Algorithms for detecting atrial arrhythmias from discriminatory signatures of ventricular cycle lengths
a technology discriminatory signature, which is applied in the field of algorithms for detecting atrial arrhythmias from discriminatory signatures of ventricular cycle length, can solve the problems of ventricular heart rate, insufficient cardiac output, and ventricular rhythm to beat too slowly, so as to improve the detection capability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
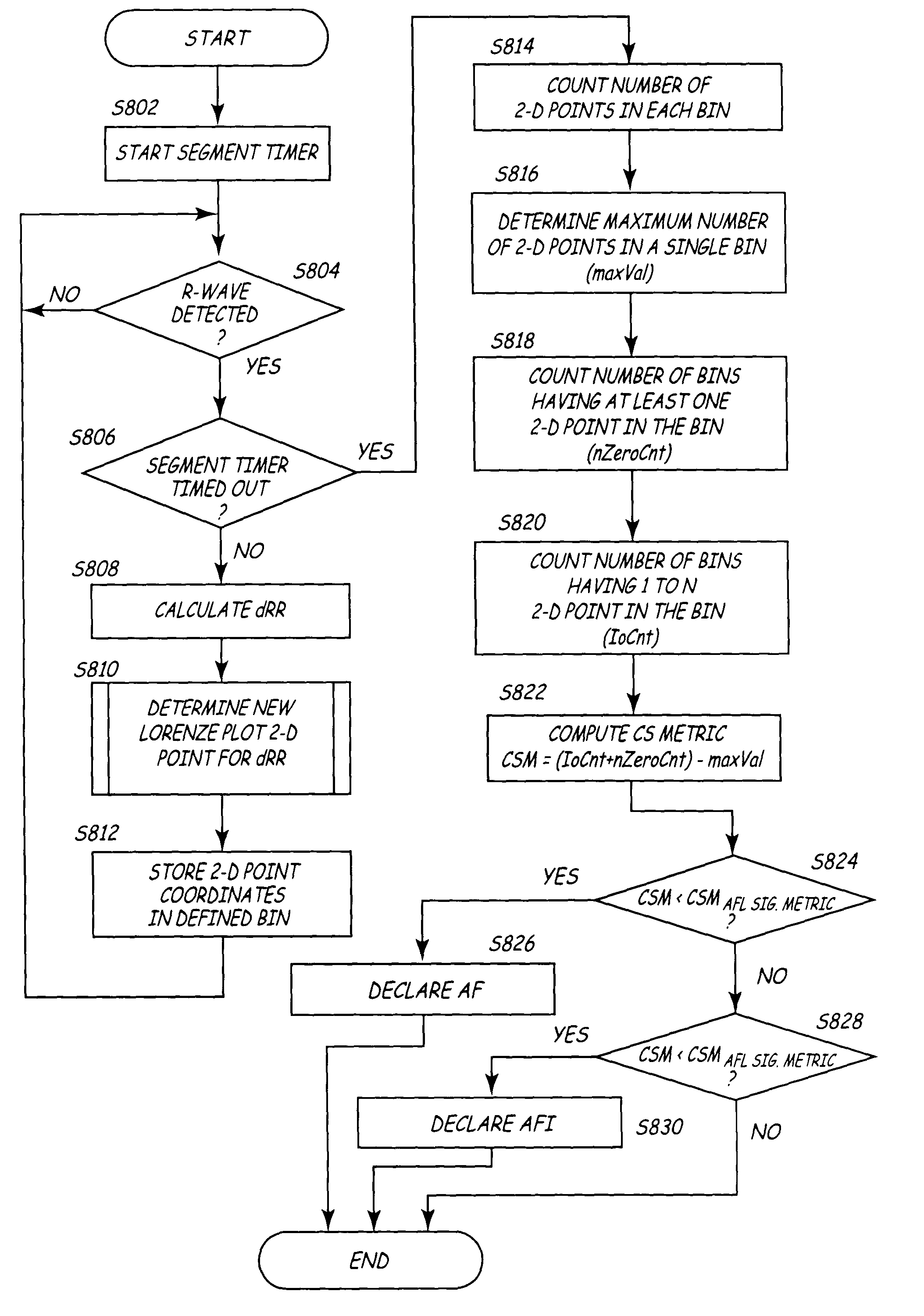
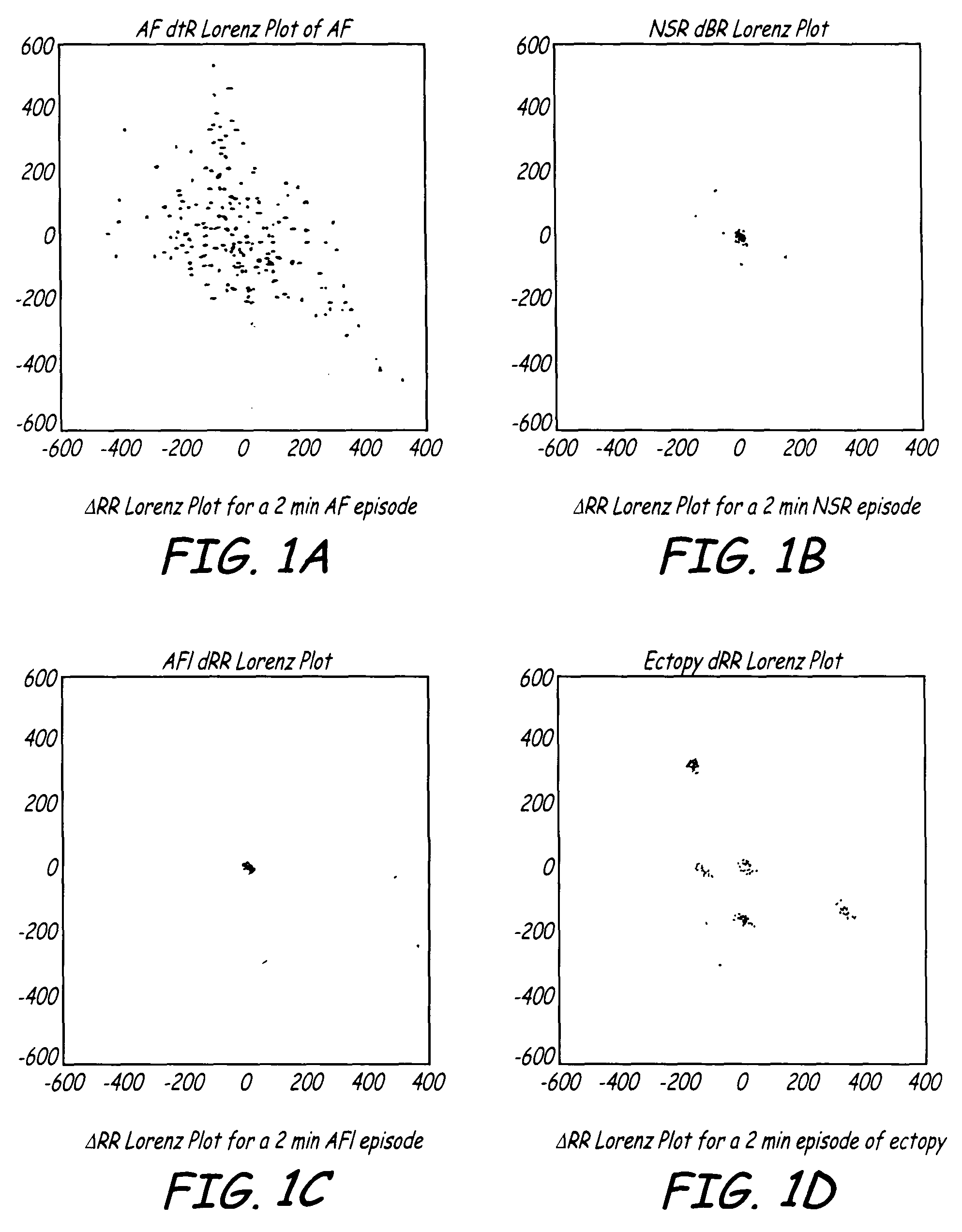
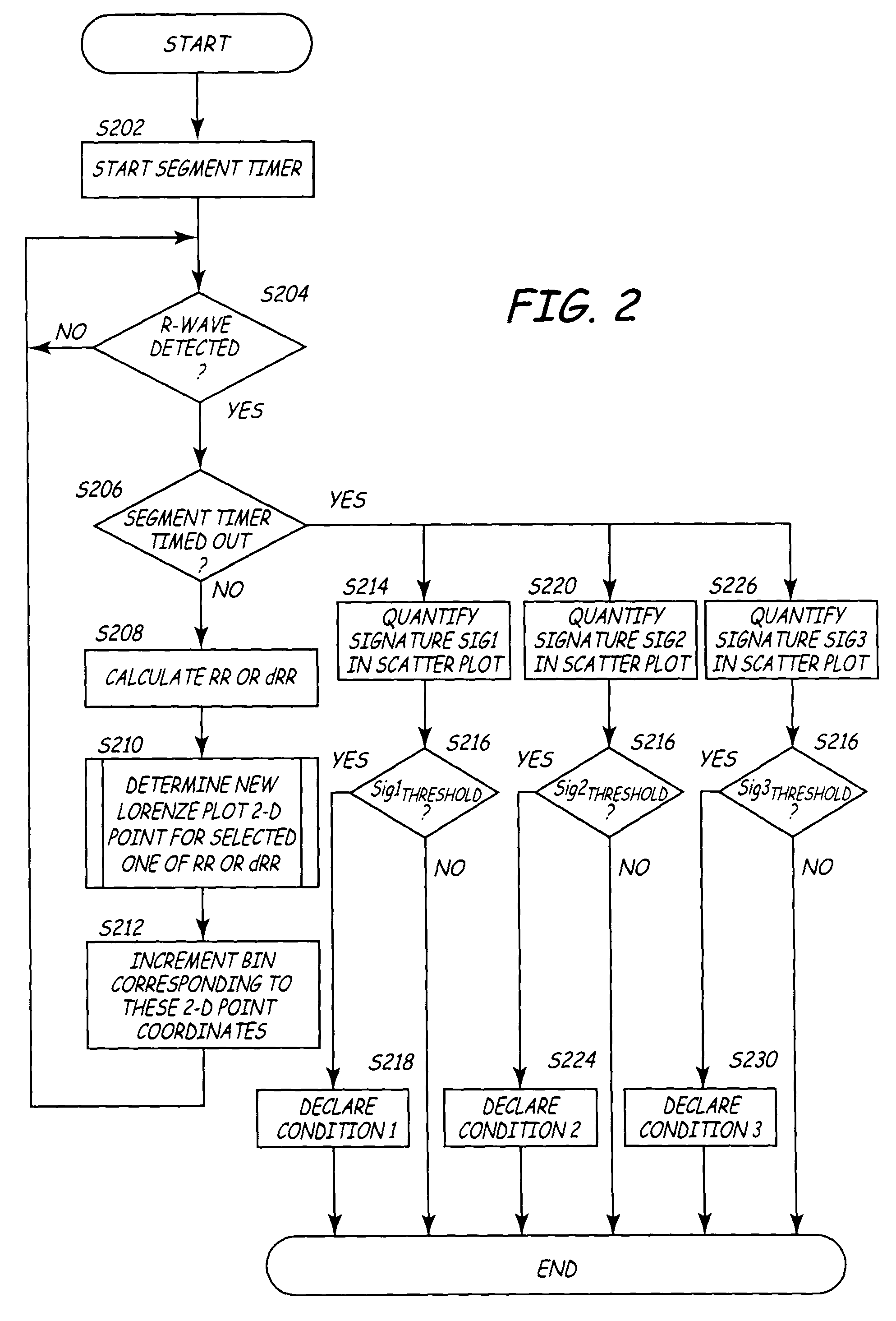
[0061]The algorithms of the present invention find particular utility embodied either in software or in firmware in cardiac EGM monitors that have EGM sense electrodes located within the patient's body either attached to the heart or located remote from the heart or a combination of both locations. The algorithms of the present invention can also be incorporated into software or in firmware of therapy delivery IMDs that would typically comprise a single chamber pacing system or ICD that senses the R-waves in the ventricles and delivers a pacing therapy or a cardioversion / defibrillation shock therapy to the ventricles. In that case, the algorithms of the present invention discriminate between high rate NSR based upon measured RR intervals and episodes of AF or AFL that are mistakenly detected as high rate NSR. However, it will be understood that the present invention is not so limited and that the algorithms of the present invention can be implemented into the firmware or software op...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com