Patents
Literature
65 results about "Patient dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
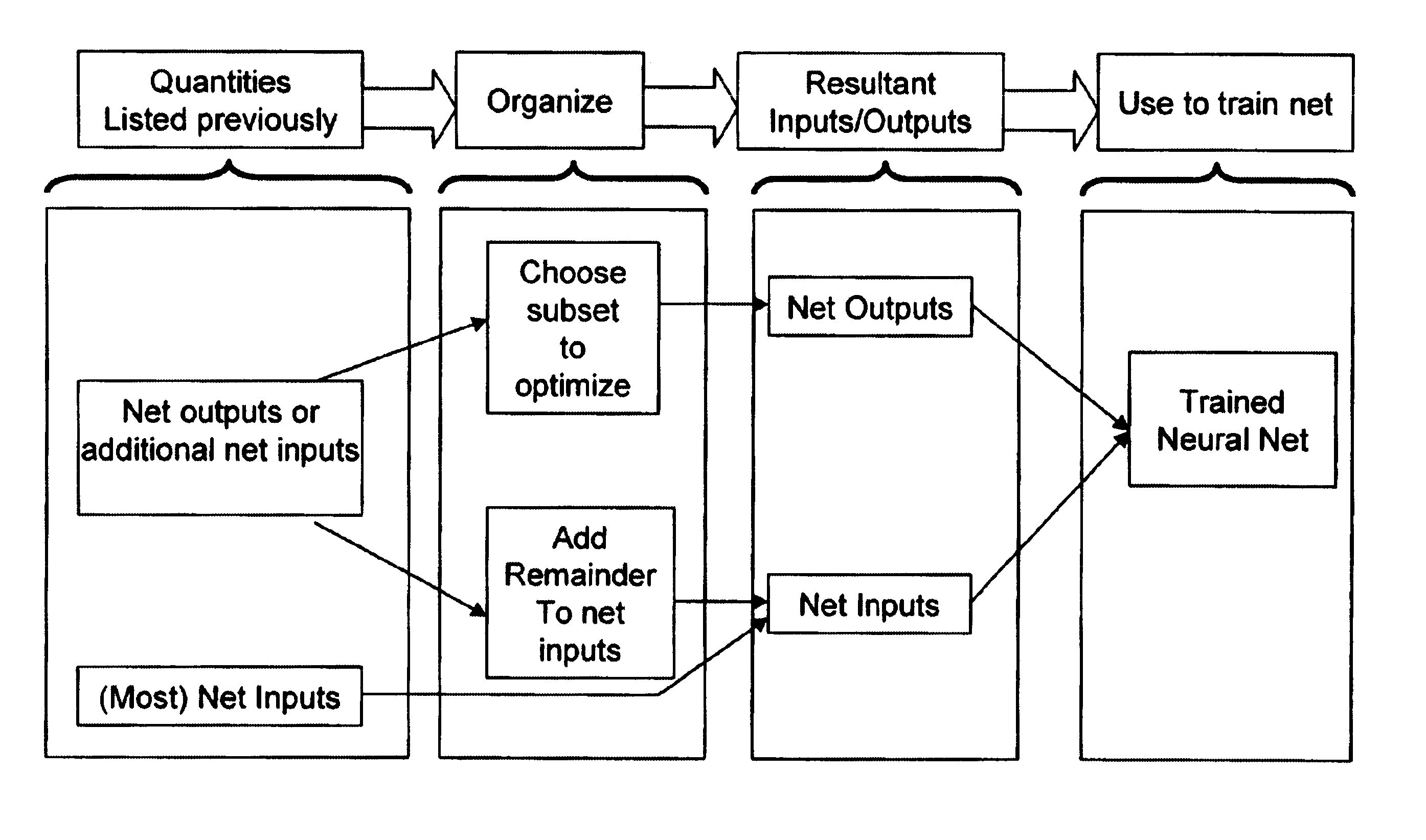
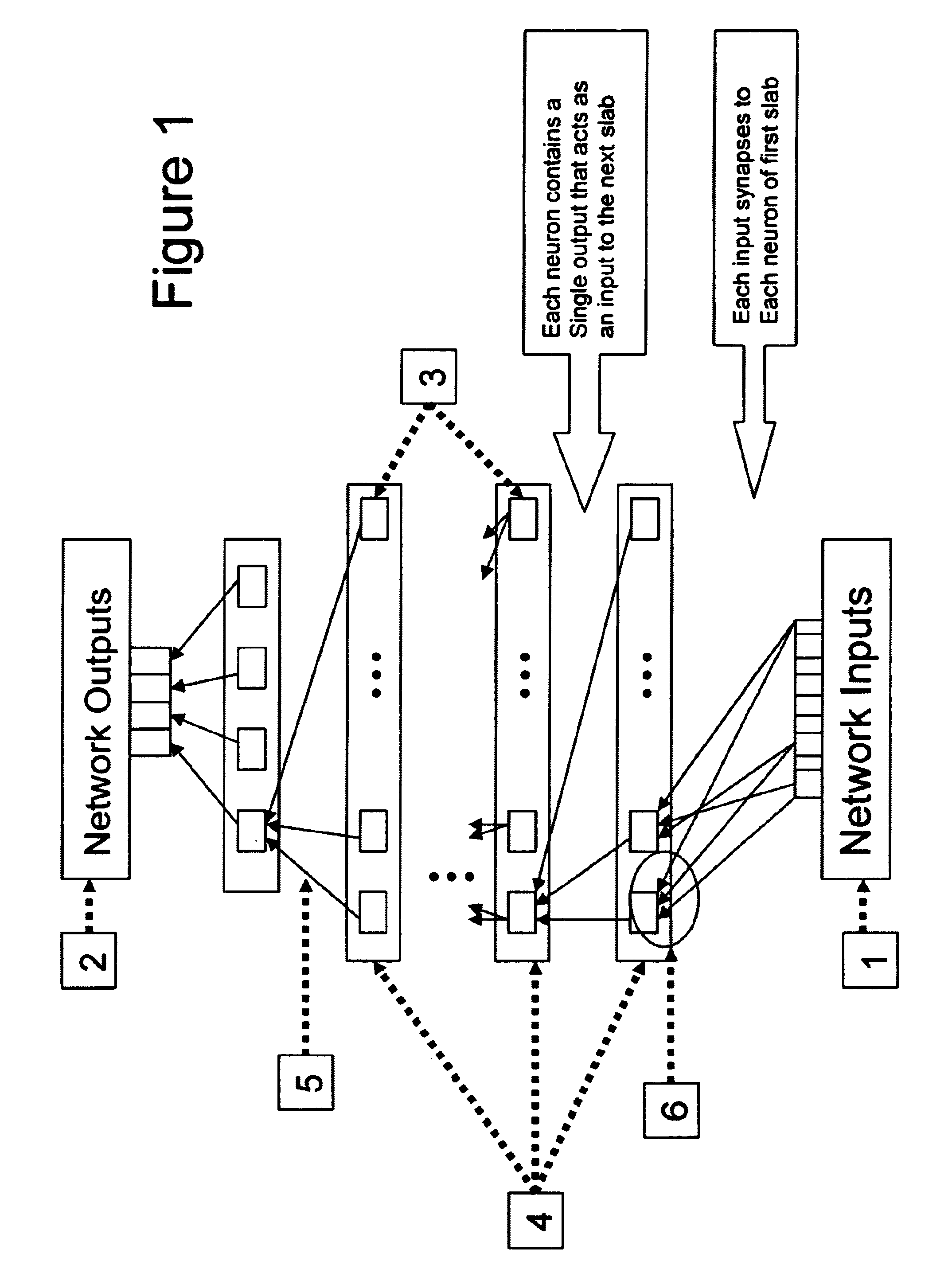
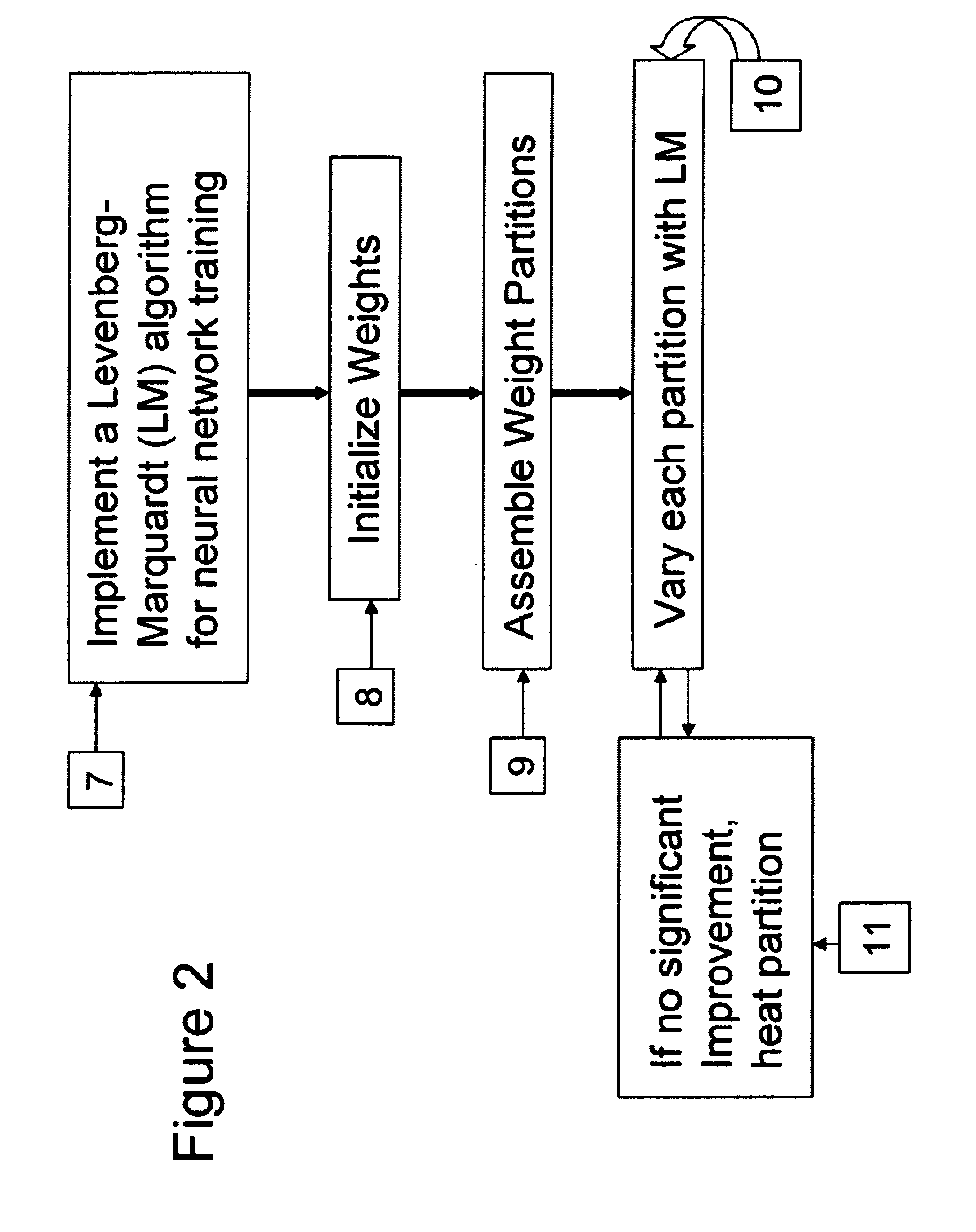
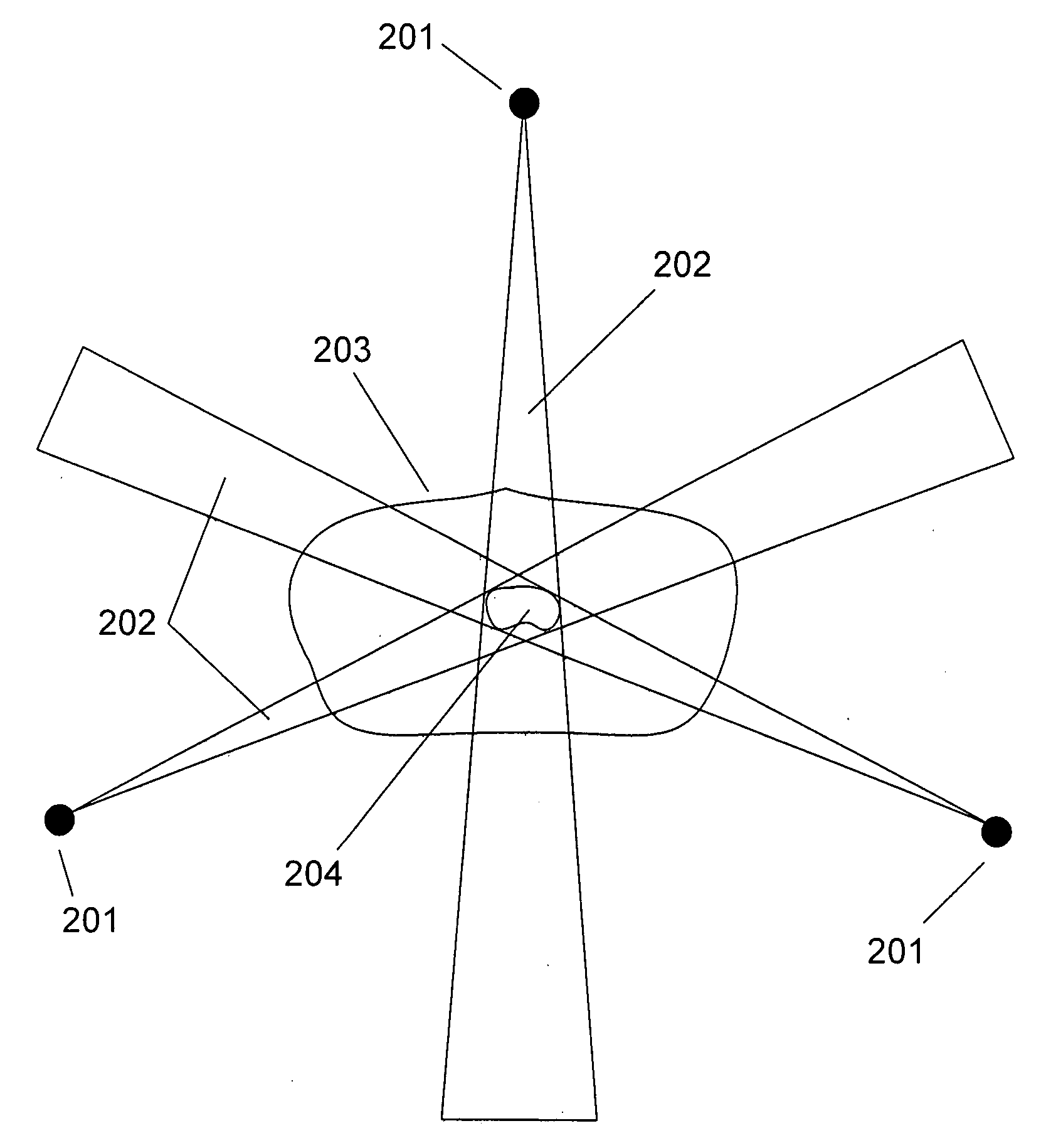
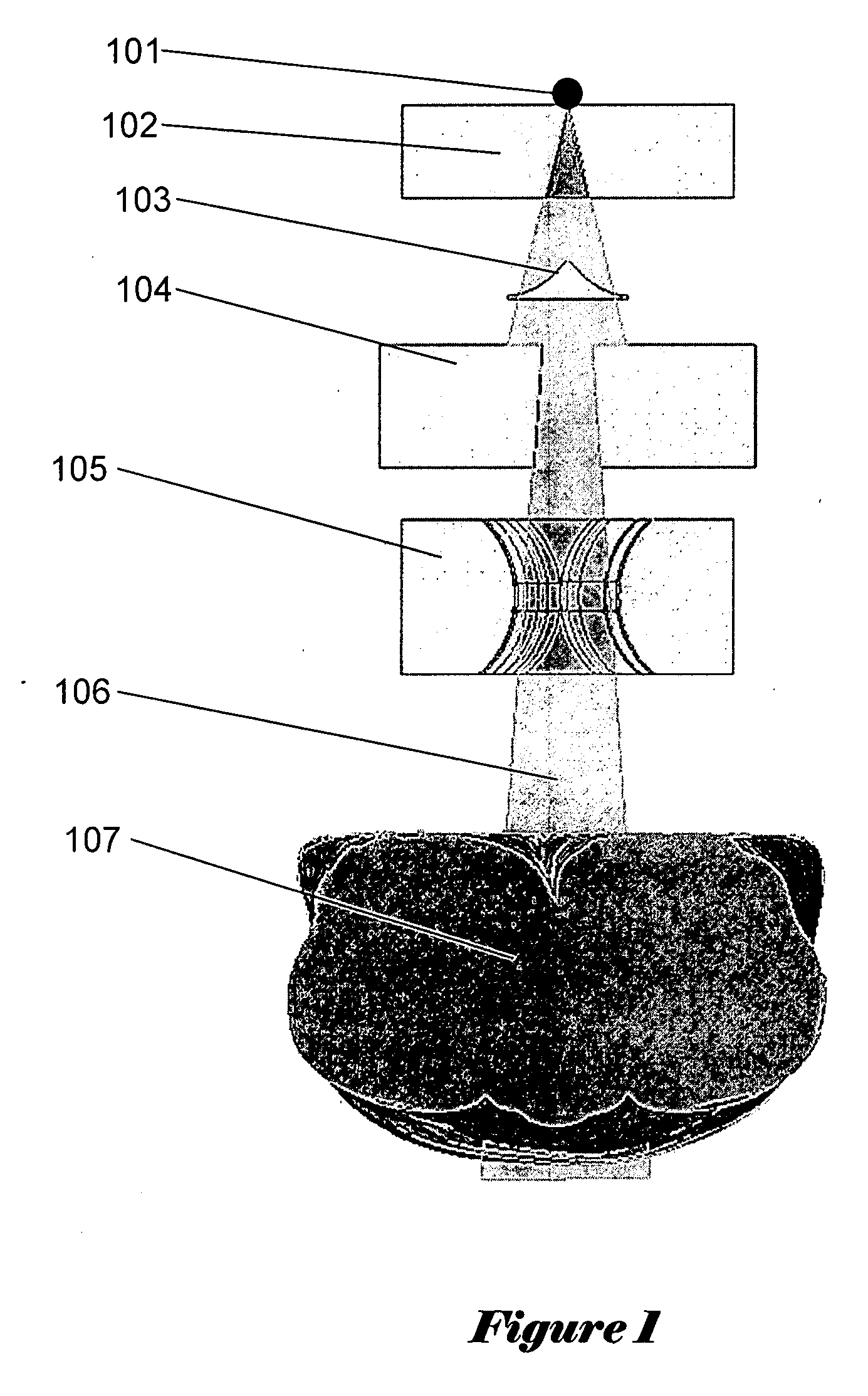
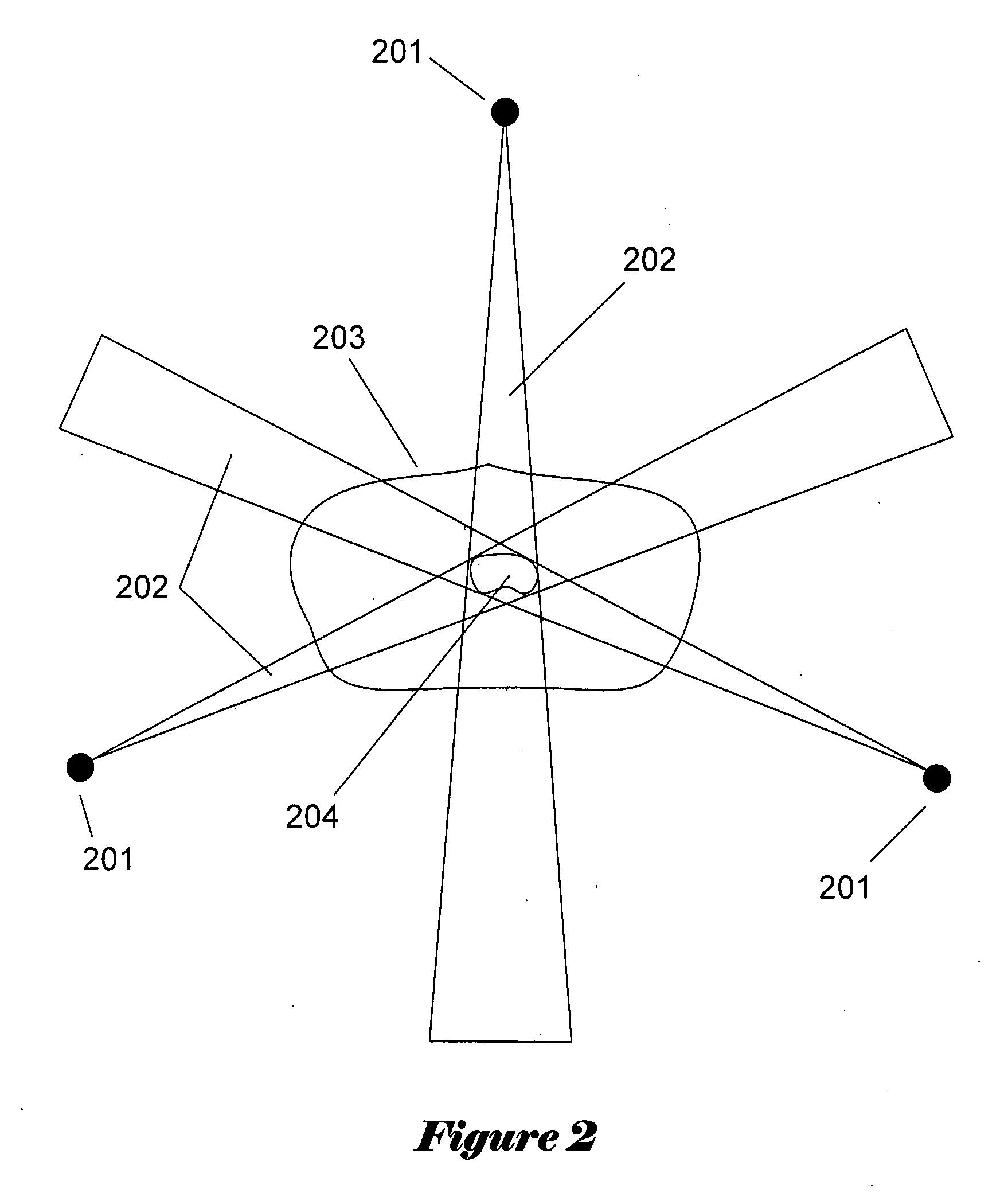
Neural network drug dosage estimation
InactiveUS6658396B1Improve accuracyGood precisionDrug and medicationsBiological neural network modelsNerve networkPatient characteristics
Neural networks are constructed (programmed), trained on historical data, and used to predict any of (1) optimal patient dosage of a single drug, (2) optimal patient dosage of one drug in respect of the patient's concurrent usage of another drug, (3a) optimal patient drug dosage in respect of diverse patient characteristics, (3b) sensitivity of recommended patient drug dosage to the patient characteristics, (4a) expected outcome versus patient drug dosage, (4b) sensitivity of the expected outcome to variant drug dosage(s), (5) expected outcome(s) from drug dosage(s) other than the projected optimal dosage. Both human and economic costs of both optimal and sub-optimal drug therapies may be extrapolated from the exercise of various optimized and trained neural networks. Heretofore little recognized sensitivities-such as, for example, patient race in the administration of psychotropic drugs-are made manifest. Individual prescribing physicians employing deviant patterns of drug therapy may be recognized. Although not intended to prescribe drugs, nor even to set prescription drug dosage, the neural networks are very sophisticated and authoritative "helps" to physicians, and to physician reviewers, in answering "what if" questions.
Owner:PREDICTION SCI
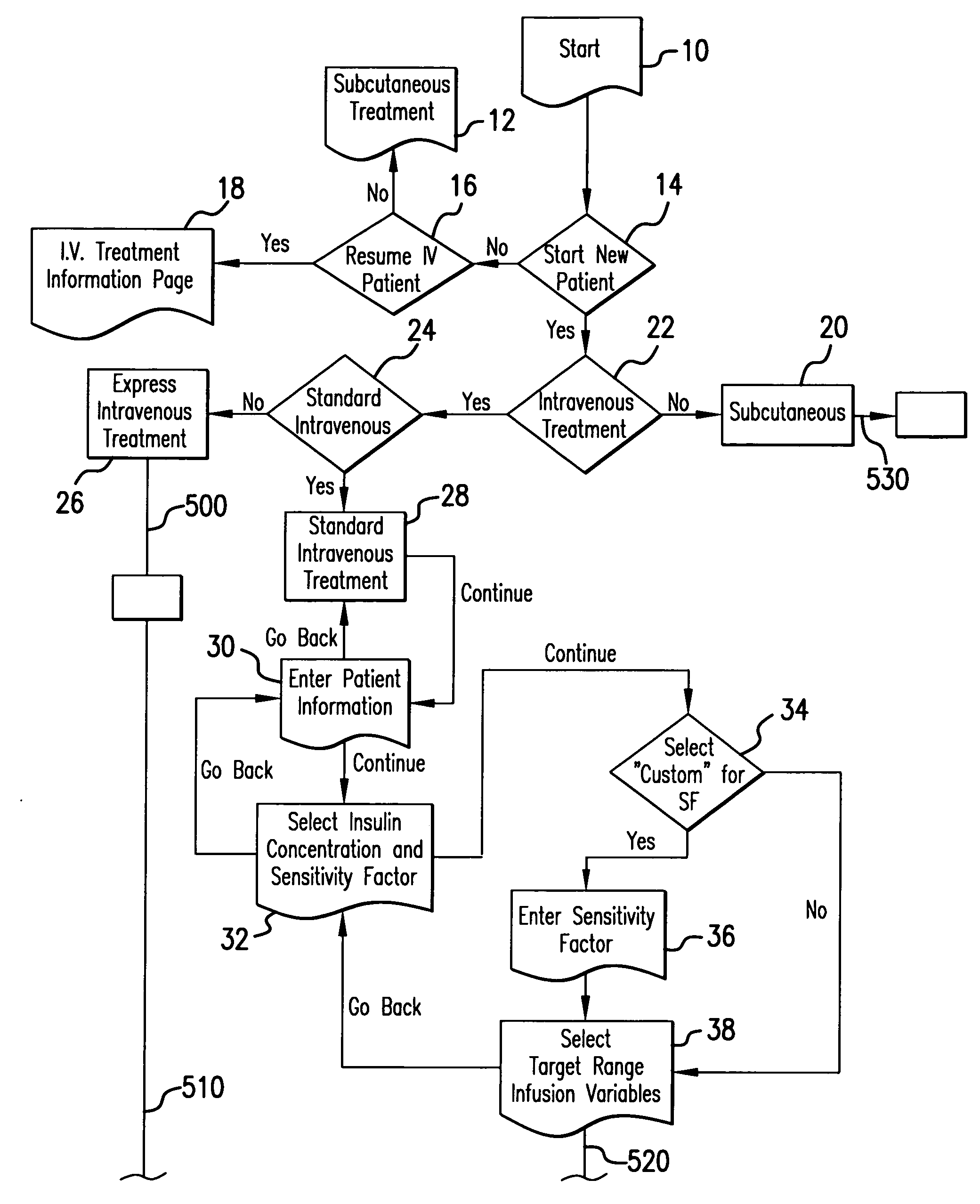
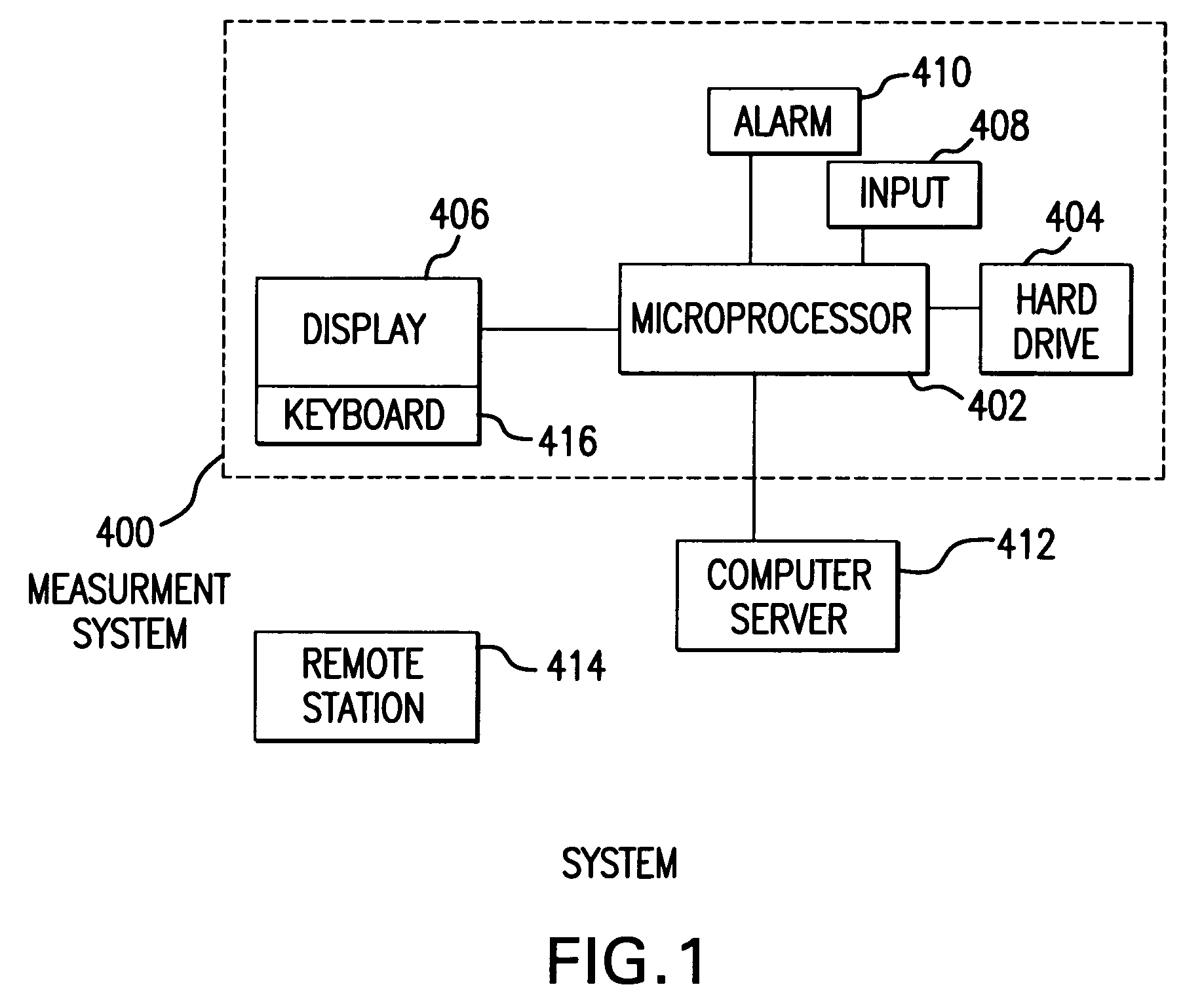
System and method for measuring and predicting insulin dosing rates
InactiveUS20070078314A1Efficient managementDrug and medicationsMedical automated diagnosisPatient dataGlucose polymers
The method and system for managing a patient's blood glucose level predicts an insulin dosing rate to bring a patient's blood glucose level into a preferred target range within a predetermined time interval. The system includes a processor which actuates a blood glucose computer program to measure and predict the patient's blood glucose level. An input mechanism allows for insertion of a preferred target range of the patient's blood glucose level and further permits input of various patient data parameters. The processor calculates the optimum insulin dosing rate for the patient based upon the type of insulin dosing whether it be intravenous dosing and / or subcutaneous dosing. A display mechanism displays the patient dosing parameters and an alarm mechanism alerts a user when the patient's blood glucose level is outside of the preferred patient blood glucose target range.
Owner:GLUCOTEC
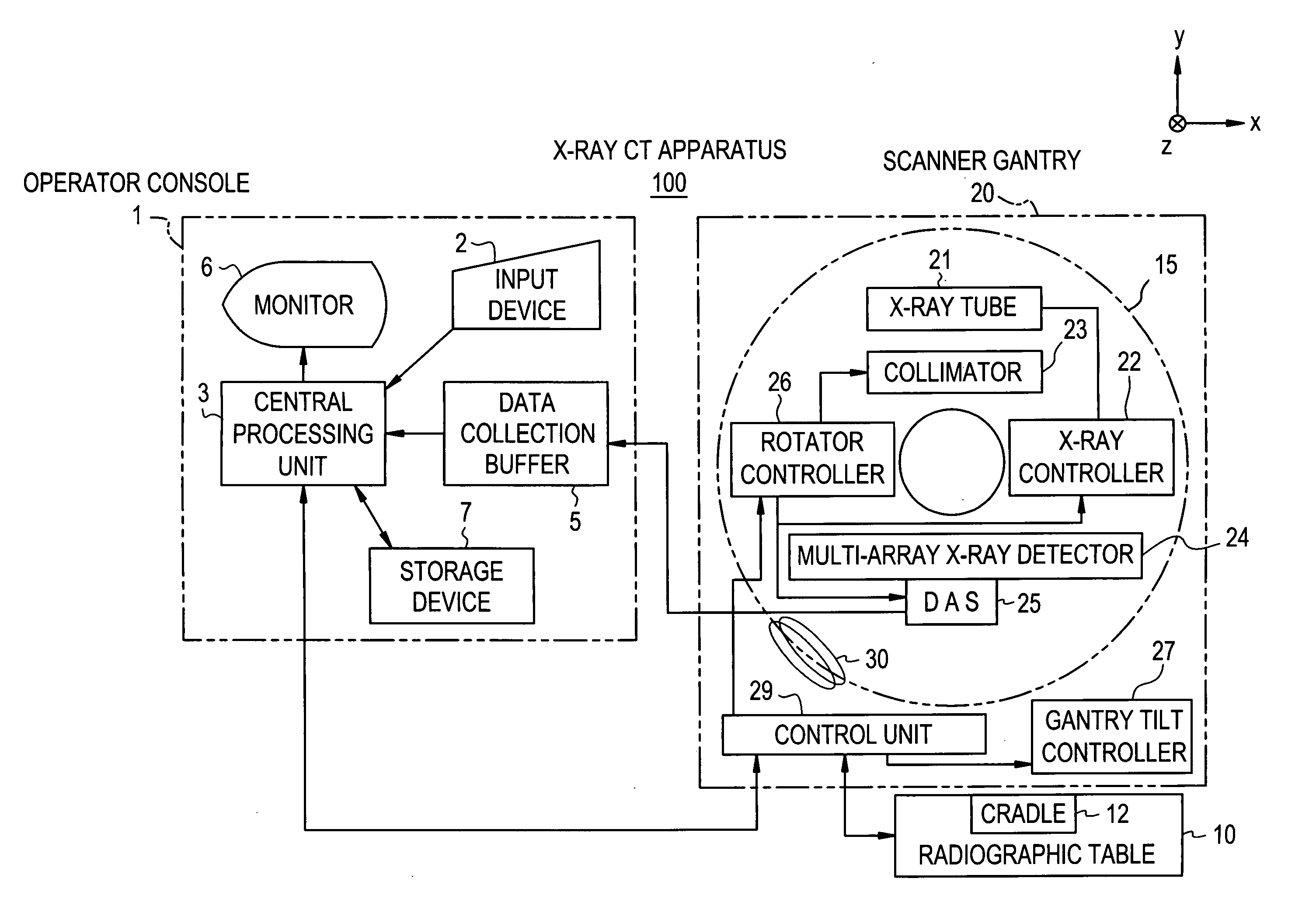
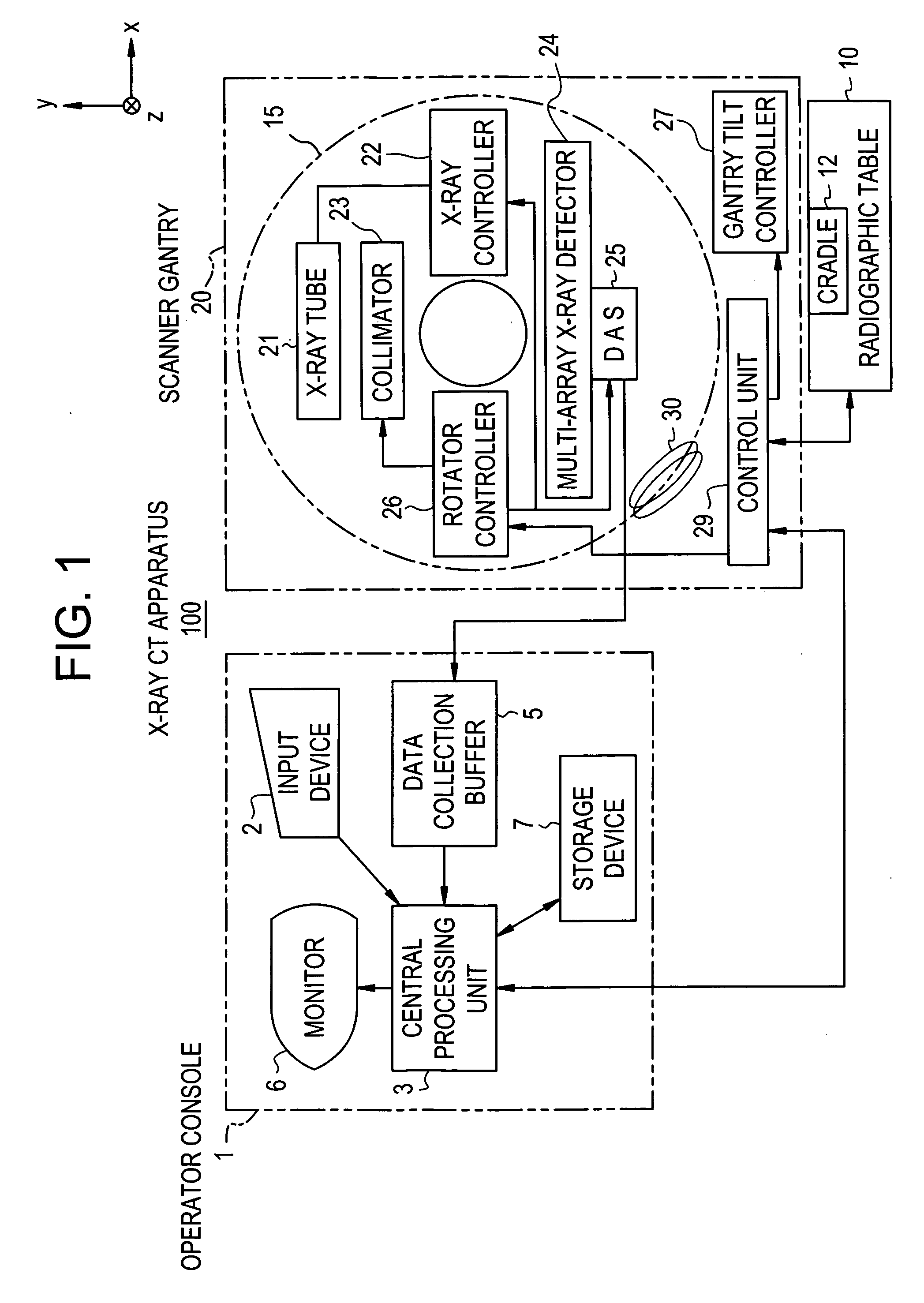
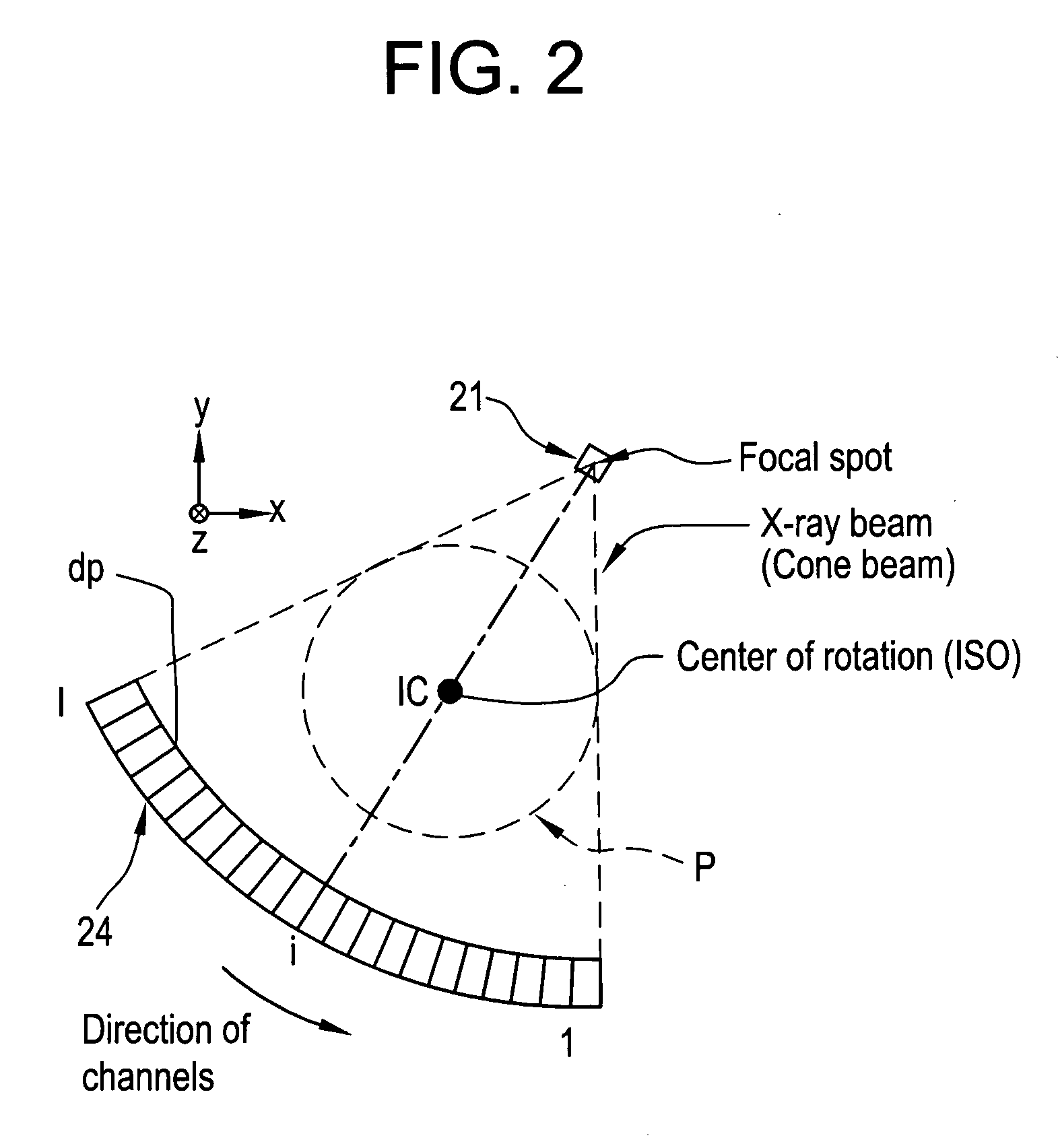
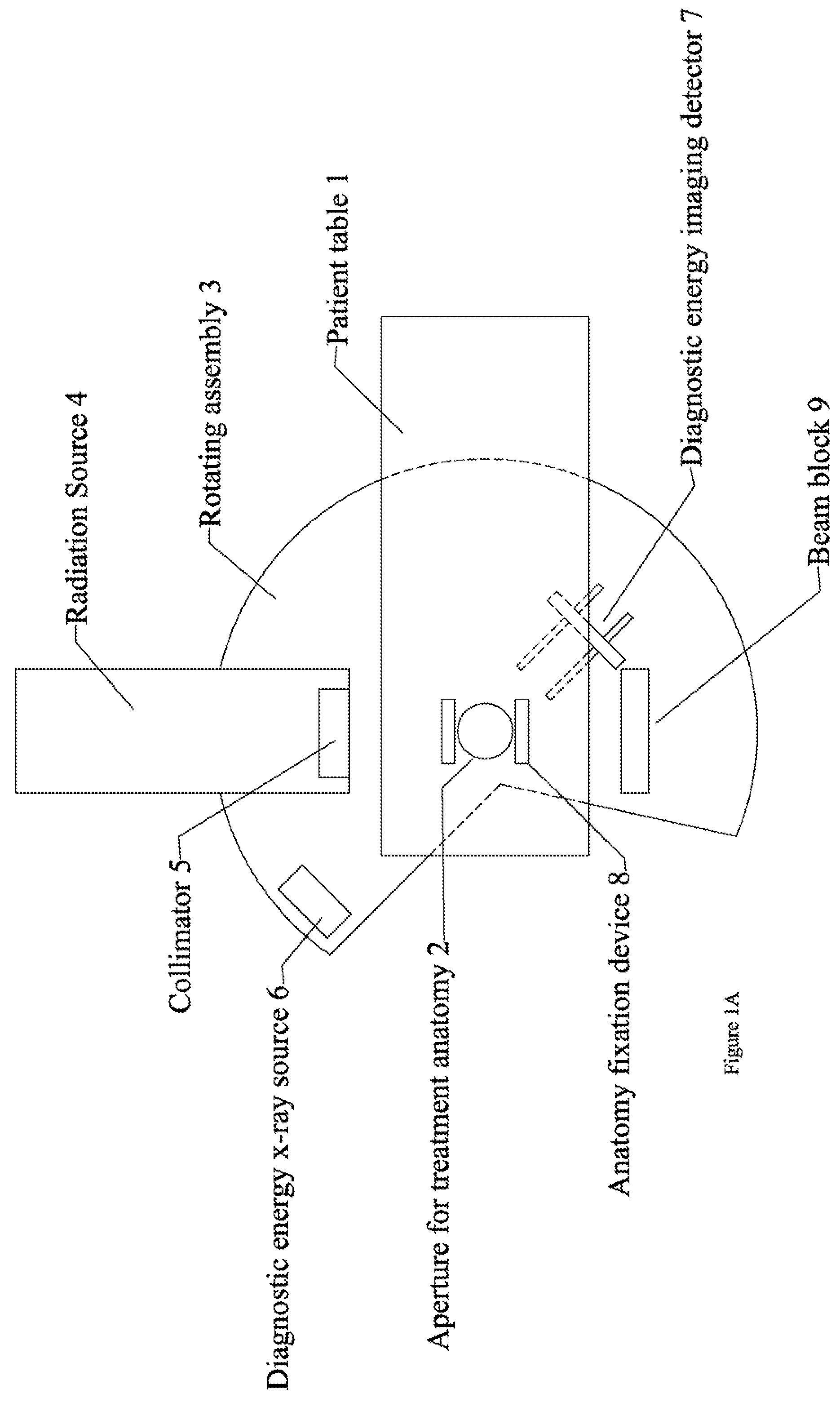
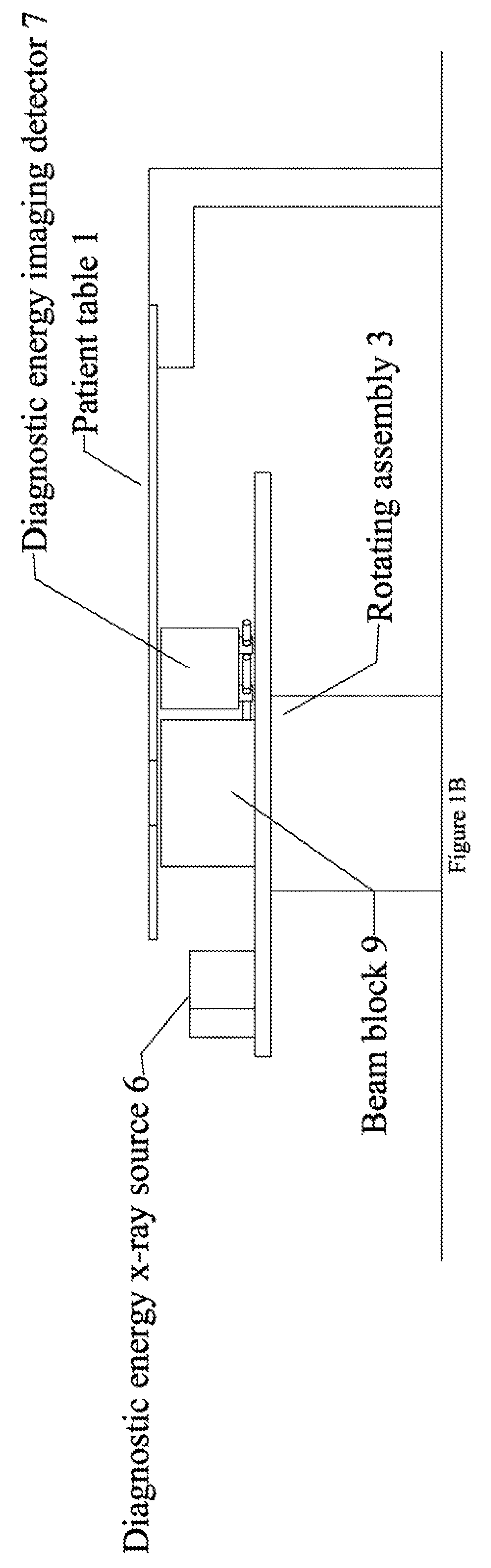
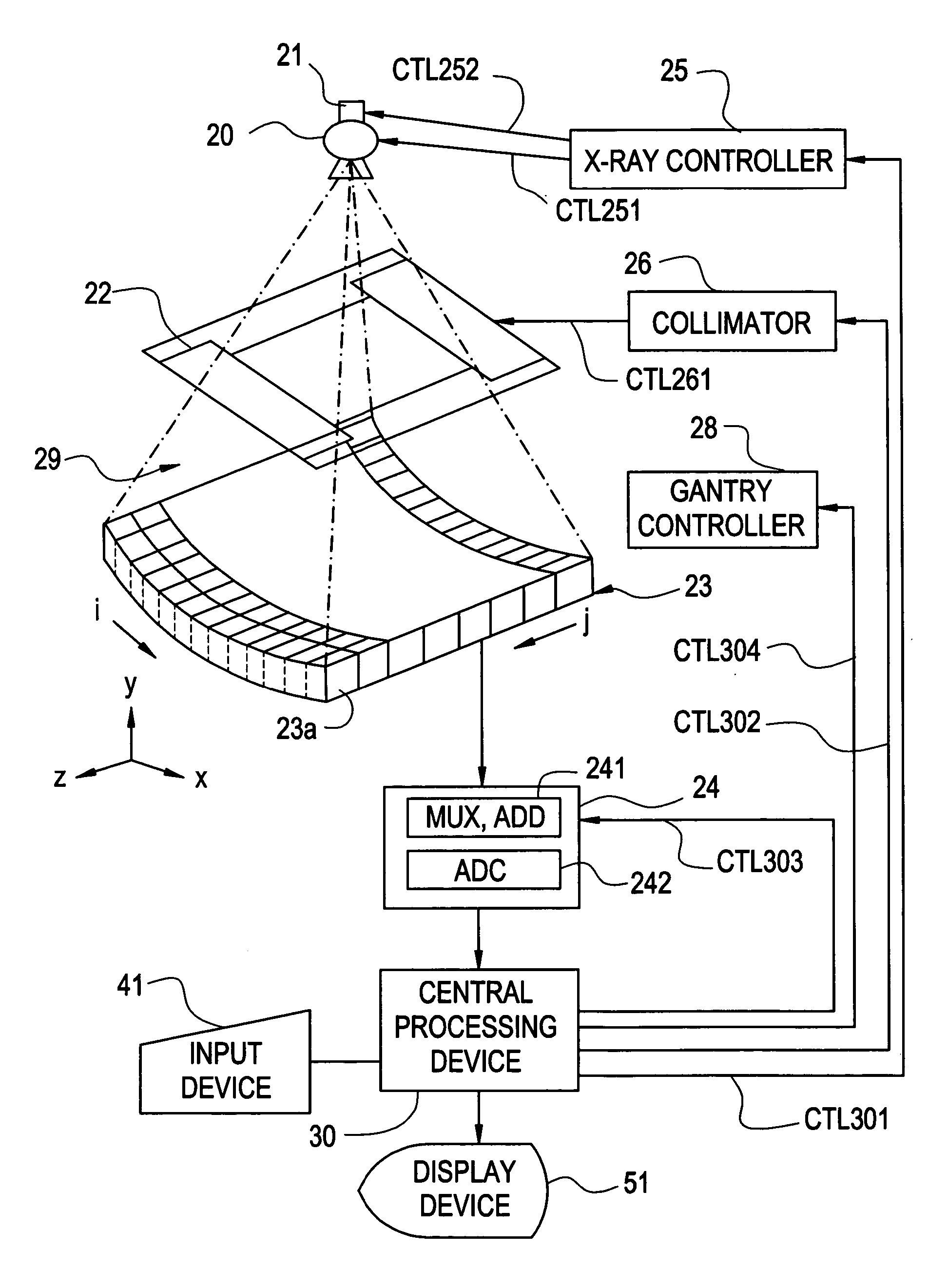
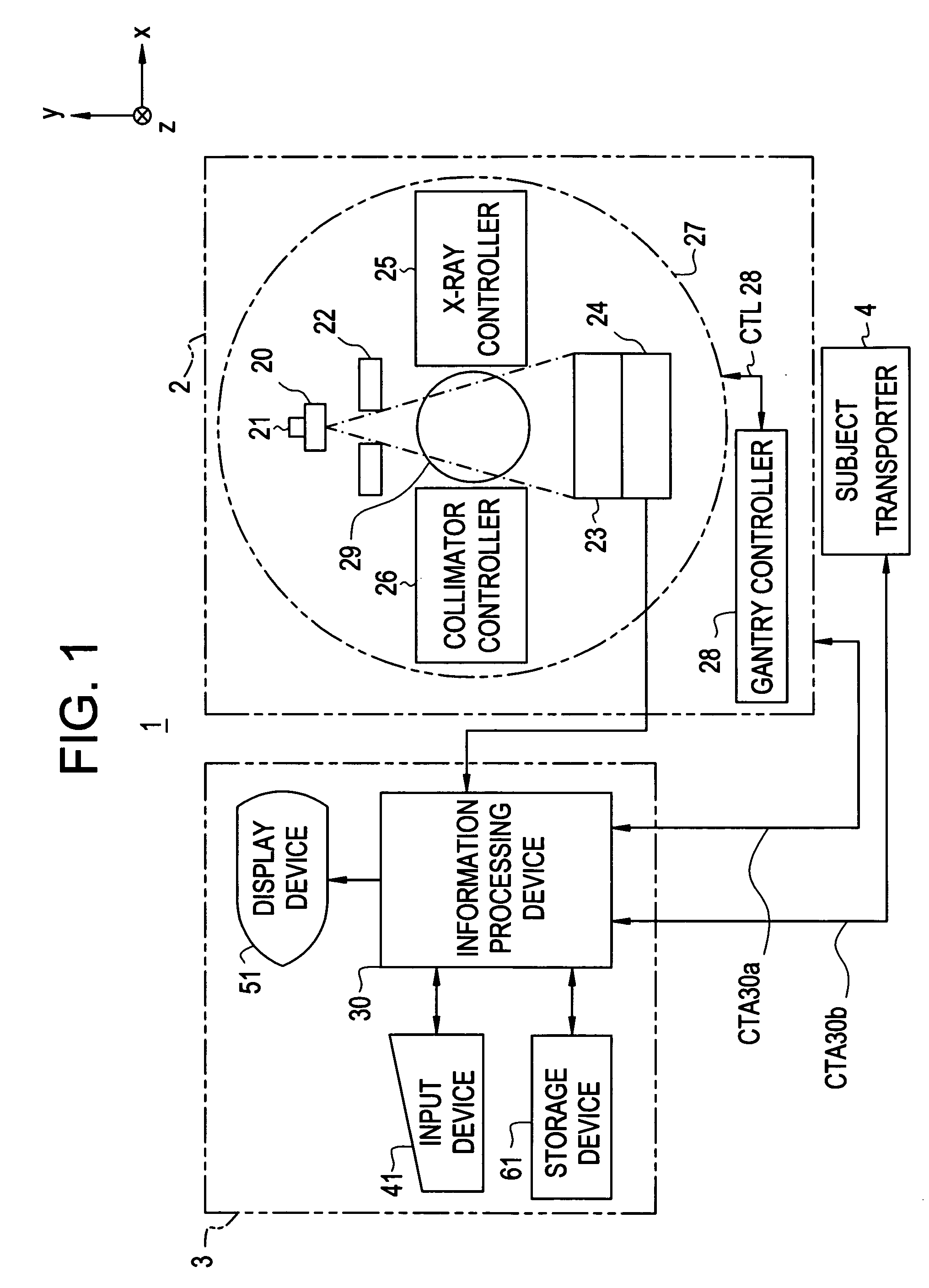
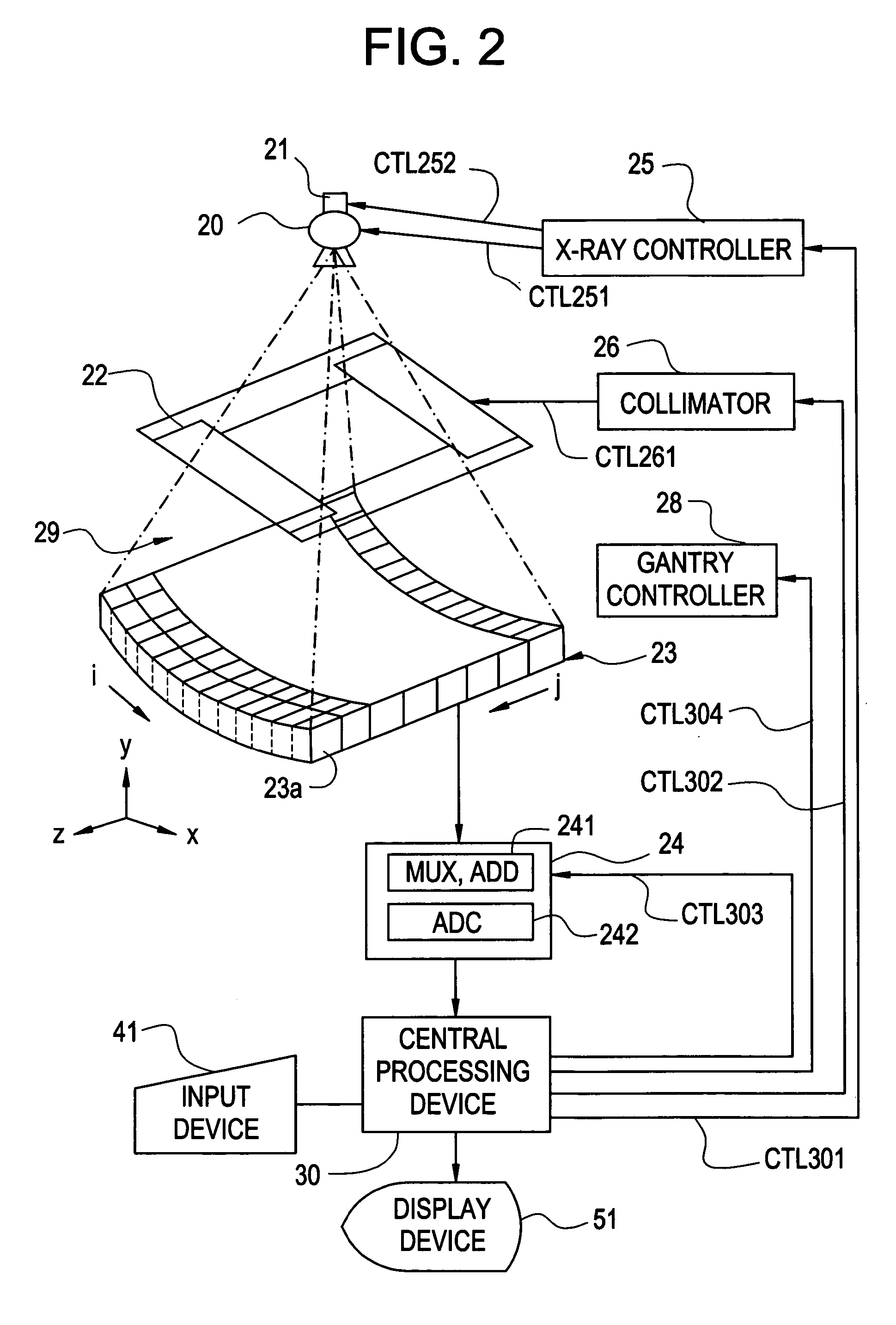
X-ray CT method and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20060291612A1Optimize radiographic conditionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-ray filterSlice thickness
In an X-ray CT apparatus, radiographic conditions (protocols) for imaging of each position represented by a z-coordinate are optimized in relation to an X-ray cone beam that spreads in a z direction. A slice thickness of a tomographic image is freely controlled in the z direction using a z filter during a conventional scan or a cine scan. For each tomographic image, a reconstruction function, an image filter, a scan field, a tomographic-image tilt angle, and a position of a tomographic image are freely adjusted or independently designated for scanning of each position in the z direction. Thus, a tomographic image is reconstructed. Moreover, the position of a beam formation X-ray filter in the z direction is shifted in order to optimize a patient dose that depends on the size of the scan field, and X-ray quality.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
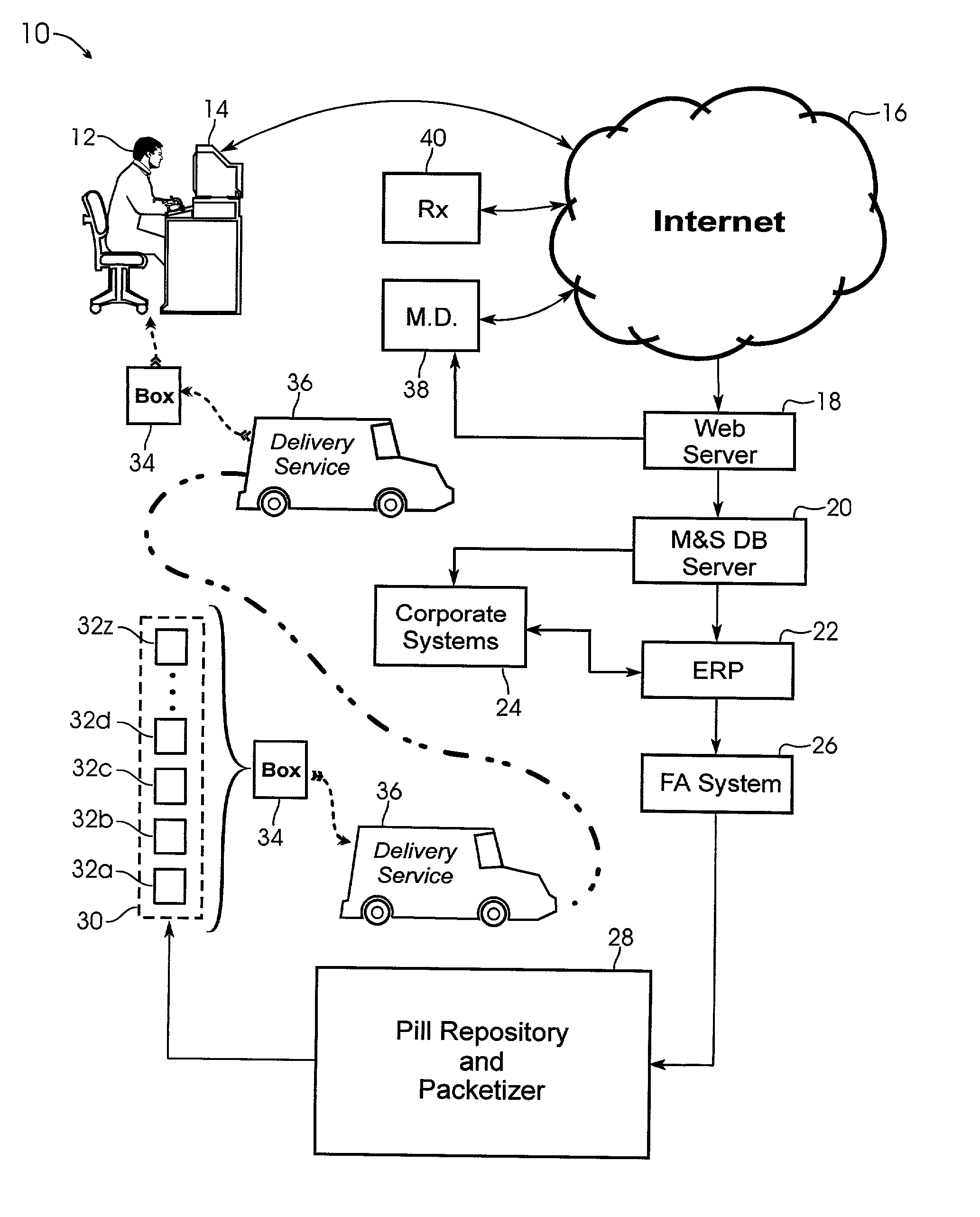
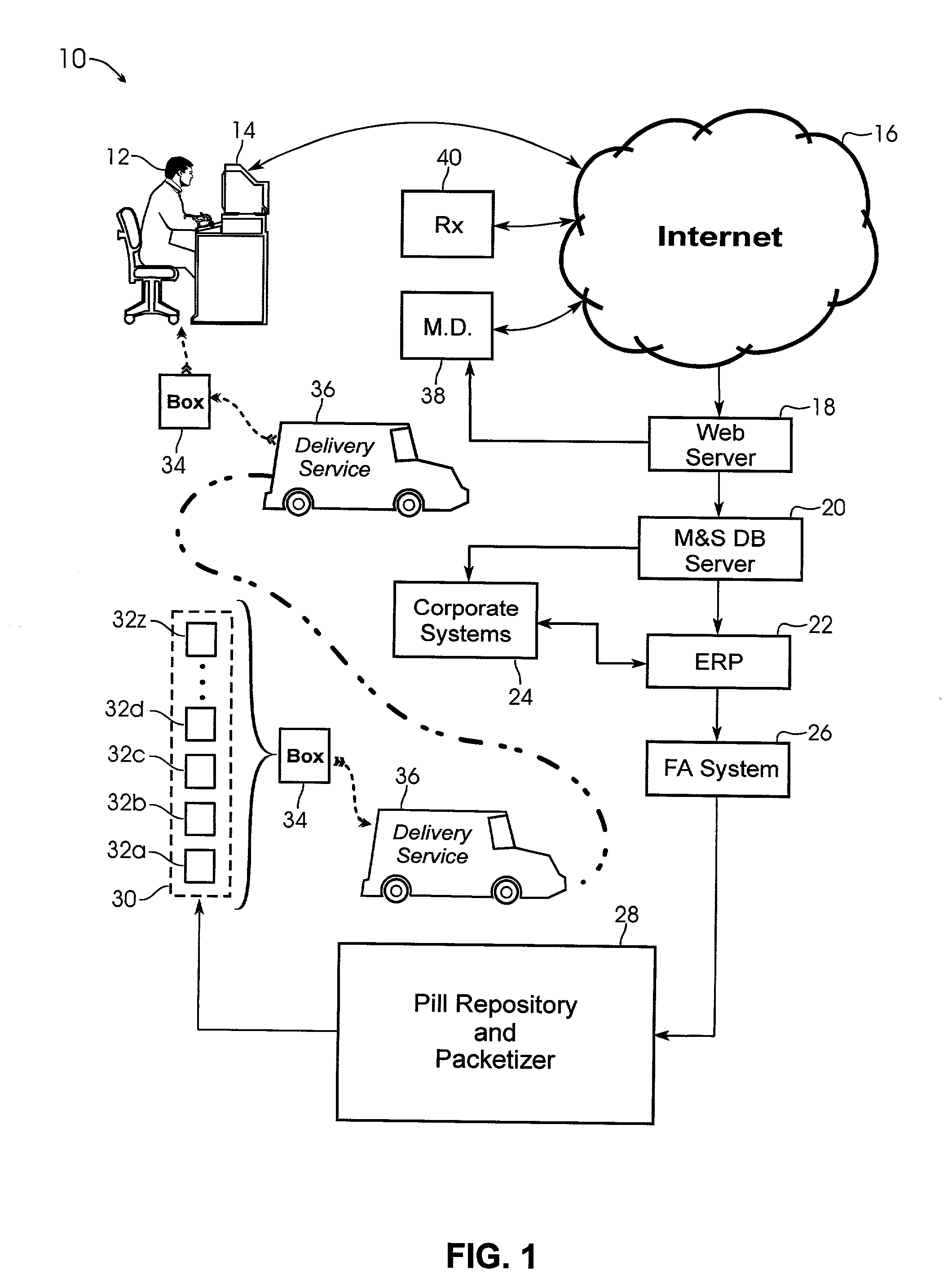
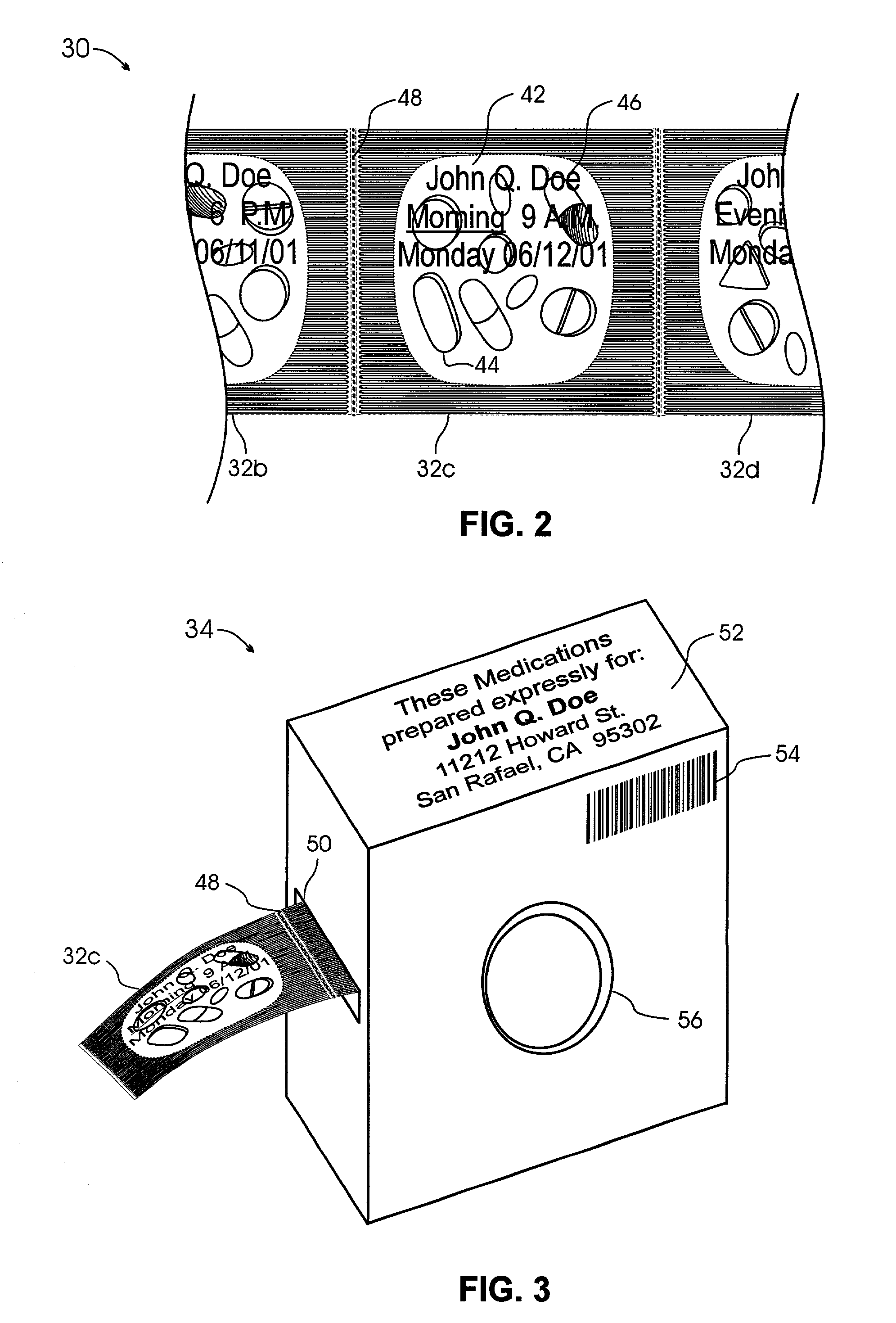
System and method for providing temporal patient dosing
InactiveUS20030200726A1Improve securityImprove reliabilityDrug and medicationsCoin-freed apparatusPersonalizationTime table
A system and method for creating a series of individualized custom doses for a consumer. The individualized doses being delivered in a package or packages, such that each individualized custom dose, comprising a plurality of medications and / or supplements, is individually separable from the remaining doses within the series. By way of example, and not of limitation, a system is described having a web based front-end interface within which the user may establish a dosing schedule, select supplements and / or medications (MS) from an MS database, elect which MS are to be included in each dose, and communicate the order to be processed by a packetizing system. The packetizing system utilizes a conveyance device which interconnects a series of pill dispensing bins. The conveyance device has compartments for collecting a series of doses which are then packetized and shipped for use by the consumer.
Owner:RAST RODGER H
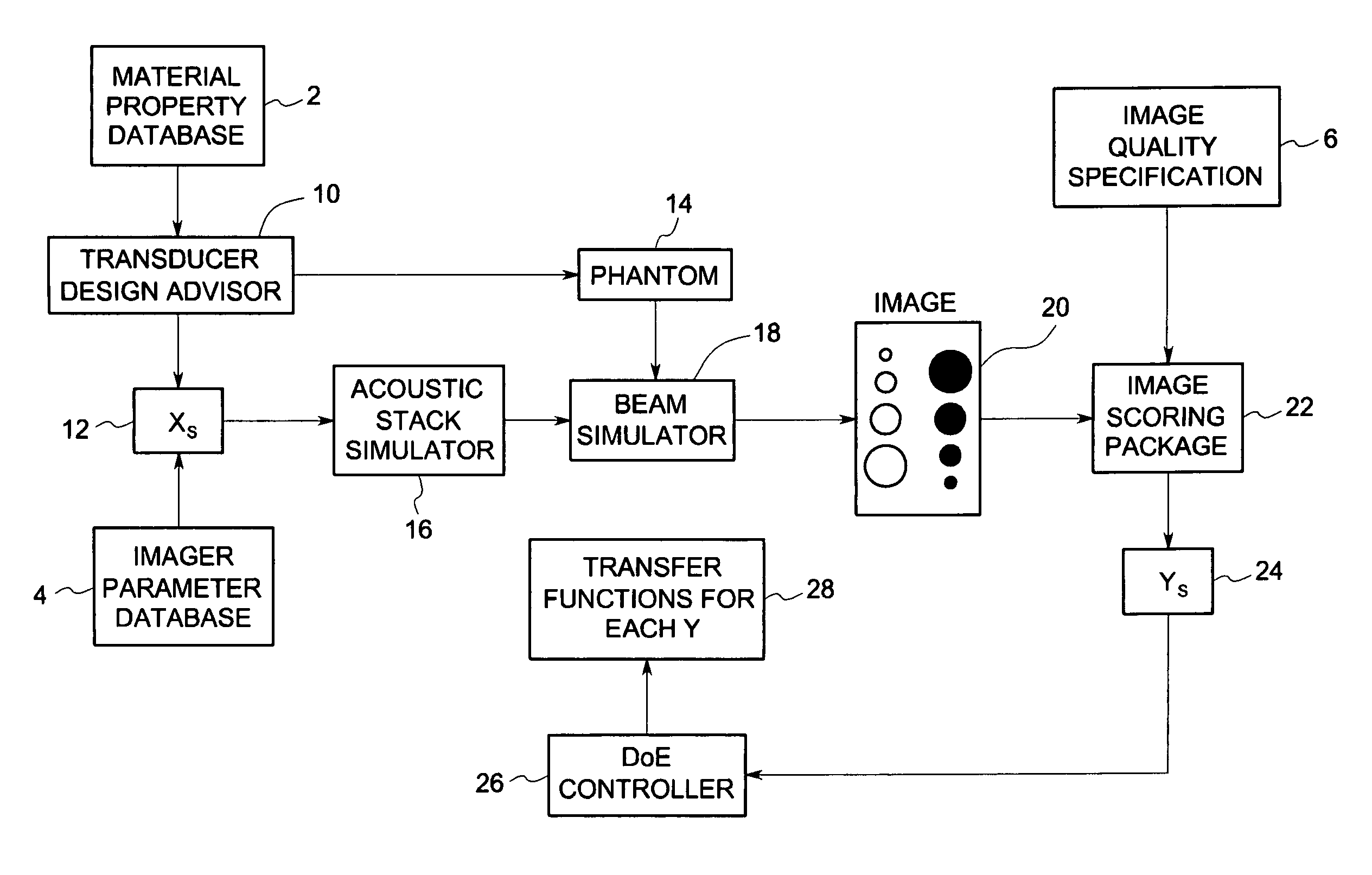
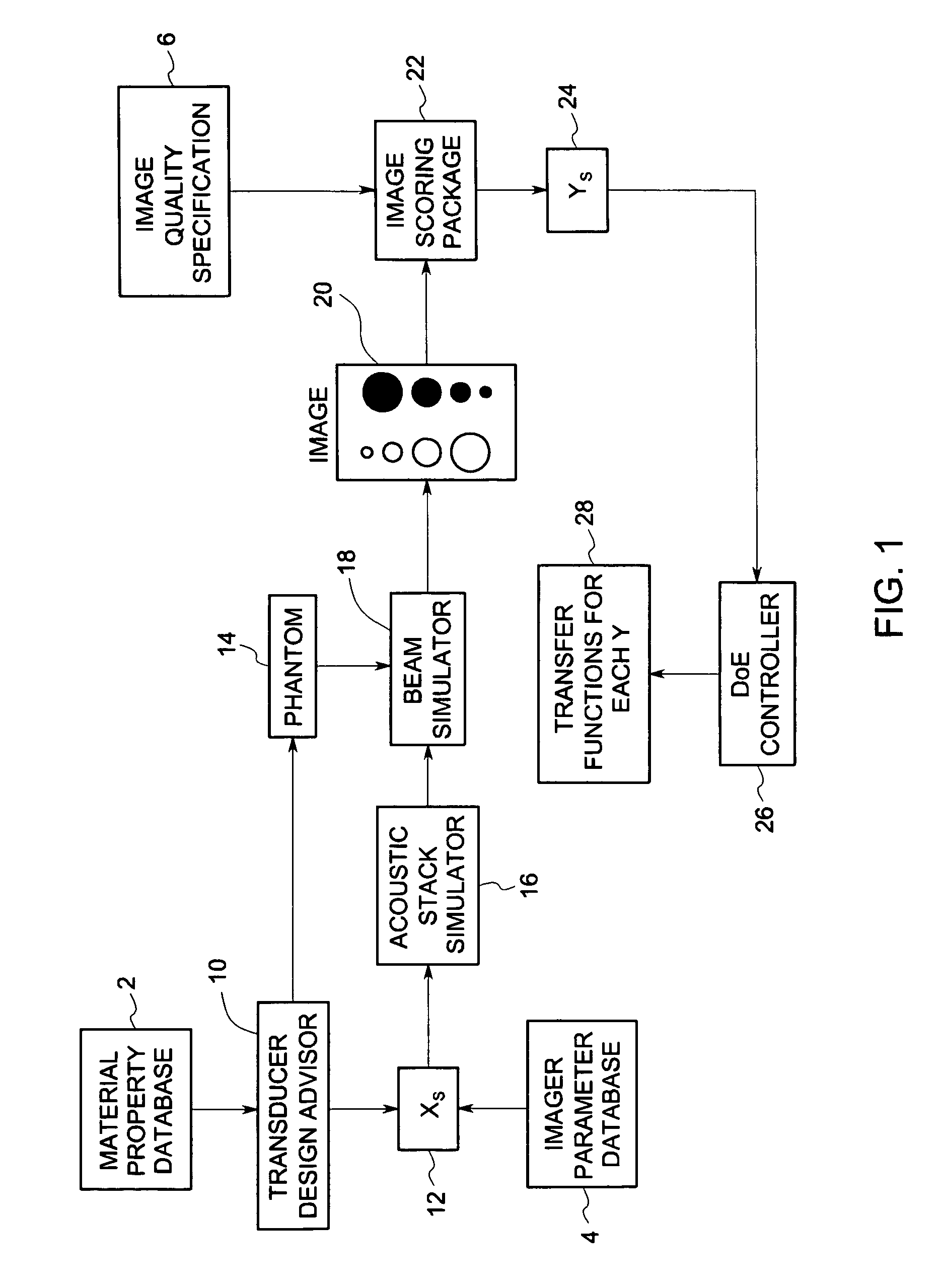
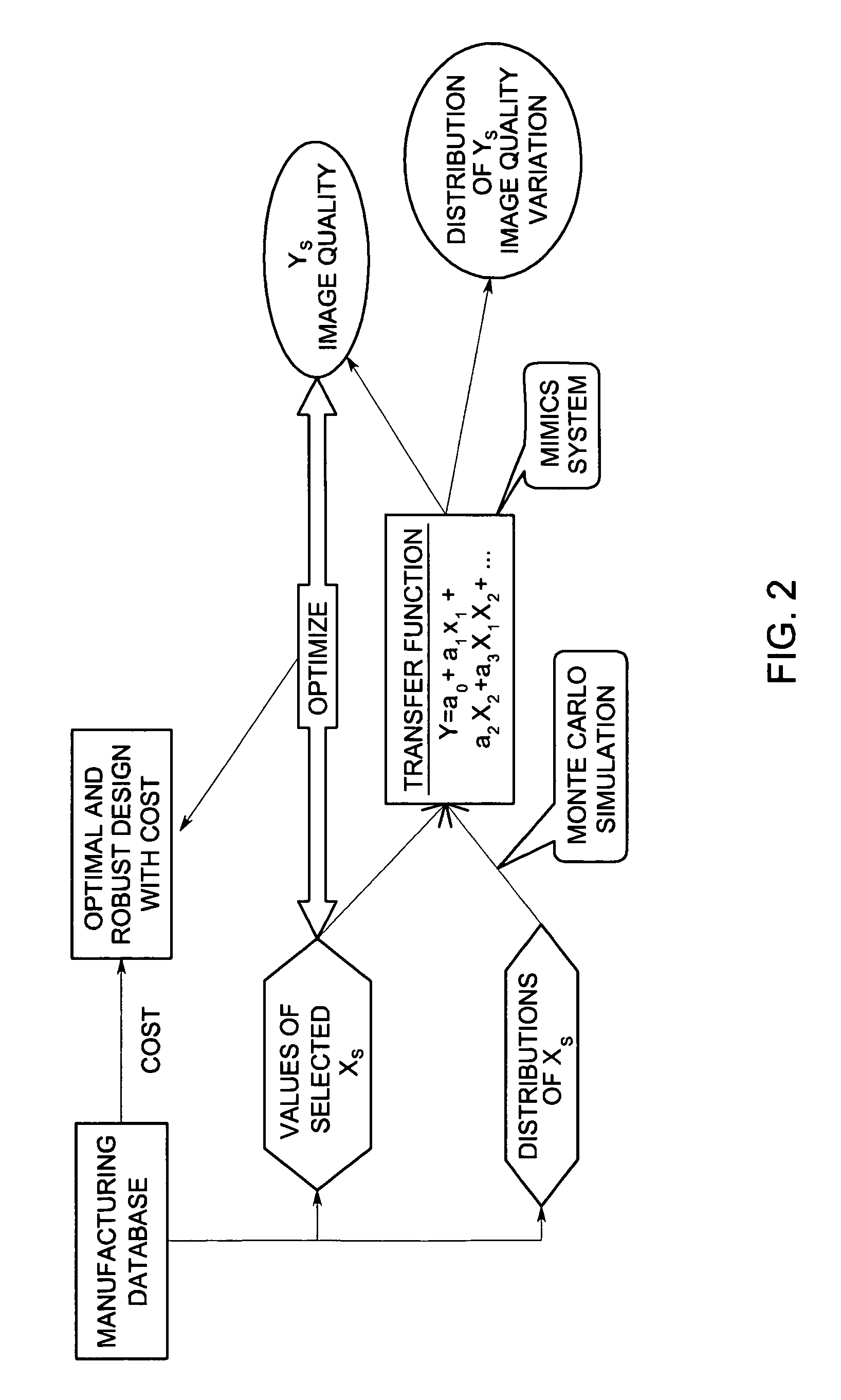
System and method for statistical design of ultrasound probe and imaging system
InactiveUS7006955B2Affect image qualityImprove image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCritical to qualitySonification
A system and method for statistical design of an ultrasound probe and imager system, and an associated graphical user interface for selecting input parameters to be used in an ultrasound simulation. The process and computer code allow the performance of a probe and imager combination to be specified and jointly optimized in image quality terms. The designs produced optimize both the image quality and other CTQ (critical to quality) parameters, such as the distribution of regulatory power indices and mechanical index. These CTQs indirectly affect image quality through their effect on patient dose. The Transducer Design Advisor incorporates a graphical user interface for facilitating selection of a parameter set to be used in the simulation. The user selects a desired parameter set by navigating across and interacting with a succession of windows. The user specifies various geometric characteristics of the transducer and how the user wants to simulate the imager system. Finally, the user specifies weights for the various CTQs at different depths. Based on these inputs, the Transducer Design Advisor creates the files needed by the ultrasound simulator.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
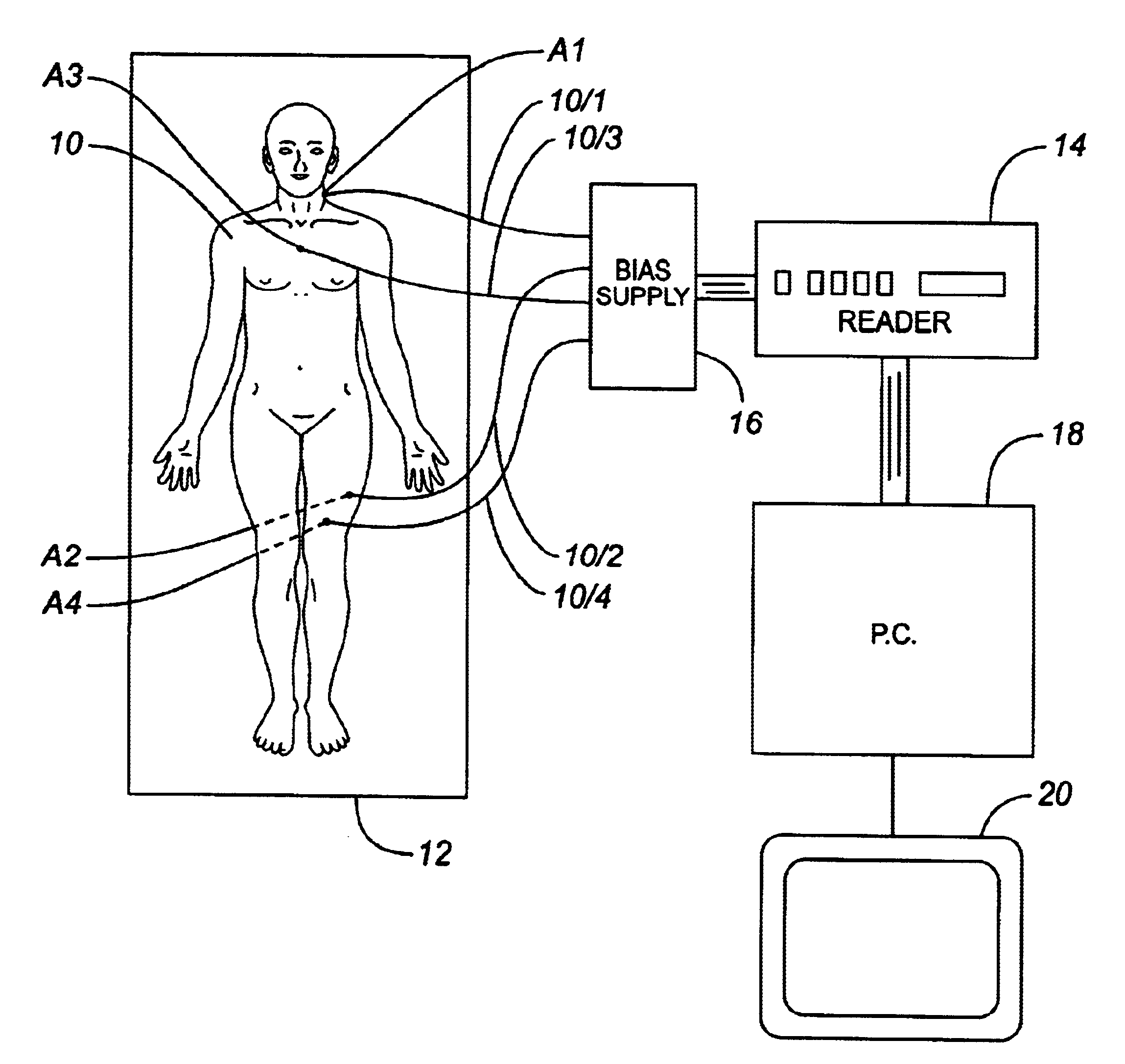
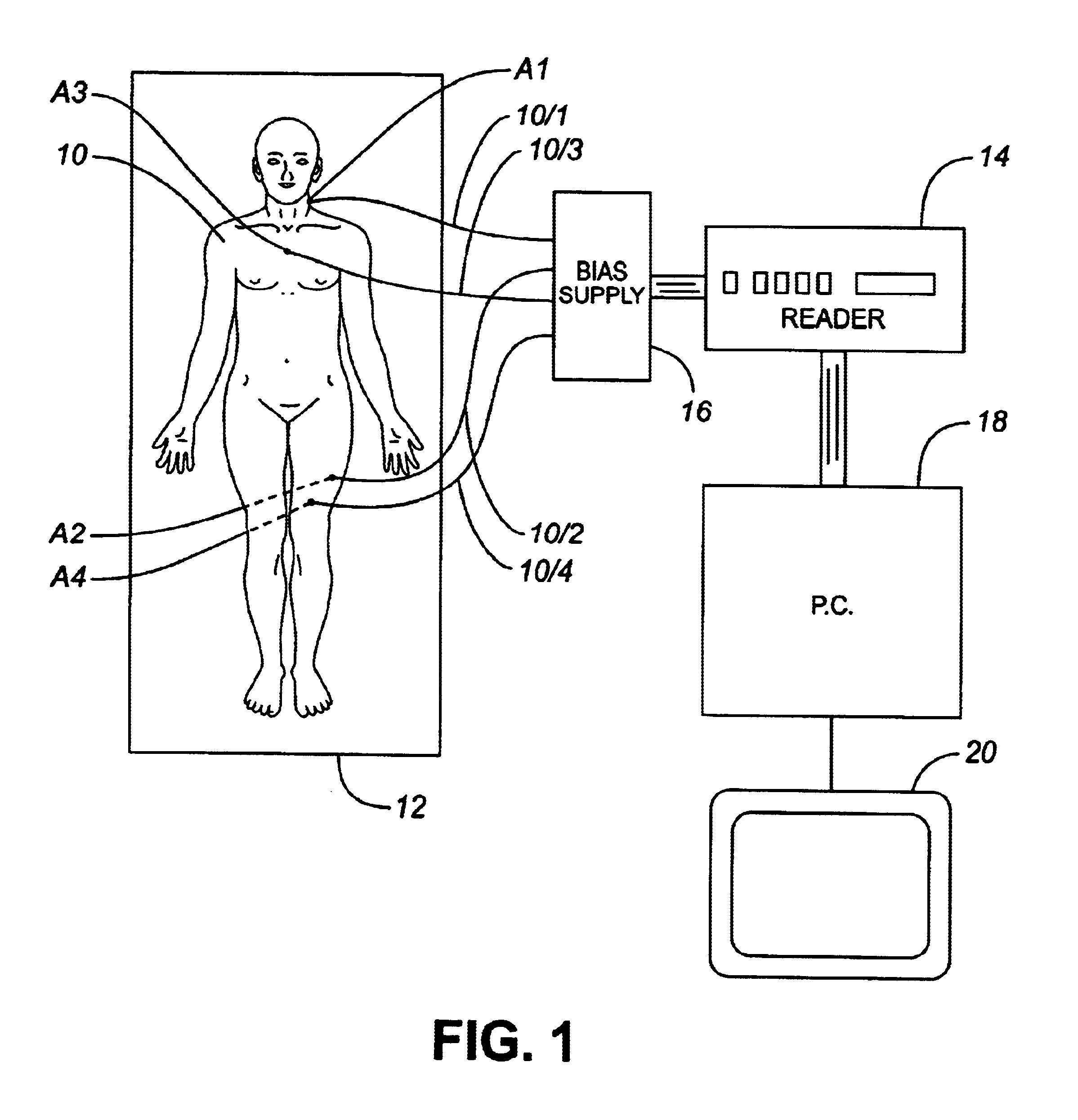
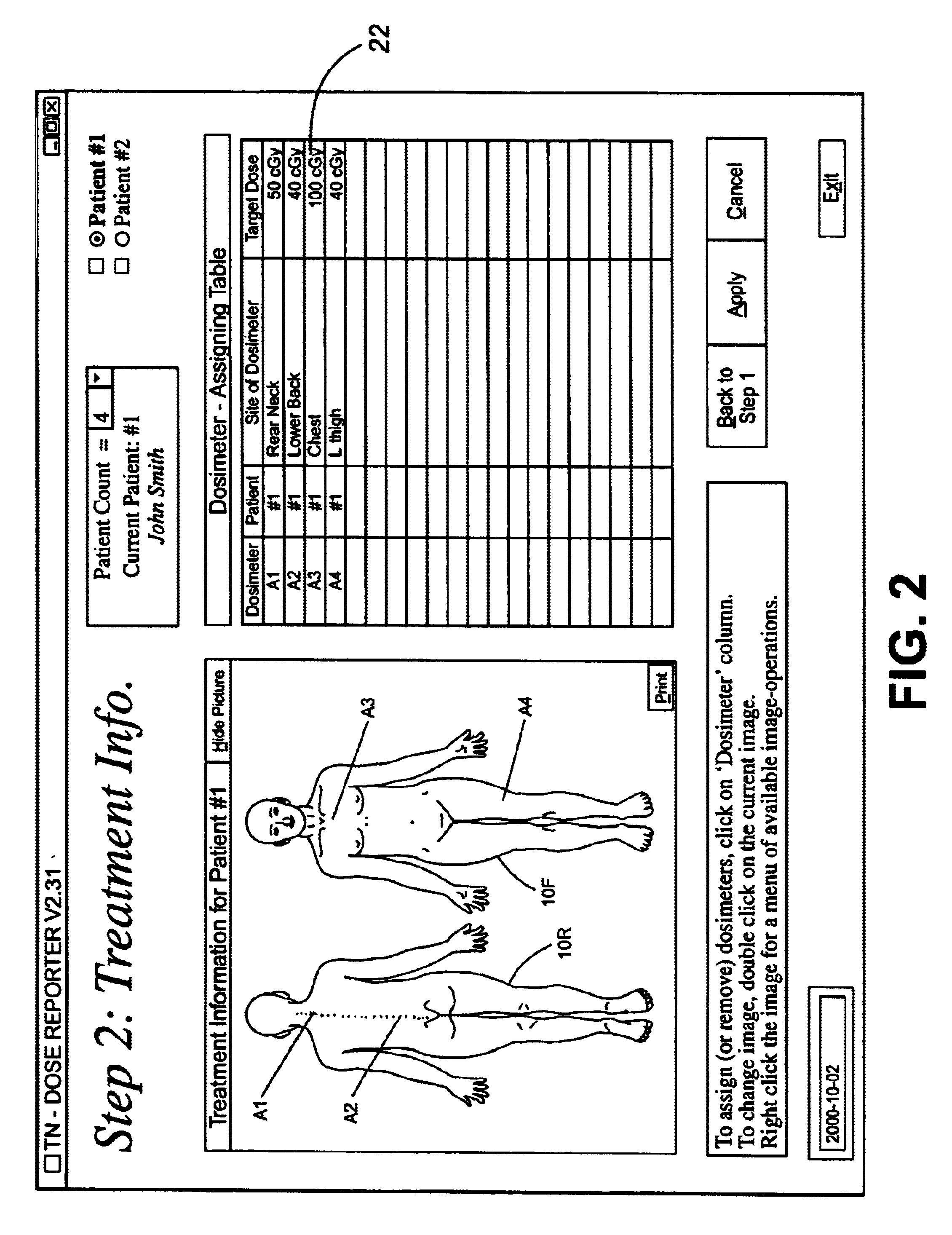
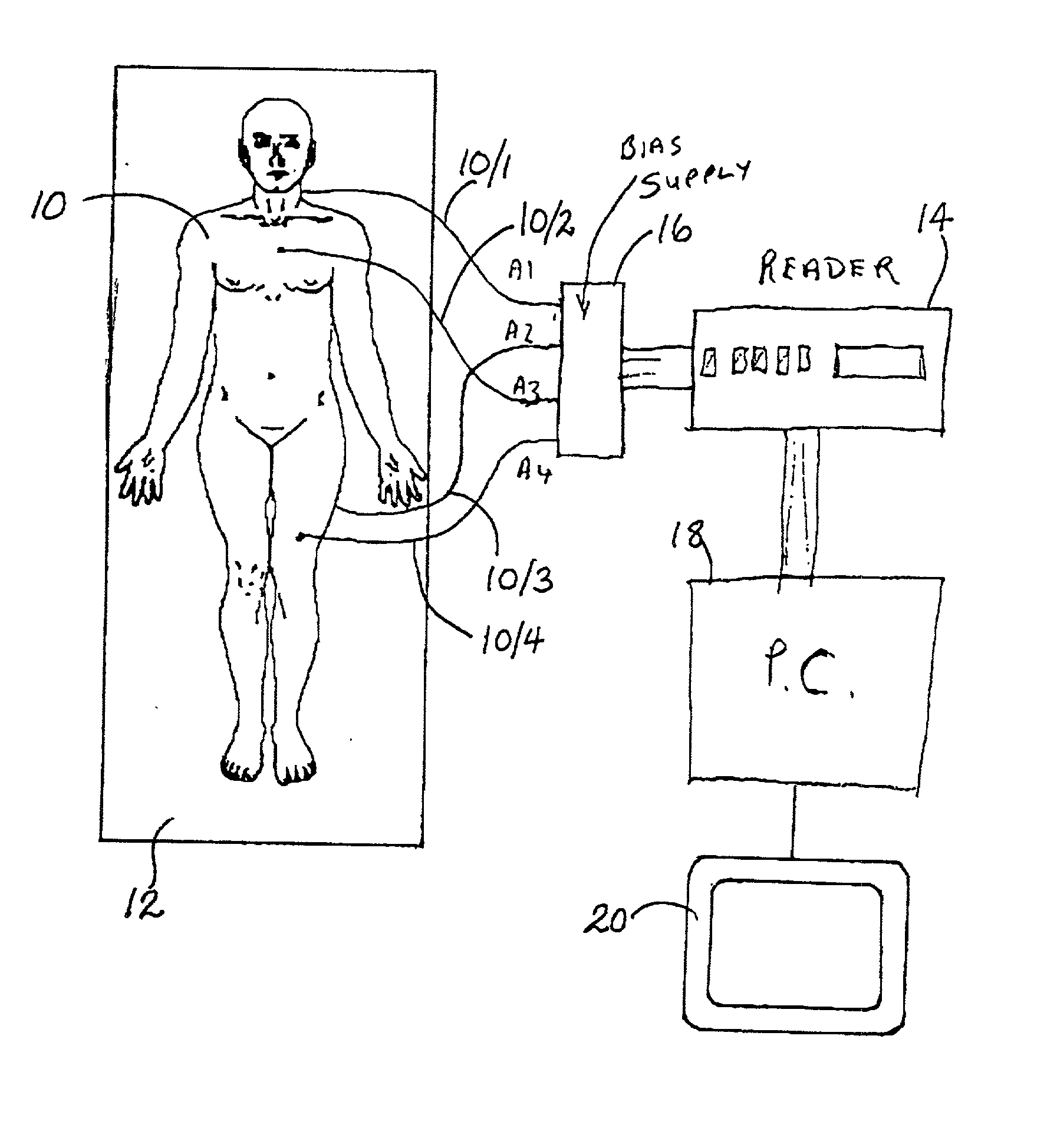
Computer assisted radiotherapy dosimeter system and a method therefor
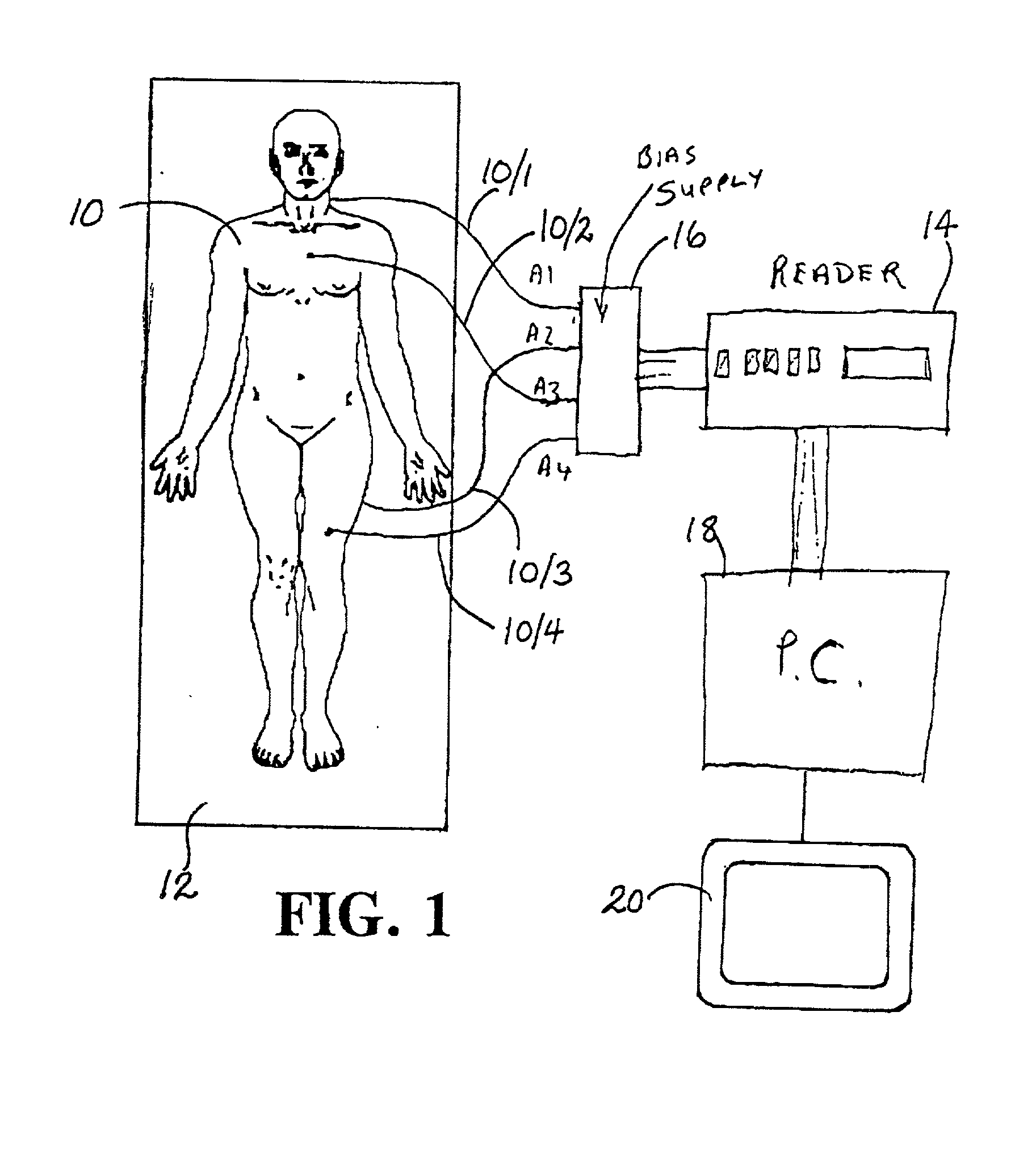
InactiveUS6650930B2Precise positioningEasy to recordSurgeryRadiation diagnosticsDosimetry radiationDosimeter
In order to facilitate the display and evaluation of data acquired while irradiating a body, e.g. a patient undergoing radiation therapy, a dosimetry system has a plurality of sensors for disposition on, in or near the body to be irradiated and connected to a sensor reading instrument which is interfaced with a display system, for example a personal computer, which is arranged to display, in use, one or more representations, for example drawings or photographs, of the body to be irradiated, along with the positions and the dose data for those specific locations where the dosimeter sensors were placed.
Owner:BEST THERATRONICS +1
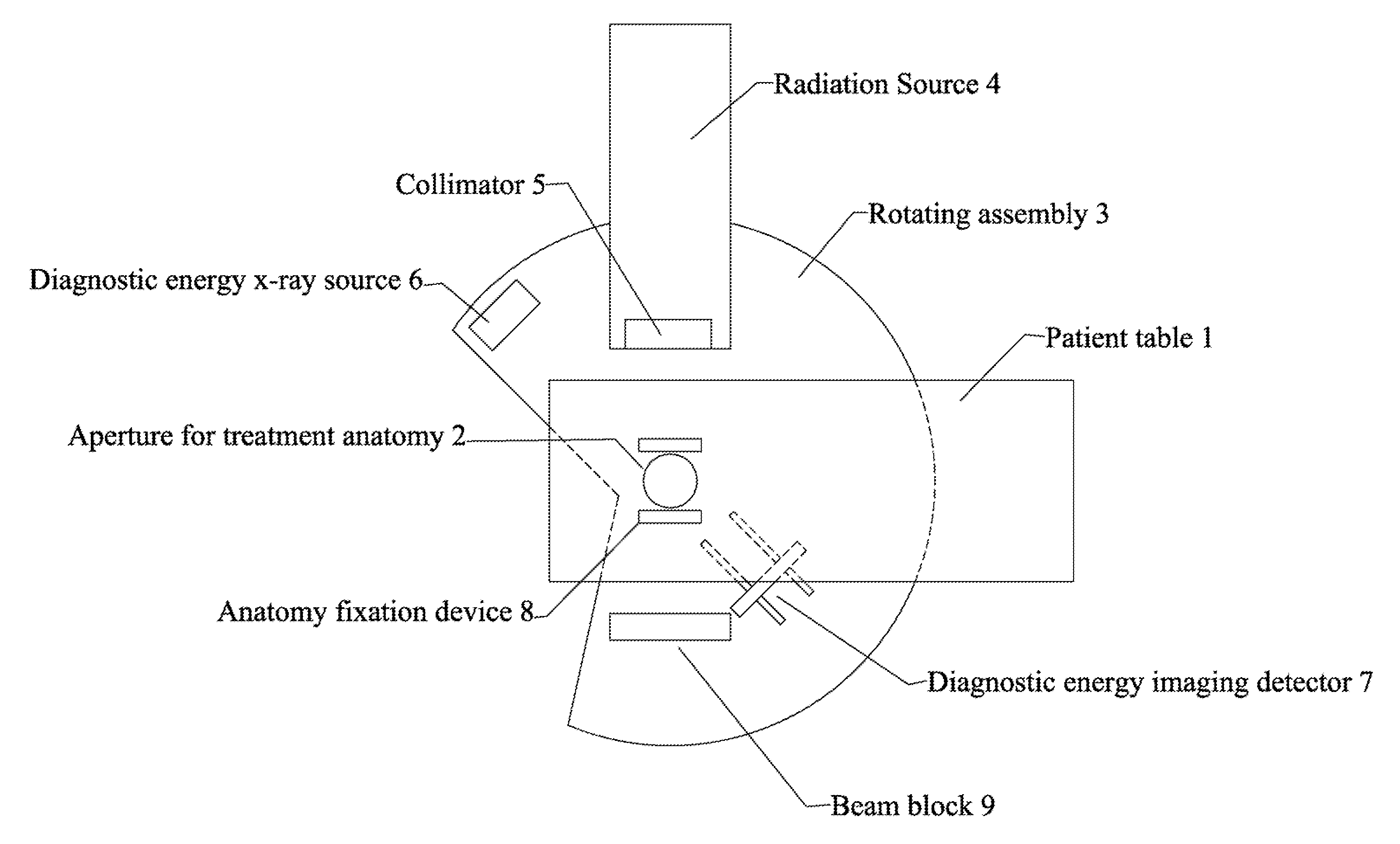
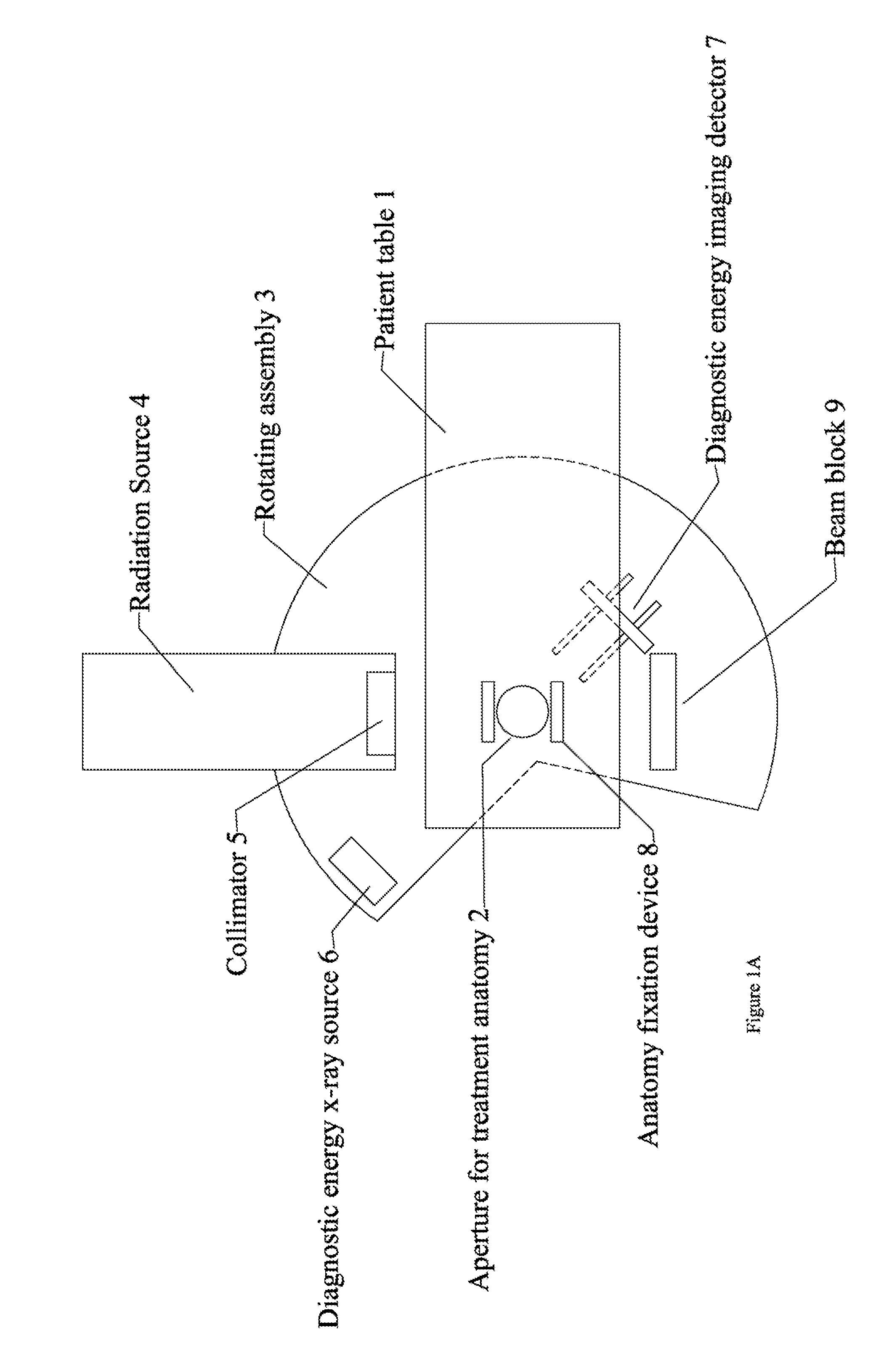
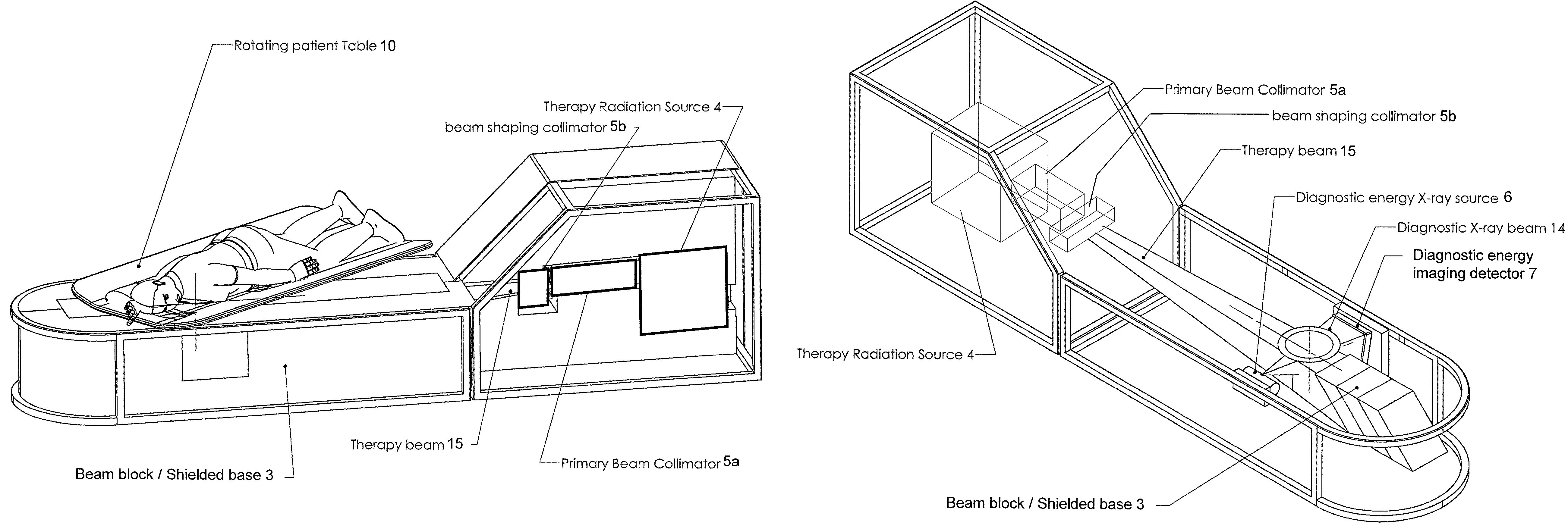
Radiation therapy system for treating breasts and extremities
InactiveUS20070211854A1Maximize separationReduce shielding requirementsPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerCritical structurePrimary disease
A radiation therapy system optimized for treating extremities such as the breast has unique geometrical features that enable the system to deliver an accurately located prescribed dose to a target volume while eliminating or reducing the collateral dose delivered to the rest of the patient. An optional integral imaging system provides accurate target volume localization for each treatment session. Utilizing the effects of gravity on a prone patient maximizes the separation of a target volume within the breast to adjacent critical structures such as the chest wall, heart and lungs, thereby reducing long term complications not associated with the primary disease. A shielded interface surface between the radiation source and the patient reduces patient dose due to scattered or stray radiation. A shielded enclosure for the radiation sources combined with the shielded interface surface eliminates the need for primary shielding in the room and allows the therapy system to be used in a transportable, mobile facility.
Owner:ORBITAL THERAPY
Method for improving clinical data quality in positron emission tomography
InactiveUS20050129170A1Improving clinical data qualitySimple calculationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData signalData quality
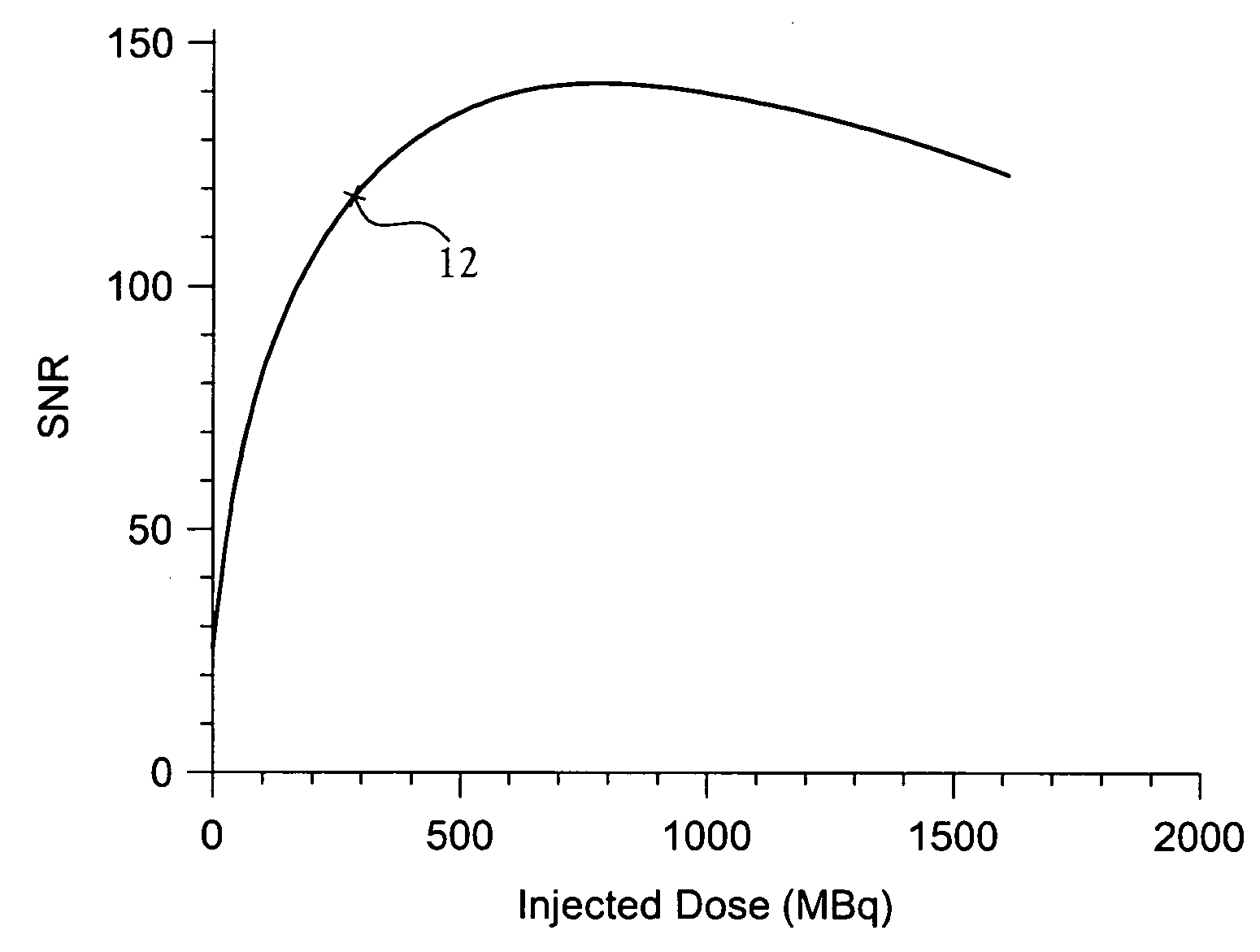
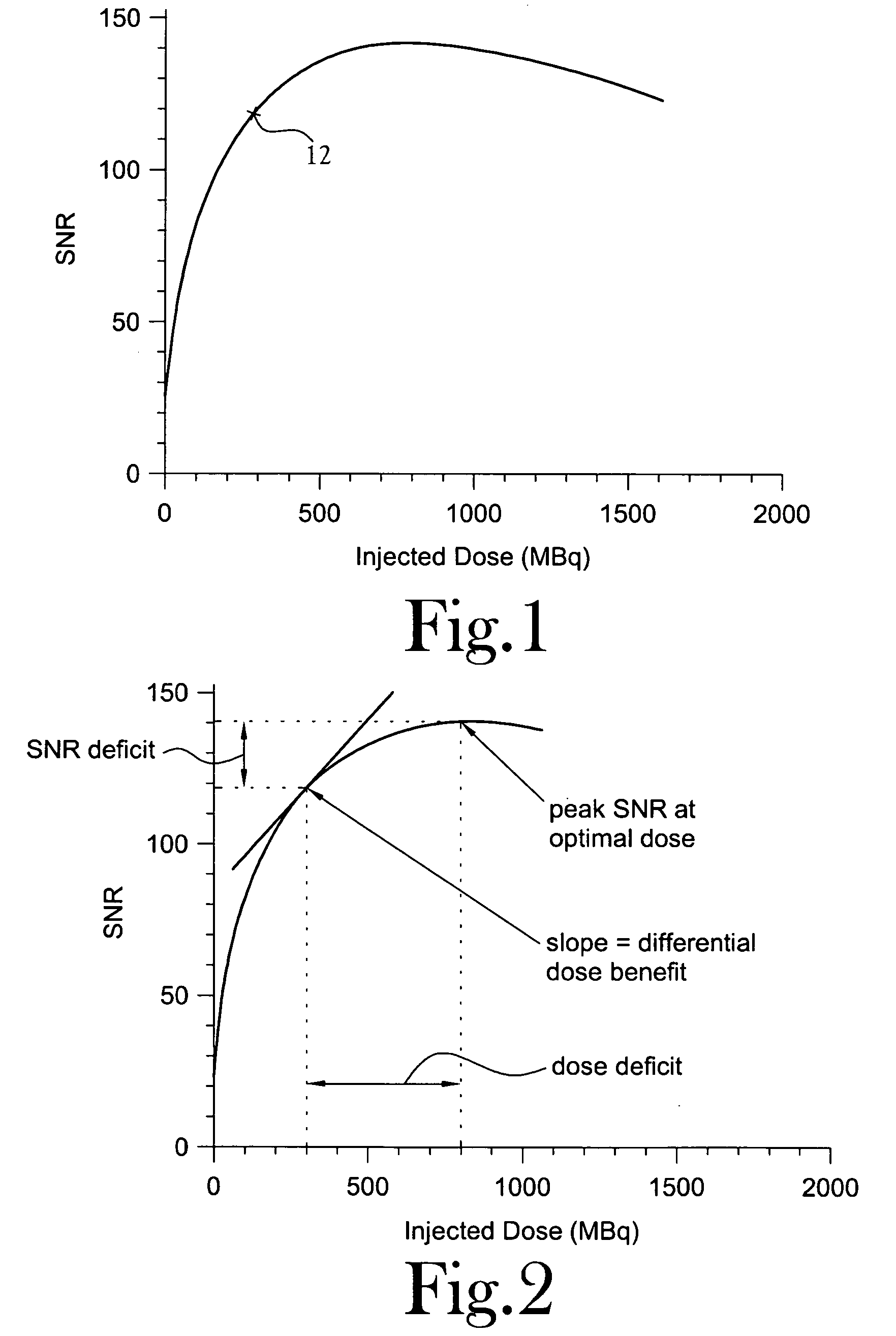
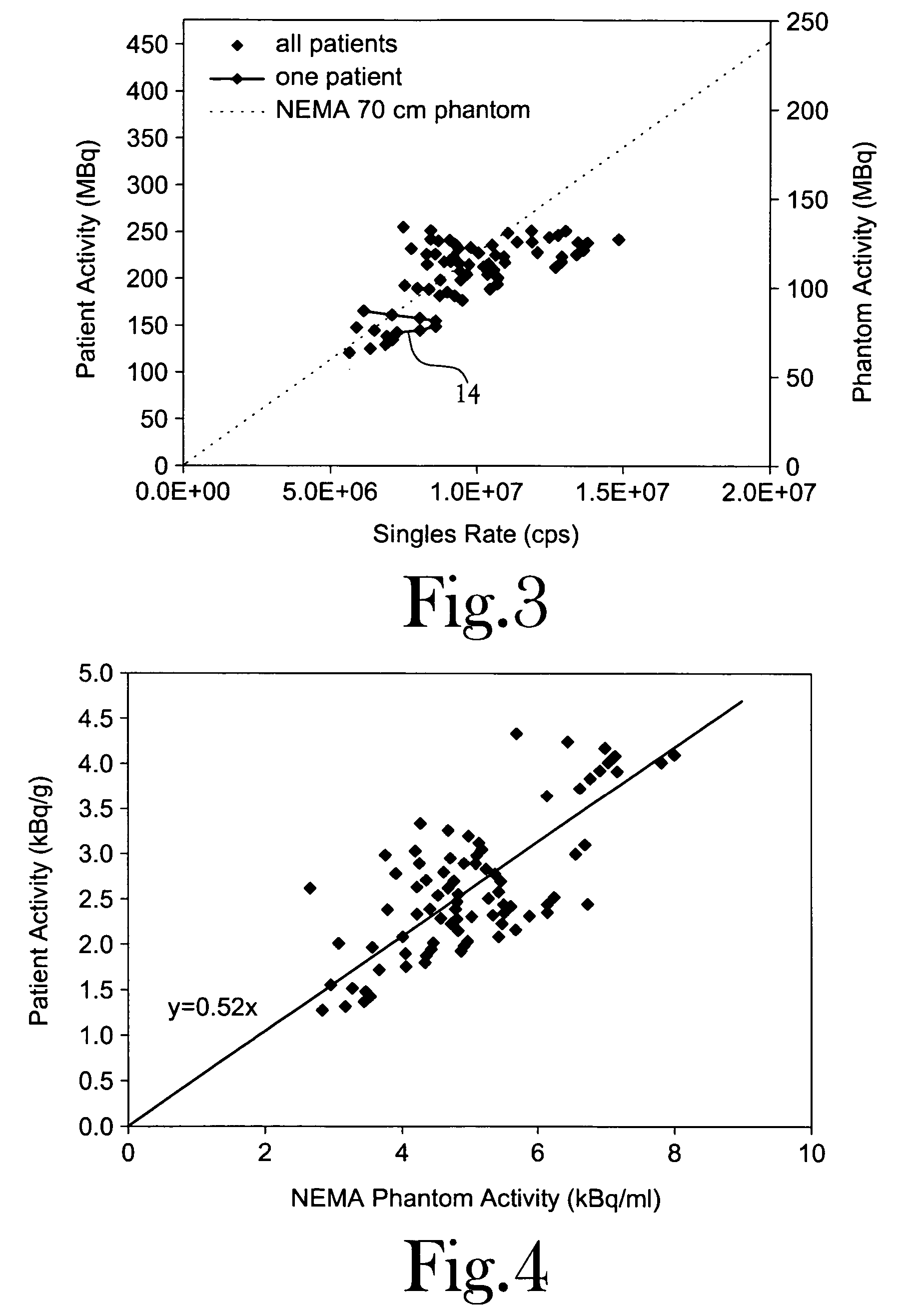
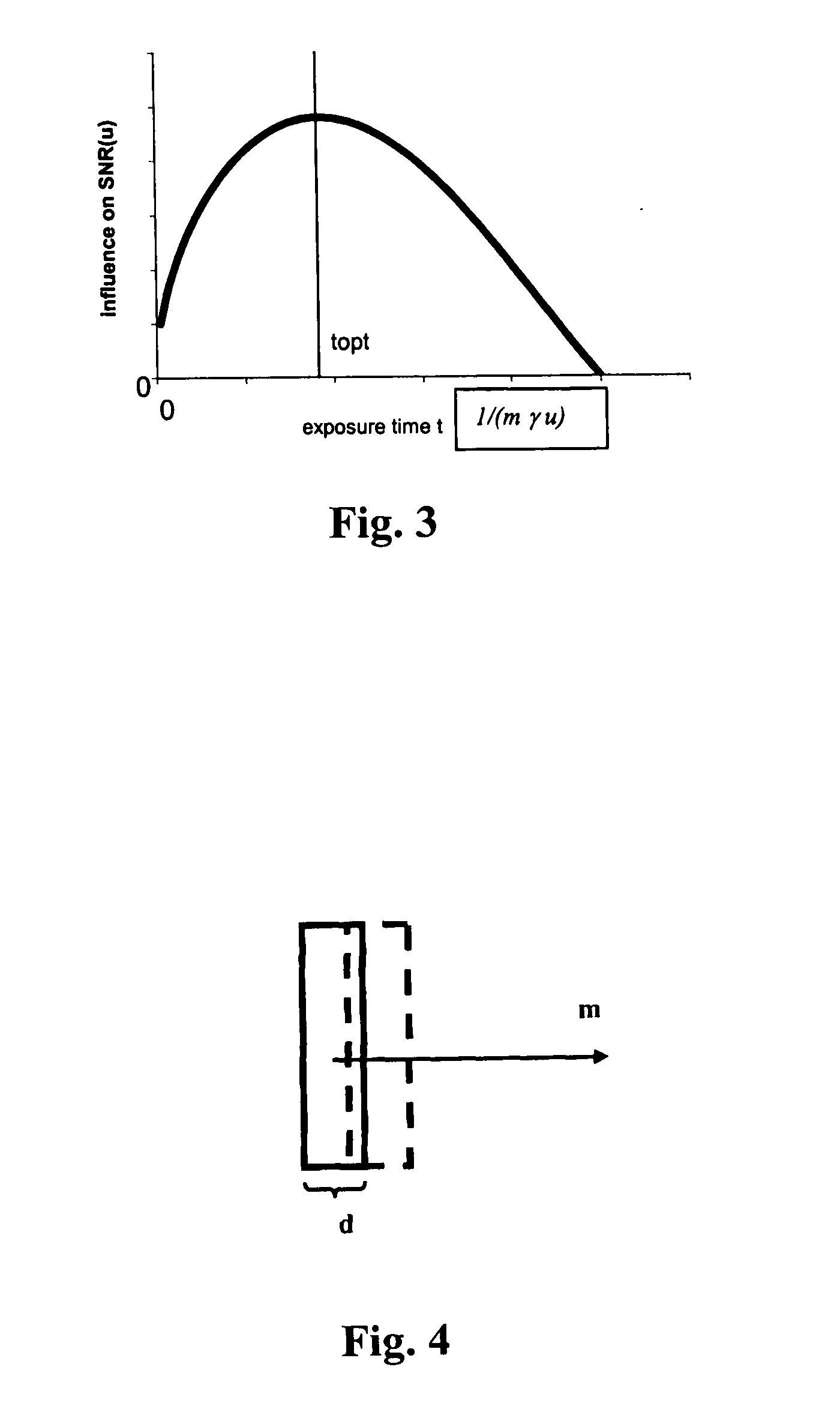
A method for improving clinical data quality in Positron Emission Tomography (PET). The method provides for the processing of PET data to accurately and efficiently determine a data signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) corresponding to each individual clinical patient scan, as a function of a singles rate in a PET scanner. The method relates an injected dose to the singles rate to determine SNR(Dinj), and provides an accurate estimate of a quantity proportional to SNR, similar in function to the SNR(Dinj). Knowledge of SNR(Dinj) permits determination of peak SNR, optimal dose, SNR deficit, dose deficit, and differential dose benefit. The patient dose is fractionated, with a small calibration dose given initially. After a short uptake, the patient is pre-scanned to determine T, S, and R. An optimal dose is then determined and the remainder injected.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
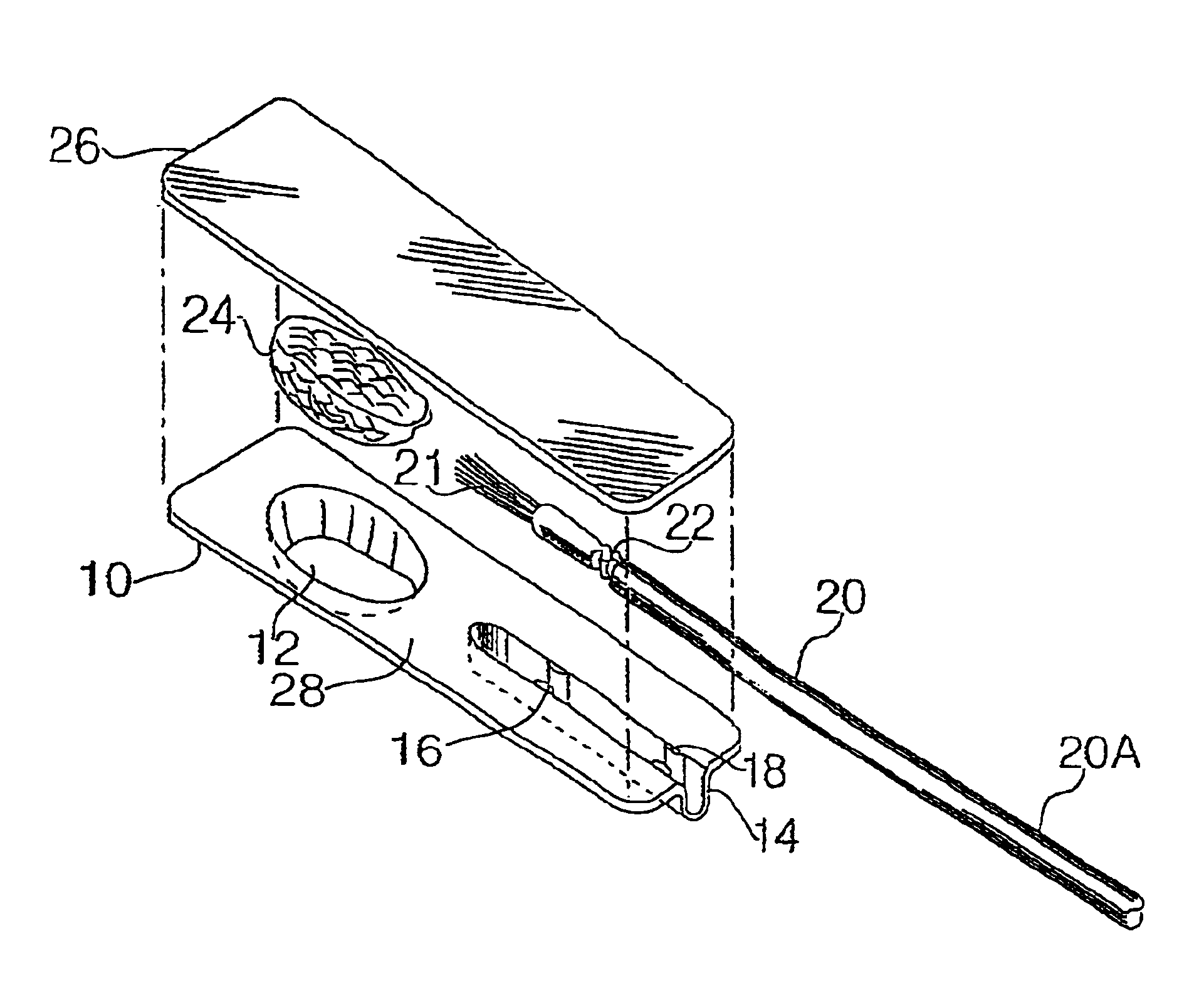
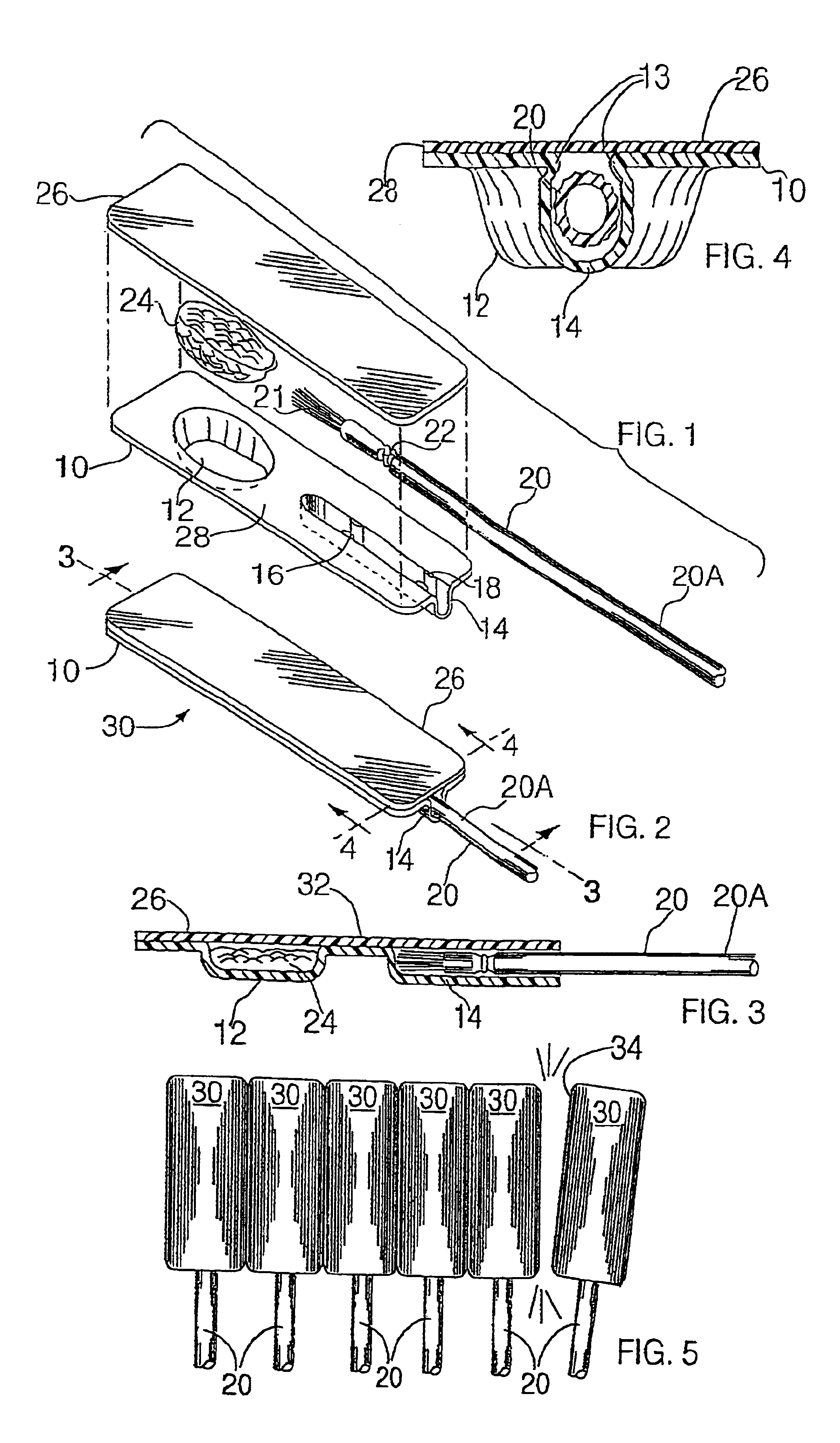
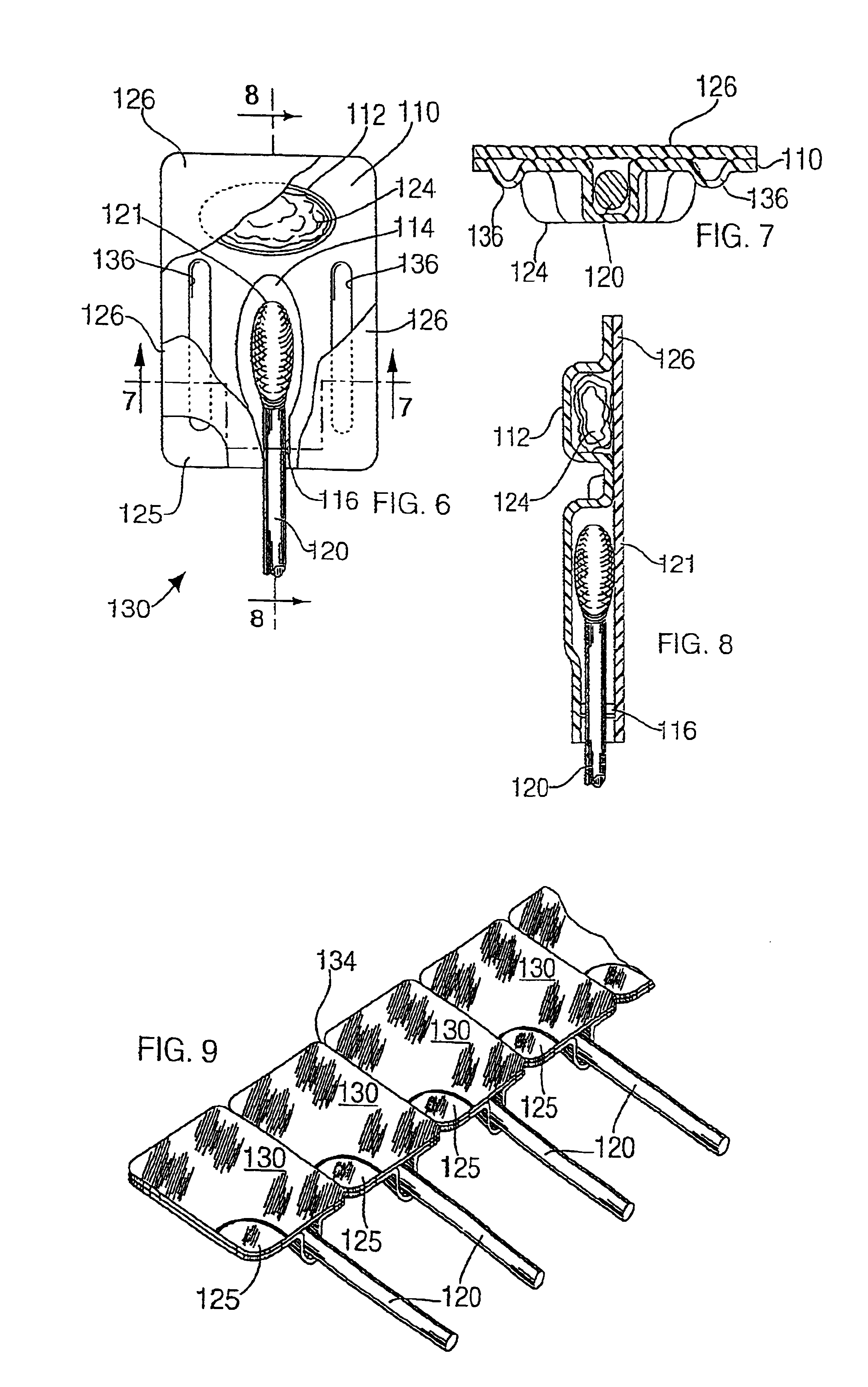
Single patient dose medicament dispenser with applicator
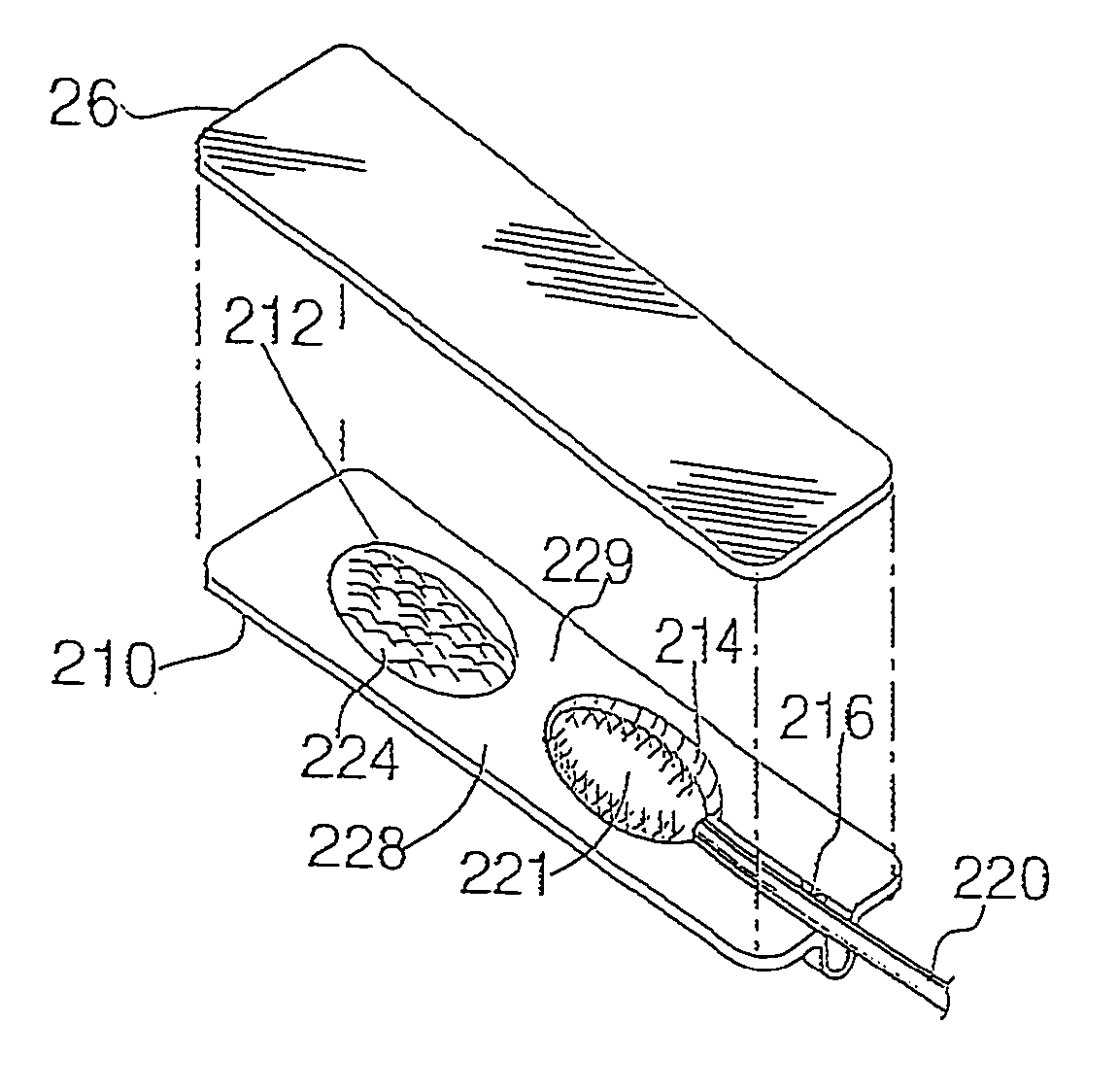
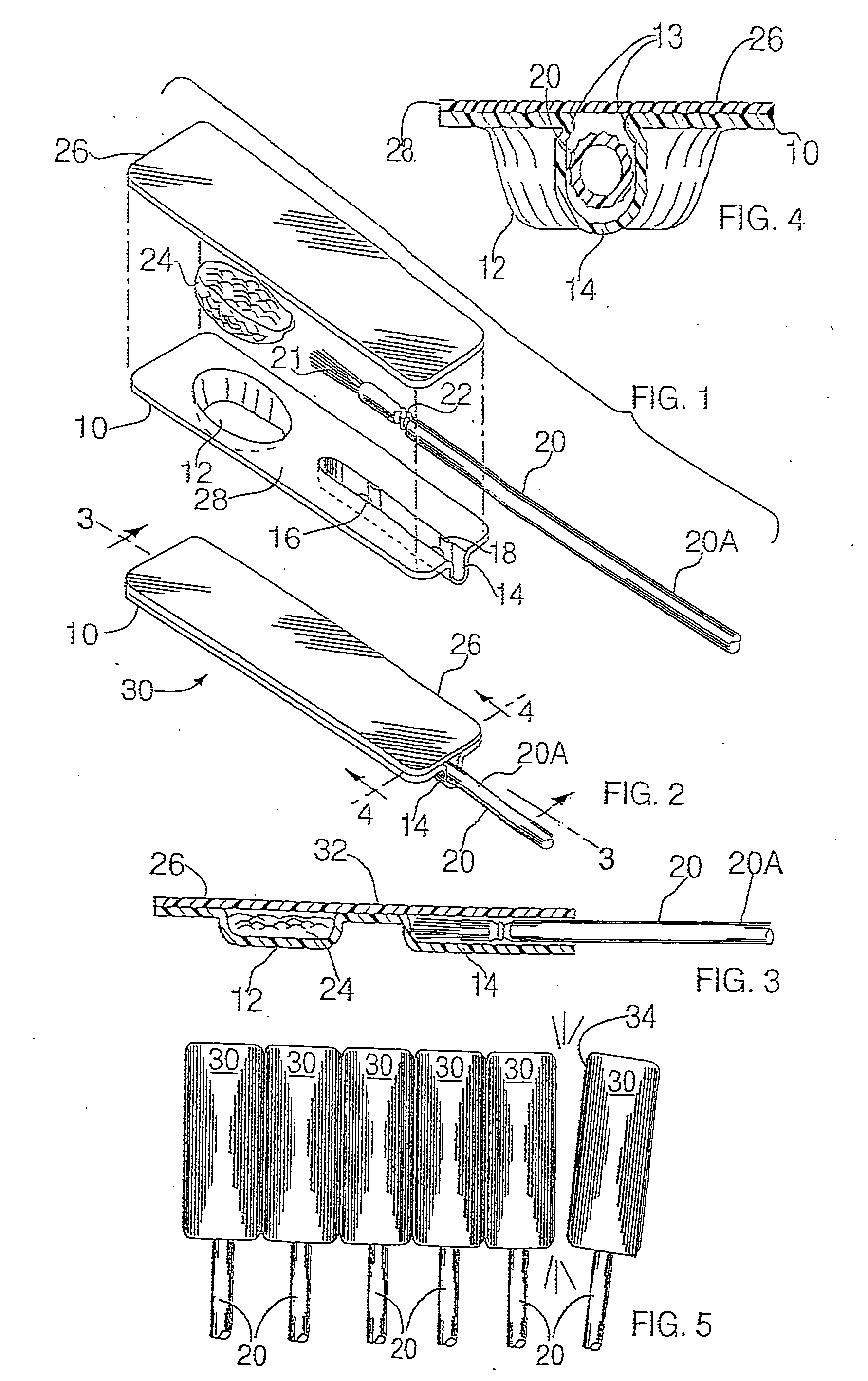
InactiveUS6959808B2Easy to openMinimal amountLiquid surface applicatorsDispensing apparatusMedication DispenserBiomedical engineering
A dose package for applying a material with an applicator having a separate material and applicator portion. In one embodiment, a portion of a cover is removable, exposing the material and applicator. In another embodiment, a plurality of material wells are used to mix different materials to be dispensed with an applicator. In another embodiment, a material well is squeezed to dispense the material onto an applicator.
Owner:CENTRIX
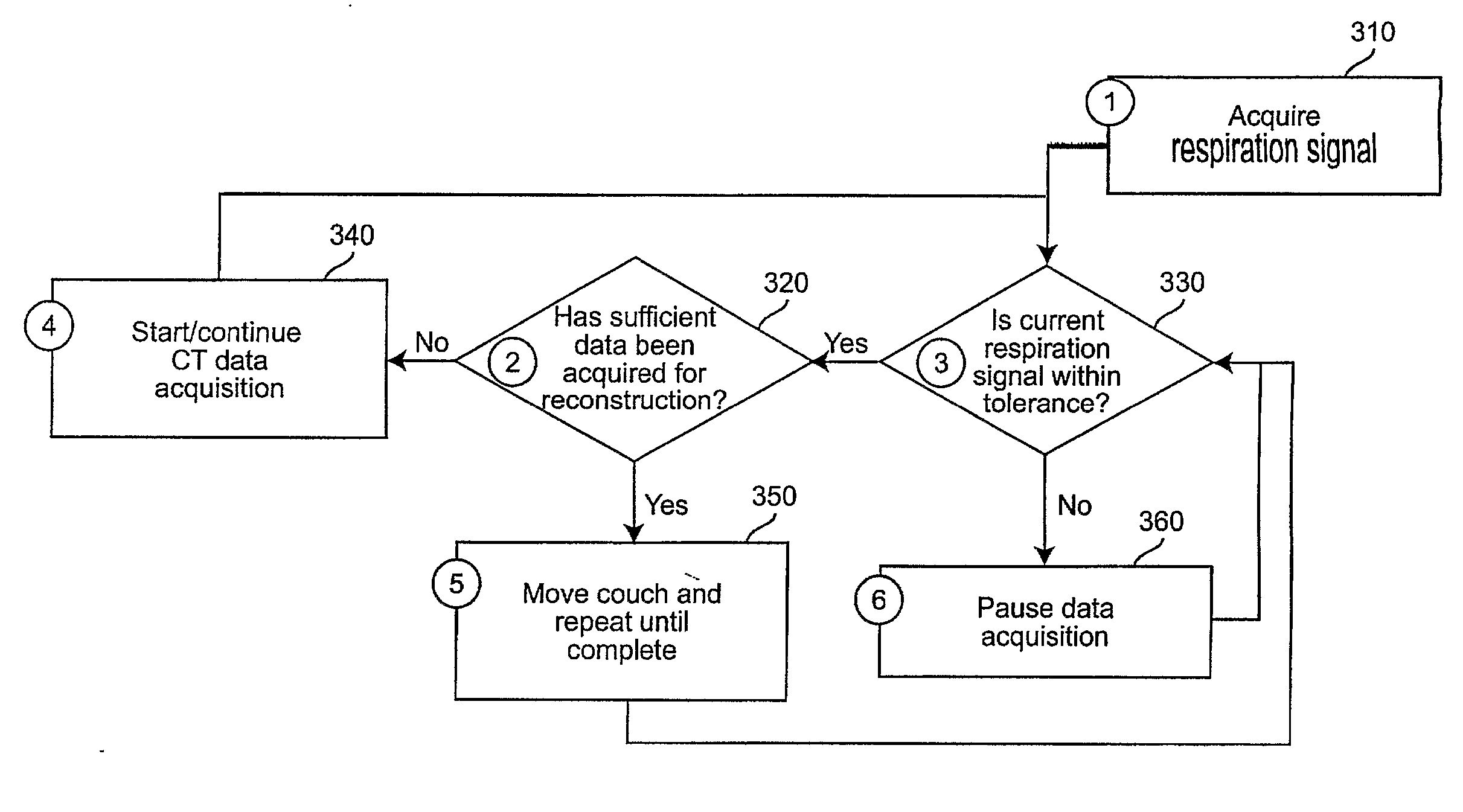
Method And System Of Adaptive Control For Reducing Motion Artifacts And Patient Dose In Four Dimensional Computed Tomography
InactiveUS20070286331A1Weakening rangeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData acquisitionFour-Dimensional Computed Tomography
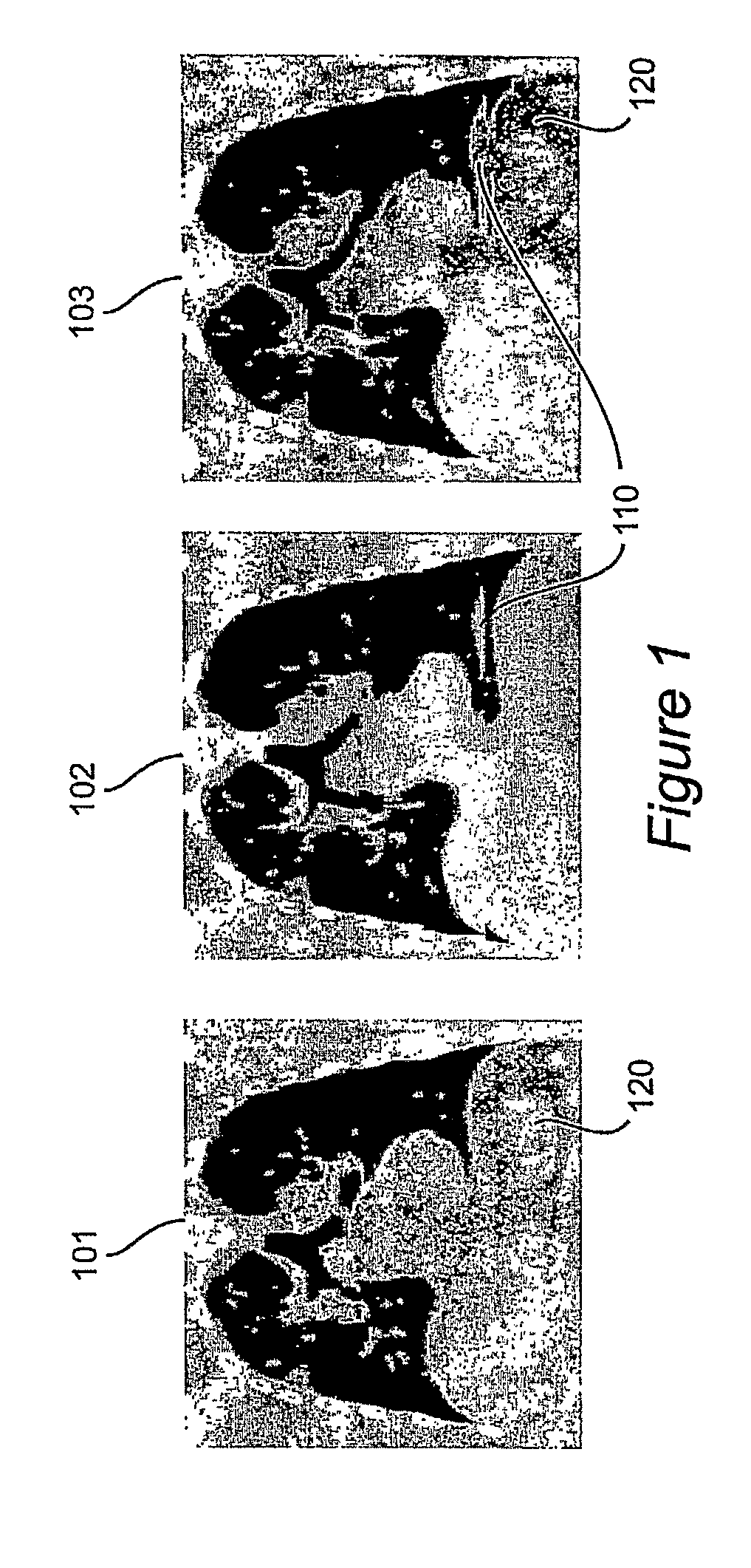
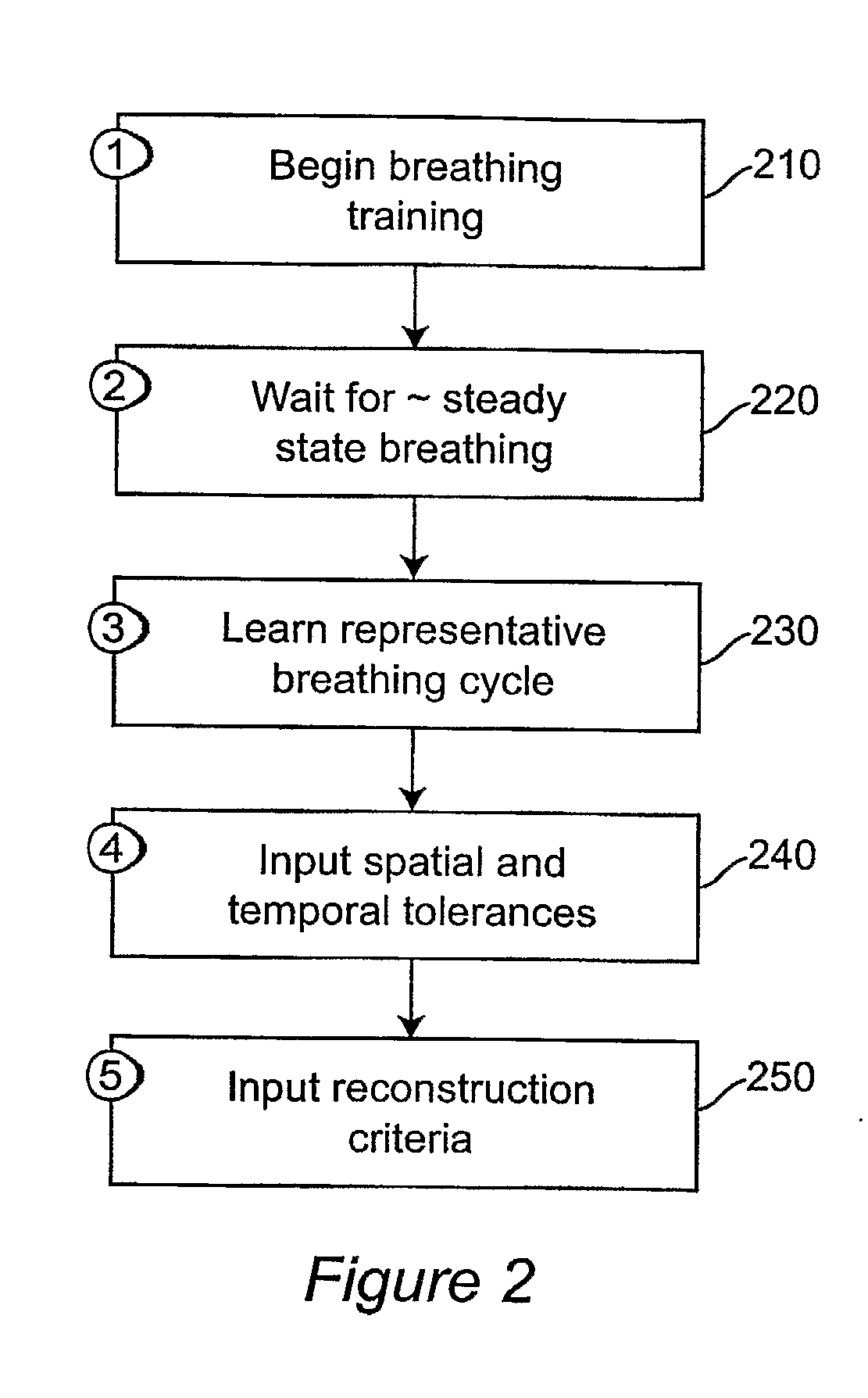
Motion artifacts and patient dose during 4D CT imaging are reduced by adaptive control of data acquisition. The respiration signal (310) and CT data acquisition (340) are linked, such that ‘bad’ data from erratic breathing cycles that cause artifacts is not acquired by pausing CT data acquisition (360) when erratic breathing is detected, and not resuming CT data acquisition until steady-state respiration is resumed. Training data is used to develop a tolerance envelope for a respiratory signal such that for erratic breathing cycles the respiratory signal is not within the tolerance envelope (330).
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
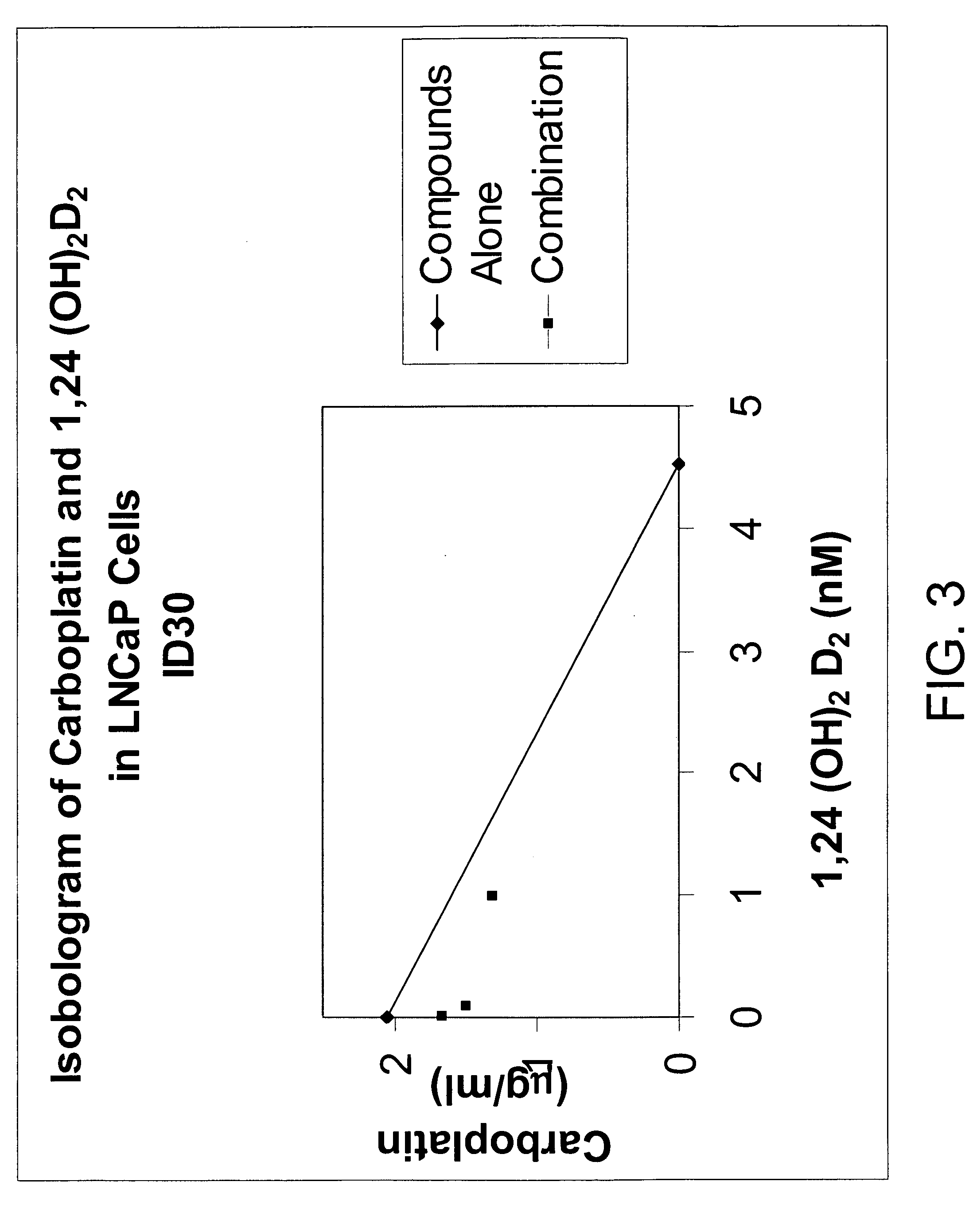
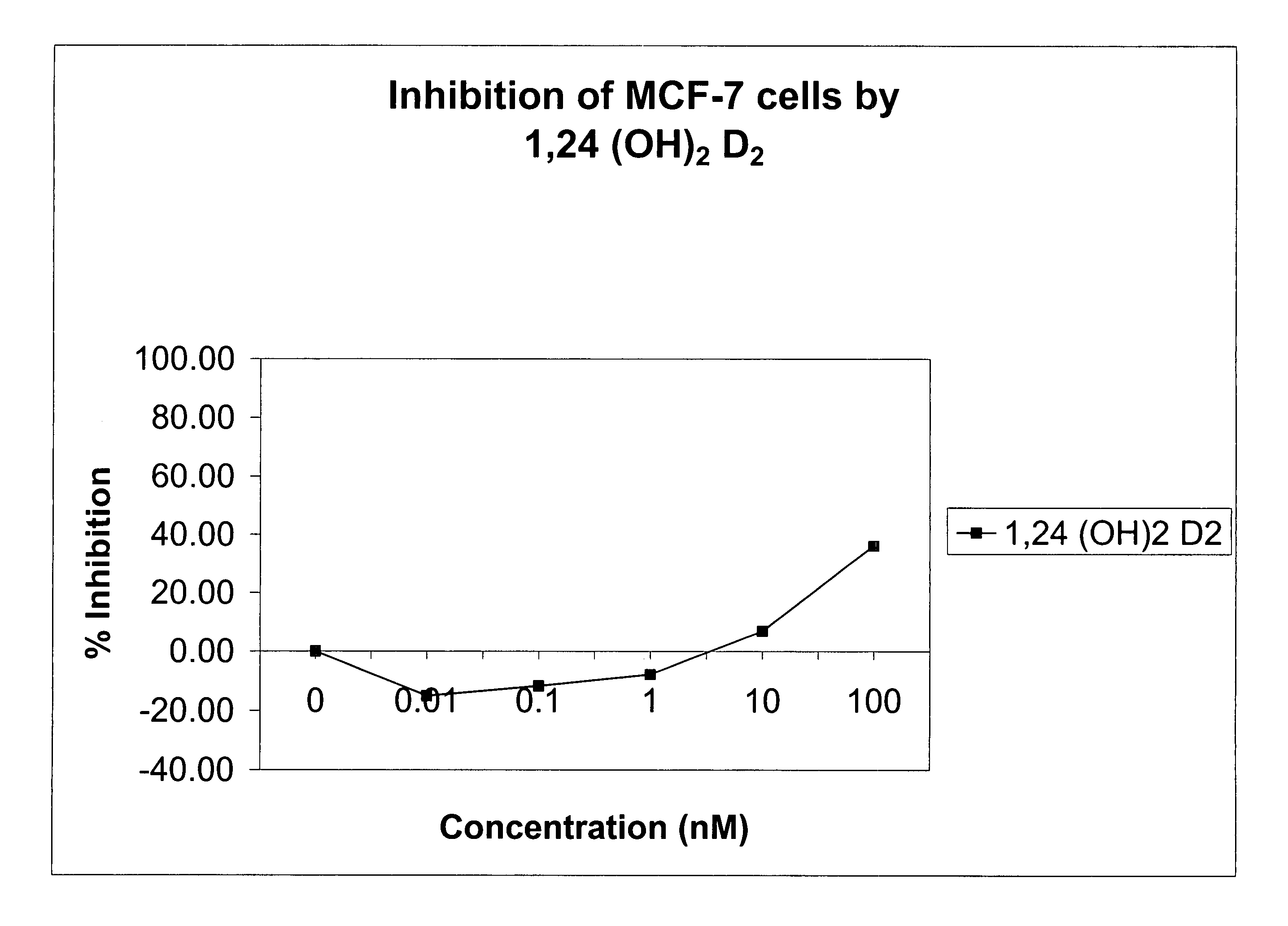
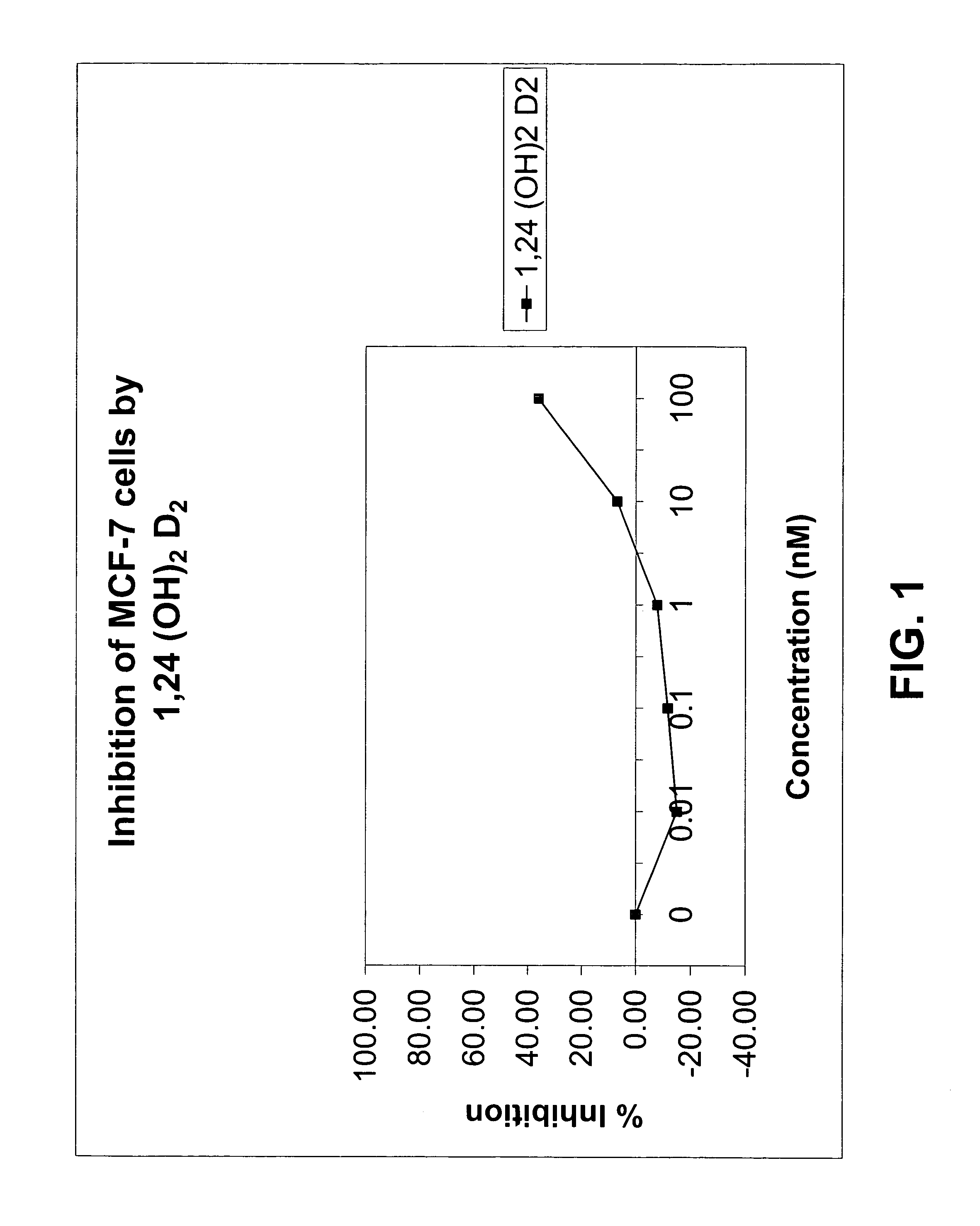
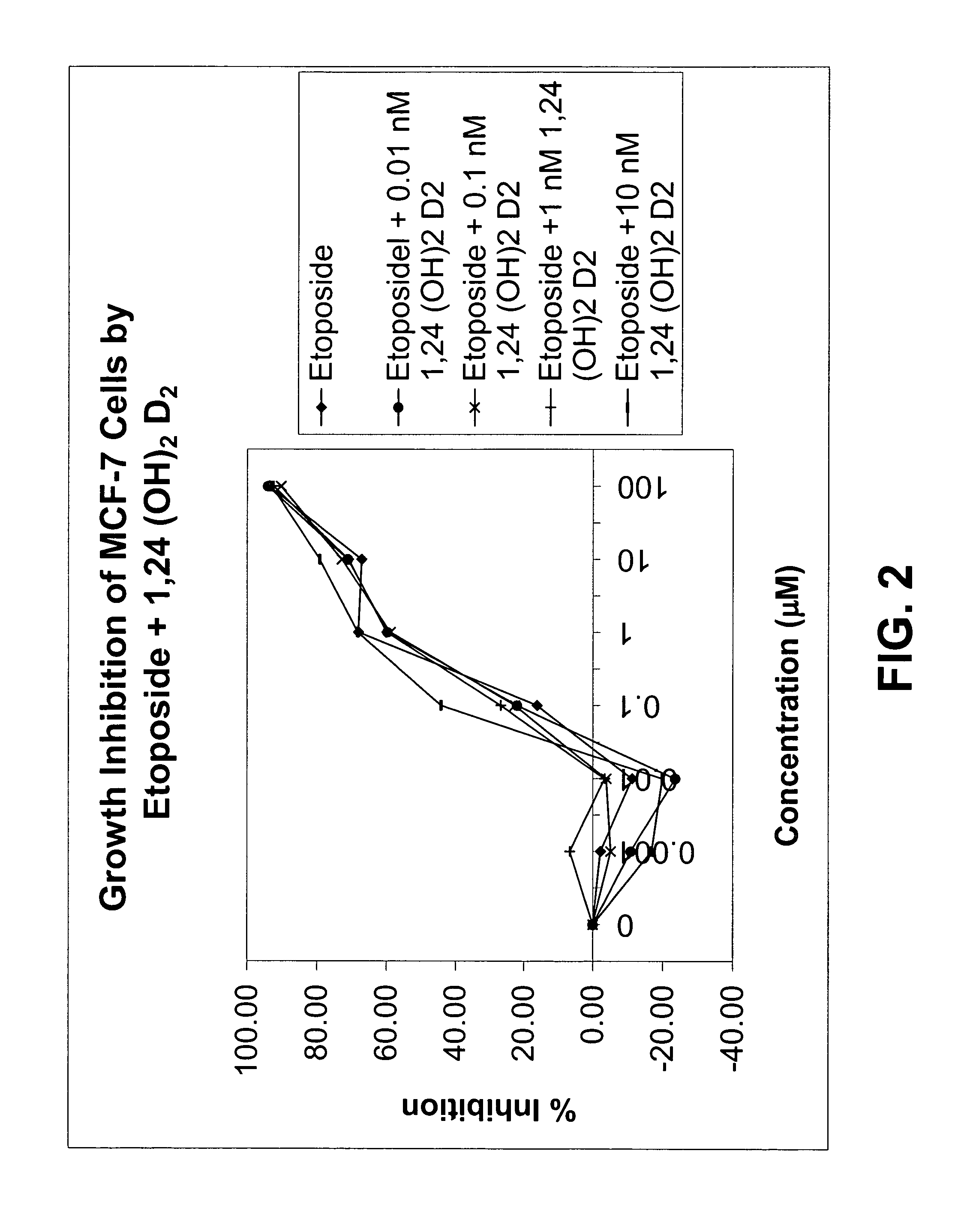
Method of treating prostatic diseases using a combination of vitamin D analogues and other agents
InactiveUS20060003950A1Reduce incidenceReduce riskBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsAnticarcinogenActive Vitamin D
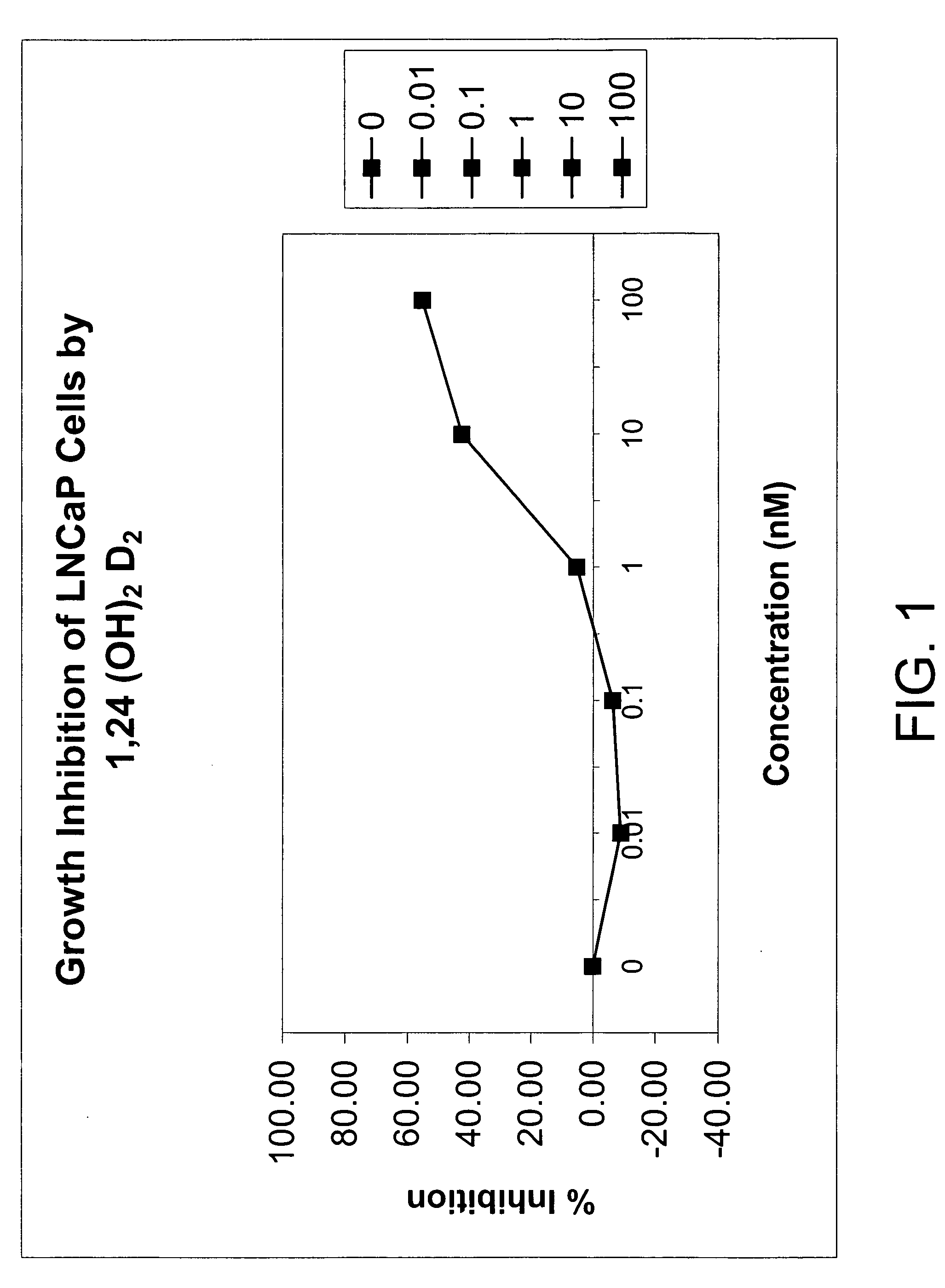
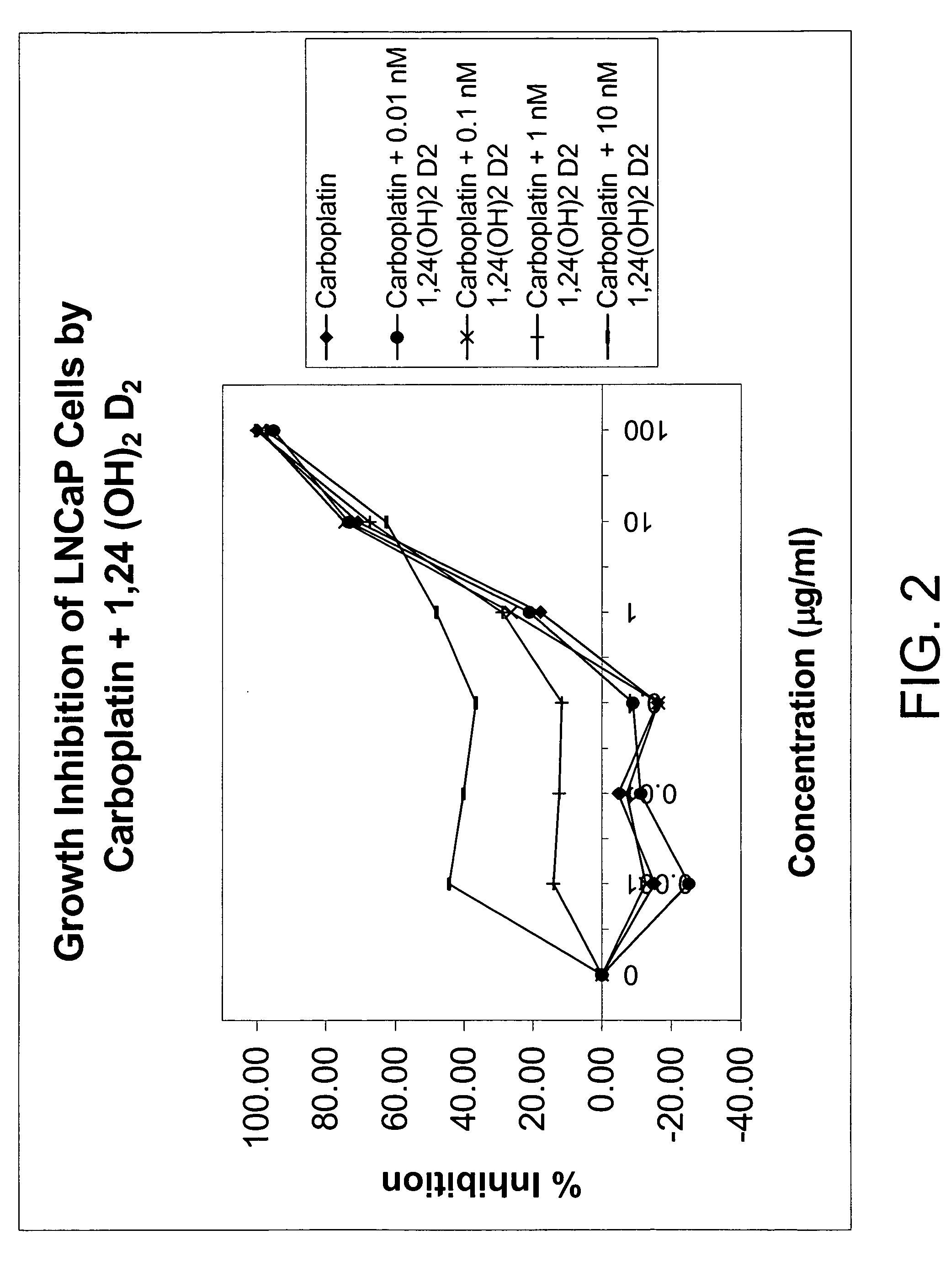
The invention provides therapeutic methods for inhibiting, ameliorating or alleviating the hyperproliferative cellular activity of diseases of the prostate, e.g., prostatic cancer and prostatic hyperplasia, which includes administering to a patient in need thereof an active vitamin D analogue and another anticancer agent. Cell differentiation is promoted, induced or enhanced without causing to the patient dose-limiting hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria.
Owner:BONE CARE INT
Method of treating breast cancer using a combination of vitamin D analogues and other agents
ActiveUS7094775B2Good treatment effectReduce in quantityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideIncreased calciumActive Vitamin D
The invention provides therapeutic methods for inhibiting, ameliorating or alleviating the hyperproliferative cellular activity of diseases of the breast, e.g., breast cancer, which includes administering to a patient in need thereof an active vitamin D analogue and another anticancer agent. Cell differentiation is promoted, induced or enhanced without causing to the patient dose-limiting hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria.
Owner:BONE CARE INT
Radiation therapy system for treating breasts and extremities
InactiveUS7526066B2Maximize separationWeaken energyPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerAnatomical structuresCritical structure
Owner:ORBITAL THERAPY
Single patient dose medicament dispenser with applicator
InactiveUS7243789B2Easy to openMinimal amountLiquid surface applicatorsDispensing apparatusMedication DispenserBiomedical engineering
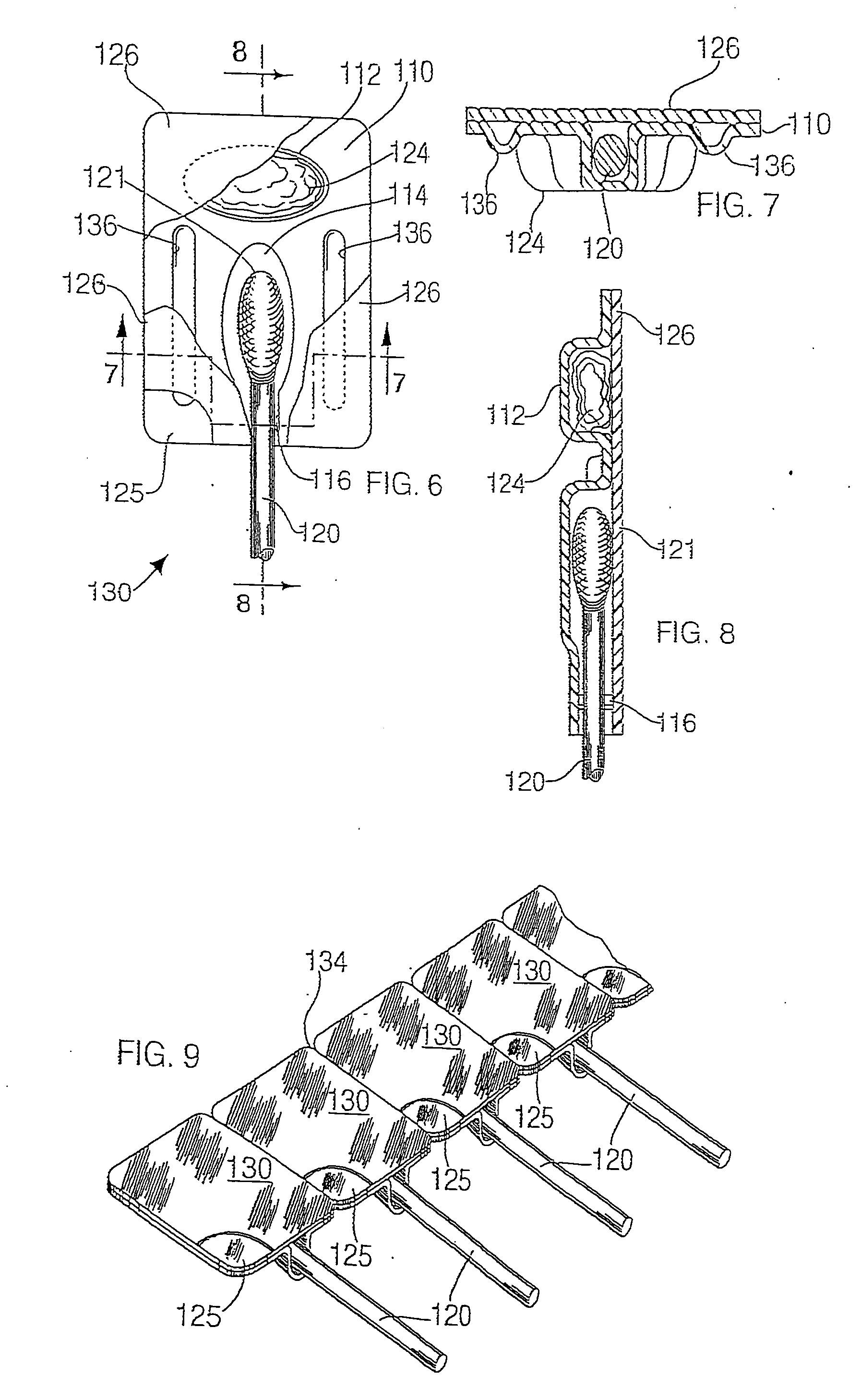
A unit dose package for applying a material with an applicator having a separate material and applicator portion. In one embodiment, a plurality of material wells is used to mix different materials to be dispensed with an applicator. In an embodiment the plurality of material wells are concentric. In another embodiment a portion of the cover is removable. In another embodiment, a material well is squeezed to dispense the material onto an applicator.
Owner:CENTRIX INC(US)
Computer assisted radiotherapy dosimeter system and a method therefor
InactiveUS20020049362A1Reduce disadvantagesPrecise positioningSurgeryRadiation diagnosticsDosimetry radiationDosimeter
In order to facilitate the display and evaluation of data acquired while irradiating a body, e.g. a patient undergoing radiation therapy, a dosimetry system has a plurality of sensors for disposition on, in or near the body to be irradiated and connected to a sensor reading instrument which is interfaced with a display system, for example a personal computer, which is arranged to display, in use, one or more representations, for example drawings or photographs, of the body to be irradiated, along with the positions and the dose data for those specific locations where the dosimeter sensors were placed.
Owner:BEST THERATRONICS +1
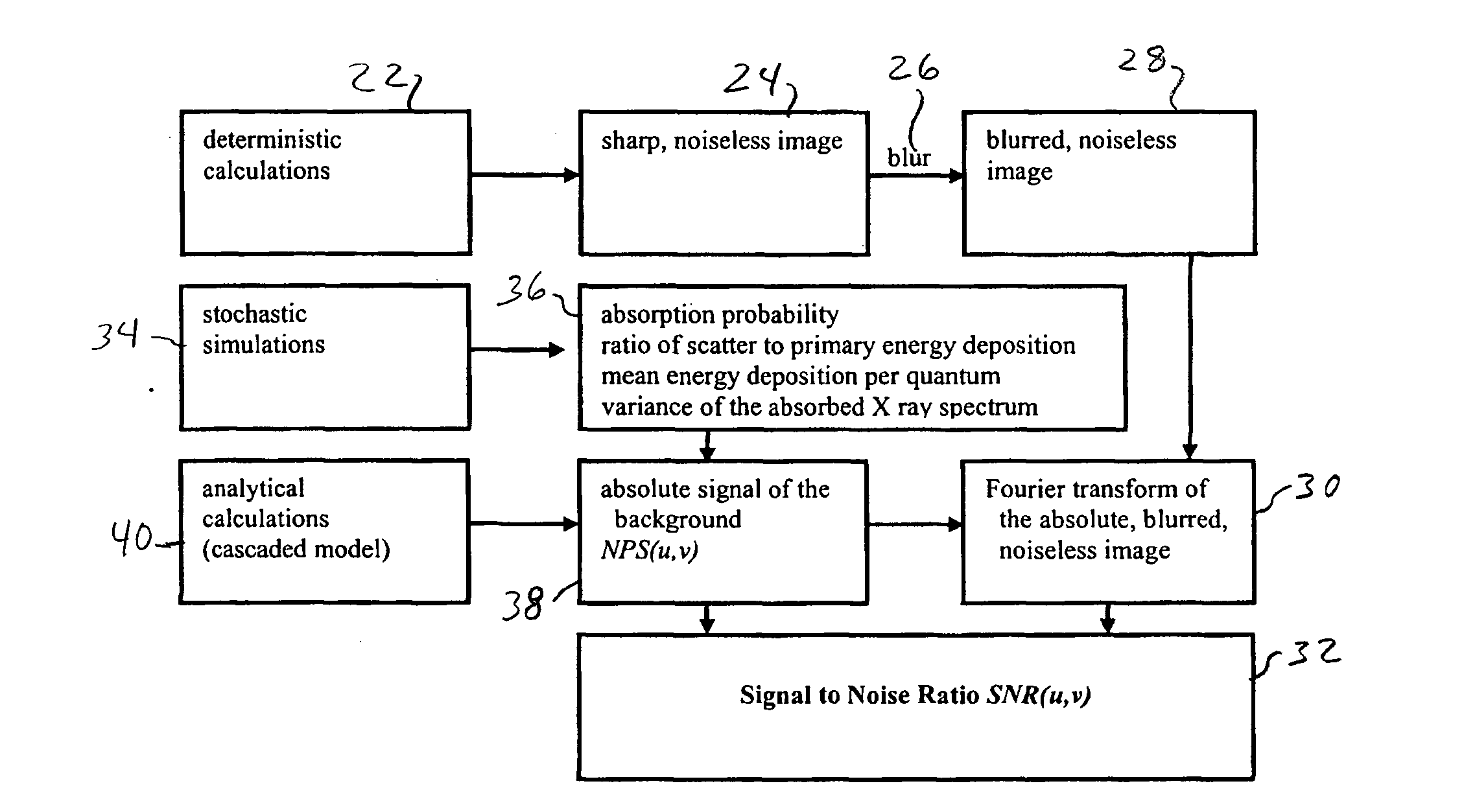
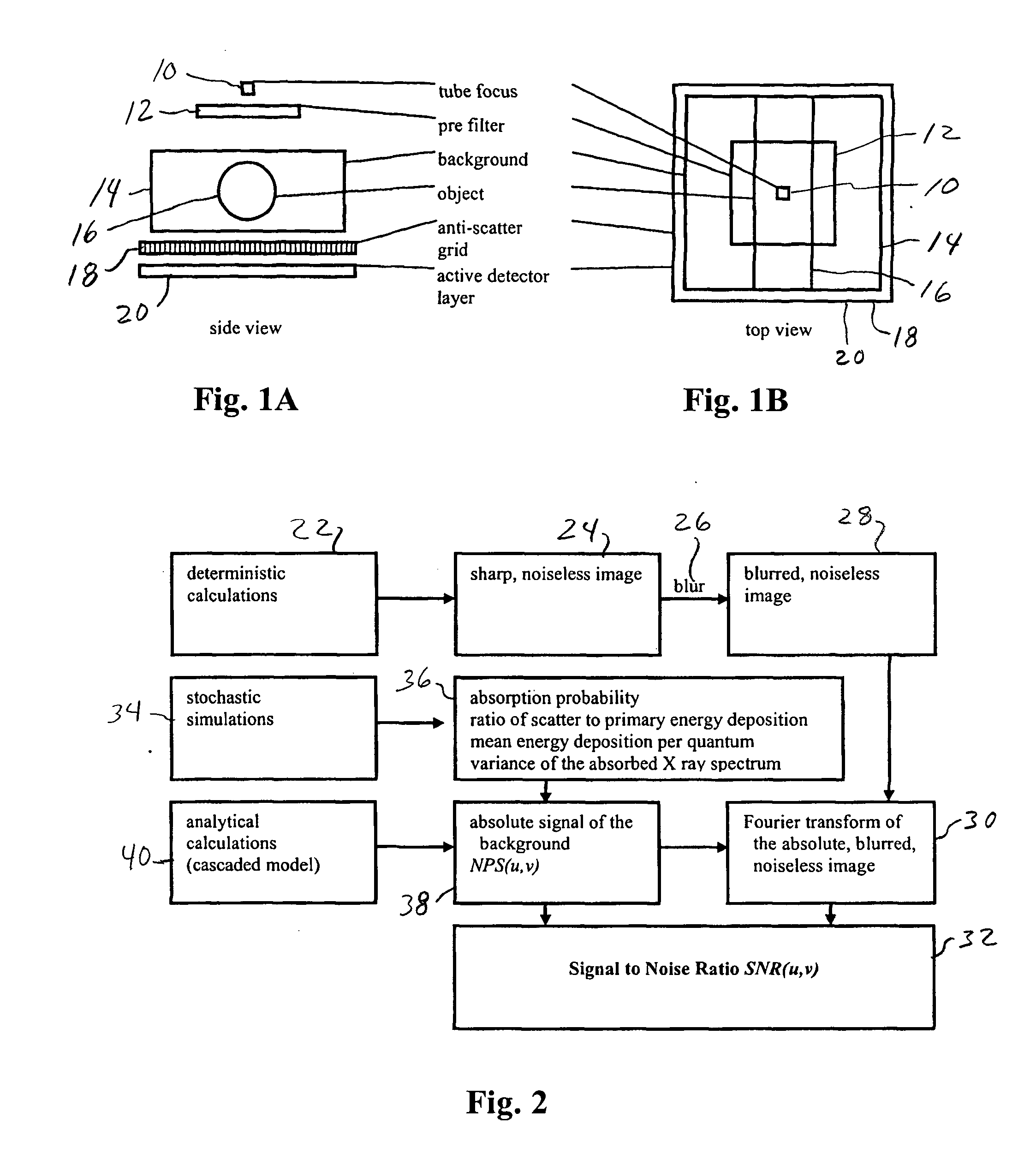
Generalized measure of image quality in medical X-ray imaging
A method for defining image quality characteristics of X-ray based medical projection imaging devices is provided. A spatial frequency-dependent signal-to-noise ratio function includes image quality parameters of spatial resolution, object contrast and noise. The detectability of an object embedded into a defined background, such as a cardiac guide wire in a patient is determined. An X-ray system may be defined and set up for obtaining an optimized image quality to determine the best object detectability for a given patient dose.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
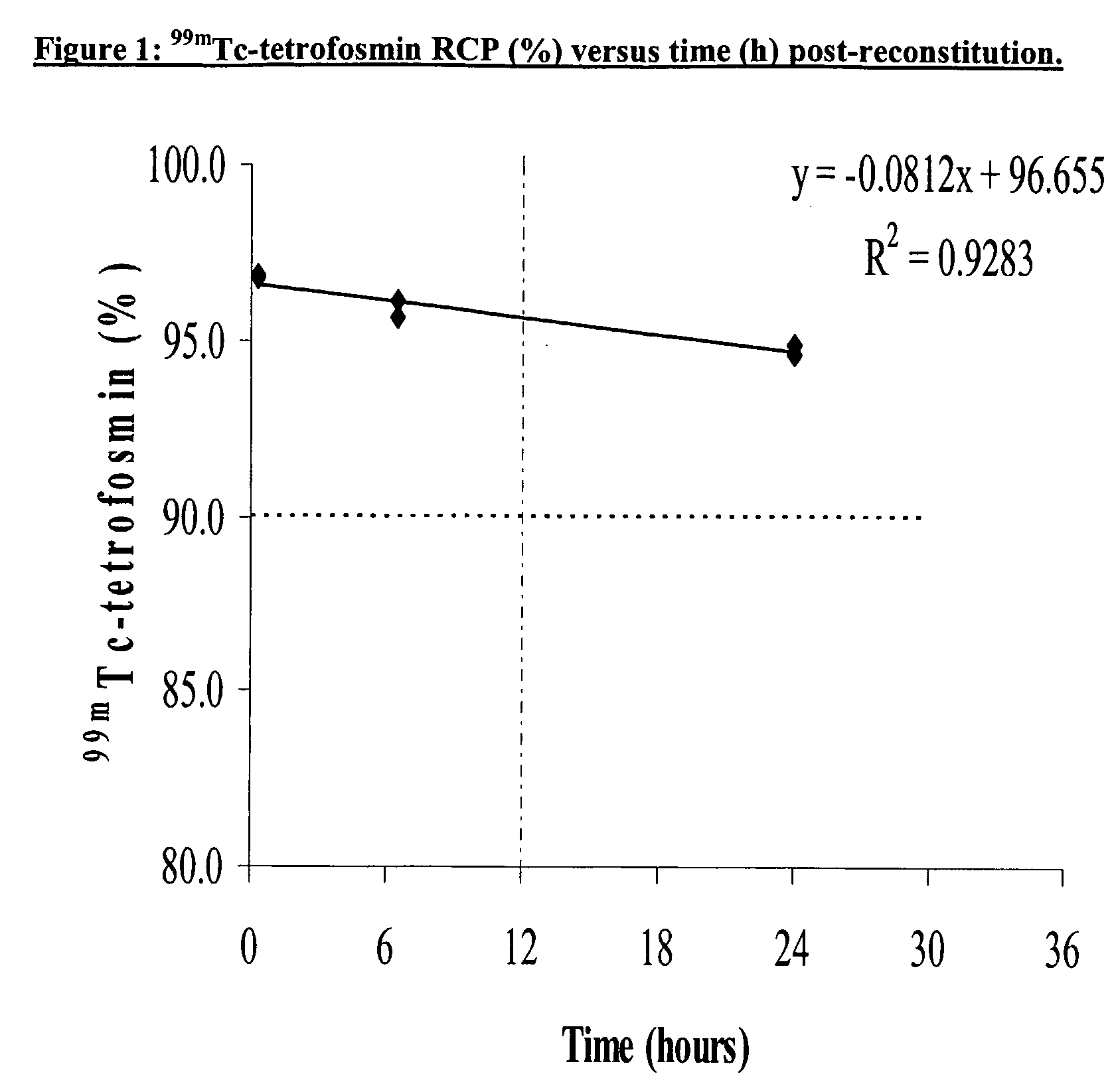
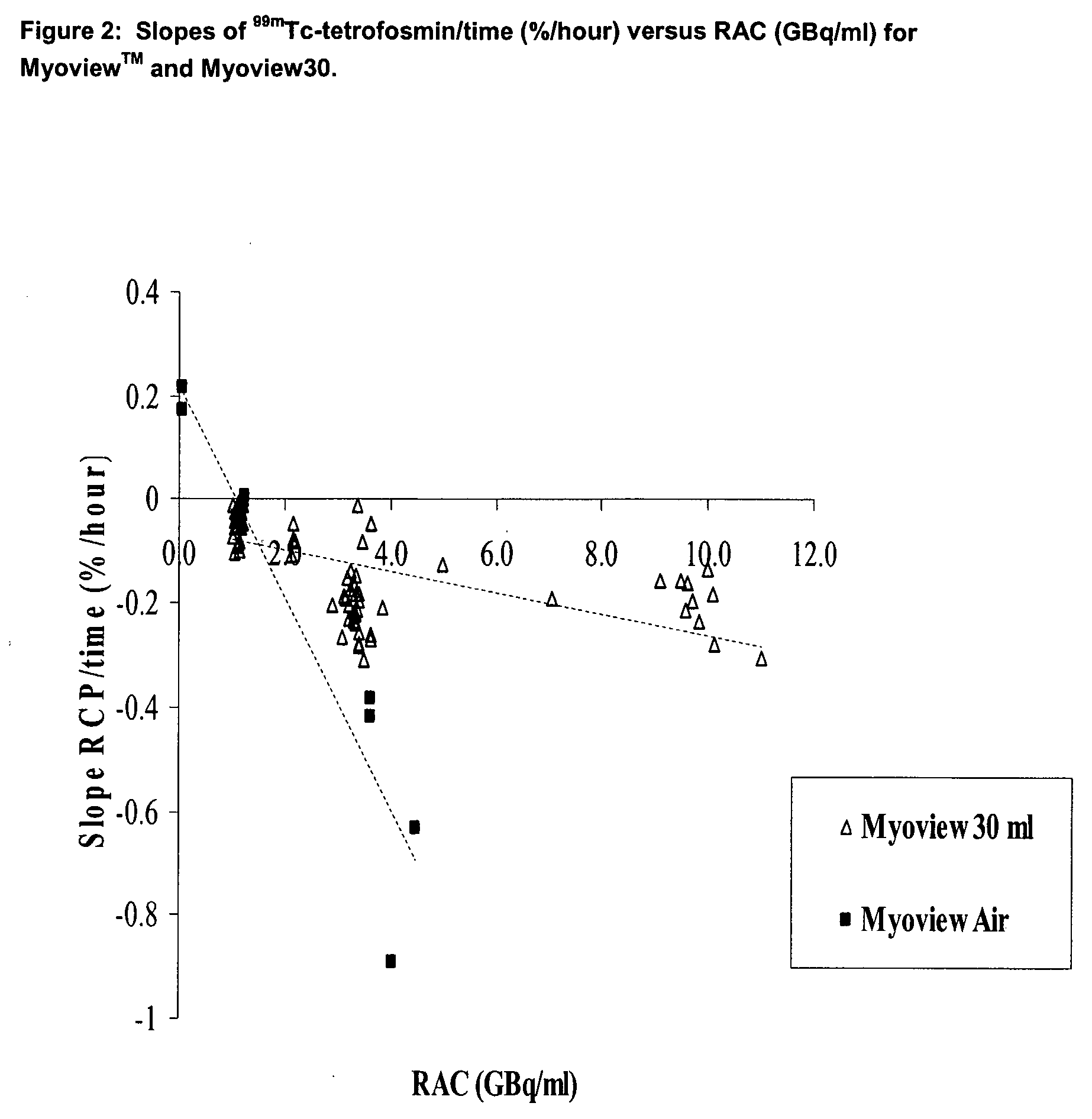
Radiopharmaceutical composition
The present invention provides a 99mTc-tetrofosmin radiopharmaceutical composition comprising tetrofosmin and a radioprotectant at a particular range of molar ratios. A kit and a multi-dose kit for the preparation of the radiopharmaceutical composition of the invention are also provided, as well as a process for the preparation of multiple unit patient doses of the radiopharmaceutical composition and a unit dose of the radiopharmaceutical composition.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
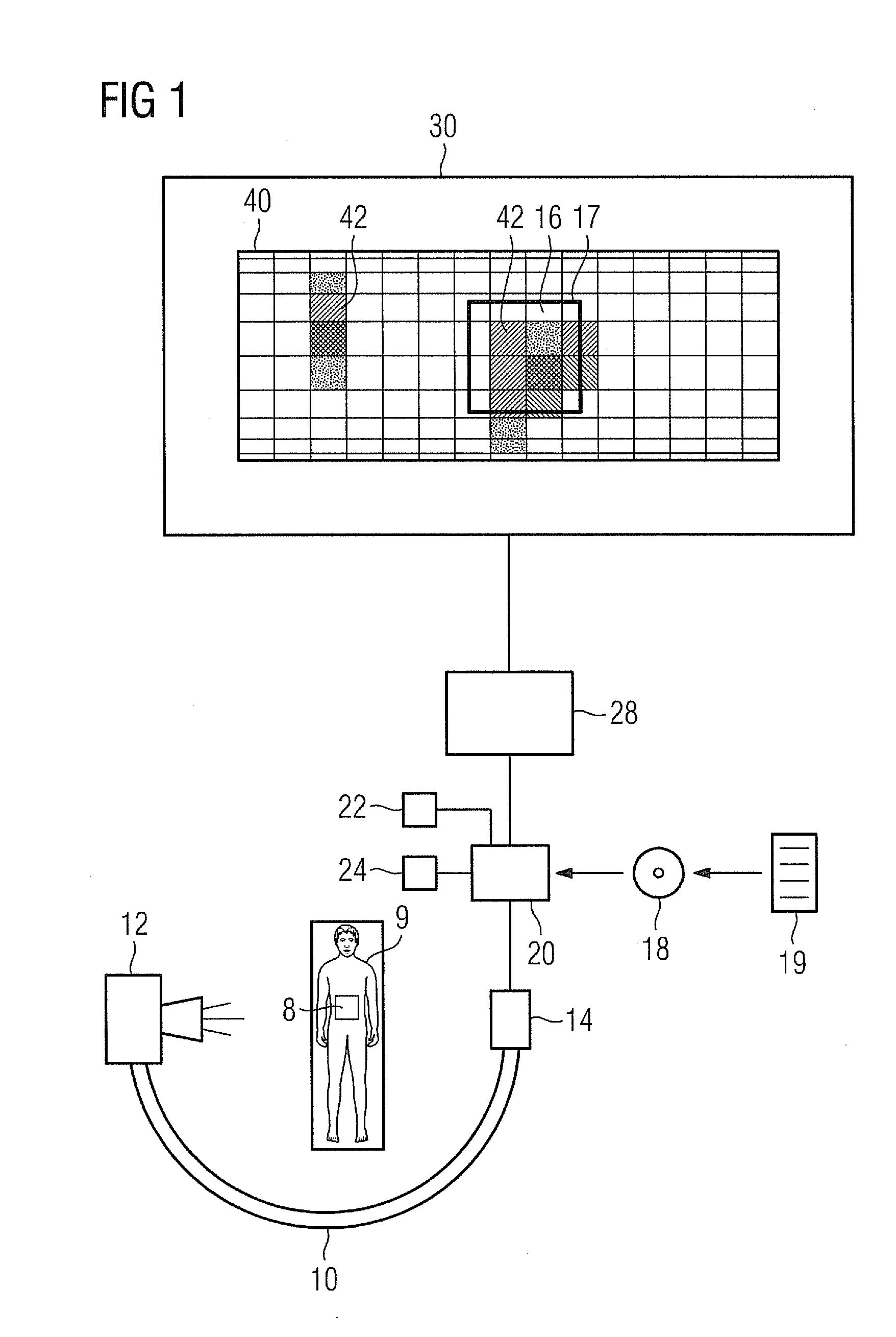
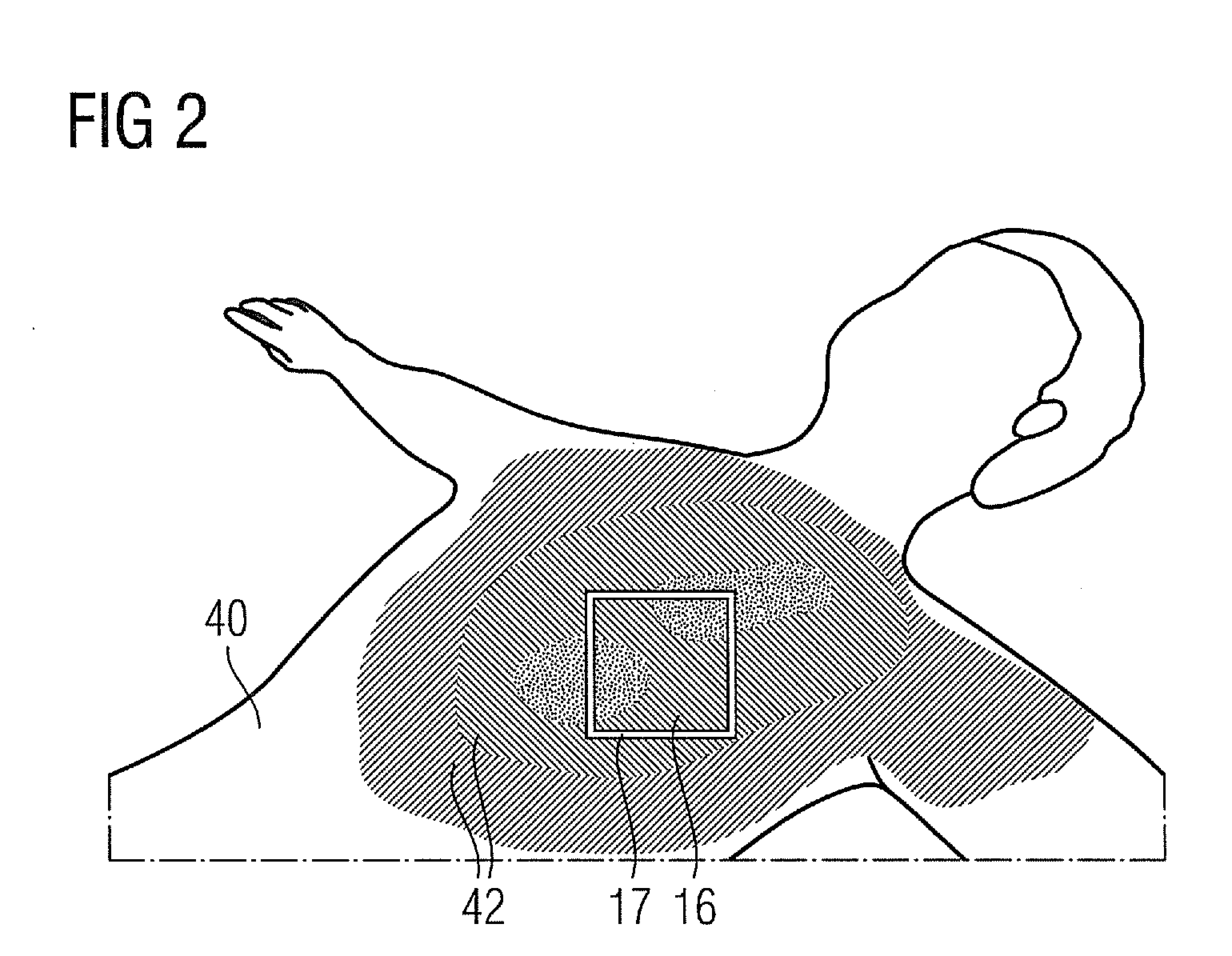
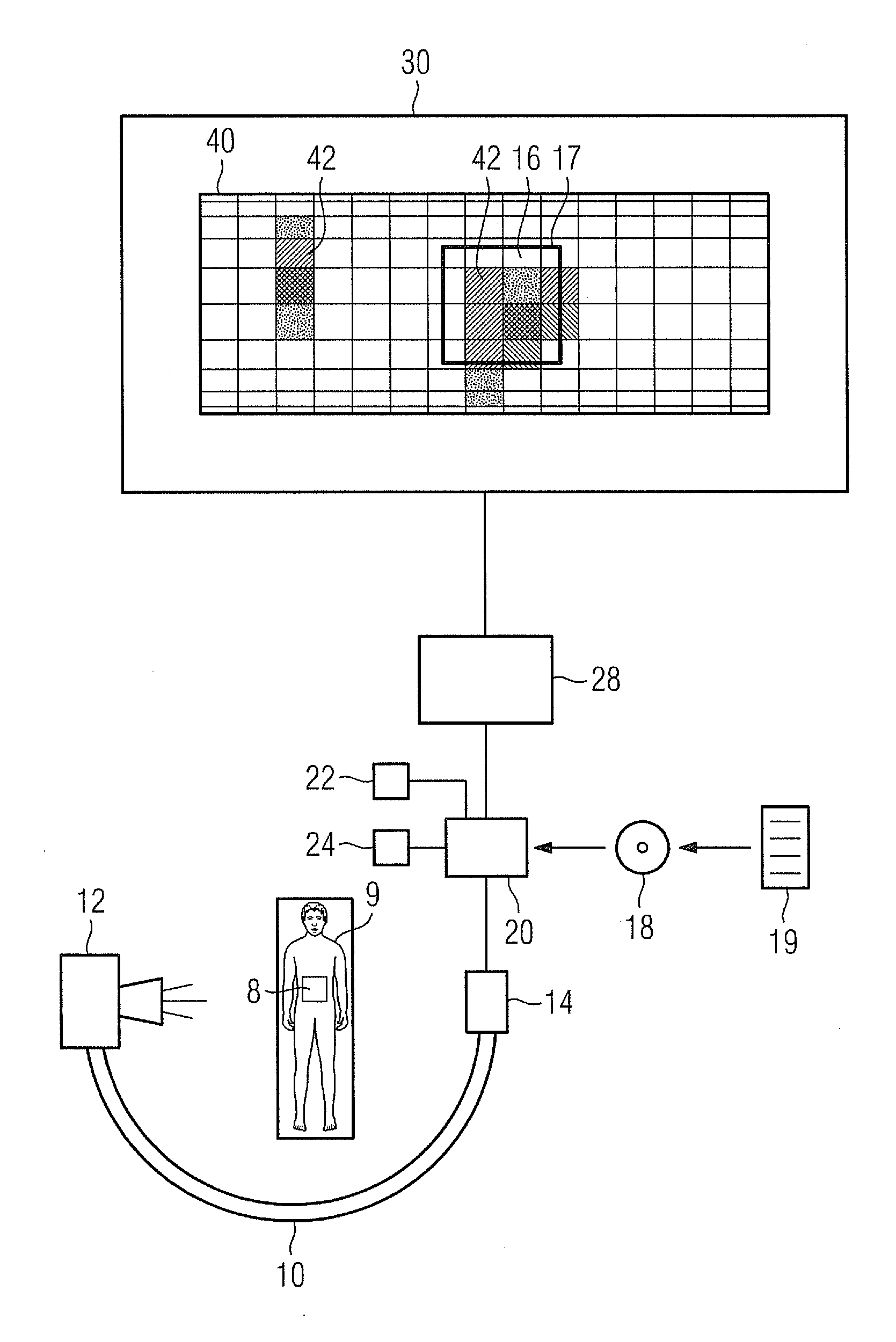
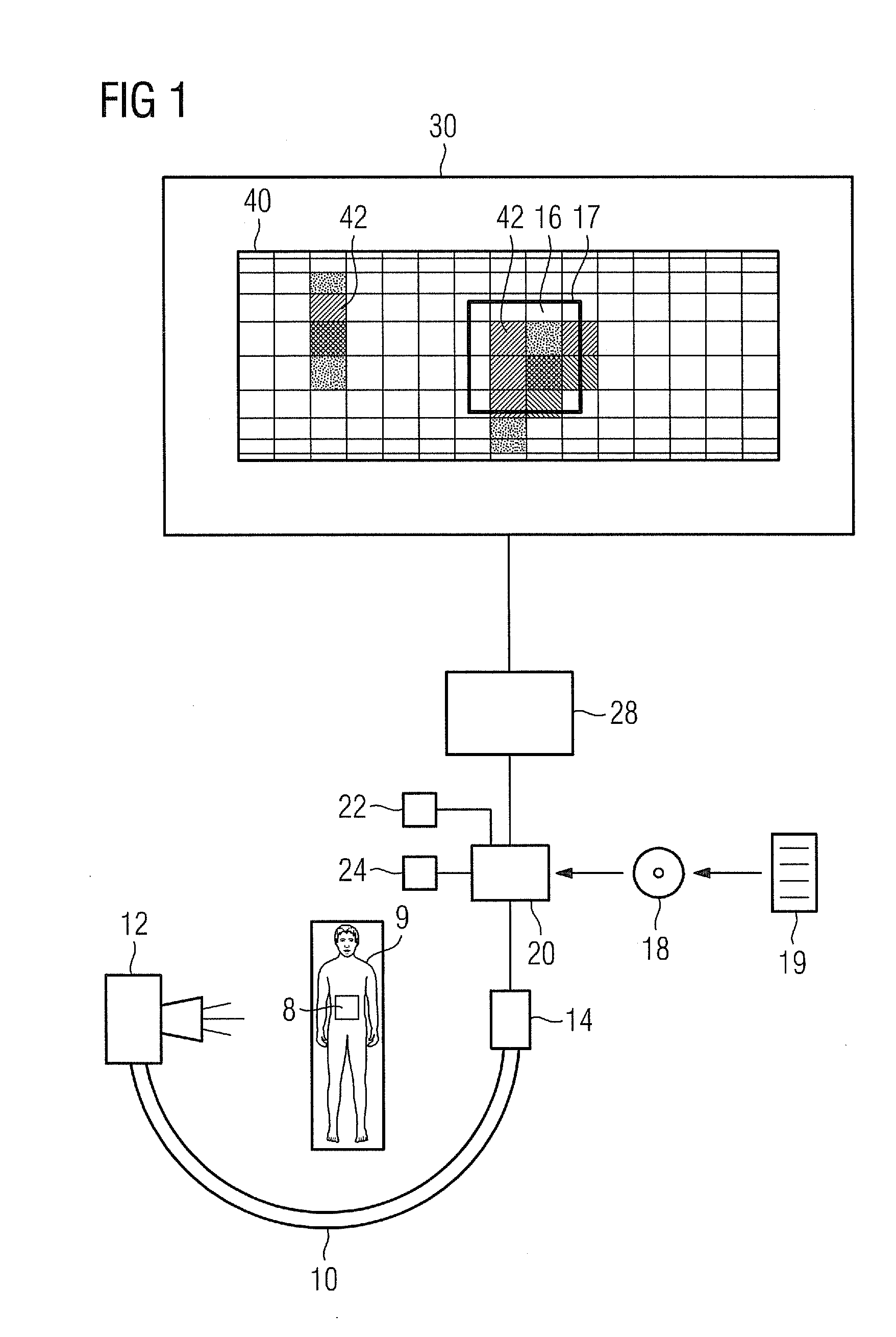
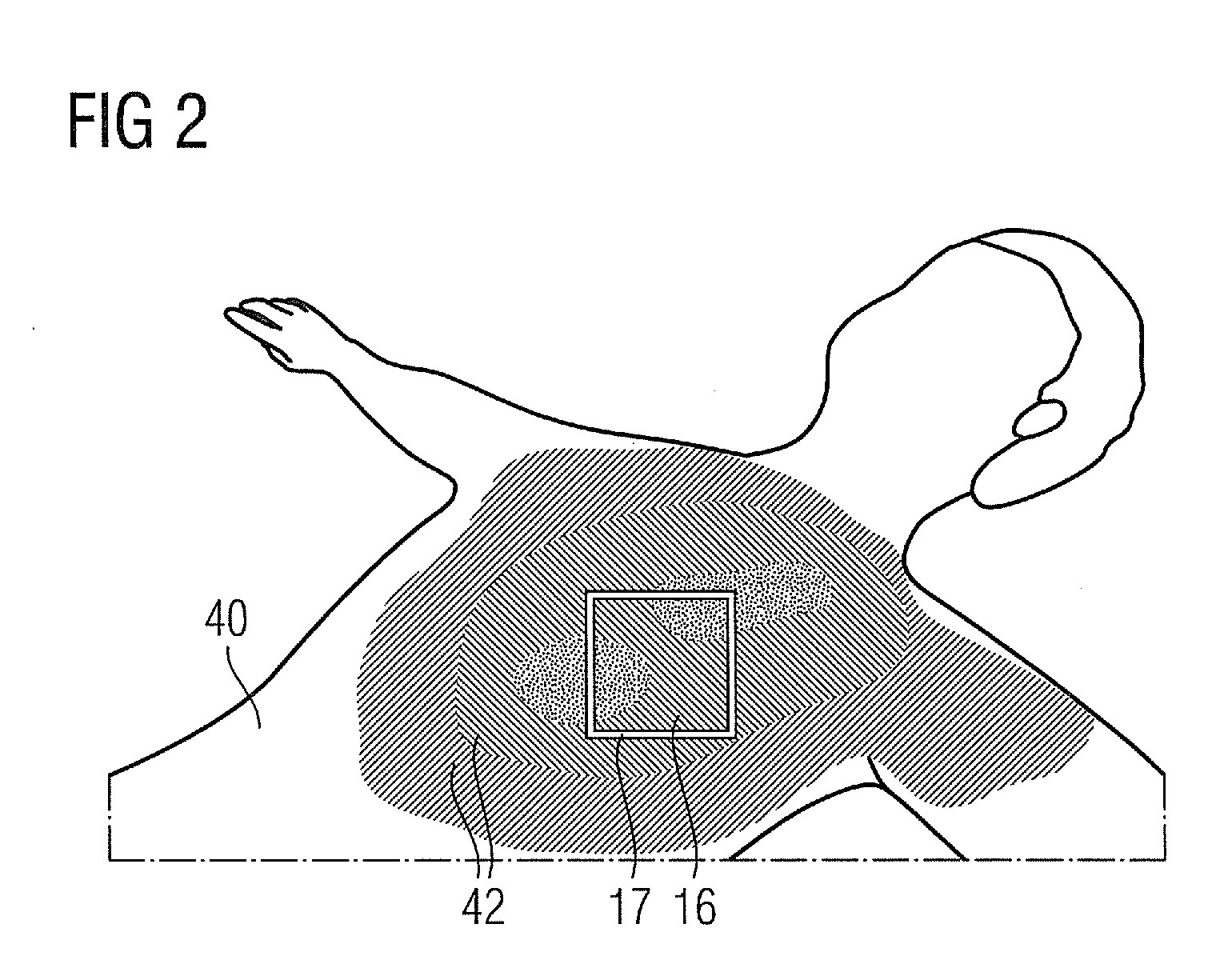
Method for Visualizing a Patient Dose, Computer Program Product and X-Ray Apparatus
A method for visualizing a dose of X-ray radiation applied to a surface of a patient in a defined time period by an X-ray apparatus is proposed. The X-ray apparatus is adjustable to different angular positions. A model of the surface of the patient is provided. The dose of X-ray radiation applied to the surface of the patient in the defined time period is calculated. The model and the calculated dose on the model is visualized. The visualization of the model and the calculated dose on the model is effected in an angular position coupled to the angular position in which the X-ray apparatus is currently disposed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
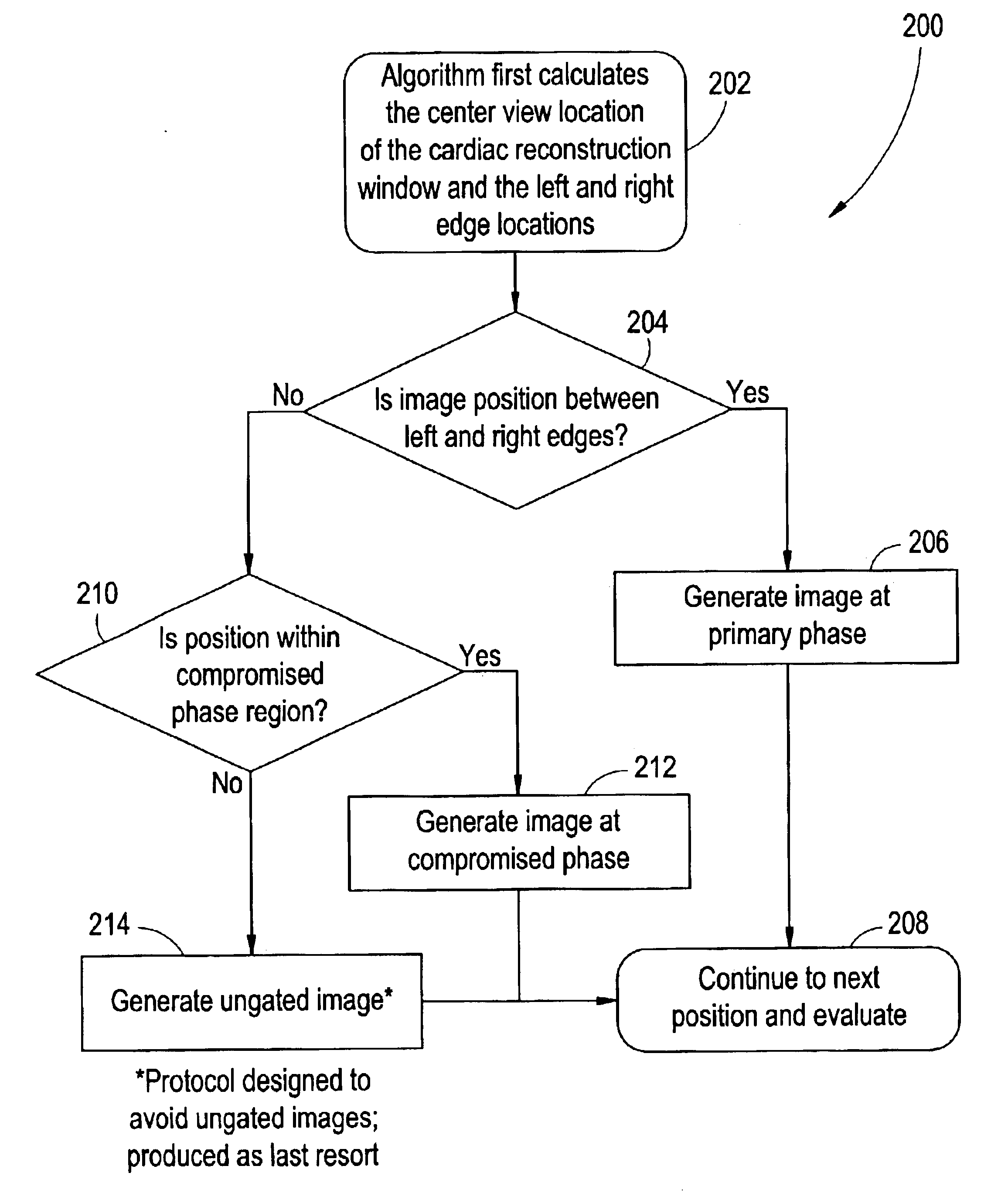
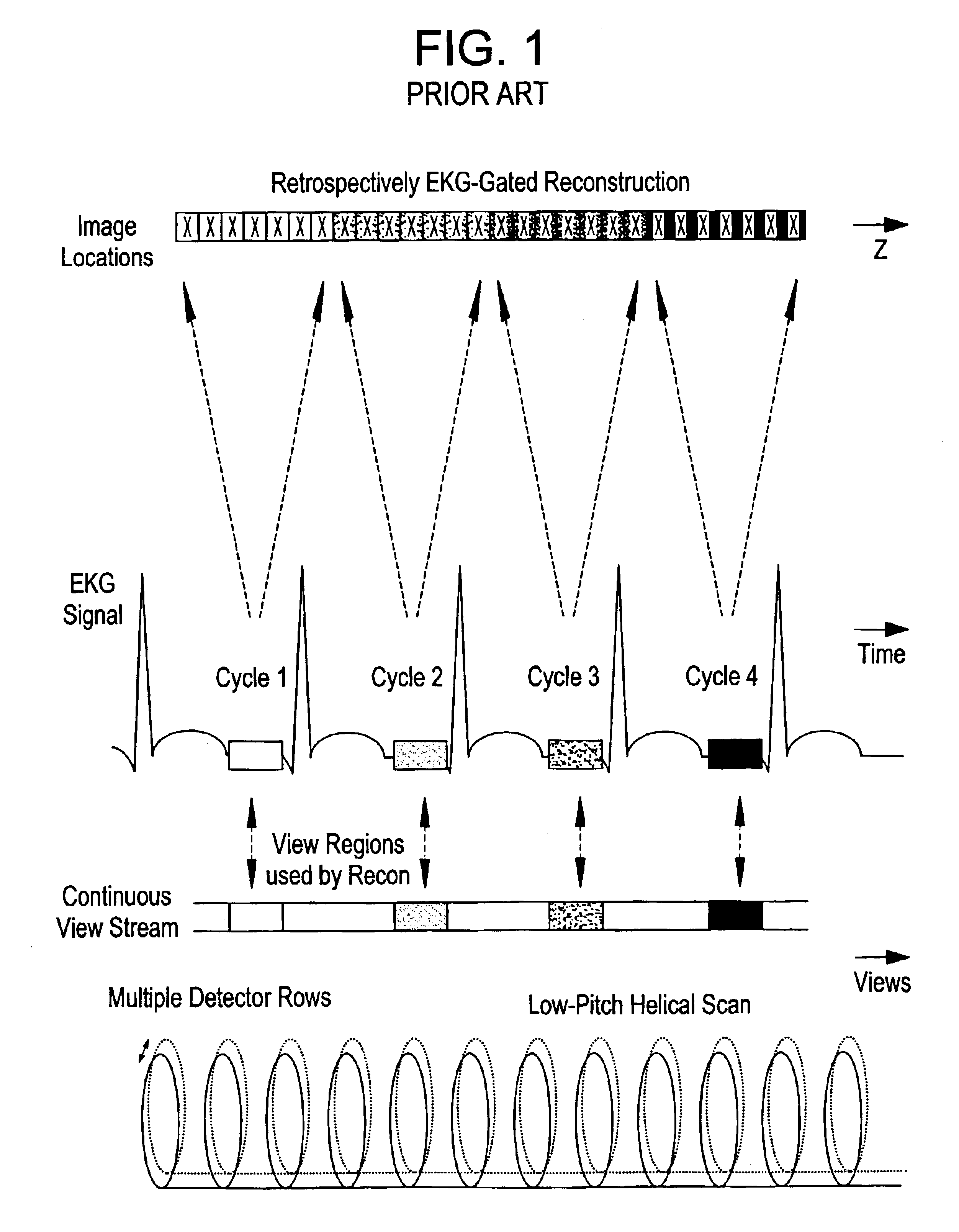
High pitch cardiac helical scan with extended reconstruction windows
InactiveUS6865250B2Reduce radiation doseIncreasing a helical scanning pitchReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanCardiac cycle
A method for image reconstruction and reducing patient dose, and an imaging system for accomplishing these methods, includes selecting a primary phase of a cardiac cycle and calculating compromised phase regions based on a selected compromised phase value. If the image position is located within the primary phase, then an image is generated at the primary phase. If the image position is not located within the primary phase, but is located within a compromised phase region, then an image is generated at the compromised phase region.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Method and system to reconstruct treatment dose to a patient from integrated exit-transit images of radiation fields taken during treatment
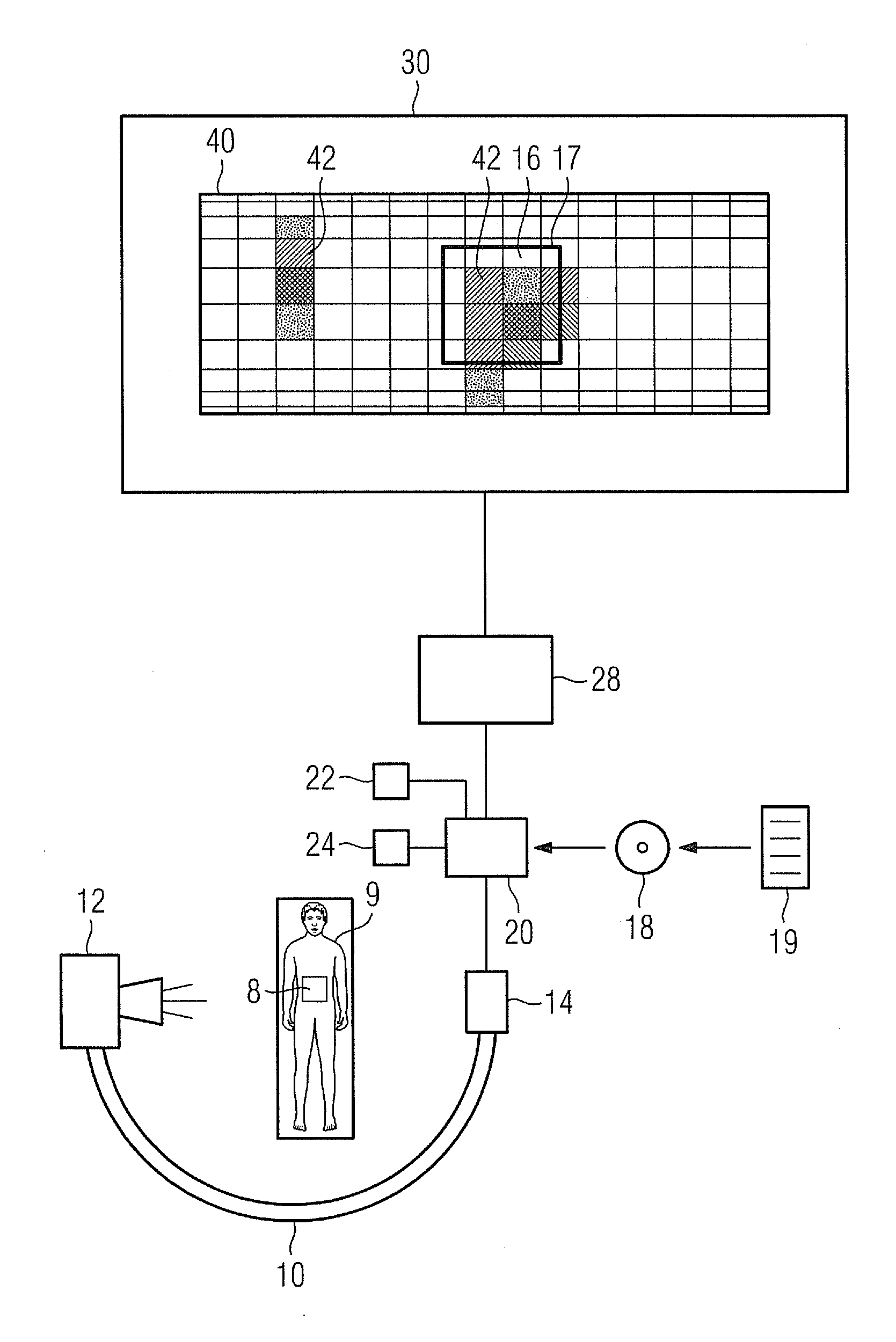
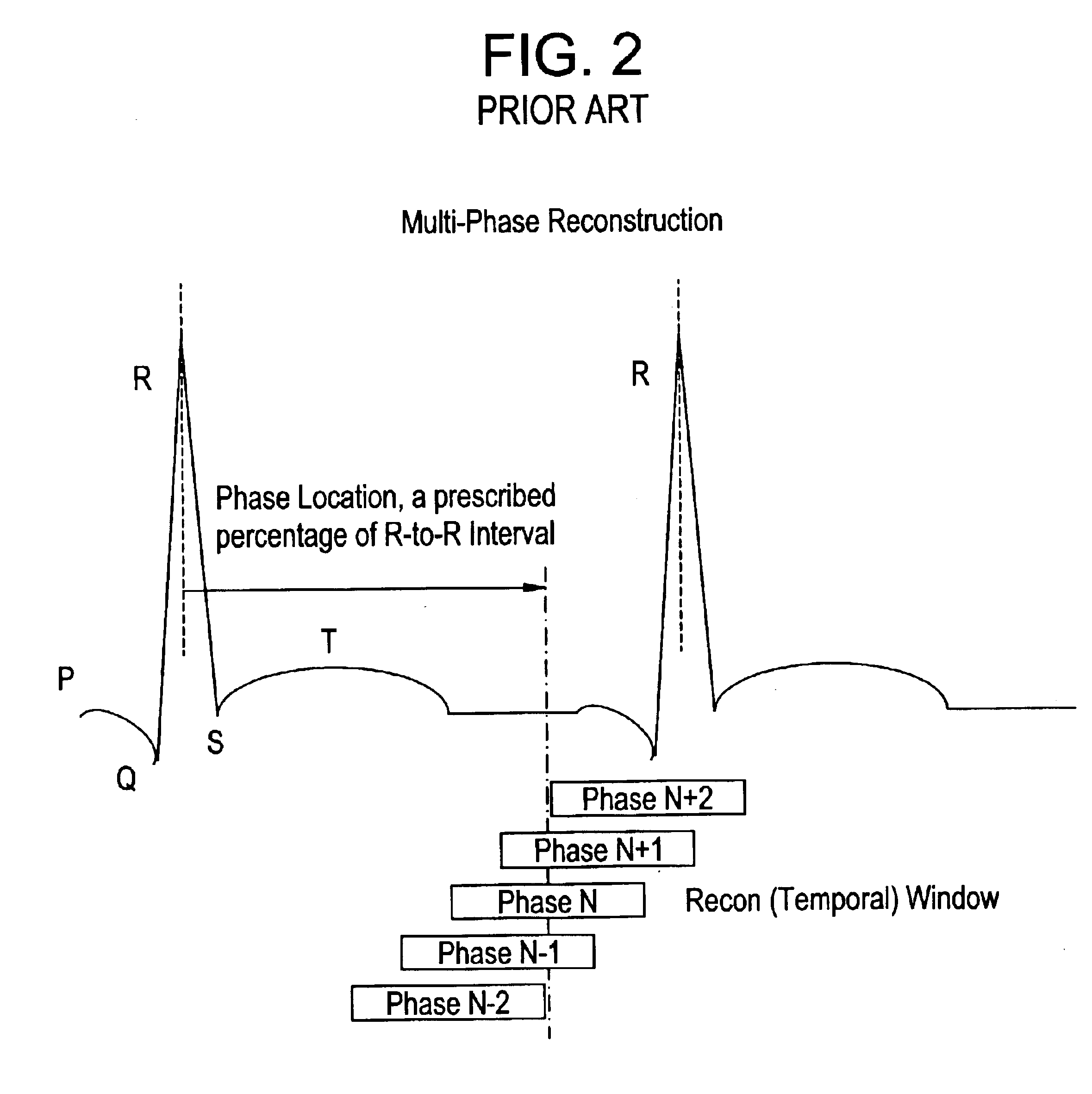
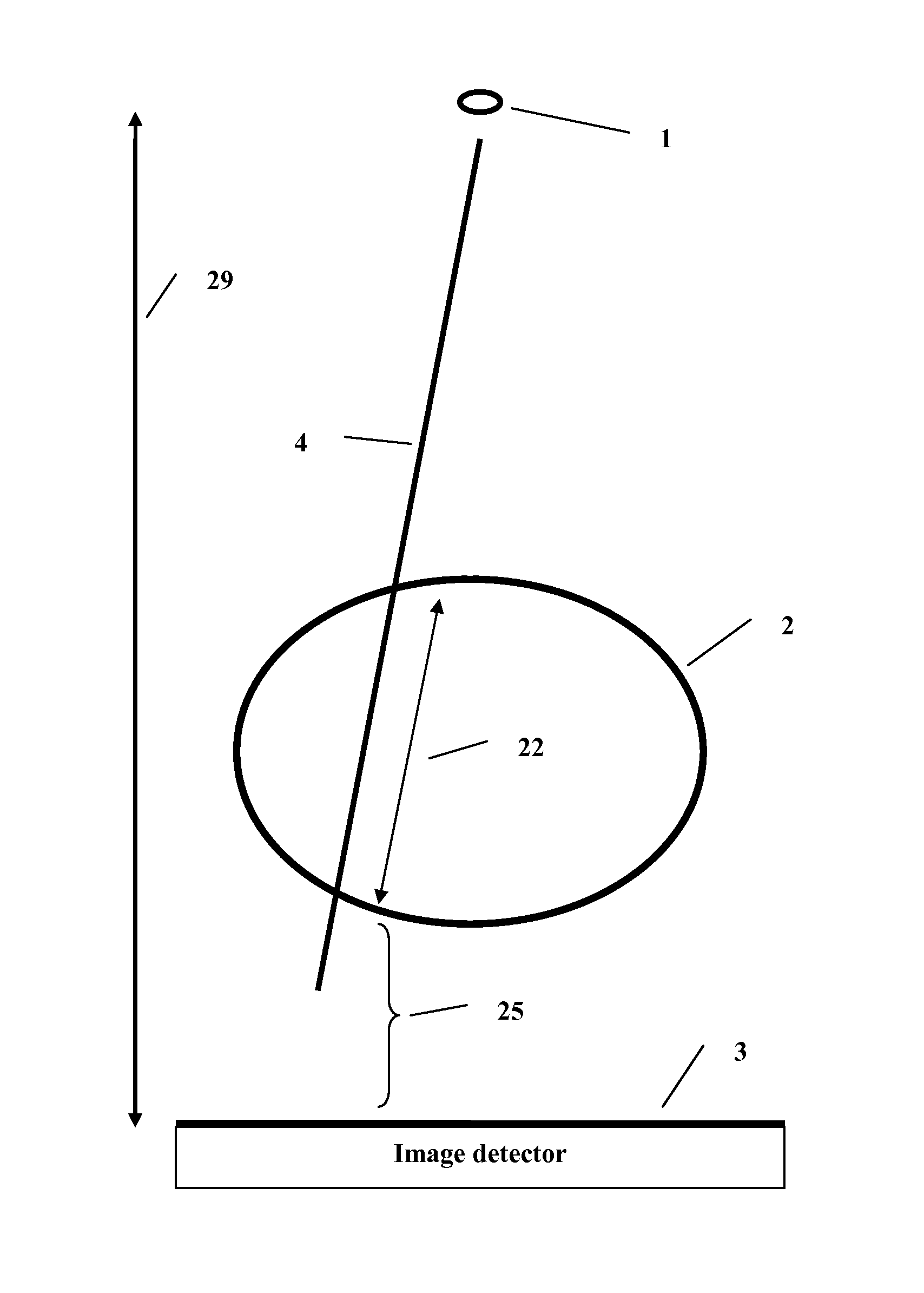
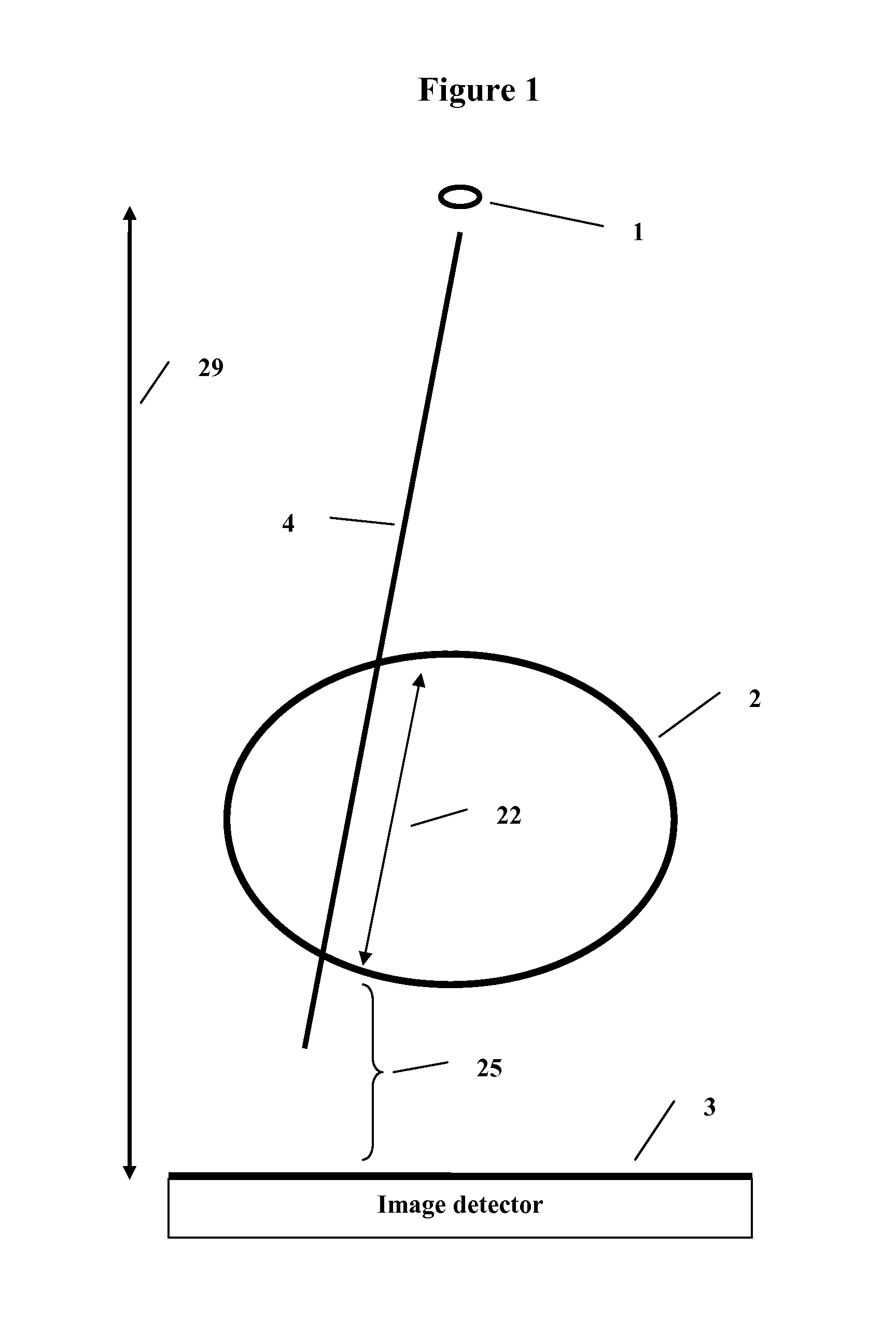
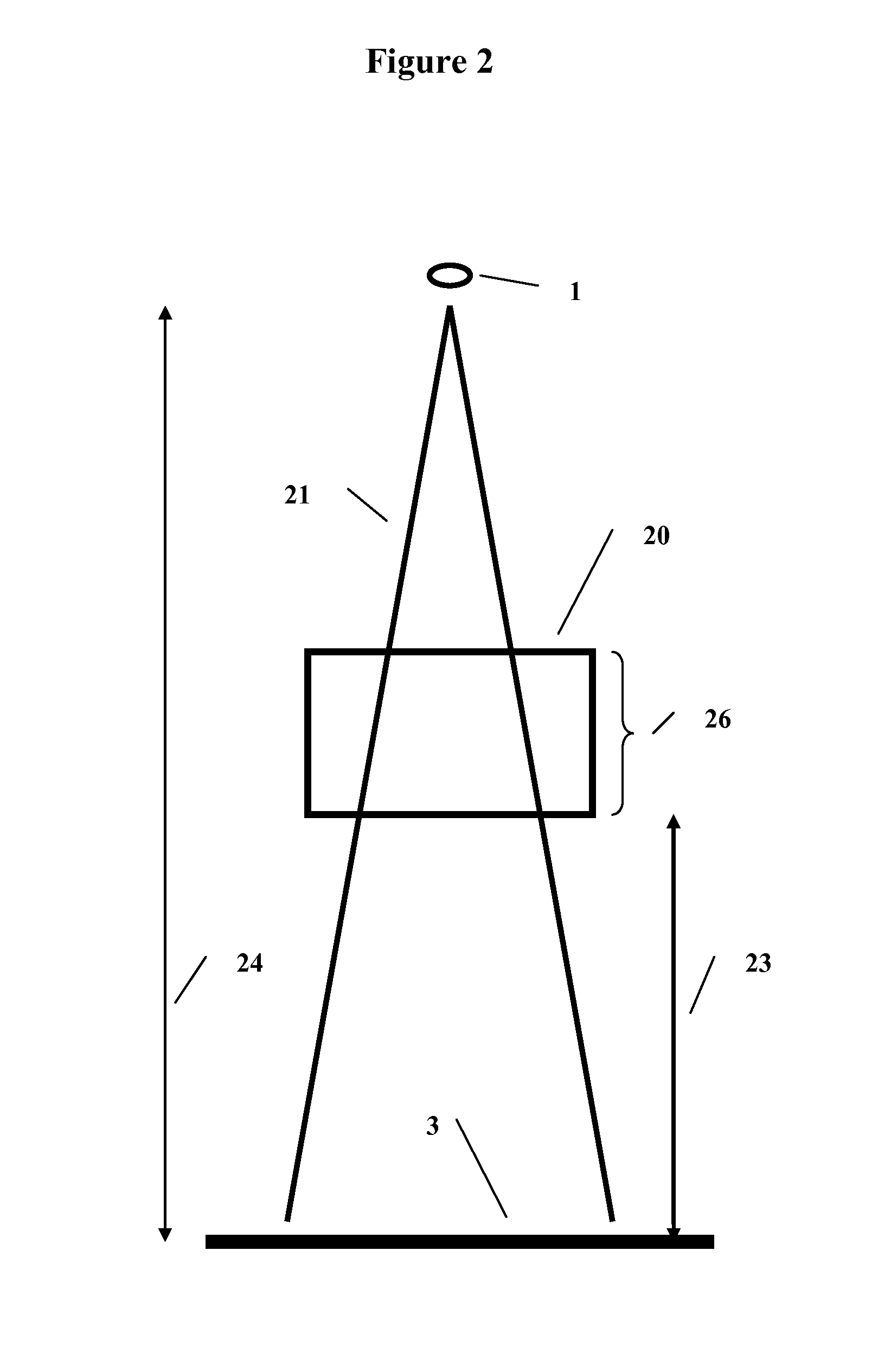
A method and system to compute the dose to a patient (2) given a captured integrated exit-transit image (5) of the radiation rays (4) traveling from the source of x-rays (1) through the patient (2) to the imaging device (3) to product the exit-transit image (5). Each radiation field image (5) is transformed (6,8,10,12) to multiple images (7,9,11,13) for each phantom thickness (26) that was measured with the imaging device (3) for a range of field sizes (21). Given the water equivalent path (22) through the patient for a ray (4) reaching a pixel (15, 16), the final pixel value (19) is interpolated from the images (9, 11) that bracket the water equivalent path through the patient (22).
Owner:LIFELINE SOFTWARE INC
Method and system for the calculation of dose responses for radiotherapy treatment planning
InactiveUS20080004845A1Rapid dose calculationQuick calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringComputation using non-denominational number representationPhoton Beam Radiation TherapyBeam direction
Method and system that allows patient dose response functions to be calculated, prior to treatment planning, for external photon beam radiotherapy. In one embodiment, for each location where a separate dose value is desired, referred to as a dose region, adjoint calculations are performed to calculate the adjoint solution fields associated with that dose region. Once potential beam directions are specified, a ray tracing process is performed to transport the adjoint solution fields out of the patient and to locations where treatment plan parameters may be specified. The output of this process is the dose response at each dose region resulting from a prescribed photon fluence, at a given location, direction, and energy.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
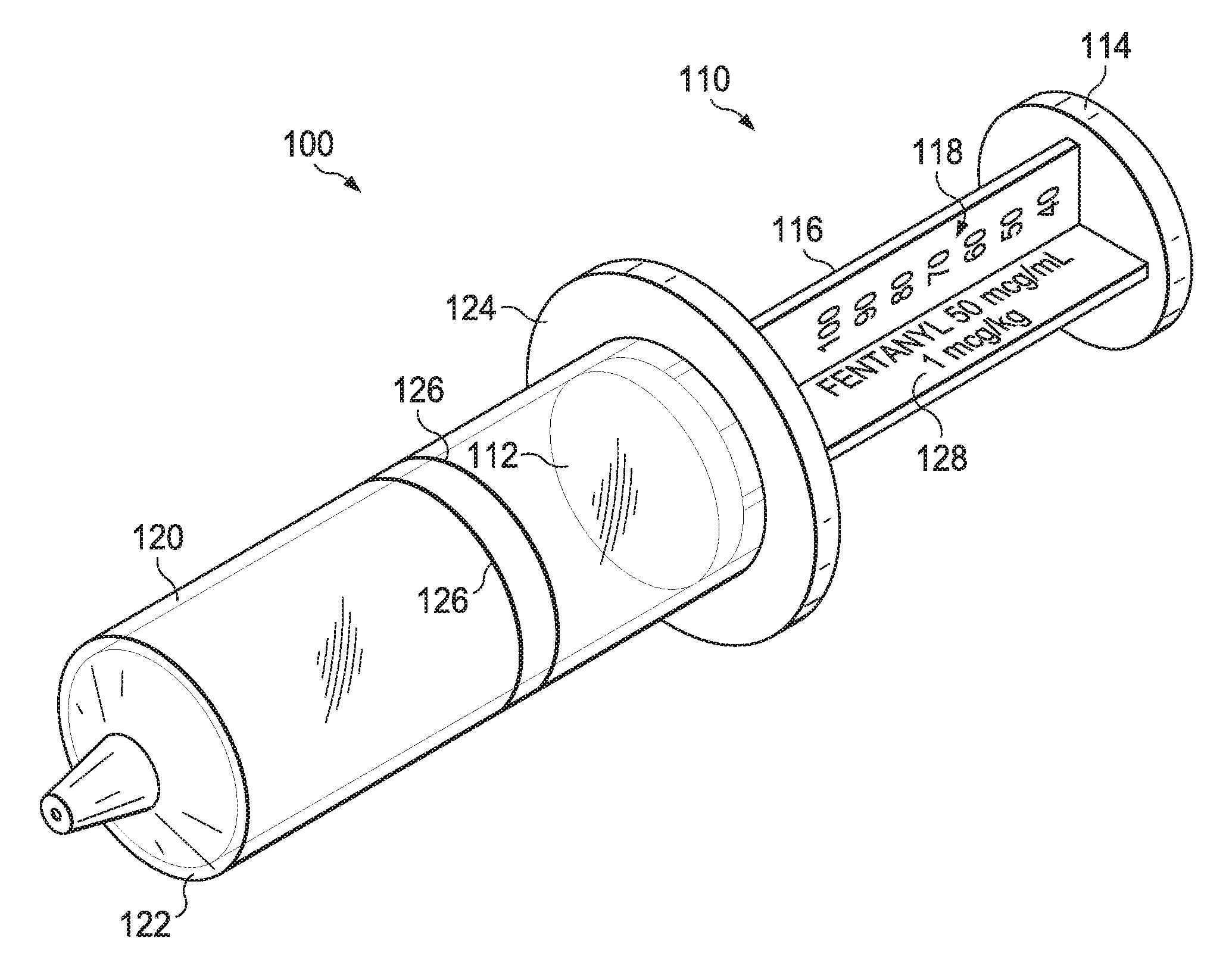
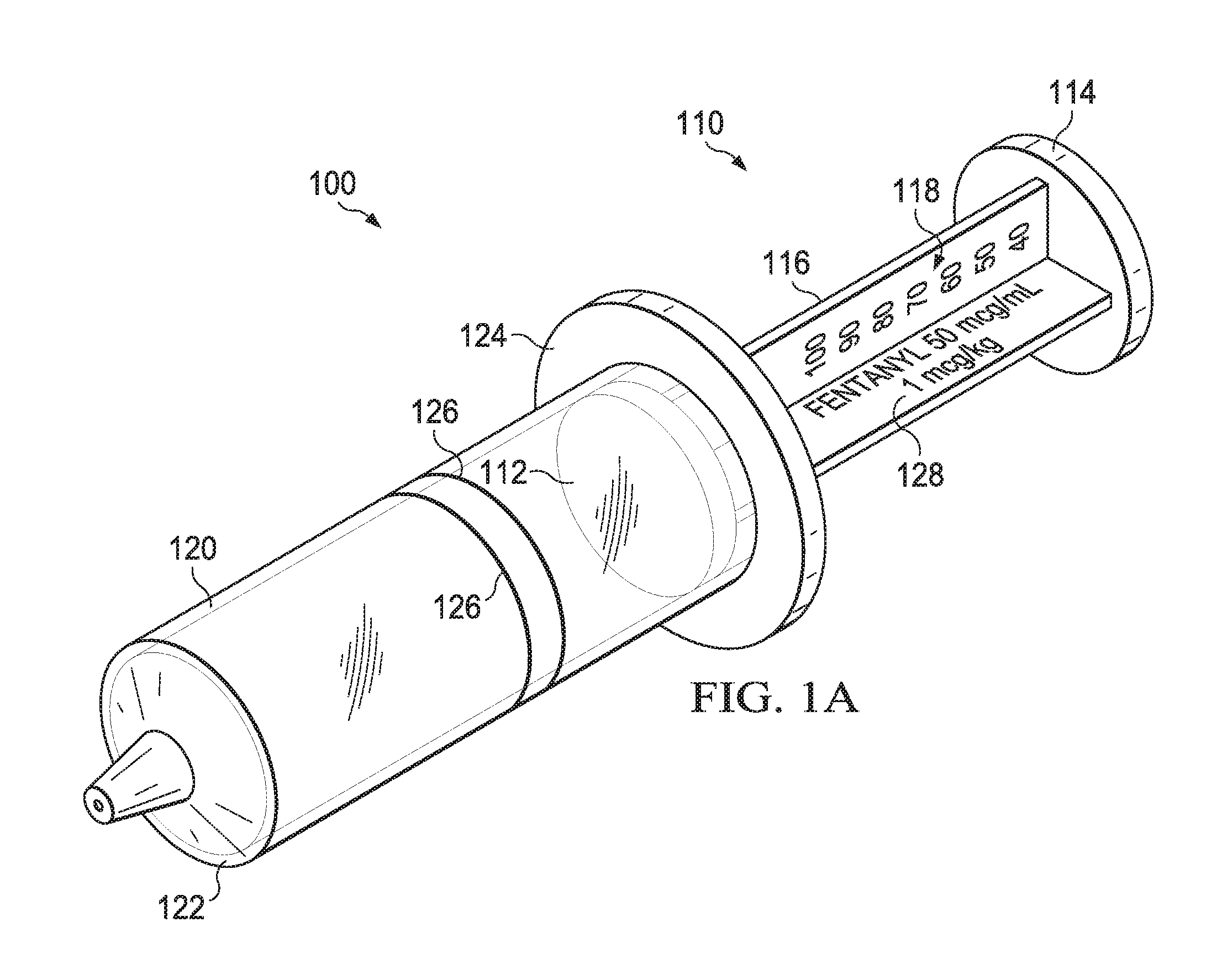
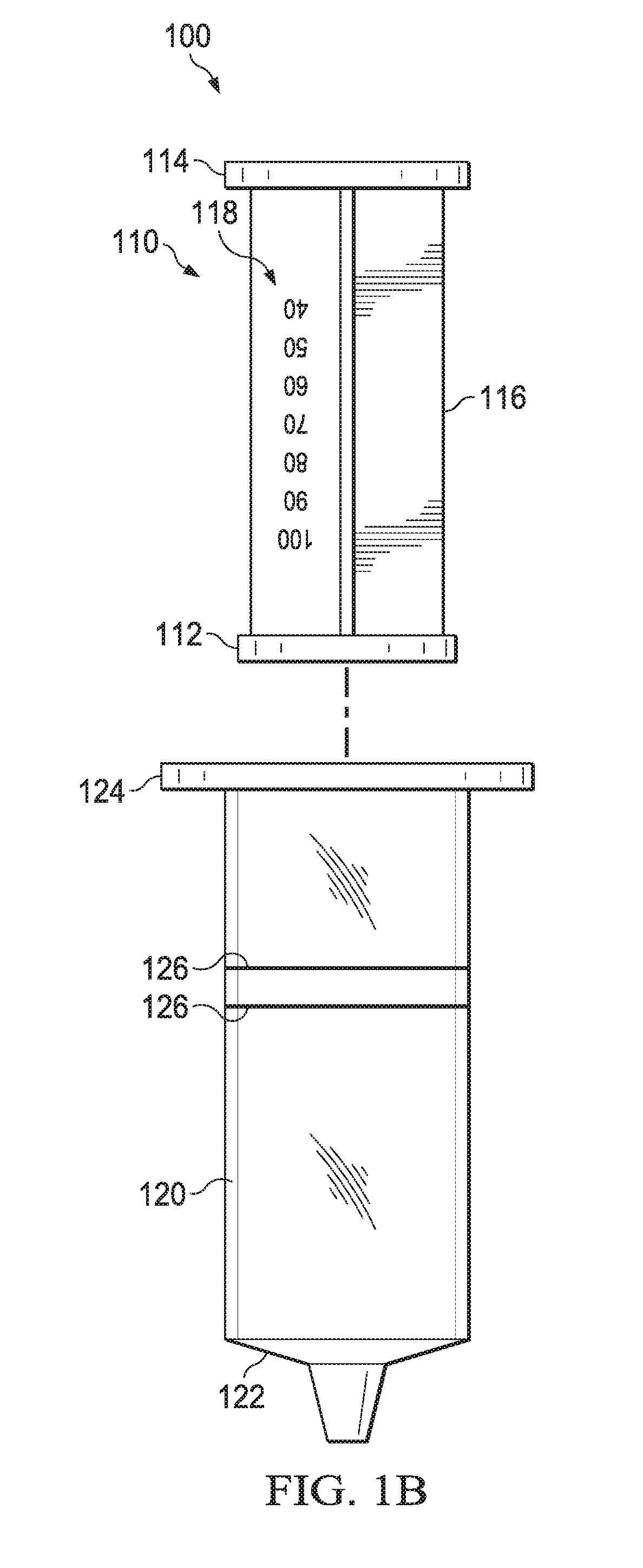
Syringe measurement marking and dosing system
ActiveUS9566388B1Reduces potential dosing errorEliminates intersectionInfusion syringesPharmaceutical containersBlood sugarPatient Base
A syringe measurement marking system for use with a syringe that includes a barrel and a plunger is marked with patient-based numerical measuring indicia on the plunger. The patient-based numerical measuring indicia is non-volumetric in nature and instead indicates patient dosing criteria such as weight, age, height, blood sugar level, or any other patient criteria by which dosing is determined. The plunger may contain more than one set of patient-based numerical measuring indicia, such as one set for adults or one set for pediatrics, or one set for a first dose of a medication and one set for a second dose, or one set based on weight in pounds and one set based on weight in kilograms. The syringe barrel will contain one or more measurement lines.
Owner:ROWDY J LLC
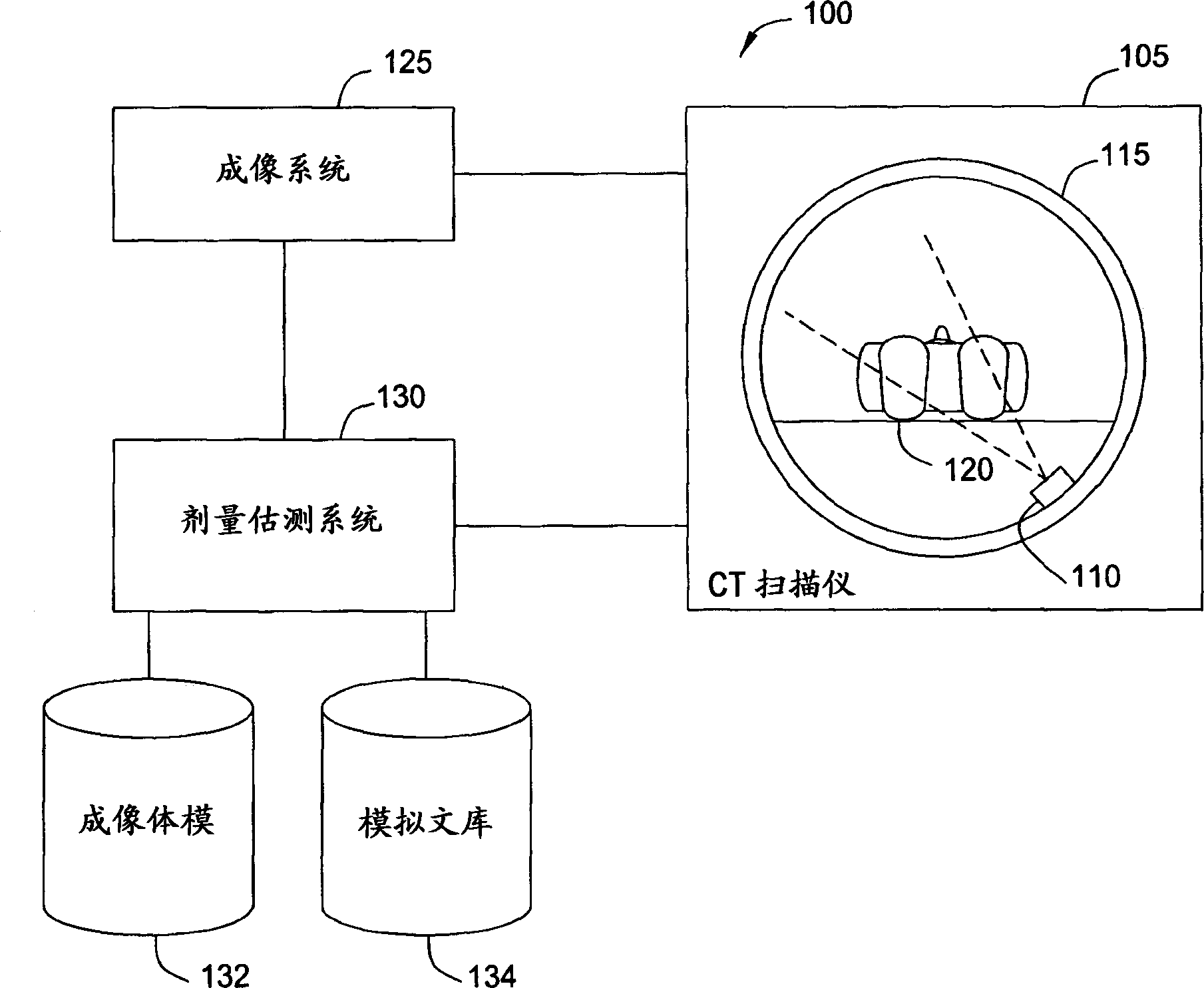
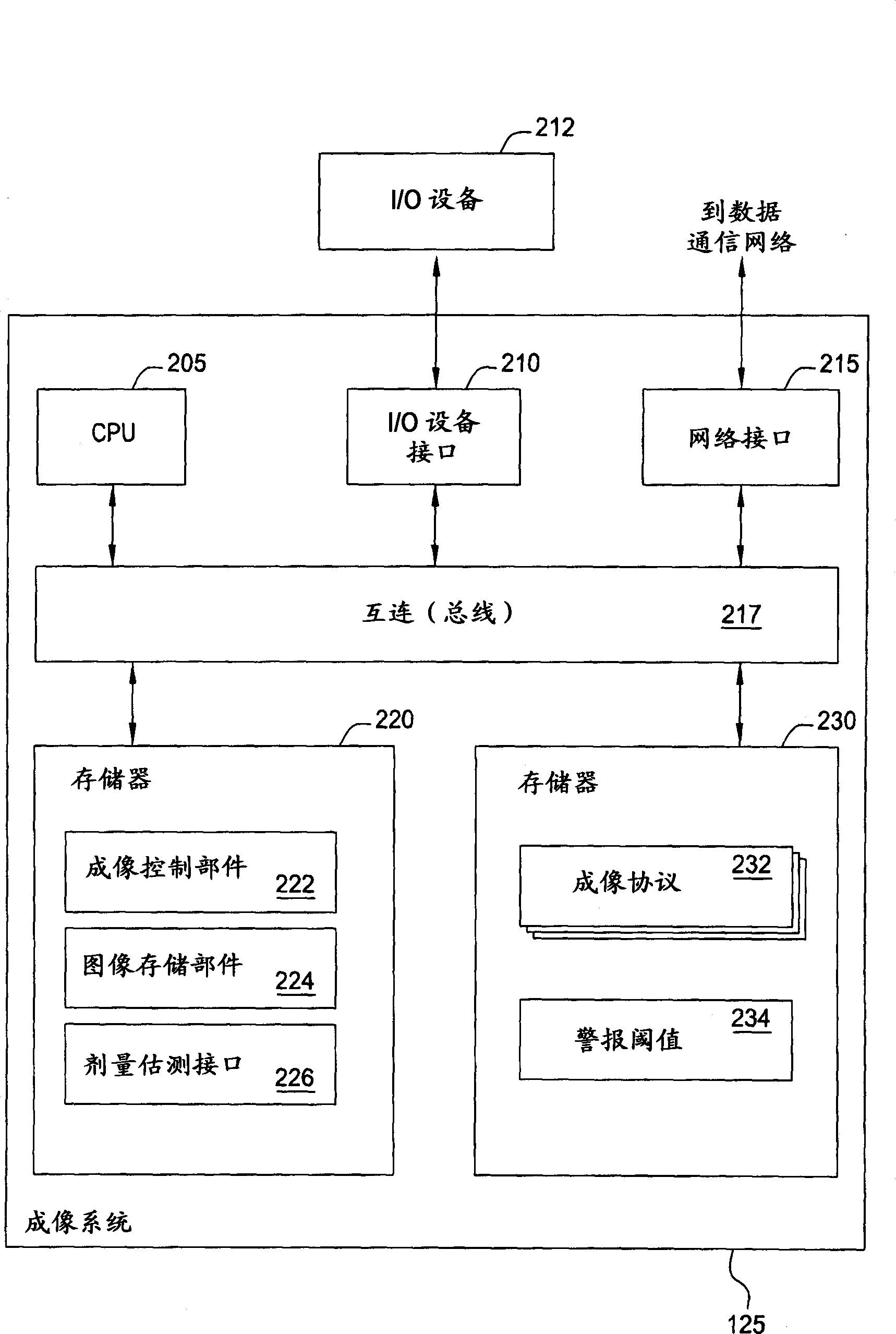
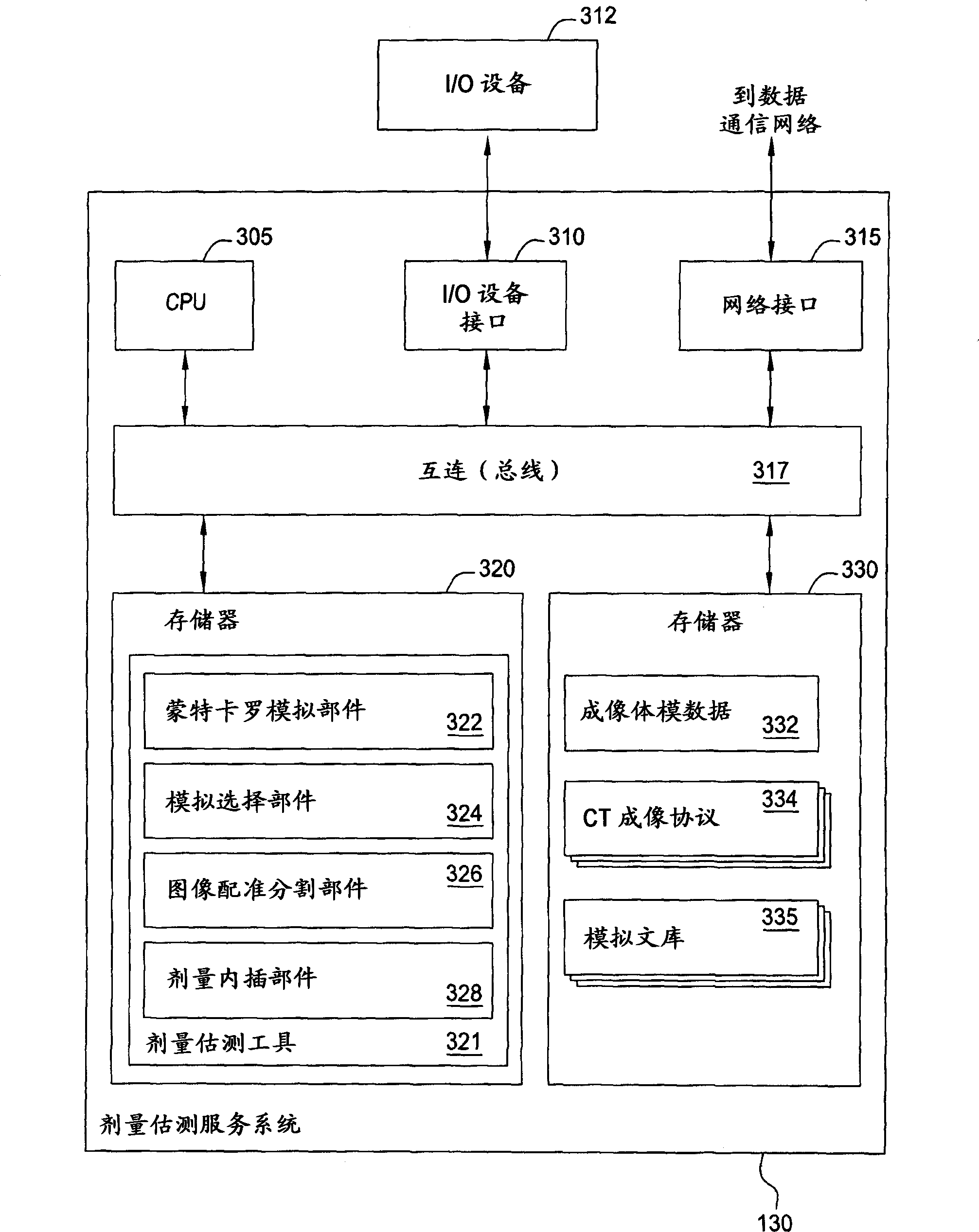
Generating a suitable model for estimating patient radiation dose resulting from medical imaging scans
Techniques are disclosed for estimating patient radiation exposure during computerized tomography (CT) scans. More specifically, embodiments of the invention provide efficient approaches for generating a suitable patient model used to make such an estimate, to approaches for estimating patient dose by interpolating the results of multiple simulations, and to approaches for a service provider to host a dose estimation service made available to multiple CT scan providers.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Single patient dose medicament dispenser with applicator
InactiveUS20050269219A1Easy to openMinimal amountLiquid surface applicatorsDispensing apparatusMedication DispenserBiomedical engineering
A unit dose package for applying a material with an applicator having a separate material and applicator portion. In one embodiment, a plurality of material wells is used to mix different materials to be dispensed with an applicator. In an embodiment the plurality of material wells are concentric. In another embodiment a portion of the cover is removable. In another embodiment, a material well is squeezed to dispense the material onto an applicator.
Owner:CENTRIX
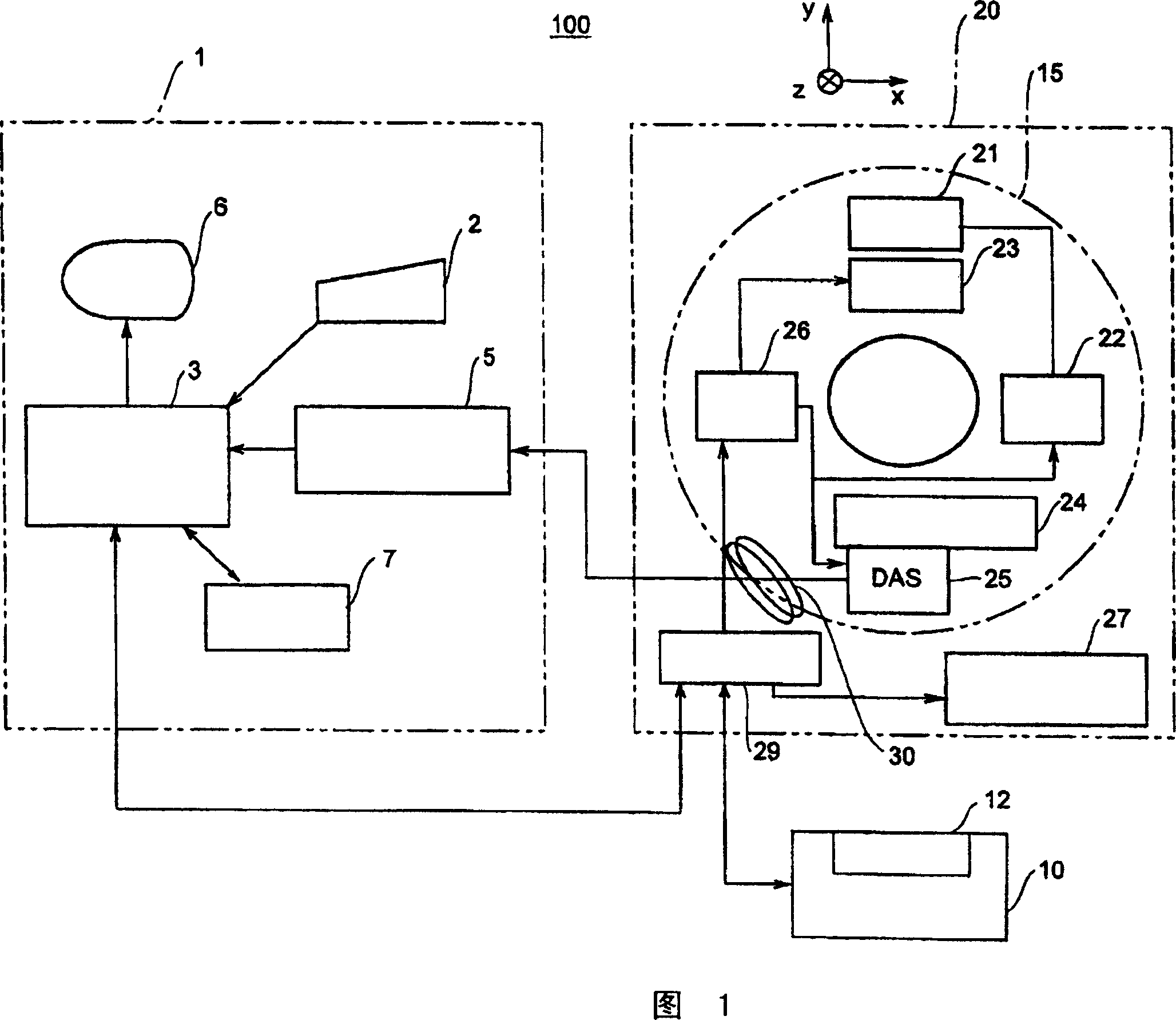
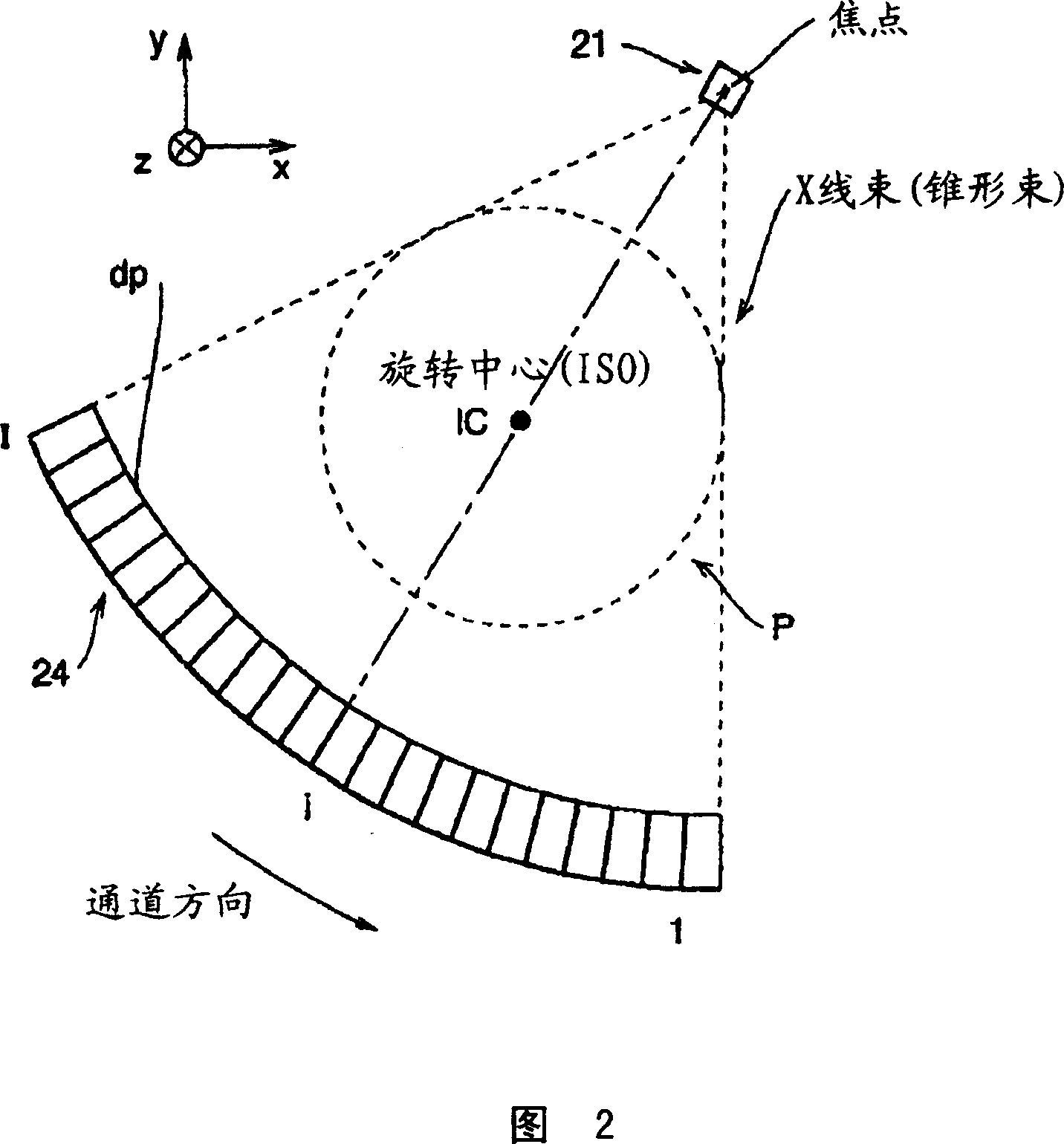
Radiography apparatus and radiography method
InactiveUS20060222142A1Easy to fallImprove diagnostic efficiencyRadiation/particle handlingTomographyBlood flowThree vessels
The present invention attempts to reduce an amount of a contrast medium or a patient dose and improve diagnostic efficiency. The conditions for a main scan are designated so that a first scan of scanning a subject with a tube current of a first tube current value fed to an X-ray tube will be performed in order to examine the blood flow in a subject's blood vessel into which a contrast medium is injected. Moreover, the conditions for a main scan are designated so that a second scan of scanning the subject with a tube current of a second tube current value fed to the X-ray tube will be performed in order to image the subject's blood vessel into which the contrast medium is injected. Images of the subject are constructed based on projection data items produced by scanning the subject under the sets of conditions for a main scan.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Method for visualizing a patient dose, computer program product and X-Ray apparatus
A method for visualizing a dose of X-ray radiation applied to a surface of a patient in a defined time period by an X-ray apparatus is proposed. The X-ray apparatus is adjustable to different angular positions. A model of the surface of the patient is provided. The dose of X-ray radiation applied to the surface of the patient in the defined time period is calculated. The model and the calculated dose on the model is visualized. The visualization of the model and the calculated dose on the model is effected in an angular position coupled to the angular position in which the X-ray apparatus is currently disposed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
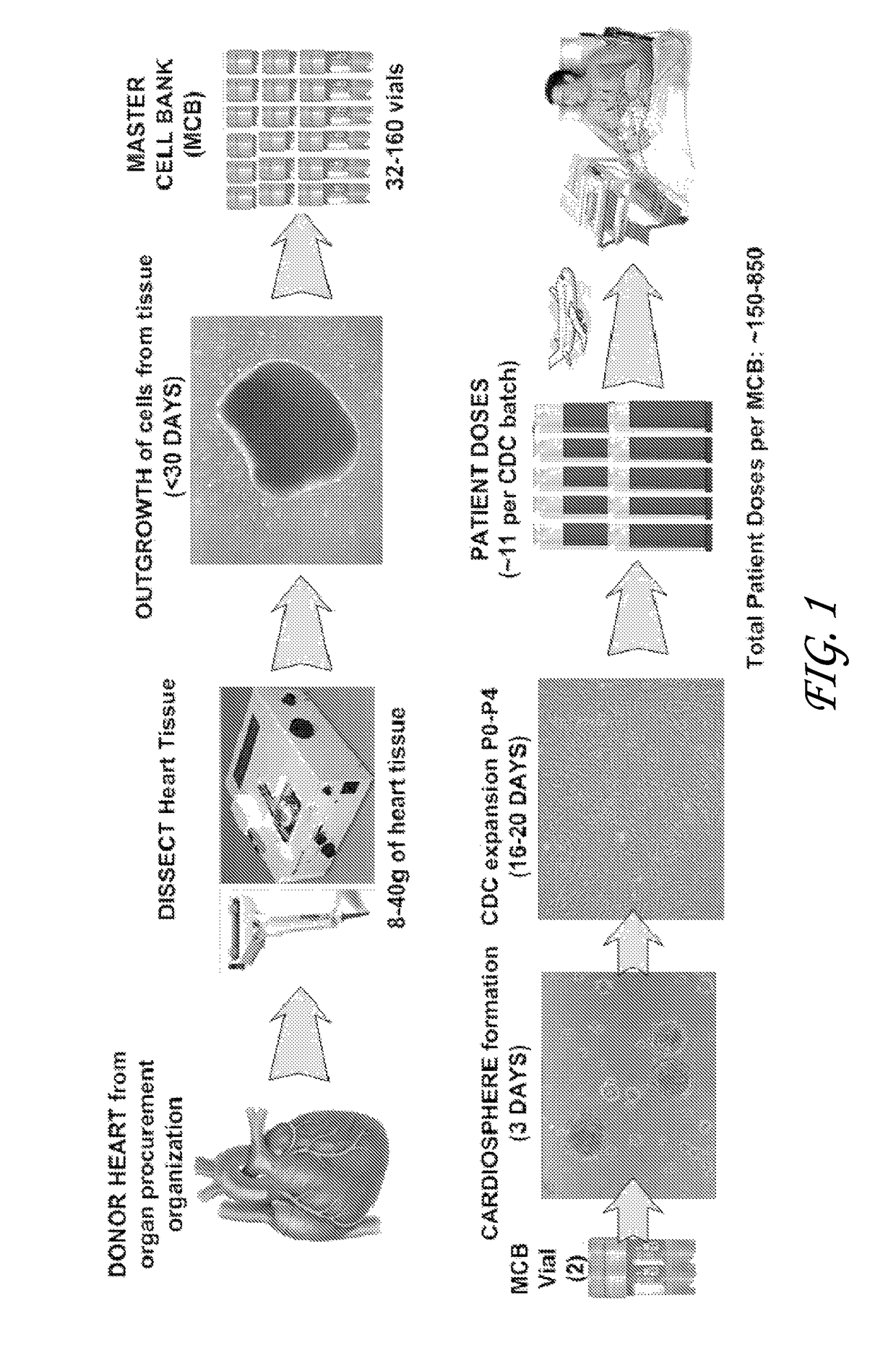
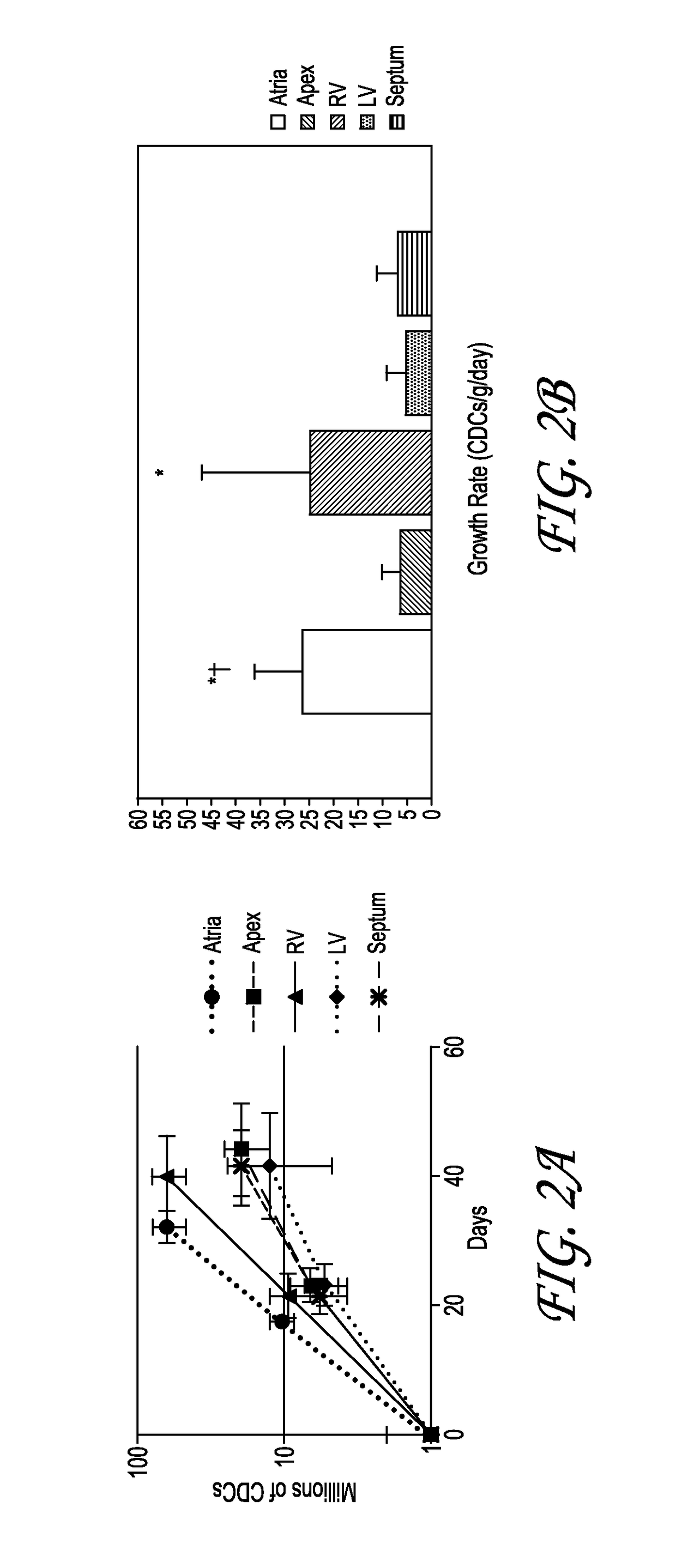
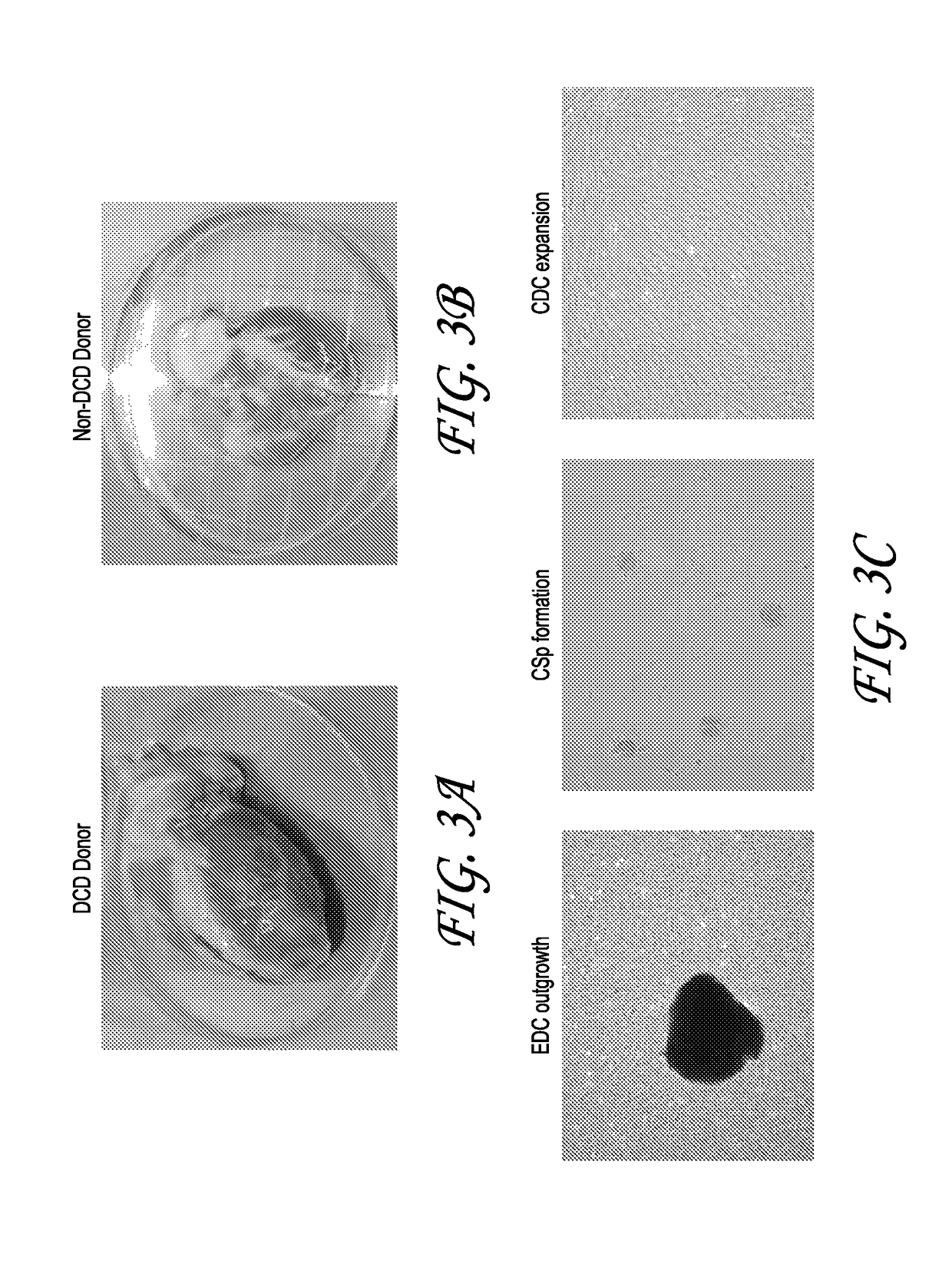
Optimized methods for generation of cardiac stem cells from cardiac tissue and their use in cardiac therapy
ActiveUS9884076B2Reduce riskReduce the risk of contaminationCell dissociation methodsCulture processCardiac Stem CellCARDIAC THERAPY
The present disclosure relates generally to methods for the increased processing of tissue for the generation of cardiac stem cells, wherein the stem cells are suitable for use in cardiac stem cell therapy. In particular, several embodiments relate to the processing of allogeneic donor cardiac tissue for the generation of multiple patient doses of cardiac stem cells.
Owner:CAPRICOR
Stabalised 99mtc compositions
ActiveUS20110008252A9Risk minimizationFast preparation timeRadioactive preparation carriersDrug compositionsMedicinePreservative
The present invention relates to stabilised 99mTc radiopharmaceutical compositions of the ligand tetrofosmin, which include an ascorbic acid or ascorbate radioprotectant, in the absence of an antimicrobial preservative. The invention also provides lyophilised kits suitable for the bulk preparation of multiple unit patient doses of 99mTc-tetrofosmin metal complexes. Also disclosed are unit doses of 99mTc-tetrofosmin, together with processes for preparing such unit doses from the lyophilised bulk vial.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
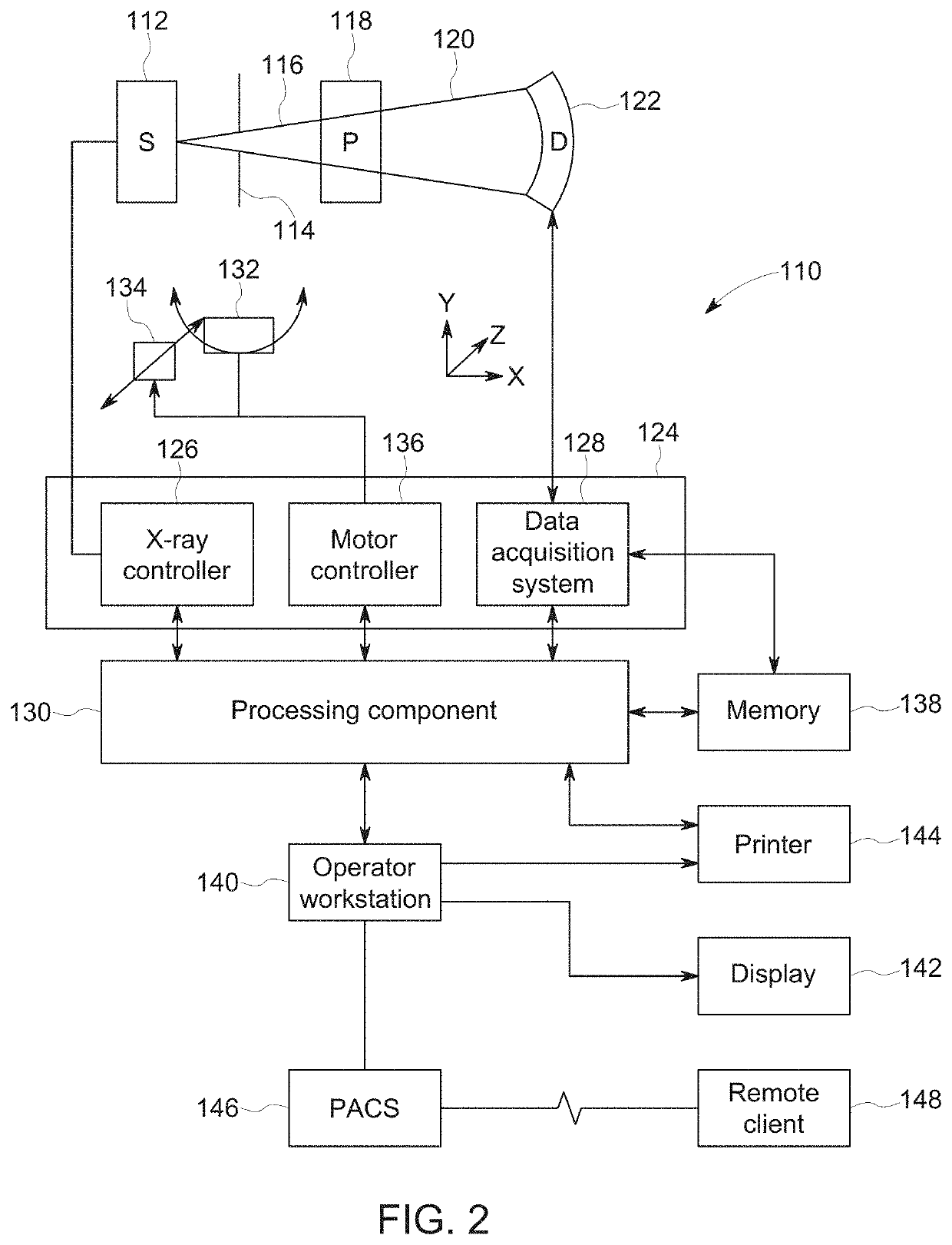
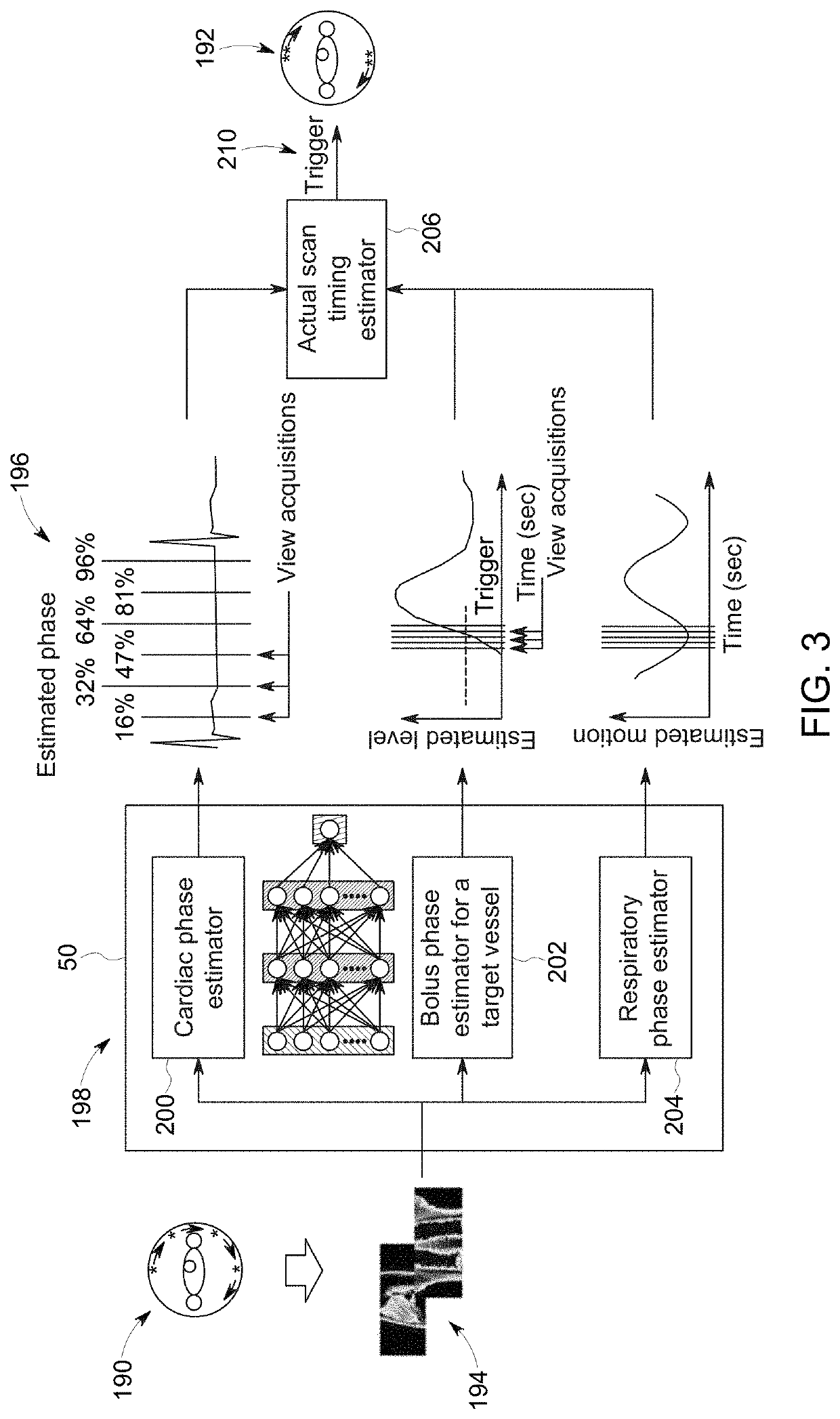
Data-based scan gating
In accordance with the present disclosure, the present technique finds a diagnostic scan timing for a non-static object (e.g., a heart or other dynamic object undergoing motion) from raw scan data, as opposed to reconstructed image data. To find the scan timing, a monitoring scan of a patient's heart is performed. In the monitoring scan, the patient dose may be limited or minimized. As the projection data is acquired during such a monitoring scan, the projection data may be subjected to sinogram analysis in a concurrent or real-time manner to determine when to start (or trigger) the diagnostic scan.
Owner:GE PRECISION HEALTHCARE LLC
X-ray ct method and x-ray ct apparatus
InactiveCN1969760AOptimizing Radiology Imaging ConditionsComputerised tomographsTomographyX-ray filterSlice thickness
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com