Patents
Literature
285 results about "Maximal energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
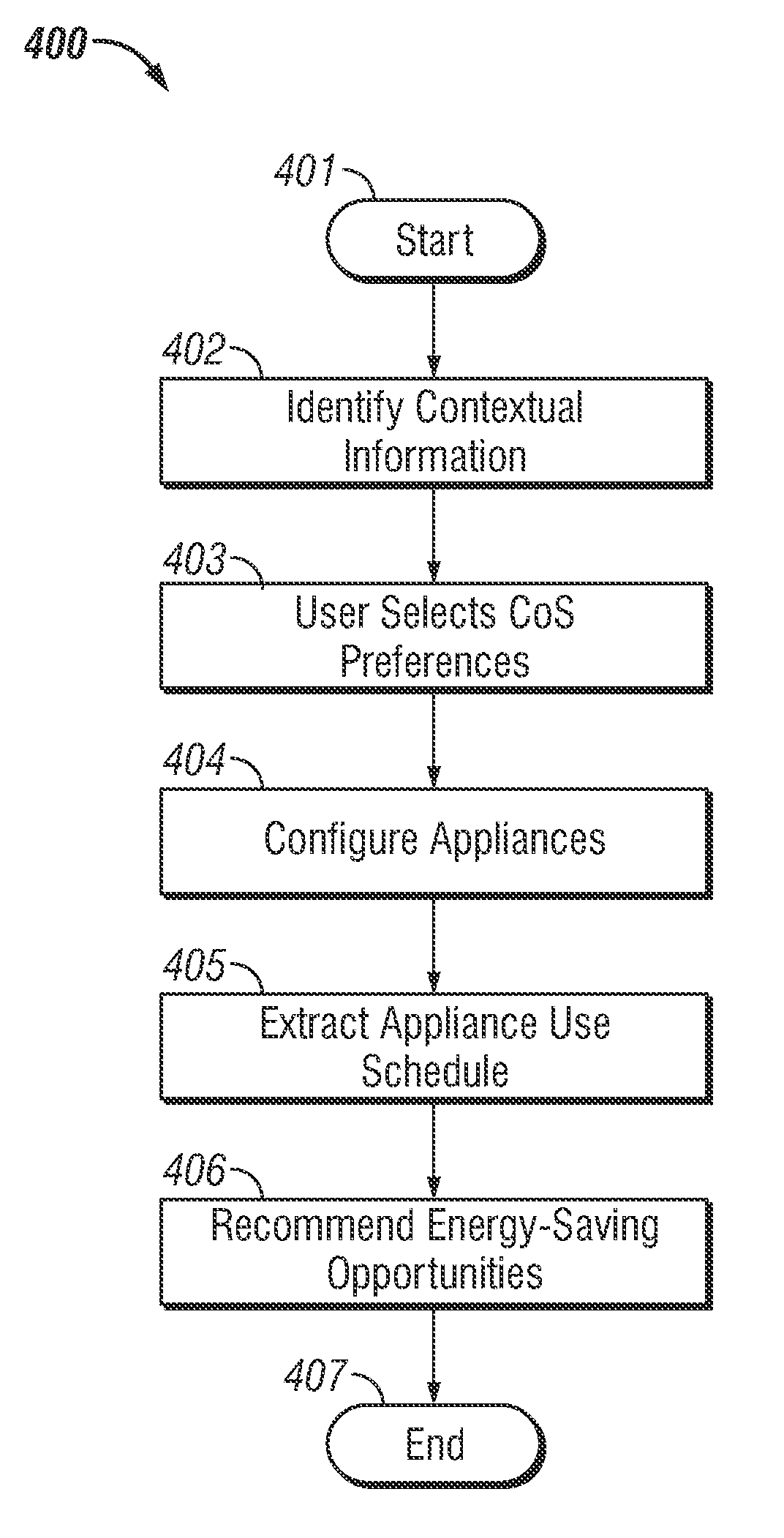
Context-aware smart home energy manager
InactiveUS20110046805A1Programme controlMechanical power/torque controlProgram instructionEngineering
A context-aware smart home energy management (CASHEM) system and method is disclosed. CASHEM dynamically schedules household energy use to reduce energy consumption by identifying contextual information within said household, selecting a comfort of service preference, wherein said comfort of service preference is based on different said contextual information, and extracting an appliance use schedule for maximum energy savings based on said contextual information in light of said comfort of service preferences, by executing a program instruction in a data processing apparatus. CASHEM correlates said contextual information with energy consumption levels to dynamically schedule said appliance based on an energy-saving condition and a user's comfort. Comfort of service preferences are gathered by CASHEM by monitoring occupant activity levels and use of said appliance. CASHEM can also recommend potential energy savings for a user to modify comfort of service preferences.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
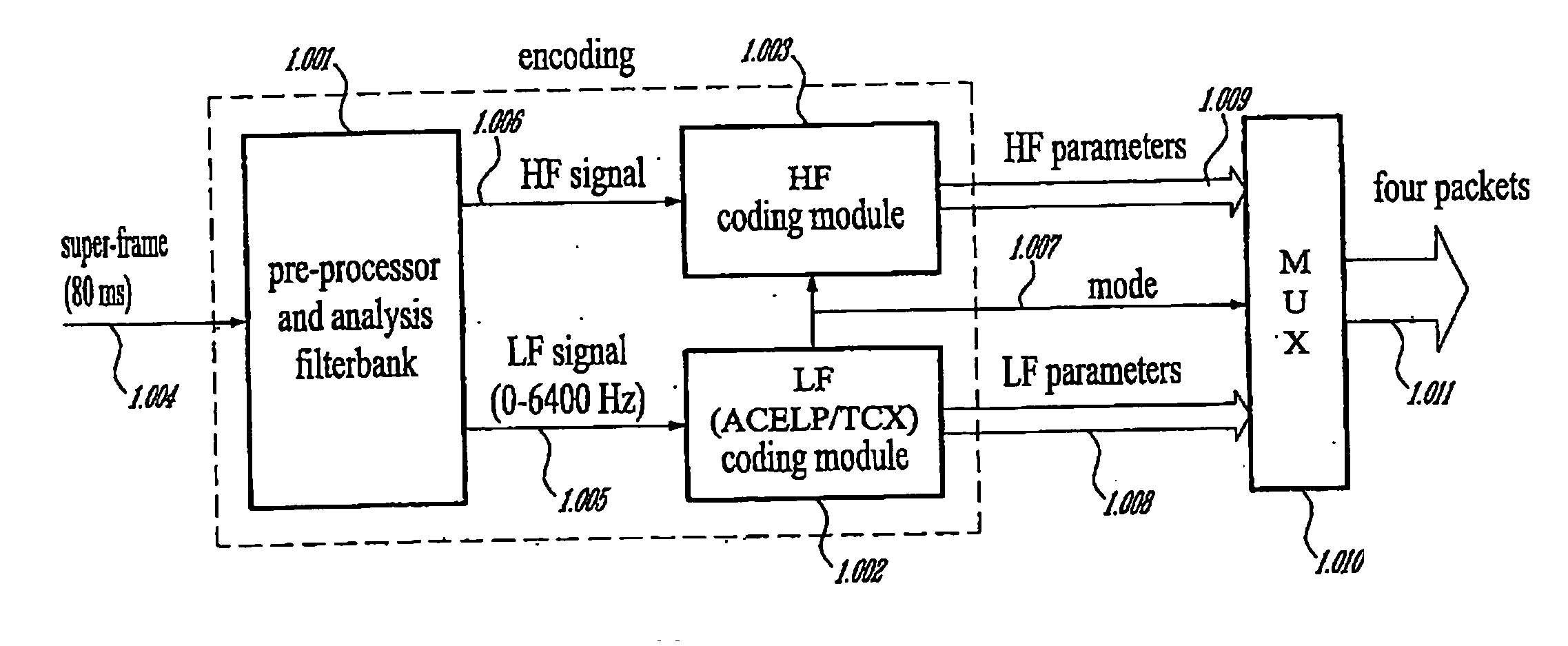
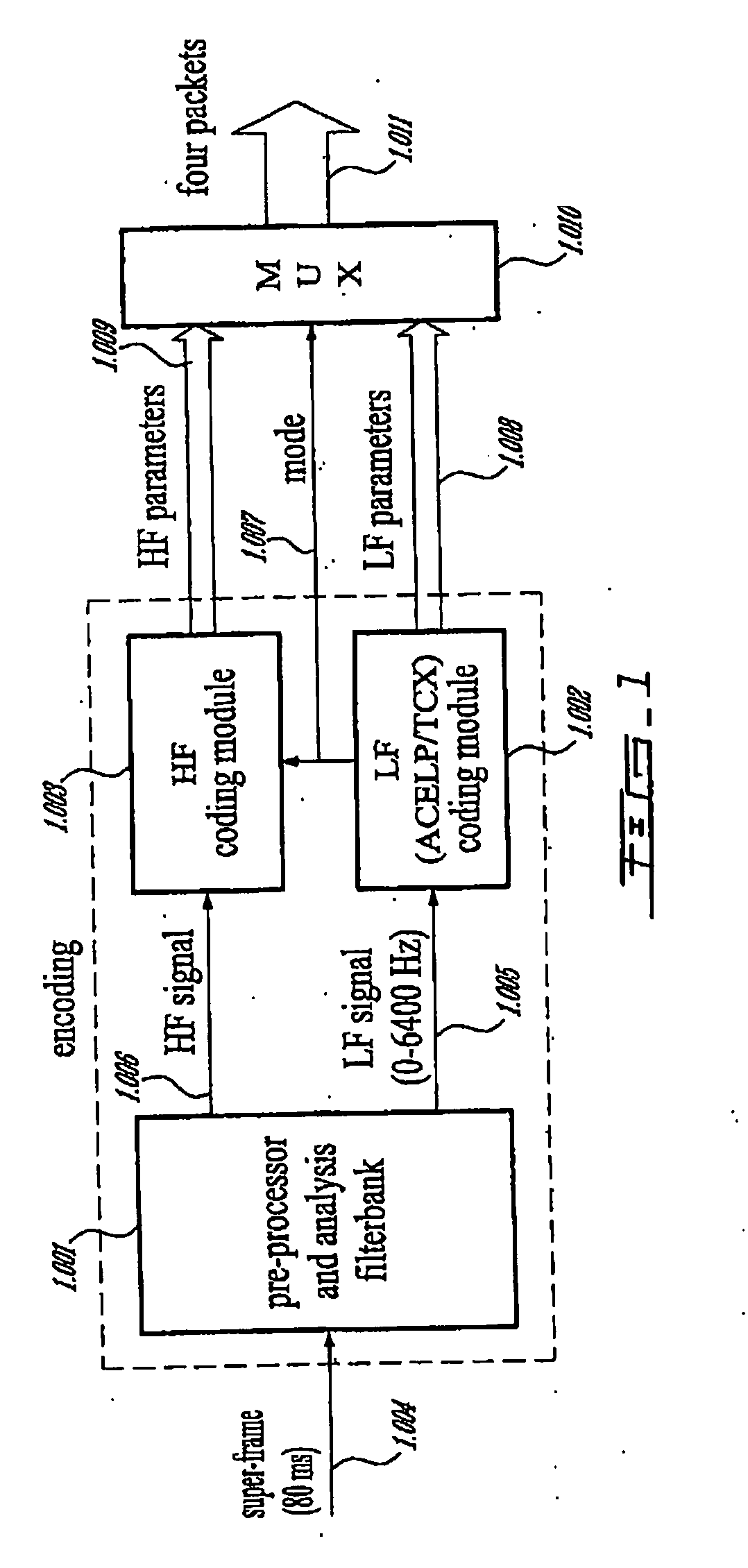
Methods and devices for low-frequency emphasis during audio compression based on ACELP/TCX
A first aspect of the present invention relates to a method for low-frequency emphasizing the spectrum of a sound signal transformed in a frequency domain and comprising transform coefficients grouped in a number of blocks, in which a maximum energy for one block is calculated and a position index of the block with maximum energy is determined, a factor is calculated for each block having a position index smaller than the position index of the block with maximum energy the calculated maximum energy and the energy of the block, and, for each block, a gain determining from the factor is applied to the transform coefficients of the block. Another aspect of the invention is concerned with an HF coding method for coding, through a bandwidth extension scheme, an HF signal obtained from separation of a full-bandwidth sound signal into the HF signal and a LF signal, in which an estimation of the an HF gain is calculated from LPC coefficients, the energy of the HF signal is calculated, the LF signal is processed to produce a synthesized version of the HF signal, the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated, a ratio between the energy of the HF signal and the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated and expressing as an HF gain, and a difference between the estimation of the HF gain and the HF gain is calculated to obtain a gain correction. A third aspect of the invention is concerned with a method for producing from a decoded target signal an overlap-add target signal in a current frame coded according to a first coding mode. According to this method, the decoded target signal of the current frame is windowed and a left portion of the window is skipped. A zero-input response of a weighting filter of the previous frame coded according to a second coding mode is calculated and windowed so that the zero-input response has an amplitude monotonically decreasing to zero after a predetermined time period. Finally, the calculated zero-input response is added to the decoded target signal to reconstruct the overlap-add target signal.
Owner:VOICEAGE CORP
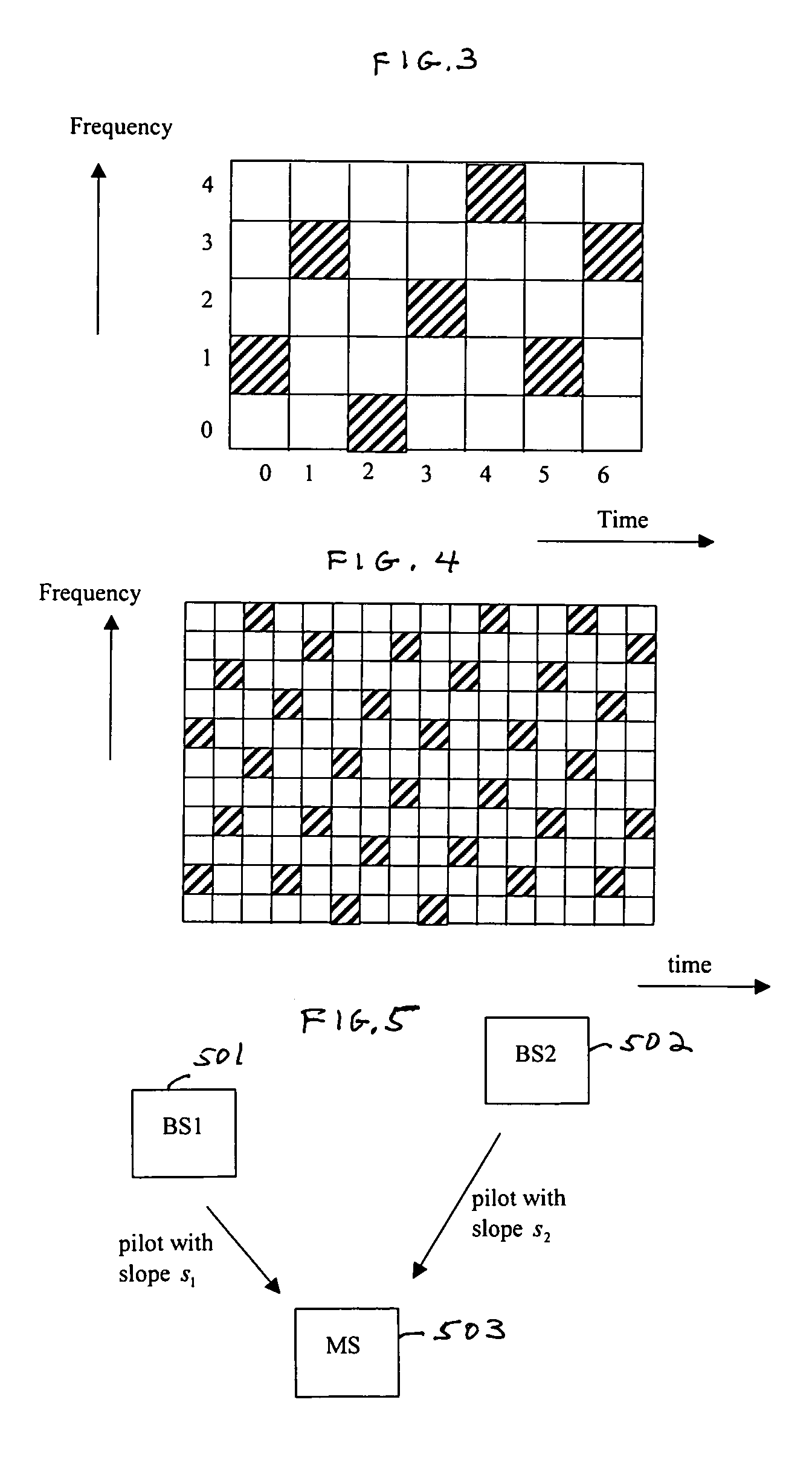
Base station identification in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing based spread spectrum multiple access systems
InactiveUS6961364B1Radio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency shiftSpread spectrum
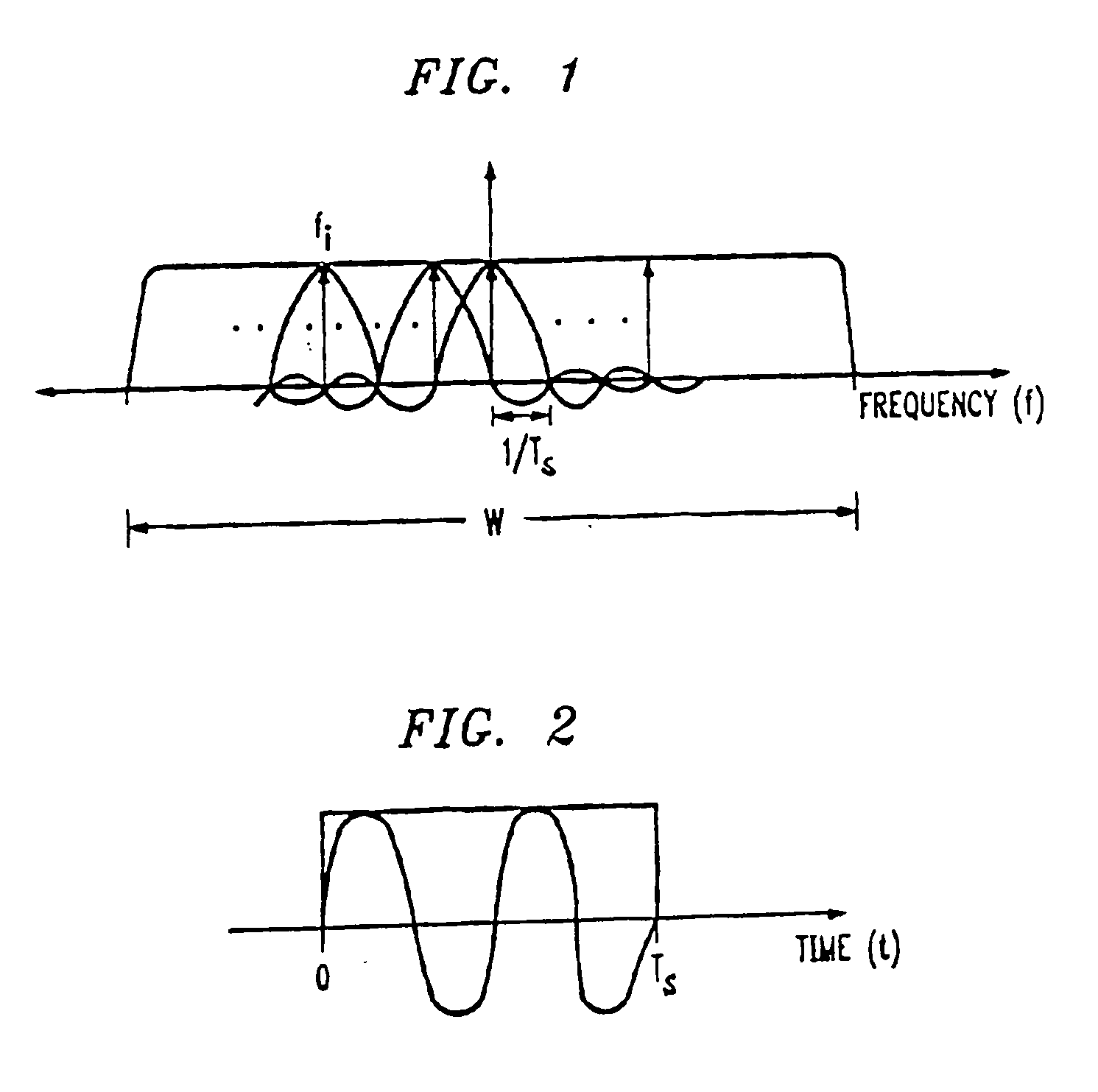
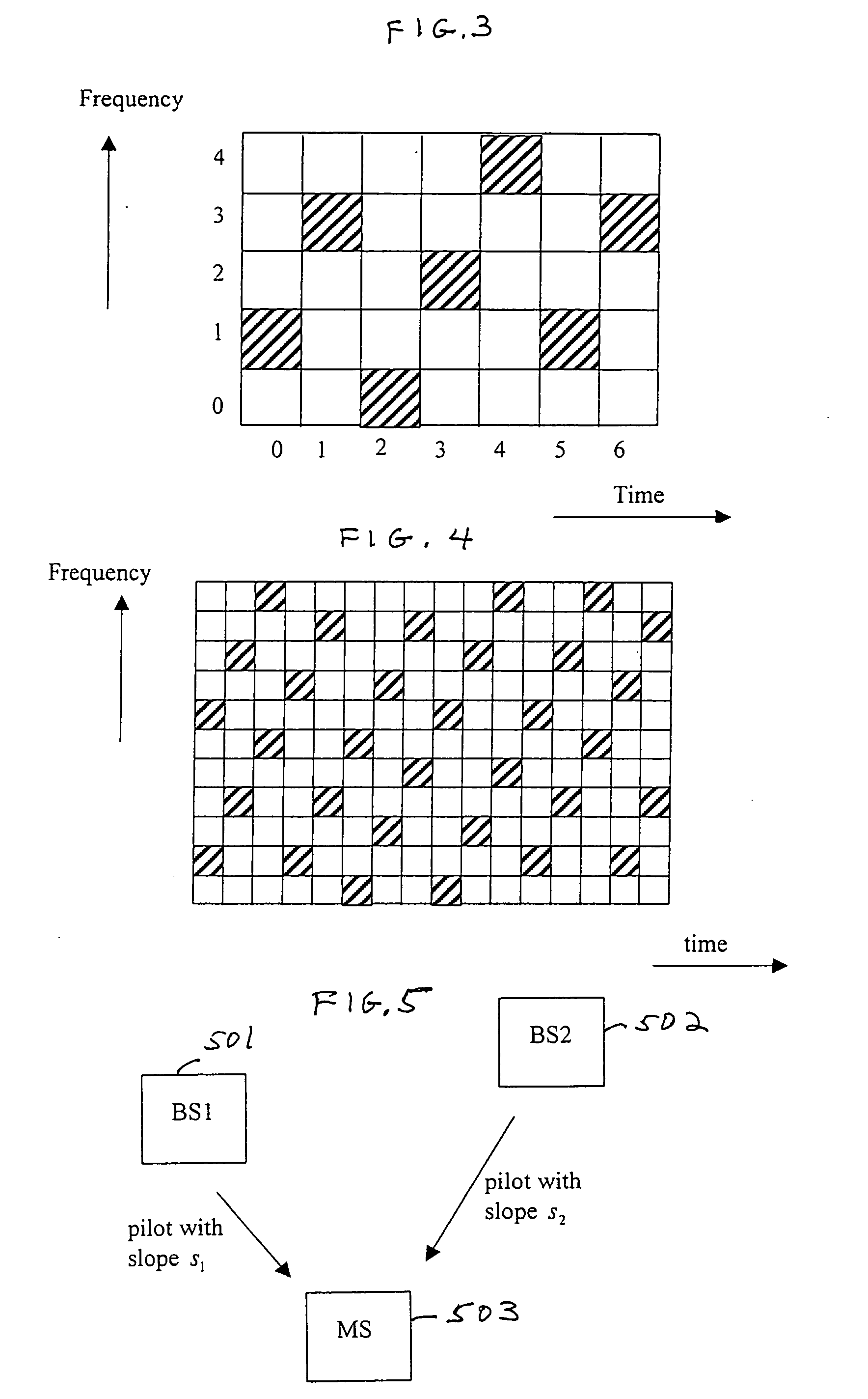
A base station having the strongest downlink signal is identified by utilizing a unique slope of a pilot tone hopping sequence being transmitted by a base station. Specifically, base station identification is realized by determining the slope of the strongest received pilot signal, i.e., the received pilot signal having the maximum energy. In an embodiment of the invention, the pilot tone hopping sequence is based on a Latin Squares sequence. With a Latin Squares based pilot tone hopping sequence, all a mobile user unit needs is to locate the frequency of the pilot tones at one time because the pilot tone locations at subsequent times can be determined from the slope of the Latin Squares pilot tone hopping sequence. The slope and initial frequency shift of the pilot tone hopping sequence with the strongest received power is determined by employing a unique maximum energy detector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
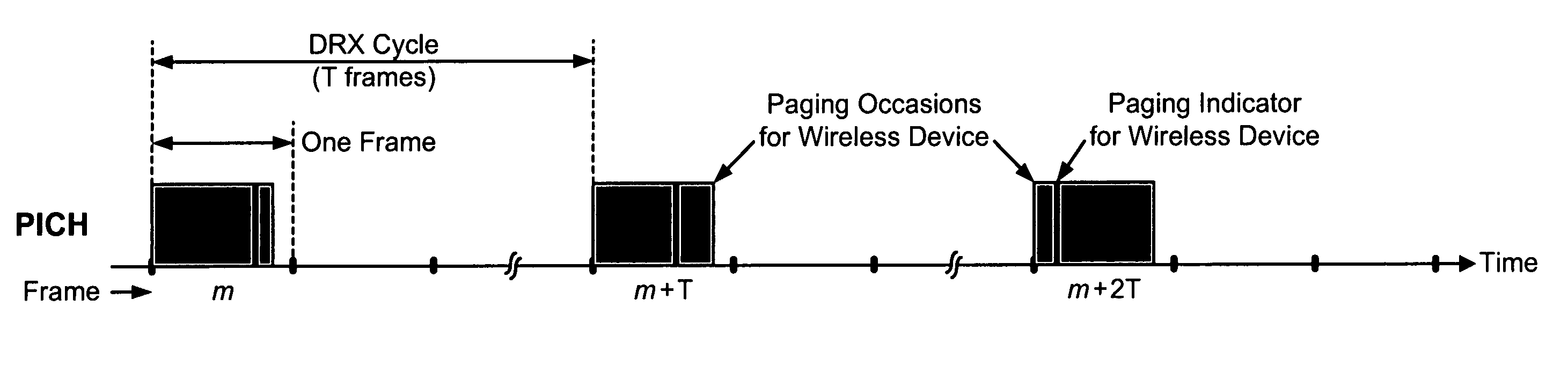
Quick detection of signaling in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20070060095A1Shorten warm-up timeExtend battery standby timePower managementCarrier regulationCommunications systemImage resolution
Quick frequency tracking (QFT), quick time tracking (QTT), and non-causal pilot filtering (NCP) are used to detect sporadically transmitted signaling, e.g., paging indicators. For QFT, multiple hypothesized frequency errors are applied to an input signal to obtain multiple rotated signals. The energies of the rotated signals are computed. The hypothesized frequency error with the largest energy is provided as a frequency error estimate. For QTT, coherent accumulation is performed on the input signal for a first set of time offsets, e.g., early, on-time, and late. Interpolation, energy computation, and non-coherent accumulation are then performed to obtain a timing error estimate with higher time resolution. For NCP, pilot symbols are filtered with a non-causal filter to obtain pilot estimates for one antenna for non-STTD and for two antennas for STTD. The frequency and timing error estimates and the pilot estimates are used to detect the signaling.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
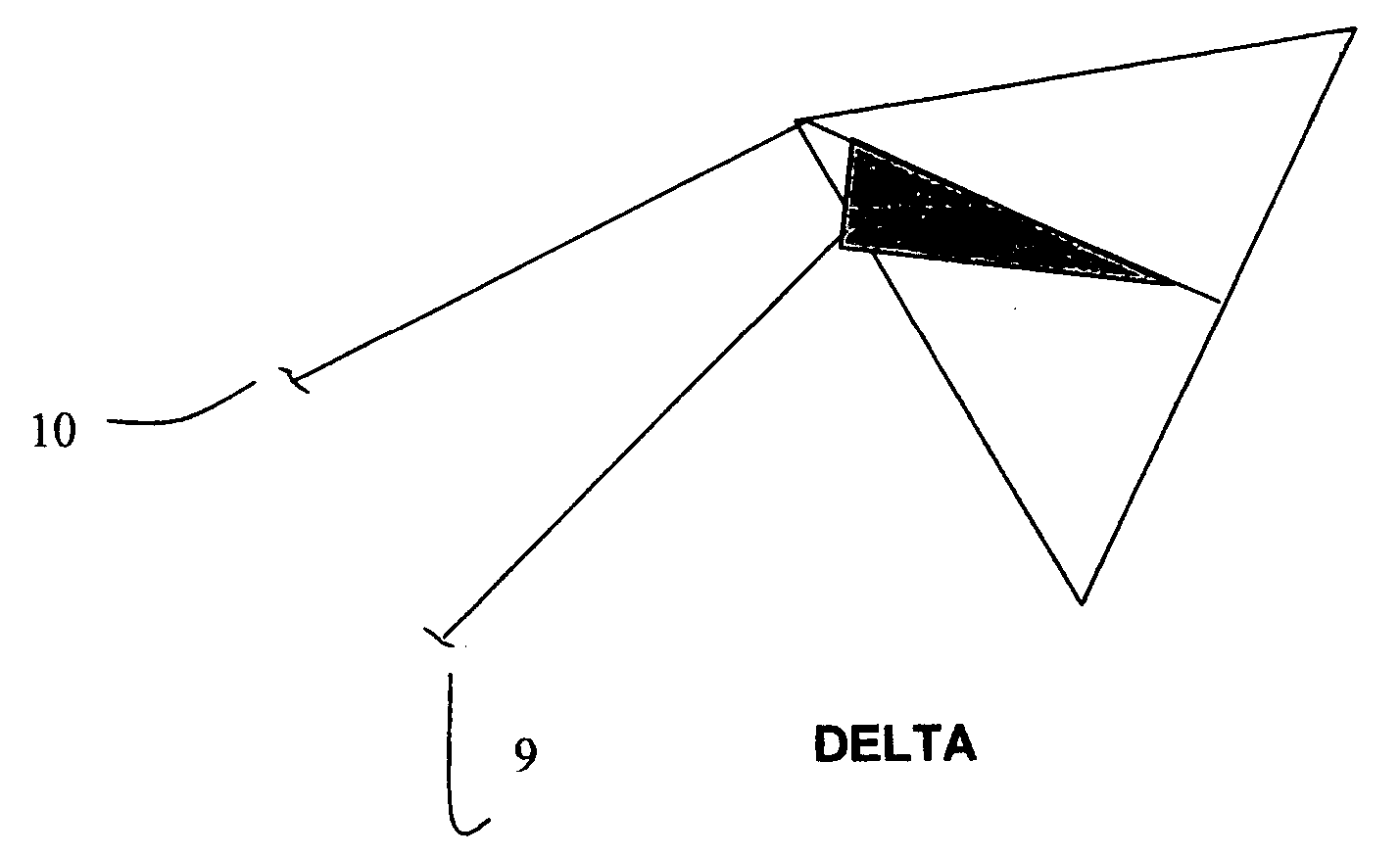
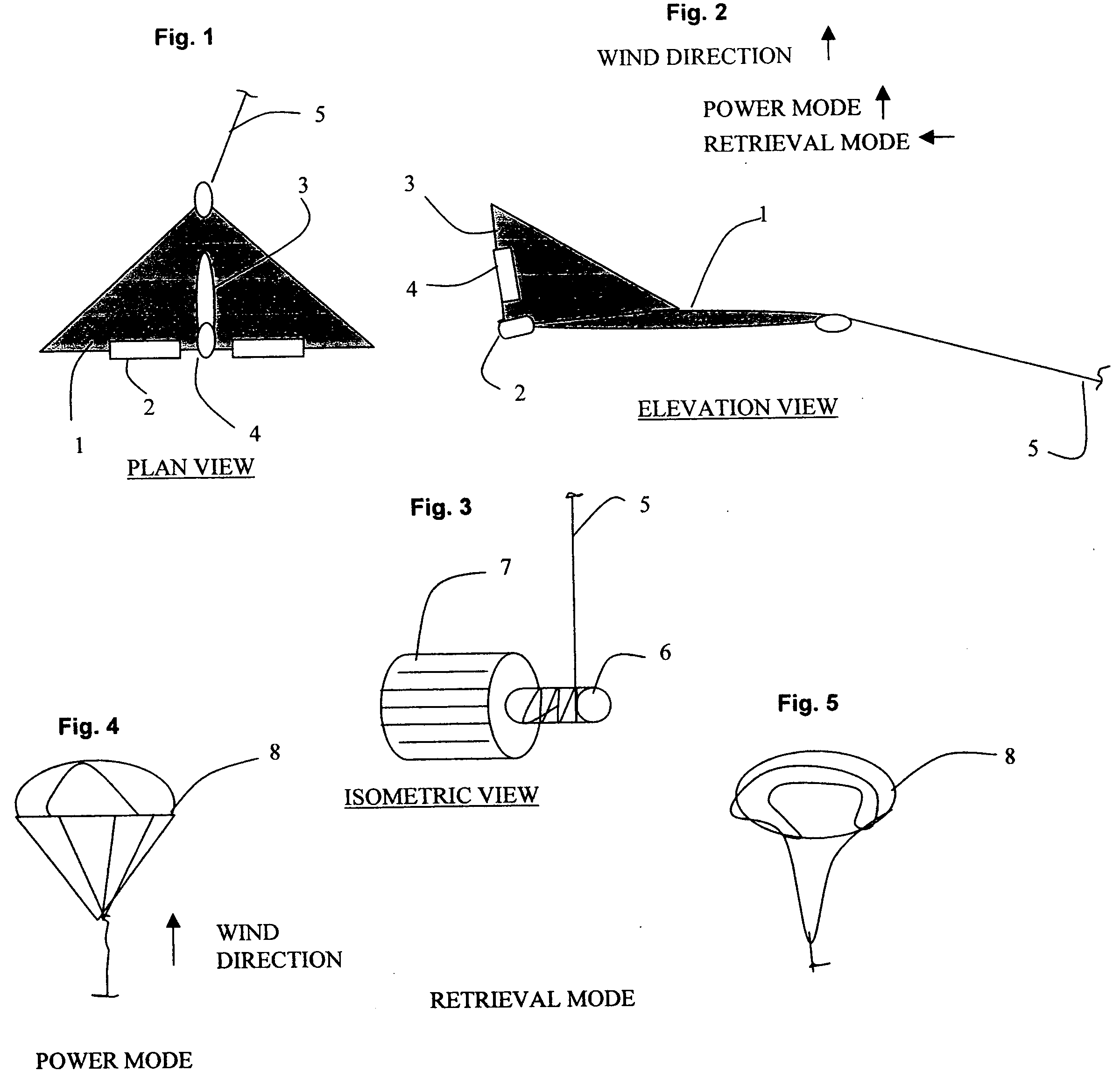
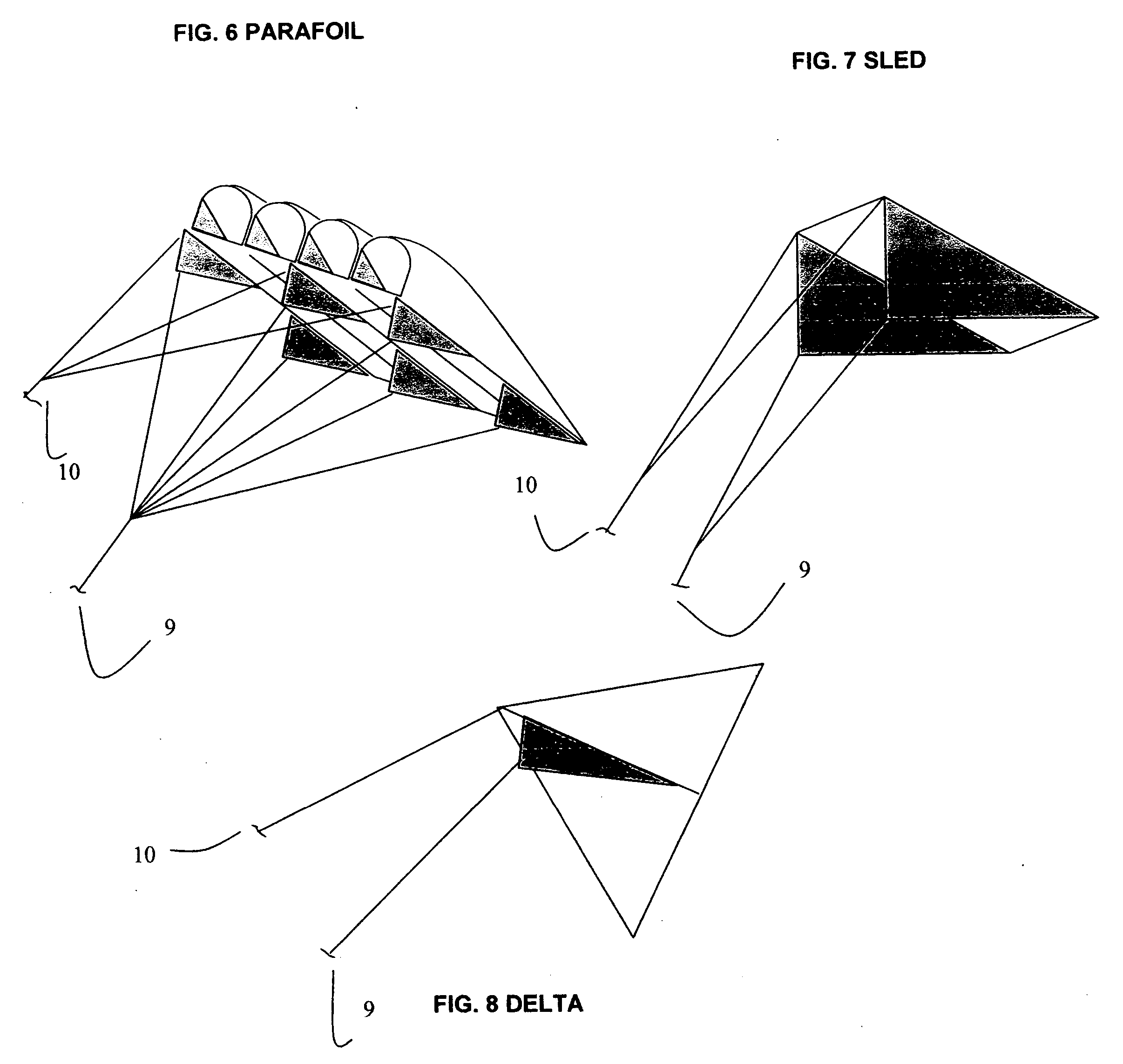
Wind energy production using kites and ground mounted power generators
Systems and methods are described for creating low cost energy using kites connected to ground mounted equipment. In power mode the kites generate maximum energy by positioning the kite at a high angle of attack relative to wind direction. The kite is allowed to travel a distance limited only by the length of line attached. The opposite end of the line is attached to a reel capable of turning a shaft to create mechanical or electrical energy. Upon reaching a controlled length, the kite is repositioned to a minimum angle of attack relative to the wind to minimize energy required to retrieve the kite. The shaft rotation is then reversed thereby winding the line on the reel. Energy is expended in retrieval mode. The difference in energy during power and retrieval mode is the net energy gain available for useful work.
Owner:KINGSLEY GORDON BRUCE
Laminated-type varistor
InactiveUS6147587ACurrent responsive resistorsResistor detailsElectrical resistance and conductancePeak current
A laminated-type varistor includes a laminated structure and a pair of external electrodes disposed on a surface of the laminated structure. The laminated structure includes effective sintered body layers and internal electrodes. The internal electrodes are connected to the external electrodes and are disposed apart from each other in the direction perpendicular to lamination surfaces. Each of the internal electrodes has a multilayer electrode structure in which a plurality of electrode layers are arranged in layers while an ineffective sintered body layer is disposed therebetween. The laminated-type varistor has increased maximum peak current and maximum energy and reduction in clamping voltage.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Wave power generator
A machine and a process to produce compressed air by sea waves, using the weight of the floating platform with its fixture using its up and down movement to compress air in both directions to absorb the maximum energy of that wave in a direct drive bidirectional pump with a single piston wherein the kinetic energy and wave bouncy force is used to compress ambient air as stored energy. This unique arrangement doubles air volume for compression in both directions in any single wave curve, doubles the energy production in both upper and lower chambers of the pump and multiplies the “psi” based on the float thrust area against the size of the piston in the pump. The preferred embodiment can be used as a stand alone unit as well as in array formation for the desired output 24 / 7.
Owner:KHAN GHAZI +1
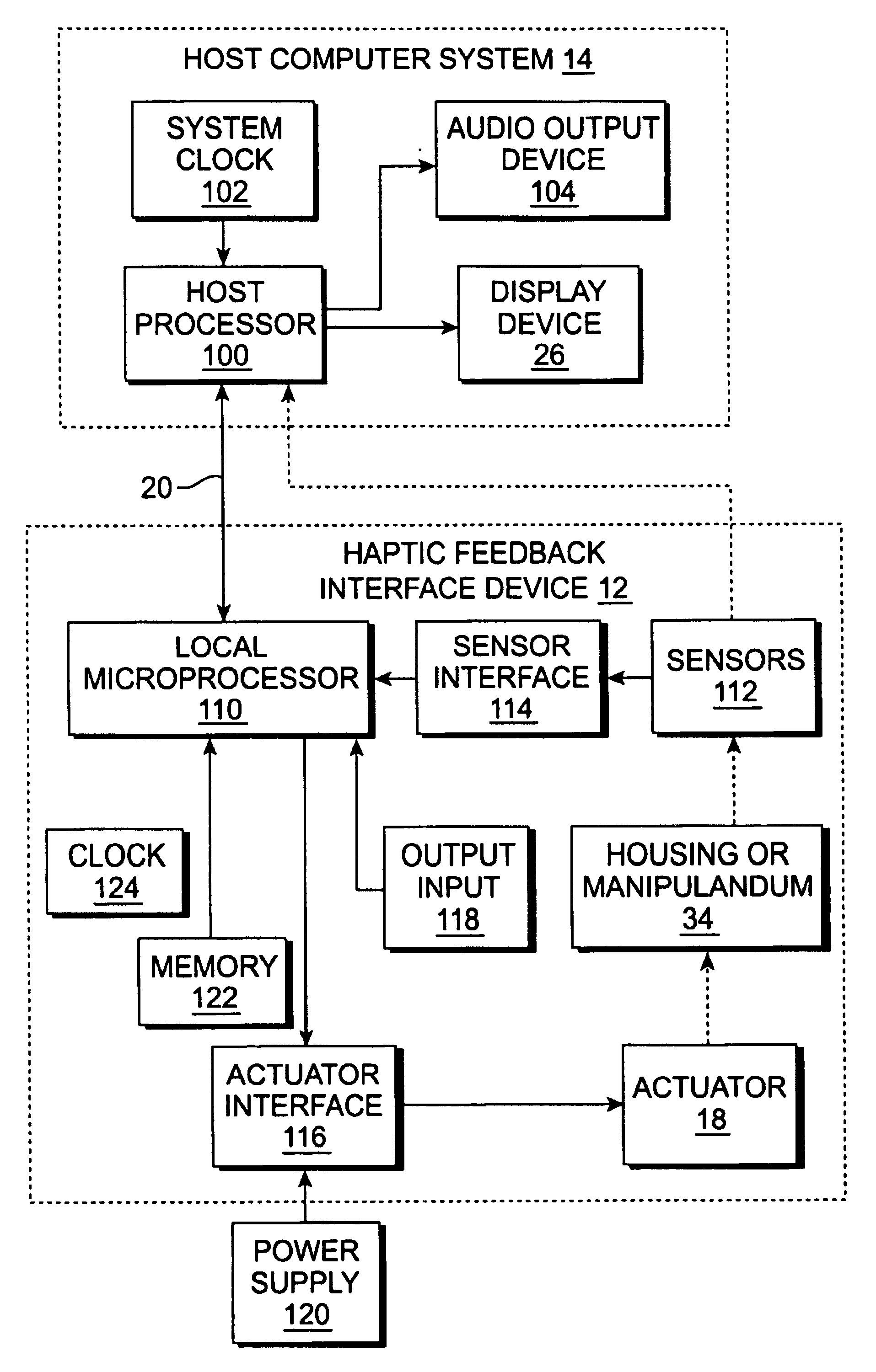
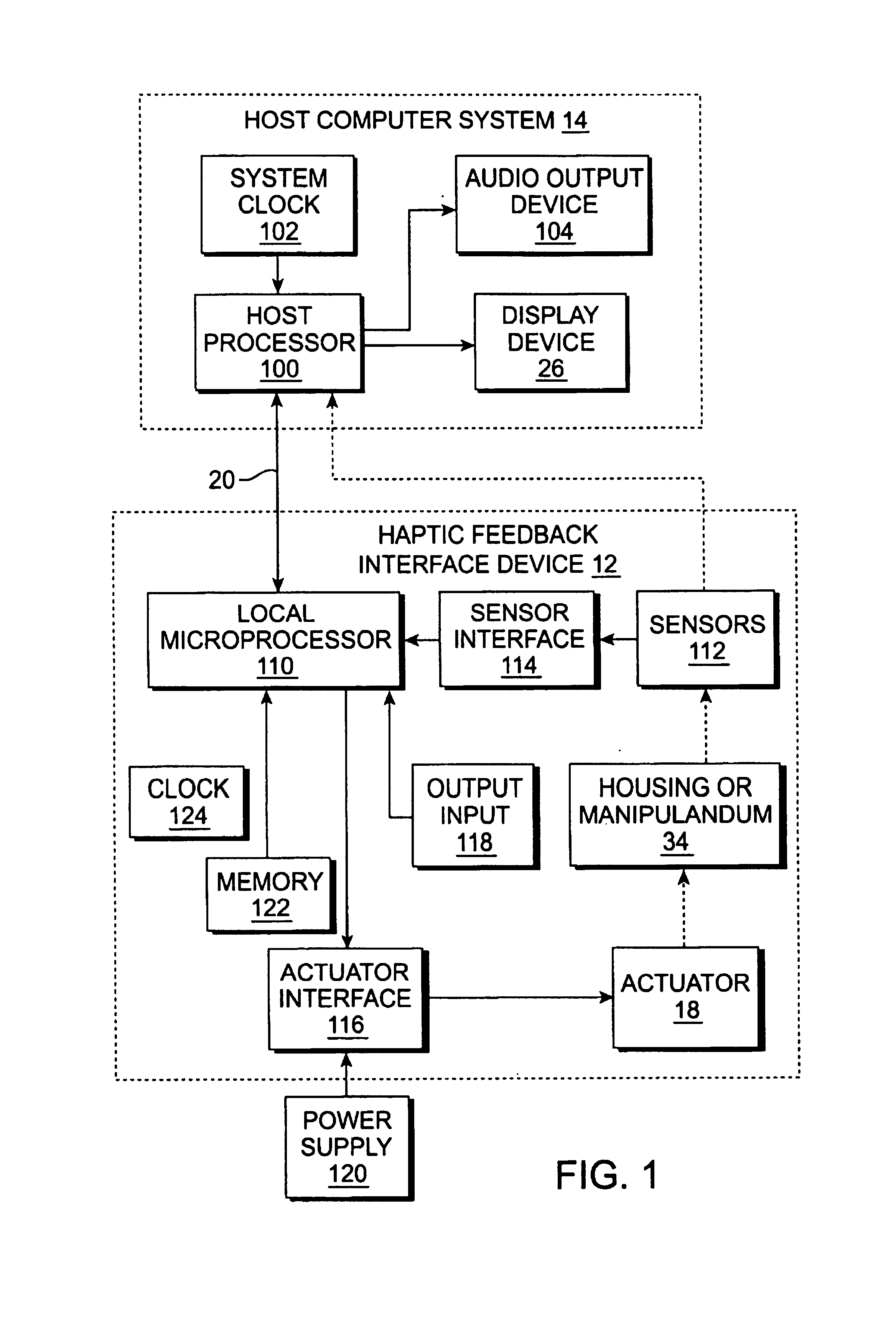
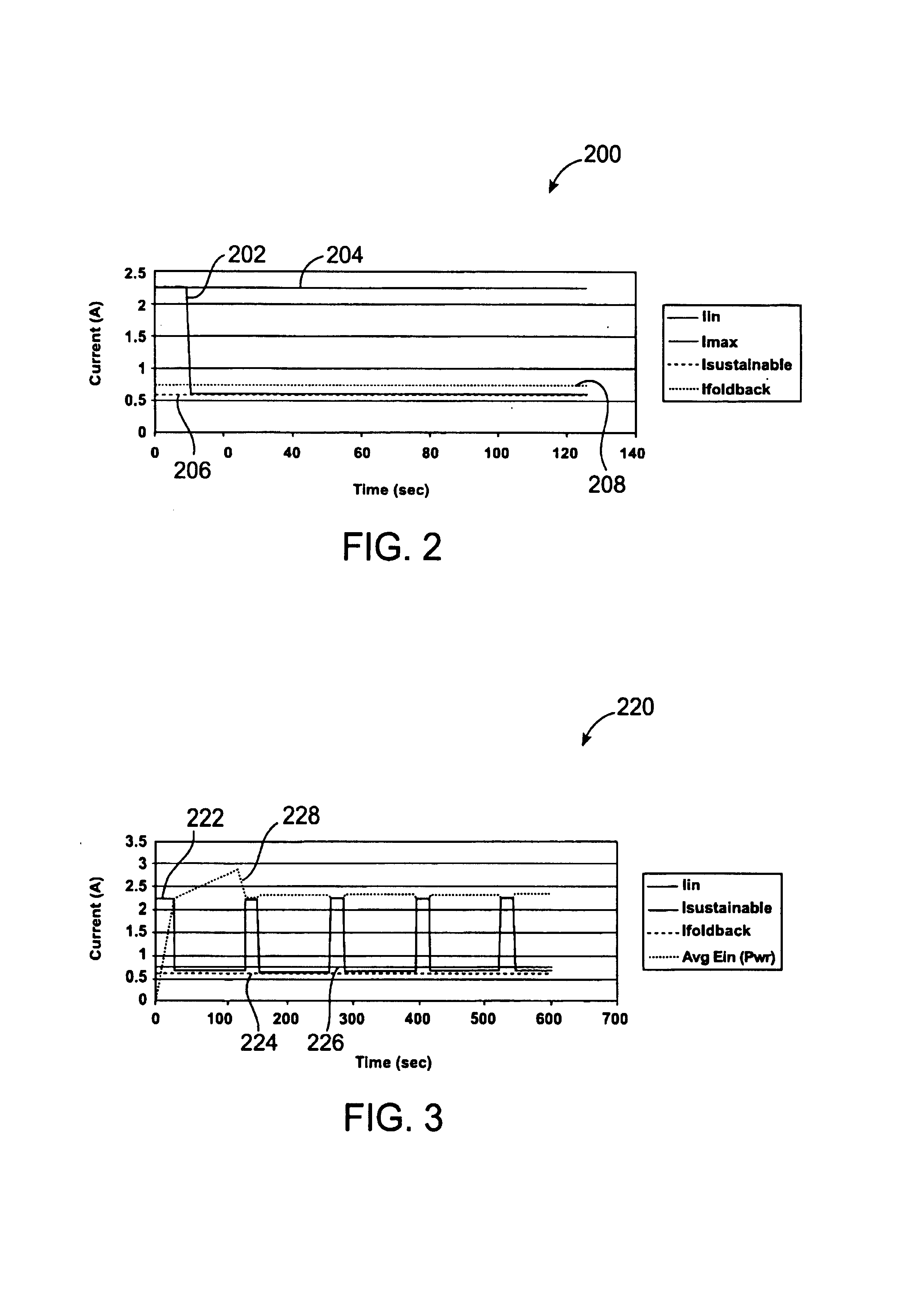
Actuator thermal protection in haptic feedback devices
InactiveUS7233476B2Reducing maximum allowable current levelReduces maximum allowable current levelInput/output for user-computer interactionEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionActuatorPersistent current
Method and apparatus for providing thermal protection for actuators used in haptic feedback interface devices. An average energy in the actuator over a predetermined period of time is determined, and the maximum allowable current level in the actuator is reduced if the average energy is determined to exceed a predetermined warning energy level. The maximum allowable current level can be reduced to a sustainable current level if the average energy reaches a maximum energy level allowed, and the maximum allowable current level in the actuator can be raised if the average energy is determined to be below the predetermined warning energy level. Preferably, the maximum allowable current level is reduced smoothly as a ramp function.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Apparatus and method for searching a base station in an asynchronous mobile communications system
InactiveUS6894996B2Improve search speedReduce search timeAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSignal on
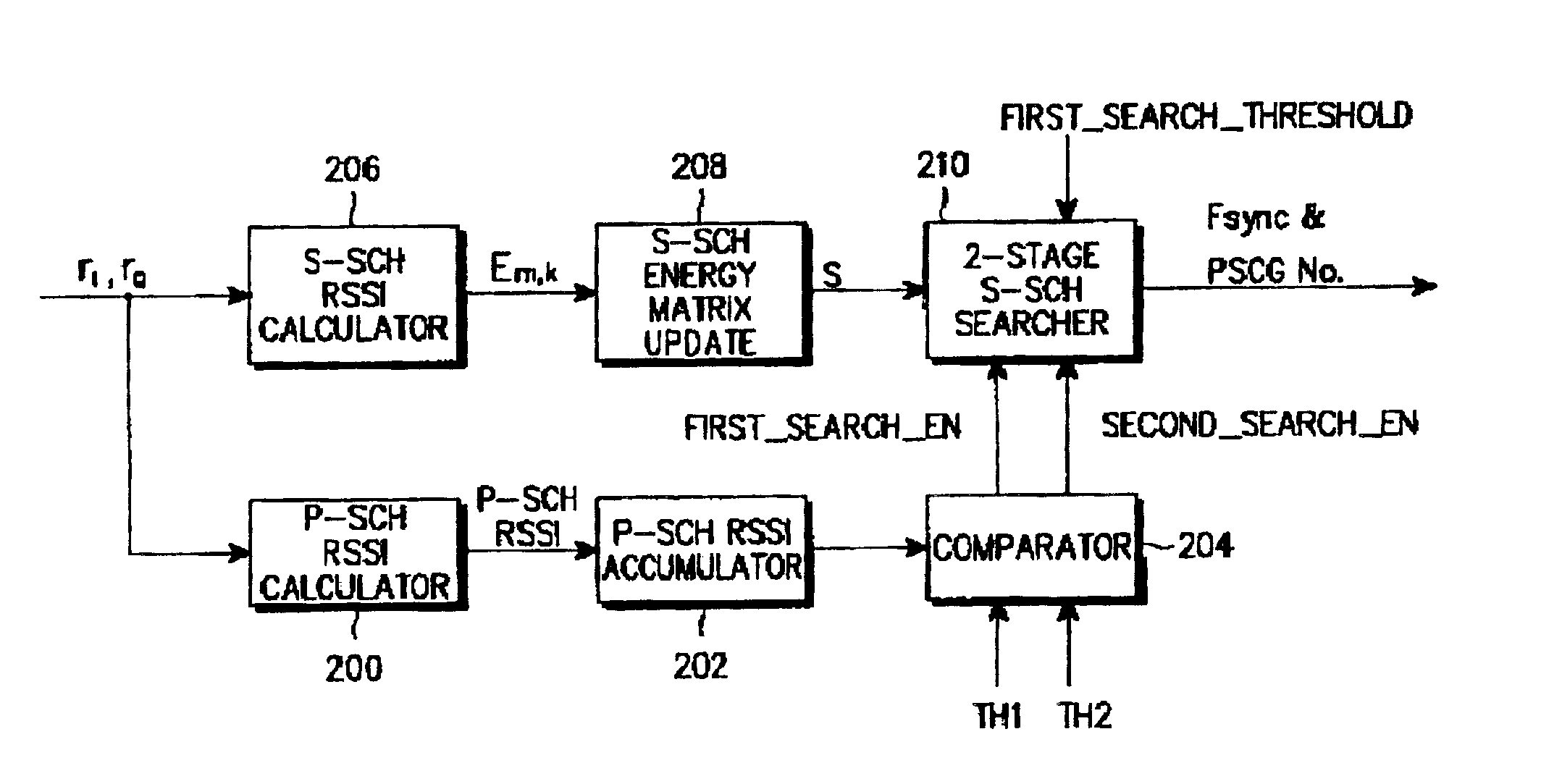
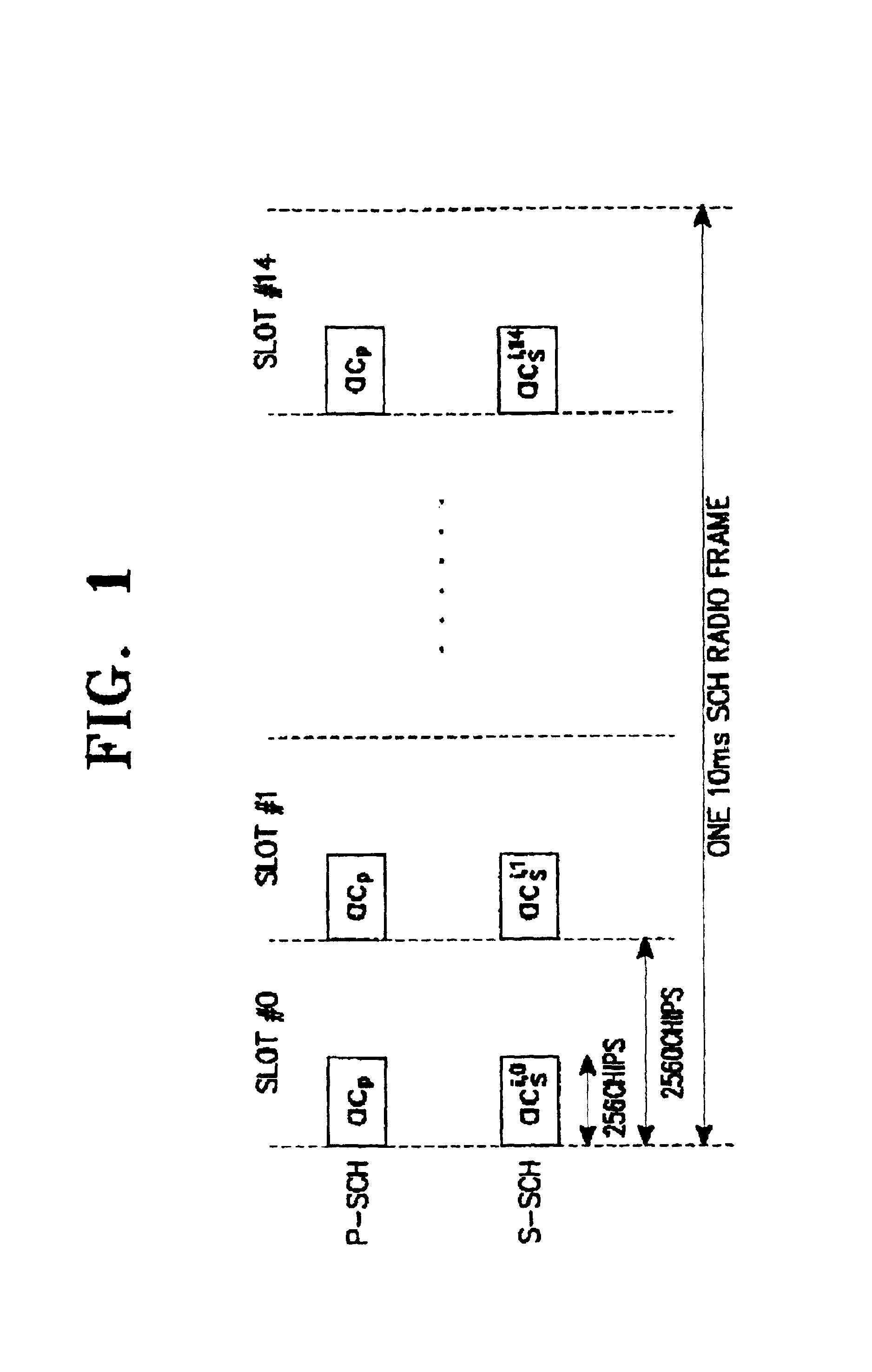
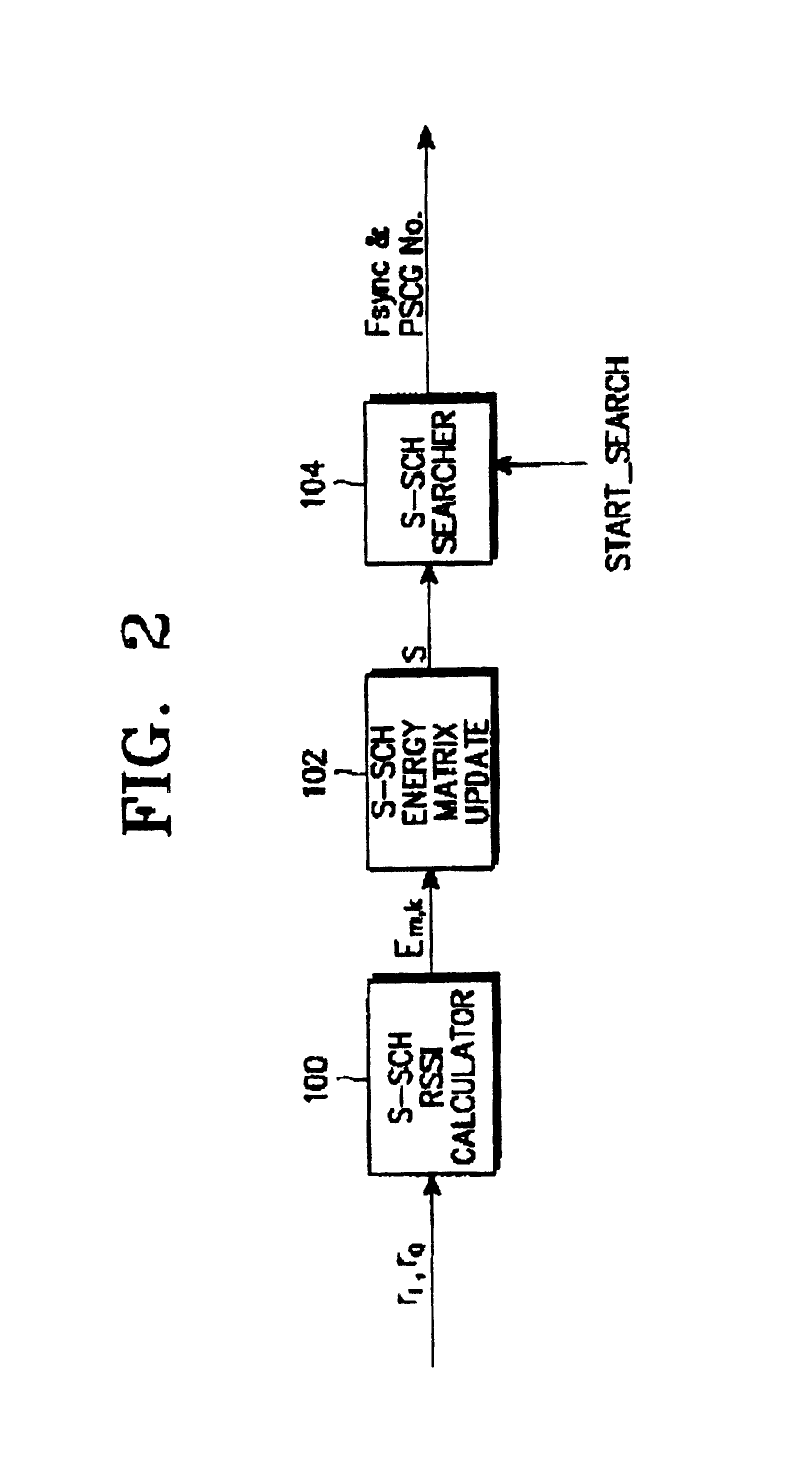
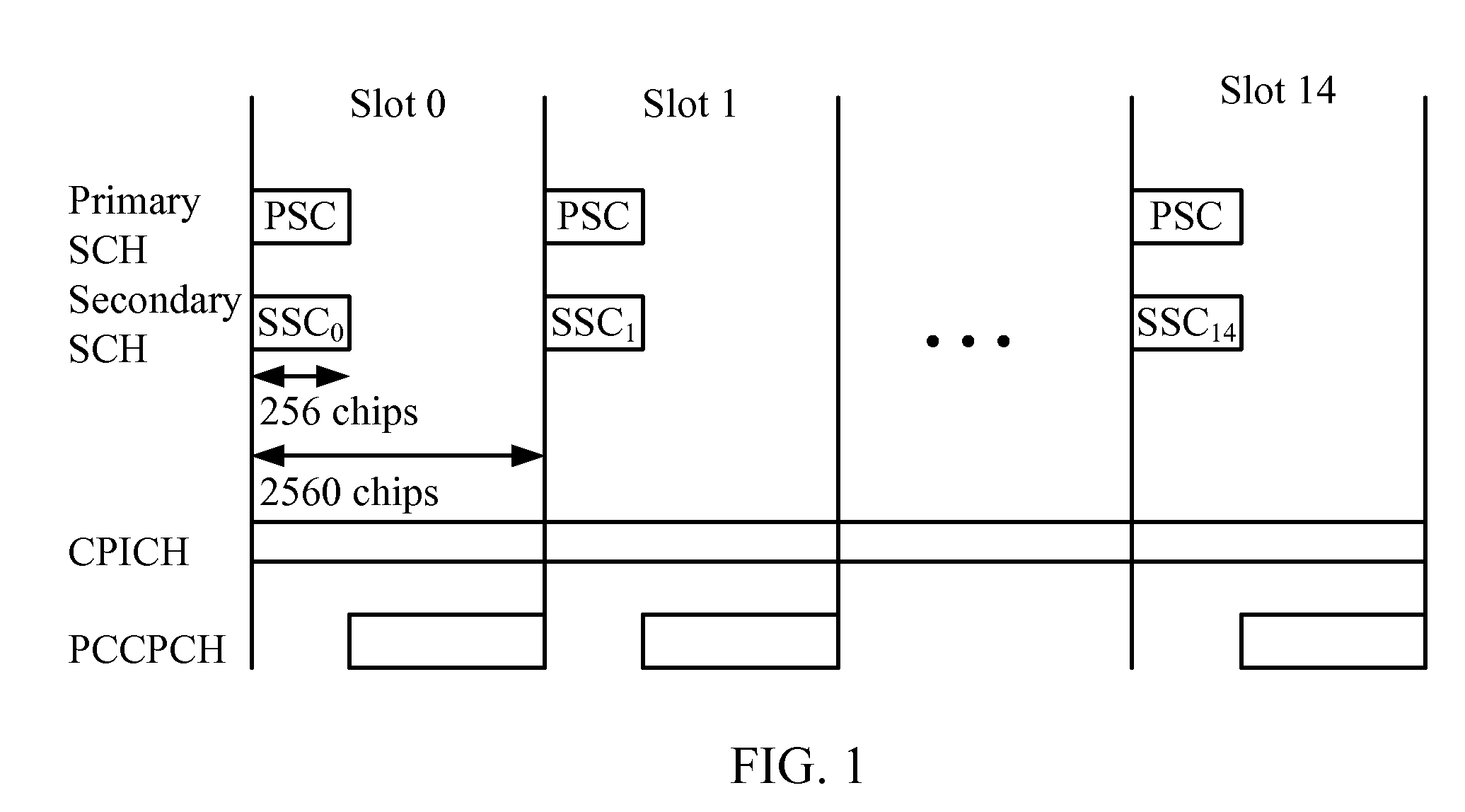
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for searching a base station in a mobile communications system, in which a mobile station acquires slot timing synchronization from a first signal on a primary sync channel (P-SCH) out of the P-SCH and a secondary sync channel (S-SCH) used for base station search, acquires frame timing synchronization (Fsync) from a second signal on the S-SCH, and determines a primary scrambling code group (PSCG) corresponding to the scrambling codes used by the respective base stations. The method comprises calculating and accumulating P-SCH RSSI values from the first signal at every slot and comparing the accumulated P-SCH RSSI values with first and second accumulation thresholds and providing the first and second search commands; and calculating S-SCH channel received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values from the second signal at every slot in one frame, and updating S-SCH RSSI values corresponding to the one frame as energy matrix values; calculating energy hypotheses corresponding to the energy matrix values using the energy matrix values and a predetermined secondary sync code (SSC) table in response to a first search command, and determining energy hypotheses having a value higher than a predetermined threshold as passed hypotheses; and calculating energy values for the passed hypotheses using the determined passed hypotheses and the SSC table in response to a second search command, and determining an energy hypothesis having a maximum energy as the Fsync and the PSCG.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Base station identification in orthongonal frequency division multiplexing based spread spectrum multiple access systems
InactiveUS20050238083A1Inherent latencyRadio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency-division multiplexingFrequency-shift keying
A base station having the strongest downlink signal is identified by utilizing a unique slope of a pilot tone hopping sequence being transmitted by a base station. Specifically, base station identification is realized by determining the slope of the strongest received pilot signal, i.e., the received pilot signal having the maximum energy. In an embodiment of the invention, the pilot tone hopping sequence is based on a Latin Squares sequence. With a Latin Squares based pilot tone hopping sequence, all a mobile user unit needs is to locate the frequency of the pilot tones at one time because the pilot tone locations at subsequent times can be determined from the slope of the Latin Squares pilot tone hopping sequence. The slope and initial frequency shift of the pilot tone hopping sequence with the strongest received power is determined by employing a unique maximum energy detector. In one embodiment, the slope and initial frequency shift of the pilot signal having the strongest received power is determined by finding the slope and initial frequency shift of a predicted set of pilot tone locations having the maximum received energy. In another embodiment, the frequency shift of the pilot signal with the strongest, i.e., maximum, received power is estimated at each of times “t”. These frequency shifts are employed in accordance with a prescribed relationship to determine the unknown slope and the initial frequency shift of the pilot signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
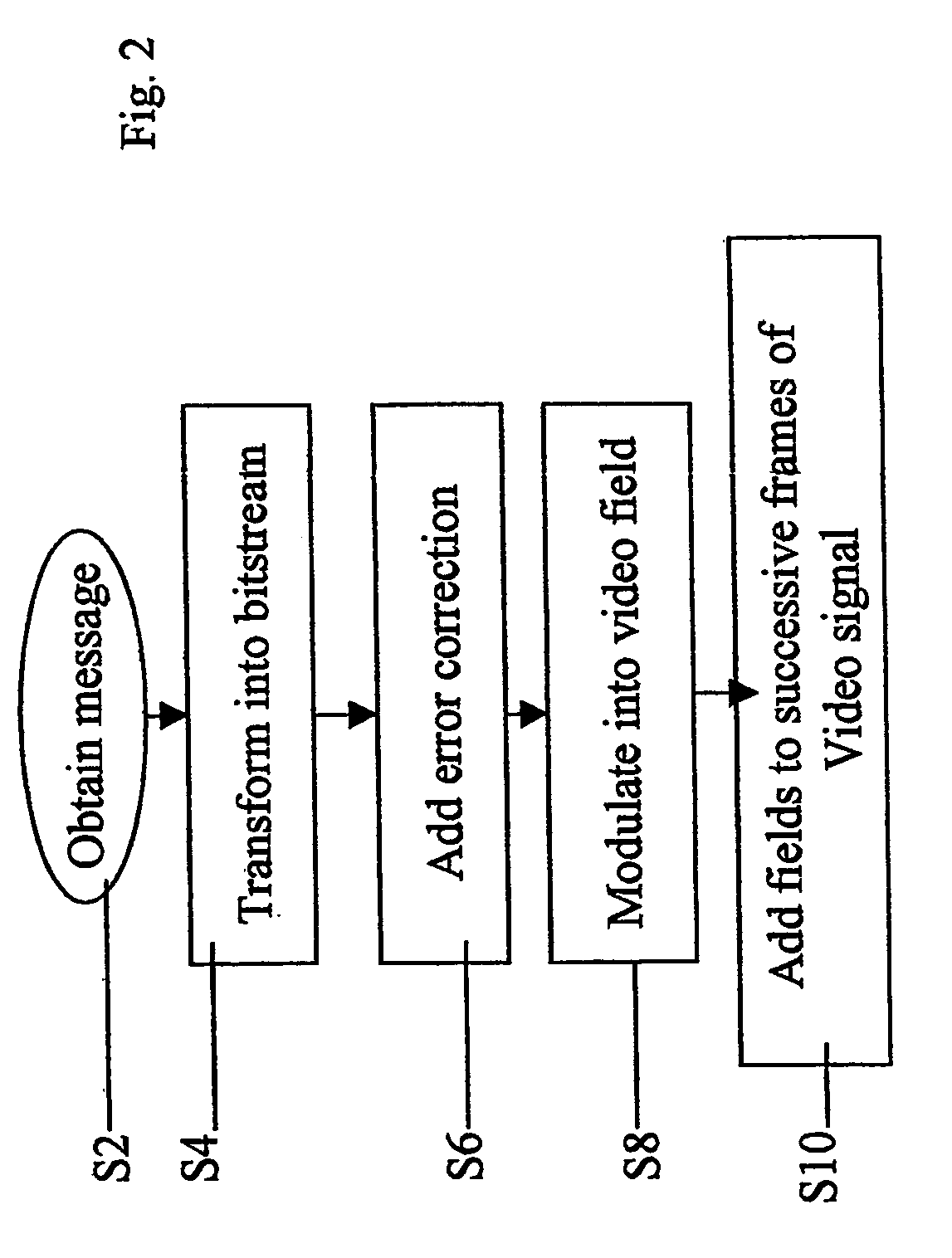
Method and apparatus for transferring data within viewable portion of video signal
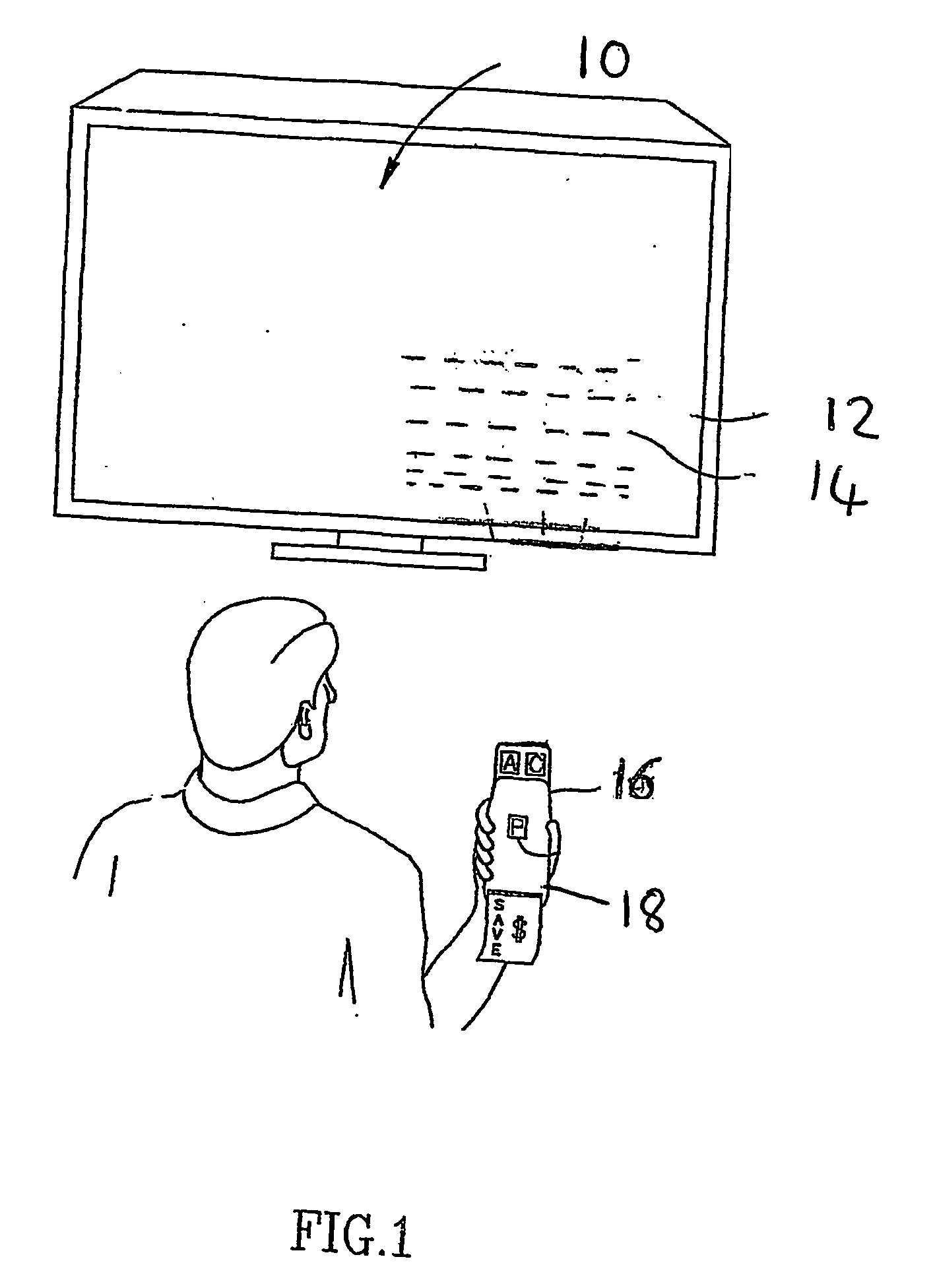
InactiveUS20050264694A1High enough bandwidthMinimal noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer scienceMaximal energy
A video signal has a visual image (12) and carries data for optical detection (54) via the image. The data for optical detection is encoded (52) as data bits in a plurality of lines within a defined region (14) within the image. A corresponding decoder (16, 58) uses maximal energy methods to detect the defined region prior to decoding the data.
Owner:OPTINETIX ISRAEL
Composite Hub for High Energy-Density Flywheel
InactiveUS20100018344A1Large energy densityPerformance maximizationMechanical energy handlingVibration suppression adjustmentsHigh peakHigh energy
A flywheel energy storage system emphasizing enhancements developed for space applications including development of a flywheel rotor system capable of achieving maximum energy density, while being capable of repeated high peak-power demands. Illustrated is a rotor system comprising a composite hub, capable of supporting an optimized high-speed composite rim and shaft, working in combination with a switched reluctance motor.
Owner:BEACON POWER LLC
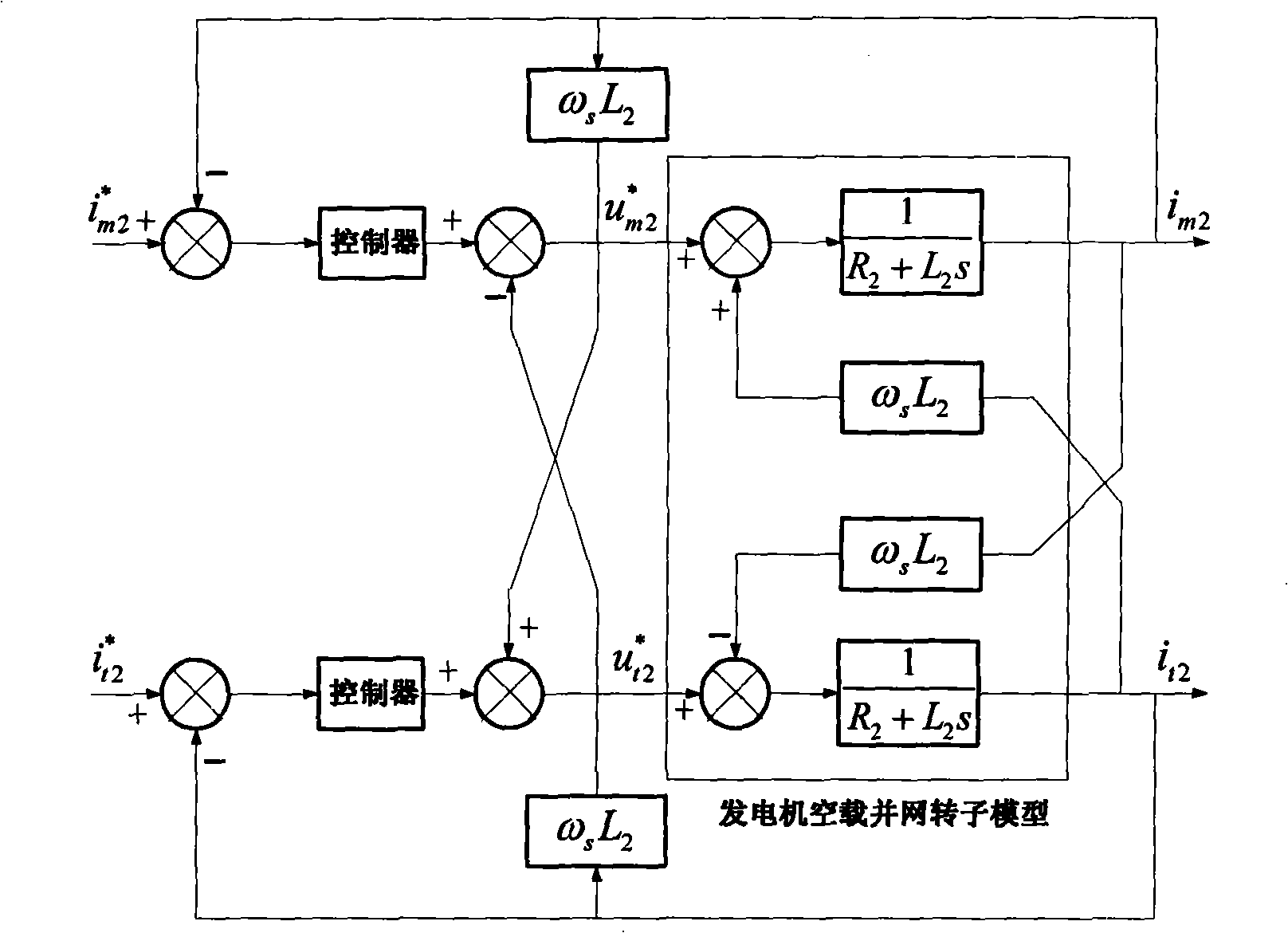
High-efficiency stable multifunctional single-stage photovoltaic single-phase grid-connected control method
InactiveCN101714763AReduce Harmonic Distortion RateImprove power qualitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationPower factorClosed loop
The invention discloses a high-efficiency stable multifunctional single-stage photovoltaic single-phase grid-connected control method, and belongs to the technical field of photovoltaic power generation control. The method is characterized in that: the method adopts a high-speed digital signal processor and applies a C language dynamic fixed-point algorithm to form a high-performance control algorithm of a whole grid-connected control system; the method adopts a single-stage grid-connected control structure and a quick smooth maximum power point tracking method to directly transmit the maximum energy sent by a photovoltaic array to a local urban power grid through first-stage DC / AC transformation; the harmonic and idle work produced by a local load can be compensated by adopting an FBD method, so the method is favorable for improving the electrical energy quality of the local power grid; and a proportional resonant converter is used to implement precise closed-loop control for the grid-connected current so that the photovoltaic grid-connected current and the commercial single-phase voltage are totally synchronous while implementing maximum power point tracking of the photovoltaic array. The power factor is high, the system efficiency is high, the operation of the whole system is safe and reliable, and the aberration rate of the grid-connected current harmonic is lower than 3 percent.
Owner:WUXI SLD POWER TECH
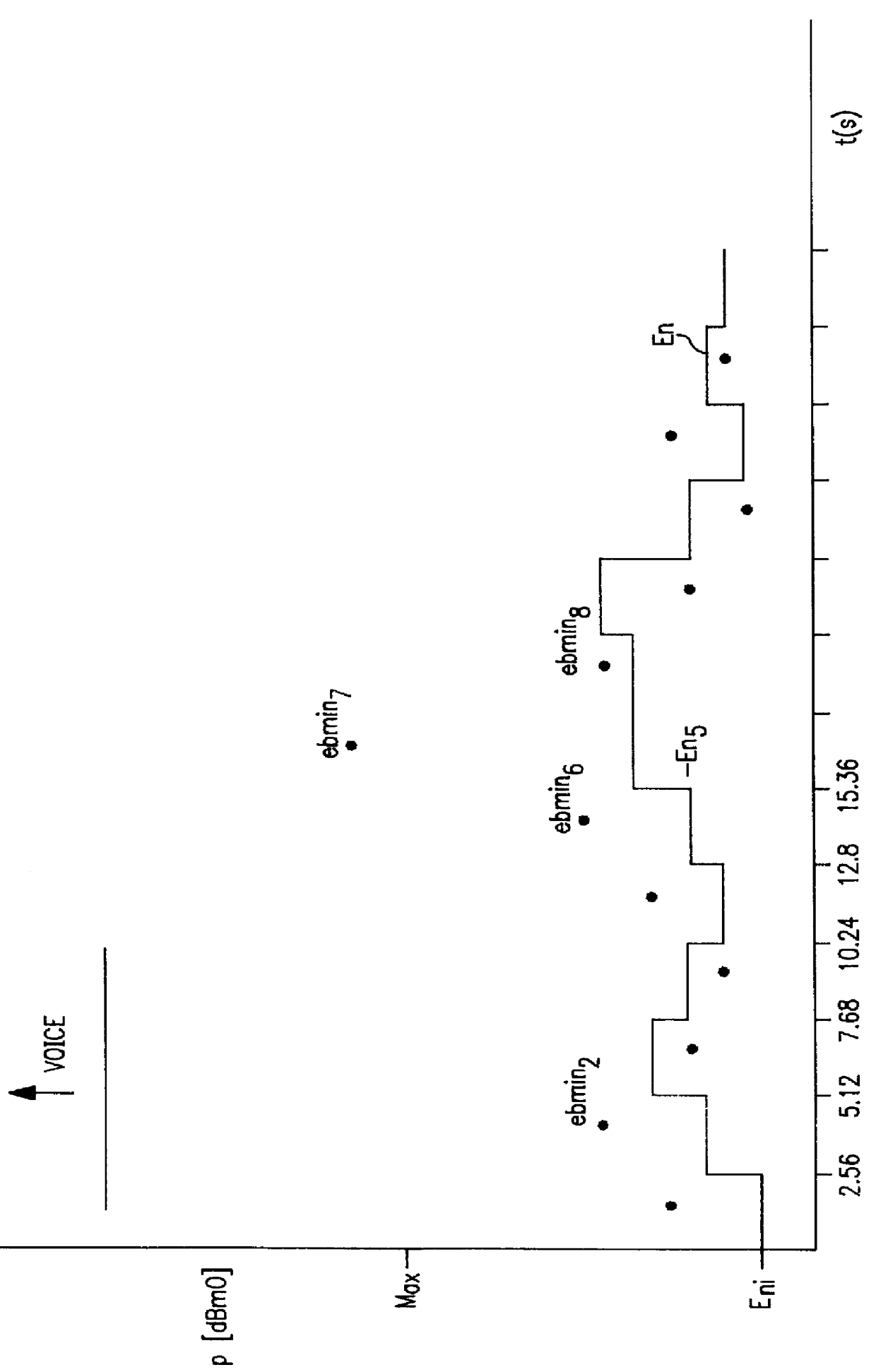
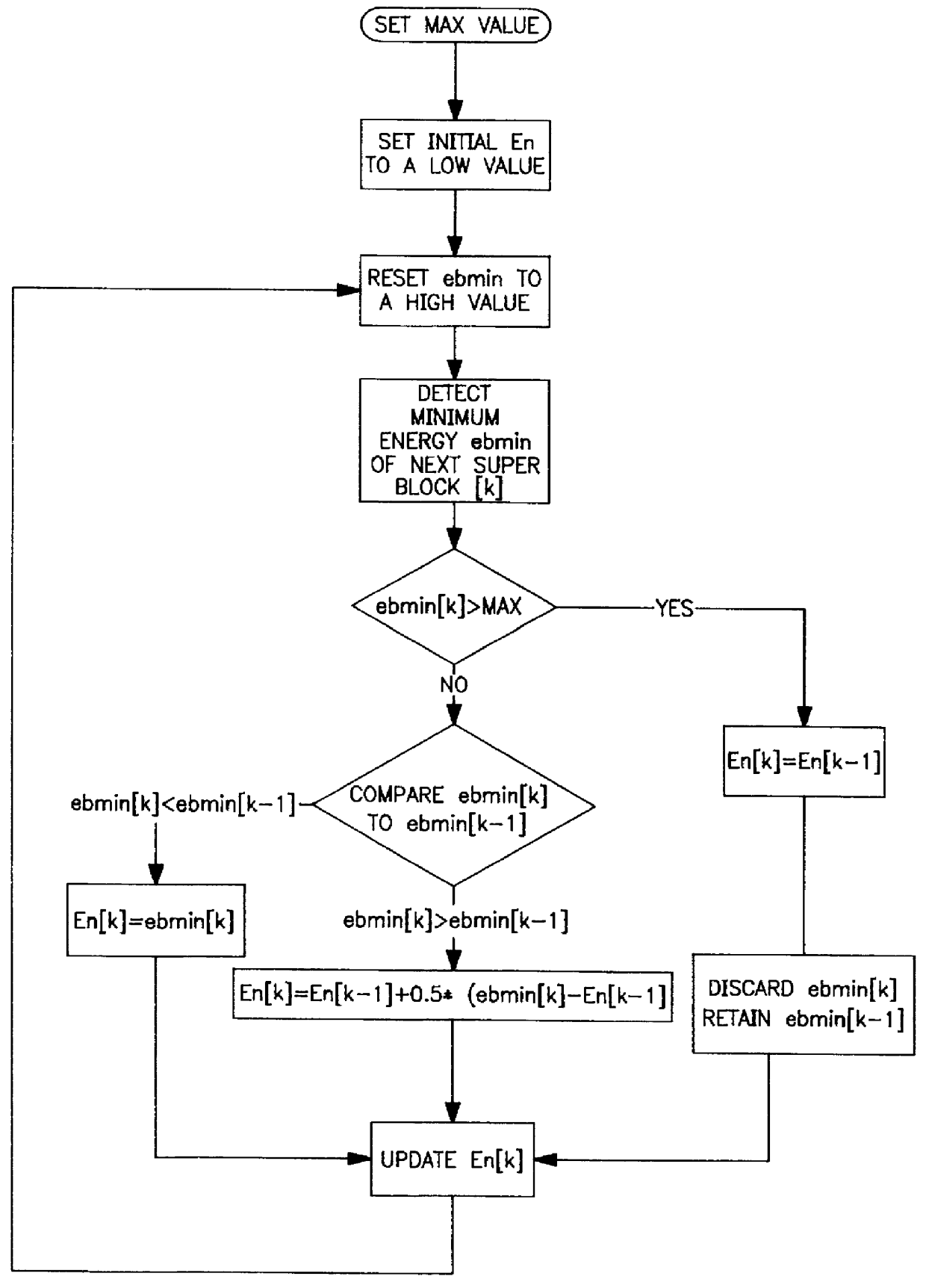
Background energy estimation
InactiveUS6157670AEstimate the background energy level accurately and reliablyEliminate energyReceivers monitoringError preventionEngineeringEnergy estimation
A method of estimating background noise in a signal. The signal is divided into blocks of equal predetermined length. The minimum energy of the signal during the length of each block is determined. The minimum energy determined for the current block is compared to a previous determination of minimum energy. If the current minimum energy exceeds a predetermined maximum energy level, the current block minimum energy is discarded and the previous determination remains unchanged. If the current block minimum energy is below the previous determination, the previous estimate is reduced by the difference between the previous determination and current minimum energy. If the current energy is above the previous determination but below the maximum, the previous estimate is increased by half of the difference between the current energy and the previous estimate. The increase factor may also be adjusted to increase the current estimated energy level by a factor of any amount between and including 0 and 1. The estimation of minimum energy, or background energy, therefore decreases in direct proportion to a drop in minimum energy determination but increases only as a partial factor of new determinations.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
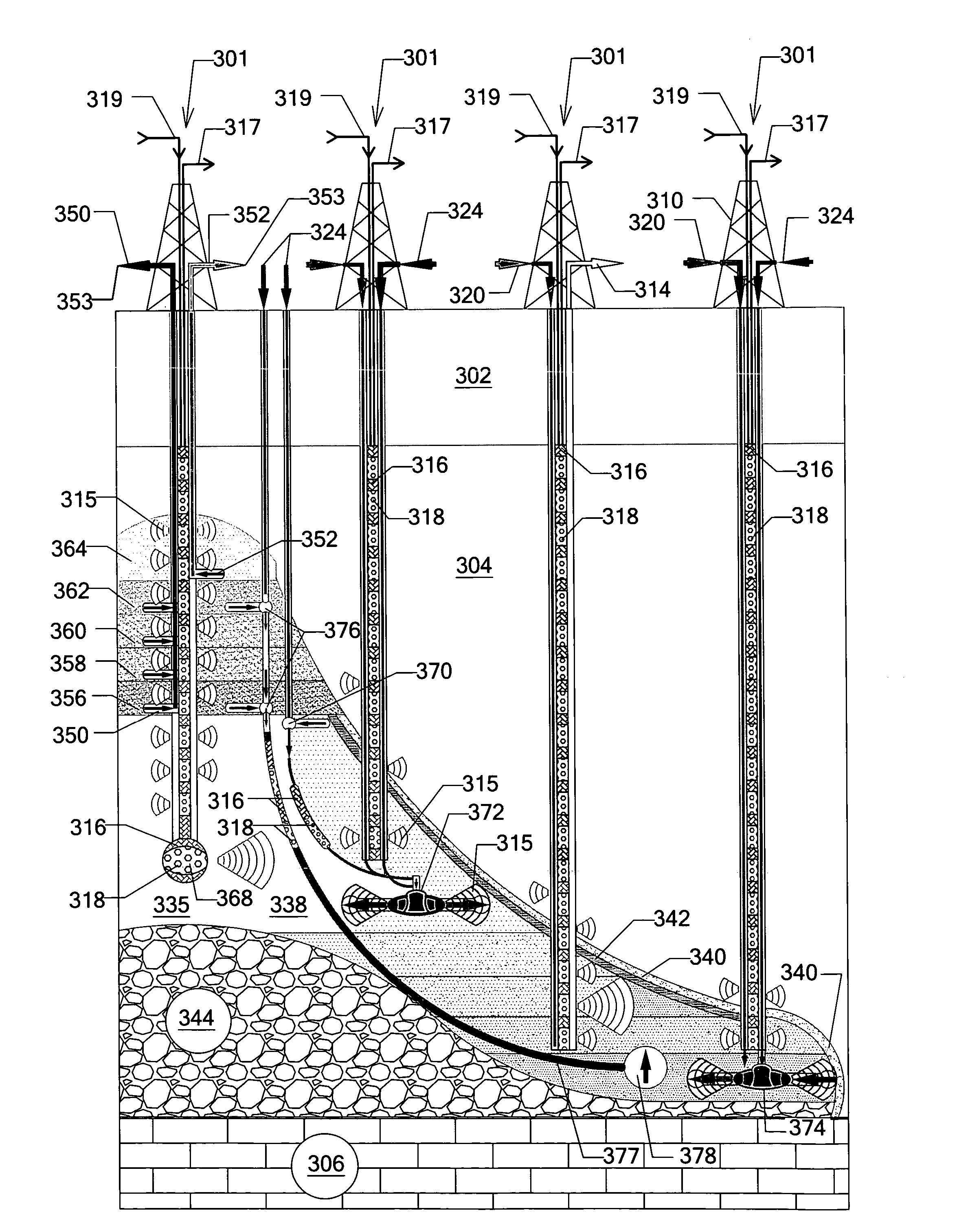
In situ processing of hydrocarbon-bearing formations with variable frequency dielectric heating
A hydrocarbon bearing formation (304) which is heated using a variable frequency capacitive radio frequency dielectric heating (334) in situ process. Hydrocarbons or other substances natural to a hydrocarbonaceous formation may be produced by heating specific chemical compositions with or without the use of a carrier medium (320) in a subterranean reservoir. Hydrocarbons or other substances natural to a hydrocarbonaceous formation are heated by maintaining specific chemical compositions in an alternating current electrical field generated by a radio frequency signal. As the targeted chemical compositions increase in temperature, maximum energy is delivered using variable frequency radio frequency dielectric heating to adjust the rate of the heating process.
Owner:HEAT ENERGY & ASSOCD TECH
Iris extraction method capable of precisely determining positions and sizes of irises in a digital face image
InactiveUS7197166B2Improved energy functionFunction increaseCharacter and pattern recognitionTemplate matchComputer vision
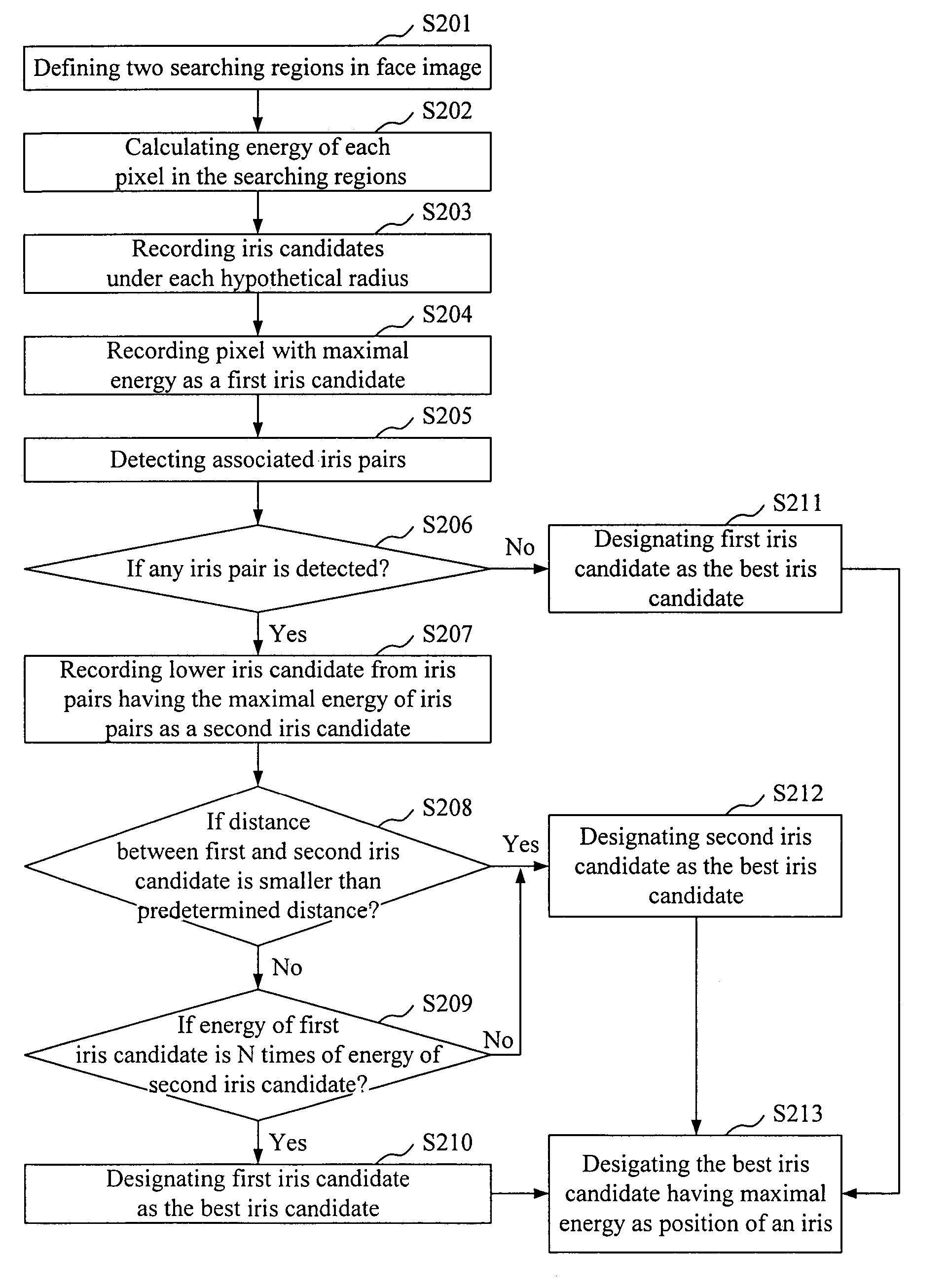
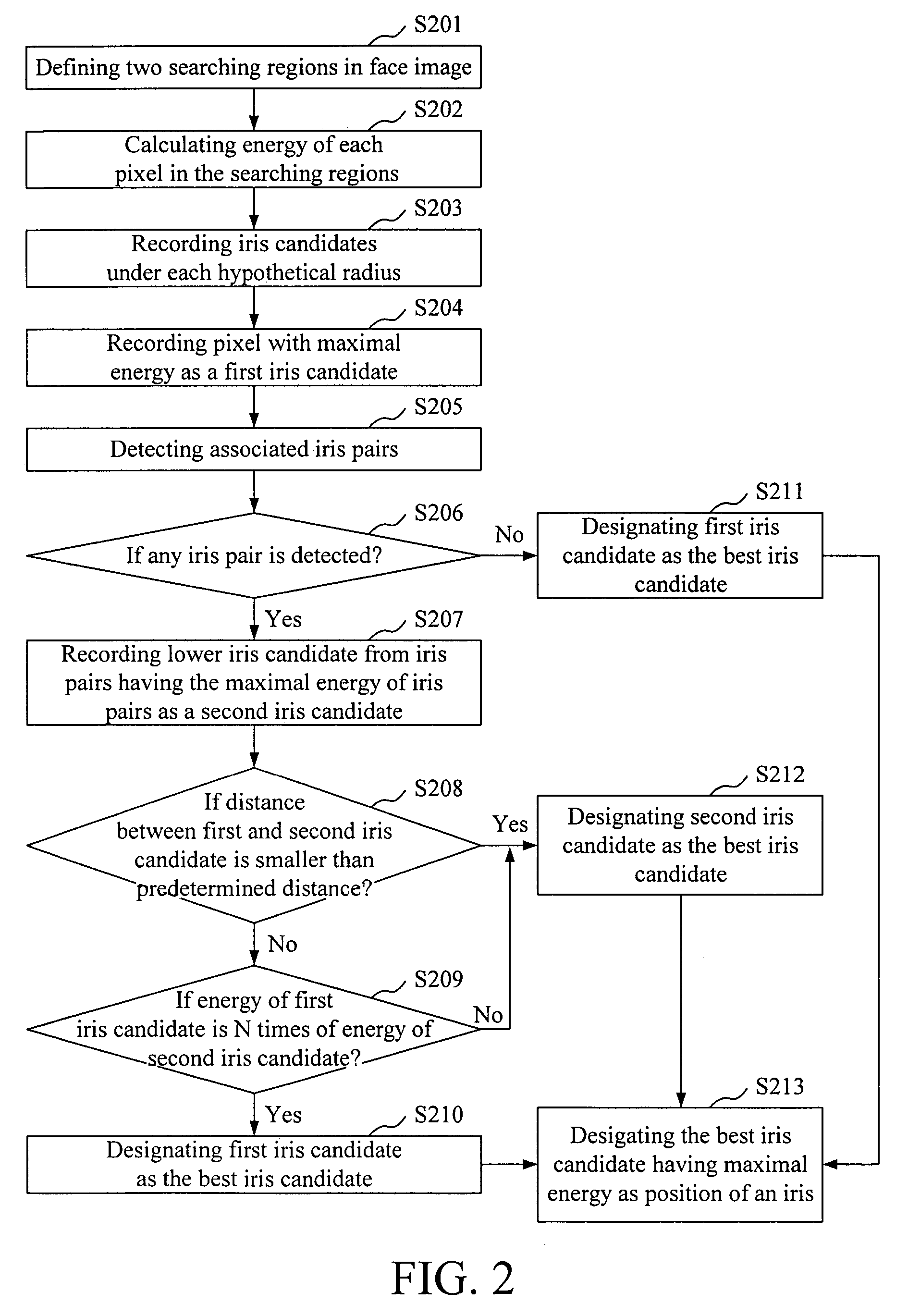
The present invention relates to an iris extraction method. In the method, two searching regions are defined in a face image. A deformable template match algorithm and an energy function are used to measure the energy of each pixel with different hypothetical circular templates within the searching region. Pixels with the same hypothetical radius having energies greater than a predetermined threshold are recorded as iris candidates, wherein the pixel having the maximal energy is recorded as first iris candidate. Further, it detects associated iris pairs from iris candidates in each searching region, records the lower iris candidate having the maximal energy of iris pairs as second iris candidate, and selects the best iris candidate from first iris candidate and second iris candidate. Finally, it designates the best iris candidate having the maximal energy of all best iris candidates with different hypothetical radius as the iris in the face image.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Optimized ridge apertures for thermally assisted magnetic recording
InactiveUS20080151360A1Combination recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEnergy absorption
Methods and devices for optimized ridge near field apertures for thermally assisted magnetic recording are disclosed. The aperture dimensions and supporting dielectric materials are optimized for maximum energy absorption at the magnetic recording layer for a light source having a wavelength of 780 nm, which can be produced by low cost laser diodes.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
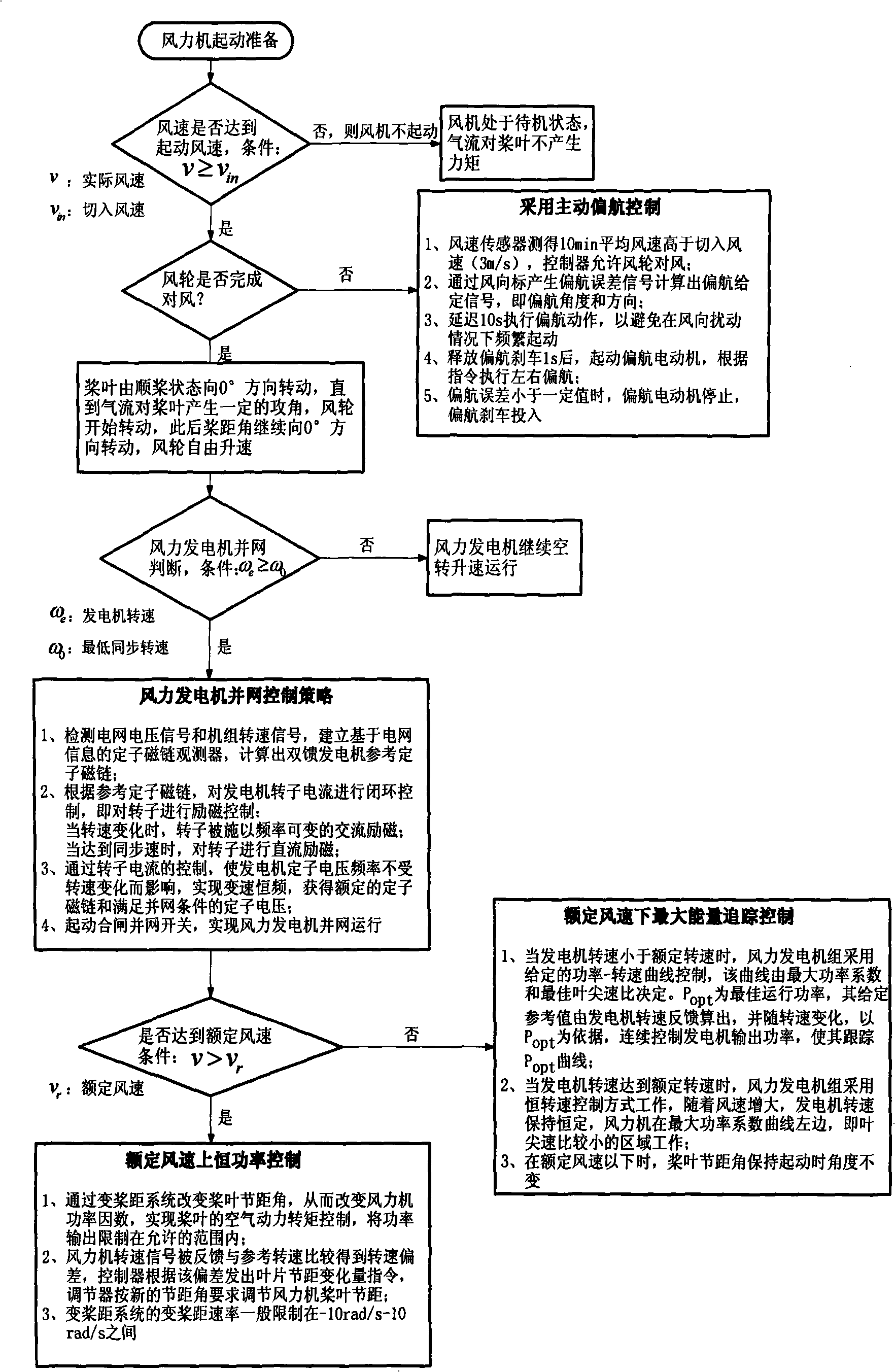
Operation control method for parallel variable-speed constant-frequency wind generator set
InactiveCN101404476AStable and accurate against the windTimely and safe releaseSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectric generator controlElectricityConstant frequency
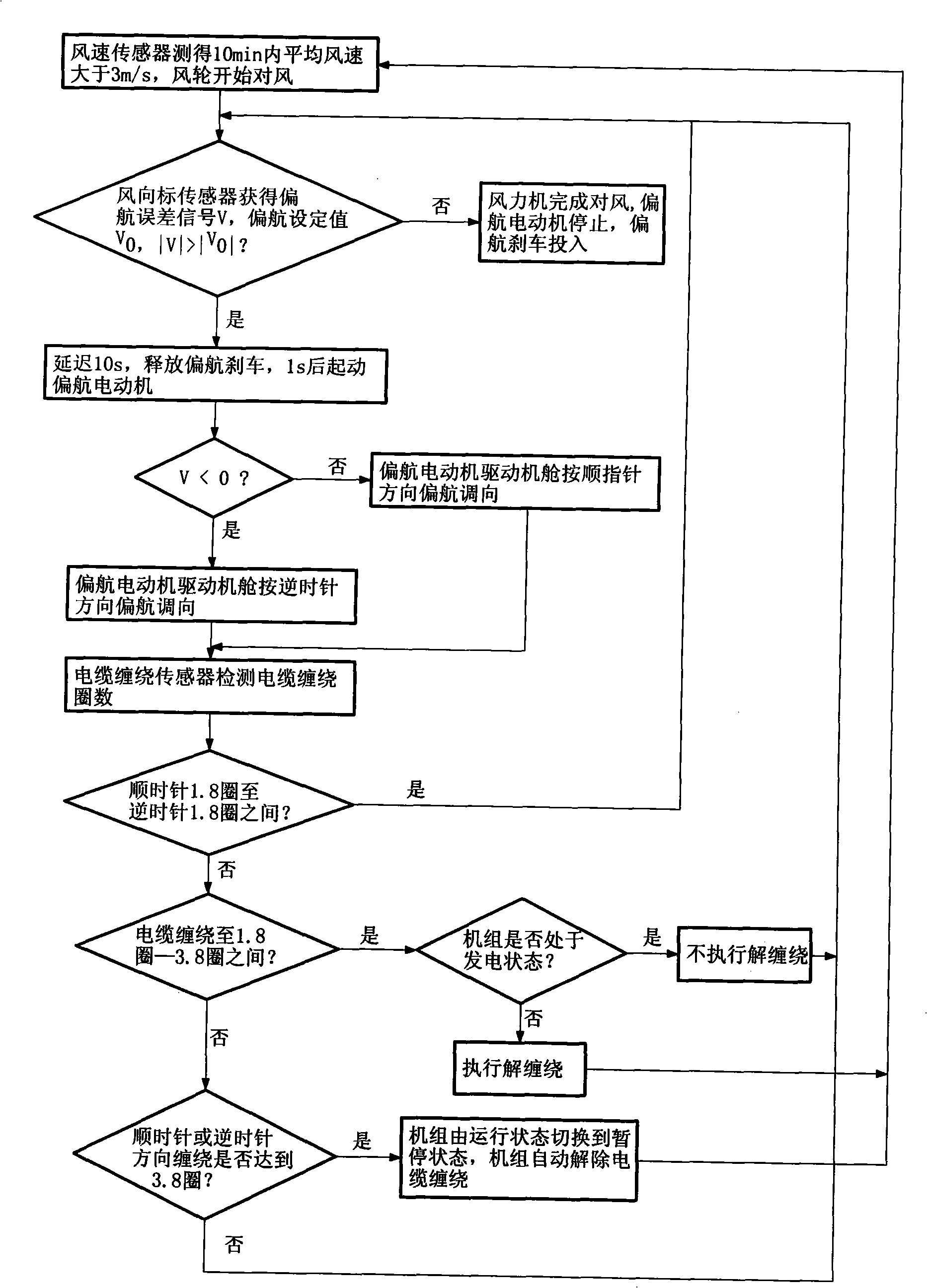
An operation control method of a synchronization variable speed constant frequency wind generating set includes the strategies of AYC, synchronization control, low wind speed ceiling capacity follow control and high wind speed constant power control which includes the AYC, the synchronization control, the low wind speed ceiling capacity follow control and the high wind speed constant power control. An anemoscope and a wind vane measure the wind speed and wind direction information to generate a yaw deviation signal; a yaw motor is driven to execute left and right yaw according to the yaw direction and angle and limit the yaw velocity and meanwhile, the steering turns of the engine room are measured with the help of cables winding around a sensor, so as to execute safe untwist action, thus ensuring that the wind generating set realizes quick, accurate and safe effect of the wind wheel against wind. All the control strategies cooperate in work from the start to synchronization power generation according to the requirement of the set and external conditions, so as to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the wind generating set.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
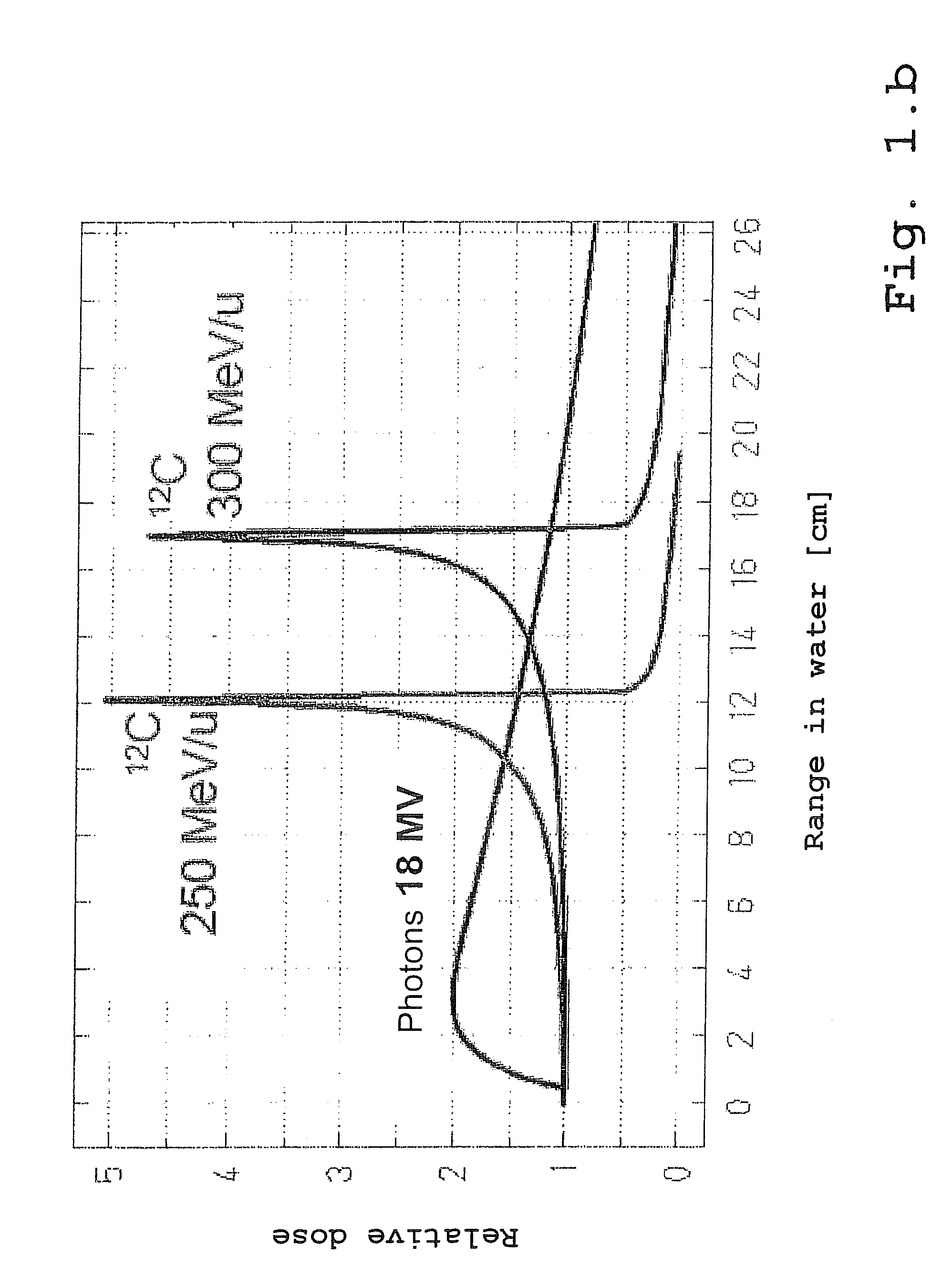
Quick Regulation of the Range of High-Energy ION Beams for Precision Irradiation of Moving Target Volumes
ActiveUS20110105821A1Reduce disadvantagesChemical conversion by chemical reactionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBragg peakHigh energy
The invention concerns a device and a process for adjusting the range of an ion beam, in particular for irradiation in tumor therapy. For this purpose, first the reference position of a target volume to be irradiated is determined. Subsequently, the range of an ion beam is configured such that said beam is adjusted to the reference position of the target volume, in such a manner that the Bragg peak, i.e. the maximal energy loss and thereby the maximal damage occurs in the region of the target volume which is to be destroyed. In the case that it has been determined that the reference position has been altered by a movement of the target volume, the ion beam is then deflected from the beam axis such that the ion beam is directed to various regions of a range modulator, in order that the ion beam experience a correspondingly adjusted energy loss in passing through the range modulator. This energy loss is adjusted to correspond to the change in position of the target volume in such a manner that the change in position is compensated for by the adjustment of the range of the ion beam, and the Bragg peak is returned to the region within the target volume.
Owner:GSI HELMHOLTZZENT FUR SCHWERIONENFORSCHUNG
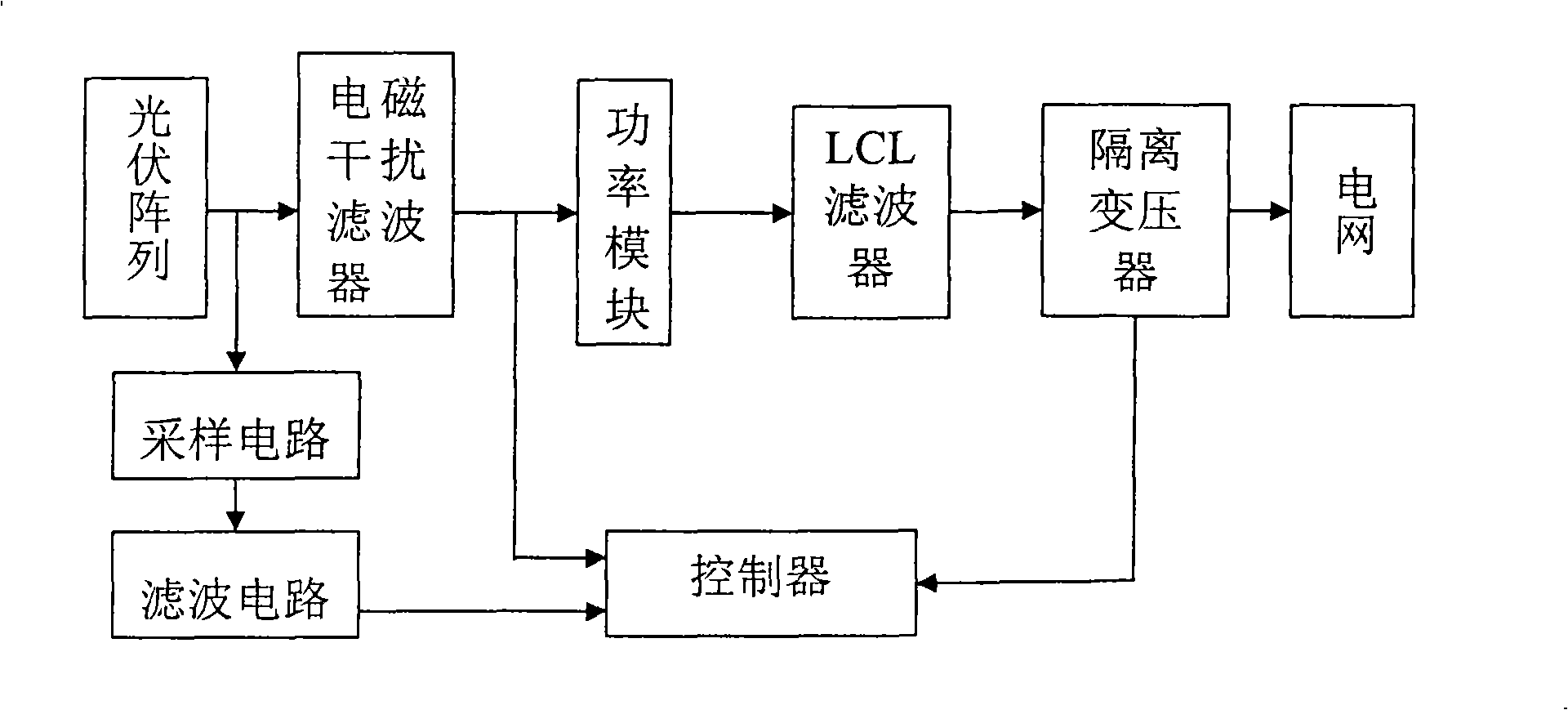
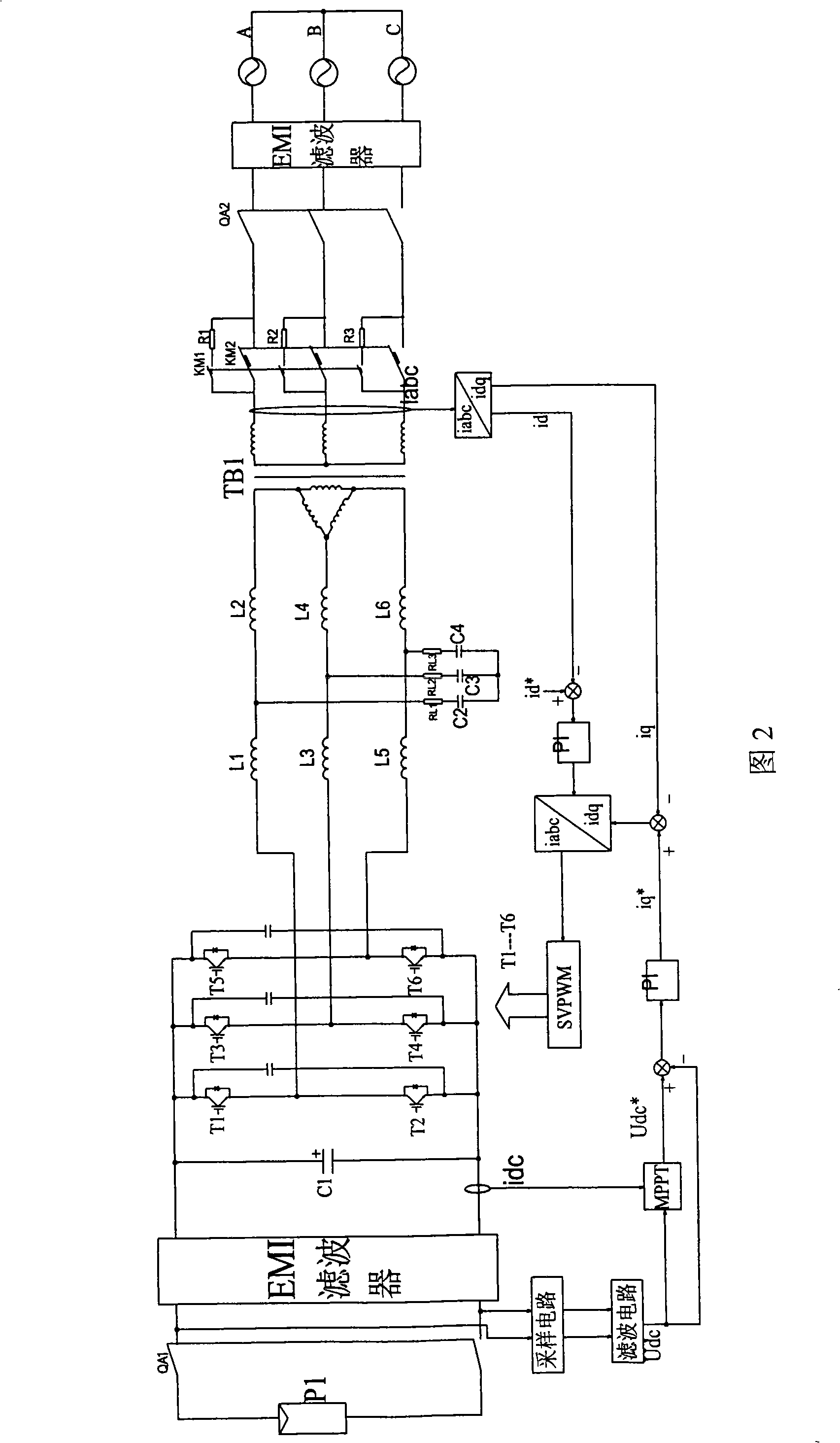
Solar photovoltaic parallel inverter control system based on LCL filtering
InactiveCN101494385AHigh technology contentEmission reductionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationFiltrationSimulated annealing
A solar energy grid-connected inverter control system based on LCL filtration comprises a photovoltaic array, an electromagnetic interference filter, namely an EMI filter, a power module, an LCL filter, an isolation transformator TB1, a sample circuit, a filter circuit and a controller which includes a maximum capacity tracking MPPT unit. MPPT adopts an intelligent algorithm based on a hybrid algorithm of a simulated annealing method and a genetic algorithm. The hybrid optimization algorithm takes the operation process of the genetic algorithm as the main process and also combines a simulated annealing mechanism that is used for further adjusting optimized instruction data. The control system has the advantages of good stability, strong performance and high efficiency and reliability.
Owner:CHANGZHOU RUSN NEW ENERGY
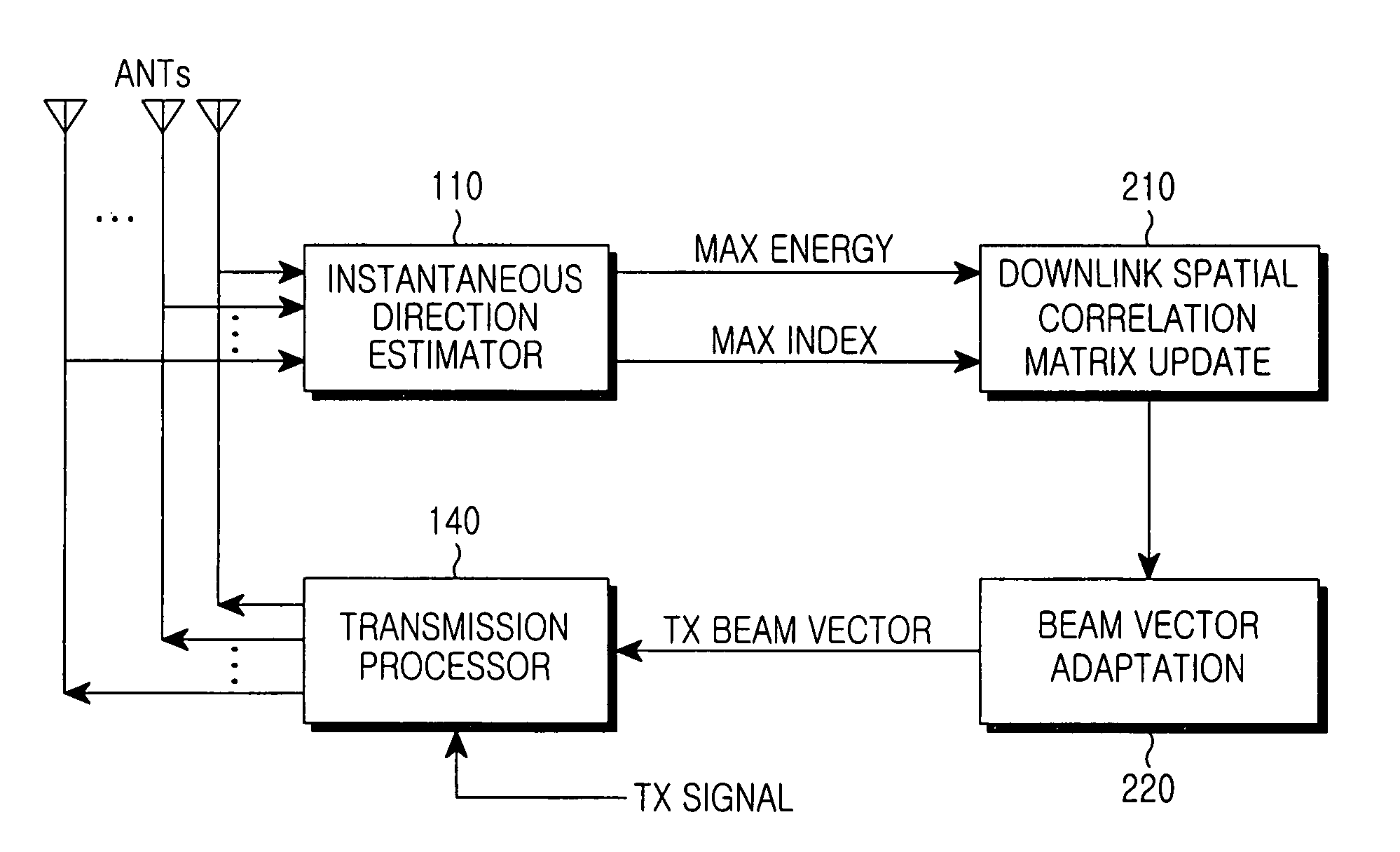
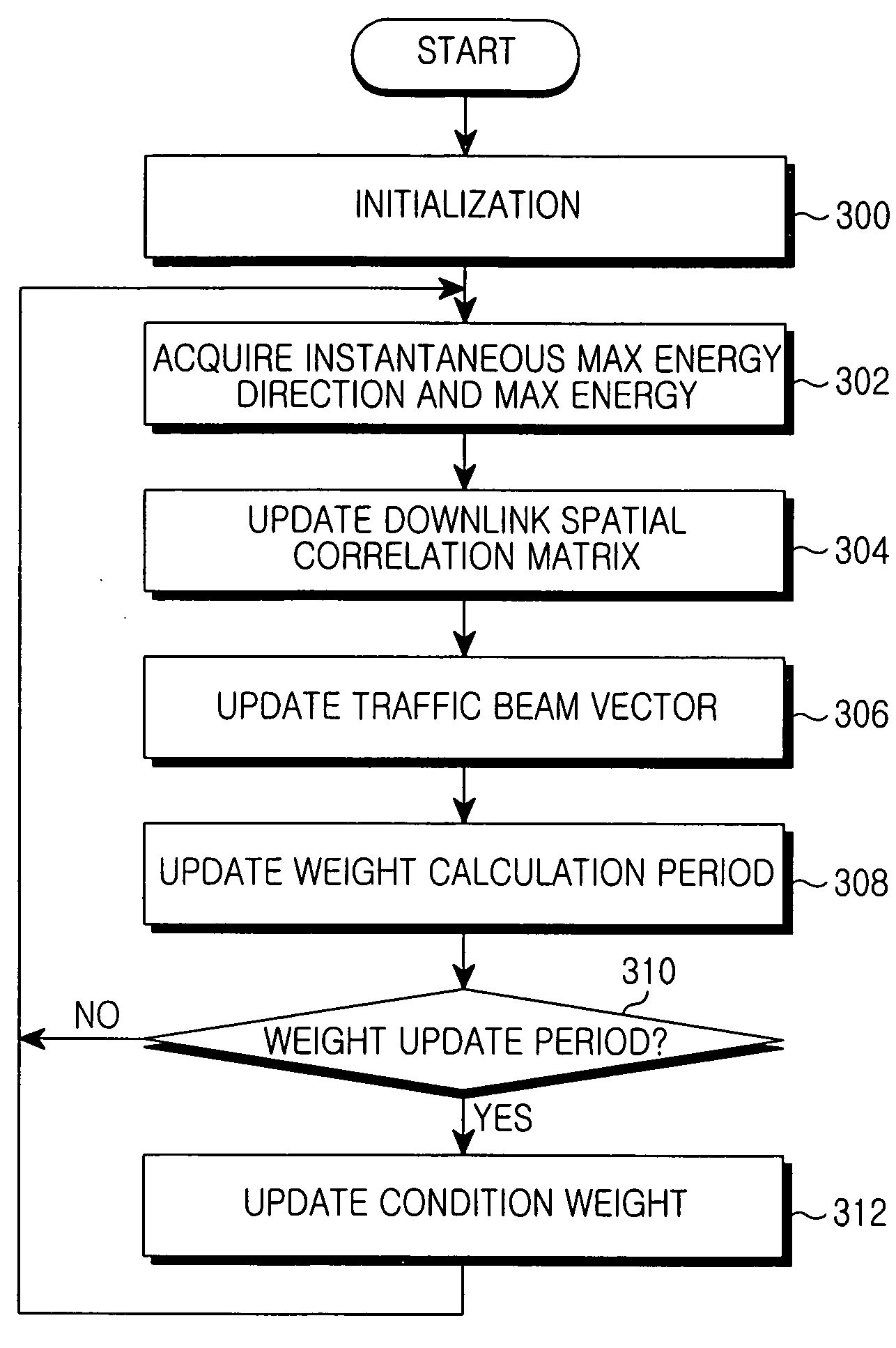
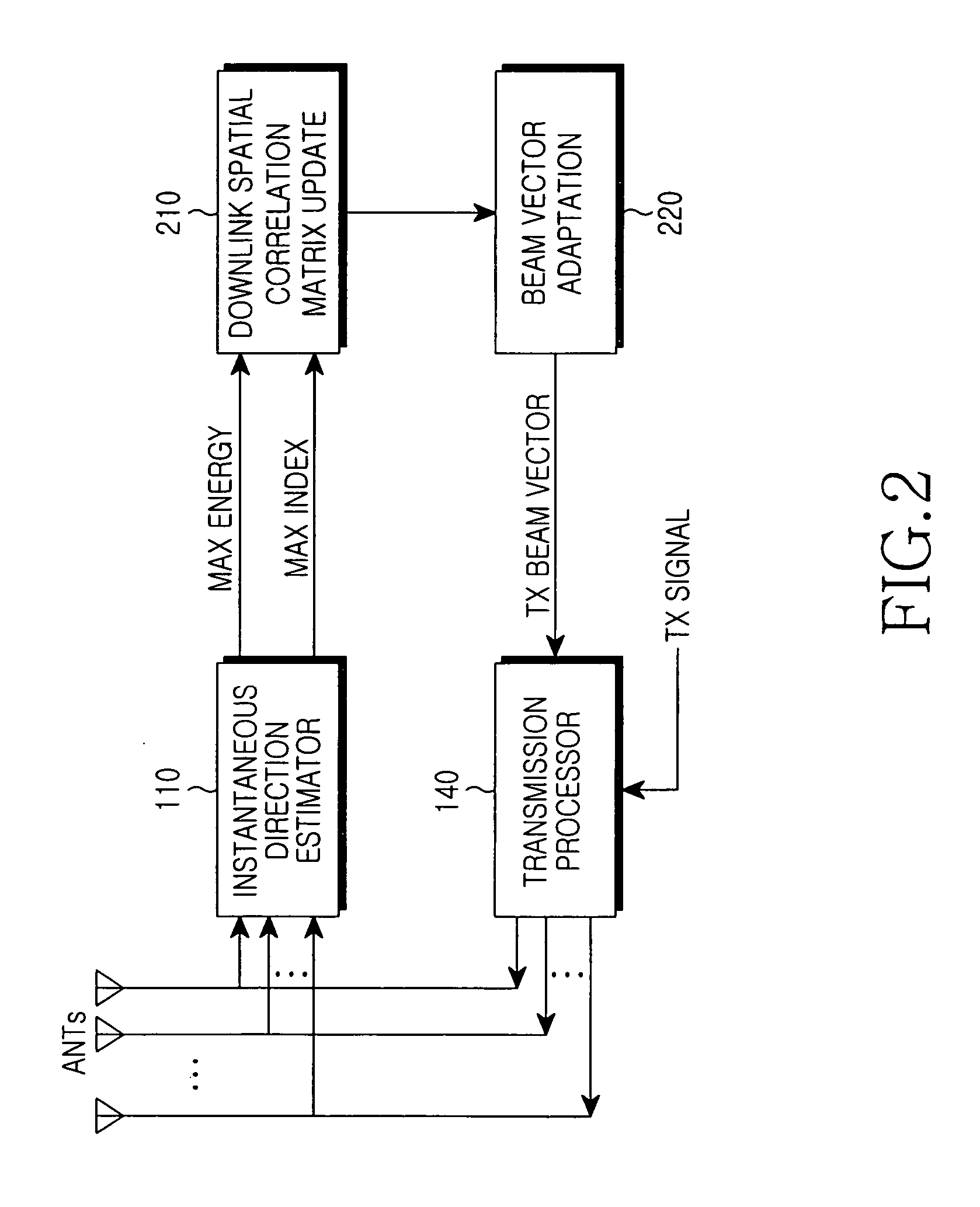
Apparatus and method for forming downlink beam in a smart antenna system
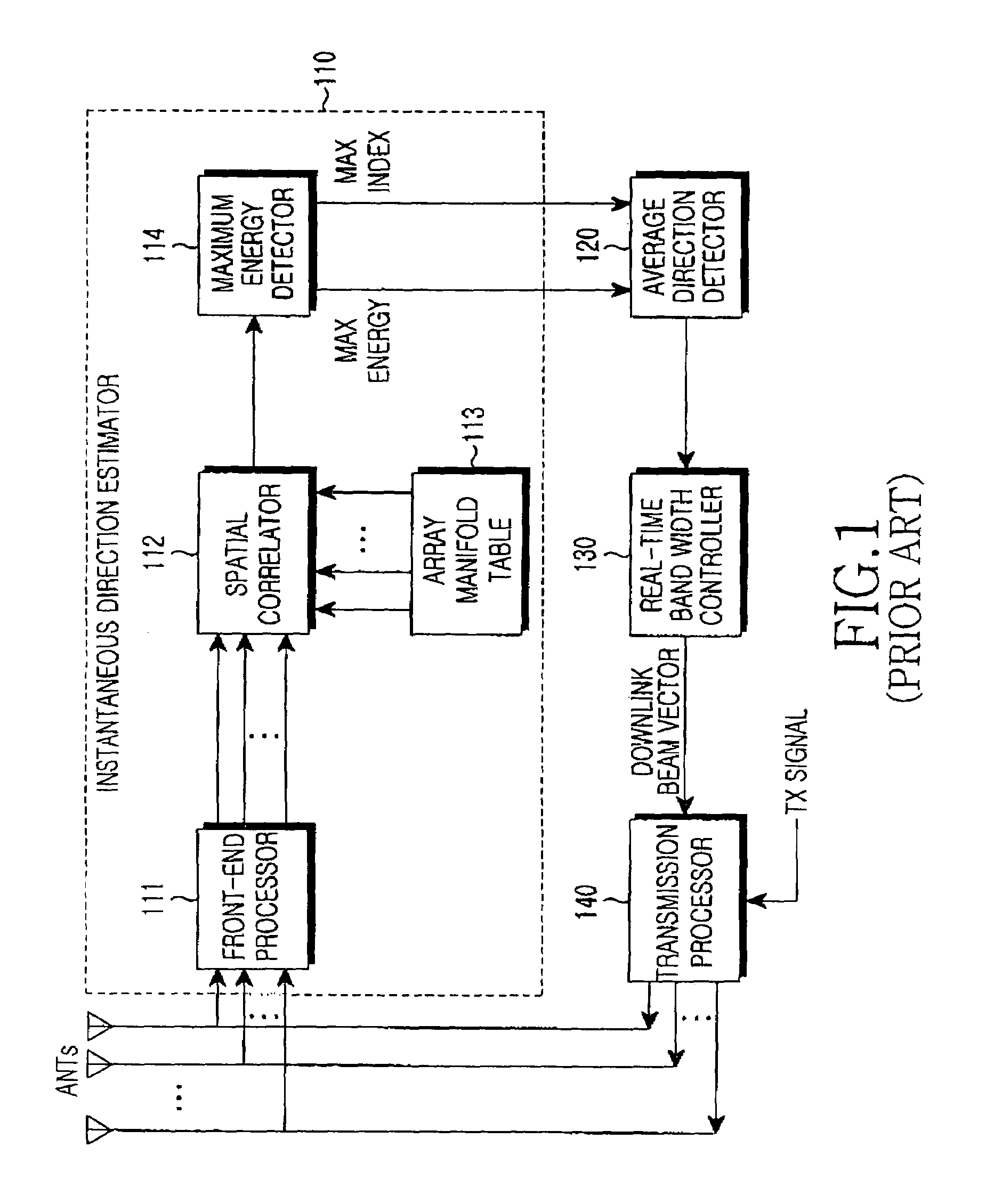
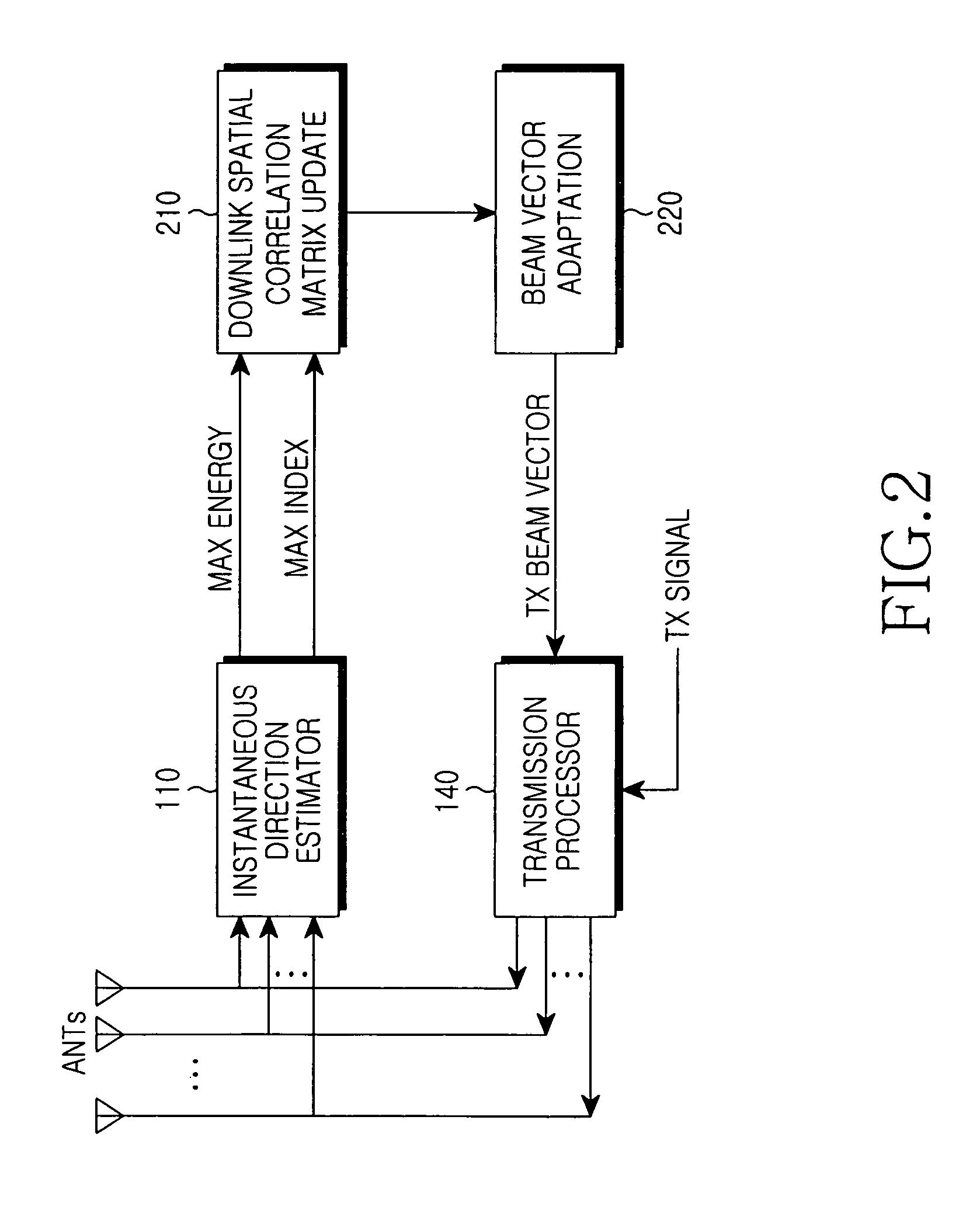
InactiveUS7239893B2Reduce errorsSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysSpatial correlationPhase difference
Disclosed is an apparatus for forming a downlink traffic beam in a base station that separately forms a traffic beam for each user using multiple antennas. In the apparatus, an instantaneous direction estimator detects a signal having maximum energy and an energy value from a received uplink signal. A downlink spatial correlation matrix update unit calculates a downlink spatial correlation matrix using an output value of the instantaneous direction estimator and a downlink antenna direction response characteristic. A beam vector adaptation unit outputs a downlink bean-forming vector by reflecting a phase difference between a common beam and a traffic beam from an output of the downlink spatial correlation matrix update unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
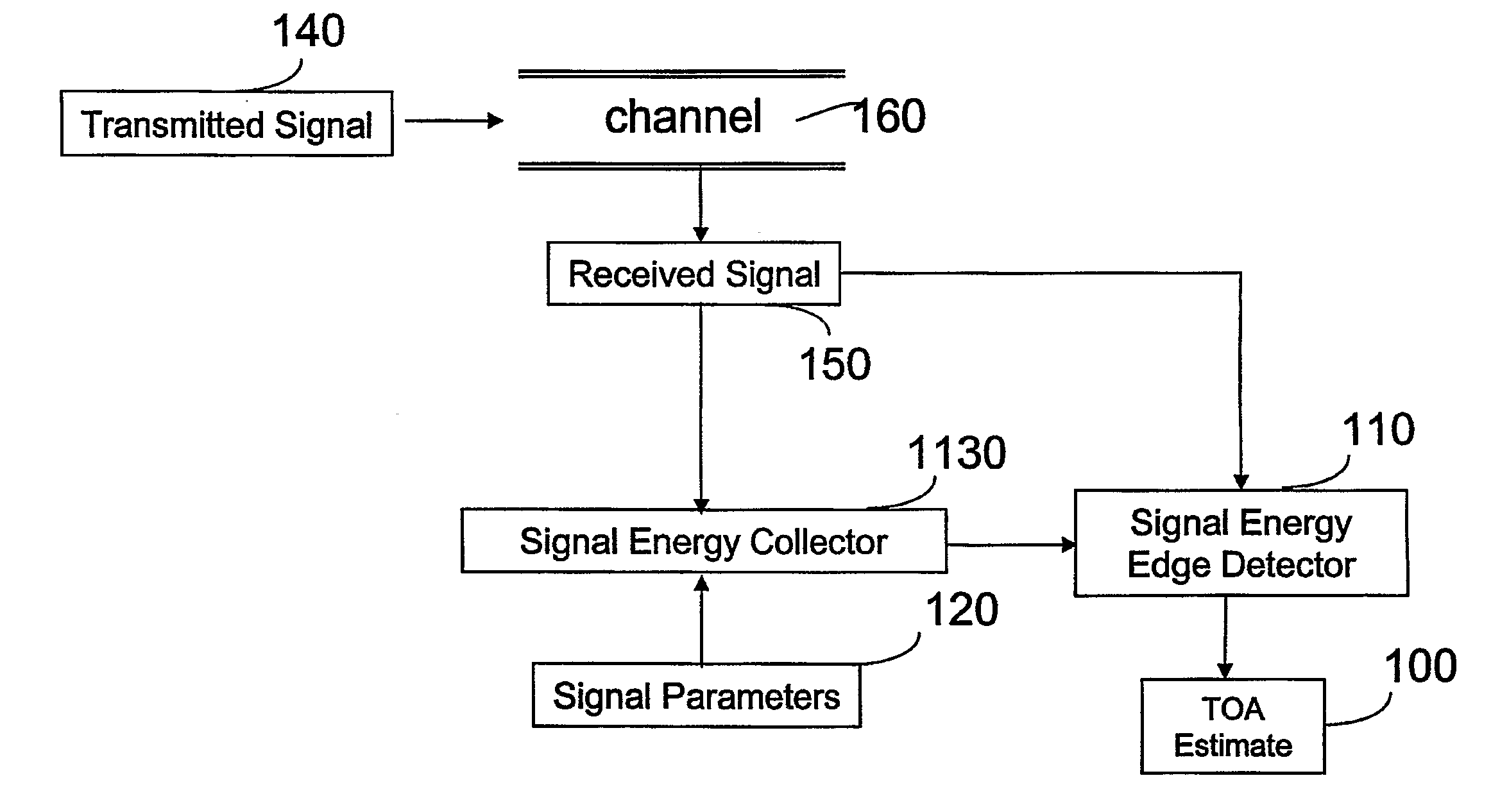
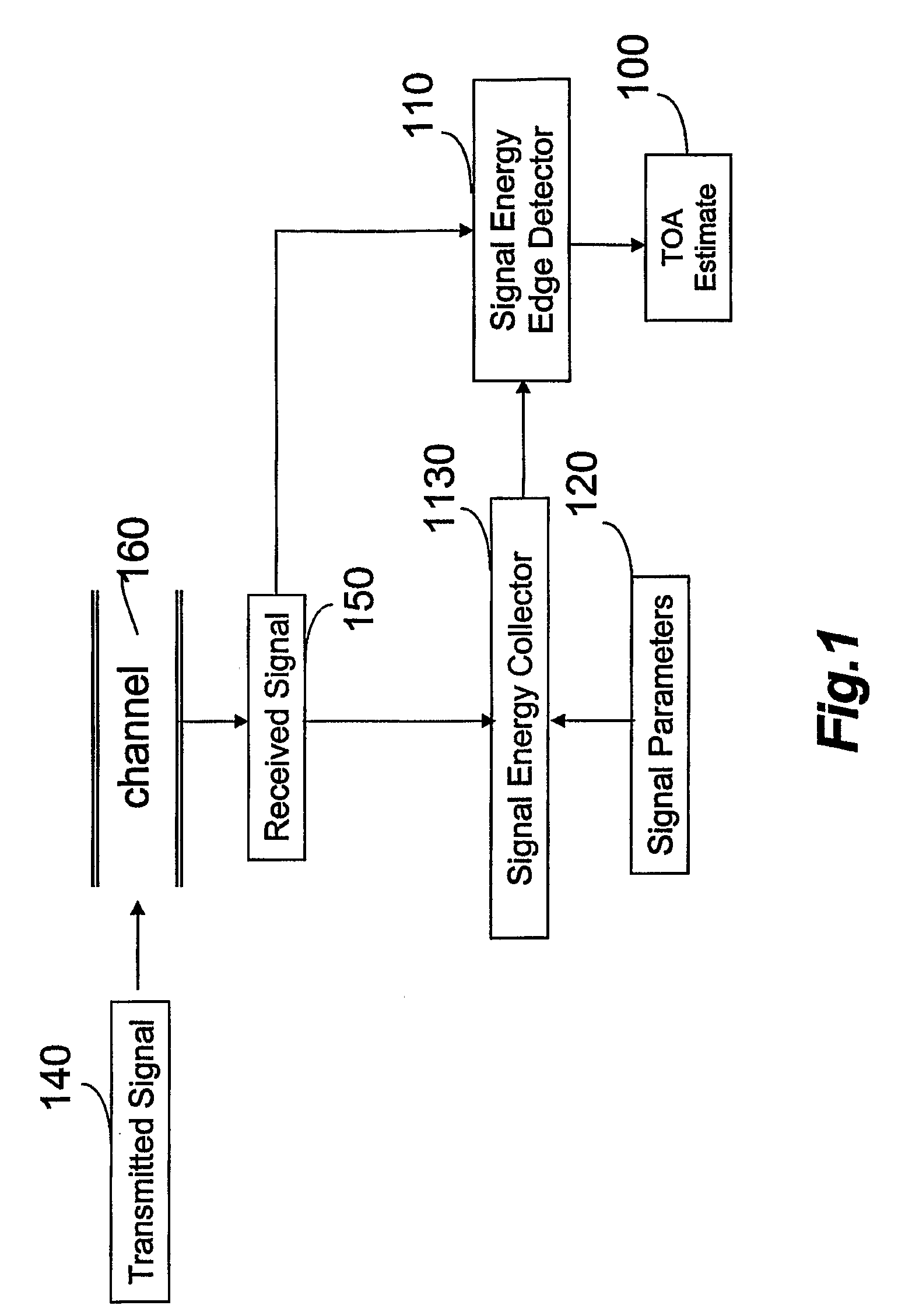
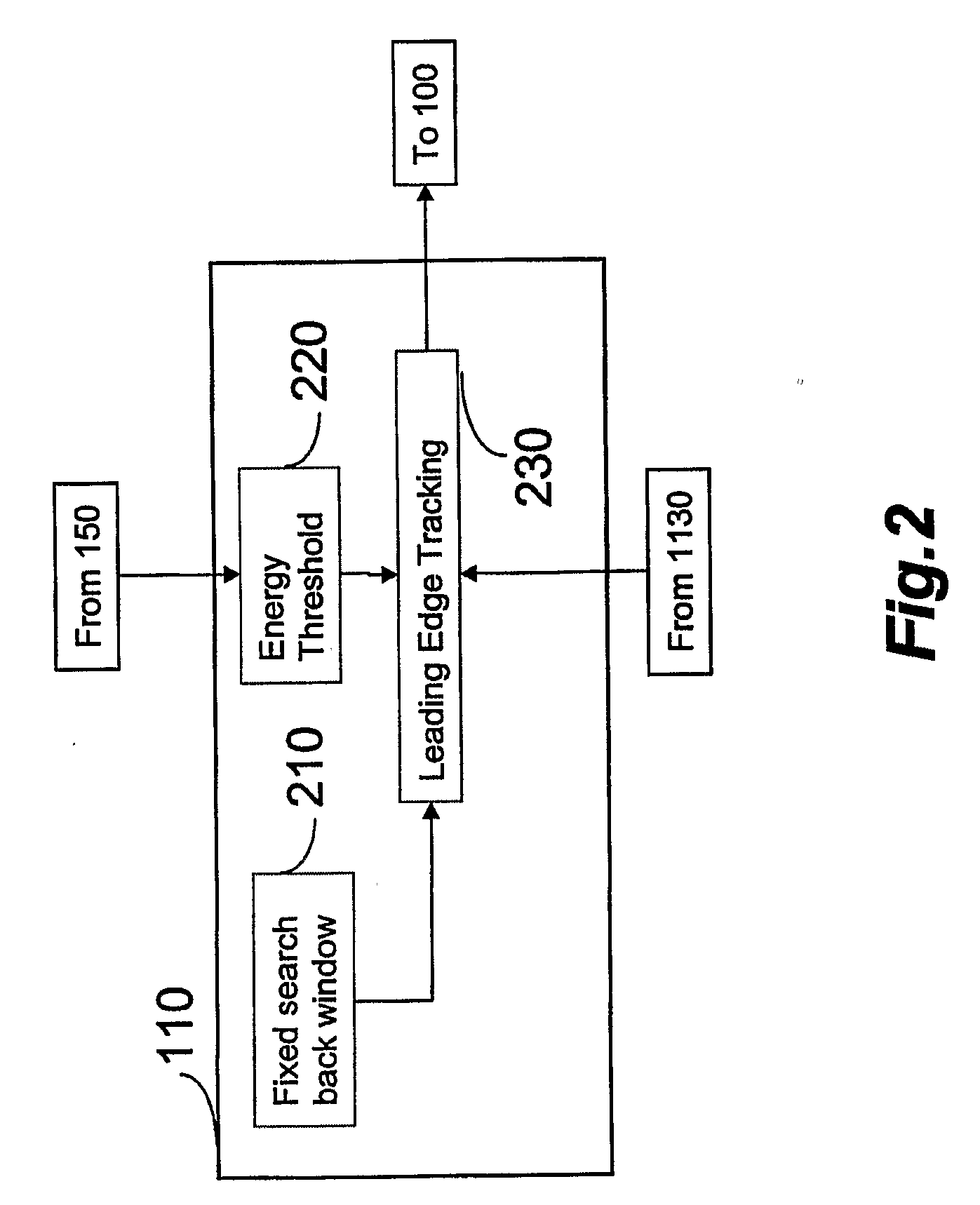
Method and Receiver for Identifying a Leading Edge Time Period in a Received Radio Signal
A method for identifying a leading edge time period of a received radio signal includes identifying a greatest energy time period in a sequence of time periods. The received radio signal has a greatest average energy in the greatest energy time period. The method also includes identifying a least energy time period in the sequence of time periods. The received radio signal has a least average energy in the least energy time period. Further, the method includes setting a threshold energy based on the greatest average energy and the least average energy, determining a number of window time periods based on a characteristic of a radio channel used by the received radio signal, and identifying as a leading edge time period an earliest time period that precedes the greatest energy time period within the number of window time periods. The received radio signal in the leading edge time period has an average energy greater than or equal to the threshold energy.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Apparatus and method for forming downlink beam in a smart antenna system
InactiveUS20050101354A1Reduce errorsSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysSpatial correlationPhase difference
Disclosed is an apparatus for forming a downlink traffic beam in a base station that separately forms a traffic beam for each user using multiple antennas. In the apparatus, an instantaneous direction estimator detects a signal having maximum energy and an energy value from a received uplink signal. A downlink spatial correlation matrix update unit calculates a downlink spatial correlation matrix using an output value of the instantaneous direction estimator and a downlink antenna direction response characteristic. A beam vector adaptation unit outputs a downlink bean-forming vector by reflecting a phase difference between a common beam and a traffic beam from an output of the downlink spatial correlation matrix update unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic core plasmon antenna with improved coupling efficiency
ActiveUS20120008229A1Efficient couplingReduce energy lossCombination recordingNanoopticsVariable thicknessMagnetic anisotropy
A TAMR (Thermal Assisted Magnetic Recording) write head uses the energy of optical-laser generated plasmons in a magnetic core plasmon antenna to locally heat a magnetic recording medium and reduce its coercivity and magnetic anisotropy. To enable the TAMR head to operate most effectively, the maximum gradient and value of the magnetic recording field should be at a point of the magnetic medium that is as close as possible to the point being heated. In addition, the coupling between the optical mode and the plasmon mode should be efficient so that maximum energy is transmitted to the medium. The present invention achieves both these objects by surrounding the magnetic core of a plasmon antenna by a variable thickness plasmon generating layer, whose thinnest and shortest portion is at the ABS end of the TAMR head and whose thickest and longest portion efficiently couples to the optical mode of a waveguide to produce a plasmon.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
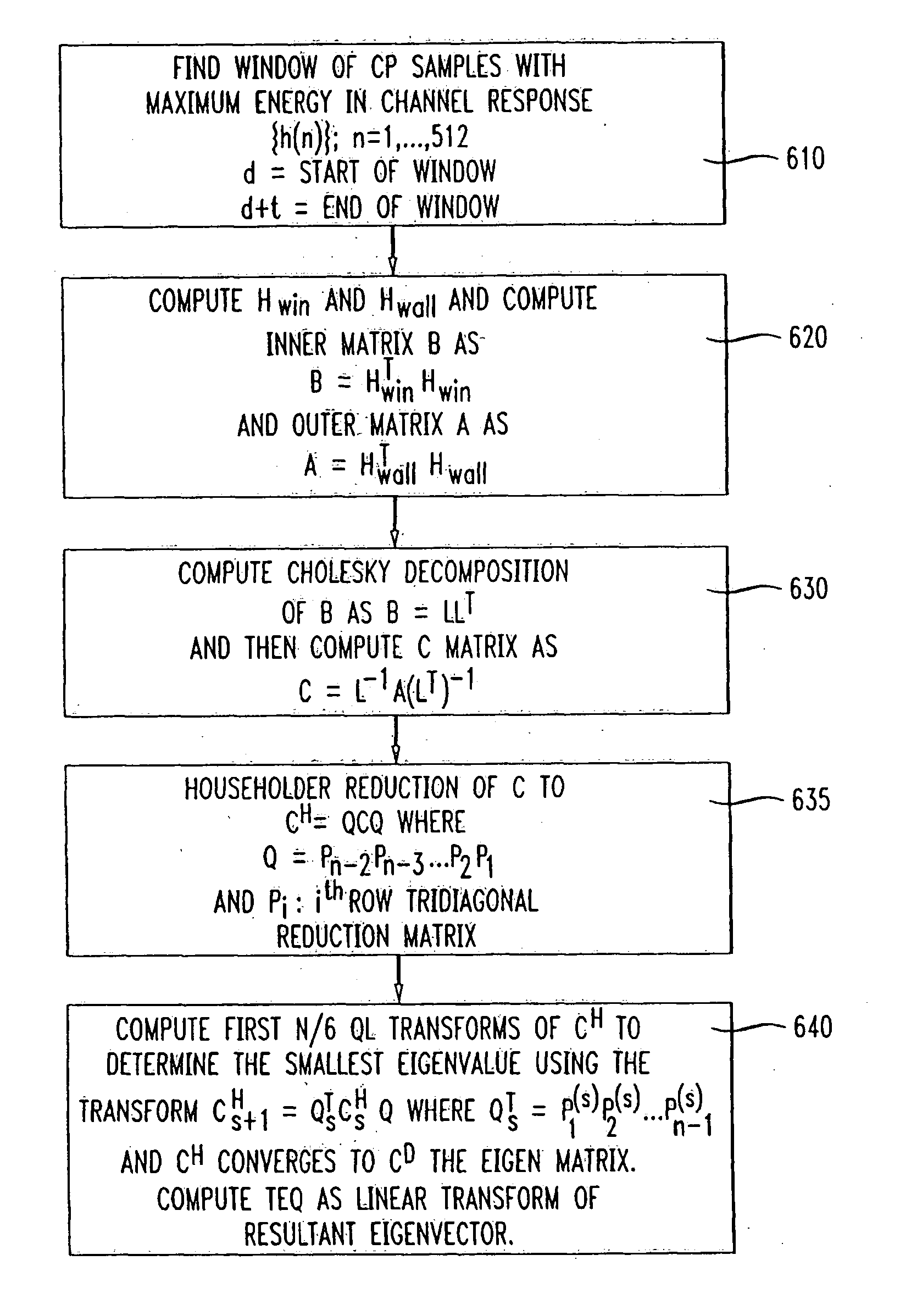
Efficient reduced complexity windowed optimal time domain equalizer for discrete multitione-based DSL modems
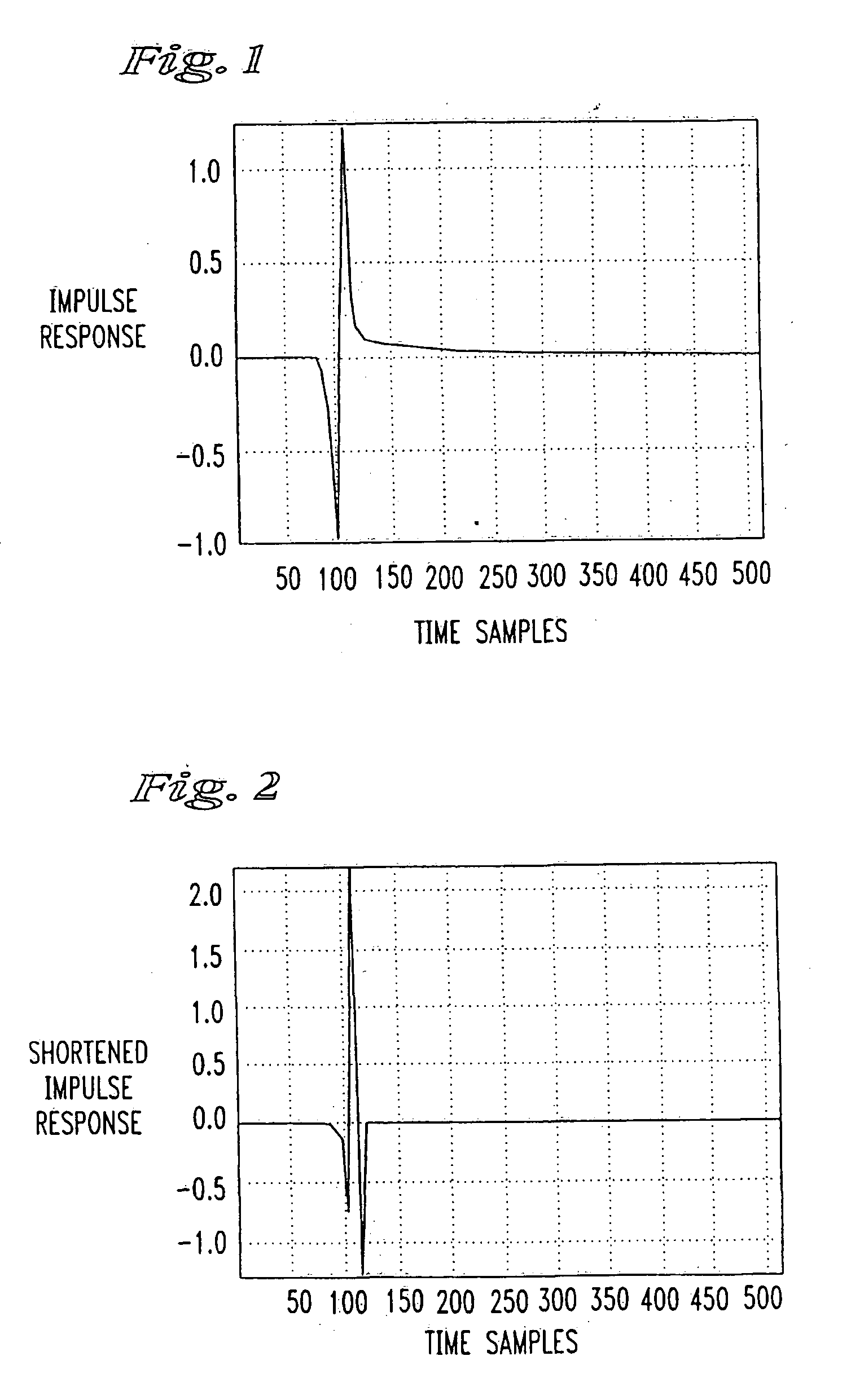
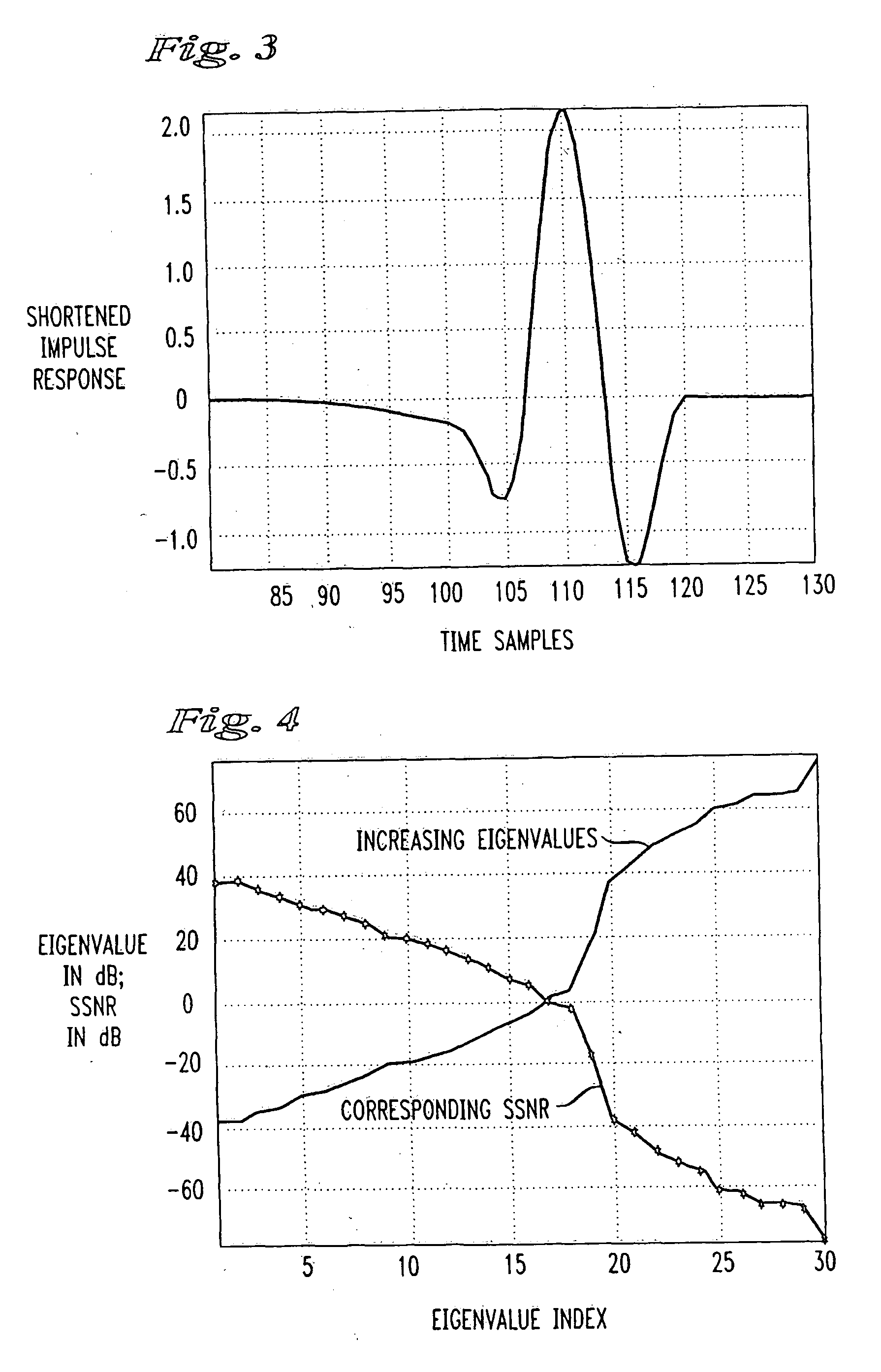
InactiveUS20060115030A1Reduce signal to noise ratioAccuracy issueMultiple-port networksTransmission path divisionDigital dataDigital signal processing
An algorithm for computing an efficient, reduced complexity, windowed optimal linear time domain equalizer for a dispersive channel comprises the steps of determining a window of maximum energy in the impulse response of length equal to or less than a number of cyclic prefix samples associated with a received digital data signal, computing the corresponding inside and outside matrices, performing an inverse Cholesky decomposition of the inside matrix, creating a resultant matrix as the product of the outer and the upper and lower square root inner matrix, followed by Householder reduction and QL transformation to thereby compute the time domain equalizer as the linear transformation of the eigenvector corresponding to the smallest eigenvalue at the receiver. The smallest eigenvalue is determined using the aforementioned orthogonal transformations without determining all the eigenvalues efficiently but without the loss accuracy associated with iterative methods like the conventional power method. The algorithm may be most conveniently implemented, for example, in the form of a thirty-two bit digital signal processor at a data receiver.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method for realizing OFDM system synchronization using circulating prefix
InactiveCN1878157AEasy to controlImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsCyclic prefixComputer science
The invention discloses a synchronizing method of circulating prefix OFDM system, which comprises the following steps: step A. finding the circulating prefix with maximum energy; step B. rotating the OFDM symbol to the corresponding position of maximum energy circulating prefix; realizing synchronous parameter of coherent estimation at receiving end. The invention simplifies effective control for PAPR, which needn't larger calculating expenditure for sending and receiving ends.
Owner:ZTE CORP
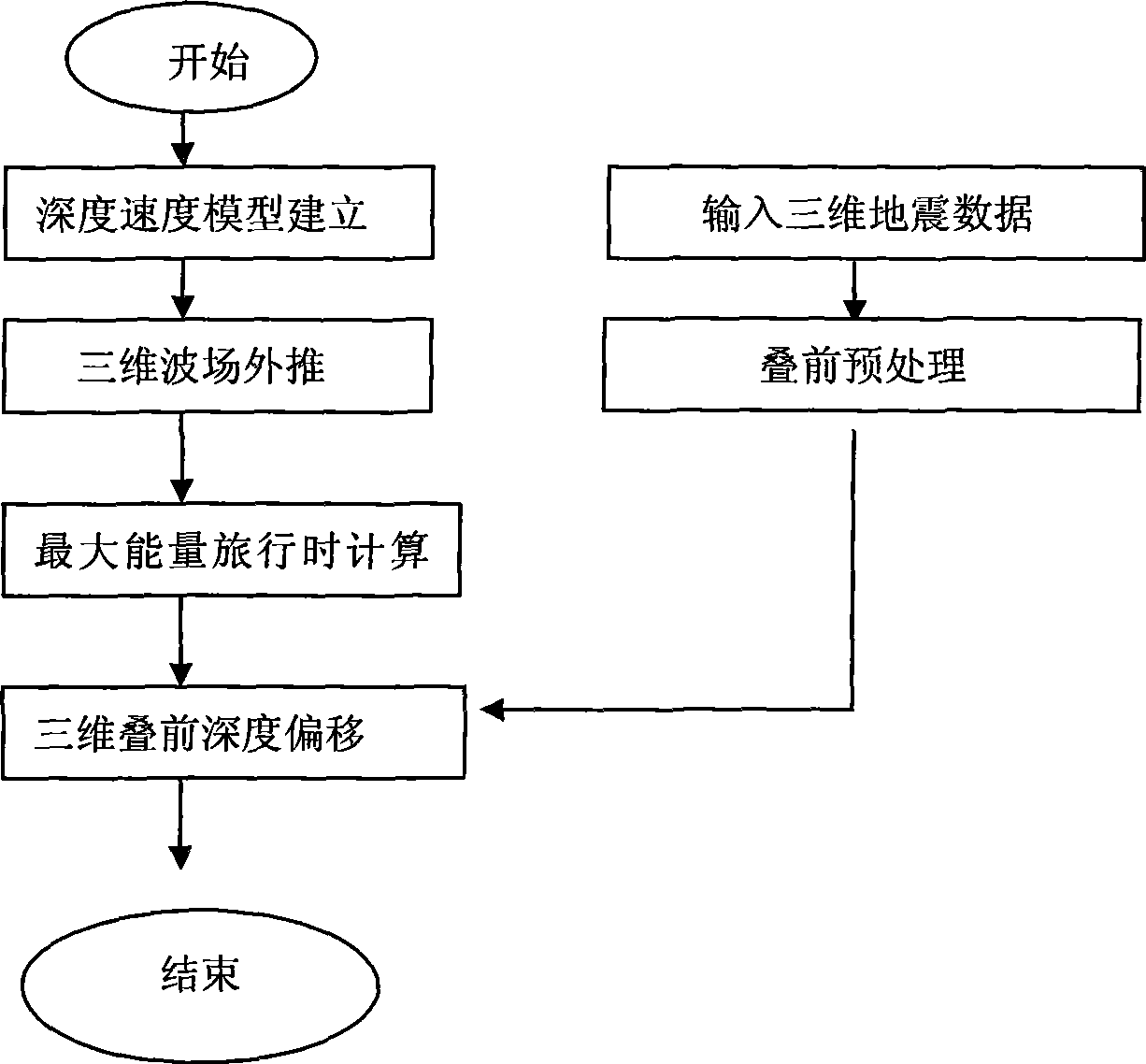
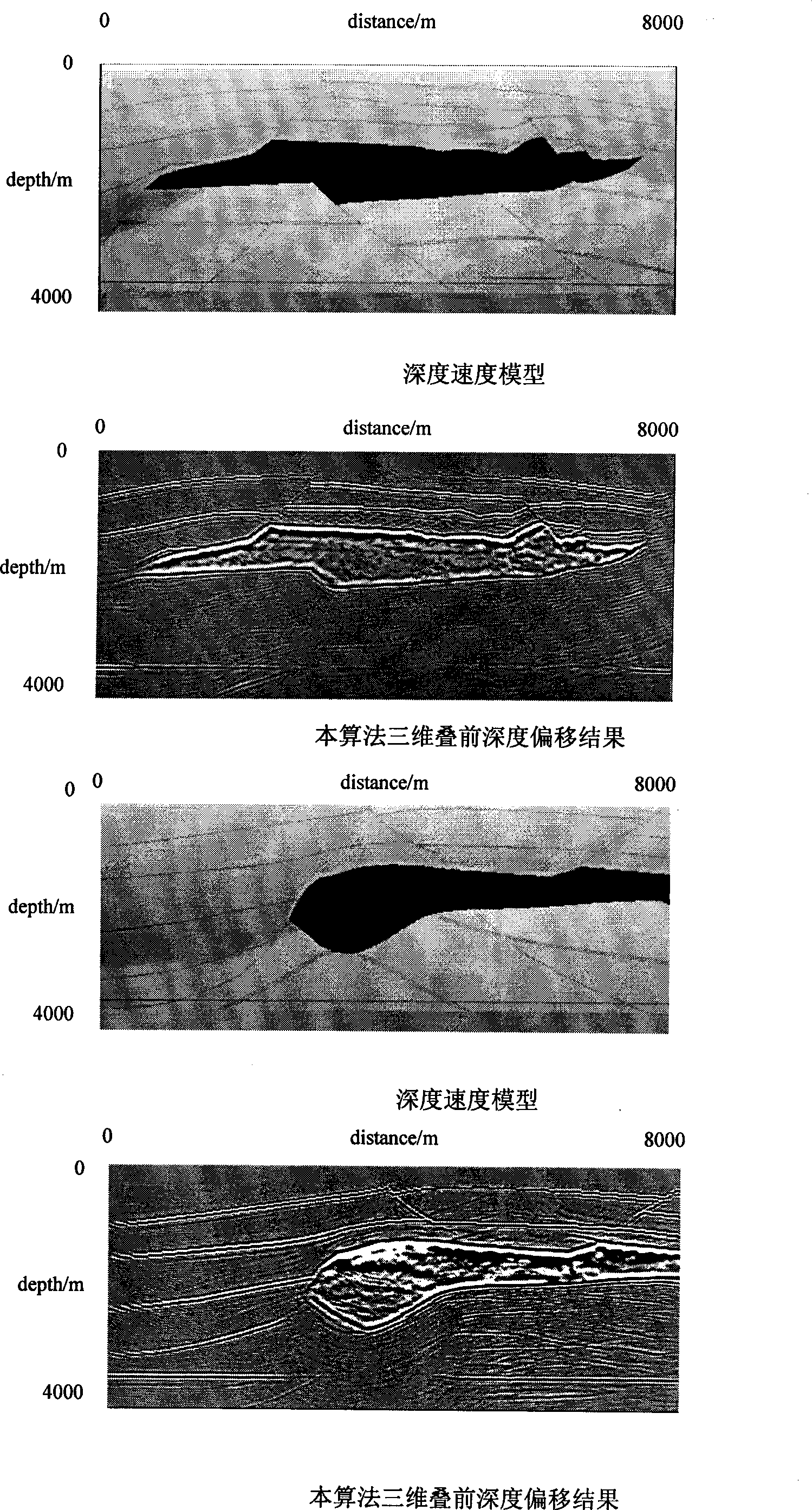
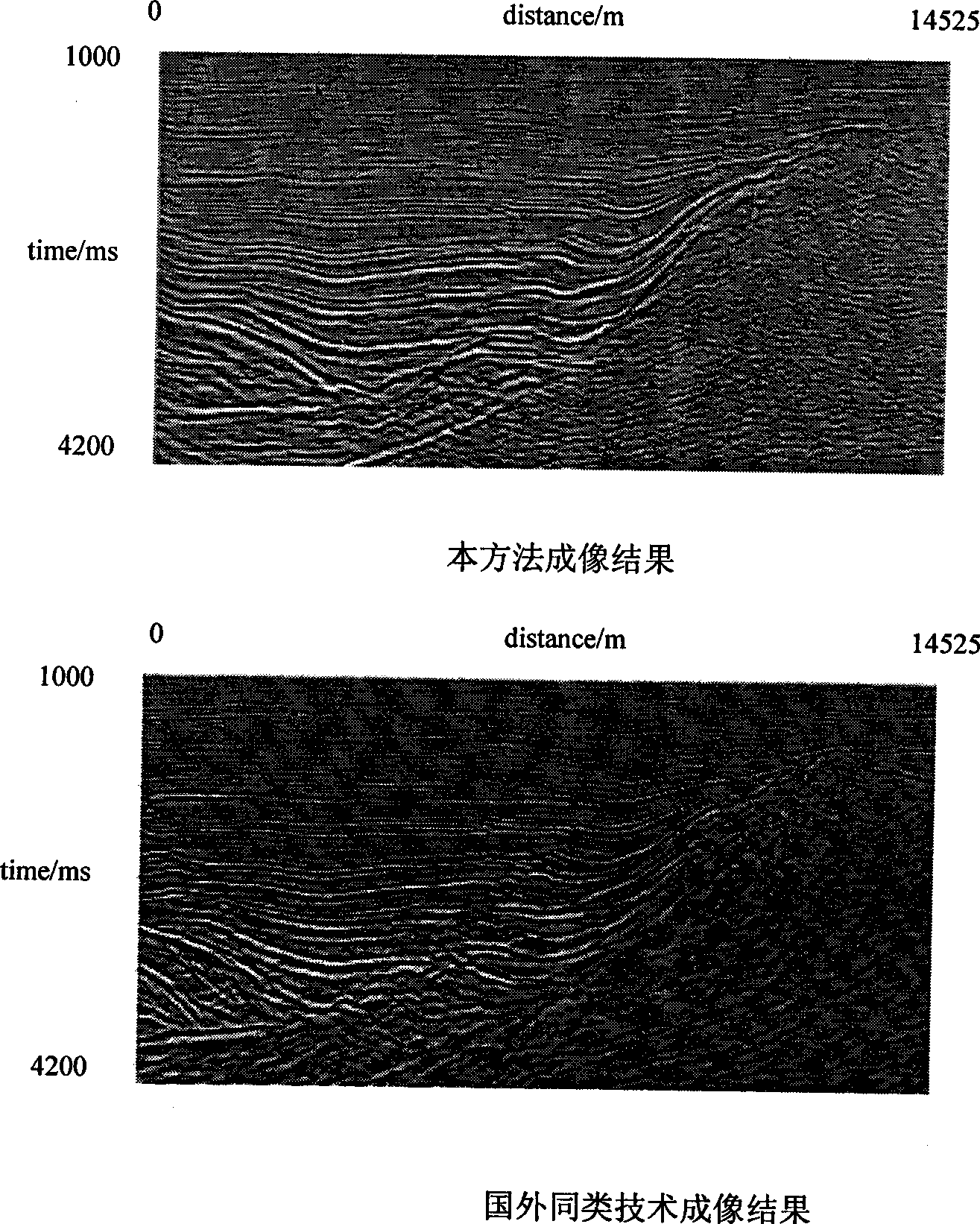
Tridimensional integral prestack depth migration method based on maximum energy travel calculation
InactiveCN101545986ASmall amount of calculationFlexible imagingSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingVibration amplitudeRectangular coordinates
The invention relates to the prestack depth migration technique during the data processing of petroleum seismic prospecting, including the following concrete steps: establishing depth rate pattern of prestack seismic data; well designing observation grids, and solving wave equation in sphere coordinate system to simulate the communication process of seismic waves; changing and converting the calculated seismic wave field of a frequency domain into a time domain, and fitting the Green function energy spectrum of the seismic wave field in the time domain to detect the arriving time and the vibration amplitude when the maximum energy arrives; transferring the travel time and the vibration amplitude field calculated in the sphere coordinate system to a rectangular coordinate system; accomplishing the maximum energy integral prestack depth migration according to the well calculated travel time and the vibration amplitude; analyzing the operation of speed to the imaging gather of the prestack depth migration to modify the depth rate pattern; and modifying the depth rate pattern by iteration, and outputting the ultimate result until the migration result meets the precision requirement. The invention provides the self-adapting variation difference grid calculation technique so as to achieve the purpose that the difference grids are automatically and gradually thinned along with radius increase, thereby guaranteeing the finite difference calculation precision.
Owner:匡斌
Searcher for multiple orthogonal channels with known data wcdma step2 search
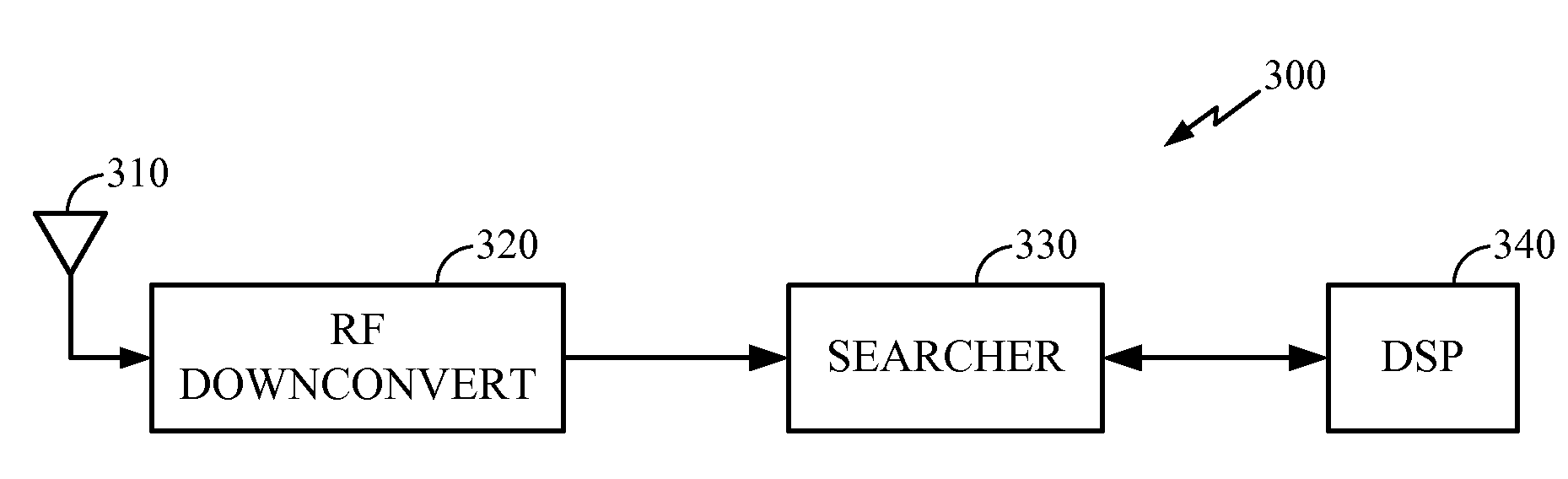
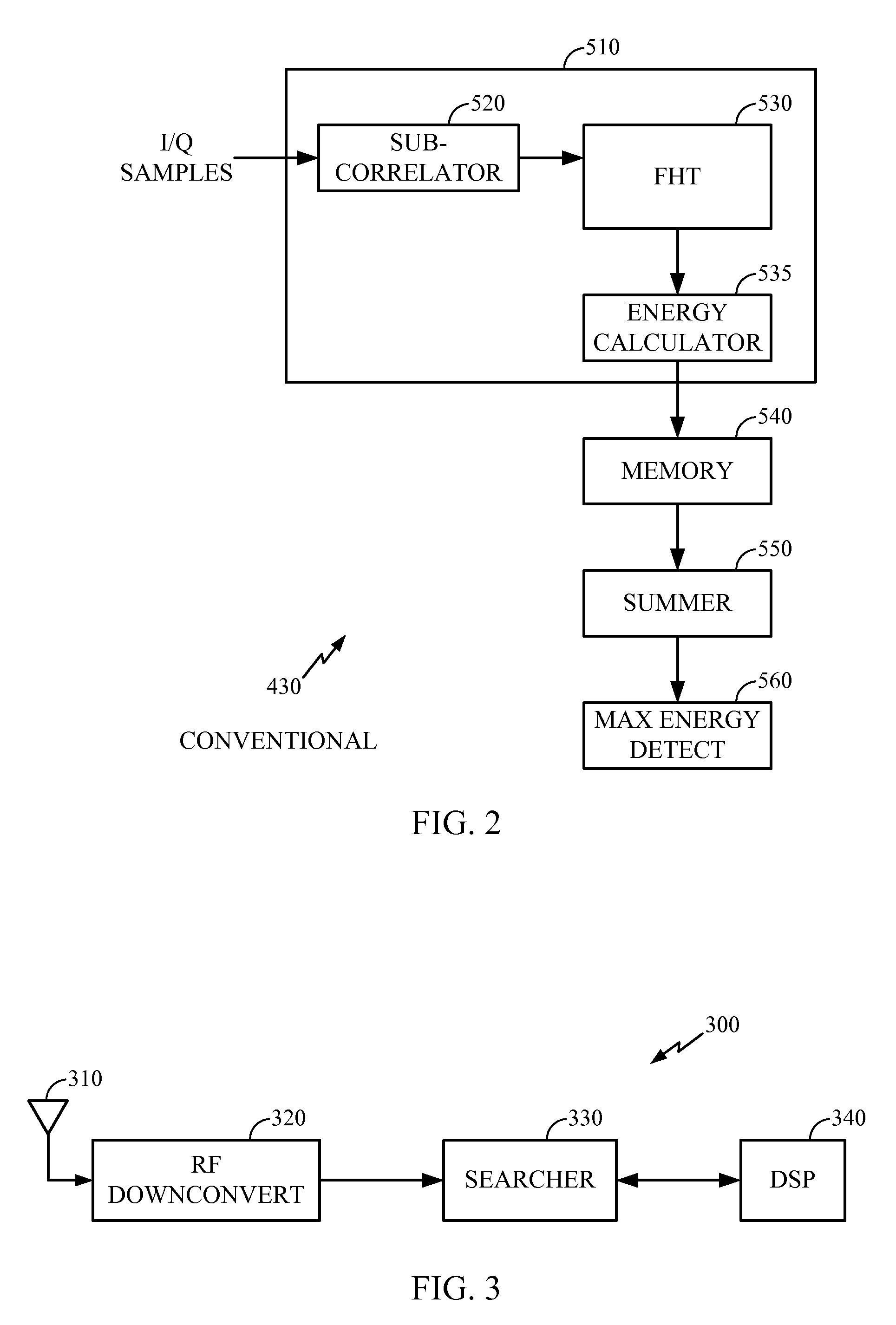
InactiveUS20090041162A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationComputer scienceCdma systems
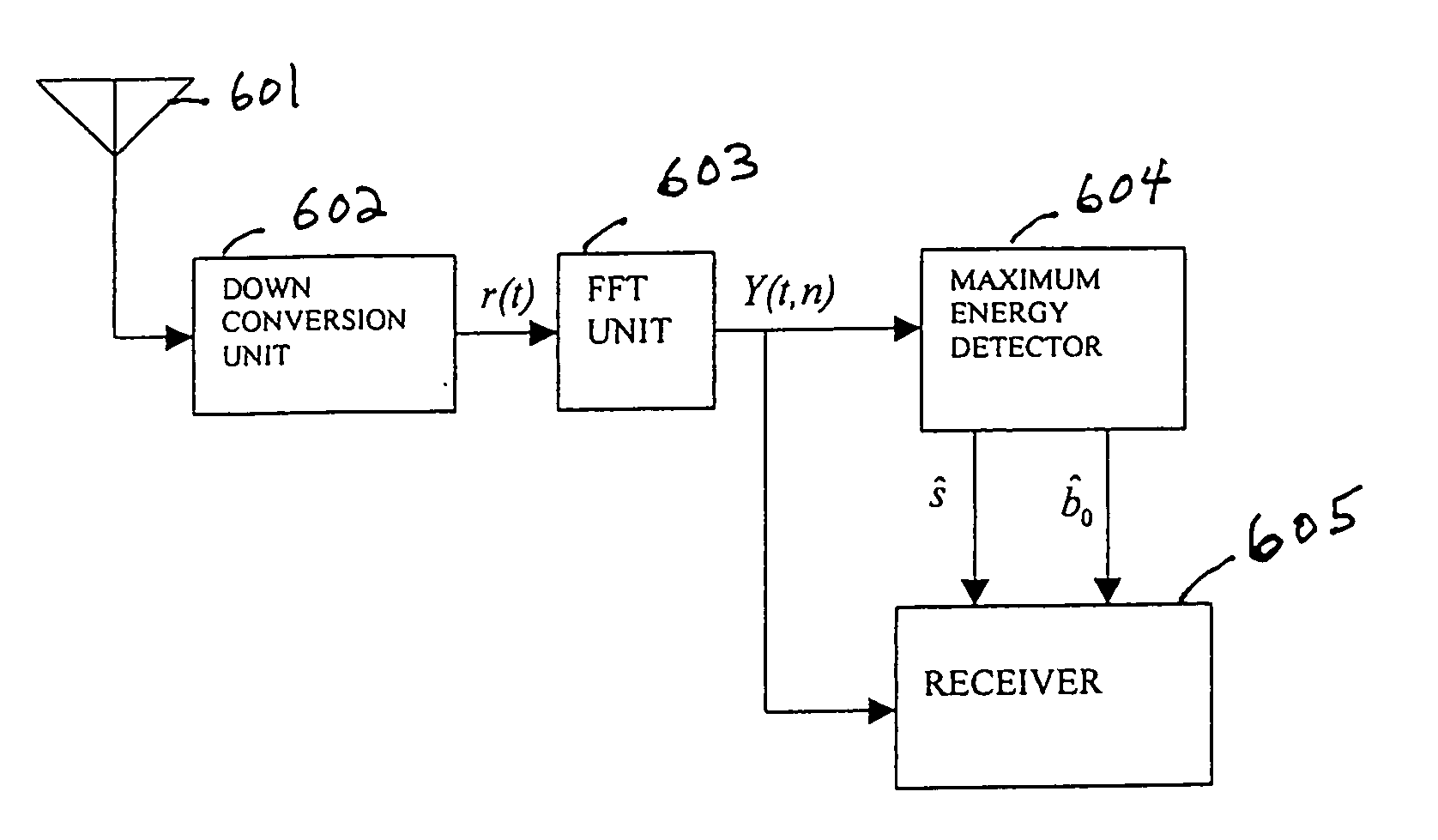
A circuit and algorithm are disclosed for a step2 search of a three step search of synchronization channels in a W-CDMA system. A mobile terminal of the CDMA system includes an RF downconverter for receiving I and Q signals. A searcher, responsive to the I and Q signals, includes a first correlator for correlating the I and Q signals with a primary synchronization code on a primary synchronization channel, and a second correlator for correlating I and Q signals with a secondary synchronization code on a secondary synchronization channel. The correlated I and Q signals are added for each of the secondary synchronization codes. An energy calculator and a maximum energy detector use the correlated I and Q signals of both the primary and secondary synchronization channels to detect the most likely scrambling code group of secondary synchronization codes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
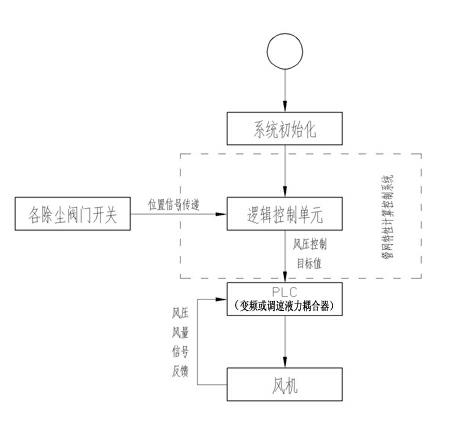
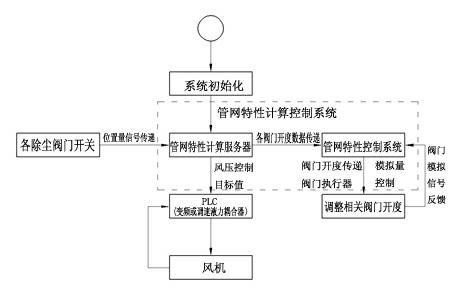
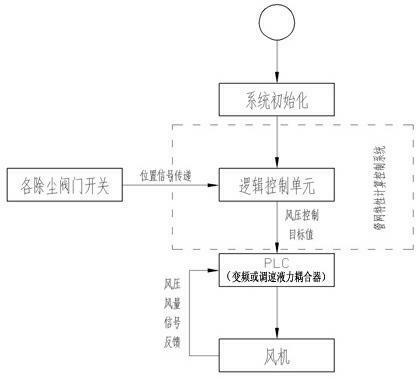
Air quantity automatic regulating method of variable working condition ventilating system
ActiveCN102635920AEasy constructionEasy to manageSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusFrequency changerFluid coupling
The invention relates to an air quantity automatic regulating method of a variable working condition ventilating system, and belongs to the technical field of ventilating and dust removing. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: inputting information of a dust removing pipe network and required air quantity of each dust collecting point into a pipe network property computing and controlling system, and determining the air pressure and air quantity of a fan according to the required air quantity of each dust collecting point in the ventilating and dust removing system under the existing working condition; and regulating the motor frequency or the number of turns of the fan automatically by a frequency converter or a speed-regulating fluid coupling and a PLC (programmable logic controller) control system according to the air pressure and air quantity which are provided by the pipe network property computing and controlling system as the standard, and performing the enclosed ring control of the fan according to the air pressure and air quantity signals fed back by a measuring sensor on the dust removing pipe network. According to the invention, the pipe network property computing and controlling system, the frequency converter or the speed-regulating fluid coupling and the PLC control system are separated, an individual functional module is formed respectively, and is convenient to construct and manage, the regulation of the fan property and the dust removing pipe network property as required according to the dust removing pipe network working condition variation is realized, and maximal energy conservation on the premises of guaranteeing the dust removing effect is realized.
Owner:唐山昊丰环保科技有限公司
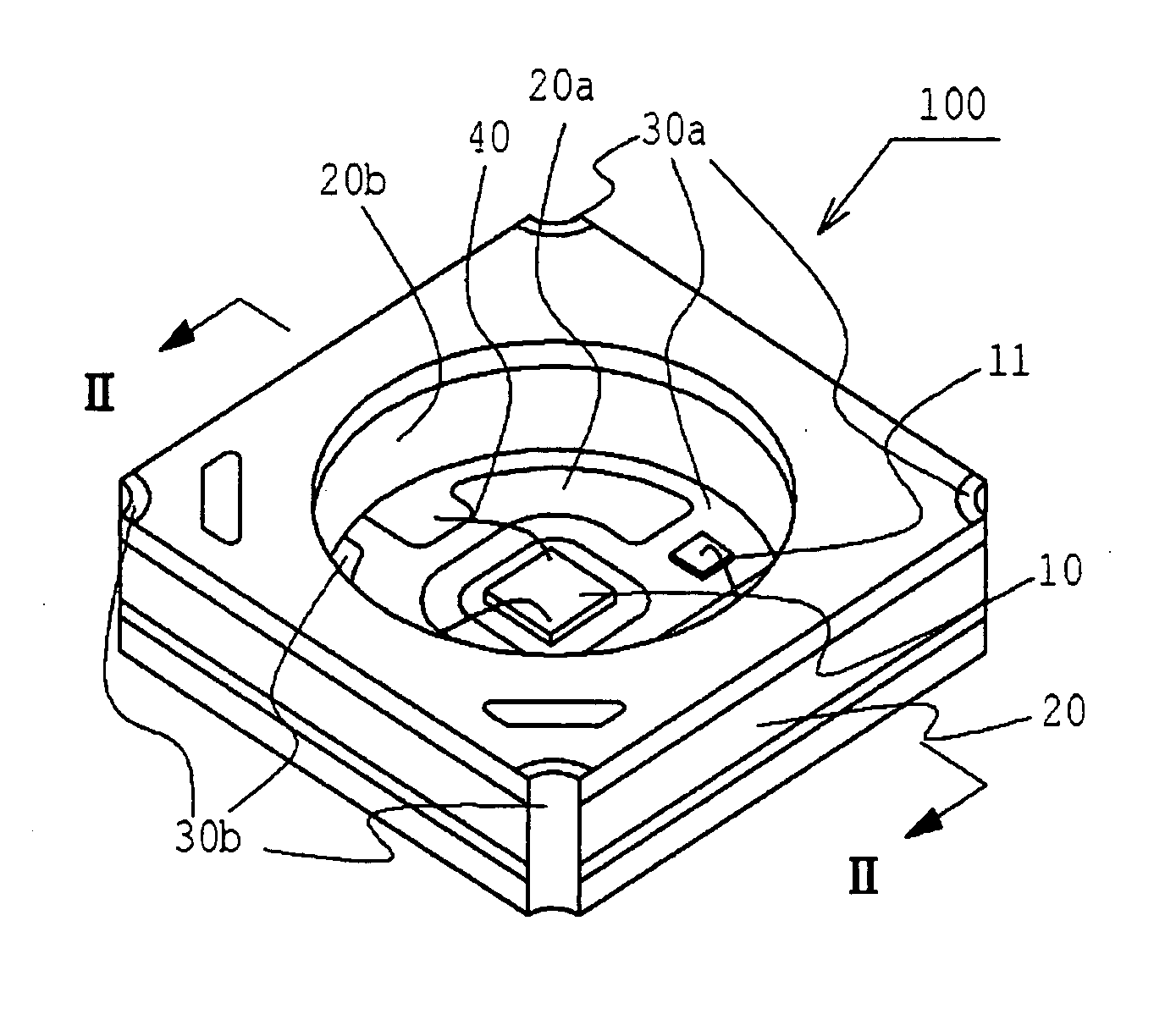
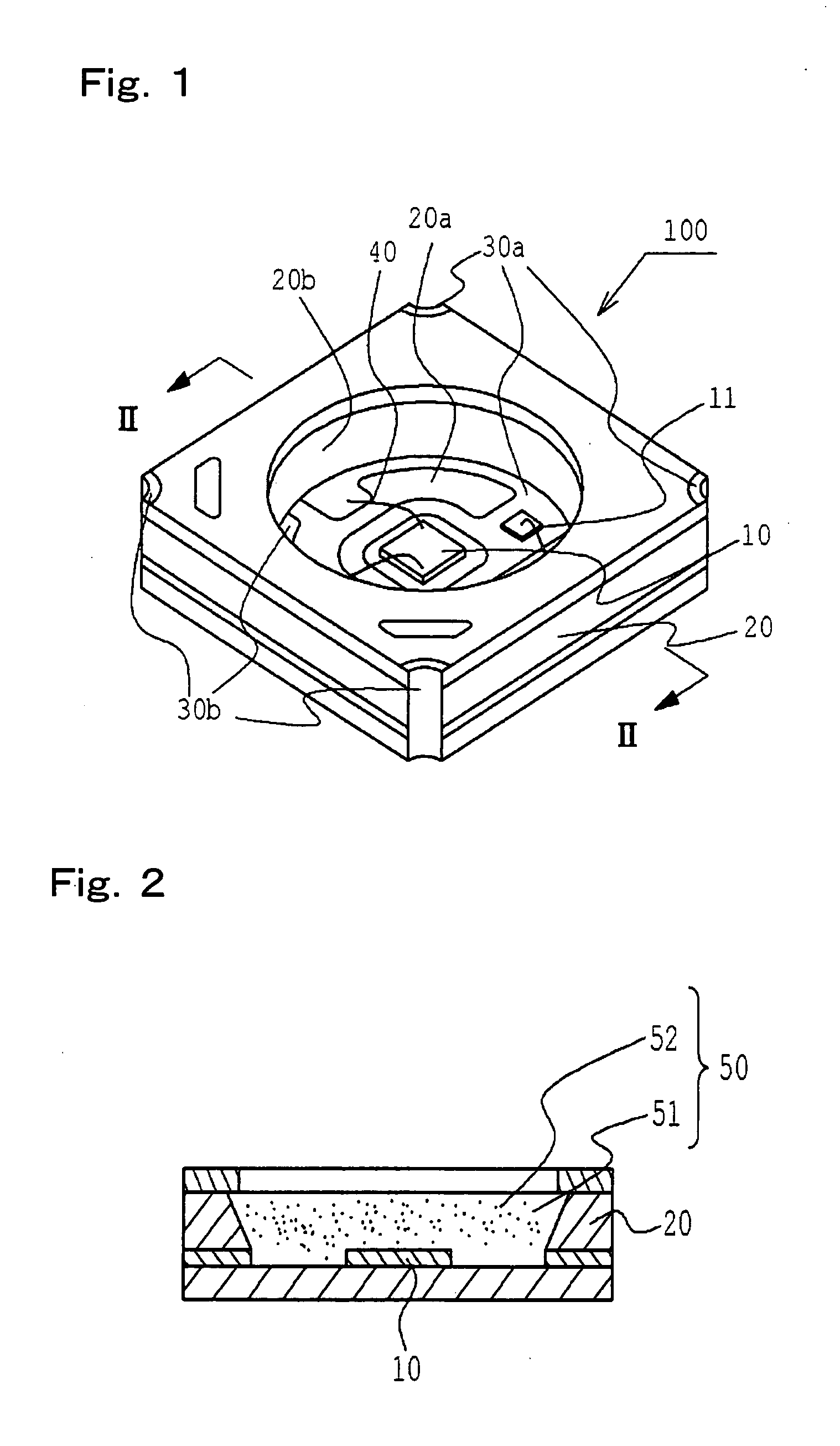
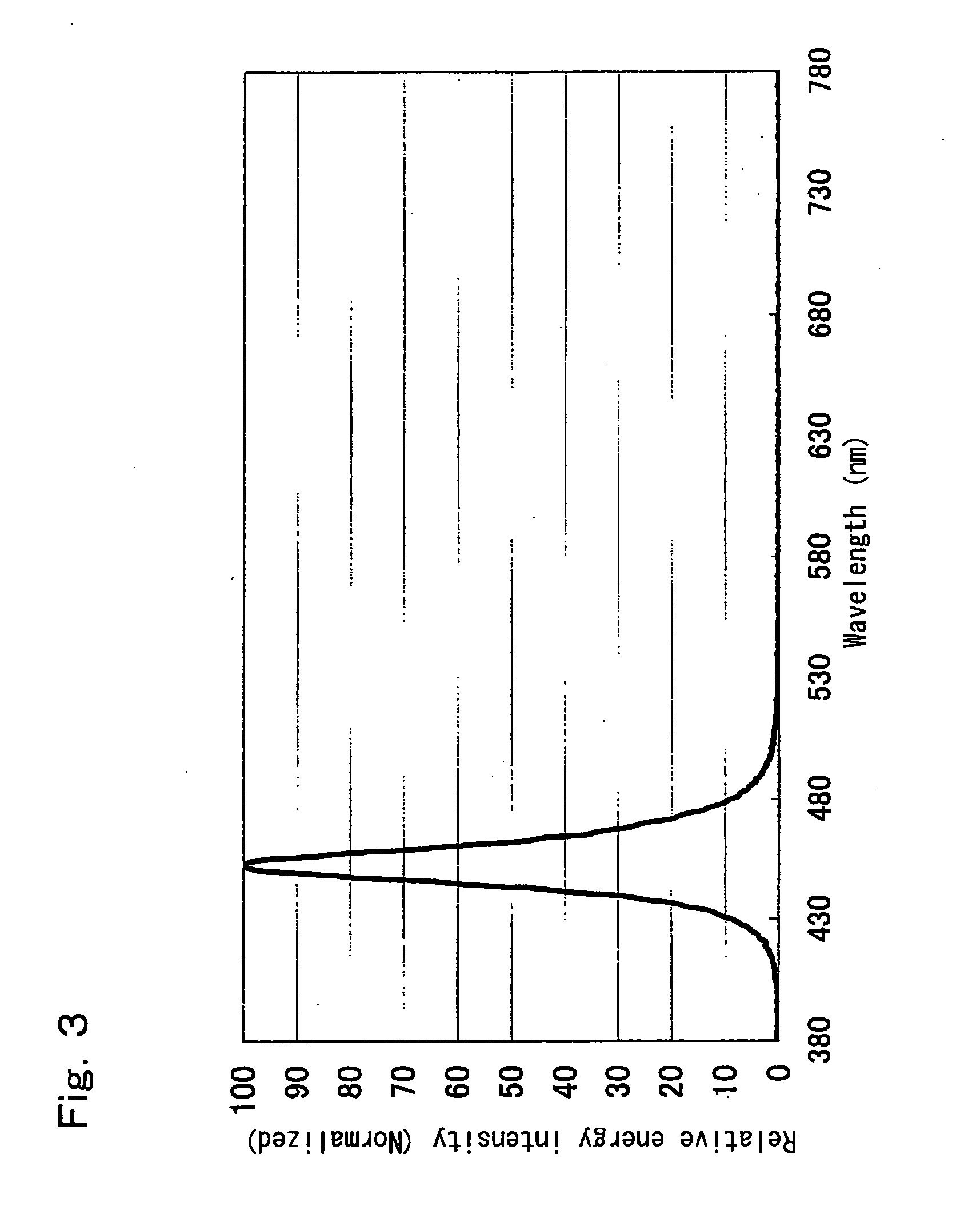
Light Emitting Device
ActiveUS20100277054A1Improve coloring performanceSmall sizeDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsLength waveLight-emitting diode
A light emitting device having a wavelength converting member for absorbing light from a pumping light source and converting its wavelength. Assuming a wavelength where the light from the pumping light source has a maximum energy intensity is a first wavelength, a wavelength where the light from the wavelength converting member has a maximum energy intensity is a second wavelength, a wavelength between the first and second wavelengths where emission spectrum of the light emitting device has a minimum energy intensity is a third wavelength, and a wavelength of 650 nm is a fourth wavelength, the ratio of energy intensity between the first and third wavelengths is 100:15-150, and the ratio of energy intensity between the first and fourth wavelengths is 100:45-200.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com