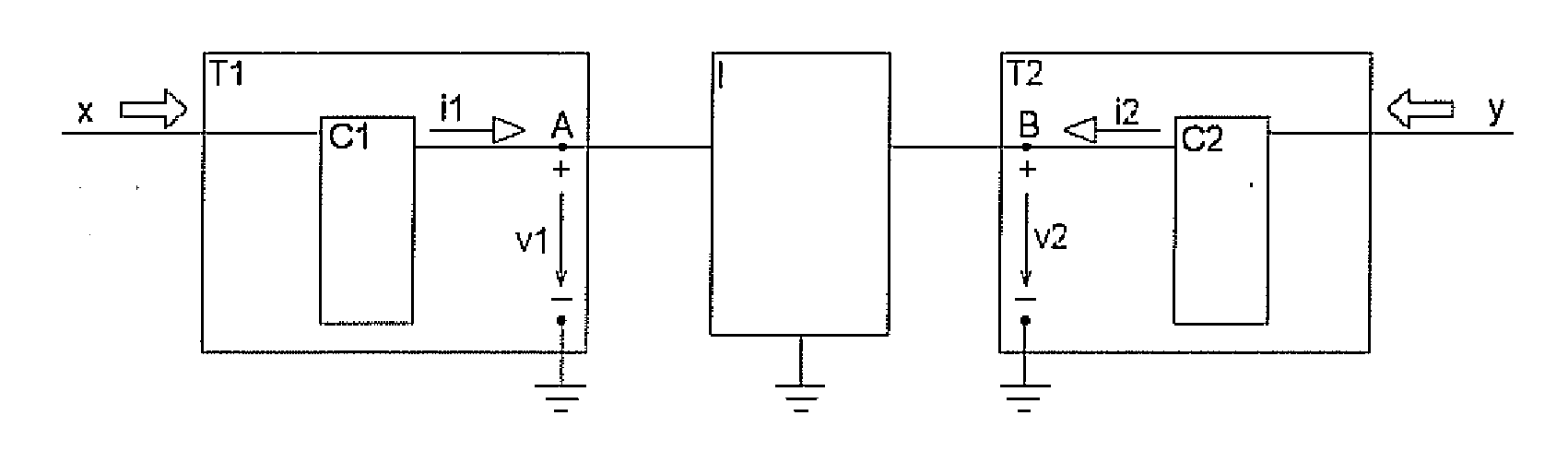
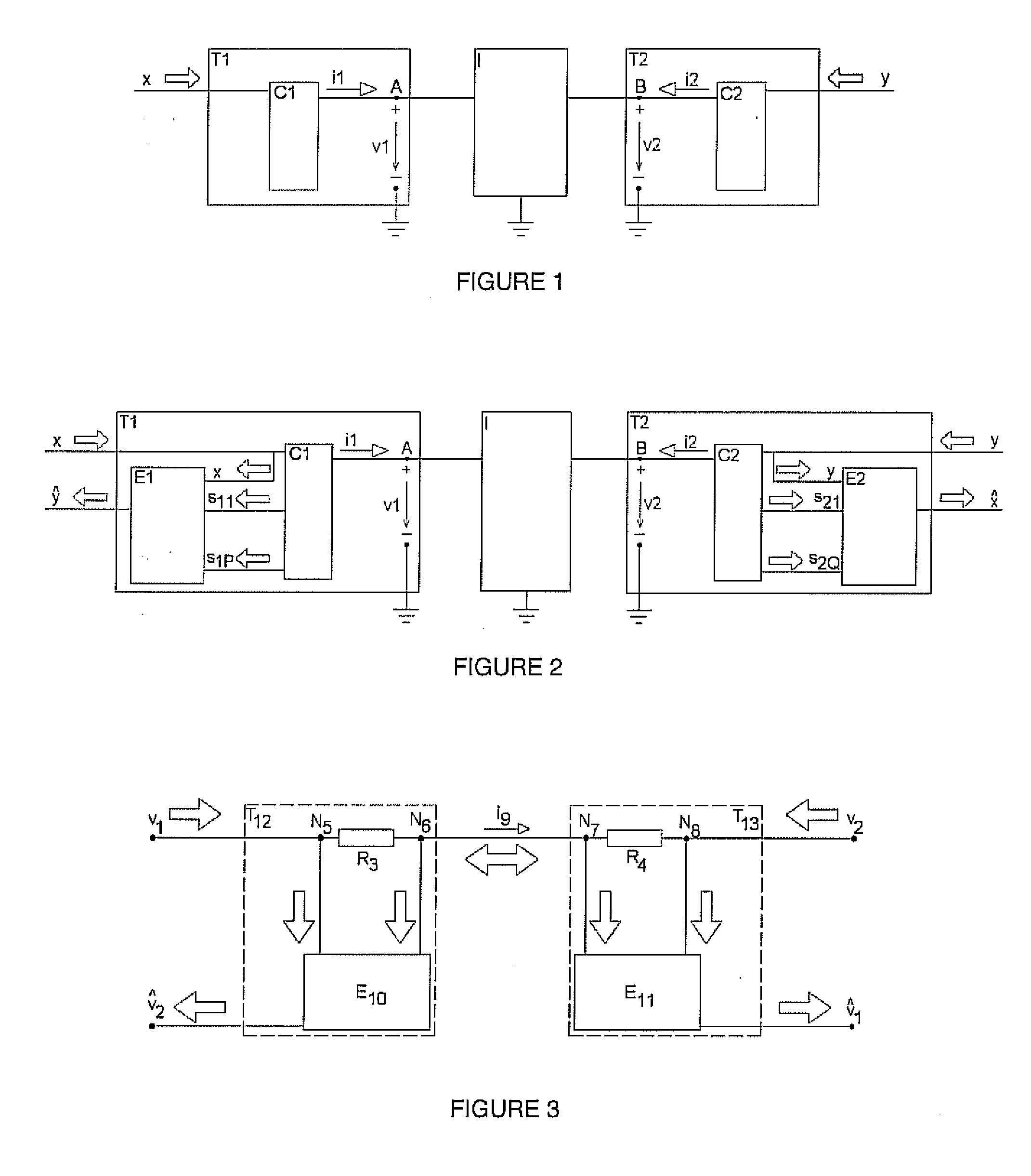
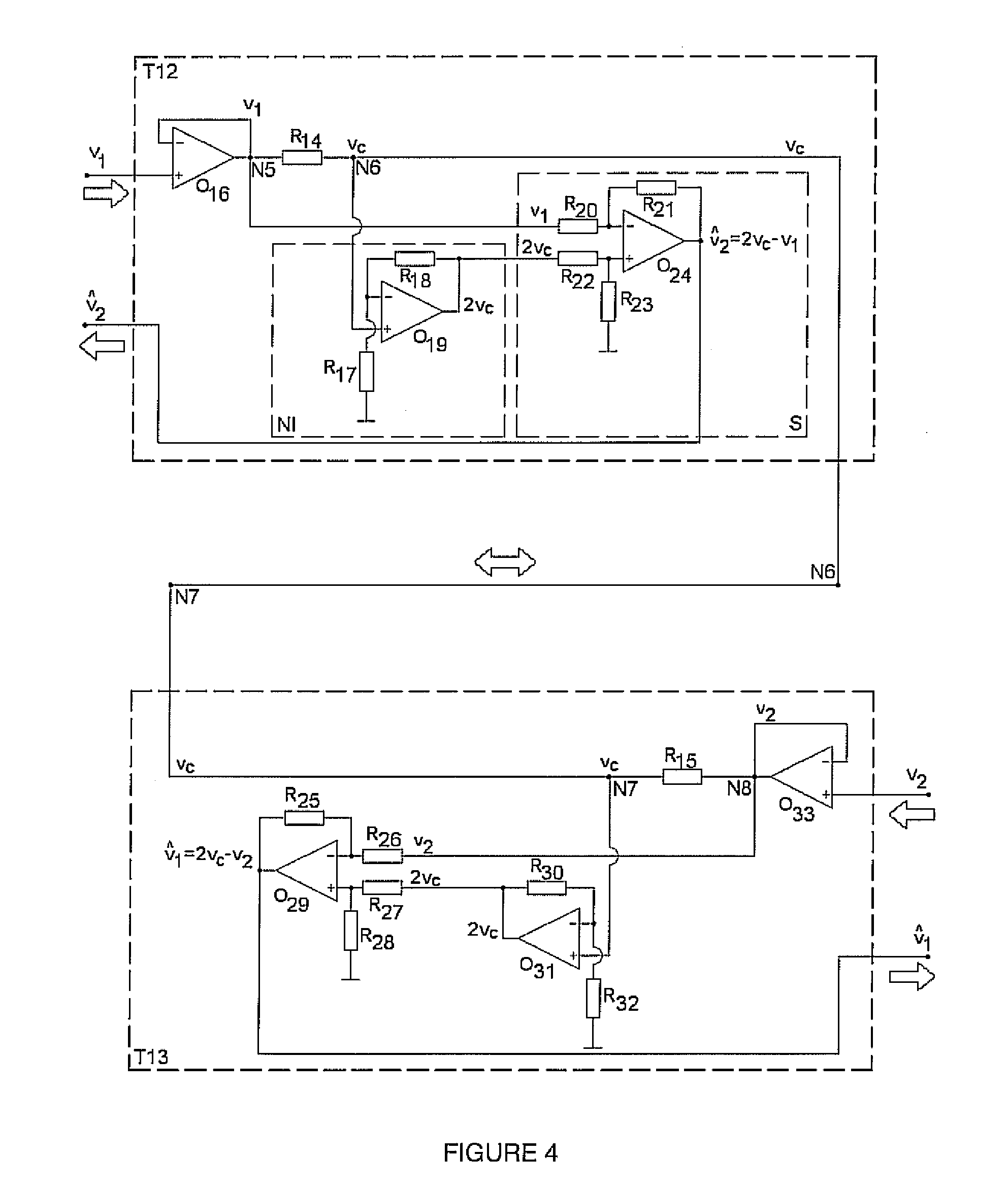
Patents
Literature
200 results about "Amplitude-shift keying" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
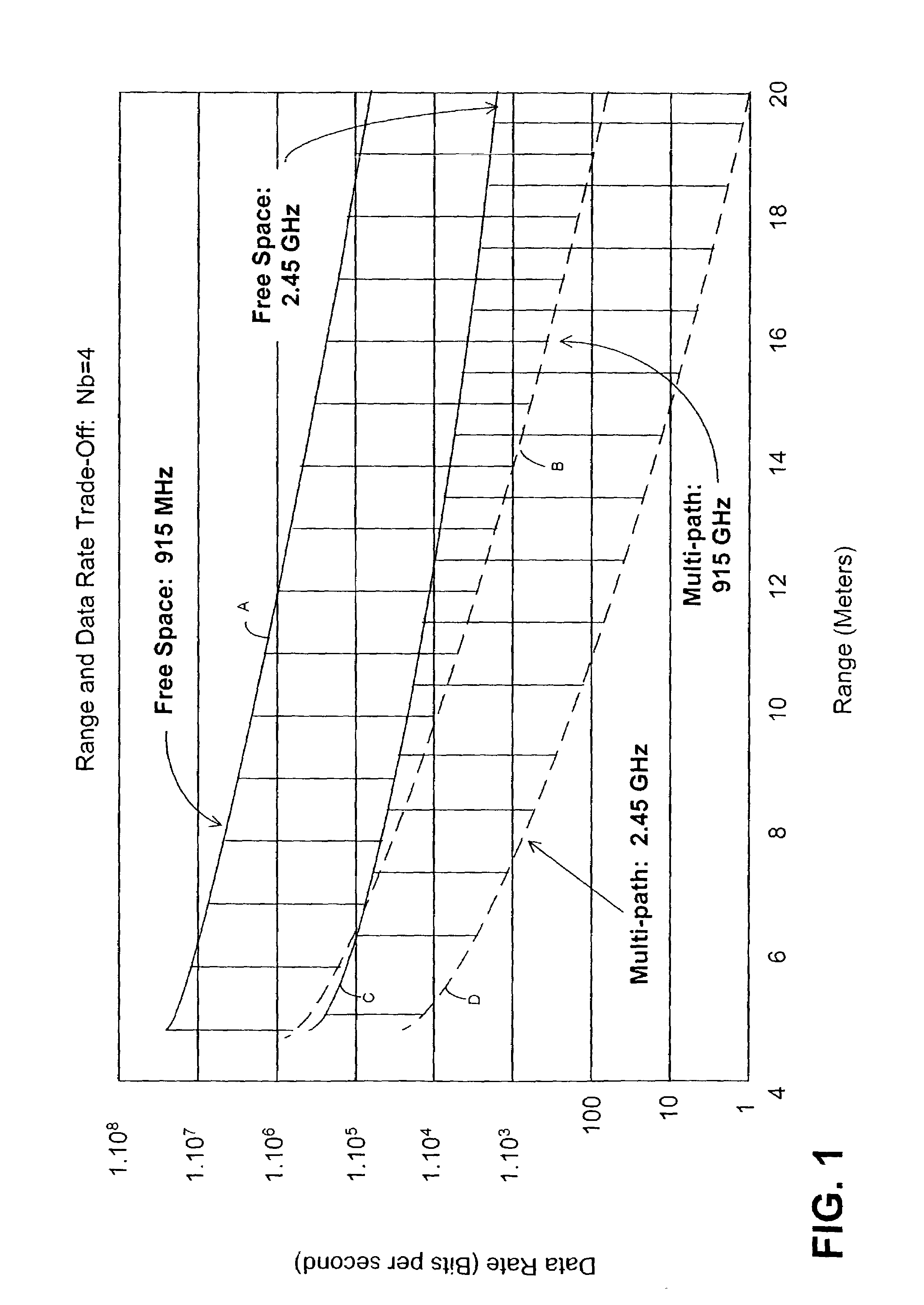
Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave. In an ASK system, the binary symbol 1 is represented by transmitting a fixed-amplitude carrier wave and fixed frequency for a bit duration of T seconds. If the signal value is 1 then the carrier signal will be transmitted; otherwise, a signal value of 0 will be transmitted.
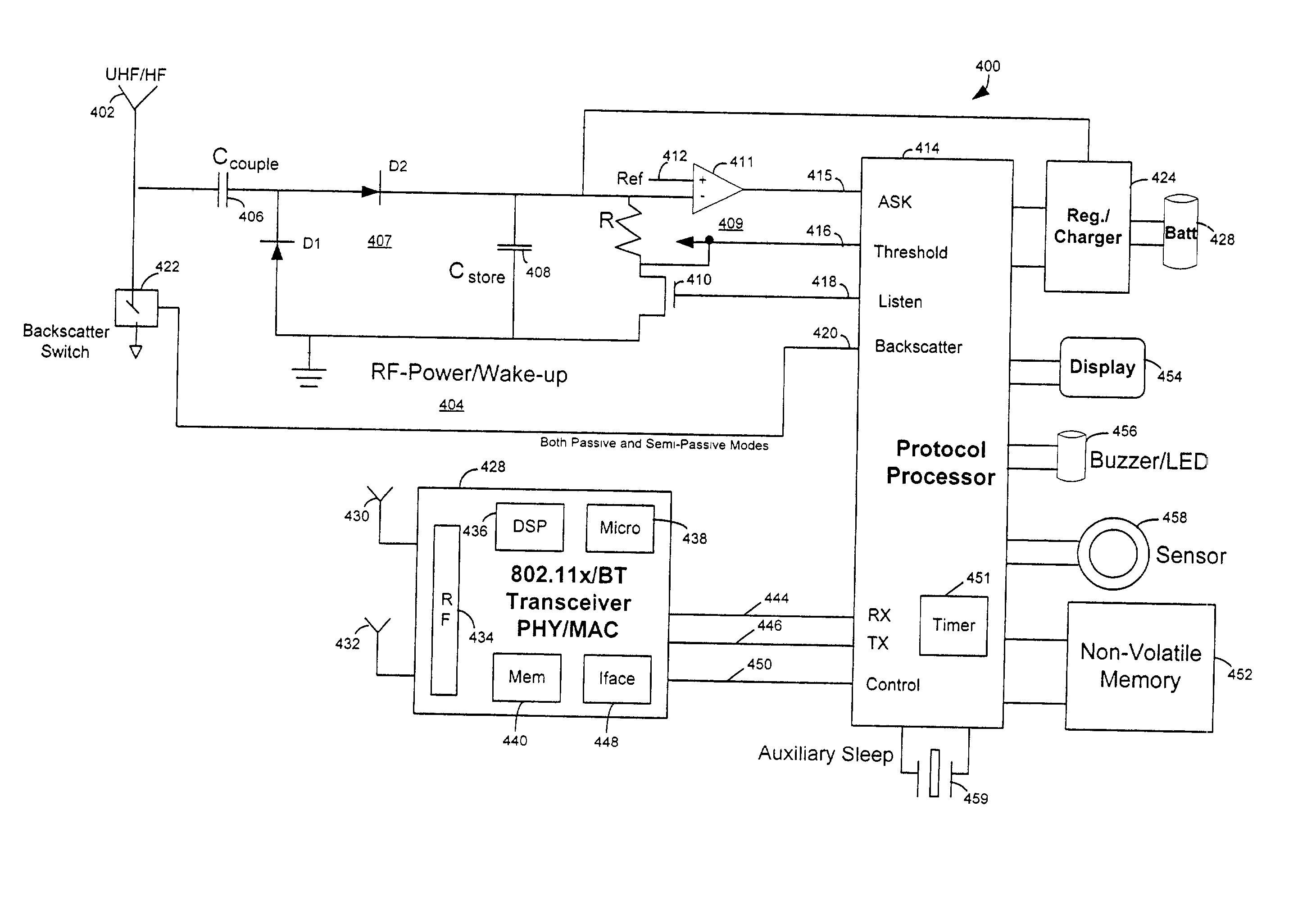
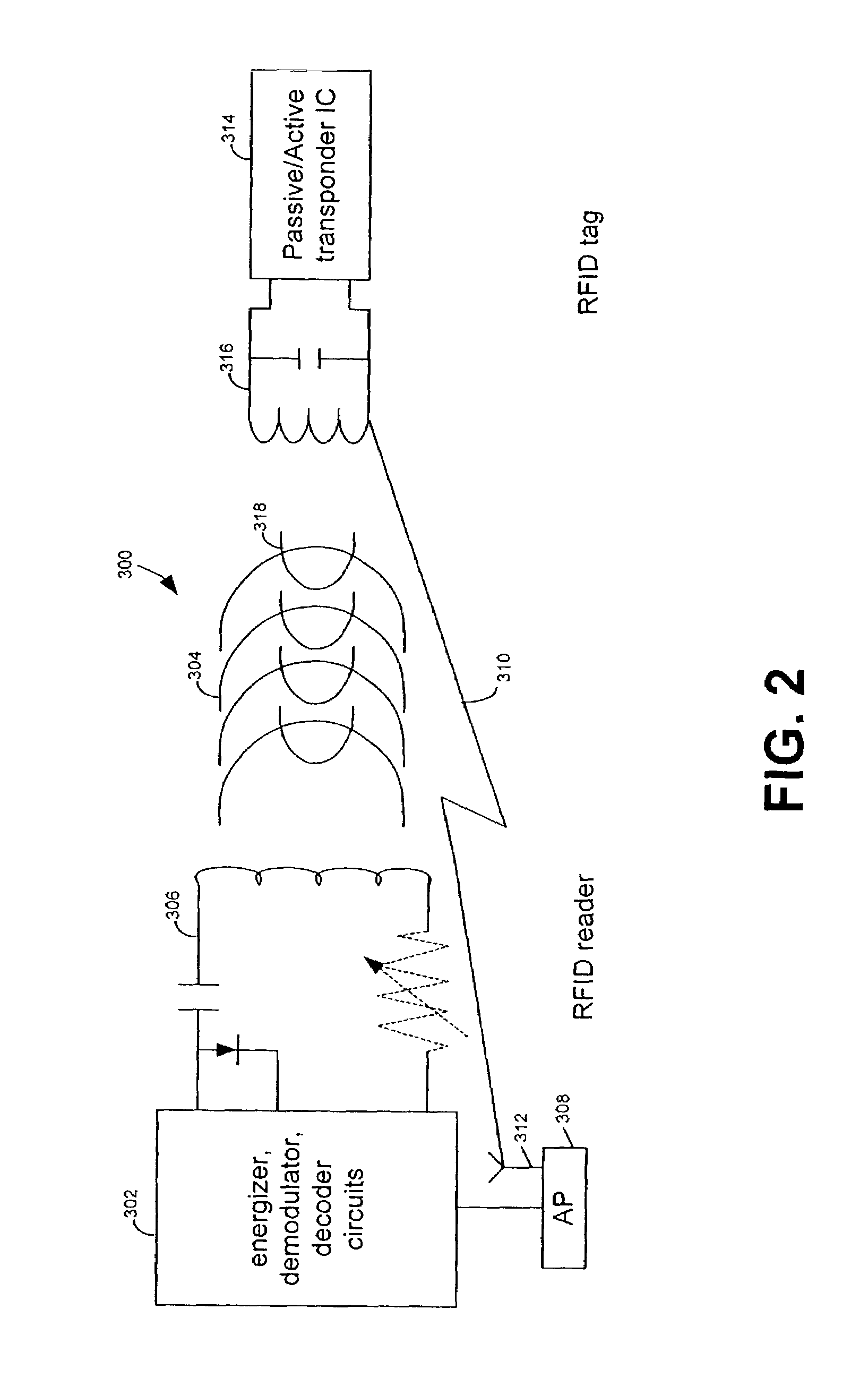
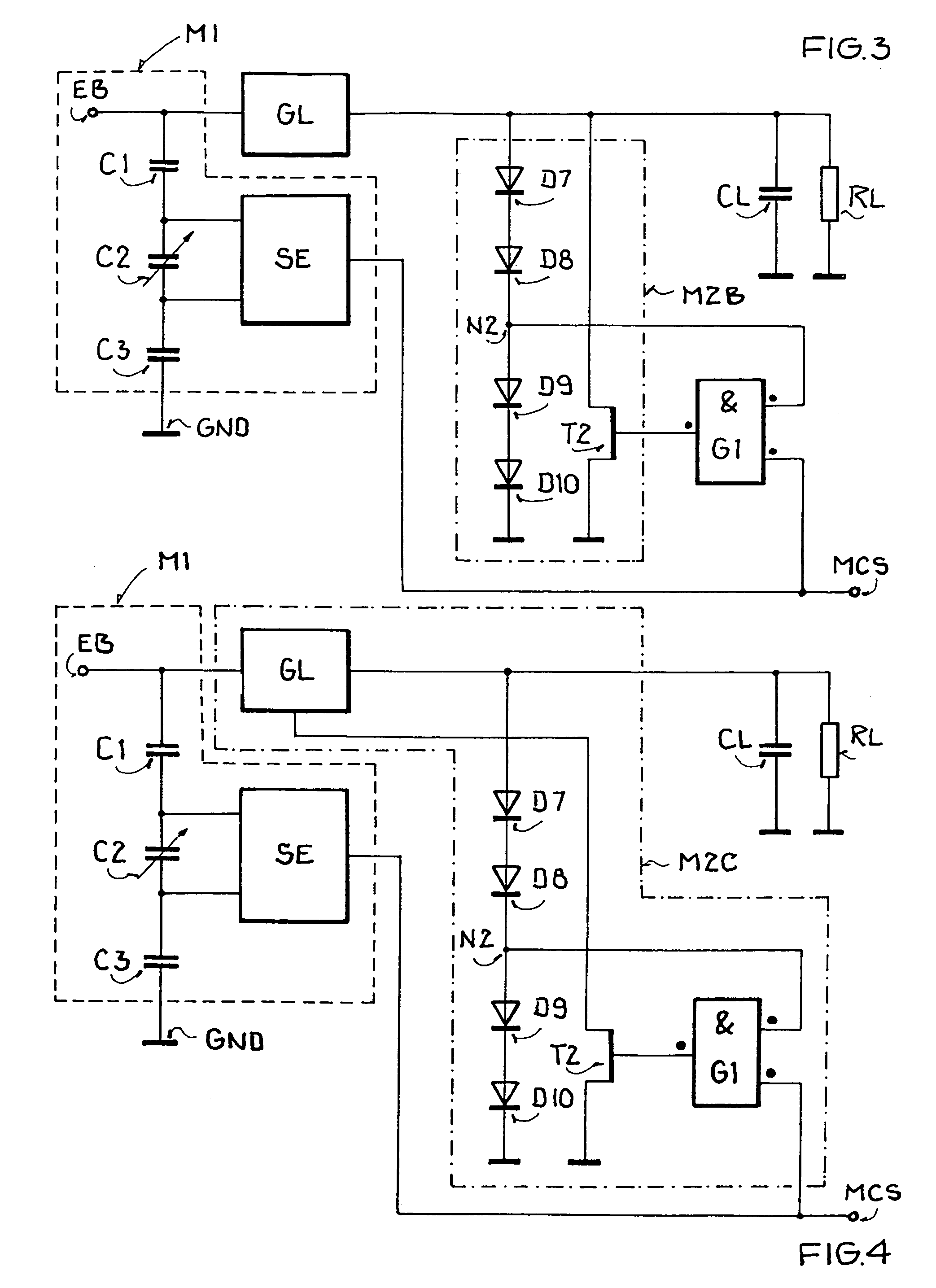
RFID device, system and method of operation including a hybrid backscatter-based RFID tag protocol compatible with RFID, bluetooth and/or IEEE 802.11x infrastructure
ActiveUS20030104848A1Near-field transmissionMemory record carrier reading problemsTransceiverAntenna impedance
An RFID system includes a hybrid backscatter-based RFID tag protocol-compatible with existing 802.11x / Bluetooth Standards as well as RFID standards. The tag is linked to a multi-protocol Interrogator via a generated RF Continuous Wave (CW) field. The tag includes an antenna coupled to an RFID and a Bluetooth / 802.11x transceiver section. A Protocol Processor services RFID and transceiver sections and is coupled to the antenna via a backscatter switch. The Interrogator can switch the tag to an RFID backscatter radiation mode where the processor switches the antenna impedance to reflect the CW signal. For transceiver operation the processor switches antenna impedance in synchronization with a frame organized bit stream. For reception, the RFID section utilizes demodulation techniques, typically Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), and provides a wake up mode within a predetermined distance of the Interrogator. The transceiver may operate in a backscatter or regular mode as directed by an Access Point.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
RFID device, system and method of operation including a hybrid backscatter-based RFID tag protocol compatible with RFID, bluetooth and/or IEEE 802.11x infrastructure
ActiveUS7215976B2Near-field transmissionMemory record carrier reading problemsTransceiverAntenna impedance
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Receiver for object locating and tracking systems and related methods
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
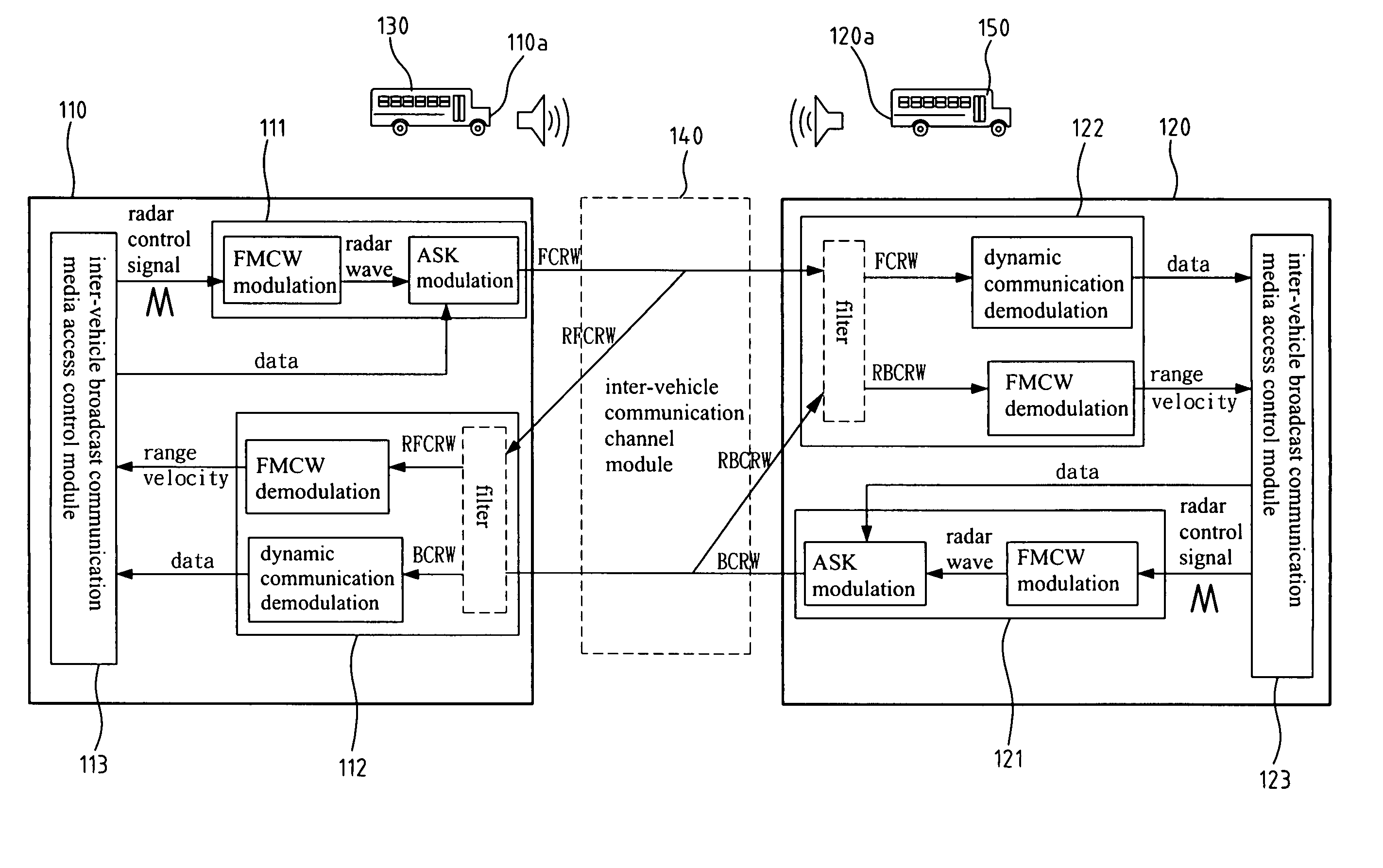
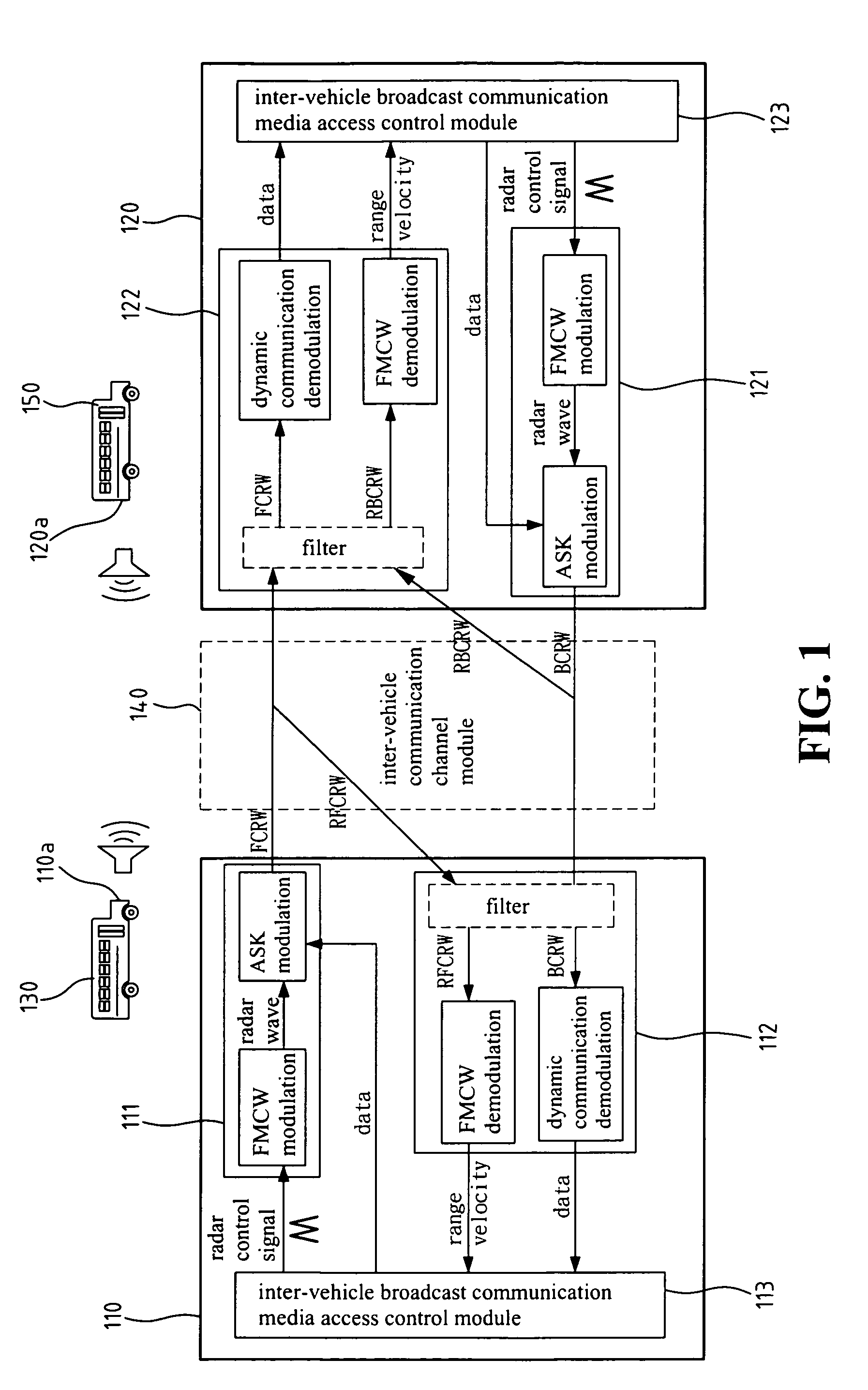
Inter-vehicle communication and warning apparatus
InactiveUS20070096885A1Enhance traffic transportation safetyEasy to transportDigital data processing detailsDetection of traffic movementRadarEngineering
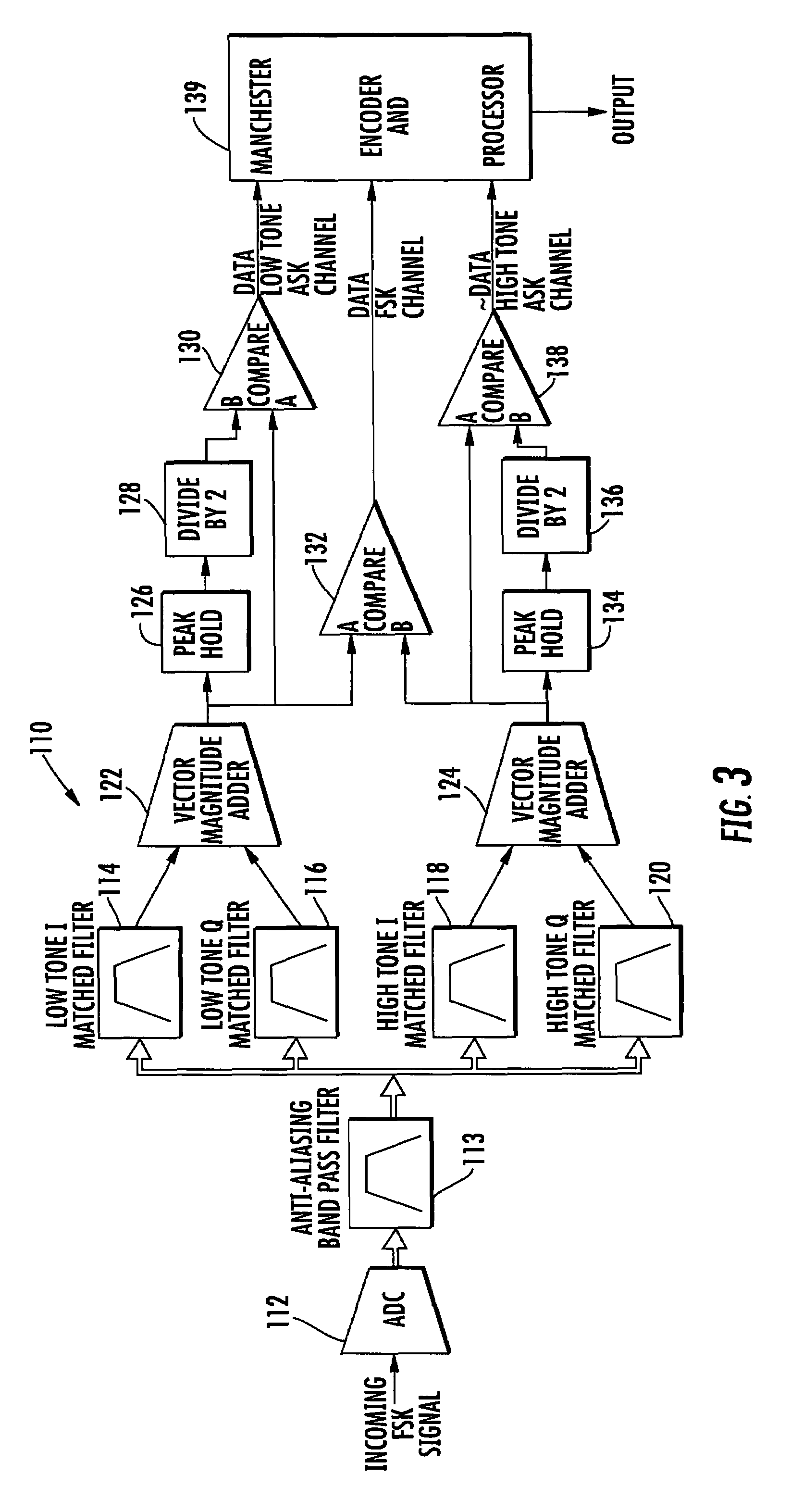
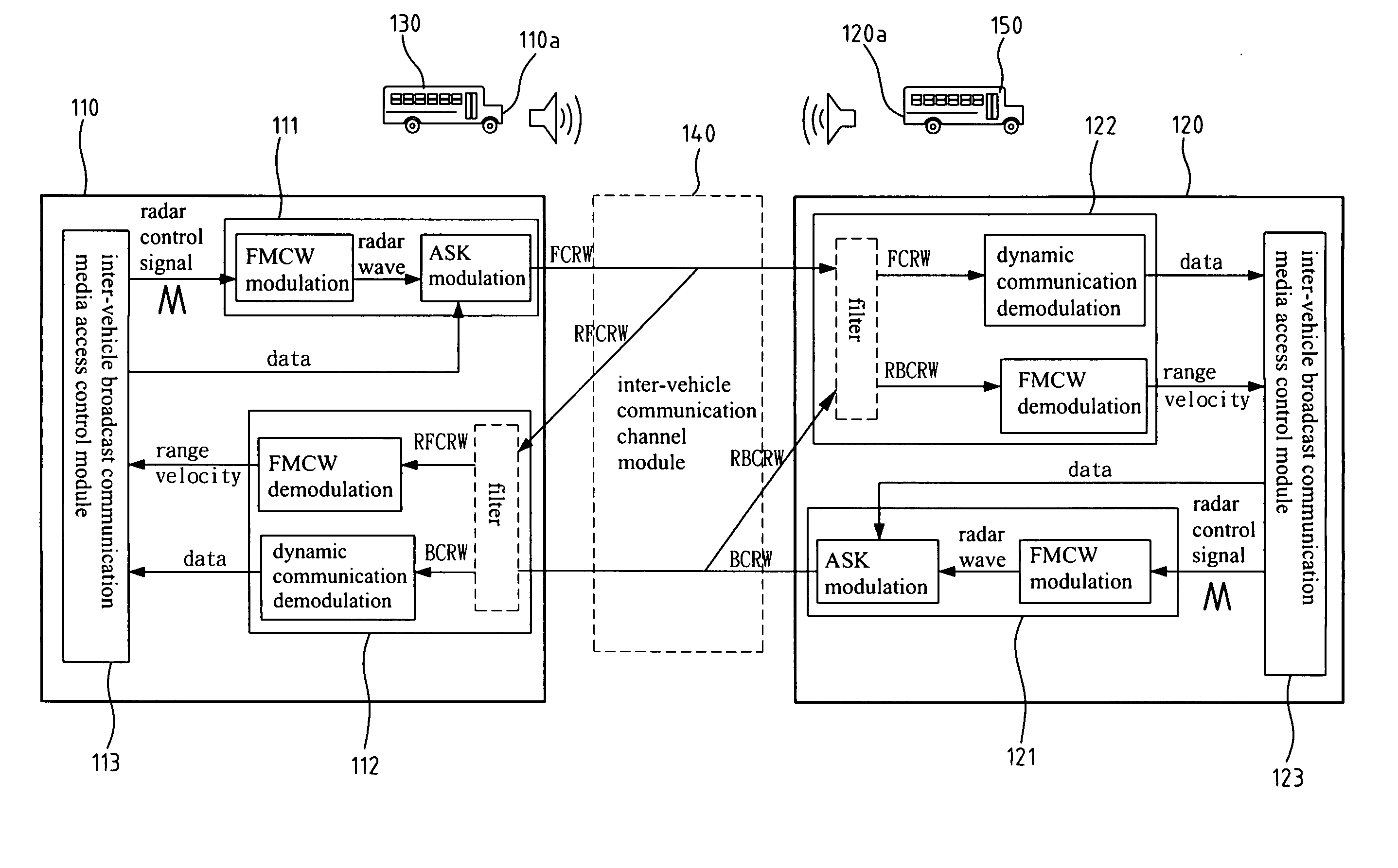
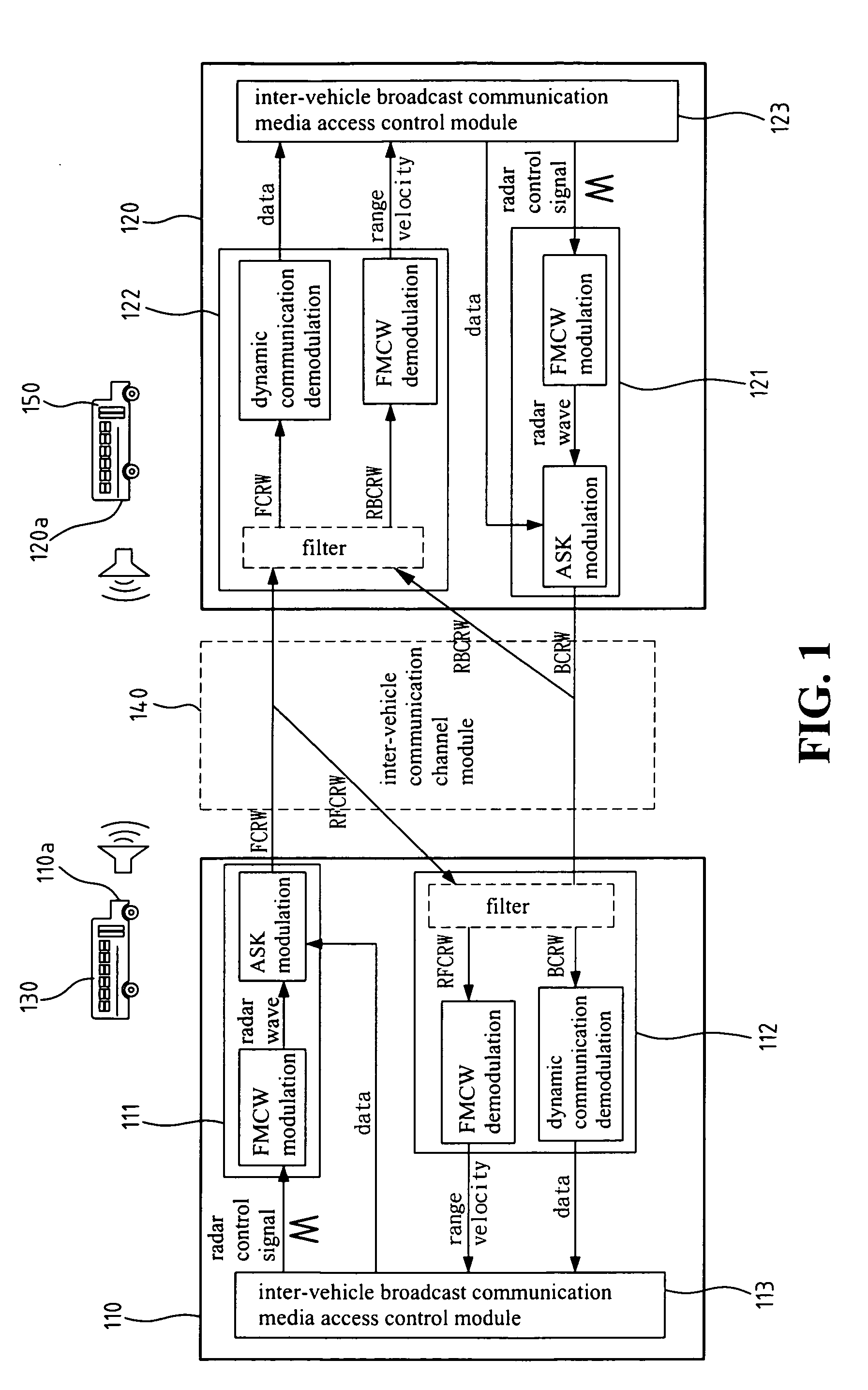
A short-range inter-vehicle communication and warning apparatus comprises a forward radar and a backward radar. The apparatus uses the radars to generate Frequency Modulation / Continuous Wave (FMCW) signals, uses amplitude shift keying for data modulation and arranges a special packet format, to realize such a low cost and fast response device of collision avoidance for vehicles. The invention has the dual capabilities of detecting and communicating simultaneously. It can also measure the relative speed of a preceding / rear vehicles and the relative inter-vehicle distance. The invention also exchanges the real-time traffic information with the preceding / rear vehicles at the same time. It is applicable to a one-to-one or one-to-many inter-vehicle channel model.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
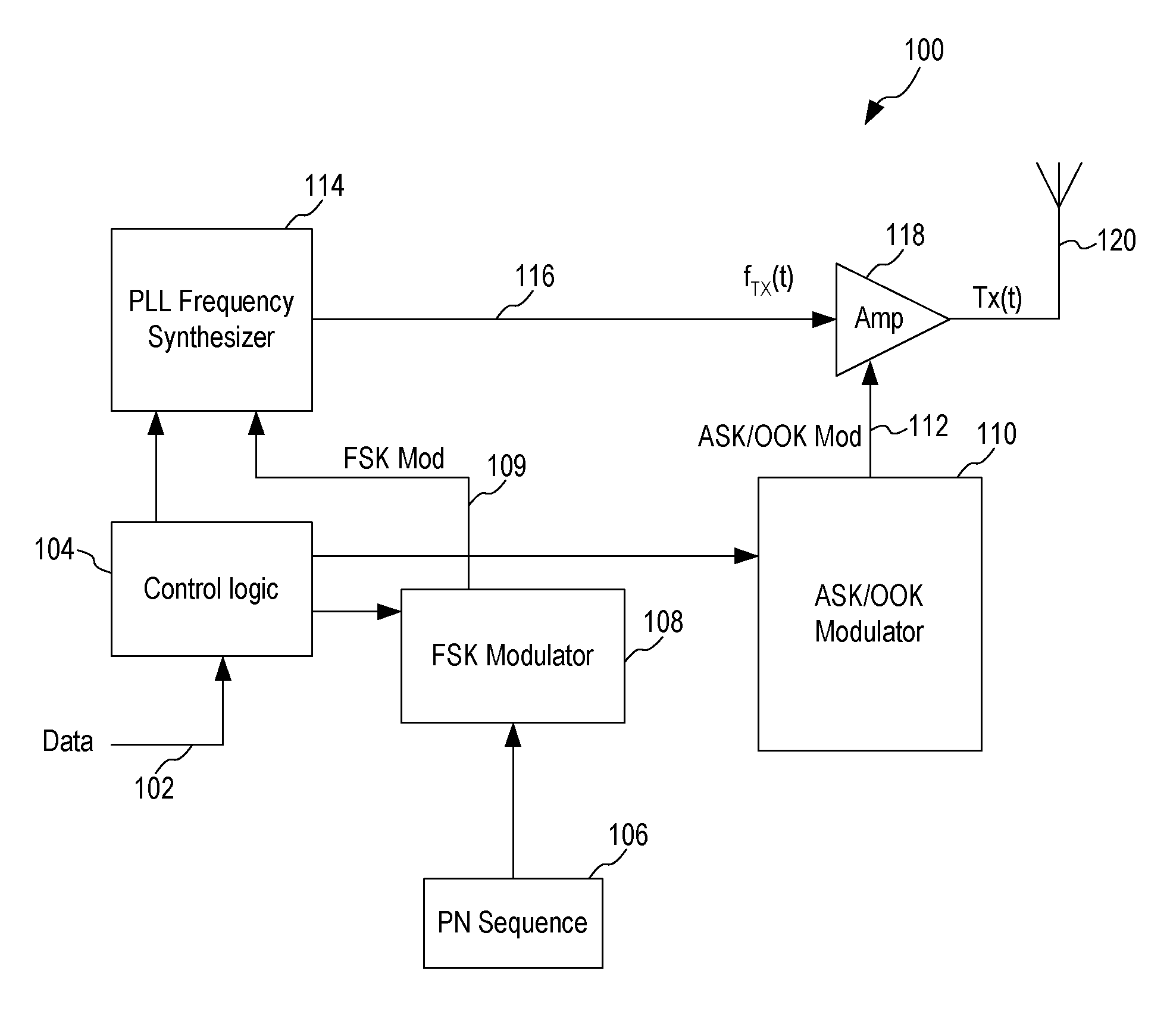
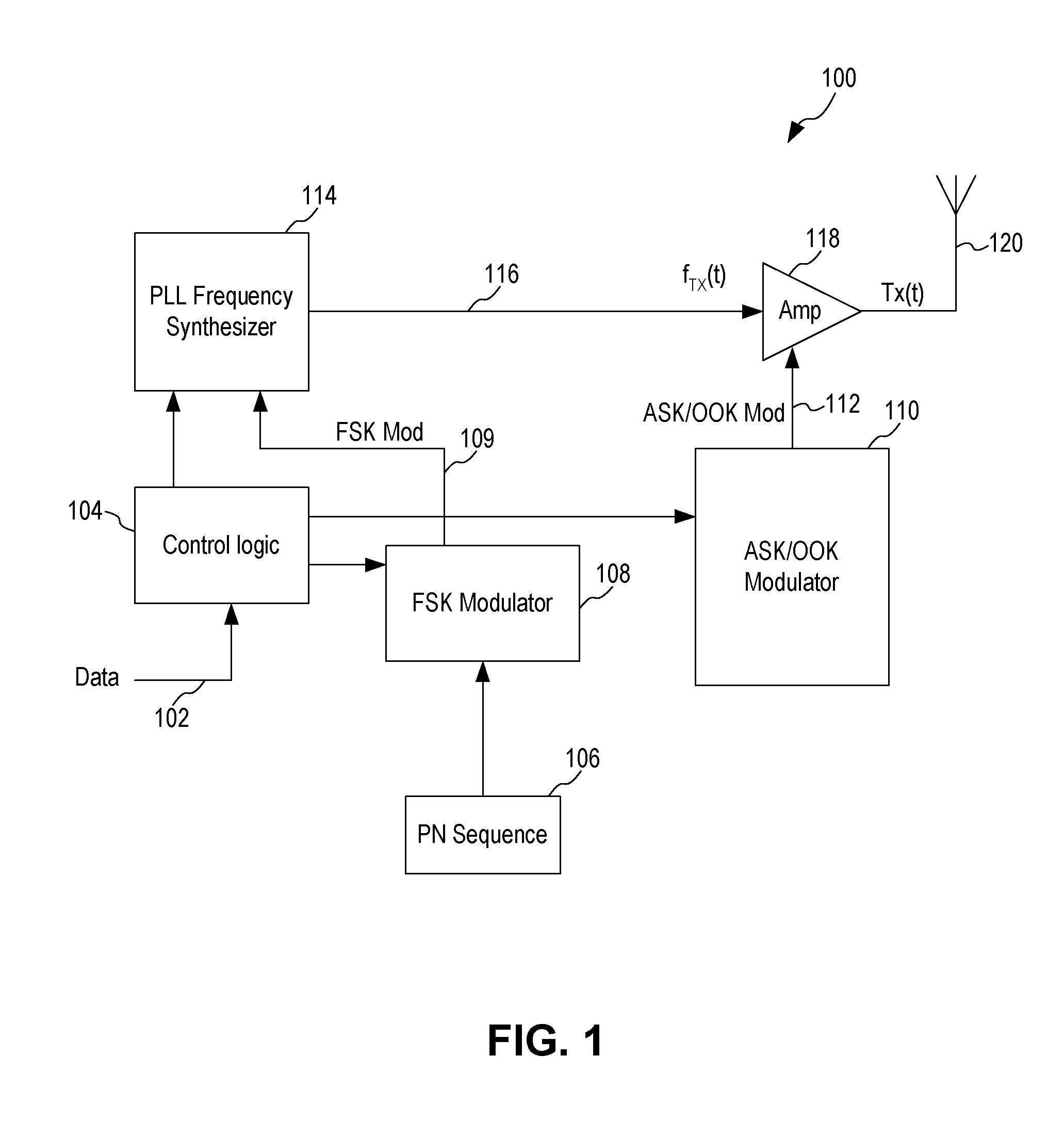
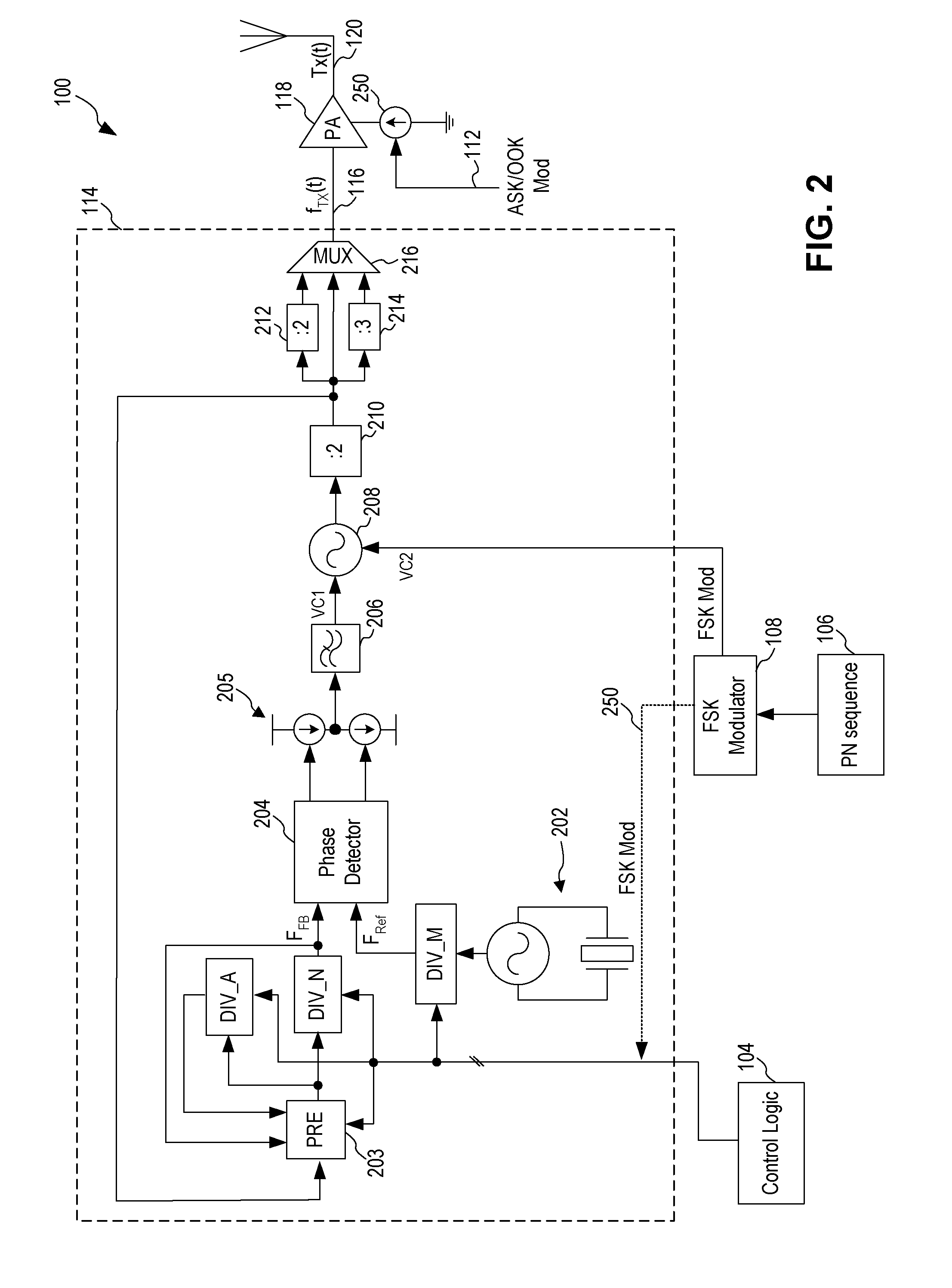
Spread Spectrum ASK/OOK Transmitter
An ASK / OOK transmitter includes a frequency-shift keying (FSK) modulator receiving an input bit sequence and generating a FSK modulation signal indicative of the input bit sequence, a frequency generation circuit receiving the FSK modulation signal and generating a carrier signal having a first frequency where the frequency of the carrier signal is shifted by the FSK modulation signal to form a wideband carrier signal, an amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulator receiving input data and generating an ASK modulation signal indicative of the input data, and a power amplifier coupled to receive the wideband carrier signal as an input signal and the ASK modulation signal as a control signal. The power amplifier provides a spread spectrum ASK transmission signal where the ASK modulation signal modulates the wideband carrier signal to form the spread spectrum ASK transmission signal.
Owner:MICREL
Inter-vehicle communication and warning apparatus
InactiveUS7315239B2Easy to transportInterference minimizationDigital data processing detailsDetection of traffic movementNetwork packetRadar
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
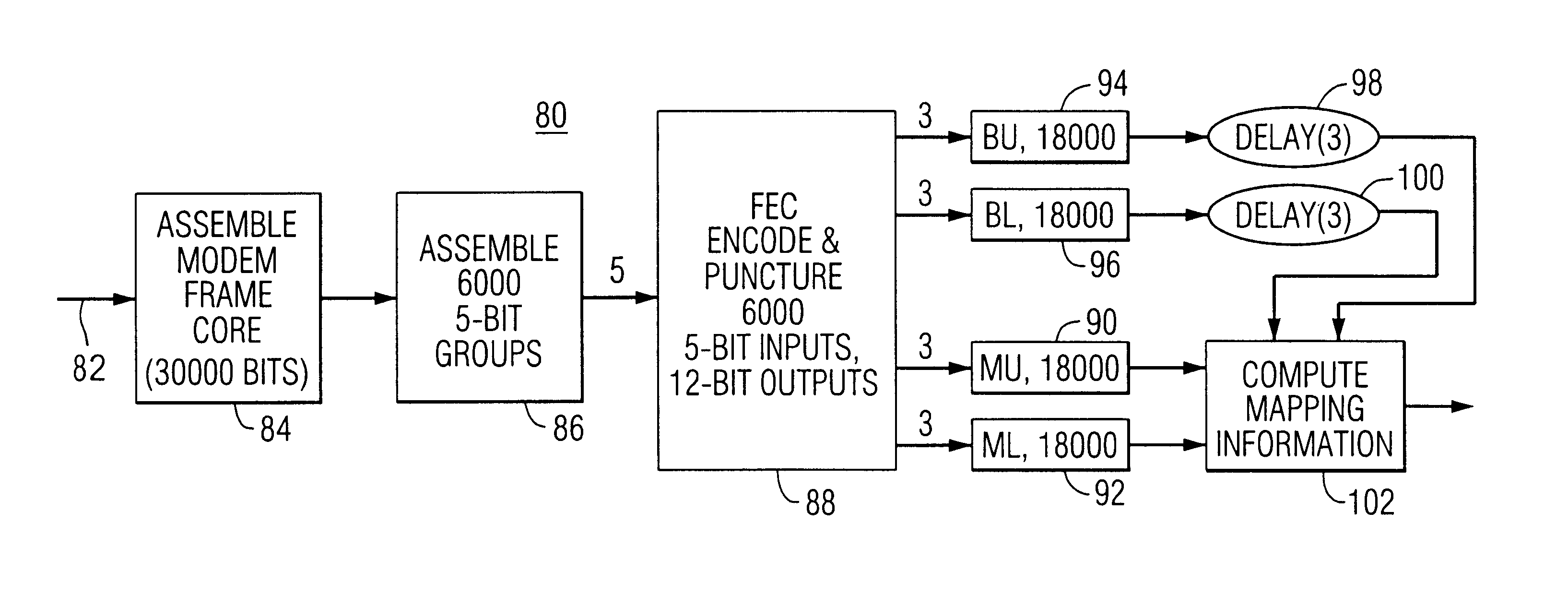
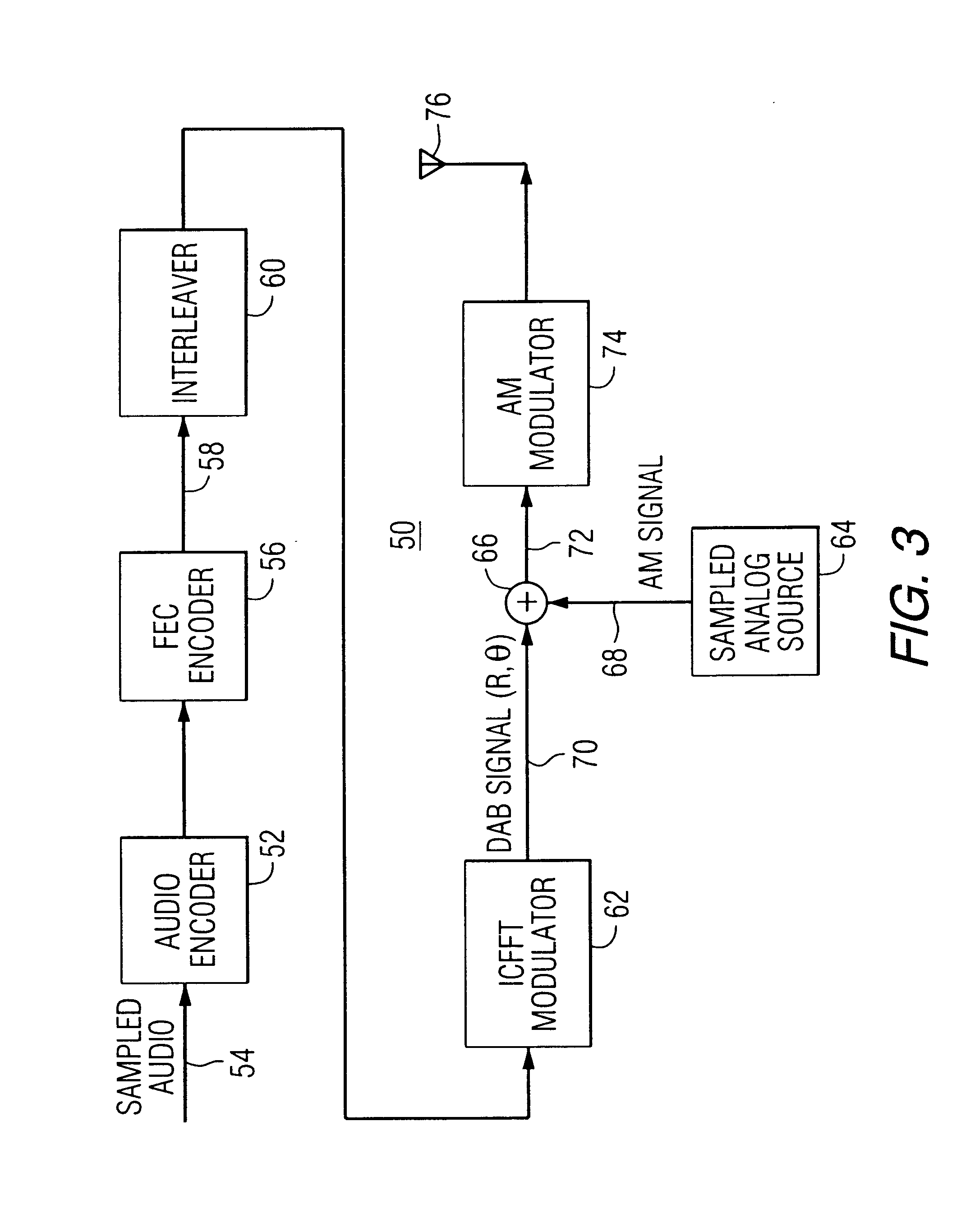
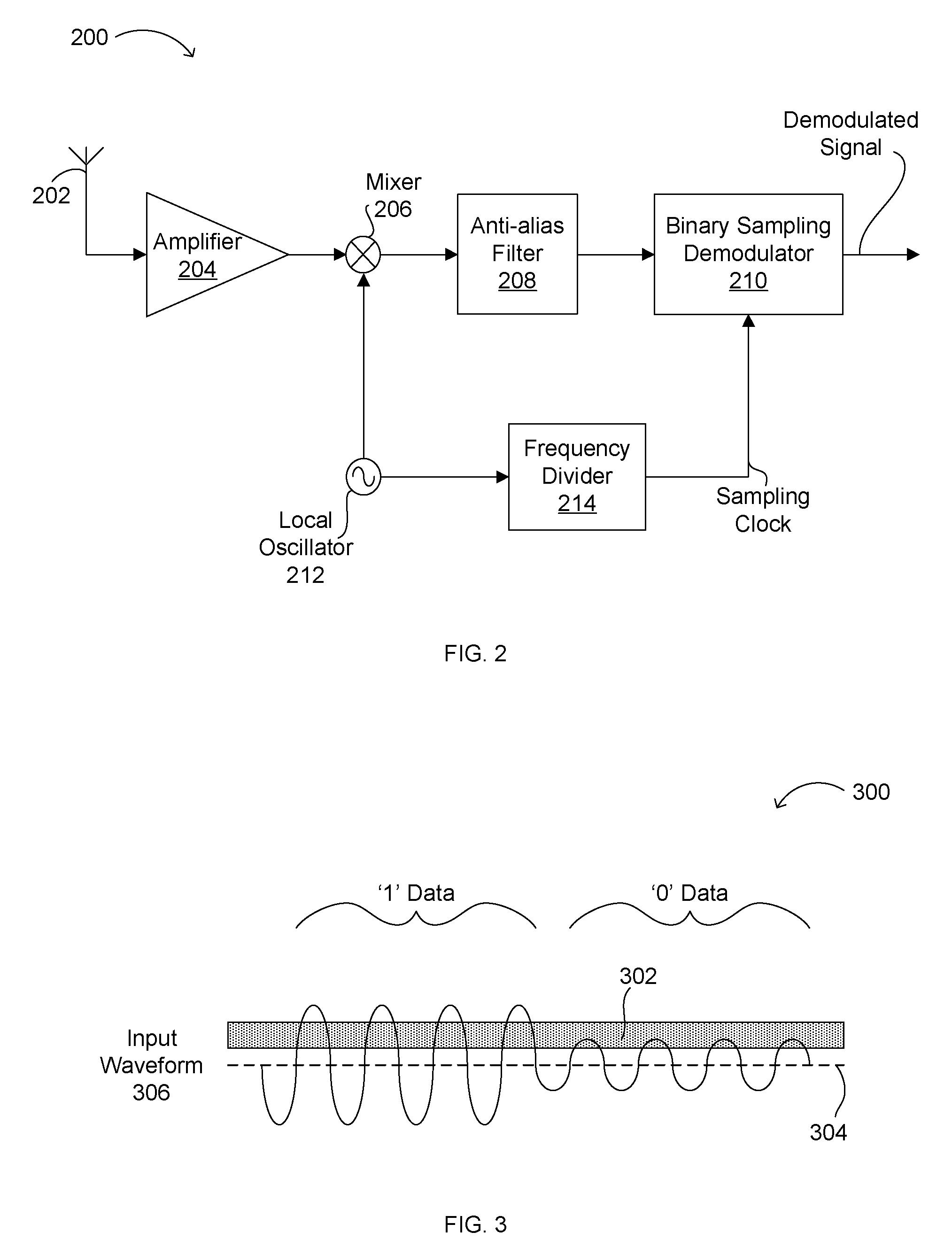
Digital audio broadcasting method and apparatus using complementary pattern-mapped convolutional codes
ActiveUS7043681B2Overcome limitationsError correction/detection using convolutional codesTransmission path divisionIn-phase and quadrature componentsCarrier signal
A method of transmitting digital information comprises the steps of forward error correction encoding a plurality of bits of digital information using complementary pattern-mapped convolutional codes, modulating a plurality of carrier signals with the forward error corrected bits, and transmitting the carrier signals. The modulation can include the step of independently amplitude shift keying in-phase and quadrature components of the QAM constellation using Gray code constellation points corresponding to amplitude levels. Transmitters that transmit signals in accordance with the method and receivers that receive such signals are also included.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
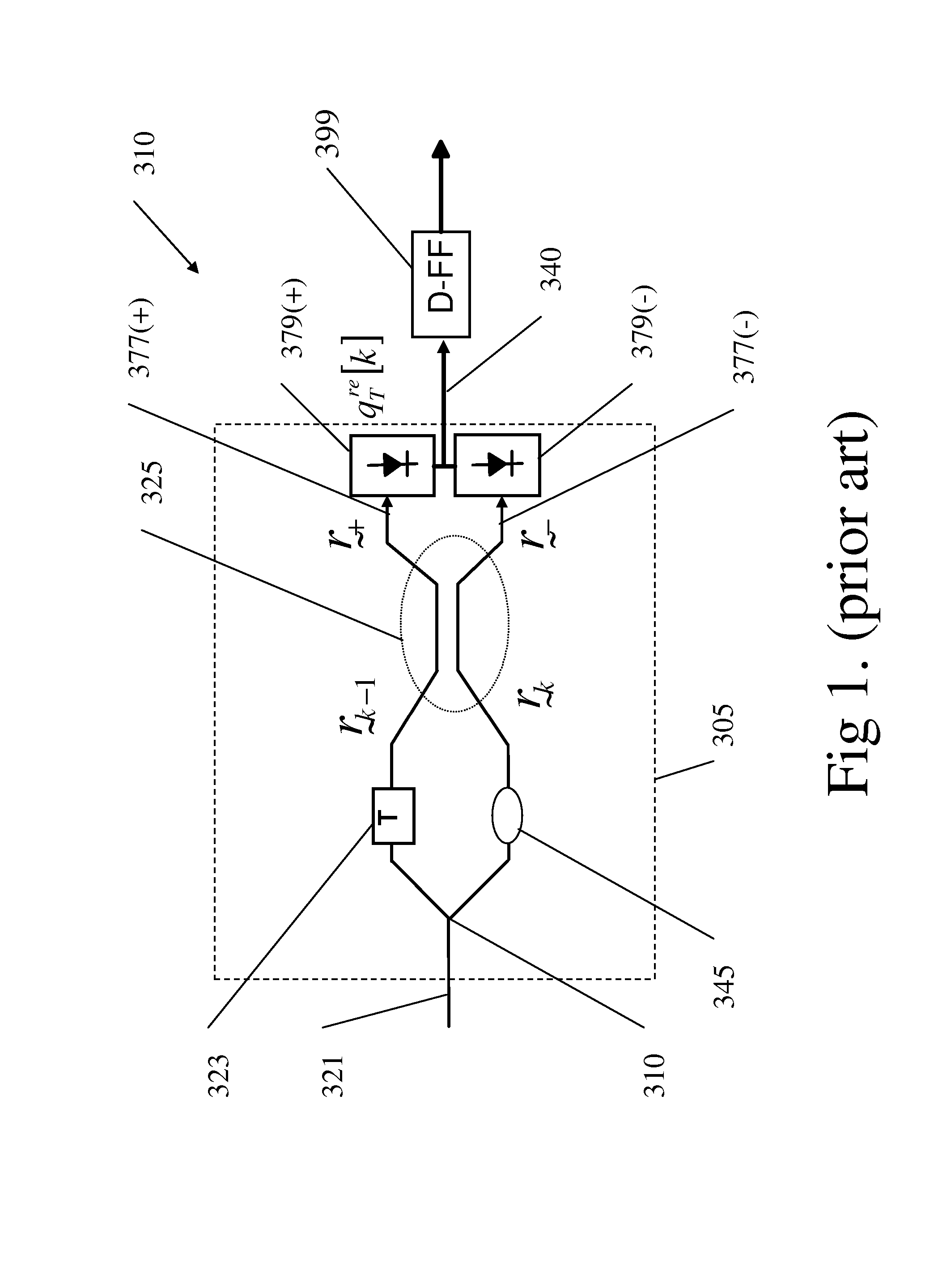
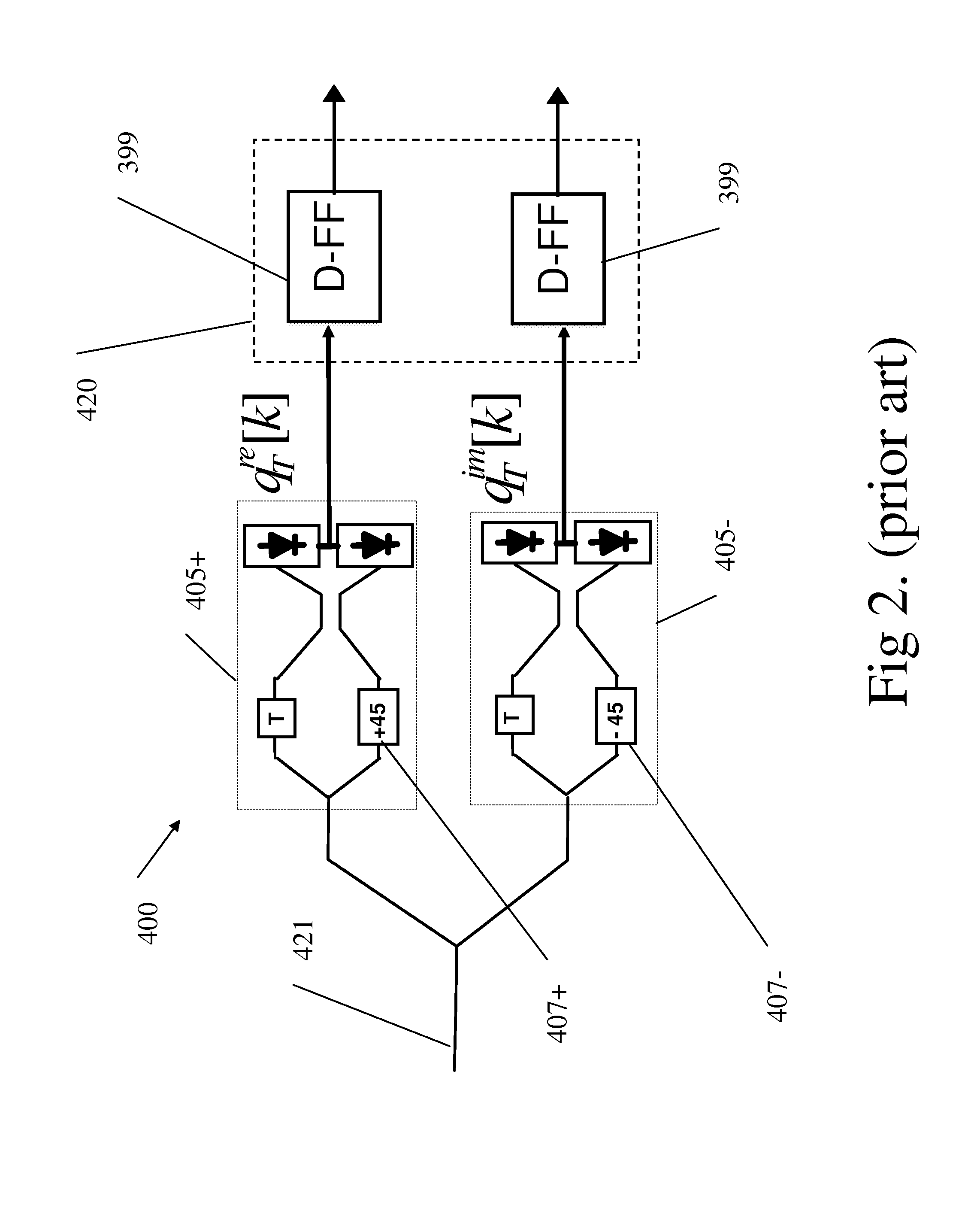
Optical differential phase shift keying receivers with multi-symbol decision feedback-based electro-optic front-end processing
Novel differential-phase shift keying optical receivers are taught based on multi-symbol differential phase shift keying detection (DPSK) aided by decision feedback (DF) from the decision bits in earlier symbol intervals. In accordance with the invention, the DF is directed to an optical front-end comprising multiple Delay Interferometers (DIs) with multiple delays T, 2T, . . . , where T is the DPSK symbol duration. In one embodiment, the DF bitstream is applied to electronically switch the polarity of DI outputs prior to additive combination and hard detection. In other embodiments the DF is applied to active phase-shifting electrodes incorporated in the DIs. In additional embodiments the DF is applied to modified DI devices which not of the conventional Mach-Zehnder asymmetric two-arms type, but rather comprise either three or more arms with appropriate couplings, or two arms, one of which comprises a recirculating delay line with delay T. These embodiments comprise pairs of active phase-shifting electrodes to be activated by the DF. In other embodiments the teachings of this invention for DPSK with DF are combined with the amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulation format, yielding improved Differential Phase Amplitude Shift Keying (DPASK) systems with decision feedback. The resulting receiver structures exhibit improved performance trade-offs between error-rate, transmission distance and bitrate, compared with conventional DPSK systems, yet are simpler to realize than prior art multi-symbol and / or DF-aided optical DPSK systems.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Transmitter modulation switching
InactiveUS20060267744A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringFrequency shift
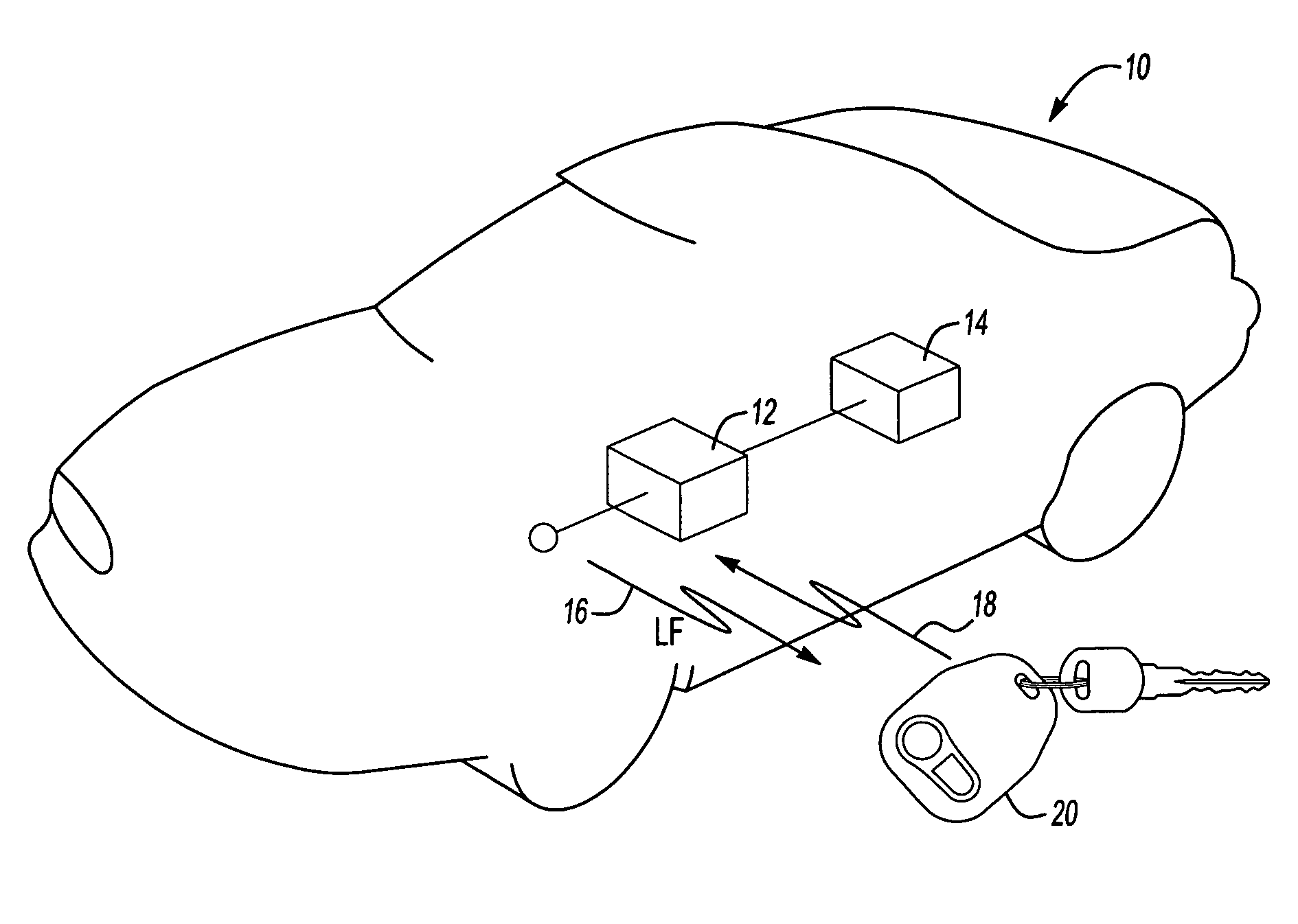
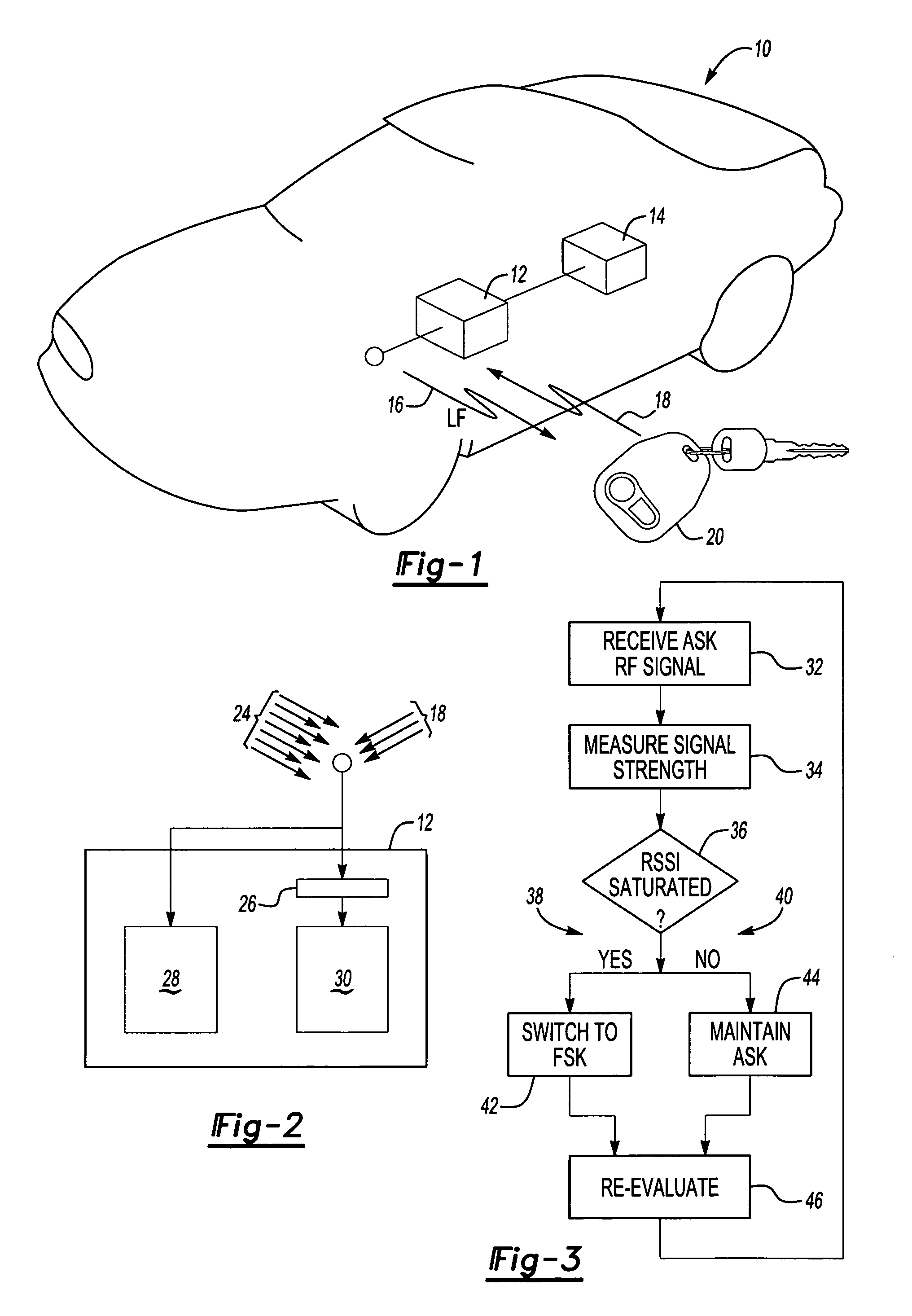
An example receiver / transmitter for a passive start and entry system switches between amplitude shift keyed modulation and frequency shift keyed modulation to maintain clear uninterrupted and dependable communication with a remote transmitter in the presence of interfering signals. The receiver / transmitter is switched to receive incoming FSK signals in response to the RSSI becoming saturated by undesired signals. The switch to FSK signal modulation occurs by signaling the remote transmitter to change over and begin sending FSK modulated signals. The FSK modulated signals are then received without significant interference.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
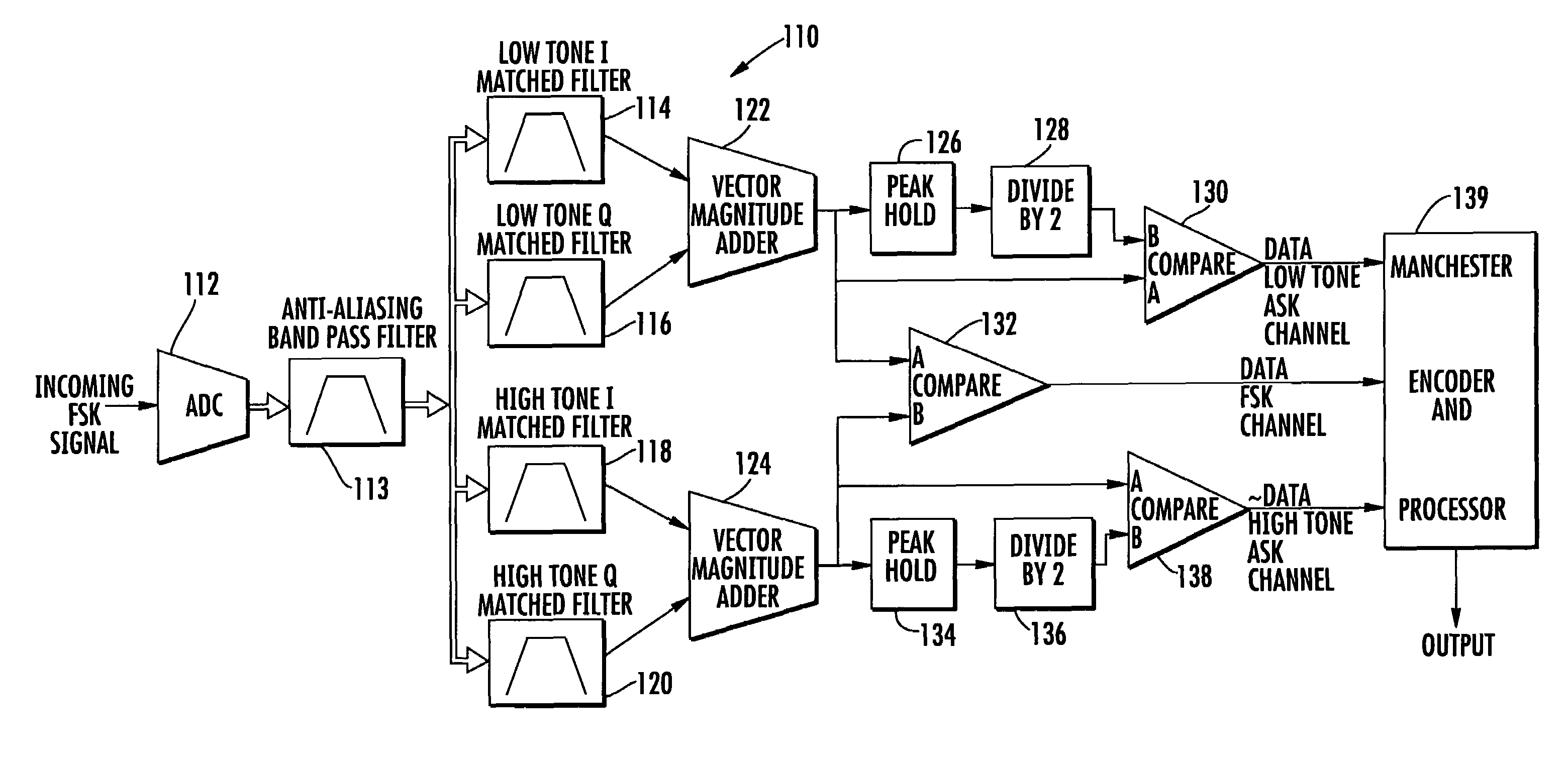
Amplitude shift keyed (ASK) demodulation pattern and use in radio frequency identification (RFID)
ActiveUS20100189196A1Increase rate of changeReduce sensitivityAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsHysteresisAc components
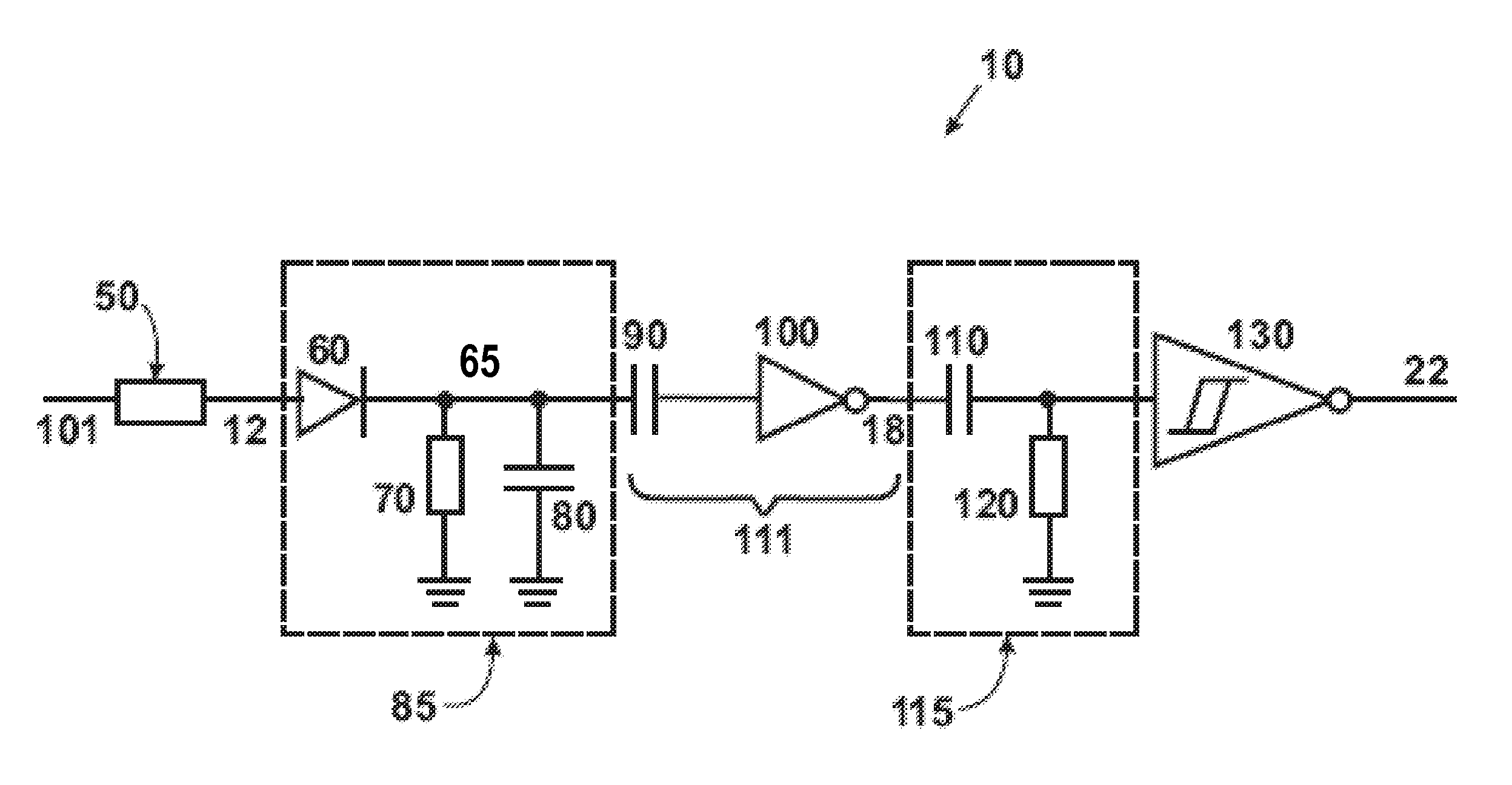
A demodulation circuit for an Amplitude Shift Keyed (ASK) modulated signal includes an envelope detector, an alternating voltage amplifier, a differentiator circuit, and a comparator having a hysteresis connected in series. The envelope detector produces an envelope signal from the received ASK signal. The amplifier blocks the DC component of the envelope signal and amplifies AC components of the envelope signal to obtain a steeper slope of the rising and falling edges. The differentiator circuit then processes the transition edges to provide a differentiated signal having positive and negative electrical pulses. The comparator converts the pulses into a binary data stream which corresponds to the transmitted data stream. The combination of the differentiated signal and comparator having a hysteresis enables better stability and sensitivity of the ASK demodulation circuit.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
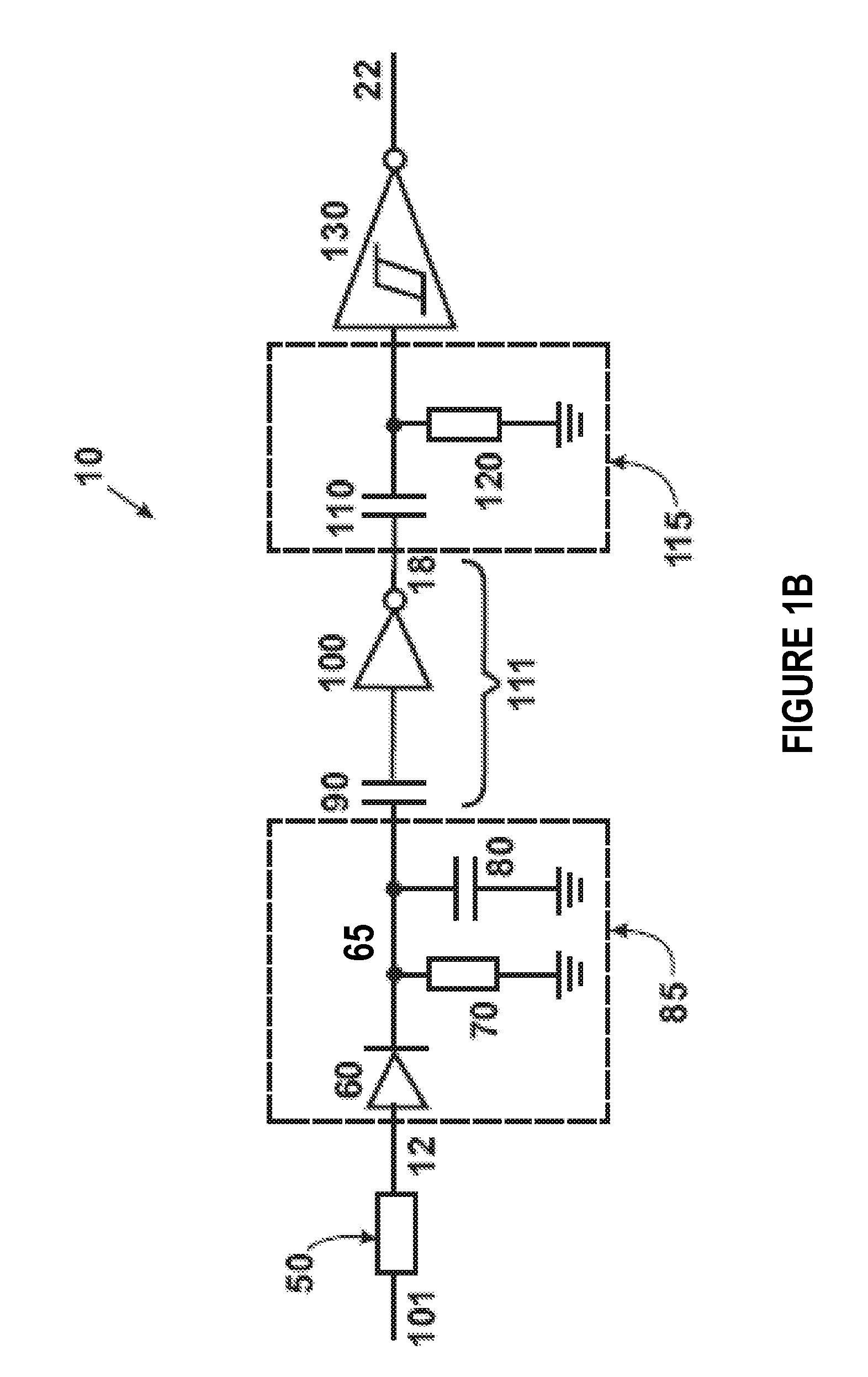
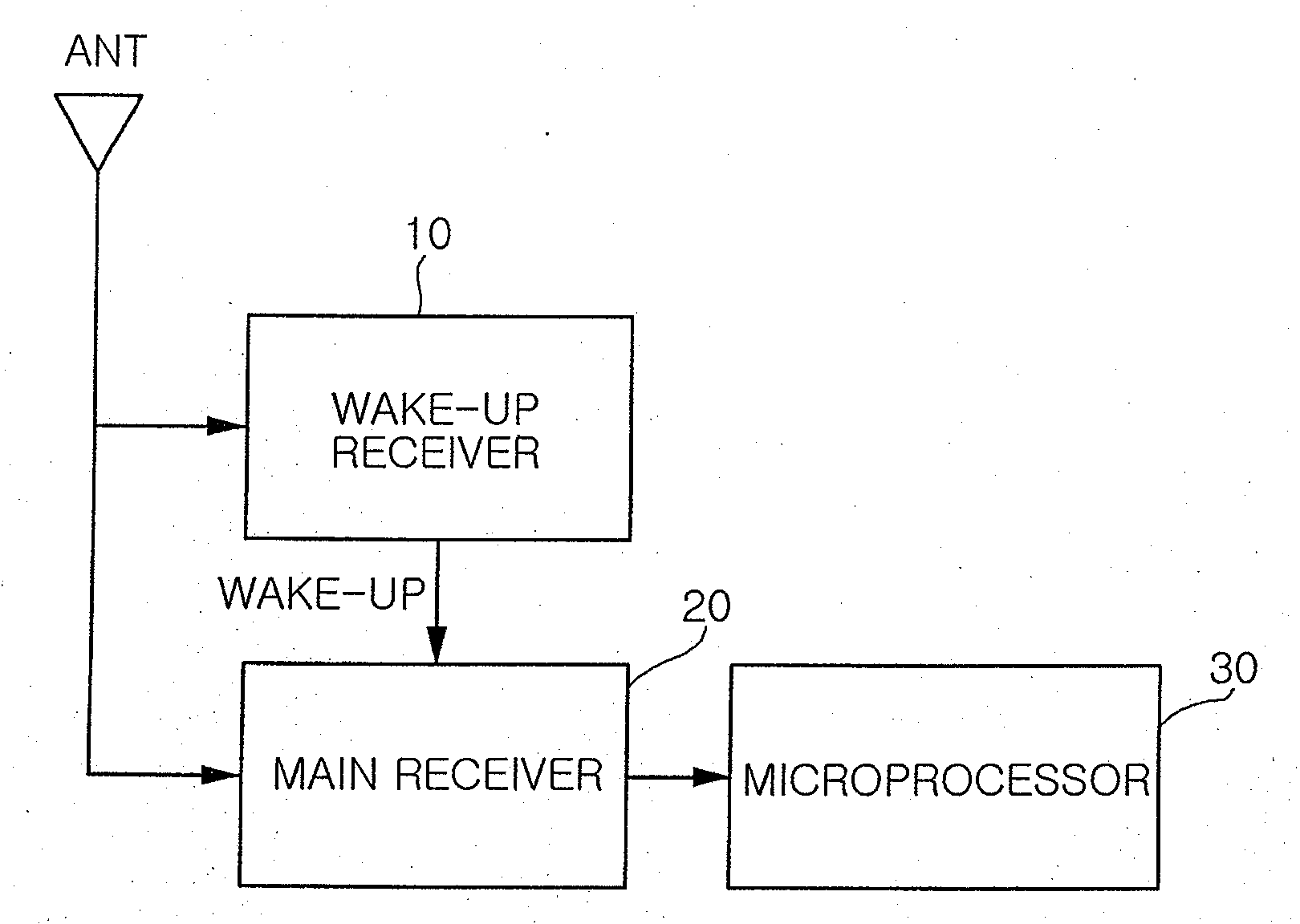
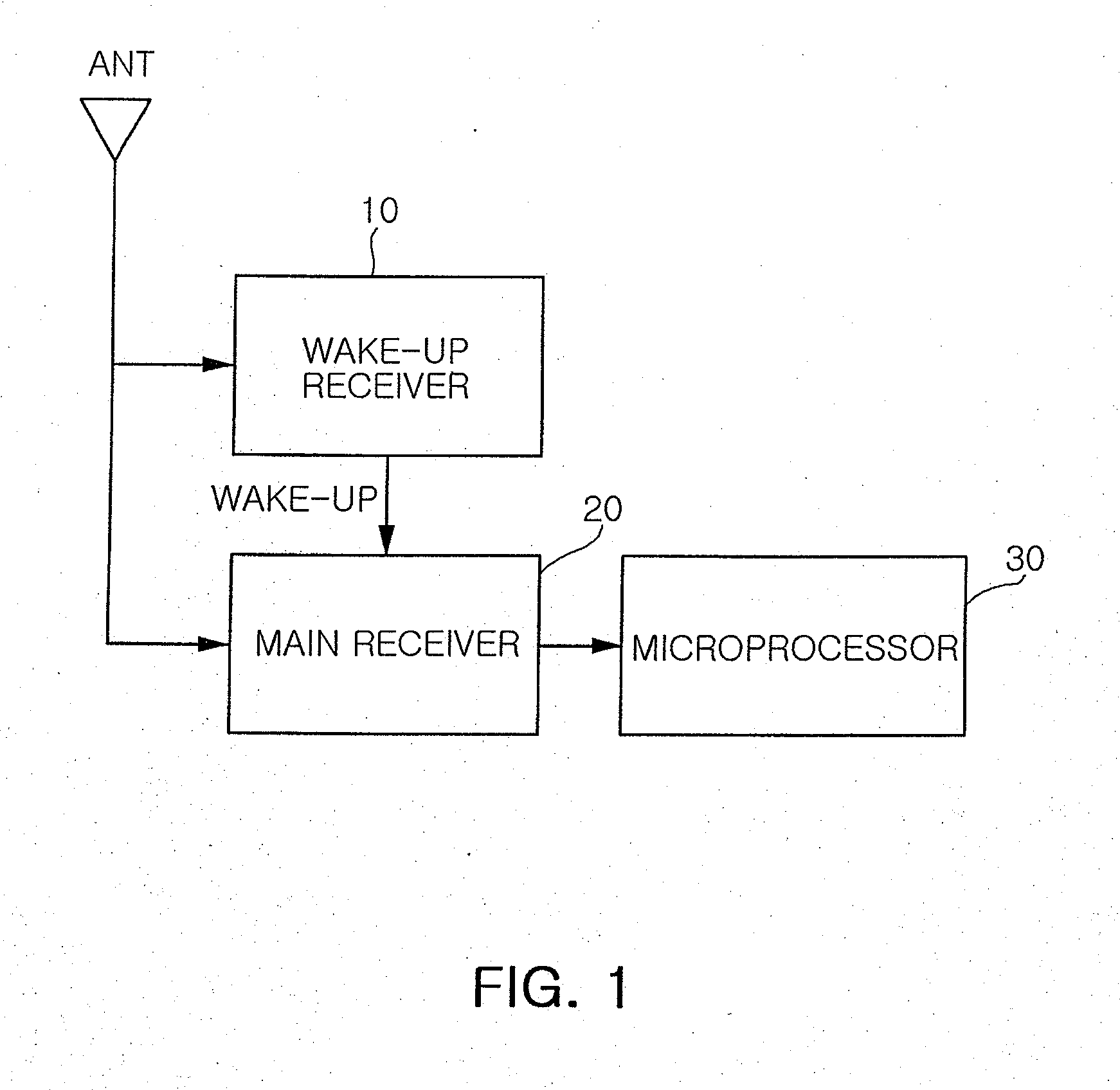
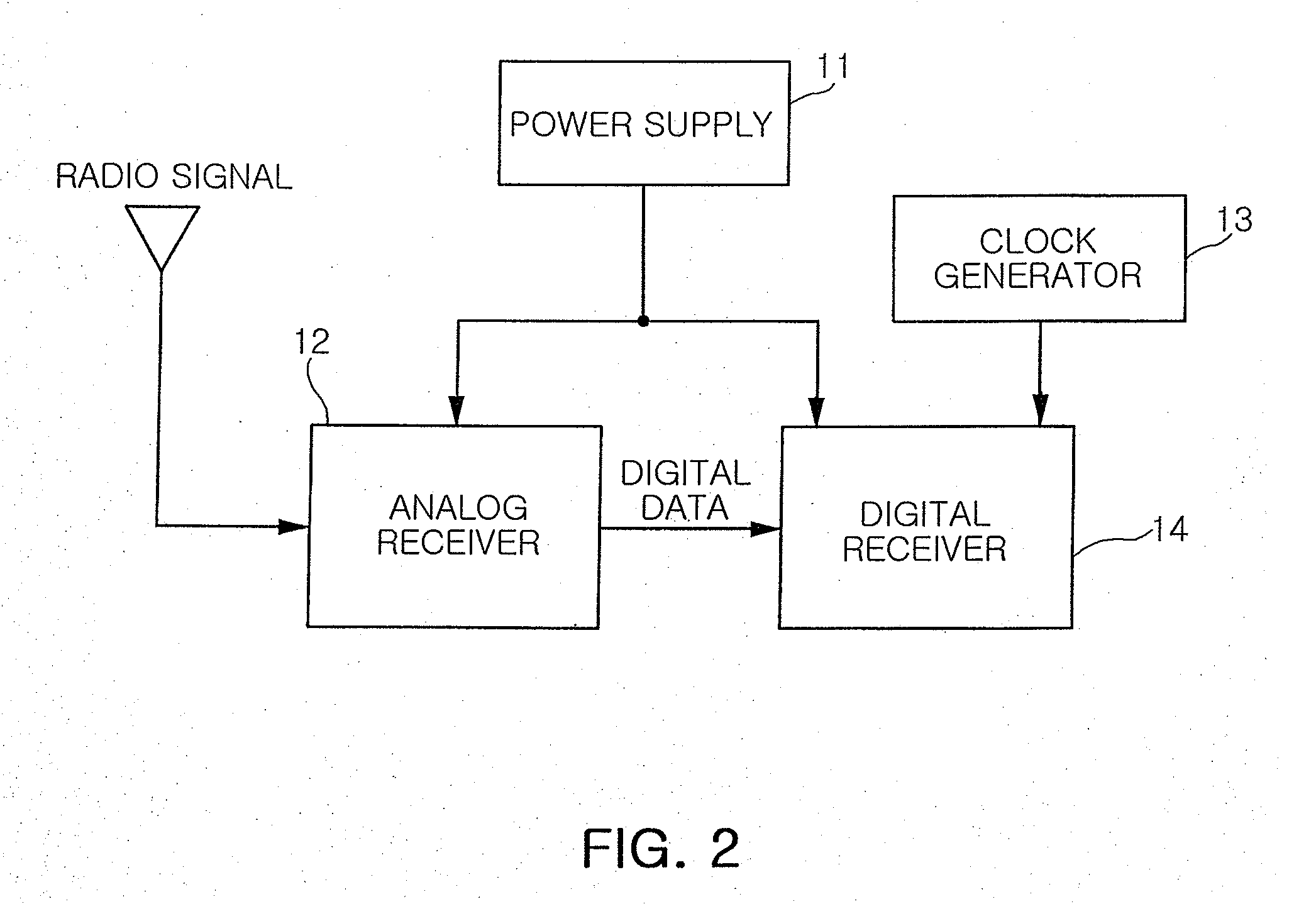
Ultra low-power wake-up receiver
InactiveUS20080108318A1Reduce power consumptionShorten operation timeEnergy efficient ICTPower managementOn-off keyingRadio reception
Provided is an ultra low-power wake-up receiver capable of reducing an operating time of an analog receiver by controlling operation on / off of the analog receiver according to a clock signal from a digital receiver in an amplitude-shift keying (ASK) or on-off keying (OOK) radio receiver. The ultra low-power wake-up receiver includes: a clock generator generating a clock signal having a predetermined frequency; an operation controller controlling analog operation-on for a predetermined time according to the clock signal from the clock generator; an analog receiver maintaining an operation-on state for a predetermined time according to the analog operation-on control performed by the operation controller, and being operated off after the predetermined time; and a digital receiver being operated on while the analog receiver maintains the operation-on state
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Optical modulating device with frequency multiplying technique for electrical signals
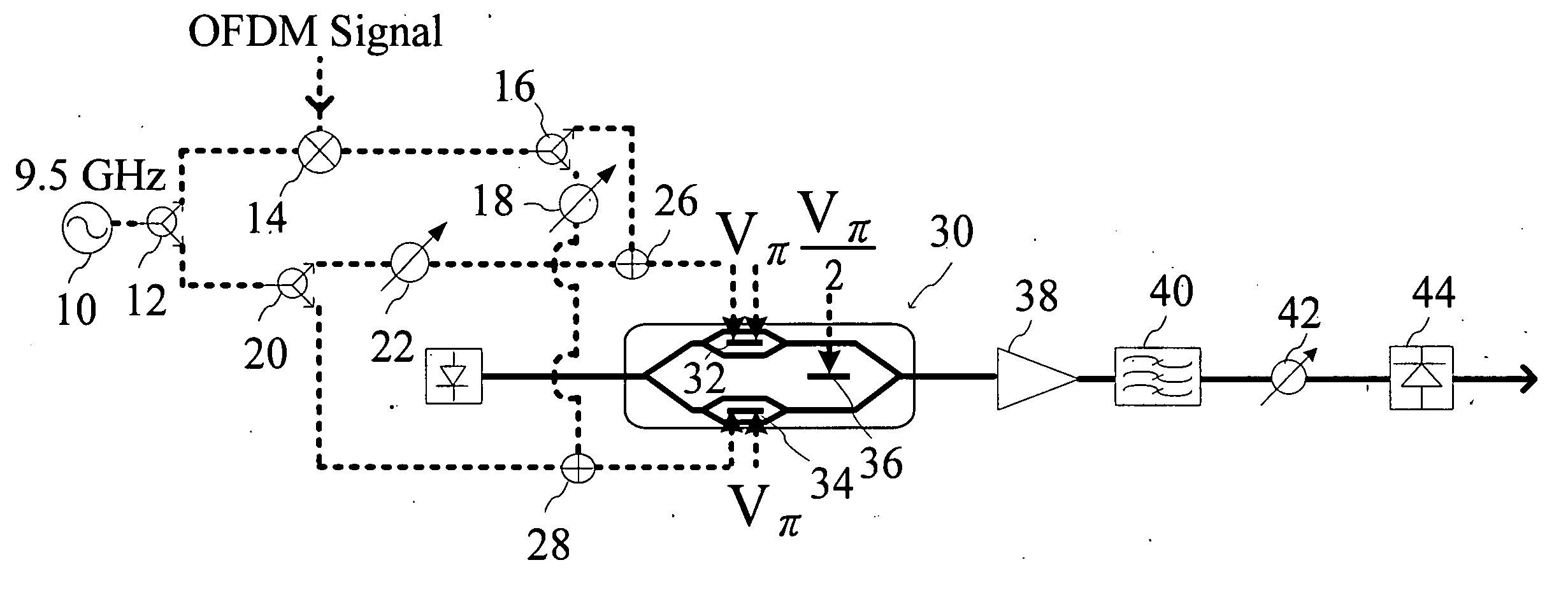
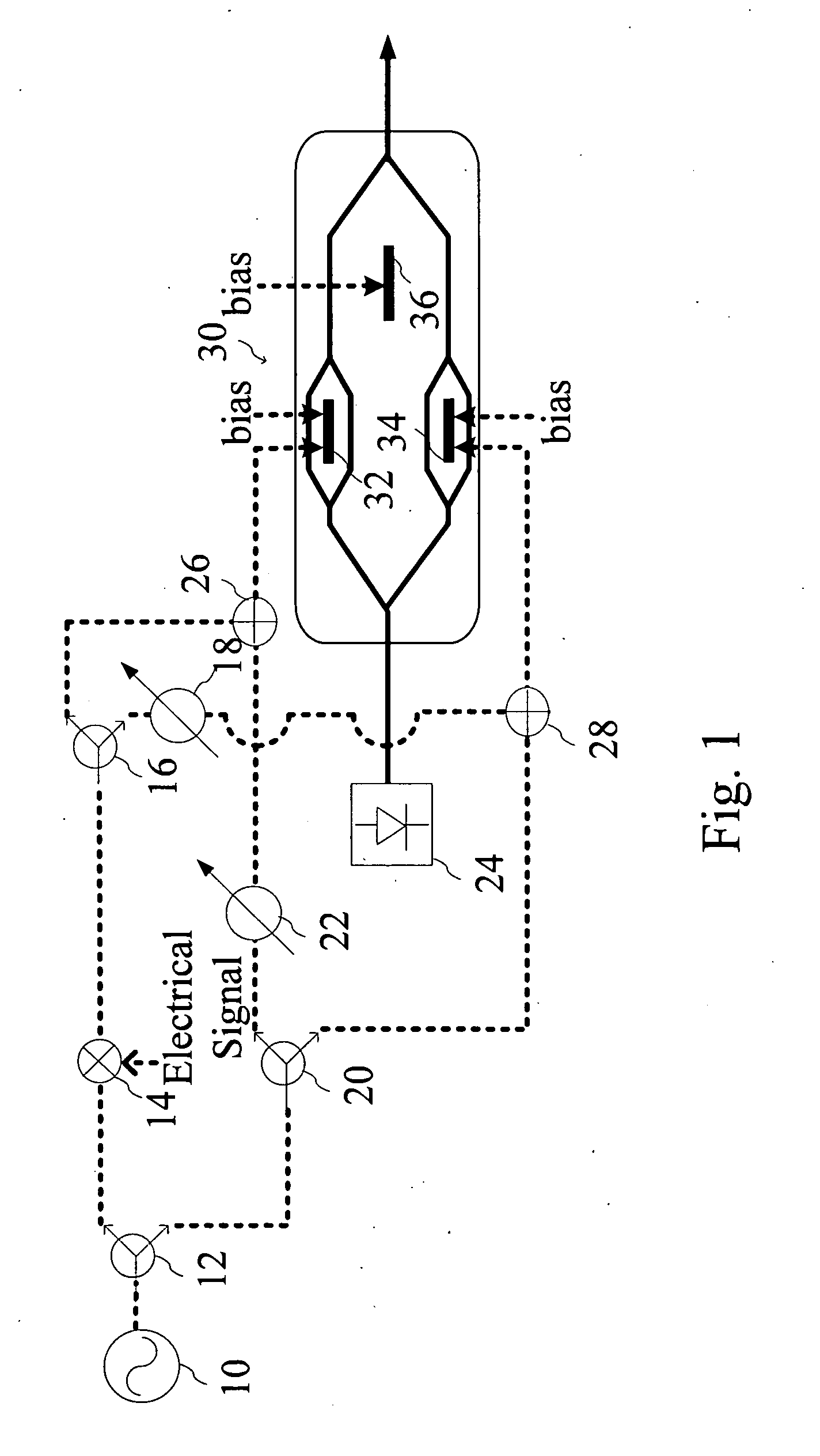
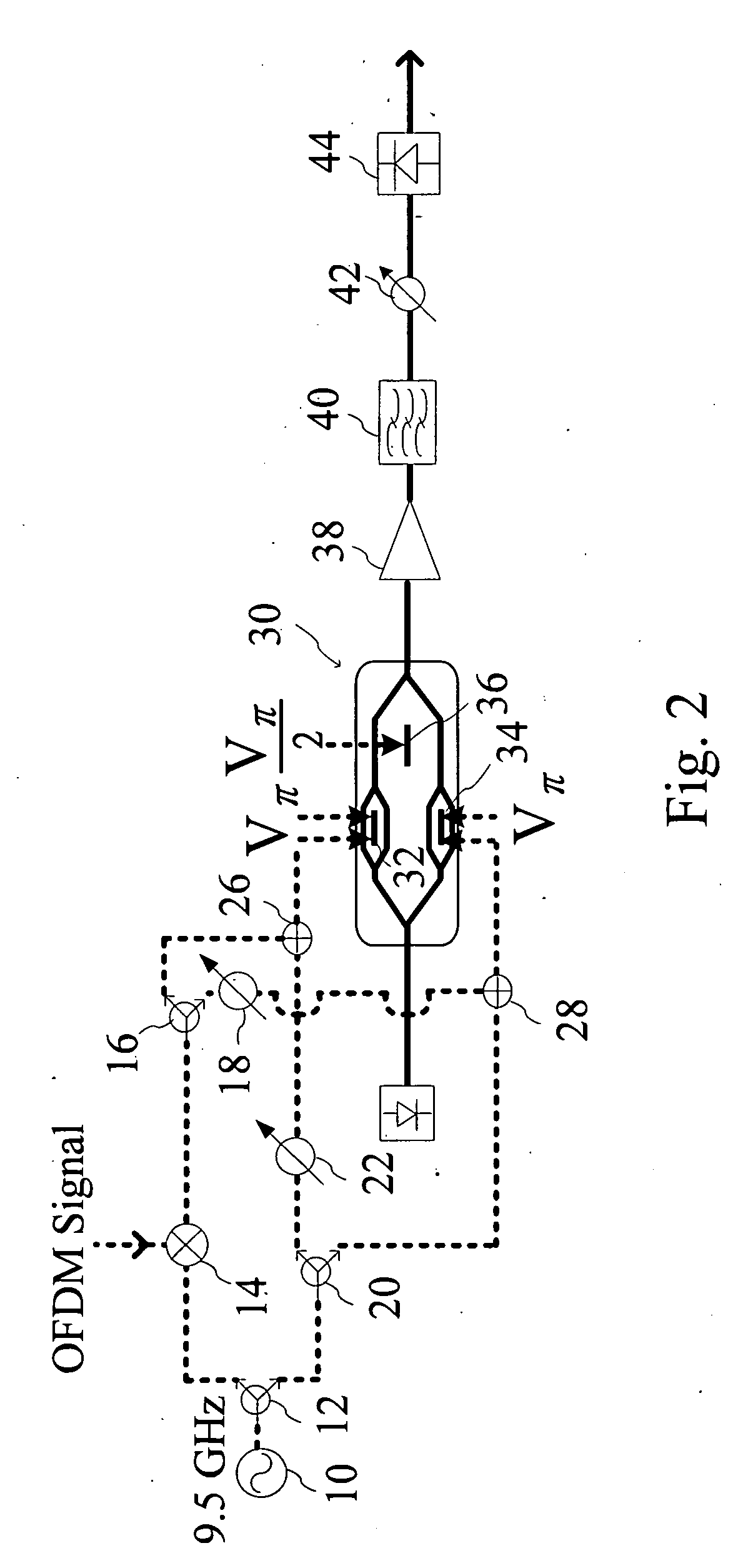
The present invention relates to an optical modulating device with frequency multiplying technique for electrical signals, which primary comprises a mixer, which generates a mixed data signal from a first electrical signal and a second electrical signal. The mixed data signal is then received by a first phase shift device to have its phase shifted and becomes a first shifted signal. The first electrical signal is further received by a second phase shift device to have its phase shifted and becomes a second shifted signal. The present invention further comprises an integrated electro-optic modulator (Mach-Zehnder modulator), which is used to receive an input optical signal, the mixed data signal, the first shifted signal, the second shifted signal and the first electrical signal mentioned above, the integrated electro-optic modulator will then modulates the input optical signal into a frequency multiplying output optical signal that carries the first electrical signal and the second electrical signal. The present invention can carry and transmit amplitude shift keying signals and vector modulation signals, thereby provides a more advanced optical communication transmission service.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
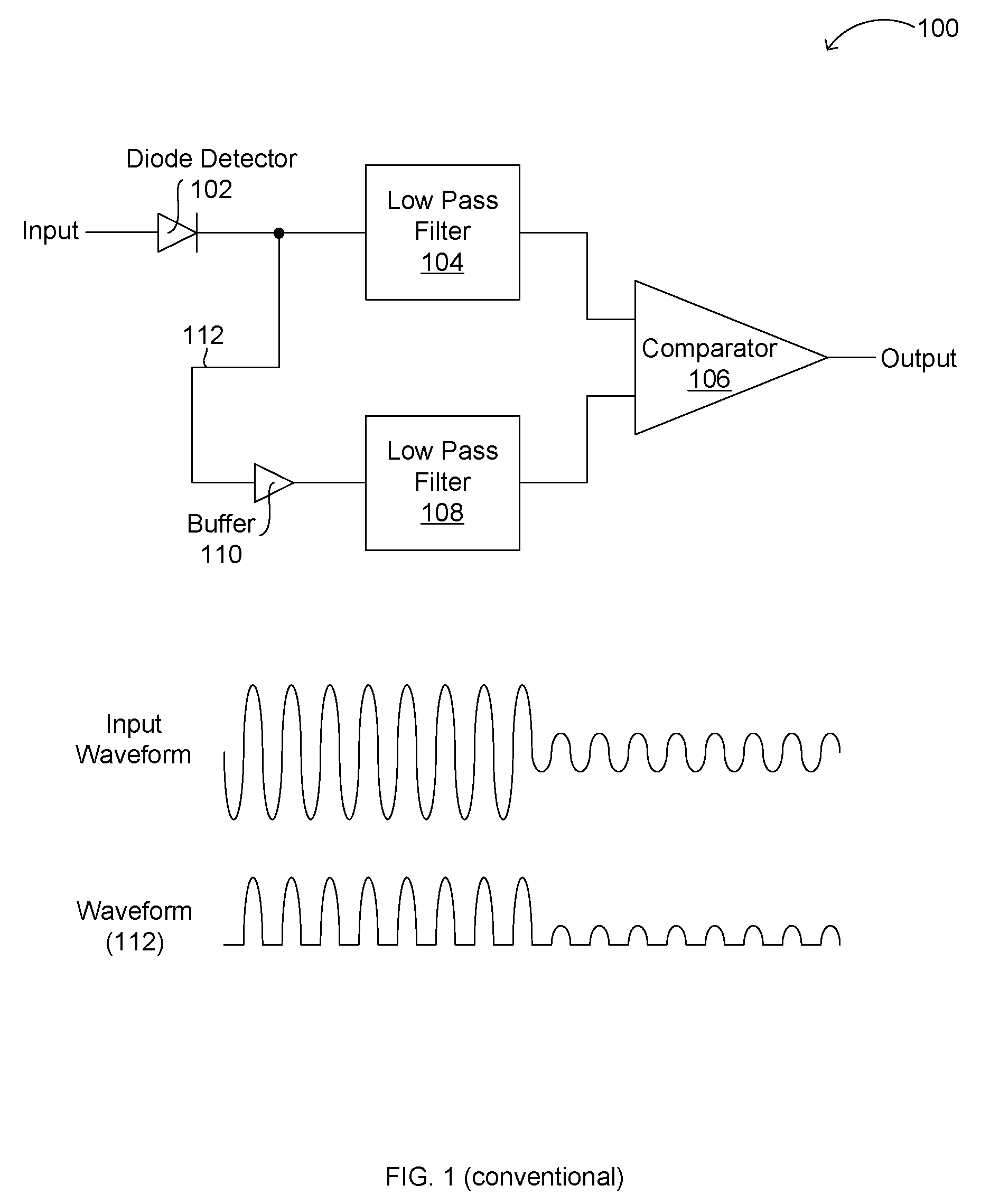
Sampling demodulator for amplitude shift keying (ASK) radio receiver
InactiveUS7885359B2Efficient integrationReliable and simplified ASKAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio receiver designRadio reception
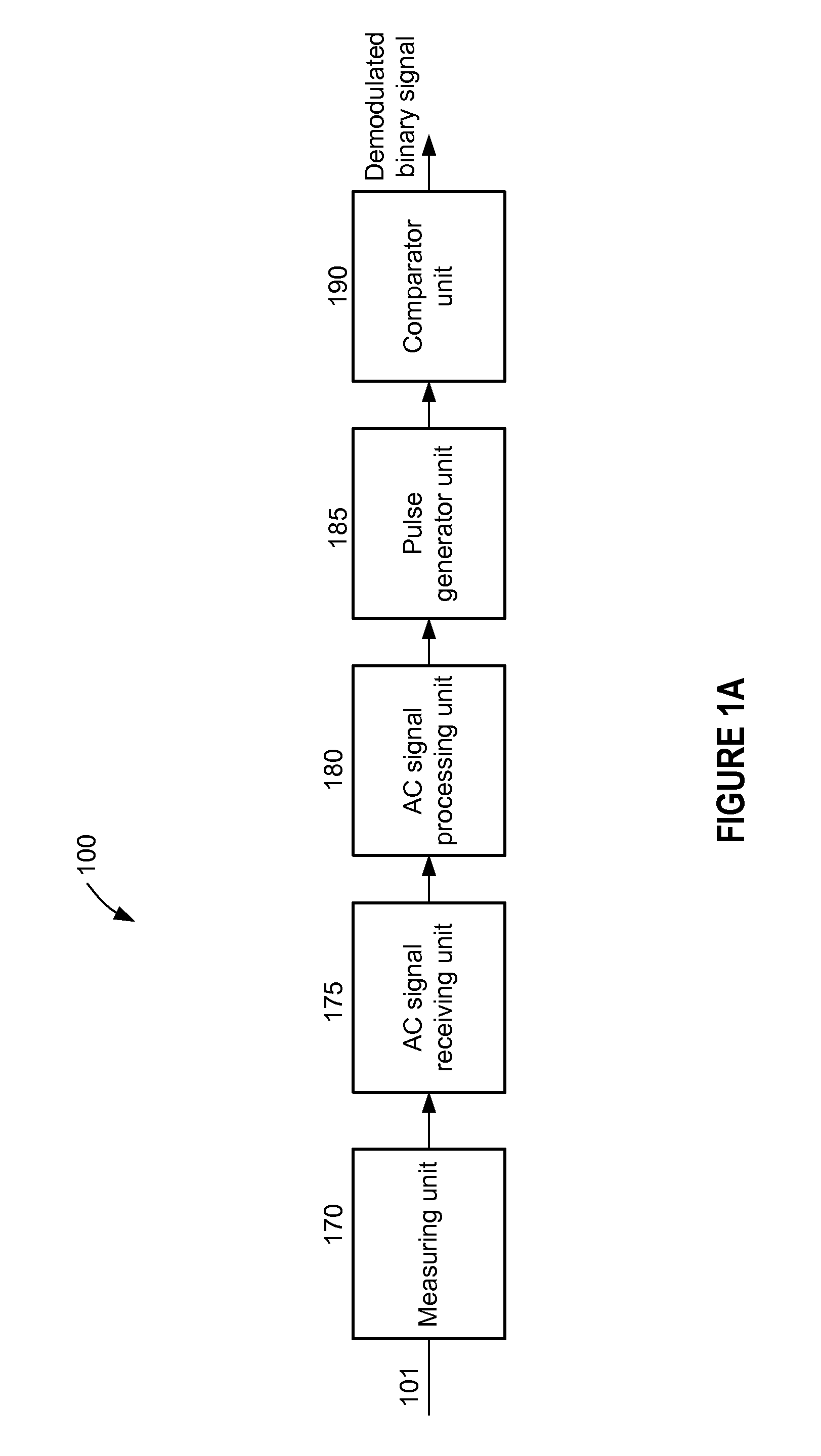
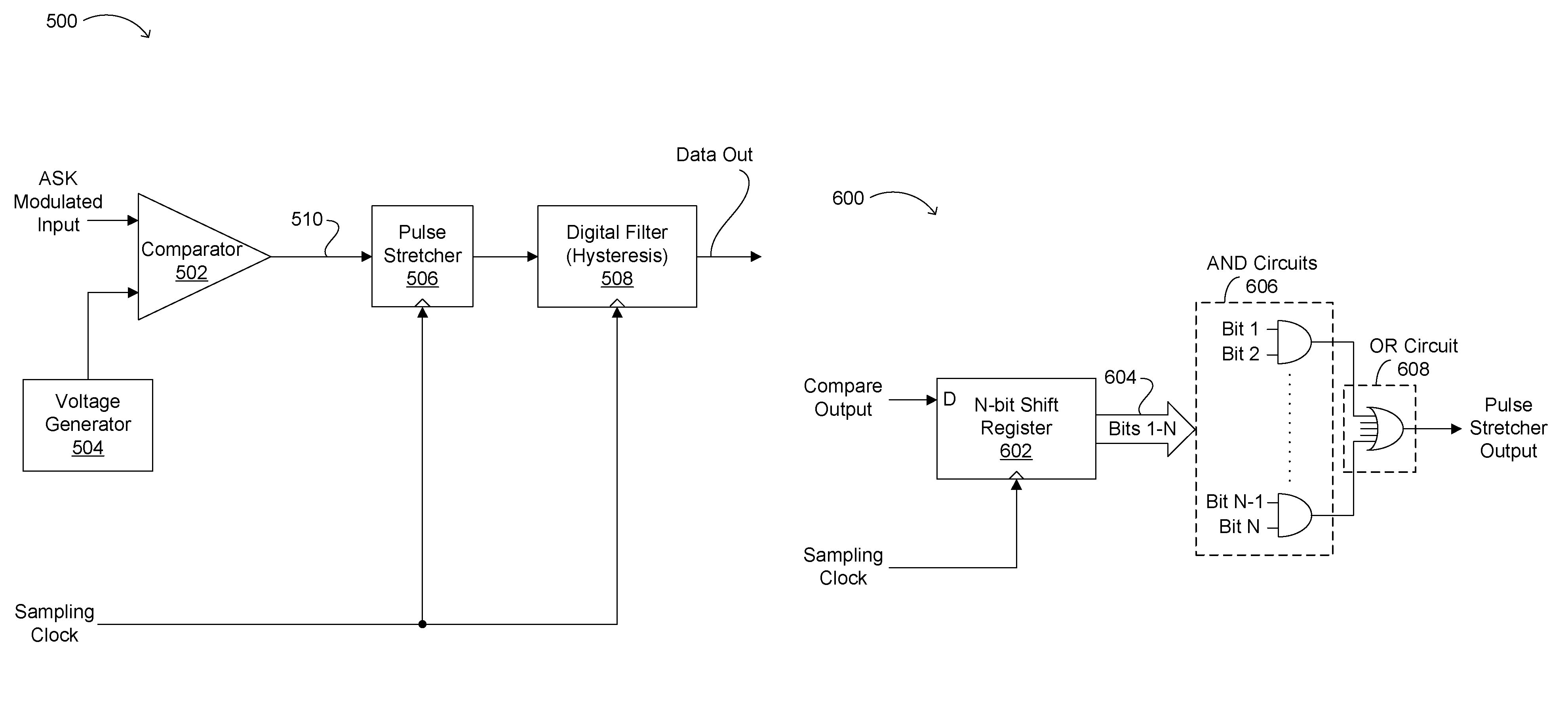
A method, algorithm, circuits, and / or systems for amplitude shift keying (ASK) modulation are disclosed. In one embodiment, a sampling demodulator includes a comparator configured to compare an ASK modulated input to a predetermined voltage level and provide a comparison result, a pulse stretcher with a sampler configured to sample the comparison result a plurality of times for each of a plurality of cycles of the ASK modulated input to generate a bit stream and digital logic configured to determine a value for each data bit in the ASK modulated input from the bit stream, and a digital filter configured to filter an output of the digital logic, thereby providing a demodulated signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
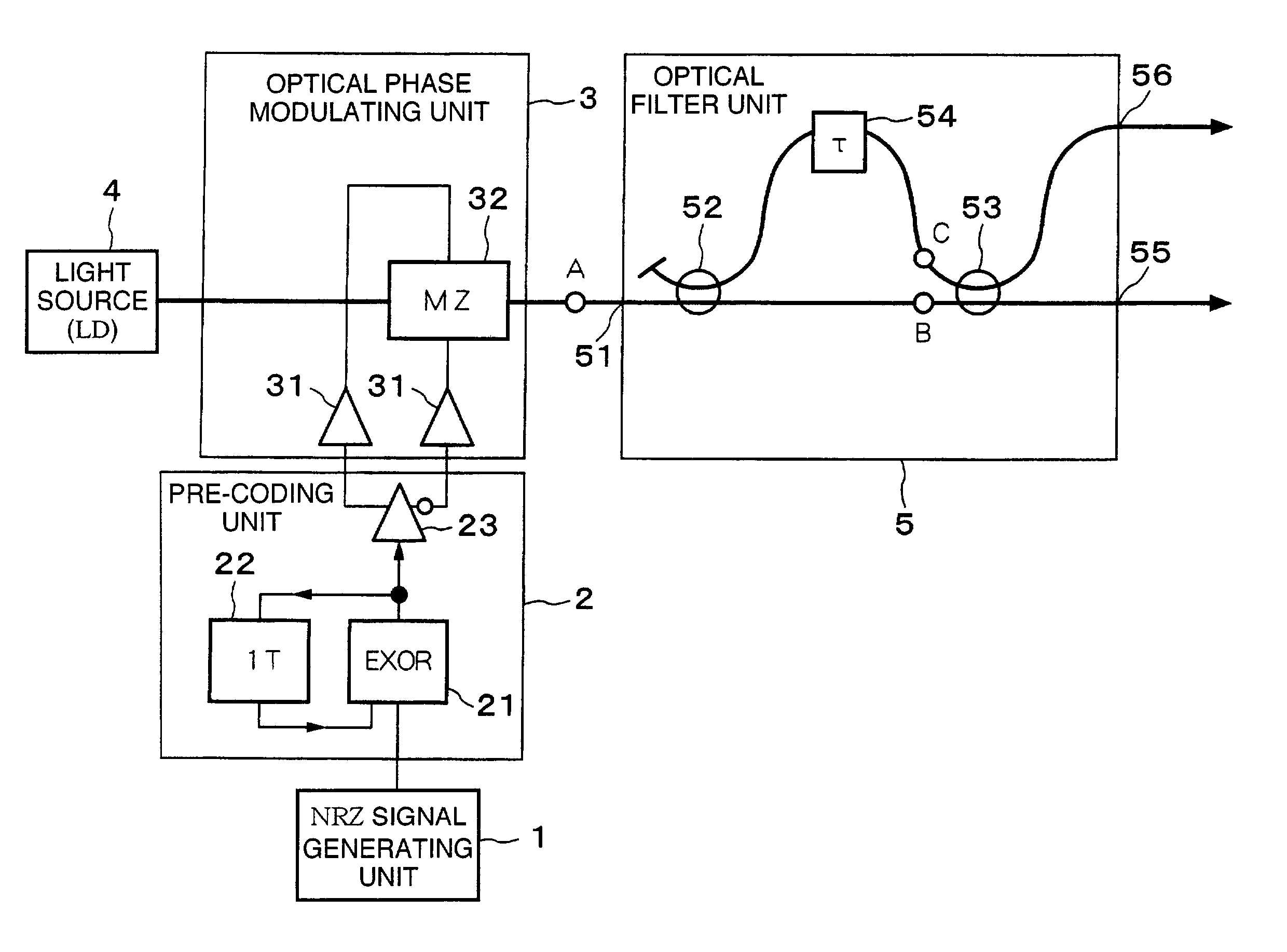
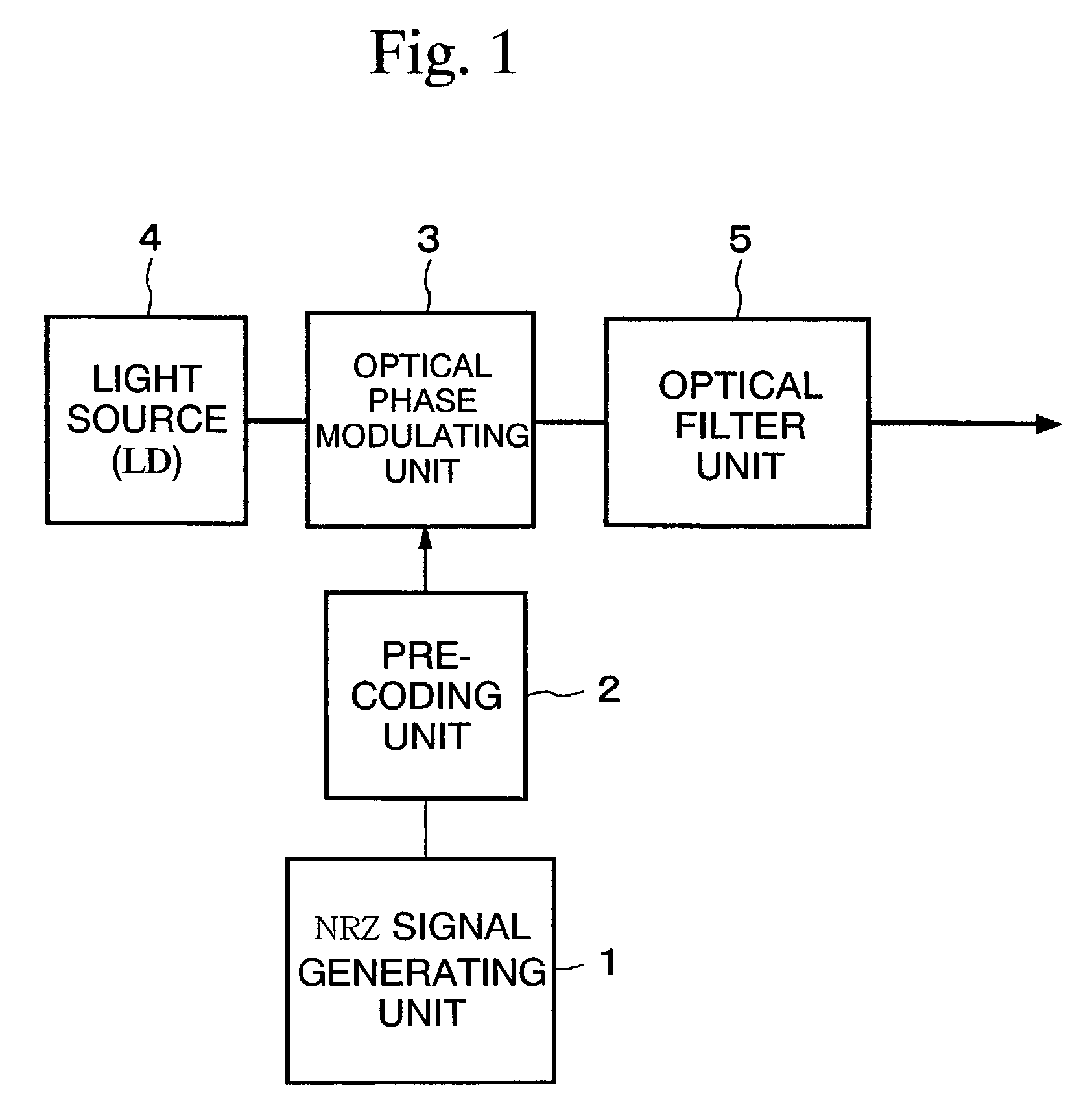
Optical transmitter and optical transmission system
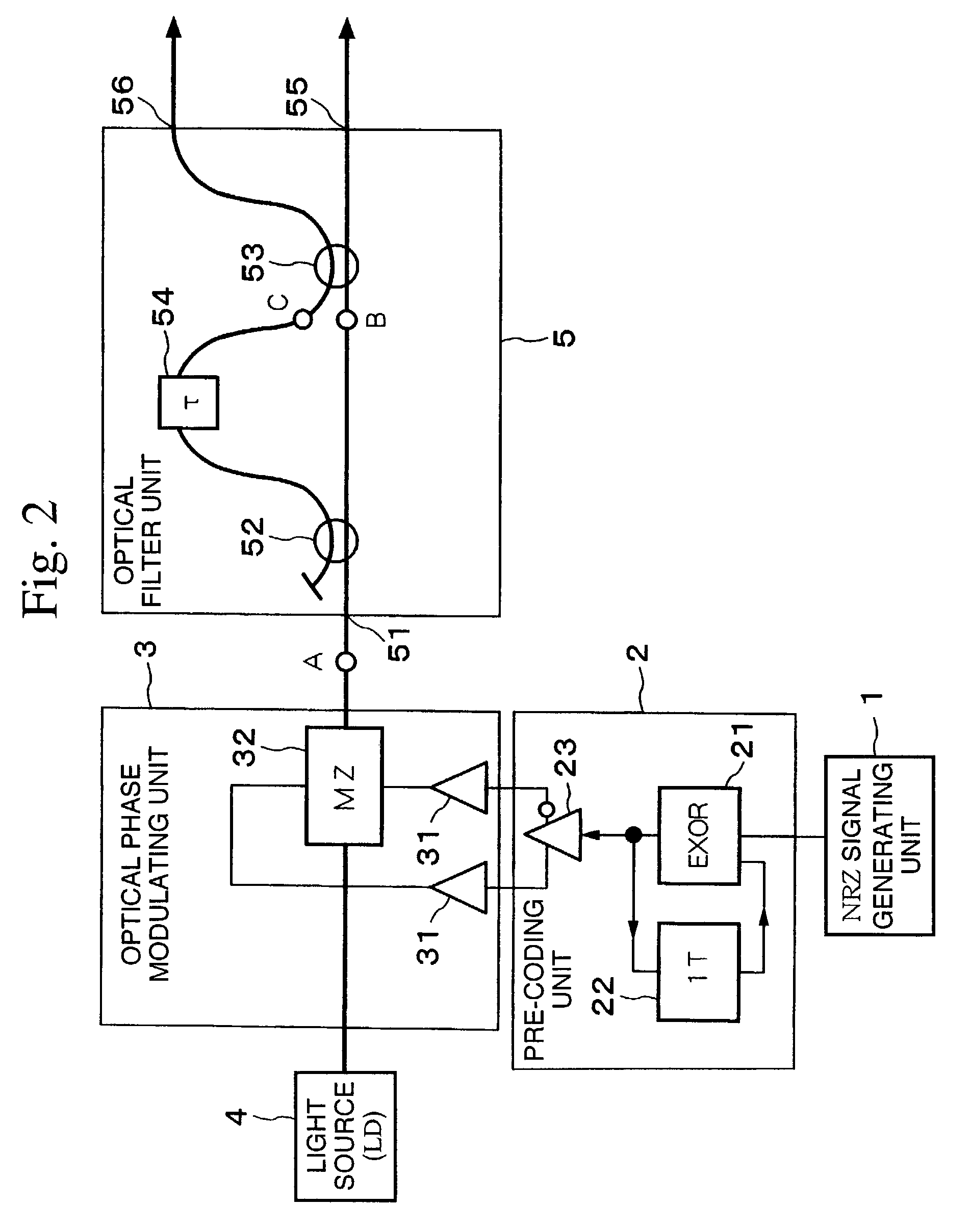
ActiveUS7116917B2Line rate can be increasedEasy to operateDistortion/dispersion eliminationOptical multiplexEngineeringTransmission quality
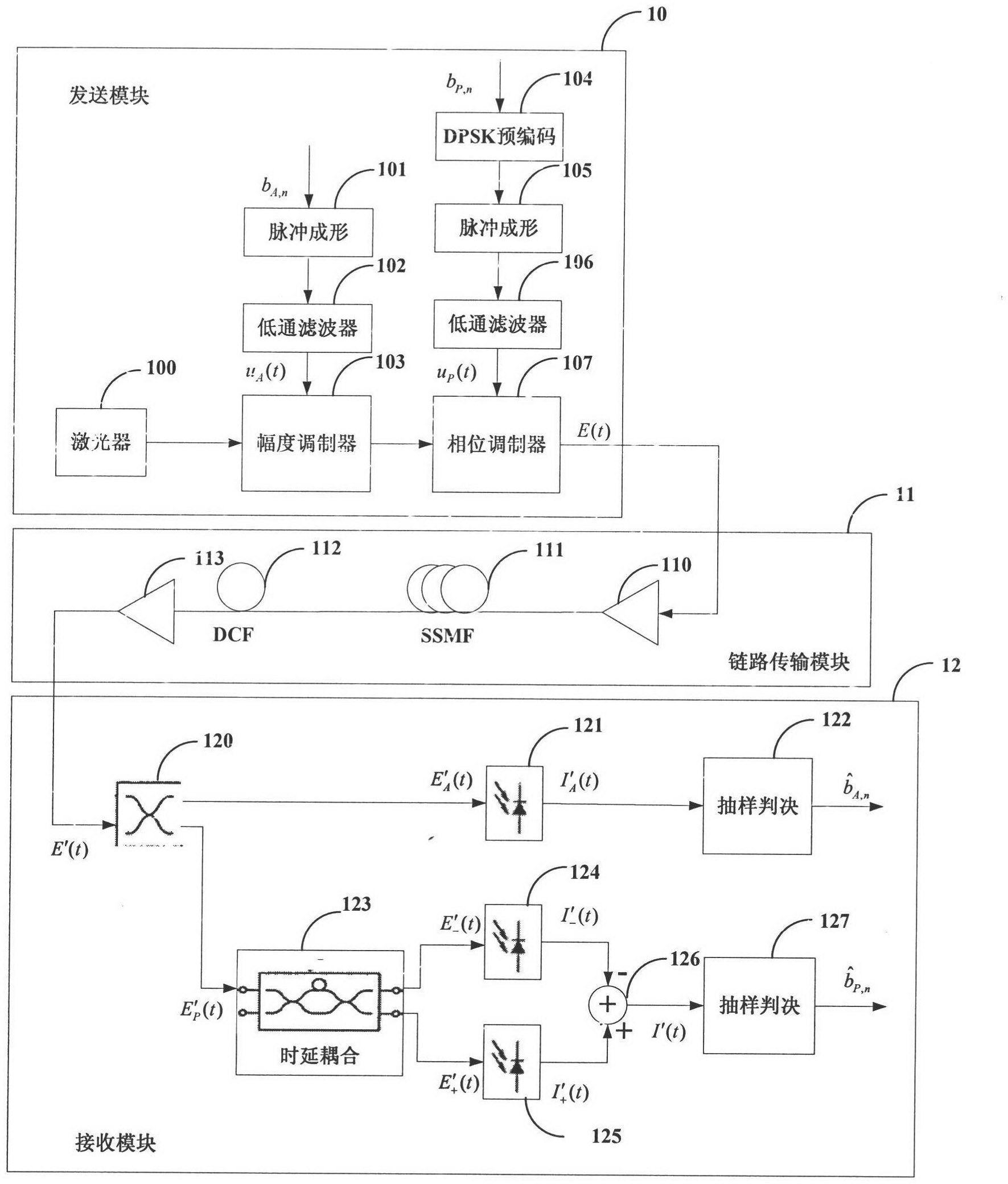
The present invention suppresses to a minimum the degradation of the transmission quality caused by chromatic dispersion characteristic of an optical transmission medium, and the interplay between the chromatic dispersion and non-linear optical effects in dense WDM transport systems. A baseband input data signal is pre-coded in advance by a pre-coding unit, phase modulation is carried out using a pre-coded signal by the optical phase modulating unit, and the phase modulated optical signal is converted to an RZ intensity modulated signal by the optical filter unit that performs phase-shift-keying to amplitude-shift-keying conversion. For example, an optical phase modulating unit generates an encoded DPSK phase modulated signal using a differential phase shirt keying (DPSK) format, and a phase modulated signal is converted to an RZ intensity modulated signal by the optical filter unit disposed downstream of the optical phase modulating unit.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
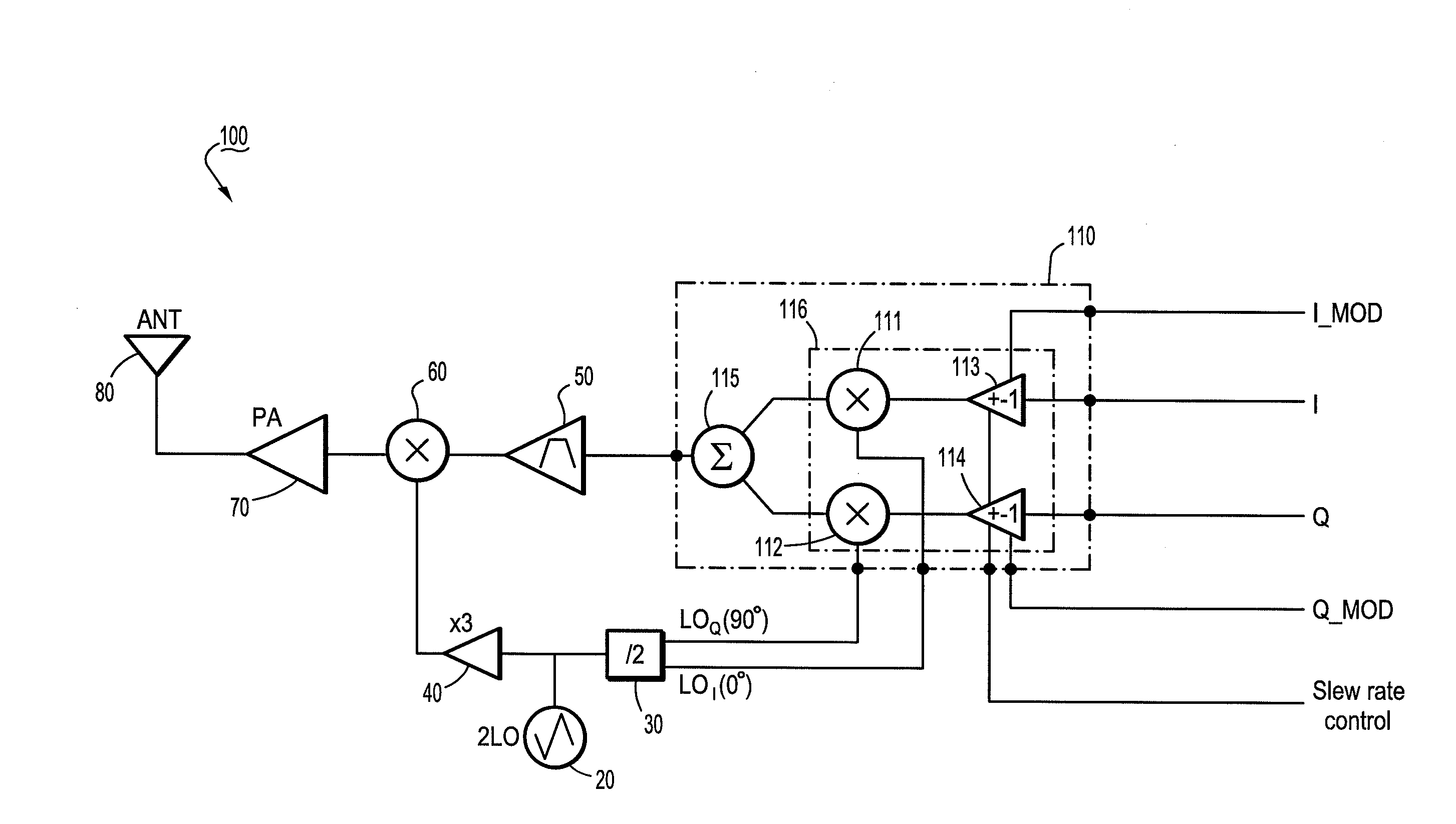
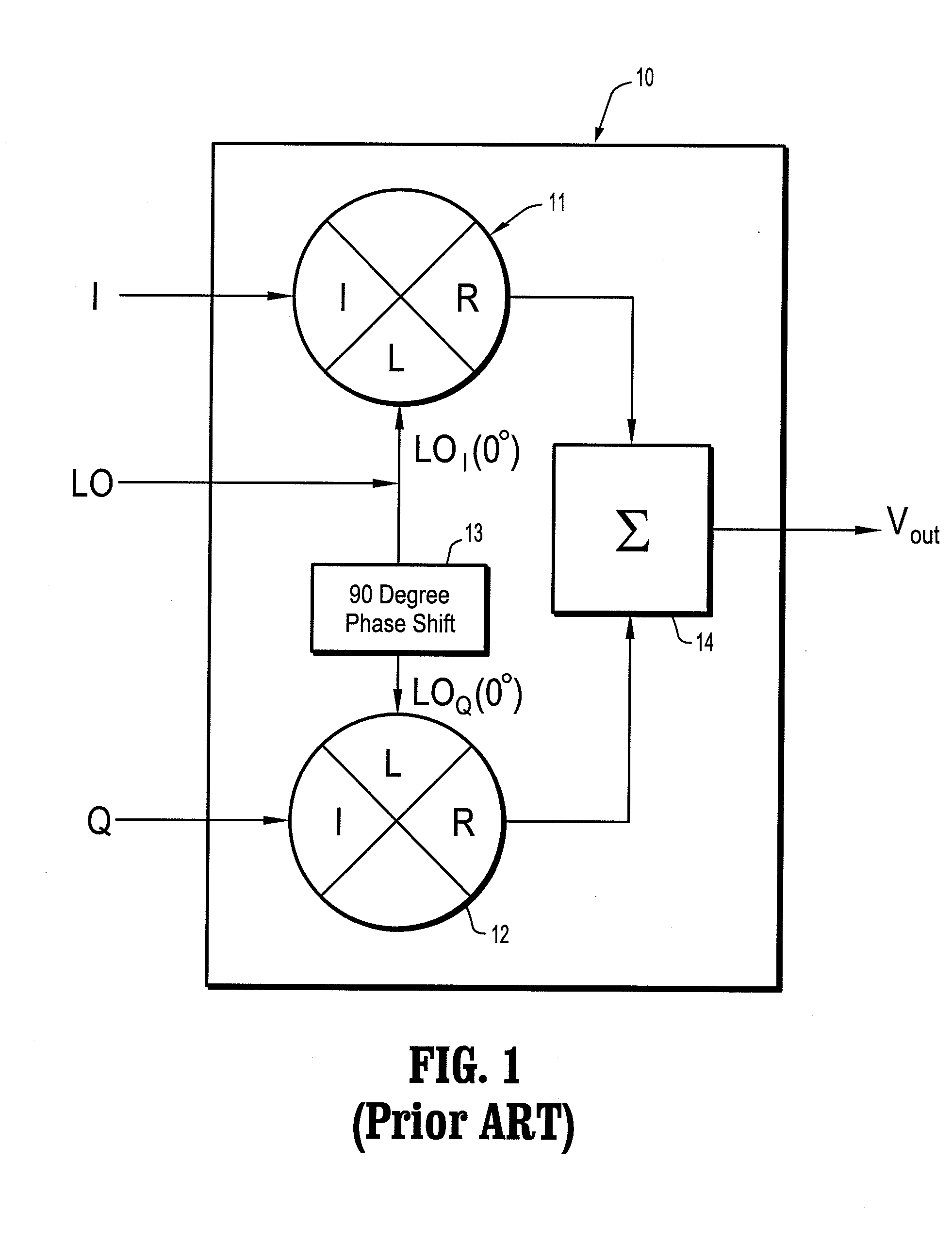
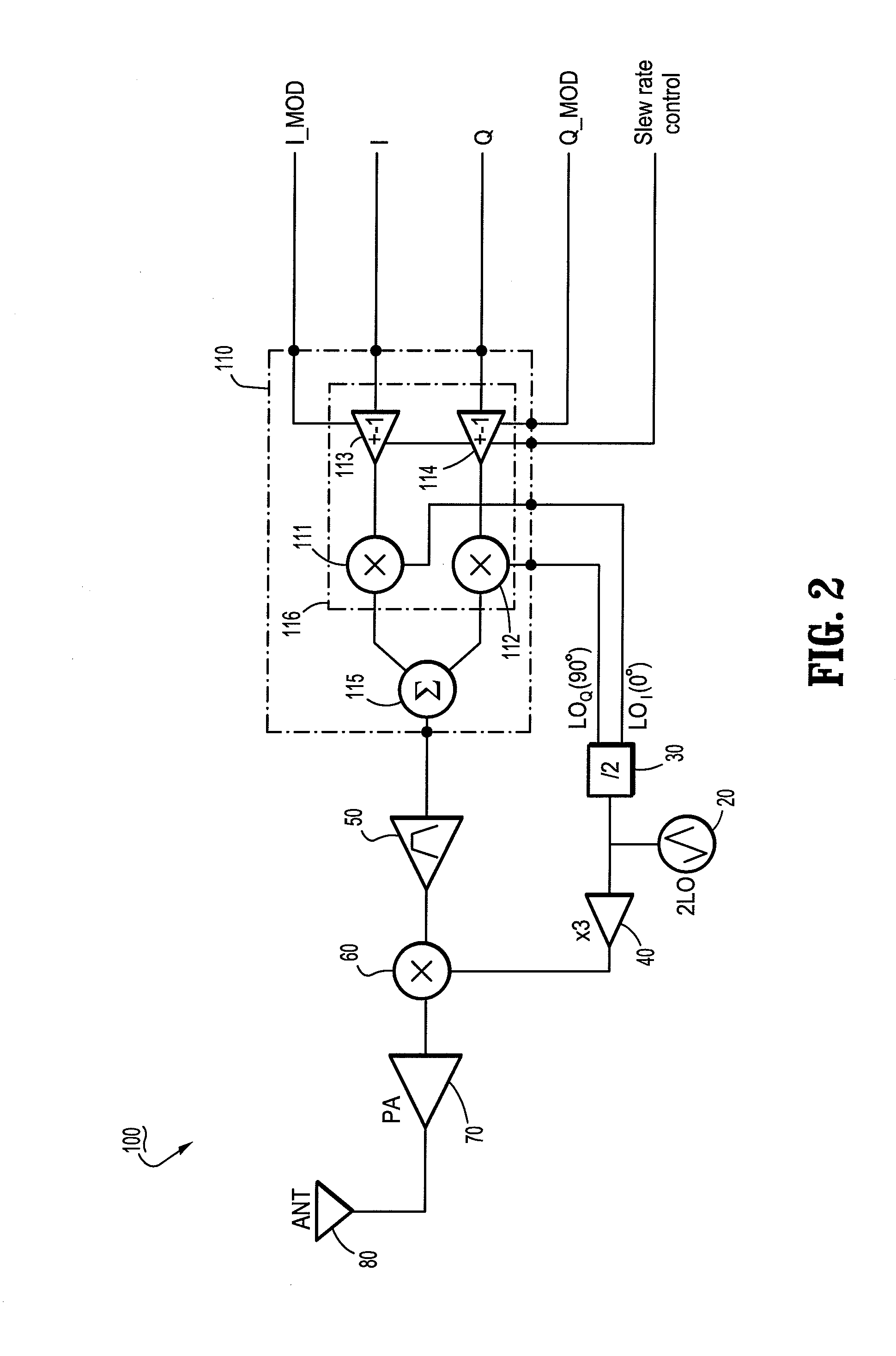
Quadrature modulation circuits and systems supporting multiple modulation modes at gigabit data rates
ActiveUS20100102895A1Minimizes spectral splatterModulation with suppressed carrierSignal channelsDigital dataQuadrature modulator
Quadrature modulation systems, circuits and methods are provided to support various modulation modes including ASK (amplitude shift key), FSK (frequency shift key) and PSK (phase shift key) modulation at high data rates (e.g., gigabit data rates). For example, a modulation circuit includes a mixer circuit including an integrated sign modulation control circuit and a plurality of mixer ports. The mixer ports include a first input port, a second input port, an output port and a sign modulation control port. The modulation circuit generates a modulated signal by operation of the mixer circuit multiplying a modulating signal applied to the first input port with a carrier signal applied to the second input port to generate a mixed signal output from the output port, and by operation of the integrated sign modulation control circuit controlling polarity switching of a signal at one of the mixer ports in response to a sign modulation control signal input to the sign modulation control port. The sign modulation control signal can be a digital data signal having binary data encoded into the modulated signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
Simultaneous full-duplex communication over a single electrical conductor
InactiveUS20070177679A1Reduce in quantityIncrease chanceOrthogonal multiplexData switching networksDigital dataElectrical conductor
Simple, inexpensive, general-purpose devices and methods achieve simultaneous, full-duplex and bi-directional communication of analog, digital or audio signals across a single conductor. “Sifudu” transceivers, which stands for “simultaneous and full-duplex,” reduce the number of cables necessary for transferring information between two or more terminals at a given rate, and / or facilitate information transfer at a higher rate than traditional circuits across the same number of cables. The transceivers can accomodate both digital and analog signals of arbitrary polarity. Since a sifudu circuit is capable of transmitting analog signals, it is also capable of transmitting digital signals in frequency, phase, or amplitude shift keyed form, thus opening the possibility of realizing higher baud rate than other simultaneous bidirectional communication systems that transfer digital data only, one bit at a time in each direction. The system not only allows one terminal to talk to more than one other terminals at a time, since there is no designated master or slave, any terminal can take on the role of the transmitter or the receiver, or both any time. The transceivers can also be connected into a multi-terminal network configurations including chain, star, tree, woods topologies, alone or in combination.
Owner:SOVENYI SZABOLCS
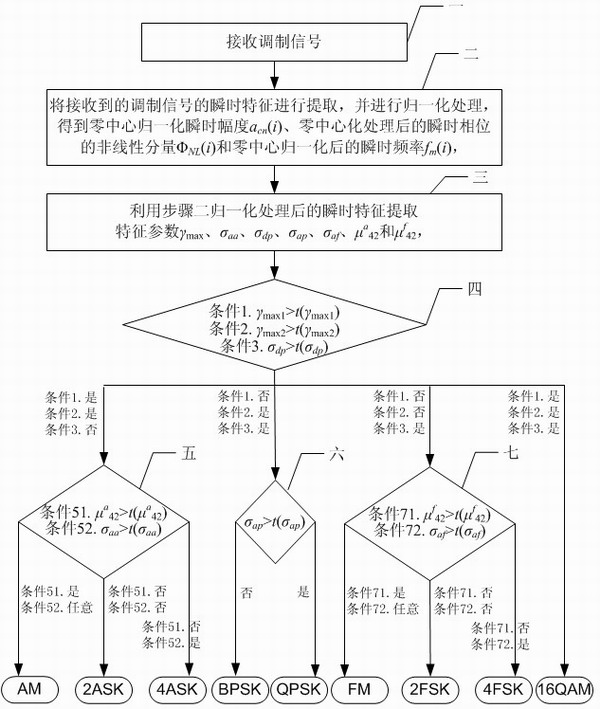
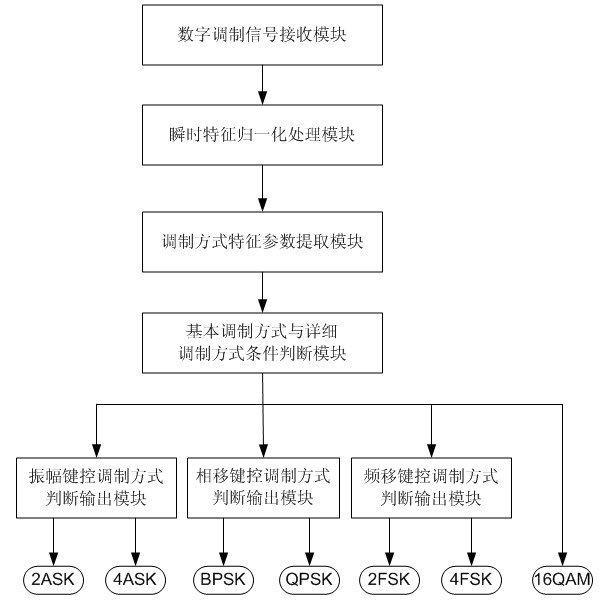
Analog-digital mixing modulation recognition device and digital modulation recognition device based on parallel judgment
InactiveCN101834819AImprove recognition accuracyAvoid the problem of order of useModulated-carrier systemsPattern recognitionPhase shifted
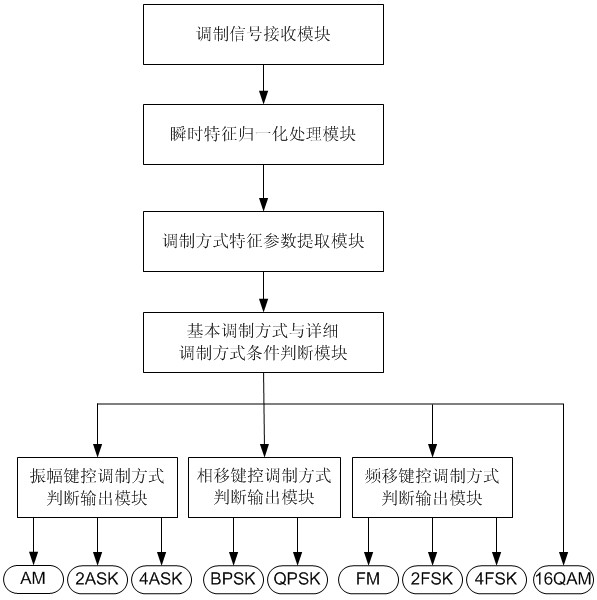
The invention discloses an analog-digital mixing modulation recognition device and a digital modulation recognition device based on parallel judgment, belonging to the communication field. The invention aims to solve the problems of low precision rate and long recognition time for providing a judgment tree by A.K. N and E.E.A zzouz. The invention is characterized in that the parallelly judged analog-digital mixing modulation recognition device comprises the following steps: a modulation signal receiving module coarsely classifies the received modulation signals through an instantaneous characteristic normalization module and a modulation mode characteristic parameter extraction module, and then the received modulation signals are particularly classified through an amplitude shift keying modulation judgment ouput module, a phase shift keying modulation judgment output module and a frequency shift keying modulation judgment output module. Compared with the analog-digital mixing modulation recognition device, the digital modulation signals received by the digital modulation recognition device based on parallel judgment have different inner structures of the modules when coarse classification and particular classification are conducted.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Receiving/backscattering arrangement and method with two modulation modes for wireless data transmission as well as modulation arrangement therefor
ActiveUS20040145452A1Guaranteed uptimeEfficient amplitude shiftSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationElectric signal transmission systemsVoltage multiplierMethod selection
For transmitting data, a receiving / backscattering arrangement receives, modulates and reflects or backscatters electromagnetic waves emitted by a base station. The modulation corresponds to the data to be transmitted and is carried out selectively using first and / or second different modulation methods depending on the received field strength of the received electromagnetic waves. Preferably, phase shift keying is used especially or at least at low field strengths at far range, while amplitude shift keying is used additionally or alternatively for high field strengths at close range. The two modulation methods can be superimposed. A circuit arrangement includes two different modulator arrangements to perform the two modulation methods depending on the received field strength. The second modulator arrangement preferably comprises a multi-stage voltage multiplier circuit with a modulated switching device intervening in one of the stages to achieve the modulation.
Owner:ATMEL GERMANY +1
Multi-band interconnect for inter-chip and intra-chip communications
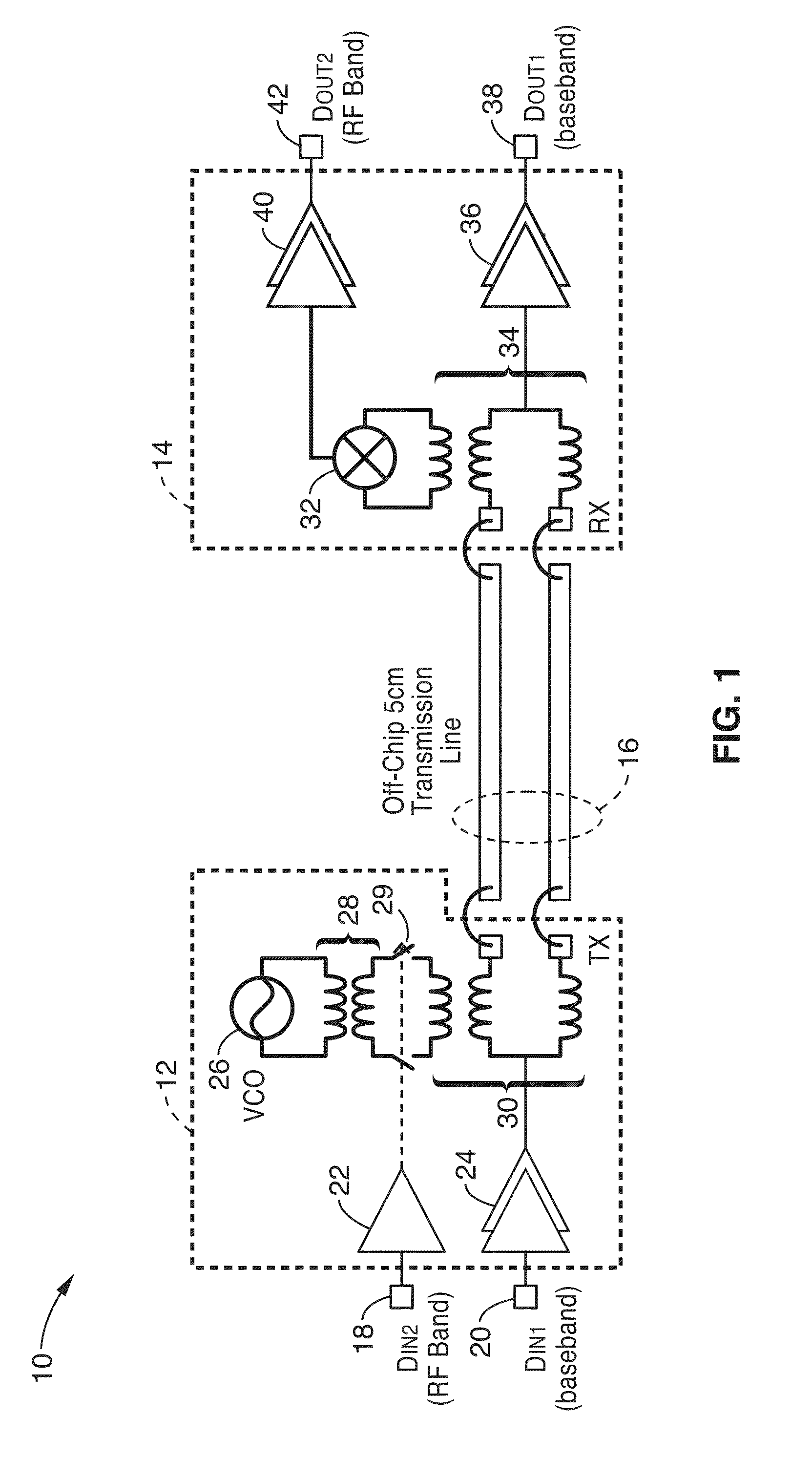
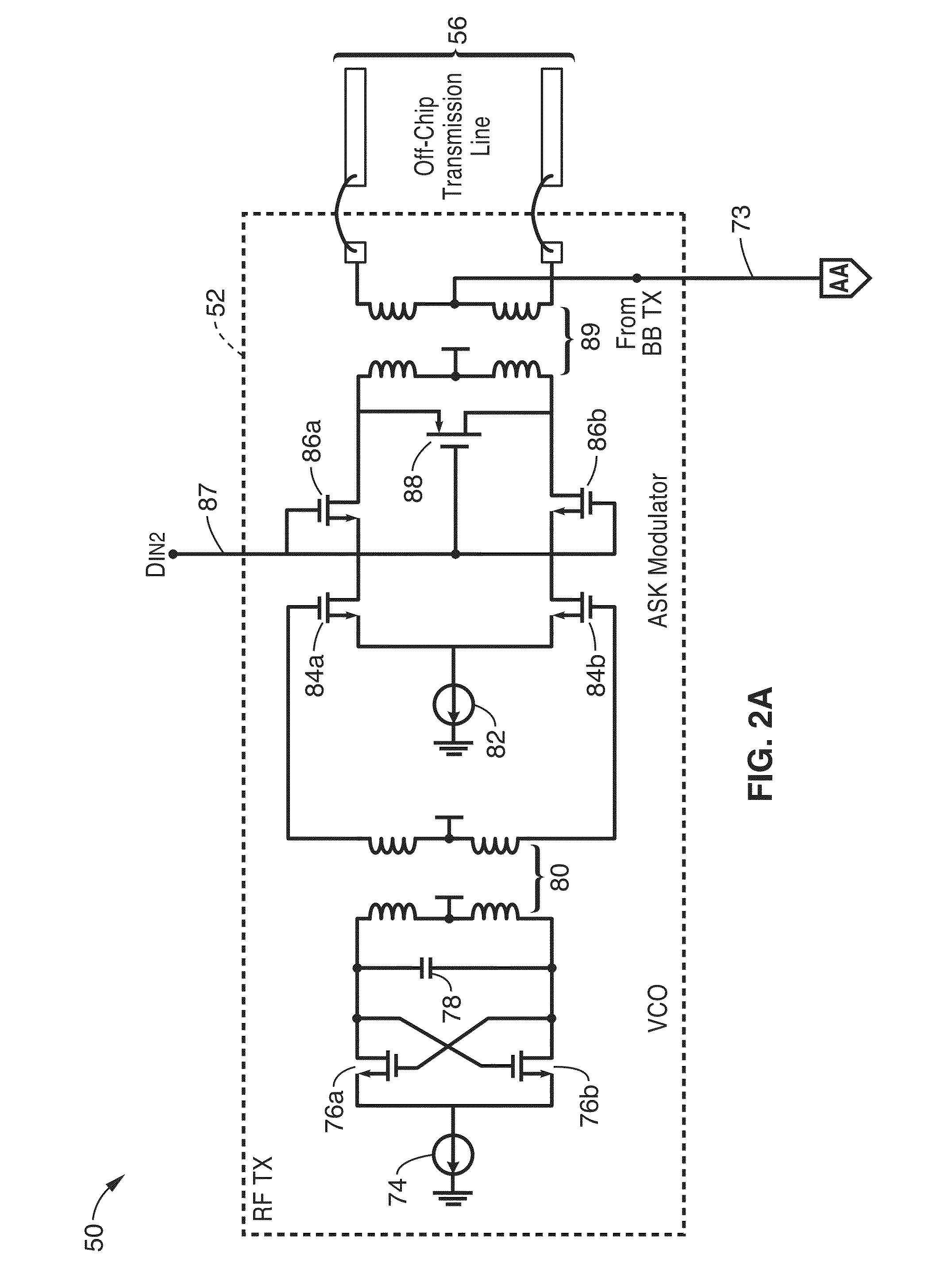
Systems, apparatus, modules, and methods of communicating with memory devices utilizing multi-band communication containing a baseband and one or more amplitude shift keyed (ASK) RF channels over each differential pair of off-chip transmission lines. Configurations are described for interfacing between microprocessors, or controllers and memory devices or modules, and within a DIMM and its DRAM devices, and between multiple DIMM memory modules.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
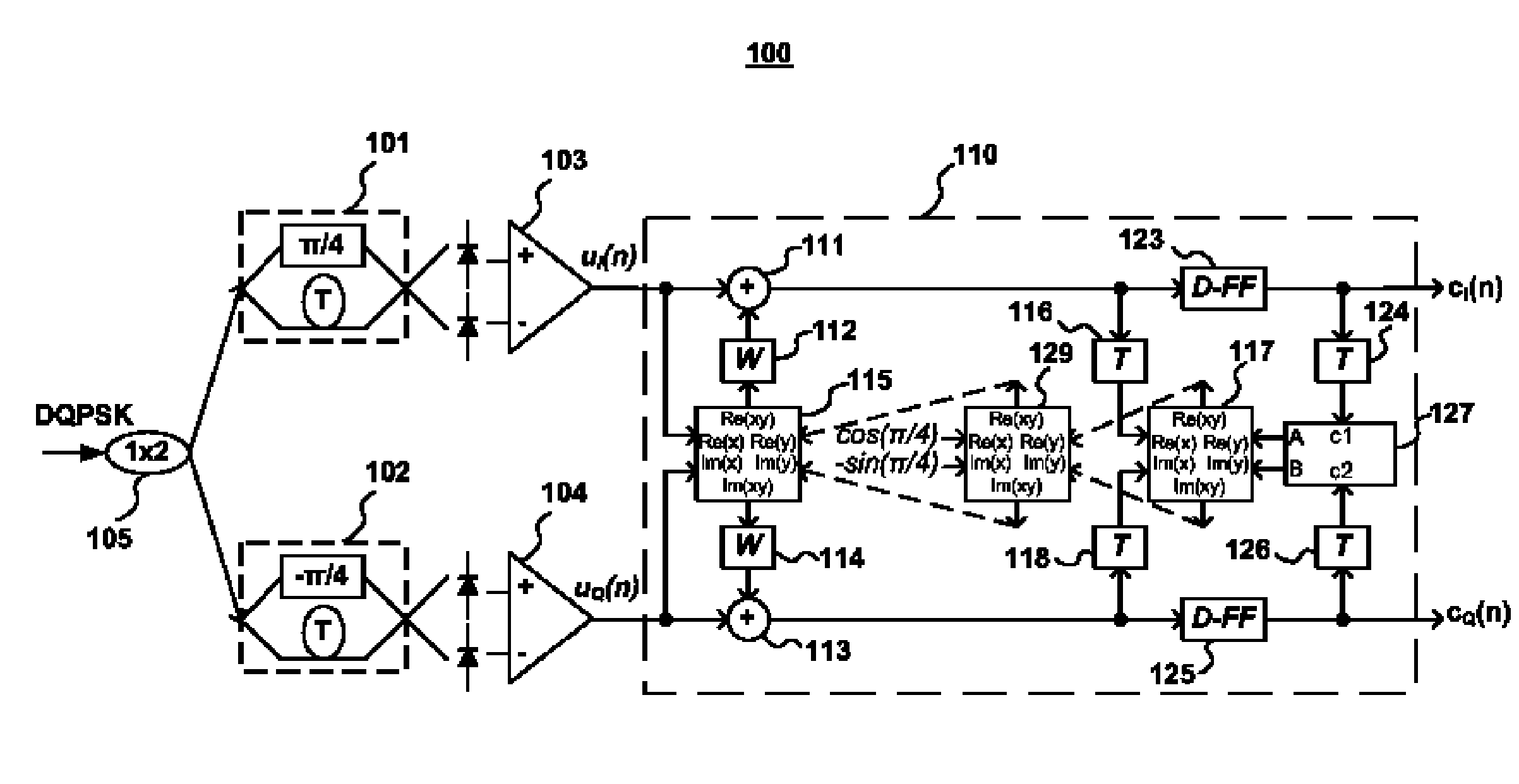
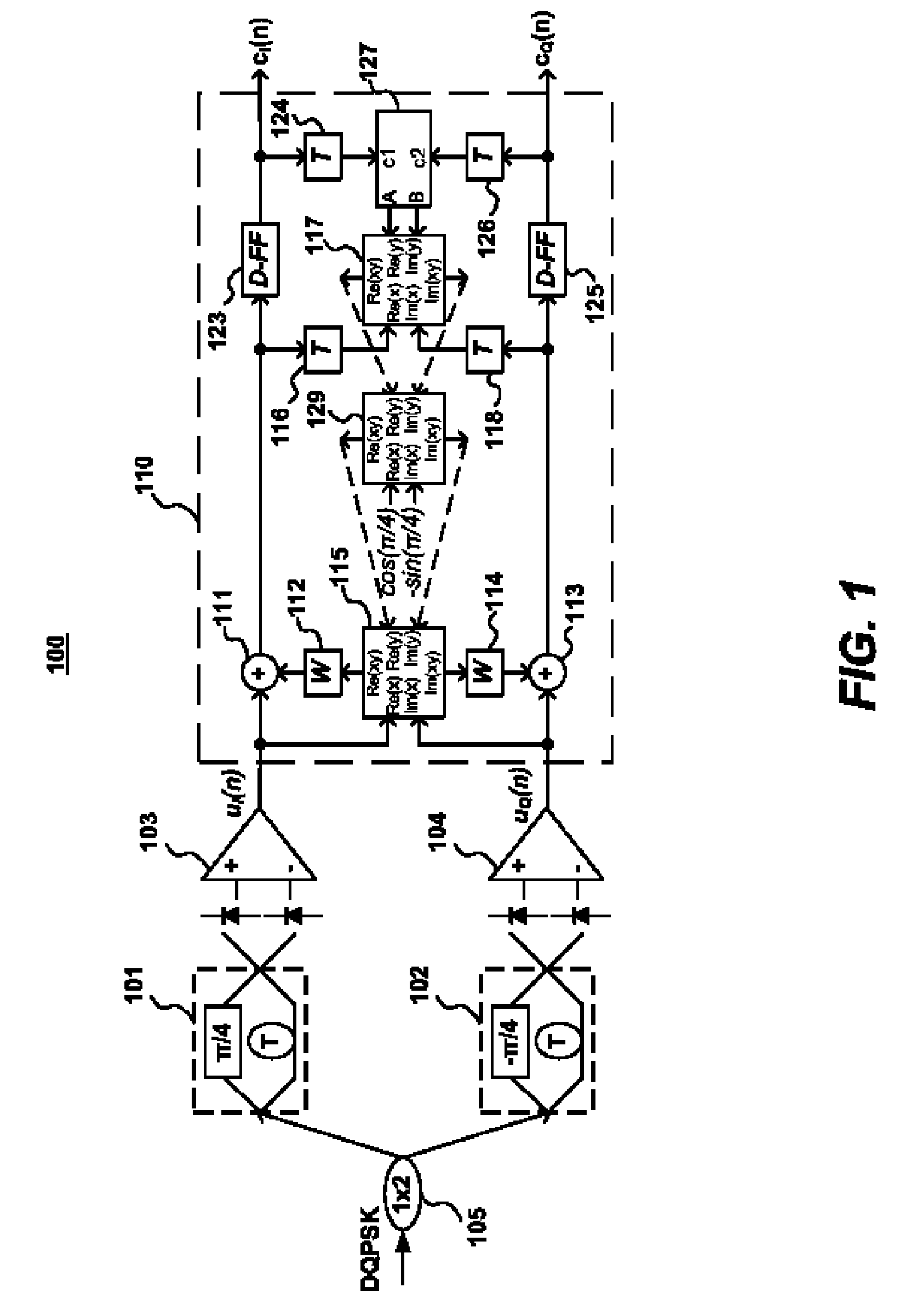
Data-aided multi-symbol phase estimation for optical differential multilevel phase-shift keying signals
InactiveUS7623796B2Reduce detectionMore spectrally efficientElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversTelecommunicationsData aided
A data-aided, multi-symbol phase estimation (MSPE) scheme is described for improving receiver sensitivity in the direct-detection of optical differential multi-level phase-shift keying (ODmPSK) signals including optical differential quadrature phase-shift keying (ODQPSK) signals, ODQPSK signals with amplitude shift keying (ODQPSK+ASK), optical differential 8-level phase-shift keying (OD8PSK) signals with eight phase levels, and optical differential phase-shift keying signals with more than eight phase levels. The use of data-aided MSPE substantially reduces the “differential detection penalty,” with receiver sensitivity approaching that of coherent detection schemes.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Method for reducing PAPR (Peak To Average Power Ratio) under APSK (Amplitude Phase Shift Keying) constellation diagram
The invention provides a method for reducing a peak average power ratio (PAPR) under APSK (Amplitude Phase Shift Keying) constellation diagram mapping in OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) modulation. According to the method provided by the invention, as the amplitude of signals is limited on a time domain, when time domain signals are converted onto frequency domain constellation points, only the constellation points at an outer layer of the APSK are expanded, only the frequency domain constellation points expanding outwards are remained, and a process of time domain amplitude limitation-frequency domain selection expansion is iterated for a plurality of times. Therefore, the rate of occurring peak signals can be reduced, and the PAPR of the OFDM signals can be reduced. According to the algorithm, an expansion area and an expansion rule are designed under the APSK constellation diagram mapping, so that the error code property cannot be worsened under the APSK modulation. The method provided by the invention can be applied to an OFDM system under the APSK constellation diagram mapping, so that the effect of reducing the PAPR can be achieved well.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Receiving/backscattering arrangement and method with two modulation modes for wireless data transmission as well as modulation arrangement therefor
ActiveUS7151436B2Guaranteed uptimeEfficient amplitude shiftSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationElectric signal transmission systemsVoltage multiplierMethod selection
For transmitting data, a receiving / backscattering arrangement receives, modulates and reflects or backscatters electromagnetic waves emitted by a base station. The modulation corresponds to the data to be transmitted and is carried out selectively using first and / or second different modulation methods depending on the received field strength of the received electromagnetic waves. Preferably, phase shift keying is used especially or at least at low field strengths at far range, while amplitude shift keying is used additionally or alternatively for high field strengths at close range. The two modulation methods can be superimposed. A circuit arrangement includes two different modulator arrangements to perform the two modulation methods depending on the received field strength. The second modulator arrangement preferably comprises a multi-stage voltage multiplier circuit with a modulated switching device intervening in one of the stages to achieve the modulation.
Owner:ATMEL GERMANY +1
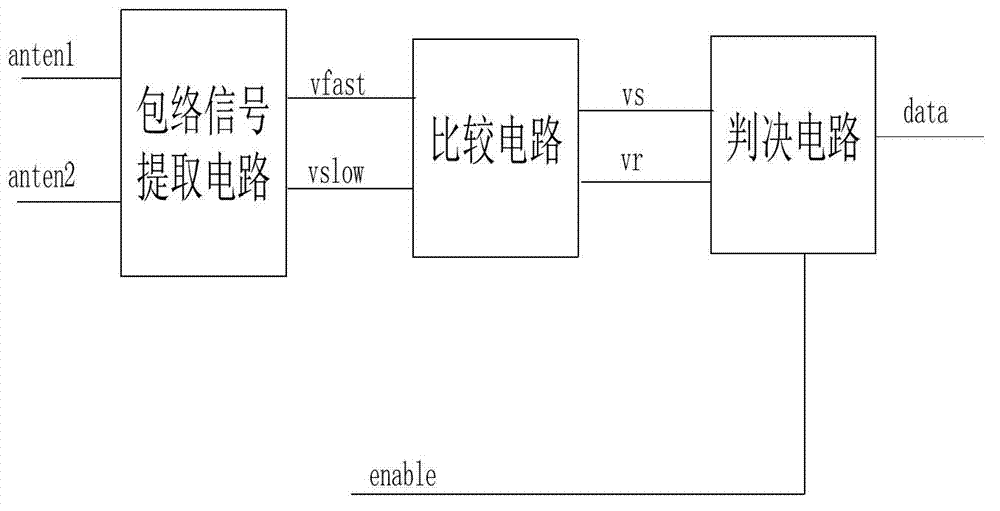
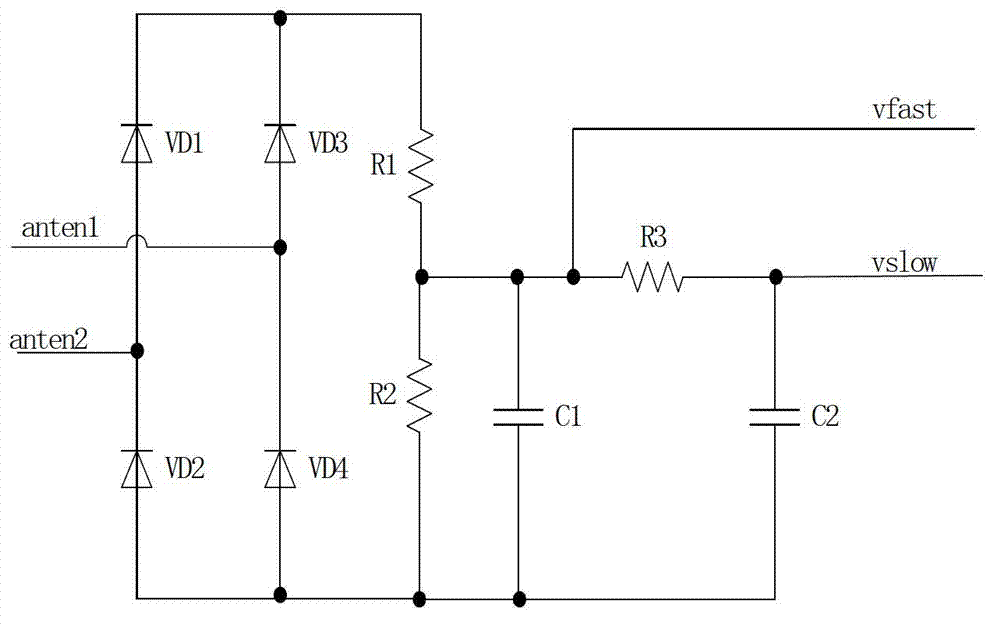
ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) demodulation circuit with wide demodulation range used for passive RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) label chips
InactiveCN102810180AAvoid influenceHigh precisionRecord carriers used with machinesDecision circuitSignal on
The invention discloses an ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) demodulation circuit with a wide demodulation range used for passive RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) label chips. The ASK demodulation circuit comprises an envelope signal extraction circuit, a comparison circuit and a decision circuit, wherein the envelope signal extraction circuit is used for extracting two antenna voltage signals received by the RFID label chip to obtain two antenna envelope signals including a fast varying envelope signal and a slowly varying envelope signal; the comparison circuit is used for comparing the sampling voltages of the two antenna envelope signals outputted by the envelope signal extraction circuit to obtain envelope changing edges of the antenna envelope signals; the decision circuit is used for deciding the output voltage of the comparison circuit to obtain and output demodulation data. According to the ASK demodulation disclosed by the invention, the influence of overshoot of the antenna envelope signals on the demodulation circuit is completely eradicated, the precision of the demodulation circuit is improved, an ASK demodulation signal of which the depth is 7%-100% can be demodulated, and the demodulation circuit has stronger anti-noise performance, and can be widely applied in the passive RFID label chips.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SYSUR MICROELECTRONICS
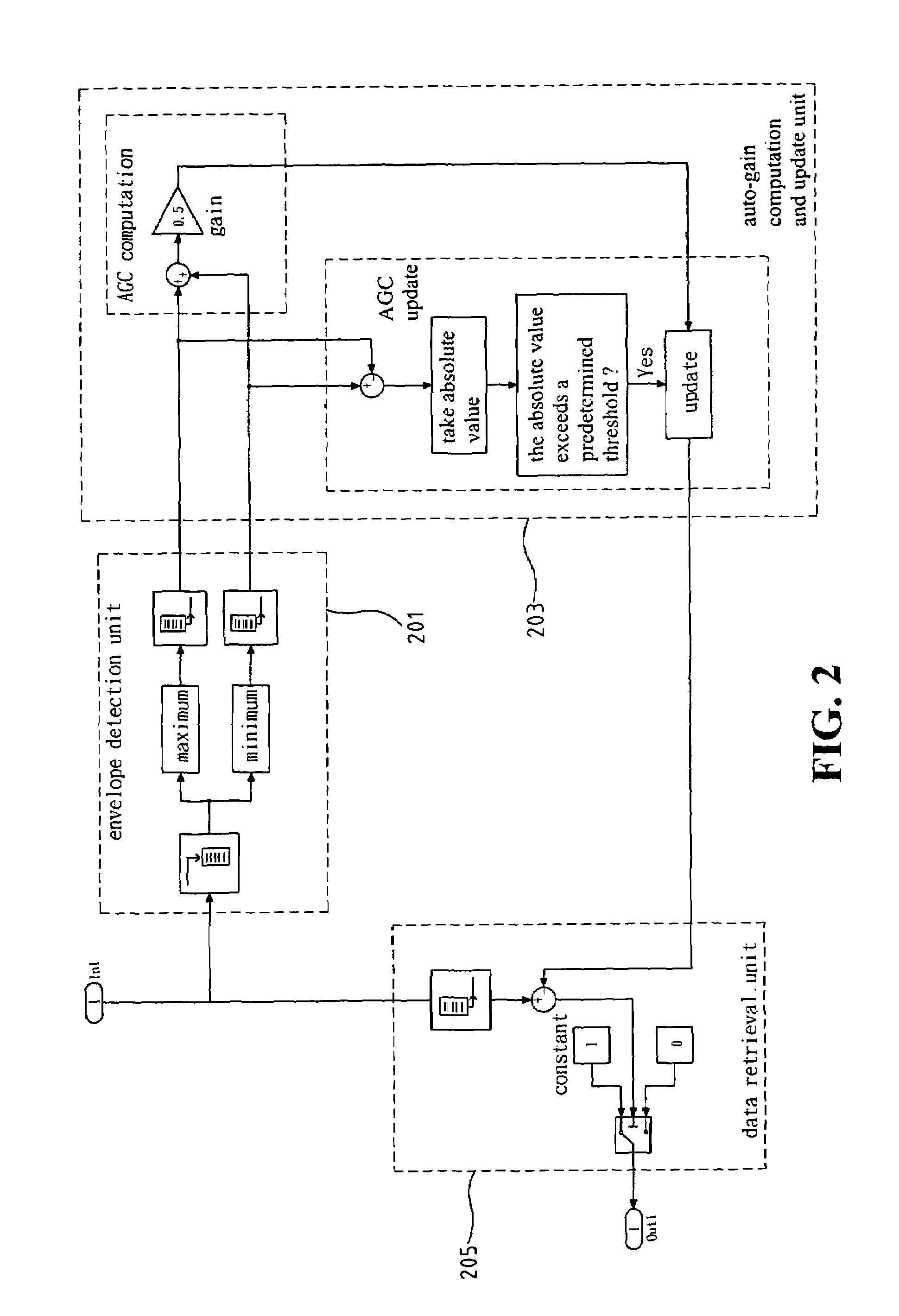
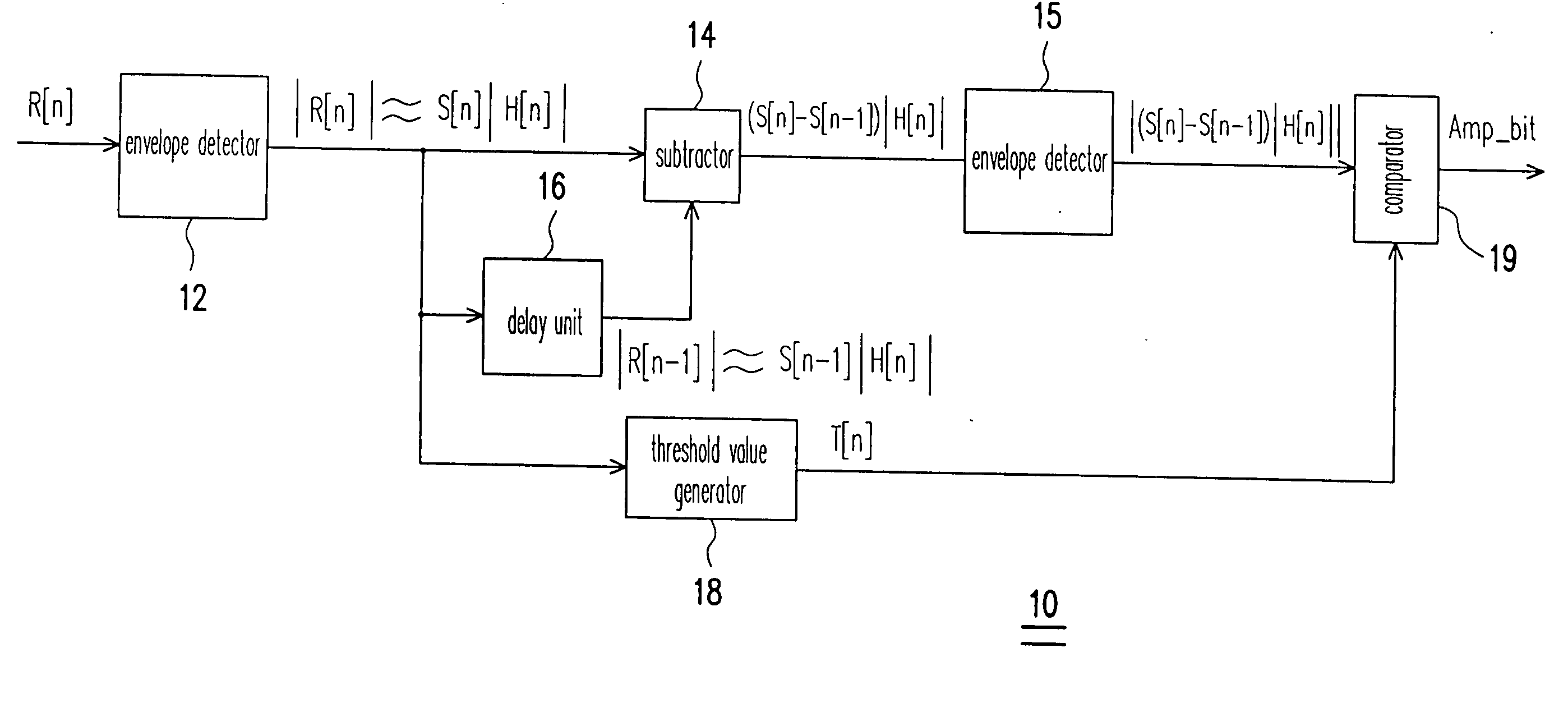
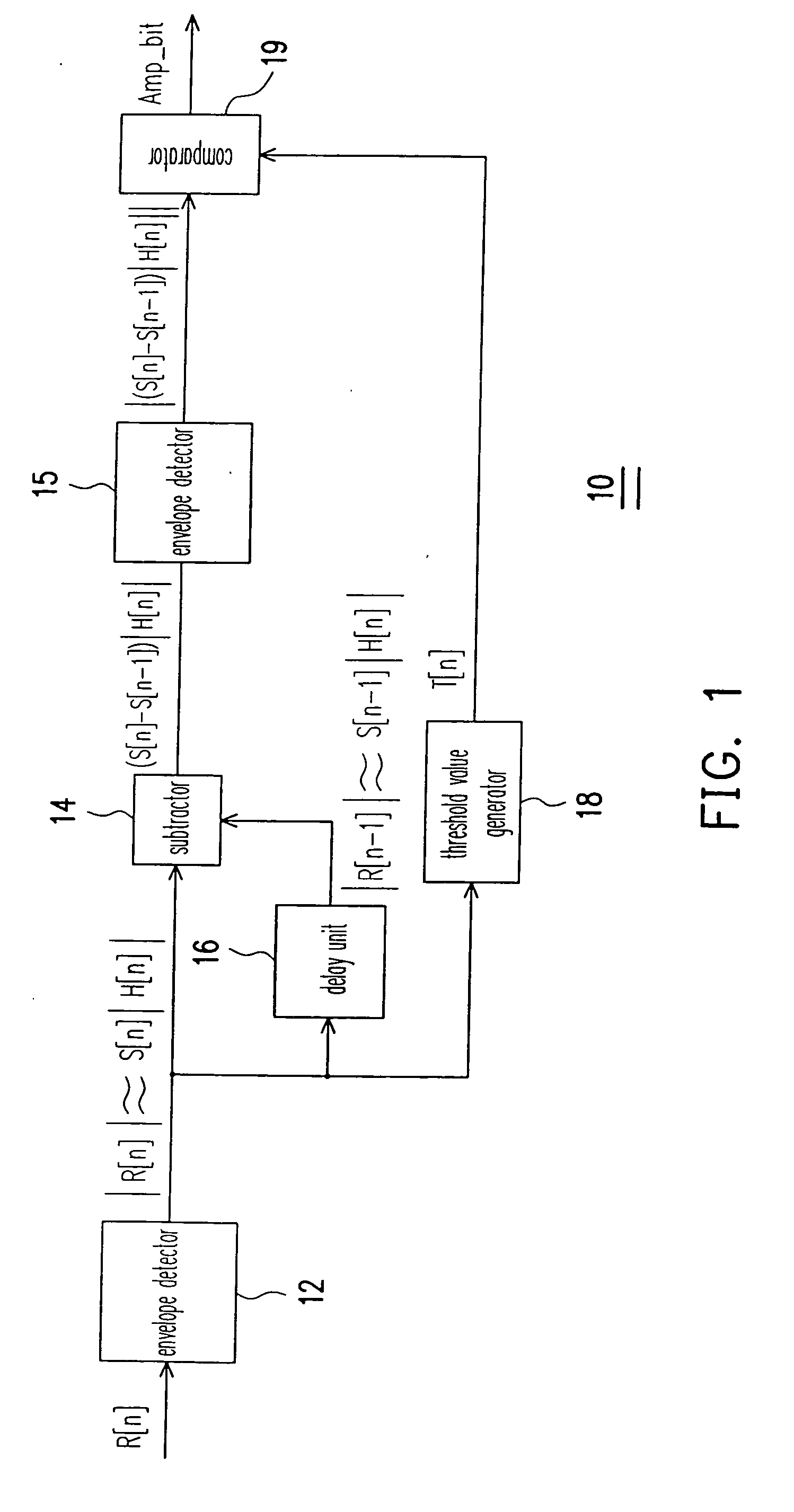
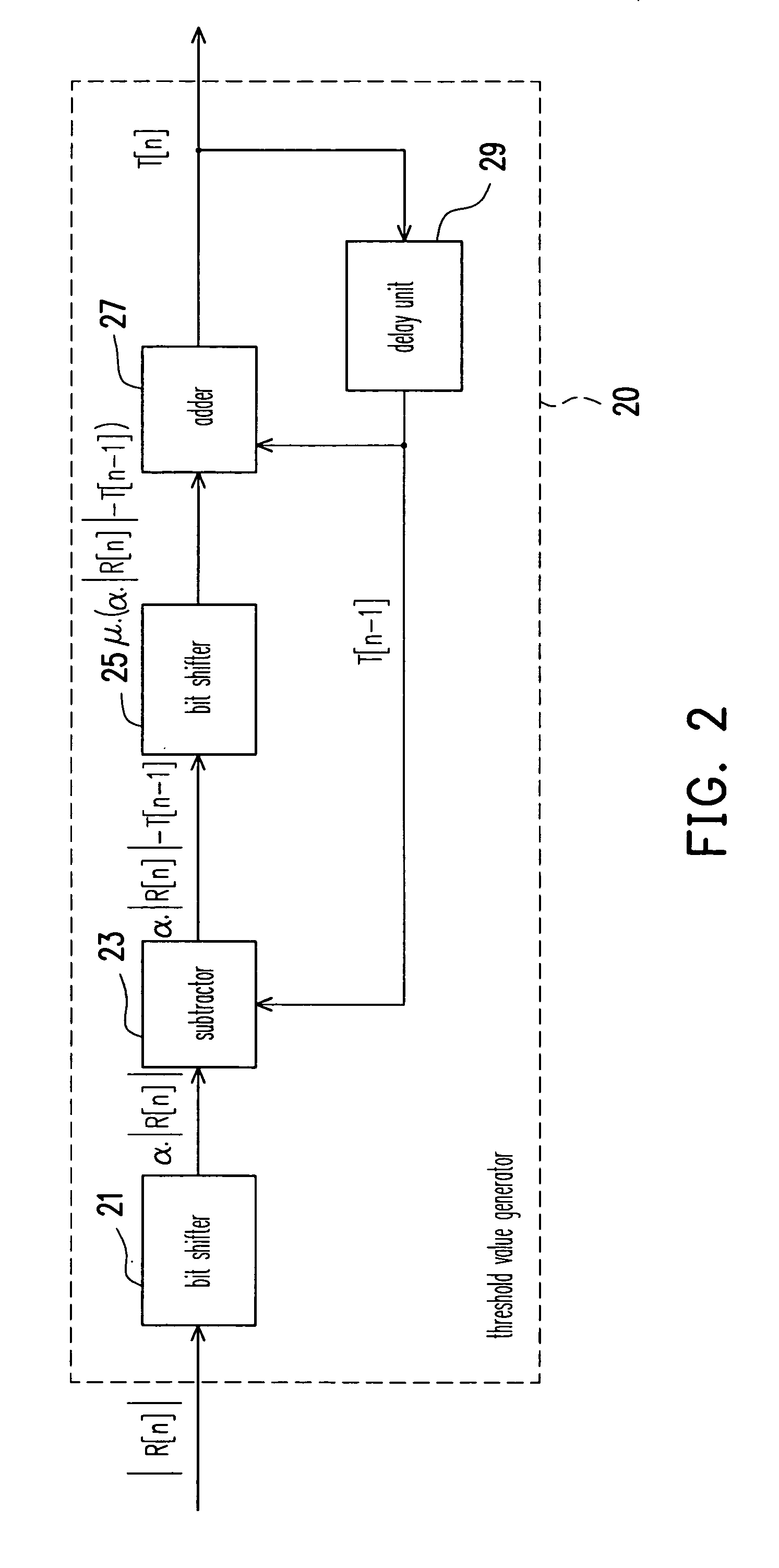
Communication system with demodulation of two-level differential amplitude-shift-keying signals
InactiveUS20070076820A1Simplify complexityImprove performanceFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationAmplitude demodulation detailsCommunications systemDemodulation
A structure and method for demodulating two-level differential amplitude-shift-keying signals using simple adding operations are provided. Threshold values are dynamically adjusted according to the channel response. By comparing the threshold values and the differential amplitude values, it can be found whether the amplitude of the received signal is changed. Furthermore, it no needs to know the changed value of received signal amplitudes and the differential two-level amplitude-shift-keying signals can be demodulated by just detecting whether the amplitude of the received signal is changed. By this idea, the complexity of the receiver implementation is simplified and the demodulator can get better performance.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
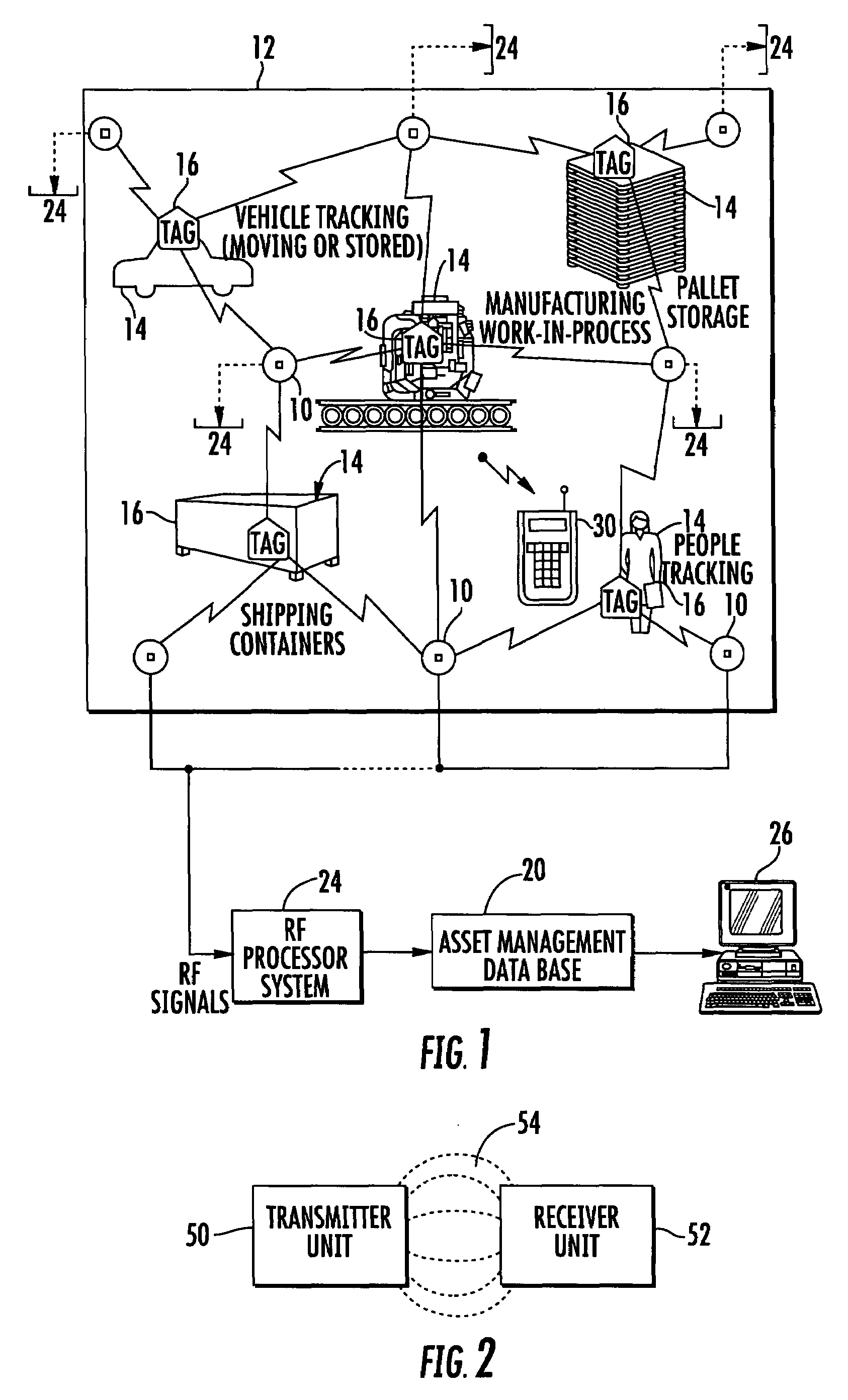
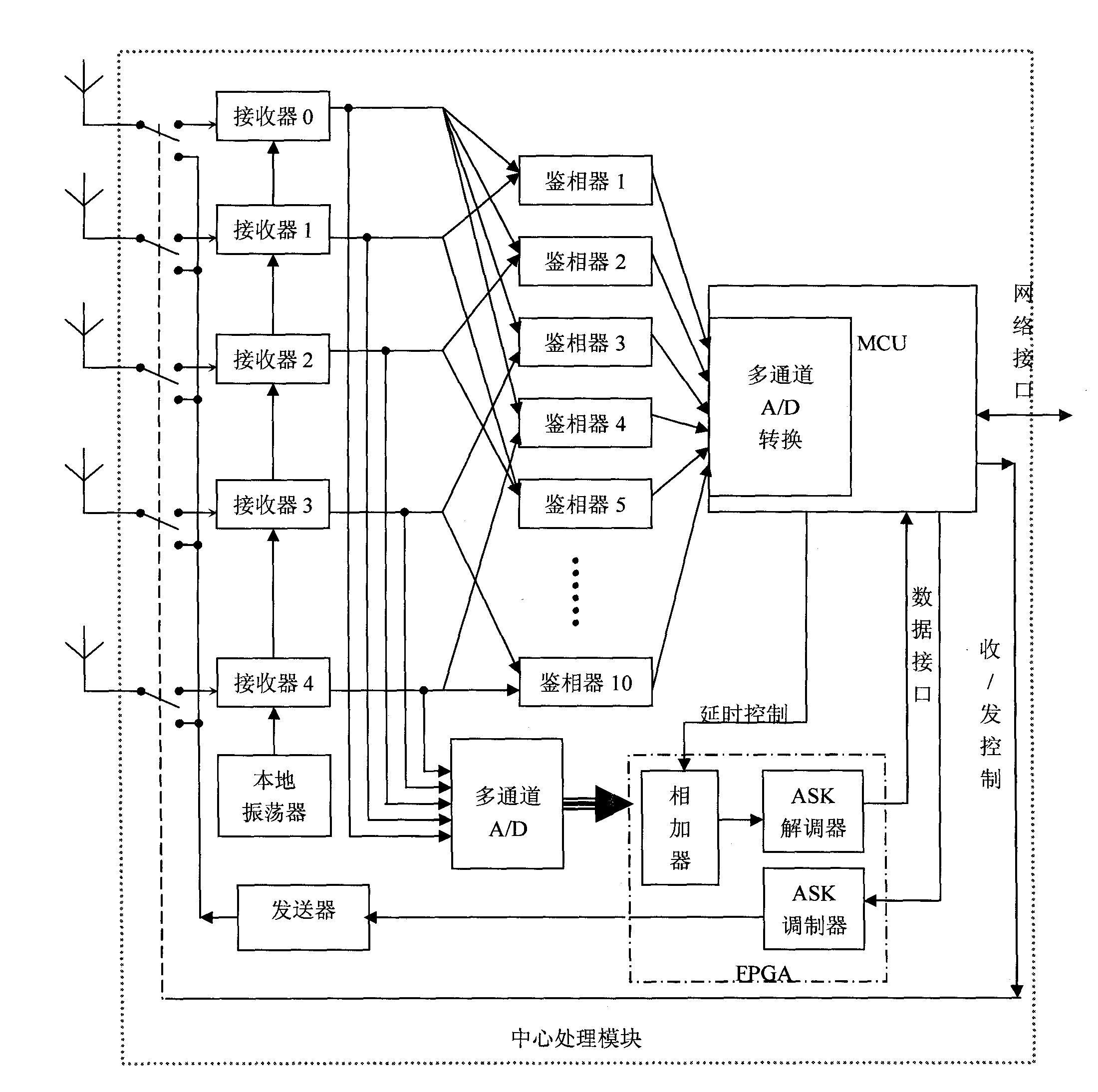
High-precision local wireless positioning system
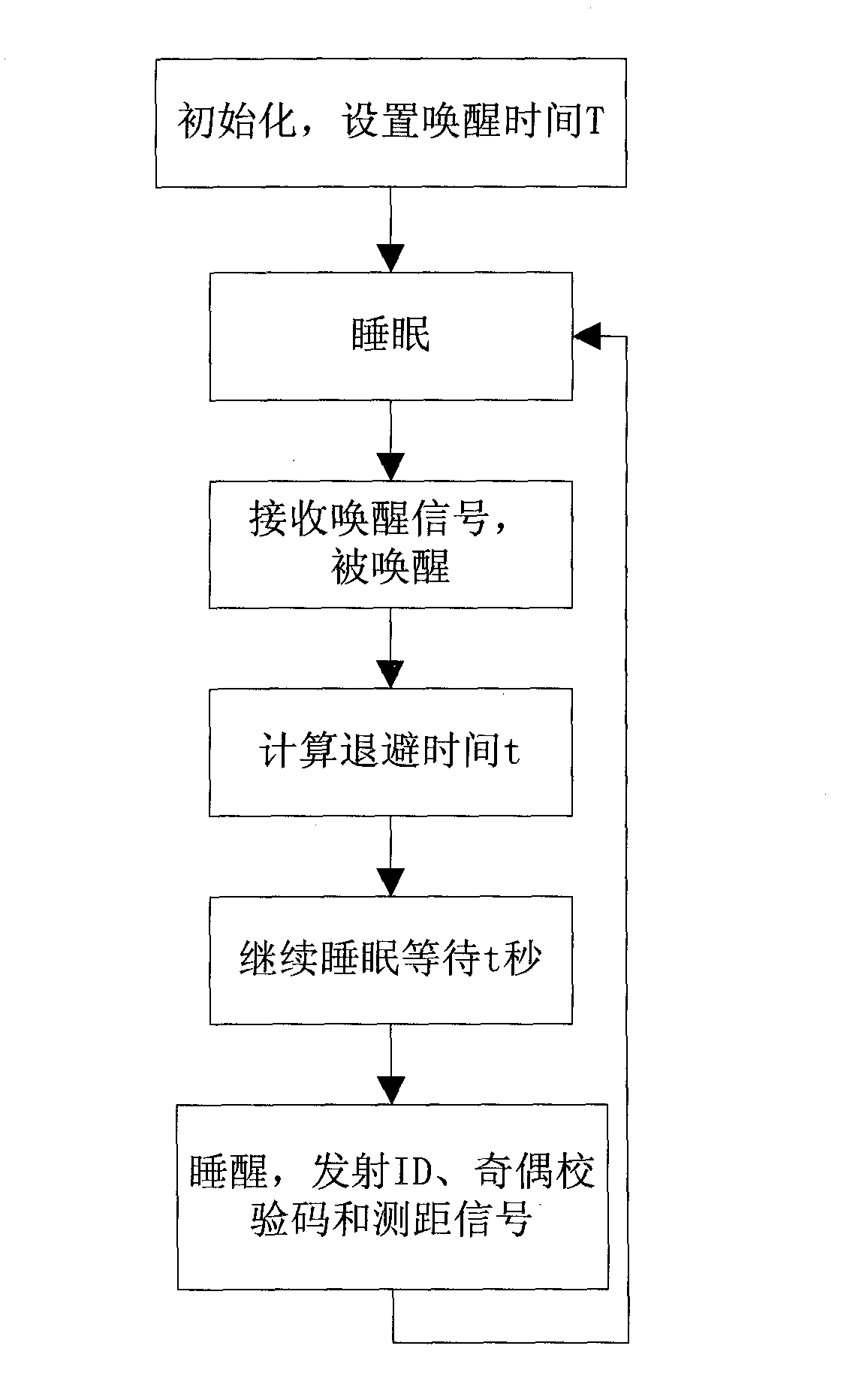
The invention discloses a high-precision local wireless positioning system which comprises anchor nodes, a positioned destination node and a central processing module, wherein the anchor nodes comprise a vertex anchor node and a central anchor node, the vertex anchor node is allocated on the vertex of a polygon on the edge of a positioned region, the central anchor node is abutted against the central processing module arranged at the center of the polygon, and each anchor node is respectively connected with the central processing module; the positioned destination node is in a sleep state in normal times, and when the node needs to be positioned, the positioned destination node is aroused, emits a wireless signal which is modulated through an ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) modulator, and then continues to sleep until being aroused the next time; and a plurality of groups of arrival time differences are obtained through the demodulation and phase discrimination processing of the anchor modes on the wireless signal and the relevant operation based on a received signal phase difference, and then the position of the positioned node is determined according to the position relation between the anchor nodes. The invention can realize the high-precision positioning within a local range (100-meter radius), and the power consumption of the positioned destination node is low.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Data-aided multi-symbol phase estimation for optical differential multilevel phase-shift keying signals
InactiveUS20070201879A1Reduction in differential detection penaltyReduce detectionElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversDifferential phaseData aided
A data-aided, multi-symbol phase estimation (MSPE) scheme is described for improving receiver sensitivity in the direct-detection of optical differential multi-level phase-shift keying (ODmPSK) signals including optical differential quadrature phase-shift keying (ODQPSK) signals, ODQPSK signals with amplitude shift keying (ODQPSK+ASK), optical differential 8-level phase-shift keying (OD8PSK) signals with eight phase levels, and optical differential phase-shift keying signals with more than eight phase levels. The use of data-aided MSPE substantially reduces the “differential detection penalty,” with receiver sensitivity approaching that of coherent detection schemes.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Amplitude shift keying (ASK)/on-off keying (OOK) radio frequency (RF) receiving circuit
InactiveCN102064841AImprove dynamic rangeImprove anti-interference abilityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsBandpass filteringCapacitance
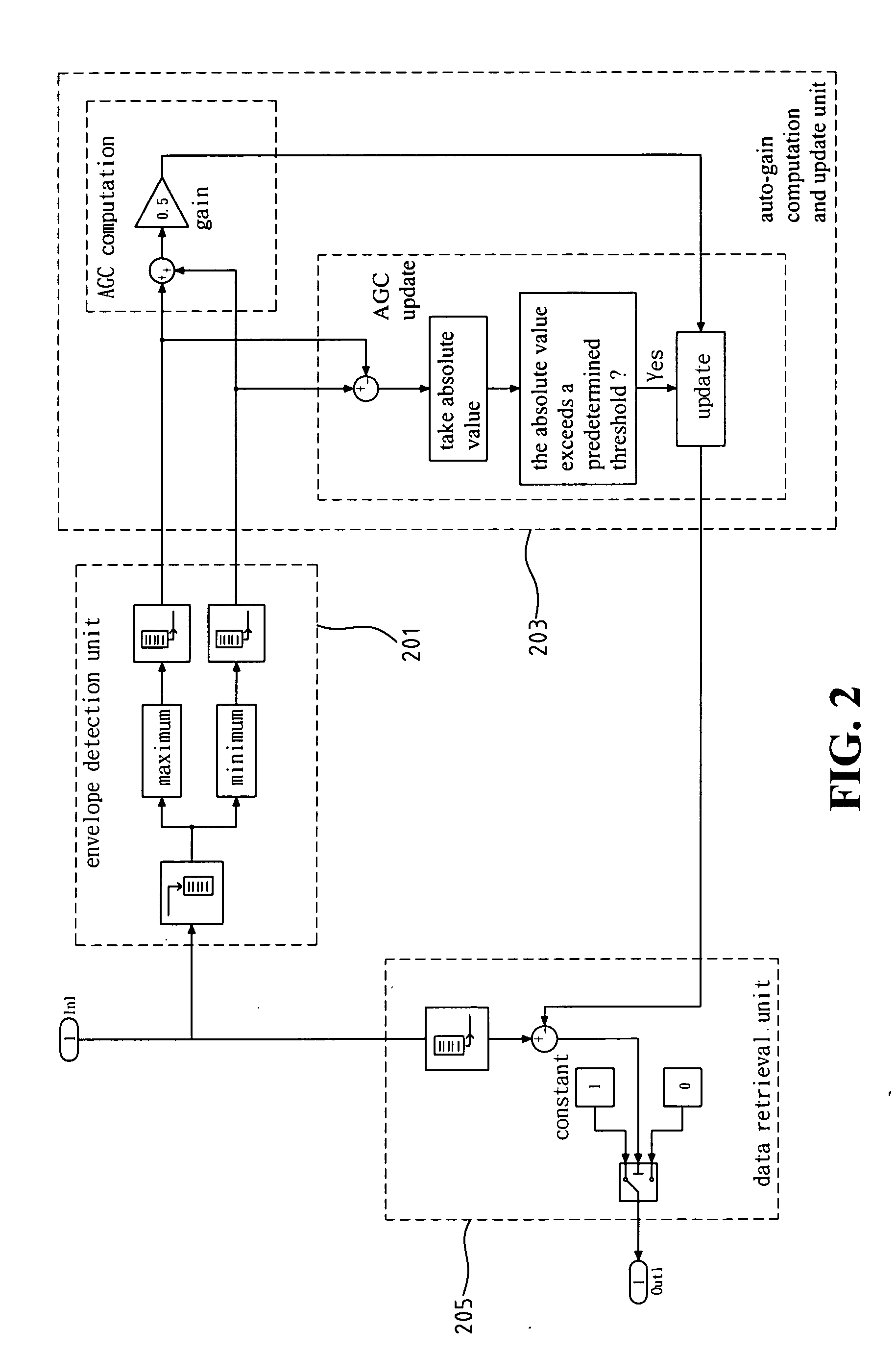
The invention provides an amplitude shift keying (ASK) / on-off keying (OOK) radio frequency (RF) receiving circuit. The receiving circuit is characterized in that after a low noise amplifier amplifies the received signal, the amplified received signal and local oscillation generated by an oscillator are jointly input into a mixer; the mixer reduces the frequency output by the low noise amplifier to intermediate frequency; the intermediate frequency signal output by the mixer is demodulated and output by a peak detection module after being amplified by a primary intermediate frequency amplifier, filtered by an intermediate frequency bandpass filter and amplified by a secondary intermediate frequency amplifier; a charge pump is driven after the peak detection output potential is compared with the fourth reference potential Vref4; the charge pump charges and discharges a capacitor to obtain gain control signals; the gain control signals are fed back to the low noise amplifier, the primary intermediate frequency amplifier and the secondary intermediate frequency amplifier to form an automatic gain control loop; and the low noise amplifier, the primary intermediate frequency amplifier and the secondary intermediate frequency amplifier respectively input the first, second and third reference potentials. The receiving circuit solves the problem of blocking during close range remote control, and meanwhile, the antijamming capability of the receiving circuit is improved and the cost is saved.
Owner:HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS
Actively regulated modulation index for contactless IC devices
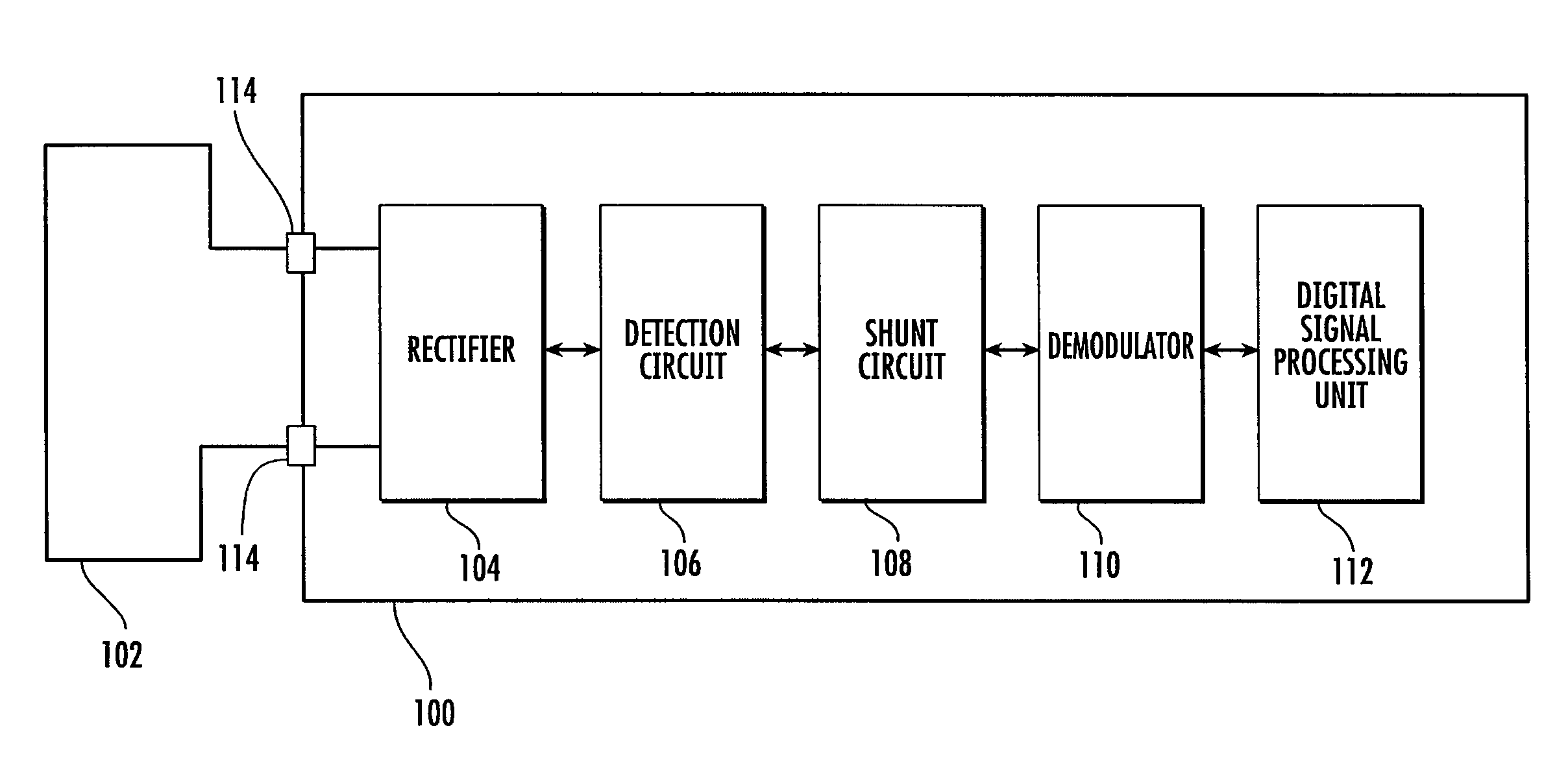
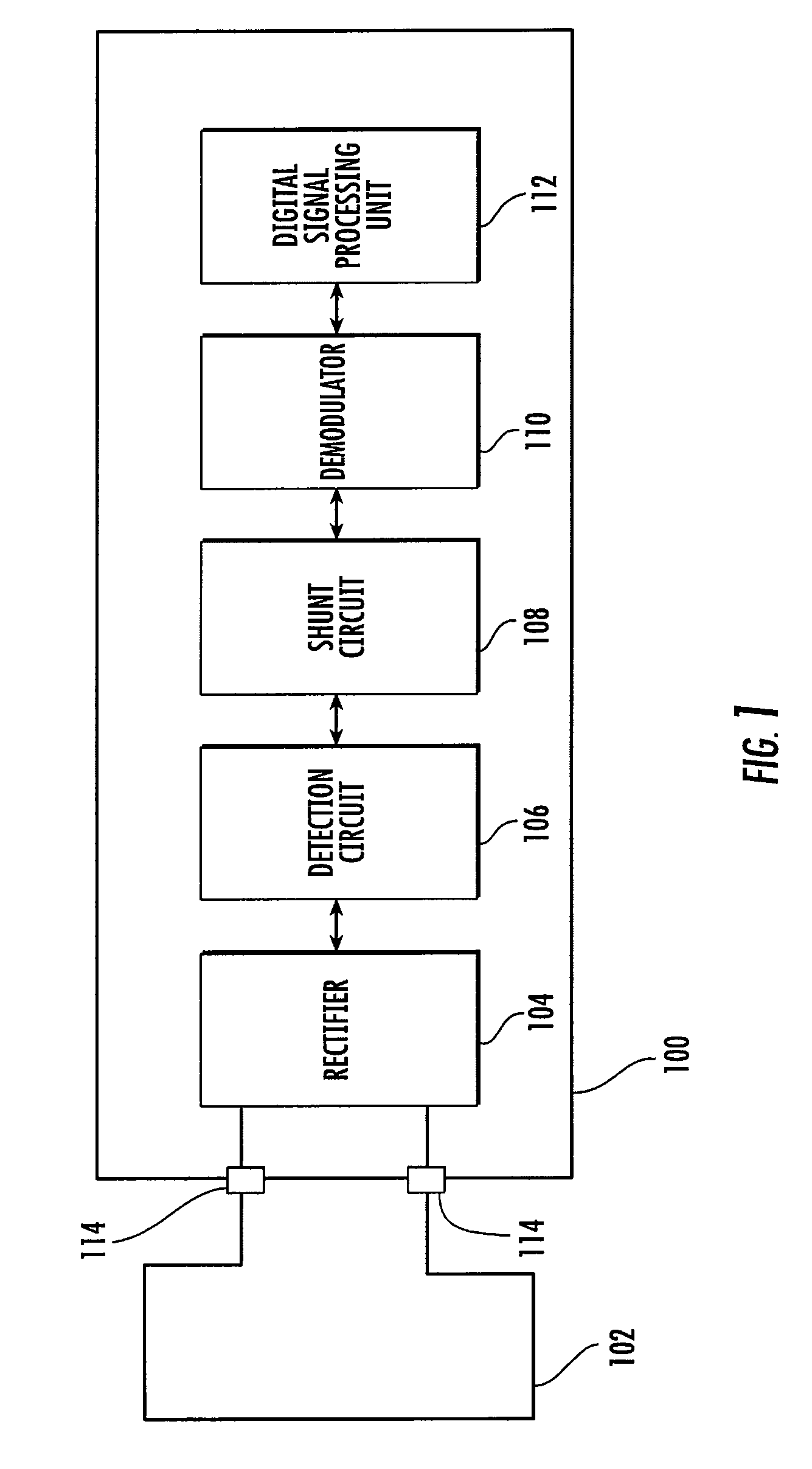
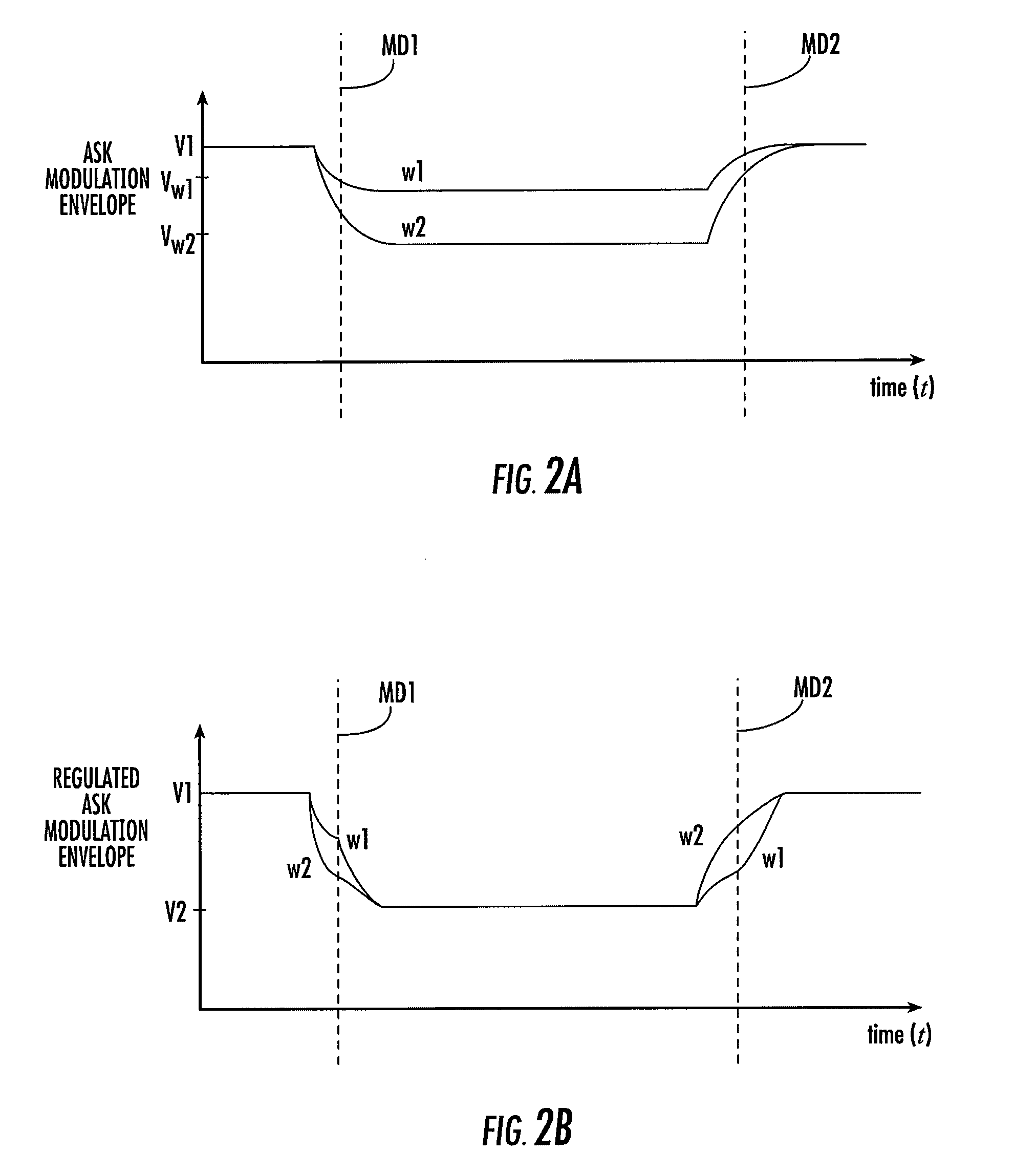
ActiveUS7971794B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsSensing record carriersDigital dataCarrier signal
A contactless IC device including a detection circuit configured to detect a carrier wave that has been amplitude shift-keying (ASK) modulated with digital data and a shunt circuit configured to regulate the carrier wave to a predetermined voltage level.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
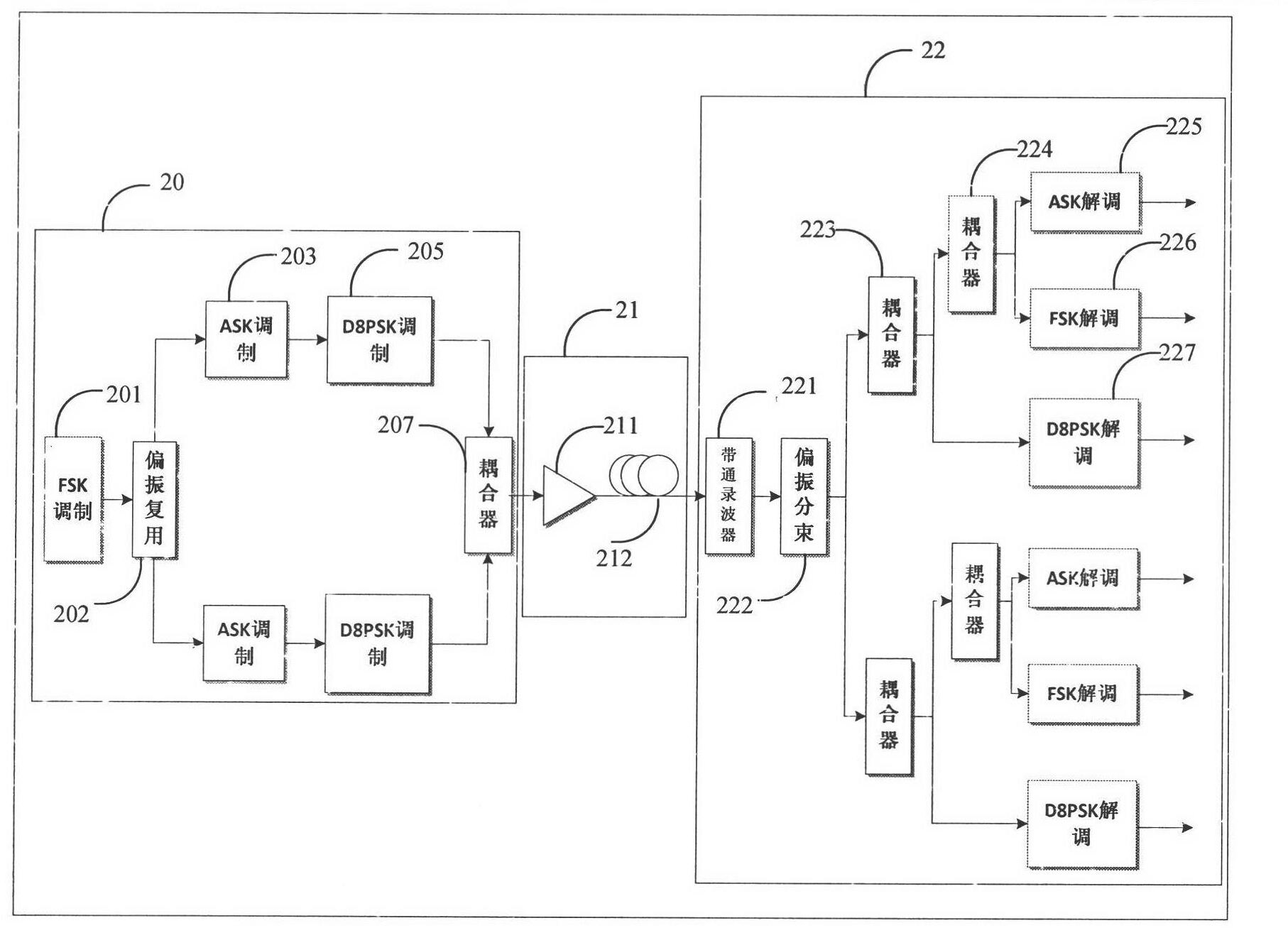
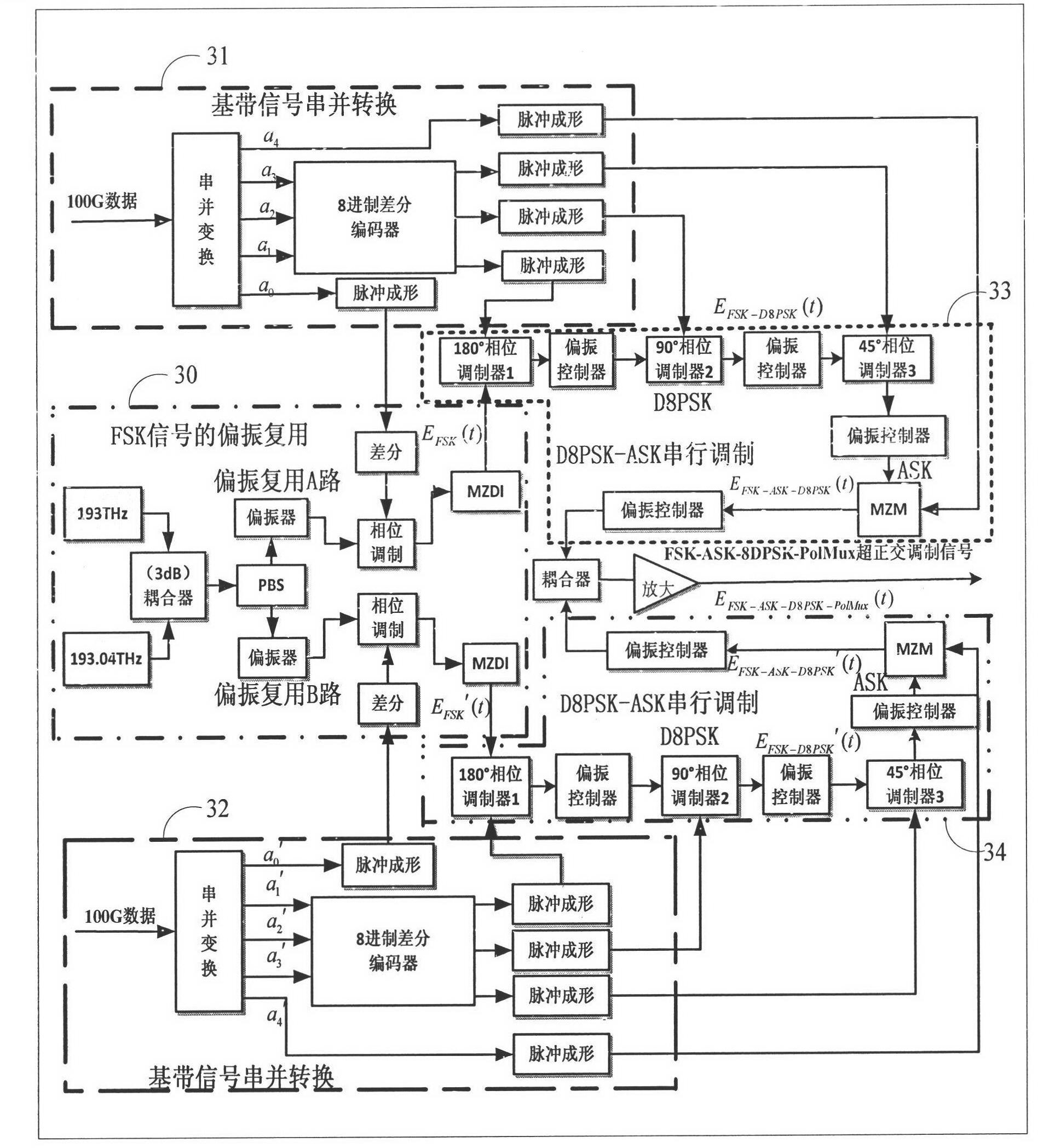
High speed optical transmission system and method based on FSK (Frequency Shift Keying)-D8PSK (Differential Eight Phase Shift Keying)-ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying)-PolMUX (multiplexer)
InactiveCN102307066AImprove frequency band utilizationImprove nonlinear toleranceMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSoftware engineeringPolarization multiplexed
The invention provides a high speed optical transmission system and method based on FSK (Frequency Shift Keying)-D8PSK (Differential Eight Phase Shift Keying)-ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying)-PolMUX (multiplexer). A sending device in the system includes the generation of an FSK-D8PSK-ASK-PolMUX signal. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, generating two paths of optical carriers by using two lasers with a 40G frequency difference, and generating two paths of FSK modulating signals at an orthogonal polarization state by using a polarization beam splitter, an M-Z interferometer and the like; then, carrying out D8PSK modulation on the FSK modulating signals respectively by using cascaded three phase modulators on an upper branch and a lower branch; then carrying out ASK modulation on the FSK-D8PSK modulating signals by using an MZM (Mach-Zehnder) modulator; and finally, combining the two paths of modulated signals by a coupler and sending to a transmission link device for transmission. The link device can amplify the received modulated optical signal, and then the optical signal is uploaded to a far-end receiving end; after the receiving device can de-polarize and multiplex the received optical signal, ASK, FSK and D8PSK parallel modulation is carried out on the optical signal so as to recover a transmitted information sequence.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
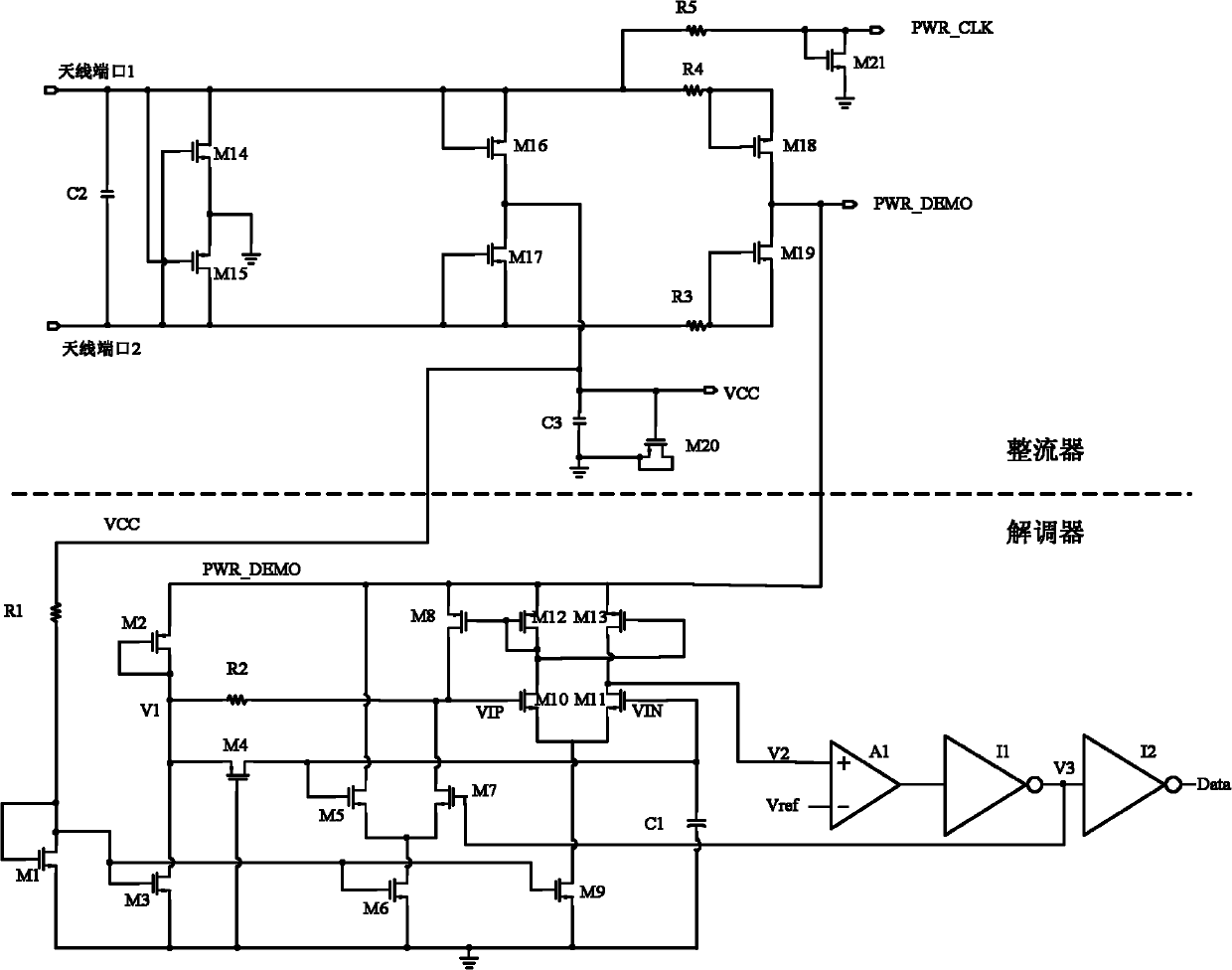
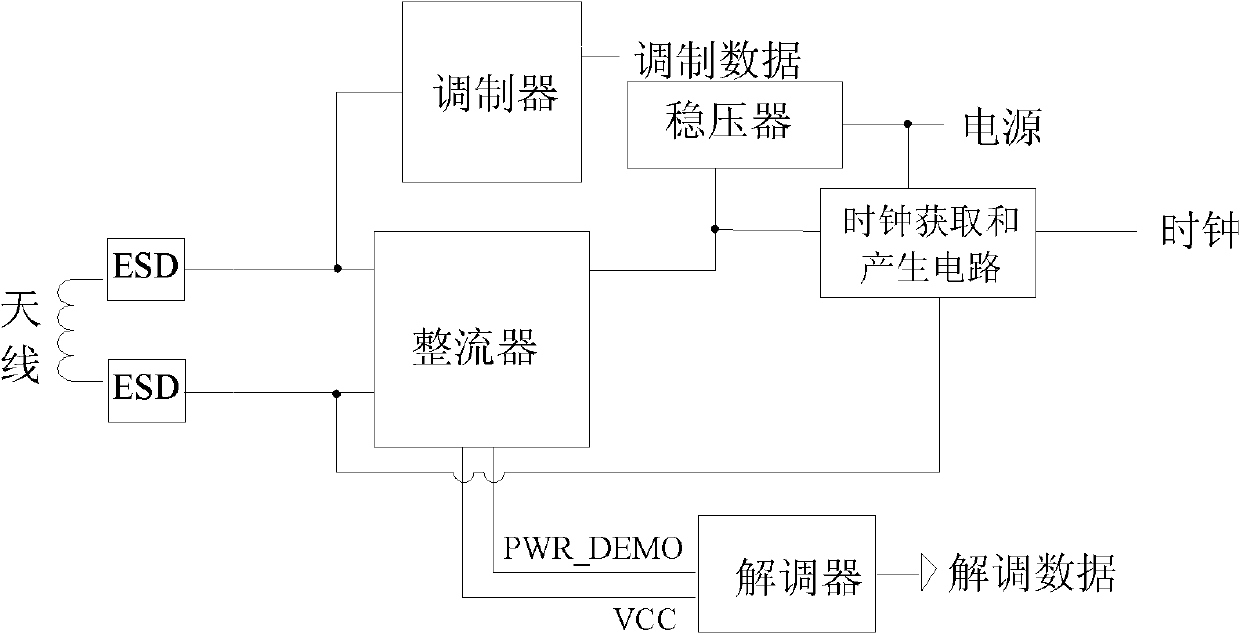
Demodulator circuit of electronic tag of RFID (radio frequency identification) system
The invention discloses a demodulator circuit of an electronic tag of an RFID system. Different from the conventional design, the demodulator circuit acquires a demodulation signal directly from a power supply PWR_DEMO outputted by a rectifier, and achieves demodulation, amplification, shaping and outputting of a weak signal by using an asymmetric circuit design. Specifically, the demodulator circuit conducts demodulation by using envelope detection method, and adopts a secondary comparison circuit. The demodulator circuit of the electronic tag of the RFID system provided by the invention can achieve demodulation of 10% ASK (amplitude shift keying) modulated signals, which are defined as type B according to the standard of ISO / IEC (International Organization for Standardization / International Electrotechnical Commission) 14443-3.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com