Position-sensitive readout modes for digital silicon photomultiplier arrays
A detector array and array technology, applied in the field of radiation detection technology, can solve the problems of unrealistic, cumbersome separation equipment, increase system complexity and cost, and achieve the effect of high temporal resolution, high spatial resolution and
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
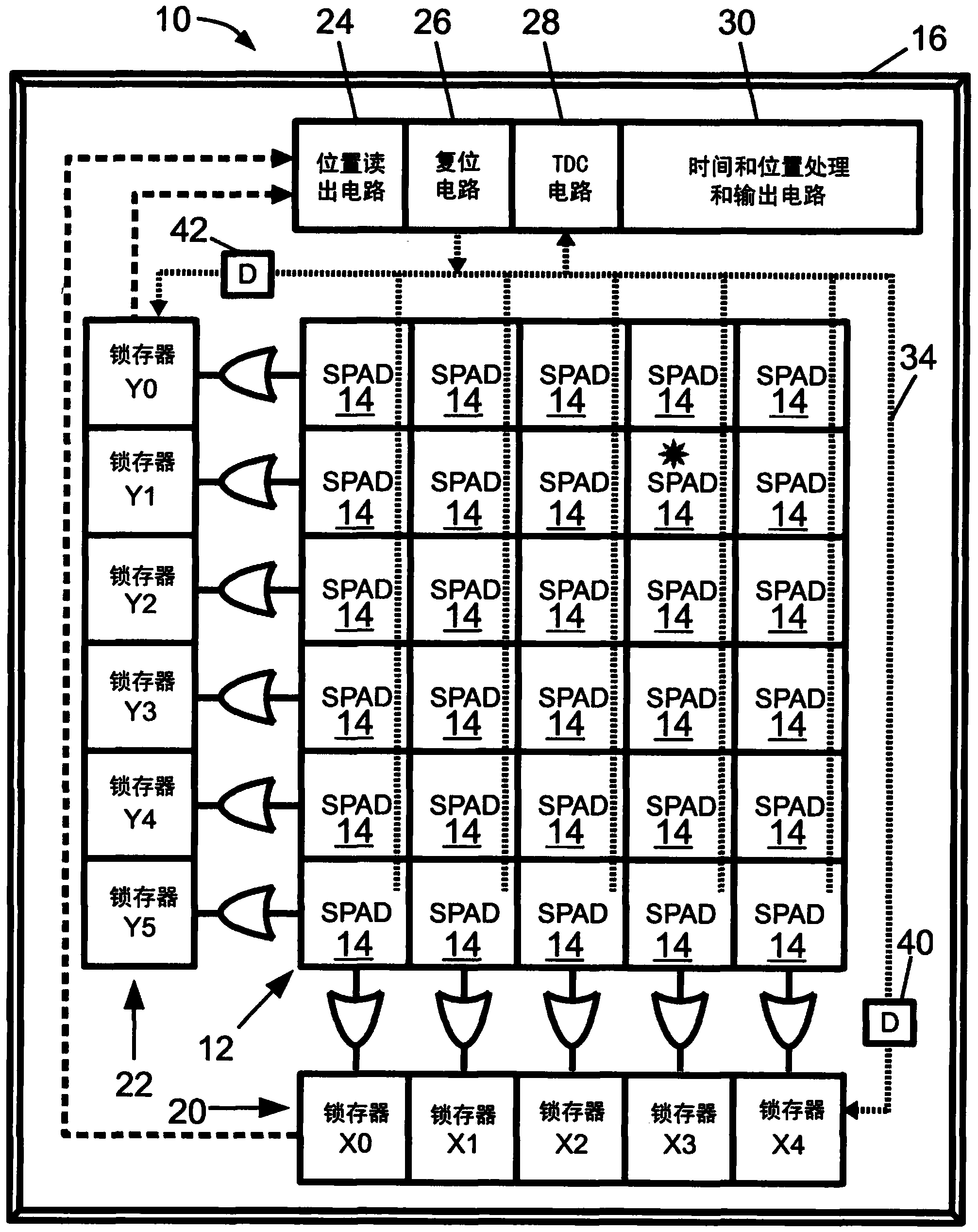
[0021] refer to figure 1 , the photon detector 10 includes a detector array 12 including an array of single photon avalanche diode (SPAD) detectors 14 . Each SPAD detector 14 suitably includes an avalanche diode reverse biased above its breakdown voltage and connected to a quenching circuit, such as a passive voltage drop placed in electrical series with the avalanche diode in some embodiments. resistors, or an active transistor based quenching circuit (details not shown). SPAD detectors operate in photon counting or Geiger mode, where the impact of a single photon on an avalanche diode results in breakdown with subsequent electron multiplication and a large current, which is then quenched by a quenching circuit. The illustrative detector array 12 includes a rectangular array having five columns identified as X0-X4 and six rows identified as Y0-Y5. This is merely illustrative, the detector array can have essentially any number of rows and columns.
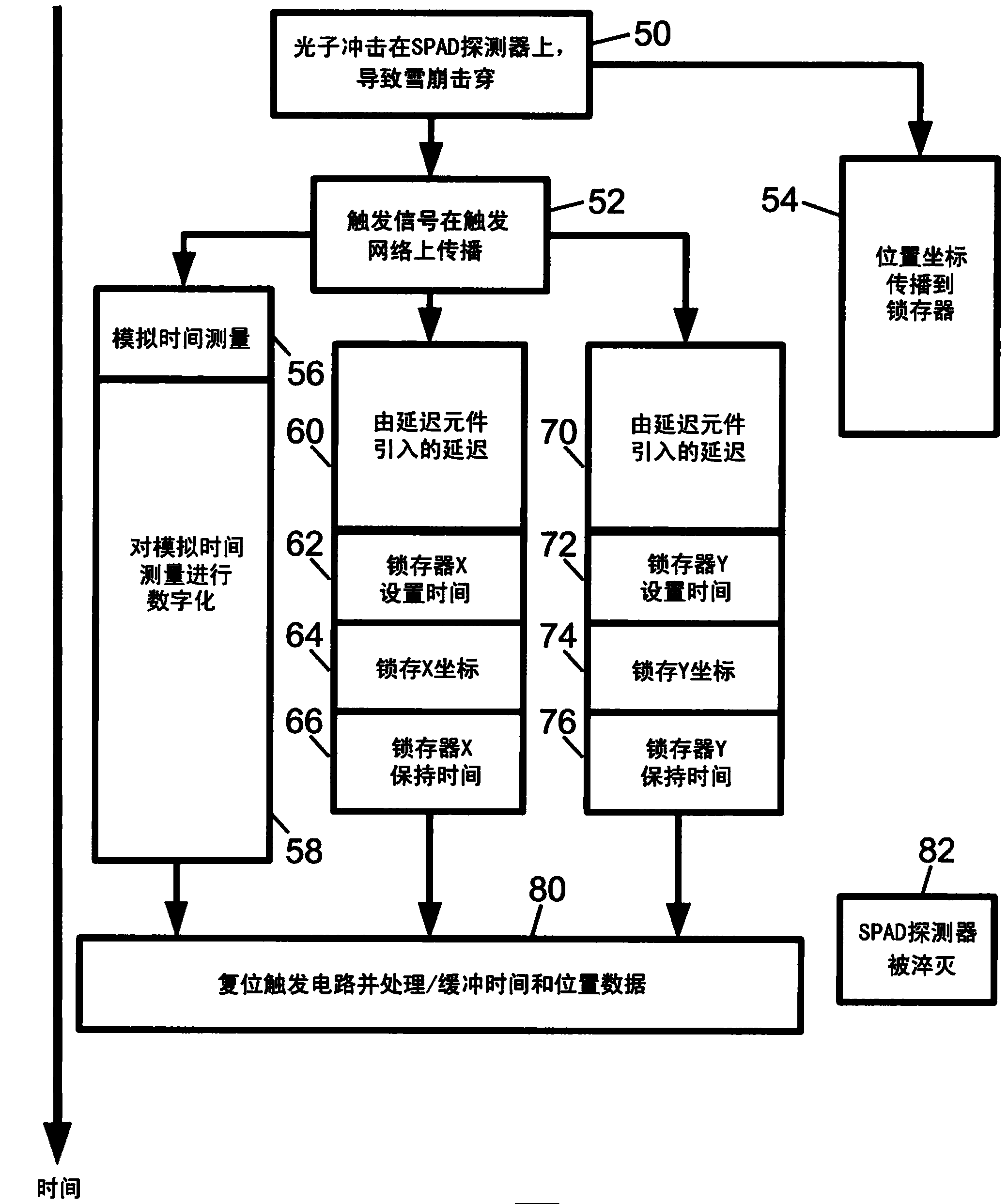
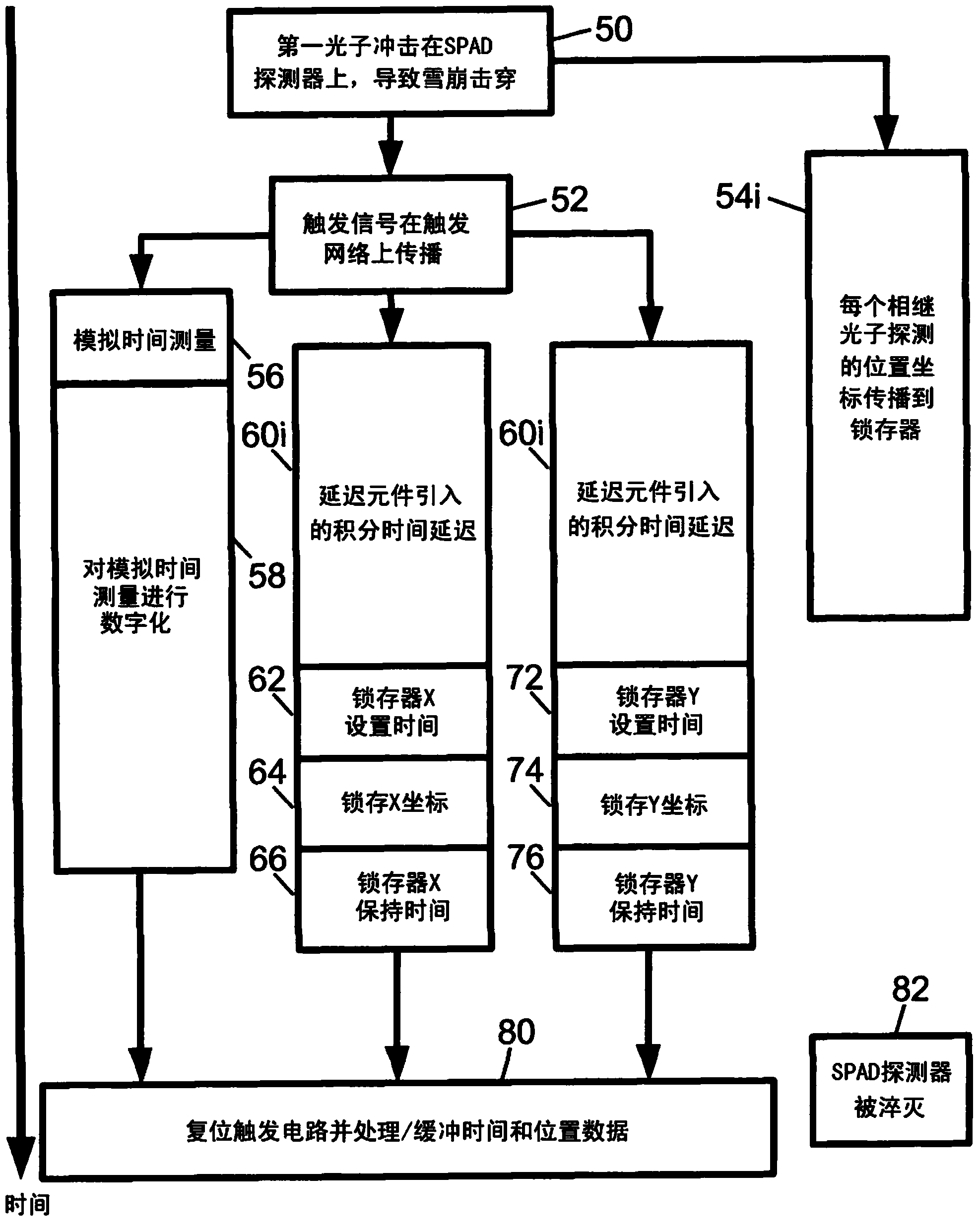
[0022] The illustrative ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com