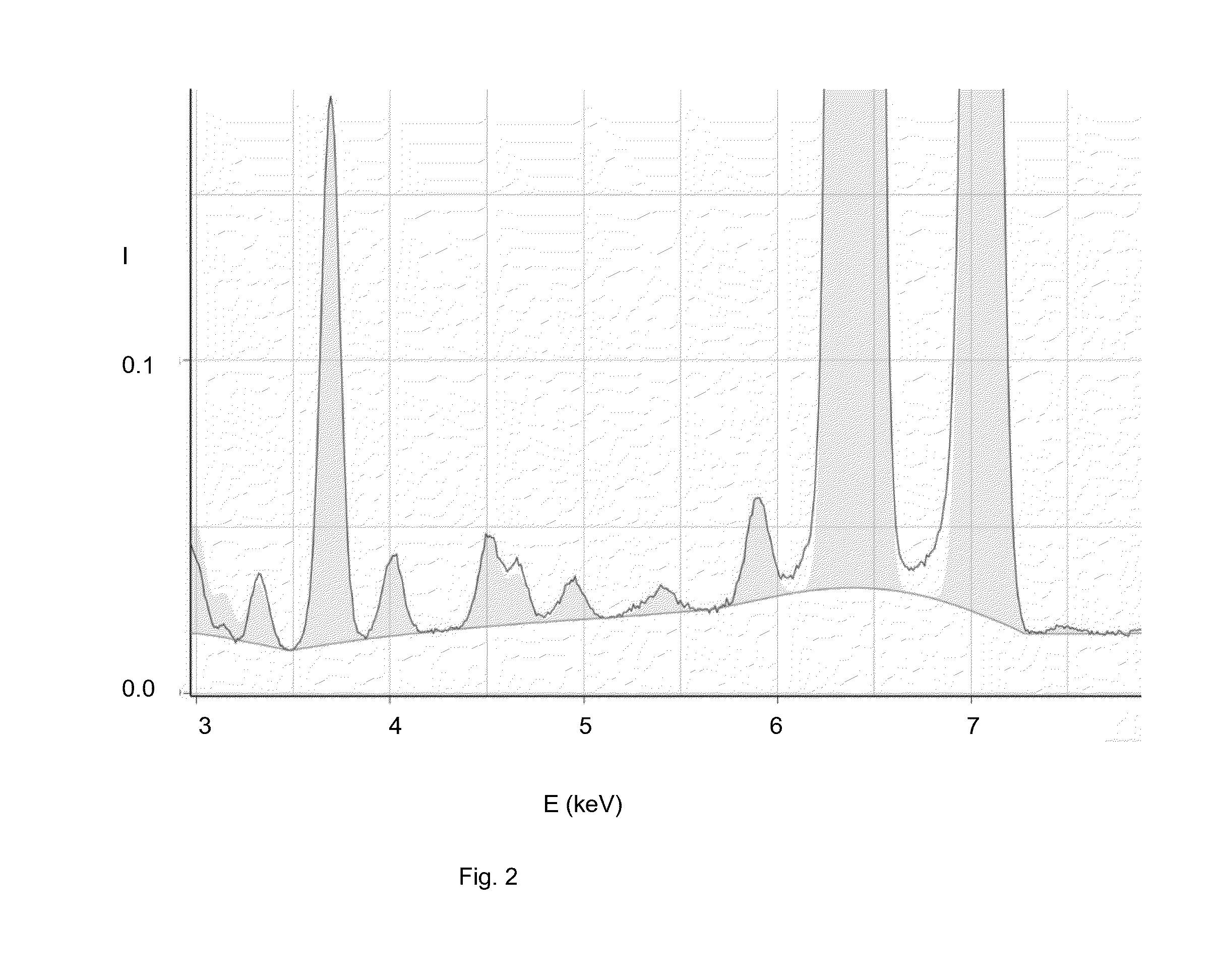
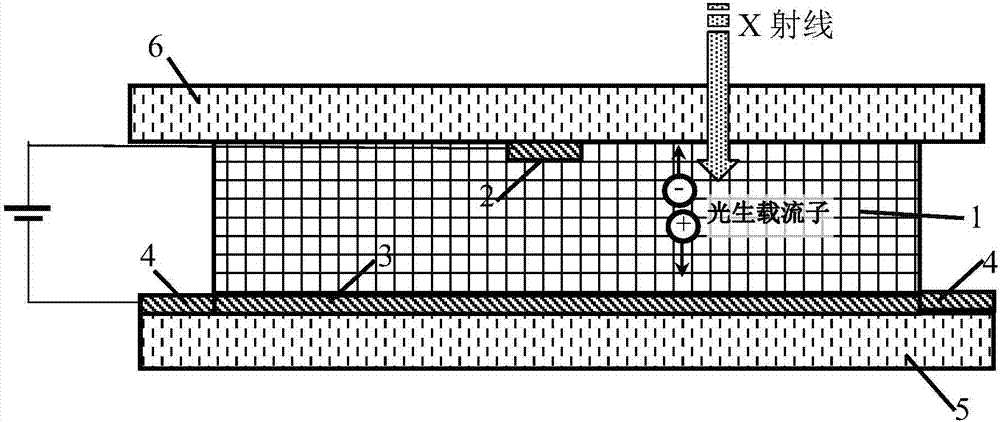
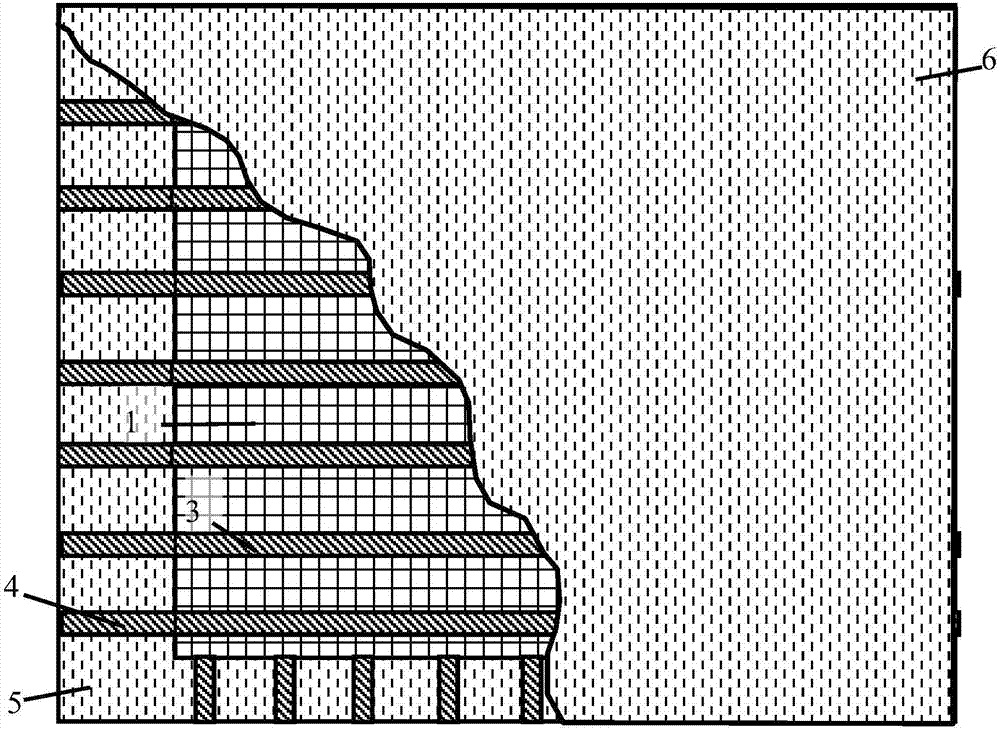
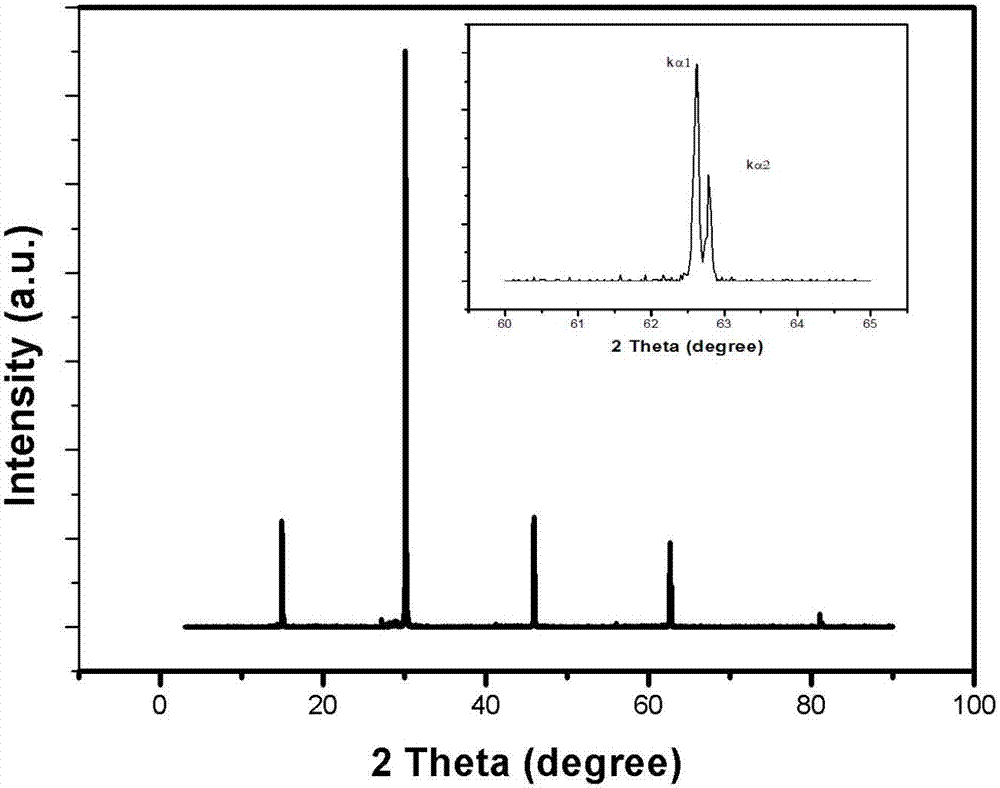
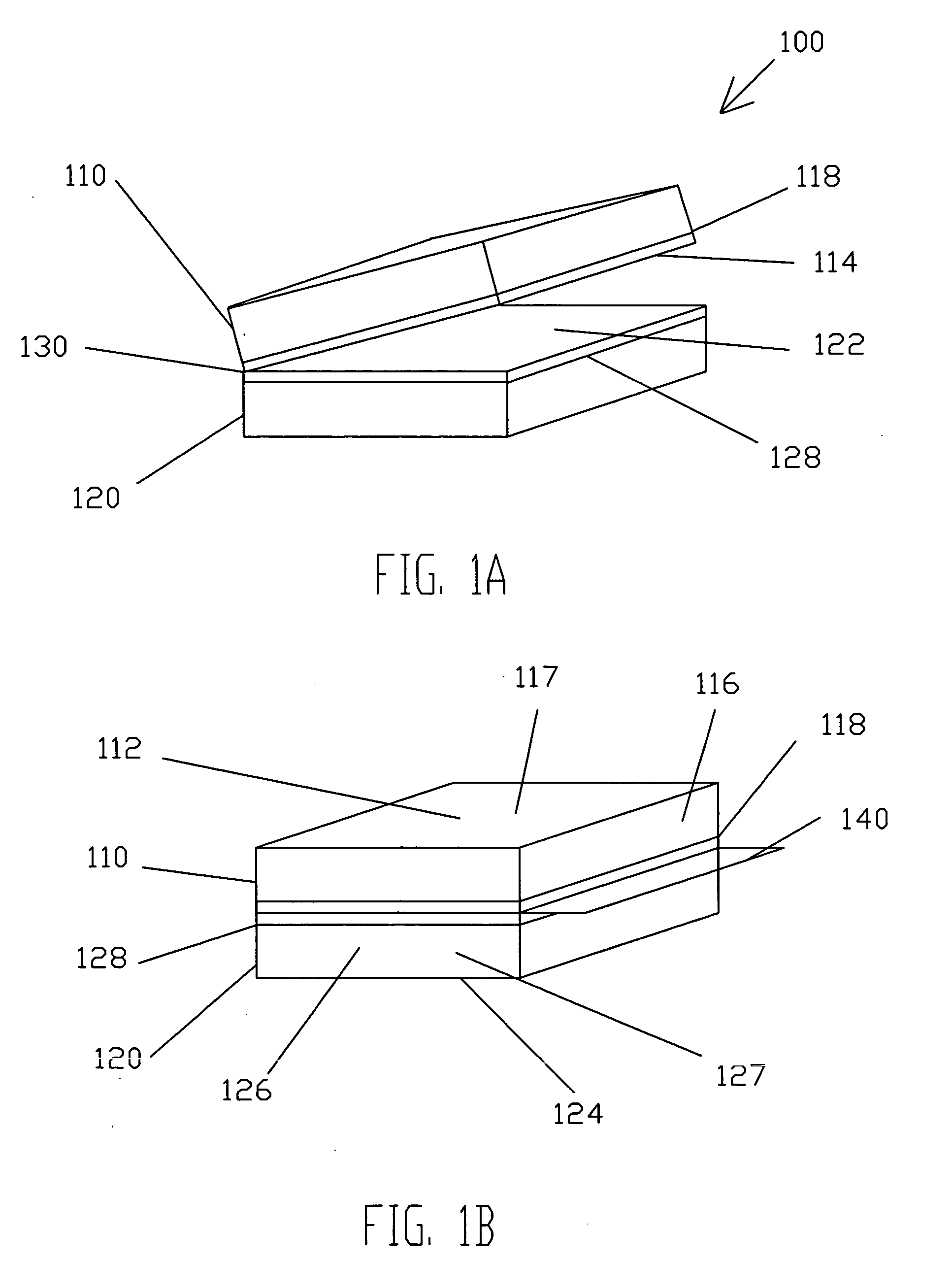
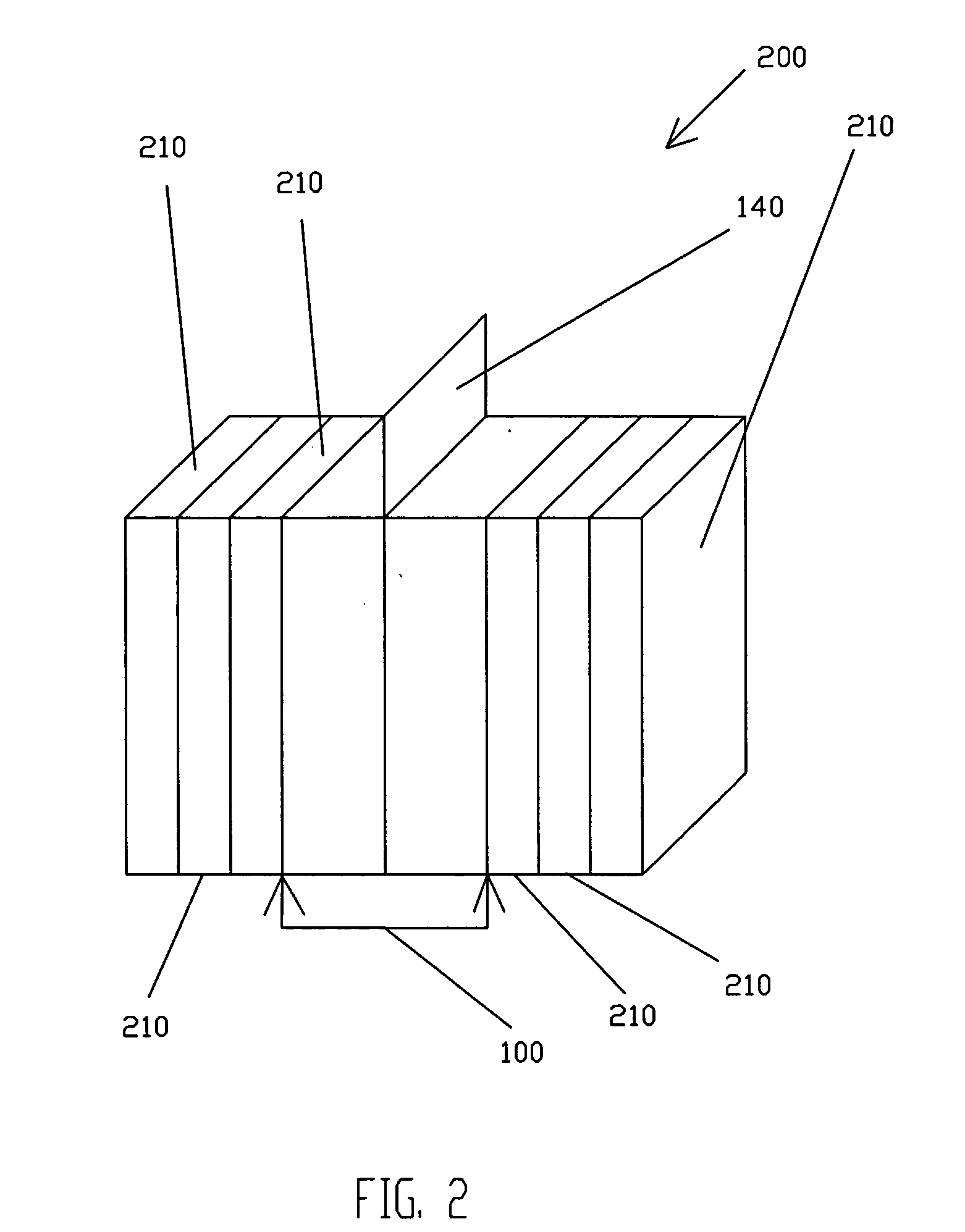
Patents
Literature
92 results about "High atomic number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Uranium (atomic number=92) is the element with the highest atomic number found in significant quantities on earth or elsewhere. The elements astatine (atomic number=85) and francium (atomic number=87), along with all the other known elements (up to atomic number 109) were discovered when first made artificially;
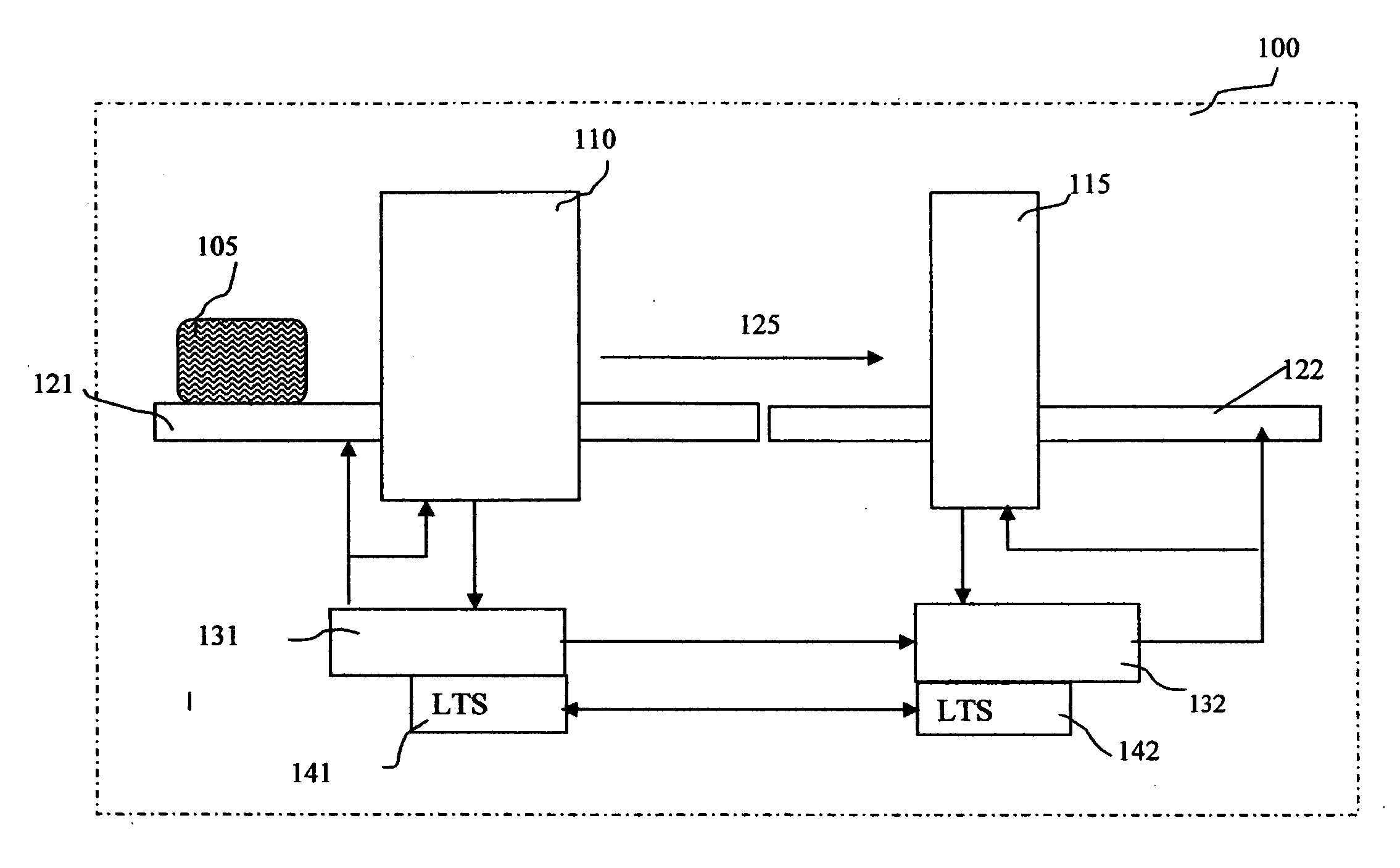
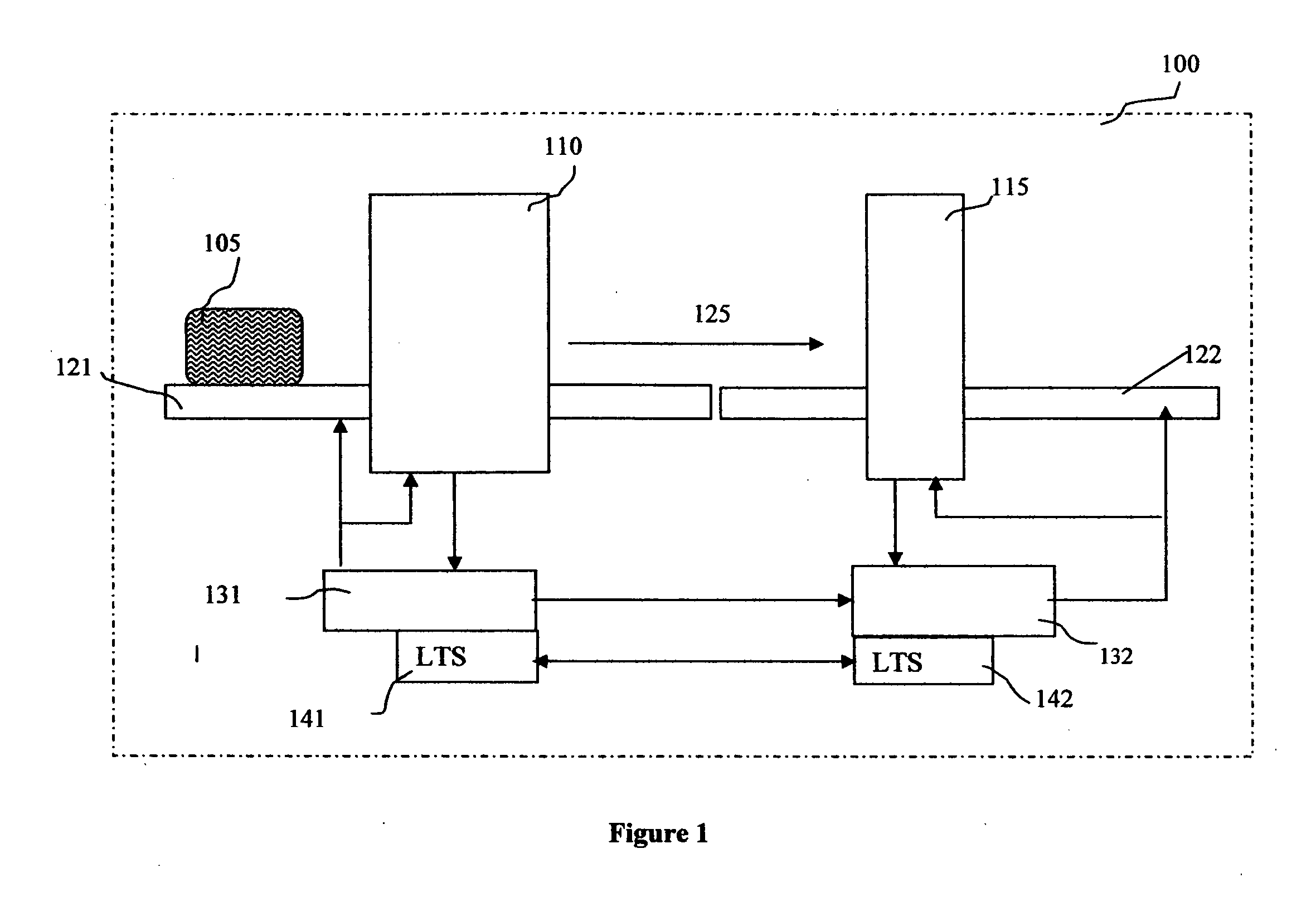
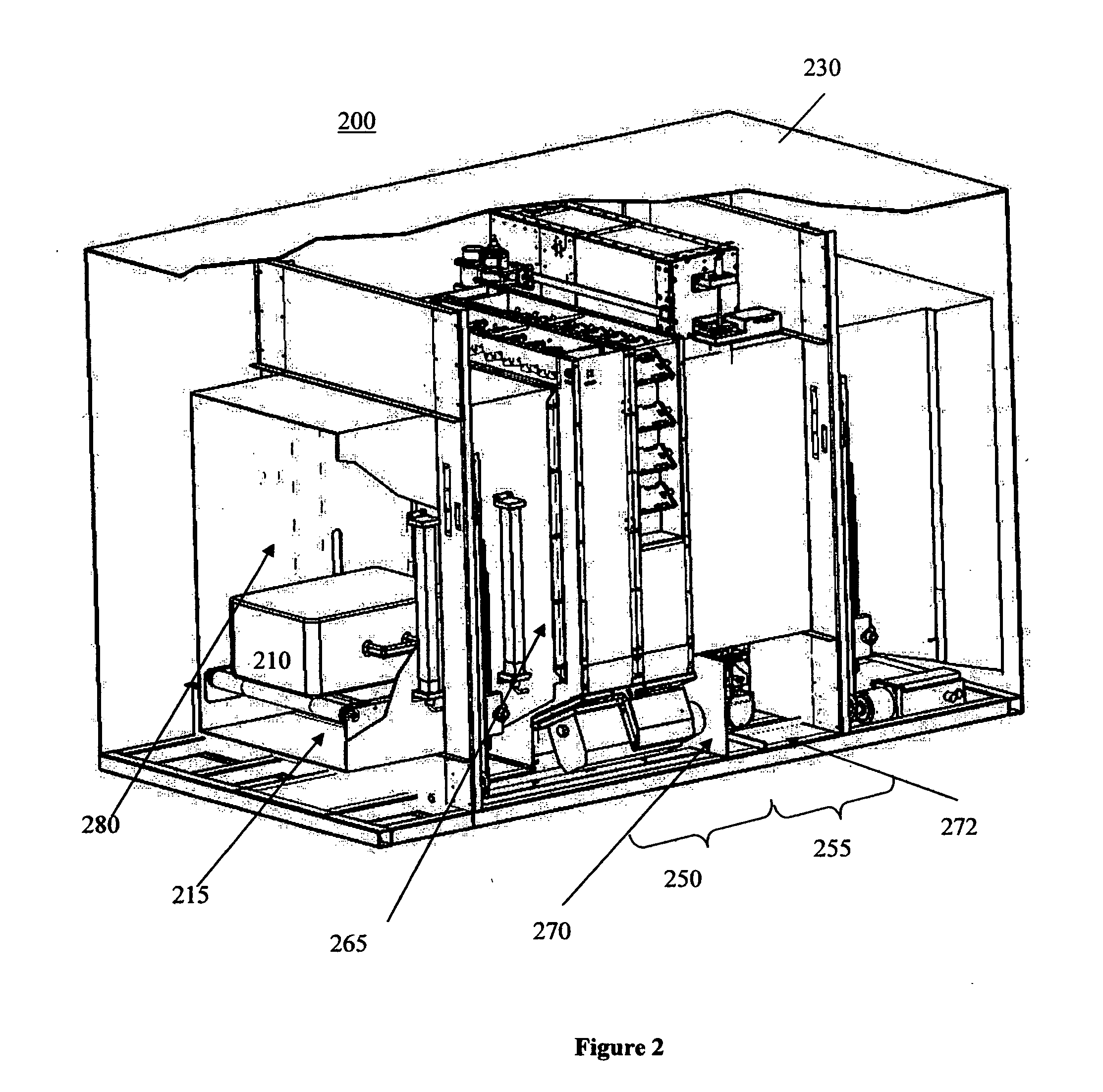
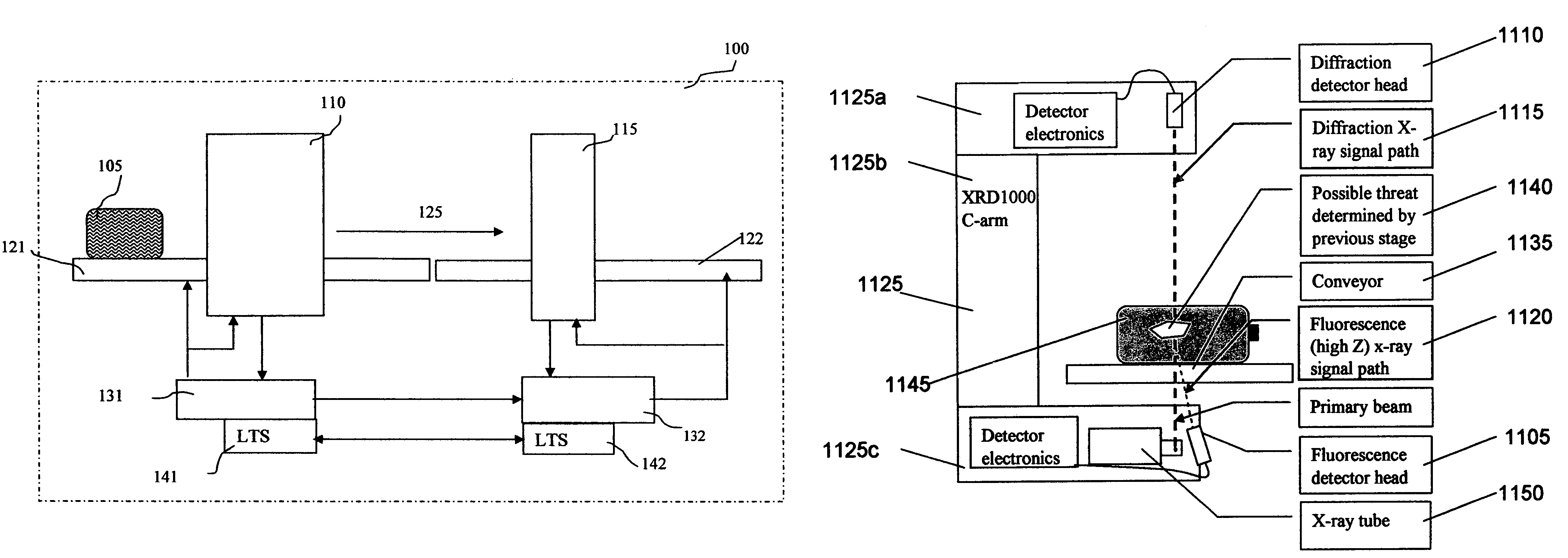
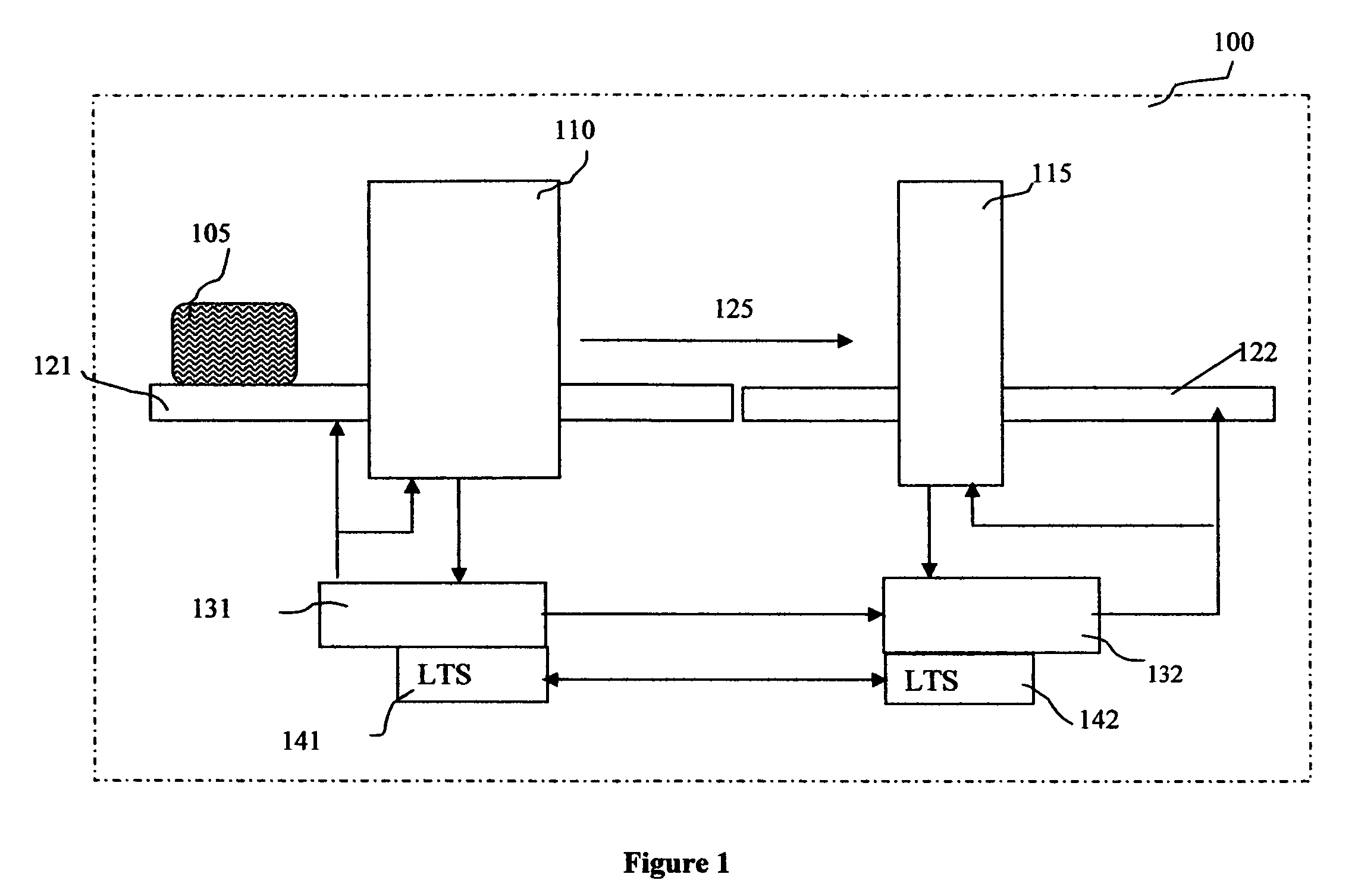
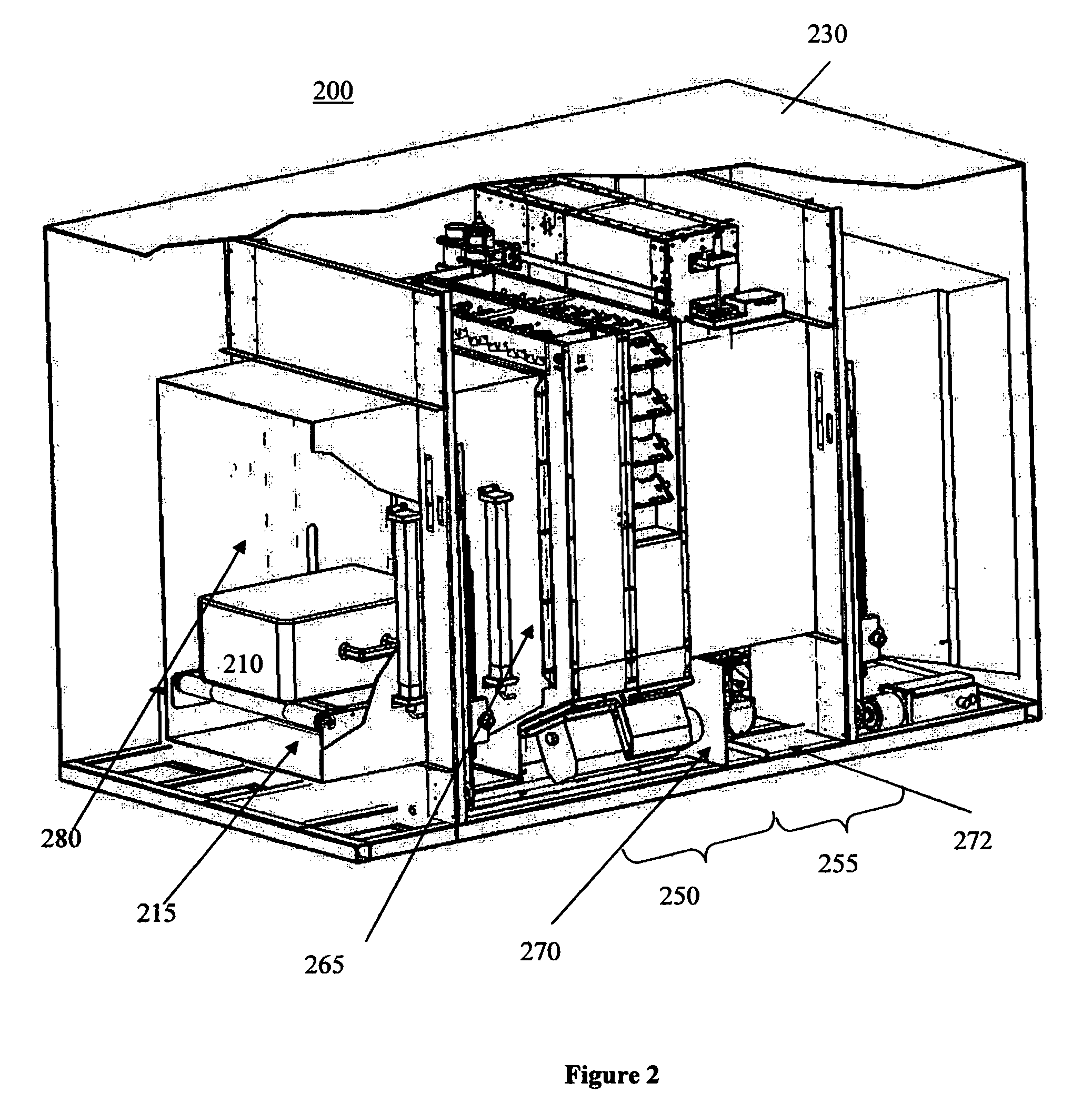
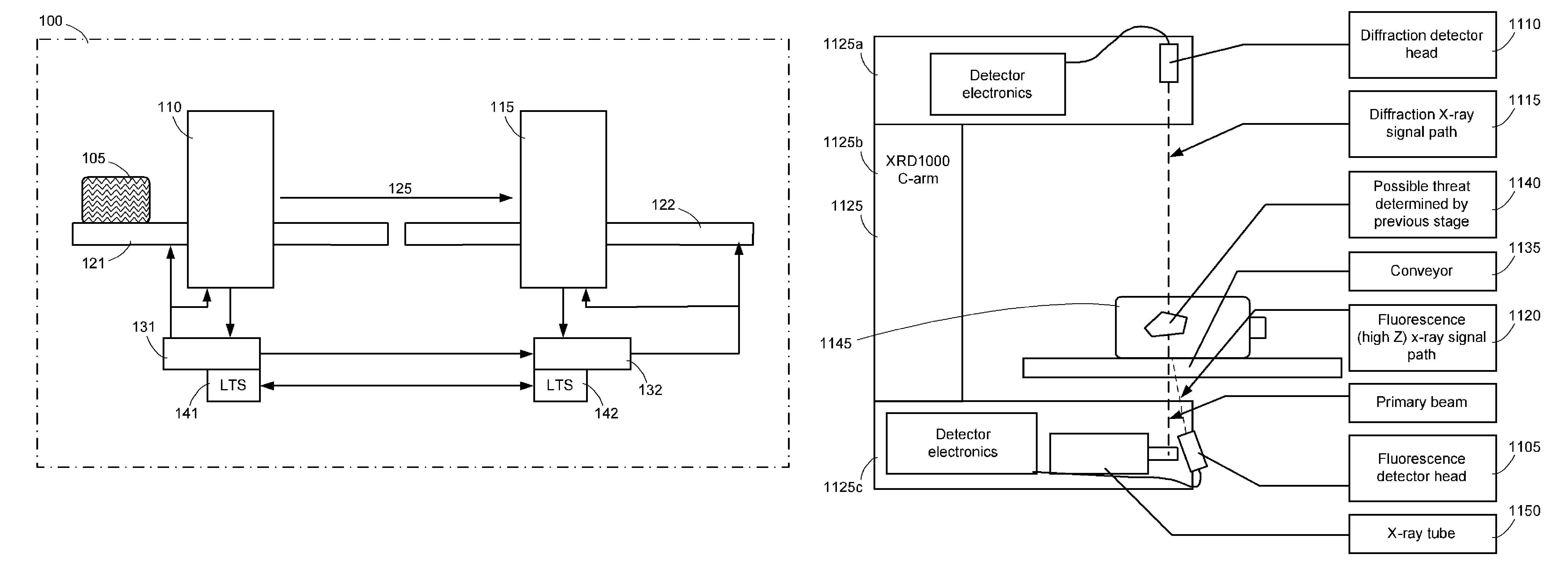
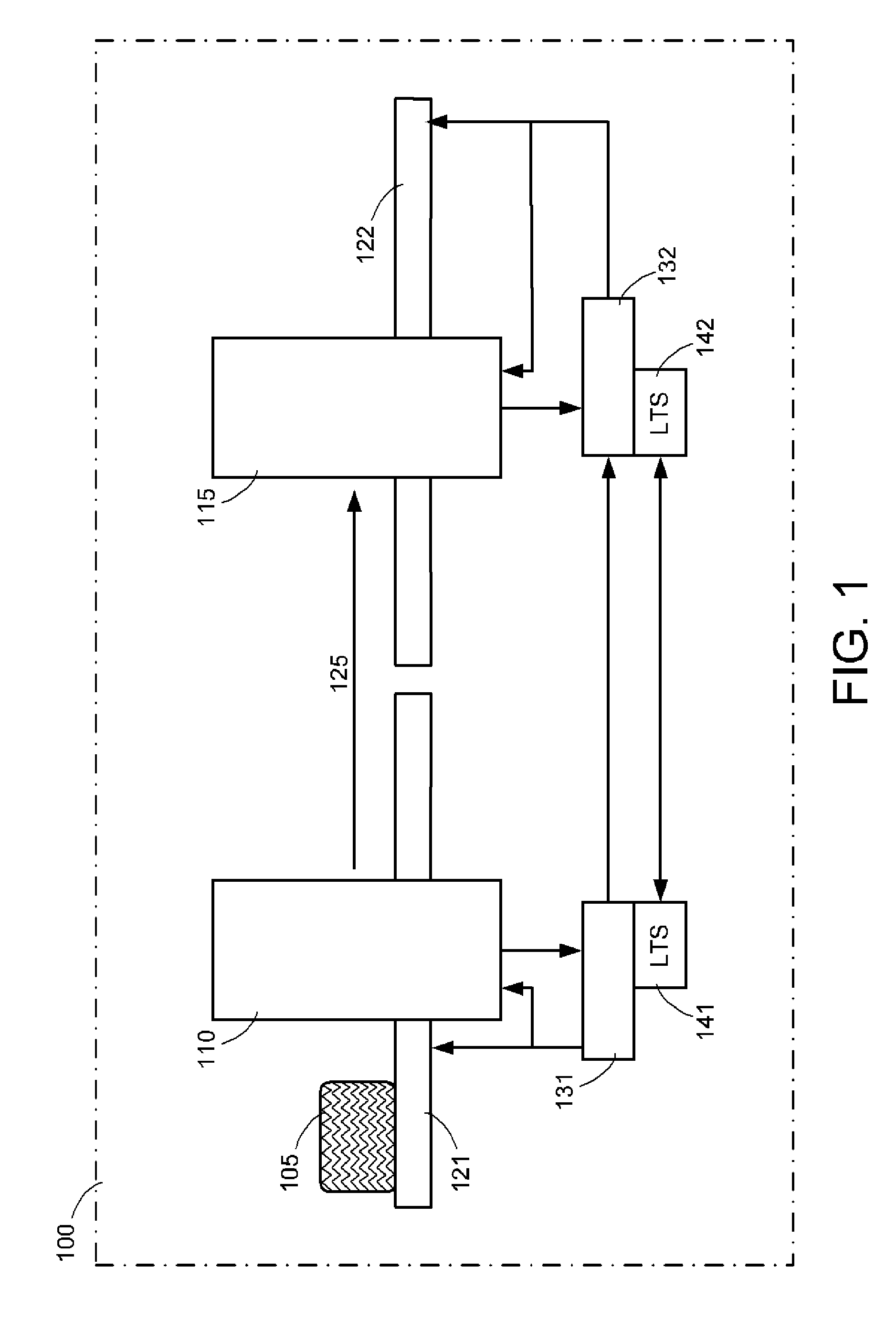
Methods and systems for rapid detection of concealed objects using fluorescence
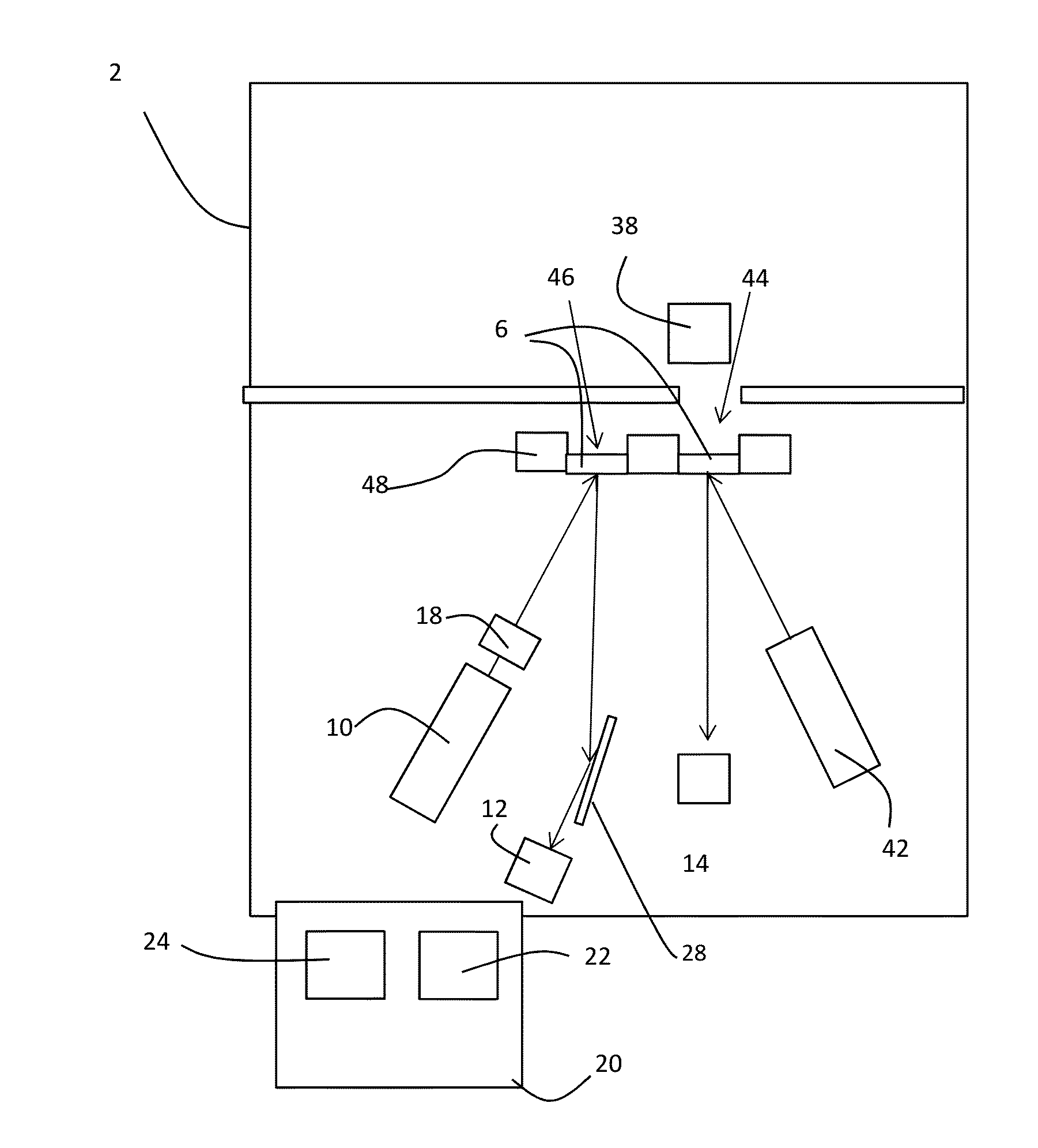
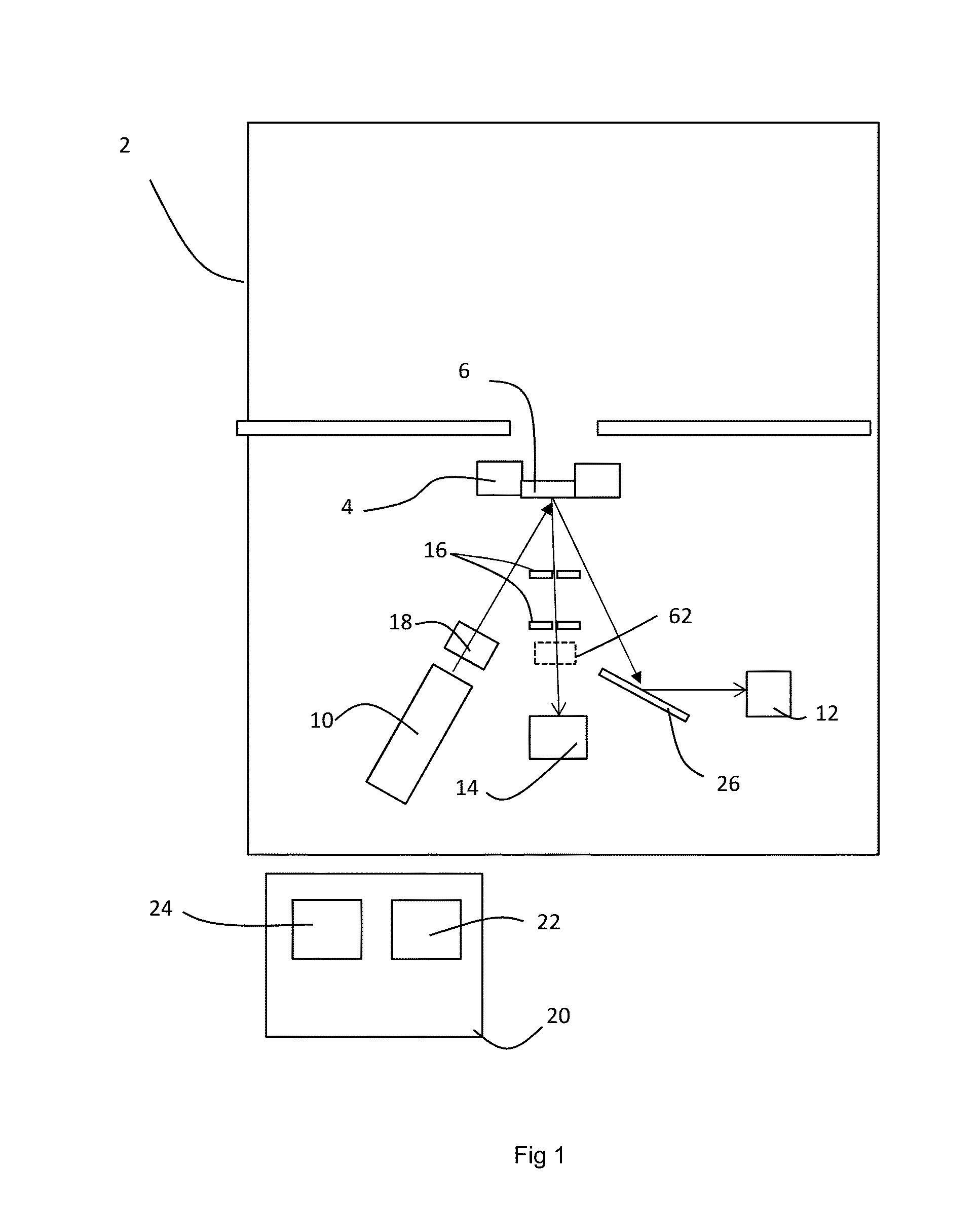
InactiveUS20060098773A1True natureImprove throughputX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging processingFluorescence
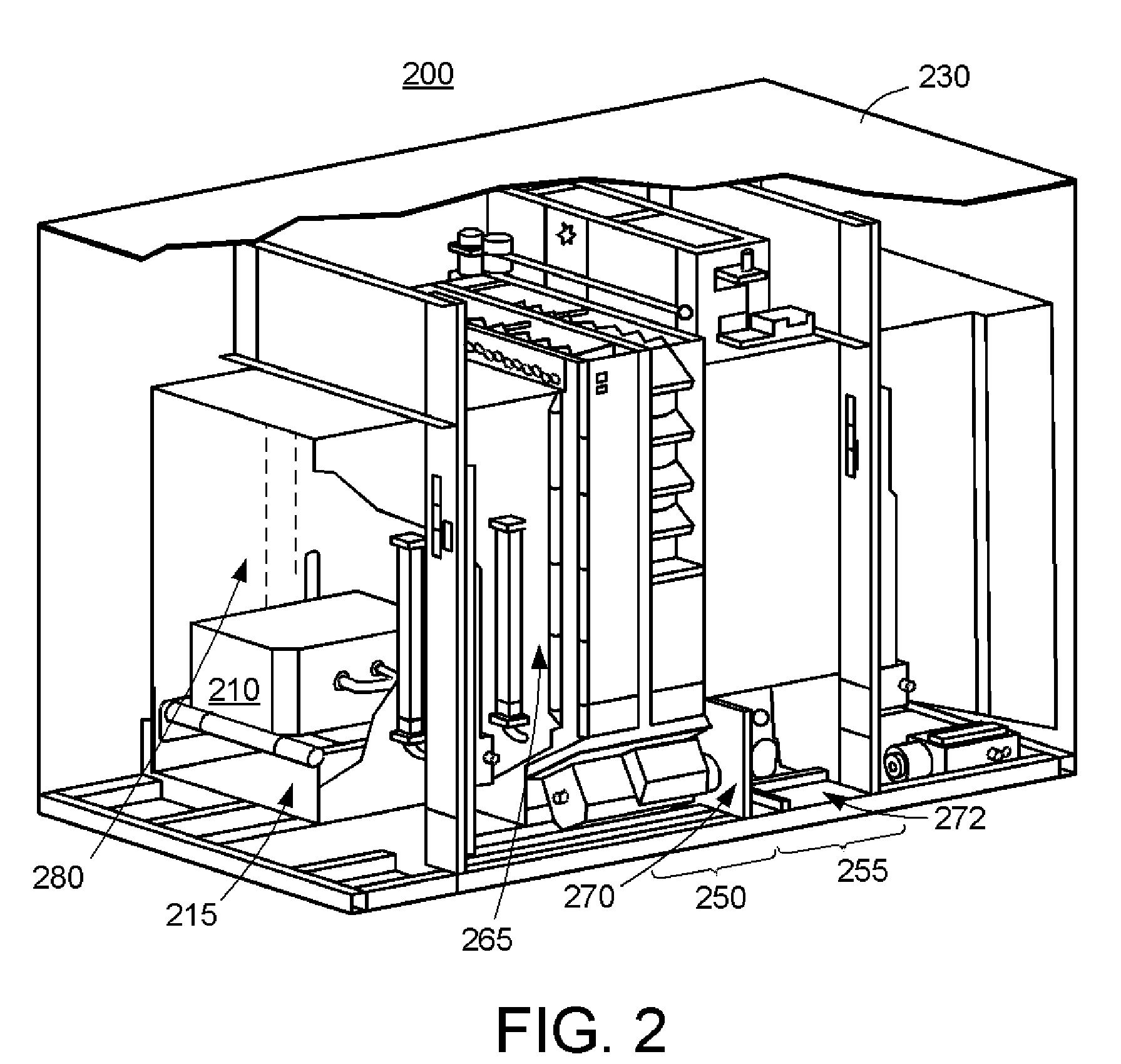
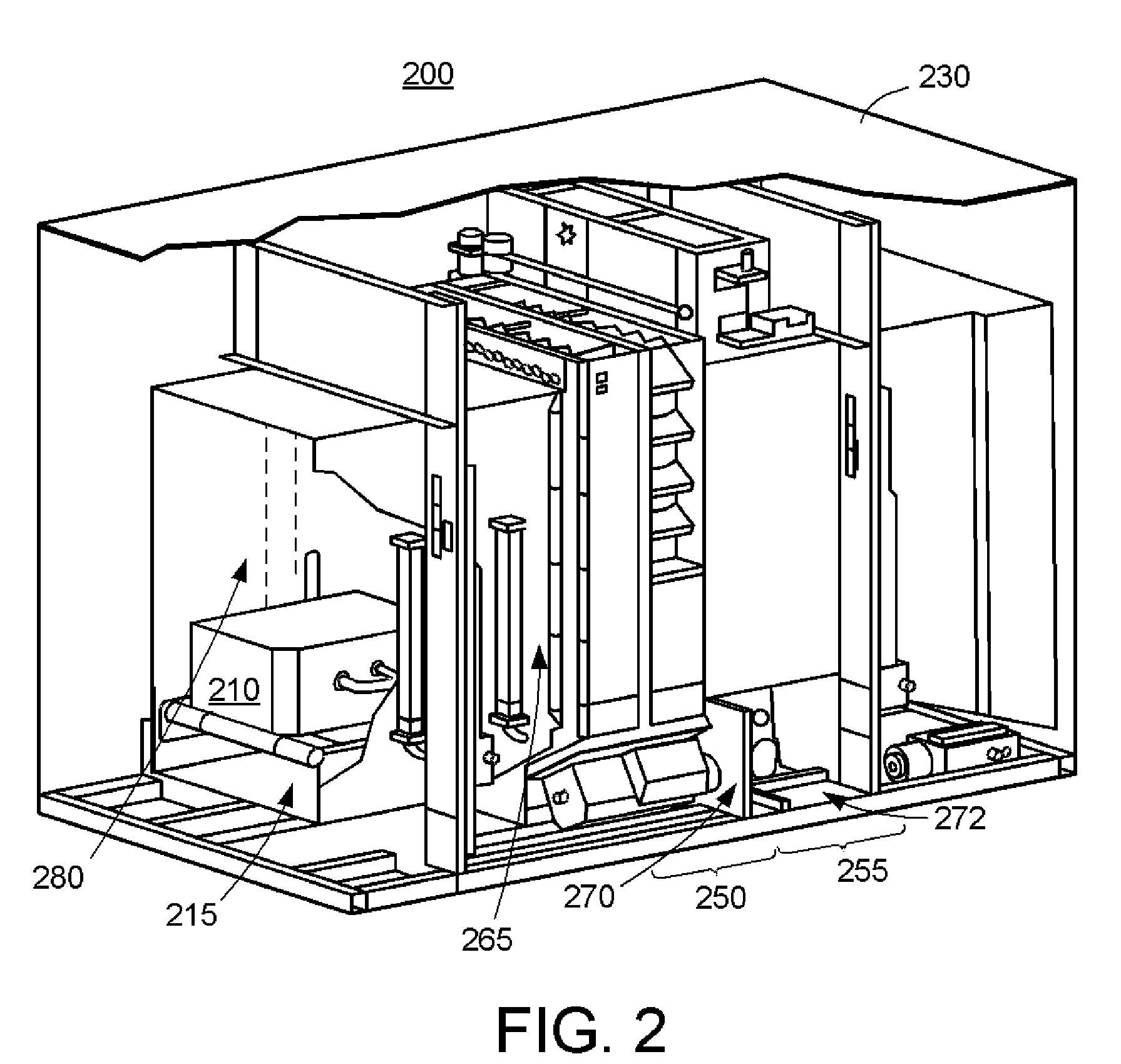
This invention is directed towards finding, locating, and confirming threat items and substances. The inspection system is designed to detect objects that are made from, but not limited to, special nuclear materials (“SNM”) and / or high atomic number materials. The system employs advanced image processing techniques to analyze images of an object under inspection (“OUI”), which includes, but is not limited to baggage, parcels, vehicles and cargo, and fluorescence detection.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Methods and systems for rapid detection of concealed objects using fluorescence
InactiveUS7366282B2True natureImprove throughputX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging processingSystems design
This invention is directed towards finding, locating, and confirming threat items and substances. The inspection system is designed to detect objects that are made from, but not limited to, special nuclear materials (“SNM”) and / or high atomic number materials. The system employs advanced image processing techniques to analyze images of an object under inspection (“OUI”), which includes, but is not limited to baggage, parcels, vehicles and cargo, and fluorescence detection.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Methods and systems for rapid detection of concealed objects using fluorescence
InactiveUS7856081B2True natureImprove throughputX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging processingSystems design
This invention is directed towards finding, locating, and confirming threat items and substances. The inspection system is designed to detect objects that are made from, but not limited to, special nuclear materials (“SNM”) and / or high atomic number materials. The system employs advanced image processing techniques to analyze images of an object under inspection (“OUI”), which includes, but is not limited to baggage, parcels, vehicles and cargo, and fluorescence detection.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Methods and Systems for Rapid Detection of Concealed Objects Using Fluorescence
InactiveUS20090010386A1True natureImprove throughputX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging processingSystems design
This invention is directed towards finding, locating, and confirming threat items and substances. The inspection system is designed to detect objects that are made from, but not limited to, special nuclear materials (“SNM”) and / or high atomic number materials. The system employs advanced image processing techniques to analyze images of an object under inspection (“OUI”), which includes, but is not limited to baggage, parcels, vehicles and cargo, and fluorescence detection.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Methods for sorting materials
ActiveUS20100219109A1Low sulfurReduce fire and explosive hazardsDifferential sedimentationSortingCarbon footprintX-ray
Disclosed herein is the use of differences in x-ray linear absorption coefficients to process ore and remove elements with higher atomic number from elements with lower atomic numbers. Use of this dry method at the mine reduces pollution and transportation costs. One example of said invention is the ejection of inclusions with sulfur, silicates, mercury, arsenic and radioactive elements from coal. This reduces the amount and toxicity of coal ash. It also reduces air emissions and the energy required to clean stack gases from coal combustion. Removal of said ejected elements improves thermal efficiency and reduces the pollution and carbon footprint for electrical production.
Owner:MINERAL SEPARATION TECH
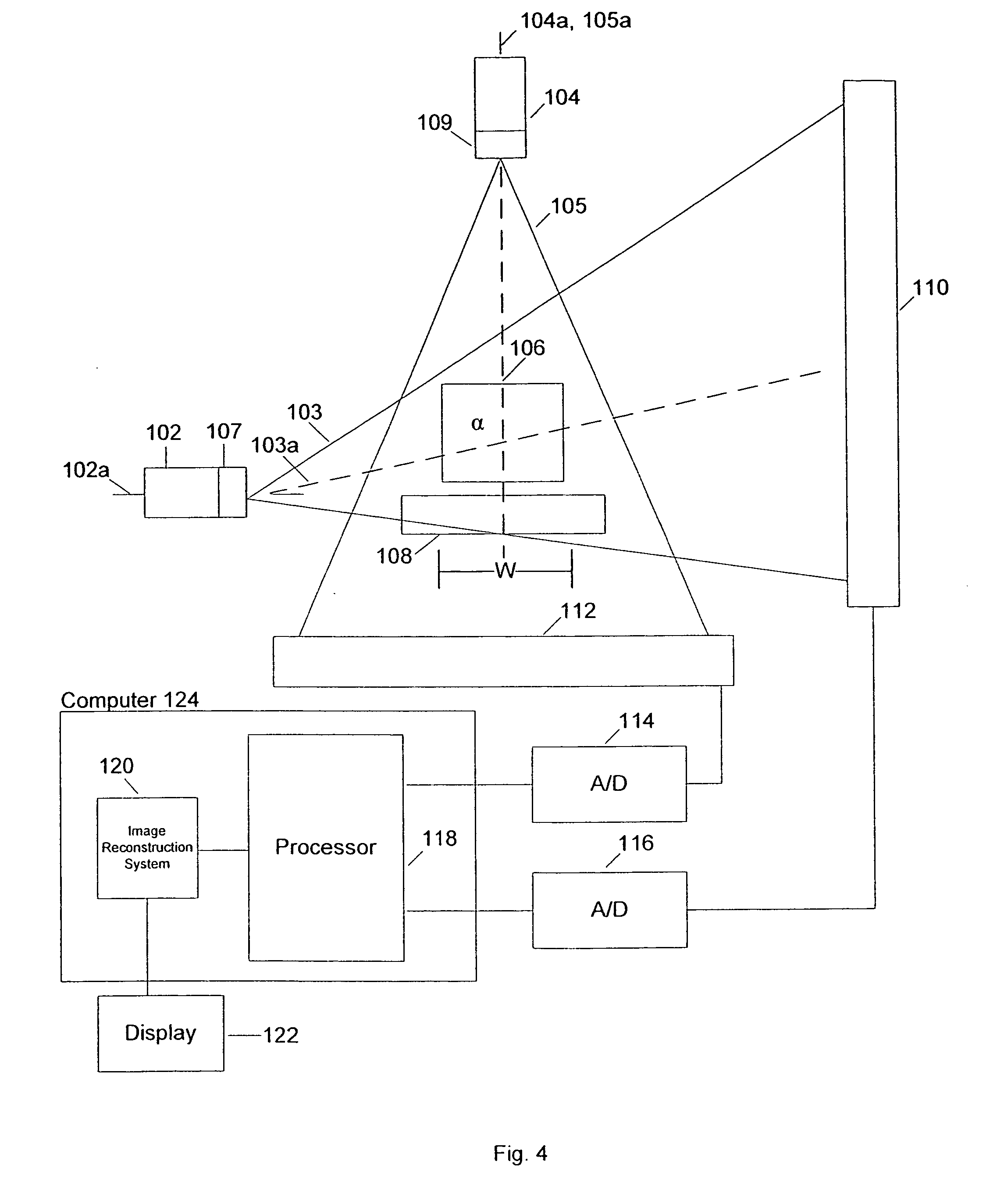
Dual angle radiation scanning of objects
ActiveUS20080014643A1Large atomic numberBiological testingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationHigh densityHigh atomic number
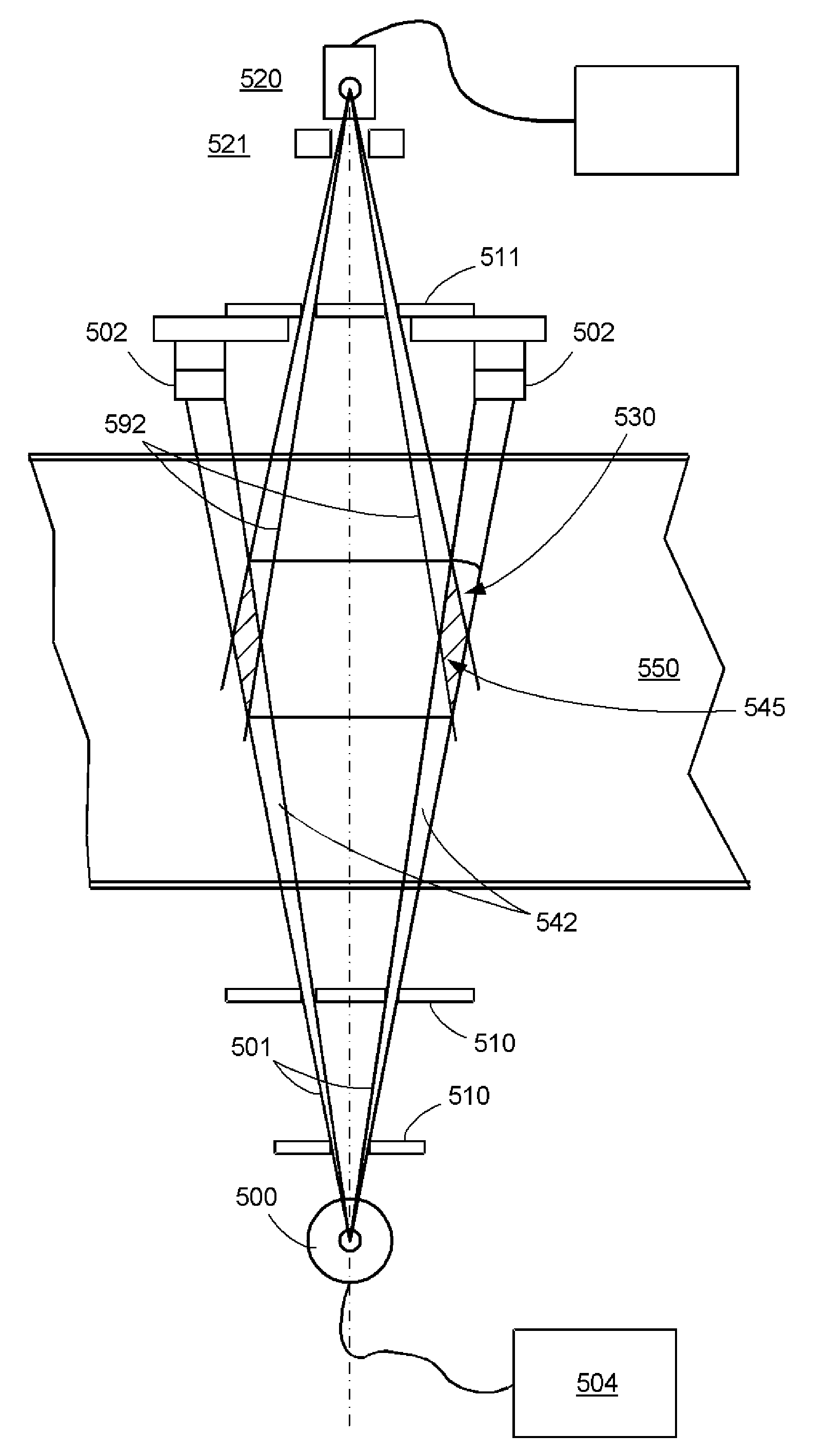
In one example, a method of examining contents of an object is disclosed comprising scanning an object by first and second radiation beams at at least first and second angles, detecting radiation at the first and second angles, and determining whether the object at least potentially comprises high atomic number material, which may be nuclear material or shielding material, based, at least in part, on the detected radiation. In one example, the detected radiation at both angles must be indicative of a region of high atomic number material by the presence of corresponding high density regions, in order for it to be concluded that high atomic number material that may be nuclear material may be present. The determination may be further based on the size of a high density region in one of the images. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Resist composition with enhanced X-ray and electron sensitivity
InactiveUS20040191669A1High sensitivityPromote absorptionMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation applicationsSoft x rayResist
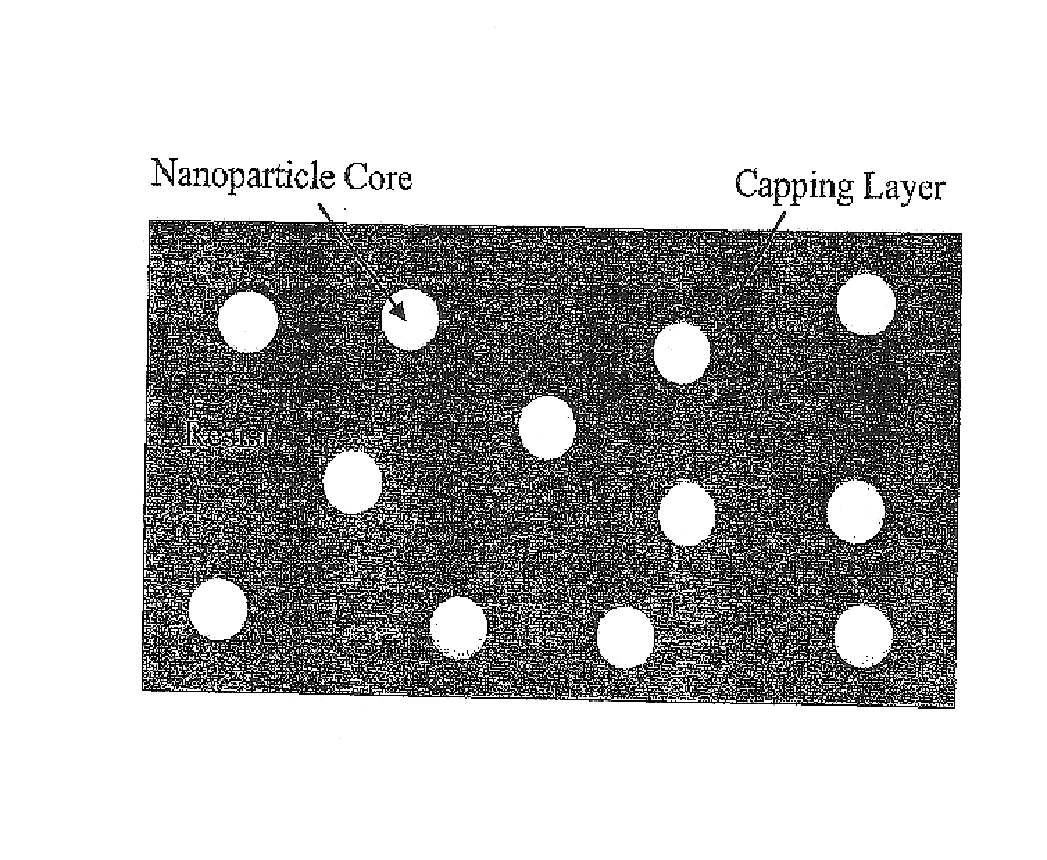
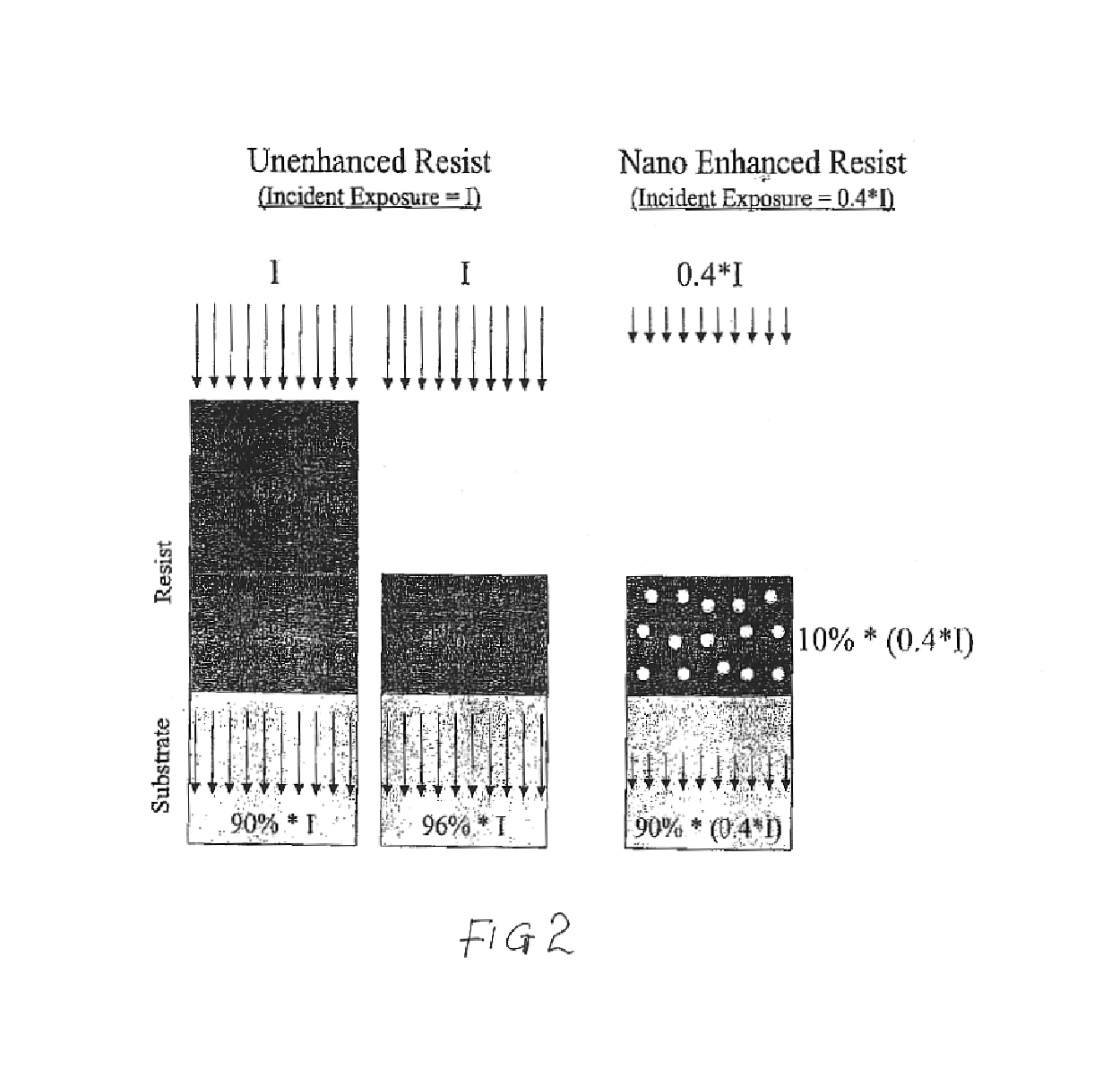
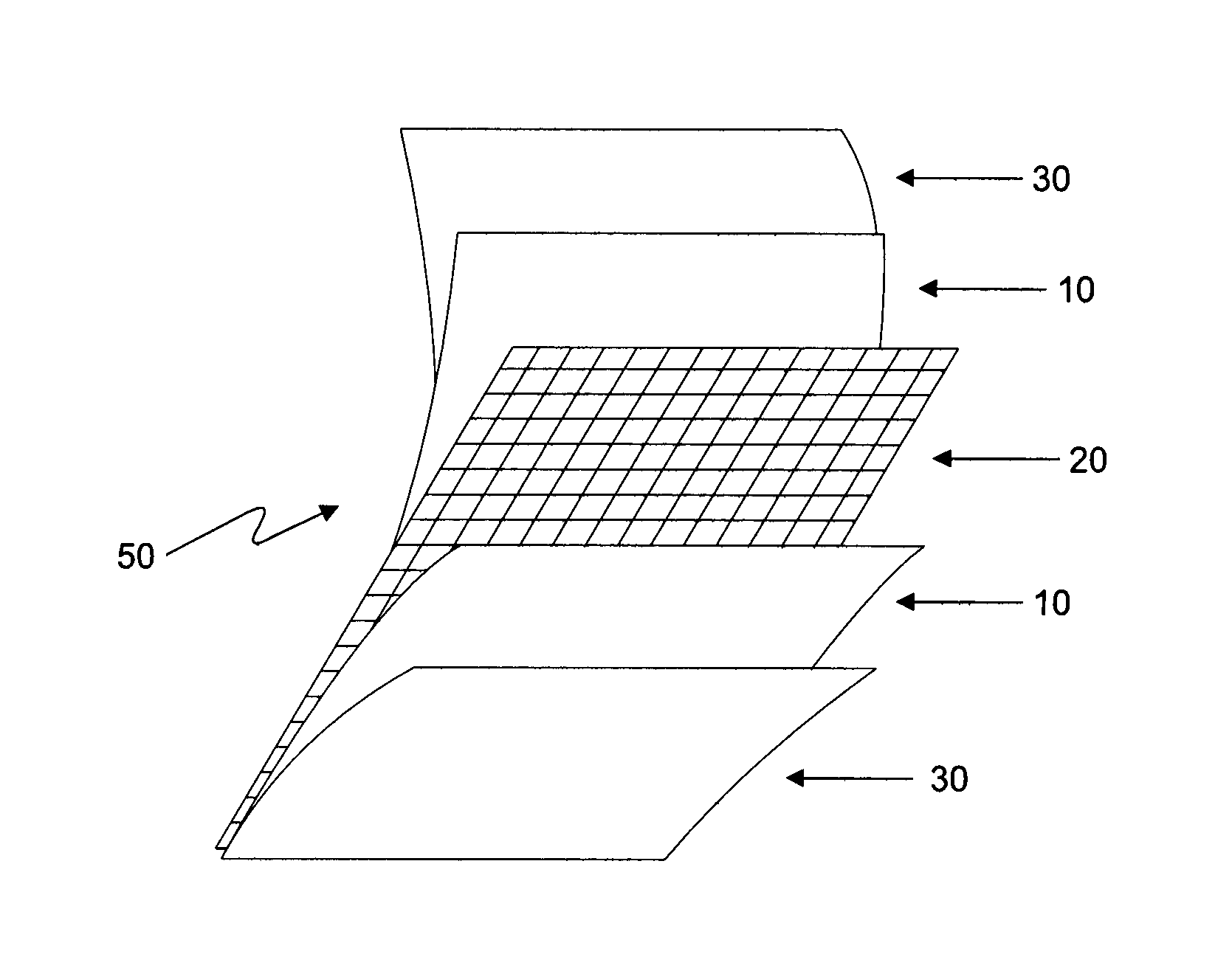
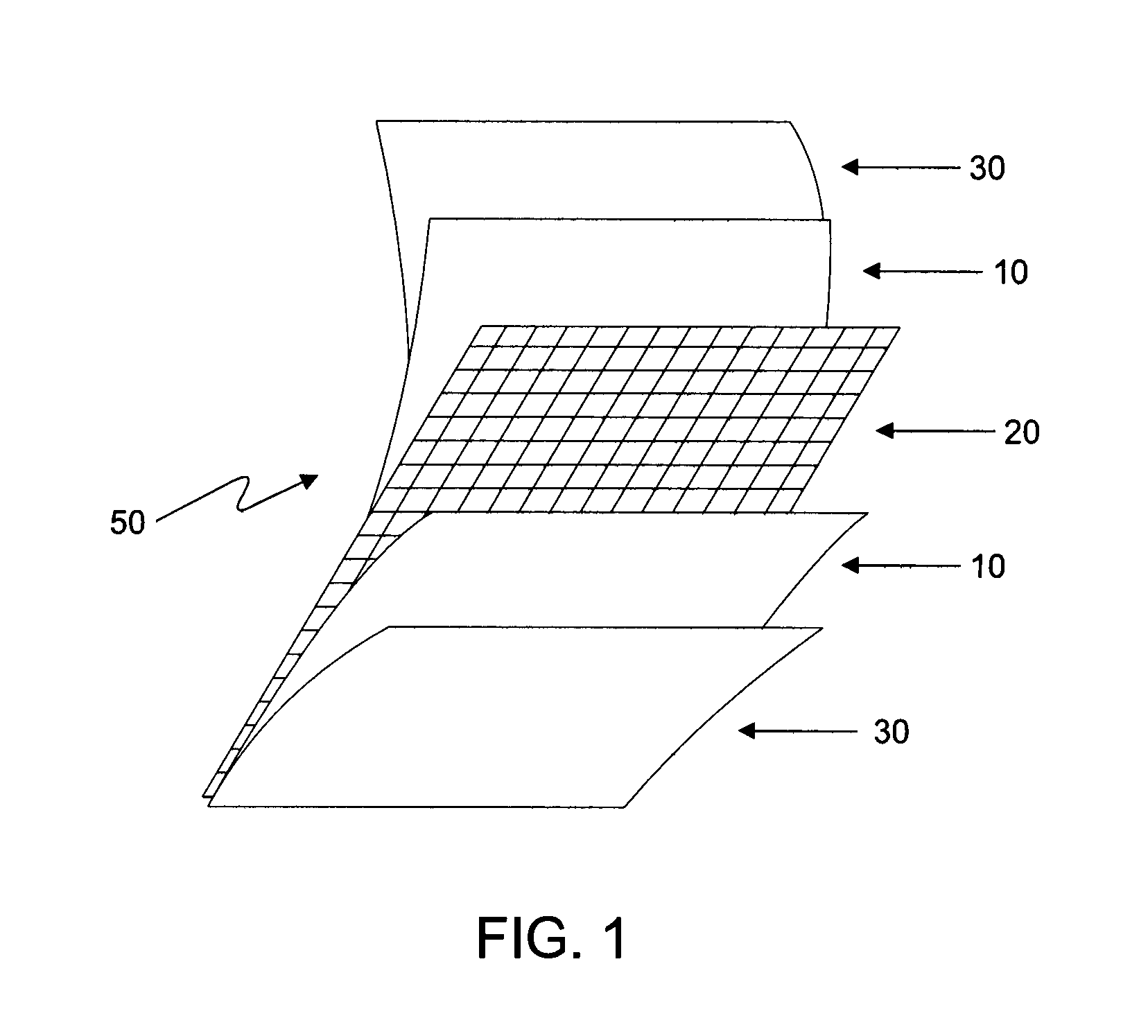
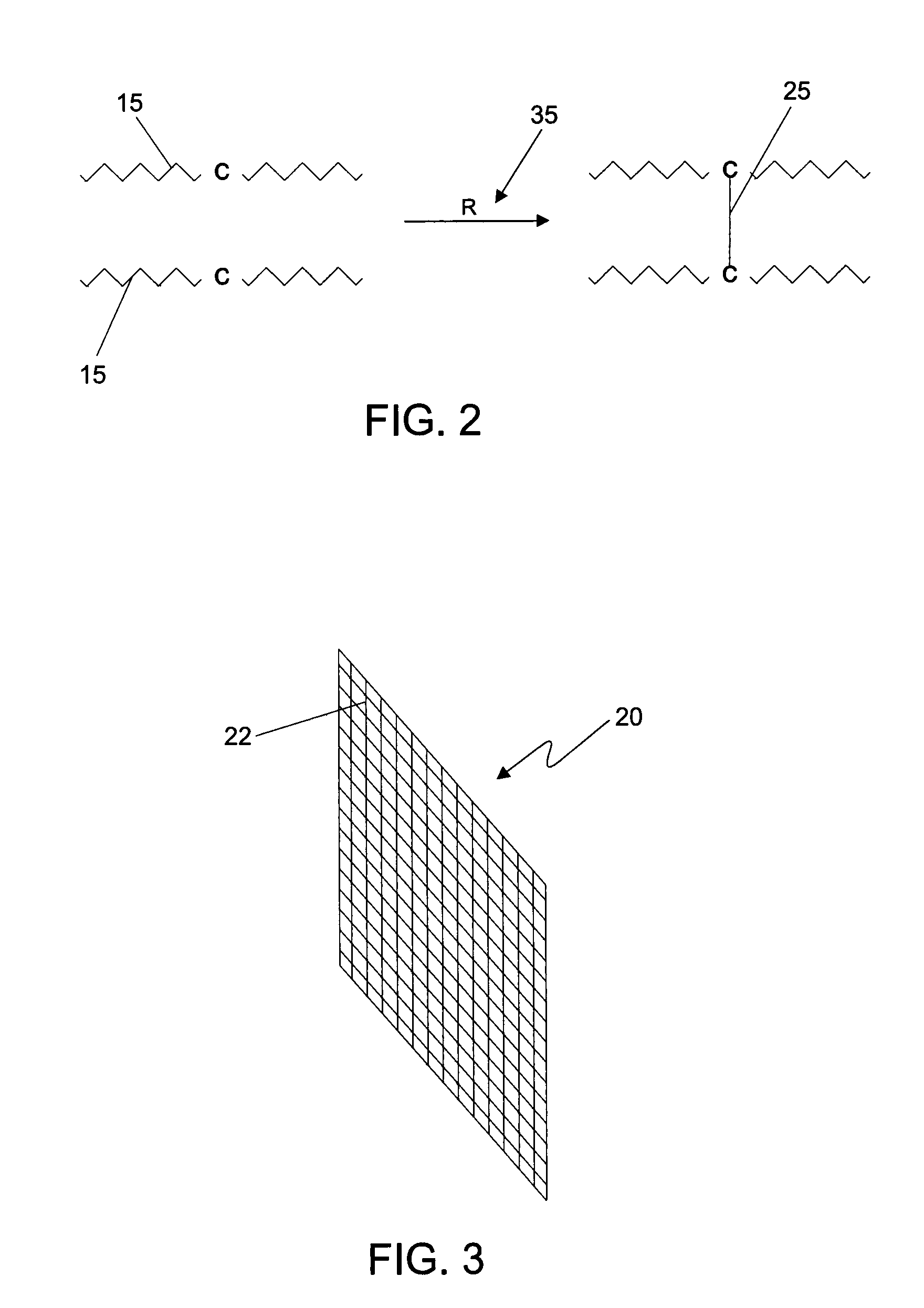
A resist composition with enhanced X-ray and electron sensitivity includes a plurality of chemically inert nanoparticles dispersed throughout a base resist material. The nanoparticles have a higher atomic number than the base resist material and each of the nanoparticles is formed by a nanoparticle core, e.g., of a noble metal, coated with an organic capping layer or shell. The latter renders the core dispersible and chemically compatible with the resist material surrounding the nanoparticle. A method of making a resist composition with enhanced X-ray and electron sensitivity is to provide a resist material and disperse chemically inert nanoparticles throughout the resist. The nanoparticles have a higher atomic number than the resist and a have core / shell structure. A resist composition with enhanced X-ray and electron sensitivity can be made by having a nanoparticle core, with a higher atomic number than the resist, that is coated with an organic capping layer. The nanoparticle with the core / shell structure is then dispersed throughout the resist material.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Isotopic response with small scintillator based gamma-ray spectrometers
ActiveUS20080251728A1Increased signal noiseImprove noisePhotometryFluorescence/phosphorescenceGamma ray spectrometerData stream
The intrinsic background of a gamma ray spectrometer is significantly reduced by surrounding the scintillator with a second scintillator. This second (external) scintillator surrounds the first scintillator and has an opening of approximately the same diameter as the smaller central scintillator in the forward direction. The second scintillator is selected to have a higher atomic number, and thus has a larger probability for a Compton scattering interaction than within the inner region. Scattering events that are essentially simultaneous in coincidence to the first and second scintillators, from an electronics perspective, are precluded electronically from the data stream. Thus, only gamma-rays that are wholly contained in the smaller central scintillator are used for analytic purposes.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
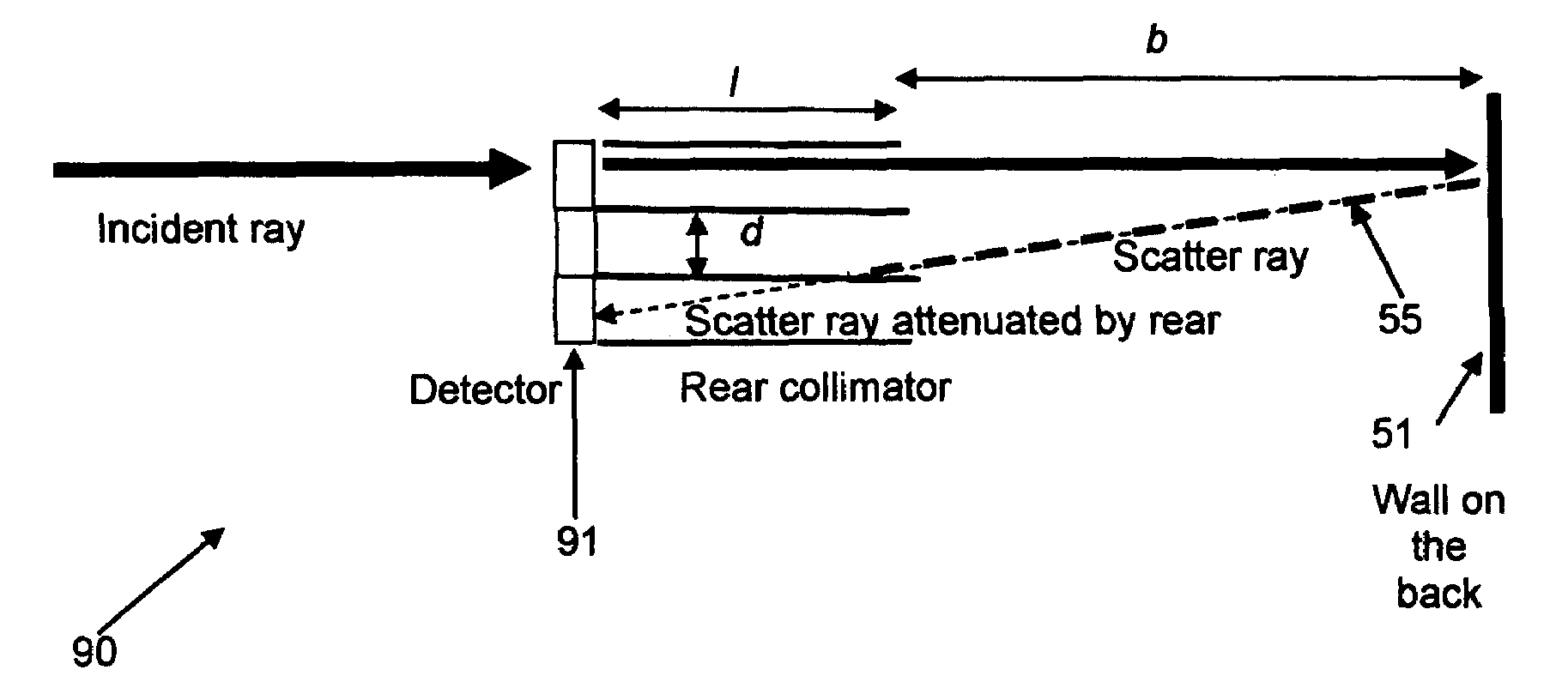
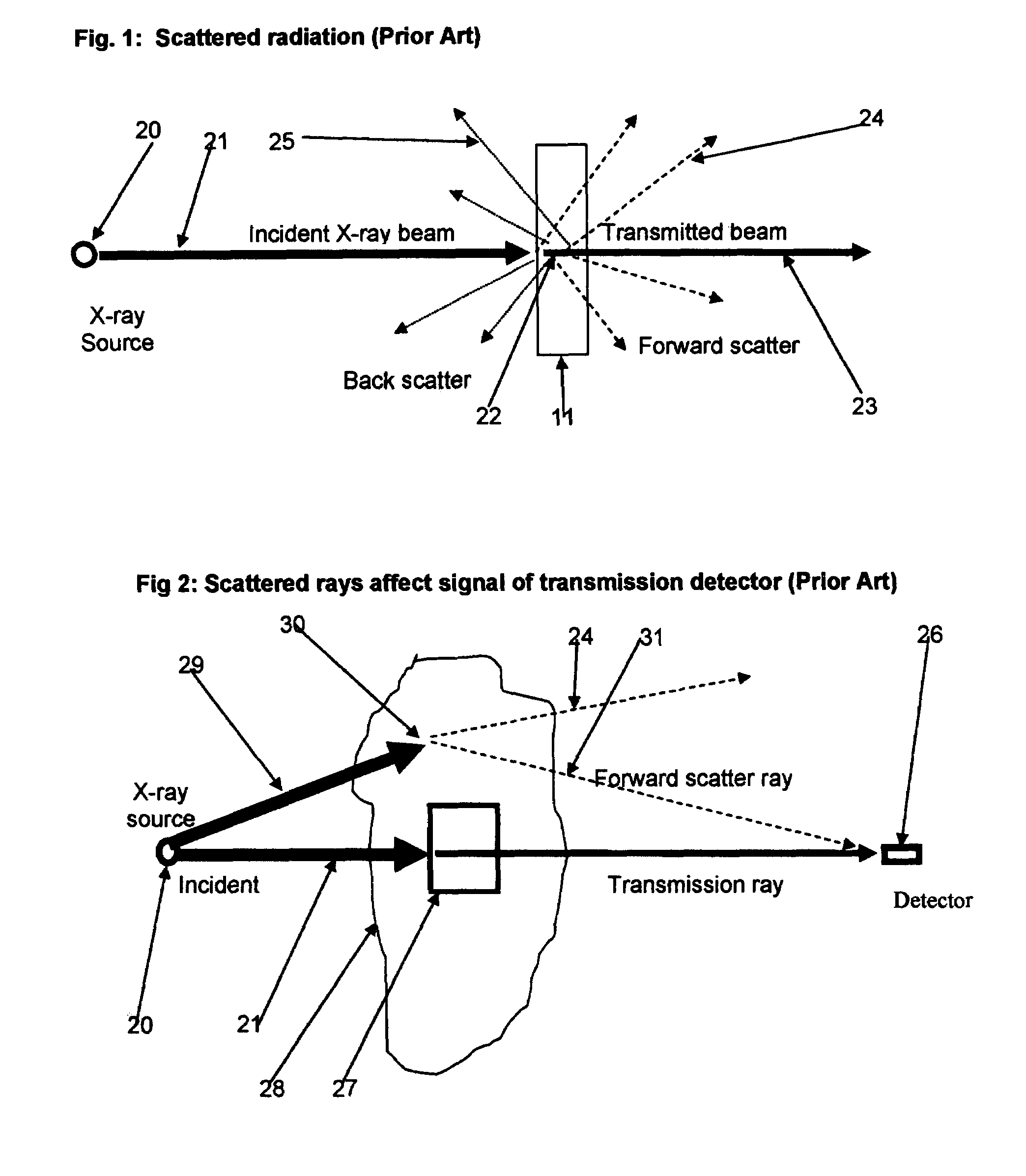
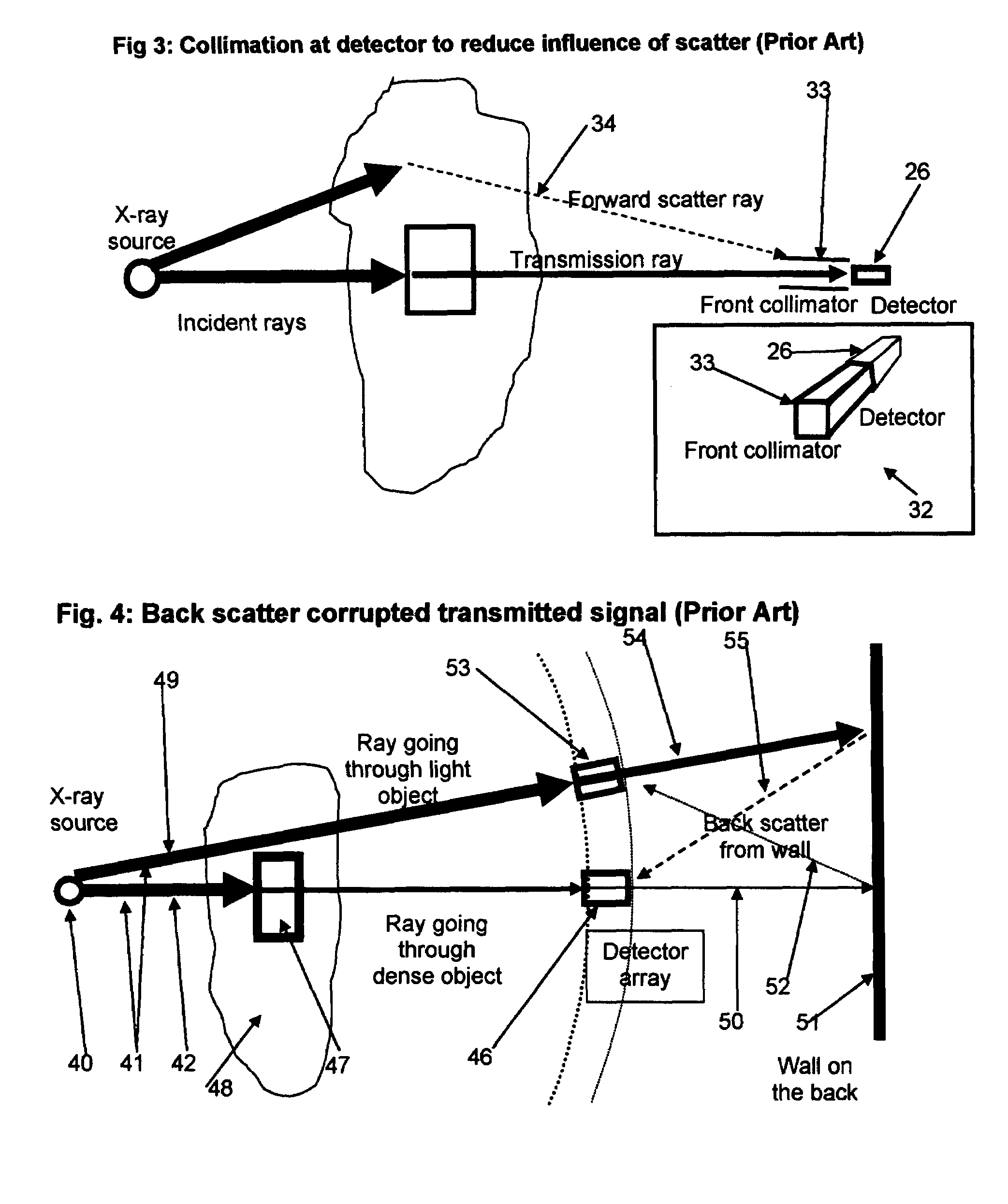
Back-scattered X-ray radiation attenuation method and apparatus
InactiveUS7336767B1Reduce intensityMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayBackscatter X-ray
A method for improving resolution of X-ray radiography systems of the type used to obtain images of internal features of human bodies or to view contents of luggage articles, cargo containers and the like comprises positioning a plurality of baffle plates between the rear surface of an X-ray radiation detector array and a back stop used to limit transmitted X-ray radiation to a safe level. The baffle plates are made of a high atomic-number metal such as iron or lead which reduces by absorption, scattering or other attenuating processes the intensity of X-ray radiation back scattered from the back-stop onto the detector array, thus reducing noise contributions to signals output from detector elements of the array and thereby improving the quality of radiographic images formed from detector output signals. A back-scattered X-ray radiation attenuation apparatus according to the present invention utilizes pairs of horizontal upper and lower baffle plates disposed longitudinally rearward from upper and lower sides of individual X-ray radiation detector elements, or groups of elements, of a detector array, and optionally includes pairs of baffle plates disposed transversely to the horizontally disposed plates to thereby form an array of tubular collimatator elements which intercept and attenuate X-ray radiation scattered from locations on a back-stop on lateral sides of as well as above and below the detector elements.
Owner:LE KHAI MINH
Scintigraphic device with avriable resolution
InactiveUS20050263717A1Reduced dimensionMass is limitedMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh densityVariable resolution
A scintigraphic device includes a case open at an application end, and coated by a shielding shell; a collimator positioned inside the case, made of a material with high atomic number and high density and having a plurality of collimation channels extending mutually parallel according to a predefined direction of measurement; a measuring member positioned inside the case in proximity to the collimator and including a scintillation crystal for converting each ionizing radiation originating from a source in exam into light radiation, and at least one photosensor, for determining the energy and the position of each detected event. The measuring member and the collimator are relatively movable to increase and / or reduce the distance between the converter and the application end and consequently to vary the total length of the collimator. The collimator may include two or more blocks at least one of which is movable relative to the others.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Cast collimators for ct detectors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20070064876A1Reduce X-ray doseLarge atomic numberMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh densityRadiology
Cast collimators for use in CT imaging systems are described, as are methods of making them. Such collimators may comprise pre-patient collimators, pre-patient filter / collimator assemblies, and / or post-patient collimators. The filters and / or collimators may be made of any suitable high-density, high atomic number material such as lead, a lead alloy, tantalum, tungsten, tungsten suspended in an epoxy matrix, tungsten suspended in a slurry, or the like. Embodiments of these collimators comprise specially-designed channels and vanes that allow them to be precision cast to the necessary degree of accuracy. These channels and vanes are preferably tapered. These collimators and filter / collimator assemblies help minimize the x-ray dose to the patient by minimizing the scattered radiation creation mechanism and by collimating out much of the scattered radiation that would otherwise be subjected to the patient. These collimators may be cast as either single piece structures, or multiple pieces that can be operatively connected together.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Scintigraphic device with variable resolution
InactiveUS7274022B2Reduced dimensionMass is limitedMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh densityScintillation crystals
A scintigraphic device includes a case open at an application end, and coated by a shielding shell; a collimator positioned inside the case, made of a material with high atomic number and high density and having a plurality of collimation channels extending mutually parallel according to a predefined direction of measurement; a measuring member positioned inside the case in proximity to the collimator and including a scintillation crystal for converting each ionizing radiation originating from a source in exam into light radiation, and at least one photosensor, for determining the energy and the position of each detected event. The measuring member and the collimator are relatively movable to increase and / or reduce the distance between the converter and the application end and consequently to vary the total length of the collimator. The collimator may include two or more blocks at least one of which is movable relative to the others.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Retrievable, shielded radiotherapy implant
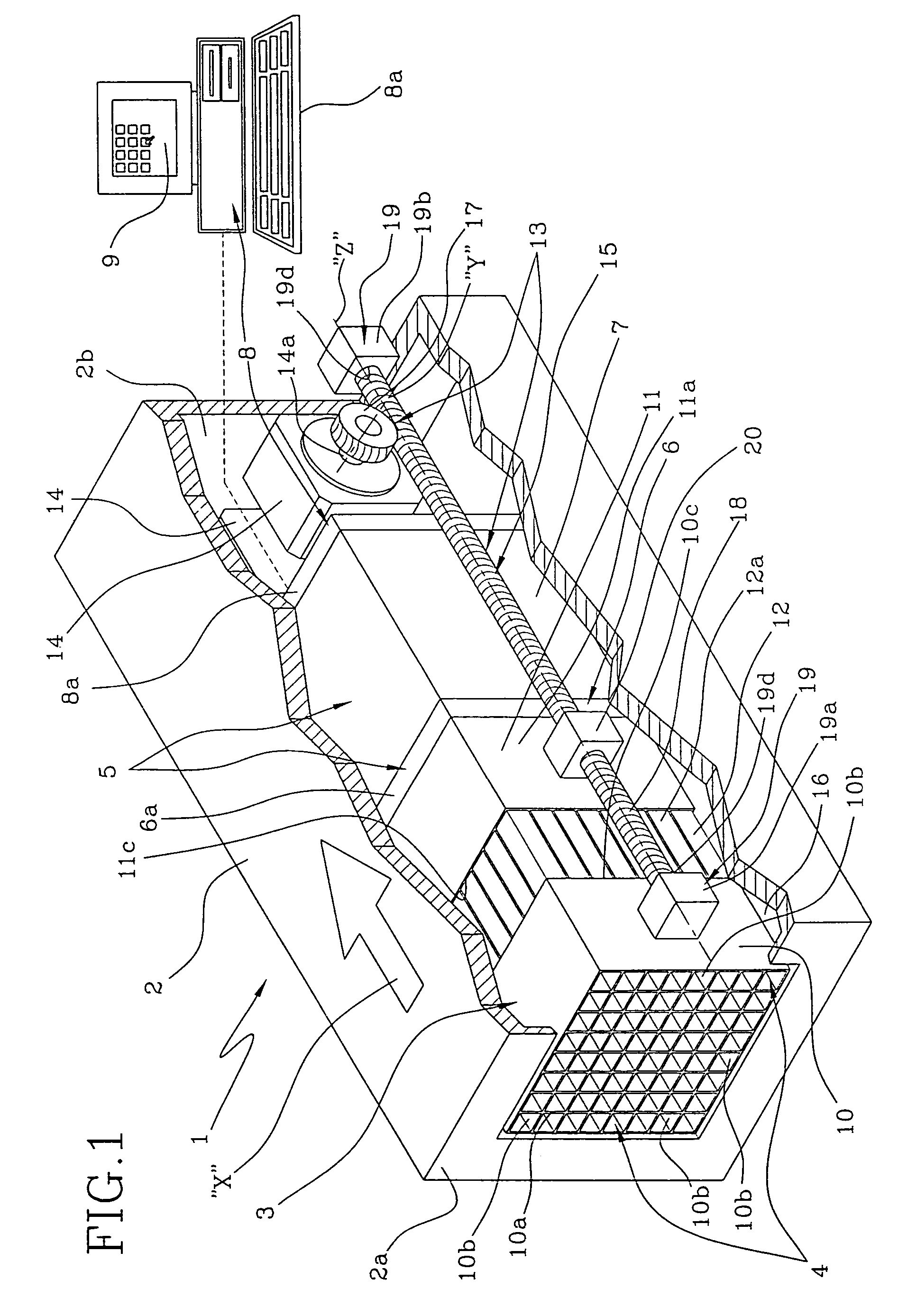
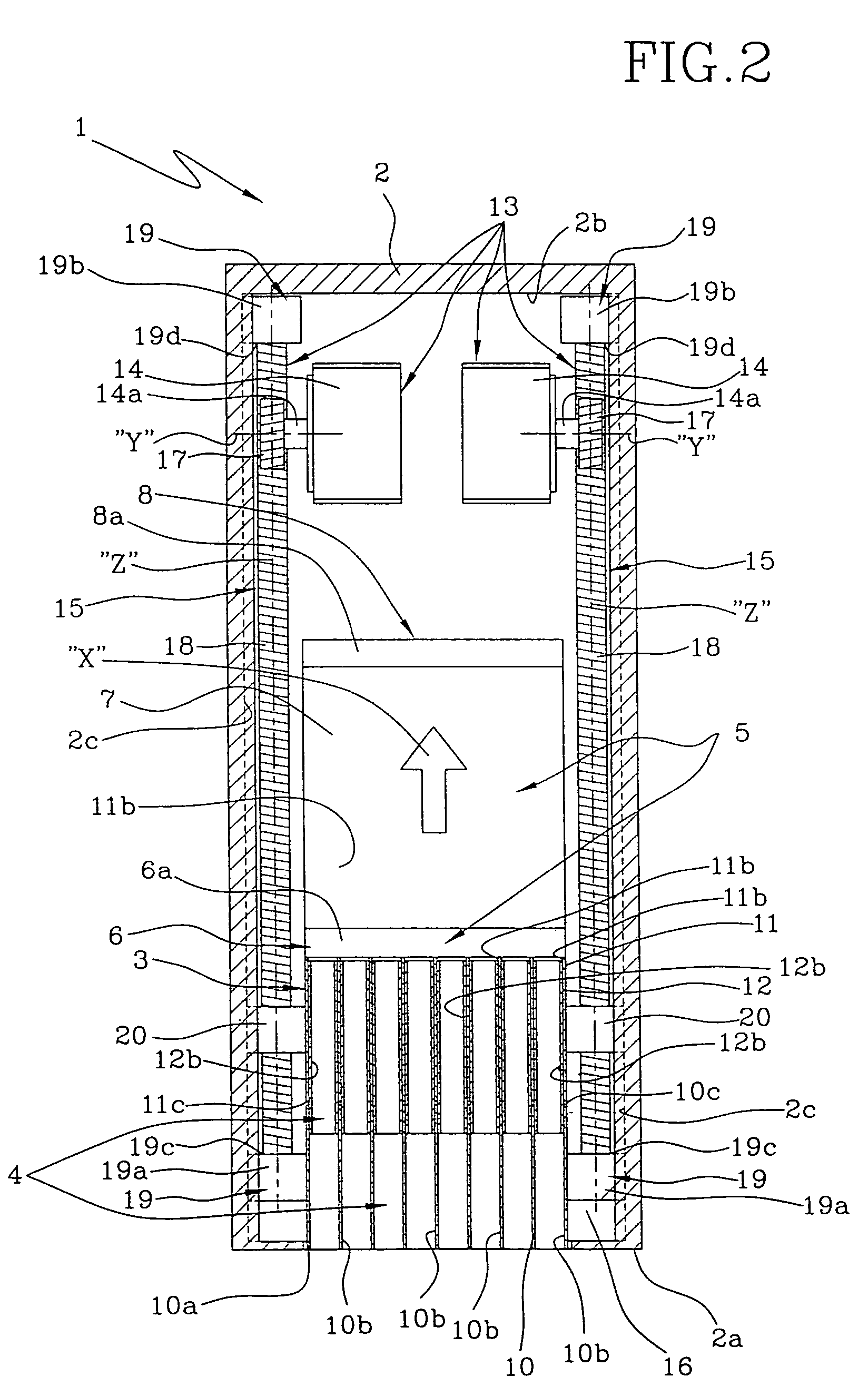
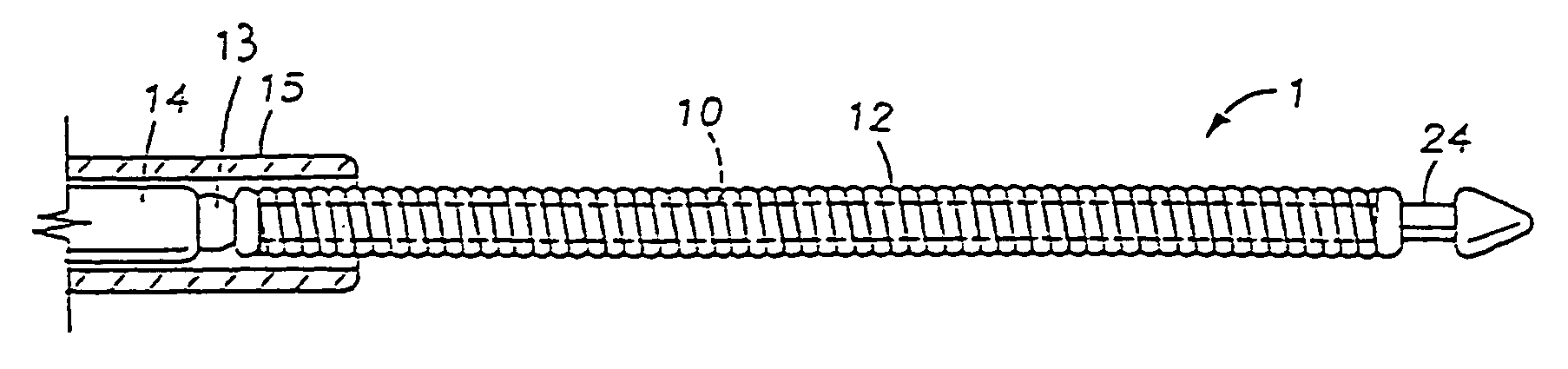
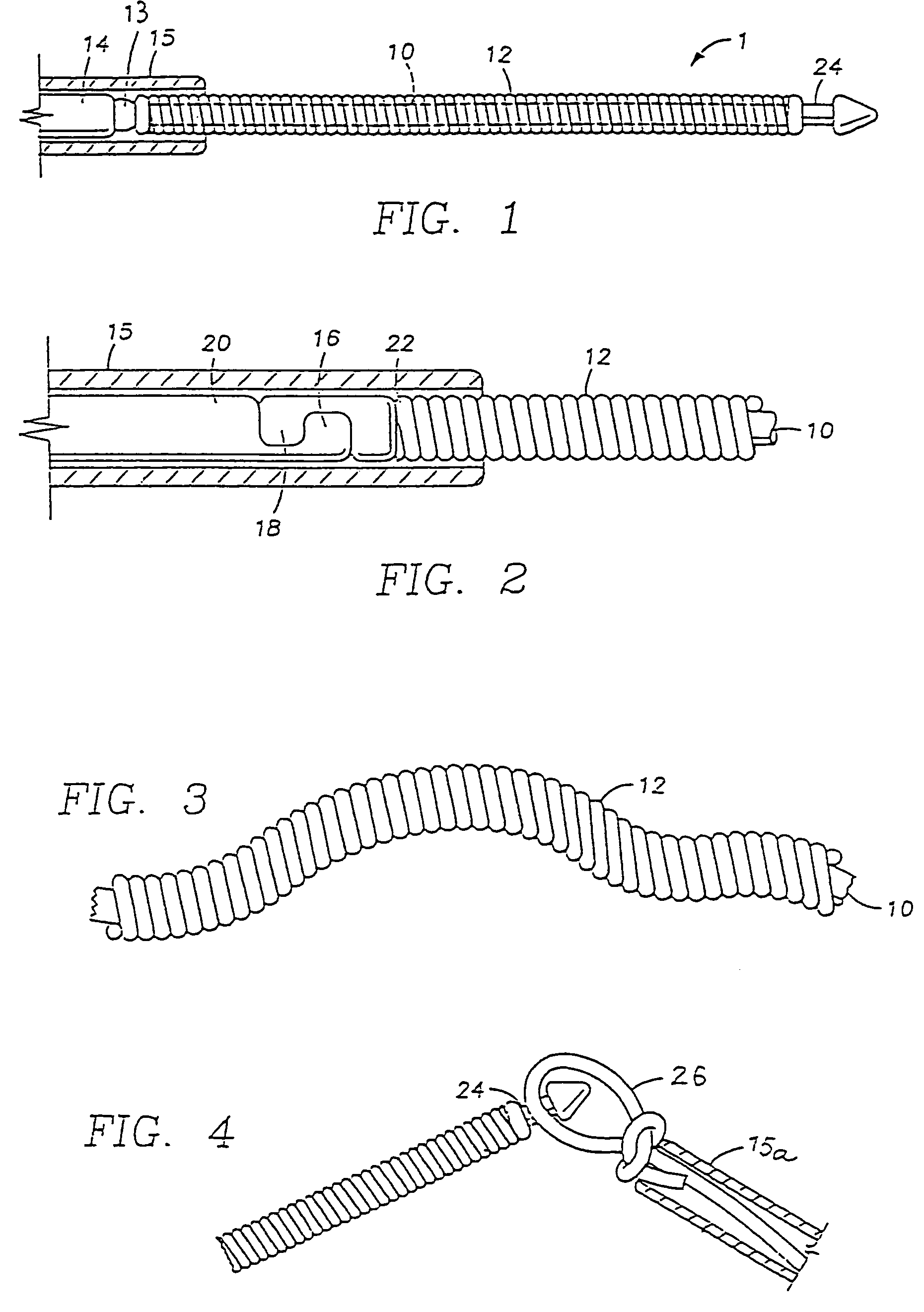
InactiveUS7083567B2Easy to pullStentsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPlatinumHelical coil
A radiotherapy device comprises a radioactive wire adapted to deliver an intended dosage of radiation to a lesion or other selected body tissues. The radioactive wire comprises an inner core about which is disposed an outer buffer layer of platinum or other suitable metal of high atomic number. The buffer layer preferably comprises a thin, continuous wire wrapped about the inner core. The radiotherapy device may be made into a variety of shapes, such as a straight wire, a helical coil, or other more complex shape, and it may be provided with an elastic memory. The device may be adapted for attachment to a delivery wire for controlled placement, as through a delivery catheter or microcatheter, at the treatment site. When accurate positioning of the device is not necessary, it can simply be injected through the delivery catheter or microcatheter, and in that event a delivery wire is not needed. The device may be provided with mechanically or electrically releasable means for attachment to the delivery wire during delivery, and for releasing the device at the treatment site. The device may be provided with a shoulder, hook, or other suitable gripping means on its distal end, which can be lassoed by a microsnare device for retrieving the device from the body.
Owner:MAWAD MICHEL E
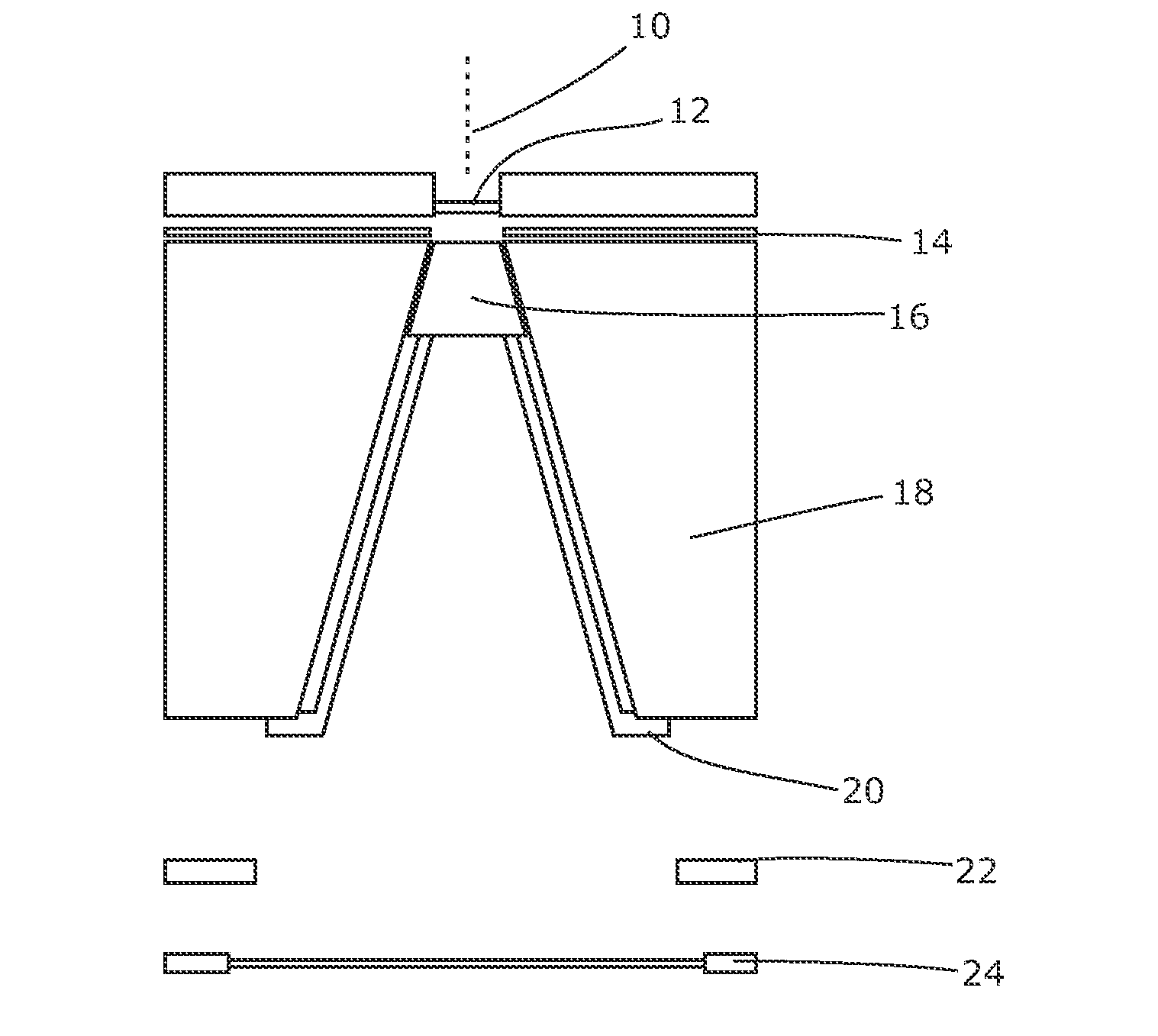
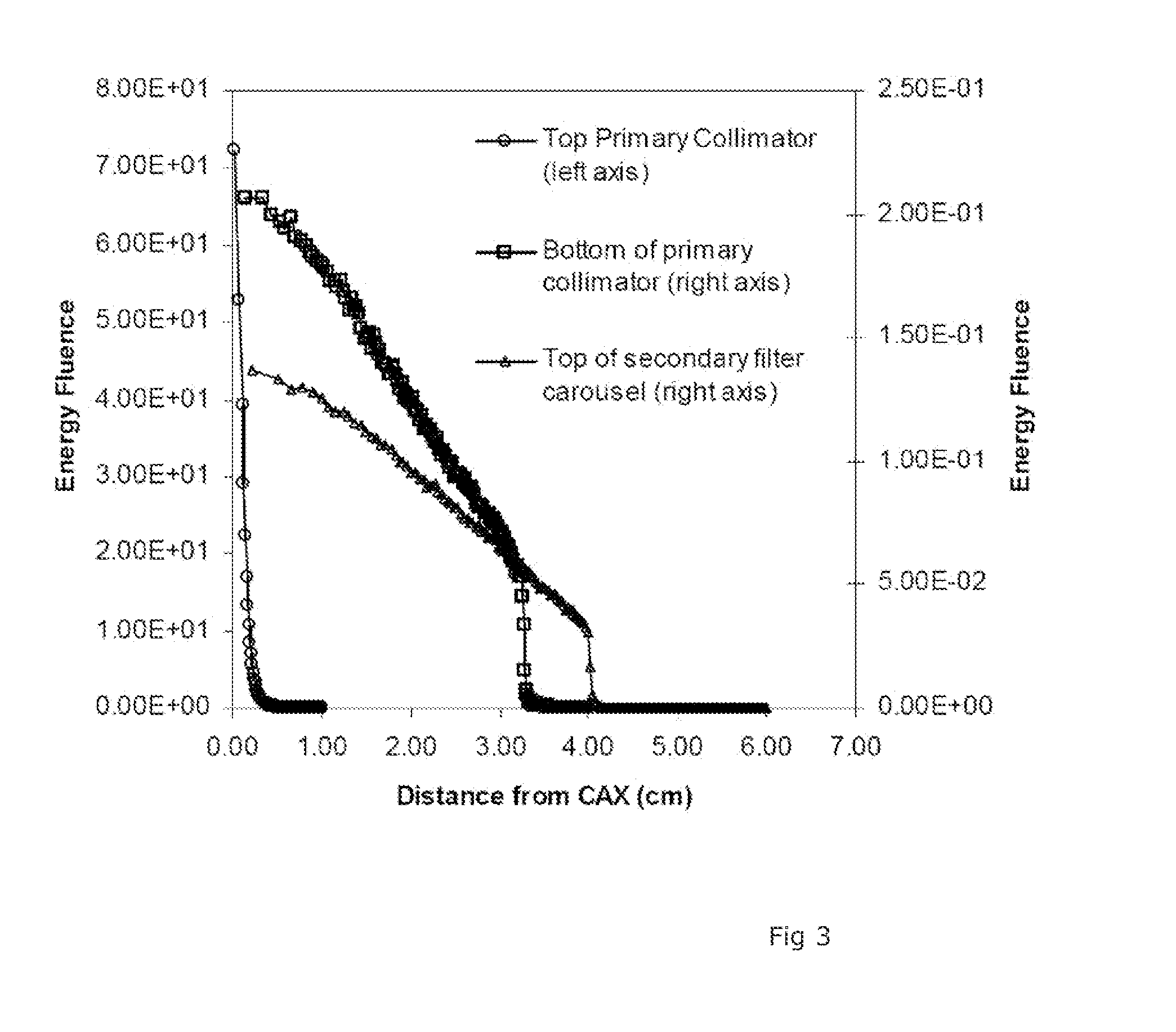
Radiotherapy Apparatus
ActiveUS20110142202A1Reduce skin doseAvoid insufficient thicknessX-ray tube electrodesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh energyX-ray
It is desirable to achieve a co-incident investigative kV source for a therapeutic MV source—a so-called “beams-eye-view” source. It has been suggested that bremsstrahlung radiation from an electron window be employed; we propose a practical structure for achieving this which can switch easily between a therapeutic beam and a beam-eye-view diagnostic beam capable of offering good image resolution. Such a radiation source comprises an electron gun, a pair of targets locatable in the path of a beam produced by the electron gun, one target of the pair being of a material with a lower atomic number than the other, and an electron absorber insertable into and withdrawable from the path of the beam. In a preferred form, the electron gun is within a vacuum chamber, and the pair of targets are located at a boundary of the vacuum chamber. The lower atomic number target can be Nickel and the higher atomic number target Copper and / or Tungsten. The electron absorber can be Carbon, and can be located within the primary collimator, or within one of a plurality of primary collimators interchangeably locatable in the path of the beam. Such a radiation source can be included within a radiotherapy apparatus, to which the present invention further relates. A flat panel imaging device for this source can be optimised for low energy x-rays rather than high energy; Caesium Iodide-based panels are therefore suitable.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Preparation method for flexible high-atomic-number material TEM (transmission electron microscope) sample
ActiveCN109374663ASolve the problem that it is difficult to form large and thin regions by sputteringImprove manufacturing precisionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationConventional transmission electron microscopeRegioselectivity
The invention discloses a preparation method for a flexible high-atomic-number material TEM (transmission electron microscope) sample. The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing a sheet sample taken down from a preparation region in a flexible high-atomic-number material block sample on a copper mesh column for TEM experiment with an H-bar Lift-out process; performing rough thinning on the sheet sample by a focused ion beam to obtain a roughly thinned sheet sample; performing transverse regional selective fine thinning on the sheet sample by the focused ion beam to obtain afine thinned sheet sample with alternative fine thinned regions and non-thinned interval regions; performing transverse and longitudinal regional selective final thinning on the sheet sample by the focused ion beam to obtain the flexible high-atomic-number material TEM sample with alternative fine thinned regions and non-thinned interval regions finally. Deformation of the flexible material sampledue to thinning to thickness of 100 nanometers or smaller is effectively prevented by self-supporting effect of the sample, and characterization analysis is facilitated.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
X-ray generator
ActiveUS20160372298A1X-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingRegular patternX-ray generator
An x-ray generator may include a plurality of electron field emitters; a target material; a plurality of energisable solenoid coils; and an electronic power and timing circuit. The generator may provide electrical current to at least one individual solenoid coil to create a magnetic field to cause the path of electrons emitted from the emitter closest to the energised solenoid coil to be defocused and / or deflected before the electrons reach the target material. The target material may comprise a low atomic number material and a high atomic number material, the high atomic number material being arranged in a regular pattern, such that, in use, the electrons may be aimed at either the high or the low atomic number material.
Owner:ADAPTIX
Radiation-proof thermal control coating and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106675391APromote absorptionEnhanced Radiation ProtectionCosmonautic radiation protectionRadiation-absorbing paintsEmissivityGreek letter epsilon
The invention discloses a radiation-proof thermal control coating. A low-atomic-number material is utilized as a surface coating of the thermal control coating, a medium-atomic-number material is utilized as an intermediate coating of the thermal control coating, and a high-atomic-number material is utilized as a bottom coating of the thermal control coating. Compared with a ZnO coating, the coating disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the radiation protection capability is improved by over 10%, the solar absorption ratio alpha s of the coating is about 0.152 and the thermal emissivity epsilon is about 0.886 and is equivalent to that of a ZnO white paint under the same surface density.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Methods for sorting materials
ActiveUS8610019B2Low sulfurReduce fire and explosive hazardsDifferential sedimentationSortingCarbon footprintX-ray
Disclosed herein is the use of differences in x-ray linear absorption coefficients to process ore and remove elements with higher atomic number from elements with lower atomic numbers. Use of this dry method at the mine reduces pollution and transportation costs. One example of said invention is the ejection of inclusions with sulfur, silicates, mercury, arsenic and radioactive elements from coal. This reduces the amount and toxicity of coal ash. It also reduces air emissions and the energy required to clean stack gases from coal combustion. Removal of said ejected elements improves thermal efficiency and reduces the pollution and carbon footprint for electrical production.
Owner:MINERAL SEPARATION TECH
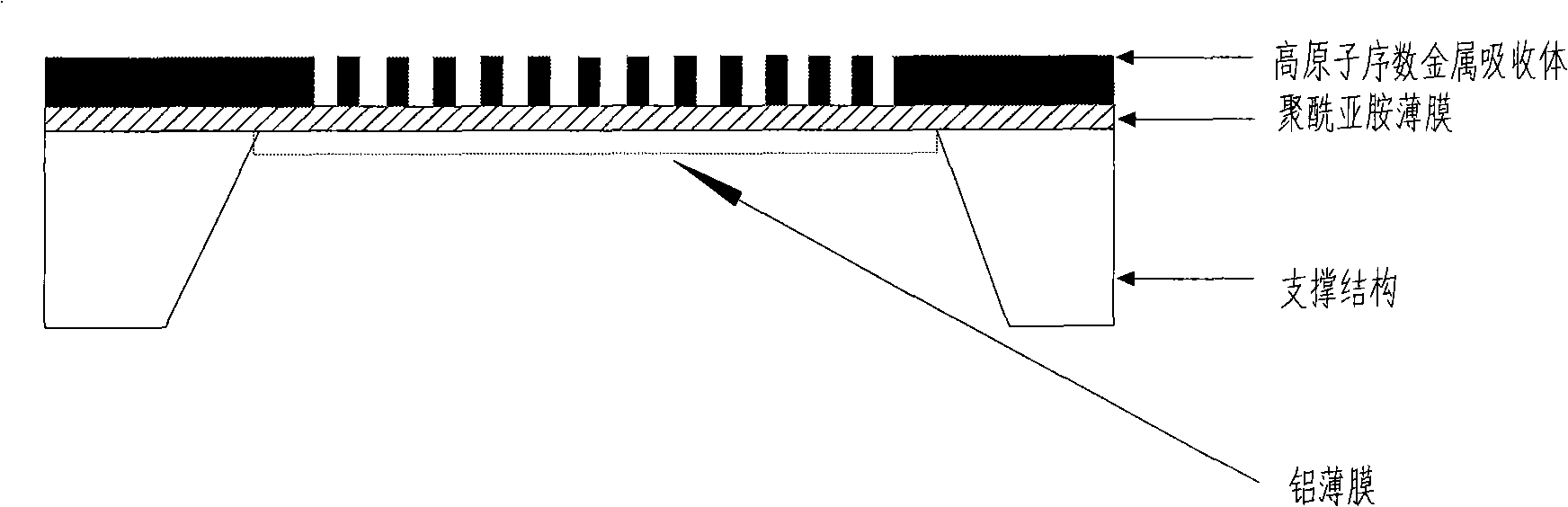
Photoetching mask structure for aeration of X-ray and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101515110ALow costSimple processPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOrganic filmHeat conducting
The invention discloses a photoetching mask structure for the aeration of X-ray. The structure, from the bottom to top, sequentially consists of a metallic film in low atomic number, a polyimide film and a metallic absorber figure in high atomic number. The invention simultaneously discloses a method for preparing the photoetching mask structure. By utilizing the method, because of the adoption of the multi-layer film structure formed by metal aluminum in low atomic number, the polyimide and the metallic absorber in high atomic number, the photoetching mask structure can be used for the X-ray photoetching on the level of micron, deep submicron and nanometer. Compared with the inorganic film based mask, the photoetching mask structure has the advantages of low cost, simple process flow and difficult cracking; and compared with the organic film based mask, the photoetching mask structure has the advantages of high mechanical strength, hard deformation and good heat conducting performance.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantitative X-ray Analysis - Multi optical path instrument
ActiveUS20160258892A1Reduced measurement timeAccurate measurementMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionX-rayEnergy based
Apparatus includes an X-ray source 10, a wavelength dispersive X-ray detector for measuring X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and an energy dispersive X-ray detector 14 again for measuring X-ray fluoresence. Selected elements are measured using the wavelength dispersive process to reduce the overall measurement time compared with using only one of the two detectors or compared to a simple approach of measuring low atomic number elements with the wavelength dispersive detector and high atomic number elements with the energy dispersive detector. The selection can take place dynamically, in particular on the basis of the results of the energy-dispersive detector.
Owner:PANALYTICAL BV
High performance X-ray sensor based on CH3NH2PbBr3 perovskite single crystals and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106856222AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyCapture moreSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic materialsX-ray
The invention discloses a high performance X-ray sensor based on CH3NH2PbBr3 perovskite single crystals and a preparation method thereof. The high performance X-ray sensor is low in cost and high in performance and can be used for digital X-ray detection. The sensor comprises 1. a CH3NH2PbBr3 perovskite single crystal substrate which is prepared by using a temperature changing crystallization method, wherein the single crystals have high crystallization quality and the preparation method is suitable for preparation of the large area substrate; 2. row electrodes which are arranged on the perovskite crystals and formed by conductive material of less X-ray absorption; and 3. column electrodes which are arranged below the perovskite crystals and mutually perpendicular to the row electrodes and formed by metal material of great conductive performance. The CH3NH2PbBr3 perovskite single crystal substrate has high thickness and high atomic number metal and has high photoelectric conversion efficiency for X-rays; besides, the recombination rate of the photo-generated carries in the CH3NH2PbBr3 perovskite single crystal substrate is low so that the X-ray sensor has high sensitivity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
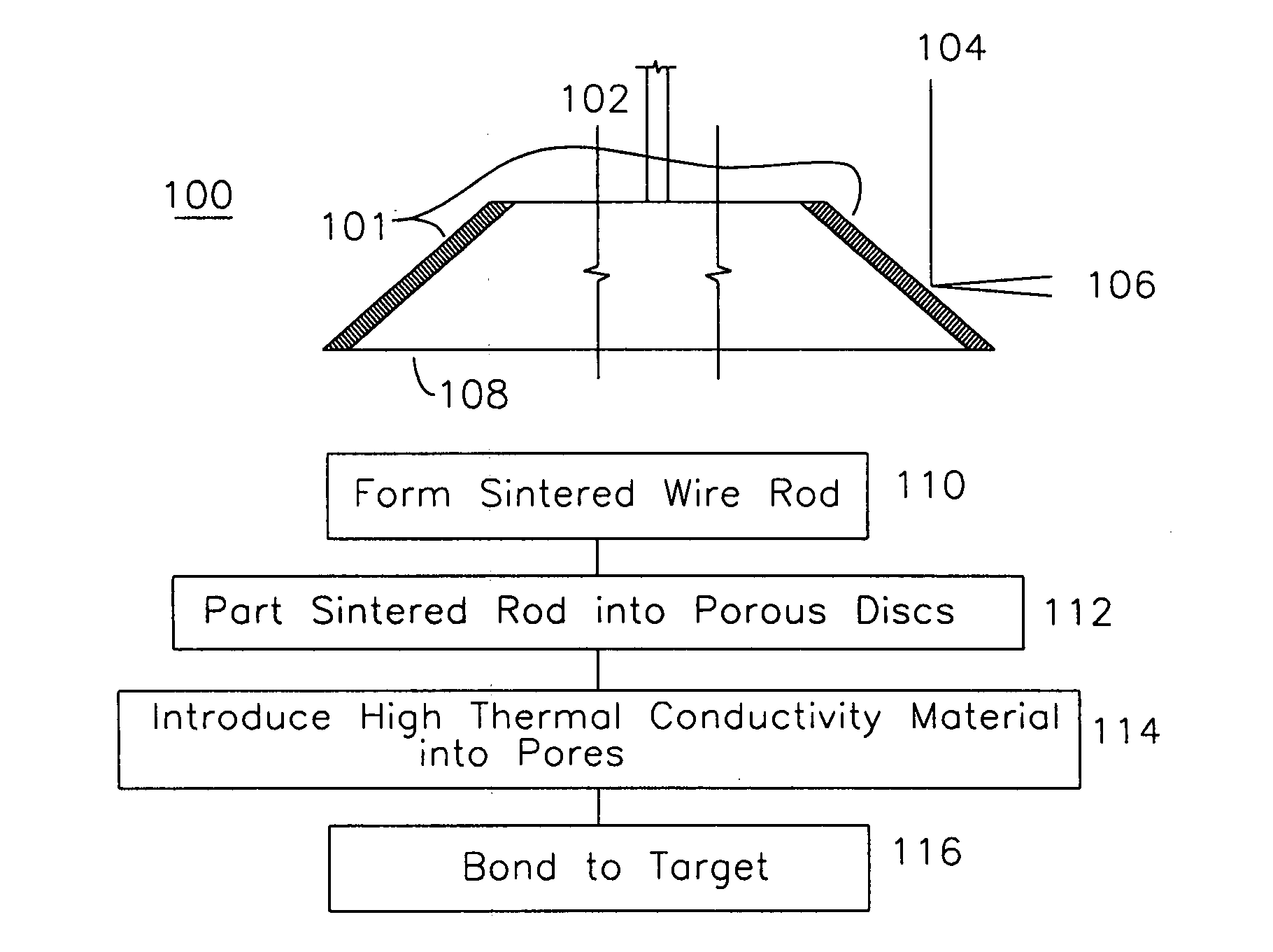
Sintered wire anode
InactiveUS7313226B1Extend cathode lifeUniform emissionX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube cathode assemblyX-rayConductive materials
A plurality of high atomic number wires are sintered together to form a porous rod that is parted into porous disks which will be used as x-ray targets. A thermally conductive material is introduced into the pores of the rod, and when a stream of electrons impinges on the sintered wire target and generates x-rays, the heat generated by the impinging x-rays is removed by the thermally conductive material interspersed in the pores of the wires.
Owner:CALABAZAS CREEK RES
Medical phantom, holder and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20050259793A1Accurate measurementAccurate verificationRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose profileEngineering
A phantom and film cassette therefor, a composition of high atomic number elements and tissue-equivalent material for a phantom, and an adjustable holder for a phantom. The film cassette comprises sections of tissue-equivalent material, wherein the sections retain a sheet of film when closed together and the phantom composition comprises tissue-equivalent material and high atomic number elements. In operation, dose distributions are determined via computation at various depths within a simulated water-equivalent phantom. After calculating dose distributions, an actual beam is delivered to a phantom containing the cassette, or utilizing a phantom containing high atomic number elements, wherein the phantom mimics human tissue, wherein the phantom houses radiographic film. Images are then generated on the film, the images are converted into an actual dose distribution, and the actual dose distribution is compared with the calculated dose distributions. Finally, a patient is treated based on the beam delivery thus verified.
Owner:YEO IN HWAN +3
Resist composition with enhanced X-ray and electron sensitivity
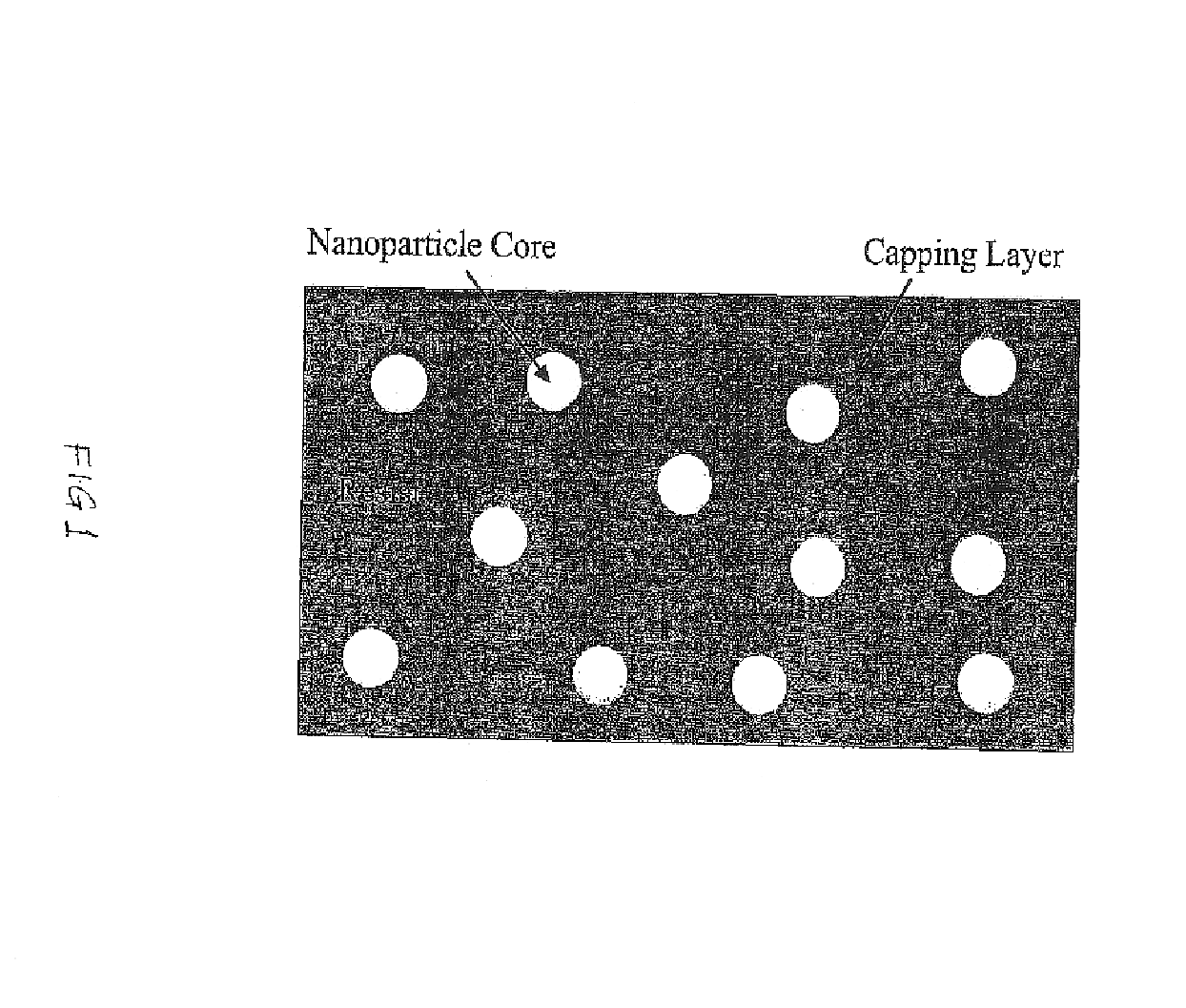
InactiveUS6858372B2High sensitivityPromote absorptionMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation applicationsSoft x rayResist
A resist composition with enhanced X-ray and electron sensitivity includes a plurality of chemically inert nanoparticles dispersed throughout a base resist material. The nanoparticles have a higher atomic number than the base resist material and each of the nanoparticles is formed by a nanoparticle core, e.g., of a noble metal, coated with an organic capping layer or shell. The latter renders the core dispersible and chemically compatible with the resist material surrounding the nanoparticle. A method of making a resist composition with enhanced X-ray and electron sensitivity is to provide a resist material and disperse chemically inert nanoparticles throughout the resist. The nanoparticles have a higher atomic number than the resist and a have core / shell structure. A resist composition with enhanced X-ray and electron sensitivity can be made by having a nanoparticle core, with a higher atomic number than the resist, that is coated with an organic capping layer. The nanoparticle with the core / shell structure is then dispersed throughout the resist material.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Radiopaque carbon-carbon linked elastomeric materials, preparation method and uses of same
InactiveUS20140106635A1Reduce mechanical resistanceHigh resistance and integrityWarp knittingAnimal housingElastomerAdhesive
An elastomeric matrix impregnated with at least 70% by weight of a high atomic number radiopaque substance, and cured with an organic peroxide, to form carbon-carbon links between elastomer molecular chains. The radiopaque elastomeric matrix may be used to create a flexible, lightweight, carbon-carbon linked, multilaminated protection material against ionizing radiation. The multilaminated protec tion material may include a mechanical reinforcement cloth layer to avoid material expansion or rupture; and additional external elastomeric layers for protection against aging, physical, biological and chemical hazards, as well as allowing mechanical memory of the material and easy cleaning, desinfection and sterilization. These layers are directly merged or incorporated into a single, fused sheet with the radiopaque elastomeric matrix, without the use of glues or adhesives, during a cure and pressure application wherein the elastomer molecules create reticulated carbon-carbon links between the internal and external elastomeric layers and through the pores of the reinforcement layer. The multilaminated material allows production of colored, flexible, lightweight, durable radiation protection articles for medical, dental, and industrial uses.
Owner:PLANIDEIA CONFECCAO DE VESTUARIO DE PROTECAO LTDA - EPP
Method for obtaining a scintillation structure
ActiveUS20090242838A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh densityScintillation crystals
A method for obtaining a scintillation body comprising the steps of readying a matrix of binding material within which is present a plurality of scintillation crystals, obtaining a plurality of channels within the matrix and around the crystals and inserting metallic material having a high atomic number and high density between mutually adjacent scintillation crystals without separating the scintillation crystals from the matrix of binding material.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Preparation and coating method of total dose radiation shielding coating layer material
ActiveCN104962128AHigh bonding strengthExtend your lifePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsSpecial surfacesSurface layerSpace environment
The invention discloses a preparation and coating method of a total dose radiation shielding coating layer material. The method concretely comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing a high atomic number material with a high-molecular polymer to obtain a mixed coating A; uniformly mixing a low atomic number material with the high-molecular polymer to obtain a mixed coating B; and coating the mixed coating A on the surface layer of a device shell in order to form a high atomic number material layer, and coating the mixed coating B on the surface of the high atomic number material layer to form a low atomic number material layer. The method for preparing the total dose radiation shielding coating layer material and coating the inner wall of the product shell allows the coating layer of the coating layer material to stand up the emission stage of a spacecraft and in-orbit space environment, and the coating layer greatly improves the space total dose radiation environment resistance of the coated product.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Isotopic response with small scintillator based gamma-ray spectrometers
ActiveUS8101919B2Improve noiseEnhances search mode of operationPhotometryFluorescence/phosphorescenceGamma ray spectrometerData stream
The intrinsic background of a gamma ray spectrometer is significantly reduced by surrounding the scintillator with a second scintillator. This second (external) scintillator surrounds the first scintillator and has an opening of approximately the same diameter as the smaller central scintillator in the forward direction. The second scintillator is selected to have a higher atomic number, and thus has a larger probability for a Compton scattering interaction than within the inner region. Scattering events that are essentially simultaneous in coincidence to the first and second scintillators, from an electronics perspective, are precluded electronically from the data stream. Thus, only gamma-rays that are wholly contained in the smaller central scintillator are used for analytic purposes.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Medical isotope generation method and device based on laser wake-field accelerator
The invention provides a medical isotope generation method and device based on a laser wake-field accelerator. Interaction between super-strong and super-short lasers and plasma is utilized to generate a strong flow relativity electron beam. The electron beam is utilized to irradiate a high atomic number target to generate high-flow-strength bremsstrahlung gamma light. The bremsstrahlung gamma light bombards an interested object target to induce a ([gamma], xn+yp) photonuclear reaction or a ([gamma], [gamma]') optical excitation reaction, and object isotopes including gamma rays, electrons, positive electrons and [alpha] particle emitters are generated. By adopting the method provided by the invention, radio isotopes higher in activity are generated, and the cost is relatively low; in addition, the device provided by the invention is compact and convenient to carry, and the device is capable of being placed near a large-sized medical mechanism to be better applied to and serve radiation diagnosis, targeting treatment and other medical applications.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com