Patents
Literature
628 results about "Frequency-shift keying" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier signal. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. The simplest FSK is binary FSK (BFSK). BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary (0s and 1s) information. With this scheme, the "1" is called the mark frequency and the "0" is called the space frequency.
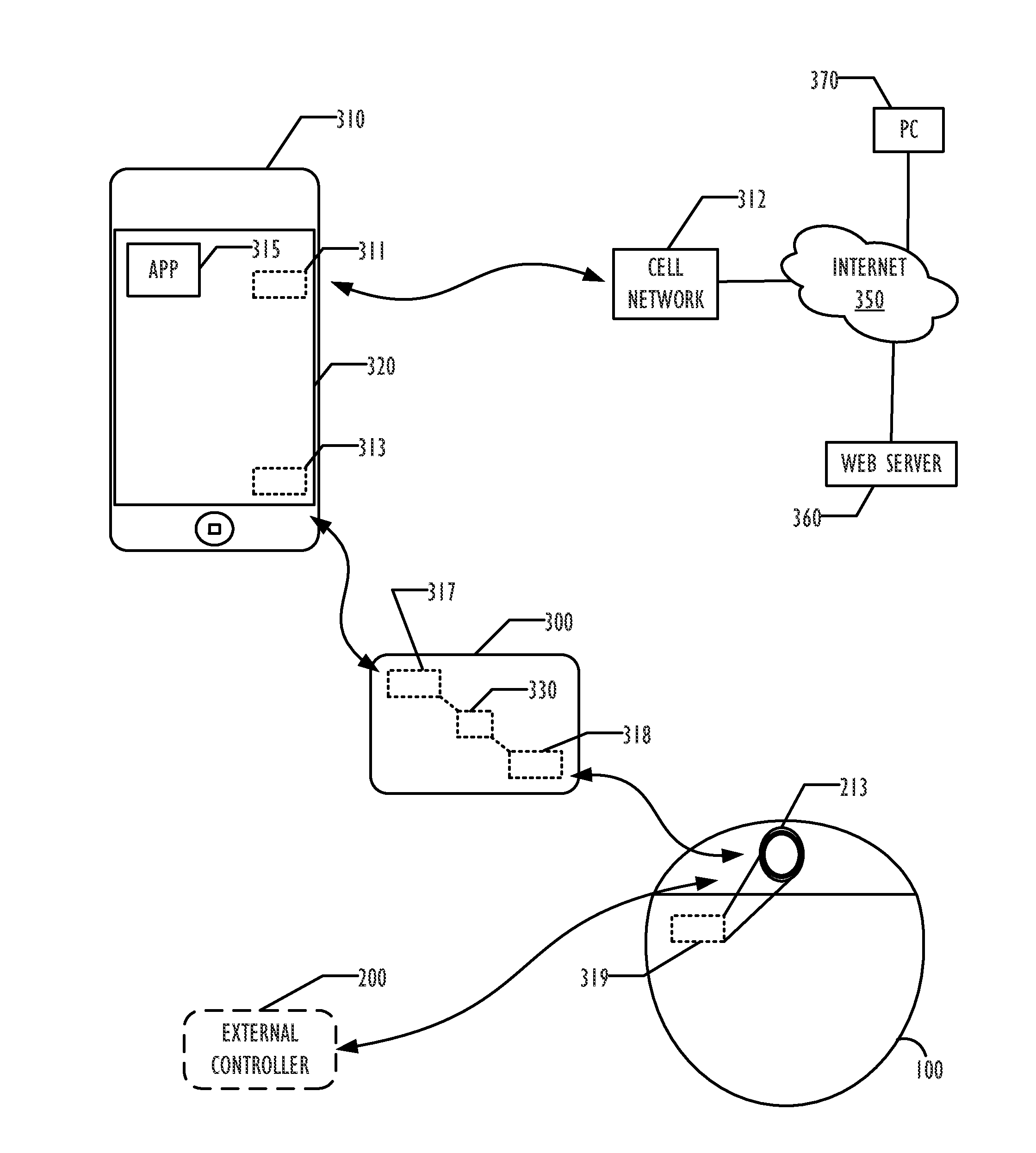
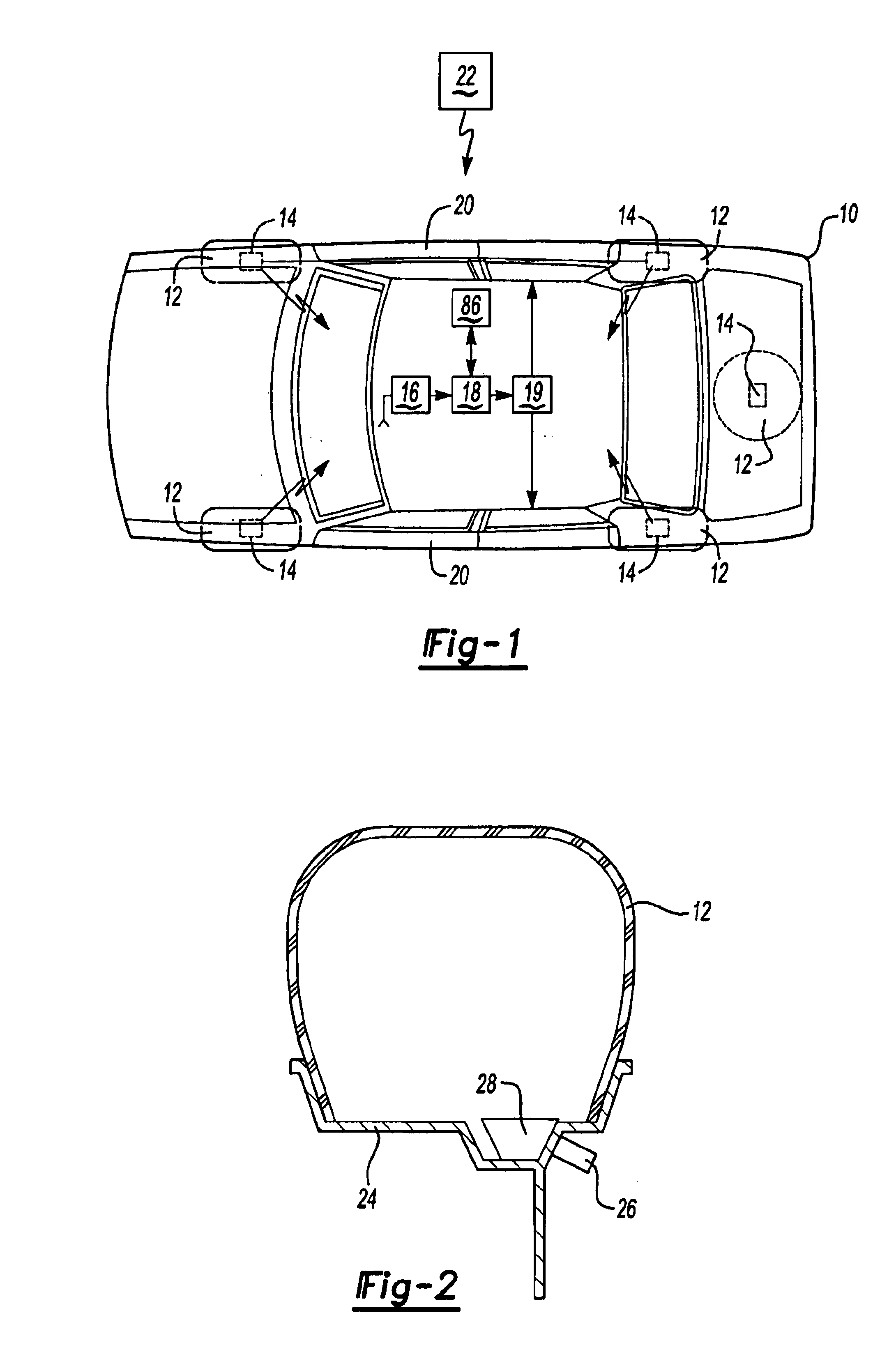
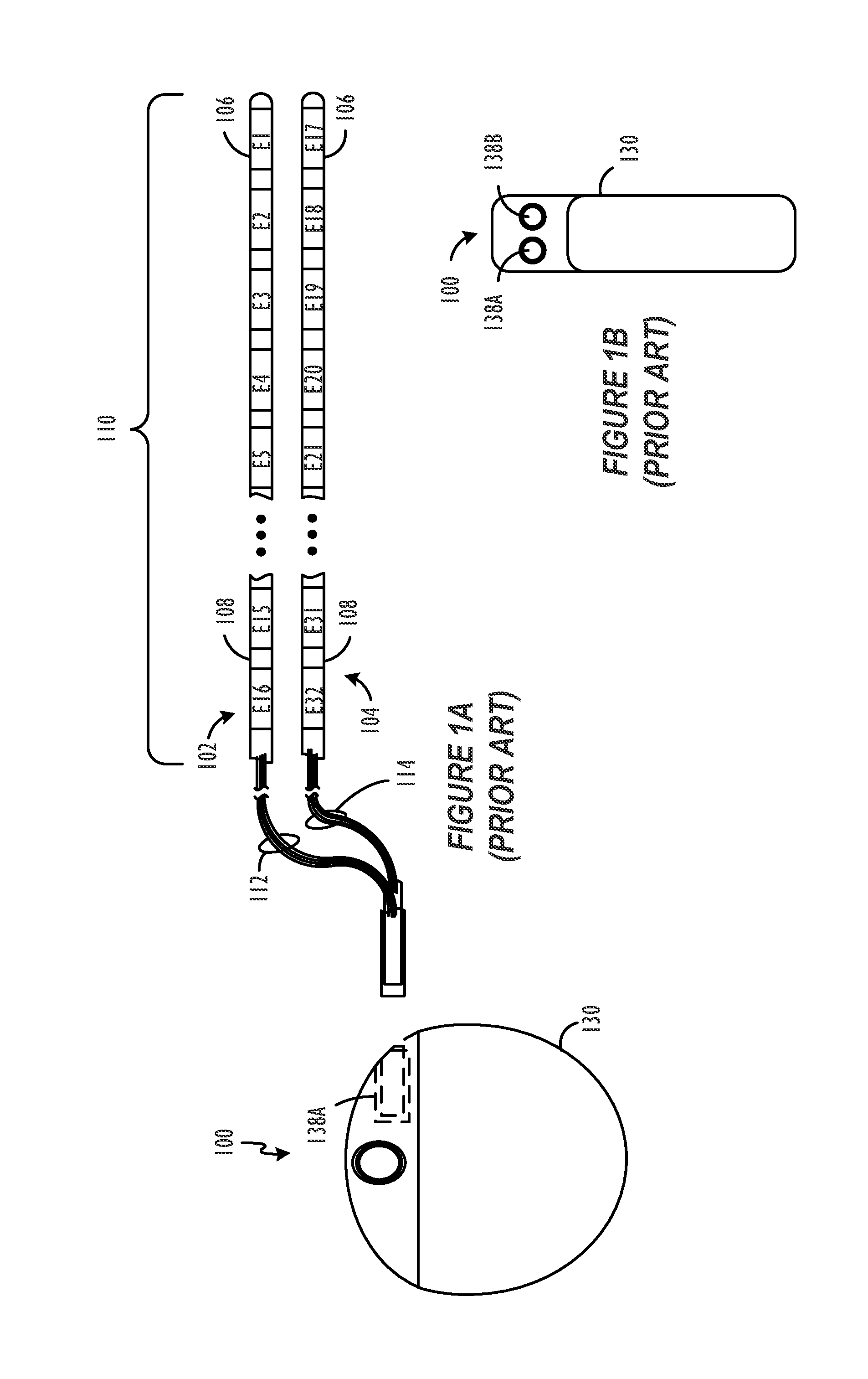
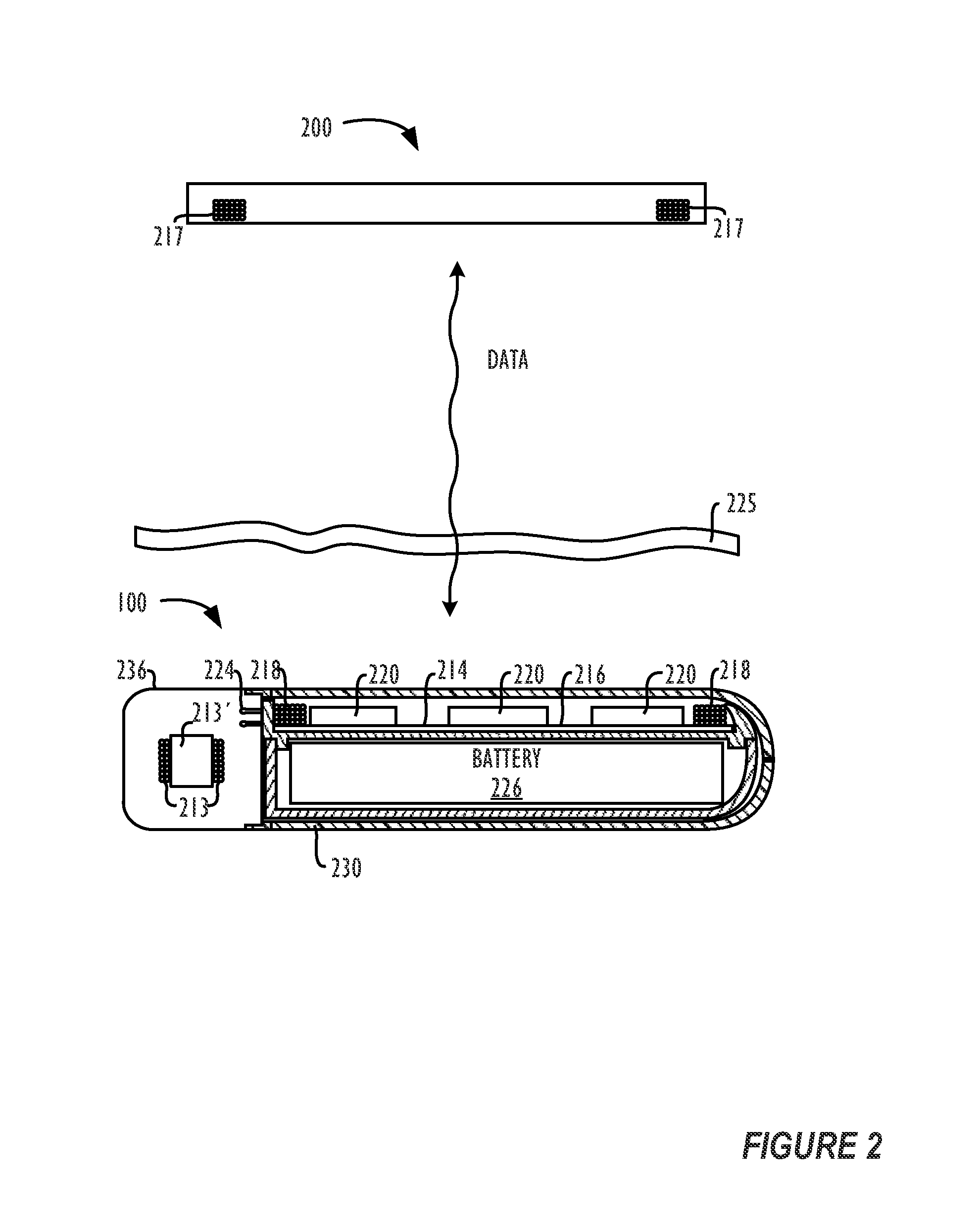
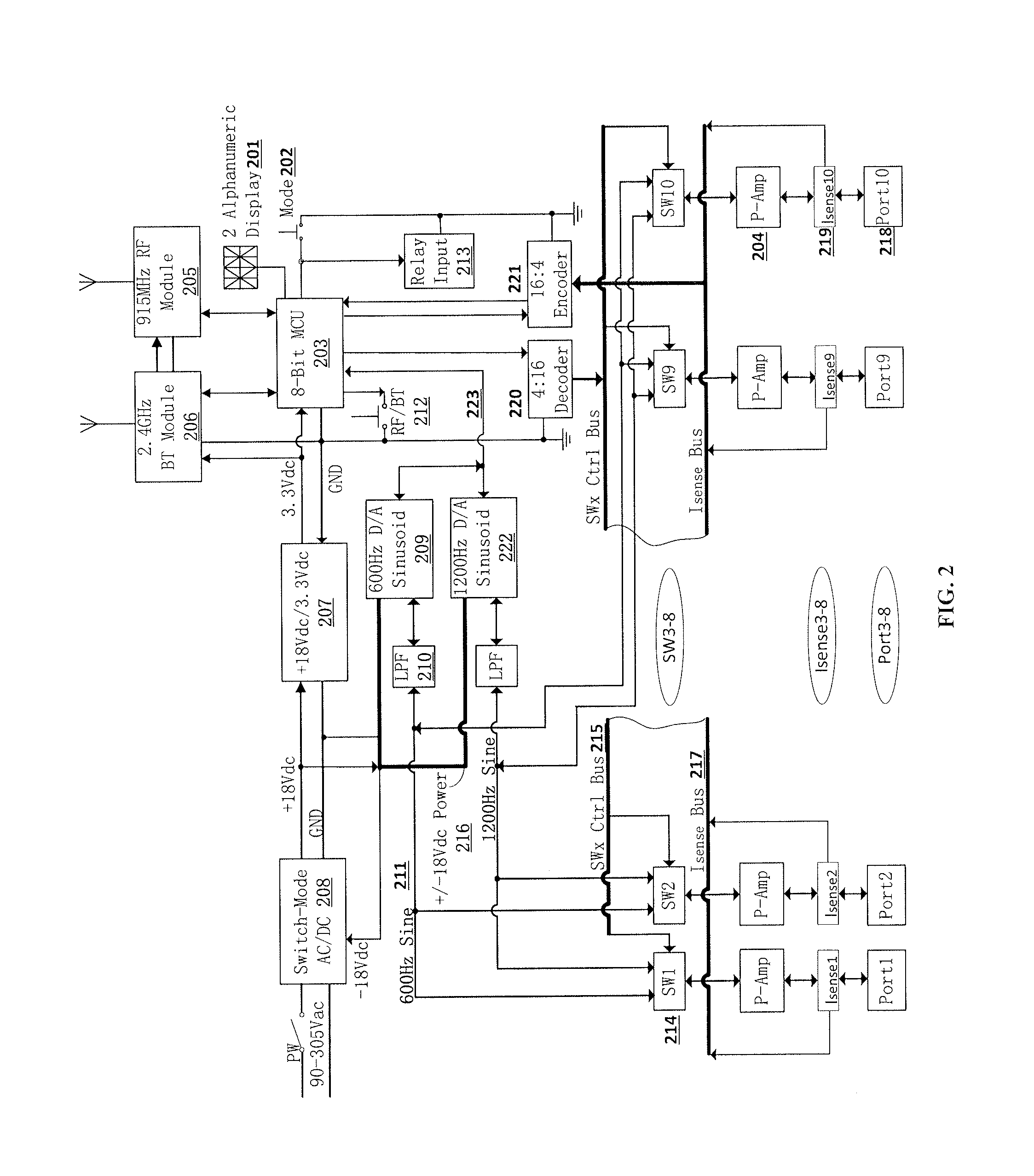
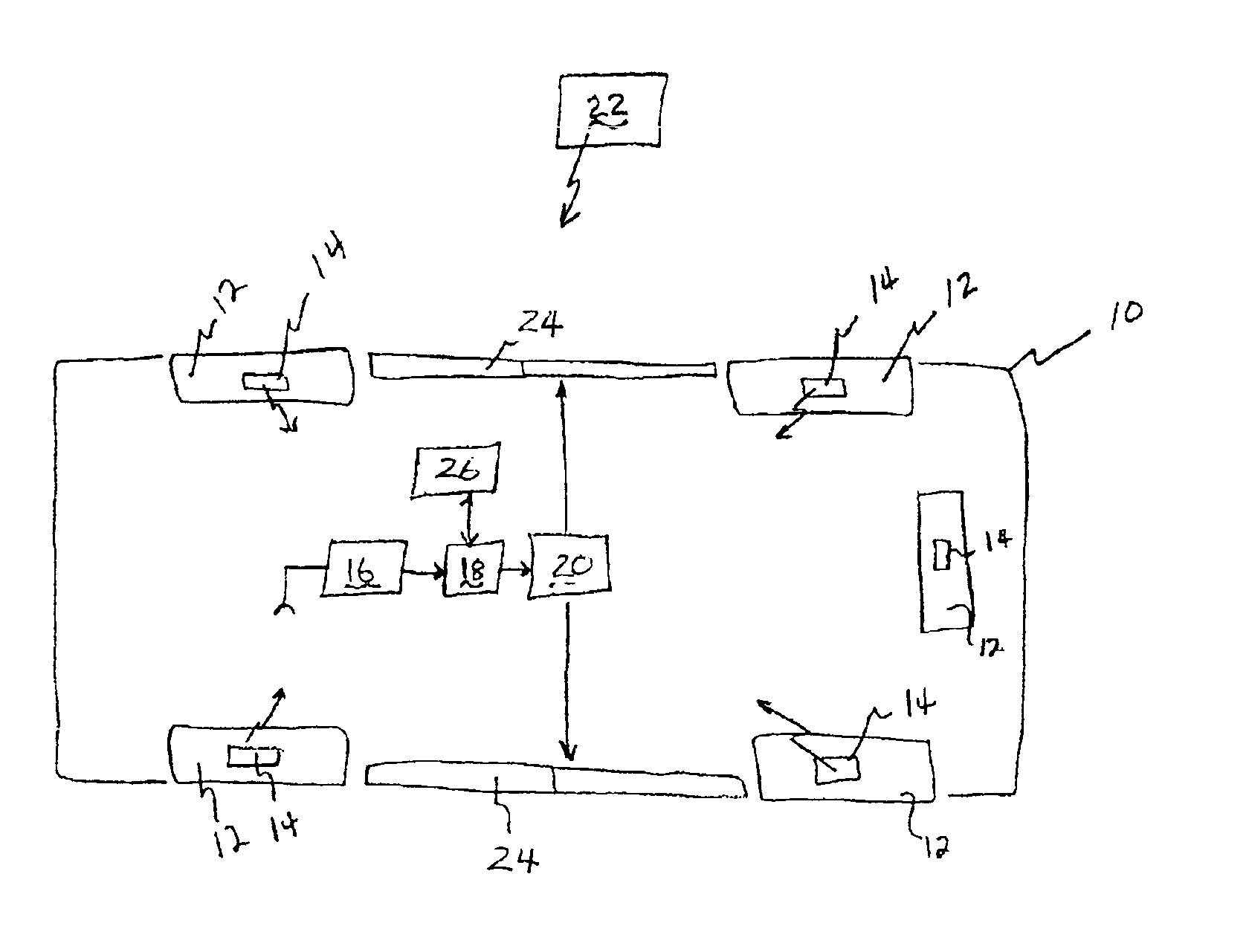
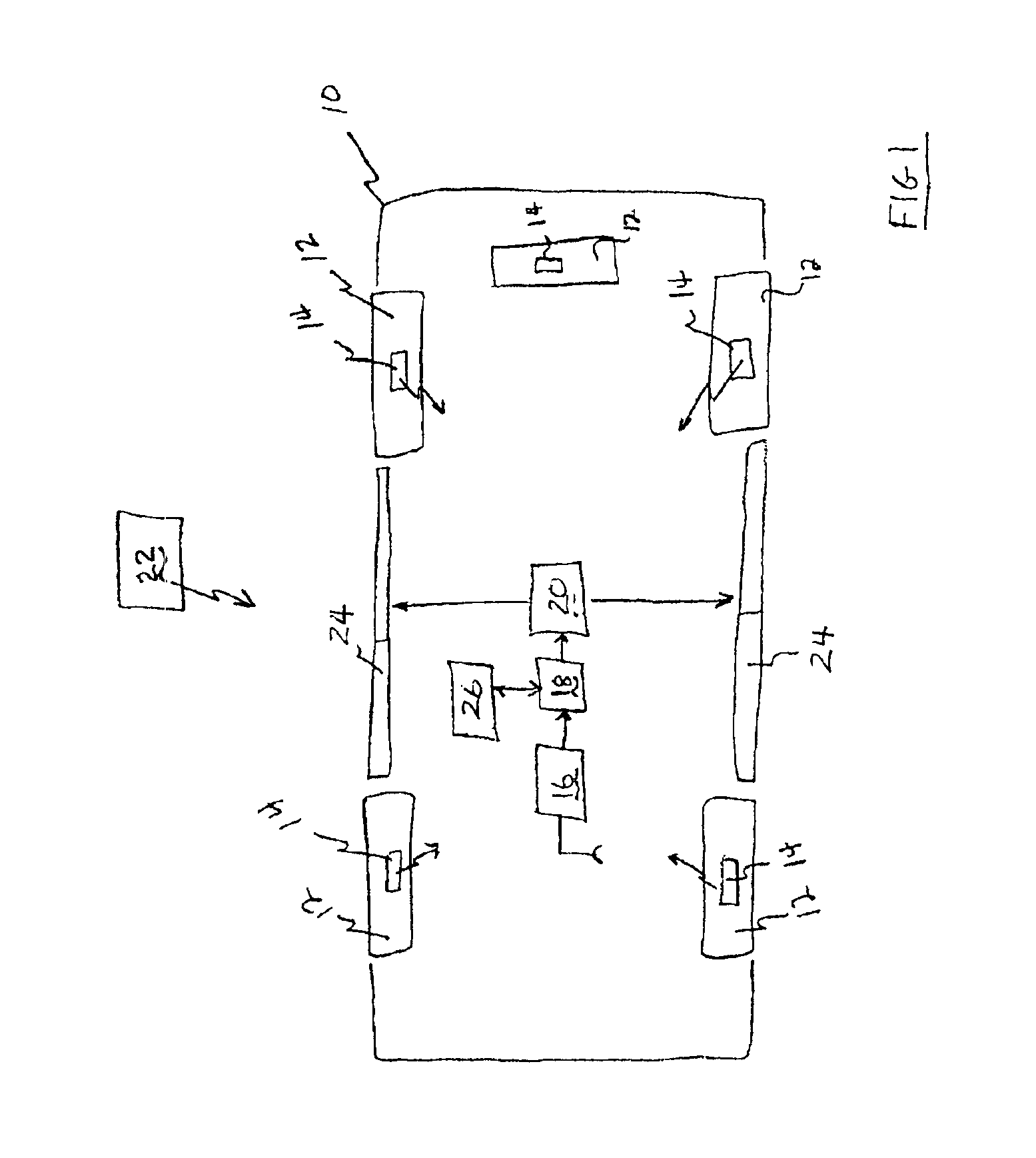
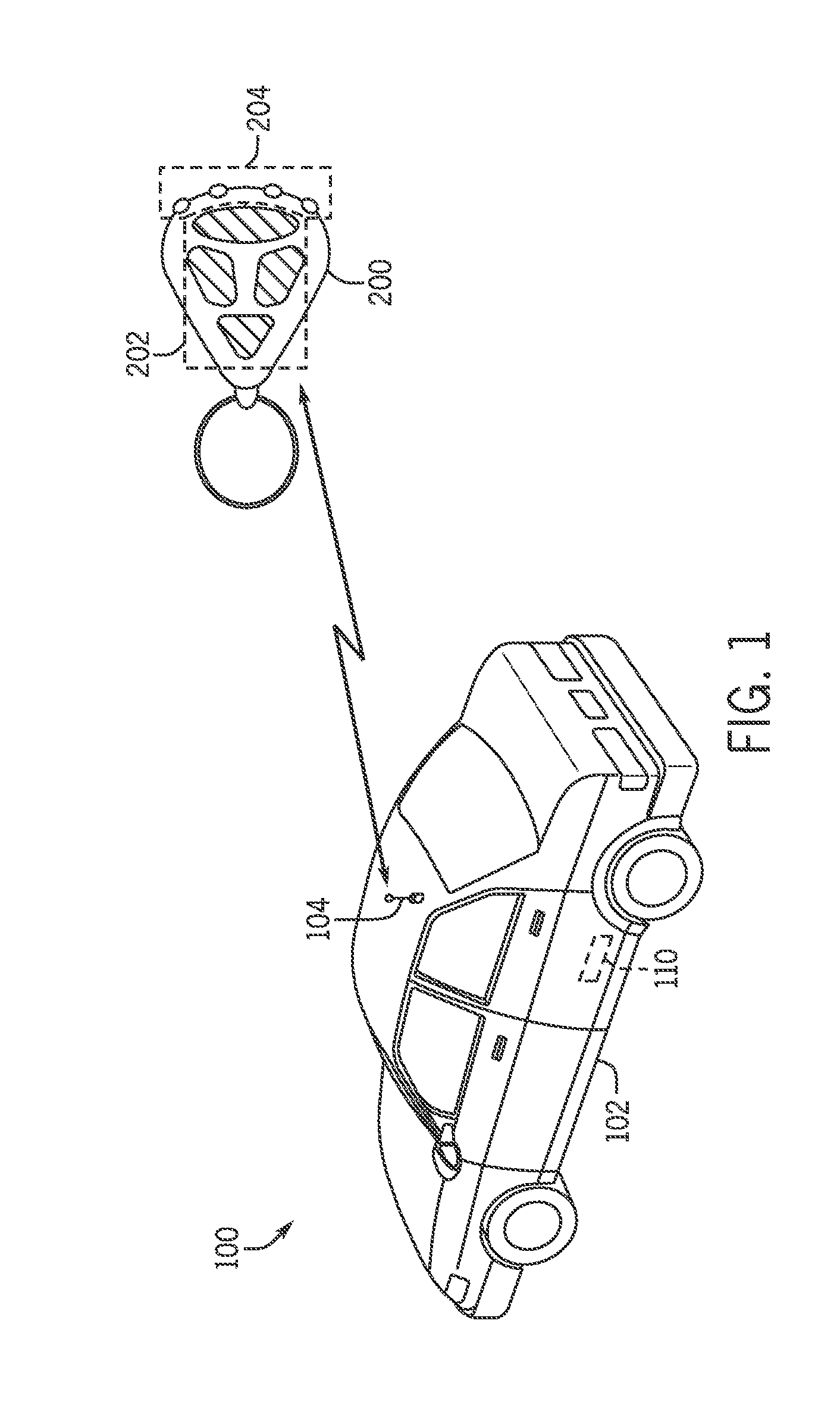
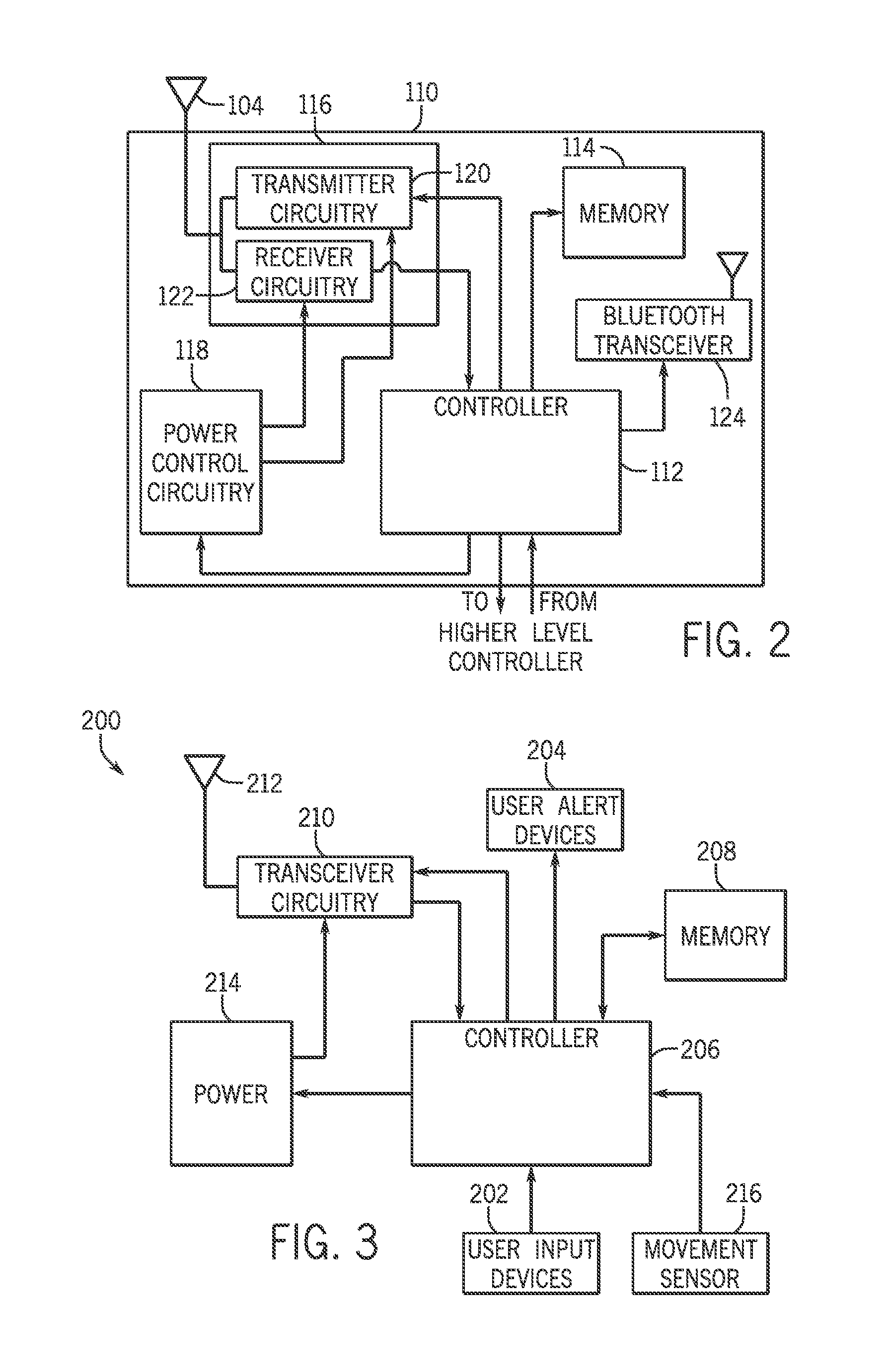
System for Communication with Implantable Medical Devices Using a Bridge Device
A communications bridge device communicates between a consumer electronics device, such as a smart telephone, and an implantable medical device. The bridge forwards instructions and data between the consumer electronics device and the implantable medical device. The bridge contains a first transceiver that operates according to a communication protocol operating in the consumer electronics device (such as Bluetooth®), and second transceiver that operates according to a communications technique operating in the implantable medical device (e.g., Frequency Shift Keying). A software application is installed on the consumer electronics device, which provides a user interface for controlling and reading the implantable medical device. The software application is downloadable using standard cellular means. The bridge is preferably small, and easily and discreetly carried by the implantable medical device patient. The bridge is preferably also simple to operate, and may have only a simple user interface, or no user interface at all.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
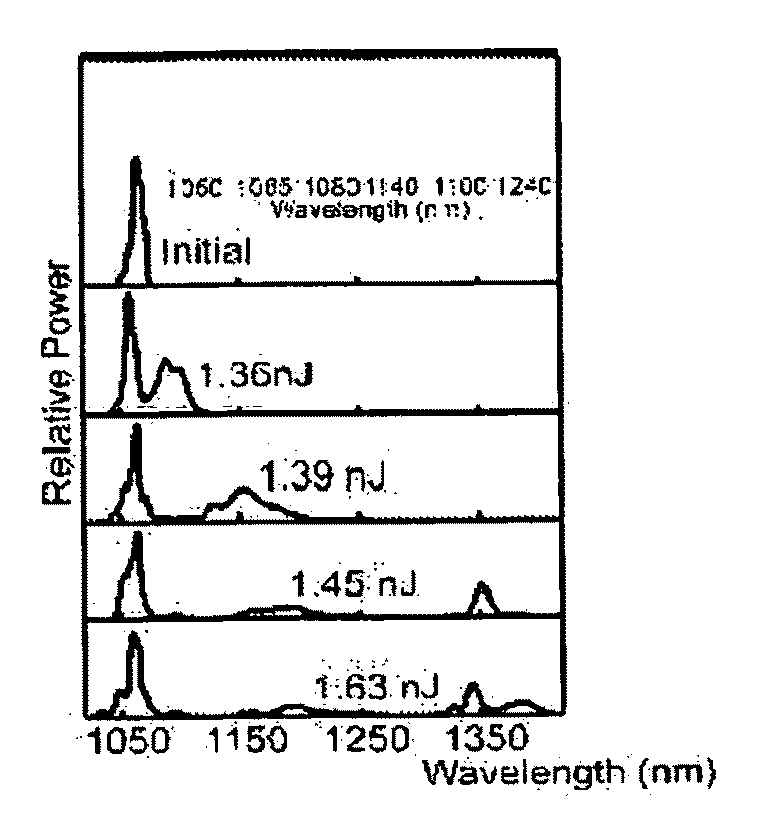
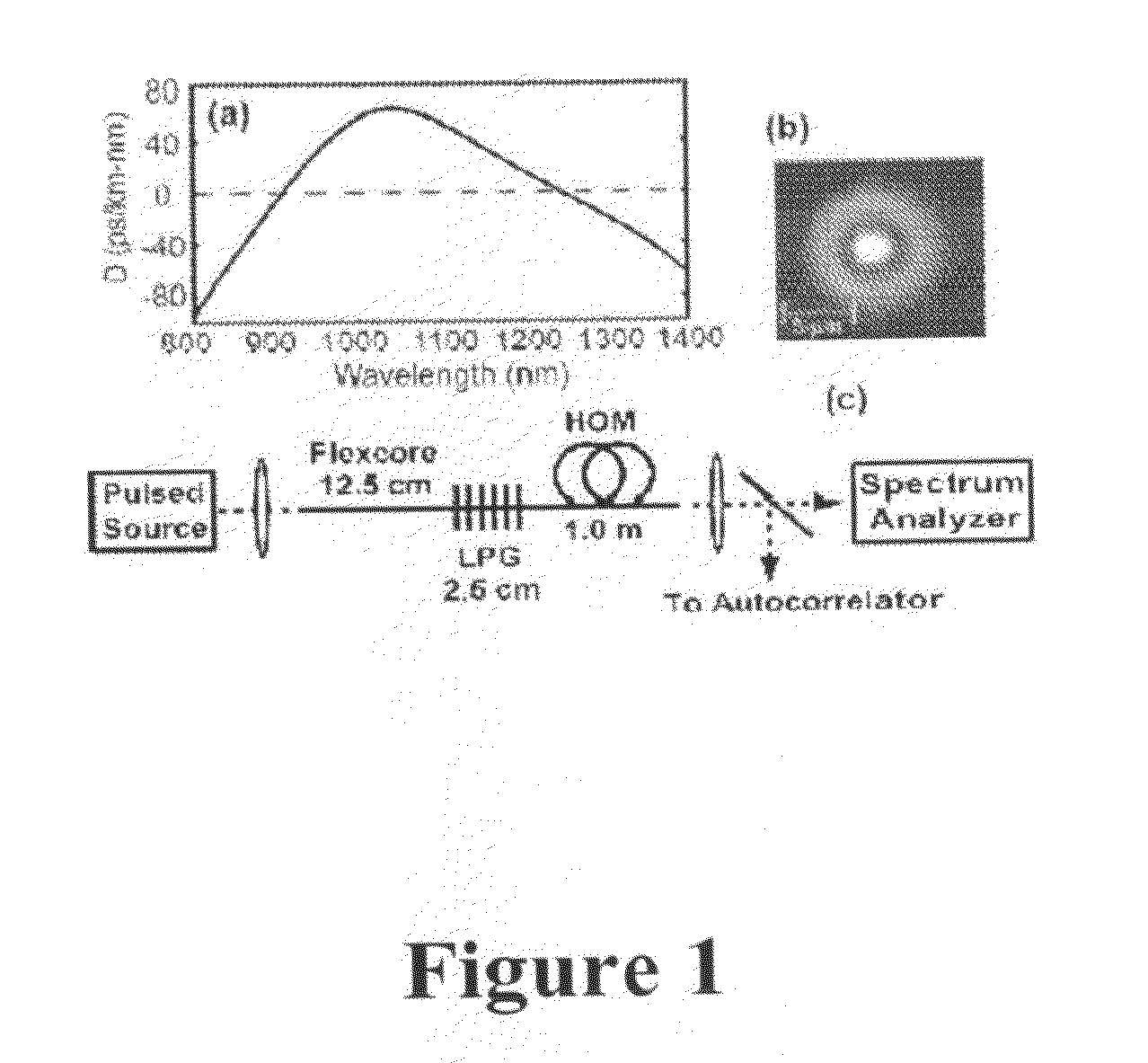
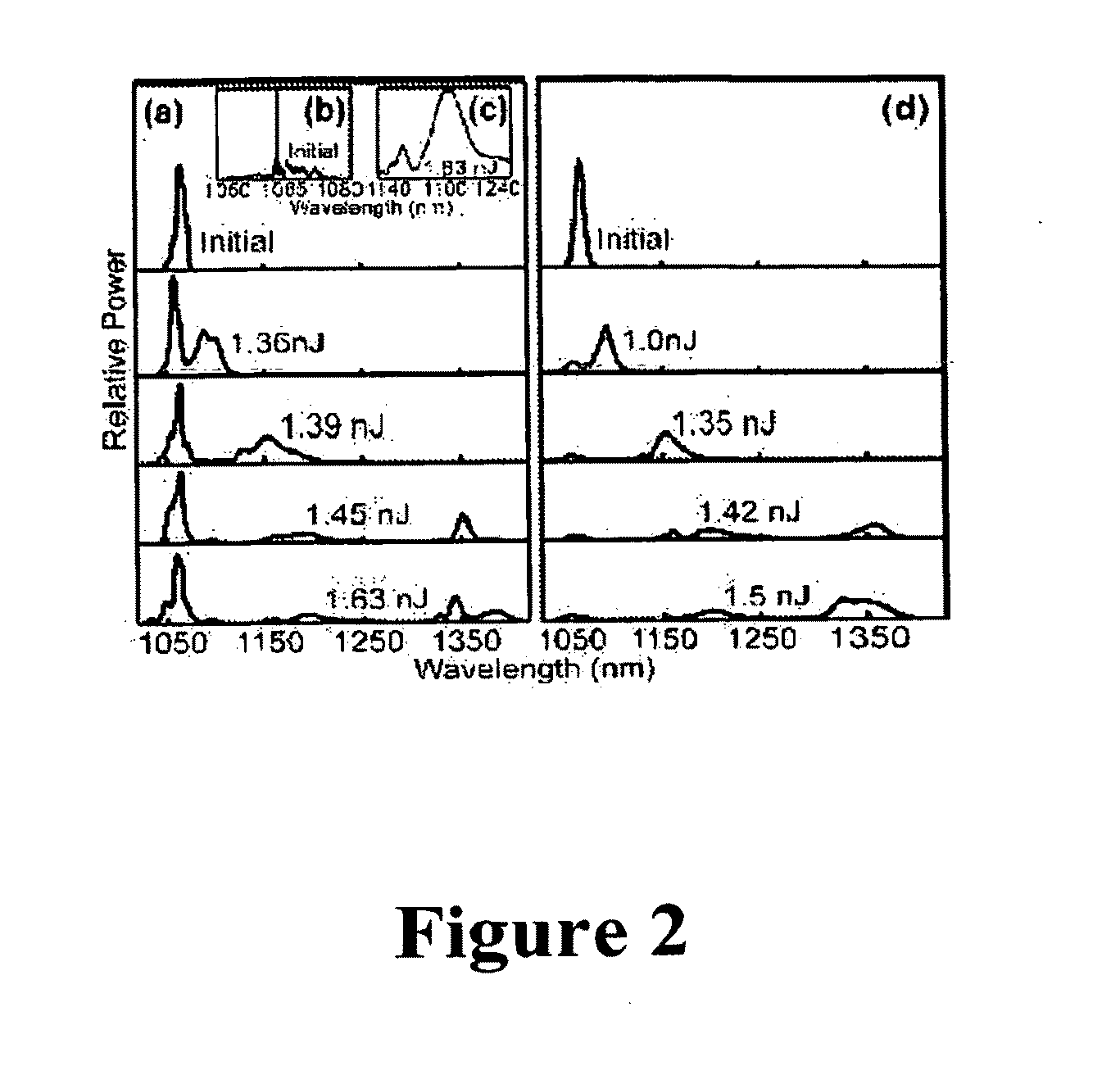
Production of optical pulses at a desired wavelength using solition self-frequency shift in higher-order-mode fiber
The present invention relates to an apparatus for producing optical pulses of a desired wavelength. The apparatus includes an optical pulse source operable to generate input optical pulses at a first wavelength. The apparatus further includes a higher-order-mode (HOM) fiber module operable to receive the input optical pulses at the first wavelength, and thereafter to produce output optical pulses at the desired wavelength by soliton self-frequency shift (SSFS). The present invention also relates to a method of producing optical pulses having a desired wavelength. This method includes generating input optical pulses using an optical pulse source, where the input optical pulses have a first wavelength and a first spatial mode. The input optical pulses are delivered into an HOM fiber module to alter the wavelength of the input optical pulses from the first wavelength to a desired wavelength by soliton self-frequency shift (SSFS) within the HOM fiber module, thereby producing output optical pulses having the desired wavelength.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
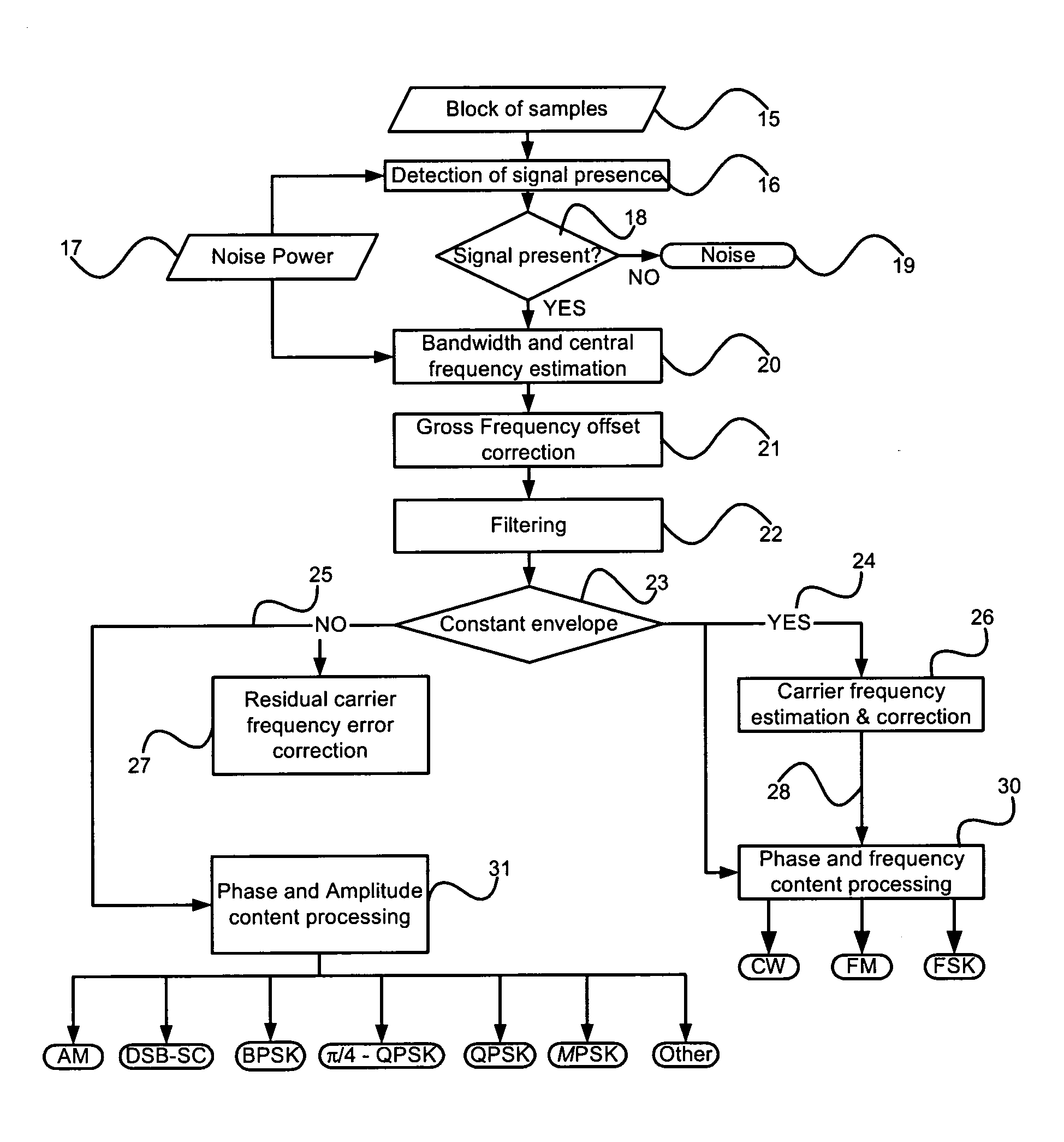
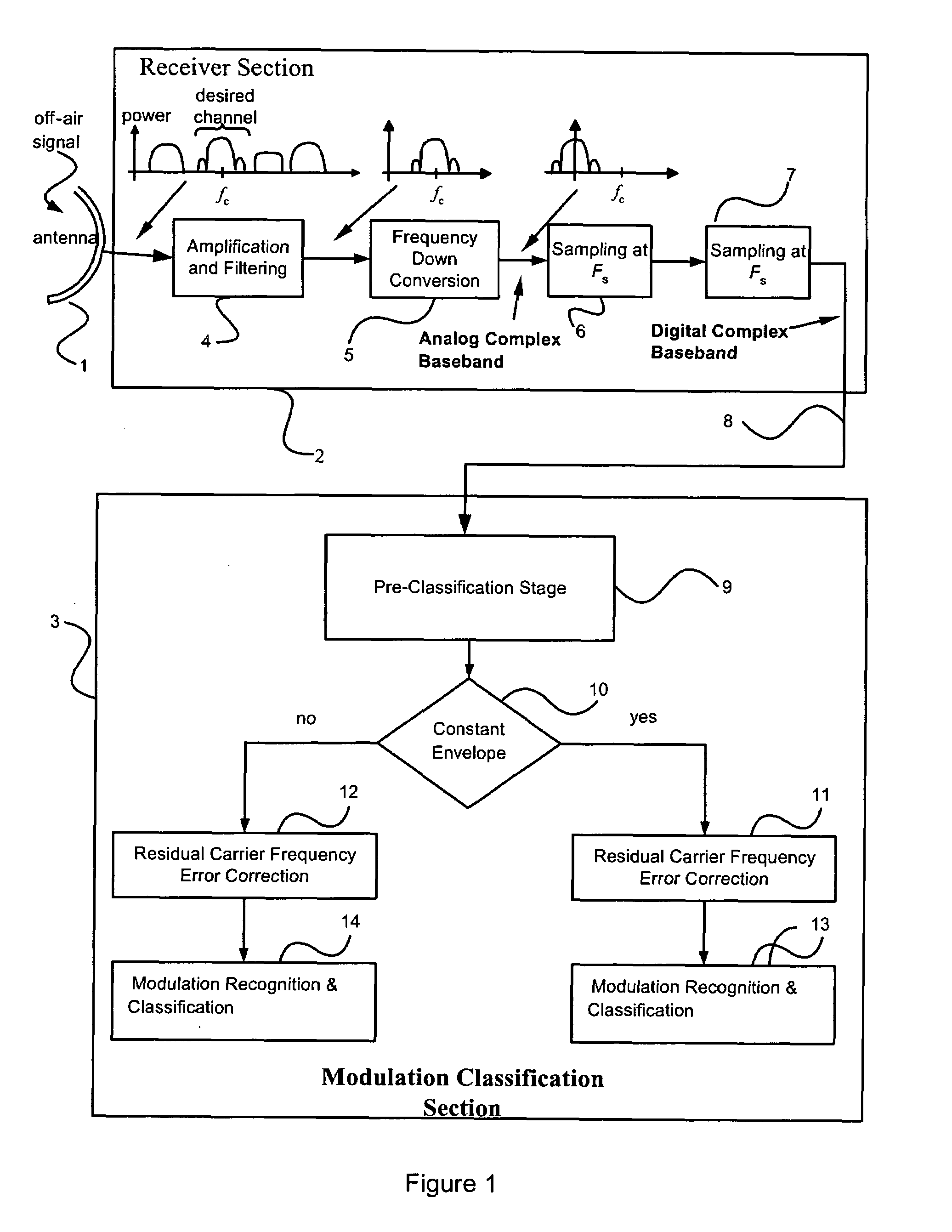
Method and system for detecting and classifying the modulation of unknown analog and digital telecommunications signals
InactiveUS7428270B1Accurate classificationHigh precisionModulation type identificationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSignal classificationCarrier signal
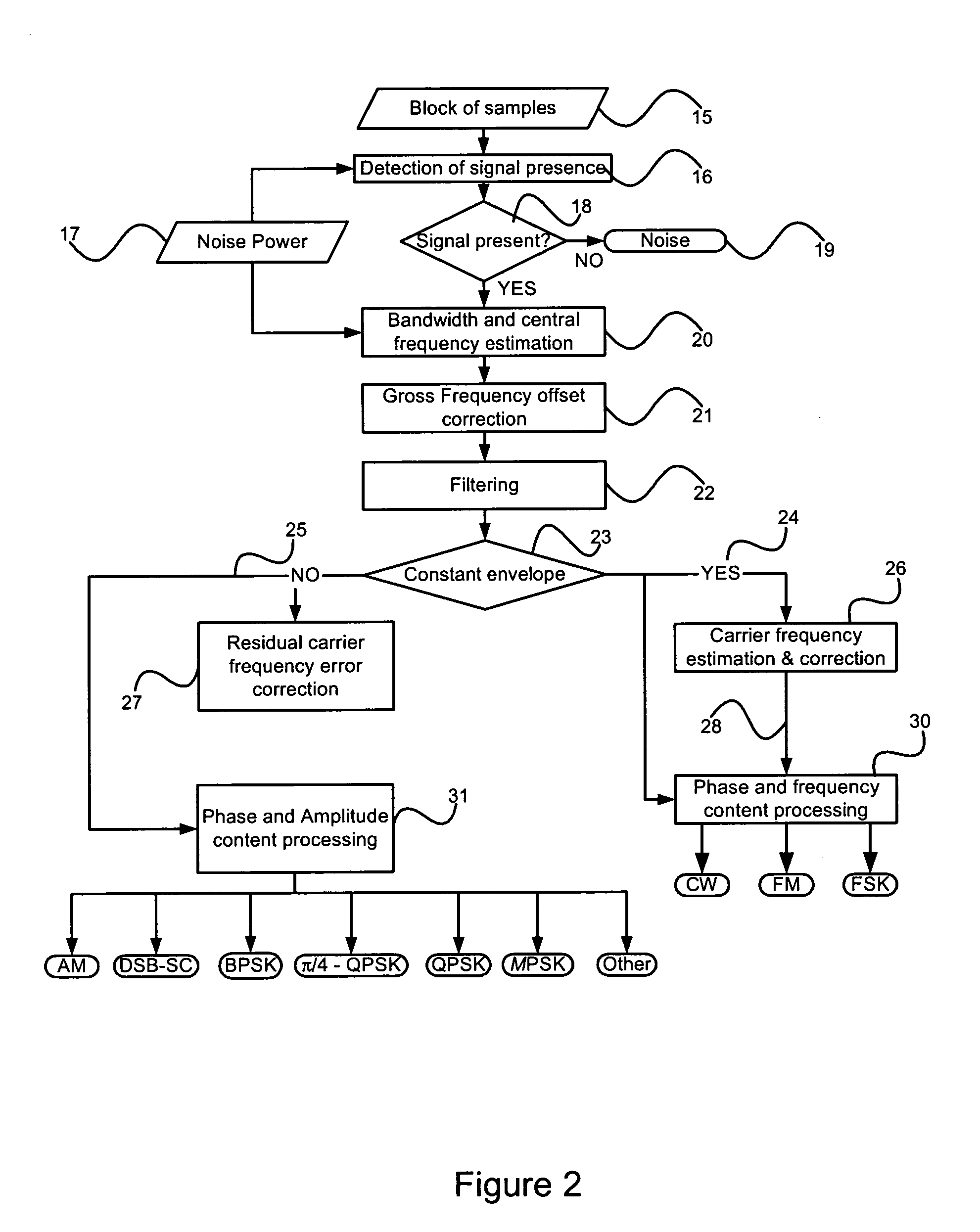
Disclosed is a unique system and method for recognizing the type of modulation embedded in an unknown complex baseband signal, comprising a receiver section for extracting the complex baseband signal from a modulated signal having a carrier frequency, and comprising an orderly series of signal processing functions for (a) estimating the bandwidth of the unknown signal, (b) removing the out-of-band noise and correcting gross carrier frequency errors, (c) discriminating between constant envelope and irregular envelope signals, (d) estimating and correcting residual carrier frequency errors, (e) classifying a constant envelope signal into one of the following modulation formats: {Continuous Wave (CW), Frequency Modulation (FM), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)}, and (f) classifying an irregular envelope signal into one of the following modulation formats: {Amplitude Modulation (AM), Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC), Binary Shift Keying (BPSK), Quaternary Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), π / 4-shifted QPSK, M-ary PSK (MPSK), and OTHER classes}.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
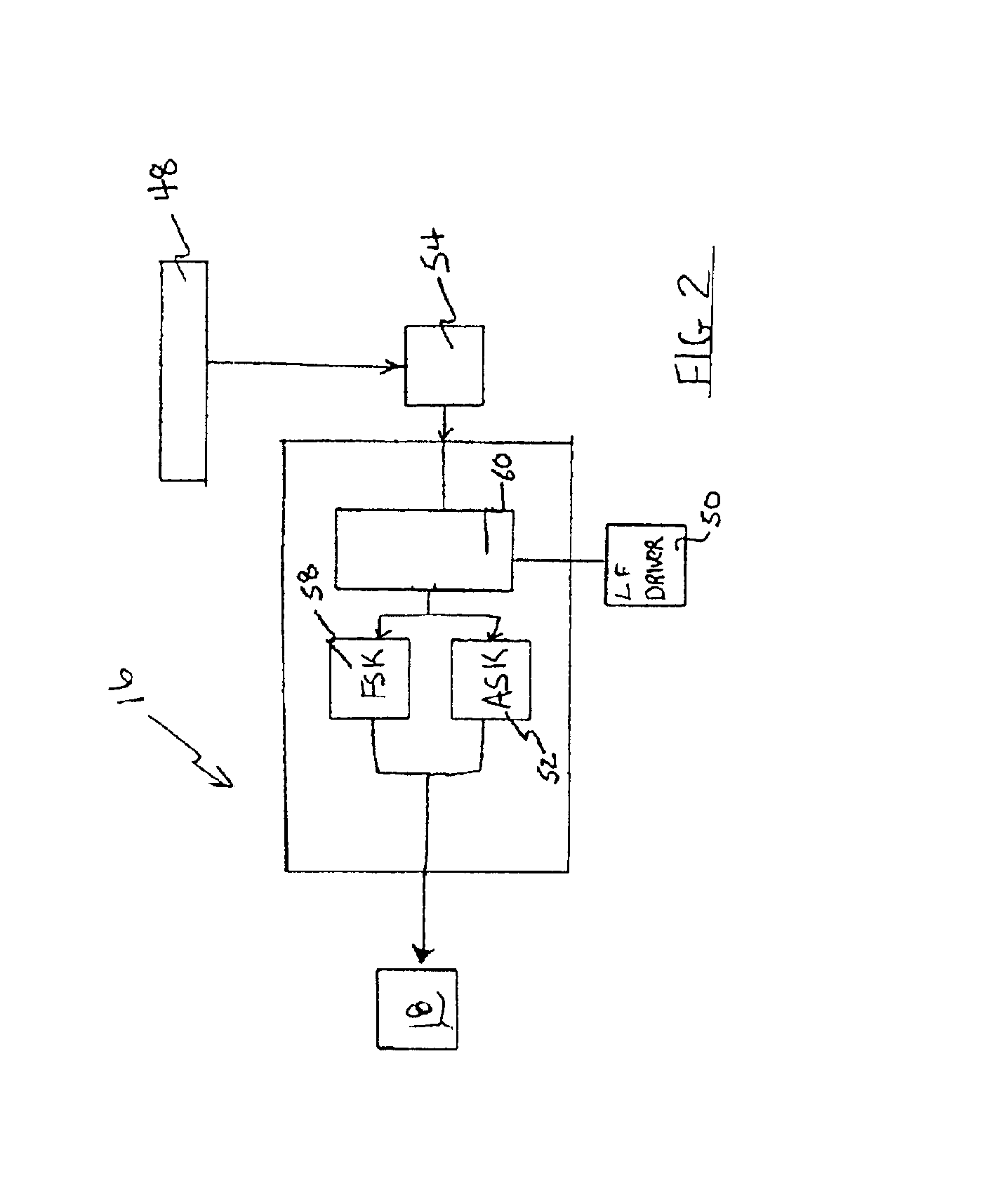
Spread Spectrum ASK/OOK Transmitter
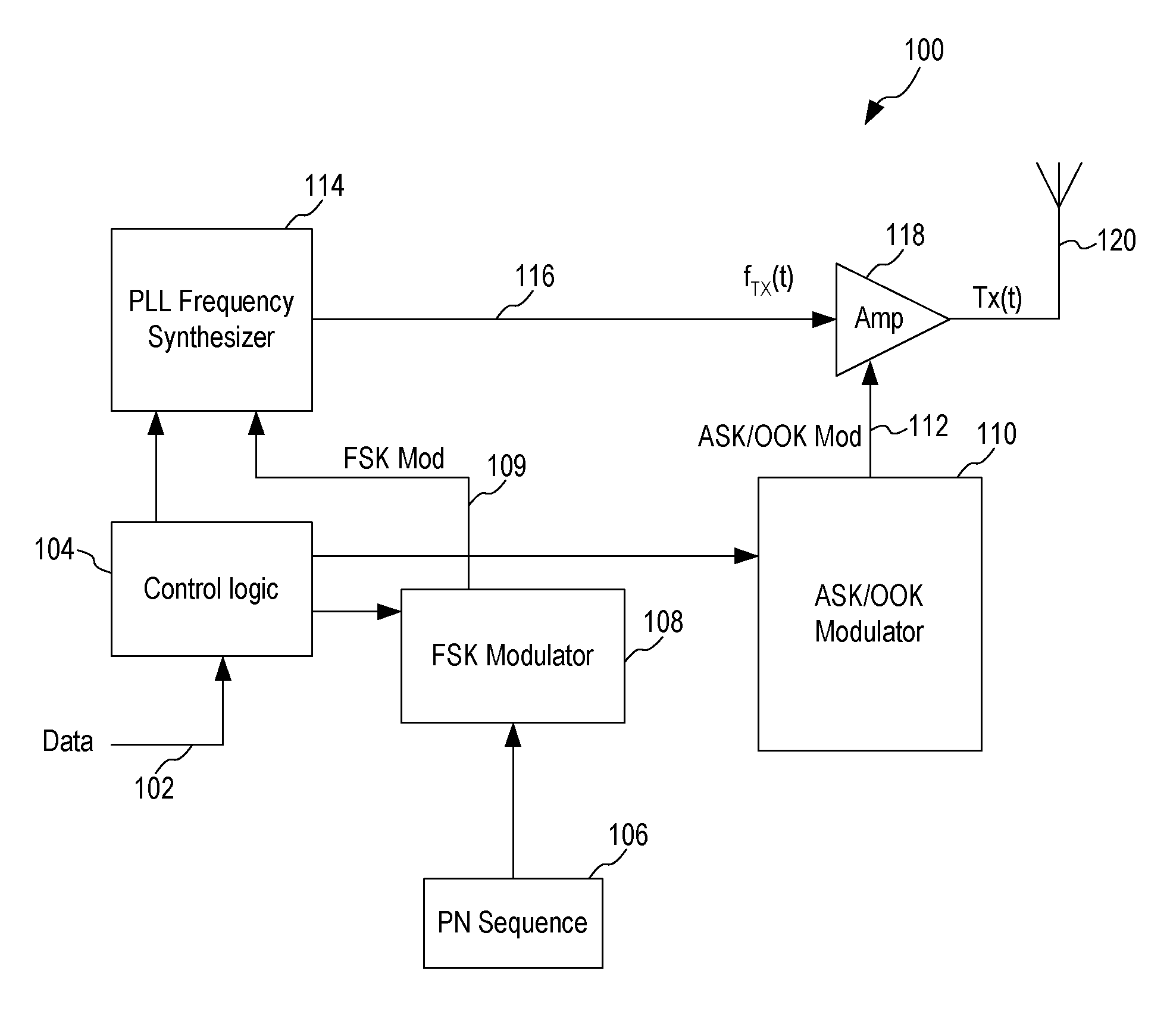
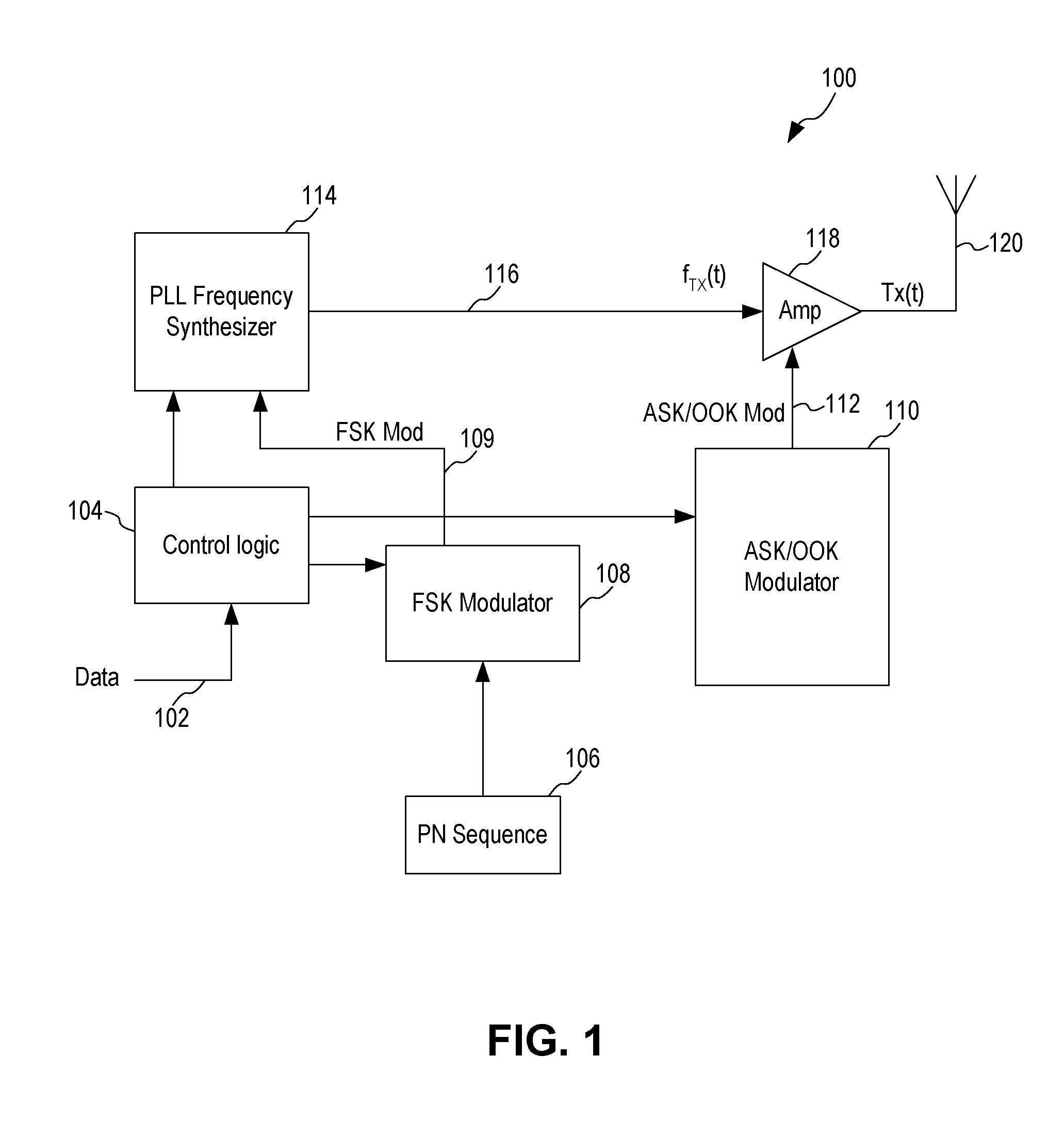
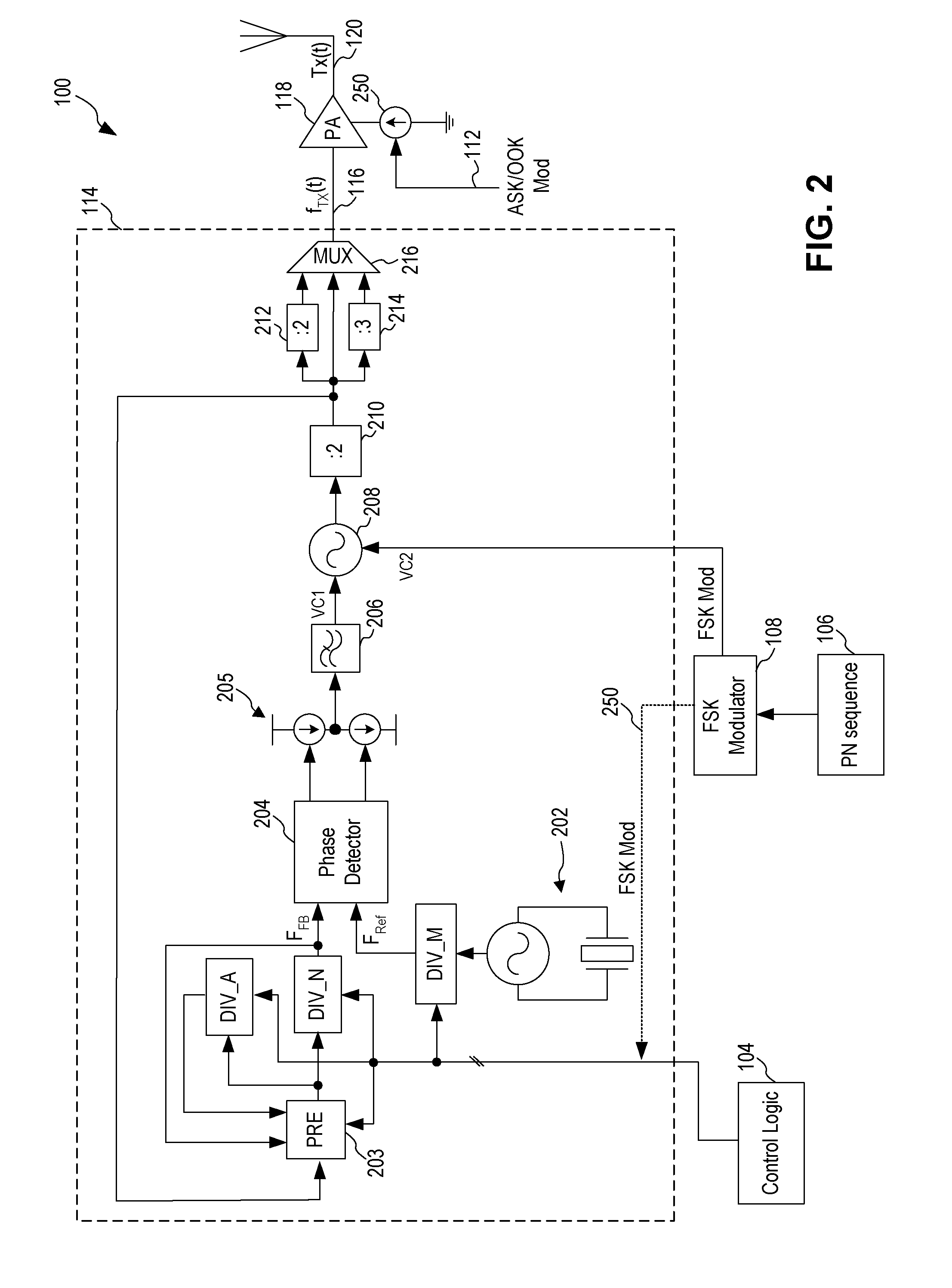
An ASK / OOK transmitter includes a frequency-shift keying (FSK) modulator receiving an input bit sequence and generating a FSK modulation signal indicative of the input bit sequence, a frequency generation circuit receiving the FSK modulation signal and generating a carrier signal having a first frequency where the frequency of the carrier signal is shifted by the FSK modulation signal to form a wideband carrier signal, an amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulator receiving input data and generating an ASK modulation signal indicative of the input data, and a power amplifier coupled to receive the wideband carrier signal as an input signal and the ASK modulation signal as a control signal. The power amplifier provides a spread spectrum ASK transmission signal where the ASK modulation signal modulates the wideband carrier signal to form the spread spectrum ASK transmission signal.
Owner:MICREL
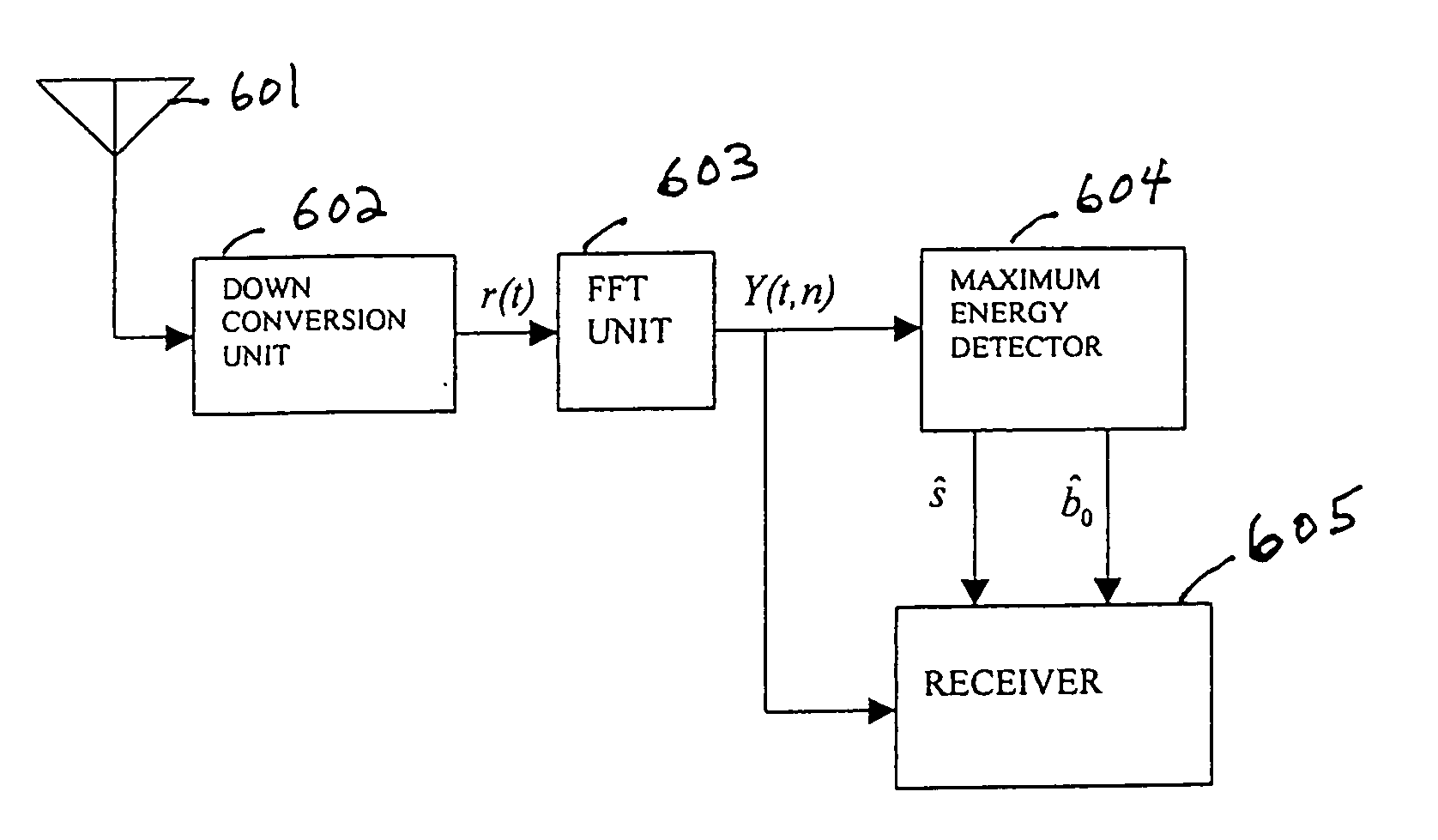
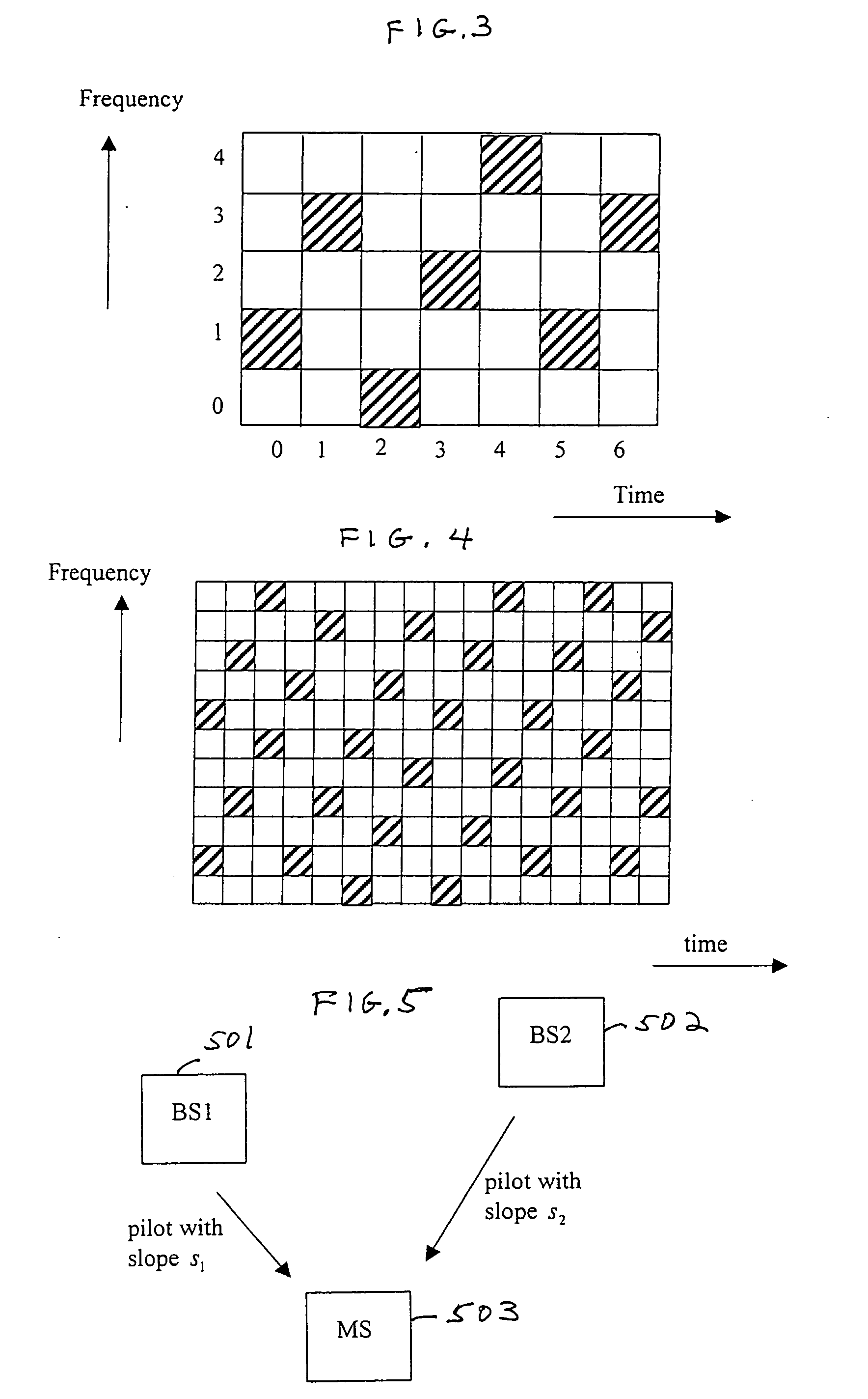
Base station identification in orthongonal frequency division multiplexing based spread spectrum multiple access systems
InactiveUS20050238083A1Inherent latencyRadio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency-division multiplexingFrequency-shift keying
A base station having the strongest downlink signal is identified by utilizing a unique slope of a pilot tone hopping sequence being transmitted by a base station. Specifically, base station identification is realized by determining the slope of the strongest received pilot signal, i.e., the received pilot signal having the maximum energy. In an embodiment of the invention, the pilot tone hopping sequence is based on a Latin Squares sequence. With a Latin Squares based pilot tone hopping sequence, all a mobile user unit needs is to locate the frequency of the pilot tones at one time because the pilot tone locations at subsequent times can be determined from the slope of the Latin Squares pilot tone hopping sequence. The slope and initial frequency shift of the pilot tone hopping sequence with the strongest received power is determined by employing a unique maximum energy detector. In one embodiment, the slope and initial frequency shift of the pilot signal having the strongest received power is determined by finding the slope and initial frequency shift of a predicted set of pilot tone locations having the maximum received energy. In another embodiment, the frequency shift of the pilot signal with the strongest, i.e., maximum, received power is estimated at each of times “t”. These frequency shifts are employed in accordance with a prescribed relationship to determine the unknown slope and the initial frequency shift of the pilot signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
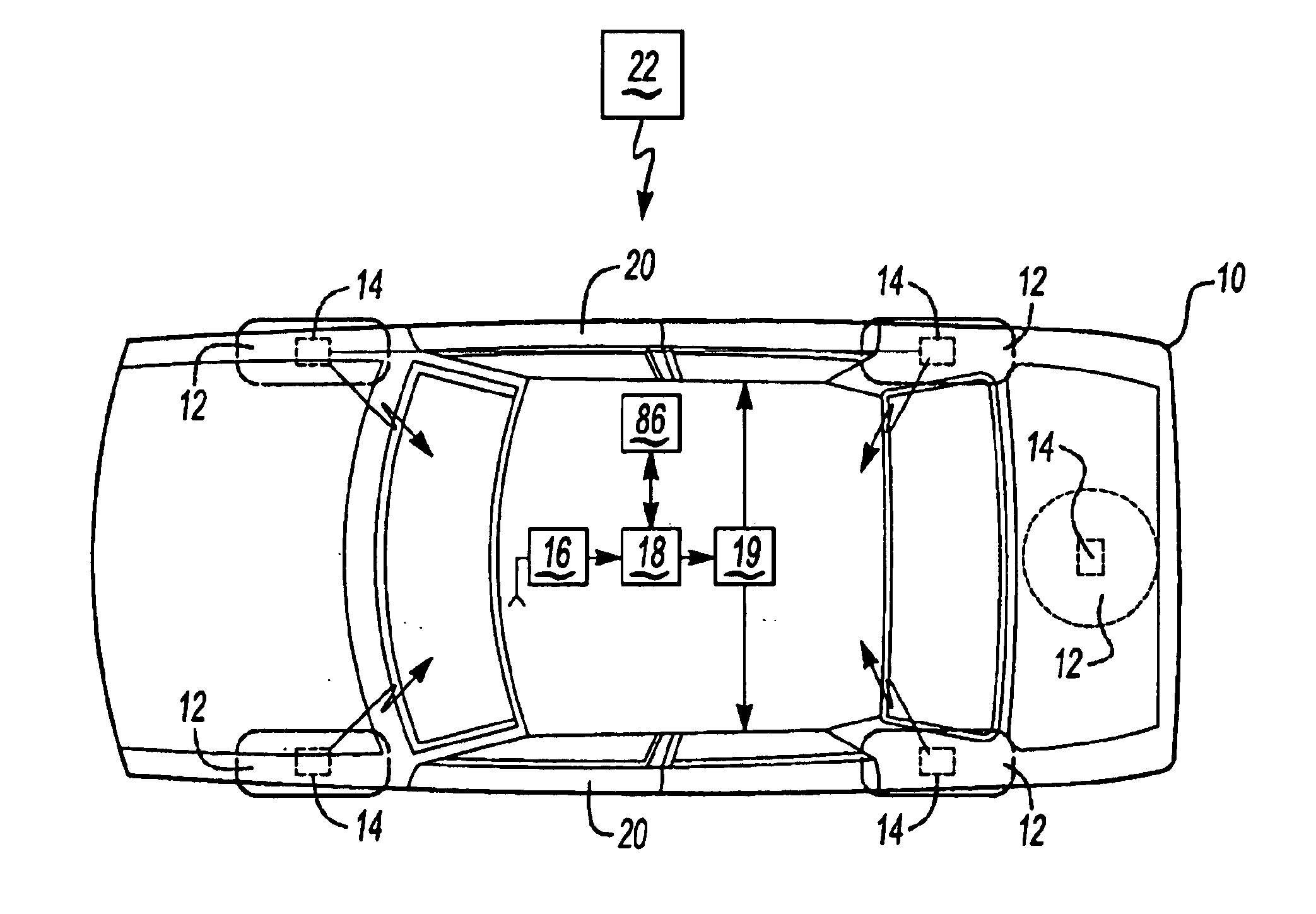
Combined tire pressure monitoring and keyless entry receiver
InactiveUS6885282B2Eliminates errant receptionReduce probabilityElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageAccelerometerMonitoring system
A system for monitoring conditions within a tire (12) including a sensor assembly (14) including a pressure sensor (36), an accelerometer (34), a temperature sensor (32), and a transmitter (40) to transmit signals indicative of current tire conditions. A remote transmitter (22) for actuating a remote keyless entry system (19) emits a signal to actuate a function of the keyless entry system (19) such as unlocking doors (20) of the motor vehicle (10). A receiver assembly (16) includes an amplitude shift keyed receiver (52) and a frequency shift keyed receiver (58) selectively engagable to receive radio frequency transmissions from the tire monitoring system or the remote keyless entry system (19).
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
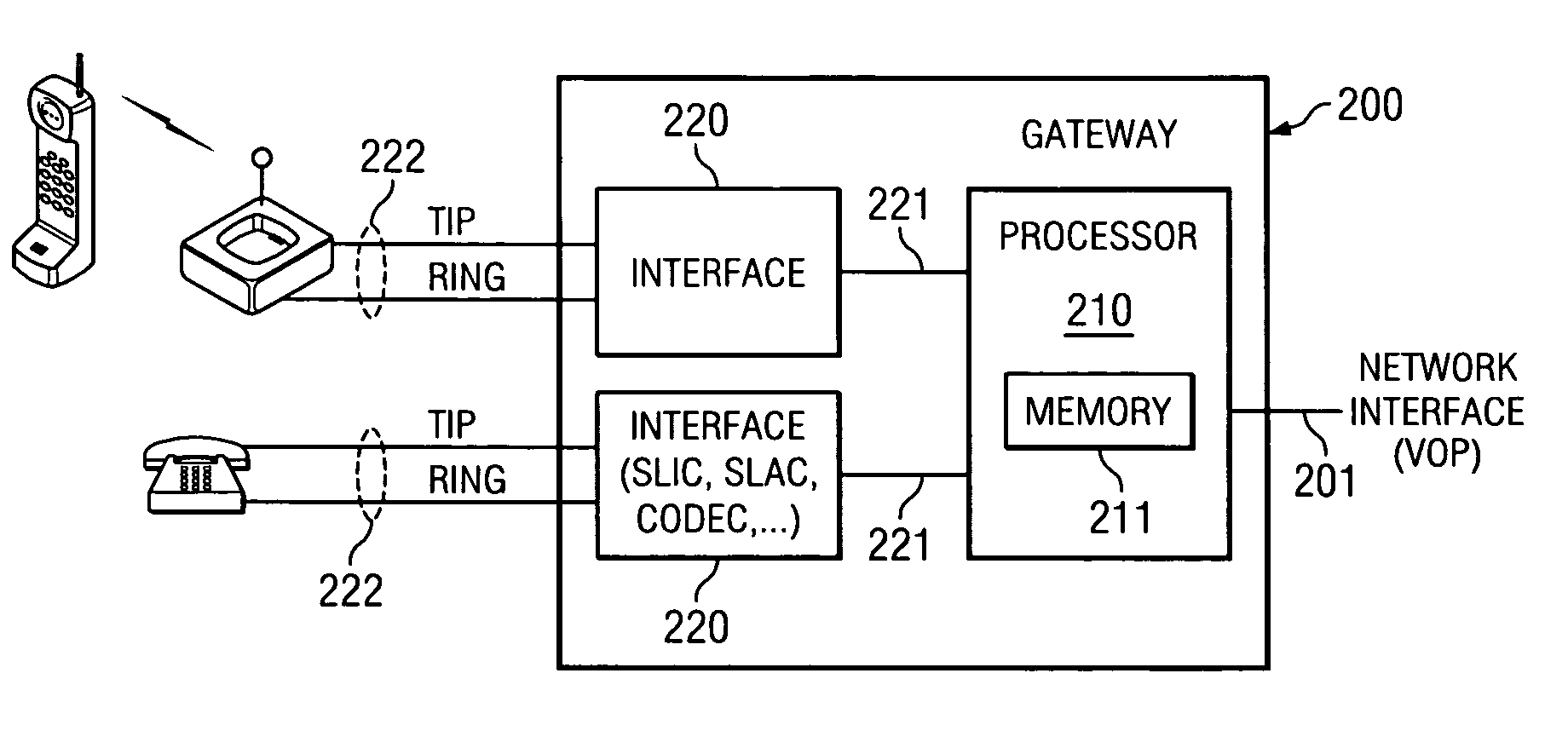
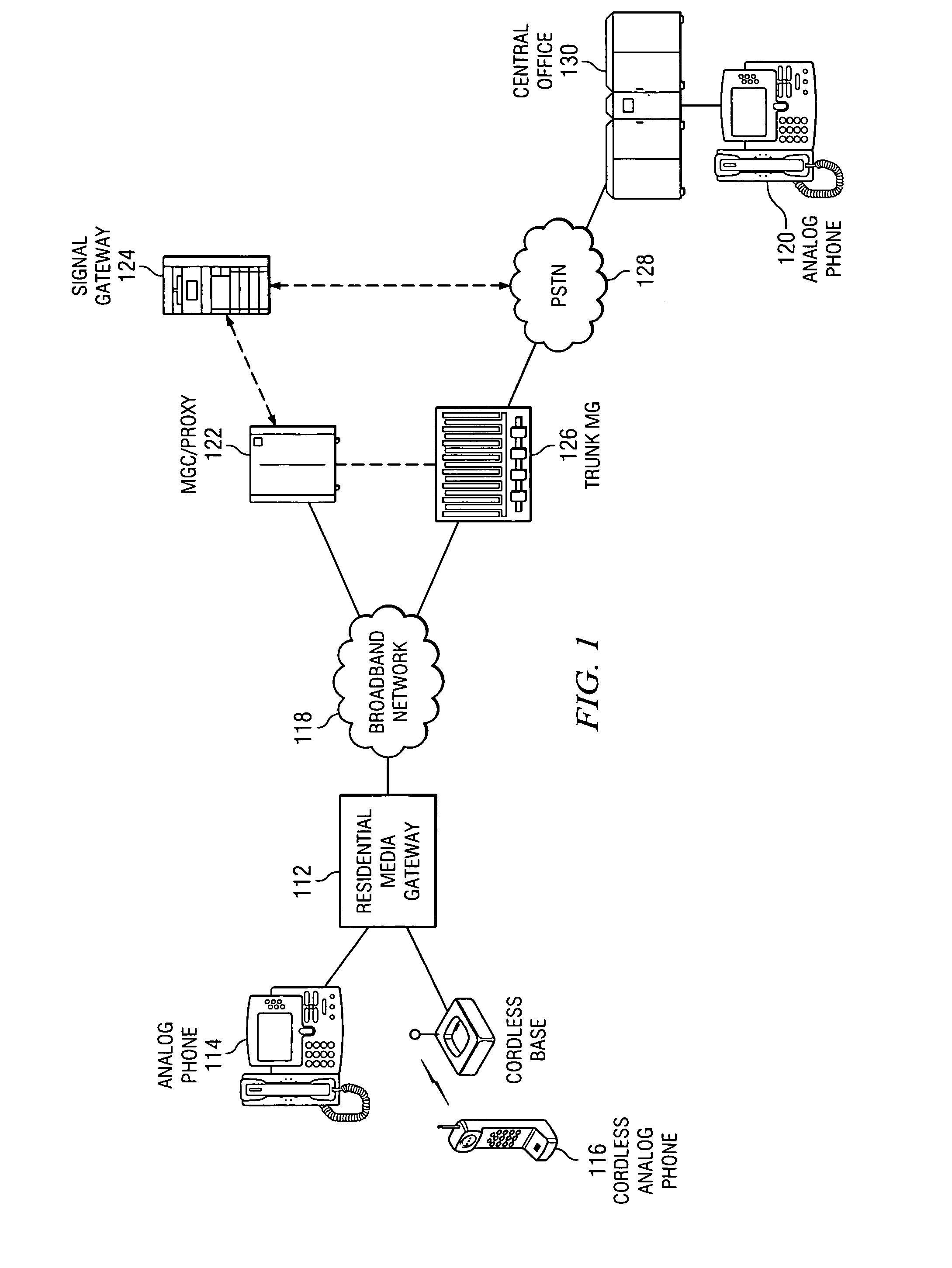
Method and apparatus for activating extended services in a user device using a voice over packet gateway
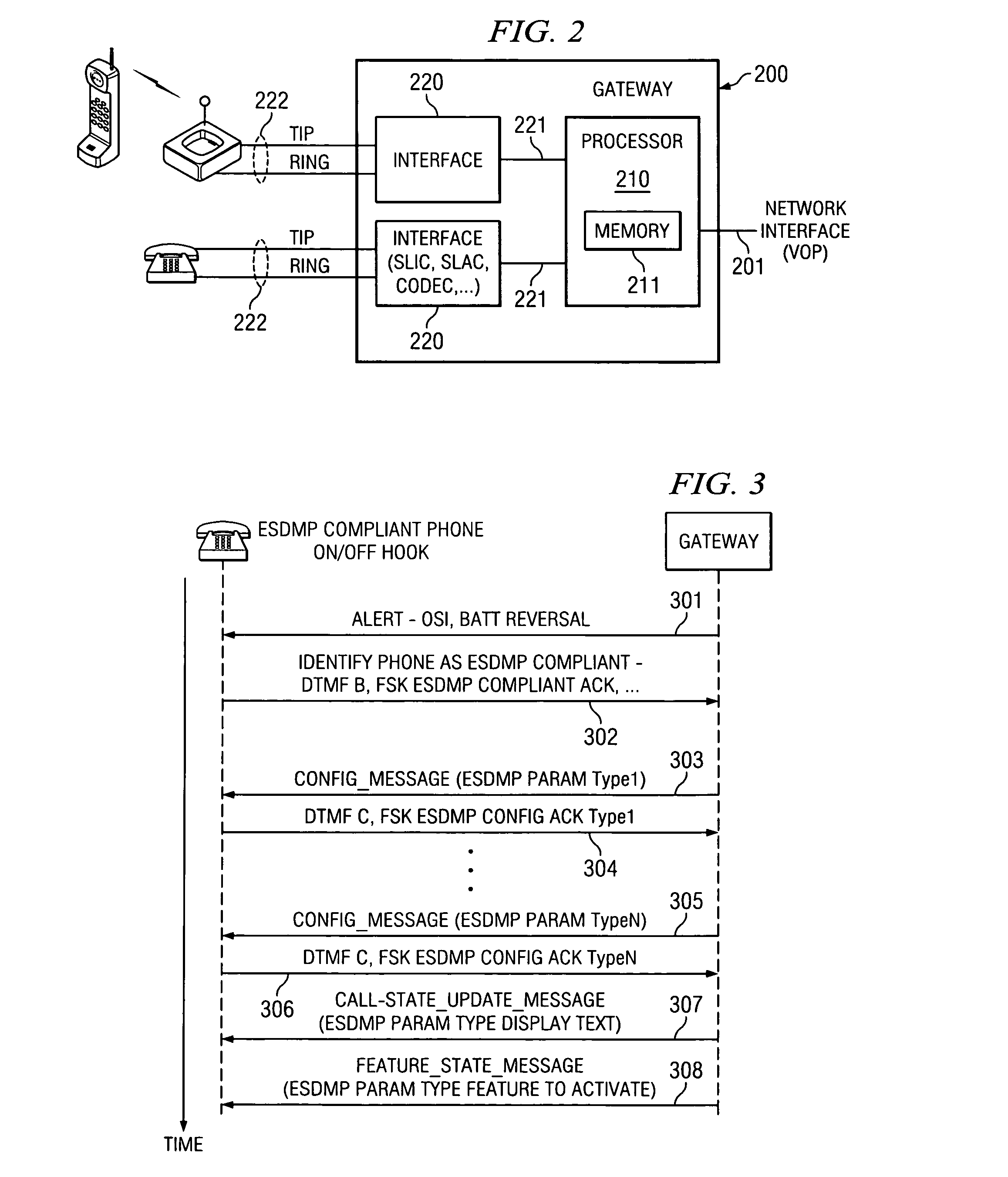
ActiveUS7403604B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareFrequency-shift keying
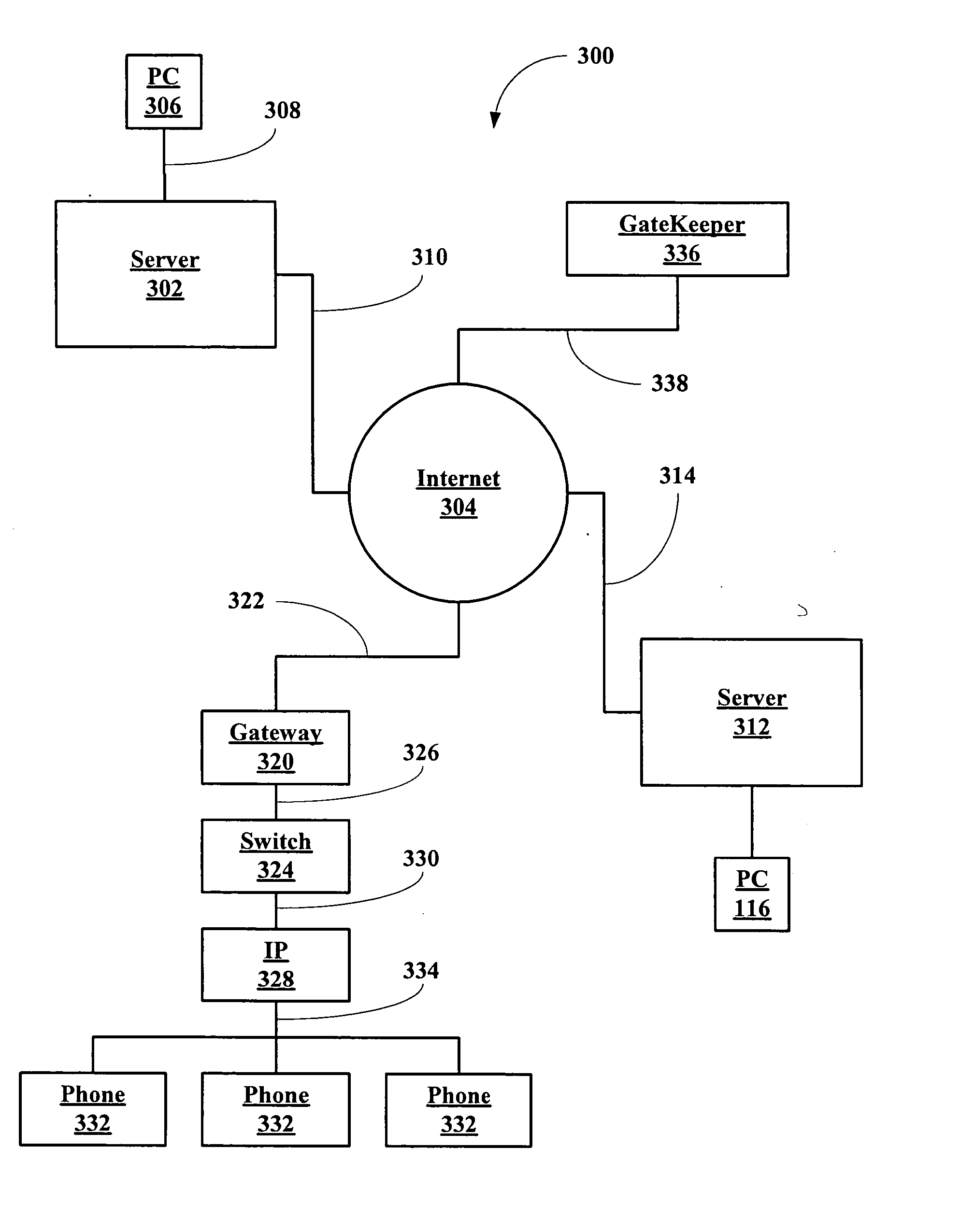
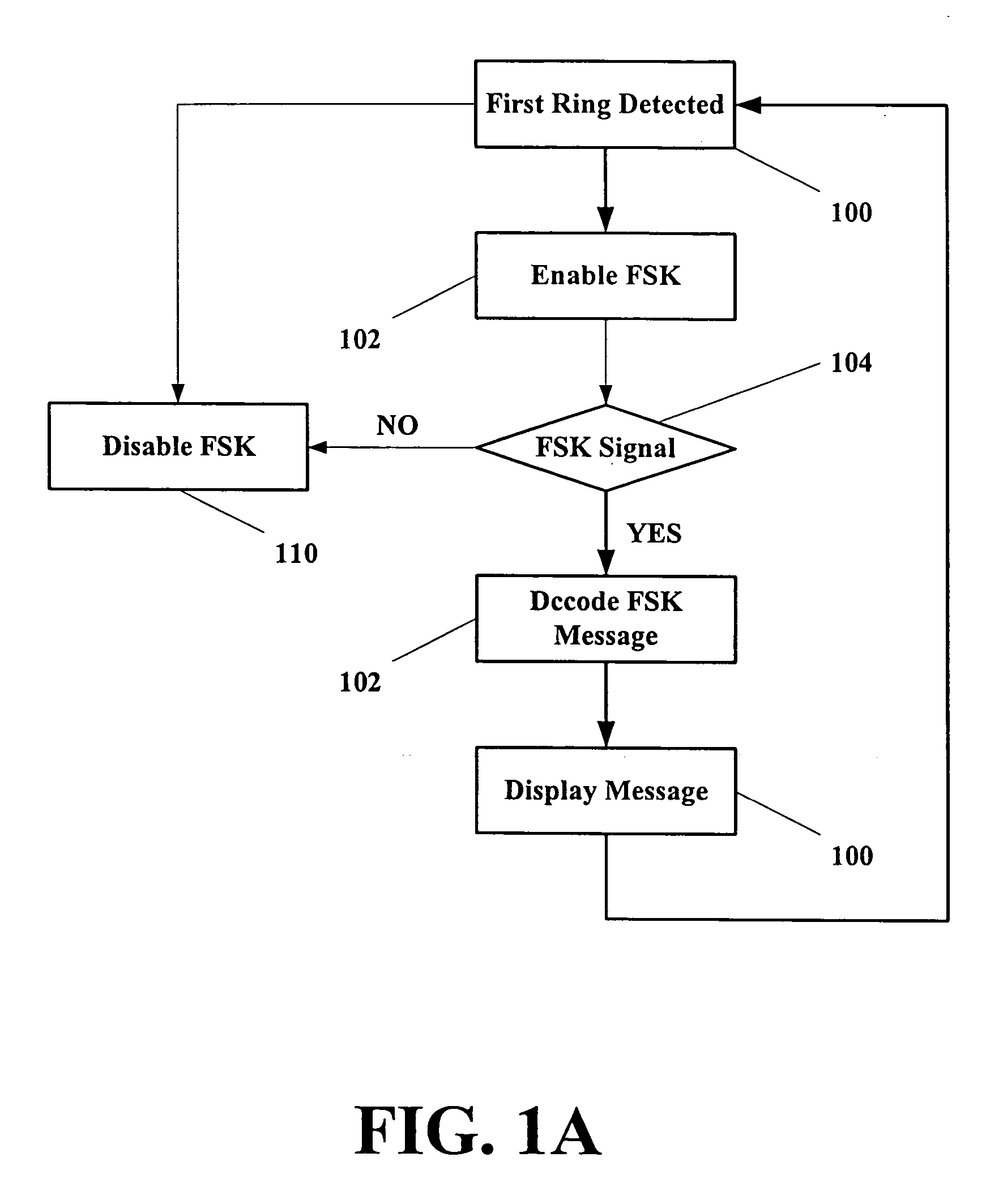
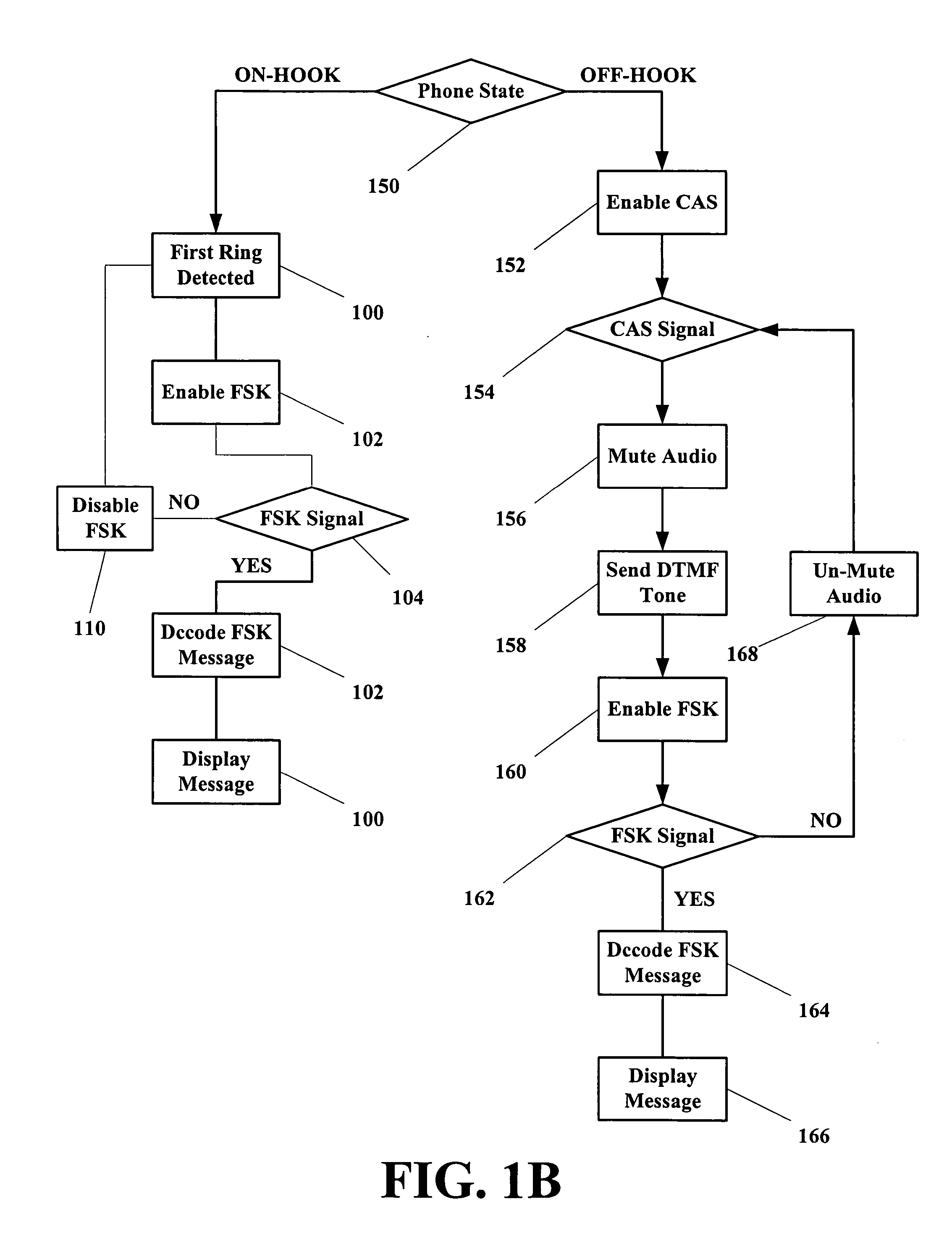
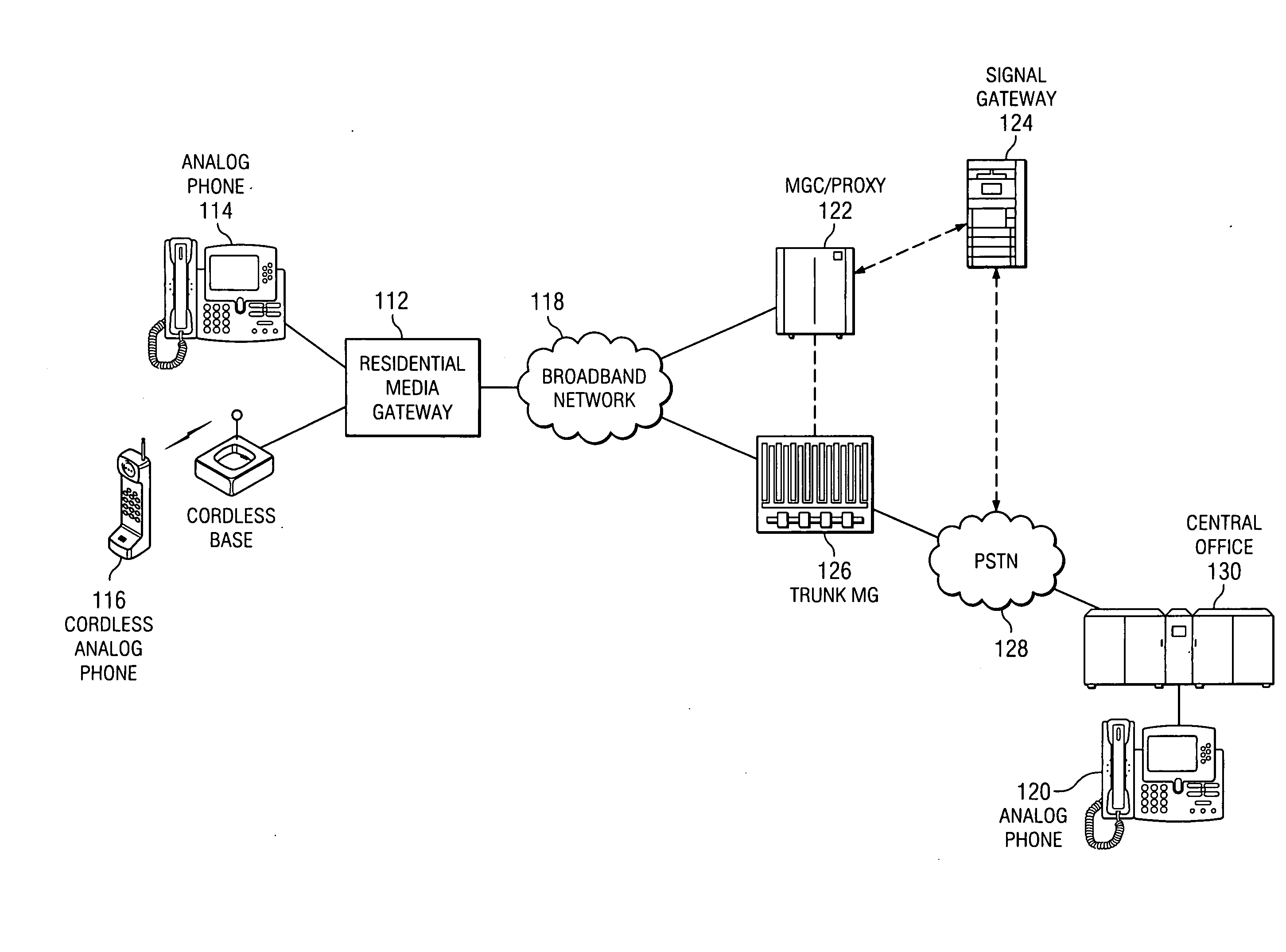
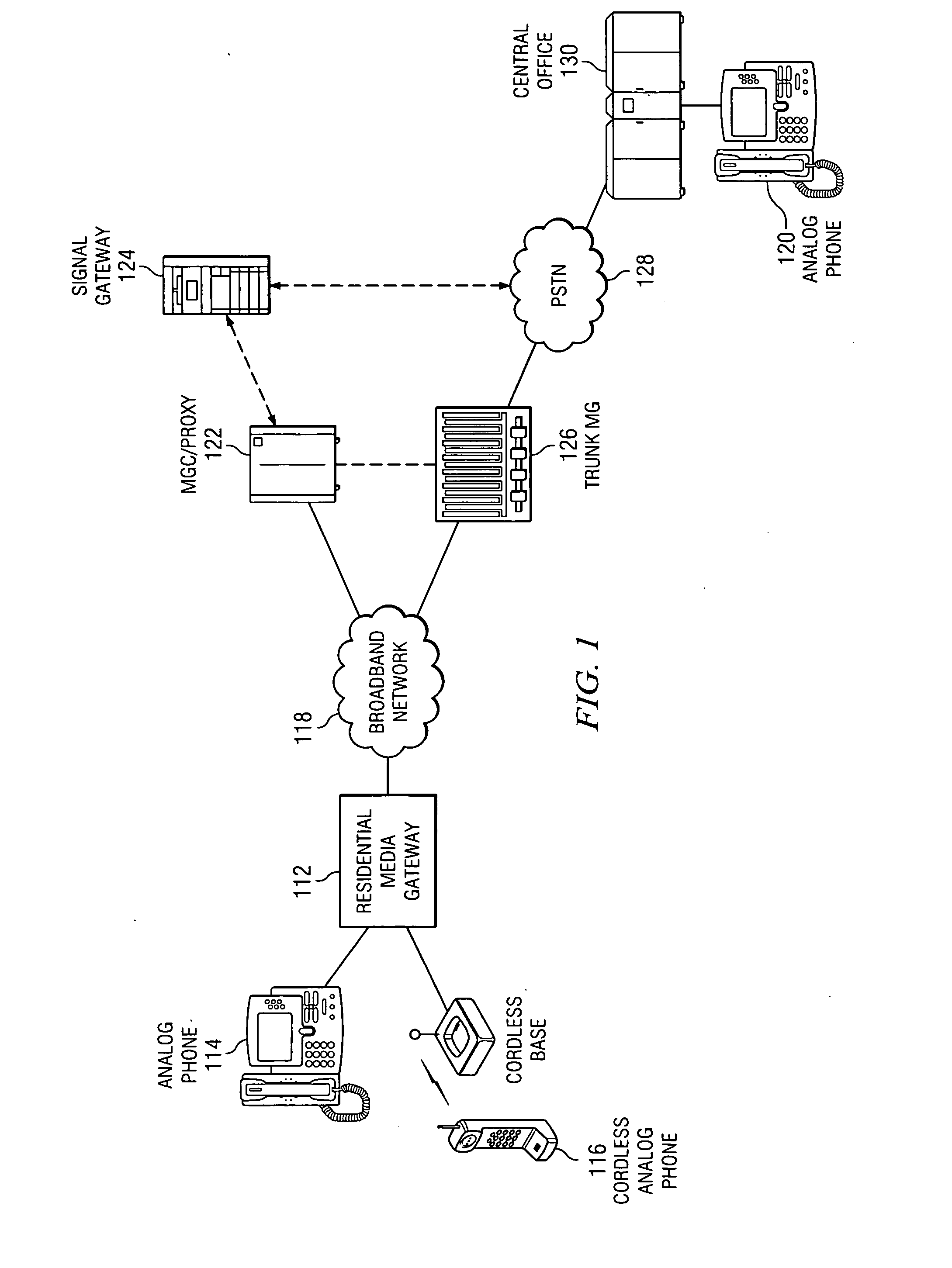
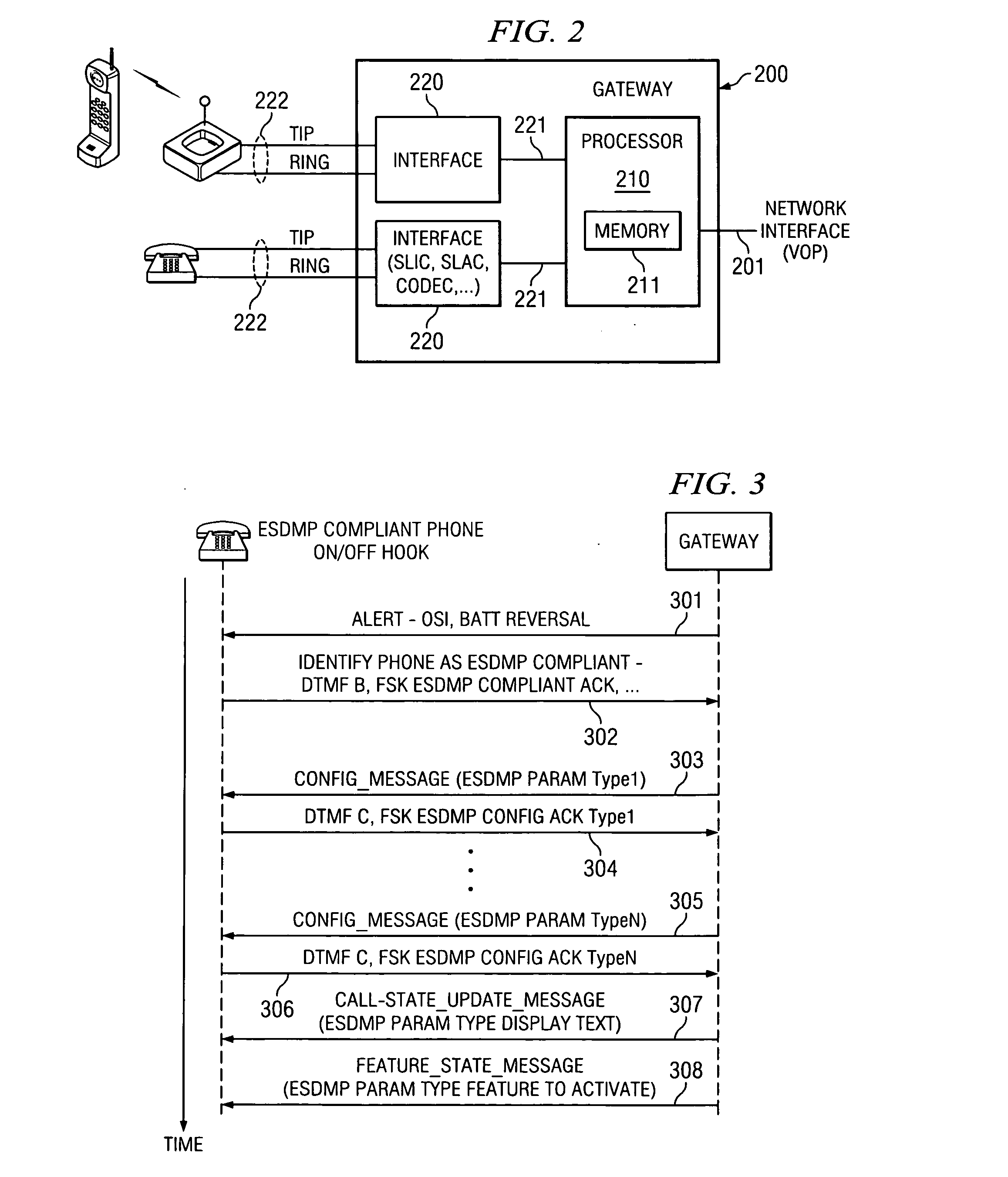
An enhanced services display message protocol (ESDMP) facilitates display of messages in a compliant analog telephony device (ATD). An exemplary gateway device in a voice over packet (VOP) network can activate enhanced services in a compliant ATD using the ESDMP and includes a controller and first and second interfaces. One of the interfaces can transmit and receive communications over a VOP network. The other interface can transmit and receive voice band message data modulated according to a frequency shift keying (FSK) protocol. The ESDMP can be used to configure the gateway to activate features supported by the ATD, to update call state information and to display feature state information.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Strong authentication token with acoustic data input
InactiveUS20120221859A1Increase chanceSimilar costDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCommon baseCommunication interface
Strong authentication tokens for generating dynamic security values having an acoustical input interface for acoustically receiving input data are disclosed. The tokens may also include an optical interface for receiving input data and may have a selection mechanism to select either the acoustical or the optical input interface to receive data. A communication interface may be provided to communicate with a removable security device such as a smart card and the token may be adapted to generate dynamic security values in cooperation with the removable security device. The acoustic signal received by the token may be modulated using a frequency shift keying modulation scheme using a plurality of coding frequencies to code the acoustical signal where each coding frequency may be an integer multiple of a common base frequency.
Owner:ONESPAN NORTH AMERICA INC
Computational bluetooth tag with backscatter
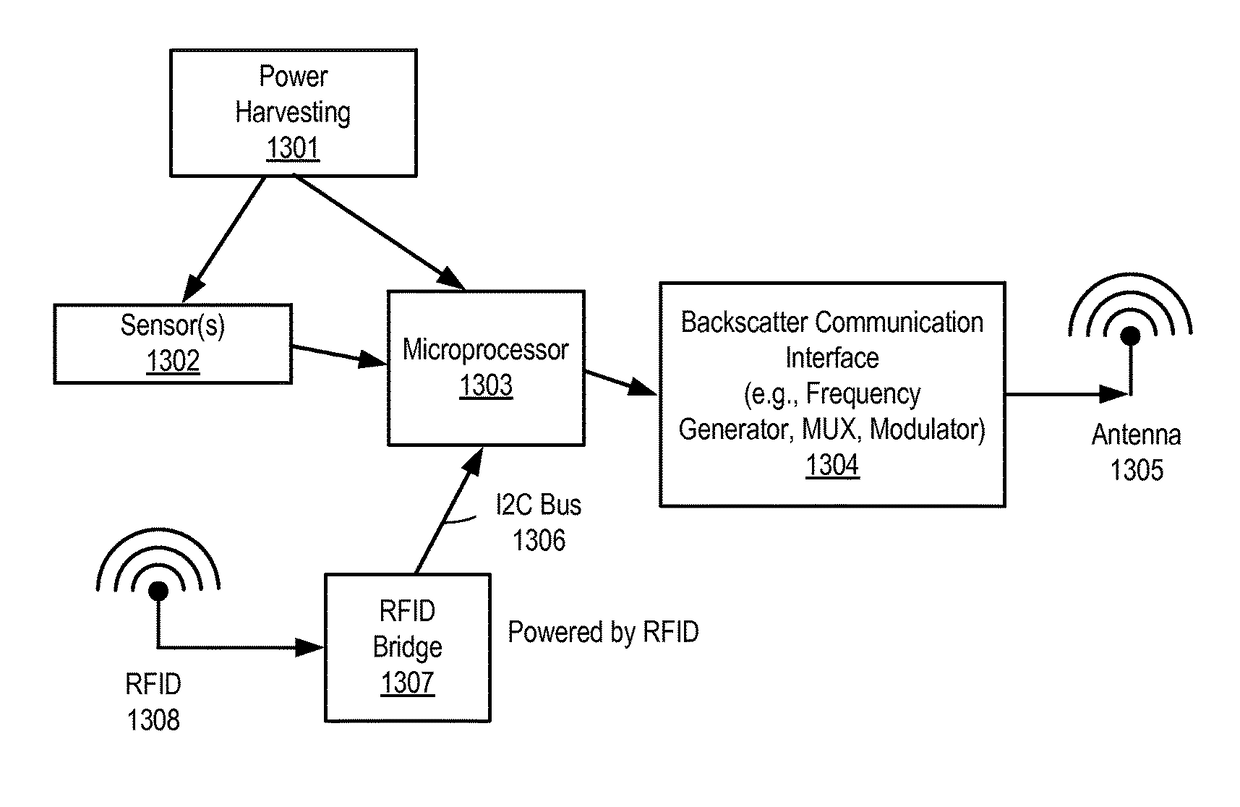
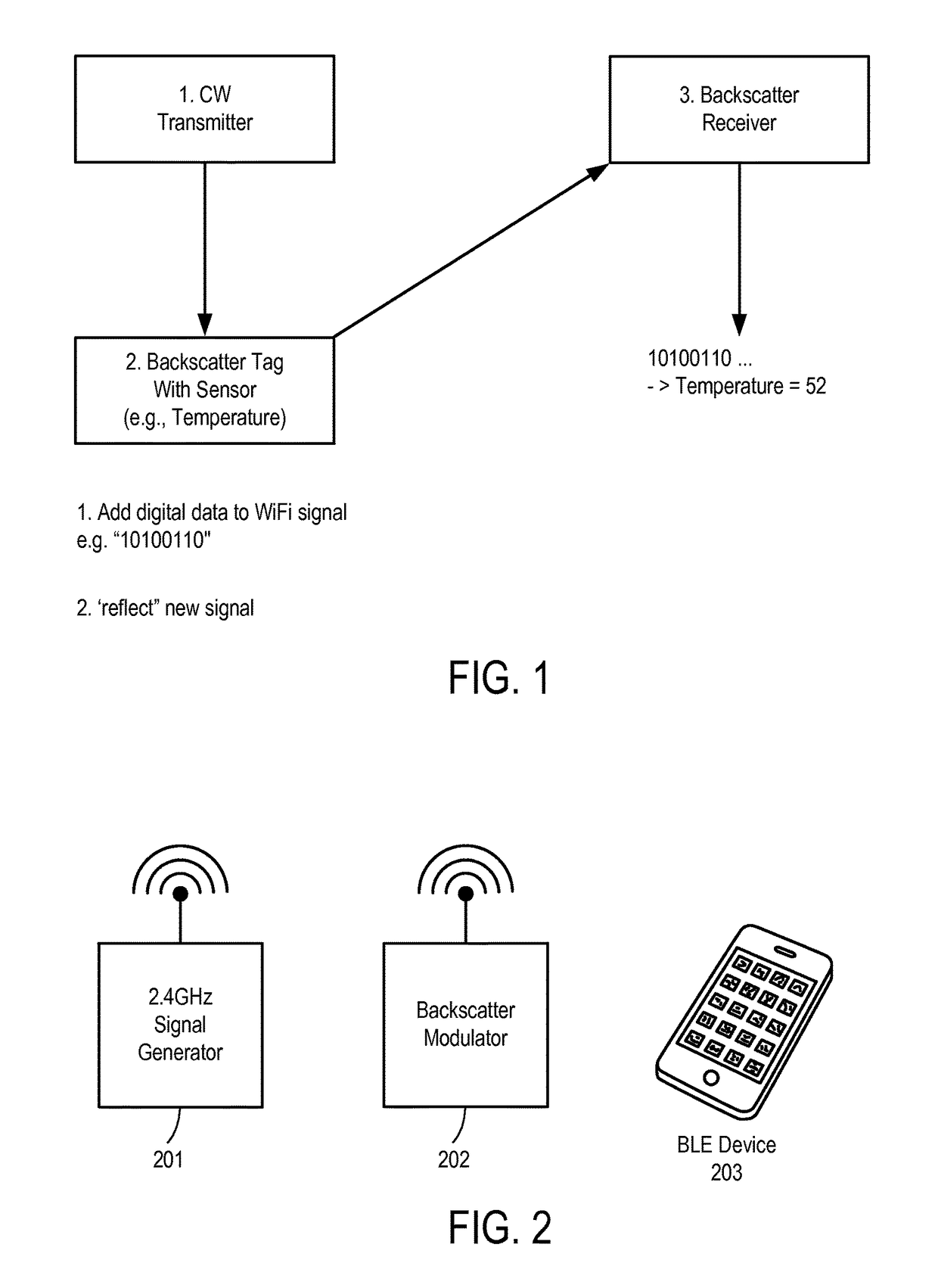
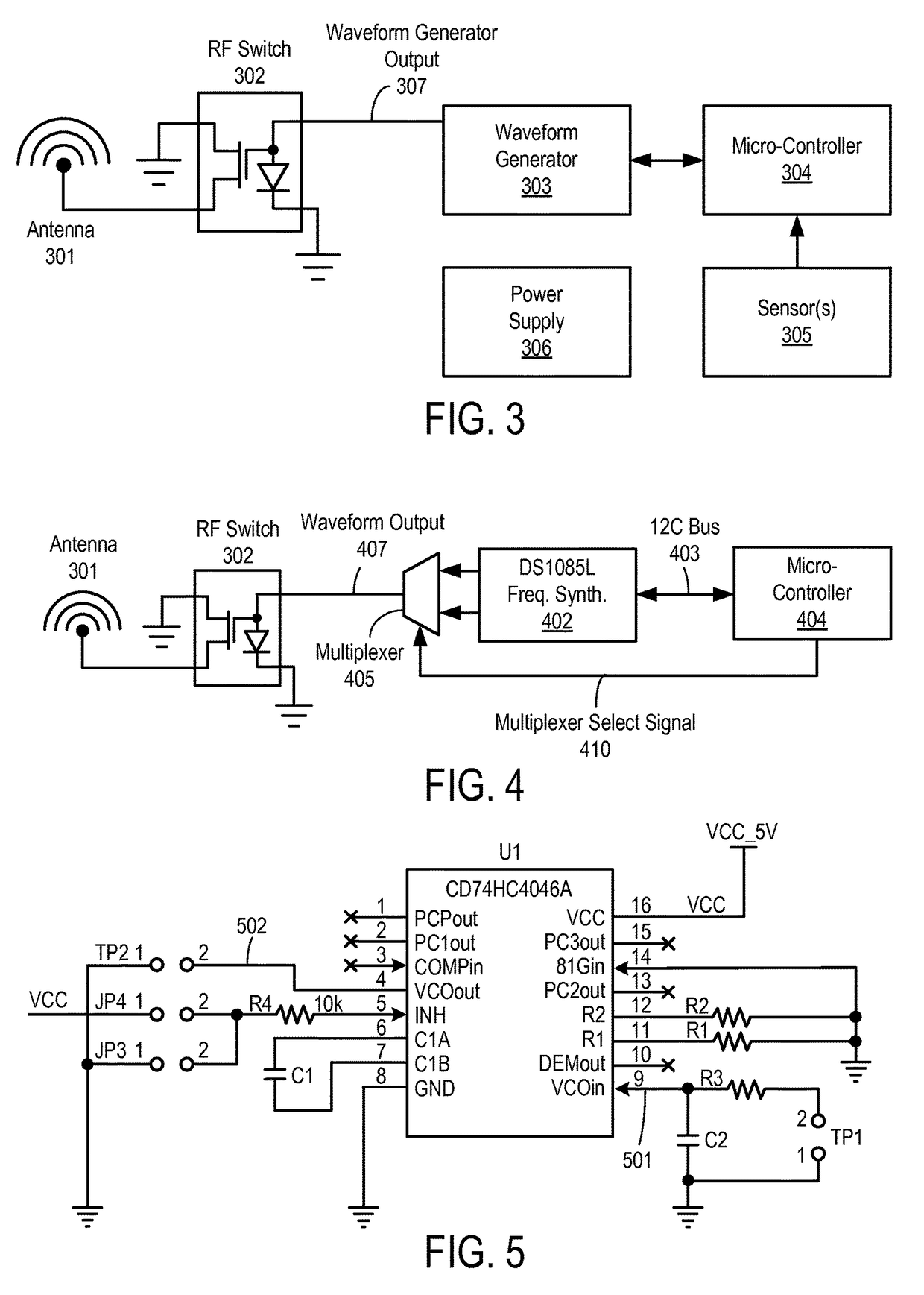
A backscatter modulation radio-frequency (RF) sensor and method for using the same are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the RF sensor comprises: an energy harvesting unit operable to convert incident RF energy to direct current (DC); a storage unit operable to store recovered DC power; one or more sensors for sensing; a backscatter communication interface to backscatter energy to communicate one or more packets using a frequency-shift keying (FSK) modulator; and a microcontroller coupled to the energy harvesting and storage units, the one or more sensors, and the backscatter communicator, the microcontroller operable to cause the backscatter communication interface to communicate sensed data from at least one of the one or more sensors while powered by energy previously harvested and stored by the energy harvesting and storage unit.
Owner:RICOH KK
System for communication with implantable medical devices using a bridge device
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
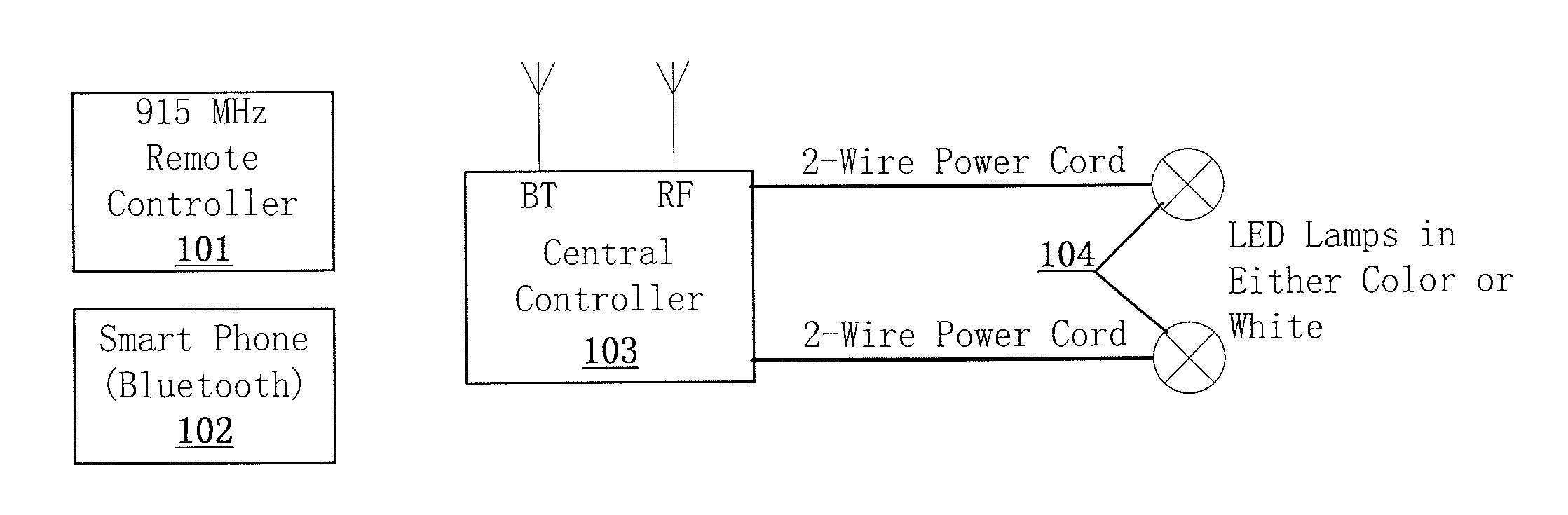
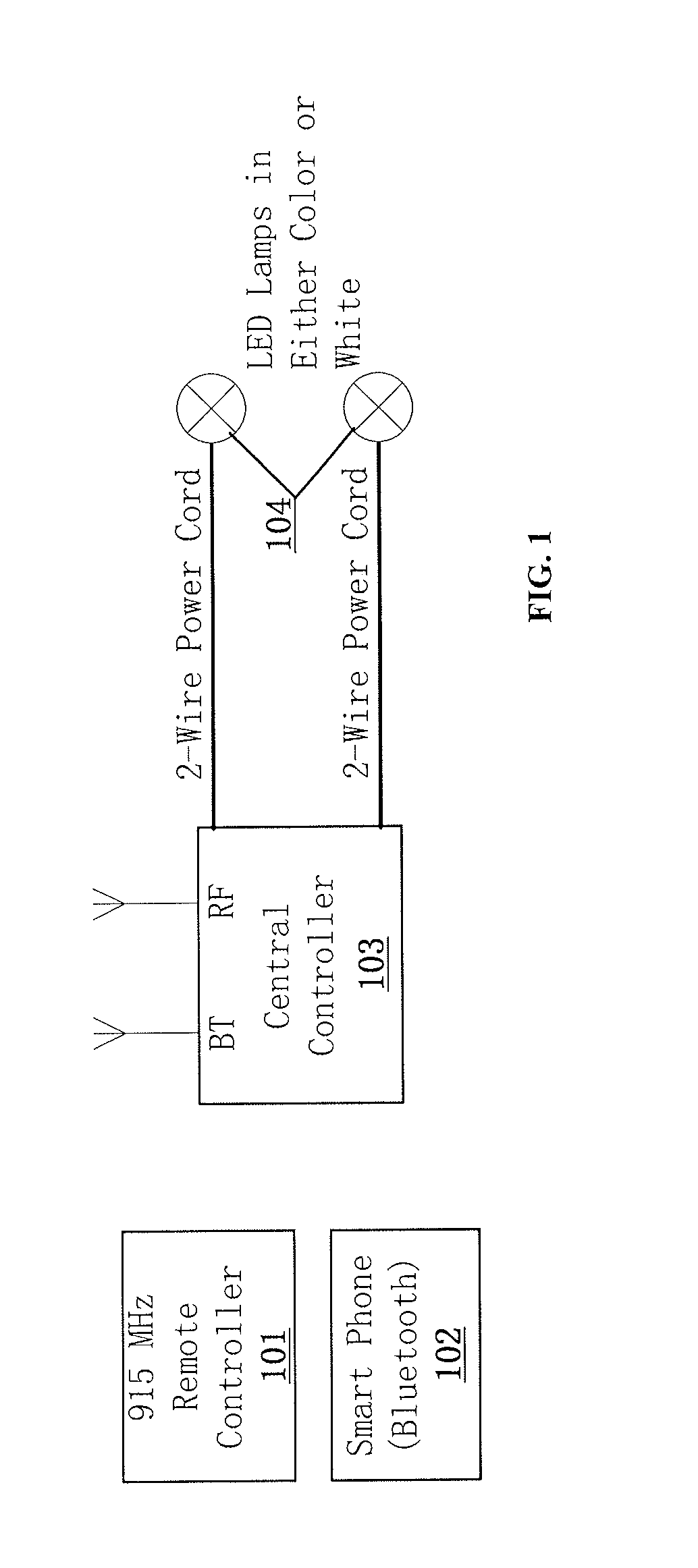
Swimming Pool LED Lighting System and Method Using Proprietary Frequency-Shift Keying Over 2-Wire Power Cord
ActiveUS20140203710A1Easy to installDischarge tube incandescent screensElectric discharge tubesPower cableControl signal
A system for controlling a lamp comprises a central controller having a waveform converter capable of modulating a control signal at more than one frequency over a two wire power cable. The control signal is capable of modifying a property of the lamp. The central controller also has a load current sensor capable of identifying the configuration of the lamp. The system further comprises a lighting control unit coupled to the lamp. The lighting control unit is powered via the two wire power cable and is capable of demodulating the control signal.
Owner:S R SMITH
UWB signal generator using optical FSK modulator
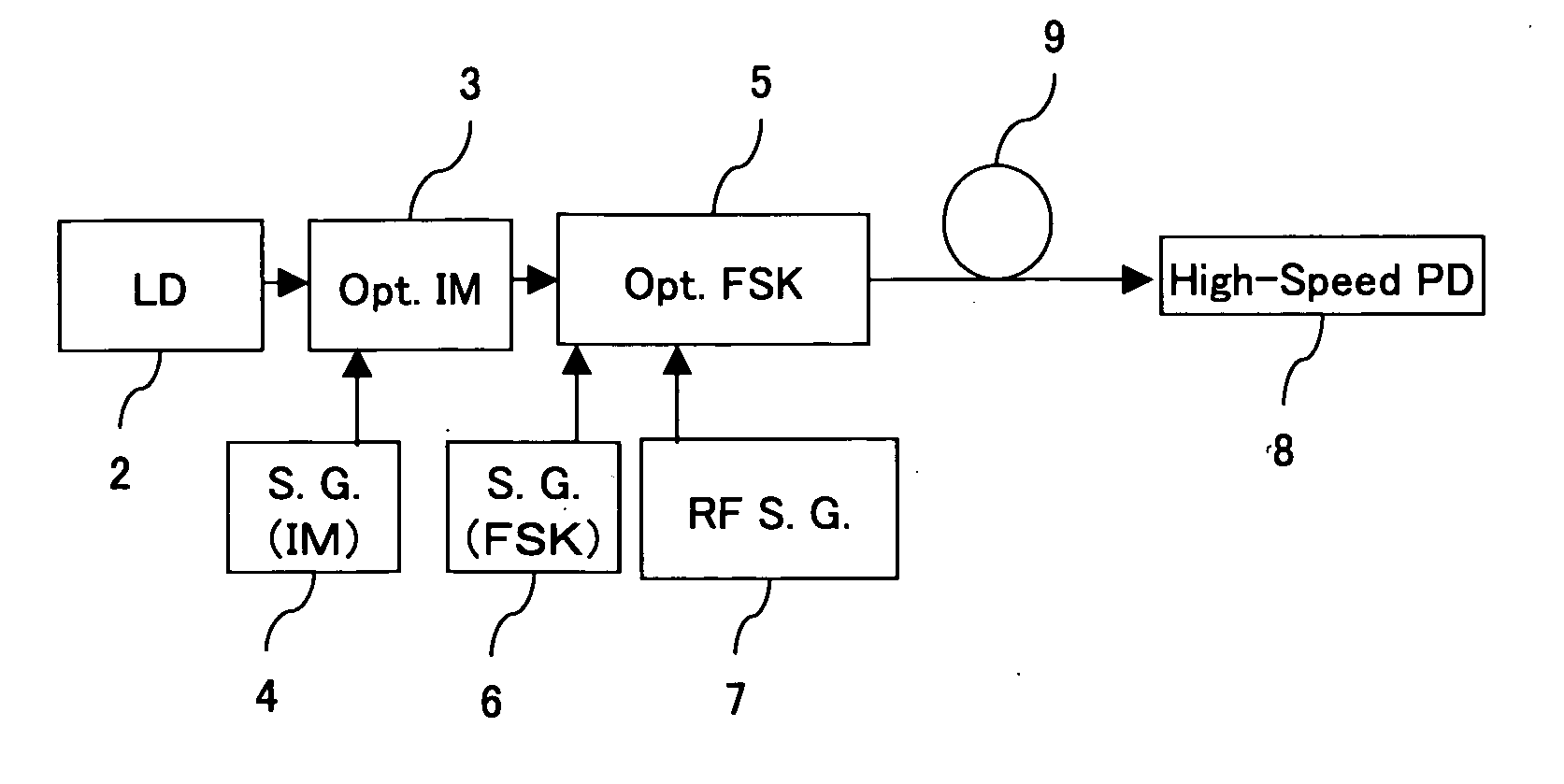
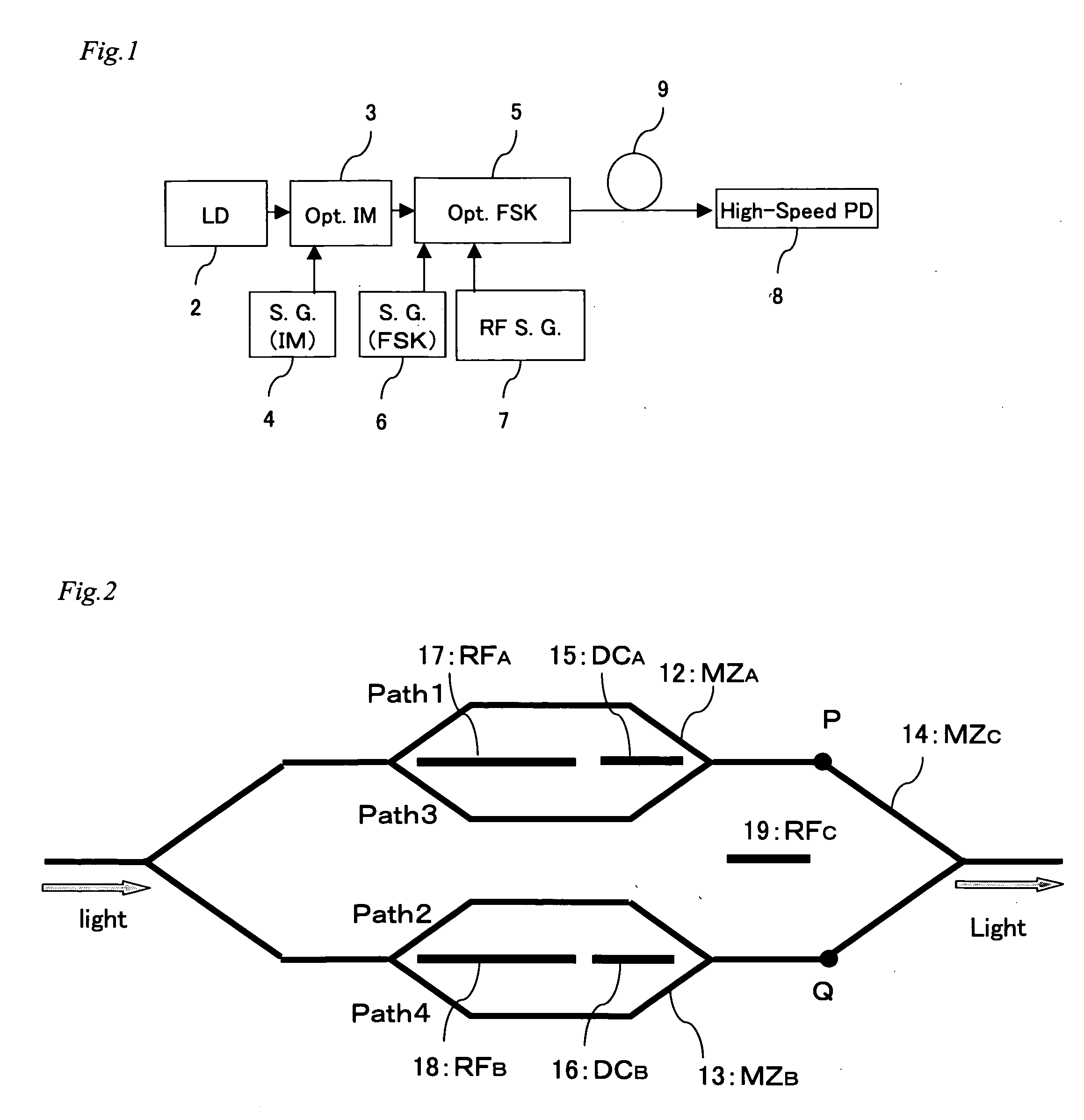
InactiveUS20050175357A1Information transmissionIncrease speedCode division multiplexElectromagnetic transmittersPhotodetectorLaser light
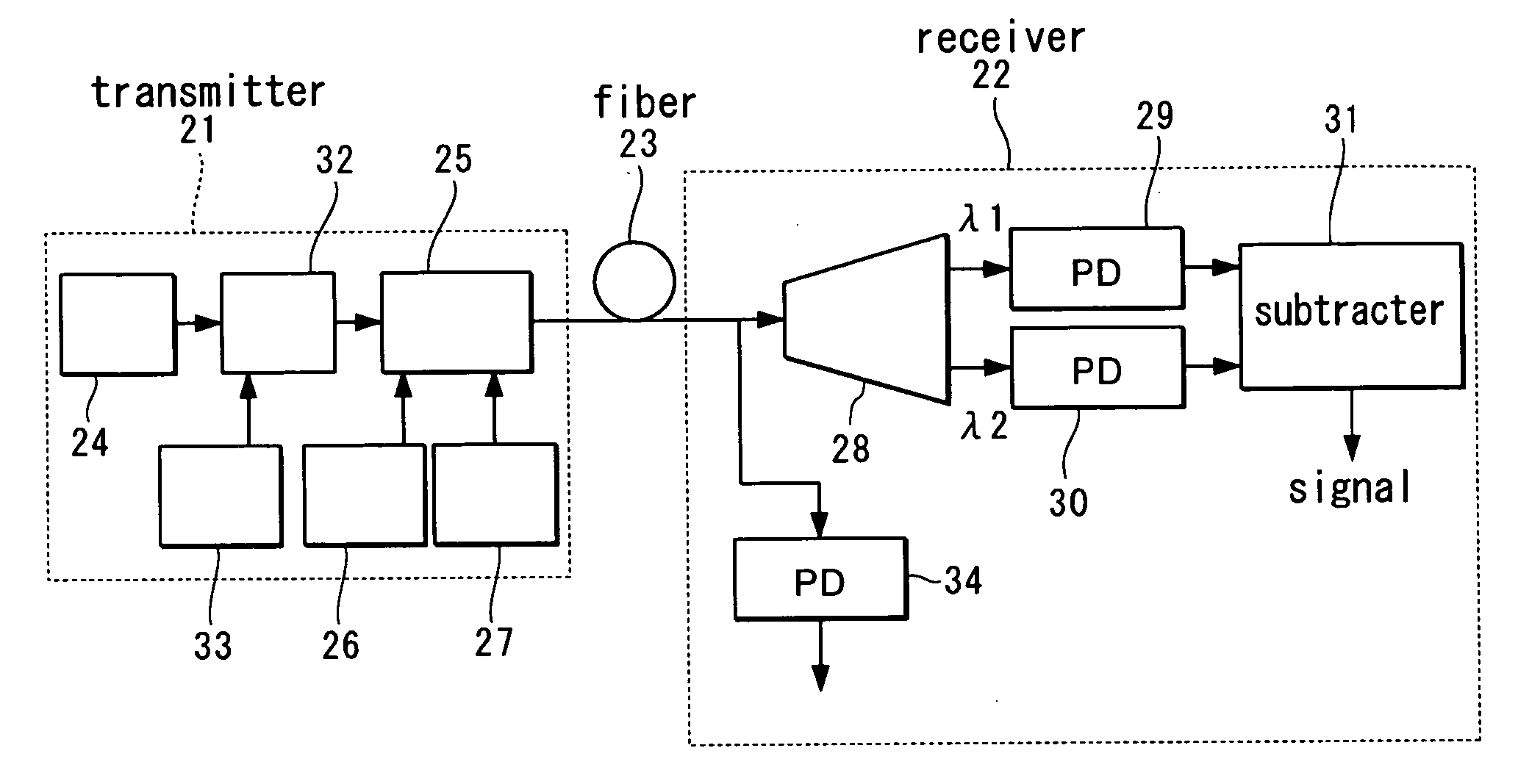
A UWB signal generator includes: a laser light source for generating laser light, an optical intensity modulator for modulating an intensity of laser light from the laser light source, a signal source of the optical intensity modulator for outputting a signal transmitted to the optical intensity modulator, an optical frequency shift keying (optical FSK) modulator to which output light from the optical intensity modulator is input, a signal source for controlling a signal transmitted to an RFC electrode of the optical FSK modulator, a high-frequency electric signal source for controlling a signal transmitted to an RFA electrode and an RFB electrode of the optical FSK modulator, and a high-speed photodetector for detecting an output from the optical FSK modulator.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Combined tire pressure monitoring and keyless entry receiver
InactiveUS6885283B2Great signal powerHigh peak output field strengthElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsMonitoring systemFrequency-shift keying
A receiver assembly (16) includes an amplitude shift keyed mode (52) and a frequency shift keyed mode (58) selectively engagable to receive radio frequency transmissions from the tire monitoring system (26) and a remote keyless entry system (20) and switches between modes in response to receipt of a wake up pattern.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
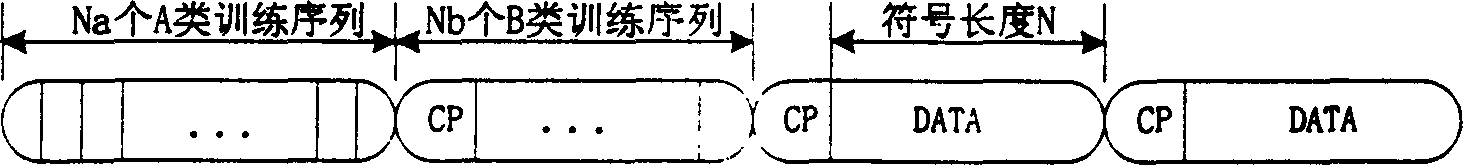
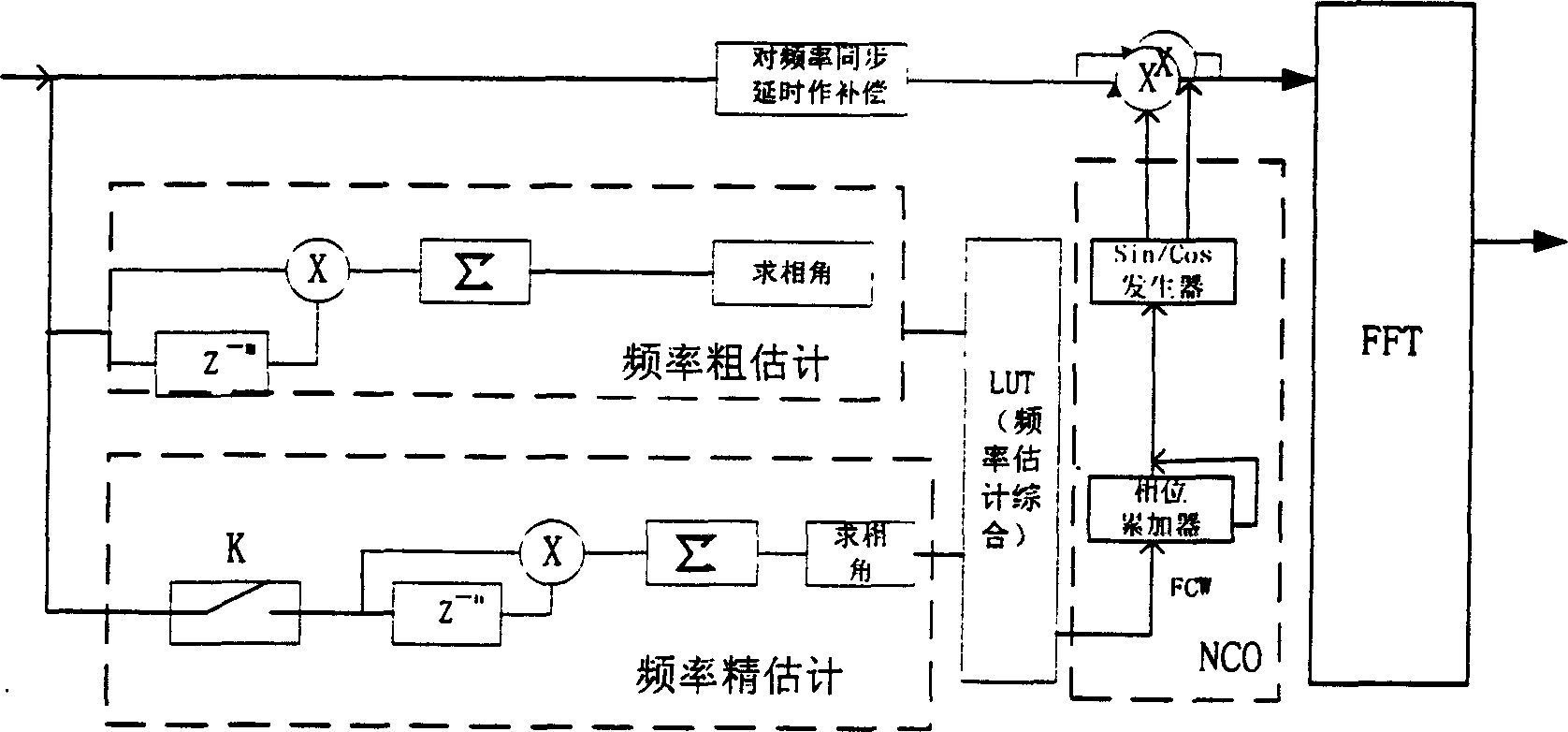
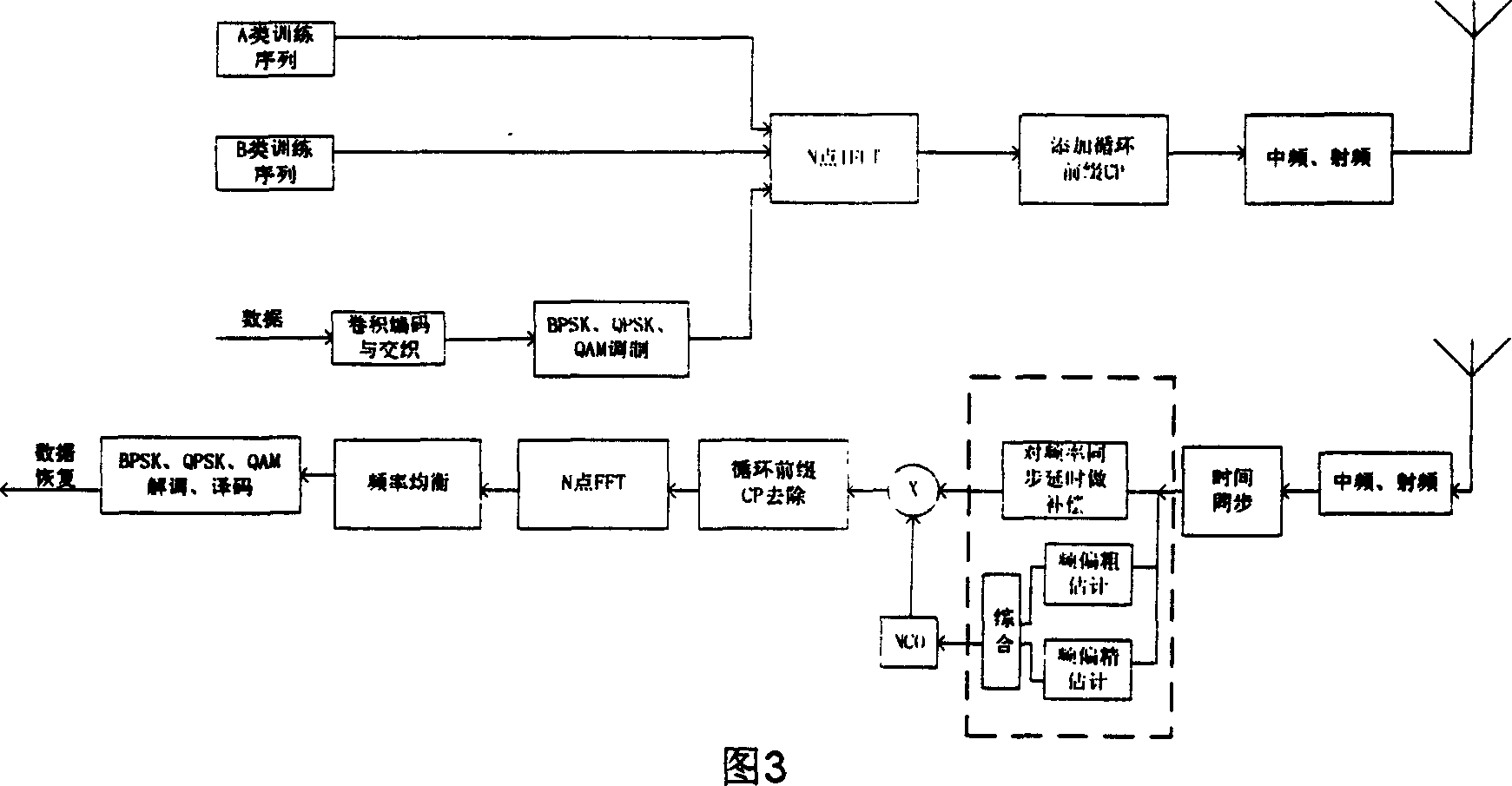
Method for estimating carrier, frequency shifts of orthogonal FDM communication system
InactiveCN1472900APromote recoveryHigh precisionOrthogonal multiplexMultiple carrier systemsTime domainNumerical control
A estimating method of OFDM communication system carrier frequency excursion, in original place of systems frame adds two training sequence that were designed especially, using the result of cross correlation of class A training sequence estimates original value of frequency excursion, namely to make rough estimation of frequency excursion, then using class B makes autocorrelation, gained frequency deviation signal was estimated precisely in small scale, namely to make frequency excursion precise estimation, then make two estimating value combined to get precise value of system frequency excursion, finally control numerical control oscillator to produce rectify value of system frequency excursion, and put it to multiply with time domain data to make compensation of frequency excursion.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
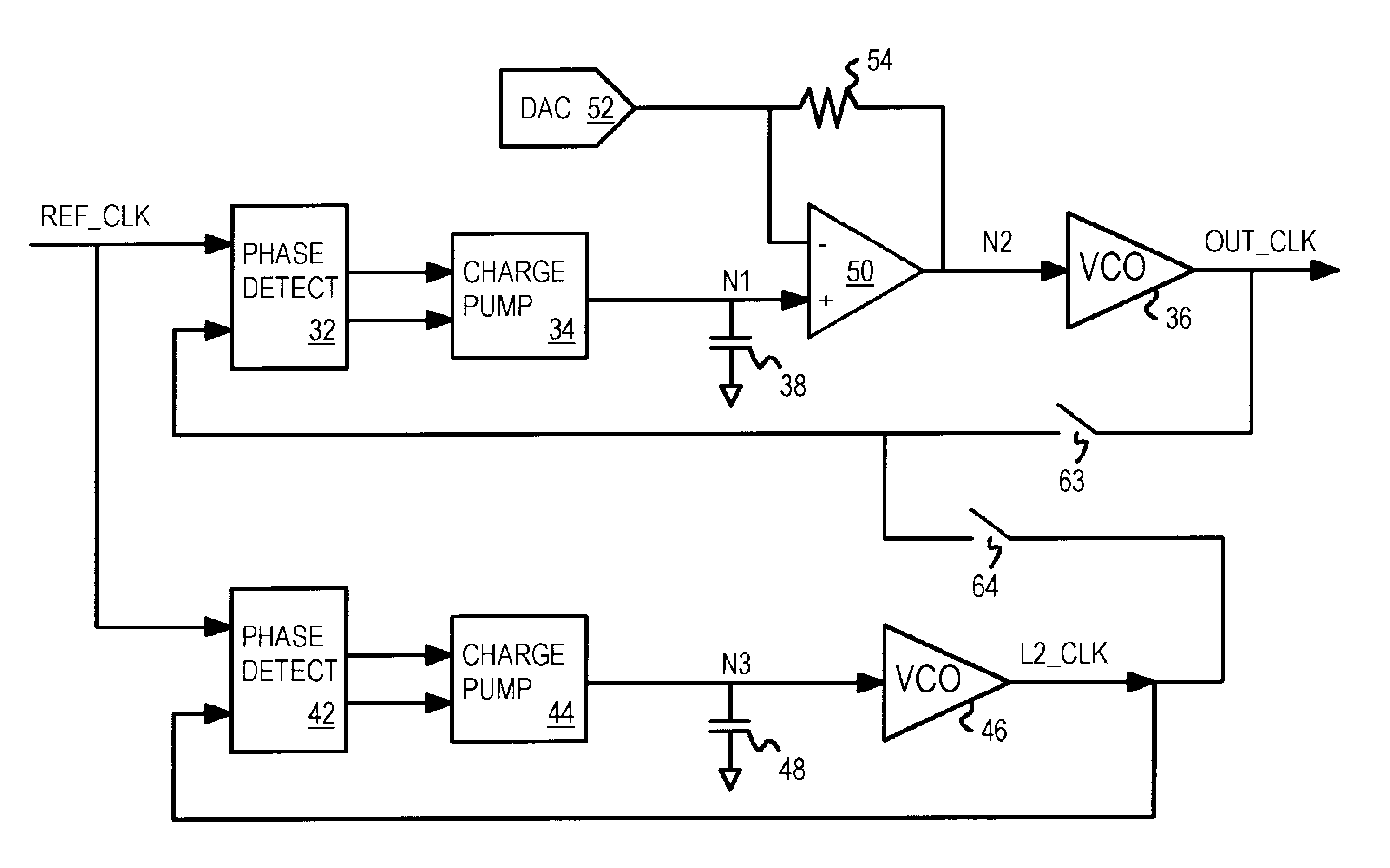
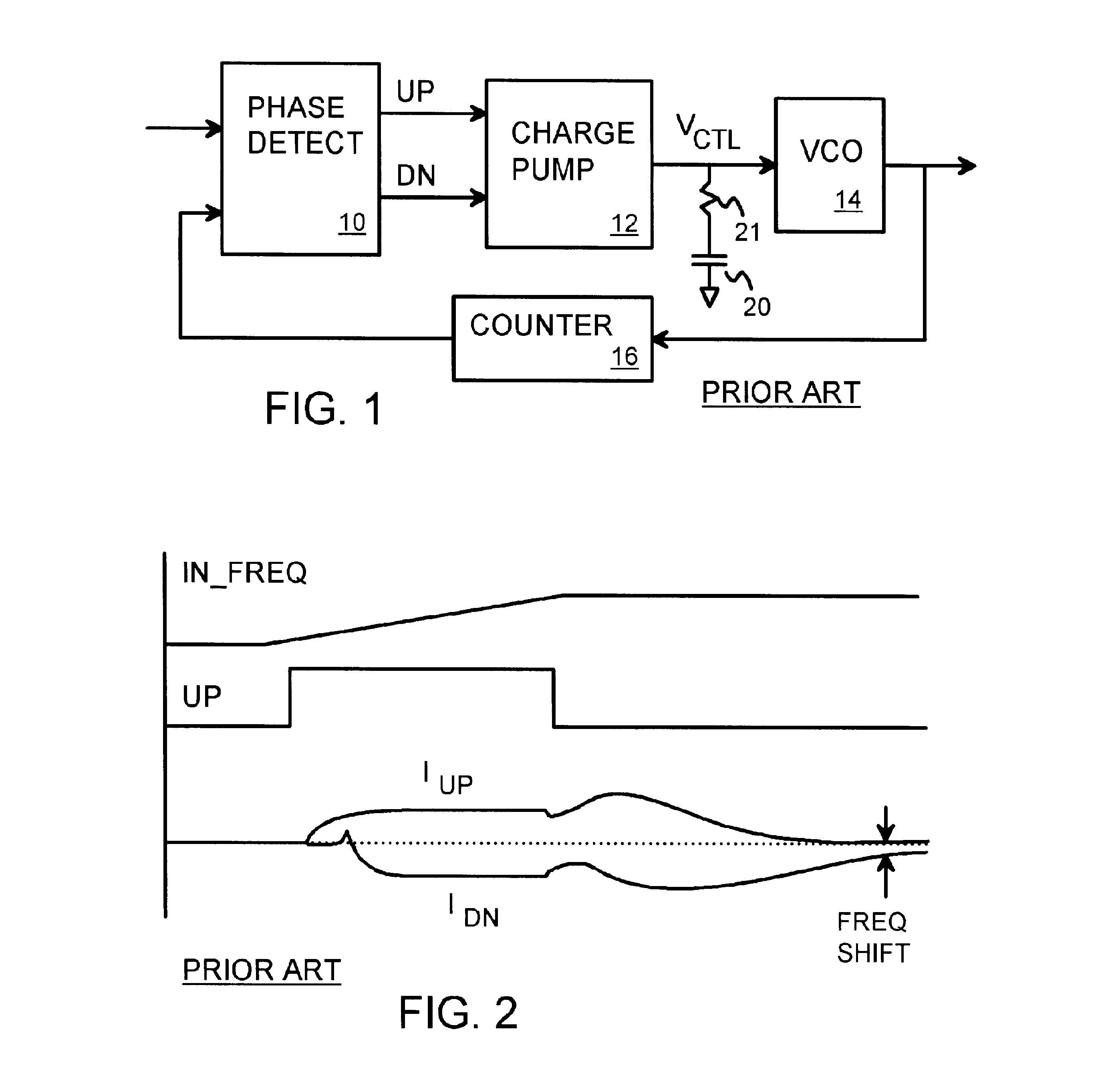
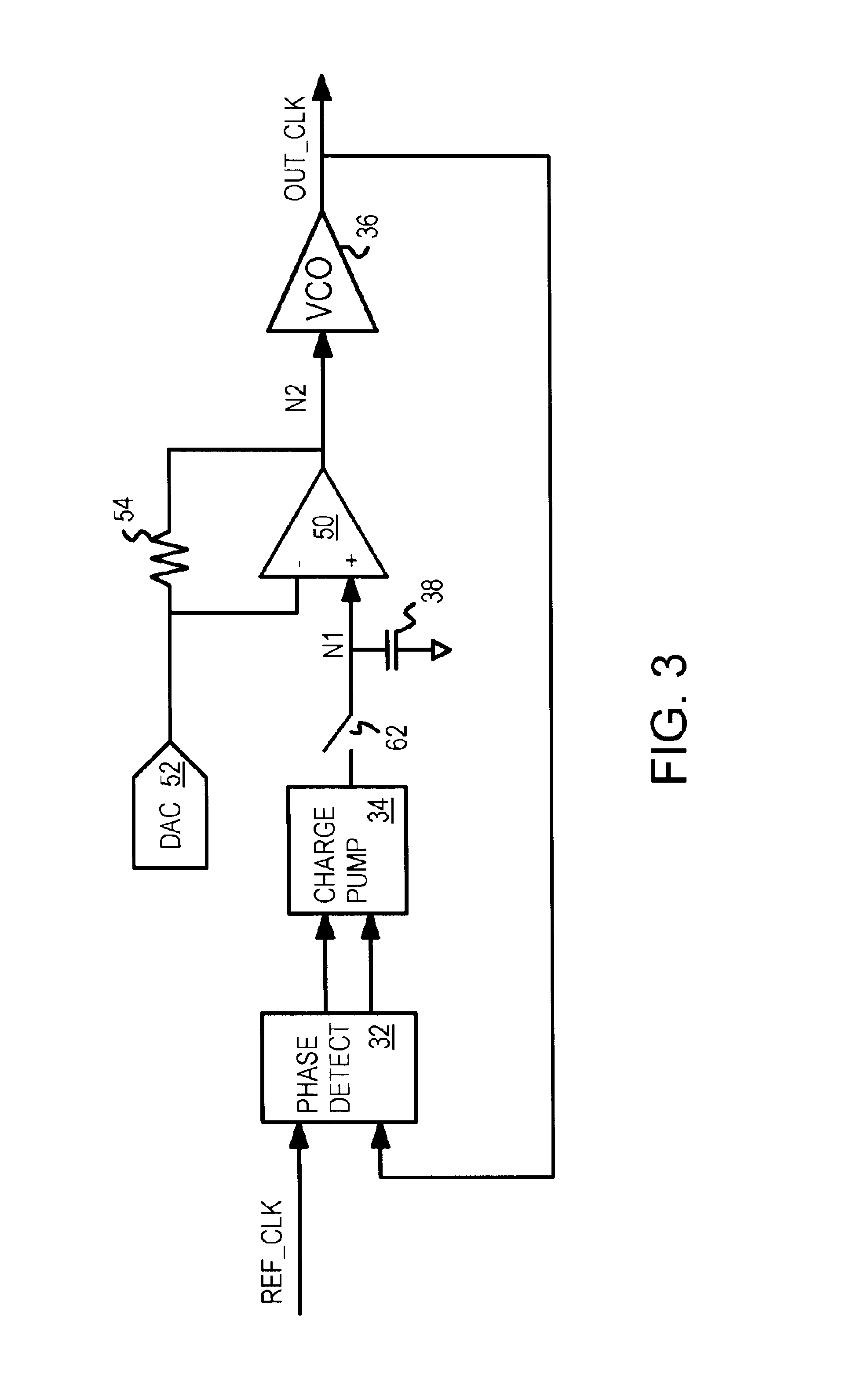
Dual-loop PLL with DAC offset for frequency shift while maintaining input tracking
A phase-locked loop (PLL) keeps tracking a reference clock when a frequency offset is introduced. The PLL has primary and secondary PLL loops. A digital-to-analog converter (DAC) generates a current that is passed through an offset resistor to generate an offset voltage. An op amp is inserted in the primary loop between a filter capacitor and a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The offset resistor is coupled between the inverting input of the op amp and the op amp's output. When the DAC offset occurs, the voltage to the VCO and the frequency of the primary loop change and the primary loop loses tracking of the reference clock. The secondary loop keeps tracking the reference clock during the DAC offset while the primary loop is open. Then the output clock of the secondary loop is applied as the feedback clock to the phase comparator of the primary loop.
Owner:DIODES INC
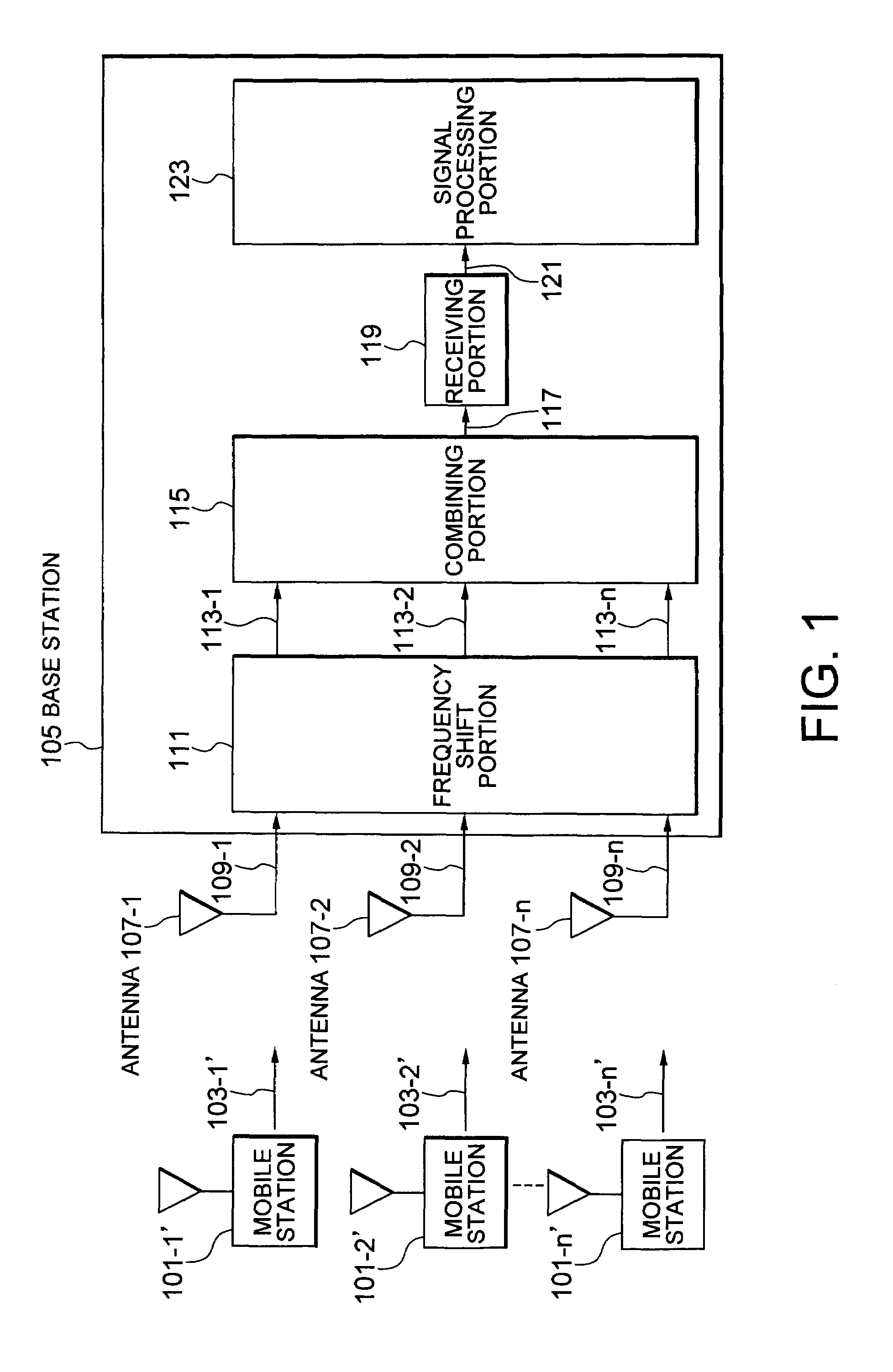
Mobile communication system having mobile stations and a base station
InactiveUS7054397B1Small sizeLow costSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityIntermediate frequencyMobile communication systems
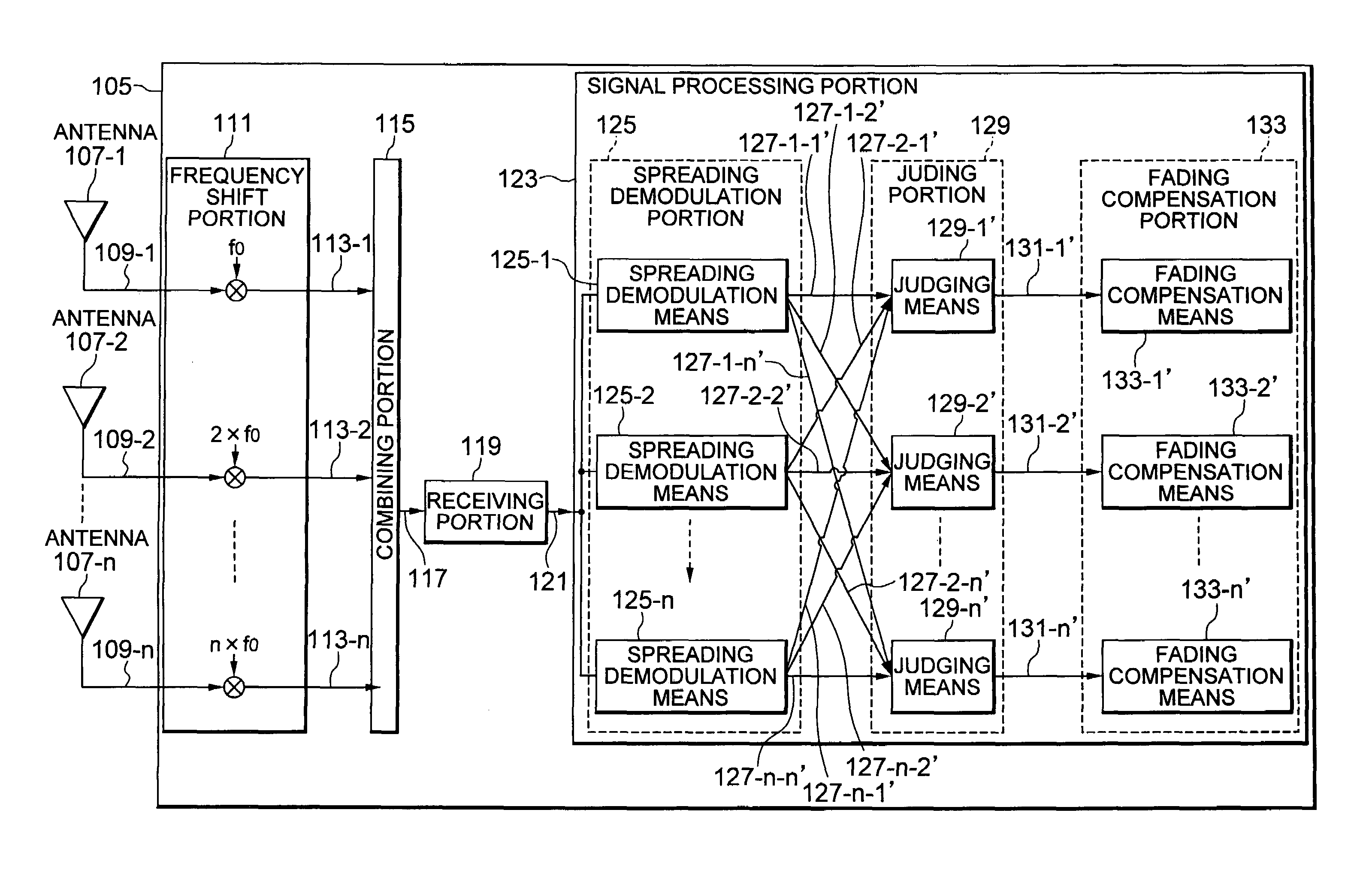
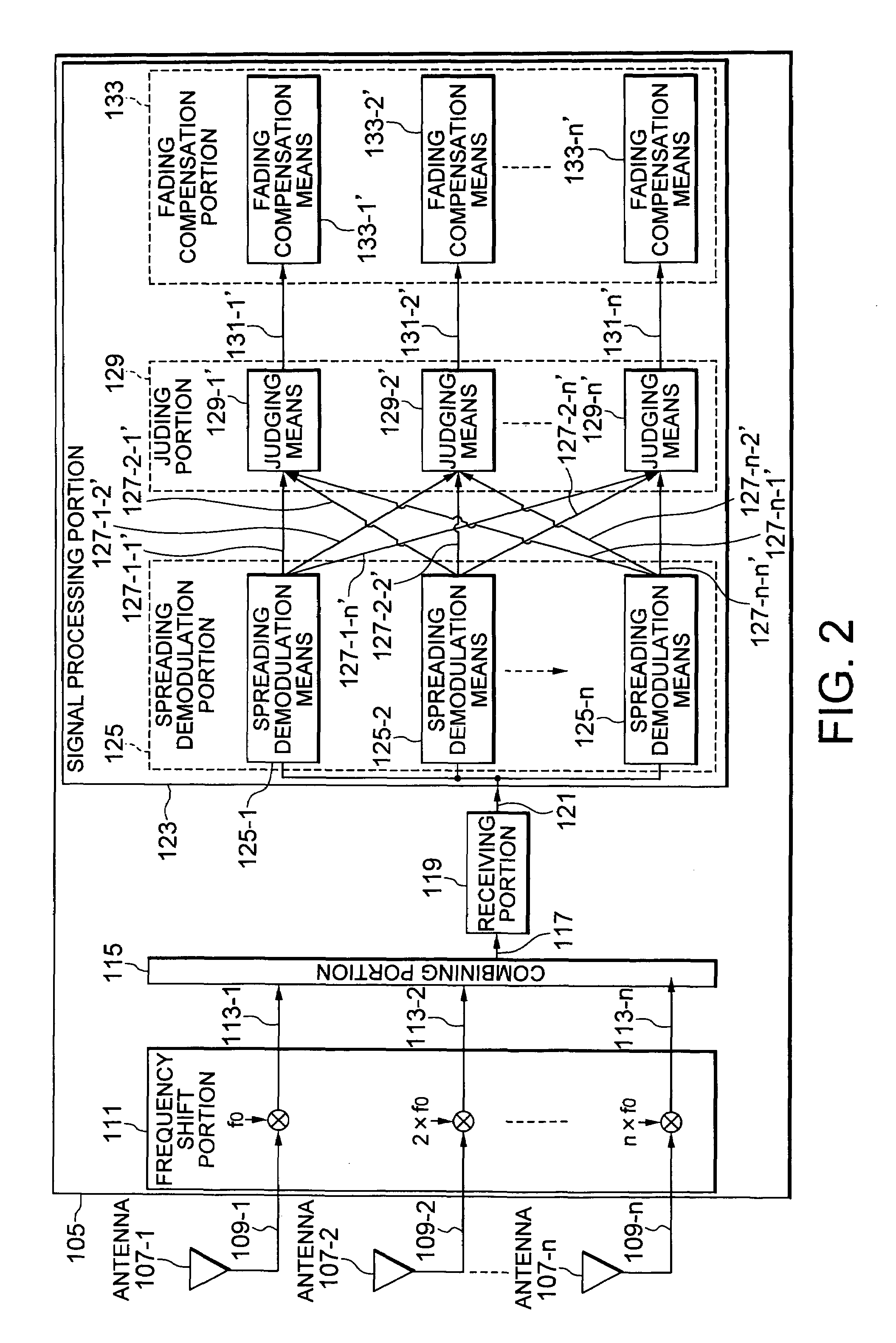
A mobile communication system has a plurality of mobile stations and a base station which includes a plurality of antennas, a frequency shift portion, a combining portion, a receiving portion and a signal processing portion. The antenna receives radio waves transmitted by the mobile stations. The frequency shift portion shifts the received signal with a frequency corresponding to each of the antennas. The combining portion determines the shifted signal as a combining signal. The receiving portion converts the combining signal in frequency to make an intermediate frequency signal, and converts the intermediate frequency signal into a digital signal. The signal processing portion includes spreading demodulation means judging means, and fading compensation means.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for realizing setting of navigating destination through bluetooth push-to-talk
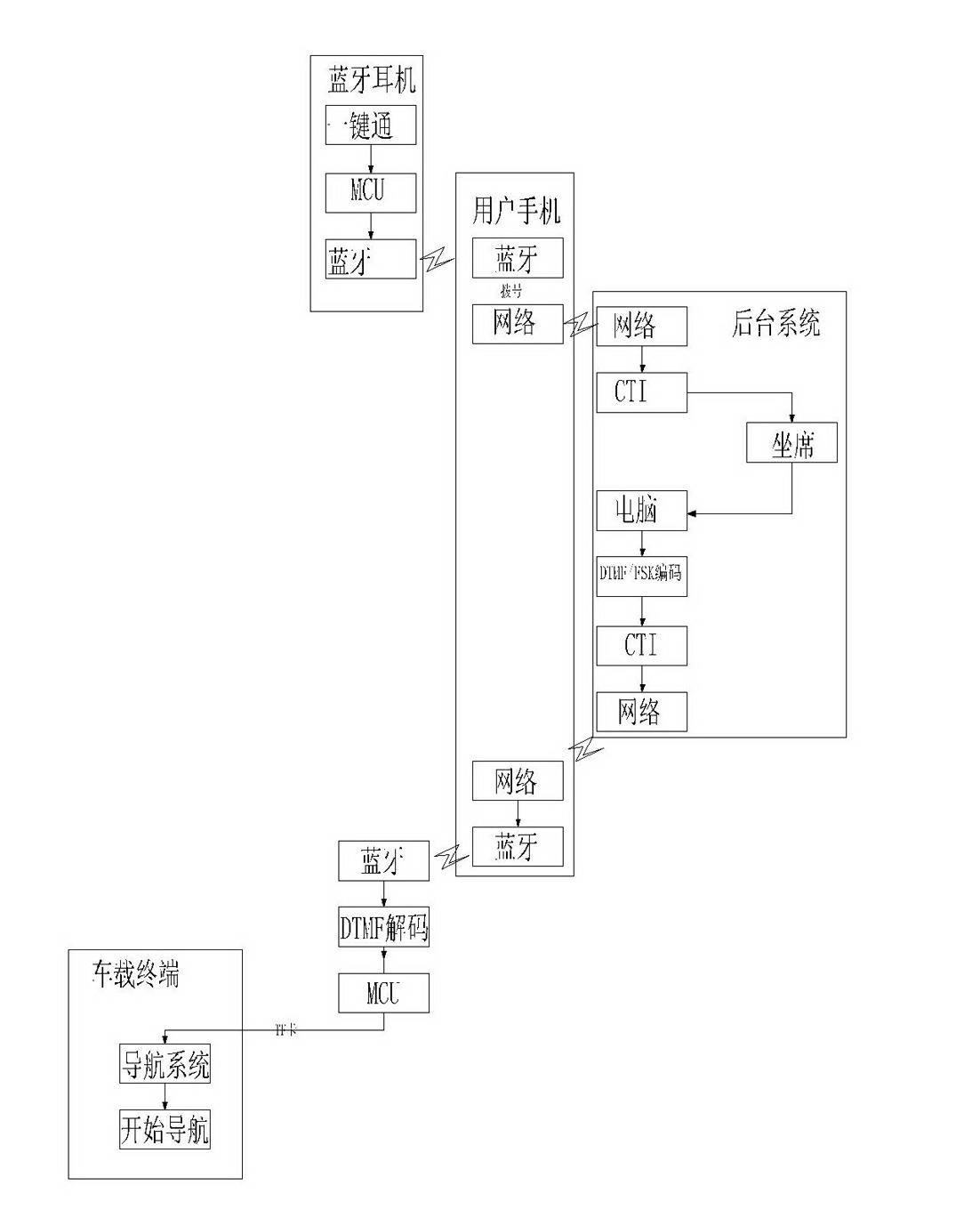
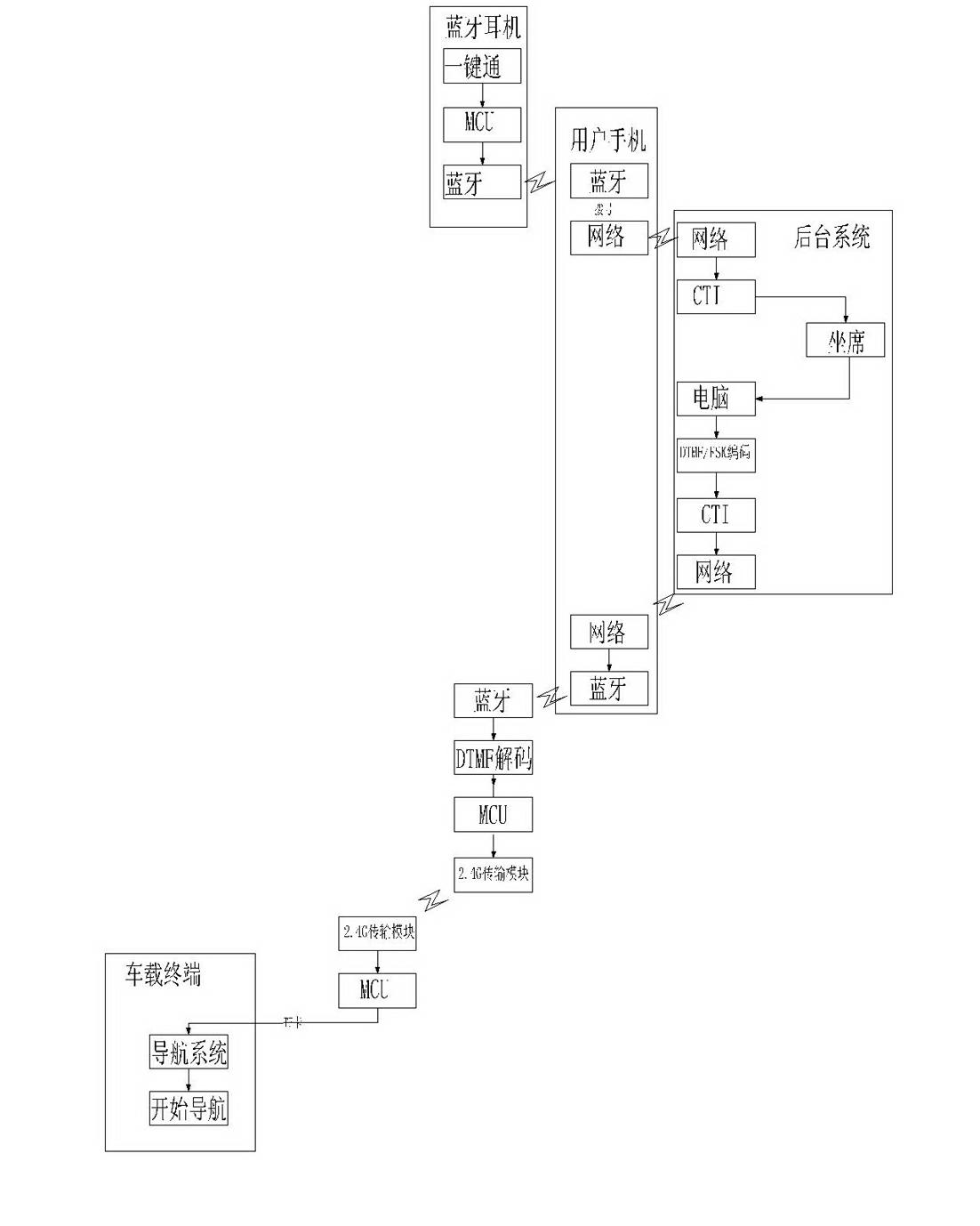
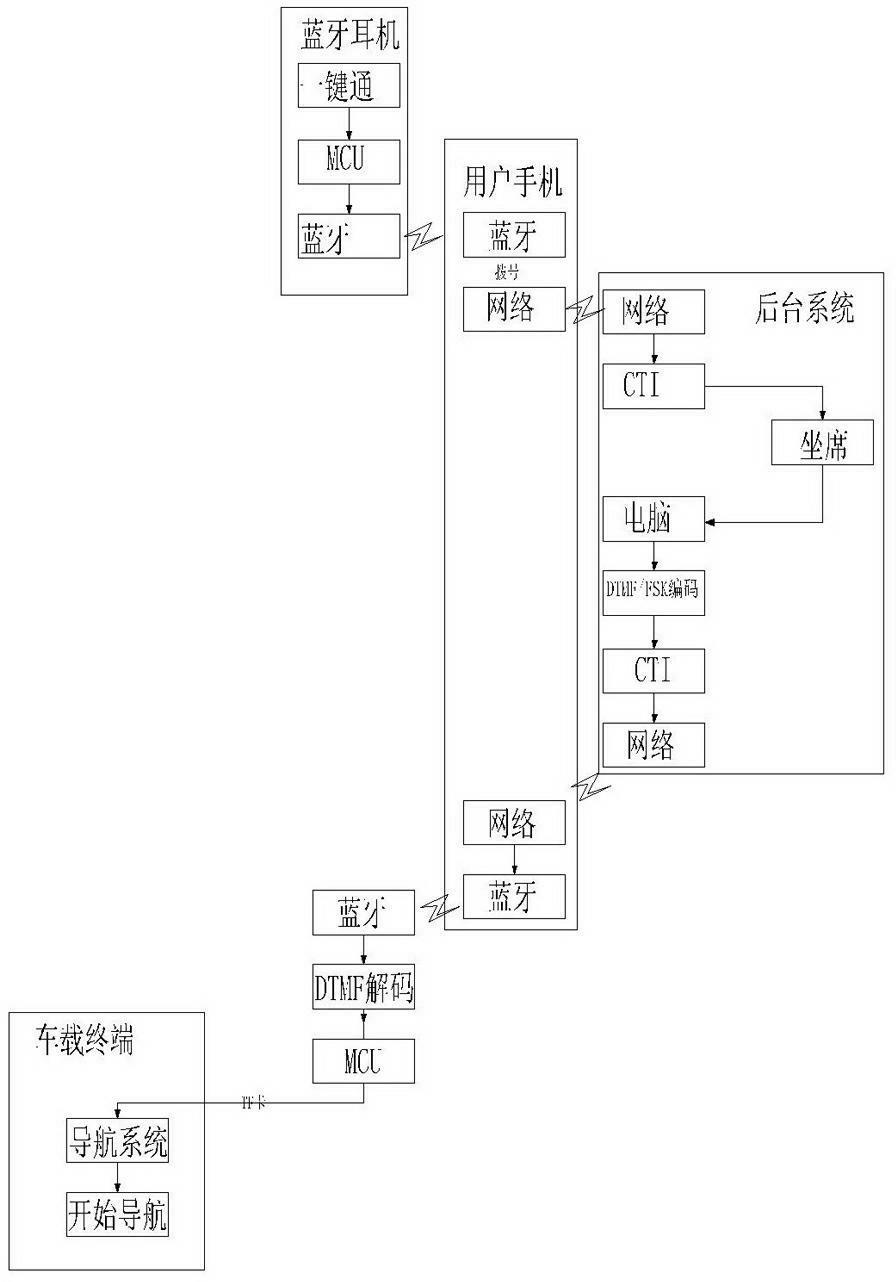
InactiveCN102625240ALow costFast decodingInstruments for road network navigationNear-field transmissionComputer moduleComputer terminal
The invention discloses a method for realizing setting of a navigating destination through bluetooth push-to-talk. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, starting a push-to-talk device which is connected with a bluetooth module; after matching the bluetooth module with a user mobile phone, dialing a background system phone number by the user mobile phone; after answering the call and understanding a user requirement by a telephone operator of the background system, operating the background system and encoding through DTMF / FSK (Dual Tone Multiple Frequency / Frequency Shift Keying) coder and decoder; returning voice signal data corresponding to map coordinate data to the user mobile phone through a mobile phone network; after receiving the voice signal data by the user mobile phone, sending the voice signal data to the DTMF / FSK decoder in the manner of mobile phone bluetooth; after decoding by the DTMF / FSK decoder, storing in a vehicle master controller MCU (Micro Controller Unit); and lastly, extracting map coordinate information from a memory by a navigating system in a vehicle-mounted terminal and starting a navigating service. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of low cost, high decoding speed and excellent popularizing value.
Owner:GUANGDONG ECAR TELEMATICS SERVICE
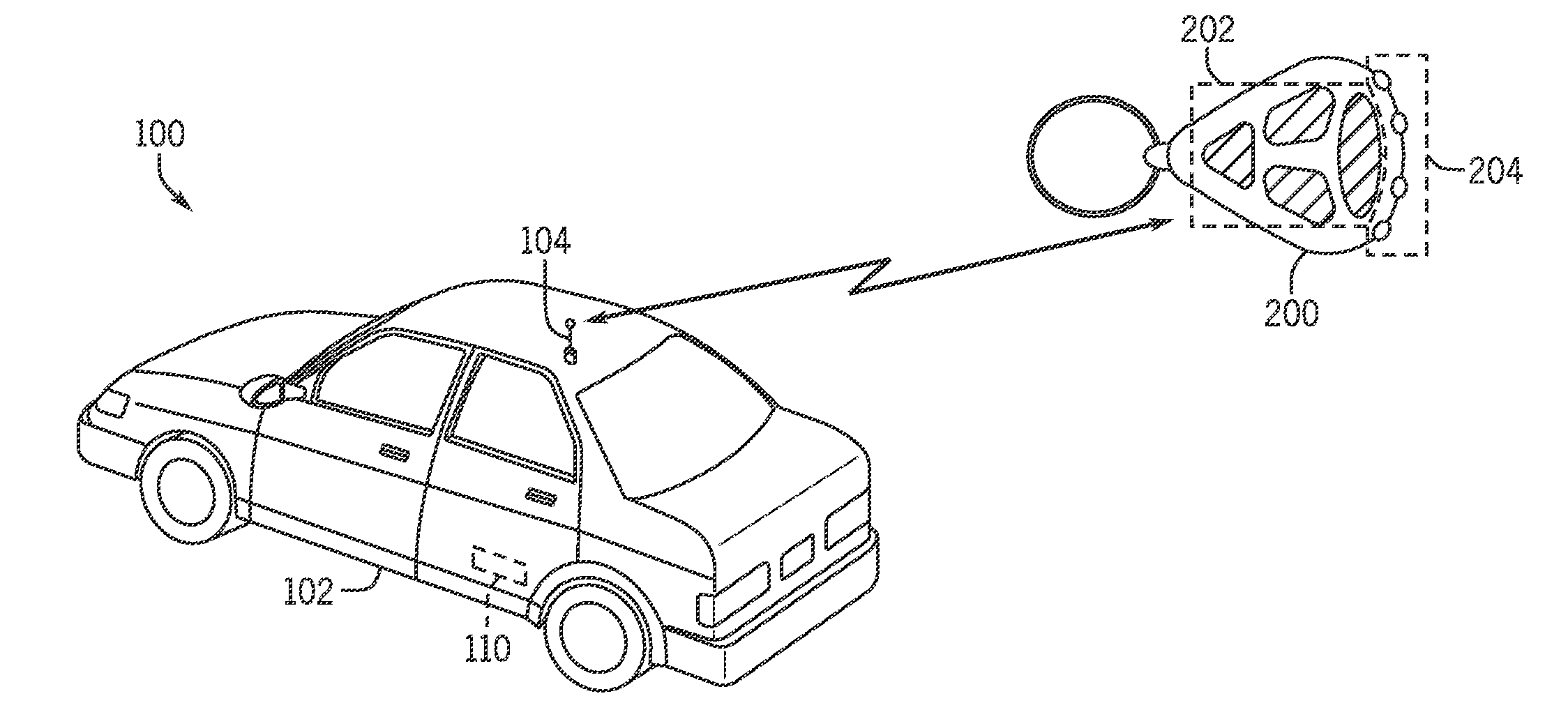
Multi-range vehicle access systems
The present disclosure addresses methods for increasing and varying the range of control of wireless systems used in vehicles. The present invention enables varying ranges which allow a user, for example, to activate lights when an authorized vehicle user is in a close range, and to start the vehicle from a distance before the authorized vehicle user leaves the house. The described systems use variable frequency shift keying, variations in power transmissions, and user defined ranges that can be modified through Bluetooth communications.
Owner:HUF NORTH AMERICA AUTOMOTIVE PARTS MFG
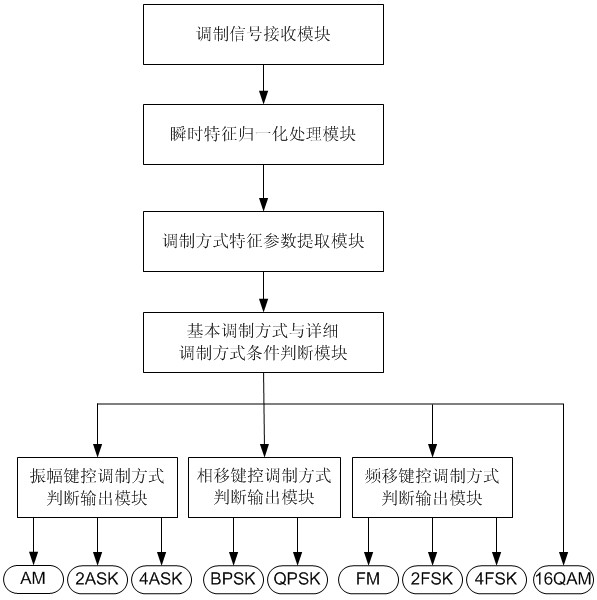
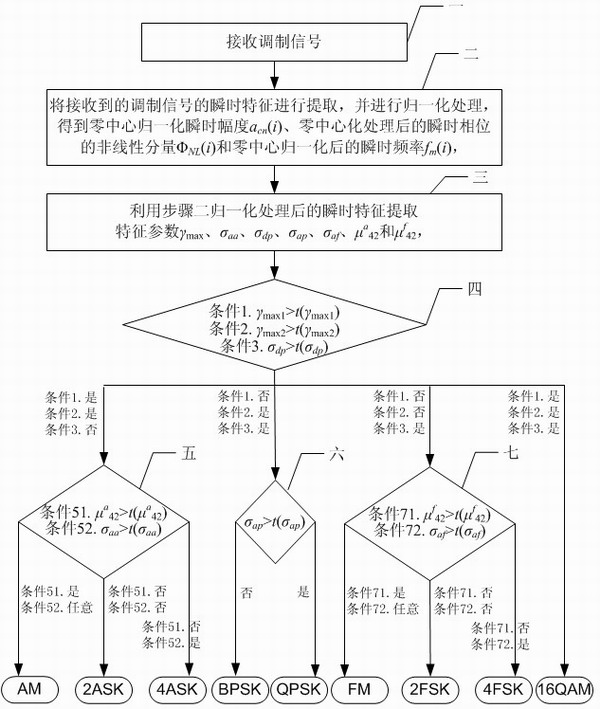
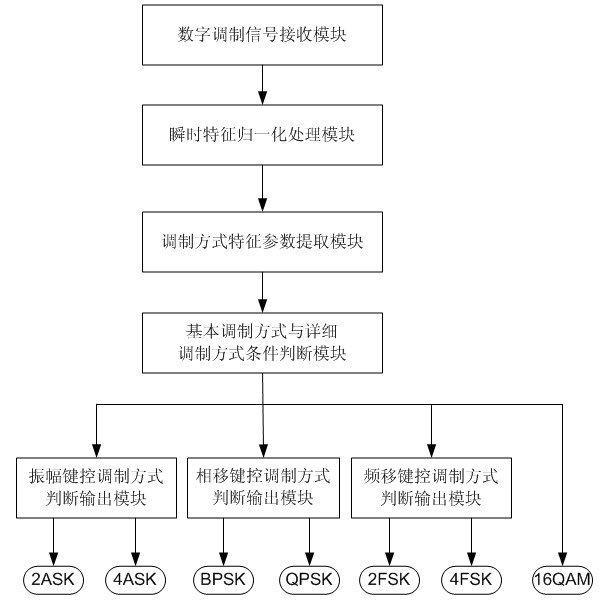
Analog-digital mixing modulation recognition device and digital modulation recognition device based on parallel judgment
InactiveCN101834819AImprove recognition accuracyAvoid the problem of order of useModulated-carrier systemsPattern recognitionPhase shifted
The invention discloses an analog-digital mixing modulation recognition device and a digital modulation recognition device based on parallel judgment, belonging to the communication field. The invention aims to solve the problems of low precision rate and long recognition time for providing a judgment tree by A.K. N and E.E.A zzouz. The invention is characterized in that the parallelly judged analog-digital mixing modulation recognition device comprises the following steps: a modulation signal receiving module coarsely classifies the received modulation signals through an instantaneous characteristic normalization module and a modulation mode characteristic parameter extraction module, and then the received modulation signals are particularly classified through an amplitude shift keying modulation judgment ouput module, a phase shift keying modulation judgment output module and a frequency shift keying modulation judgment output module. Compared with the analog-digital mixing modulation recognition device, the digital modulation signals received by the digital modulation recognition device based on parallel judgment have different inner structures of the modules when coarse classification and particular classification are conducted.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
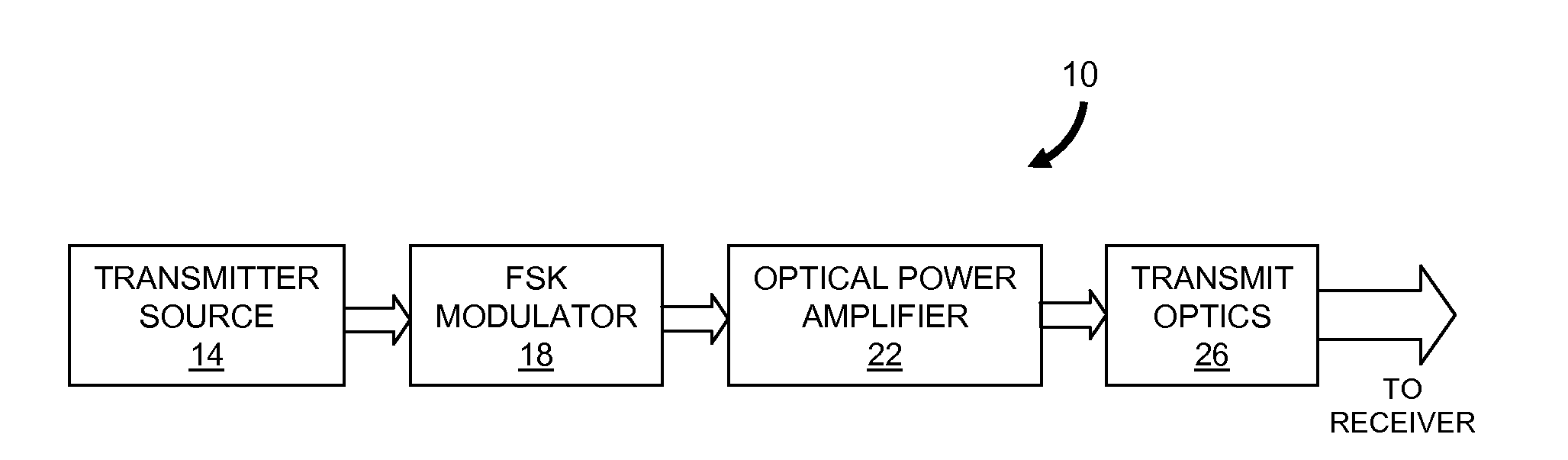
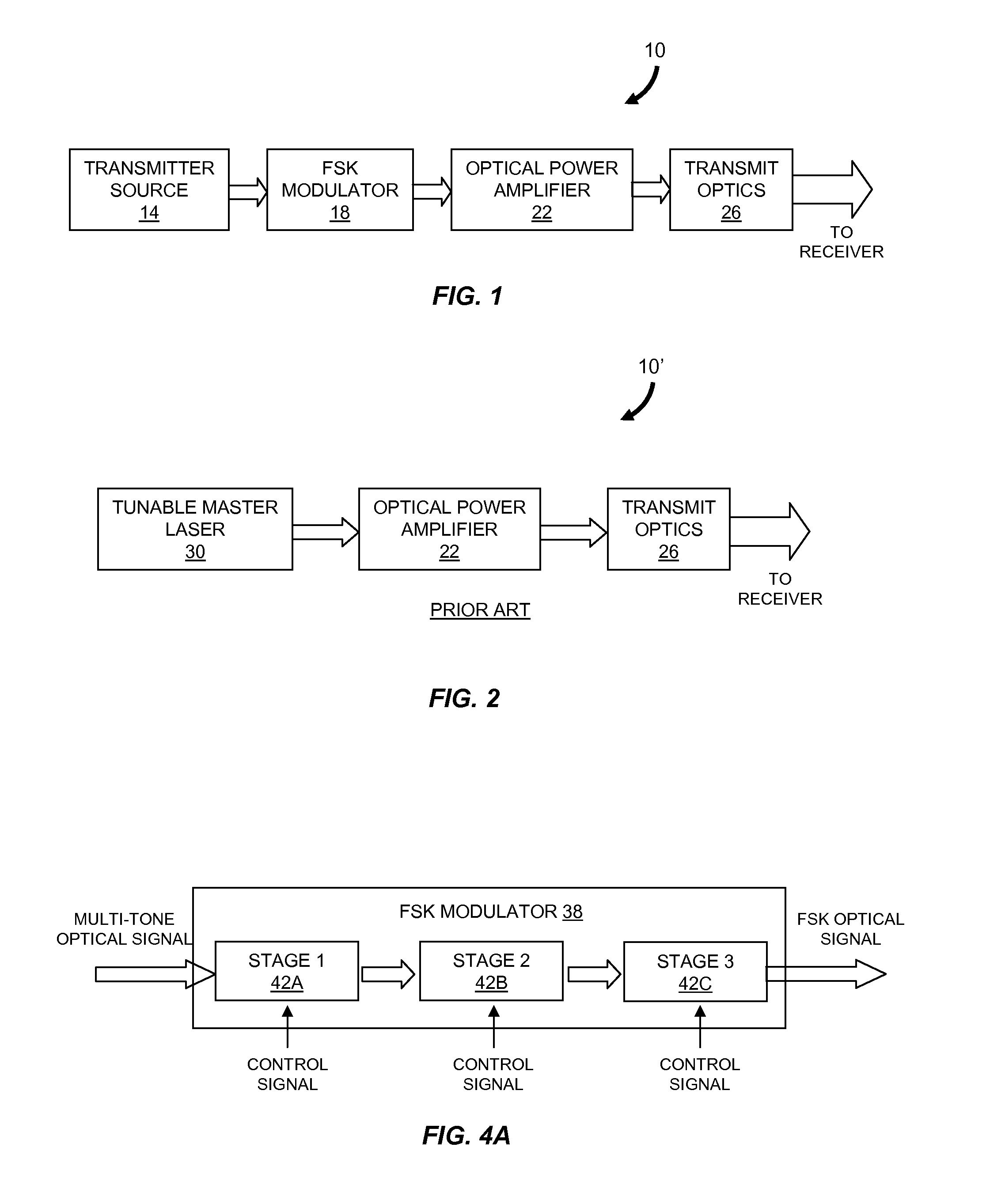
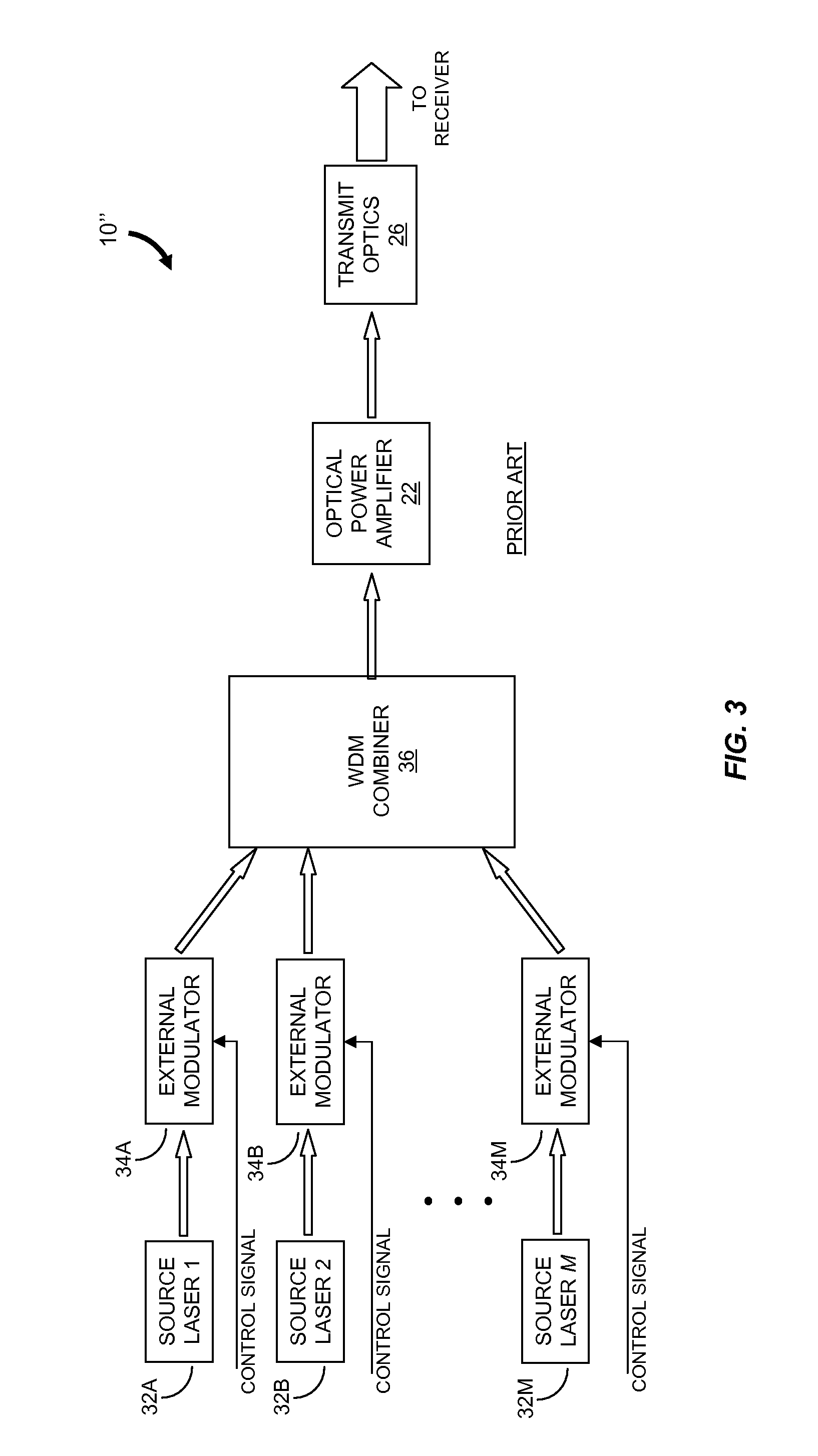
Modulator for frequency-shift keying of optical signals
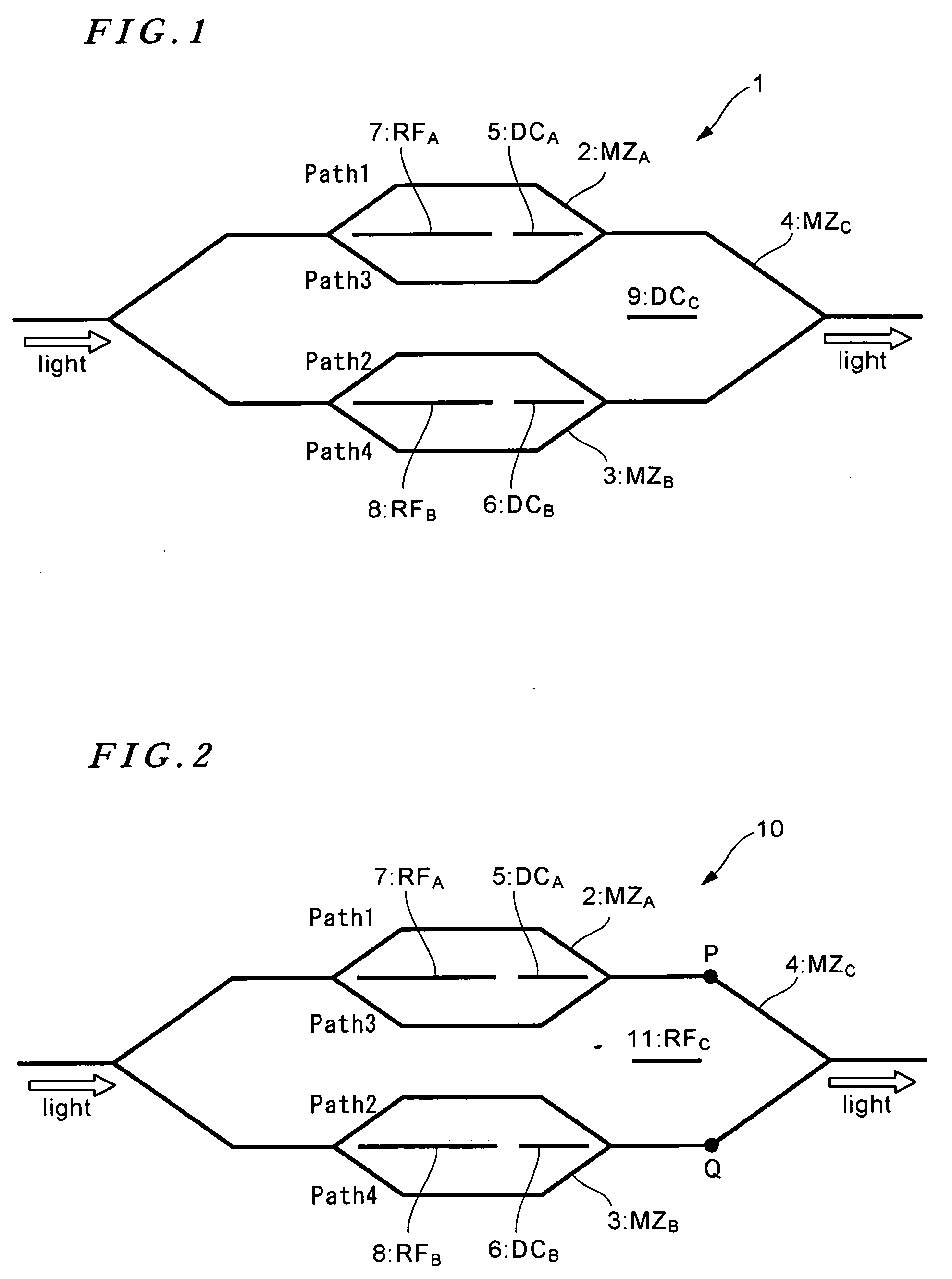
ActiveUS20100104277A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringResonator filterMach–Zehnder interferometer
Described are an FSK modulator and a method for large-alphabet FSK modulation. The FSK modulator and the method are based on filtering of a multi-tone optical source such as a mode-locked laser which provides a comb distribution of tones. A frequency-selective component selects for transmission a subset of the tones. In various embodiments the frequency-selective component is a Mach-Zehnder interferometer filter or a microring resonator filter. A second frequency-selective component selects a subset of the tones from the comb distribution provided by the first frequency-selective component. Still more frequency-selective components can be used according to the number of tones supplied by the multi-tone optical source to the FSK modulator. The optical signal exiting the last frequency-selective component includes only a single tone which corresponds to the symbol to be transmitted.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Long range phasing voltmeter
ActiveUS8283911B1Accurate measurementCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage-current phase angleElectrical conductorPhase difference
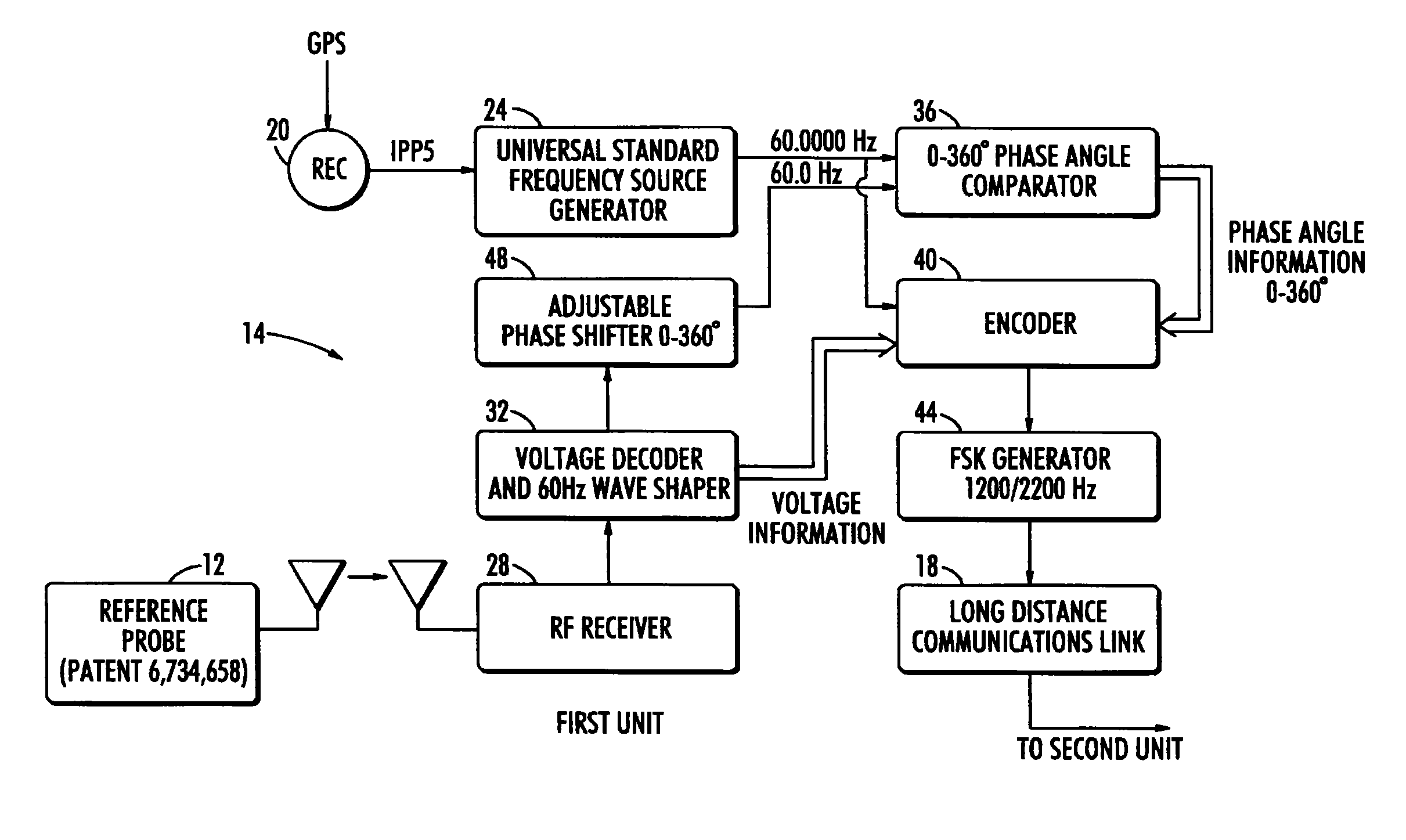
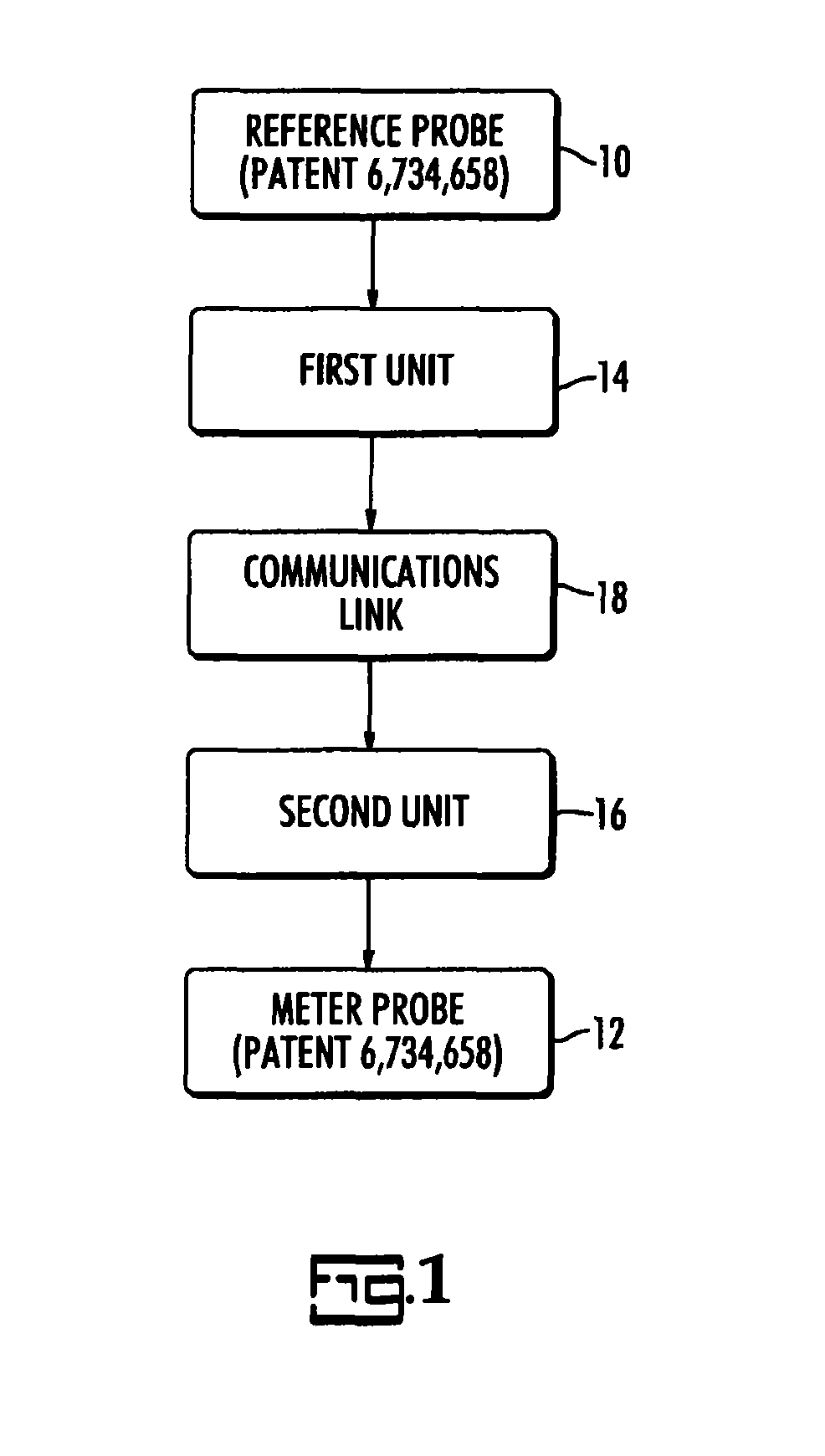
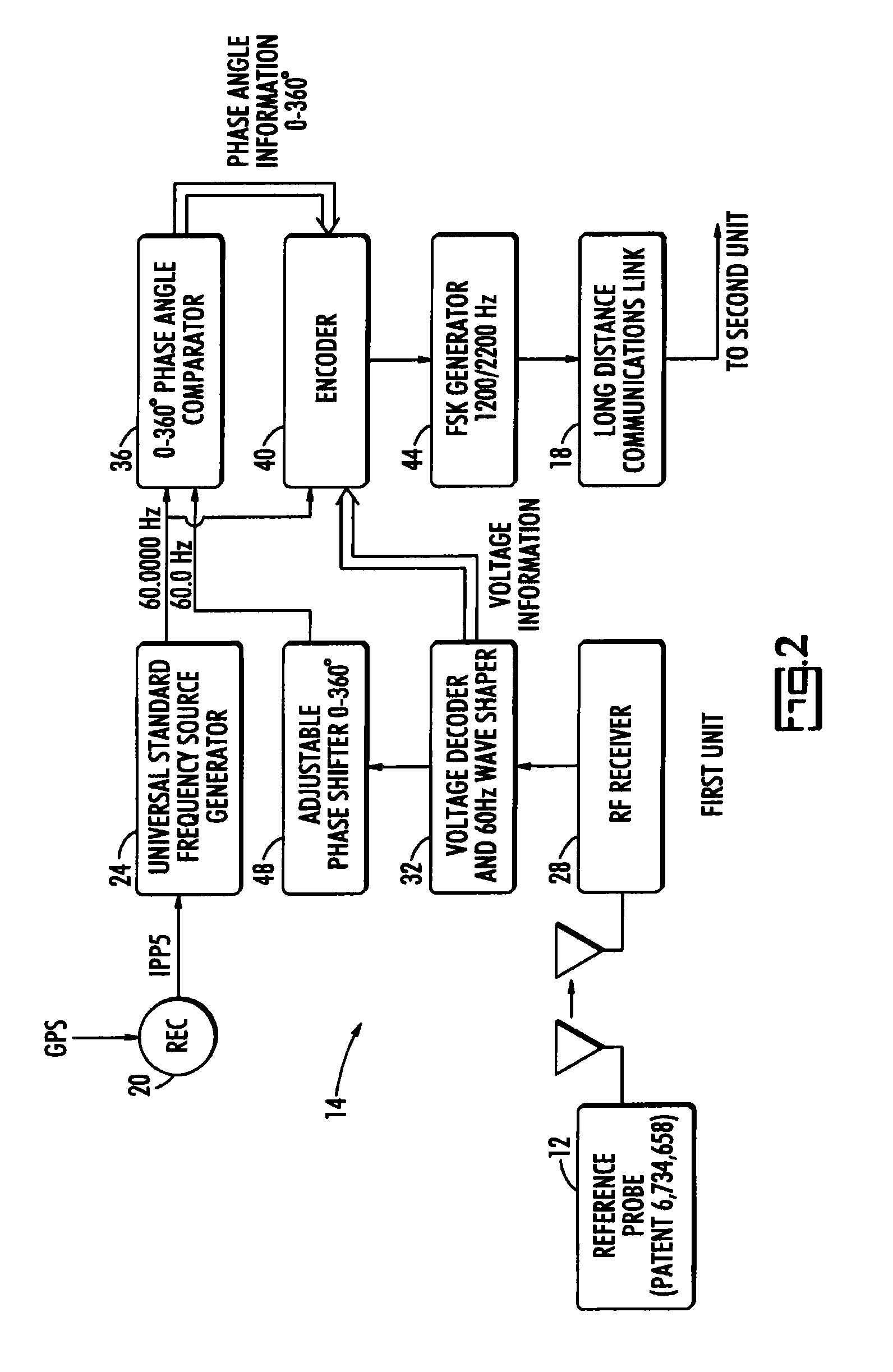
A long range wireless phasing voltmeter determines the phase difference between the time-varying voltage carried on a reference electrical conductor and another, field conductor. The voltage signal from the reference conductor is measured by a reference probe and compared by a first unit in communication with that reference probe to a precision 60 Hz signal generated from a GPS receiver. The phase difference between these, in the form of a nine-bit, audible signal using frequency shift keying to modulate the carrier frequency, is transmitted by the first unit to a second unit perhaps miles away. A receiver in the second unit decodes the signal and uses another precision 60 Hz signal generated from another GPS receiver to re-create a surrogate of the original reference voltage signal. This surrogate signal is forwarded to a meter probe that is measuring the signal on a field conductor. The meter probe can then compare the two signals to determine the phase angle difference between them.
Owner:BIERER WALTER S
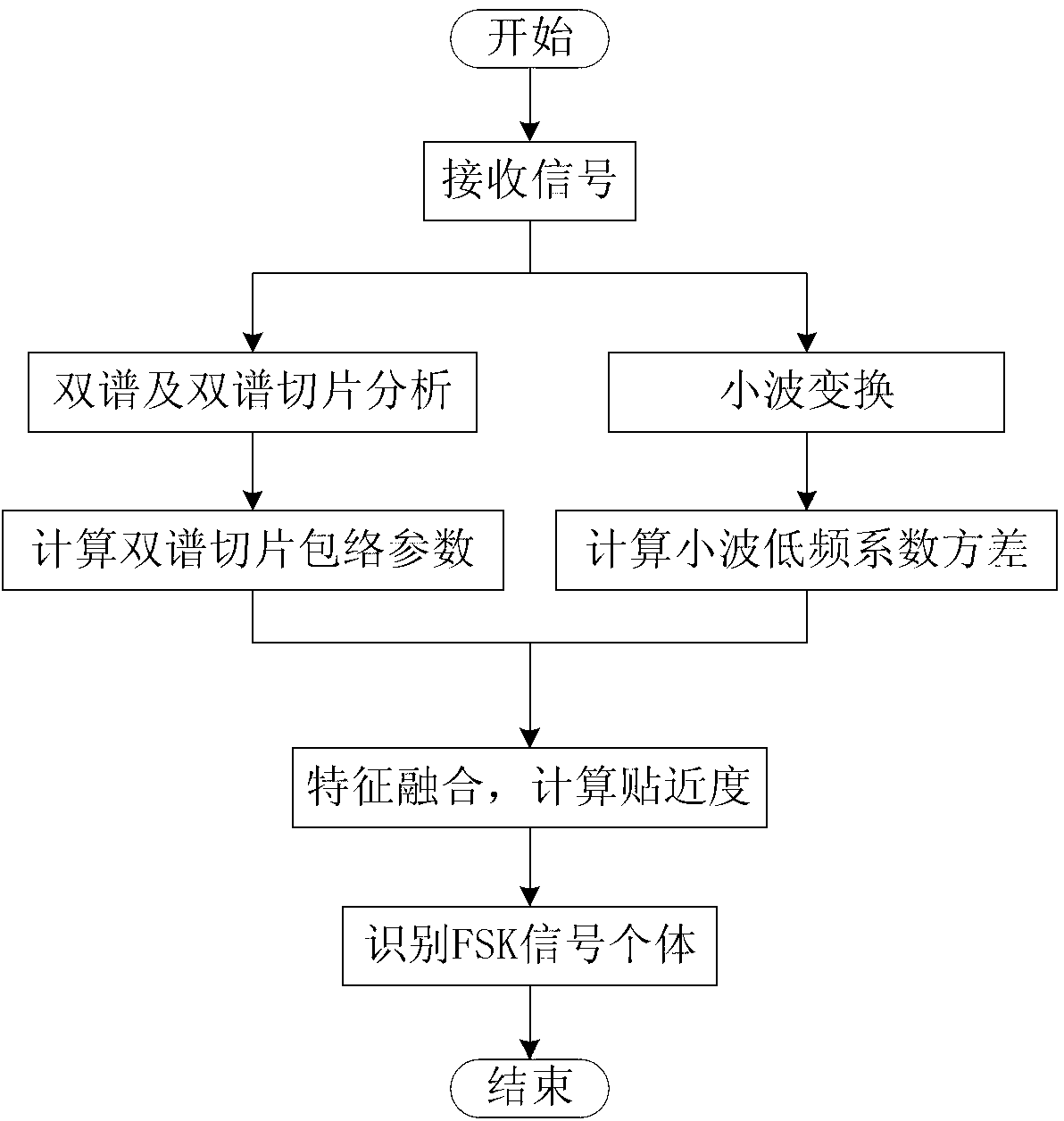
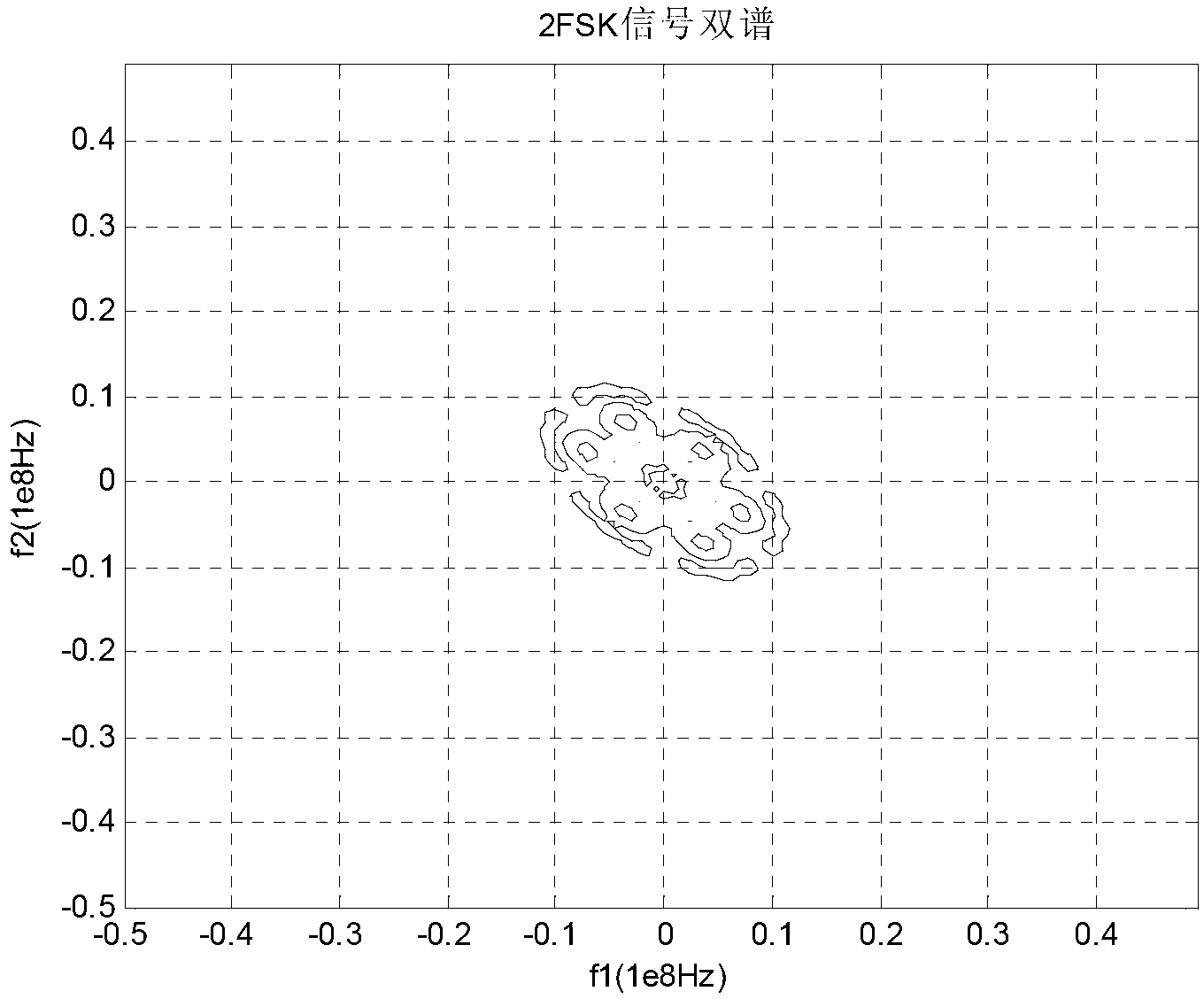
Individual identification method of FSK (frequency-shift keying) signal based on slice bi-spectrum and wavelet transformation
InactiveCN102916917AReal-time individual identificationTo overcome the lack of high signal-to-noise ratio requirementsModulated-carrier systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The aim of the invention is to provide an individual identification method of an FSK (frequency-shift keying) signal based on slice bi-spectrum and wavelet transformation. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out bi-spectrum and slice bi-spectrum analysis on the received signal to obtain a spectrogram of the slice bi-spectrum of the signal; respectively building envelope parameter characteristic databases under different signal to noise ratios; carrying out wavelet transformation on the received signal, and extracting a mean value of low-frequency wavelet coefficients; simultaneously building characteristic databases of 4FSK signals of different M numbers and different modulation parameters under different signal to noise ratios; fusing the slice bi-spectrum envelope parameter characteristics and the low-frequency wavelet coefficients; identifying the modulation type of the FSK signal, and achieving individual identification of the 4FSK signals of different parameters by the same signal processing process. According to the individual identification method, the defects of high requirements on the signal to noise ratios of the existing class modulation identification method can be overcome, and individual identification on the FSK signal is carried out in real time under the conditions of low signal to noise ratio and less priori knowledge.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Home appliance information communication system of asymmetric power line carrier and wireless communication
InactiveCN102098077ARealize online displayRealize remote controlEnergy efficient ICTPower distribution line transmissionElectric power systemLow voltage
The invention provides a home appliance information communication system of asymmetric power line carrier and wireless communication. The system comprises an electric energy meter gateway, a ZB-APLC (zinc borate-active power line conditioner) and a white information home appliance, wherein the white information home appliance comprises an APLC standard white information home appliance and a ZigBee standard white information home appliance; an APLC communication circuit of the APLC electric energy meter gateway is arranged in an electric energy meter, and the APLC electric energy meter gateway is accessed between a phase line and an N phase of a three-phase four-wire system at a lower voltage side of a 10kV / 0.4kV distribution transformer of an electric power system; a ZB-APLC network bridge is electrically connected with the load of the white information home appliance, and the ZB-APLC network bridge is accessed into the electric system by the APLC electric energy meter gateway; digital communication is performed between the APLC electric energy meter gateway and the ZB-APLC network bridge by the asymmetric power line carrier communication, the communication between the APLC electric energy meter gateway and the ZB-APLC network bridge adopts a voltage type FSK (frequency shift keying) or S-FSK (spread frequency shift keying) modulating signal, and the communication between the ZB-APLC network bridge and the APLC electric energy meter gateway adopts a current type FSK or S-FSK modulating signal; and the information exchange between the ZB-APLC network bridge and the ZigBee standard white information home appliance can be realized by the ZigBee wireless communication.
Owner:郭建国 +2
System for transmitting emergency and notification messages over a phone line
InactiveUS20050008004A1Special service for subscribersData switching by path configurationDatabase serverThe Internet
A method of communication utilizing the Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN) and the Internet is disclosed which includes receiving on a database server, a query transmitted from a first computer, which query includes a set of instructions encapsulated in a string of data including a telephone number, time, date and a short fifteen character message that will be accessed by a third computer which is running a telephone soft switch server, the soft switch server will then place a call to the telephone number and deliver the string of data using Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) and SMS even while the recipient's phone is ringing or while off hook as call wait caller id (CWCID).
Owner:TELCONCEPT USA HLDG
Method for wirelessly updating firmware in a wide area network
ActiveUS20180024828A1Reduce throughputReducing “ path balance ”Hybrid transportFrequency-modulated carrier systemsUltrasound attenuationTransceiver
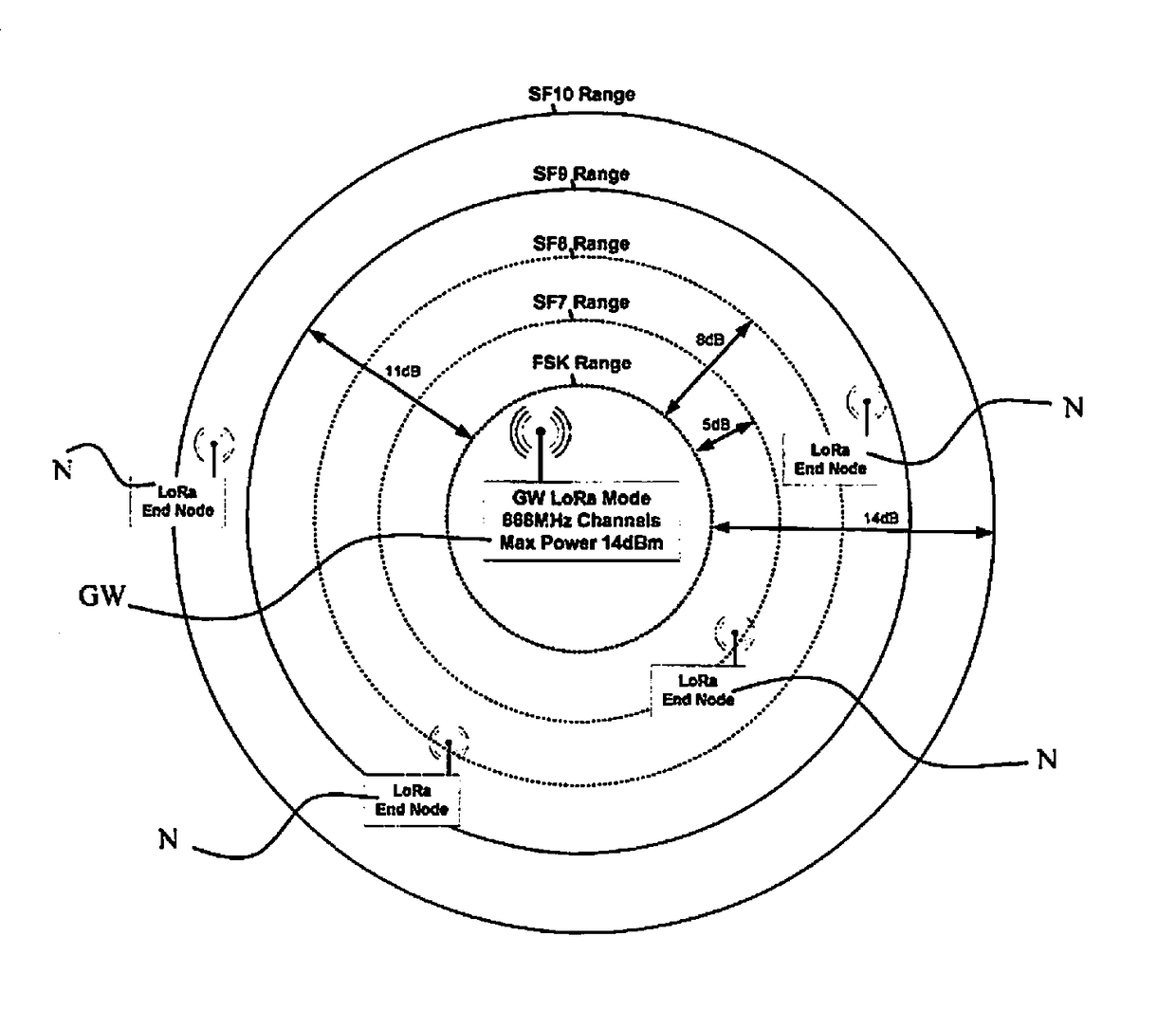
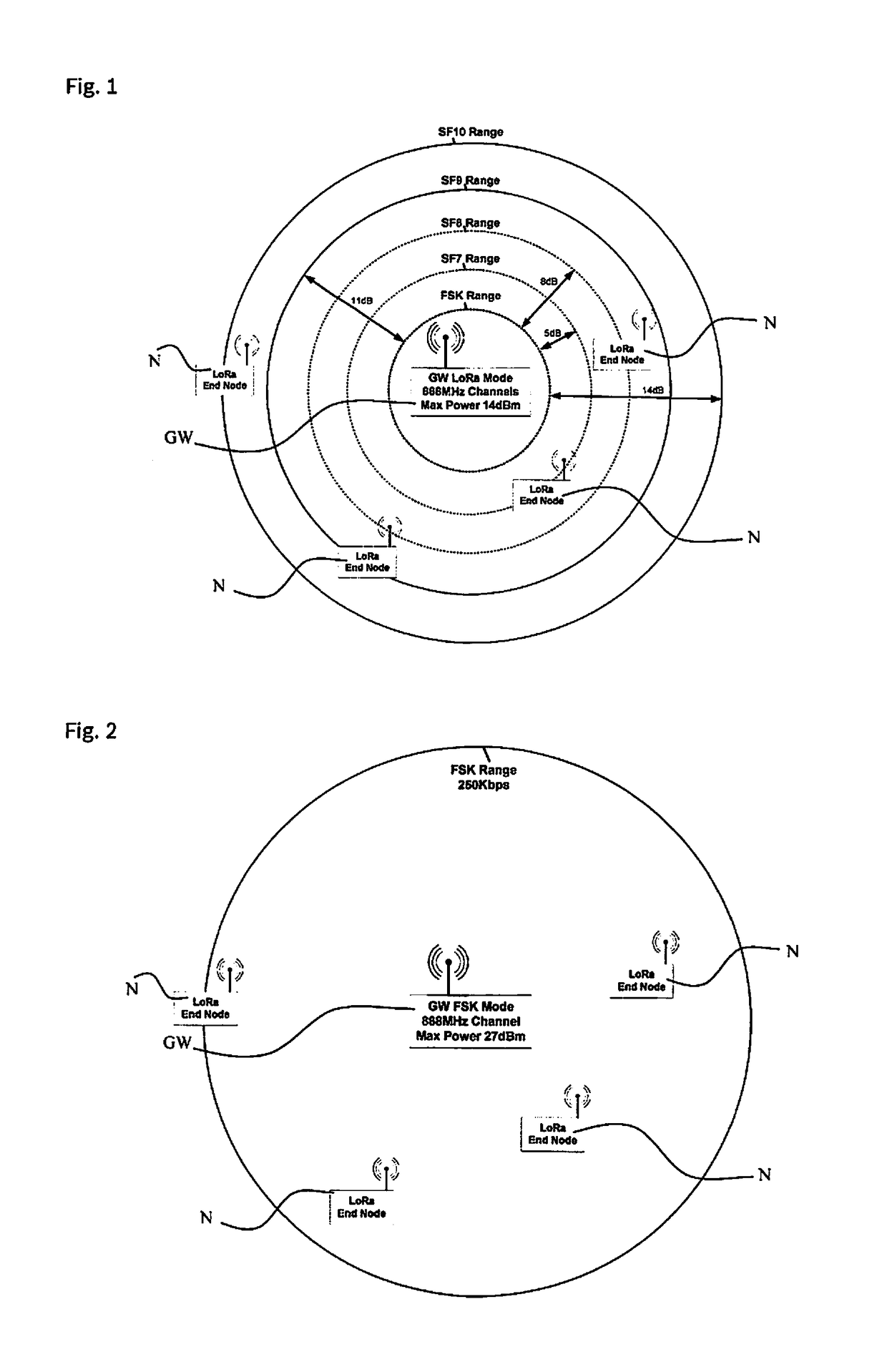
Executing a FOTA (firmware over the air) method in a LoRa network having low throughput and low power. the transceivers used in the end nodes and in the LoRa gateway are capable of selecting a certain frequency channel and deactivating the LoRa mode. If the spread-spectrum LoRa mode is deactivated, both transceivers at the end node and the gateway function instead using a basic FSK (frequency-shift keying) modulation scheme. This modulation scheme is capable of providing a higher data rate at the expense of reducing the “path balance,” which indicates how much attenuation the transmitted signal may sustain while still being able to be decoded at the receiver. When using the FSK modulation scheme at a high data rate, a FOTA method may be easily carried out, since the end node must have its receiver activated only for a short time.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method and apparatus for activating extended services in a user device using a voice over packet gateway
ActiveUS20080123670A1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareFrequency shift
An enhanced services display message protocol (ESDMP) facilitates display of messages in a compliant analog telephony device (ATD). An exemplary gateway device in a voice over packet (VOP) network can activate enhanced services in a compliant ATD using the ESDMP and includes a controller and first and second interfaces. One of the interfaces can transmit and receive communications over a VOP network. The other interface can transmit and receive voice band message data modulated according to a frequency shift keying (FSK) protocol. The ESDMP can be used to configure the gateway to activate features supported by the ATD, to update call state information and to display feature state information.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Frequency offset compensation in a digital frequency shift keying receiver
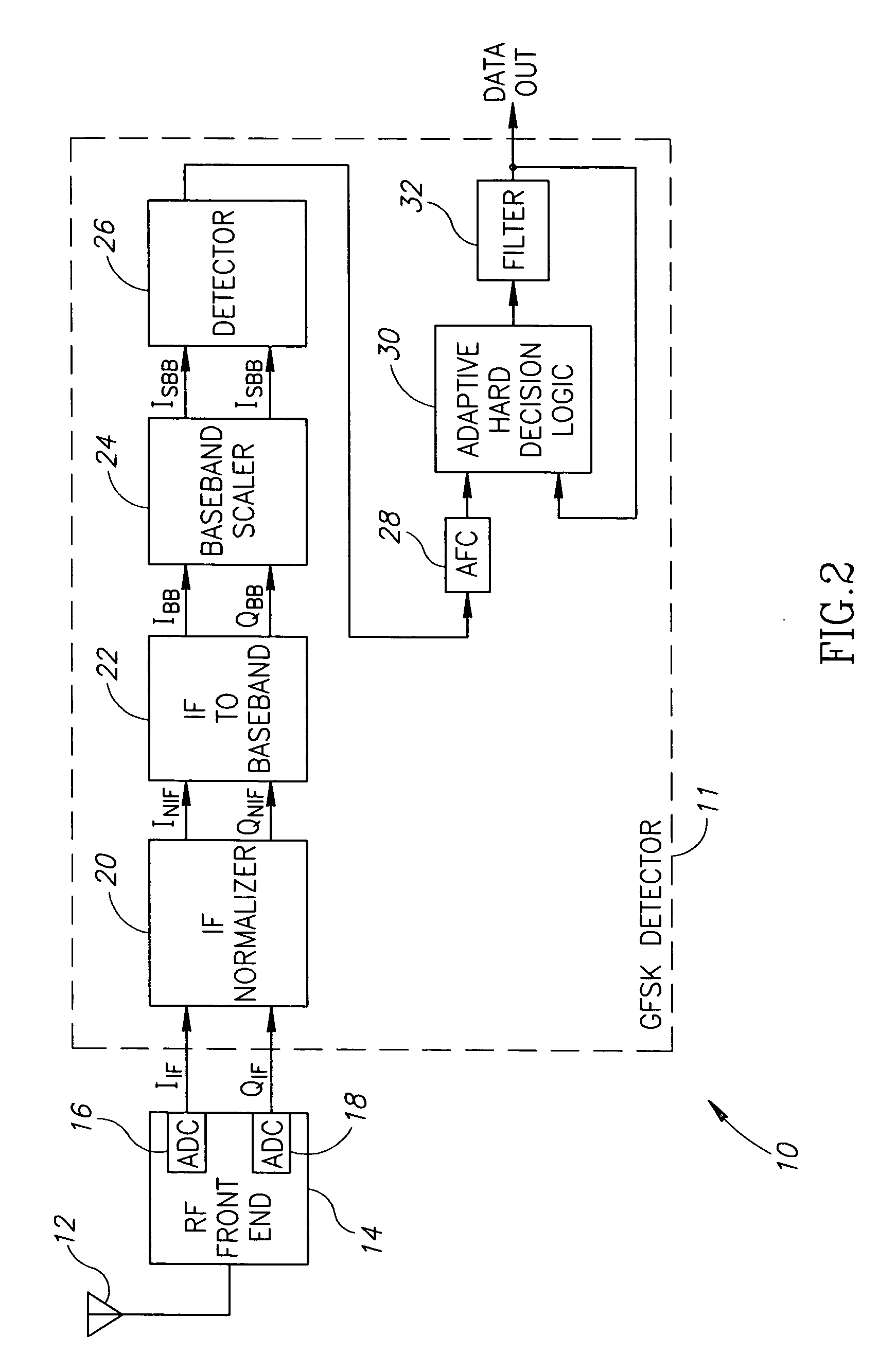
ActiveUS20050164639A1Simplifies and accelerates simulation based developmentSimplifies and accelerates and verificationDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationEngineeringPeak value
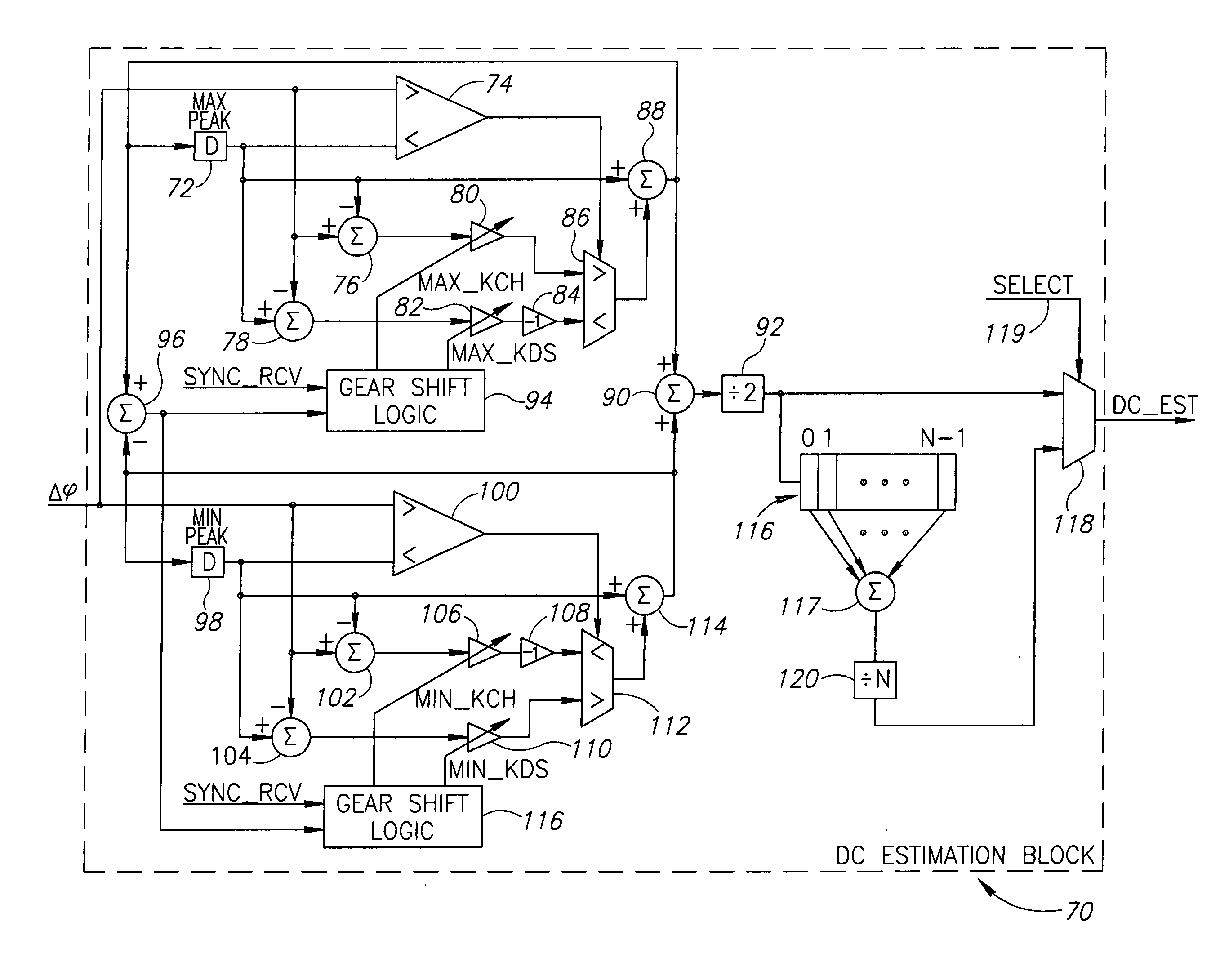
A digital nonlinear adaptive mechanism for frequency offset compensation for use in a digital Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) receiver such as a Bluetooth GFSK receiver. The mechanism is intended to aid in the recovery of a frequency-modulated signal in the presence of an unknown additive frequency offset, which could be greater than the peak frequency deviation and which must be suppressed to enable proper data recovery in the receiver. The mechanism utilizes a demodulator to convert the frequency offset into a digitally represented DC level. This level is extracted by a non-linear estimator based on peak detectors and filters. Active suppression of the DC level is achieved by feed-forwarding the estimated value into a subtractor that removes it from the digital signal. A gear shift mechanism incorporated within the DC estimation block enables the dynamic control of the DC estimation process. Charge and discharge coefficients are configured dynamically to provide fast frequency offset compensation during the reception of the redundant header at the beginning of a packet and relatively slow frequency offset compensation during the subsequent reception of the payload portion of the packet, thus minimizing both the acquisition time and the payload's BER in the receiver.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Optical frequency shift keying modulator
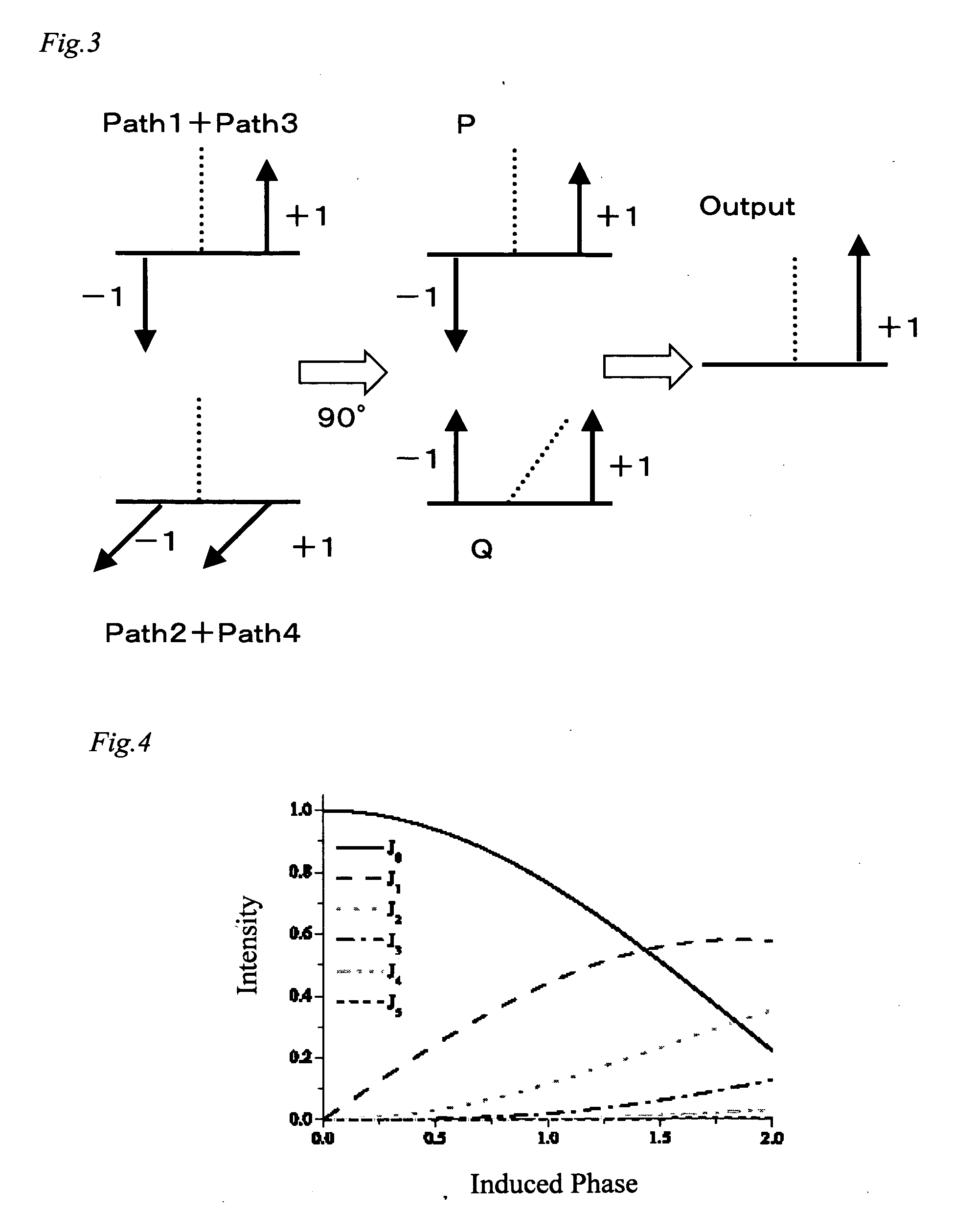
ActiveUS20050111853A1Improve transfer rateAvoid it happening againCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency-shift keyingRadio frequency
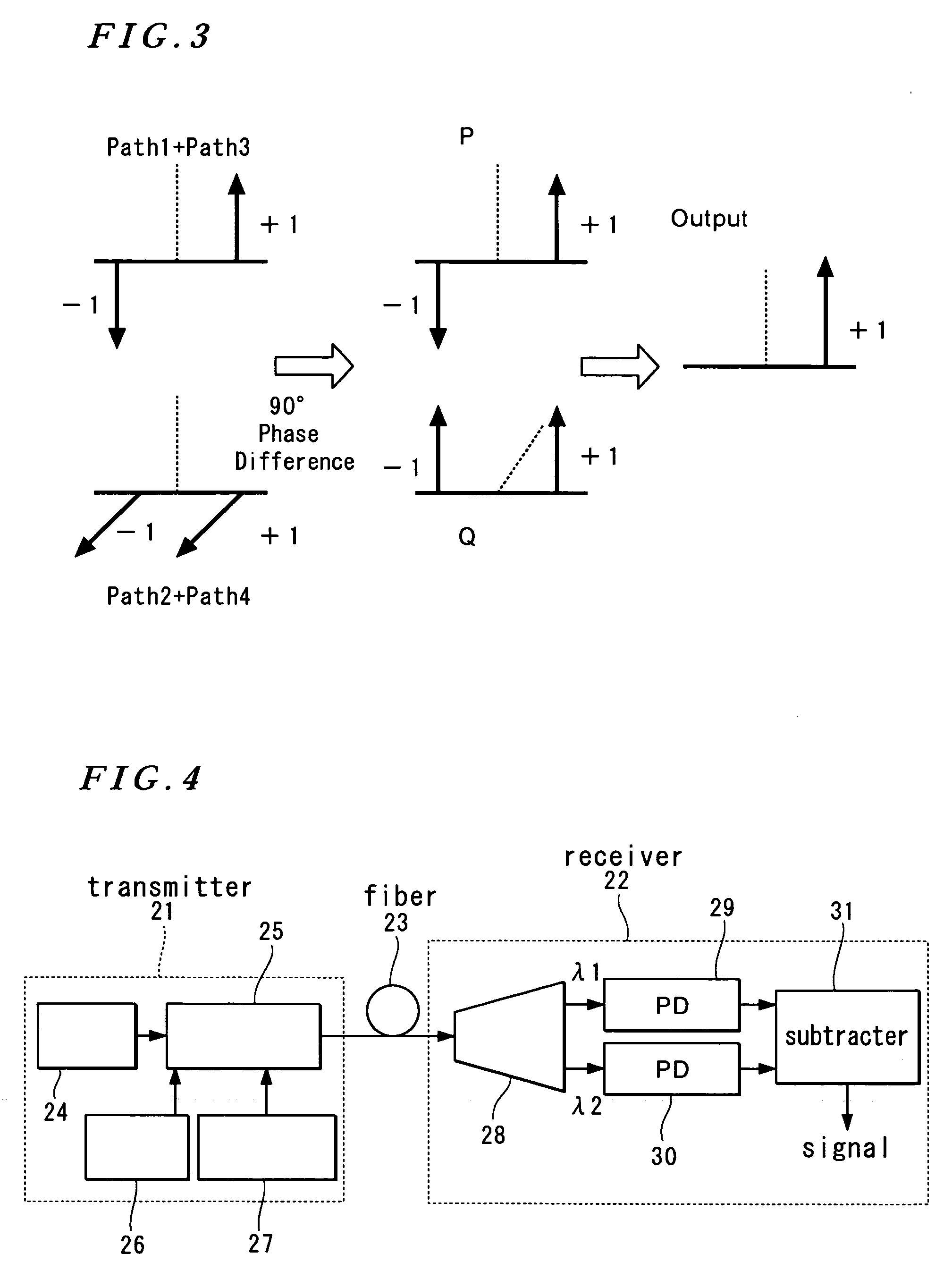
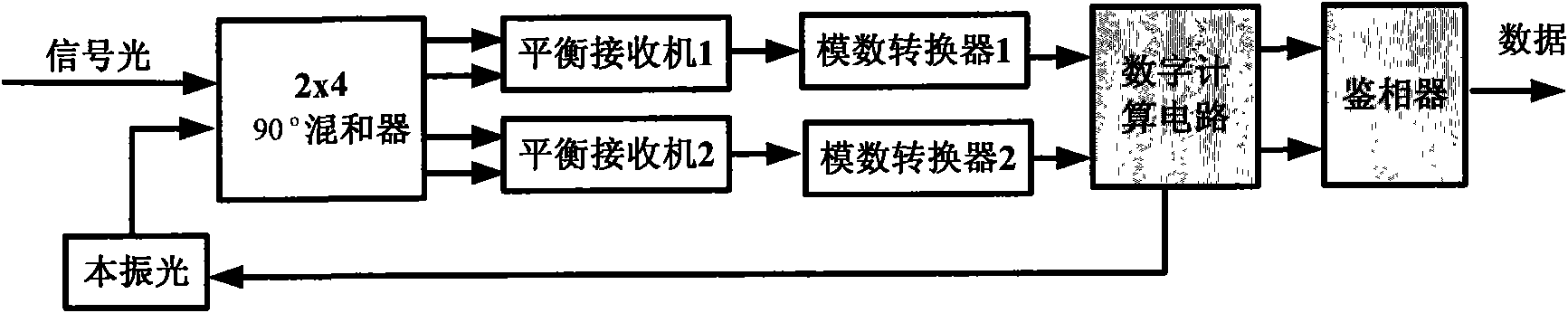
An optical FSK modulator which can be used for an optical information communication is provided. The optical FSK is provided with: a second sub Mach-Zehnder waveguide (MZB) 3; a main Mach-Zehnder waveguide (MZC) 4 including the MZA and MZB and provided with a light input portion and a modulated light output portion; a first direct-current or low-frequency electrode (DCA electrode) 5 controlling a bias voltage between two arms composing the MZA, thereby controlling a phase of light propagating in the two arms of the MZA; a second direct-current or low-frequency electrode (DCB electrode) 6 controlling a bias voltage between two arms composing the MZB, thereby controlling a phase of light propagating in the two arms of the MZB; a first RF electrode (RFA electrode) 7 inputting a radio frequency (RF) signal to the two arms composing the MZA; a second RF electrode (RFB electrode) 8 inputting an RF signal to the two arms composing the MZB; and a traveling-wave-type electrode (RFC electrode) 11 controlling a voltage of the RF signal inputted, thereby controlling a frequency of light outputted from the output portion.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Optical signal receiving method, optical signal receiving device and optical transmission system
ActiveCN101867418ACompensate for phase errorReduce bit error rateOptical multiplexElectromagnetic receiversTransport systemPhase shifted
The invention relates to an optical signal receiving method, an optical signal receiving device and an optical transmission system; the method comprises the following steps: receiving a 16QAM optical signal and local oscillator light, carrying out coherent detection to the signal and the light to obtain a 16QAM signal; according to the nonlinear phase shift factor and the drift phase error make-up corresponding to a previous 16QAM signal, pre-compensating for the phase of a current 16QAM signal, calculating the nonlinear phase shift factor and the shift phase error corresponding to the current 16QAM and takes the same as the nonlinear phase shift factor and the shift phase error required by compensating for a next 16QAM signal. The realization of the embodiment of the invention not only can effectively compensate for the shift phase error caused by frequency shift and phase shift between optical carrier and the local oscillator light, but also can compensate for the nonlinear phase shift of the 16QAM optical signal when transmitted in an optical fiber caused by nonlinear effect, thereby greatly reducing the error rate of the system and not producing format effect.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
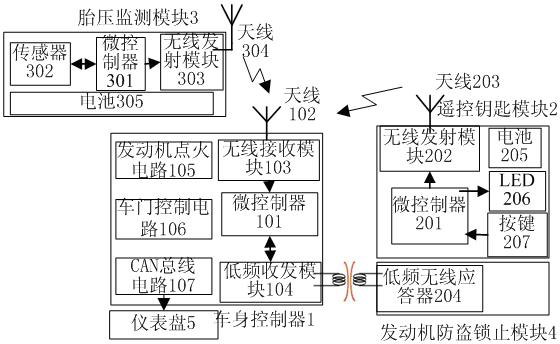
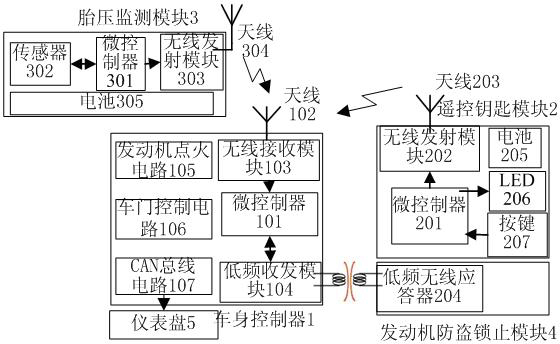
Remote control key, tire pressure monitoring and engine anti-theft locking system
InactiveCN102424032AReduced hardware redundancySmall space volumeAnti-theft devicesTyre measurementsFailure rateWireless data
The invention discloses a remote control key, tire pressure monitoring and engine anti-theft locking system, which comprises an automobile body controller, a tire pressure monitoring module, a remote control key module and an engine anti-theft locking module, wherein on the basis of the system integration technology, an automobile remote control entry system, an engine anti-theft locking system and a tire pressure monitoring system are combined into a whole, and the hardware redundancy is reduced. The remote control key module and the tire pressure monitoring module are connected with the automobile body controller in a wireless way of 434MHz, and the engine anti-theft locking module is connected with the automobile body controller in a low-frequency wireless way of 125MHz. Wireless data emitted by the remote control key and the tire pressure monitoring module adopts a 434MHz frequency range, a frequency shift keying modulation mode and a Manchester data encoding mode. The remote control key data after the Keeloq rolling code encryption is distinguished from the tire pressure monitoring data through matching codes. The system has the advantages that the hardware redundancy is reduced, the cost is low, the failure rate is low, and the space size is small.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com