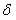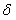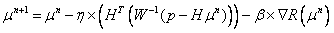Patents
Literature
1264results about How to "Reduce radiation dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
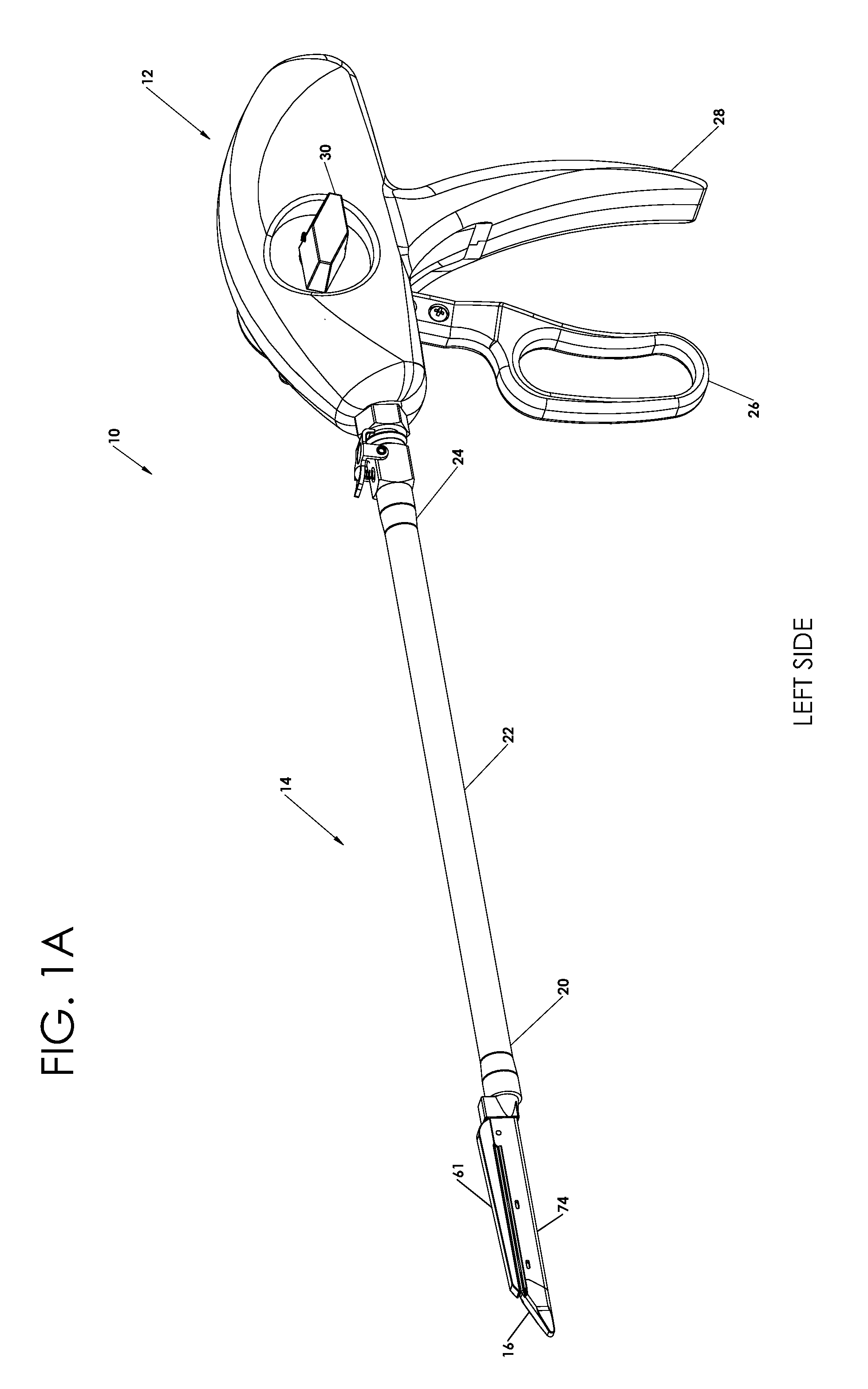
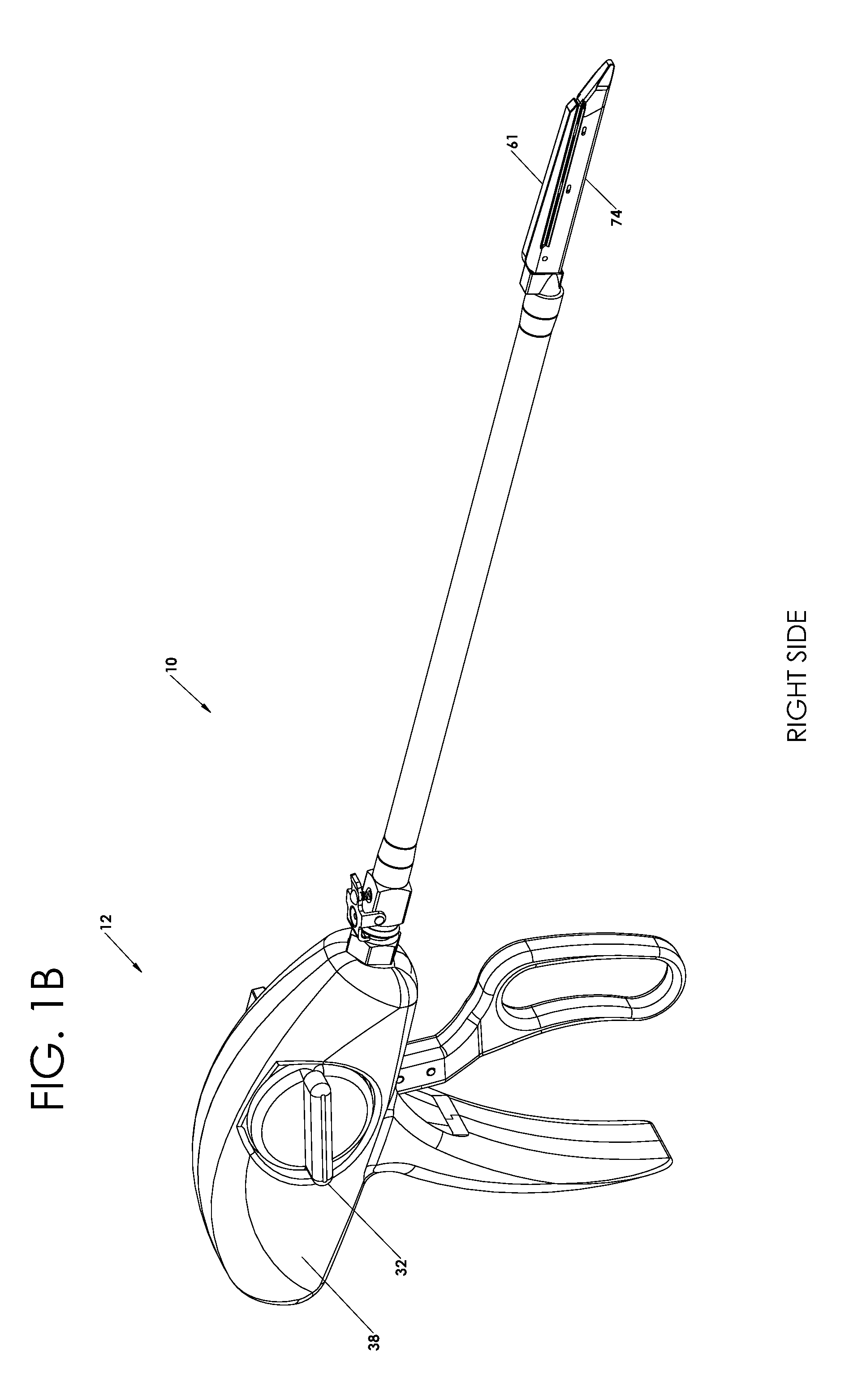
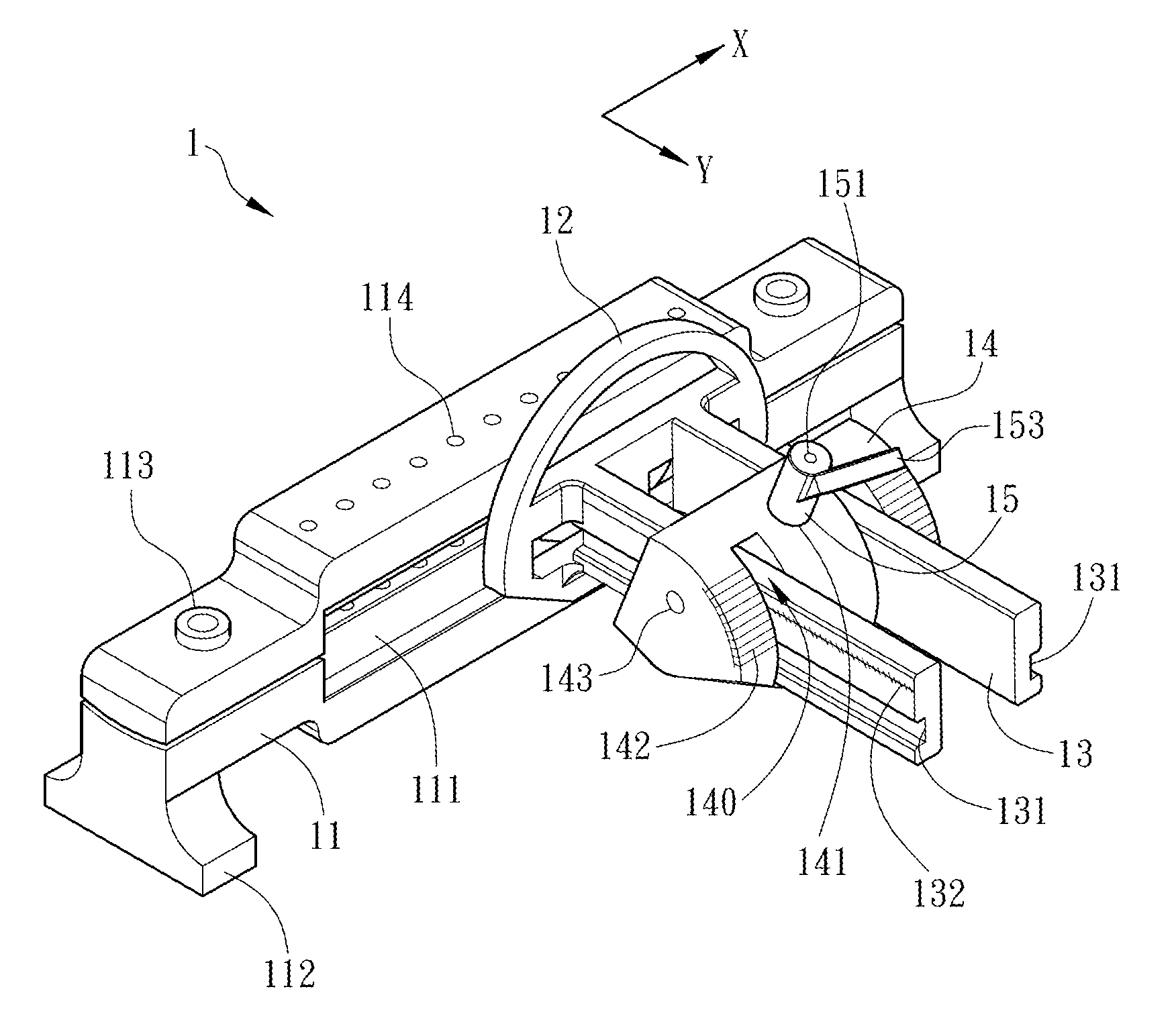
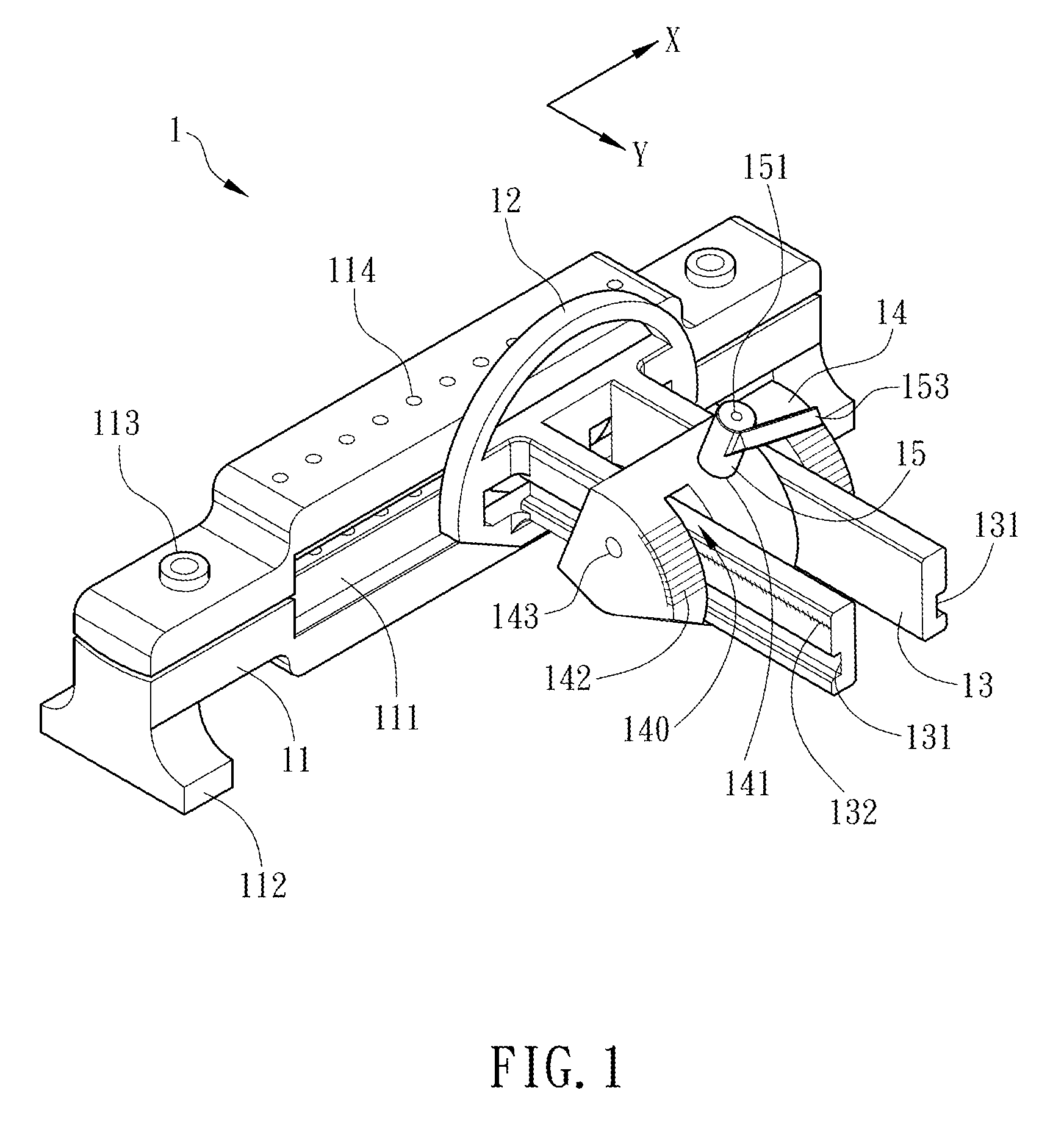
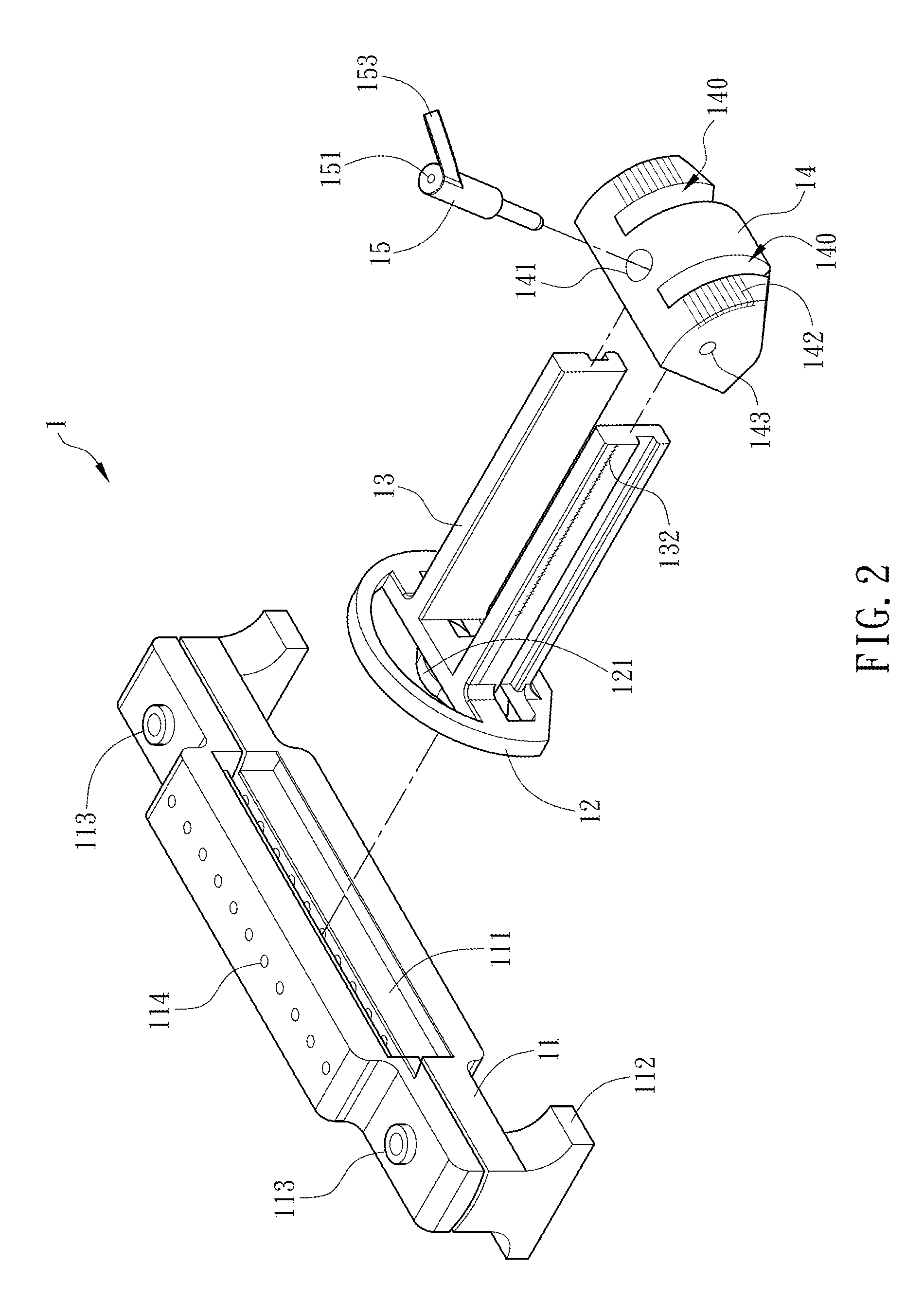
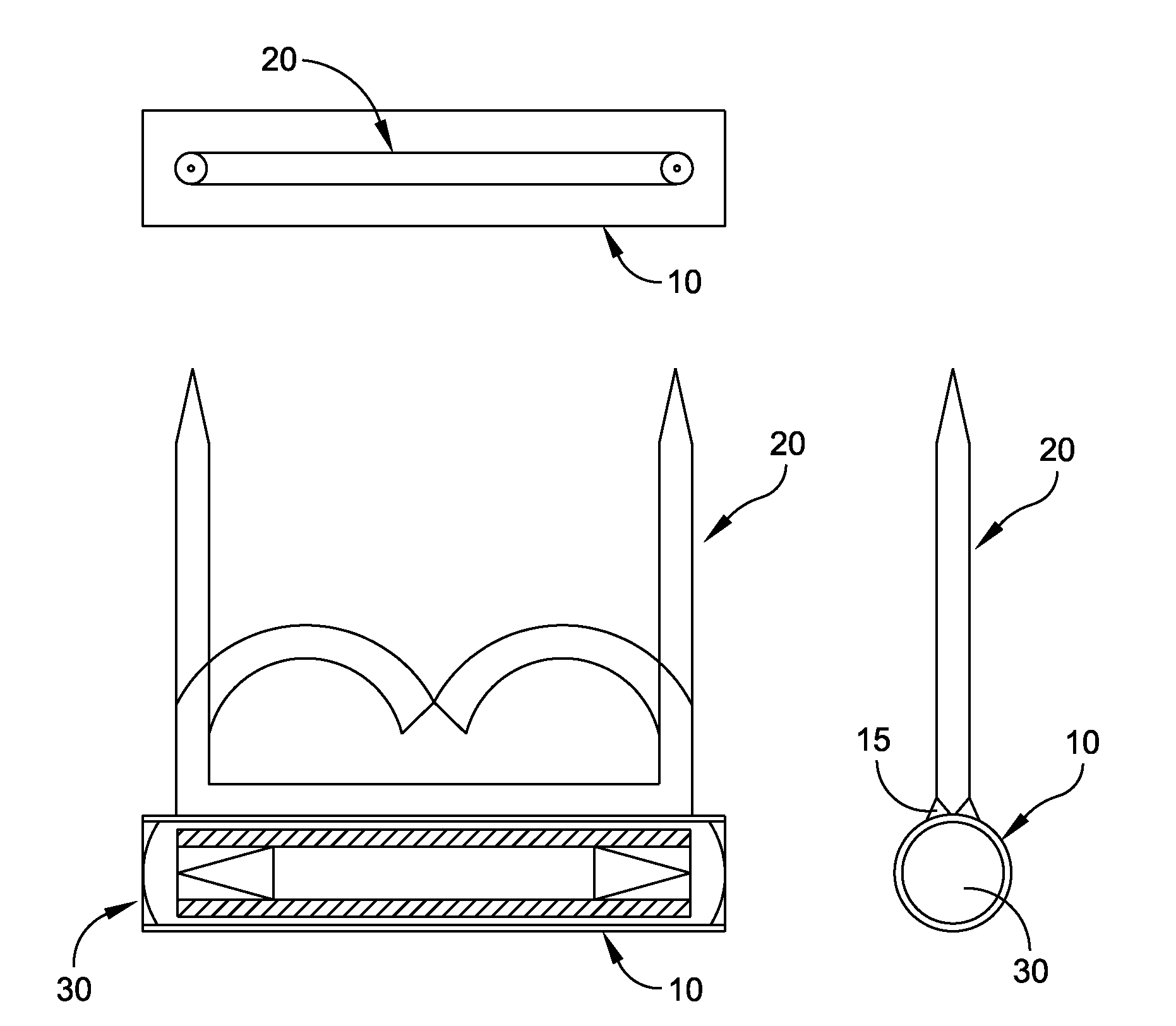
Radioactive therapeutic fastening instrument
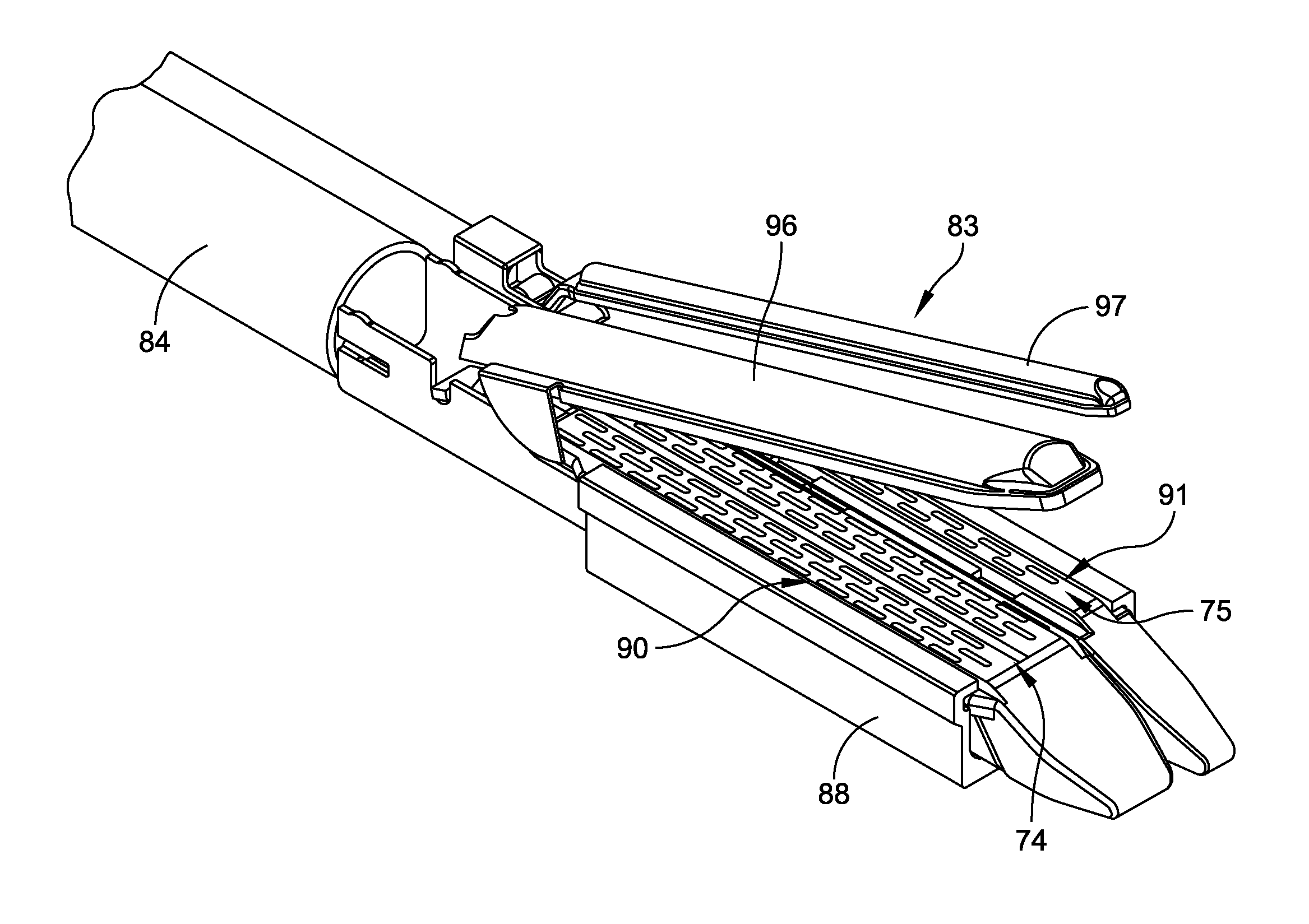
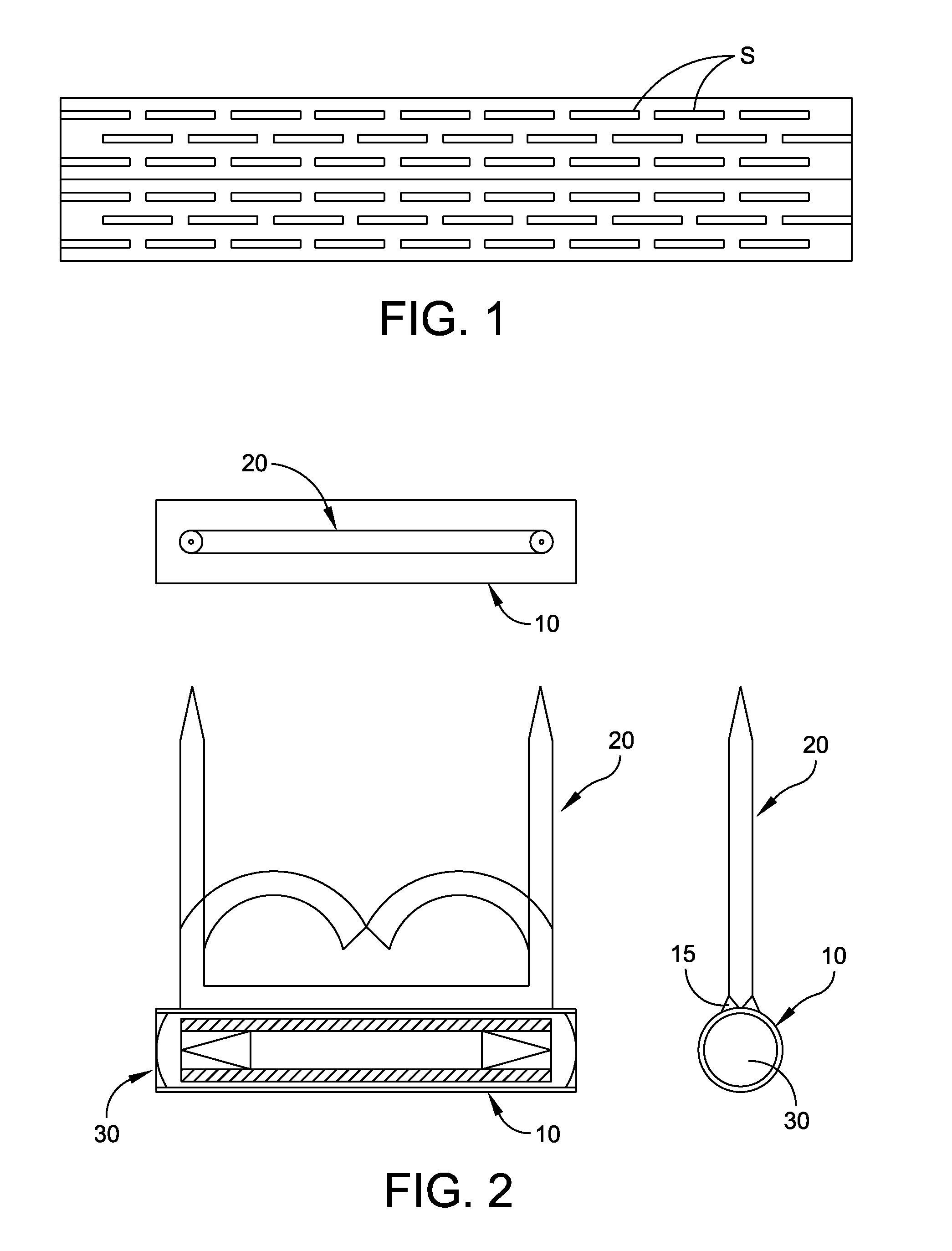
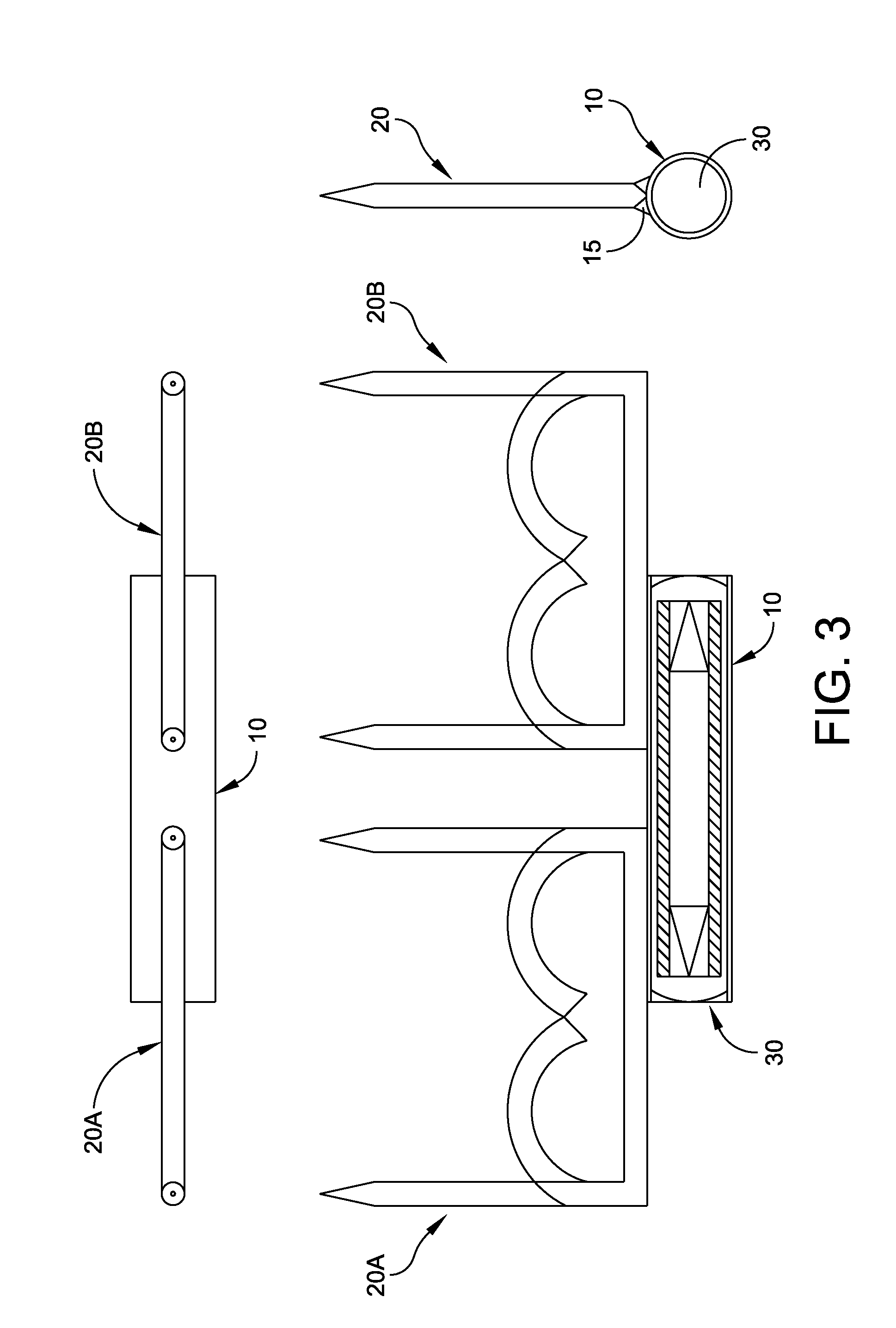
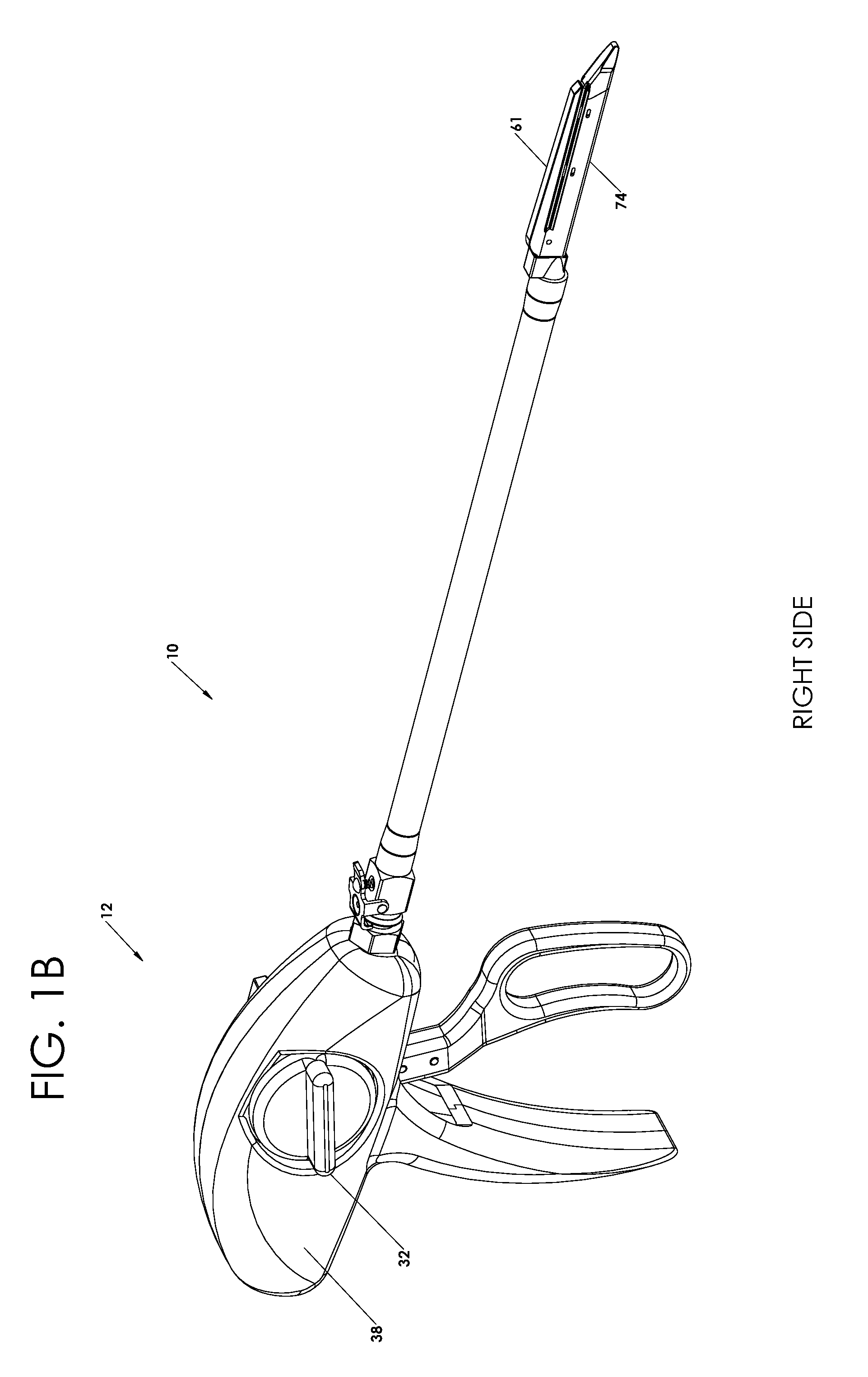
ActiveUS8267849B2For accurate placementReduce doseSuture equipmentsStapling toolsBrachytherapyEngineering
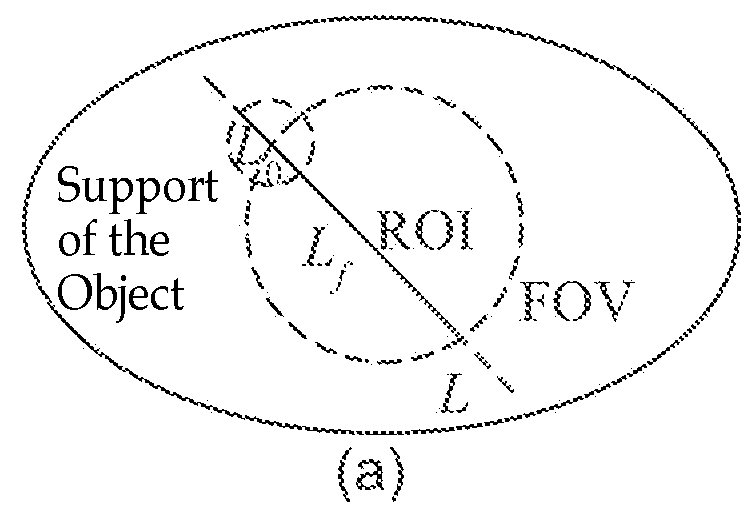
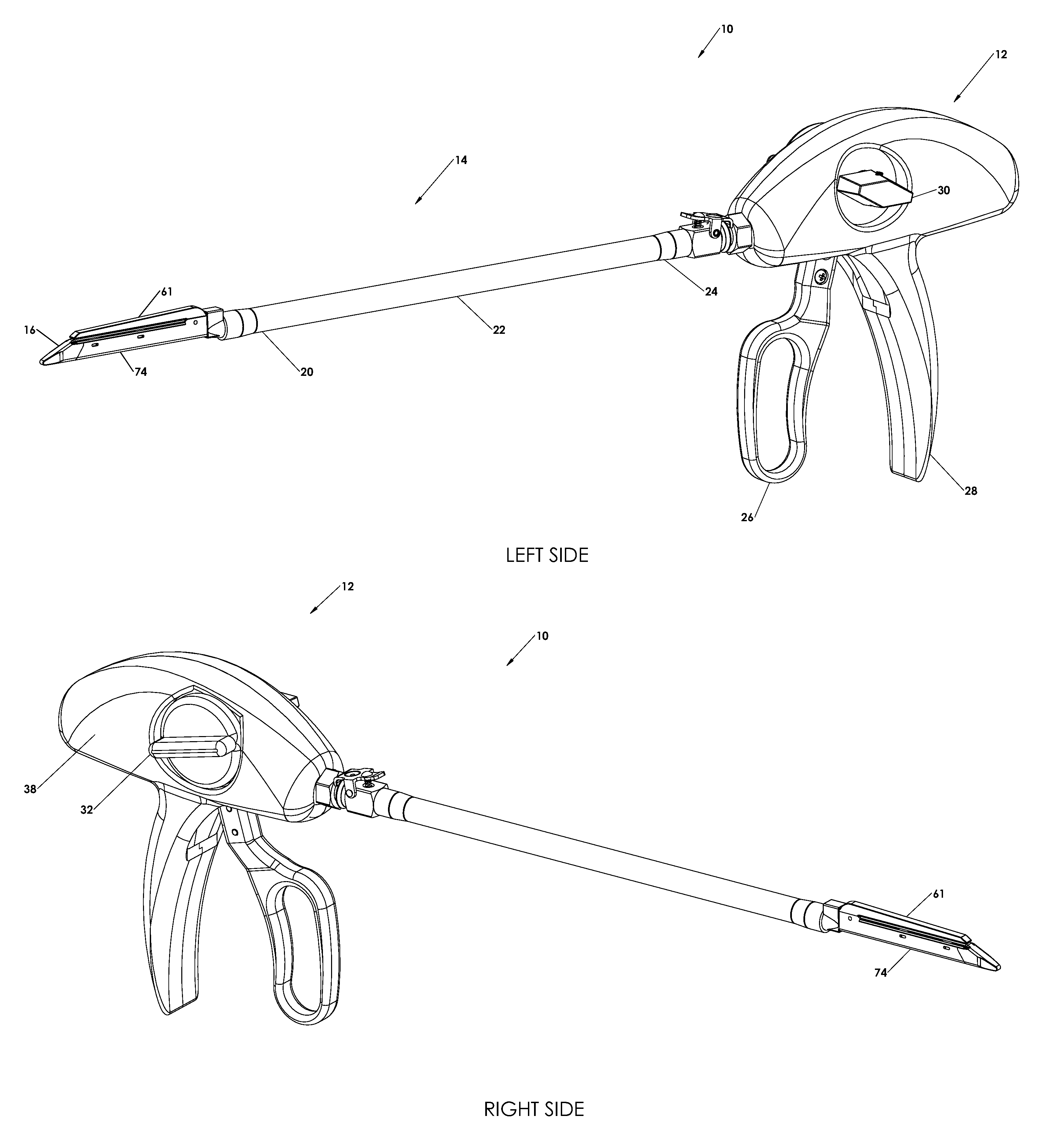
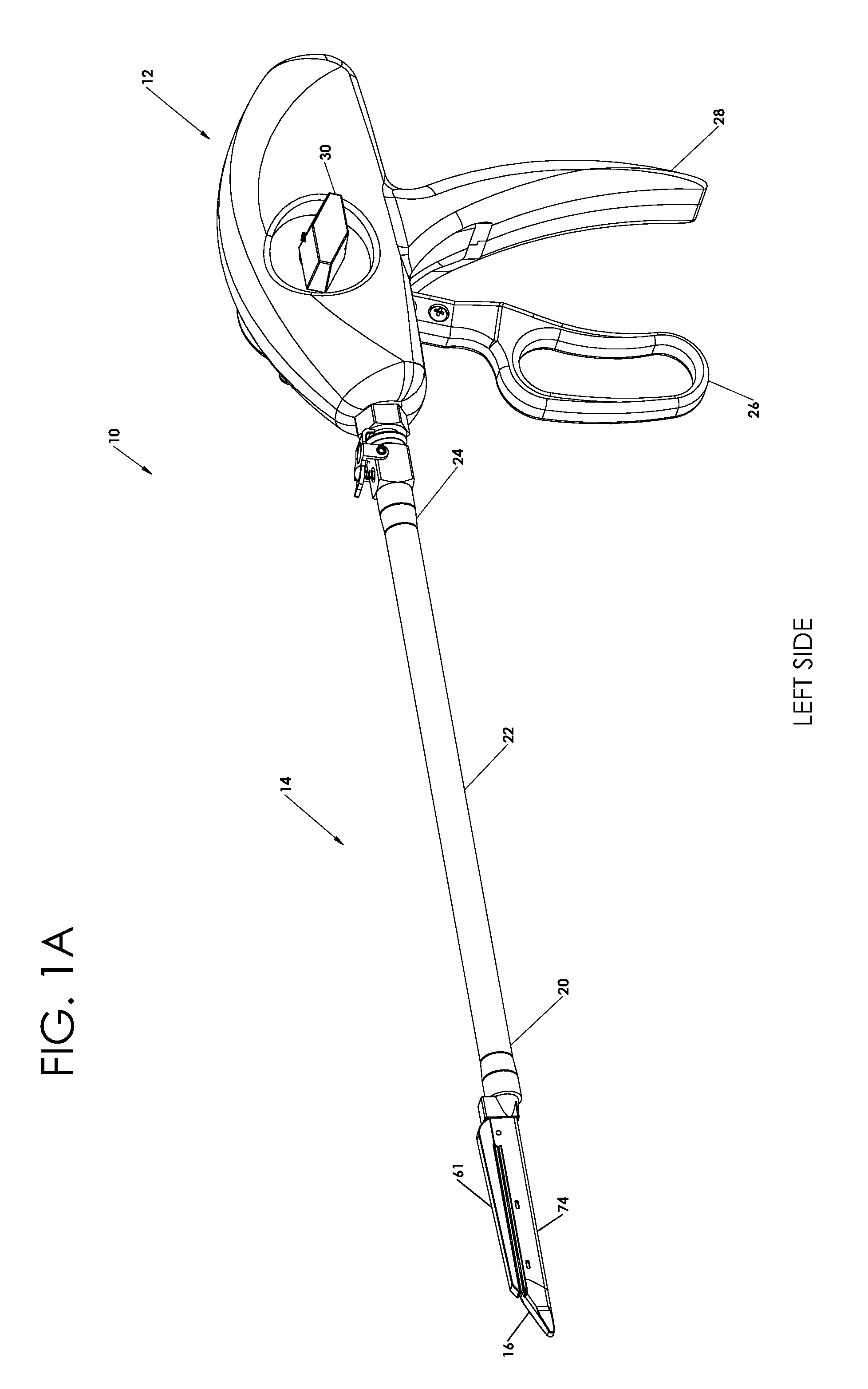
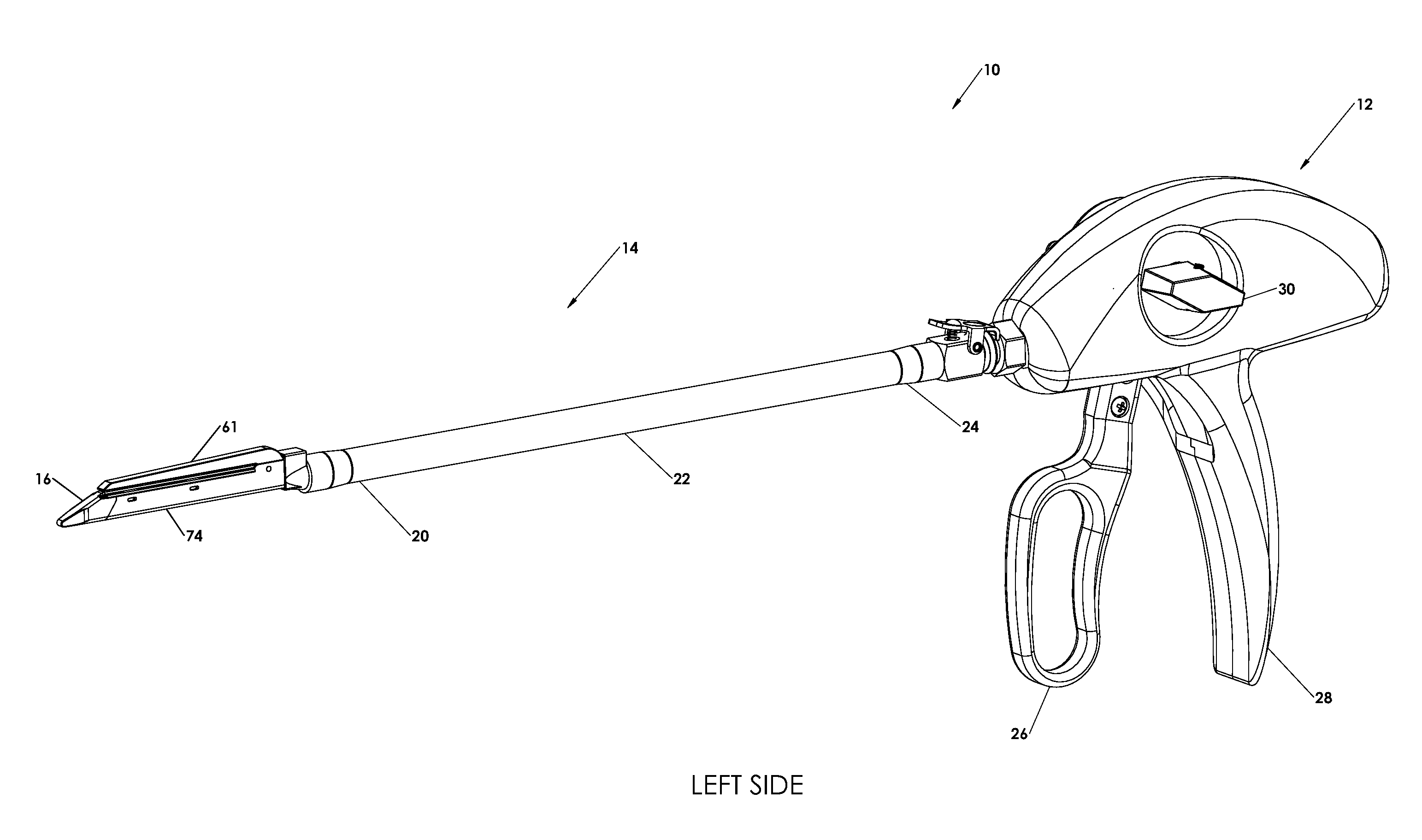
An instrument used for brachytherapy delivery in the treatment of cancer by radiation therapy including a handle having first and second handle actuators; an end effector; and an instrument shaft that connects the handle with the end effector. The end effector has first and second adjacent disposed staple mechanisms that each retain a set of staples. The first mechanism is for holding standard staples in a first array, and dispensing the standard staples under control of the corresponding first handle actuator. The second mechanism is for holding radioactive source staples in a second array, and dispensing said radioactive source staples under control of the corresponding second handle actuator. A holder is for receiving the first and second mechanisms in a substantially parallel array so that the standard staples close the incision at a surgical margin while the source staples are secured adjacent thereto.
Owner:POINT SOURCE TECH
Computer tomography imaging device and method
ActiveUS9380984B2Increase speedReduce hardware costsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayTomography
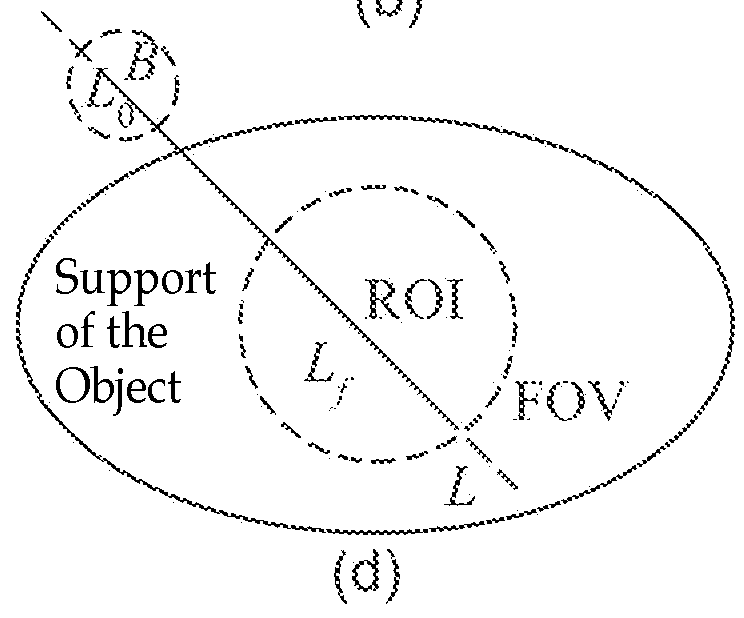
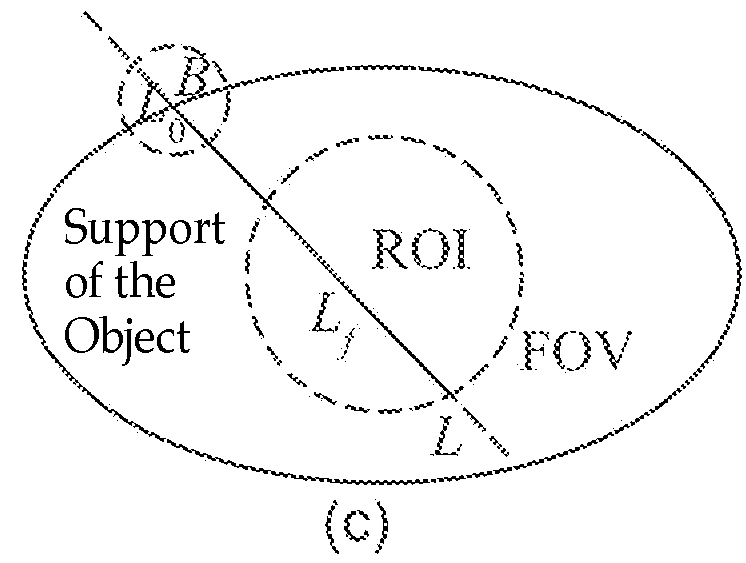
The present invention discloses a method for performing CT imaging on a region of interest of an object under examination, comprising: acquiring the CT projection data of the region of interest; acquiring the CT projection data of region B; selecting a group of PI line segments covering the region of interest, and calculating the reconstruction image value for each PI line segment in the group; and combining the reconstruction image values in all the PI line segments to obtain the image of the region of interest. The present invention further discloses a CT imaging device using this method and a data processor therein. Since the 2D / 3D slice image of the region of interest can be exactly reconstructed and obtained as long as the X-ray beam covers the region of interest and the region B, it is possible to use a small-sized detector to perform CT imaging on the region of interest at any position of a large-sized object, which reduces to a great extent the radiation dose of the X-ray during the CT scanning.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Delivery applicator for radioactive staples for brachytherapy medical treatment
InactiveUS8833631B2EffectiveMinimizing radiation doseSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleBrachytherapy
Owner:SOURCE PRODN & EQUIP
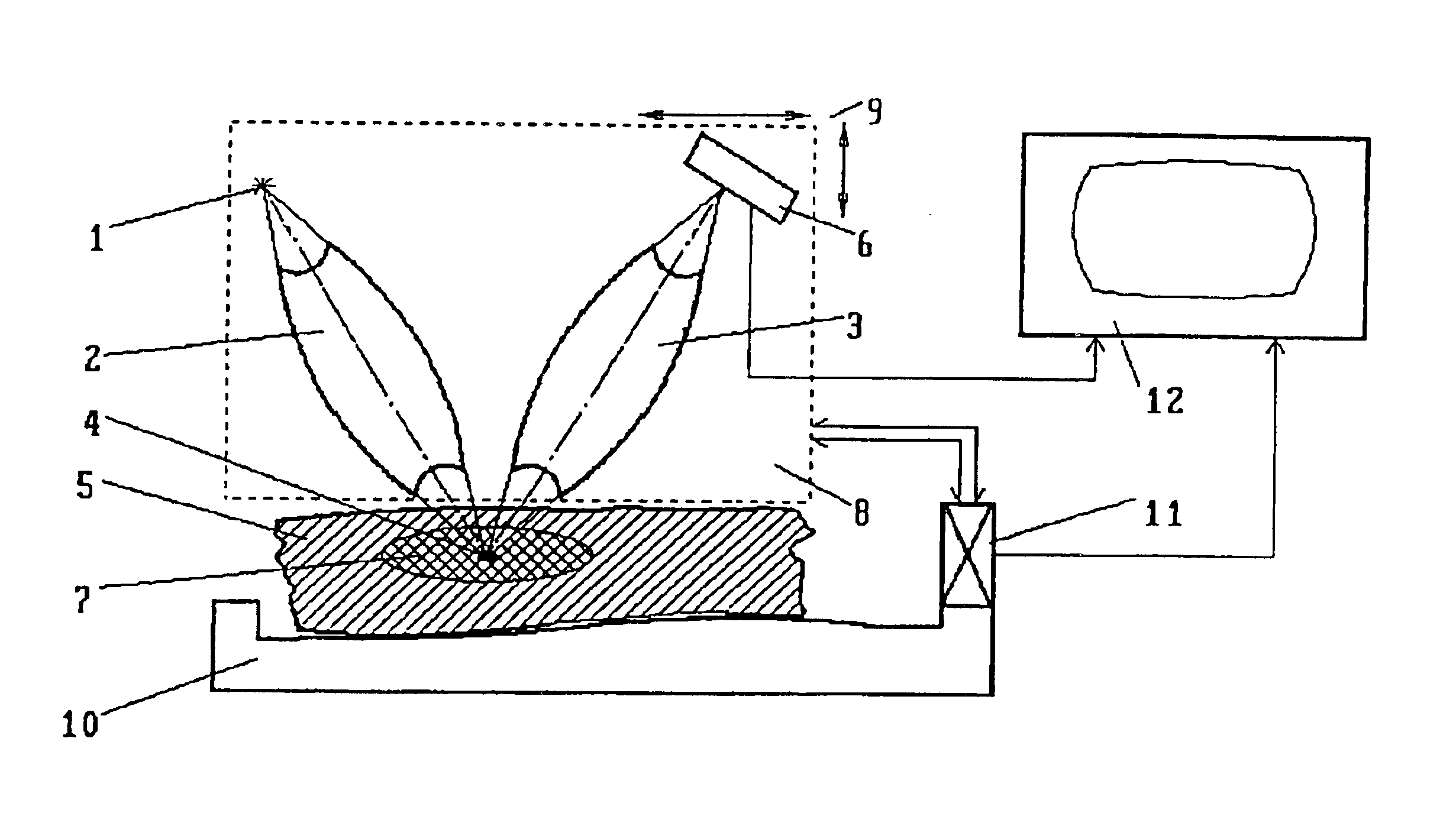
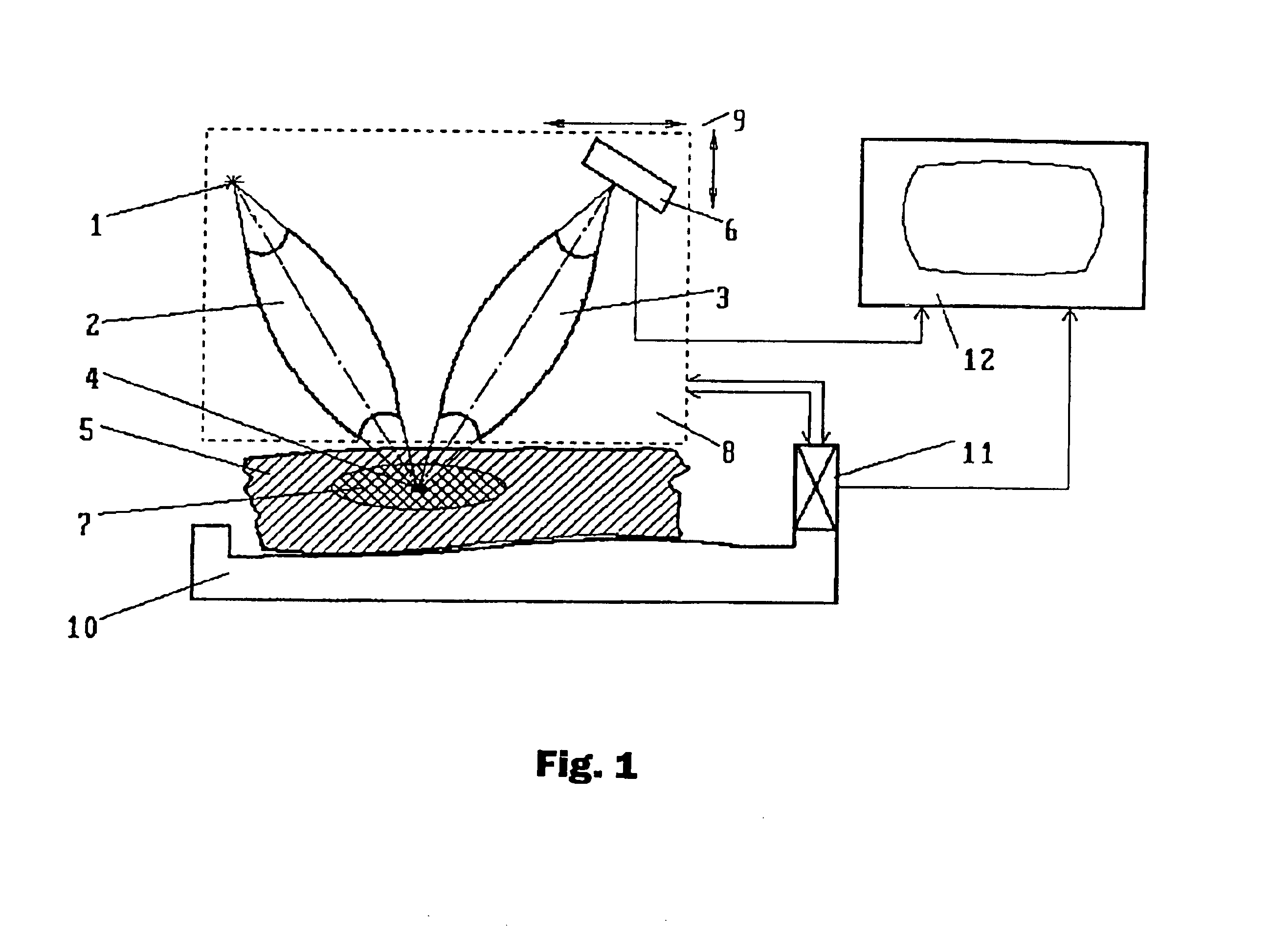
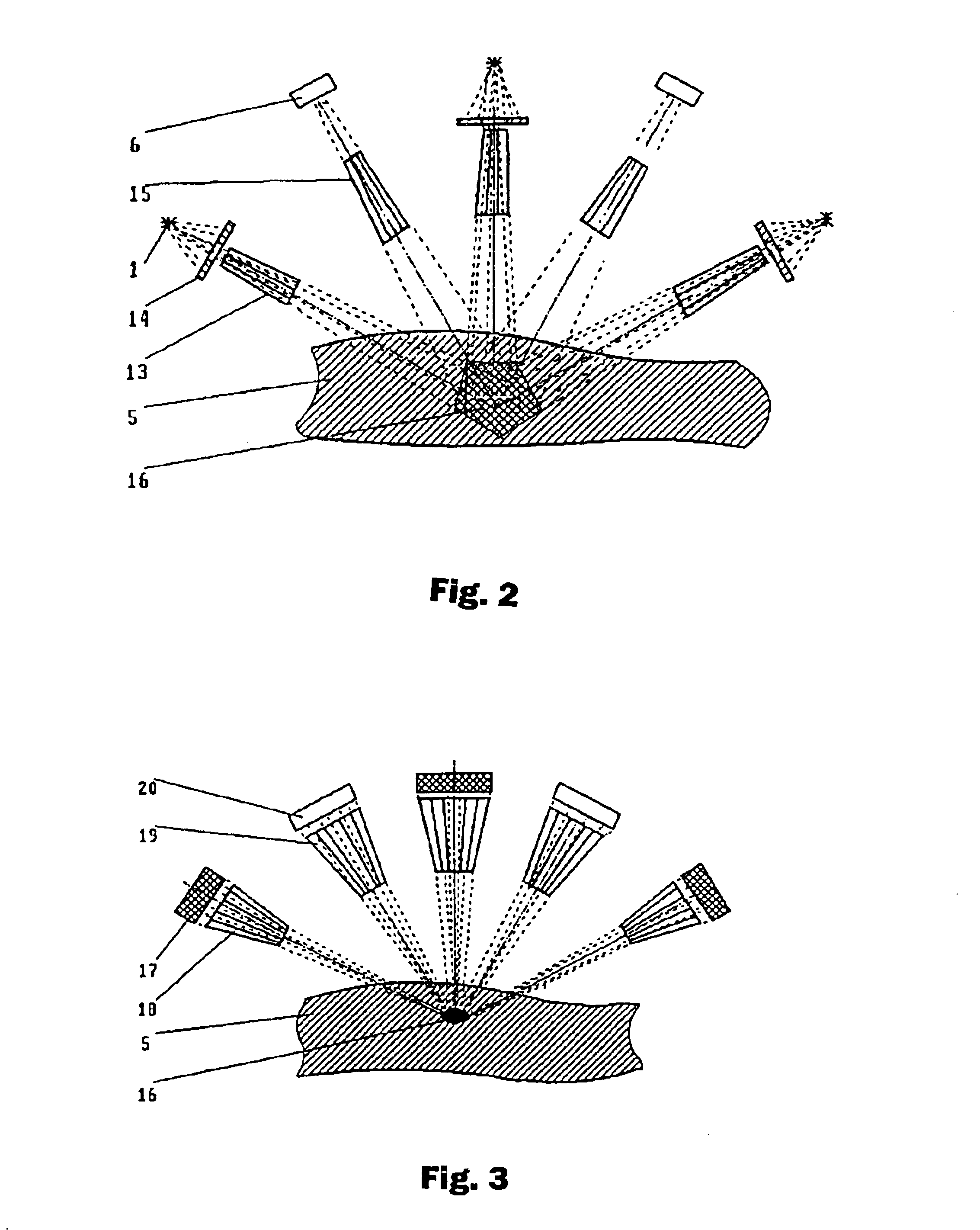
Method for obtaining a picture of the internal structure of an object using x-ray radiation and device for the implementation thereof
InactiveUS6754304B1Improve accuracyReduce usageX-ray spectral distribution measurementHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX-rayX ray dose
Owner:KUMAKHOV MURADIN ABUBEKIROVICH
Tomosynthesis in a limited angular range
InactiveUS6813334B2The process is simple and fastReduce speedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhysicsProjection image
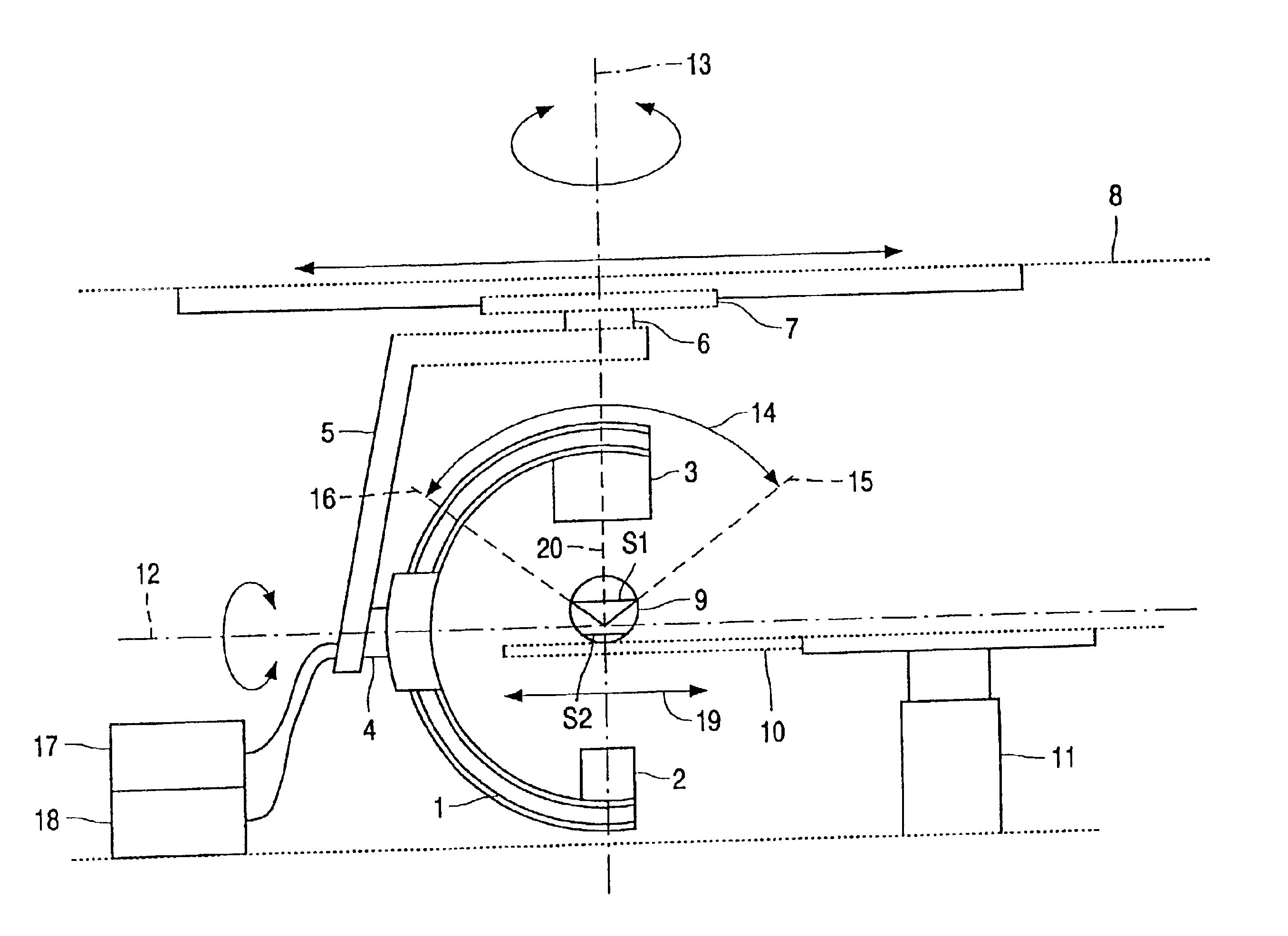
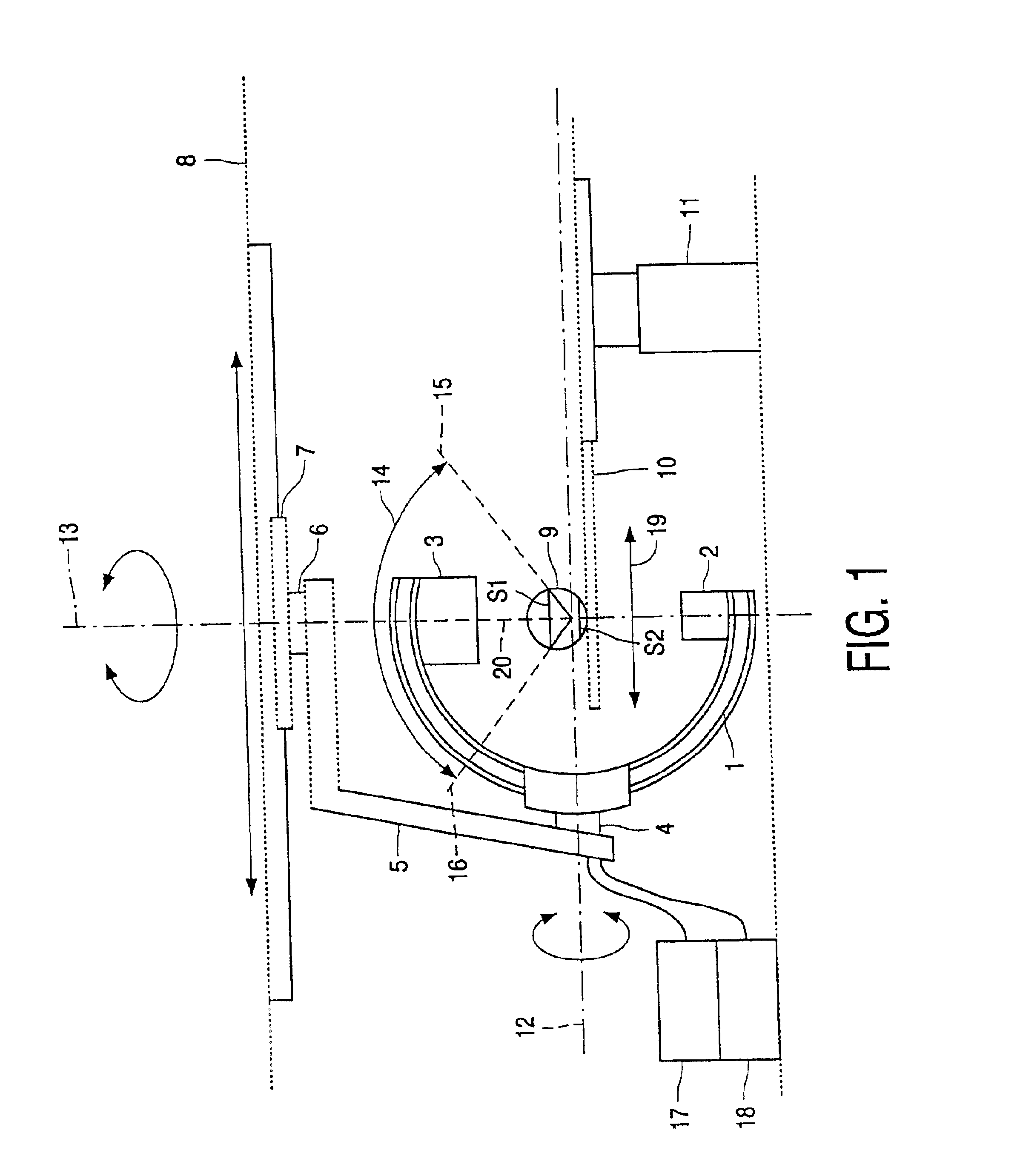
A method and system of forming an X-ray layer image of an object being examined by an X-ray device having an X-ray source and an X-ray detector is described. At least one of the X-ray source and the X-ray detector can be displaced in an angular range around the object in order that X-ray projection images are acquired from different directions. When forming only a single X-ray layer image, or a plurality of X-ray layer images of parallel layers of the object, the time required for the acquisition of the X-ray projection images is notably reduced by forming the X-ray layer image directly from the X-ray projection images, where the resulting X-ray layer image is situated in a plane which extends essentially perpendicularly to the bisector of the angular range of displacement. The angular range of displacement can be less then 180°. The system and method is notably applicable to a C-arm X-ray device, in which the angular range can be chosen at will.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Delivery Applicator for Radioactive Staples for Brachytherapy Medical Treatment
InactiveUS20120292369A1Effective treatmentMinimizing radiation doseSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleBrachytherapy
A staple delivery applicator for delivering radioactive staples during brachytherapy medical treatment has an actuating device for at source staples located distally from the actuating device. The actuating device is removably attachable to an actuator arm on a proximal end. A staple applicator cartridge holder is attached to the actuator arm on a distal end. The staple applicator cartridge is mountable in the holder and having a plurality of slots for mounting of radioactive source staples therein. An anvil therein crimps the staples. The staple applicator cartridge holder is removably mountable in a connector and the connector is also removably mounted to a surgical staple holder. A trigger device being one of the actuating devices has a control for closing the anvil of the cartridge holder and for firing of the source staples in the cartridge therein to cause the staples to crimp, and a control for opening the anvil and releasing the trigger device from the actuator arm.
Owner:SOURCE PRODN & EQUIP
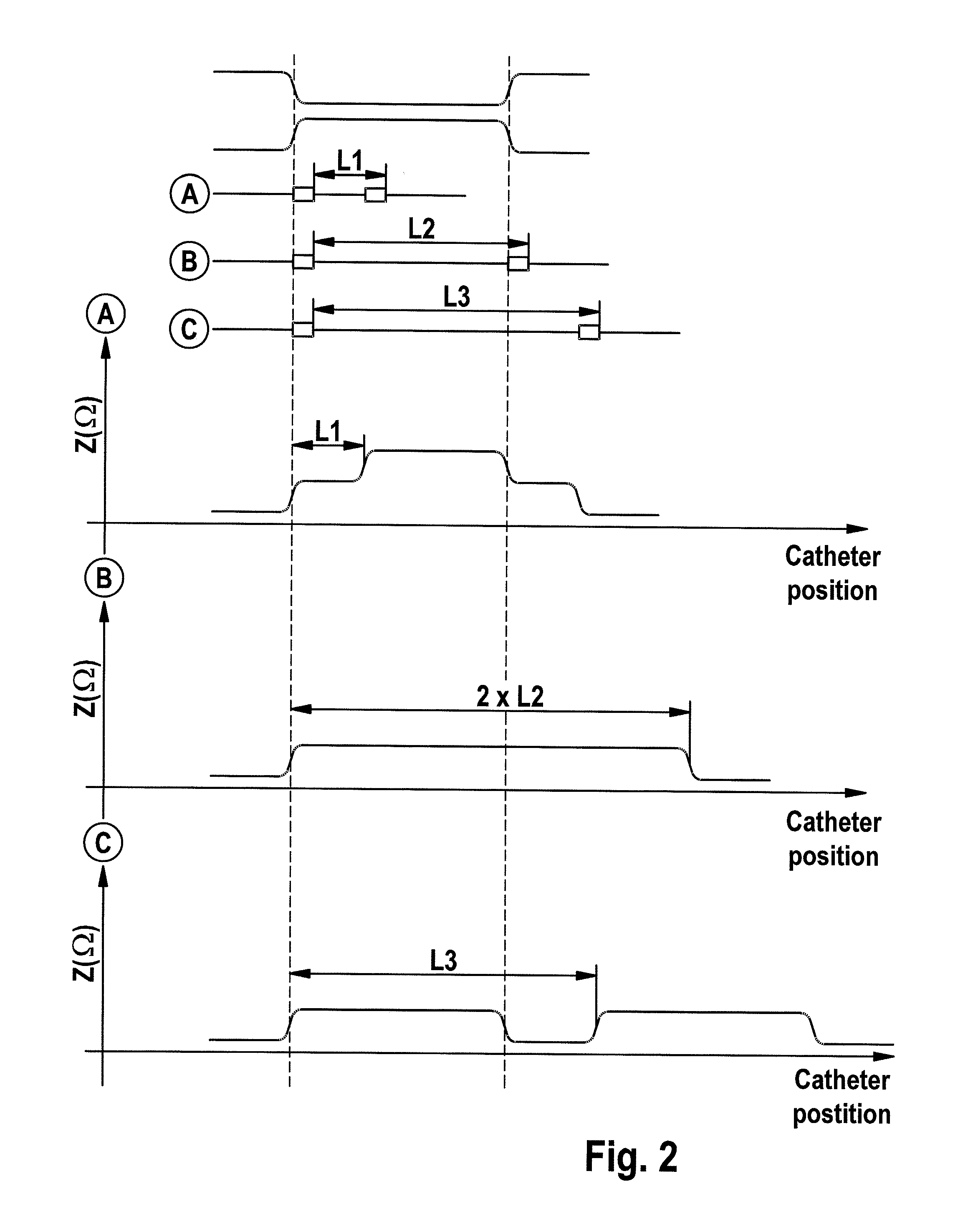
Positioning catheters using impedance measurement
InactiveUS20120078342A1Improving impedanceLower impedanceStentsCatheterElectrical impedanceBlood vessel
The invention relates to a method for determining the position of a catheter in a blood vessel relative to a change in the vascular cross section, comprising the steps: providing a catheter that includes at least two electrodes which can be brought into electrically conductive contact with the surrounding blood while the catheter is being positioned in the blood vessel, wherein the two electrodes are installed on the catheter along the longitudinal axis at a defined distance from each other; advancing the catheter in the vessel to be treated, toward the change in the vascular cross section; and measuring the impedance across the two electrodes while the catheter is being advanced; and to a catheter for use in a method of this type.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
All field simultaneous radiation therapy
InactiveUS8173983B1Increase dose rateOvercome disadvantagesRadiation pyrometryElectrotherapyProstate cancerEstrogen receptor
This invention describes a system for generating multiple simultaneous tunable electron and photon beams and monochromatic x-rays for all field simultaneous radiation therapy (AFSRT), tumor specific AFSRT and screening for concealed elements worn on to the body or contained in a container. Inverse Compton scattering renders variable energy spent electron and tunable monochromatic x-rays. It's spent electron beam is reused for radiation with electron beam or to generate photon beam. Tumor specific radiation with Auger transformation radiation is facilitated by exposing high affinity tumor bound heavy elements with external monochromatic x-rays. Heavy elements like directly iodinated steroid molecule that has high affinity binding to estrogen receptor in breast cancer and to iodinated testosterone in prostate cancer or with directly implanted nanoparticles into the tumor are exposed with tuned external monochromatic x-rays for tumor specific radiation therapy. Likewise, screening element's atom's k, l, m, n shell specific Auger transformation radiation generated by its exposure to external monochromatic x-rays is used to screen for concealed objects. Multiple beam segments from a beam storage ring or from octagonal beam lines are simultaneously switched on for simultaneous radiation with multiple beams. The beam on time to expose a tumor or an object is only a few seconds. It also facilitates breathing synchronized radiation therapy. The intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and intensity modulated screening for concealed objects (IMSFCO) is rendered by varying beam intensities of multiple simultaneous beams. The isocentric additive high dose rate from simultaneously converging multiple beams, the concomitant hyperthermia and chemotherapy and tumor specific radiation therapy and the AFSRT's very low radiation to the normal tissue all are used to treat a tumor with lower radiation dose and to treat a radioresistant and multiple times recurrent tumors that heave no other alternative treatments.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
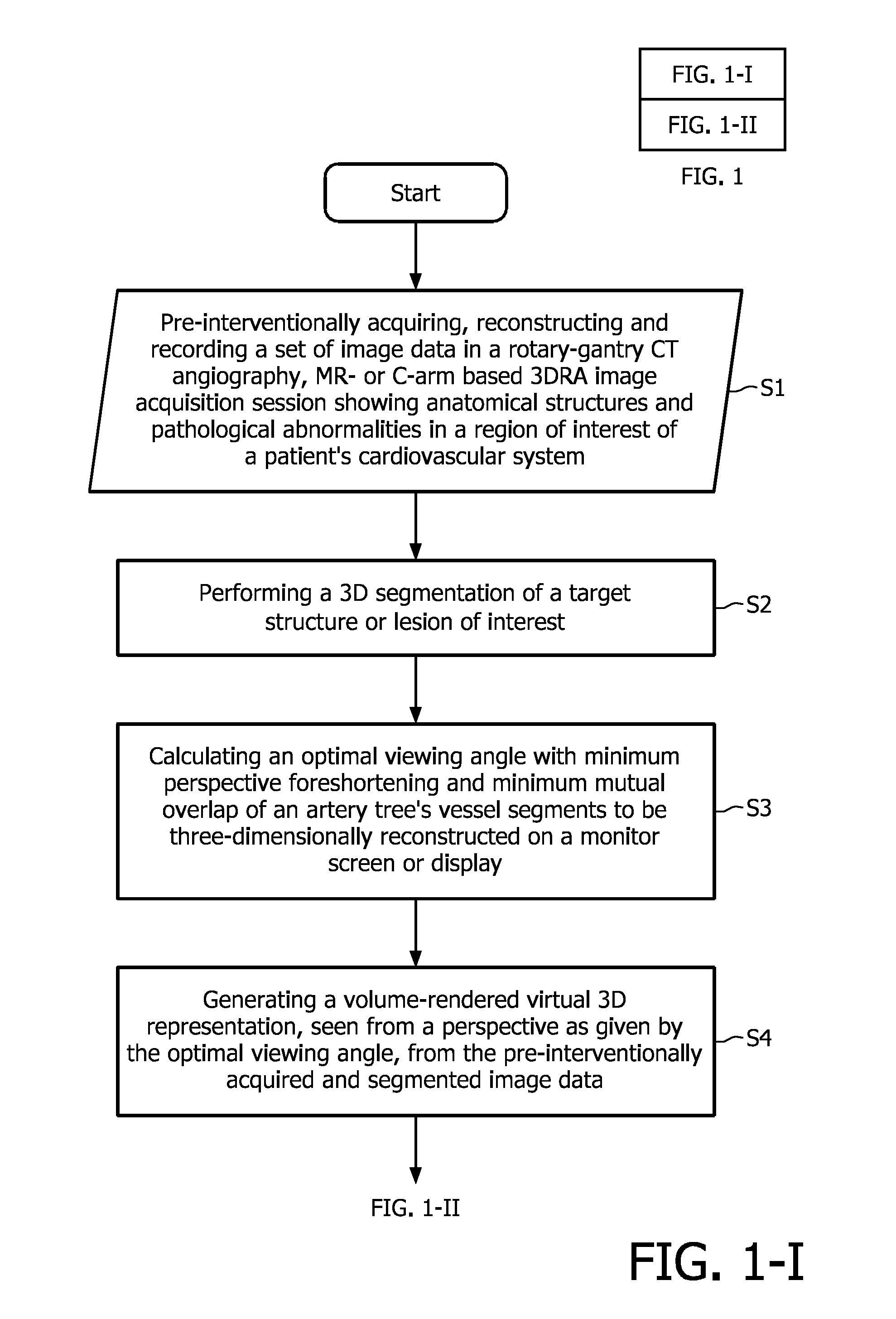
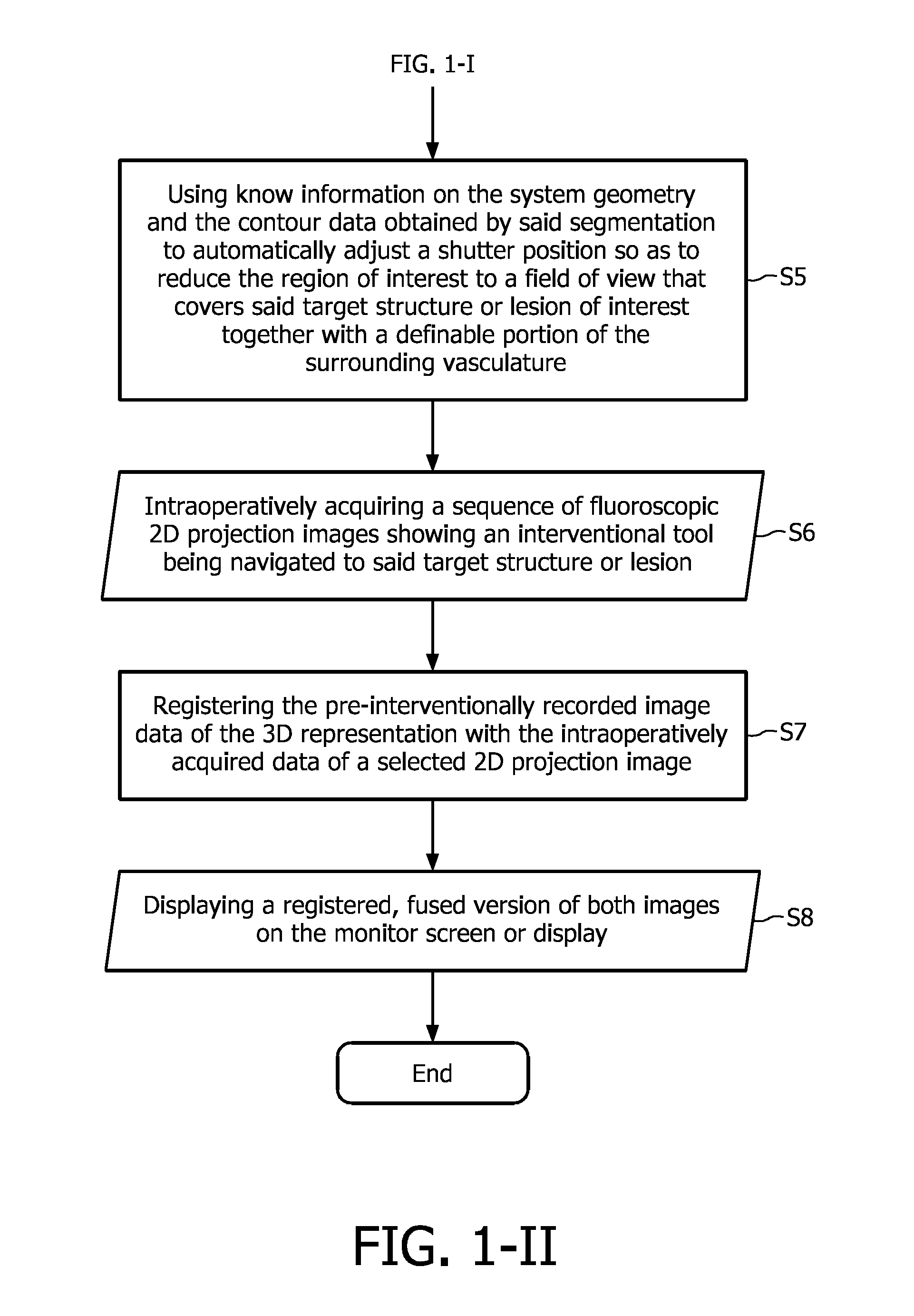
Angiographic image acquisition system and method with automatic shutter adaptation for yielding a reduced field of view covering a segmented target structure or lesion for decreasing x-radiation dose in minimally invasive x-ray-guided interventions
ActiveUS20110182492A1Decrease radiation doseReduce radiation doseReconstruction from projectionLocal control/monitoring3d rotational angiographyWire source
The present invention refers to an angiographic image acquisition system and method which can beneficially be used in the scope of minimally invasive image-guided interventions. In particular, the present invention relates to a system and method for graphically visualizing a pre-interventionally virtual 3D representation of a patient's coronary artery tree's vessel segments in a region of interest of a patient's cardiovascular system to be three-dimensionally reconstructed. Optionally, this 3D representation can then be fused with an intraoperatively acquired fluoroscopic 2D live image of an interventional tool. According to the present invention, said method comprises the steps of subjecting the image data set of the 3D representation associated with the precalculated optimal viewing angle to a 3D segmentation algorithm (S4) in order to find the contours of a target structure or lesion to be examined and interventionally treated within a region of interest and automatically adjusting (S5) a collimator wedge position and / or aperture of a shutter mechanism used for collimating an X-ray beam emitted by an X-ray source of a C-arm-based 3D rotational angiography device or rotational gantry-based CT imaging system to which the patient is exposed during an image-guided radiographic examination procedure based on data obtained as a result of said segmentation which indicate the contour and size of said target structure or lesion. The aim is to reduce the region of interest to a field of view that covers said target structure or lesion together with a user-definable portion of the surrounding vasculature.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Device and method for coronary artery calcification detection and quantification in CTA image
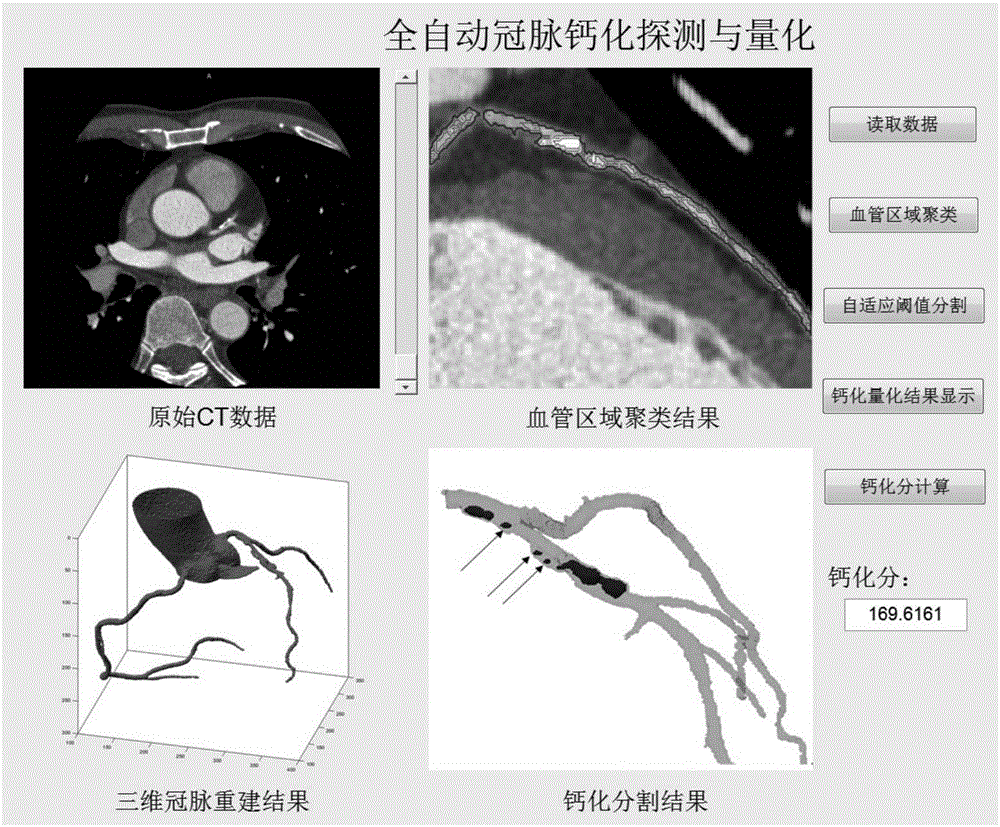
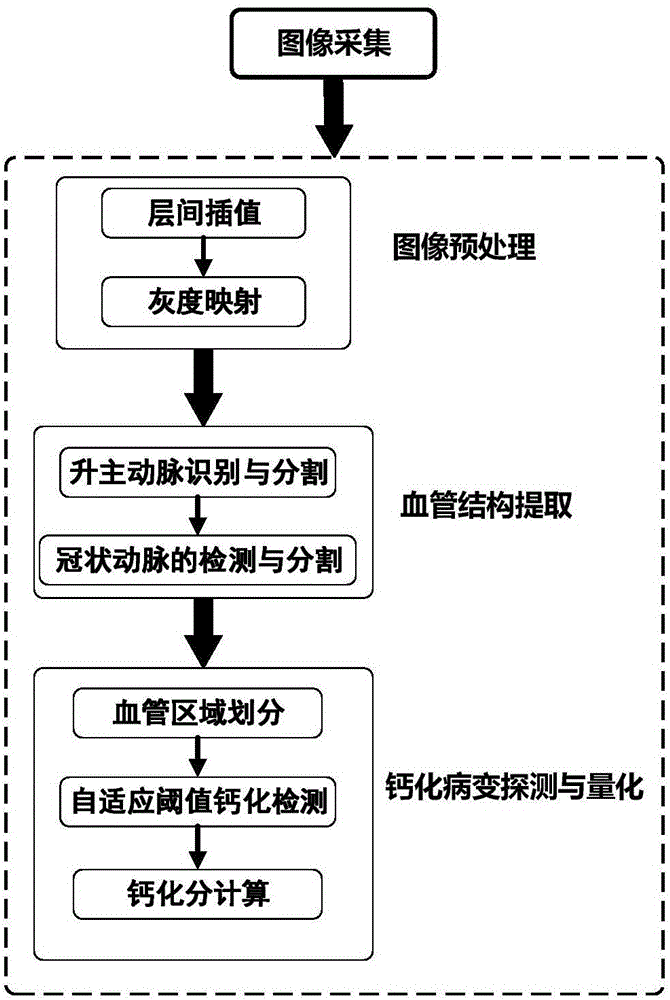
InactiveCN106447645AEasy to identifyGood overcoming abilityImage analysisCoronary arteriesCluster algorithm
The present invention relates to an image processing technique for effectively suppressing noise by providing a fully automatic calcification patch detection, segmentation and quantization apparatus and method based on fuzzy super pixel clustering in CTA data. The technical scheme adopted in the present invention is the method for the enhancement of coronary artery calcification detection and quantification in CT image. The method comprises the following steps: first, using a seed point to automatically choose a low threshold region to grow and obtain a coronary artery region containing the calcification patch; then using the fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm to divide the above-mentioned blood vessel region into a finite number of super-pixel sets according to the Euclidean distances among the pixel points and the gray scale differences of the pixels in the region; and finally, using a threshold selection method based on gray histogram to screen the super pixel sets to obtain the final measurement and quantification result of the calcification patch, and completing the calcification score calculation of the blood vessel according to the segmentation result. The invention is used mainly in image processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
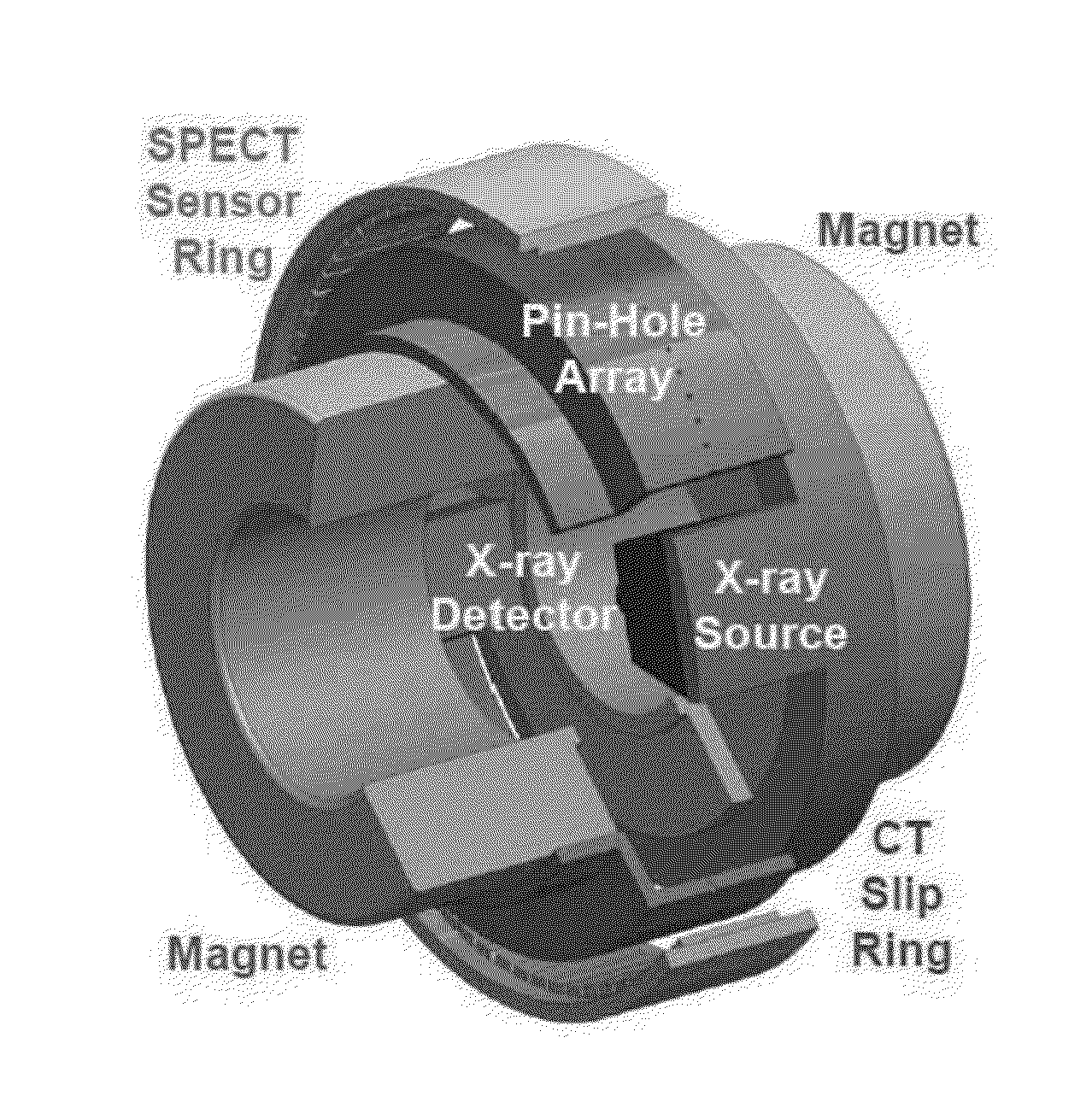
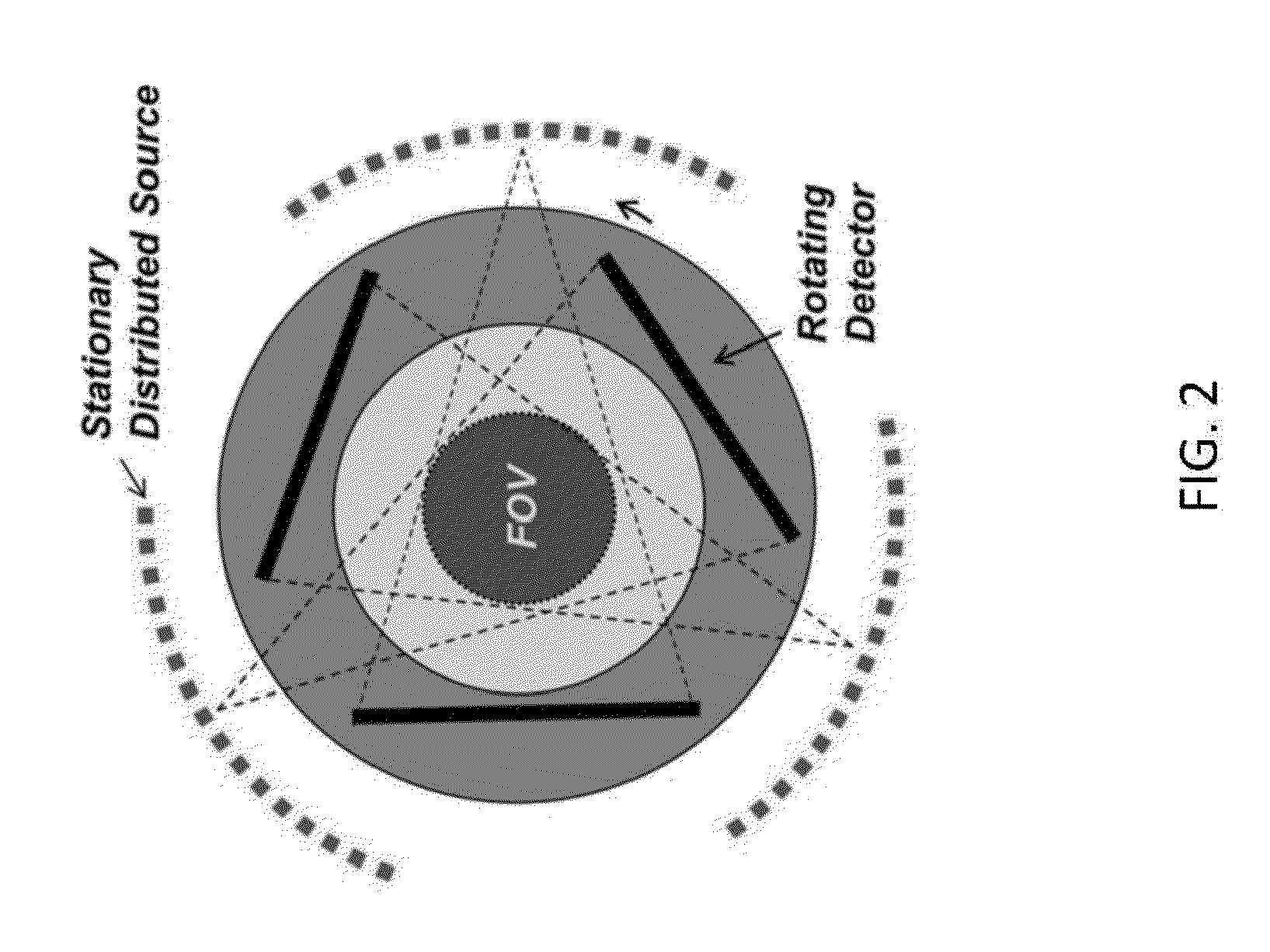
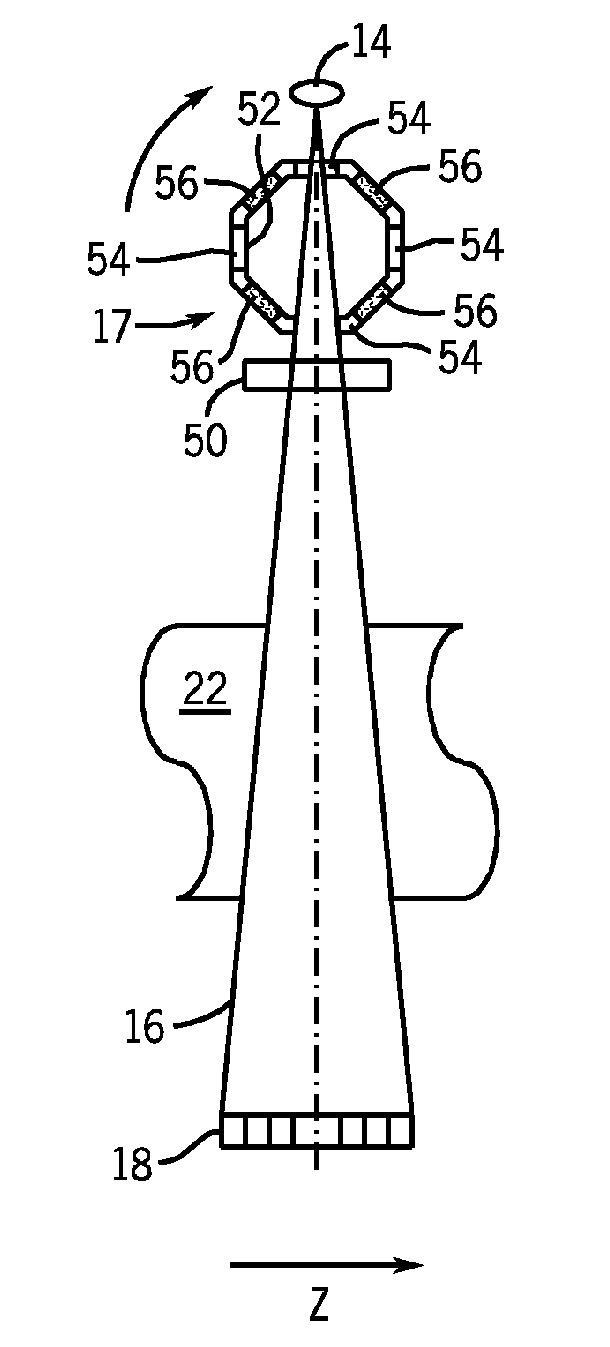
Stationary source computed tomography and ct-mri systems
ActiveUS20150230766A1Quick fixReduce radiation doseDiagnostics using lightComputerised tomographsTemporal resolutionImage resolution
The present invention provides stationary CT architecture for imaging at a faster temporal resolution and lower radiation dose. In embodiments, the architecture features stationary distributed x-ray sources and rotating x-ray detectors. Provided is a stationary source computed tomography (CT) architecture comprising: a detector disposed on a rotatable gantry; an x-ray source disposed on a fixed ring; wherein the detector is disposed on the gantry in a manner such that the detector is capable of rotating around a subject and of receiving a signal from the x-ray source. Embodiments of the invention include a CT-MRI scanner comprising the stationary CT architecture.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Assistant device and guiding assembly for percutaneous surgery
InactiveUS9131948B2Improve accuracyImprove stabilityDiagnosticsSurgical needlesEngineeringPercutaneous surgery
An assistant device for percutaneous puncture is disclosed. The assistance device includes a fixing element, a first rotatable element, a supporting element and a second rotatable element. The fixing element has a first rail, and the first rotatable element is slidably disposed on the first rail. The supporting element is connected to the first rotatable element. The second rotatable element is slidably disposed on the supporting element and has a puncture restraint pore.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Mobile computed tomography (CT) scanner and operation method thereof
InactiveCN102697517AExtended service lifeReduce operating costsComputerised tomographsTomographyCt scannersImaging quality
The invention discloses a mobile computed tomography (CT) scanner. The mobile CT scanner comprises a bottom plate platform, a machine frame, a rotary plate, an X-ray emitting source, and a detector and data acquisition system. The bottom plate platform is provided with a linear guide rail; and one end of the machine frame is provided with a guide rail sliding block which is slidably connected with the linear guide rail, and the other end of the machine frame is connected with the rotary plate. The rotary plate can rotate relative to the machine frame. The X-ray emitting source and the detector and data acquisition system are arranged on the rotary plate and are respectively positioned at two ends of the same diameter of the rotary plate. The X-ray emitting source comprises a grid controlled carbon nano tube-based field emission cathode X-ray tube. The invention also provides an operation method for the mobile CT scanner. The mobile CT scanner is simple in structure, low in radiation dosage, and high in imaging quality, and has two purposes.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH
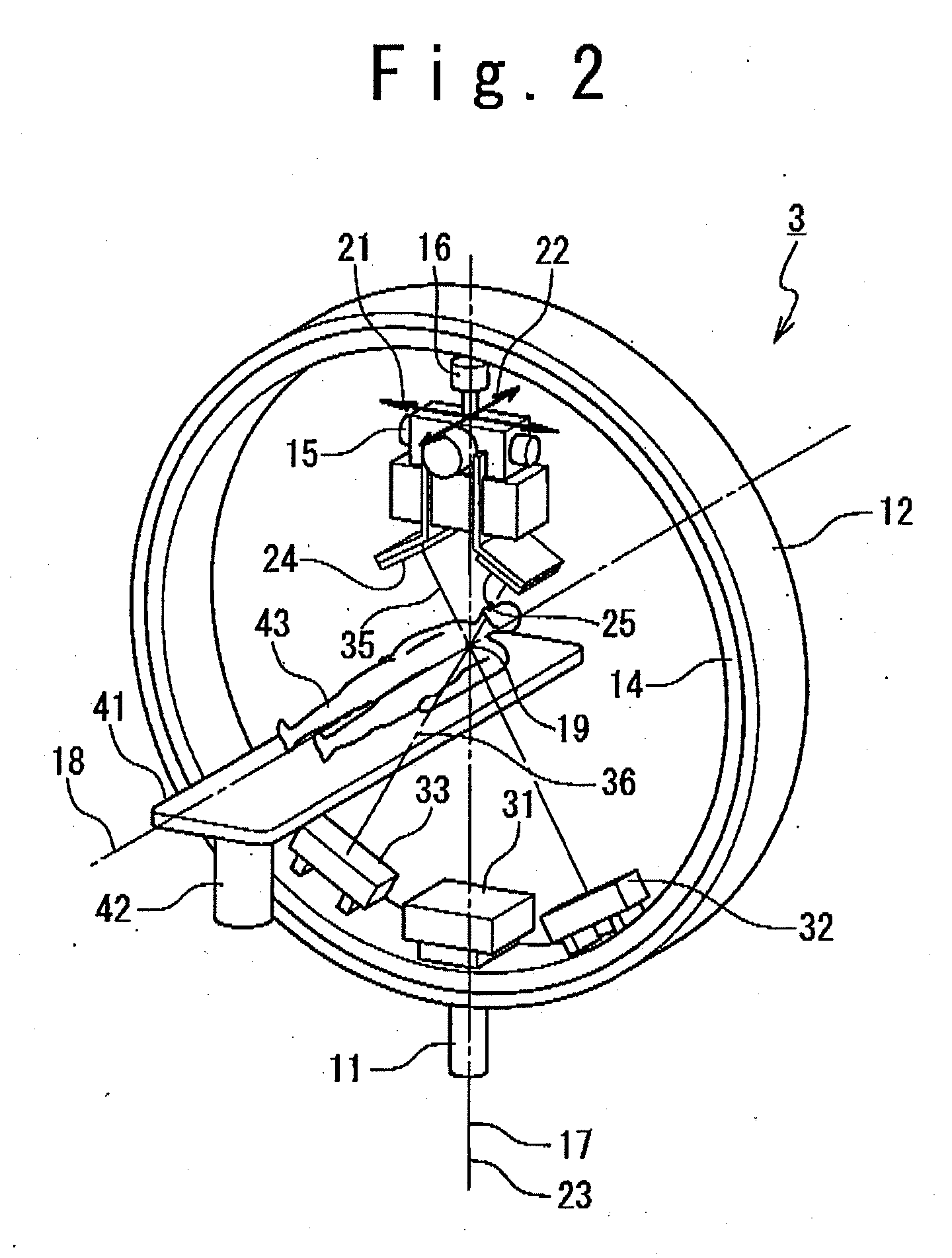
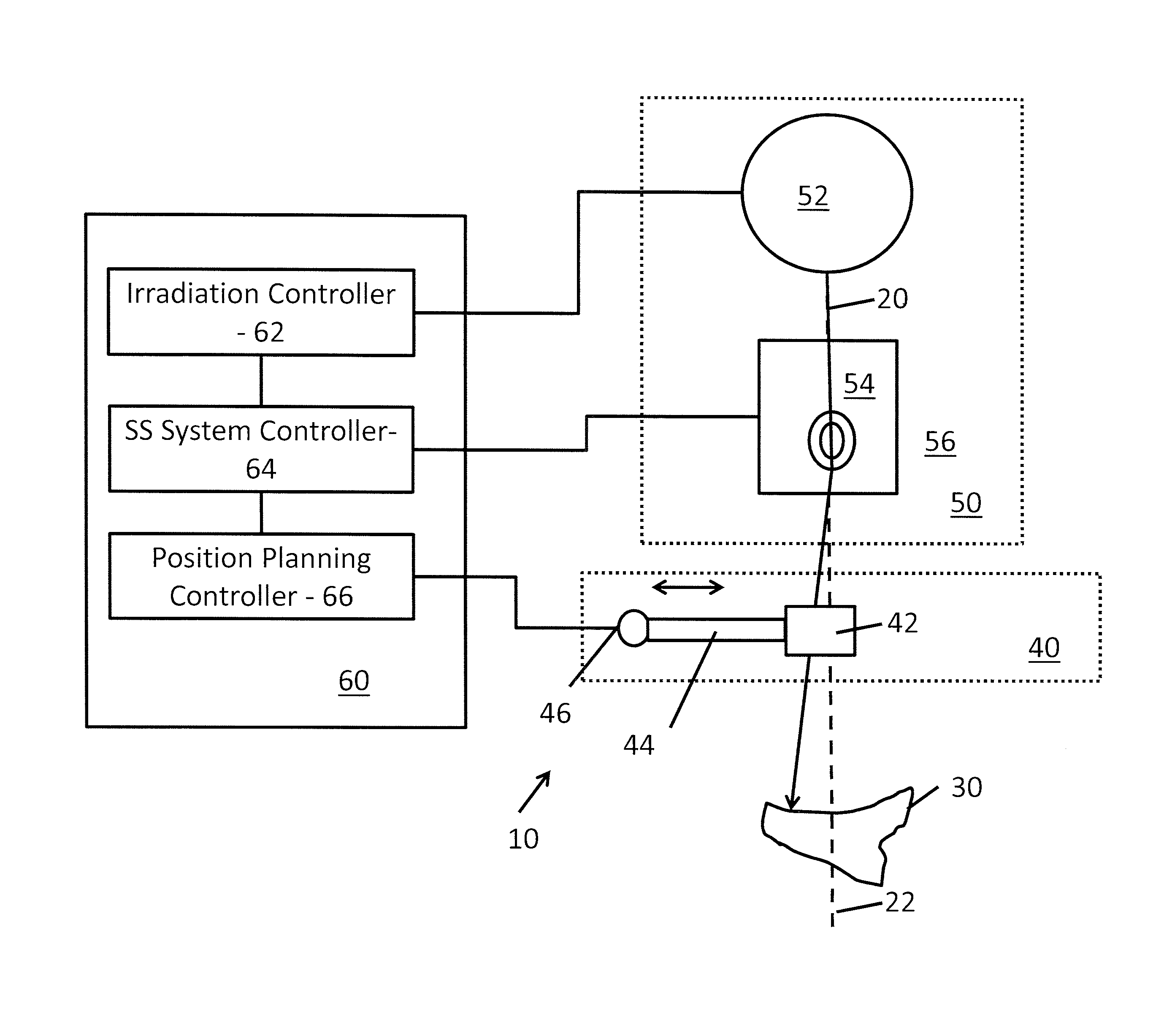
Radiation therapy planning apparatus and radiation therapy planning method
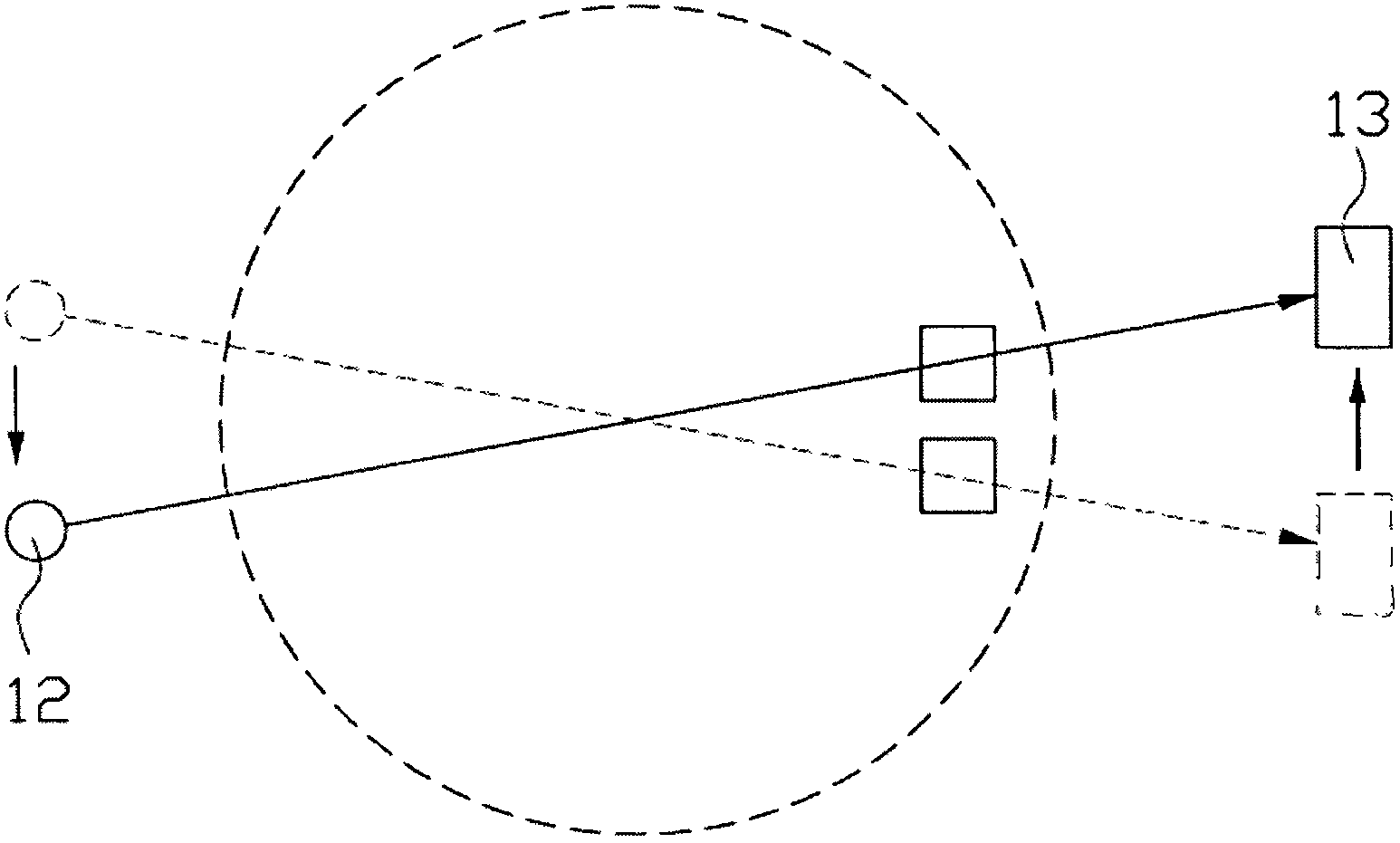
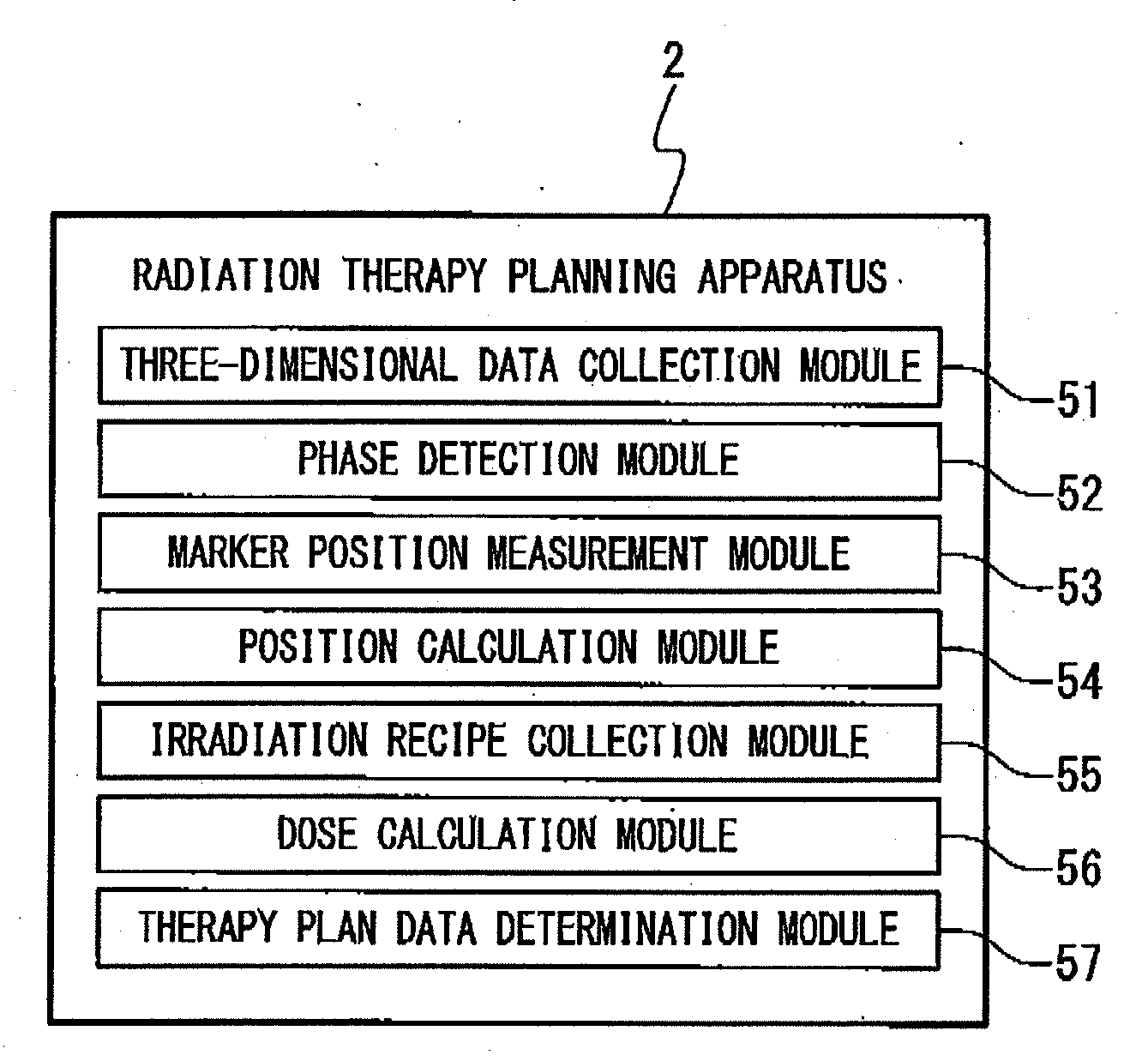
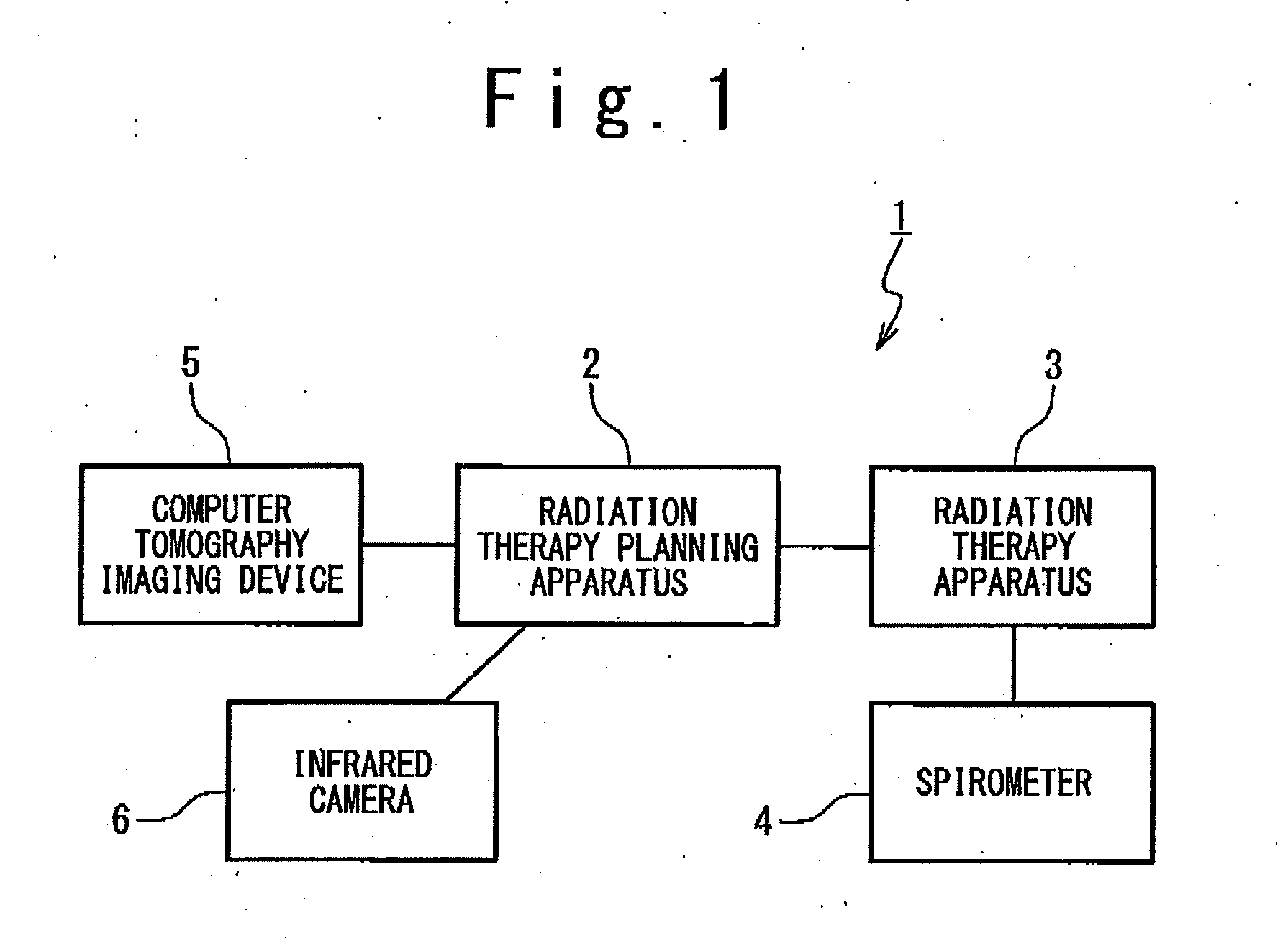
ActiveUS20110044429A1Reduce the burden onReduce doseX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySubject matterTherapy radiation
A radiation therapy planning apparatus is provided with; a three-dimensional data collection part collecting three-dimensional data representing a plurality of positions where a plurality of portions of a subject are positioned; a marker position measurement part measuring a motion of a marker; and a dose calculation part calculating, when the subject is irradiated with therapeutic radiation changing on the basis of the motion of the subject, the dose of the therapeutic radiation with which each of the plurality of portions is irradiated, based on the motion and the three-dimensional data. The radiation therapy planning apparatus thus constructed can calculate the dose of the therapeutic radiation with which each of the respective portions of the subject is irradiated, more accurately, and reduce the dose of radiation with which the subject is irradiated in calculating the motions of the plurality of portions of the subject.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
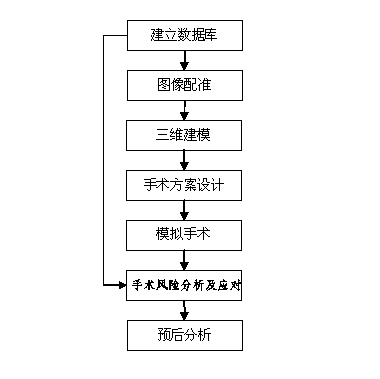
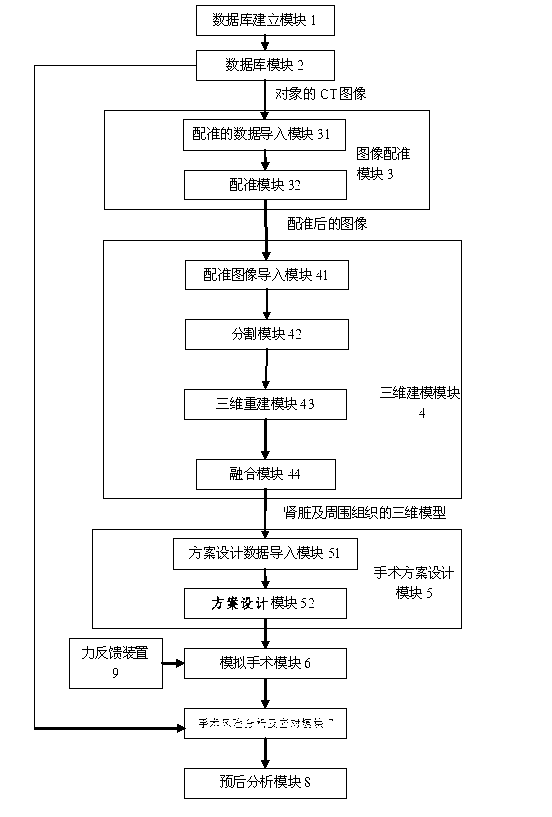
Three-dimensional kidney neoplasm surgery simulation method and platform based on computed tomography (CT) film
ActiveCN102982238AImprove surgical skillsImprove proficiencySpecial data processing applicationsSurgical riskGuideline
The invention discloses a three-dimensional kidney neoplasm surgery simulation method and a platform based on a computed tomography (CT) film. The method includes that firstly, a data base including object resources is built, multiple manners including CT film scanning are inputted into a CT faultage image, a sequence image is registered according to the sequence based on an outline gradient principle, a registered CT image is utilized to reconstruct segmentation tissue of an arterial phase, a venous phase and a lag phase by adopting of a three-dimensional reconstruction technology, and the segmentation tissue of the arterial phase, the venous phase and the lag phase are effectively fused in the same coordinate space. According to an imaging staging criteria and a treatment guideline of kidney neoplasm, and based on modeling results, various peration plan designing, operation stimulation, surgical risk analysis and response, and prognostic analysis are carried out, a personalized and benefit maximization treatment plan can be provided for an object, and skills and degree of proficiency of an operation can be improved, and the three-dimensional kidney neoplasm surgery simulation method can be used in medical teaching.
Owner:江苏瑞影医疗科技有限公司
X-ray flux management device
ActiveUS20070104320A1Reduced dynamic rangeReduce radiation doseHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh fluxX-ray
The invention is directed to an x-ray flux management device that adaptively attenuates an x-ray beam to limit the incident flux reaching a subject and radiographic detectors in potentially high-flux areas while not affecting the incident flux and detector measurements in low-flux regions. While the invention is particularly well-suited for CT, the invention is also applicable with other x-ray imaging systems. In addition to reducing the required detector system dynamic range, the present invention provides an added advantage of reducing radiation dose.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Histone deacelylase inhibitors in diagnosis and treatment of thyroid neoplasms
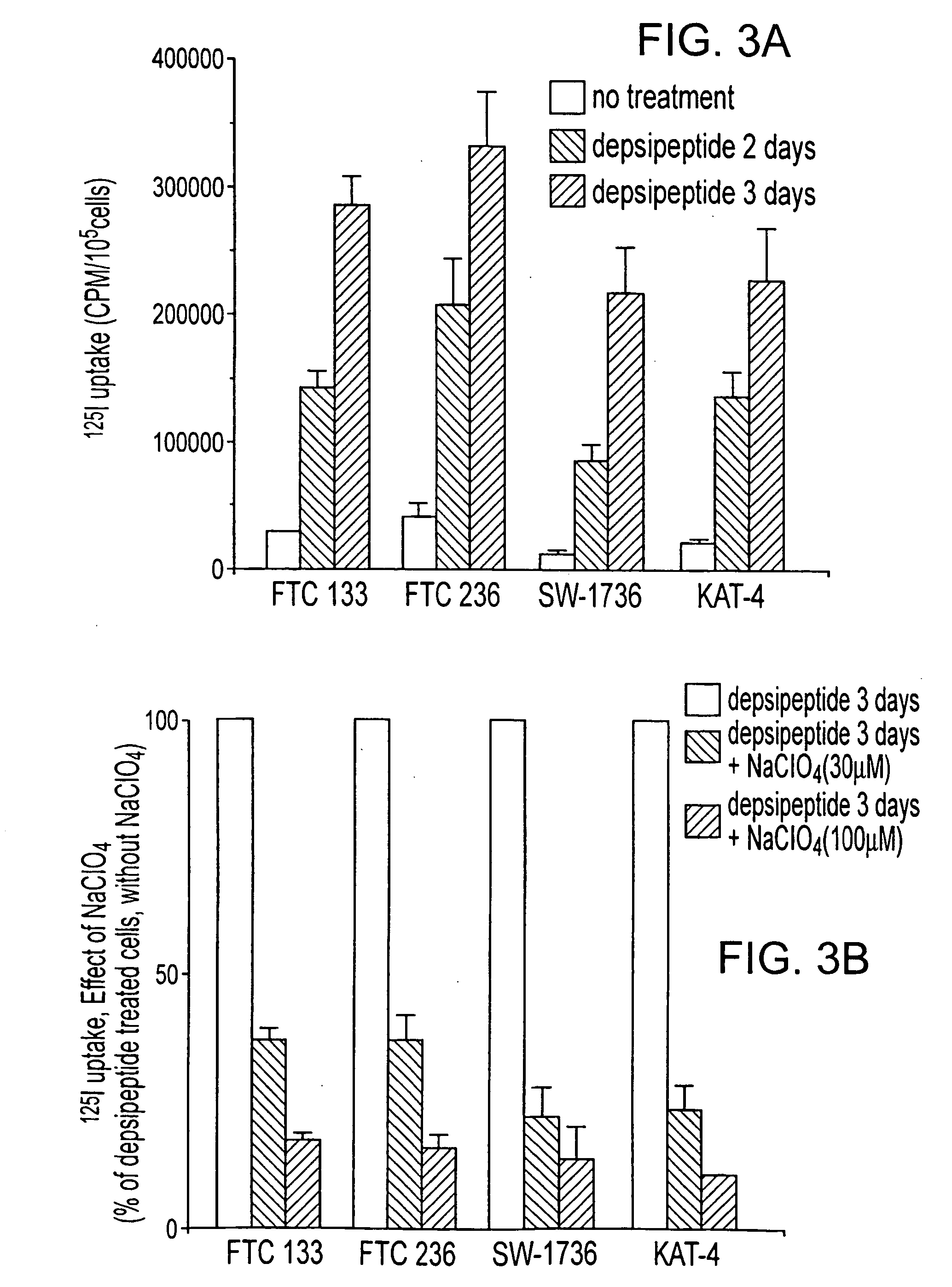
InactiveUS20040132643A1Increase count rateAdequate imagingBiocideRadioactive preparation carriersLymphatic SpreadRadioactive iodine therapy
Disclosed herein are novel approaches to thyroid cancer therapy. These approaches include methods to enhance thyroid specific gene expression, for example methods to enhance expression of thyroglobulin and / or the Na<+> / I<-> symporter in thyroid cancer cells. Enhanced expression of thyroid-specific genes promotes cellular differentiation and reduces biologically aggressive behavior such as invasion and metastasis. In addition, enhanced expression of thyroglobulin and / or the Na<+> / I<31 > symporter increases the ability of thyroid cancer cells to concentrate iodine or iodide, thereby making the cells more susceptible to radioactive iodine therapy. Also disclosed herein are methods for detecting thyroid neoplasms in a subject, by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a histone deacetylase inhibitor, administering a detectable agent whose uptake or concentration in thyroid cells is increased by administration of the histone deacetylase inhibitor, and detecting the detectable agent.
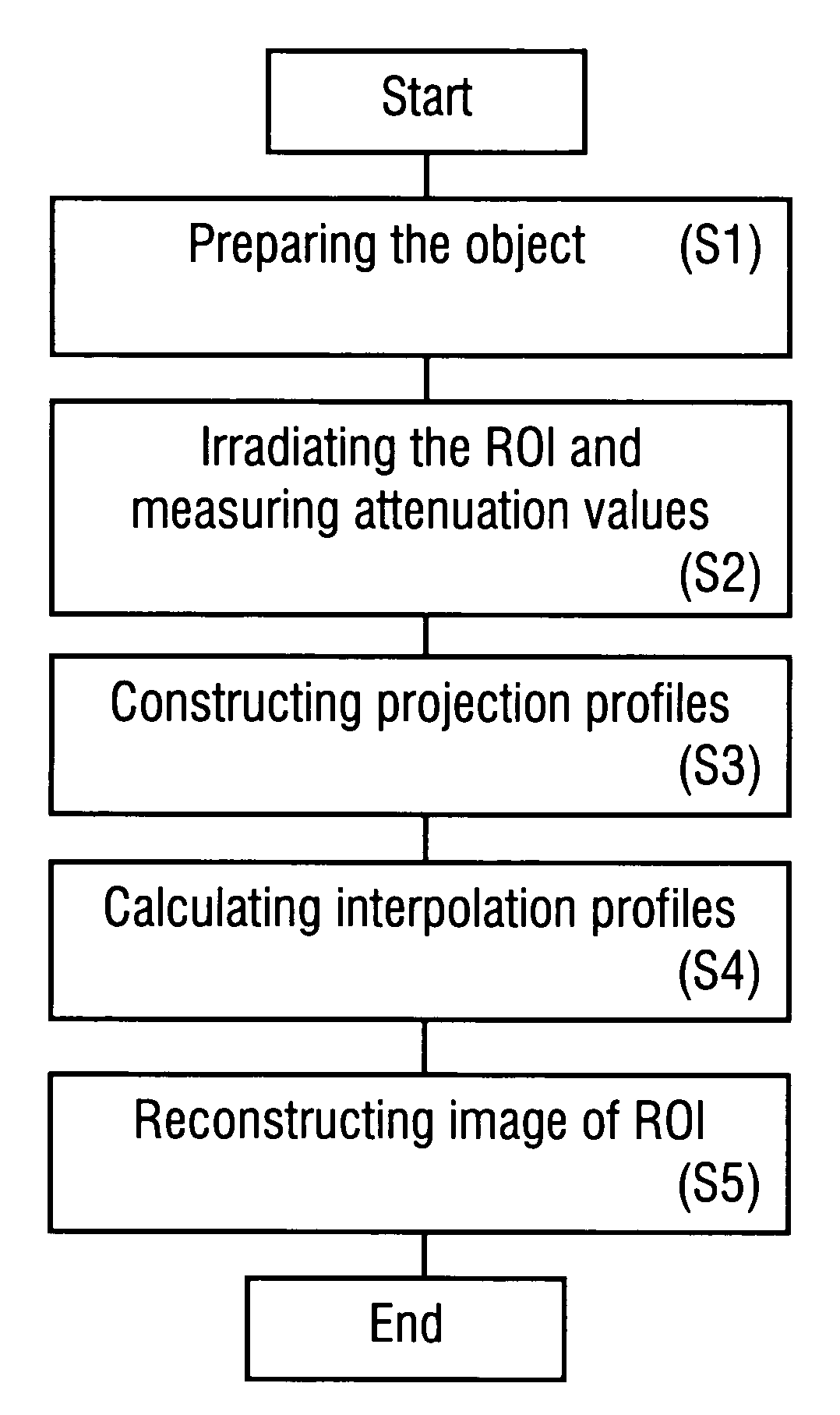
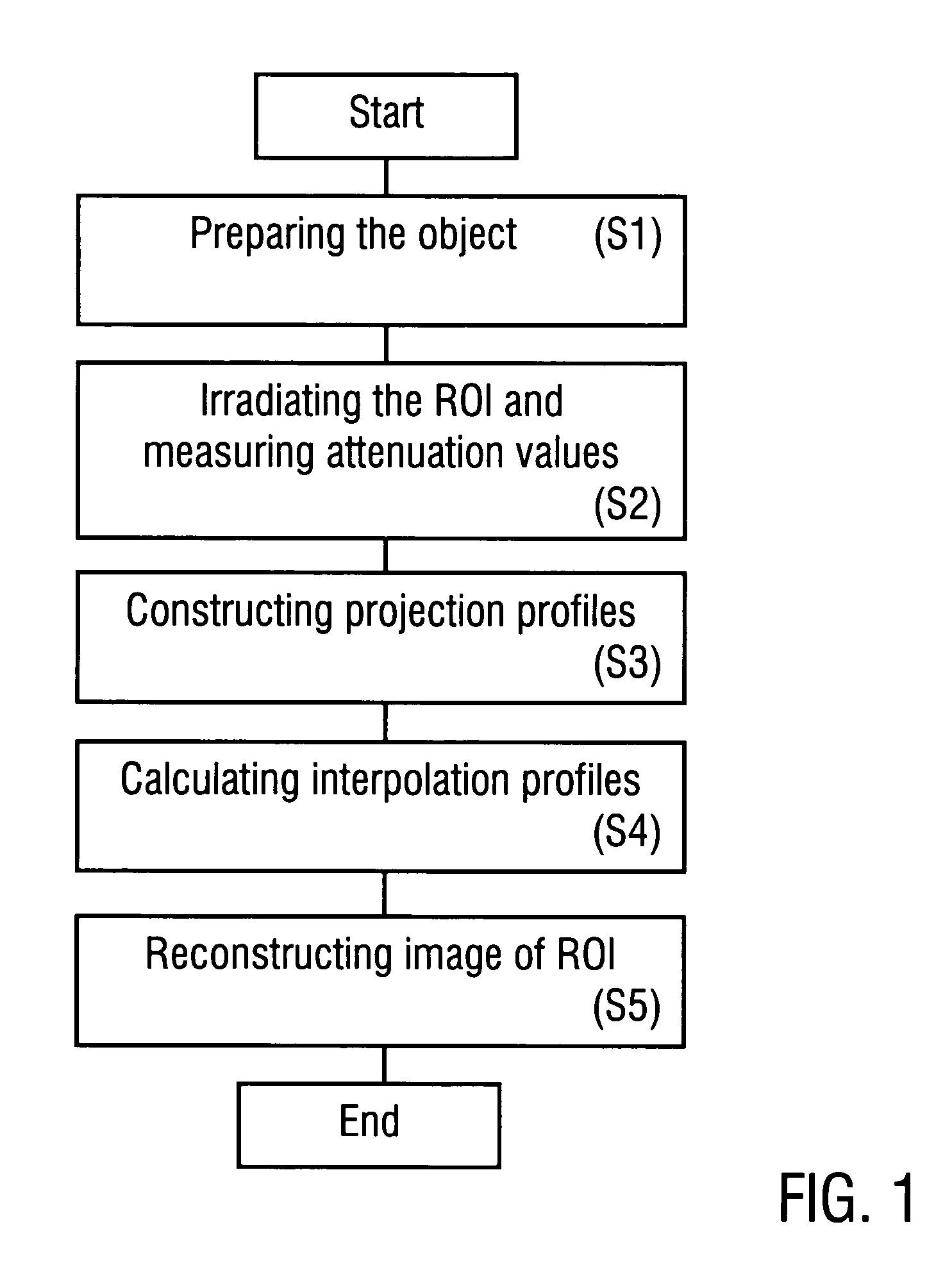
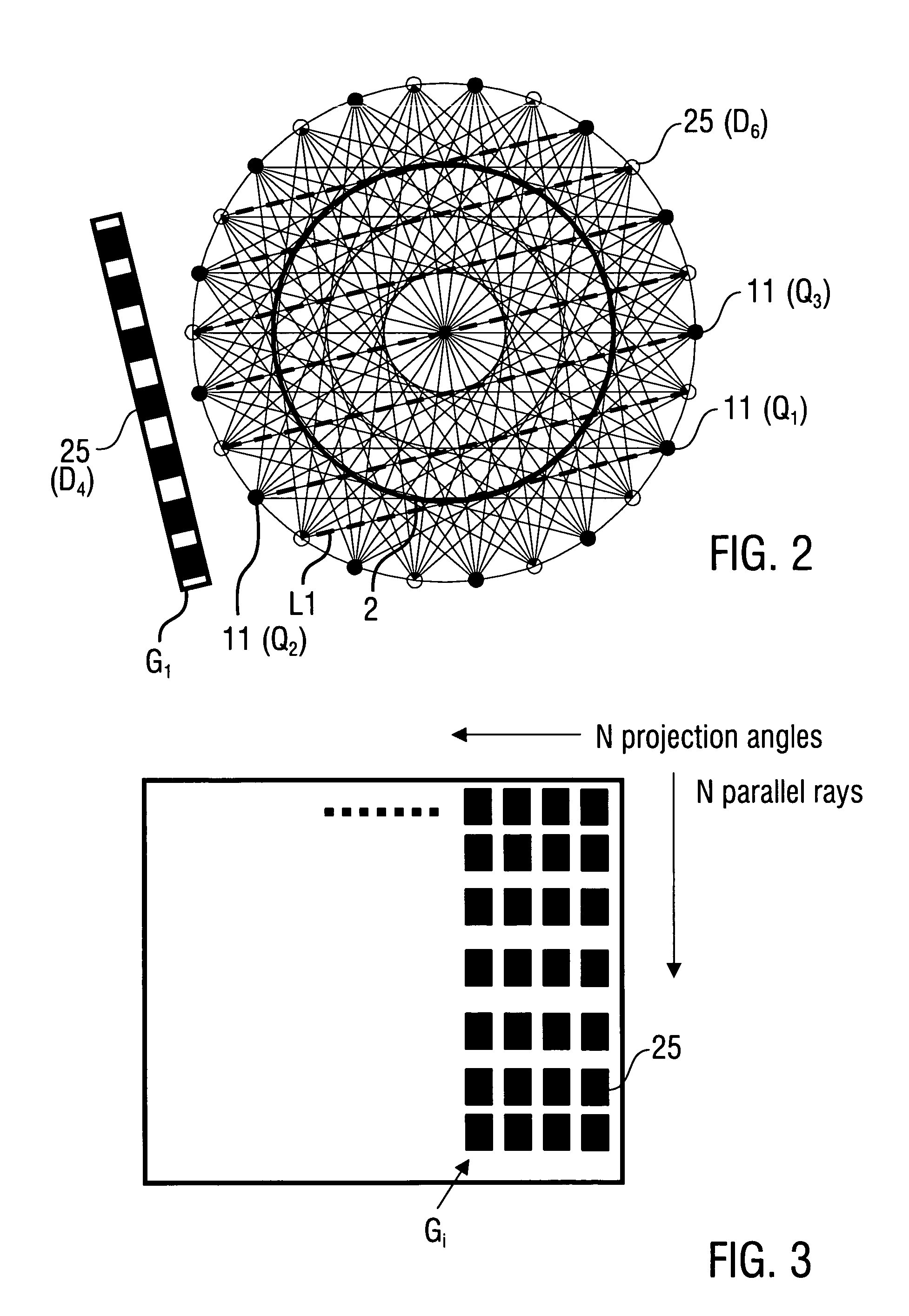
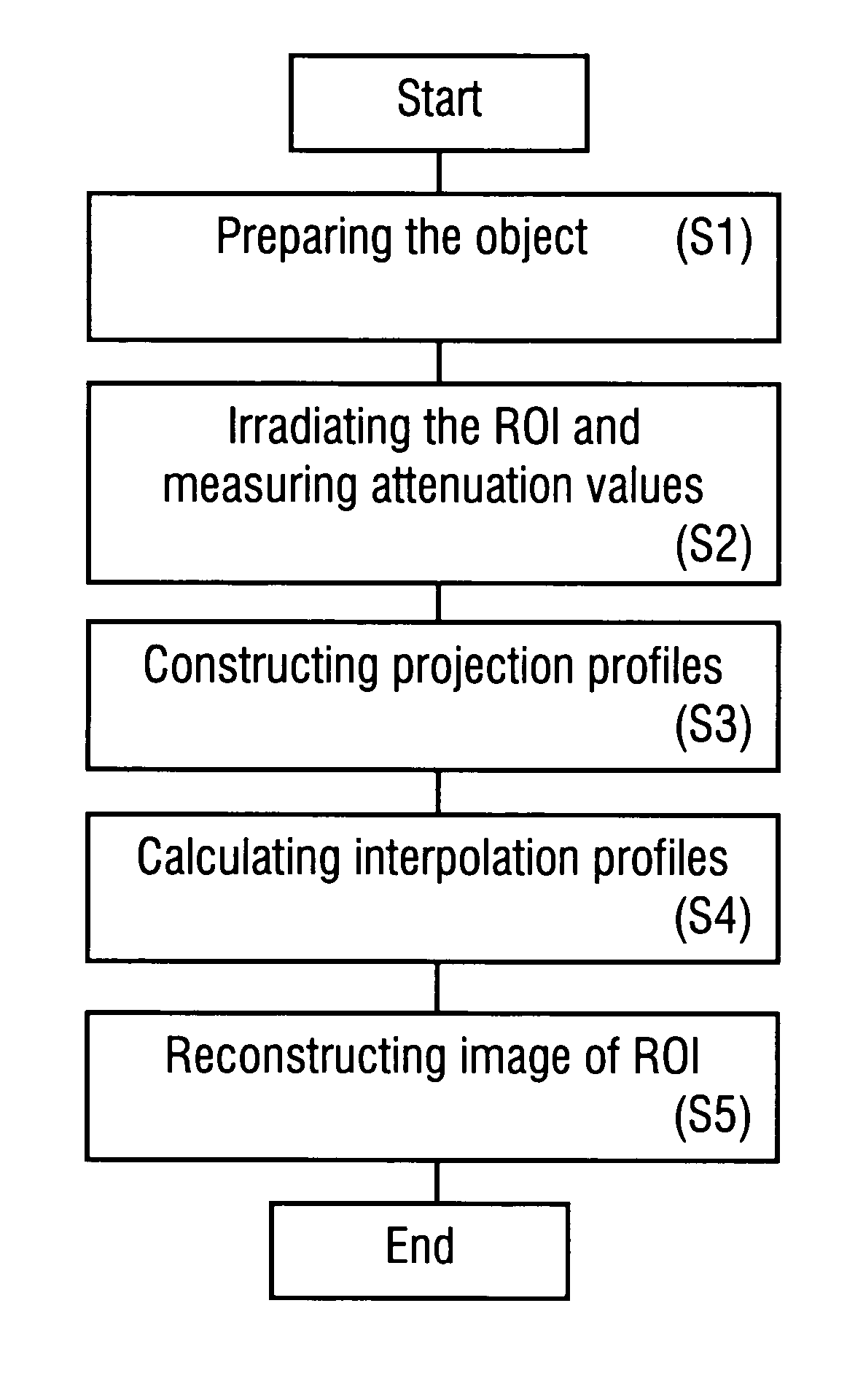
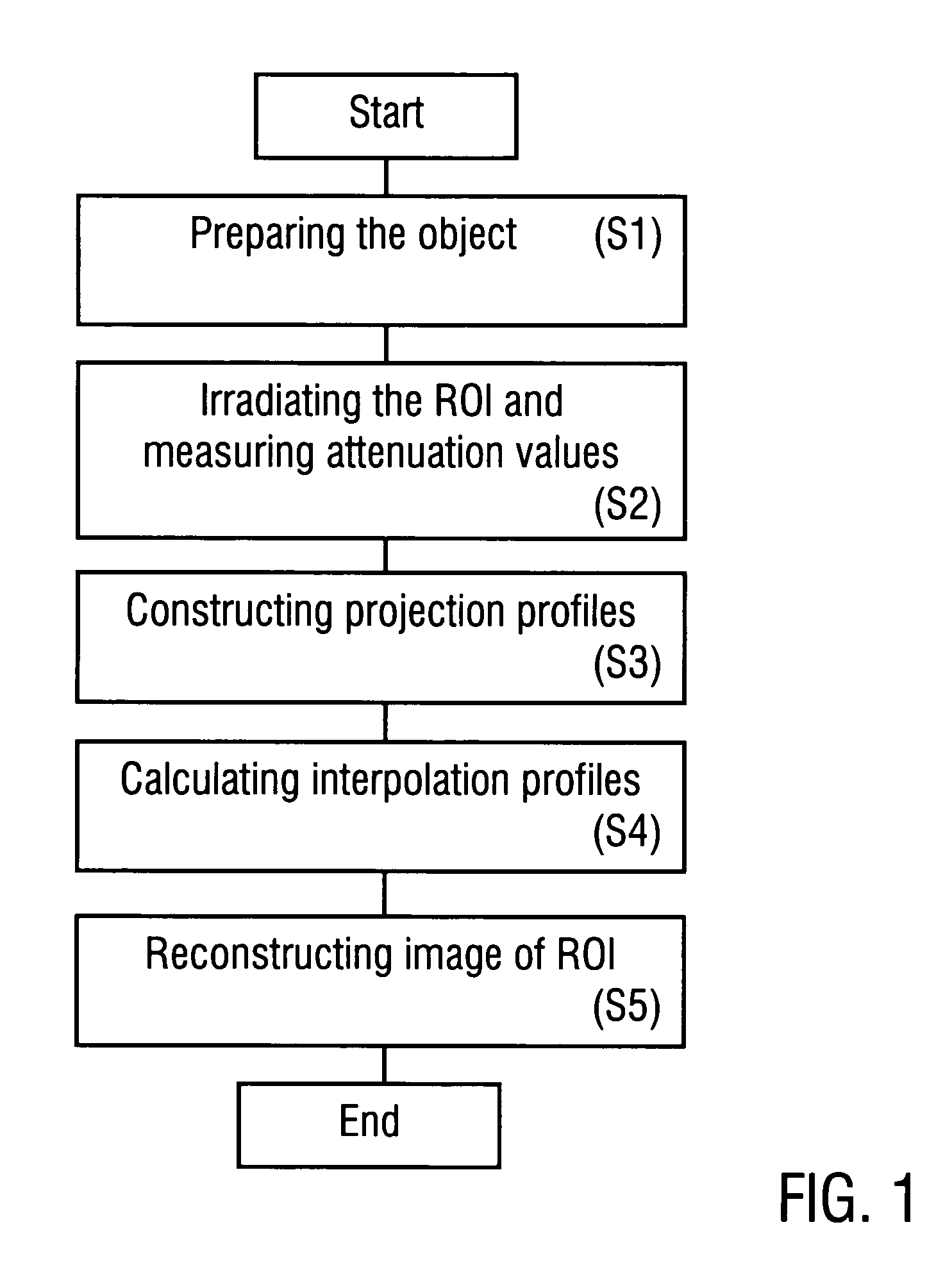
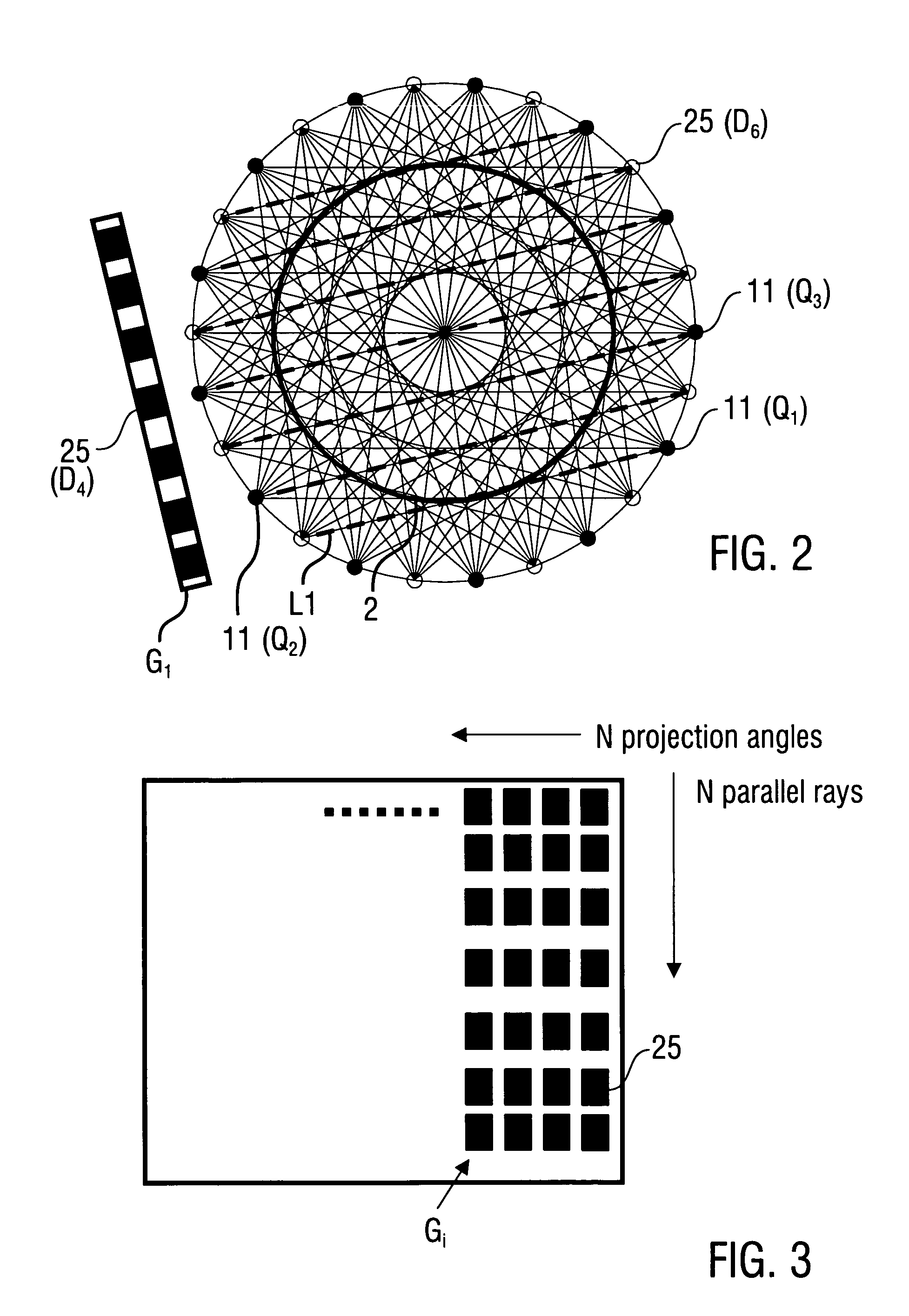
Method of reconstructing an image function from radon data
InactiveUS20090297009A1Increase the scope of applicationImprove imaging resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationReconstruction algorithmImage fusion
A method of reconstructing an image function on the basis of a plurality of projection profiles corresponding to a plurality of projection directions through a region of investigation, each projection profile including a series of value positions, wherein measured projection values corresponding to projection lines parallel to the respective projection direction are assigned to respective value positions and a plurality of remaining value positions are empty, comprises the steps of (a) assigning first interpolation values to the empty value positions for constructing a plurality of interpolation profiles on the basis of the projection profiles, wherein the first interpolation values are obtained from a first interpolation within a group of measured projection values having the same value position in different projection profiles, and (b) determining the image function by applying a predetermined reconstruction algorithm on the interpolation profiles.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OREGON +1
Positioning method for use in image-guided radiotherapy
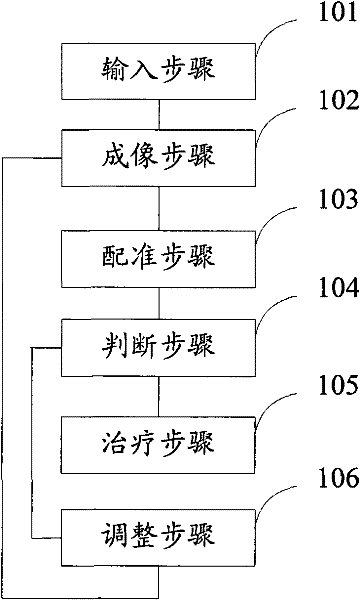
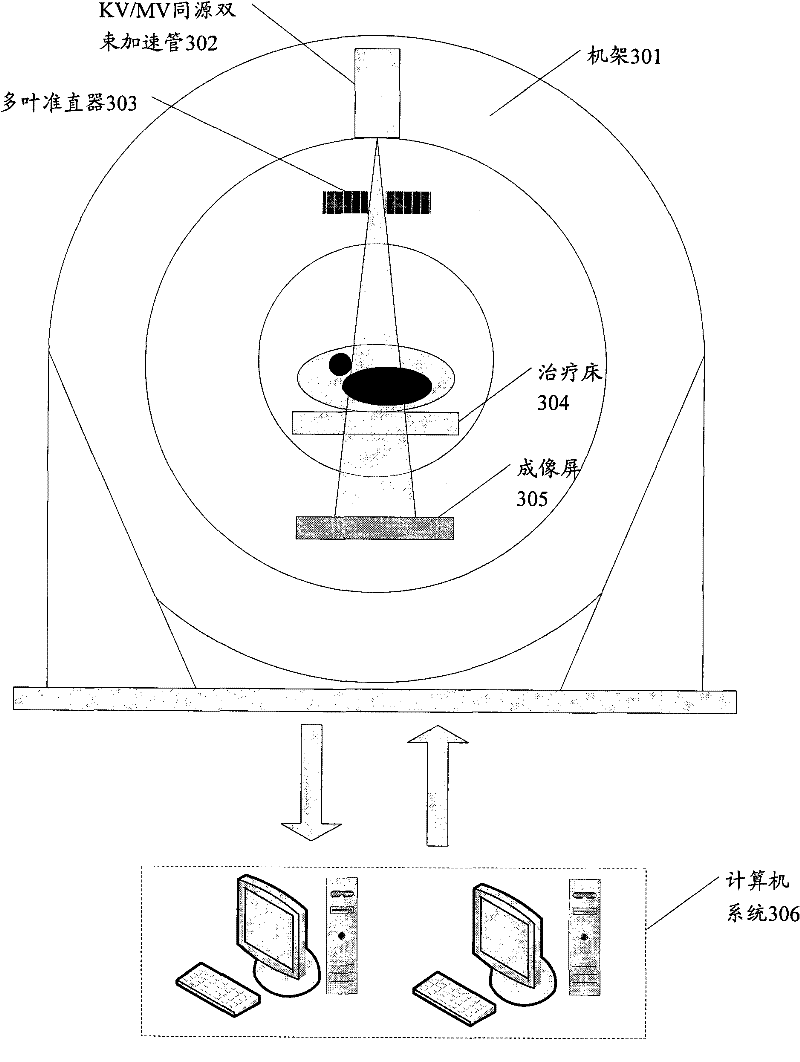
InactiveCN102232835AReflect postural errorAccurately determineRadiation diagnosticsX-rayComputer science
The invention provides a positioning method for use in image-guided radiotherapy, which comprises the following: a step of input, which is to input a radiotherapy plant image; a step of imaging, which is o acquire the image data of a patient by using KV-grade X-rays and acquire the image of a patient according to the image data; a step of registering, which is to register the image of the patient with the radiotherapy plant image; a step of judging, which to judge whether the positions of the two images are consistent according to the registration results, and execute a step of treatment if the positions of the two images are consistent or execute a step of regulation if the positions of the two images are inconsistent; a step of treatment, which is to treat the patient by using an MV-grade X-rays, wherein the KV-grade X-rays and the MV-grade X-rays are from the same accelerating tube; and the step of regulation, which is to regulate the position of a patient according to the registration result and return to the step of imaging. The positioning method is used for improving the positioning accuracy of image-guided radiotherapy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Radioactive therapeutic fastening instrument
ActiveUS20110245578A1For accurate placementReduce radiation doseSuture equipmentsStapling toolsBrachytherapyEngineering
An instrument used for brachytherapy delivery in the treatment of cancer by radiation therapy including a handle having first and second handle actuators; an end effector; and an instrument shaft that connects the handle with the end effector. The end effector has first and second adjacent disposed staple mechanisms that each retain a set of staples. The first mechanism is for holding standard staples in a first array, and dispensing the standard staples under control of the corresponding first handle actuator. The second mechanism is for holding radioactive source staples in a second array, and dispensing said radioactive source staples under control of the corresponding second handle actuator. A holder is for receiving the first and second mechanisms in a substantially parallel array so that the standard staples close the incision at a surgical margin while the source staples are secured adjacent thereto.
Owner:POINT SOURCE TECH
CT system, CT system scanning positioning method and CT system calibration method
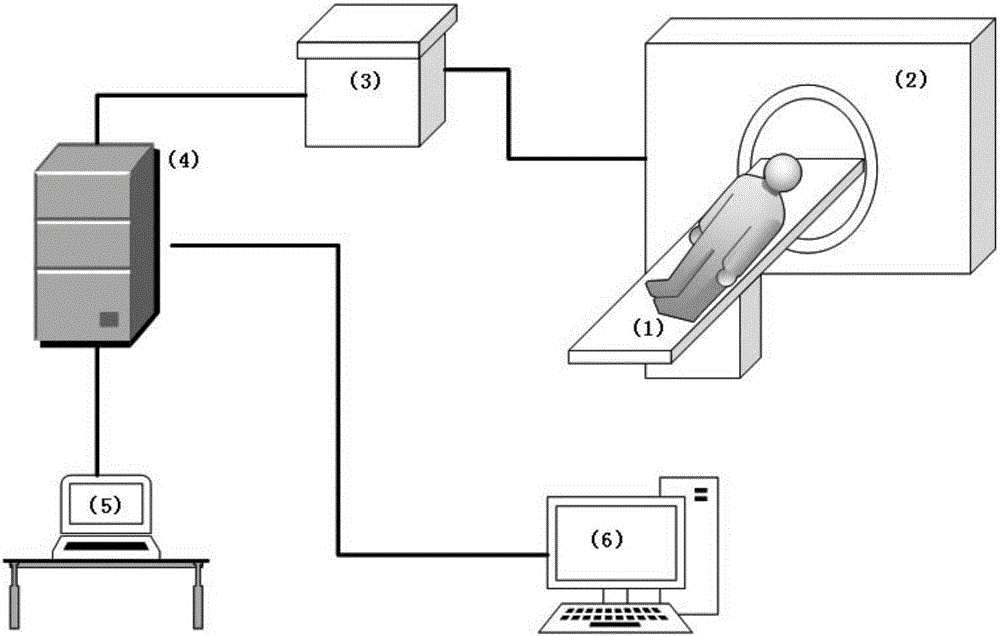
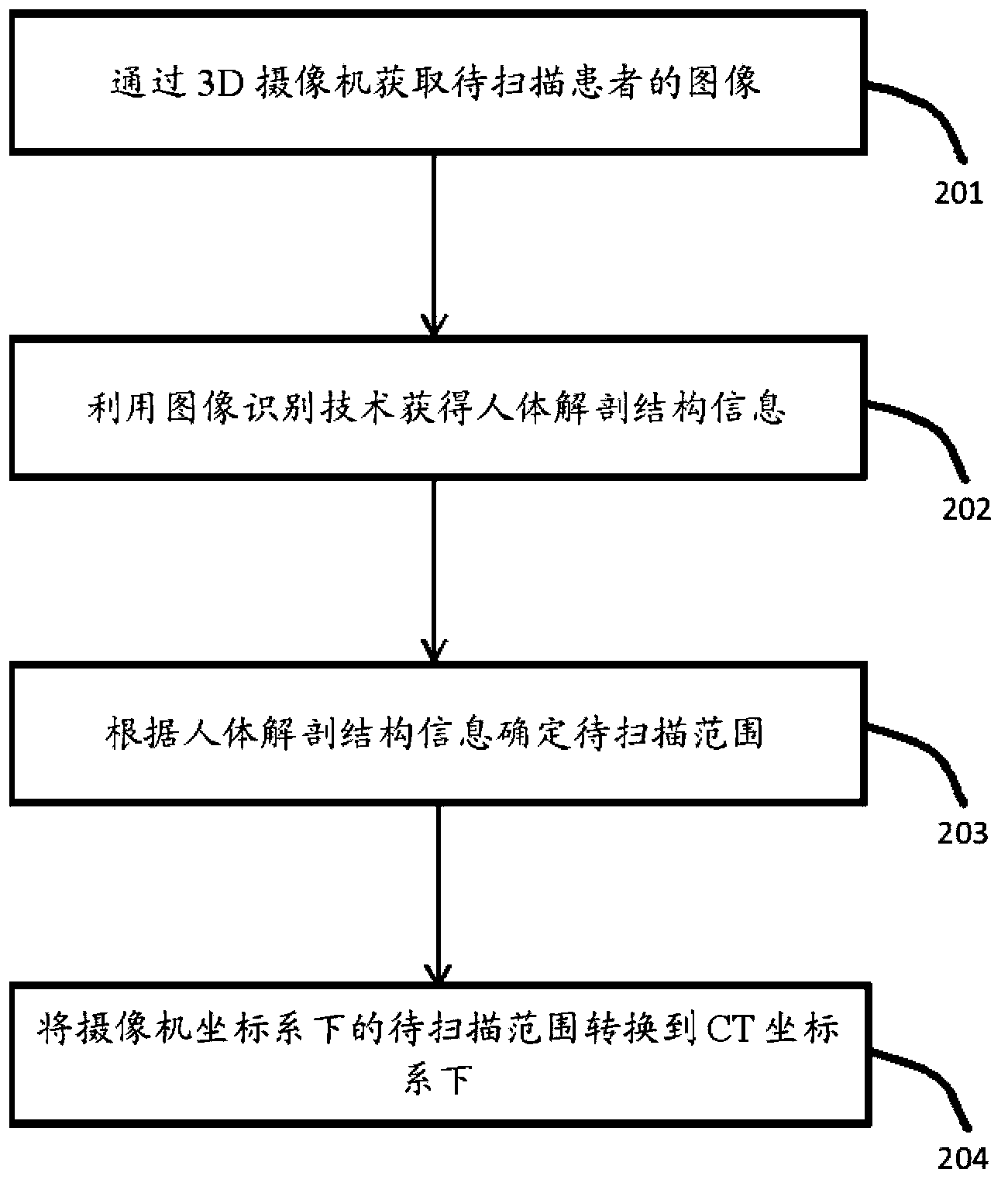
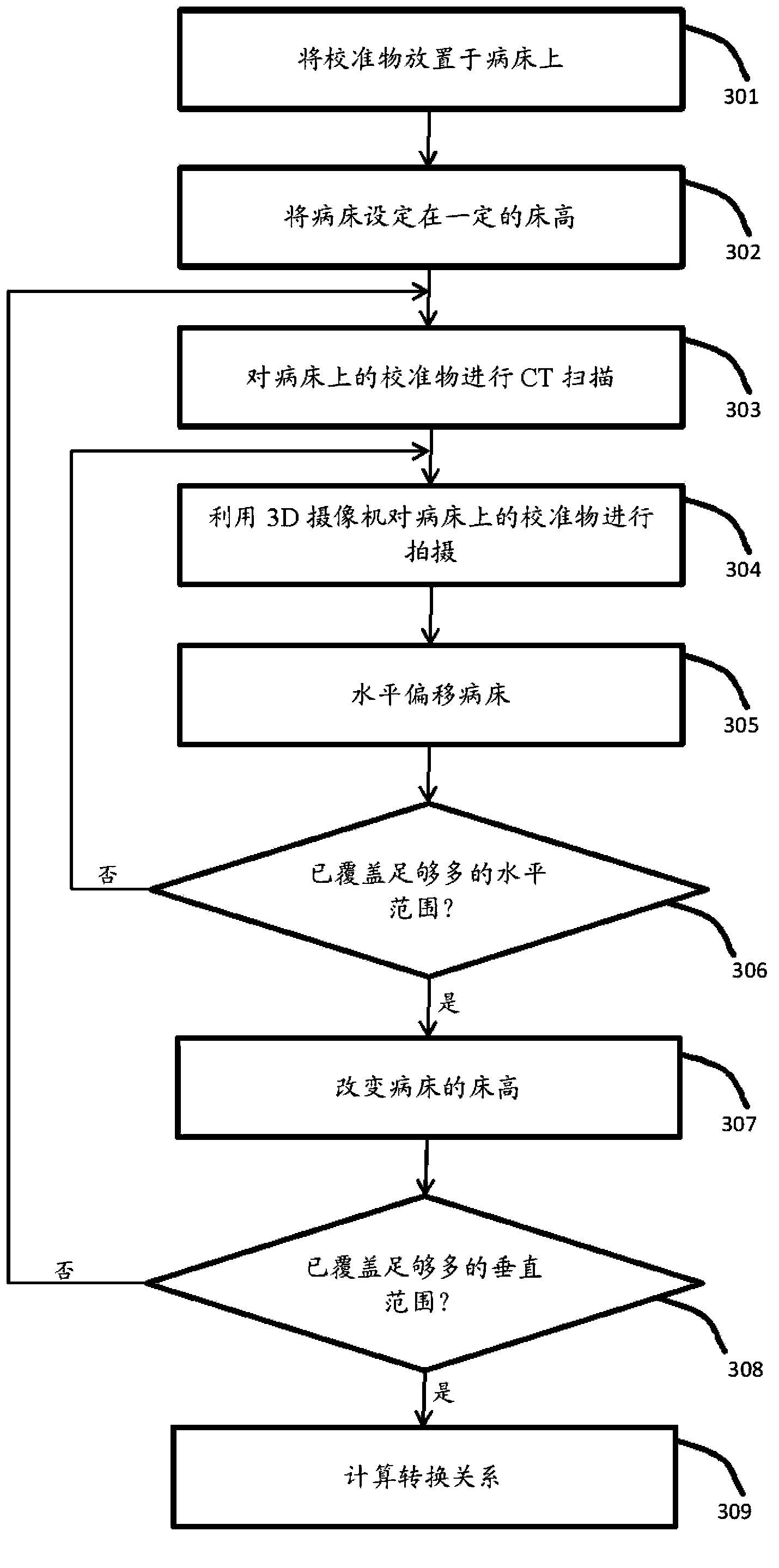
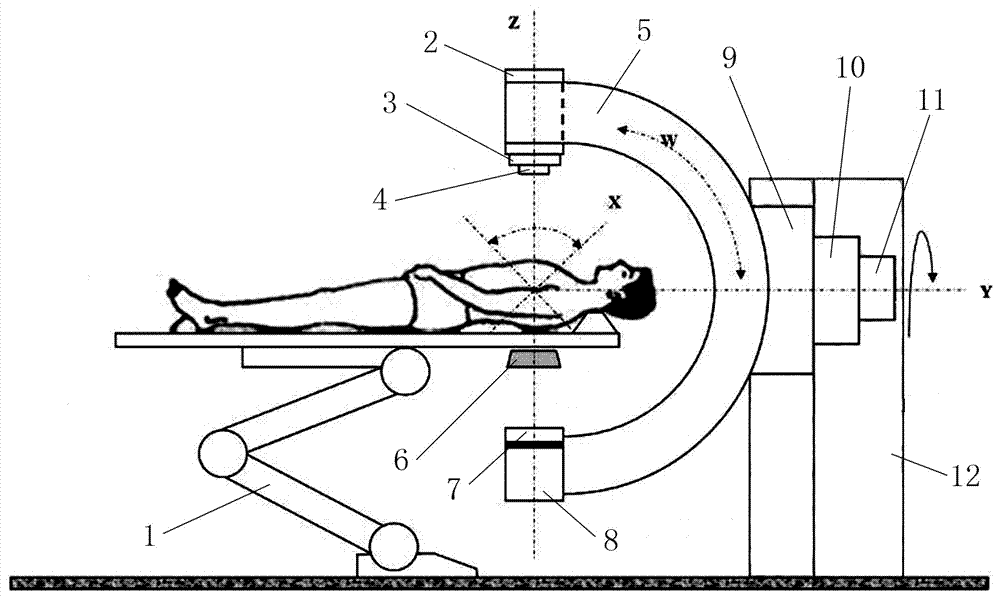
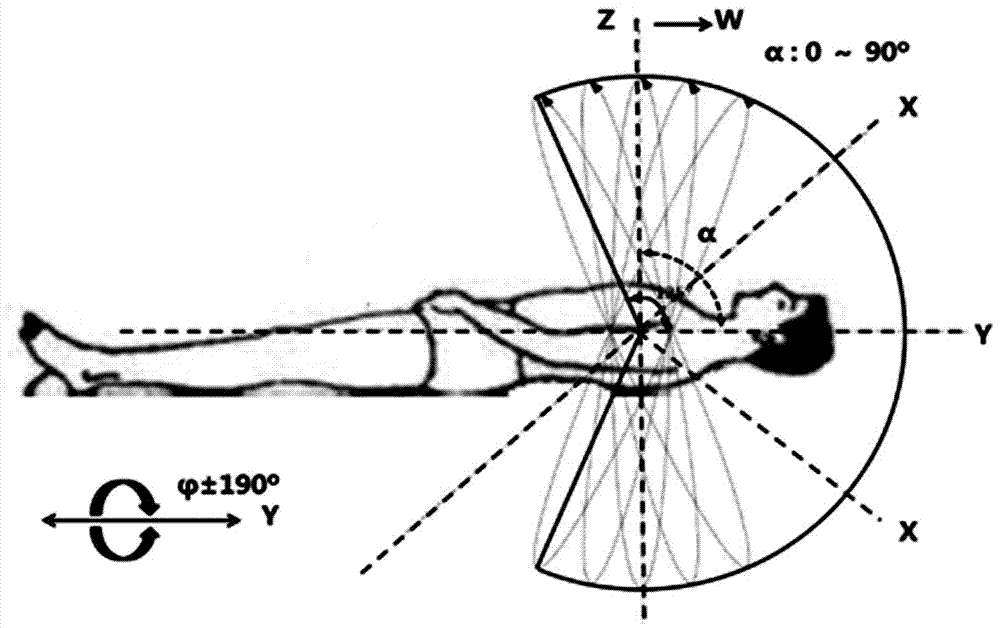
ActiveCN104224212AHigh precisionReduce scan timeComputerised tomographsTomographyHuman anatomyComputed tomography
The invention relates to a CT system, a CT system scanning positioning method and a CT system calibration method. The CT system comprises a hospital bed, CT scanning and imaging equipment, a 3D video camera and a processing unit. The hospital bed is used for supporting a patient to be scanned on the hospital bed. The CT scanning and imaging equipment is used for conducting CT scanning and imaging on the patient to be scanned. The 3D video camera is used for shooting a 3D image of the patient to be scanned on the hospital bed. The processing unit is used for acquiring human anatomy structural information of the patient to be scanned according to the 3D image shot by the 3D video camera so as to determine the range to be scanned and for converting the range to be scanned of the 3D video camera under a space coordinate system to the range to be scanned of the CT scanning and imaging equipment under a space coordinate system. The CT scanning and imaging equipment conducts scanning and imaging on the patient to be scanned according to the converted range to be scanned of the CT scanning and imaging equipment under the space coordinate system. By means of the CT system, the CT system scanning positioning method and the CT system calibration method, the precision of the scanned range can be improved, scanning time is shortened, and radiation dosage is lowered.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Targeted nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and treatment
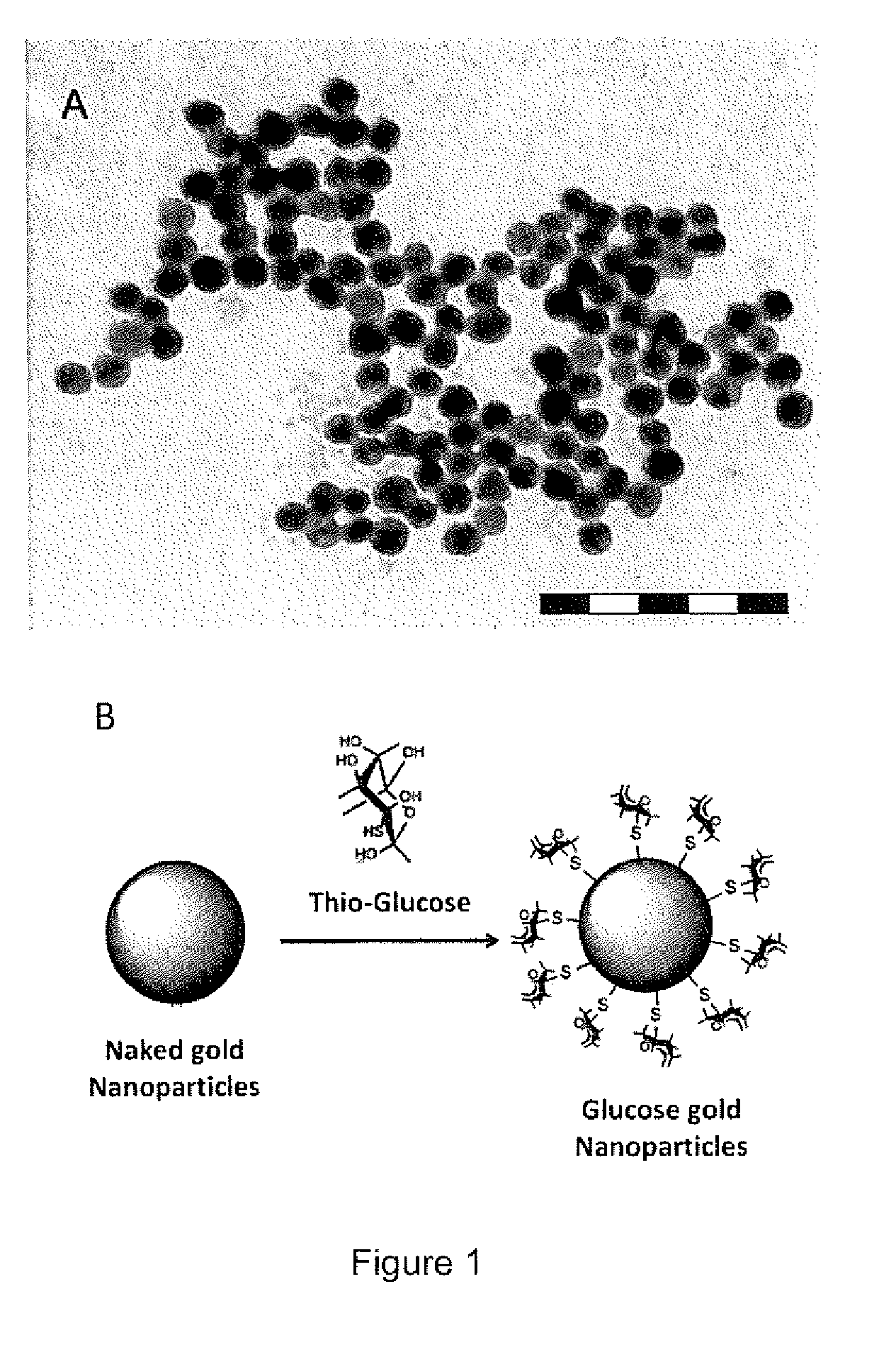
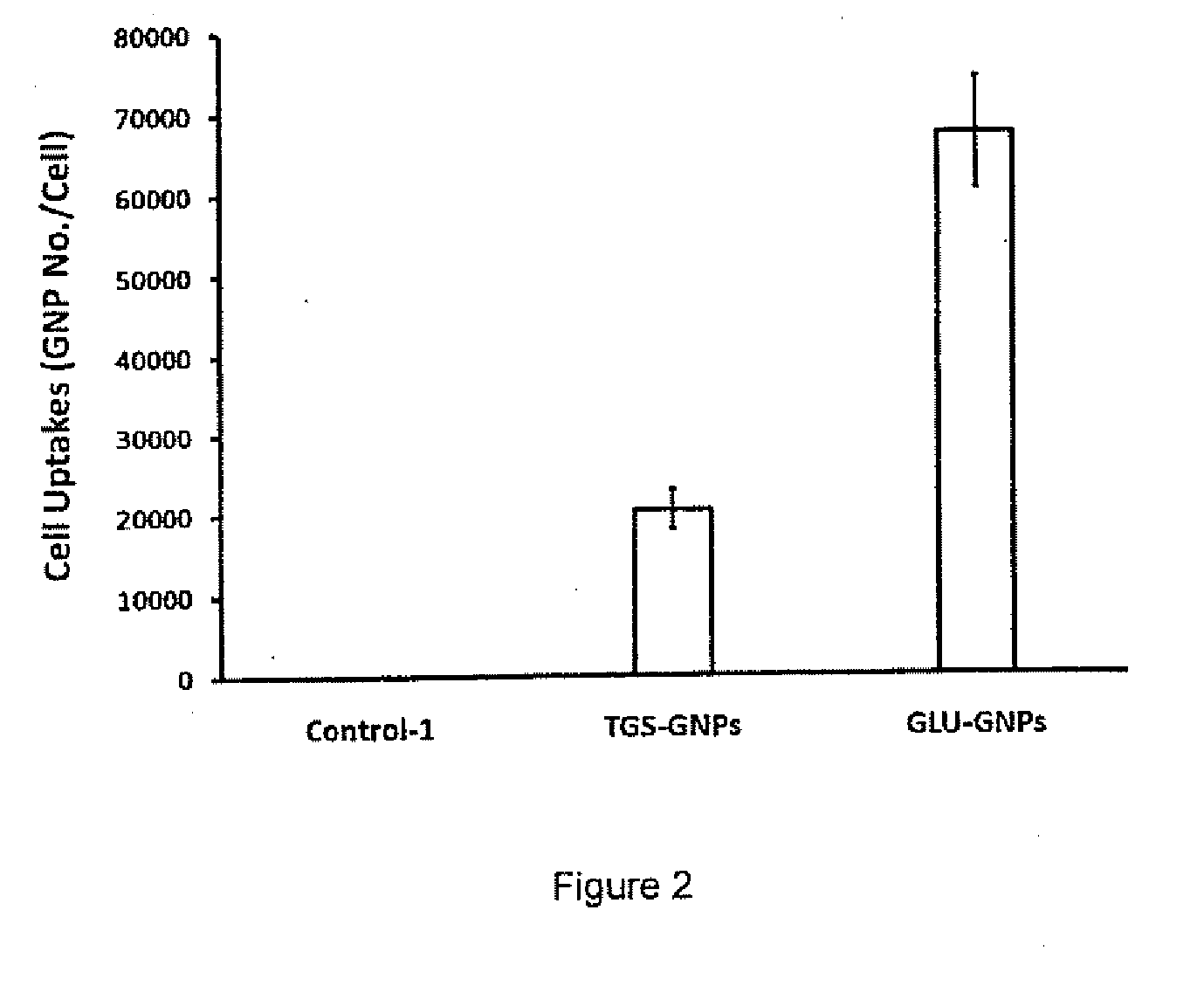
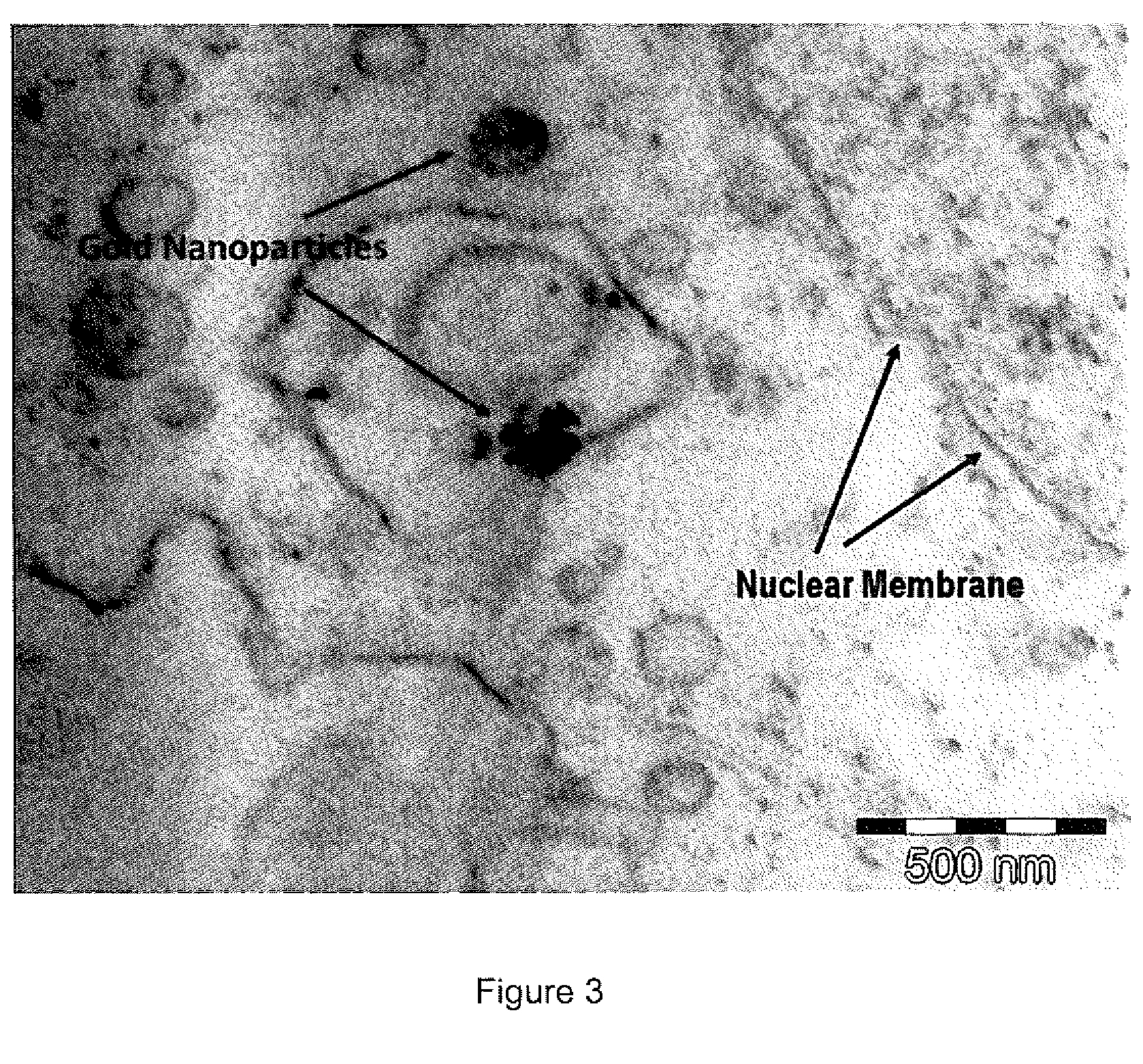
InactiveUS20100034735A1Increase local concentrationGood choicePowder deliveryIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCancers diagnosis
The invention provides modified gold nanoparticles that enable a non-invasive, real time, targeted cancer imaging-therapeutic in one step. After reaching the cancer targets, the designed targeted gold nanoparticles significantly enhance conventional treatment modalities at the cellular level. In this aspect the gold nanoparticles of the invention are modified to be bound to a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) tracer.
Owner:ALBERTA HEALTH SERVICES +1
Preparation process of ethylene propylene diene rubber foaming materials
InactiveCN101824189AUniform Radiation VulcanizationIncreased Radiation Processing EnergyCross-linkVulcanization
The invention discloses a preparation process of ethylene propylene diene rubber foaming materials. A rubber compounding recipe of the invention consists of ingredients of rubber base materials, an anti-aging system, a filling system, a plasticizing agent, a vulcanizing system, a foaming system and a radiation cross linking sensitizing agent. The ethylene propylene diene rubber foaming materials are prepared through vulcanization foaming and demolding after the pretreatment of compounding, sheet cutting and electronic beam radiation pretreatment. The rubber sheets of the invention after radiation pretreatment have a certain pre-cross-linking degree before the heating vulcanization foaming, the fit of the vulcanization speed and the foaming velocity can be realized, the integral performance of products can be improved, the pre-vulcanization time can be shortened, energy sources can be saved, and the production efficiency can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING RADIATION APPL RES CENT
Method of reconstructing an image function from Radon data
InactiveUS8094910B2Improve imaging resolutionSimple methodReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationReconstruction algorithmImage fusion
A method of reconstructing an image function on the basis of a plurality of projection profiles corresponding to a plurality of projection directions through a region of investigation, each projection profile including a series of value positions, wherein measured projection values corresponding to projection lines parallel to the respective projection direction are assigned to respective value positions and a plurality of remaining value positions are empty, comprises the steps of (a) assigning first interpolation values to the empty value positions for constructing a plurality of interpolation profiles on the basis of the projection profiles, wherein the first interpolation values are obtained from a first interpolation within a group of measured projection values having the same value position in different projection profiles, and (b) determining the image function by applying a predetermined reconstruction algorithm on the interpolation profiles.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OREGON +1
Sparse angle X-ray captive test (CT) imaging method
InactiveCN103136773ARemove Motion ArtifactsQuality rebuild2D-image generationRadiologyNuclear medicine
A sparse angle X-ray captive test (CT) imaging method comprises the following steps: (1) system parameters, all angle projection data scanned previously and sparse angle projection data scanned previously in different periods are obtained; (2) image reconstruction is respectively performed to the all angle projection data scanned previously and the sparse angle projection data scanned previously which are obtained in step (1) so that a previously scanned CT image and a currently reconstructed CT image are obtained; (3) weighting even filtering processing is performed to the previously scanned CT image and the currently reconstructed CT image which are obtained in the step (2) so that a prior image is obtained; (4) a sparse angle CT image reconstruction model is constructed by the prior image obtained in the step (3); and (5) a final reconstructed image is obtained through optimization solution. According to the sparse angle X-ray CT imaging method, motion artifact caused by mismatching of imaging positions between the previously scanned CT image and the currently reconstructed CT image is removed so that high quality reconstruction of a low dose CT image is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
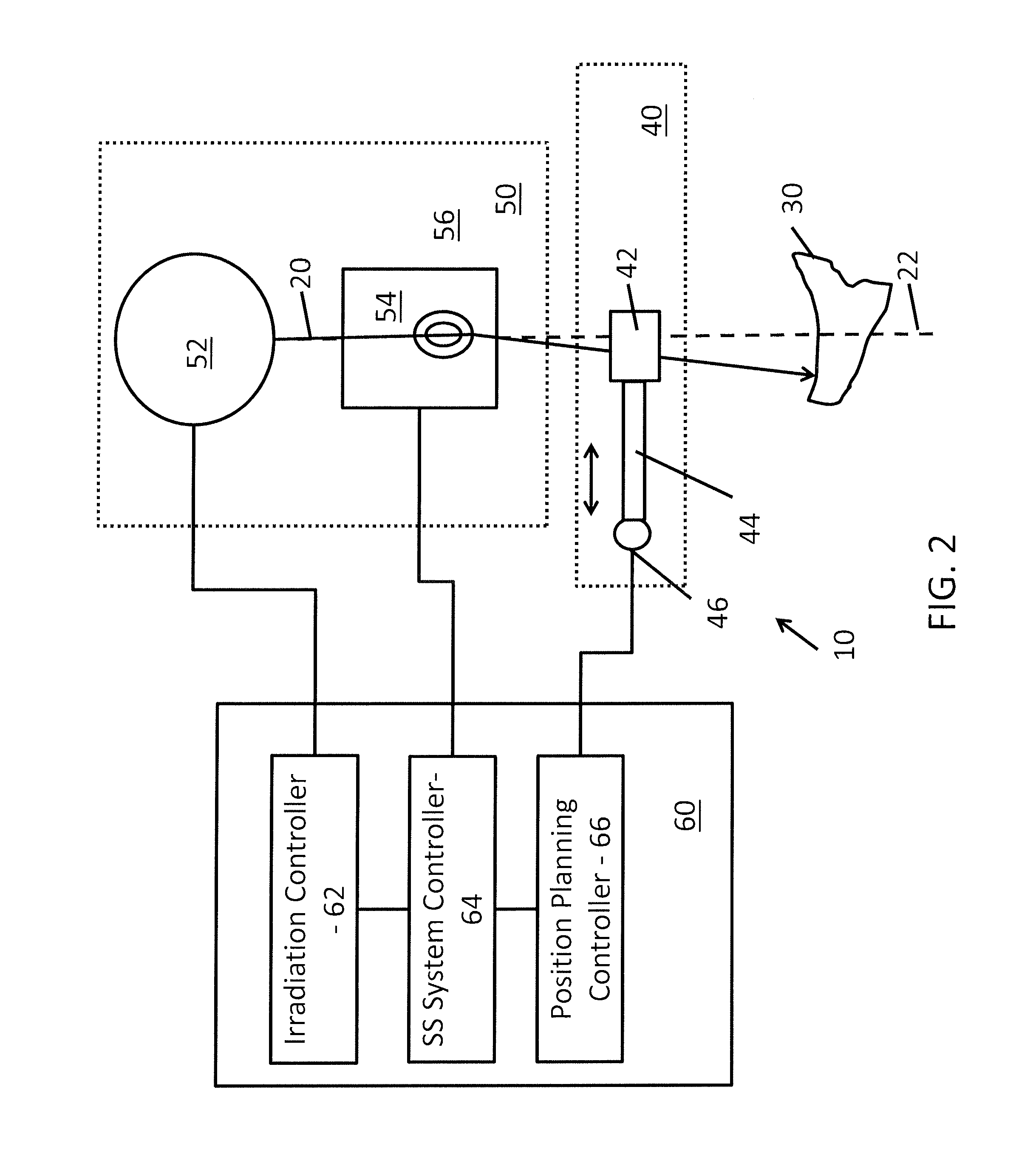
Method and system for dynamically-trimmed spot scanning for ion therapy
ActiveUS20160199667A1Reduce deliveryImproves SS ion therapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiation doseIon
A spot scanning (SS) ion therapy system configured for dynamic trimming of an ion particle pencil beam to reduce the amount of the radiation dosage outside of a target boundary.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device
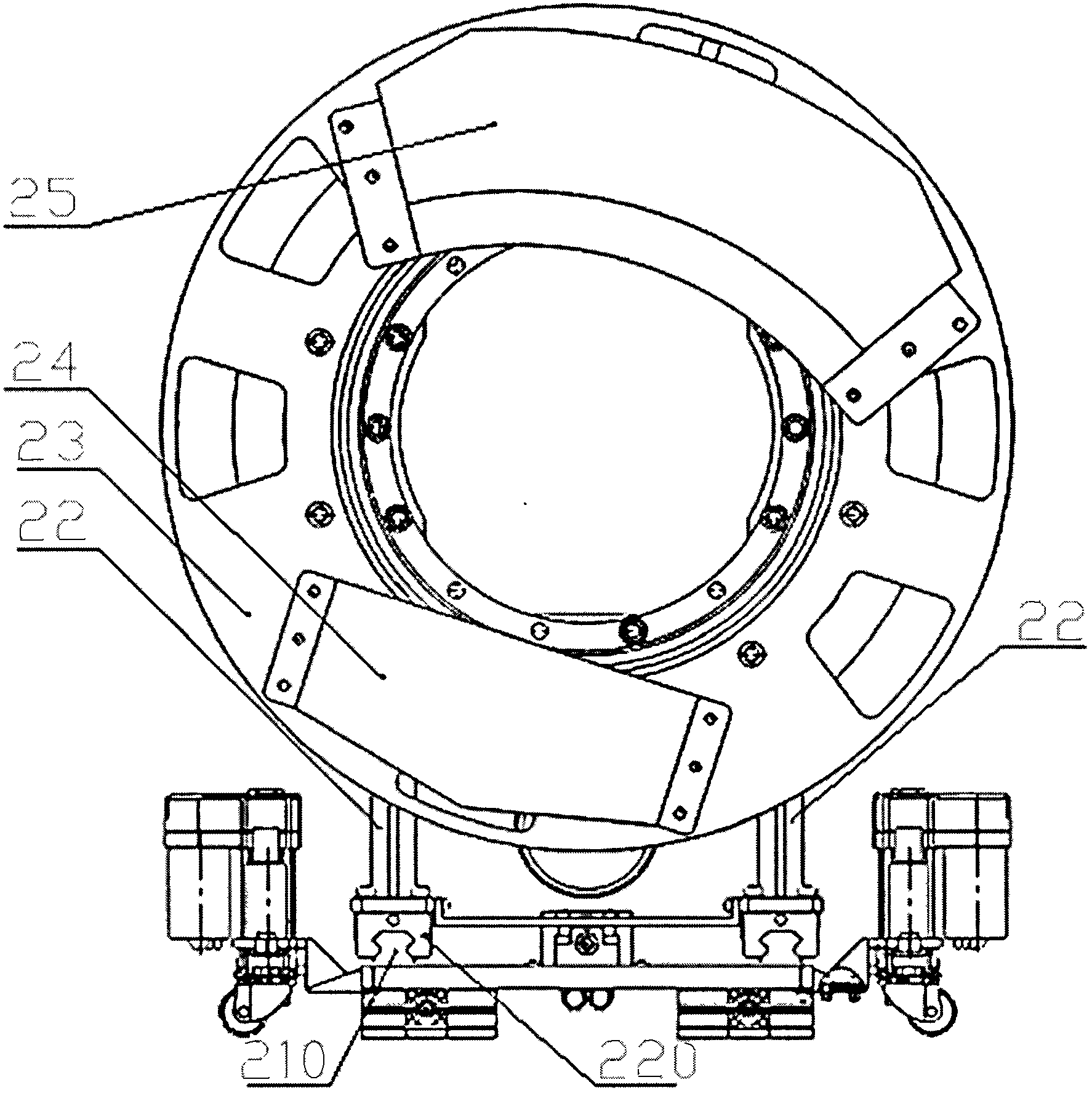
InactiveCN107362464AMechanical balance counterweight problem solvingReduce shielding requirementsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiosurgeryEngineering
The invention provides an accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device which belongs to the field of a medical device. The accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device is composed of a radiation device system, a six-dimensional robot treatment bed 1 and a treatment planning system. The radiation device system is composed of a frame 12 and a C-shaped machine arm 5. The frame 12 is provided with a rotating shaft 10. The rotating shaft 10 is connected with a guiderail 9 and controls rotation of the guiderail 9. The C-shaped machine arm 5 is mounted on the guiderail 9 and performs arc-shaped motion along the guiderail 9. One end of the C-shaped machine arm 5 is provided with a radiation source 2. The bottom end of the radiation source 2 is provided with a small machine head 3. The bottom end of the small machine head 3 is provided with a collimator. The other end of the C-shaped machine arm 5 is provided with a telescopic electronic portal imaging device 7 and a movable shielding protecting counterweight 8. A target organ positioning and detecting device 6 is mounted at the side part or the lower part of the six-dimensional robot treatment bed 1. The radiation treatment head of the accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device can perform 90-degree (or + / -45-degree) rotation around an X axis so that rays can be transmitted in a 4pi non-coplanar track.
Owner:吴大可
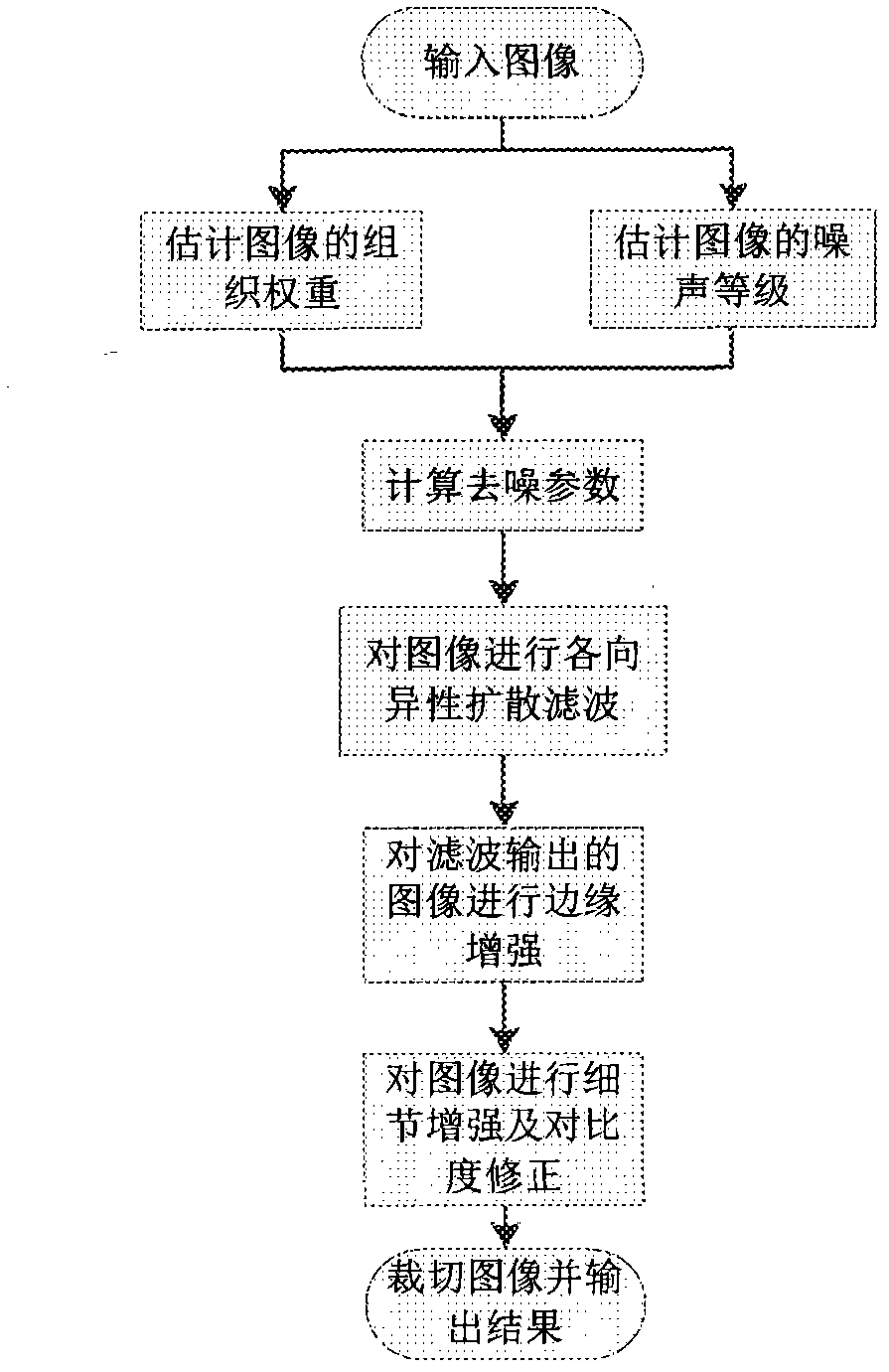
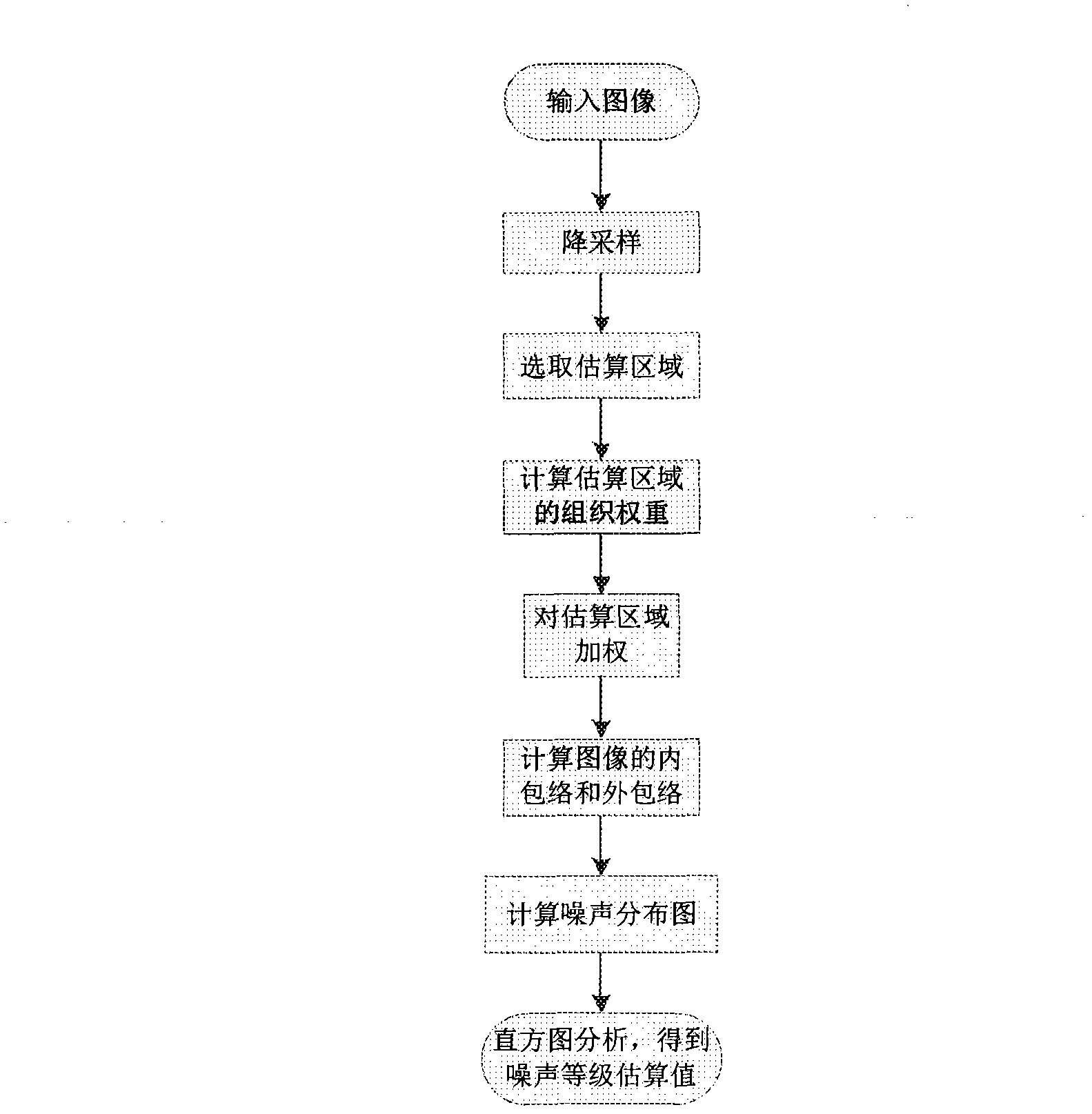
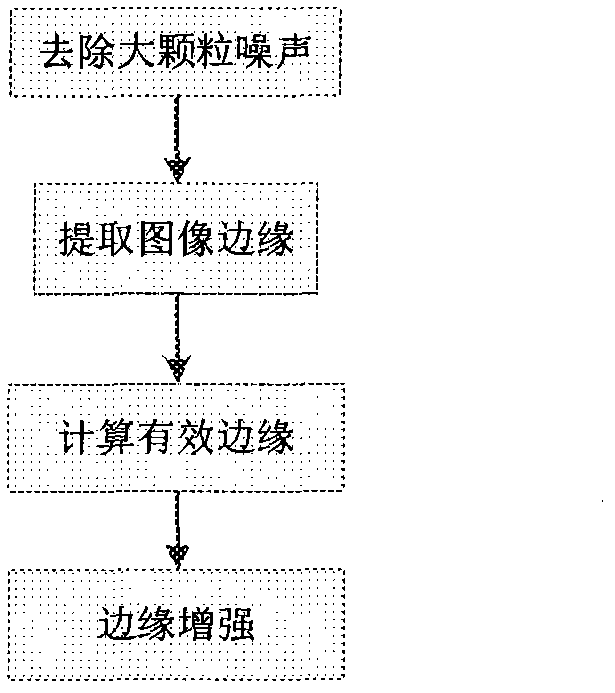
Method and device for removing CT (computed tomography) image noises
ActiveCN103186888AKeep detailsDoes not weaken contrastImage enhancementComputed tomographyNoise level
The invention discloses a method and a device for removing CT (computed tomography) image noises, and relates to the technical field of image noise removal. The method comprises the following steps of: estimating the tissue weight of an image, estimating the noise level of the image, calculating a noise removing parameter, carrying out anisotropic diffusion filtering on the image, carrying out edge enhancement on the image subjected to filtering output, enhancing details of the image and correcting the contrast ratio, cutting the image, and outputting the result. The device comprises a module for estimating the tissue weight of the image, a module for estimating the noise level of the image, a module for calculating the noise removing parameter, a module for carrying out anisotropic diffusion filtering on the image, a module for carrying out edge enhancement on the image subjected to filtering output, a module for performing detail enhancement and contrast ratio rectification on the image, and a module for cutting images and outputting the result. The method and the device can maintain the image edge and the original contrast ratio of the image while effectively removing the high-frequency noises of the CT images.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
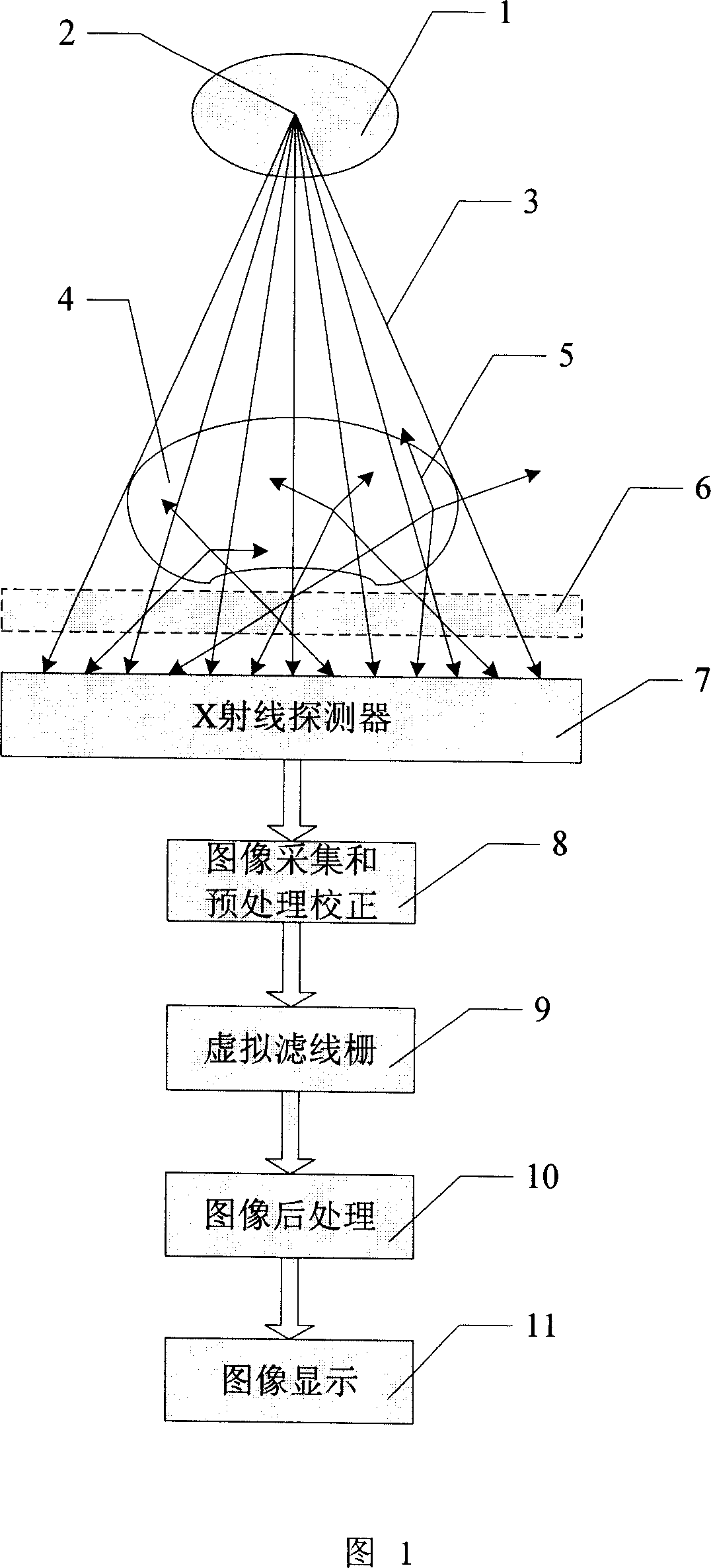
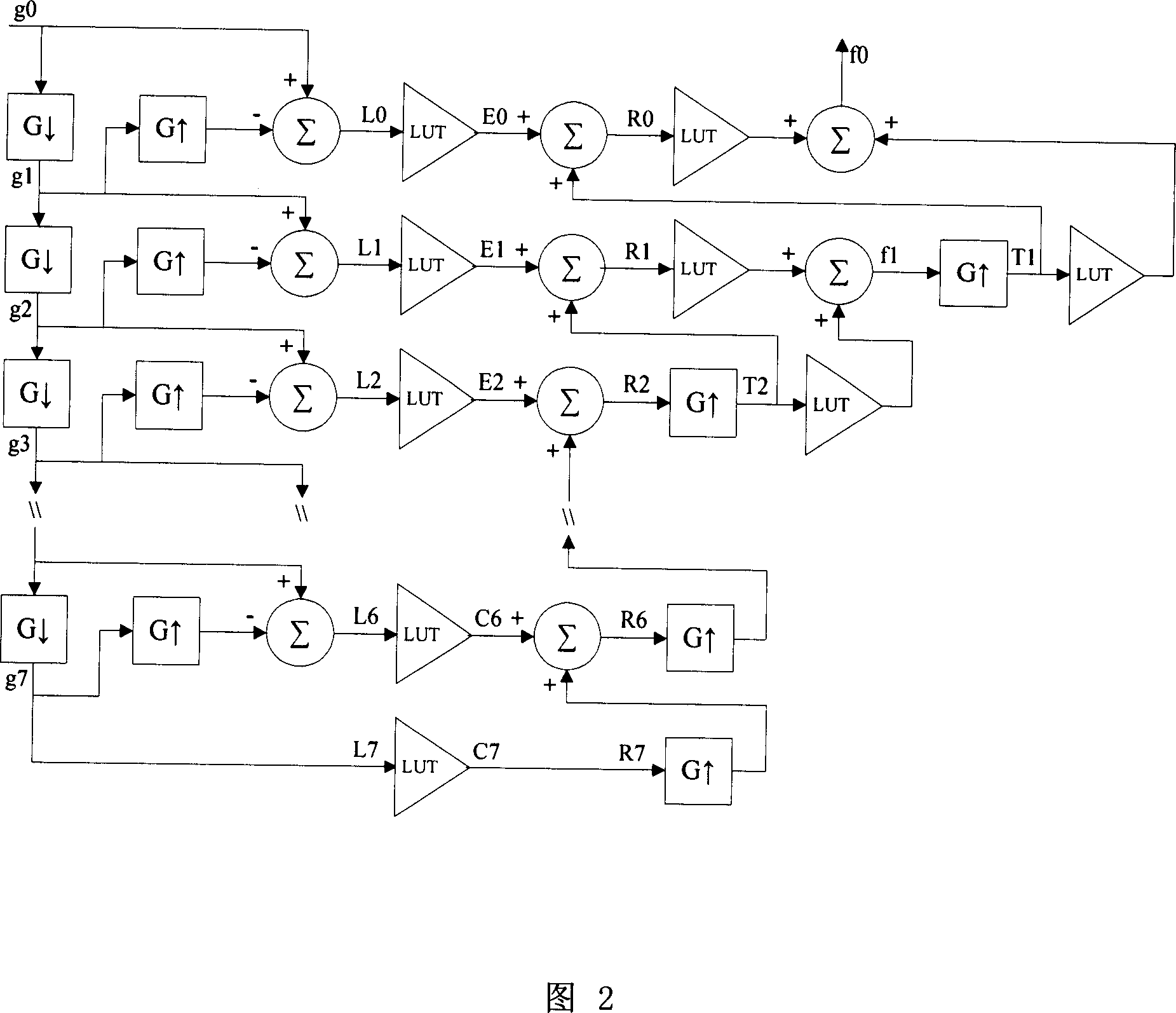
Virtual grid imaging method and system used for eliminating influence of scattered radiation
ActiveCN101109718AEliminate the effects ofIncrease contrastImage enhancementImage analysisVirtual screenRadiology
The invention discloses an imaging method and system for a virtual screen grid that can remove any radiation and scattering effect. The method is essentially used in a high-energy ray imaging. The scattering rays arriving at the detector surface are not filtered first, all the scattering rays and direct-emitting rays are sampled, then the sampled data go through separation and suppression of the components of scattering rays, so as to remove the components of scattering rays in the images. The procedures are: (1) a digital image is discomposed into a multi-frequency image from high to low frequency; (2) the low-frequency images are de-scattered; (3) the contrast of the hi-frequency images are enhanced; (4) images of different frequencies got by (2) and (3) are combined, and output images are formed. According to experiments, in digital X-ray imaging, the invention can obviously remove the radiation and scattering effect, and can greatly reduce the dosage of rays, which is 1 / 3 of ordinary screen grid with a given image brightness.
Owner:TCL HEALTHCARE EQUIP SHANGHAI CO LTD
Radiation detector and radiation detection system
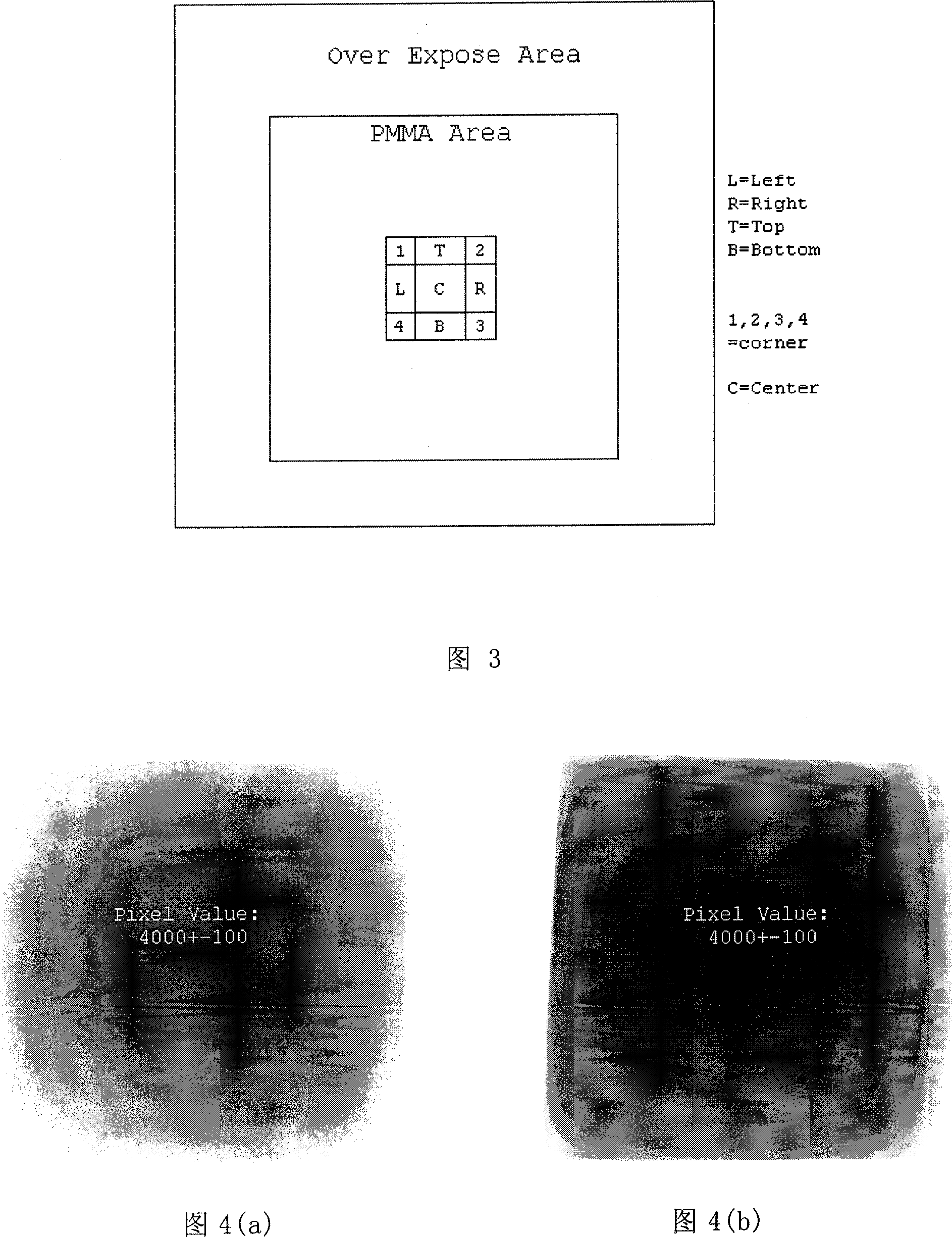
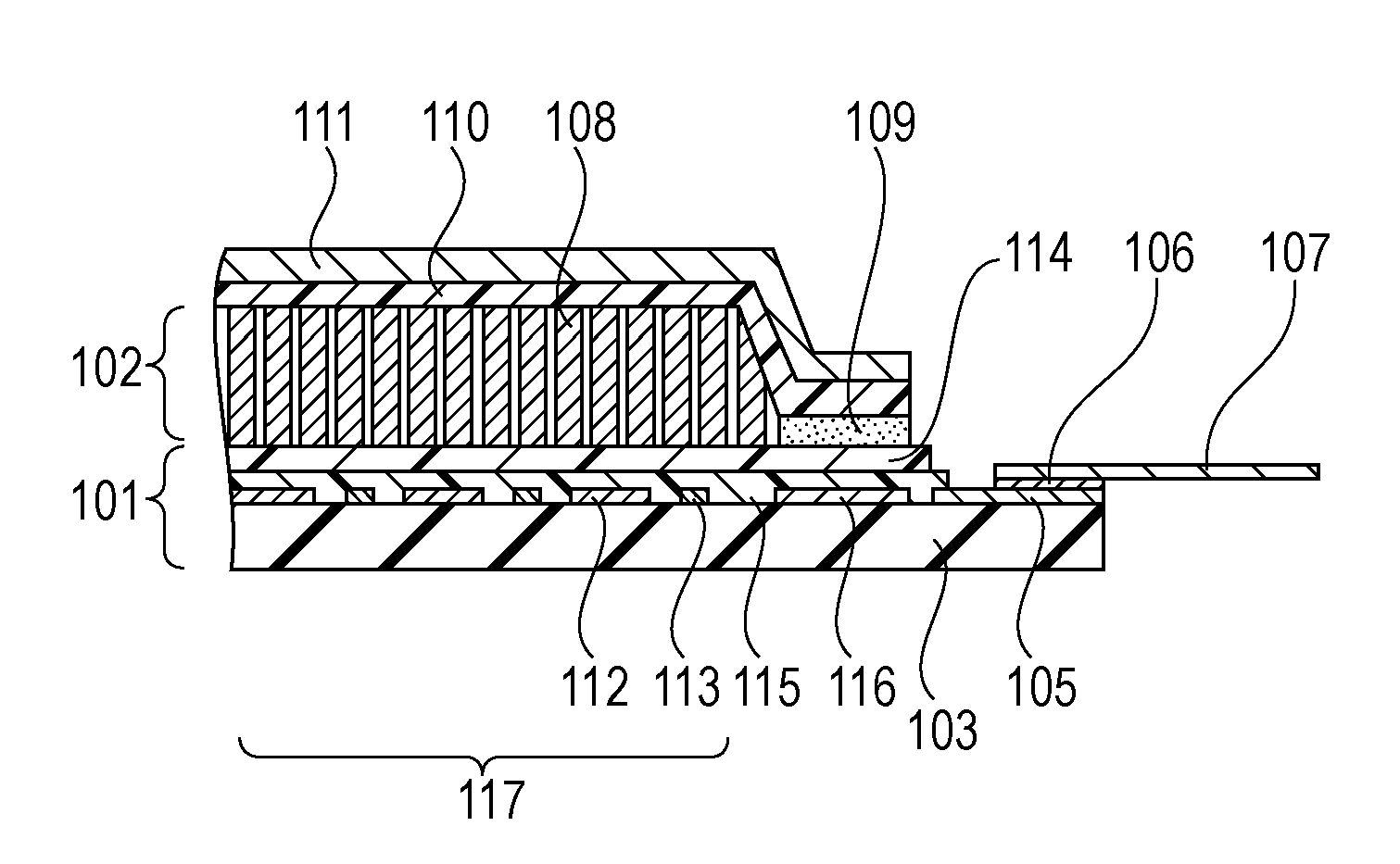
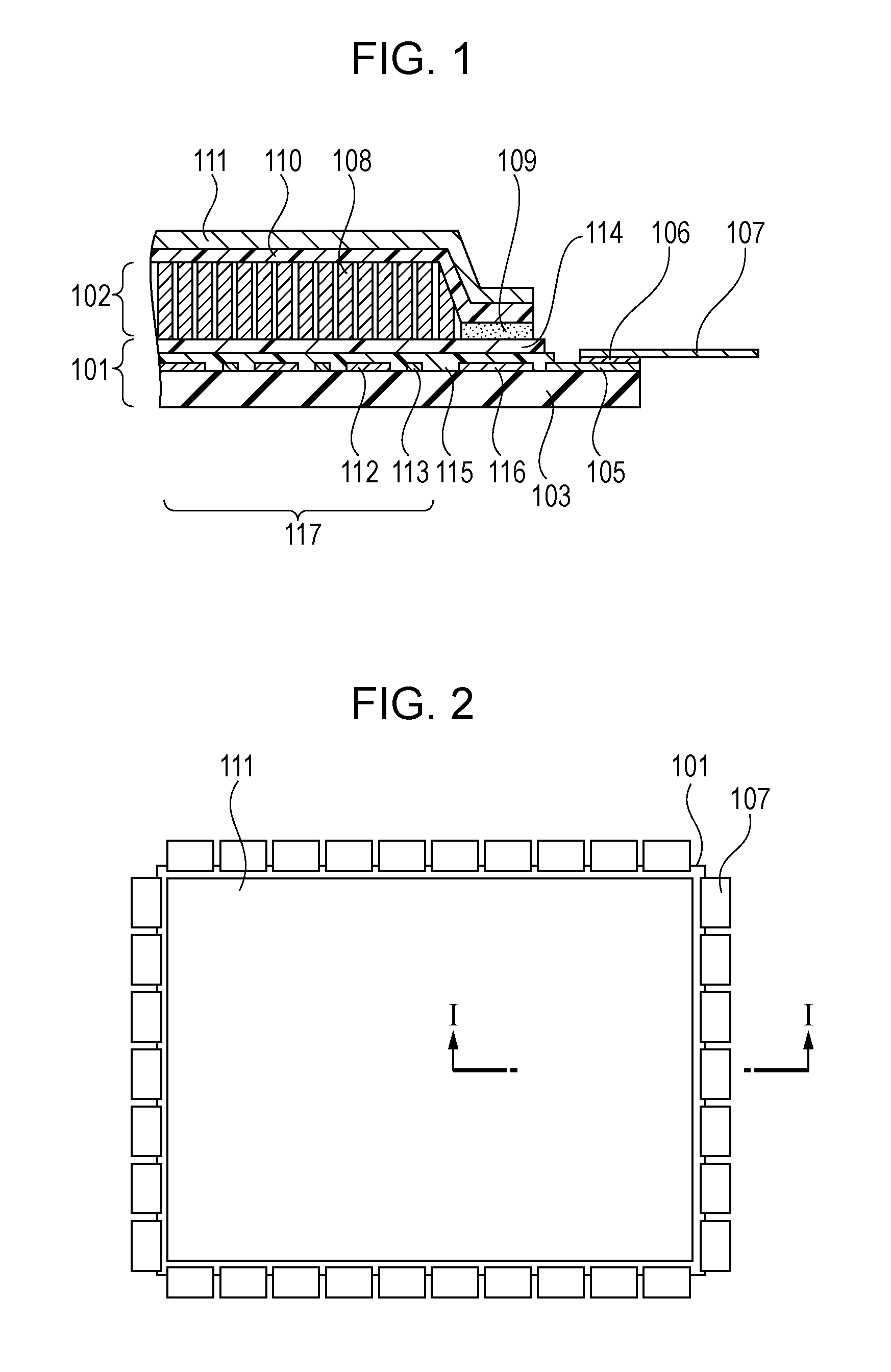
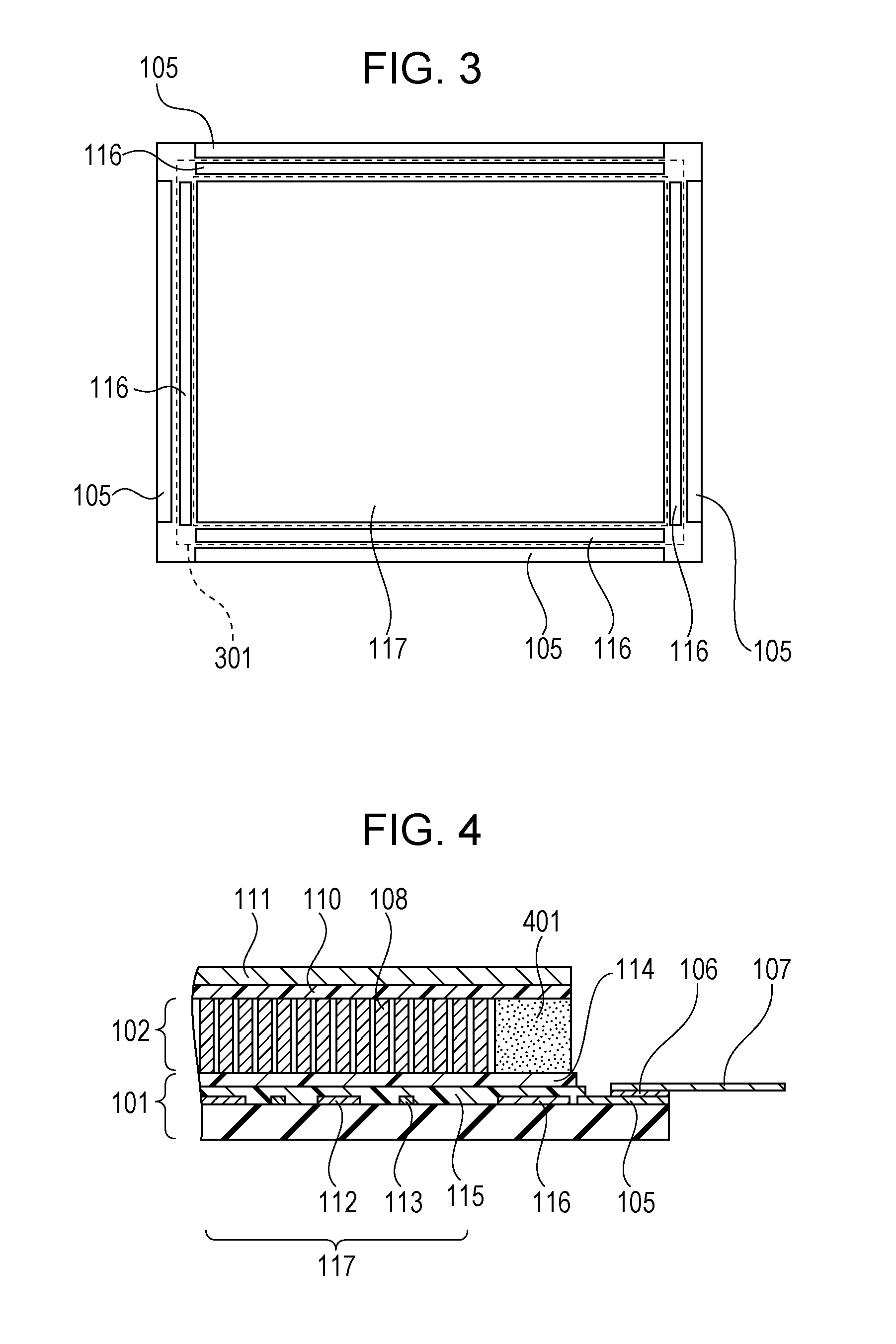
InactiveUS20110198505A1Reduce radiation doseReduce harmHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsRadar-absorbent material
A radiation detector includes a sensor panel including a photodetector and peripheral circuitry, the photodetector includes a two-dimensional array of photoelectric conversion elements arranged on a substrate, the peripheral circuitry is electrically connected to the photoelectric conversion elements and is disposed on the periphery of the photodetector; a scintillator layer is disposed on the photodetector of the sensor panel, the scintillator layer converts radiation into light that is detectable by the photoelectric conversion elements; a scintillator protection member covers the scintillator layer; and a sealing resin seals the scintillator layer, the sealing resin is disposed between the sensor panel and the scintillator protection member on the periphery of the scintillator layer; the sealing resin is disposed on top of the peripheral circuitry; and particles containing a radiation-absorbing material are dispersed in the sealing resin.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com