Patents
Literature
1855 results about "Feature detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Feature detection is a process by which specialized nerve cells in the brain respond to specific features of a visual stimulus, such as lines, edges, angle, or movement. The nerve cells fire selectively in response to stimuli that have specific characteristics E.G shape, angle, or movement. Feature detection was discovered by David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel of Harvard University, an accomplishment which won them the 1981 Nobel Prize. In the area of computer vision, feature detection usually refers to the computation of local image features as intermediate results of making local decisions about the local information contents in the image; see also the article on interest point detection. In the area of psychology, the feature detectors are neurons in the visual cortex that receive visual information and respond to certain features such as lines, angles, movements, etc. When the visual information changes, the feature detector neurons will quiet down, to be replaced with other more responsive neurons.
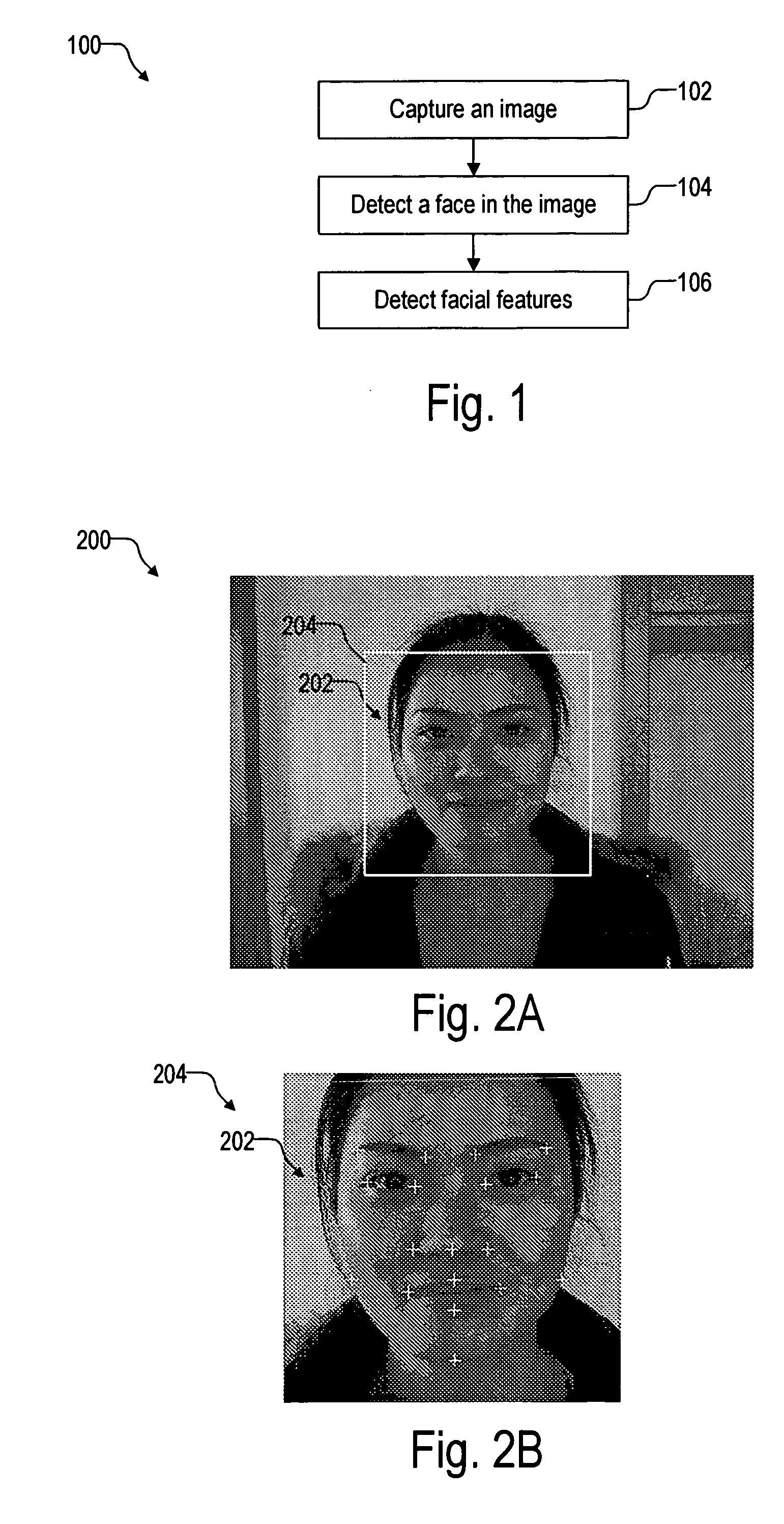
Method and system for real-time facial image enhancement
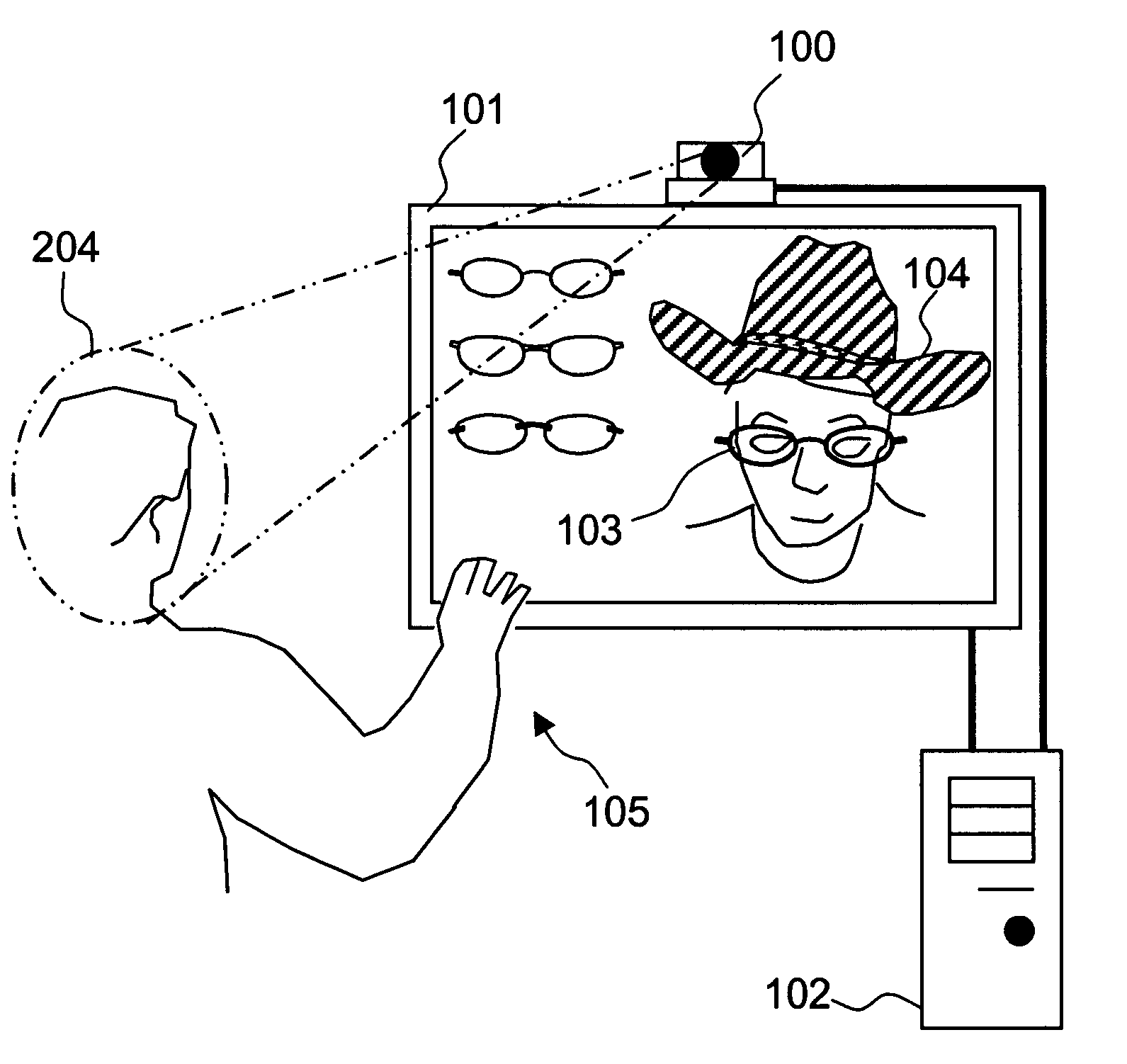
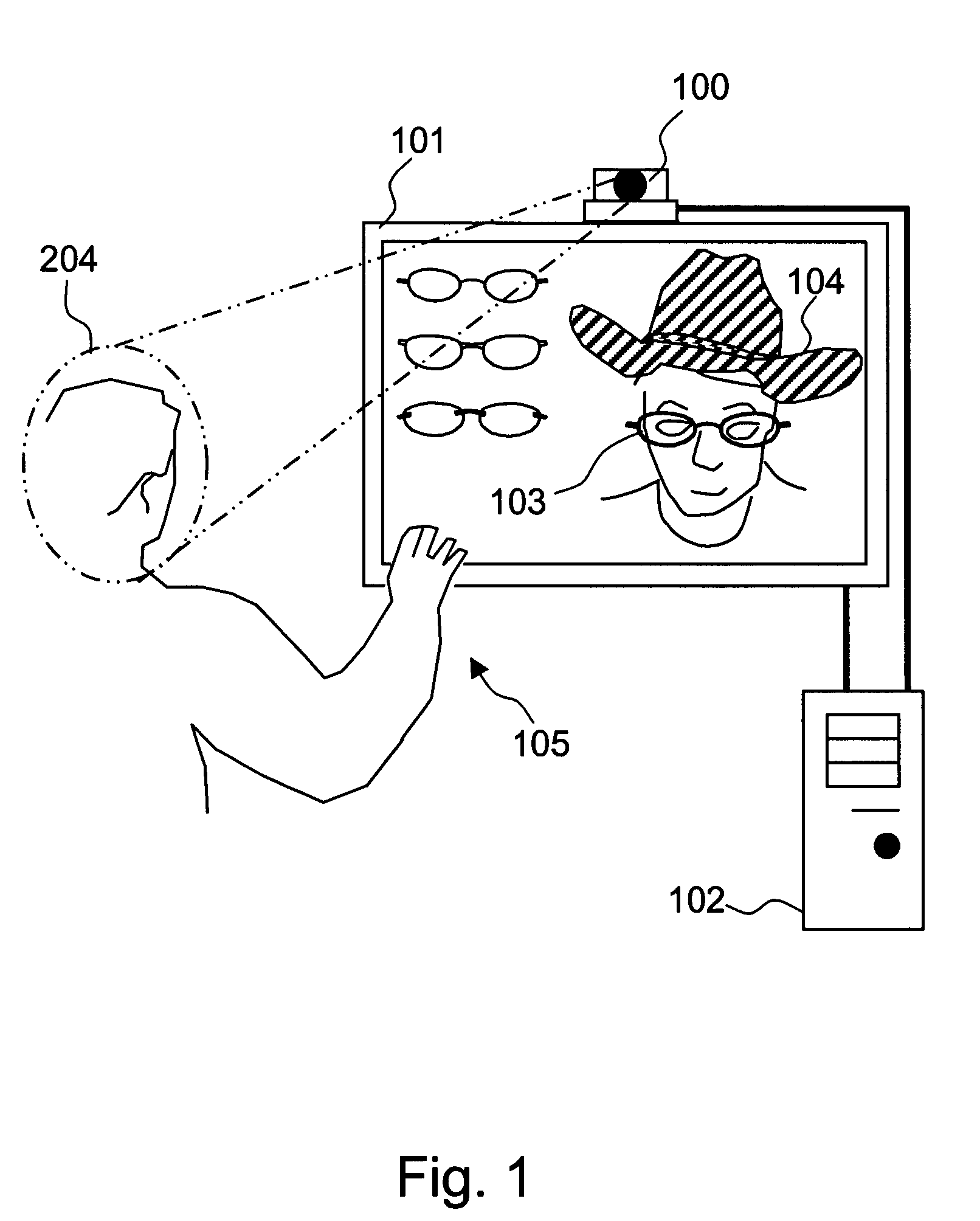
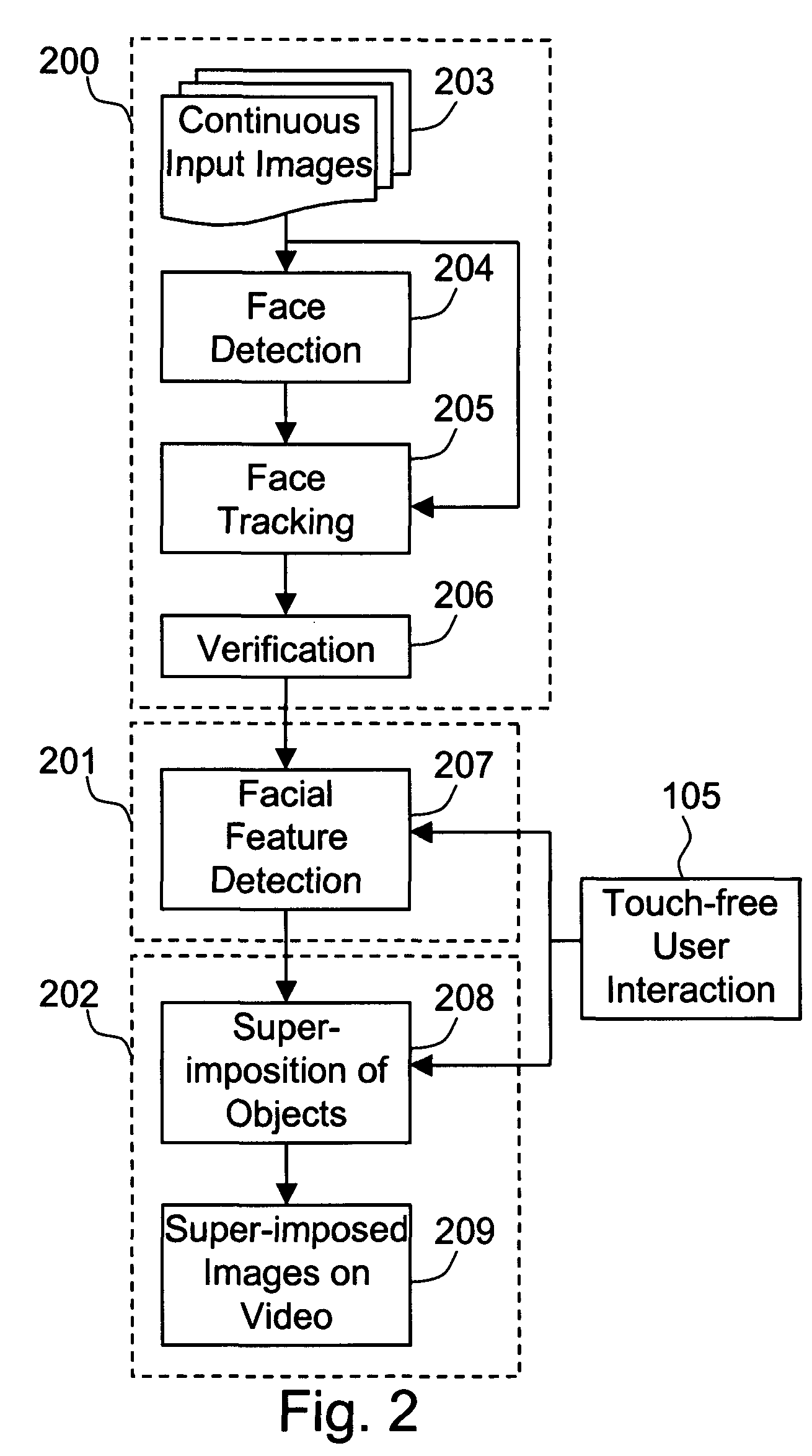
The present invention is a system and method for detecting facial features of humans in a continuous video and superimposing virtual objects onto the features automatically and dynamically in real-time. The suggested system is named Facial Enhancement Technology (FET). The FET system consists of three major modules, initialization module, facial feature detection module, and superimposition module. Each module requires demanding processing time and resources by nature, but the FET system integrates these modules in such a way that real time processing is possible. The users can interact with the system and select the objects on the screen. The superimposed image moves along with the user's random motion dynamically. The FET system enables the user to experience something that was not possible before by augmenting the person's facial images. The hardware of the FET system comprises the continuous image-capturing device, image processing and controlling system, and output display system.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
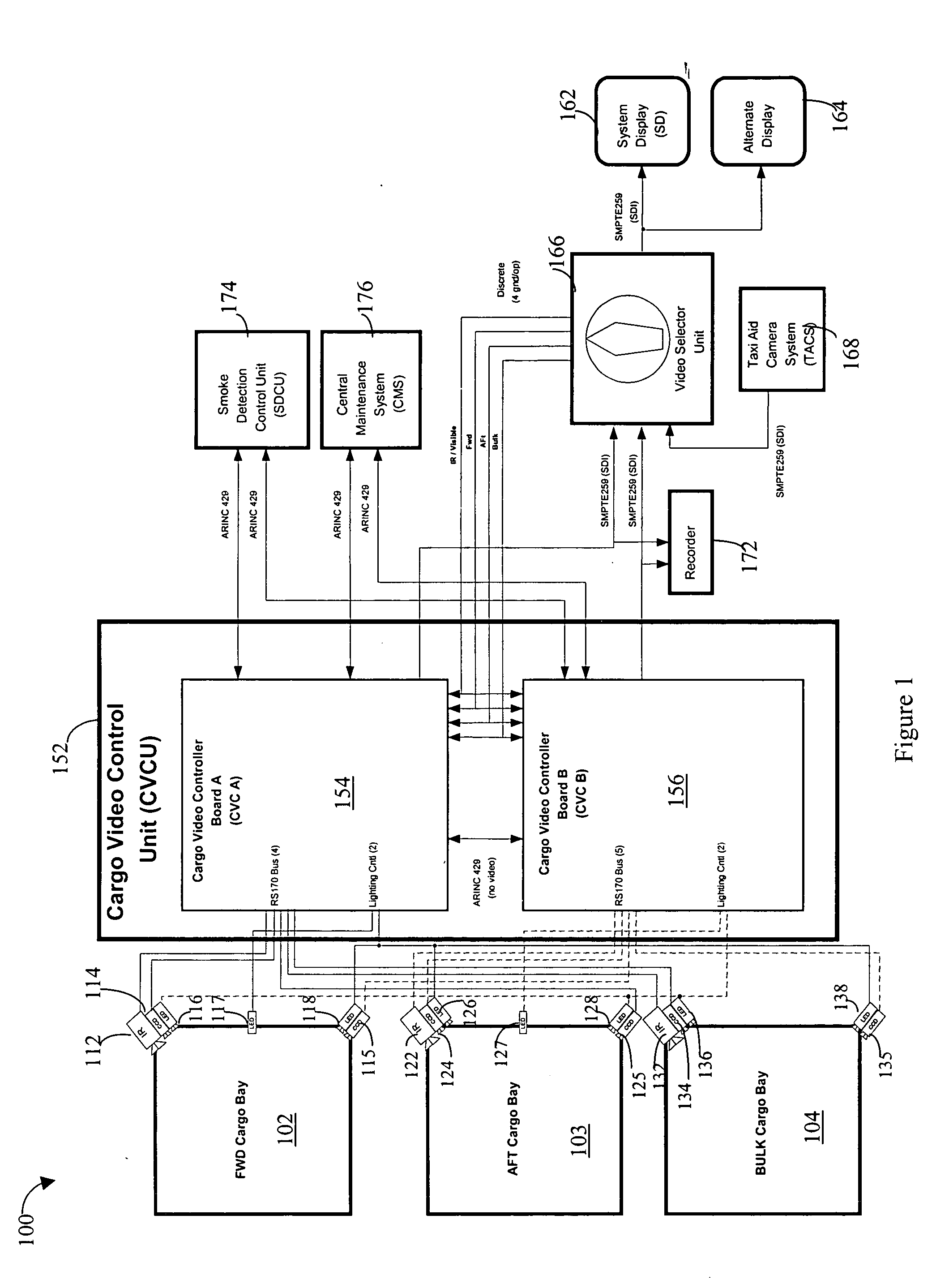
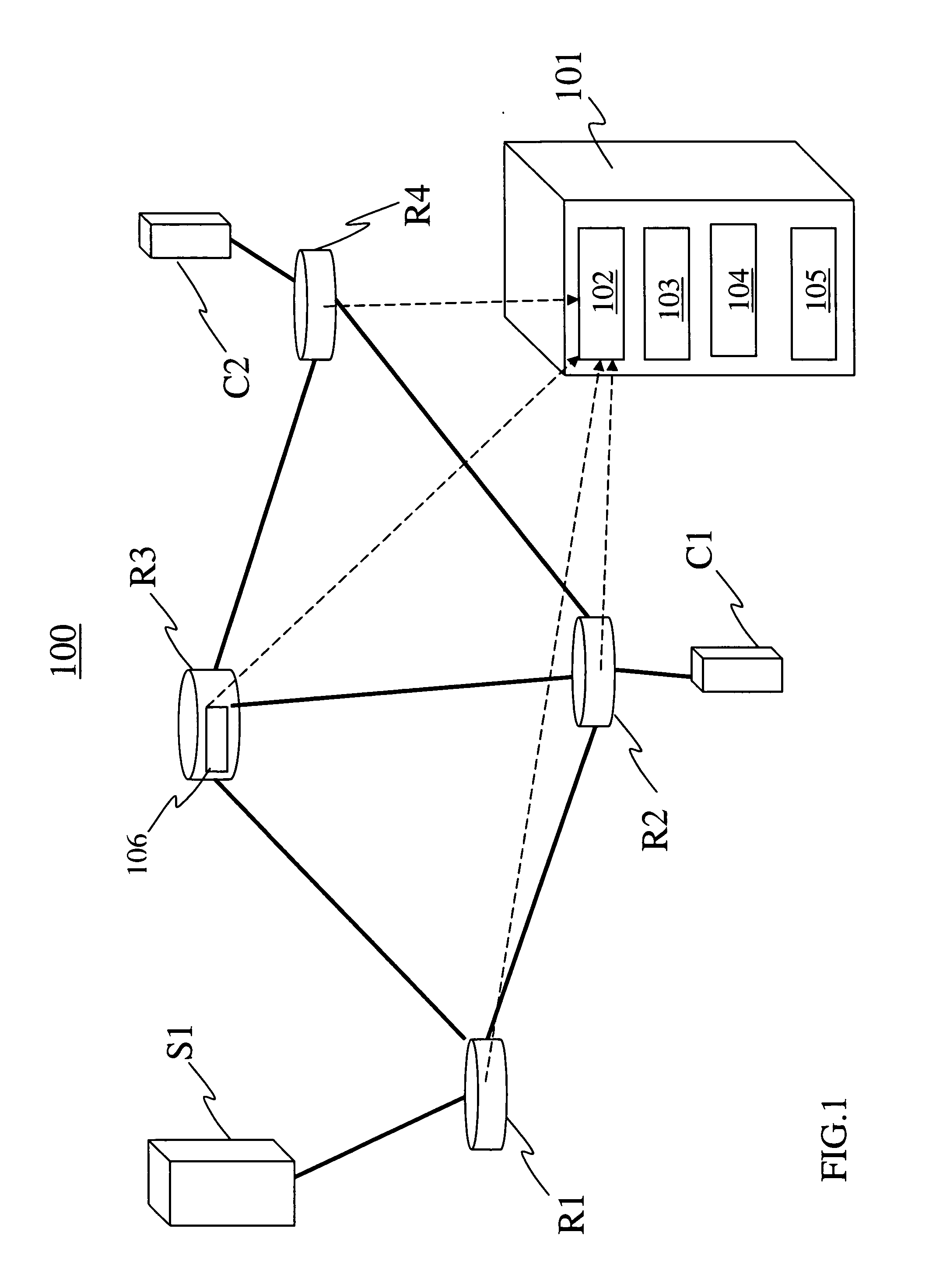
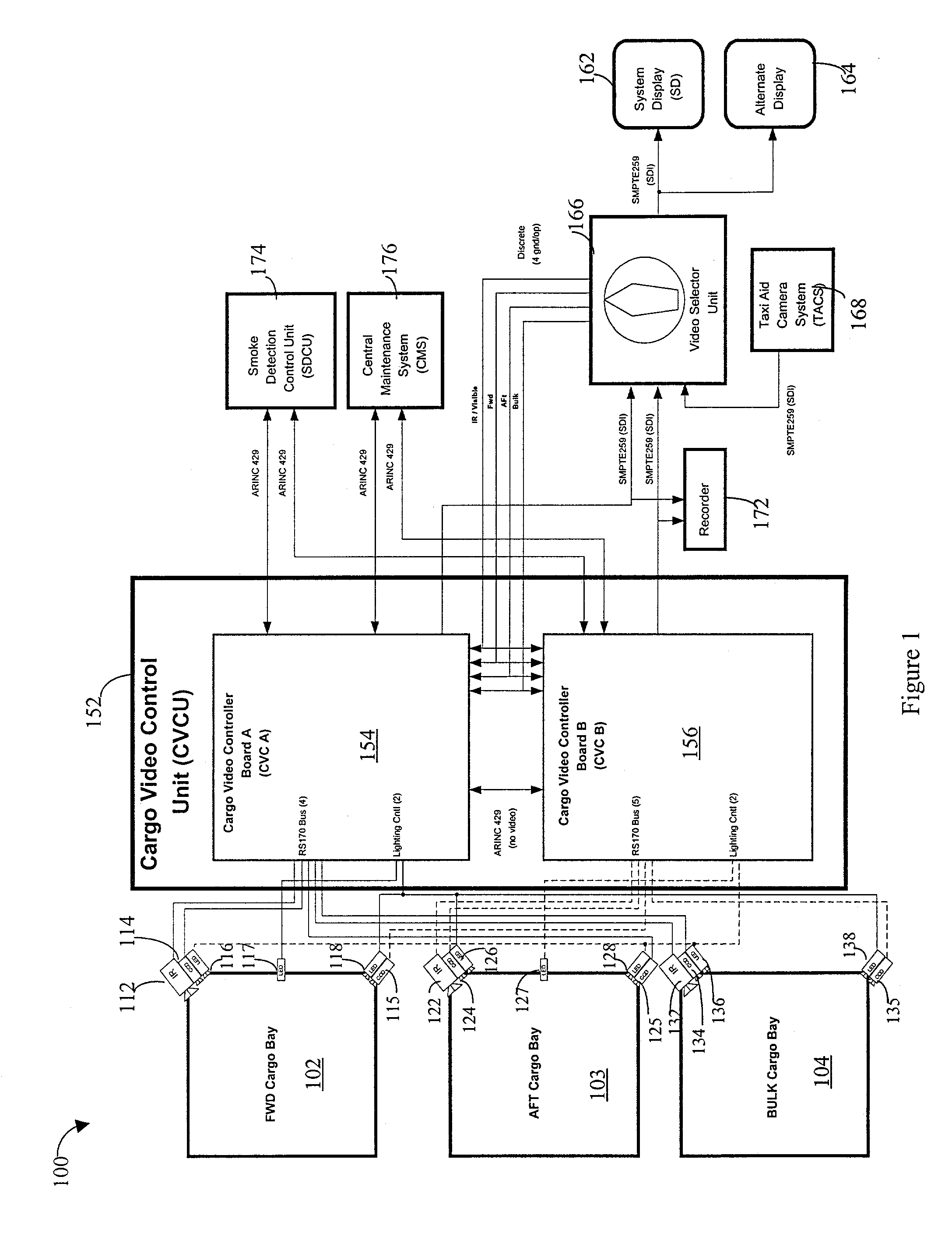
Method for detection and recognition of fog presence within an aircraft compartment using video images
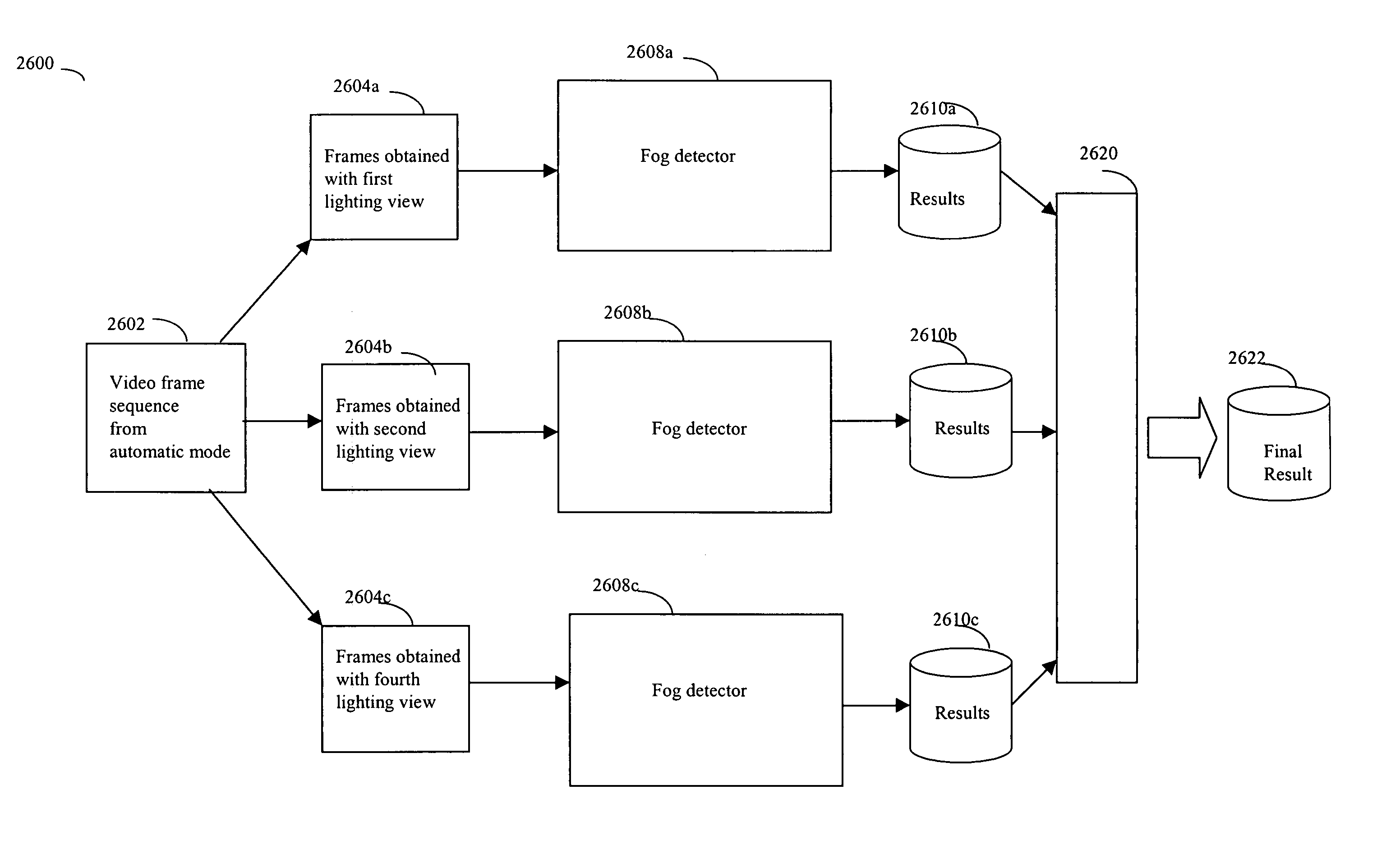
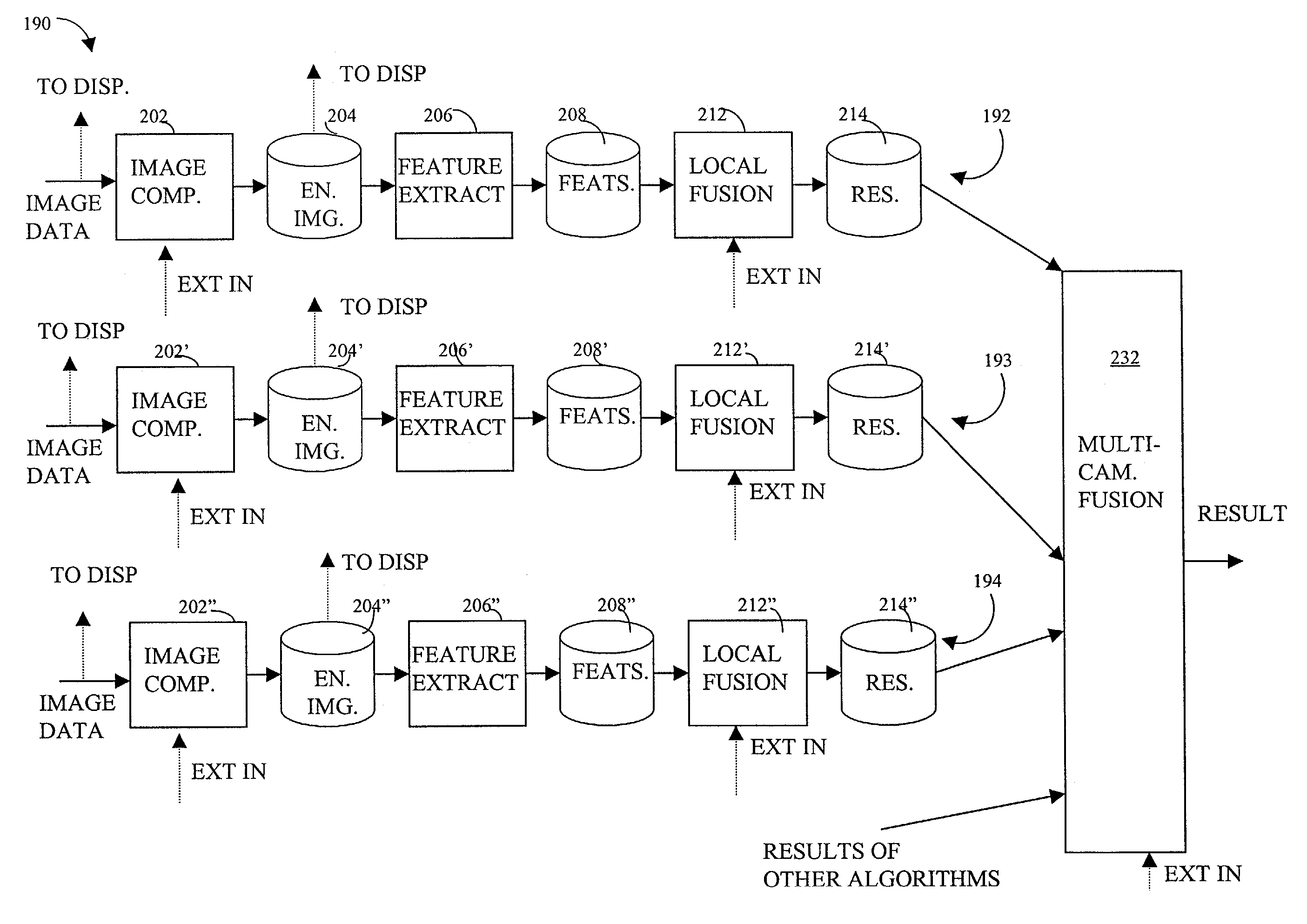
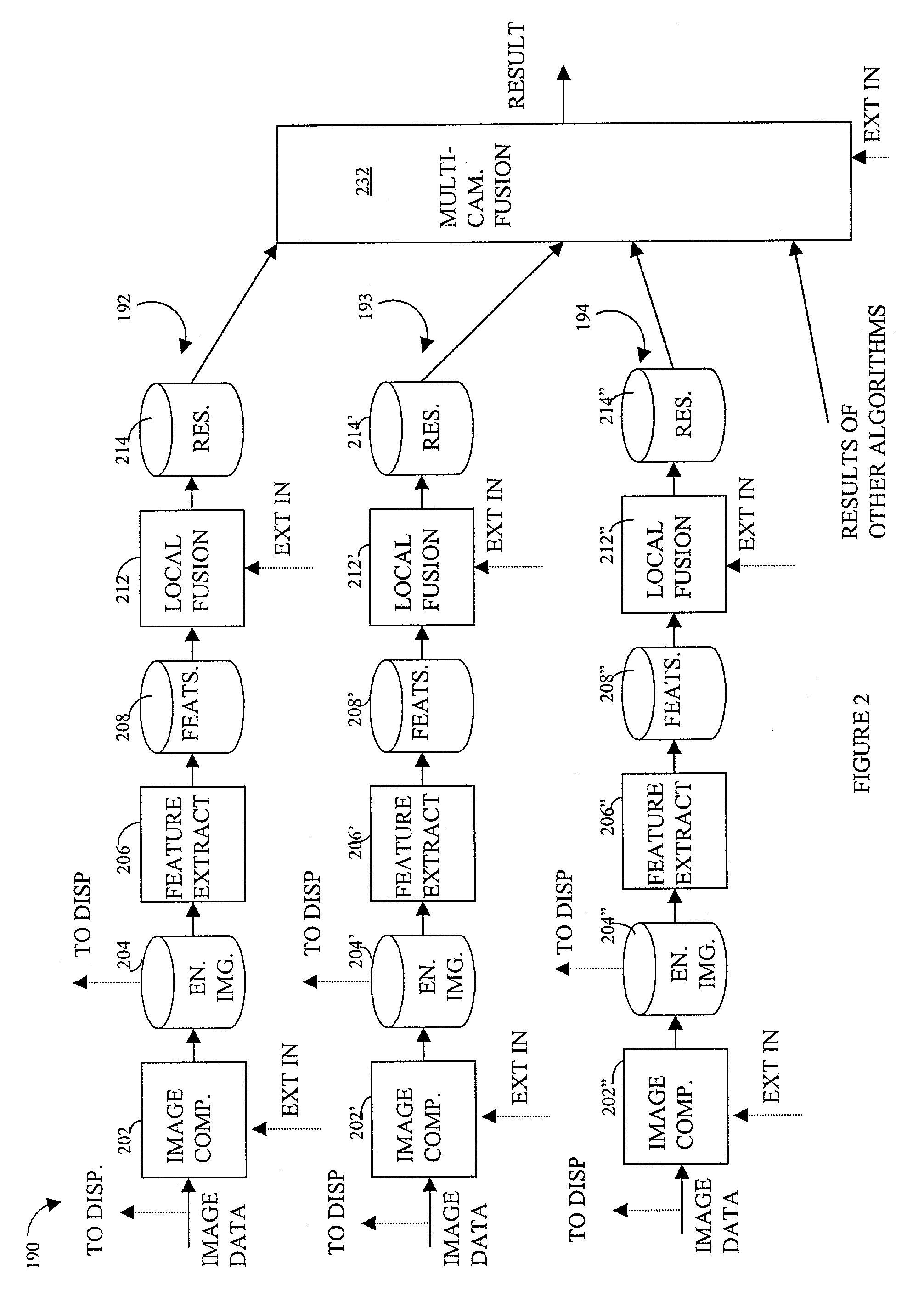
Detecting video phenomena, such as fire in an aircraft cargo bay, includes receiving a plurality of video images from a plurality of sources, compensating the images to provide enhanced images, extracting features from the enhanced images, and combining the features from the plurality of sources to detect the video phenomena. Extracting features may include determining an energy indicator for each of a subset of the plurality of frames. Detecting video phenomena may also include comparing energy indicators for each of the subset of the plurality of frames to a reference frame. The reference frame corresponds to a video frame taken when no fire is present, video frame immediately preceding each of the subset of the plurality of frames, or a video frame immediately preceding a frame that is immediately preceding each of the subset of the plurality of frames. Image-based and non-image based techniques are described herein in connection with fire detection and / or verification and other applications.
Owner:SIMMONDS PRECISION PRODS
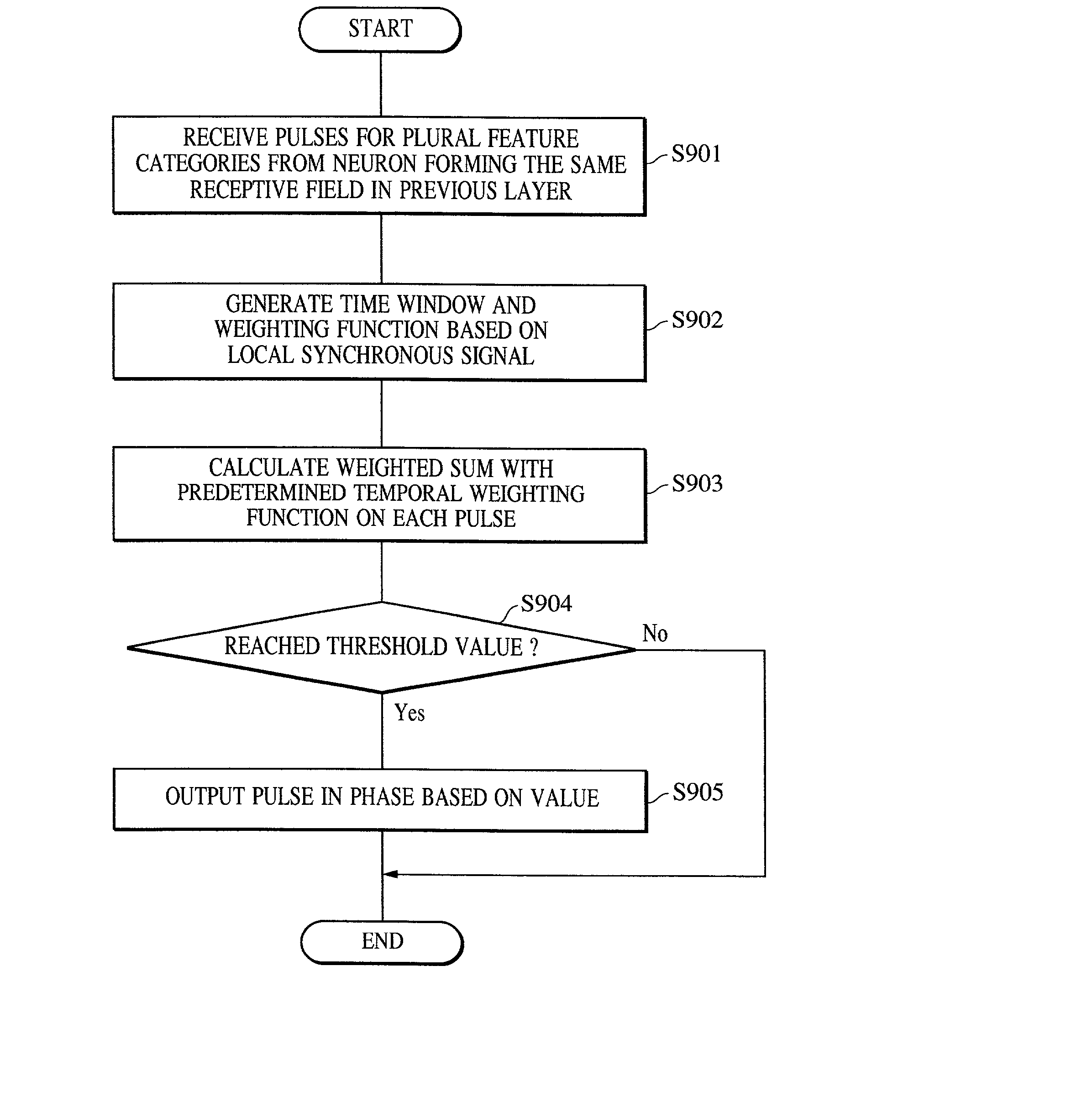
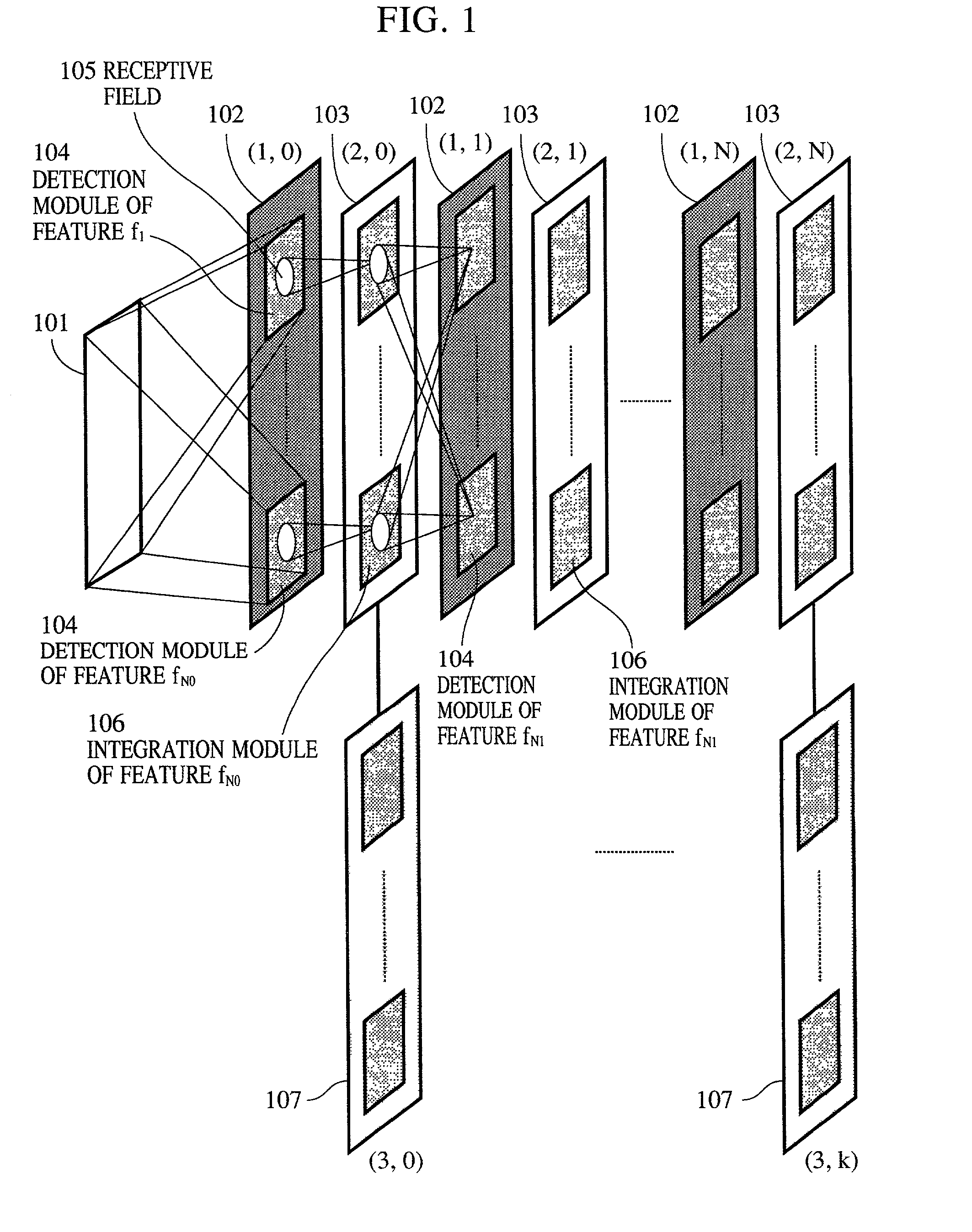
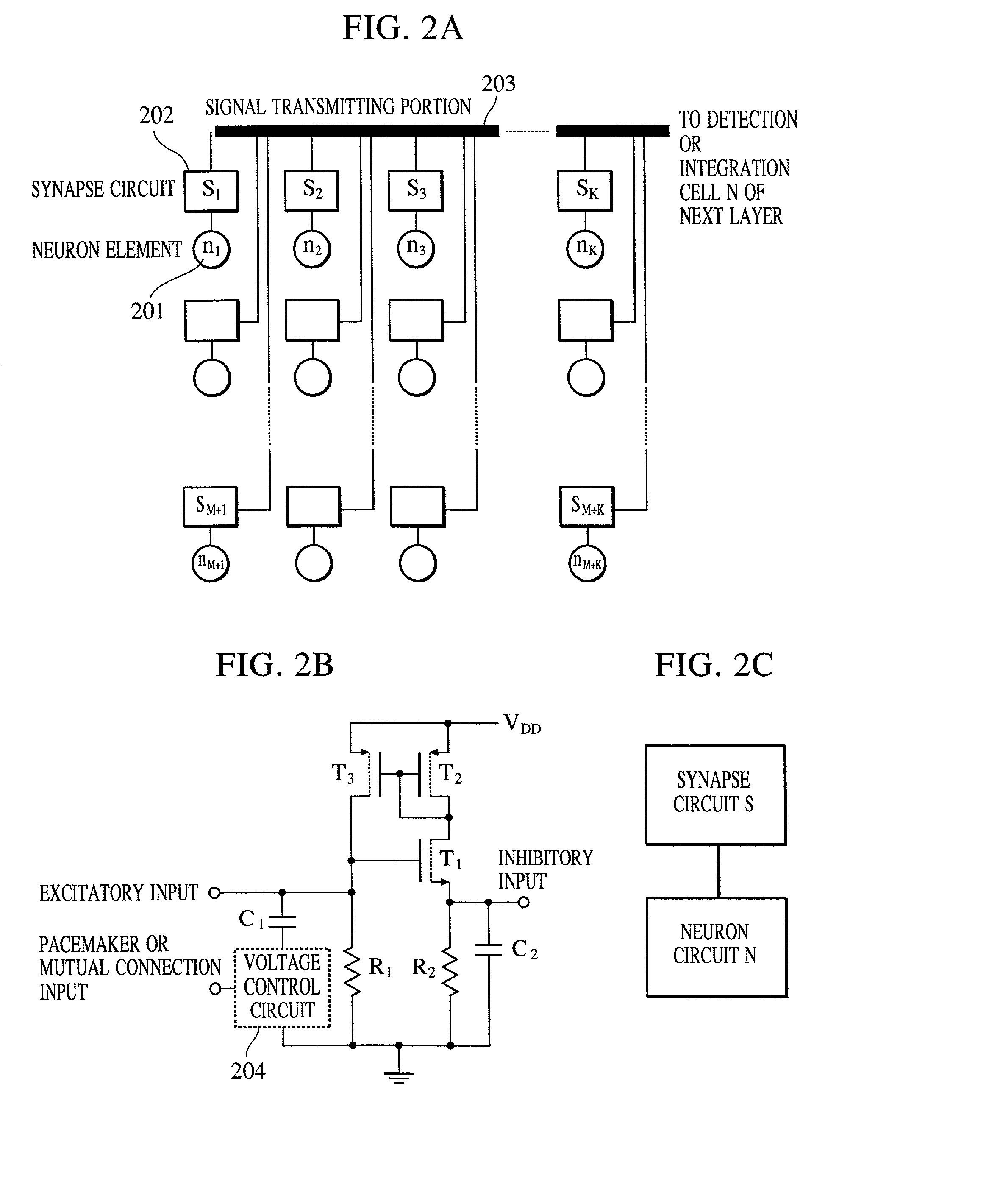
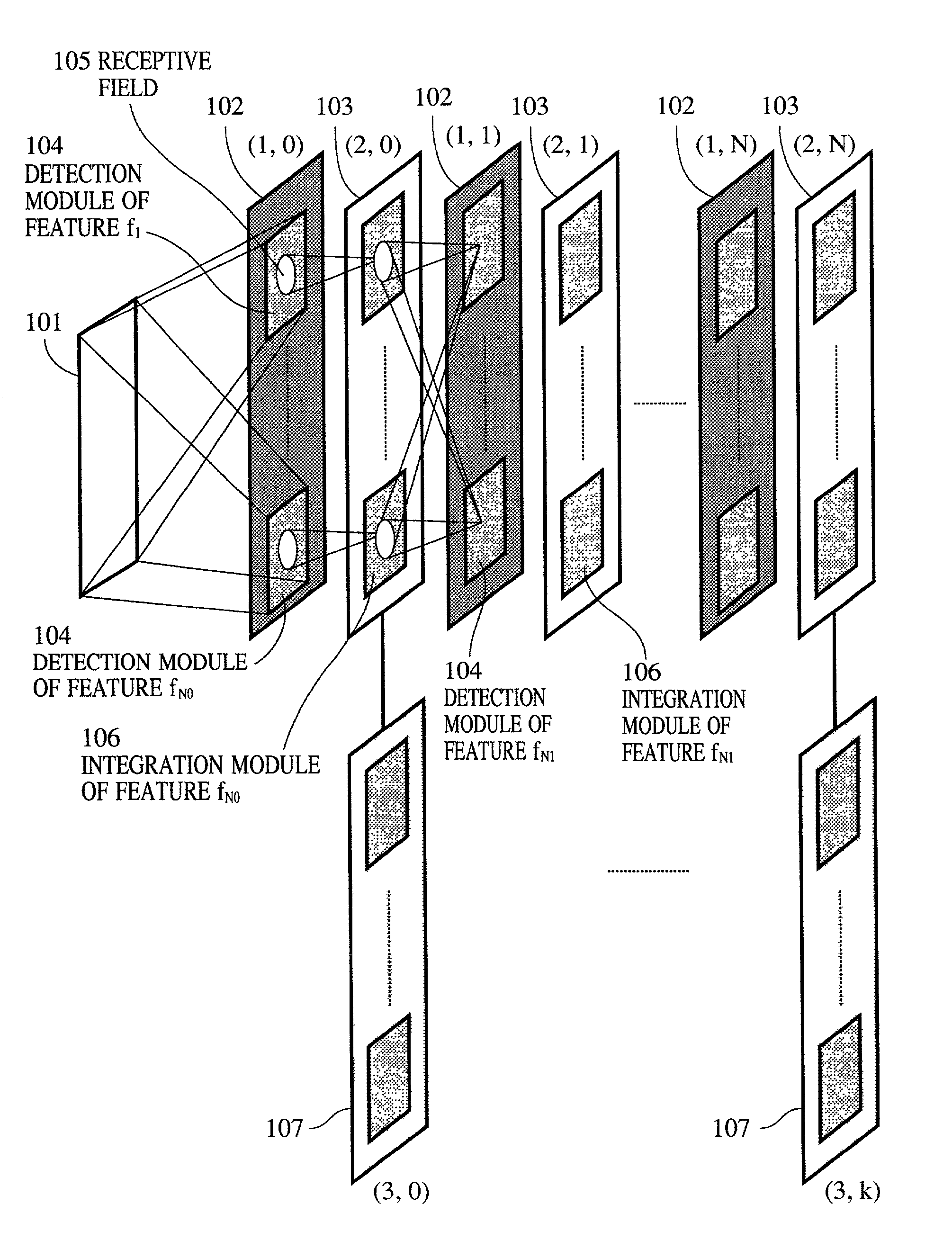
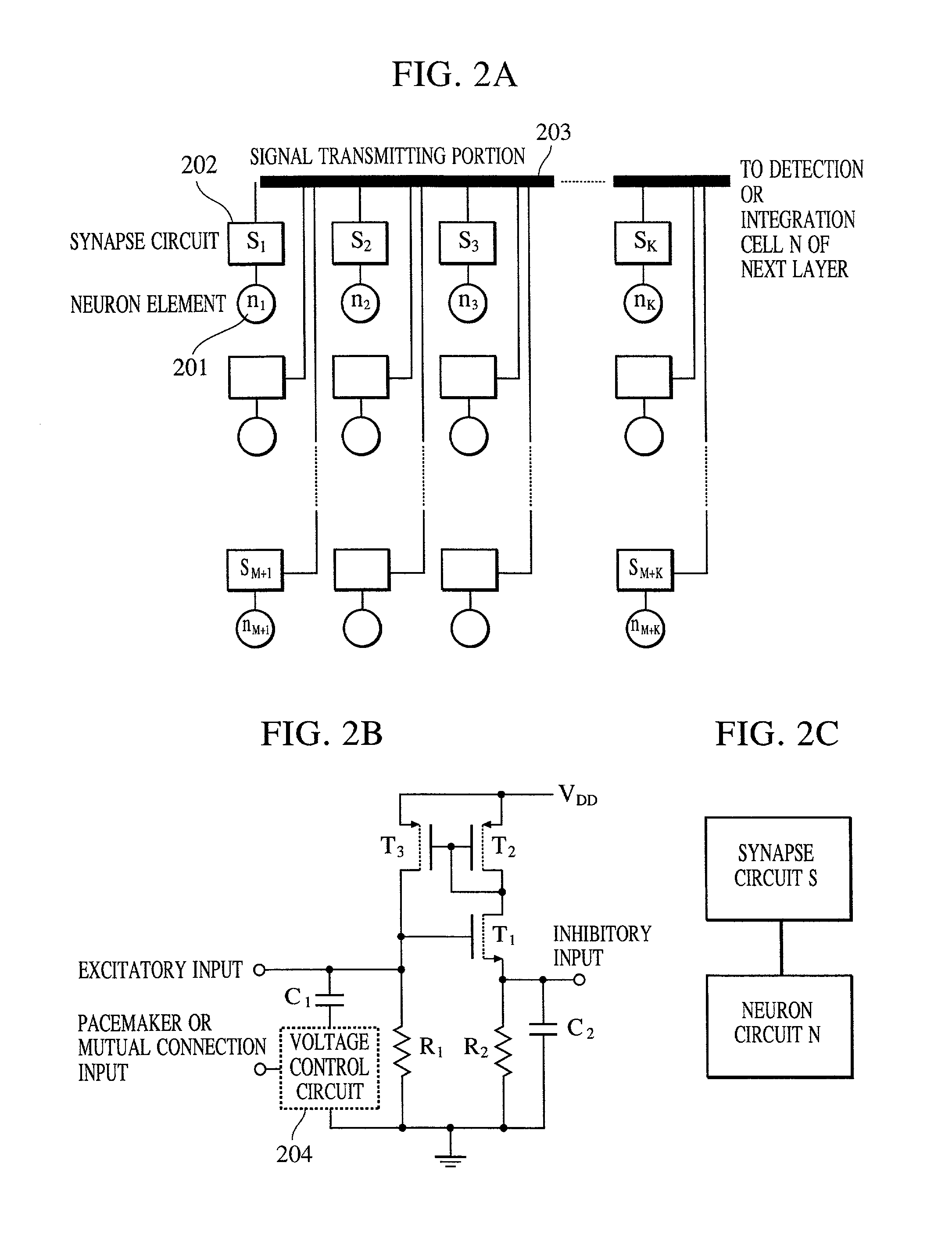
Apparatus and method for detecting or recognizing pattern by employing a plurality of feature detecting elements
InactiveUS20020038294A1Easy constructionReduce in quantityDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSynapsePattern detection
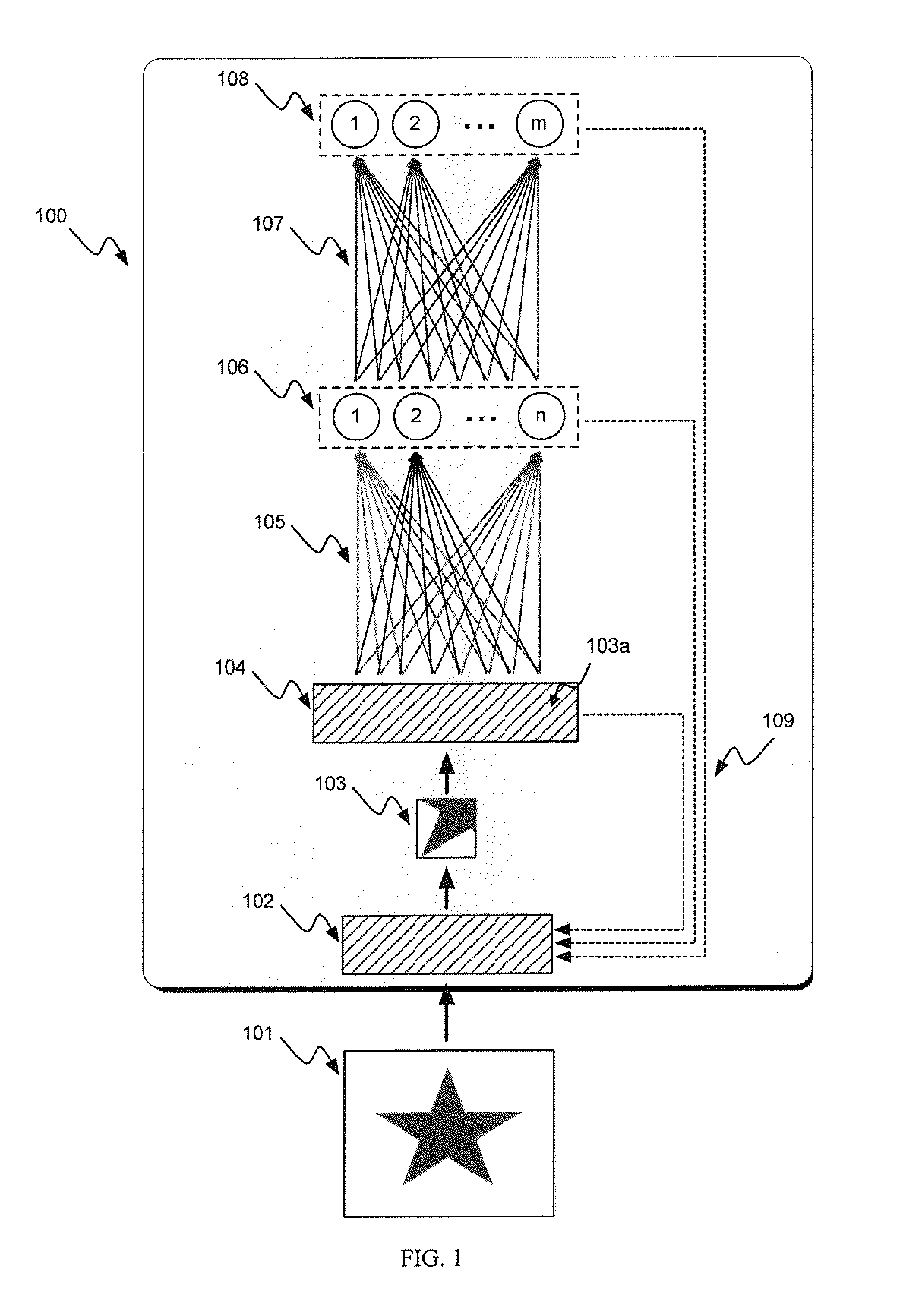
A pattern detecting apparatus has a plurality of hierarchized neuron elements to detect a predetermined pattern included in input patterns. Pulse signals output from the plurality of neuron elements are given specific delays by synapse circuits associated with the individual elements. This makes it possible to transmit the pulse signals to the neuron elements of the succeeding layer through a common bus line so that they can be identified on a time base. The neuron elements of the succeeding layer output the pulse signals at output levels based on a arrival time pattern of the plurality of pulse signals received from the plurality of neuron elements of the preceding layer within a predetermined time window. Thus, the reliability of pattern detection can be improved, and the number of wires interconnecting the elements can be reduced by the use of the common bus line, leading to a small scale of circuit and reduced power consumption.
Owner:CANON KK
Associating application states with a physical object
InactiveUS7397464B1Simple methodCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingApplication softwareInteractive displays
An application state of a computer program is stored and associated with a physical object and can be subsequently retrieved when the physical object is detected adjacent to an interactive display surface. An identifying characteristic presented by the physical object, such as a reflective pattern applied to the object, is detected when the physical object is positioned on the interactive display surface. The user or the system can initiate a save of the application state. For example, the state of an electronic game using the interactive display surface can be saved. Attributes representative of the state are stored and associated with the identifying characteristic of the physical object. When the physical object is again placed on the interactive display surface, the physical object is detected based on its identifying characteristic, and the attributes representative of the state can be selectively retrieved and used to recreate the state of the application.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
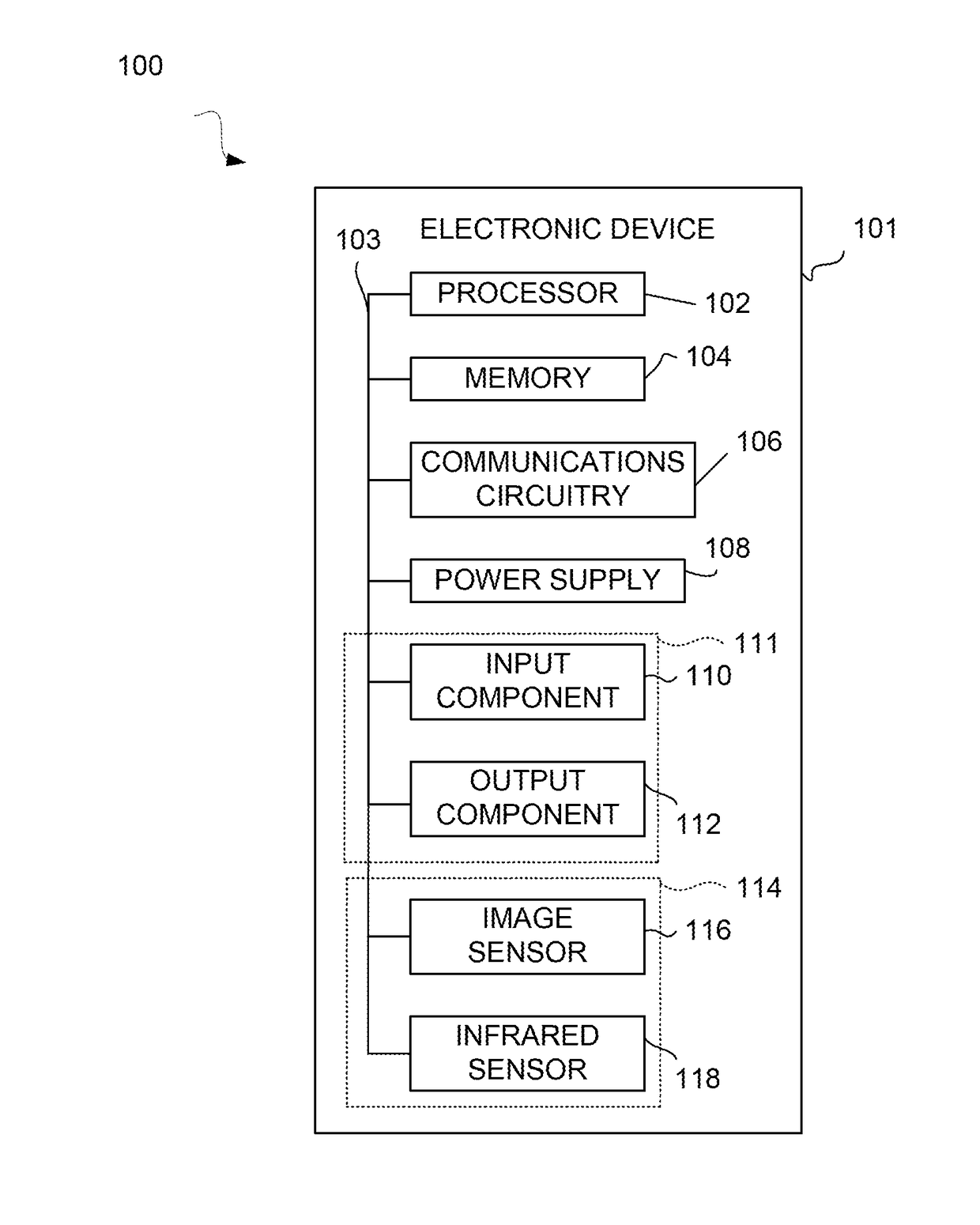
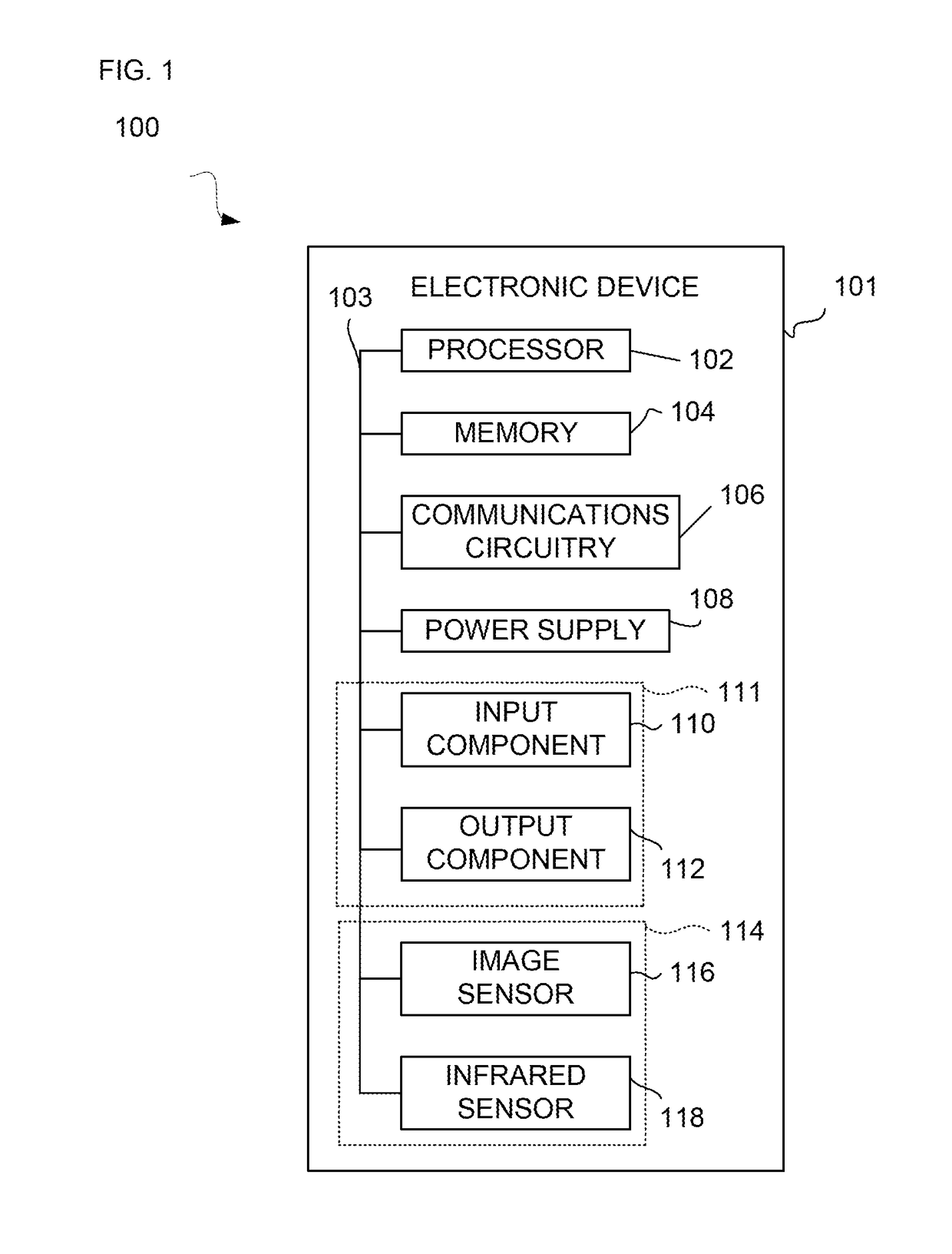
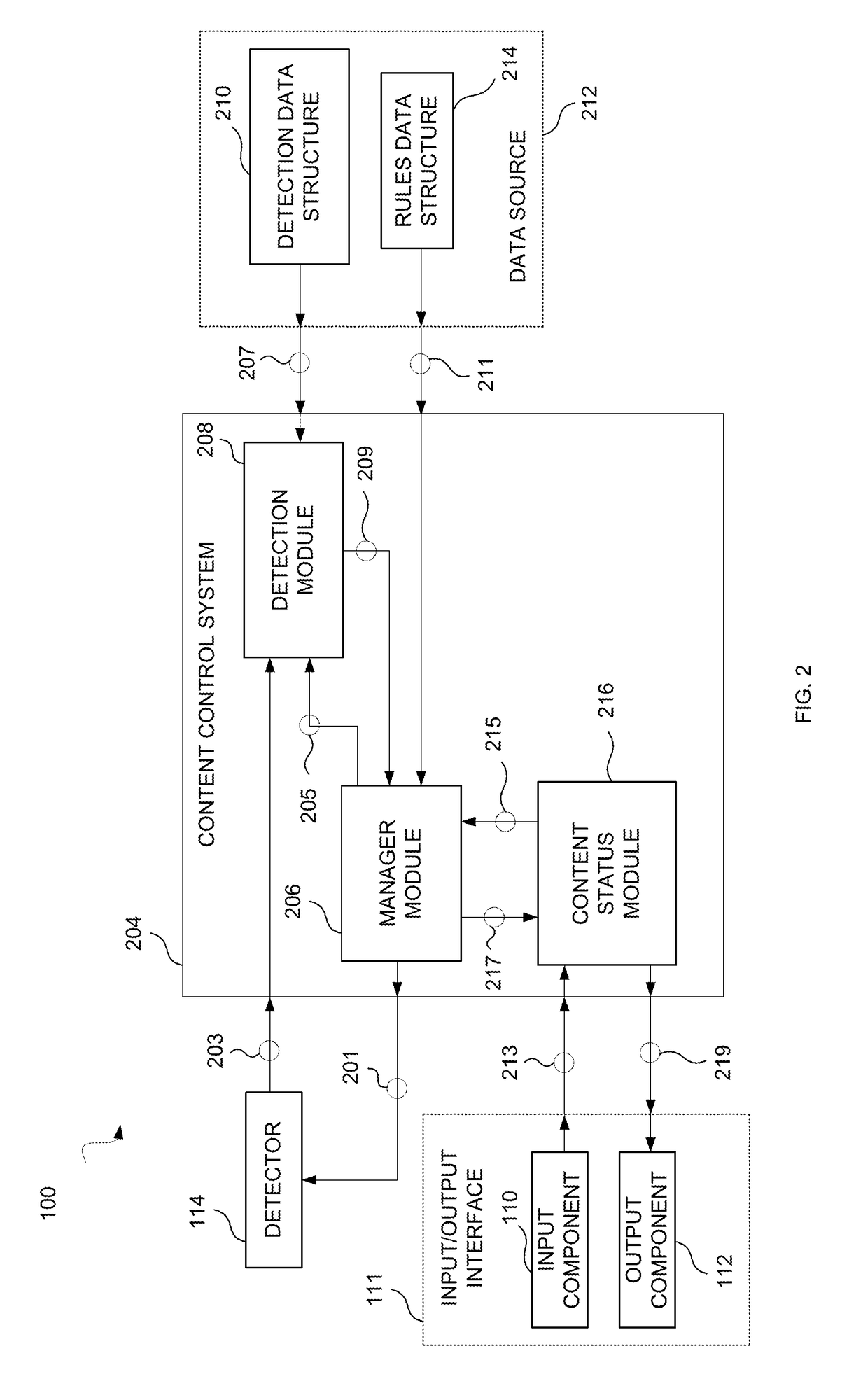
Systems and methods for controlling output of content based on human recognition data detection
Systems and methods for controlling output of content based on human recognition data captured by one or more sensors of an electronic device are provided. The control of the output of particular content may be based on an action of a rule defined for the particular content, and may be performed when at least one human feature detection related condition of the rule is satisfied. In some embodiments, the action may include granting access to requested content when detected human feature data satisfies at least one human feature detection related condition of a rule defined for the requested content. In other embodiments the action may include altering a presentation of content, during the presentation of the content, when detected human feature data satisfies at least one human feature detection related condition of a rule defined for the presented content.
Owner:APPLE INC
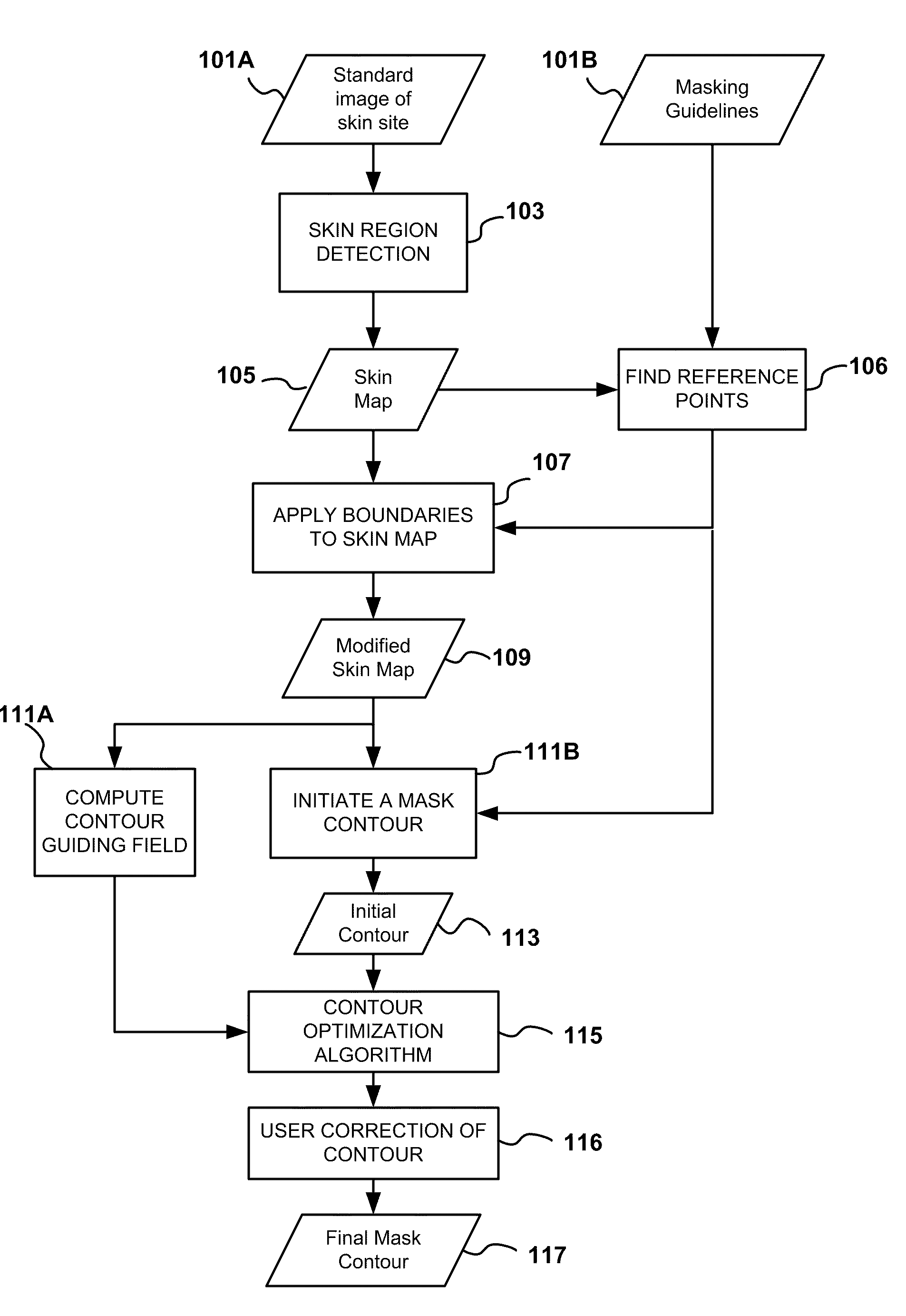
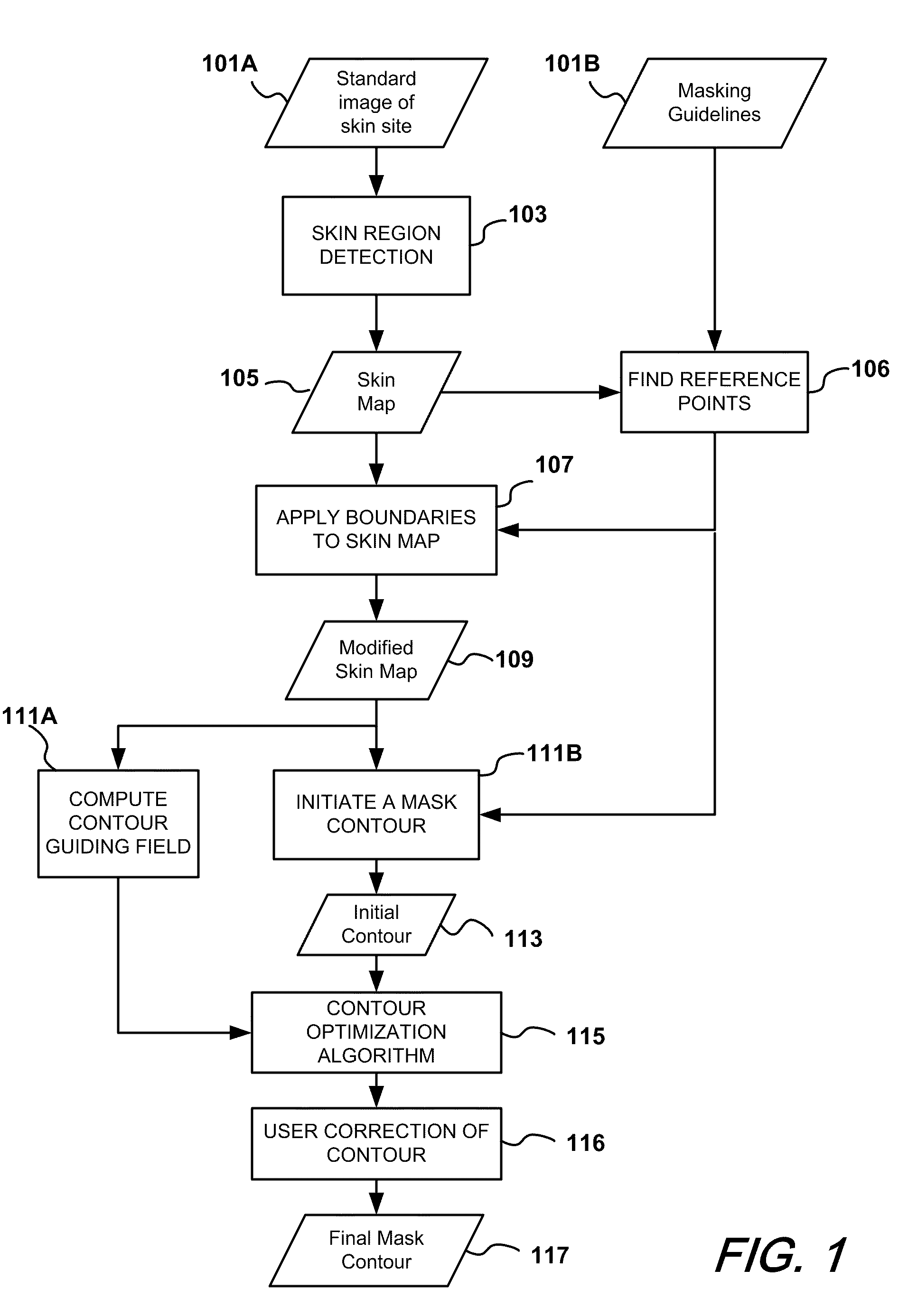
Automatic mask design and registration and feature detection for computer-aided skin analysis
ActiveUS20090196475A1Avoiding skin regions not useful or amenableCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityNose
Methods and systems for automatically generating a mask delineating a region of interest (ROI) within an image containing skin are disclosed. The image may be of an anatomical area containing skin, such as the face, neck, chest, shoulders, arms or hands, among others, or may be of portions of such areas, such as the cheek, forehead, or nose, among others. The mask that is generated is based on the locations of anatomical features or landmarks in the image, such as the eyes, nose, eyebrows and lips, which can vary from subject to subject and image to image. As such, masks can be adapted to individual subjects and to different images of the same subjects, while delineating anatomically standardized ROIs, thereby facilitating standardized, reproducible skin analysis over multiple subjects and / or over multiple images of each subject. Moreover, the masks can be limited to skin regions that include uniformly illuminated portions of skin while excluding skin regions in shadow or hot-spot areas that would otherwise provide erroneous feature analysis results. Methods and systems are also disclosed for automatically registering a skin mask delineating a skin ROI in a first image captured in one imaging modality (e.g., standard white light, UV light, polarized light, multi-spectral absorption or fluorescence imaging, etc.) onto a second image of the ROI captured in the same or another imaging modality. Such registration can be done using linear as well as non-linear spatial transformation techniques.
Owner:CANFIELD SCI
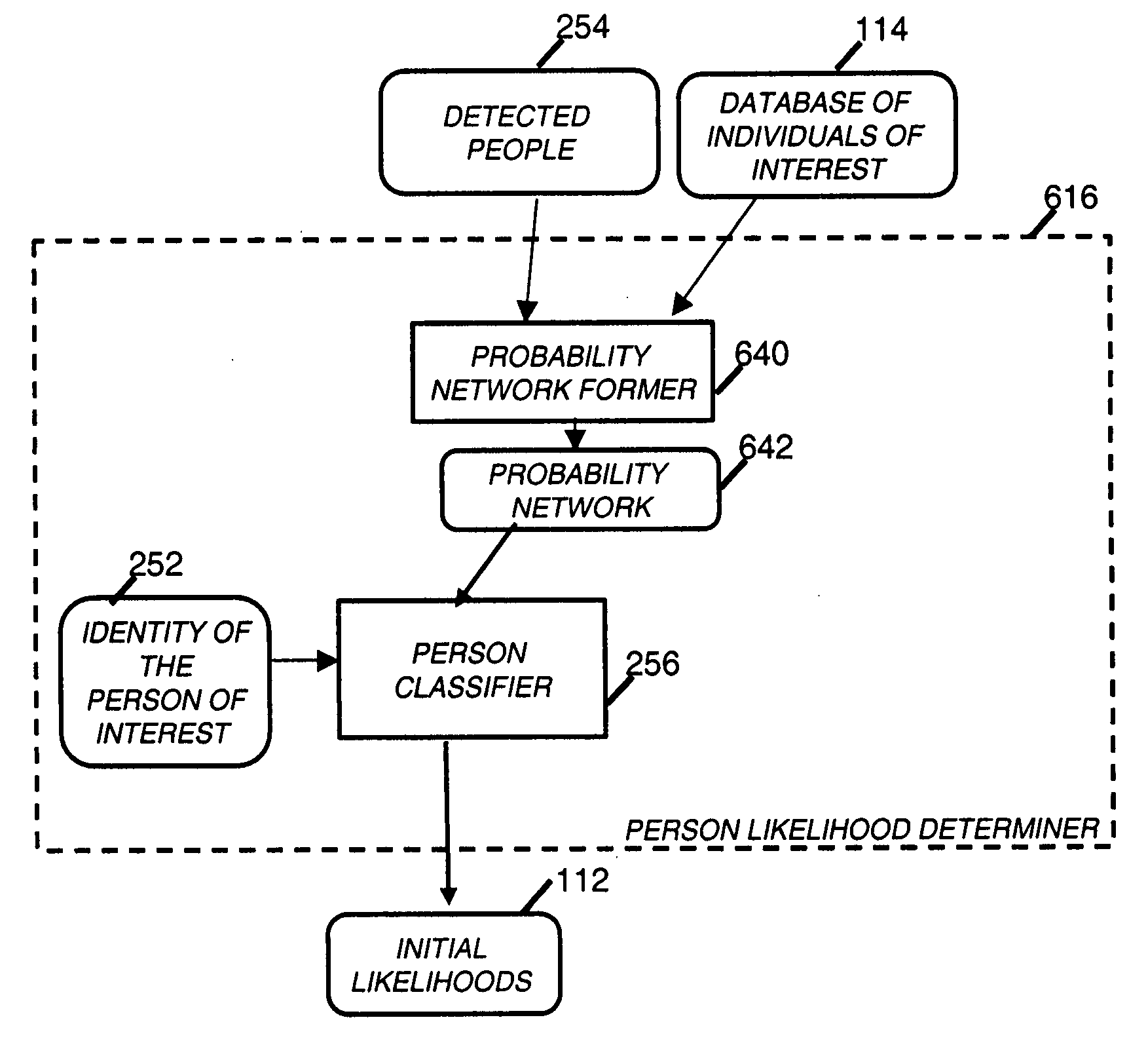
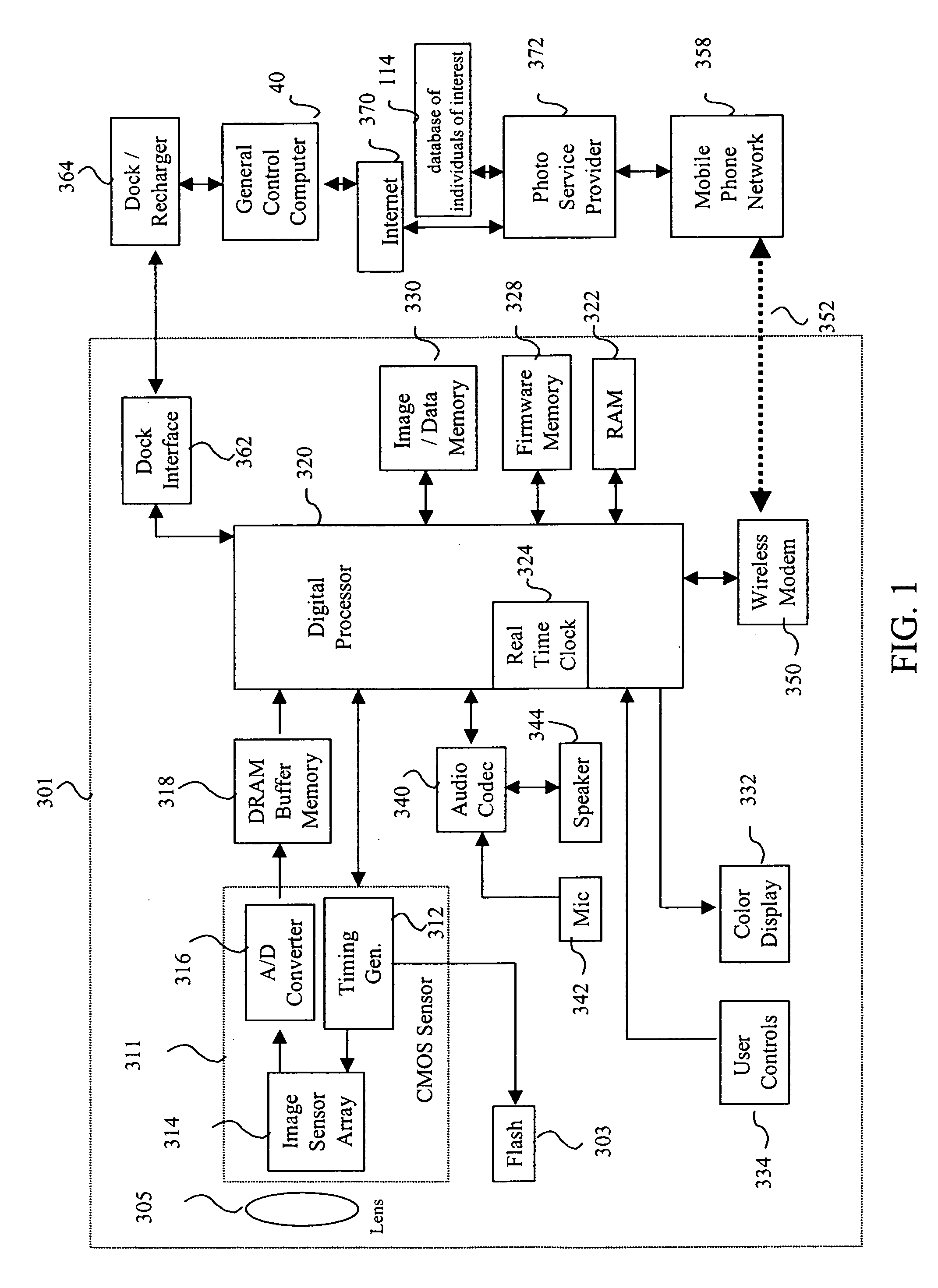
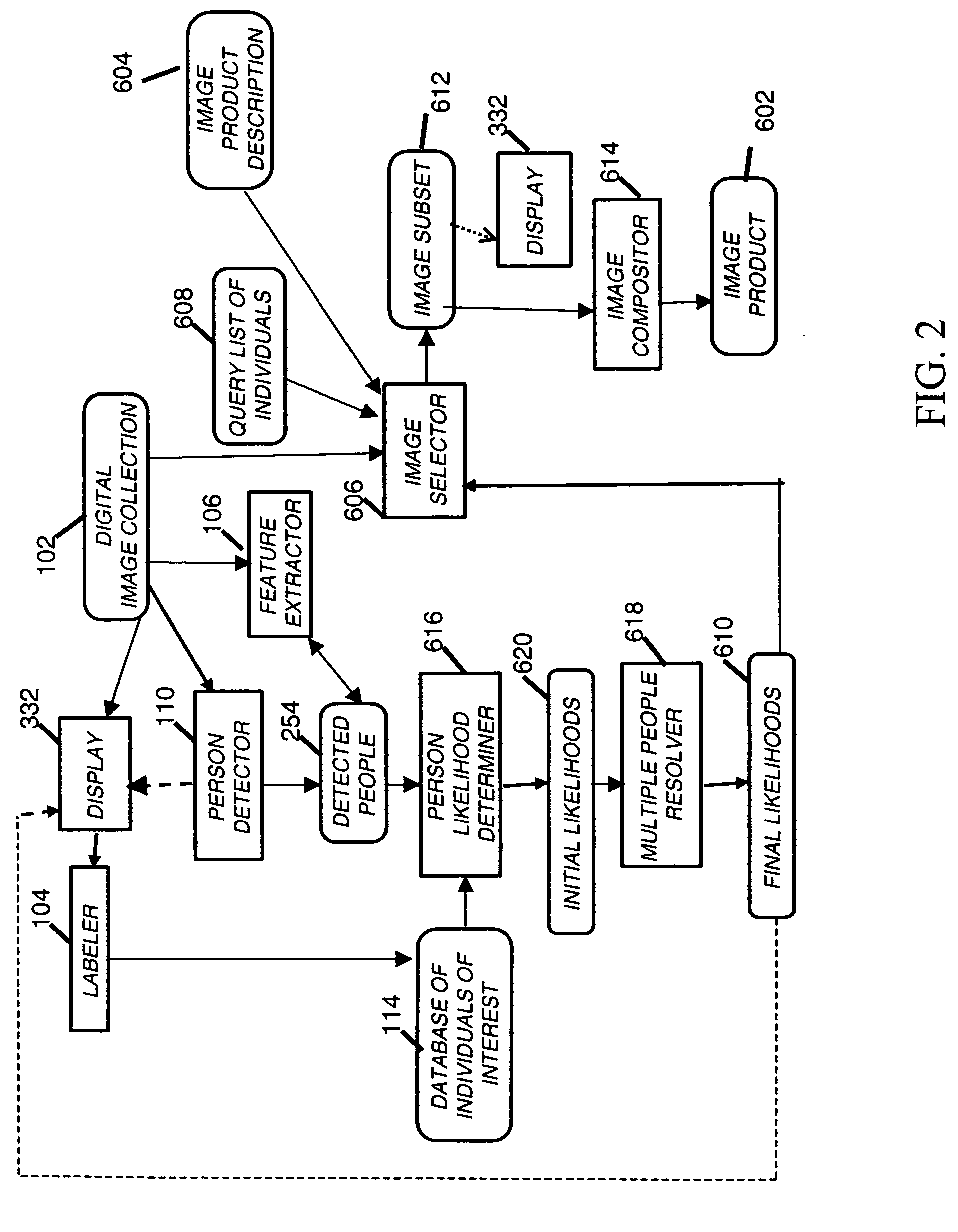
Finding images with multiple people or objects
InactiveUS20070177805A1Character and pattern recognitionMetadata still image retrievalPattern recognitionRadiology
A method of searching through a collection of images, includes providing a list of individuals of interest and features associated with such individuals; detecting people in the collection images; determining the likelihood(s) for each listed individual of appearing in each collection image in response to the detected people and the features associated with the listed individuals; and selecting in response to the determined likelihood(s) a number of collection images such that each individual from the list appears in the selected number of collection images.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
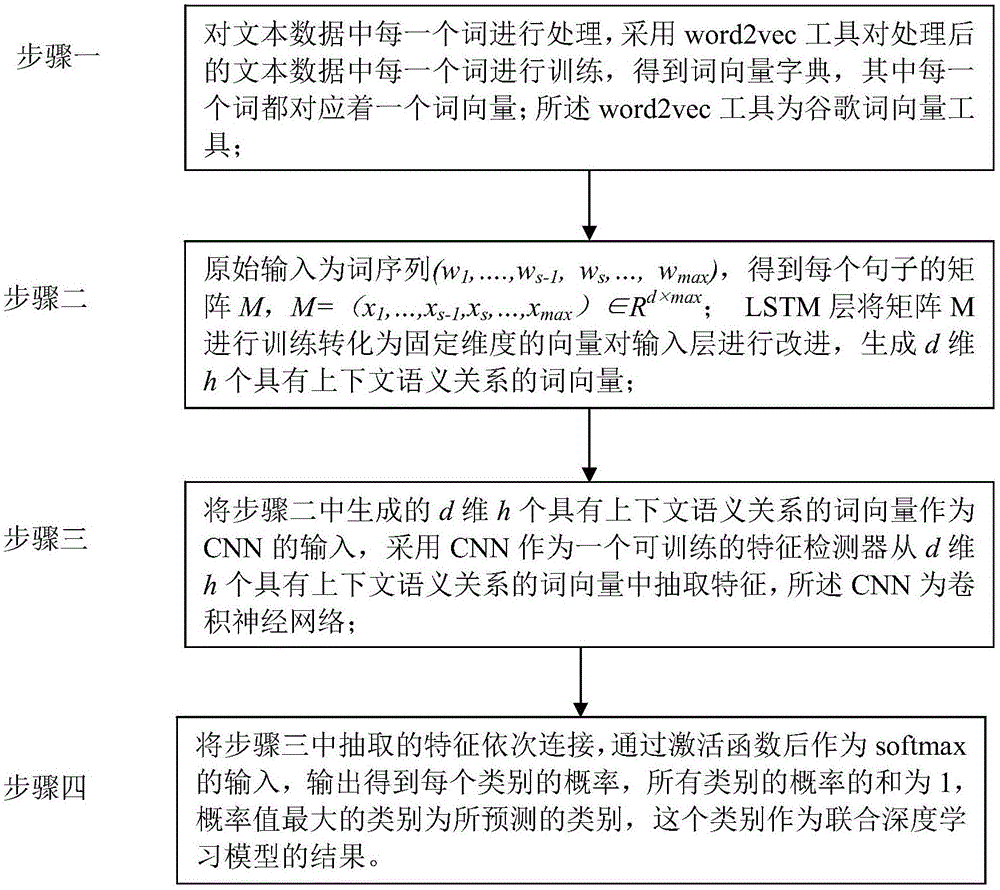
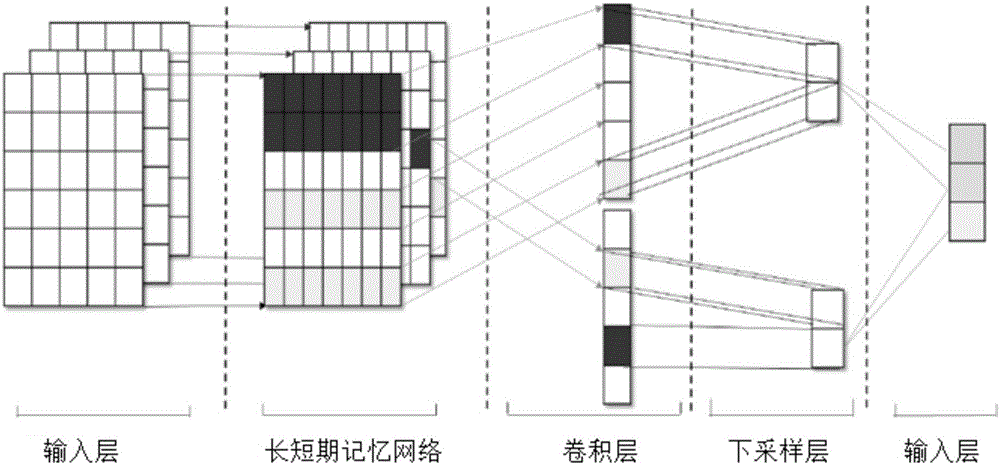
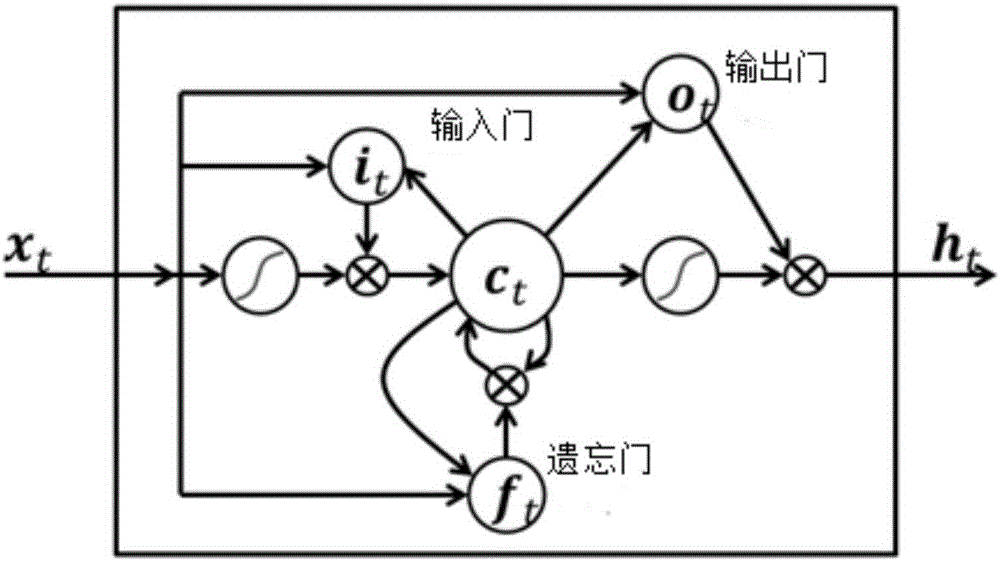
Text emotion classification method based on the joint deep learning model
InactiveCN106599933AImprove classification performanceGreat photo effectCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSupport vector machineCurse of dimensionality
The invention provides a text emotion classification method based on the joint deep learning model which relates to the text emotion classification method. The method is designed with the object of solving the problems with the dimension disaster and sparse data incurred from the existing support vector machine and other shallow layer classification methods. The method comprises: 1) processing each word in the text data; using the word2vec tool to train each processed word in the text data so as to obtain a word vector dictionary; 2) obtaining the matrix M of each sentence; training the matrix M by the LSTM layer and converting it into vector with fixed dimensions; improving the input layer; generating d-dimensional h word vectors with context semantic relations; 3) using a CNN as a trainable characteristic detector to extract characteristics from the d-dimensional h word vectors with context semantic relations; and 4) connecting the extracted characteristics in order; outputting to obtain the probability of each classification wherein the classification with the maximal probability value is the predicated classification. The invention is applied to the natural language processing field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
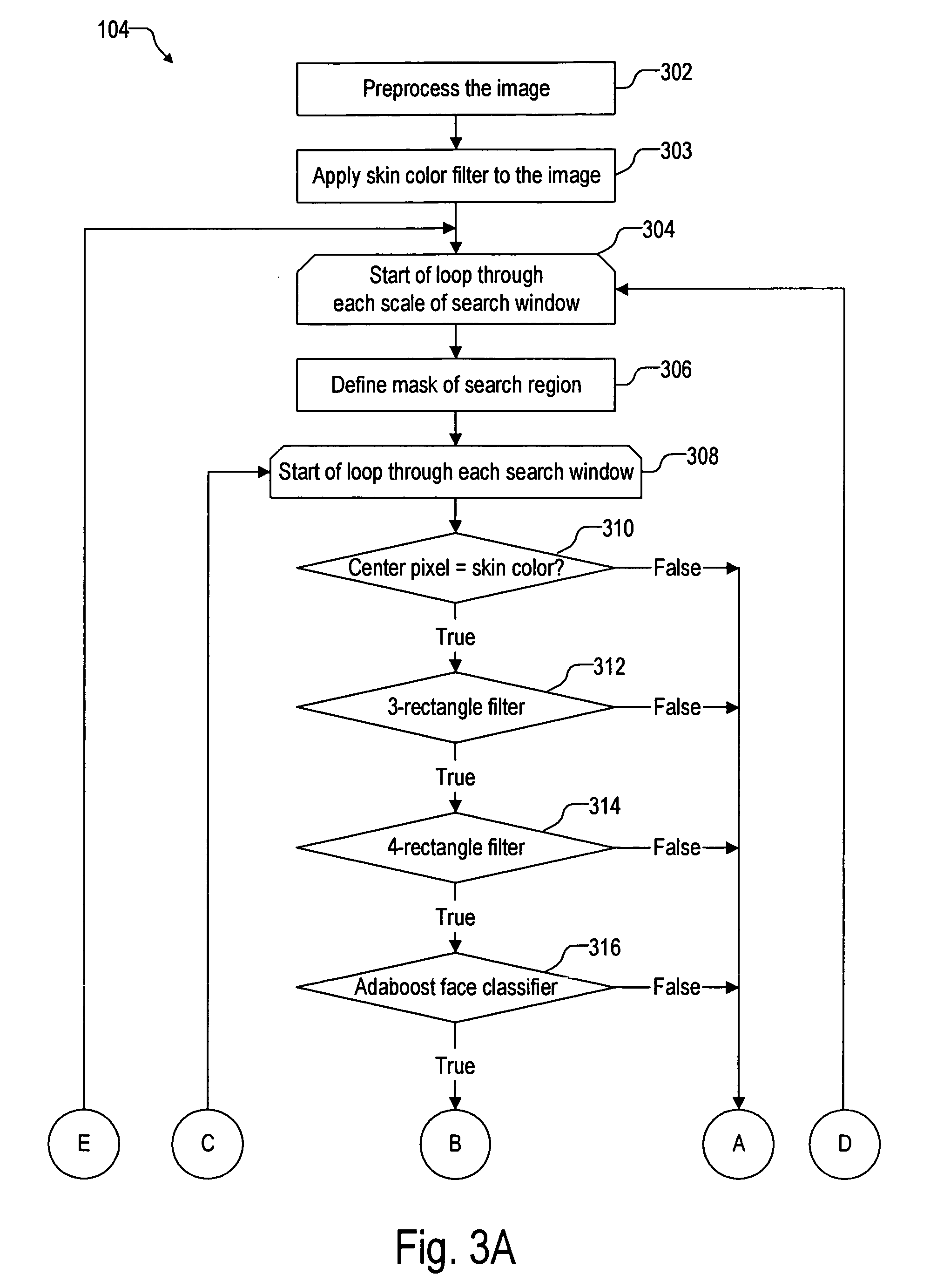
Facial feature detection on mobile devices
Locating an eye includes generating an intensity response map by applying a 3-rectangle filter and applying K-mean clustering to the map to determine the eye. Locating an eye corner includes applying logarithm transform and grayscale stretching to generate a grayscale eye patch, generating a binary map of the patch by using a threshold based on a histogram of the patch, and estimating the eye corner by averaging coordinates weighted by minimal eigenvalues of spatial gradient matrices in a search region based on the binary map. Locating a mouth corner includes generating another intensity response map and generating another binary map using another threshold based on another histogram of the intensity response map. Locating a chin or a cheek includes applying angle constrained gradient analysis to reject locations that cannot be the chin or cheek. Locating a cheek further includes removing falsely detected cheeks by parabola fitting curves through the cheeks.
Owner:ARCSOFT
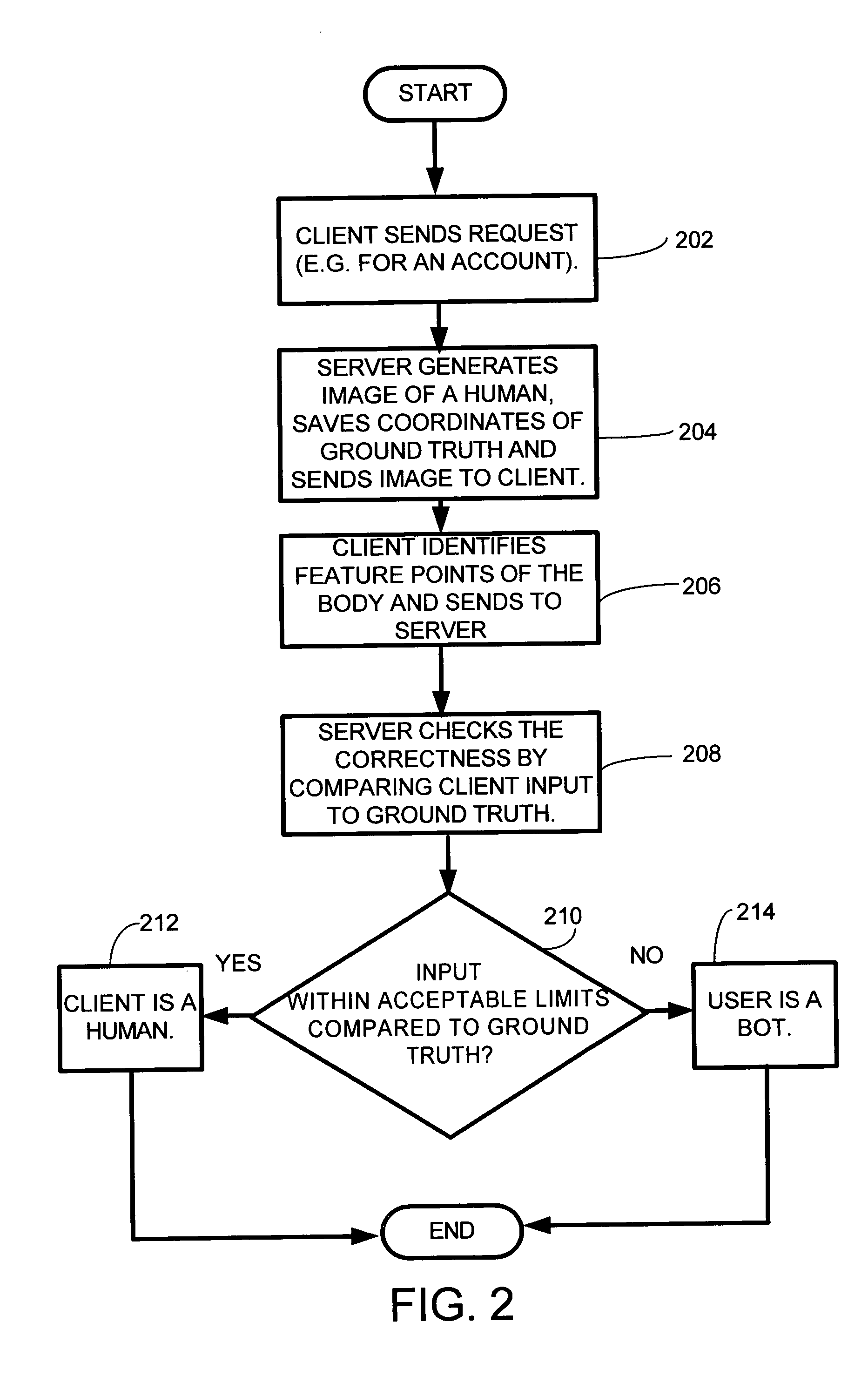
System and method for devising a human interactive proof that determines whether a remote client is a human or a computer program
InactiveUS20050065802A1Character and pattern recognitionComputer security arrangementsGuidelineUsability
A system and method for automatically determining if a remote client is a human or a computer. A set of HIP design guidelines which are important to ensure the security and usability of a HIP system are described. Furthermore, one embodiment of this new HIP system and method is based on human face and facial feature detection. Because human face is the most familiar object to all human users the embodiment of the invention employing a face is possibly the most universal HIP system so far.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
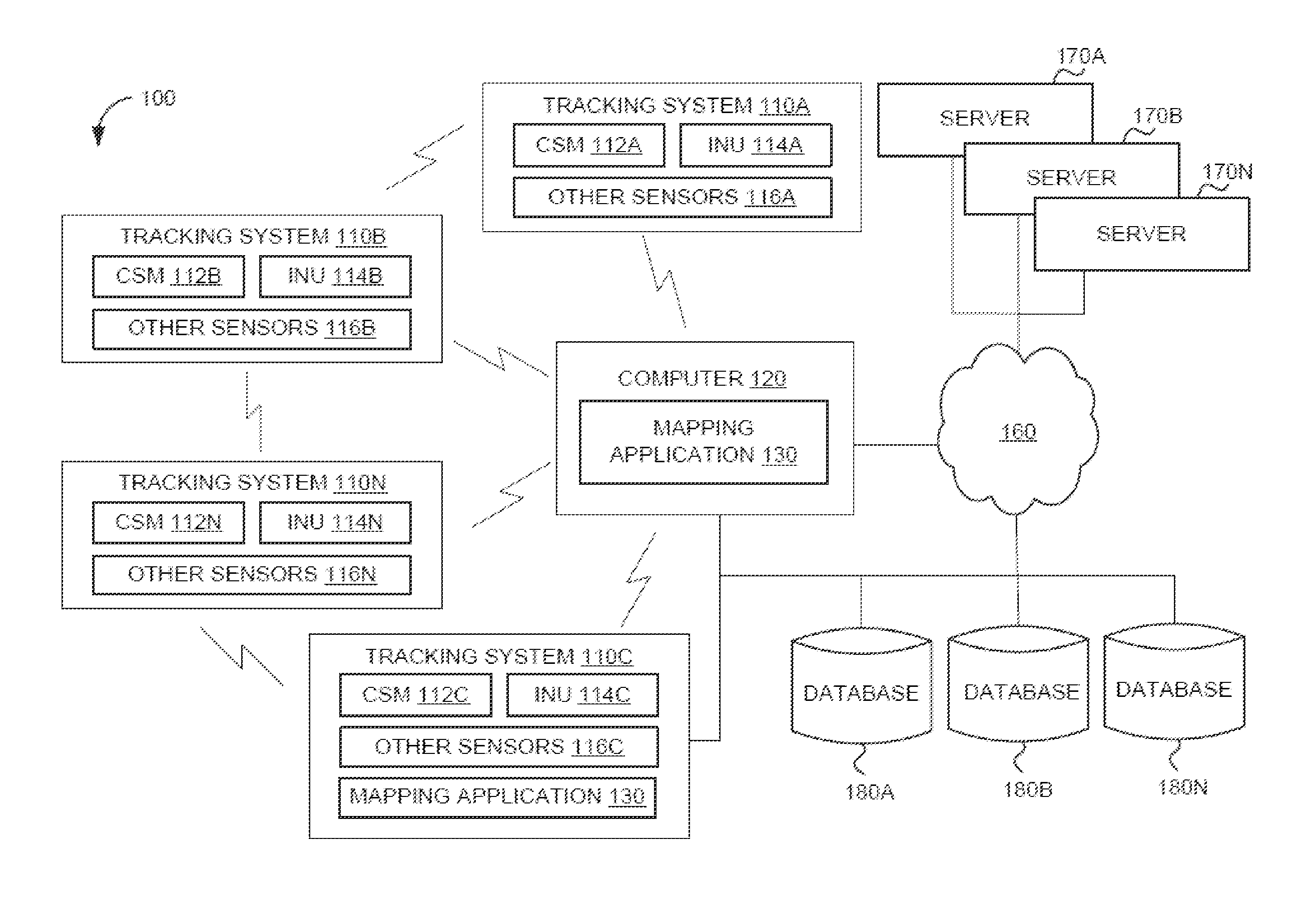
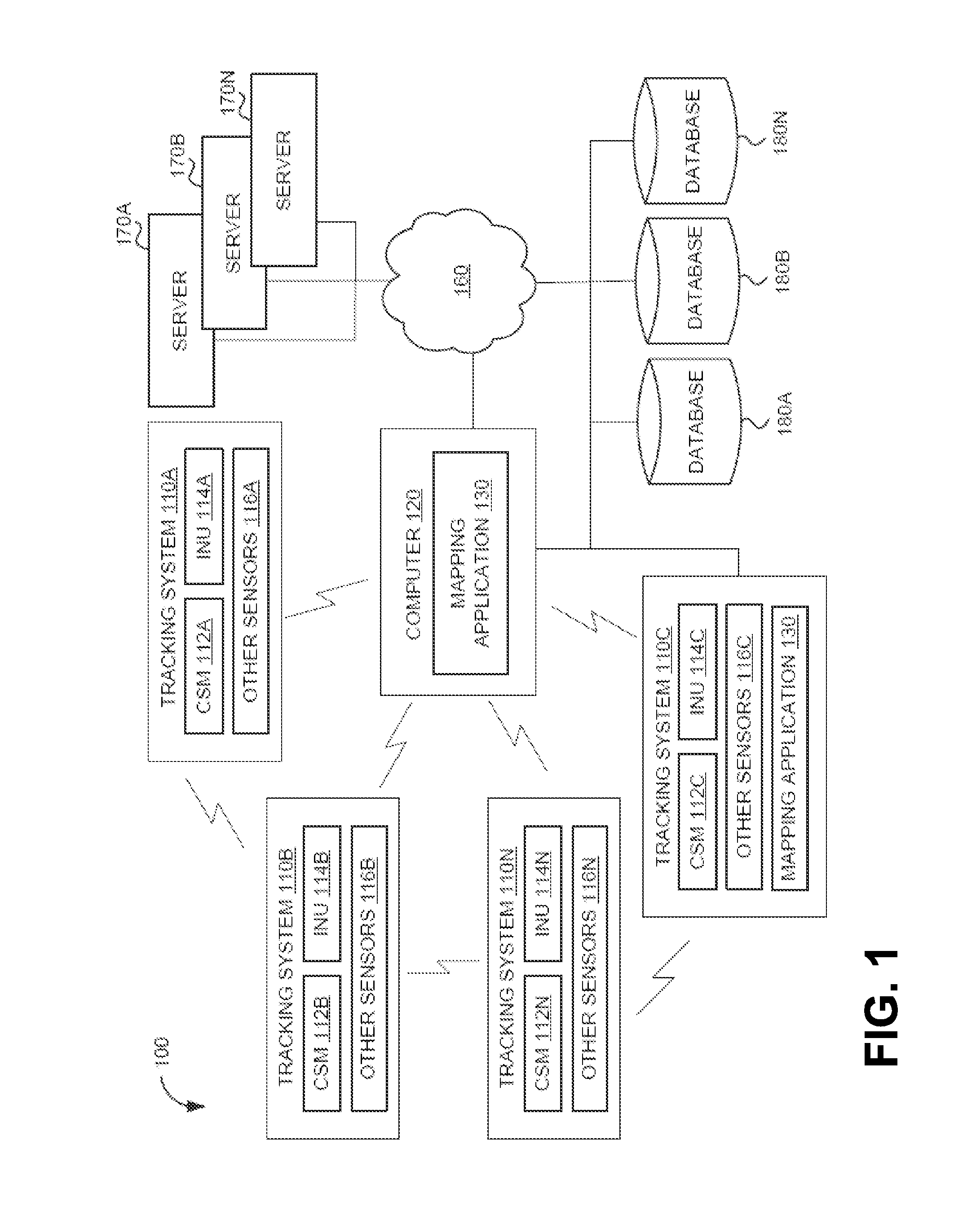
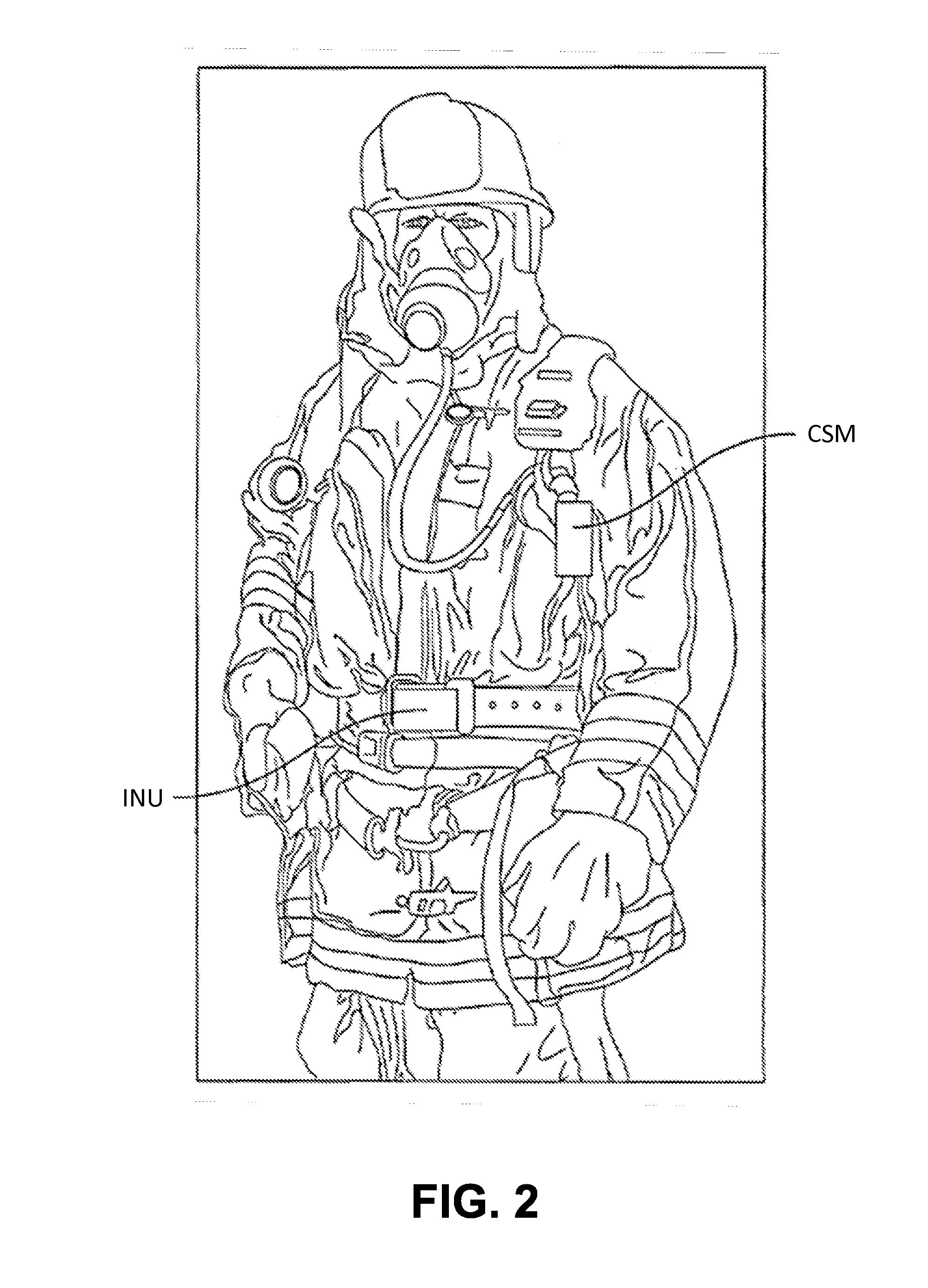
System and method for localizing a trackee at a location and mapping the location using inertial sensor information
ActiveUS20130332064A1Long durationNavigational calculation instrumentsRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition dependentNetwork communication
A system and method for recognizing features for location correction in Simultaneous Localization And Mapping operations, thus facilitating longer duration navigation, is provided. The system may detect features from magnetic, inertial, GPS, light sensors, and / or other sensors that can be associated with a location and recognized when revisited. Feature detection may be implemented on a generally portable tracking system, which may facilitate the use of higher sample rate data for more precise localization of features, improved tracking when network communications are unavailable, and improved ability of the tracking system to act as a smart standalone positioning system to provide rich input to higher level navigation algorithms / systems. The system may detect a transition from structured (such as indoors, in caves, etc.) to unstructured (such as outdoor) environments and from pedestrian motion to travel in a vehicle. The system may include an integrated self-tracking unit that can localize and self-correct such localizations.
Owner:TRX SYST
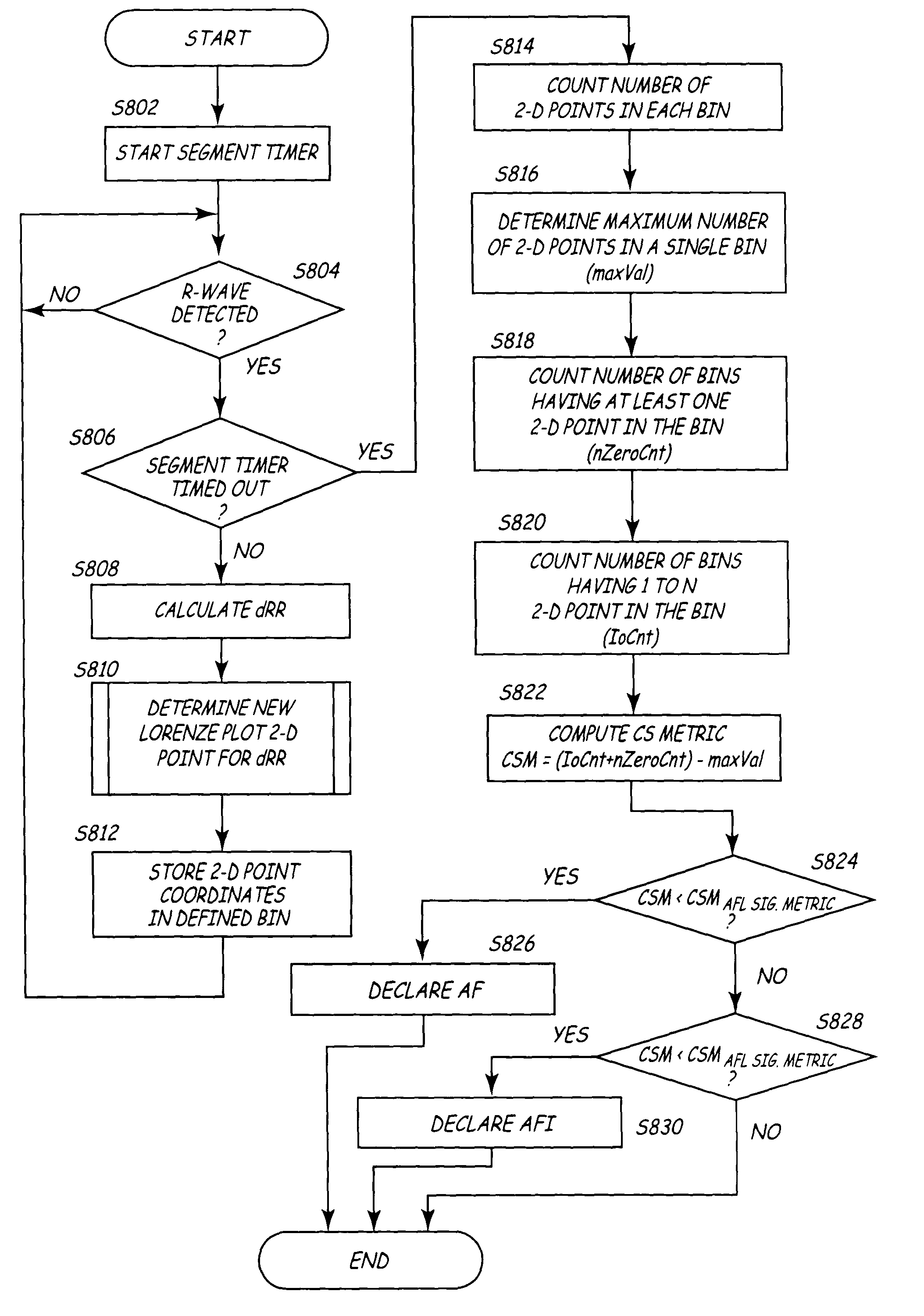
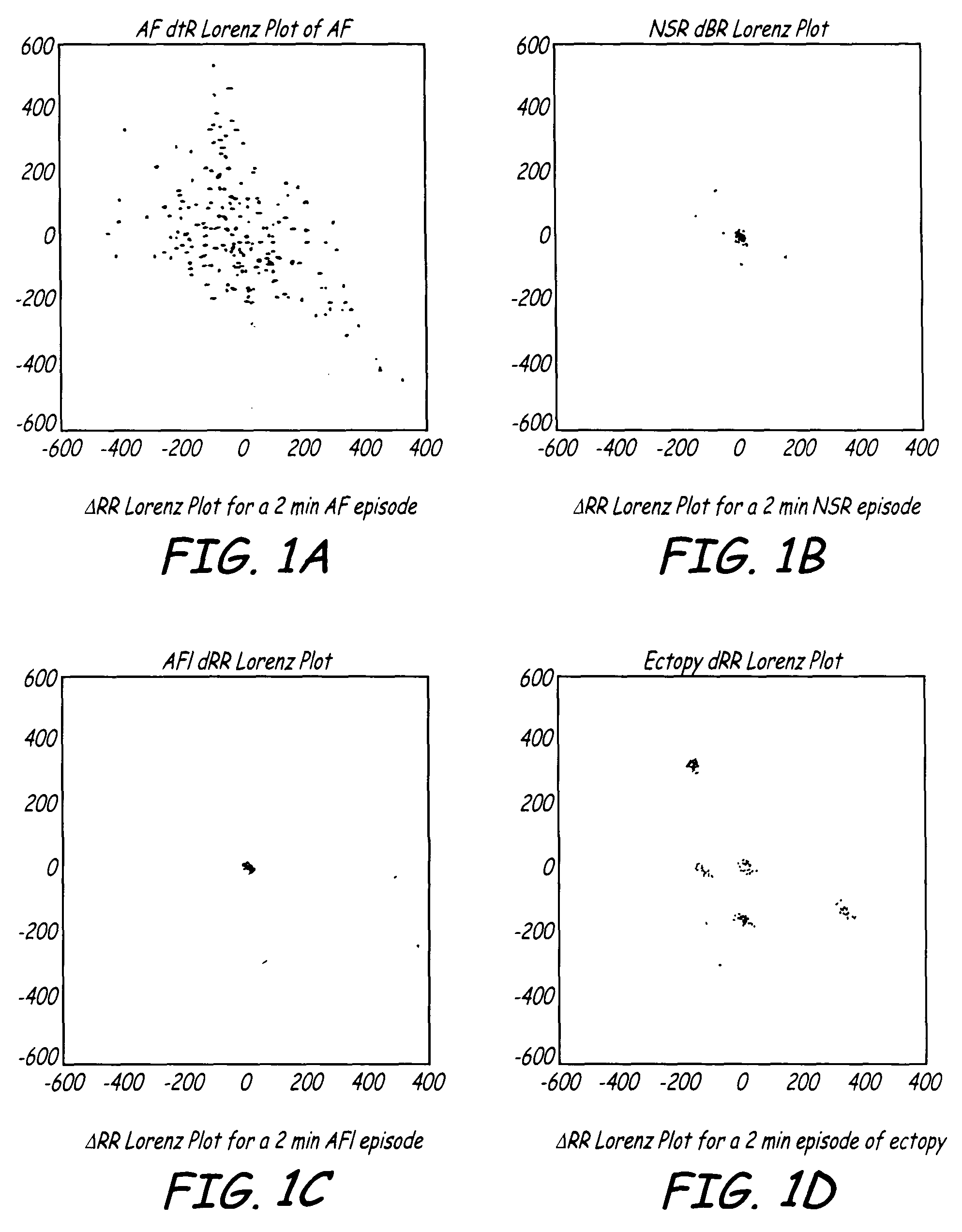
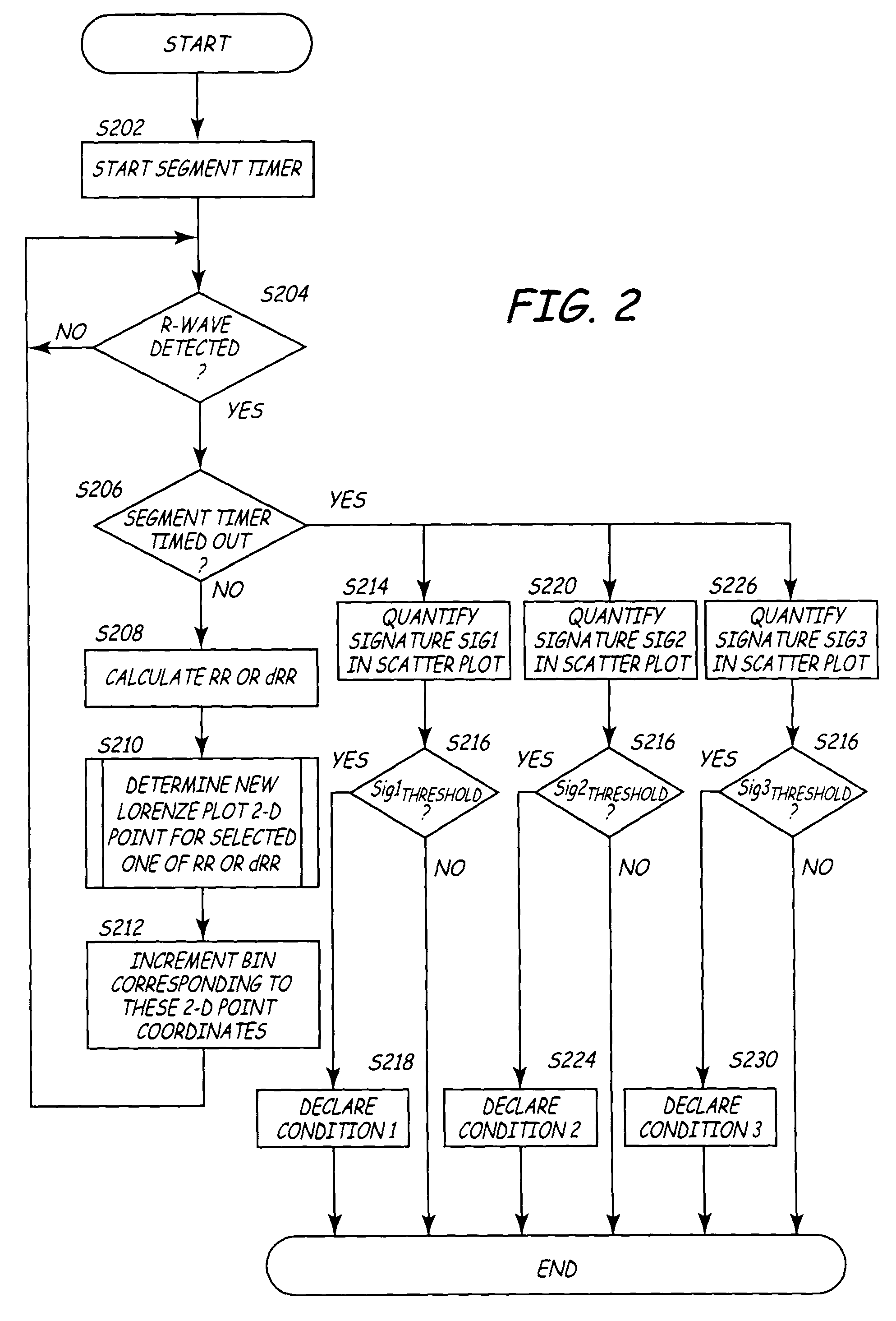
Algorithms for detecting atrial arrhythmias from discriminatory signatures of ventricular cycle lengths
ActiveUS7031765B2Enhances and improves detectionElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsCardiac arrhythmiaComputer science
Detection of arrhythmias is facilitated using irregularity of ventricular beats measured by delta-RR (ΔRR) intervals that exhibit discriminatory signatures when plotted in a Lorenz scatter-plot. An “AF signature metric” is established characteristic of episodes of AF that exhibit highly scattered (sparse) distributions or formations of 2-D data points. An “AFL signature metric” is established characteristic of episodes of AFL that exhibit a highly concentrated (clustered) distribution or formation of 2-D data points. A set of heart beat interval data is quantified to generate highly scattered (sparse) formations as a first discrimination metric and highly concentrated (clustered) distributions or formations as a second discrimination metric. The first discrimination metric is compared to the AF signature metric, and / or the second discrimination metric is compared to the AFL signature metric. AF or HFL is declared if the first discrimination metric satisfies either one of the AF signature metric.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140016858A1Reduce image dataCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesContent distributionNeuron network
Apparatus and methods for detecting salient features. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. A dedicated inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the remaining neurons within the network. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the remaining neurons thereby facilitating salient feature detection within the image by the network. Salient feature detection can be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
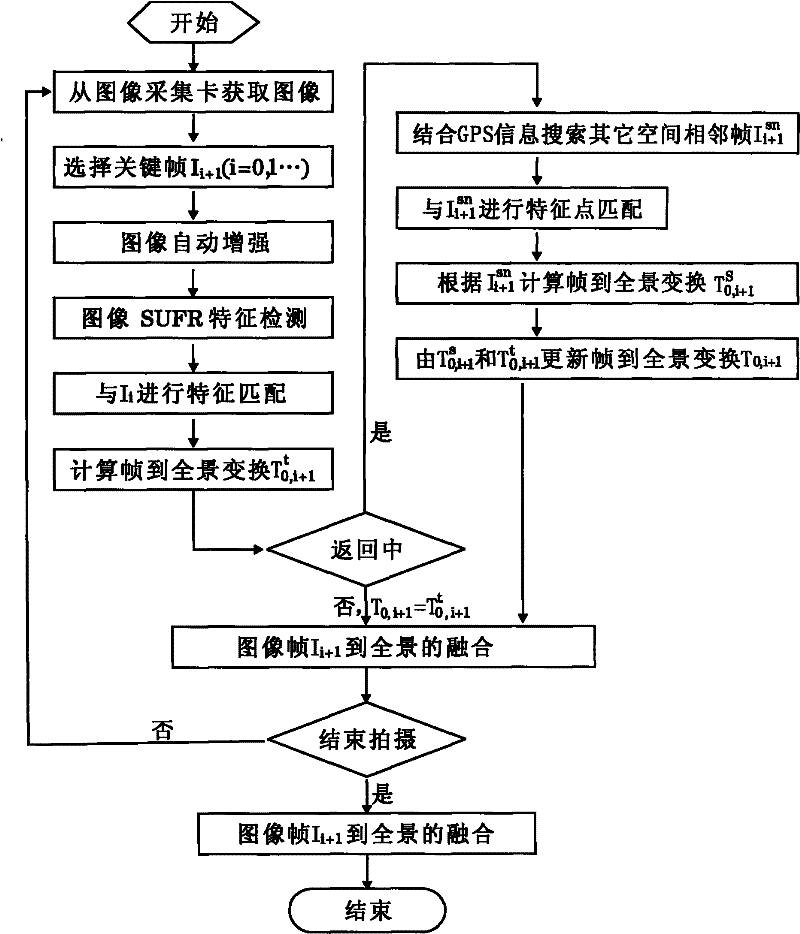
Real-time panoramic image stitching method of aerial videos shot by unmanned plane
ActiveCN102201115ARealize the transformation relationshipQuickly achieve registrationTelevision system detailsImage enhancementGlobal Positioning SystemTime effect
The invention discloses a real-time panoramic image stitching method of aerial videos shot by an unmanned plane. The method comprises the steps of: utilizing a video acquisition card to acquire images which are transmitted to a base station in real time by an unmanned plane through microwave channels, carrying out key frame selection on an image sequence, and carrying out image enhancement on key frames; in the image splicing process, firstly carrying out characteristic detection and interframe matching on image frames by adopting an SURF (speeded up robust features) detection method with good robustness; then reducing the series-multiplication accumulative errors of images in a frame-to-mosaic image transformation mode, determining images which are not adjacent in time sequence but adjacent in space on a flight path according to the GPS (global positioning system) position information of the unmanned plane, optimizing the frame-to-mosaic transformation relation, determining image overlapping areas, thereby realizing image fusion and the panoramic image construction and realizing real-time effect of carrying out flying and stitching simultaneously; and in image transformation, based on adjacent frame information in a vision field and adjacent frame information in airspace, optimizing image transformation to obtain the accurate panoramic images. The stitching method has good real-time performance, is fast and accurate and meets the requirements of application occasions in multiple fields.
Owner:HUNAN AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for detecting or recognizing pattern by employing a plurality of feature detecting elements
InactiveUS7054850B2High-precision detectionImprove process capabilityDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSynapsePattern detection
Owner:CANON KK
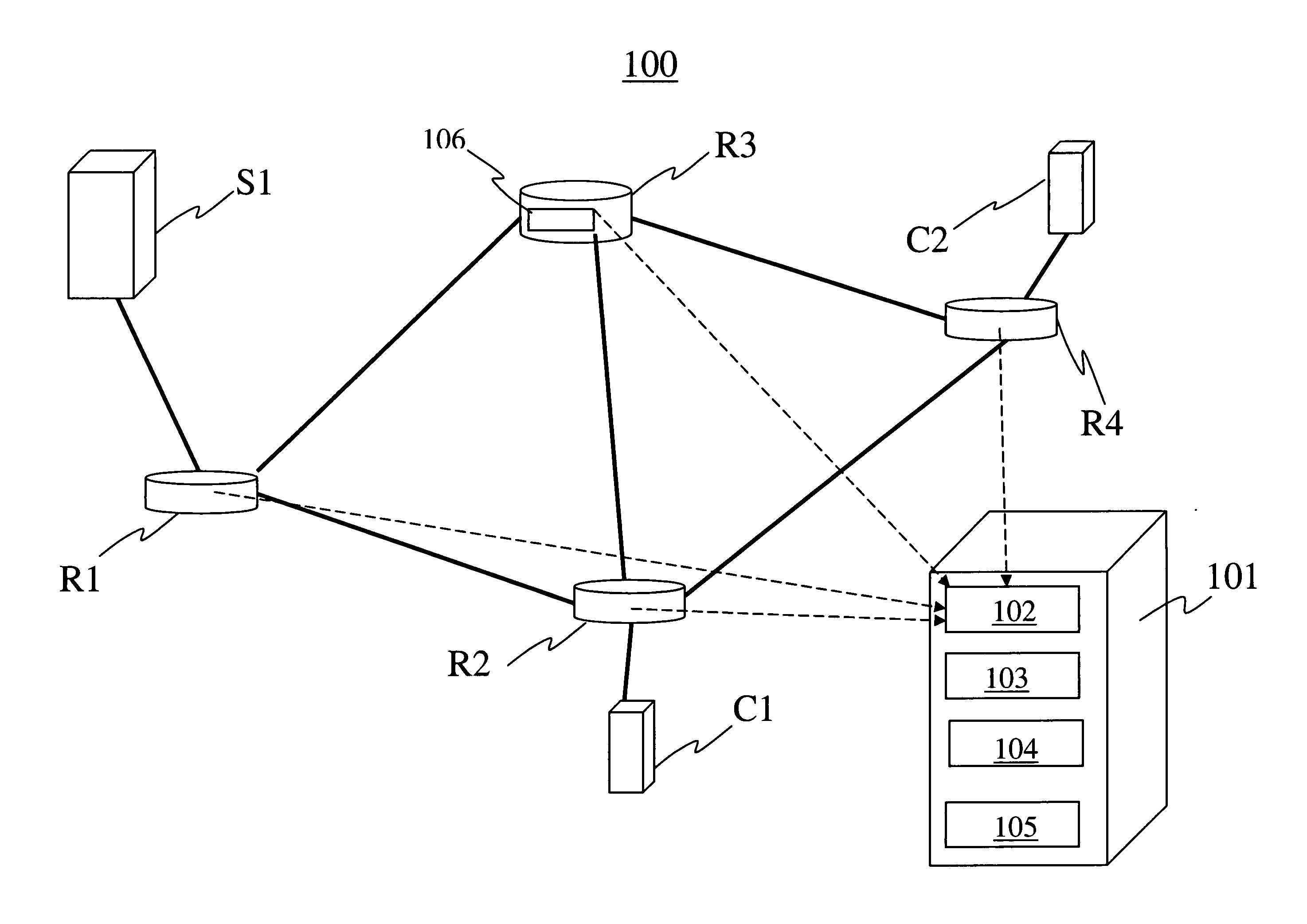
Web-based client/server communication channel with automated client-side channel endpoint feature detection and selection
A TCP / IP-based software application client / server communication channel construction mechanism is presented. The mechanism constructs a dedicated bi-directional data transmission for a single client / server session. The server software, running on a server host computer, provides session-based data services to one or more software clients. The client process supports one or more execution environments including: text-based scripting, Java or ActiveX components. The invoked code executing within the client computer detects the most attractive execution environment available within its execution environments, and uses the services of that execution environment client process to establish an optimal communication channel back to the server software process. Depending on the execution environment(s) available to the invoked code, the communication channel may be: (a) a content-independent, bi-directional transmission control protocol (TCP) connection, or (b) a content-dependent TCP connection, such as a TCP connection supporting only a single HTTP request / response pair.
Owner:PATH RELIABILITY
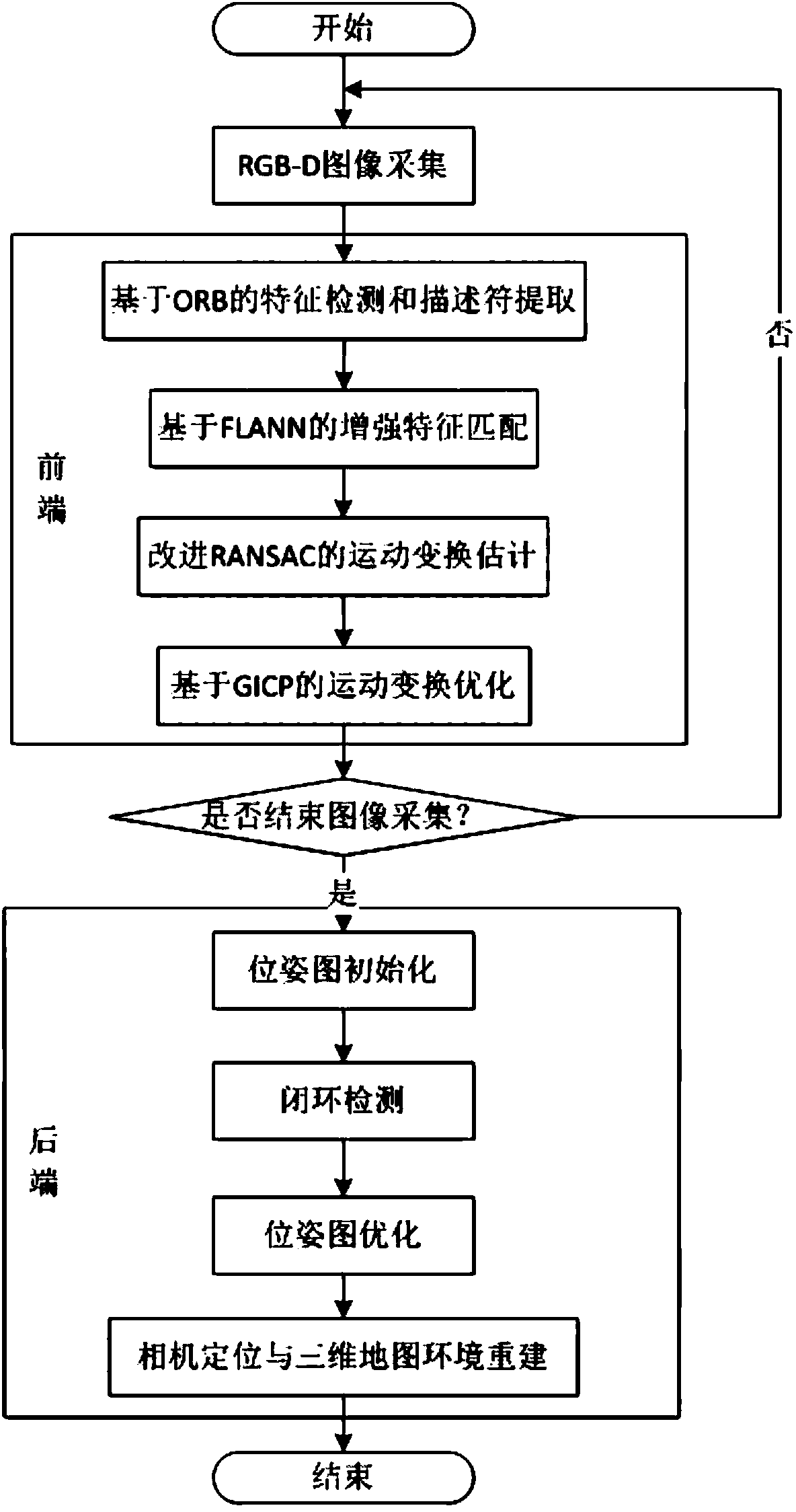
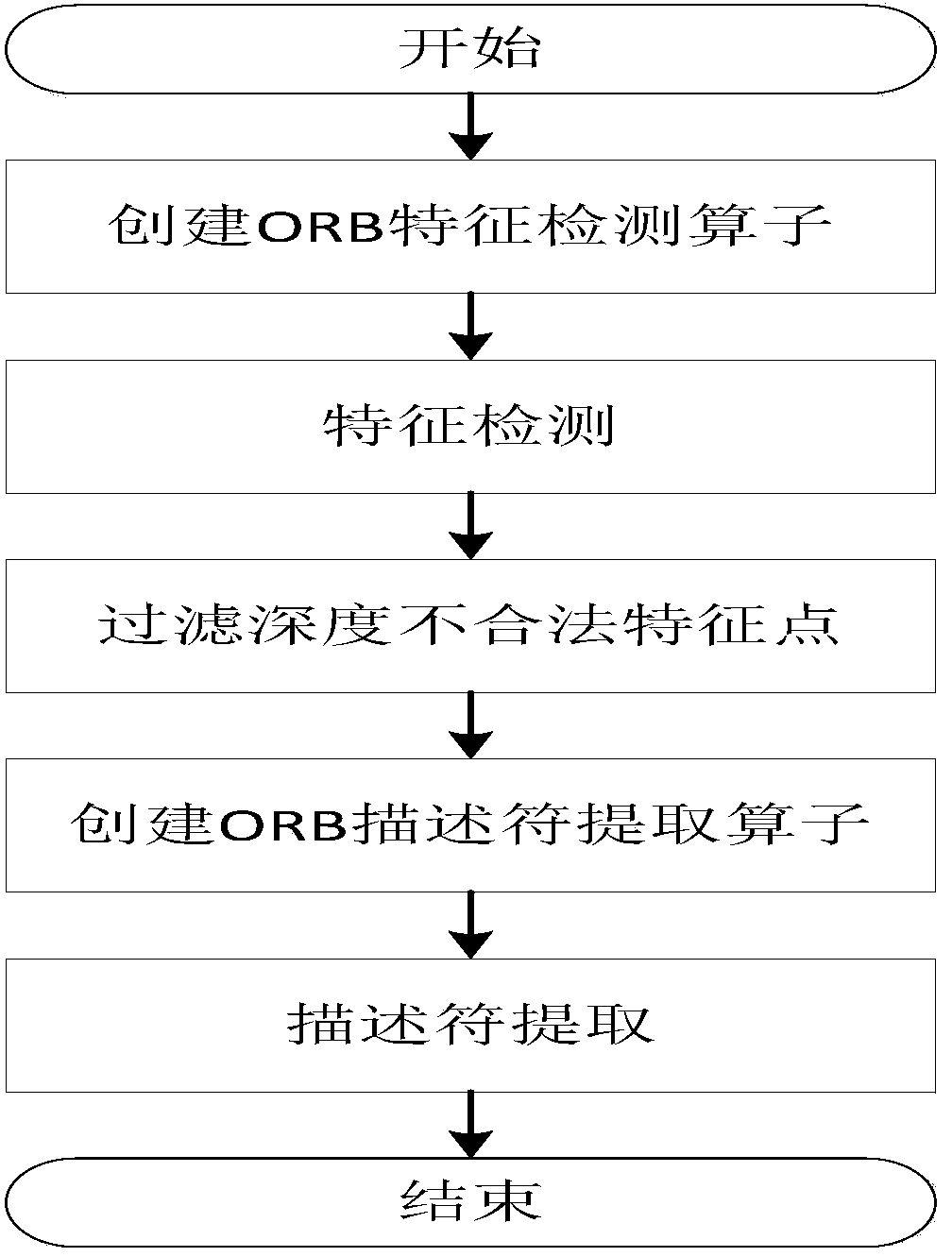
Improved method of RGB-D-based SLAM algorithm
InactiveCN104851094AMatching result optimizationHigh speedImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudEstimation methods
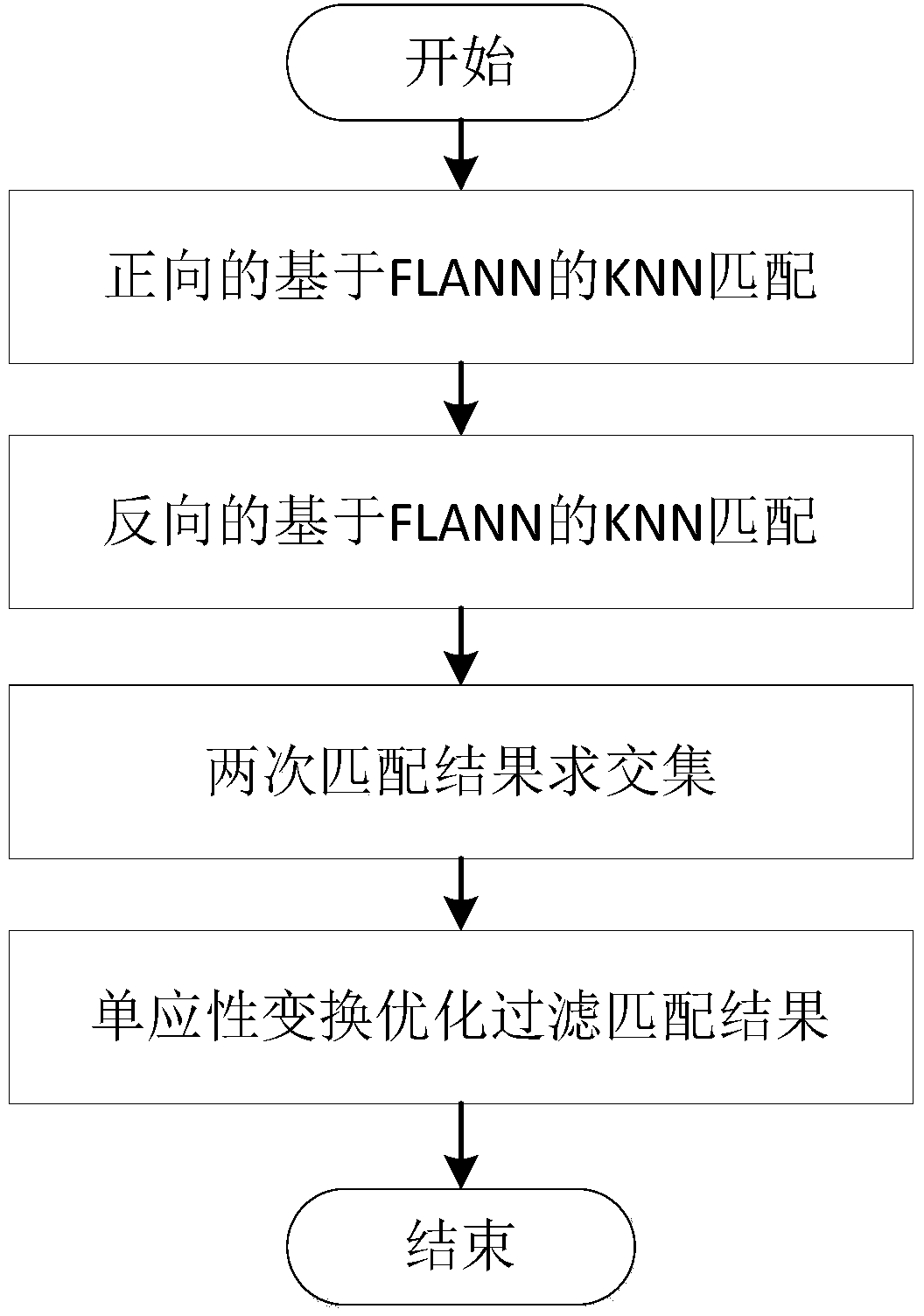
Disclosed in the invention is an improved method of a RGB-D-based simultaneously localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm. The method comprises two parts: a front-end part and a rear-end part. The front-end part is as follows: feature detection and descriptor extraction, feature matching, motion conversion estimation, and motion conversion optimization. And the rear-end part is as follows: a 6-D motion conversion relation initialization pose graph obtained by the front-end part is used for carrying out closed-loop detection to add a closed-loop constraint condition; a non-linear error function optimization method is used for carrying out pose graph optimization to obtain a global optimal camera pose and a camera motion track; and three-dimensional environment reconstruction is carried out. According to the invention, the feature detection and descriptor extraction are carried out by using an ORB method and feature points with illegal depth information are filtered; bidirectional feature matching is carried out by using a FLANN-based KNN method and a matching result is optimized by using homography matrix conversion; a precise inliners matching point pair is obtained by using an improved RANSAC motion conversion estimation method; and the speed and precision of point cloud registration are improved by using a GICP-based motion conversion optimization method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Video surveillance using stationary-dynamic camera assemblies for wide-area video surveillance and allow for selective focus-of-attention
InactiveUS20060203090A1Wide-area coverageSelective focus-of-attentionCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsVideo monitoringObject motion
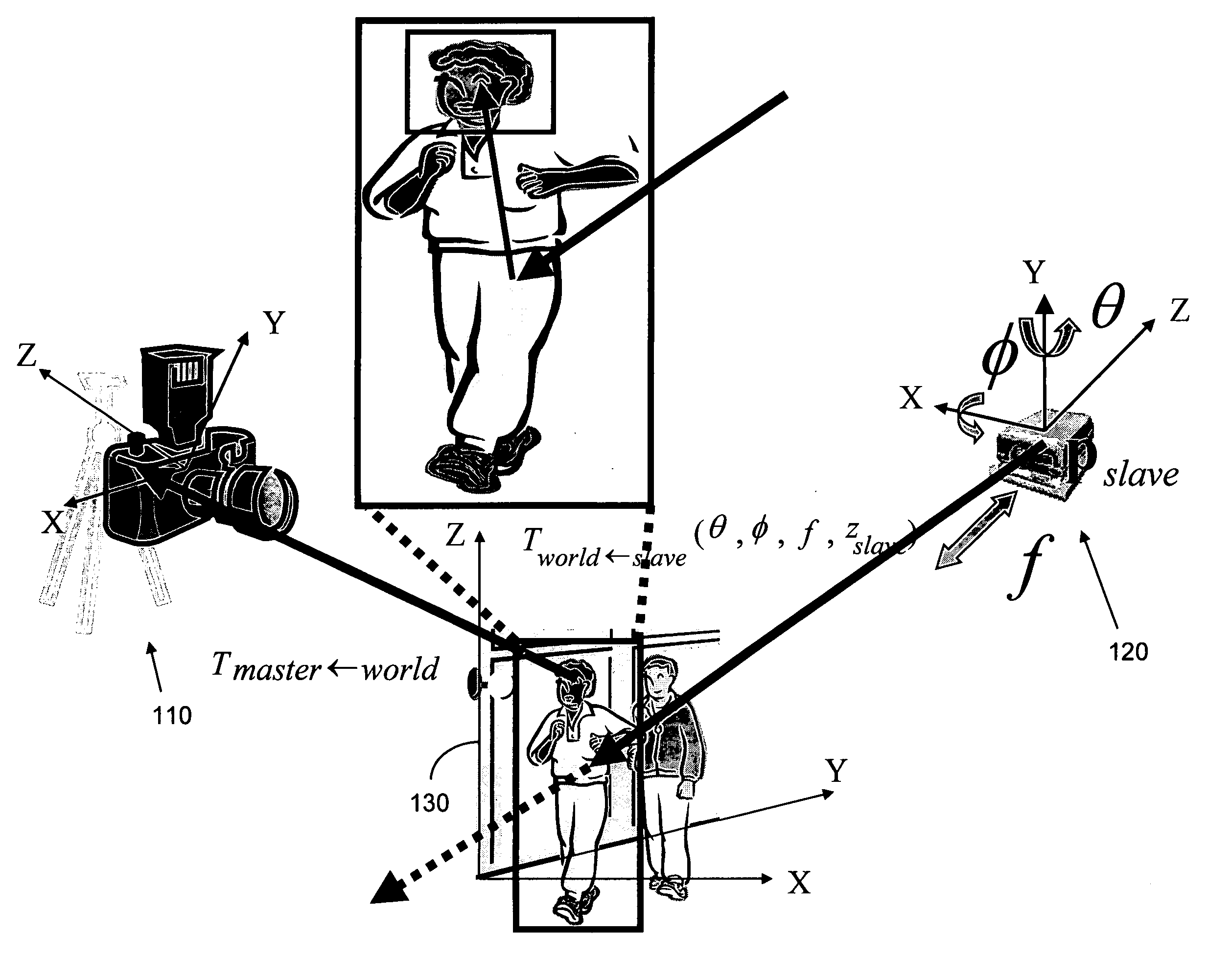
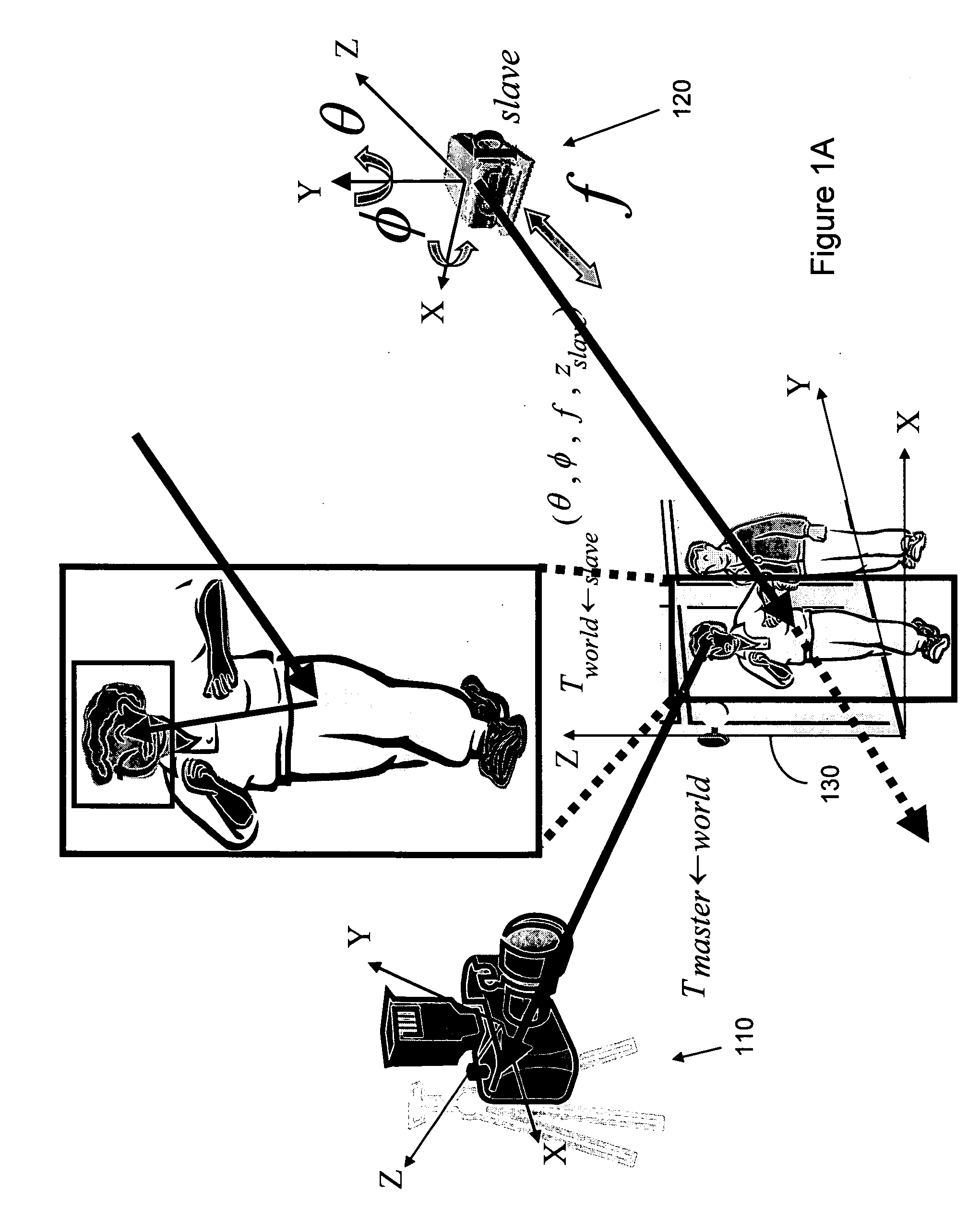
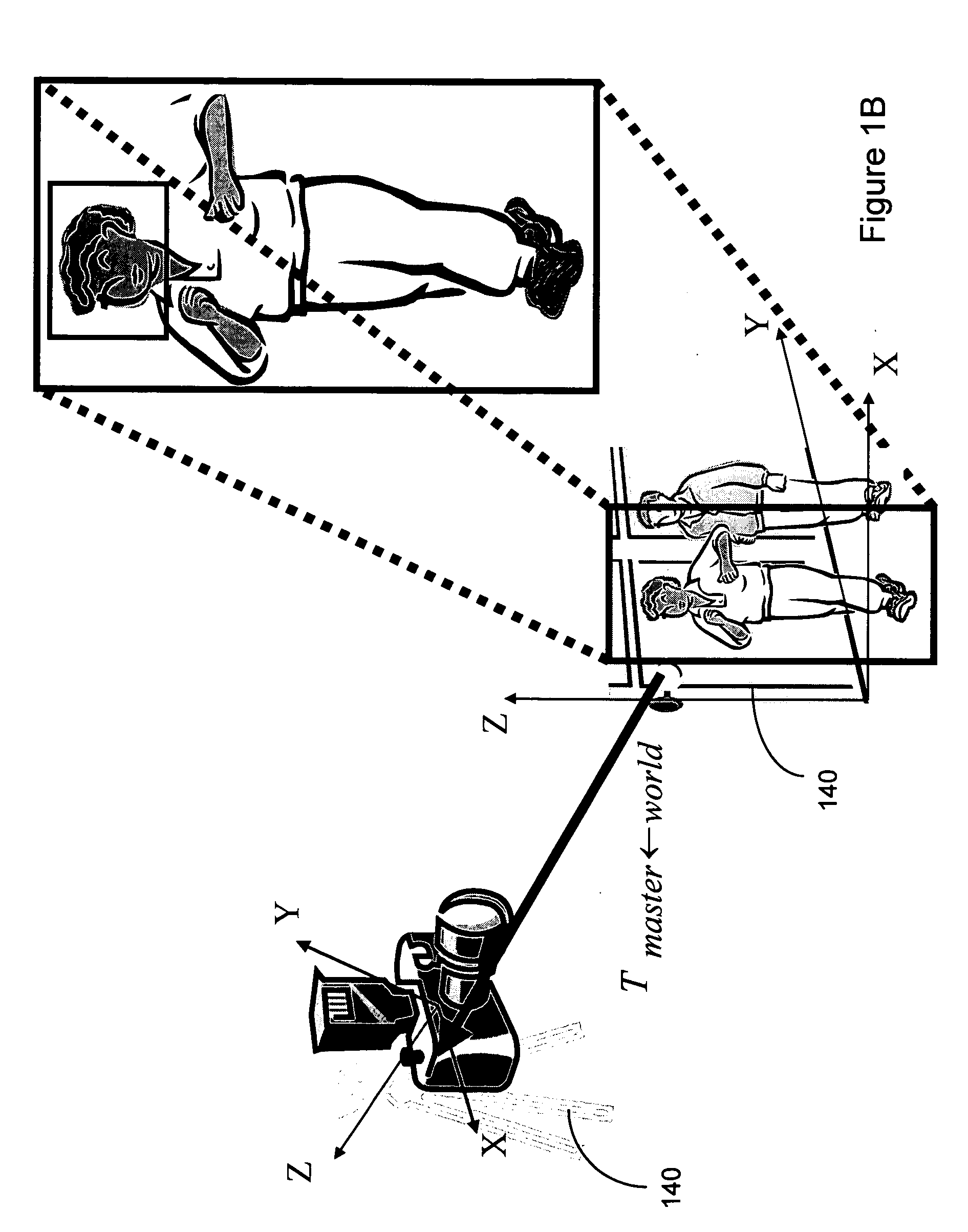
A video surveillance system includes multiple video cameras. The surveillance system is configured with an arrangement to separate the surveillance functions and assign different surveillance functions to different cameras. A master camera is assigned the surveillance of large area surveillance and tracking of object movement while one or more slave cameras are provided to dynamically rotate and adjust focus to obtain clear image of the moving objects as detected by the master camera. Algorithms to adjust the focus-of-attention are disclosed to effectively carry out the tasks by a slave camera under the command of a master camera to obtain images of a moving object with clear feature detections.
Owner:PROXIMEX CORP
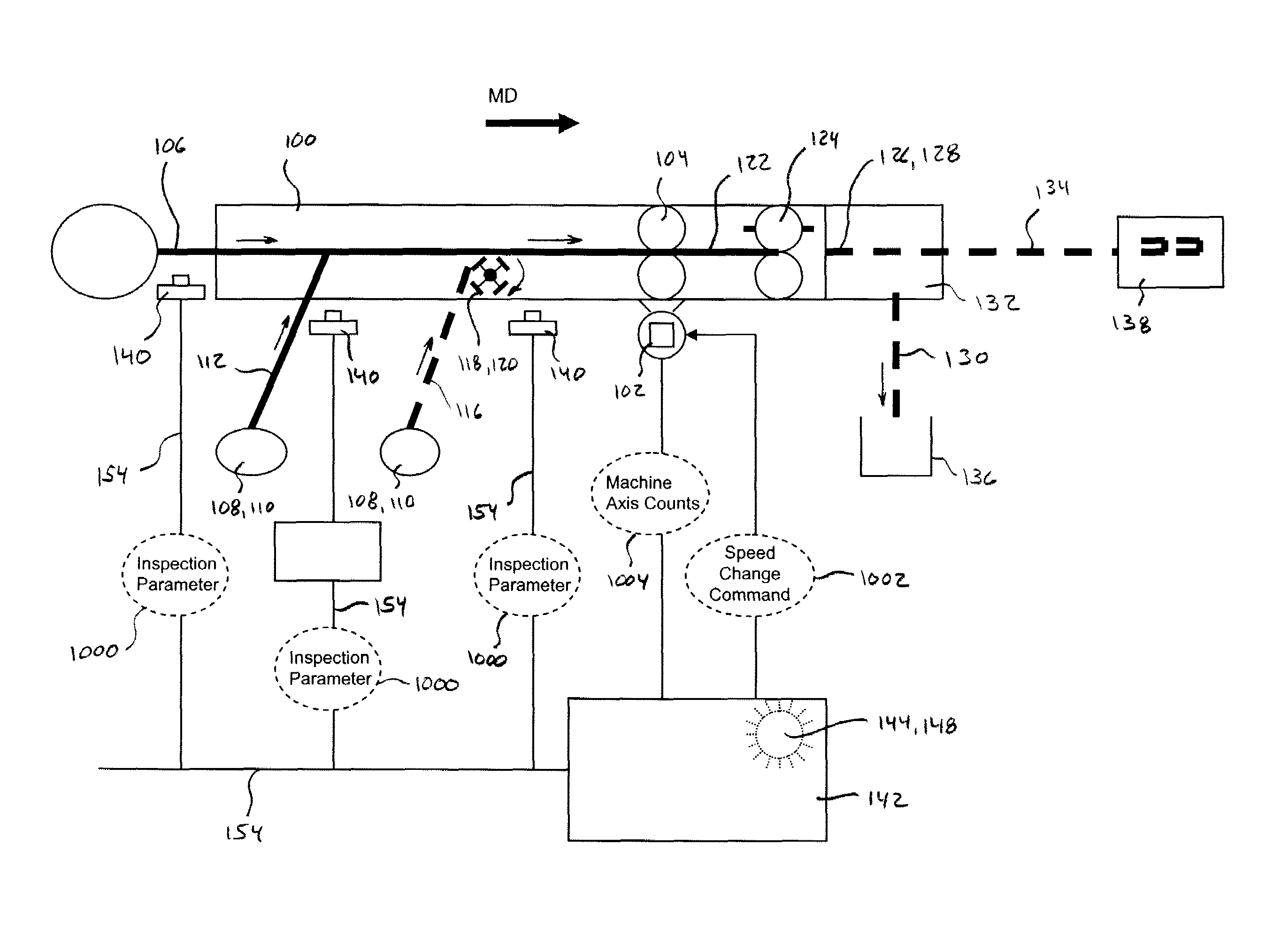
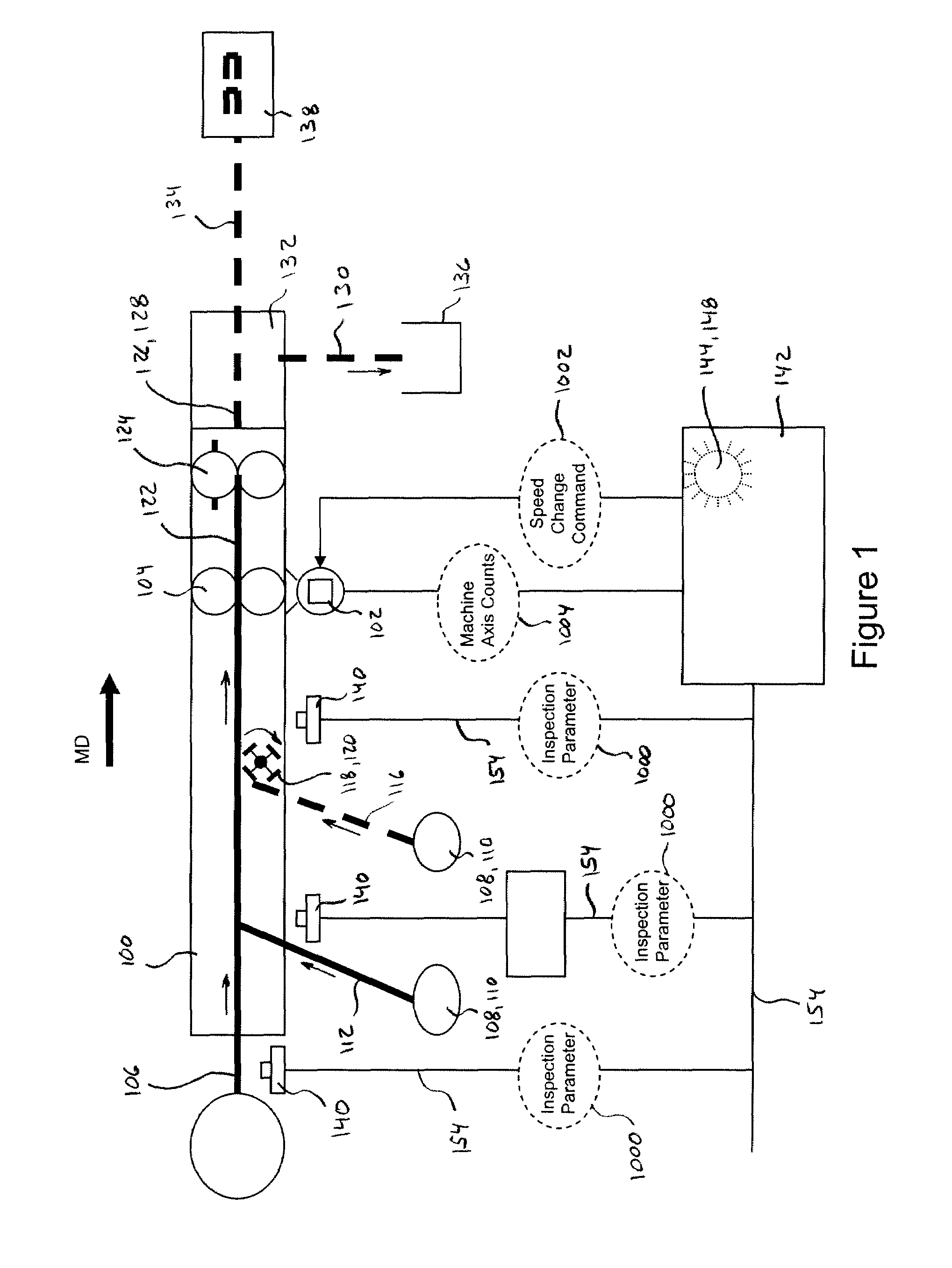
Systems and methods for controlling registration of advancing substrates in absorbent article converting lines
ActiveUS8145343B2Precise applicationMaterial analysis by optical meansMultiple digital computer combinationsControl systemEngineering
The present disclosure relates to systems and processes for controlling the registration of advancing substrates in absorbent article converting lines. The systems and methods may utilize feedback from technologies, such as vision systems, sensors, remote input and output stations, and controllers with synchronized embedded clocks to accurately correlate registration feature detections and substrate speed control on an absorbent article converting process. The systems and methods may accurately apply the use of precision clock synchronization for both instrumentation and control system devices on a non-deterministic communications network. In turn, the clock synchronized control and instrumentation network may be used to control the substrate speed. As such, the controller may be programmed to track registration features on substrates and components along the converting line without having to account for undeterminable delays.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
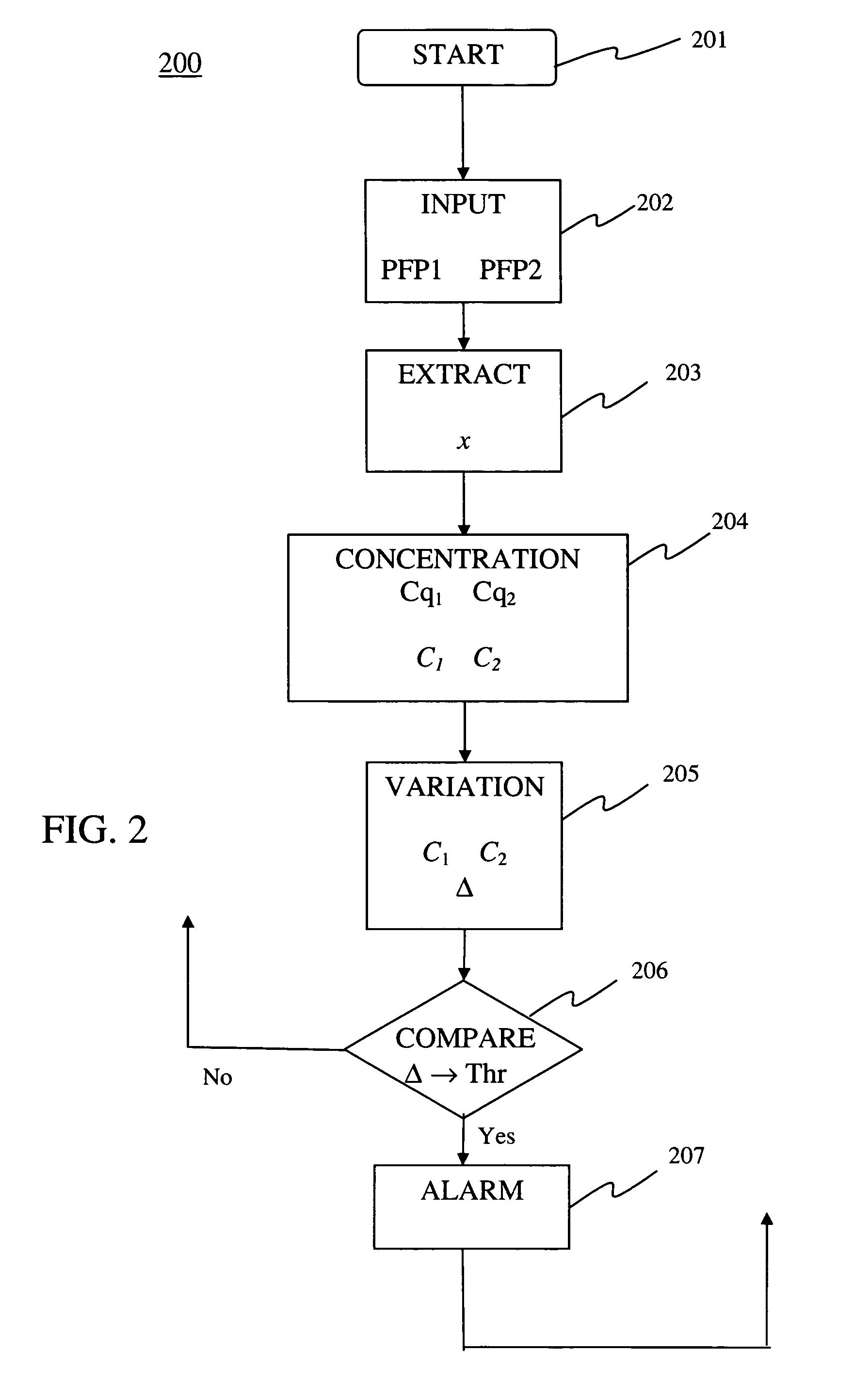
Method of detecting anomalies in a communication system using symbolic packet features
ActiveUS20100284282A1Improve reliabilityReduce computational complexityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsState dependentCommunications system
A method of detecting anomalies in a communication system includes: providing a first packet flow portion and a second packet flow portion; extracting samples of a symbolic packet feature associated with a traffic status of the first and second packet flow portions; computing from the extracted samples a first statistical concentration quantity and a second statistical concentration quantity of the symbolic feature associated with the first and second packet flow portions, respectively; computing from the concentration quantities a variation quantity representing a concentration change from the first packet flow portion to the second packet flow portion; comparing the variation quantity with a comparison value; and detecting an anomaly in the system in response to the comparison.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Laser radar projection with object feature detection and ranging
A 3D pulsed laser projection system scans an object to produce a dense 3D point cloud and projects a laser light beam onto an object as a glowing template. A high-sensitivity optical feedback system receives and detects a feedback beam of the output beam light diffusely reflected from the object. The feedback light and projected beam share the same beam path between steering mirrors and the object. A light suppression component controls stray scattered light, including ambient light, from being detected. A time-of-flight measurement subsystem provides a distance-to-object measurement for projected pulses. An acousto-optical modulator, variable gain detected signal amplification and variable photo-detector power together produce a dynamic range for detected reflected feedback signals of at least 100,000, and up to 500,000. Optical fiber cables spatially filter scattered light and isolate the photo-detectors thermally. The laser is preferably pulsed at least 50 kHz, with sampling of the projected and feedback reflected optical pulse signals at a sampling rate of up to 10 gigasamples per second.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
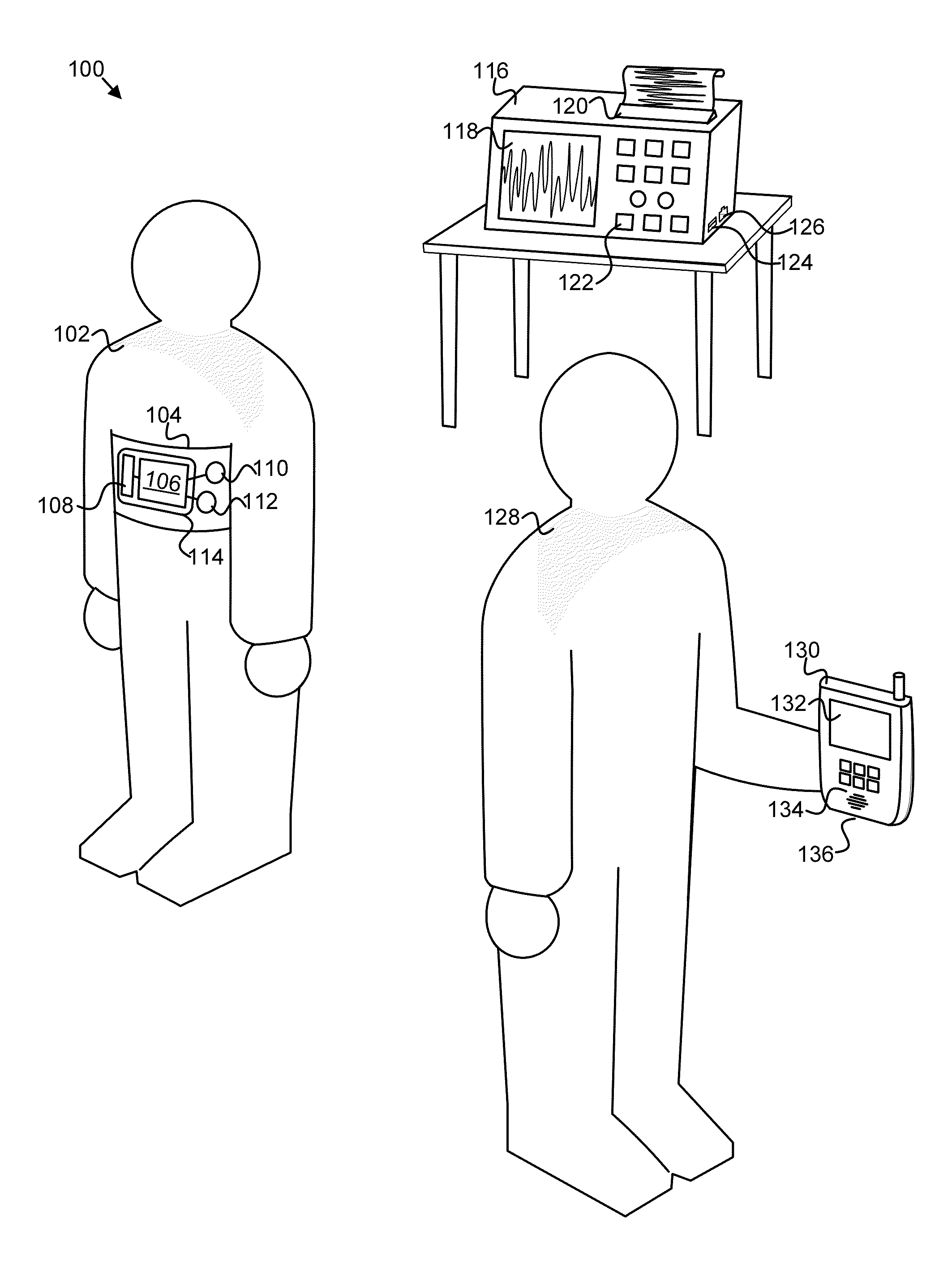
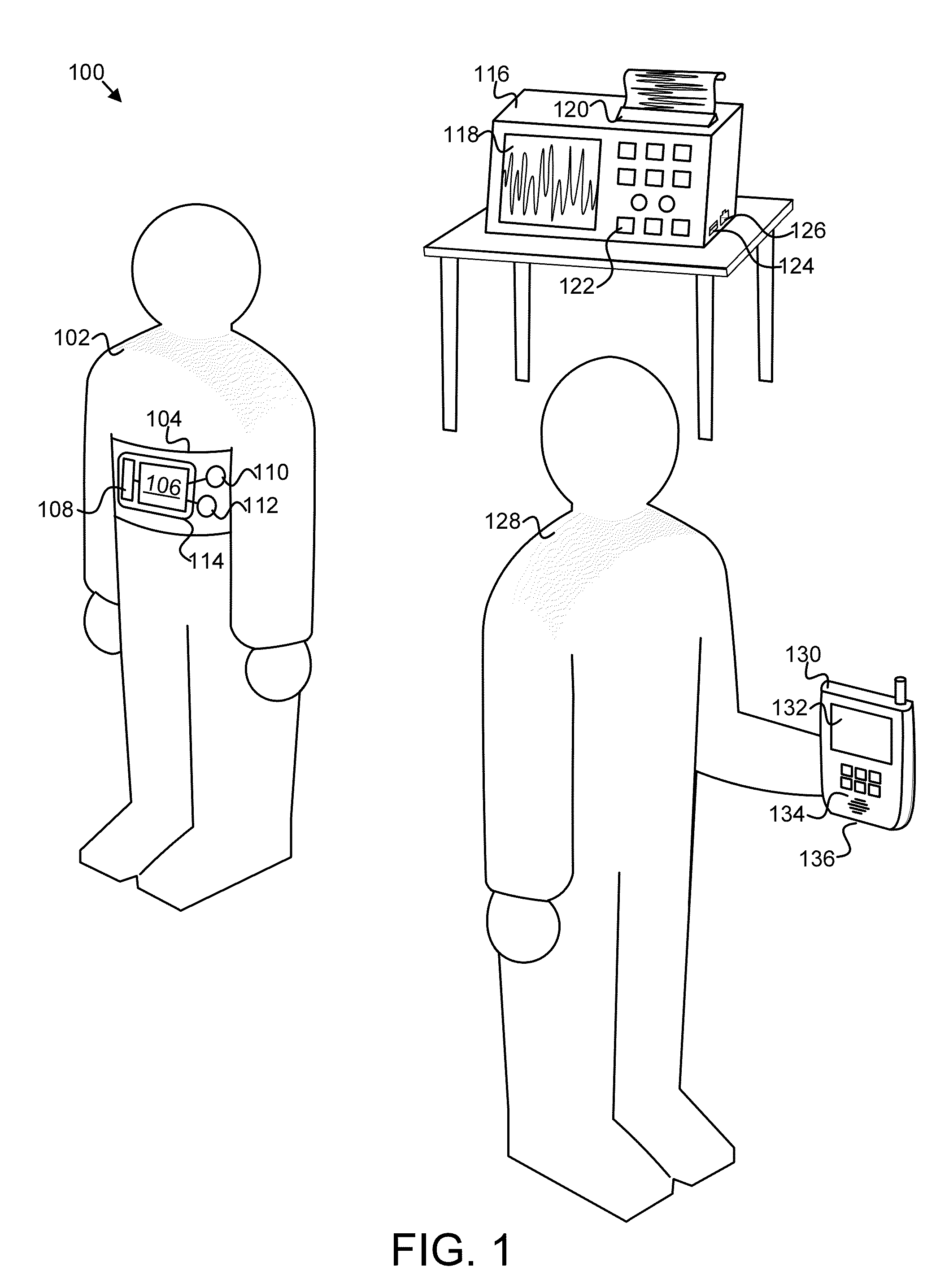
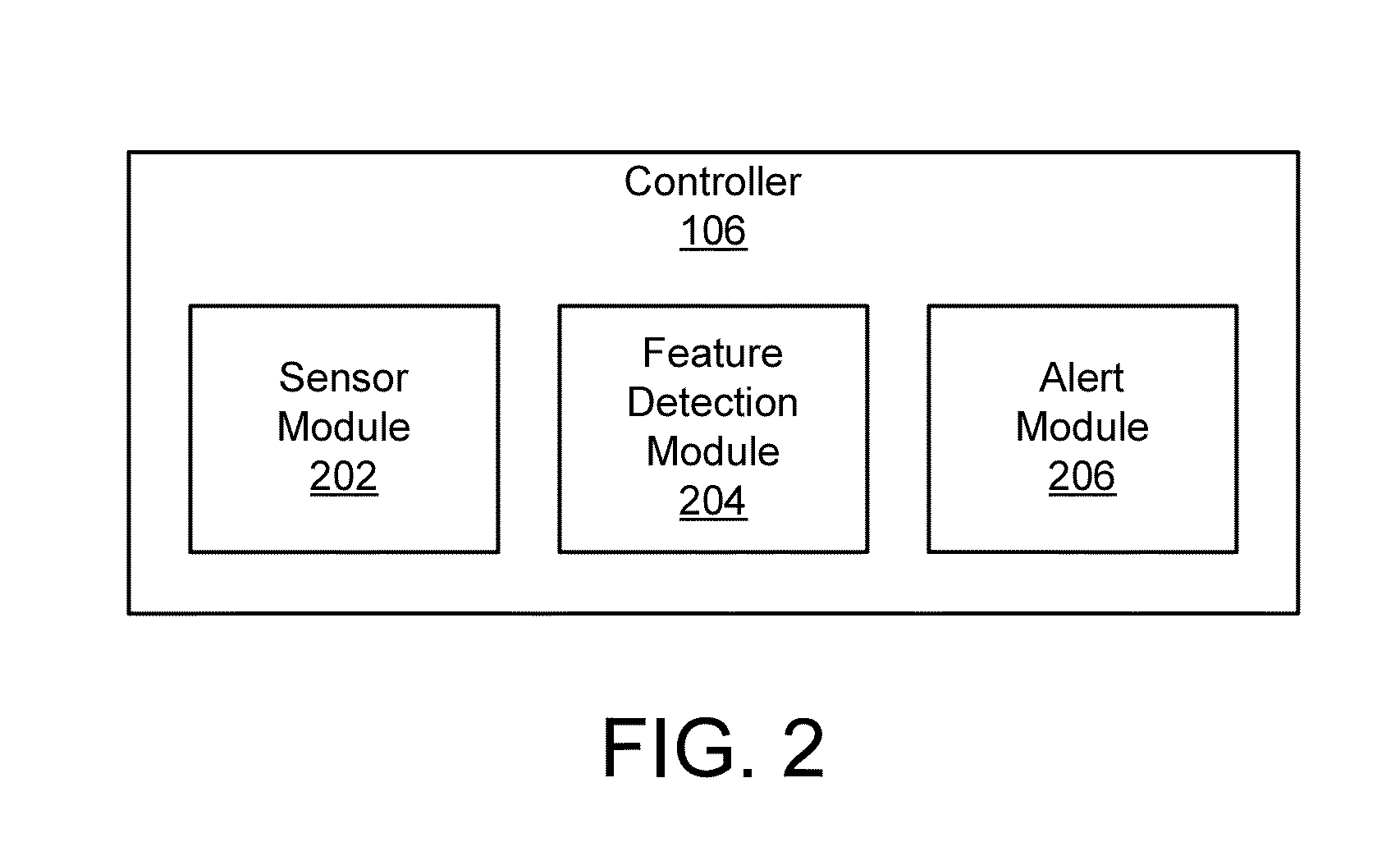
Apparatus, system, and method for seizure symptom detection
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for detecting seizure symptoms in an individual 102. A sensor module 202 receives physiological data for an individual 102 from one or more sensors 110, 112, such as a heart activity sensor. A feature detection module 204 detects a predefined feature 500, 520, 530, 540 in the physiological data. The predefined feature 500, 520, 530, 540 is associated with a seizure or another medical condition. An alert module 206 broadcasts an alert in response to the feature detection module 204 detecting the predefined feature 500, 520, 530, 540.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Systems and methods for feature detection in retinal images
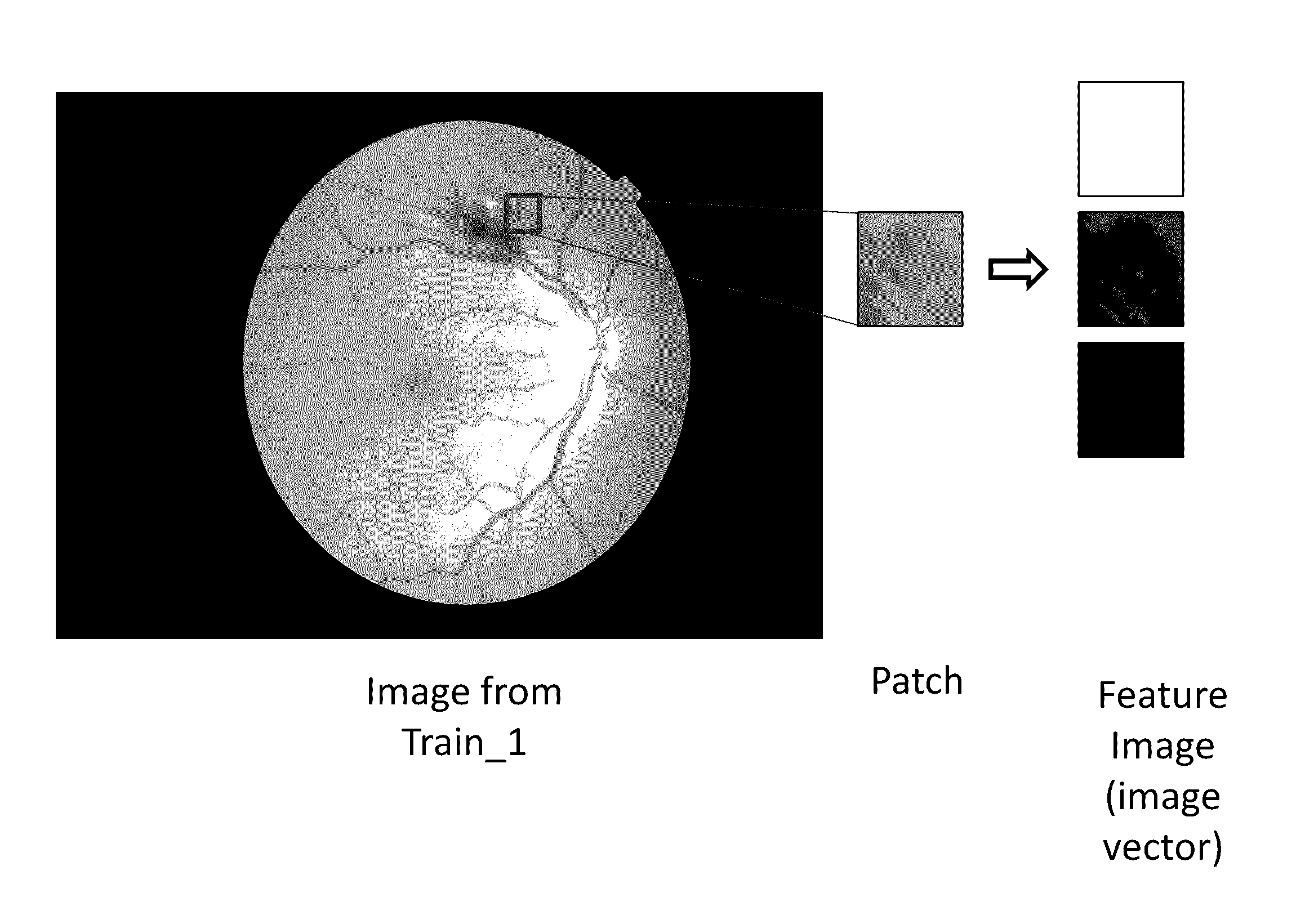
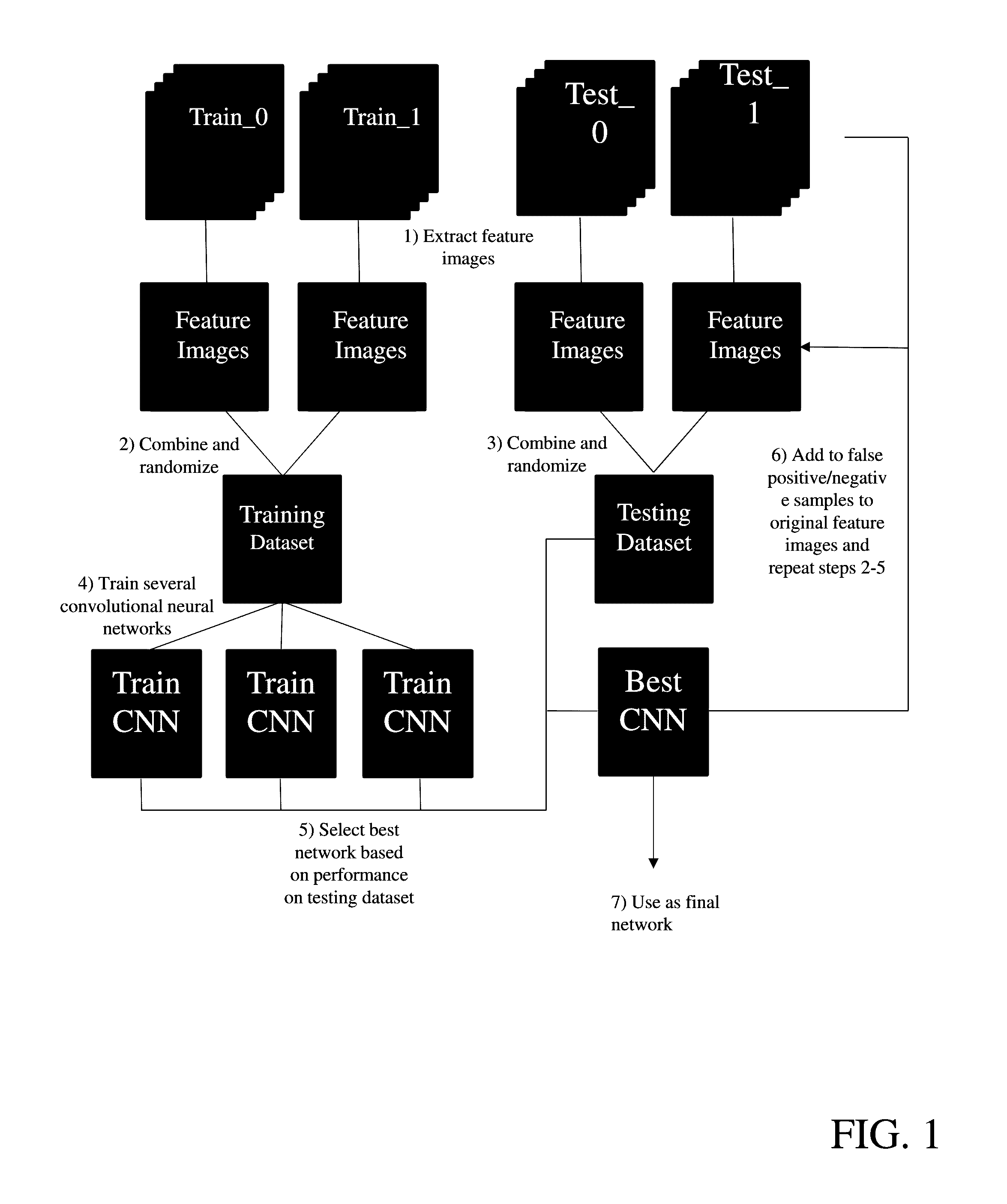
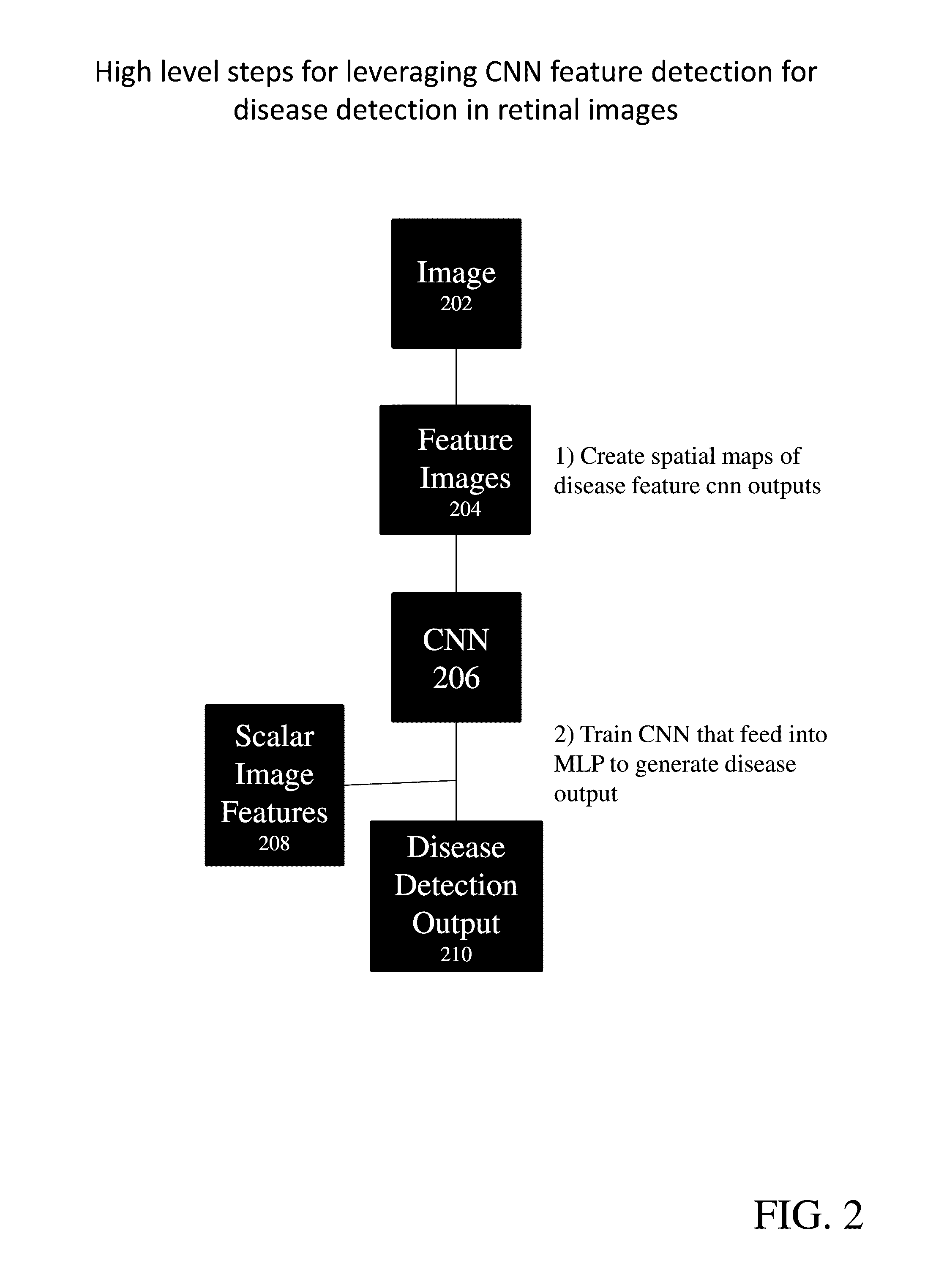
Provide are systems methods and devices for diagnosing disease in medical images. In certain aspects, disclosed is a method for training a neural network to detect features in a retinal image including the steps of: a) extracting one or more features images from a Train_0 set, a Test_0 set, a Train_1 set and a Test_1 set; b) combining and randomizing the feature images from Train_0 and Train_1 into a Training data set; c) combining and randomizing the feature images from Test_0 and Test_1 into a testing dataset; d) training a plurality of neural networks having different architectures using a subset of the training dataset while testing on a subset of the testing dataset; e) identifying the best neural network based on each of the plurality of neural networks performance on the testing data set; f) inputting images from Test_0, Train_1, Train_0 and Test_1 to the best neural network and identifying a limited number of false positives and false negative and adding the false positives and false negatives to the training dataset and testing dataset; and g) repeating steps d)-g) until an objective performance threshold is reached.
Owner:DIGITAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
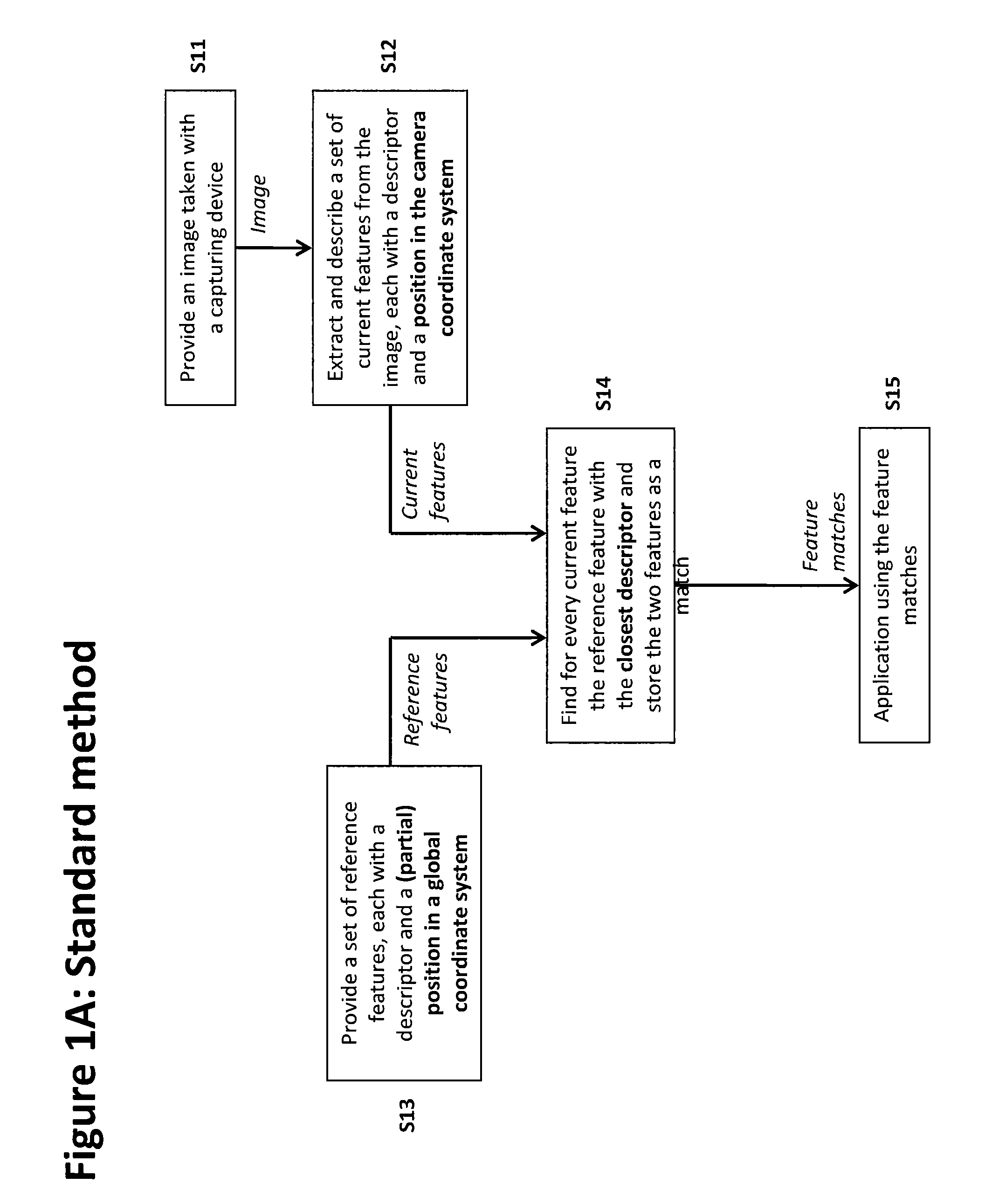
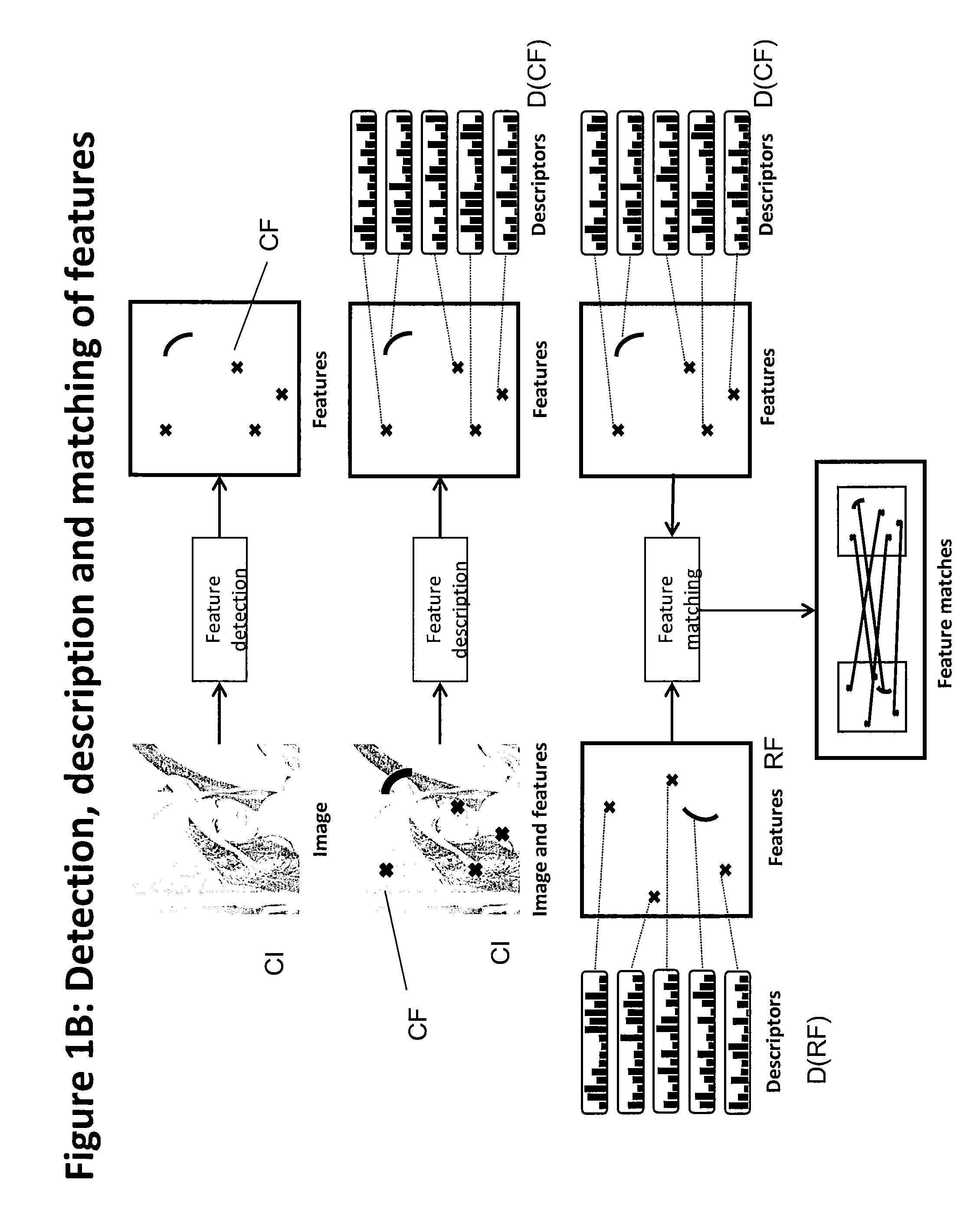
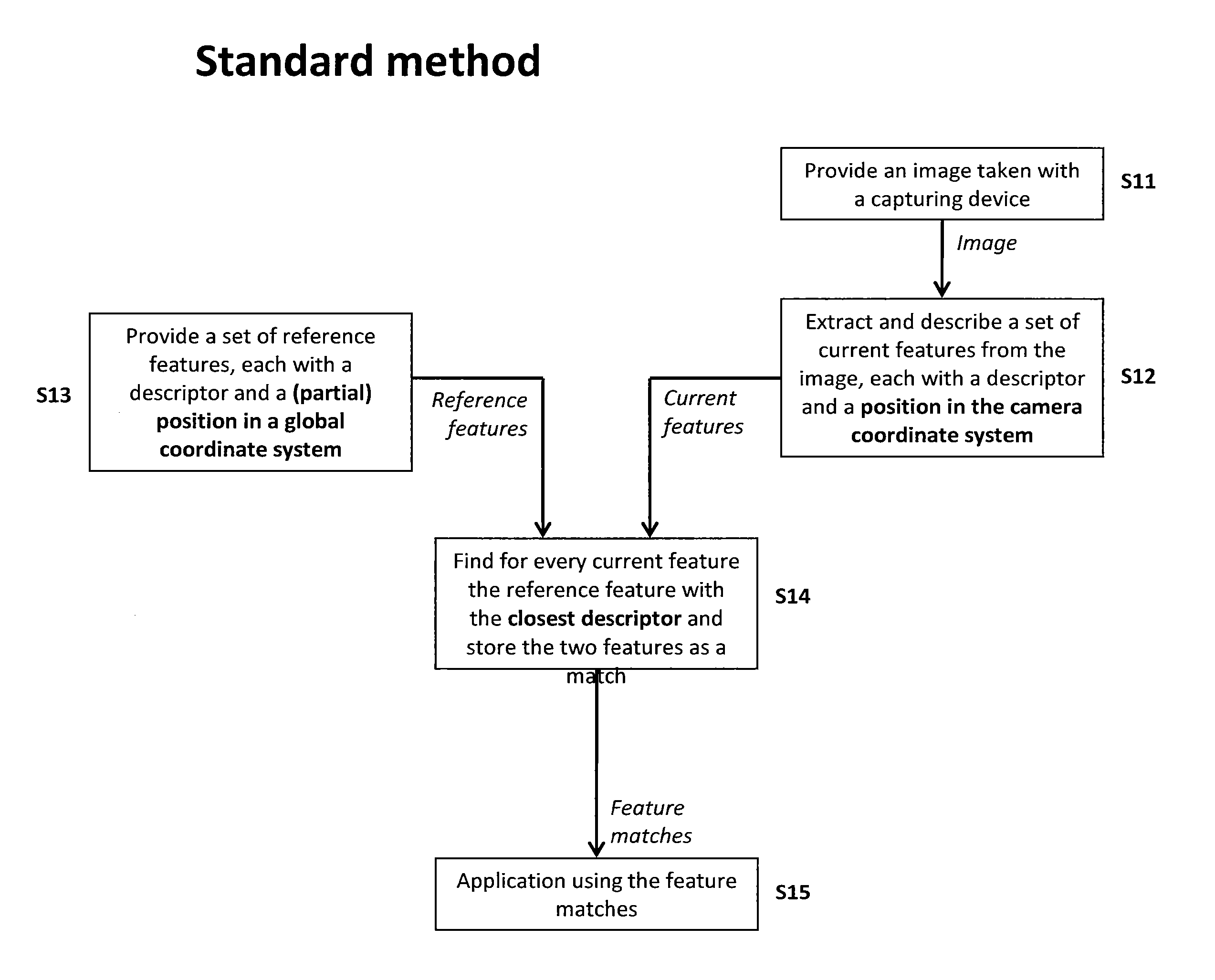
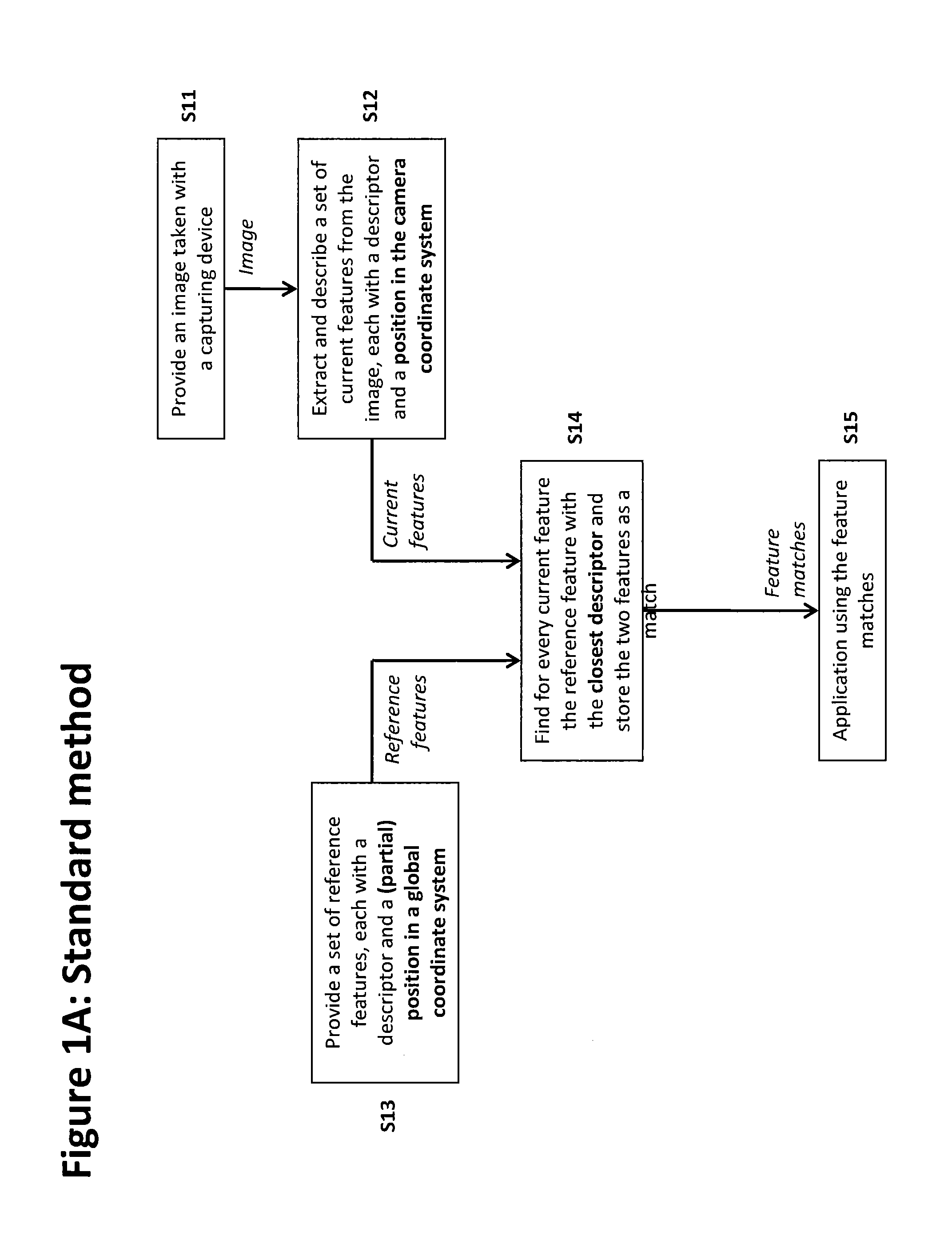
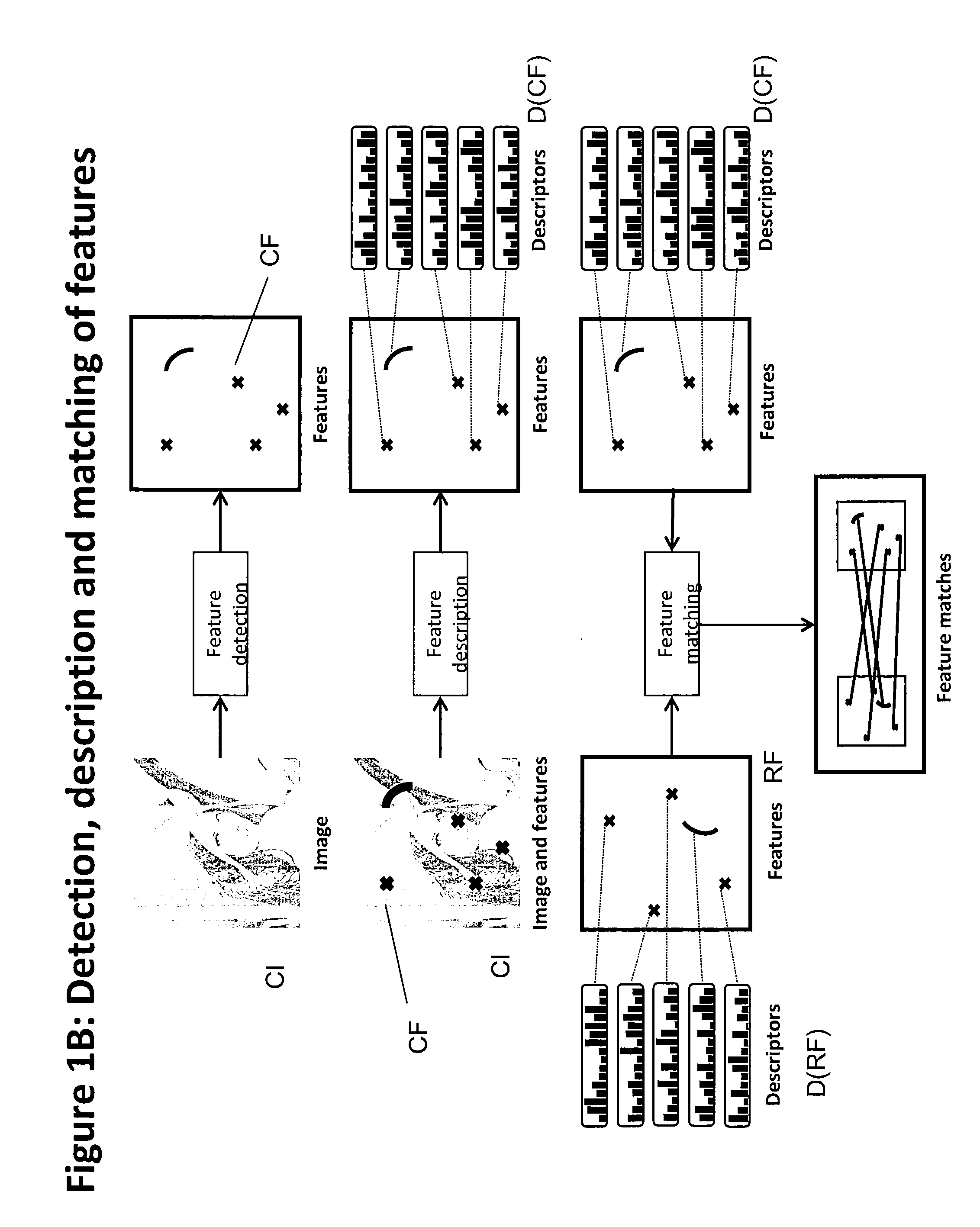
Method of matching image features with reference features
ActiveUS9400941B2Increase weightReduce uncertaintyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging FeatureSimilarity measure
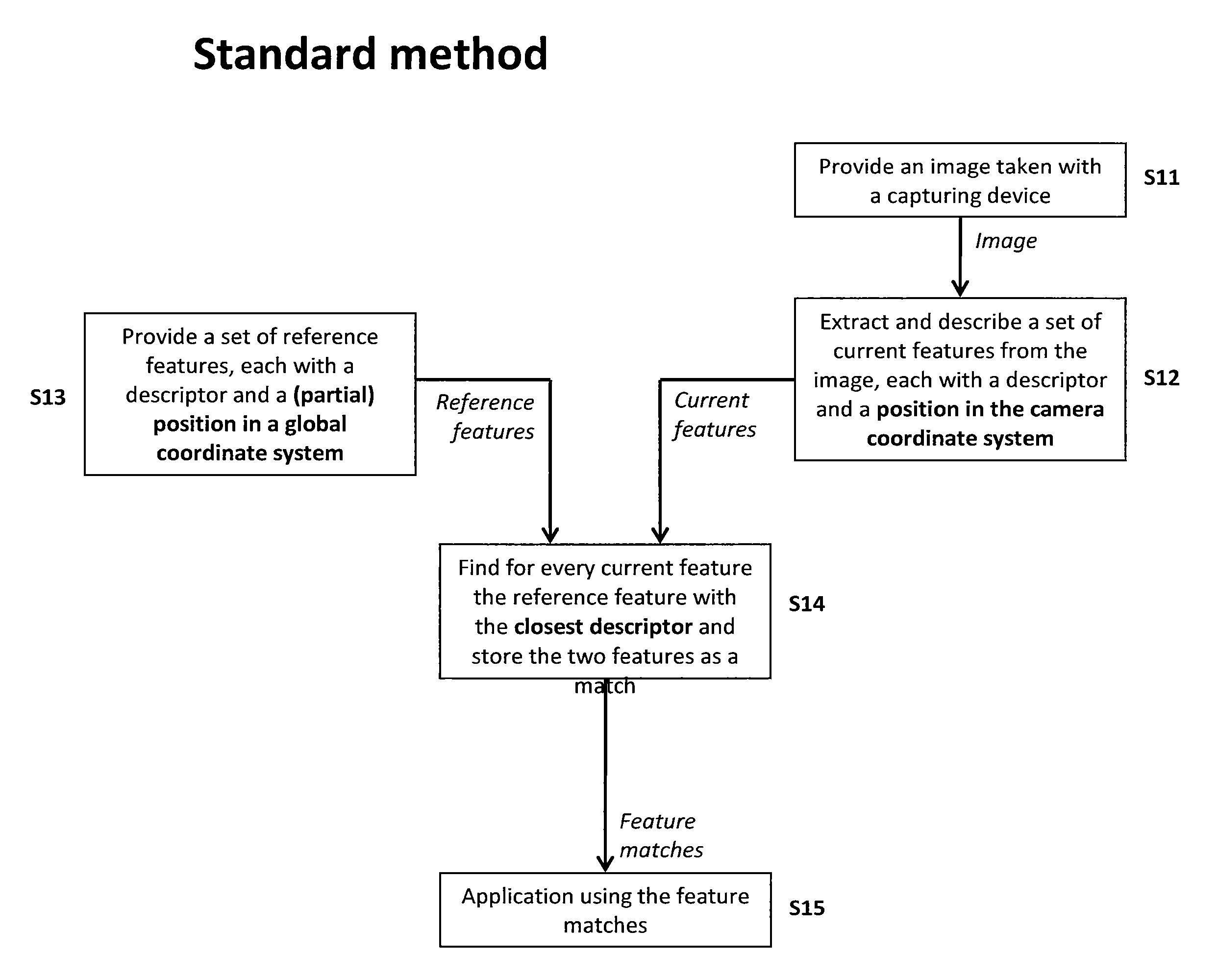
A method of matching image features with reference features comprises the steps of providing a current image, providing a set of reference features, wherein each of the reference features comprises at least one first parameter which is at least partially indicative of a position and / or orientation of the reference feature with respect to a global coordinate system, wherein the global coordinate system is an earth coordinate system or an object coordinate system, or at least partially indicative of a position of the reference feature with respect to an altitude, detecting at least one feature in the current image in a feature detection process, associating with the detected feature at least one second parameter which is at least partially indicative of a position and / or orientation of the detected feature, or which is at least partially indicative of a position of the detected feature with respect to an altitude, and matching the detected feature with a reference feature by determining a similarity measure.
Owner:APPLE INC
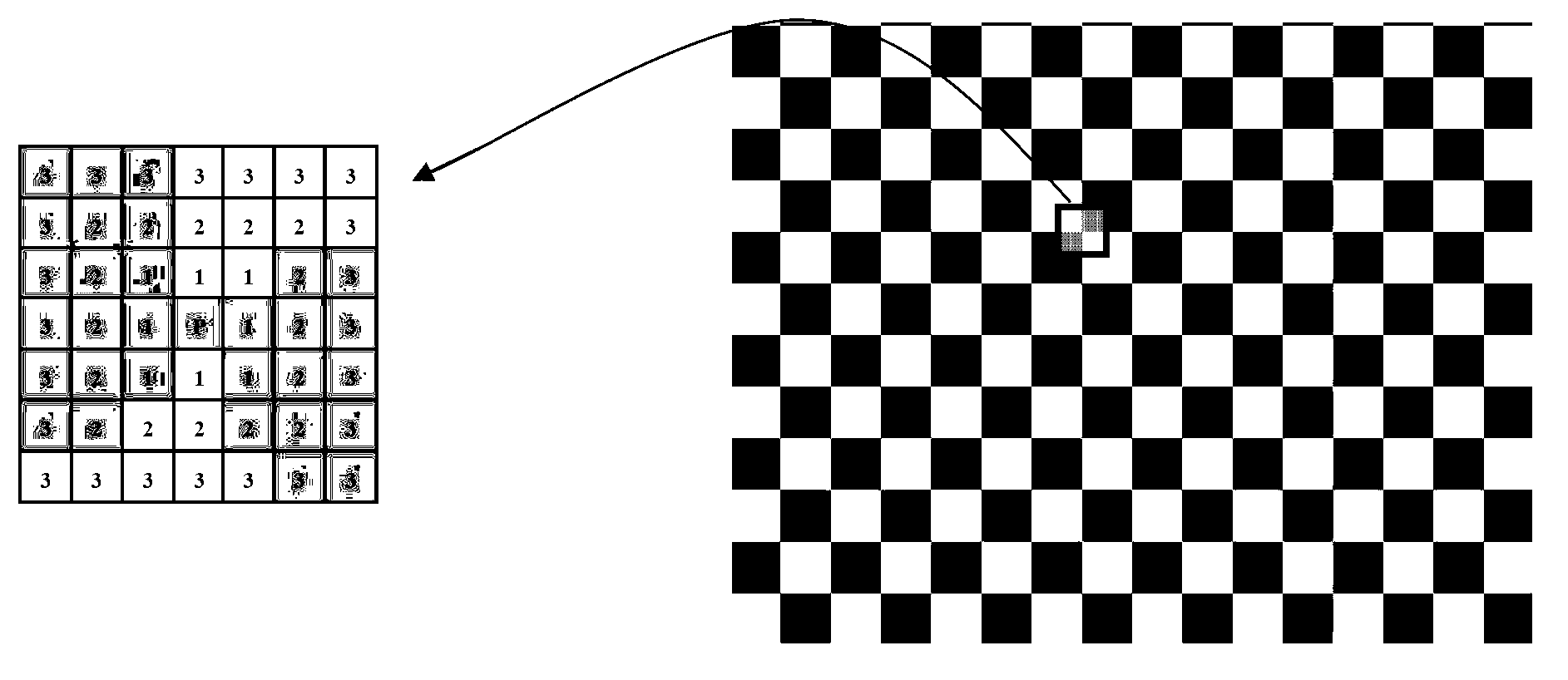
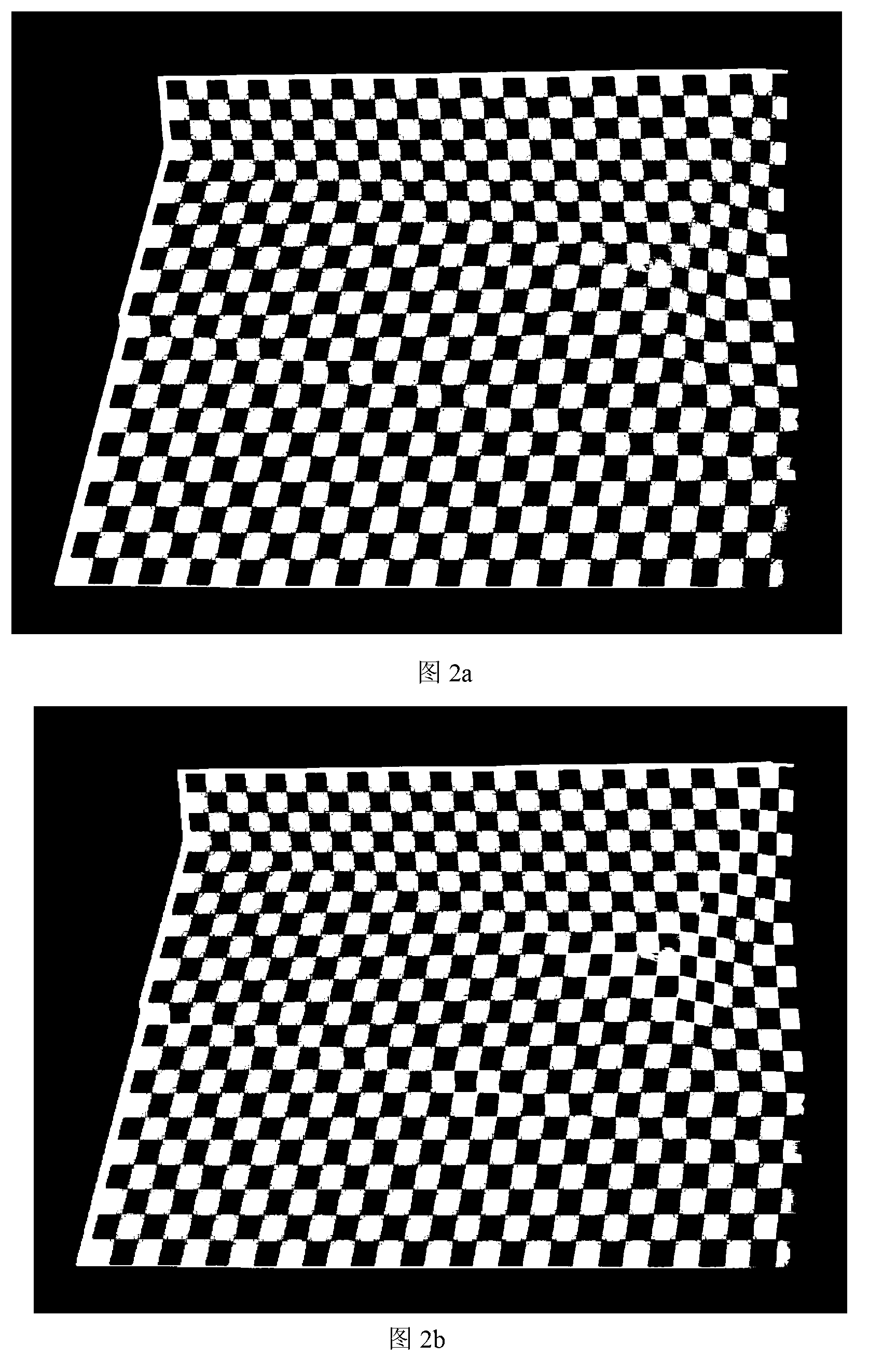
Method for automatic correction and tiled display of plug-and-play large screen projections
ActiveCN103019643ASmart and Simple PreprocessingEasy to detectTelevision system detailsProjectorsLarge screenFeature detection
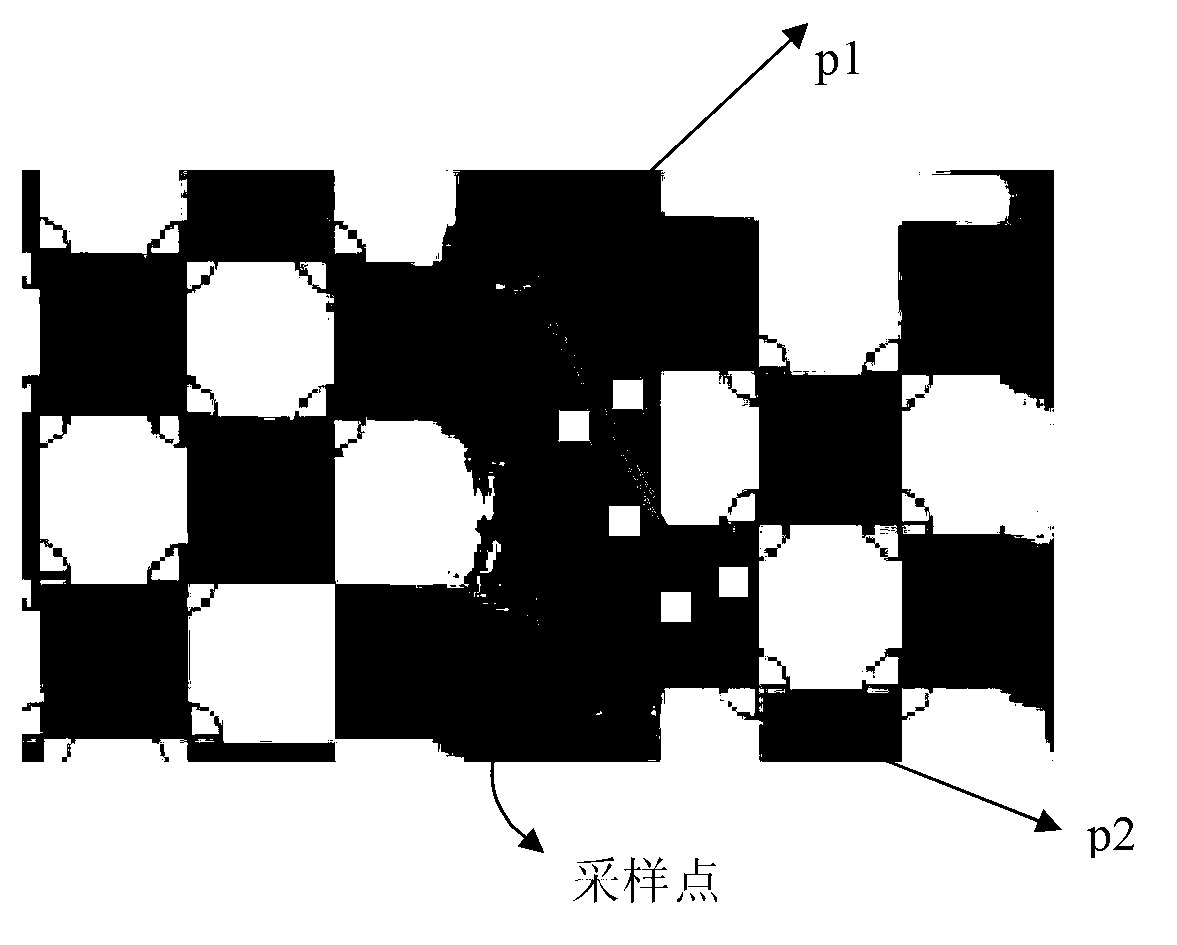
The invention discloses a method for automatic correction and tiled display of plug-and-play large screen projections. The method comprises the steps as follows: adaptively generating a checker pattern with a certain resolution ratio, projecting by projectors in sequence, capturing by cameras, carrying out feature detection and identification on complicated projection surfaces or checkers under the illumination condition with a multi-feature detection method based on color and geometry, and creating a Bezier curve function to represent a corresponding relation of points between projector images and camera images; and obtaining effective display areas for screen projection with a quick approach method, determining a corresponding relation of the projection contents of the projectors and the display areas, carrying out geometrical distortion on the images to be projected for geometrical correction, and calculating weight values of pixels in projection overlapping areas with a distance-based nonlinear weight value distribution method for fusion of edge brightness. According to the invention, a plurality of projection images of irregular surfaces can be aligned and seamlessly spliced, and the whole method is simple and easy to use, higher in autonomy and better in seamless splicing performance.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Devices, systems and methods for security using magnetic field based identification
ActiveUS8752200B2Data taking preventionDigital data processing detailsInternet privacyIdentification device
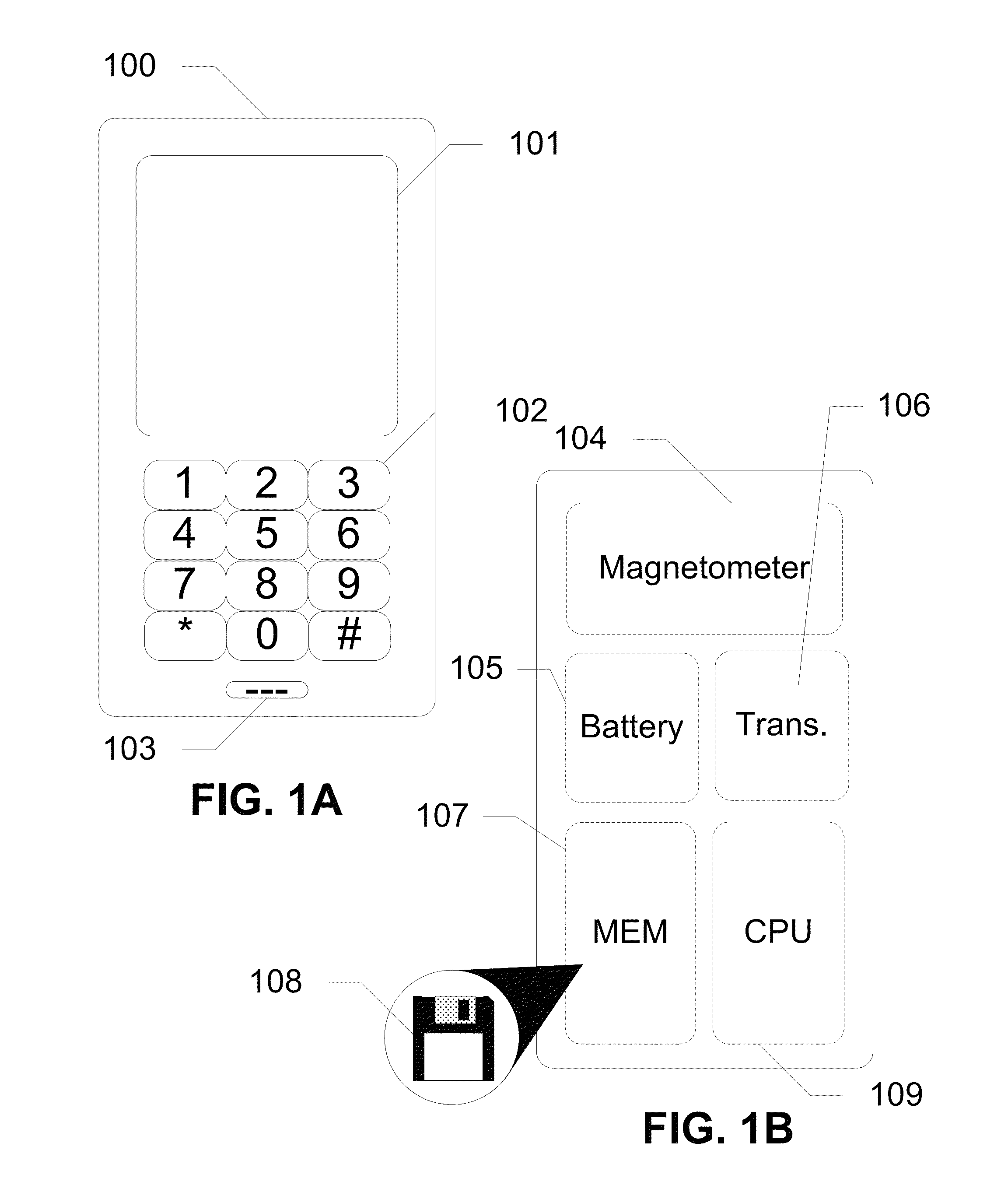
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for determining an electromagnetic signature for authenticating a device, a user, and / or a location. In exemplary embodiments, a magnetometer captures an electromagnetic signature which is then compared with one or more authorized electromagnetic signatures. If the electromagnetic signature matches an authorized electromagnetic signature, then access is granted. The magnetometer is integrated into a communication device having a processor and a logic. The magnetometer captures an electromagnetic signature of a surrounding environment and detects motion of the communication device through the captured electromagnetic signature. The logic on the communication device locks or unlocks features of the device based upon the captured electromagnetic signature. In further embodiments of the subject disclosure, the magnetometer is in communication with a server which authenticates a user or communication device to provide access to a remote location.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Method of matching image features with reference features
ActiveUS20150161476A1Increase weightWeight increaseImage enhancementImage analysisImaging FeatureSimilarity measure
A method of matching image features with reference features comprises the steps of providing a current image, providing a set of reference features, wherein each of the reference features comprises at least one first parameter which is at least partially indicative of a position and / or orientation of the reference feature with respect to a global coordinate system, wherein the global coordinate system is an earth coordinate system or an object coordinate system, or at least partially indicative of a position of the reference feature with respect to an altitude, detecting at least one feature in the current image in a feature detection process, associating with the detected feature at least one second parameter which is at least partially indicative of a position and / or orientation of the detected feature, or which is at least partially indicative of a position of the detected feature with respect to an altitude, and matching the detected feature with a reference feature by determining a similarity measure.
Owner:APPLE INC
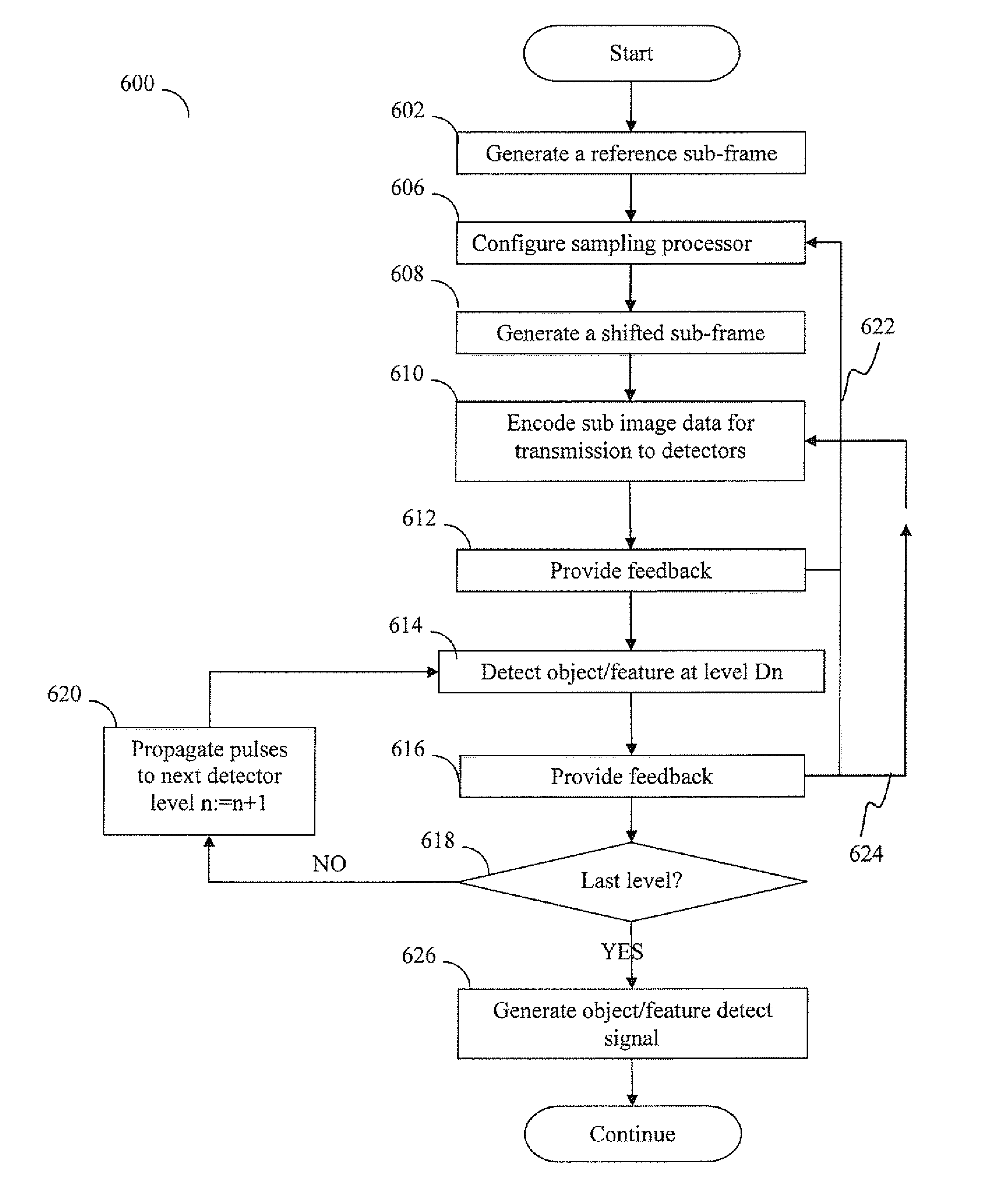
Sensory input processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140064609A1Easy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFrame sequenceAdaptive encoding
Sensory input processing apparatus and methods useful for adaptive encoding and decoding of features. In one embodiment, the apparatus receives an input frame having a representation of the object feature, generates a sequence of sub-frames that are displaced from one another (and correspond to different areas within the frame), and encodes the sub-frame sequence into groups of pulses. The patterns of pulses are directed via transmission channels to detection apparatus configured to generate an output pulse upon detecting a predetermined pattern within received groups of pulses that is associated with the feature. Upon detecting a particular pattern, the detection apparatus provides feedback to the displacement module in order to optimize sub-frame displacement for detecting the feature of interest. In another embodiment, the detections apparatus elevates its sensitivity (and / or channel characteristics) to that particular pulse pattern when processing subsequent pulse group inputs, thereby increasing the likelihood of feature detection.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
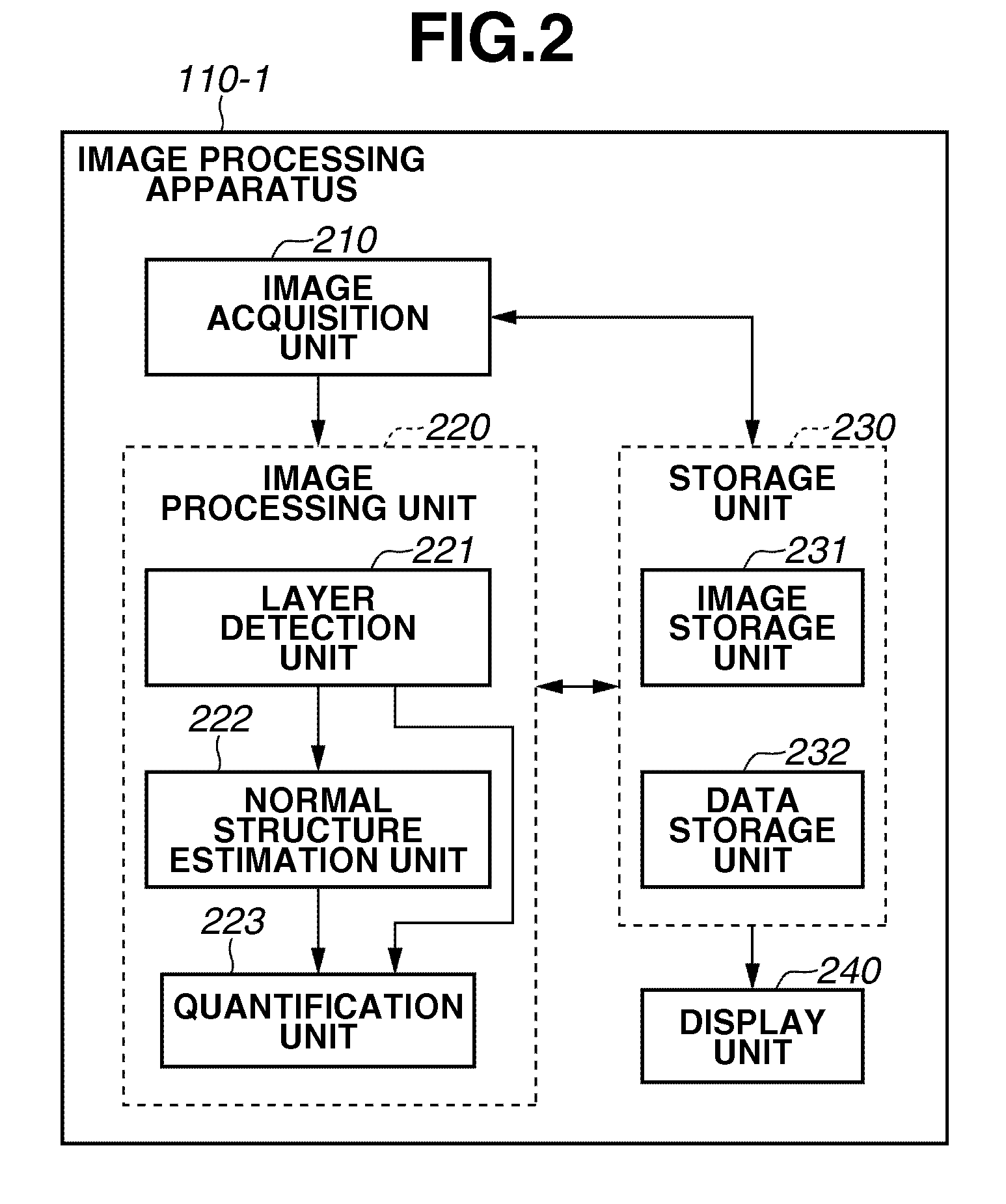
Image processing apparatus and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20100220914A1Accurate estimateImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingTomographic image
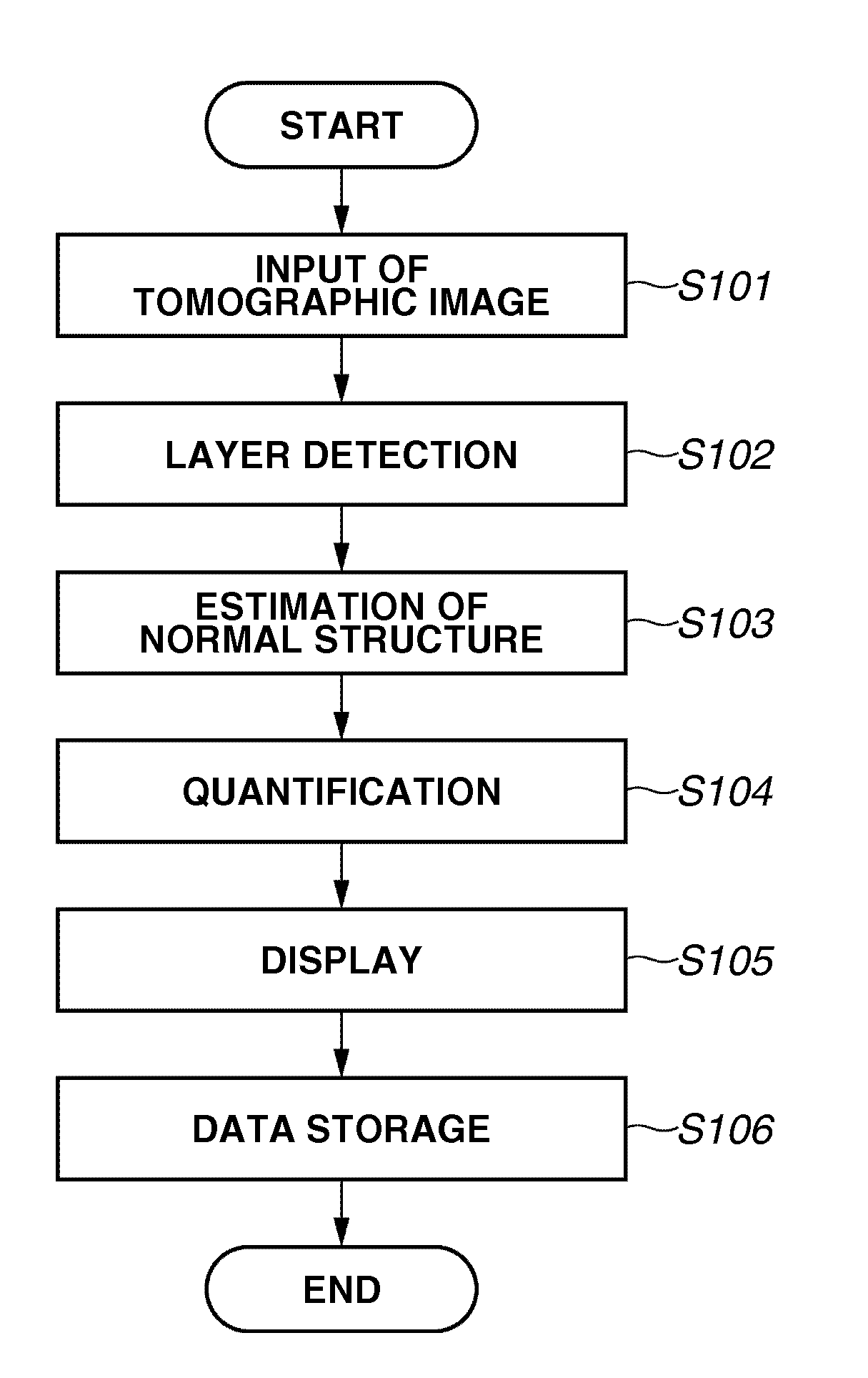
An image processing apparatus includes an image acquisition unit configured to acquire a tomographic image of an object, a layer detection unit configured to detect a layer that constitutes the object from the tomographic image acquired by the image acquisition unit, and a normal structure estimation unit configured to estimate a normal structure of the layer based on the layer detected by the layer detection unit and a feature that is modified by a lesion of the layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Video detection/verification system
InactiveUS20030215141A1Character and pattern recognitionFire alarm radiation actuationMicrometerEnergy indicators
Detecting video phenomena, such as fire in an aircraft cargo bay, includes receiving a plurality of video images from a plurality of sources, compensating the images to provide enhanced images, extracting features from the enhanced images, and combining the features from the plurality of sources to detect the video phenomena. The plurality of sources may include cameras having a sensitivity of between 400 nm and 1000 nm and / or may include cameras having a sensitivity of between 7 and 14 micrometers. Extracting features may include determining an energy indicator for each of a subset of the plurality of frames. Detecting video phenomena may also include comparing energy indicators for each of the subset of the plurality of frames to a reference frame. The reference frame corresponds to a video frame taken when no fire is present, video frame immediately preceding each of the subset of the plurality of frames, or a video frame immediately preceding a frame that is immediately preceding each of the subset of the plurality of frames.
Owner:SIMMONDS PRECISION PRODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com