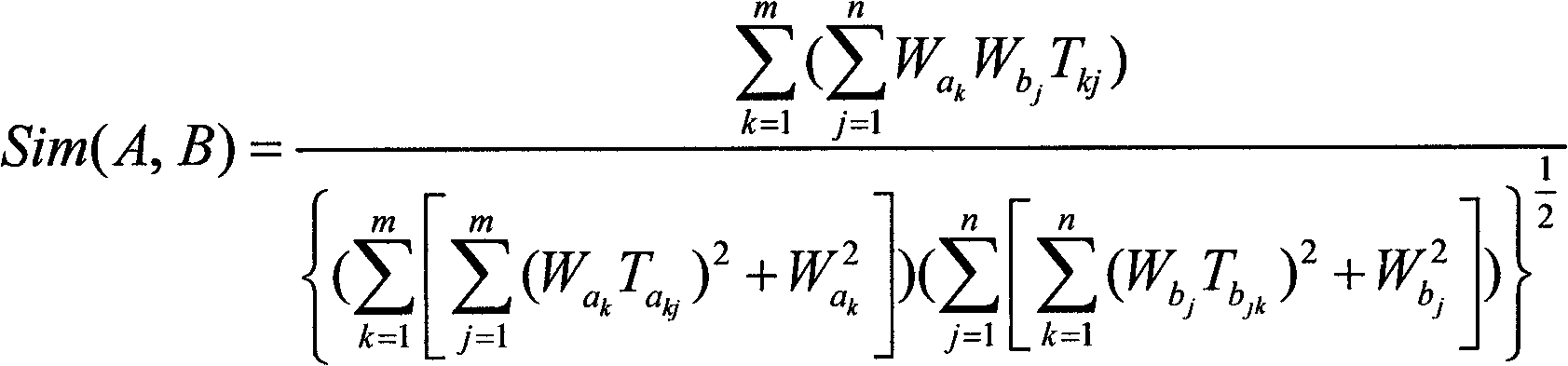Patents
Literature
83 results about "Patient model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
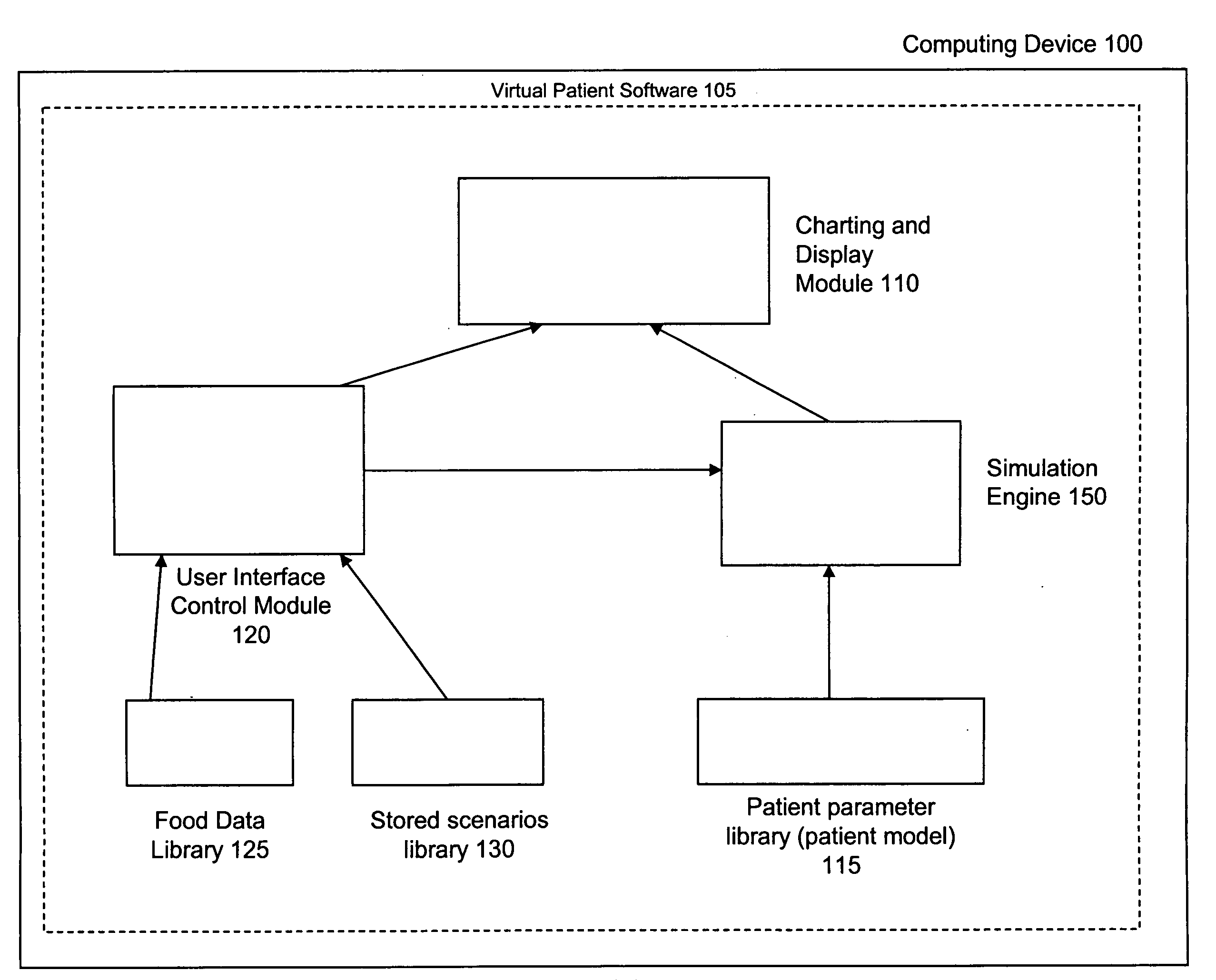
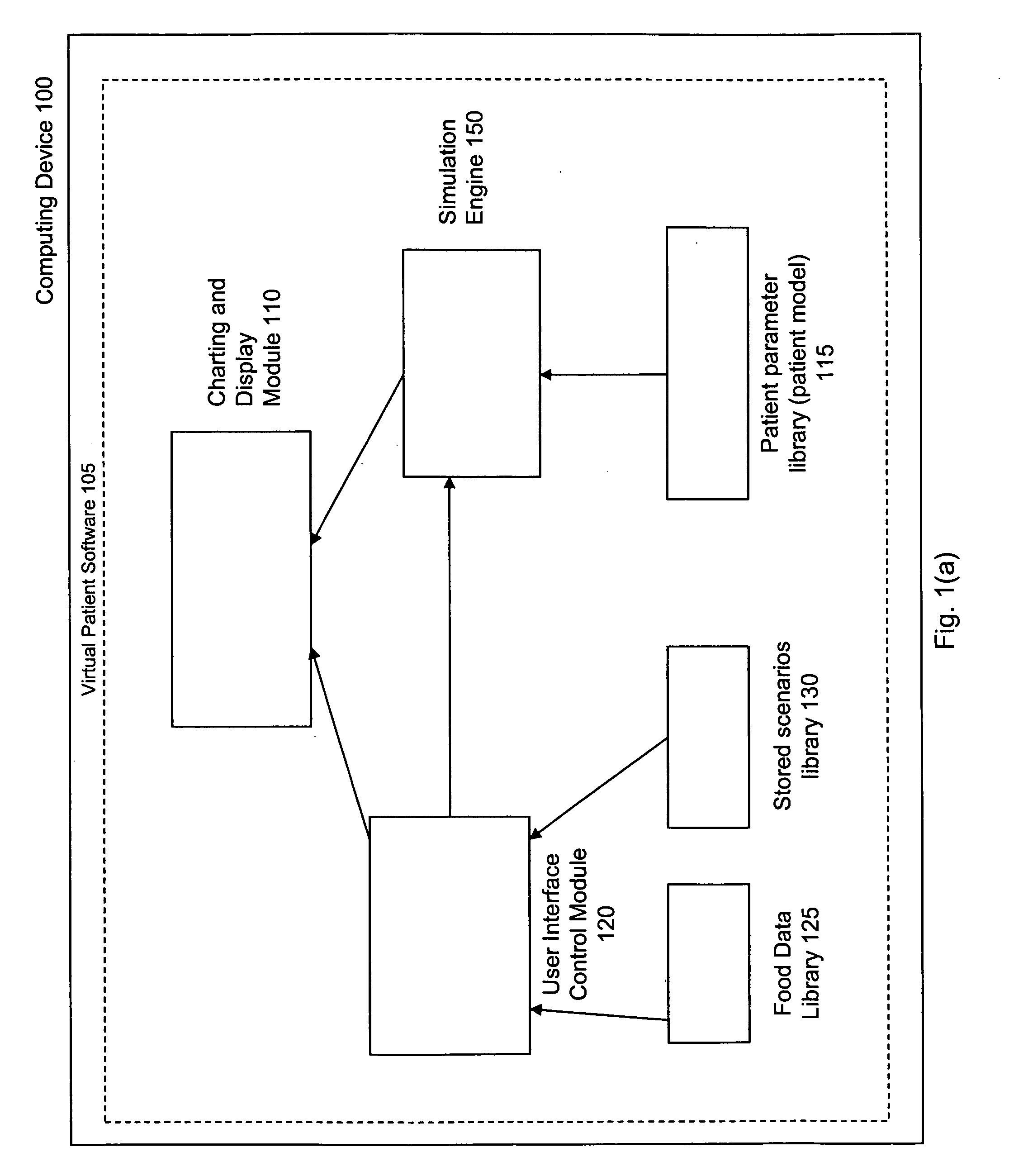
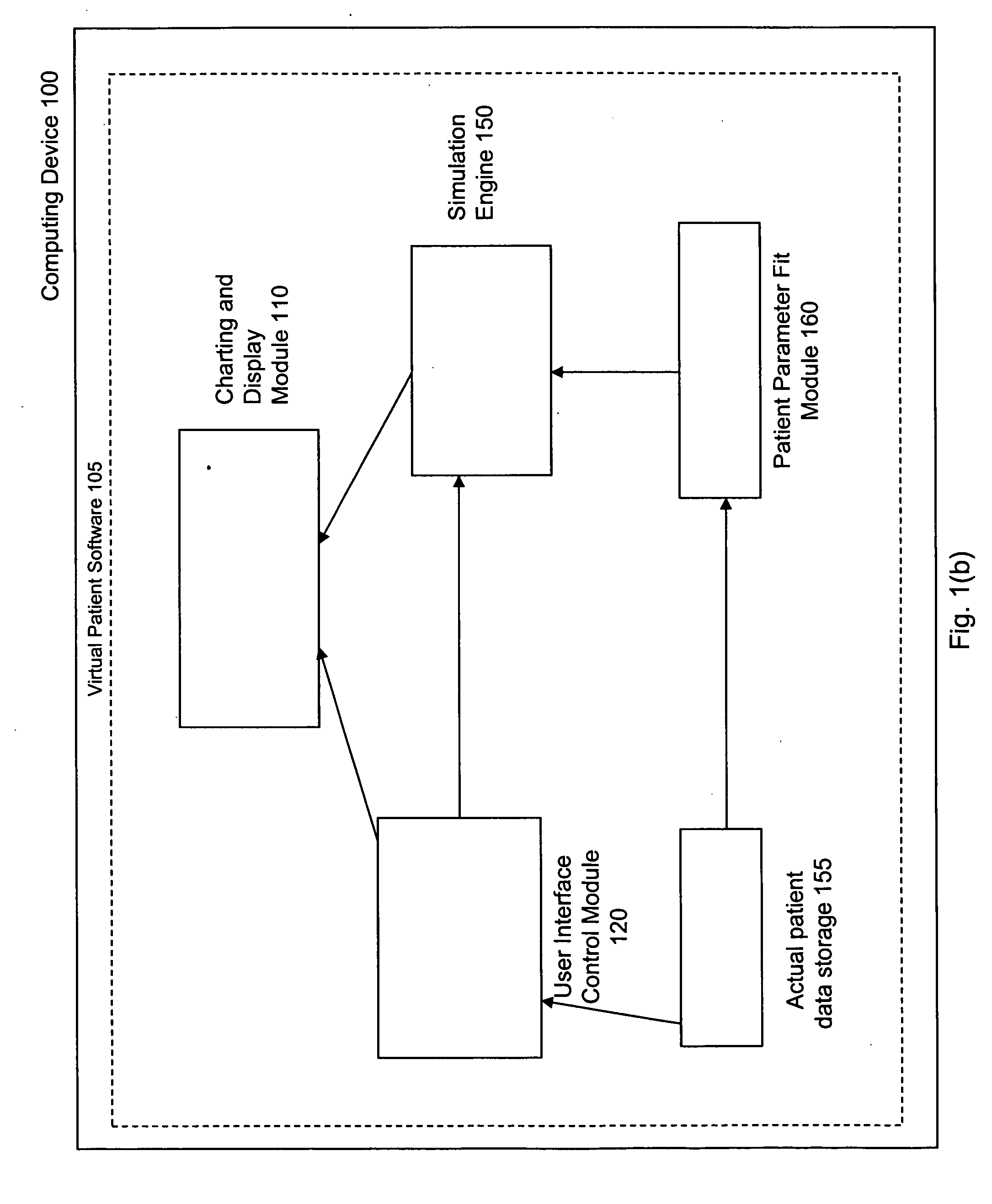
Virtual patient software system for educating and treating individuals with diabetes
A system to assist an individual in developing a therapy in diabetes treatment of a patient includes a user interface control module, a simulation engine, a charting and display module. The user interface control module receives an input related to the patient and captures a current time of the simulation. The simulation engine receives the input, generates a plurality of blood glucose readings for the patient up to the current time of the simulation based on the input, and to transfers the plurality of blood glucose readings. The charting and display module receives the plurality of blood glucose readings and display the plurality of blood glucose readings. The simulation engine receives patient parameters from a patient parameter library based on a selected patient model.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
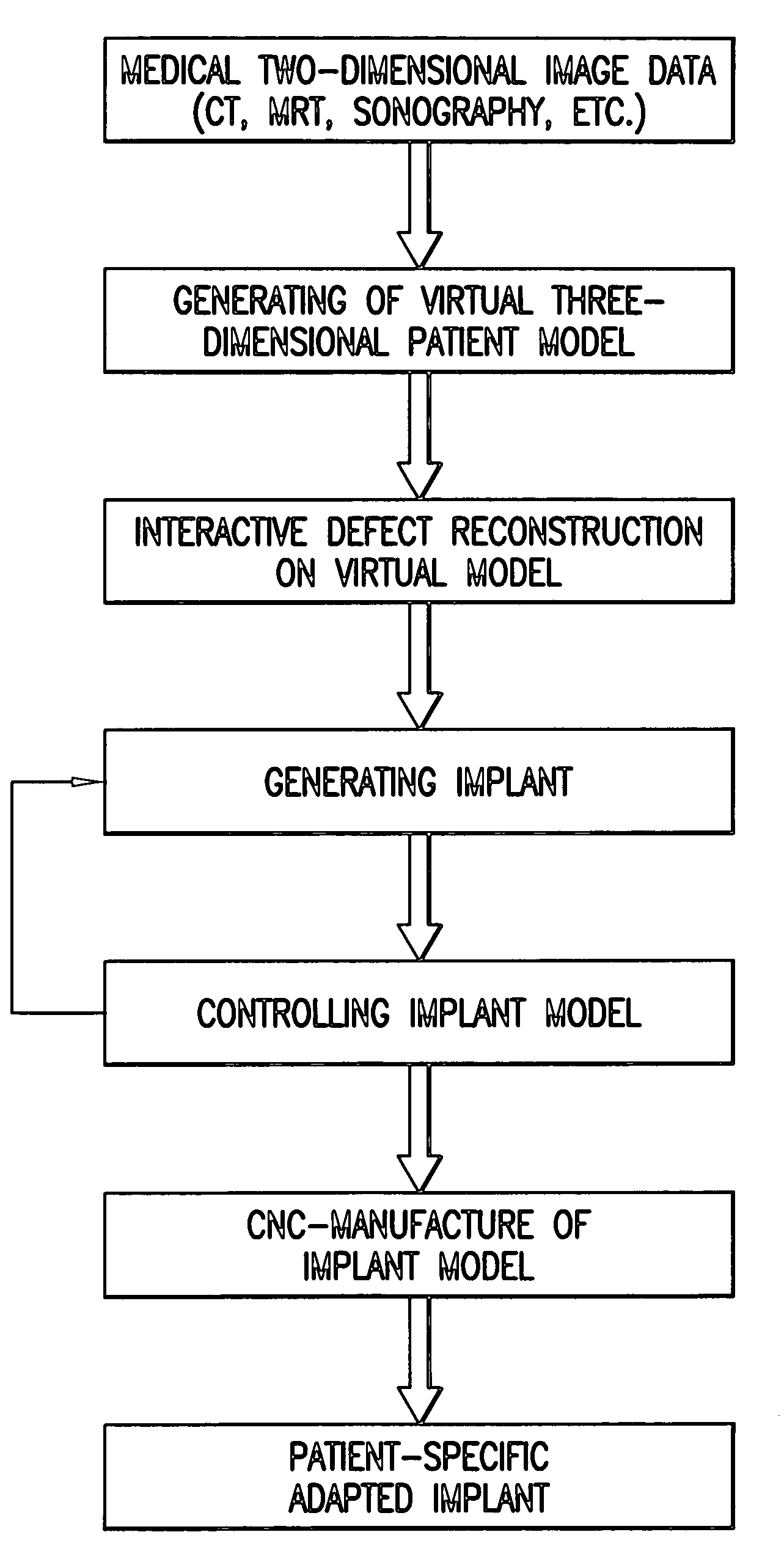
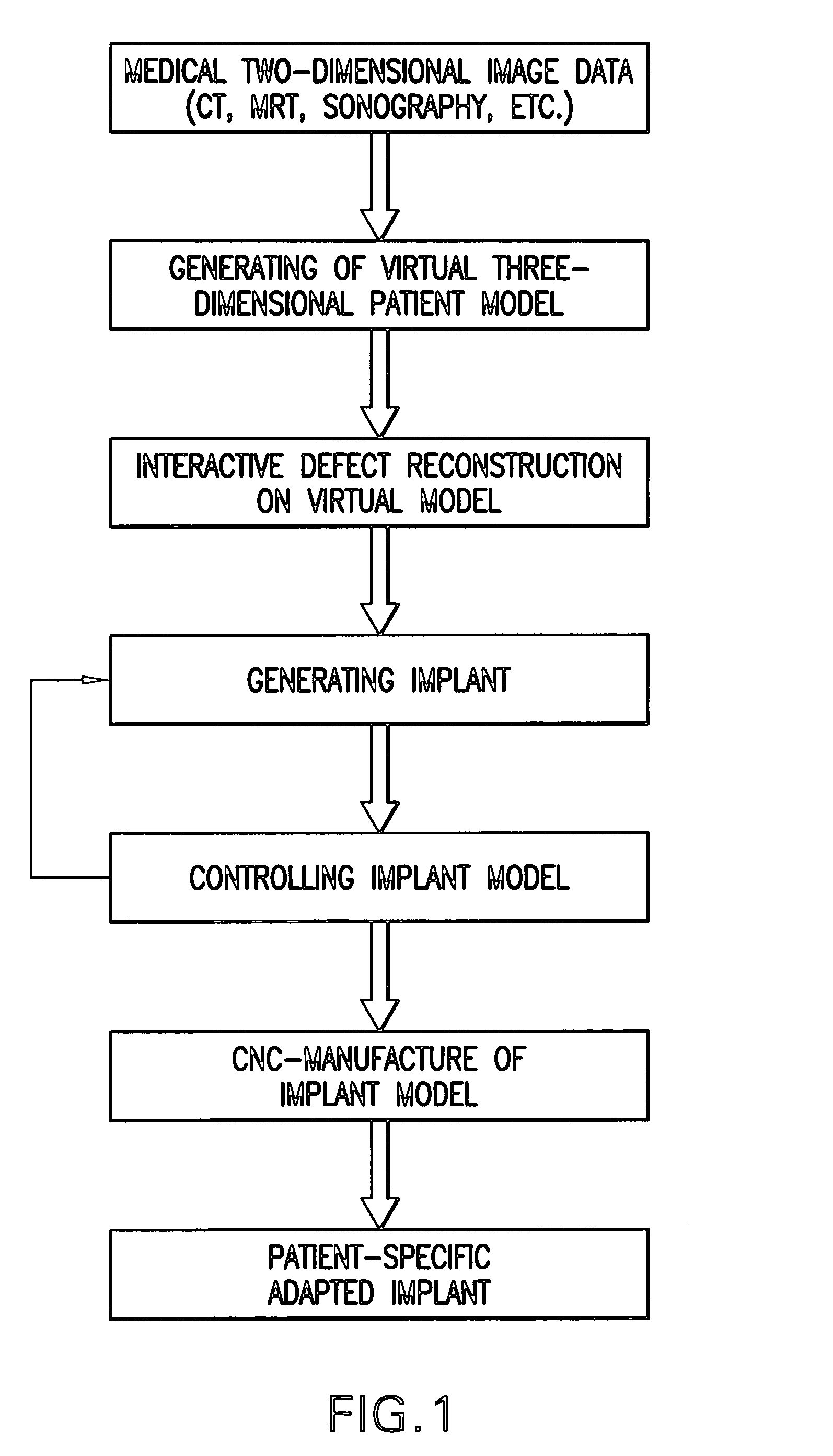
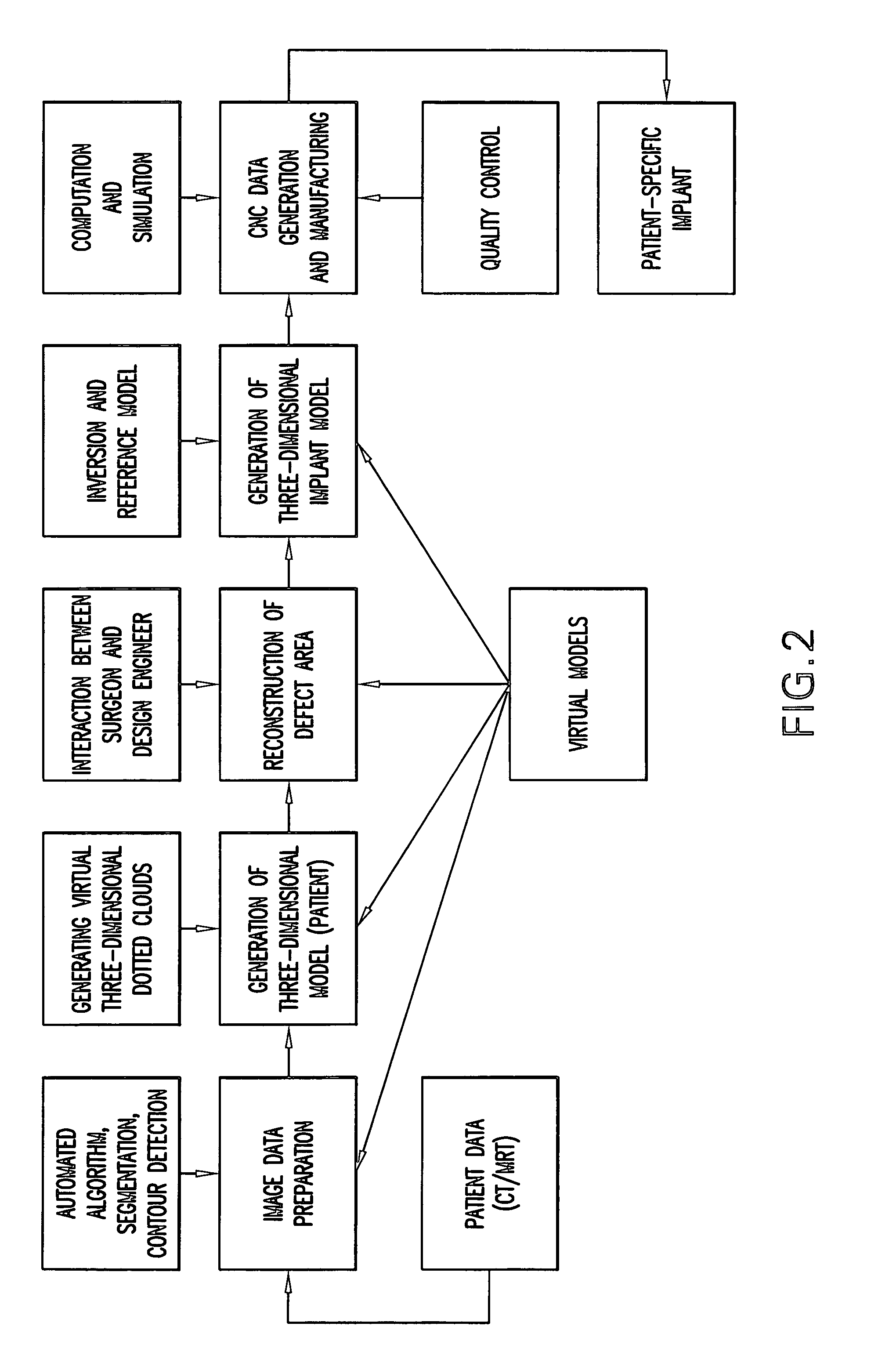
Method for generating patient-specific implants
InactiveUS6932842B1Exact fitShorten the timeProgramme controlComputer controlReference modelPatient model
An implant is generated which is functionally and aesthetically adapted to the patient with a greater degree of precision, irrespective of the size, form and complexity of the defect, whereby the implant can be produced and operatively inserted into the patient over a short time period and in a simple manner. A virtual three-dimensional model of the patient which is formed from existing recorded (two-dimensional) image data of the patient is compared with real medical reference data. The comparison which is, for example, carried out using a data bank with test person data enables a reference model object which is most suited to the patient or closest to the patient model to be selected or formed and a virtual implant model is generated accordingly. Computer numeric control data is directly generated from the implant model which is generated virtually in the computer for program-assisted production of the implant.
Owner:3DI
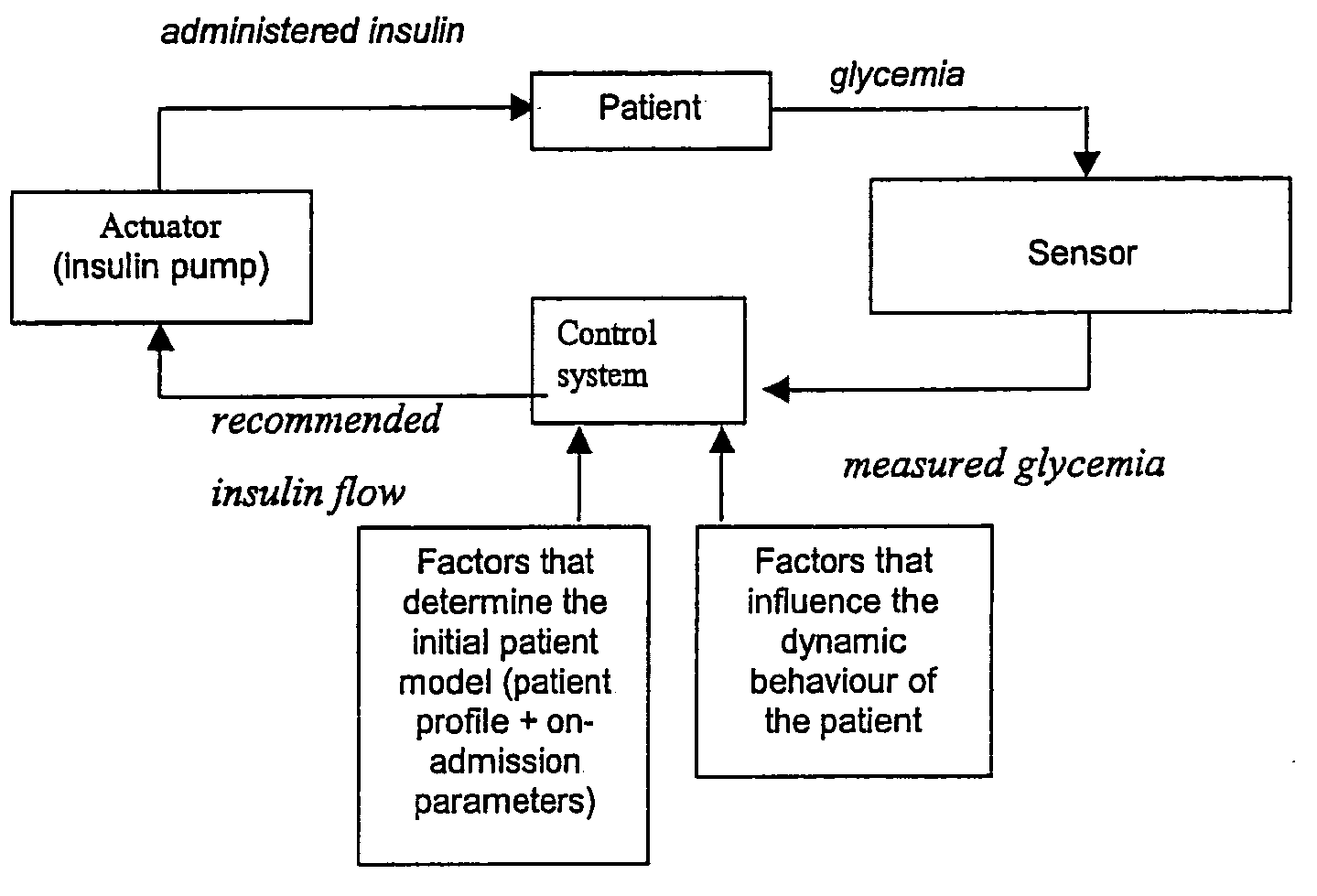
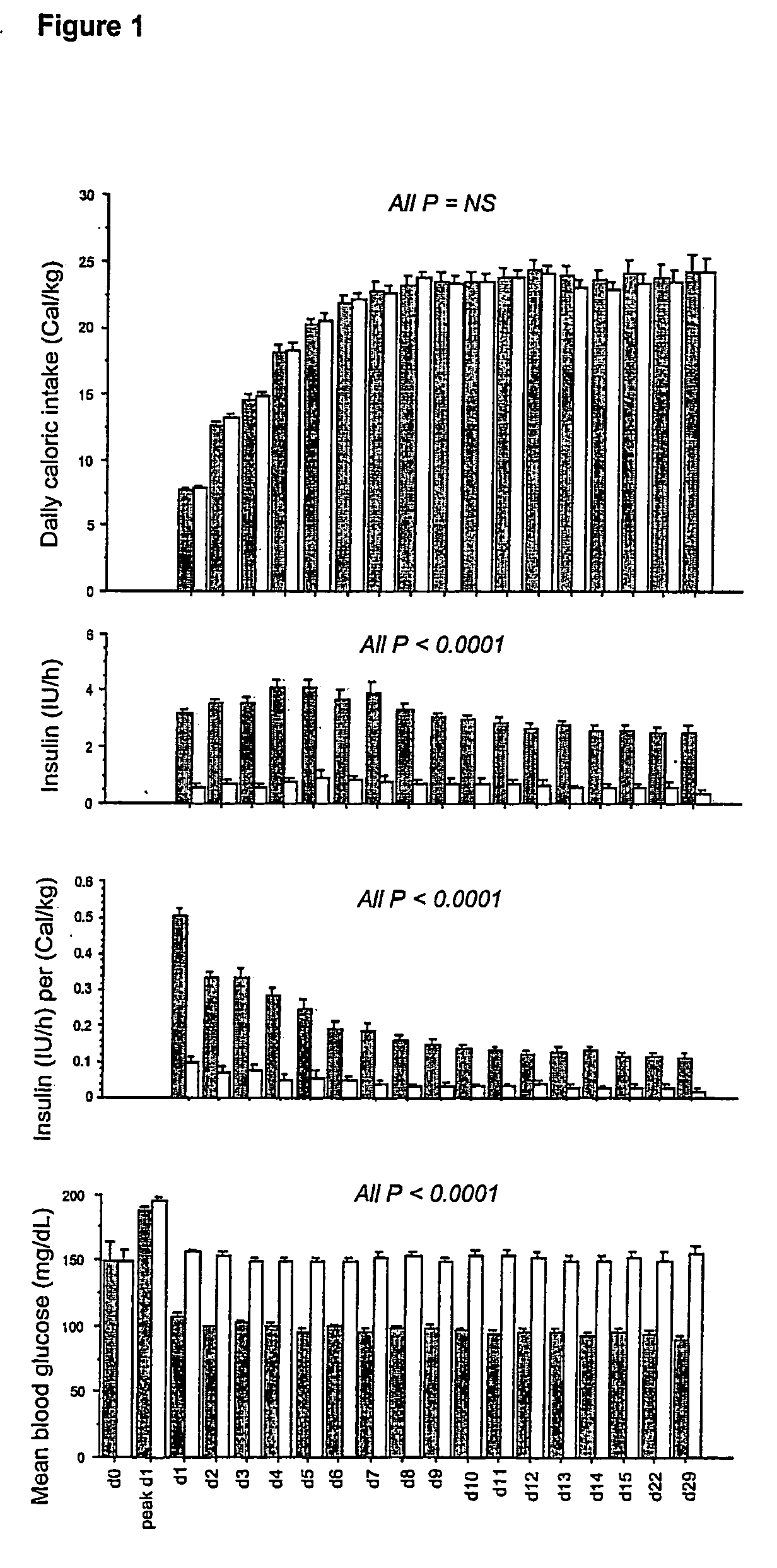
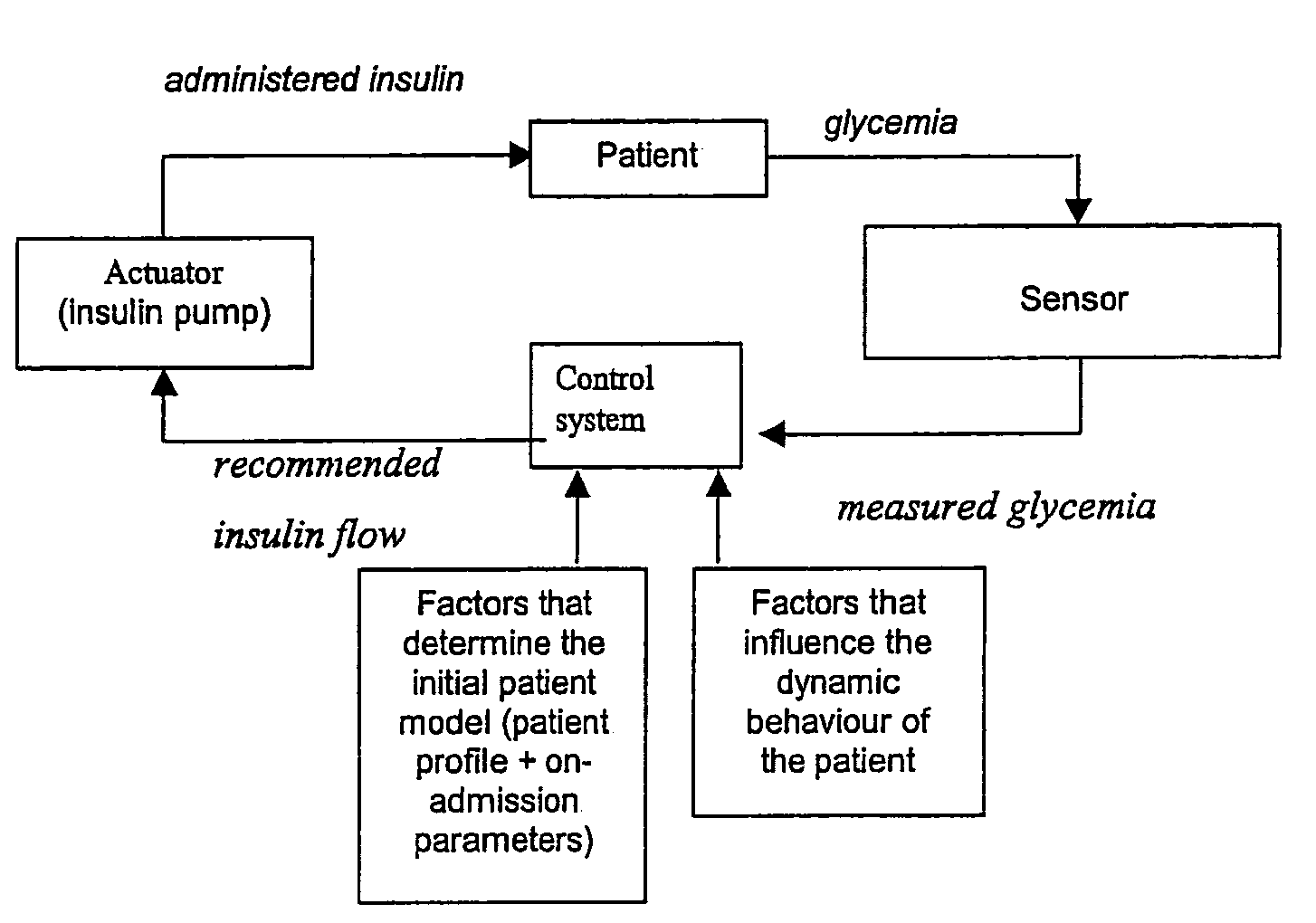
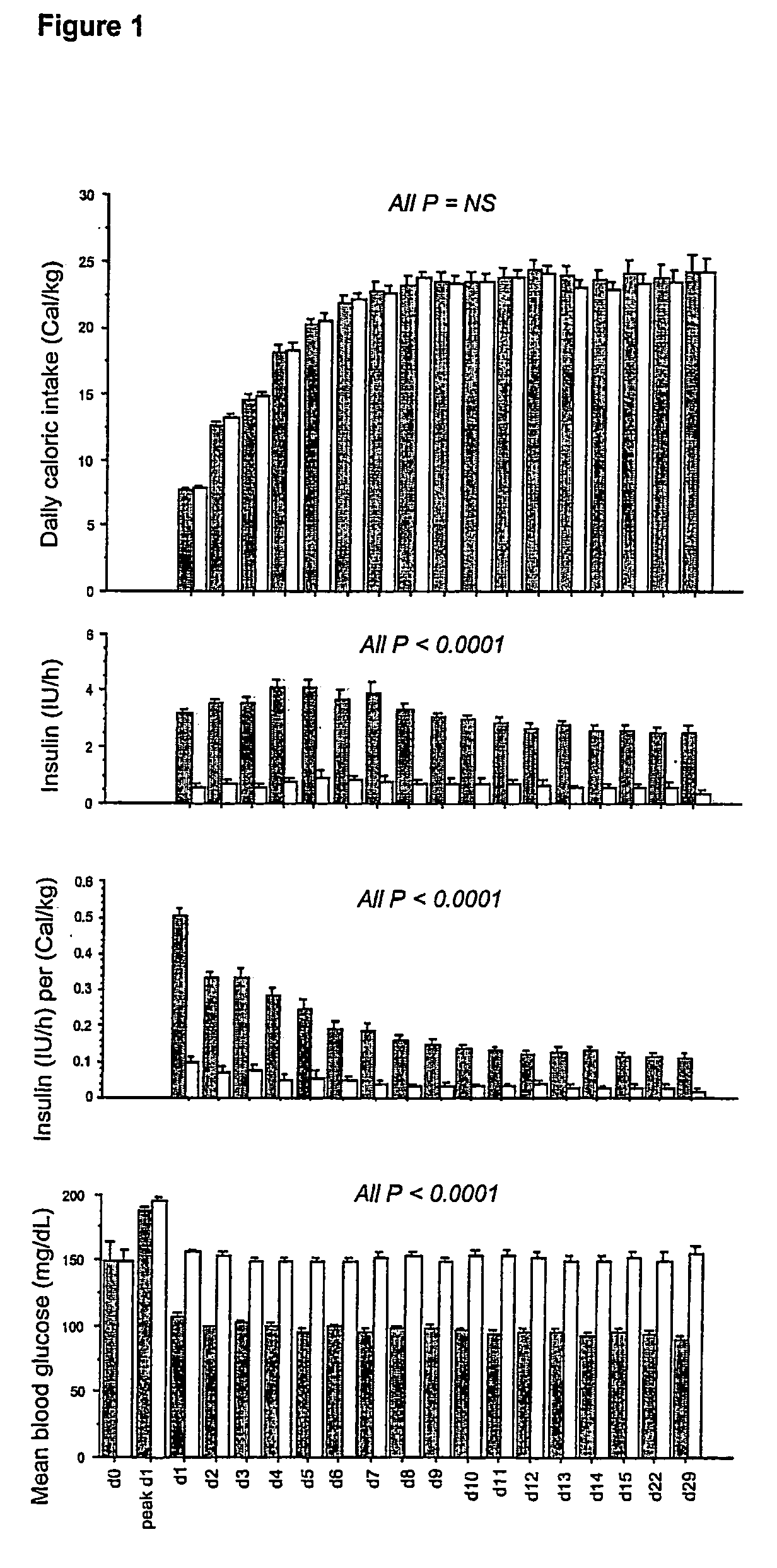
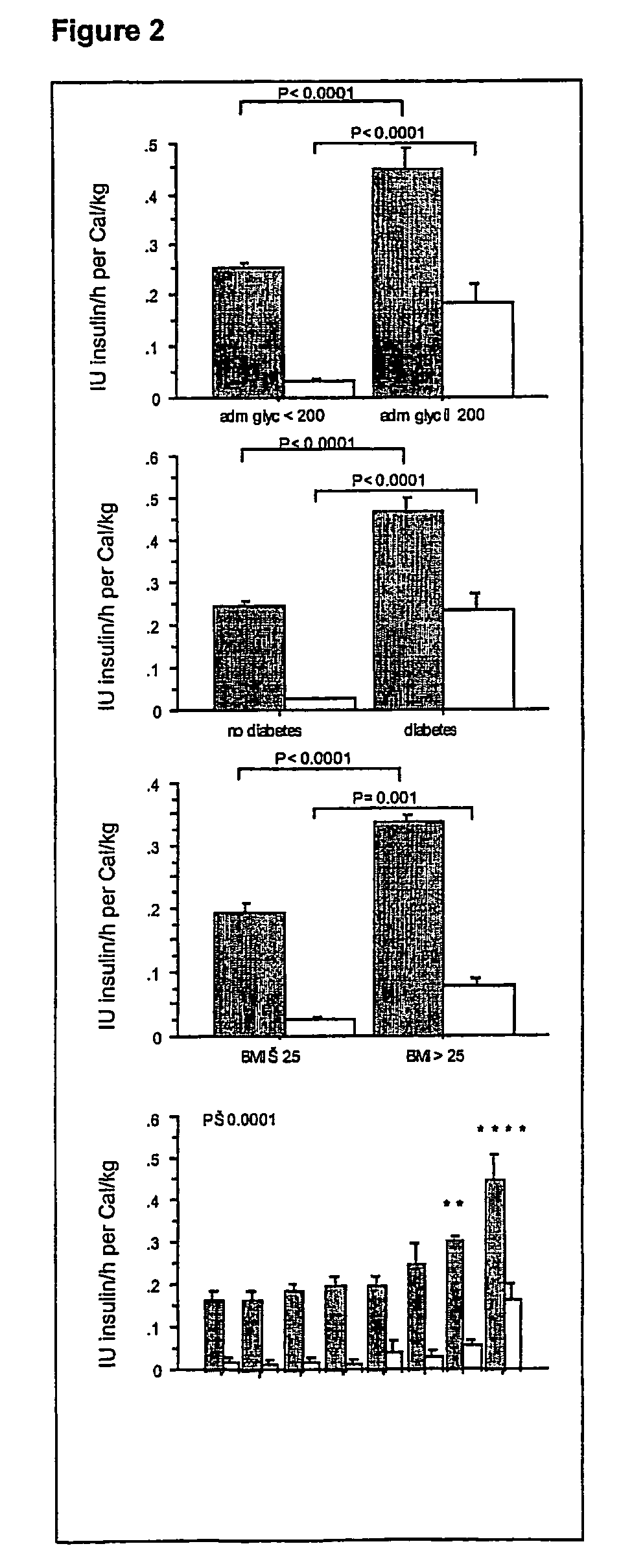
Automatic infusion system based on an adaptive patient model
ActiveUS20050171503A1Ensuring wound repairReduces intensive care and hospital mortality and morbidityMedical devicesPressure infusionPatient modelDisease
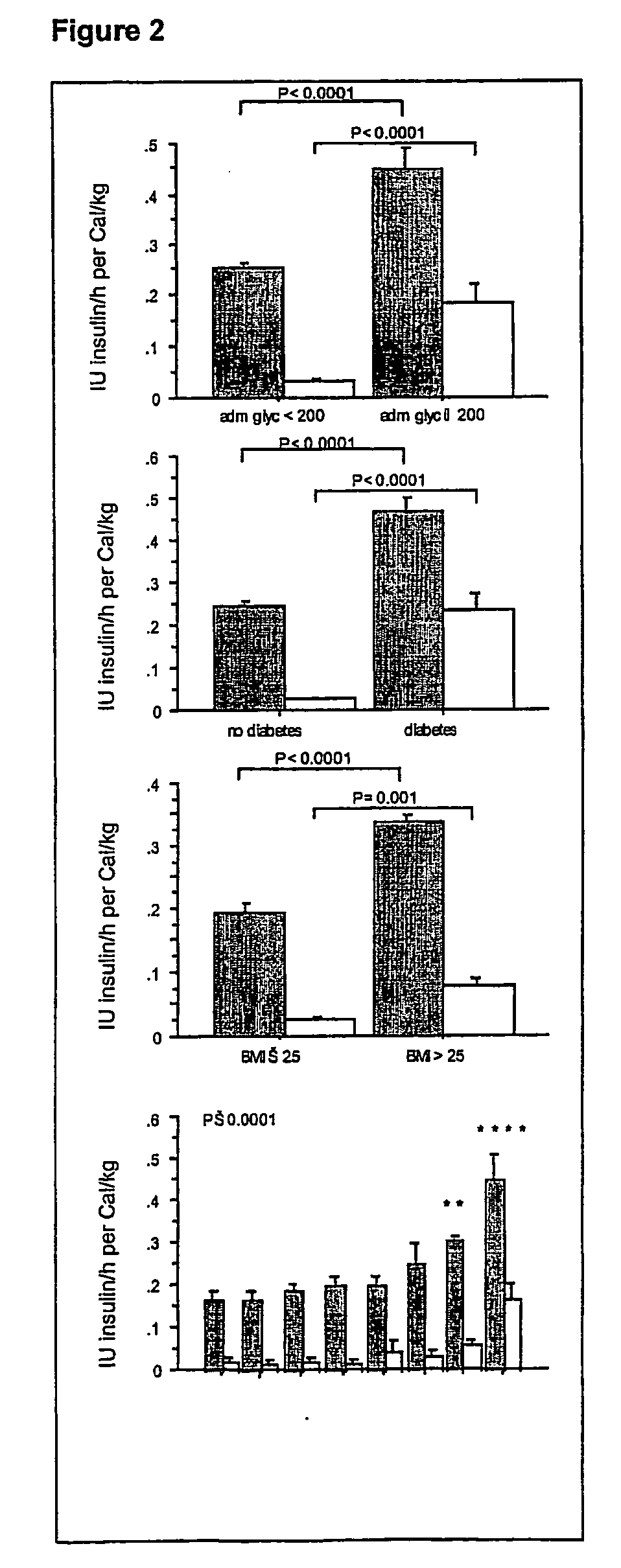
Present invention is a system of blood glucose monitoring and intensive insulin therapy in a ICU for strict maintenance of normoglycemia which reduces intensive care and hospital mortality and morbidity of critically ill adult patients. The findings of present study also reveal factors determining insulin doses needed to maintain normoglycemia as well as the impact of insulin dose versus blood glucose level on the observed outcome benefits have been established. The invention provides a control system that adapts the flow of the insulin infusion based on insulin requirement calculated by blood glucose levels and clinical parameters such as history of diabetes, Body Mass Index, blood glucose level on admission, reason of ICU admission, time in the ICU, type and severity of illness, caloric intake, obesity, drugs affecting insulin sensitivity). This automated insulin monitoring systems significantly reduces the workload and human resource management problems for intensive insulin therapy in patients in the ICU.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV
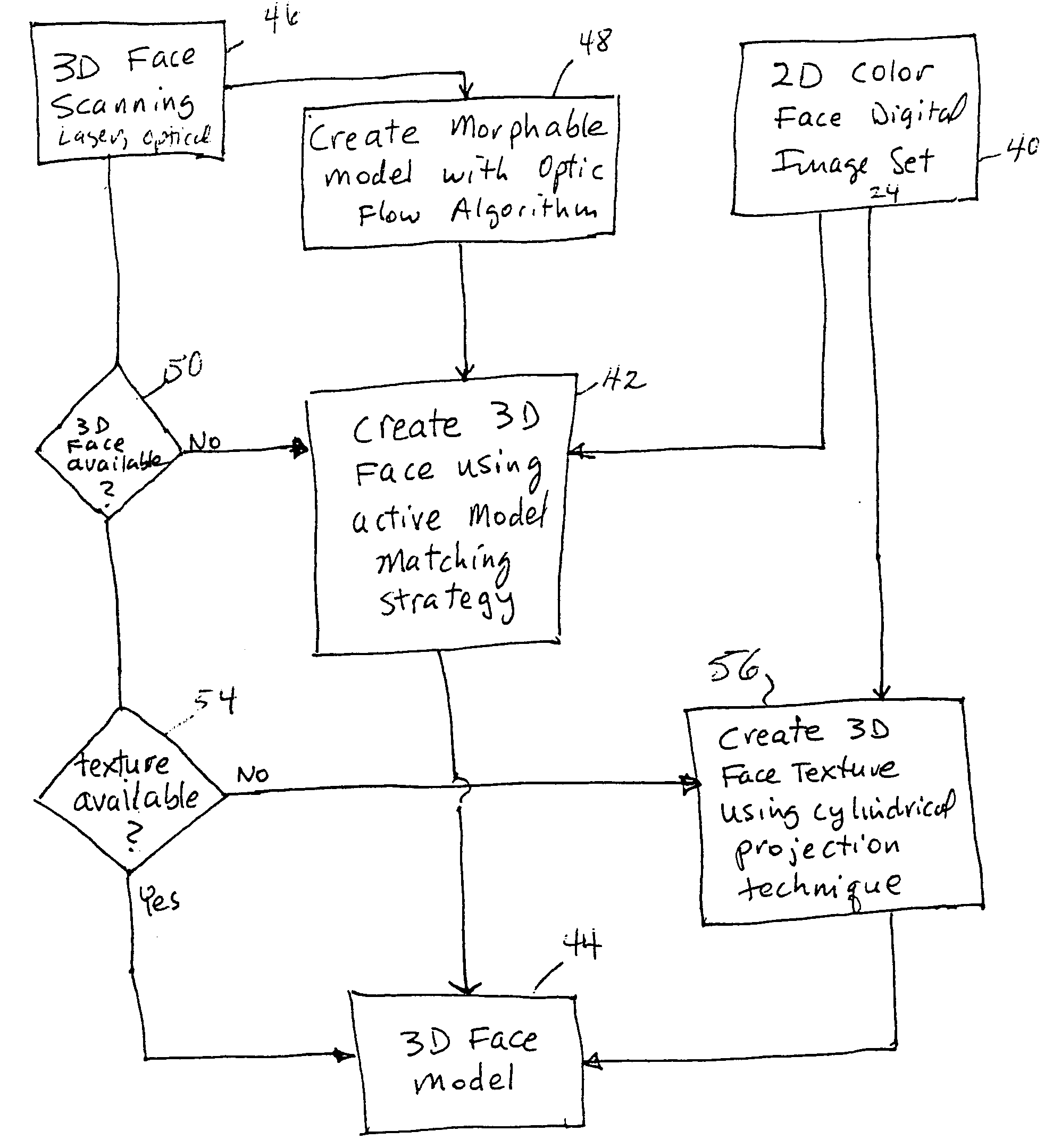
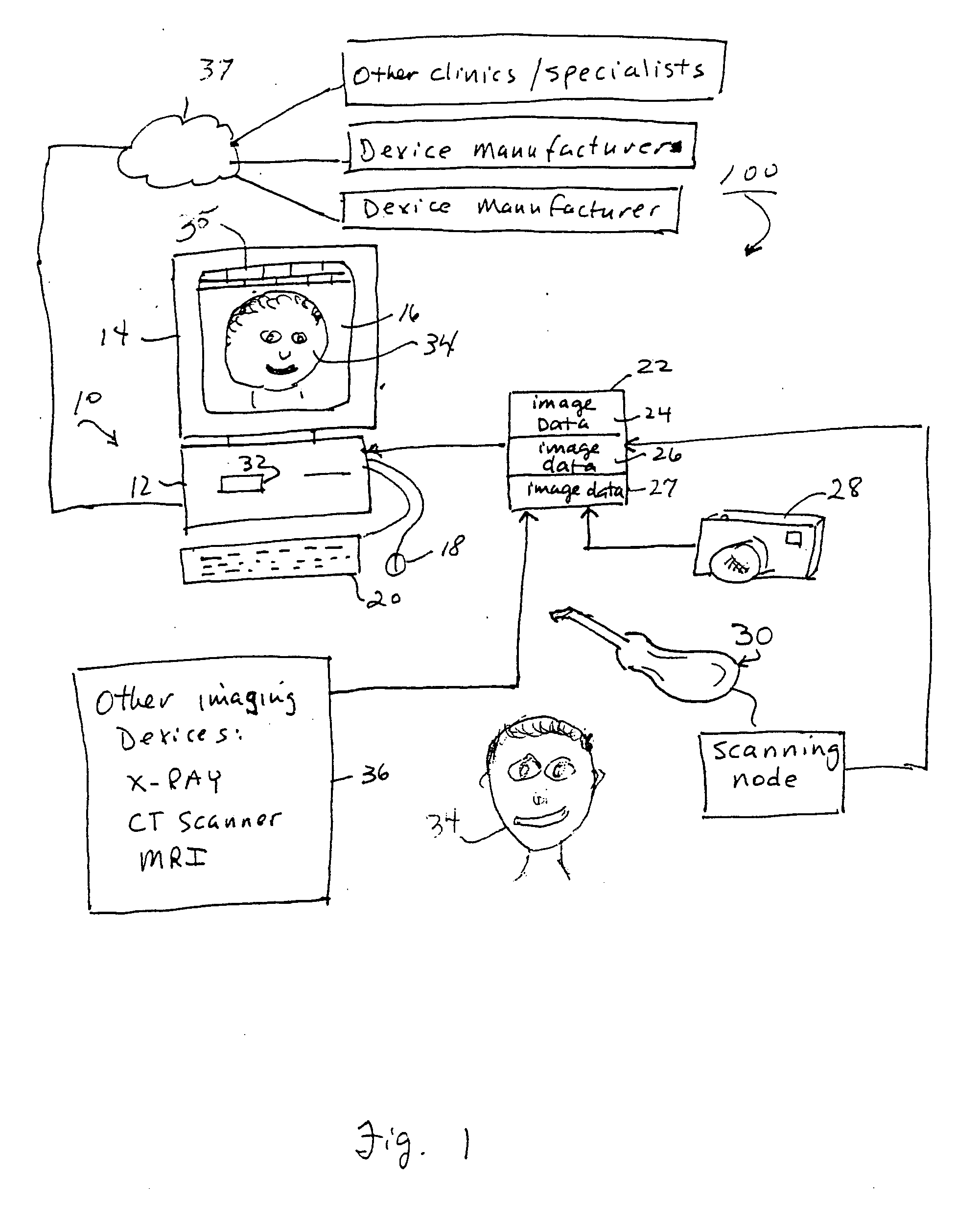
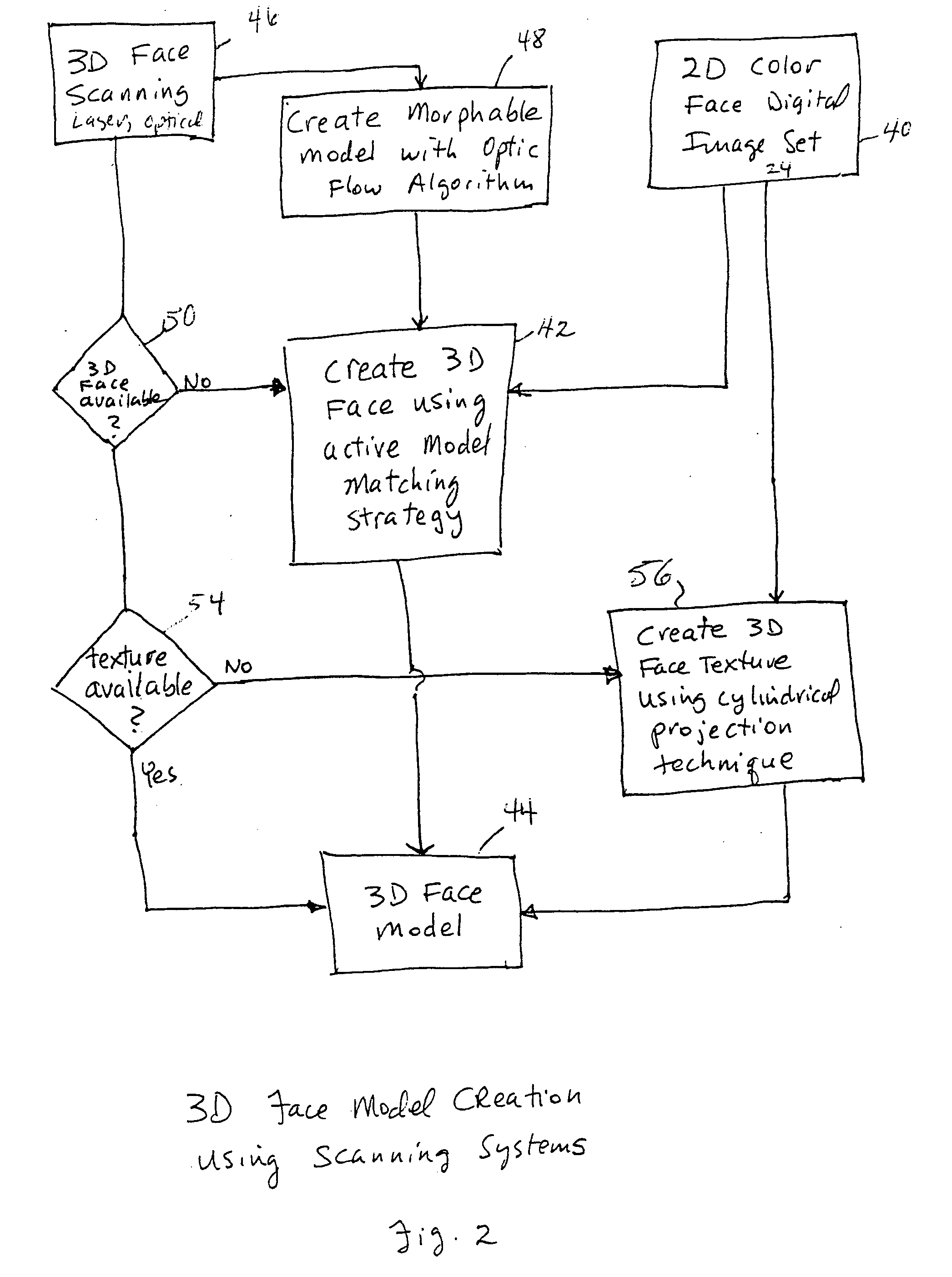
Unified workstation for virtual craniofacial diagnosis, treatment planning and therapeutics
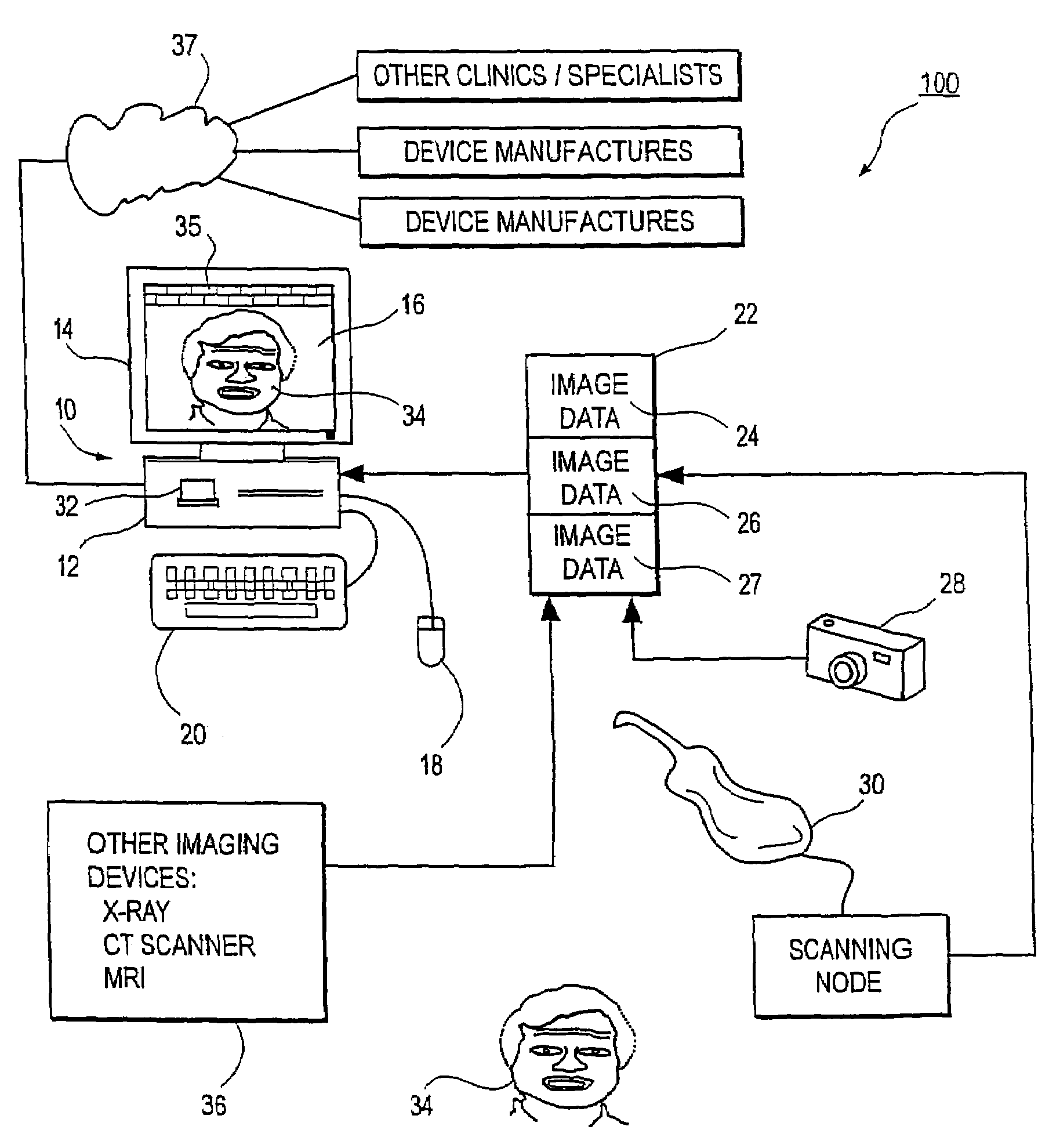
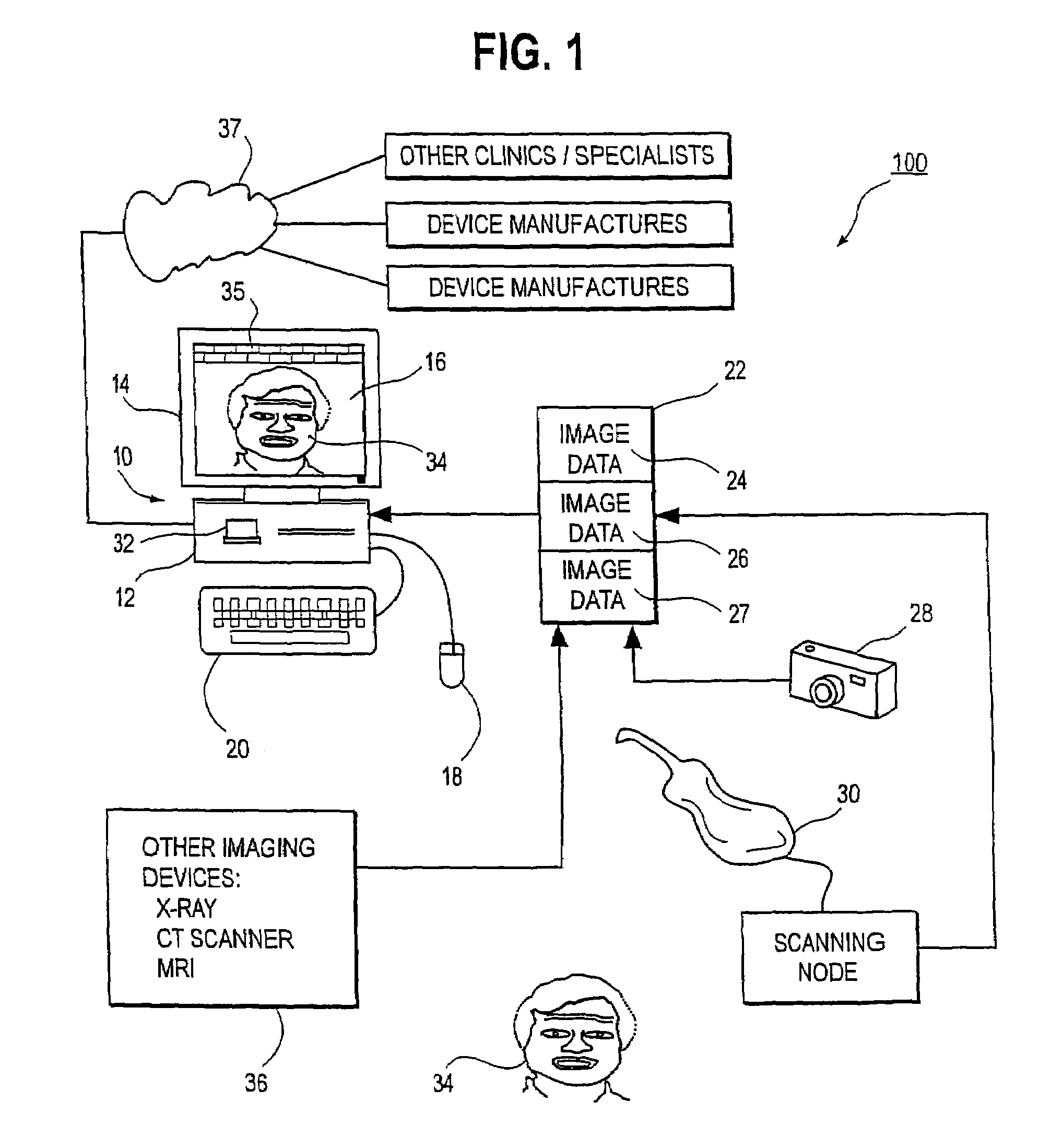
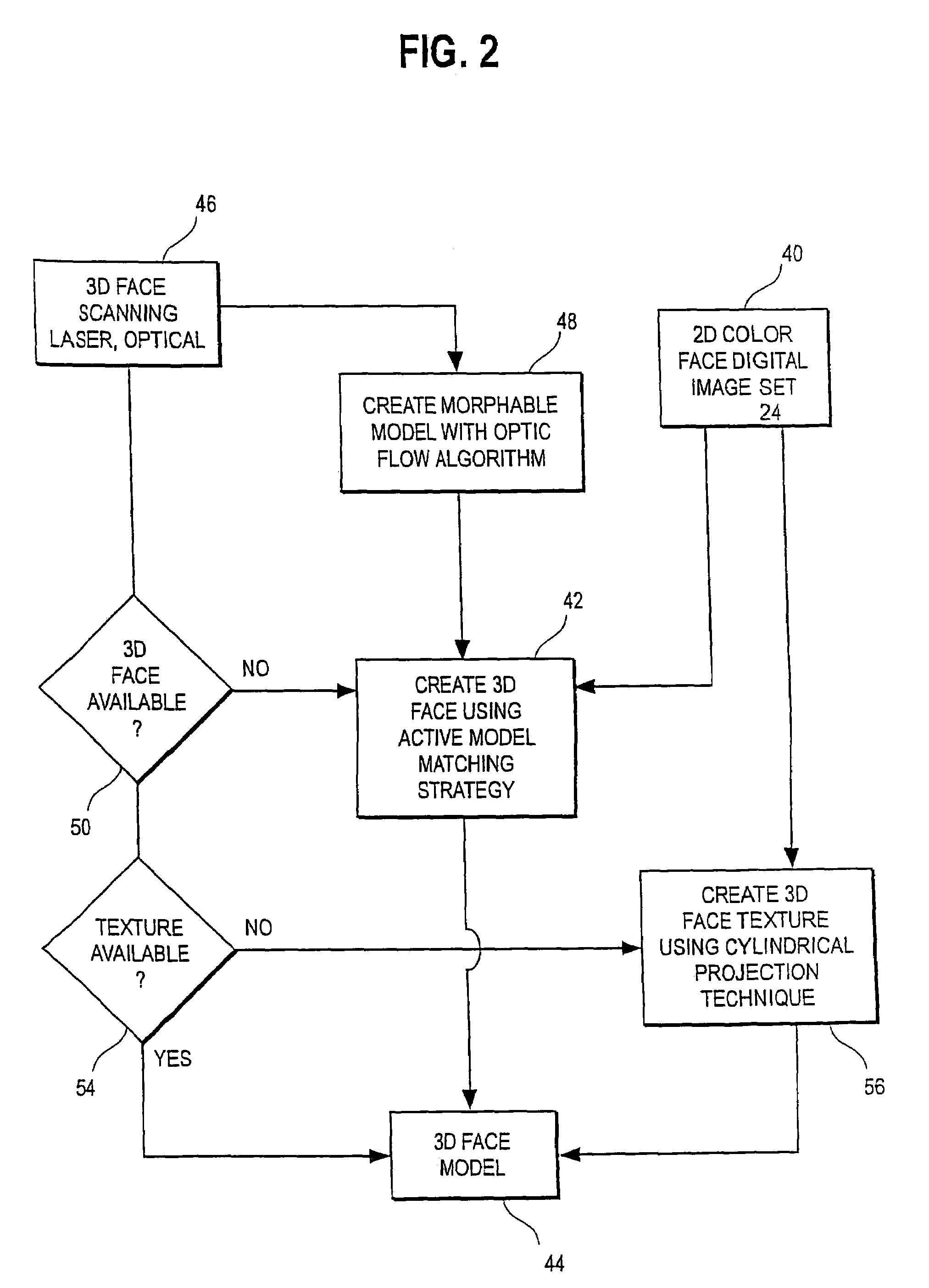
InactiveUS7234937B2Quick analysisPowerful toolDental implantsImpression capsPlan treatmentPatient model
An integrated system is described in which digital image data of a patient, obtained from a variety of image sources, including CT scanner, X-Ray, 2D or 3D scanners and color photographs, are combined into a common coordinate system to create a virtual three-dimensional patient model. Software tools are provided for manipulating the virtual patient model to simulation changes in position or orientation of craniofacial structures (e.g., jaw or teeth) and simulate their affect on the appearance of the patient. The simulation (which may be pure simulations or may be so-called “morphing” type simulations) enables a comprehensive approach to planning treatment for the patient. In one embodiment, the treatment may encompass orthodontic treatment. Similarly, surgical treatment plans can be created. Data is extracted from the virtual patient model or simulations thereof for purposes of manufacture of customized therapeutic devices for any component of the craniofacial structures, e.g., orthodontic appliances.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
Automatic infusion system based on an adaptive patient model
ActiveUS7491187B2Reduces intensive care and hospital mortality and morbiditySafely reachedJet injection syringesMedical devicesPatient modelDisease
Present invention is a system of blood glucose monitoring and intensive insulin therapy in a ICU for strict maintenance of normoglycemia which reduces intensive care and hospital mortality and morbidity of critically ill adult patients. The findings of present study also reveal factors determining insulin doses needed to maintain normoglycemia as well as the impact of insulin dose versus blood glucose level on the observed outcome benefits have been established. The invention provides a control system that adapts the flow of the insulin infusion based on insulin requirement calculated by blood glucose levels and clinical parameters such as history of diabetes, Body Mass Index, blood glucose level on admission, reason of ICU admission, time in the ICU, type and severity of illness, caloric intake, obesity, drugs affecting insulin sensitivity). This automated insulin monitoring systems significantly reduces the workload and human resource management problems for intensive insulin therapy in patients in the ICU.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV
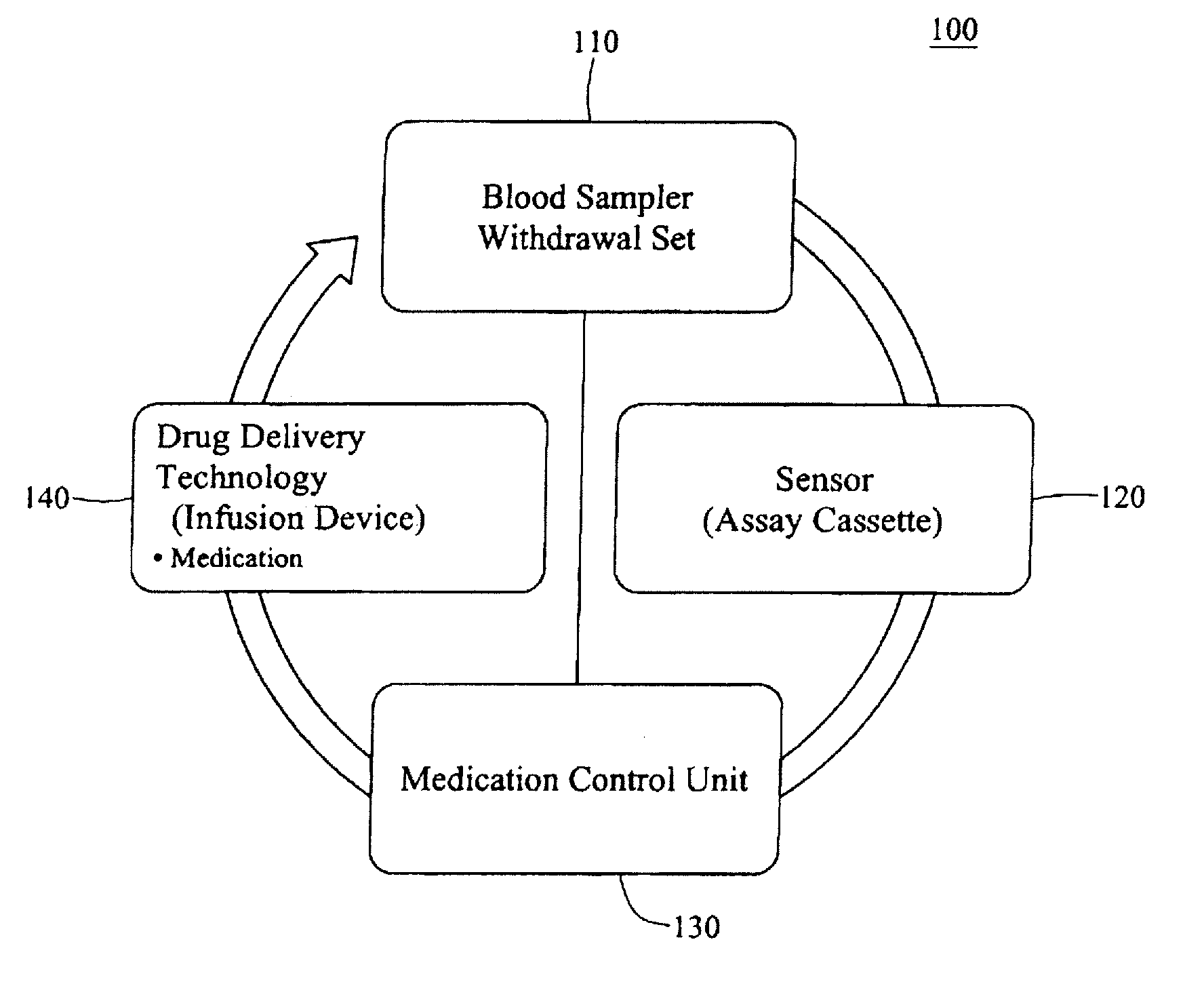
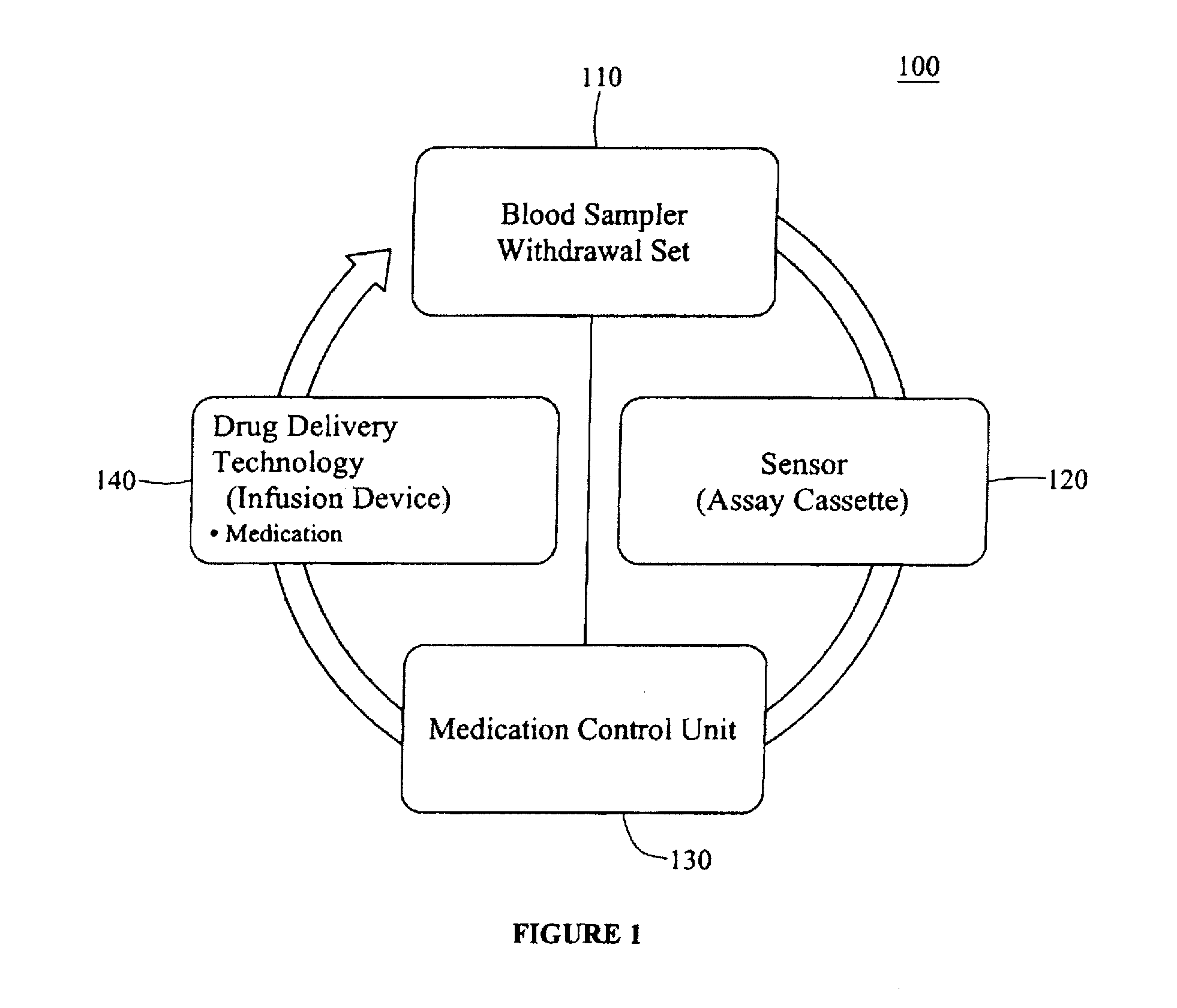
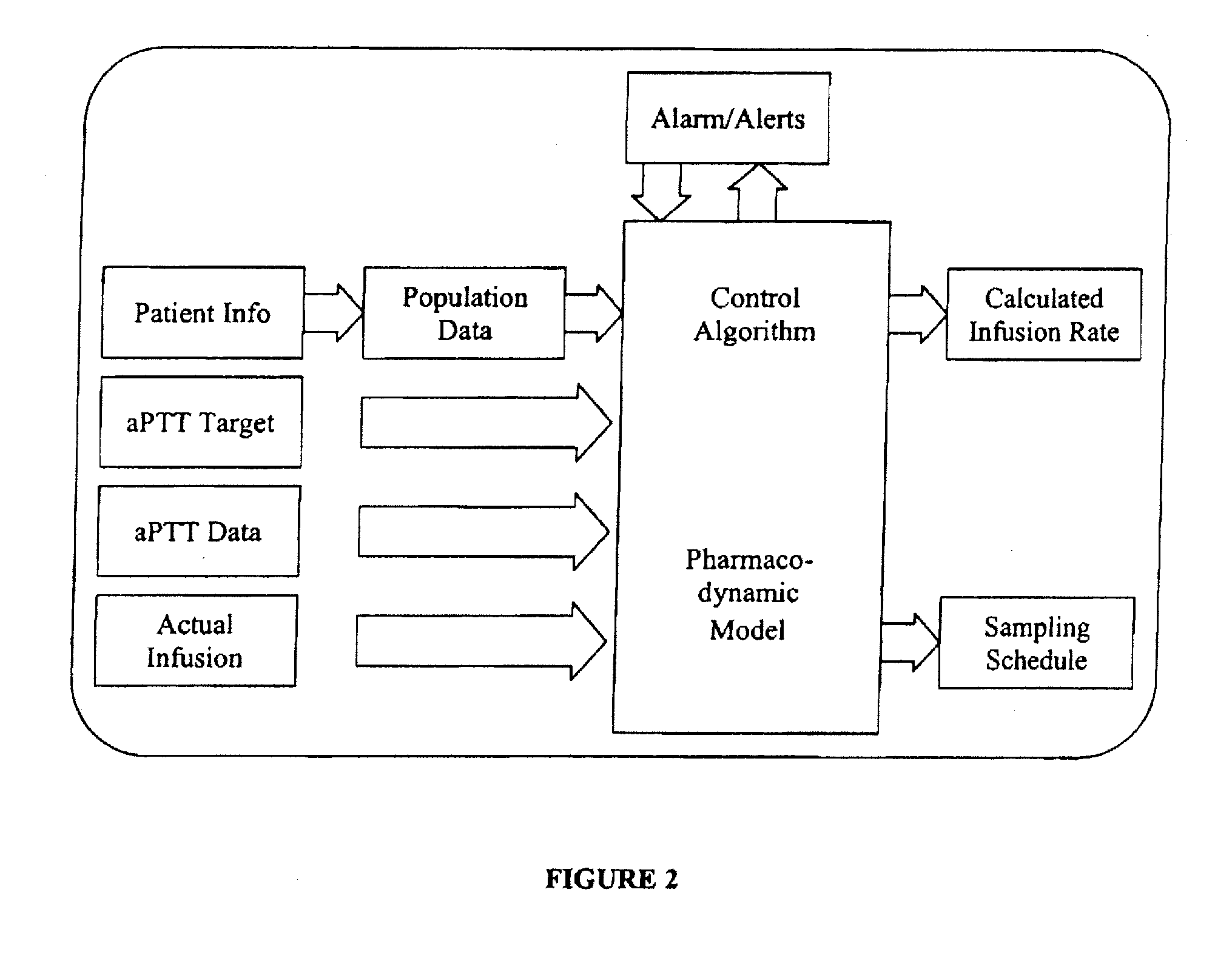
Integrated patient management and control system for medication delivery
InactiveUS20100273738A1Quality improvementOrganic active ingredientsDrug and medicationsPatient modelMeasurement device
An integrated patient monitoring and control system is provided which includes a closed-loop control system for monitoring and adjusting the heparin infusion rate for a patient. The system includes a processor which uses a dynamic patient model that is continuously adjusted based on the patient's aPTT measurements to calculate an optimal heparin infusion rate to achieve an operator-input aPTT target range. The processor also includes a forecasting model to calculate the optimum sample time interval for measuring the patient's aPTT to calculate a new infusion rate. An automated sampling system, which includes a storage device for storing a series of assay devices, an advancement mechanism for moving the assay devices to a sample area, and a measurement device for analyzing a sample dispensed on the assay, is provided. The sampling system is used to repeatedly measure the patient's aPTT according to the sample time interval determined by the processor.
Owner:AUTOMEDICS MEDICAL SYST
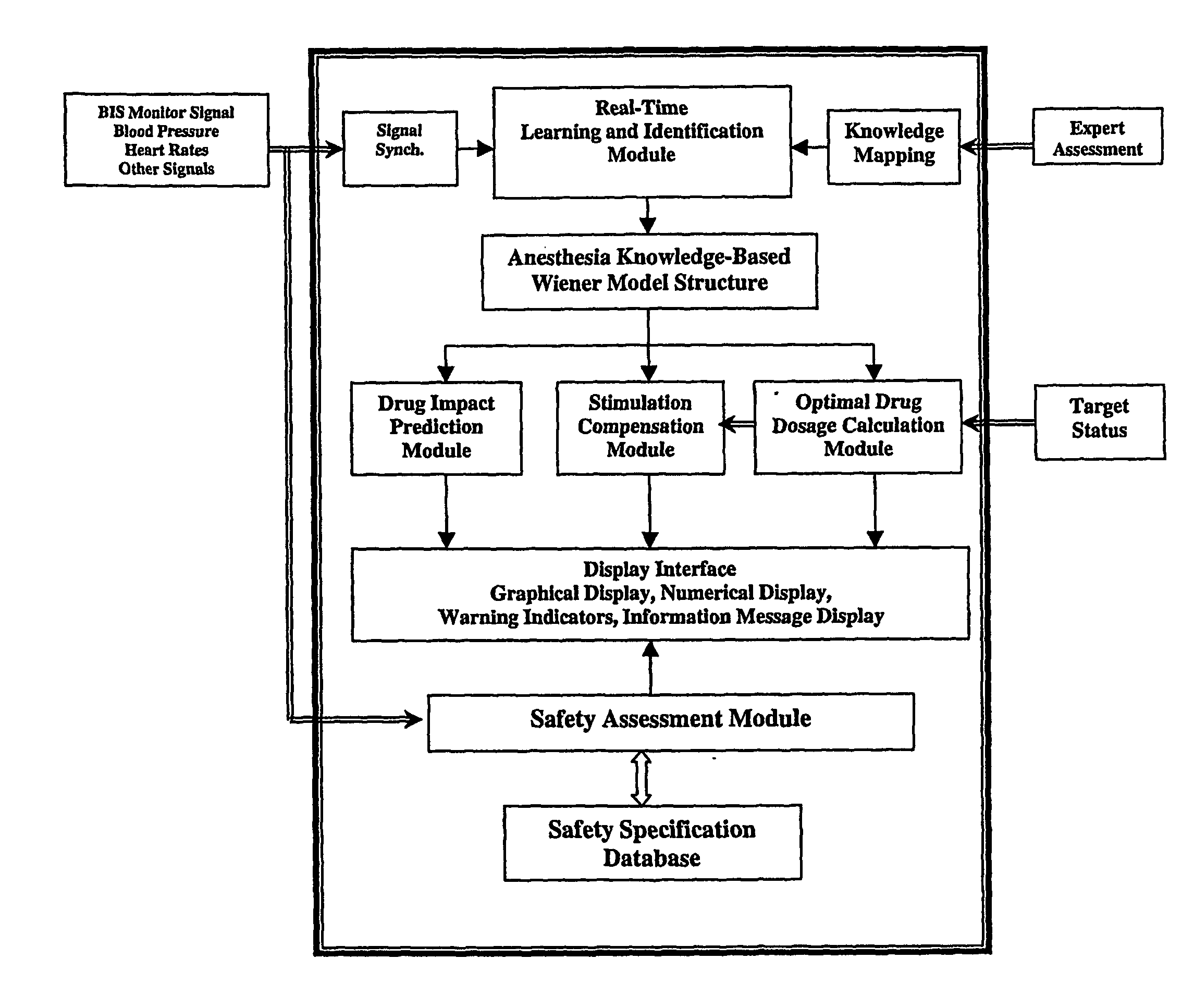
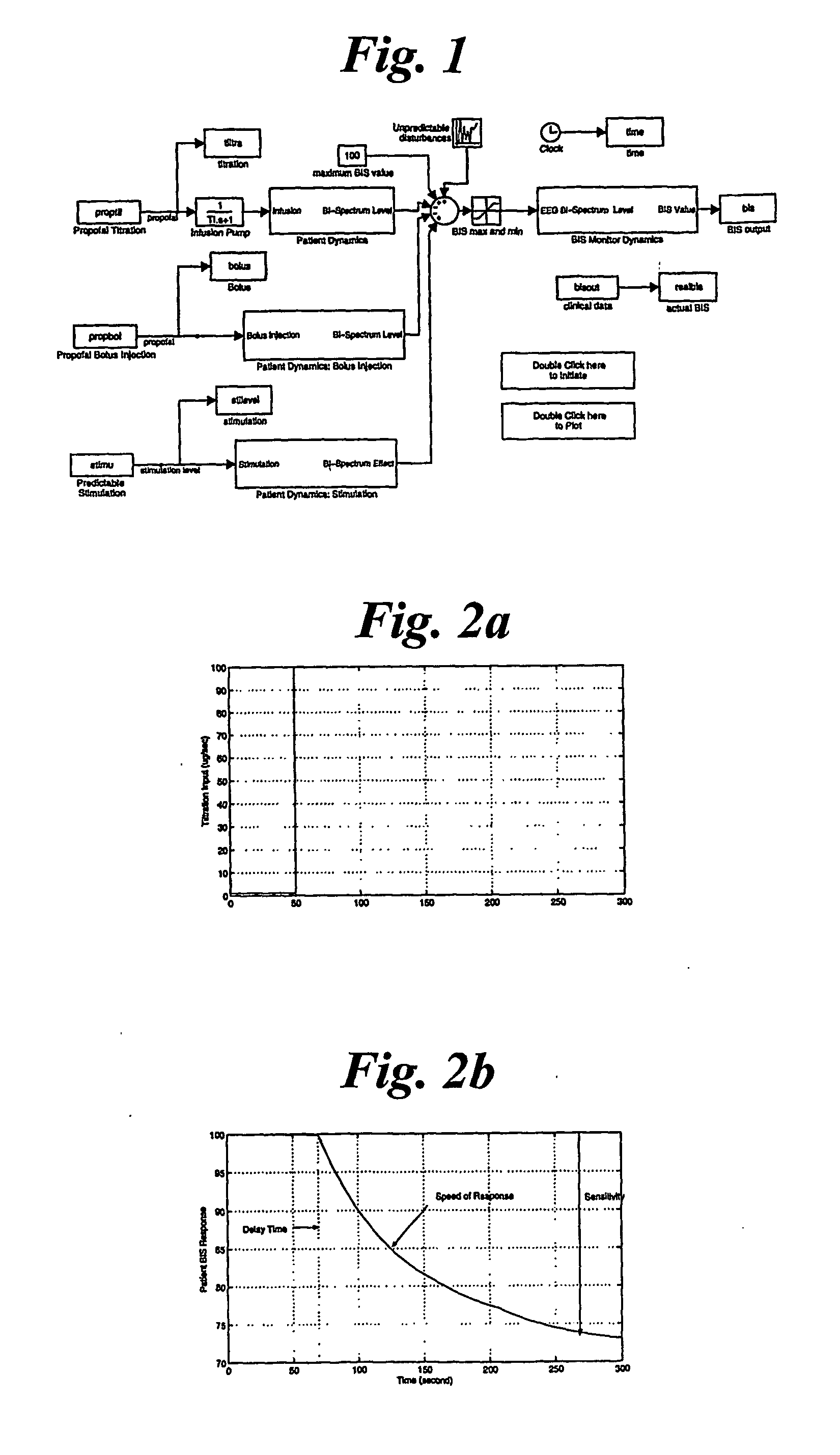
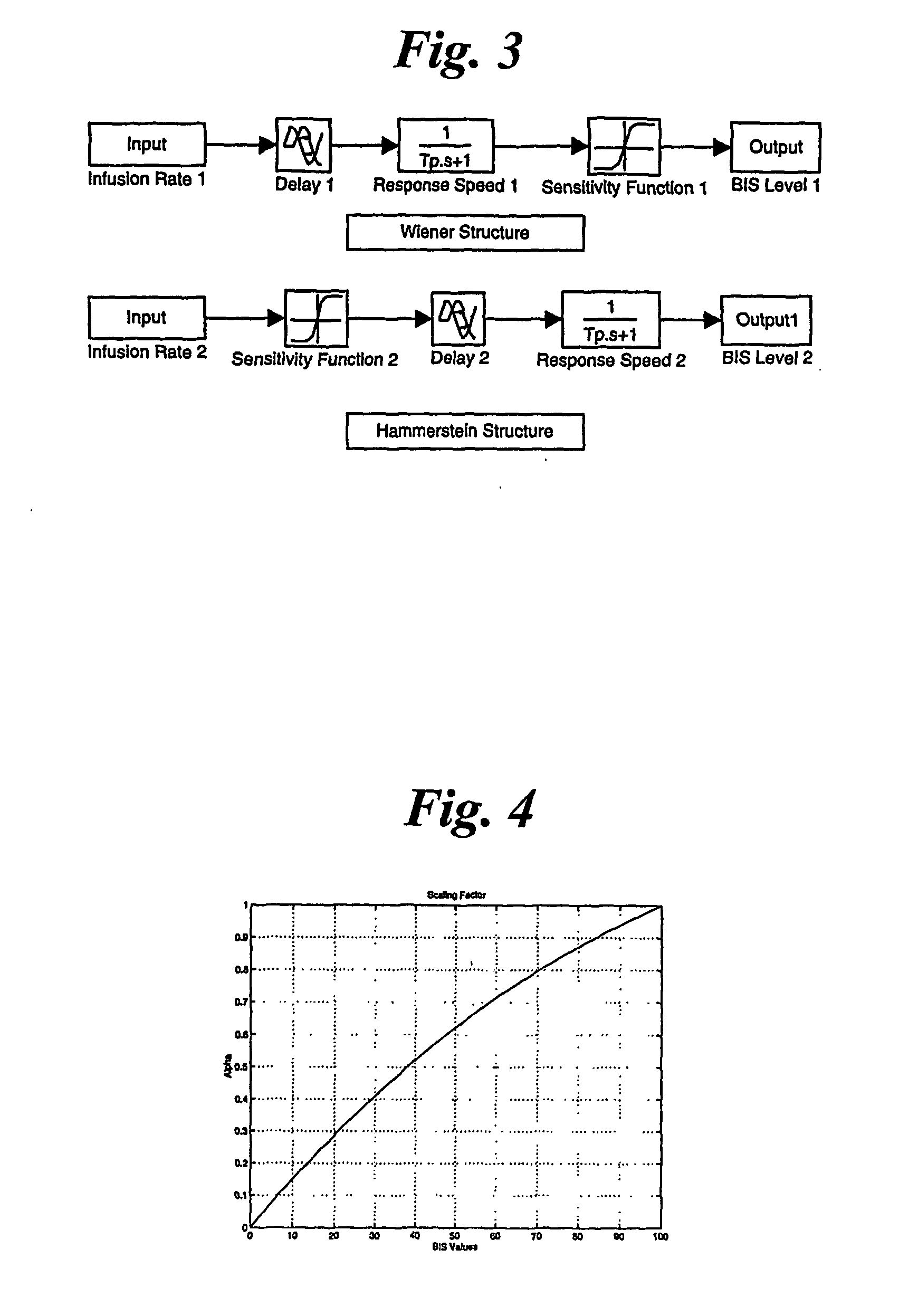
System for identifying patient response to anesthesia infusion
InactiveUS20070015972A1Avoid large fluctuations in BIS valuesReduce the valueElectroencephalographyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPatient modelDrugs sensitivity
A generic model structure captures basic characteristics in BIS-based patients' responses to anesthesia and surgical stimulation, the model being used in combination with the insight of an anesthesiologist. The model structure represents the patient response with a time delay, a time constant for response speed, and a nonlinear function for drug sensitivity. Clinical data confirms the model structure and is used to establish parameters and function forms for individual patients. A feedback and predictive control strategy for anesthesia drug infusion is then introduced on the basis of the patient model. Feedback control alone cannot avoid large fluctuations in BIS values when significant surgical stimulation is imposed, as a result of time delays in a patient's response to drug infusion. Predictive control attenuates fluctuations of BIS levels from surgical stimulation.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Unified workstation for virtual craniofacial diagnosis, treatment planning and therapeutics
An integrated system is described in which digital image data of a patient, obtained from a variety of image sources, including CT scanner, X-Ray, 2D or 3D scanners and color photographs, are combined into a common coordinate system to create a virtual three-dimensional patient model. Software tools are provided for manipulating the virtual patient model to simulation changes in position or orientation of craniofacial structures (e.g., jaw or teeth) and simulate their affect on the appearance of the patient. The simulation (which may be pure simulations or may be so-called “morphing” type simulations) enables a comprehensive approach to planning treatment for the patient. In one embodiment, the treatment may encompass orthodontic treatment. Similarly, surgical treatment plans can be created. Data is extracted from the virtual patient model or simulations thereof for purposes of manufacture of customized therapeutic devices for any component of the craniofacial structures, e.g., orthodontic appliances.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
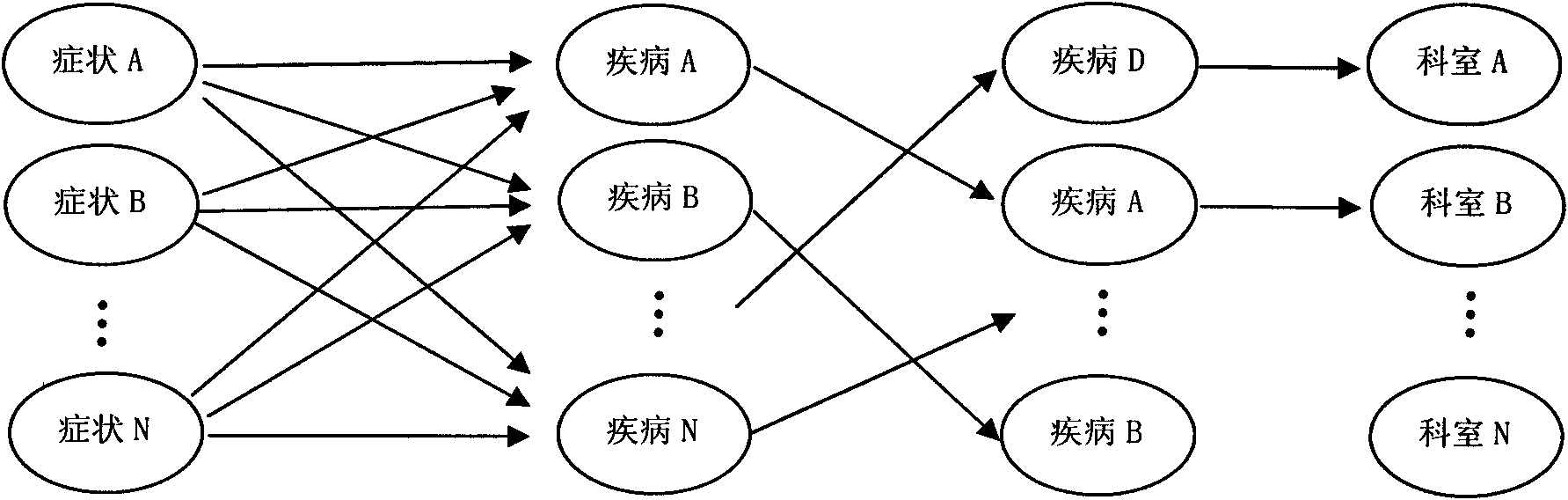
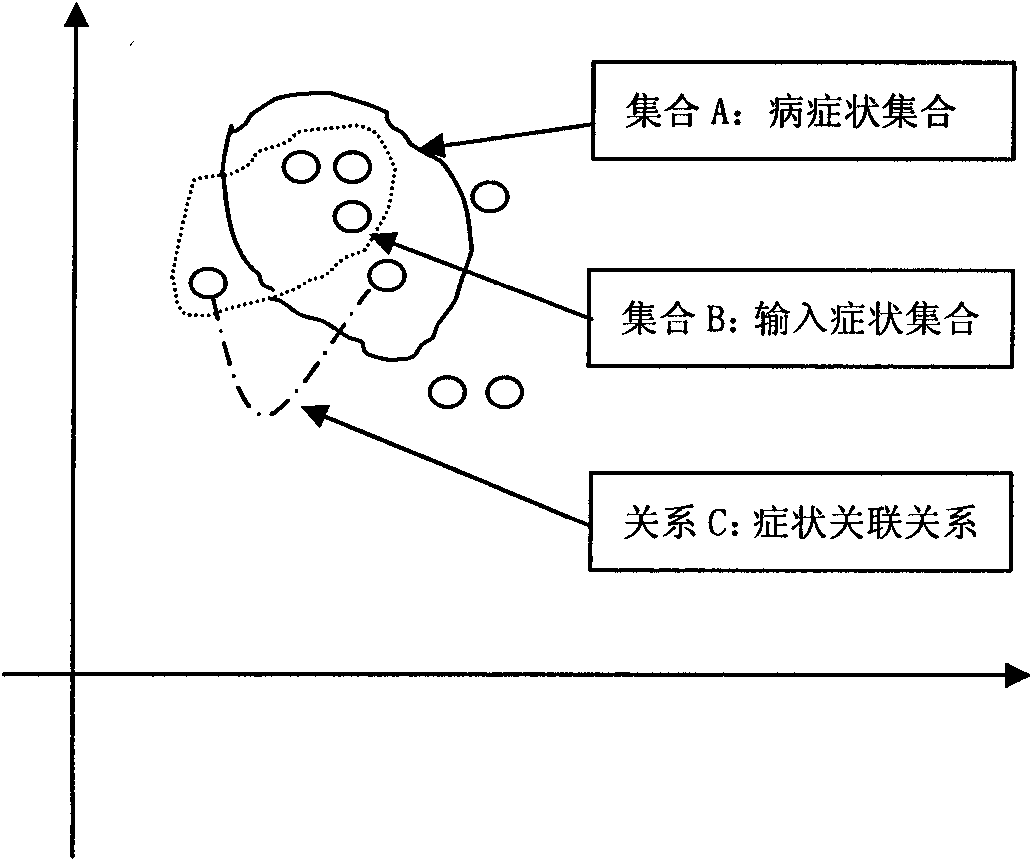
Hospital decision-making aiding method based on symptom similarity analysis
InactiveCN102156812AWeaken errors interfere with resultsAchieve correctnessSpecial data processing applicationsPatient modelInformation analysis
The invention provides a hospital decision-making aiding method based on symptom similarity analysis, belonging to the field of information analysis and decision-making aid. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a disease database, a symptom database, a department database and a correlating relationship; establishing a patient model for symptoms input by users, and calculating the similarity between the patient model and a disease model; and searching one department with corresponding suspected diseases in the department model to serve as hospital reference. The method has the advantages that an error interrupted result is weakened under a condition that a user takes an error symptom as a reasoning condition; a correct symptom participates in the reasoning operation by combining the correlating relationship between the error symptom and the convention symptoms according to the error symptom condition so as to realize the correctness and interruption resistance of reasoning; and a hospital department list is obtained by utilizing the mapping relationship between the disease and the department. The method can be used in electronic reception or health consulting systems, as well as in medical training or clinical reference.
Owner:中国医学科学院医学信息研究所
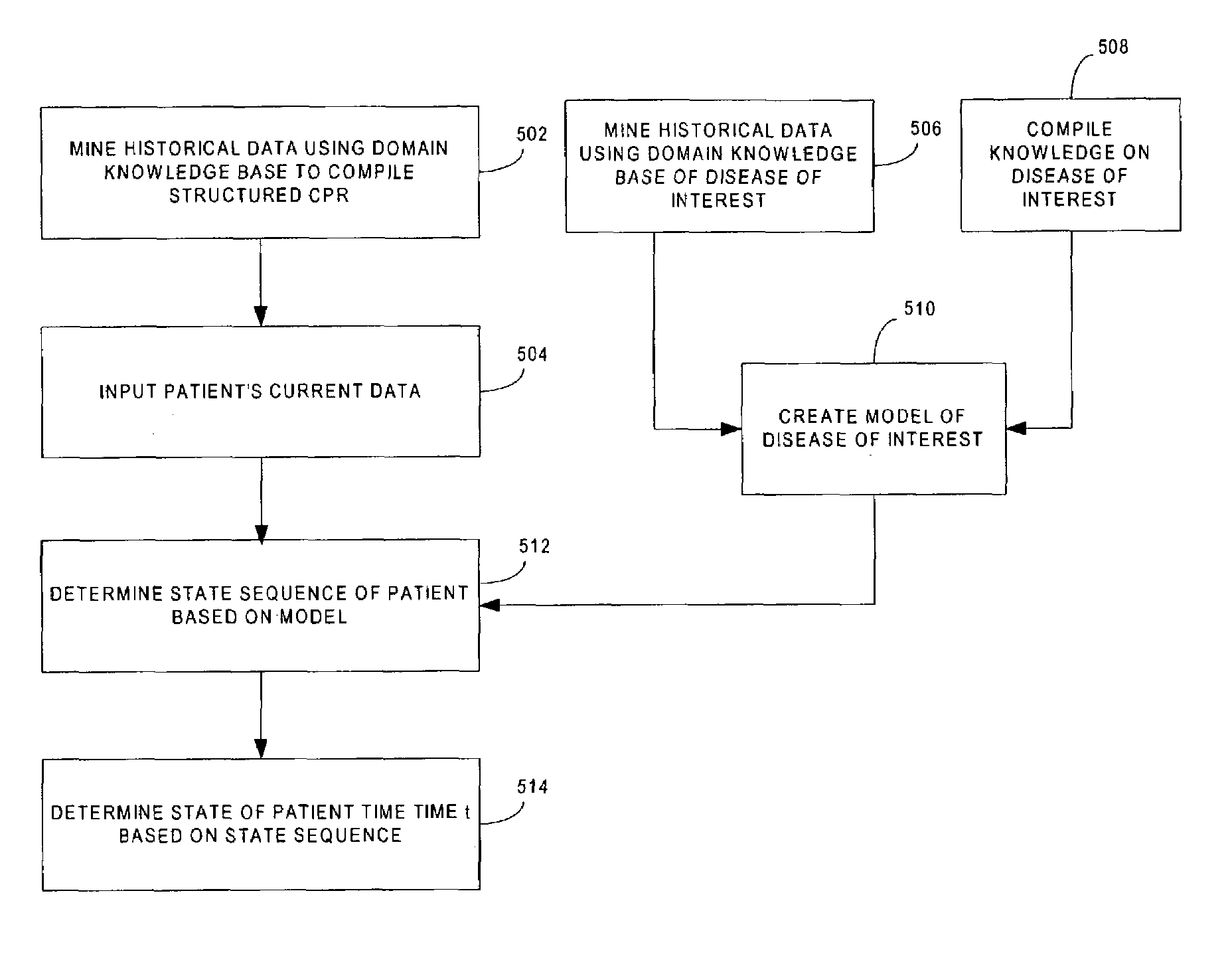
Patient data mining for diagnosis and projections of patient states
ActiveUS7181375B2Digital data processing detailsComputer-assisted treatment prescription/deliveryPatient modelPatient data
Owner:CERNER HEALTH SERVICES
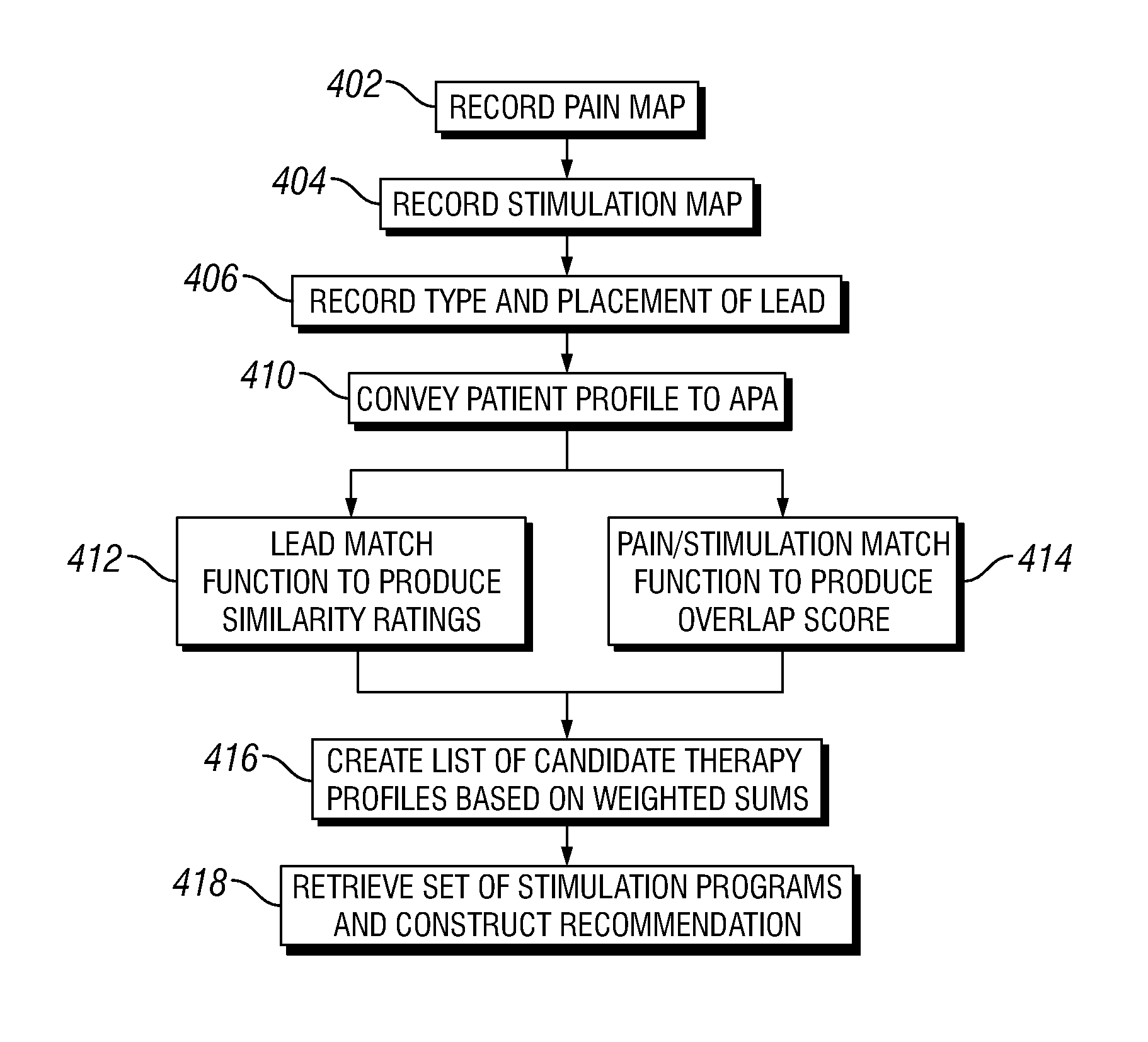
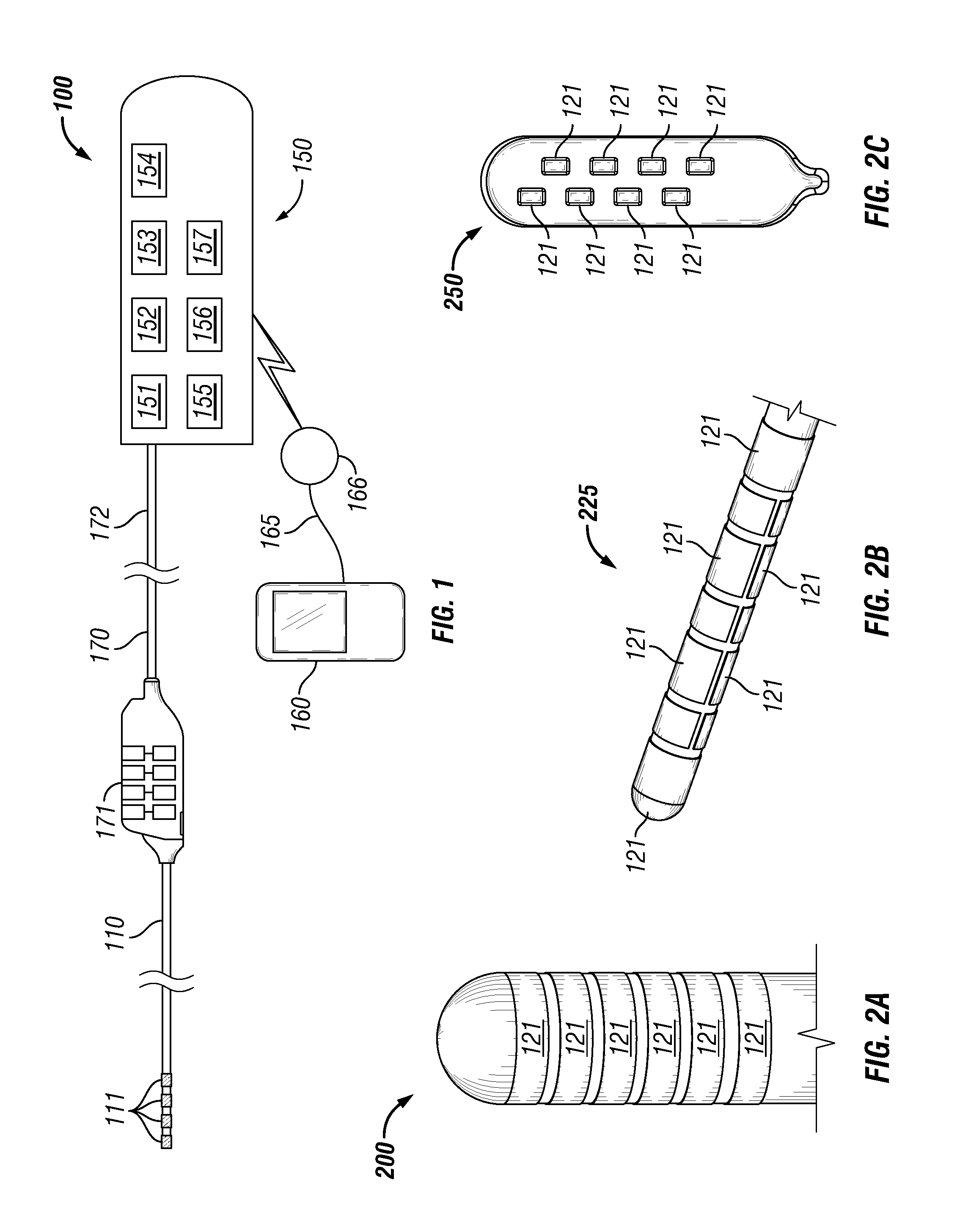
Method and system to facilitate neurostimulator programming based on pre-existing therapy profiles
ActiveUS20130023950A1Increase probabilityAccelerated programElectrotherapyArtificial respirationPatient modelEmergency medicine
A method and system are provided to assist in programming of a neurostimulator based on a collection of pre-existing therapy profiles. The method and system access a collection of pre-existing therapy profiles derived from prior actual patients or patient models. The pre-existing therapy profiles include stimulation programs mapped to pre-existing patient profiles. The pre-existing patient profiles have at least one of i) prior lead attribute, ii) prior pain maps, and iii) prior stimulation maps for prior patients or models of patients. The method and system further compare the new patient profile with at least a portion of the collection of pre-existing patient profiles to generate profile matching scores indicating an amount of similarity between the pre-existing patient and the new therapy profile.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
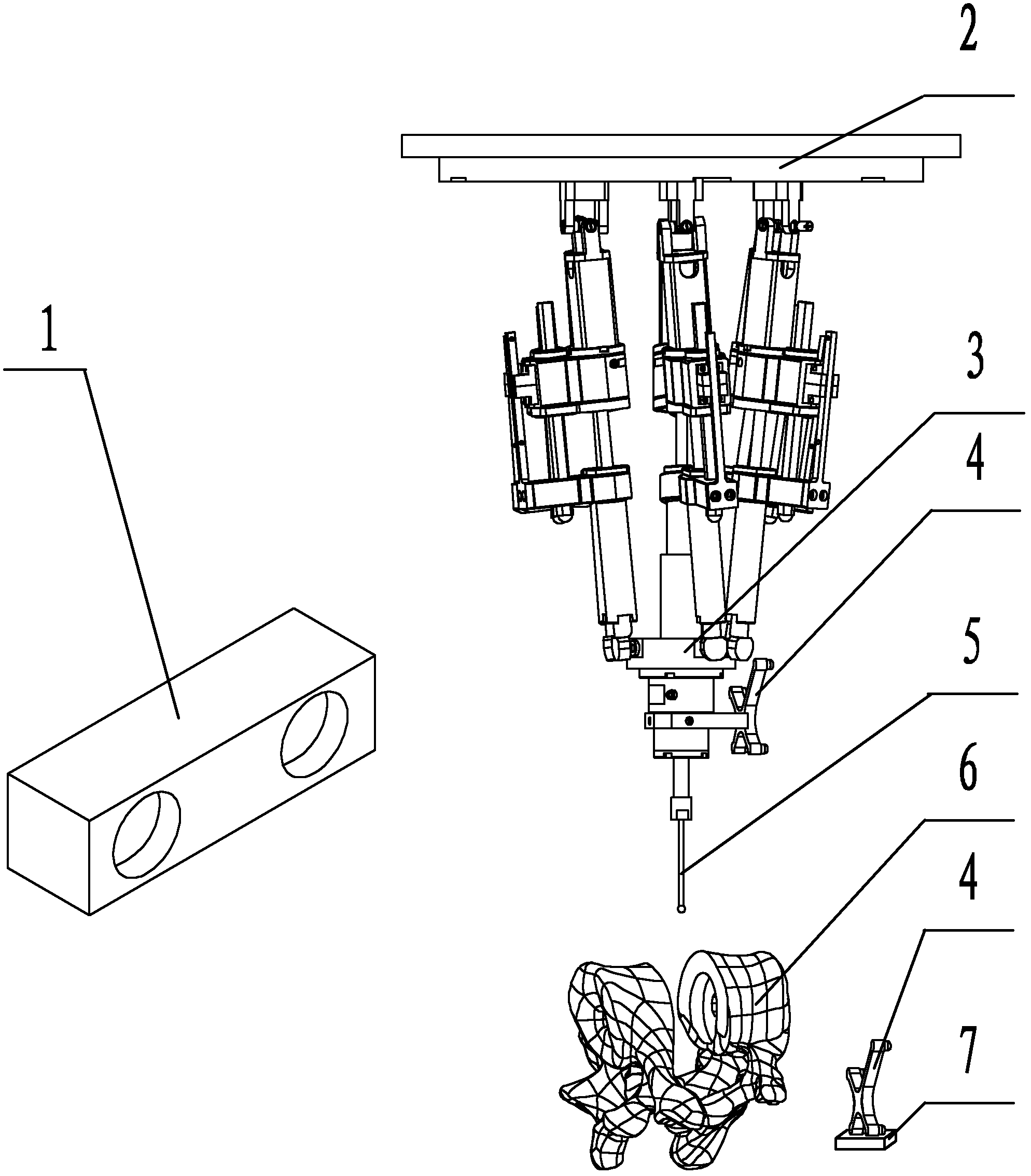
Image navigation-based parallel robot-assisted artificial cervical intervertebral disc replacement surgery positioning method
InactiveCN102429726AAchieve positioningSolve the lack of precisionDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsPatient modelSurgical operation
The invention discloses an image navigation-based parallel robot-assisted artificial cervical intervertebral disc replacement surgery positioning method, which belongs to application of a parallel robot in the field of surgical operation and is used for making sure that the pose relation between a practical surgery abrasive drilling and a patient is consistent with the pose relation between a virtual abrasive drilling and a patient model determined by a doctor in a virtual environment. According to technical key points, the method comprises the following steps of: performing three-dimensional reestablishment on a CT (Computerized Tomography) image by using a VTK (Visualization Tool Kit) software package to obtain a three-dimensional model of the silk cervical vertebra of a patient; introducing the virtual abrasive drilling into an image space and making the doctor complete virtual positioning on a computer; establishing a position and pose mapping relation among the image, the patient and the robot by using an optical positioning system and an ICP (Iterative Closest Point) algorithm; and controlling the parallel robot to move to finally complete positioning of the abrasive drilling of the parallel robot and the patient.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
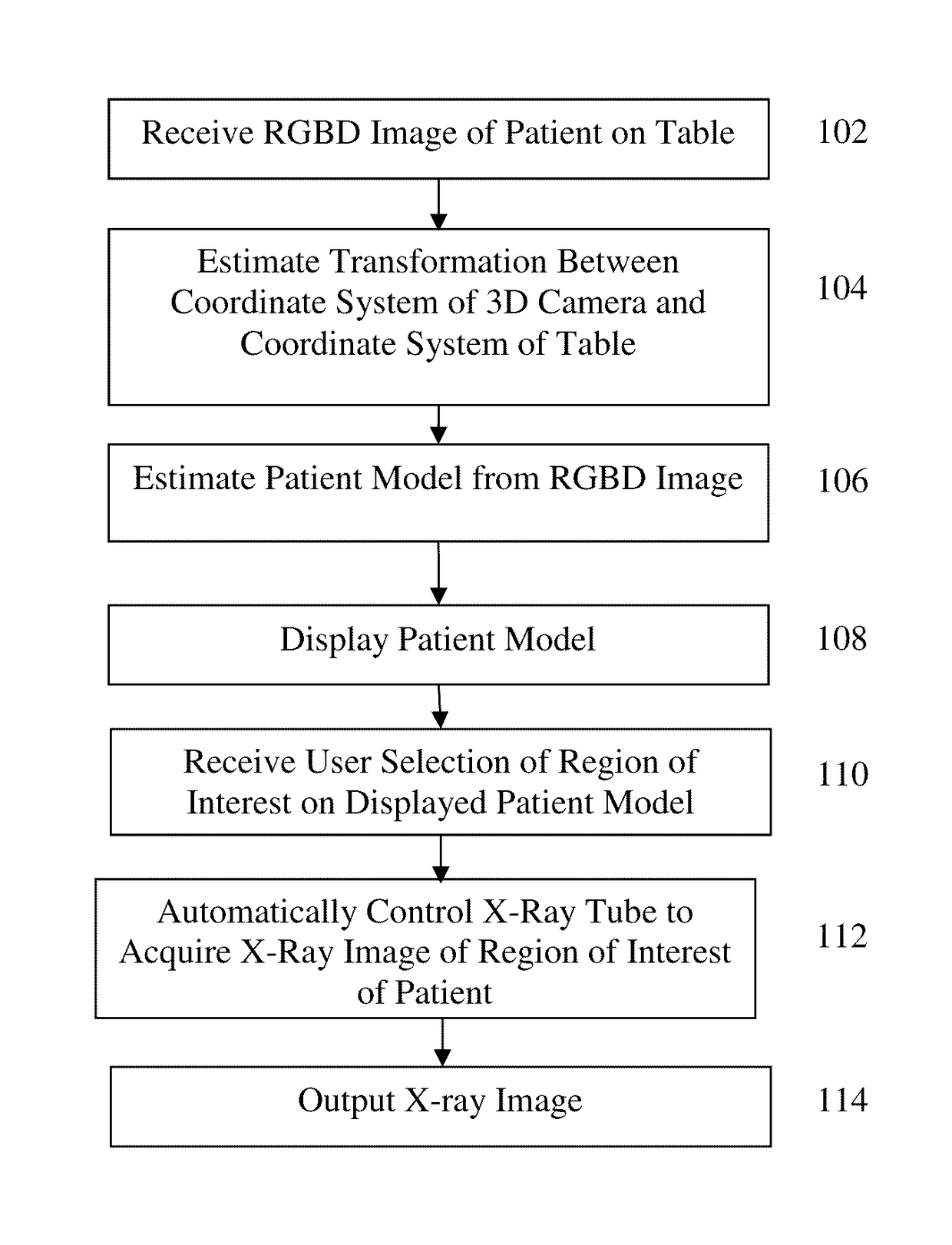
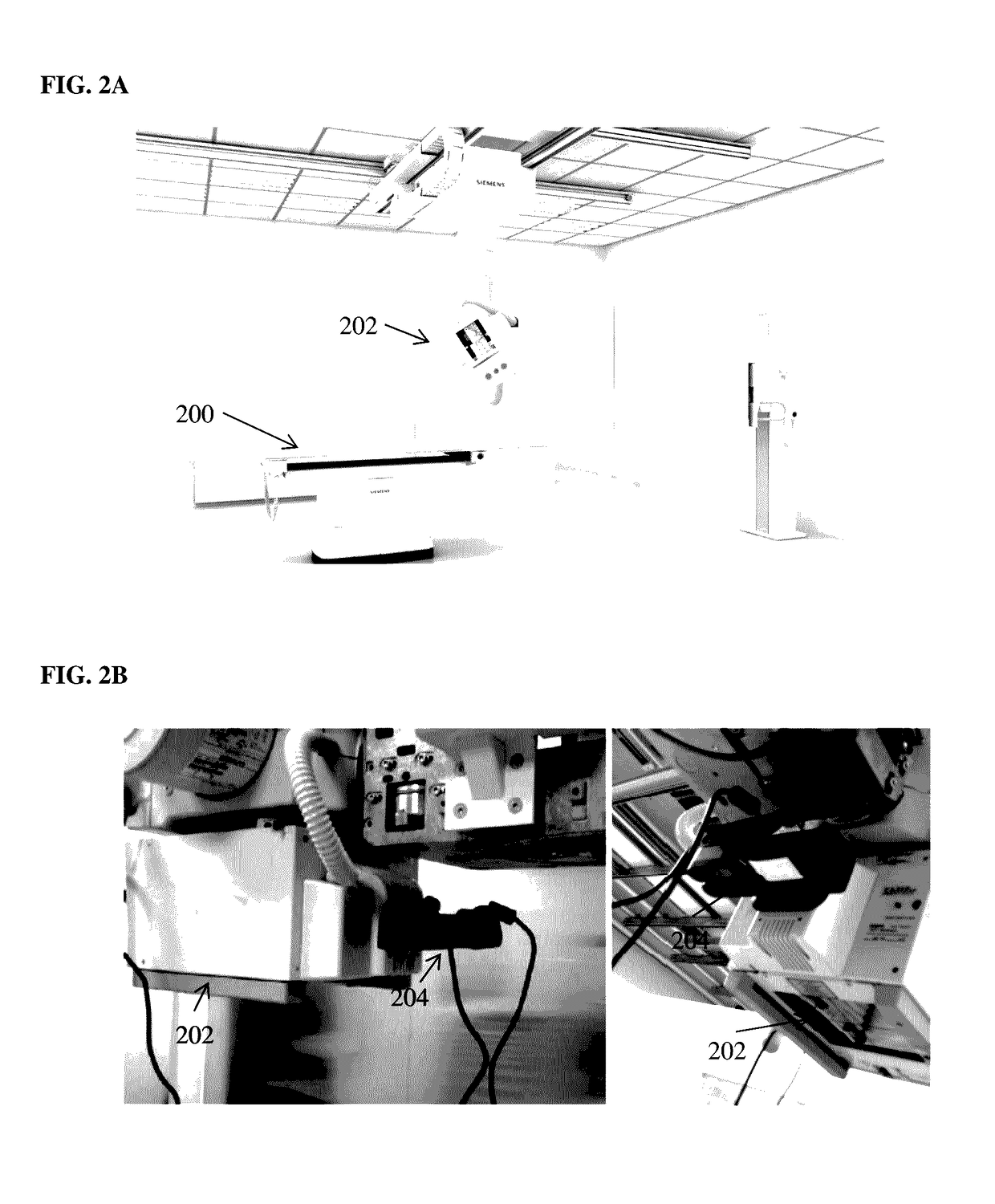
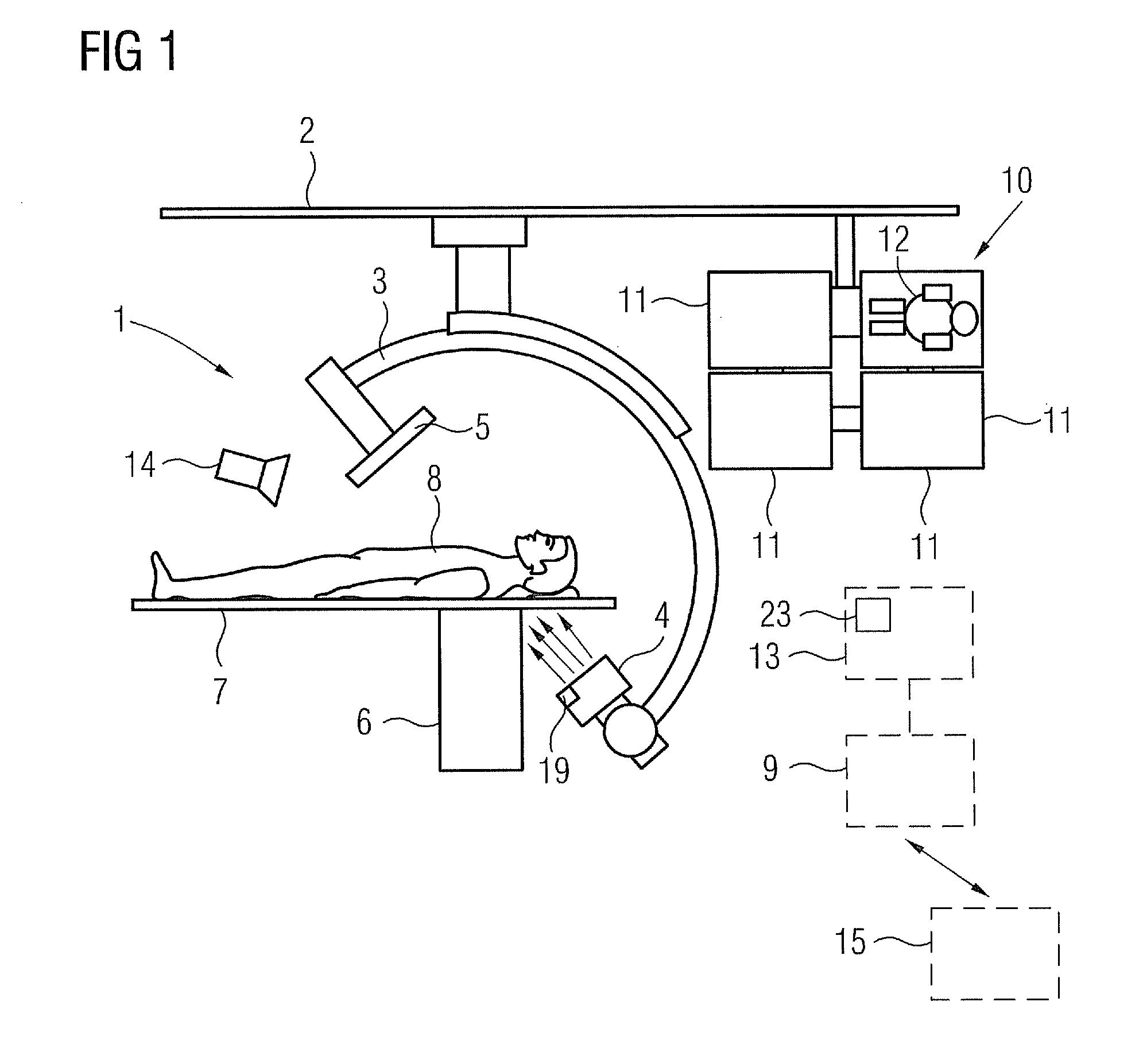
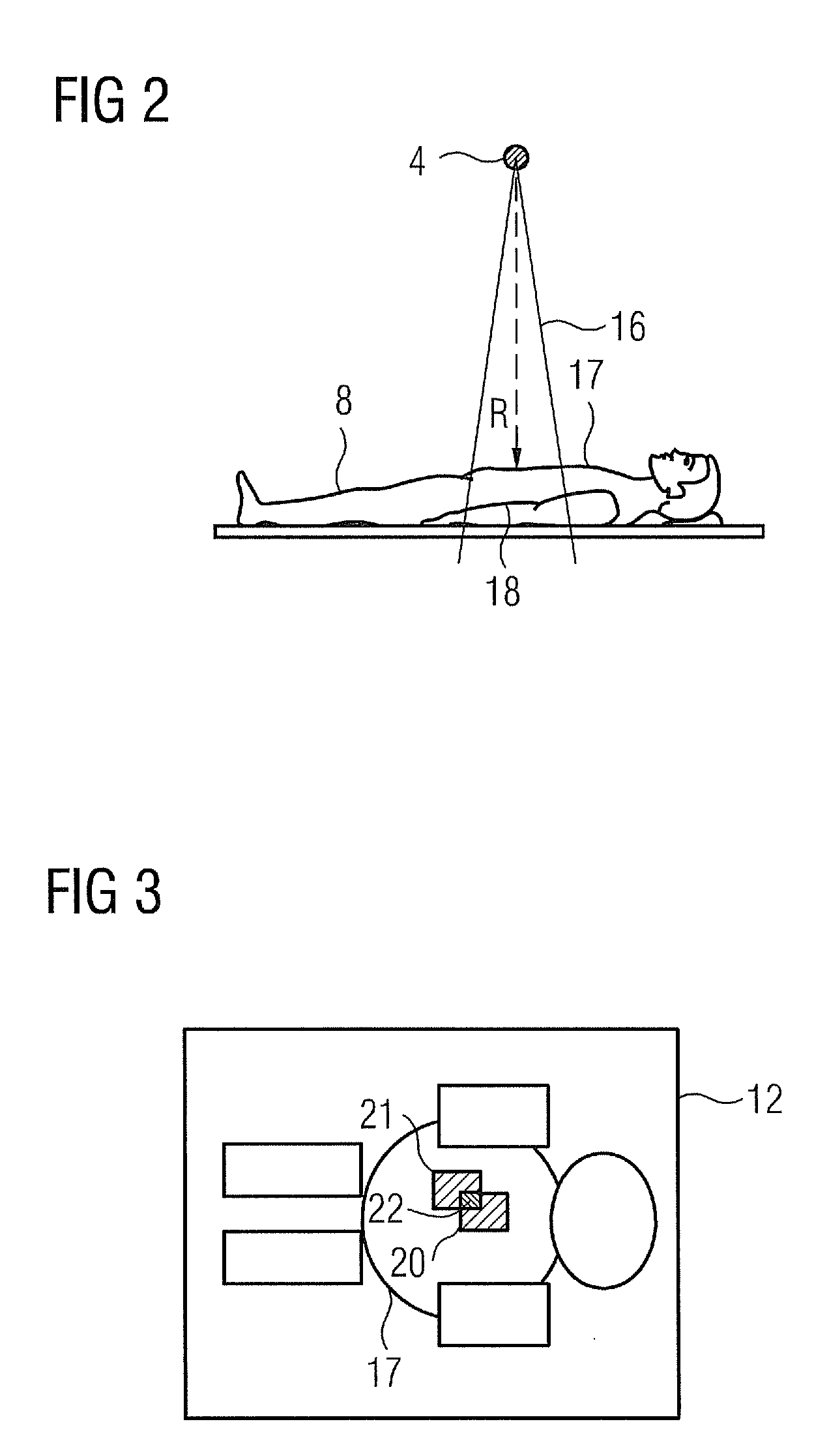
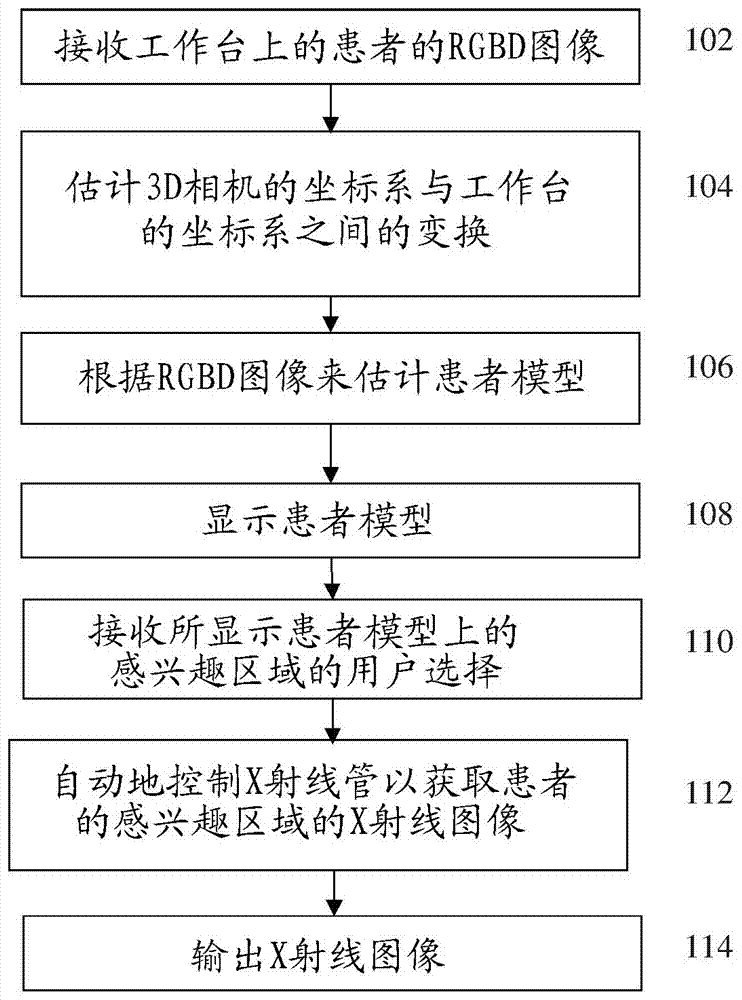
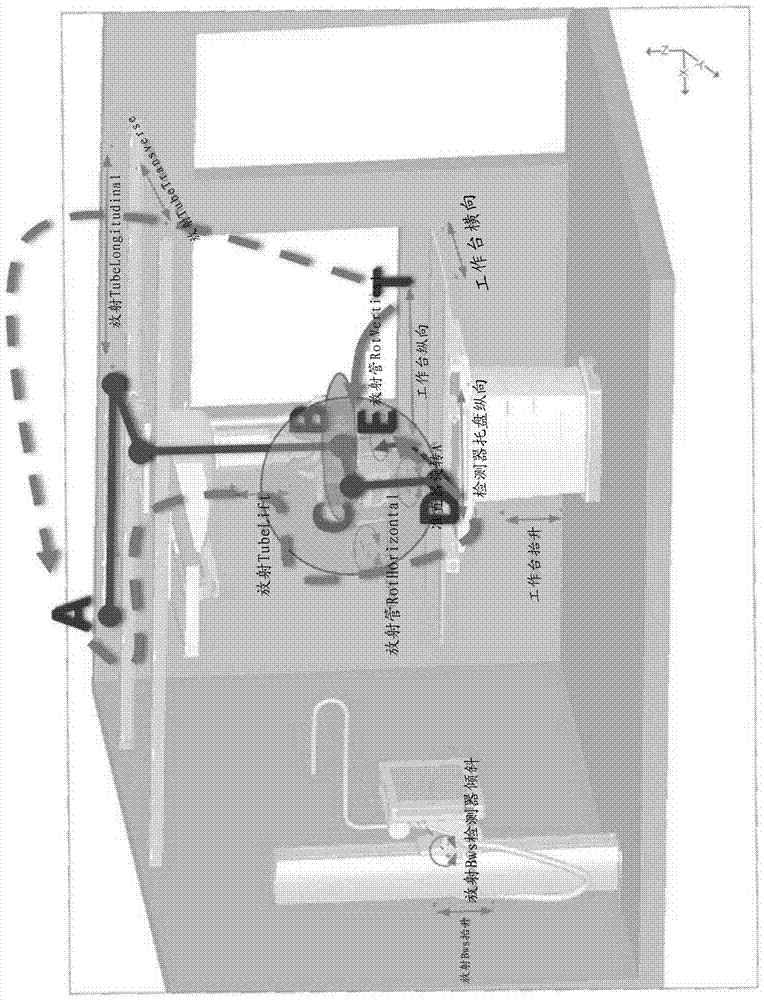
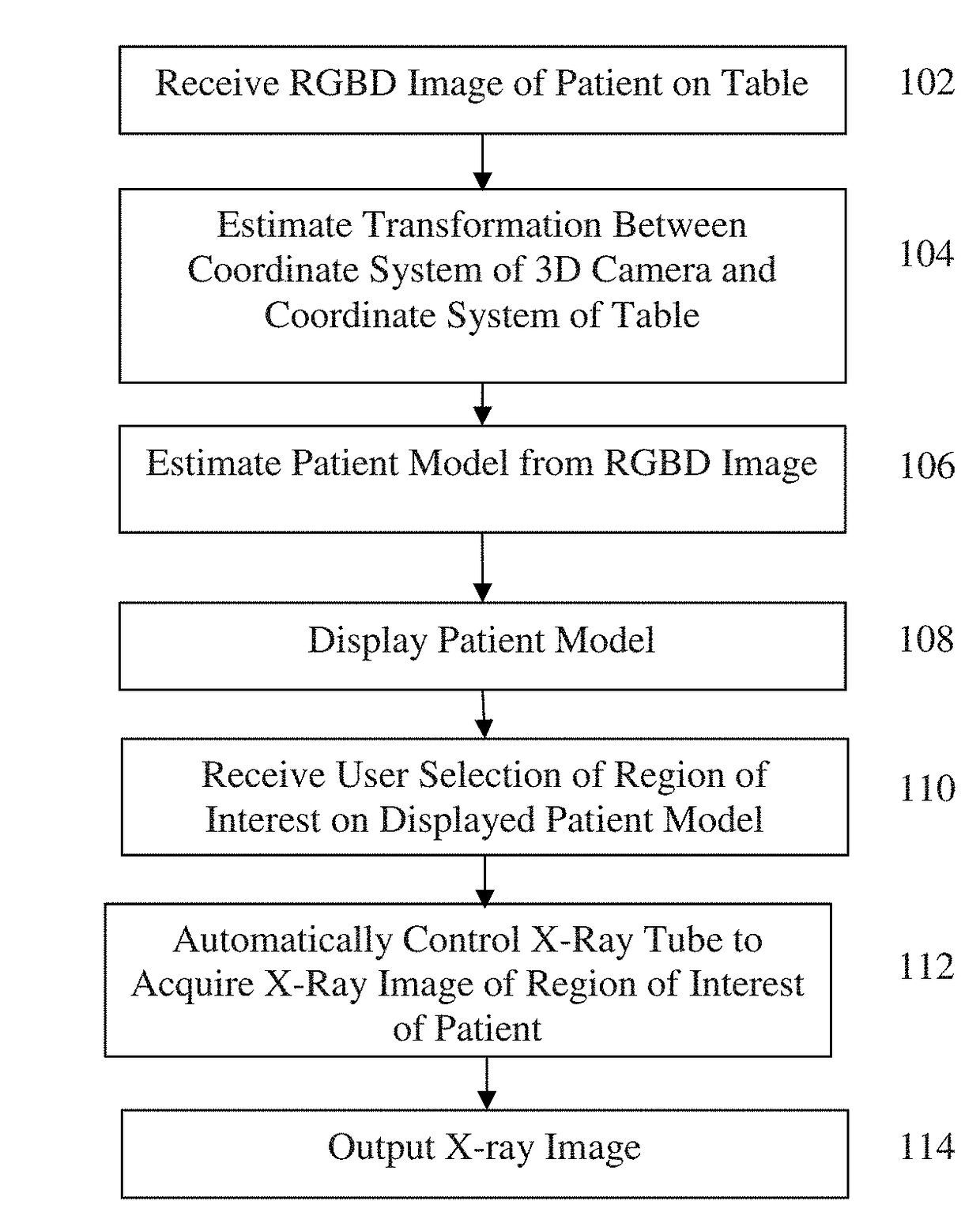
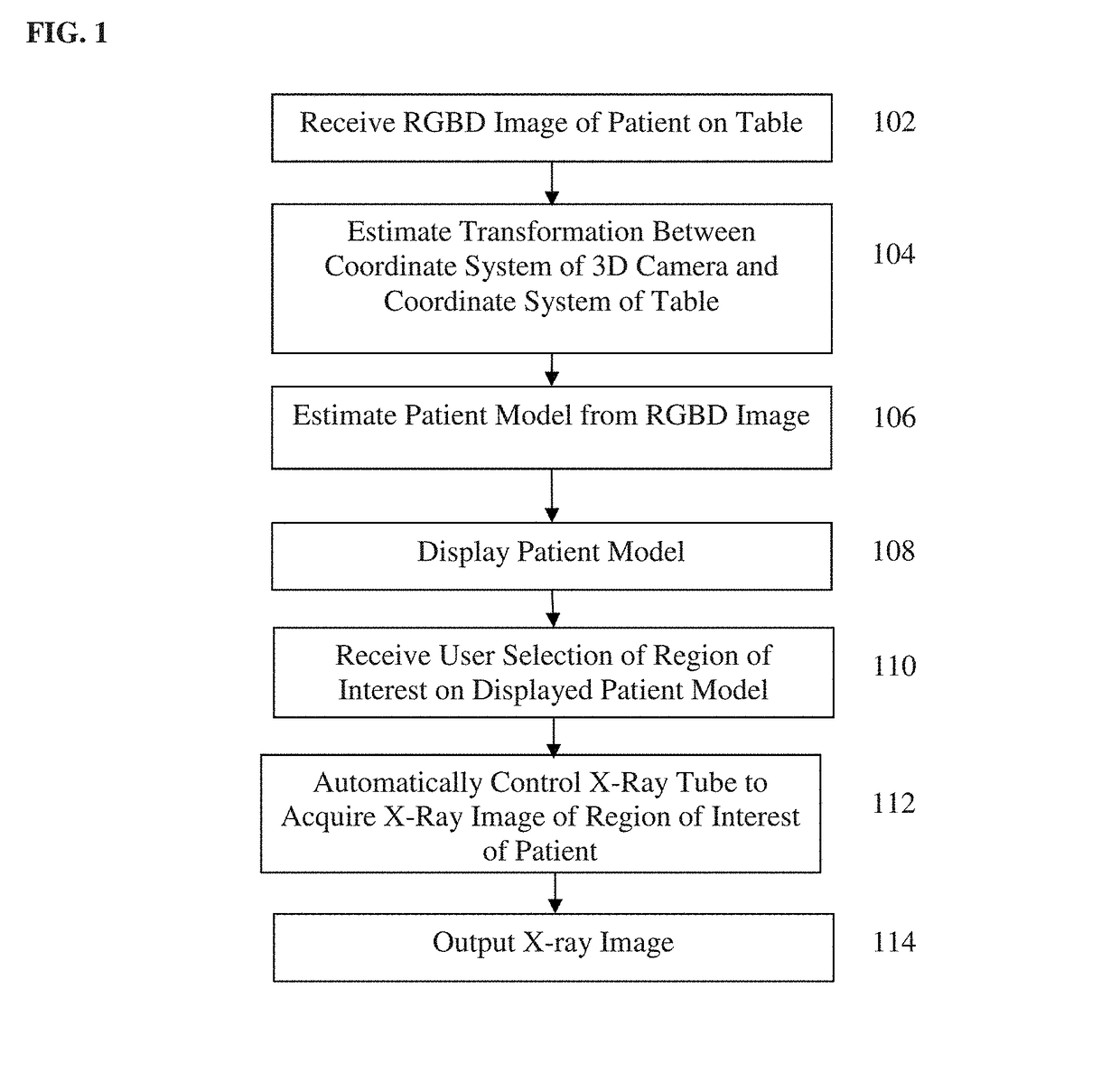
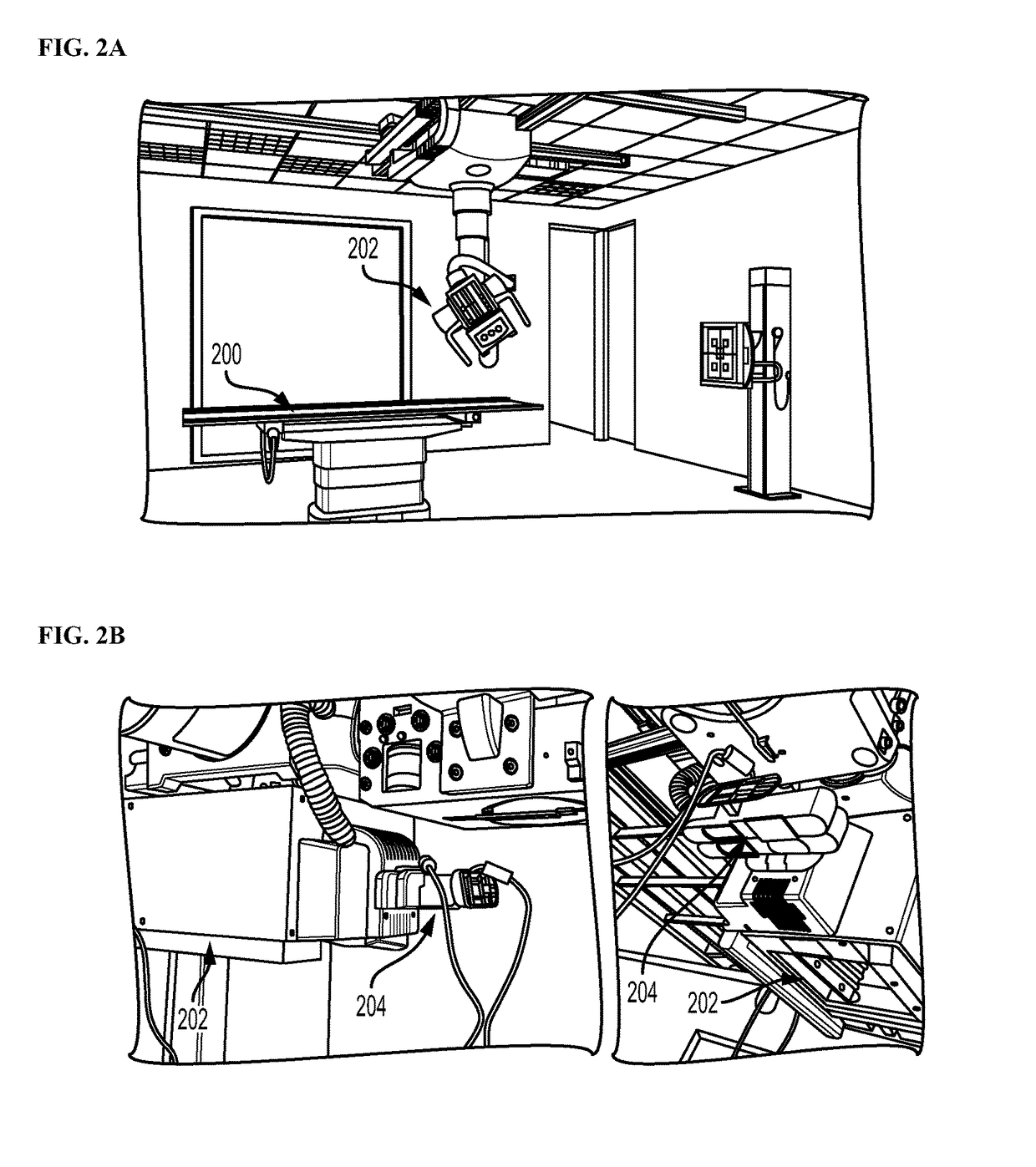
Method and System of Scanner Automation for X-Ray Tube with 3D Camera
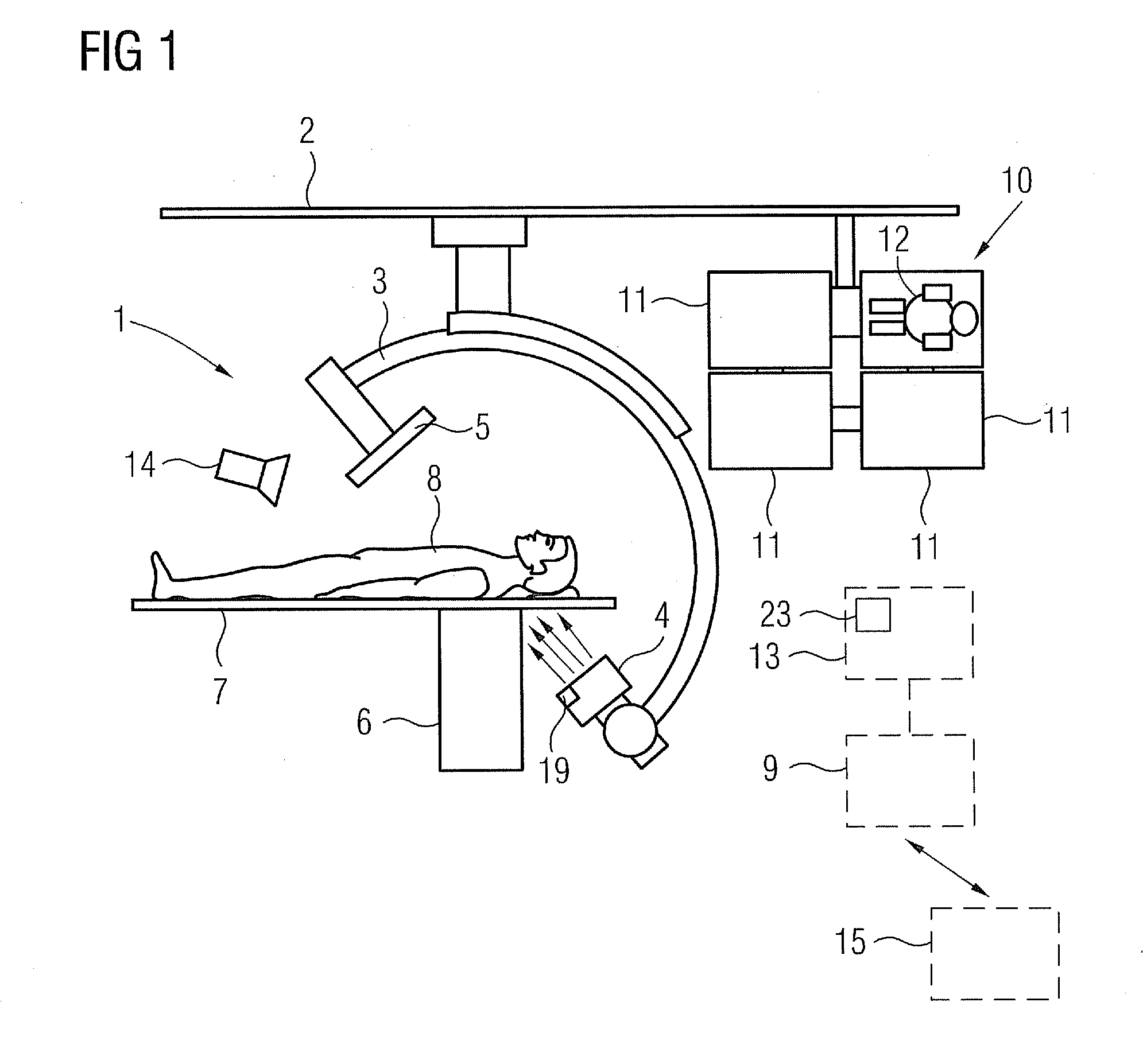
A method and apparatus for X-ray tube scanner automation using a 3D camera is disclosed. An RGBD image of a patient on a patient table is received from a 3D camera mounted on an X-ray tube. A transformation between a coordinate system of the 3D camera and a coordinate system of the patient table is calculated. A patient model is estimated from the RGBD image of the patient. The X-ray tube is automatically controlled to acquire an X-ray image of a region of interest of the patient based on the patient model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
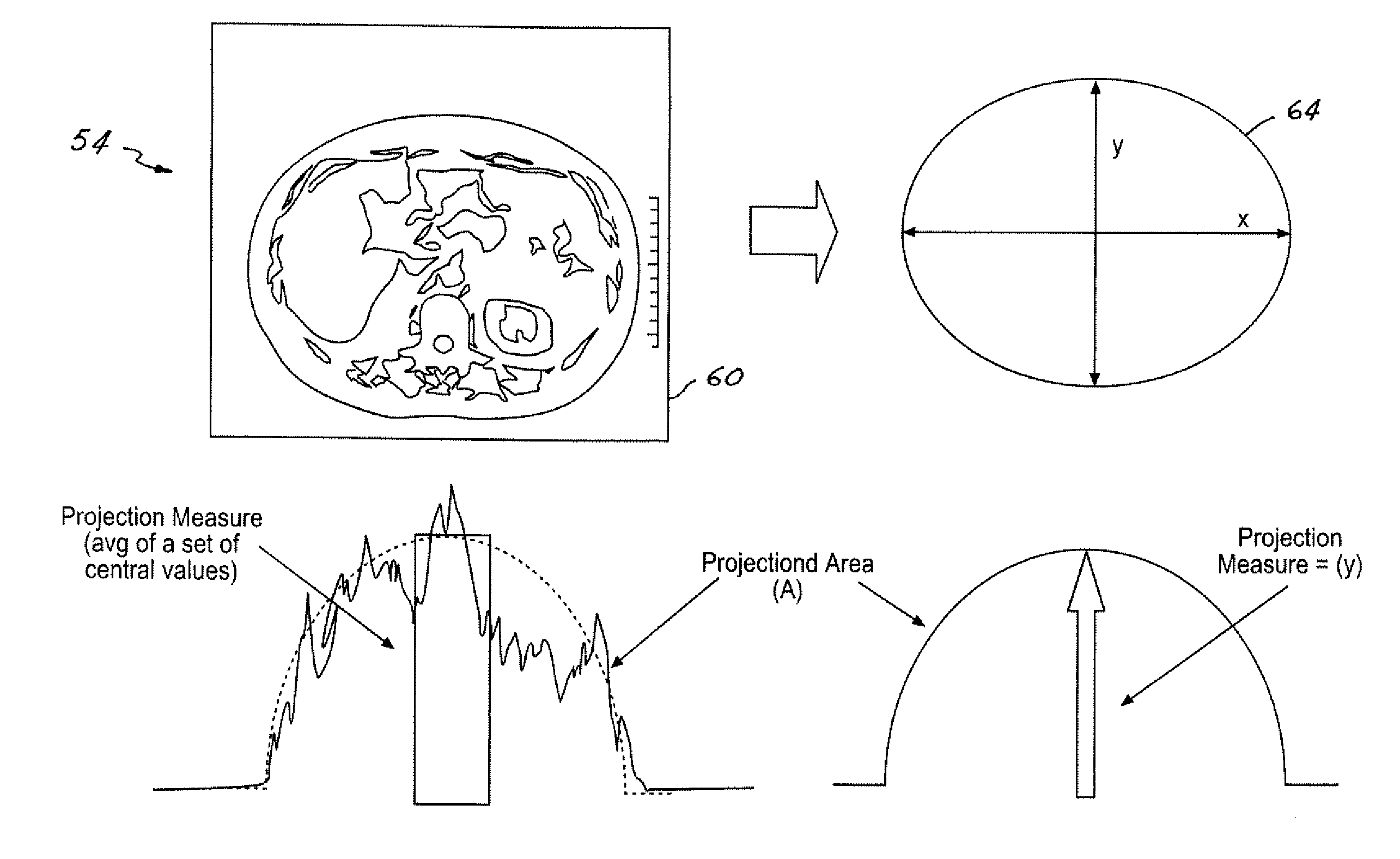
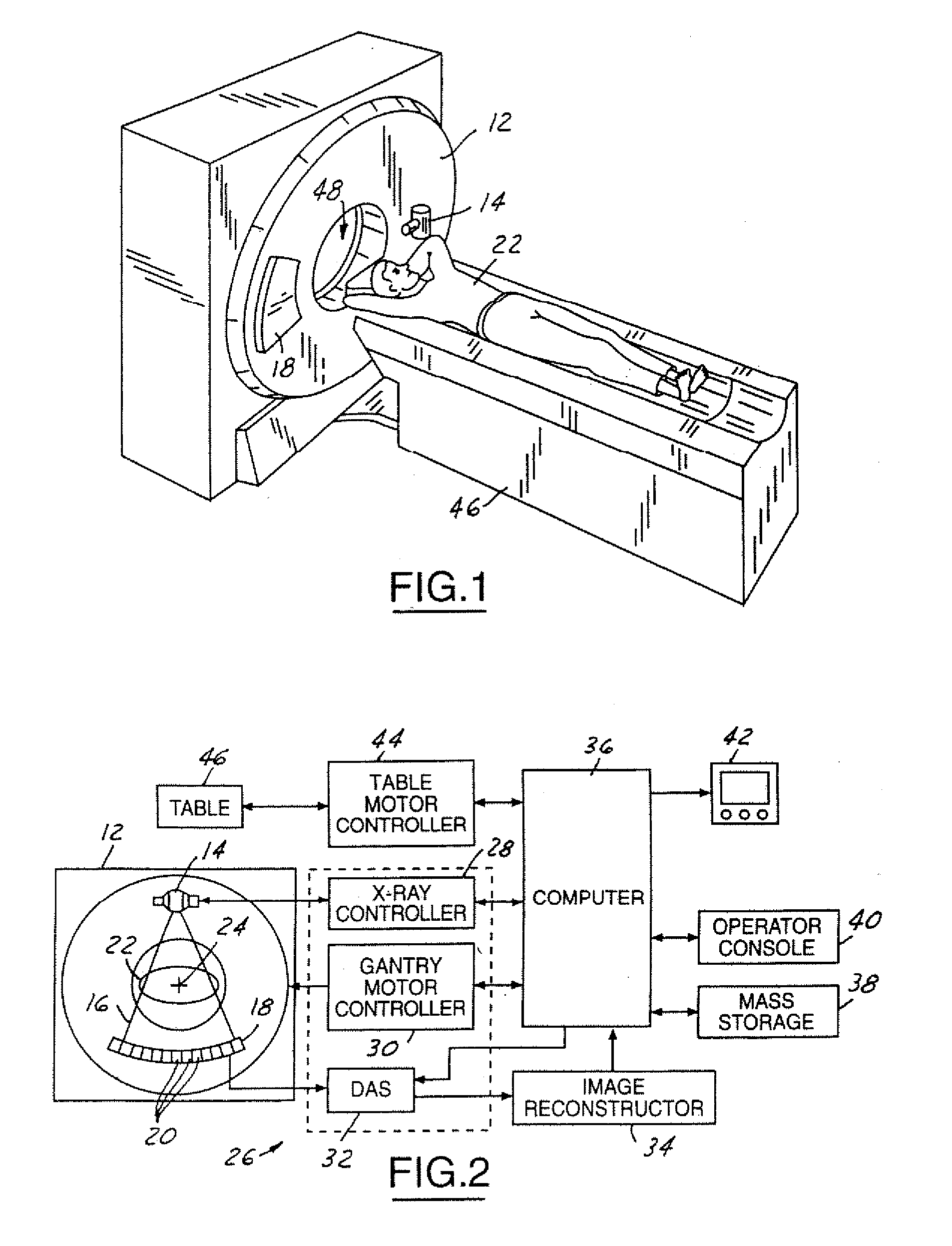
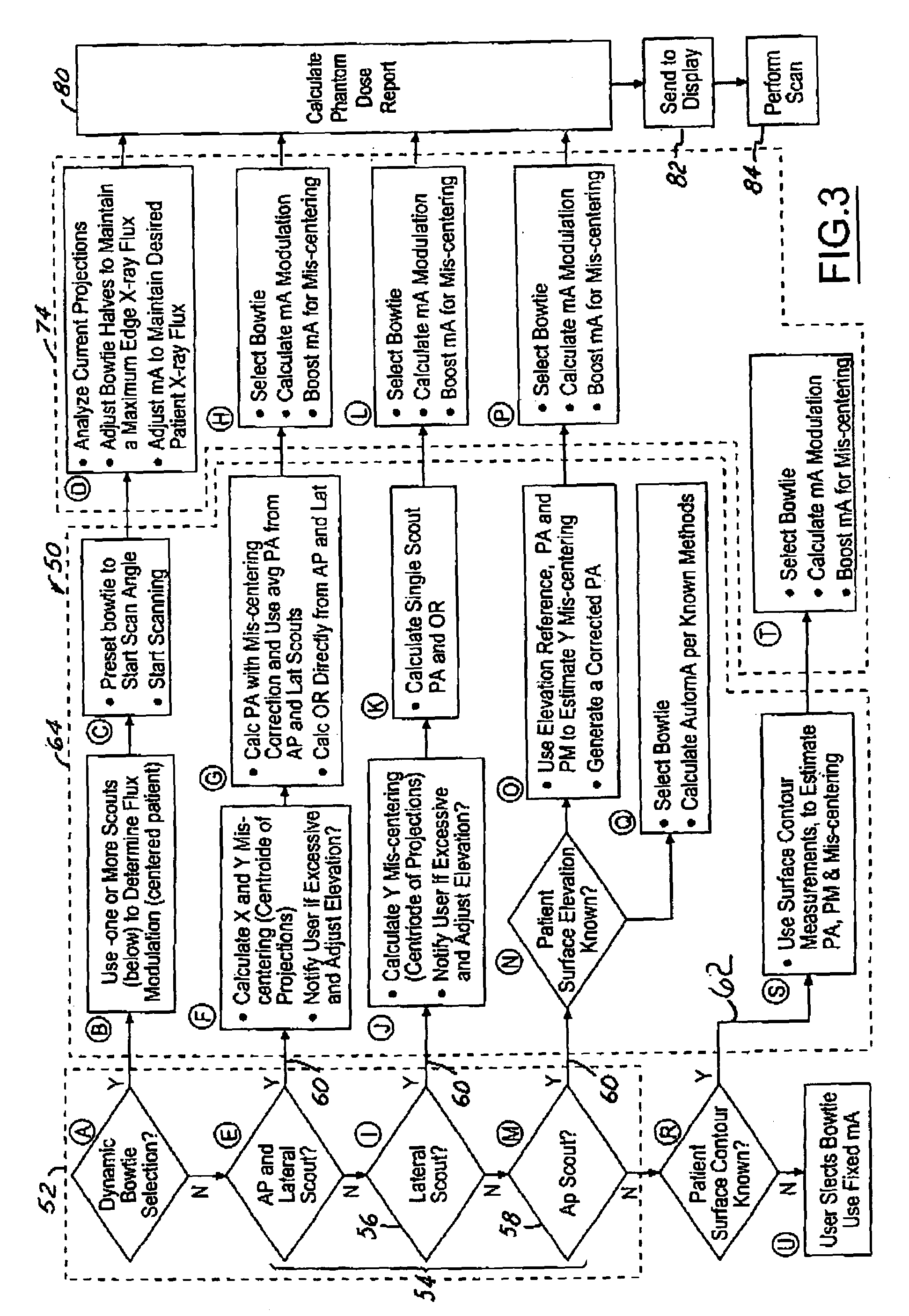
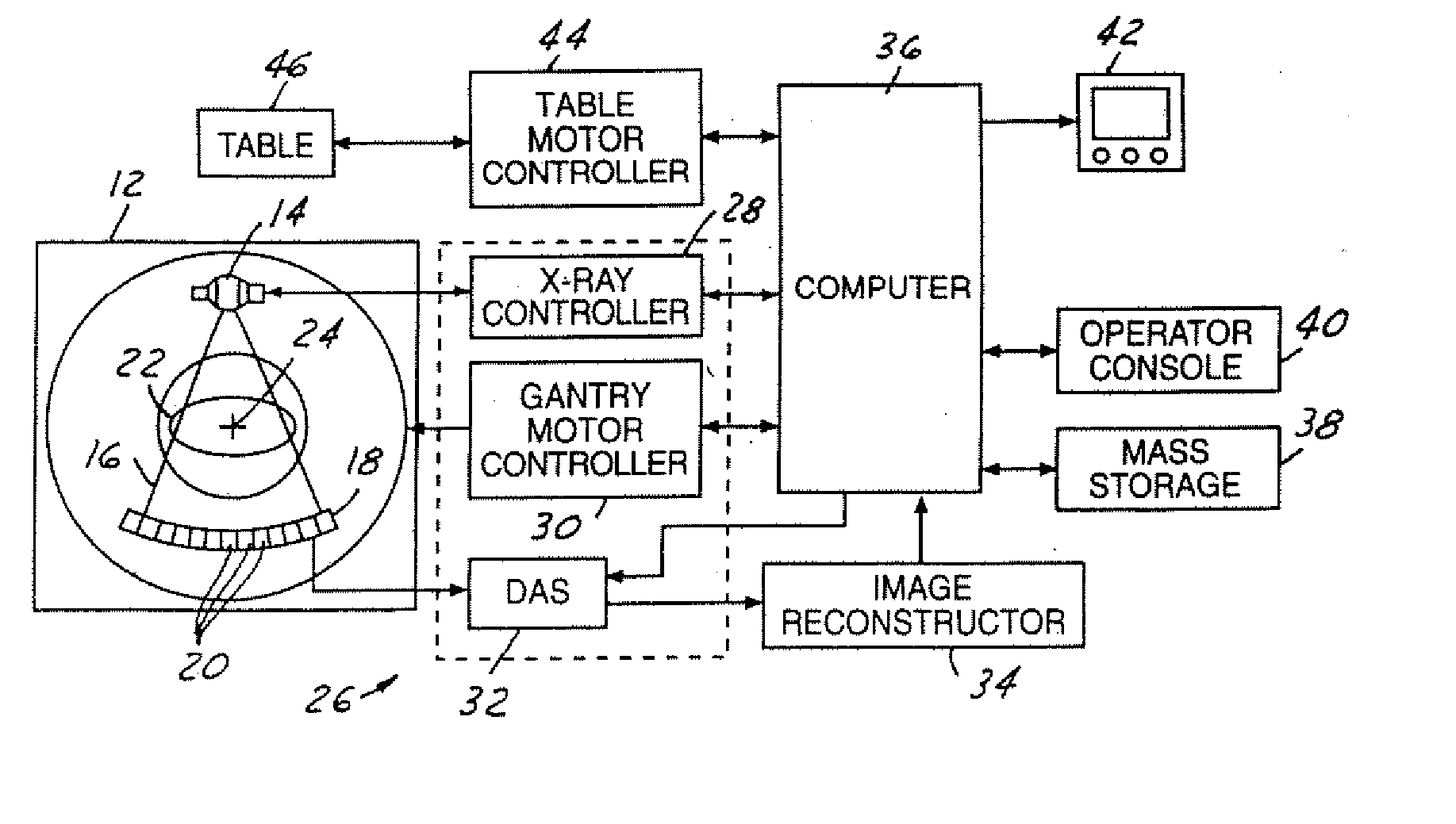
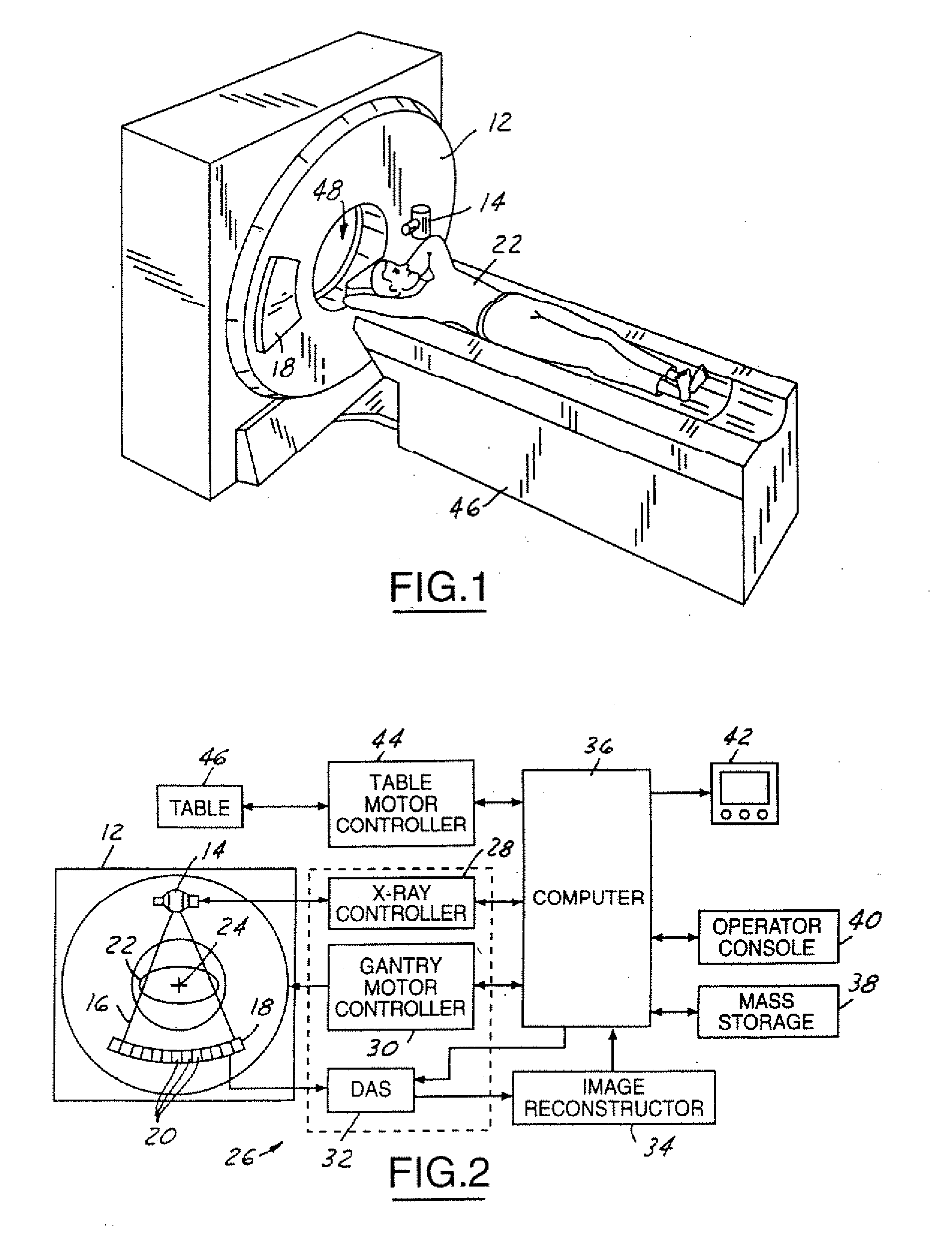
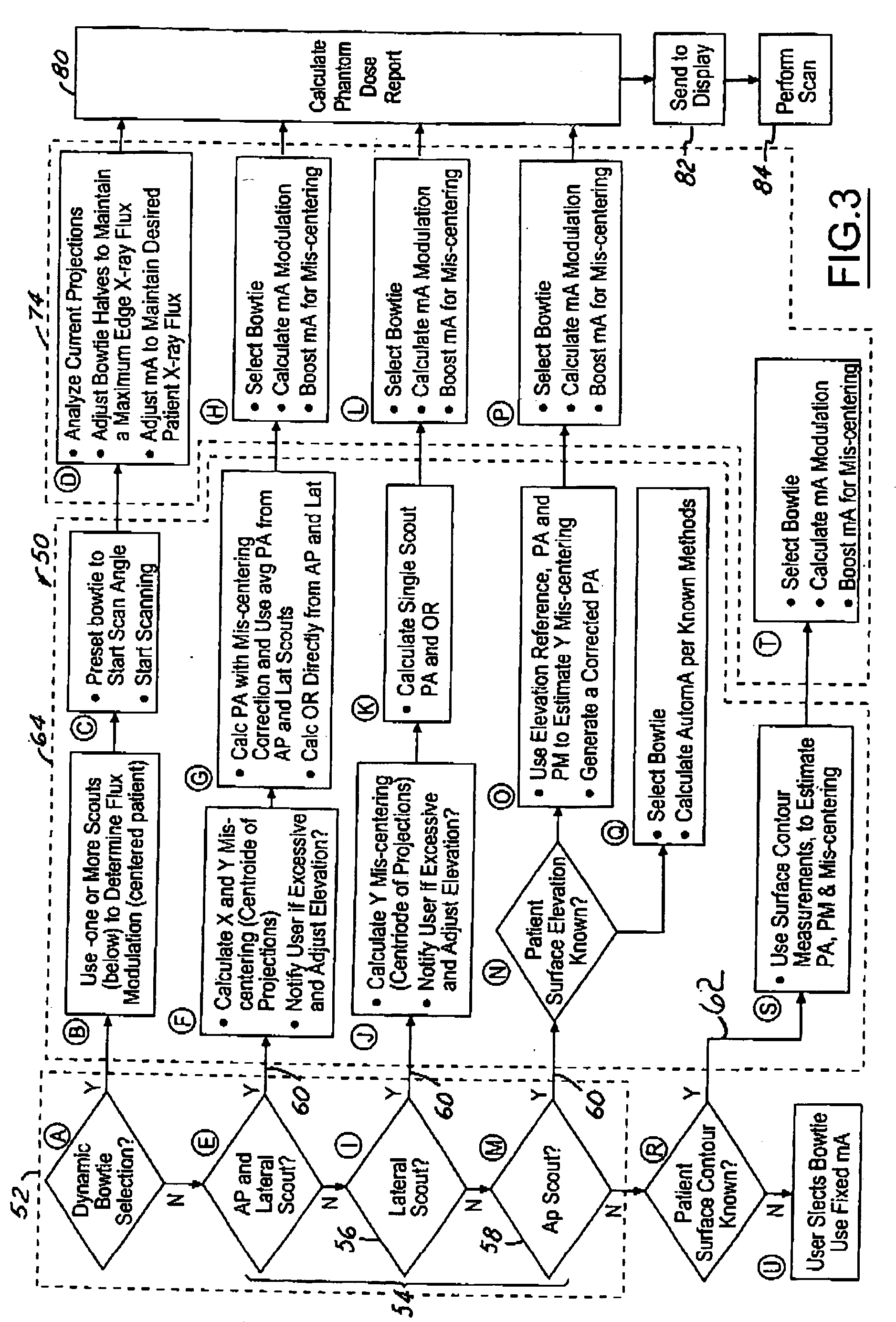
Computed tomography dose indexing phantom selection for dose reporting
ActiveUS7082183B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPatient modelSoft x ray
A computed tomography assembly is providing including an x-ray gantry assembly, an x-ray source projecting a beam of x-rays, a detector assembly positioned opposite the x-ray source and receiving the beam of x-rays, and a control mechanism in communication with the x-ray source and the detector assembly. The control mechanism includes logic adapted to: execute at least one scout scan of the object to produce a first scout scan image; generate an elliptical patient model based on the first scout scan image; match the elliptical patient model to a phantom diameter approximation; generate a dose report based on the phantom diameter approximation; and display said dose report on a display in communication with the control mechanism.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Computed tomography dose indexing phantom selection for dose reporting
ActiveUS20060018435A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPatient modelX-ray
A computed tomography assembly is providing including an x-ray gantry assembly, an x-ray source projecting a beam of x-rays, a detector assembly positioned opposite the x-ray source and receiving the beam of x-rays, and a control mechanism in communication with the x-ray source and the detector assembly. The control mechanism includes logic adapted to: execute at least one scout scan of the object to produce a first scout scan image; generate an elliptical patient model based on the first scout scan image; match the elliptical patient model to a phantom diameter approximation; generate a dose report based on the phantom diameter approximation; and display said dose report on a display in communication with the control mechanism.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
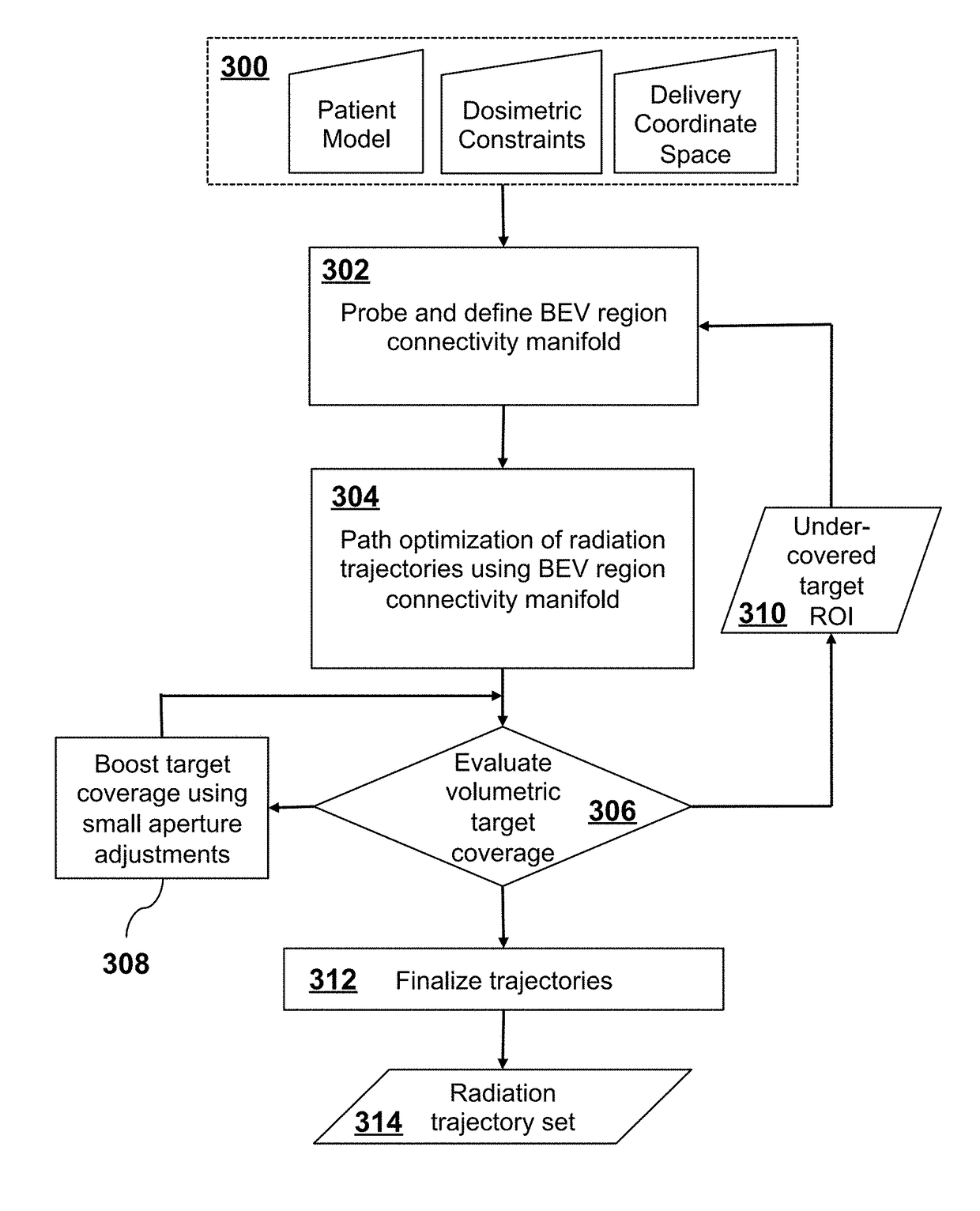
Trajectory Optimization in Radiotherapy Using Sectioning
ActiveUS20170354832A1Avoids degradation of trajectory optimization qualityOptimal trajectoryX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPatient modelBeam trajectory
A radiation therapy treatment method includes providing a patient model, dosimetric constraints, delivery motion constraints, and delivery coordinate space of a radiation delivery device, where the delivery coordinate space is represented as a mesh with vertices connected by edges, where the vertices correspond to directions of a beam eye view (BEV) of the radiation delivery device, where each BEV has corresponding area elements resulting from beam collimation. BEV region connectivity manifolds are constructed from the patient model, the dosimetric constraints, the delivery coordinate space, and existing beam trajectories, wherein each of the BEV region connectivity manifolds represents connections between contiguous 2D target regions, where each of the 2D target regions is defined at each of the vertices of the delivery coordinate space. Beam trajectories are selected based on region connectedness information in the BEV region connectivity manifolds, the dosimetric constraints, the delivery motion constraints, and the existing beam trajectories. Radiation is delivered using the radiation delivery device in accordance with the beam trajectories.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for monitoring the X-ray dosage administered to a patient by a radiation source when using an X-ray device, and X-ray device
ActiveUS20100290591A1Ease of evaluationConvenience to workDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSoft x rayPatient model
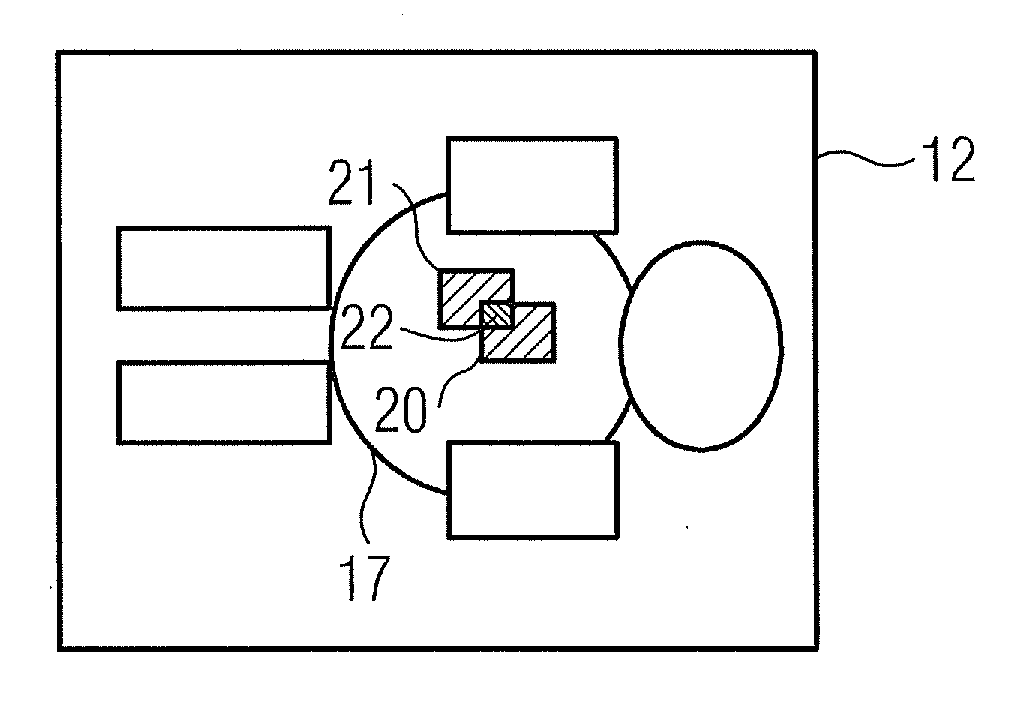
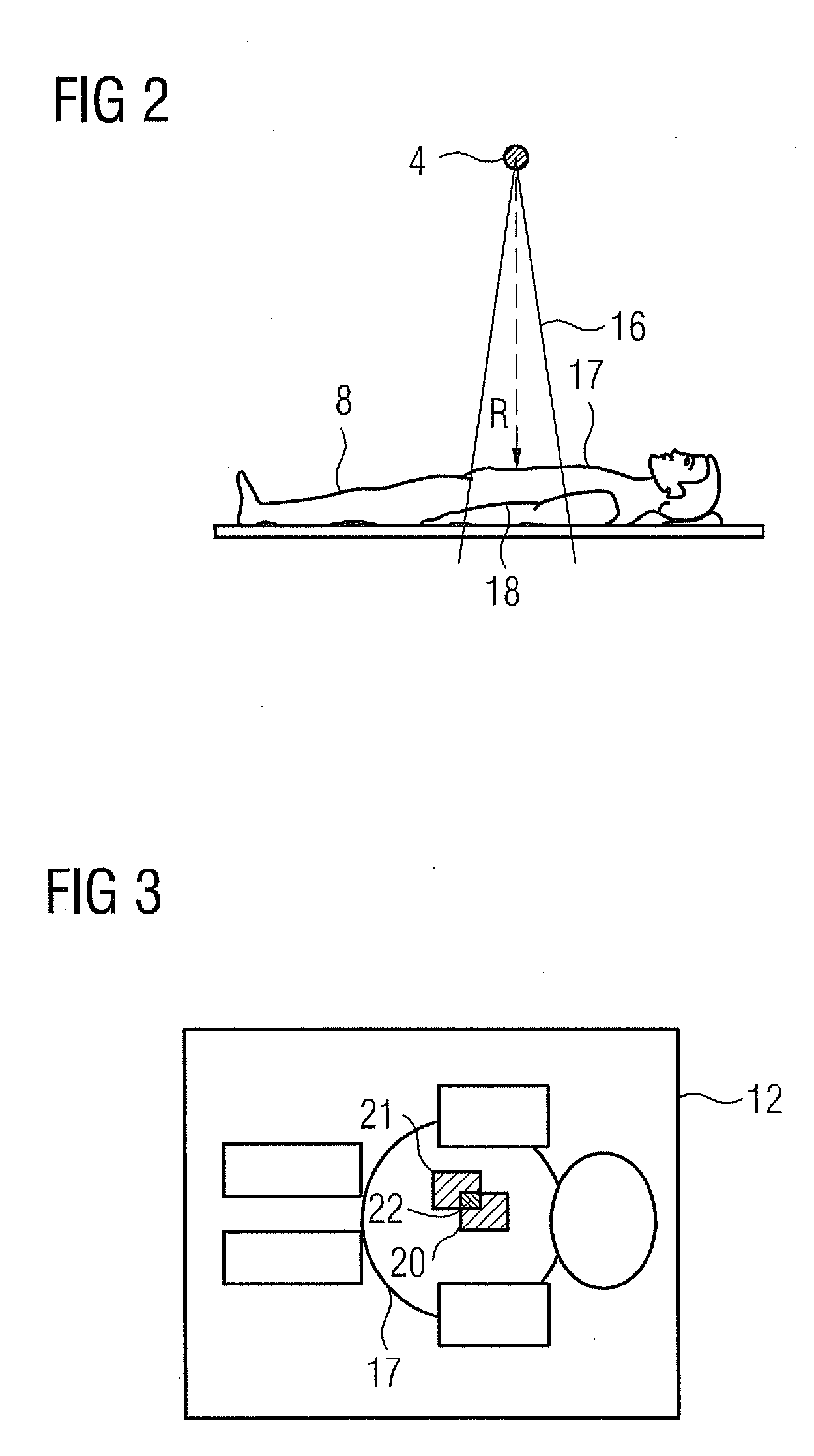
A method for monitoring the X-ray dosage administered to a patient by a radiation source when using an X-ray device is proposed. The X-ray device is in particular a C-arm X-ray device. A location-dependent dosage value on the surface of the patient is determined with reference to parameters which describe the recording geometry and the radiation that is administered. The surface is described by a patient model in particular. A representation of the dosage value and / or of a value derived therefrom is displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
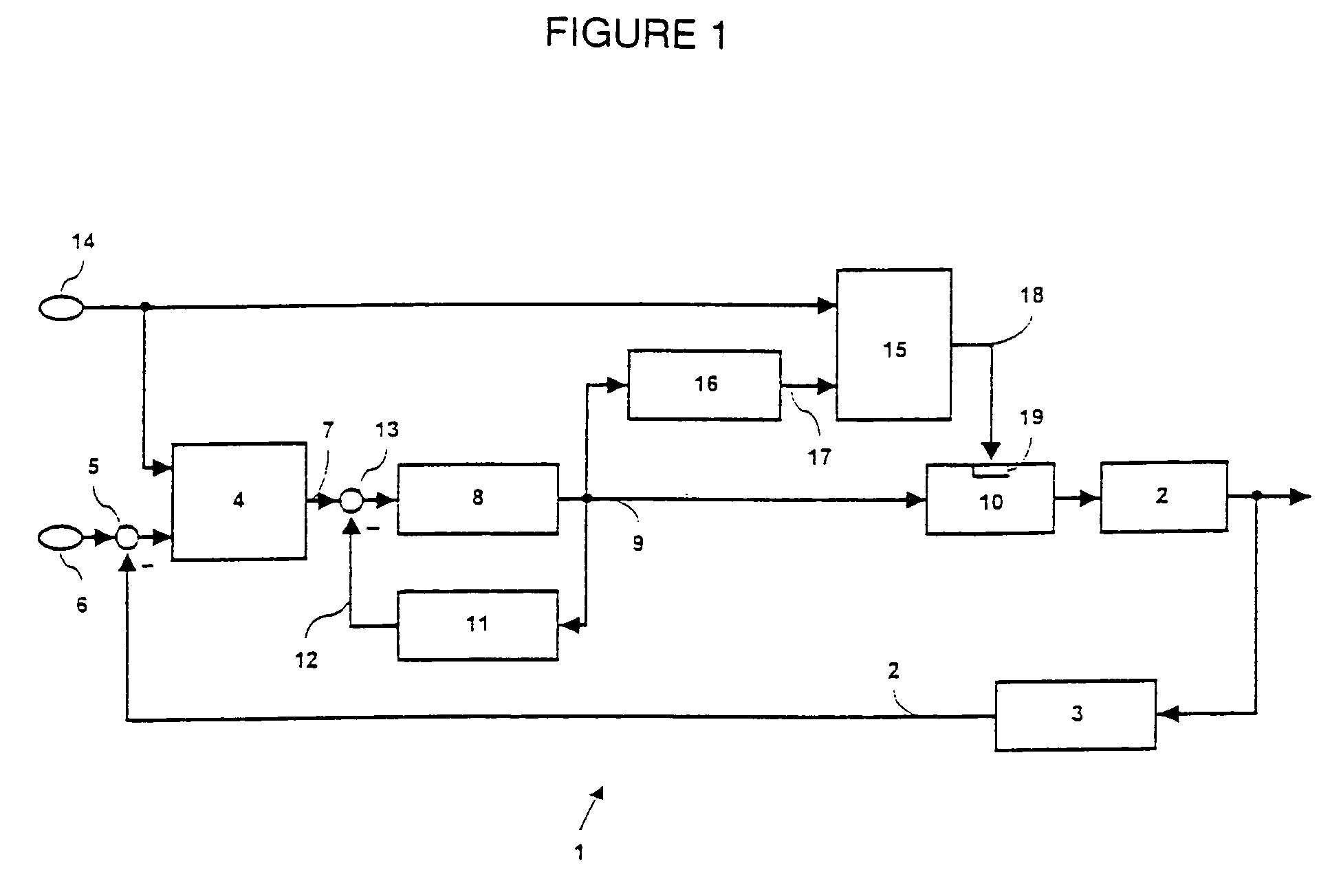
Apparatus for controlling the delivery of medical fluids
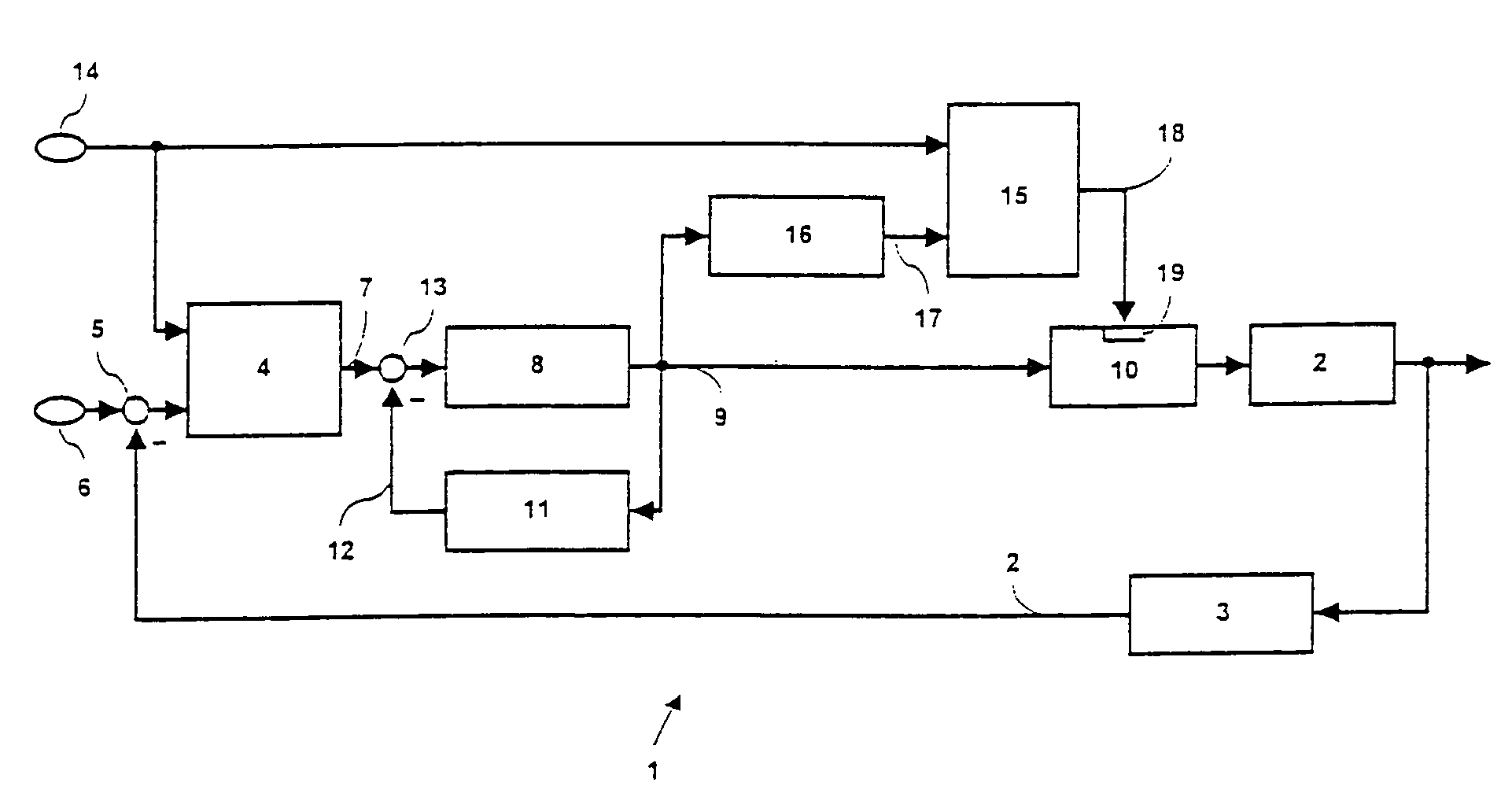
An apparatus for medical fluid delivery is to be improved for the sake of simple monitoring of the quantity of medical fluid delivered. For attaining this object, a safety device (15) with a patient model (16) is provided, which from past values and current values of the dosage rate of the medical fluid extrapolates a future medical fluid concentration (17) and switches off the dosage unit (10) for the medical fluid if the extrapolated medical fluid concentration (17) exceeds a predetermined limit value (14).
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Orthodontic surgery training system and training method
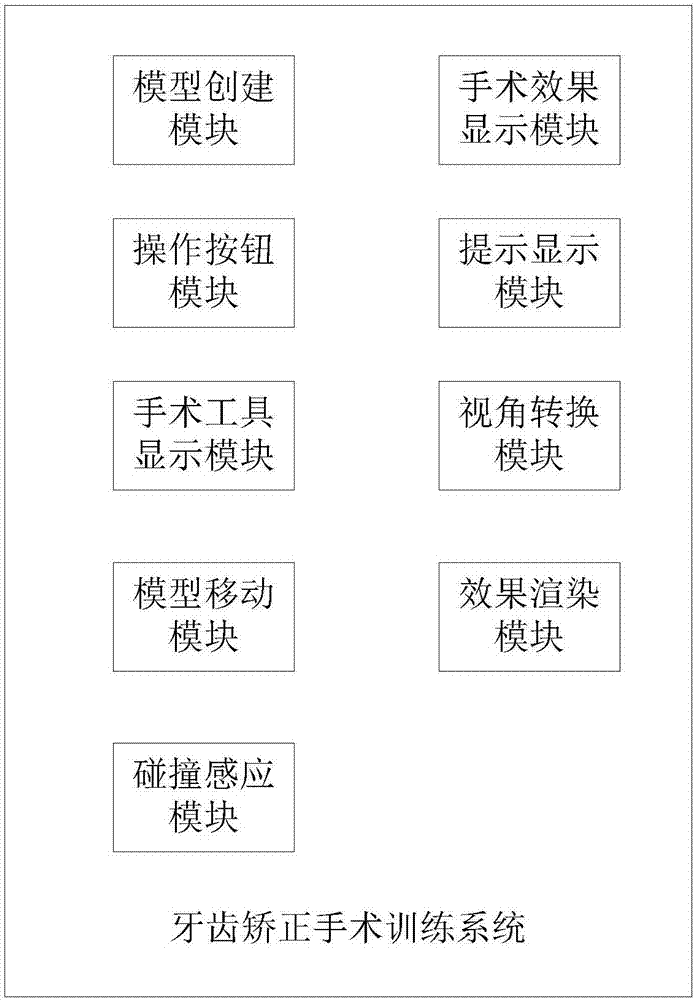
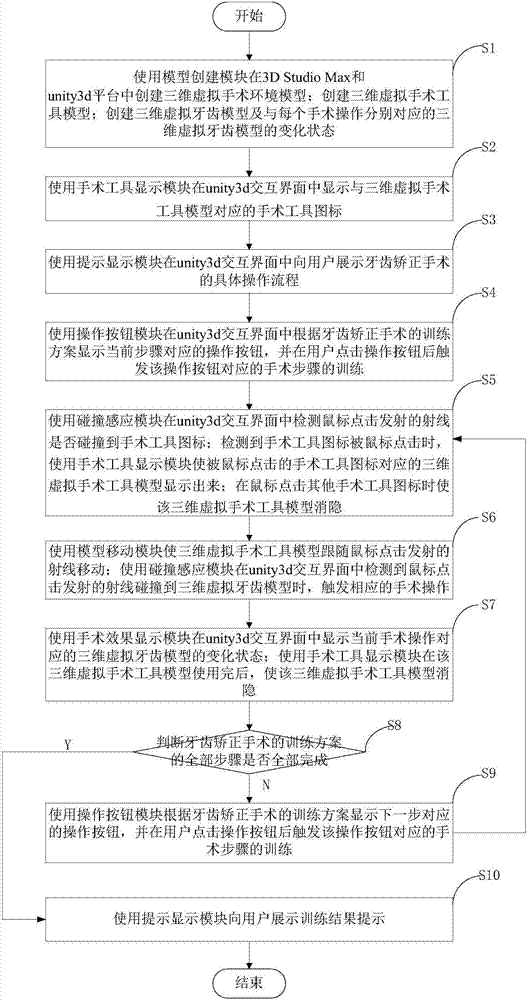
ActiveCN107240343ASave teaching resourcesImprove learning efficiencyEducational modelsVirtual realityTraining methods
The present invention discloses an orthodontic surgery training system, which relates to the field of virtual reality technology and comprises a model creating module, an operation button module, a surgical tool display module, a model moving module, a collision sensing module, a surgical effect display module and a prompt display module, Inventing 3D Virtual Operating Room and Patient Models, 3D Virtual Surgical Tool Models, and 3D Virtual Dental Models Using the Model Creation Module in 3D Studio Max and Unity3d Platforms Using the Action Button Module, Surgical Tool Display Module, Model Mobility Module, Collision Sensing Module , The operation effect display module and the prompt display module realize the virtual surgery training according to the orthodontic training program. With each operation of the user, the three-dimensional virtual surgical tool model and the three-dimensional virtual dental model may move or change correspondingly. The invention also discloses a dental orthodontic training method.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
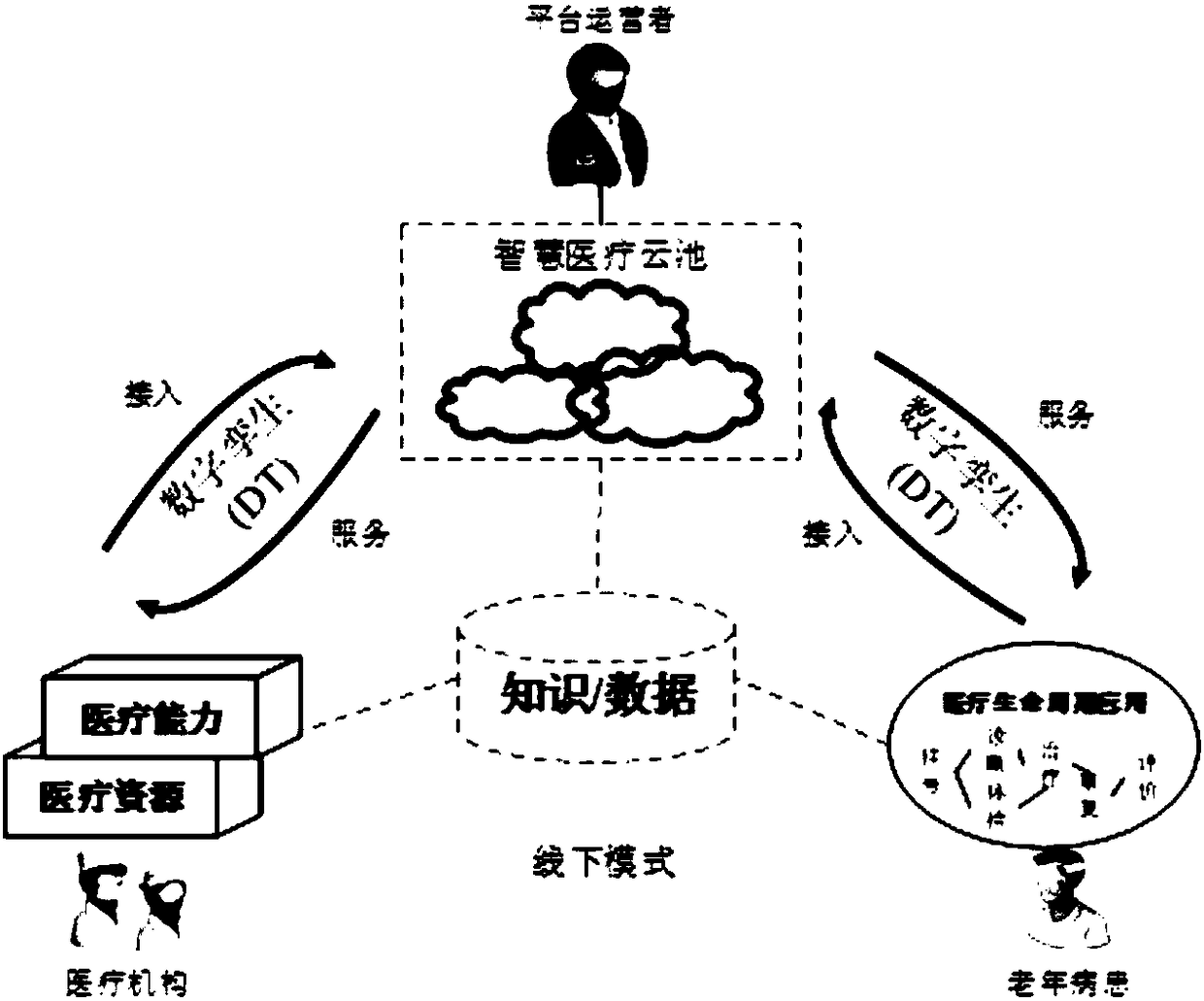
Digital twin-based cloud medical simulation platform building method and cloud medical system
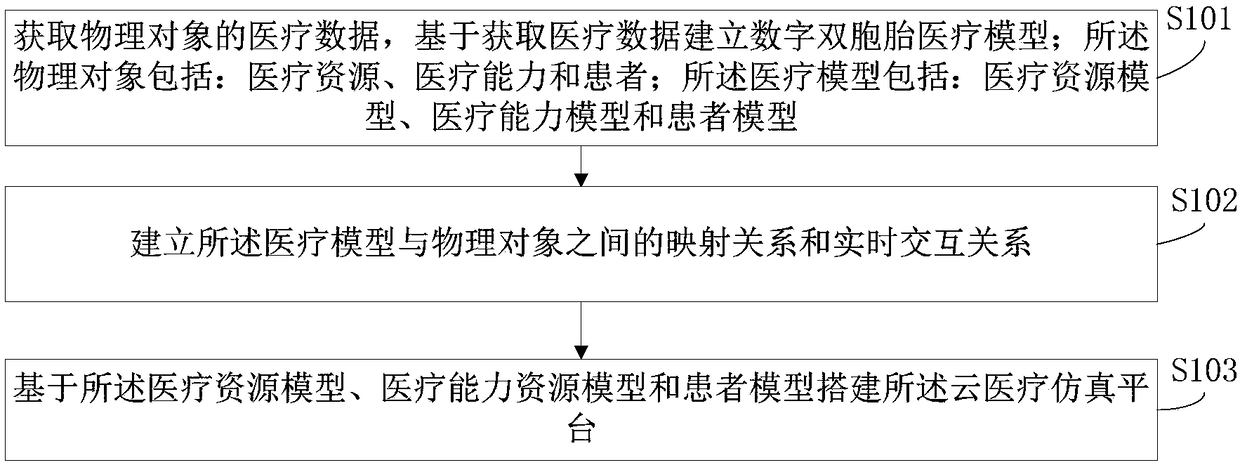
PendingCN108428477AReal time monitoringReal-time warningMedical simulationMedical communicationPatient modelReal-time simulation
The invention provides a digital twin-based cloud medical simulation platform building method and a cloud medical system. The method comprises the steps that medical data of physical objects is obtained, and a digital twin medical model is built; the physical objects comprise medical resources, medical capacity and patients; the digital twin medical model comprises a medical resource model, a medical capacity model and a patient model; interconnection among the medical model, the physical object and the cloud medical service system is built; a cloud medical simulation platform is built on thebasis of the digital twin medical platform. Accordingly, precise modeling is conducted on the patients and medical equipment through a digital twin technology and a cloud architecture, the medical process can be subjected to real-time simulation, medical service can be subjected to optimal management, and the patients can be monitored and pre-warned in real time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Virtual operating room layout planning and analysis tool
ActiveUS20190307510A1Computer-aided planning/modellingMedical equipmentPatient modelOperating theatres
A method and system to generate an operating room layout plan for a surgical procedure involving a patient and a trajectory of access. A patient model is positioned in a virtual coordinate space representing the operating room, and is rendered, along with the trajectory of access relative to the patient, on a display. The trajectory of access defines a zone of operation in the virtual coordinate space. The planning system receives selection of a navigation camera location in the virtual coordinate space; renders a navigation camera model visually indicating an operative field of view; determines whether the navigation camera has a direct line-of-sight to the zone of operation and, if not, indicates an error; and outputs the operating room layout plan based on the location of the models in the virtual coordinate space.
Owner:SYNAPTIVE MEDICAL INC
Method for planning a dental treatment
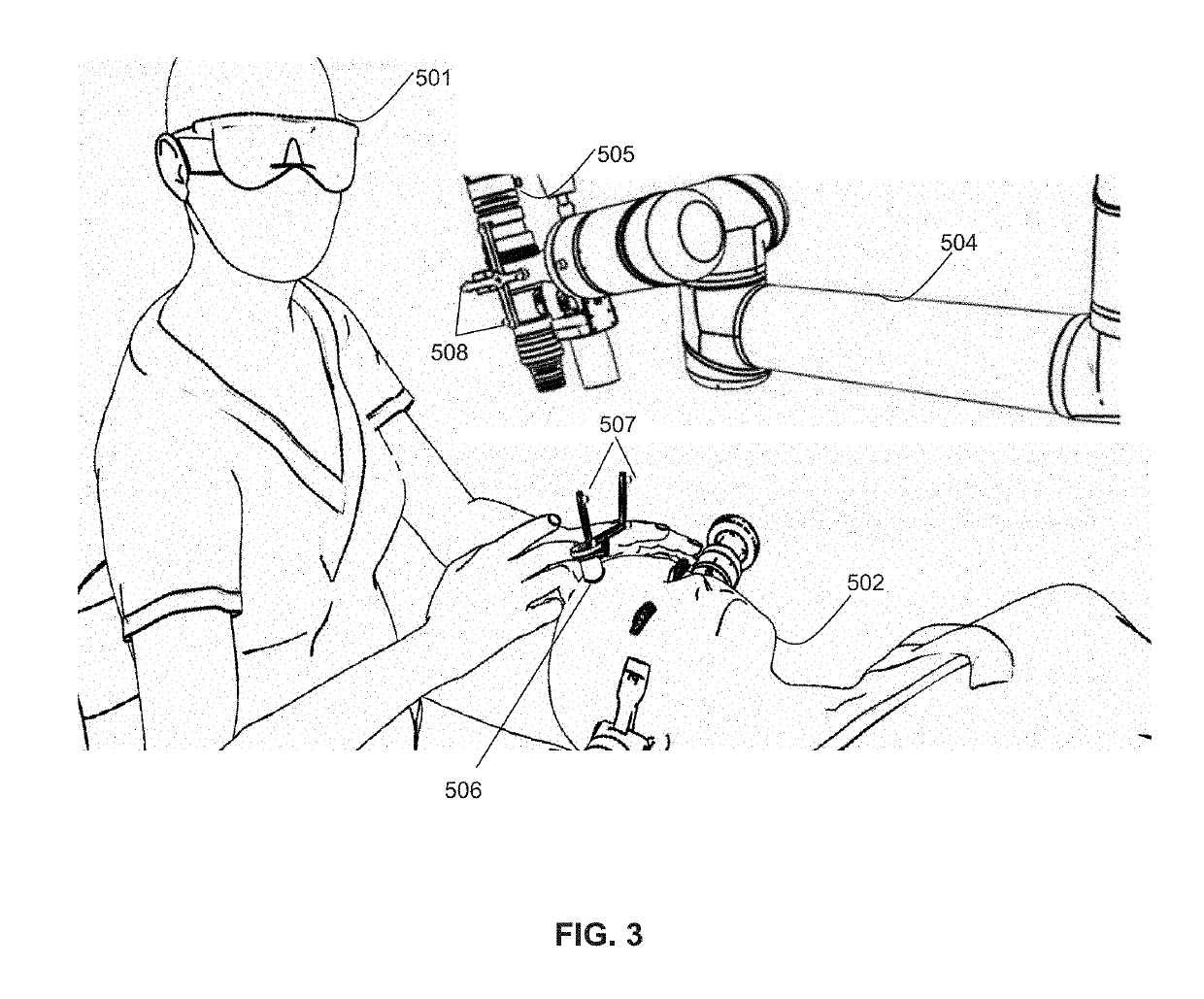
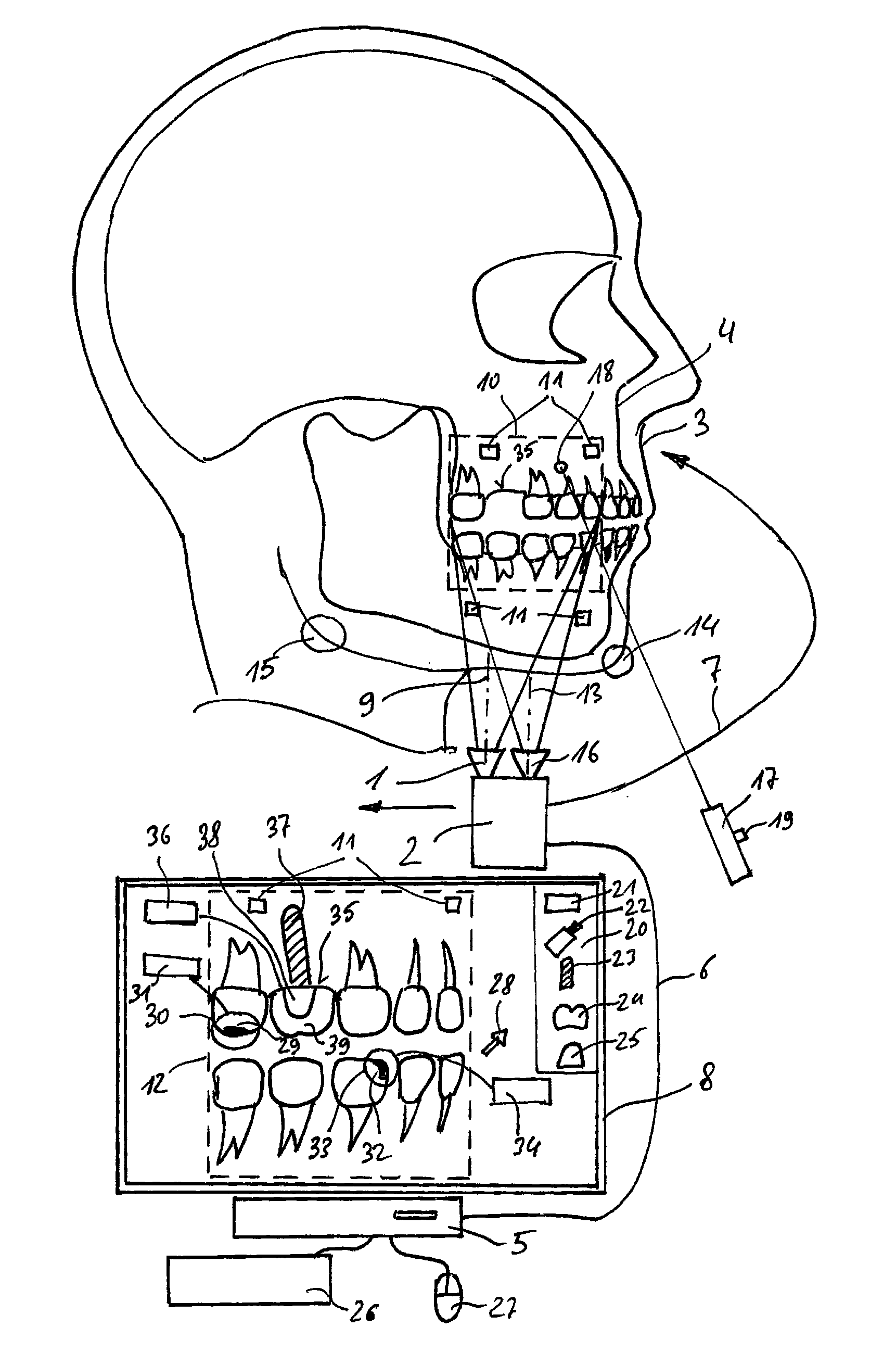
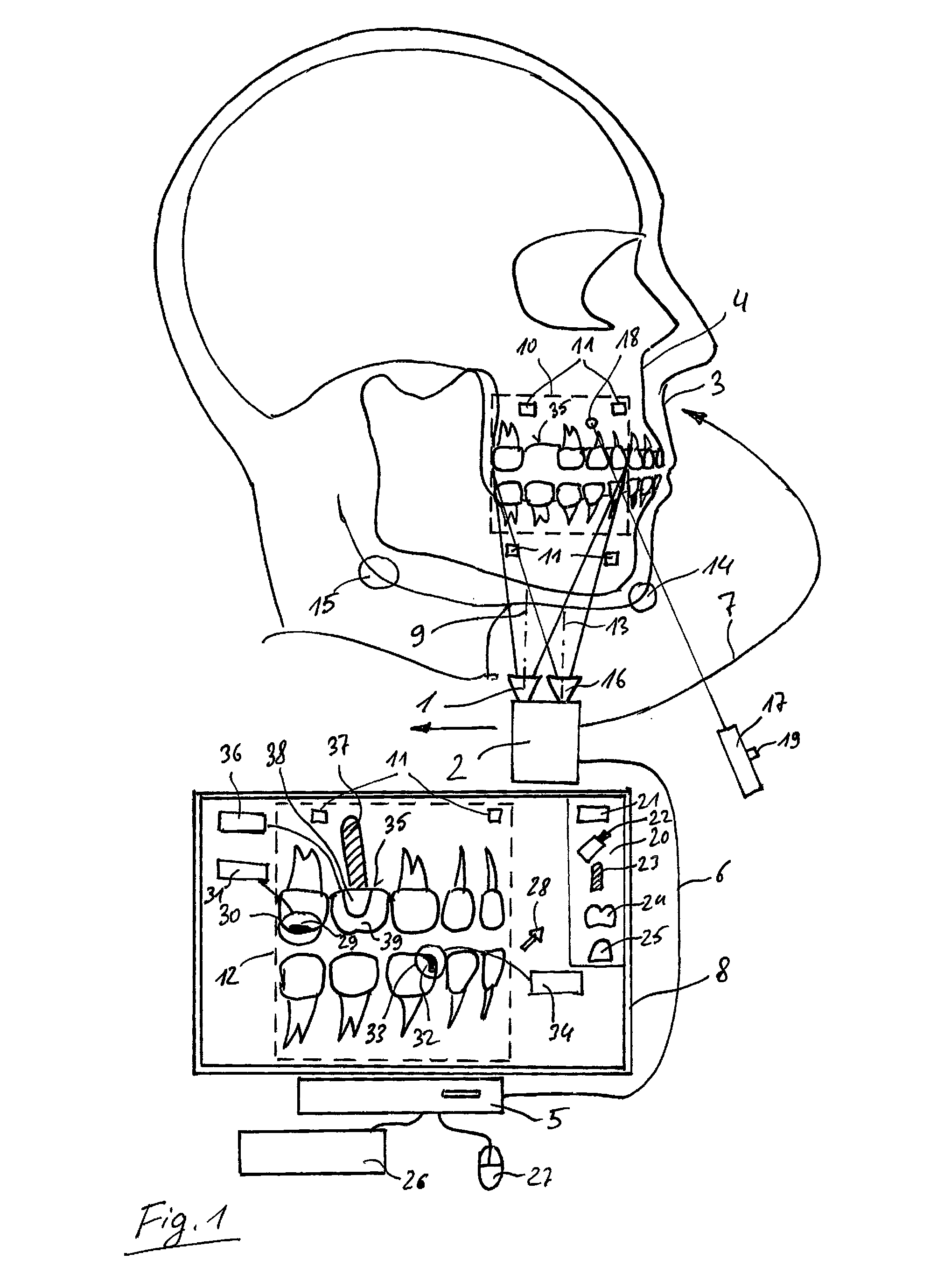
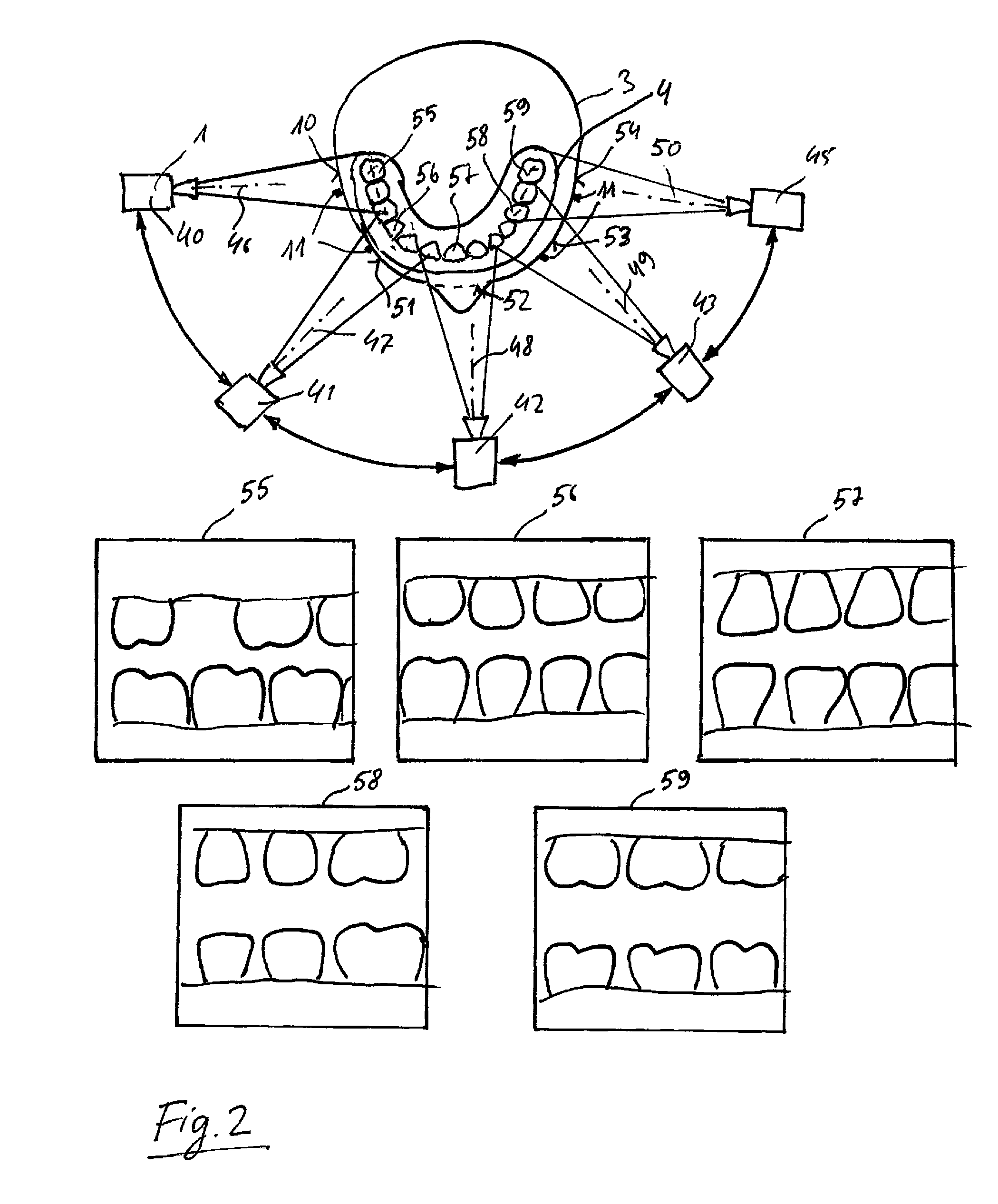
ActiveUS20150296184A1Easy to planPrecise positioningTelevision system detailsImpression capsPatient modelComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a method for planning or for checking the planning of a dental and / or a maxillofacial treatment, wherein at least one video recording of an object (3) is recorded by means of at least one video camera (1). A patient model (4) is available which comprises image data of the object (3), wherein the video recording is virtually coupled to the patient model (4) in such a way that a viewing direction (13) of the view of the patient model (4) is changed in dependence on a changing recording direction (9, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50) of the video recording when the video camera (1) is moved in relation to the object (3).
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
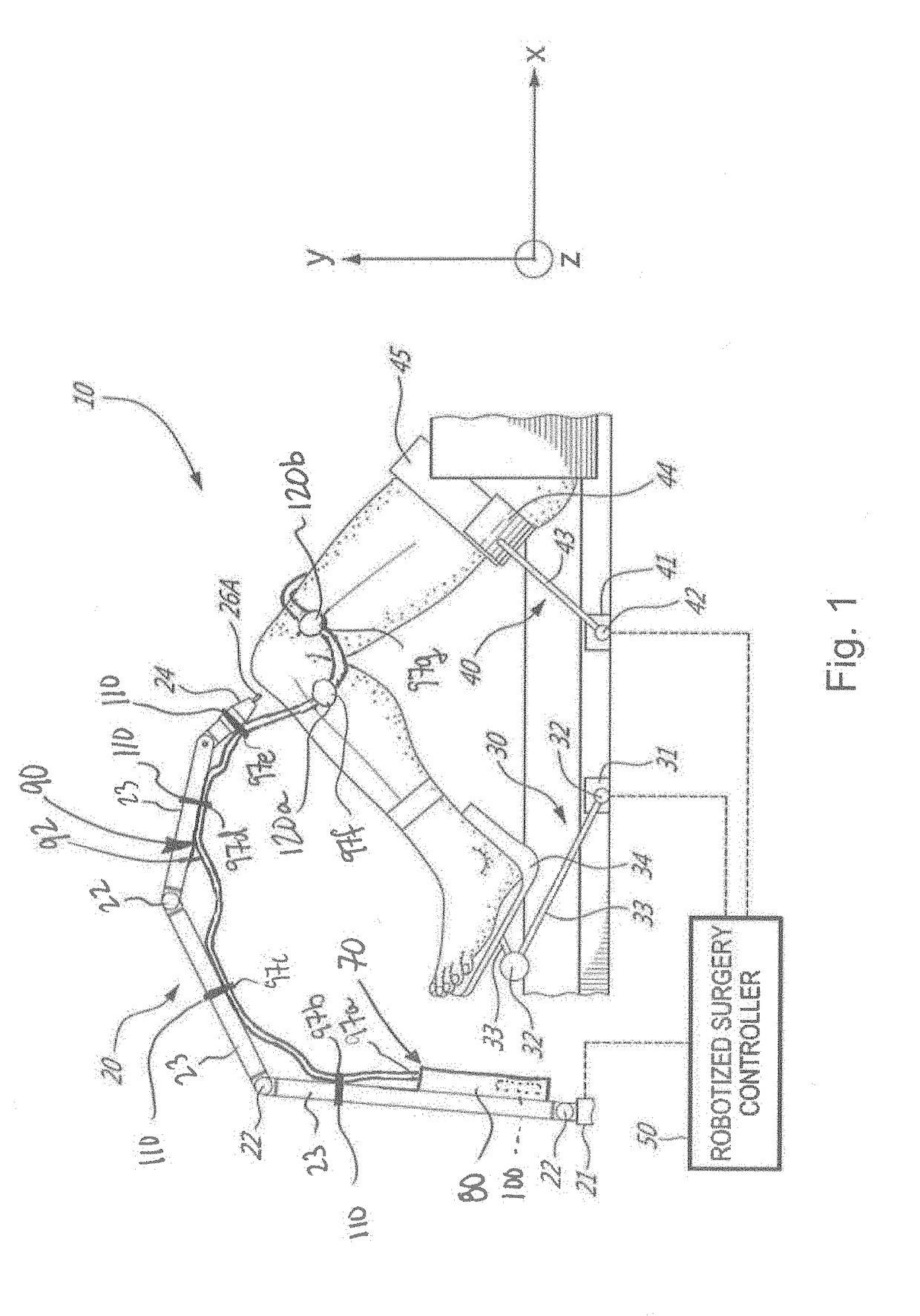
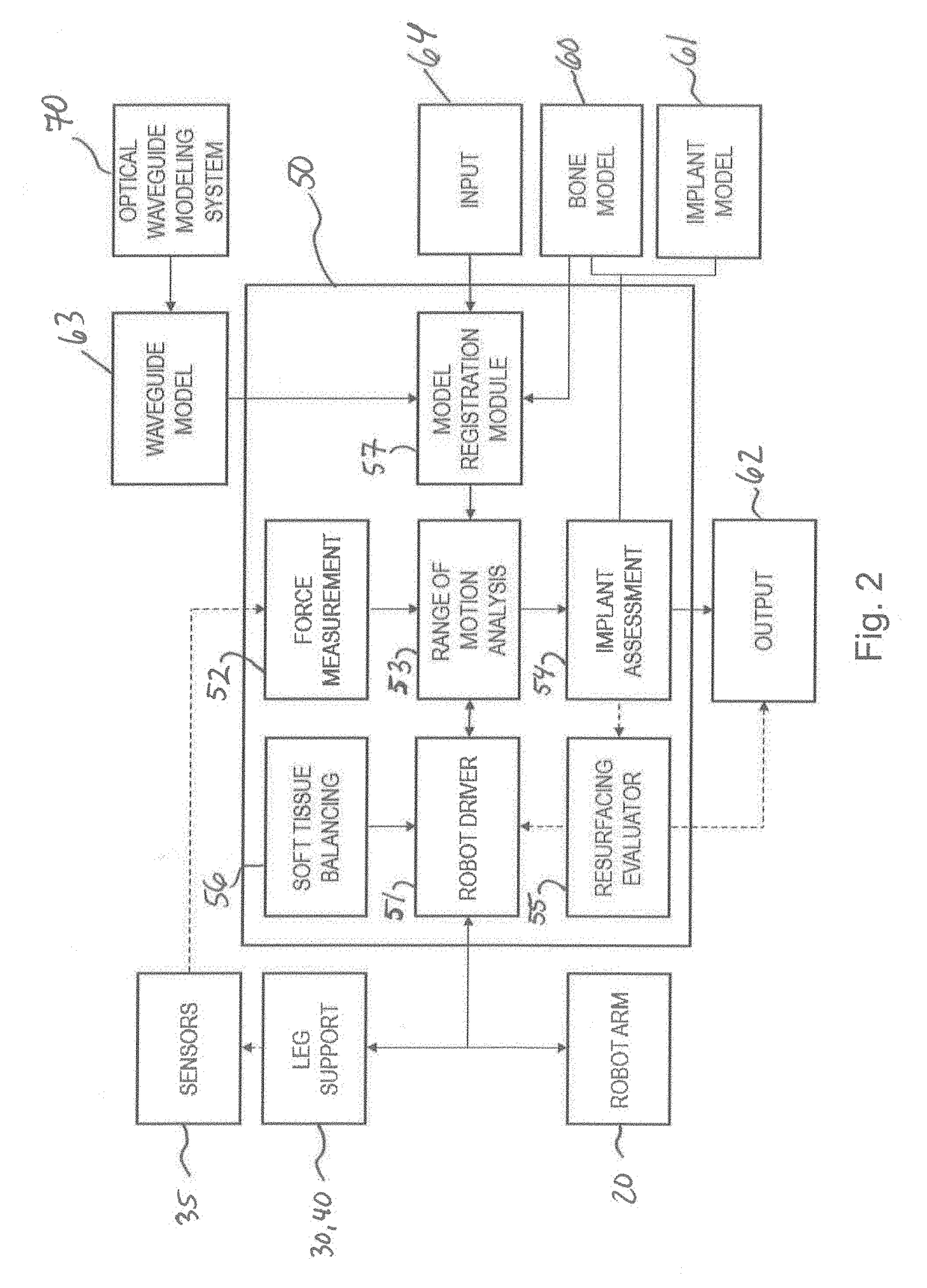
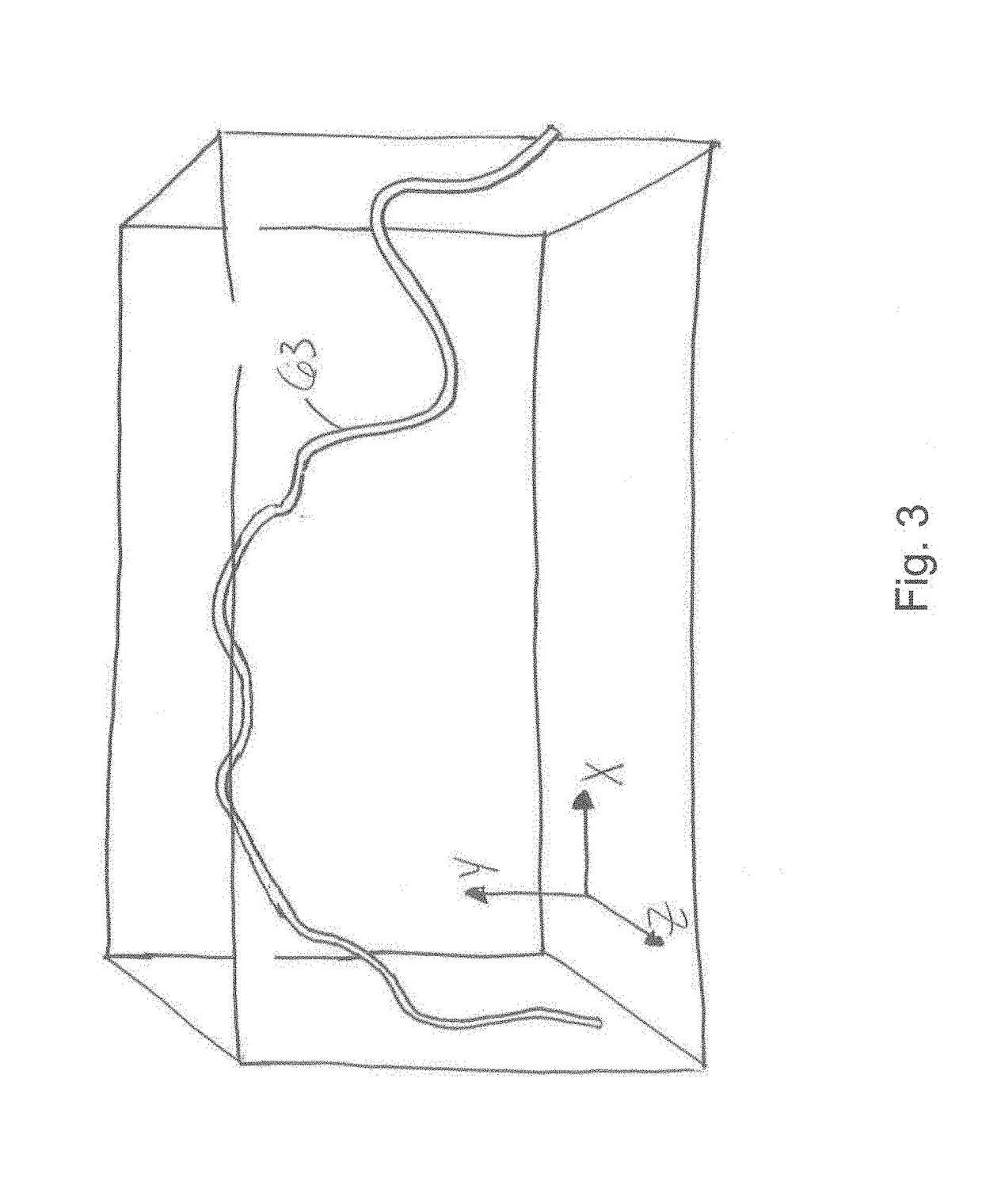
Bone and tool tracking with optical waveguide modeling system in computer-assisted surgery
ActiveUS20190029759A1Easy to optimizeSurgical navigation systemsMulticore optical fibrePatient modelComputer-assisted surgery
There is described a method for tracking a patient in a coordinate system of a surgical tool using an optical waveguide modeling system having one multicore optical fiber with a portion attached to the surgical tool and a portion attached to the patient. The method generally includes receiving a patient model representing a shape and orientation of at least one of a limb and a bone of the patient, generating a waveguide model representing a shape and orientation of the multicore optical fiber as attached to the surgical tool and to the patient, and tracking the patient model in the coordinate system by registering the patient model in the coordinate system using the waveguide model and known spatial relationships relating to the surgical tool, the portion of the multicore optical fiber attached to the surgical tool, and the portion of the multicore optical fiber attached to the patient.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
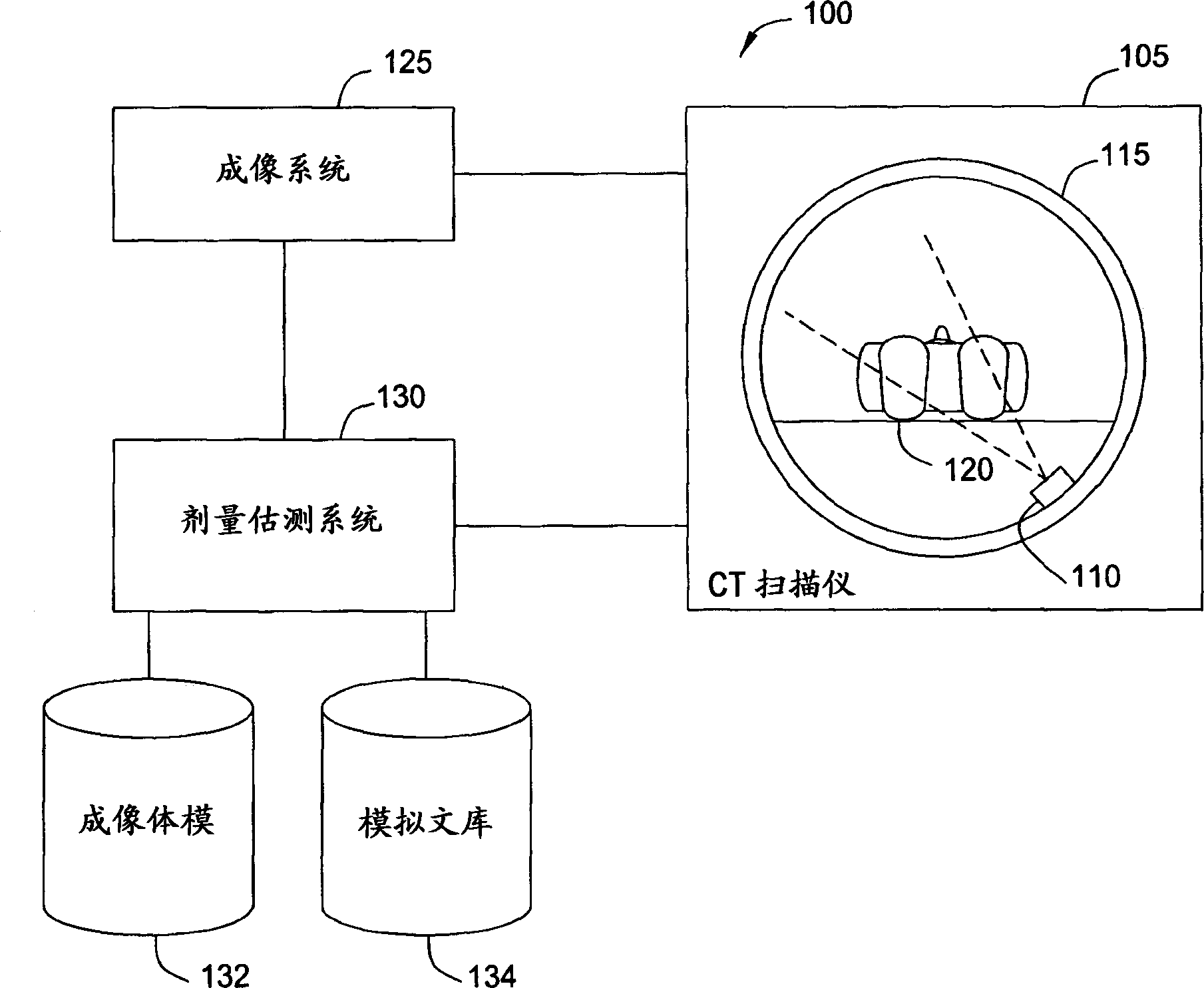
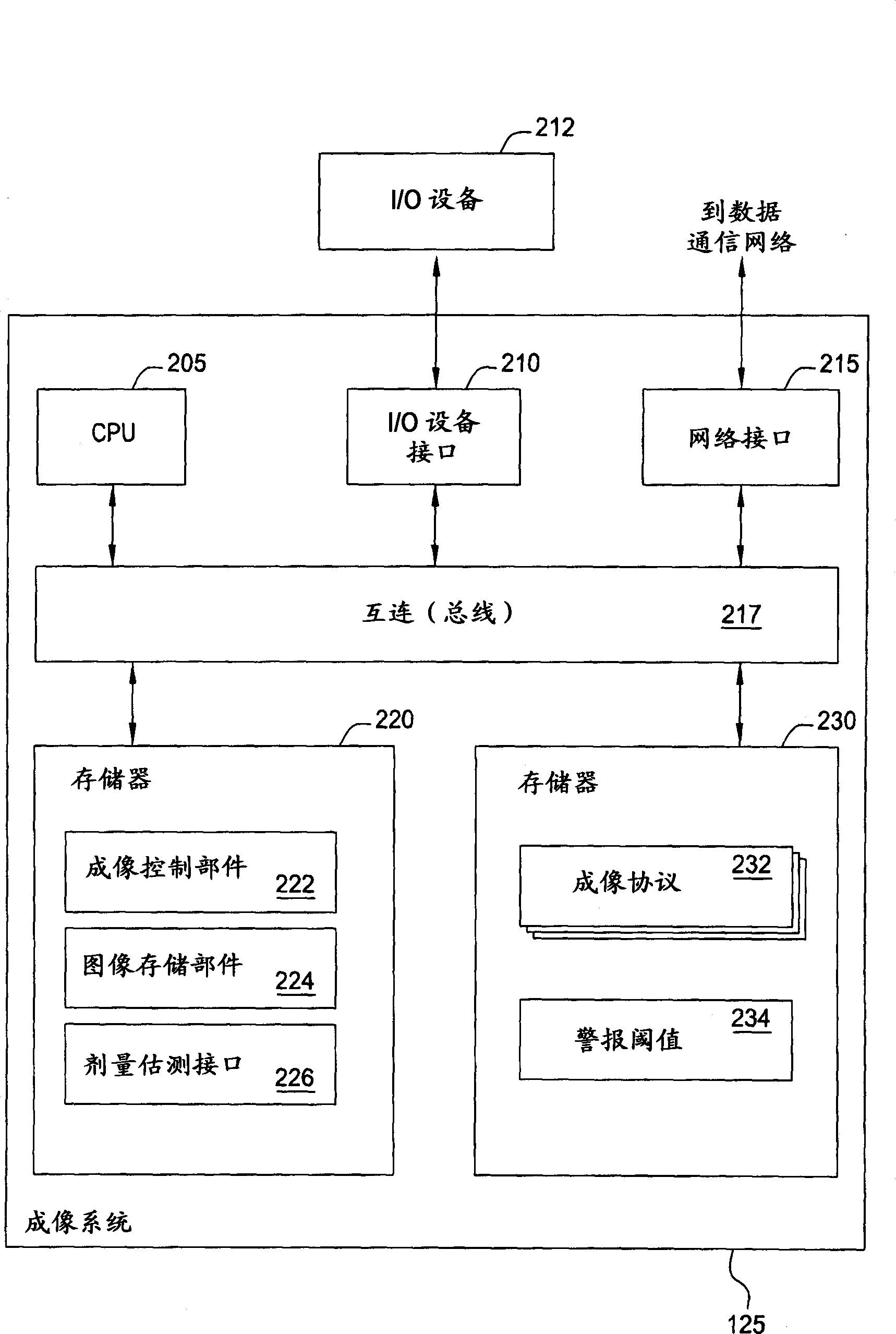
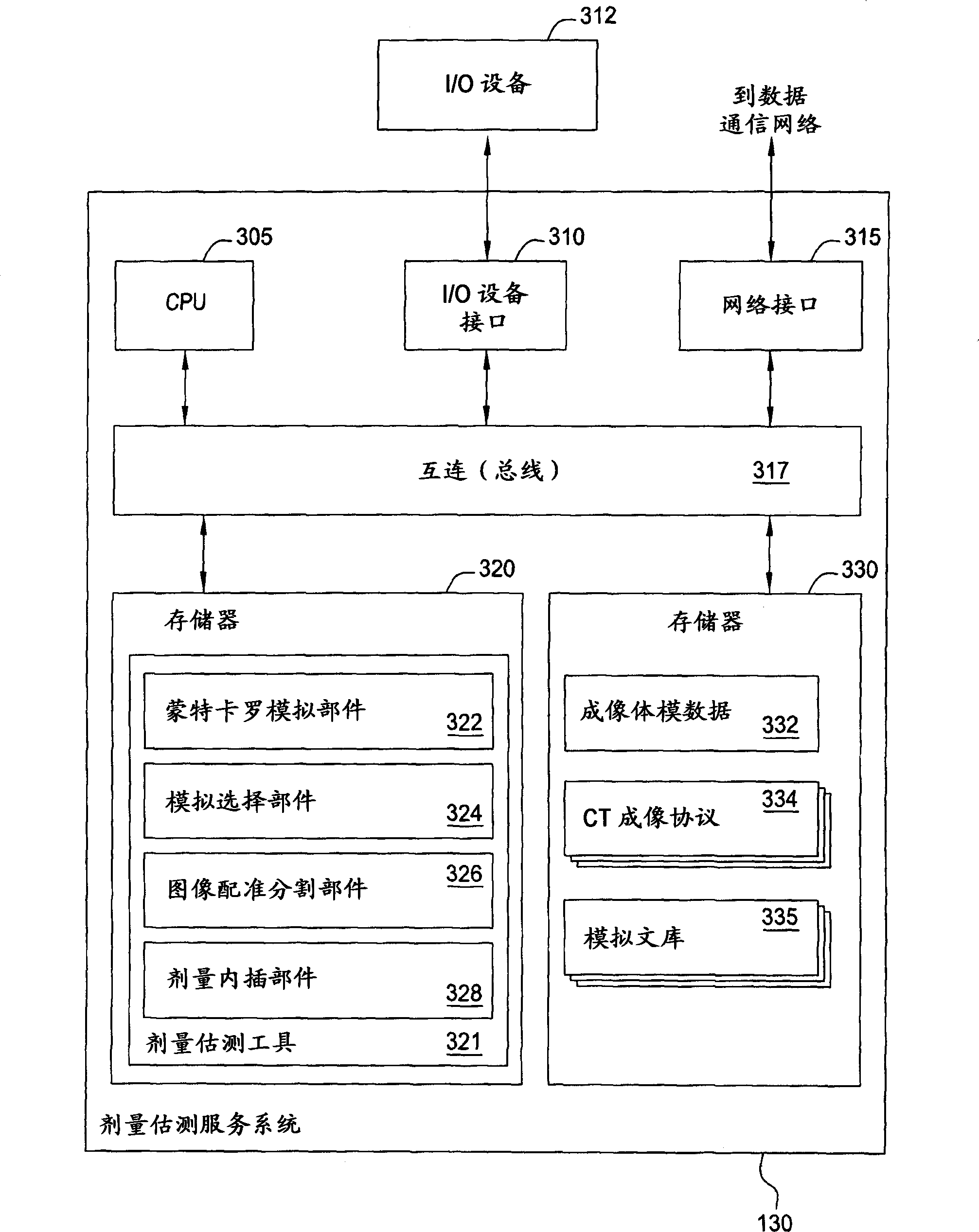
Generating a suitable model for estimating patient radiation dose resulting from medical imaging scans
Techniques are disclosed for estimating patient radiation exposure during computerized tomography (CT) scans. More specifically, embodiments of the invention provide efficient approaches for generating a suitable patient model used to make such an estimate, to approaches for estimating patient dose by interpolating the results of multiple simulations, and to approaches for a service provider to host a dose estimation service made available to multiple CT scan providers.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Method and system to facilitate neurostimulator programming based on pre-existing therapy profiles
ActiveUS8918177B2Increase probabilityAccelerated programInternal electrodesExternal electrodesPatient modelEmergency medicine
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
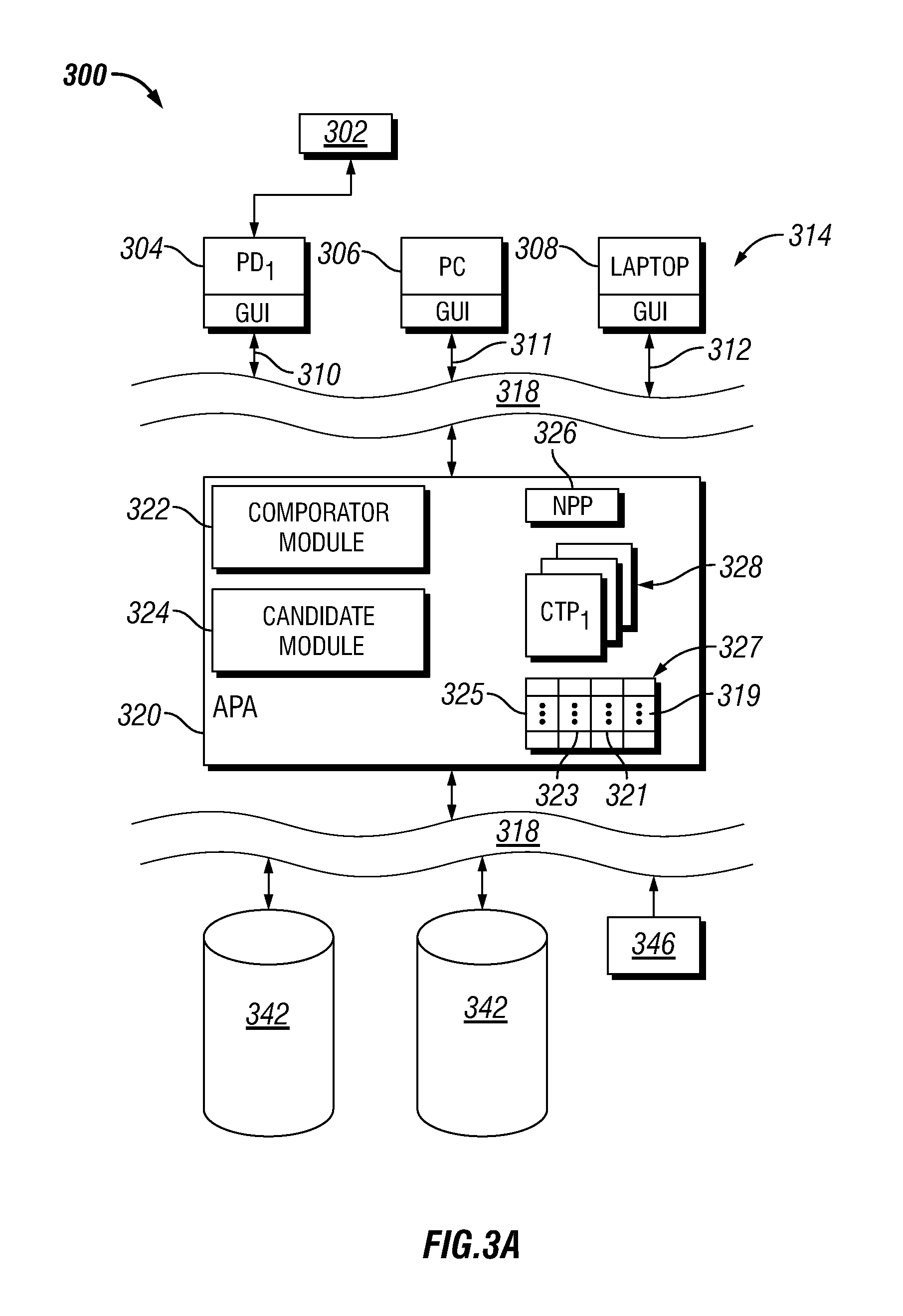
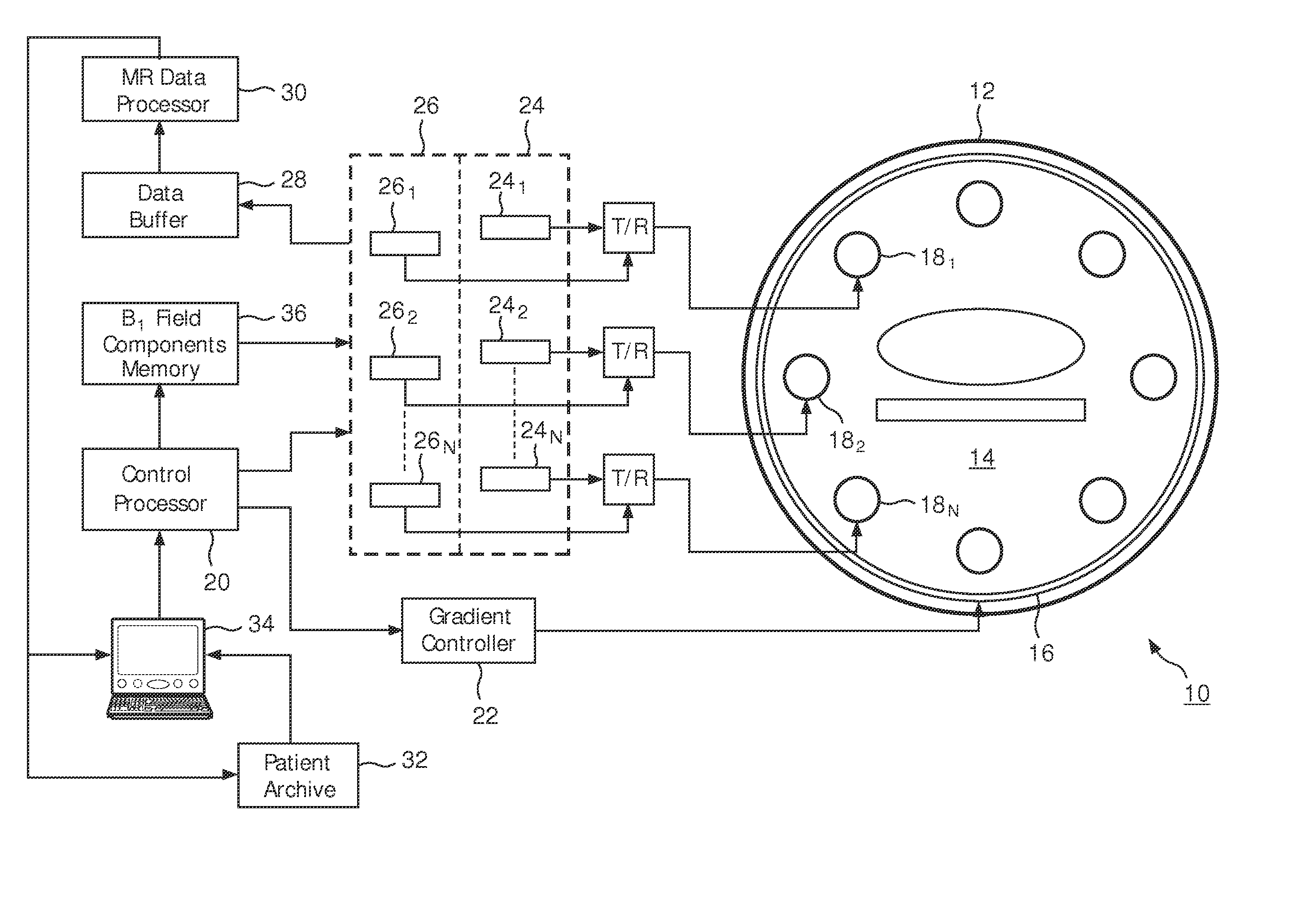
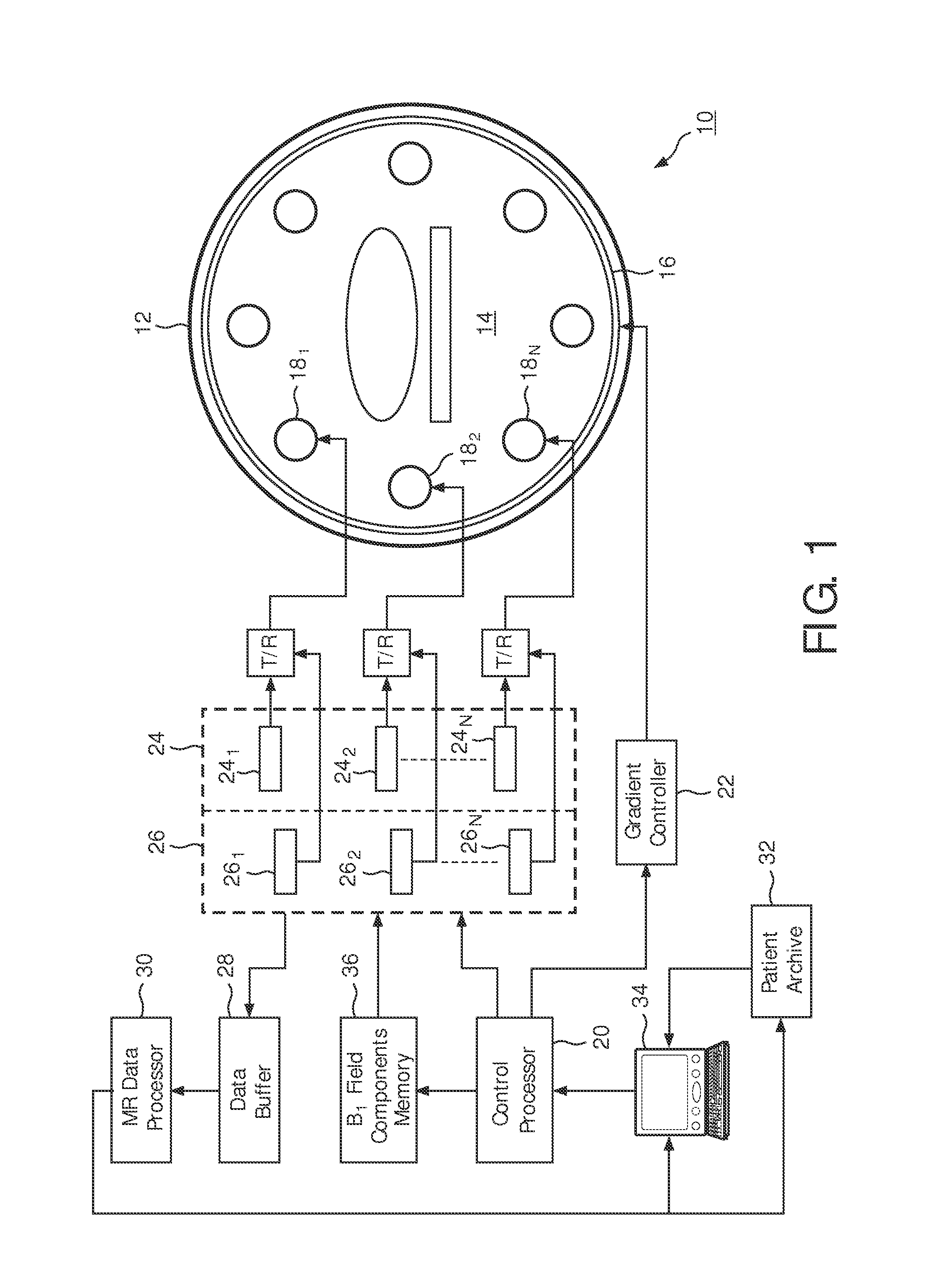
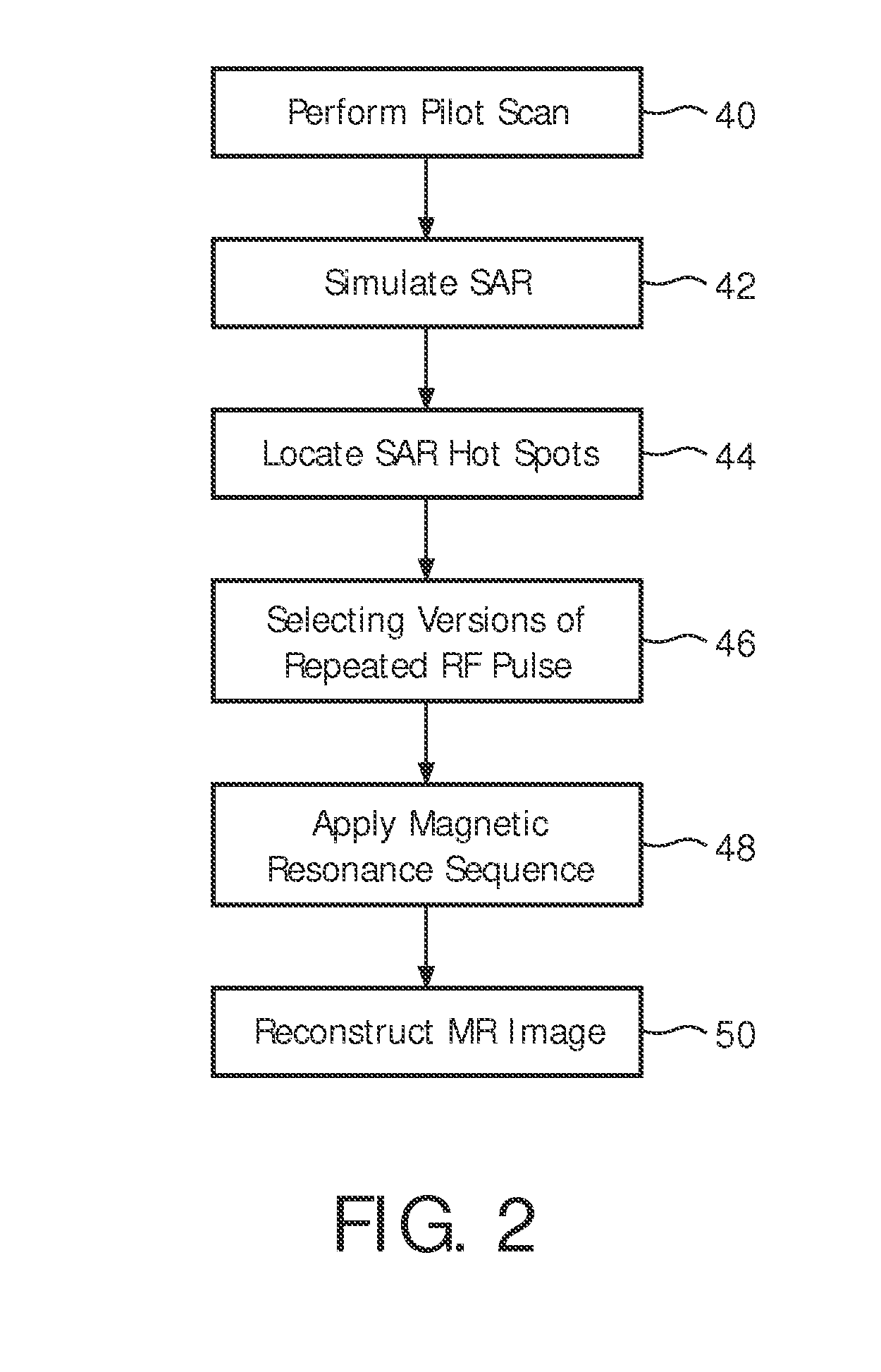
SAR hotspot reduction by temporal averaging in parallel transmission MRI
ActiveUS20120013337A1Increased duty cycleIncreased flip angleElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRPatient modelSpecific absorption rate
A magnetic resonance sequence includes a repetitively applied radiofrequency B1 pulse capable of causing a specific absorption rate (SAR) hot spot. The composition of the repetitive B1 pulse is varied to generate versions of the repetitive B1 pulse such that the SAR hot spot changes locations with subsequent applications of the repetitive B1 pulse. To generate versions of the B1 pulse, a pilot scan is performed to generate a patient model. A simulation of the SAR response to each of the versions of the repetitive B1 pulse is performed to determine the location of SAR hot spot(s). A plurality of versions of the repetitive B1 pulse is selected to be used in the magnetic resonance sequence.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for delivering a biphasic defibrillation pulse with variable energy
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Method for monitoring the X-ray dosage administered to a patient by a radiation source when using an X-ray device, and X-ray device
ActiveUS8611499B2Comprehensible and quick to graspEase of evaluationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPatient modelSoft x ray
A method for monitoring the X-ray dosage administered to a patient by a radiation source when using an X-ray device is proposed. The X-ray device is in particular a C-arm X-ray device. A location-dependent dosage value on the surface of the patient is determined with reference to parameters which describe the recording geometry and the radiation that is administered. The surface is described by a patient model in particular. A representation of the dosage value and / or of a value derived therefrom is displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and System of Scanner Automation for X-Ray Tube with 3D Camera
A method and apparatus for X-ray tube scanner automation using a 3D camera is disclosed. An RGBD image of a patient on a patient table is received from a 3D camera mounted on an X-ray tube. A transformation between a coordinate system of the 3D camera and a coordinate system of the patient table is calculated. A patient model is estimated from the RGBD image of the patient. The X-ray tube is automatically controlled to acquire an X-ray image of a region of interest of the patient based on the patient model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system of scanner automation for X-ray tube with 3D camera
A method and apparatus for X-ray tube scanner automation using a 3D camera is disclosed. An RGBD image of a patient on a patient table is received from a 3D camera mounted on an X-ray tube. A transformation between a coordinate system of the 3D camera and a coordinate system of the patient table is calculated. A patient model is estimated from the RGBD image of the patient. The X-ray tube is automatically controlled to acquire an X-ray image of a region of interest of the patient based on the patient model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com