Patents
Literature
82results about How to "High spatial resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
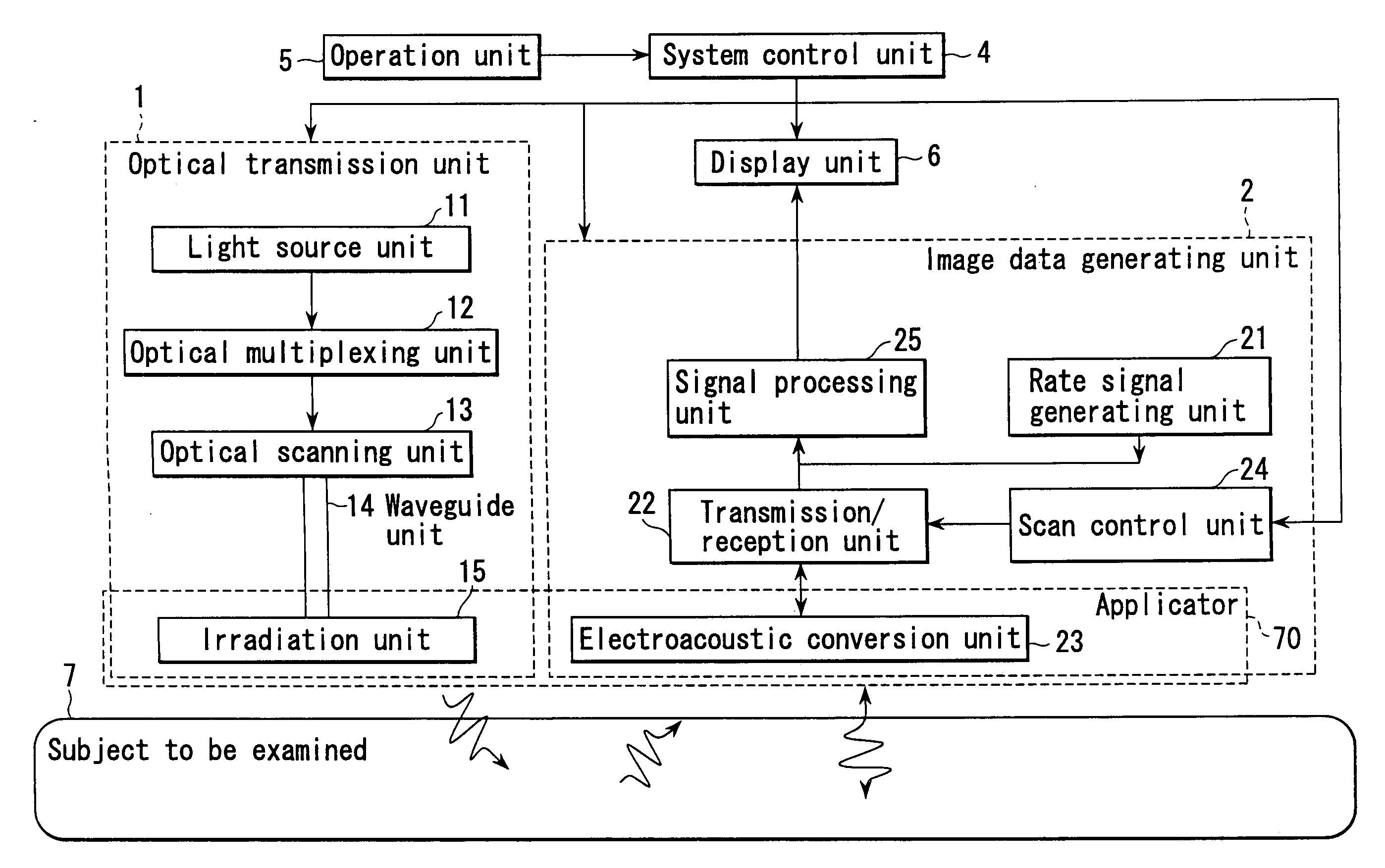
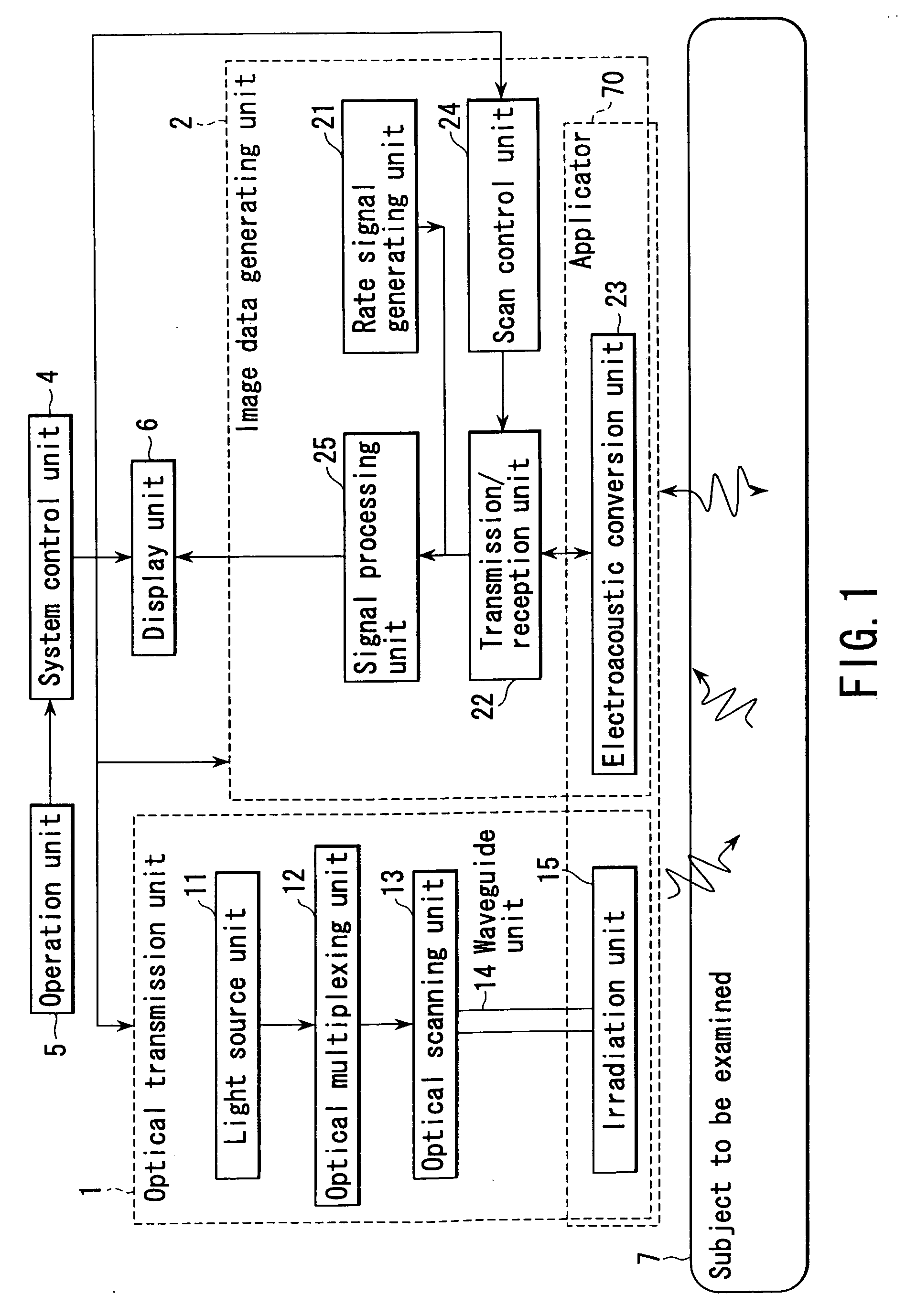
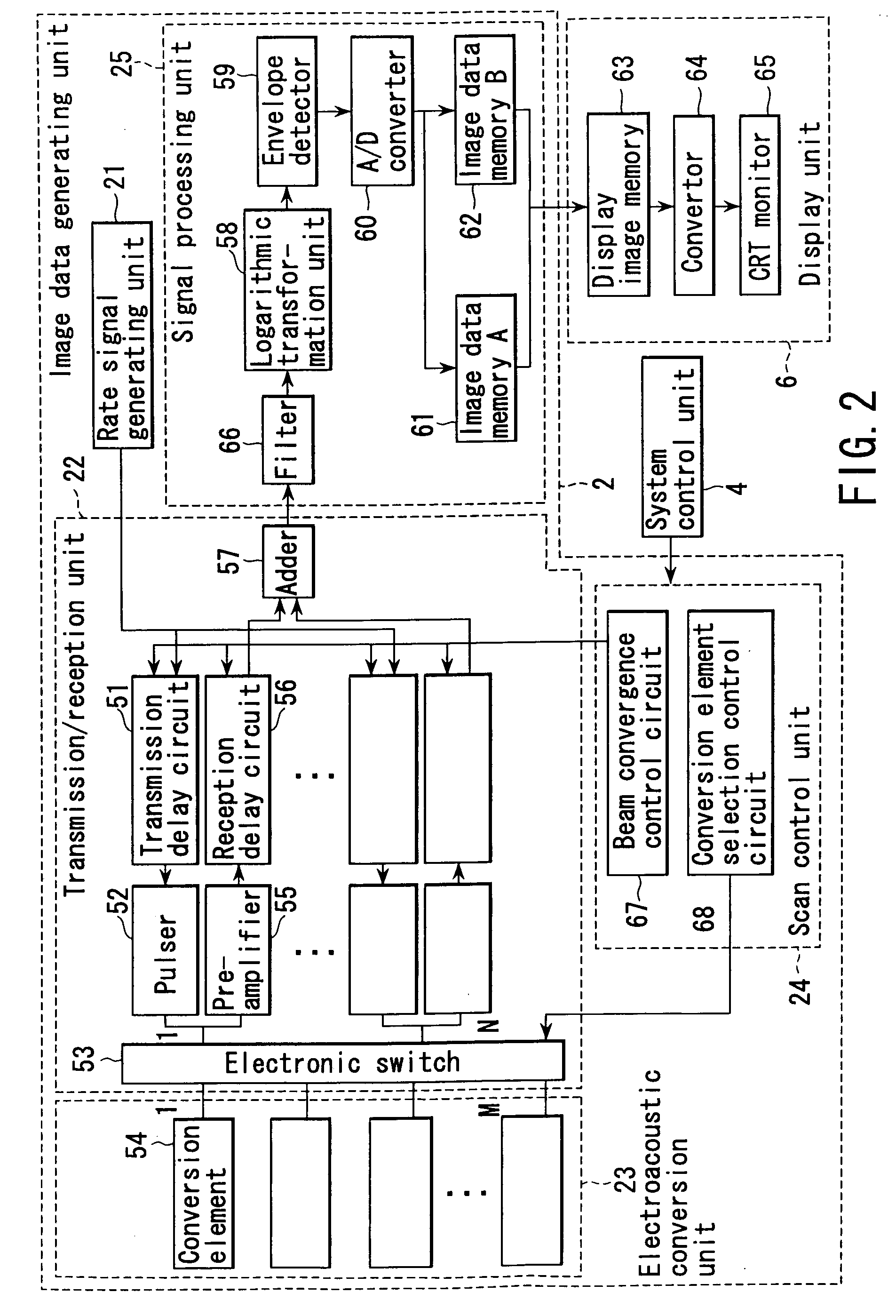
Method and apparatus for forming an image that shows information about a subject
ActiveUS20050004458A1Easy to operateImprove spatial resolutionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionAcoustic waveLength wave
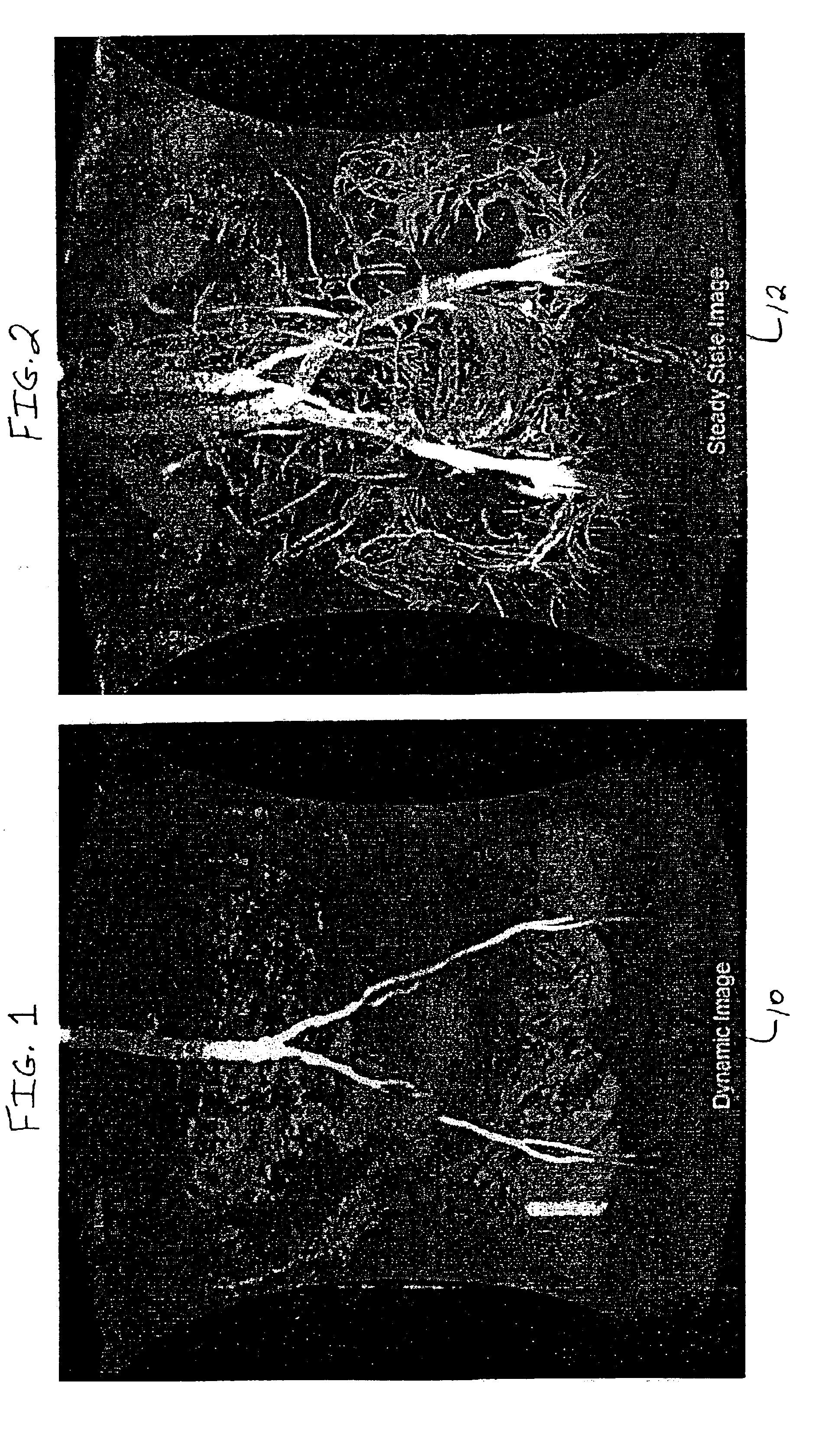
An apparatus includes an optical transmission unit which irradiates a subject to be examined with light containing a specific wavelength component, an electroacoustic conversion unit which receives acoustic waves generated inside the subject by the light radiated by the optical transmission unit and converts them into electrical signals, an image data generating unit which generates first image data on the basis of the reception signals obtained by the electroacoustic conversion unit, an electroacoustic conversion unit which receives ultrasonic reflection signals obtained by transmitting ultrasonic waves to the subject and converts them into electrical signals, an image data generating unit which generates second image data on the basis of the reception signals obtained by the electroacoustic conversion unit, and a display unit which combines the first and second image data and displays the resultant data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Stereoscopic System for Minimally Invasive Surgery Visualization
Embodiments of the present invention provide improved visualization systems and methods for minimally invasive surgery. Some embodiments include the use of reverse kinematic positioning of camera systems to provide rapid and manual surgeon controllable positioning of camera systems as well as display of 3D surgical area images along the line of sight between a surgeon's eyes and the surgical area itself.
Owner:VANTAGE SURGICAL SYST
Miniaturized terahertz radiation source
InactiveUS6909104B1High spatial resolutionHighly coherentLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusPhysicsElectrostatic lens
A miniaturized terahertz radiation source based on the Smith-Purcell effect is provided, in which, from a focused electron source, a high-energy bundle of electrons is transmitted at a defined distance over a reflection diffraction grating composed of transversely disposed grating rods, so that, in response to oscillating image charges, electromagnetic waves of one wavelength are emitted, the wavelength being adjustable as a function of the periodicity of the lines and of the electron velocity. The elements of the radiation source, such as field emitter (1), electrostatic lens (4), beam deflector (5), grating (7) of metal, and a second anode (8), are integrated on a semiconductor chip using additive nanolithographic methods. The field electron source is constructed to project, as a wire, out of the surface, using additive nanolithography, and is made of readily conductive material having stabilizing series resistance. The wire is constructed, using computer-controlled deposition lithography, in a straight or curved, free-standing design. In its surface area, the base material bears a conductor structure for the electrical terminals and connections (2), including controllable voltage sources (3) for supplying the field emitter tips (1), lens (4), and control electrodes (5, 8). The terahertz radiation source is designed to be a powerful component that is available in modular form and is usable in any spatial situation.
Owner:NAWOTEC
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for dynamic magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20080021304A1High temporalHigh spatial resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMR - Magnetic resonanceData set
The invention concerns a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for acquisition and generation of a time-resolved image series of an anatomical organ with a quasi-periodical movement in a subject, k-space is sampled in segments with a number of partial data sets, with the sampling points of each partial data set corresponding to grid points of a Cartesian sampling grid of a k-space segment, and the Cartesian sampling grids of the k-space segments being rotated relative to one another. A series of sub-data sets is incompletely acquired for each partial data set using alternating sampling schemes. Each incomplete sub-data set is associated with one of the individual images. For at least some of the partial data sets, complete sub-data sets are reconstructed from the incomplete sub-data sets. For the reconstruction of the individual images, in each of the individual images, at least some of the complete sub-data sets that are associated with this individual image are used.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for the preparation of compound micro array chips and the compound micro array chips produced according to said method
InactiveUS6423552B1IndexHigh correctnessMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsMicroarray cghReagent
The present invention relates to a method for the preparation of compound of microarray chips, especially the method by repeatedly impressing reagents at fixed locations on a substrate to synthesize said chips; and also realtes to a compound microarray chips produced according to said method.
Owner:ZUHONG LU
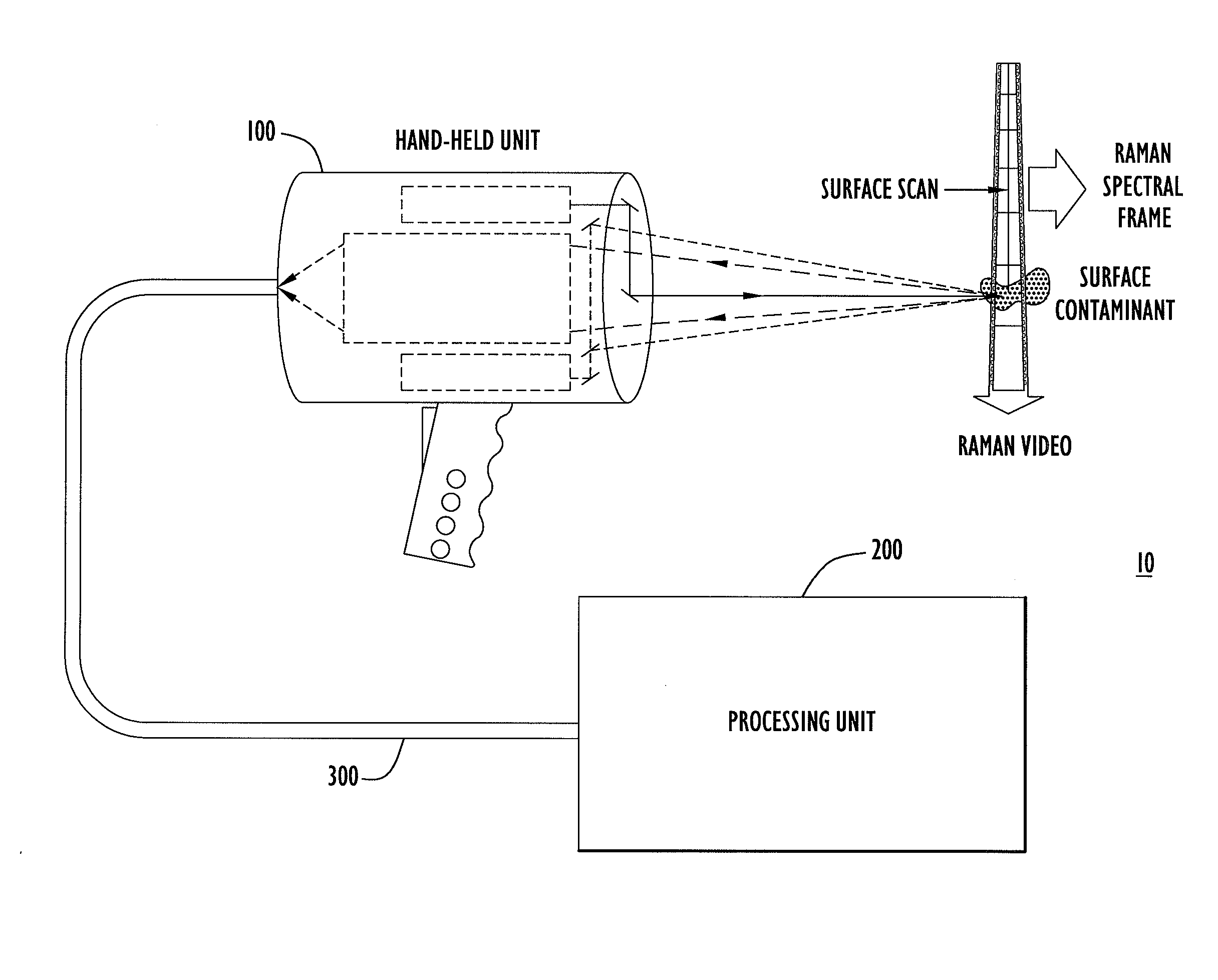
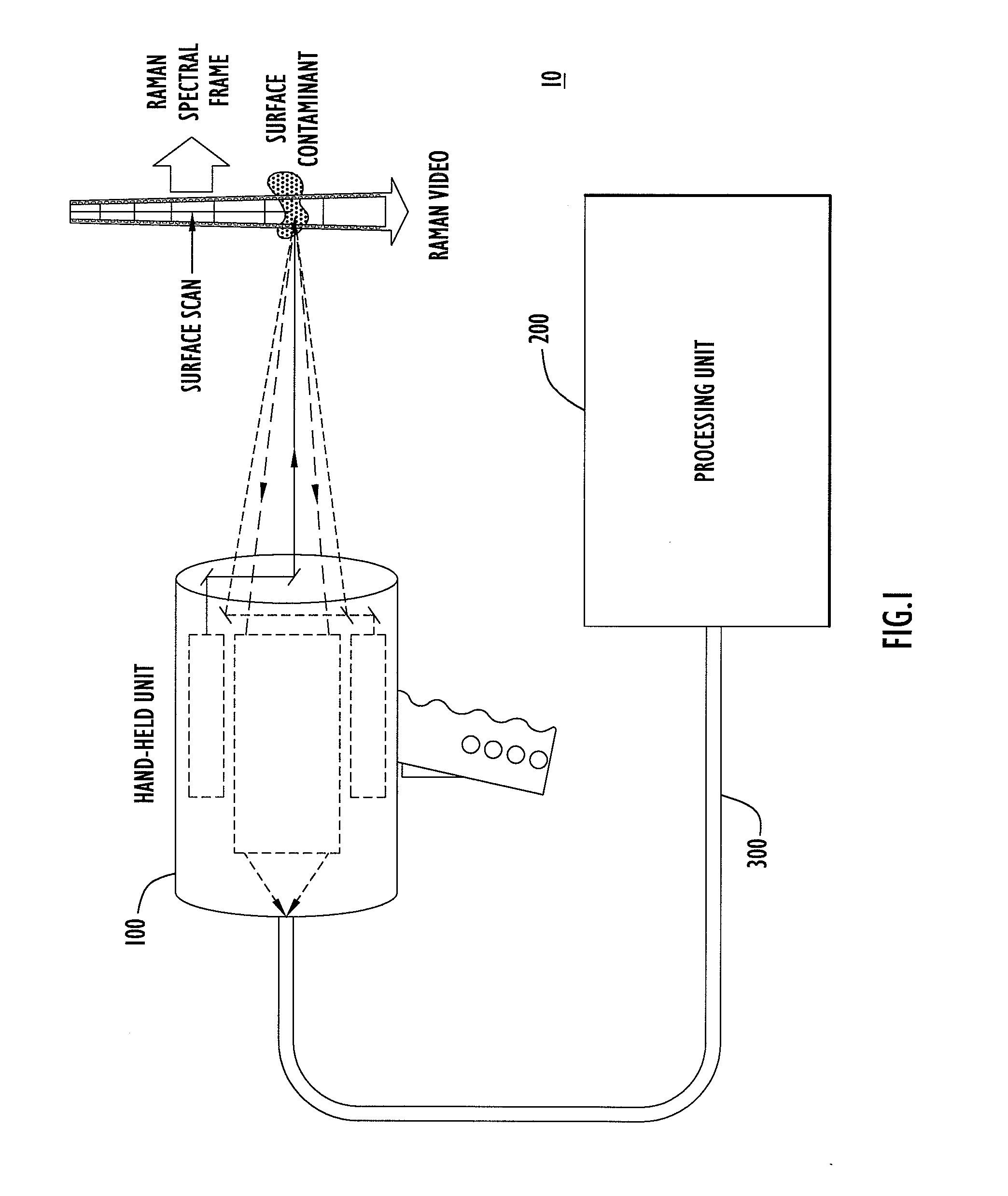
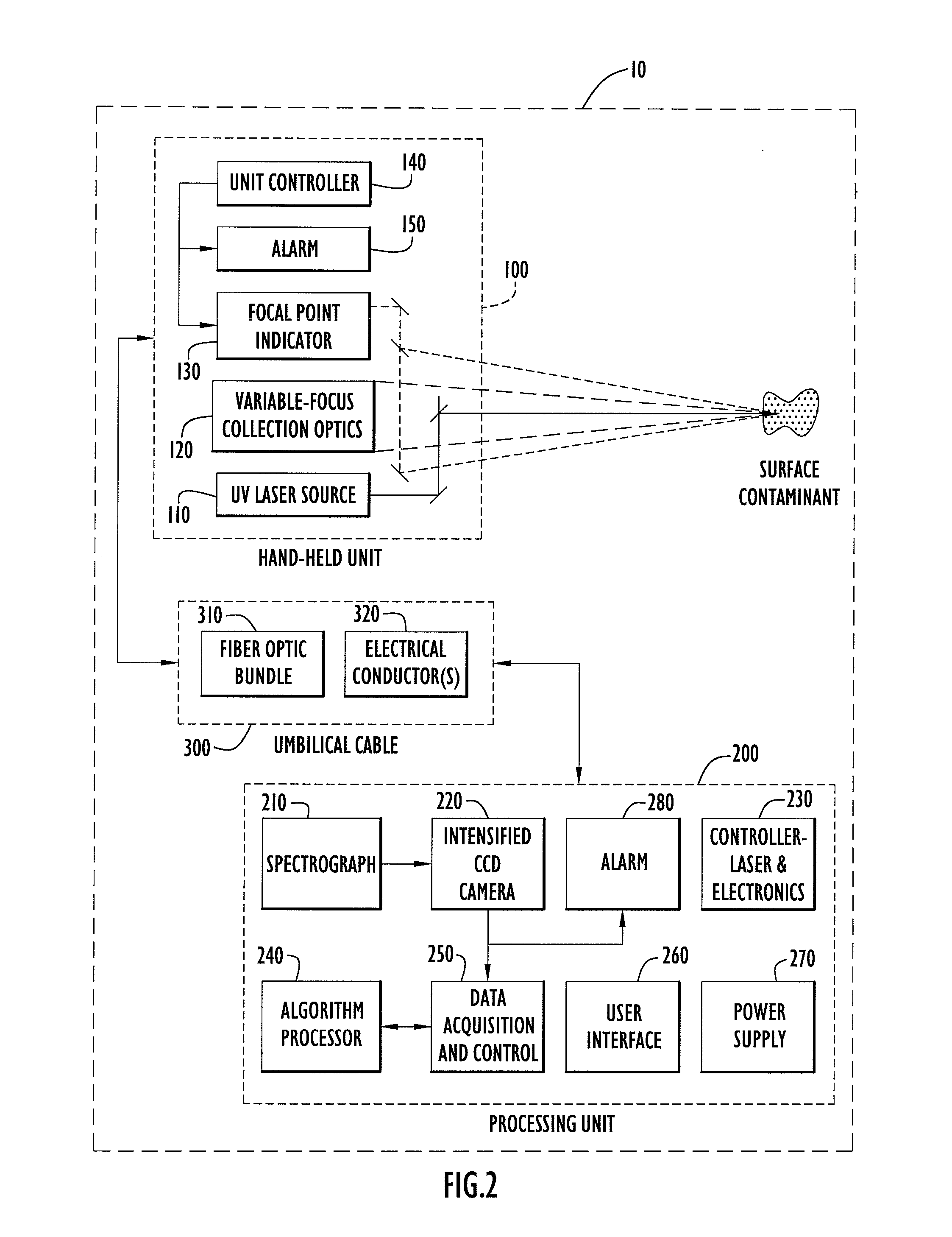
Method, Apparatus and System for Rapid and Sensitive Standoff Detection of Surface Contaminants
ActiveUS20070222981A1Fast and sensitive standoffImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringExcitation beamHazardous substance
Systems and methods for fast and sensitive standoff surface-hazard detection with high data throughput, high spatial resolution and high degree of pointing flexibility. The system comprises a first hand-held unit that directs an excitation beam onto a surface that is located a distance away from the first unit and an optical subsystem that captures scattered radiation from the surface as a result of the beam of light. The first unit is connected via a link that includes a bundle of optical fibers, to a second unit, called the processing unit. The processing unit comprises a fiber-coupled spectrograph to convert scattered radiation to spectral data, and a processor that analyzes the collected spectral data to detect and / or identify a hazardous substance. The second unit may be contained within a body-wearable housing or apparatus so that the first unit and second unit together form a man-portable detection assembly. In one embodiment, the system can continuously and without interruptions scan a surface from a 1-meter standoff while generating Raman spectral-frames at rates of 25 Hz.
Owner:PERATON INC
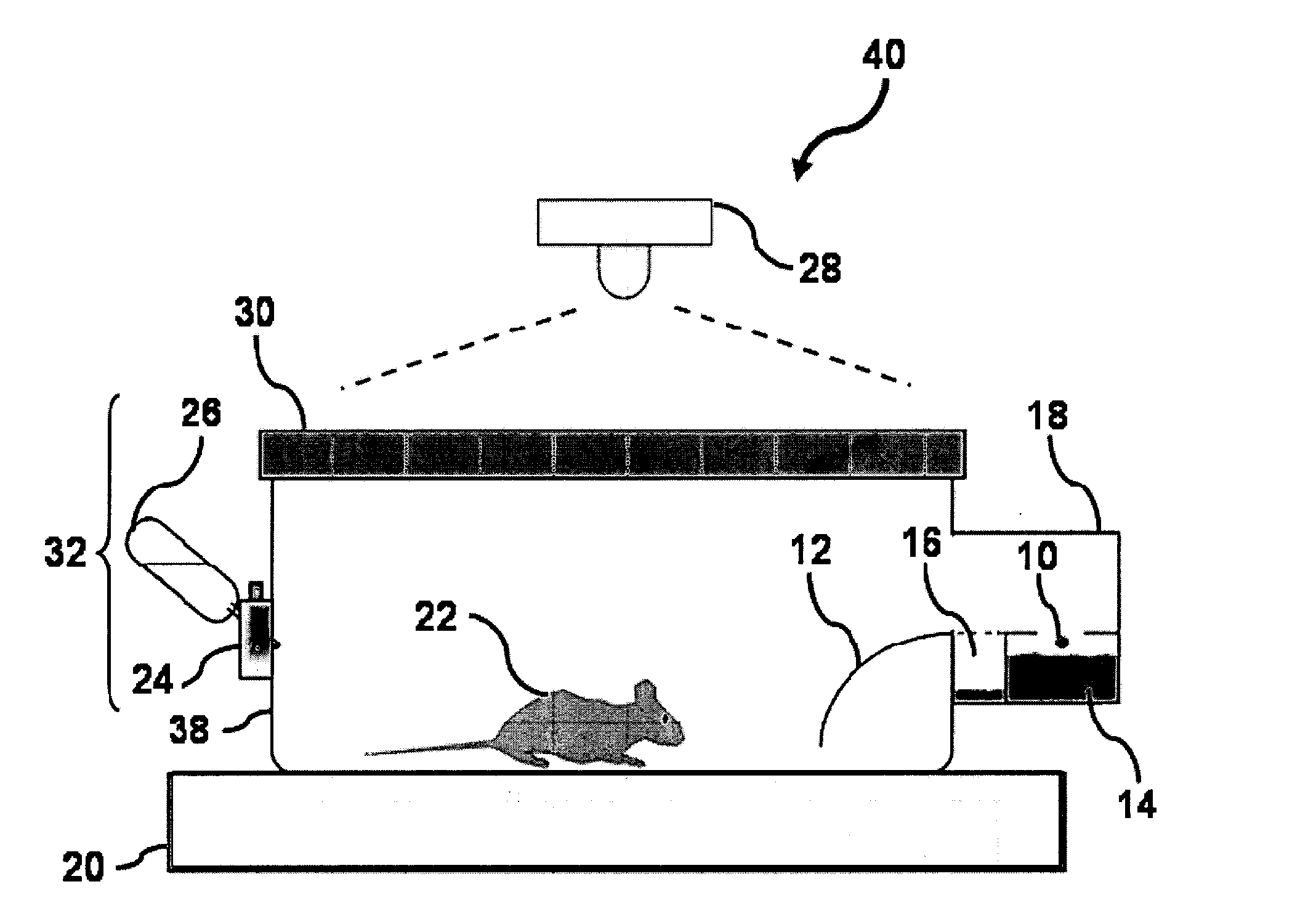
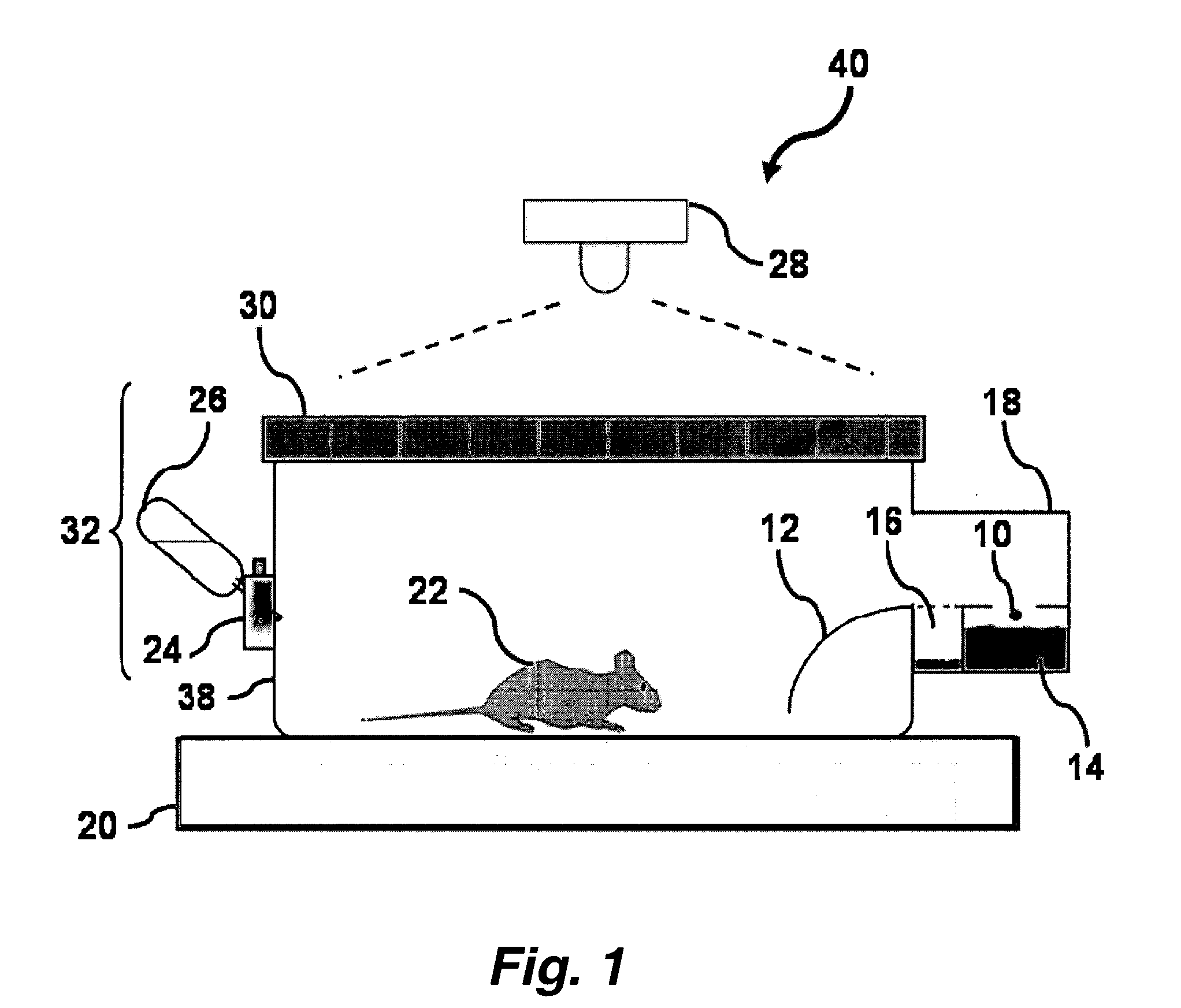
Animal cage behavior system
InactiveUS20050066910A1High temporalHigh spatial resolutionAnimal housingOther apparatusTemporal resolutionImage resolution
This invention pertains to a novel behavioral monitoring system useful for the analysis of complex behaviors in a number of animal species. The monitoring systems of this invention allow continuous monitoring of feeding, drinking and movement of animals with high temporal and spatial resolution. In certain embodiments, teh system comprises an enclosure comprising: an animal position indicator; a food consumption indicator; and a fluid consumption indicator, where the system reports behavioral data at a temporal resolution of 20 seconds or lower.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
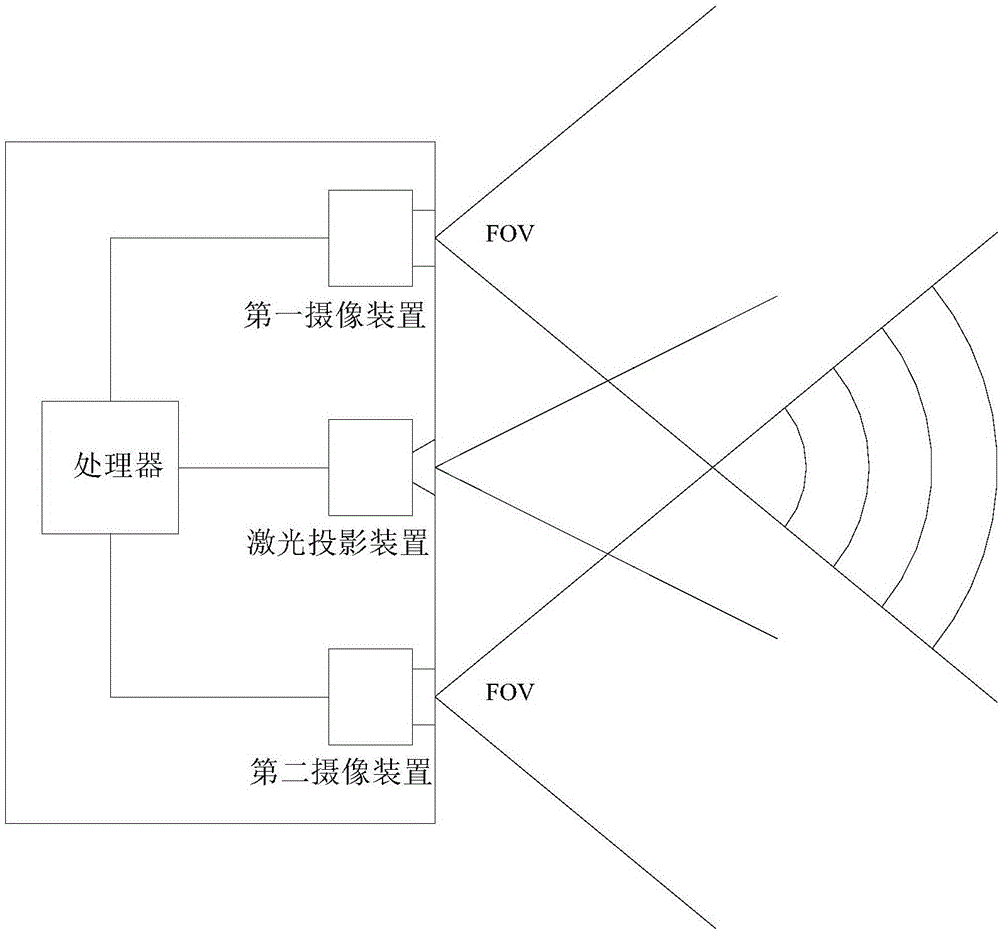
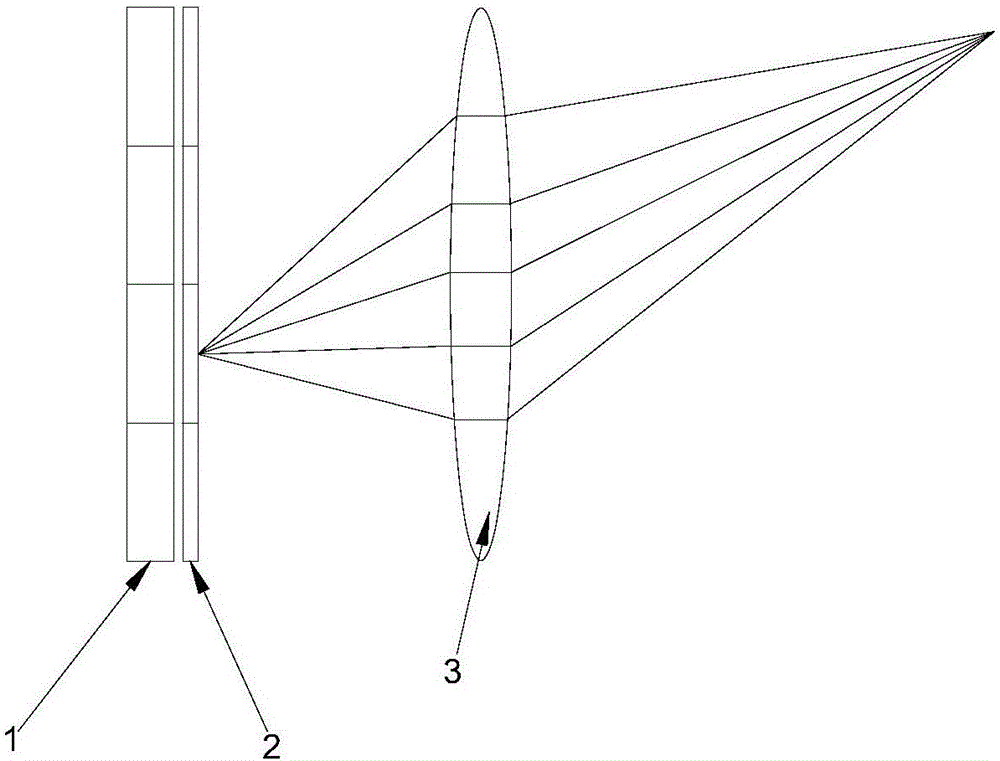
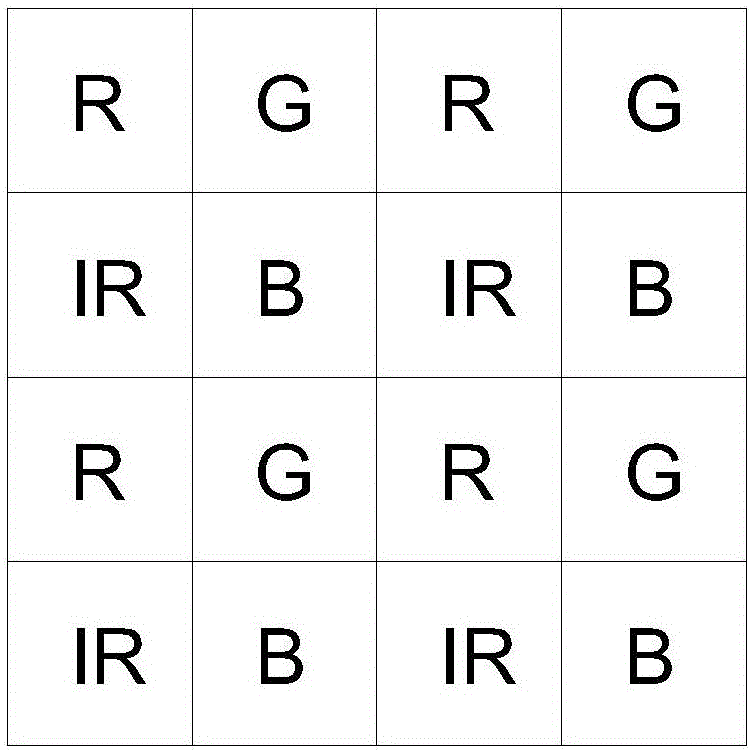
Combined camera shooting system, mobile terminal and image processing method
ActiveCN106454287ALarge synthetic depth rangeHigh spatial resolutionPicture reproducers using projection devicesPicture signal generatorsImaging processingHigh spatial resolution
The invention discloses a combined camera shooting system, a mobile terminal and an image processing method. According to the combined camera shooting system, a laser projection device is used for projecting a structured light pattern of invisible laser to a shared field of view of a first camera shooting device and the second camera shooting device; the first camera shooting device is used for collecting a first visible light image and a first invisible light image synchronously; the second camera shooting device is used for collecting a second visible light image and a second invisible light image synchronously; and a processor is used for calculating a first depth image through utilization of the first invisible light image, calculating a second depth image through utilization of the second invisible light image, synthesizing the first depth image and the second depth image to obtain a third depth image, and carrying out visual motion tracking through utilization of the second visible light image. According to the system, the mobile terminal and the method, collection of the visible light image, collection of the target depth images and the visual motion tracking can be synthesized, and the depth image with a wider depth range and higher spatial resolution can be synthesized.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
Passively controlled smart microjet cooling array
ActiveUS20140204532A1Reduce heat transferHigh spatial resolutionSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsShock coolingEngineering
An impingement cooling system for cooling electronic components includes a nozzle array having a plurality of nozzles in fluid communication with a source of cooling fluid, each nozzle including a deflection structure that deforms above a threshold temperature. A plurality of thermally conductive pins respectively are in thermal contact with the deflection structures and conduct heat from at least one of the electronic components to the deflection structures. When a heated nozzle within the nozzle array reaches a temperature above the threshold temperature due to heat conducted from the respective thermally conductive pin, the deflection structure of the heated nozzle deforms from a closed position to an open position to permit cooling fluid to impinge upon the electronic component. The deflection structure may be a deflection plate formed of a bimetallic material having layers of different thermal expansion coefficients, or a thermally responsive two-way shape memory material.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
System comprising a cellular network of capacitive pressure and shear-stress sensors and manufacturing process
ActiveUS20170176266A1High spatial resolutionReduce numberInsolesForce measurementElectrically conductiveCellular network
Disclosed is a system and to a process for manufacturing a system including a network of sensors including a sheet of dielectric material that is elastically deformable under compressive and shear stress, each cell of the network including a first capacitive sensor for sensing normal pressure in a first direction, a second capacitive sensor for sensing shear stress in a second direction and a third capacitive sensor for sensing shear stress in a third direction. Each capacitive sensor includes a first electrode fixed to the first side of the sheet of dielectric material and a second electrode fixed to the second side of the sheet of dielectric material, the first electrodes of the capacitive sensors of a given cell being connected in series to a first electrically conductive track connecting a row of cells of the network of sensors.
Owner:FEETME
Switch probe for multiple electrode measurement of impedance
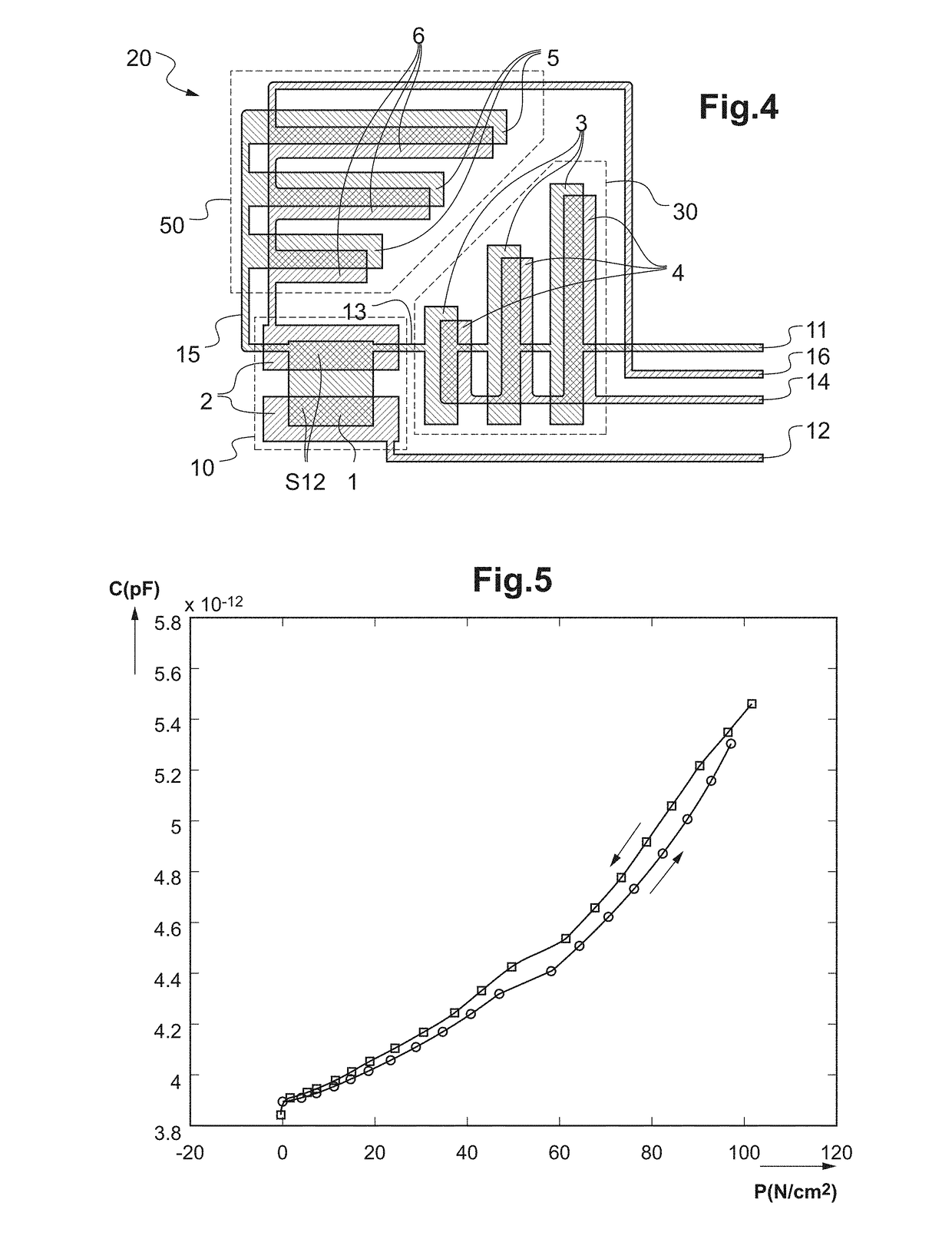
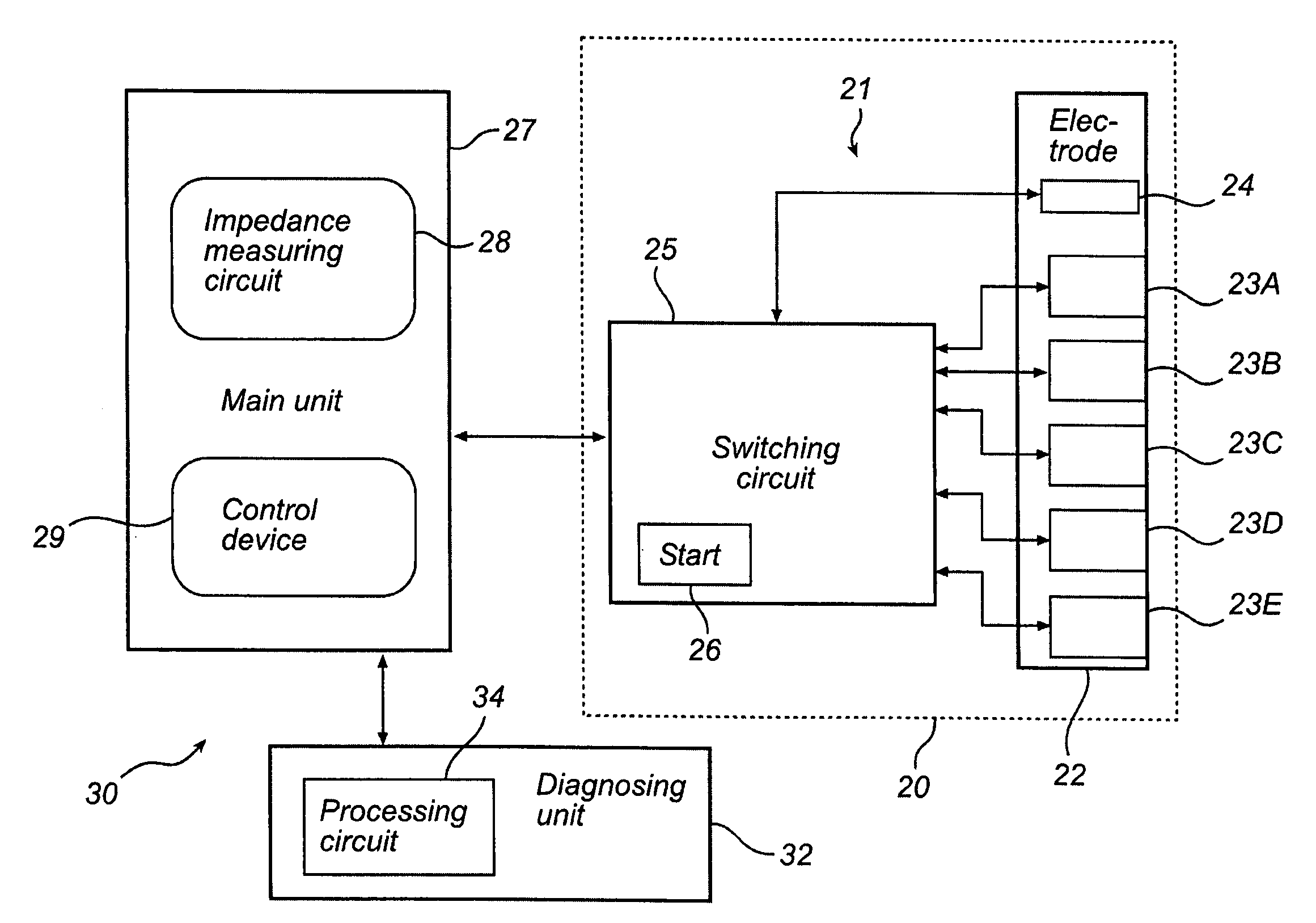
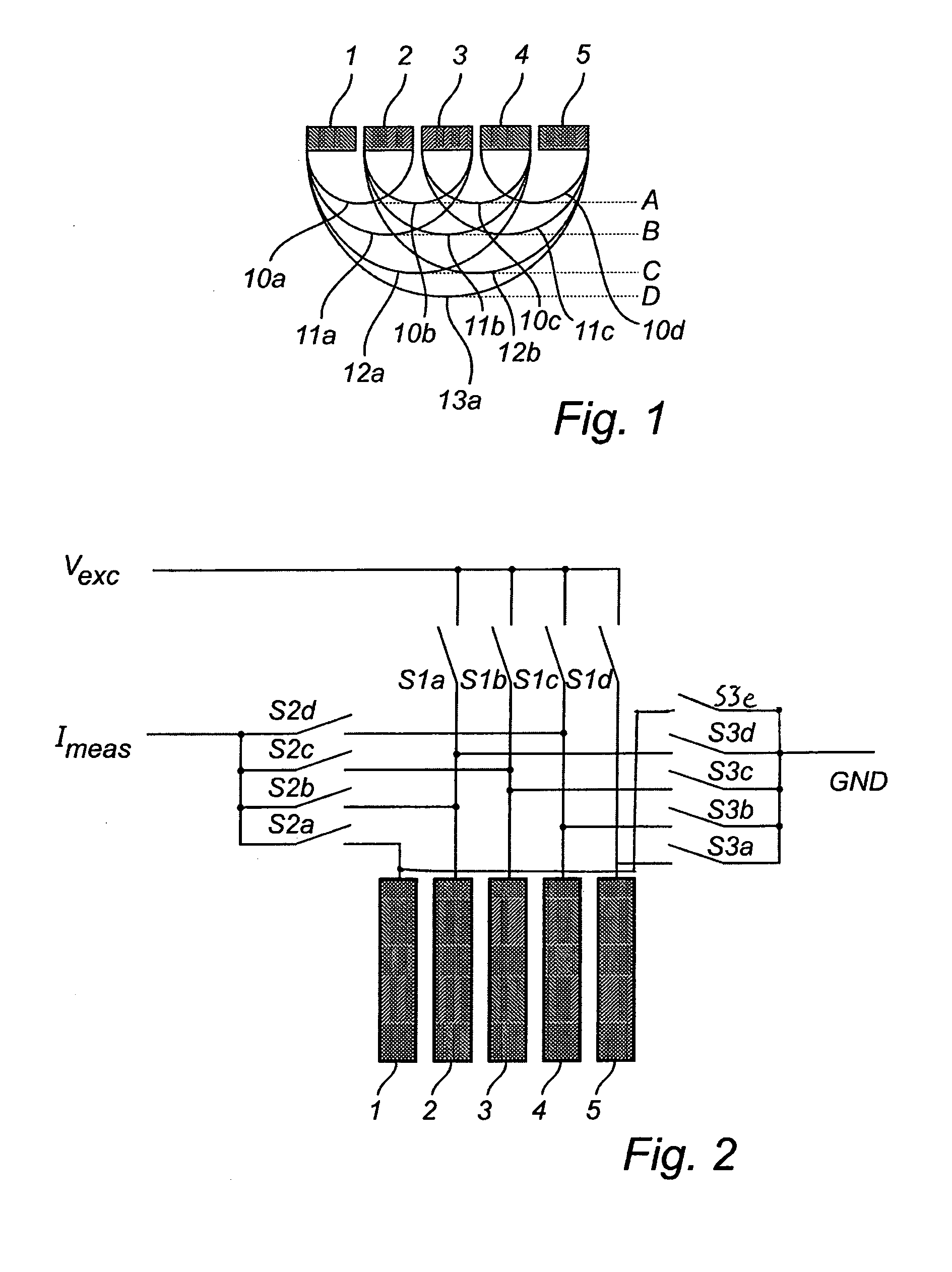
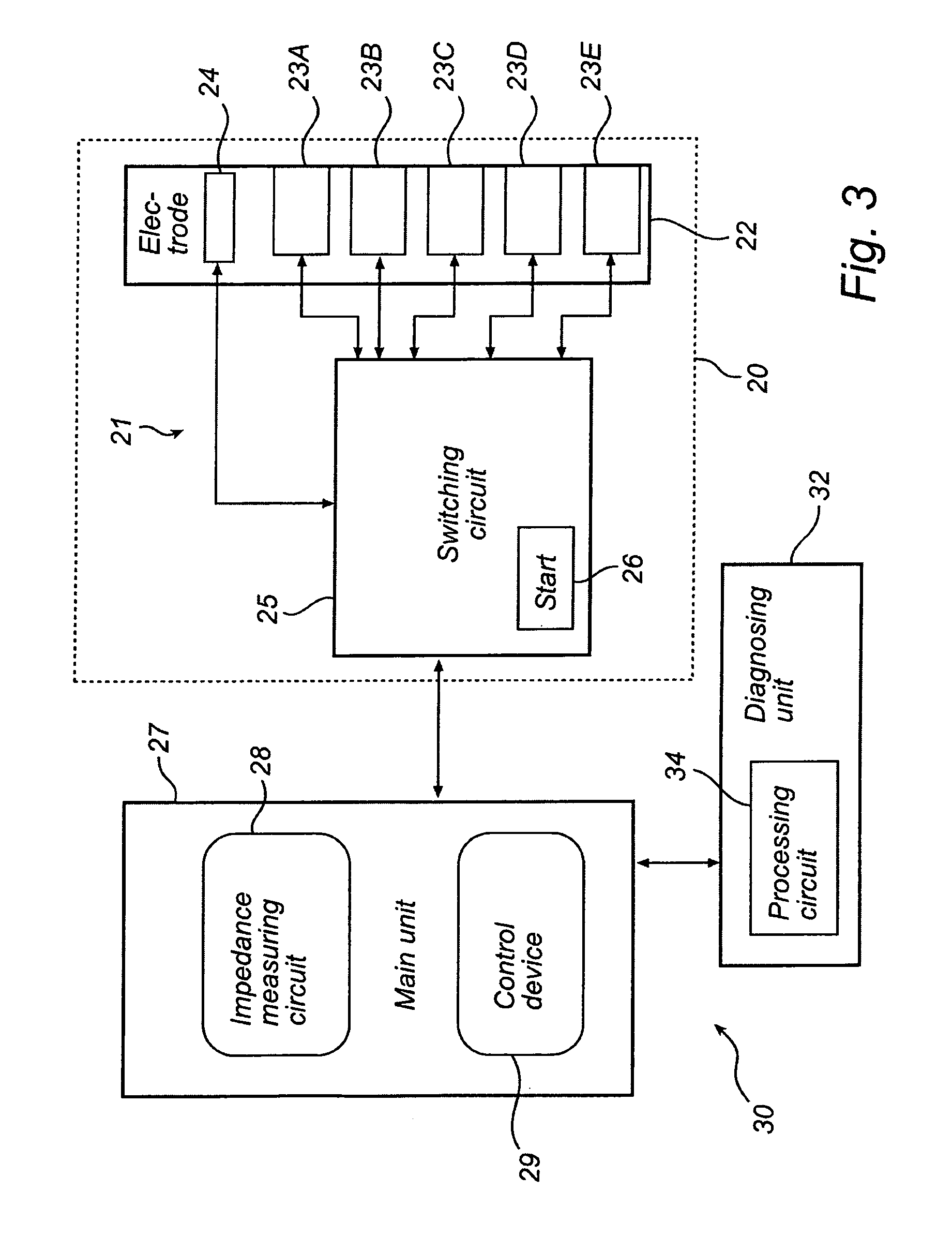
ActiveUS20110282180A1High degree of accuracyImprove reliabilityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostic recording/measuringMelanomaImage resolution
The present invention provides impedance data having an improved spatial resolution, both with regard to depth and lateral extension, which enables a detection of diseased skin conditions, such a malignant melanoma, at an early stage. Specifically, the present invention is implemented in a probe, medical devices and medical systems including such a probe, and methods using such a probe for measuring electrical impedance of tissue of a subject. A switching circuit is arranged for selectively activate electrode pairs of the probe in accordance with a predetermined activation scheme, the predetermined activation scheme including to activate adjacent electrodes in a successive manner, to gradually scan tissue of the subject at a first tissue depth so as to obtain a sequence of impedance signals from the tissue depth.
Owner:SCIBASE
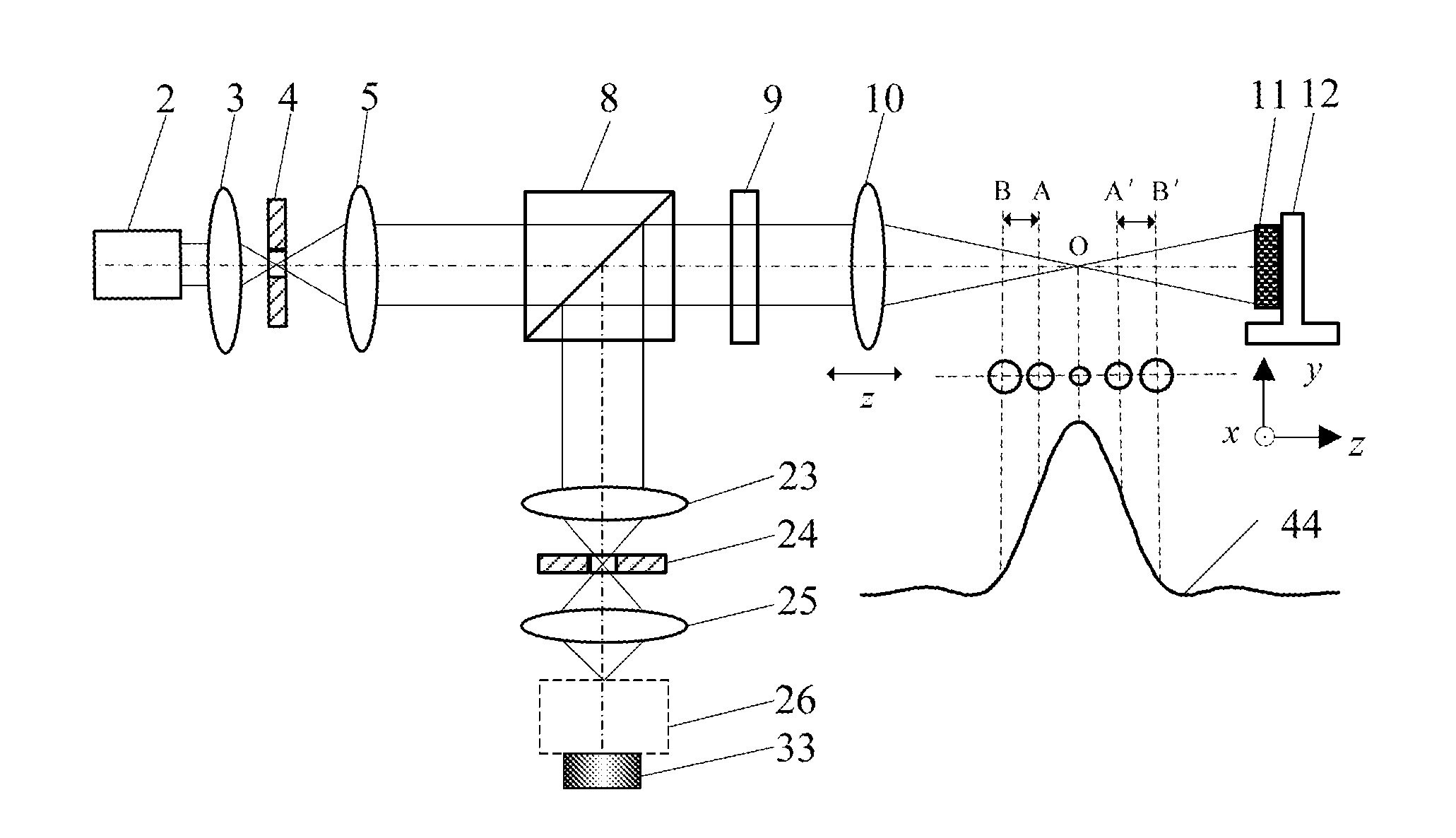
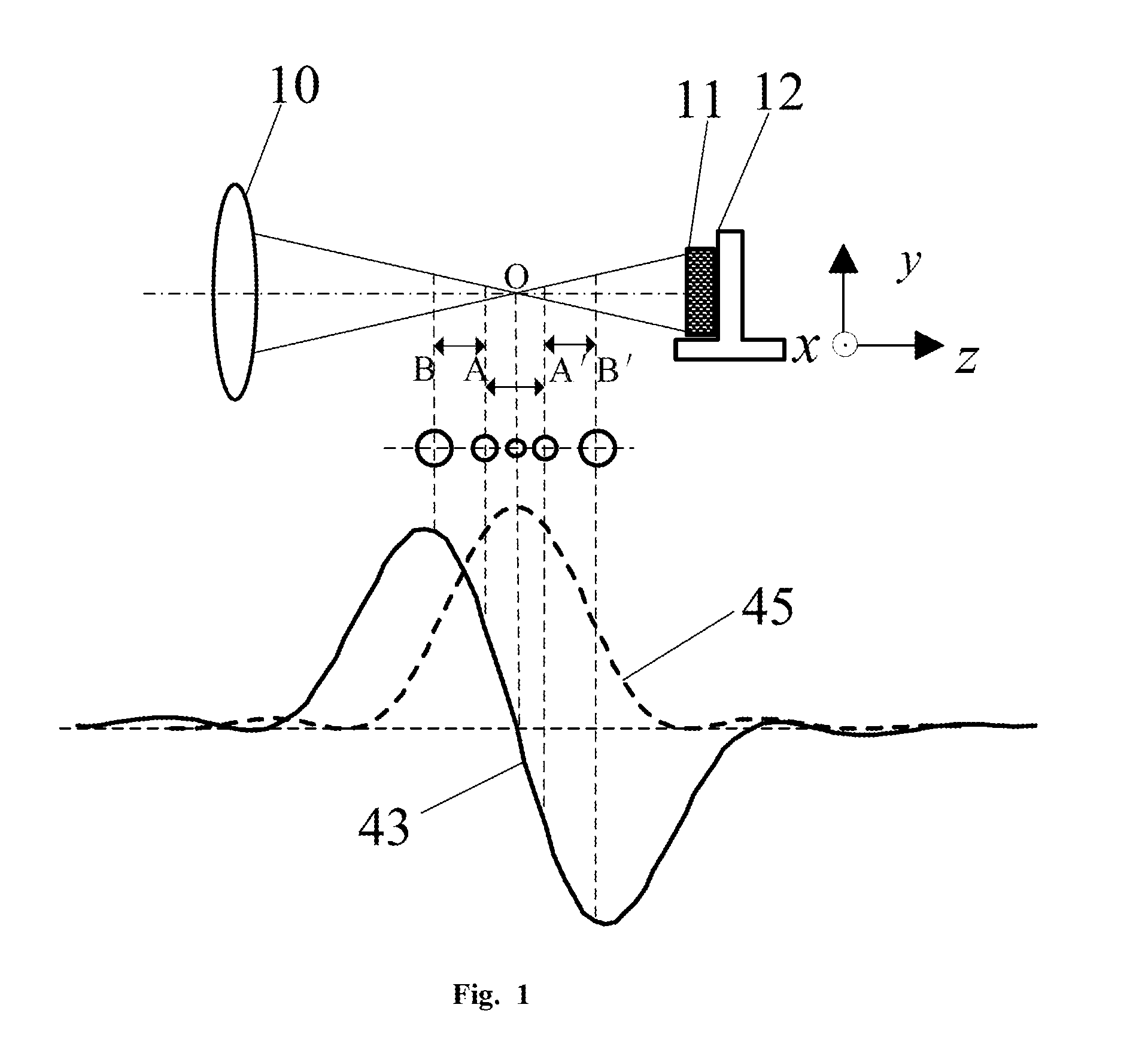
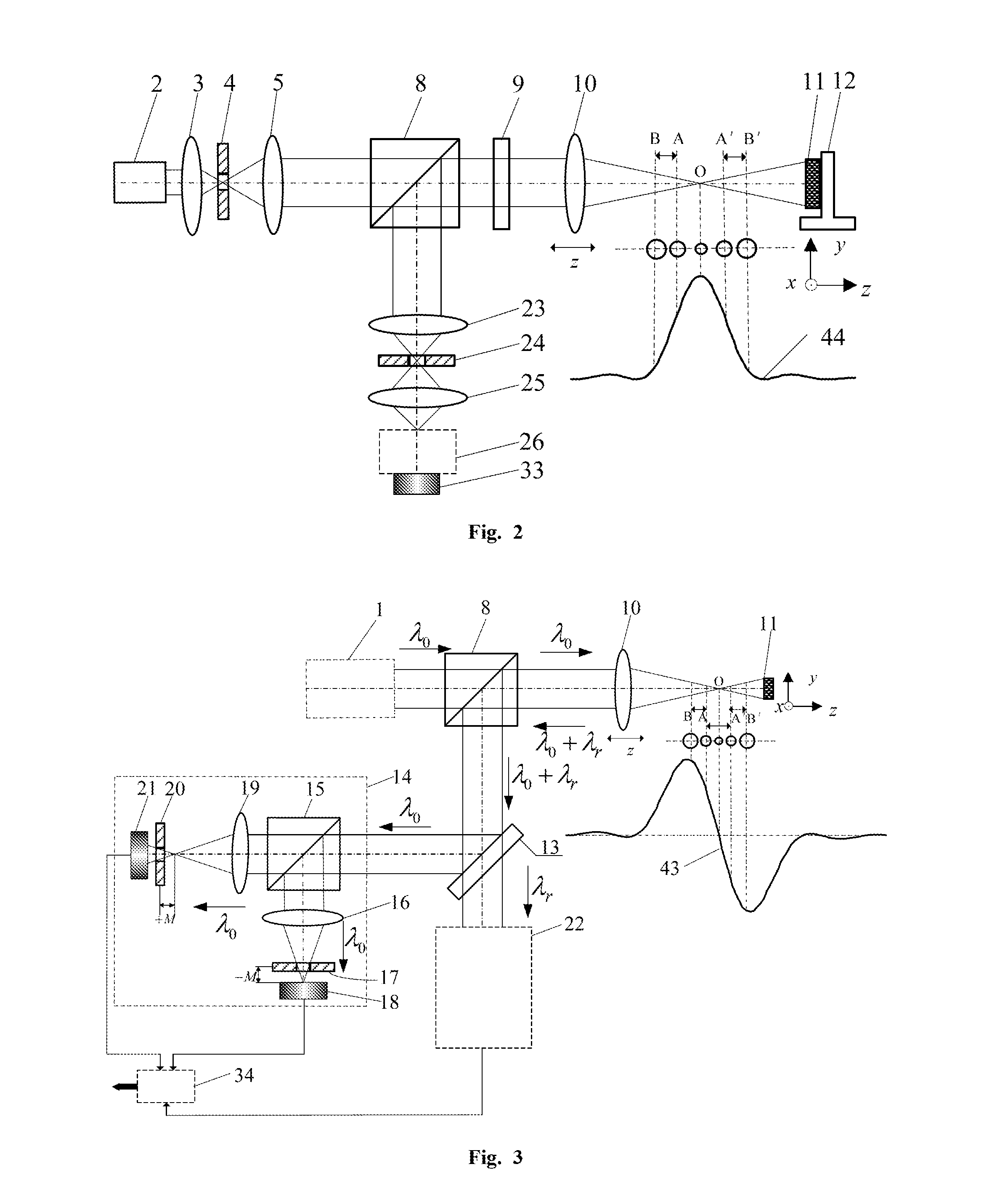
Laser Differential Confocal Mapping-Spectrum Microscopic Imaging Method and Device
ActiveUS20150346101A1Improve spatial resolutionSize of the detection area of the sample to be controllableRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splittingImage resolution
The present invention belongs to a technical field of optical microscopic imaging and spectral measurement, and discloses a laser differential confocal mapping-spectrum microscopic imaging method and device. The core concept of the present invention is to combine the differential confocal detection and the spectrum detection techniques and use a dichroic beam splitting system (13) to separate the Rayleigh light for geometric position detection from the Raman scattering light for spectrum detection, by mean of the property that the zero-cross point of the differential confocal curve (43) accurately corresponds to the focus of the objective, the spectral information at focus of the excitation spot being accurately captured by the zero trigger to accomplish the spectrum detection with high spatial resolution. Therefore, the present invention provides a method and device that may be able to accomplish the spectrum detection with high spatial resolution to a micro-area of a sample.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
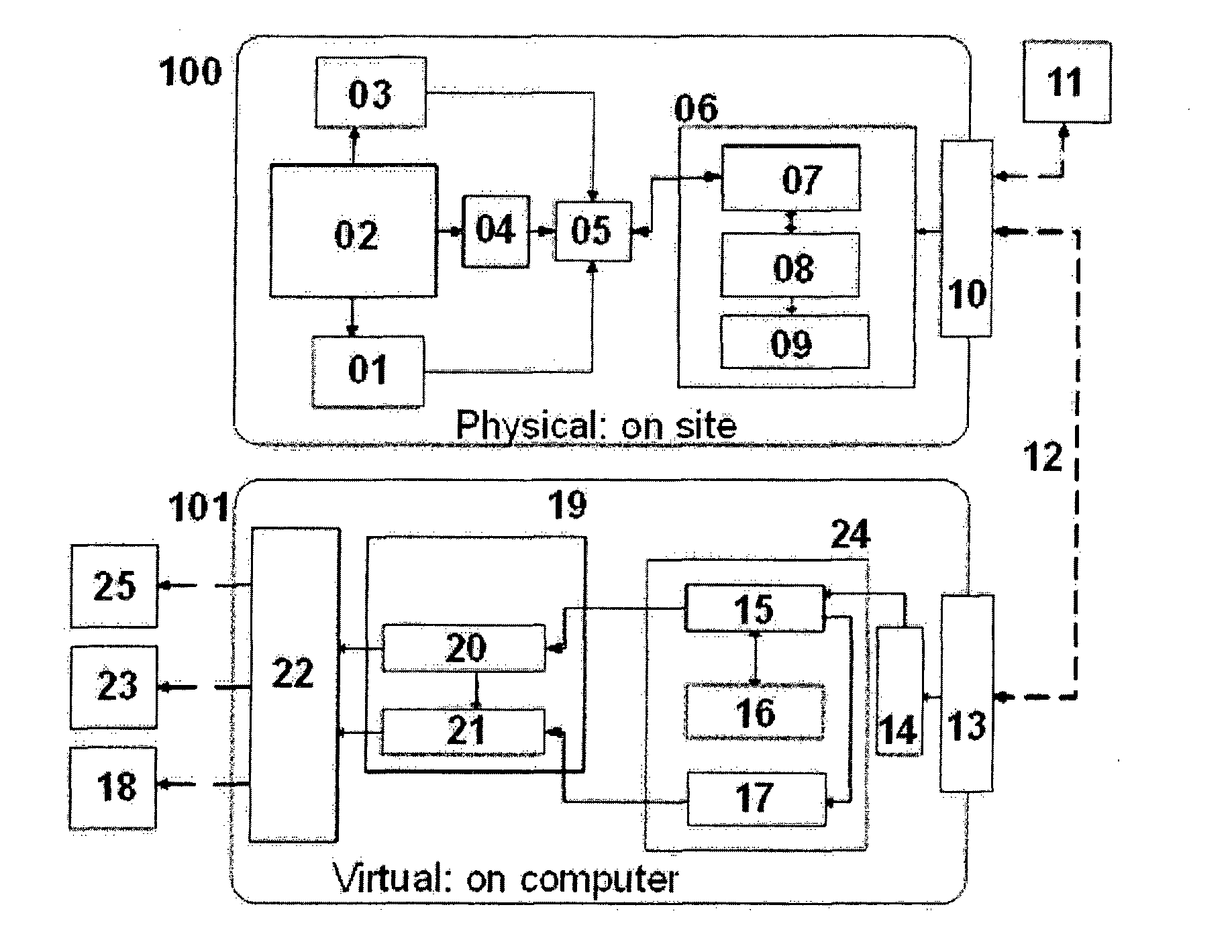
Structural health management system and method based on combined physical and simulated data
InactiveUS20140058709A1Storage and low levelHigh spatial resolutionTesting/monitoring control systemsComputation using non-denominational number representationDecision-makingSimulated data
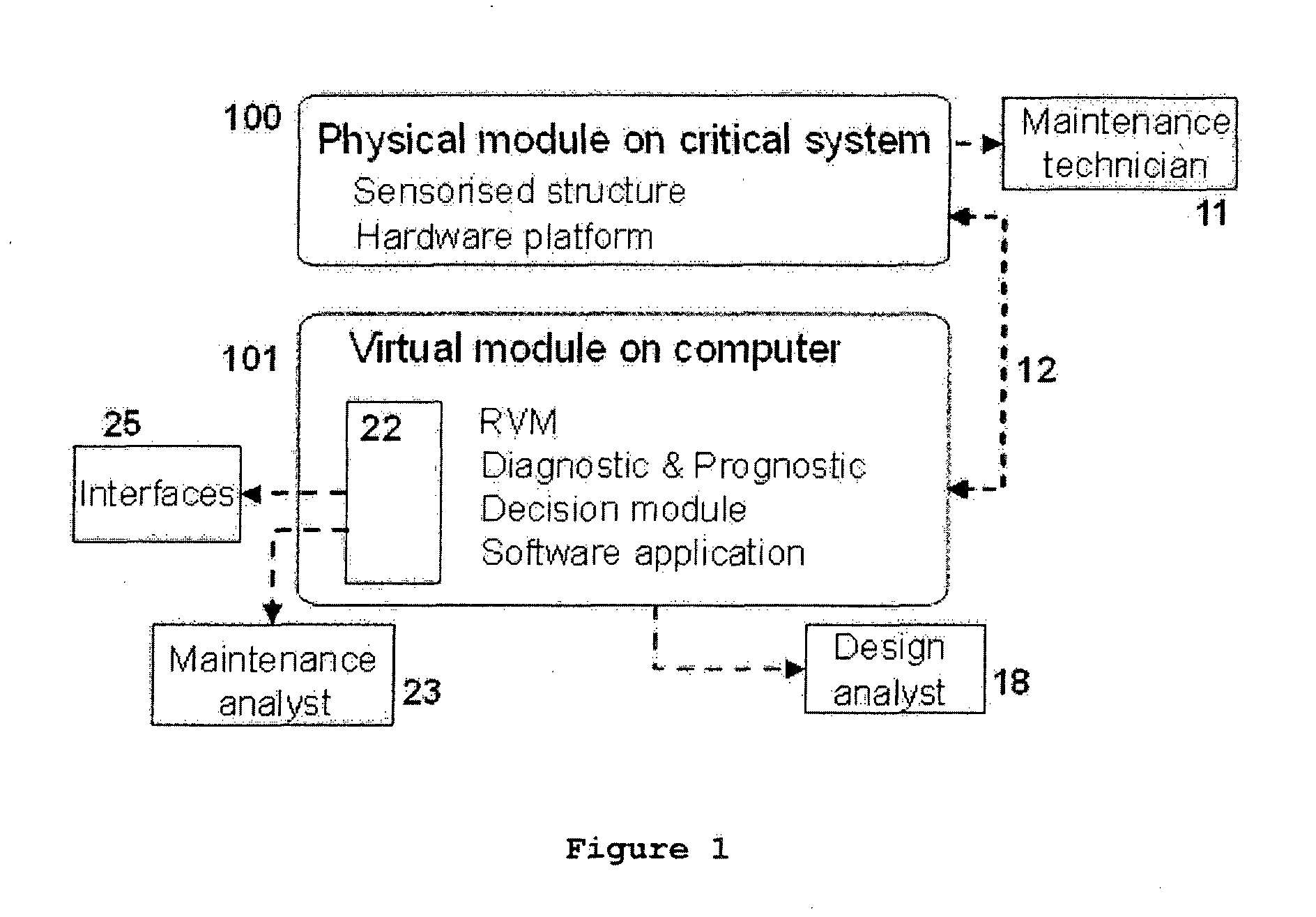
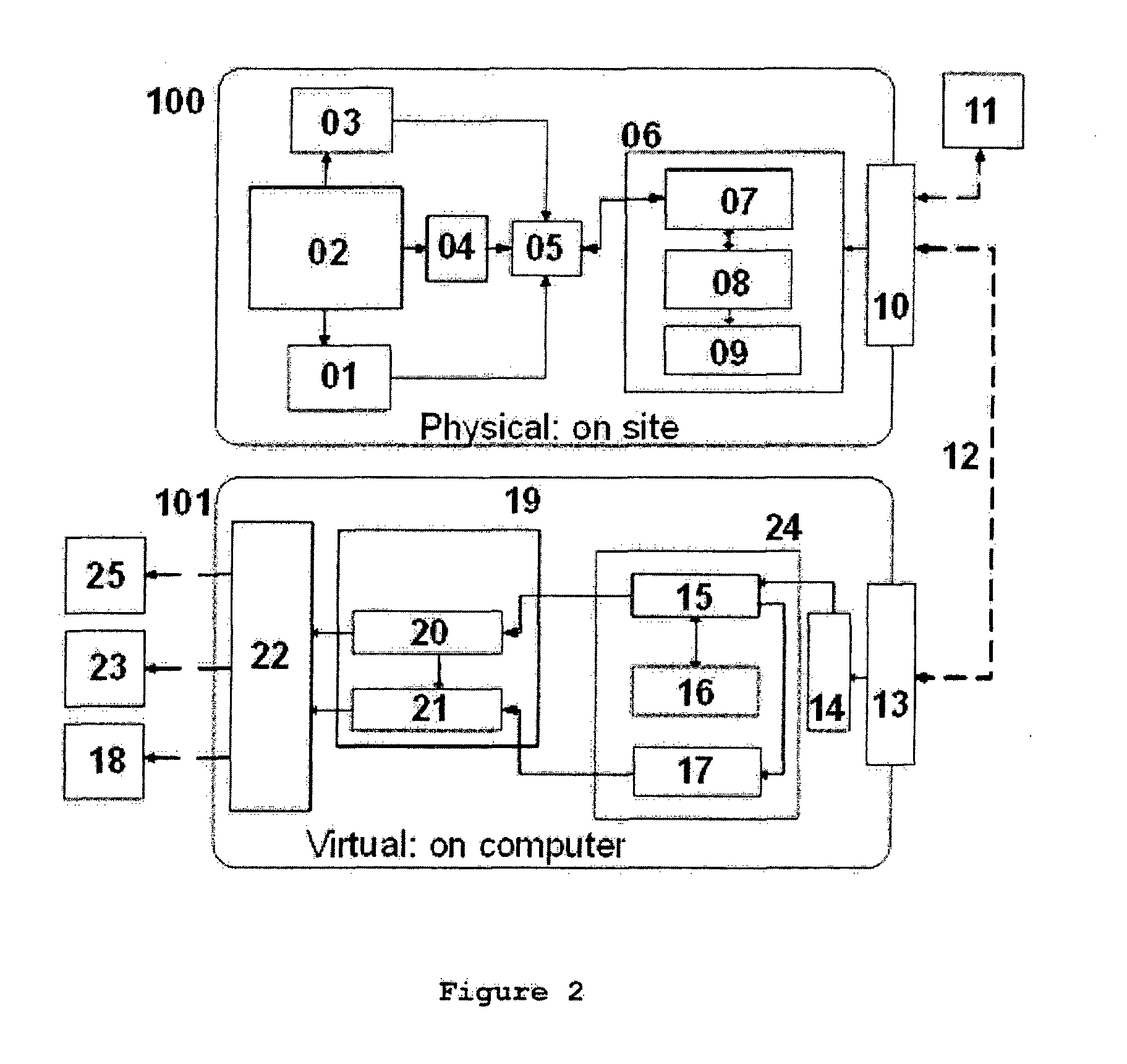
System and method to manage the structural integrity of critical systems for decision-making support actions based upon their condition, in a structural health management system, analysing information from physical sensors through a computational model (101) of the system. The invention comprises an optimal sensor placement method, a data acquisition system with multi-sensor capability mounted / embedded in the critical system (100), a sampling algorithm for balanced compacted information flow from sensor to storage, a data exchange channel (12) linking the physical module (100) with the virtual one (101), a simulated model of the components / structures combined with the adequate solver for the actual physics involved on the problem and an optimization tool, a database to store data and manage results, a decision module for diagnostics and prognostics of the component / structure integrity status, and a data treatment and visualisation tools (22). These modules support decision-making actions (11, 23, 25) and new components / structures design (18).
Owner:CRITICAL MATERIALS LDA
Magneto-Optical Sensor
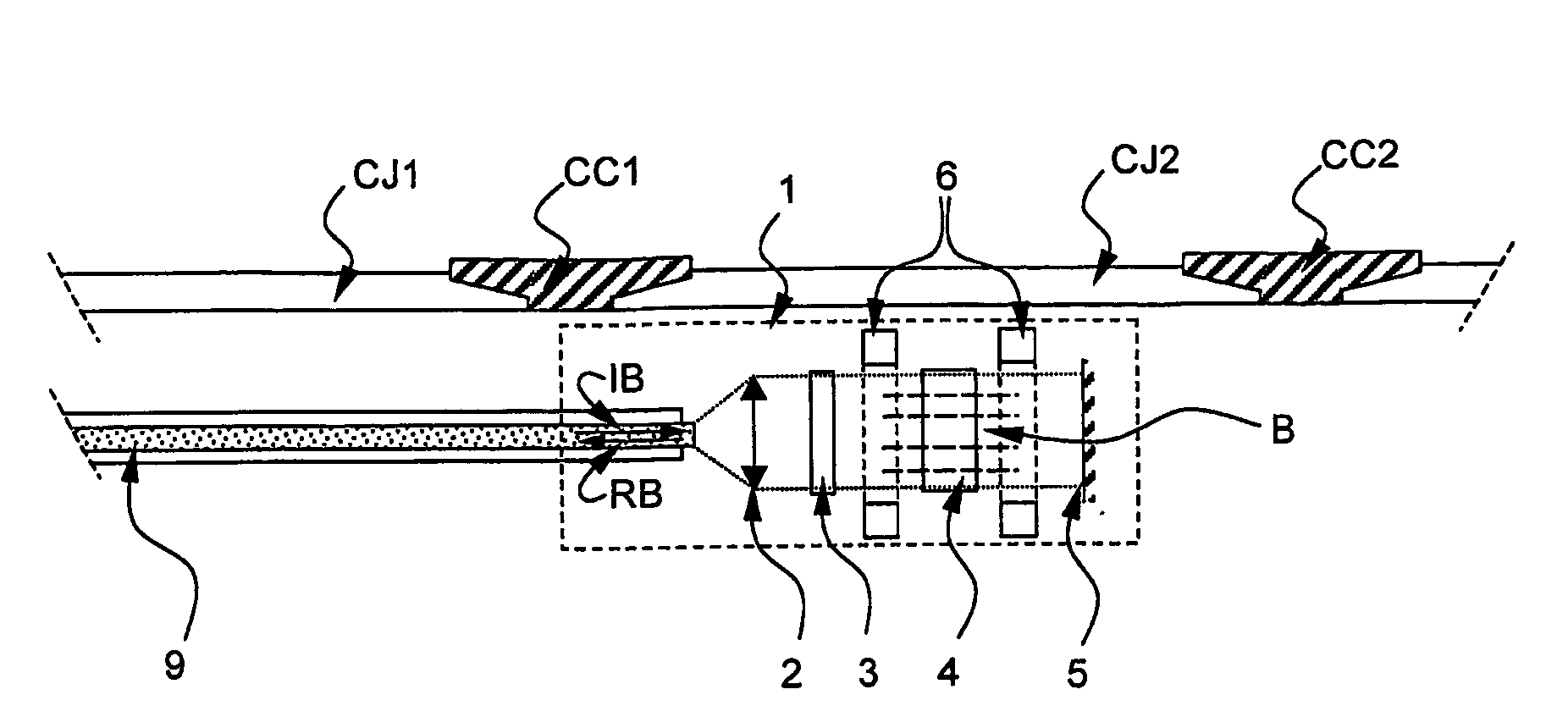
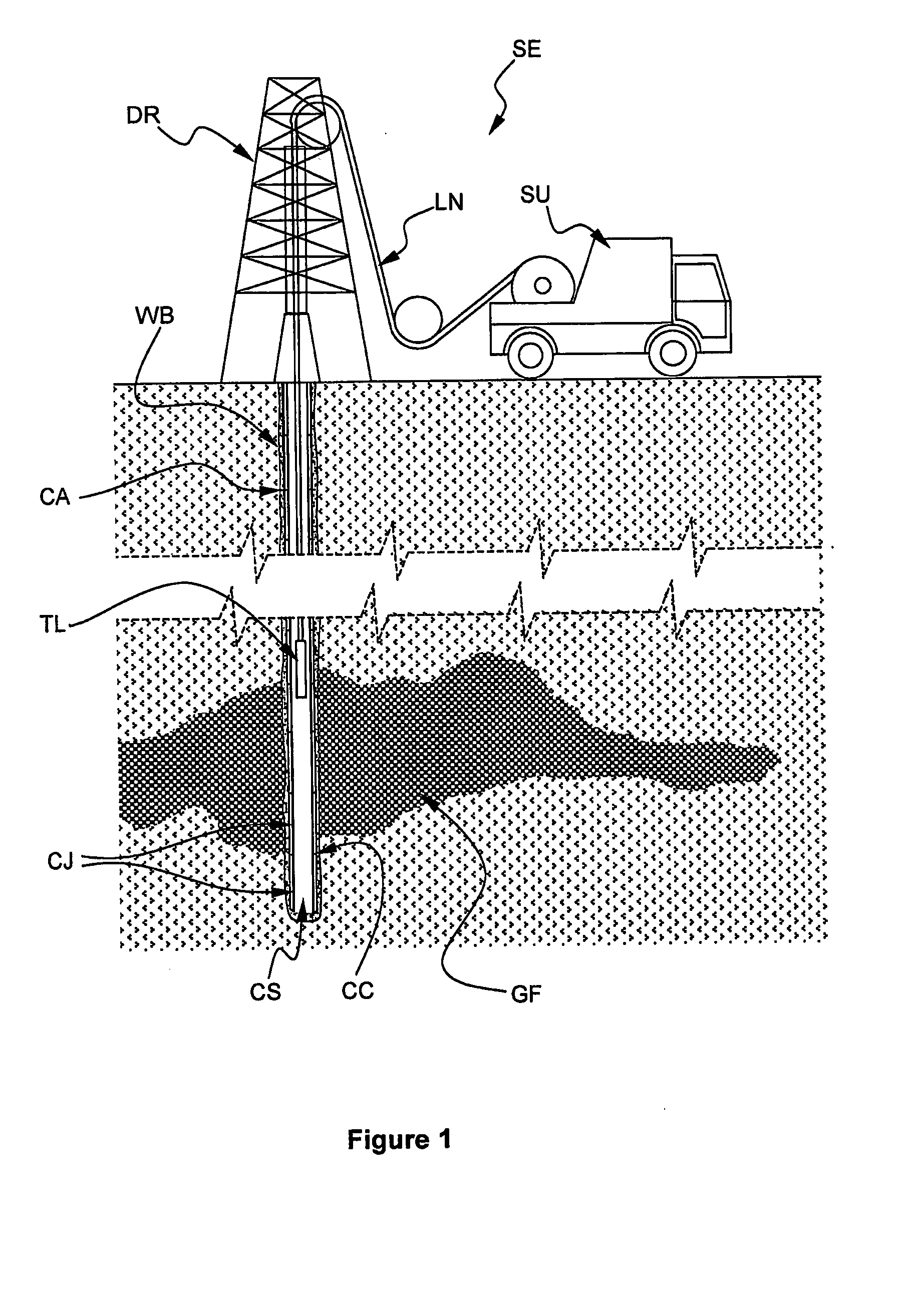
InactiveUS20090250213A1High spatial resolutionImprove measurement sensitivitySurveyConstructionsMagnetoMagneto optical
A magneto-optic sensor for oilfield application, the sensor (1, 1′, 101, 101′) receives an incident beam IB, IBA, IBB, IBC, IBD and comprises a polarizing element (3, 103) for providing a determined state of polarization beam and a Faraday rotator (4, 104) for providing a response beam having a modified state of polarization. The sensor provides a response beam (RB, RBA, RBB, RBC, RBD having an intensity dependent on an external magnetic field representative of a particular characteristic of a well-bore casing CC, CR applied on the Faraday rotator (4, 104).
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Optimized high-speed magnetic resonance imaging method and system using hyperpolarized noble gases
ActiveUS20040260173A1Easily tradedImprove spatial resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTemporal resolutionNoble gas
A system and method for using hyperpolarized noble gases together with an appropriately designed and optimized magnetic resonance imaging pulse sequence to rapidly acquire static or dynamic magnetic resonance images. The strong magnetic resonance signal from hyperpolarized gases, combined with the present magnetic resonance imaging technique, presents the opportunity for the imaging of gases with both high spatial and high temporal resolution. One potential application for such a method is the direct, dynamic visualization of gas flow, which would be extremely useful for characterizing a variety of fluid systems. In the medical field, one such system of substantial importance is the lung. The system and method provides for visualizing regional ventilatory patterns throughout the respiratory cycle with high temporal and high spatial resolution. The low sensitivity to susceptibility artifacts permits good image quality to be obtained in various orientations. Depending on the application, temporal resolution can be traded for anatomical coverage. Such application of dynamic imaging of the lung using hyperpolarized gases will provide unique information on the physiology and pathophysiology of the lung, and has the potential for many clinically-relevant applications.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
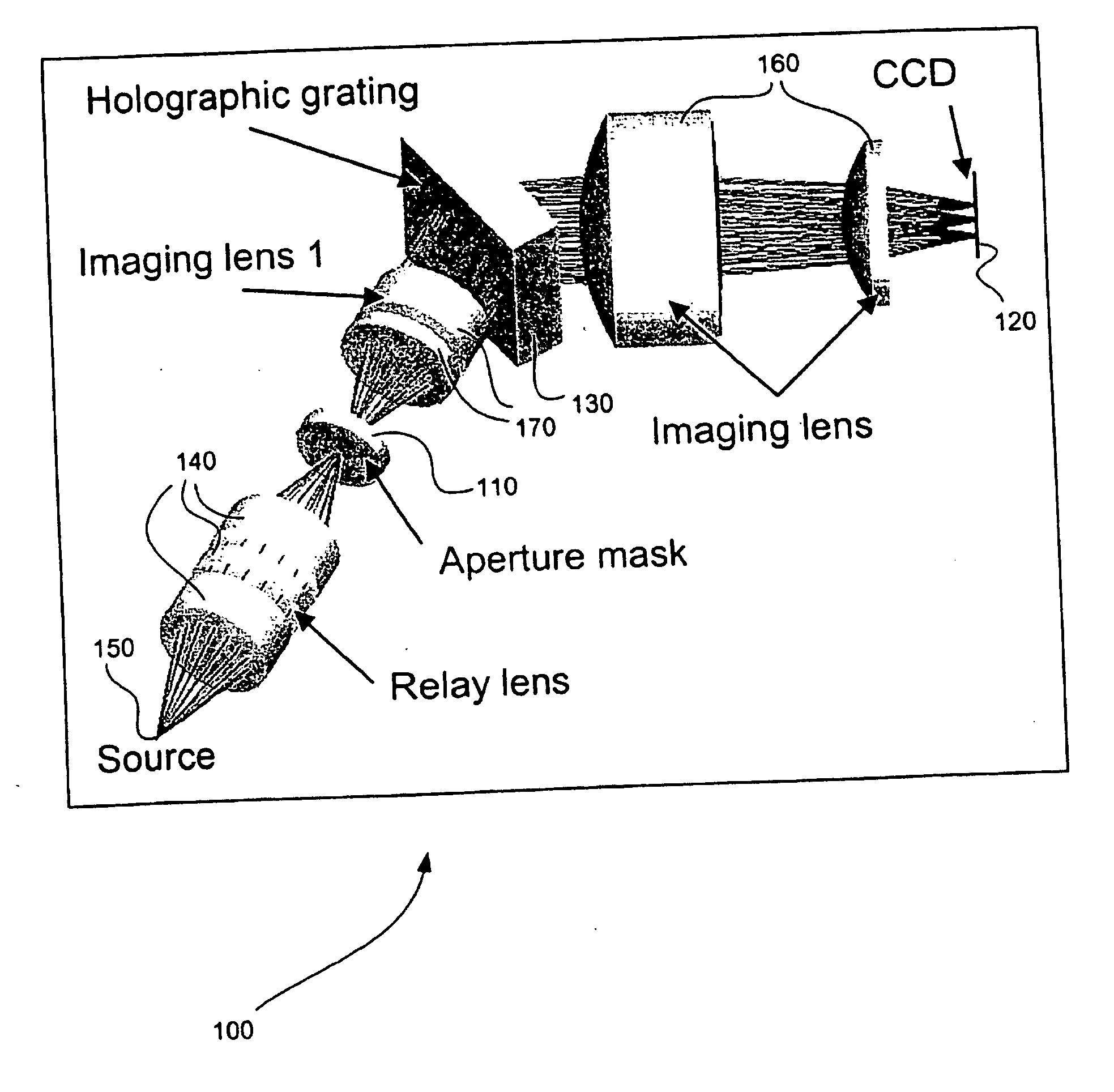
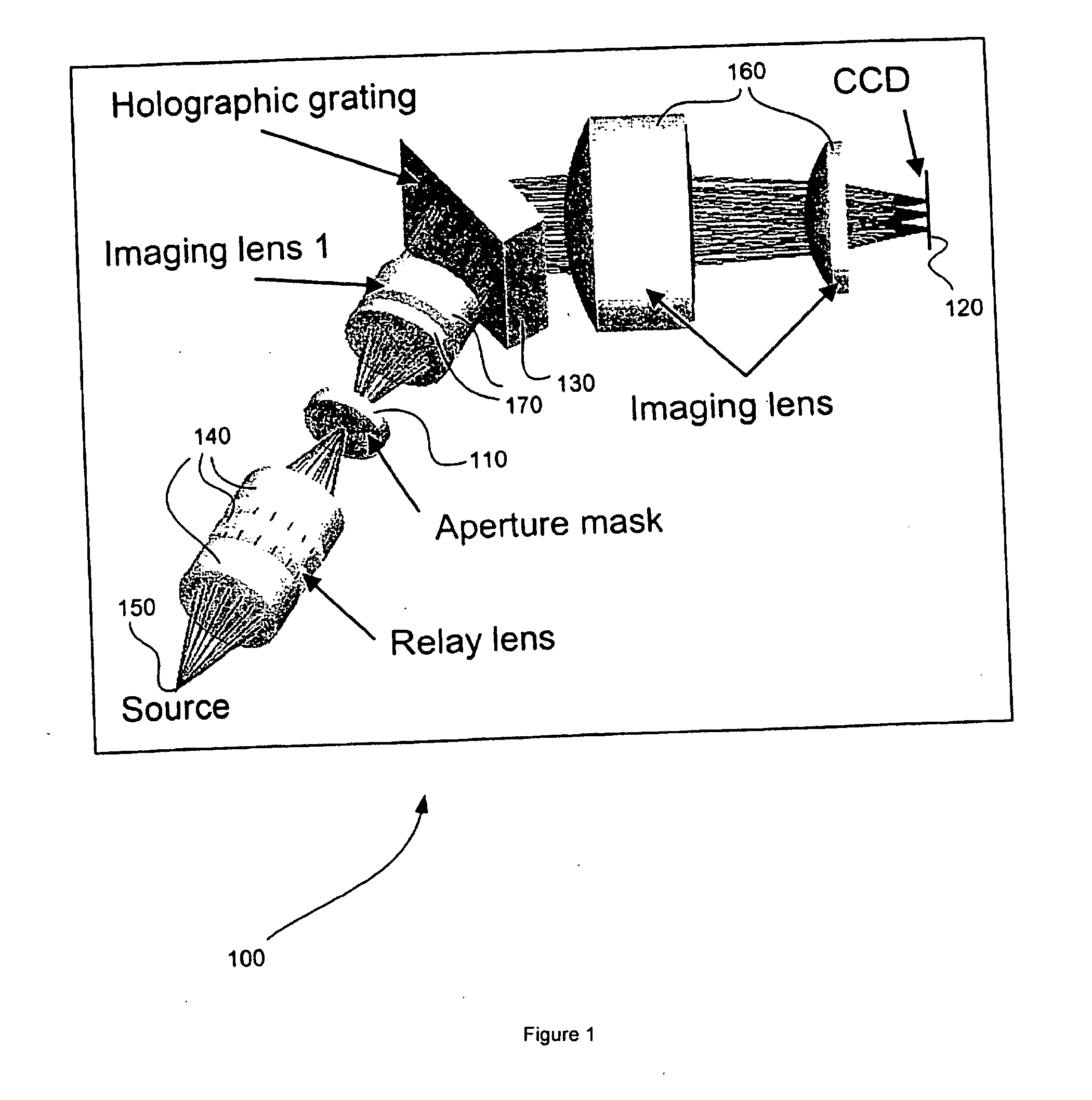
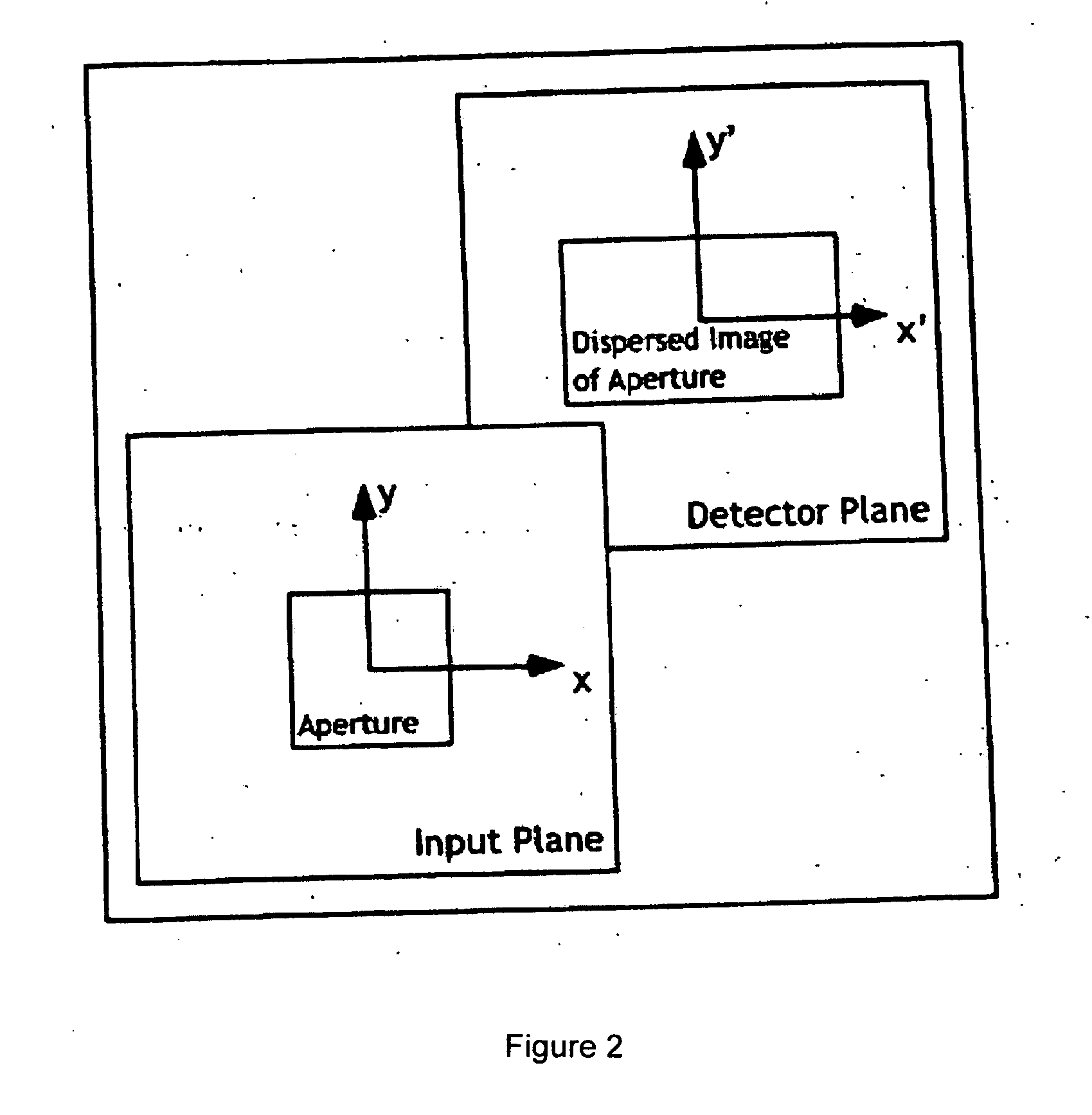
Static two-dimensional aperture coding for multimodal multiplex spectroscopy
ActiveUS20070081158A1High throughputHigh spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectroscopyImage resolution
A class of aperture coded spectrometer is optimized for the spectral characterization of diffuse sources. The instrument achieves high throughput and high spatial resolution by replacing the slit of conventional dispersive spectrometers with a spatial filter or mask. A number of masks can be used including Harmonic masks, Legendre masks, and Hadamard masks.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
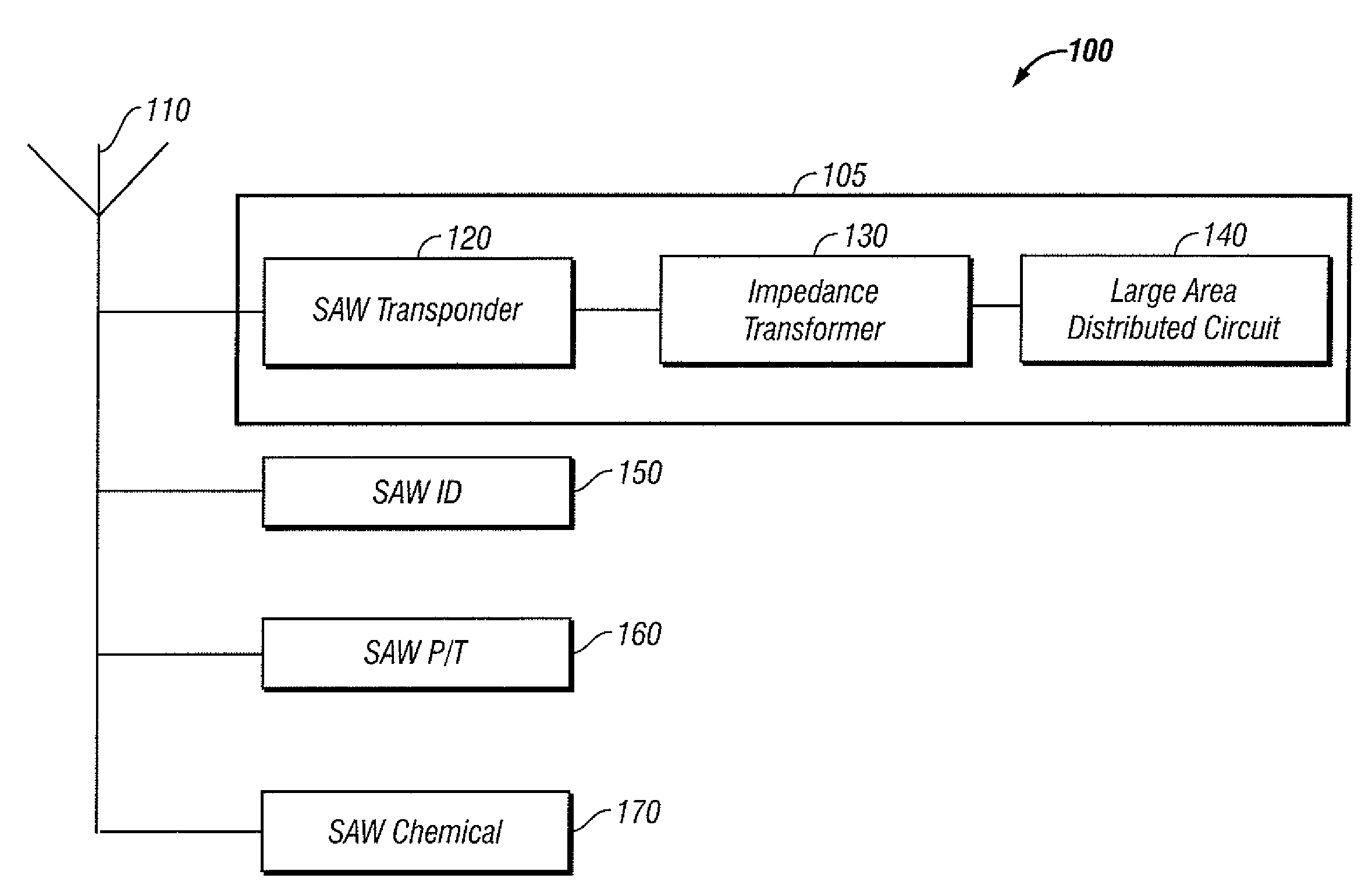
Intelligent packaging method and system based on acoustic wave devices
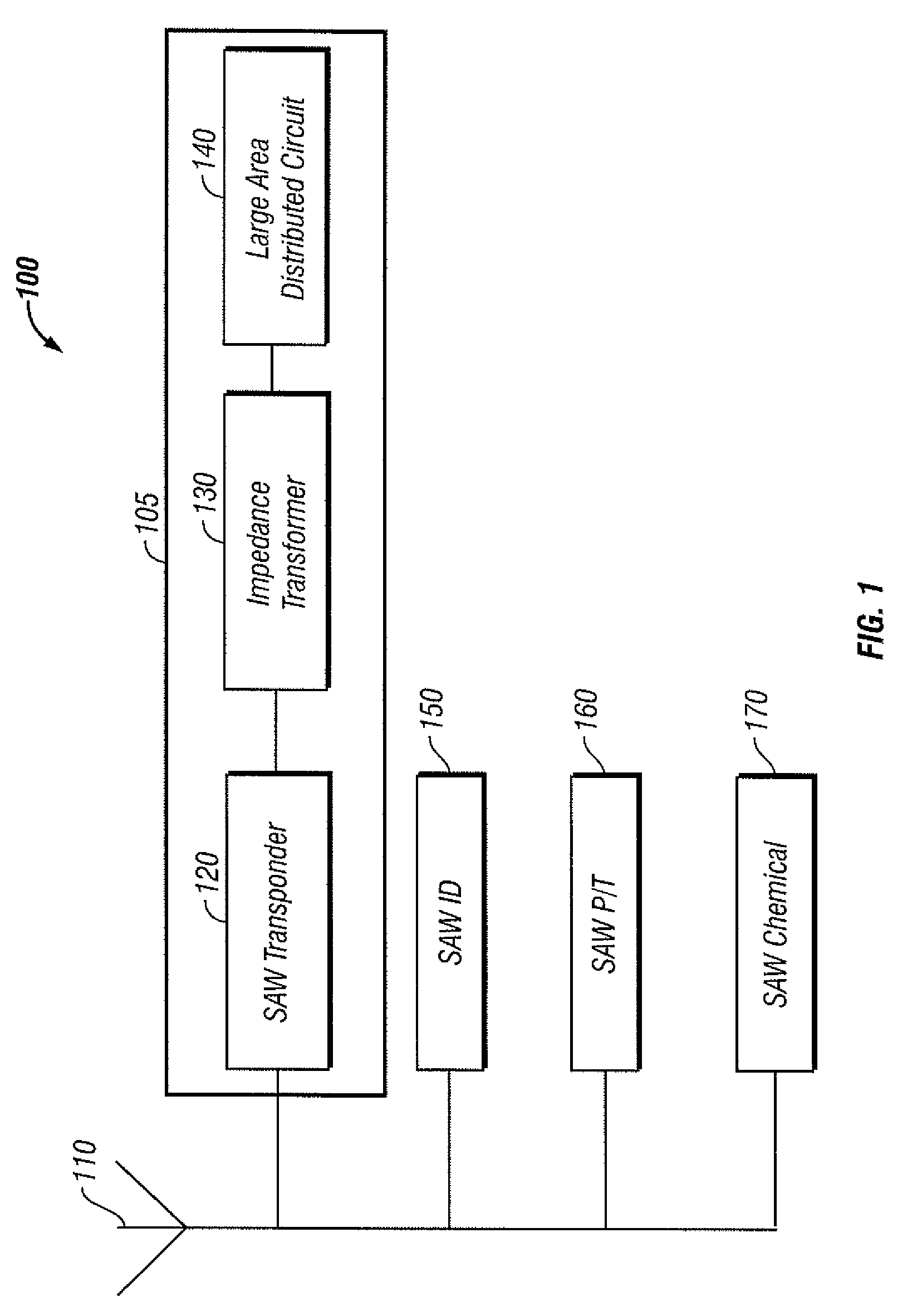
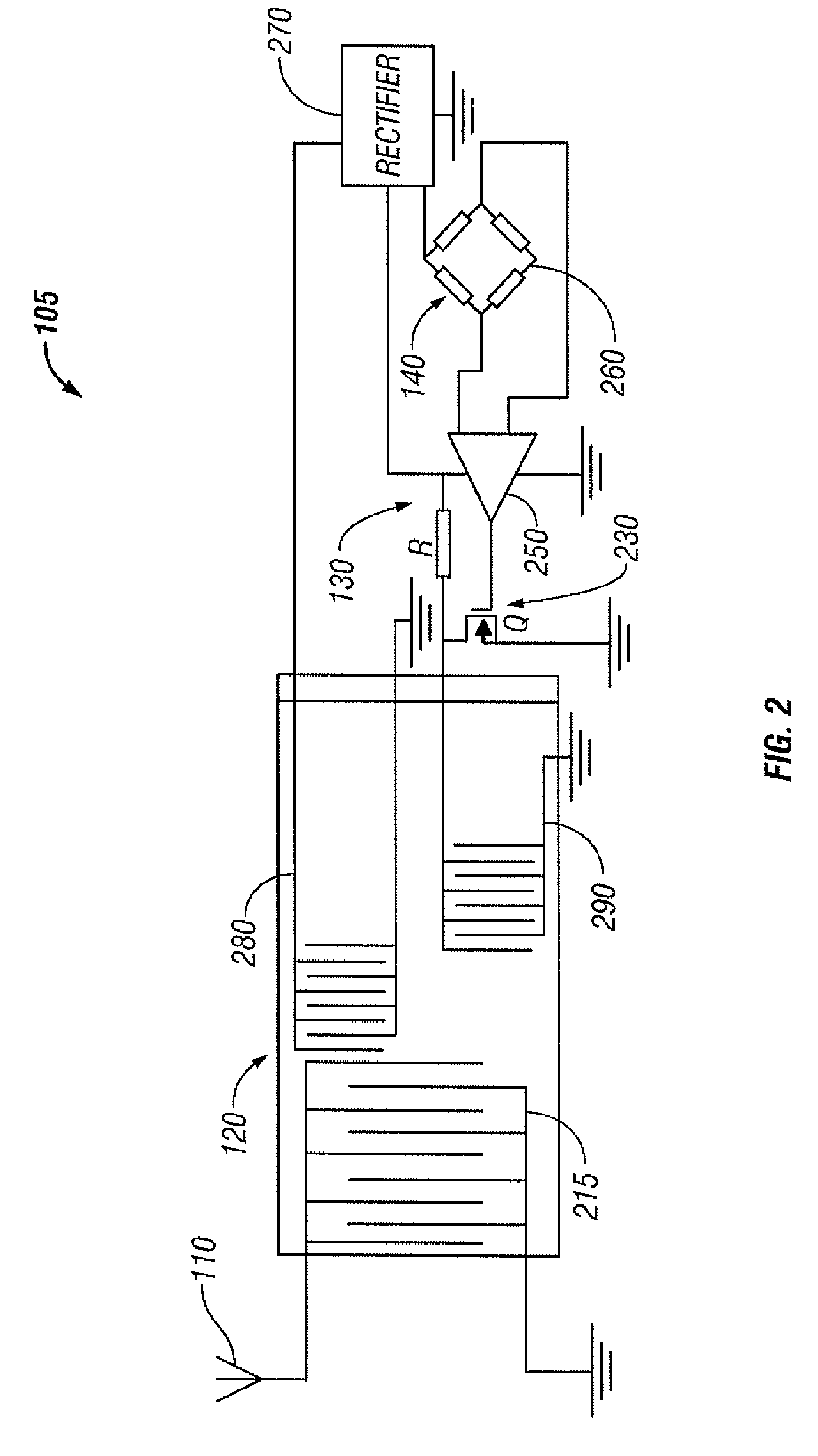
InactiveUS20090267761A1High spatial resolutionSimple methodContainer decorationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImpedance transformerRadio frequency
An intelligent packaging system utilizing acoustic wave devices includes an electronic module, a SAW ID, various passive SAW sensors and a printed antenna. The passive SAW sensors include a SAW pressure sensor, a SAW temperature sensor and one or more SAW chemical sensors for monitoring physical parameters of a package content. The electronic module generally includes a printed large area distributed electrical circuit, an impedance transformer and a SAW transponder for realizing passive wireless monitoring of the structural integrity of the package. A separate power harvesting antenna and / or a separate dual band antenna can generate radio frequency (RF) power for biasing components associated with the electronic module.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
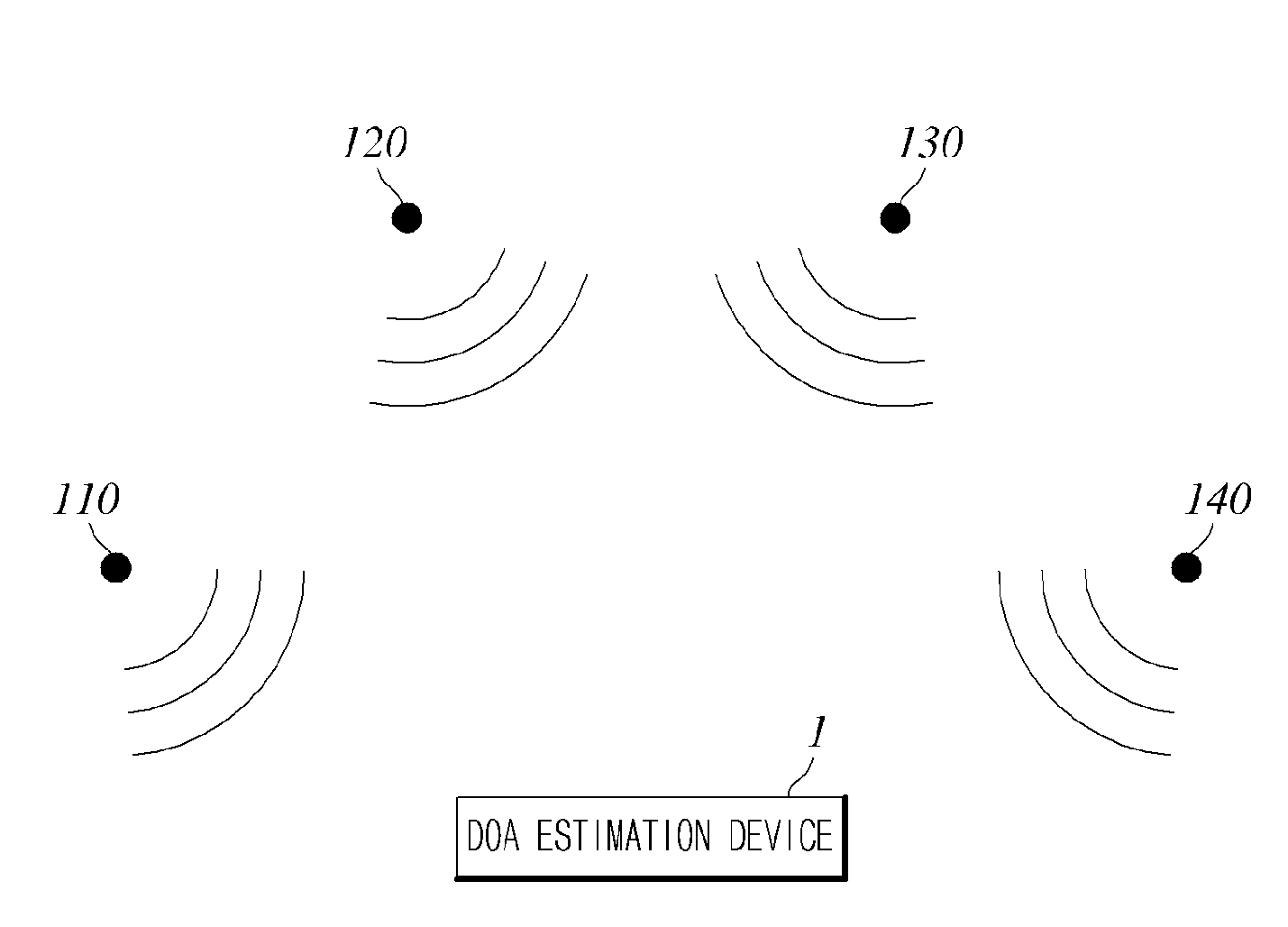
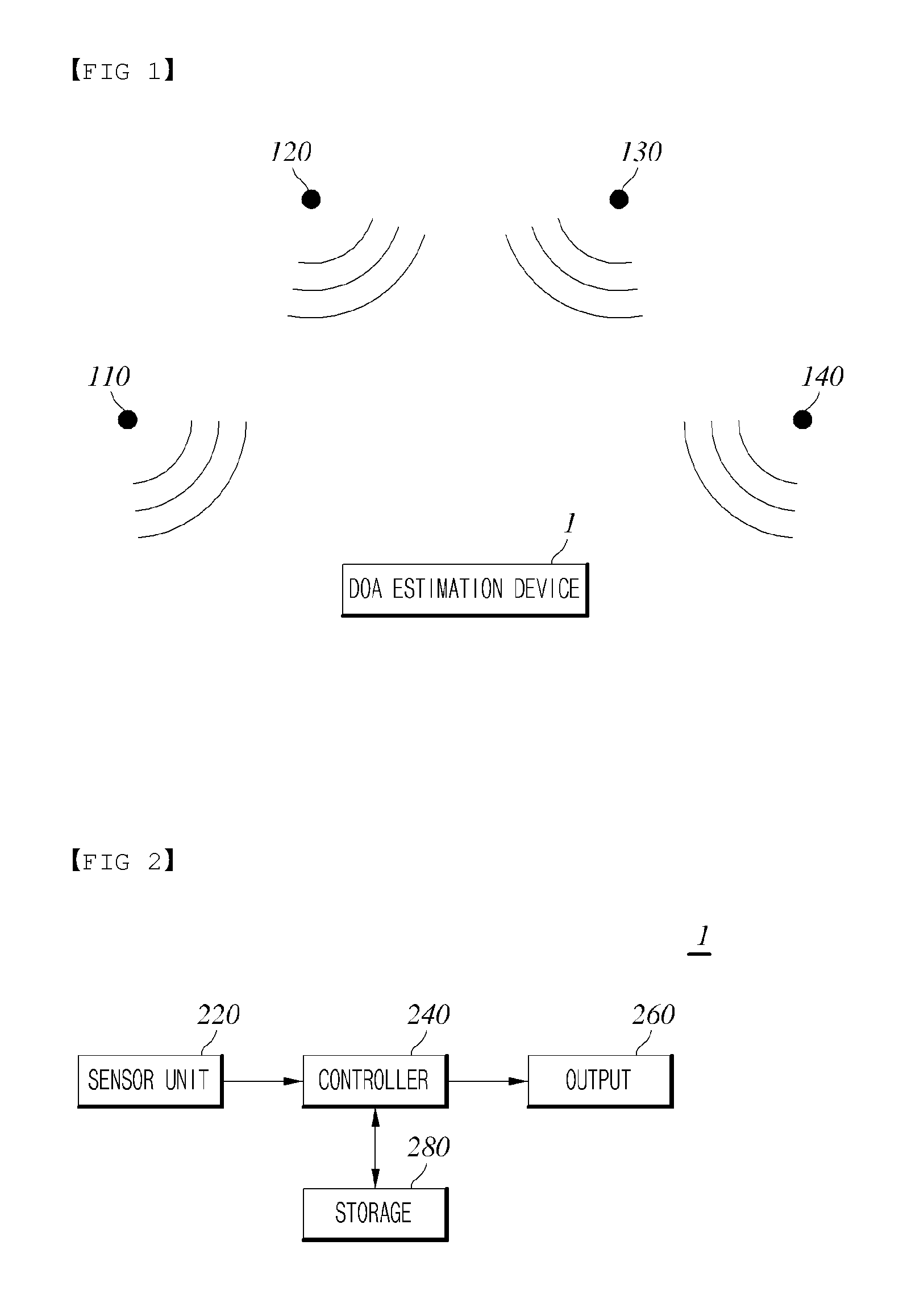
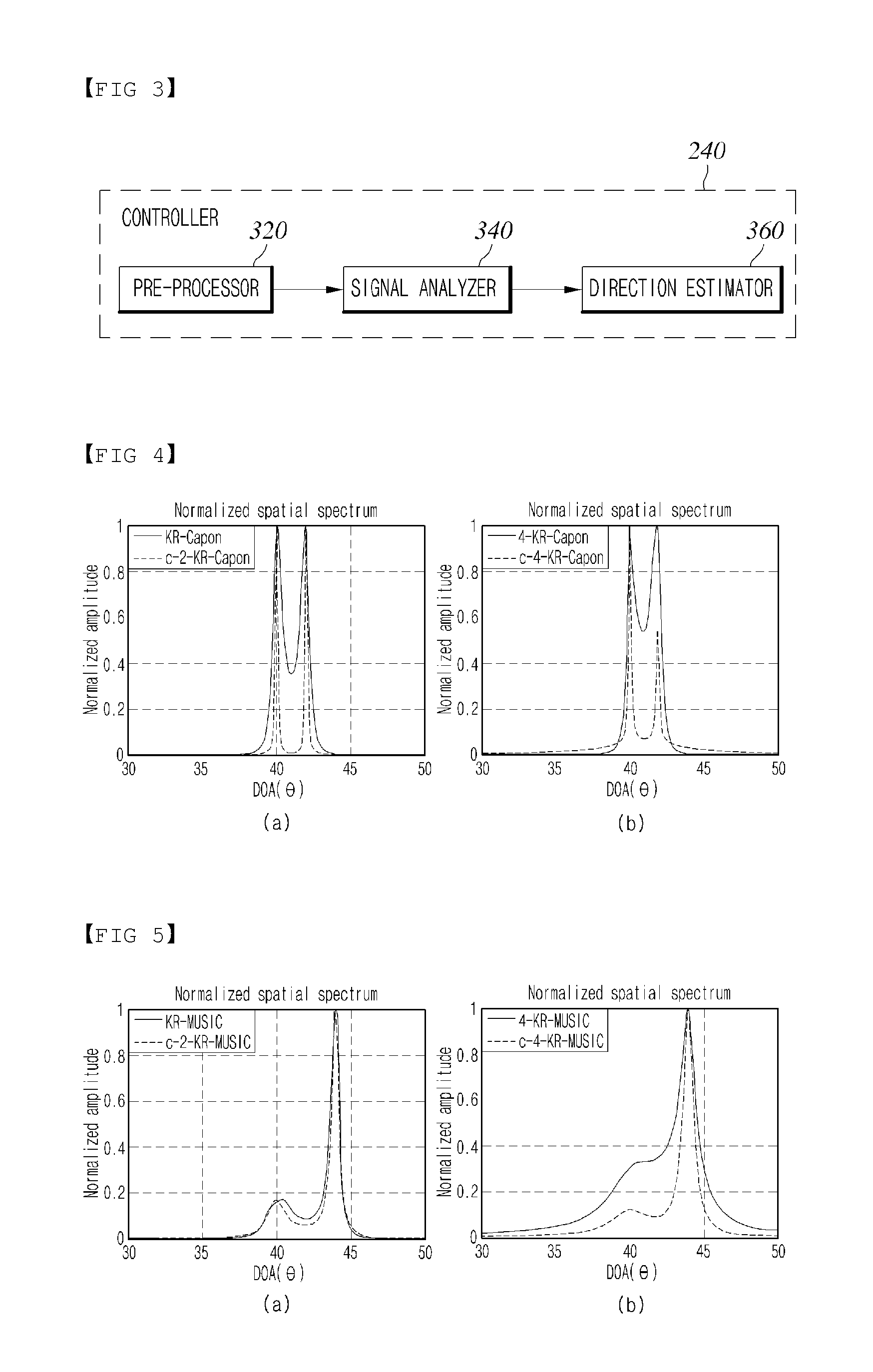
Direction of Arrival (DOA) Estimation Device and Method
InactiveUS20140334265A1High spatial resolutionHigh accuracyRadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsEngineeringDirection of arrival
A direction of arrival (DOA) estimation device and method are provided, in which the DOA estimation device includes a sensor unit configured to detect a signal and comprising two or more sensors to output sensor signals as a detect signal in response to the detected signal, and a controller configured to calculate statistical distribution data indicative of statistical distribution of each of the sensor signals outputted from the two or more sensors, respectively, retrieve statistical distribution data indicative of statistical distribution of source signal which is non-stationary signal entrained in the signal of the calculated statistical distribution data, and estimate DOA of the source signal based on the retrieved statistical distribution data.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
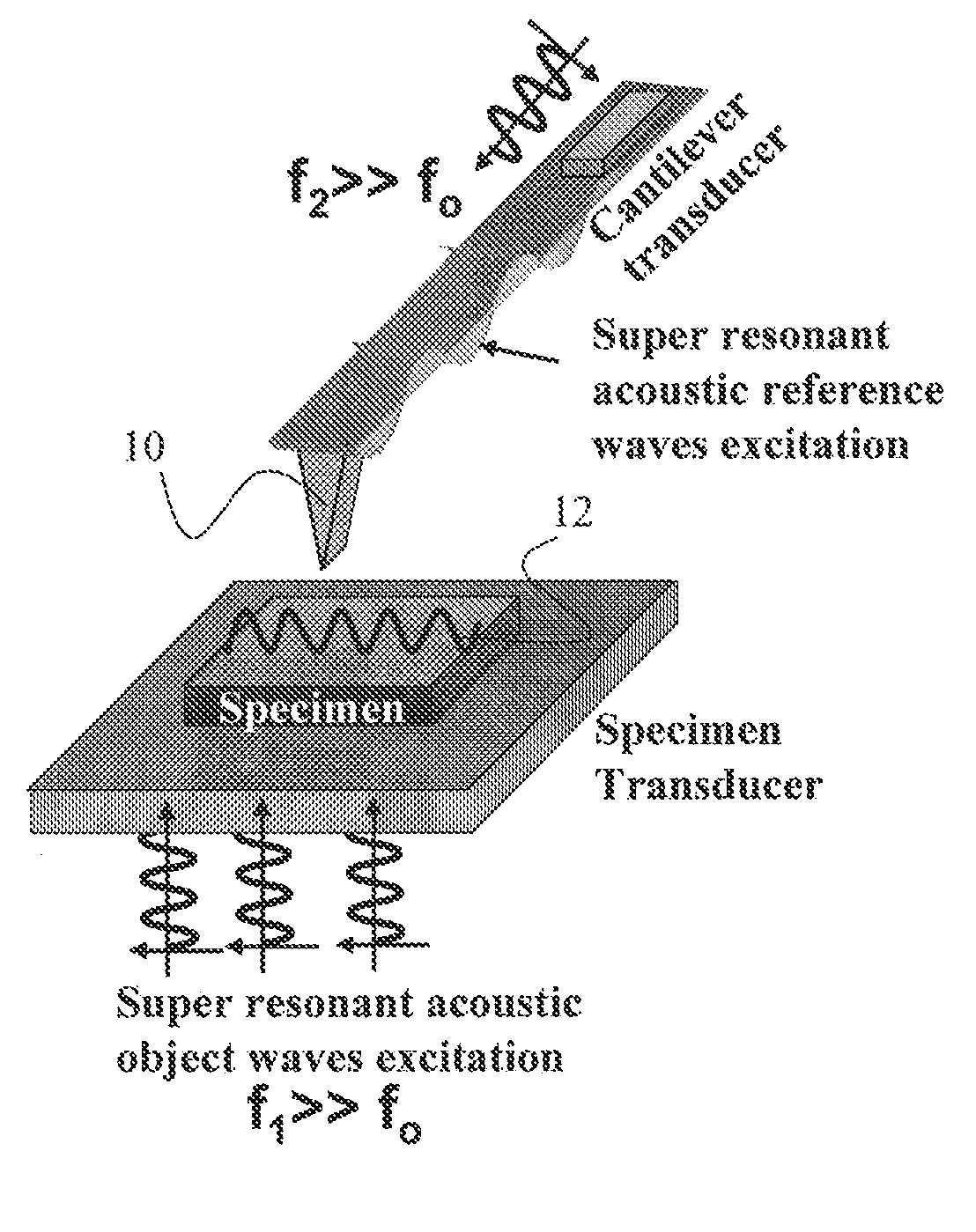
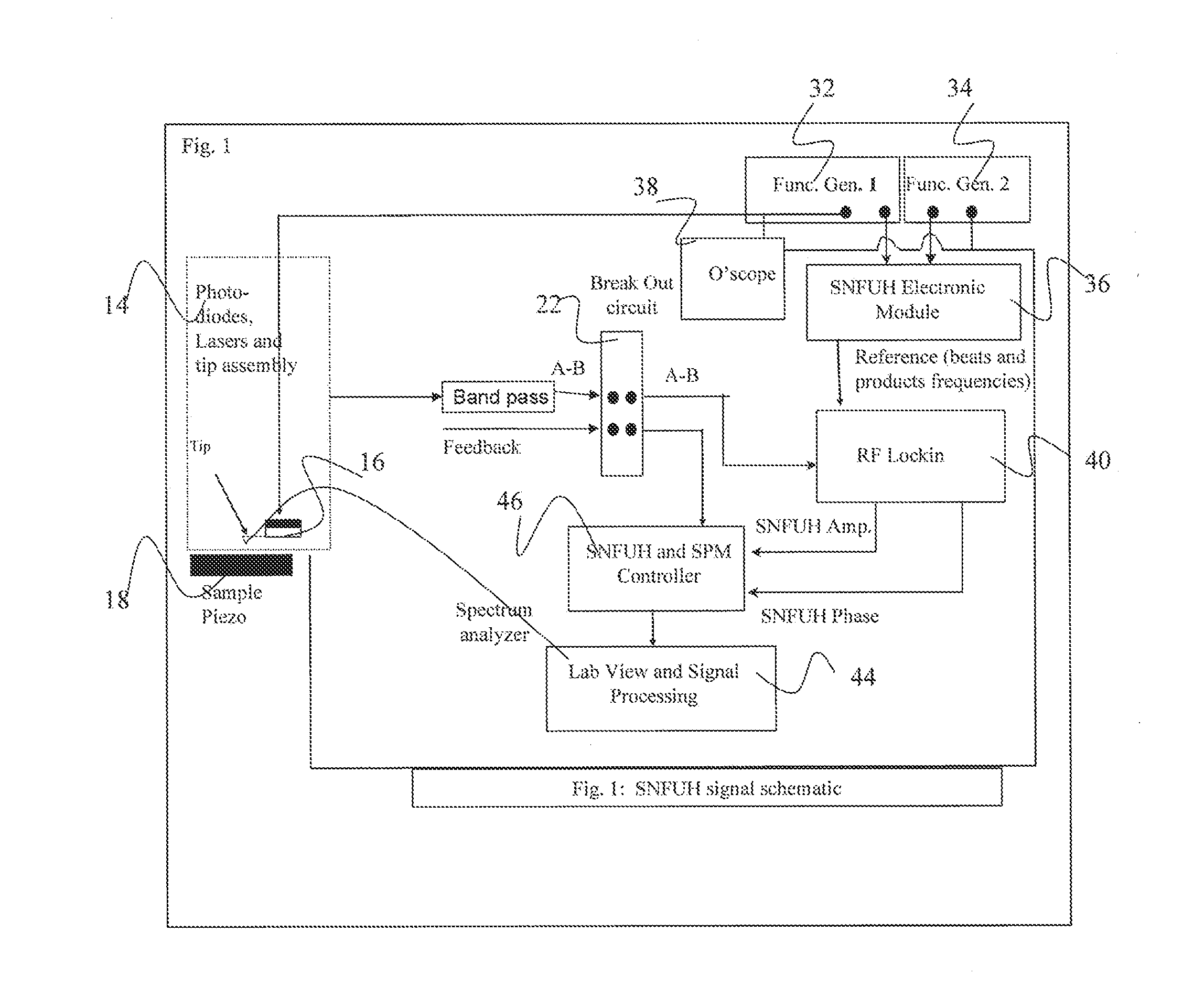
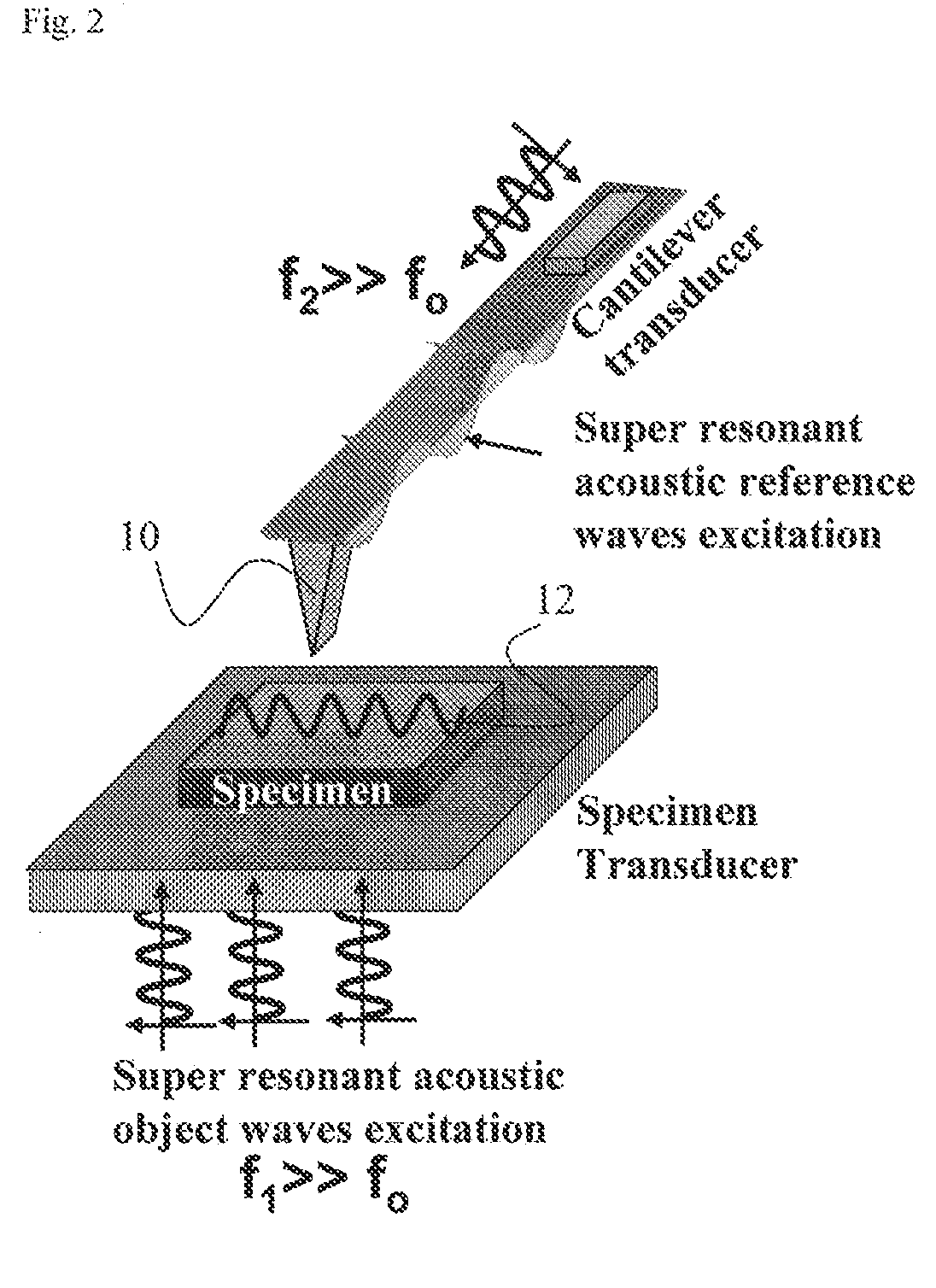
Scanning Near Field Thermoelastic Acoustic Holography (SNFTAH)
InactiveUS20110036170A1High spatial resolutionImprove spatial resolutionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsMicroscopeLight source
A system and method for analyzing a sample is described. The system may include, for example, a light source and a scanning probe microscope probe. The light source may generate a coherent laser beam that is modulated by a waveform of a lower frequency. The modulated laser beam is absorbed by the sample causing thermally induced expansion and resulting in an excitation of acoustic waves. The probe is locally deployed near the sample and detects, in real time, perturbations in the excited acoustic waves to detect surface and buried structures of the sample.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
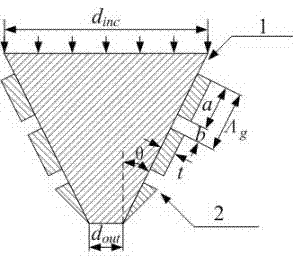
Micro-medium cone and nanometal grating-compounded optical probe
The invention provides a micro-medium cone and nanometal grating-compounded optical probe with high spatial resolution and high sensitivity. The optical probe consists of a micro-medium cone and nanometal gratings, wherein the nanometal gratings are distributed along the outer surface of the micro-medium cone, the micro-medium cone collects incident light energy with larger aperture as far as possible and gathers the light engery towards a cone top, the gathered light energy is efficiently coupled and converted into surface plasmons by the nanometal gratings, so that the surface plasmons can be continuously compressed and focused along with a cone surface, and a nano-focused high-local area strong field is formed at the tip end of the cone. In addition, regulation and optimization of nano focus can be realized through changing and optimizing the apex angle of the micro-medium cone, the structure and parameters of the gratings, and the size of an outlet. The optical probe can be used as a probe of a near field scanning microscope, an atomic force microscope and a tip-enhanced raman spectrometer, the strong nano focus formed by the optical probe can be used as a light source of nano lithography and sub-wavelength optical communication, and has important application values in the fields of nanosensing, nanoimaging, nano lithography, sub-wavelength optical communication and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
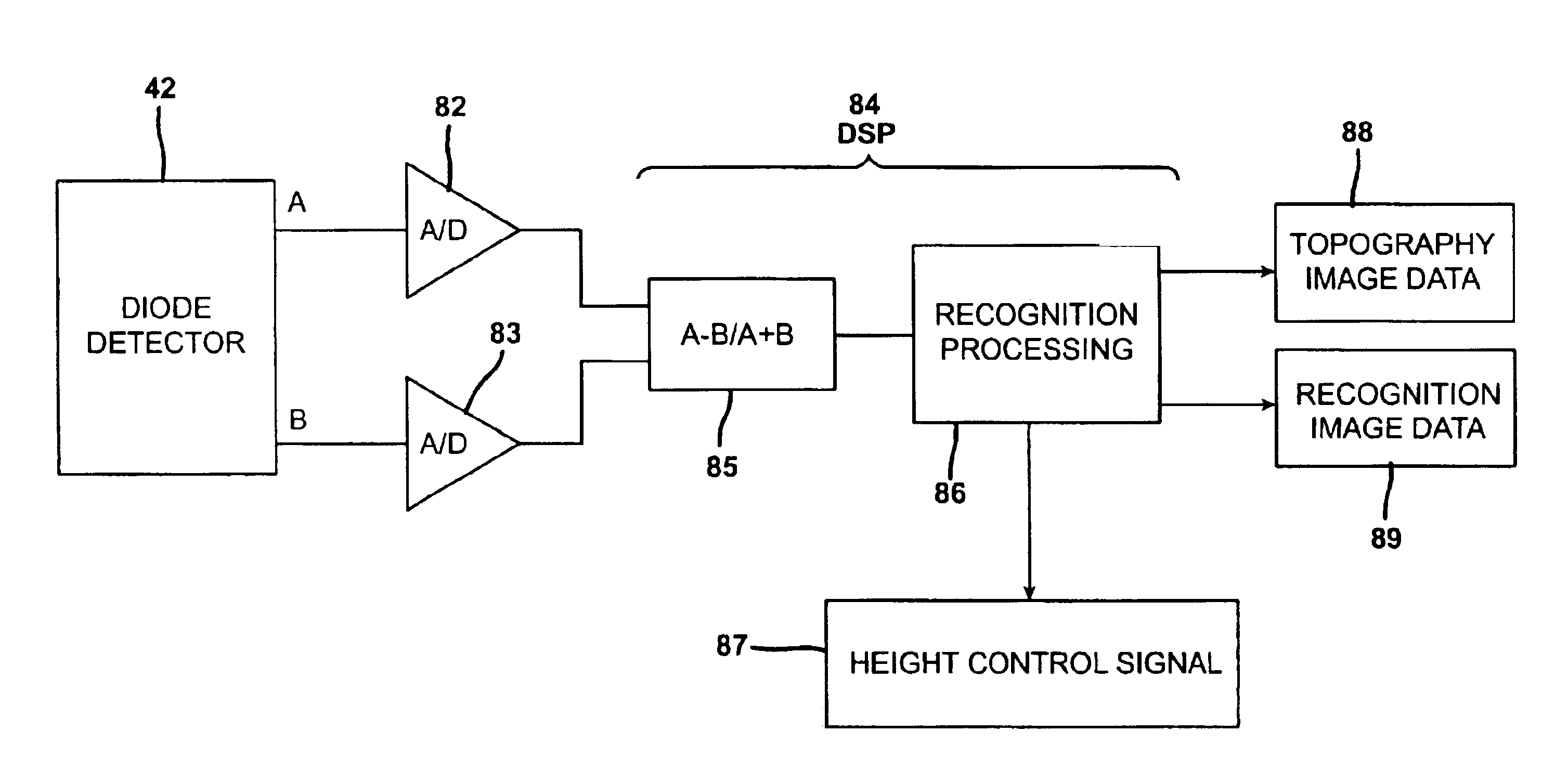
Topography and recognition imaging atomic force microscope and method of operation
ActiveUS6952952B2Rapid quantitative measurementHigh spatial resolutionNanotechMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationQ factorMicroscope
A recognition force microscope for detecting interactions between a probe and a sensed agent on a scanned surface and methods for its operation are provided. The microscope includes a scanning probe having a tip that is sensitive to a property of the scanned surface, and the probe is adapted to oscillate with a low mechanical Q factor. Operation of the microscope includes recording the displacement of the probe tip as a function of time and simultaneously recording both topographic images and the spatial location of interactions between said probe and one or more sensed agents on the surface.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
X-ray measuring apparatus
InactiveUS6895080B2High spatial resolutionHigh sensitivityHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentPhysicsImage resolution
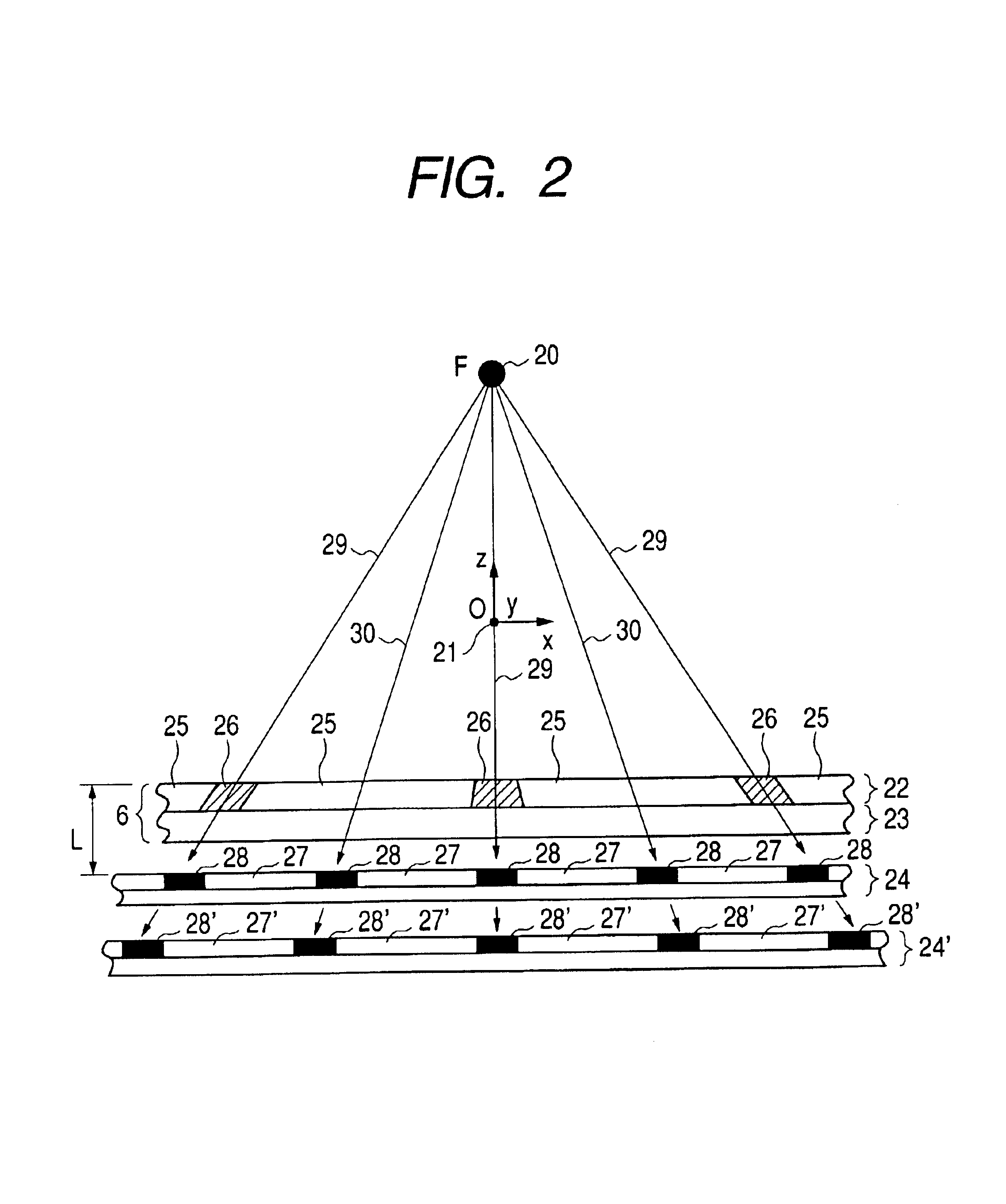
The present invention provides an x-ray measuring apparatus for diagnosis having high spatial resolution and high sensitivity, which includes: an x-ray source for emitting x-rays from an x-ray focal spot; an x-ray detector in which a plurality of sensing elements each having a sensitive part and a blind part surrounding the sensitive part are arranged two-dimensionally; data processing means for collecting output signals of the sensing elements and performing data processing; and an anti-scatter grid disposed between the x-ray focal spot and the x-ray detector with predetermined distance from the position of the x-ray focal spot and in which an x-ray transmitting member and an x-ray shielding member are alternately arranged in a first direction. A pitch in the first direction of linear images projected on a sensing surface of the x-ray detector of the x-ray shielding member by the x-ray is set to be substantially an integral multiple of two or larger of the pitch of arrangement of the sensing elements in the first direction. In such a manner, a moiré-free image of a wide field of view is obtained.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Multi-parameter distributed measurement system and measuring method of dual-core weak grating array based on dark pulse light source
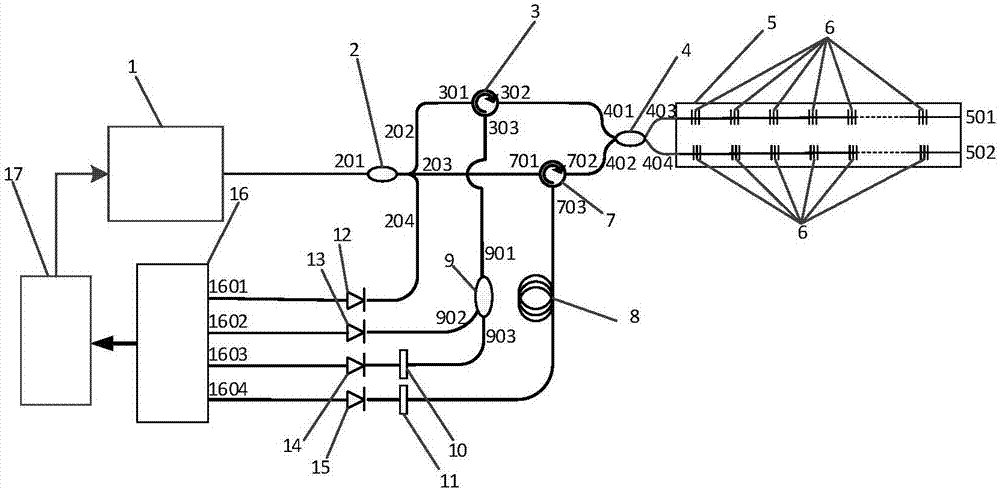
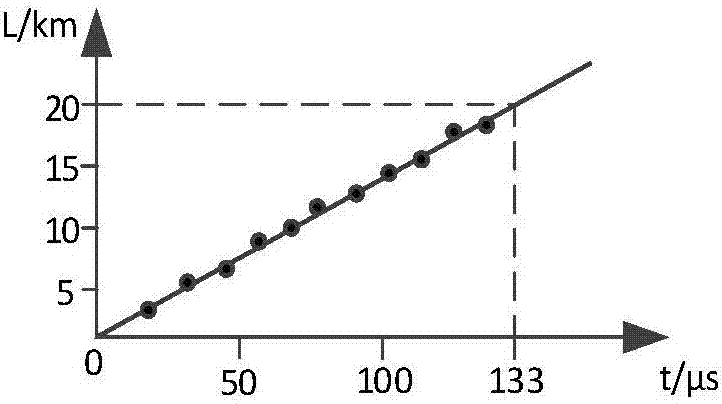
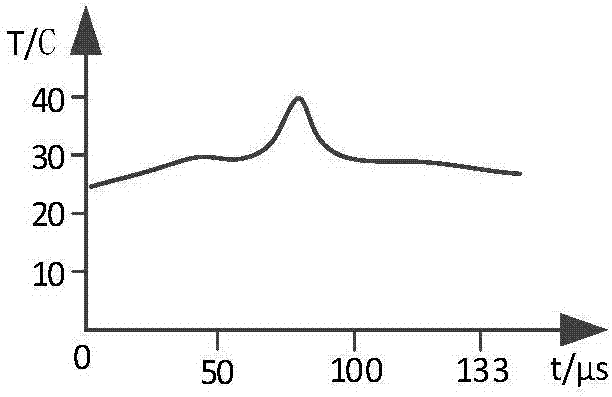
ActiveCN107036733AImprove spatial resolutionHigh measurement accuracyForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiberFiber coupler
The invention relates to a multi-parameter distributed measurement system and measuring method of a dual-core weak grating array based on a dark pulsed light source. The system includes a broadband dark pulse light source, a weak grating array, a dual-core fiber, a photoelectric conversion unit, a fiber delay line, a notch filter, an information collection unit, a computer, a dual-core fiber coupler. The system utilizes high-intensity Rayleigh scattered light excited by high-power stable background light of a pulse width tunable dark pulse light source for distributed measurement; meantime, the system uses the dark pulse and weak grating array of the light source to carry out spatial segmented positioning of the Rayleigh scattering in the whole fiber range in order to improve the spatial resolution and measurement precision of a sensing system, and realizes simultaneous precise measurement of temperature and strain and precise positioning in an interval. The system has the advantages of simple structure, fast response speed and high spatial resolution, and can realize the distributed optical fiber sensing measurement of temperature and strain parameters at the same time with high precision.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic resonance angiography data
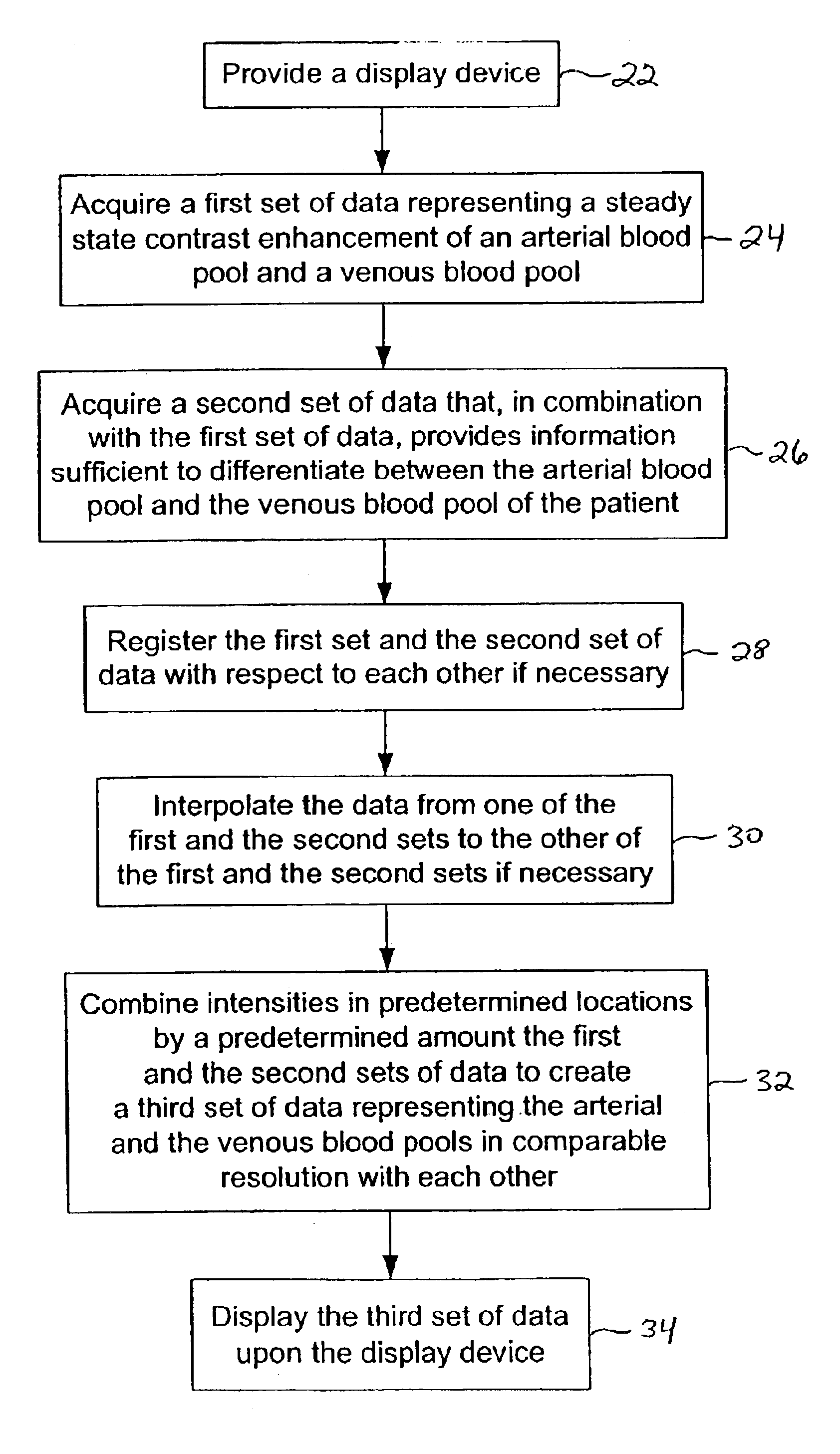
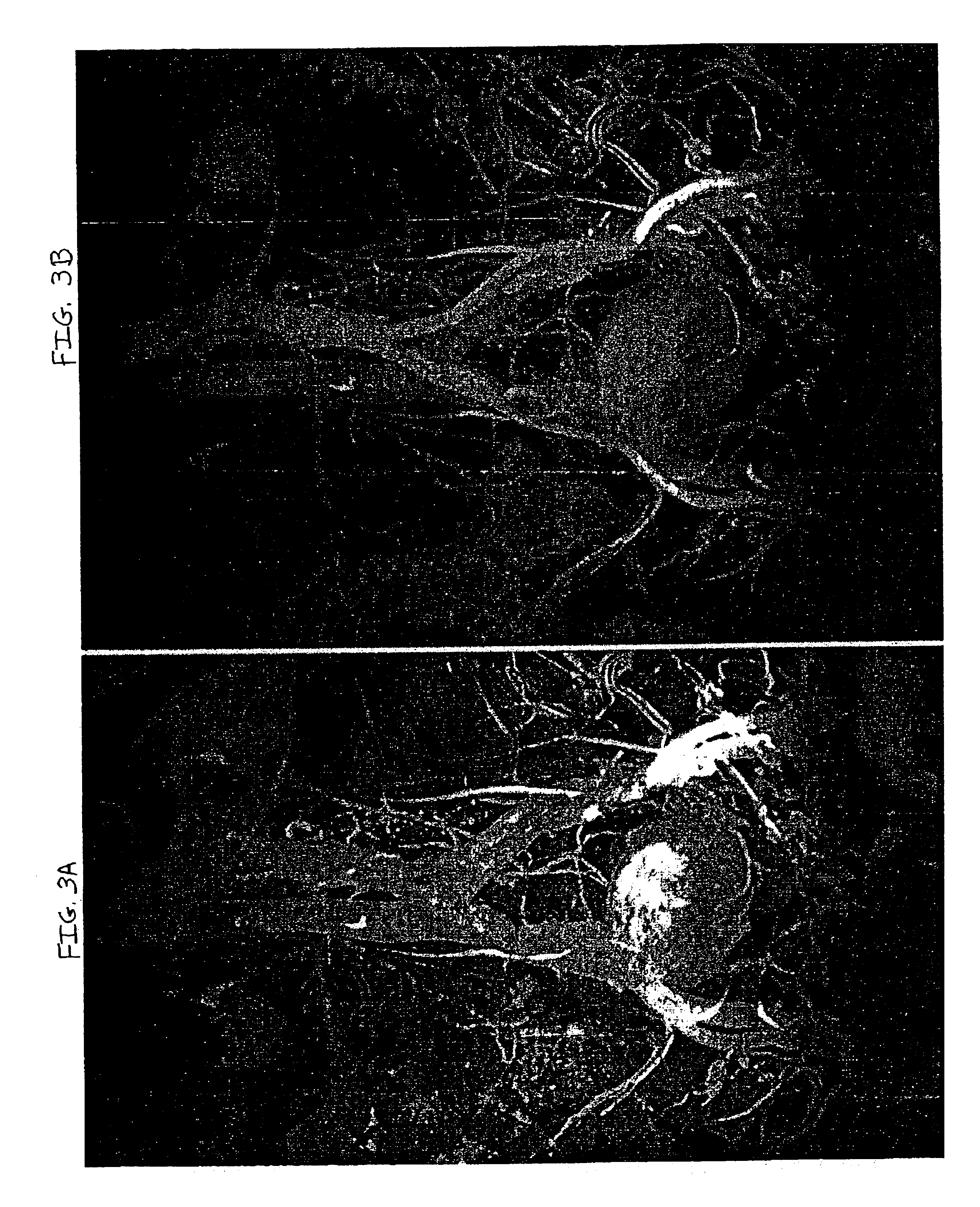
InactiveUS6925321B2Improve visualizationHigh spatial resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisVascular structureVenous blood
A method is provided for improved visualization of vascular structures contained within magnetic resonance angiograms, particularly steady-state contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiograms. The disclosed methods include manipulating the relative enhancement levels of the arterial and venous blood pools images with respect to each other and to the surrounding anatomy. This manipulation is meant to optimize visualization of one or both of the individual blood pools without the necessity of completely obscuring or removing the supporting information given by presentation of the other blood pool and / or the surrounding anatomy.
Owner:LANTHEUS MEDICAL IMAGING INC
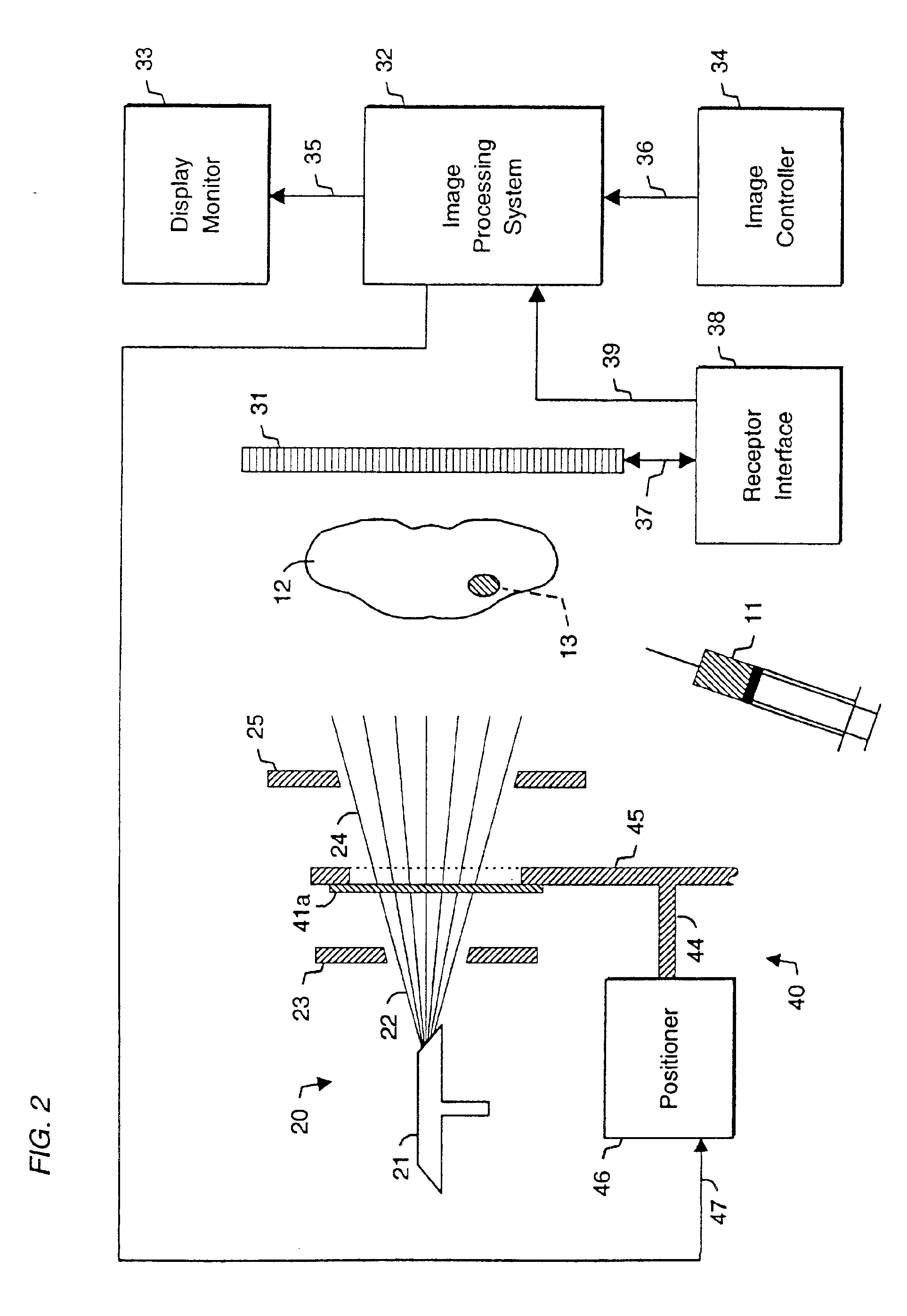
System and method for radiographic imaging of tissue
InactiveUS6923950B2High anatomical detailHigh spatial resolutionIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSugar derivativesAnatomical structuresX-ray
System and method for radiographic imaging of tissue using a non-radioactive, radio-opaque imaging agent that accumulates intracellularly in tissue in proportion to its functional, or physiological, activity. In one embodiment, the imaging agent is a cell-membrane permeable, radio-opaque, high affinity ligand for the intracellular enzyme hexokinase. The imaging agent is administered to a patient, and after an accumulation interval, radiographic images are acquired. The imaging agent preferentially accumulates in malignant tissue and increases its radio-opacity because of its elevated glucose metabolic rate relative to benign and normal tissue. The tissue being examined is transilluminated by X-ray beams with preselected different mean energy spectra, and a separate radiographic image is acquired during transillumination by each beam. An image processing system performs a weighted combination of the acquired images to produce a single displayed image. The image processing procedure isolates the radiographic density contributed solely by differential accumulation of the imaging agent in malignant, benign, and normal tissue. The system and method thus provides a functional image displayed with the anatomical detail and spatial resolution of a radiographic image. The viewer may interactively control the relative proportion of radiographic density contributed by imaging agent, soft tissue, and bone to the displayed image, allowing the display of functional and anatomical information in complete registration, and facilitating localization of malignant tissue in relation to nearby anatomical structures. In other embodiments, the system and method may be used to detect enzymes, nucleic acids, coenzymes, fatty acids, and other cellular targets in diagnostic imaging applications.
Owner:VERITAS PHARM INC
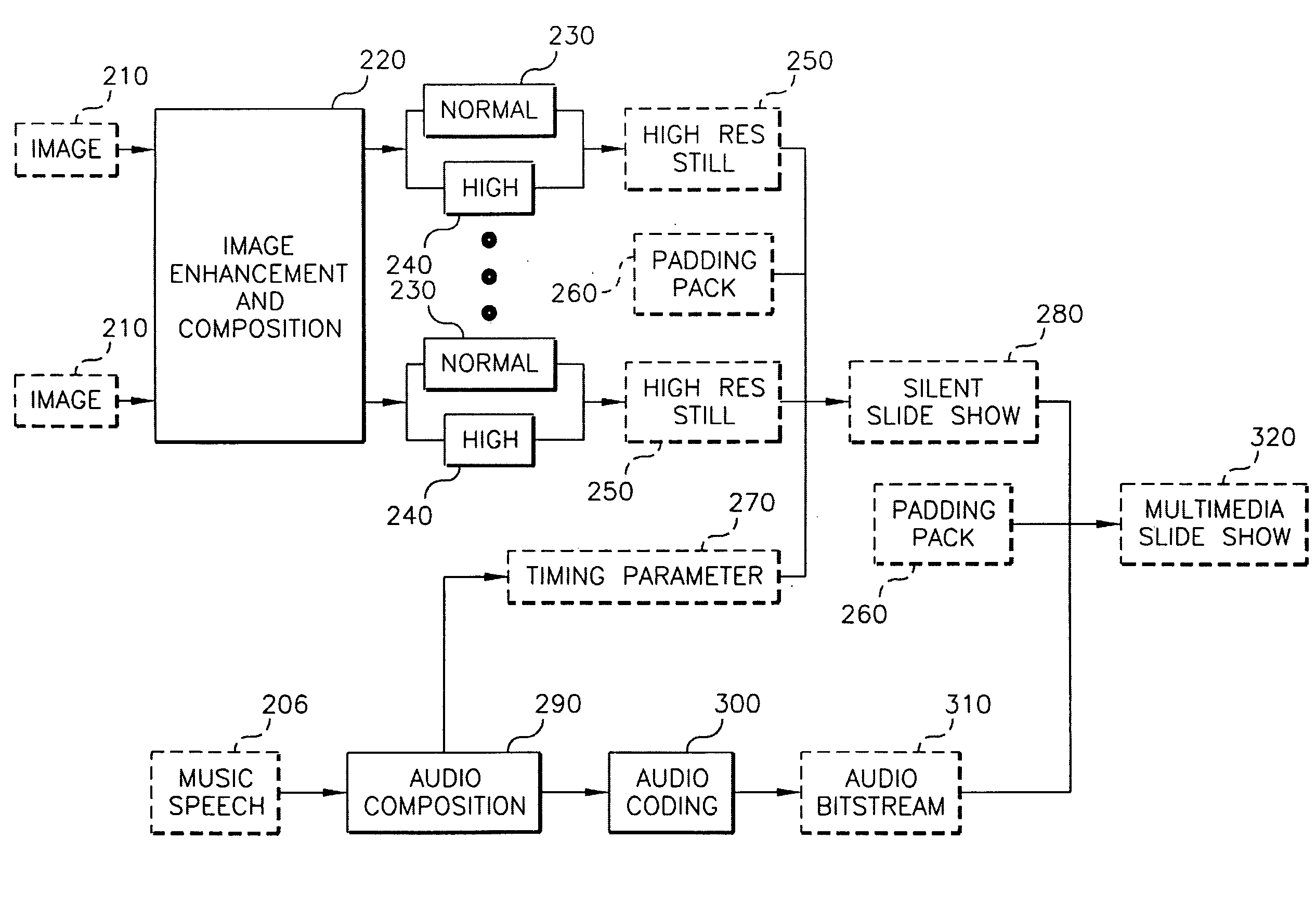
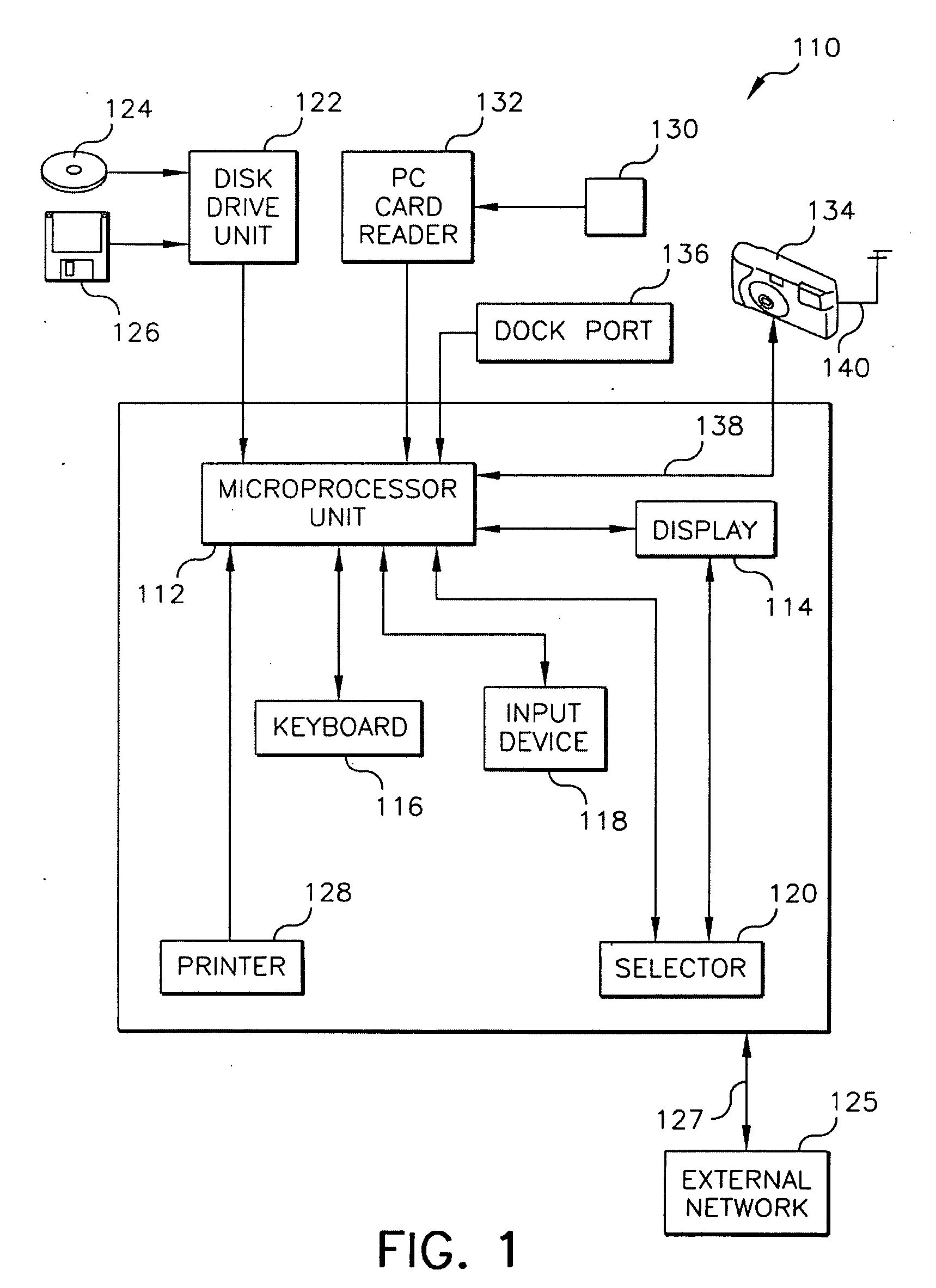
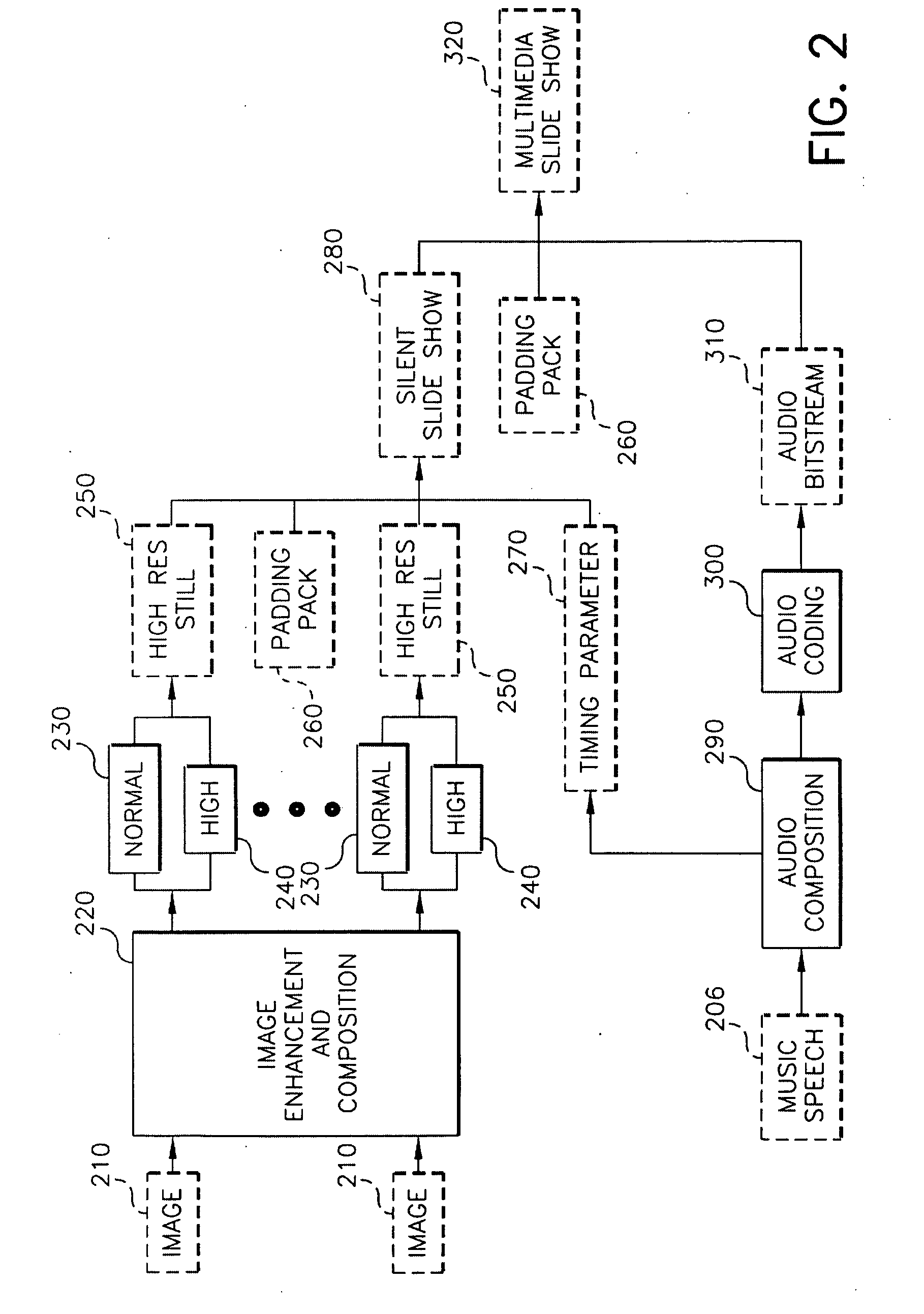
System and method to compose a slide show
InactiveUS20080247458A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVideo bitstreamComputer graphics (images)
A method of composing a multimedia slide show. In a preferred embodiment, the method comprises the steps of: selecting a plurality of digital images; encoding each of the plurality of digital images to generate a normal resolution image portion and a high resolution image portion; multiplexing each corresponding normal and high resolution image portion to generate a single high resolution still image; determining a time parameter for each of the high resolution still images; selecting an audio portion for at least one of the plurality of digital images; concatenating the plurality of high resolution still images to generate a video bitstream; generating an audio bitstream by encoding the audio portion; and multiplexing the video bitstream and audio bitstream to generate the multimedia slide show.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO +15
Method and device for imaging soft body tissue using x-ray projection and optical tomography
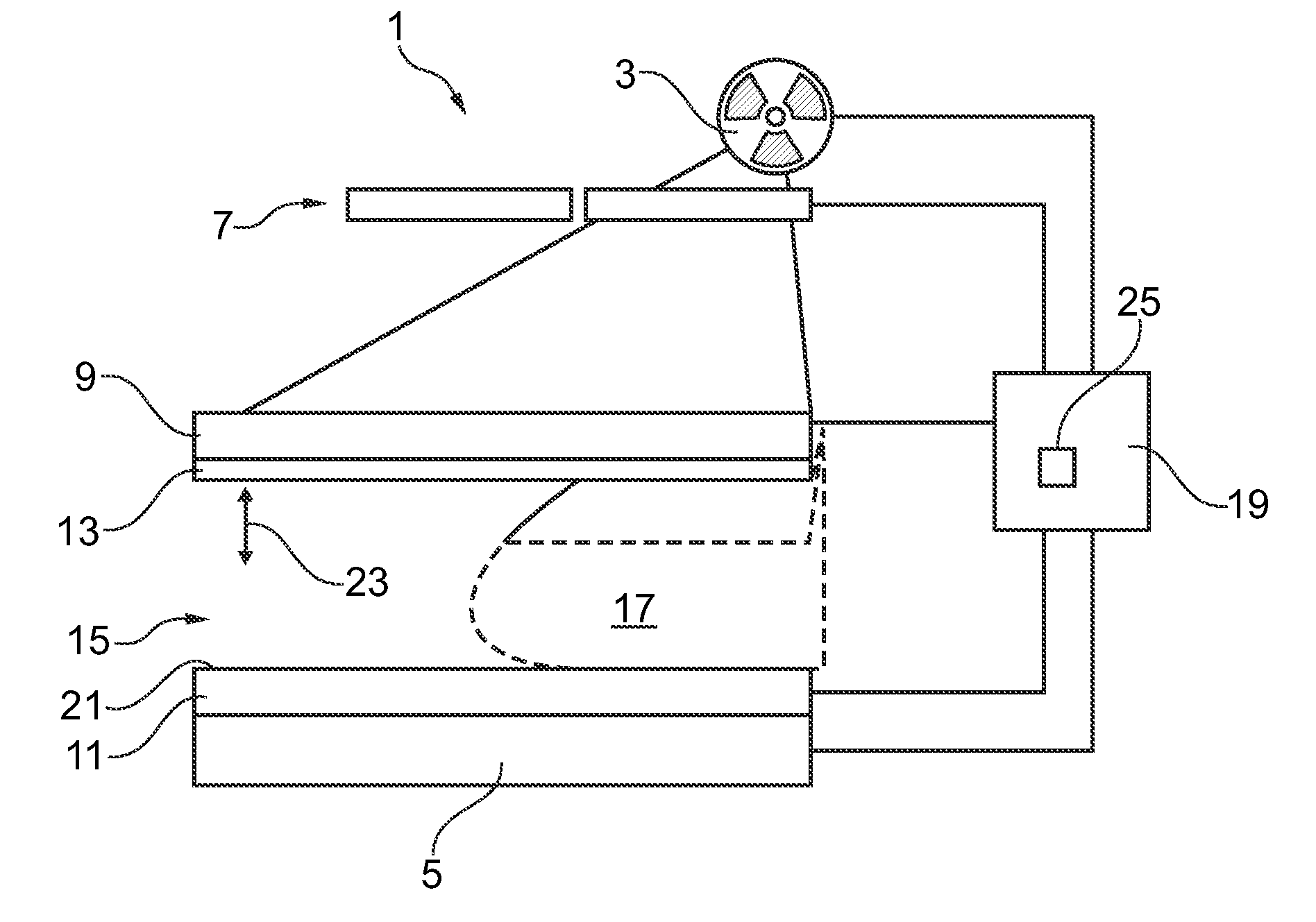
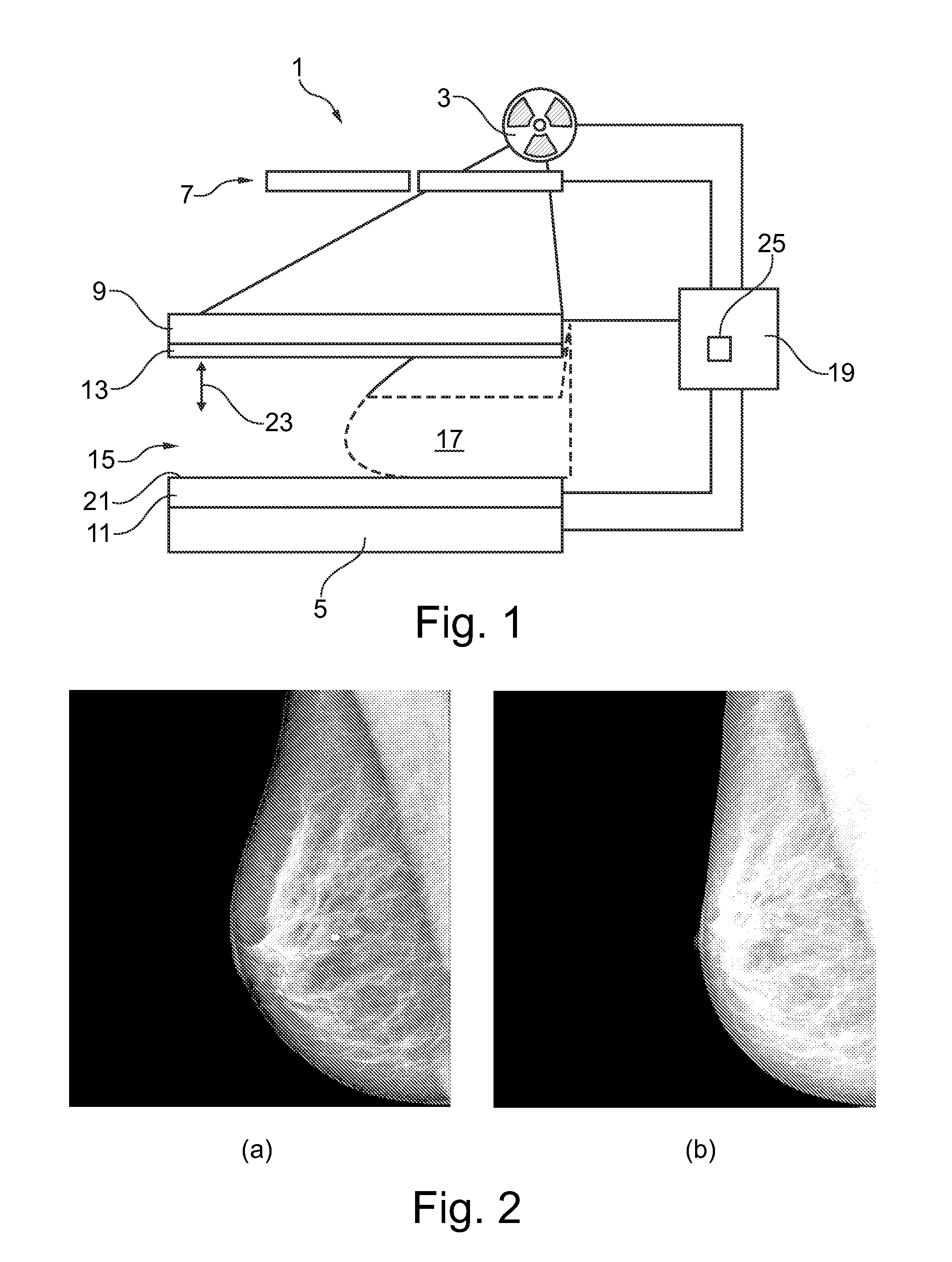
ActiveUS20140288420A1Improve reconstructionHigh spatial resolutionRadiation diagnostic device controlHealth-index calculationXeromammogramPhysics
A method and device (1) for imaging soft body tissue such as a female breast is proposed. X-ray projection techniques and optical tomography techniques are combined. First image data for a first image of a breast (17) may be acquired by X-ray projection using an X-ray source (3) and an X-ray detector (5). Second image data for a second image may be acquired using optical tomography equipment comprising a light source (9) and a light detector (11). From the first image data, estimated bulk optical properties of the breast (17) are be derived. Based on such estimated bulk optical properties, an optical tomography image is reconstructed from the second image data with high image quality. Performing mammography acquisition at different compression states of the breast (17) may improve patient comfort. Mammograms may be acquired at two different compression states wherein a first compression state is adapted to provide high image resolution. At a second compression state, another mammogram may be acquired together with an optical tomography image. The two mammograms may be used for image registration thereby possibly providing information for a deformation prior. Additional information on tissue composition within the breast may be received by acquiring the first and second mammogram at different X-ray settings.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Fluorescence Microscope and Fluorescence Microscope Method
InactiveUS20080215272A1High spatial resolutionBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsDigital computer detailsLaser lightMicroscope
To increase spatial resolution by observing a sample based on saturated fluorescence components. A fluorescence microscope according to the present invention includes: a laser light source 10 emitting laser light as excitation light; an objective lens 13 focusing the laser light and applying the focused laser light to a sample 14; a detector 22 detecting fluorescence generated in the sample 14 with the laser light; and a stage 15 scanning the sample 14 while moving the sample 14 relative to the laser light, wherein the laser light is applied to the sample with varying intensities such that saturation of fluorescence occurs at the maximum intensity of the laser light, and fluorescence is detected with the detector in accordance with intensity of the laser light, and the sample is observed based on the saturation components of fluorescence.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Systems and methods for placing heart leads
InactiveUS20100010503A1High spatial resolutionAccurate treatmentSurgeryCatheterAnatomical structuresLesion
Devices, systems, and methods for the localization of body lumen junctions and other intraluminal structure are disclosed. Various embodiments permit clinicians to identify and locate lesions and / or anatomical structures within a lumen and accurately place leads and / or devices within a lumen, through determining the intralumen conductance and / or cross-sectional area at a plurality of locations within the body lumen.
Owner:DTHERAPEUTICS
Magnetic recording disk drive having read head with high cross-track resolution and disk with low bit-aspect-ratio
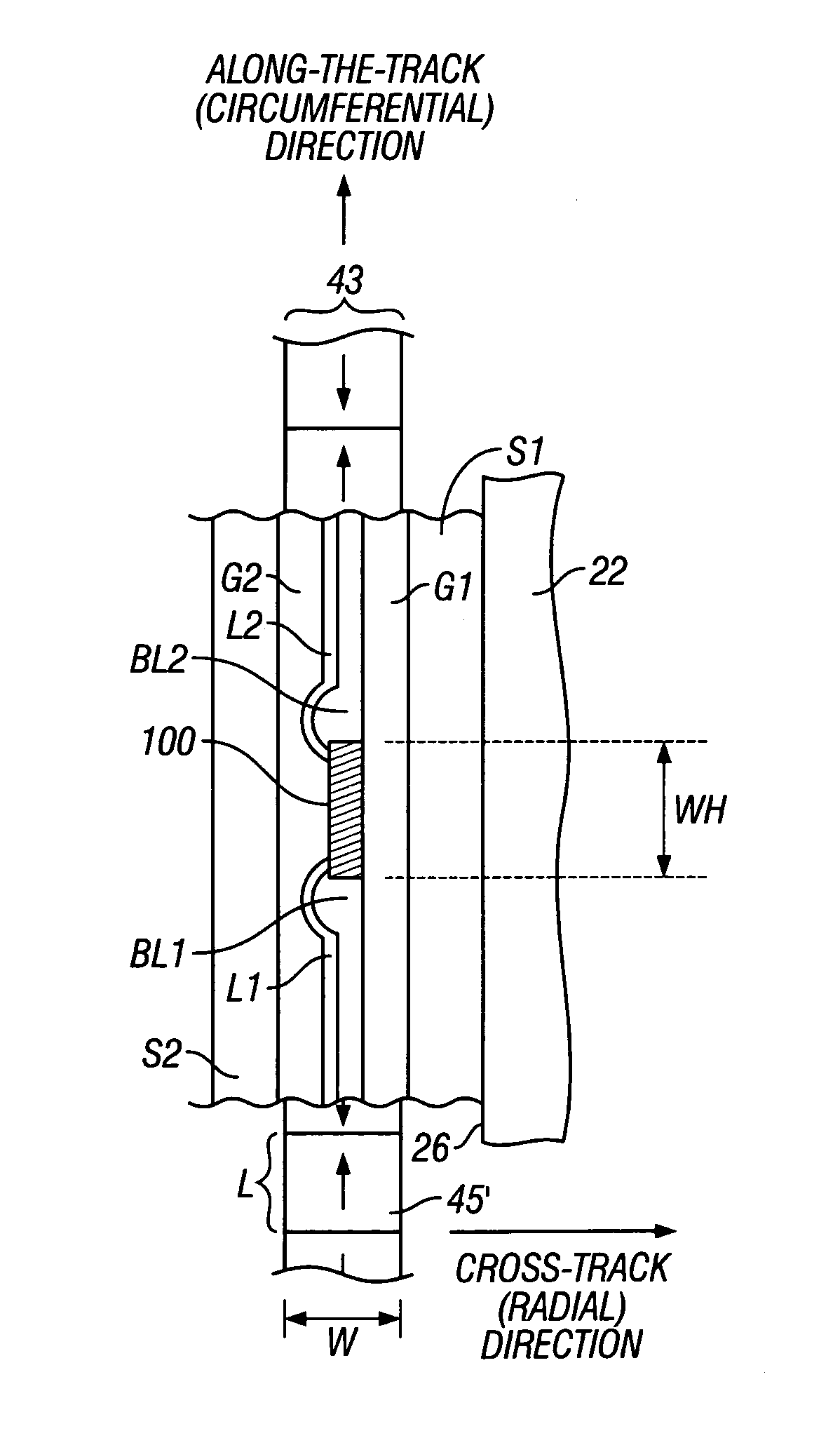
InactiveUS20060285257A1High spatial resolutionReduce amountNanoinformaticsPatterned record carriersTrack densityAspect ratio
A continuous-media or patterned-media disk drive with a low ratio of linear bit density in bits per inch (BPI) in the along-the-track direction to track density in tracks per inch (TPI) in the cross-track direction has a magnetoresistive read head with high cross-track spatial resolution. The read head is located between two magnetic shields, with the shields and read head formed on a side surface of the head carrier perpendicular to the carrier's disk-facing surface. The carrier is supported by the disk drive actuator with the side surface of the carrier oriented generally parallel to the data tracks. In this arrangement the high-spatial-resolution direction of the read head (the transverse direction perpendicular to the side surface on which the head is formed) is in the radial or cross-track direction.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com