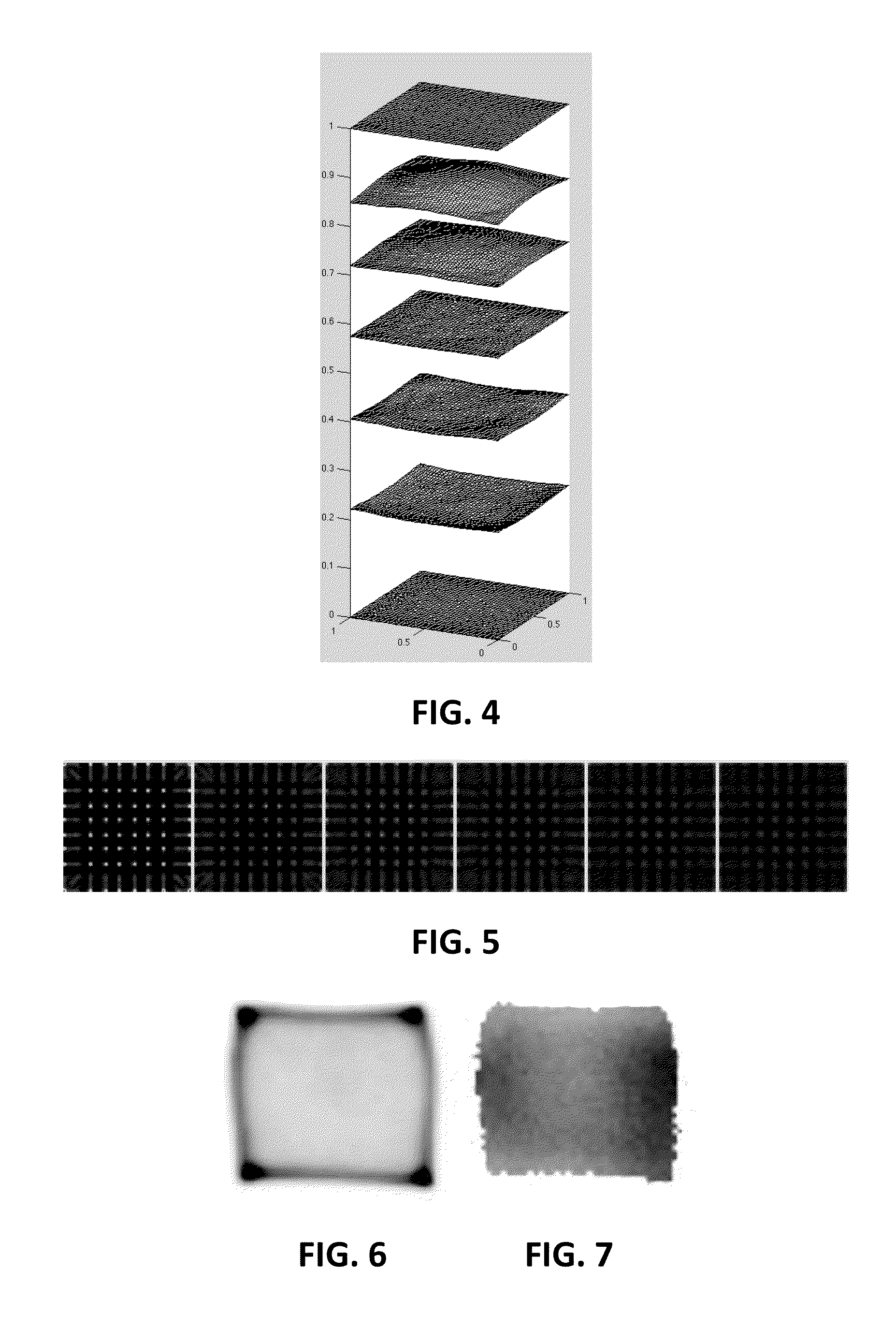
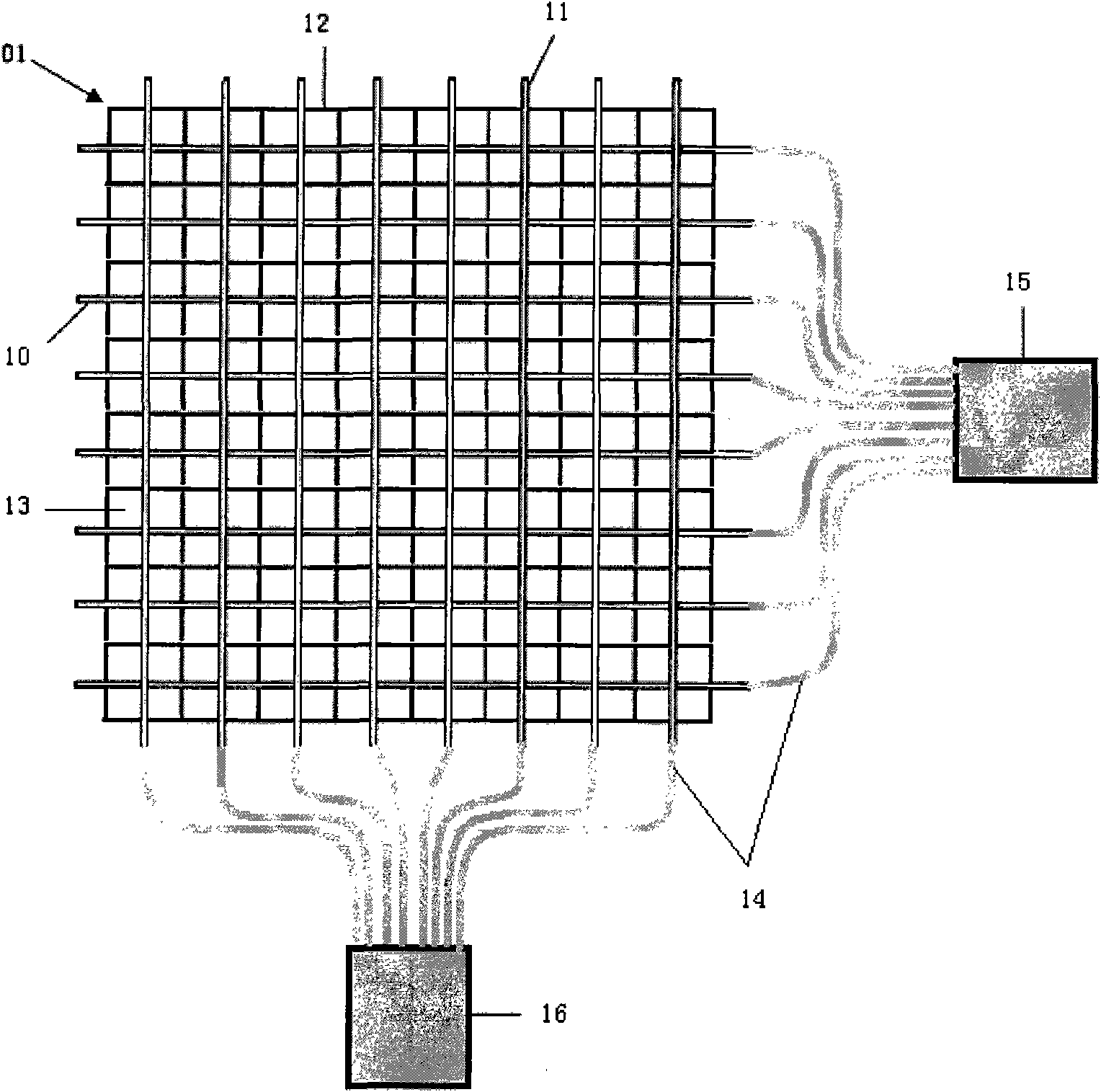
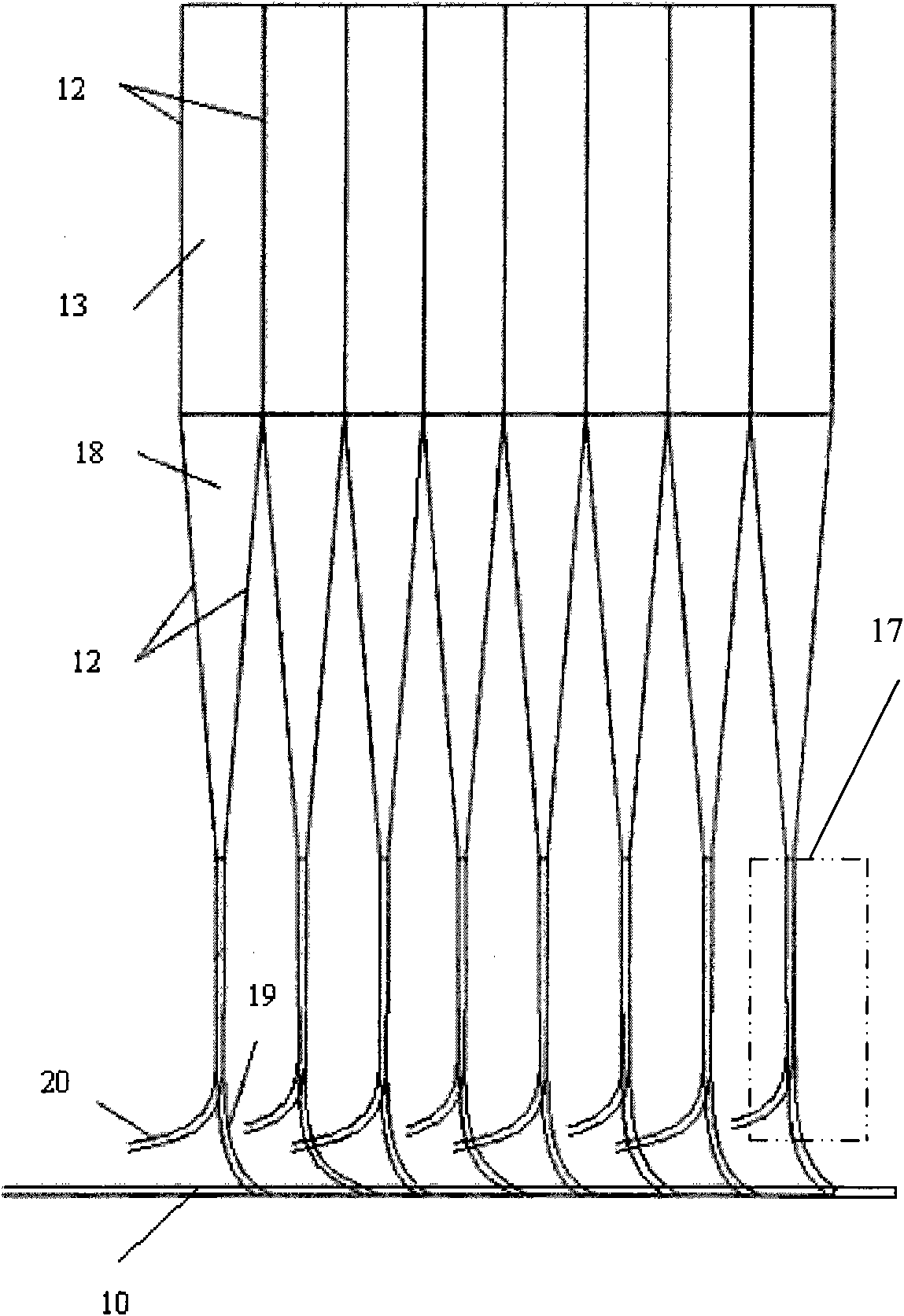
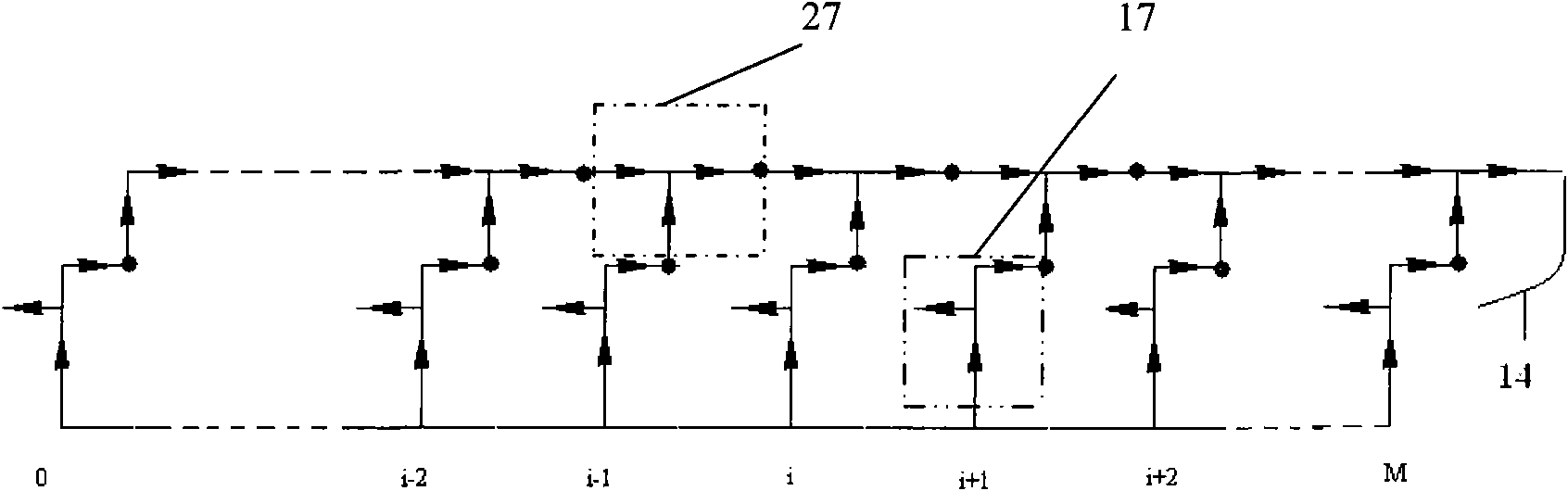
Patents
Literature
667 results about "Scintillation crystals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
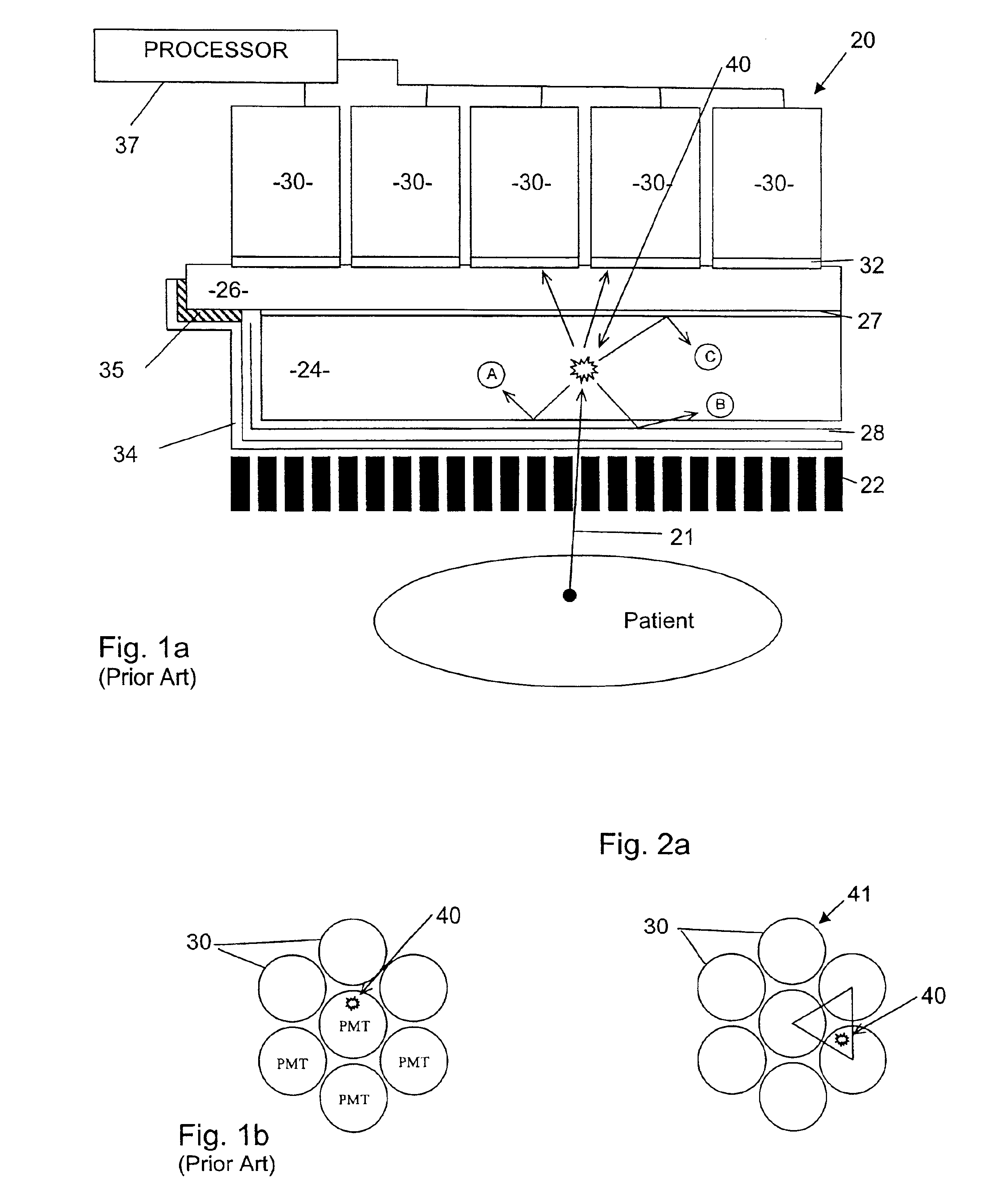
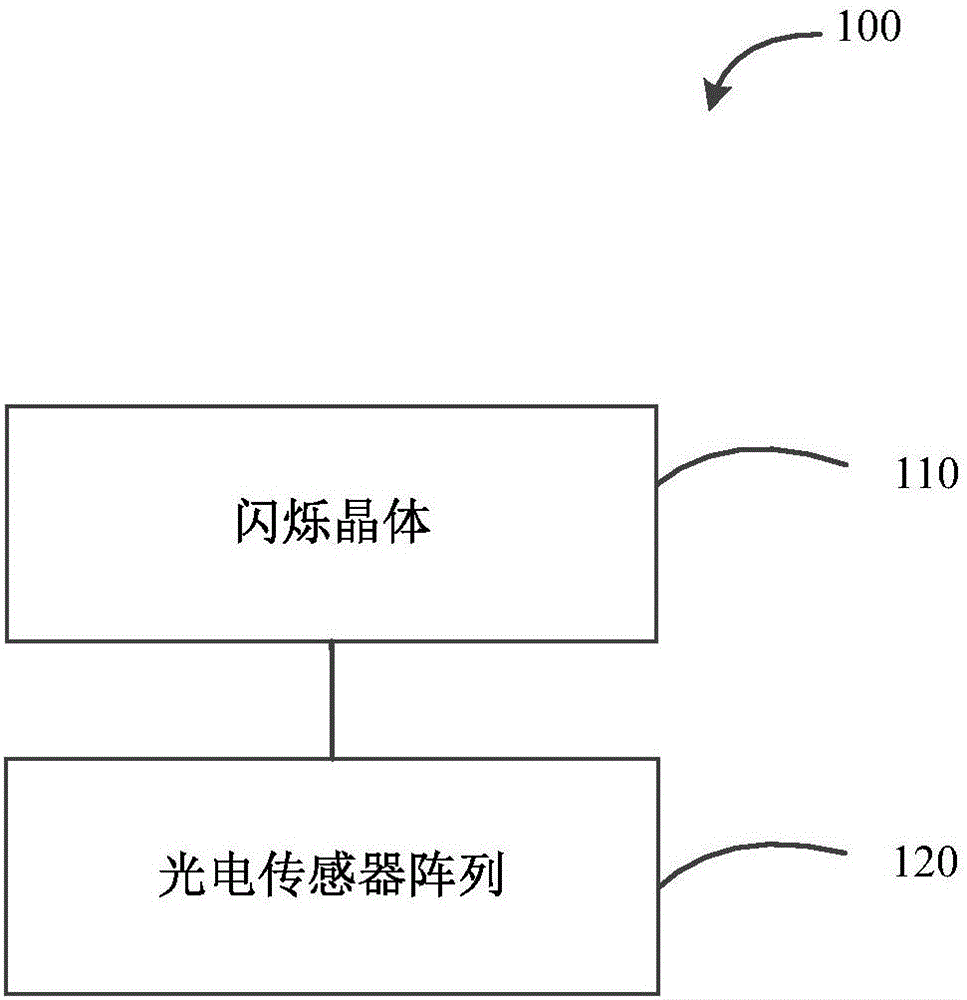
Scintillation crystals are used in detectors to convert X-rays or Gamma rays into light pulses that are subsequently detected by either a photomultiplier tube (PMT) or a photodiode (SiPM).
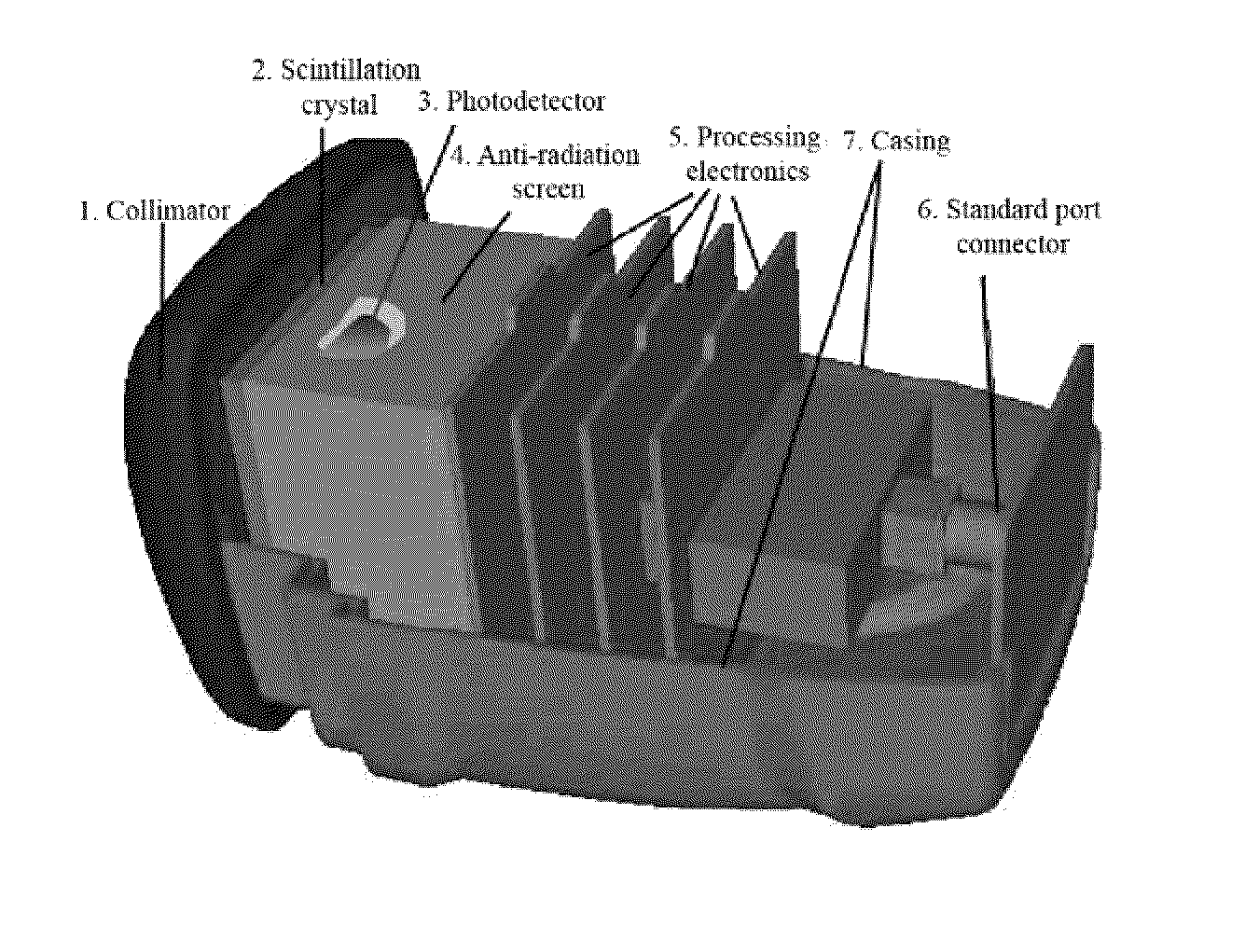
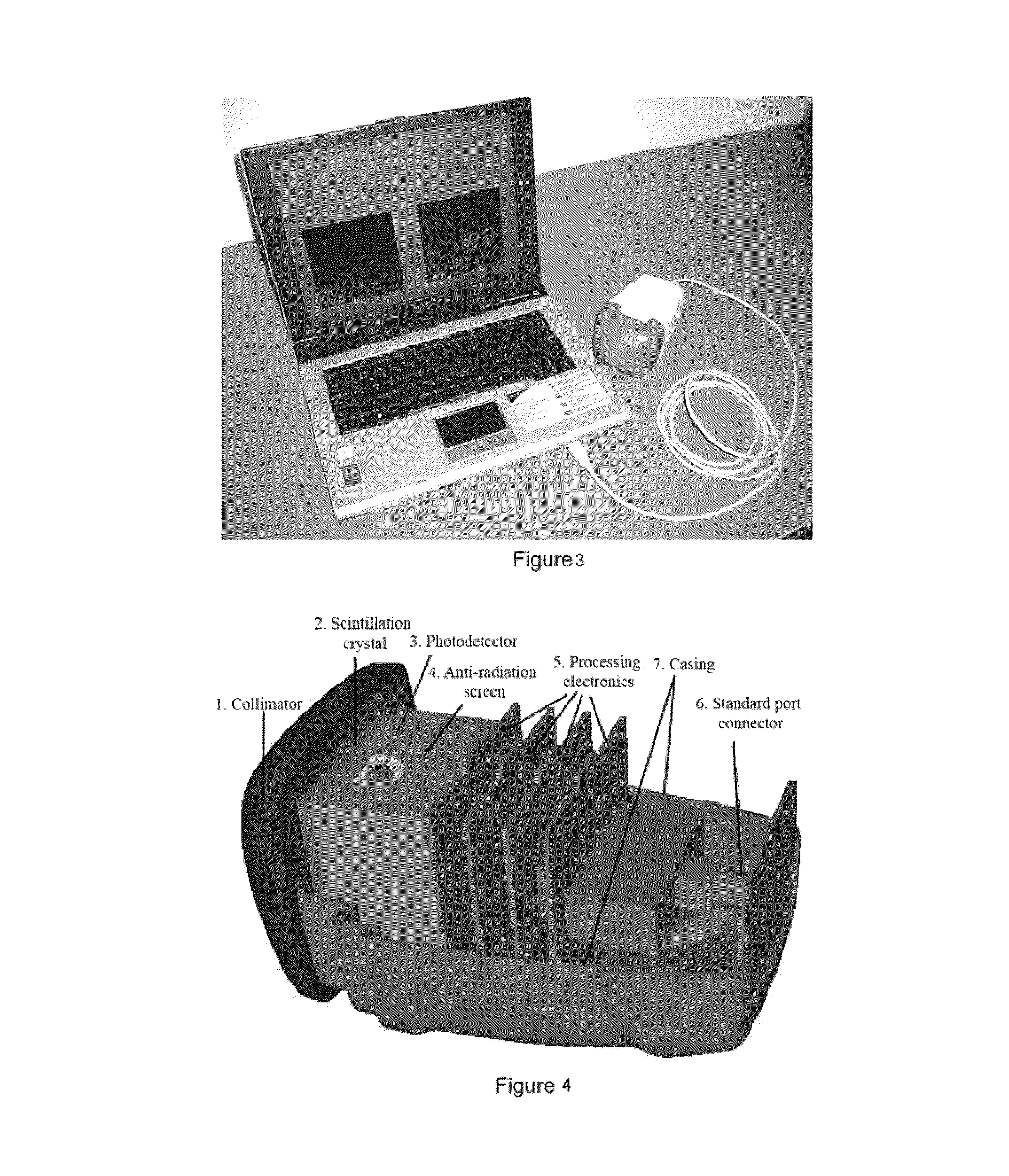
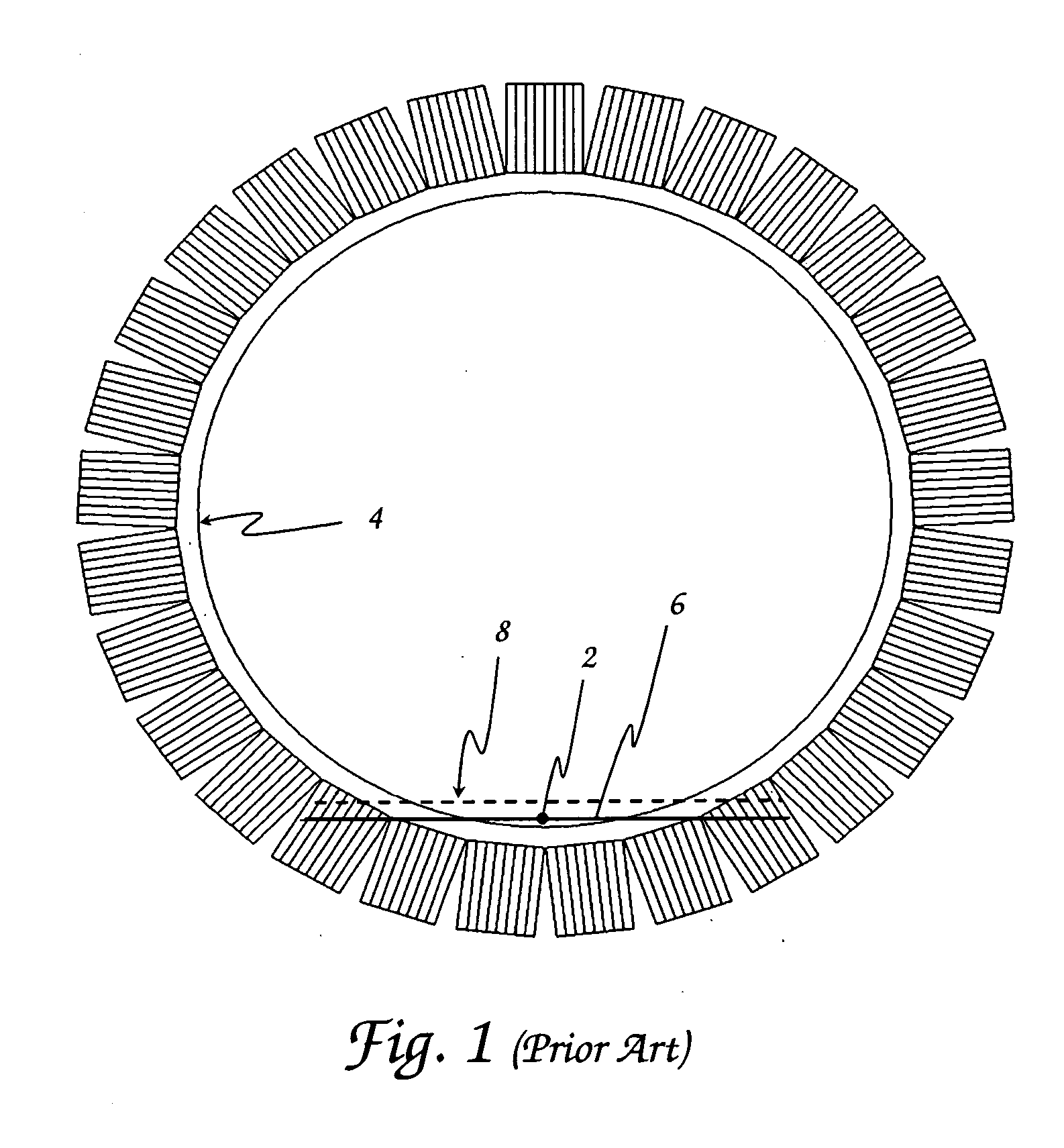
Stand-alone mini gamma camera including a localization system for intrasurgical use
ActiveUS8450694B2Surgical navigation systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansLocalization systemThe Internet
The invention relates to a portable mini gamma camera for intrasurgical use. The inventive camera is based on scintillation crystals and comprises a stand-alone device, i.e. all of the necessary systems have been integrated next to the sensor head and no other system is required. The camera can be hot-swapped to any computer using different types of interface, such as to meet medical grade specifications. The camera can be self-powered, can save energy and enables software and firmware to be updated from the Internet and images to be formed in real time. Any gamma ray detector based on continuous scintillation crystals can be provided with a system for focusing the scintillation light emitted by the gamma ray in order to improve spatial resolution. The invention also relates to novel methods for locating radiation-emitting objects and for measuring physical variables, based on radioactive and laser emission pointers.
Owner:GENERAL EQUIP FOR MEDICAL IMAGING SL +2
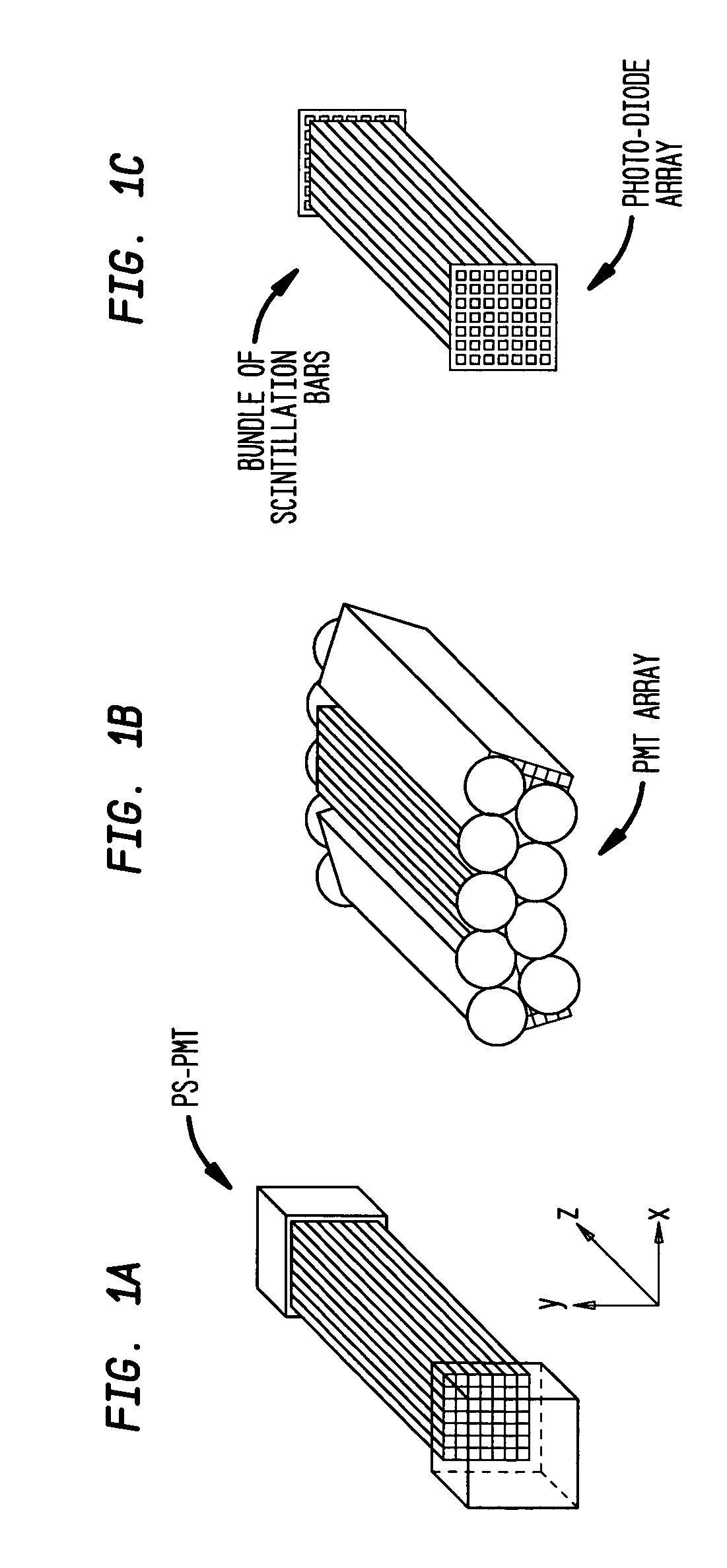
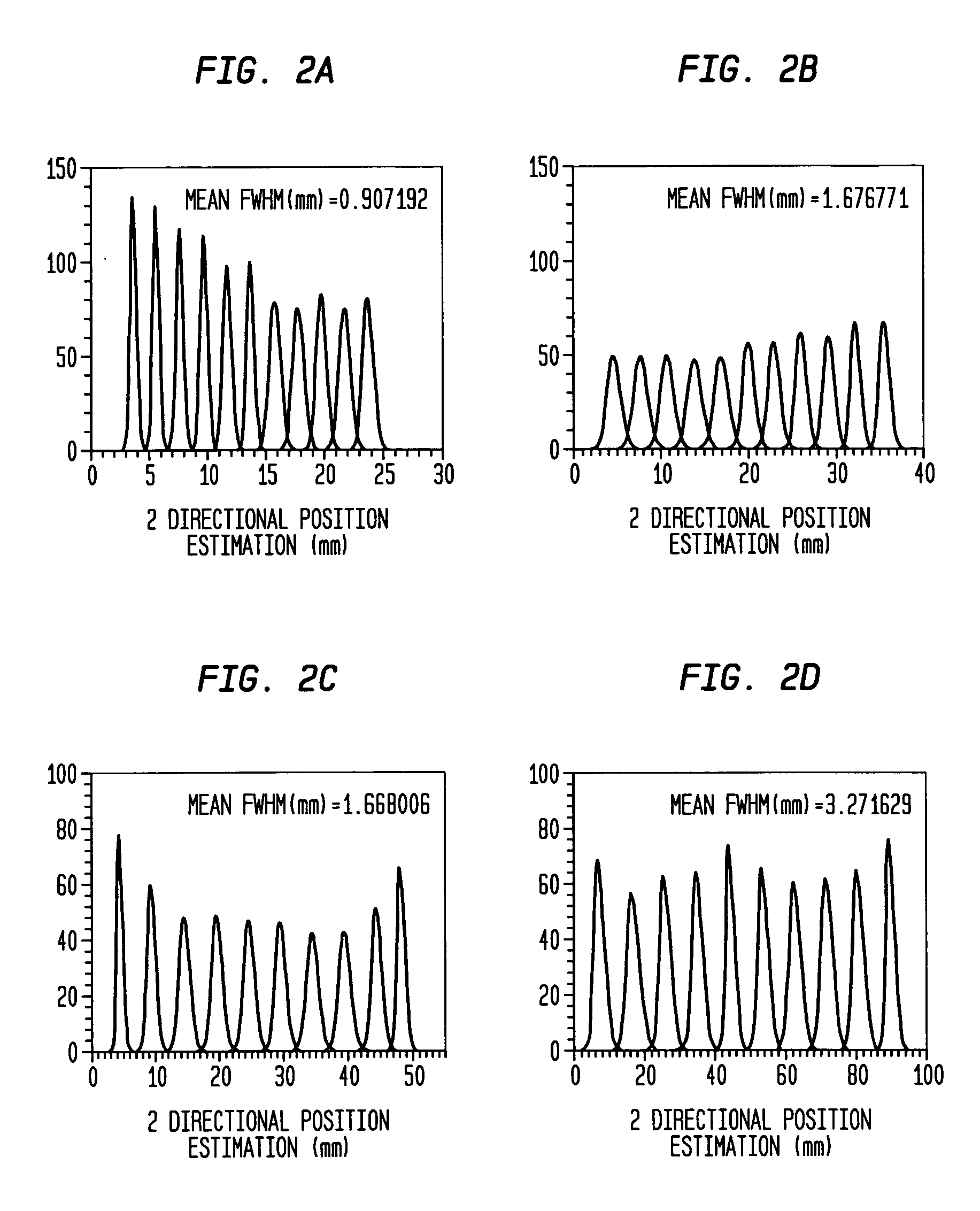
Nuclear imaging system using scintillation bar detectors and method for event position calculation using the same
InactiveUS20050006589A1Improve spatial resolutionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansScintillation crystalsCompanion animal
A gamma camera having a scintillation detector formed of multiple bar detector modules. The bar detector modules in turn are formed of multiple scintillation crystal bars, each being designed to have physical characteristics, such as light yield, to achieve a sufficient spatial resolution for nuclear medical imaging applications. According to another aspect of the invention, the bar detector modules are arranged in a three-dimensional array, where each module is made up of a two-dimensional array of bar detectors with at least one photosensor optically coupled to each end of the module. Such a camera can be used for both PET (coincidence) and single photon imaging applications. According to another aspect of the invention, a bar detector gamma camera is provided, which utilizes an improved positioning algorithm that greatly enhances spatial resolution in the z-axis direction (i.e., the direction along the length of the scintillation crystal bar).
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Multiplexing readout scheme for a gamma ray detector
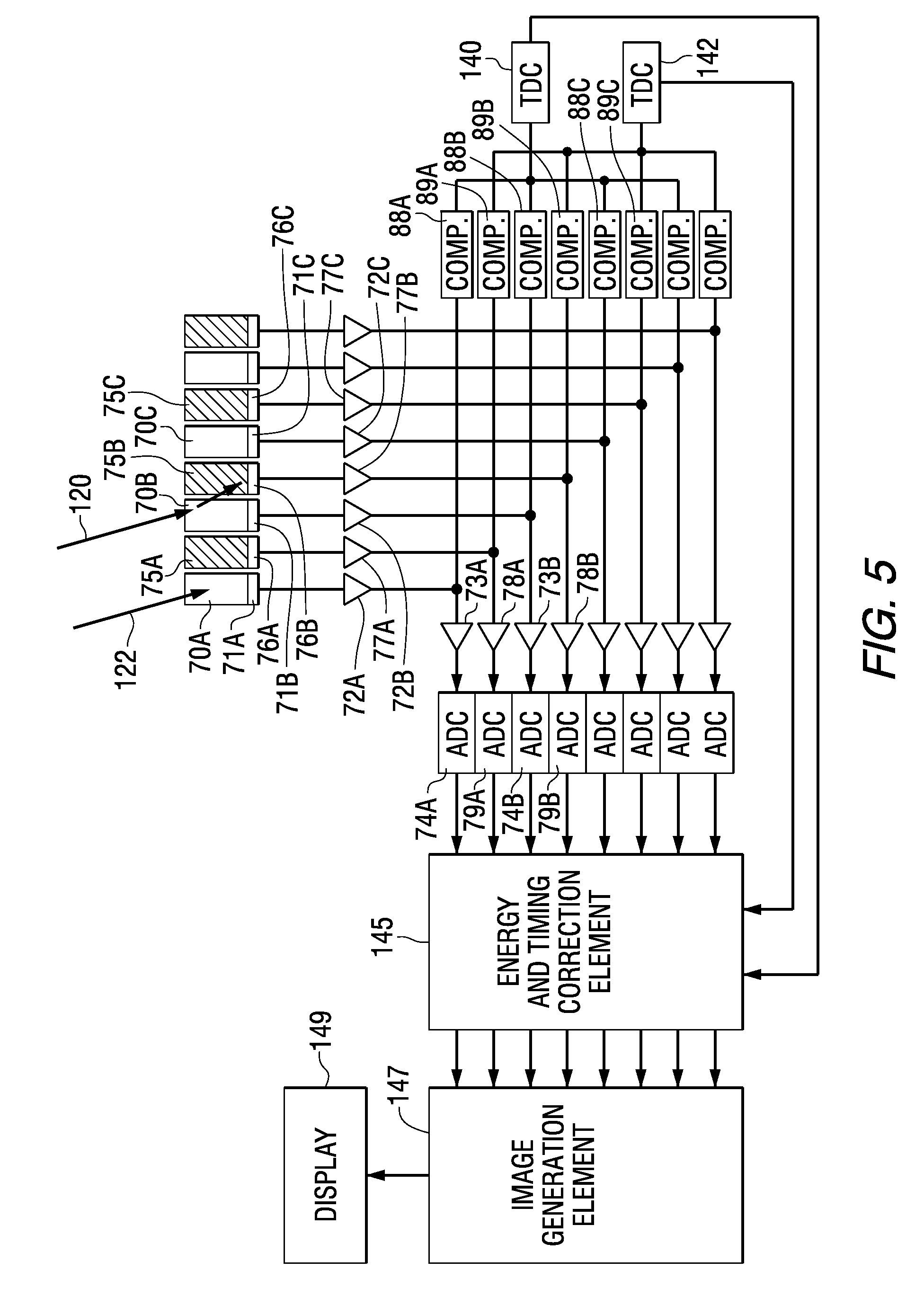
A method for producing a PET image of a tissue using a PET scanner, the scanner comprising a plurality of scintillation crystals (70X / 75X) and a plurality of detectors (71X / 76X). The method comprises forming a first crystal group (160X) including a first subset of the plurality of crystals; forming a second crystal group (164X) including a second subset of the plurality of crystals, wherein crystals comprising the first crystal group (160X) are different from crystals comprising the second crystal group (164X); converting a first beam (120) striking one or more crystals of the first crystal group (70X / 160X) to a first electrical signal (94); converting a second beam striking one or more crystals of the second crystal group (75X / 164X) to a second electrical signal (98), wherein the second beam is scattered from the first beam; determining one or both of a first and a second timing relationship, wherein the first timing relationship (Δt2) is a time interval between a value of the first electrical signal (94) and a time reference (t1), and the second timing relationship (Δt3) is a time interval between a value of the second electrical signal (98) and the time reference (t1); correcting the second electrical signal (98) to produce a corrected second electrical signal using a correction factor derived from at least one of the first and the second timing relationships to compensate for energy in the second signal scattered from the first signal; and creating an image of the tissue (12) using the corrected second electrical signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Gamma-ray spectrometry
InactiveUS6940071B2Improve resolutionEnhanced signalX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansΓ ray spectrometryImage resolution
Different geometries of scintillation spectrometers are disclosed which provide improved resolution over prior art scintillation spectrometers. By ensuring that photons generated by scintillation events occurring in different locations within the scintillation material generate similar light profiles on the photo-detector, the output signal is made less sensitive to the initial interaction site. This can be achieved in a number of ways, such as: by limiting the exit window of the scintillation crystal to a smaller detector, by introducing an optical spacer (94) between the scintillation crystal and detector (99), and / or by making the crystal longer than necessary to stop the gamma rays. A principal advantage of these new geometries is that deconvolution of the raw-data is more effective, thus improving resolution.
Owner:SYMETRICA
Positron emission tomography detector for multilayer scintillation crystal
ActiveCN102707310AImprove detection efficiencyImprove spatial resolutionMeasurement with scintillation detectorsRadiation diagnosticsImaging qualityScintillation crystals
A positron emission tomography detector for a multilayer scintillation crystal comprises a plurality of layers of scintillation crystals, a photoelectric detector system and an algorithm system, wherein the multilayer scintillation crystals comprises n layers of array scintillation crystals and m layers of continuous scintillation crystals, both n and m are integers which are greater than or equal to 1, the sum of n and m is smaller than or equal to 10, the array scintillation crystals are formed by arraying strip-type scintillation crystals along the width and length directions, the continuous scintillation crystals are scintillation crystals which have uncut inner parts, the array scintillation crystals and the continuous scintillation crystals are sequentially coupled along the height direction of the strip-type scintillation crystals to form the multilayer scintillation crystals, and the bottoms of the continuous scintillation crystals are coupled with the photoelectric detector system. The positron emission tomography detector can more accurately obtain the position and the time of energy deposition of gamma photon in the scintillation crystal, and has higher detection efficiency of the gamma photon, the spatial resolution, the time resolution and the flexibility of a positron emission tomographic imaging system can be improved when the positron emission tomography detector is applied to the positron emission tomographic imaging system, and further, the imaging quality of the system can be improved.
Owner:RAYCAN TECH CO LTD SU ZHOU
Scintillation detector, system and method providing energy and position information
InactiveUS6909097B2Lower performance requirementsMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementScintillation crystalsSingle crystal
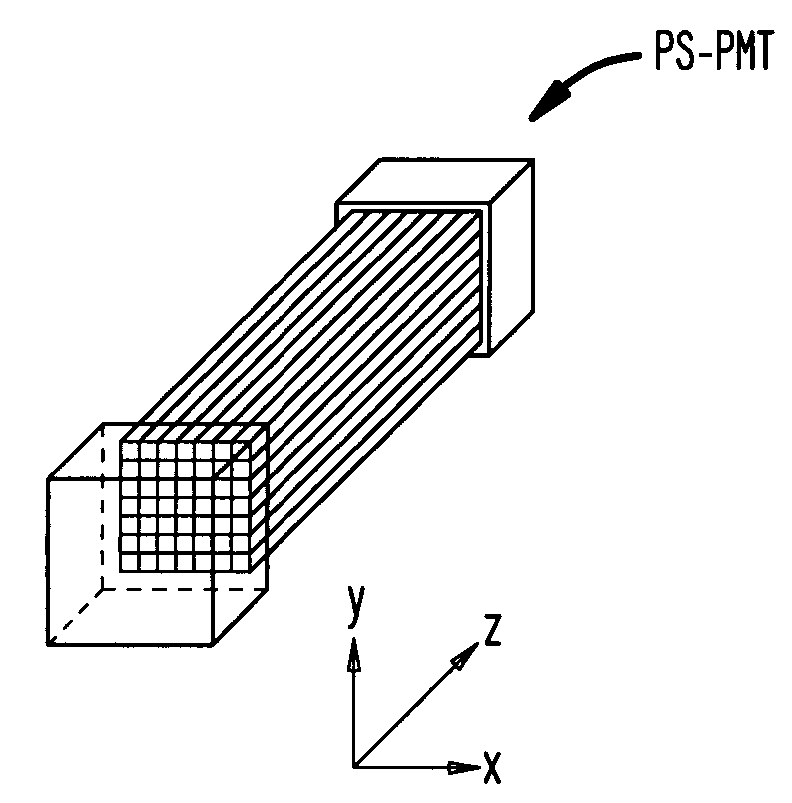
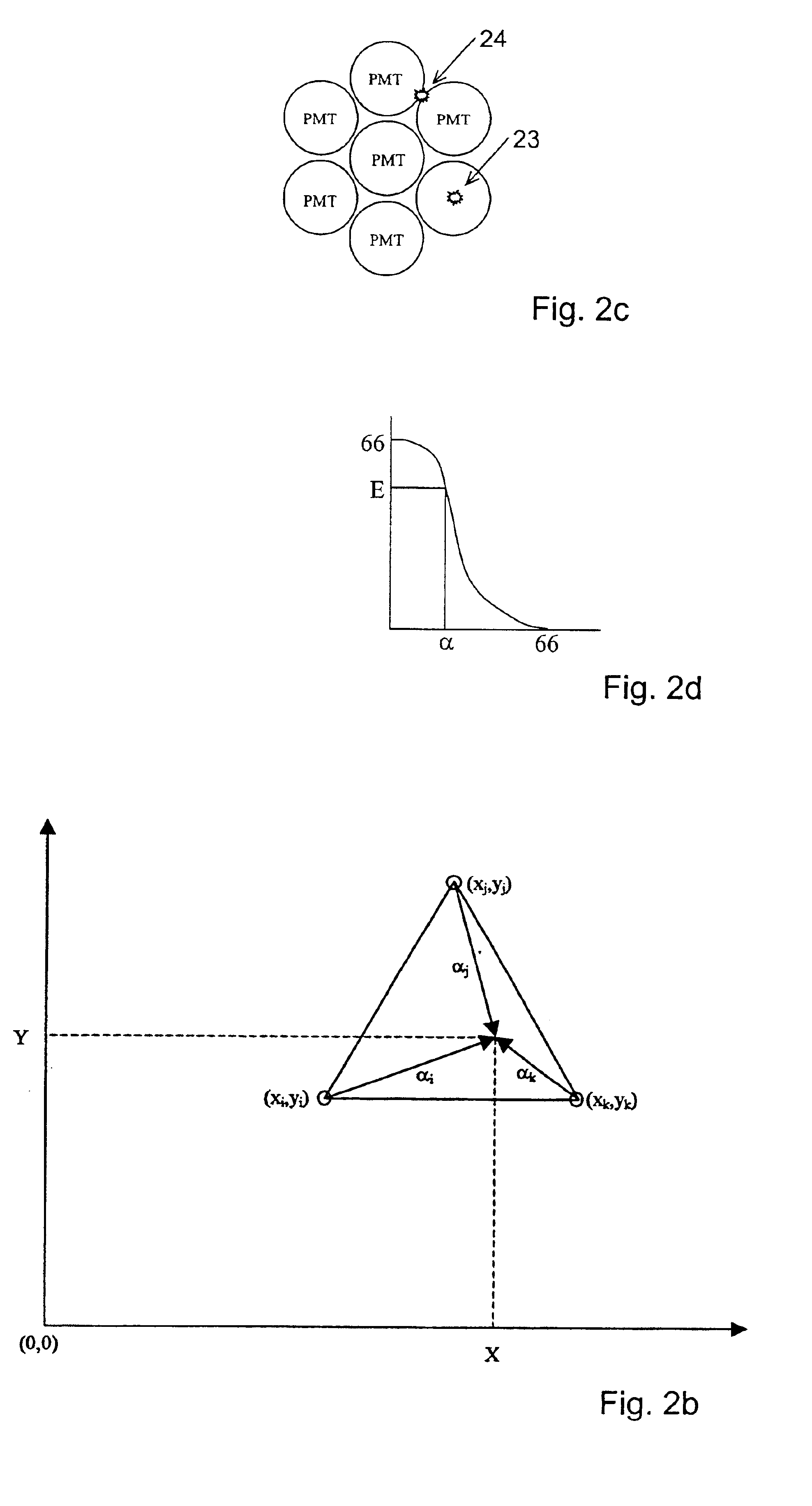
A radiation detector, in particular a gamma camera, is constructed and operated in such a fashion that only a predetermined number of light sensors (such as PMT's) adjoining each other in a cluster are used to generate a signal with amplitude and event position information. The camera may also use an array of individual scintillation elements (crystals) in place of a single crystal, with certain advantages obtained thereby. According to another aspect of the invention, there is a reflector sheet that defines an array of apertures through which scintillation light can pass from the scintillation crystal to a plurality of light sensors optically coupled to an optical window in an array corresponding to the array of apertures in the reflector.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CERAMICS & PLASTICS INC
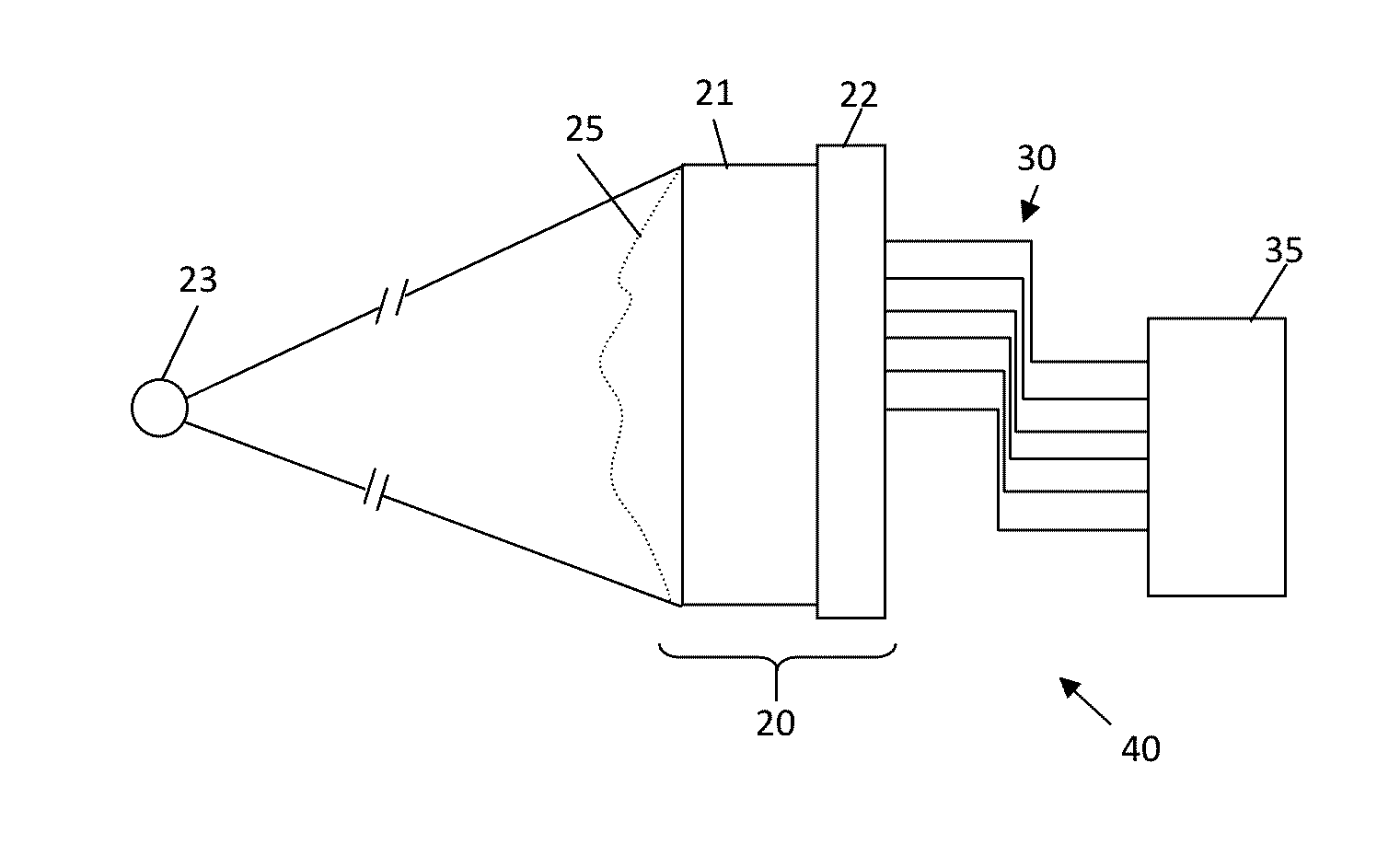
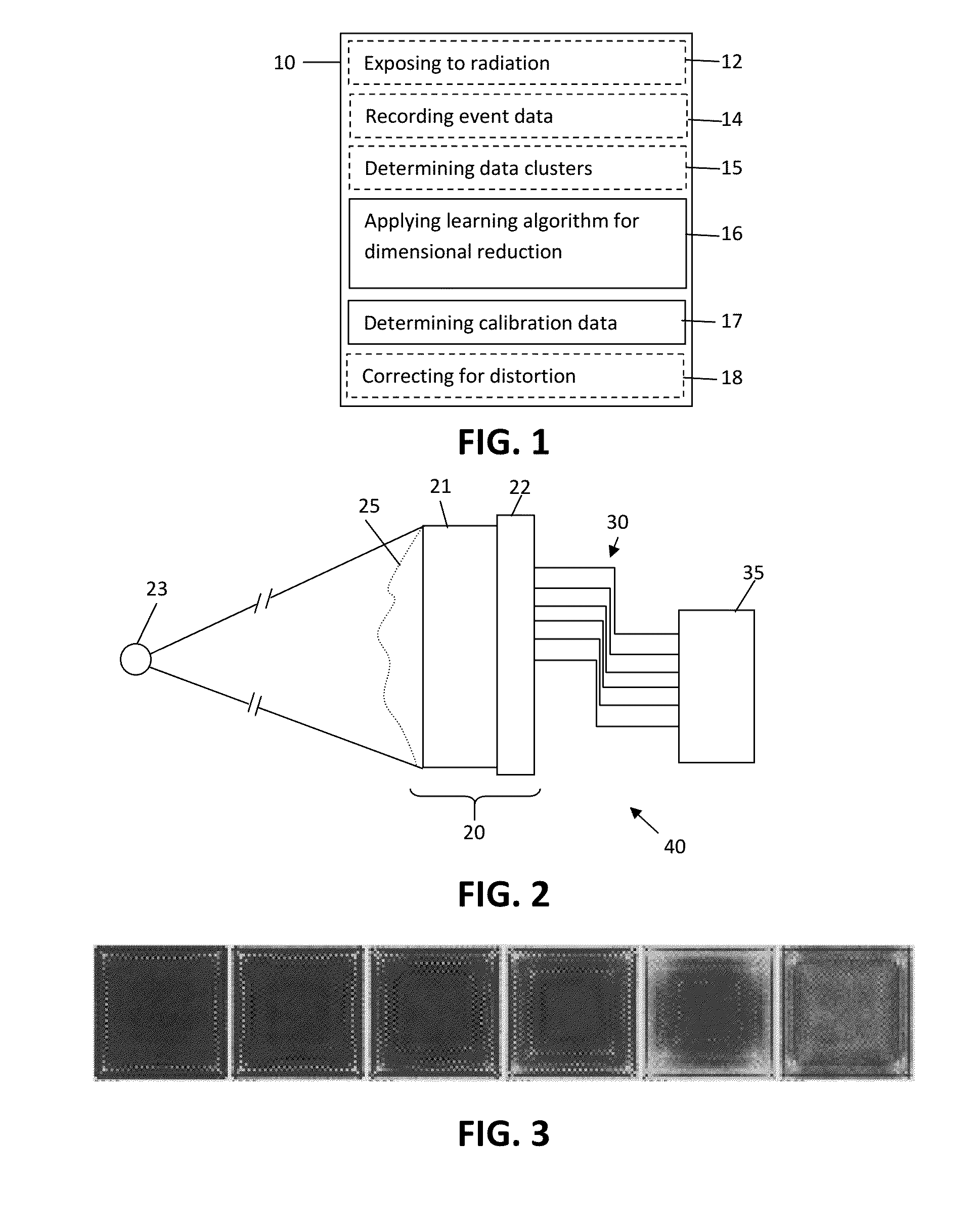
Calibration of monolithic crystal-based detectors
ActiveUS20150276953A1Simple and efficient calibrationCheap and simple methodTesting/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsScintillation crystalsEvent data
A calibration method for calibrating at least one gamma radiation detector includes a monolithic scintillation crystal. The calibration method comprises obtaining event data for a plurality of scintillation events. The event data for each scintillation event includes a plurality of location sensitive signals observed by the at least one gamma radiation detector to be calibrated, applying an unsupervised learning algorithm to embed the event data on a low-dimensional manifold, and obtaining calibration data considering the low-dimensional manifold embedding.
Owner:MOLECUBES
Scintillation crystal array detecting device
InactiveCN101644780AReduce the numberLow costX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentImage resolutionLight guide
The invention relates to a scintillation crystal array detecting device, which comprises a crystal array, M*N light guides, an optical fiber splitter unit, an optical fiber merging unit and an opticalfiber signal reading unit, wherein the crystal array comprises M*N crystals for generating fluorescence photons, M represents the number of rows, and N represents the number of columns; each light guide is connected with the surface of a crystal to collect and transmit the fluorescence photons generated by the crystal; the optical fiber splitter unit is used for splitting fluorescence photons transmitted by each light guide into two paths of optical fibers which are a row transmission optical fiber and a column transmission optical fiber to transmit the fluorescence photons; the optical fibermerging unit is used for fusing row transmission optical fibers corresponding to light guides connected with the same row of crystals into a row optical fiber and fusing column transmission optical fibers corresponding to light guides connected with the same column of crystals into a column optical fiber; and the optical fiber signal reading unit is connected with the row optical fibers and the column optical fibers to recognize the numbers of the rows in which the row optical fibers transmitting the fluorescence photons are and the numbers of the columns in which the column optical fibers transmitting the fluorescence photons are to further determine the position of scintillation crystals and detect the total quantity and energy of received fluorescence photons. The device is reduced incost, volume and weight and has high position resolution and fluorescence collection efficiency.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Data acquisition system for nuclein and fluorescent dual module integral small animal molecules imaging
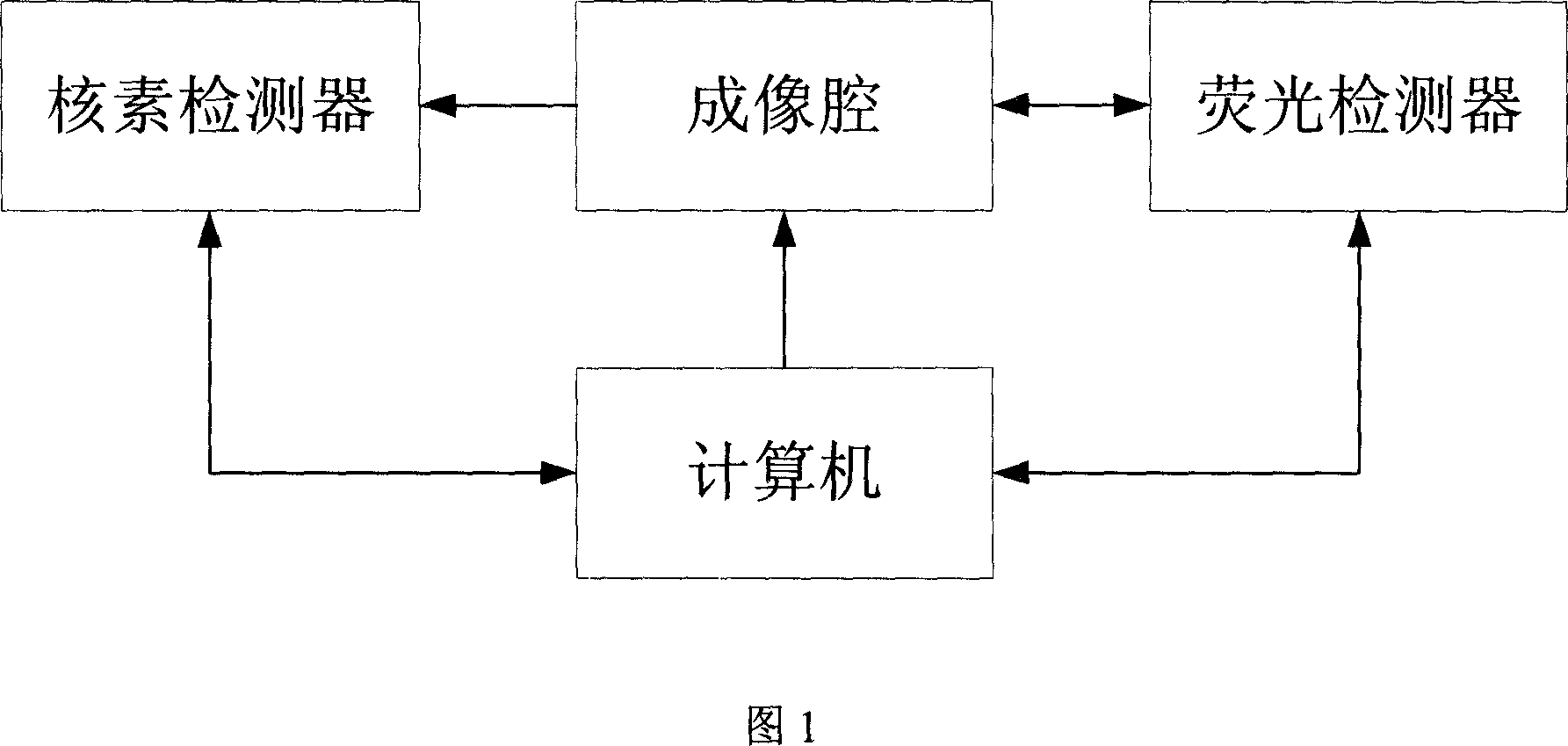
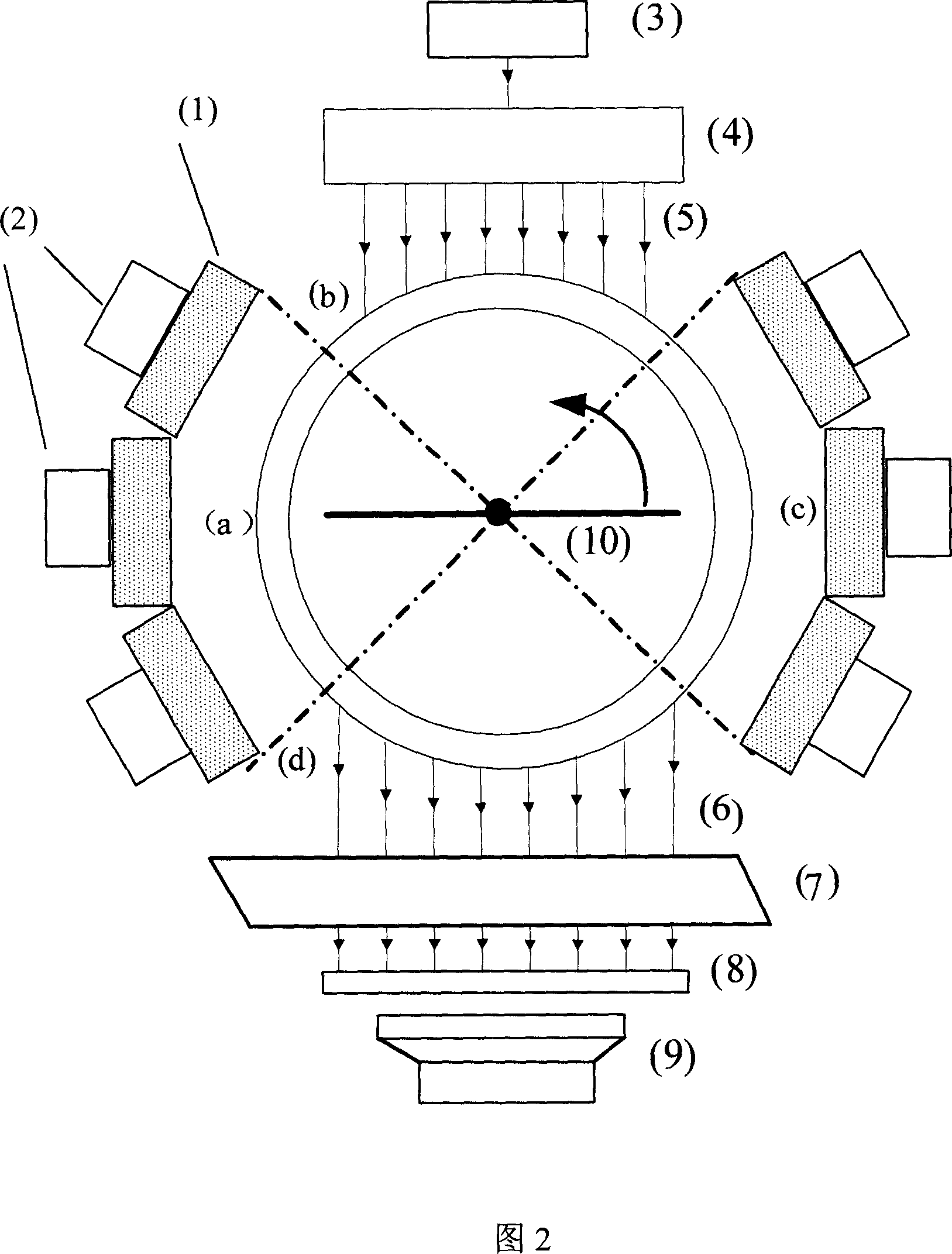
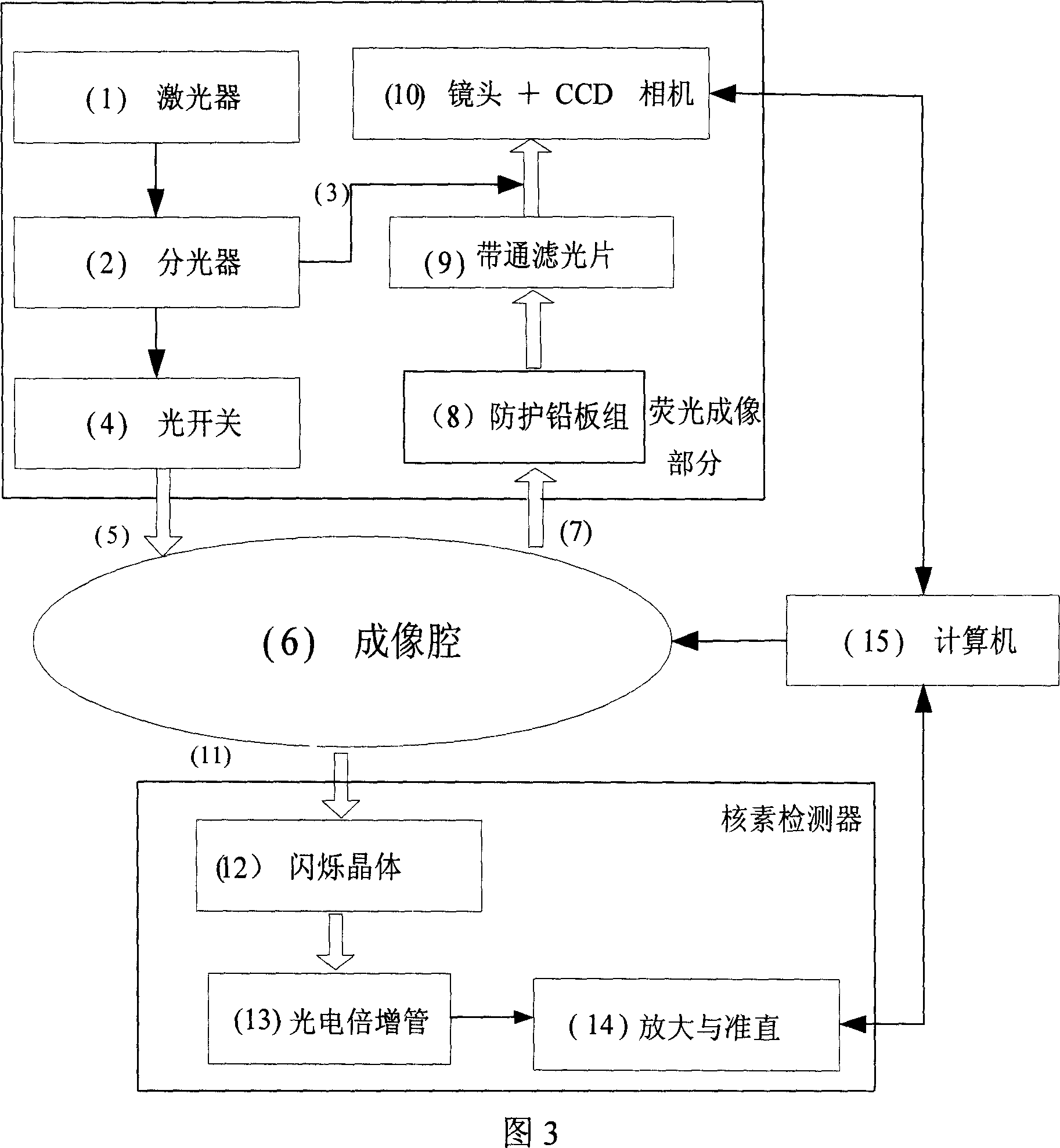
InactiveCN101057788ASmall doseEasy to implementSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsQuantum yieldScintillation crystals
The invention belongs to the field of application of near-infrared laser, nuclear irradiation, electron and image rebuild in systematic biology and medicine. It is characterized in that high-specificity nuclear species and fluorescent probe are implanted in live animal to realize double mark of muscle deep layer or internal organ tumor cell. The emission signal of nuclear species is checked by sensitive electron-multiplier phototube in array copulation position of scintillation crystal; feeble fluorescent signal generated by visible light or infrared agitation is checked by high quantum yield CCD camera. The two checking systems are orthogonally arranged in the same surface, the live nuclear species and fluorescent signal can be checked simultaneously through rotary image cavity, and double module three dimensional tomography image of small animal can be rebuilt with software algorism. The invention is characterized by multi-image forming modules, abundant information and simple operation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
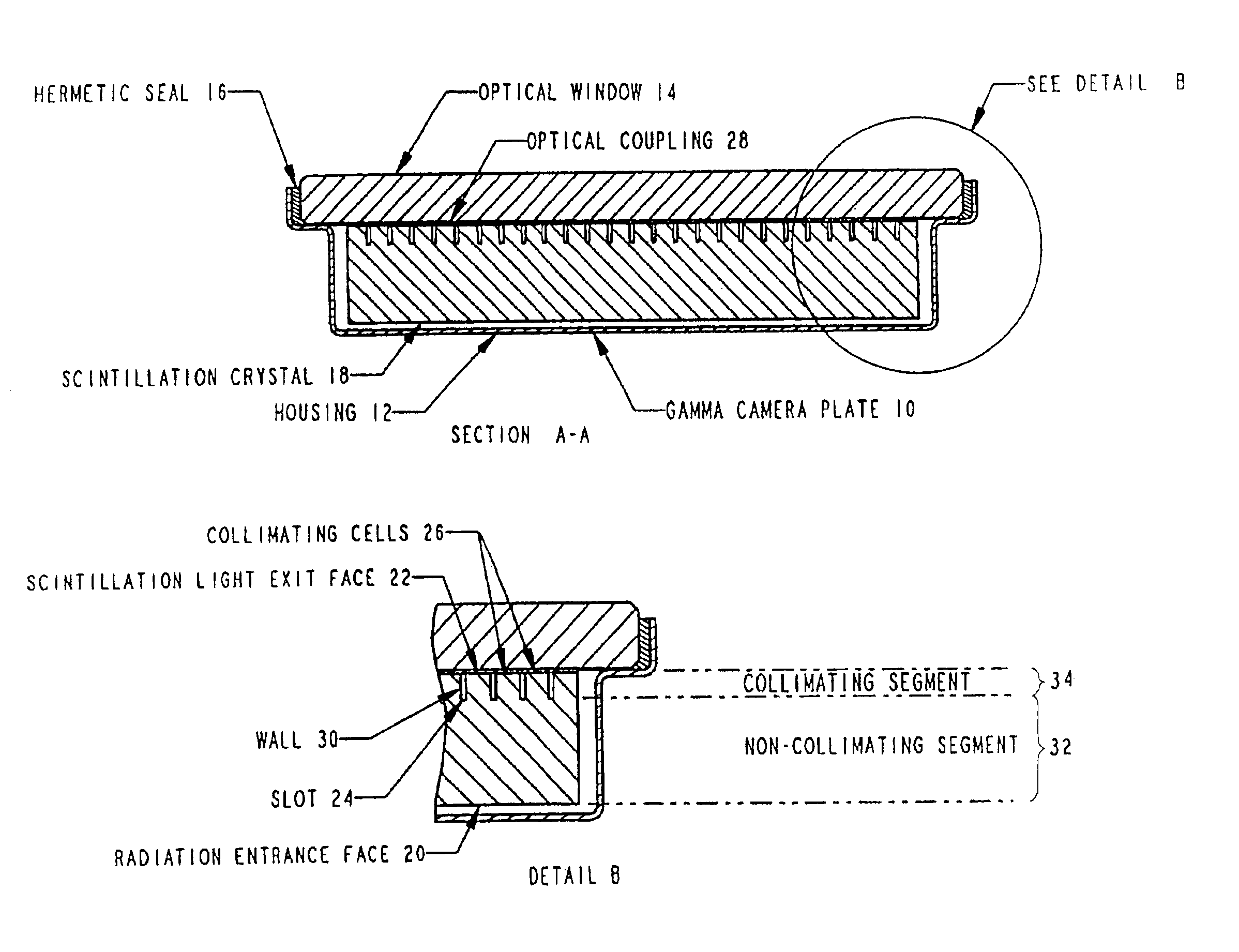
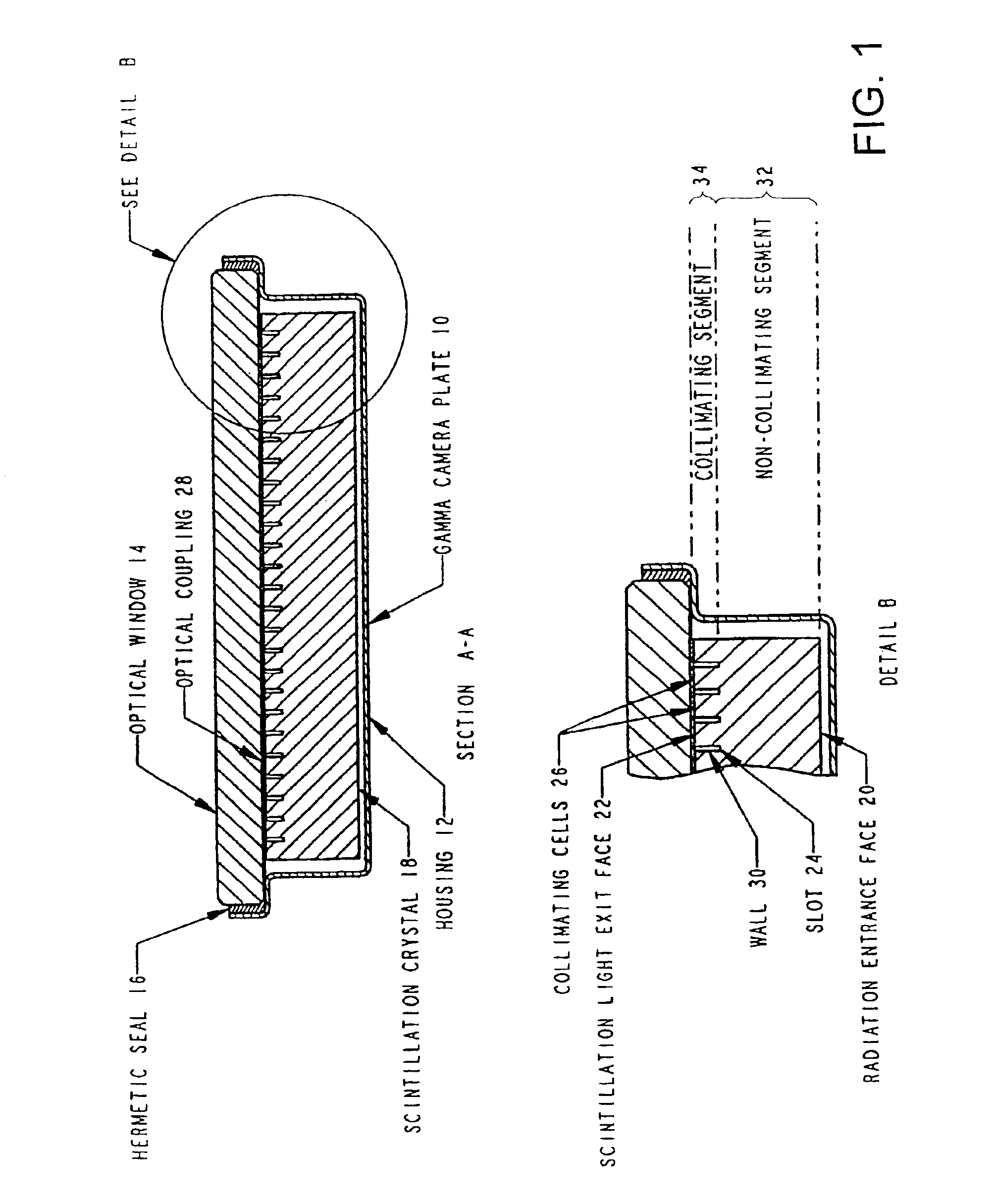
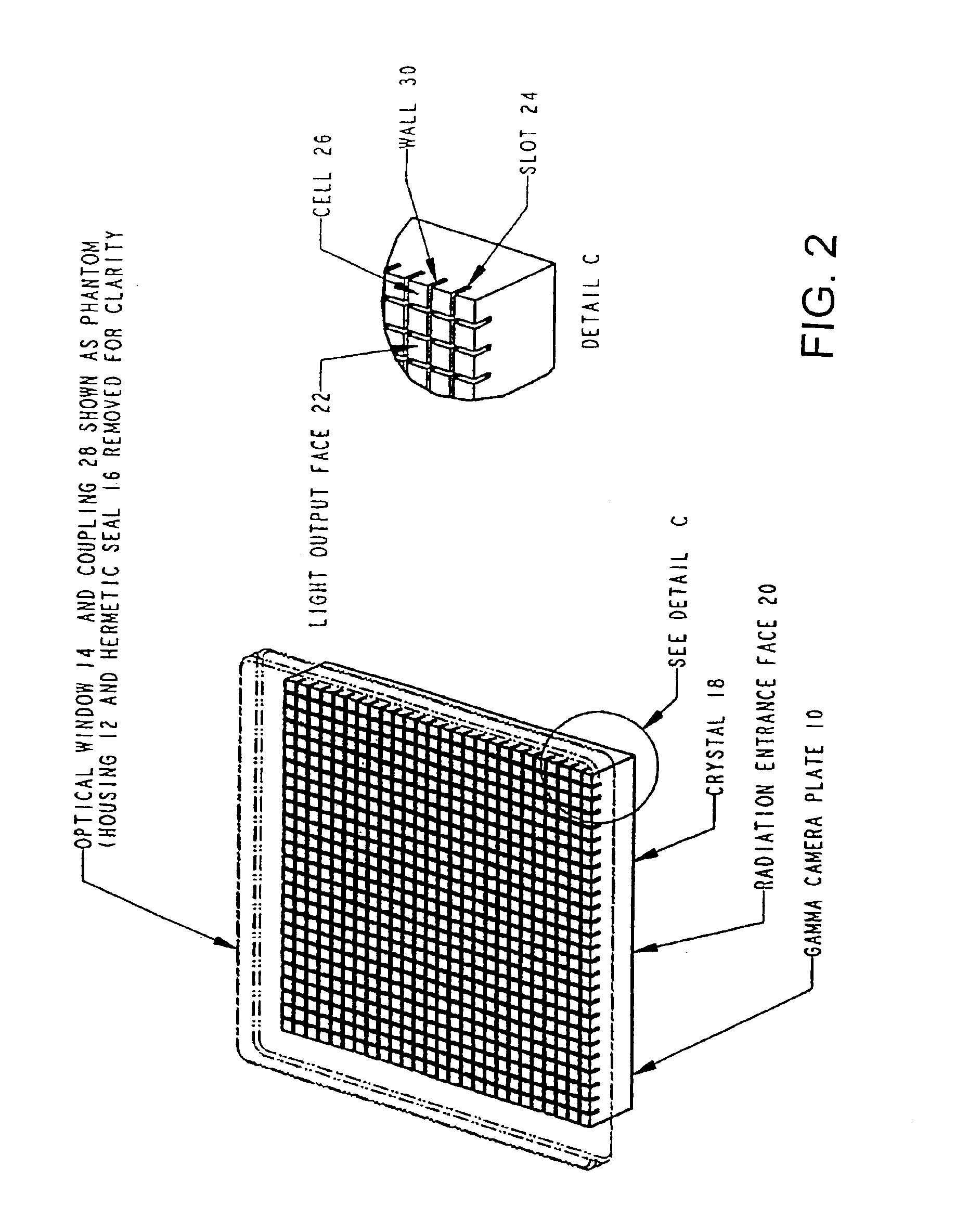
Thick scintillation plate with internal light collimation
InactiveUS6881960B2Satisfactory resolutionReduce light spreadPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh energyScintillation crystals
A gamma camera plate incorporates scintillation crystal which is sufficiently thick to effectively capture high energy radiation. The crystal is provided on its light output side with an array of light path-modifying partitions which extend partly through its thickness. These partitions define individual light collimating cells which reduce the light spreading which would otherwise prevent effective use of the plate for low energy radiation.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN IND CERAMICS INC
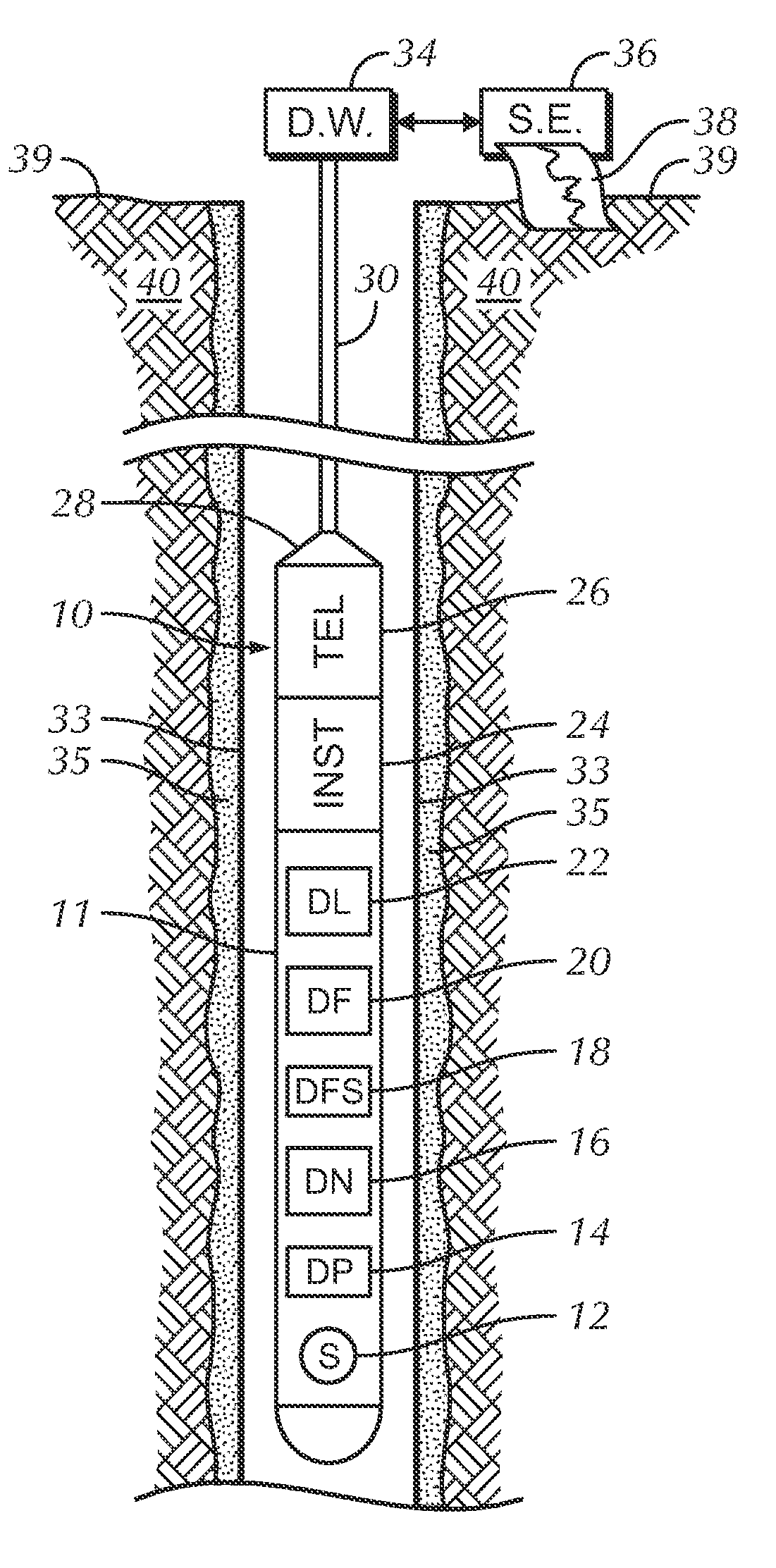
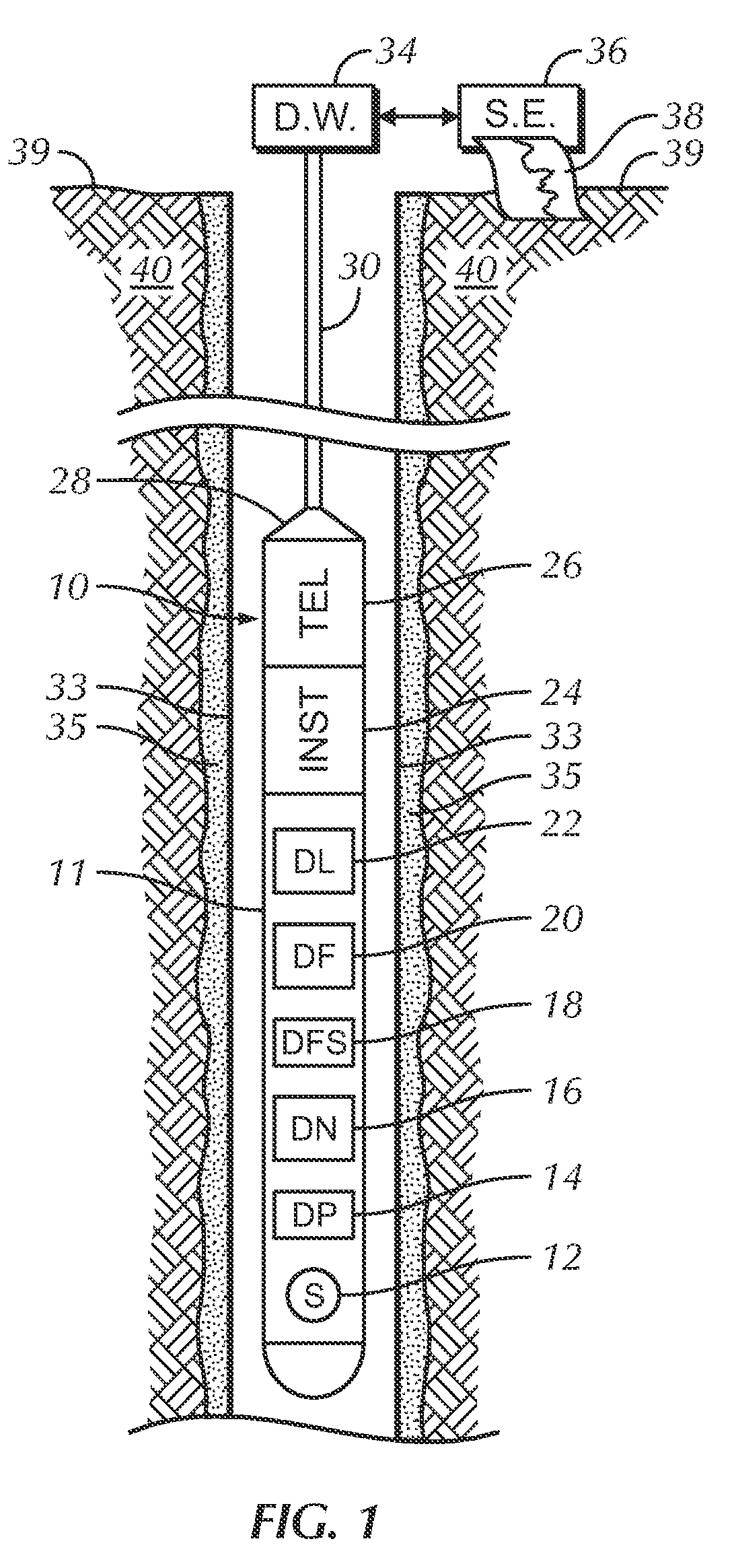
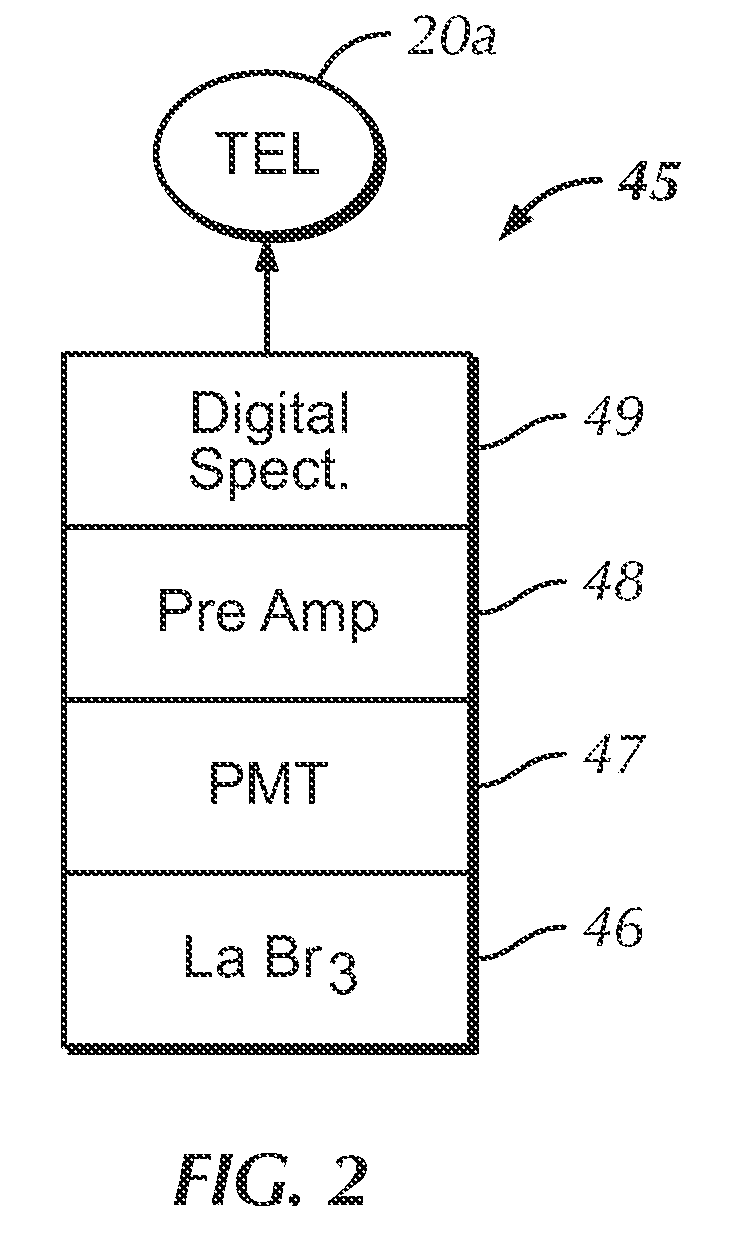
Borehole measurements using a fast and high energy resolution gamma ray detector assembly
ActiveUS7999220B2Energy optimizationFast emission timeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDead timePulse height
A gamma ray detector assembly for a borehole logging system that requires the measure of gamma radiation with optimized gamma ray energy resolution and with fast emission times required to obtain meaningful measurements in high radiation fields. The detector assembly comprises a lanthanum bromide (LaBr3) scintillation crystal and a digital spectrometer that cooperates with the crystal to maximize pulse processing throughput by digital filtering and digital pile-up inspection of the pulses. The detector assembly is capable of digital pulse measurement and digital pile-up inspection with dead-time less than 600 nanoseconds per event. Pulse height can be accurately measured (corrected for pile-up effects) for 2 pulses separated by as little as 150 nanoseconds. Although the invention is applicable to virtually any borehole logging methodology that uses the measure of gamma radiation in harsh borehole conditions, the invention is particularly applicable to carbon / oxygen logging.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
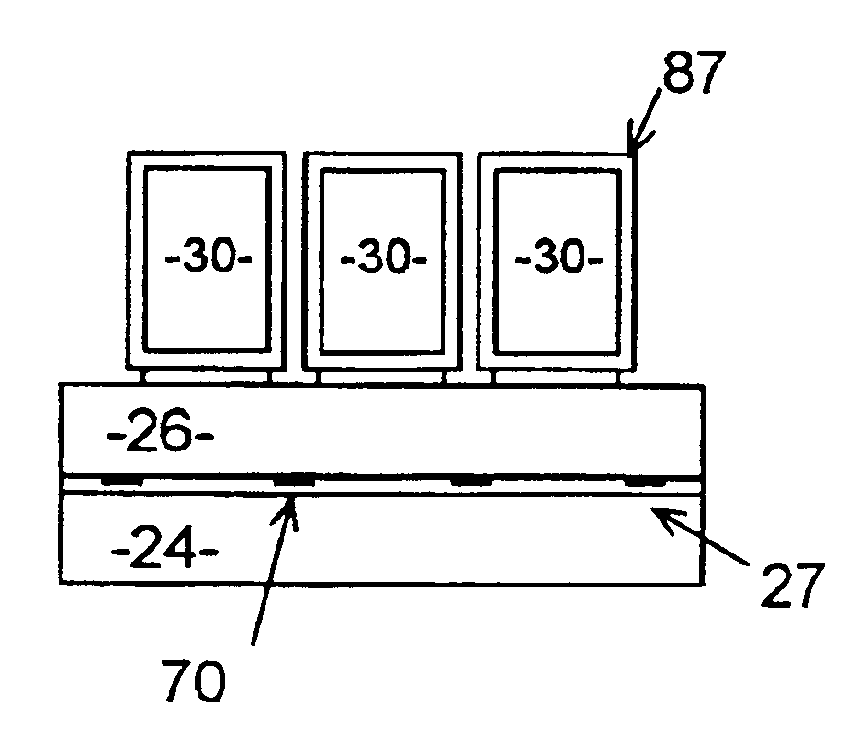
Detector module and medical imaging device
The invention provides a detector module and a medical imaging device. The detector module comprises a scintillation crystal array, a photoelectric detector array and a readout circuit board, wherein the scintillation crystal array is connected with the photoelectric detector array, and the photoelectric detector array outputs a collected signal through the readout circuit board; the detector module further comprises support blocks positioned on the end part of the scintillation crystal array, and a support board positioned between the photoelectric detector array and the readout circuit board, wherein the support blocks are connected through the support board, and the end blocks, namely, the support blocks and the support board define the space for accommodating the scintillation crystal array and the photoelectric detector array. The detector module disclosed by the invention is high in structural strength, and the coupling between a photoelectric detector and scintillation crystal is good.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Production method for making position-sensitive radiation detector arrays
InactiveUS6956214B2Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDetector arrayScintillation crystals
Systems and methods are described for a production method for making position-sensitive radiation detector arrays. A method includes applying a plurality of masks to a plurality of scintillation crystal slabs; coupling the plurality of scintillation crystal slabs to form a sandwich structure; cutting a plurality of slices from the sandwich structure; and coupling at least two of the plurality of slices to form a detector array.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
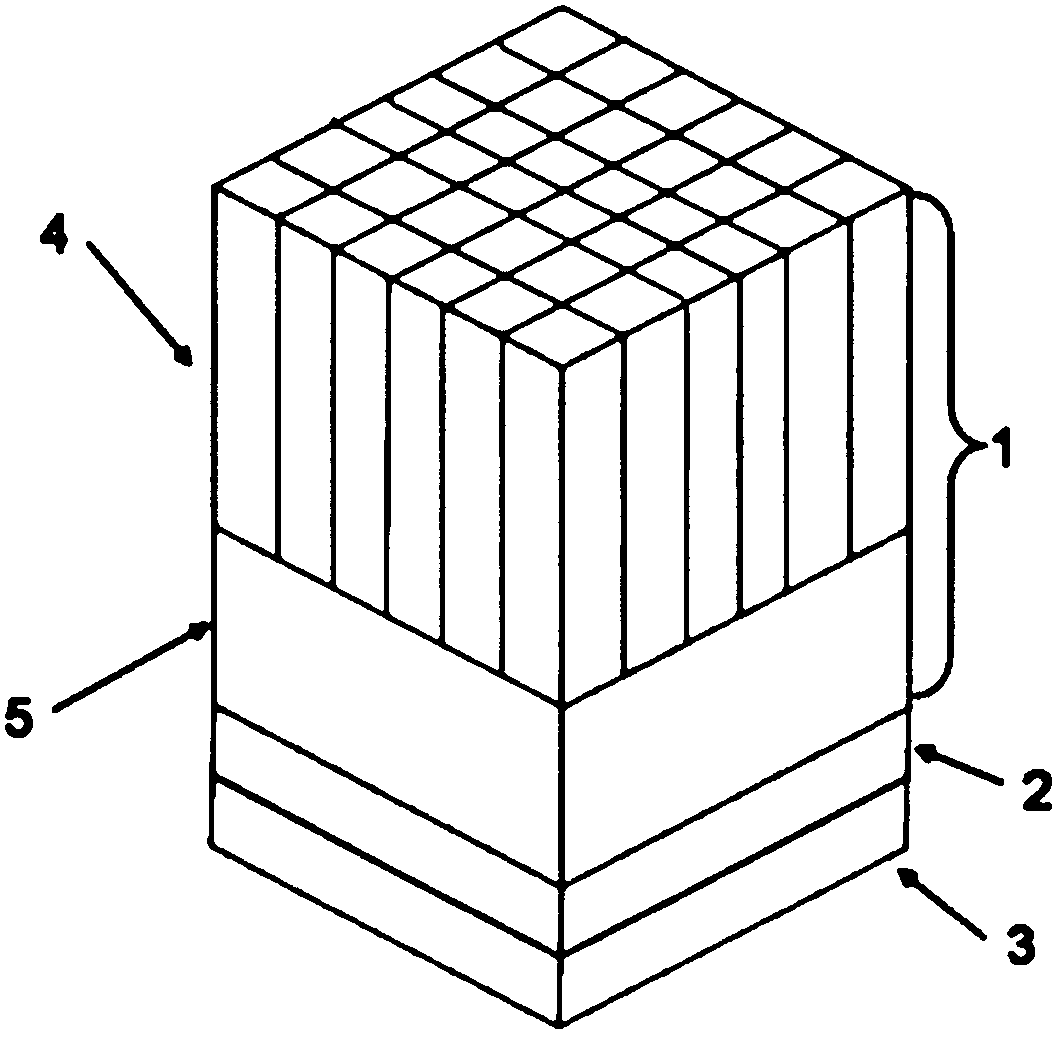
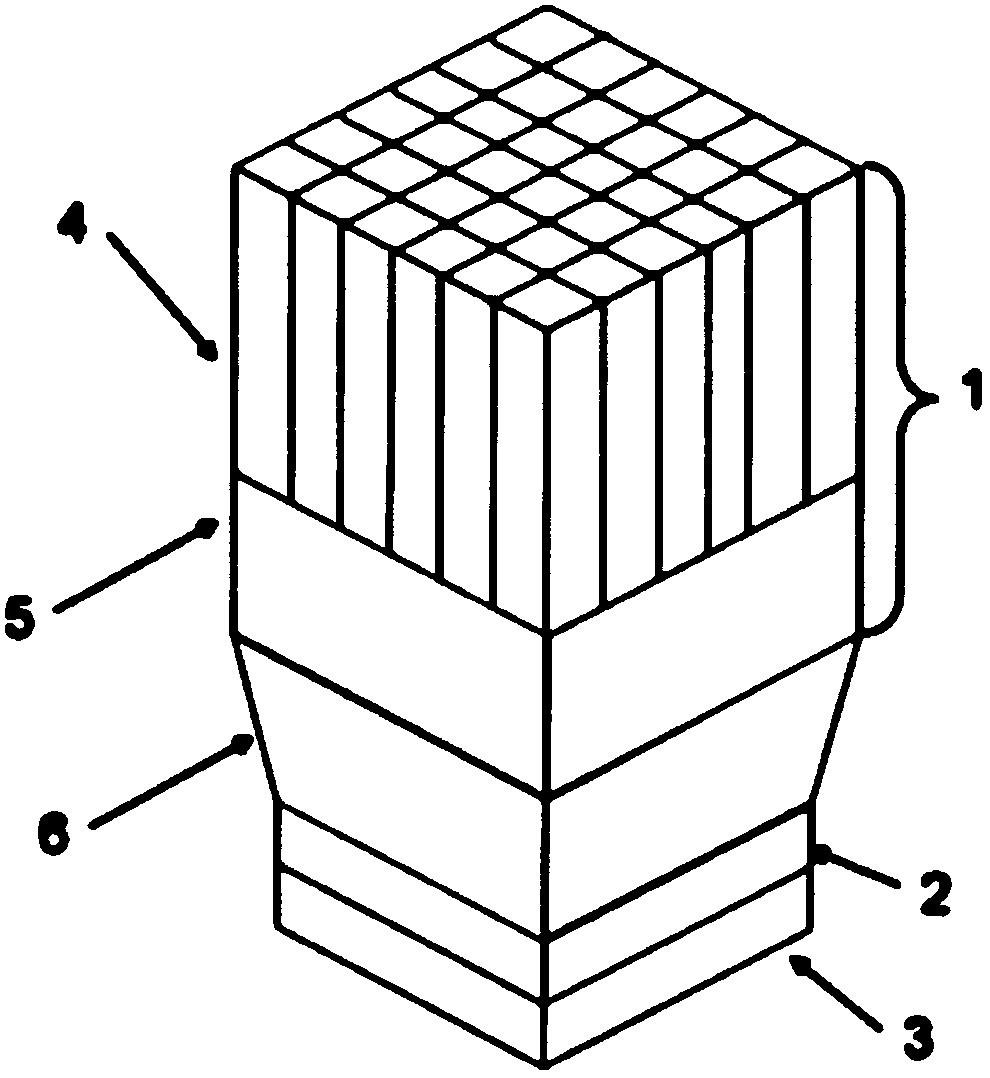
Scintillation crystal array and scintillation detector possessing the same
ActiveCN102565841AIncrease flexibilityReduce blind areaX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentScintillation crystalsSilicone oil
The invention provides a scintillation crystal array and a scintillation detector possessing the same. The scintillation crystal array of the invention is formed through arranging a plurality of crystal units according to a predetermined design. And the crystal units are connected with each other through an optical cement or silicone oil. One part of an external surface of the each crystal unit is coated with a reflective film so that the reflective films on a plurality of crystal units can define a light emission surface of the scintillation crystal array together. The scintillation detectorof the invention has the following advantages that flexibility is high; reflectivity is high; the structure is compact; mass production is easy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Photoelectric converter, detector and scanning equipment
ActiveCN105655435AReduce volumeGuaranteed tight arrangementX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSemiconductor devicesSilicon photomultiplierElectronic systems
The invention relates to a photoelectric converter, a detector and scanning equipment. The photoelectric converter comprises a silicon photomultiplier array and a light guide coupled with the silicon photomultiplier array, wherein the silicon photomultiplier array comprises i*j silicon photomultipliers spliced on a horizontal plane, and the i and the j are both integers greater than or equal to 2. The detector comprises a scintillation crystal, an electronic system, a light guide and silicon photomultipliers. The scanning equipment comprises a detection device and a frame, wherein the detection device comprises the detector, and the detector comprises the photoelectric converter. According to the photoelectric converter, the detector and the scanning equipment, a photoelectric conversion scheme of the photoelectric silicon photomultipliers is mainly employed, the silicon photomultipliers have small volumes and are closely arranged, the silicon photomultipliers in proper dimensions and in proper quantity are matched with the light guide in proper shape, a PET detector with high spatial resolution can be established, so the spatial resolution of the whole PET system can be improved, the PET detector having DOI and TOF performances is proper to establish, application to PET / MRI can be realized, and low cost is further realized.
Owner:RAYCAN TECH CO LTD SU ZHOU
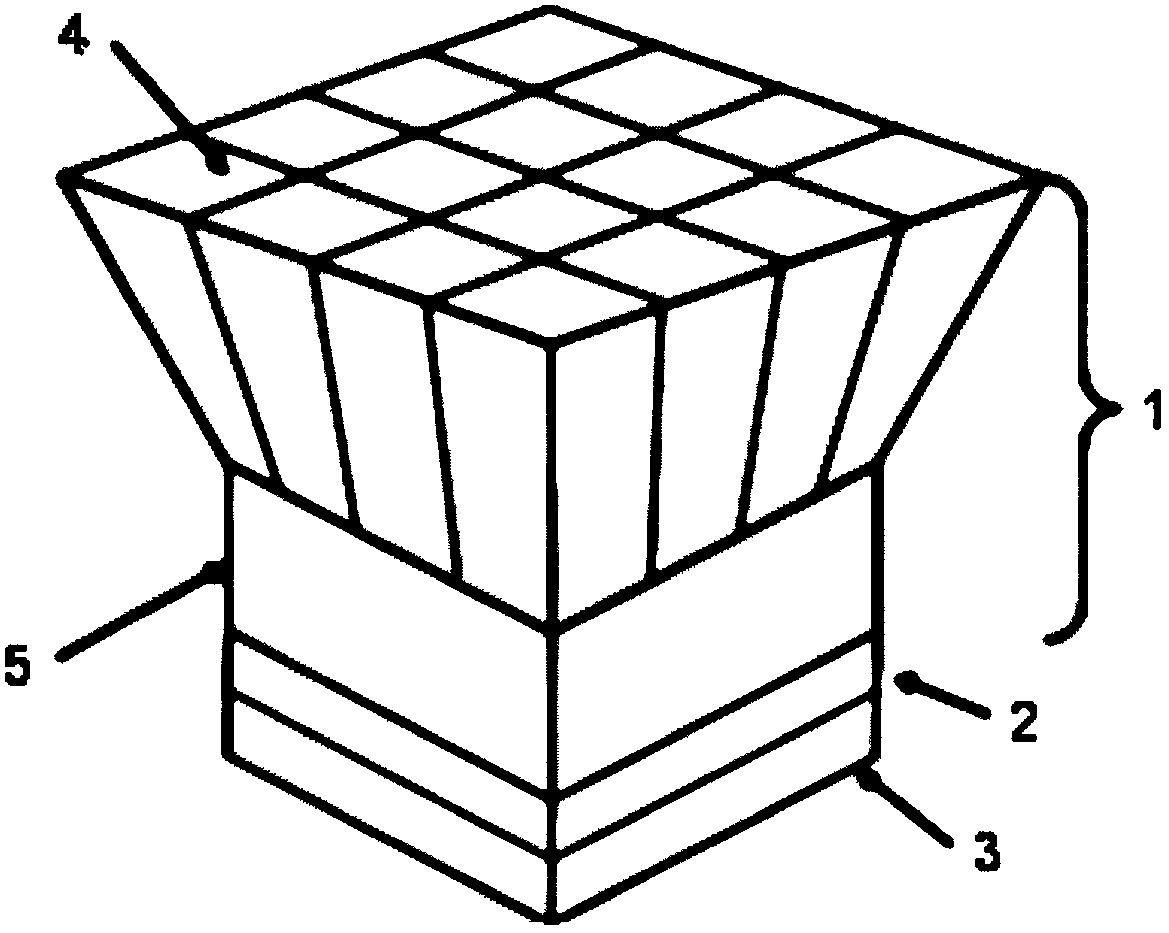
Conical scintillation crystal module and processing method thereof
ActiveCN102129082AHigh sensitivityReduce the problem of missing collectionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentImaging qualityImage resolution
The invention discloses a conical scintillation crystal module and a processing method thereof. The stereo shape of the appearance of the scintillation crystal module is of a conical table, the top surface of the conical table is mutually parallel to the bottom surface, the top surface is rectangular, and the area of the top surface is greater than that of the bottom surface. The scintillation crystal module is formed by splicing and bonding m*n crystal strips. The processing method comprises the following steps of: calculating the size of each crystal strip according to the size of the conical scintillation crystal module and the array number of the crystal strips, assembling and polishing the crystal strips obtained by processing a batch of crystal strip blanks, and processing the crystal strips into the conical scintillation crystal module as required. By designing the conical scintillation crystal module directly coupled with a photoelectric conversion device, the advantages of improving the sensitivity of a medical imaging system, reducing the problems on data acquisition deletion and improving the imaging quality of the system can be achieved under the condition that the energy resolution and the time resolution of the system are not affected.
Owner:NANJING RAYCAN INFORMATION TECH
Method and device for correcting energy value
InactiveCN104035122AEliminate offsetDoes not reduce statsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentScintillation crystalsPeak value
The invention provides a method and a device for correcting an energy value. The method comprises the following steps: presetting an energy correction coefficient table; calculating the product of the to-be-corrected energy value of each to-be-corrected single event and the energy correction coefficient of the each to-be-corrected single event to obtain the corrected energy value of the each to-be-corrected single event; counting an energy value-count value curve according to the corrected energy value. The energy correction coefficient is the ratio of a theoretical energy peak value in the energy valve-count value curve obtained by counting an extensive source radiation scintillation crystal array to a detected energy peak, thus the obtained corrected energy value of each to-be-corrected single event deviates towards the theoretical energy value of information about the position of the to-be-corrected single event, thereby eliminating the deviation between an energy value corresponding to a detected count peak value and an energy value corresponding to the theoretical count peak value on the premise of not reducing the statistical information of a scintillation crystal array edge single event.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
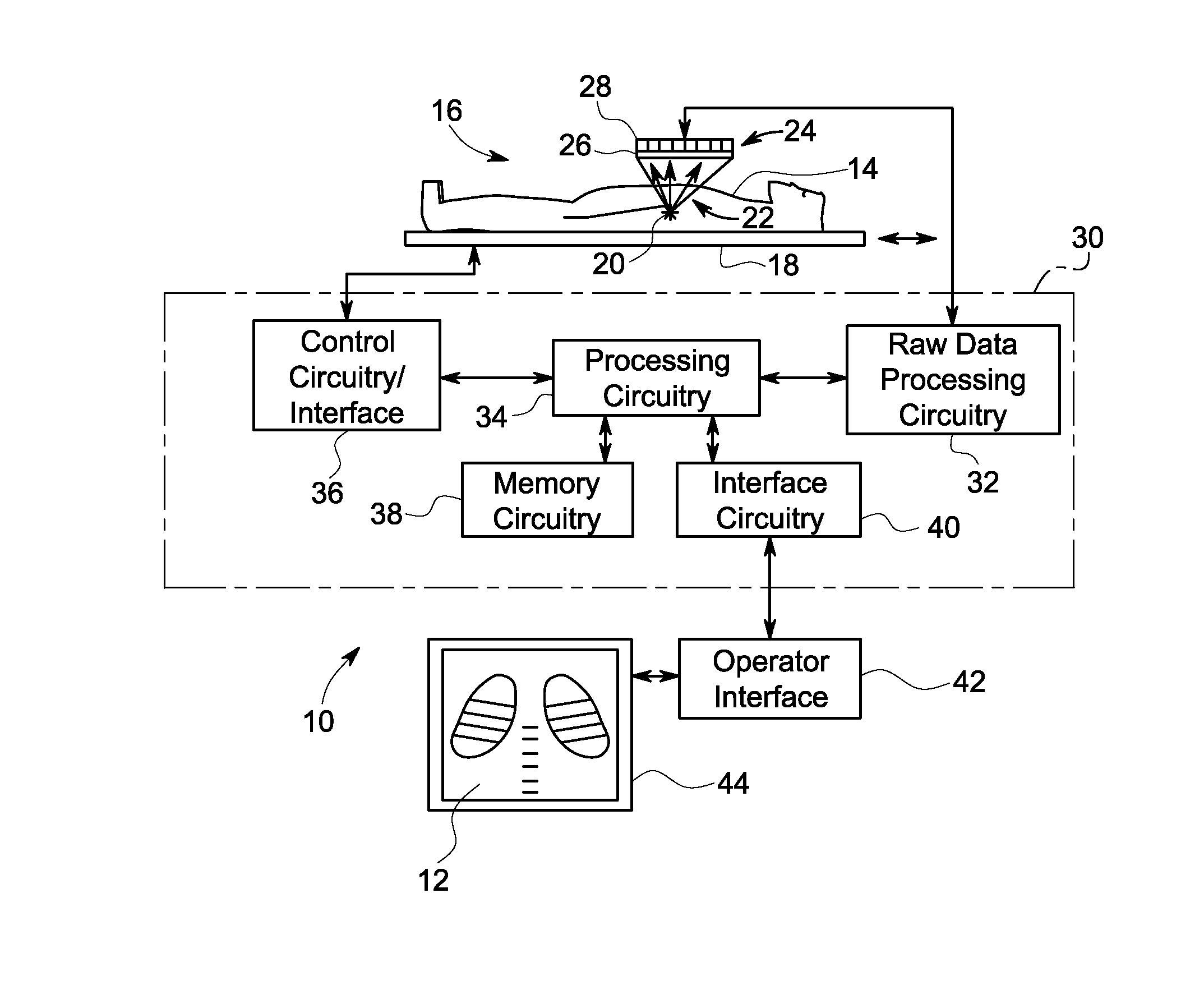
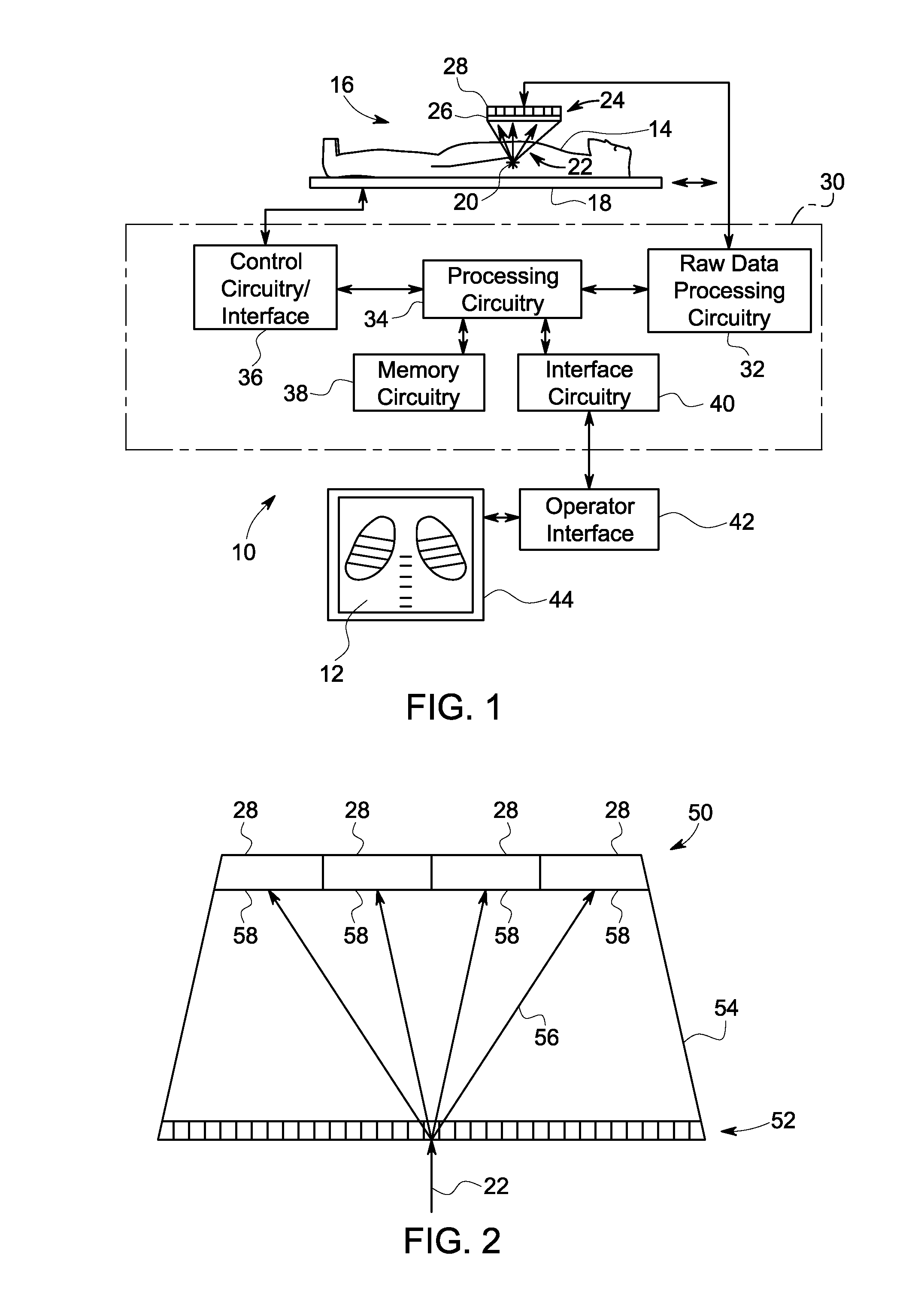
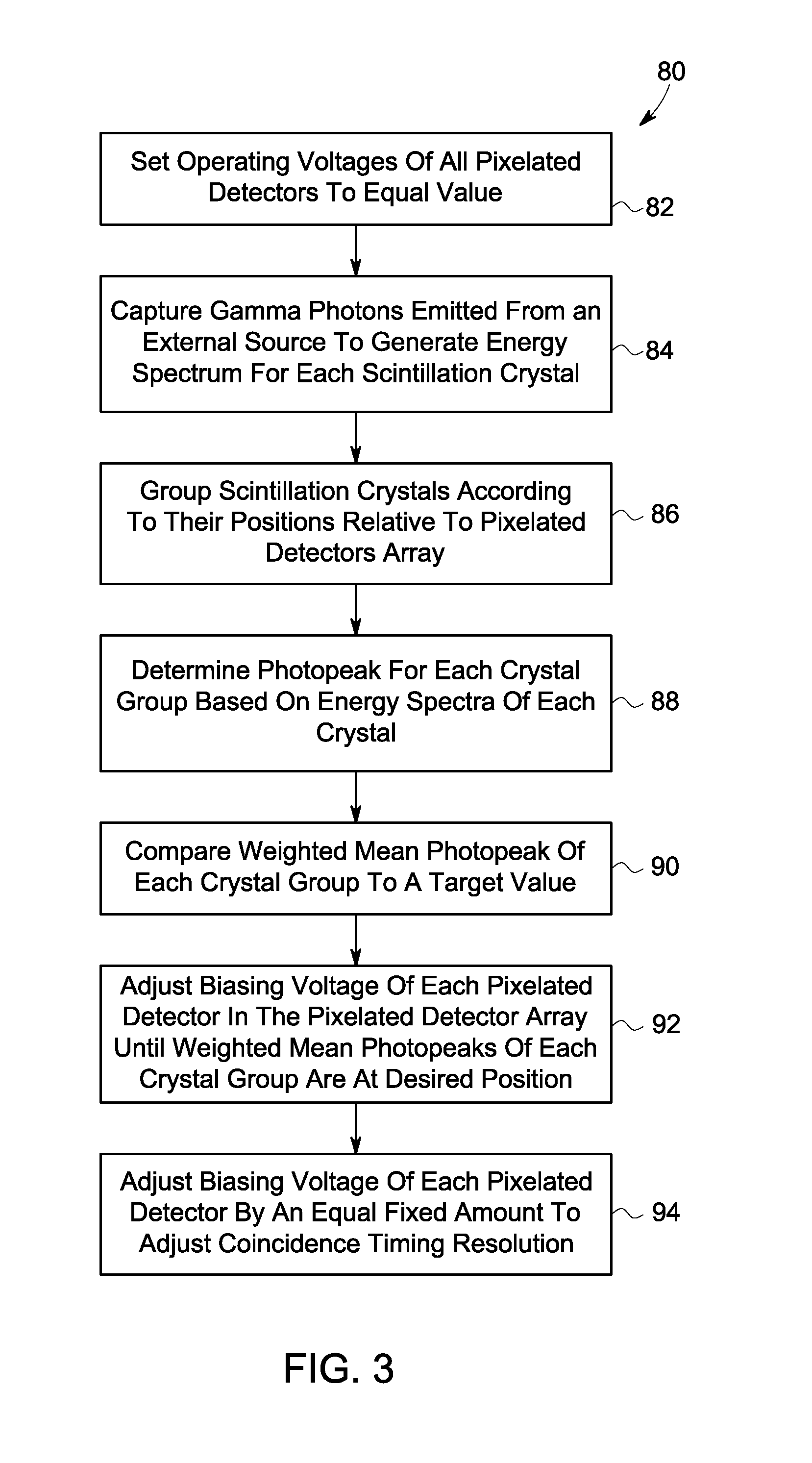
System and method for pixelated detector calibration
ActiveUS20130193330A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementScintillation crystalsPeak value
Present embodiments relate to the calibration of detectors having one or more arrays of pixelated detectors. According to an embodiment, a method includes detecting optical outputs generated by a plurality of scintillation crystals of a detector with an array of pixelated detectors, generating, with the array of pixelated detectors, respective signals indicative of the optical outputs, generating, from the respective signals, a unique energy spectrum correlated to each of the plurality of scintillation crystals, grouping subsets of the plurality of scintillation crystals into macrocrystals, determining a representative energy spectrum peak for each macrocrystal based on the respective energy spectra of the scintillation crystals in the macrocrystal, comparing a value of the representative energy spectrum peak for each macrocrystal with a target peak value, and adjusting an operating parameter of at least one pixelated detector in the array of pixelated detectors as a result of the comparison.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for detection, location, and identification of gamma sources
InactiveUS8067742B2Improve responseIncrease pointsMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersPhotodetectorScintillation crystals
An apparatus for detecting and determining a source azimuth for gamma radiation includes at least two scintillation crystals at angular offsets and directed toward a common plane of detection, photodetectors adjacent to each of the scintillation crystals for converting the light response of the scintillation crystals into distinct electrical signals, and a digital processing system configured to analyze spectral data from each electrical signal produced for each crystal. The digital processing system monitors a finite number of spectral windows corresponding to a selected set of radioisotopes, and uses one or more of the electrical signals to determine a signal intensity and a likely source azimuth for a detected radioisotope in the plane of detection. Another scintillation crystal directed outside of the common plane of detection may be used for three-dimensional detection. Related methods for detection and location of gamma ray sources are discussed.
Owner:SPACE MICRO A CORP OF DELAWARE
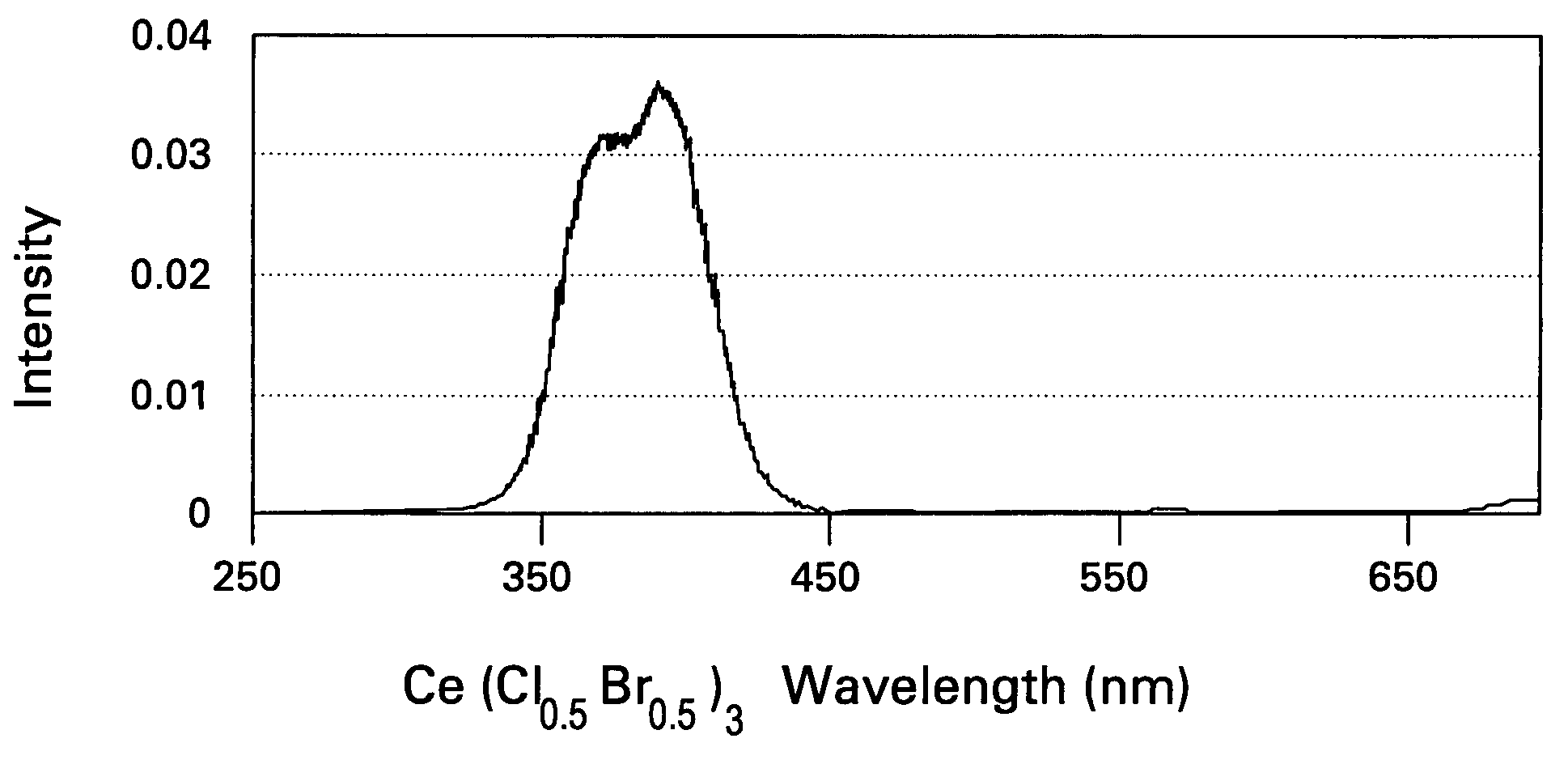
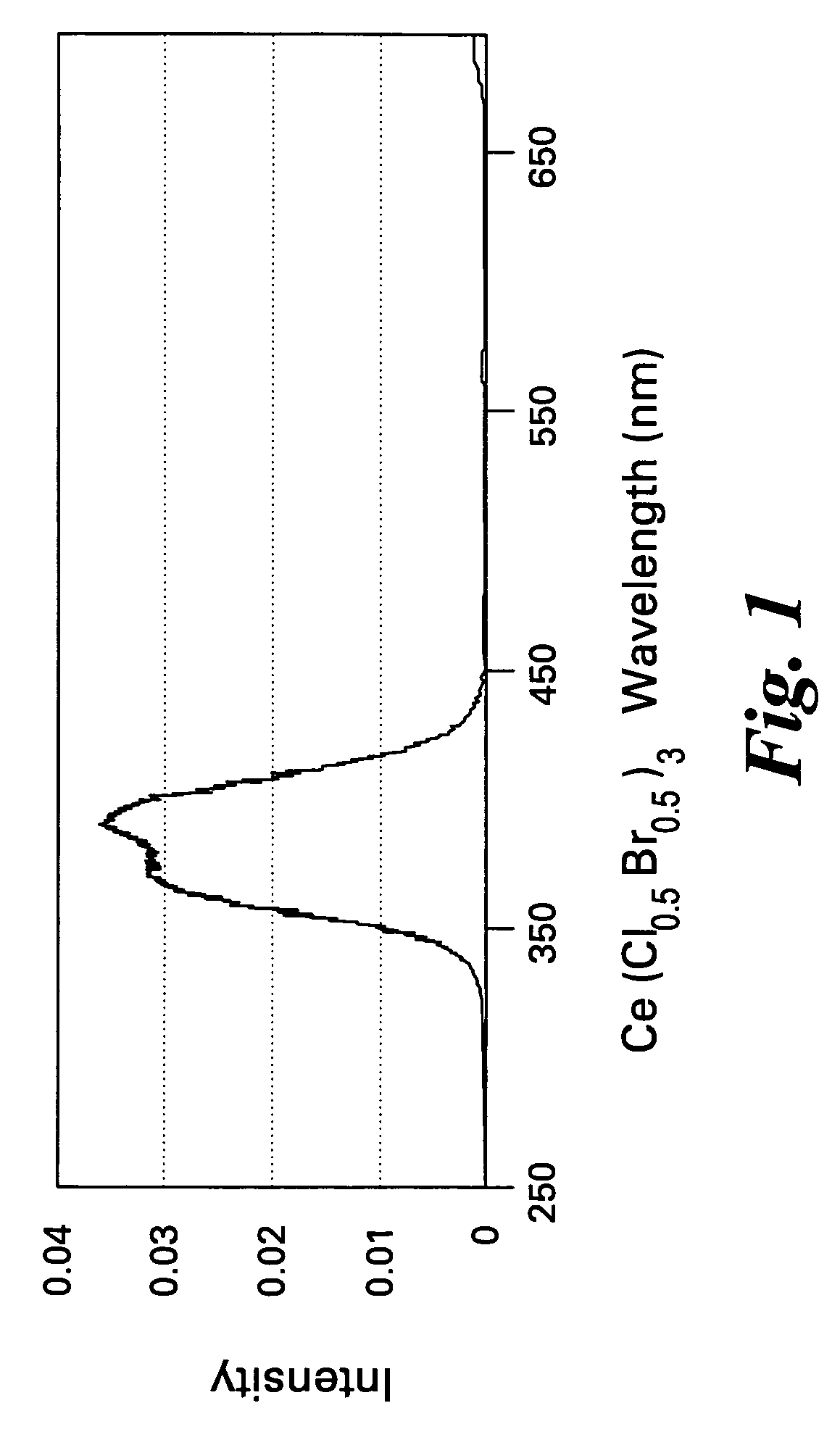
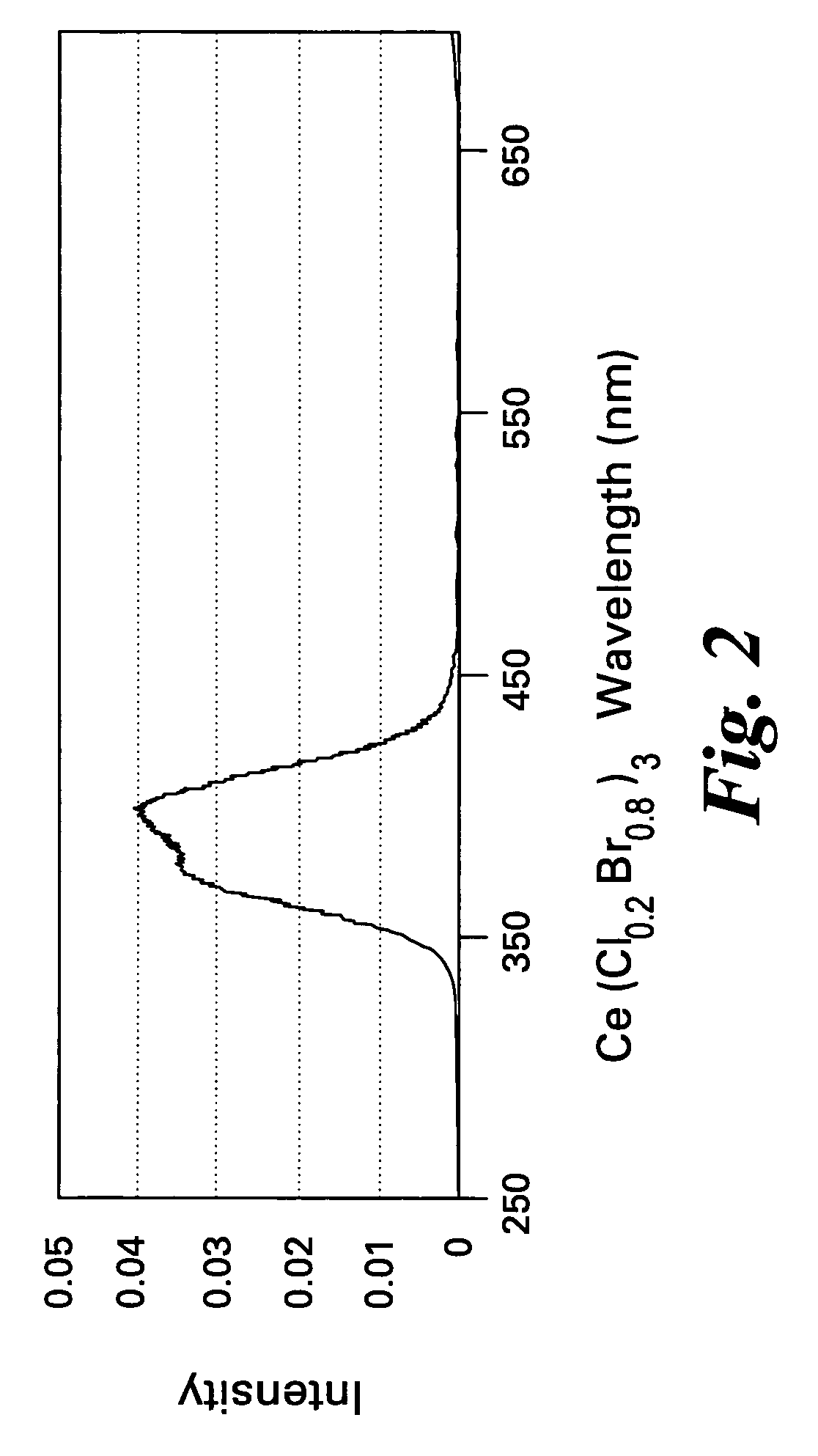
Scintillator compositions of cerium halides, and related articles and processes
ActiveUS7202477B2Material analysis by optical meansRare earth metal compoundsPhotovoltaic detectorsHigh energy
A scintillator composition is disclosed, containing a solid solution of at least two cerium halides. A radiation detector for detecting high-energy radiation is also described herein. The detector includes the scintillator composition mentioned above, along with a photodetector optically coupled to the scintillator. A method for detecting high-energy radiation with a scintillation detector is also described, wherein the scintillation crystal is based on a mixture of cerium halides.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
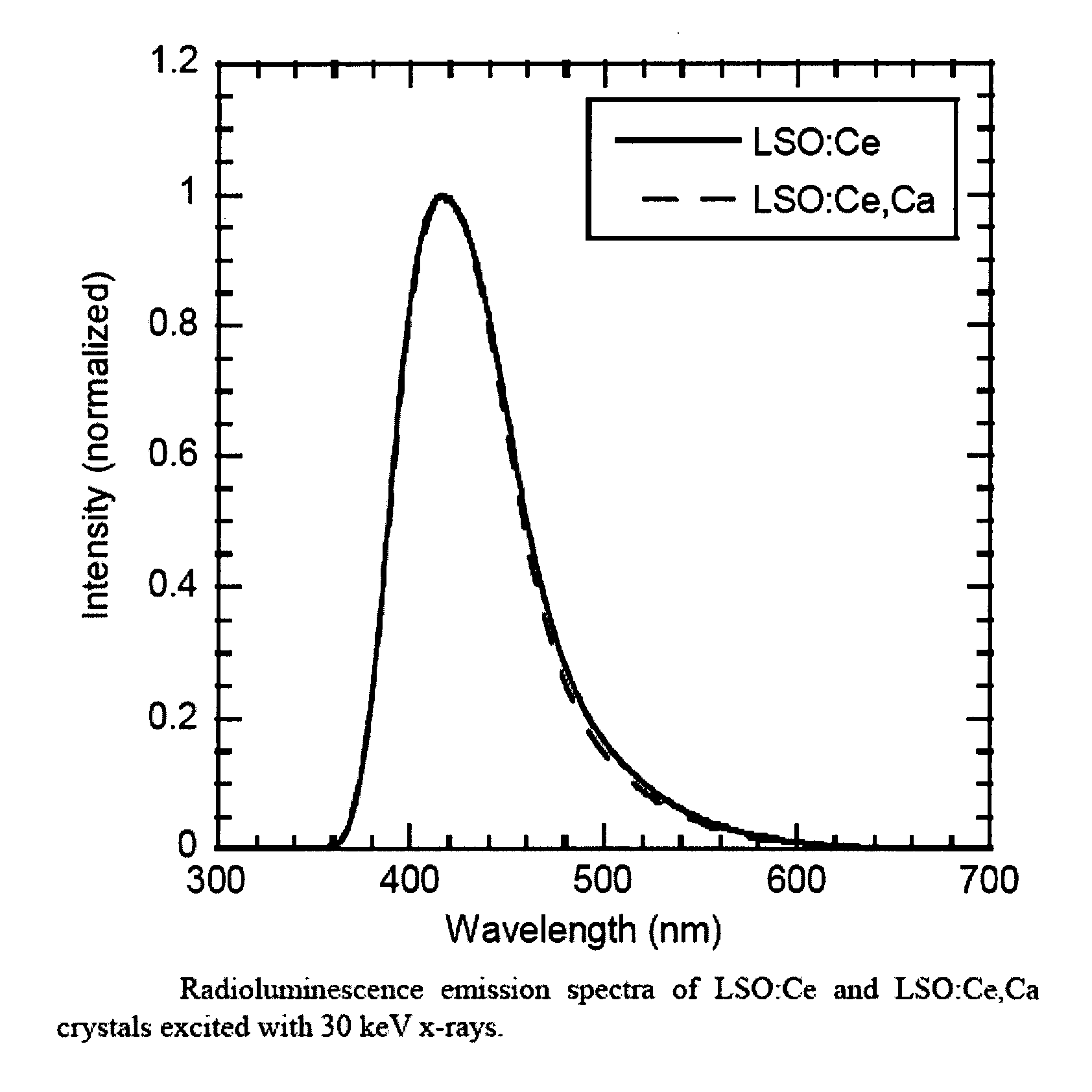
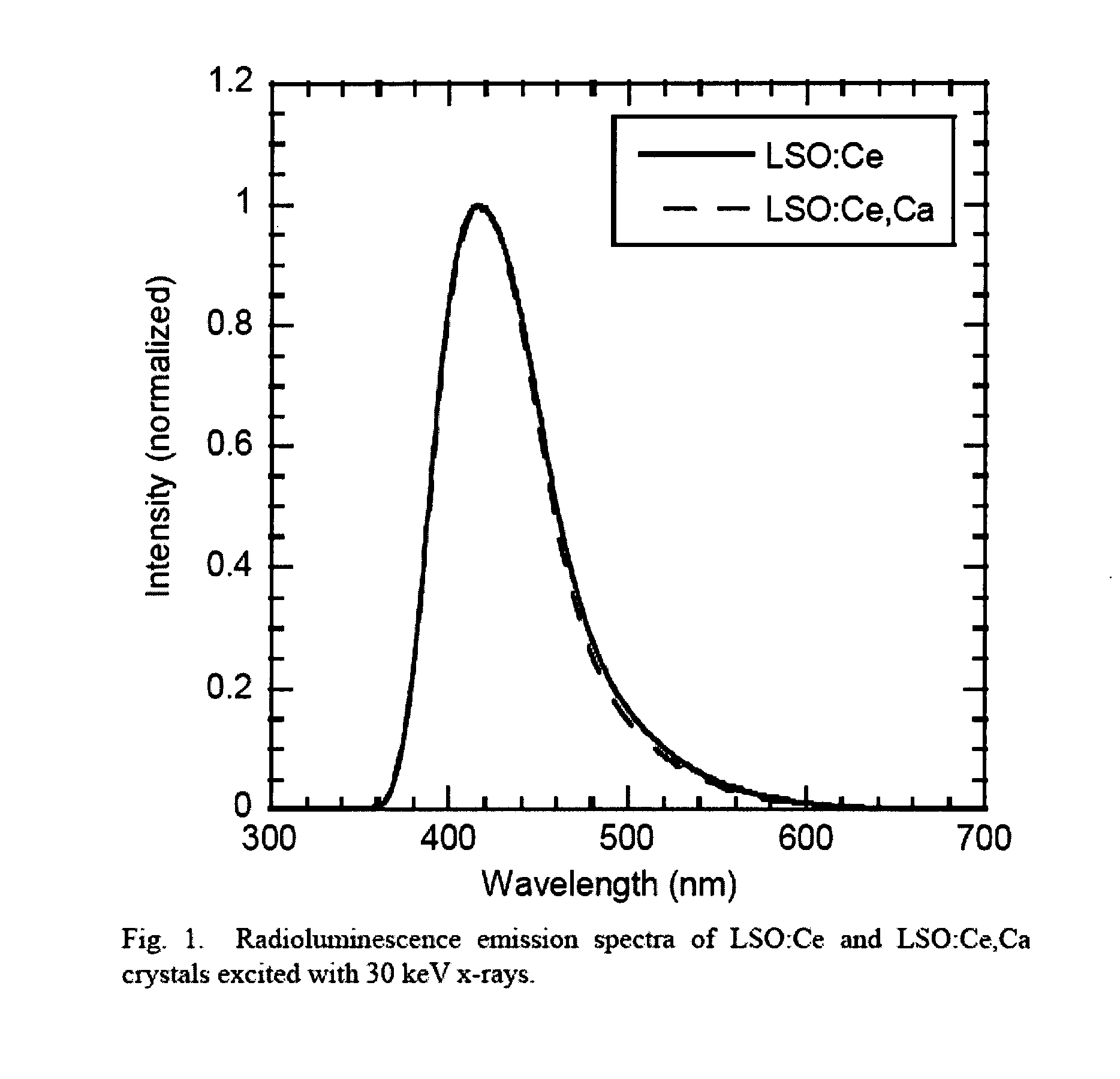
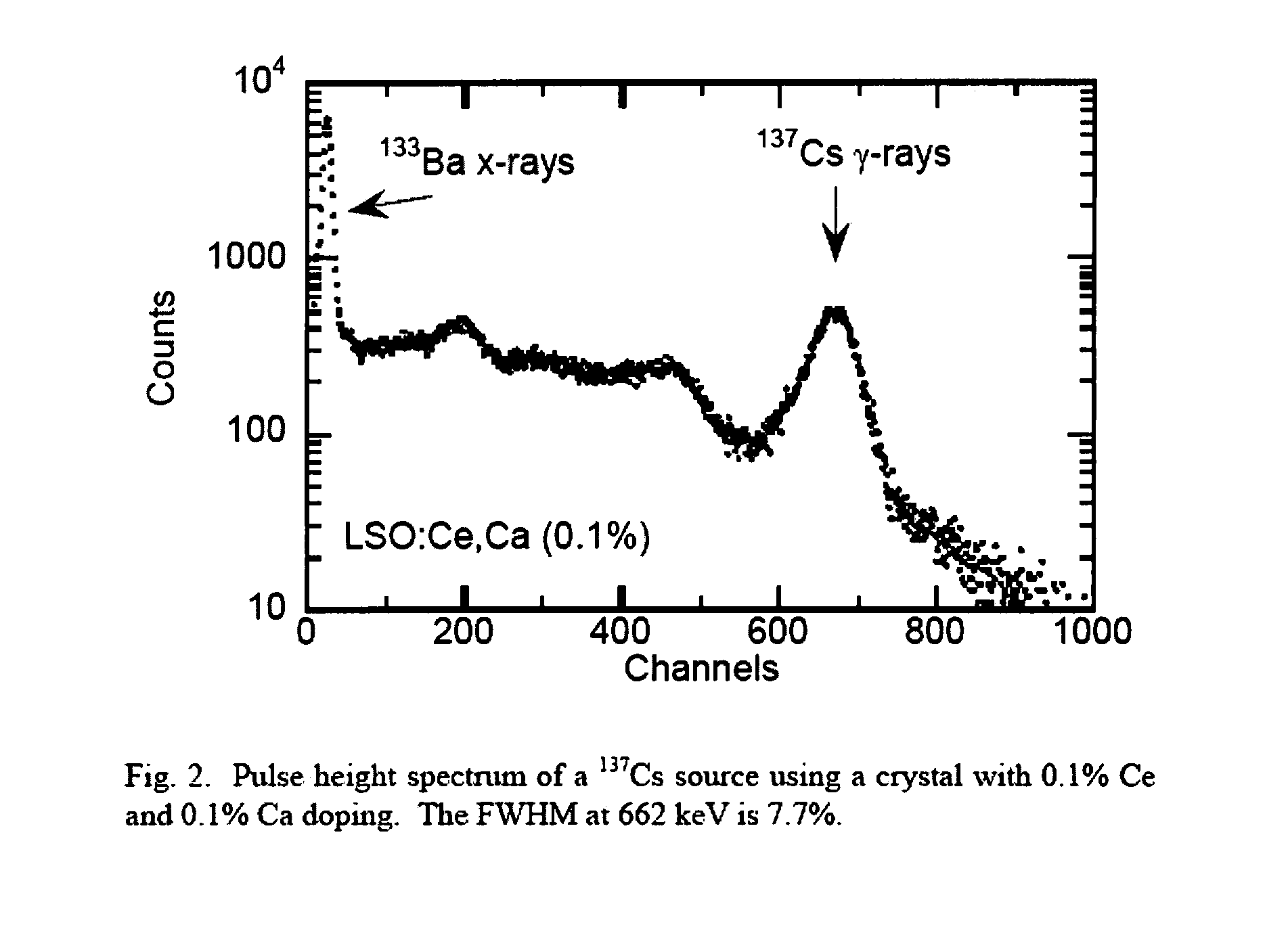
Lutetium oxyorthosilicate scintillator having improved scintillation and optical properties and method of making the same
ActiveUS8278624B2Improve flickeringChange propertiesPolycrystalline material growthMaterial analysis by optical meansScintillation crystalsCerium
LSO scintillation crystals with improved scintillation and optical properties are achieved by controlled co-doping a LSO crystal melt with amounts of cerium and an additional codopant such as calcium or other divalent cations. Crystal growth atmosphere is optimized by controlling the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere. Zinc is added as an additional material to restabilize crystal growth where calcium co-dopant is added. The decay time of the scintillation crystal can be controlled by controlling the concentration of co-dopant added.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
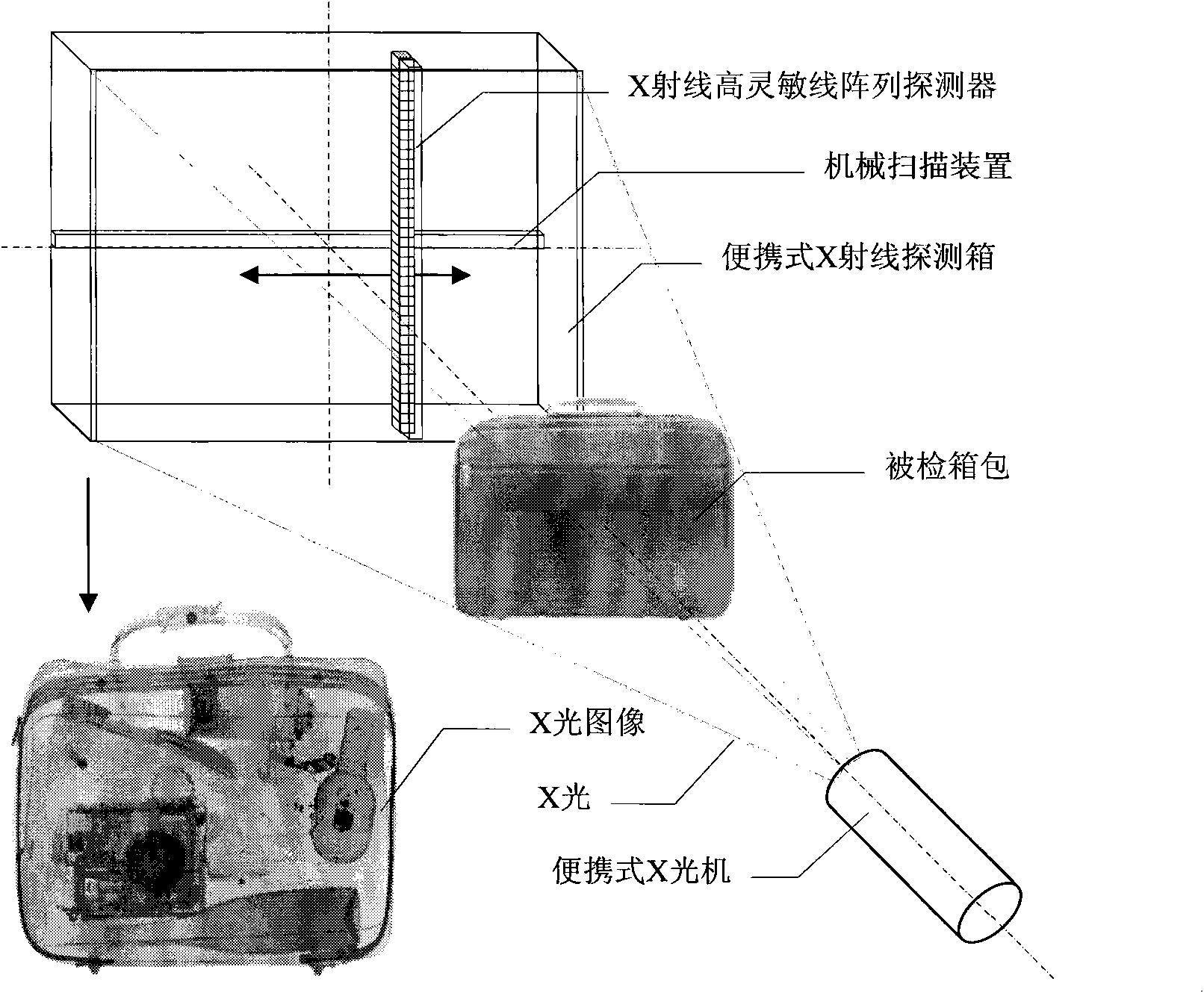
Portable X-ray detector based on highly sensitive line array detector
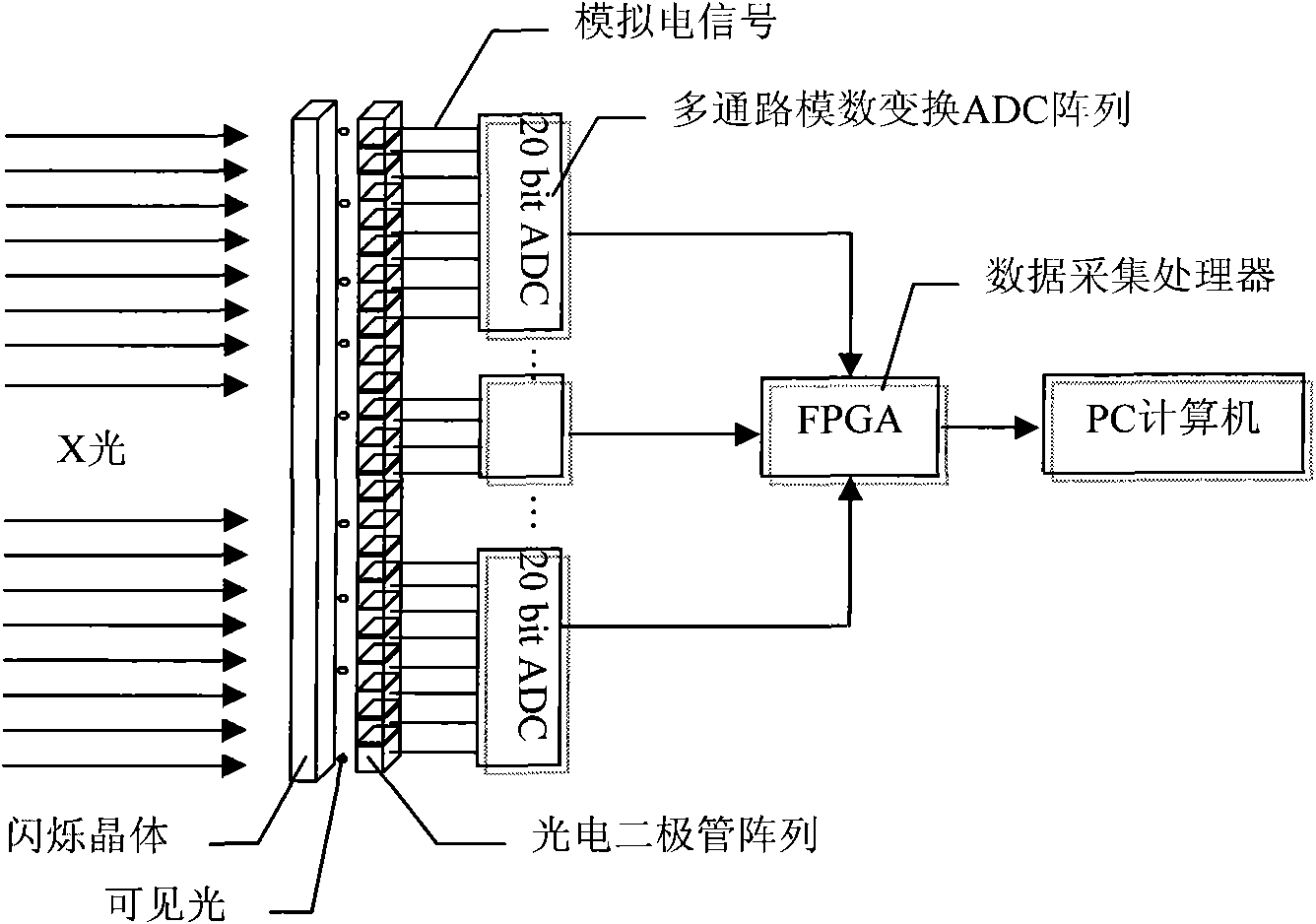
ActiveCN101576514AHigh detection sensitivityImprove image contrastX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayData acquisition
The invention discloses a portable X-ray detector based on a highly sensitive line array detector, which comprises a portable X light source and a portable X-ray detection box that is internally provided with an X-ray highly sensitive line array detector; the X-ray highly sensitive line array detector driven by a mechanical scanning device comprises a scintillation crystal and a photodiode array; the scintillation crystal detects the X-ray signal sent out by the X light source and inputs the X-ray signal to the photodiode array which converts the received X-ray signal into a current signal, and then the current signal is converted into a digital signal by a multi-channel analog-digital conversion ADC array to be input to a data acquisition processor; and the data acquisition processor obtains the digital signals of multi-row pixels output by the multi-channel analog-digital conversion ADC array for forming an X-ray perspective image. The image has good contrast, high detection sensitivity and smaller volume.
Owner:PURPLE SQUARE TECH +1
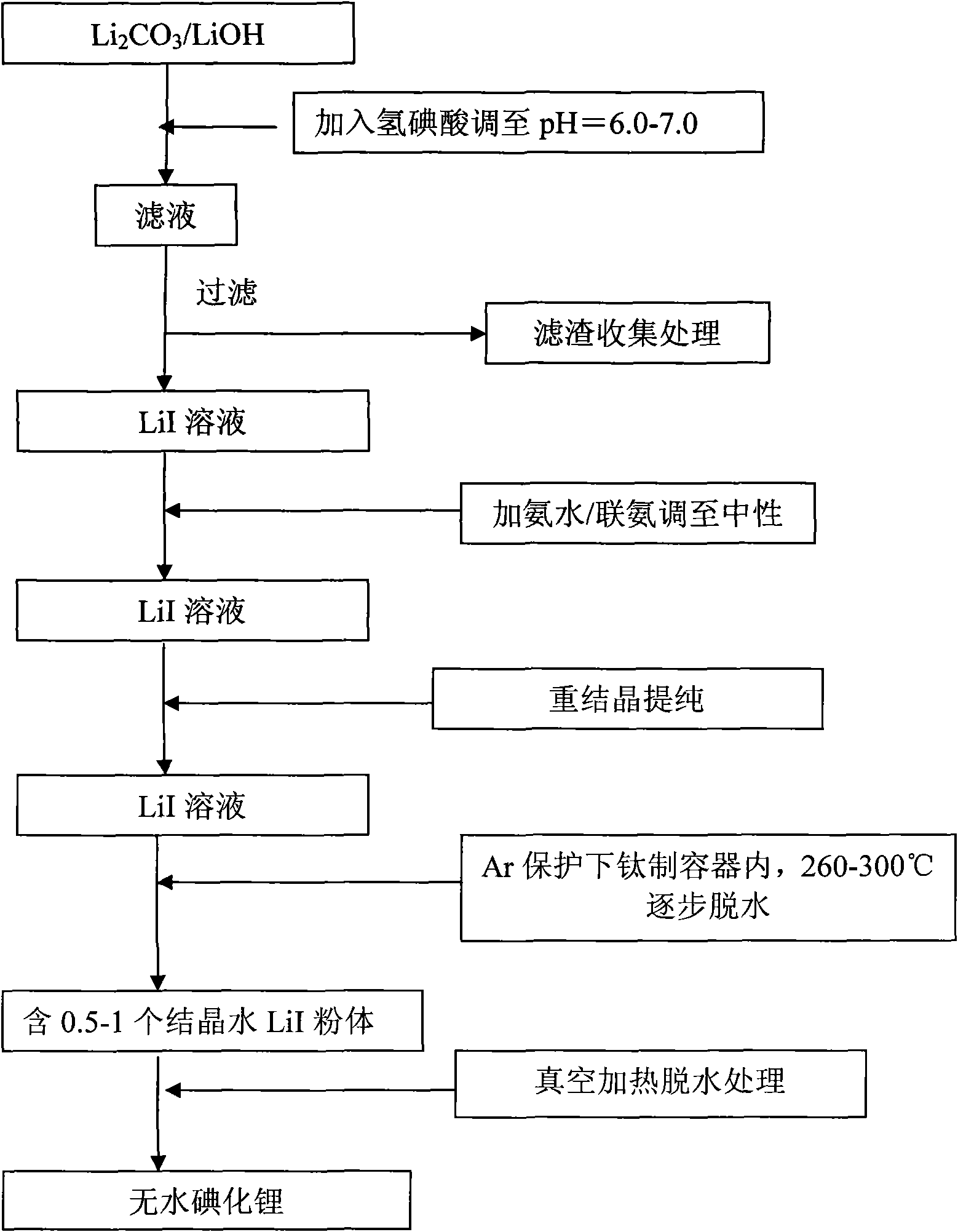
Methods for preparing anhydrous lithium iodide and scintillation crystal doped with lithium iodide
ActiveCN101565192AEasy to operateSimple processPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsBridgman methodScintillation crystals
The invention discloses a method for preparing an anhydrous lithium iodide, comprising the following operation steps of: dehydrating the lithium iodide water solution to the lithium iodide powders containing 0.5-1 crystal water; and subsequently carrying out heating and dehydration treatment in vacuum to obtain the anhydrous lithium iodide. The invention also discloses a method for preparing a scintillation crystal doped with the lithium iodide, comprising the following operation steps of: dehydrating the lithium iodide water solution to the lithium iodide powders containing 0.5-1 crystal water; mixing the lithium iodide powder with the doped compound; subsequently carrying out heating and dehydration treatment in vacuum; and subsequently carrying out crystal growth under a vacuum state by adopting a Bridgman method, thus obtaining the scintillation crystal doped with the lithium iodide. The method for preparing the anhydrous lithium iodide has simple operation and no environmental pollution and is easy for large-scale industrial production; the method for preparing the scintillation crystal doped with the lithium iodide has simple process, is not easy to be oxidized at high temperature during the preparation process and can produce the high-quality scintillation crystal doped with the lithium iodide in batches.
Owner:上海新漫传感科技有限公司
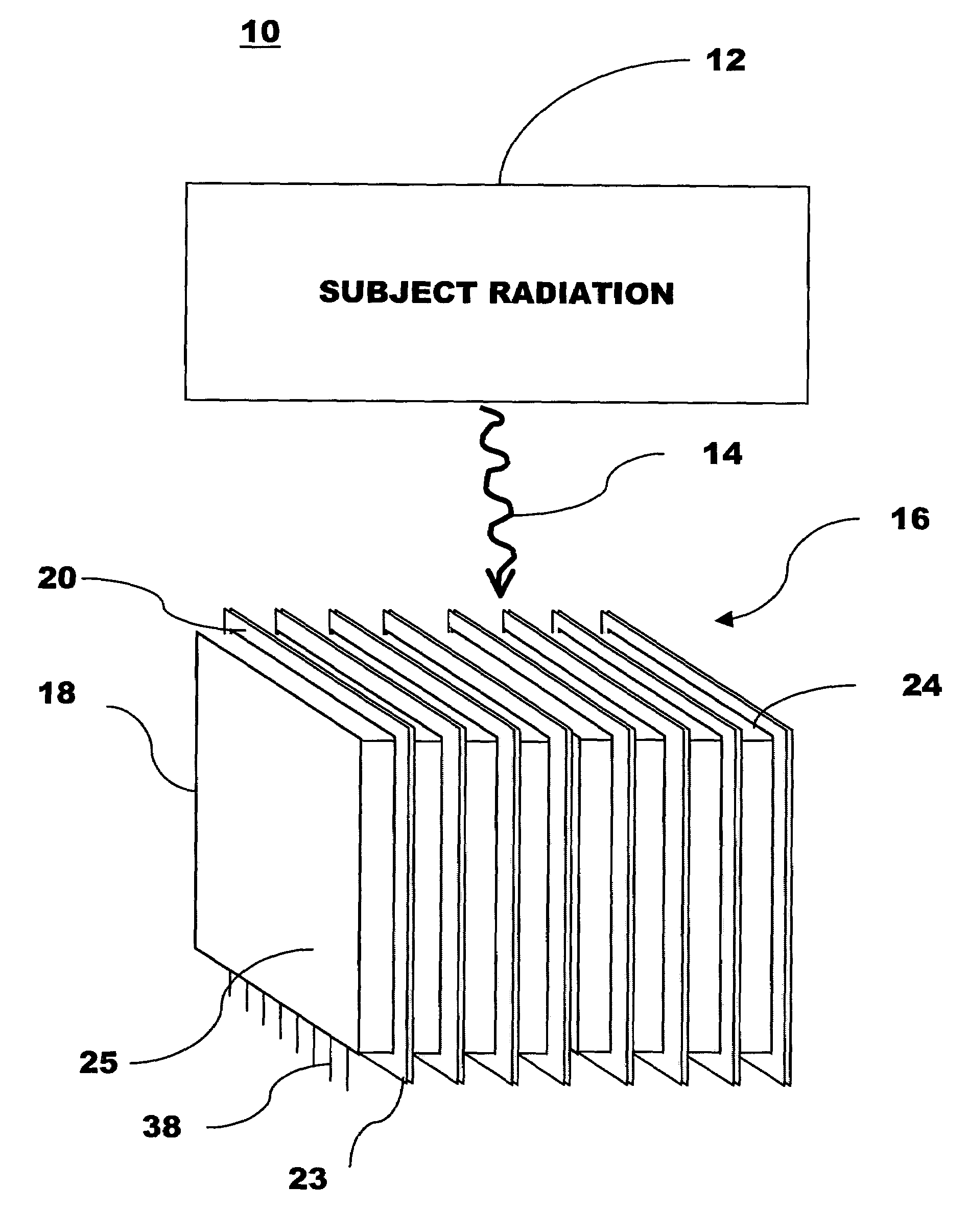
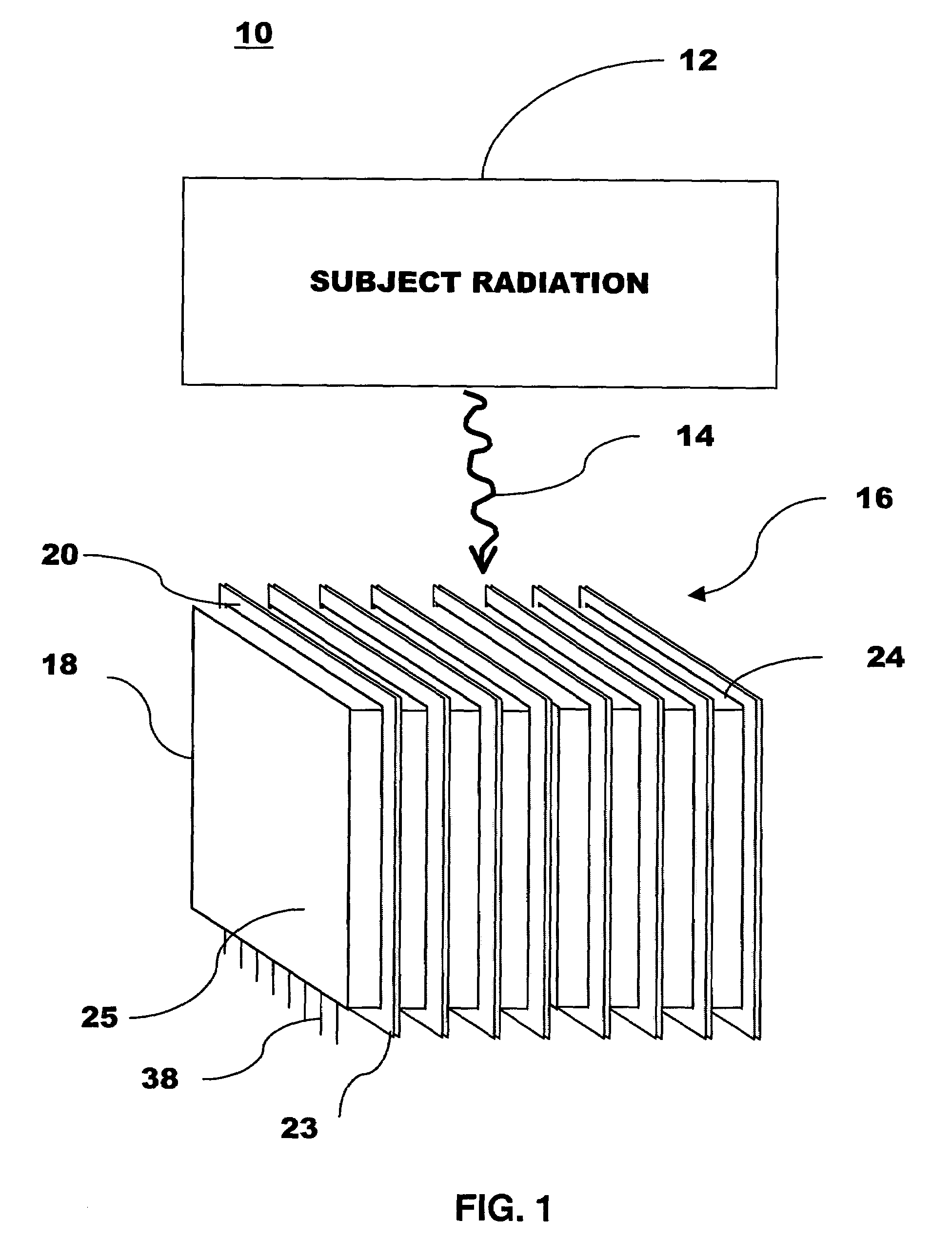
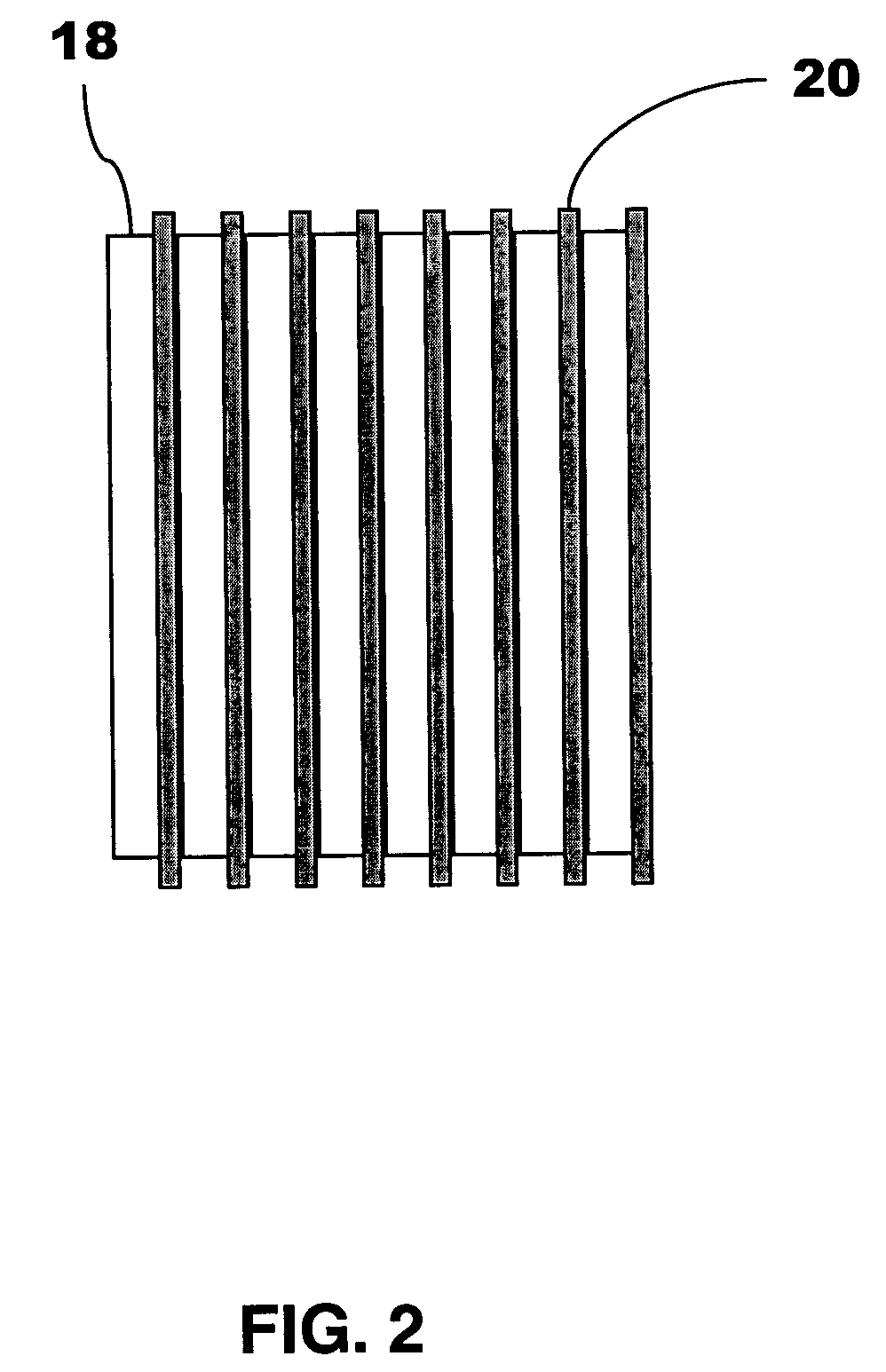
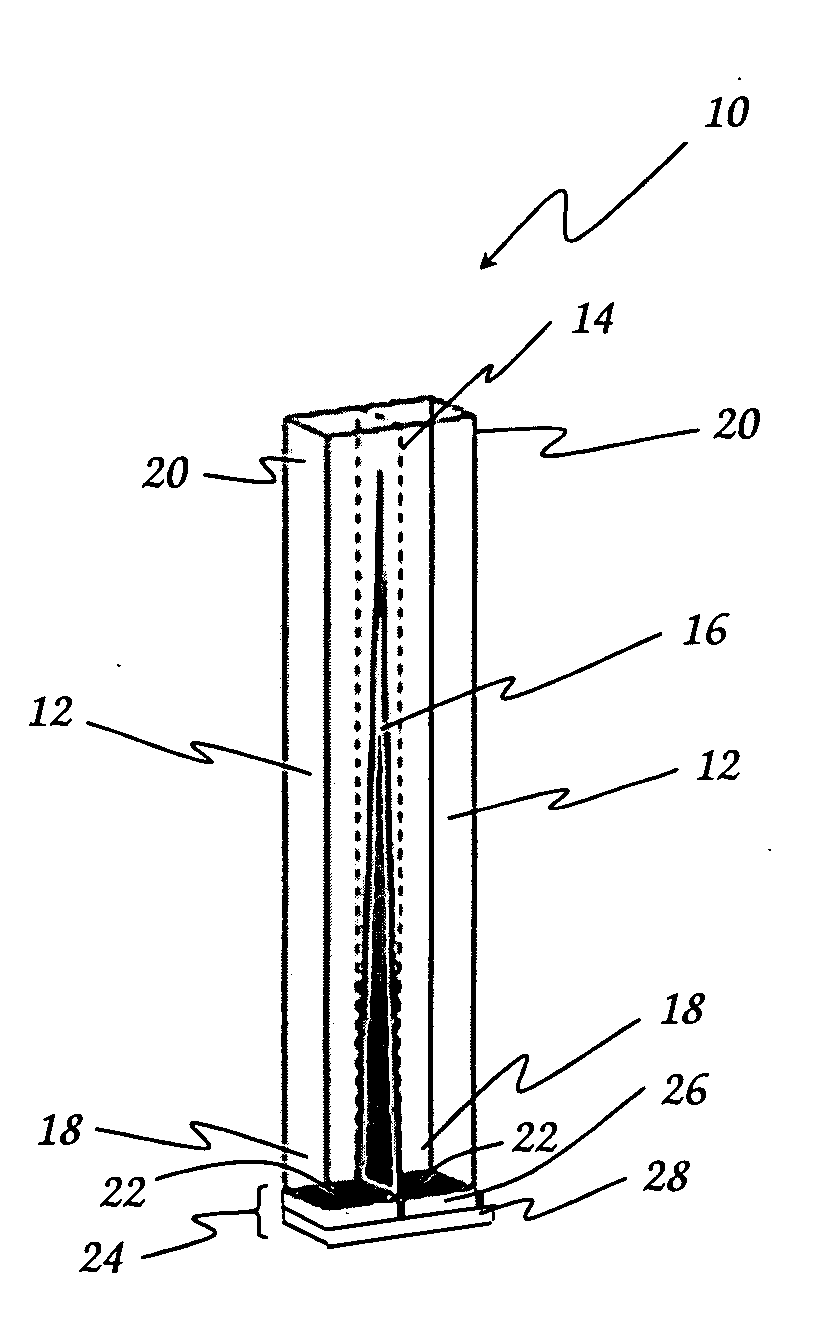
Scintillation crystal detection arrays for radiation imaging devices
ActiveUS7049600B2Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A radiation imaging device includes scintillation crystal sheets arranged in parallel to each other. Semiconductor photodetector positional detectors read light from large faces of the scintillation crystal sheets to detect interactions in the scintillation crystal sheets and independently provide positional information concerning the interactions relative to at least one axis. The structures of the photodetectors and crystal sheets provide for very small spaces between the sheets.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Detector for positron emission imaging equipment, and positron emission imaging equipment
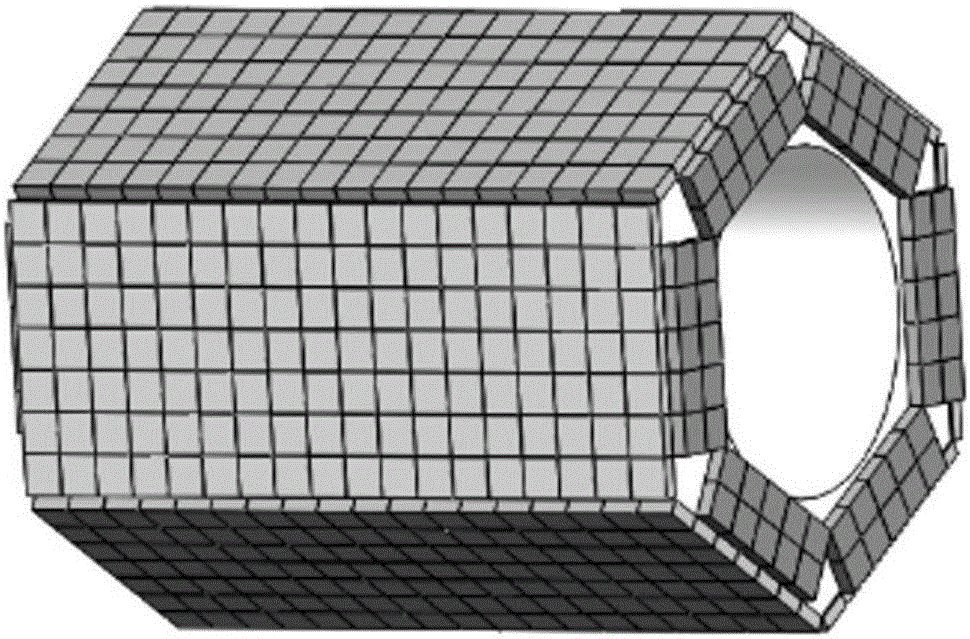
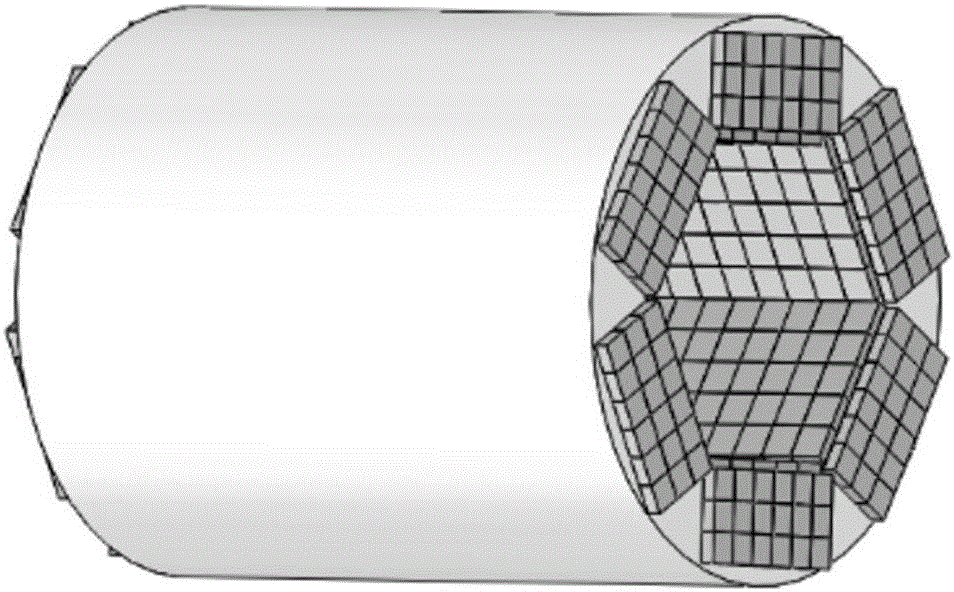
InactiveCN106562799AHigh positioning accuracyHigh sensitivityComputerised tomographsTomographyGamma photonScintillation crystals
The invention provides a detector for positron emission imaging equipment, and positron emission imaging equipment. The detector includes a scintillation crystal and at least one photoelectric sensor array, wherein the scintillation crystal is an integrated scintillation crystal, and is provided with a through hole; the through hole is used for accommodating an object waiting for imaging; the photoelectric sensor array is coupled with the scintillation crystal, and is used for detecting a visible photon which is generated when a gamma photon and the scintillation crystal react; and the gamma photon is generated through positron annihilation effect which occurs in the object waiting for imaging. The detector for positron emission imaging equipment enables the positron emission imaging equipment using the detector to be high in positioning accuracy of the gamma photon, to be high in sensitivity, to be weak in edge effect and to be low in mechanical design difficulty.
Owner:WUHAN ZHONGPAI TECH CO LTD
Composite crystal, gamma ray detector and their preparation methods
InactiveCN102787360AImprove spatial resolutionSimple processAfter-treatment detailsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentAdhesiveScintillation crystals
The invention discloses a composite crystal, a gamma ray detector and their preparation methods. The gamma ray detector comprises a composite crystal array and a photomultiplier. The composite crystal array is coupled with the photomultiplier by an optical coupling agent. The composite crystal array comprises the multiple composite crystal wires and light reflective layers having different lengths are filled between the multiple composite crystal wires. The multiple composite crystal wires are cut, grinded and polished to form the composite crystal. The composite crystal comprises scintillation crystals and a photoconductive material. The scintillation crystals and the photoconductive material are bonded by an adhesive and are aligned with each other without deviation, wherein the adhesive is optical cement. The gamma ray detector provided by the invention has a high space resolution ratio. The preparation method of the composite crystal has simple processes, can be realized easily, and adopts a high-stability and high-repeatability assembling technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT OF BIOMEDICAL ENG
Flicker activity meter
InactiveCN1952689AHigh sensitivityWork lessRadiation intensity measurementMeasuring instrumentScintillation crystals
The invention relates to a twinkled activity indicator belonging to the field of nuclear technique applications and measuring instruments. The activity indicator contains a probe bracket, the partial pressure resistance is mounted on the bracket, and the photomultiplier is mounted on the partial pressure resistance, the scintillator is mounted on the photomultiplier, under the bracket there are signal output connections which connect with the anode of photomultiplier and high pressure connections which connect with photomultiplier via the partial pressure resistance. Because the detecting head is scintillation crystal not the ionization chamber with thick wall, the energy-limiting valve of testing nuclide and the work voltage can be dropped, the alpha, beta charged particles can be detected, and the efficiency of detecting the low energy photon nuclide can be improved. Because of the photomultiplier, the pulsing signals can be measured, and the sensibility of the detecting head can be improved. According to the kinds of the nuclides, you can choose detector with different crystals that it can drop the cost, and it is economic and practical for medium-sized, pint-sized or county hospitals.
Owner:HTA CO LTD
Scintillation detector for positron emission tomography
InactiveUS20090224164A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementGamma photonPhotodetector
The invention disclosed herein is directed to scintillation detectors capable of detecting the position or depth of gamma photon interactions occurring within a scintillator, thereby improving the resolution of ring based positron emission tomography (PET) imaging systems. In one embodiment, the invention is directed to a scintillation detector that comprises at least one pair of side-by-side conjunct scintillation crystal bars having a shared interface between, and a solid-state semiconductor photodetector optically coupled to each output window of each individual scintillation crystal bar. The solid-state semiconductor photodetector includes an array of discrete sensitive areas disposed across a top surface of a common substrate, wherein each sensitive area contains an array of discrete micro-pixelated avalanche photodiodes, and wherein the output window of each scintillation crystal bar is optically coupled to each respective sensitive area in a one-on-one relationship.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Reaction position positioning method and apparatus
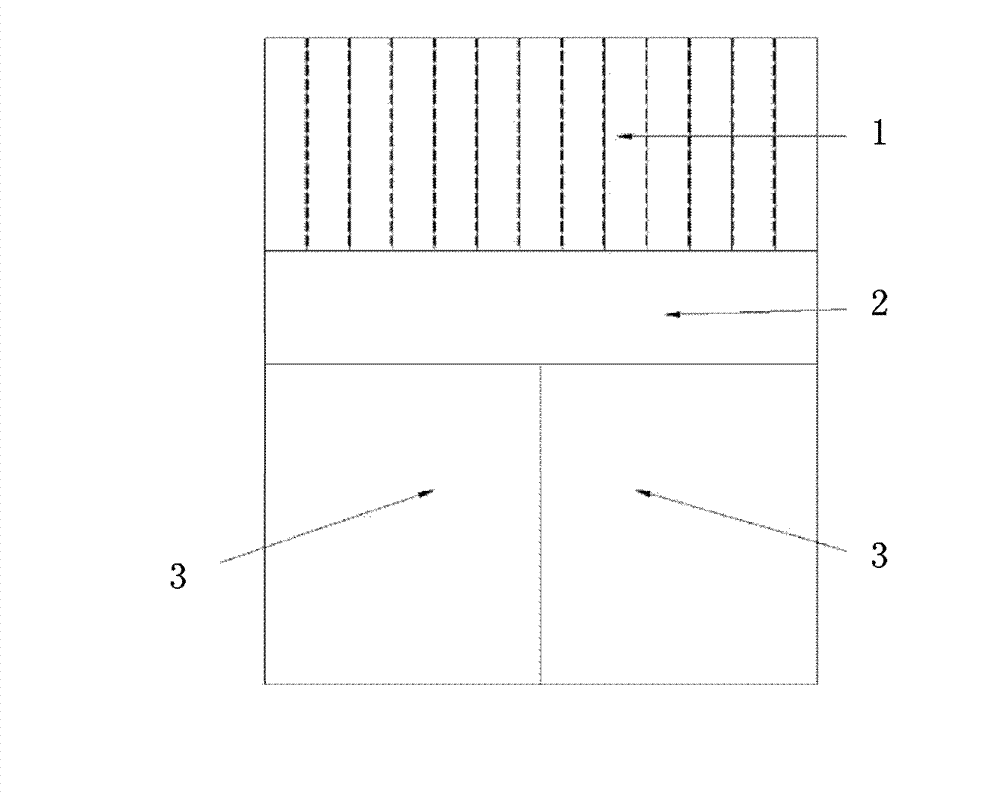
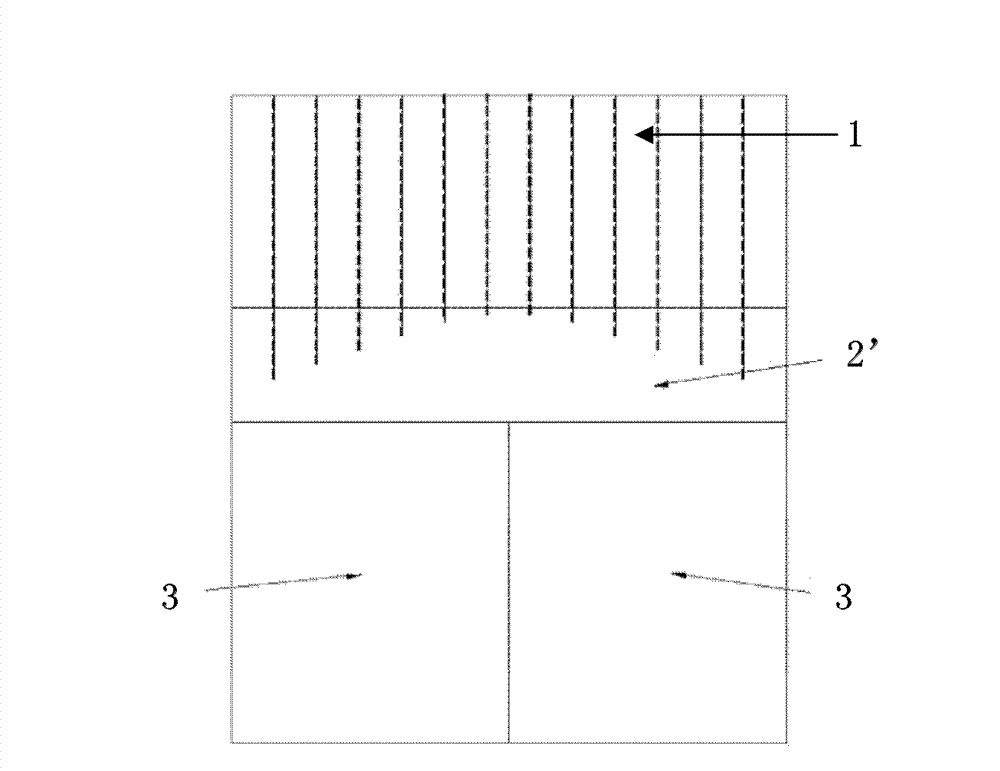
ActiveCN106556857ASolve the problem that it cannot be applied to the above-mentioned modified positron emission imaging equipmentX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentGamma photonScintillation crystals
The invention provides a reaction position positioning method and apparatus. The method includes receiving the energy information of the visible photon coupled to a scintillation crystal, detected by at least one photoelectric sensor array, and generated by the reaction of the gamma photon with the scintillation crystal, wherein the scintillation crystal is an integrated scintillation crystal and has a through hole for receiving an object to be imaged, and the gamma photon is generated by the positron annihilation effect in the object to be imaged; and determining the reaction position of the gamma photon in the scintillation crystal according to the received energy information, wherein the reaction position is represented by a cylindrical coordinate system. According to the invention, by providing a way for positioning the reaction position of the gamma photon for a positron emission imaging apparatus with the integrated scintillation crystal, the problem that a conventional position calculation method is not suitable for the improved positron emission imaging apparatus can be solved.
Owner:WUHAN ZHONGPAI TECH CO LTD
Scintigraphic device with avriable resolution
InactiveUS20050263717A1Reduced dimensionMass is limitedMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh densityVariable resolution
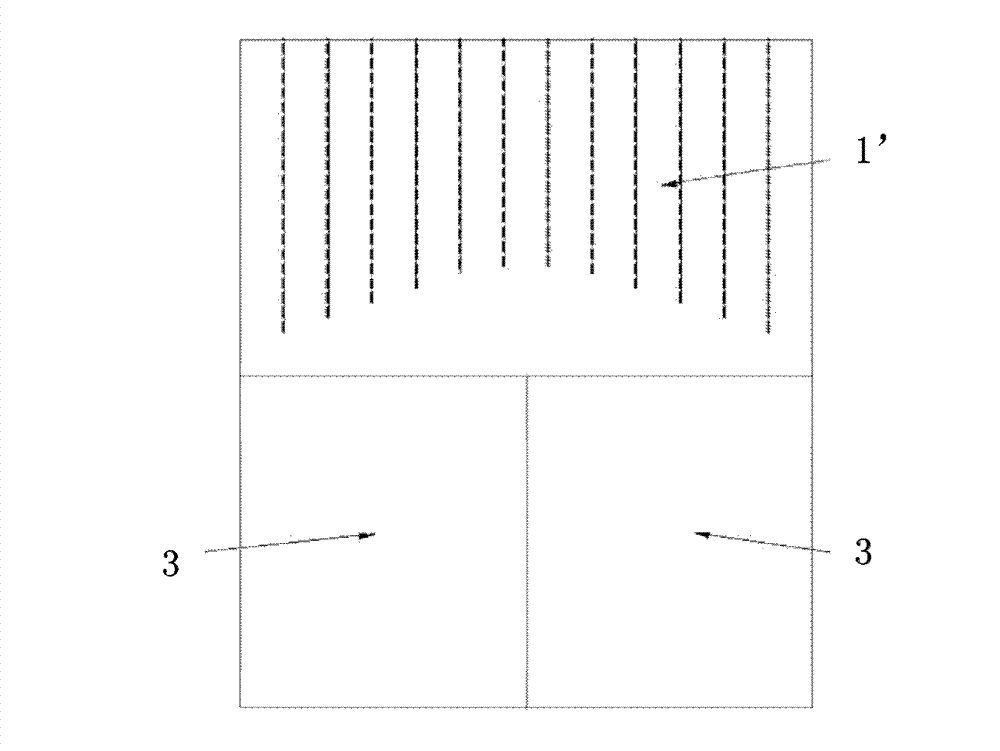
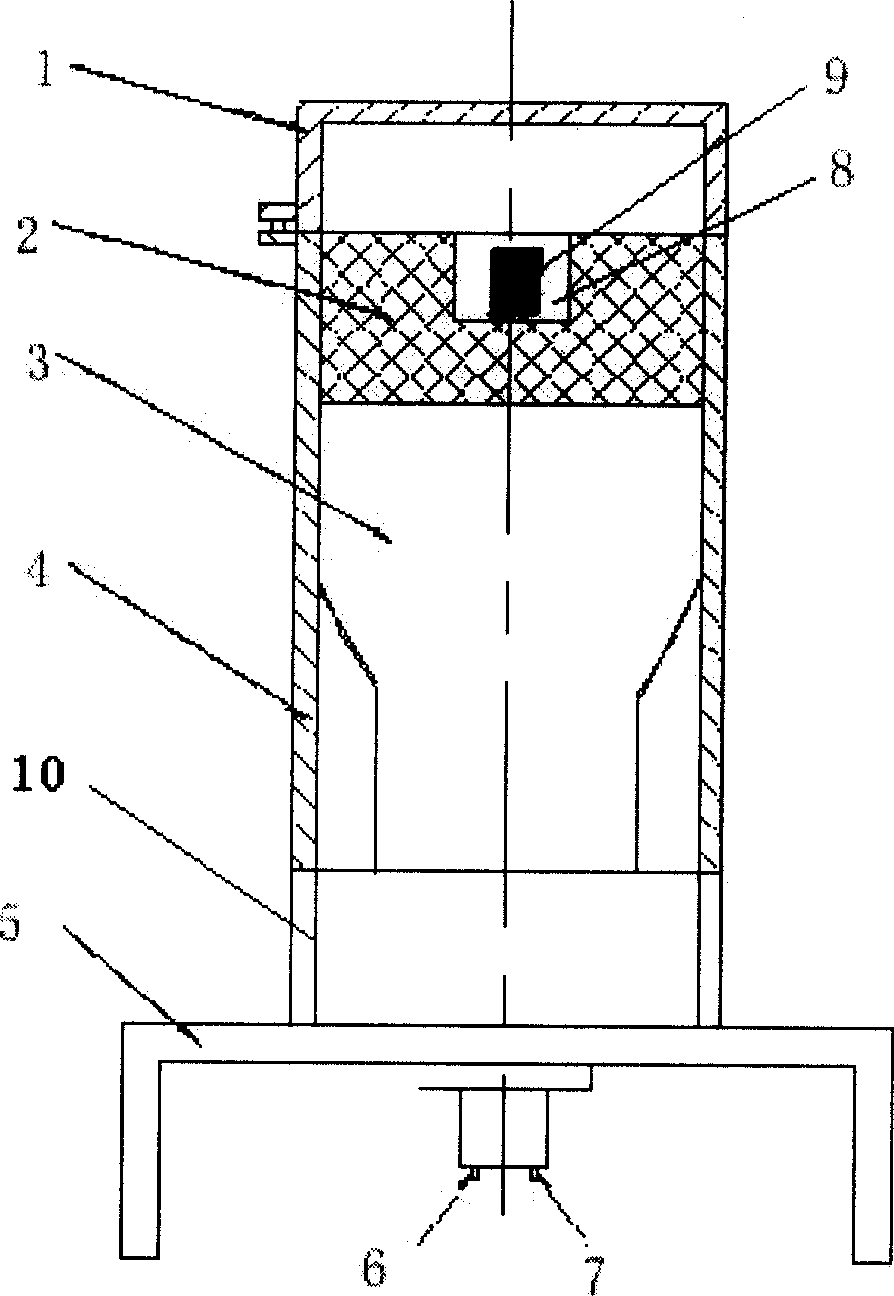
A scintigraphic device includes a case open at an application end, and coated by a shielding shell; a collimator positioned inside the case, made of a material with high atomic number and high density and having a plurality of collimation channels extending mutually parallel according to a predefined direction of measurement; a measuring member positioned inside the case in proximity to the collimator and including a scintillation crystal for converting each ionizing radiation originating from a source in exam into light radiation, and at least one photosensor, for determining the energy and the position of each detected event. The measuring member and the collimator are relatively movable to increase and / or reduce the distance between the converter and the application end and consequently to vary the total length of the collimator. The collimator may include two or more blocks at least one of which is movable relative to the others.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com