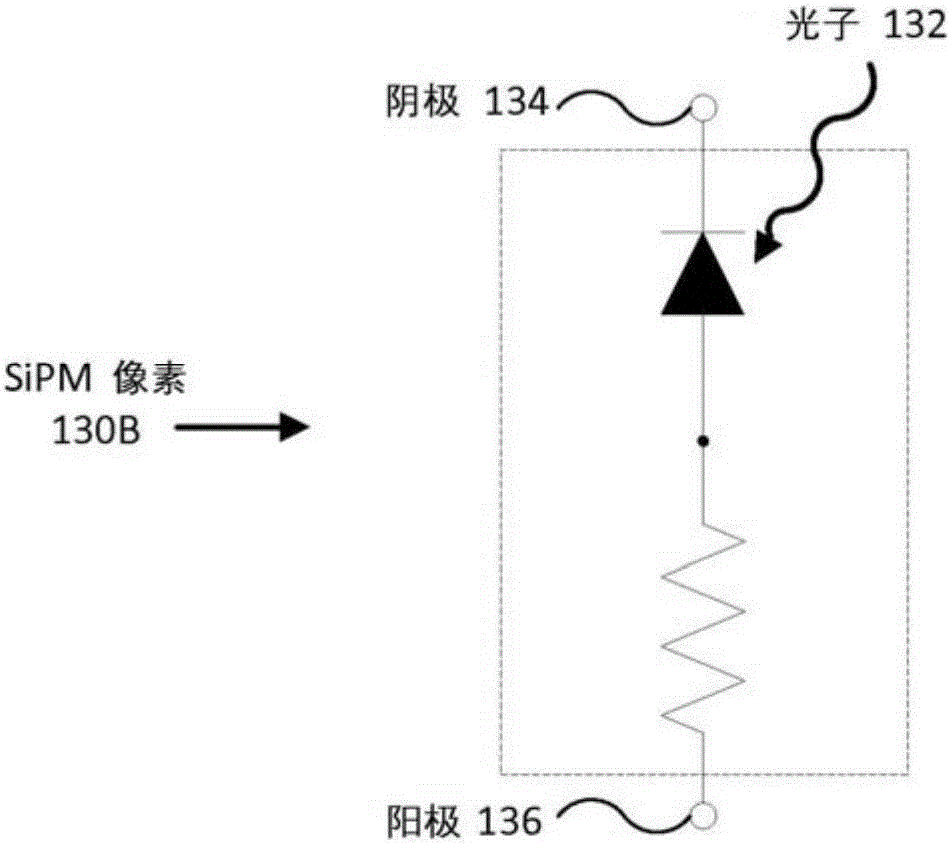
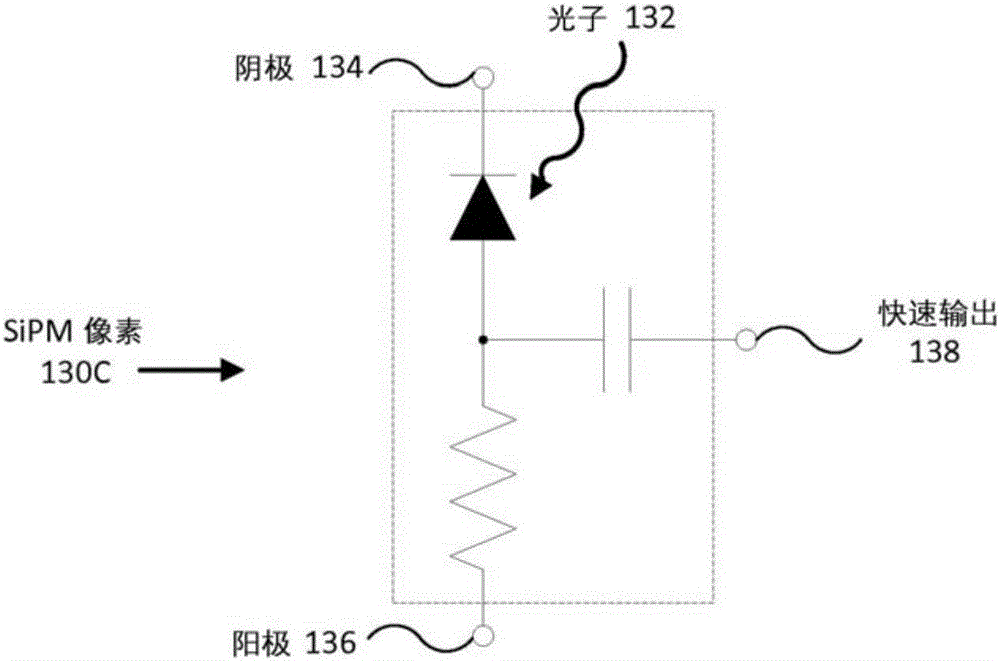
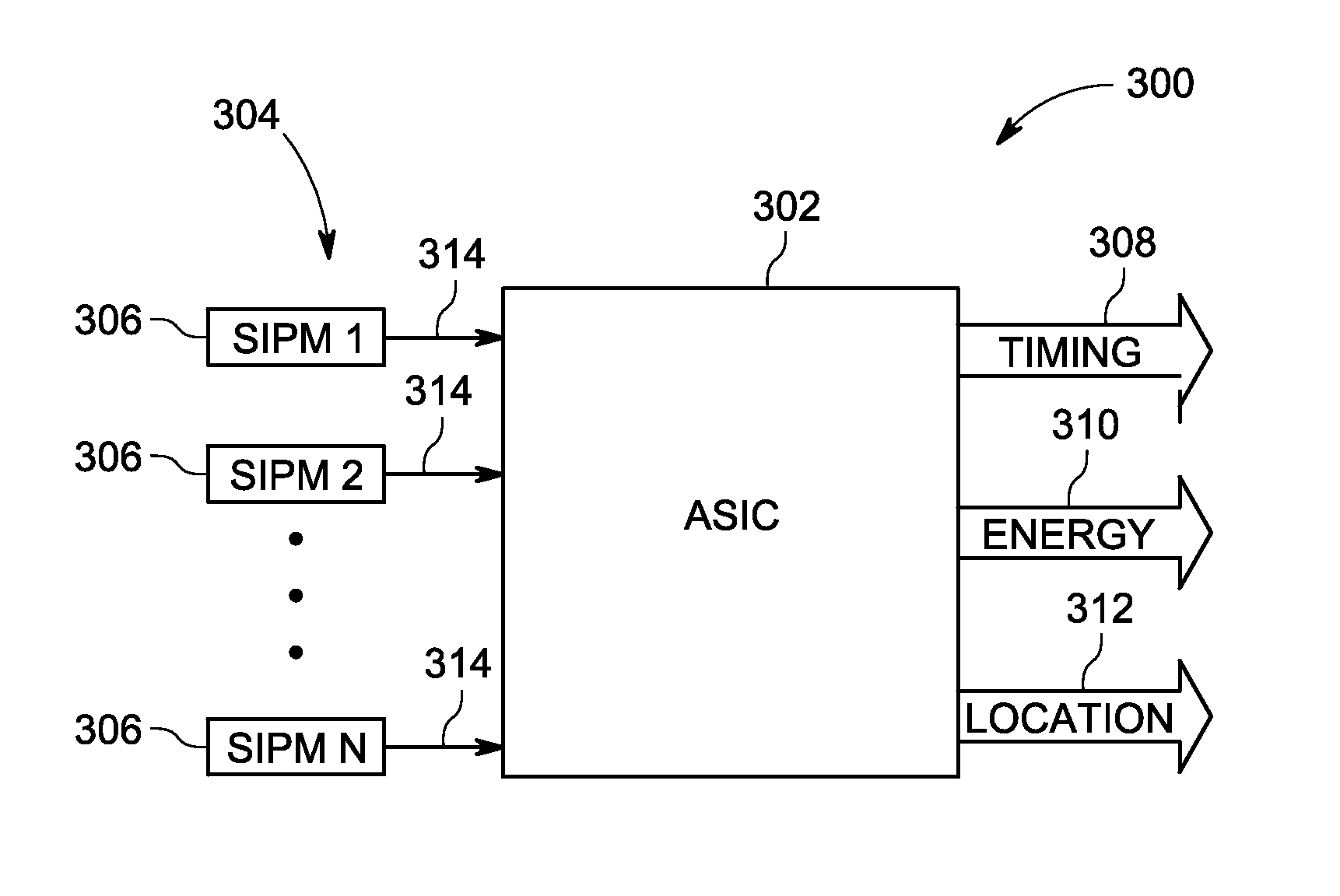
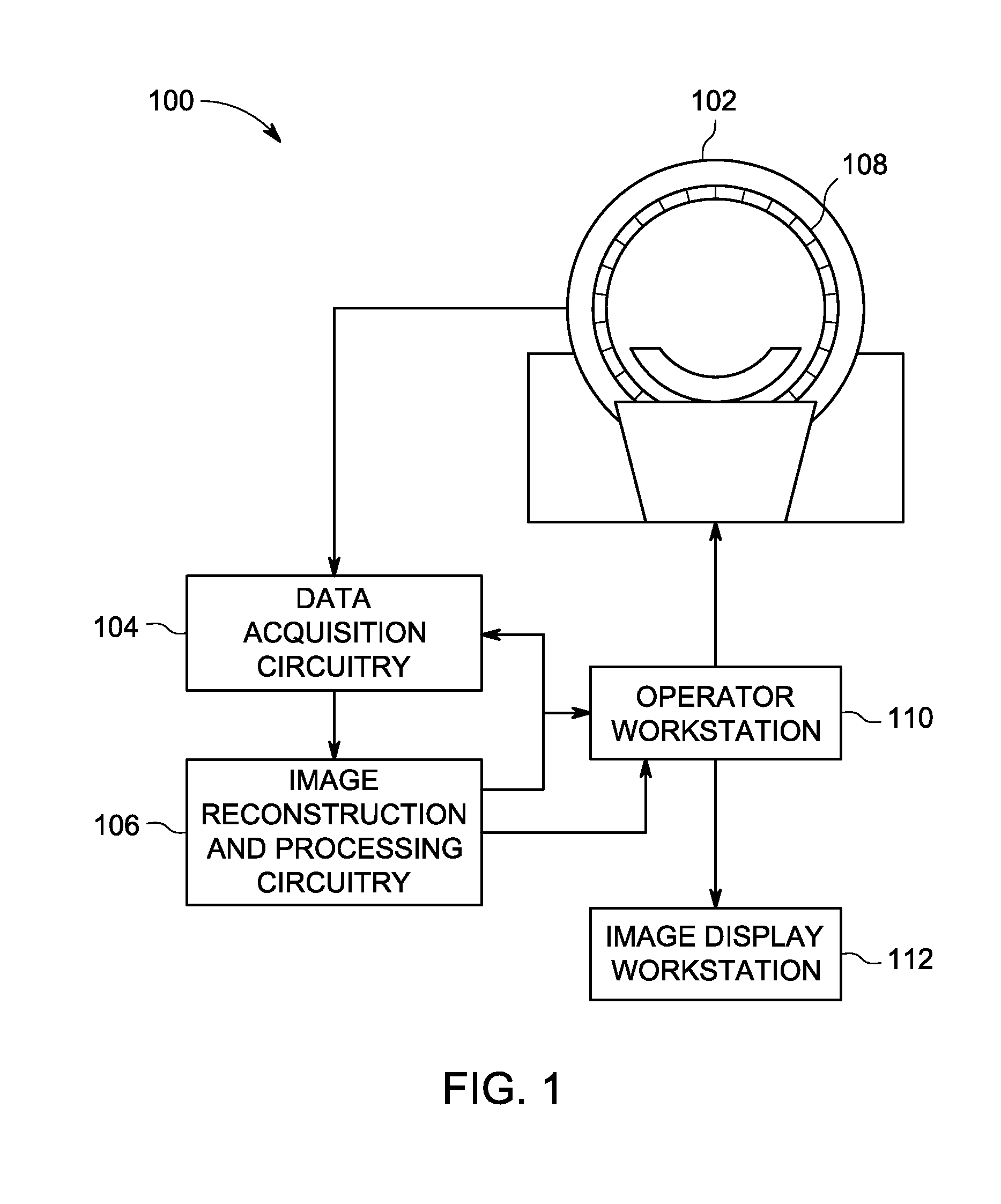
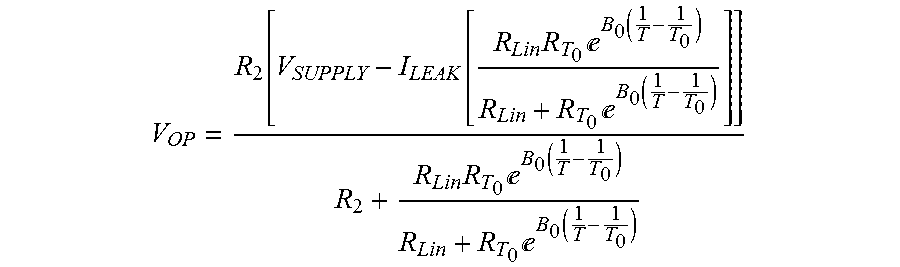Patents
Literature
199 results about "Silicon photomultiplier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
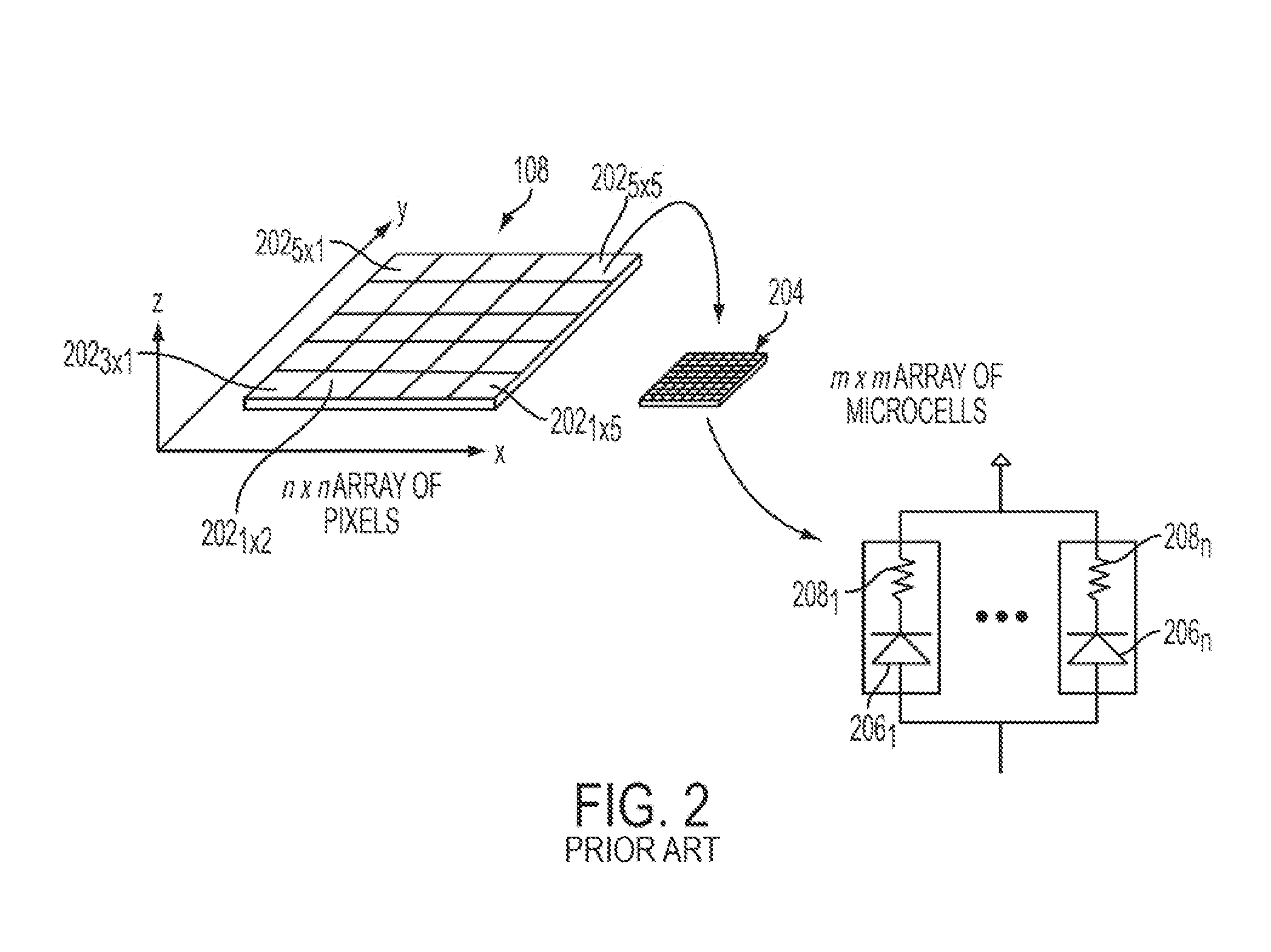
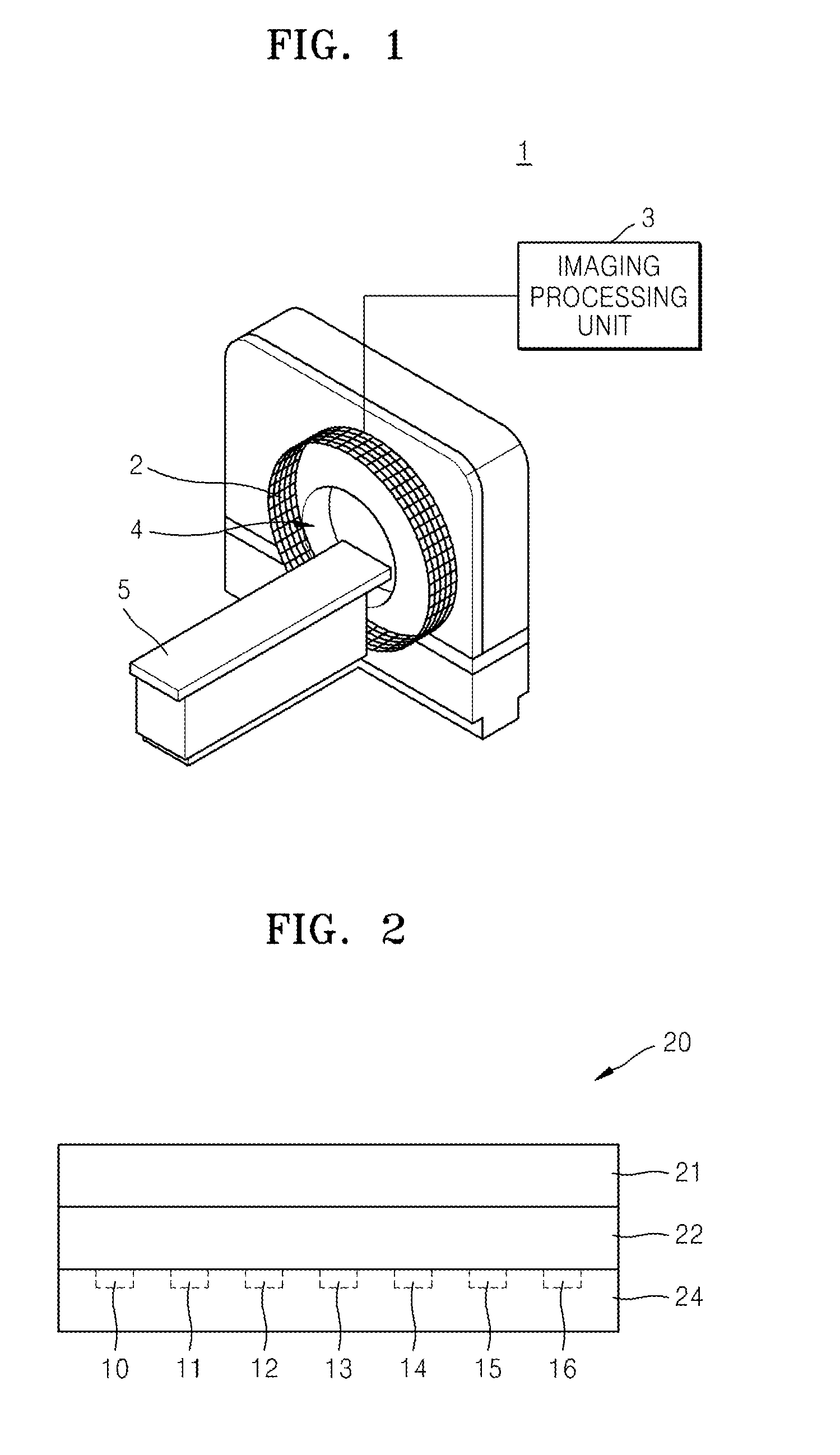
Silicon photomultipliers, often called "SiPM" in the literature, are solid-state single-photon-sensitive devices based on Single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) implemented on common silicon substrate. The dimension of each single SPAD can vary from 10 to 100 micrometres, and their density can be up to 10000 per square millimeter. Every SPAD in SiPM operates in Geiger mode and is coupled with the others by a metal or polysilicon quenching resistor. Although the device works in digital/switching mode, most of SiPM are an analog device because all the microcells are read in parallel, making it possible to generate signals within a dynamic range from a single photon to 1000 photons for a device with just a square-millimeter area. More advanced readout schemes are utilized for the lidar applications. The supply voltage (Vb) depends on APD technology used and typically varies between 20 V and 100 V, thus being from 15 to 75 times lower than the voltage required for a traditional photomultiplier tube's (PMT) operation.
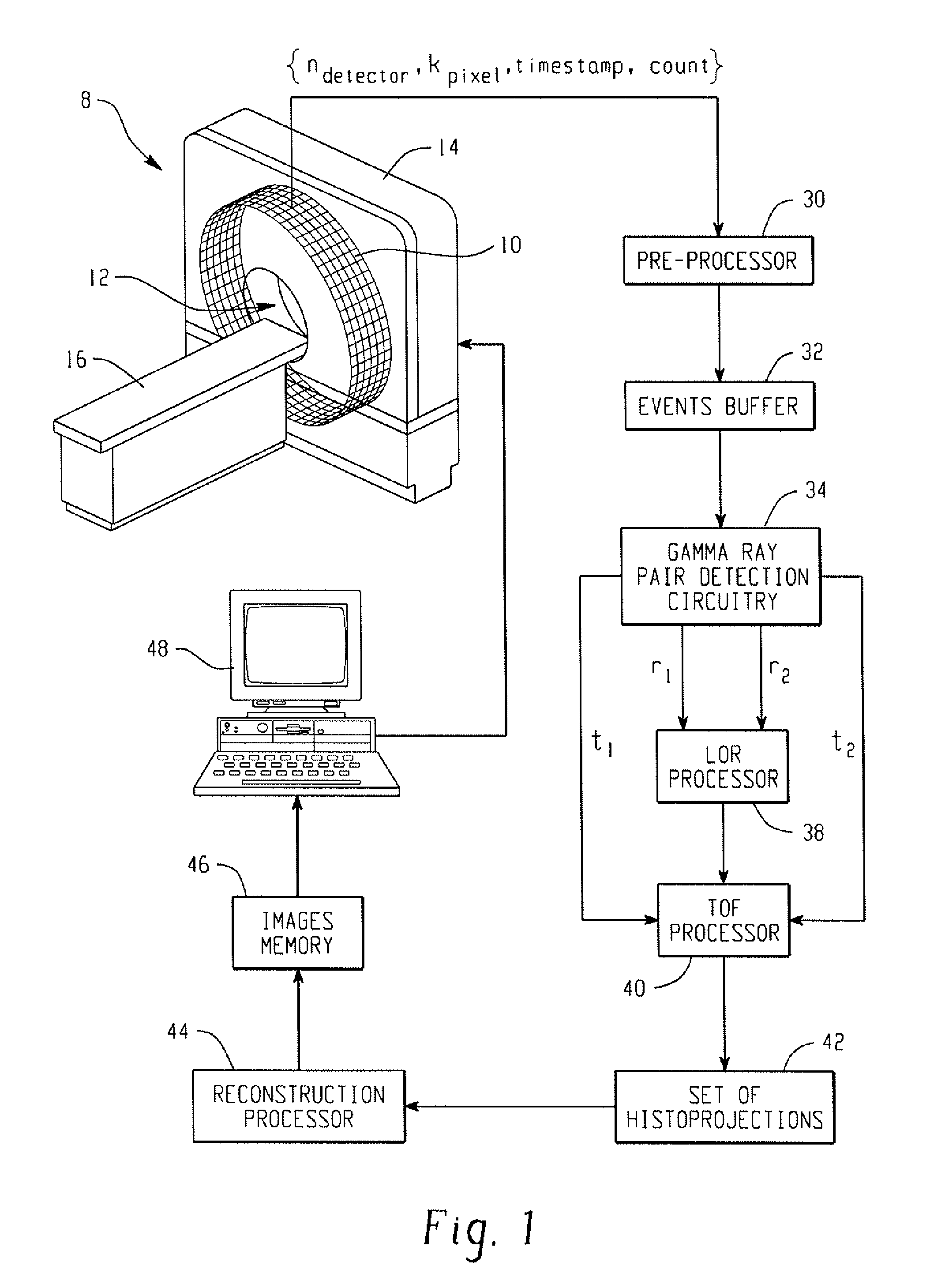
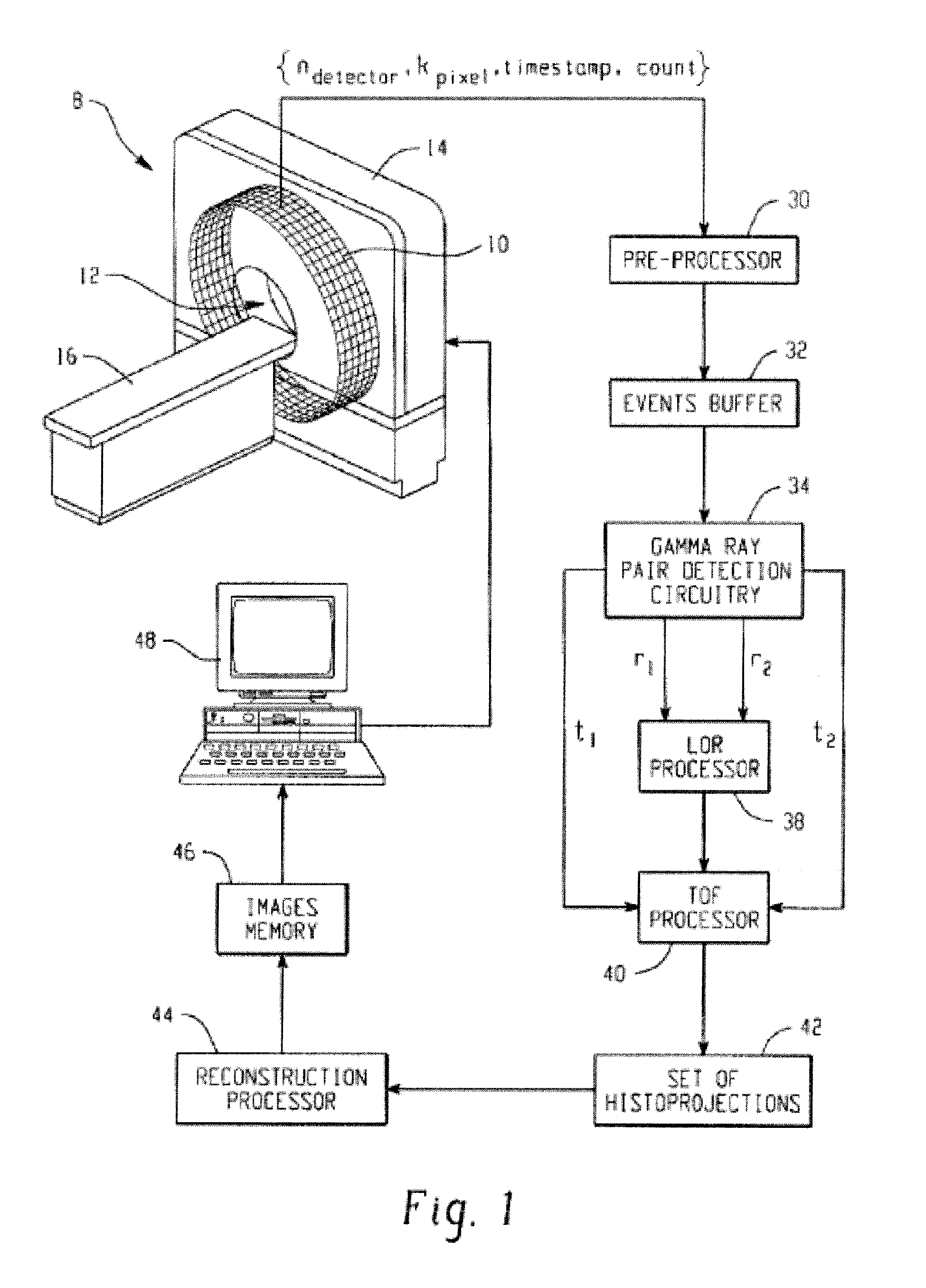
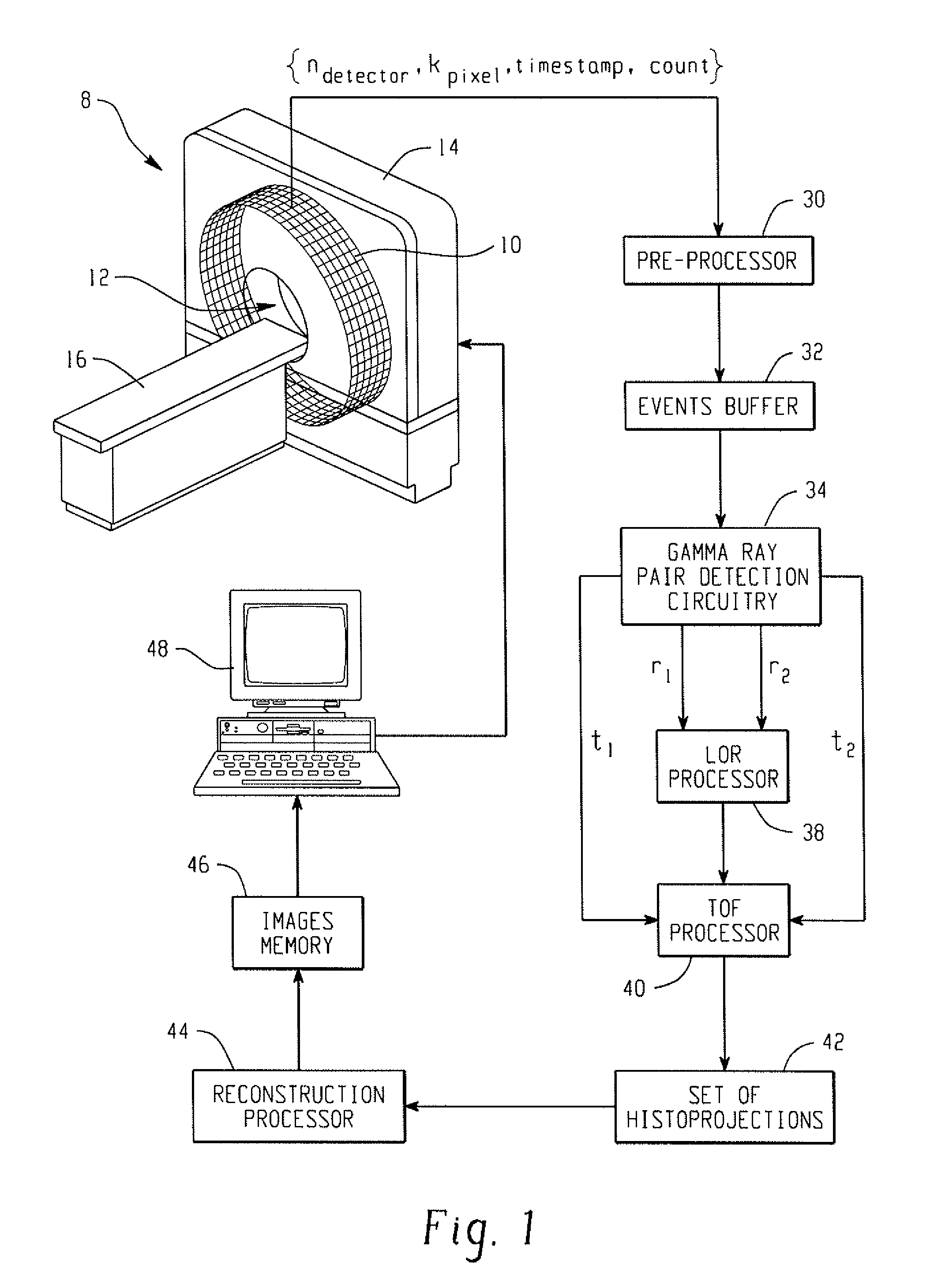
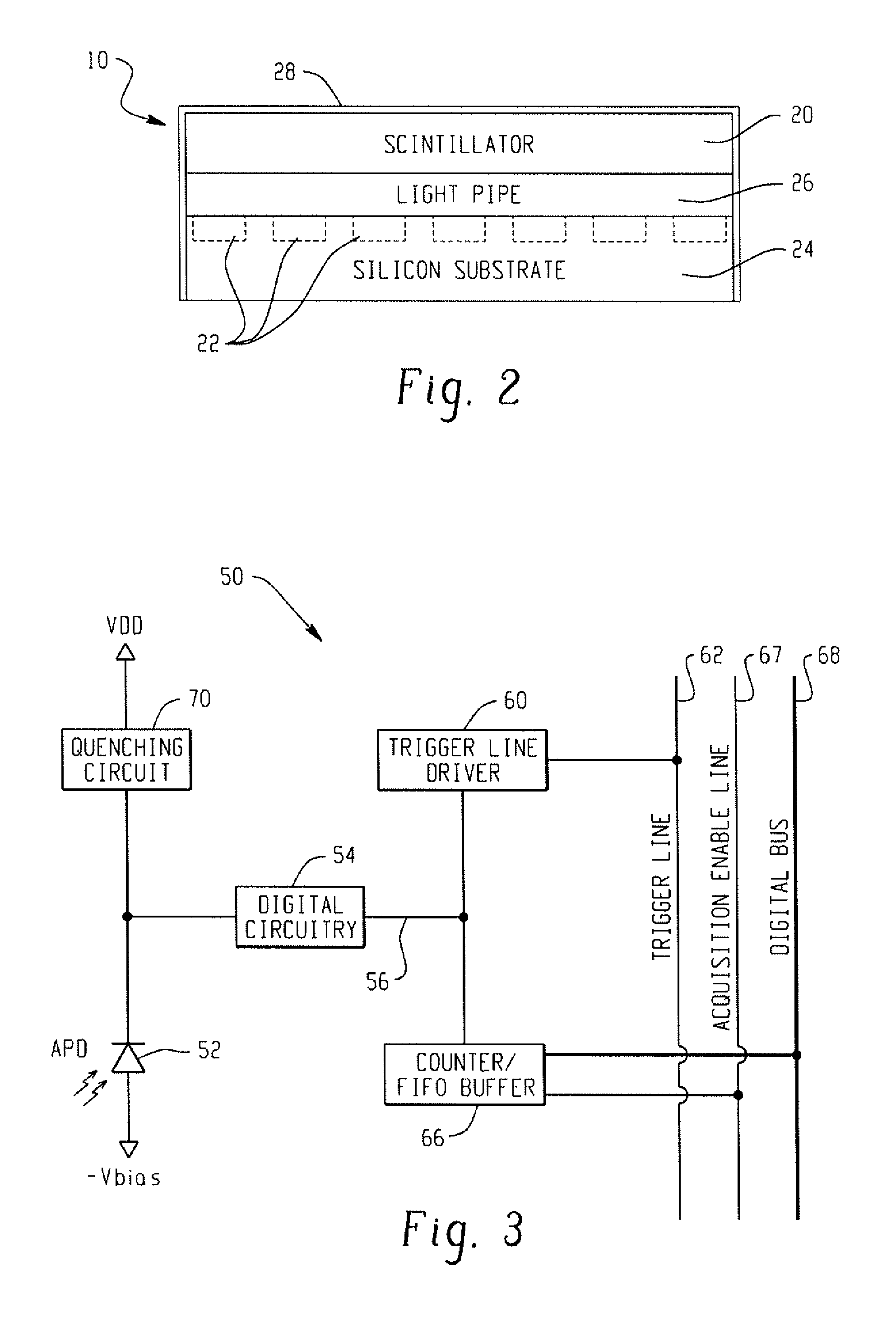
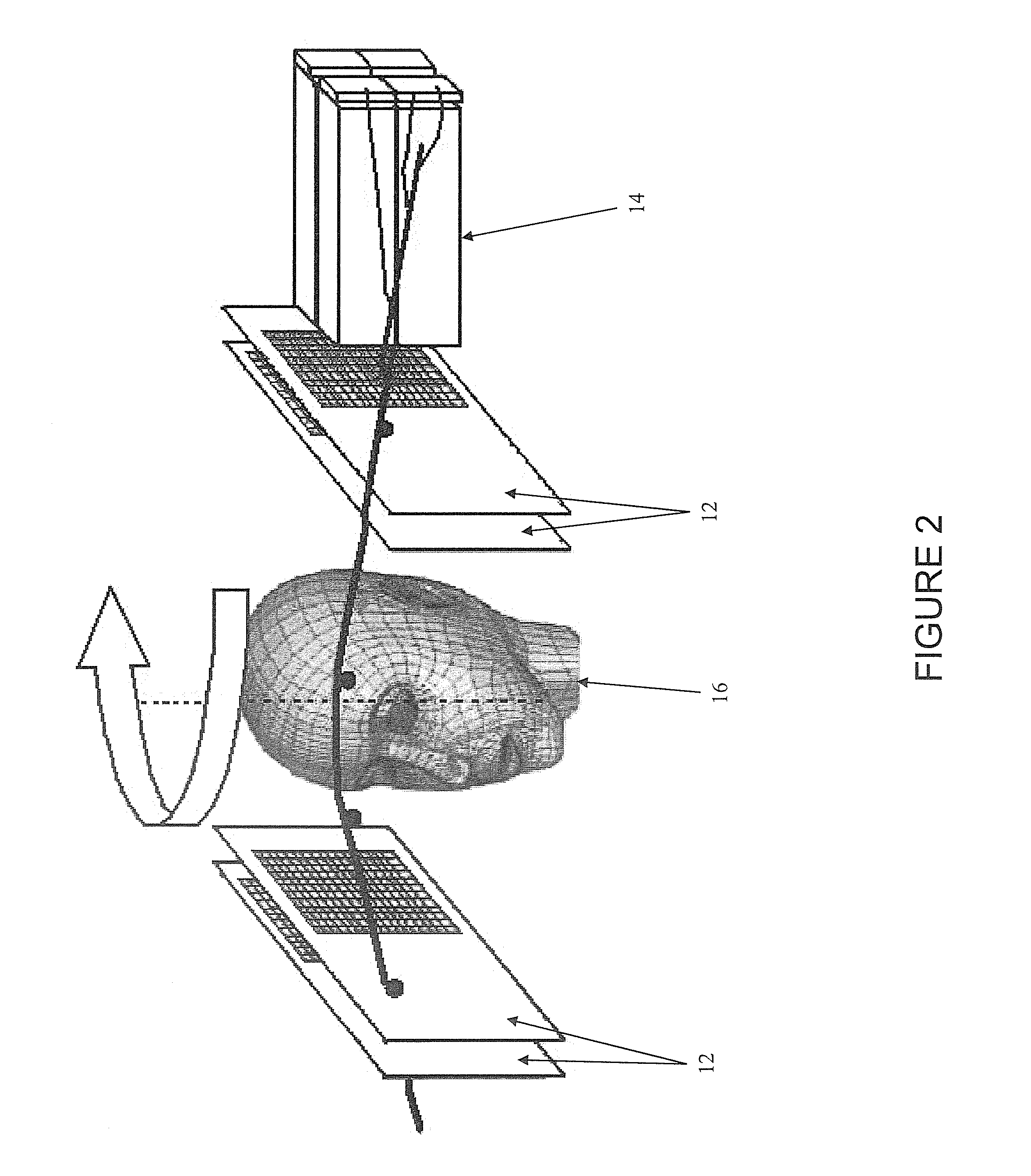
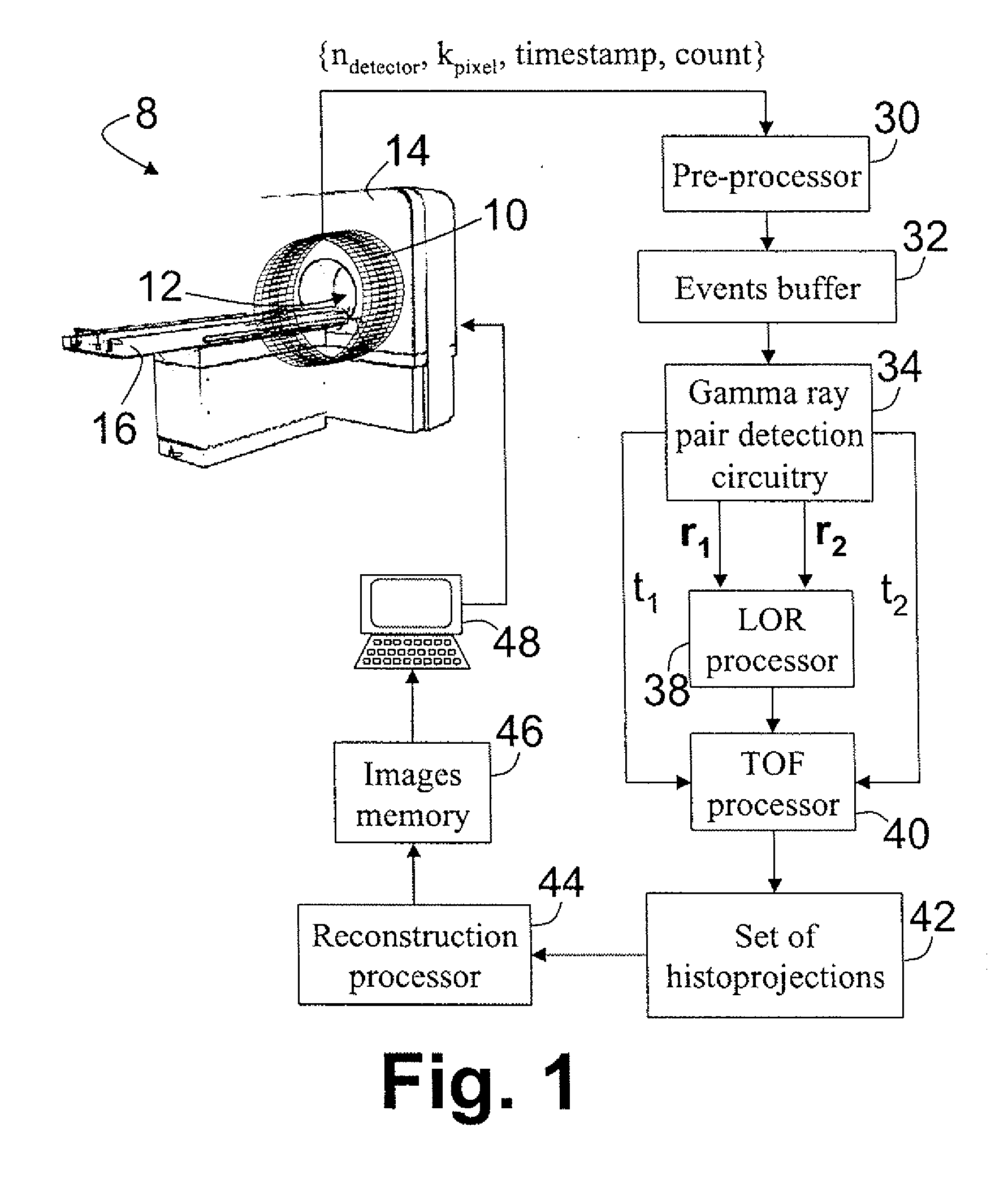
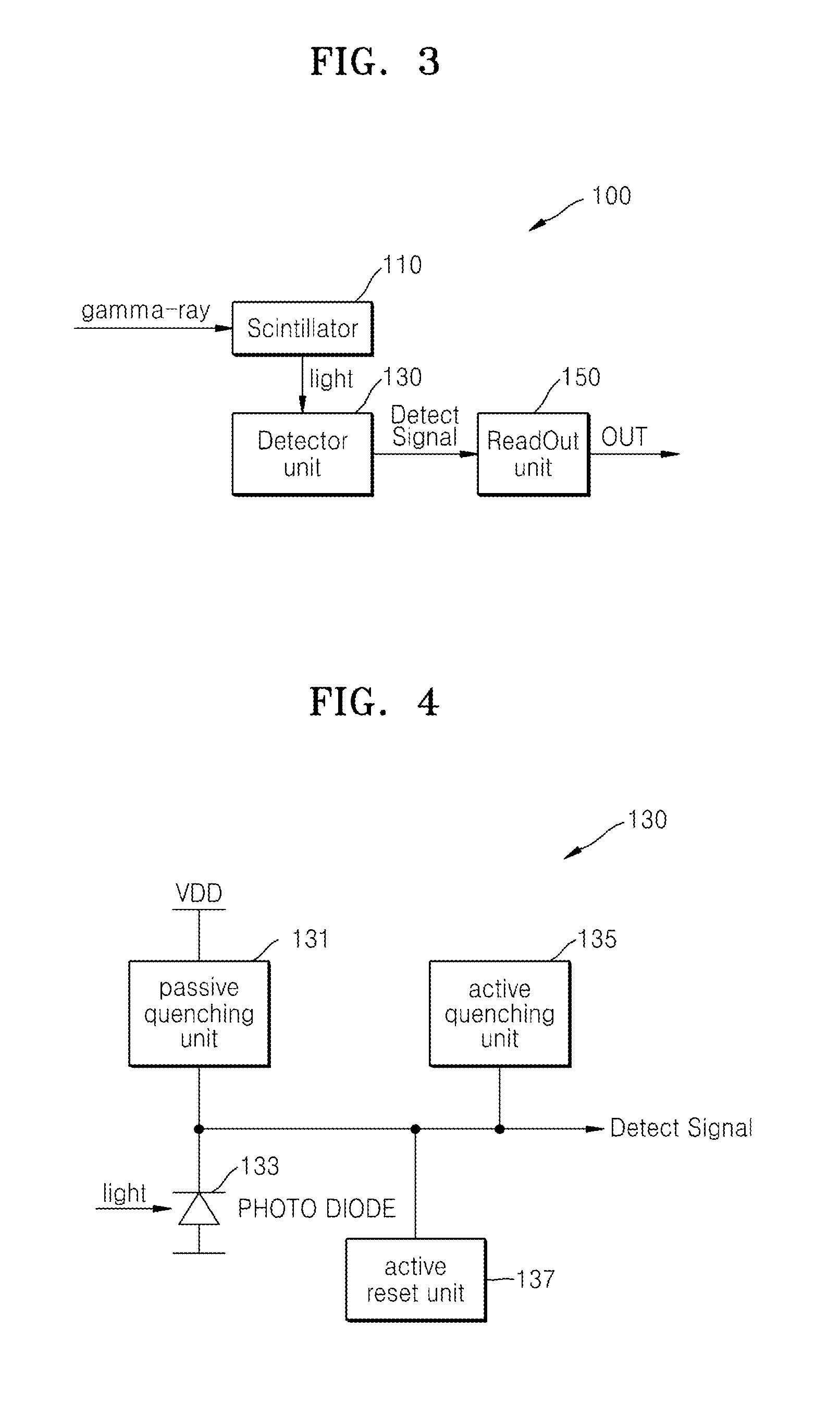
Digital silicon photomultiplier for TOF-PET
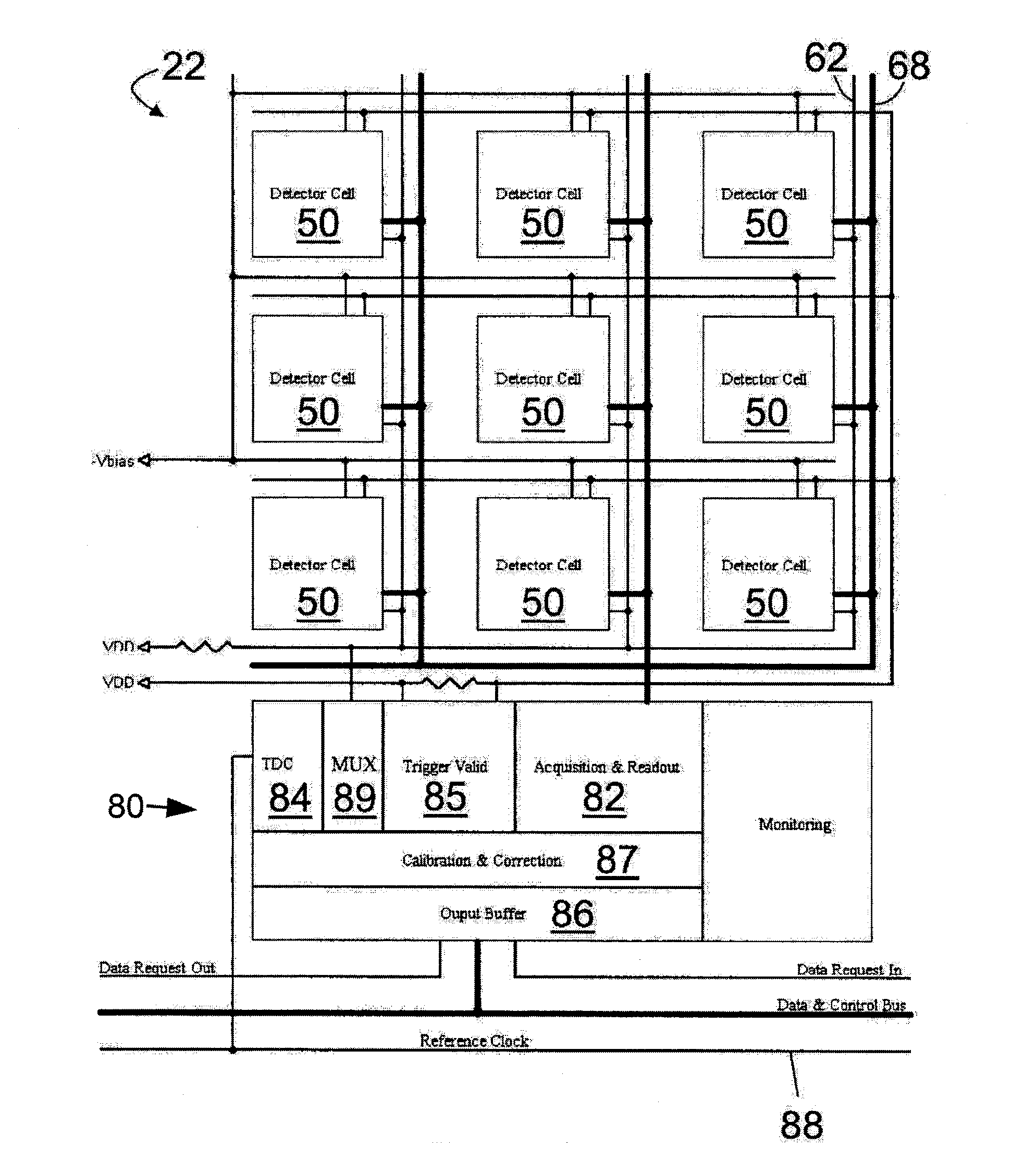
ActiveUS20080203309A1High data-rate radiation detectionImproved spatial detector resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyQuiescent stateSilicon photomultiplier
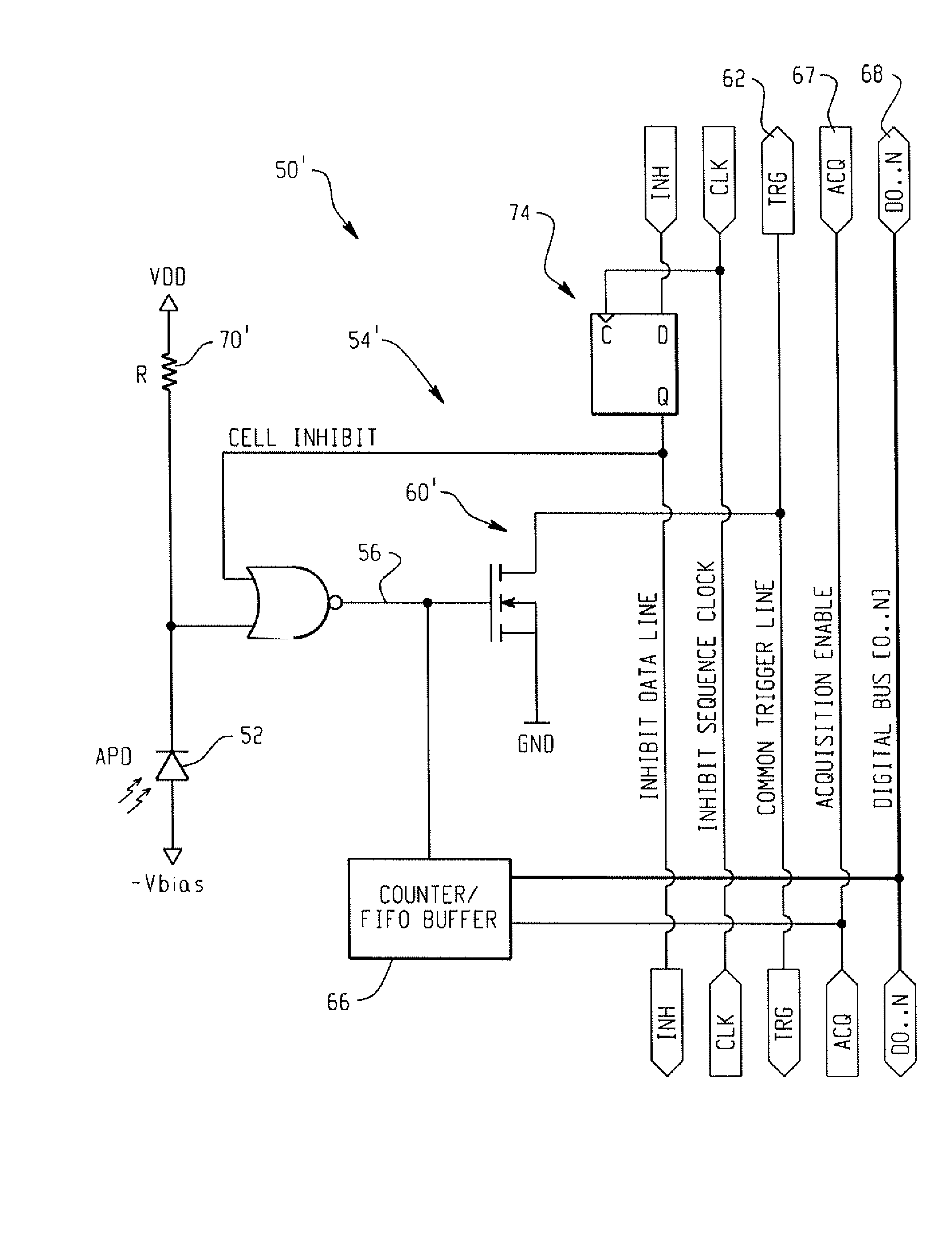
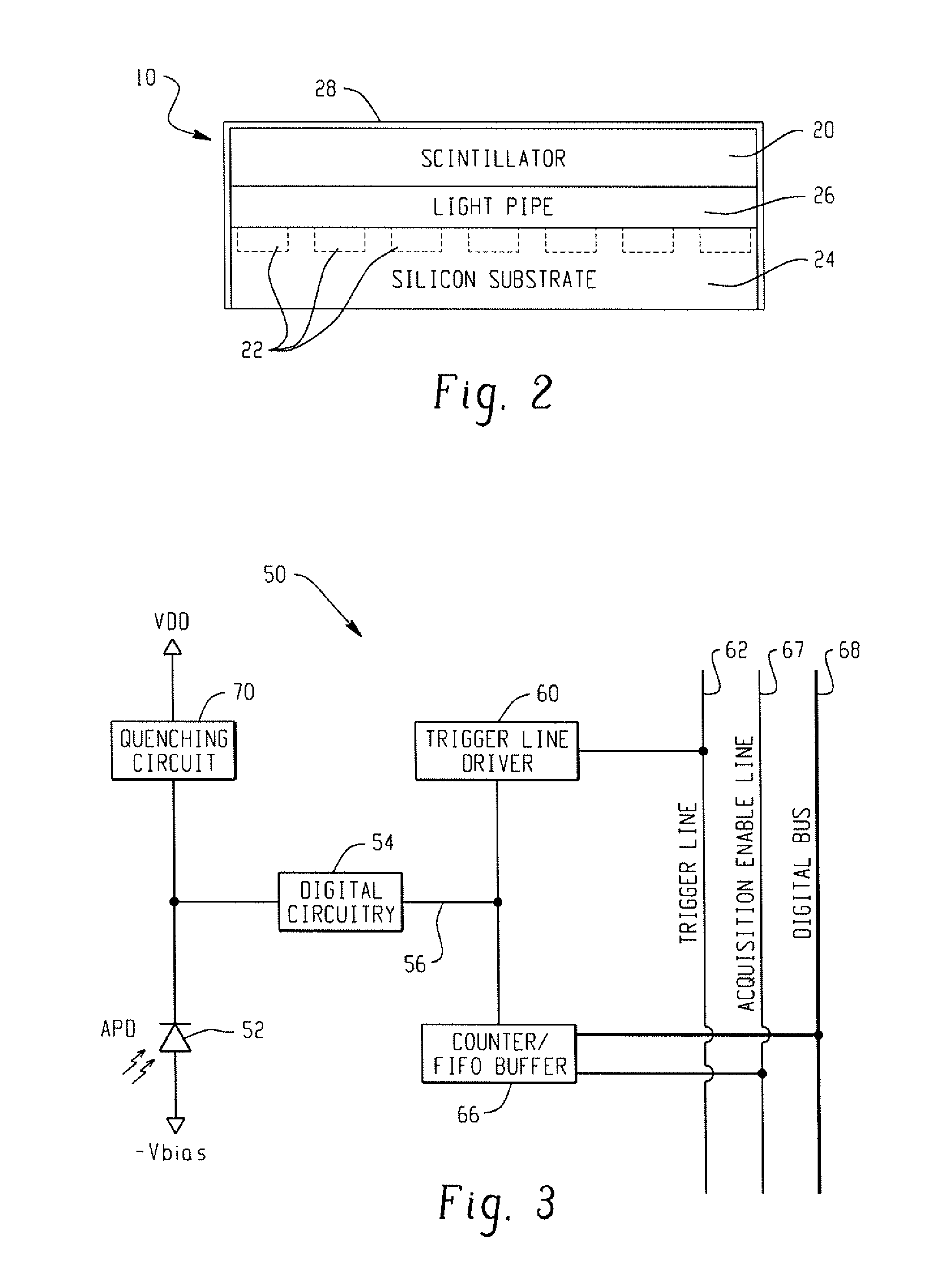
A radiation detector includes an array of detector pixels each including an array of detector cells. Each detector cell includes a photodiode biased in a breakdown region and digital circuitry coupled with the photodiode and configured to output a first digital value in a quiescent state and a second digital value responsive to photon detection by the photodiode. Digital triggering circuitry is configured to output a trigger signal indicative of a start of an integration time period responsive to a selected number of one or more of the detector cells tranisitioning from the first digital value to the second digital value. Readout digital circuitry accumulates a count of a number of transitions of detector cells of the array of detector cells from the first digital state to the second digital state over the integration time period.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Digital silicon photomultiplier for TOF PET
ActiveUS8395127B1High data-rate radiation detectionImproved spatial detector resolutionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansQuiescent stateSilicon photomultiplier
A radiation detector includes an array of detector pixels each including an array of detector cells. Each detector cell includes a photodiode biased in a breakdown region and digital circuitry coupled with the photodiode and configured to output a first digital value in a quiescent state and a second digital value responsive to photon detection by the photodiode. Digital triggering circuitry is configured to output a trigger signal indicative of a start of an integration time period responsive to a selected number of one or more of the detector cells transitioning from the first digital value to the second digital value. Readout digital circuitry accumulates a count of a number of transitions of detector cells of the array of detector cells from the first digital state to the second digital state over the integration time period.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
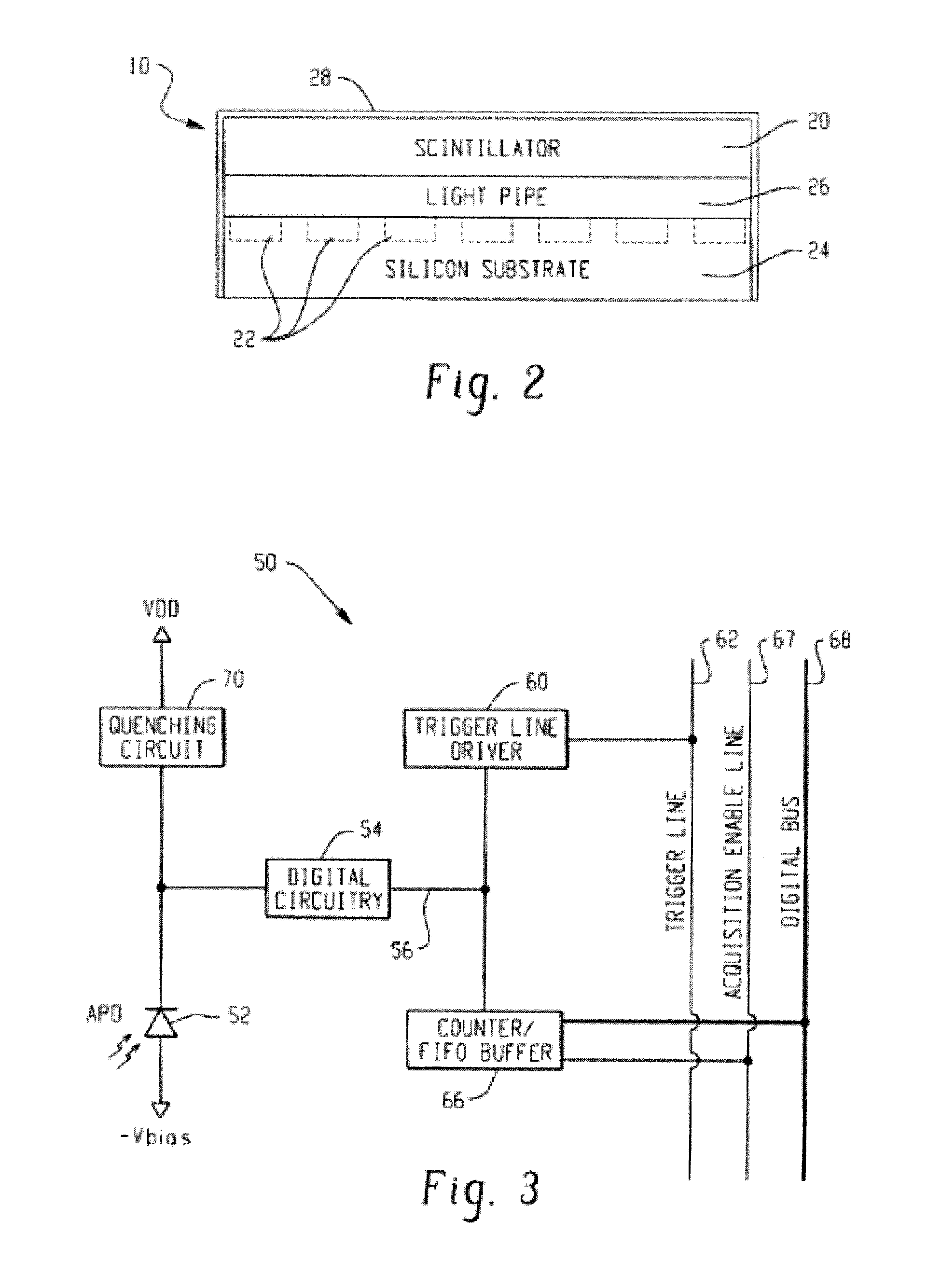
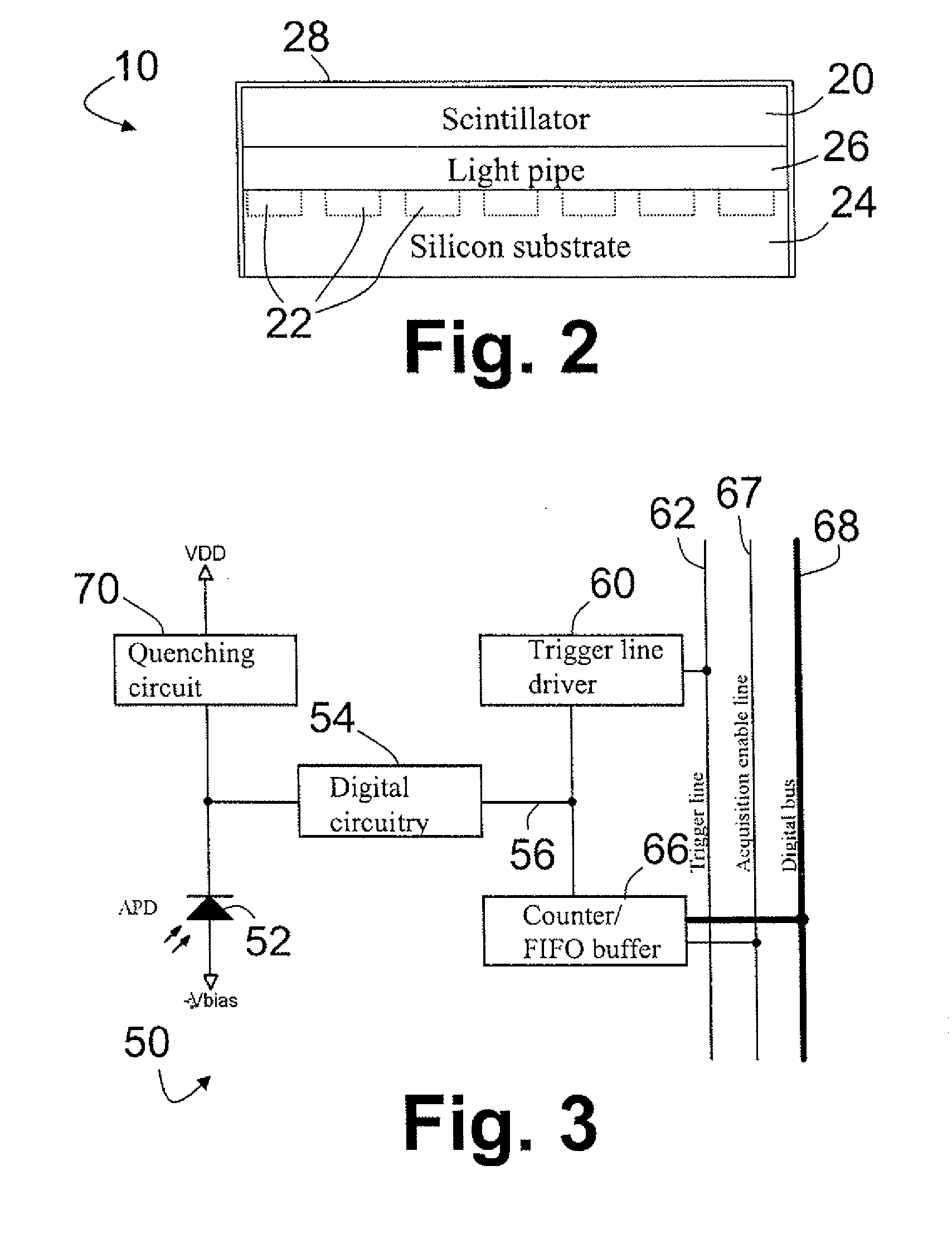
Silicon photomultiplier detector for computed tomography
InactiveUS20100316184A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x raySilicon photomultiplier
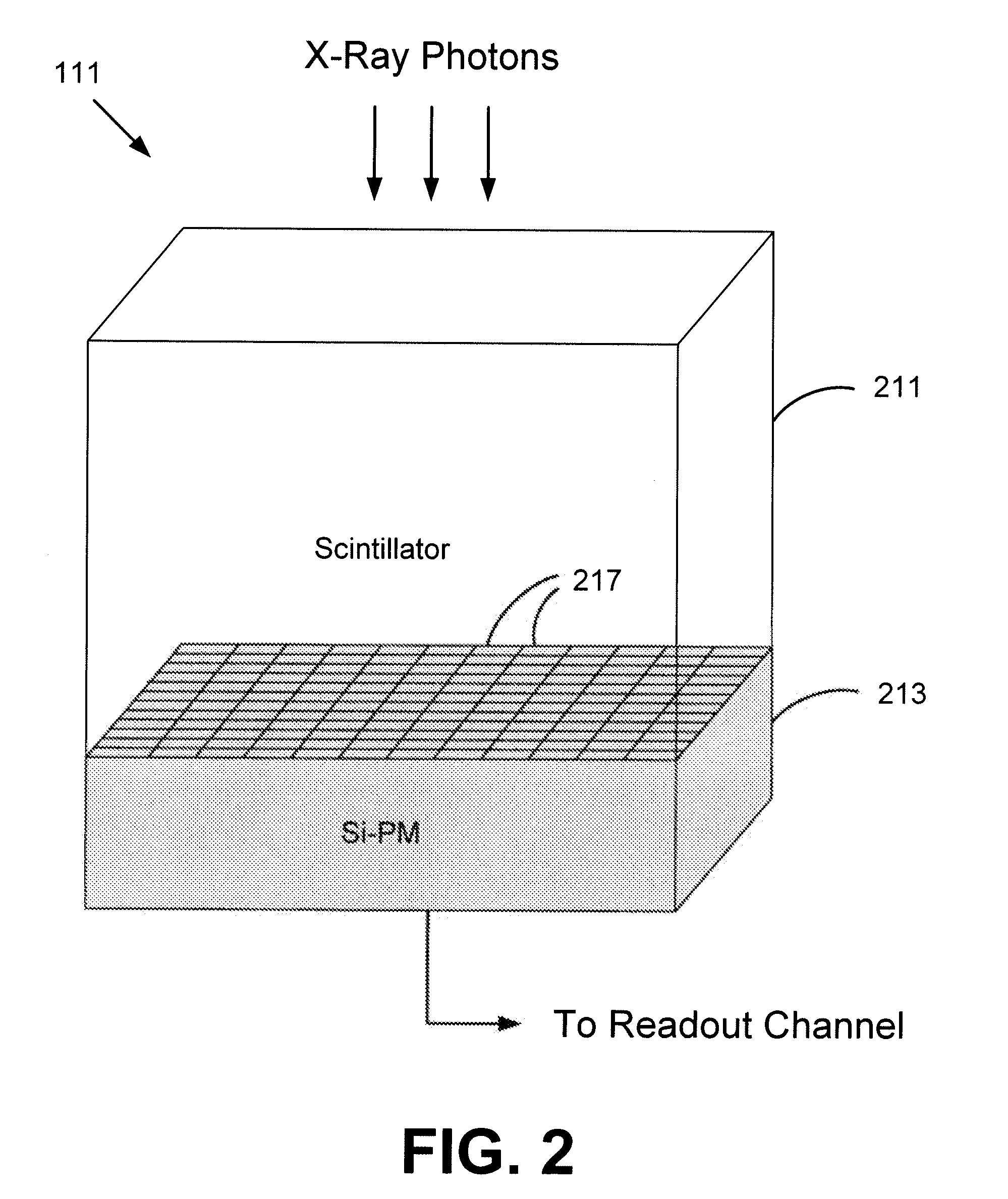
An x-ray detector module including a silicon photomultiplier and a computed tomography imaging system including the same is provided. The x-ray detector module includes optically coupled scintillation materials and silicon photomultiplier pixels. The x-ray detector pixels may have a constant axial profile with a polygonal cross section, which may be rectangular. A plurality of the x-ray detector pixels are generally arranged into 2D arrays. Each x-ray detector pixel may be connected to a dedicated electronic readout channel. In operation, the scintillation materials interact with incident x-ray photons to generate visible-light photons. The silicon photomultiplier pixels generate electrical signals in accordance with the number of visible-light photons generated by an incident x-ray photon. The electronic readout channels process the electrical signals to determine characteristics of the incident x-ray photons. Information of a plurality of x-ray photons are compiled to generate computed tomography images.
Owner:DXRAY
Silicon Photomultiplier Based TOF-PET Detector
ActiveUS20150285922A1Reducing electronic circuit complexityReduced Power RequirementsMaterial analysis by optical meansComputerised tomographsSensor arraySilicon photomultiplier
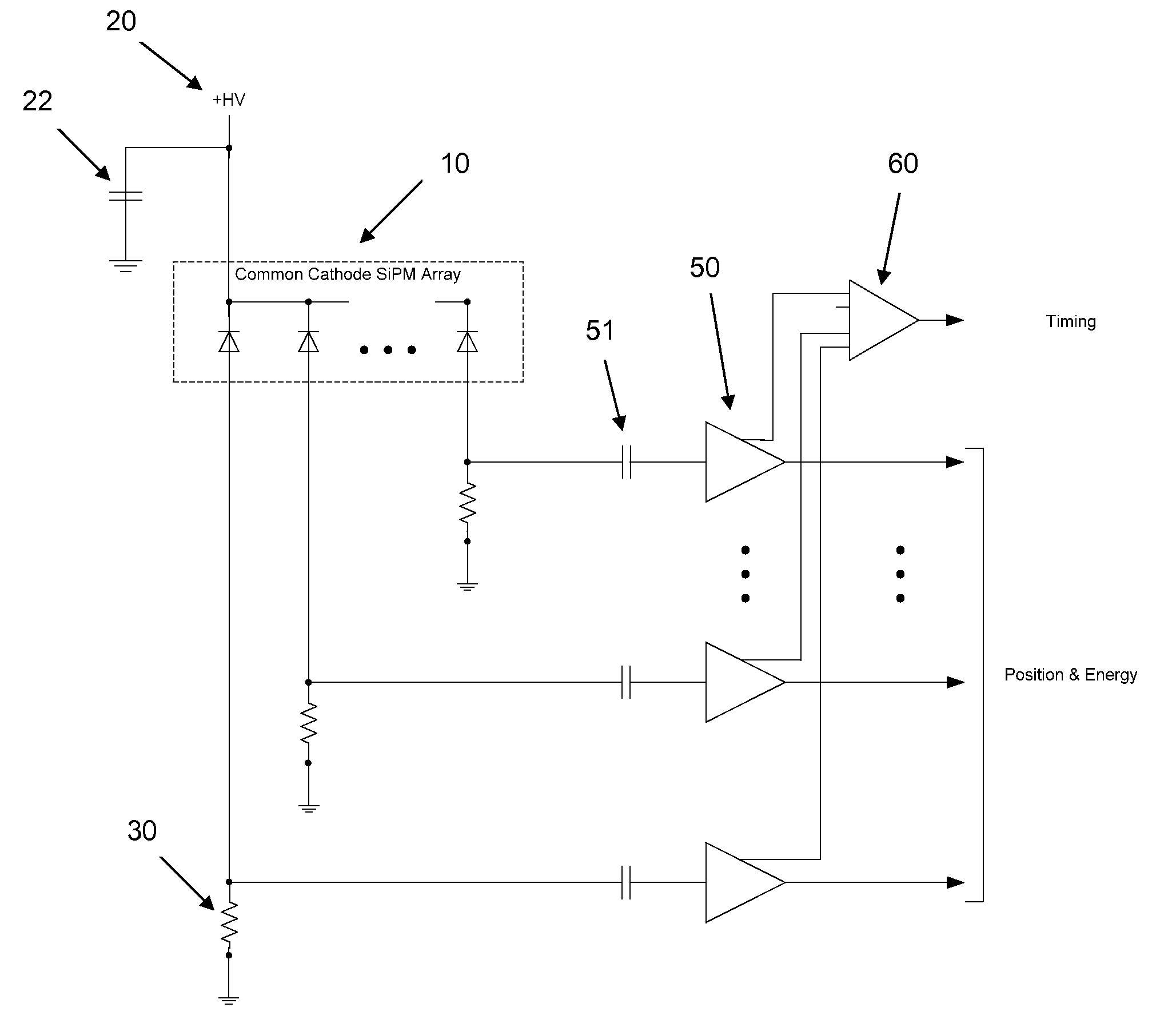
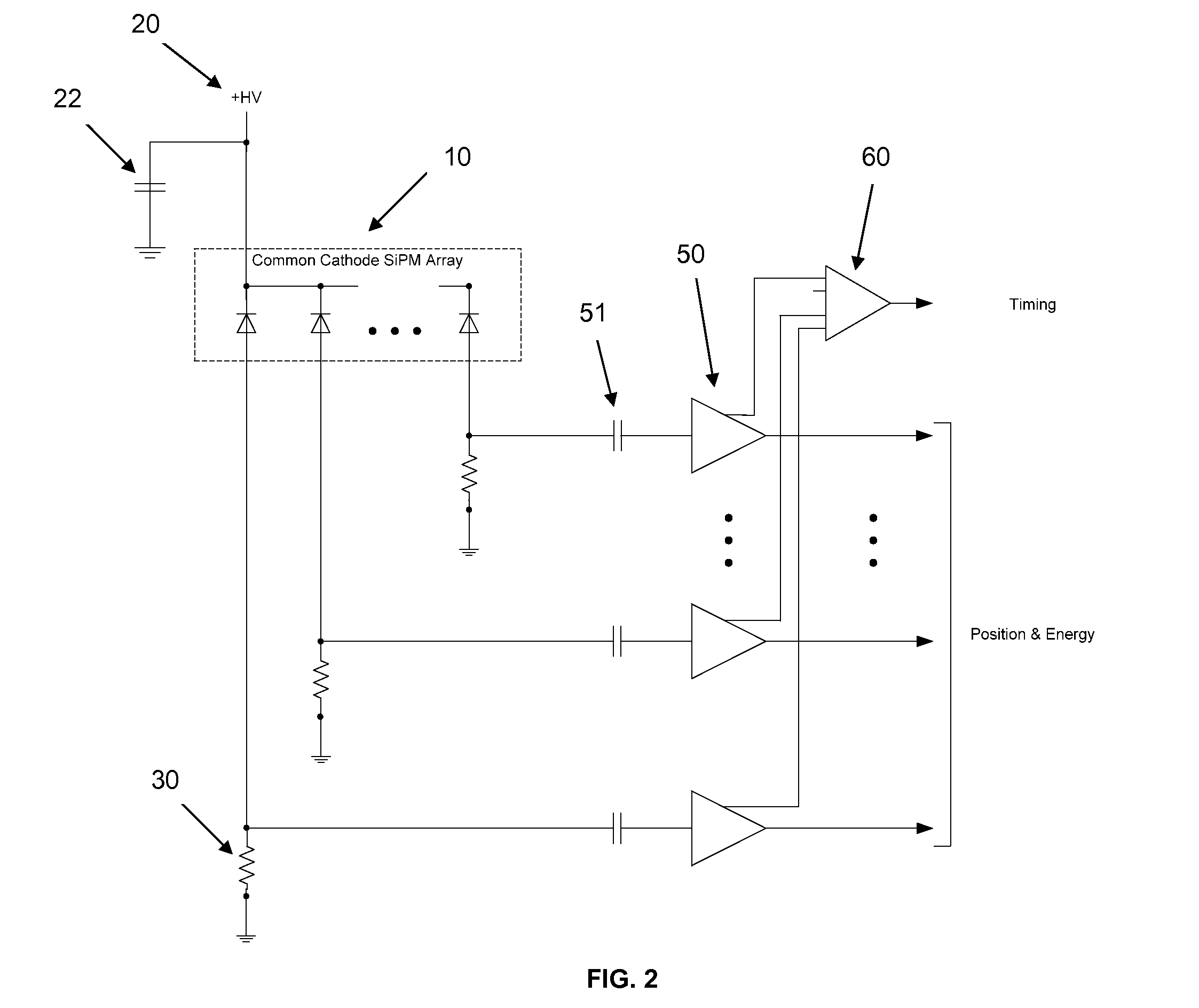
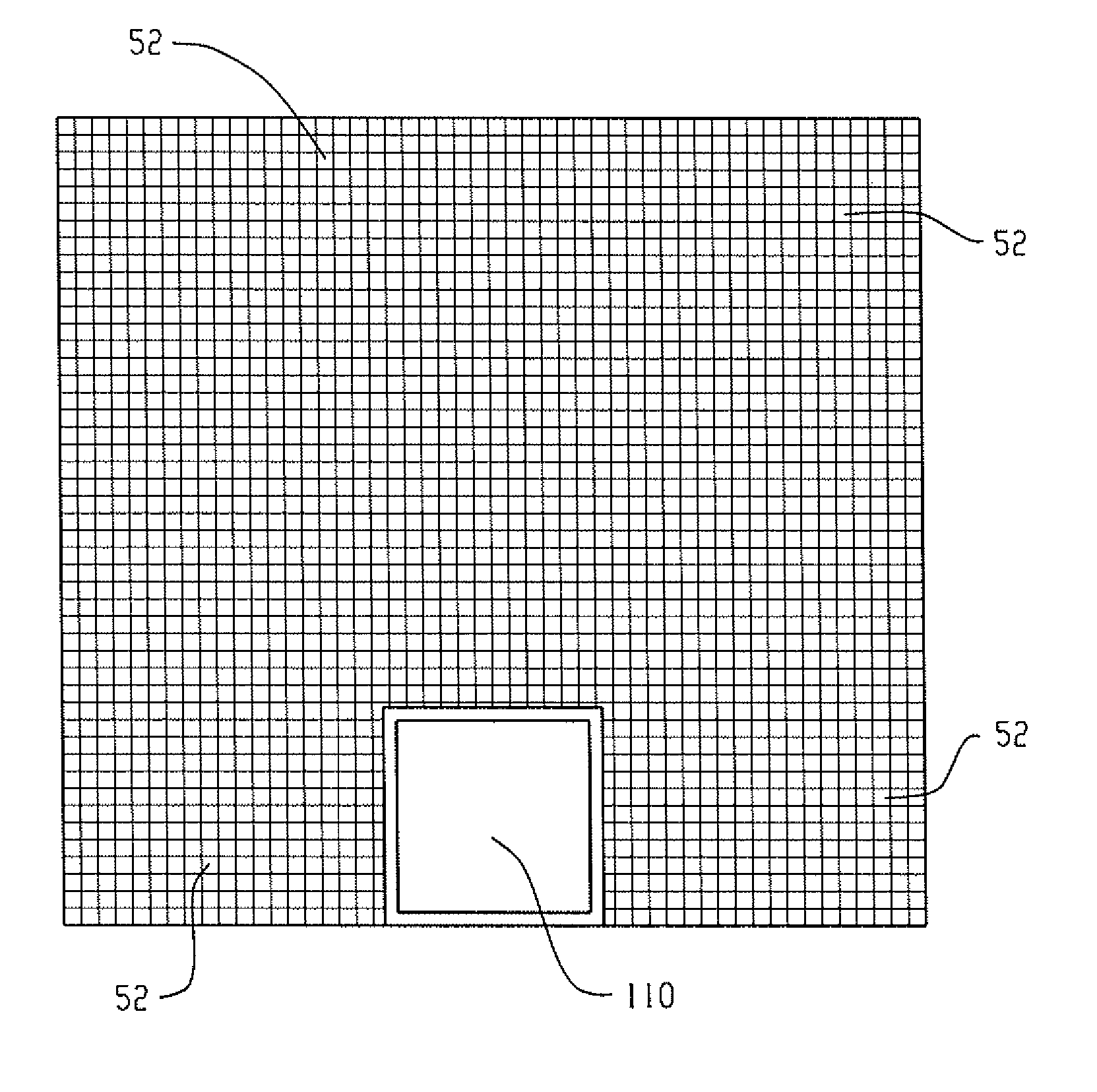
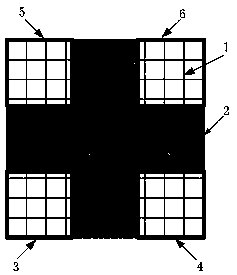
A scintillation block detector employs an array of optically air coupled scintillation pixels, the array being wrapped in reflector material and optically coupled to an array of silicon photomultiplier light sensors with common-cathode signal timing pickoff and individual anode signal position and energy determination. The design features afford an optimized combination of photopeak energy event sensitivity and timing, while reducing electronic circuit complexity and power requirements, and easing necessary fabrication methods. Four of these small blocks, or “miniblocks,” can be combined as optically and electrically separated quadrants of a larger single detector in order to recover detection efficiency that would otherwise be lost due to scattering between them. Events are validated for total energy by summing the contributions from the four quadrants, while the trigger is generated from either the timing signal of the quadrant with the highest energy deposition, the first timing signal derived from the four quadrant time-pickoff signals, or a statistically optimum combination of the individual quadrant event times, so as to maintain good timing for scatter events. This further reduces the number of electronic channels required per unit detector area while avoiding the timing degradation characteristic of excessively large SiPM arrays.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Digital silicon photomultiplier for TOF-PET
ActiveUS7723694B2Improve manufacturing yieldReduce sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyQuiescent stateSilicon photomultiplier
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
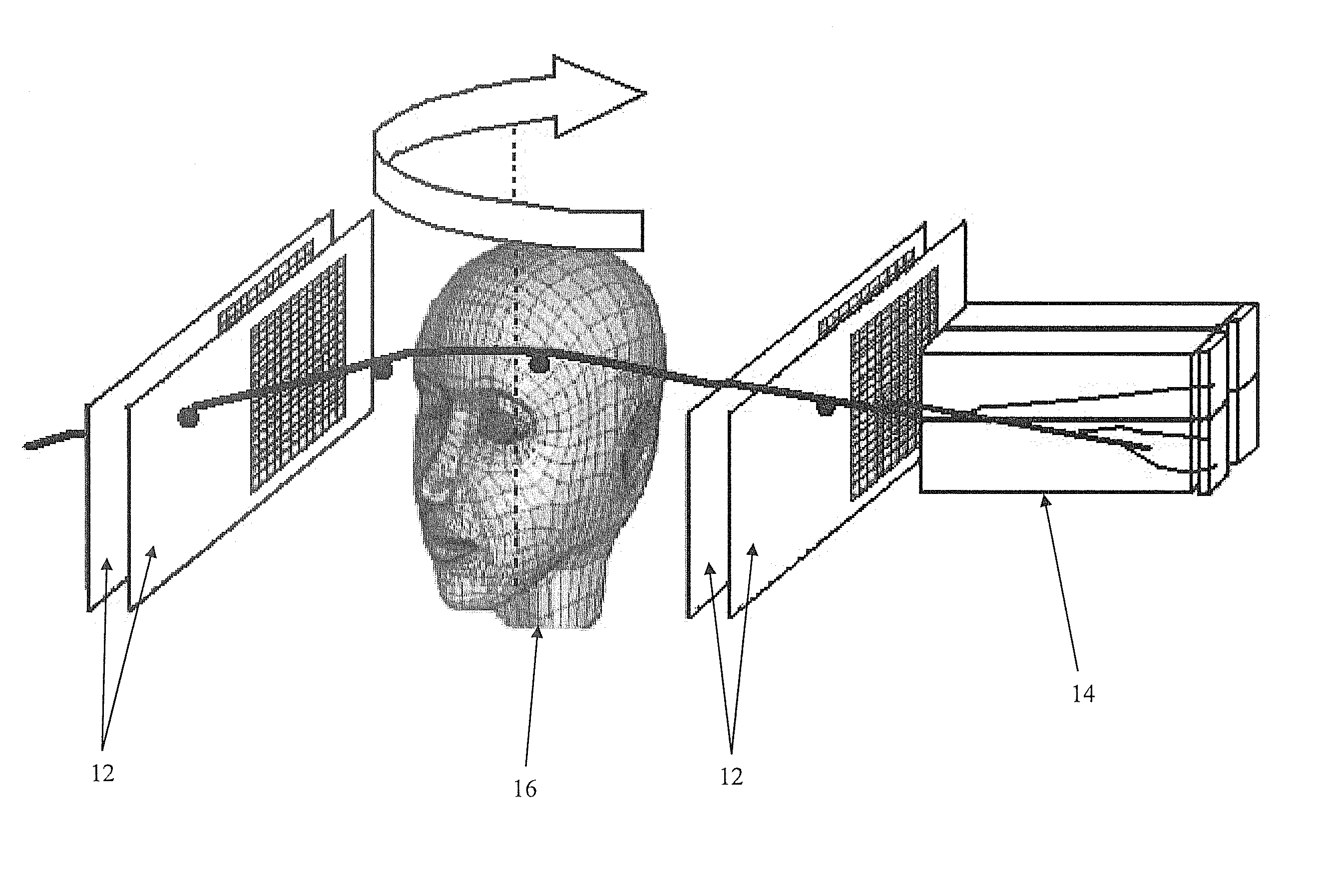
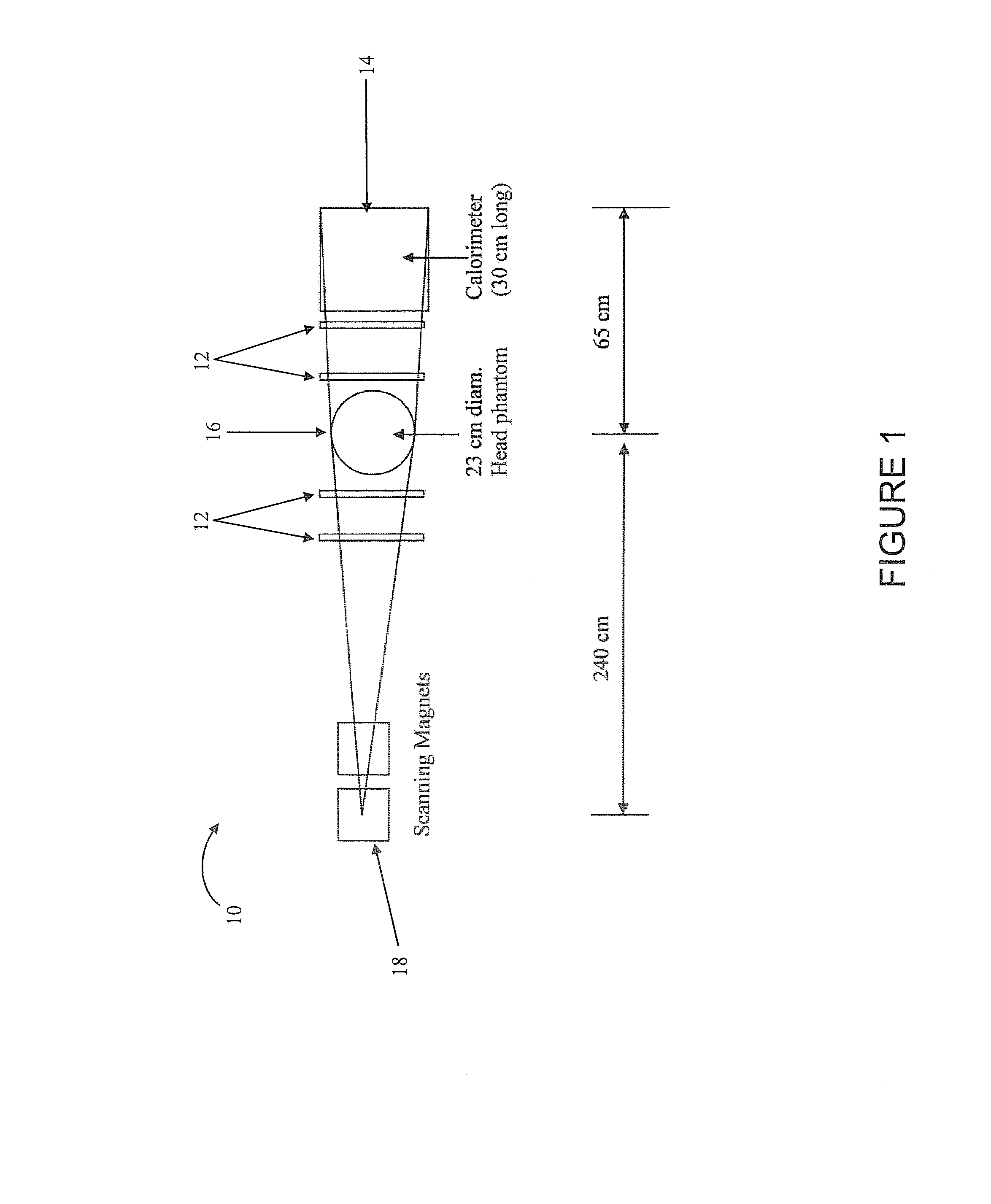
High performance computing for three dimensional proton computed tomography (hpc-pct)
ActiveUS20130015352A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation diagnosticsFiberComputer cluster
A proton computed tomography (pCT) detector system, including two tracking detectors in sequence on a first side of an object to be imaged, two tracking detectors in sequence on an opposite side of the object to be imaged, a calorimeter, and a computer cluster, wherein the tracking detectors include plastic scintillation fibers. All fibers in the detector system are read out by Silicon Photomultipliers (SiPM). A method of imaging an object by emitting protons from a source through two tracking detectors, through and around the object, and through two opposite tracking detectors, detecting energy of the protons with a calorimeter, and imaging the object.
Owner:UNIV OF WOLLONGONG +2
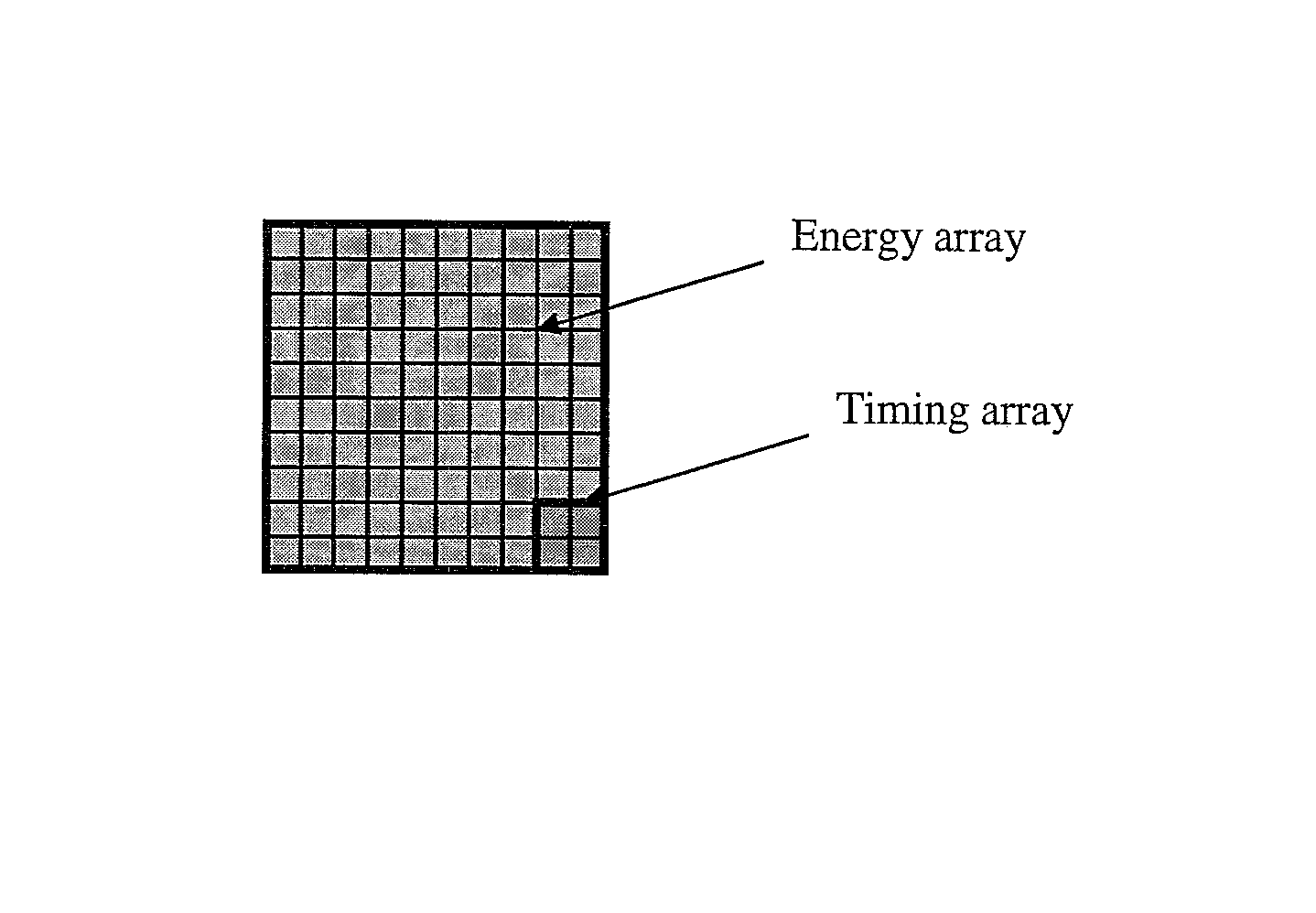
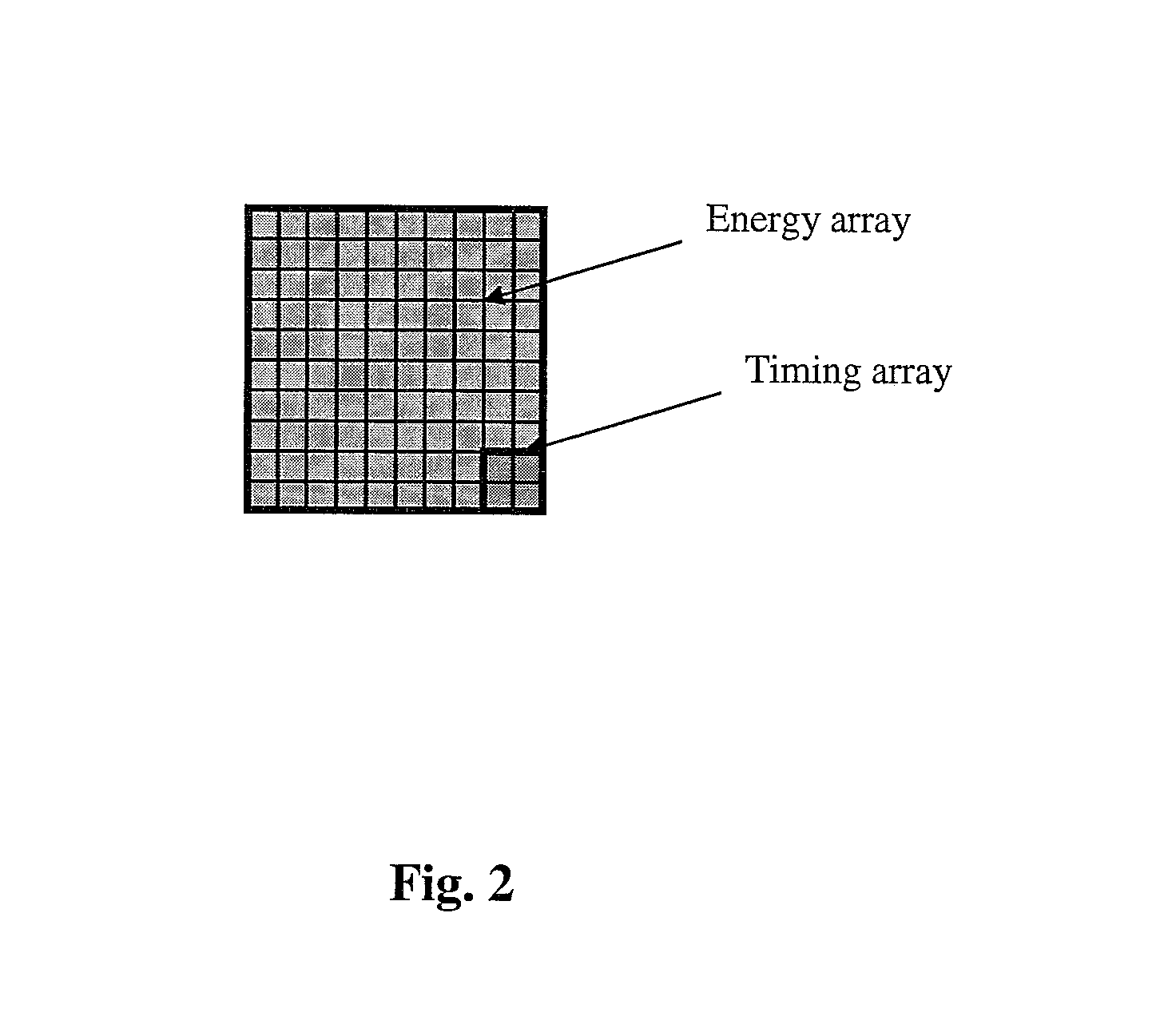
Dual channel SiPM for optimal energy and fast timing
ActiveUS7439509B1High gainReduce noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansLow noiseSilicon photomultiplier
Dual channel silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs) can replace PMTs and APDs for use in PET and other radiation detectors. The devices are compact, have high gain, high QE and low noise. Due to their timing performance, these devices can be used in time-of-flight PET applications. By dividing the device into two separate channels, one for timing resolution and one for energy resolution, both can be optimized simultaneously.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
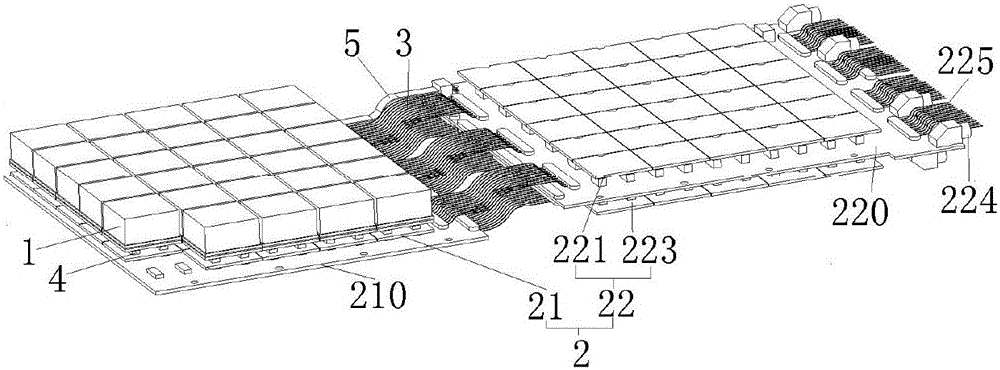
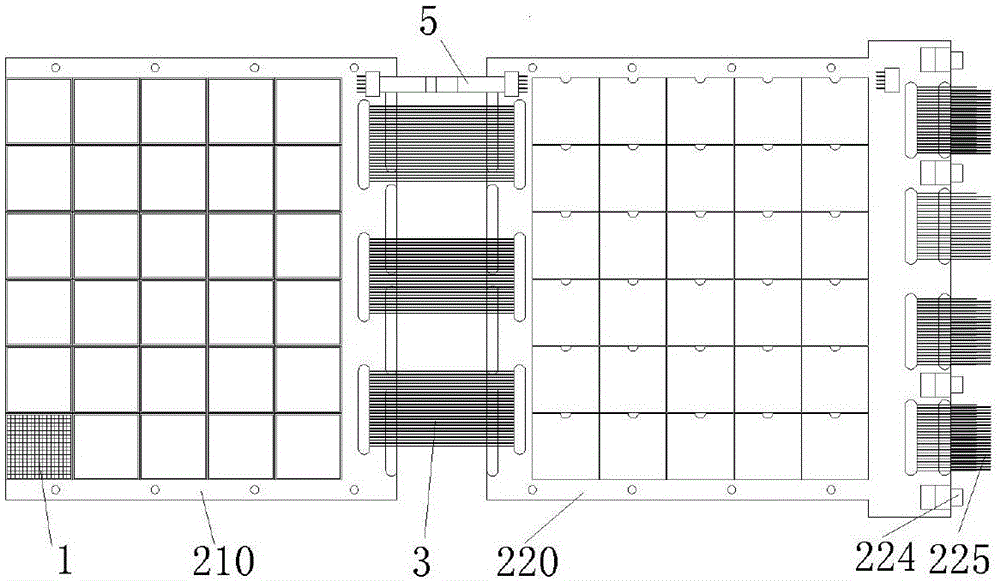
Photoelectric converter, detector and scanning equipment
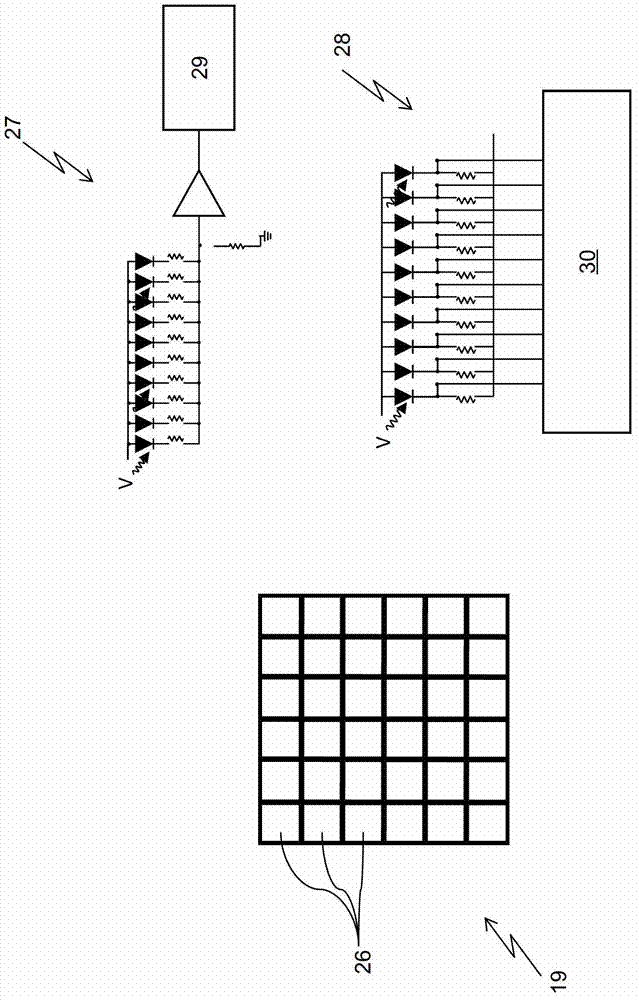
ActiveCN105655435AReduce volumeGuaranteed tight arrangementX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSemiconductor devicesSilicon photomultiplierElectronic systems
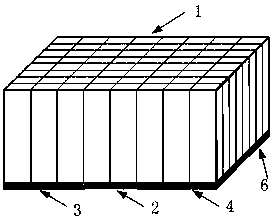
The invention relates to a photoelectric converter, a detector and scanning equipment. The photoelectric converter comprises a silicon photomultiplier array and a light guide coupled with the silicon photomultiplier array, wherein the silicon photomultiplier array comprises i*j silicon photomultipliers spliced on a horizontal plane, and the i and the j are both integers greater than or equal to 2. The detector comprises a scintillation crystal, an electronic system, a light guide and silicon photomultipliers. The scanning equipment comprises a detection device and a frame, wherein the detection device comprises the detector, and the detector comprises the photoelectric converter. According to the photoelectric converter, the detector and the scanning equipment, a photoelectric conversion scheme of the photoelectric silicon photomultipliers is mainly employed, the silicon photomultipliers have small volumes and are closely arranged, the silicon photomultipliers in proper dimensions and in proper quantity are matched with the light guide in proper shape, a PET detector with high spatial resolution can be established, so the spatial resolution of the whole PET system can be improved, the PET detector having DOI and TOF performances is proper to establish, application to PET / MRI can be realized, and low cost is further realized.
Owner:RAYCAN TECH CO LTD SU ZHOU
SiPM-BASED RADIATION DETECTION SYSTEMS AND METHODS
The invention discloses a SiPM-based radiation detection systems and methods. According to the invention, techniques are disclosed for systems and methods using silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) based radiation detectors to detect radiation in an environment. A SiPM-based radiation detection system may include a number of detector assemblies, each including at least one scintillator providing light to a corresponding SiPM in response to ionizing radiation entering the scintillator. The radiation detection system may include a logic device and a number of other electronic modules to facilitate reporting, calibration, and other processes. The logic device may be adapted to process detection signals from the SiPMs to implement different types of radiation detection procedures. The logic device may also be adapted to use a communication module to report detected radiation to an indicator, a display, and / or a user interface.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
System and method of simplifying a direct control scheme for a detector
ActiveUS20150168567A1Material analysis by optical meansComputerised tomographsSilicon photomultiplierGain
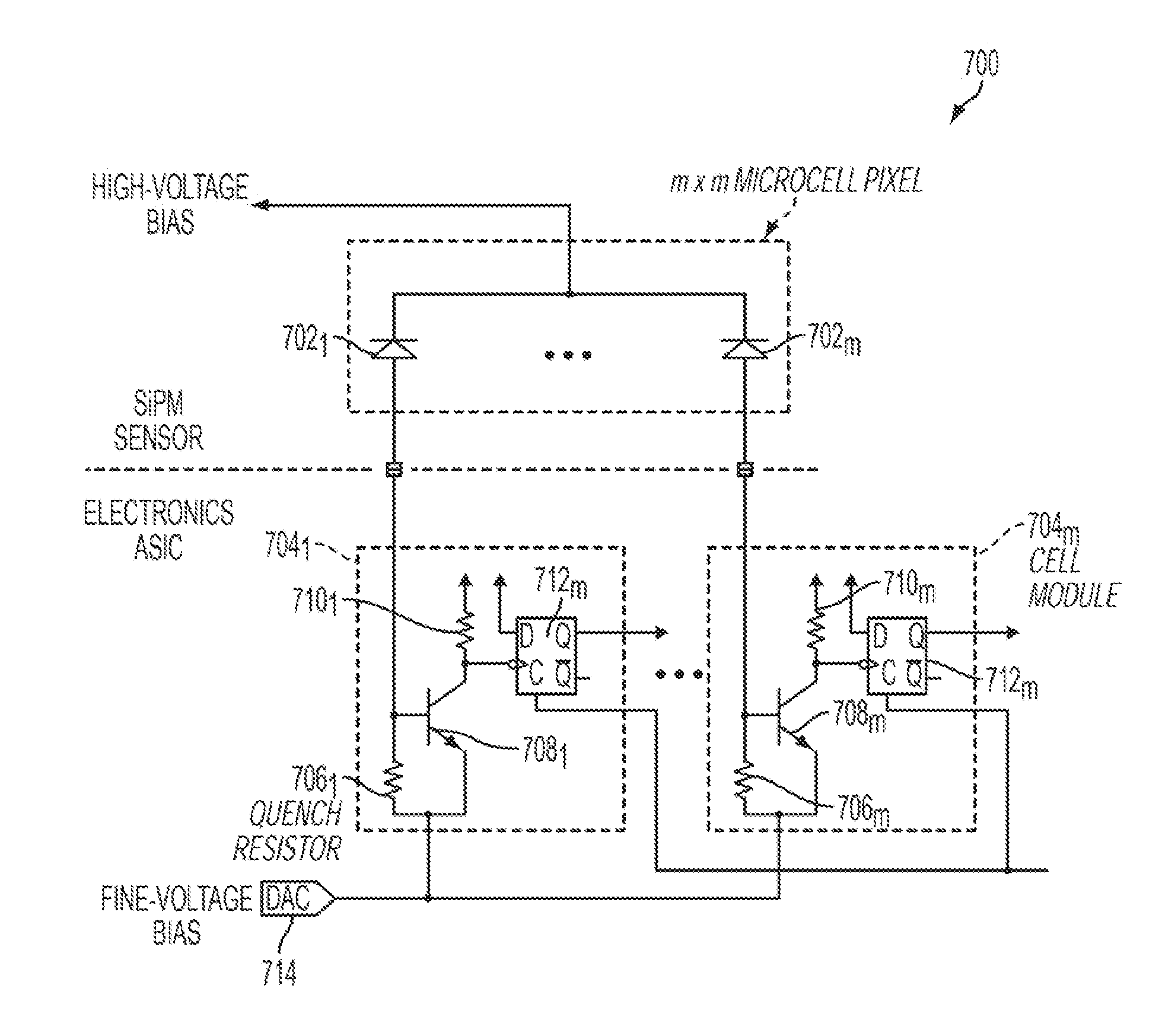
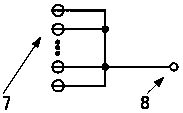
An imaging system includes a first silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) comprising an array of microcells. Each microcell is an avalanche photodiode (APD) operated in a Geiger mode, a first area of the first SiPM, comprising at least one of the microcells, is electrically isolated from all other microcells, and a signal from the first area, resulting from at least one photon pulse, is used to determine a gain of the first SiPM.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Position-sensitive readout modes for digital silicon photomultiplier arrays
ActiveCN103733609AImprove spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSingle-photon avalanche diodeSilicon photomultiplier
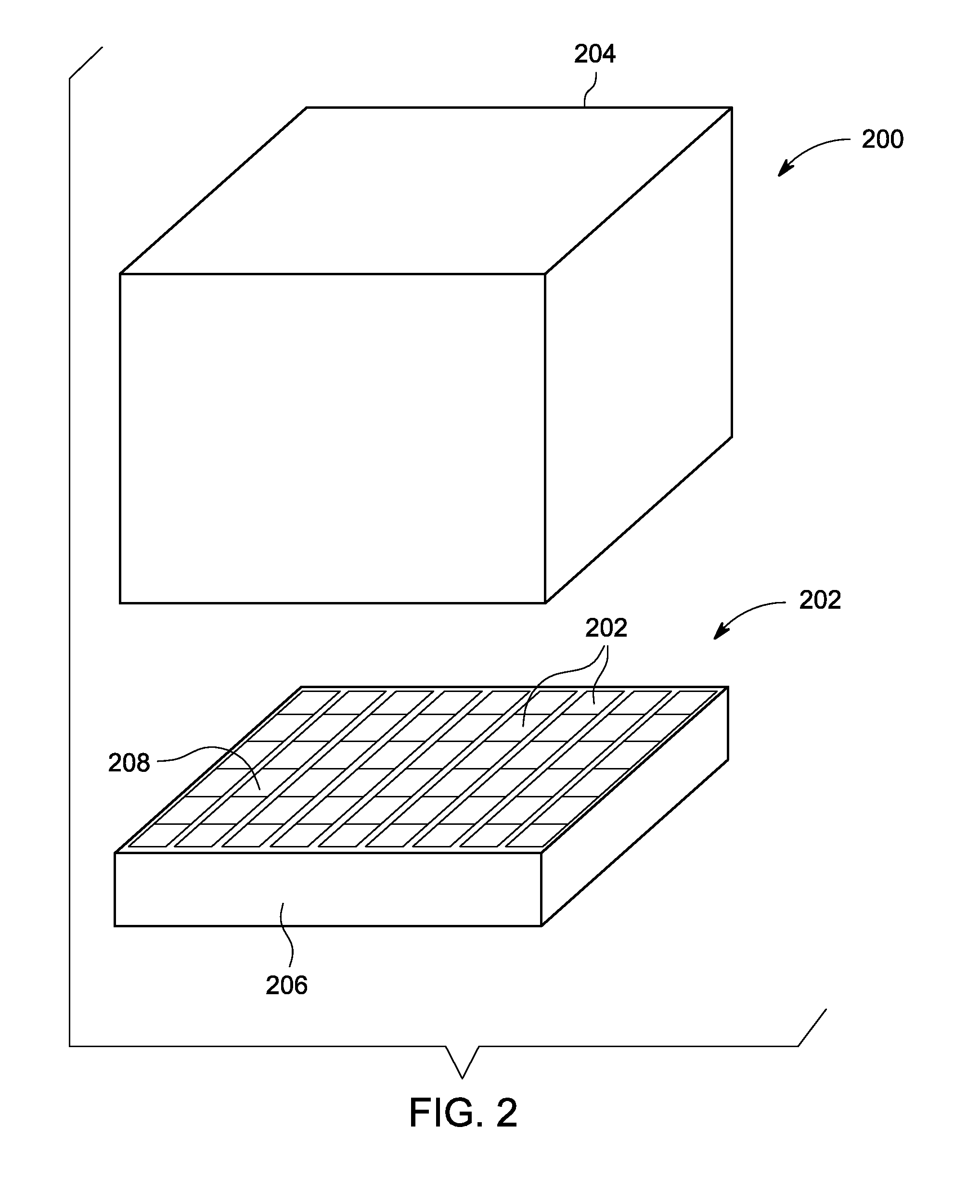
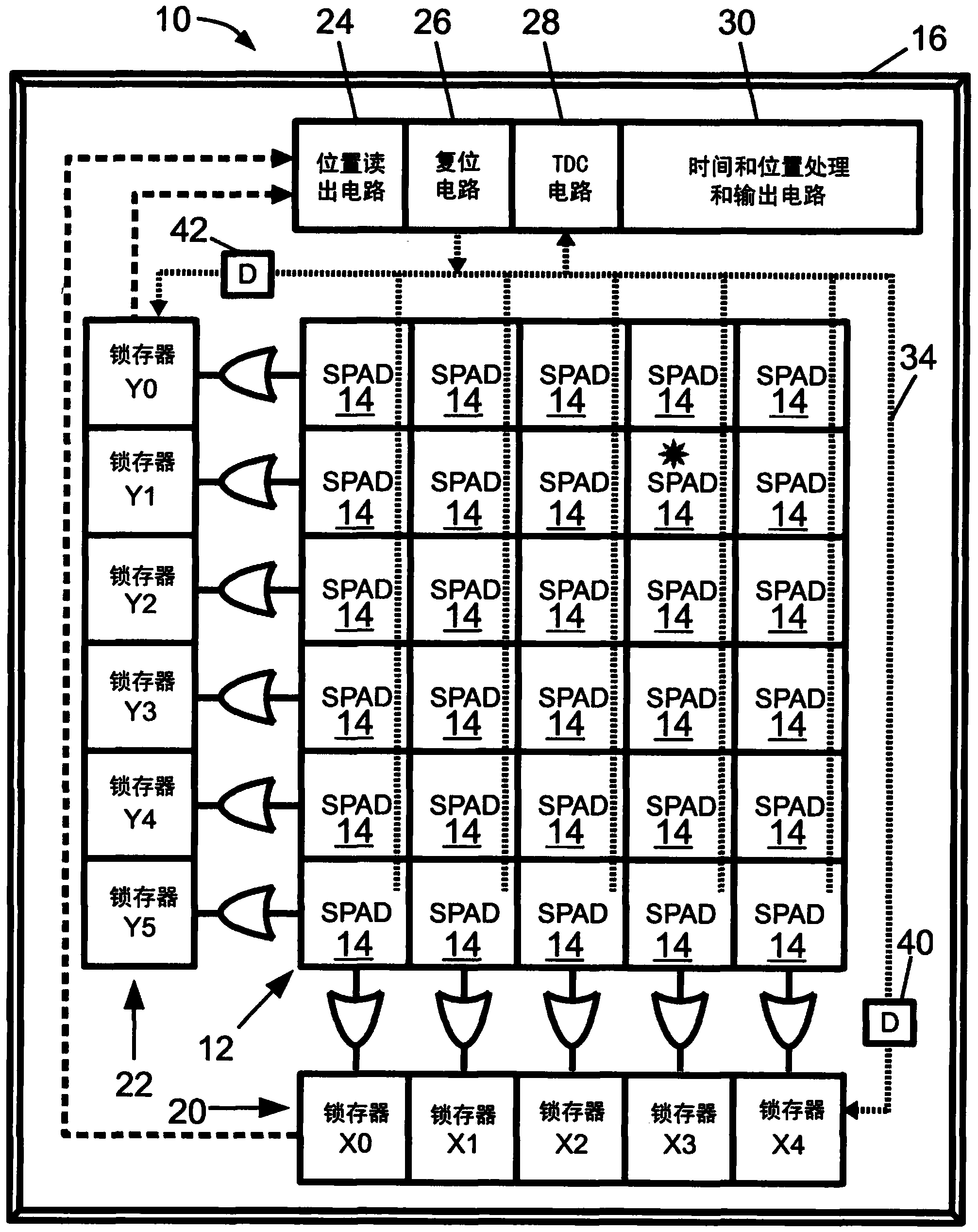
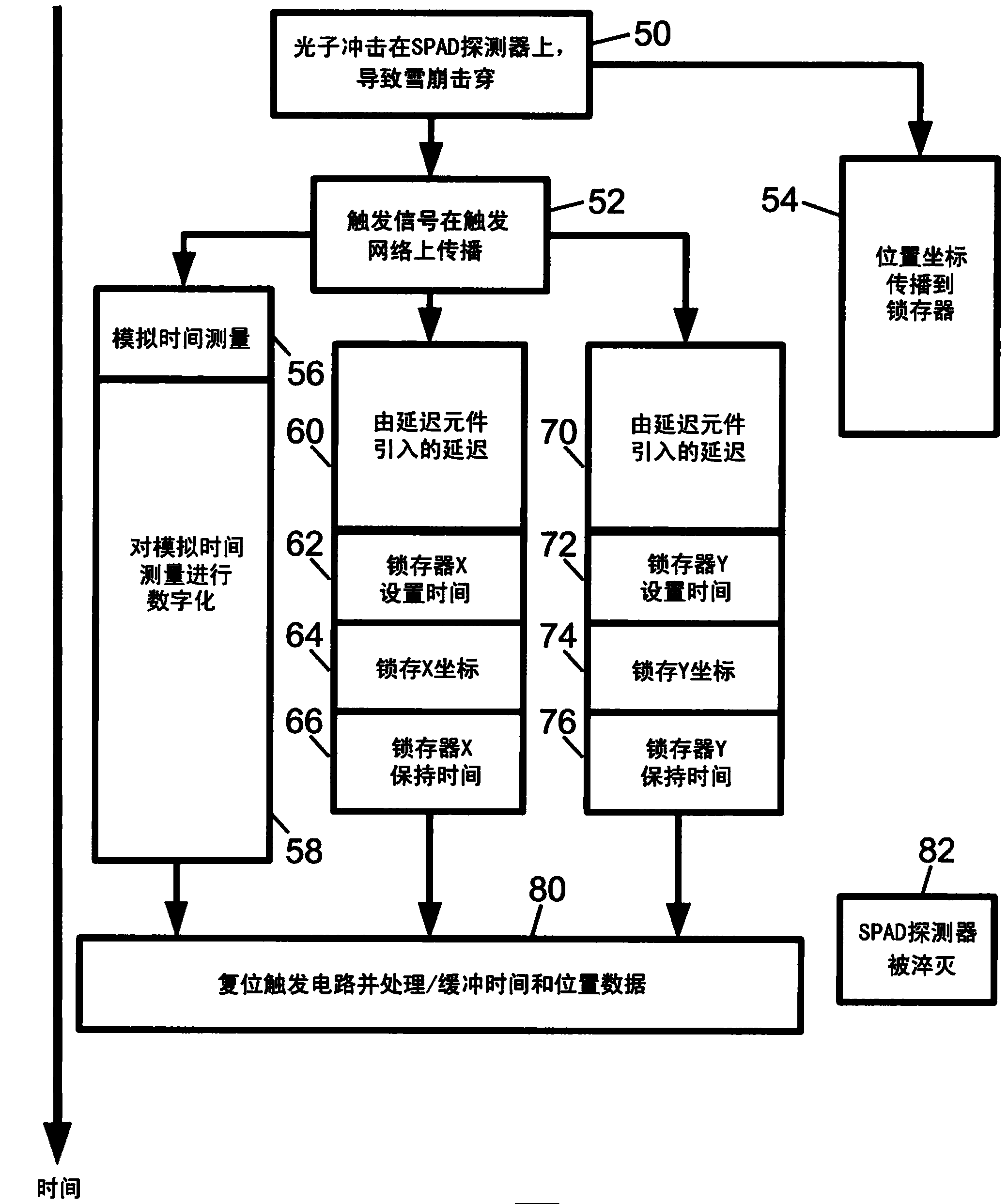
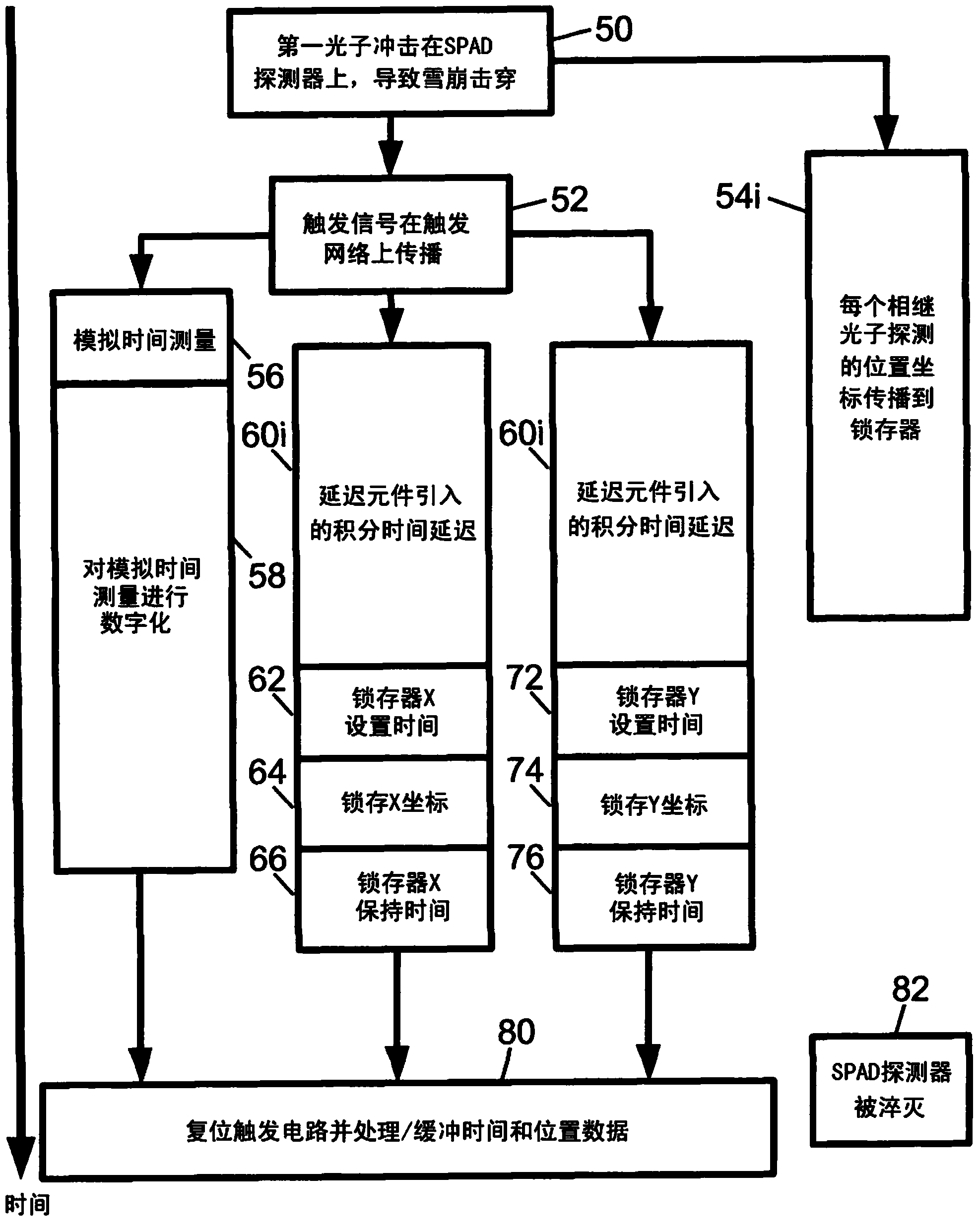
A photon detector (10) includes a detector array (12) comprising single photon avalanche diode (SPAD) detectors (14) configured to break down responsive to impingement of a photon. Trigger circuitry (34) is configured to generate a trigger signal responsive to break down of a SPAD detector of the detector array. Latches (20, 22) are configured to store position coordinates of SPAD detectors of the detector array that are in break down. The latches are configured to latch responsive to a trigger signal generated by the trigger circuitry. The latches may include row latches (22) each connecting with a logical "OR" combination of SPAD detectors of a corresponding row of the detector array, and column latches (20) each connecting with a logical "OR" combination of SPAD detectors of a corresponding column of the detector array. Time to digital converter (TDC) circuitry (28) may generate a digital time stamp for the trigger signal.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
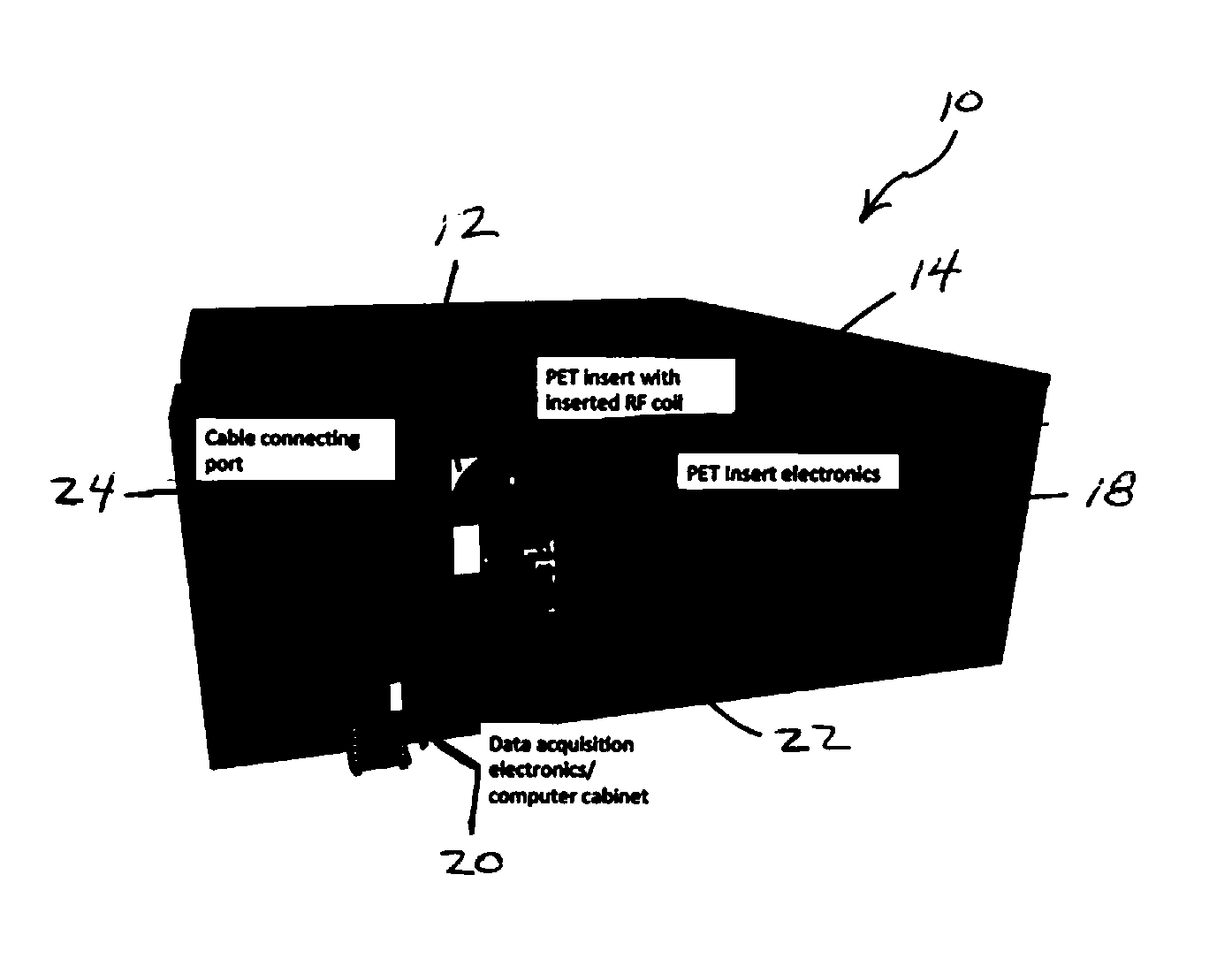
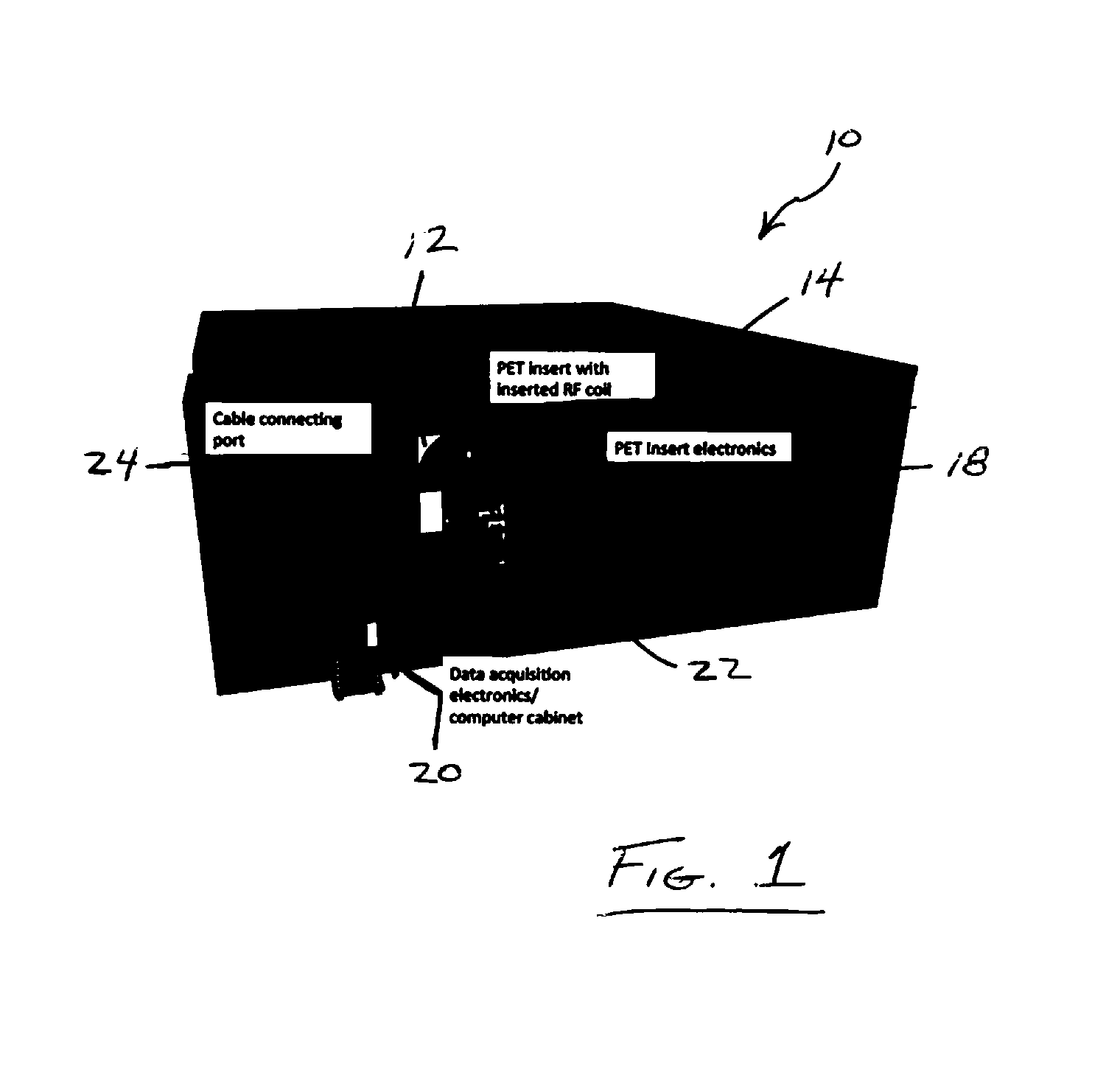
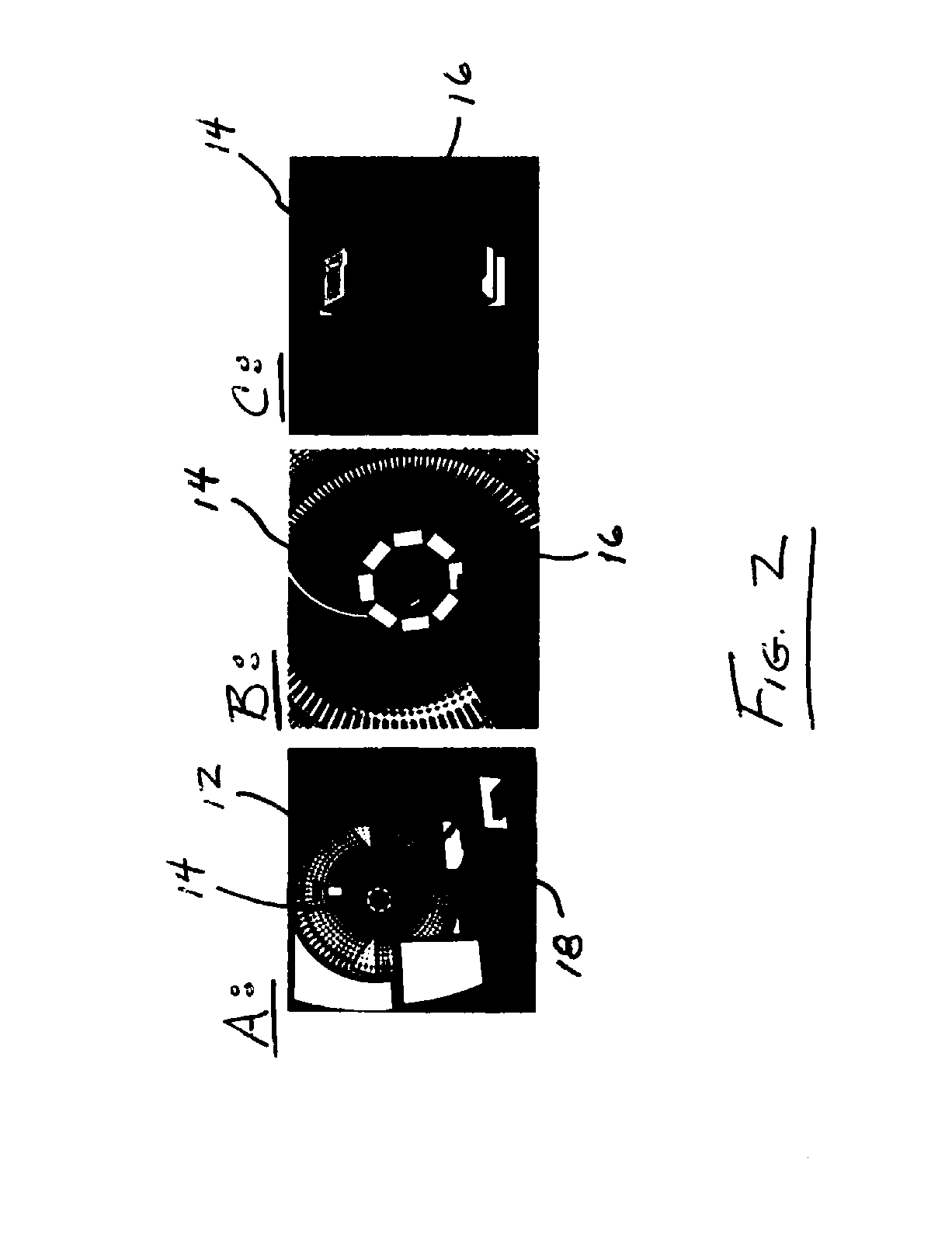
Apparatus and Implementation Method of a Set of Universal Compact Portable MR-Compatible PET Inserts to Convert Whole-Body MRI Scanners Into Organ-Specific Hybrid PET/MRI Imagers
ActiveUS20140275965A1Comprehensive anatomical and metabolic profile imageEnhanced radiationDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSilicon photomultiplierPhotodetector
A Positron Emission Tomography (PET″) insert for use with a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (“MRI”) scanning device, the PET insert including a plurality of photodetector modules provided adjacent each other in an array, the plurality of photodetector modules configured for placement adjacent a body of a patient and sized to be received in a magnetic bore of the MRI scanning device with the patient, the photodetector modules providing detection of gamma annihilation photons, and a Radio Frequency (“RF”) coil provided between the patient and the plurality of photodetector modules. Each of the plurality of photodetector modules includes a pixelated scintillator array provided for alignment adjacent the patient's body, and a shielding block including silicon photomultiplier pads and passive electronic circuitry only.
Owner:WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
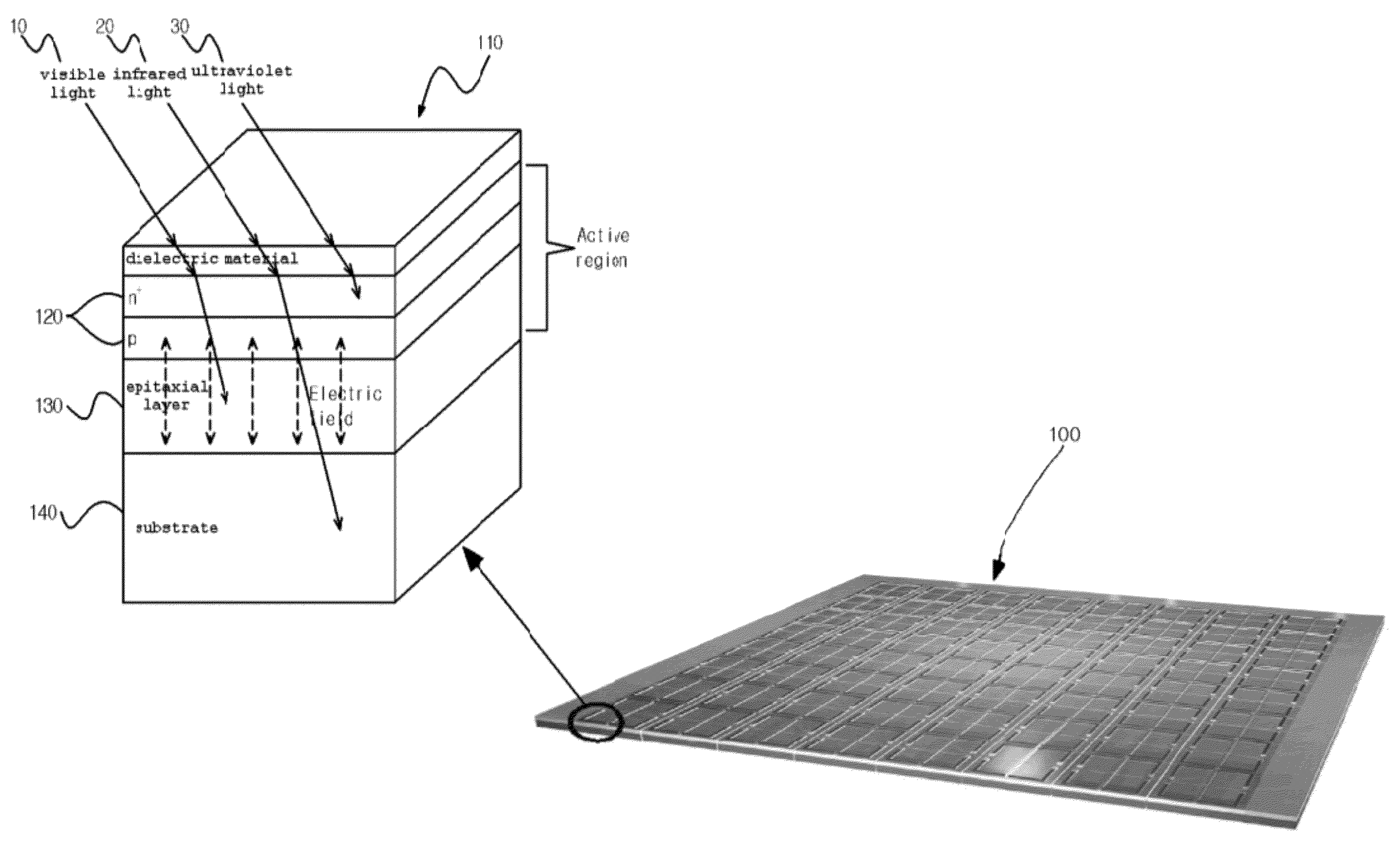
Vertical silicon photomultipler with superior quantum efficiency at optical wavelengths
InactiveUS20120025340A1Maximize efficiencyUsing liquid separation agentSolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyElectron hole
The vertical silicon photomultiplier according to the present invention includes a trench electrode and a PN-junction layer perpendicular to the trench electrode forms and can maximize the quantum efficiency at optical wavelengths, 200˜900 nm in such a way that: it generates electric fields horizontal thereto, by applying a reverse bias voltage to between the trench electrode and the PN junction layer, so that, although ultraviolet light does not reach the PN-junction layer but is incident on the surface, electron-hole pairs can be produced by the horizontally generated electric fields although and an avalanche breakdown can be thus generated, and it allows ultraviolet light, capable of being transmitted to a relatively deep depth, to react with the PN-junction layer.
Owner:SATBYUL CO LTD
Integrated Digital Discriminator For a Silicon Photomultiplier
ActiveUS20140029715A1Minimize impactMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansDiscriminatorSilicon photomultiplier
Apparatuses and methods are provided that minimize the effects of dark-current pulses. For example, in one embodiment of the invention, a method is provided where a first pixel is struck (i.e., a primary pixel). Pixels struck within a fixed time frame after the primary pixel is struck are referred to as secondary pixels. After a short fixed time frame has expired, the number of primary and secondary pixels is added. If the count exceeds a threshold, the primary pixel was activated by the first (or early) photon from a true gamma event. If the threshold is not met then it is likely the primary pixel generated a dark pulse that should be ignored.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
On-line type energy spectrum analysis anti-coincidence measurement detector
InactiveCN104820232ASolve processing problemsAddress analysis measurement impactRadiation intensity measurementSilicon photomultiplierSodium iodide
The invention relates to the field of radiation measurement and provides an on-line type energy spectrum analysis anti-coincidence measurement detector. The detector comprises a sodium iodide scintillator for recording a gamma ray, a photomultiplier for converting an optical signal of the sodium iodide scintillator into a weak pulse signal, a plastic scintillator for deducting Compton flashing of the sodium iodide scintillator, a silicon photomultiplier for converting an optical signal of the plastic scintillator into a weak pulse signal, a lead shielding body for shielding an environment radiation band alignment hole and a lead plug, and a forward amplifying plate for amplifying the weak signals. The detector can achieve complex environment, Compton flashing and serious background interference always on-line measuring, eliminate the influence of nuclear site Compton flashing on 50keV-1.5MeV middle and low energy section radionuclide analysis measurement, and, at the same time, solve the difficulty that anti-coincidence measurement is unlikely to be achieved on a nuclear site.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Crystal arranging method and probe thereof
ActiveCN103064102AHigh-resolutionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSilicon photomultiplierImage resolution
The invention relates to a crystal arranging method and a probe thereof. A crystal is formed by array configuration of a plurality of crystal units, each crystal unit comprises a flicker crystal block and a flicker crystal block with a processed outgoing face, a portion of the processed outgoing face of the flicker crystal block is processed in a shading mode. The crystal arranging method comprises that upper and lower adjacent crystal units are arranged in a manner that the flicker crystal block and the processed flicker crystal block are mutually interval, and left and right adjacent crystal units are arranged in a manner that a shading face and a non-shading face of the outgoing face of the processed flicker crystal block are mutually interval. The crystal is adopted by the probe, and the probe comprises a silicon photomultiplier (SPM). Multiple signal units are arranged on the SPM, the signal units correspond to the crystal units one by one, and the signal units can receive light signals which are sent by the crystal units. The probe breaks through size limitation of signal units of an existing SPM, and under the condition that sizes of the signal units of the SPM are not reduced, and resolution ratio of the probe is greatly improved.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN MINFOUND MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Device and method for detecting light
ActiveCN102879088AAvoid repetitionPhotometry using reference valueSpectrum investigationSingle-photon avalanche diodeSilicon photomultiplier
A device for detecting light includes at least one silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) having an array of a plurality of single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs), the array being larger in area than an incident light. The device is configured so as to at least one of activate and analyze only the SPADs upon which a specific minimum intensity of light impinges.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
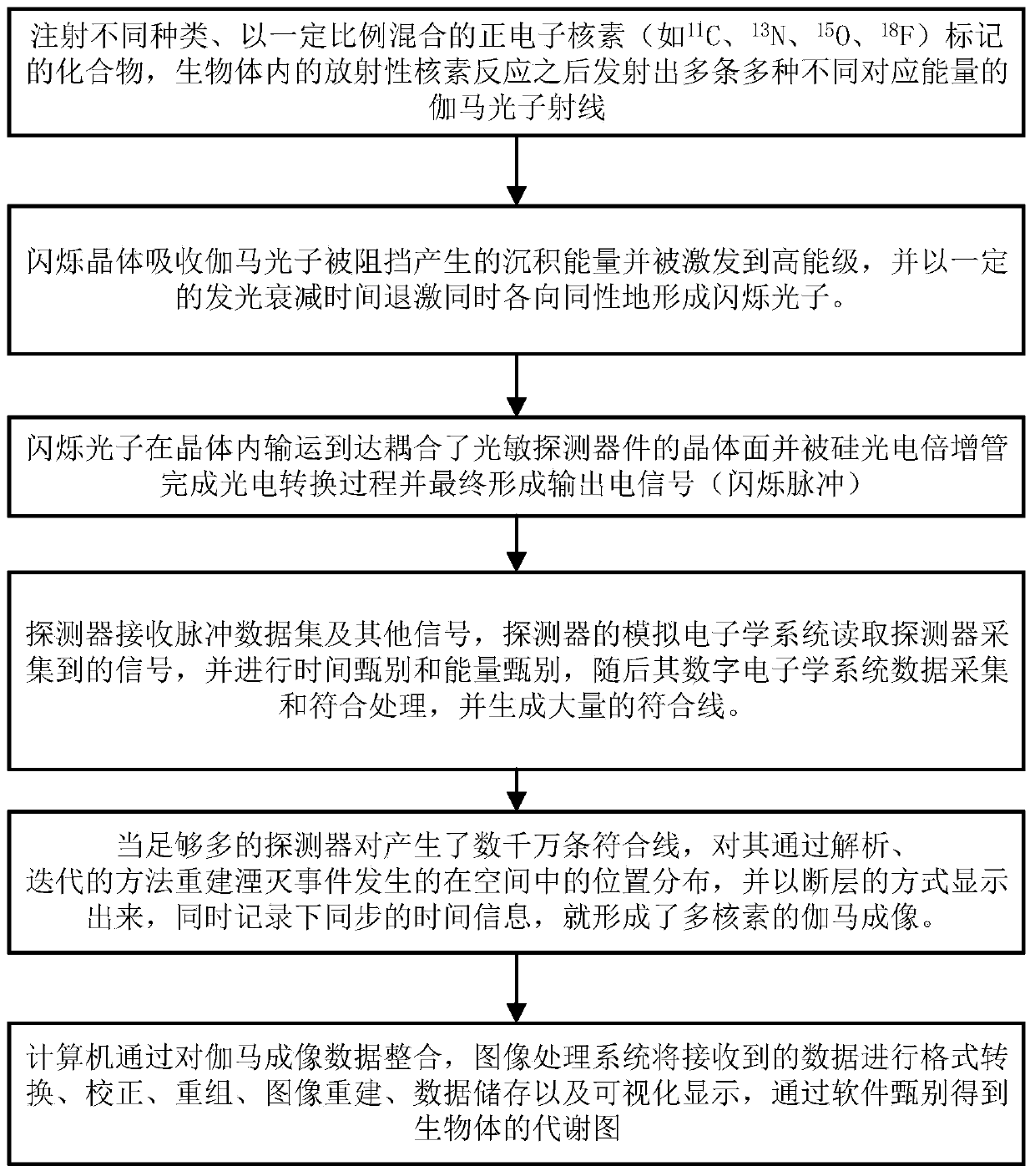
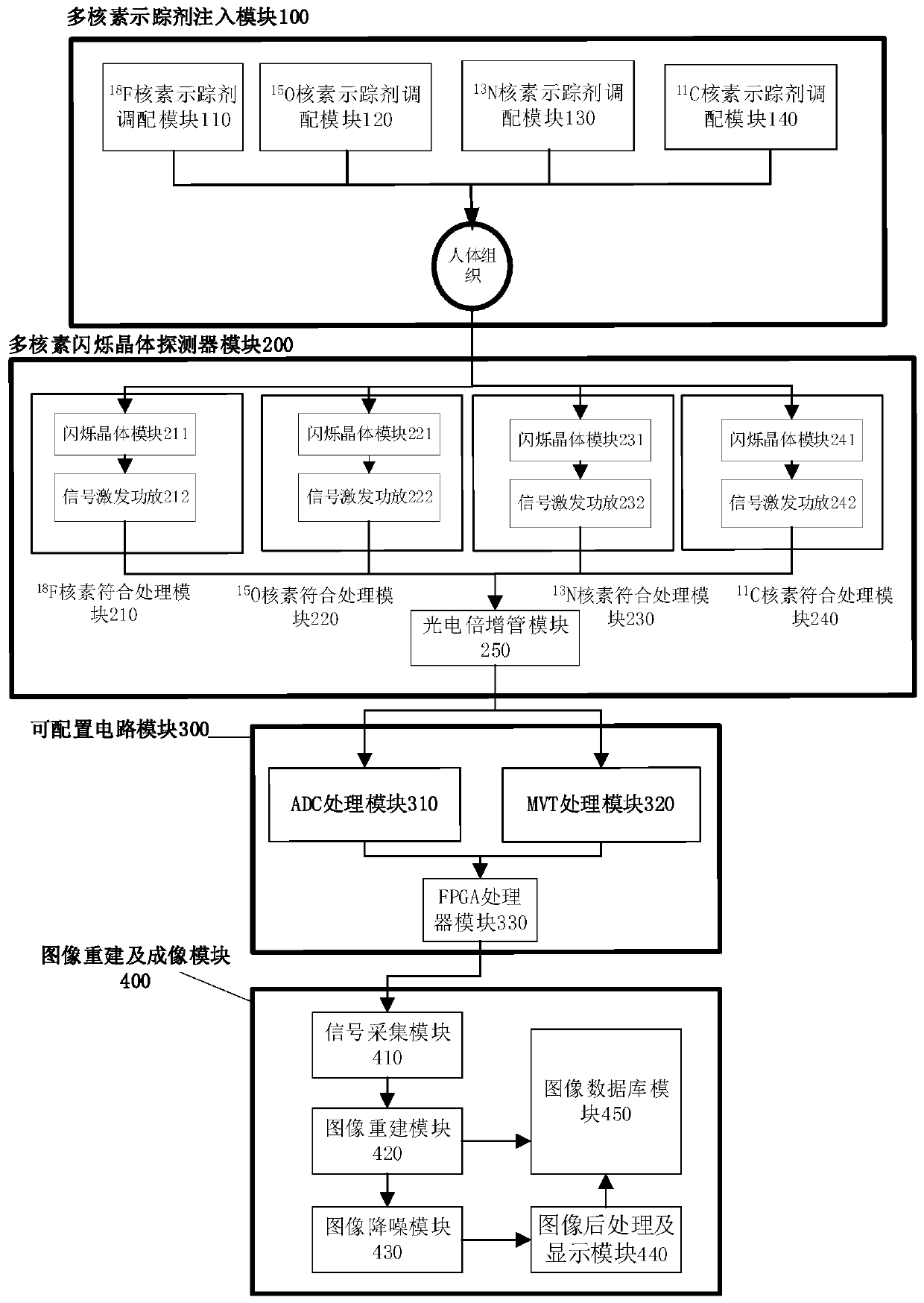
Multiple-nuclide gamma imaging system and method
InactiveCN110772274AReduce the need for total countsReduce risk of exposureComputerised tomographsTomographySilicon photomultiplierData set
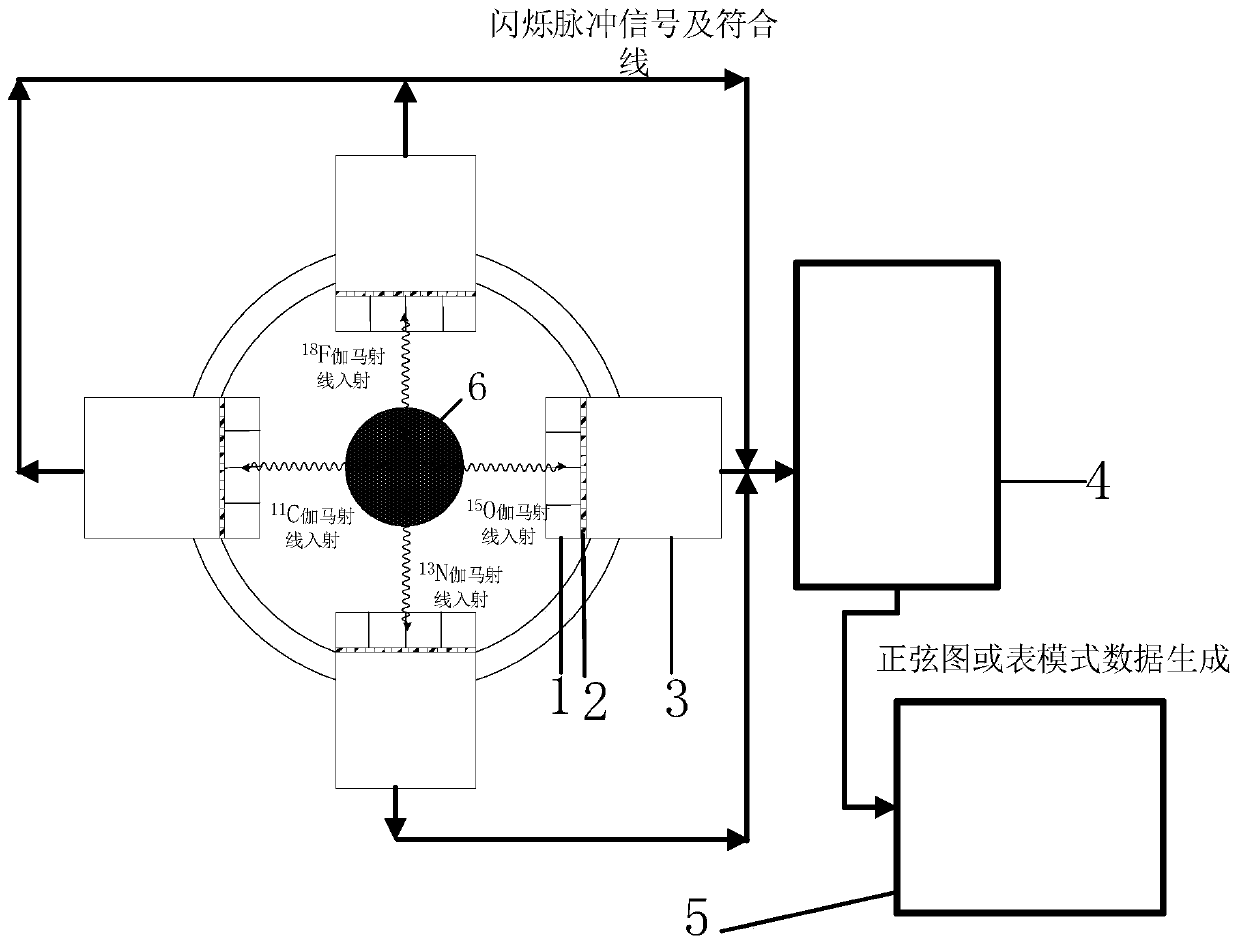
The present invention discloses a multiple-nuclide gamma imaging system and method and belongs to the field of medical imaging. The multiple-nuclide gamma imaging system comprises a multiple-nuclide tracer injection module, a multi-nuclide scintillation crystal detector module, a configurable circuit module and an image reconstruction and imaging module. The multiple-nuclide gamma imaging method comprises the following steps: S1, starting the imaging system, setting acquisition time of the imaging system, and injecting 11C, 13N, 15O and 18F labeled compounds into an imaging object; S2, obtaining a decay event emission gamma pulse data set by positioning a gamma detector; S3, outputting an electrical signal (scintillation pulse) by a silicon photomultiplier; S4, conducting time discrimination, energy discrimination, data acquisition and coincidence processing by a detector; and S5, displaying images in a tomographic manner by a computer. The disclosed multiple-nuclide gamma imaging system and method can obtain more comprehensive data than the prior art, comprehensively analyze multi-molecule events and related influences, reduce requirements on the total gamma photon counting, reduce irradiation risks on organisms and improve a signal-to-noise ratio of reconstructed images.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Detector for ray position and energy measurement and signal read-out method
ActiveCN107728188ABig gapReduce usageX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSilicon photomultiplierTransducer
The invention discloses a detector for the ray position and the energy measurement and a signal read-out method. The detector comprises a scintillation crystal array, a photolectric transducer array and a high-reflective-rate medium, wherein the photolectric transducer array is composed of multiple pieces of silicon photomultiplier tube arrays distributed in the longitudinal and transverse arrangement. A gap is reserved between adjacent silicon photomultiplier tube arrays and the gap is filled with the high-reflective-rate material so as to improve the collection efficiency of the scintillation light. Through enlarging the gap between adjacent silicon photomultiplier tube arrays, the number of silicon photomultiplier tube arrays is greatly reduced and the cost is obviously reduced. All output signals of one piece of the silicon photomultiplier tube array are connected in parallel into one output signal and then the signal is digitized. In this way, the number of signal channels is greatly reduced. The parallel output signals of the multiple pieces of silicon photomultiplier tube arrays are processed by a preprocessing circuit, and then are digitized. As a result, the number of signal channels is further reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG MADIC TECH CO LTD
SiPM (Silicon Photomultiplier)-based nuclear medical imaging plate flat panel detector
ActiveCN105759301AImprove stabilityImprove performanceX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSilicon photomultiplierScintillation crystals
The invention discloses a SiPM (Silicon Photomultiplier)-based nuclear medical imaging plate flat panel detector, which comprises multiple detection modules and a processing circuit module, wherein each detection module comprises a scintillation crystal array and a SiPM array coupled with the scintillation crystal array, the scintillation crystal array comprises multiple scintillation crystals for detecting gamma rays and generating optical signals, and the SiPM array comprises multiple SiPMs for converting the optical signals generated through the scintillation crystal array into electric signals; and the processing circuit module receives and processes the electric signals from the SiPMs to generate output signals as a detection result, and comprises a passive processing circuit module and an active processing circuit module arranged separately, the active processing circuit module leads out the electric signals generated by the SiPM array, and the active processing circuit module receives and processes the electric signals from the passive processing circuit module and generates the output signals. the flat panel detector of the invention has the advantages of compact structure, good performance and strong stability.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Digital silicon photomultiplier for tof-pet
ActiveUS20100252723A1Improve manufacturing yieldReduce sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansQuiescent stateSilicon photomultiplier
A radiation detector includes an array of detector pixels each including an array of detector cells. Each detector cell includes a photodiode biased in a breakdown region and digital circuitry coupled with the photodiode and configured to output a first digital value in a quiescent state and a second digital value responsive to photon detection by the photodiode. Digital triggering circuitry is configured to output a trigger signal indicative of a start of an integration time period responsive to a selected number of one or more of the detector cells transitioning from the first digital value to the second digital value. Readout digital circuitry accumulates a count of a number of transitions of detector cells of the array of detector cells from the first digital state to the second digital state over the integration time period.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
Digital silicon photomultiplier detector cells
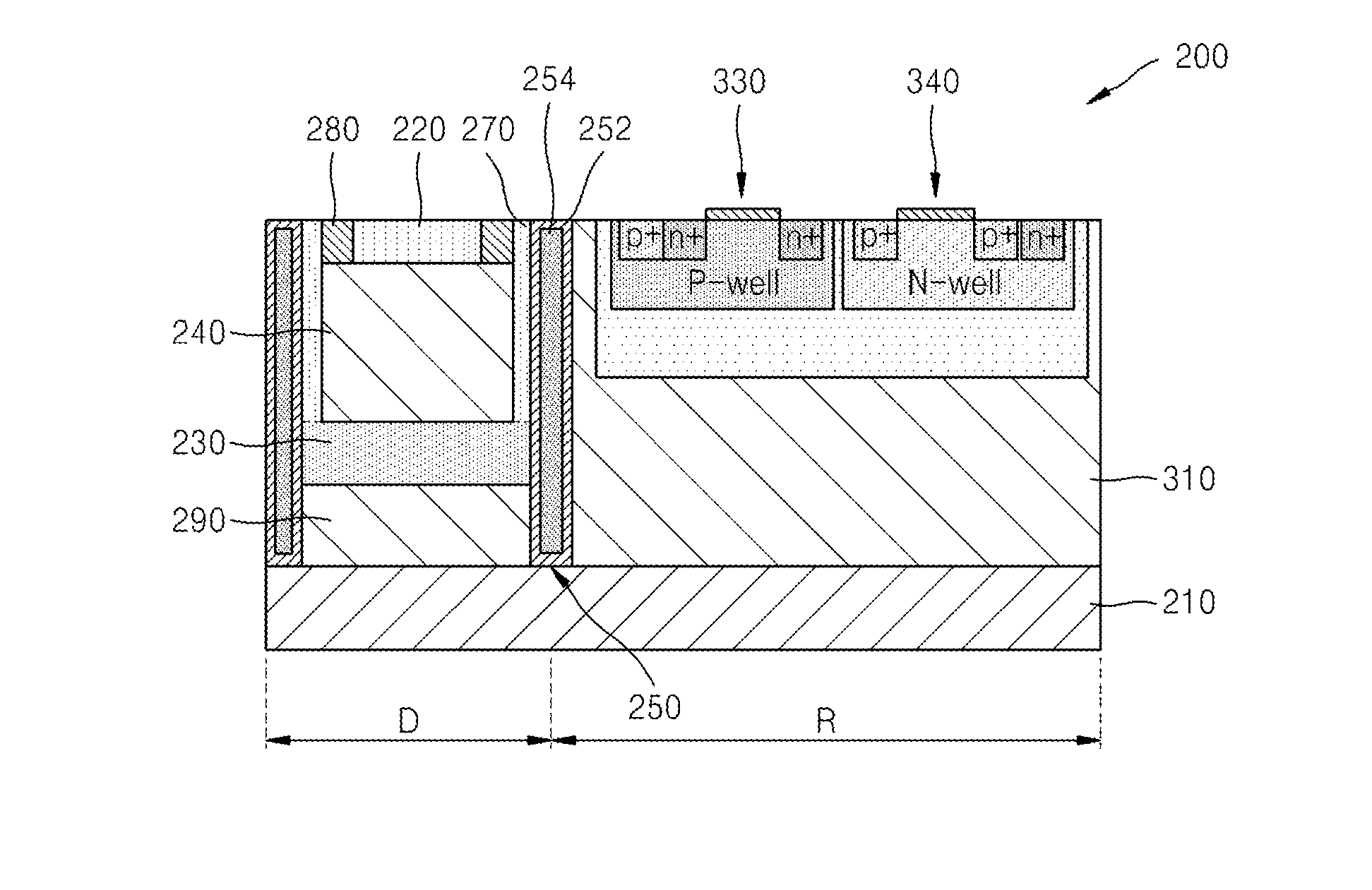
ActiveUS20140210035A1Increasing photo detection efficiencyImprove detection efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorSilicon photomultiplier
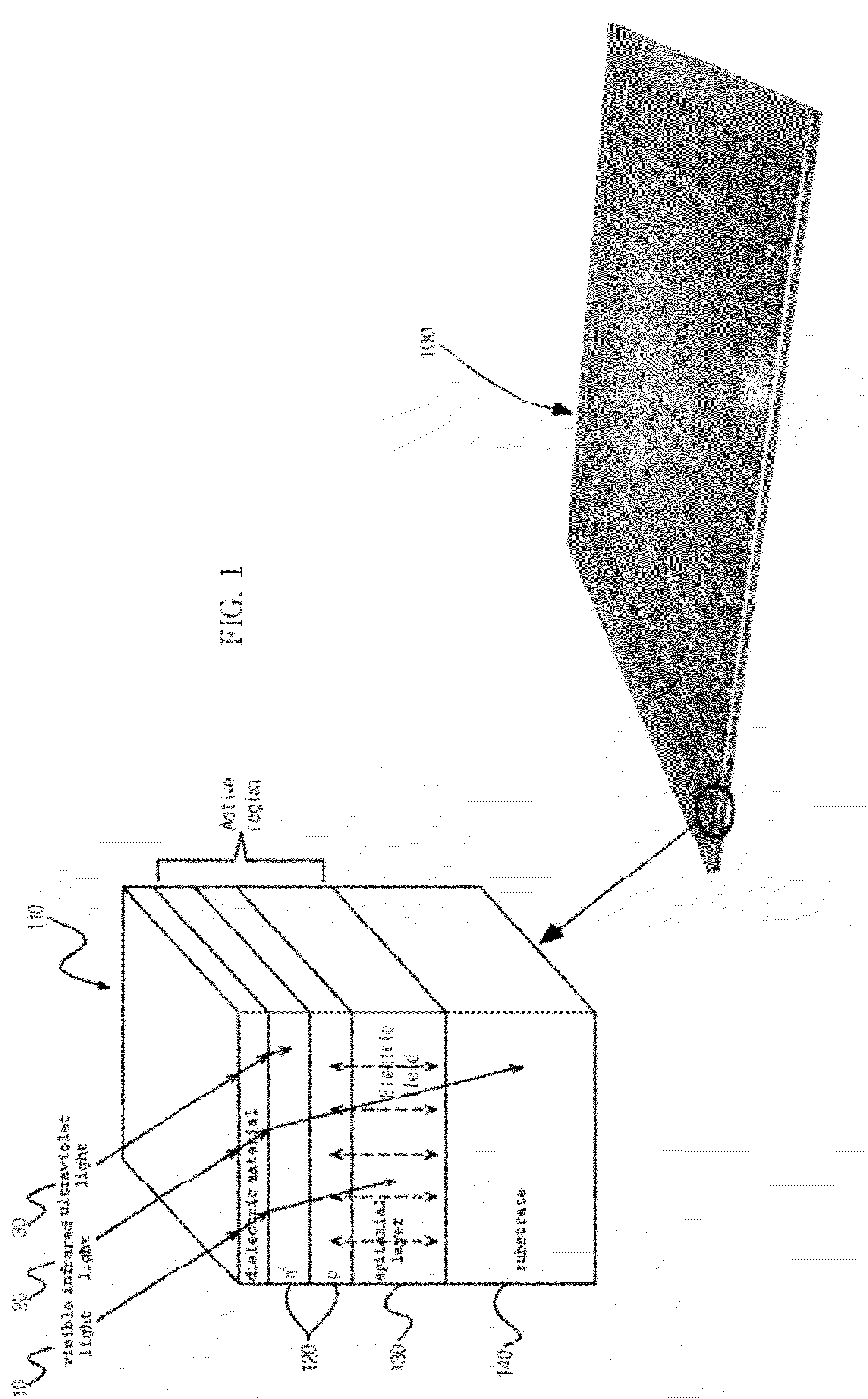
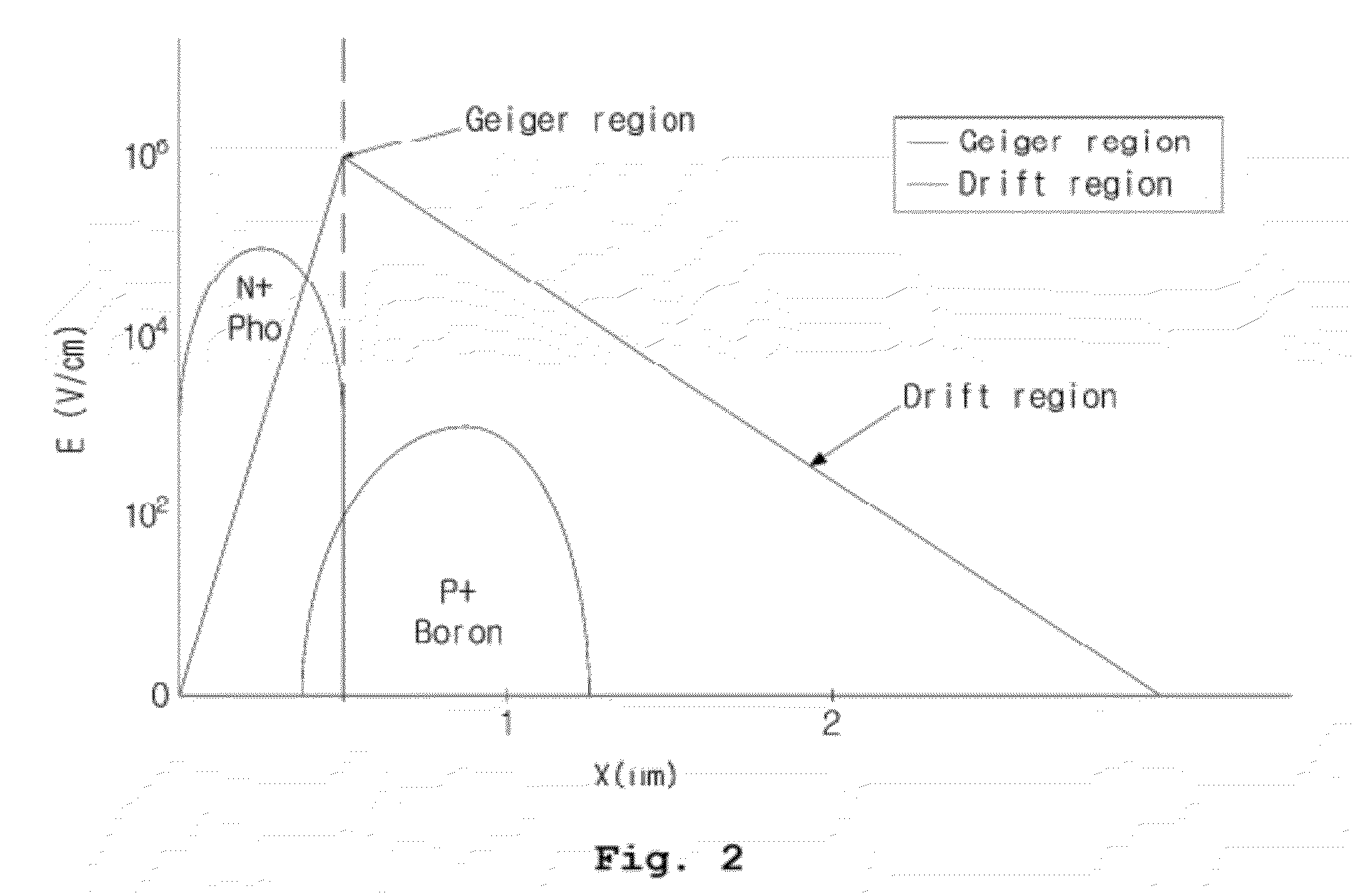
A silicon photomultiplier detector cell may include a photodiode region and a readout circuit region formed on a same substrate. The photodiode region may include a first semiconductor layer exposed on a surface of the silicon photomultiplier detector cell and doped with first type impurities; a second semiconductor layer doped with second type impurities; and / or a first epitaxial layer between the first semiconductor layer and the second semiconductor layer. The first epitaxial layer may contact the first semiconductor layer and the second semiconductor layer. The first epitaxial layer may be doped with the first type impurities at a concentration lower than a concentration of the first type impurities of the first semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High resolution PET breast imager with improved detection efficiency
InactiveUS20100074399A1Prevent rotationMaterial analysis by optical meansPatient positioning for diagnosticsPhotovoltaic detectorsSilicon photomultiplier
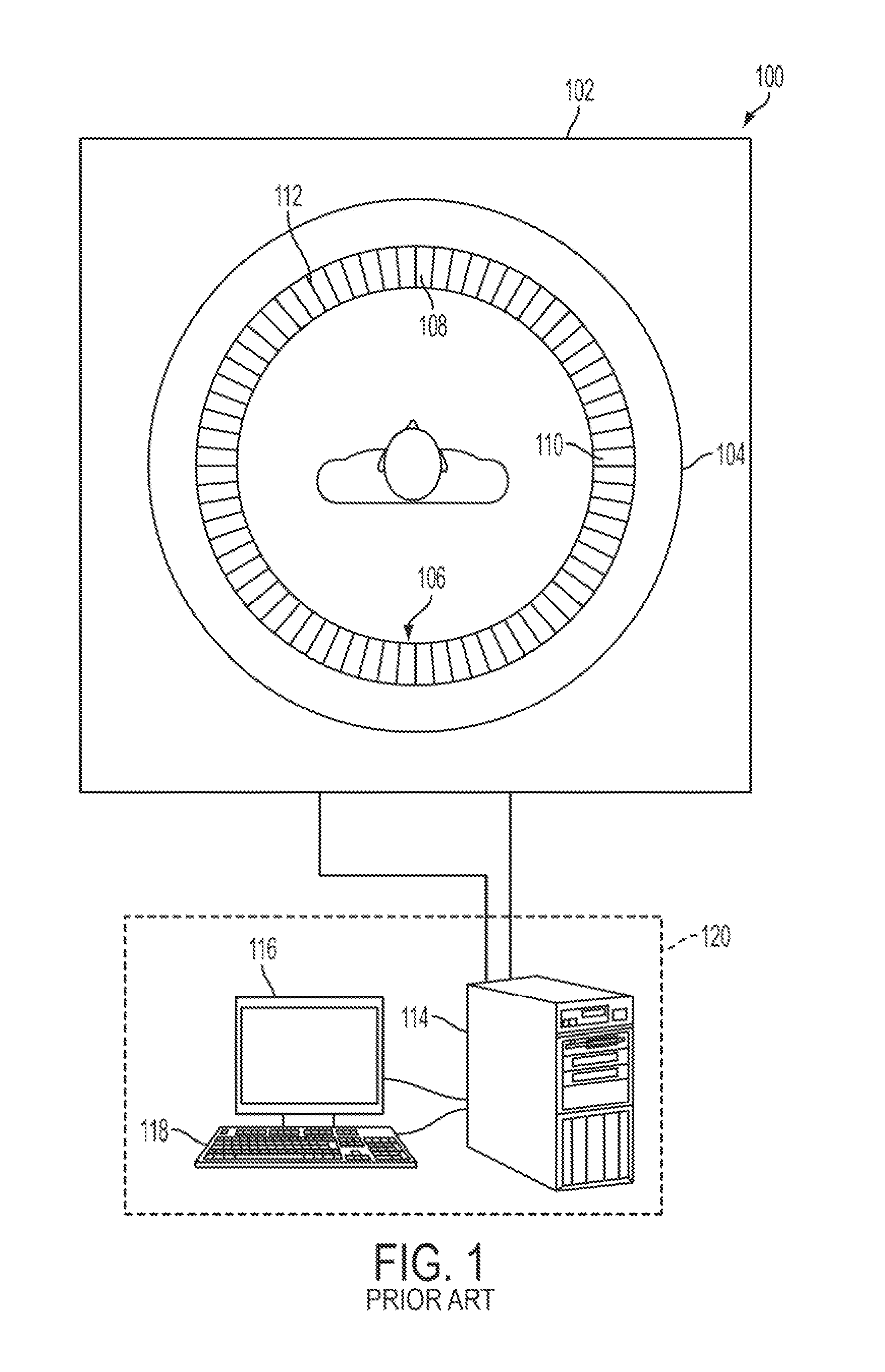
A highly efficient PET breast imager for detecting lesions in the entire breast including those located close to the patient's chest wall. The breast imager includes a ring of imaging modules surrounding the imaged breast. Each imaging module includes a slant imaging light guide inserted between a gamma radiation sensor and a photodetector. The slant light guide permits the gamma radiation sensors to be placed in close proximity to the skin of the chest wall thereby extending the sensitive region of the imager to the base of the breast. Several types of photodetectors are proposed for use in the detector modules, with compact silicon photomultipliers as the preferred choice, due to its high compactness. The geometry of the detector heads and the arrangement of the detector ring significantly reduce dead regions thereby improving detection efficiency for lesions located close to the chest wall.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Silicon photomultiplier tube
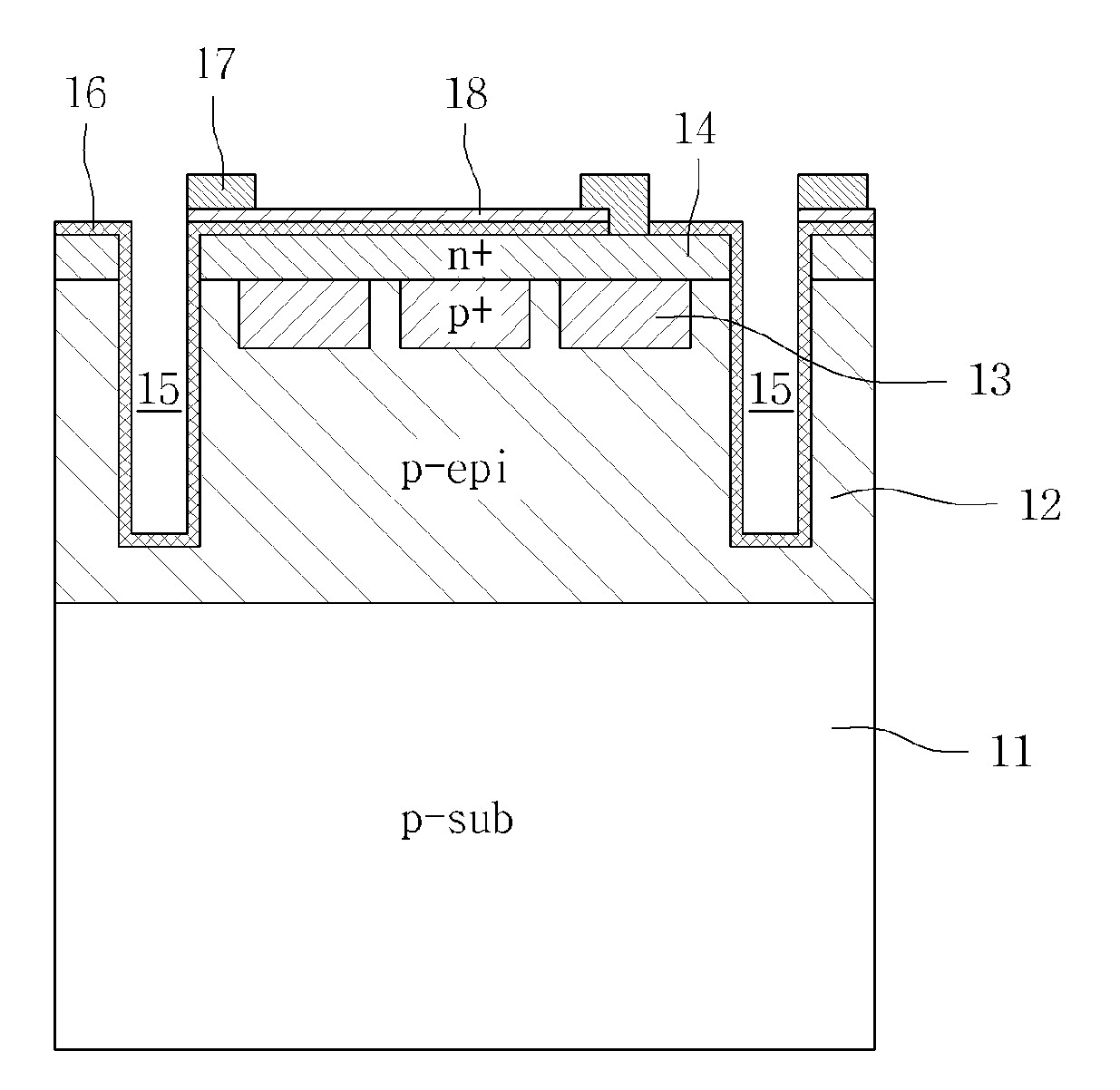
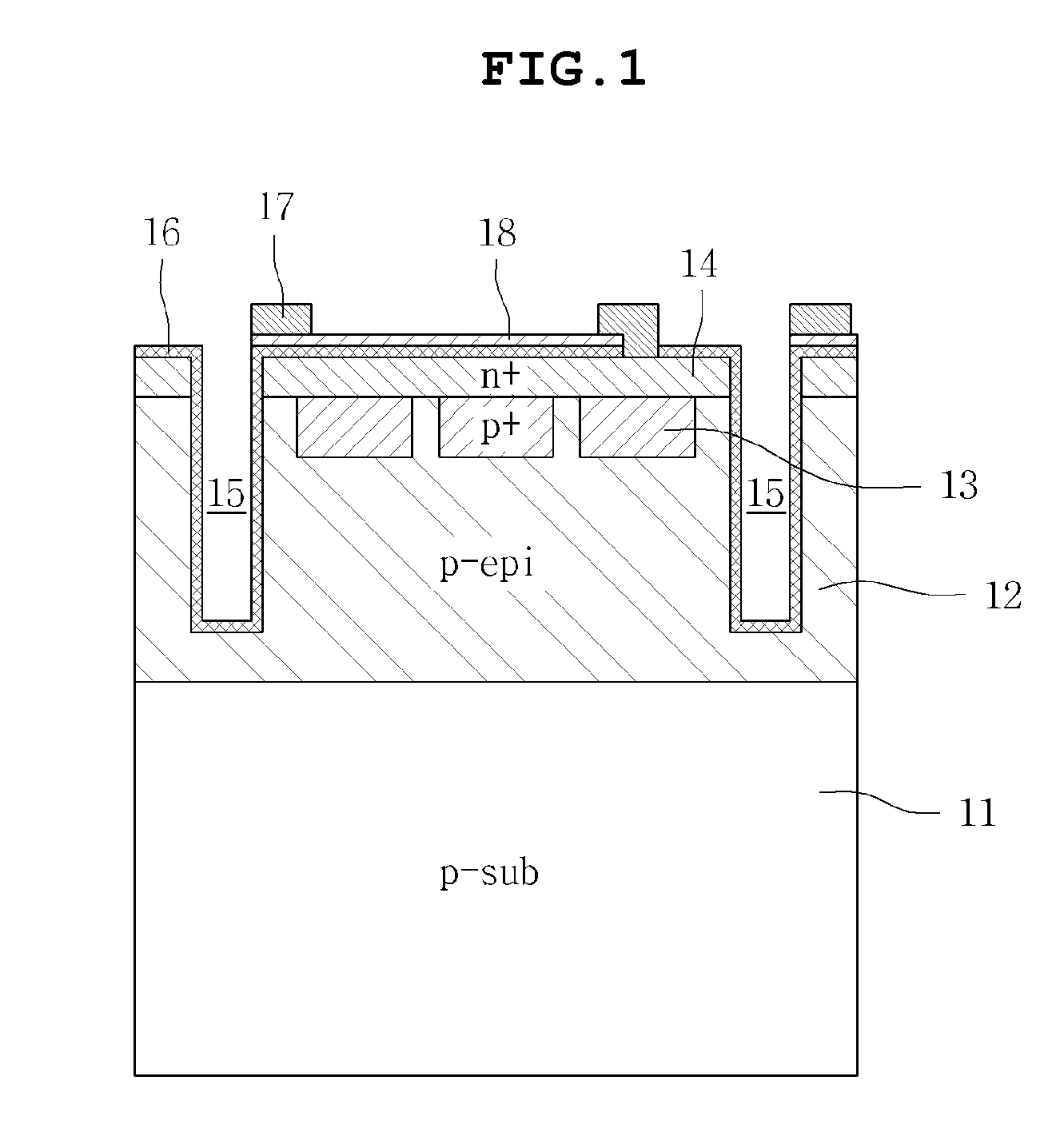
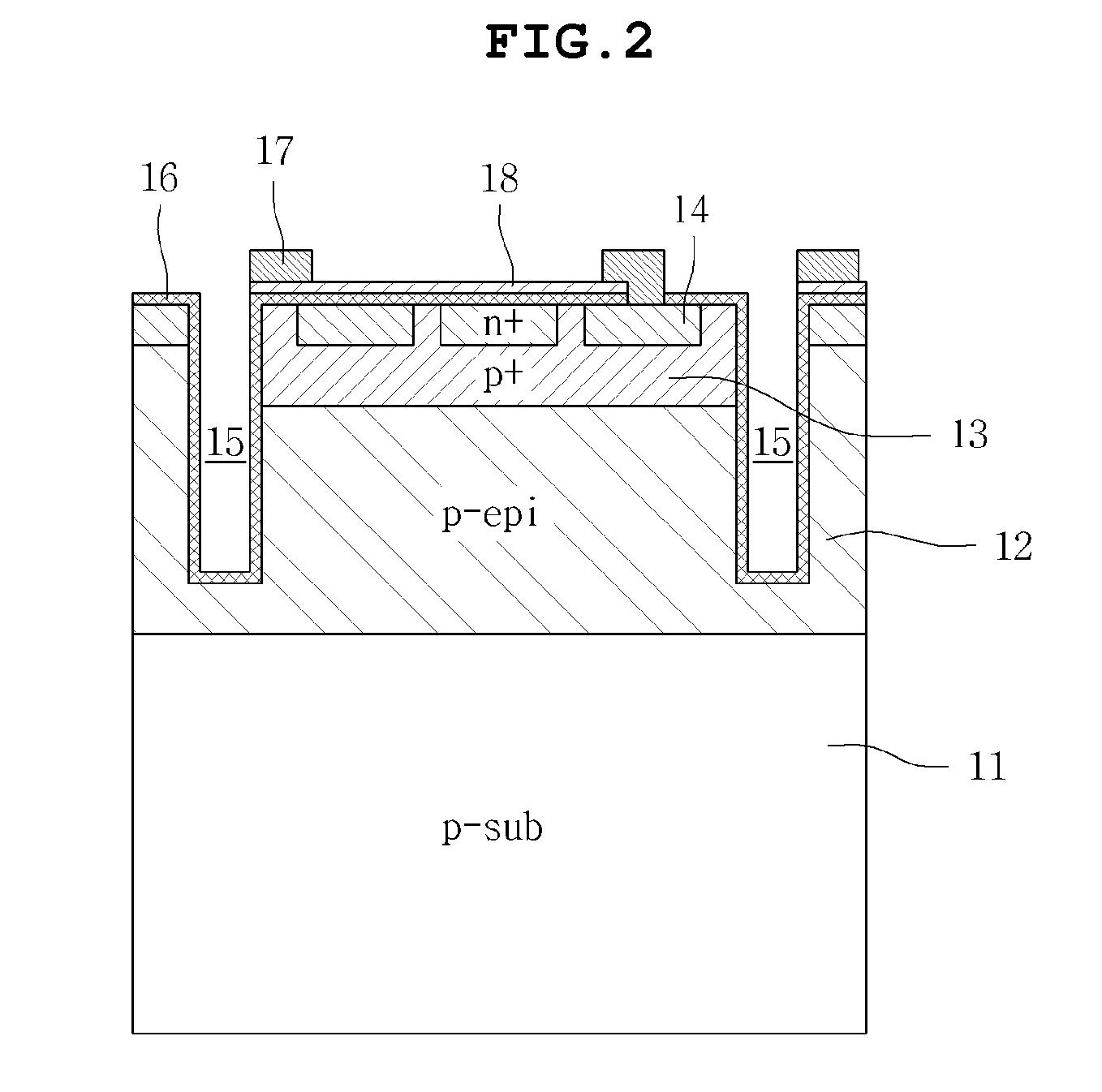
InactiveUS20110074283A1Improve efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMutiple dynode arrangementsSilicon photomultiplierSilicon
Disclosed herein is a silicon photomultiplier tube, including: a first type silicon substrate; a cell, each including a first type epitaxial layer formed on the first type silicon substrate, a first type conductive layer formed on the first type epitaxial layer, and a second type conductive layer formed on the first type conductive layer; a separating element located between the cell and a cell adjacent to the cell to separate the cells from each other; and an antireflection coating layer formed on a top surface of the second type conductive layer and an inner wall of the separating element, wherein any one of the first type conductive layer and the second type conductive layer is formed in a plurality of rows.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
PET detection module, PET detector and PET system
ActiveCN104166151AExpanded imaging field of viewImprove spatial resolutionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentDiseaseSilicon photomultiplier
The invention discloses a PET detection module, a PET detector and a PET system. The PET detection module includes a plurality of detection units, and each detection unit includes a scintillation crystal and a silicon photoelectric multiplier tube which is in one-to-one coupling with the scintillation crystal so as to read scintillation signals of the scintillation crystal, and a part between two adjacent scintillation crystals is filled with a blocking material used for blocking rays. The PET detection module has the advantages of being high in space resolution, low in error positioning probability, and capable of improving imaging quality of the PET system and improving accuracy of disease diagnosis and the like.
Owner:BEIJING NOVEL MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
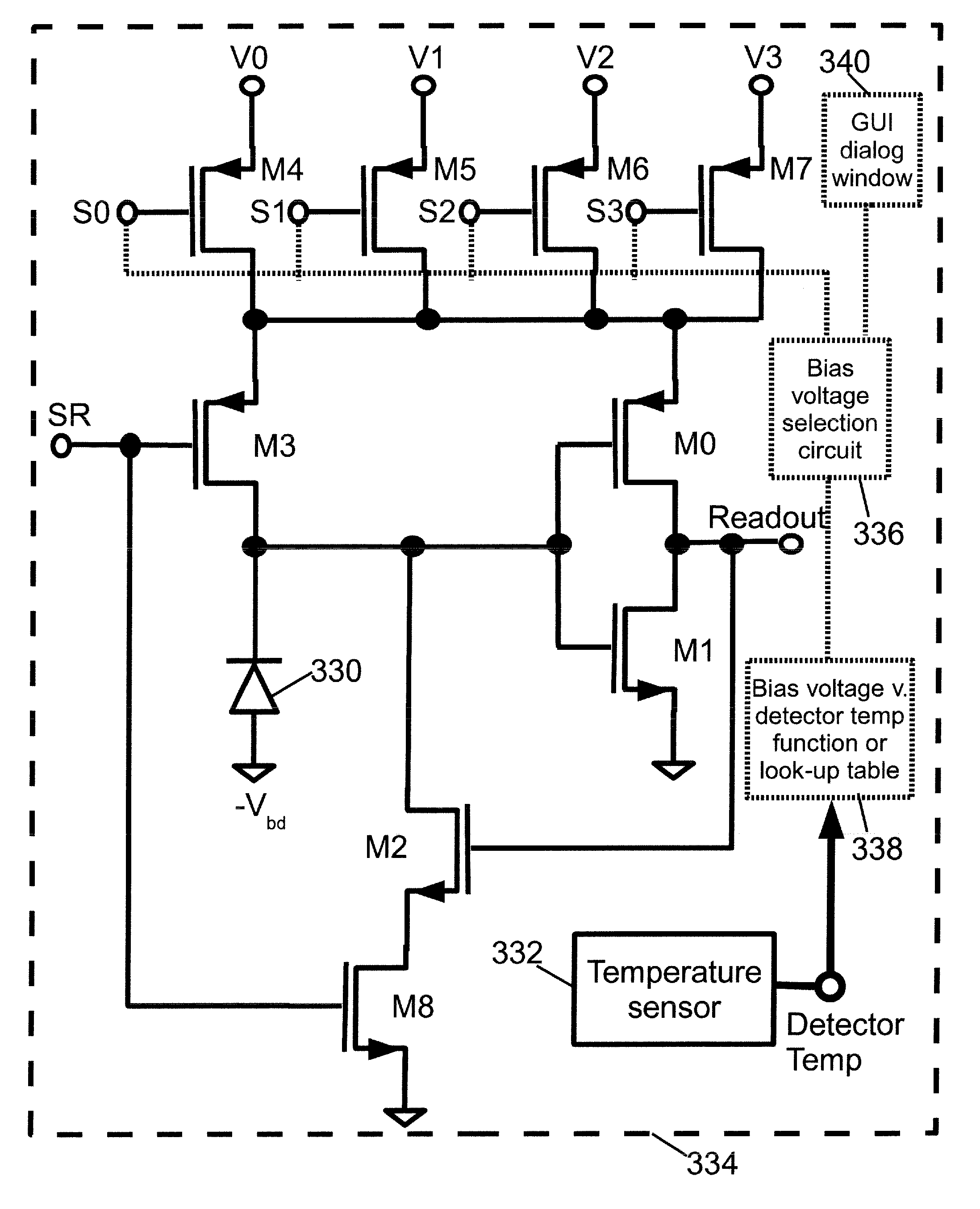
Method for passively compensating for temperature coefficient of gain in silicon photomultipliers and similar devices
ActiveUS9123611B1Small setGood energyDiodeRadiation controlled devicesSilicon photomultiplierEngineering
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Multifunctional detector capable of simultaneously measuring alpha, beta, gamma and neutrons
InactiveCN111060953AReduce distractionsMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMeasurement with scintillation detectorsSilicon photomultiplierScintillation crystals
The invention discloses a multifunctional detector capable of simultaneously measuring alpha, beta, gamma and neutrons. A plastic scintillator sprayed with zinc sulfide (ZnS (Ag)) and scintillation crystals with gamma and neutron detection and discrimination capability such as Cs2LiLaBr6: Ce (CLLB), Cs2LiYCl6: Ce (CLYC) and Cs2LiLa (Br, Cl) 6: Ce (CLLBC) are coupled together to form a coincidencecrystal, and a silicon photomultiplier is coupled with the coincidence crystal to form the detector. Alpha, beta, gamma and neutron rays are discriminated by using a pulse shape discrimination (PSD) method, and the interference of gamma rays on alpha and beta detectors can be greatly reduced by using a digital anticoincidence technology.
Owner:中国人民解放军96901部队23分队
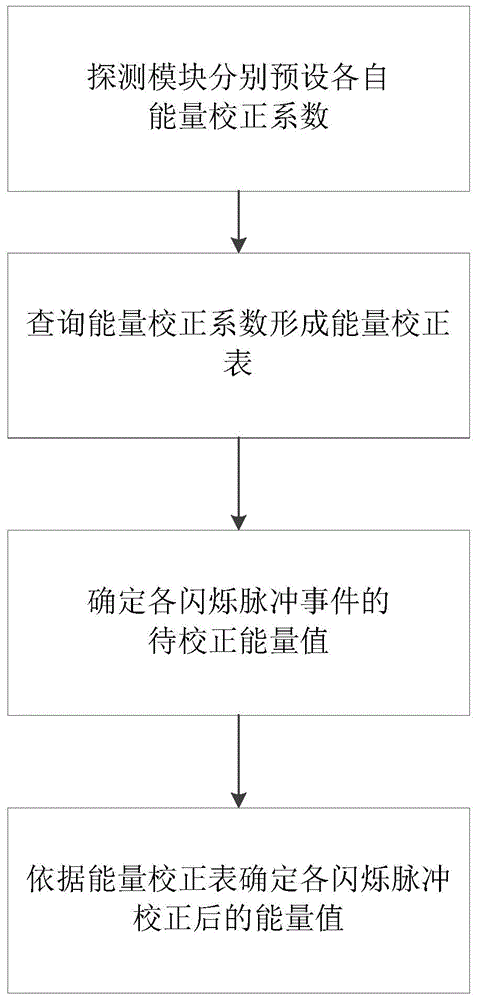
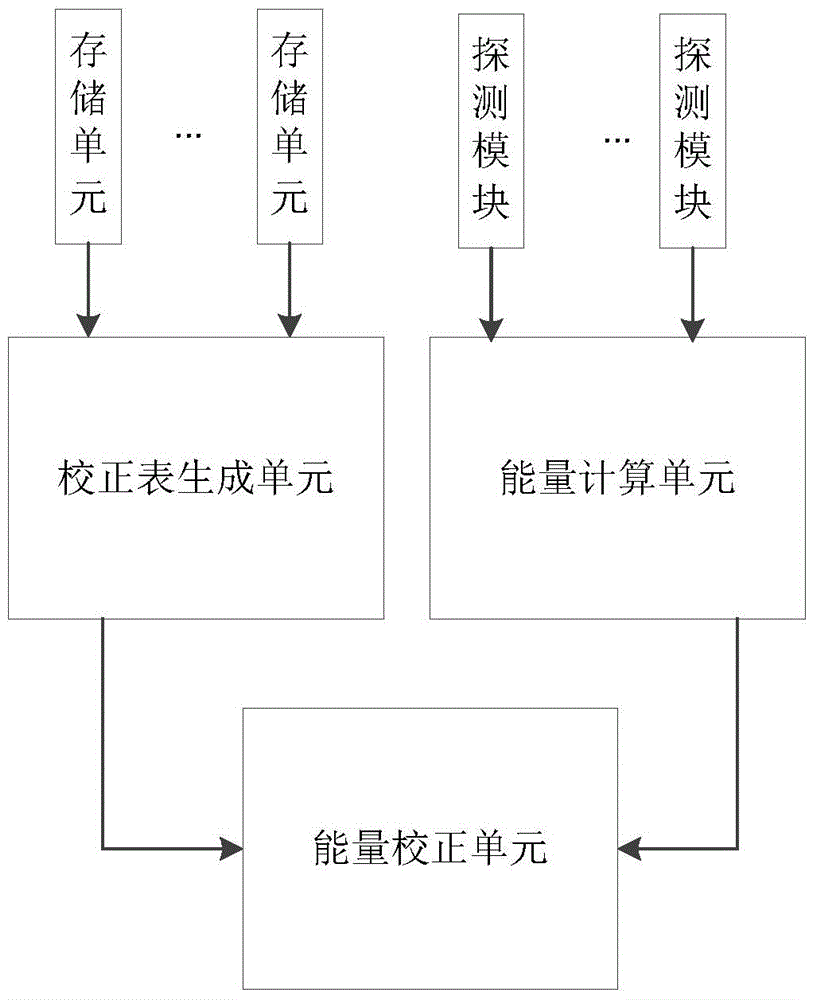
Digital PET energy parameterization calibration method and system
InactiveCN105115994AIncrease job securityImprove calibration efficiencyMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSilicon photomultiplierEngineering
The invention discloses a digital PET energy parameterization calibration method. According to the digital PET energy parameterization calibration method, each detector module is provided with corresponding energy calibration coefficients via presetting; each detector module comprises one-to-one coupled crystal strips and silicon photomultipliers. The digital PET energy parameterization calibration method comprises following steps: (1) an upper computer is used for inquiring the preset energy calibration coefficients in each detector module so as to obtain an energy calibration chart; (2) the upper computer is used for acquiring energy values for calibration of each scintillation pulse event generated by the detector modules; and (3) the upper computer is used for calibrating the energy values for calibration based on the energy calibration chart so as to obtain energy values after calibration of the scintillation pulse events. According to the digital PET energy parameterization calibration method, the upper computer is used for reading the energy calibration coefficients of the detector modules and complete energy calibration of the corresponding scintillation pulse events, no radiation source is needed, the whole energy calibration process is completed in the upper computer, efficiency is high, and accuracy is high.
Owner:RAYSOLUTION DIGITAL MEDICAL IMAGING CO LTD
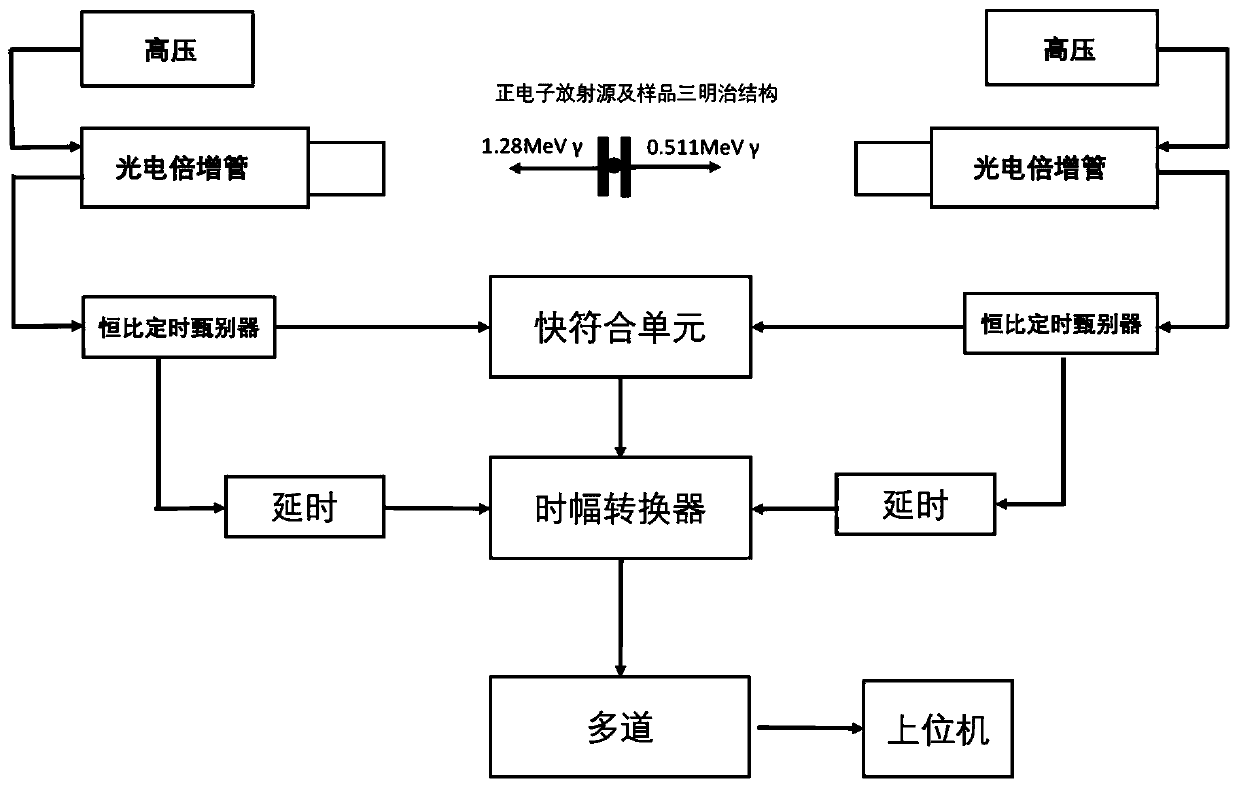
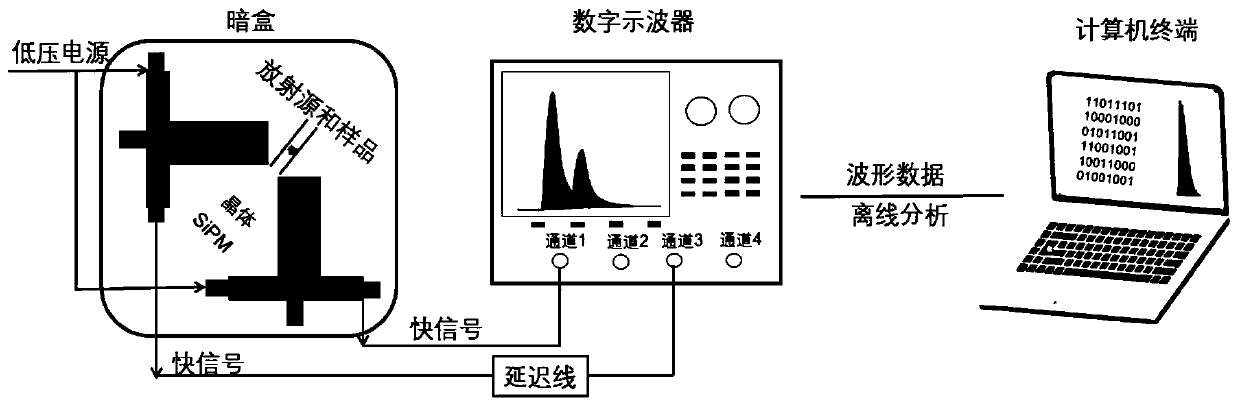
Positron annihilation lifetime spectrometer based on silicon photomultiplier (SiPM)
ActiveCN110082368AGood single photon response abilityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementTime informationSilicon photomultiplier
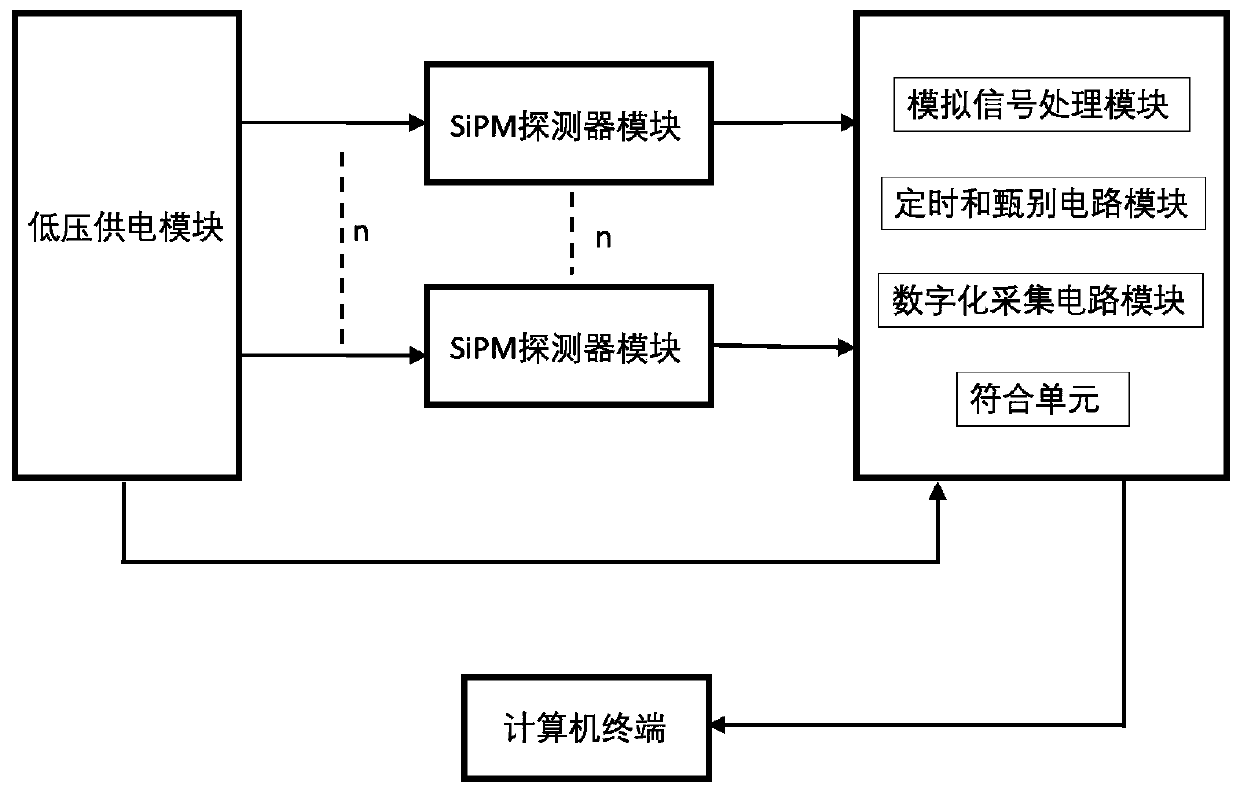
The invention discloses a positron annihilation lifetime spectrometer based on a silicon photomultiplier (SiPM), and the lifetime spectrometer comprises a SiPM detector module, an analog signal processing module, a timing and discrimination circuit module, a digital acquisition circuit module, a matching unit and a low voltage power supply module, wherein the SiPM detector receives gamma photons and generates scintillation light, which is converted into a photoelectric signal by the SiPM; the photoelectric signal is processed into a pulse signal through further amplification, noise reduction and the like by the analog signal processing module; the pulse signal is timed and discriminated by the timing and discrimination circuit module to obtain position information, energy information and time information of the gamma photons; the information is acquired by the digital acquisition circuit module and filtered by the matching unit to a meeting event; and all the modules are powered by thelow voltage power supply module. The positron annihilation lifetime spectrometer can improve measurement accuracy, reduce measurement time, greatly reduce cost, reduce power supply requirements and simplify the spectrometer structure.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
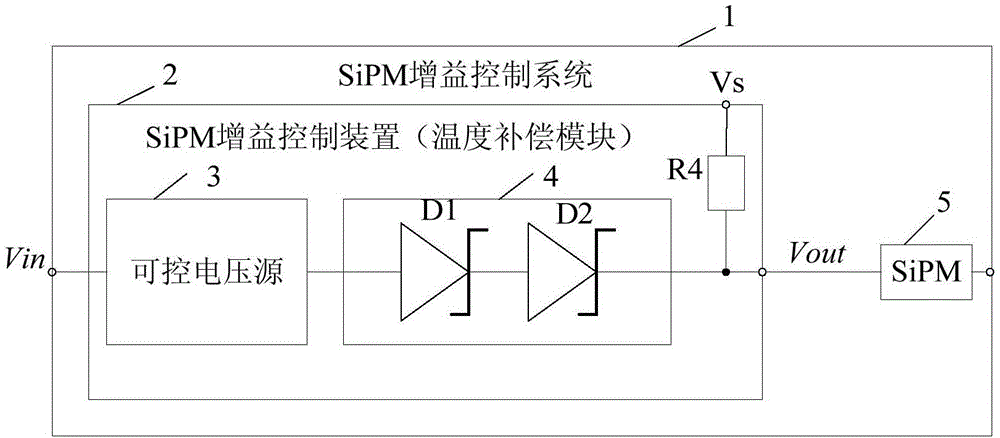
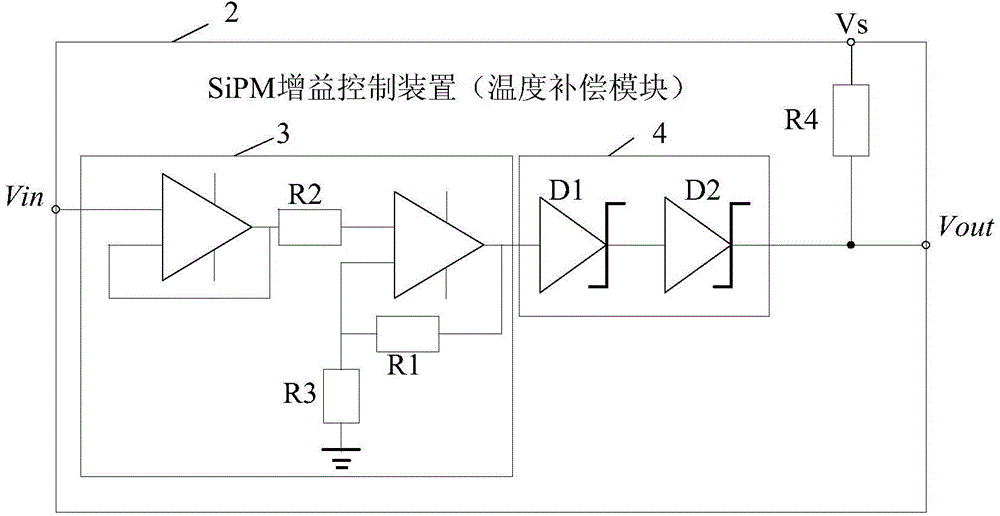
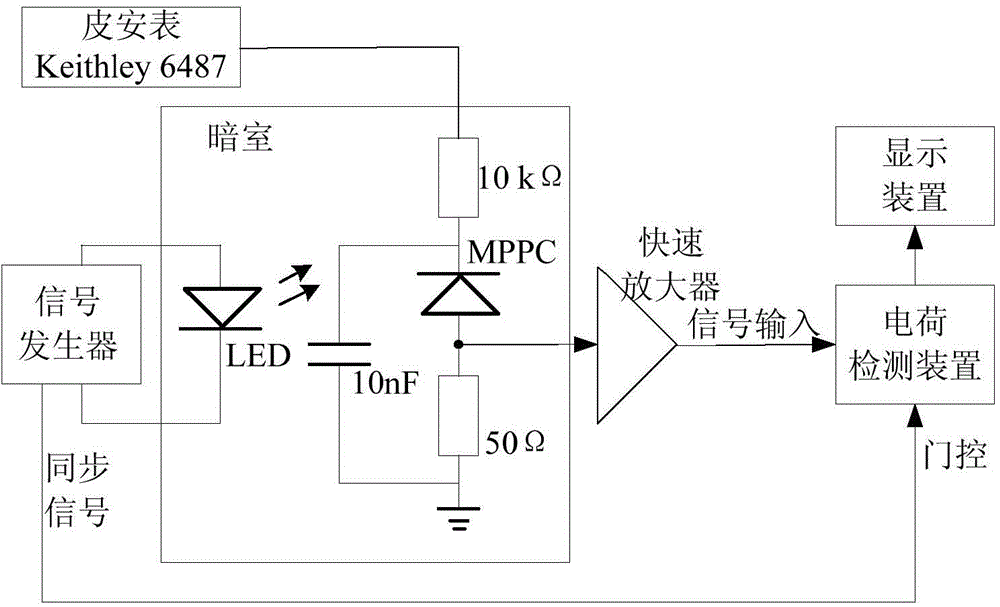
Gain control device, system and method for silicon photomultiplier
ActiveCN104570043AReduce usageSimple technical solutionRadiation intensity measurementSilicon photomultiplierControl system
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com