Patents
Literature
170 results about "High temporal resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The technical term “temporal resolution” refers to the distance of time between two images of the same area. Geostationary satellites acquire images of the same section of the surface of the earth so they have a very high temporal resolution. Polar orbiting systems, in turn, have a low temporal but a high spatial resolution.
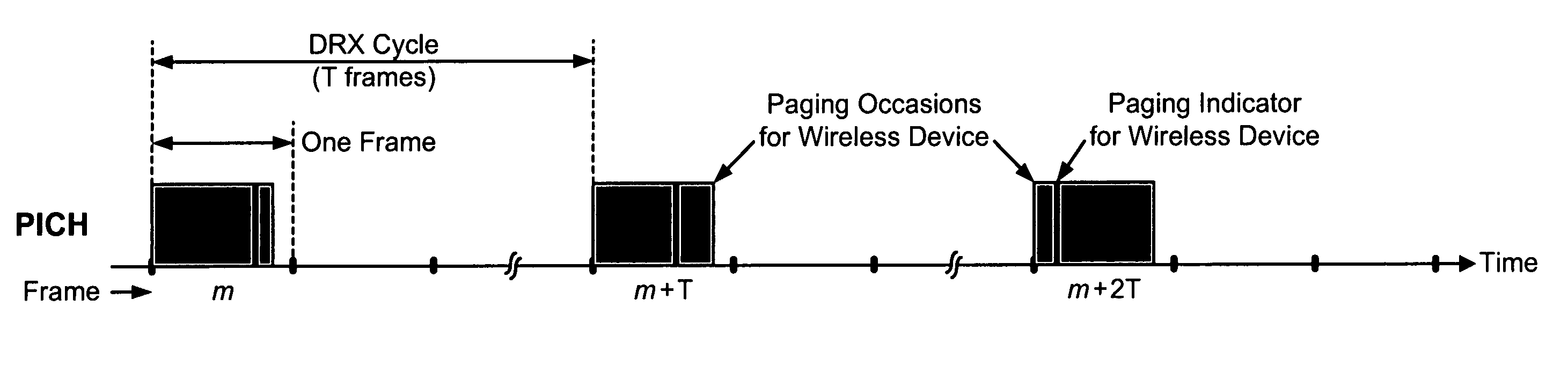
Quick detection of signaling in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20070060095A1Shorten warm-up timeExtend battery standby timePower managementCarrier regulationCommunications systemImage resolution
Quick frequency tracking (QFT), quick time tracking (QTT), and non-causal pilot filtering (NCP) are used to detect sporadically transmitted signaling, e.g., paging indicators. For QFT, multiple hypothesized frequency errors are applied to an input signal to obtain multiple rotated signals. The energies of the rotated signals are computed. The hypothesized frequency error with the largest energy is provided as a frequency error estimate. For QTT, coherent accumulation is performed on the input signal for a first set of time offsets, e.g., early, on-time, and late. Interpolation, energy computation, and non-coherent accumulation are then performed to obtain a timing error estimate with higher time resolution. For NCP, pilot symbols are filtered with a non-causal filter to obtain pilot estimates for one antenna for non-STTD and for two antennas for STTD. The frequency and timing error estimates and the pilot estimates are used to detect the signaling.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
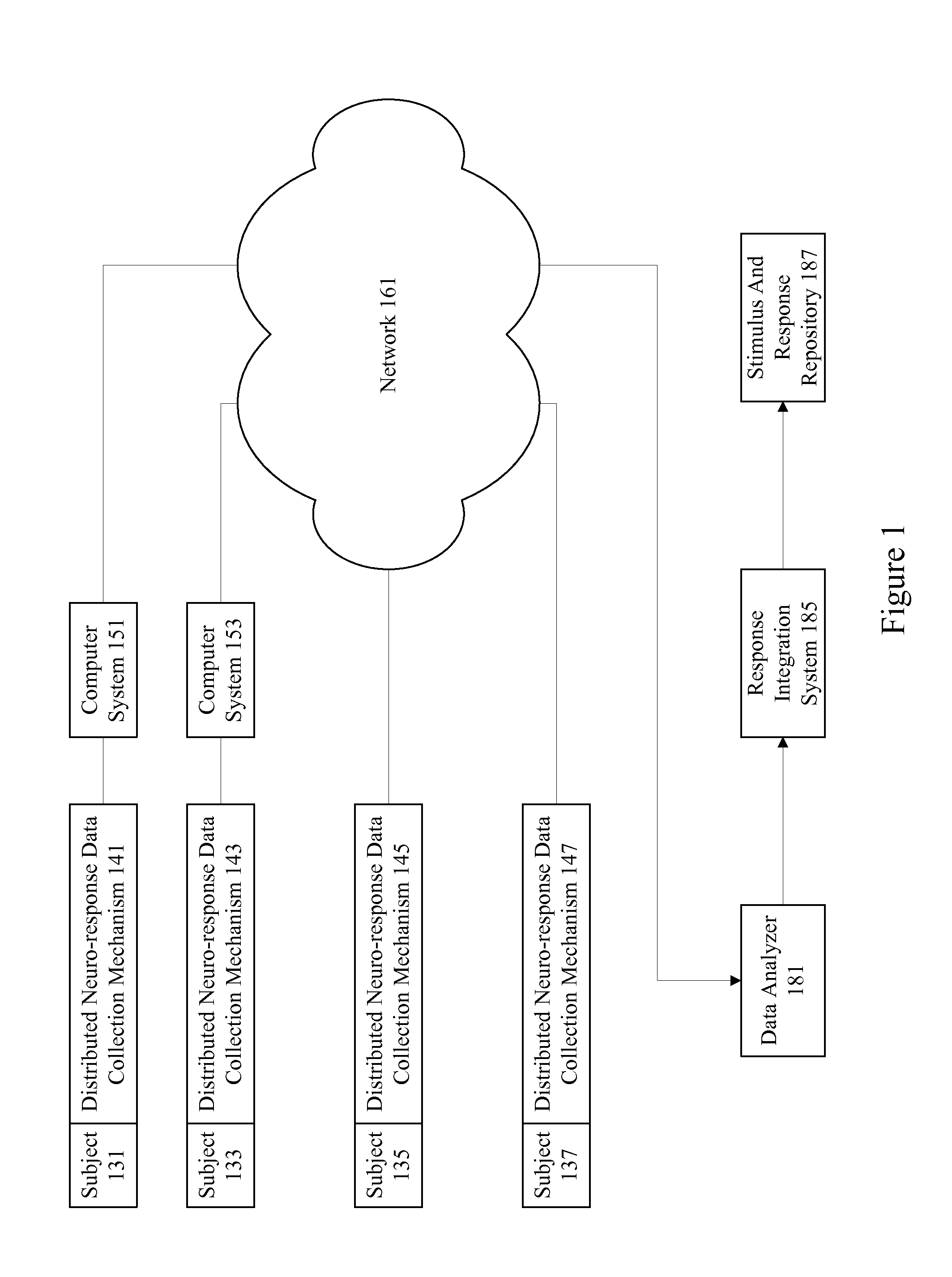
Neurological sentiment tracking system
Distributed mechanisms are provided for implementing a neurological sentiment tracking system to collect and analyze consumer and business sentiment. Neuro-response data as well as optional survey and interview data may be collected from subjects about personal finance expectations, anticipated hiring expectations, views on prospects for the economy in the short and long term, purchase expectations, etc. Neuro-response data collection mechanisms such as Electroencephalography (EEG) and / or facial emotion encoding can be used along with surveys and interviews to collect data from subjects in a variety of environments. Collected data may be aggregated to aid in economic forecasting and modeling. Data may be continuously collected to provide high temporal resolution. Analysis may also be performed to determine impacts of particular events on sentiment.
Owner:THE NIELSEN CO (US) LLC
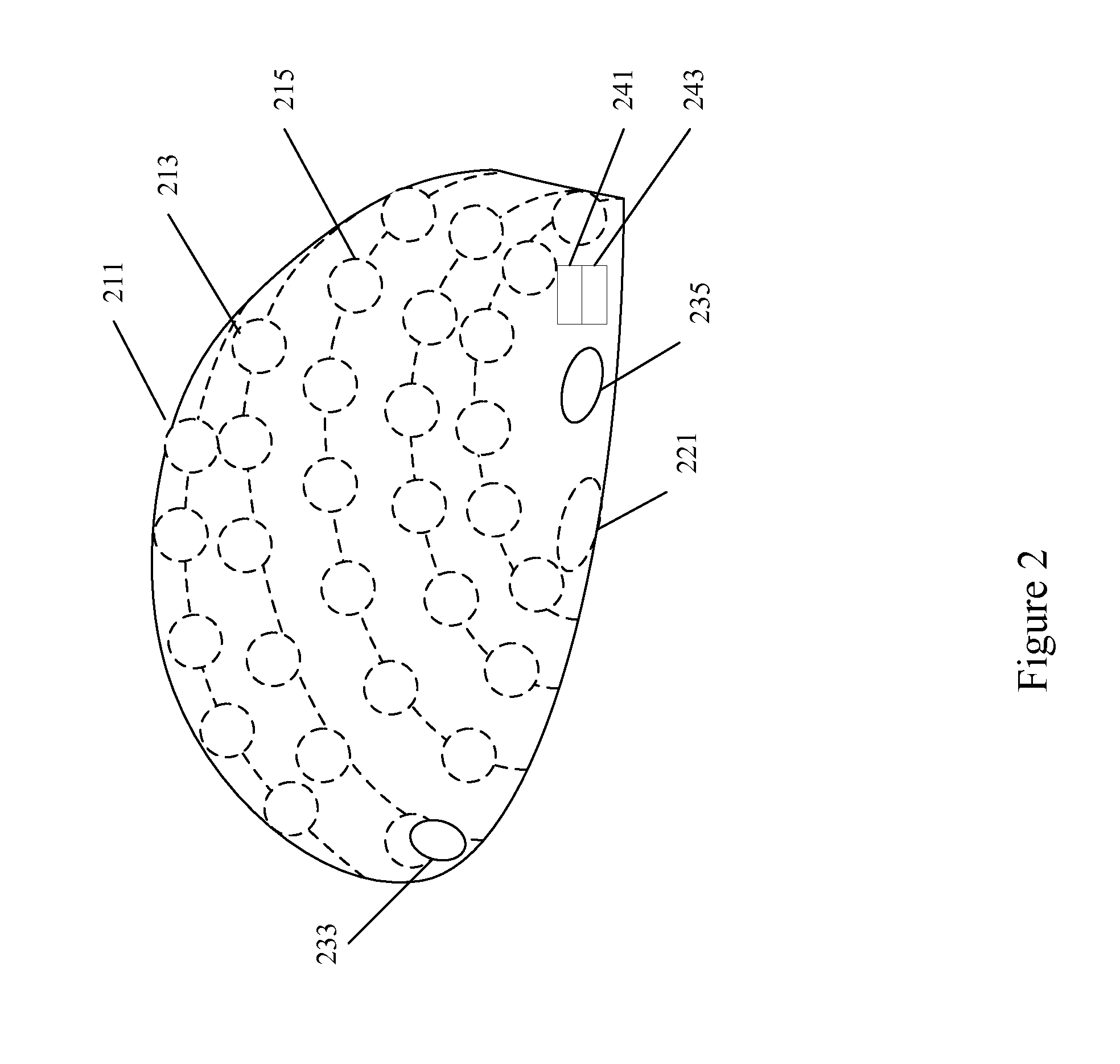
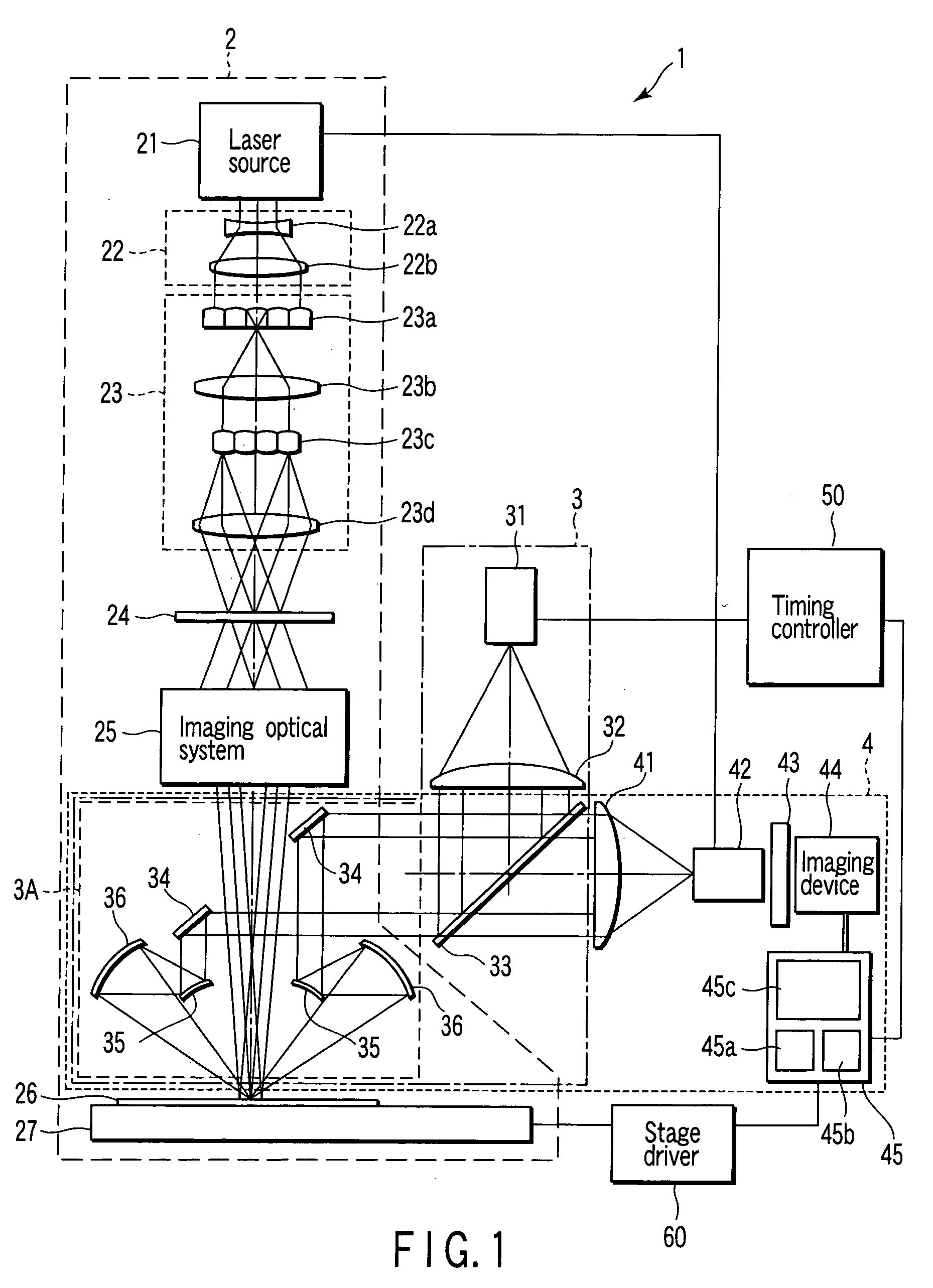
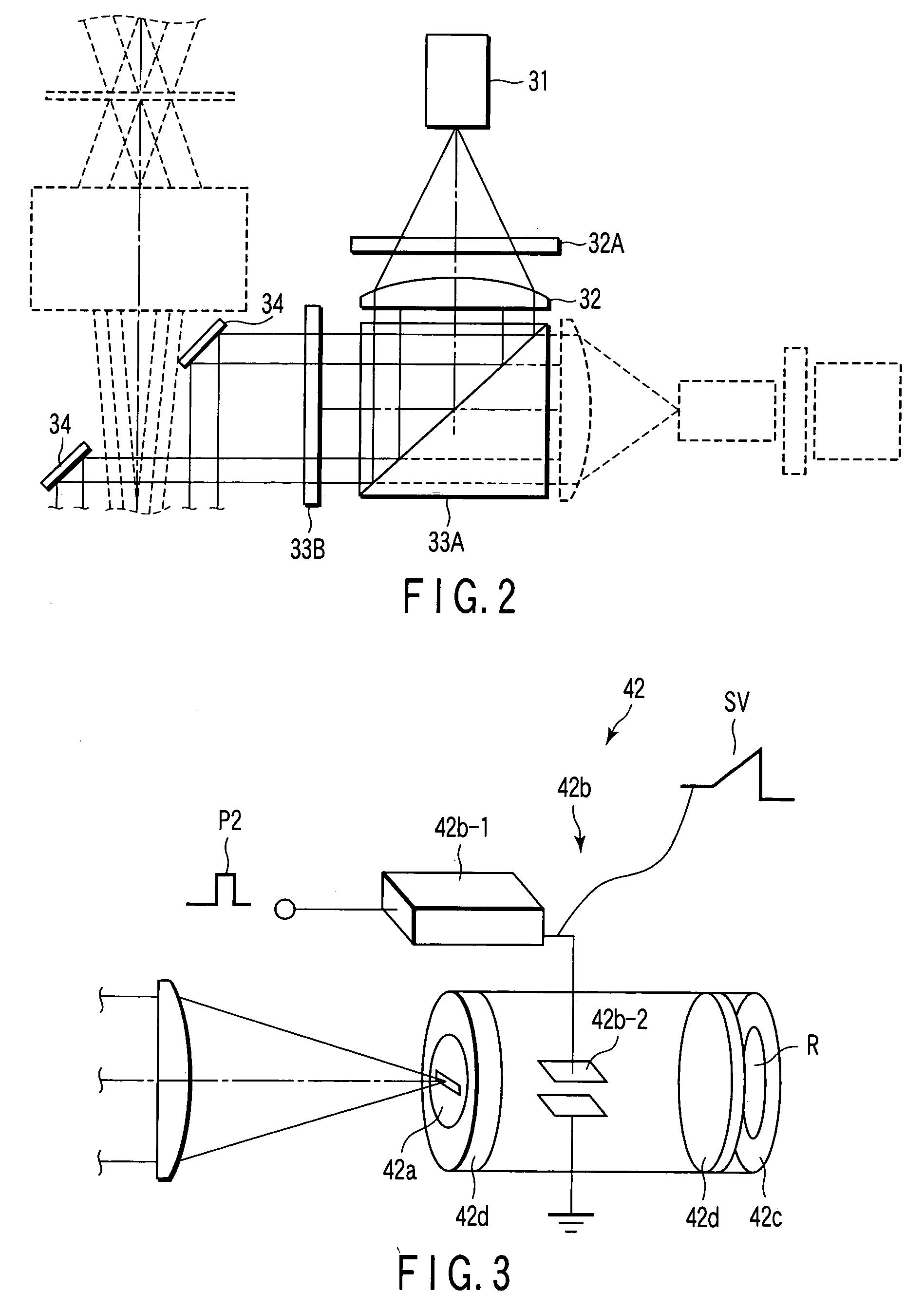
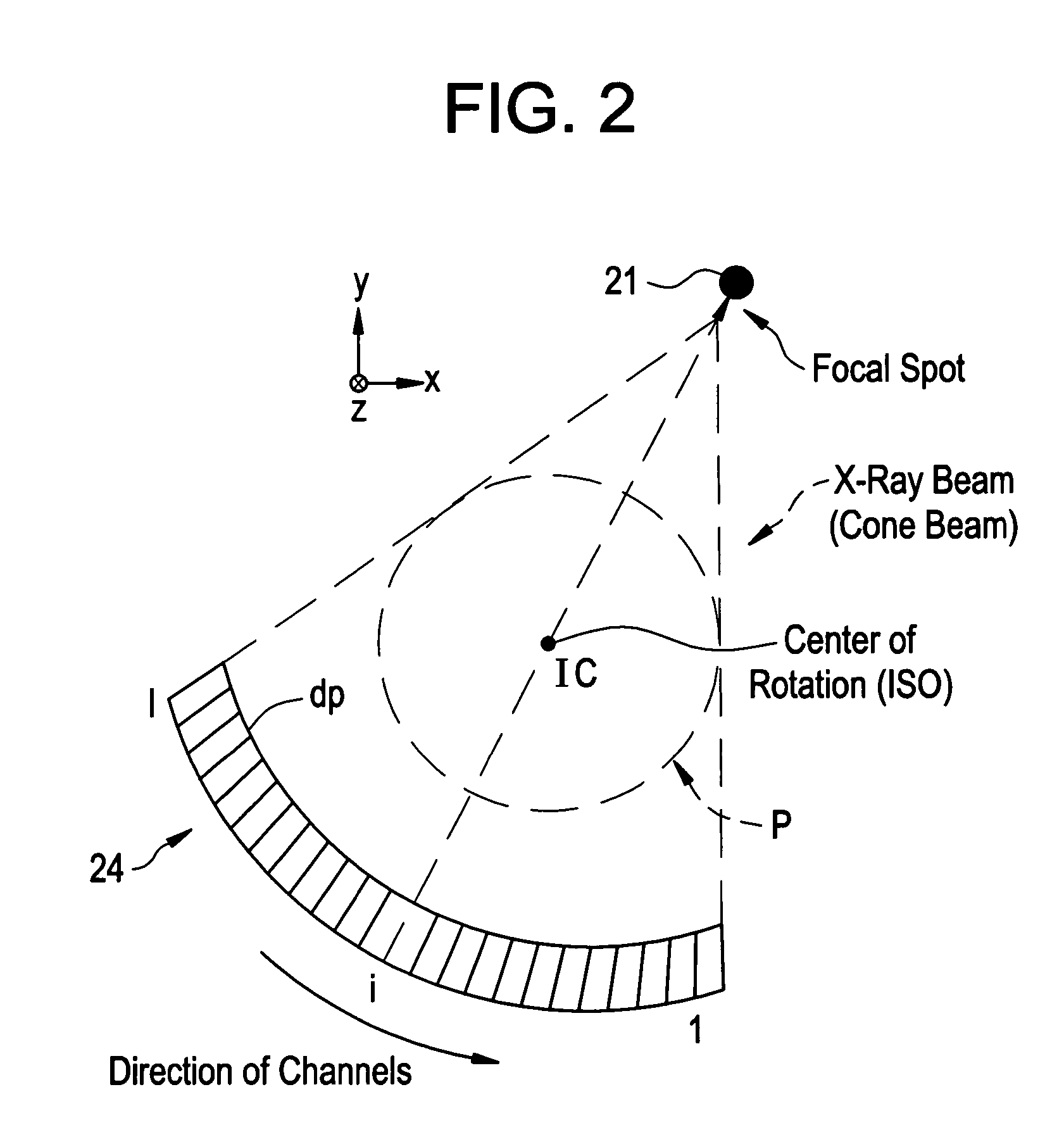
Radiotomography apparatus
ActiveUS20070189436A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove temporal resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTemporal resolutionData segment
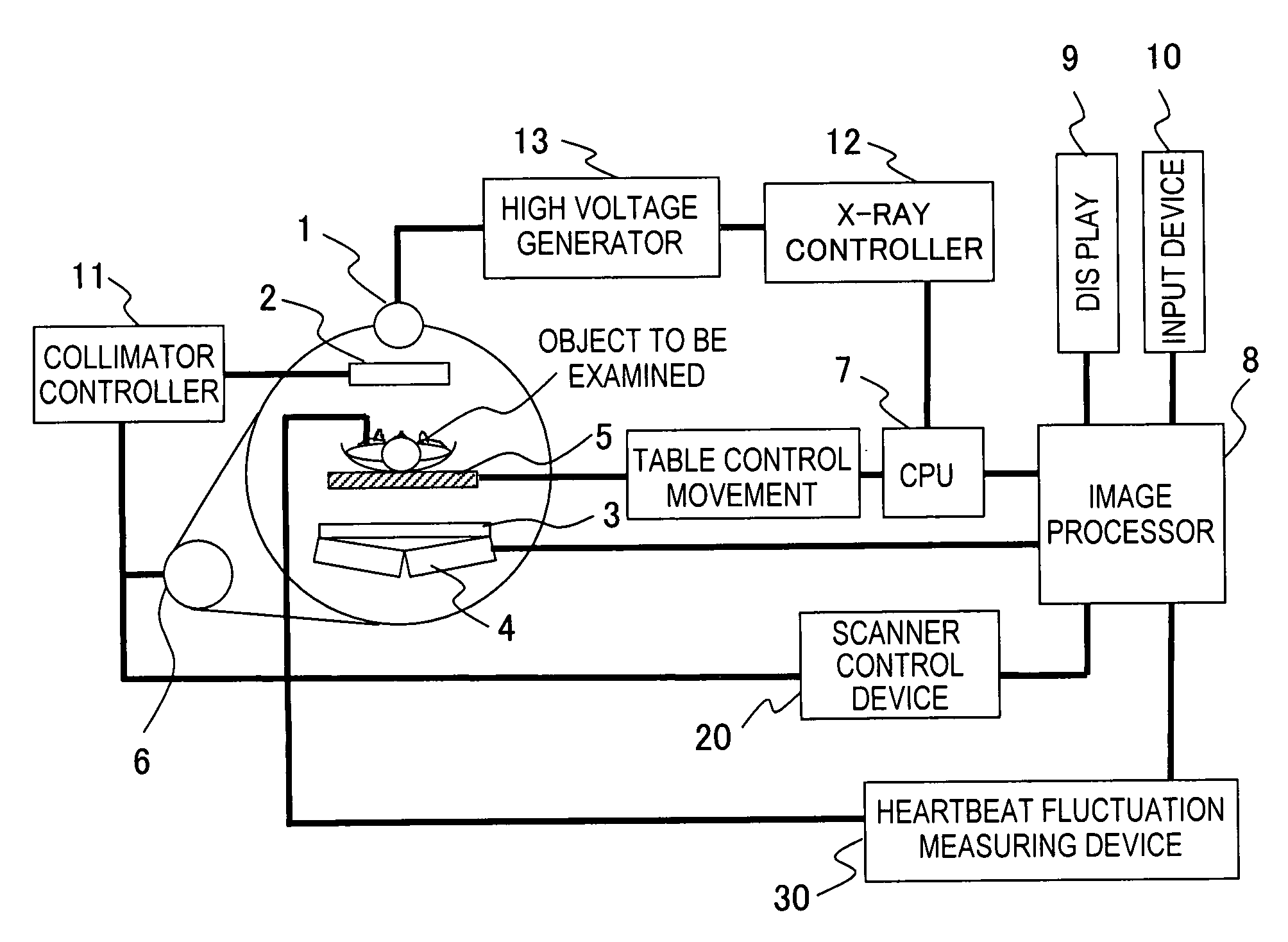
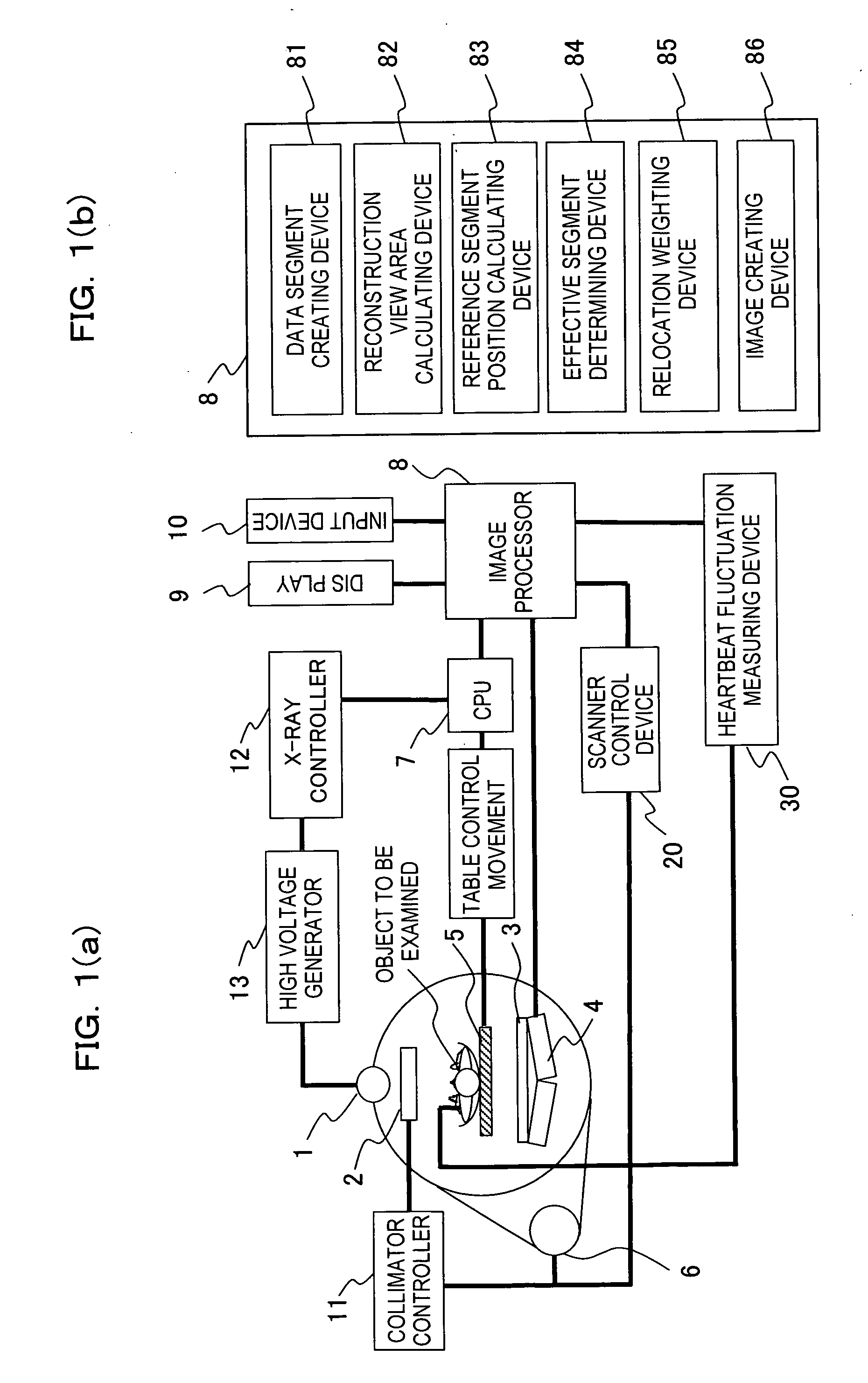
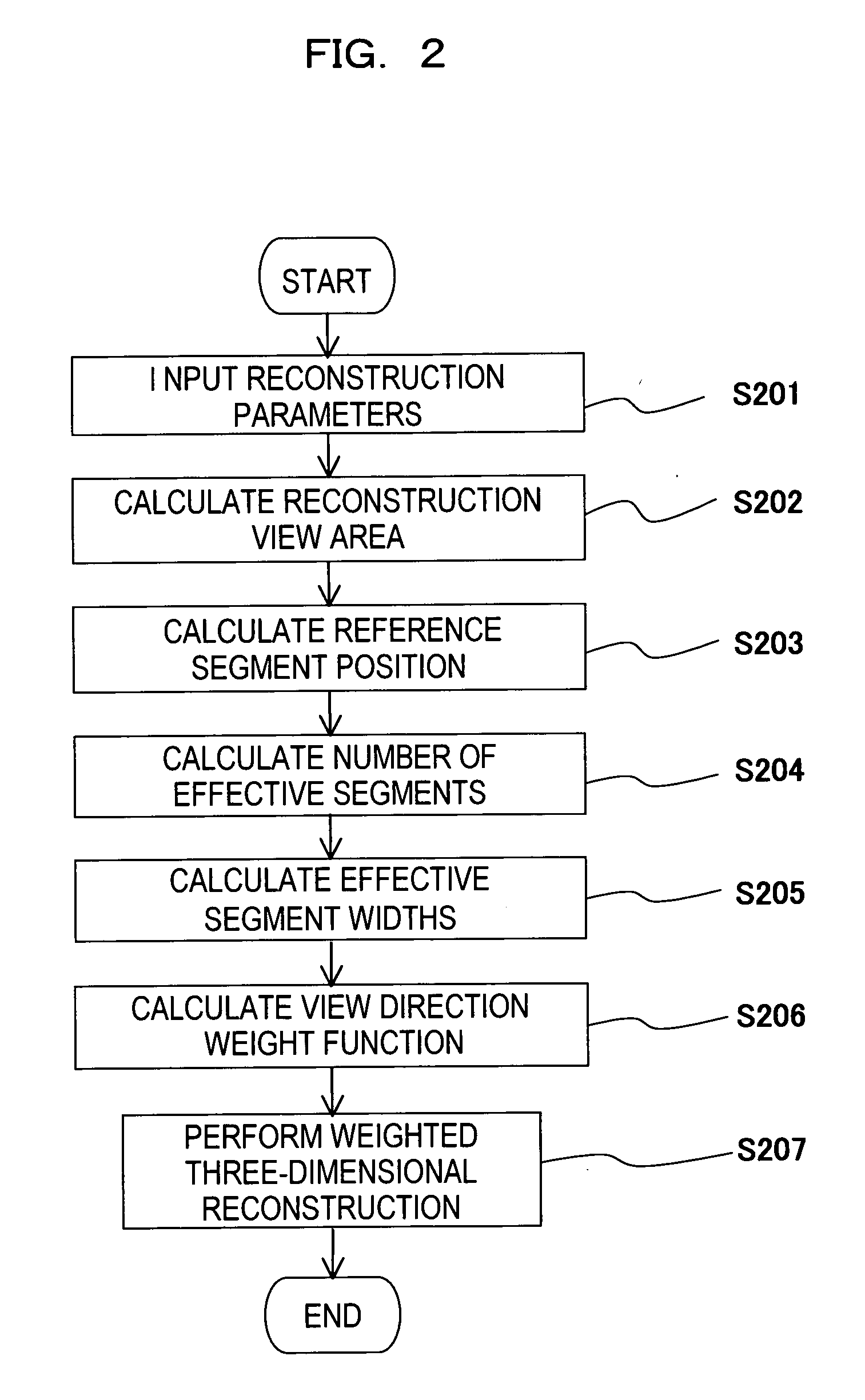
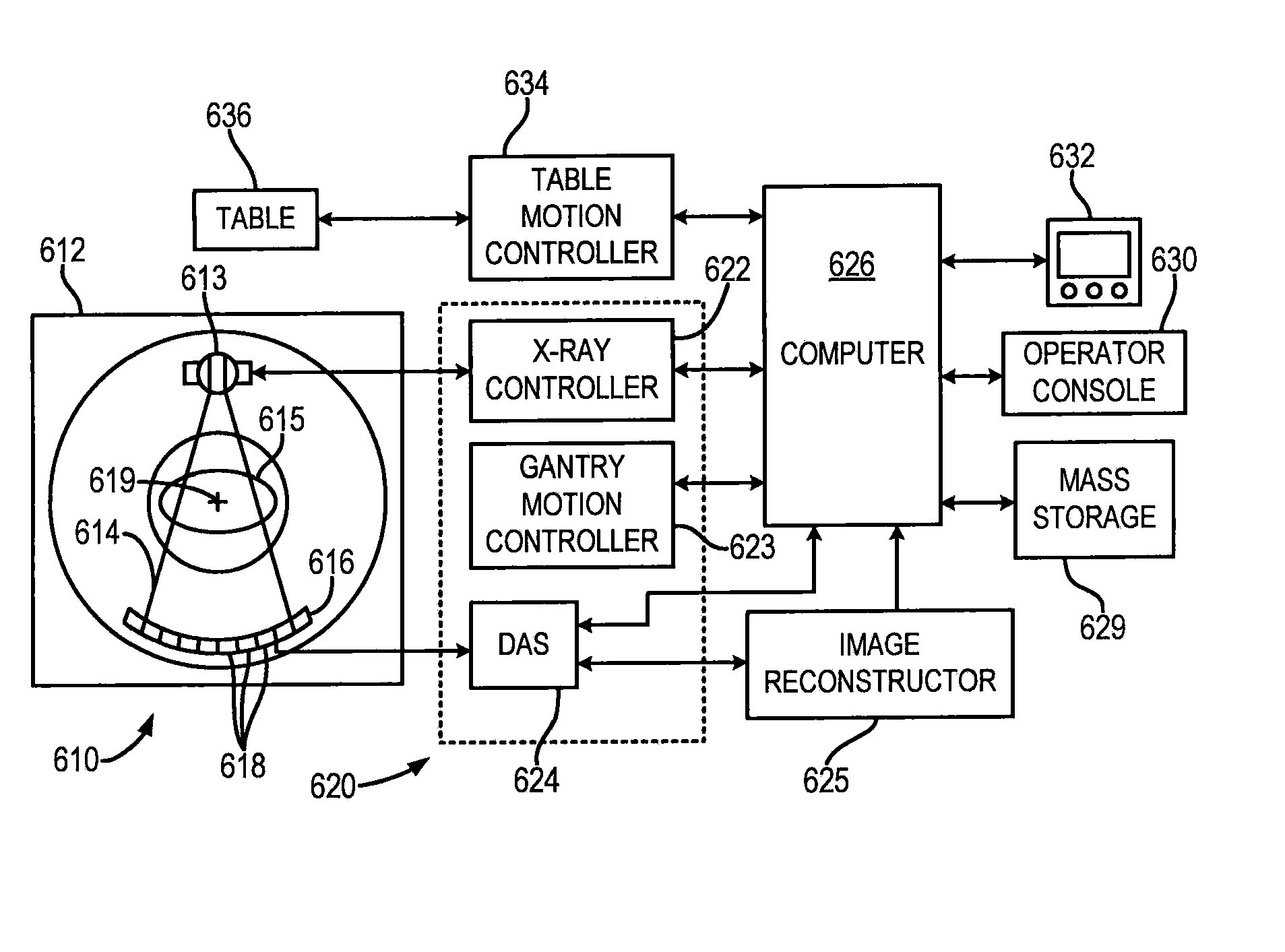
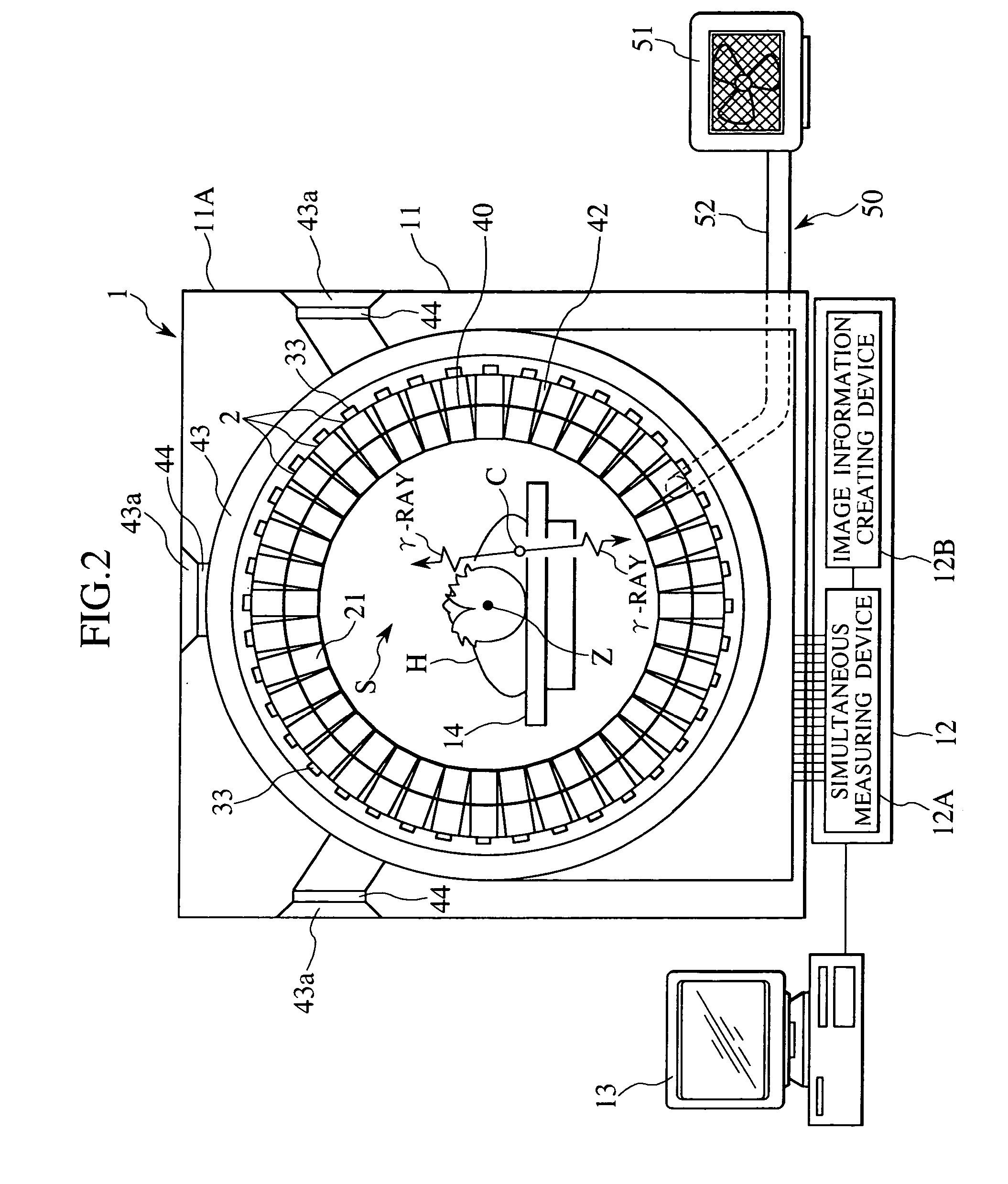
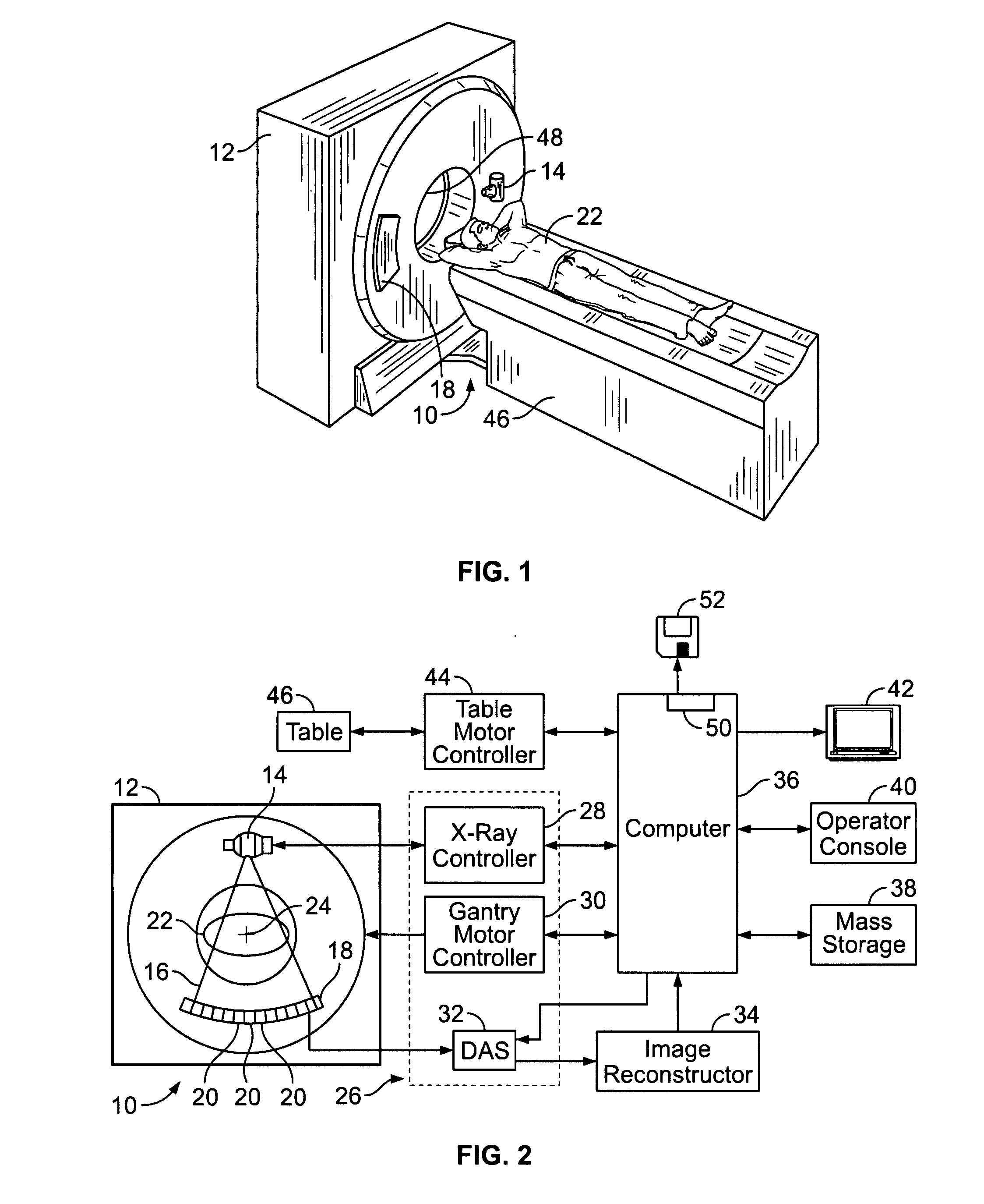
A radiotomography apparatus according to the present invention includes a radiation detection device that irradiates radiation from a radiation source in multiple directions around an object to be examined and detects radiation transmitted through the object from the multiple directions; a table on which the object lies and which can move the object in a body axis direction of the object; reconstruction parameter setting device that sets reconstruction parameters that include an amount of movement of the table in the body axis direction, and that are used to reconstruct an image of the object; a reconstruction view area calculating device that calculates a reconstruction view area for at least one data segment that is necessary for a reconstruction calculation that is determined for each spatial position that is reconstructed based on the set reconstruction parameters; a reference segment position setting device that sets a reference segment position in the calculated reconstruction view area according to a phase signal that is obtained by dynamic analysis of the object; an effective segment calculating device that calculates a data segment including the set reference segment position as an effective segment using a predetermined weight function; and an image creating device that creates an image by reconstructing the calculated effective segments. It is thus possible to provide a radiotomography apparatus that can both enhance temporal resolution and reduce ineffective radiation exposure.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Temporal and spatial shaping of multi-channel audio signals
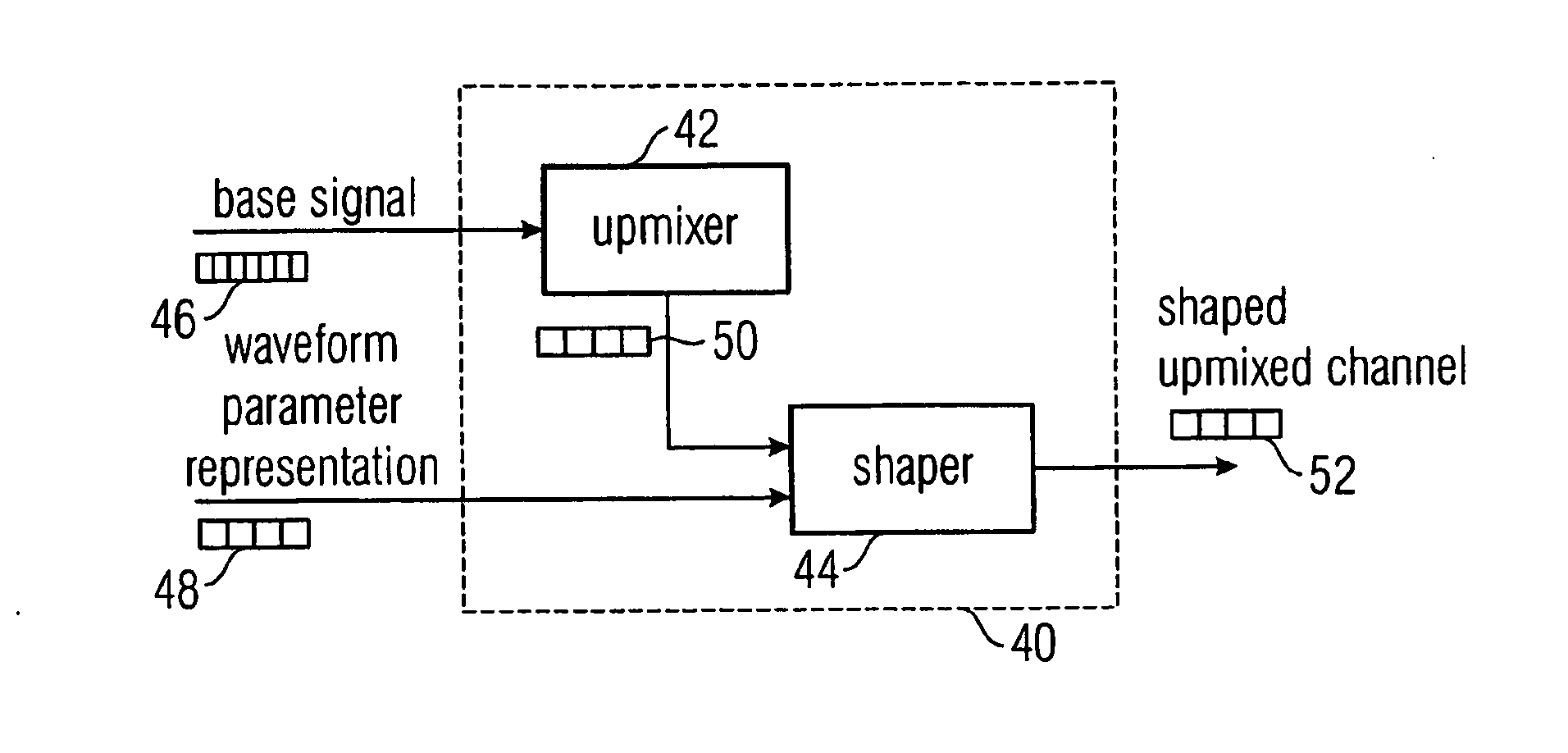
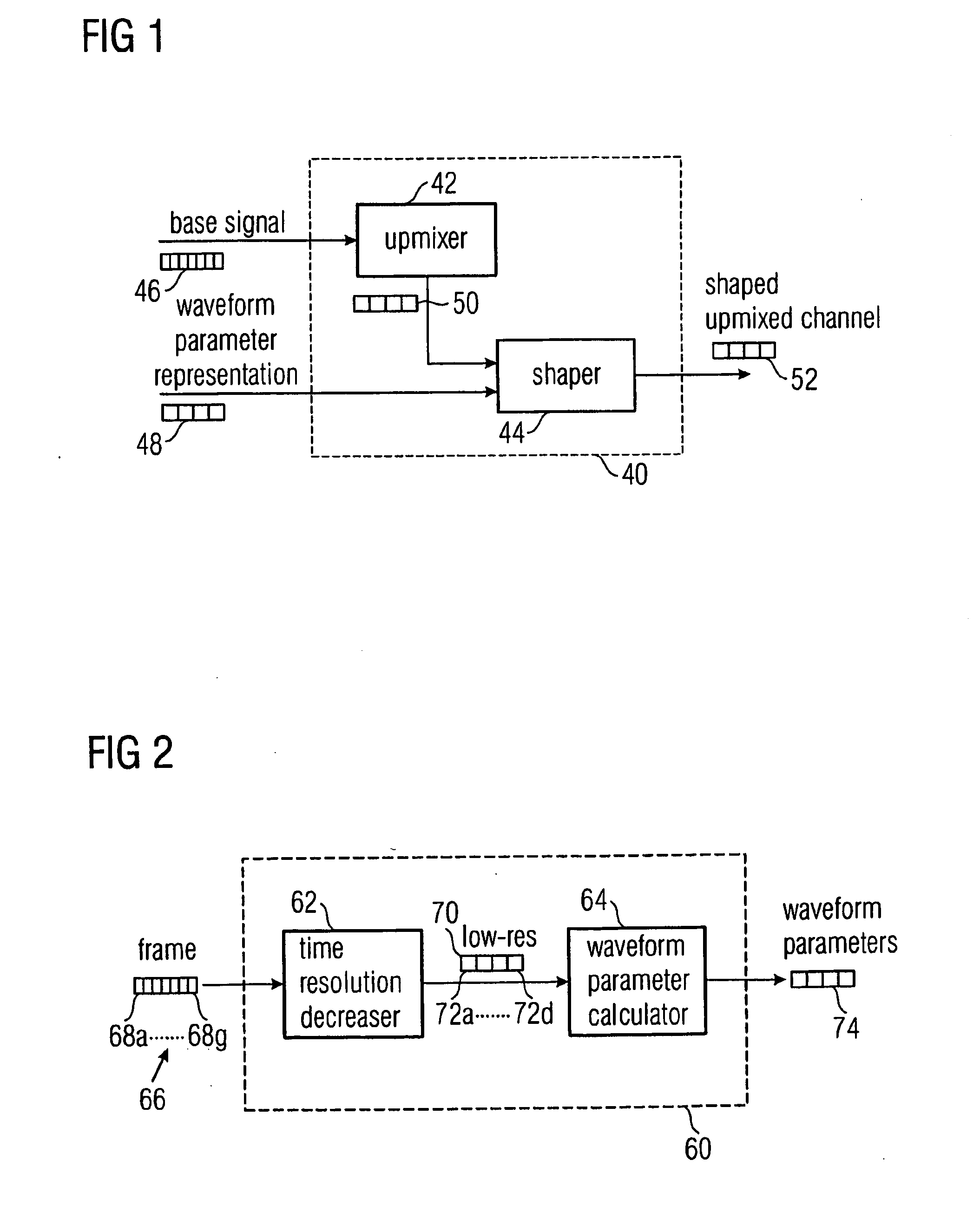
A selected channel of a multi-channel signal which is represented by frames composed from sampling values having a high time resolution can be encoded with higher quality when a wave form parameter representation representing a wave form of an intermediate resolution representation of the selected channel is derived, the wave form parameter representation including a sequence of intermediate wave form parameters having a time resolution lower than the high time resolution of the sampling values and higher than a time resolution defined by a frame repetition rate. The wave form parameter representation with the intermediate resolution can be used to shape a reconstructed channel to retrieve a channel having a signal envelope close to that one of the selected original channel. The time scale on which the shaping is performed is shorter than the time scale of a framewise processing, thus enhancing the quality of the reconstructed channel. On the other hand, the shaping time scale is larger than the time scale of the sampling values, significantly reducing the amount of data needed by the wave form parameter representation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +2
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveUS20060161060A1Faster and accurate perfusion mapImprove time resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac phaseRadio frequency
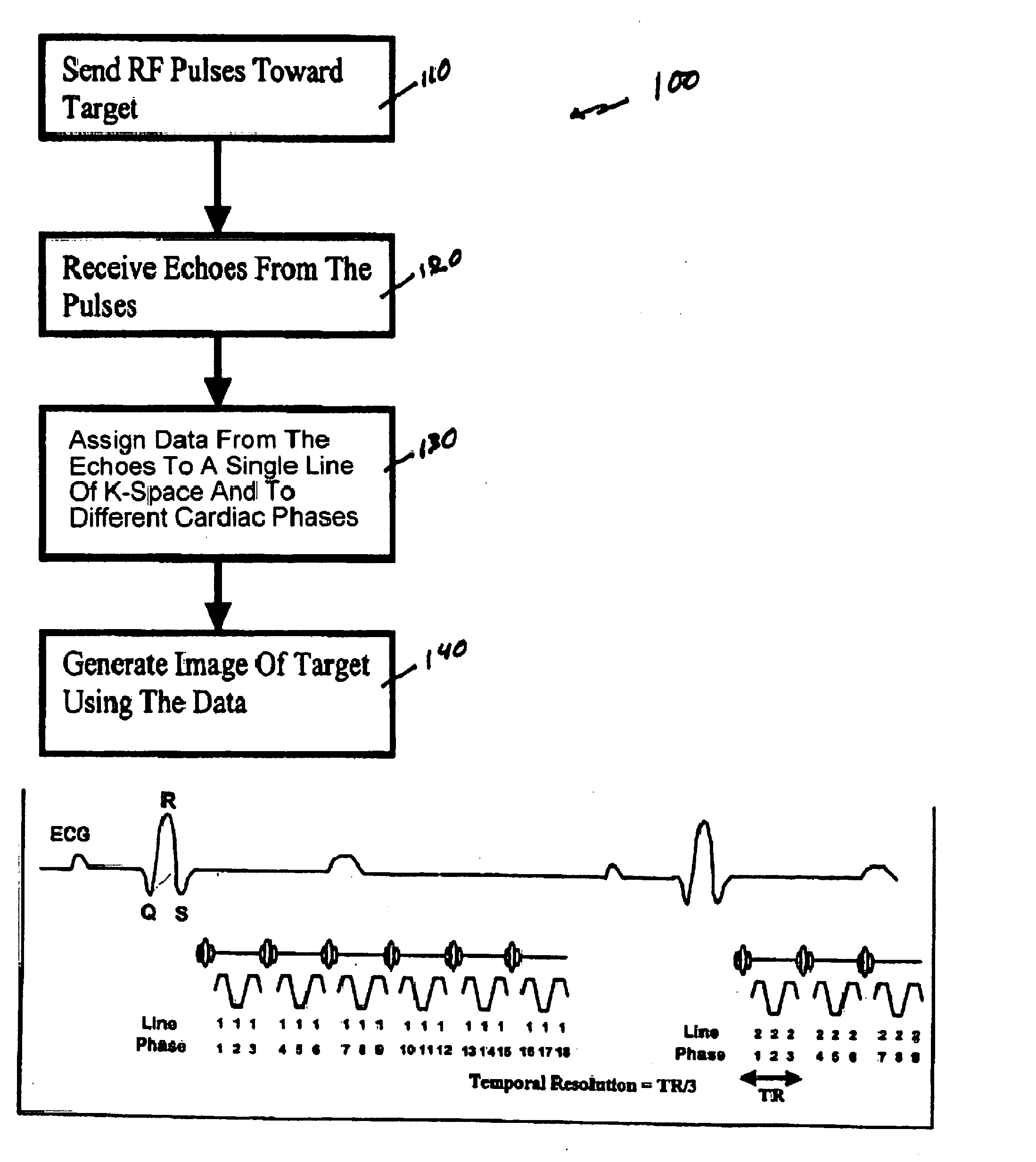
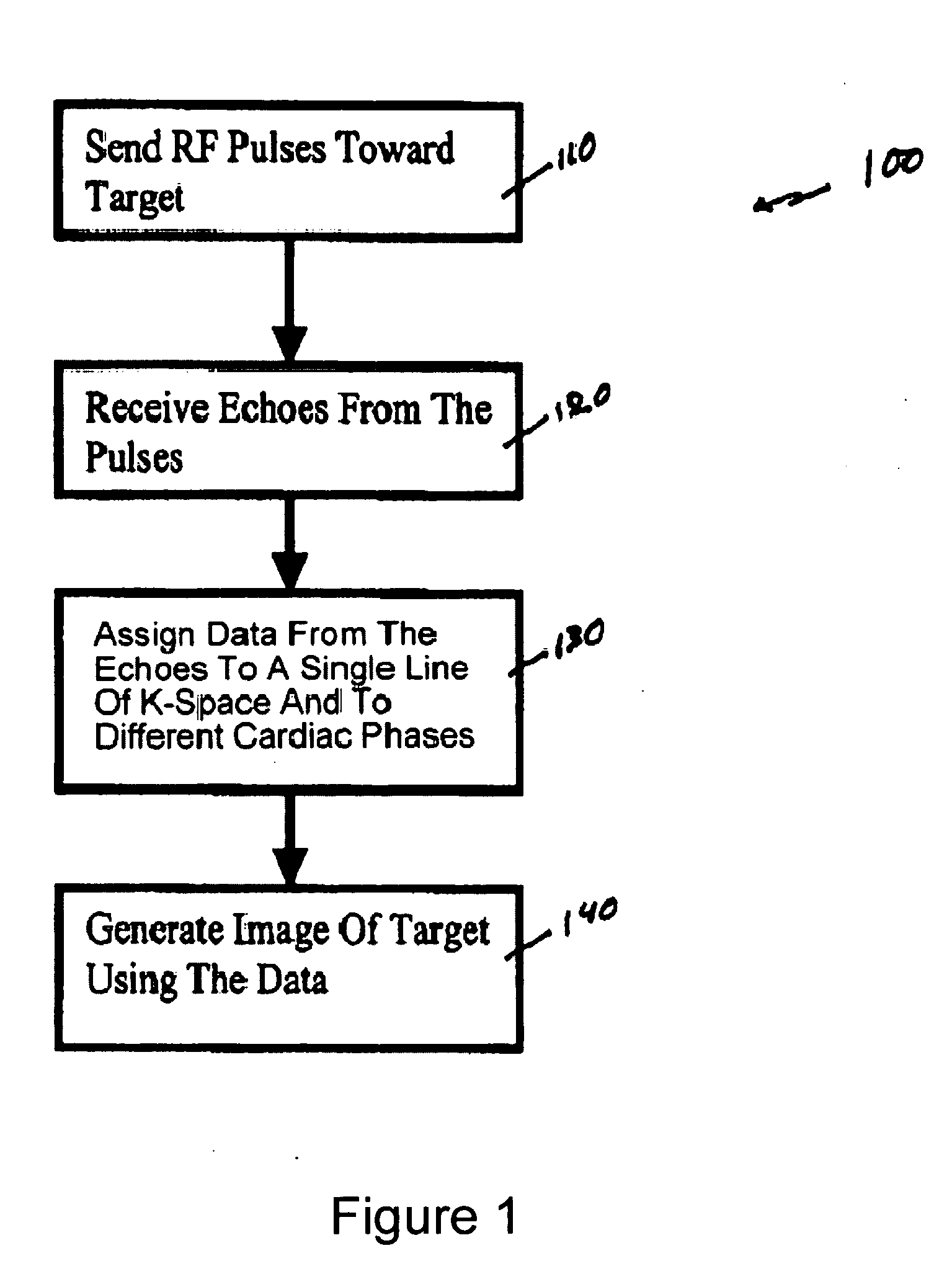
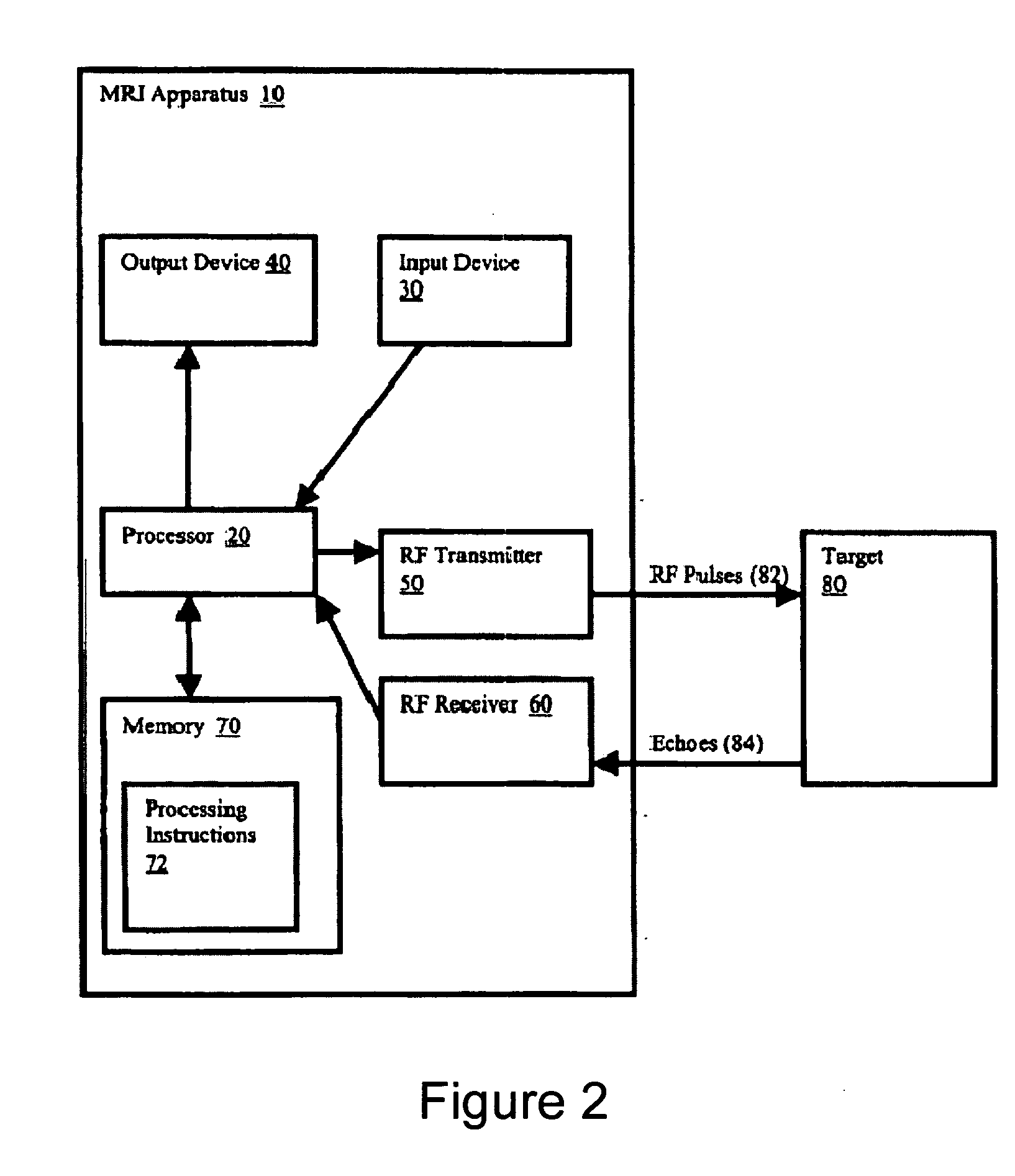
Method, systems and arrangements are provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target, such as a cardiac region of a patient. Radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by, e.g., an RF transmitter of an MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to the plurality of pulses may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, acceleration data and / or velocity data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes may be assigned to the same k-space line, and to different cardiac phases. In one further embodiment, parallel processing may be used to improve the resolution of the image acquired during a single breath-hold duration. In yet another embodiment, utilizing a segmented implementation, multiples lines of k-space are acquired for a given cardiac phase (or time stamp) per trigger signal. The present invention may be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest for the evaluation and study of flow dynamics with very high temporal resolution.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Small-sized low-power dissipation short-range radar that can arbitrarily change delay time between transmission and reception with high time resolution and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20070132633A1Improve time resolutionSimple configurationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionEngineering
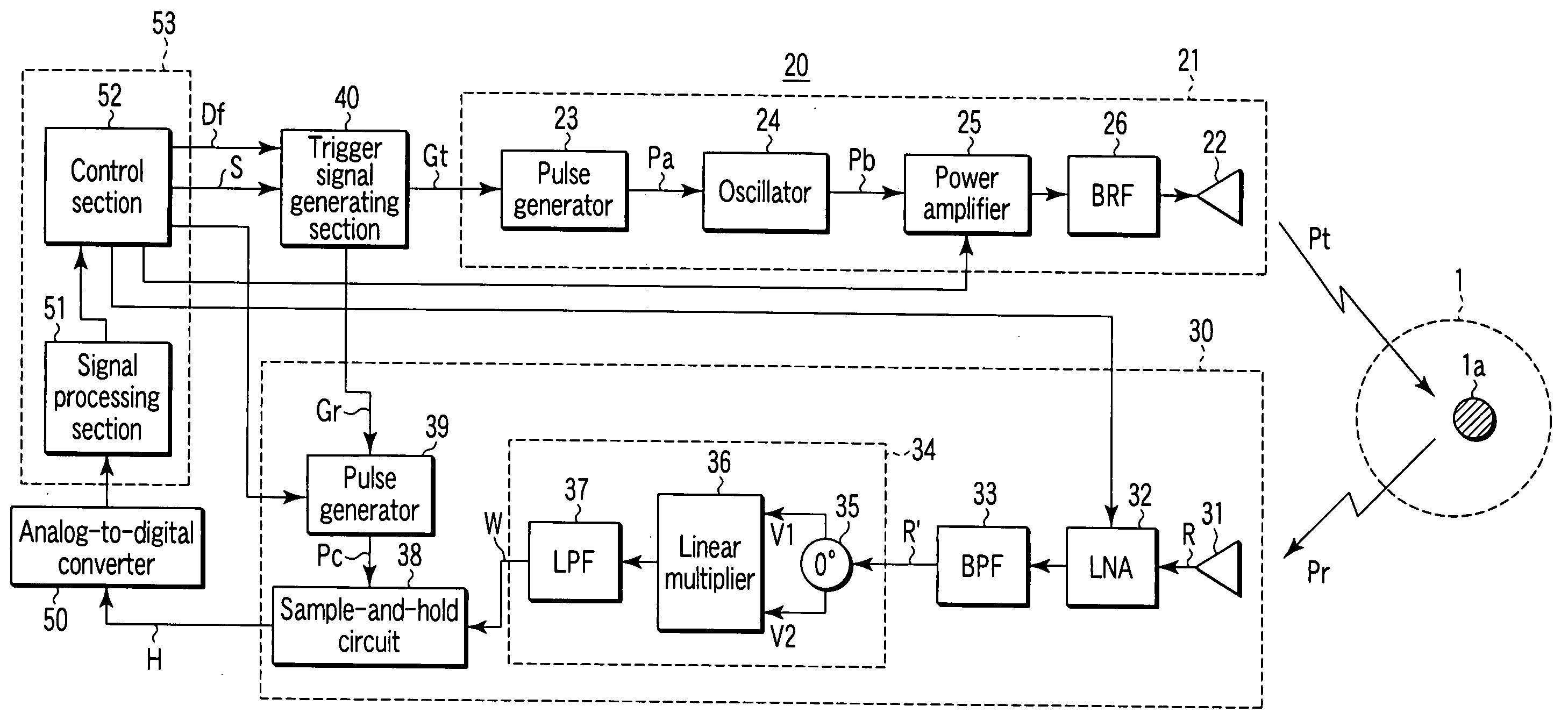
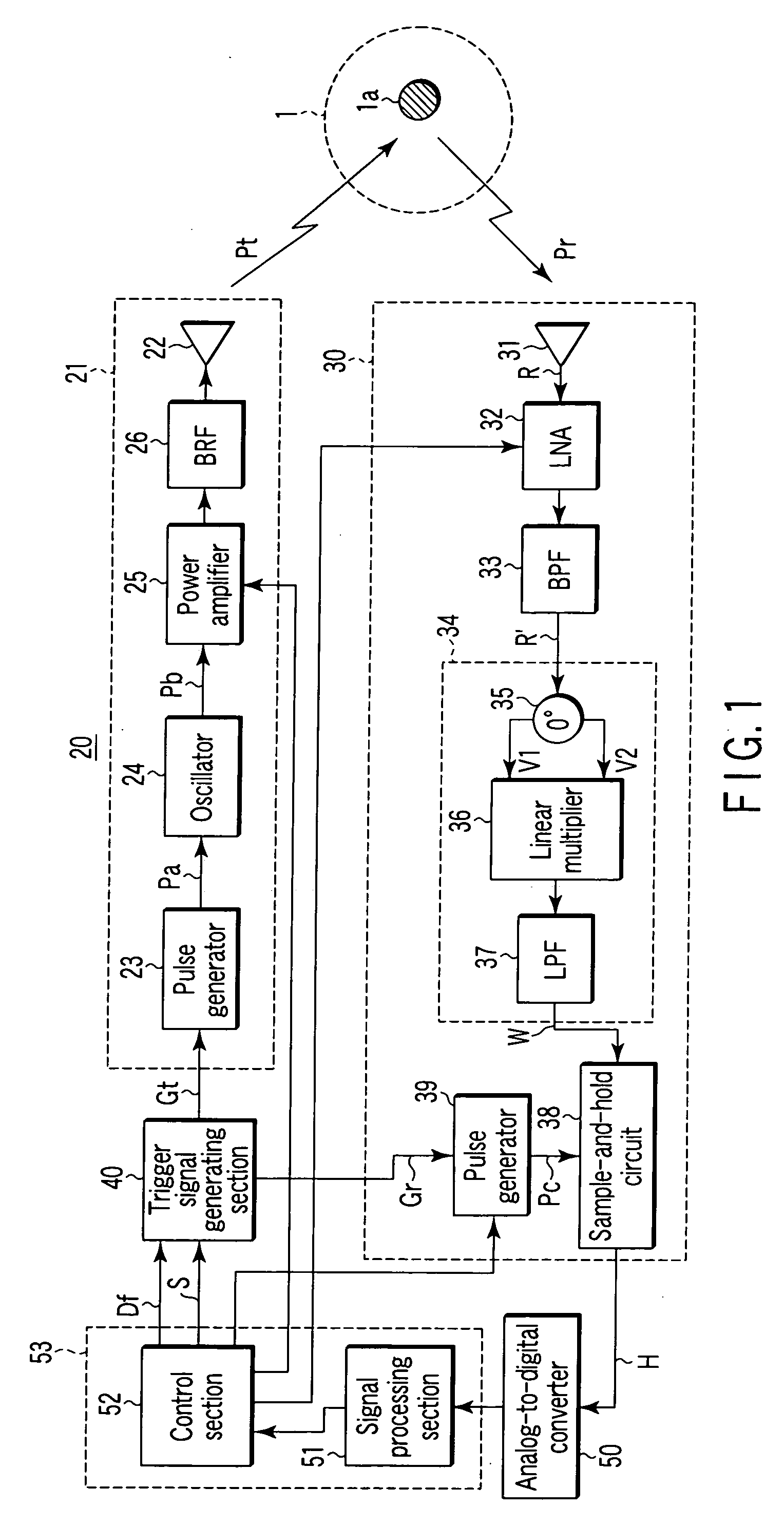
In a configuration according to a short-range radar of the present invention and a method of controlling the same, the timing at which a variable-period pulse output from a variable-period pulse generator including a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) has shifted in level first since reception of a search instruction is used as a reference timing, so that a signal that shifts in level at the reference timing or a fixed lapse of time later than the reference timing is generated and output as a transmission trigger signal, and a signal that shifts in level at a timing delayed by half a period of the variable-period pulse or its integral multiple from the timing at which the transmission trigger signal is output is generated and output as a reception trigger signal. With this, by varying beforehand frequency data of the DDS based on the relationship between the frequency data and delay time between transmission and reception stored in a memory, it is possible to vary delay time between the transmission trigger signal and the reception trigger signal. It is thus possible to arbitrarily vary the delay time between transmission and reception at a high time resolution by using a simple configuration and low power dissipation.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP +1
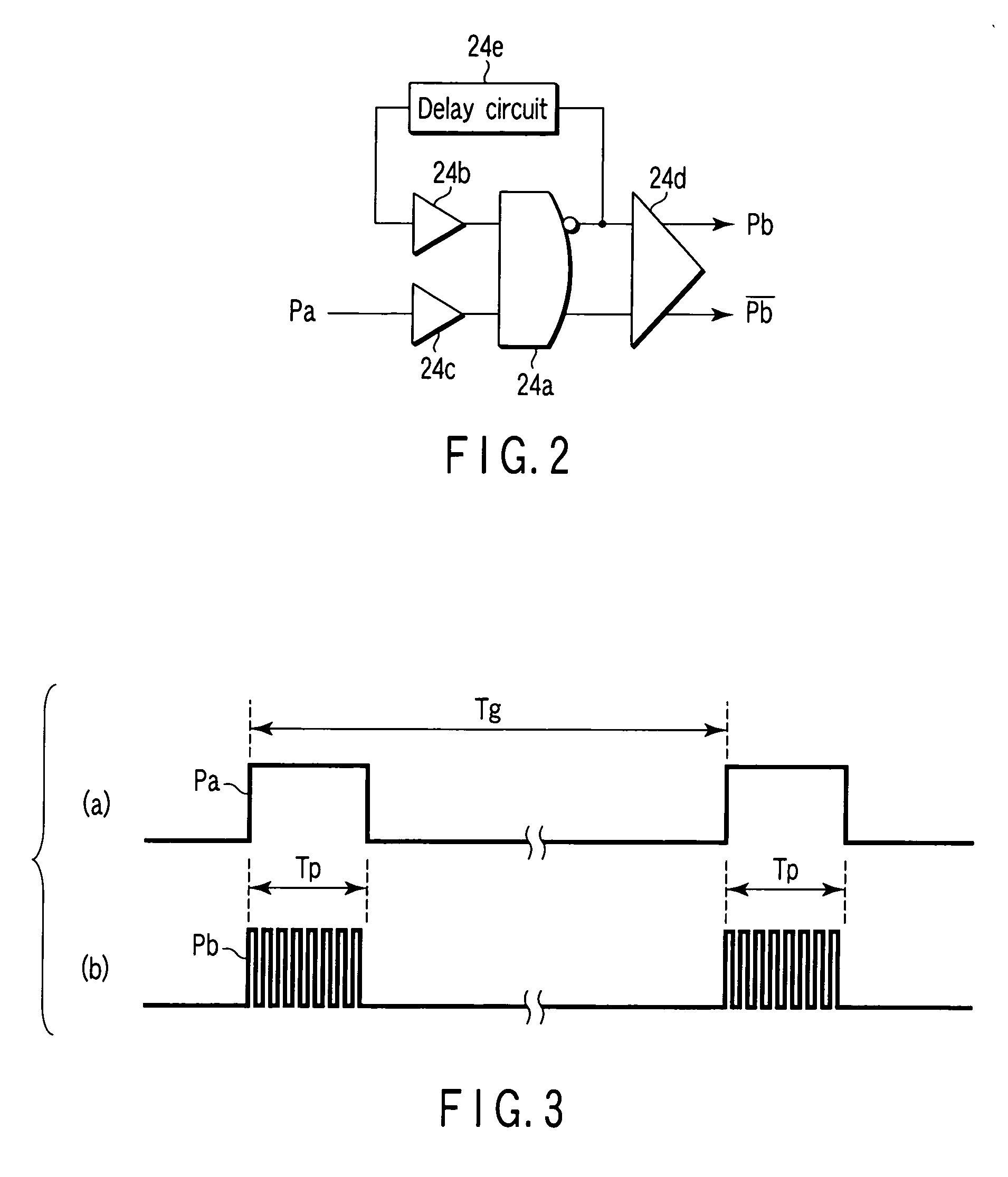
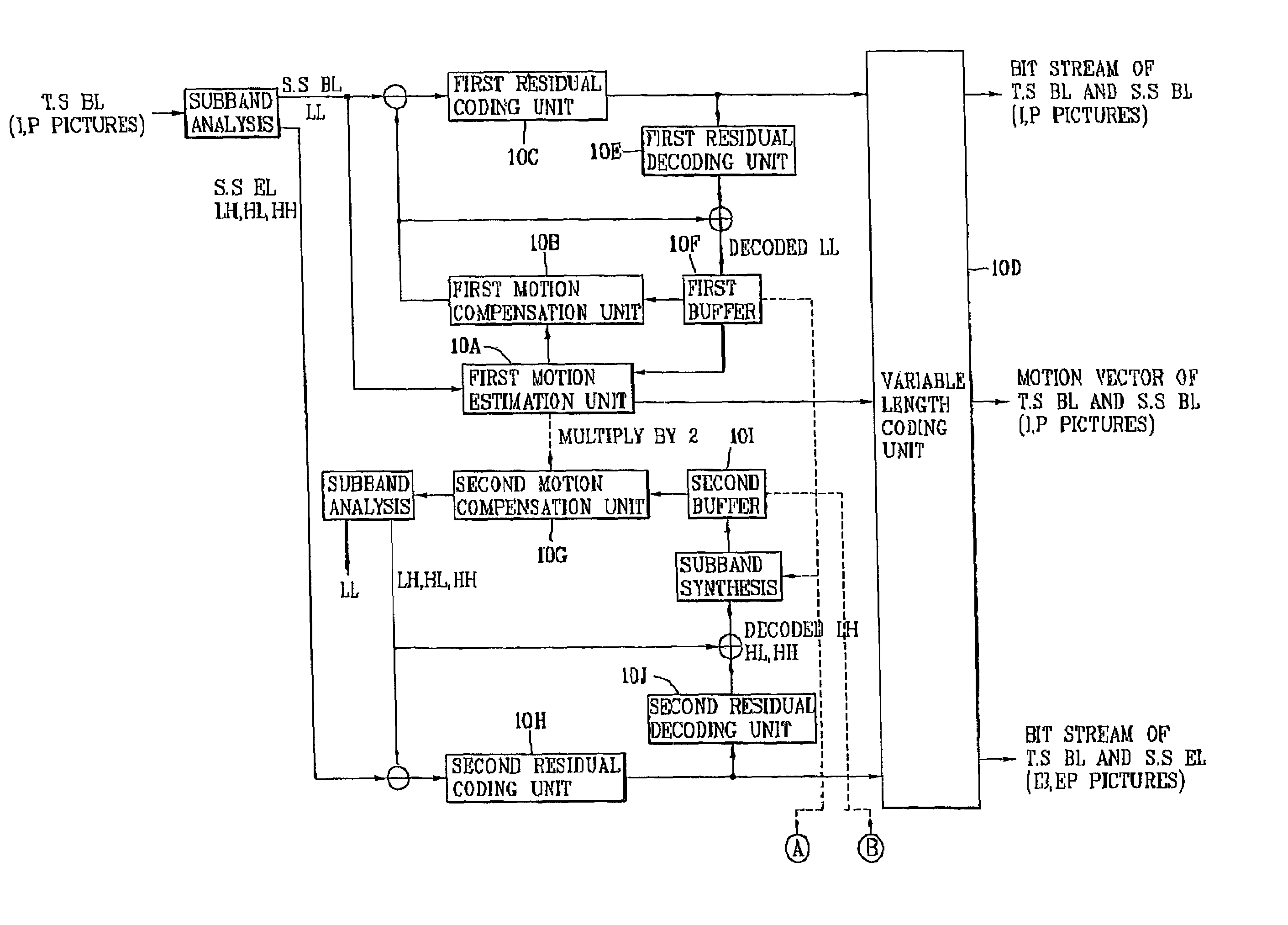
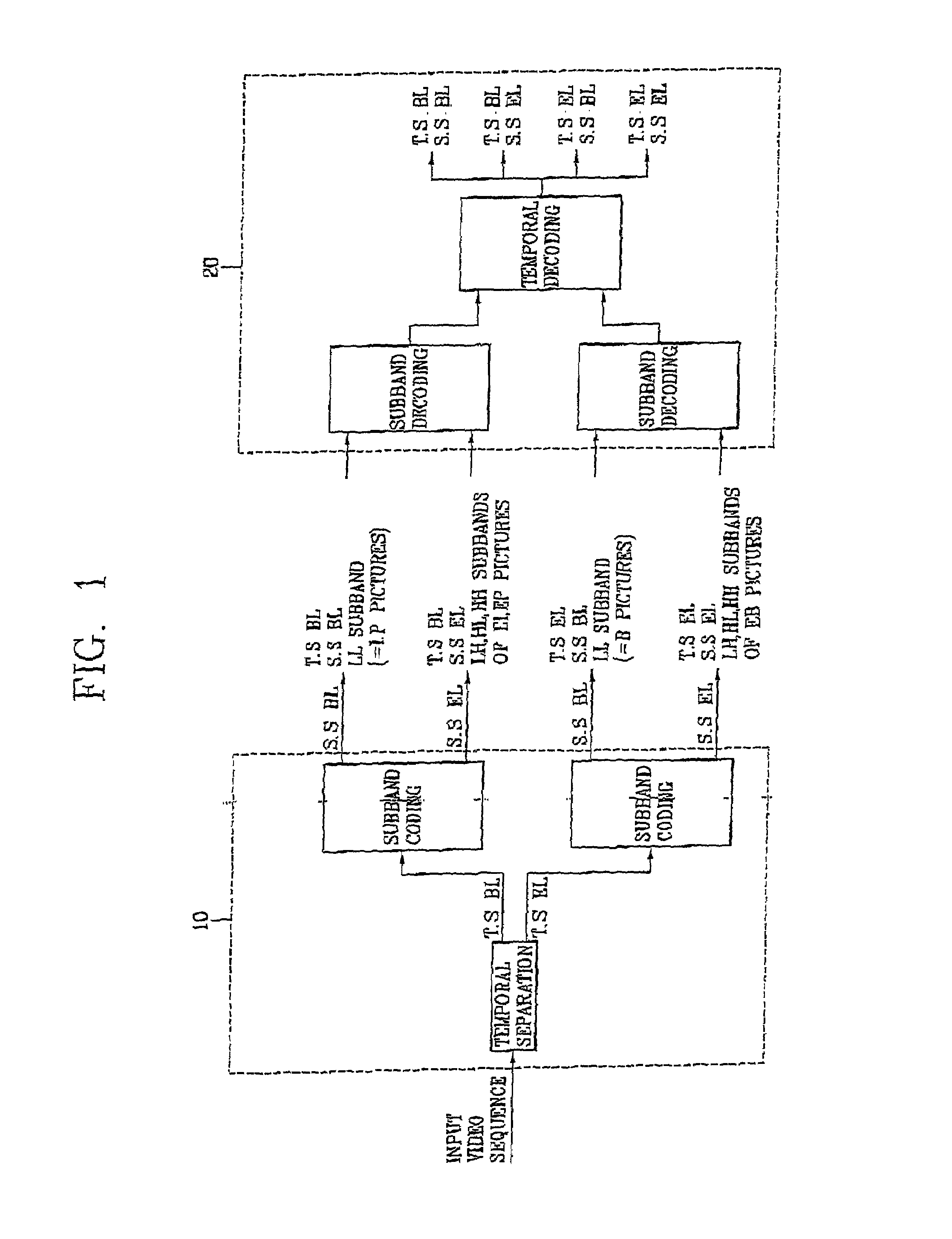
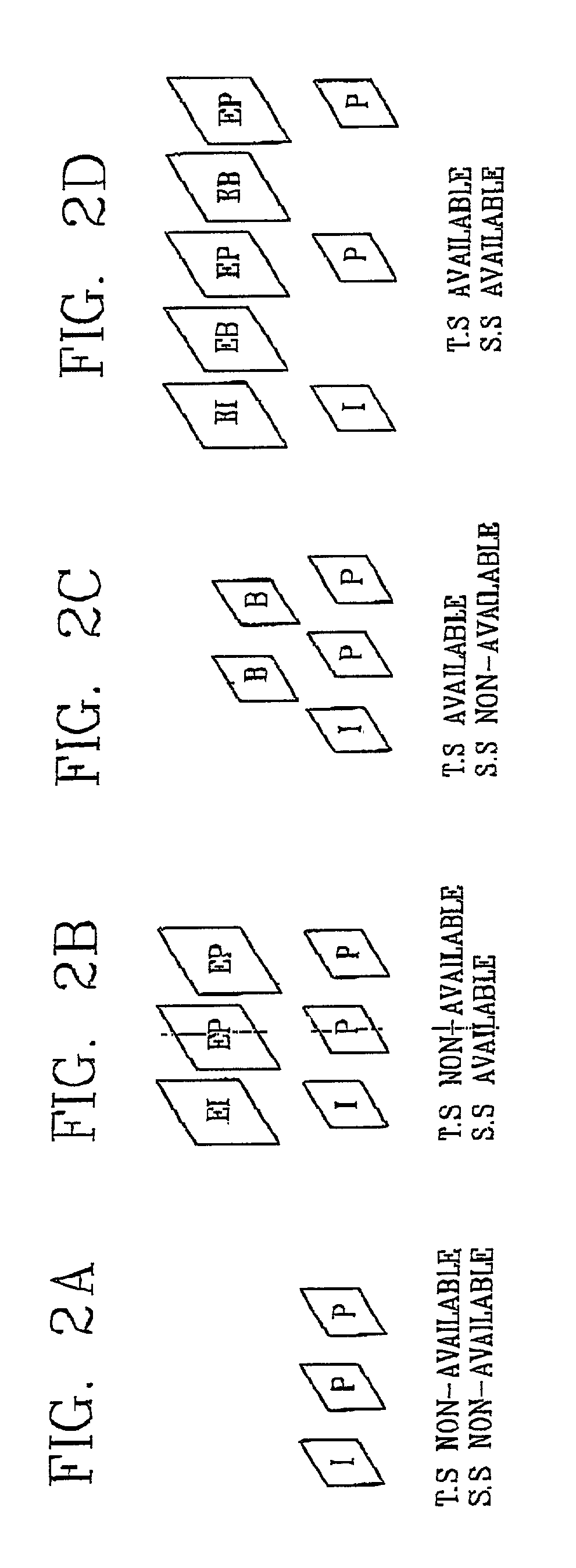
Spatio-temporal hybrid scalable video coding apparatus using subband decomposition and method
InactiveUS7027512B2Maximize efficiencyReduce the ratioPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesTemporal resolutionComputation complexity
In video coding techniques, in order to improve a coding efficiency and reduce a computational complexity sharply by mixing a temporal scalability and a spatial scalability, a spatio-temporal hybrid scalable video coding method using subband decomposition in accordance with the present invention includes classifying an input picture sequence into a picture of a low frame frequency BL (base layer) and a picture of a high frame frequency EL (enhancement layer) by sampling the sequence according to a time axis; decomposing the pictures on the BL and the EL into four subbands (LL, LH, HL, HH), coding the low frequency element subband (LL) at the spatial scalability BL having a low spatial resolution and coding the rest subbands (LH, HL, HH) at the EL having a high spatial resolution; decoding coding data of the temporal scalability BL in order to get a picture having a low temporal resolution and decoding coding data of the temporal scalability BL and the temporal scalability EL together in order to get a picture having a high temporal resolution; and decoding the subband (LL) of the spatial scalability BL in order to get a picture having a low spatial resolution and decoding the low frequency element subband (LL) and the high frequency element subbands (LH, HL, HH) together in order to get a picture having a high spatial resolution.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
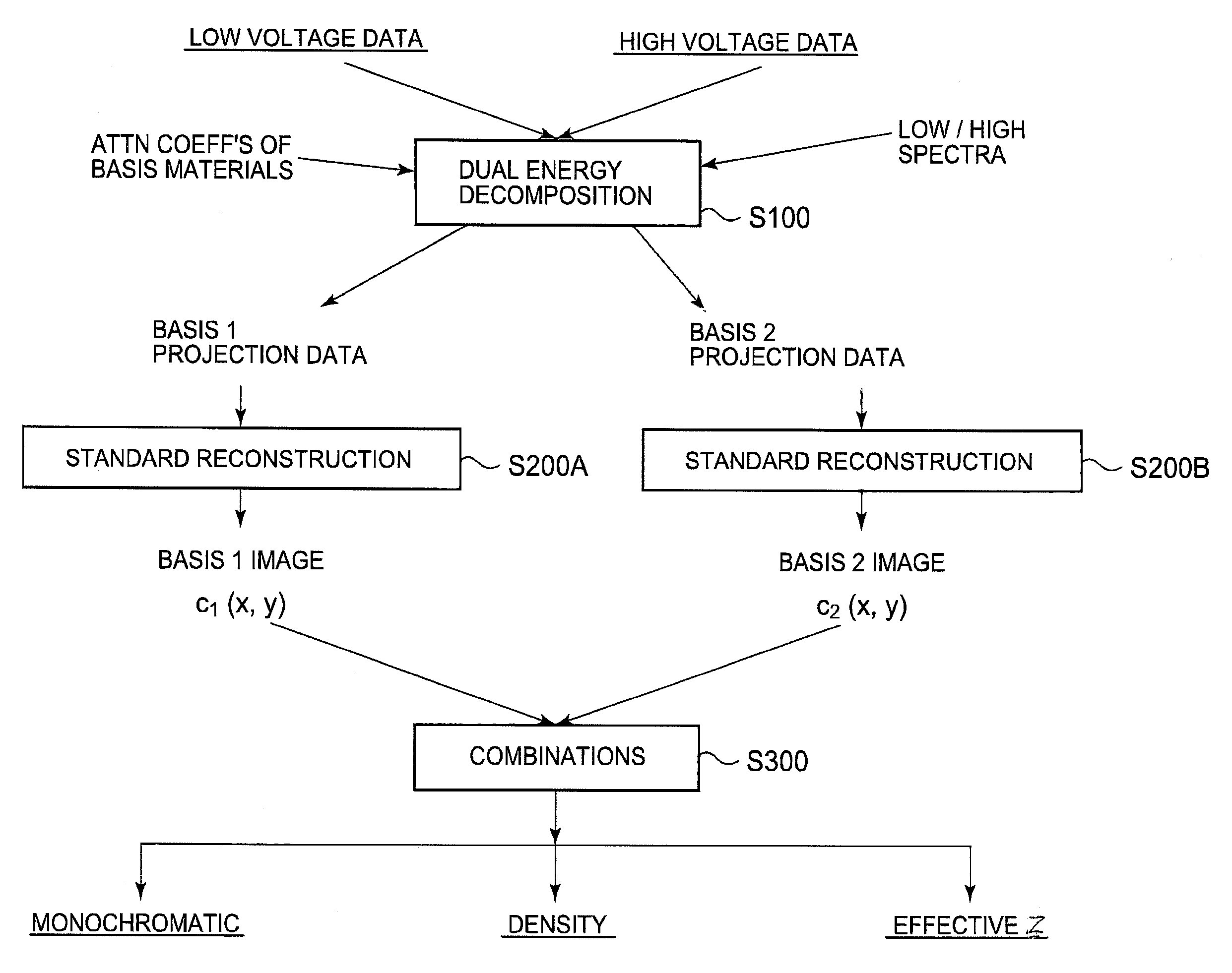
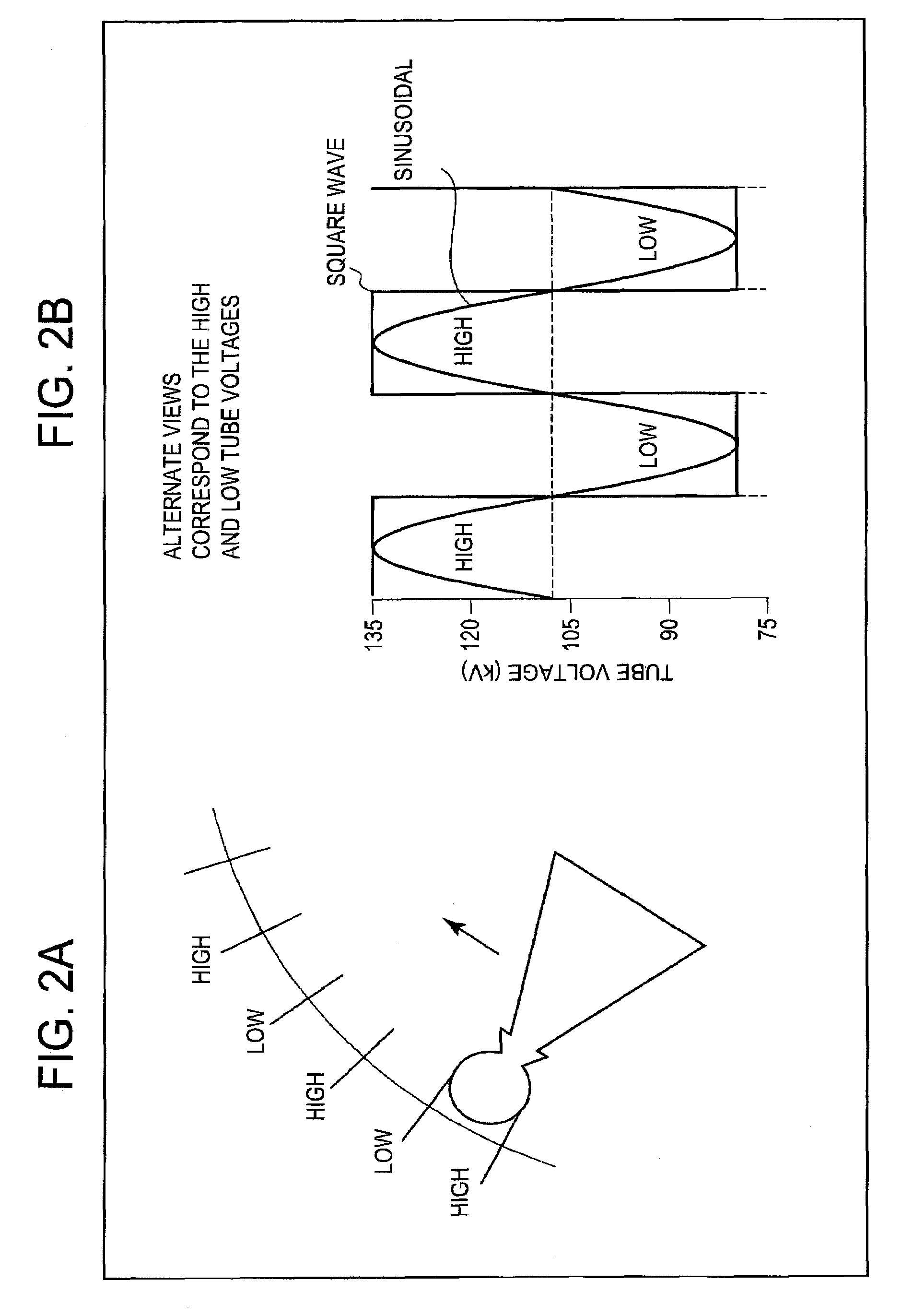
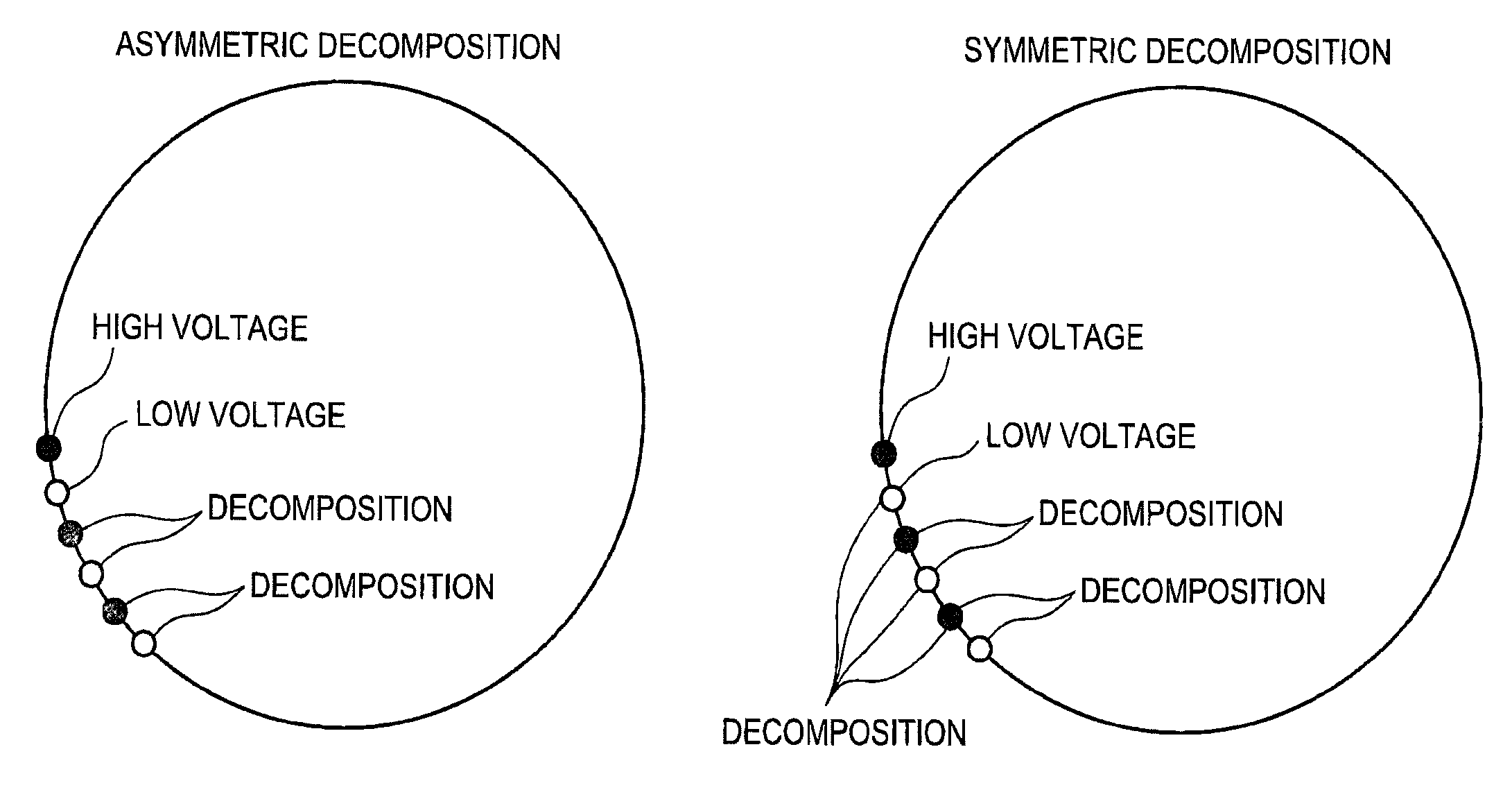
METHOD OF PRE-RECONSTRUCTION DECOMPOSITION FOR FAST kV-SWITCHING ACQUISITION IN DUAL ENERGY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT)
ActiveUS20100189212A1Quick switchReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFrequency spectrumLow voltage
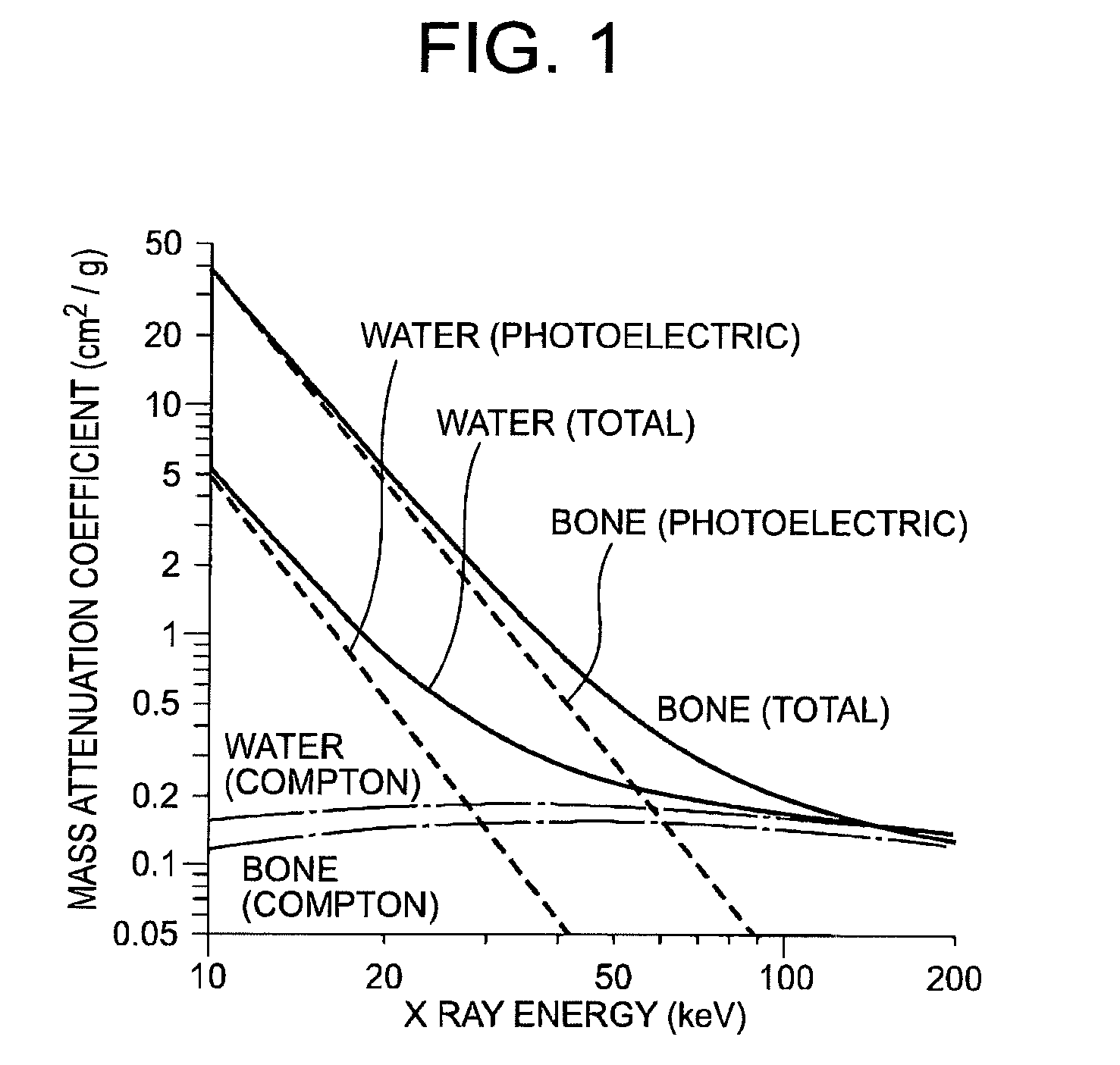
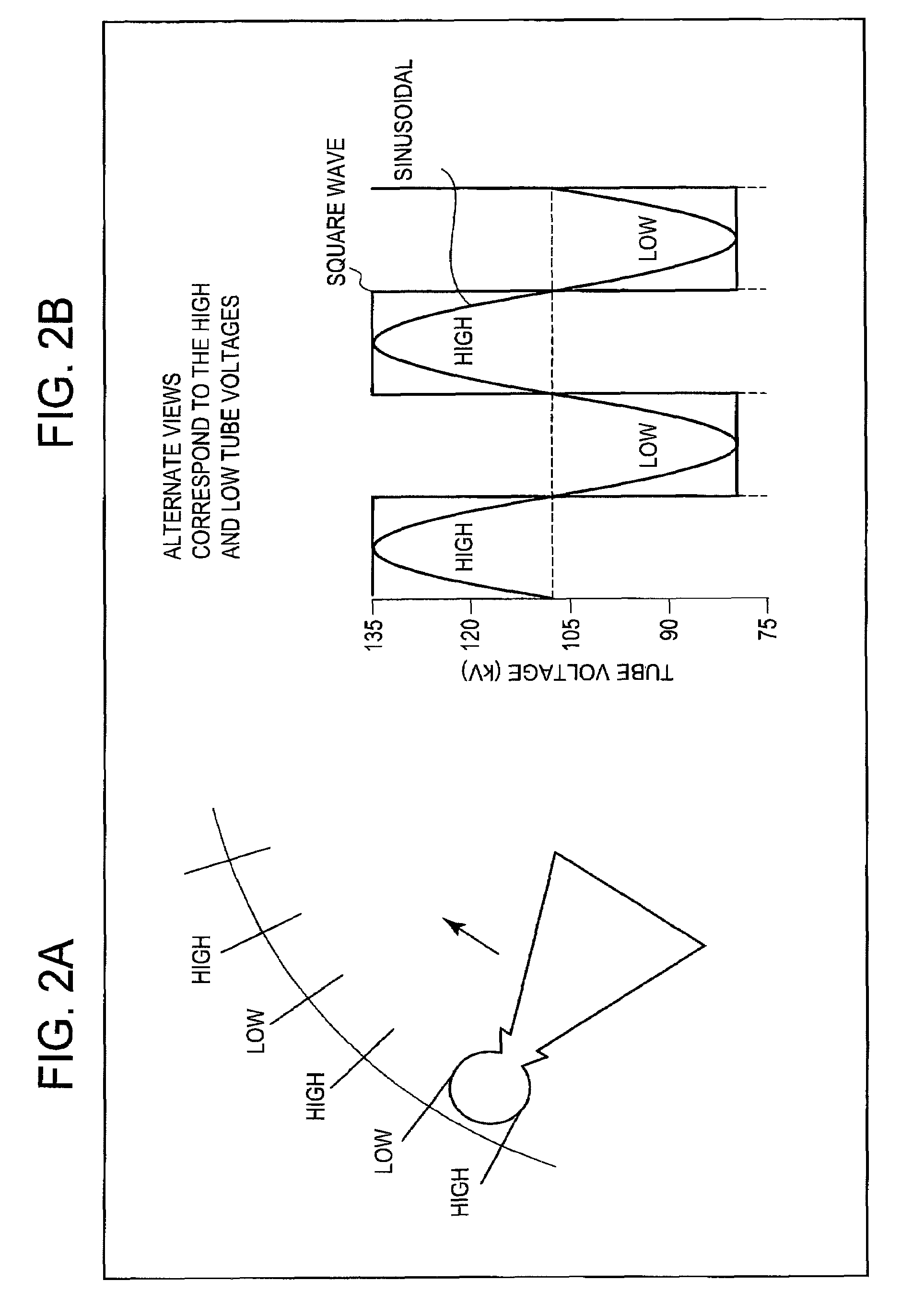
Fast kV-switching is a dual energy acquisition technique in computed tomography (CT) in which alternating views correspond to the low and high tube voltages. Its high temporal resolution and its suitability to a variety of source trajectories make it an attractive option for dual energy data acquisition. Its disadvantages include a one-view misregistration between the data for high and low voltages, the potentially poor spectrum separation due to the more-like a sine wave rather than the desired square wave in fast kV-switching, and the higher noise in the low voltage data because of the technical difficulty in swinging the tube current to counter the loss of x-ray production efficiency and loss of penetration at lower tube voltages. Despite the disadvantages, symmetric view matching according to the current invention substantially improves streaks and other artifacts due to the view misregistration, sufficient spectrum separation even in a sinusoidal waveform swinging between 80 kV and 135 kV, and contrast-to-noise for the simulated imaging task maximized at monochromatic energy of 75 keV.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
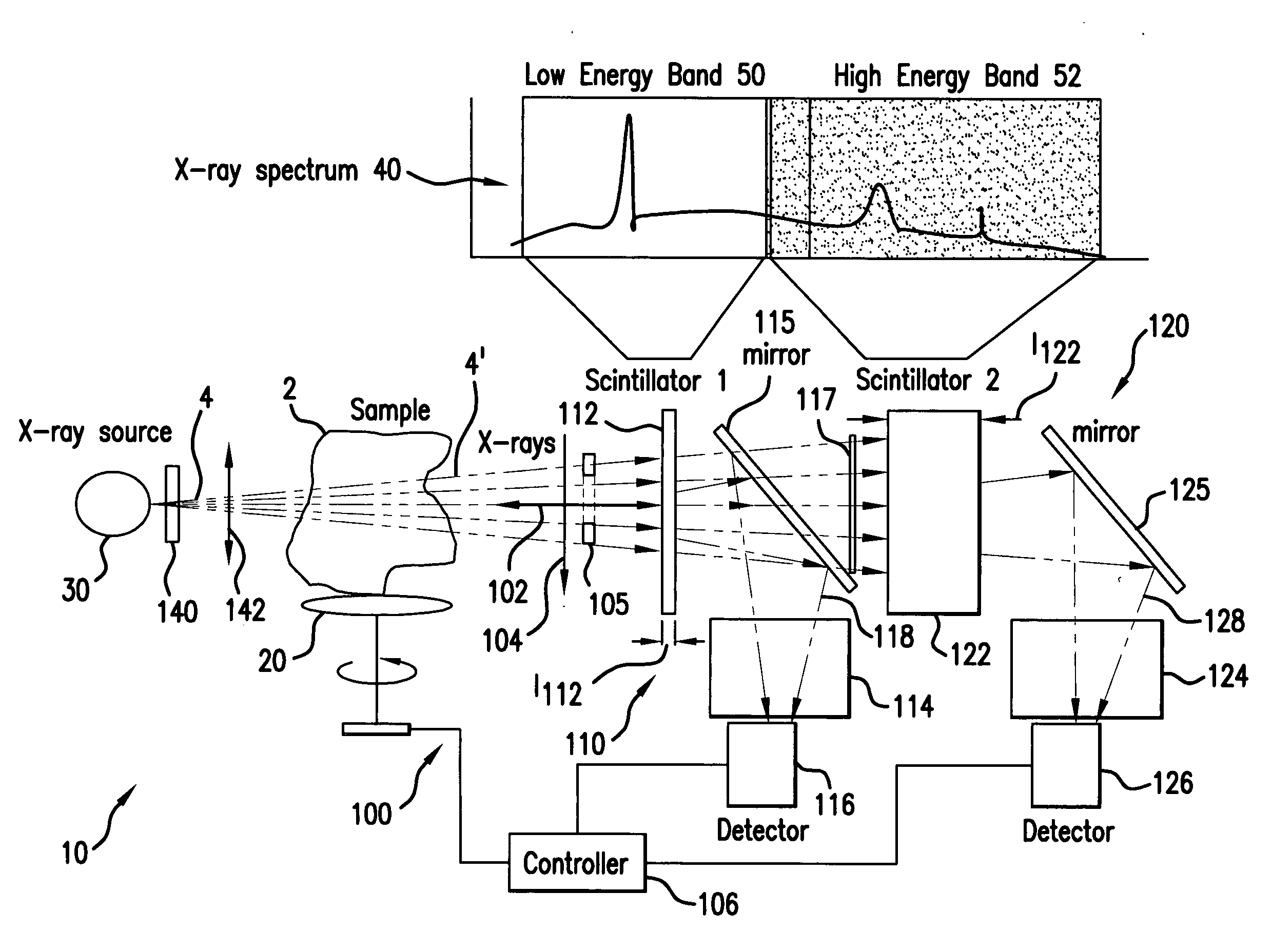
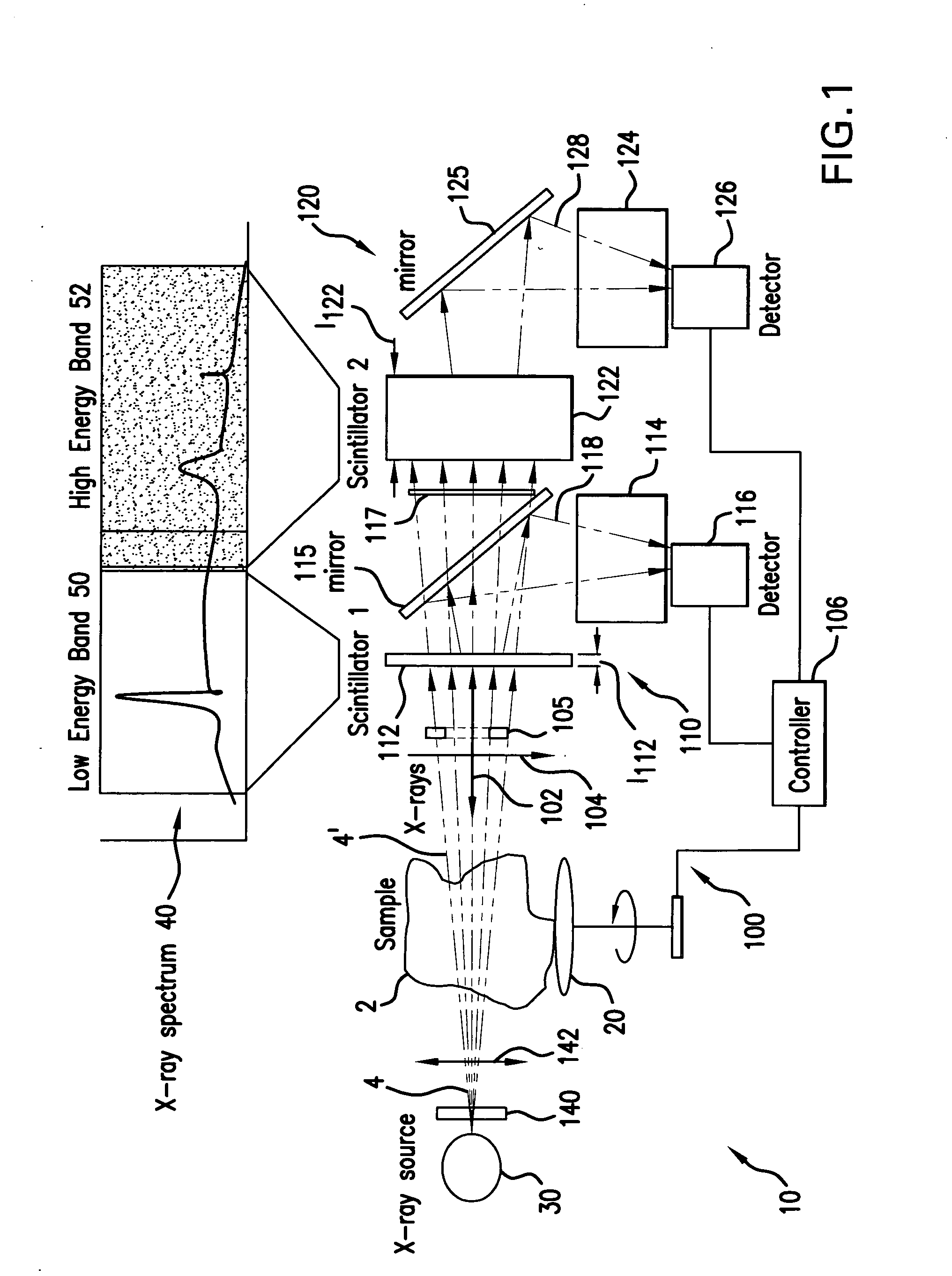
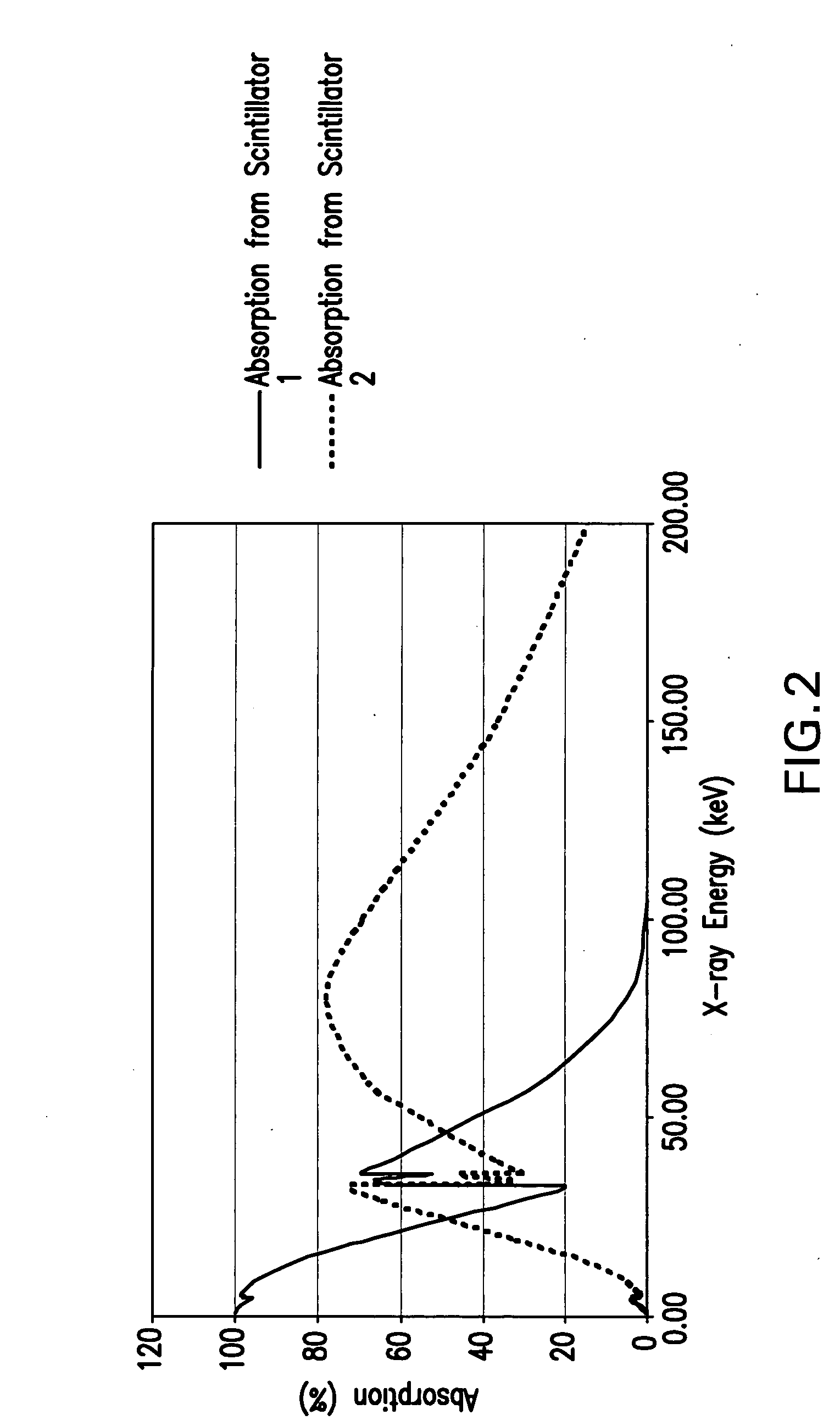
Dual-band detector system for x-ray imaging of biological samples
ActiveUS20050226376A1Easy to implementEasy to deployImaging devicesPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsX-rayHigh temporal resolution
A digital dual-band detector functions as an imaging platform capable of extracting hard and soft tissue images, for example. The detector has a first detector system comprising a first scintillator for converting x-rays from a sample to an first optical signal, and a first detector for detecting the first optical signal in combination with a second detector system comprising a second scintillator for converting x-rays from the sample and passing through the first scintillator to a second optical signal, and a second detector for detecting the second optical signal. The detector can facilitate the implementation and deployment of recent developments and can permit low cost practical deployment in clinical applications as well as biomedical research applications where significant improvement in spatial resolution and image contrast is required. These improvements include an increase of feature detection sensitivity by more than an order of magnitude, simultaneous imaging of soft and hard (or mineralized) tissue at extremely high time resolution that is not limited by detector readout speed, and an increase in the signal to noise ratio of images by reducing the substantial background resulting from Compton scattering.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Atmospheric detection laser radar based on superconducting single-photon detector
ActiveCN106054209AImprove time resolutionHigh range resolutionElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationPhoton detectionOptical processing
The invention discloses an atmospheric detection laser radar based on a superconducting single-photon detector. Optical pulse emitted by a laser pulse generation unit points to a detected atmosphere through a transmitting telescope and a laser scanning unit, background noise of an atmospheric echo signal is filtered out by an optical preprocessing unit, an optical processing unit extracts atmospheric information, a superconducting single-photon detection unit detects the atmospheric echo signal, a data acquisition card collects the signal, and finally, a subsequent data inversion and display unit inverts and displays atmospheric parameter information. The atmospheric detection laser radar of the invention is different from the existing atmospheric detection laser radar in that the atmospheric detection laser radar of the invention uses a superconducting single-photon detector with low dark count, high quantum efficiency, wide wavelength response and low time jitter as a detection unit. By using the superconducting single-photon detector, the atmospheric detection laser radar has the advantages of high spatial resolution, high temporal resolution, large detection distance, high detection precision, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
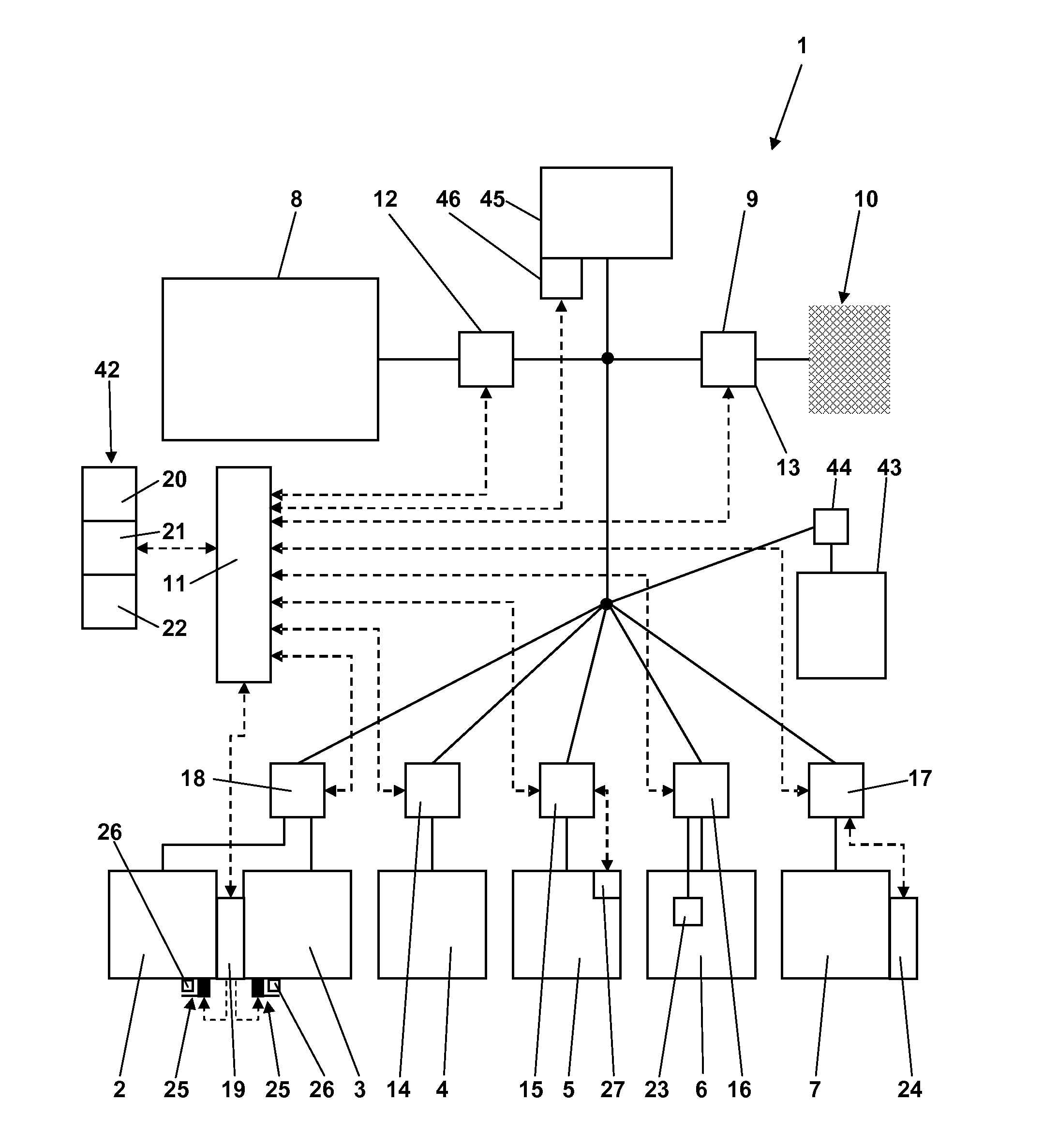
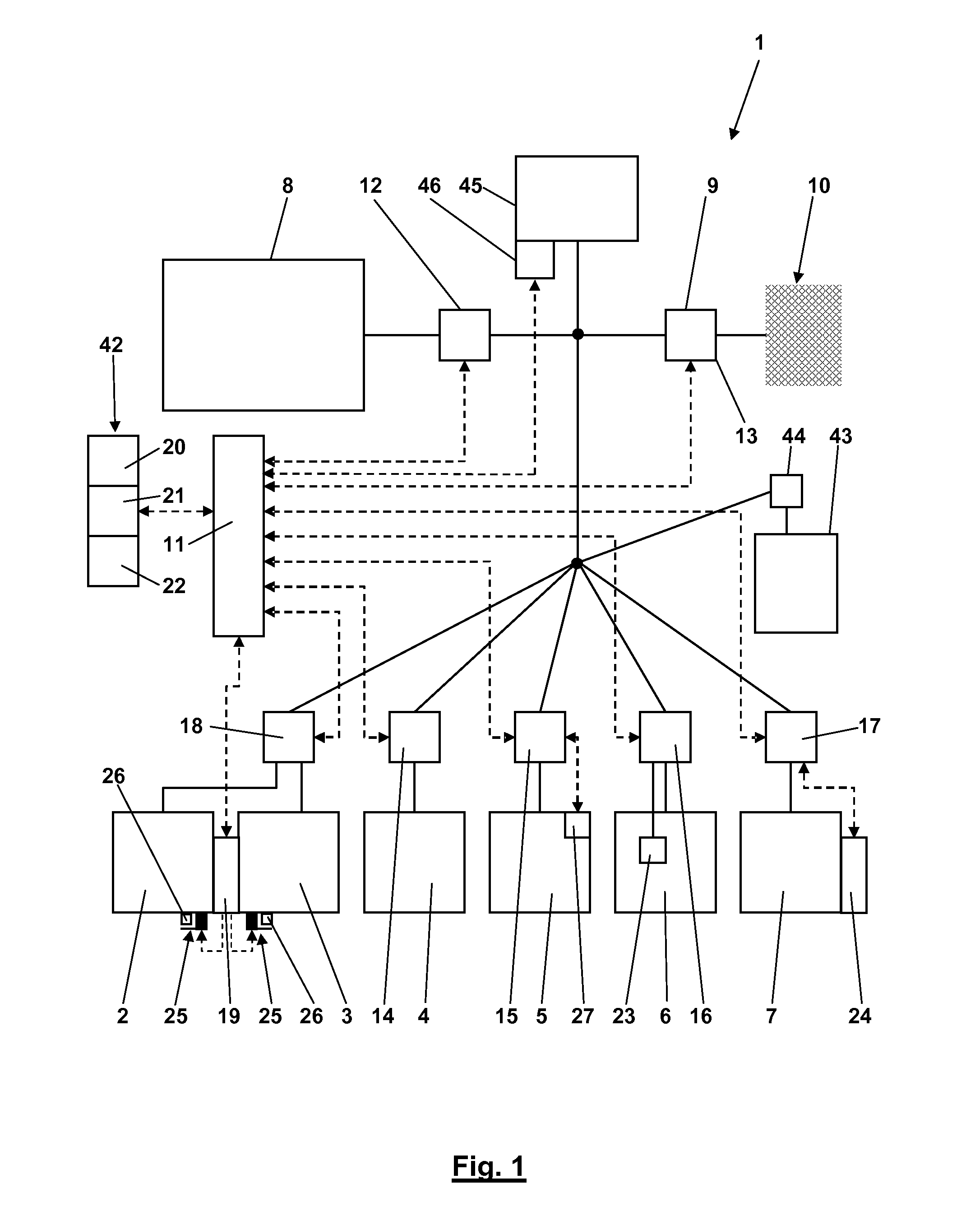
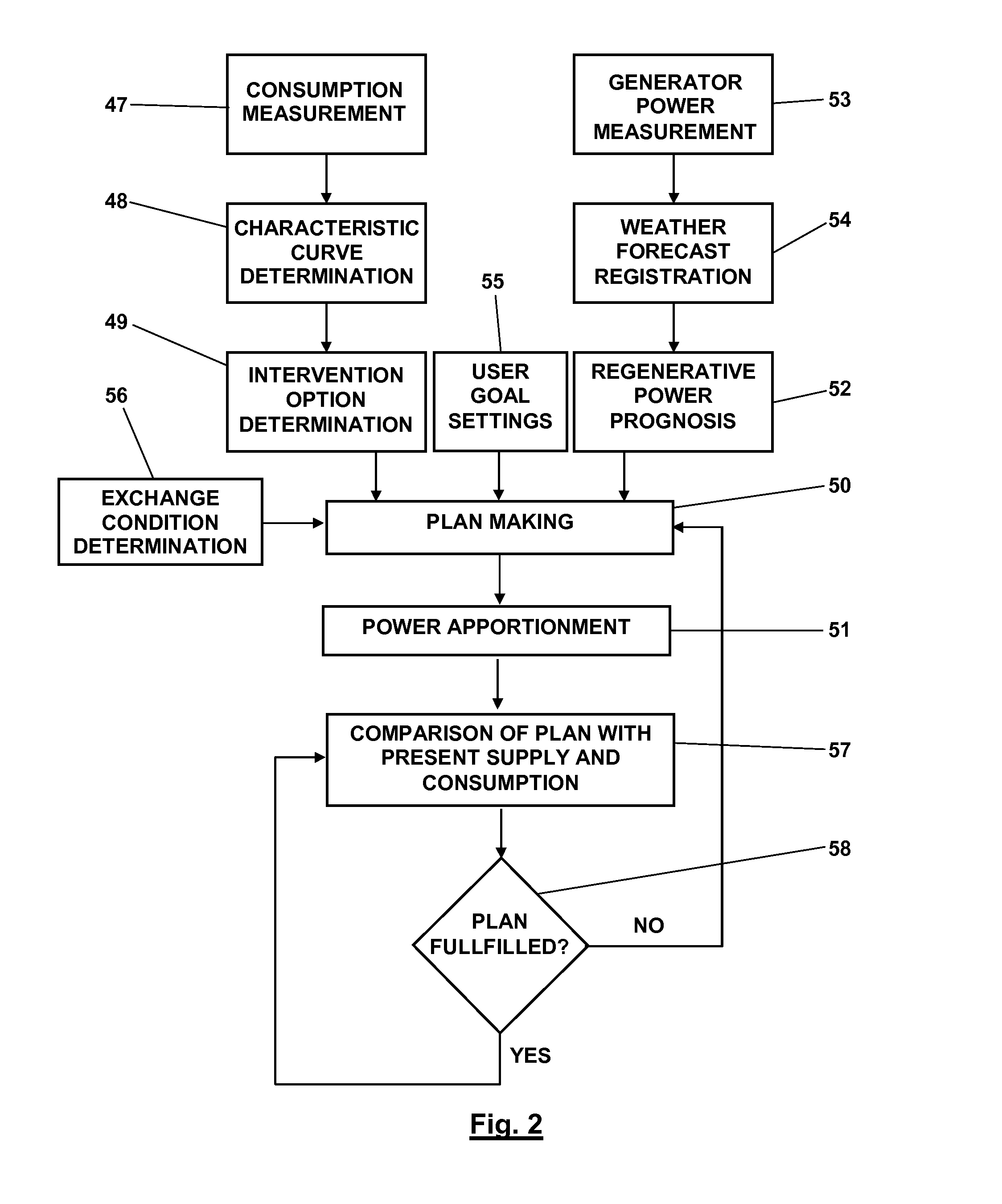
Optimized Load Management
ActiveUS20140046495A1Mechanical power/torque controlData processing applicationsSolar generatorElectric power system
For optimizing a chronological development of consumption of electric power by a group of different consumers with regard to a supply of electric power including electric power from at least one wind or solar power generator, characteristic time curves of the consumption of electric power are determined at a high temporal resolution. A prognosis is made of a chronological development of the supply of electric power from the at least one power generator for a future period of time, and a plan for apportioning electric power to the individual consumers within the future period of time is made based on the characteristic time curves of the consumption of electric power by the individual consumers, the prognosis, and user goal setting by a user of the consumers resulting in different weightings of consumption of electric power by different consumers and supply of electric power by different power sources.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
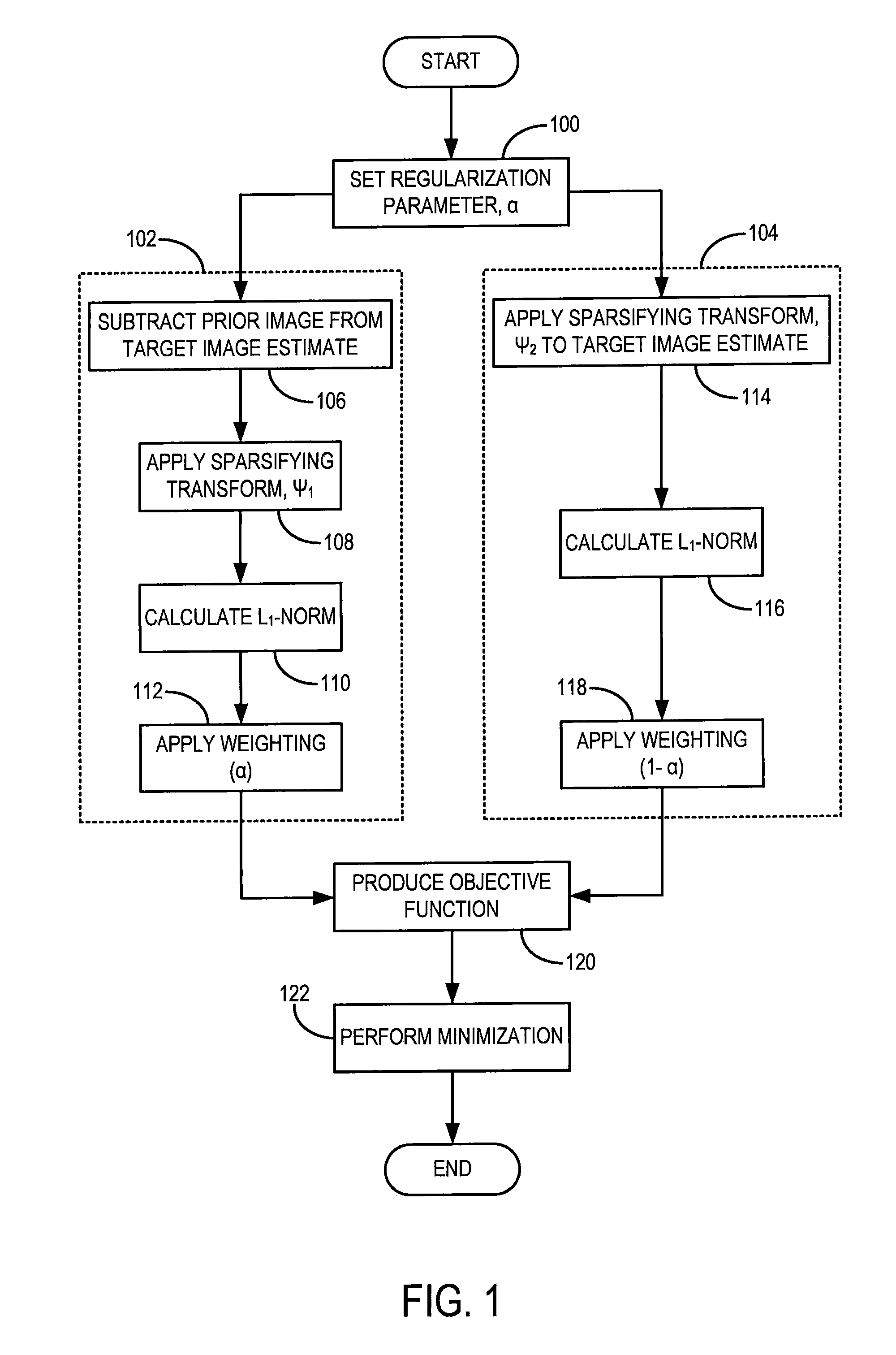
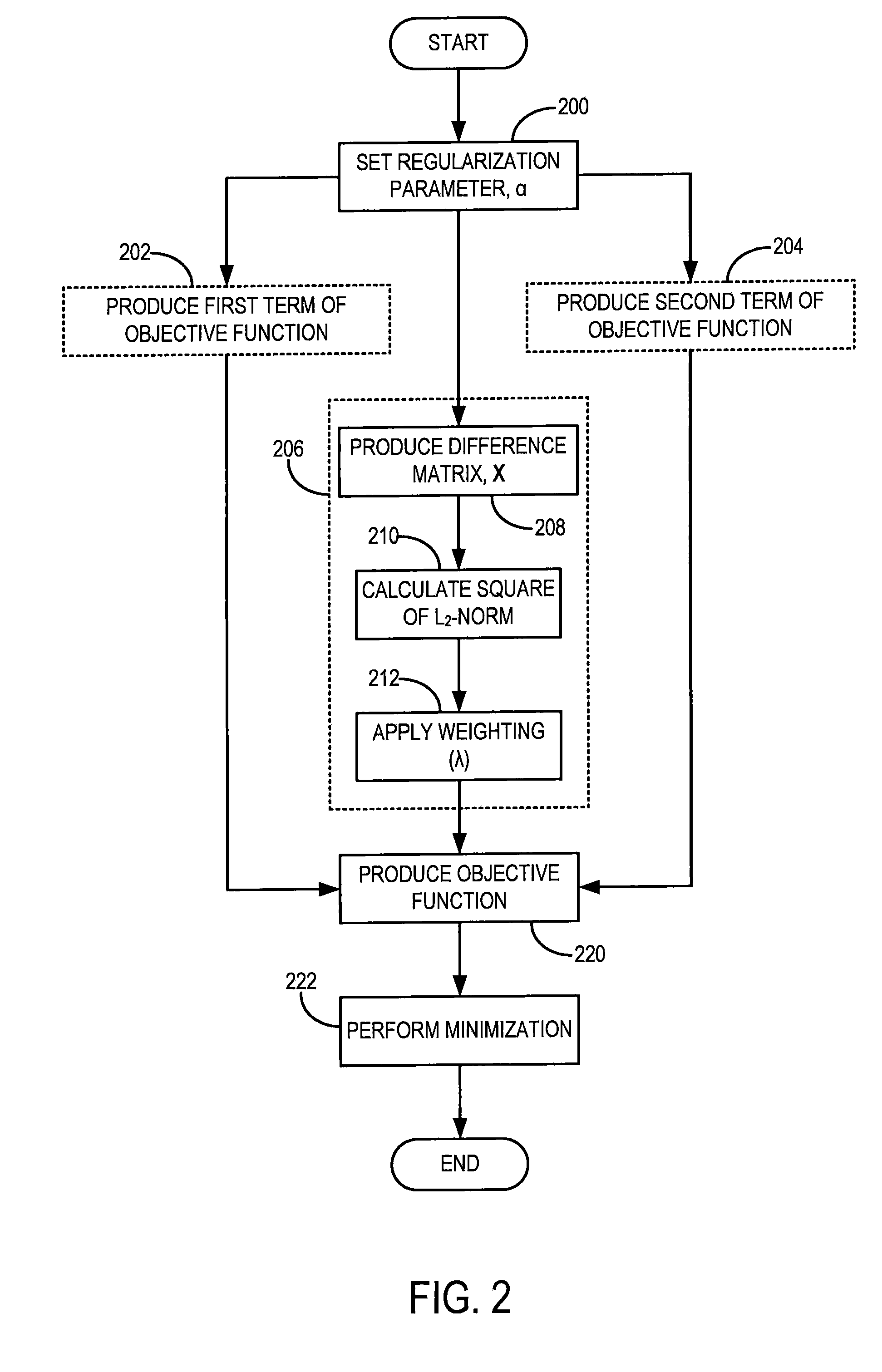
Method for Dynamic Prior Image Constrained Image Reconstruction
ActiveUS20100310144A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging modalitiesImage resolution
A method for reconstructing a high quality image from undersampled image data is provided. The image reconstruction method is applicable to a number of different imaging modalities. Specifically, the present invention provides an image reconstruction method that incorporates an appropriate prior image into the image reconstruction process. One aspect of the invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that produces a time series of desired images indicative of a higher temporal resolution than is ordinarily achievable with the imaging system, while mitigating undesired image artifacts. This is generally achieved by incorporating a limited amount of additional image data into the data consistency condition imposed during a prior image constrained image reconstruction. For example, cardiac phase images can be produced with high temporal resolution using a state-of-the-art multi-detector CT system with either fast gantry rotation speed or CT imaging system with a slow gantry rotation speed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
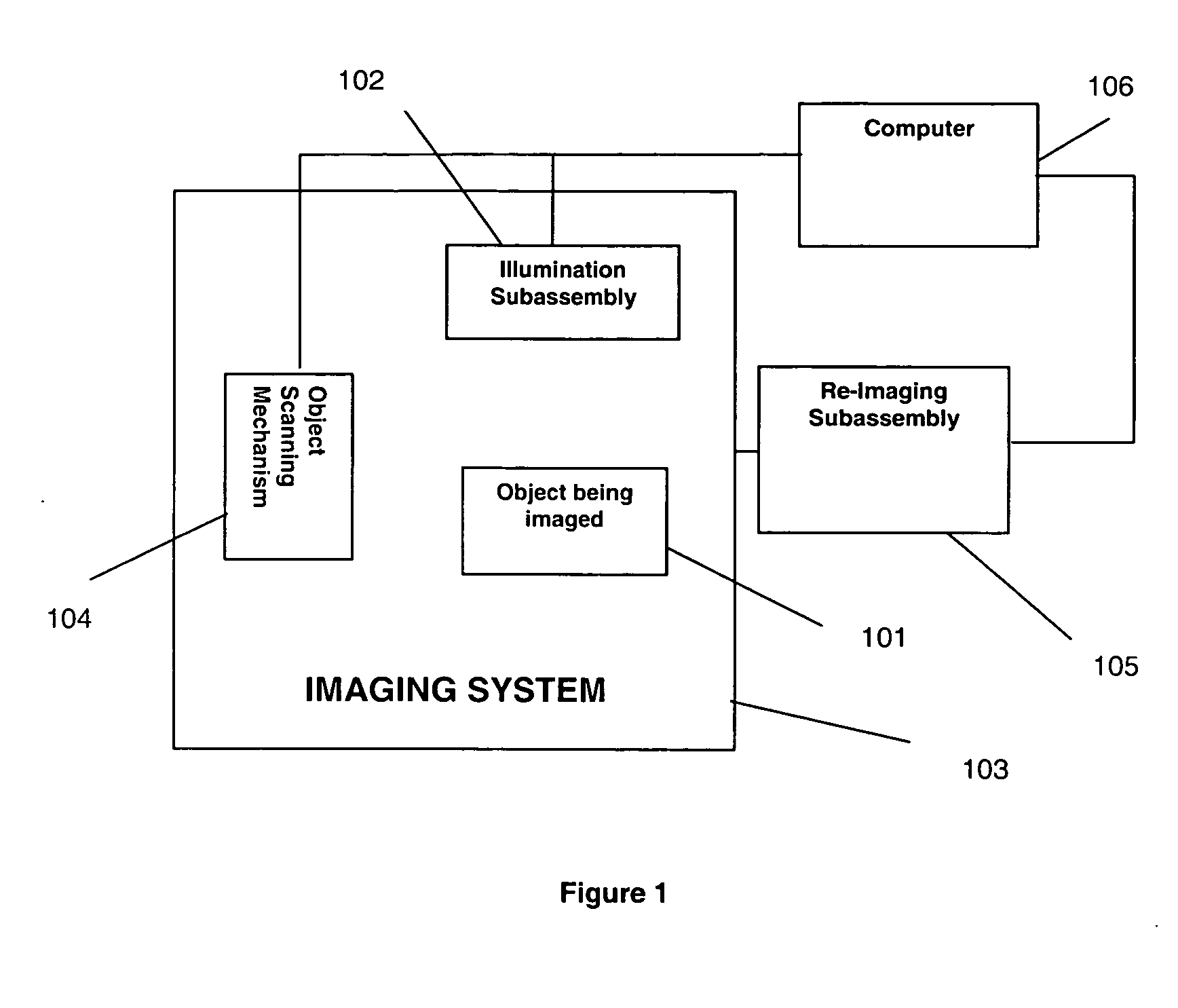
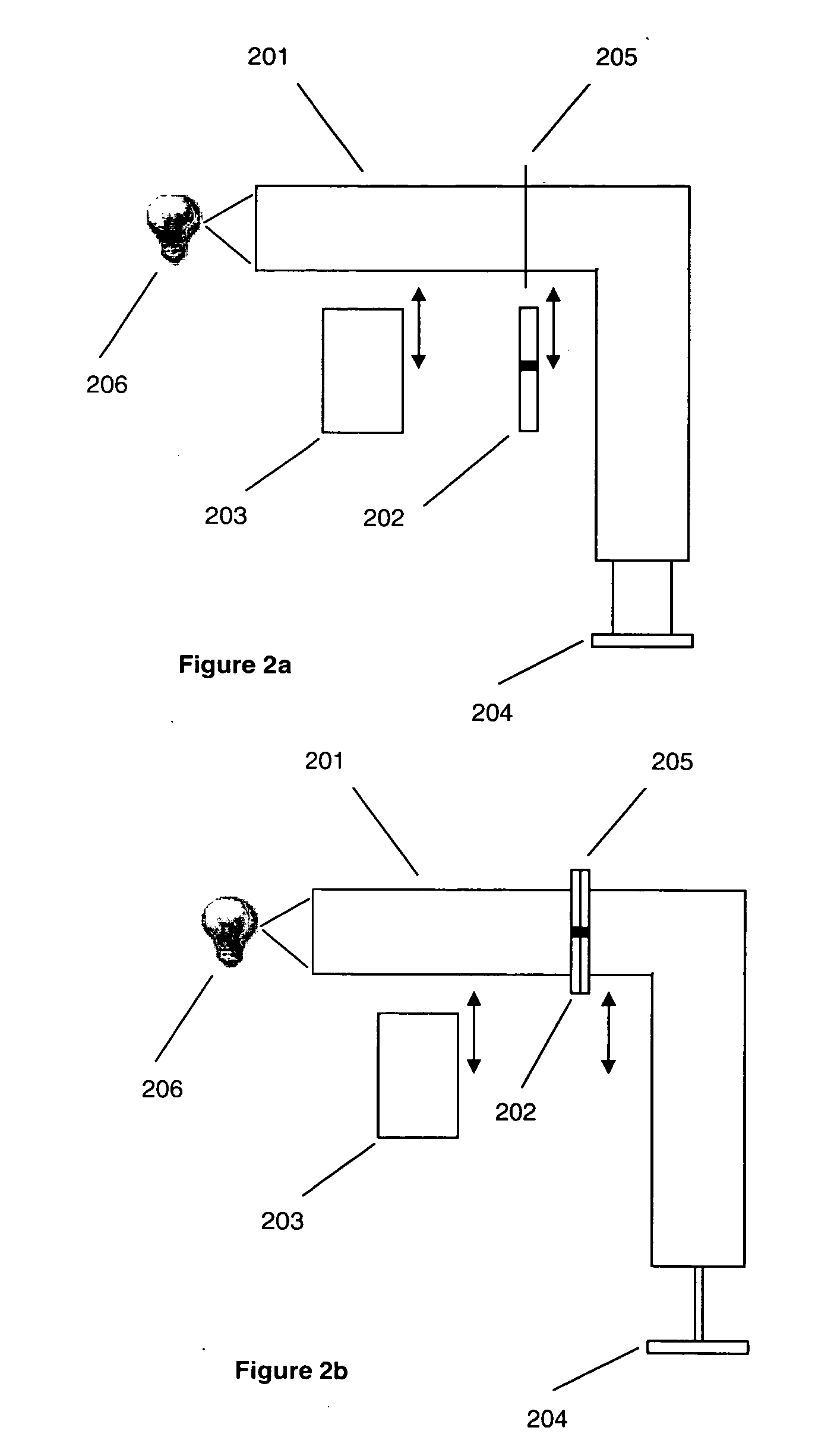
Method and apparatus for multi-mode spectral imaging
A method and apparatus is disclosed for multi-mode spectral imaging. In one embodiment, the present invention comprises the steps of illuminating an object with a modified illumination profile, producing a reflected, transmitted or fluorescence image of the illuminated object, scanning the object, and re-imaging the reflected, transmitted or fluorescence light after modifying the light's optical state. The present invention preferably works in conjunction with other imaging systems to provide both high-spectral resolution images with lower temporal resolution and multiple image acquisition with high temporal resolution.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING US INC
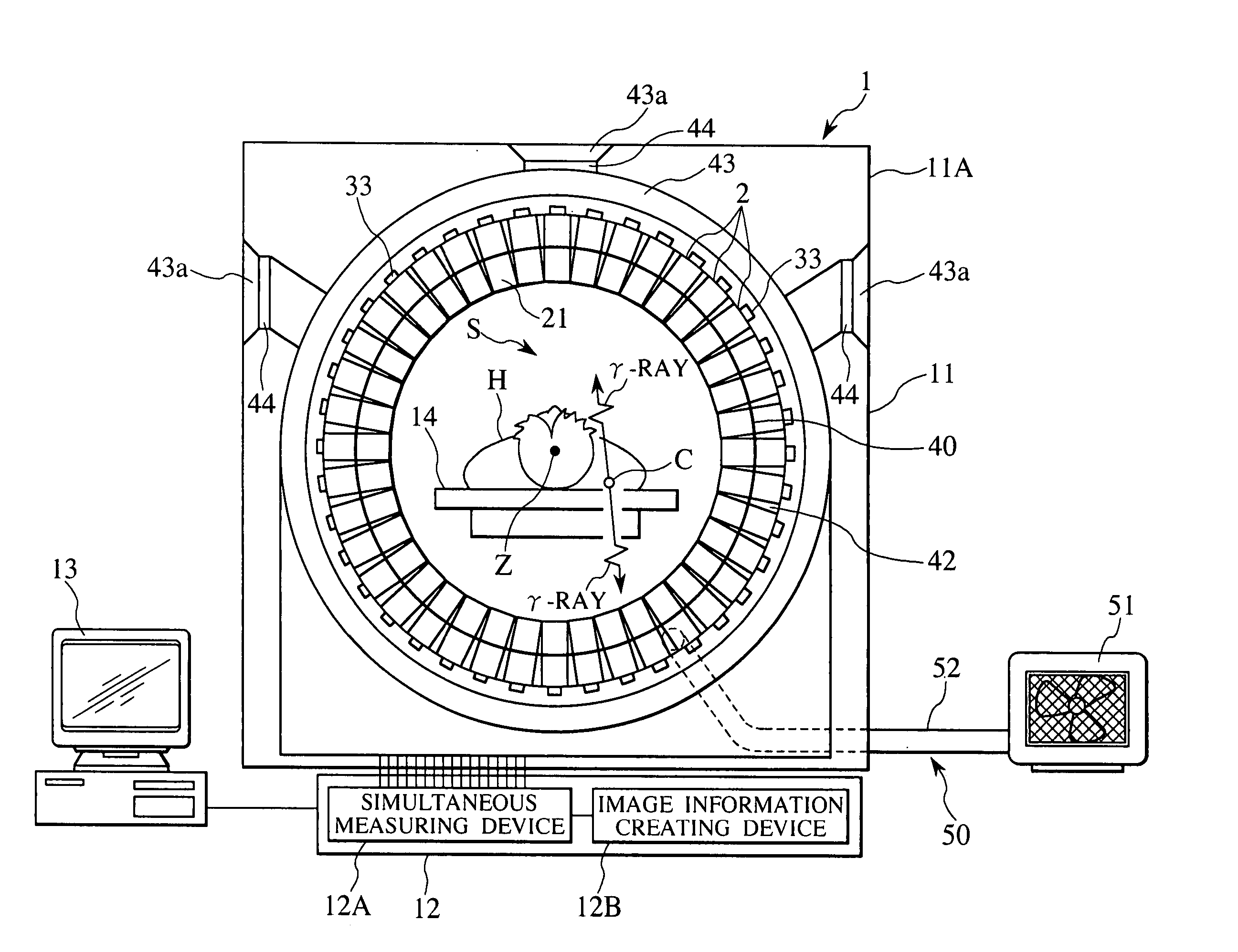
Nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus, positron emission computed tomography apparatus, and detector units
InactiveUS20070080296A1Increase current leakageReduces energy resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyHigh temporal resolutionMoisture
Owner:HITACHI LTD
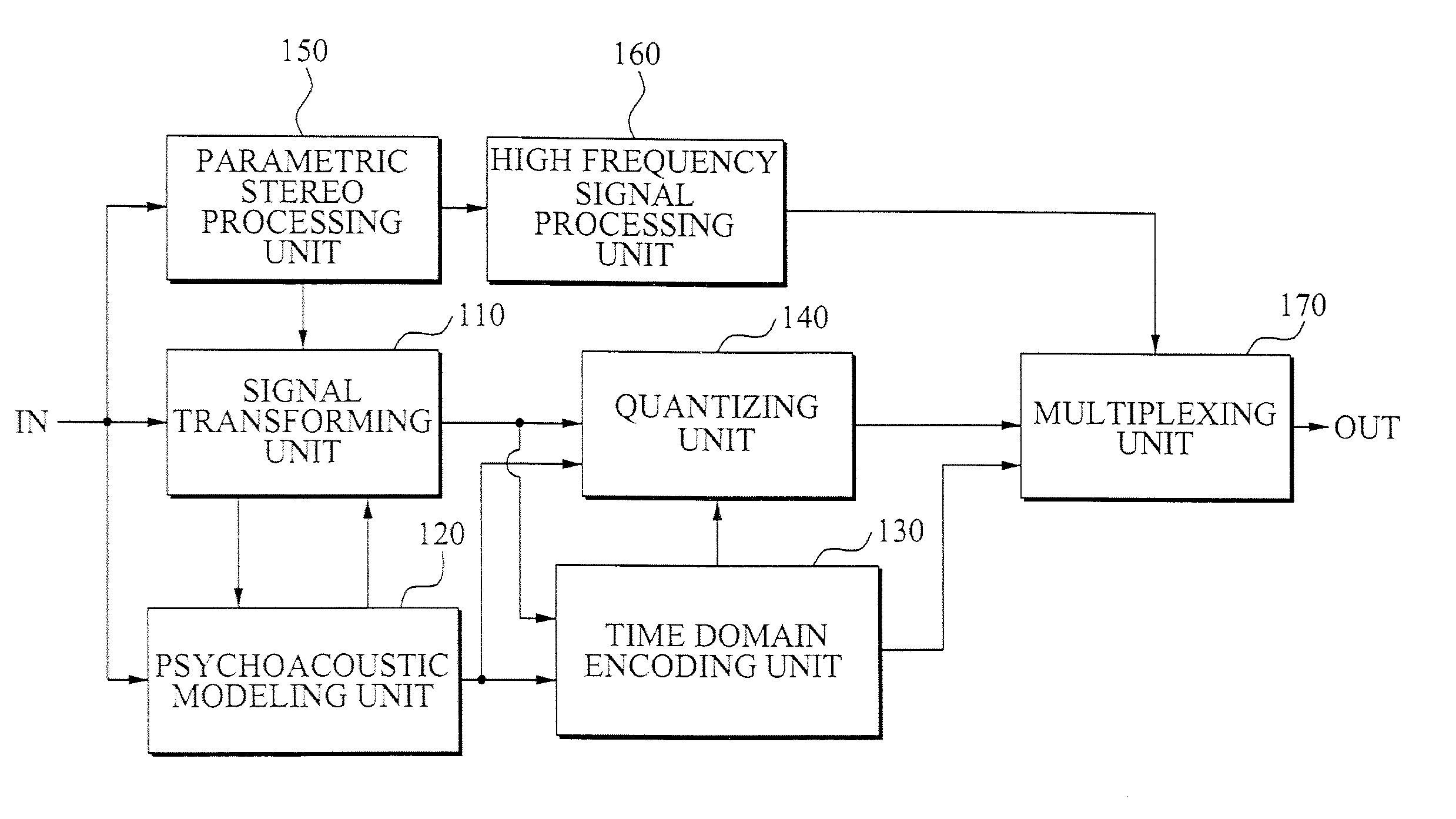
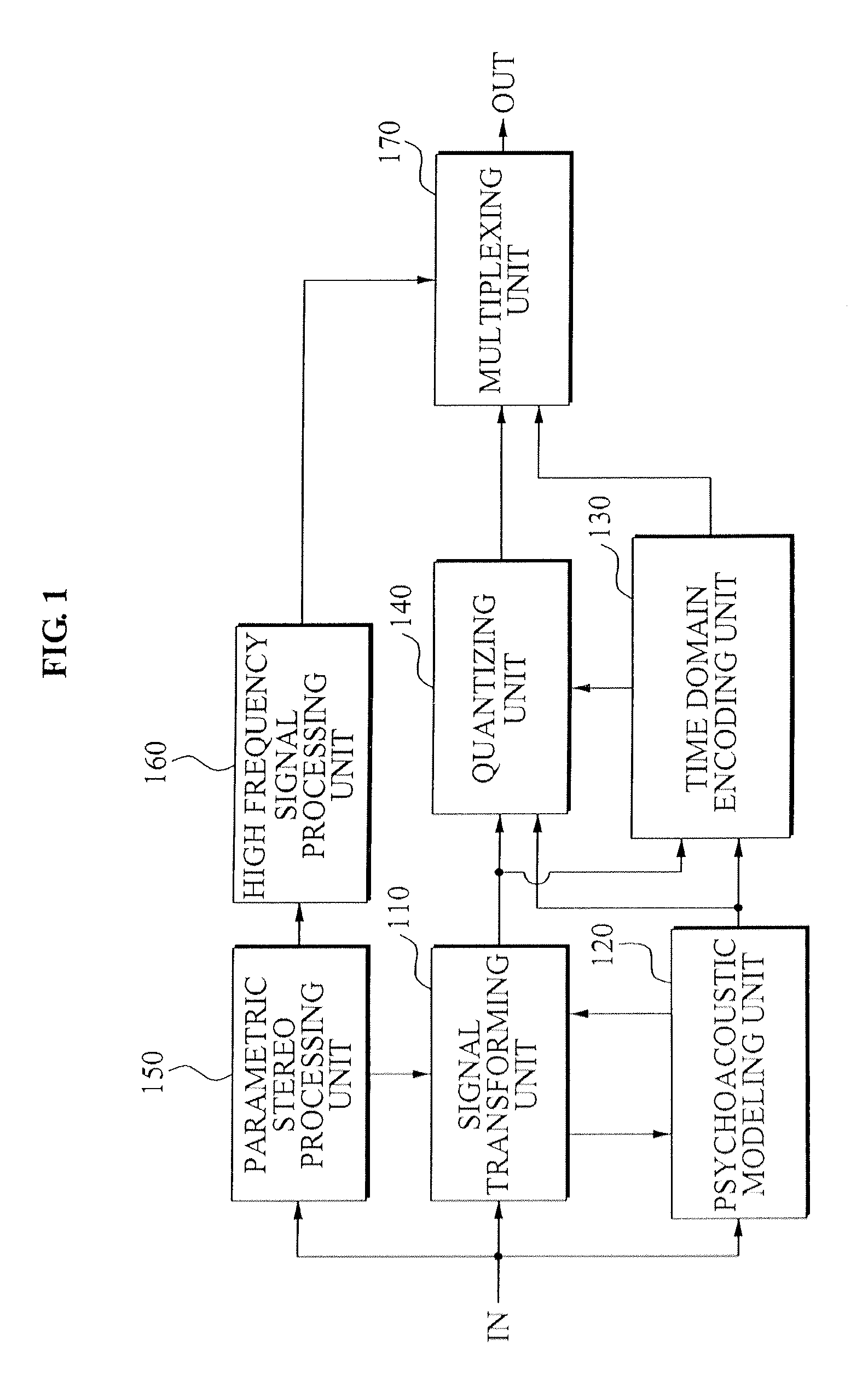
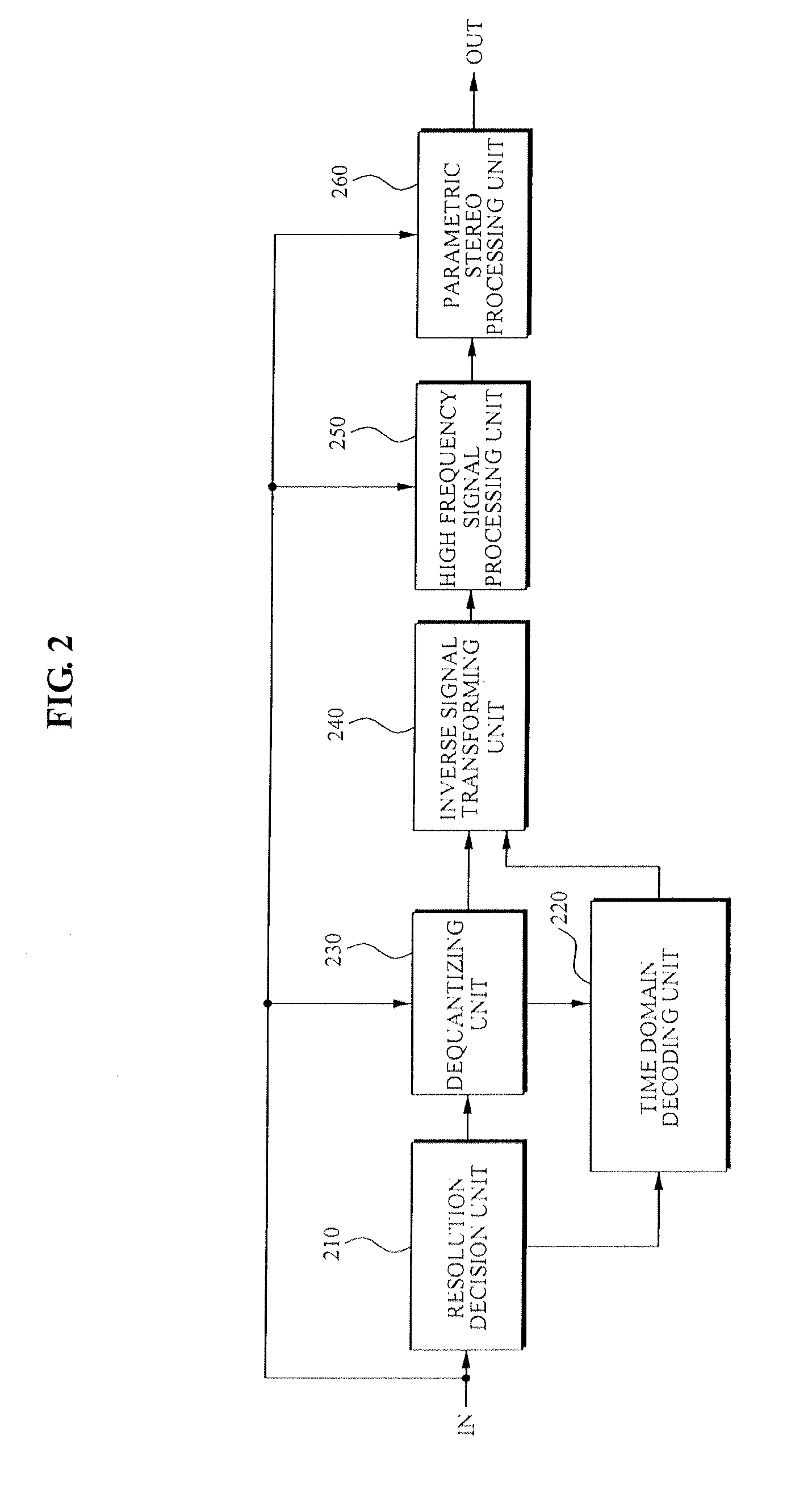
Apparatus and method for encoding an audio signal and apparatus and method for decoding an encoded audio signal
ActiveUS7275031B2Higher-quality and still efficient audio encoding/decodingImprove encoding qualitySpeech analysisImage resolutionHigh temporal resolution
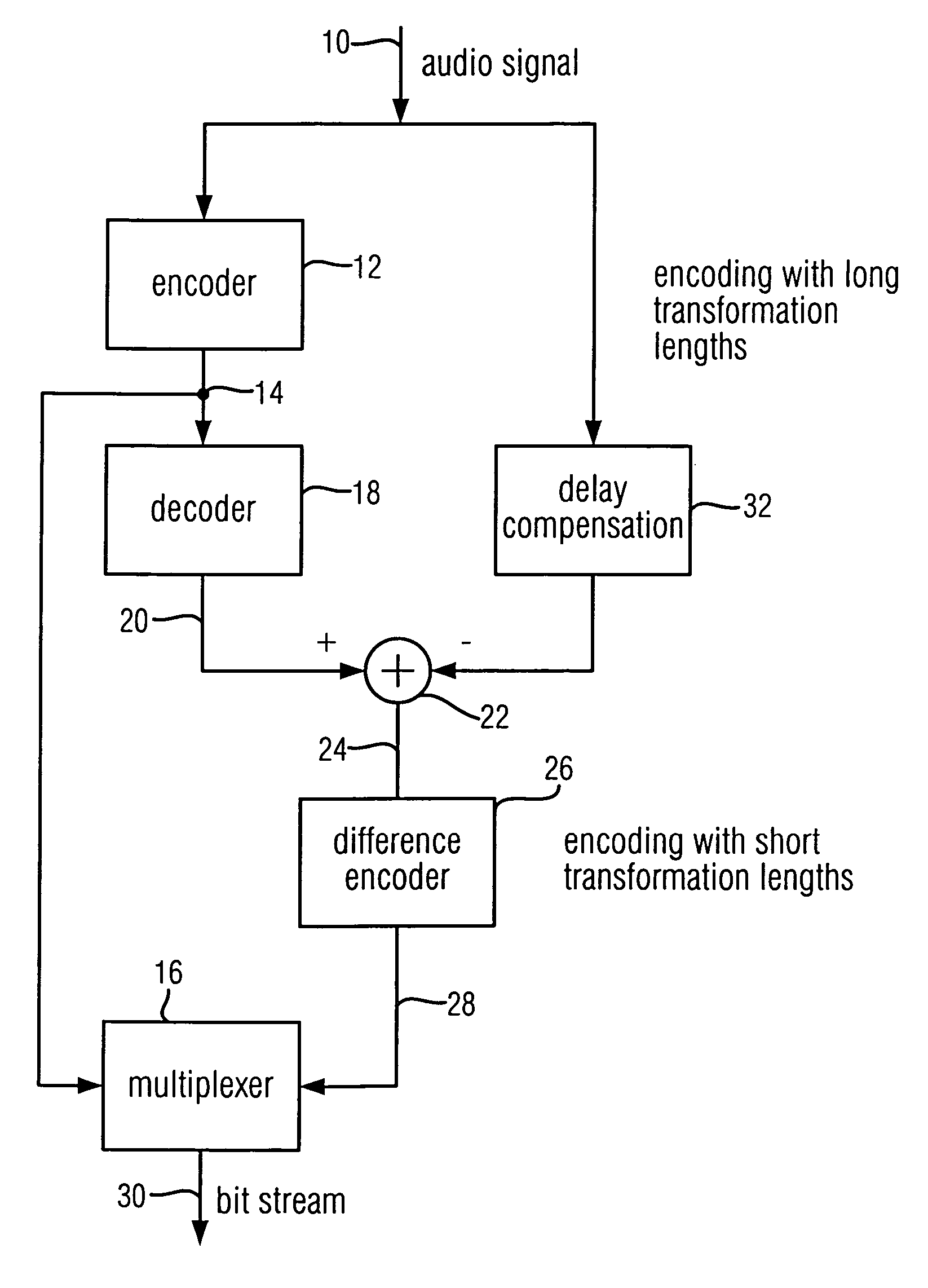
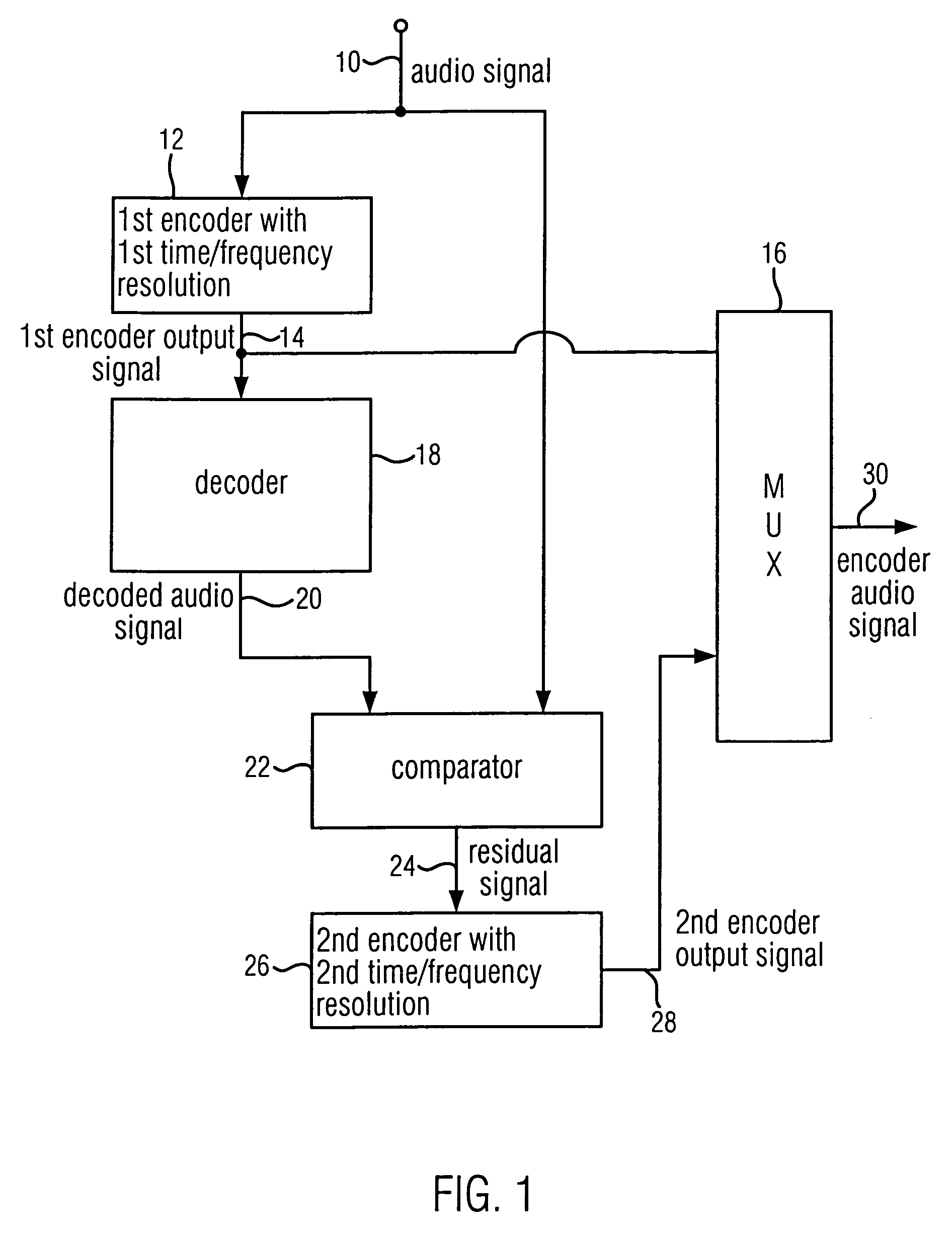
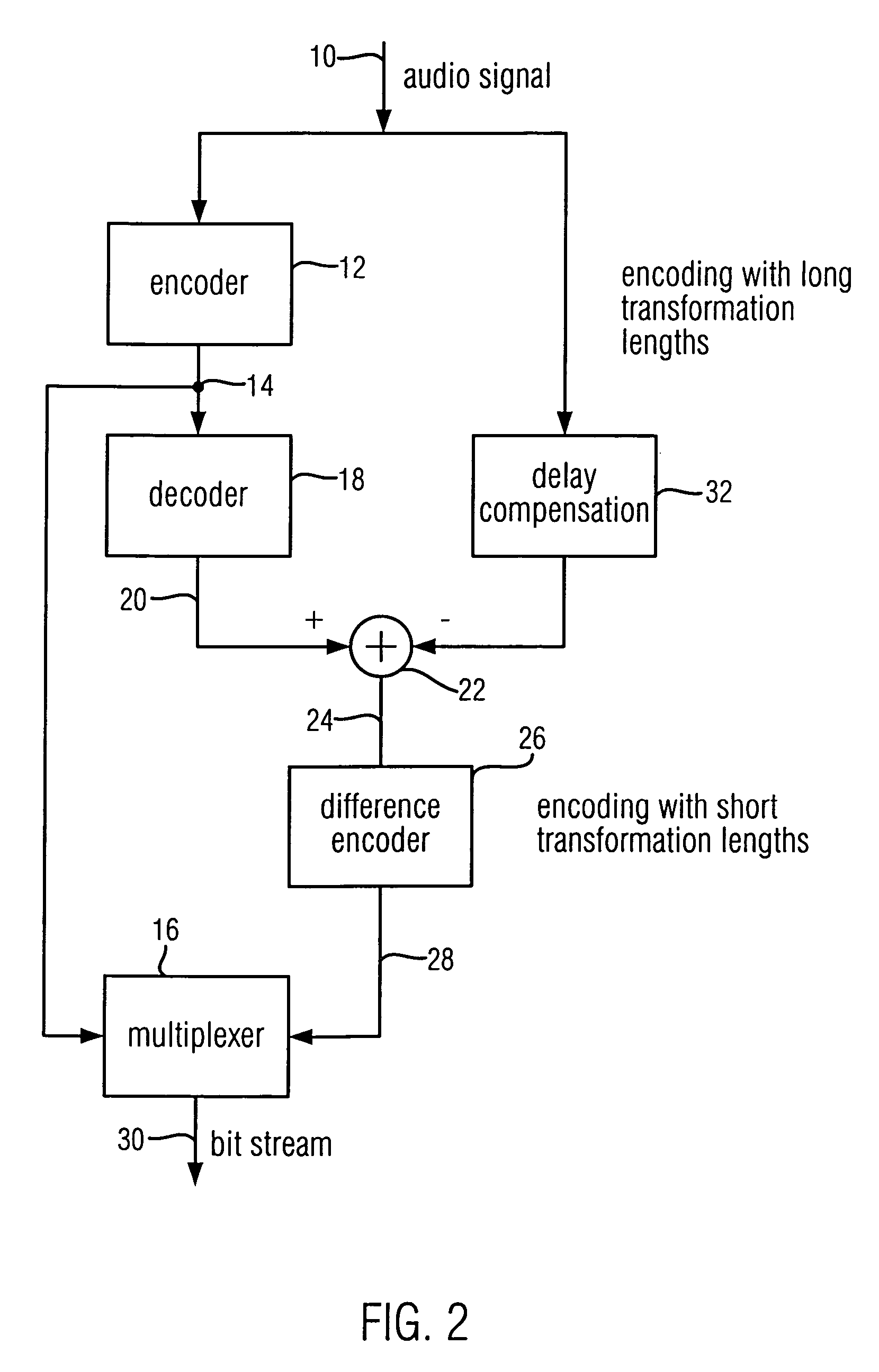
When encoding an audio signal, the audio signal is first encoded with the first encoder to obtain a first encoder output signal. This first encoder output signal is written into a bit stream. It is further decoded by a decoder to provide a decoded audio signal. The decoded audio signal is compared with the original audio signal to obtain a residual signal. The residual signal is then encoded via a second encoder to provide a second encoder output signal which is also written into a bit stream. The first encoder has a first time or frequency resolution. The second encoder has a second time or frequency resolution. The first resolution differs from the second resolution, so that in a respective decoder, an audio signal with both a high time resolution as well as a high frequency resolution can be retrieved.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Method and apparatus to encode and decode an audio/speech signal
ActiveUS20100010807A1Efficient codingSpeech analysisNetwork connectionsImage resolutionHigh temporal resolution
A method and apparatus to encode and decode an audio / speech signal is provided. An inputted audio signal or speech signal may be transformed into at least one of a high frequency resolution signal and a high temporal resolution signal. The signal may be encoded by determining an appropriate resolution, the encoded signal may be decoded, and thus the audio signal, the speech signal, and a mixed signal of the audio signal and the speech signal may be processed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
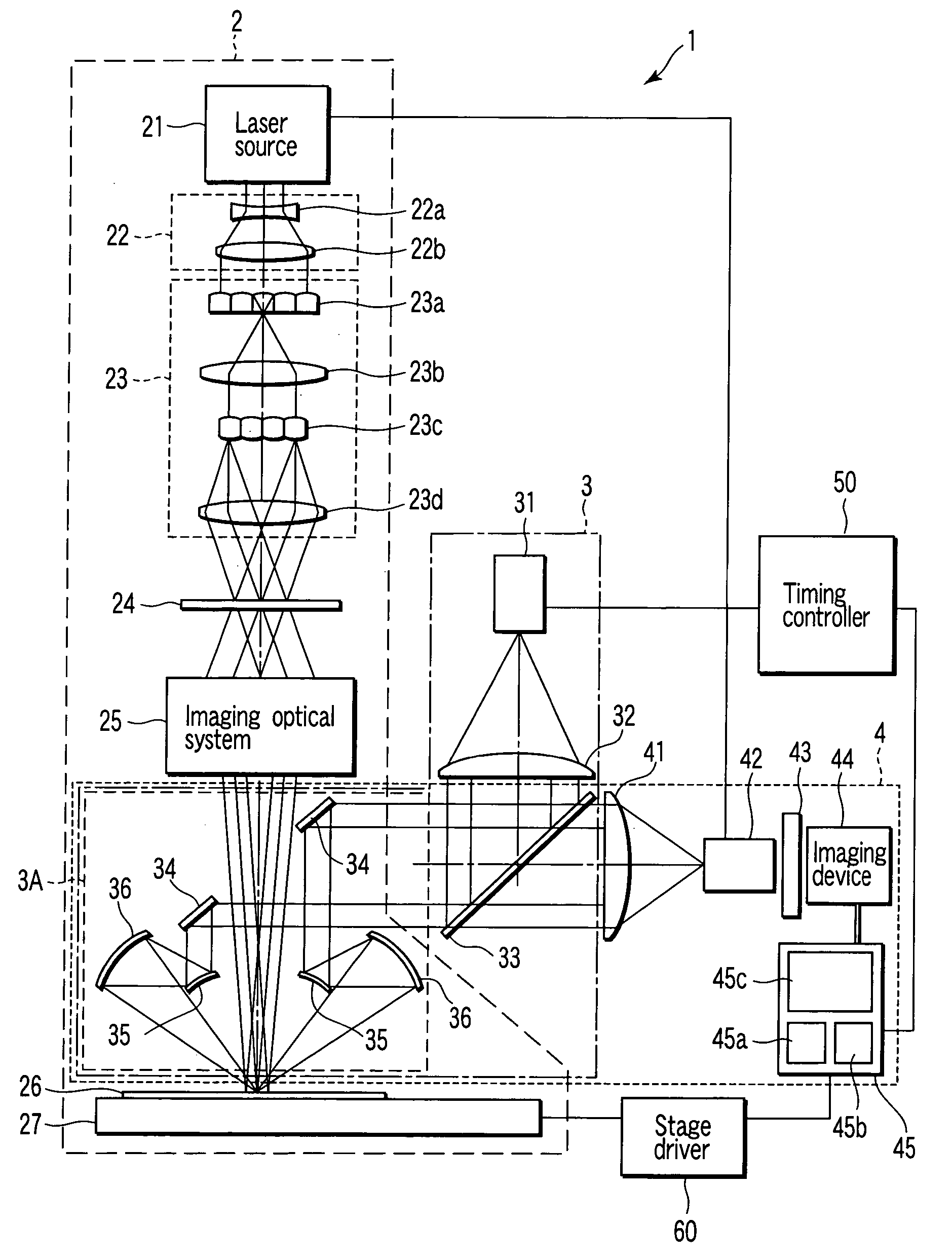
Laser crystallization apparatus and laser crystallization method
InactiveUS20050199596A1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementNanosecondImage resolution
A laser crystallization apparatus, which enables an observation of a high spatial resolution with several μm and a high temporal resolution with several nanoseconds, comprising a crystallization optical system to irradiate a laser light to a thin film provided on a substrate and to melt and crystallize the thin film, the laser crystallization apparatus comprises an illumination light source disposed out of an optical path of the laser light and emitting an illumination light for observation to illuminate the thin film, an illumination optical system comprising an annular optical element which has the optical path of the laser light in the center and which leads the illumination light from the illumination light source to the thin film along the optical path, and an observation optical system which displays a magnified image of the substrate including the thin film.
Owner:ADVANCED LCD TECH DEVMENT CENT
Exact local computed tomography based on compressive sampling
ActiveUS8811700B2Faithful resolution of featureMinimize L normReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTemporal resolutionRadiation Dosages
A system and method for tomographic image reconstruction using truncated projection data that allows exact interior reconstruction (interior tomography) of a region of interest (ROI) based on the known sparsity models of the ROI, thereby improving image quality while reducing radiation dosage. In addition, the method includes parallel interior tomography using multiple sources beamed at multiple angles through an ROI and that enables higher temporal resolution.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
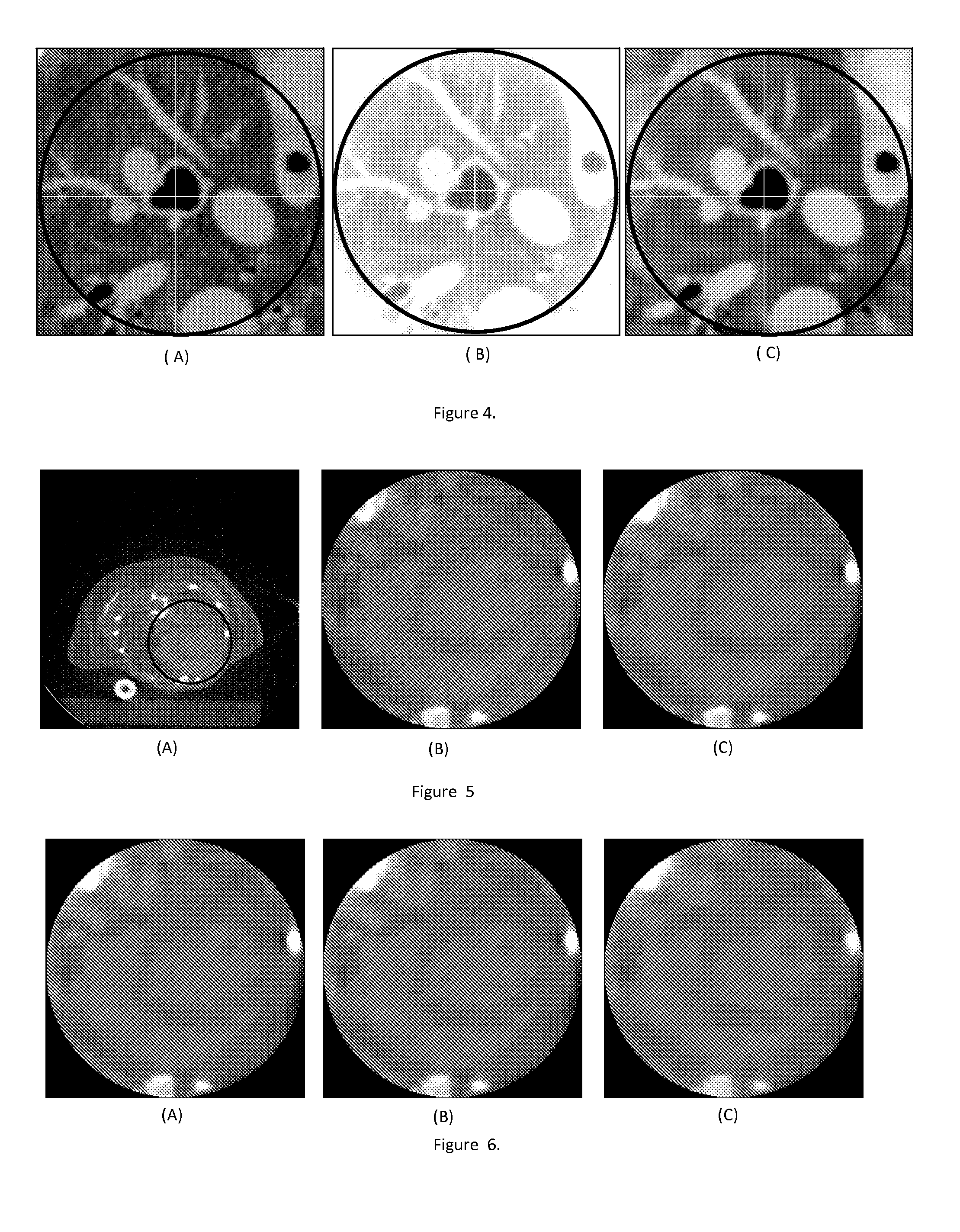
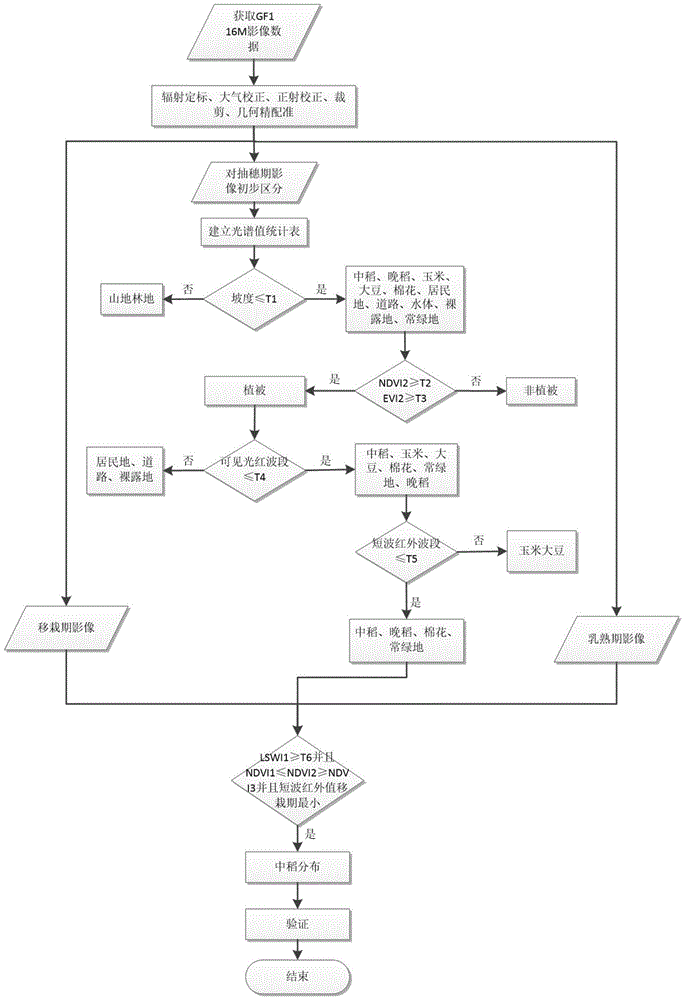
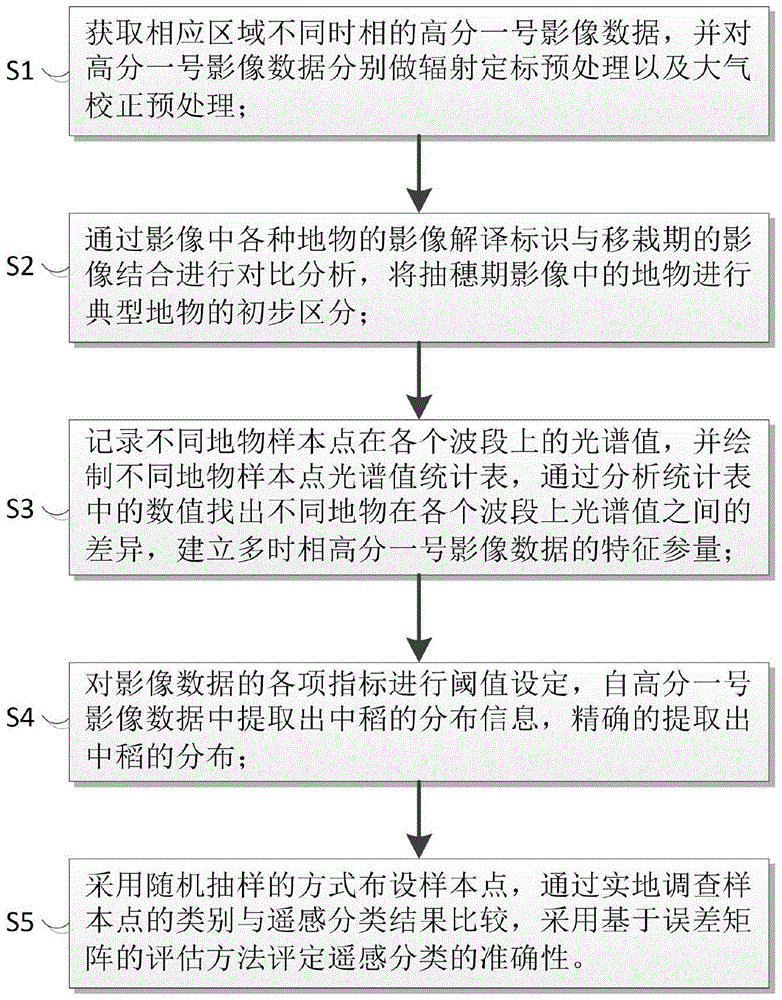
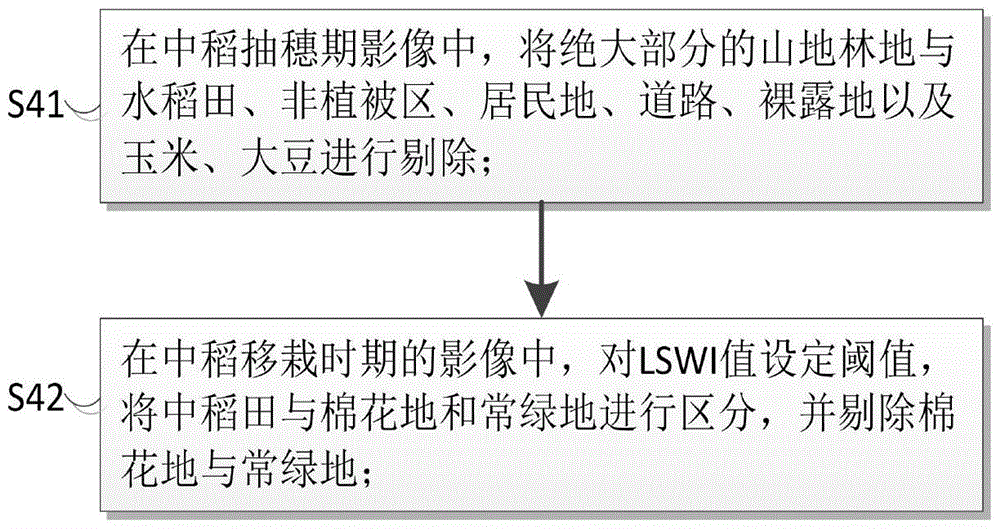
Middle-season rice information decision tree classification method based on multi-temporal data feature extraction
ActiveCN105740759AImprove spatial resolutionImprove time resolutionCharacter and pattern recognitionForeign matterClassification methods
According to a middle-season rice information decision tree classification method based on multi-temporal data feature extraction of the invention, selected GF-1 image data has the advantages of high spatial resolution and high temporal resolution. On the basis, a variety of characteristic parameters for rice distribution extraction based on a single-temporal image are used, the advantages of timing analysis based on a multi-temporal image are utilized, multiple parameters and multiple temporal phases are combined organically, and the distribution of middle-season rice is extracted by means of knowledge decision tree classification. Through use of a variety of characteristic parameters, non-target surface features can be eliminated better. Multi-temporal analysis is conducive to the elimination of wrongly-classified surface features caused by 'different surface features, same spectrum' and the extraction of target surface features. Decision tree classification has the characteristics of being flexible, visual, efficient, and the like. Therefore, by integrating all the advantages, the precision of middle-season rice extraction is further improved. The method is of positive significance both to the food security system of a country and to the commercial application of remote sensing in agriculture.
Owner:武汉珈和科技有限公司
Image processing apparatus, image processing method and program
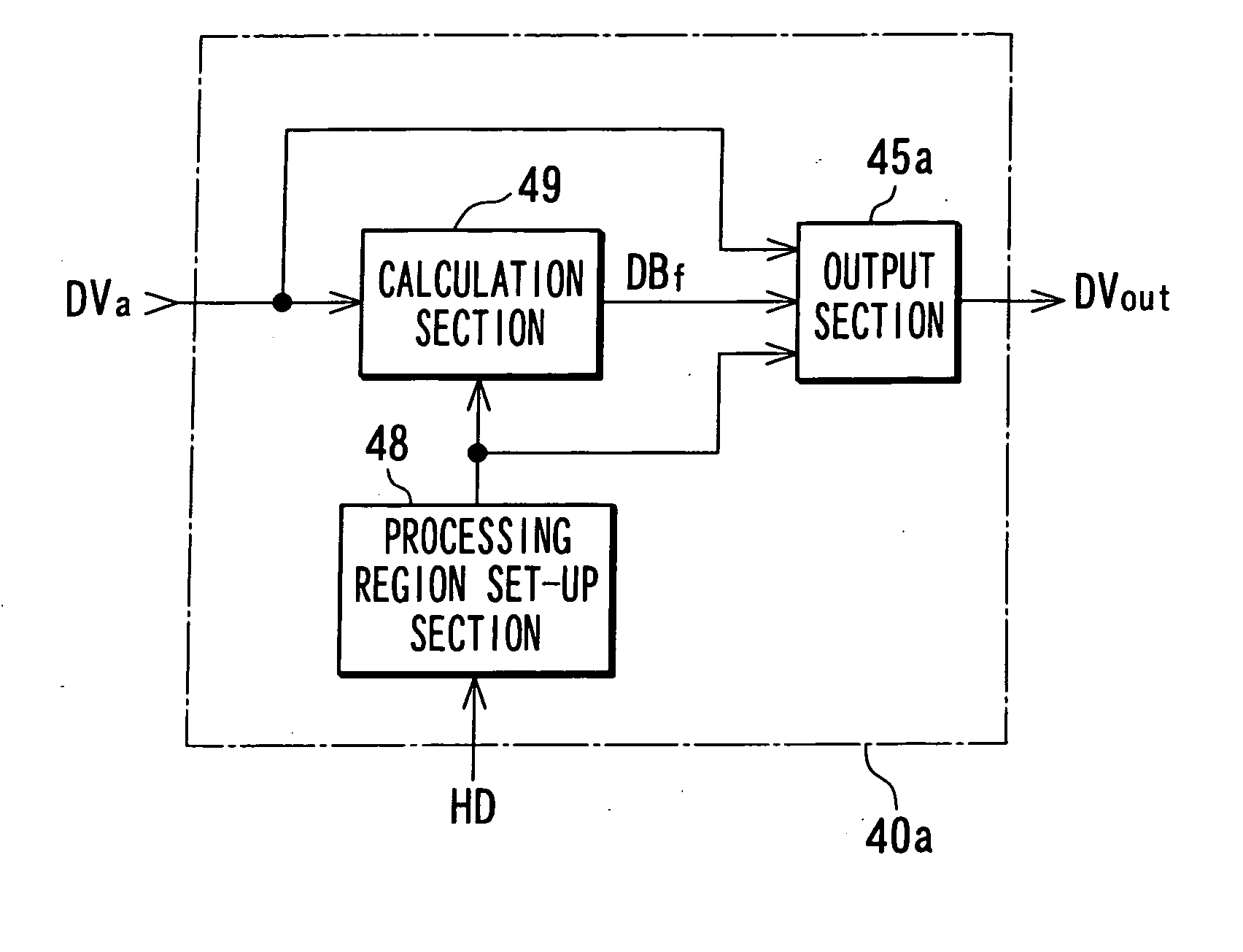
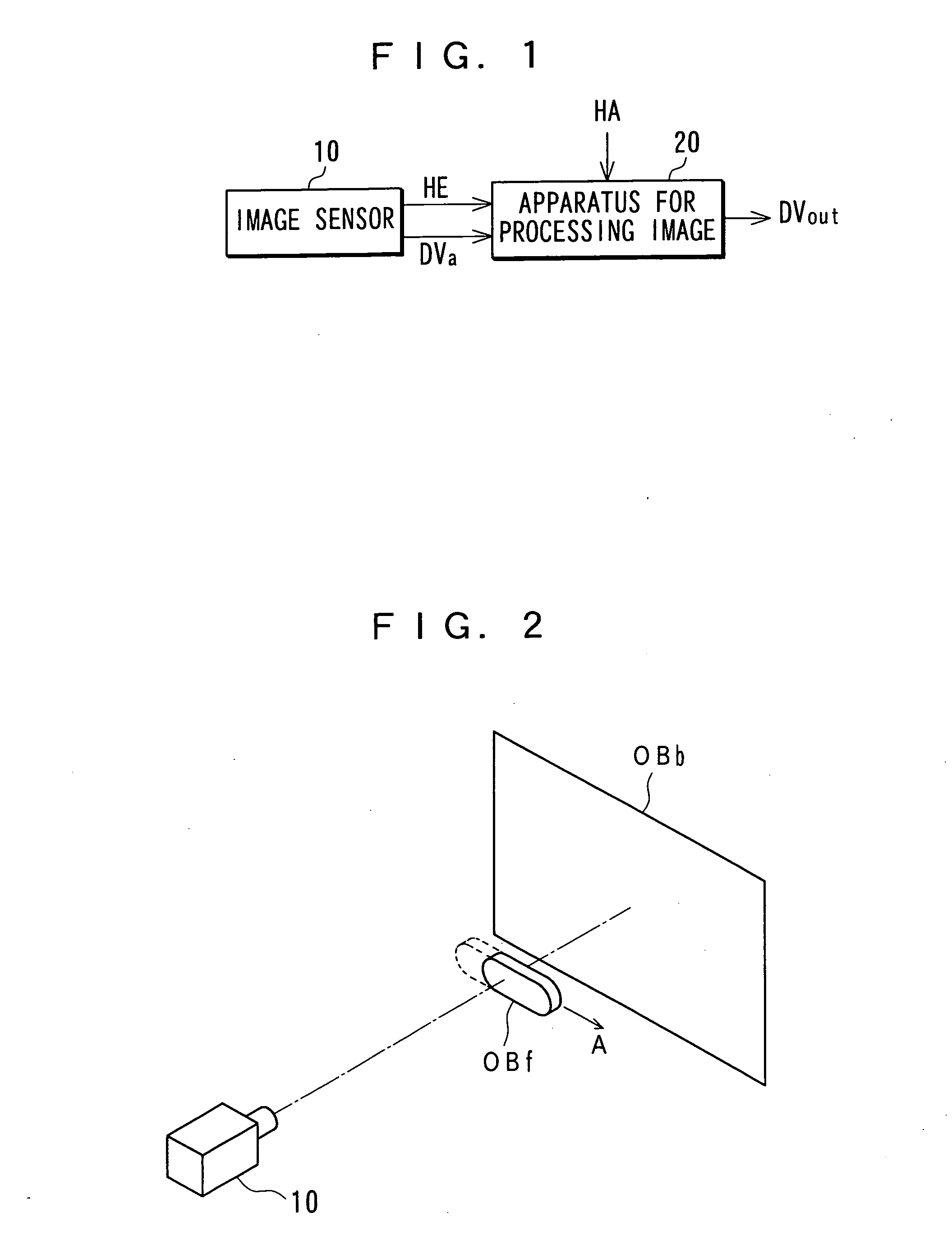
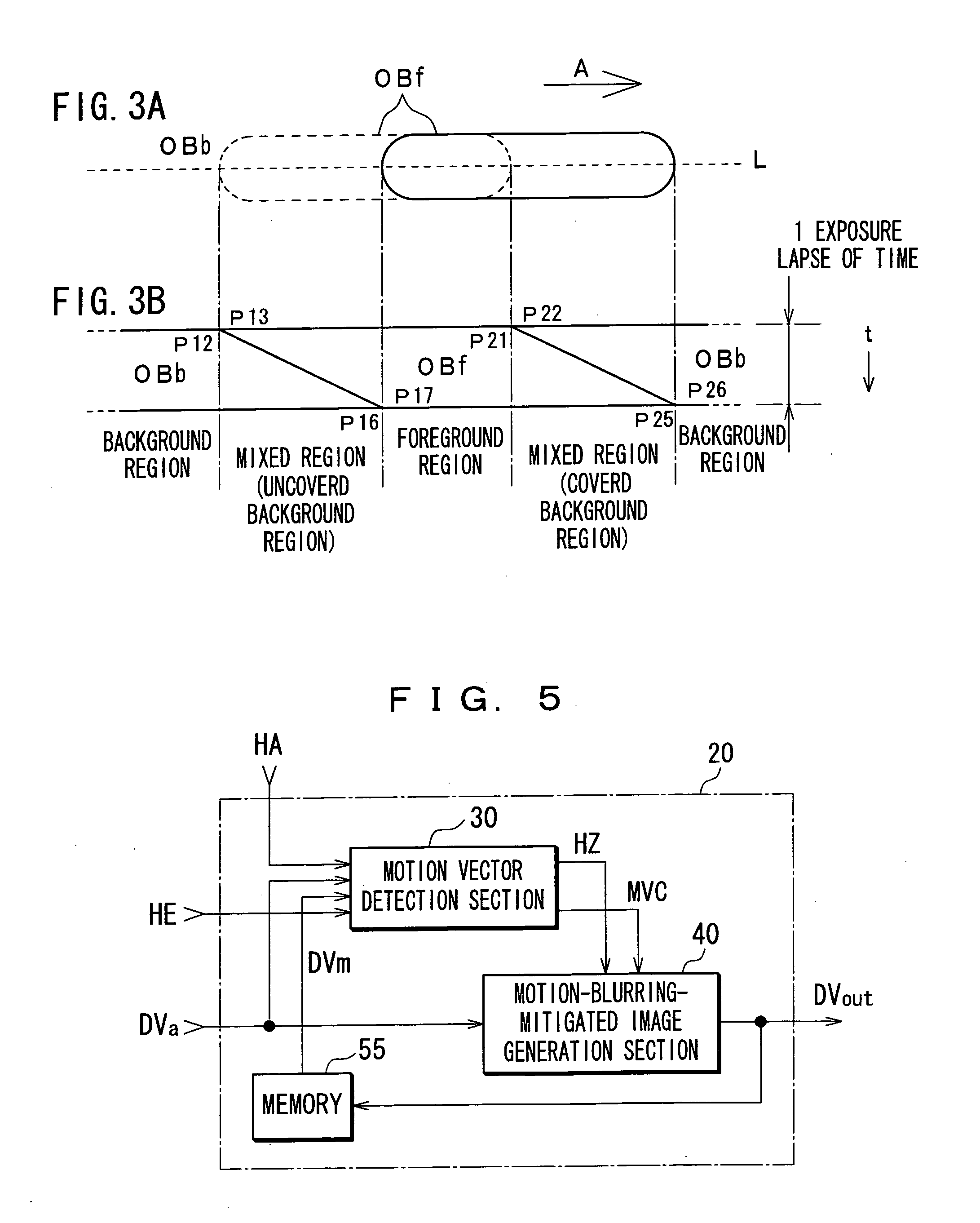
InactiveUS20070040918A1Convenient timeReduce relative motionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingMotion vector
A motion vector detection section 30a detects a motion vector by using an image that is made up of multiple pixels and acquired by an image sensor having time integration effects. A time resolution creation section 90 generates an image that has a higher time resolution by using the detected motion vector and the image made up of the multiple pixels. A motion-blurring-mitigated image generation section 40 generates a motion-blurring-mitigated image in which motion blurring of a moving object is mitigated by using the detected motion vector on the assumption that a pixel value of pixel of the moving object in the image is a value obtained by integrating, in a time direction, a pixel value of each pixel in which no motion blurring that corresponds to the moving object occur as it is moved.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of pre-reconstruction decomposition for fast kV-switching acquisition in dual energy computed tomography (CT)
ActiveUS8165264B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFrequency spectrumDecomposition
Fast kV-switching is a dual energy acquisition technique in computed tomography (CT) in which alternating views correspond to the low and high tube voltages. Its high temporal resolution and its suitability to a variety of source trajectories make it an attractive option for dual energy data acquisition. Its disadvantages include a one-view misregistration between the data for high and low voltages, the potentially poor spectrum separation due to the more-like a sine wave rather than the desired square wave in fast kV-switching, and the higher noise in the low voltage data because of the technical difficulty in swinging the tube current to counter the loss of x-ray production efficiency and loss of penetration at lower tube voltages. Despite the disadvantages, symmetric view matching according to the current invention substantially improves streaks and other artifacts due to the view misregistration, sufficient spectrum separation even in a sinusoidal waveform swinging between 80 kV and 135 kV, and contrast-to-noise for the simulated imaging task maximized at monochromatic energy of 75 keV.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
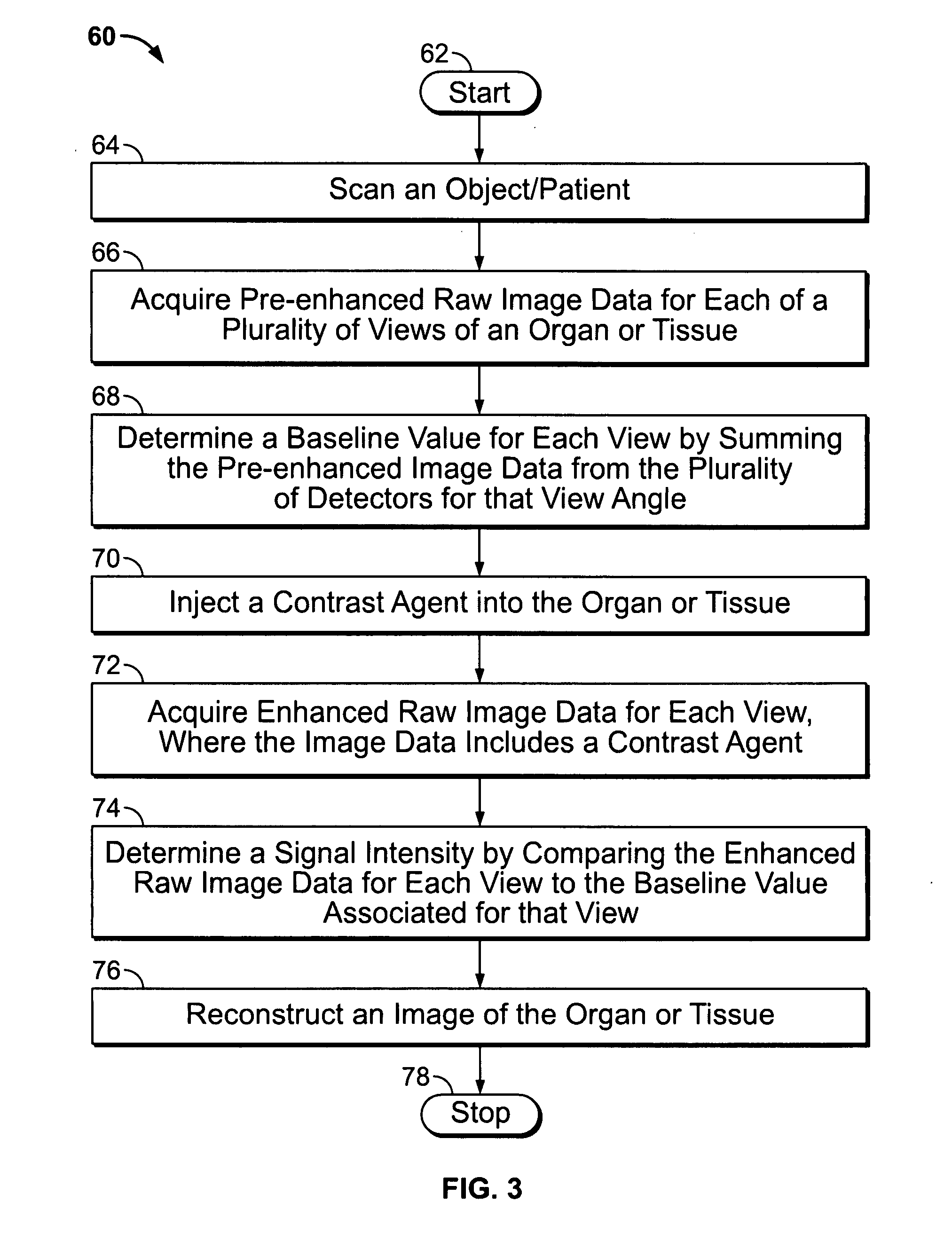
Method and system for performing high temporal resolution bolus detection using CT image projection data
A method of evaluating changes in contrast of an image using a diagnostic imaging system is provided. The method provides acquiring raw image data of an organ or tissue, calculating a baseline of data based on the raw image data acquired before arrival of an agent, and determining changes in a signal intensity of the agent based on changes in the raw image data compared to the baseline. The agent may be an imaging agent, a contrast agent, a biomedical agent, a needle, a catheter, a biomedical device, and the like.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
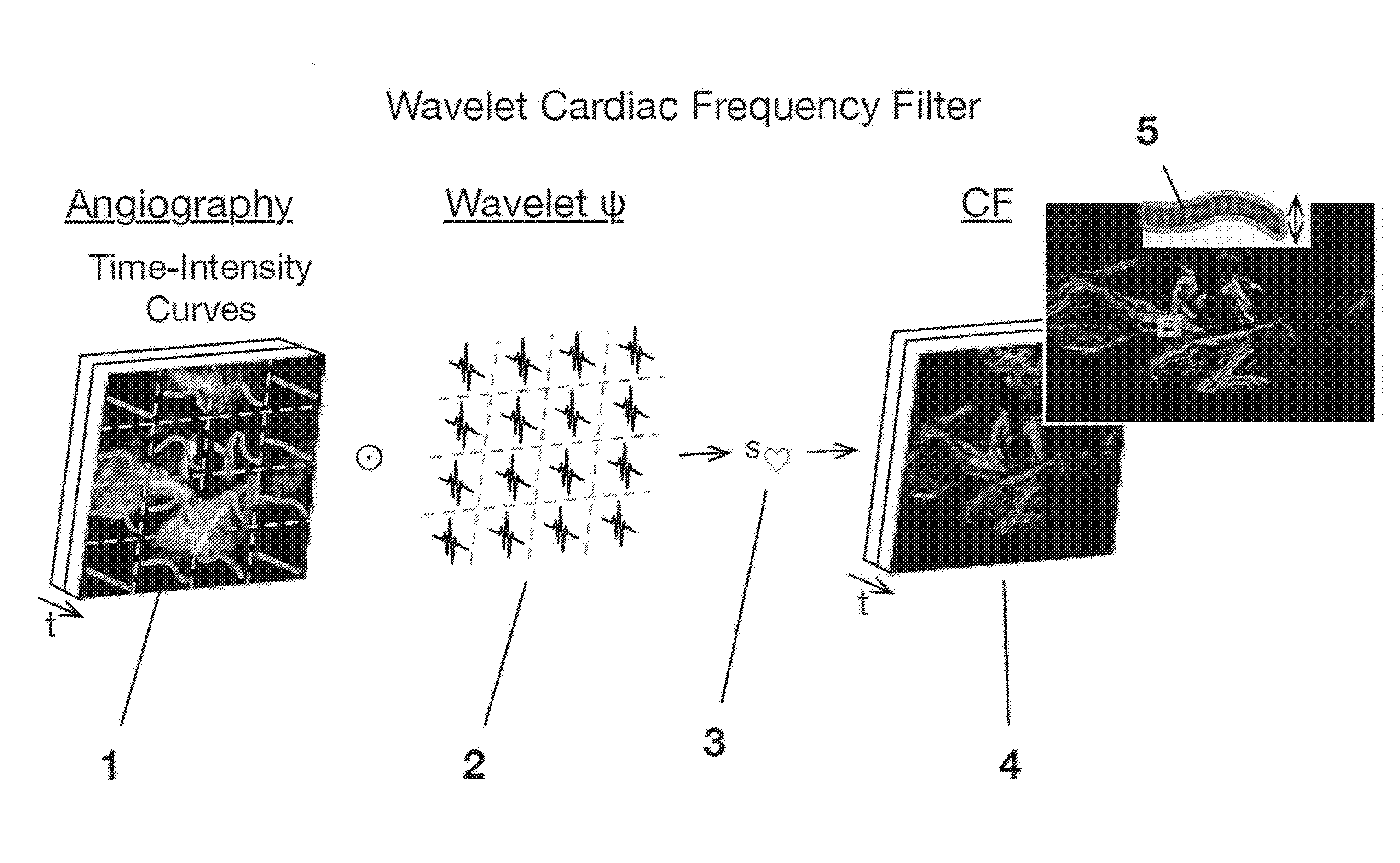
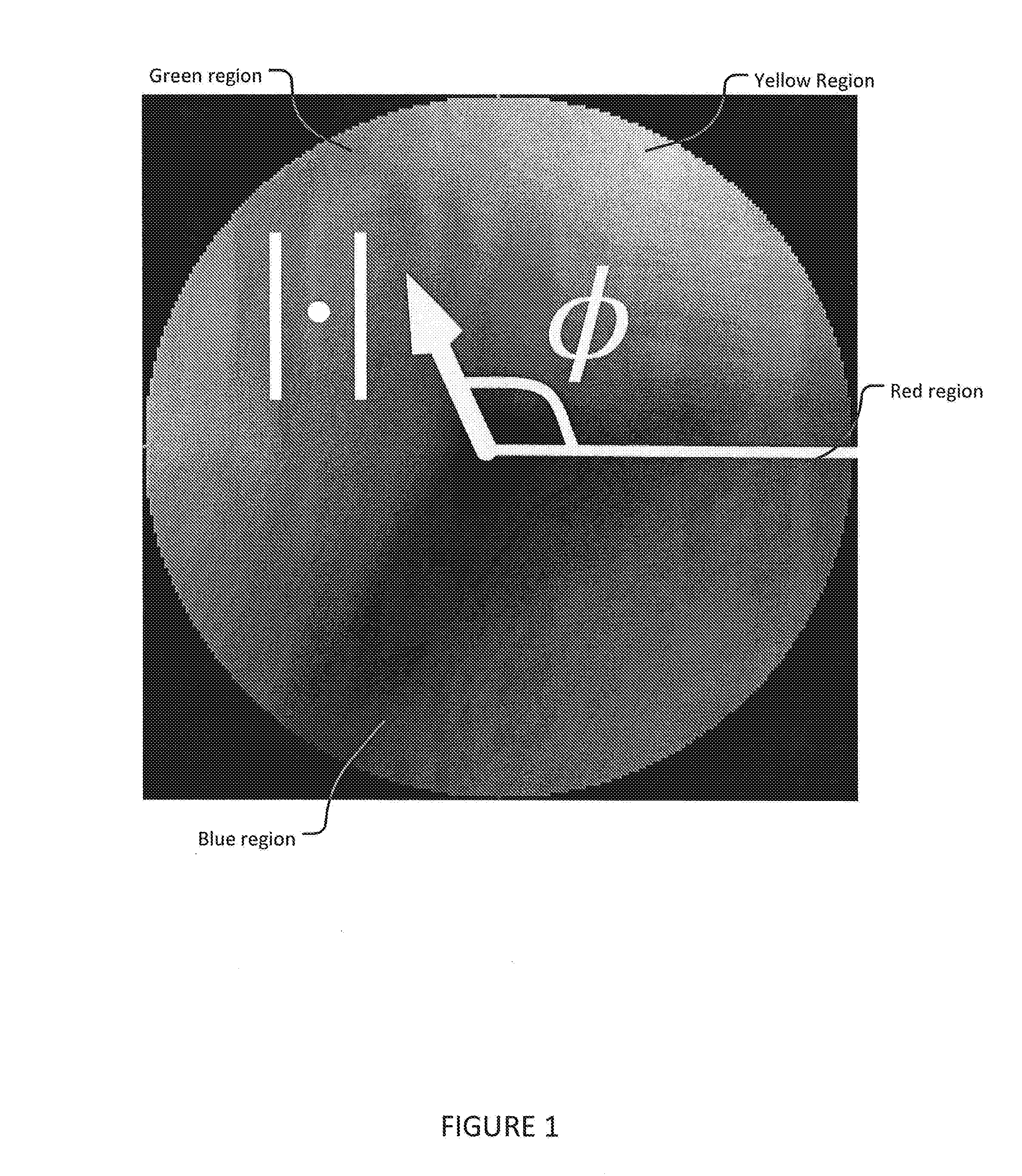
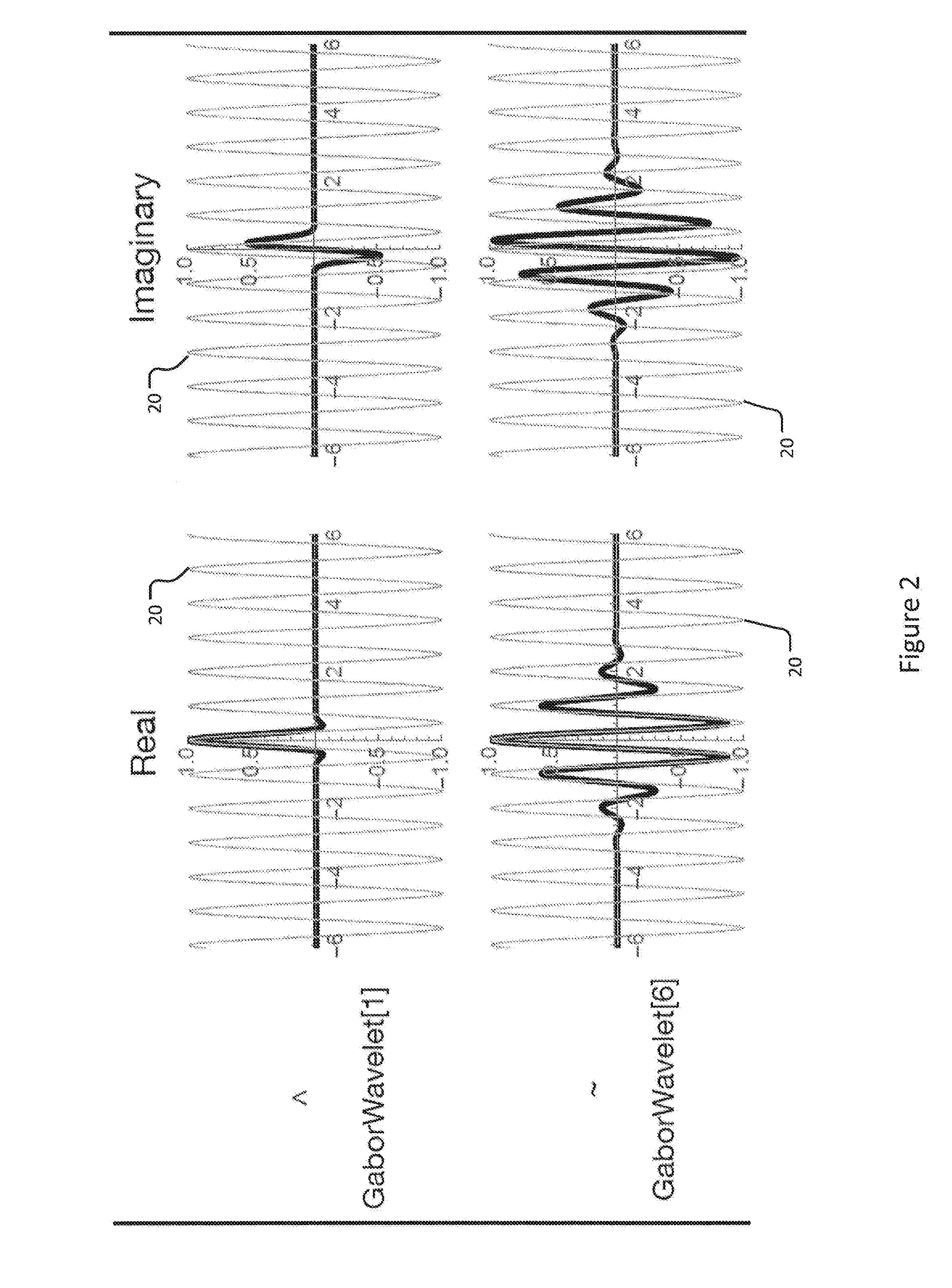
Device and method for spatiotemporal reconstruction of a moving vascular pulse wave in the brain and other organs
ActiveUS20170000441A1Reduce relative motionImage enhancementImage analysisHigh temporal resolutionTime signal
The brain appears to have organized cardiac frequency angiographic phenomena with such coherence as to qualify as vascular pulse waves. Separate arterial and venous vascular pulse waves may be resolved. This disclosure states the method of extracting a spatiotemporal reconstruction of the cardiac frequency phenomena present in an angiogram obtained at faster than cardiac frequency. A wavelet transform is applied to each of the pixel-wise time signals of the angiogram. If there is motion alias then instead a high frequency resolution wavelet transform of the overall angiographic time intensity curve is cross-correlated to high temporal resolution wavelet transforms of the pixel-wise time signals. The result is filtered for cardiac wavelet scale then pixel-wise inverse wavelet transformed. This gives a complex-valued spatiotemporal grid of cardiac frequency angiographic phenomena. It may be rendered with a brightness-hue color model or subjected to further analysis.
Owner:BUTLER WILLIAM E
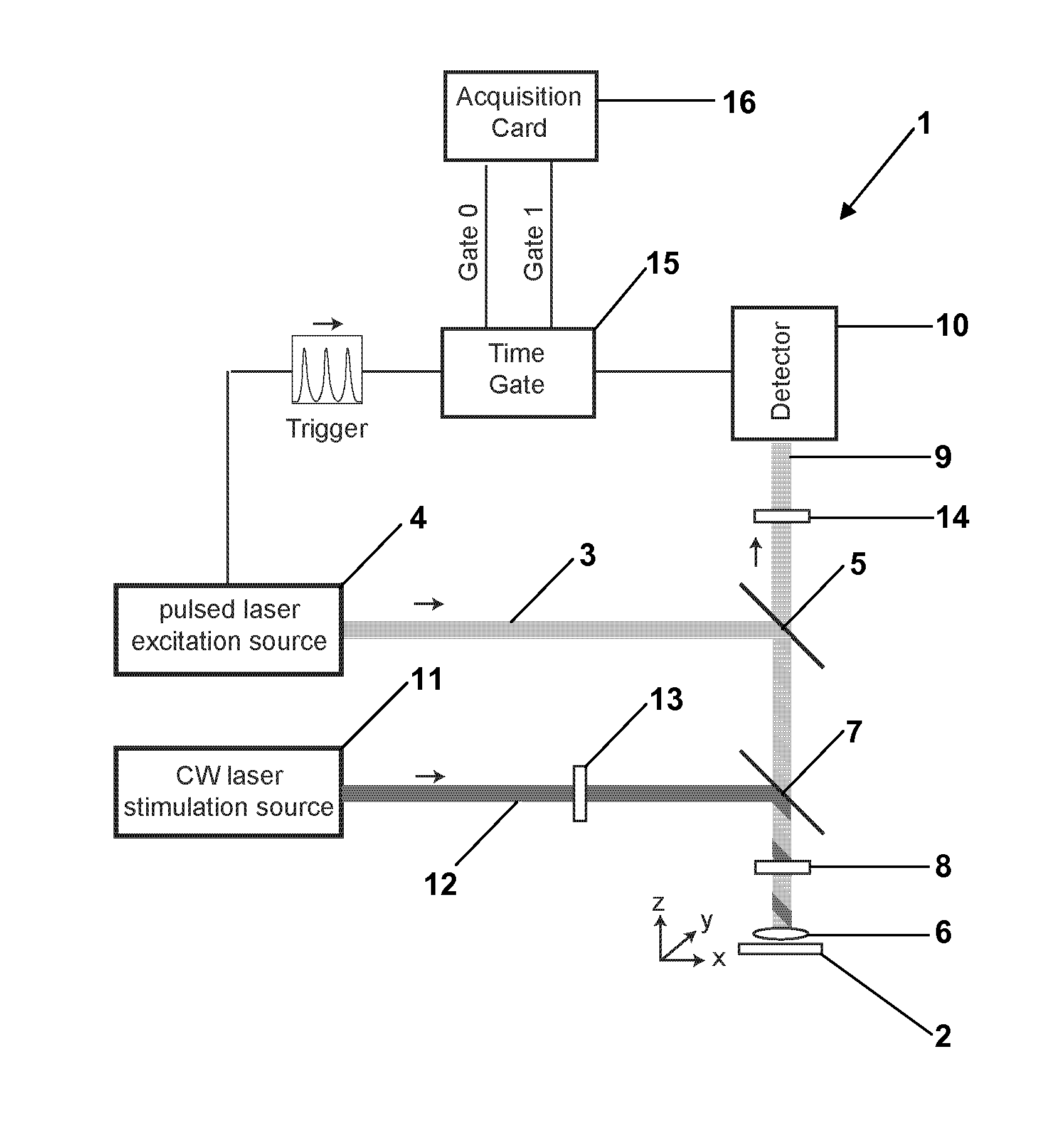
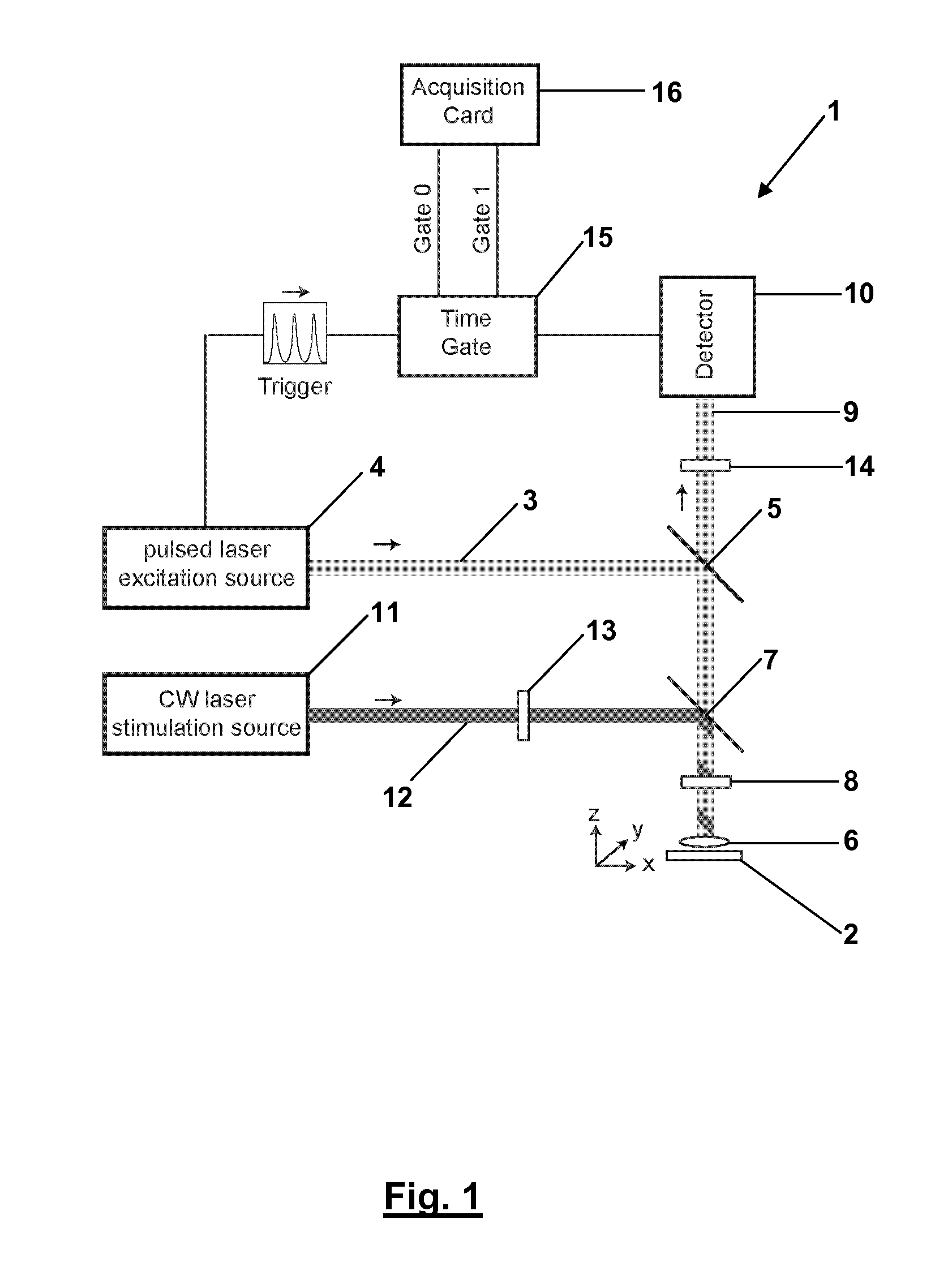
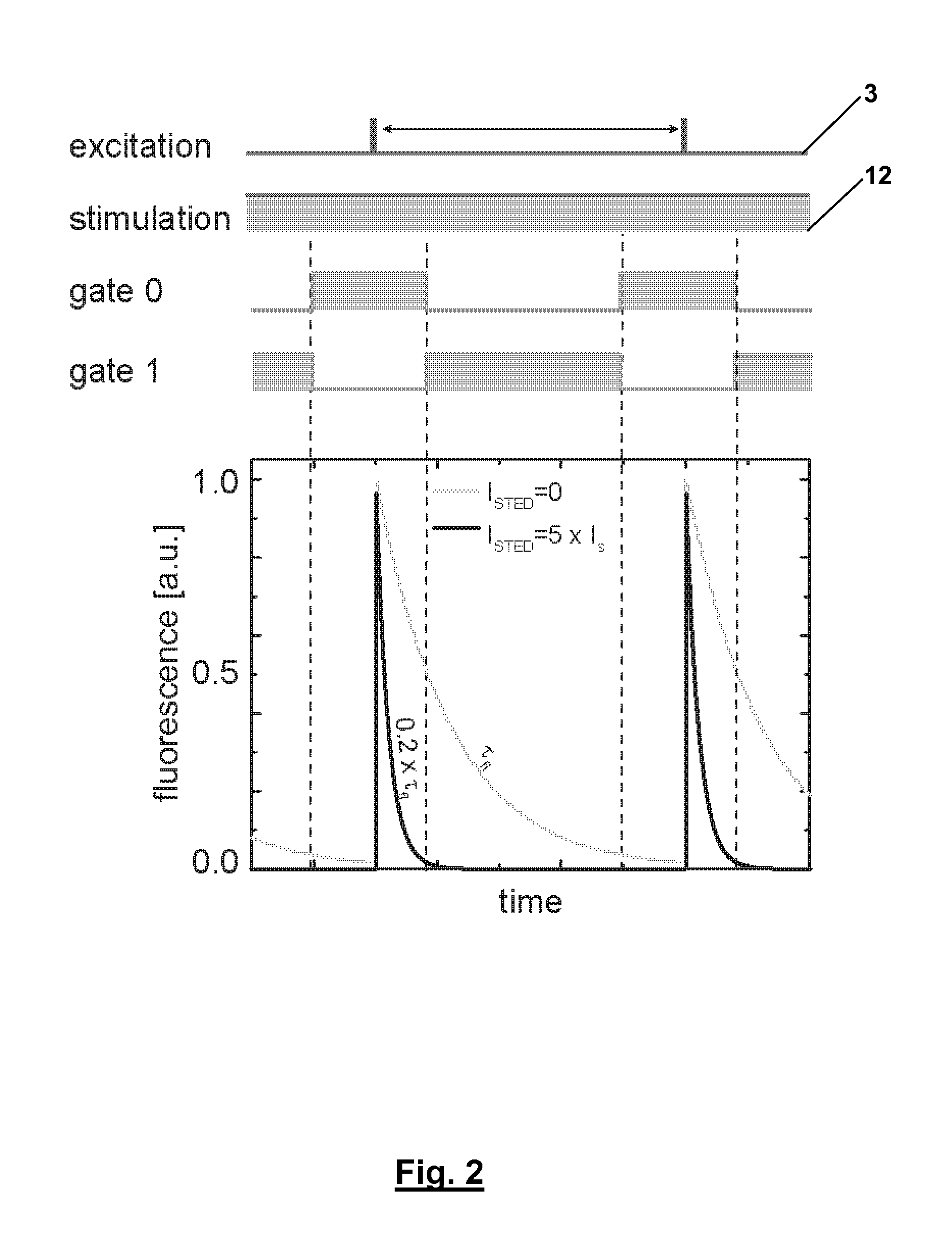
STED Microscopy With Pulsed Excitation, Continuous Stimulation, And Gated Registration Of Spontaneously Emitted Fluorescence Light
ActiveUS20130256564A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometryImage resolutionOptoelectronics
In a STED fluorescence light microscope pulses of excitation light (3) are applied to a sample, which excite fluorescent entities contained in the sample for fluorescence, and which are focused on at least one focal area. Further, de-excitation light (12) is applied to the sample, which de-excites the excited fluorescent entities and which comprises an intensity zero point in the at least one focal area, as a continuous wave. Fluorescence light emitted by the excited fluorescent entities in the sample is registered after each pulse of the excitation light (3) and overlapping with applying the de-excitation light (13) with high temporal resolution between consecutive pulses of the excitation light (3).
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS +1
Hand-held optical scanner for real-time imaging of body composition and metabolism
ActiveUS20170209083A1High-resolution characterizationFaster data acquisitionRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsLipid formationOptical scanners
A low cost portable high speed quantitative system for diffuse optical spectroscopic imaging of human tissue. The hybrid system (CWFD) can measure absolute optical properties from 660 nm to 980 nm and recover all tissue chromophore concentrations. The standalone FD module can be utilized to measure scattering at every measurement and recover deoxygenated and oxygenated hemoglobin concentrations. The CW module can operate concurrently with the FD module to also measure water and lipid. The high temporal resolution and large signal-to-noise ratio of the CWFD system may be used to explore tissue oximetry, vascular occlusion, and paced breathing models to measure and analyze tissue hemodynamics response to changes in blood flow. Continuous monitoring of vasculature response to various modified blood perfusion conditions can provide information about local tissue metabolism and physiological state (dysfunction).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
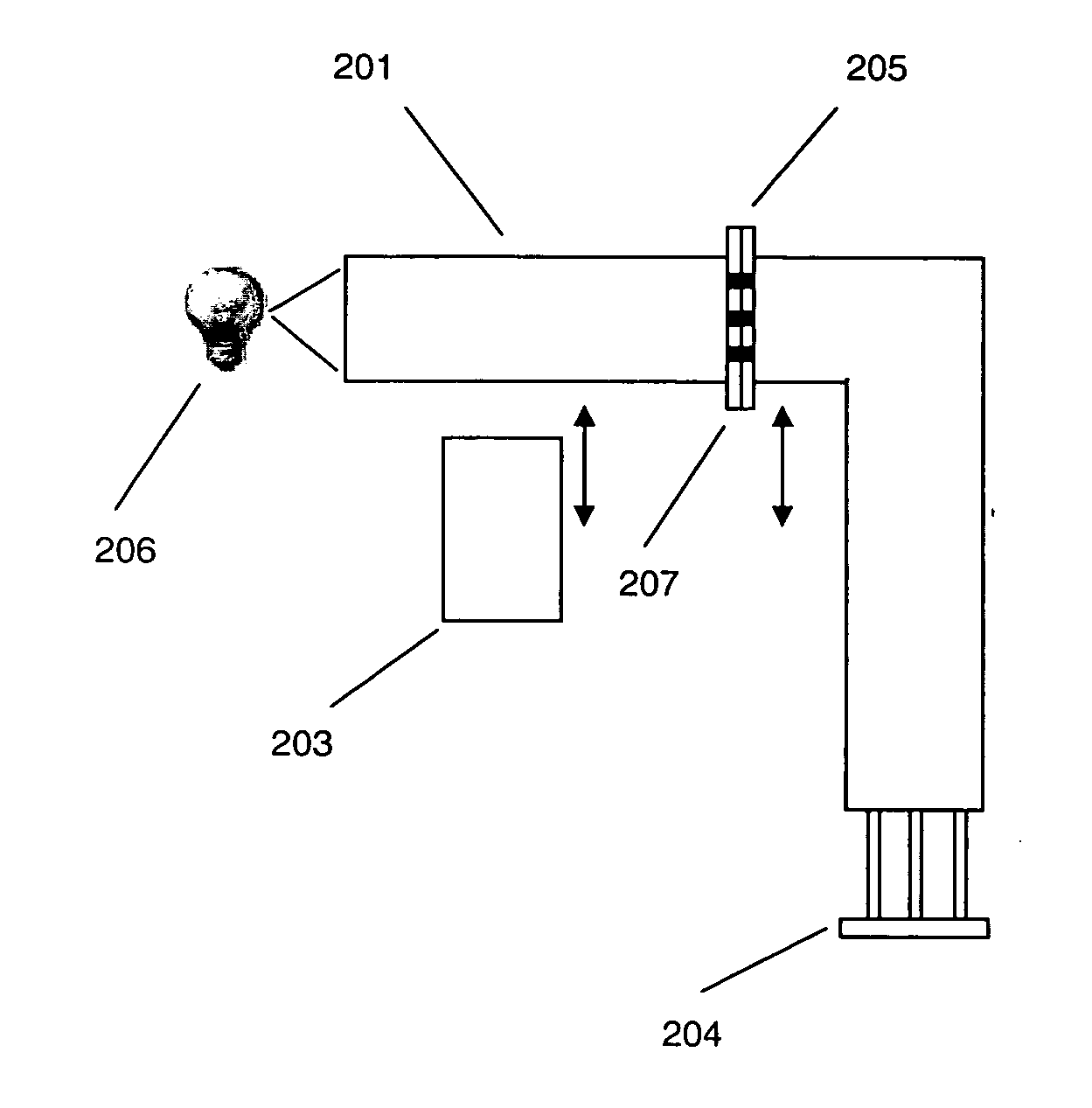
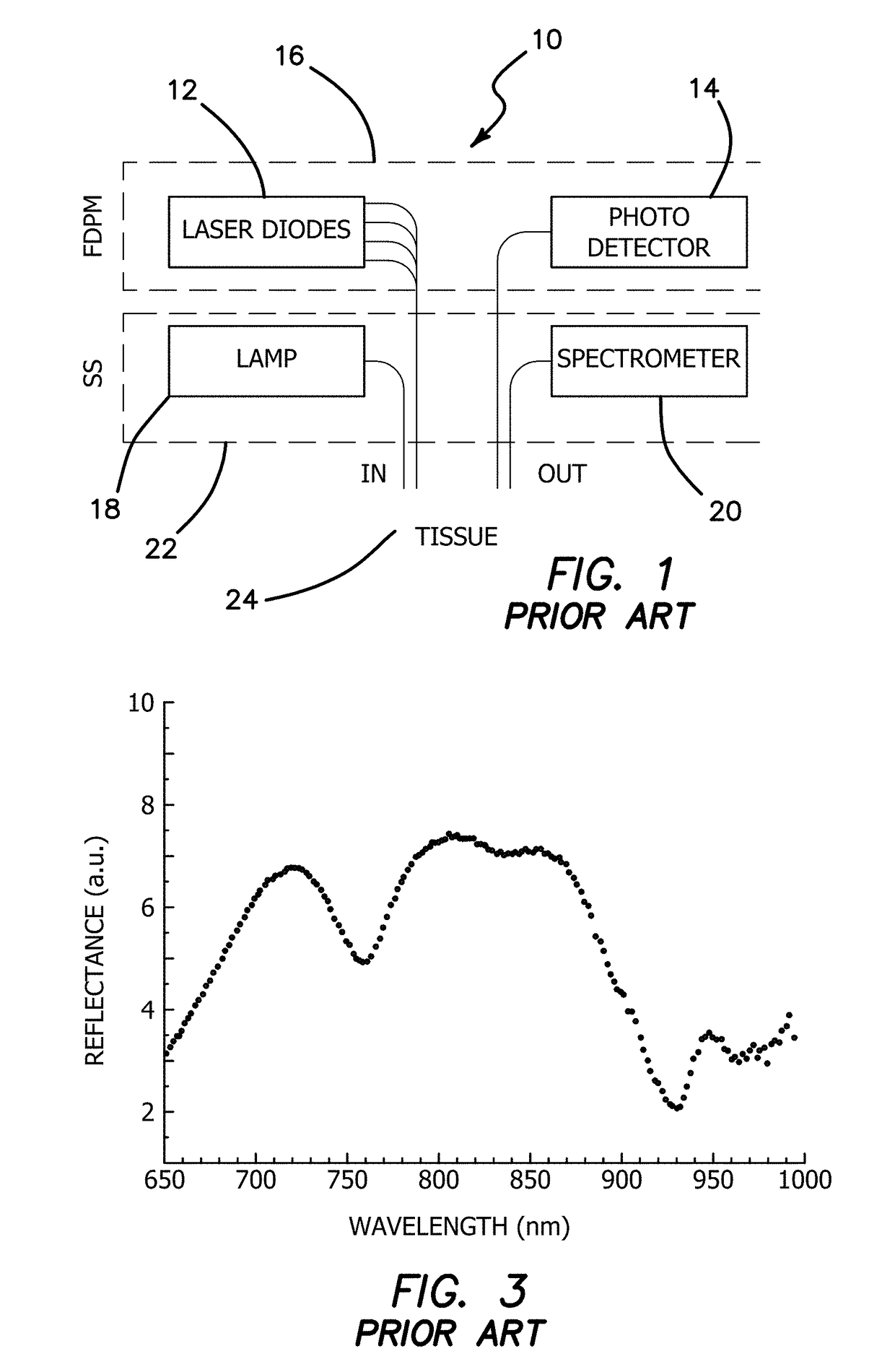
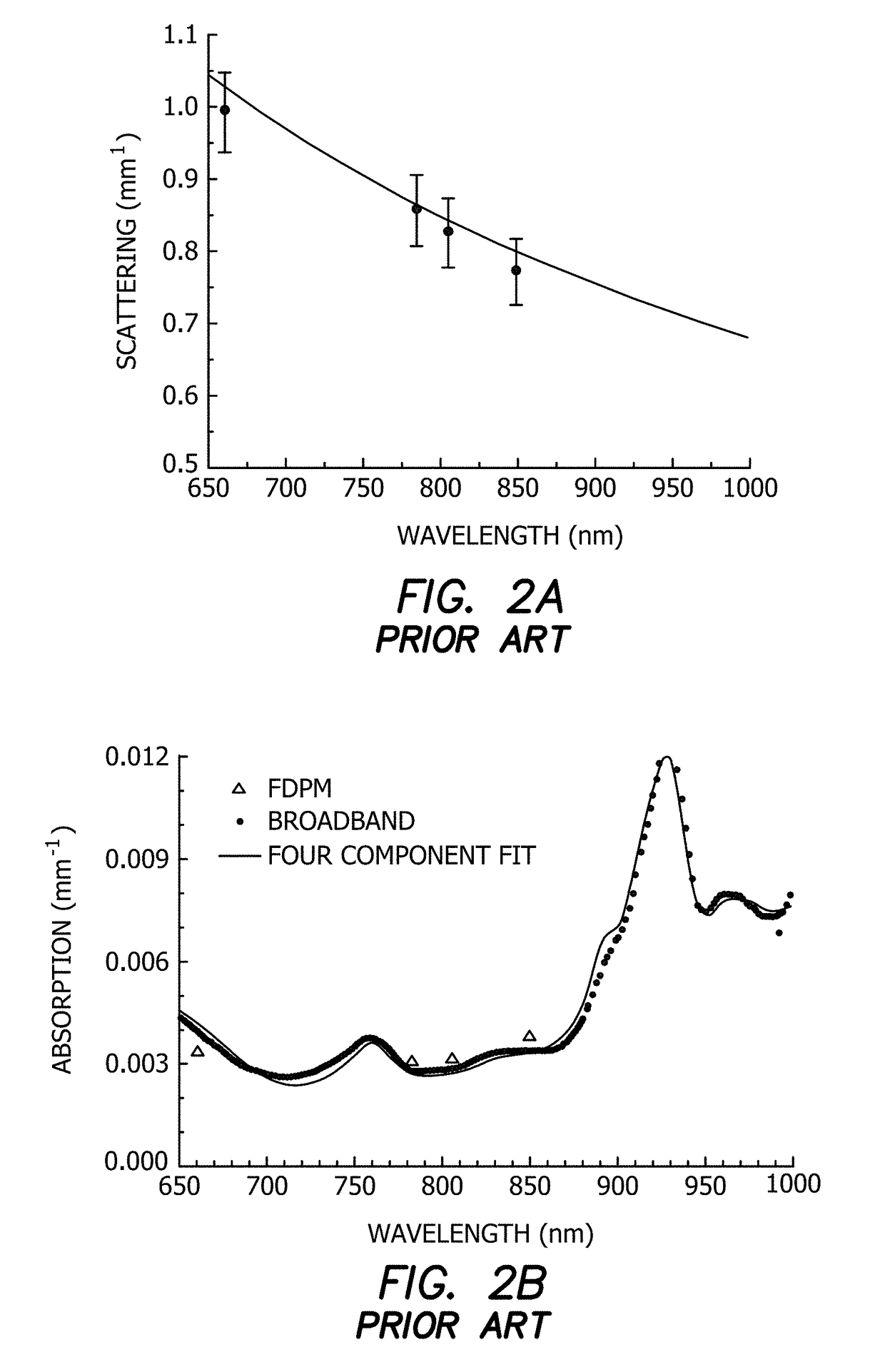
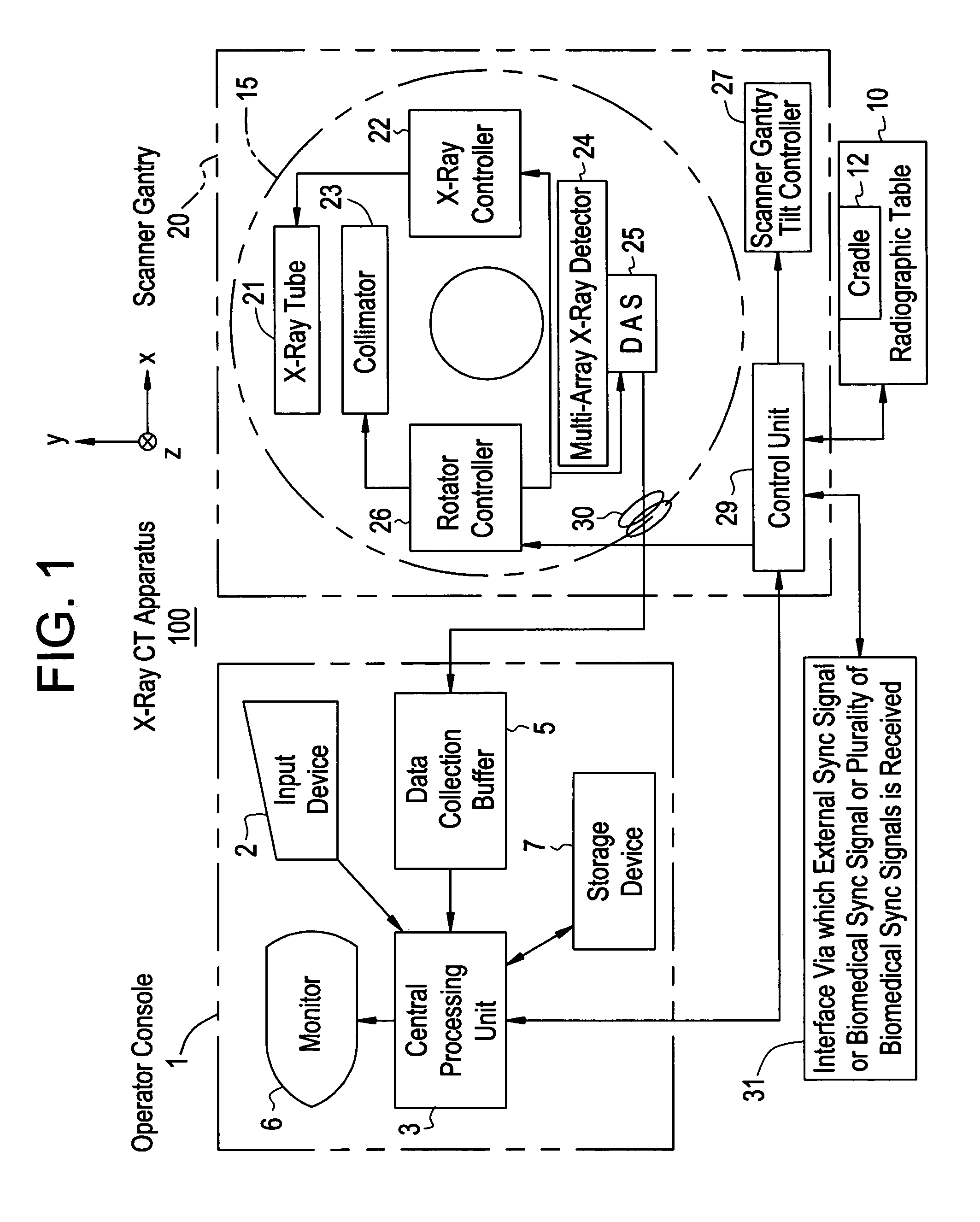
X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20060291615A1Improve image qualityImprove time resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImage resolutionLight beam
When an X-ray CT apparatus including a two-dimensional X-ray area detector performs a conventional (axial) scan or a cine scan, a plurality of segments of projection data items detected synchronously with an external signal or a biomedical signal is sampled from projection data items acquired during one scan or a plurality of scans. Projection data items corresponding to those detected during a half scan of rotating an X-ray tube by an angle of 180° plus the angle of a fan beam falling on the detector or during a 360° full scan are used to reconstruct a three-dimensional image. Thus, a three-dimensional tomographic image enjoying a high temporal resolution is displayed. Moreover, successive three-dimensional display images showing states of a subject synchronized with respective phases of the external signal or biomedical signal may be displayed as a four-dimensional image.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
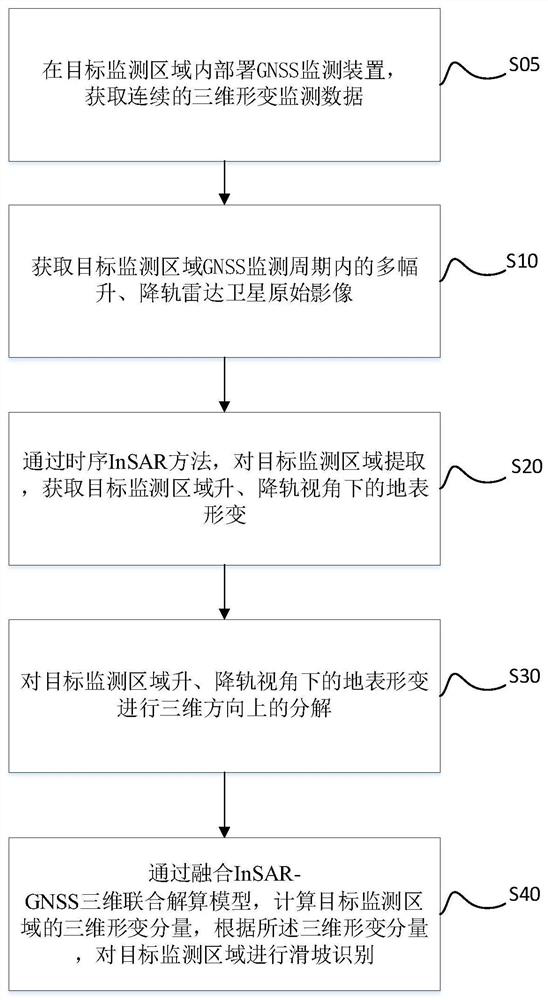
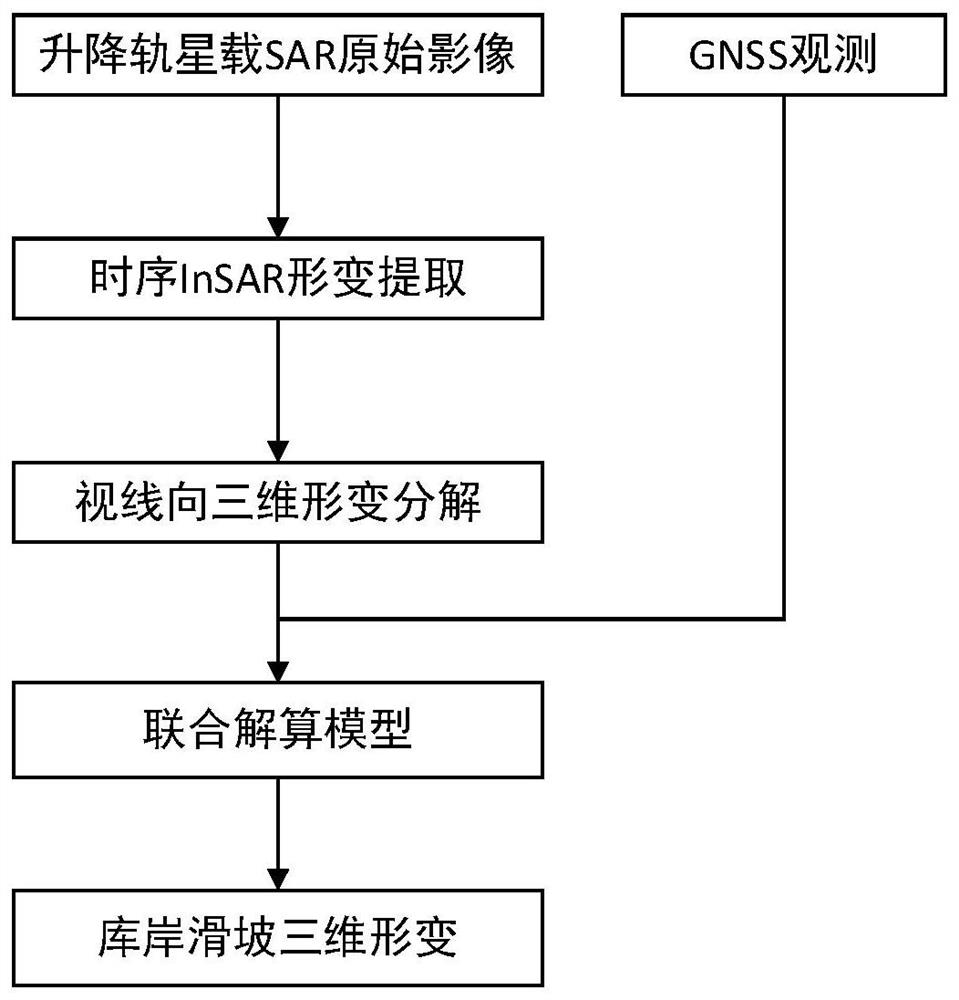
Landslide three-dimensional deformation resolving method and system fusing GNSS and ascending and descending orbit time sequence InSAR
PendingCN112540369ASatellite radio beaconingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh temporal resolutionPhysics
The invention discloses a landslide three-dimensional deformation calculation method fusing GNSS and ascending and descending orbit time sequence InSAR, which belongs to the technical field of risk identification, and is used for solving the technical problem of incomplete results of an existing detection mode. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a plurality of ascending and descending orbit radar satellite original images in a GNSS monitoring period of a target monitoring area; acquiring surface deformation of the target monitoring area under the view angle of a ascending and descending orbit radar through a time sequence InSAR method; decomposing the surface deformation of the target monitoring area in the three-dimensional direction under the view angle of the ascending and descending orbit radar; and calculating three-dimensional deformation of the target monitoring area by fusing an InSAR-GNSS three-dimensional joint calculation model, and performing landslide identification on the target monitoring area according to the three-dimensional deformation. According to the method, the problem that it is difficult for InSAR to obtain three-dimensional deformationis effectively solved, effective unification of high time resolution and high plane position precision of GNSS and high spatial resolution and elevation deformation precision of the InSAR technology is realized, and the method has very high practicability for obtaining a landslide three-dimensional deformation field.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV +2
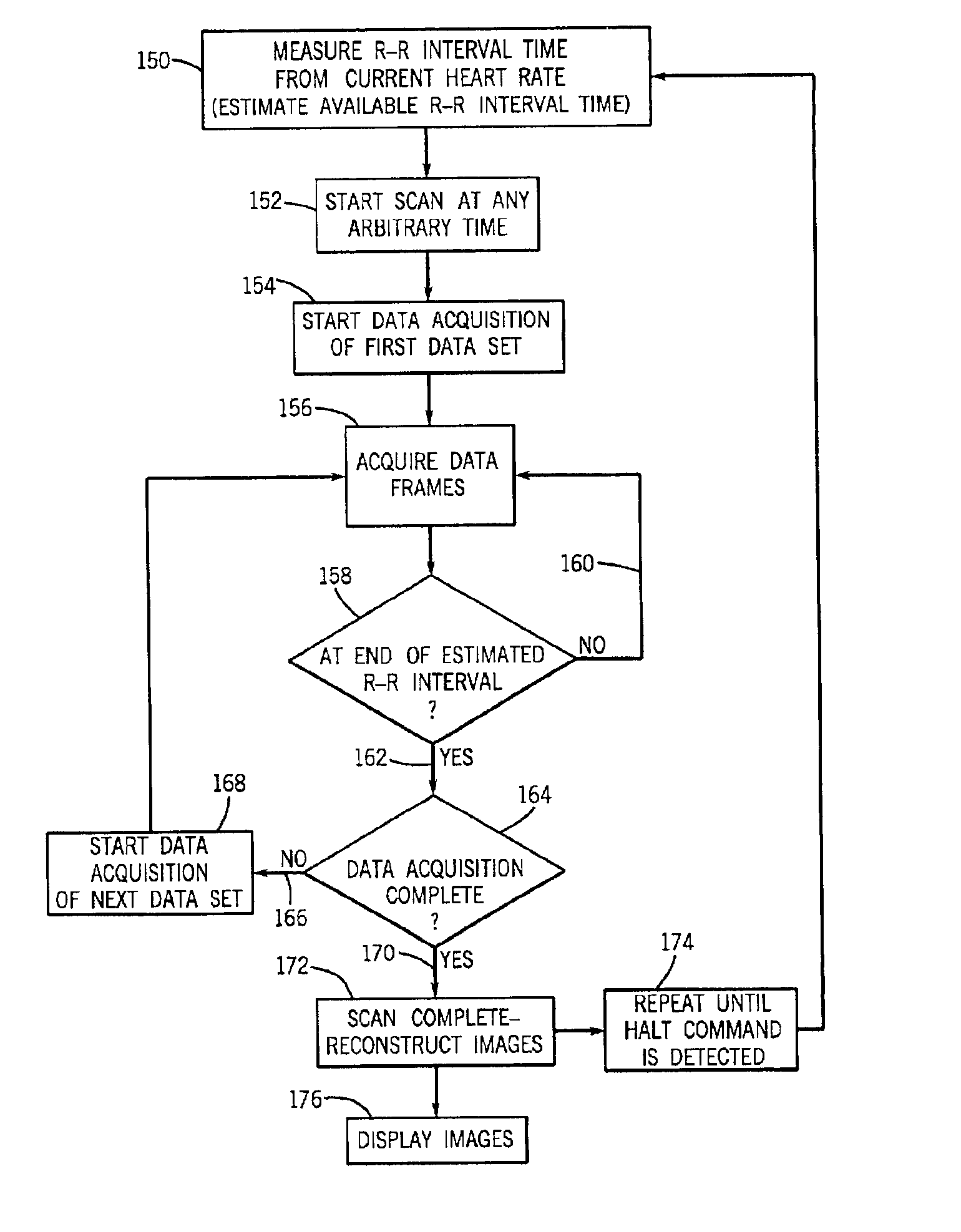
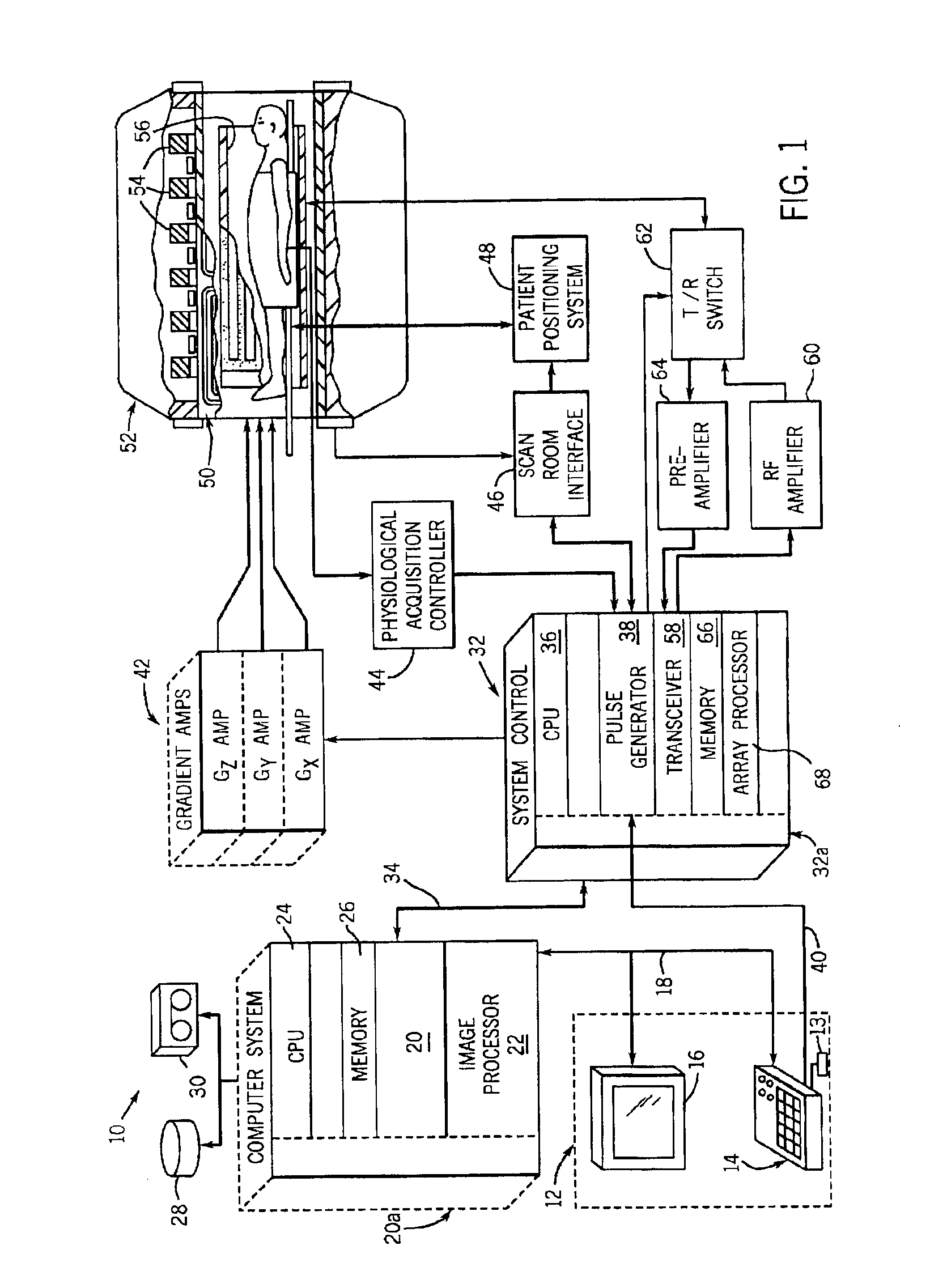
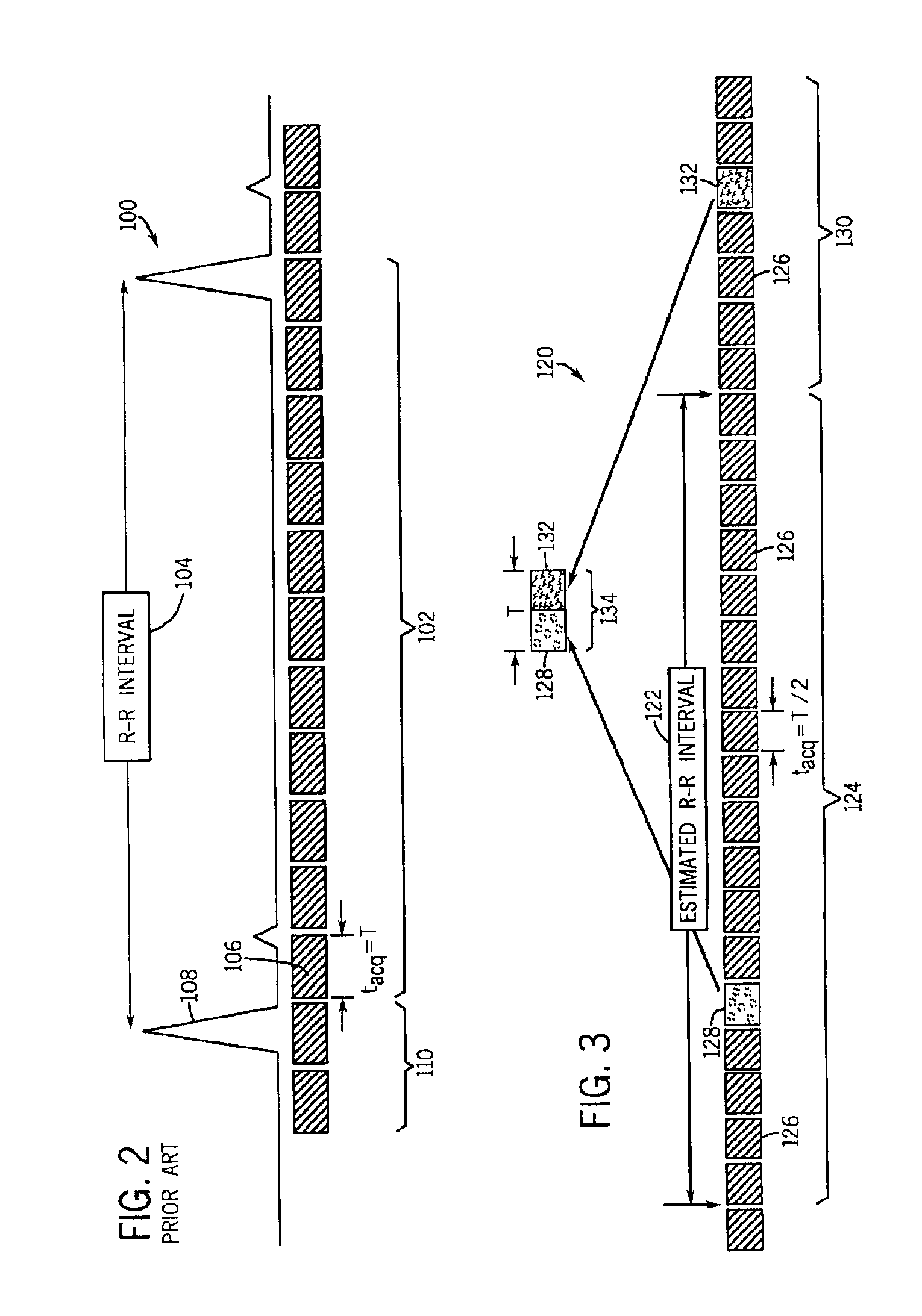
Acquisition of high-temporal free-breathing MR images
InactiveUS6889071B2Short acquisition timeHigh resolution imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImage resolutionTime segment
A system and method are disclosed to acquire high temporal resolution free-breathing cardiac MR images. The technique includes monitoring heart rate of a patient just prior to image acquisition to acquire a time period of an R—R interval, and using this time period from the heart rate monitoring to prospectively estimate future R—R intervals. The acquisition of MR data can then commence at any point in an R—R interval and extend for the time period recorded. The data acquisition can be segmented and acquired in successive R—R intervals, then combined to create high temporal resolution images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
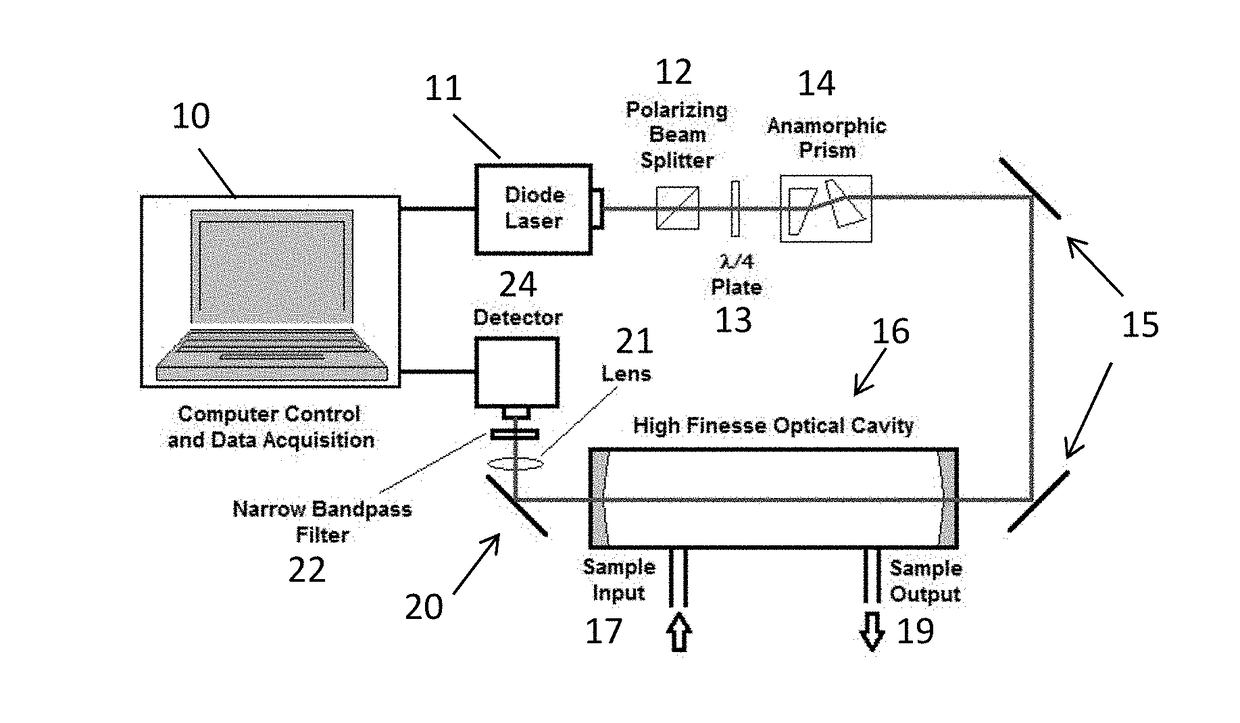
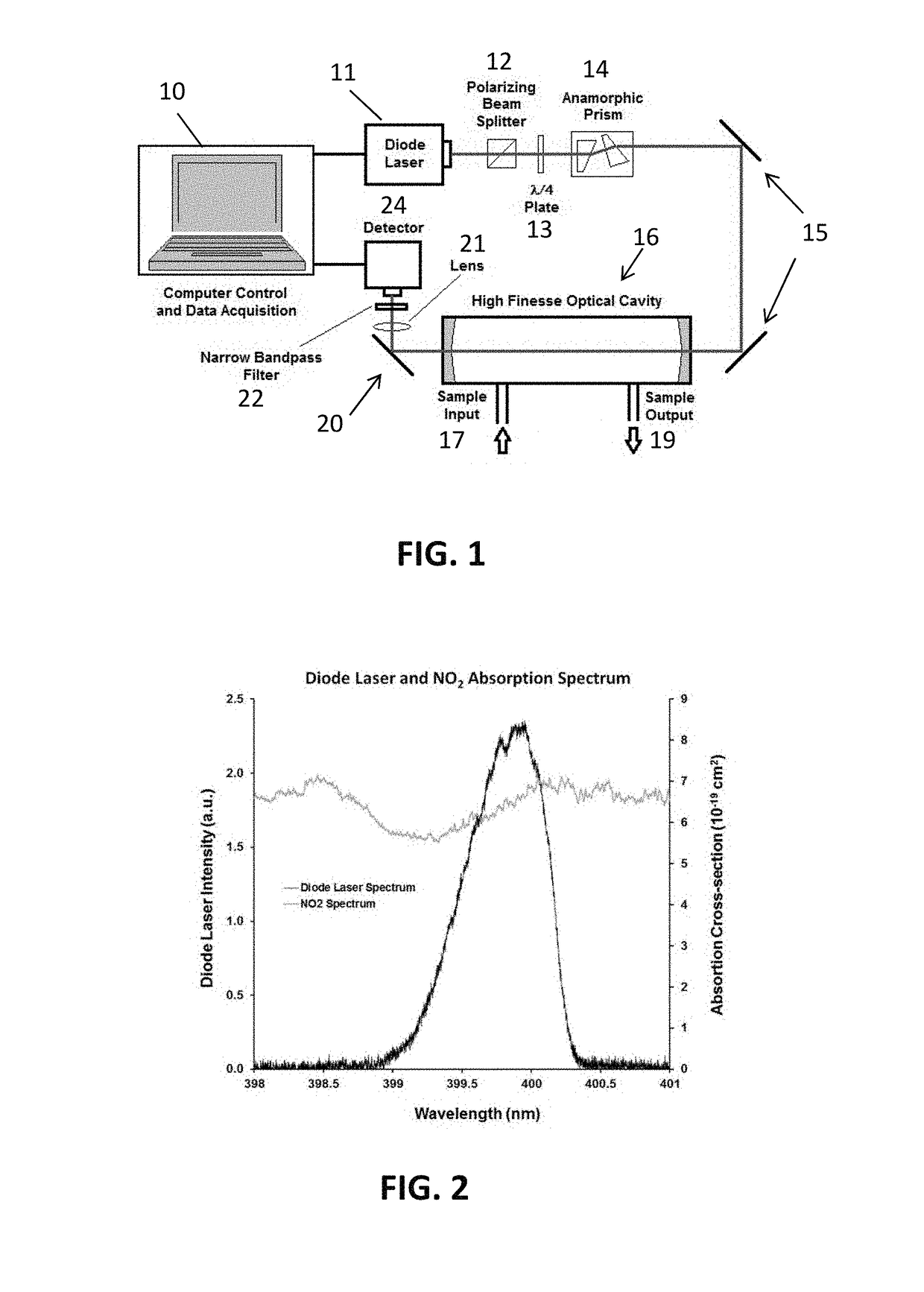
Ultra-sensitive, real-time trace gas detection using a high-power, multi-mode semiconductor laser and cavity ringdown spectroscopy
InactiveUS20180306713A1Sensitive measurementSimple structureLaser detailsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyHigh temporal resolutionUltra sensitive
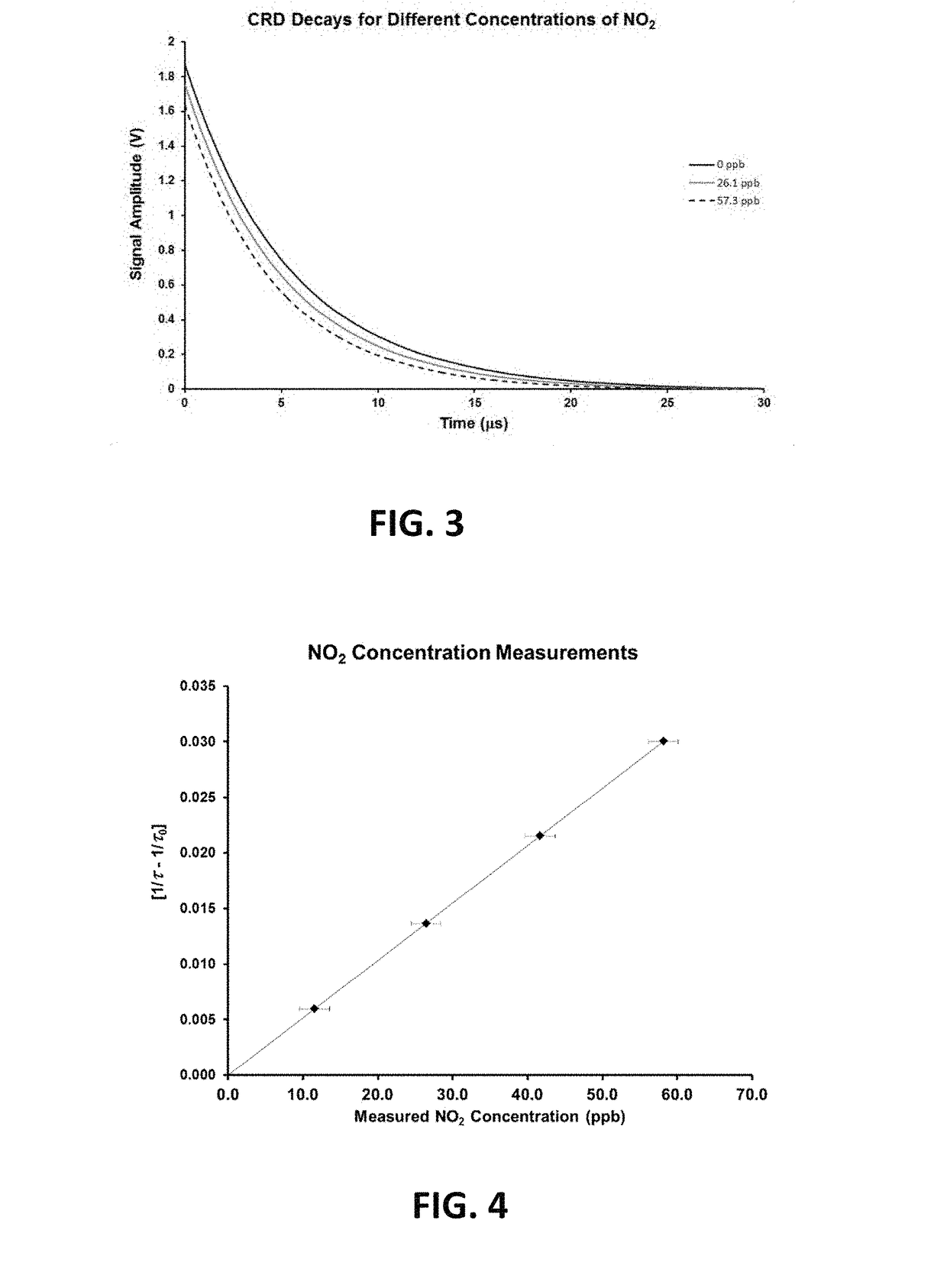
A highly sensitive trace gas sensor based on Cavity Ring-down Spectroscopy (CRDS) makes use of a high power, multi-mode Fabry-Perot (FP) semiconductor laser with a broad wavelength range to excite a large number of cavity modes and multiple molecular transitions, thereby reducing the detector's susceptibility to vibration and making it well suited for field deployment. The laser beam is aligned on-axis to the cavity, improving the signal-noise-ratio while maintaining its vibration insensitivity. The use of a FP semiconductor laser has the added advantages of being inexpensive, compact and insensitive to vibration. The technique is demonstrated using a laser with an output power of at least 200 mW, preferably over 1.0 Watt, (λ=400 nm) to measure low concentrations of Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) in zero air. For single-shot detection, 530 ppt sensitivity is demonstrated with a measurement time of 60 μs which allows for sensitive measurements with high temporal resolution.
Owner:ADELPHI UNIVERSITY
Large-Area Monitoring Using Infrared Imaging System
InactiveUS20150161779A1Improve time resolutionImage enhancementSolar heating energyThermal monitoringFisheye lens
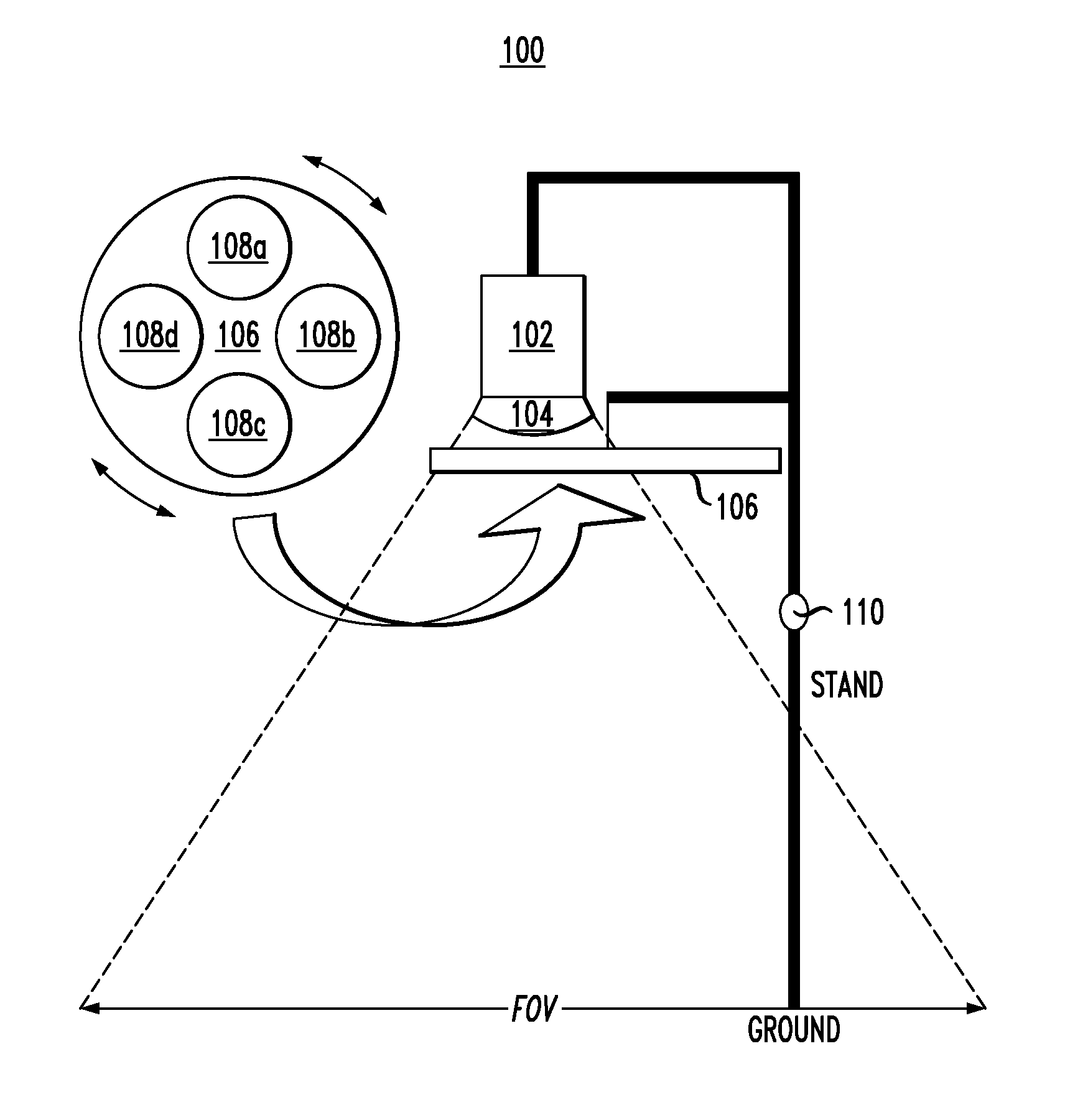
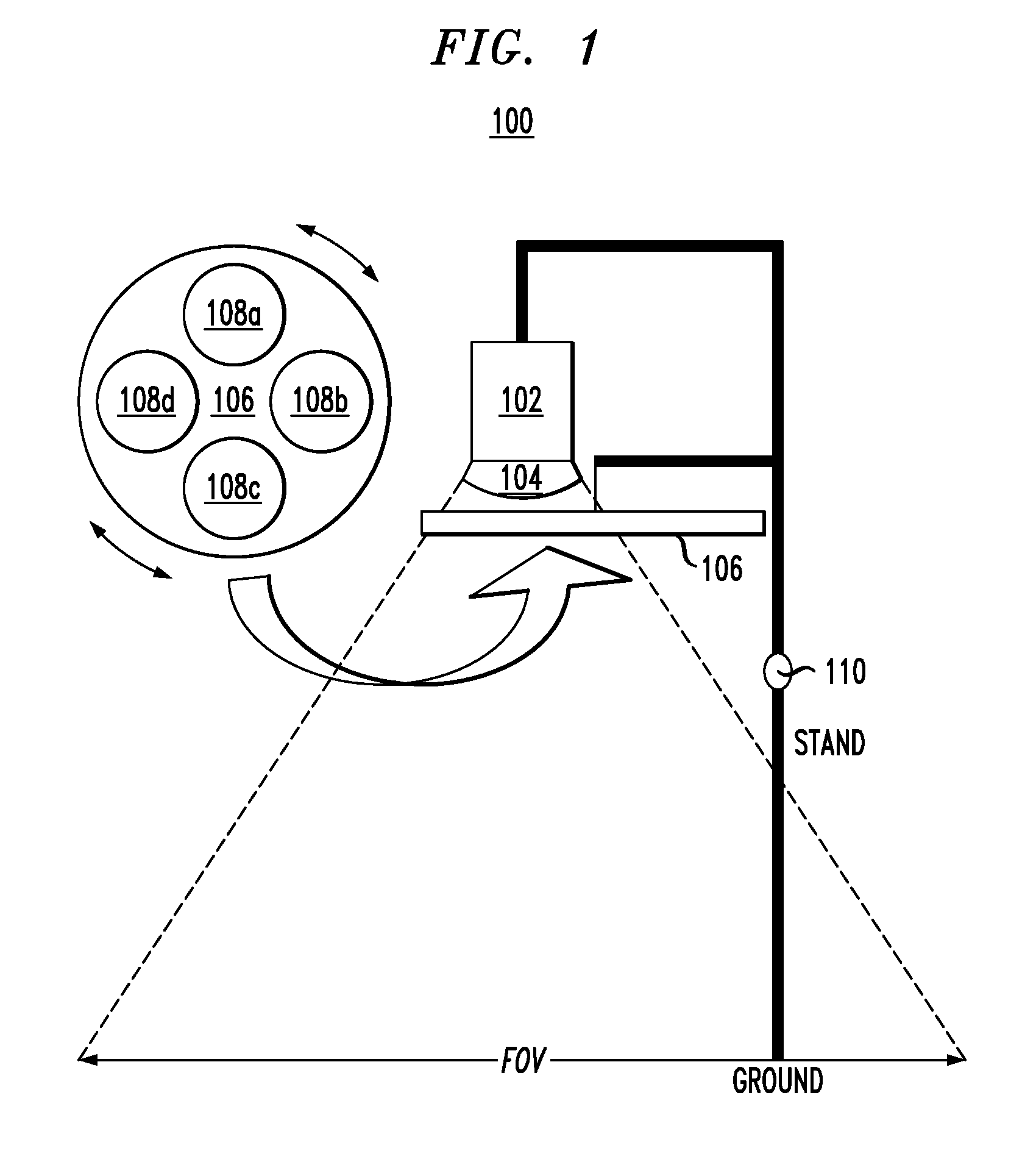
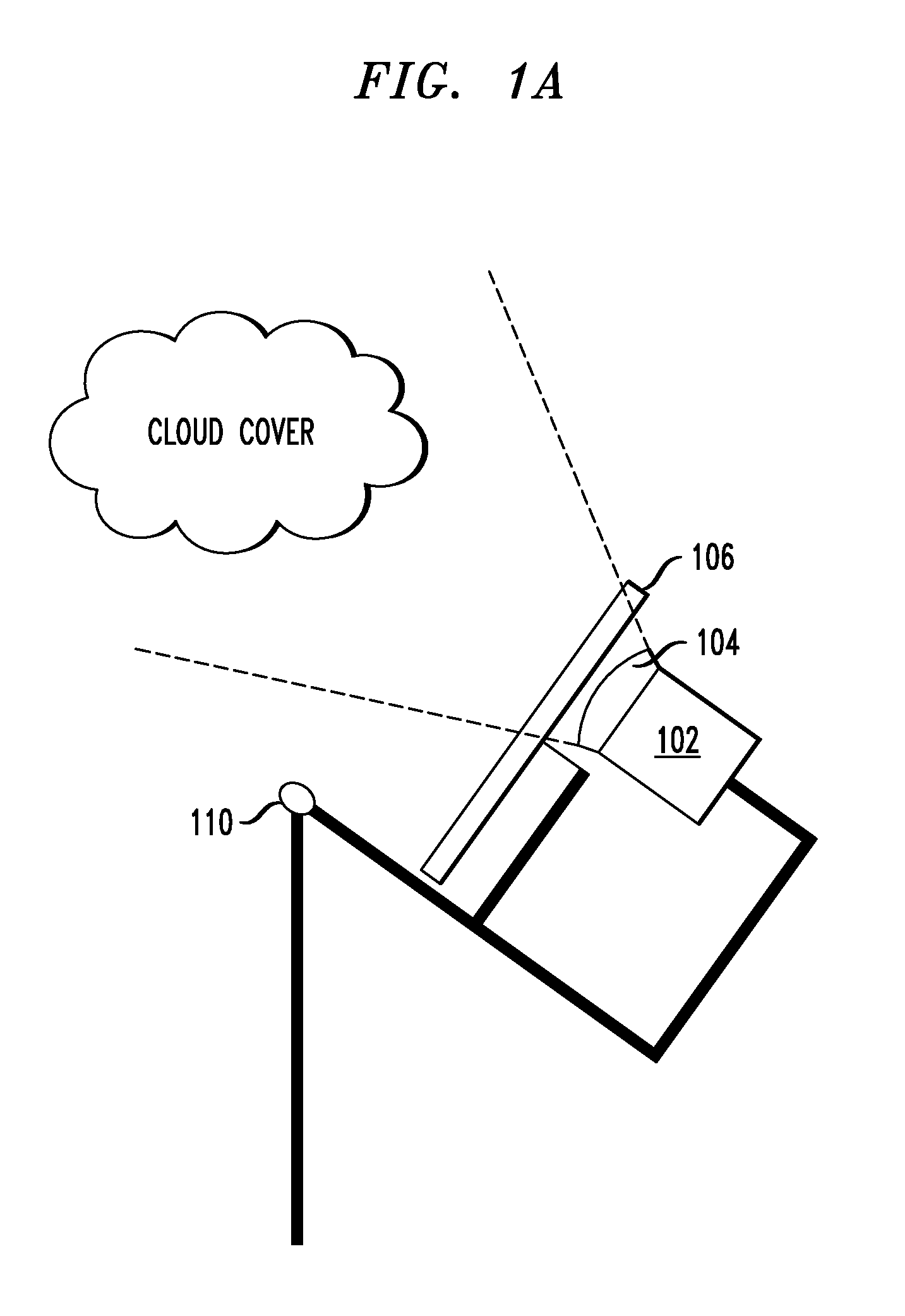
An imaging system and use thereof for large-area monitoring with very high temporal resolution are provided. In one aspect, an imaging system includes a camera equipped with curved optics having a field of view of from about 0.01 miles to about 1.5 miles; and interchangeable light filters positioned in front of the camera configured to change one or more of an intensity and an amplitude of light captured by the imaging system. The curved optics may include a hemispherical mirror configured to reflect an image of objects in front of the mirror, and the camera may be positioned facing a reflective surface of the hemispherical mirror so as to capture the image reflected in the hemispherical mirror. Alternatively, the curved optics may include a fisheye lens mounted to the camera. An imaging network of the present imaging systems and a method for use thereof for thermal monitoring are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com