Patents
Literature
95 results about "Therapy radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
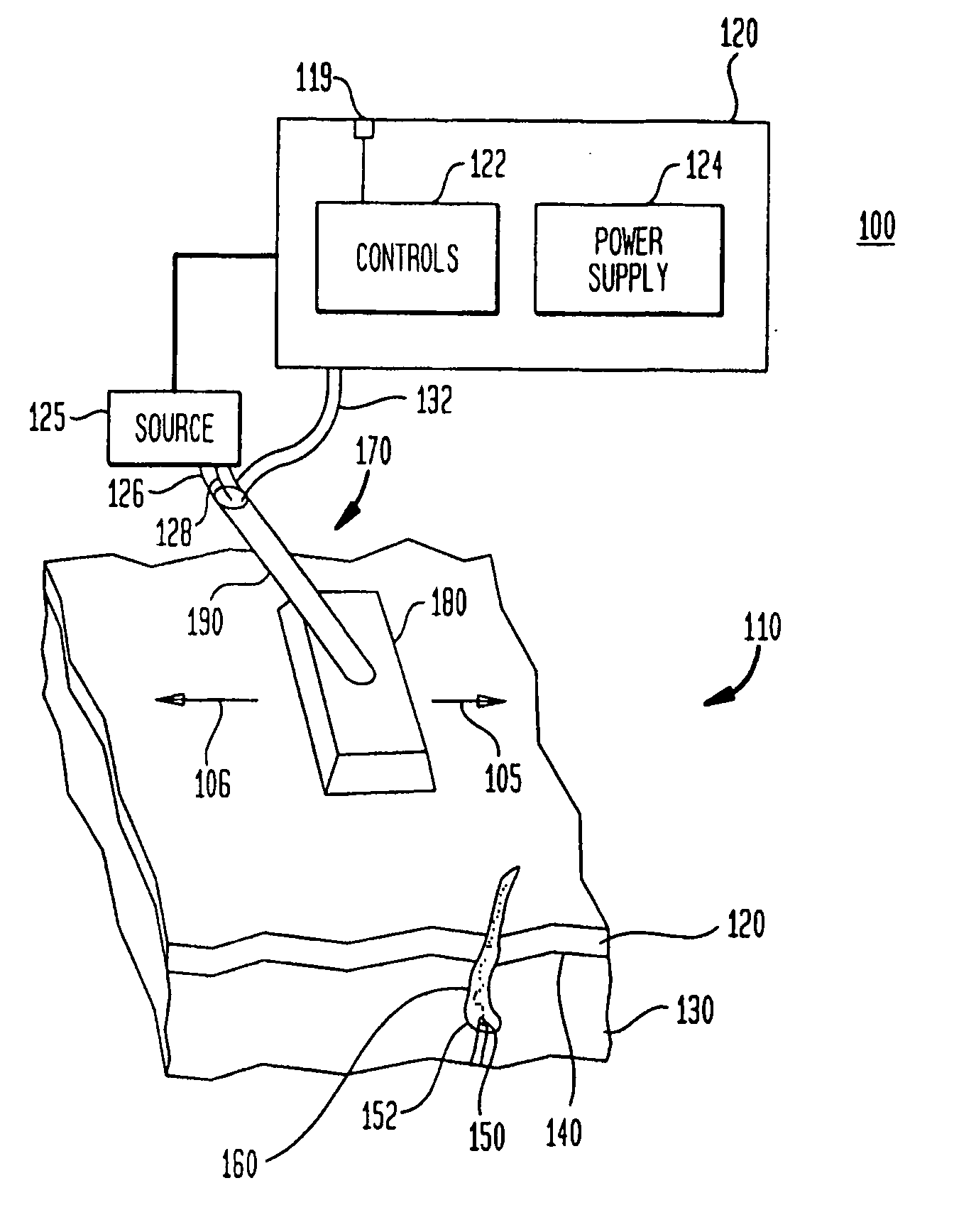
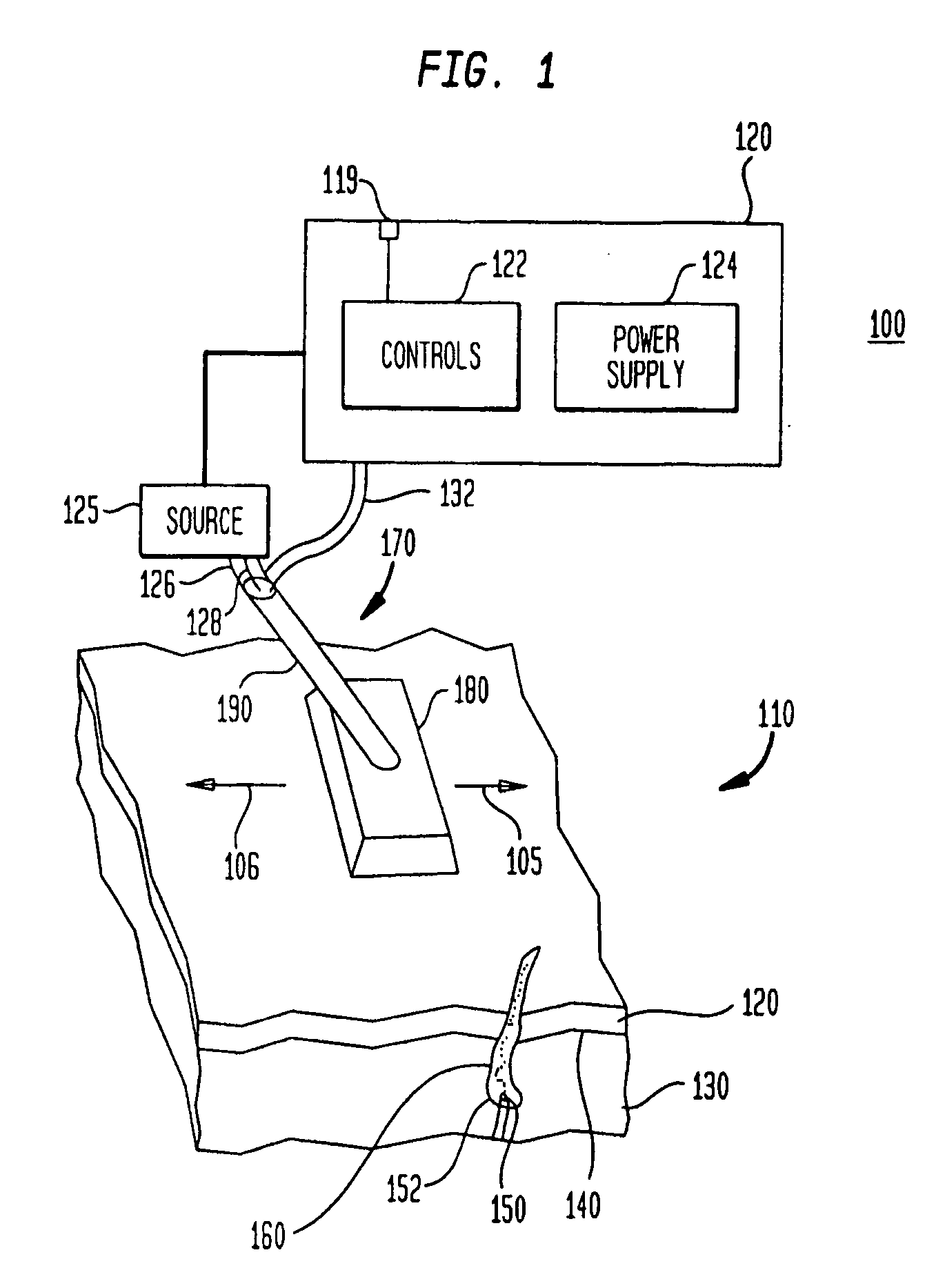
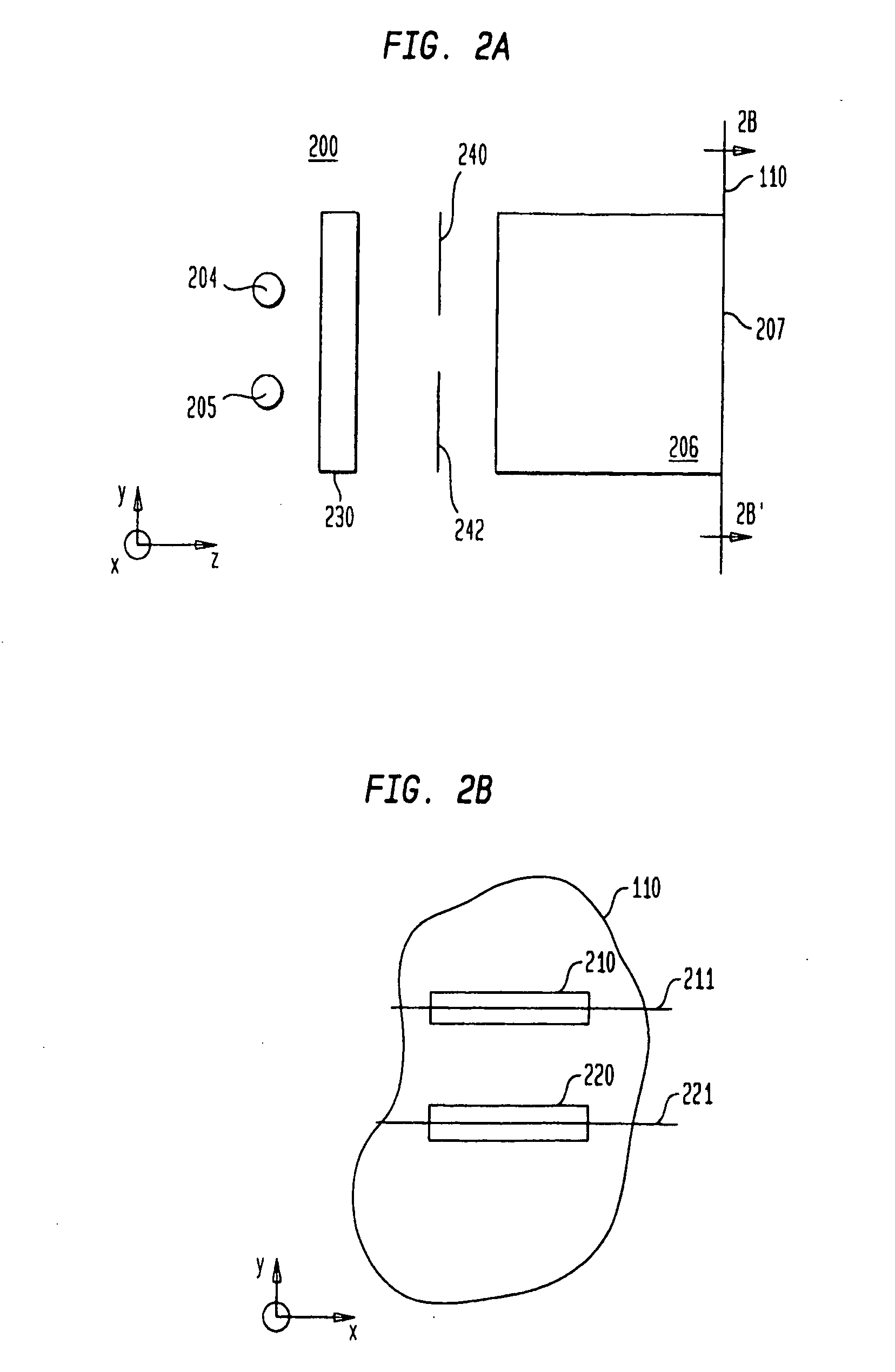
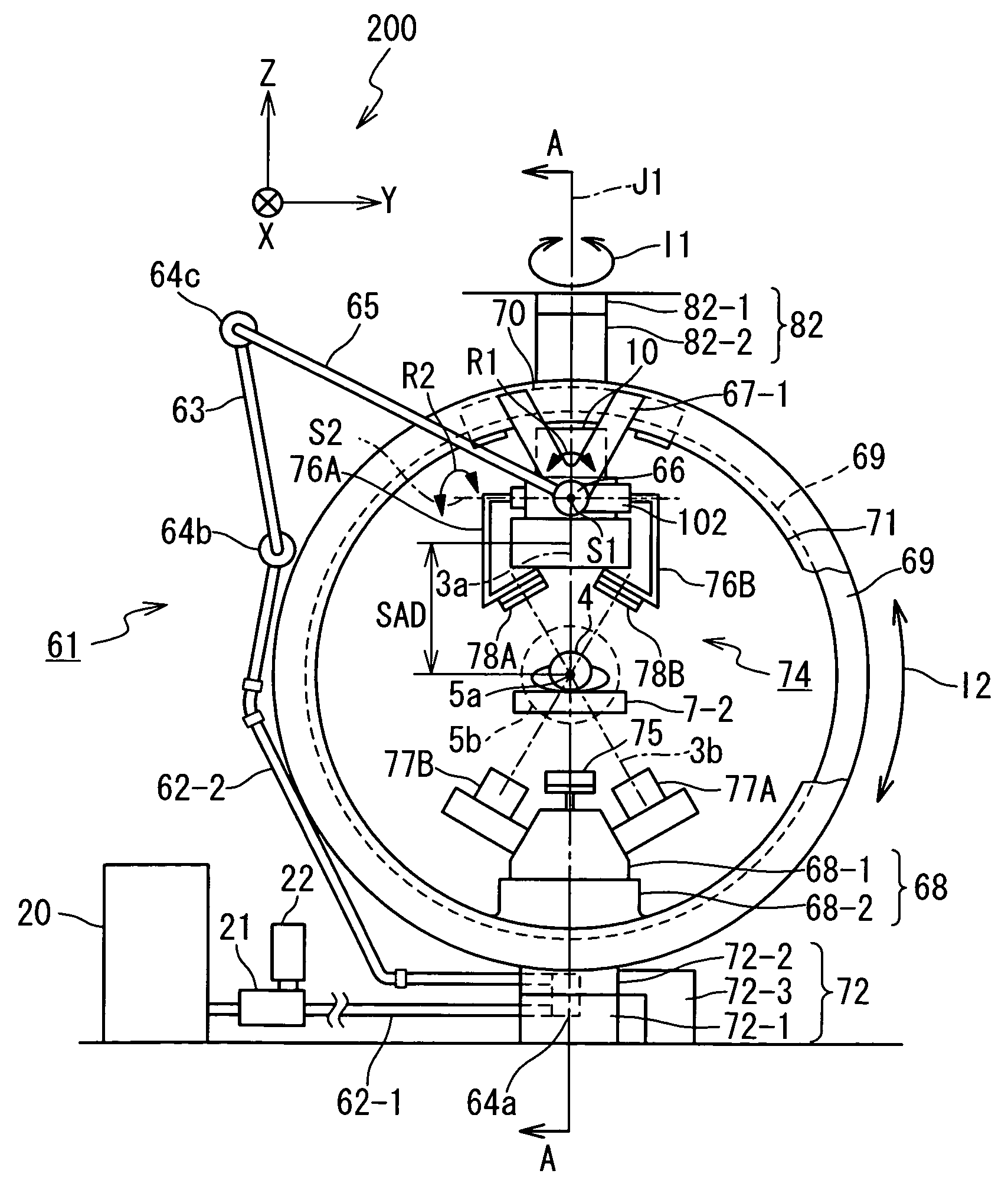
In radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), invisible high-energy rays or beams of subatomic particles are used to damage cancer cells and can stop them from growing and dividing. This ultimately can kill the cancer cells treated with radiation. A specialist in radiation therapy is called a radiation oncologist.
Cooling system for a photocosmetic device
Photocosmetic device for use in medical or non-medical environments (e.g., a home, barbershop, or spa), which can be used for a variety of tissue treatments. Radiation is delivered to the tissue via optical systems designed to pattern the radiation and project the radiation to a particular depth. The device has a variety of cooling systems including phase change cooling solids and liquids to cool treated skin and the radiation sources. Contact sensors and motion sensor may be used to enhance treatment. The device may be modular to facilitate manufacture and replacement of parts.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
Radiotherapy apparatus monitoring therapeutic field in real-time during treatment
ActiveUS20060193435A1Exclude influenceEasy to adjustSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arrayX-ray
A radiotherapy apparatus includes an irradiation head section, an X-ray source section and a sensor array section. The irradiation head section irradiates therapeutic radiation to a therapeutic field of a target substance. The X-ray source section irradiates diagnostic X-rays to the therapeutic field of the target subject. The sensor array section detects the diagnostic X-rays which have transmitted the target subject, and outputs diagnostic X-ray image data based on the detected diagnostic X-rays. The sensor array section moves in conjunction with movement of the irradiation head section.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
All field simultaneous radiation therapy
InactiveUS8173983B1Increase dose rateOvercome disadvantagesRadiation pyrometryElectrotherapyProstate cancerEstrogen receptor
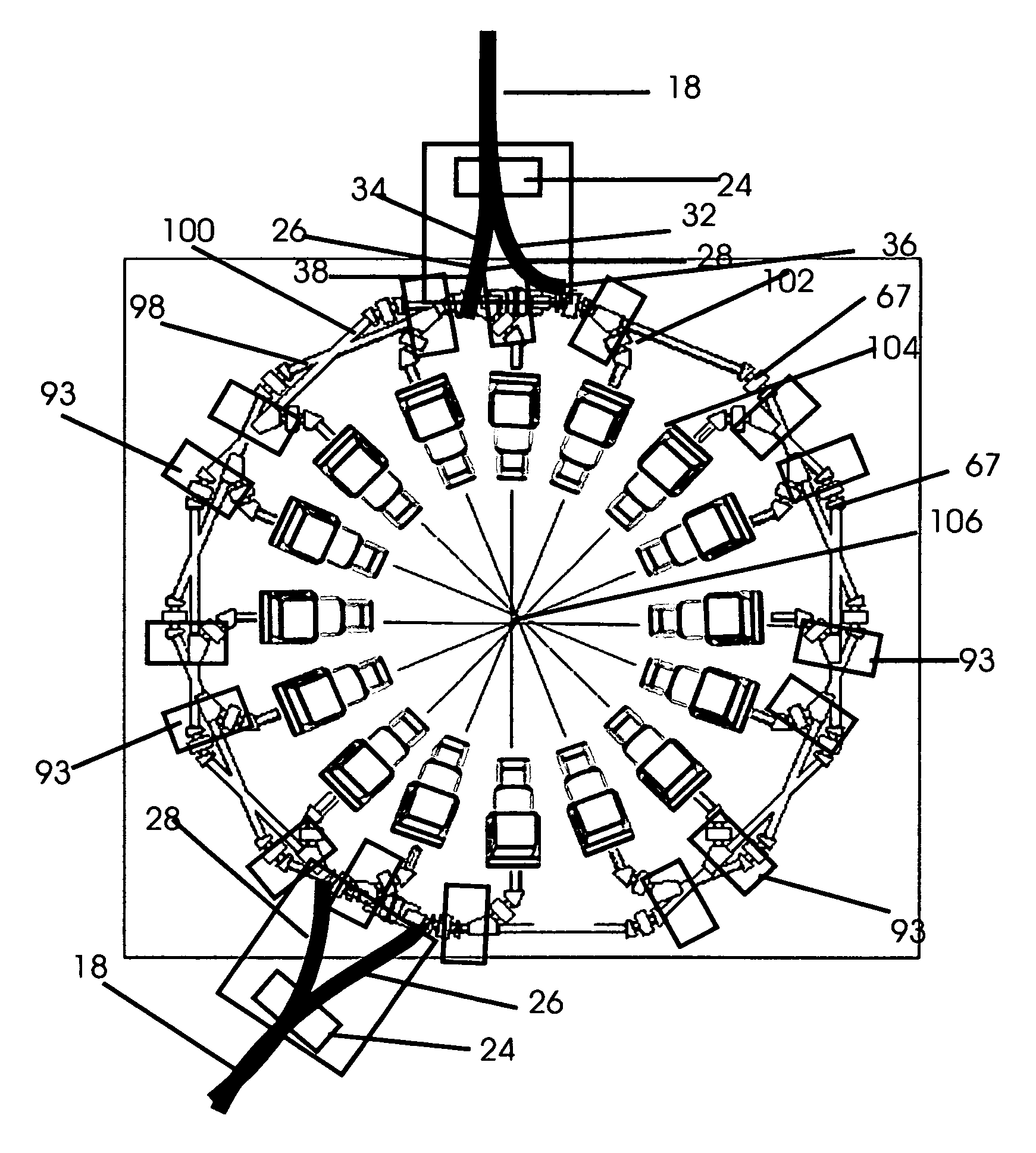
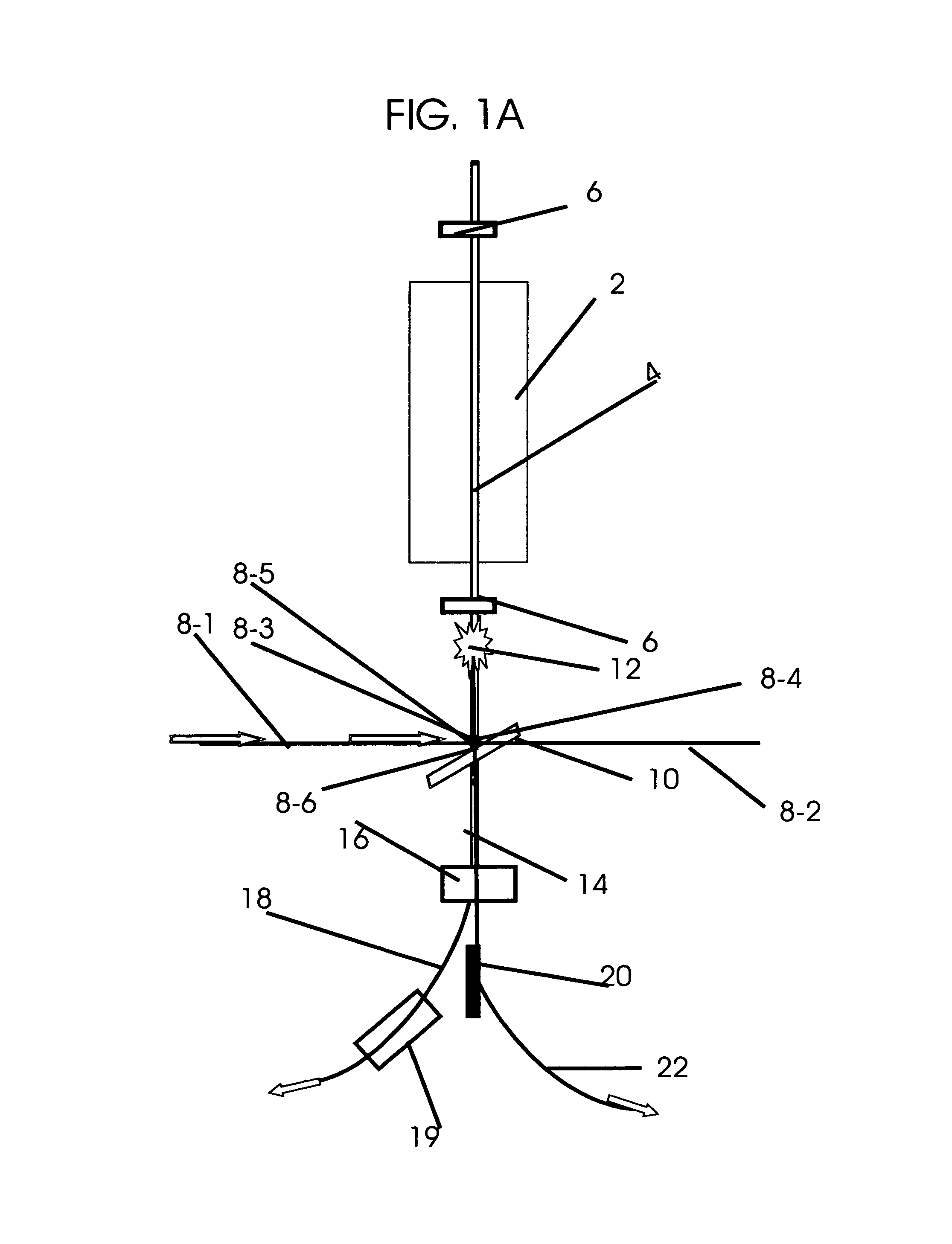
This invention describes a system for generating multiple simultaneous tunable electron and photon beams and monochromatic x-rays for all field simultaneous radiation therapy (AFSRT), tumor specific AFSRT and screening for concealed elements worn on to the body or contained in a container. Inverse Compton scattering renders variable energy spent electron and tunable monochromatic x-rays. It's spent electron beam is reused for radiation with electron beam or to generate photon beam. Tumor specific radiation with Auger transformation radiation is facilitated by exposing high affinity tumor bound heavy elements with external monochromatic x-rays. Heavy elements like directly iodinated steroid molecule that has high affinity binding to estrogen receptor in breast cancer and to iodinated testosterone in prostate cancer or with directly implanted nanoparticles into the tumor are exposed with tuned external monochromatic x-rays for tumor specific radiation therapy. Likewise, screening element's atom's k, l, m, n shell specific Auger transformation radiation generated by its exposure to external monochromatic x-rays is used to screen for concealed objects. Multiple beam segments from a beam storage ring or from octagonal beam lines are simultaneously switched on for simultaneous radiation with multiple beams. The beam on time to expose a tumor or an object is only a few seconds. It also facilitates breathing synchronized radiation therapy. The intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and intensity modulated screening for concealed objects (IMSFCO) is rendered by varying beam intensities of multiple simultaneous beams. The isocentric additive high dose rate from simultaneously converging multiple beams, the concomitant hyperthermia and chemotherapy and tumor specific radiation therapy and the AFSRT's very low radiation to the normal tissue all are used to treat a tumor with lower radiation dose and to treat a radioresistant and multiple times recurrent tumors that heave no other alternative treatments.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Method for verification of intensity modulated radiation therapy
InactiveUS20070071169A1Improve accuracyAccurate calculationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose levelIntensity-modulated radiation therapy
An accurate method for inversely verifying a therapeutic radiation dose delivered to a patient via an x-ray delivery system without involving any computational iteration was developed. The usage of it includes detecting the transmitted radiation dose image after passage through the patient, imaging the patient during treatment to anatomically record information of the patient, followed by inversely verifying through use of both the detected radiation image and the imaging data, the actual radiation dose delivered to the patient, and comparing the level of the dose delivered to a previously planned dose to determine whether the planned dose was delivered, or whether an overdose or underdose occurred.
Owner:NJ UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF +1
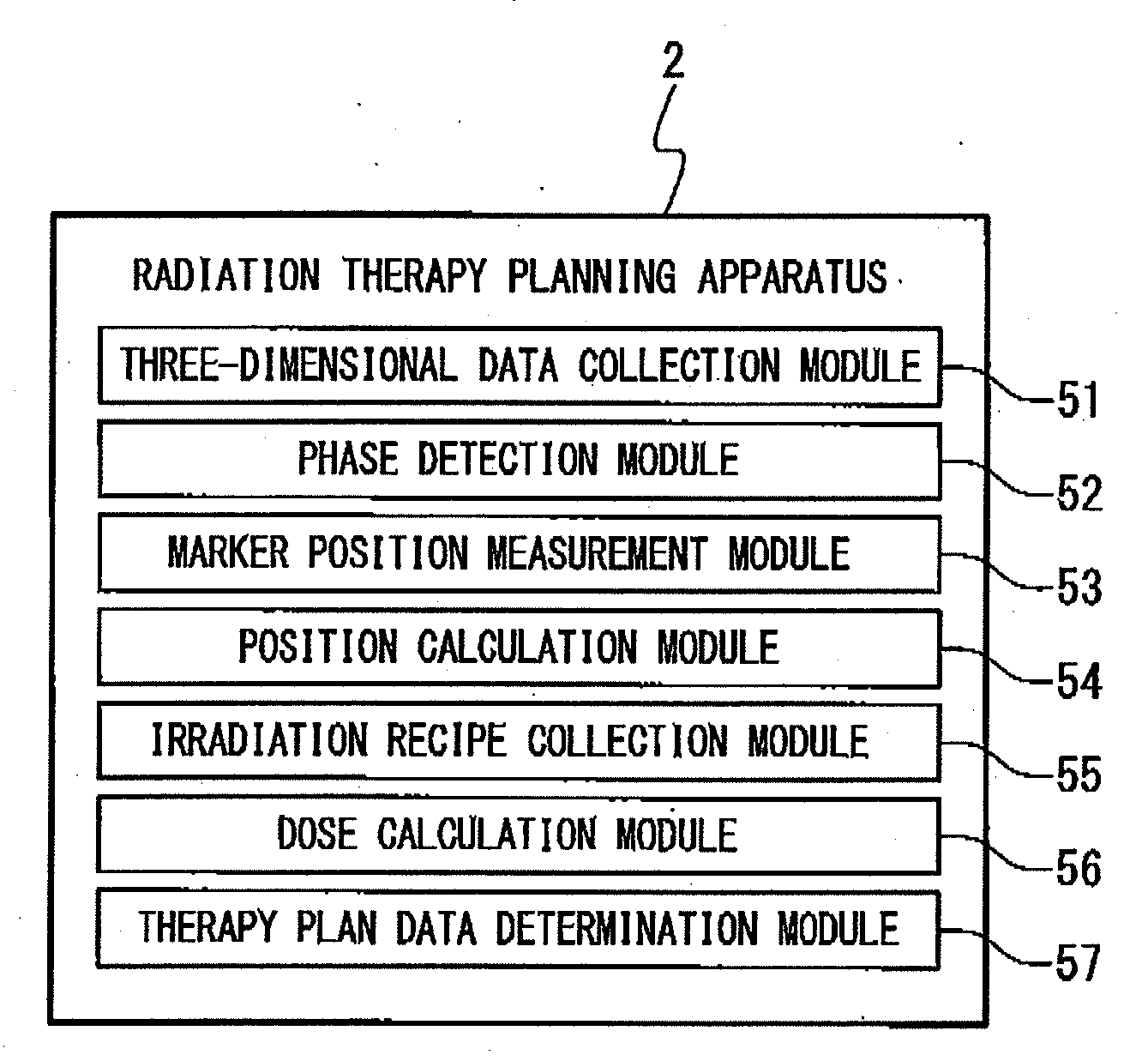
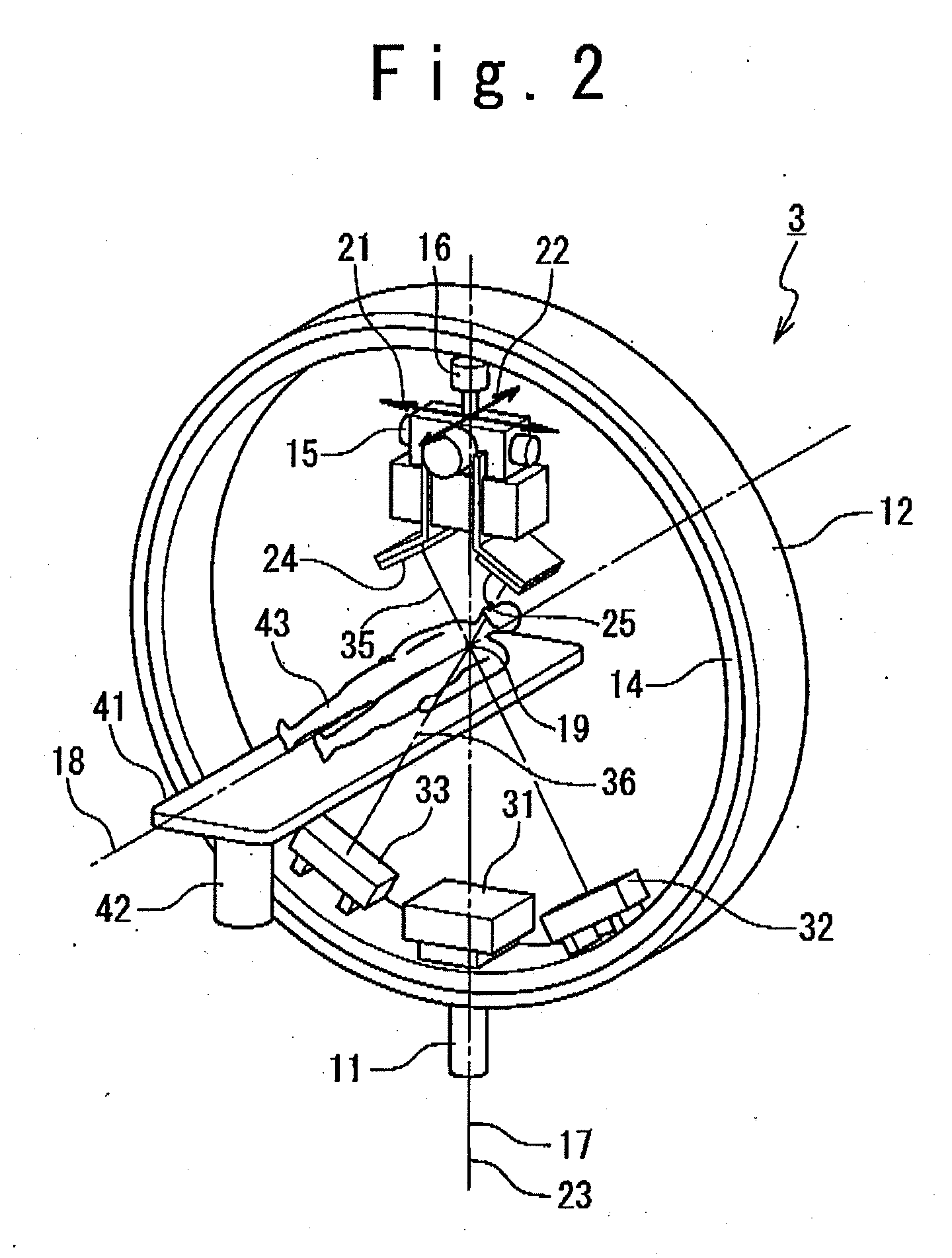
Radiation therapy planning apparatus and radiation therapy planning method
ActiveUS20110044429A1Reduce the burden onReduce doseX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySubject matterTherapy radiation
A radiation therapy planning apparatus is provided with; a three-dimensional data collection part collecting three-dimensional data representing a plurality of positions where a plurality of portions of a subject are positioned; a marker position measurement part measuring a motion of a marker; and a dose calculation part calculating, when the subject is irradiated with therapeutic radiation changing on the basis of the motion of the subject, the dose of the therapeutic radiation with which each of the plurality of portions is irradiated, based on the motion and the three-dimensional data. The radiation therapy planning apparatus thus constructed can calculate the dose of the therapeutic radiation with which each of the respective portions of the subject is irradiated, more accurately, and reduce the dose of radiation with which the subject is irradiated in calculating the motions of the plurality of portions of the subject.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
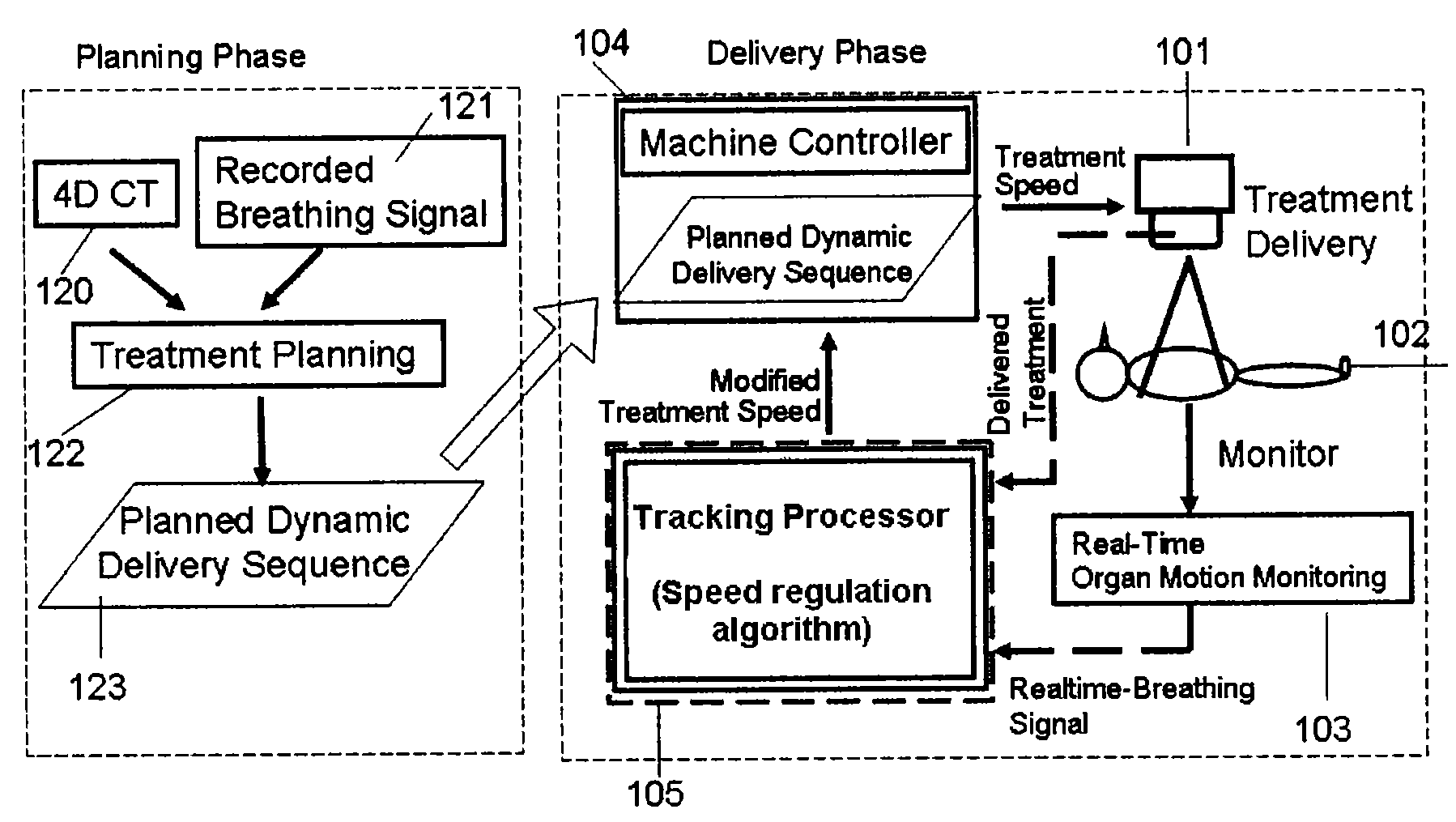
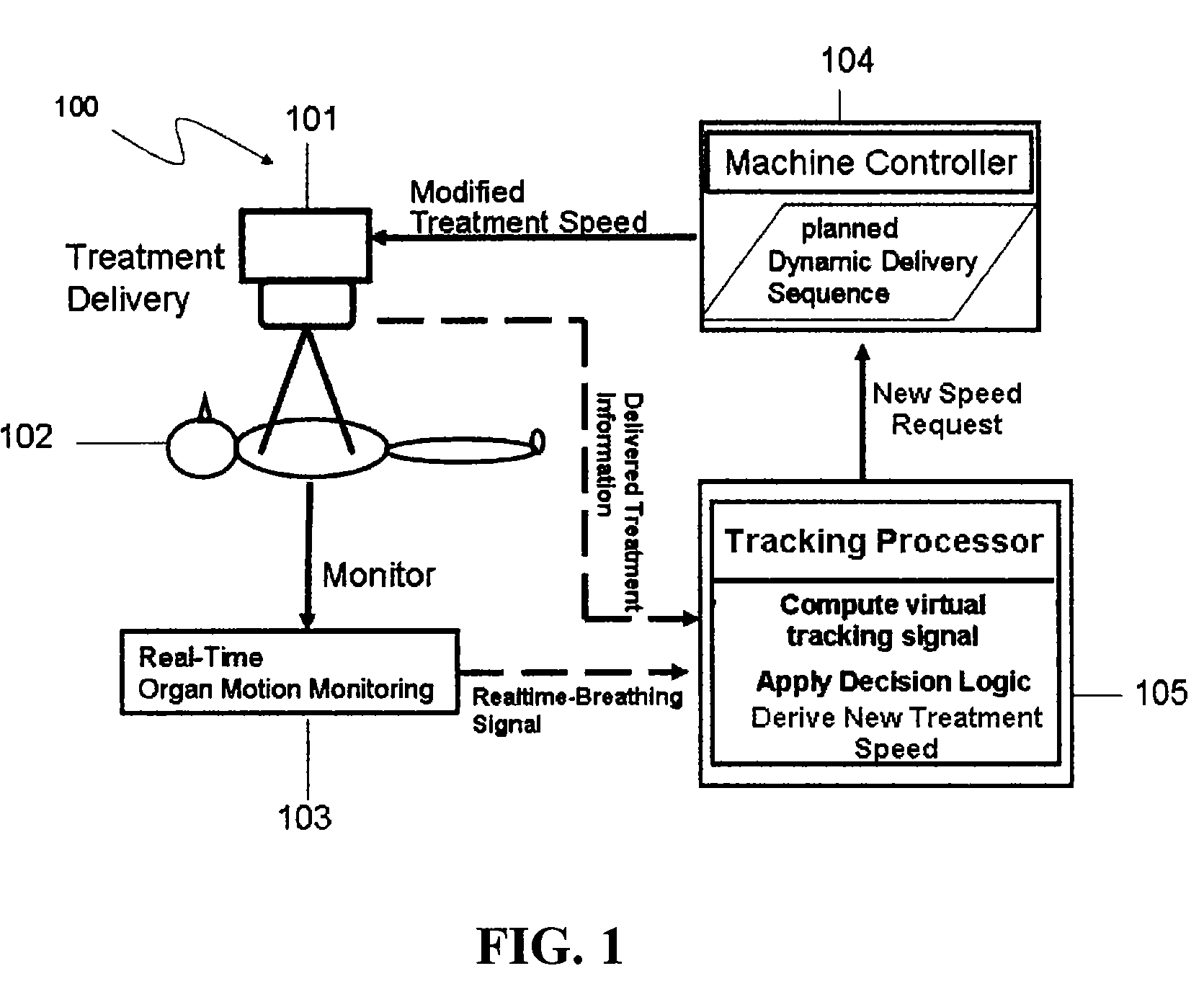
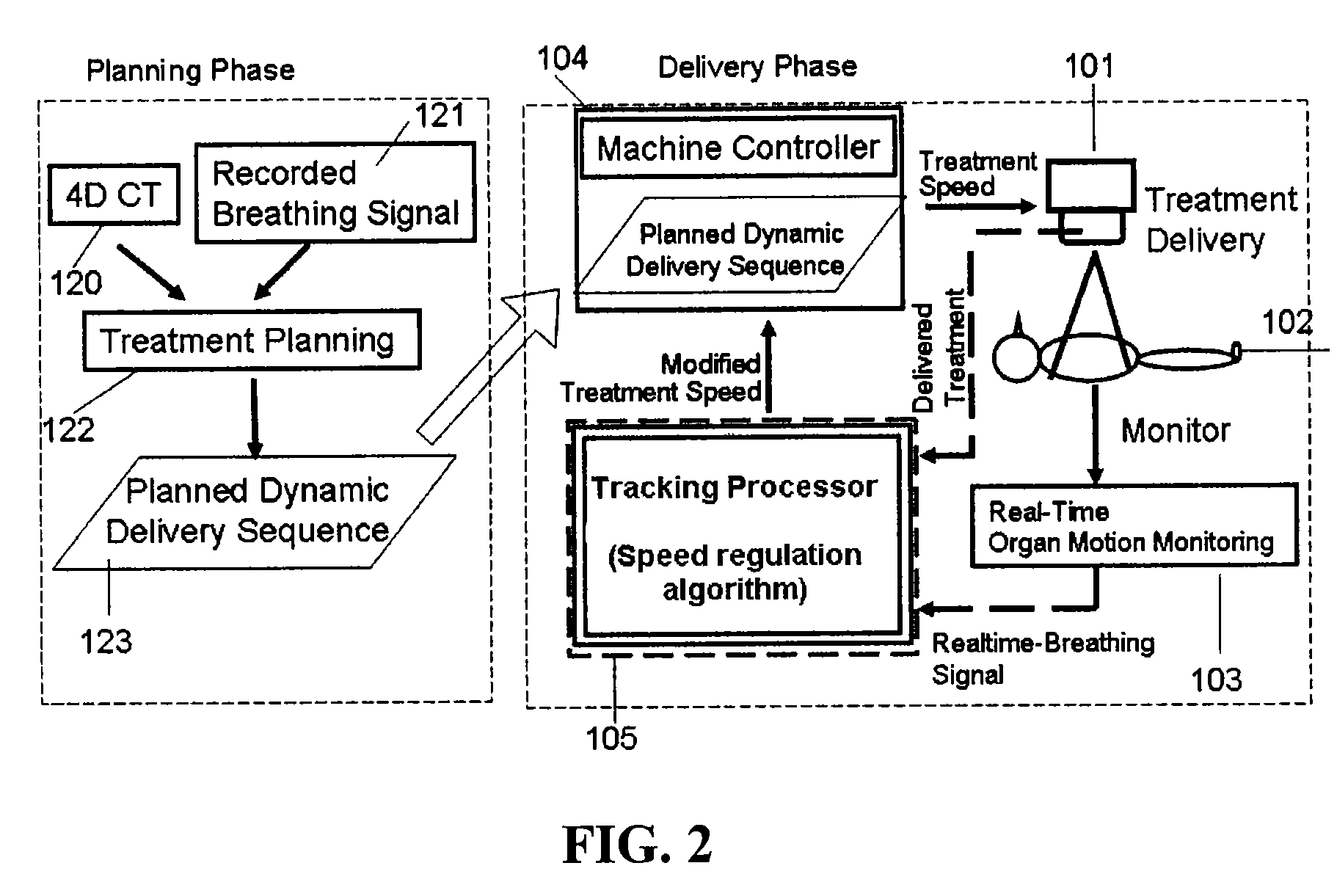
Treatment-speed regulated tumor-tracking
ActiveUS7609810B2Eliminate distractionsEffective trackingX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatments proceduresTherapeutic radiation
Owner:YI BYONG YONG +2
Methods for treating radiation or chemical injury
InactiveUS20140017209A1Reduce impactRelieve symptomsBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsStromal cellChemical Injury
Methods for treating radiation or chemical injury are described that comprise administering to a subject a therapeutically effective amount of adherent stromal cells. Methods of preparing adherent stromal cells and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the cells are also described.
Owner:PLURISTEAM LTD
Method for verification of intensity modulated radiation therapy
InactiveUS7450687B2Improve accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity-modulated radiation therapyTherapeutic radiation
An accurate method for inversely verifying a therapeutic radiation dose delivered to a patient via an x-ray delivery system without involving any computational iteration was developed. The usage of it includes detecting the transmitted radiation dose image after passage through the patient, imaging the patient during treatment to anatomically record information of the patient, followed by inversely verifying through use of both the detected radiation image and the imaging data, the actual radiation dose delivered to the patient, and comparing the level of the dose delivered to a previously planned dose to determine whether the planned dose was delivered, or whether an overdose or underdose occurred.
Owner:NJ UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF +1
Multiplexed Radiation Therapy
InactiveUS20130066134A1Precise deliveryPatient positioning for diagnosticsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayTherapeutic radiation
A radiation system is provided comprising a single source of therapeutic radiation that is directed toward at least two treatment spaces in succession. Each treatment space houses a patient to be treated, each patient being secured generally by a separate supporting device adapted to support the patient in a generally sitting or standing or horizontal position. The x-ray source first delivers at least one beam to the first patient in the first space and then the x-ray source / patient relationship is adjusted so as to deliver an at least one beam to an at least second patient in a second space.
Owner:CAROL MARK
Radiation therapeutical irradiation device
ActiveCN1919374ARealize real-time monitoringRealize verificationRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLow activityGamma ray
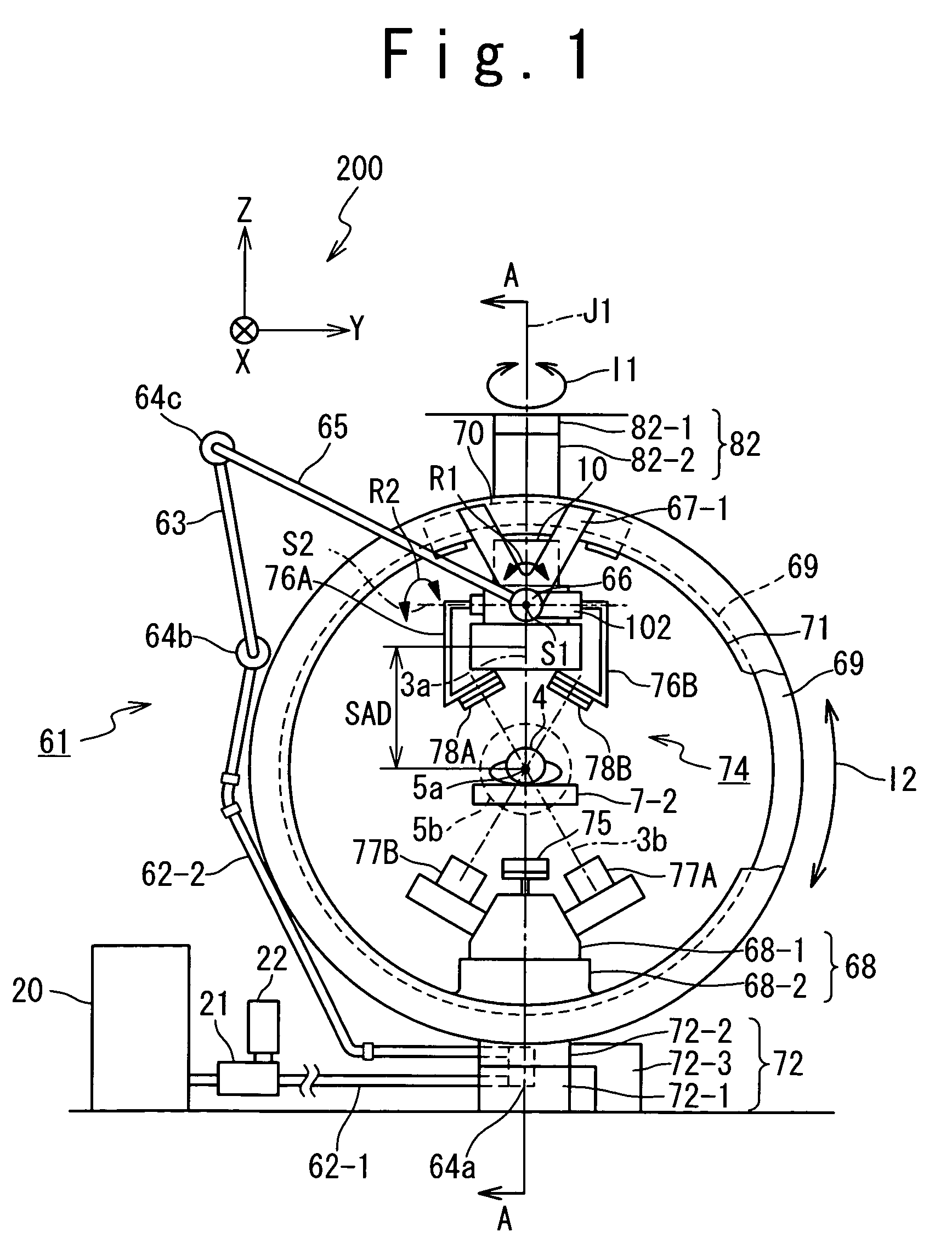
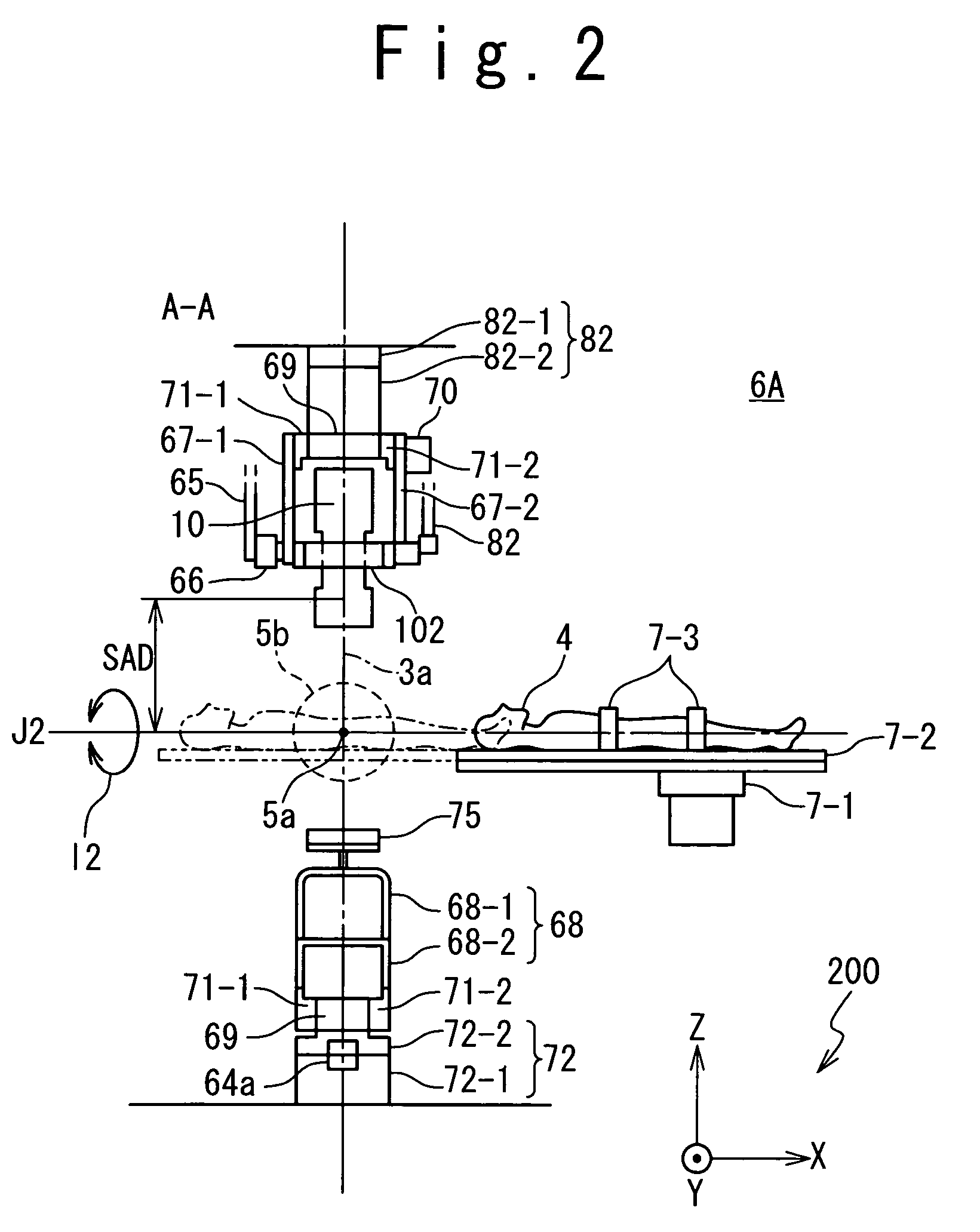
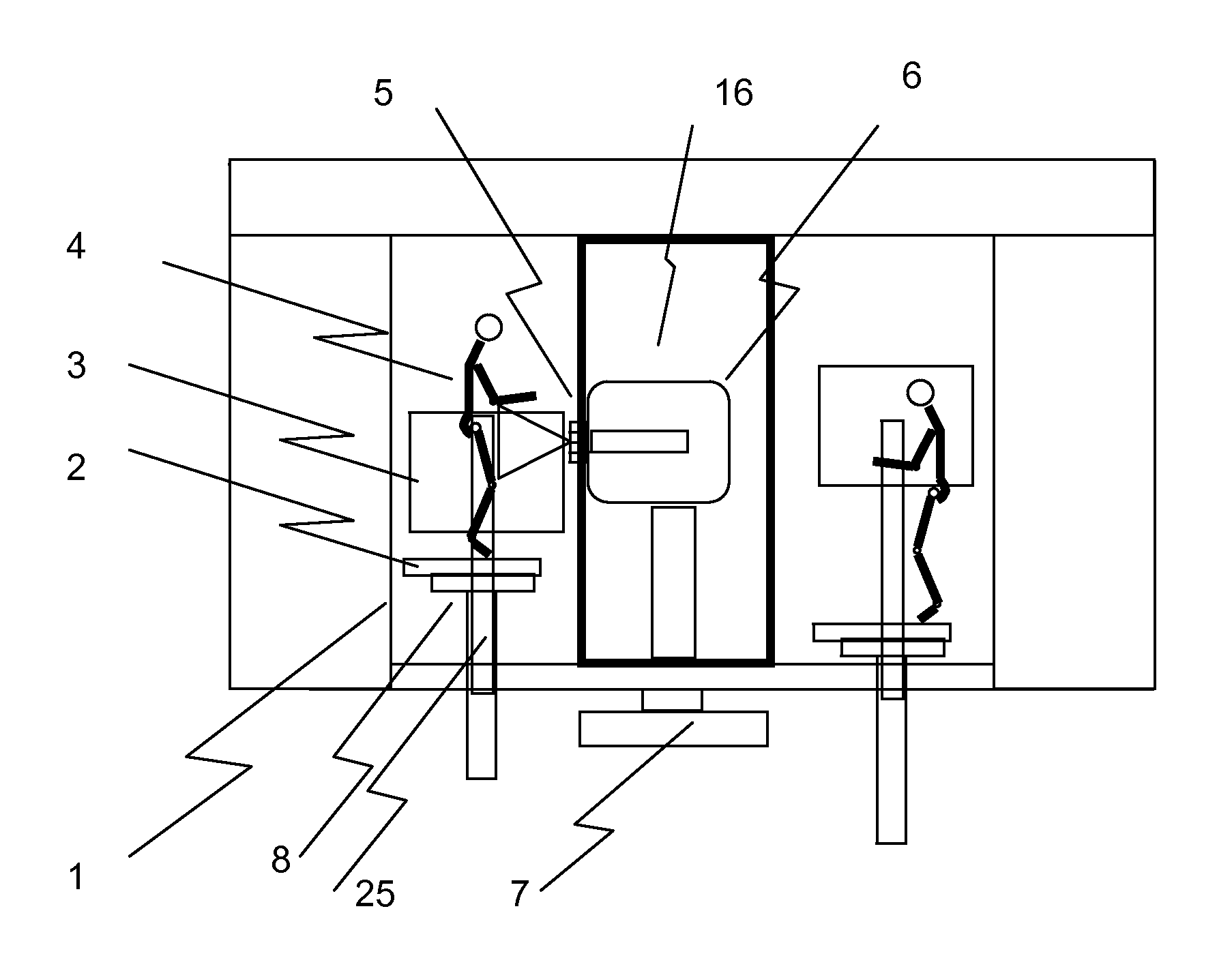
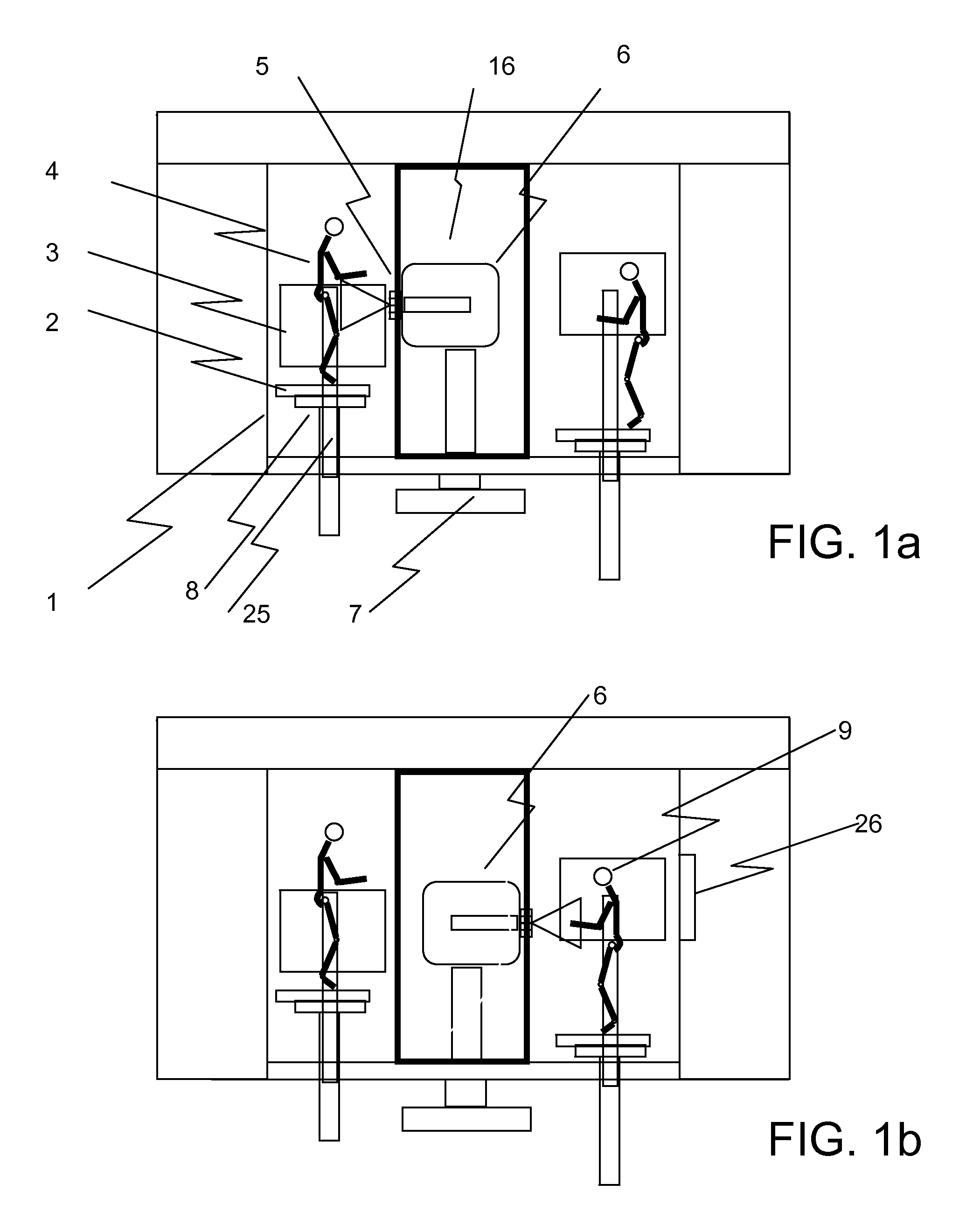
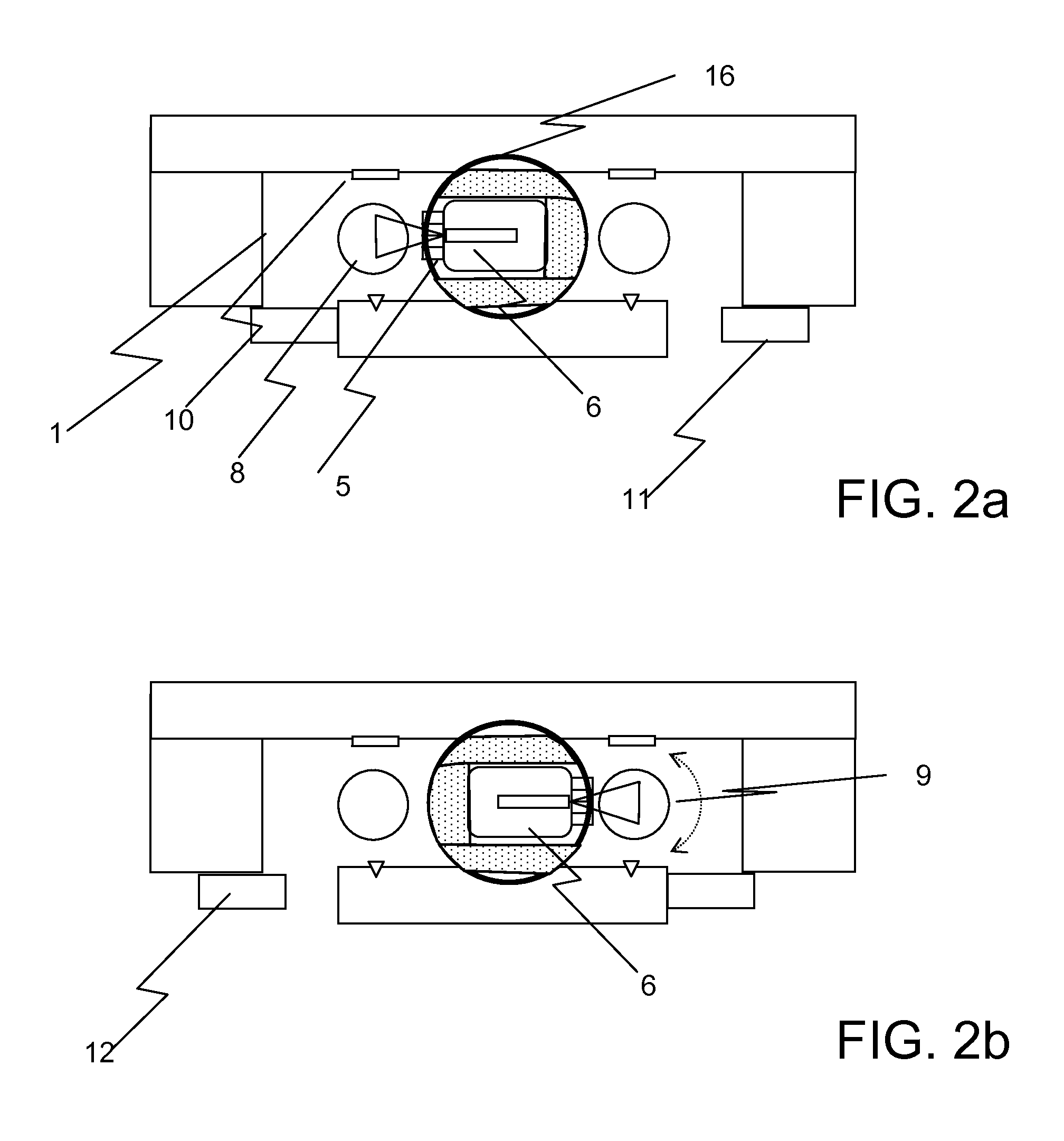
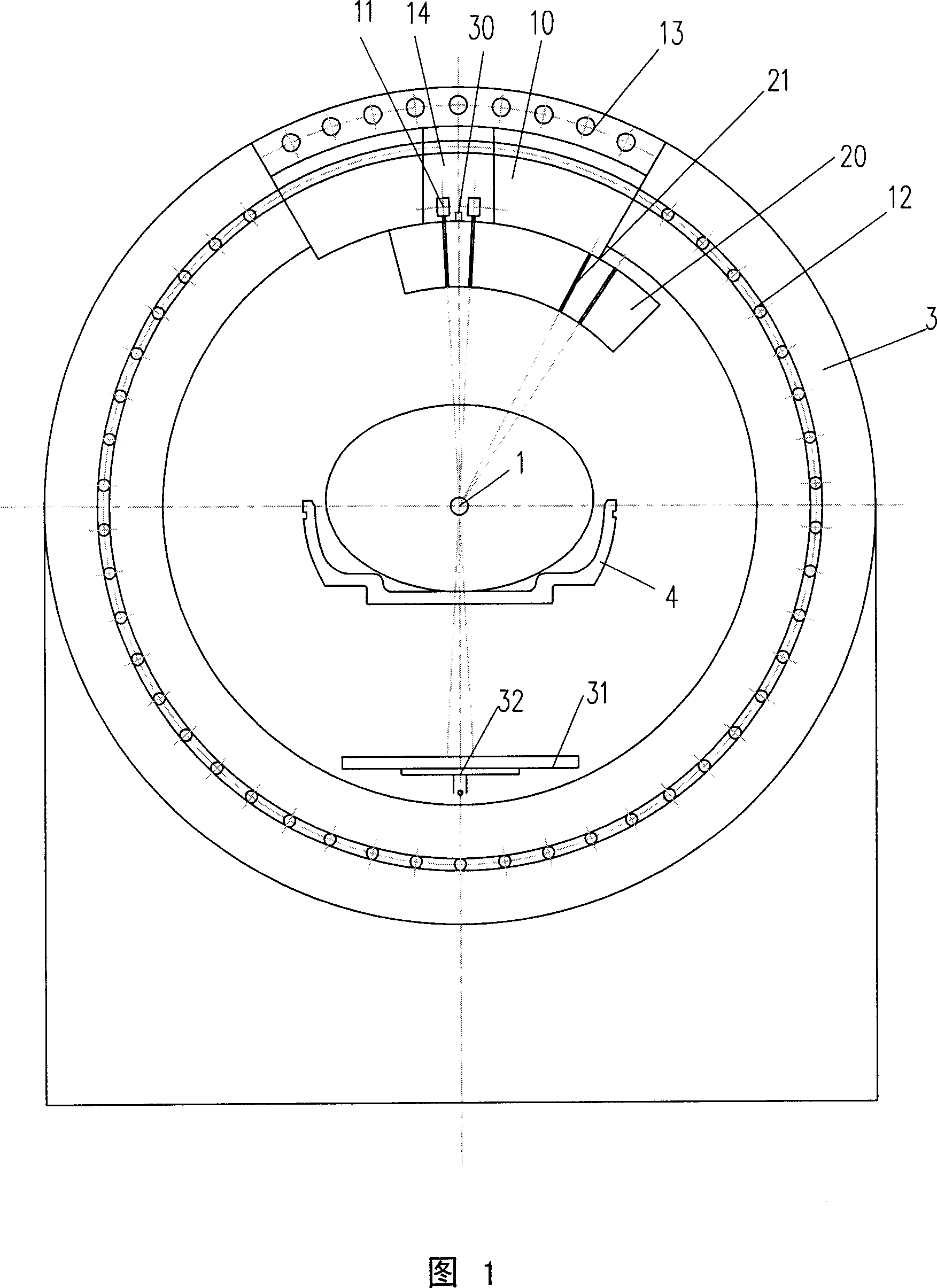
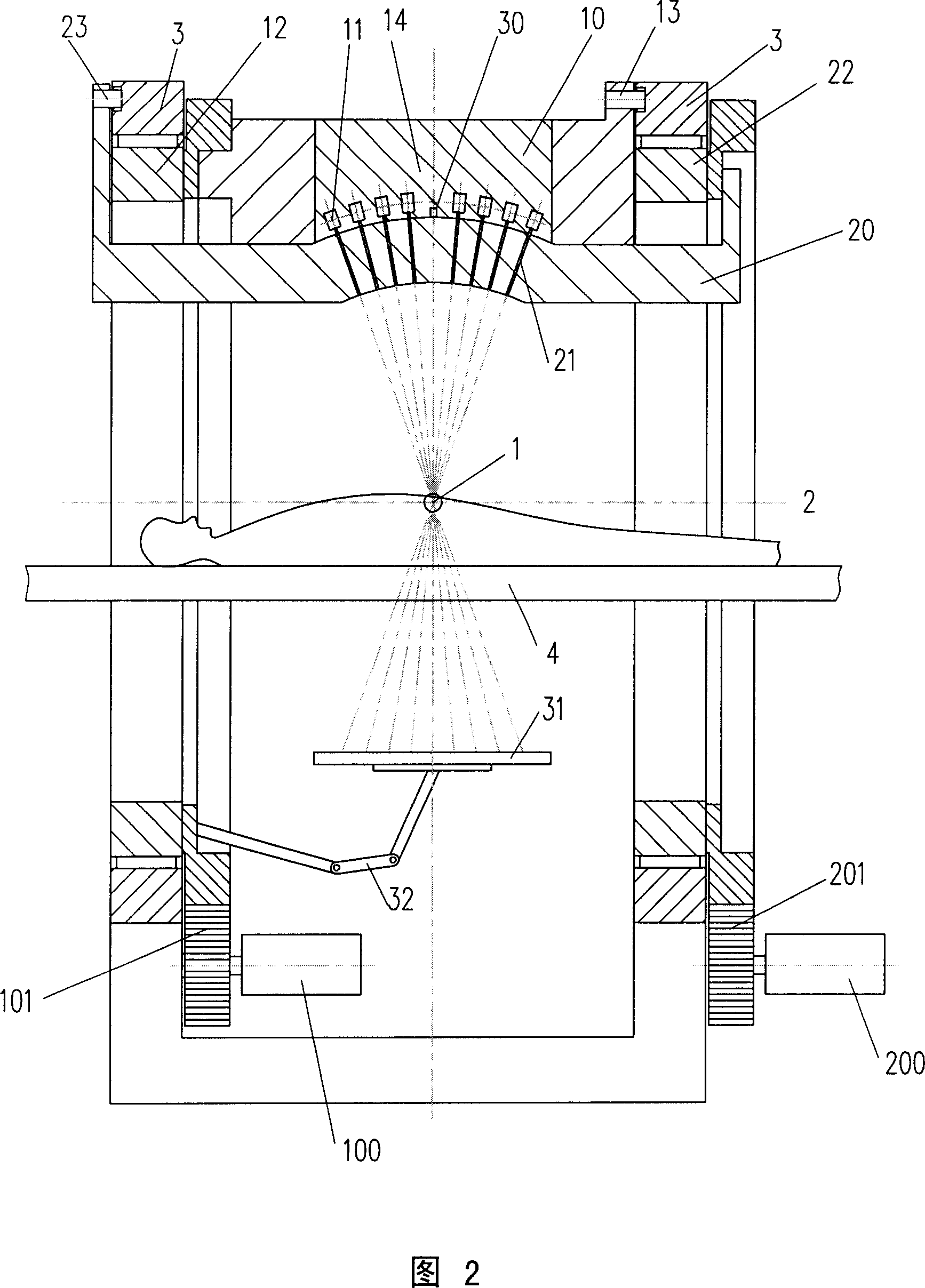
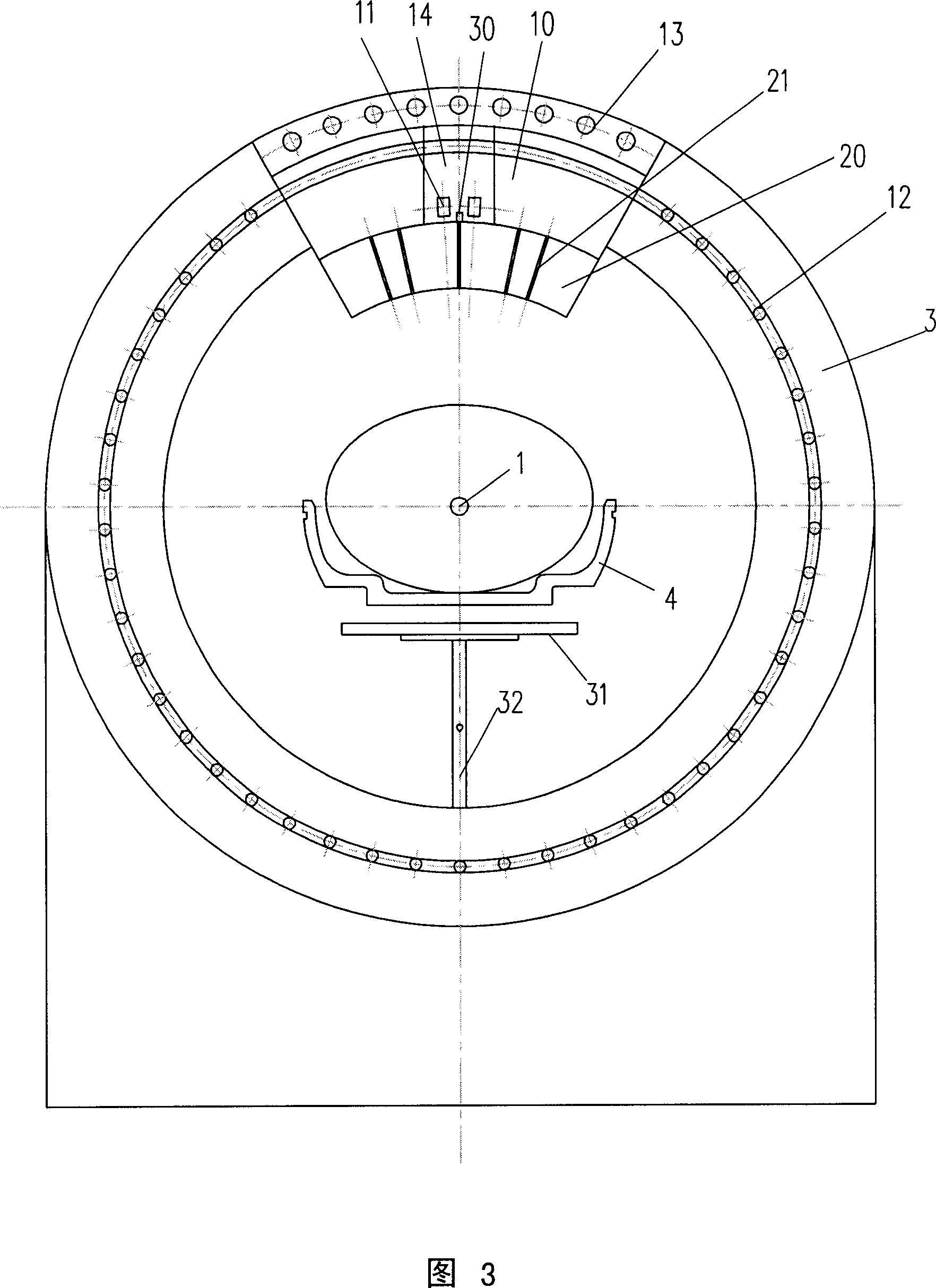
The invention discloses a radiation device of radiation treatment through rotating focus of gamma ray, which comprises the following parts: rotary ring, source bulk and detector, wherein multiple radiation sources are set in the source bulk, which emits ray to focus on the public focal point on the shaft line of rotary ring, one end of source bulk and detector is connected on the rotary ring, which are distributed symmetrically along radial direction of rotary ring, the high-activity treating radiation source and low-activity diagnosis radiation source are set in the source bulk, the beam of radiation source pierces the shaft line of rotary ring, the detector receives radiation information, which responds to output detecting information.
Owner:SHEN ZHEN HYPER TECH SHENZHEN
Method and device for fast raster beam scanning in intensity-modulated ion beam therapy
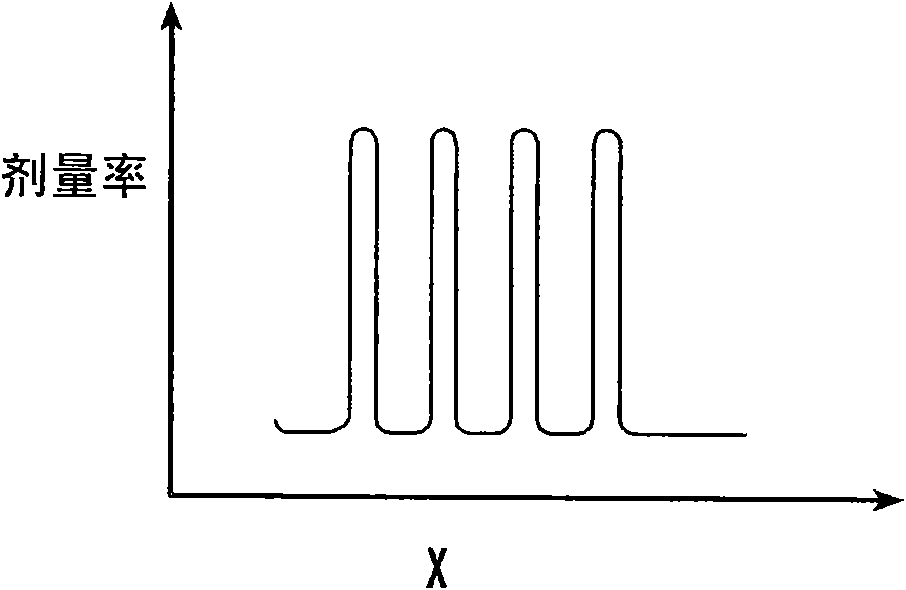
InactiveUS20160030769A1Continuous motionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment implementationDose profile
A method and device are designed to deliver intensity-modulated ion beam therapy radiation doses closely conforming to tumors of arbitrary shape, via a series of two-dimensional (2-D) continuous raster scans of a pencil beam, wherein each scan takes no more than about 100 milliseconds to complete. The device includes a fast scanning nozzle for the exit of an ion beam delivery gantry. The fast scanning nozzle has a fast combined-function X-Y steering magnet, and is coupled to a rastering control system capable of adjusting the length of each scan line, continuously varying the beam intensity along each scan line, and executing multiple rescans of a tumor depth layer within a single patient breathing cycle. An in-beam absolute dose and dose profile monitoring system is capable of millimeter-scale position resolution and millisecond-scale feedback to the control system to ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment implementation.
Owner:PHENIX MEDICAL
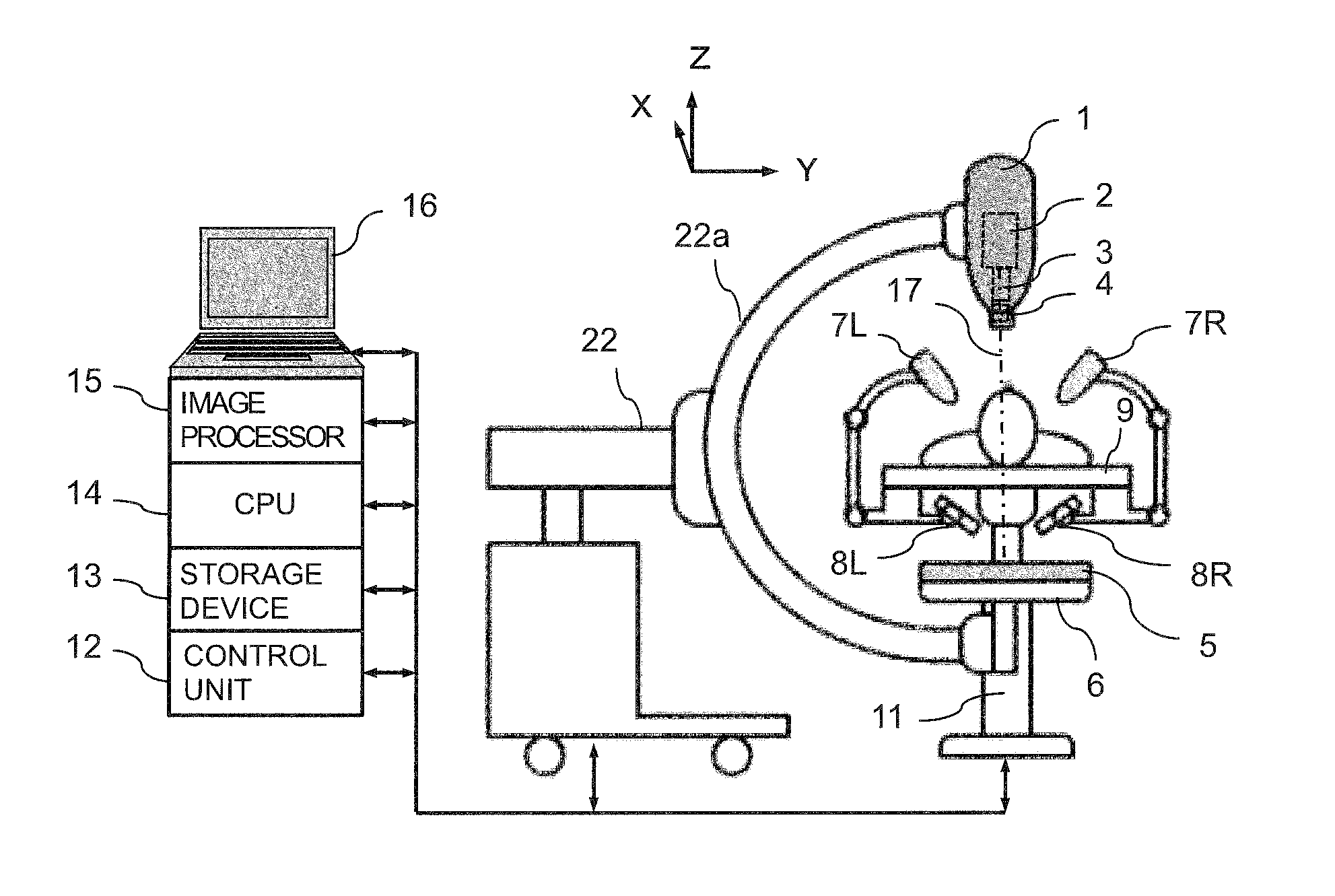
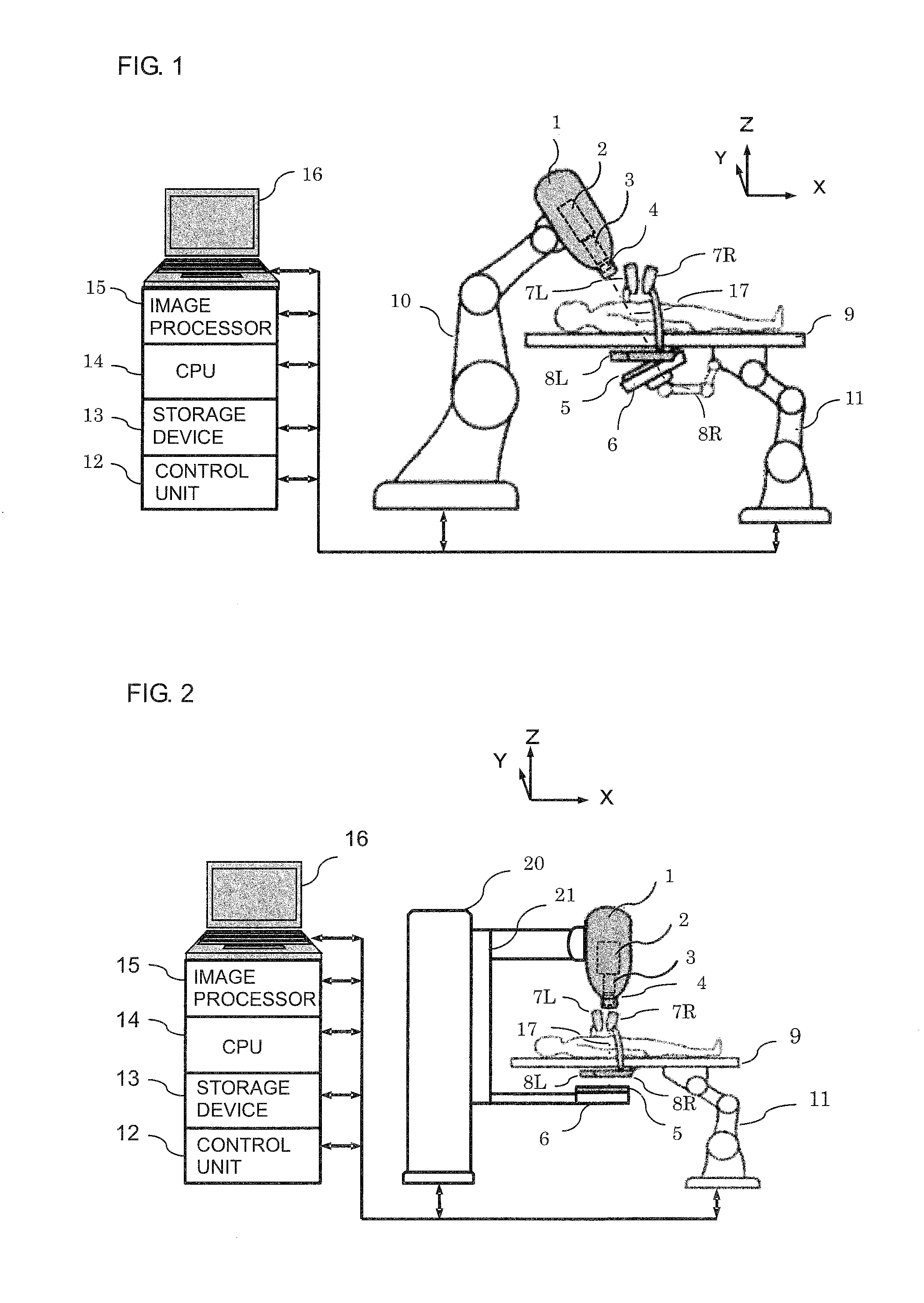
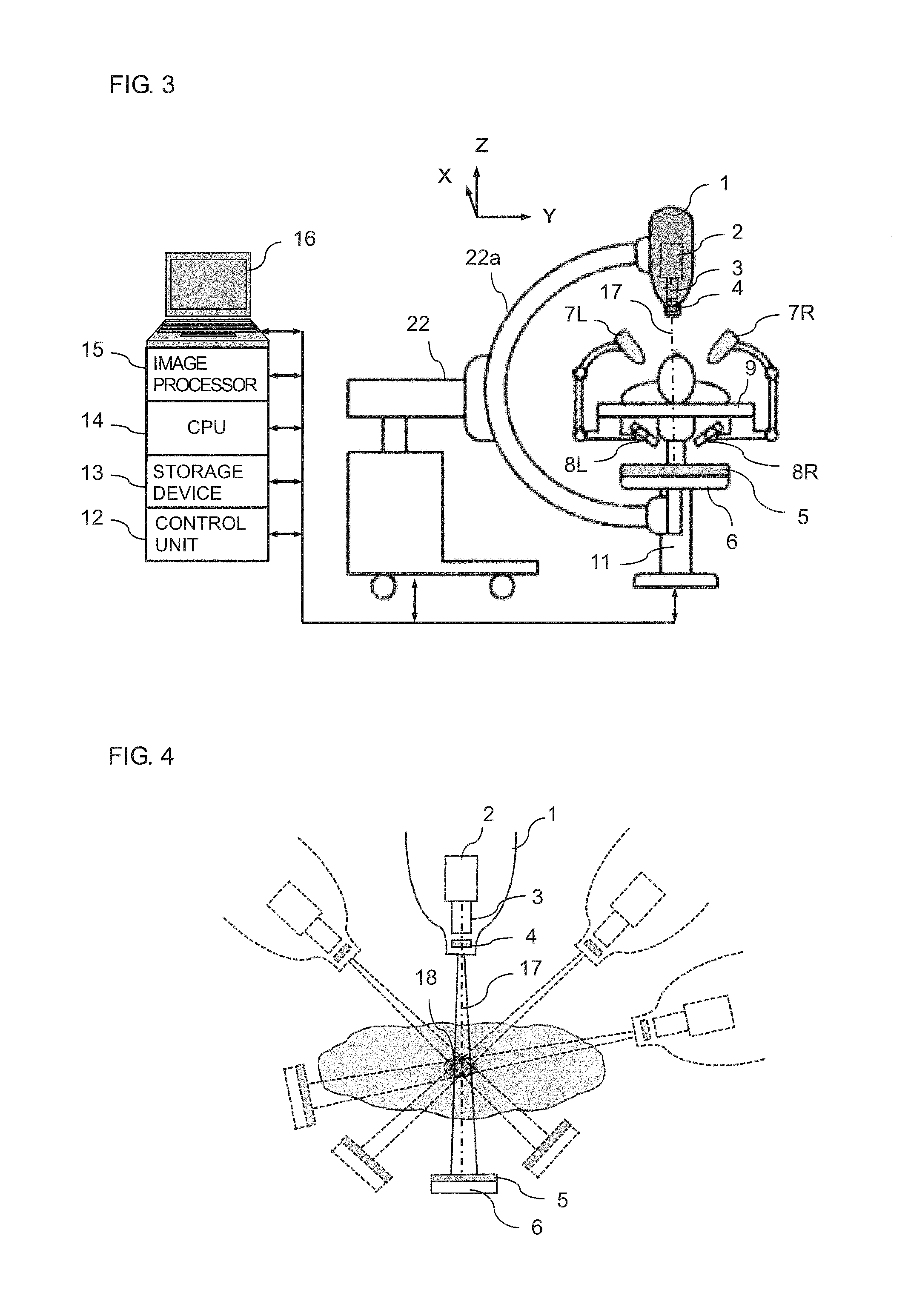
Real-Time Three-Dimensional Radiation Therapy Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20130336449A1High precisionIncrease speedMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyX-rayTreatment targets
A radiation therapy apparatus including a robot supporting a robot head; a therapeutic radiation source attached to the robot head; a collimator for adjusting a radiation field shape of therapeutic radiation radiated from the therapeutic radiation source; a first therapeutic radiation detector attached to the robot head; a couch configured to support a patient lying supine thereon; a second therapeutic radiation detector for detecting the therapeutic radiation, disposed opposite the first therapeutic radiation detector with the couch disposed therebetween; at least two X-ray sources and detectors for position detection of a marker and / or a treatment target; an image processor for reconstructing an image of the treatment target; and a CPU that computes the intensity, irradiation direction, dose, and dose distribution of the therapeutic radiation, and dose absorbed by the treatment target, radiation field shape, and position of the treatment target in real time for feedback to a next irradiation.
Owner:ACCUTHERA
Radiotherapeutic apparatus
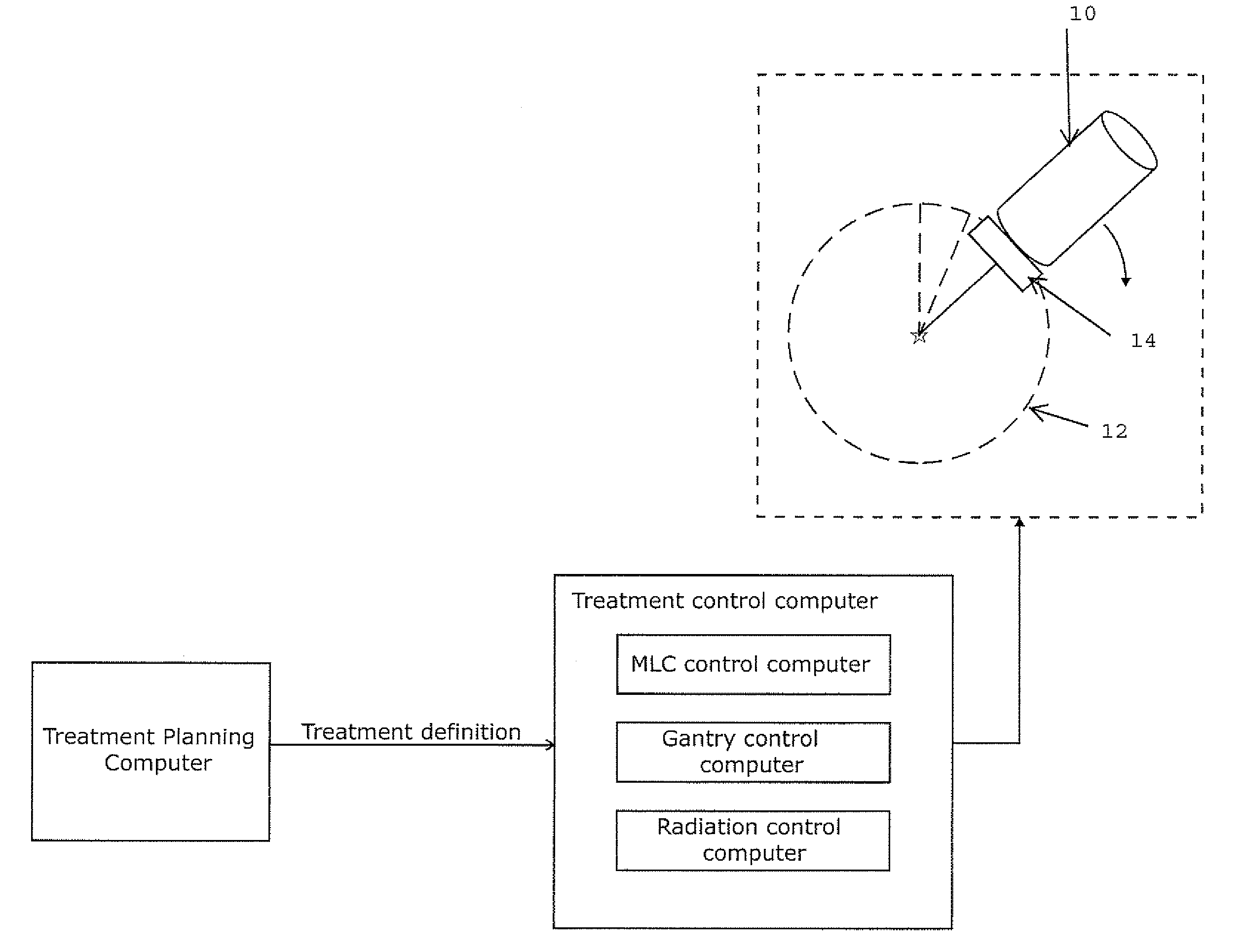
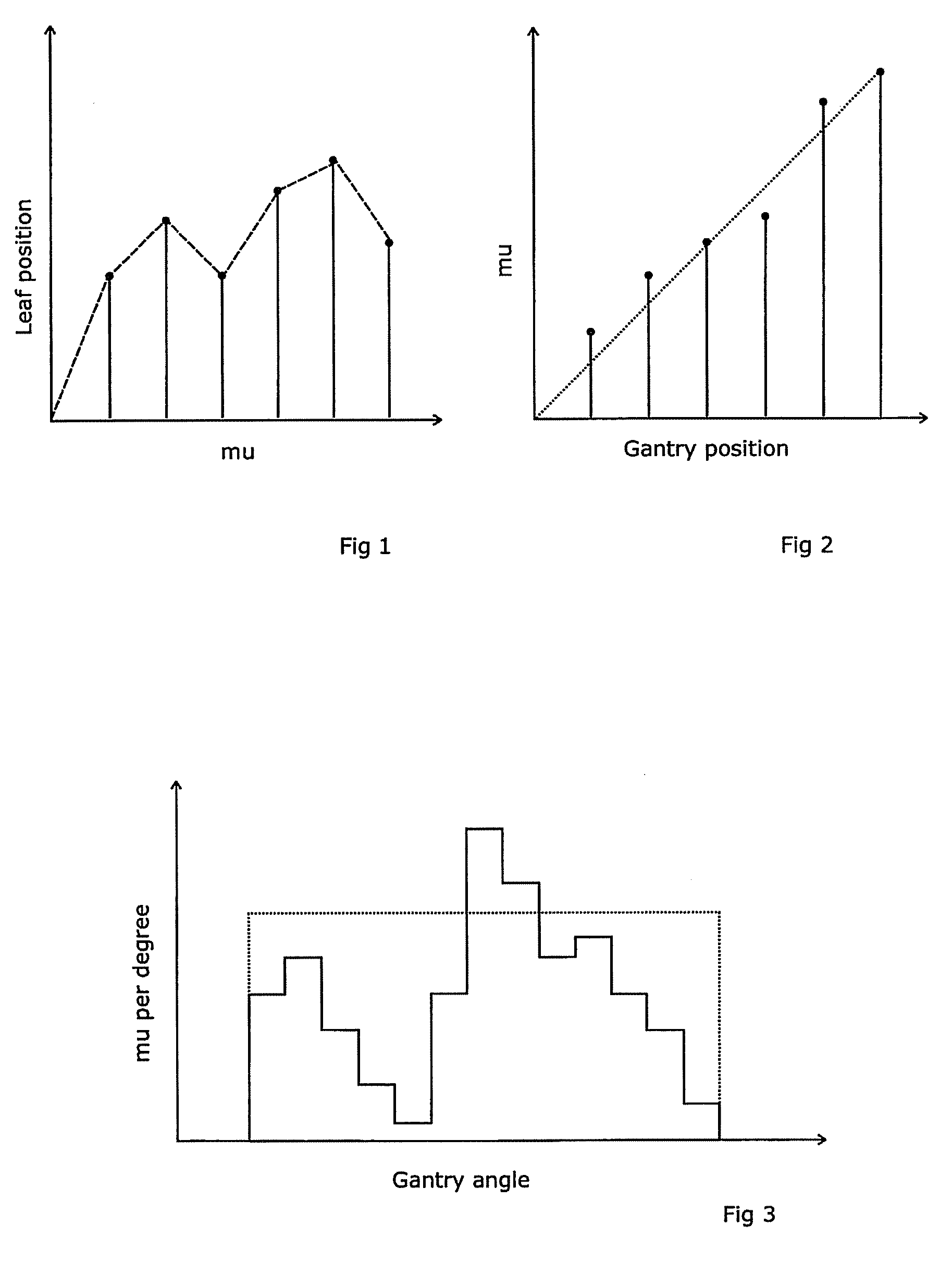
ActiveUS7961843B2Avoid less flexibilityReduce doseX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorClassical mechanics
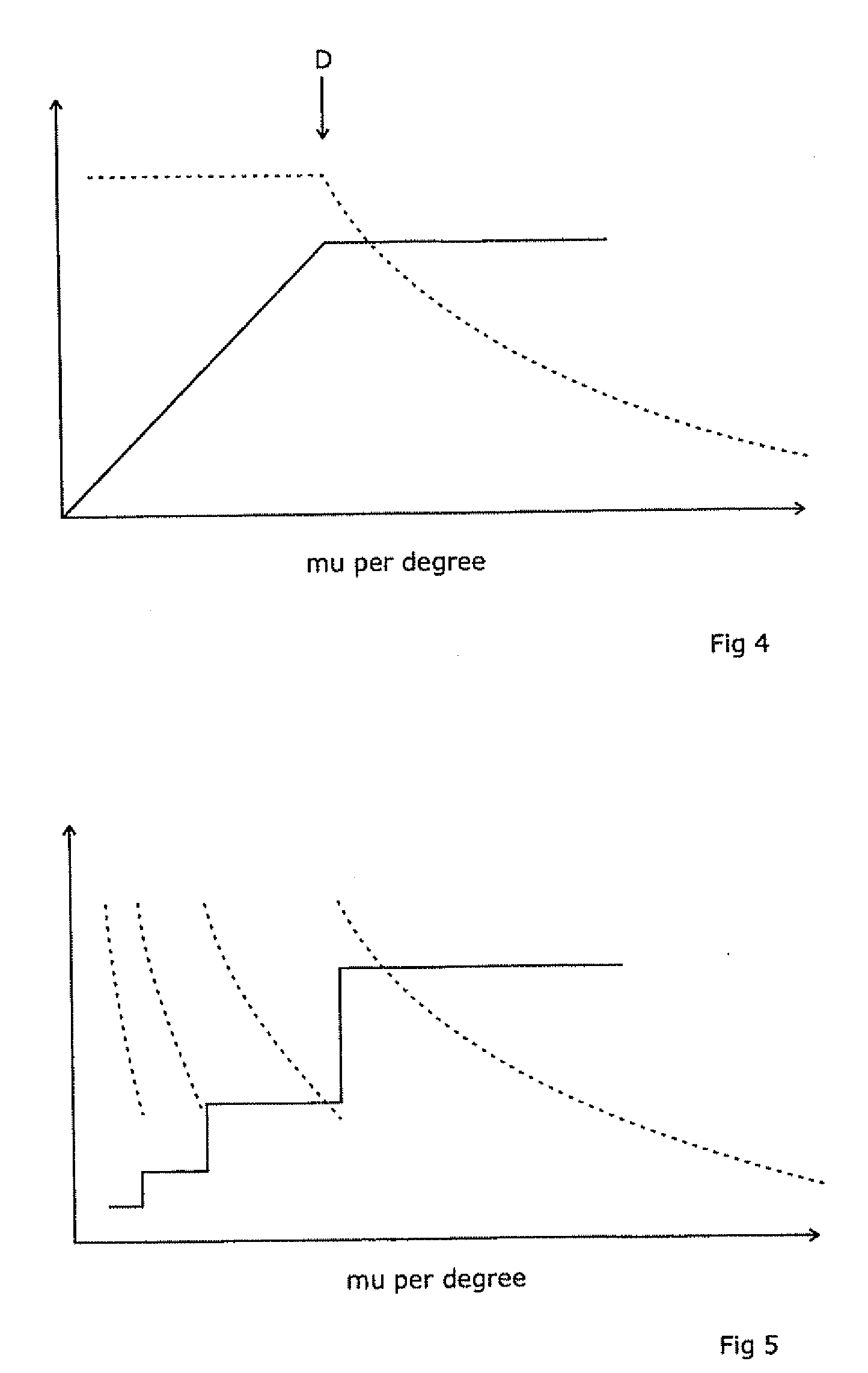
A radiotherapeutic apparatus comprises a source able to emit a beam of therapeutic radiation along a beam axis, a multi-leaf collimator arranged to collimate the beam to a desired shape, wherein the source is rotatable about a rotation axis that is substantially orthogonal and intersects with the beam axis thereby to describe an arc around that axis, and further comprises a control means able to control the dose / time rate of the source, the rotation speed of the source, and the multi-leaf collimator position. The control means is arranged to control the source in accordance with a treatment plan over first and second arc-segments such that at least the multi-leaf collimator changes shape at a different rate per degree in the second arc-segment as to the first arc-segment.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Advanced cherenkov-based imaging systems, tools, and methods of feedback control, temporal control sequence image capture, and quantification in high resolution dose images
ActiveUS20200061391A1Simple, accurate, quick, robust, real-time, water-equivalent characterizationRapid and economic characterizationRadiation intensity measurementX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyClinical settingsTherapy radiation
The present invention relates to advanced Cherenkov-based imaging systems, tools, and methods of feedback control, temporal control sequence image capture, and quantification in high resolution dose images. In particular, the present invention provides a system and method for simple, accurate, quick, robust, real-time, water-equivalent characterization of beams from LINACs and other systems producing external-therapy radiation for purposes including optimization, commissioning, routine quality auditing, R&D, and manufacture. The present invention also provides a system and method for rapid and economic characterization of complex radiation treatment plans prior to patient exposure. Further, the present invention also provides a system and method of economically detecting Cherenkov radiation emitted by tissue and other media in real-world clinical settings (e.g., settings illuminated by visible light).
Owner:DOSEOPTICS LLC
Radiotherapeutic apparatus
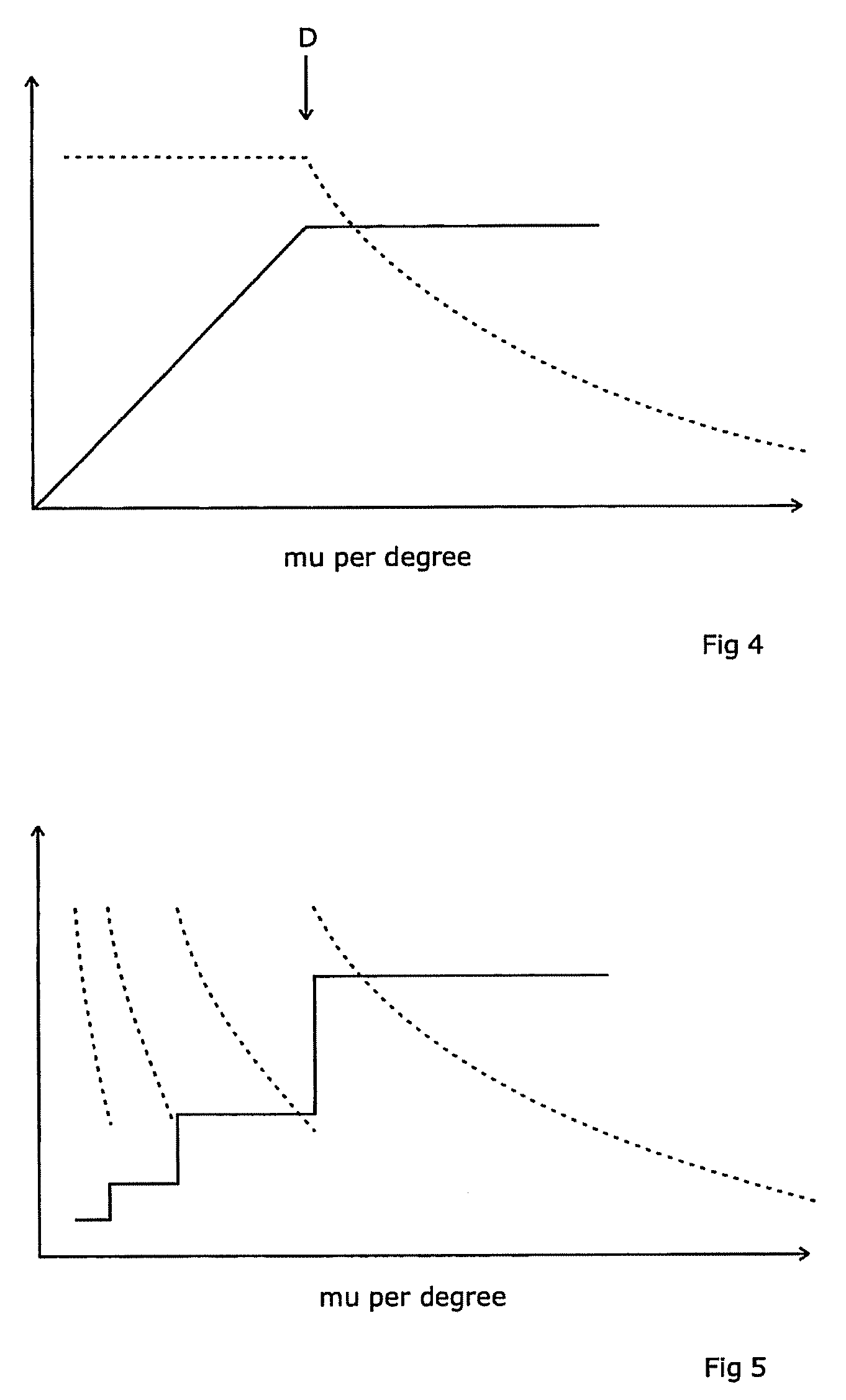
ActiveUS20100329422A1Reduce unwanted doseAvoid less flexibilityX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTherapeutic radiationRotation velocity
A radiotherapeutic apparatus comprises a source able to emit a beam of therapeutic radiation along a beam axis, a multi-leaf collimator arranged to collimate the beam to a desired shape, wherein the source is rotateable about a rotation axis that is substantially orthogonal and intersects with the beam axis thereby to describe an arc around that axis, and further comprises a control means able to control the dose / time rate of the source, the rotation speed of the source, and the multi-leaf collimator position. The control means is arranged to receive a treatment plan in which the arc is divided into a plurality of notional arc-segments, and specifying the total dose for the arc-segment and a Start and end MLC position. It then controls the source in accordance with that plan over an first arc-segment such that at least one of the rotation speed and dose rate are constant and the multi-leaf collimator changes shape, and a second arc segment such that at least one of the rotation speed and dose rate are constant at a level different to the constant level adopted during the first arc-segment. It achieves this by calculating the total time required for the arc segment for a plurality of factors including an MLC leaf movement from a prescribed position at the start of the arc-segment to a prescribed position at the end of the arc-segment, at a maximum leaf speed, rotation of the source from the start to the end of the arc-segment at a maximum source rotation speed, delivery of the dose at a maximum dose rate per time, selecting the factor dictating the longest time, and Controlling the apparatus so that the selected factor operates at its respective maximum and the remaining factors are operated at a reduced rate selected to match that longest time, wherein the total time required for the arc segment for at least one factor relating to a moving geometry item is the greater of (a); a time required to complete the segment at a continuous defined upper speed for the geometry item and (b) a time required to accelerate the geometry item until it is travelling at the defined upper speed. Generally, the time required to accelerate the geometry item to the defined upper speed will include a time to accelerate the geometry item to that speed, and a further time to accelerate the geometry item beyond that speed and subsequently decelerate it until travelling at that speed.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Therapeutic use of radiation and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20060064008A1Extension of timeComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringTreatment deliveryProjection image
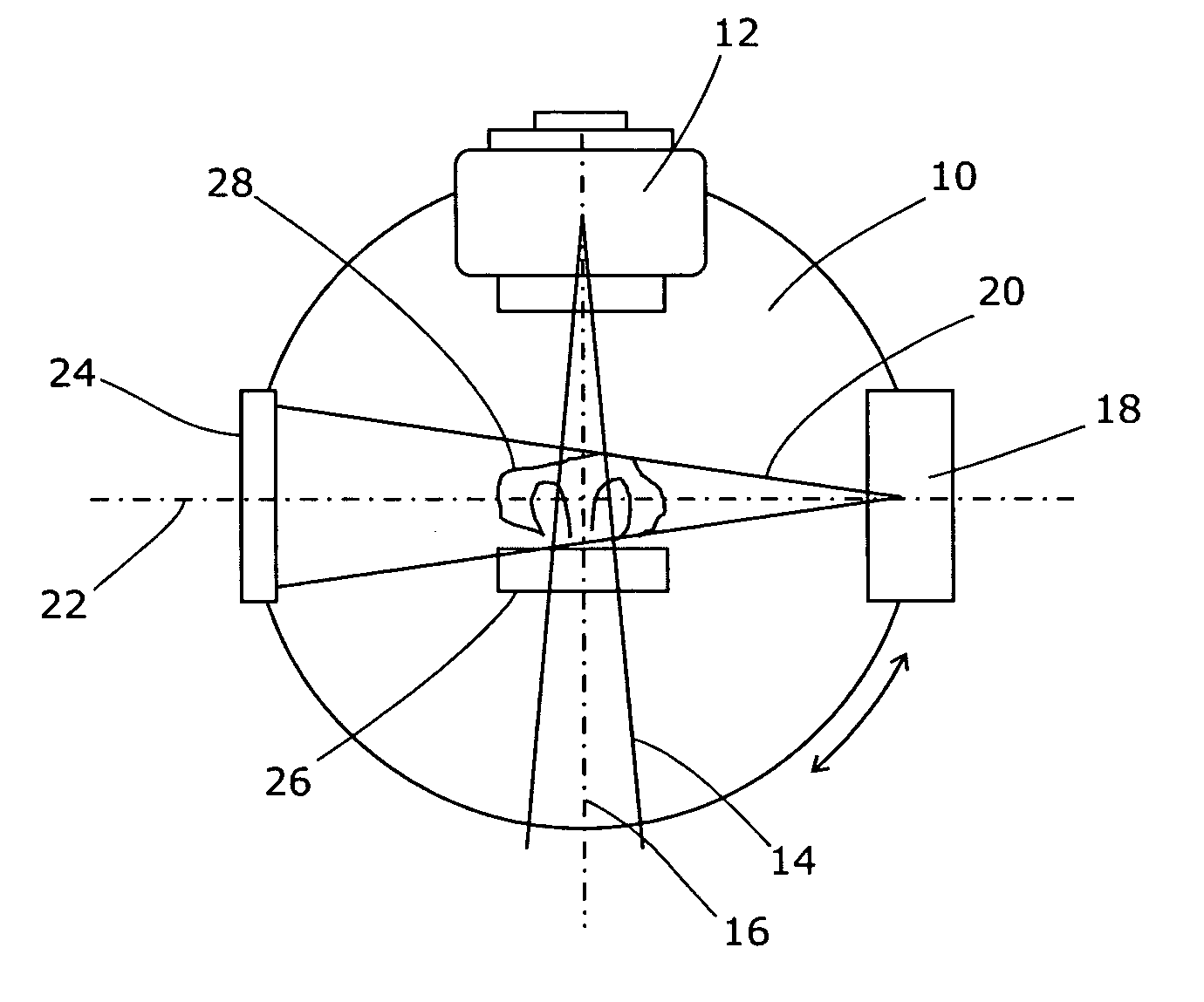
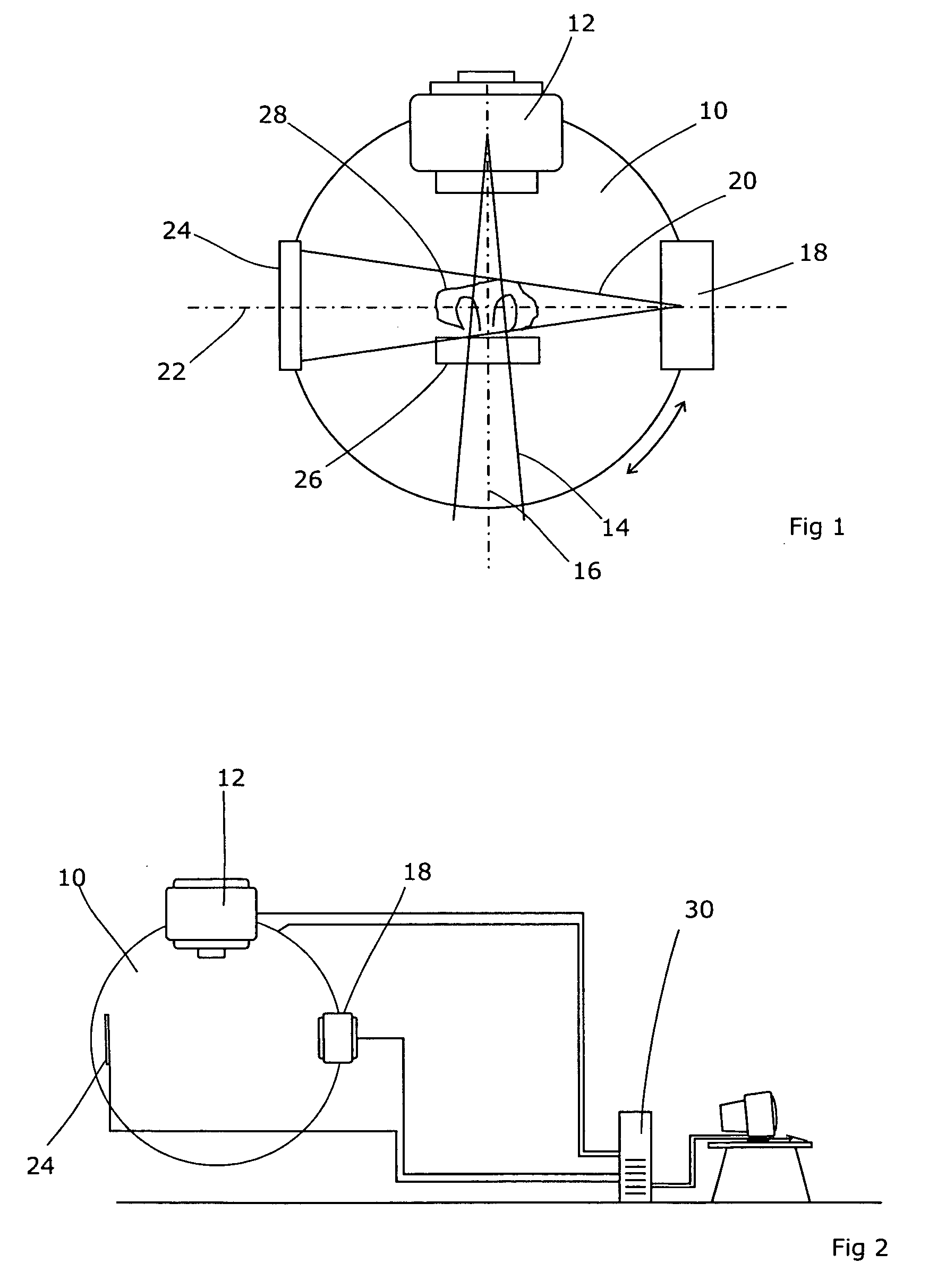
A radiotherapy apparatus comprises a source of therapeutic radiation adapted to emit radiation along a therapeutic beam axis a source of diagnostic radiation adapted to emit radiation along a diagnostic beam axis, and a detector therefor, the two sources being rotateable in unison about a common axis intersecting with the therapeutic beam axis and the diagnostic beam axis; and a control unit arranged to move the therapeutic source to a first position by rotation thereof, activate the therapeutic source thereby to provide a first dose segment, de-activate the therapeutic source, rotate the sources together while the diagnostic source is active and while acquiring images from the detector, and re-activate the therapeutic source thereby to provide a second dose segment. A corresponding operation method is also disclosed, together with a reconstruction module. The invention demonstrates the feasibility of integrating cone beam imaging into normal treatment delivery, using kV projection images acquired during the gantry rotation between each treatment beam.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Compact microbeam radiation therapy systems and methods for cancer treatment and research
ActiveCN101927065ARadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose rateCarbon nanotube
The present subject matter relates to compact, non-synchrotron microbeam radiation therapy (MRT) systems and methods for cancer research and treatment based on a carbon nanotube distributed x-ray source array technology. The systems and methods can deliver microscopically discrete x-ray radiation at peak dose rate of 10 Gy per second or higher. The x-ray radiation can be provided by a spatially distributed x-ray source array. The technology can be used, for example and without limitation, for human cancer treatment, for intra-operative radiation therapy, and for pre-clinical cancer research on animal cancer models.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
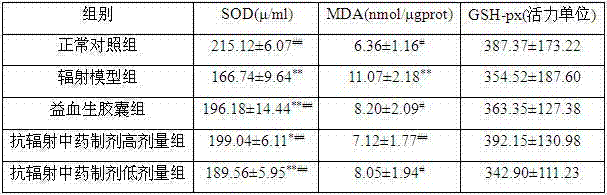
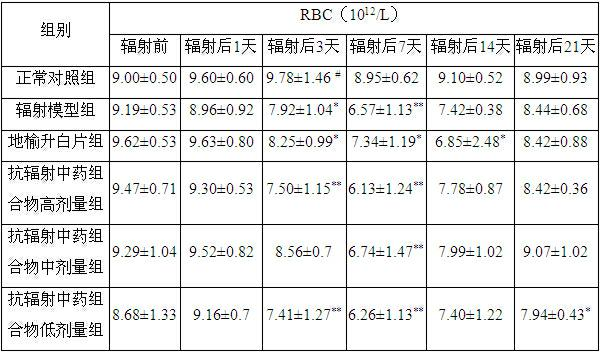
Anti-radiation Chinese medicine preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102389511ASmall toxicityEasy to prepareAntinoxious agentsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAngelica Sinensis RootTherapy radiation
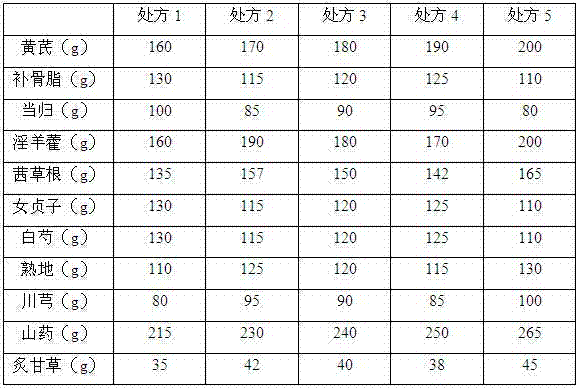
The invention discloses an anti-radiation Chinese medicine preparation and a preparation method thereof. The preparation is a capsule which is prepared by mixing extract powder of a Chinese medicine composition and microcrystalline cellulose with the weight ratio of 2:1, wherein the Chinese medicine composition consists of ingredients according to parts by weight: 160-200 parts of astragalus mongholicus, 110-130 parts of fructus psoraleae, 80-100 parts of angelica sinensis, 160-200 parts of herba epimedii, 135-165 parts of madder root, 110-130 parts of fructus ligustri lucidi, 110-130 parts of radix paeoniae alba, 110-130 parts of radix rehmanniae preparata, 80-100 parts of ligusticum wallichii, 215-265 parts of rhizoma dioscoreae and 35-45 parts of radix glycyrrhizae preparata, and the extract powder is dry powder of ethanol solution extract of the Chinese medicine composition. The anti-radiation Chinese medicine preparation is precise in anti-radiation treatment effect, low in toxicside effects, simple in preparation method, low in cost, convenient to carry, easy to store, convenient to take and accurate in dosage, thus having good development and application prospect in the prevention and treatment of radiation injury.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
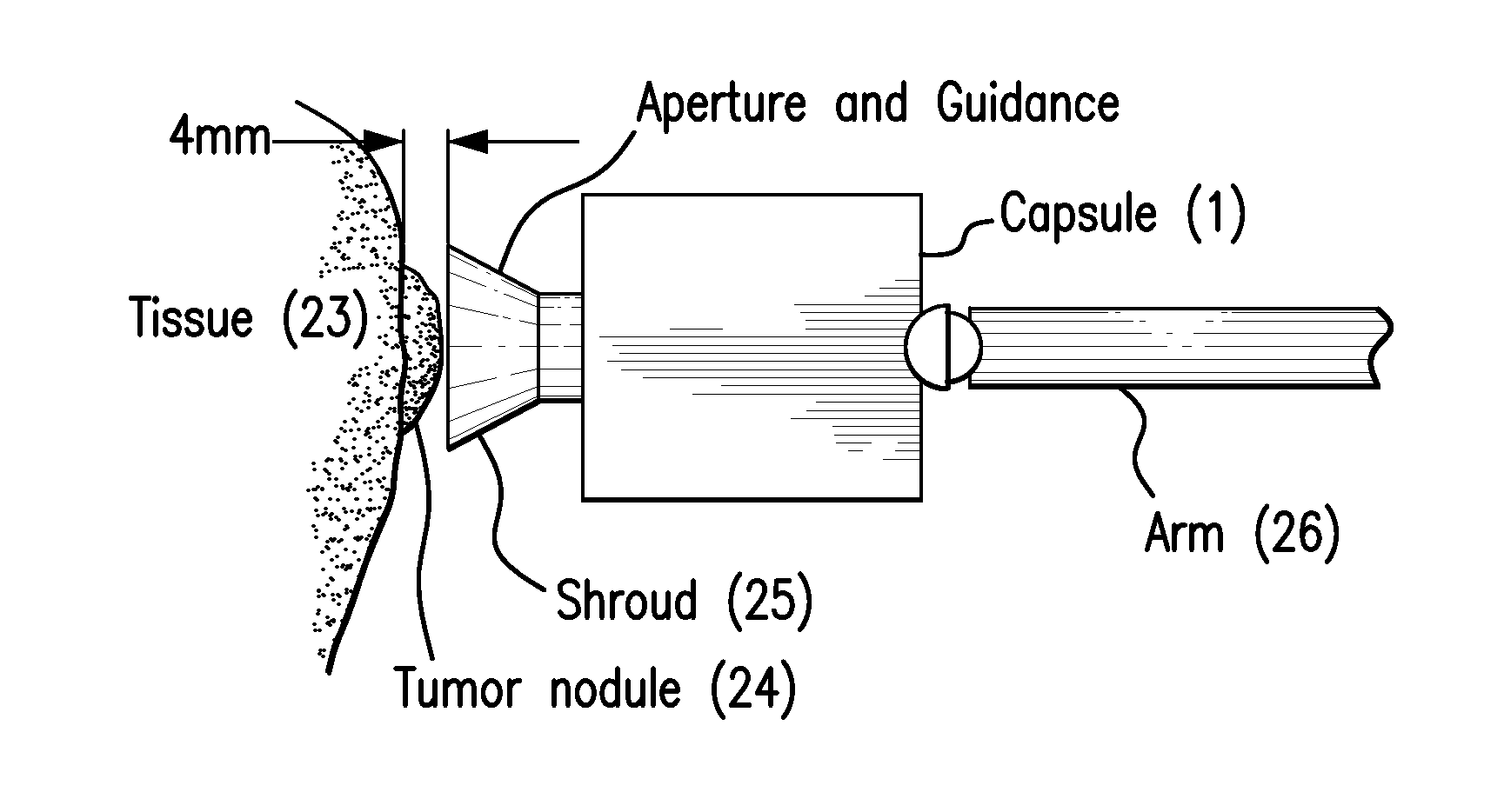
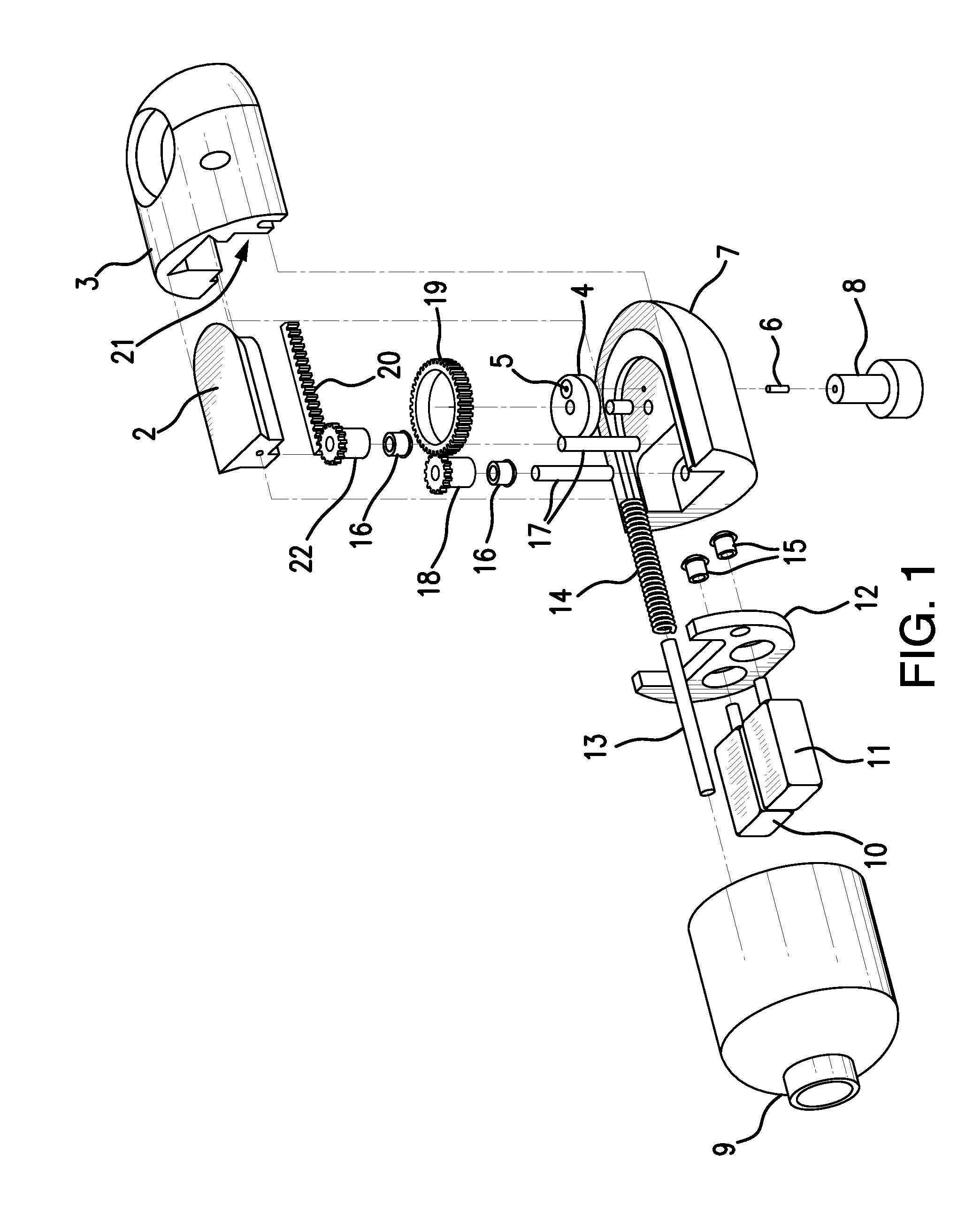
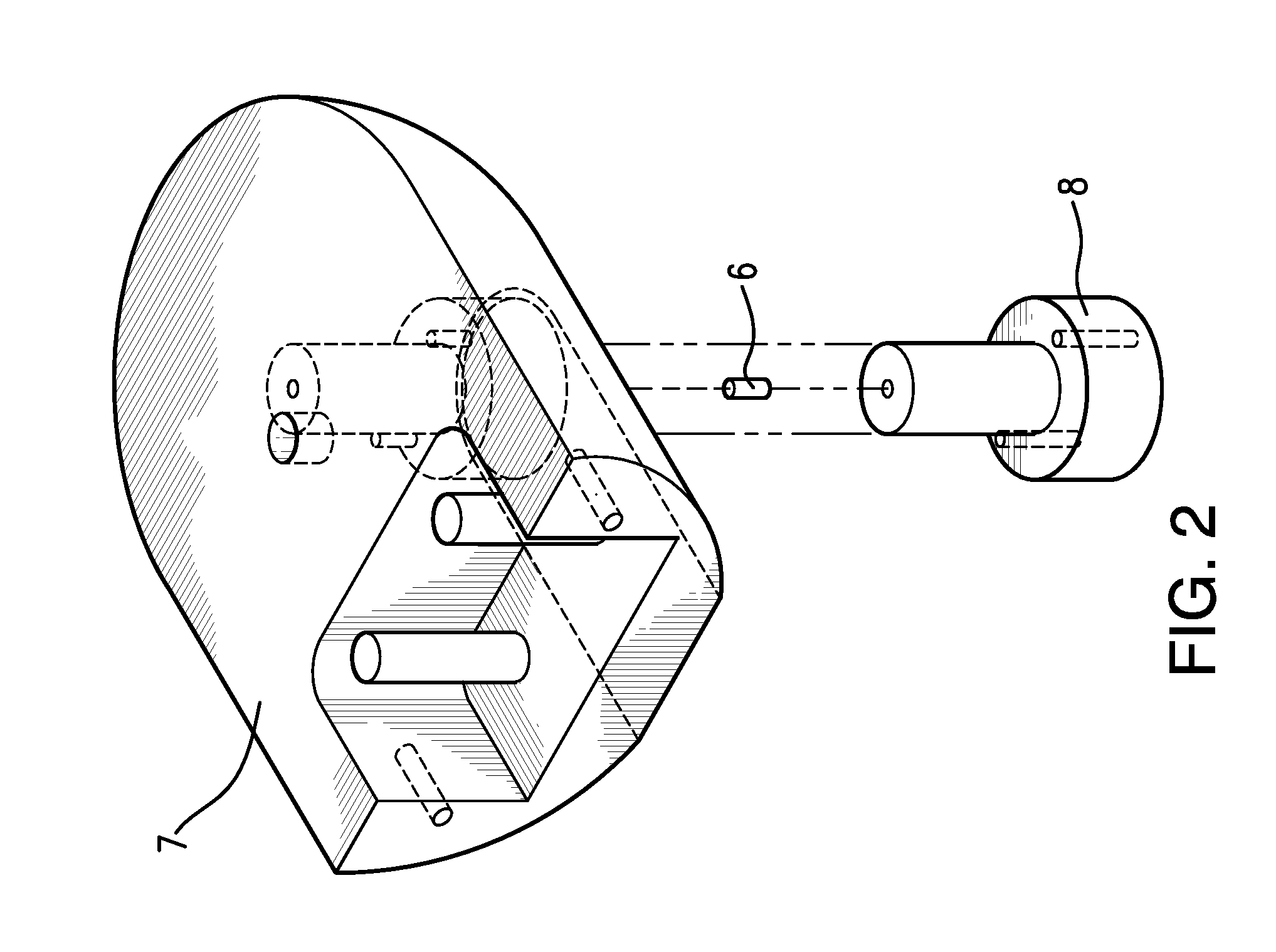
Direct visualization Robotic Intra-Operative Radiation Therapy Device with Radiation Ablation Capsule and Shutter System
This invention proposes a robotic applicator device to be deployed internally to a patient having a capsule (also referred to as a cassette) and aperture with a means of alternately occluding and exposing a radioactive source through the aperture. The capsule and aperture will be integrated with a surgical robot to create a robotic IORT (intra-operative radiation therapy) applicator device as more fully described below. The capsule, radiation source, and IORT applicator arm would be integrated to enable a physician, physicist or technician to interactively internally view and select tissue for exposure to ionizing radiation in sufficient quantities to deliver therapeutic radiation doses to tissue. Via the robotic manipulation device, the physician and physicist would remotely apply radiation to not only the tissue to be exposed, but also control the length of time of the exposure. Control means would be added to identify and calculate margin and depth of tissue to be treated and the proper radiation source or radioactive isotope (which can be any particle emitter, including neutron, x-ray, alpha, beta or gamma emitter) to obtain the desired therapeutic effects. The invention enables stereotactical surgery and close confines radiation therapy adjacent to radiosensitive tissue.
Owner:ROBERTS WALTER A +1
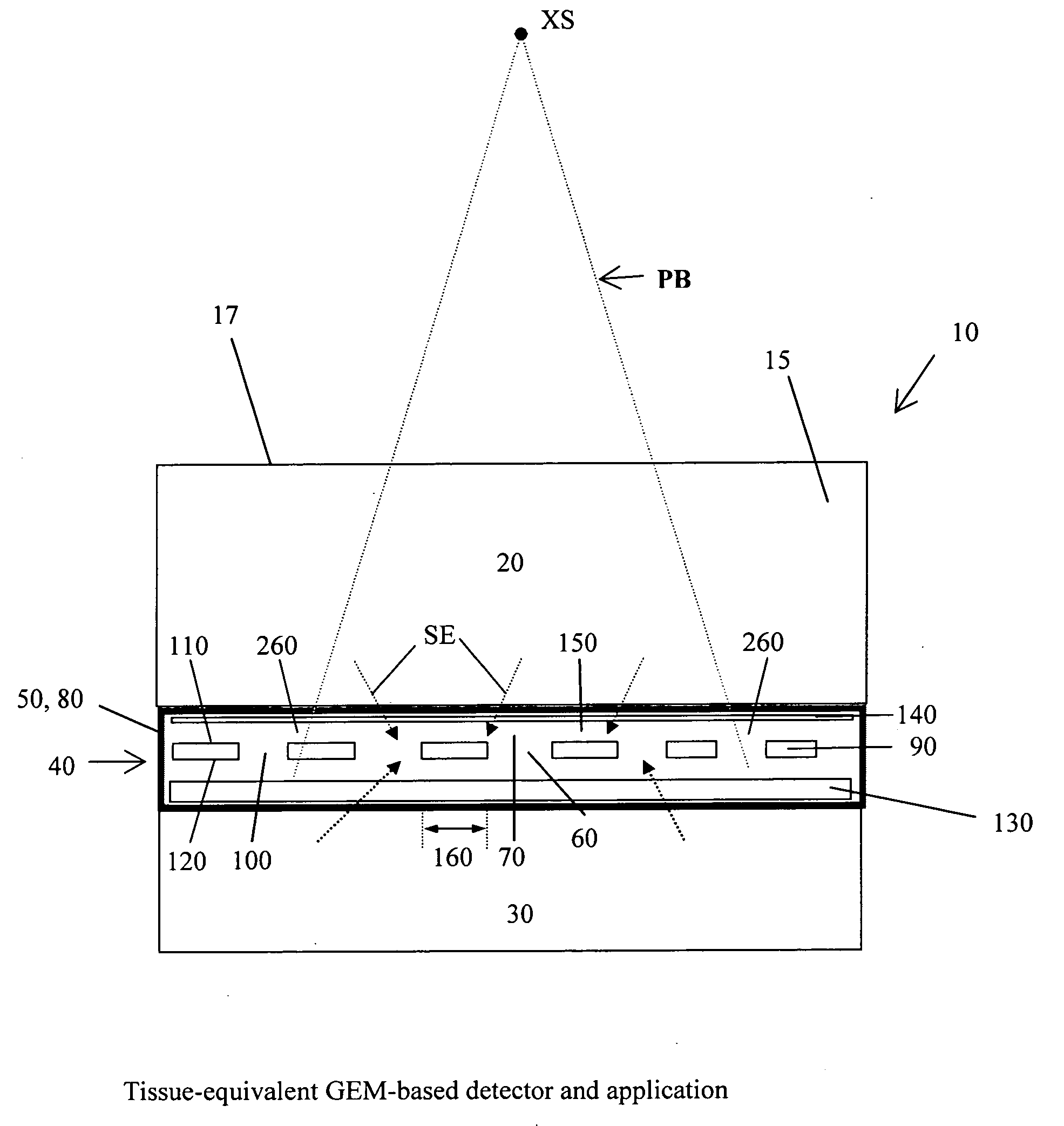
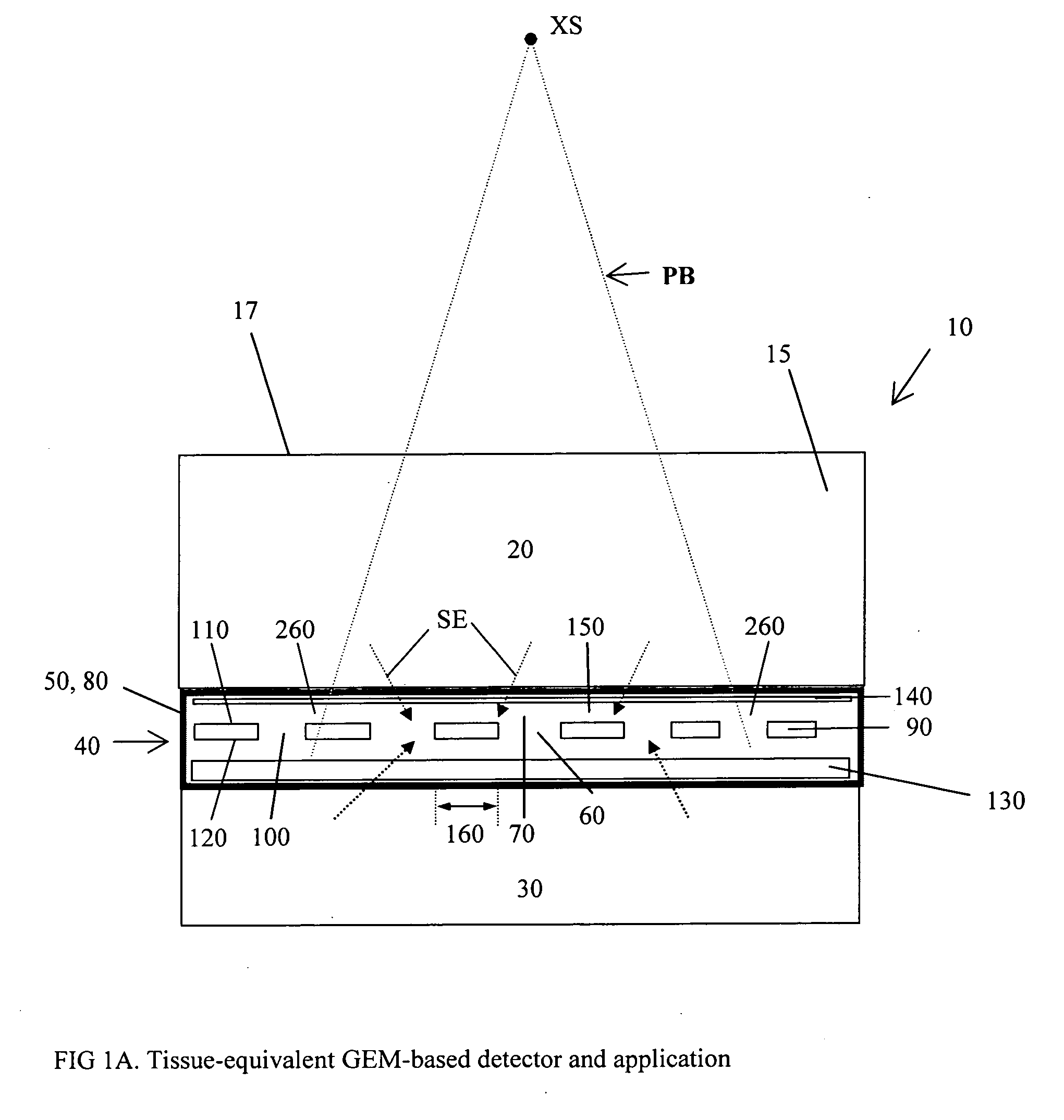
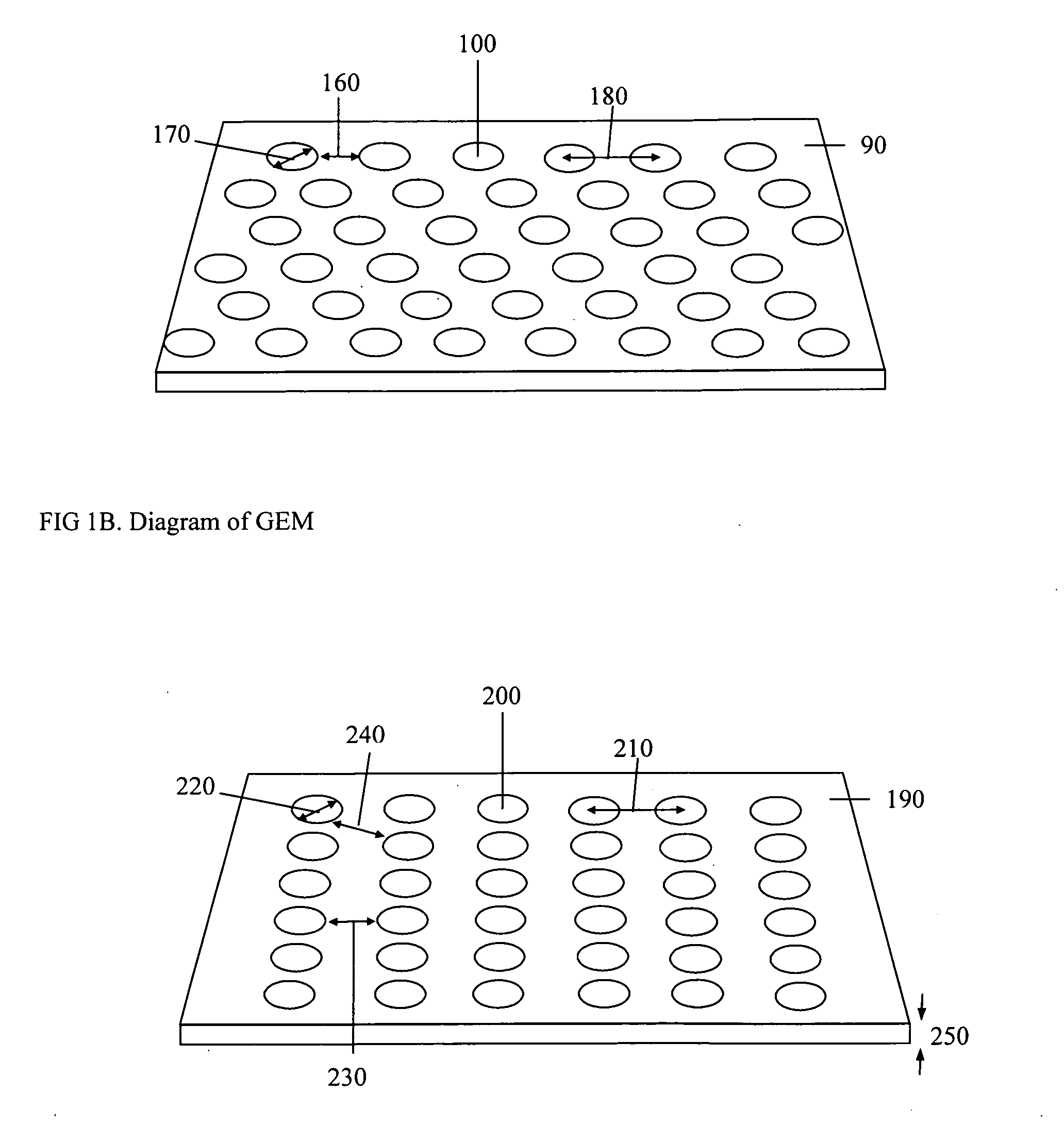
Dosimeter based on a gas electron multiplier for dose measurements of therapeutic radiation
InactiveUS20080029709A1Real-time acquisitionFacilitate sandwichingElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansDosimeterTherapeutic radiation
A dosimeter based on a gas electron multiplier and method of use thereof for measurement of doses of therapeutic radiation to which a tissue-phantom is exposed. Subsequent to the in-phantom measurement and verification of radiation beam delivery, radiation can be effectively delivered to a human target organ, based on the verification of radiation quantities to which the phantom was exposed. Use of a gas electron multiplier-based dosimeter facilitates precise and accurate verification of the radiation dose within a phantom by taking measurements in real time, with no need for subsequent film processing.
Owner:PRECISION DOSIMETRY SYST
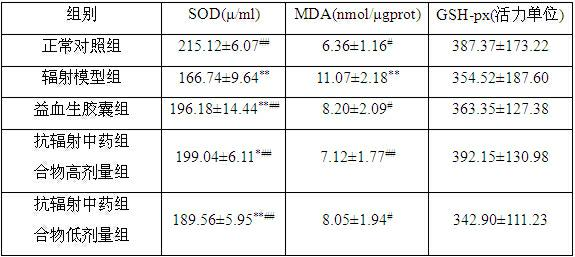
Anti-radiation traditional Chinese medicine composition
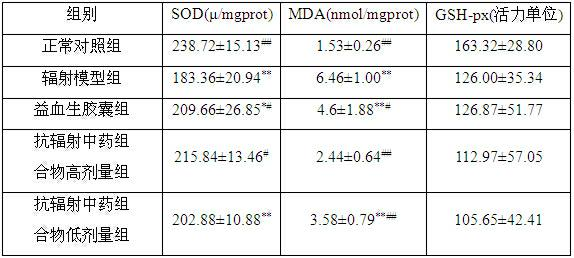
InactiveCN102380016AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove securityAntinoxious agentsDermatological disorderBiotechnologyMedicinal herbs
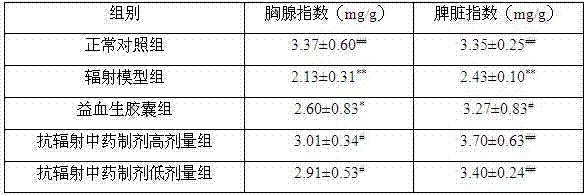
The invention discloses an anti-radiation traditional Chinese medicine composition which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 160-200 parts of membranous milkvetch root, 110-130 parts of scurfy pea, 80-100 parts of Chinese angelica, 160-200 parts of epimedium, 135-165 parts of madder root, 110-130 parts of glossy privet fruit, 110-130 parts of white paeony root, 110-130 parts ofradix rehmanniae preparata, 80-100 parts of Szechuan lovage rhizome, 215-265 parts of Chinese yam and 35-45 parts of prepared liquoric root. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can increase thymus index and spleen index of a 60Co gamma-radiated mouse and protect immune organs; improve the activity of superoxide dismutase in blood serum and the liver of the 60Co gamma-radiated mouse, reduce the content of malonaldehyde and improve the anti-oxidation capability of an organism; increase peripheral white blood cells of the 60Co gamma-radiated mouse and improve the hematogenesis function;and reduce the micronuclear rate of marrow cells of the 60Co gamma-radiated mouse and inhibit the action of causing chromosomal aberration of 60Co gamma rays. In addition, the traditional Chinese medicine composition is low in toxicity and side effects, and medicinal materials in the formula are low in price and easy to obtain, thereby having great development and application prospects in the aspects of preventing and treating radiation injuries.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method and device for fast raster beam scanning in intensity-modulated ion beam therapy
InactiveCN106604762ASurgical instrument detailsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment implementationDose profile
A method and device are designed to deliver intensity-modulated ion beam therapy radiation doses closely conforming to tumors of arbitrary shape, via a series of two-dimensional (2-D) continuous raster scans of a pencil beam, wherein each scan takes no more than about 100 milliseconds to complete. The device includes a fast scanning nozzle for the exit of an ion beam delivery gantry. The fast scanning nozzle has a fast combined-function X-Y steering magnet, and is coupled to a rastering control system capable of adjusting the length of each scan line, continuously varying the beam intensity along each scan line, and executing multiple rescans of a tumor depth layer within a single patient breathing cycle. An in-beam absolute dose and dose profile monitoring system is capable of millimeter-scale position resolution and millisecond-scale feedback to the control system to ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment implementation.
Owner:PHENIX MEDICAL
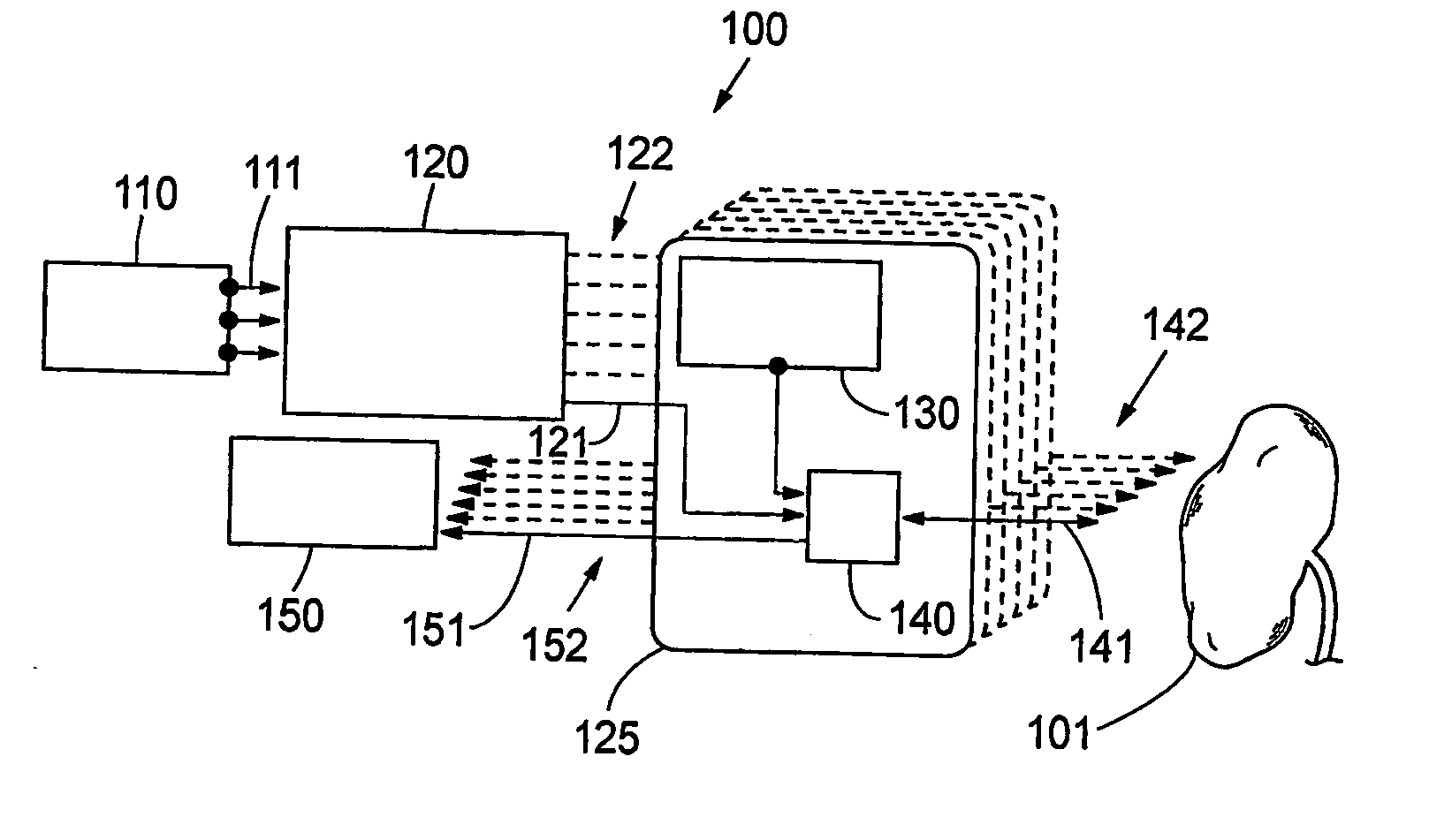
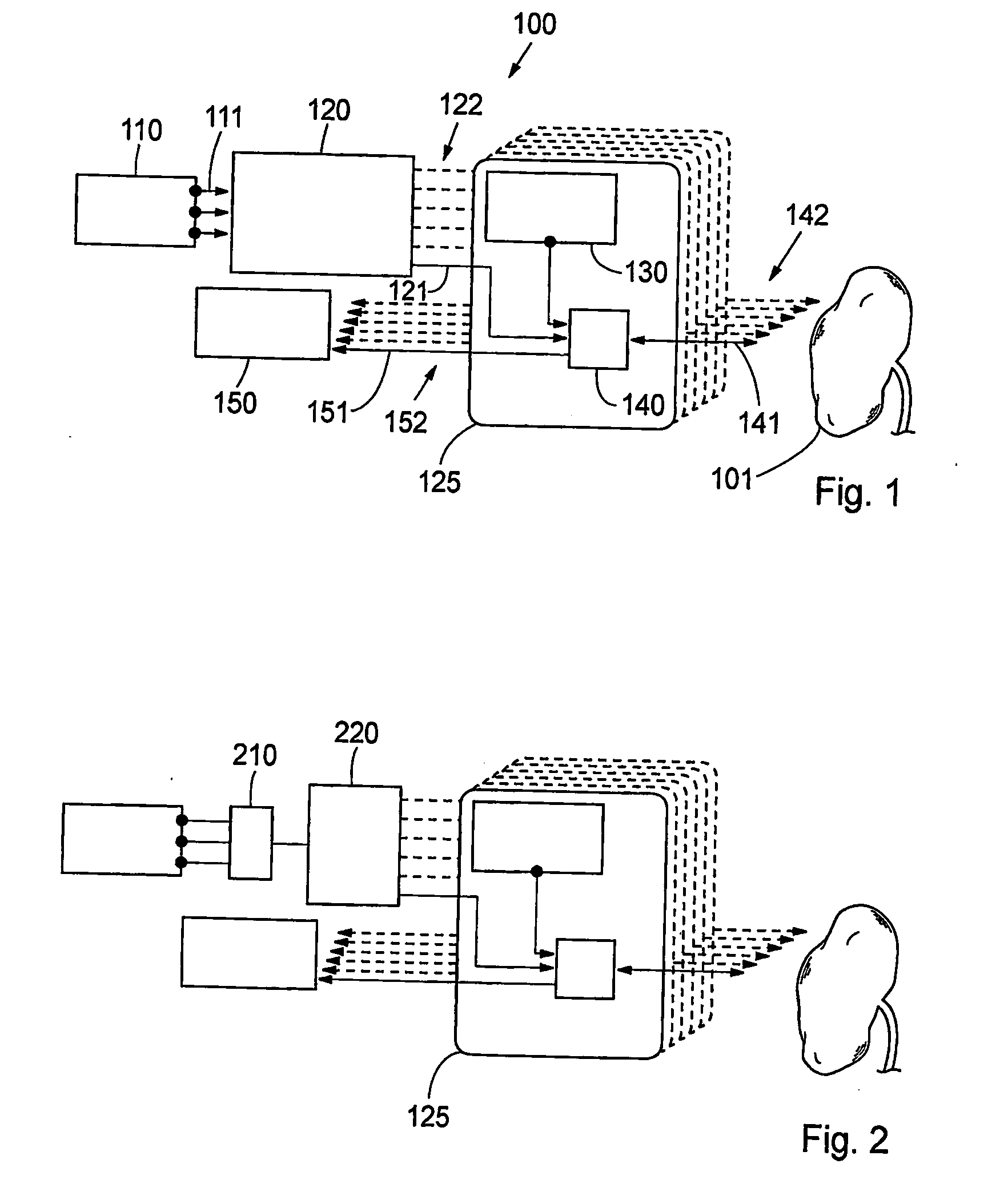
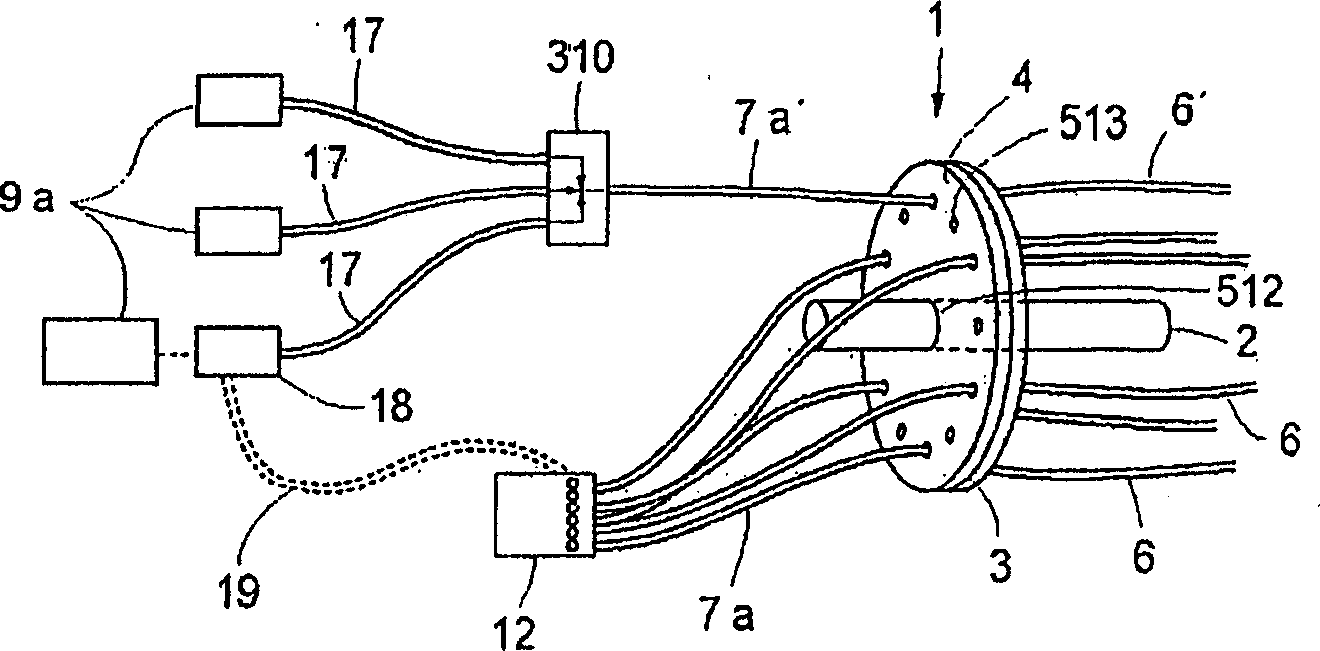
System and method for therapy and diagnosis comprising optical components for distribution of radiation
ActiveUS20070060804A1Fast switching speedCompactness and stabilityHeart defibrillatorsDianostics using fluorescence emissionElectrical conductorOperation mode
A system and method for interactive therapy and diagnosis of a human or animal comprising at least one first radiation source for emission of a diagnostic radiation, at least one second radiation source for emission of a therapeutic radiation, and at least one radiation conductor adapted to conduct radiation to a tumour site at or in said human or animal. A non-mechanical operation mode selector directs the therapeutic radiation and / or the diagnostic radiation to the tumour site through the radiation conductors. The operation mode selector means is preferably a non-mechanical optical switch and / or an optical combiner. The system may be used for interactive interstitial photodynamic tumour therapy.
Owner:SPECTRACURE
Radiotherapy
InactiveUS20130034211A1Excessive leakageReduce complexityX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTherapeutic radiationCollimator
Radiotherapy apparatus is disclosed, comprising a radiation source capable of emitting a beam of therapeutic radiation along a beam axis, collimation apparatus for delimiting the beam and comprising (i) a block of sufficient width to extend across the width of the beam, selectively movable into the beam from a first side of the beam axis, and (ii) an array of individually moveable elongate narrow leaves arranged side-by-side in a direction perpendicular to the beam, each being moveable longitudinally into the beam from a second and opposing side of the beam axis, in which there is no array of individually moveable elongate narrow leaves arranged side-by-side in a direction perpendicular to the beam moveable longitudinally into the beam from the first side of the beam axis. Thus, there is in effect a single bank of MLC leaves on one side of the aperture and a block collimator on the other.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Use of ancillary devices/accessories in radiotherapy systems
ActiveUS10668302B2X-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTherapeutic radiationTherapy radiation
Owner:ELEKTA AB
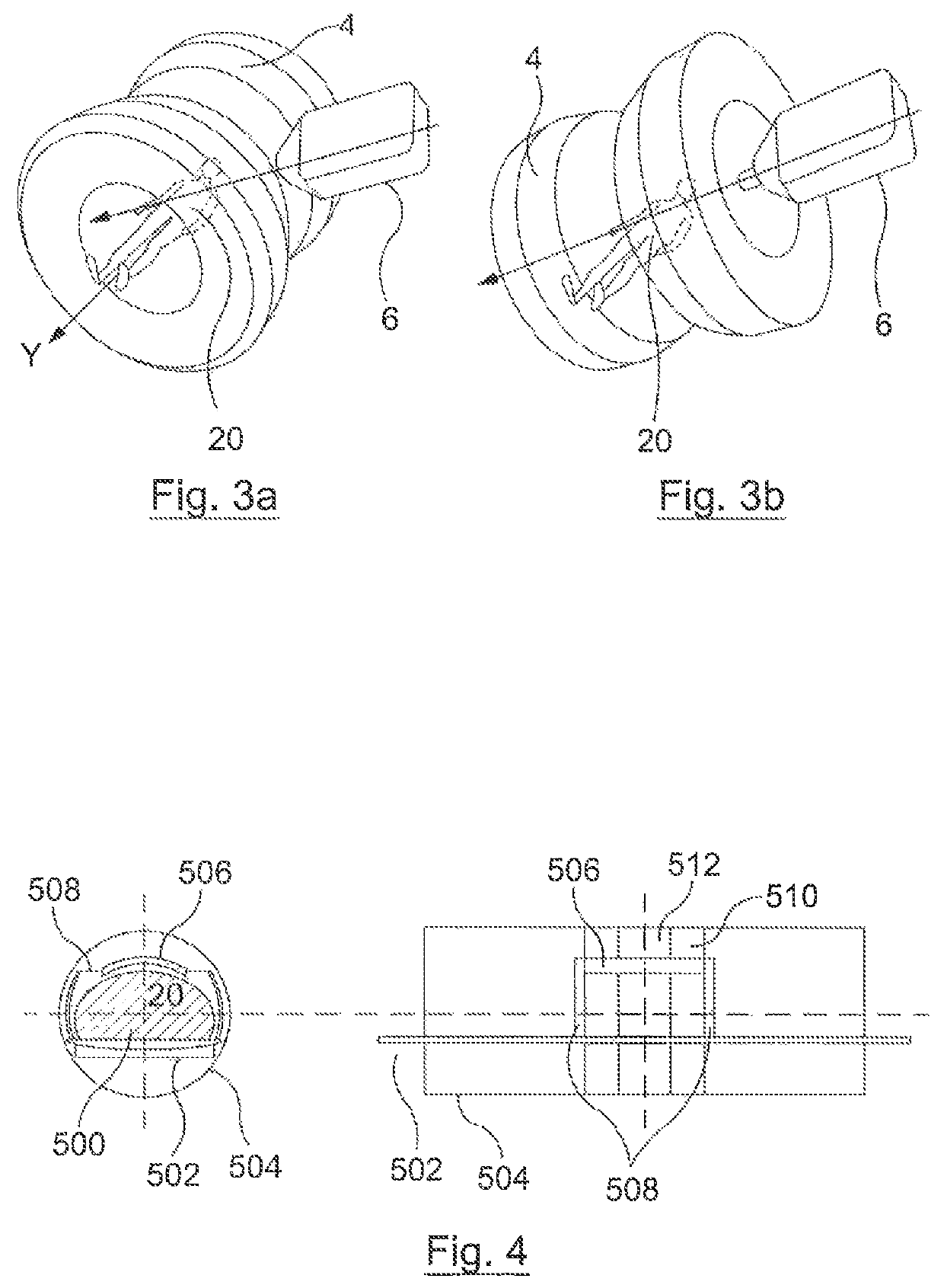
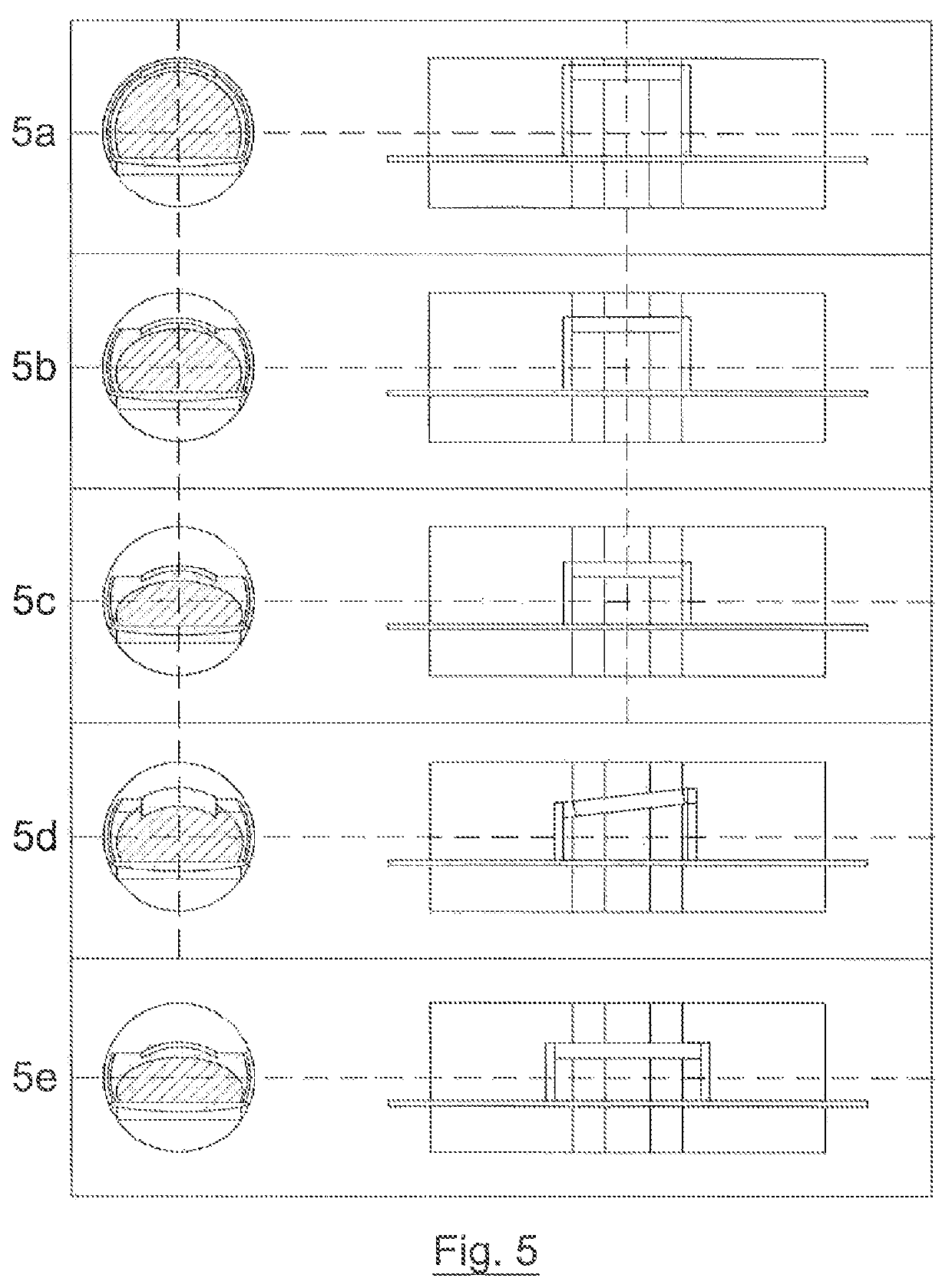
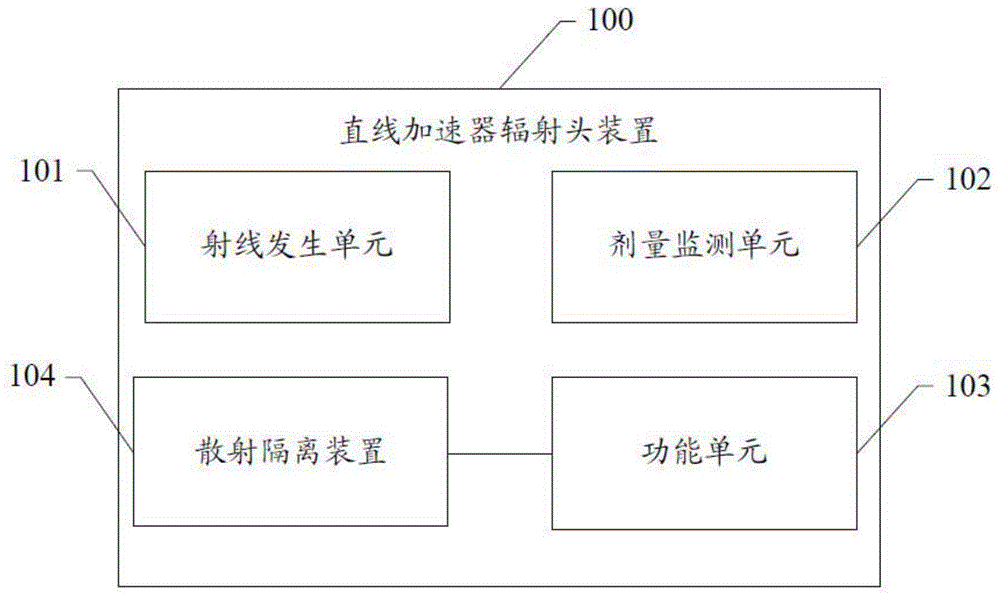
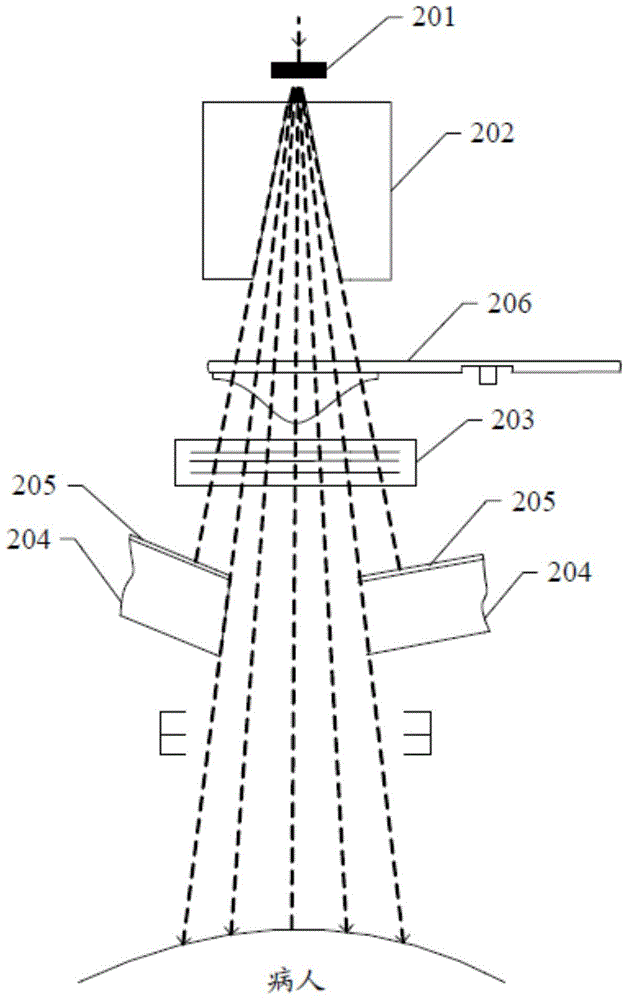
Radiation head device for linear accelerator
ActiveCN104399188AImprove accuracySimple structureLight therapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyScattering functionIonization chamber
A radiation head device for a linear accelerator comprises a ray generation unit, a dose monitoring unit, a function unit and a scattering isolating unit, wherein the ray generation unit is suitable for generating and emitting therapy radiation beam; the dose monitoring unit is used for measuring a dose of the radiation beam emitted by the ray generation unit in real time; the function unit is used for achieving at least one function of beam limiting, intensity modulation, flattening, shielding or filtering; the scattering isolating unit is covered on the outer surface of the function unit and is used for isolating the influences of scattering particles on radiation beam dose measurement in the dose monitoring unit, and the scattering particles are generated by a scattering function of the function unit on the radiation beam. By means of the above technical scheme, the accuracy of dose monitoring of an ionization chamber can be effectively improved, the structure is simple and convenience and practicality are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
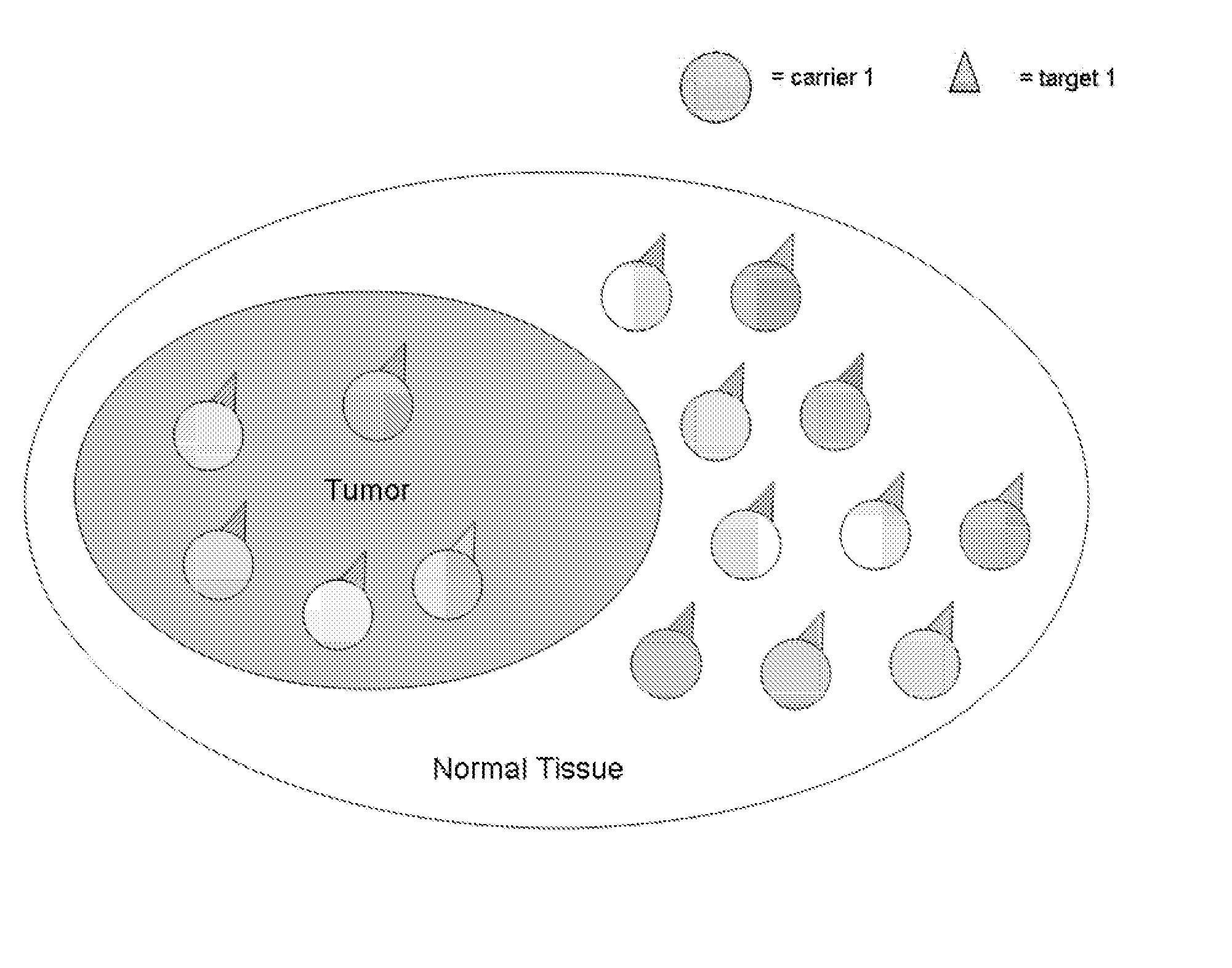
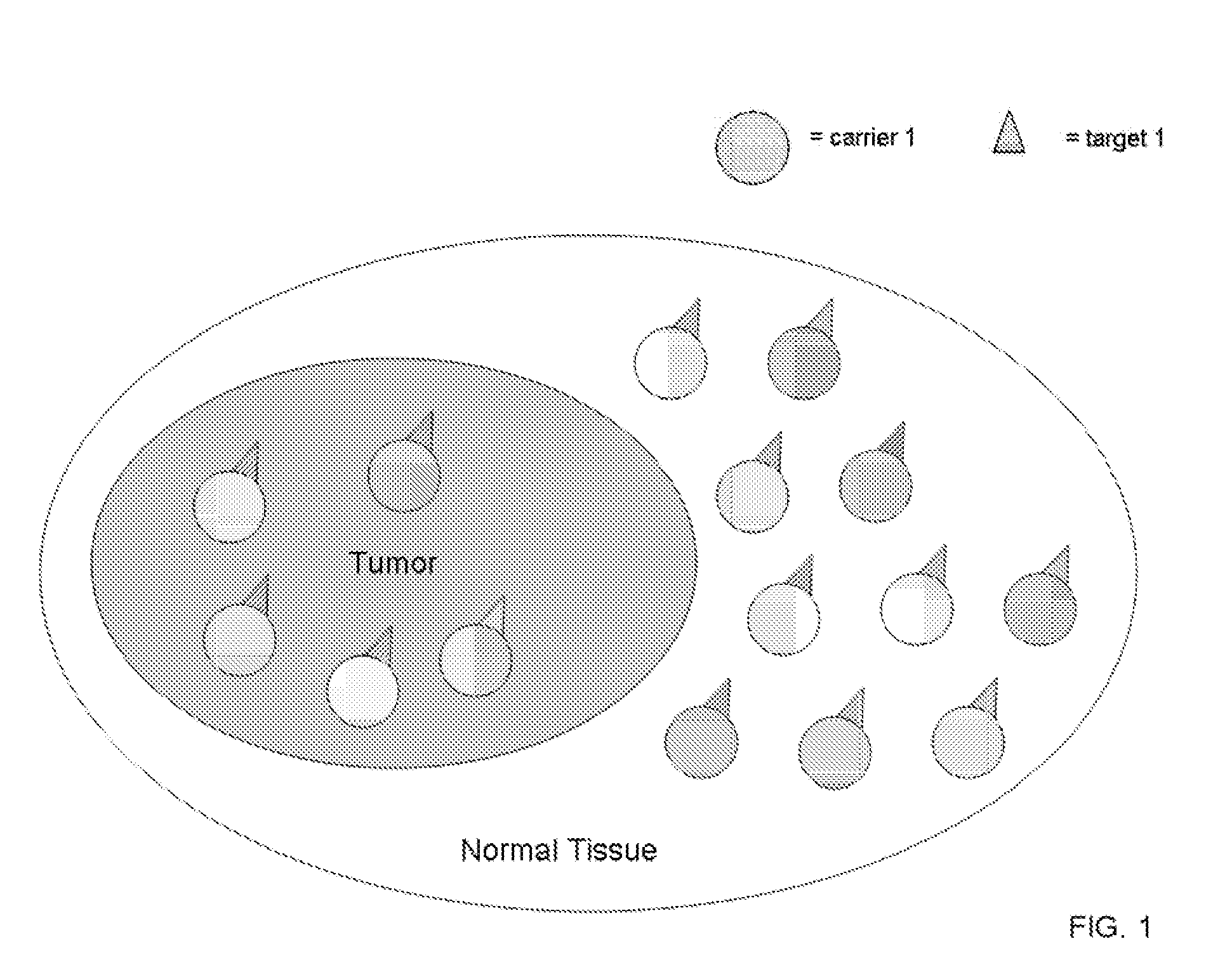
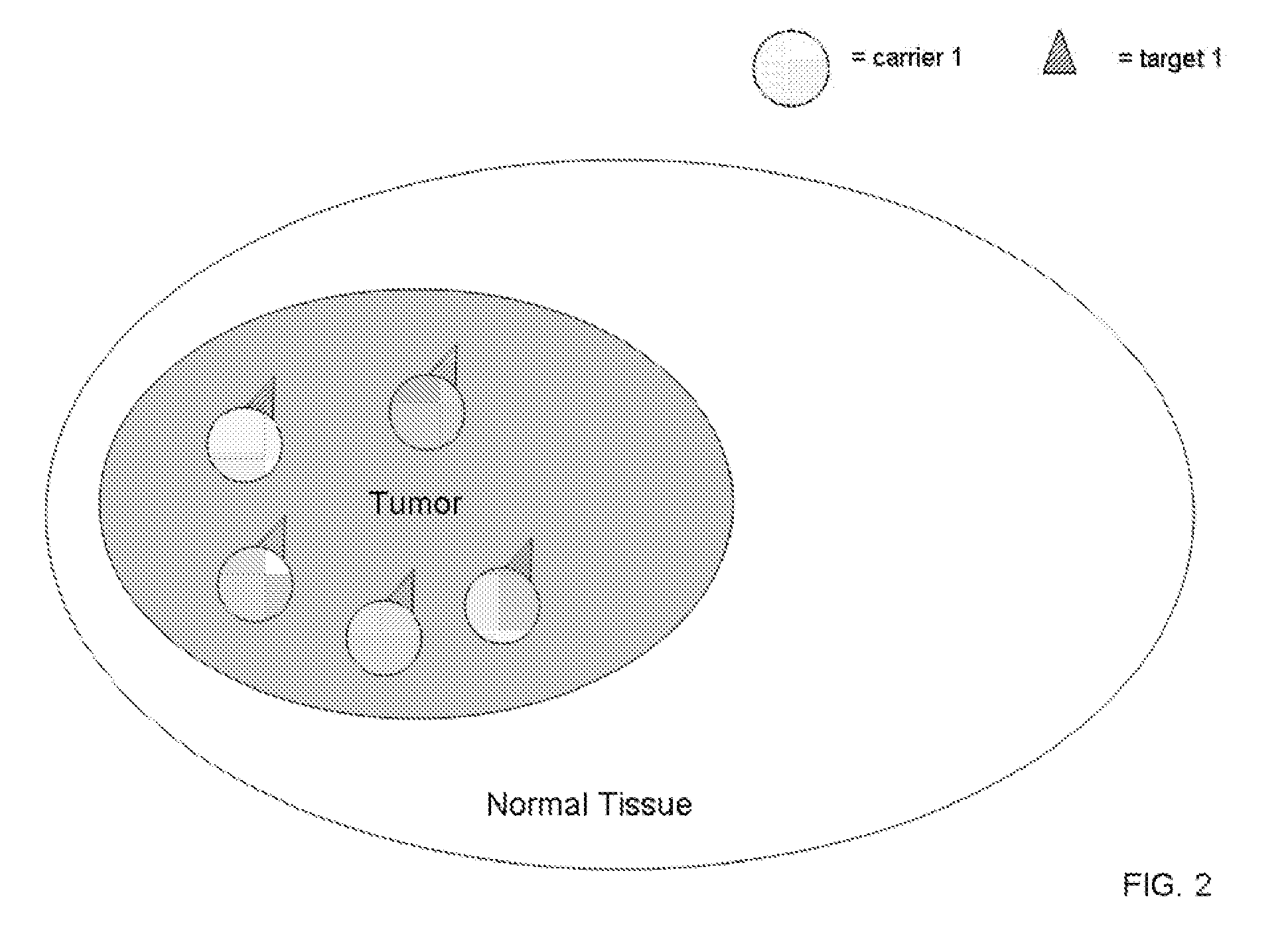
Coupled Carriers for Enhancing Therapy
InactiveUS20070280418A1Promote absorptionFacilitate depositionRadioactive preparation carriersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAbnormal tissue growthSide effect
Radiation has been used for many years to treat cancer patients. In the case of ionizing electromagnetic radiation, the incidental, extra dose to tissues surrounding the tumor is significant. The aim of this invention is to provide compounds and methods to enhance the absorbed radiation dose ratio, or other therapeutic compounds, in tumors verses normal tissue. The system concentrates contrast agents with high atomic number elements preferentially at the site of the tumor prior to administering radiotherapy, or preferentially concentrates other therapeutic compounds in the abnormal region. The agents are concentrated in a pathologic lesion following systemic or direct administration. Interaction of the ionizing radiation with the coupled compounds of this invention results in a significantly higher radiation dose to the tumor compared to surrounding tissues. The result is greater therapeutic efficacy with fewer side effects following treatment with low-energy radiation, or other agents. These compounds permit diagnostic uses in combination with the therapeutic use.
Owner:SIRIUS MEDICINE
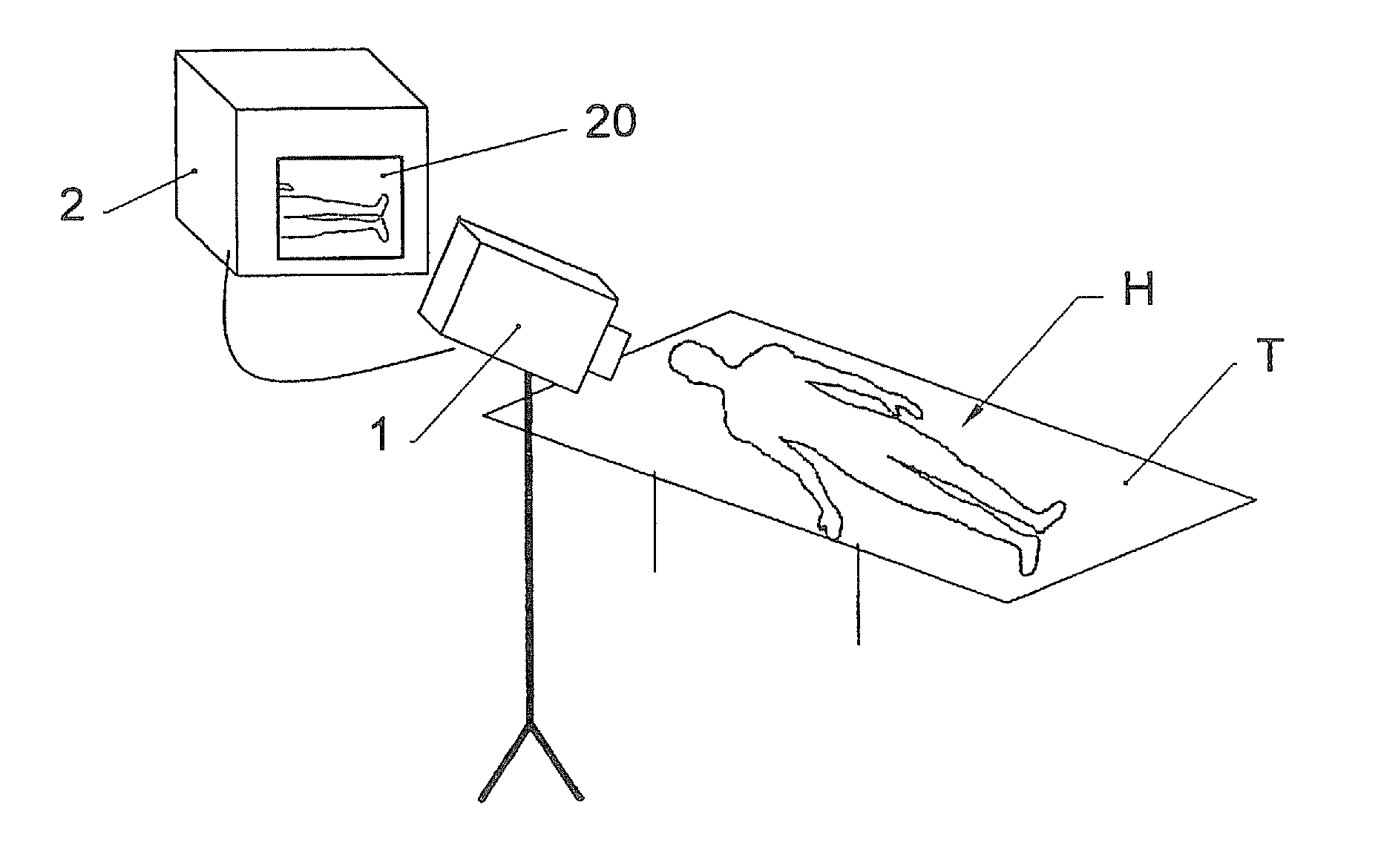
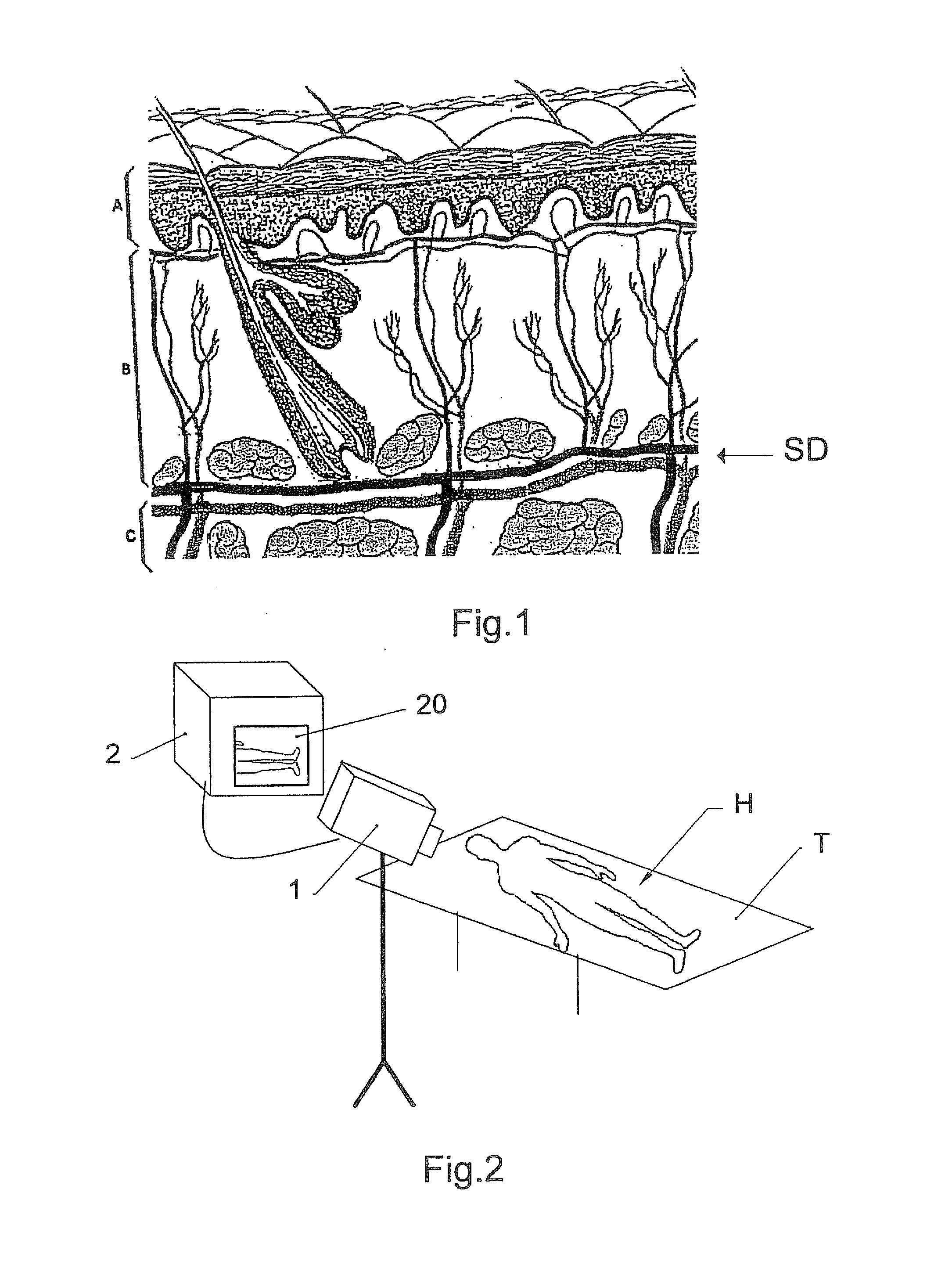
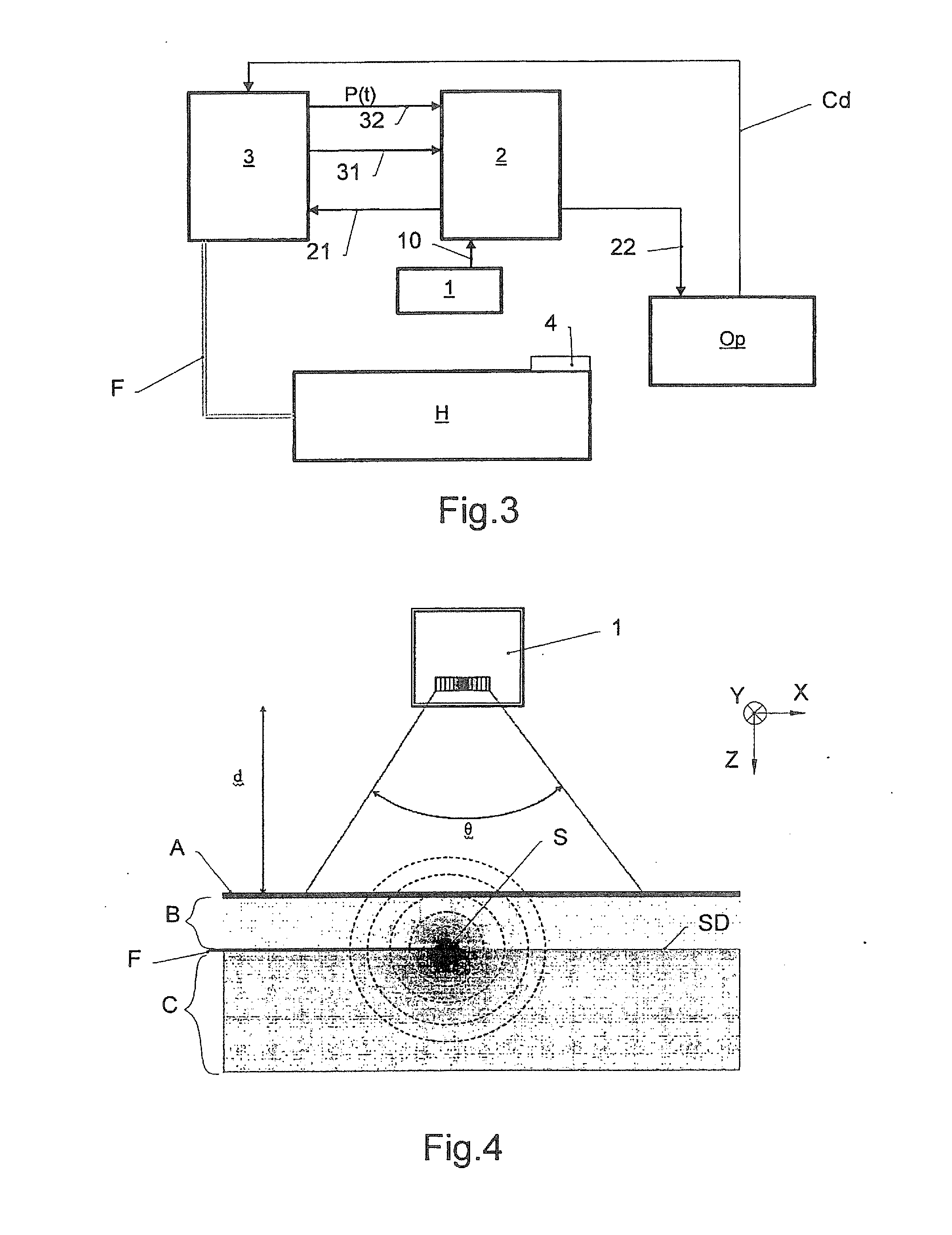
Method and control system for a treatment by subcutaneous or intracutaneous irradiation by means of electromagnetic radiation
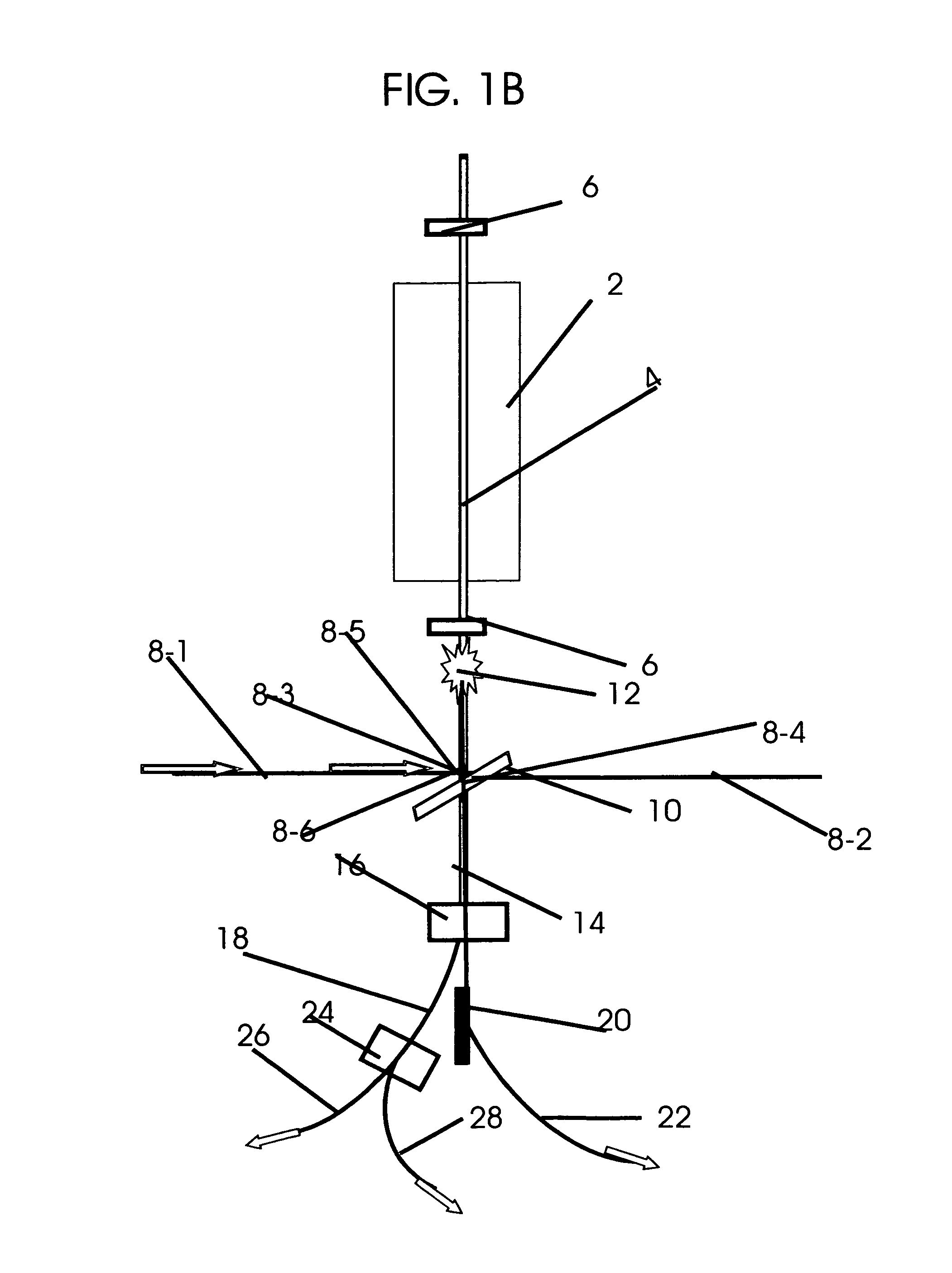
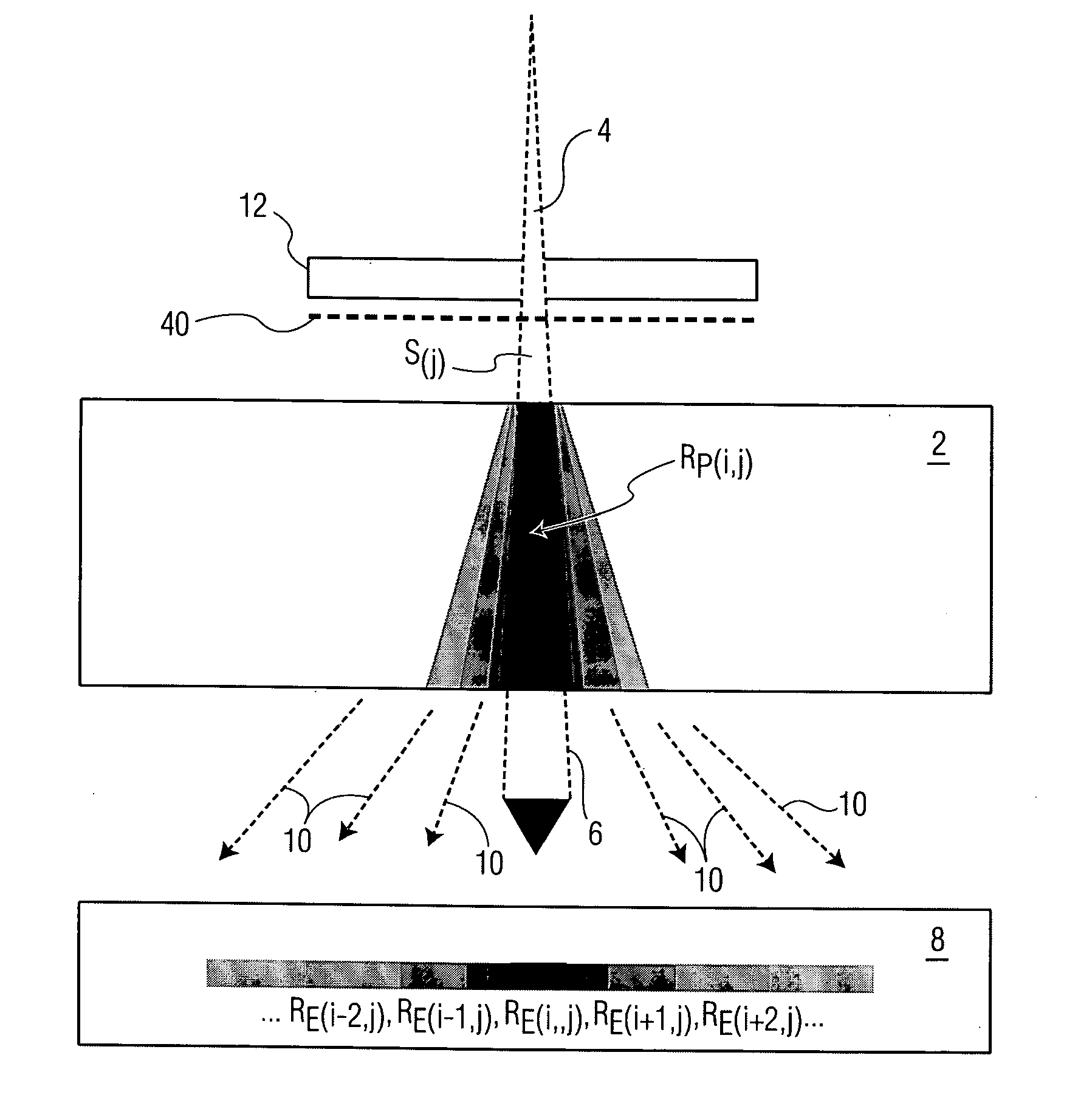
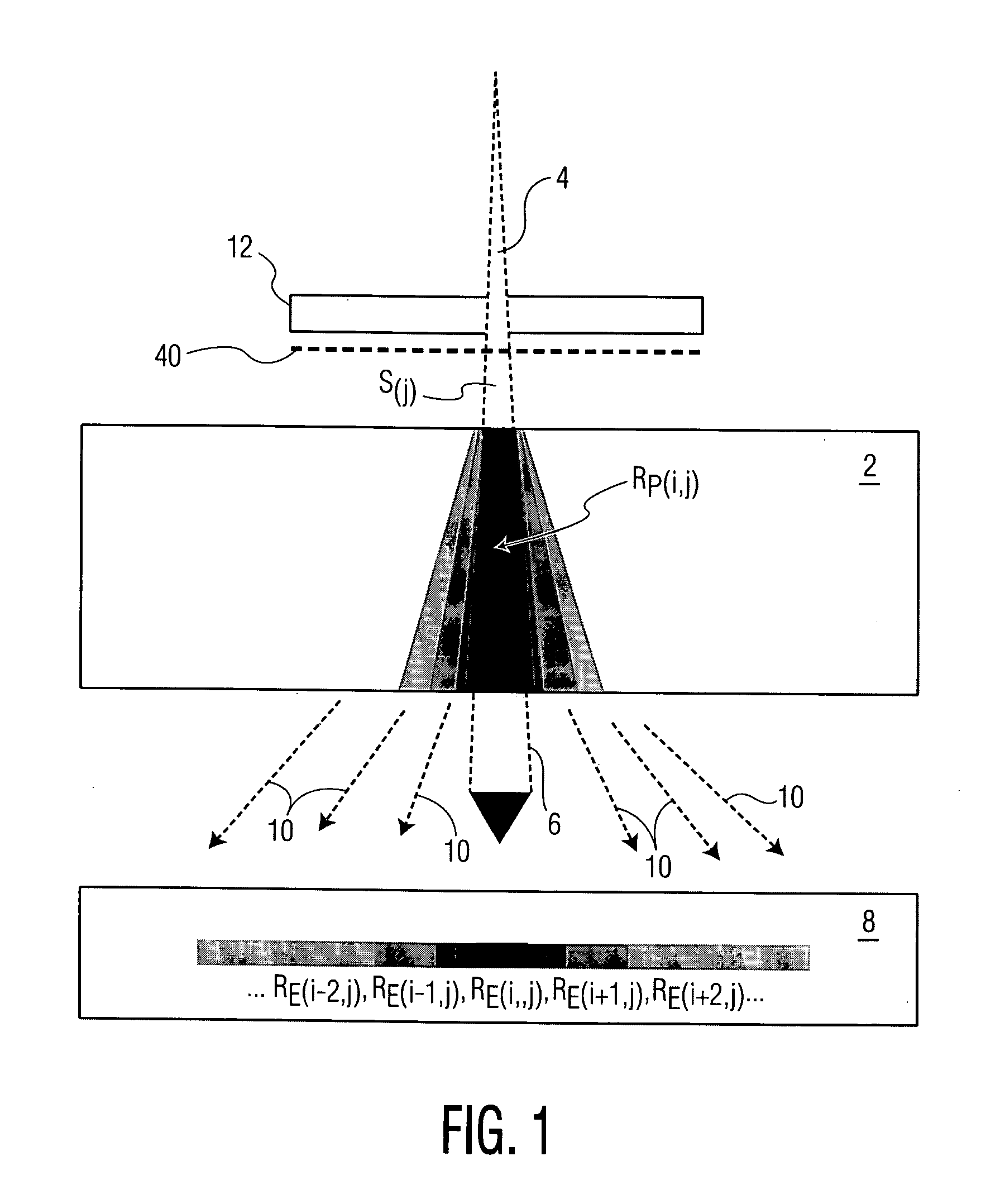
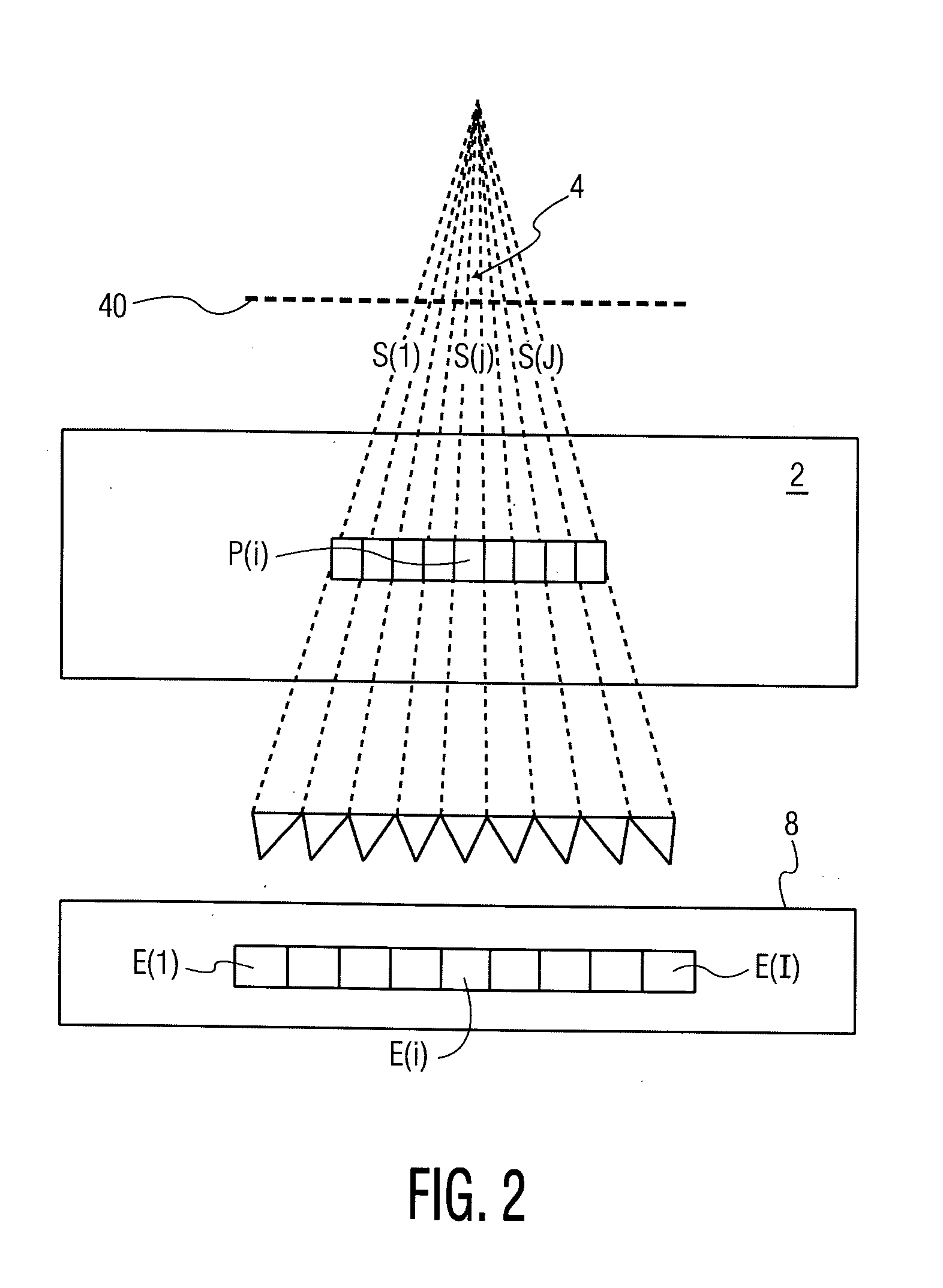
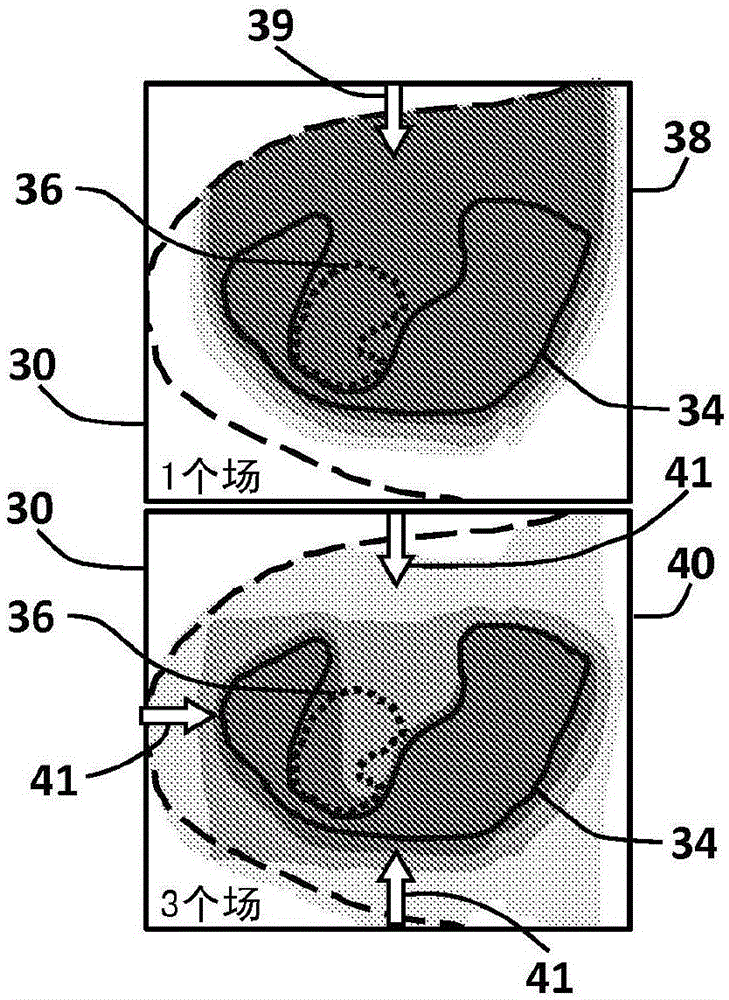
InactiveUS20110319971A1Limited supplyEfficiently obtainedDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsAutomatic controlControl system
To automatically control a treatment during which subcutaneous or intracutaneous irradiation by means of electromagnetic treatment radiation and possibly targeted electromagnetic radiation is carried out, the following steps are implemented: acquisition of several successive images l(t) of the treated zone by means of an external sensor (1), which is sensitive to the wavelength or the range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic treatment radiation or of the targeted electromagnetic radiation, the time interval (τ) between two successive images [l(t−1); l(t)] being known, detection and localisation in each image l(t) of a light spot p(t) corresponding to the irradiation spot (S) of the electromagnetic treatment radiation or the targeted electromagnetic radiation, calculation for each light spot p(t) of at least one of the following parameters: the energy [eij(t) or Eij(t)] supplied from the power P(t) of the electromagnetic treatment radiation and the time interval (τ) between two successive images [l(t−1); l(t)]; the displacement speed v(t) of the irradiation spot (S) from the positions of two light spots [p(t−1); p(t)] in two different images [l(t−1); l(t)] and the time interval between these two images [l(t−1); l(t)].
Owner:OSYRIS MEDICAL
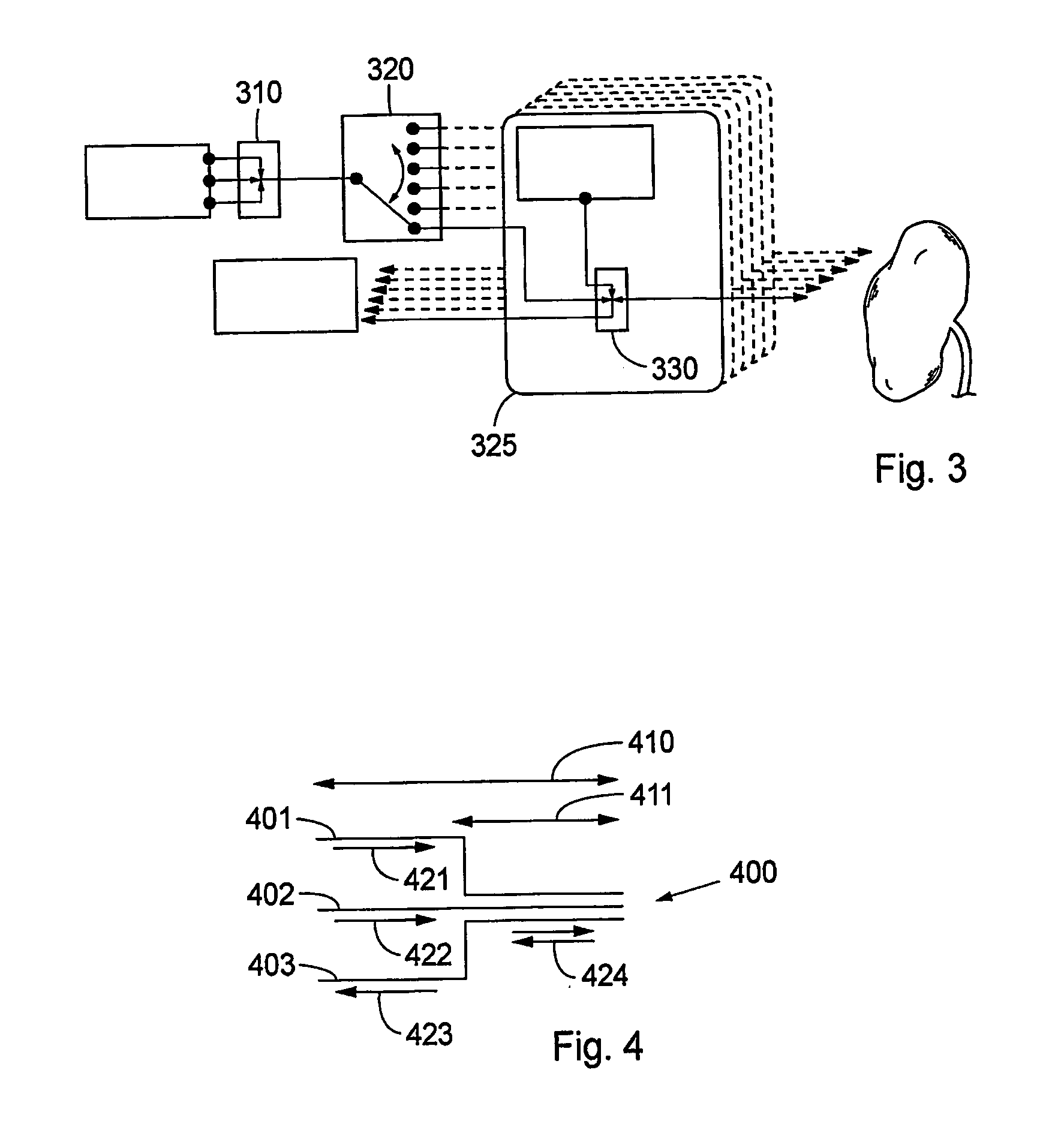
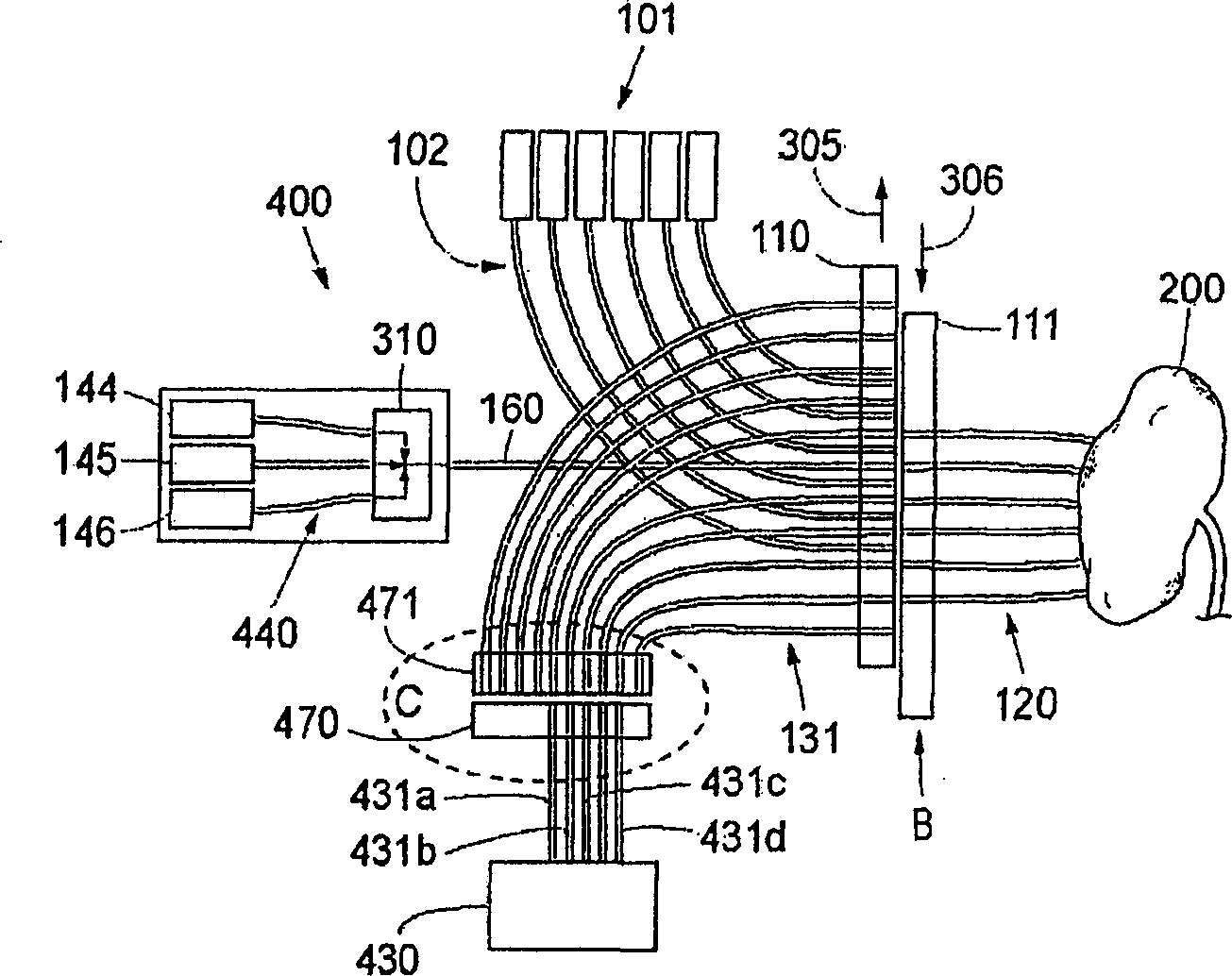
System and method for therapy and diagnosis comprising in combination non-mechanical and mechanical distributors for distribution of radiation
ActiveCN1787776AFast switching speedImprove compactnessDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionOptical radiationMedicine
A system and method for interactive interstitial photo-dynamic tumour therapy and / or photothermal tumour therapy of a human or animal, said system comprising at least one radiation distributor, which is arranged for distribution of optical radiation from at least one radiation source to a reaction site, or from the reaction site to at least one radiation sensor. The radiation distributor comprises at least one translatory displacement element being translatory movable relatively to another element. First ends of first radiation conductors are fixed to the first translatory displacement element and first ends of second radiation conductors are fixed to the other element, wherein the first and the second radiation conductors are connectable to each other in different constellations through translatory movement of the translatory displacement element and the other element relative each other in order to obtain different operation modes of said system.
Owner:SPECTRACURE
Radiation therapy apparatus
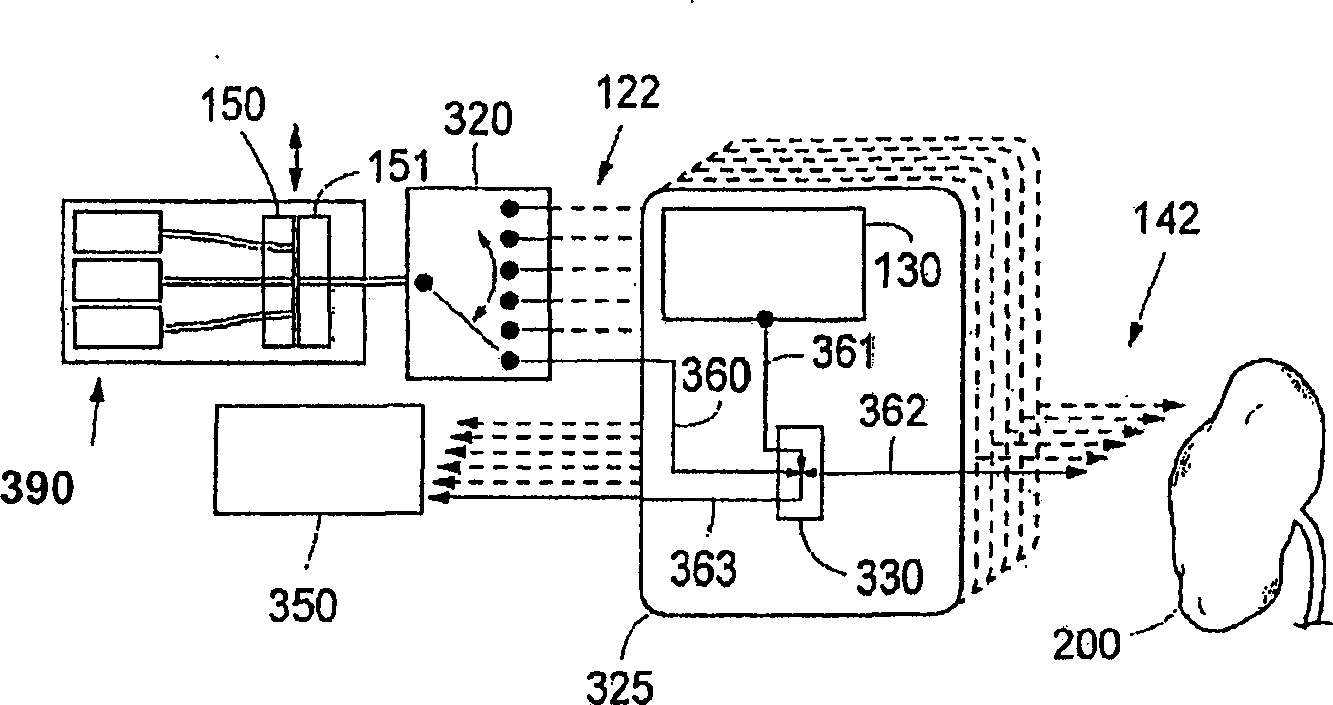
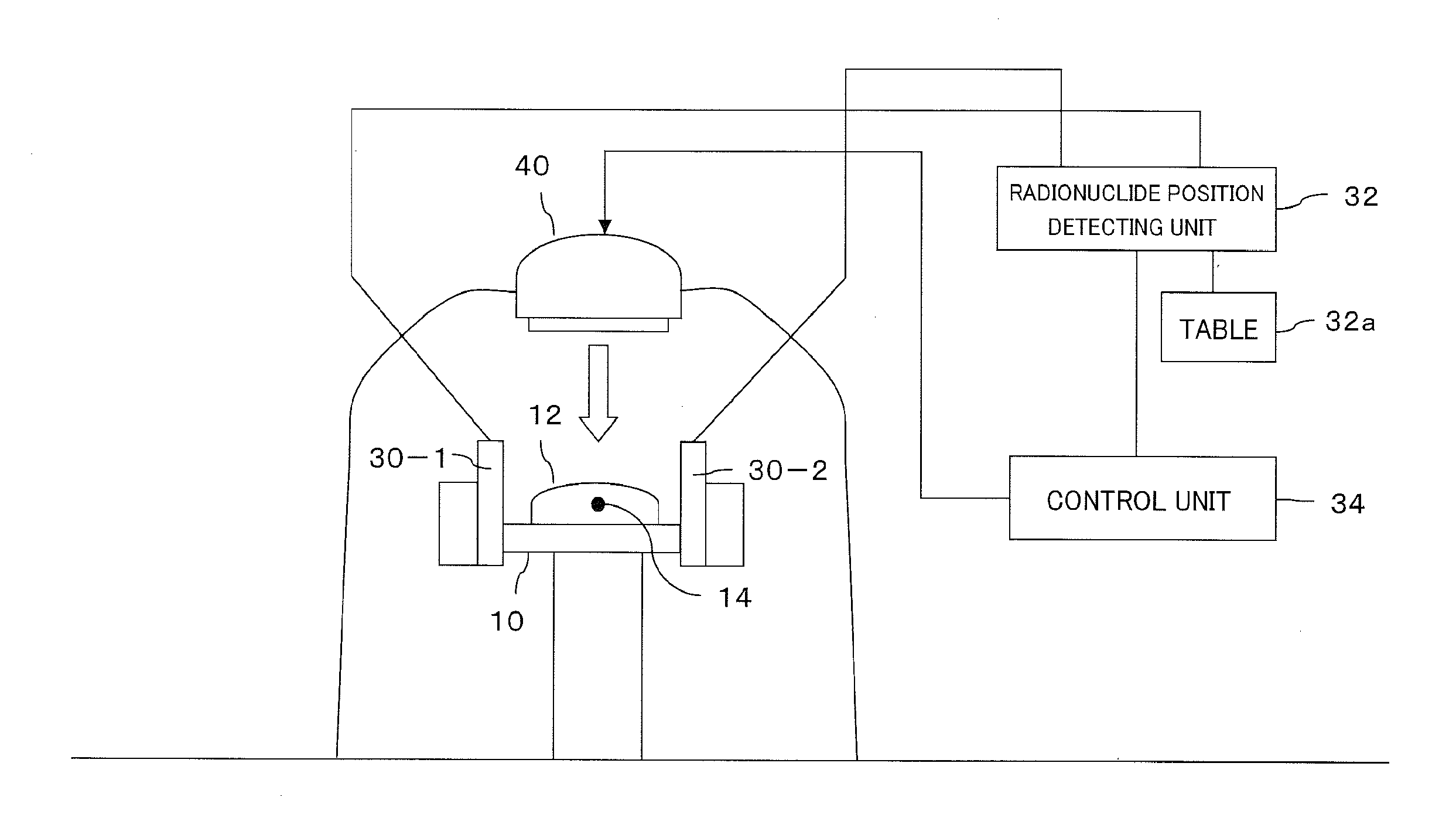
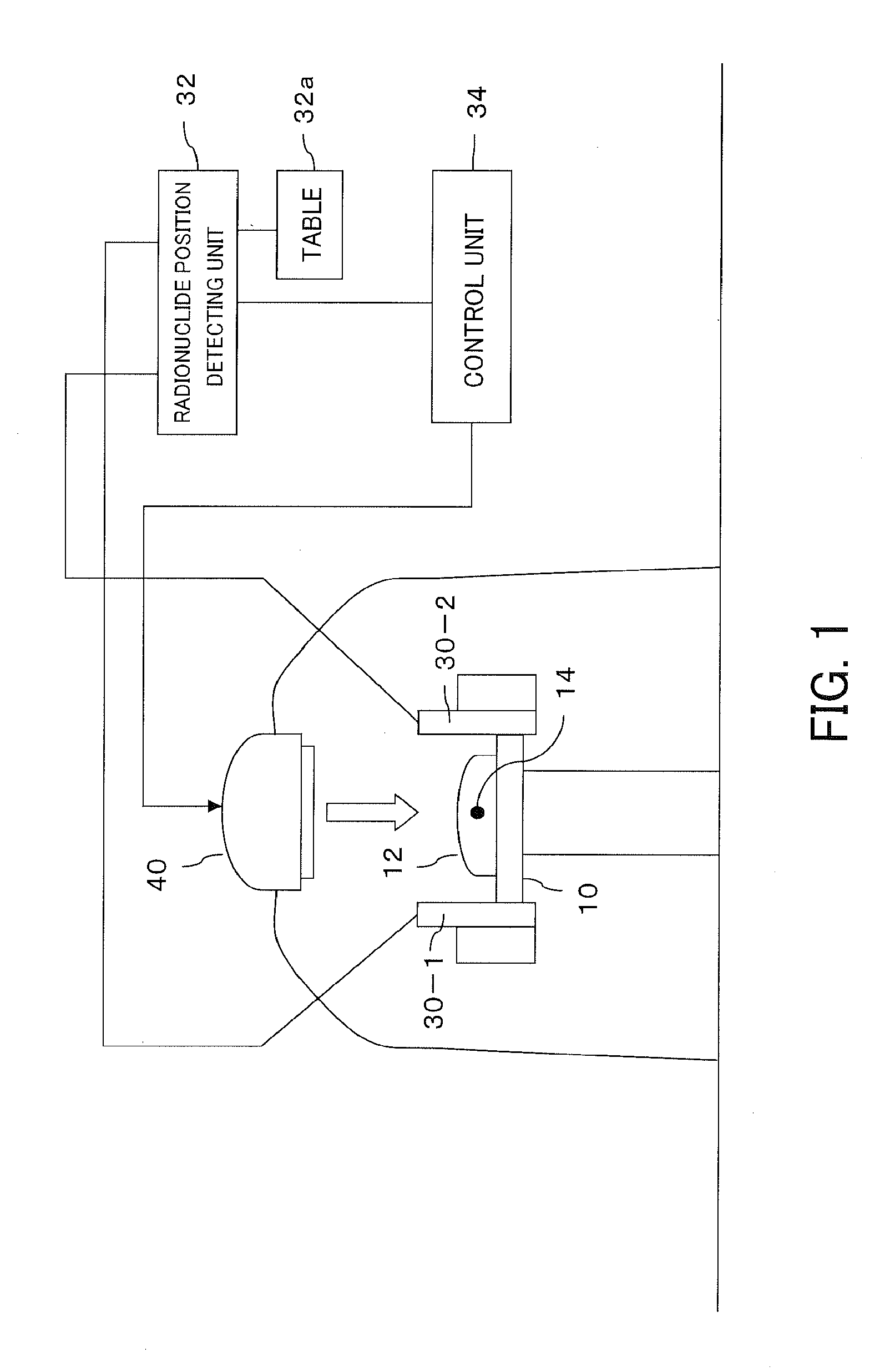
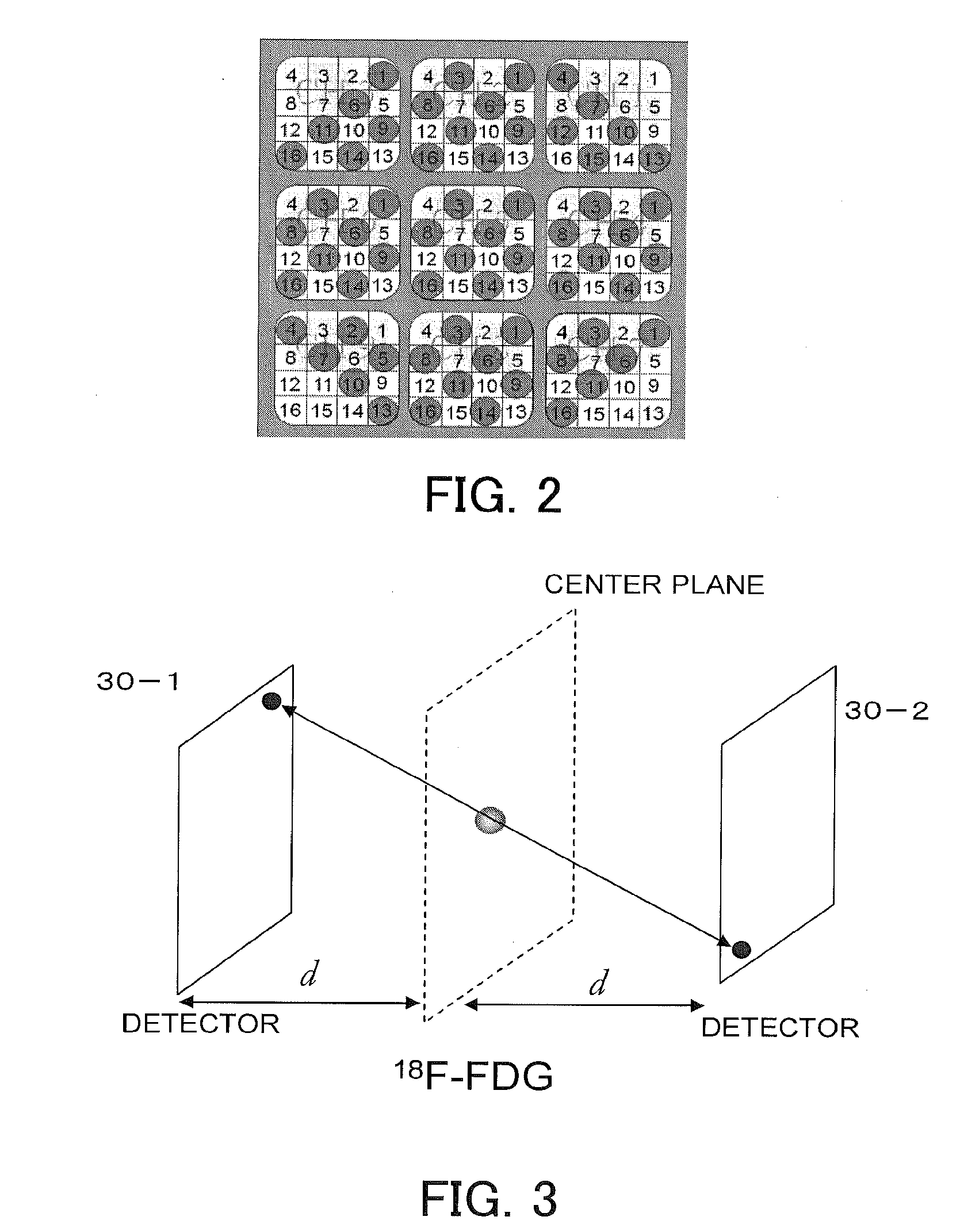
ActiveUS20120006990A1Image analysisRadiation diagnostic image/data processingBiological bodyTherapy radiation
An organism is irradiated with therapeutic radiation from a radiation irradiation device. A pair of two-dimensional radiation detectors are arranged so as to face one another with the irradiated therapeutic radiation passing therebetween, and detect the two-dimensional positions irradiated by a pair of annihilation γ rays produced when a positron emitted from a positron-emitting radionuclide is annihilated. On the basis of a pair of positions detected by the pair of two-dimensional radiation detectors, a radionuclide position detecting unit detects the position of the positron-emitting radionuclide, and the radiation irradiation device irradiates the position of the positron-emitting radionuclide with therapeutic radiation.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com