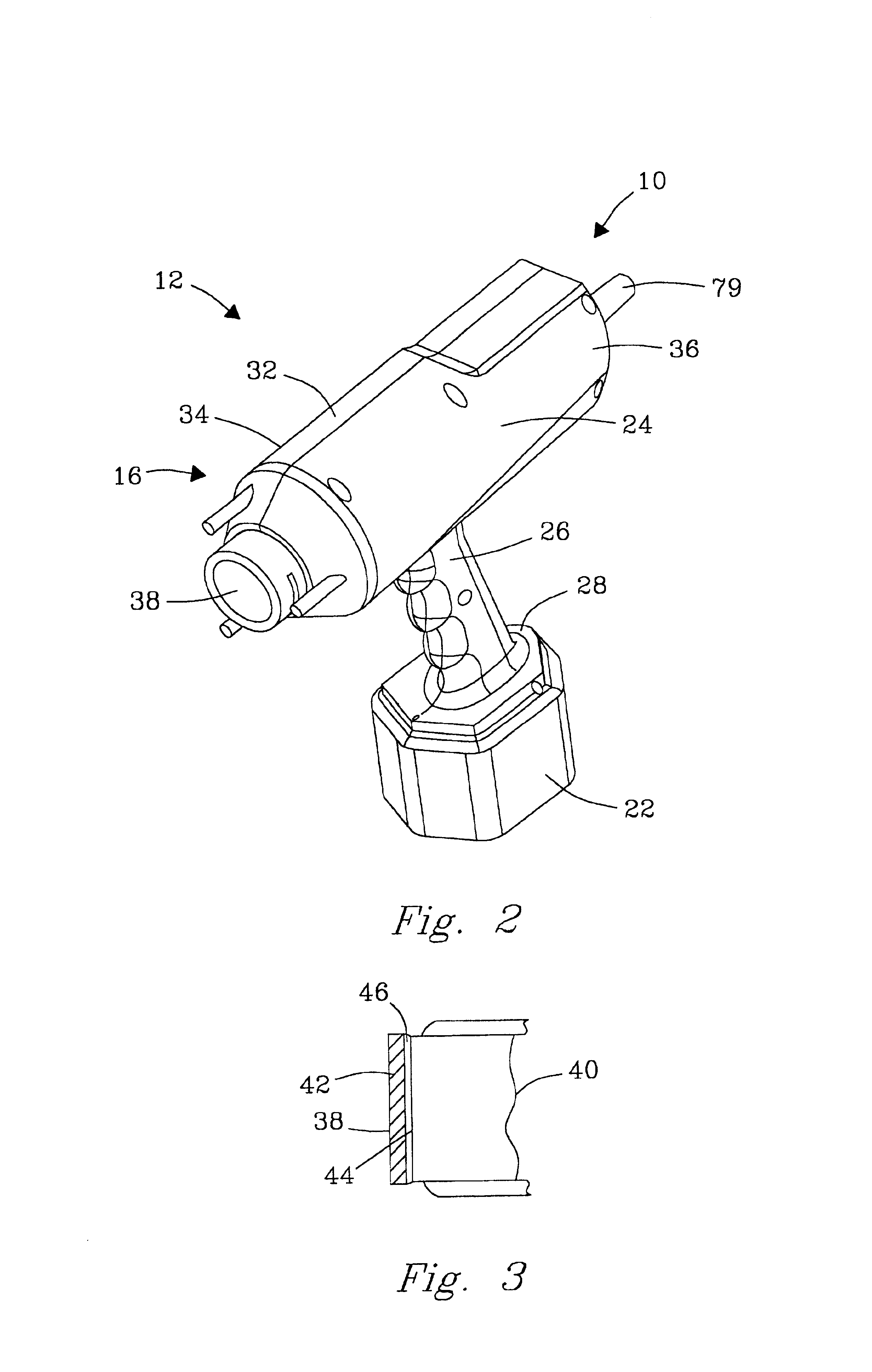
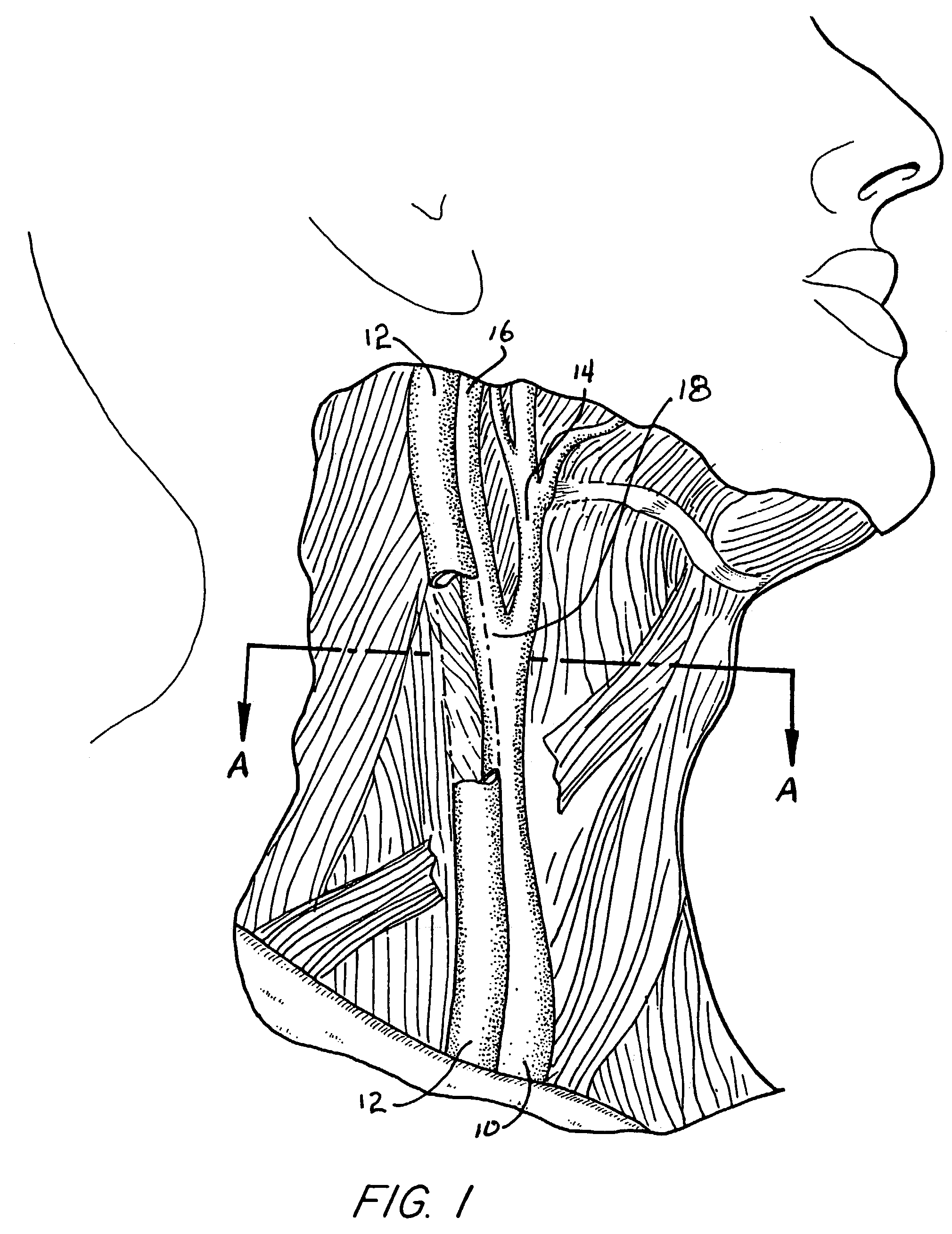
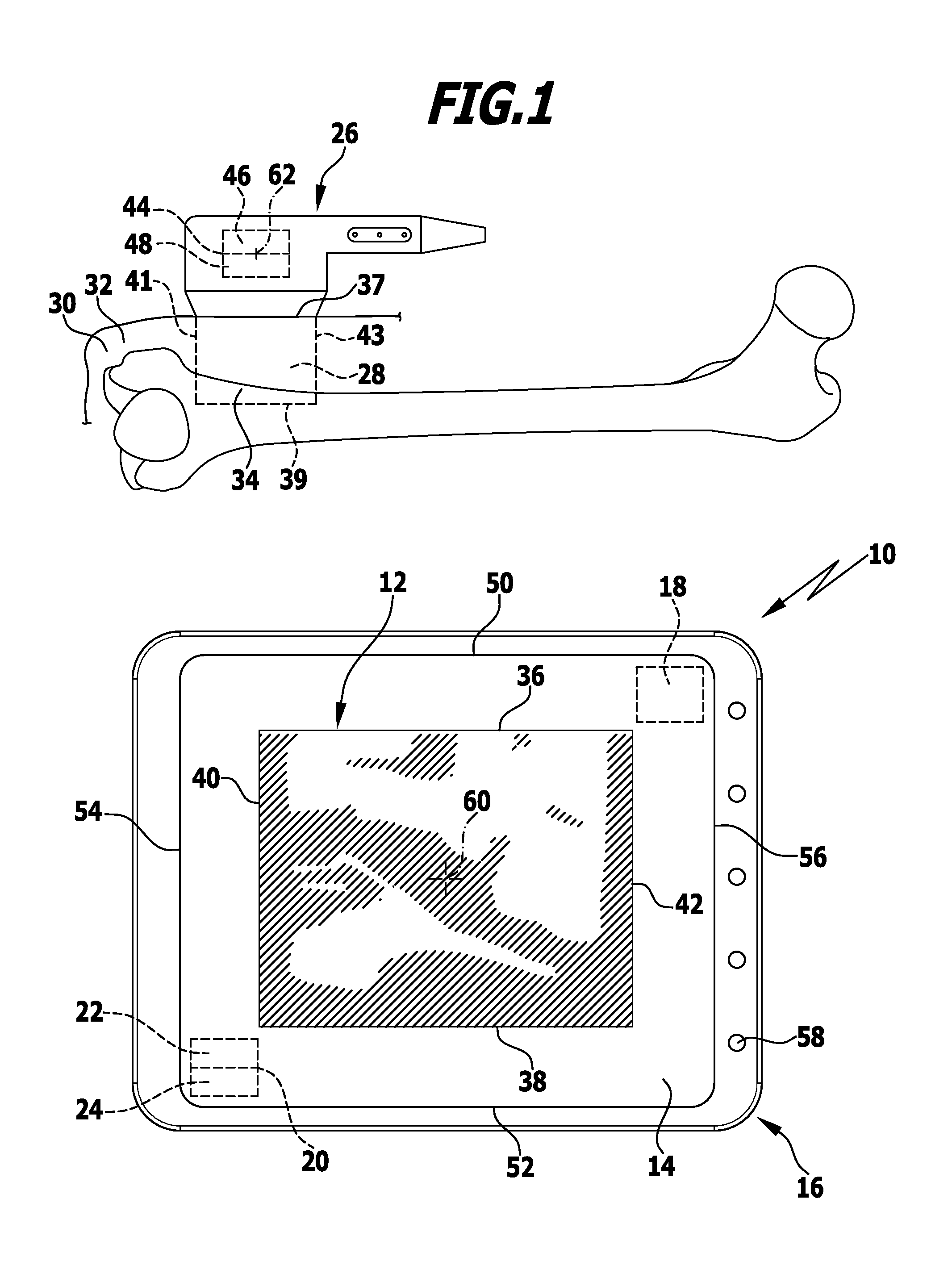
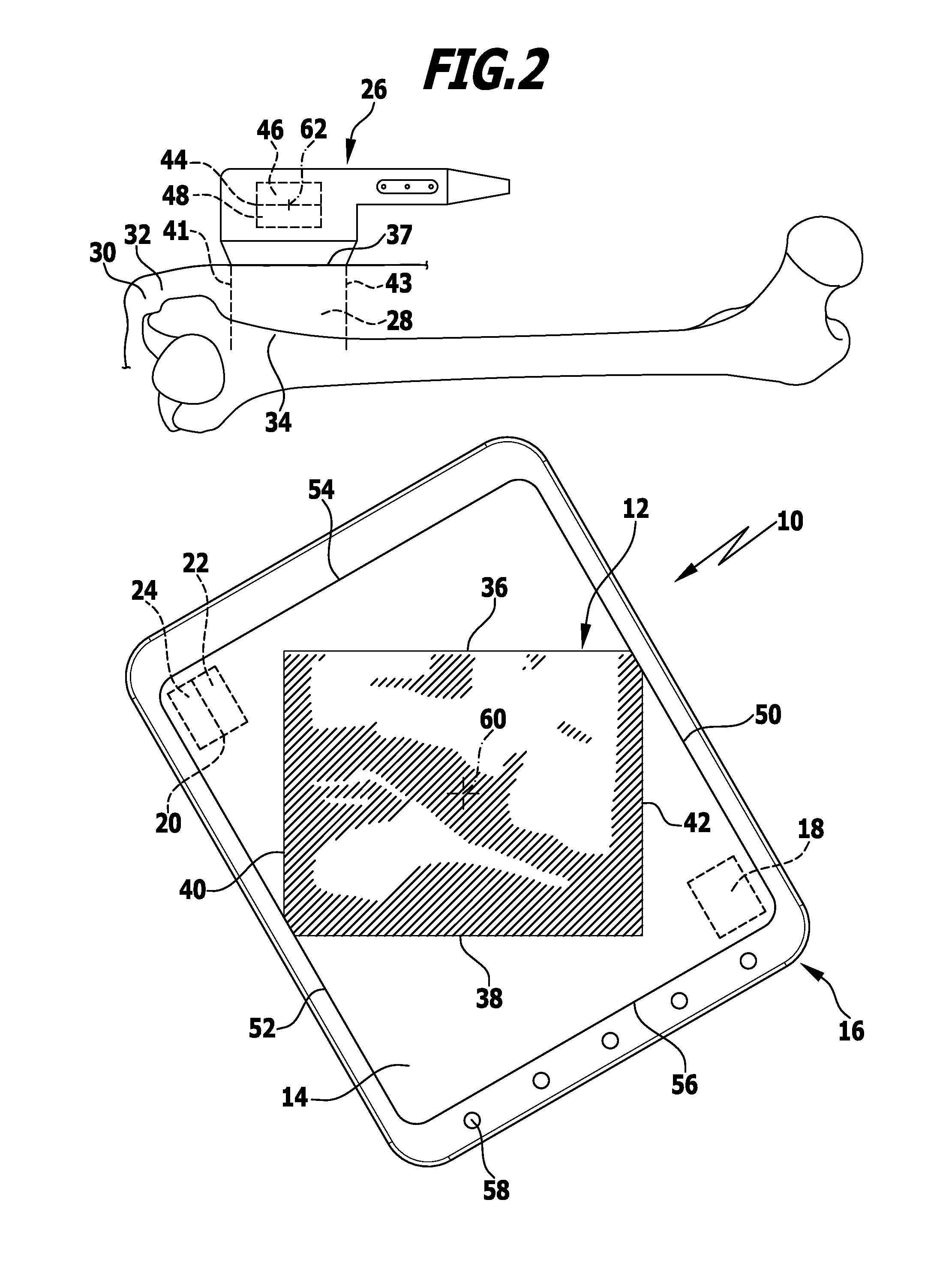
Apparatus and method for marking tissue
InactiveUS20050234336A1Eliminate needPrecise positioningSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsUltrasound sonographyX-ray
The present invention includes methods and materials for implantable devices (markers) which are disclosed for permanently marking the location of a biopsy or surgery for the purpose of identification. The devices are remotely delivered, preferably percutaneously. Visualization of the markers is readily accomplished using various state of the art imaging systems. Preferred visualization is through MRI, X-ray and ultrasound. The markers function to provide evidence of the location of the lesion after the procedure is complete for reference during future examinations or procedures.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
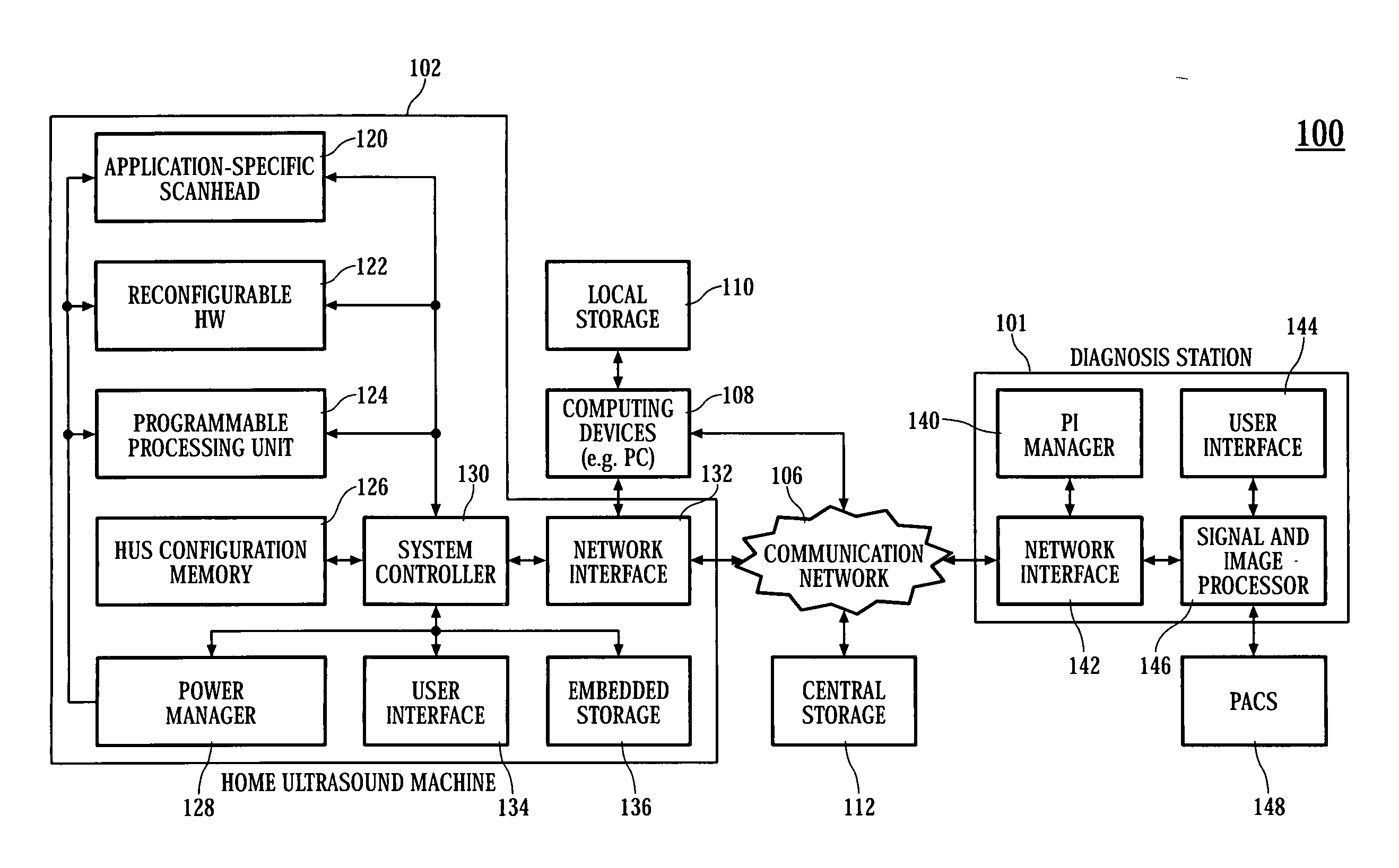
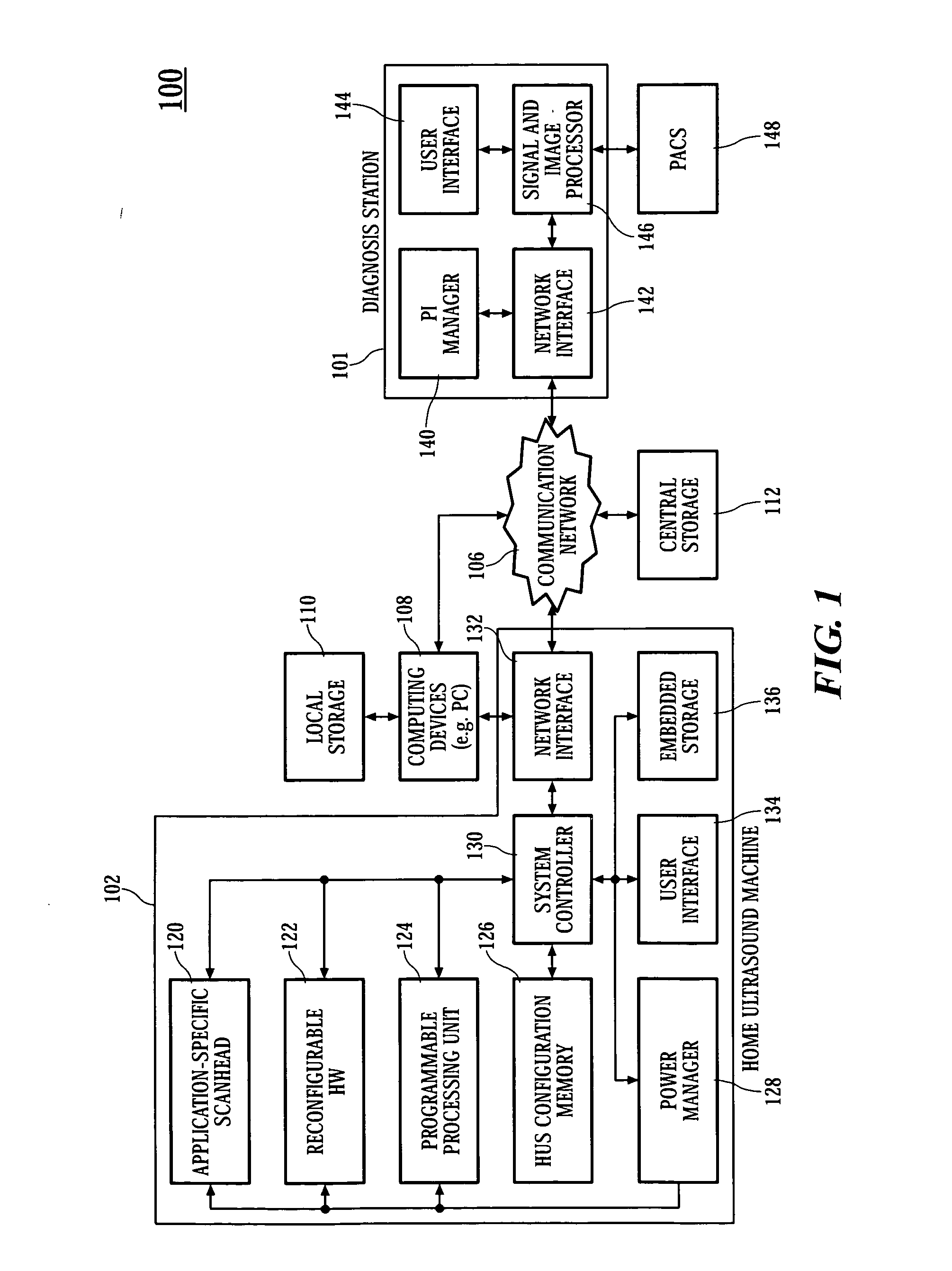
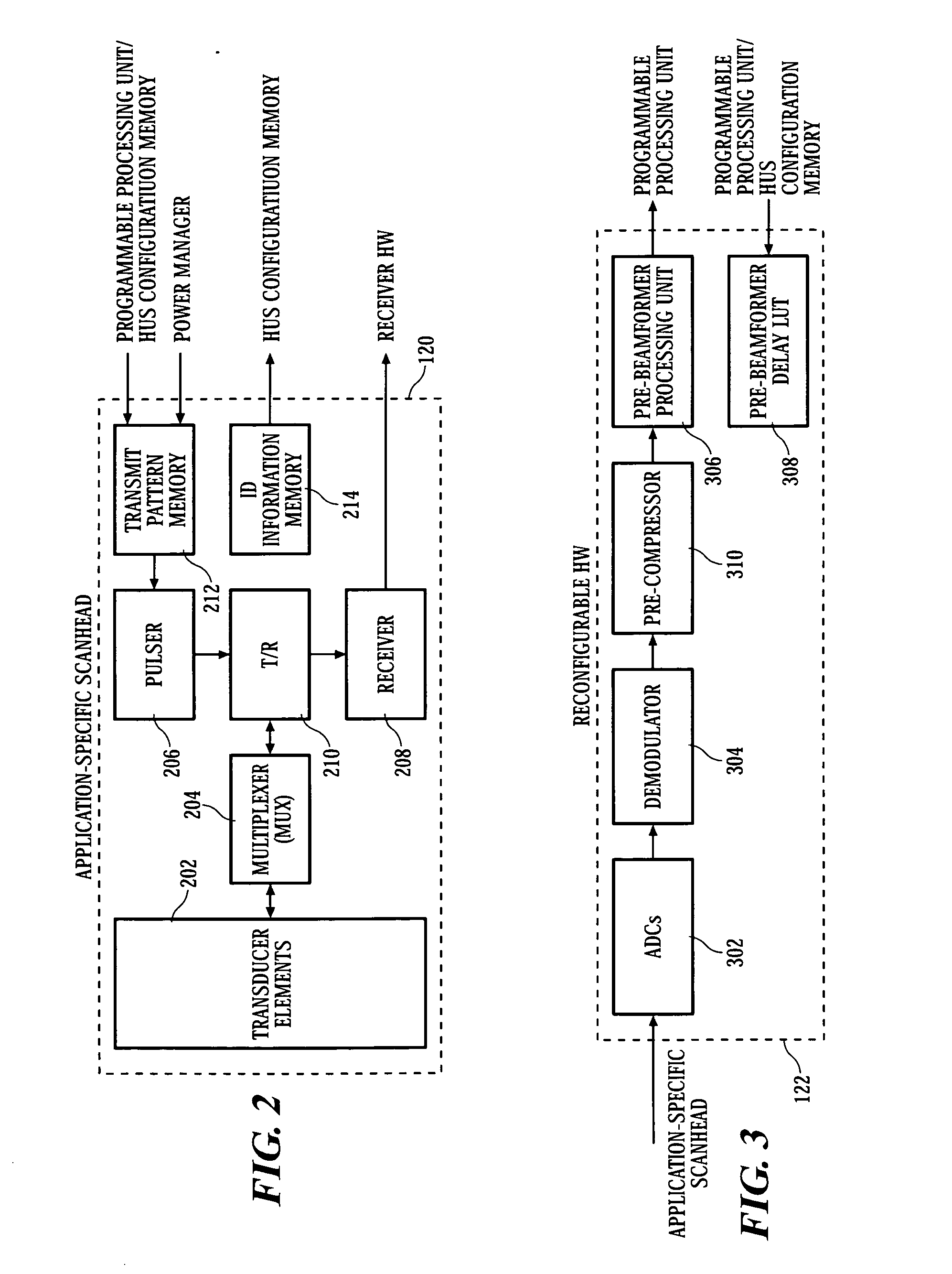
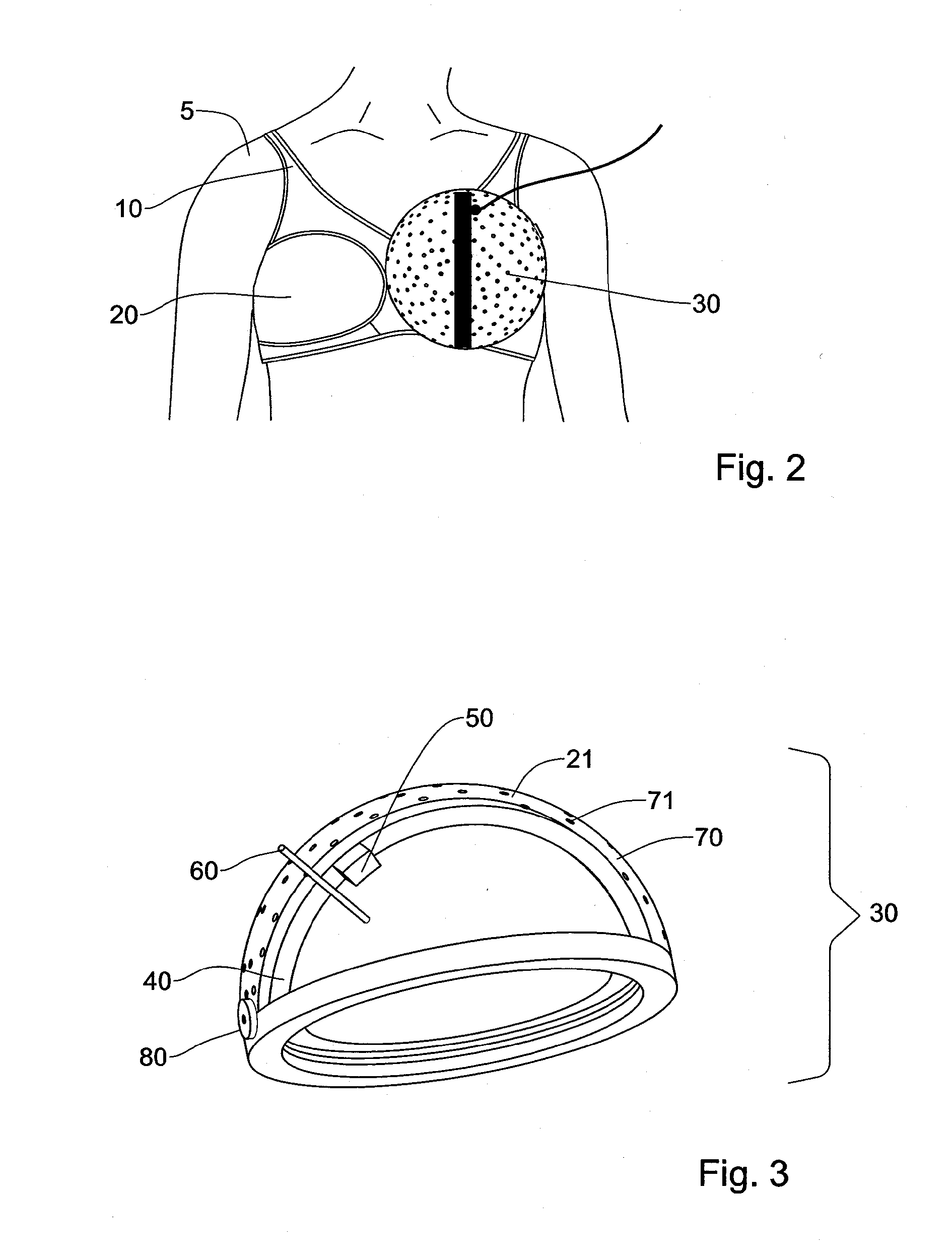
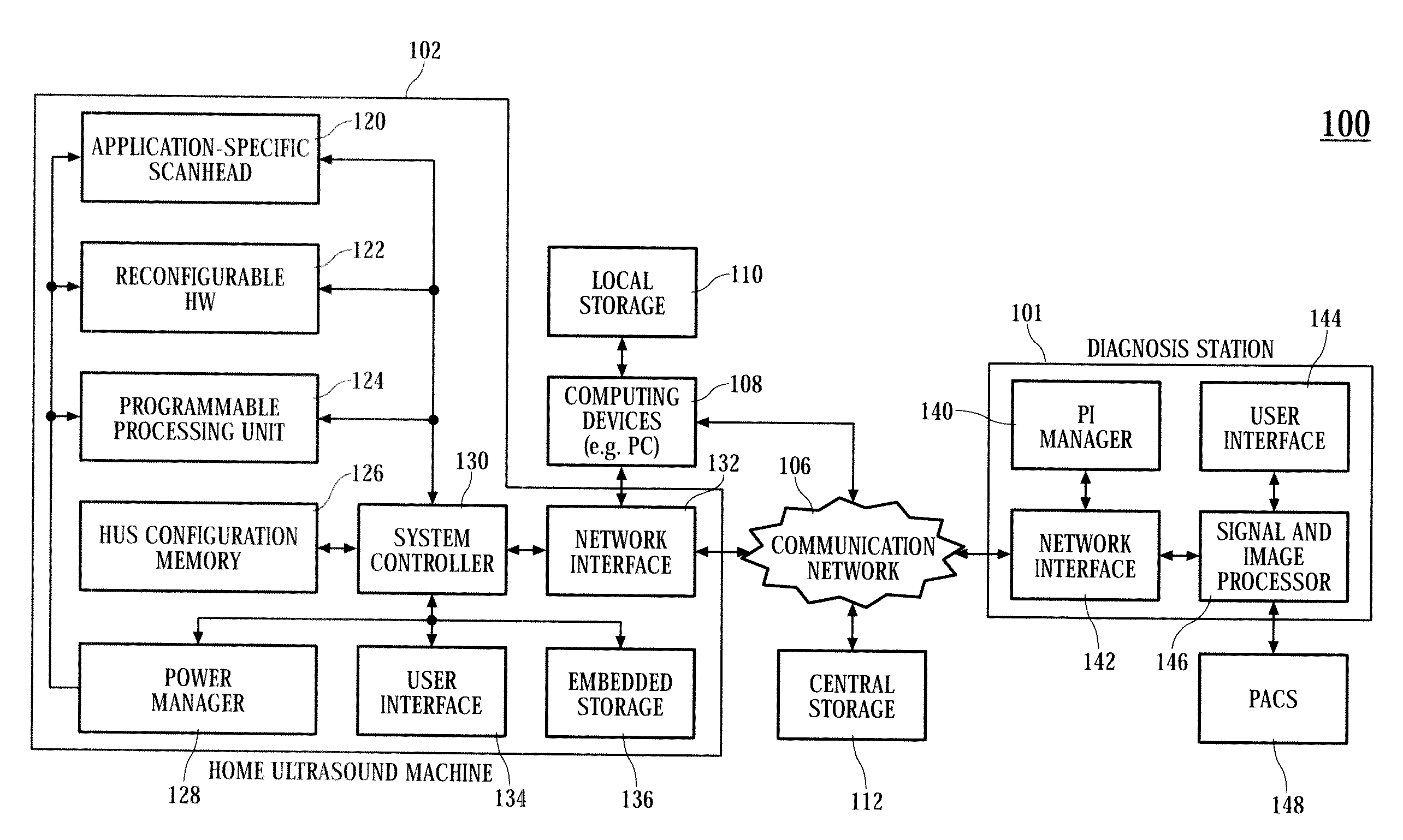
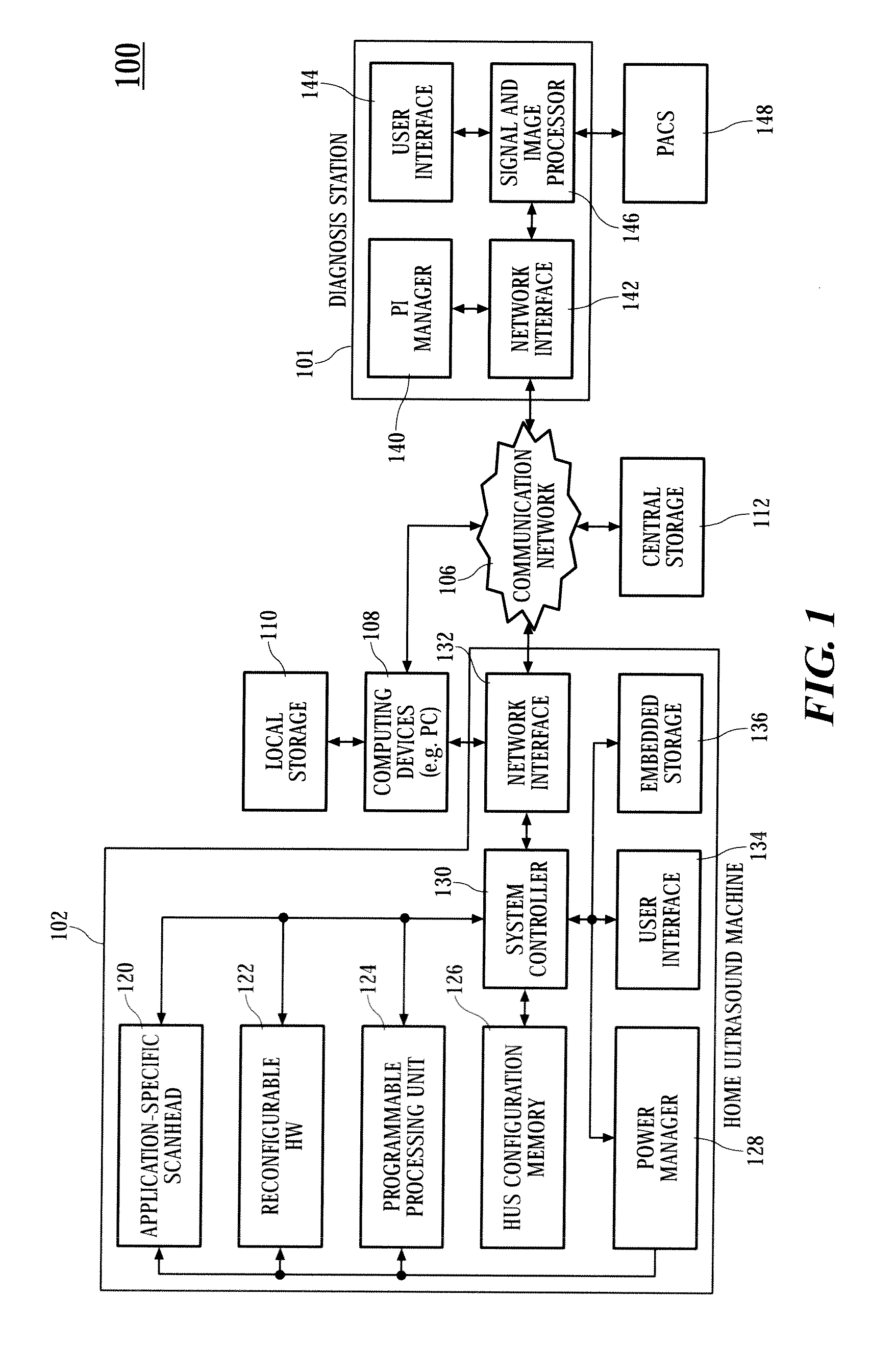
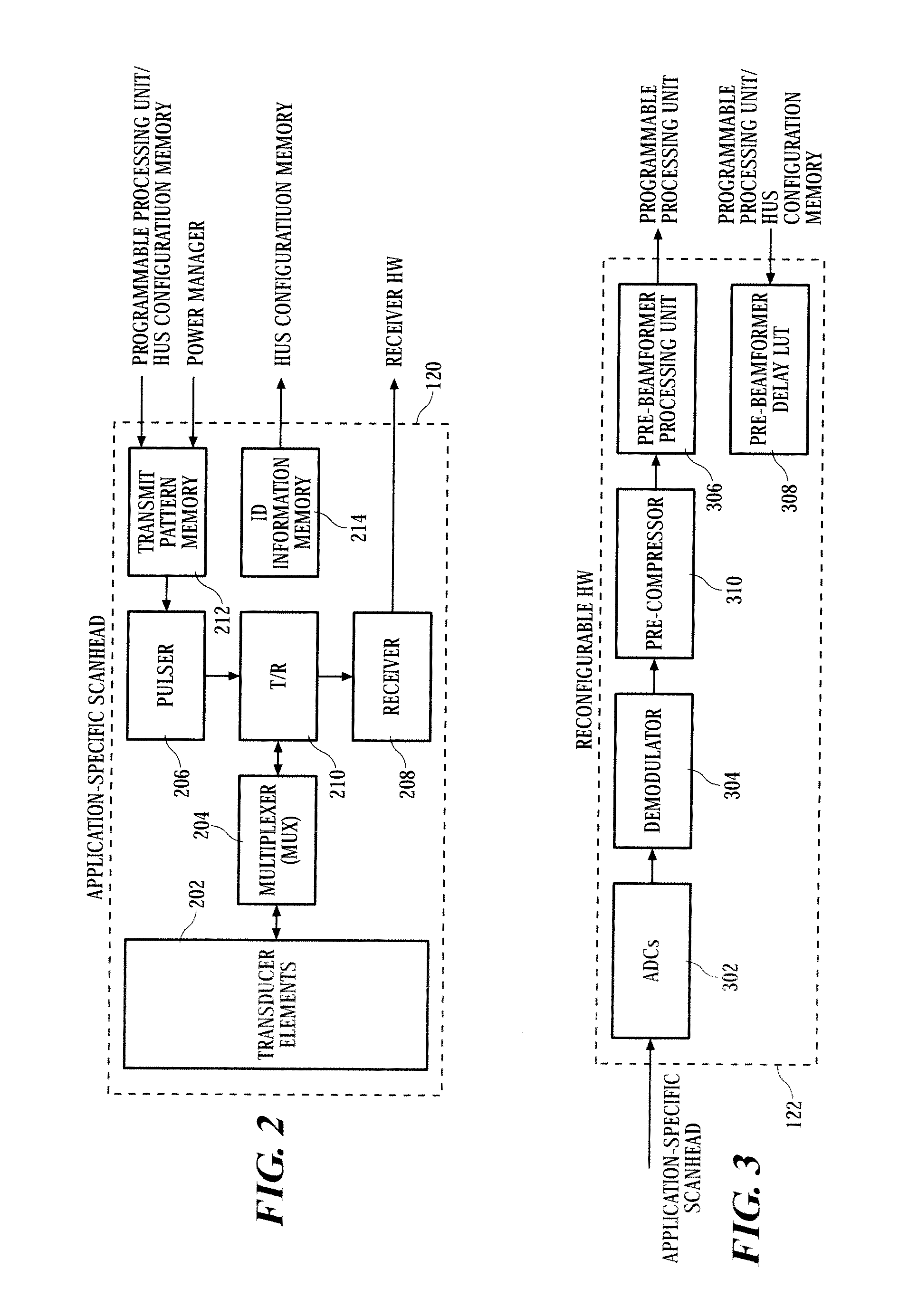
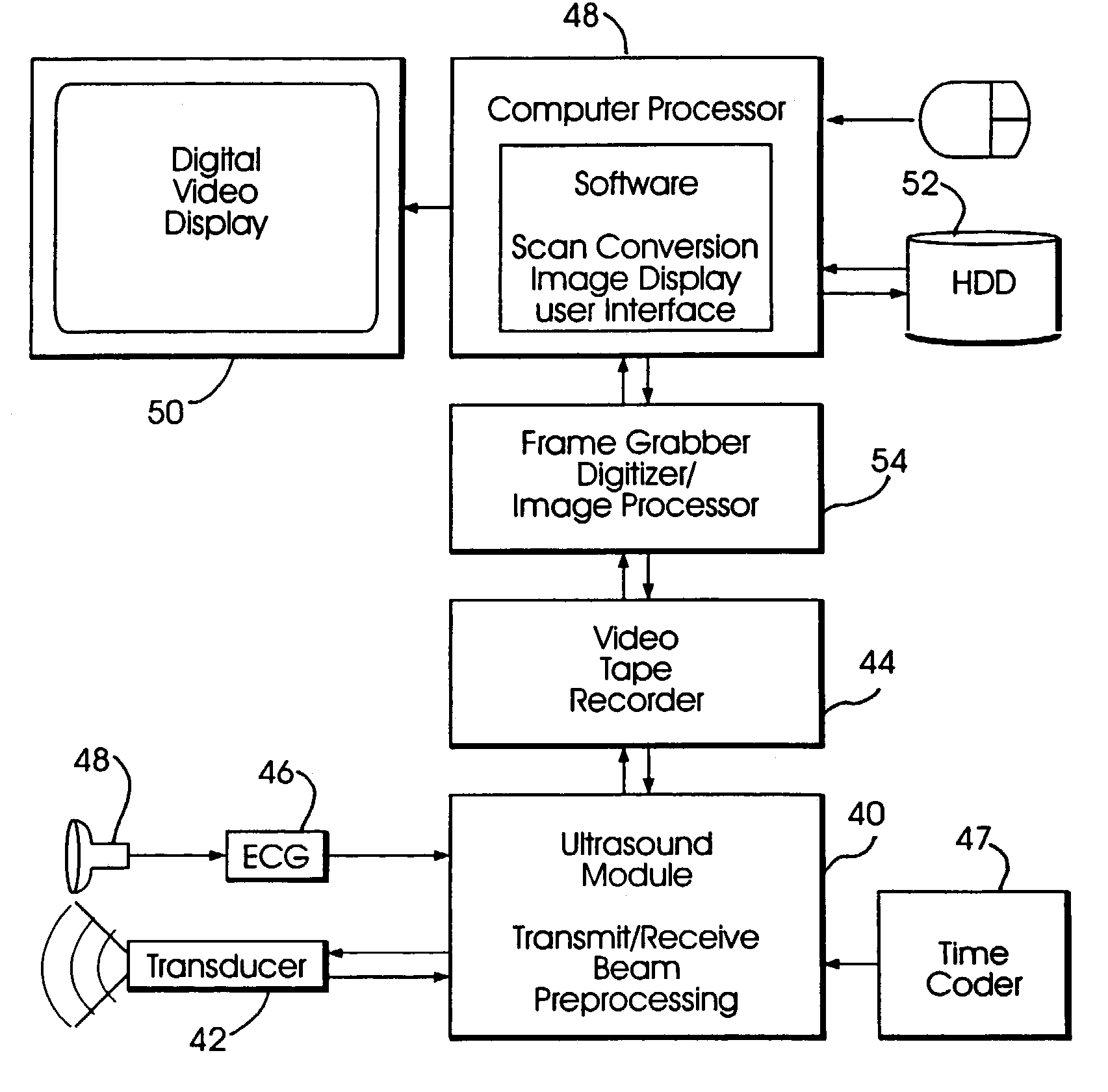
Home ultrasound system
InactiveUS20060074320A1Improve portabilityImprove battery lifeOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationUltrasound sonography
In embodiments of the present invention, an ultrasound system includes an ultrasound machine, which may be located in a hospital, clinic, vehicle, home, etc., coupled to a remotely located diagnosis station via a communication network. For some embodiments, the ultrasound machine includes an application-specific scan head that has identification information that allows the home ultrasound machine to notify a user whether the attached scan head is appropriate for the type of examination to be performed. For other embodiments, a first stage of beamforming is conducted in reconfigurable hardware and a second stage of beamforming is conducted in programmable software digital signal processor. The diagnosis station may transfer information associated with a scanning protocol for the ultrasound examination to the ultrasound machine via the communication network, and the ultrasound machine may transfer measurement values acquired during the ultrasound examination to the diagnosis station via the communication network.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
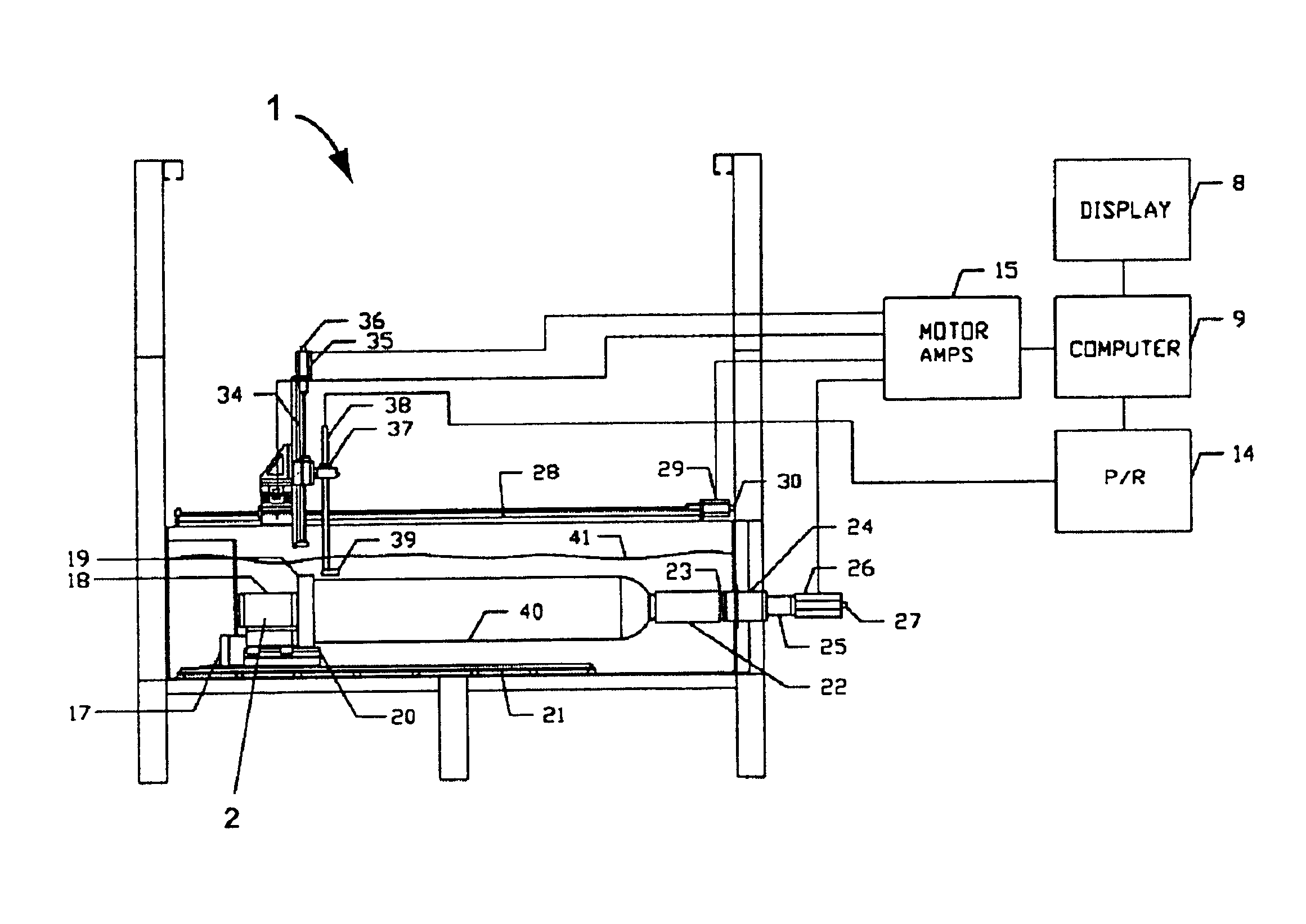
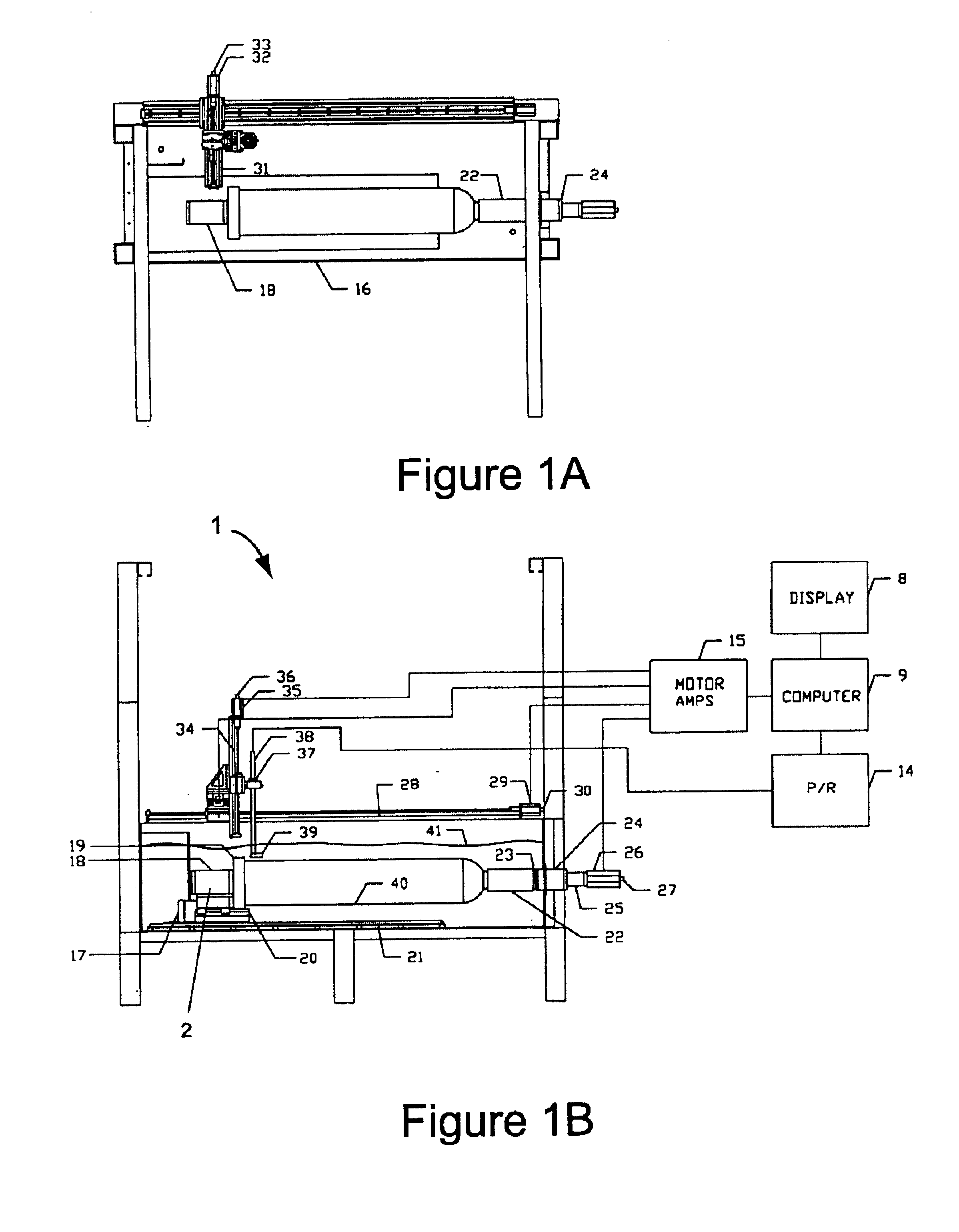
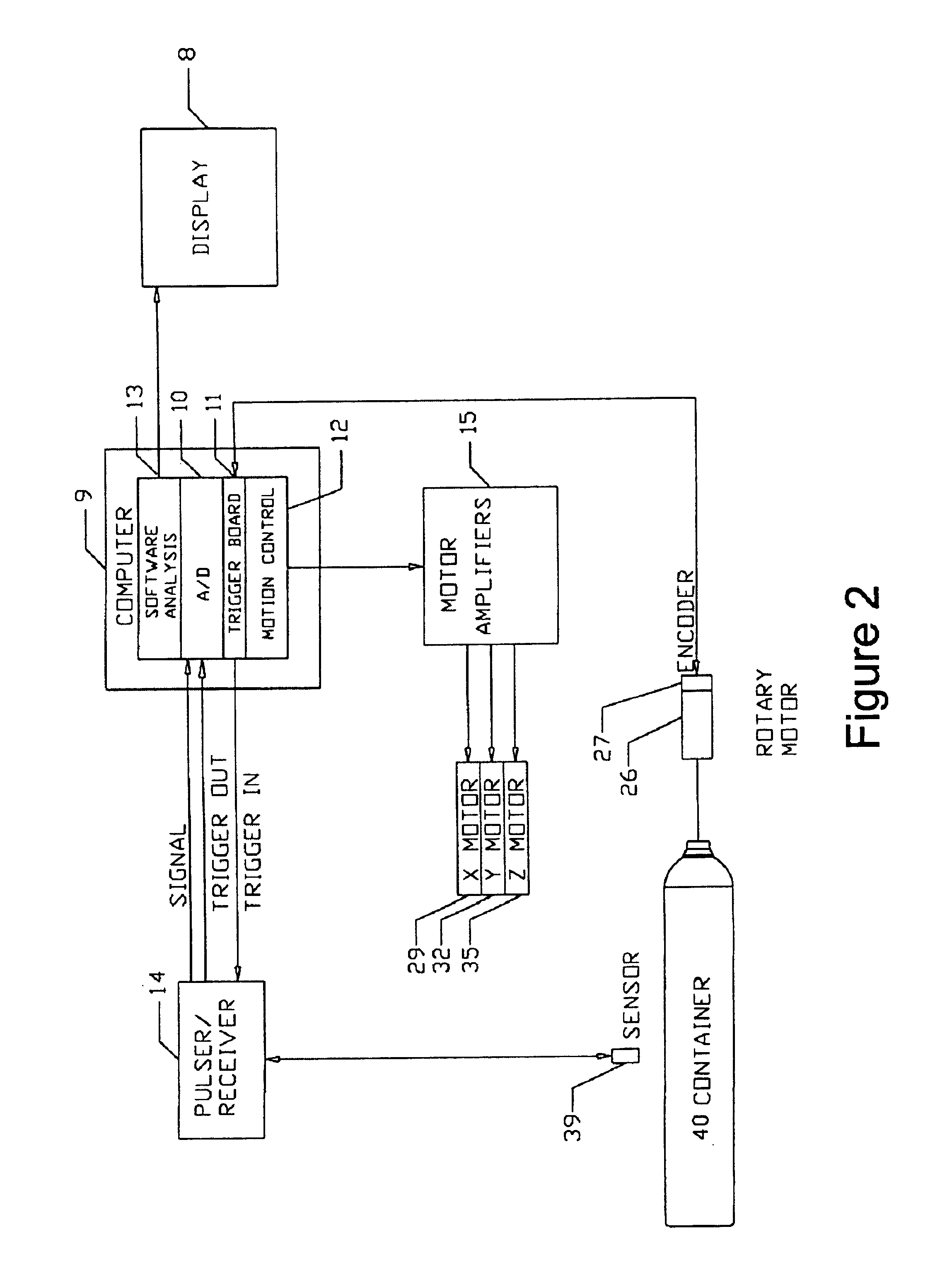
Acoustic inspection device
InactiveUS6938488B2Minimal noise figureRapid determinationUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansMagnetic property measurementsUltrasound sonographyTransducer
An ultrasound inspection apparatus particularly adapted to examine containers (sealed or unsealed) containing a liquid or solid bulk material. The apparatus has an overall configuration of a hand held pistol with a front transducer contact surface that is positioned against a front wall of the container. An ultrasound pulse is transmitted from the apparatus to be reflected from a back wall of a container being investigated. The received echo pulse is converted to a digital waveform. The waveform is analyzed relative to temperature, travel distance of the pulse(s), and time of travel to ascertain characteristics of the liquid or other materials and to provide identification of the same.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Electronic stethoscope system
InactiveUS20090316925A1Auxiliary diagnosisStethoscopeAcoustic sensorsAbnormal bowel soundsSonification
An electronic stethoscope head includes a head member having a contact surface for contact with a patient's body, a transducer in the head member, and an adhesive on the contact surface. A processing system for an electronic stethoscope includes a conditioning circuit configured to receive a transducer signal from a transducer and to be capable of amplifying and / or filtering the transducer signal, to yield a conditioned signal. There is also a signal processor system configured to subject the conditioned signal to an audio editing process. Bodily sounds are detected by applying an electronic stethoscope head a patient's body; generating a patient sonograph of the patient's bodily sounds; and comparing the patient sonograph to a reference sonograph. An electronic stethoscope system may include an accessory device and control circuitry to control the accessory device when abnormal bowel sounds are detected or no bowel sounds are detected for a predetermined interval.
Owner:EISENFELD LEONARD
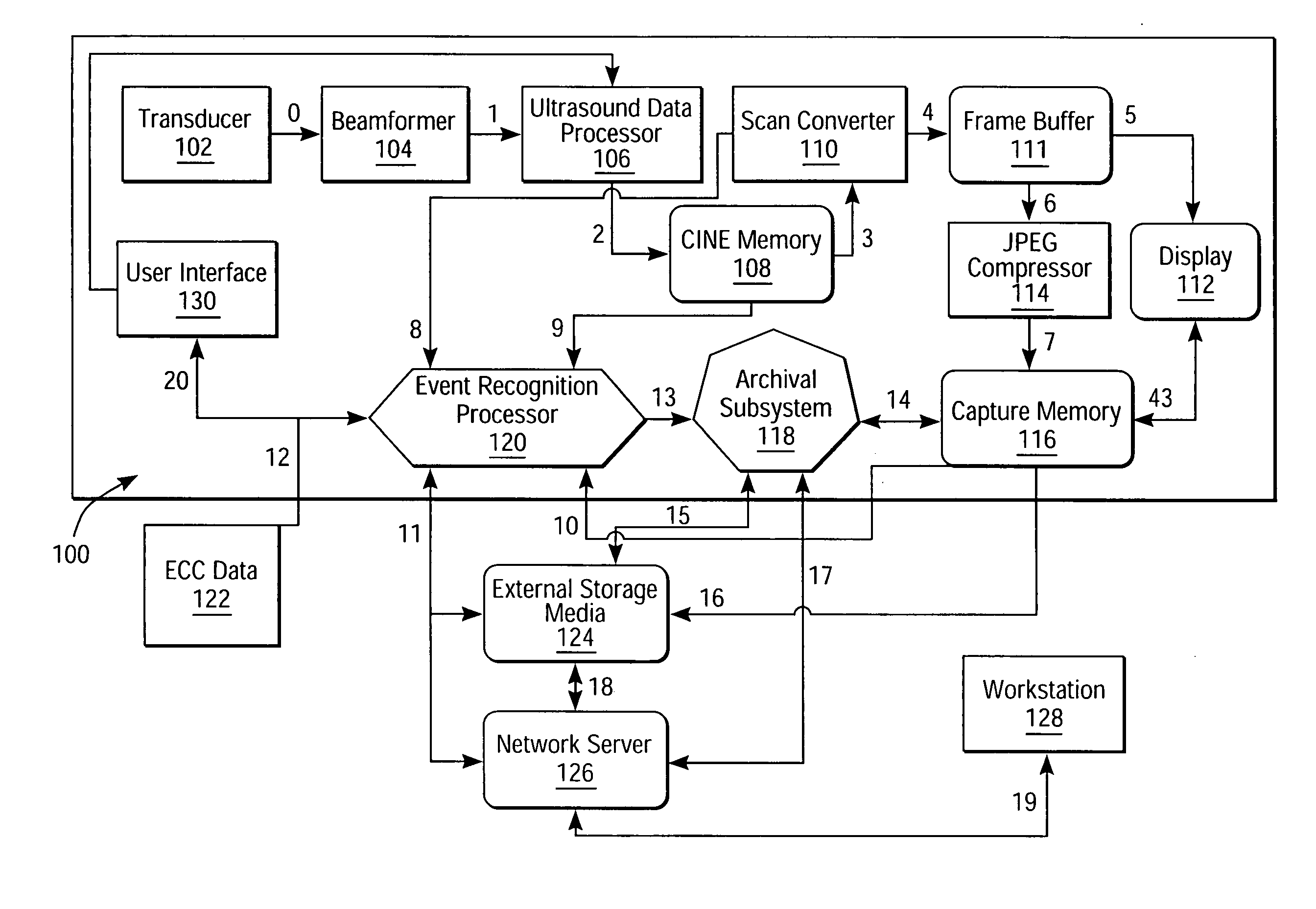
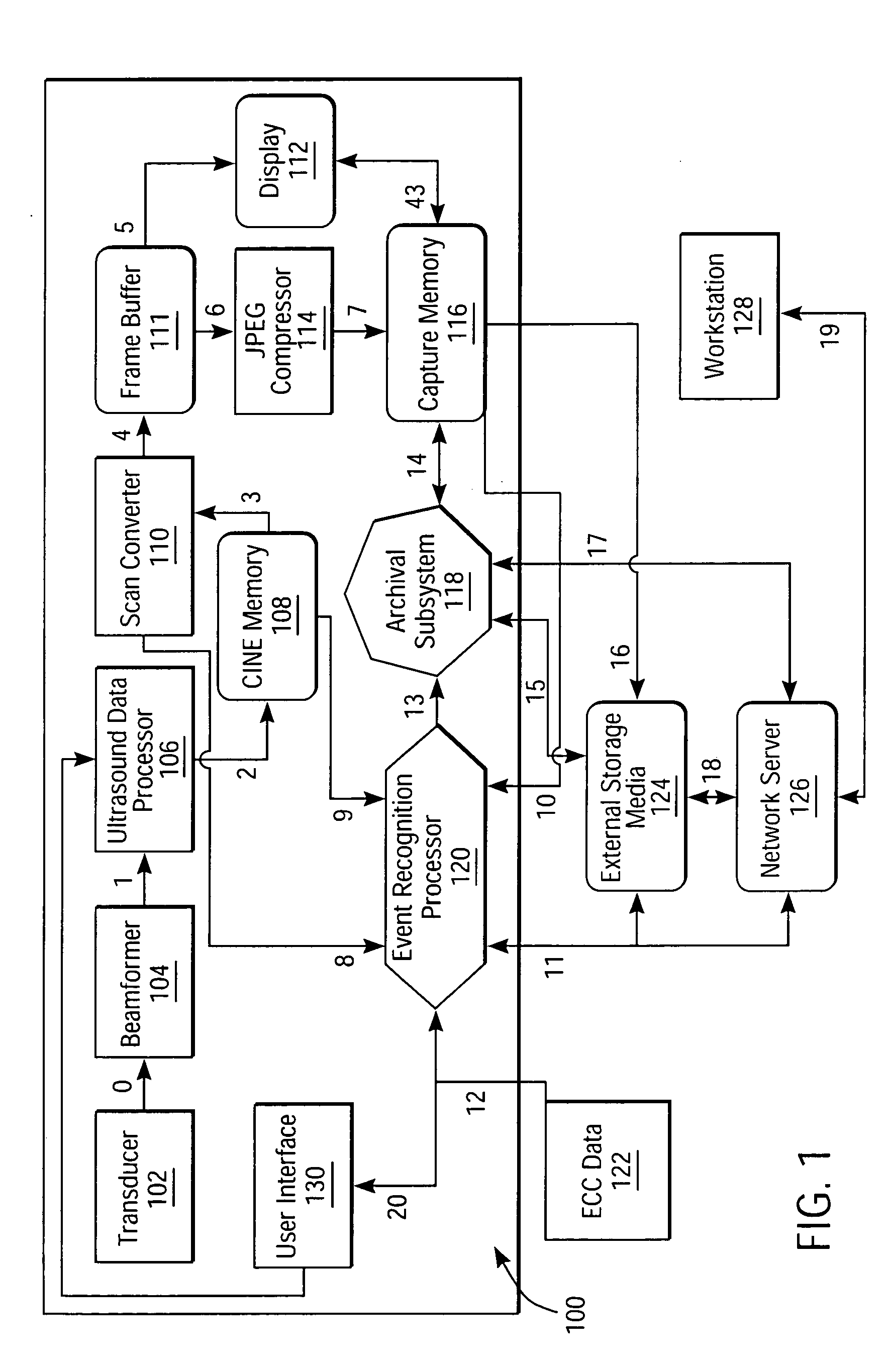
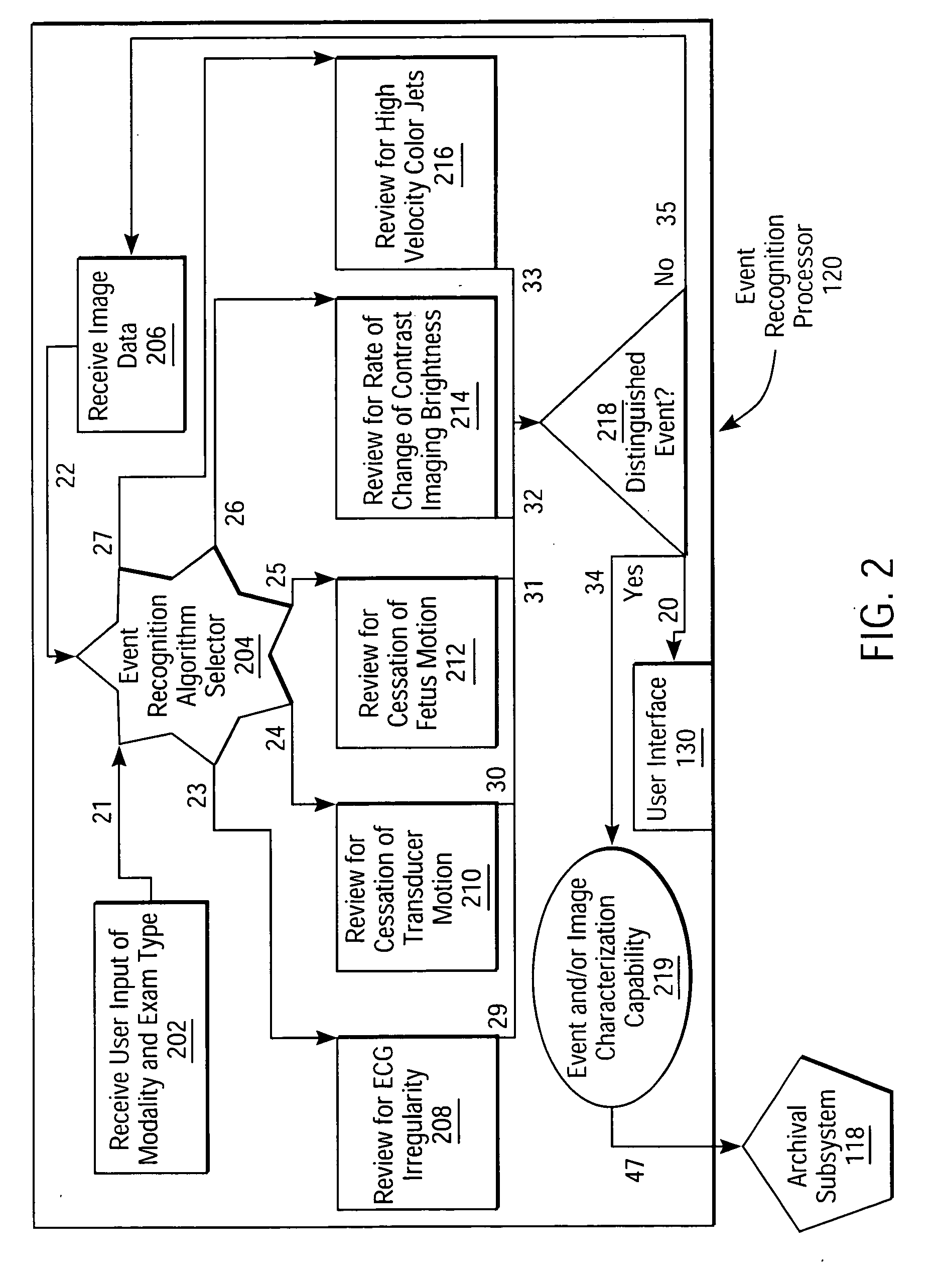
Intelligent ultrasound examination storage system
ActiveUS20050096539A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionSystems analysisUltrasound sonography
An intelligent ultrasound examination storage system is disclosed, which permits a sonographer to focus entirely on the examination process while the system analyses image data and marks events of interest for post-examination review or storage.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
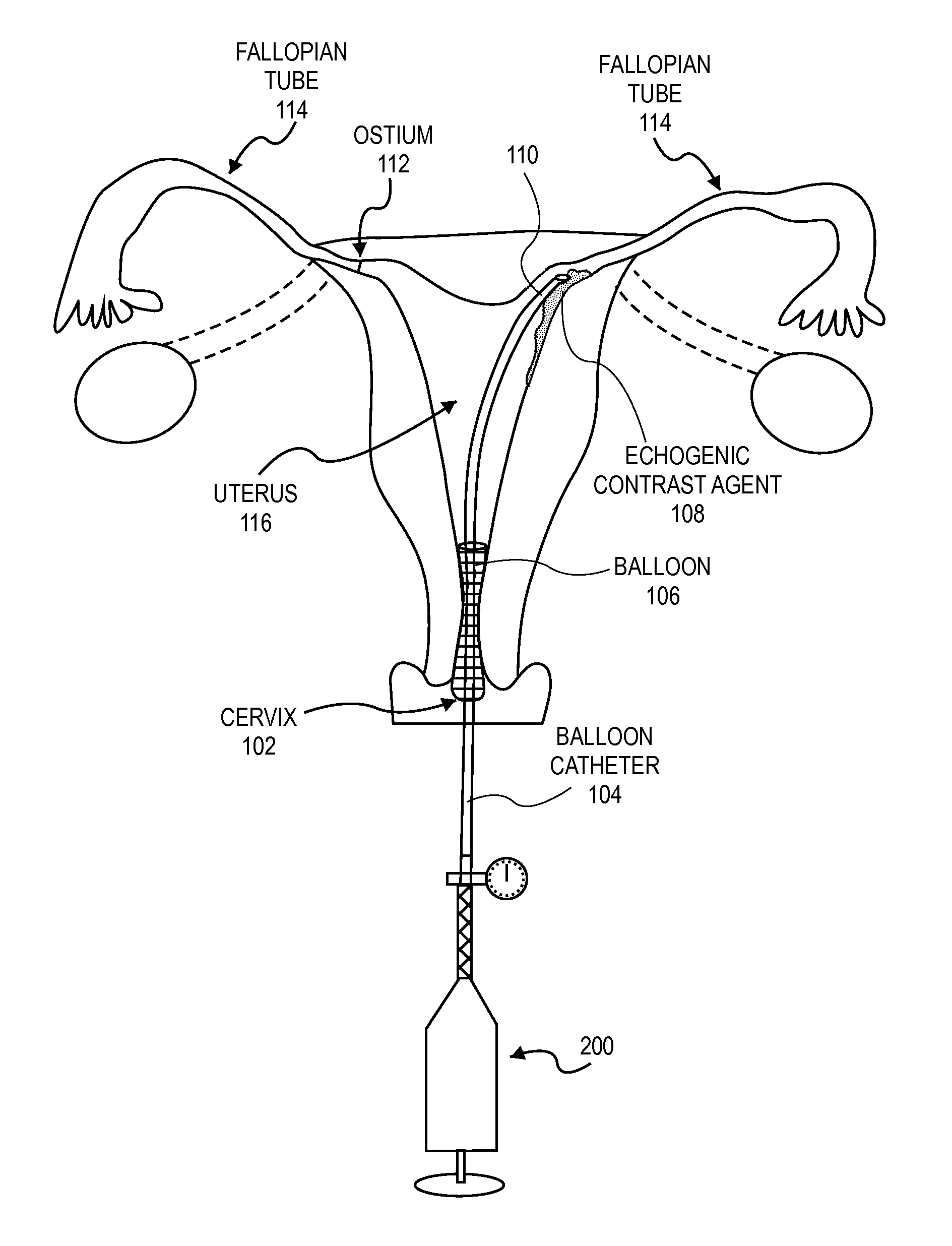
Methods and devices for determining lumen occlusion
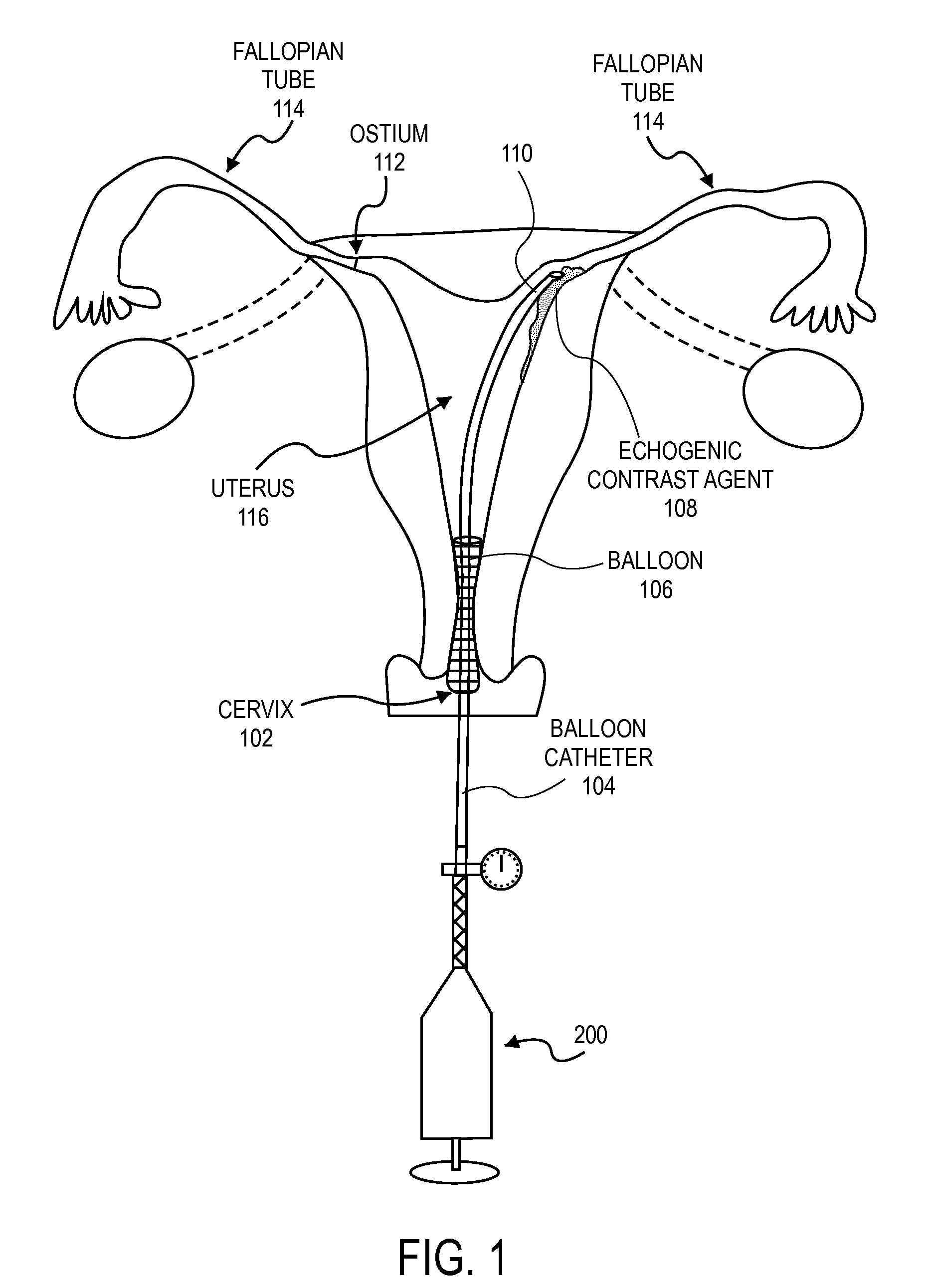
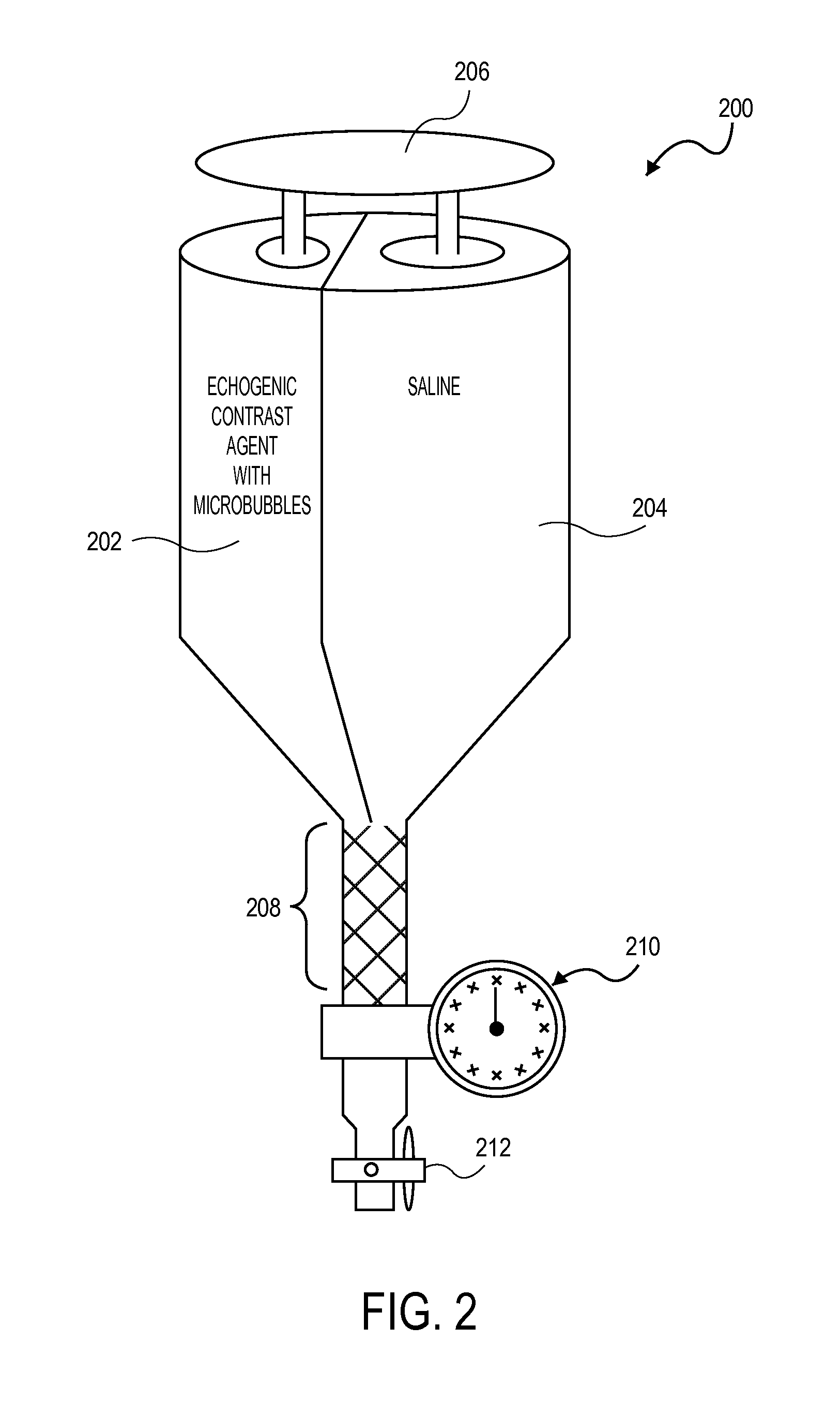
InactiveUS20110137150A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryMicrobubblesContrast enhance ultrasound
Embodiments of the present invention describe methods of determining the occlusion of body lumens and apparatuses for doing so. In one particular embodiment, the occlusion of the fallopian tubes by an intrafallopian contraceptive device may be confirmed by contrast enhanced ultrasonography (also known as stimulated acoustic emission hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography). In these embodiments a contrast agent containing microbubbles is used.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Pipe inspection systems and methods
InactiveUS6782751B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionElastomerUltrasound device
Systems and methods for ultrasonically inspecting pipe, the pipe having a longitudinal axis, the methods in certain aspects including compressing with a compressing force an elastomeric element between an ultrasonic probe of an ultrasonic pipe inspection system and a pipe to be inspected; and, in certain aspects, the systems and methods including placing a coupling between the elastomeric element and the pipe, wherein the elastomeric element surrounds the pipe; and, in certain aspects, a system for ultrasonically inspecting pipe, the system with a housing, a packer element in the housing with an opening through which a pipe to be inspected is passable, and at least one ultrasonic probe in or on the housing useful in conjunction with an ultrasonic apparatus for inspecting pipe.
Owner:COILED TUBING ENG SERVICES
System and method for improving ultrasound image acquisition and replication for repeatable measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS20040116812A1ElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical landmarkUltrasonic sensor
High resolution B-mode ultrasound images of the common carotid artery are obtained with an ultrasound transducer using a standardized methodology. Subjects are supine with the head counter-rotated 45 degrees using a head pillow. The jugular vein and carotid artery are located and positioned in a vertical stacked orientation. The transducer is rotated 90 degrees around the centerline of the transverse image of the stacked structure to obtain a longitudinal image while maintaining the vessels in a stacked position. A computerized methodology assists operators to accurately replicate images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time "live" ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. By viewing both images, whether simultaneously or alternately, while manually adjusting the ultrasound transducer, an operator is able to bring into view the real-time image that best matches a selected image from the earlier ultrasound examination. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. All images contain anatomical landmarks for reproducing probe angulation, including visualization of the carotid bulb, stacking of the jugular vein above the carotid artery, and initial instrumentation settings, used at a baseline measurement are maintained during all follow-up examinations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Device and method designed for ultrasonically inspecting cylinders for longitudinal and circumferential defects and to measure wall thickness
InactiveUS6851319B2Good flexibilitySimpler and flexibleAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorUltrasound sonography
Methods and apparatus for ultrasonically scanning cylinders are provided. The methods and apparatus employ as few as one ultrasonic sensor for full immersion scanning and defect detection. Self-centering fixturing spins the cylinder, reducing vibration, allowing for fast ultrasonic scans. To create the 45 degree angle beam shear waves for the circumferential scans, the ultrasonic sensor is offset from the centerline of the cylinder, creating the correct angle for excitation of the shear wave.
Owner:DIGITAL WAVE CORP
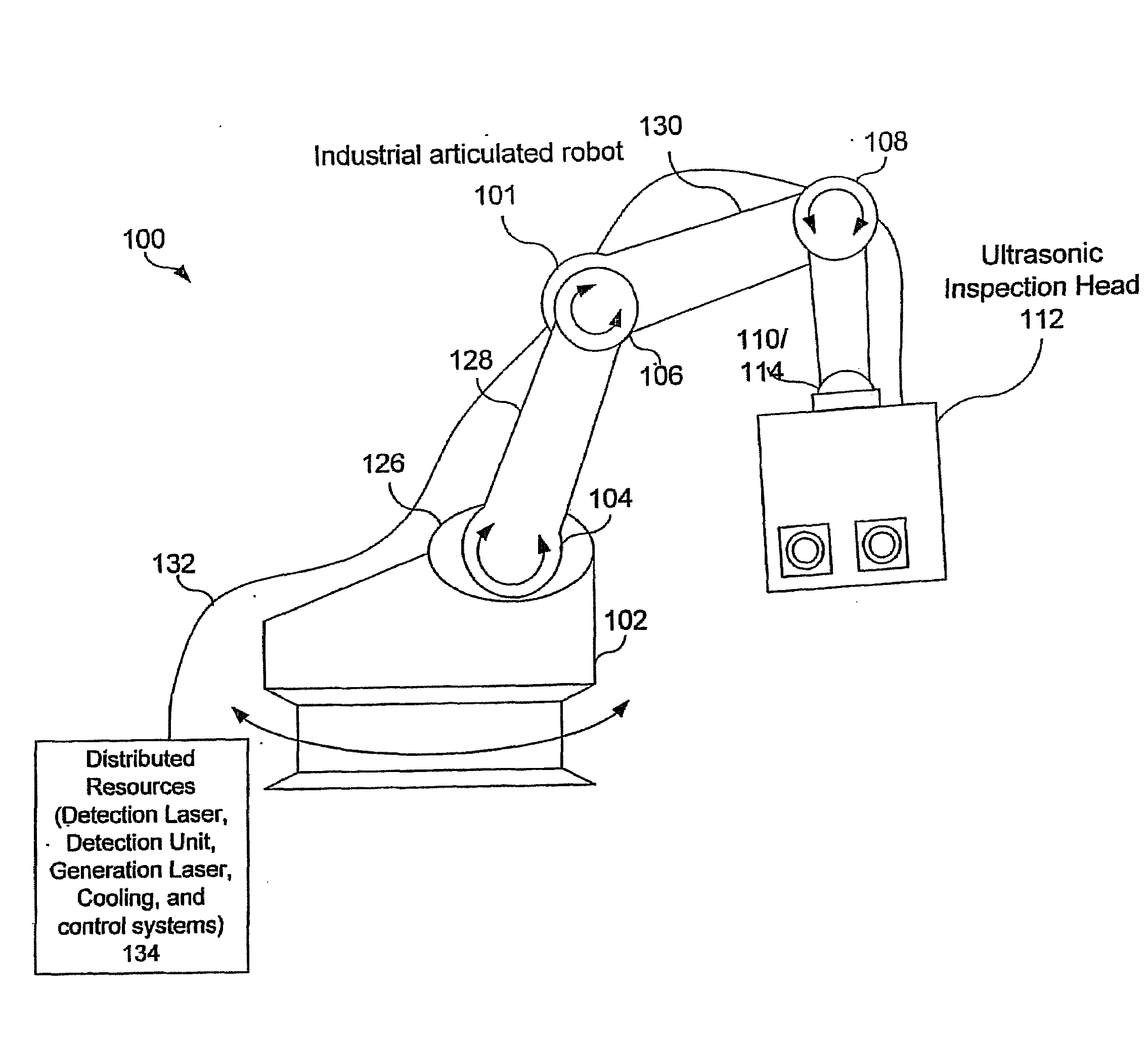
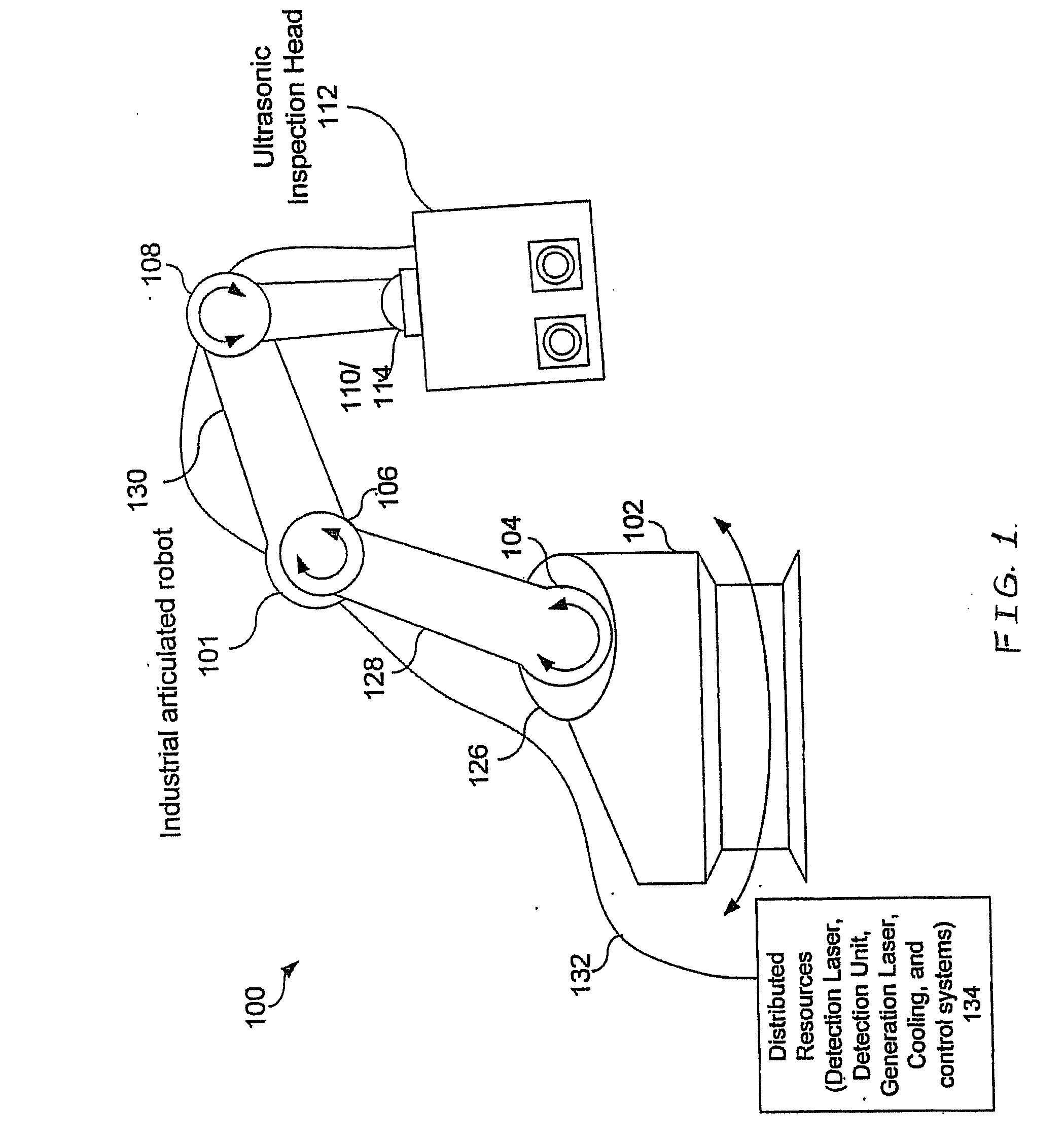
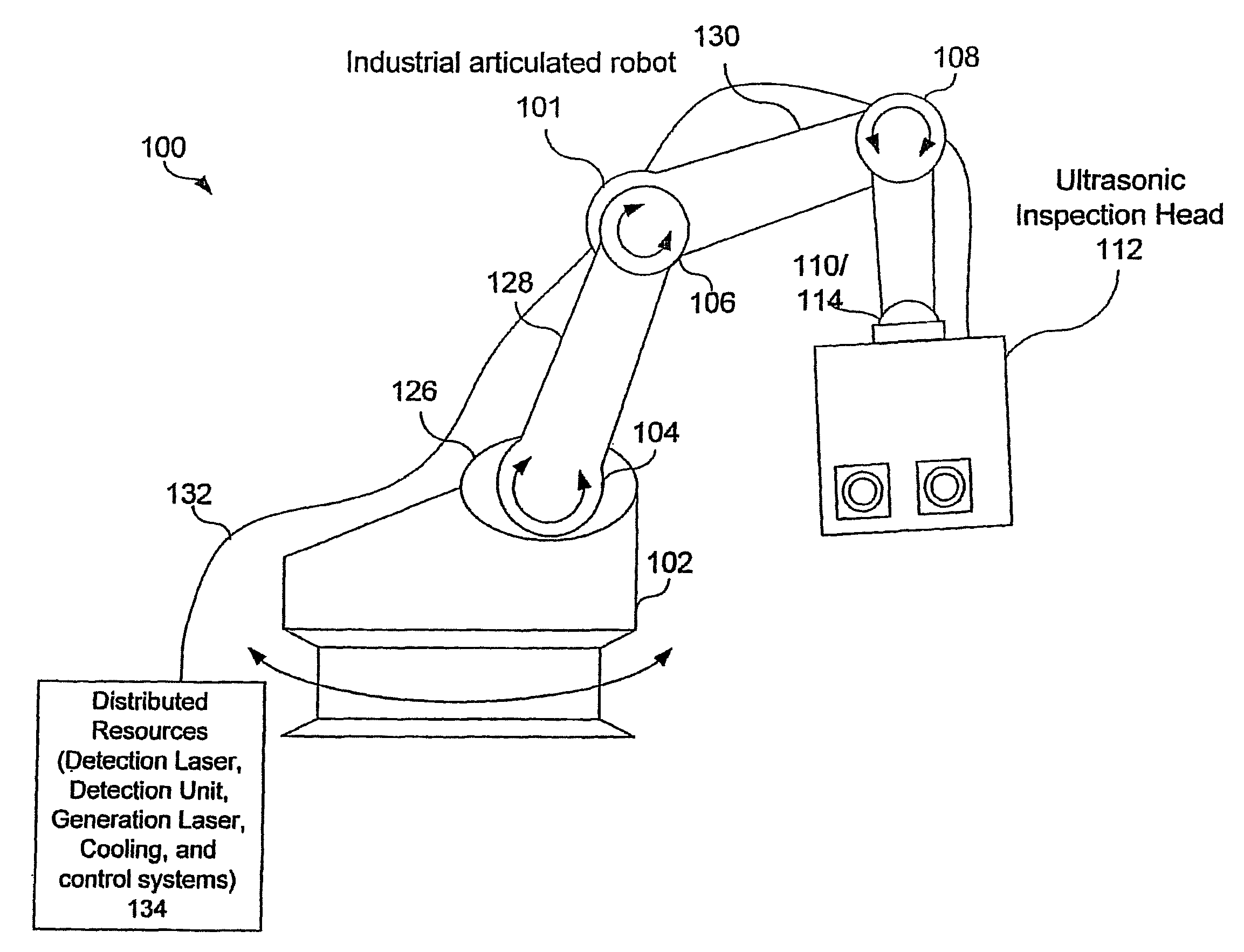
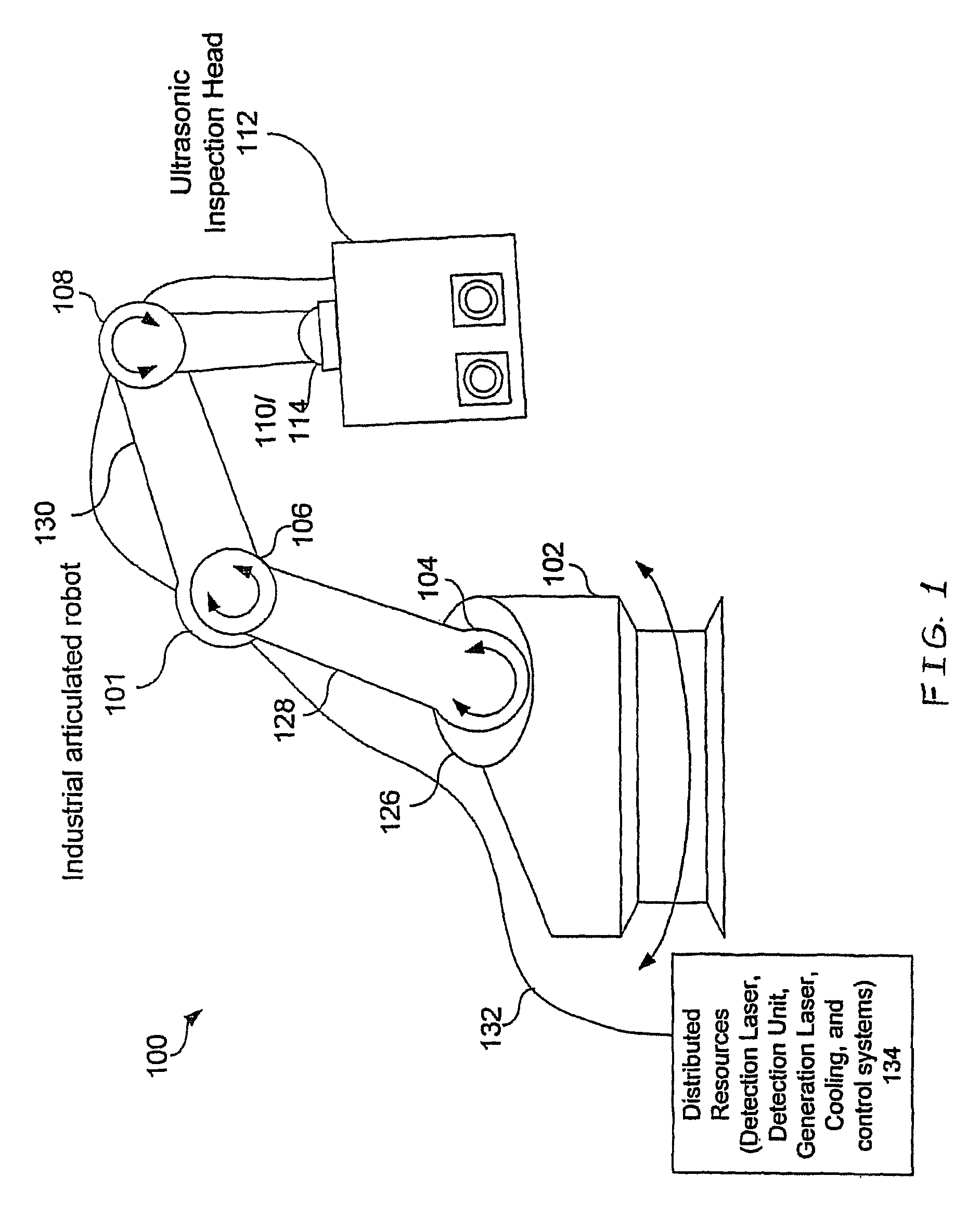
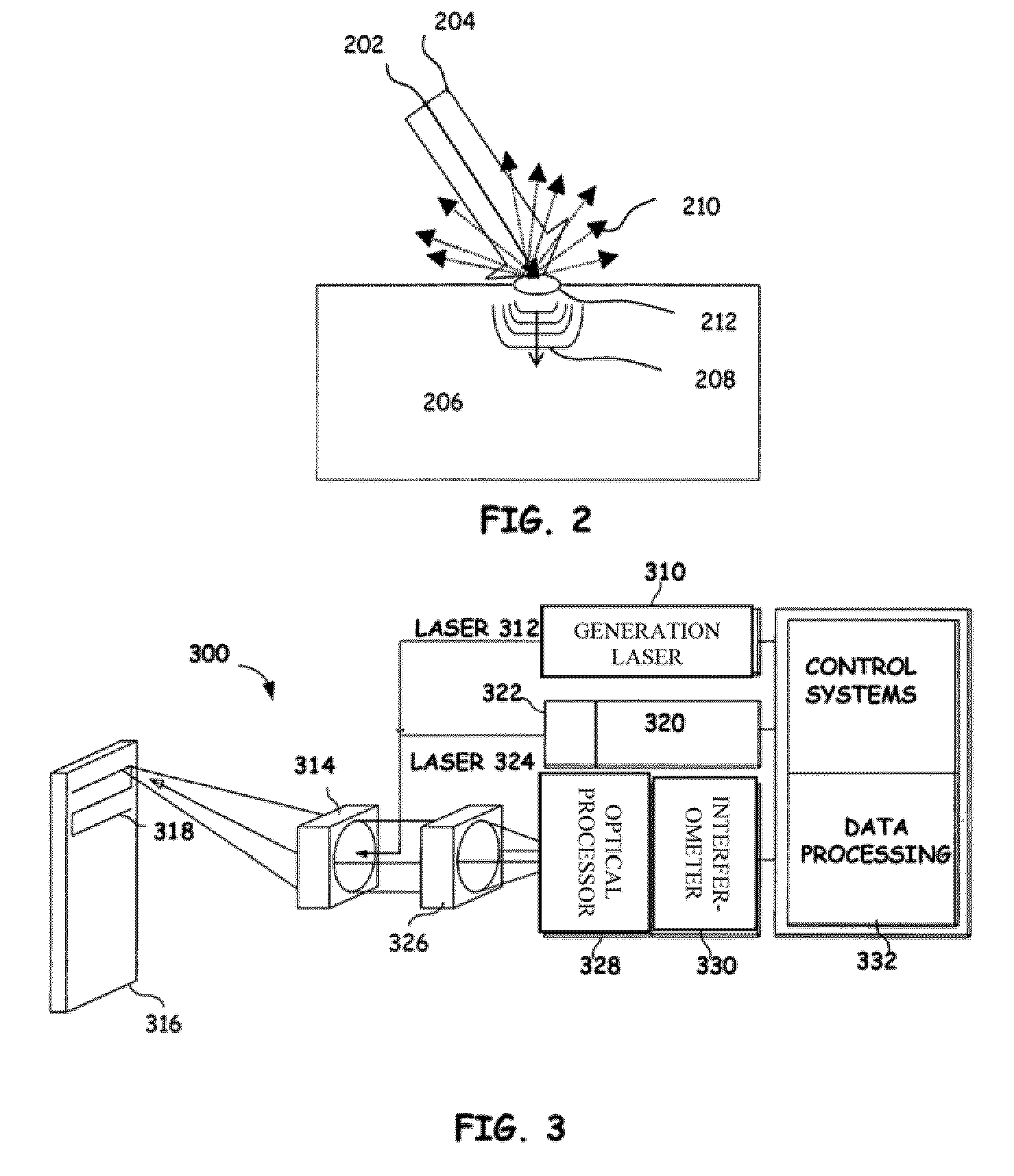
Articulated robot for laser ultrasonic inspection
ActiveUS20090010285A1Cost-effectiveMore compact robotsLaser using scattering effectsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveUltrasound sonography
An ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation (NDE) system operable to inspect target materials is provided. This ultrasonic NDE system includes an articulated robot, an ultrasound inspection head, a processing module, and a control module. The ultrasound inspection head couples to or mounts on the articulated robot. The ultrasound inspection head is operable to deliver a generation laser beam, a detection laser beam, and collect phase modulated light scattered by the target materials. The processing module processes the phase modulated light and produces information about the internal structure of the target materials. The control module directs the articulated robot to position the ultrasound inspection head according to a pre-determined scan plan.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
System and method for ultrasonic examination of the breast
InactiveUS20130267850A1Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingUltrasonic radiation
The invention provides a system and method for limited view ultrasound imaging of a 2D section or a 3D volume of a body part. Ultrasound sensors configured are spatially or temporally arrayed in a limited view circular arc or over at least part of a concave surface such as a hemisphere. A processor calculates from detected ultrasound radiation a beam forming (BF) functional and calculates from the free amplitudes a point spread function (PSF). A filter g(k) is calculated from the Fourier transform HBF(k) of the PSF that is used to generate an image of the 2D section or the 3D volume of the body part.
Owner:BERMAN MICHAEL
Home ultrasound system
InactiveUS20110301464A1Improve portabilityImprove battery lifeOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound sonographyEngineering
In embodiments of the present invention, an ultrasound system includes an ultrasound machine, which may be located in a hospital, clinic, vehicle, home, etc., coupled to a remotely located diagnosis station via a communication network. For some embodiments, the ultrasound machine includes an application-specific scan head that has identification information that allows the home ultrasound machine to notify a user whether the attached scan head is appropriate for the type of examination to be performed. For other embodiments, a first stage of beamforming is conducted in reconfigurable hardware and a second stage of beamforming is conducted in programmable software digital signal processor. The diagnosis station may transfer information associated with a scanning protocol for the ultrasound examination to the ultrasound machine via the communication network, and the ultrasound machine may transfer measurement values acquired during the ultrasound examination to the diagnosis station via the communication network.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
System and method for improving ultrasound image acquisition and replication for repeatable measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS7074187B2ElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical landmarkUltrasonic sensor
High resolution B-mode ultrasound images of the common carotid artery are obtained with an ultrasound transducer using a standardized methodology. Subjects are supine with the head counter-rotated 45 degrees using a head pillow. The jugular vein and carotid artery are located and positioned in a vertical stacked orientation. The transducer is rotated 90 degrees around the centerline of the transverse image of the stacked structure to obtain a longitudinal image while maintaining the vessels in a stacked position. A computerized methodology assists operators to accurately replicate images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time “live” ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. By viewing both images, whether simultaneously or alternately, while manually adjusting the ultrasound transducer, an operator is able to bring into view the real-time image that best matches a selected image from the earlier ultrasound examination. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. All images contain anatomical landmarks for reproducing probe angulation, including visualization of the carotid bulb, stacking of the jugular vein above the carotid artery, and initial instrumentation settings, used at a baseline measurement are maintained during all follow-up examinations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Handheld volumetric ultrasound scanning
InactiveUS20100179429A1Improve positional stabilityProcess stabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationImaging quality
Systems, methods, and related computer program products for ultrasonic examination of a tissue volume, such as a human breast, are described. A handheld volumetric ultrasound scanning probe, which is characterized by a two-dimensional scan area with a substantially rigid cap extending across the two-dimensional scan area, is provided with a texturably couplant-porous material sheet covering the substantially rigid cap over at least a portion of the two-dimensional scan area. The texturably couplant-porous material sheet facilitates positional stability of the handheld volumetric ultrasound scanning probe while positioned against a skin surface of the tissue volume. Advantageously, while the texturably couplant-porous material sheet brings about a more stable physical interface at the skin surface, the texturably couplant-porous material sheet brings about little or no degradation in acquired image quality. Also described are systems and related methods for elastography imaging using the handheld volumetric ultrasound scanning probe.
Owner:U SYST
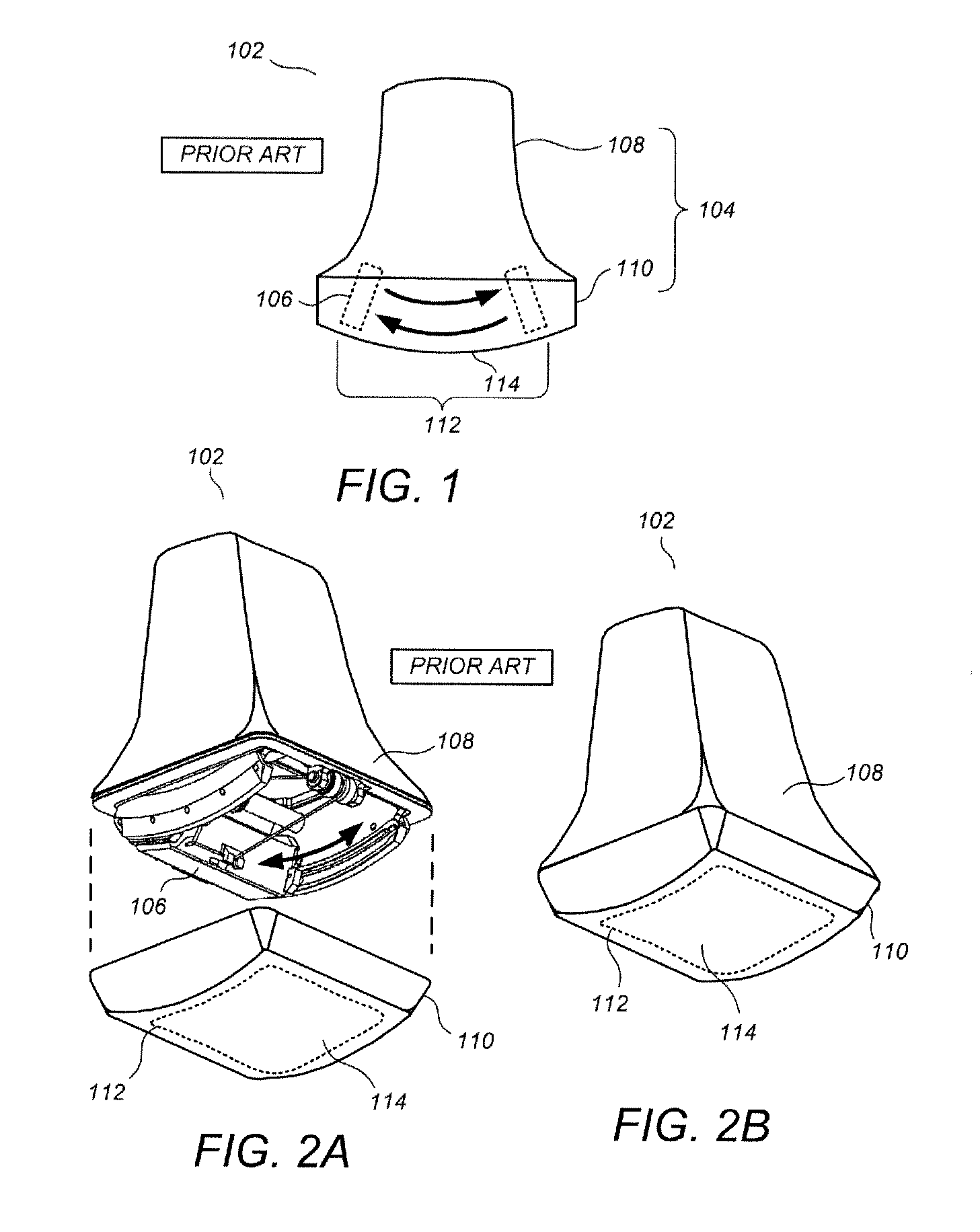
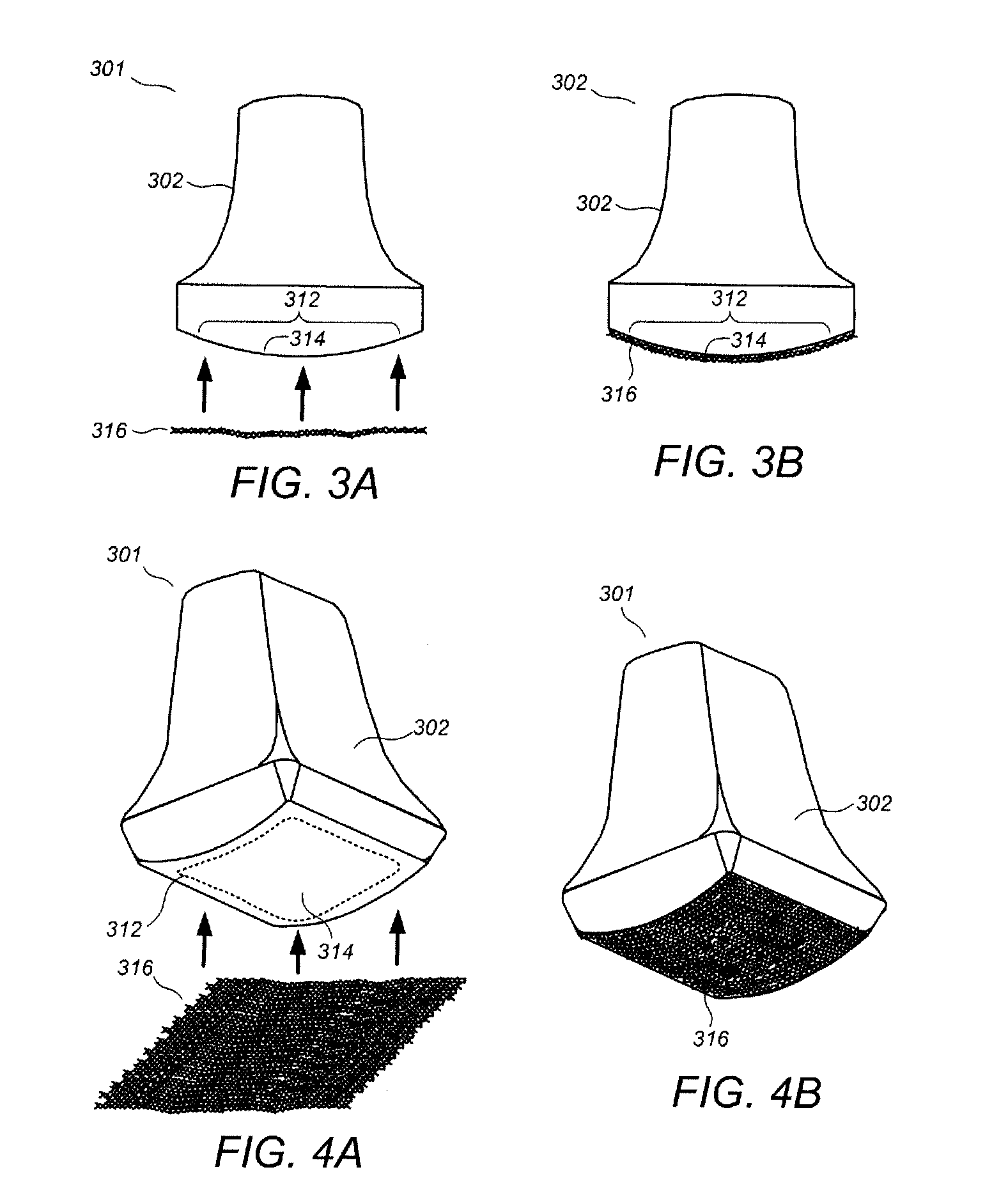
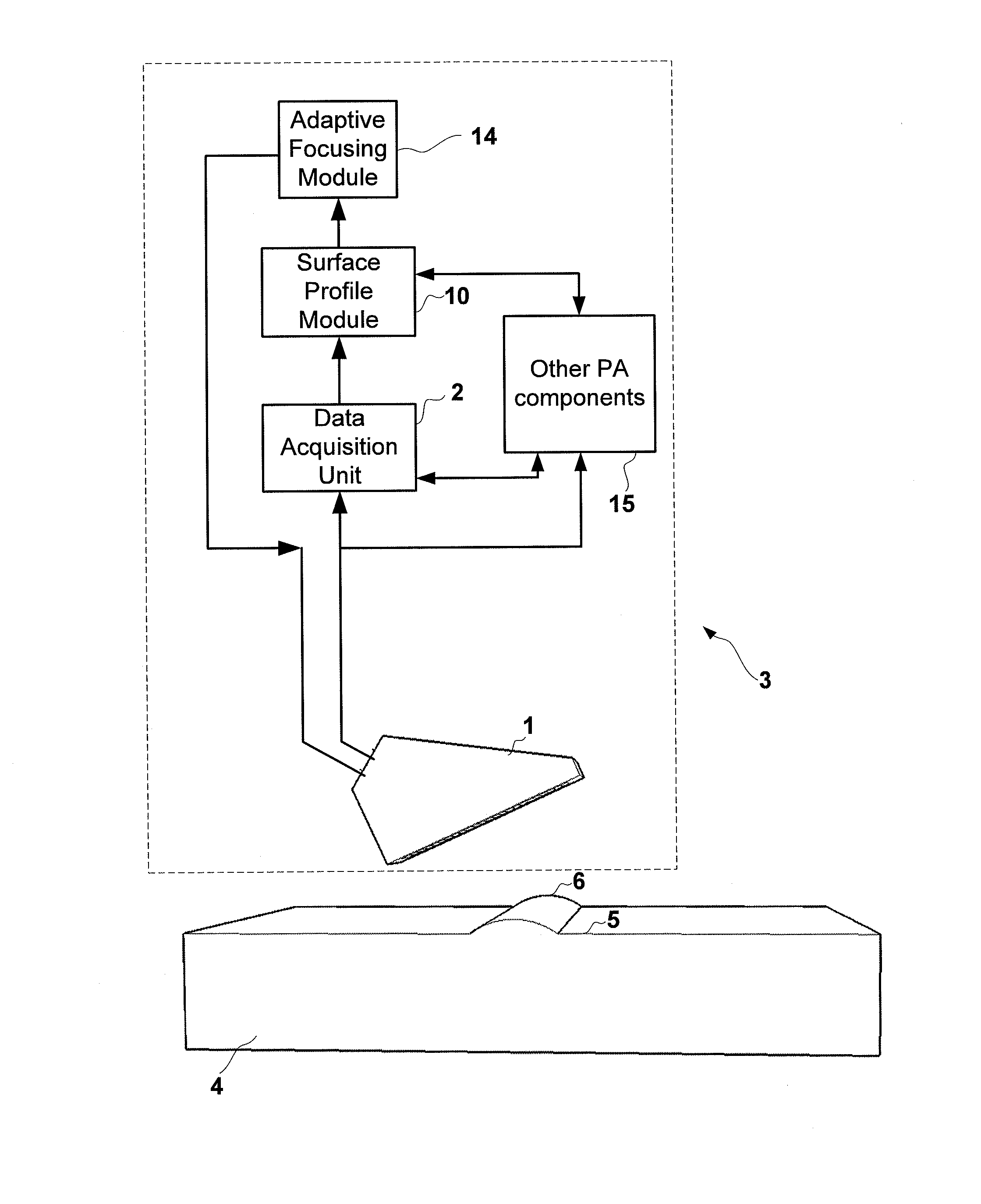
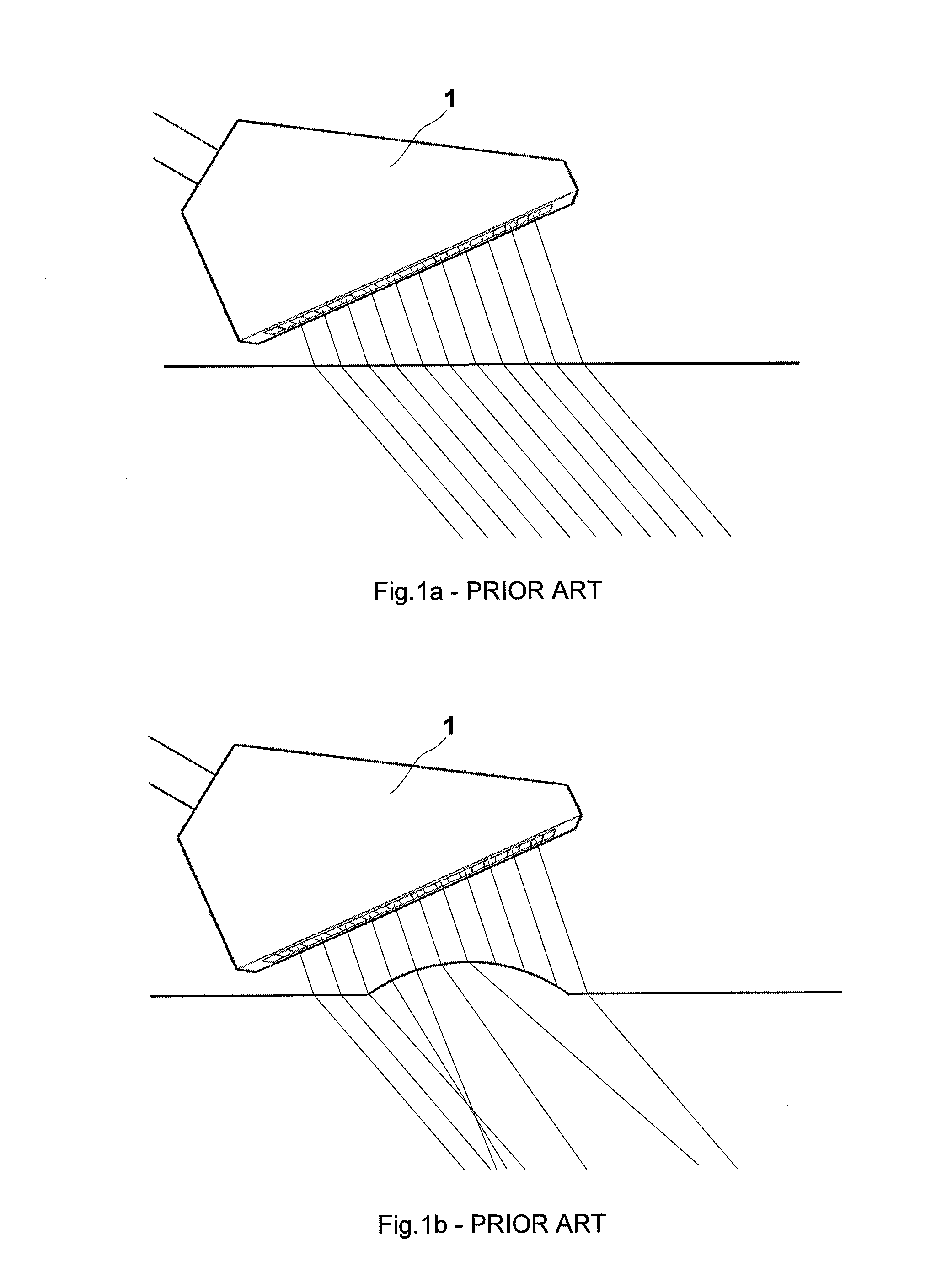
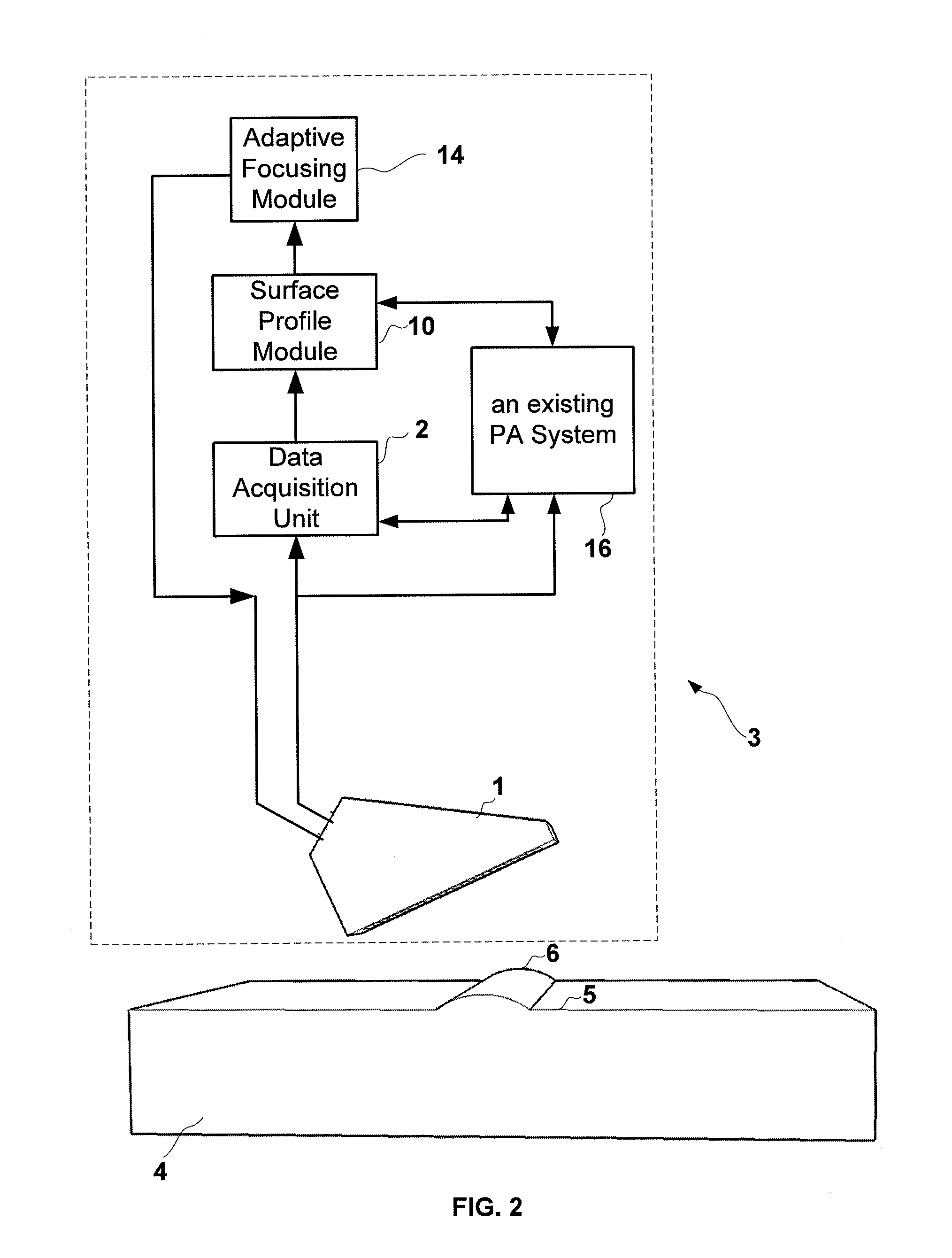
System and a method of adaptive focusing in a phased array ultrasonic system
InactiveUS20140283611A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansSonificationUltrasound sonography
Disclosed in the present disclosure is a phased array system configured to ultrasonically inspect test targets complex surfaces while employing the surface profiling capability of phased-array linear and sectorial scans. Adaptive focusing is employed for inspecting the test target by using customized apertures according to the surface profiles to generate a plurality of beams that are evenly and thoroughly spaced along a scan line inside the test target.
Owner:OLYMPUS NDT
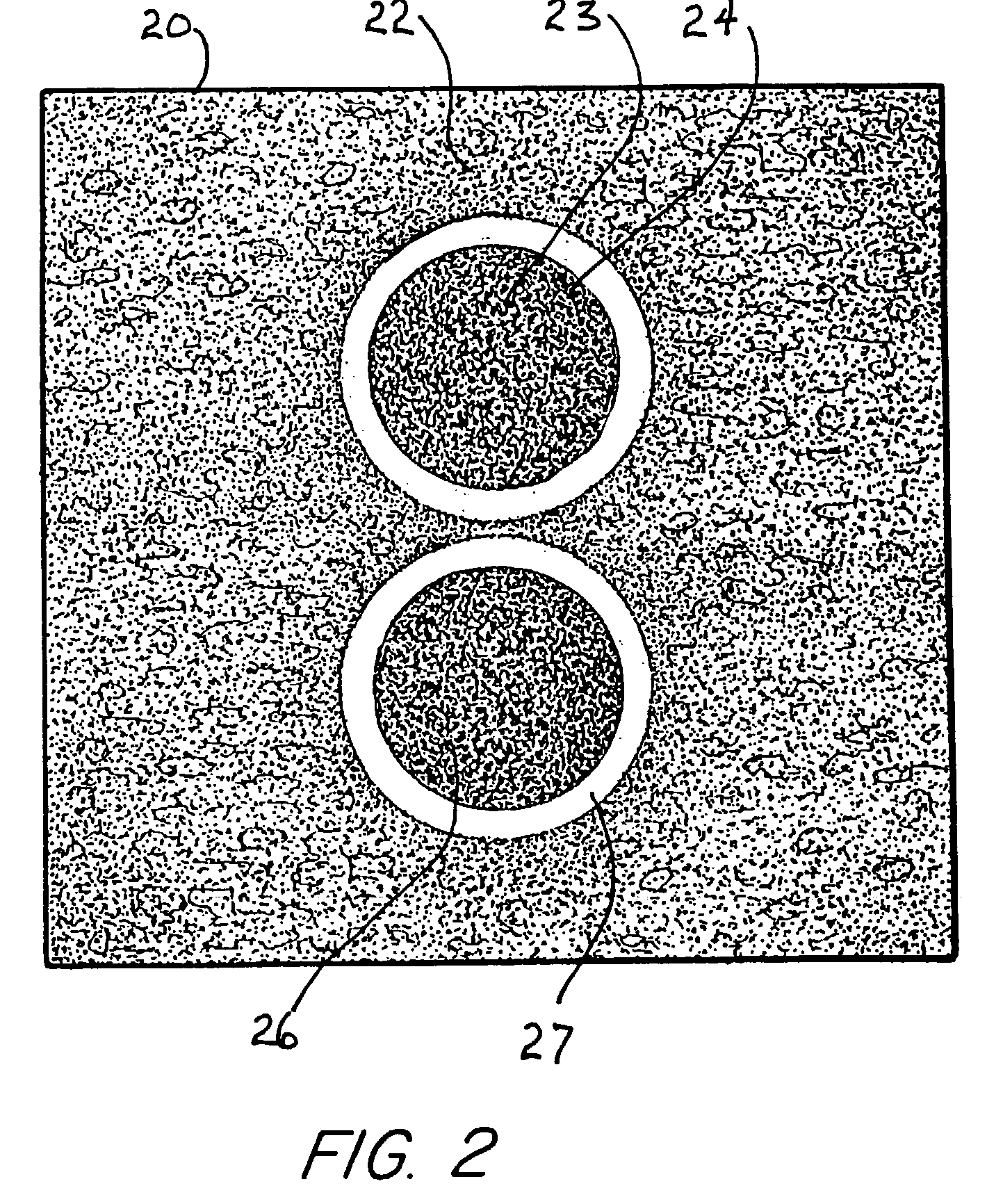
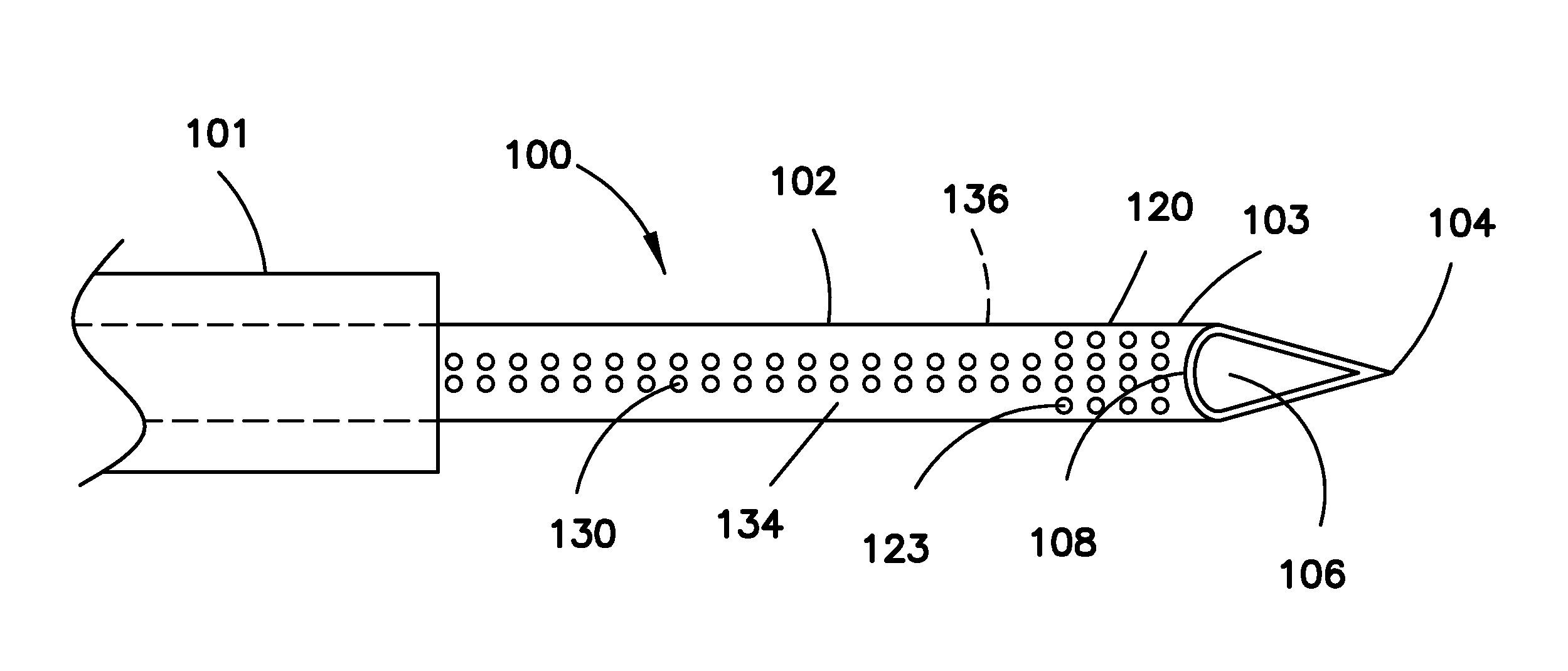
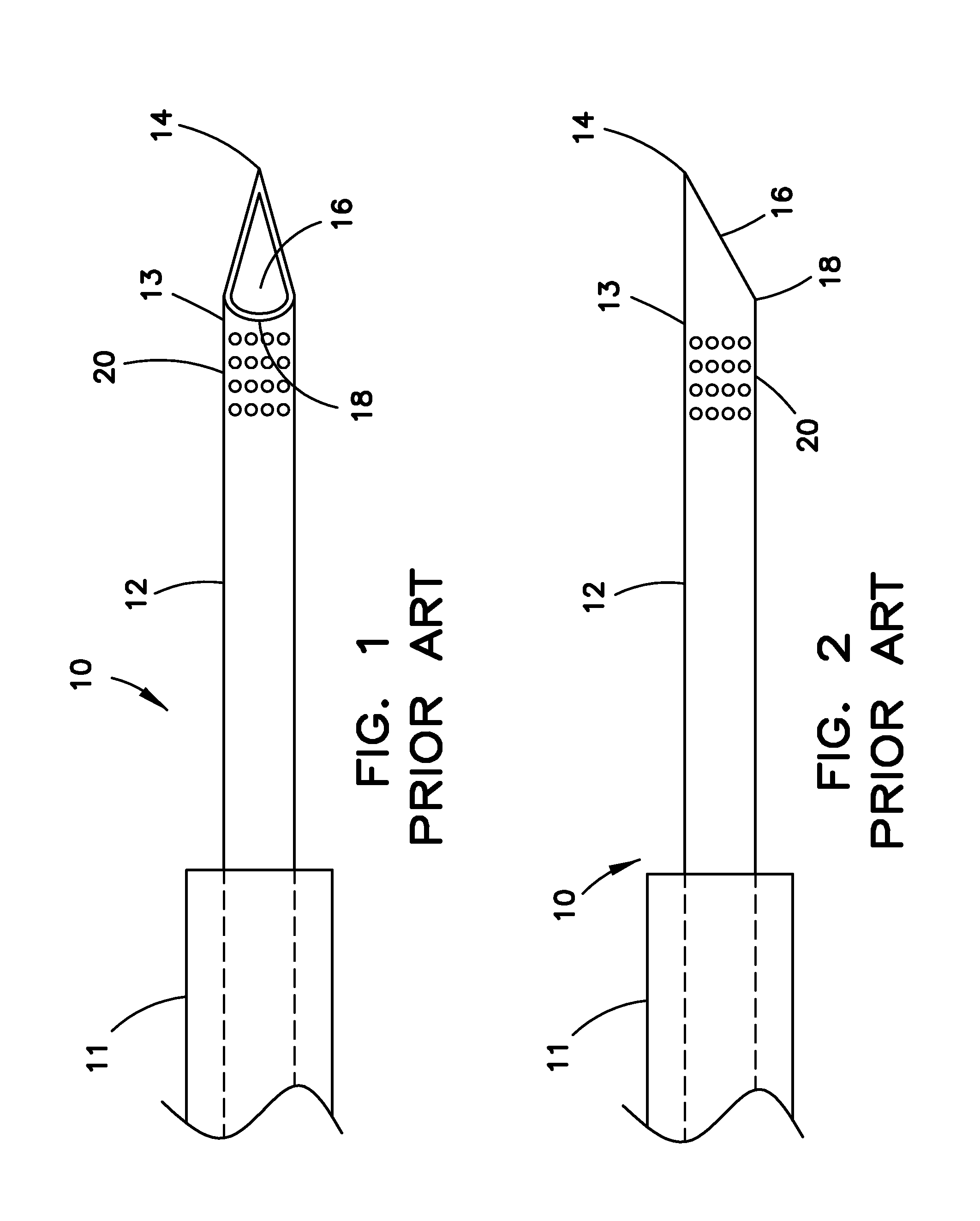
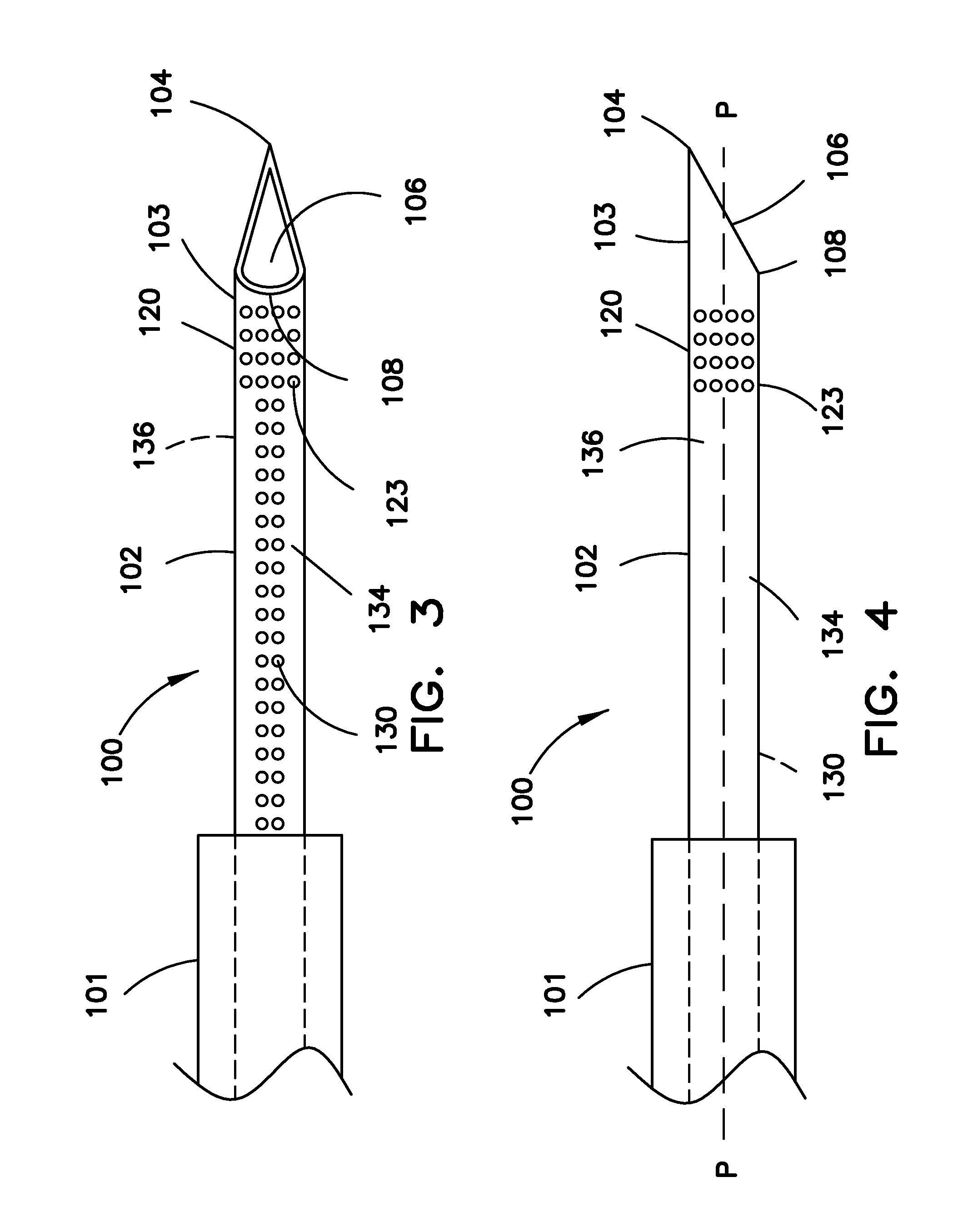
Echogenic medical device
InactiveUS20130190609A1Increase echogenicityOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesUltrasound sonographyDistal portion
An echogenic medical device includes a shaft having a proximal portion, a distal portion, first and second opposing longitudinal sides, and a passageway extending therethrough. The distal end includes a beveled opening communicating with the passageway, and extending between a distal tip portion disposed along the first longitudinal side and a heel portion disposed along the second longitudinal side. A first echogenic region extends circumferentially around the shaft at the distal portion. The first echogenic region is structured for providing a signal visible along the circumference of the shaft under ultrasound visualization. A second echogenic region extends along a length of the second longitudinal side and is substantially aligned with the heel portion. The second echogenic region is structured and arranged for providing a generally linear signal visible under ultrasound examination along the second longitudinal side, and substantially not visible along the first longitudinal side.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for area limited-access through transmission ultrasonic inspection
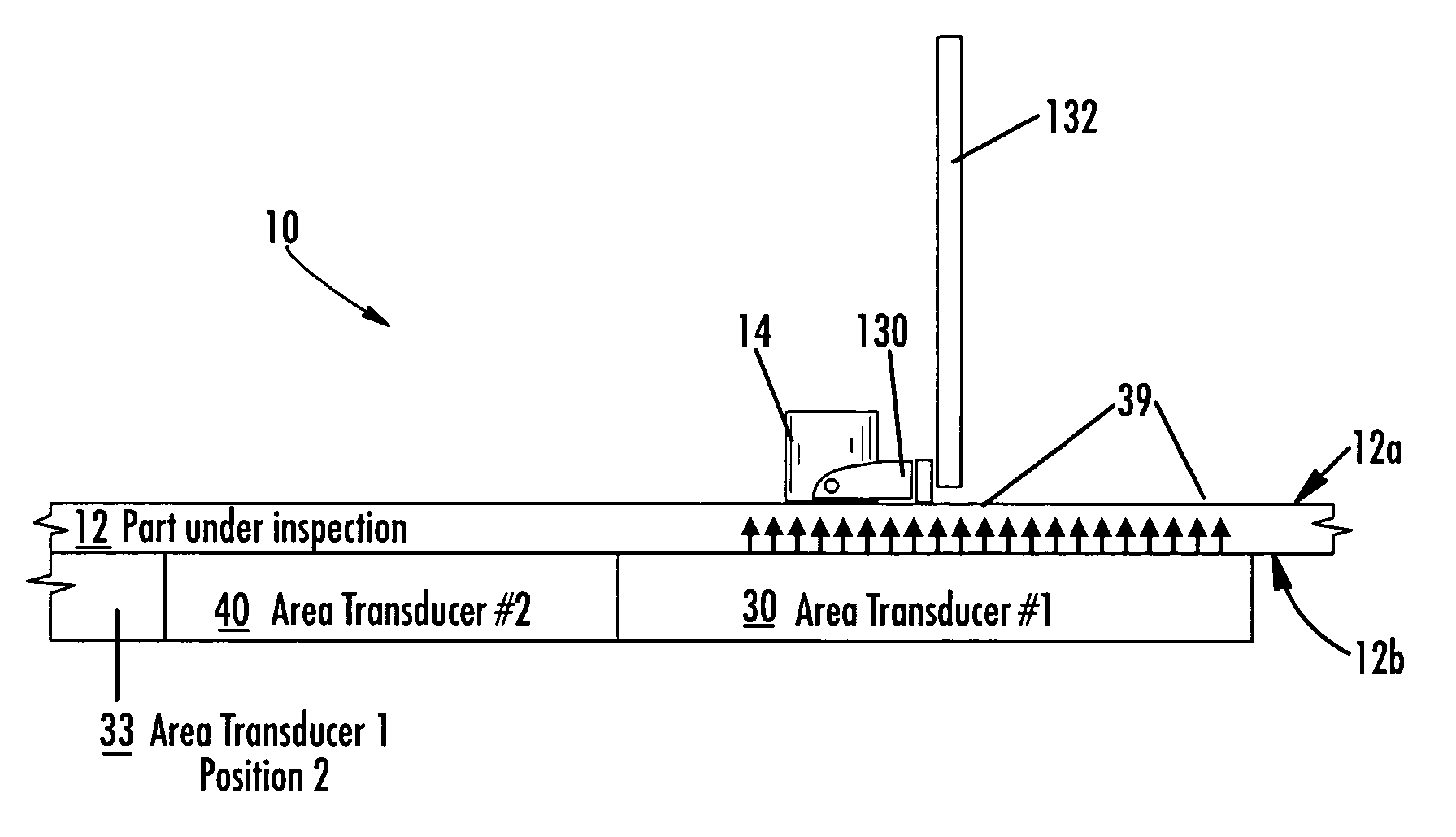
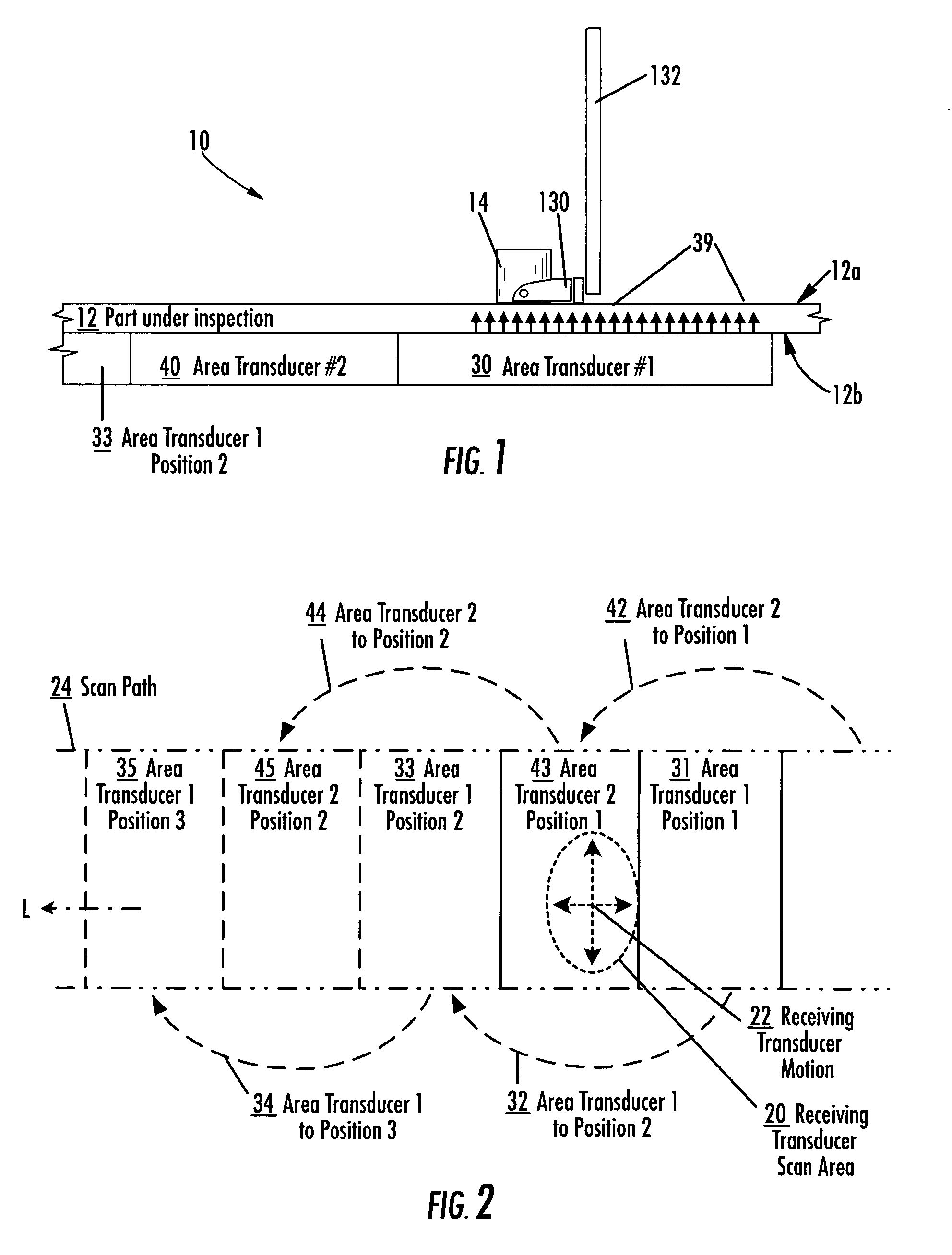
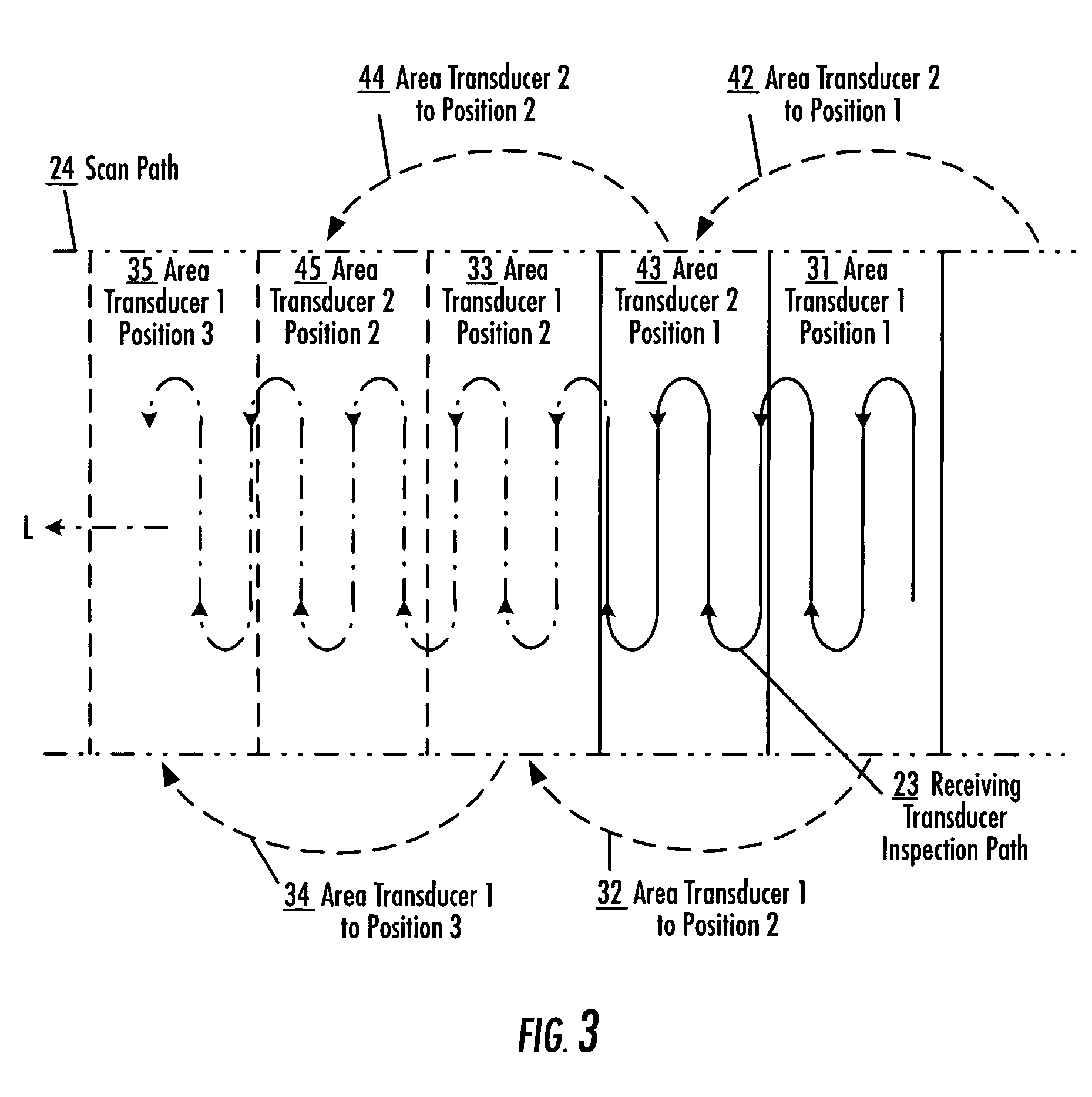
ActiveUS20060053891A1Increase speedImprove efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProximateLimited access
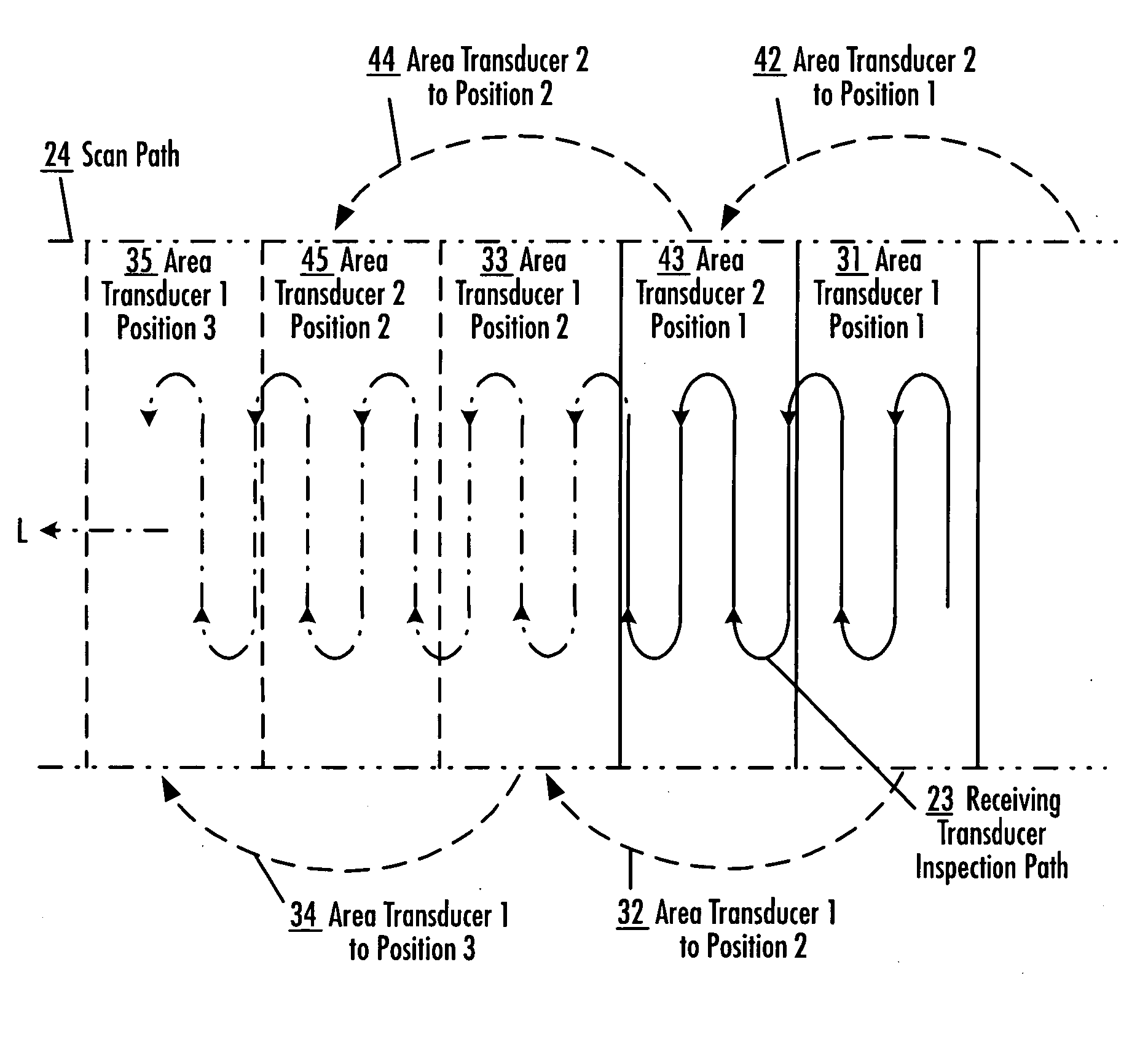
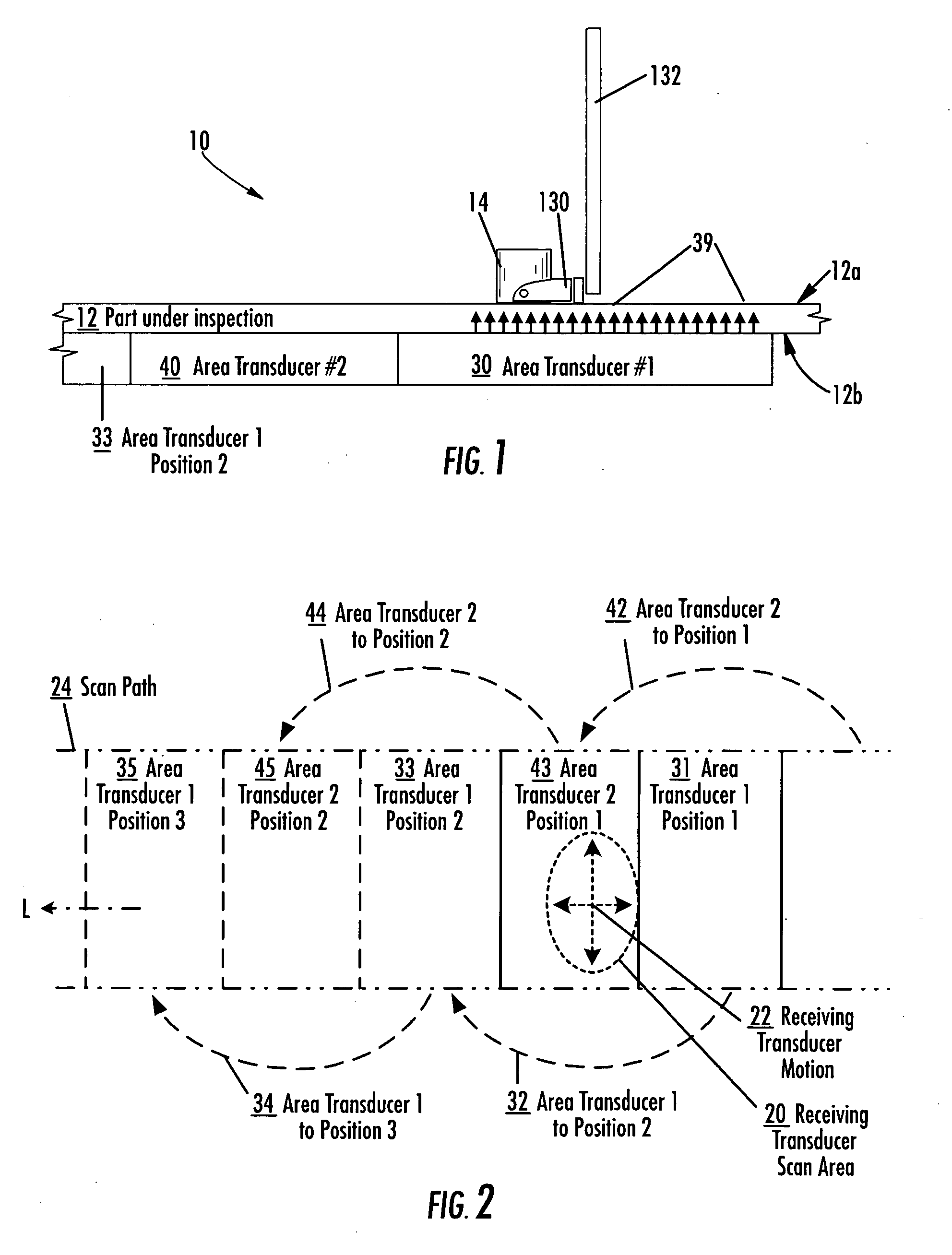
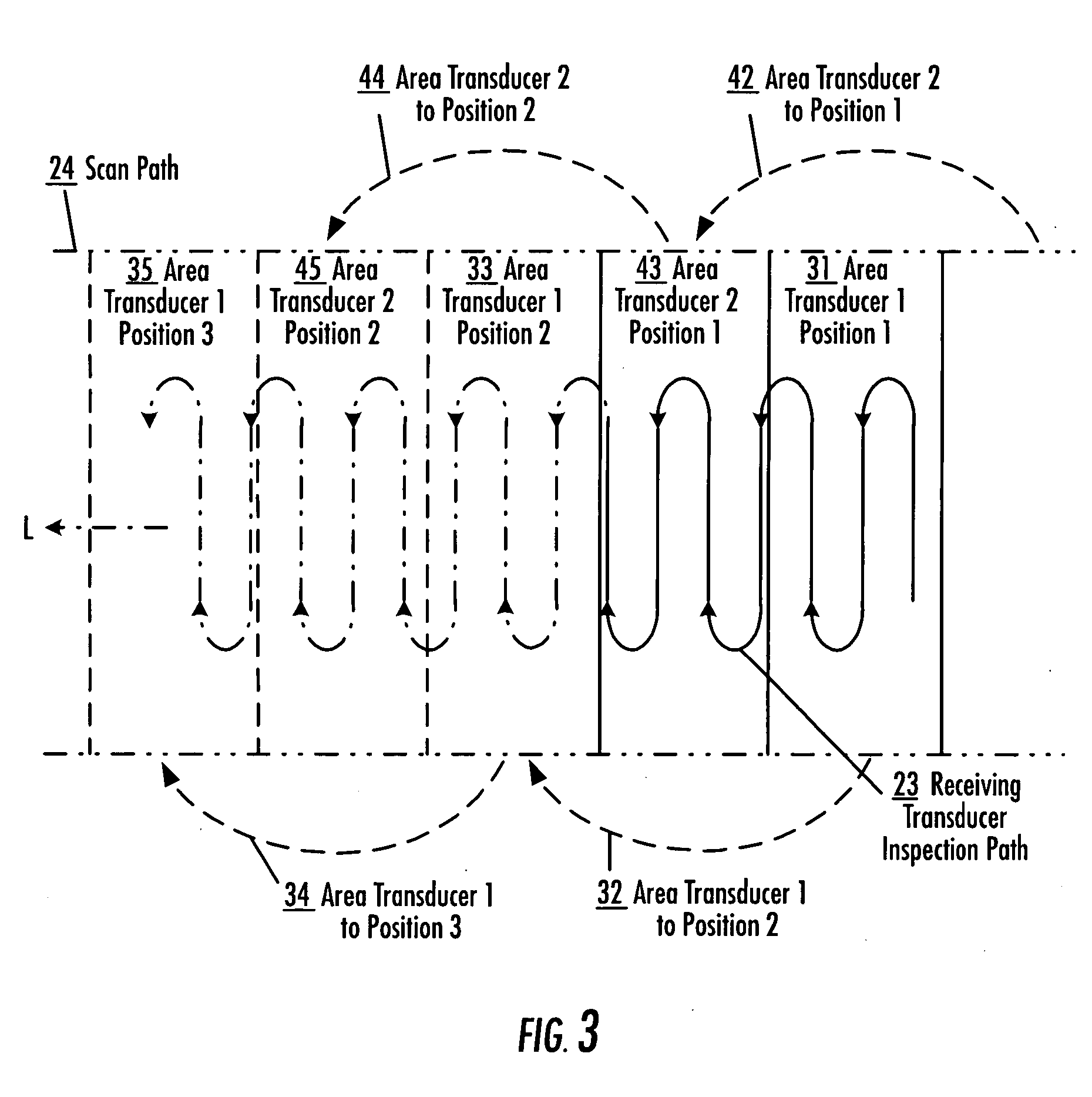
An apparatus and method for inspecting a structure are provided which include receiving probes and area transducers disposed proximate opposite surfaces of a structure under inspection. An area transducer uniformly emits ultrasonic signals over an area which may be scanned by a receiving probe without corresponding movement of the area transducer. An area transducer may be moved over the surface of the structure or repositioned to provide additional inspection area for the receiving probe to scan, including to provide for continuous inspection. Multiple area transducers may be used in sequence to provide for continuous inspection. Multiple receiving probes may be used, independently or collectively as an array, to increase inspection of a structure, taking advantage of the large area of ultrasonic signals emitted by one or more area transducers.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
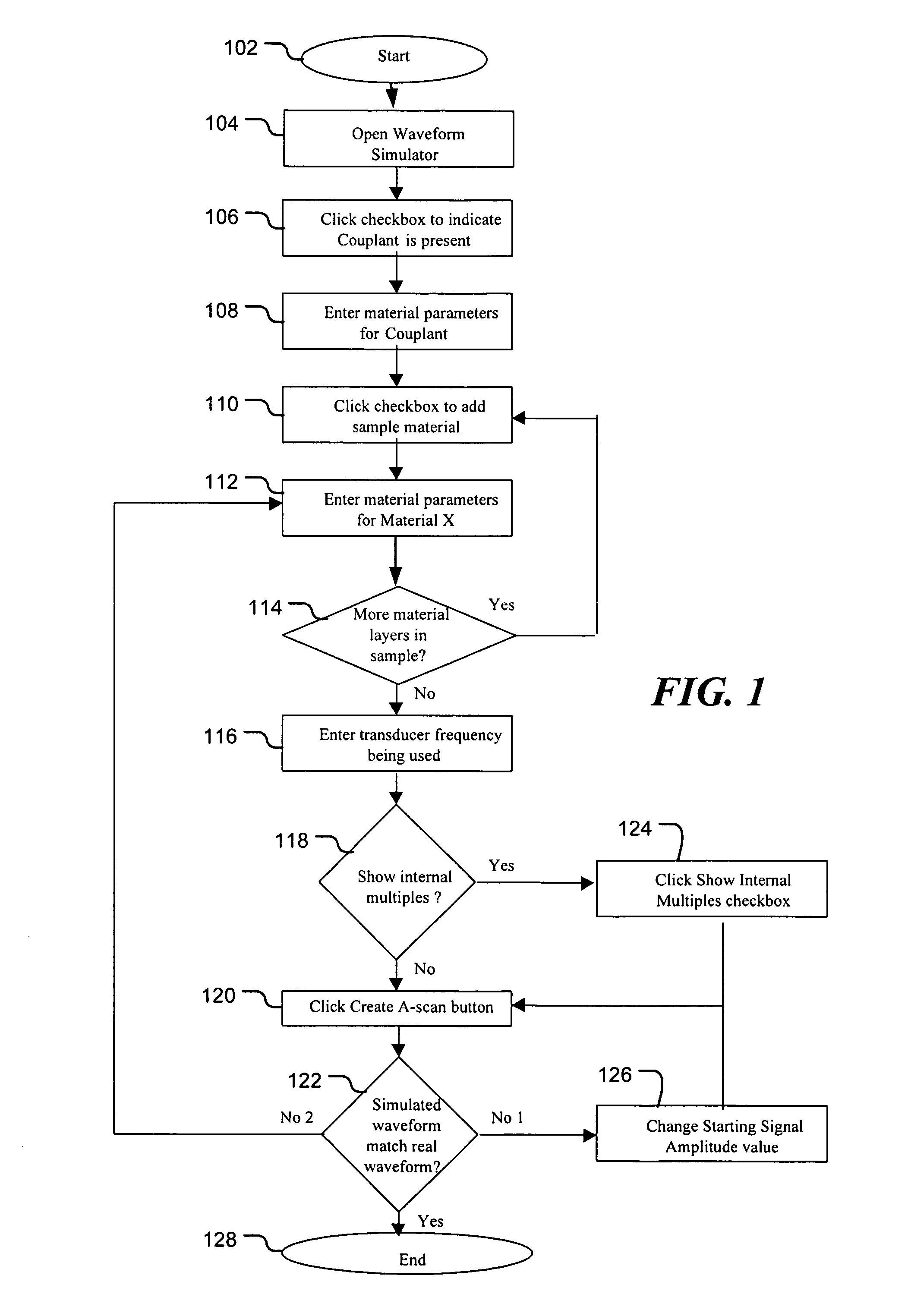
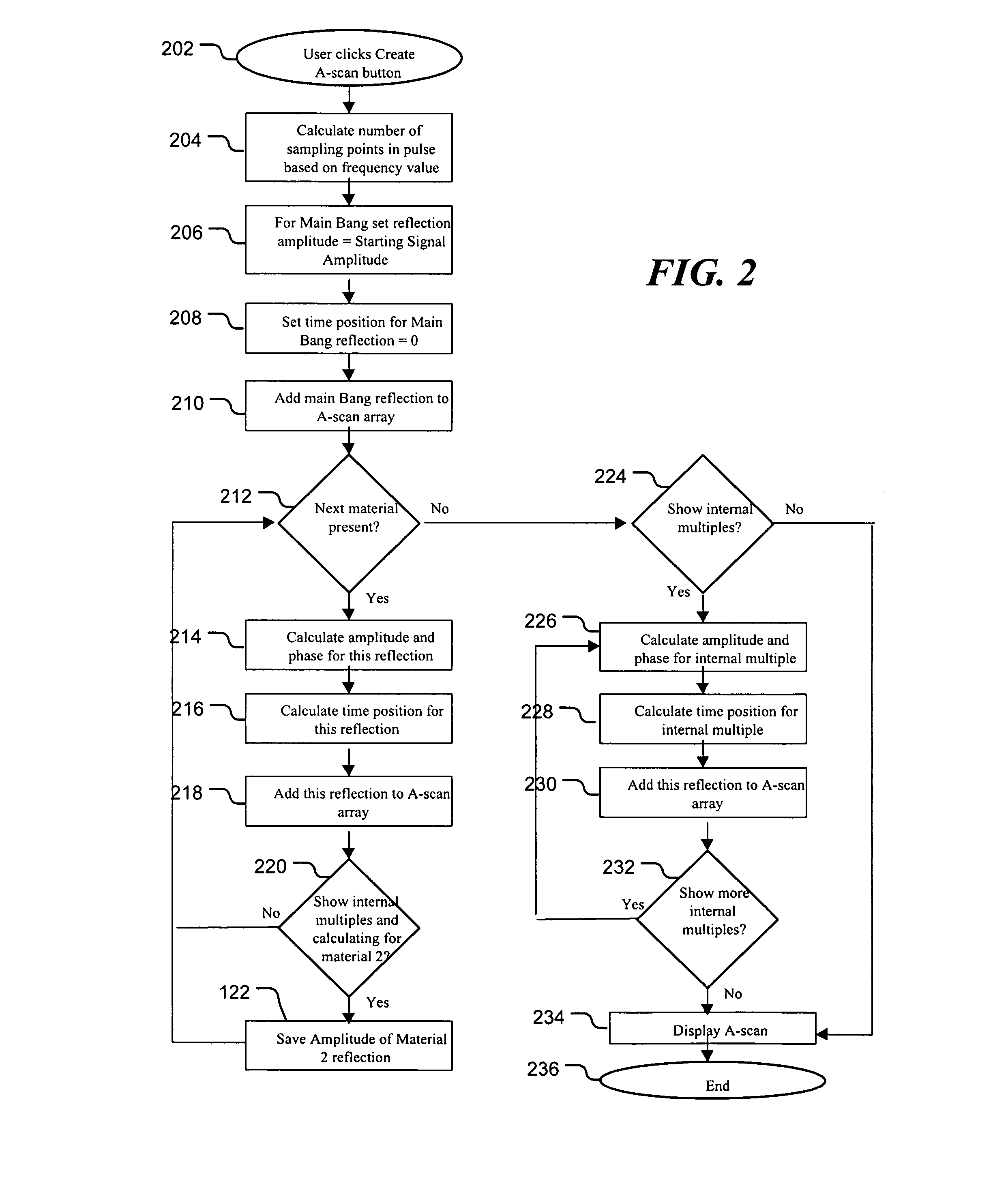
Ultrasonic inspection using acoustic modeling
ActiveUS7917317B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalogue computers for electric apparatusTime gatingSonification
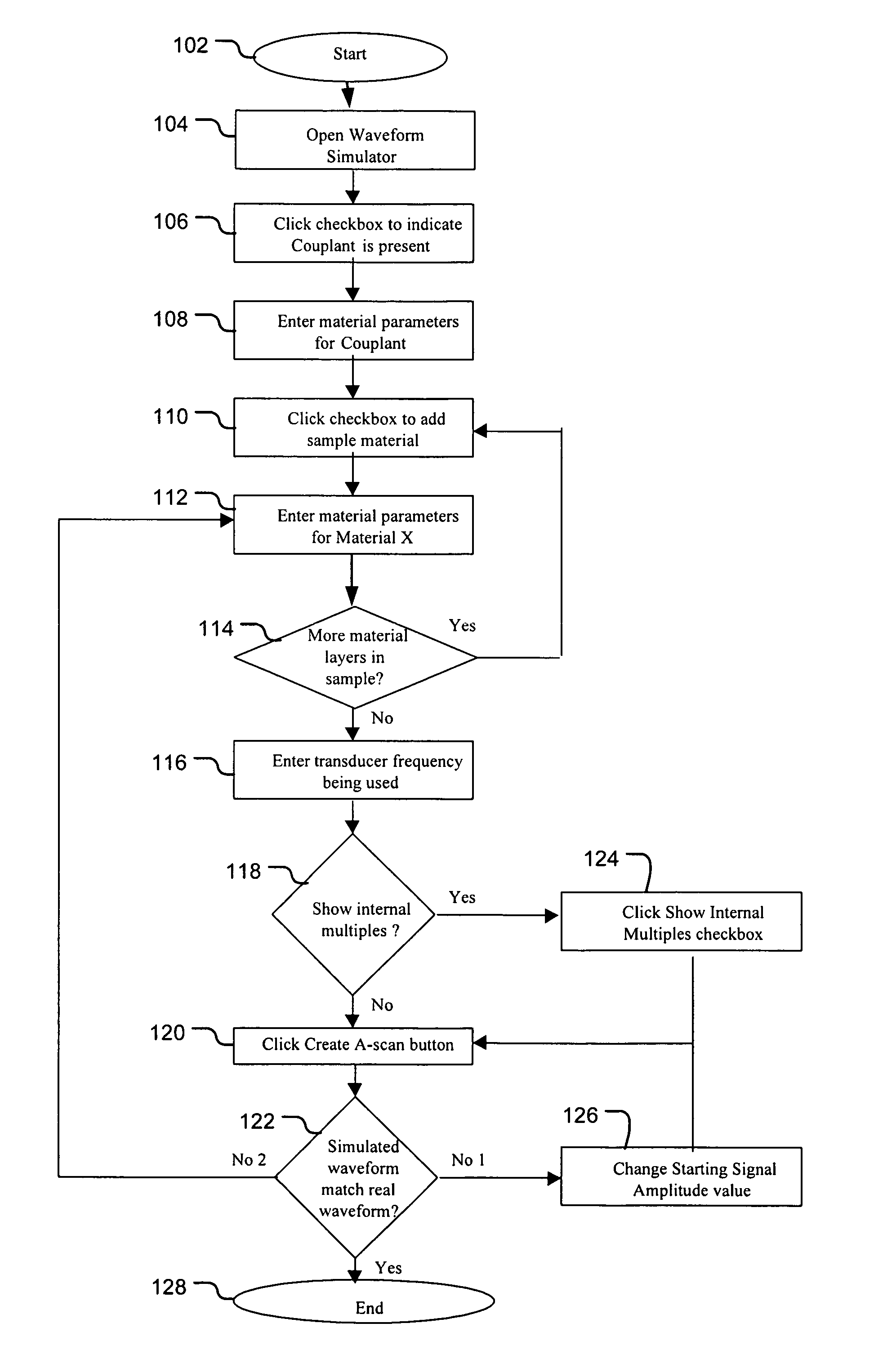
Configuration of an ultrasonic inspection system is facilitated using an ultrasound response predicted by a simulation tool. In one embodiment, estimated material properties of an object to be inspected are input to the simulation tool. Also input to the simulation tool is at least one estimated property of an ultrasonic transducer of the ultrasonic inspection. The simulation tool predicts the response of the object to ultrasound from the ultrasonic transducer. This response is dependent upon the estimated material properties of the object to be inspected and the at least one estimated property of the ultrasonic transducer. The ultrasonic inspection system is then configured dependent upon a feature of the predicted response. The system may be configured, for example, by setting the position of a time gate, selecting an appropriate ultrasonic transducer, selecting the position of the transducer to achieve good focus, or selecting parameters for signal processing.
Owner:SONIC CORP
Articulated robot for laser ultrasonic inspection
ActiveUS7784348B2Cost-effectiveMore compact robotsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLaser using scattering effectsNon destructiveUltrasound sonography
An ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation (NDE) system operable to inspect target materials is provided. This ultrasonic NDE system includes an articulated robot, an ultrasound inspection head, a processing module, and a control module. The ultrasound inspection head couples to or mounts on the articulated robot. The ultrasound inspection head is operable to deliver a generation laser beam, a detection laser beam, and collect phase modulated light scattered by the target materials. The processing module processes the phase modulated light and produces information about the internal structure of the target materials. The control module directs the articulated robot to position the ultrasound inspection head according to a pre-determined scan plan.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
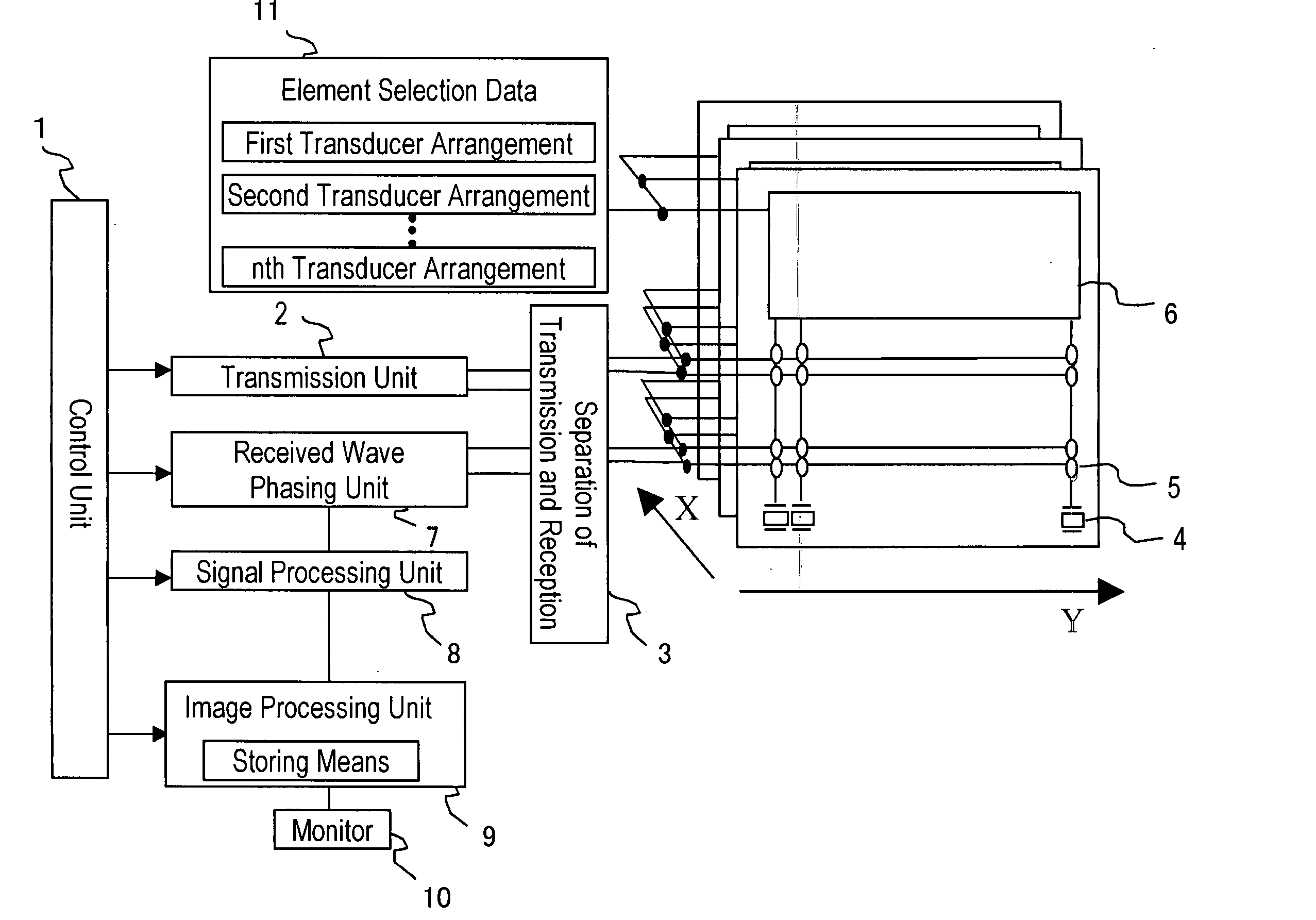
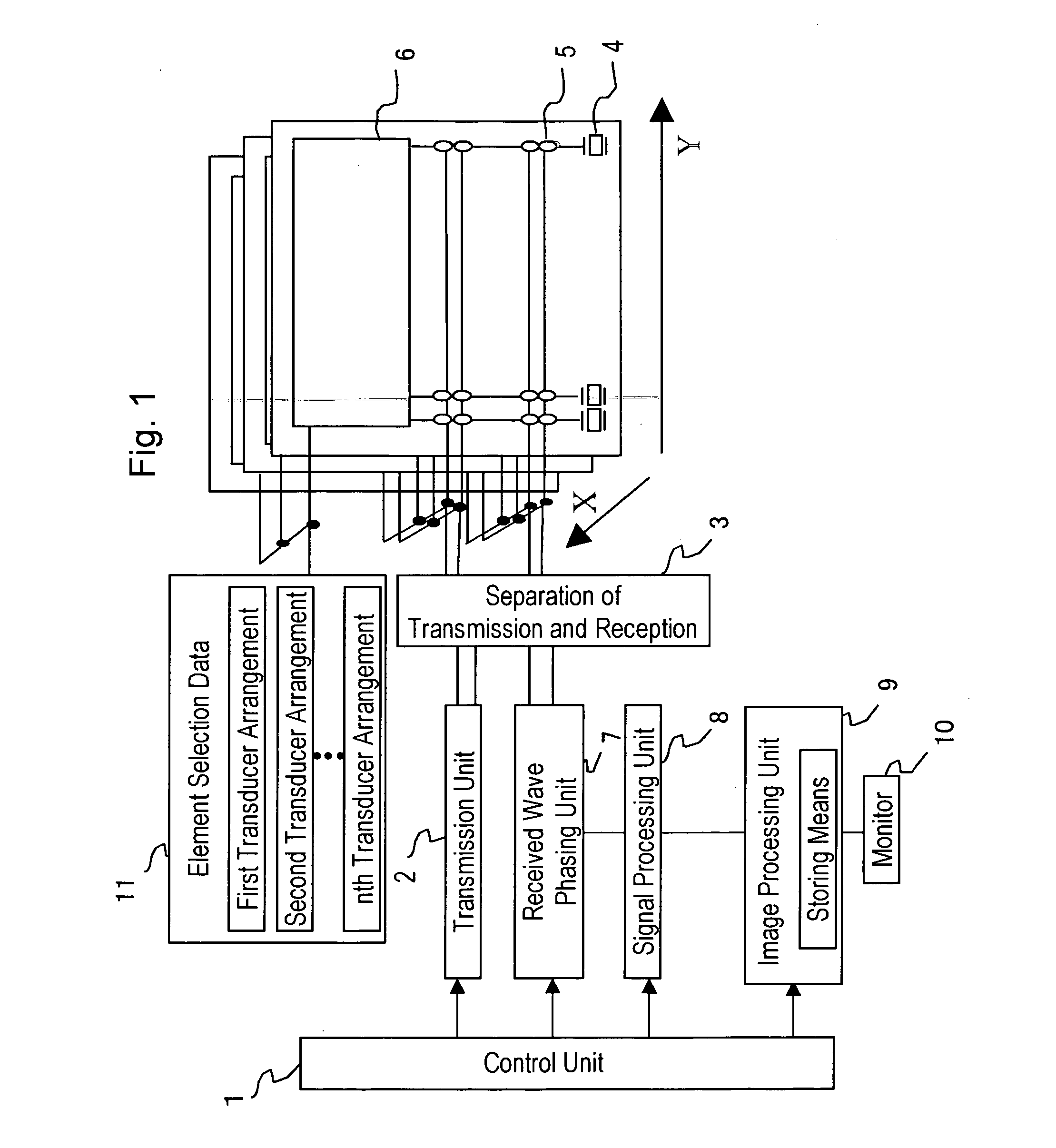
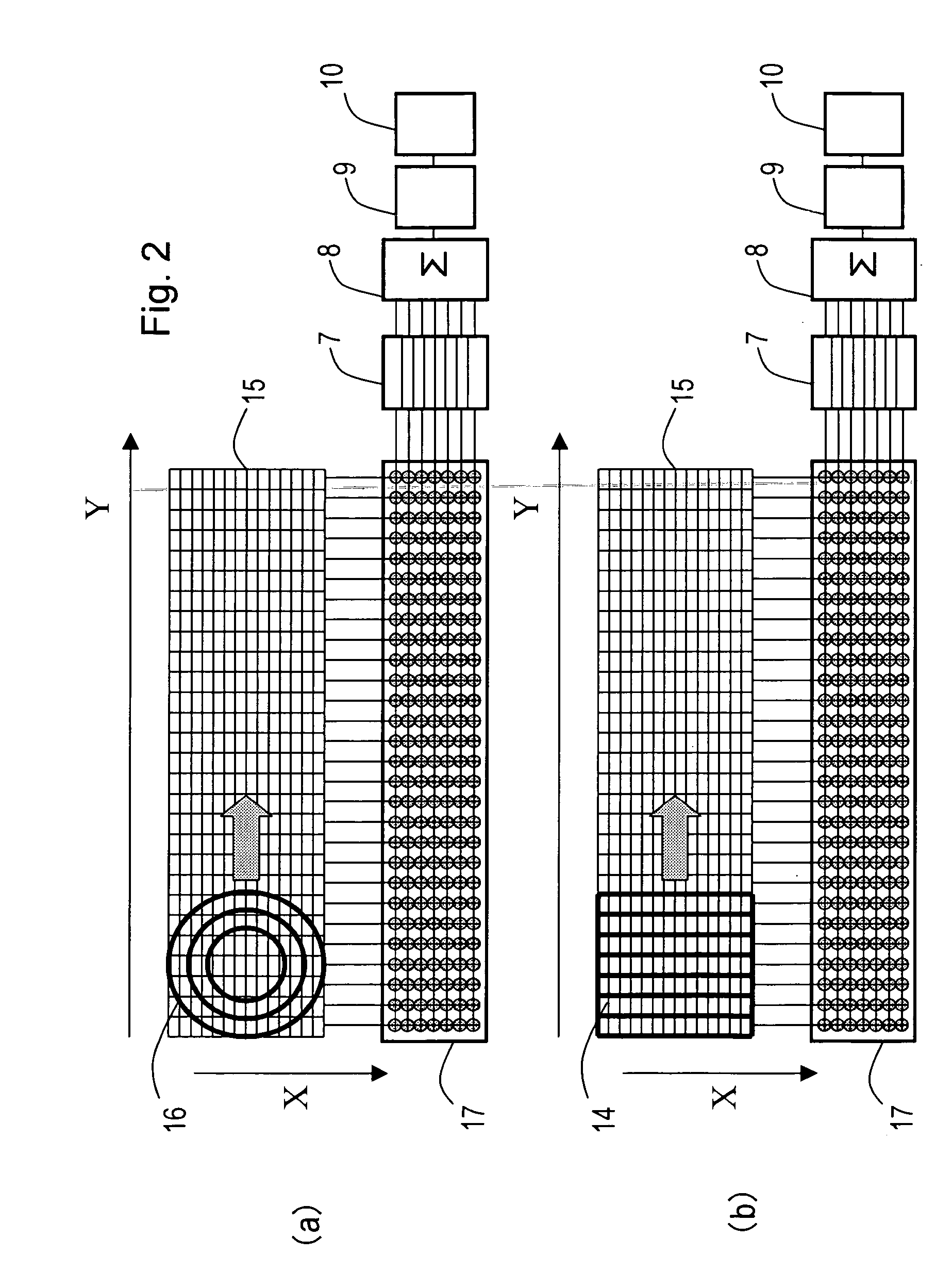
Ultrasonograph
InactiveUS20050124880A1Improve scaleImprove image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging processingUltrasound sonography
An ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus includes an ultrasound probe having two-dimensionally arranged transducer elements for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves to an object, a transducer element selector for selecting transducer elements used in transmission and reception, a signal processing unit for applying a delay to a signal received by a selected transducer element, an image processing unit for generating an image based on the output signal of the signal processing unit, and an image display unit. The image processing unit stores a first ultrasound image obtained by a scan of a first transducer arrangement selected by the transducer element selector and a second ultrasound image obtained by a scan of a second transducer arrangement selected by the transducer element selector so as to irradiate an ultrasound beam in a different direction than the beam direction of the first transducer arrangement, and combines the first ultrasound image and the second ultrasound image.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Ultrasonic inspection method
ActiveUS20080121040A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalUltrasound sonographyLight beam
A method for ultrasonically inspecting components with wavy or uneven surfaces. A multi-element array ultrasonic transducer is operated with a substantial fluid layer, such as water, between the array transducer and the component surface. This fluid layer may be maintained by immersing the component in liquid or by using a captive couplant column between the probe and the component surface. The component is scanned, measuring the two dimensional surface profile using either a mechanical stylus, laser, or ultrasonic technique. Once an accurate surface profile of the component's surface has been obtained, data processing parameters are calculated for processing the ultrasonic signals reflected from the interior of the component that eliminate beam distortion effects and reflector mis-location that would otherwise occur due to the uneven surfaces.
Owner:BWXT NUCLEAR OPERATIONS GRP
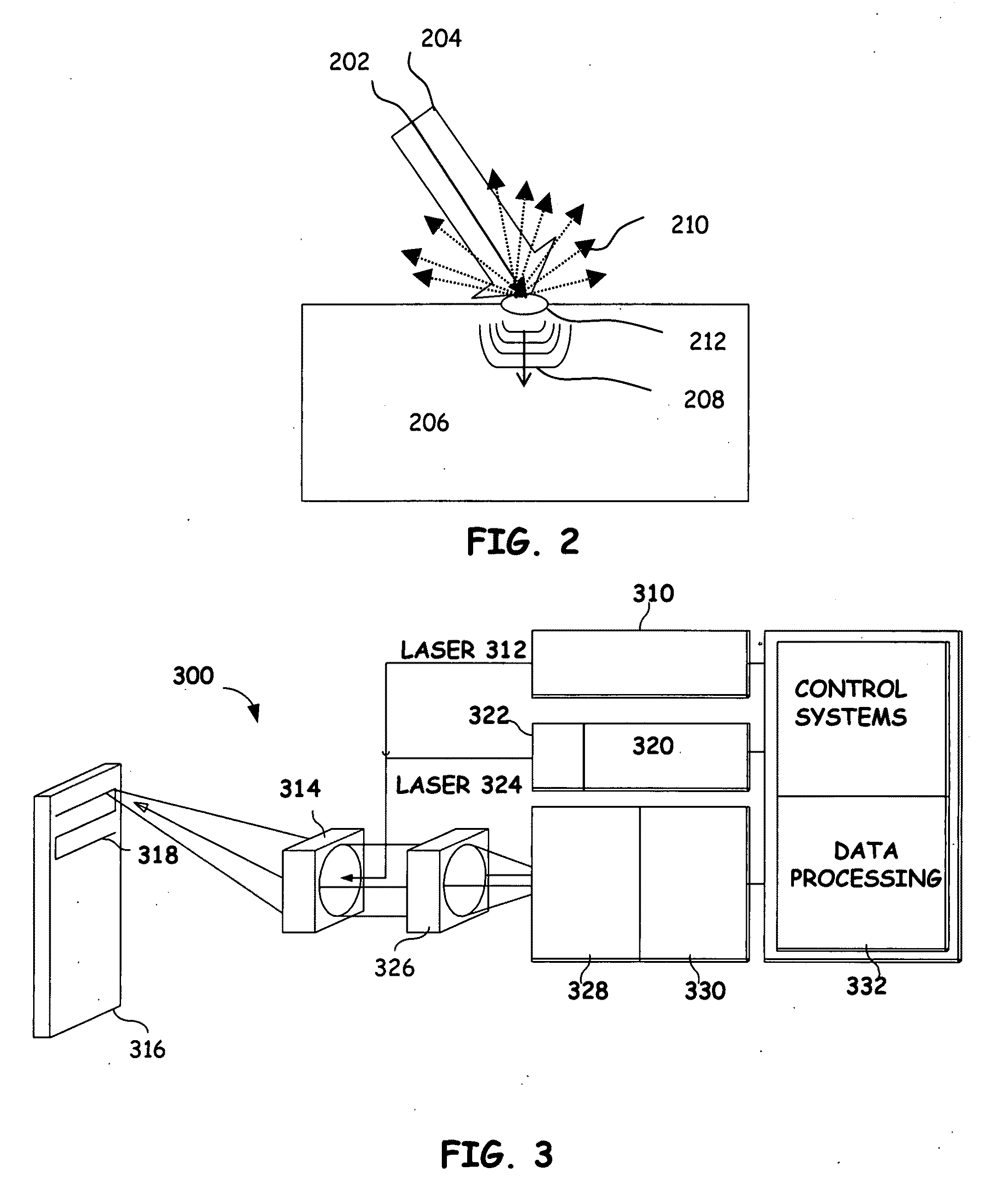
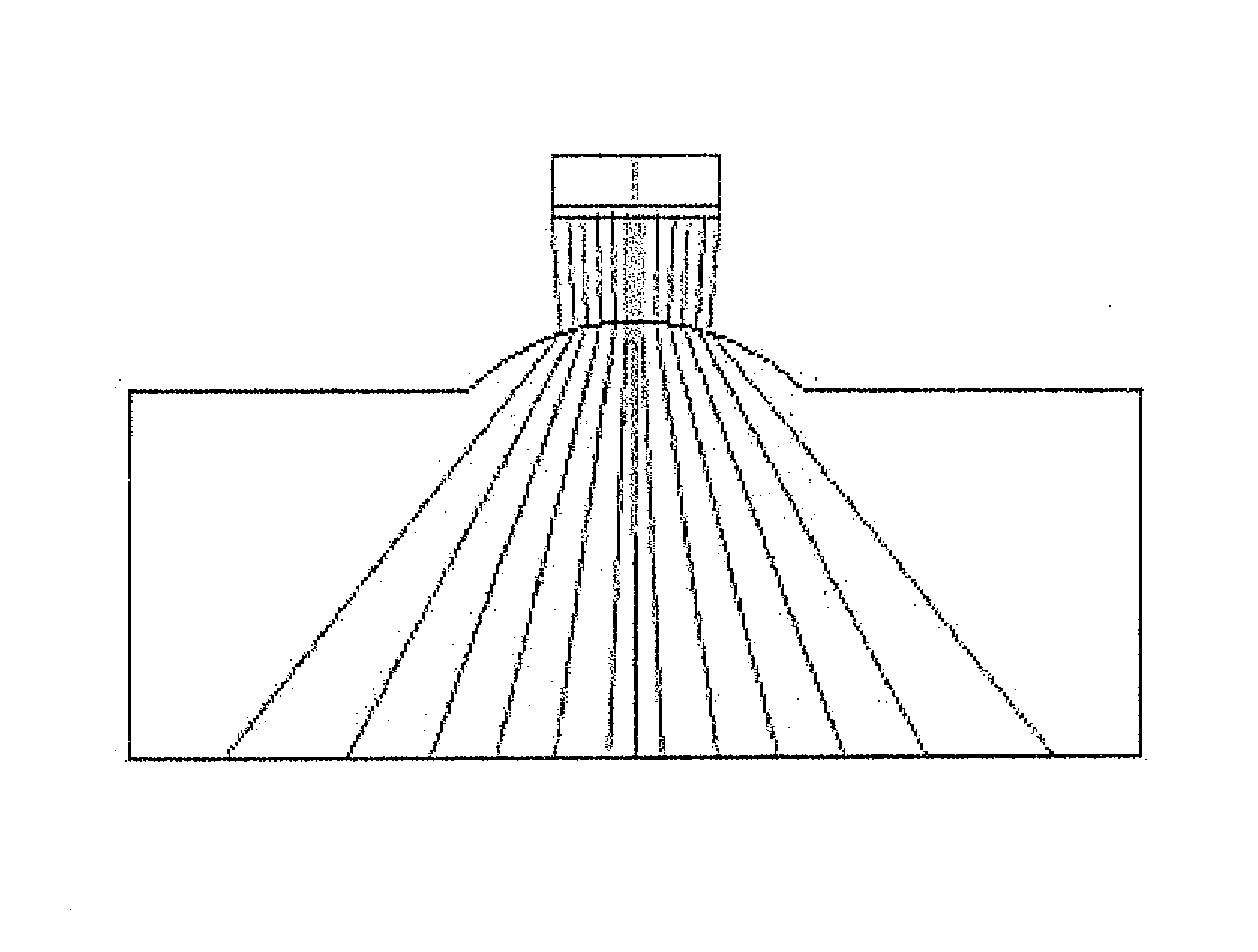
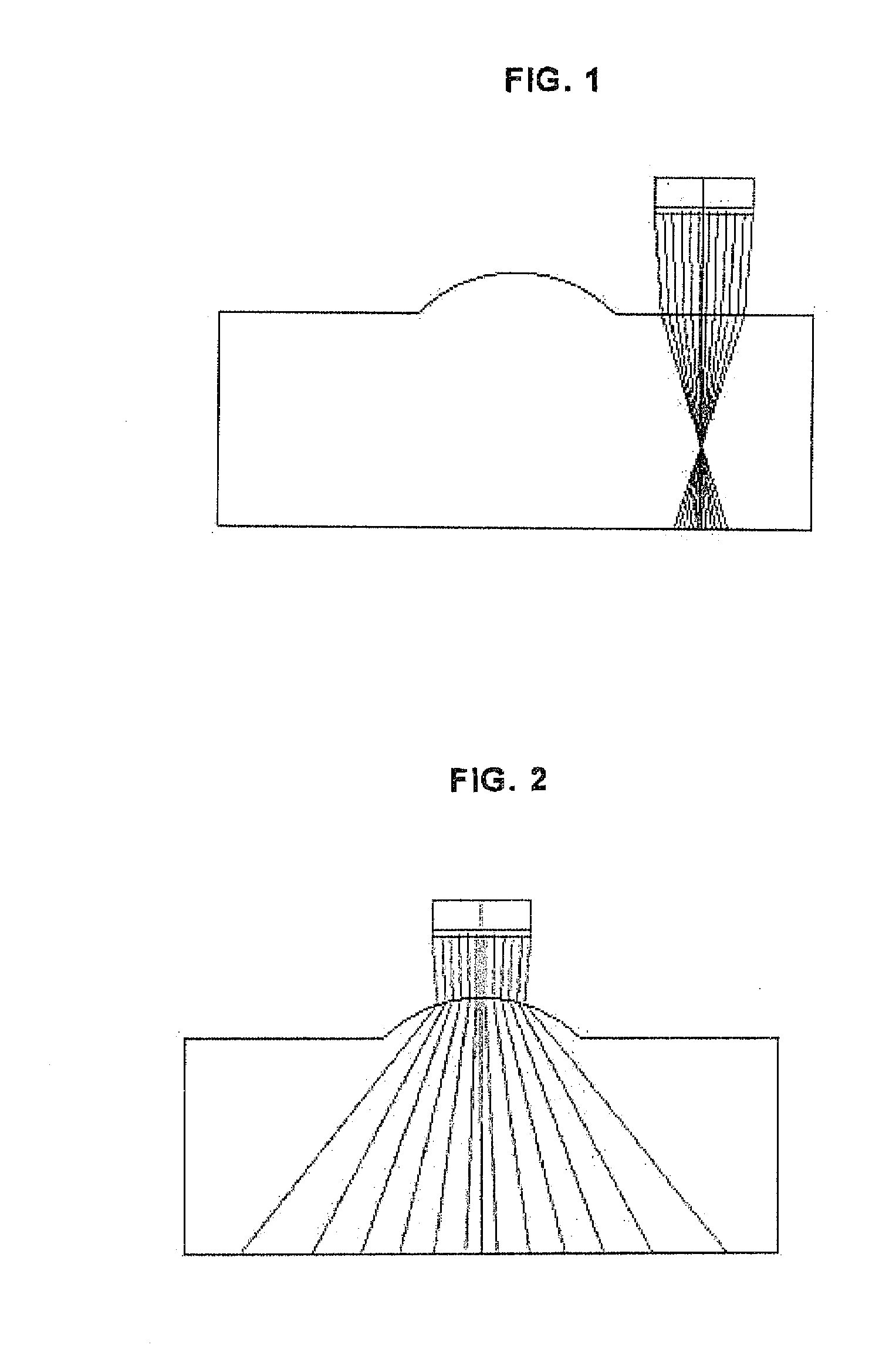
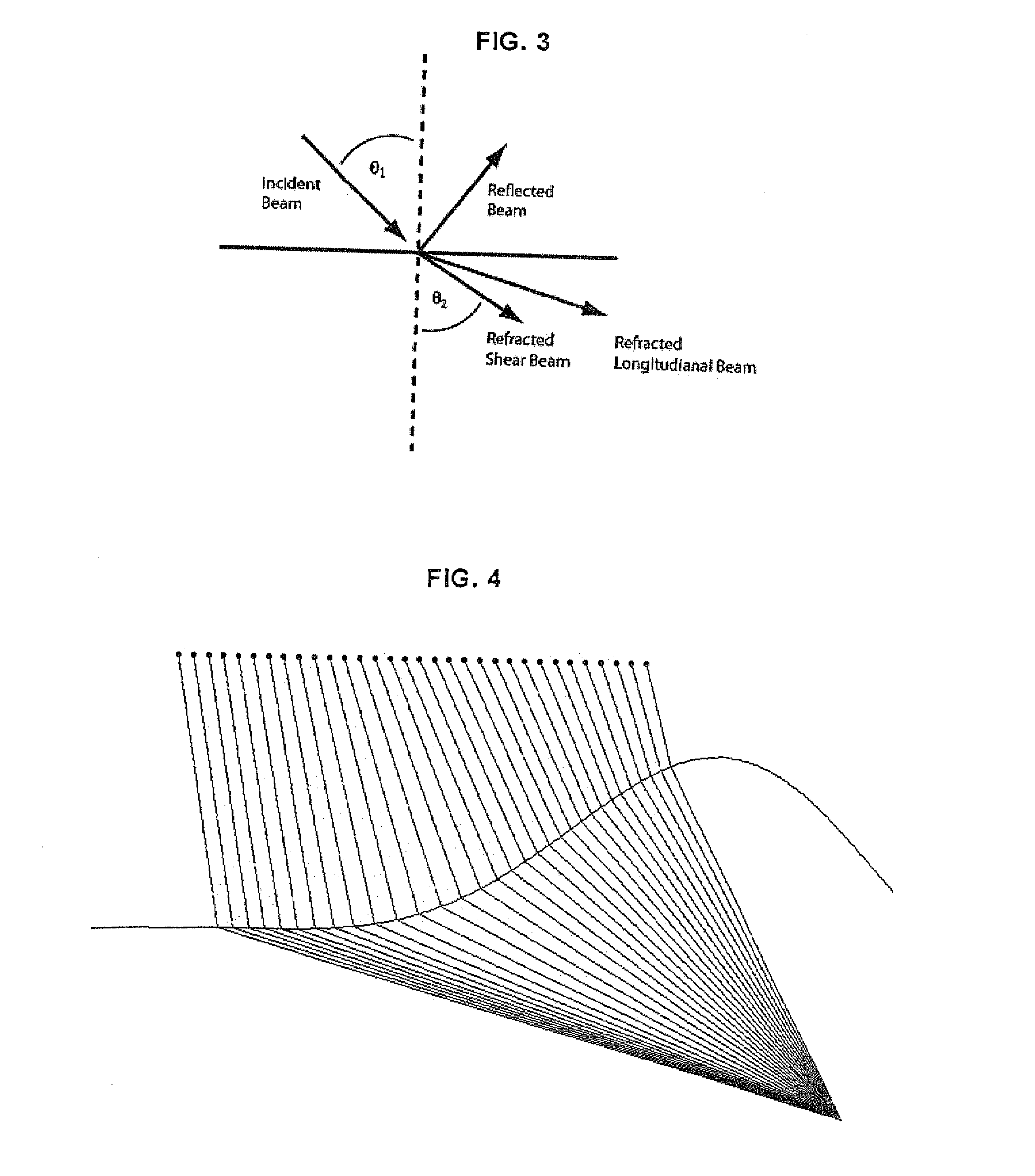
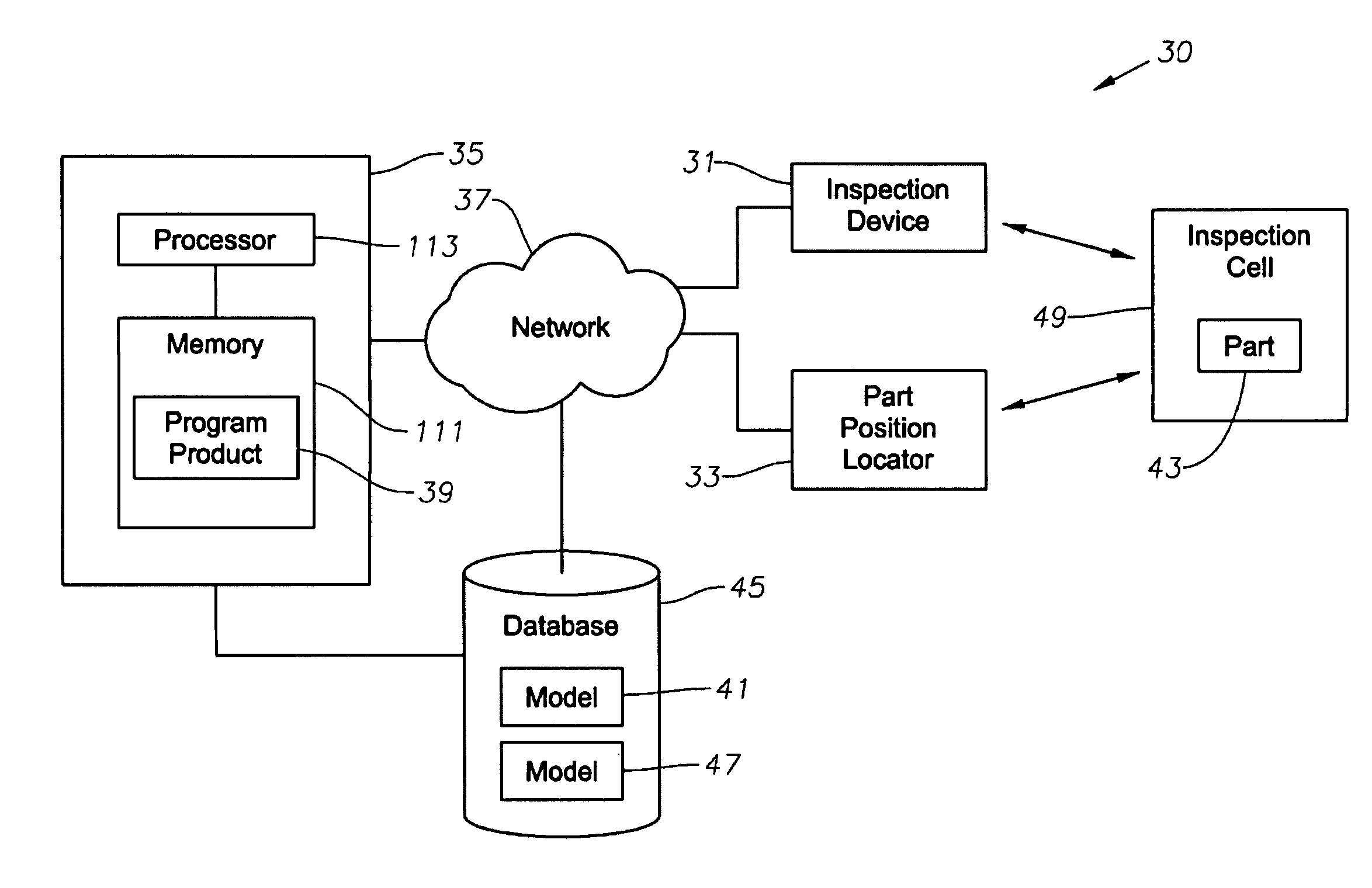
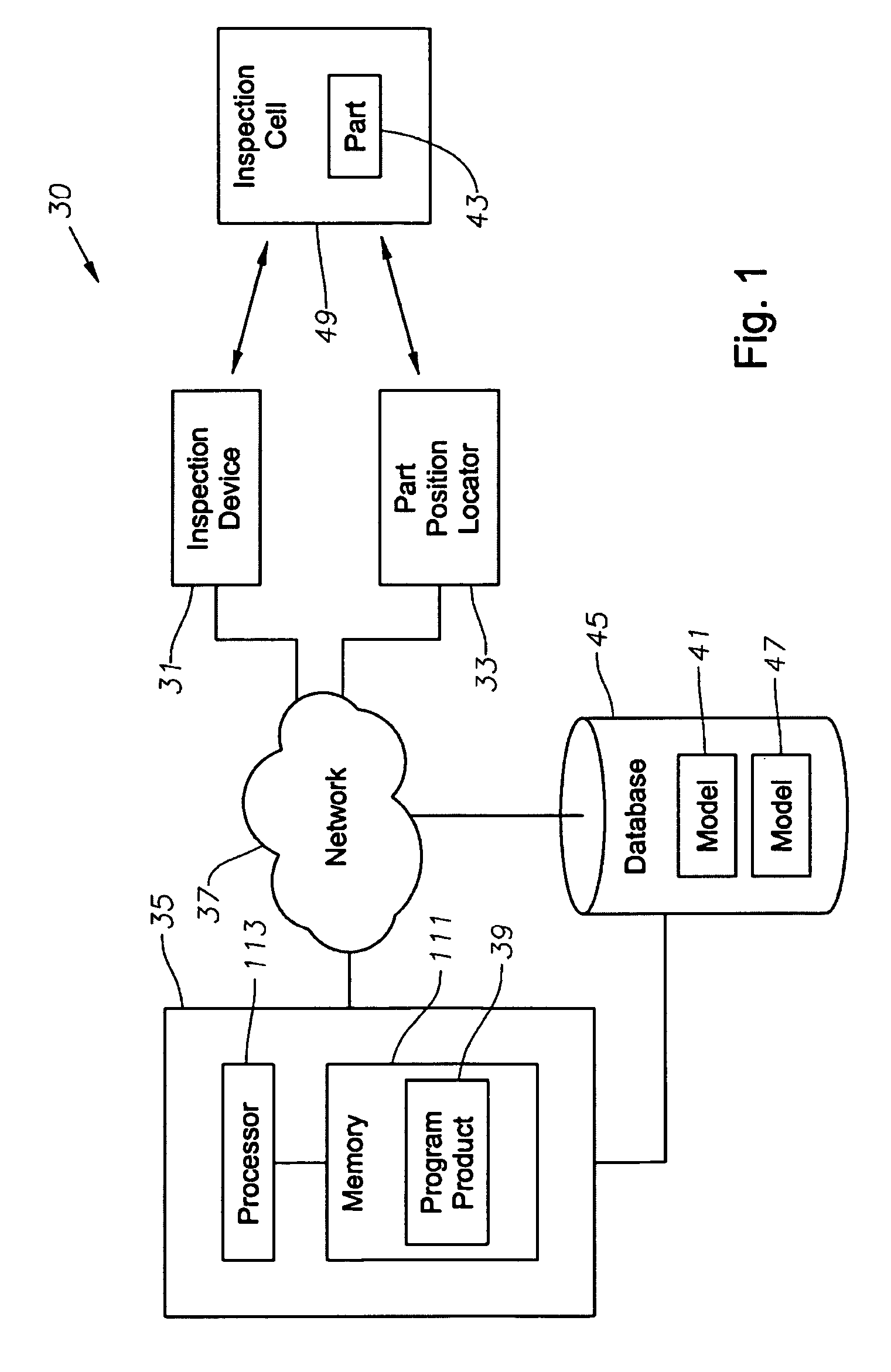
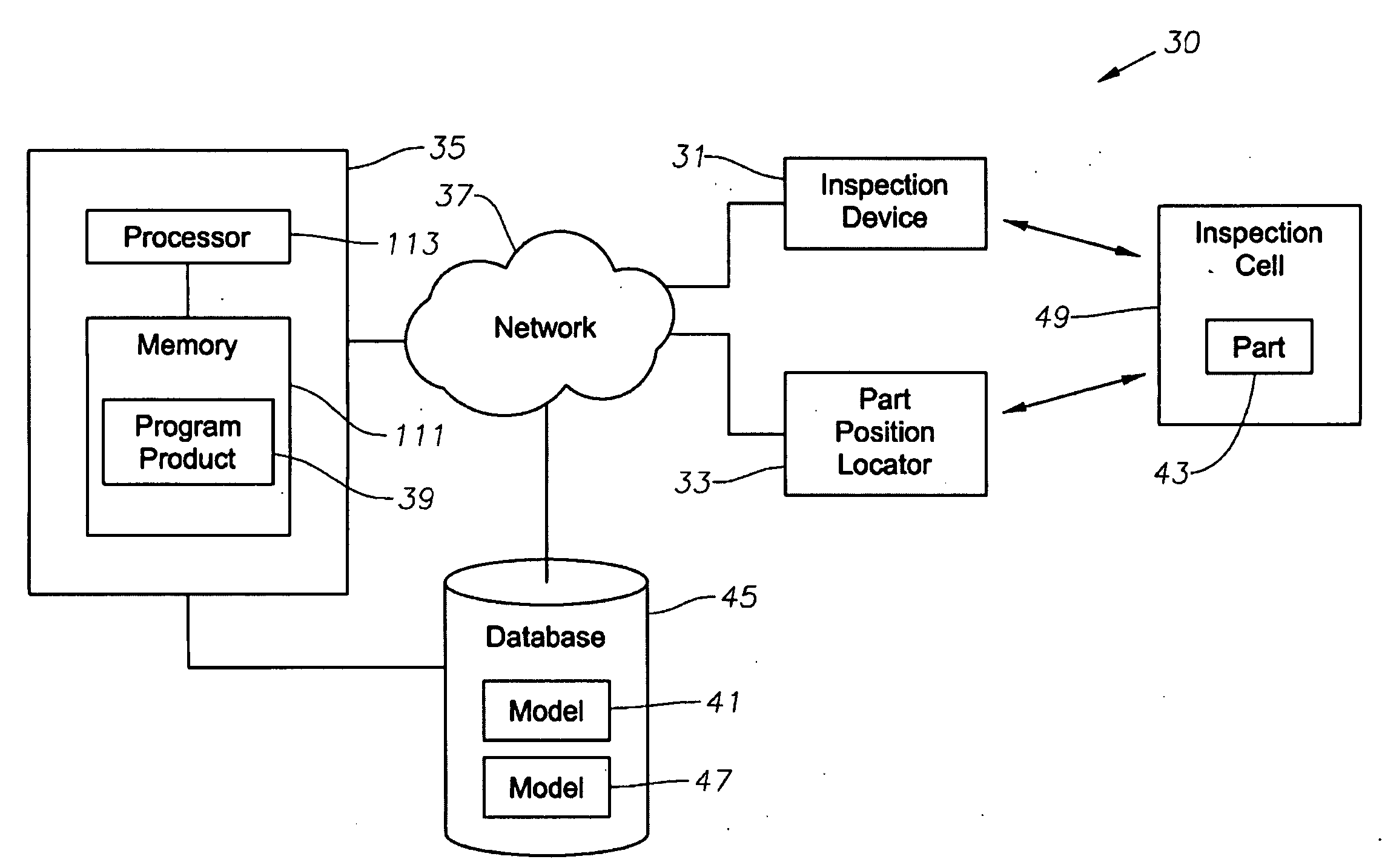
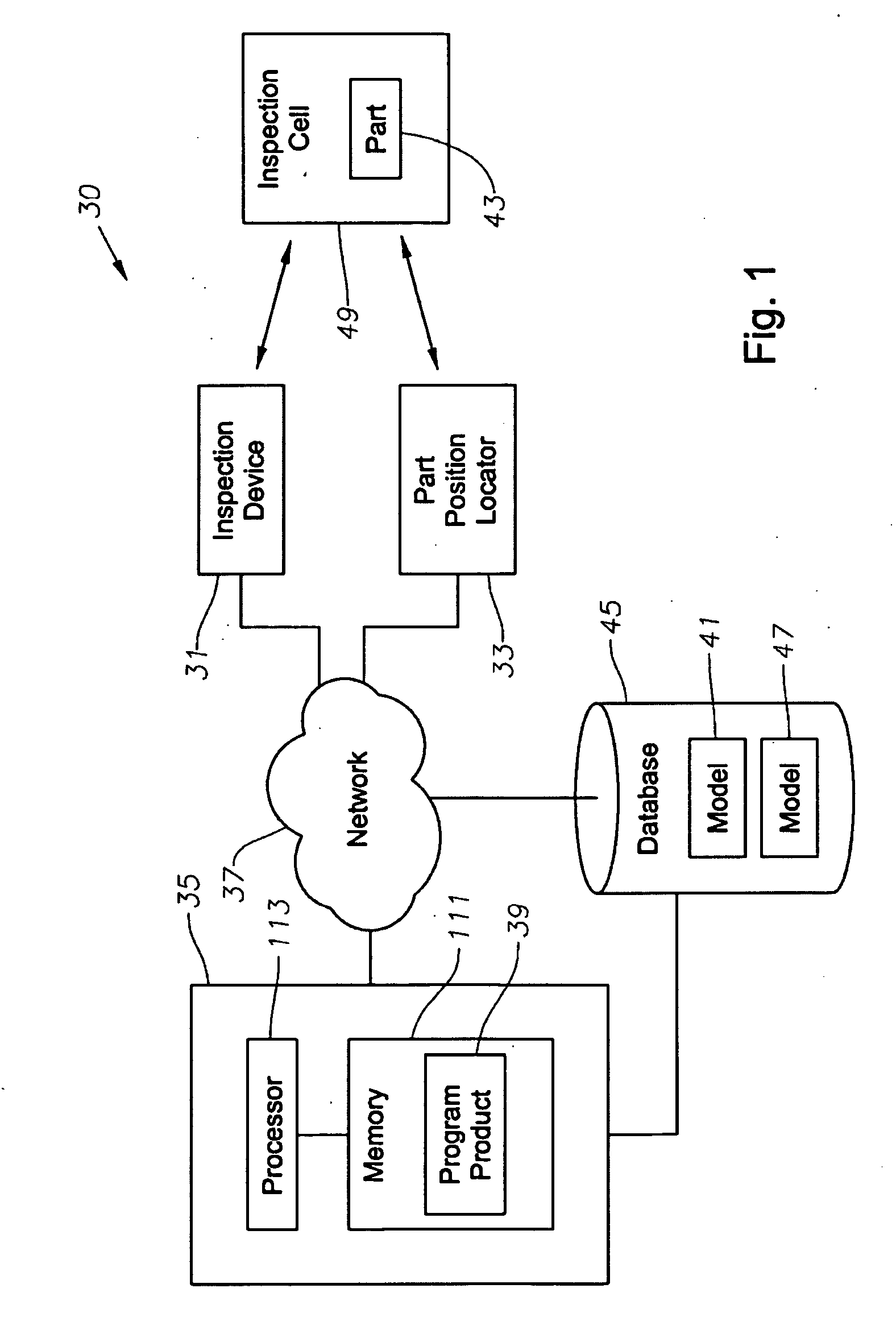
System, program product, and related methods for registering three-dimensional models to point data representing the pose of a part
ActiveUS7865316B2Improve visualizationVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComputer Aided DesignSonification
A system, program product, and method to perform automated three-dimensional image registration of a part within an inspection cell, are provided. The system can include a laser-ultrasound inspection device having a scanning head to generate ultrasonic surface displacements in a part, an inspection laser, and an interferometer to collect phase modulated light reflected by the part. The system can also include a part position locator positioned to measure a distance between points on a surface of the part and a scanning laser reference location. The system can also include a database containing computer-aided design models for each part of interest, and a model of the inspection cell. The system can further include a laser ultrasound inspection computer communication with the laser-ultrasound detection device and the part position locator, and laser ultrasound inspection program product adapted to perform automated three-dimensional image registration of the part.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
System, program product, and related methods for registering three-dimensional models to point data representing the pose of a part
ActiveUS20090248323A1Improve visualizationVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComputer Aided DesignSonification
A system, program product, and method to perform automated three-dimensional image registration of a part within an inspection cell, are provided. The system can include a laser-ultrasound inspection device having a scanning head to generate ultrasonic surface displacements in a part, an inspection laser, and an interferometer to collect phase modulated light reflected by the part. The system can also include a part position locator positioned to measure a distance between points on a surface of the part and a scanning laser reference location. The system can also include a database containing computer-aided design models for each part of interest, and a model of the inspection cell. The system can further include a laser ultrasound inspection computer communication with the laser-ultrasound detection device and the part position locator, and laser ultrasound inspection program product adapted to perform automated three-dimensional image registration of the part.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Probe coupler for ultrasound examination system
InactiveUS6039695AHigh strengthImprove accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasound sonographyEngineering
An ultrasound probe coupler for electrically and rotationally coupling an ultrasound probe with a probe control unit of an ultrasound examination system. The probe coupler essentially includes a tail end connector provided at the tail end of a flexible cord to be connected to the probe control unit. The tail end connector is provided with a stationary ring which is fixedly connected to a tail end portion of the flexible cord, and a rotational coupler having a series of rotary rings, including at least one electrode ring, for coupling the flexible shaft with a rotational drive means and an electrode on the part of the probe control unit. The rotational coupler further includes a rotation transmission member detachably connected to one of the rotating electrode rings and projected radially outward of the inner periphery of the stationary ring for engagement with a rotational drive member on the part of the probe control unit.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Method and apparatus for washing a probe or the like using ultrasonic energy
InactiveUS20060179946A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMechanical vibrations separationUltrasound sonographyUltrasonic generator
An apparatus and corresponding method for ultrasonically washing a probe or the like are disclosed. The apparatus comprises an ultrasonic wave generator and an ultrasonic wave concentrator. The ultrasonic wave concentrator includes a body portion having a wash cavity. The wash cavity is shaped to generally conform to an exterior portion of the probe. A first end of the ultrasonic wave concentrator is adapted to receive ultrasonic energy produced by the ultrasonic wave generator. The ultrasonic energy received at the first end of the concentrator is focused into the wash cavity where it is used to wash the probe (or other object). A second end of the ultrasonic wave concentrator includes an aperture that is open to the wash cavity and is adapted to receive the probe and allow it to enter the wash cavity.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method and apparatus for displaying an ultrasound image
InactiveUS20130190624A1Diagnostic probe attachmentInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound sonographyDisplay device
A method for displaying an ultrasound image on a display device is provided. Image signals are generated with an ultrasound probe during examination of an item under examination with ultrasound and are transferred to a data processing device. The image signals are displayed by the data processing device as an ultrasound image on a display device. In order to make it easier for an operator to observe the ultrasound image, by means of an orientation detection device, a change in orientation of the display device in space is detected and an associated change in orientation signal is provided to the data processing device and the orientation of the ultrasound image on the display device is changed by the data processing device as a function of the change in orientation of the display device in space. An apparatus for carrying out the method is also provided.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
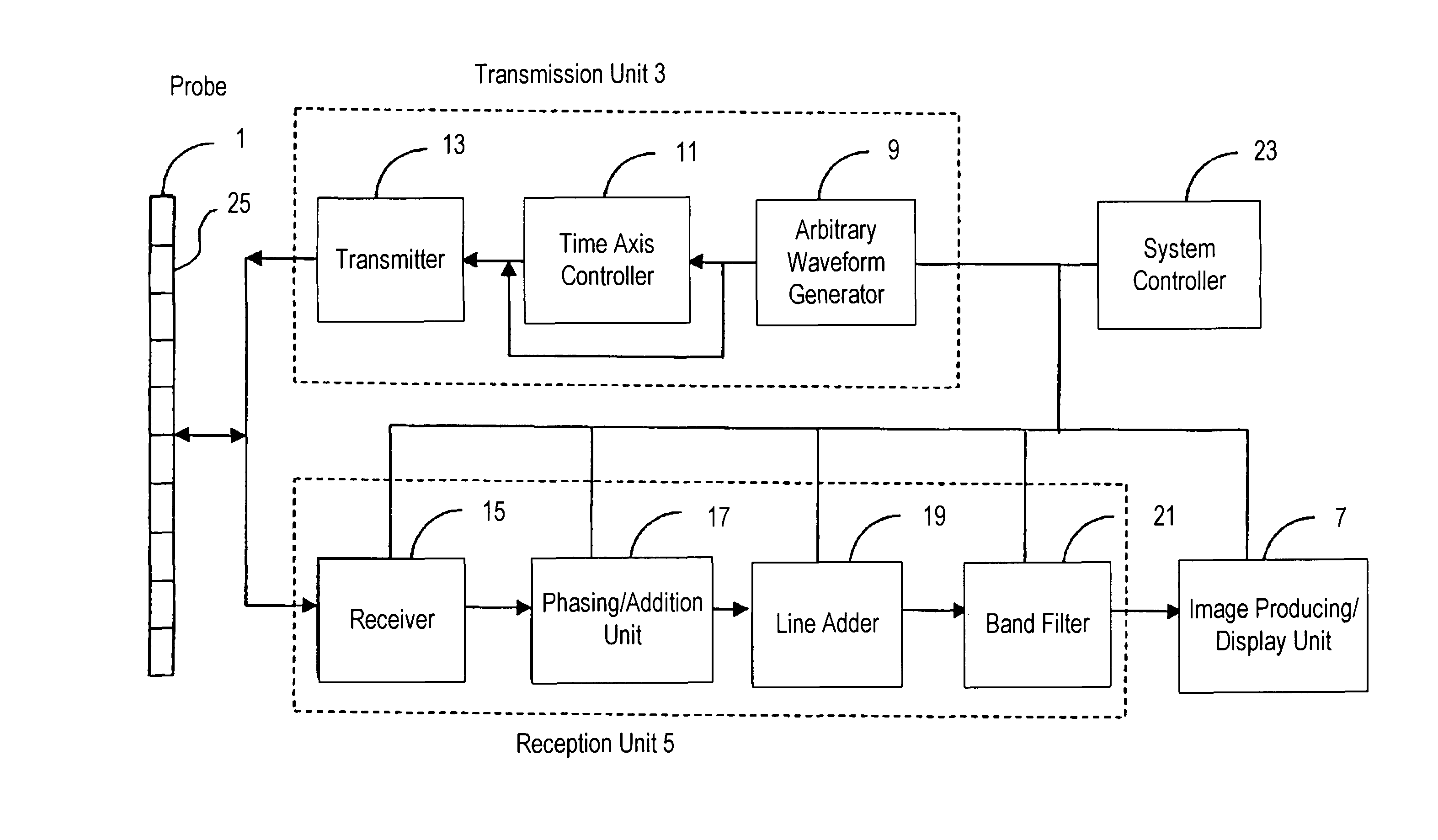
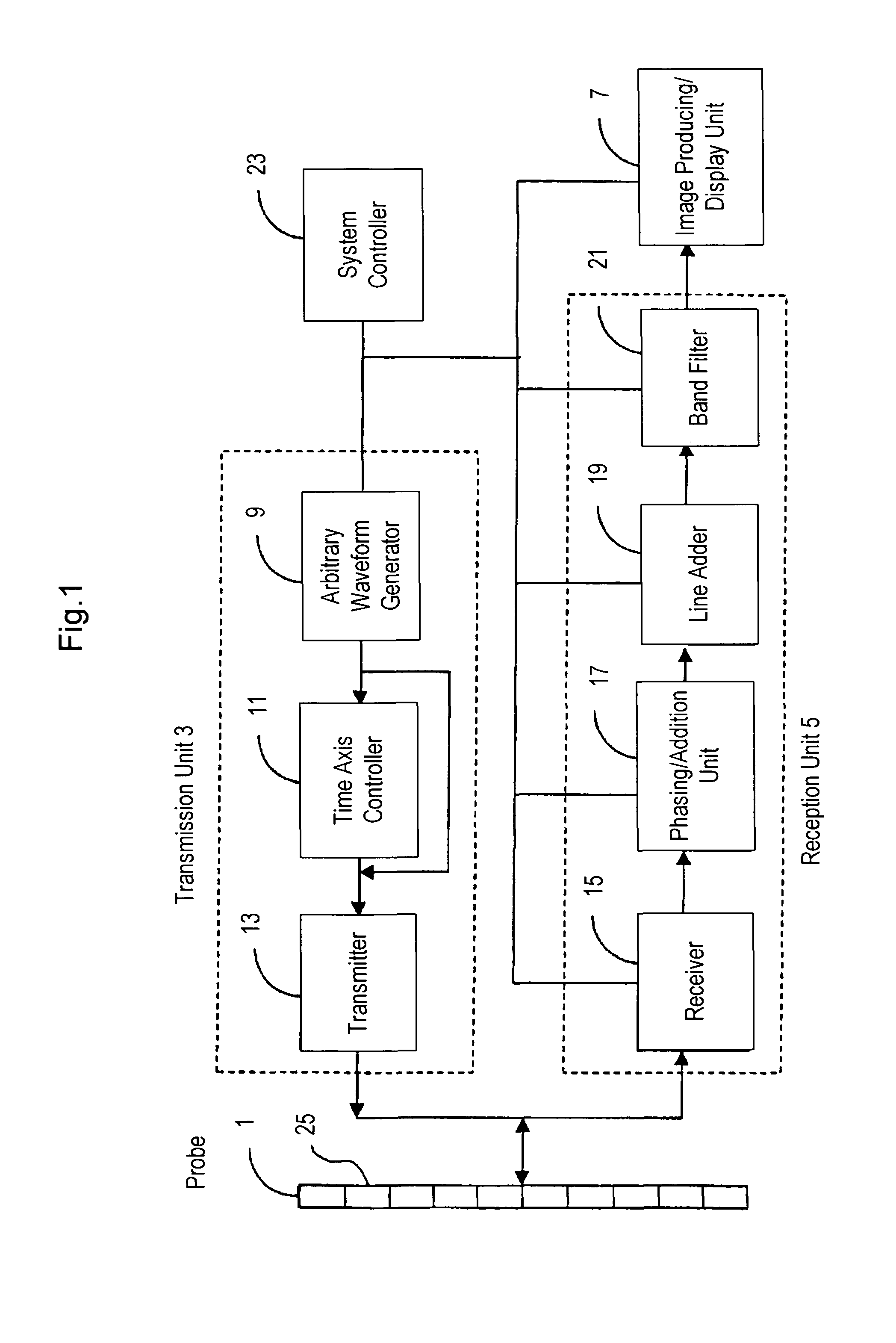
Ultrasonograph
InactiveUS8043220B2Enhance the imageReduce resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationImage resolution
An ultrasound diagnostic apparatus includes an ultrasound probe, a transmission unit for transmitting an ultrasound signal to an object to be examined via the ultrasound probe, a reception unit for processing a signal received by the ultrasound probe, and an image generating unit for generating an image on the basis of the received signal processed by the reception unit, wherein the transmission unit has a function of transmitting the ultrasound signals with varying frequency plural times in an identical direction at predetermined time intervals. The ultrasound signal transmitted plural times includes a first waveform in which the frequency increases and a second waveform in which the frequency decreases, and the reception unit has a function of phasing and adding received signals respectively corresponding to the first waveform and the second waveform, whereby, in tissue harmonic imaging, the penetration is improved, while the resolution is maintained.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
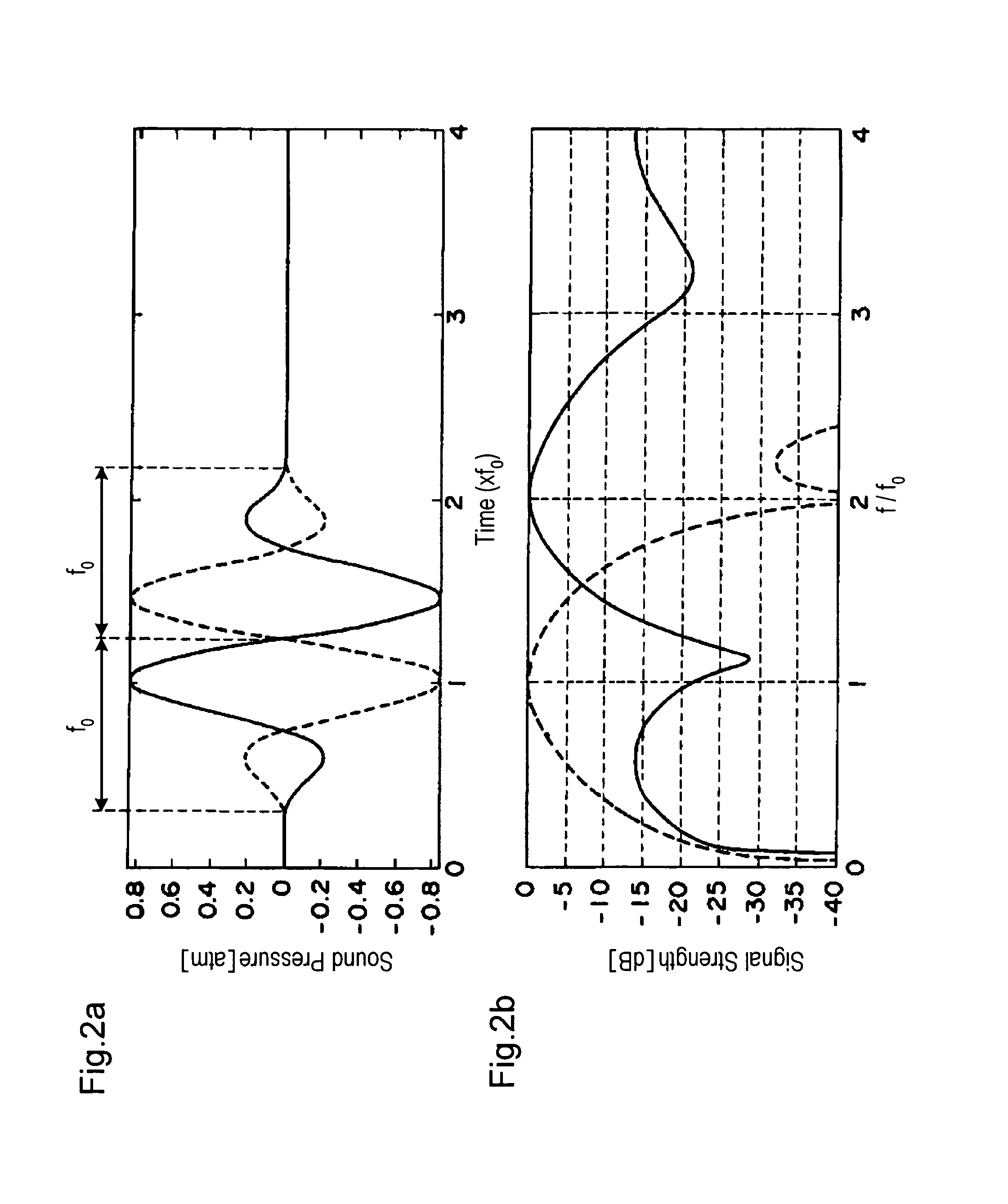
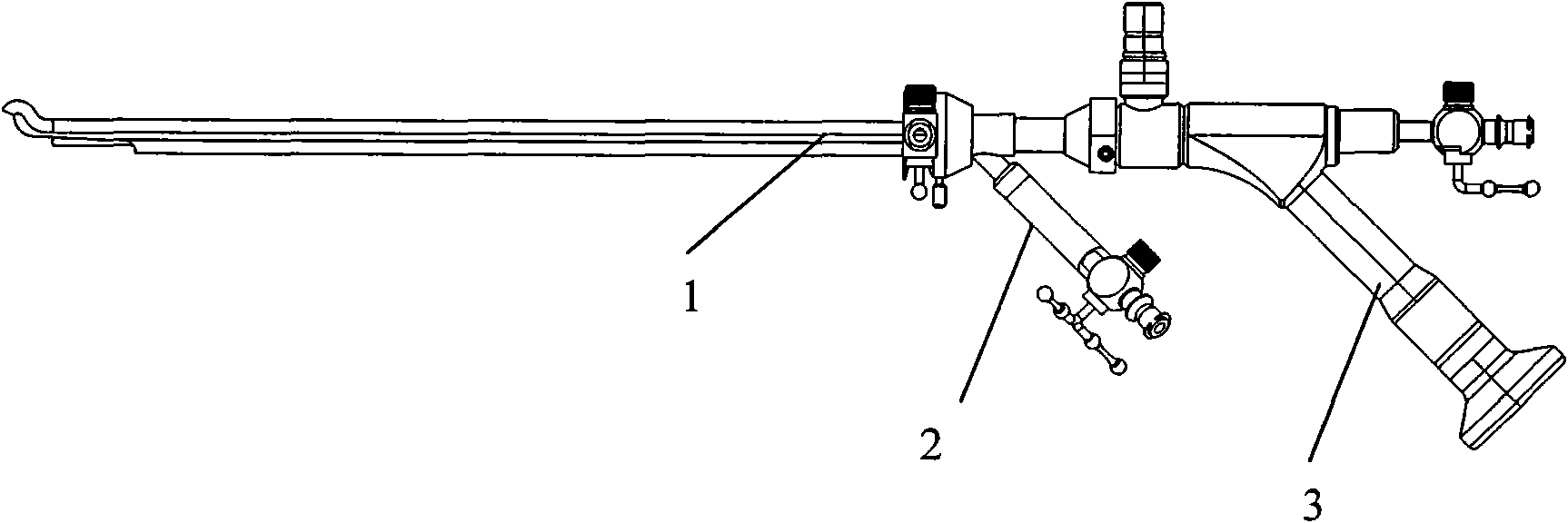
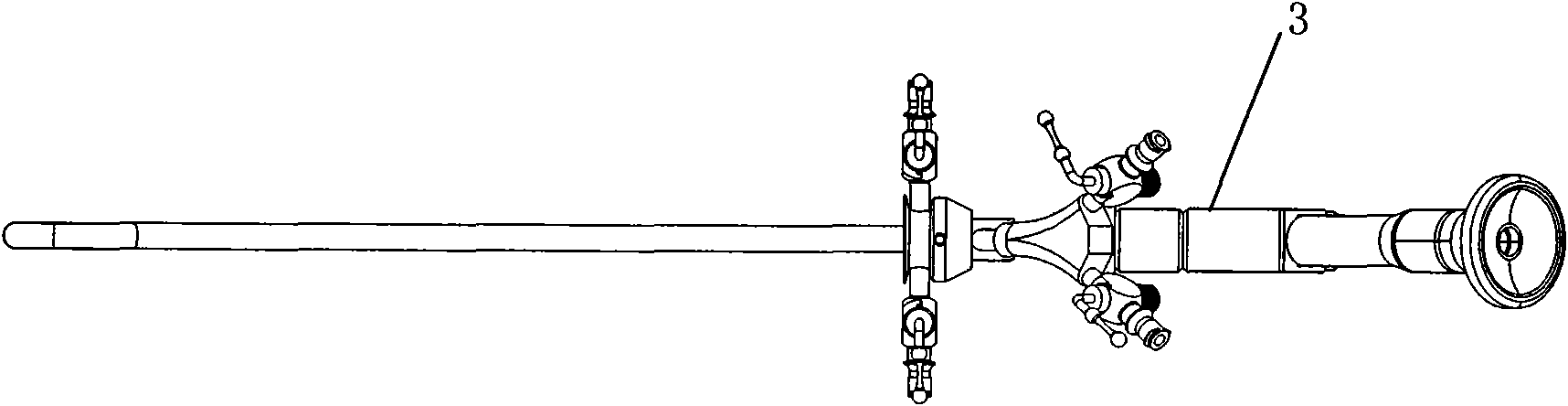
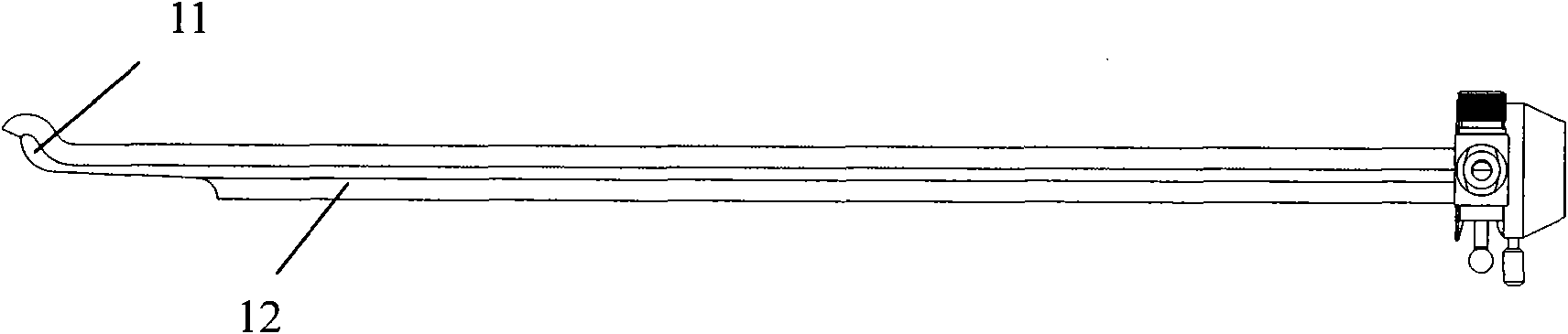
Ultrasonic cystoscope
The invention discloses an ultrasonic cystoscope which belongs to the technical field of medical apparatuses. The ultrasonic cystoscope is formed by organically combing an altered scleroid cystoscope with a miniature ultrasonic probe, and has the functions of a cystoscope and ultrasonic inspection. The ultrasonic cystoscope comprises an endoscope main body. The endoscope main body comprises a scleroid endoscope end part, and an apparatus passage, a cold light source input end and an eye lens input end which are communicated with the scleroid endoscope end part. A lens sheath is arranged outside the endoscope main body, and an operator with at least one apparatus passage is connected with the lens sheath. The miniature ultrasonic probe used for carrying out real-time ultrasonic scanning on bladders is arranged in the apparatus passage of the endoscope main body. The ultrasonic cystoscope can exactly fix the position, the size, the appearance and the range of focus, enhance the accuracy of bladder examination, diagnosis and operation, make up the shortage of the current diagnosis and treat methods and better diagnose and treat various bladder diseases. In addition, the ultrasonic cystoscope has favorable grippage, which is convenient for operations to be carried out successfully.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAODAN MEDICAL INSTR TECH
Apparatus and method for area limited-access through transmission ultrasonic inspection
ActiveUS7703327B2Low costReduced SophisticationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationProximate
An apparatus and method for inspecting a structure are provided which include receiving probes and area transducers disposed proximate opposite surfaces of a structure under inspection. An area transducer uniformly emits ultrasonic signals over an area which may be scanned by a receiving probe without corresponding movement of the area transducer. An area transducer may be moved over the surface of the structure or repositioned to provide additional inspection area for the receiving probe to scan, including to provide for continuous inspection. Multiple area transducers may be used in sequence to provide for continuous inspection. Multiple receiving probes may be used, independently or collectively as an array, to increase inspection of a structure, taking advantage of the large area of ultrasonic signals emitted by one or more area transducers.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
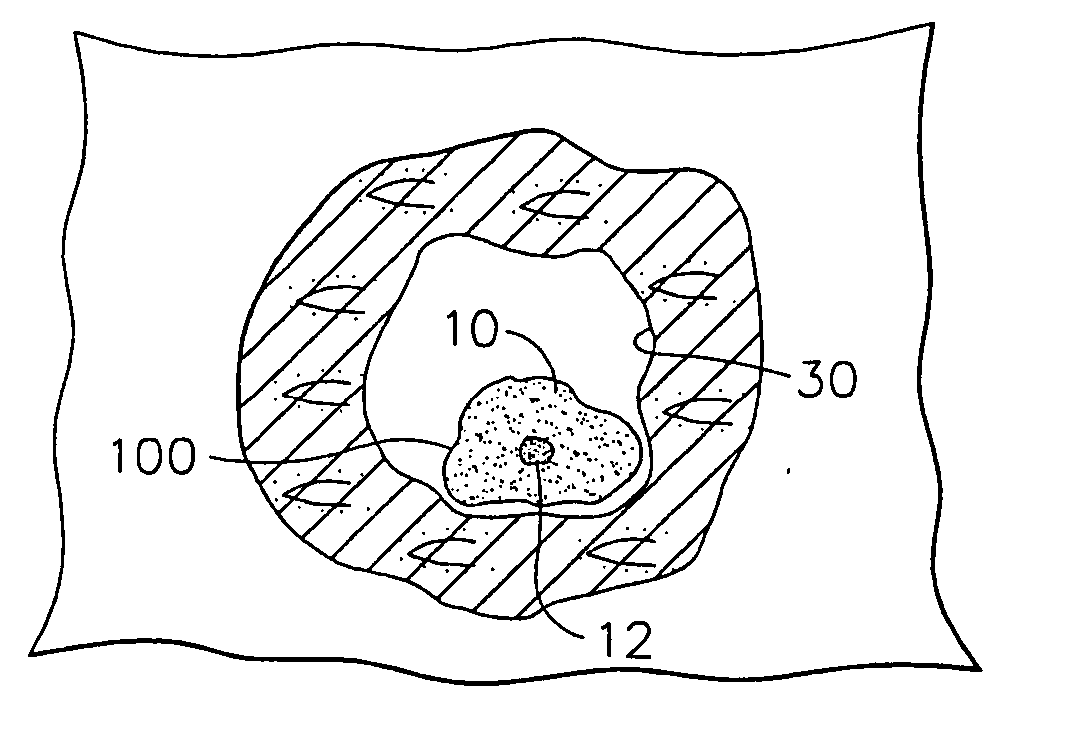
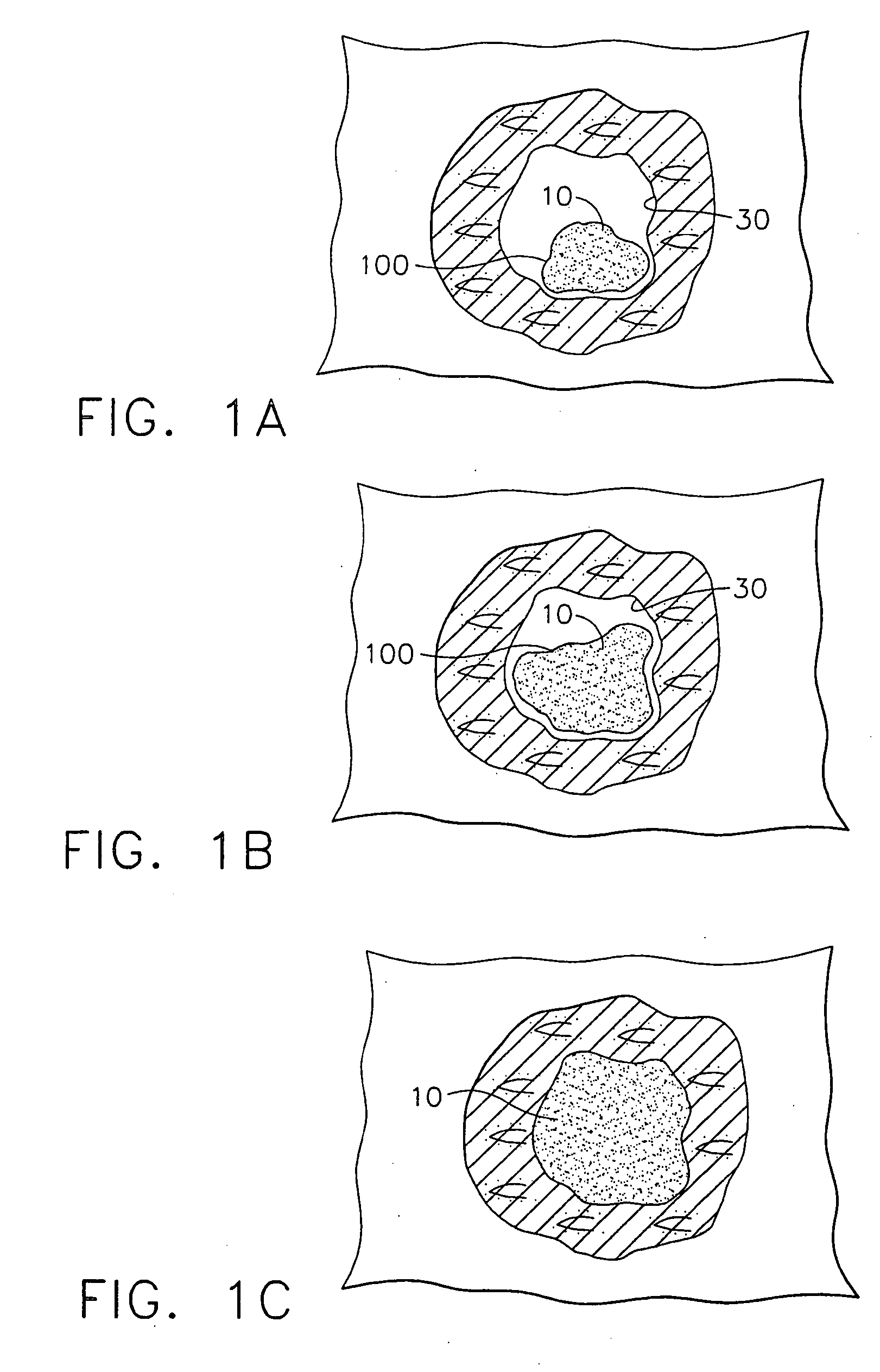
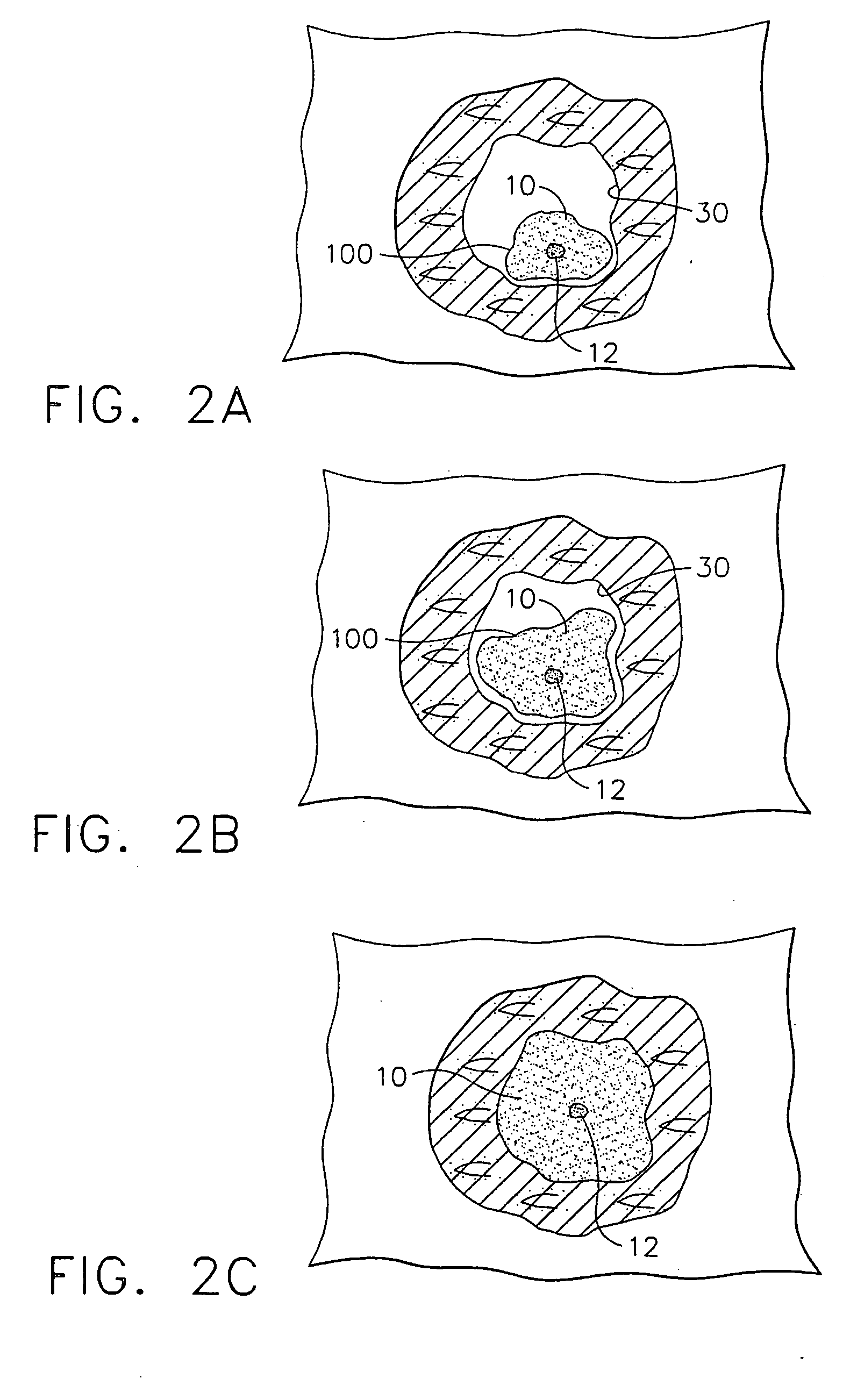
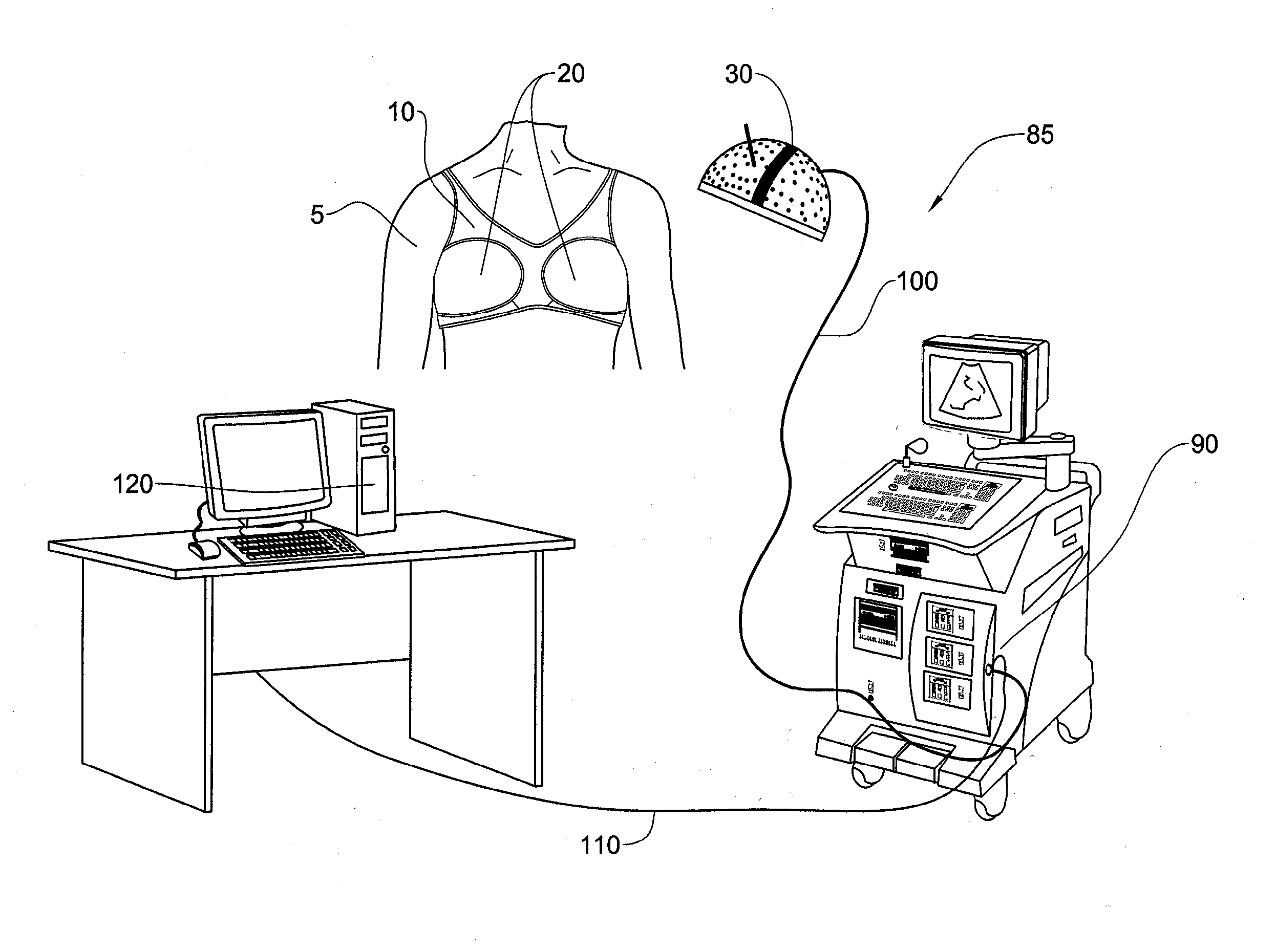
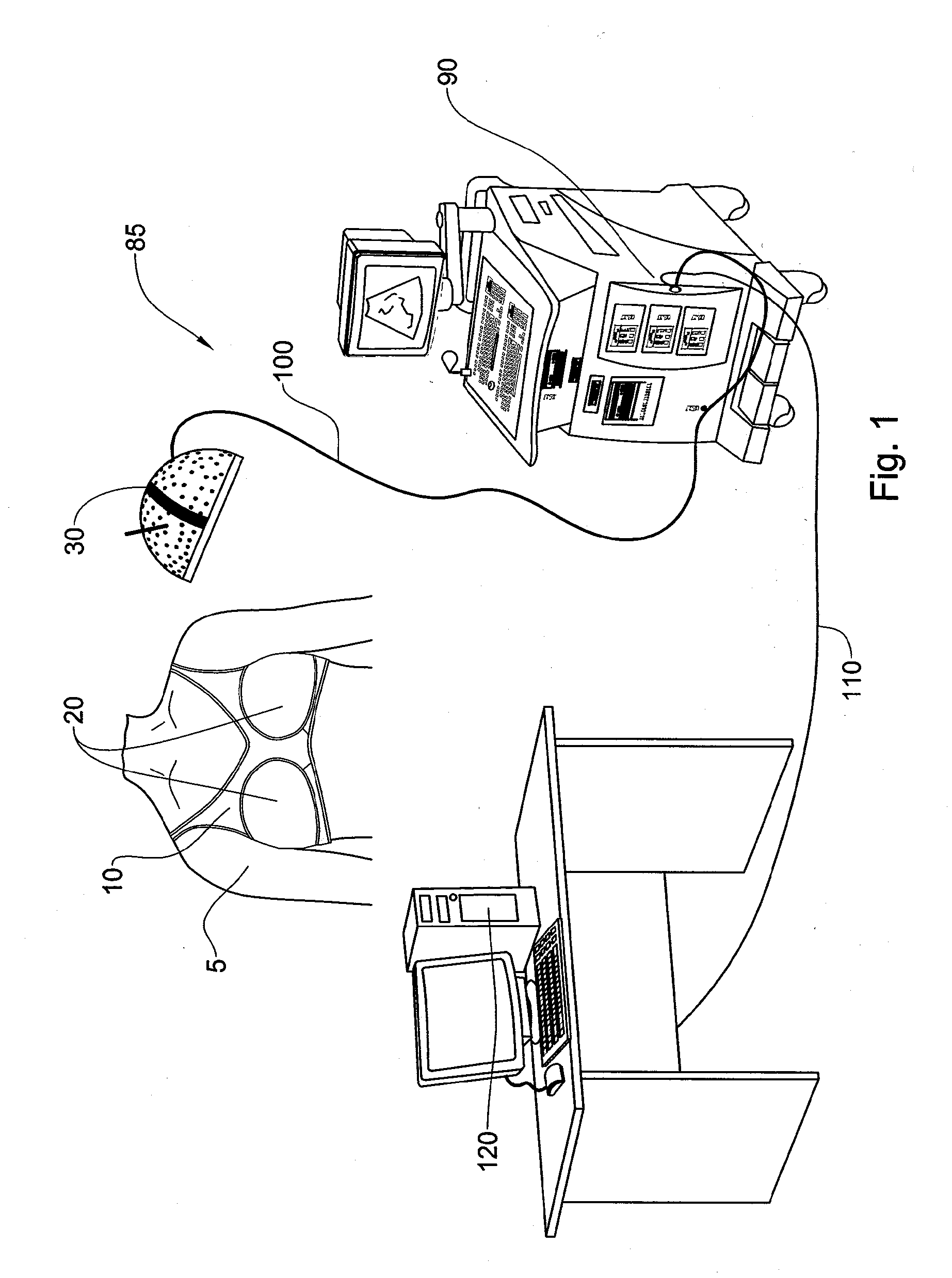
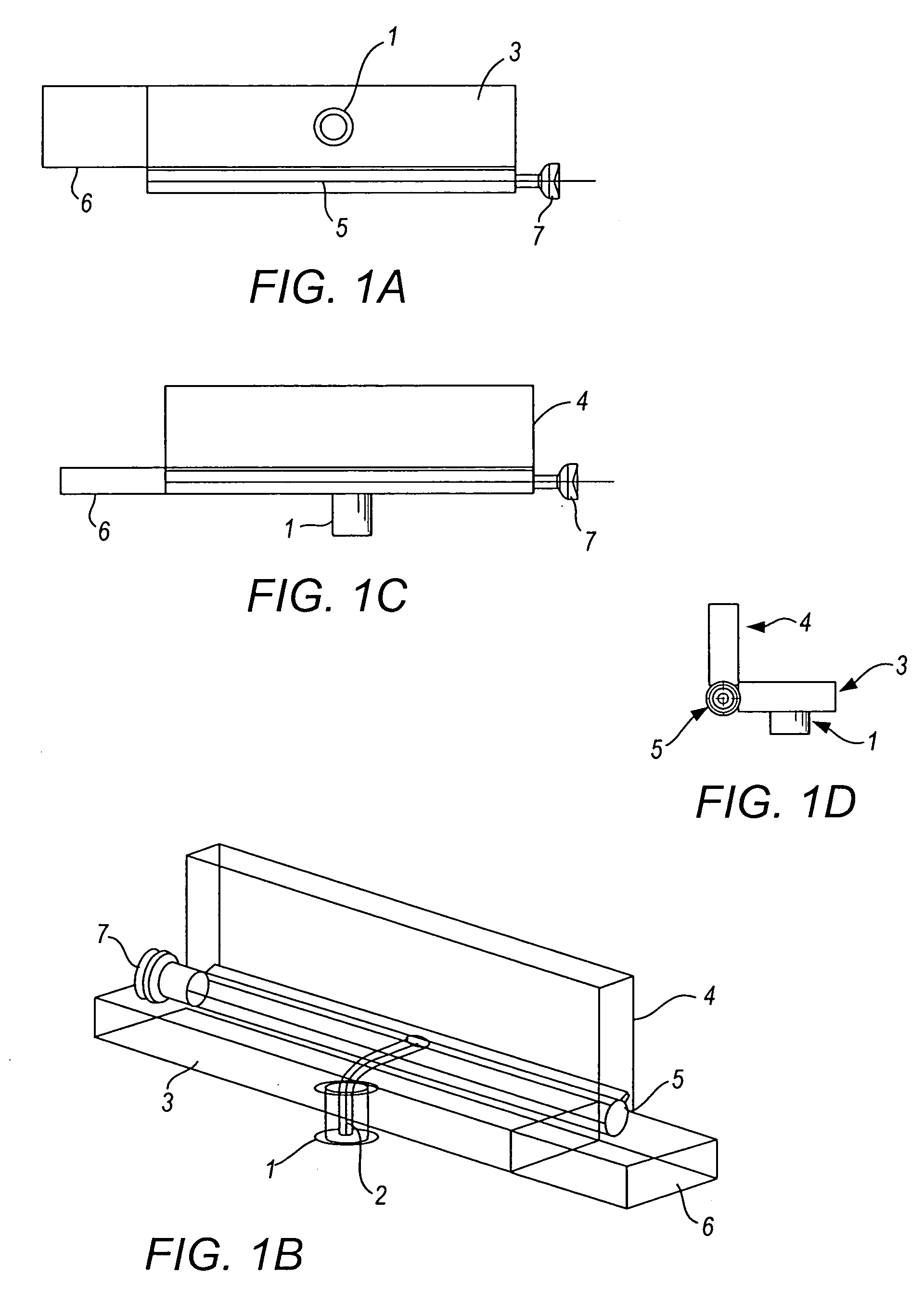
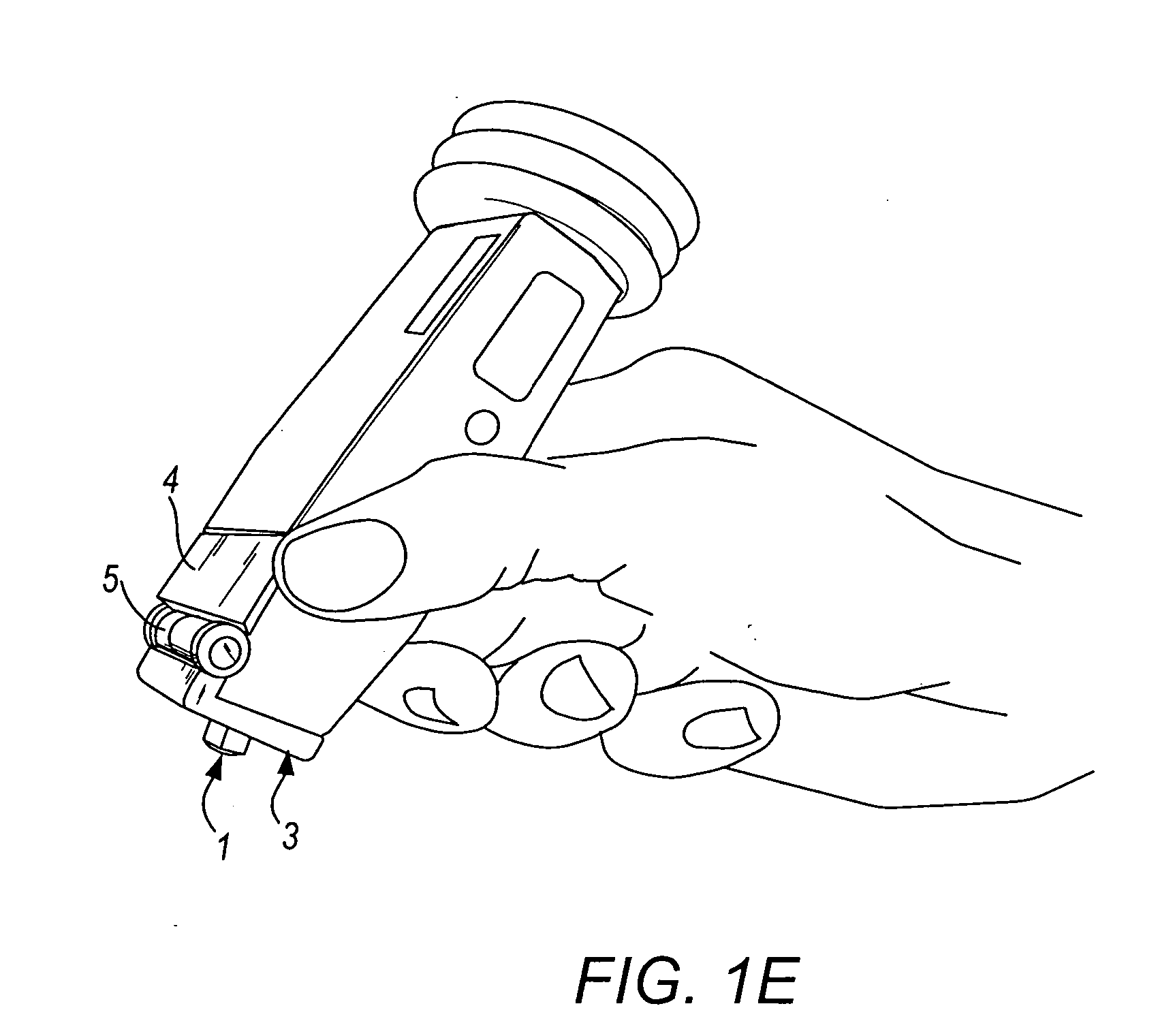
Method and device for marking skin during an ultrasound examination
InactiveUS20050085727A1Ensure high efficiency and accuracyEasy to produceDiagnostic probe attachmentInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic sensorUltrasound sonography
A method and device for marking a patient's skin during an ultrasound examination to denote a feature of interest. The device comprises a first portion and a second portion. The first portion is adapted for attachment of the device to an ultrasound transducer. The second portion is adapted for marking the skin of the patient to denote the feature of interest. The first and second portions are rotatably attached to each other. During an ultrasound examination of the patient to locate the feature of interest, the second portion is rotated so that it is spaced away from the patient's skin. The ultrasound examination is conducted in the normal manner until the feature of interest is located, at which time the second portion is rotated so that it contacts and marks the patient's skin to denote the feature of interest.
Owner:SWANBOM REBECCA L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com