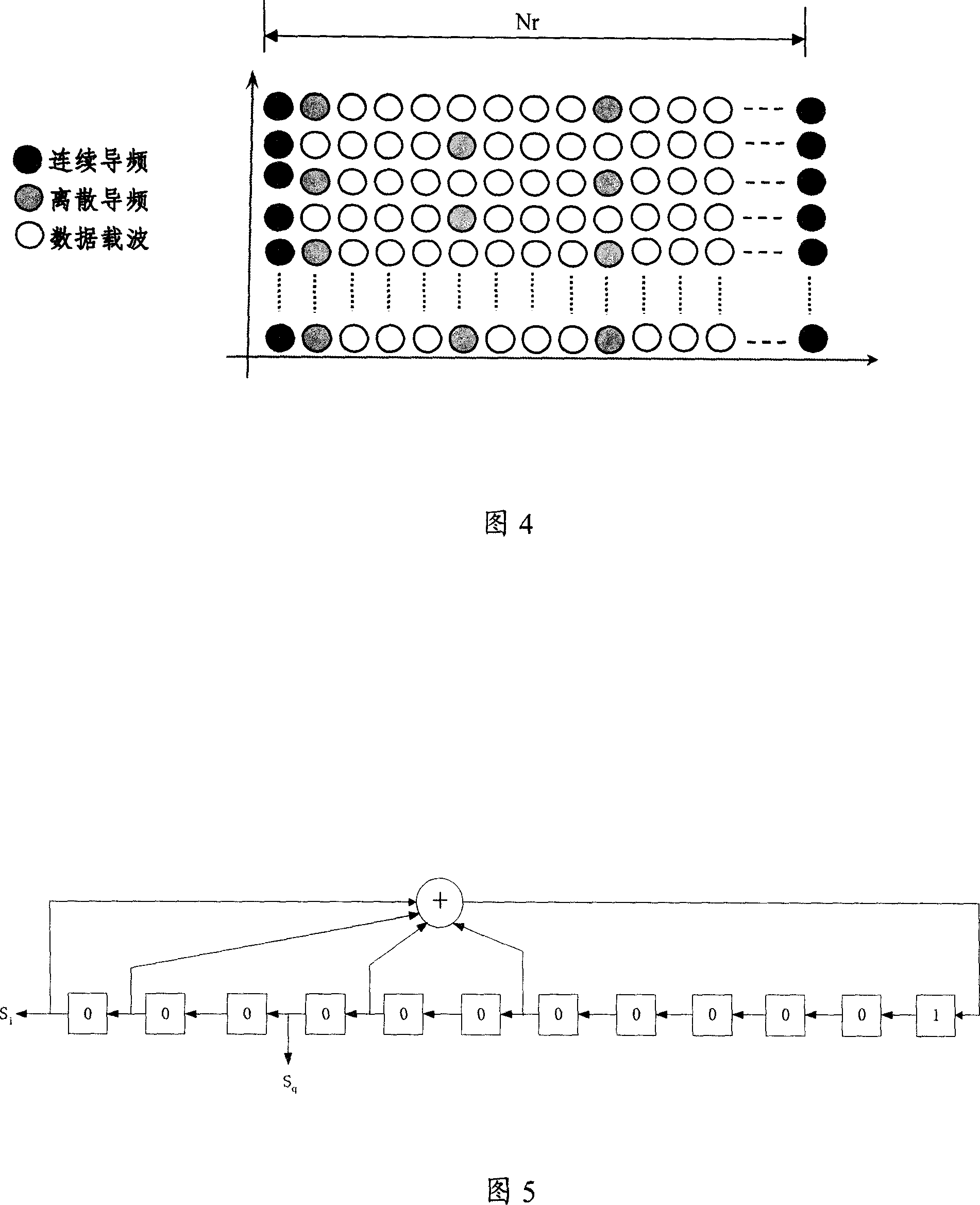
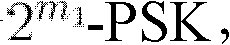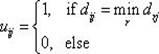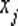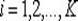Patents
Literature
305 results about "QAM" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
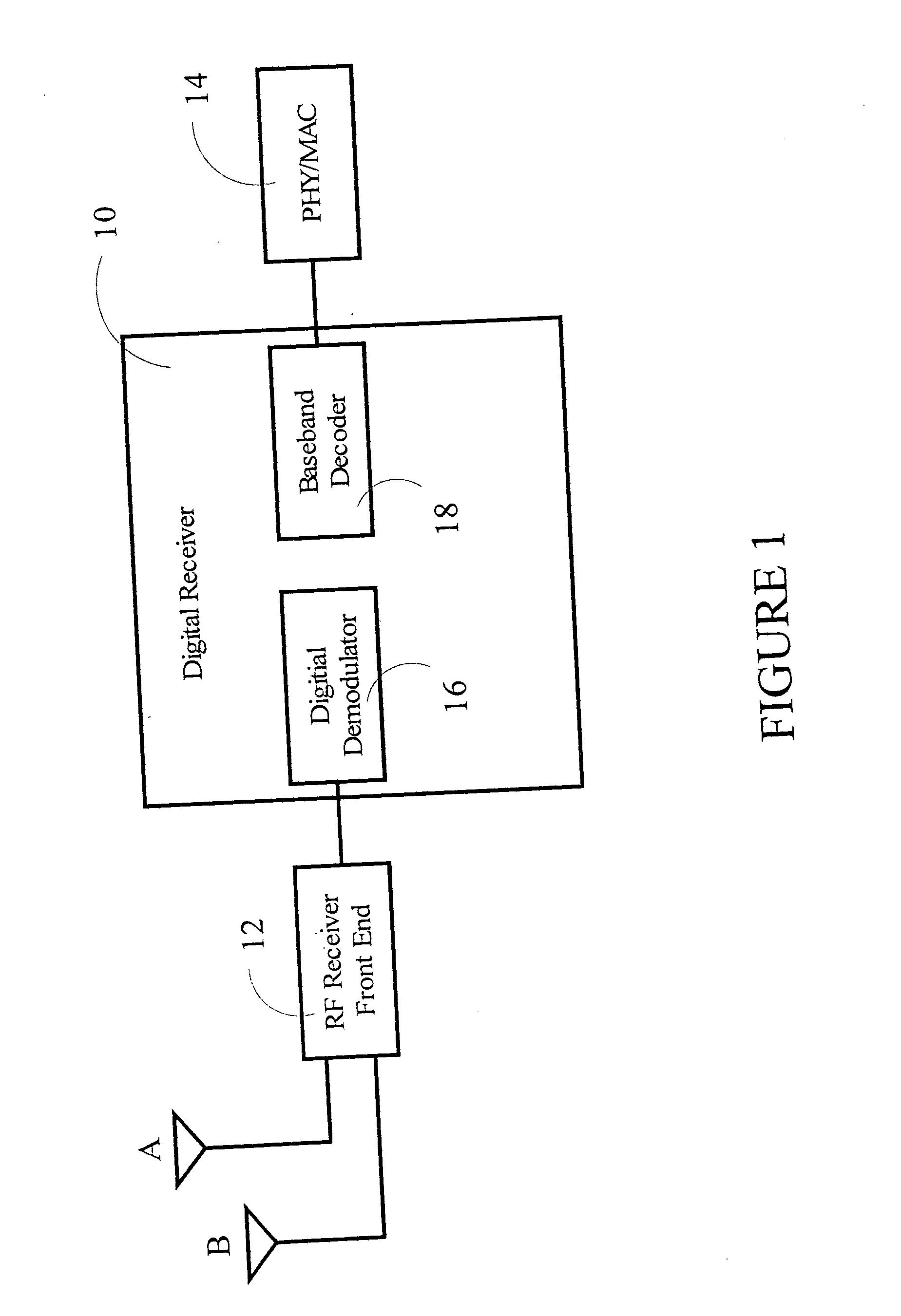
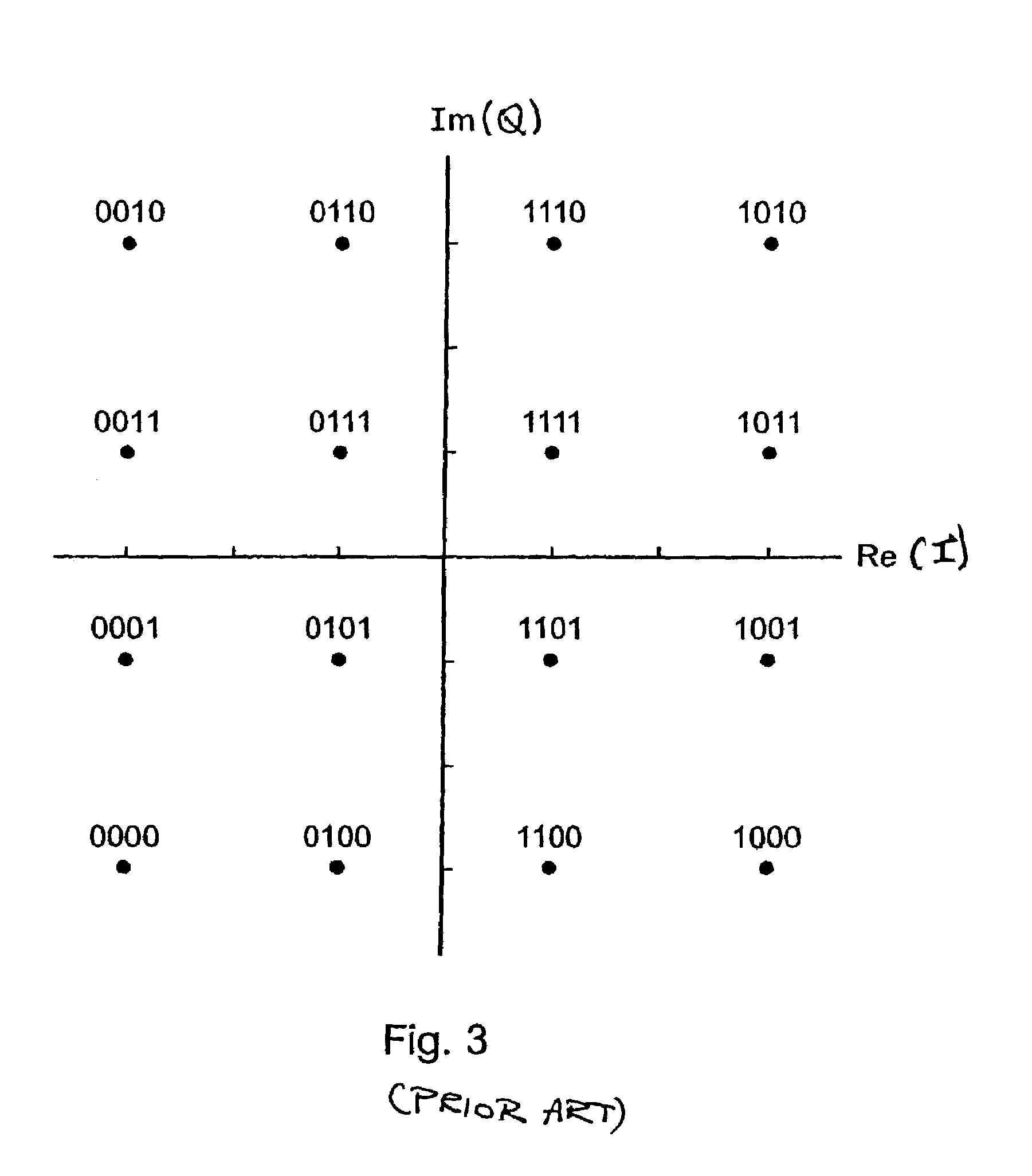
QAM is a digital television standard using quadrature amplitude modulation. It is the format by which digital cable channels are encoded and transmitted via cable television providers. QAM is used in a variety of communications systems such as Dial-up modems and WiFi. In cable systems, a QAM tuner is linked to the cable in a manner that is equivalent to an ATSC tuner which is required to receive over-the-air (OTA) digital channels broadcast by local television stations when attached to an antenna. Most new HDTV digital televisions support both of these standards. QAM uses the same 6 MHz bandwidth as ATSC, using a standard known as ITU-T Recommendation J.83 Annex B ("J.83b").
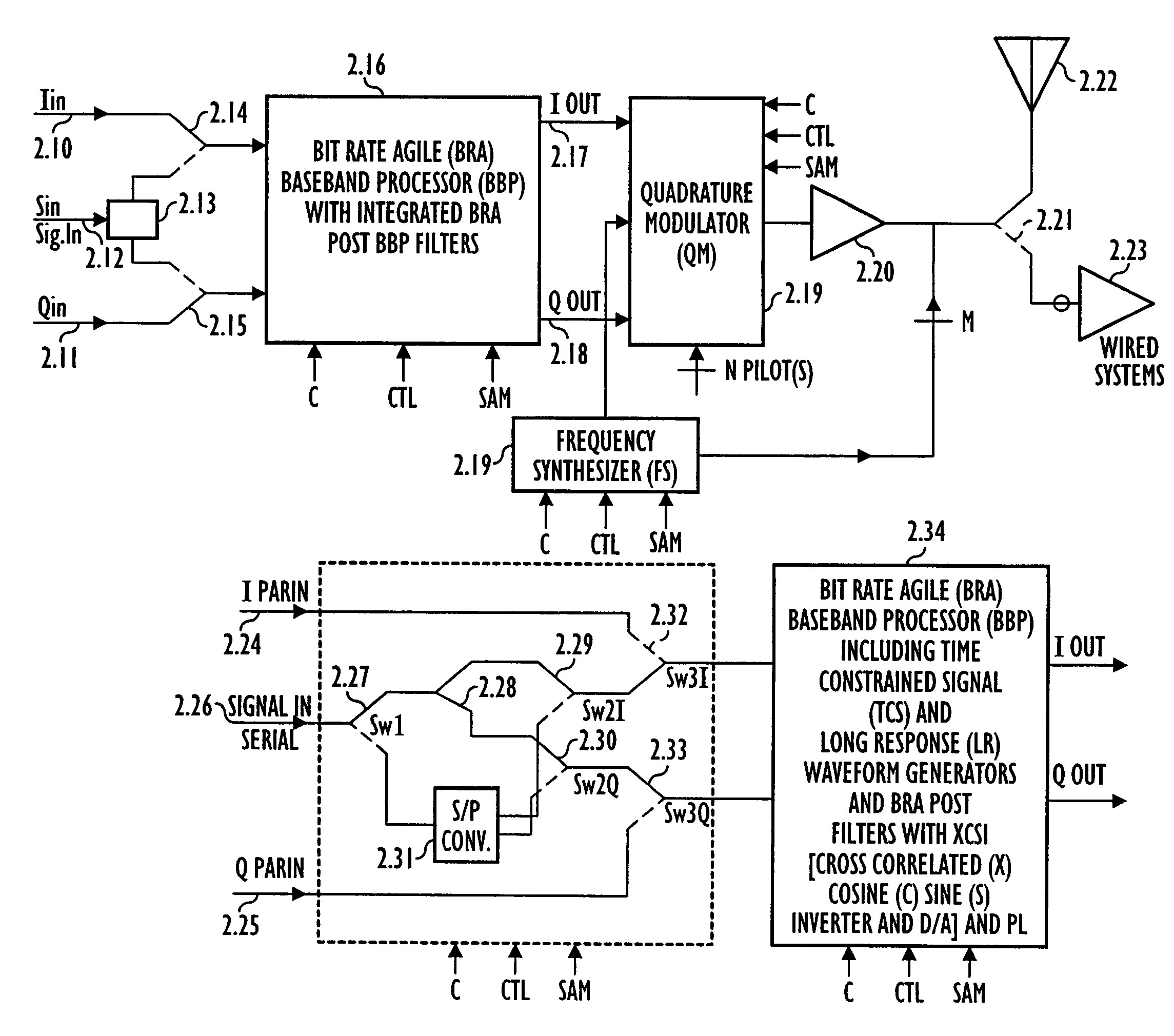
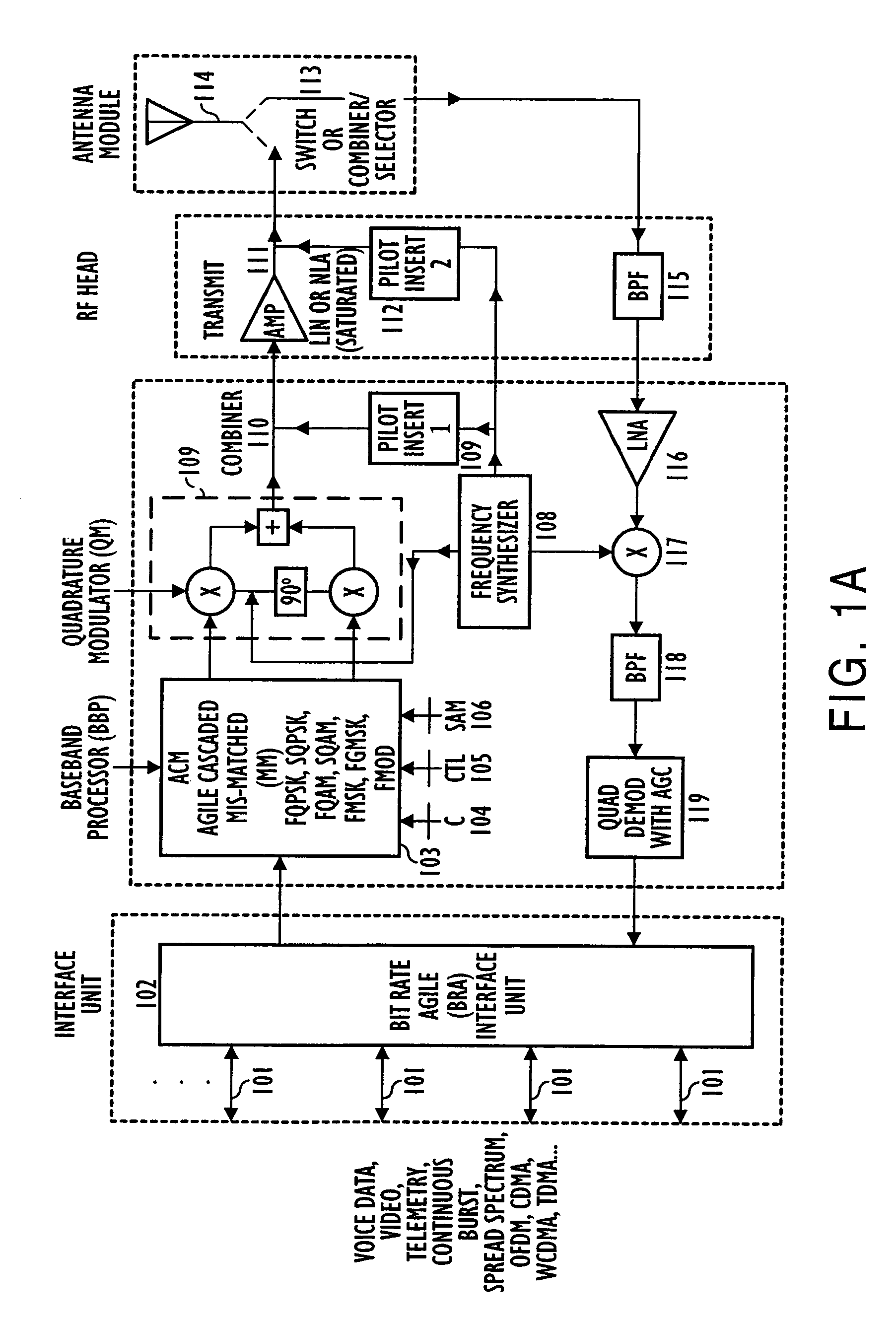
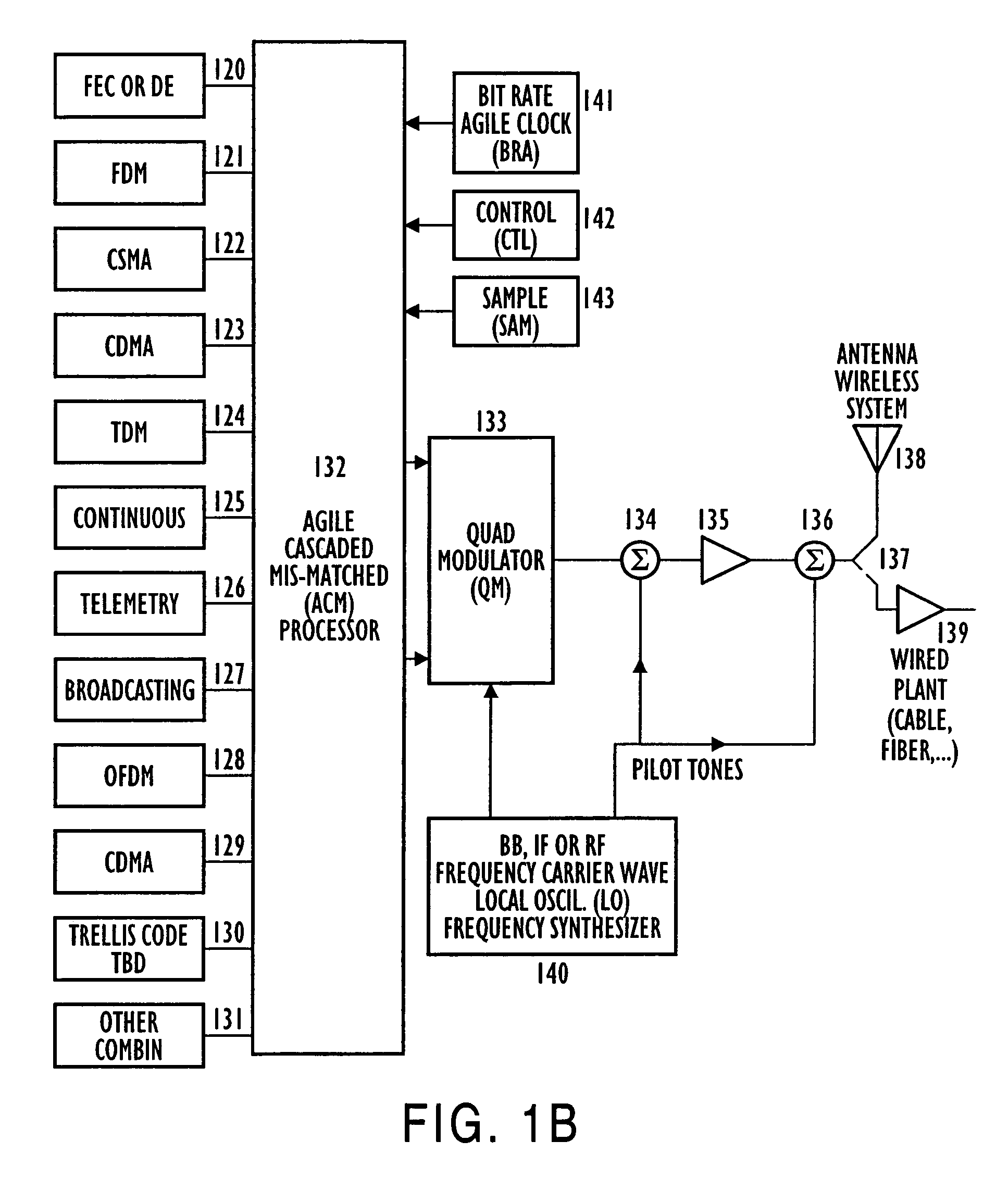
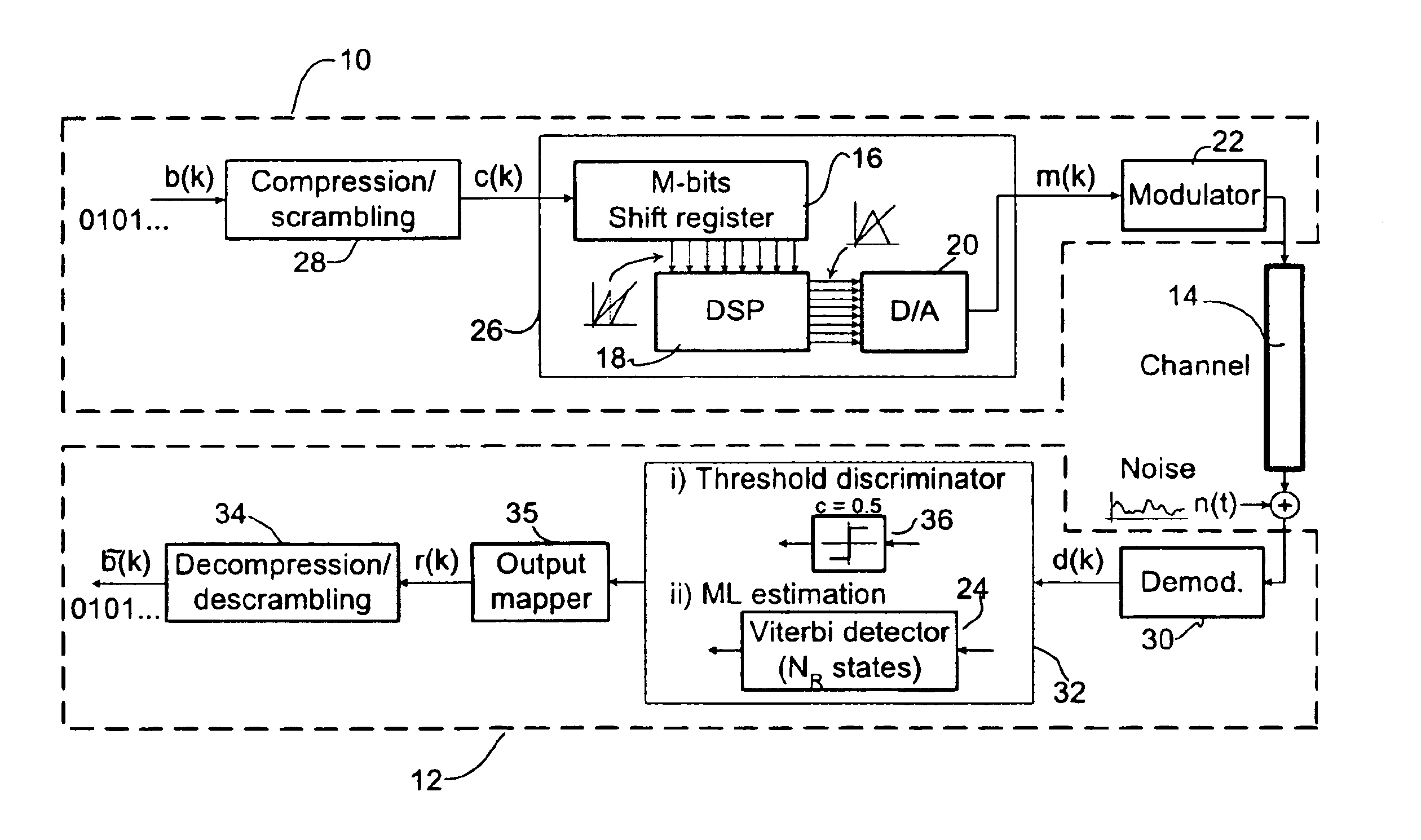
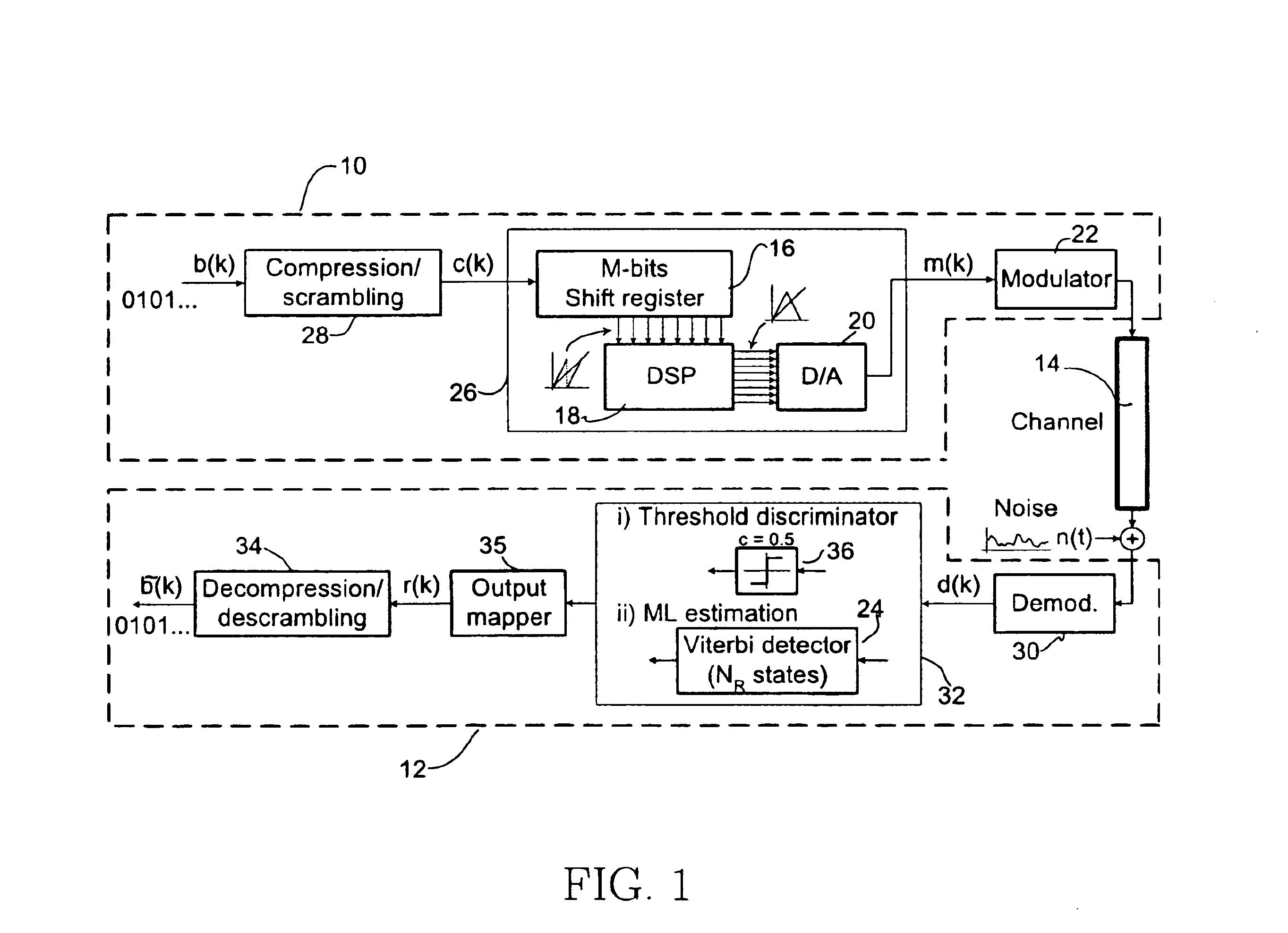
Adaptive receivers for bit rate agile (BRA) and modulation demodulation (modem) format selectable (MFS) signals
InactiveUS7376180B2Improve performanceSignificant spectral saving advantageMultiple-port networksSecret communicationModem deviceThird generation
Systems, apparatus, and methods for new generations of wireless systems, including multiple standard, interoperable Third-Generation (3G) and Second-Generation (2G), Spread Spectrum CDMA, WCDMA, GSM, Enhanced GSM systems and CSMA, TDMA and OFDM. Bit Rate Agile (BRA), Modulation and Code Selectable processing techniques of Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK), Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM), and of Mis-Matched demodulator filters in which the demodulator filter set is mismatched to the filter set of the signal modulator.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
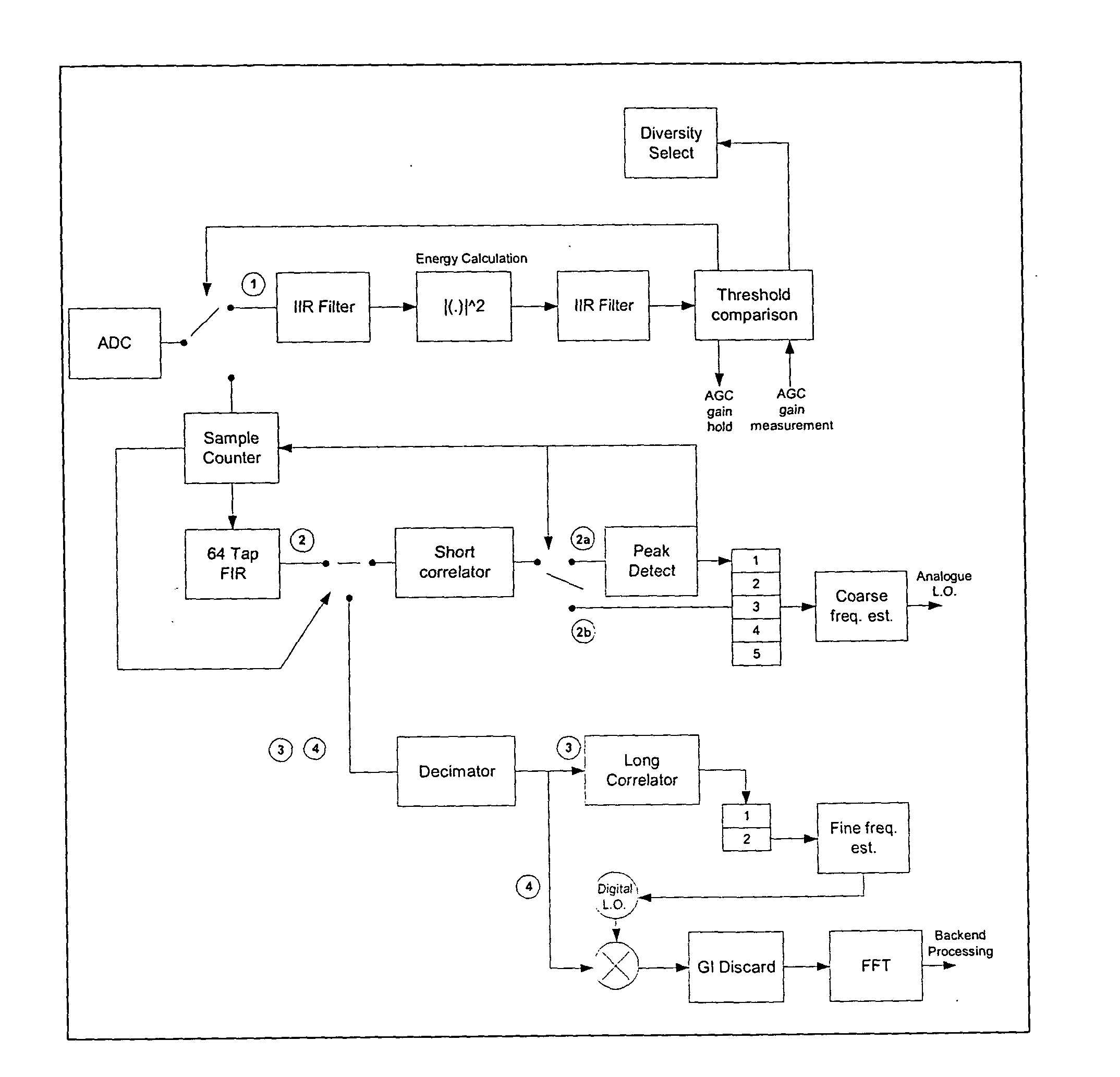
Method for amplitude insensitive packet detection
ActiveUS20050058227A1High outputEasy to detectAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPhase correlationComputer science
The invention relates generally to the field of wireless communications and more particularly to a method of and device for detecting the presence of a received data packet in a digital receiver. The present invention proposes a simplified method of correlation by removing dependency on the amplitude fluctuations while at the same time maintaining phase relevancy. The key advancement involves mapping the complex quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) preamble to a quantized phase shift keying (PSK) constellation before application to a matched complex correlator. The proposed process essentially “amplitude normalizes” the input signal without the use or complexity associated with a divider. This simplified normalization scheme makes the packet detection algorithm robust against amplitude variations in the input signal, while still allowing for good correlation output. In applications where interference is superimposed on the I / Q input signals, the invention improves the detection capability over automatic gain control (AGC) normalization methods.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
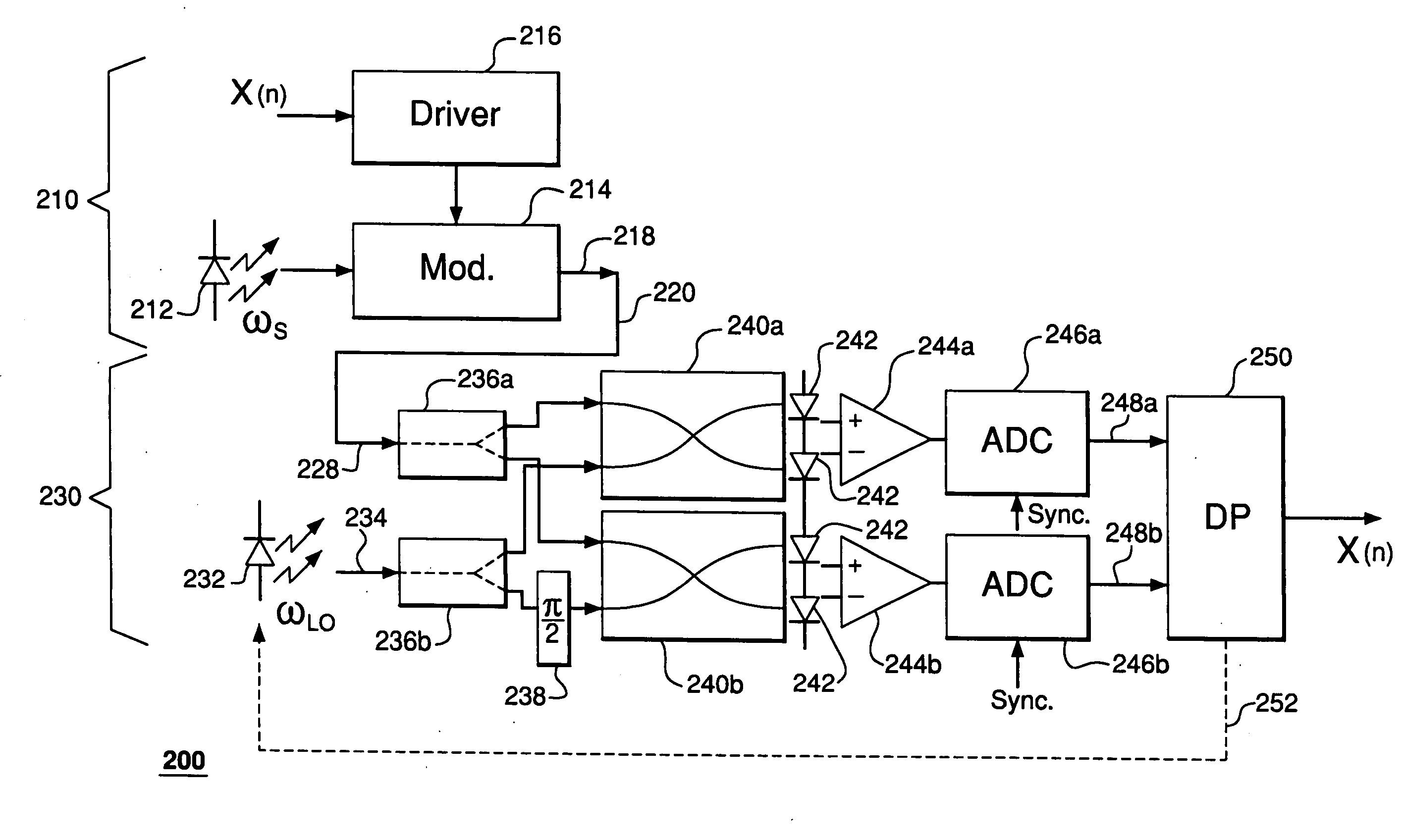
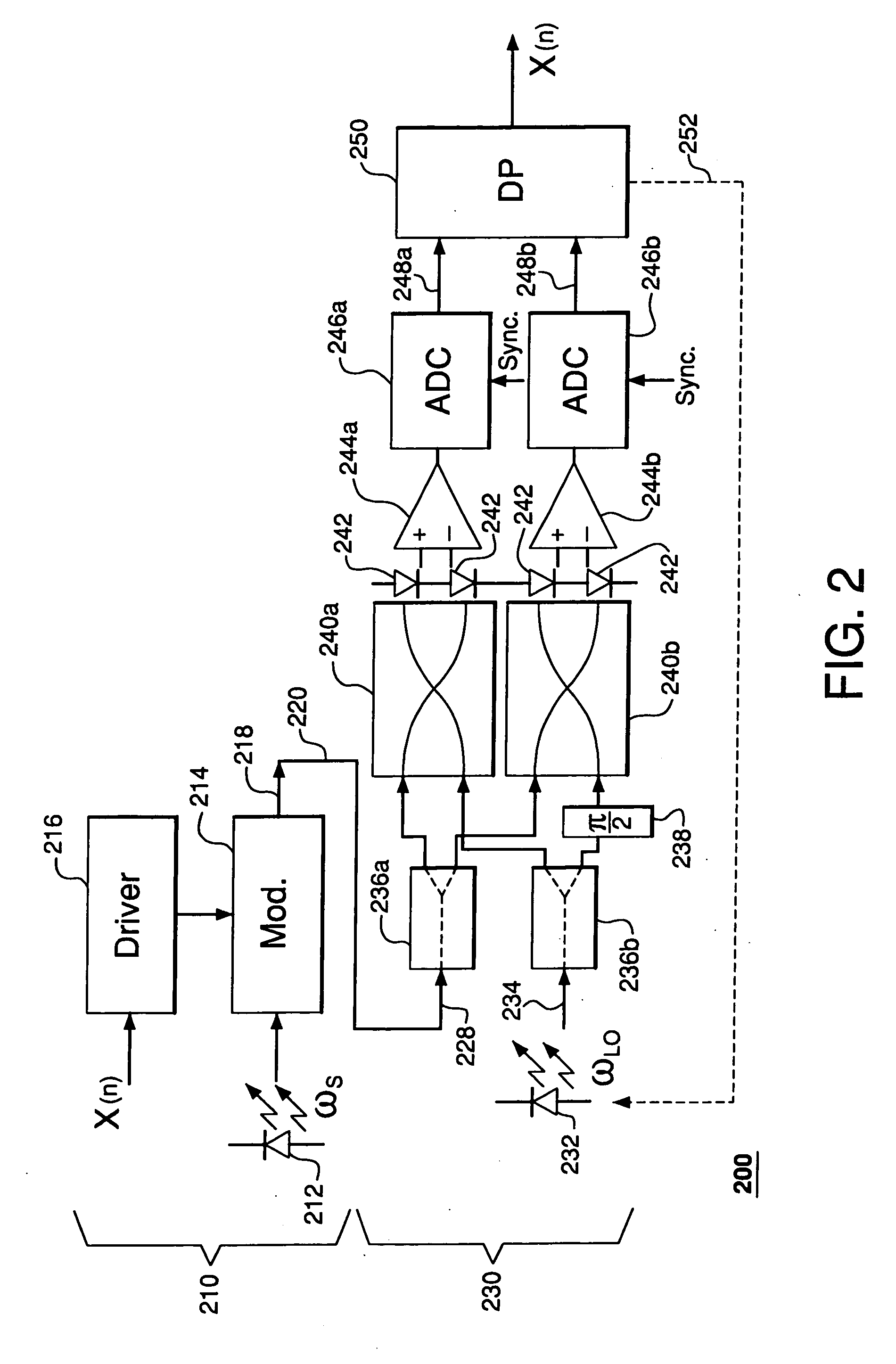
Optical quadrature-amplitude modulation receiver
In one embodiment, a receiver of the invention has an optical detector coupled to a digital processor. The optical detector is adapted to mix the received optical quadrature-amplitude modulation (QAM) signal with an optical local oscillator (LO) signal having a time-varying phase offset with respect to the carrier frequency of the QAM signal to produce two digital measures of the QAM signal. The digital processor is adapted to: (i) determine the amplitude and phase differentials for each QAM-symbol transition based on these digital measures; (ii) adjust each phase differential for an amount of phase drift associated with the time-varying phase offset; (iii) map each QAM-symbol transition onto a constellation point of a 2D decision map using the transition's amplitude differential and adjusted phase differential; and (iv) based on the mapping results, recover the data encoded in the optical QAM signal.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
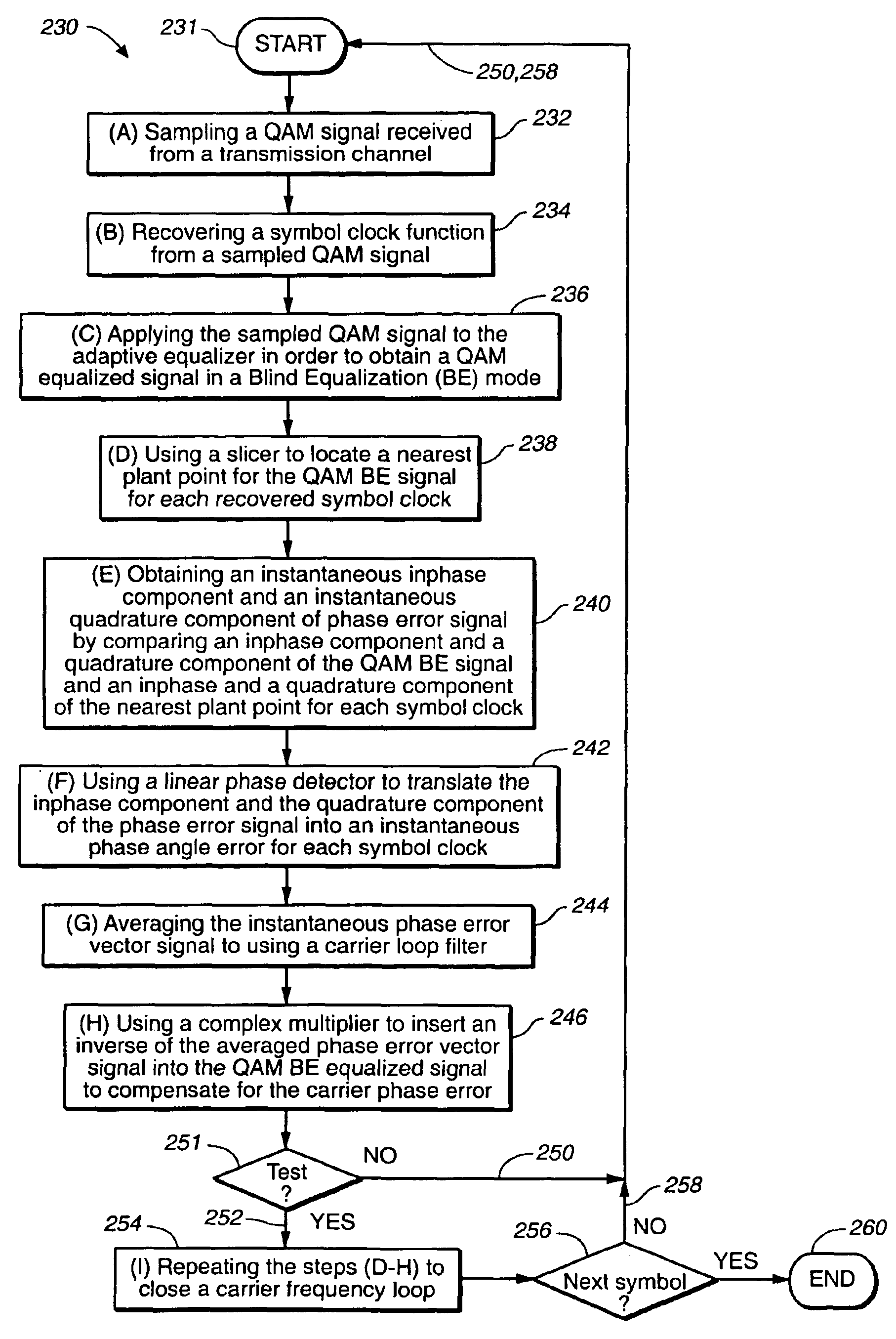
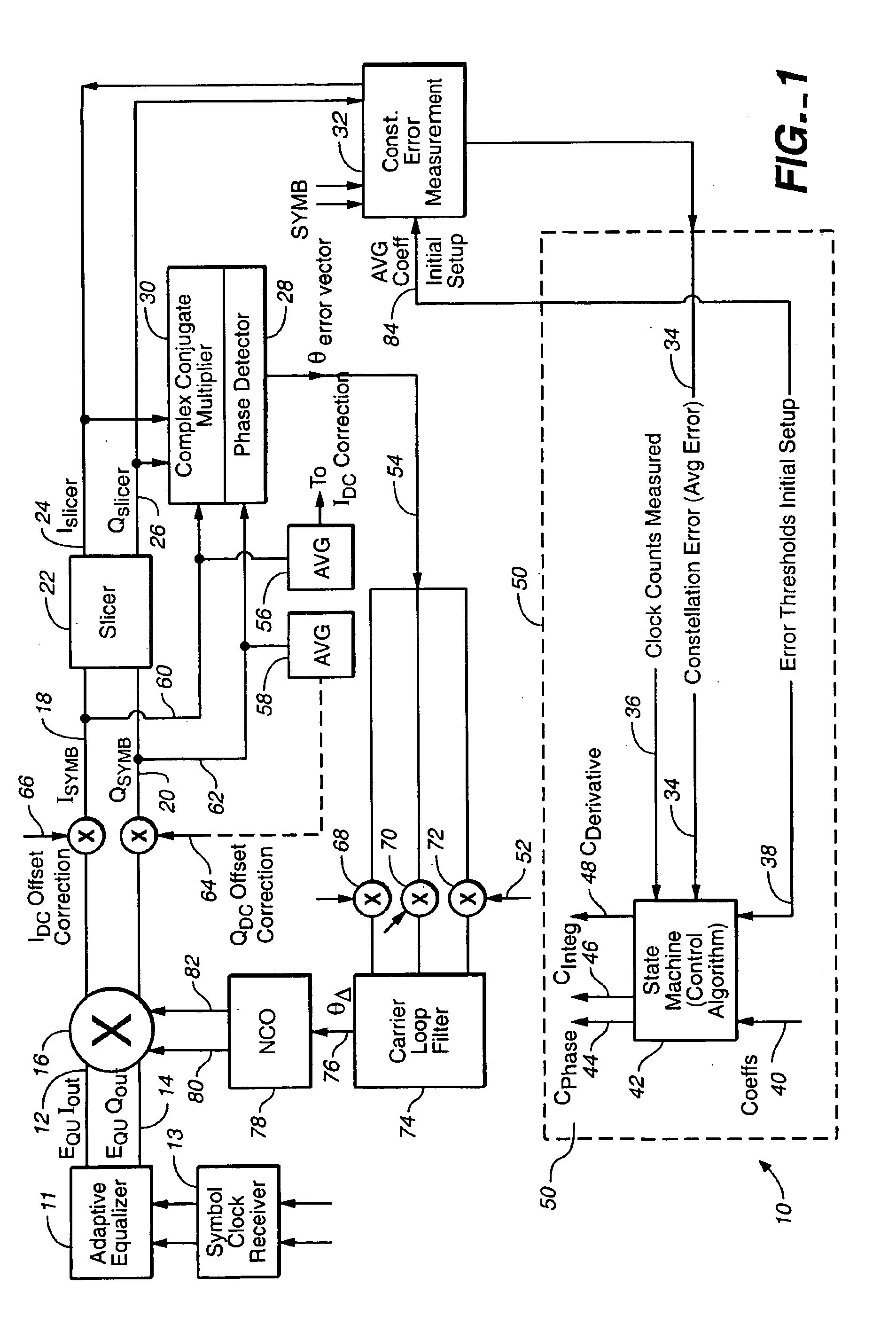
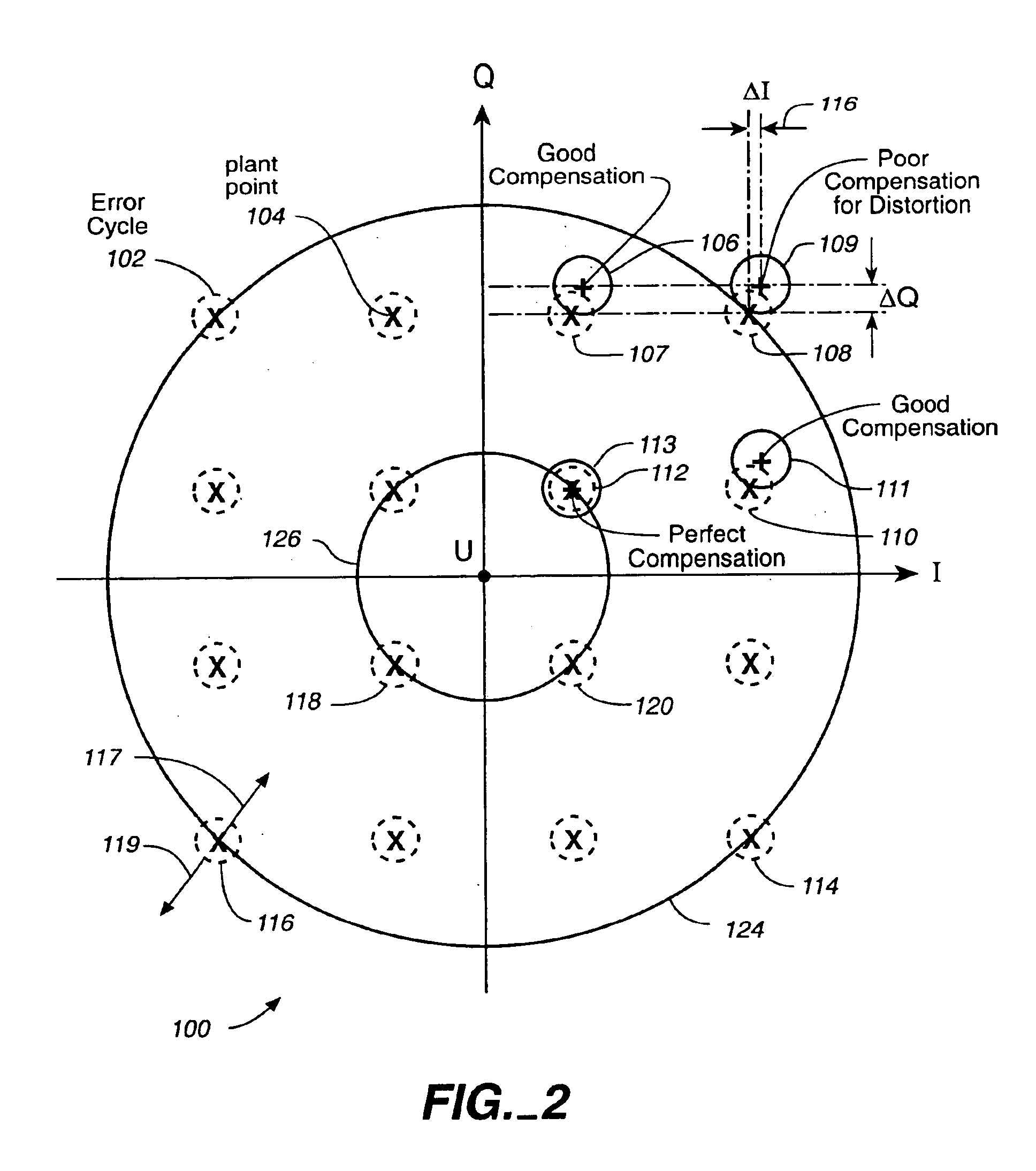
Linear phase robust carrier recovery for QAM modems
InactiveUS6904098B1Large loop bandwidthLower latencyDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAutomatic frequency control detailsQam modulationBlind equalization
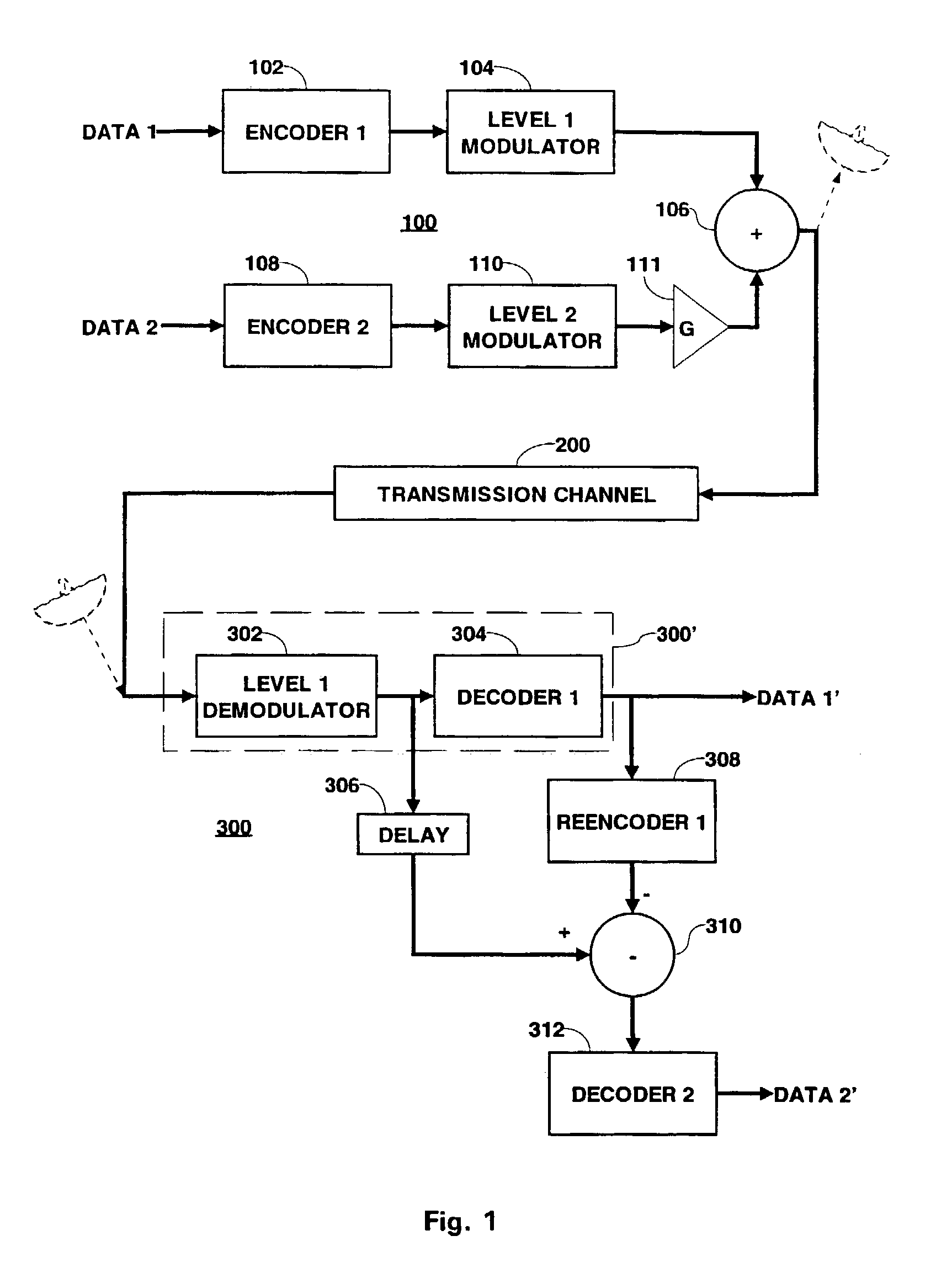
In a QAM demodulator including an adaptive equalizer, a method of carrier tracking comprising the following steps is disclosed: (A) sampling a QAM signal received from a transmission channel; (B) recovering a symbol clock function from the sampled QAM signal; (C) applying the sampled QAM signal to the adaptive equalizer in order to obtain a QAM equalized signal in a Blind Equalization (BE) mode; (D) using a slicer to locate a nearest plant point for the QAM Blind equalized signal for each recovered symbol clock; (E) using a complex conjugate multiplier to obtain an instantaneous inphase component and an instantaneous quadrature component of a phase angle error signal; (F) using a linear phase detector to obtain an instantaneous phase angle error for each symbol clock; (G) averaging the instantaneous phase angle error signal by using a carrier loop filter; (H) using a complex multiplier to insert an inverse of the averaged phase angle error signal into the QAM Blind equalized signal to compensate for the carrier phase angle error; and (I) repeating the steps (D-H) to close a carrier frequency loop.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
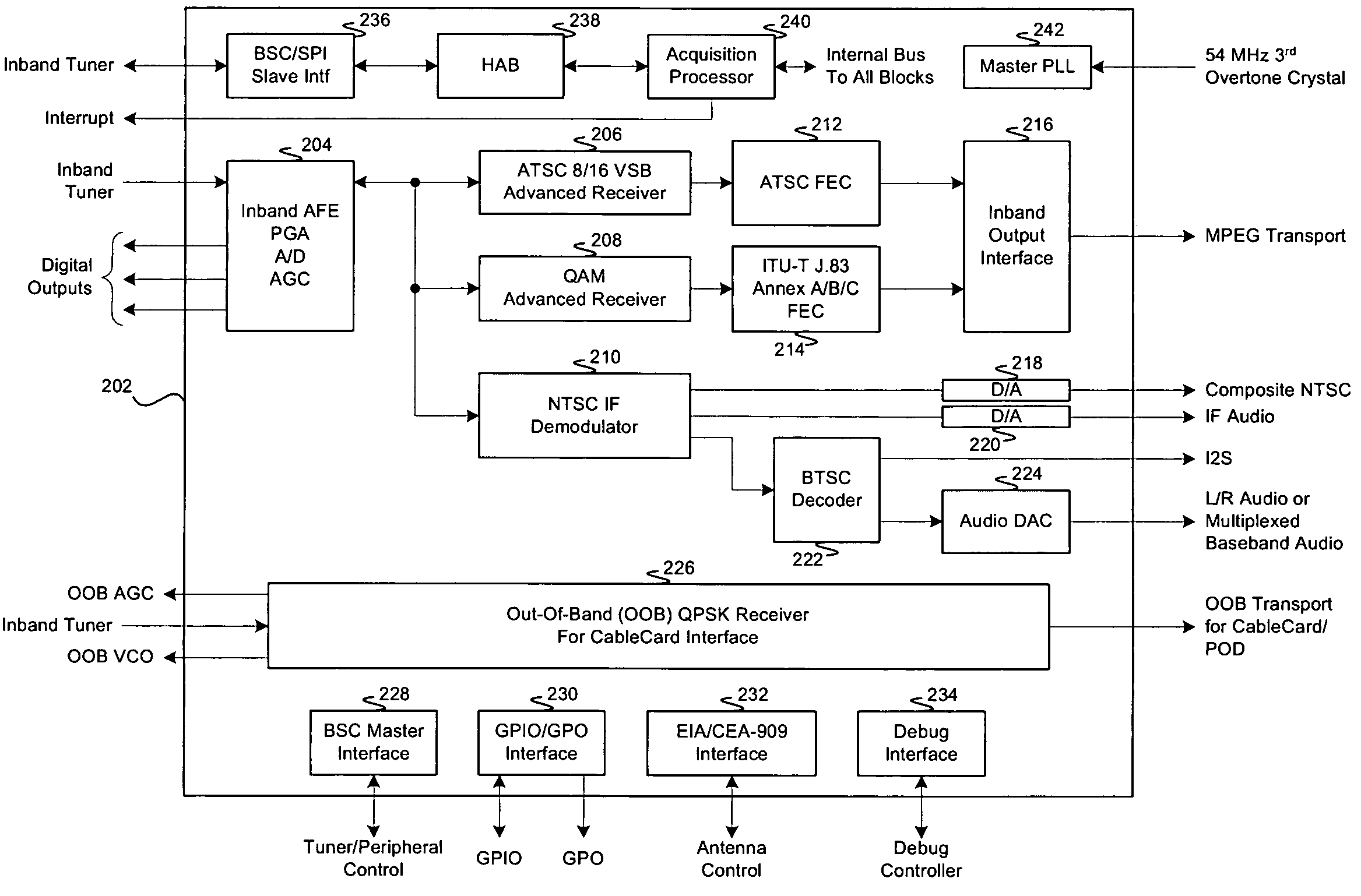
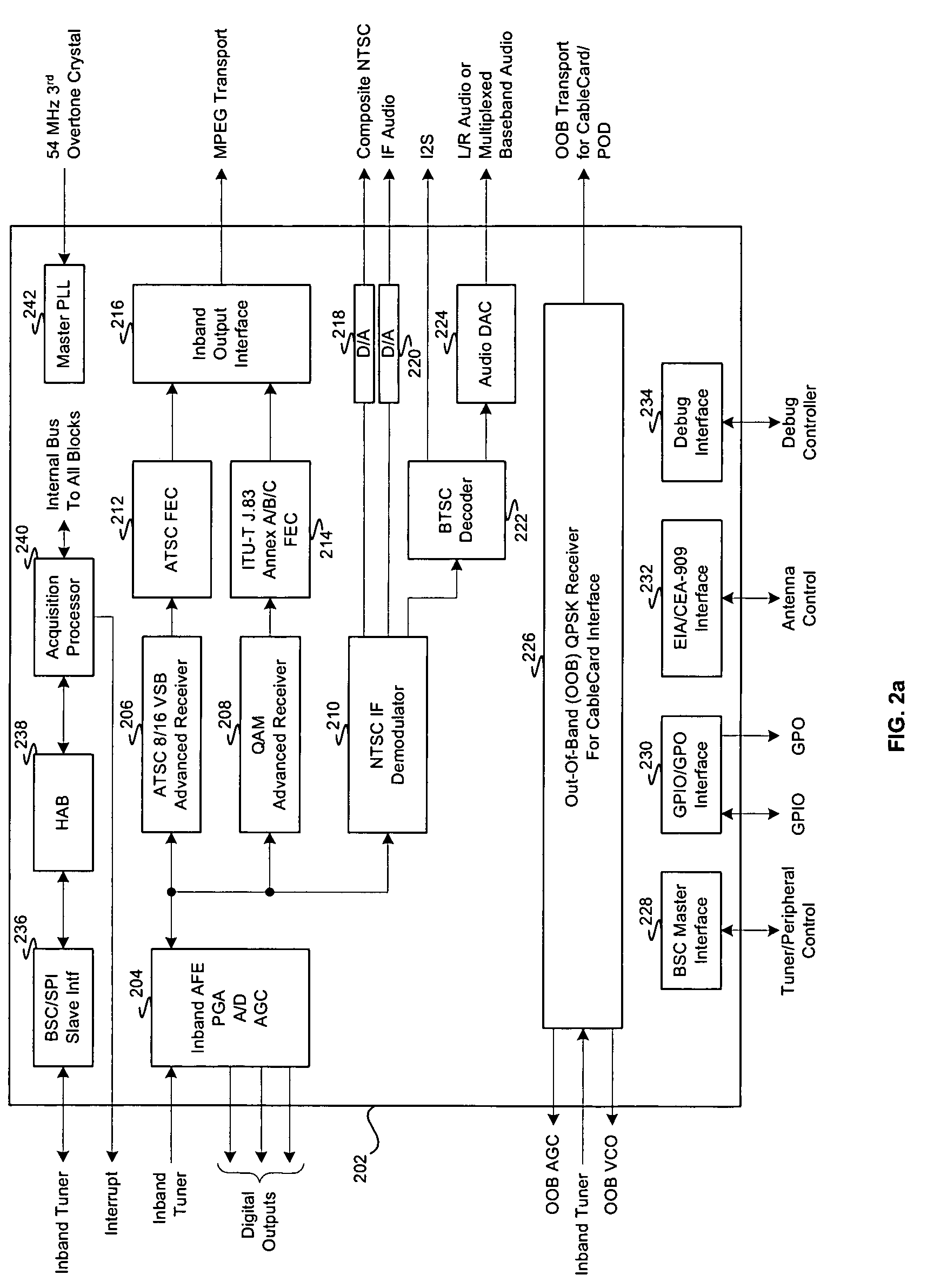
Method and system for an integrated VSB/QAM/NTSC/OOB plug-and-play DTV receiver
ActiveUS20050177860A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDTV receiverOutside broadcasting
Certain embodiments of the invention may be found in a method and system for a vestigial side band (VSB), quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), NTSC, out-of-band (OOB) receiver that is integrated in a single chip. The single chip integrated digital television (DTV) receiver provides plug and play DTV receiver capability for handling both North American digital cable television and digital terrestrial broadcast television compatible systems. The integrated DTV receiver may receive all standard-definition and high-definition digital formats (SDTV / HDTV) and an on-chip NTSC demodulator handles NTSC video. An output of the NTSC demodulator may be directed to an external broadcast television system committee (BTSC) or Zweiton M decoder, or it may be sent to an on-chip audio BTSC compliant decoder. The single chip integrated DTV receiver may also comprise an integrated out-of-band QPSK receiver, which may be adapted to, for example, handle a CableCard compliant with the CableCard Specification.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
Gray encoding for hierarchical QAM transmission systems
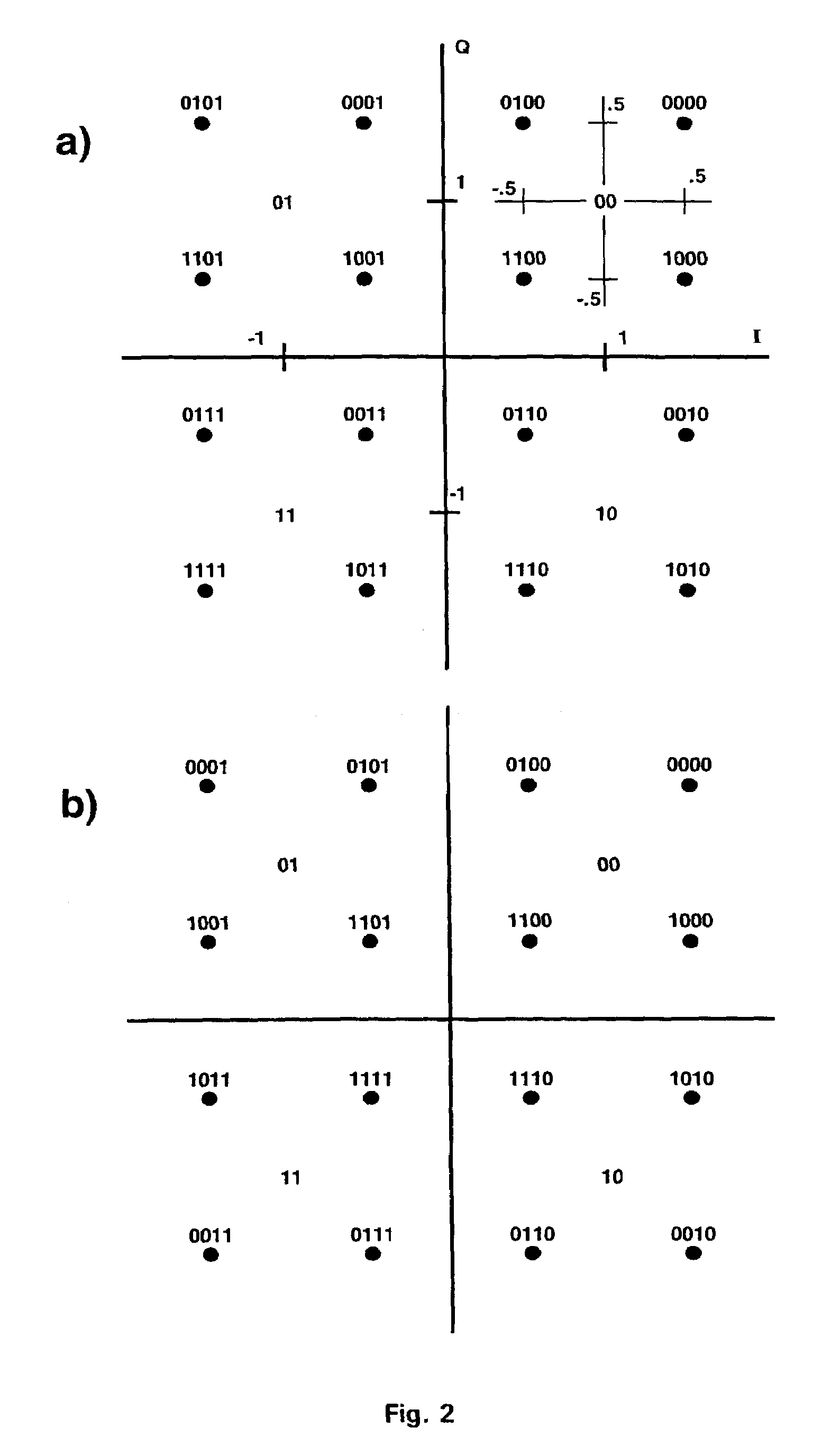
A hierarchical QAM system allows the transmission of different sources by embedding the relative constellation points. At the transmitter the constellations generated by the different sources are remapped by a grey coder and then combined. At the receiver, the different source data are decoded by using a corresponding grey code demapper.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method and apparatus for clock timing recovery in χDSL particularly VDSL modems
InactiveUS6922436B1Lower control costsStable and accurate control voltageFrequency-modulated carrier systemsDigital-analogue convertorsModem deviceLow-pass filter
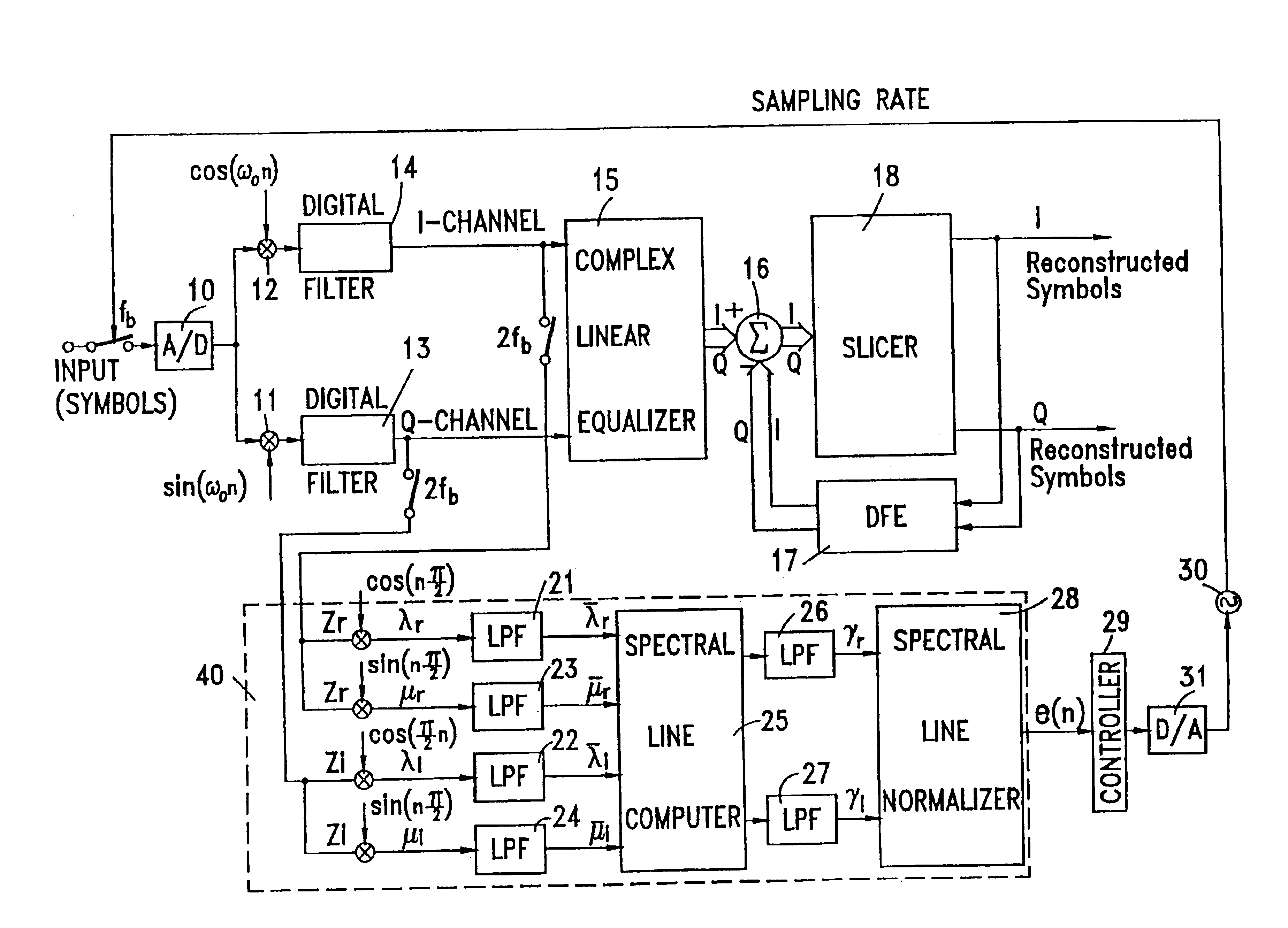
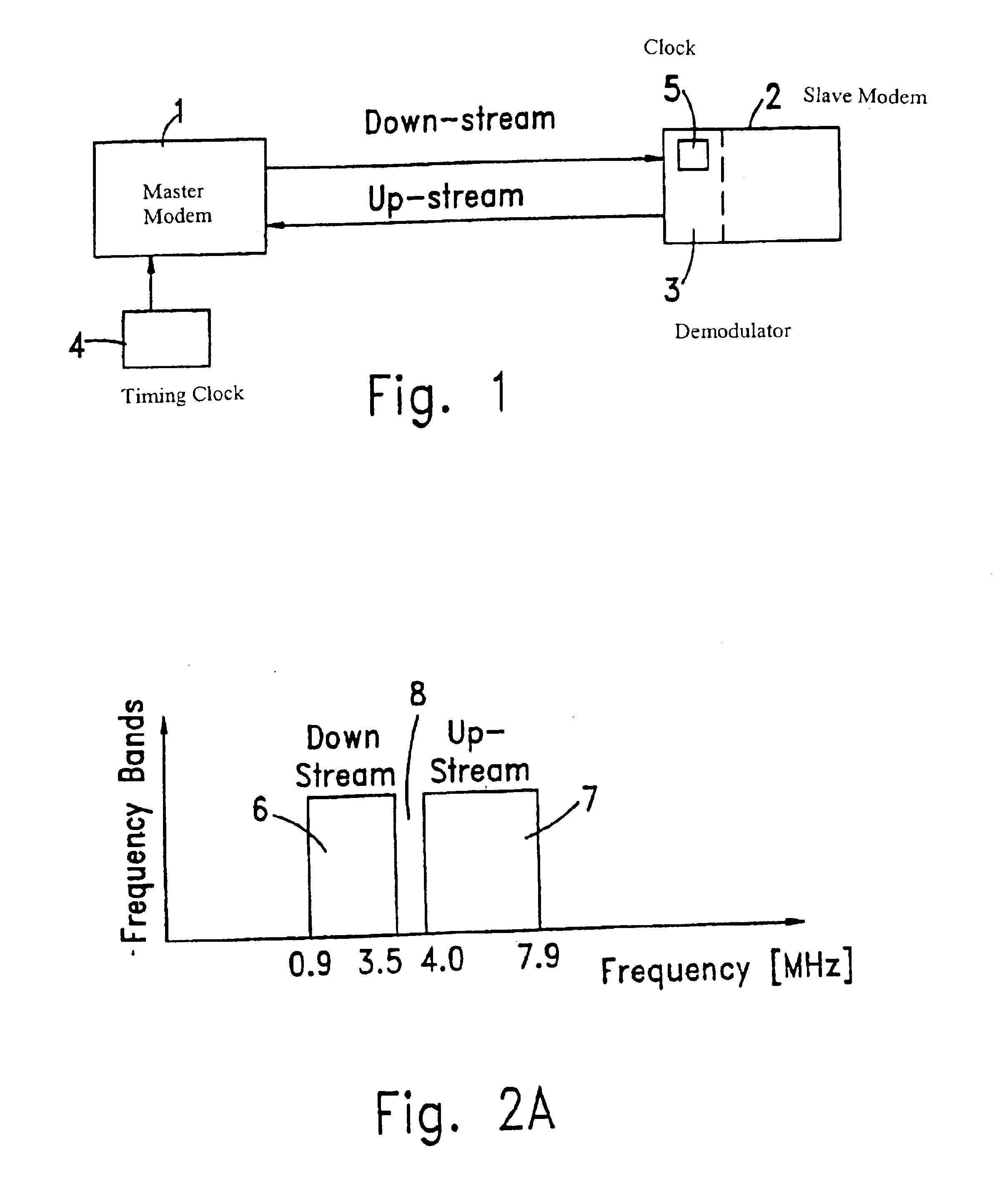
Method and modem for fast timing recovery of transmitted data between a master χDSL modem and a slave χDSL modem, over a noisy, high loss, high distortion wiring. Transmitted QAM symbols are received and sampled at the slave modem. The sampled data is split into in-phase and quadrature channel, each of which is filtered by matched filter. The filtered outputs are sampled at twice the symbol rate and the lower and upper band edge components are extracted by modulating each of the sampled sequences of outputs with two discrete time sequences: cos(0.5 π n)=. . . 1,0,−1,0 . . . and sin(0.5 π n)=. . . 0,1,0,−1 . . . . Each of the resulting products is filtered with a first order low-pass filters and re-sampled again at the symbol rate. The Bit Error Rate is computed, and the slave modem switches from blind timing recovery mode, to data directed timing recovery mode, after the Bit Error Rate has sufficiently decreased.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Method and apparatus for high-speed data transfer employing self-synchronizing quadrature amplitude modulation
ActiveUS20100225752A1Reduce signal to noise ratioBroaden applicationColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsQuadrature modulationClock recovery
A Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) method and apparatus including a QAM transmit modulator with at least one unbalanced mixer, which creates an asymmetric two-dimensional (2-D) QAM symbol constellation. The asymmetrical symbol constellation provides baseband symbol clock signal leakage sufficient to facilitate quick and simple baseband symbol clock recovery and signal channel compensation at the QAM receiver without significantly degrading the system bit-error rate (BER). While slightly degrading static BER, overall system performance is improved when considering baseband symbol clock recovery and received signal compensation for an imperfect signal channel. This allows QAM to be deployed in systems where QAM is otherwise prohibitively expensive and improves overall system performance for any existing QAM system application without additional bandwidth, cost or complexity.
Owner:SEEKTECH
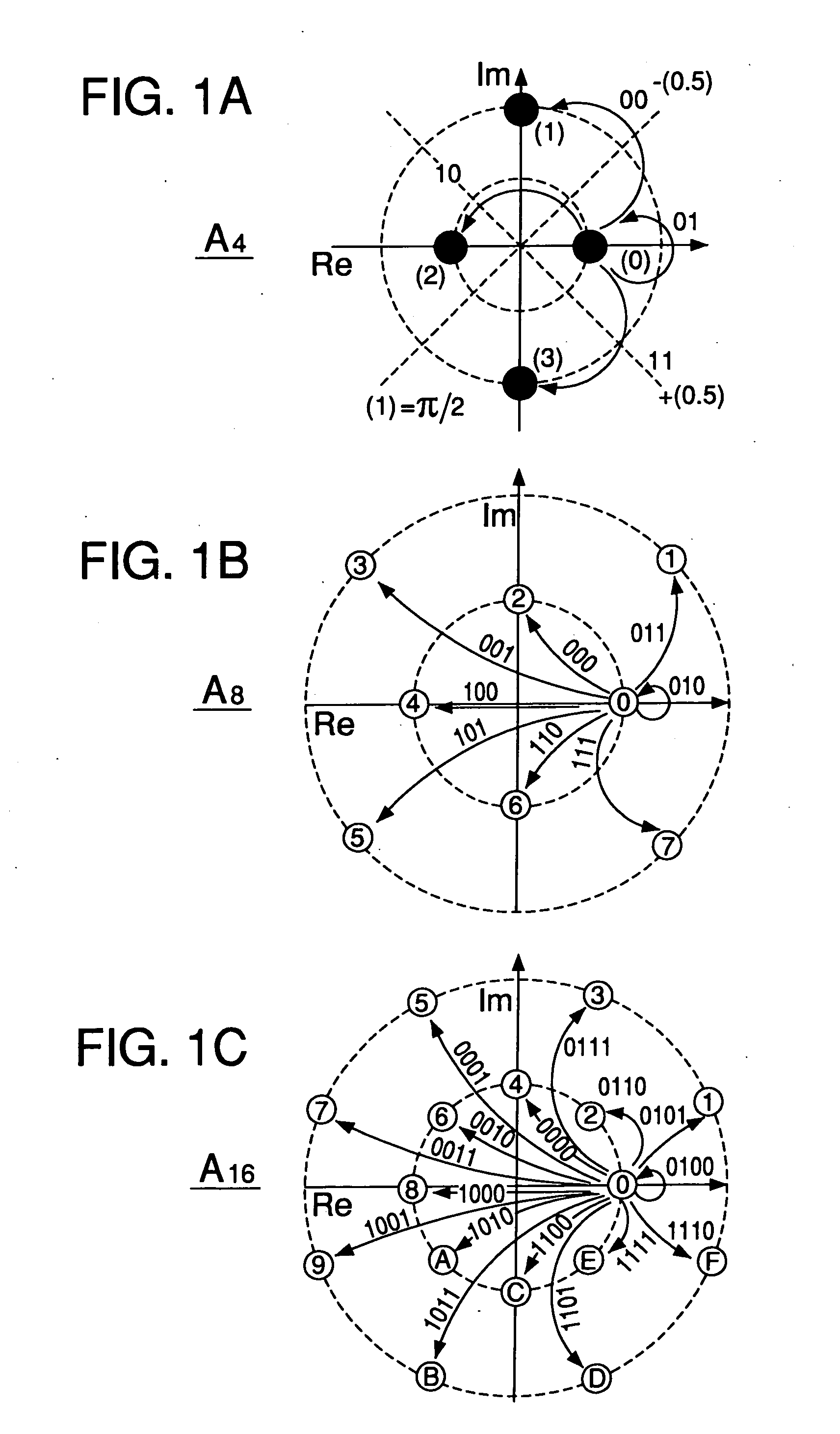
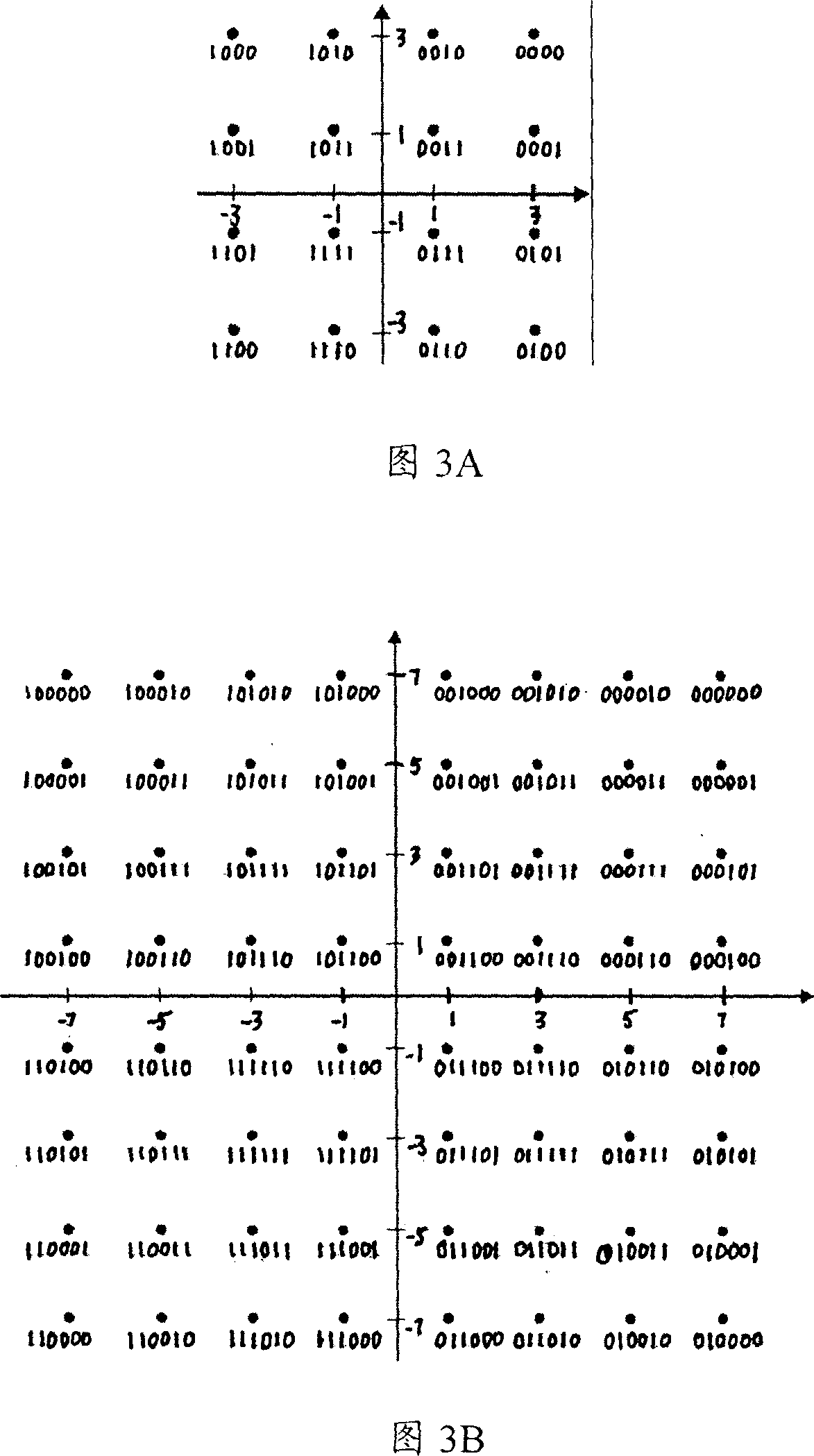
Constellation mapping method based on absolute phase shift keying (APSK) constellation map, coded modulation method and system
ActiveCN102752261AImprove performanceError preventionMultiple carrier systemsComputer scienceQam constellations
The invention discloses a constellation mapping method based on an absolute phase shift keying (APSK) constellation map. The constellation mapping method is characterized in that the order M of an APSK constellation is equal to 2<m>; the number n1 of points on each ring is equal to a value of powers to 2, namely n1=2<m1>, the number n1=2<m1>-PSK (phase shift keying), the number of rings R=2<m2>, and a set consisting of different ring radiuses is a special 2<m2>-PAM(pulse amplitude modulation ), wherein m1+m2=m; and the phase deflection theta1 of all the rings are the same. The method comprises the following steps of: B1, for a bit vector which is m in length, setting m1 bits to be only related to the phase, and adopting PSK Gray mapping between the m1 bits and the 2<m1>-PSK; and B2, setting the rest m2 bits to be only related to the amplitude, and adopting PAM Gray mapping between the m2 bits and the 2<m2>-PAM. The invention has the advantages that compared with the conventional coded modulation system adopting quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) constellation map mapping, the coded modulation system adopting the APSM constellation map Gray mapping can acquire a considerable error control performance gain regardless of adopting independent demapping or iterative demapping by a receiving end.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
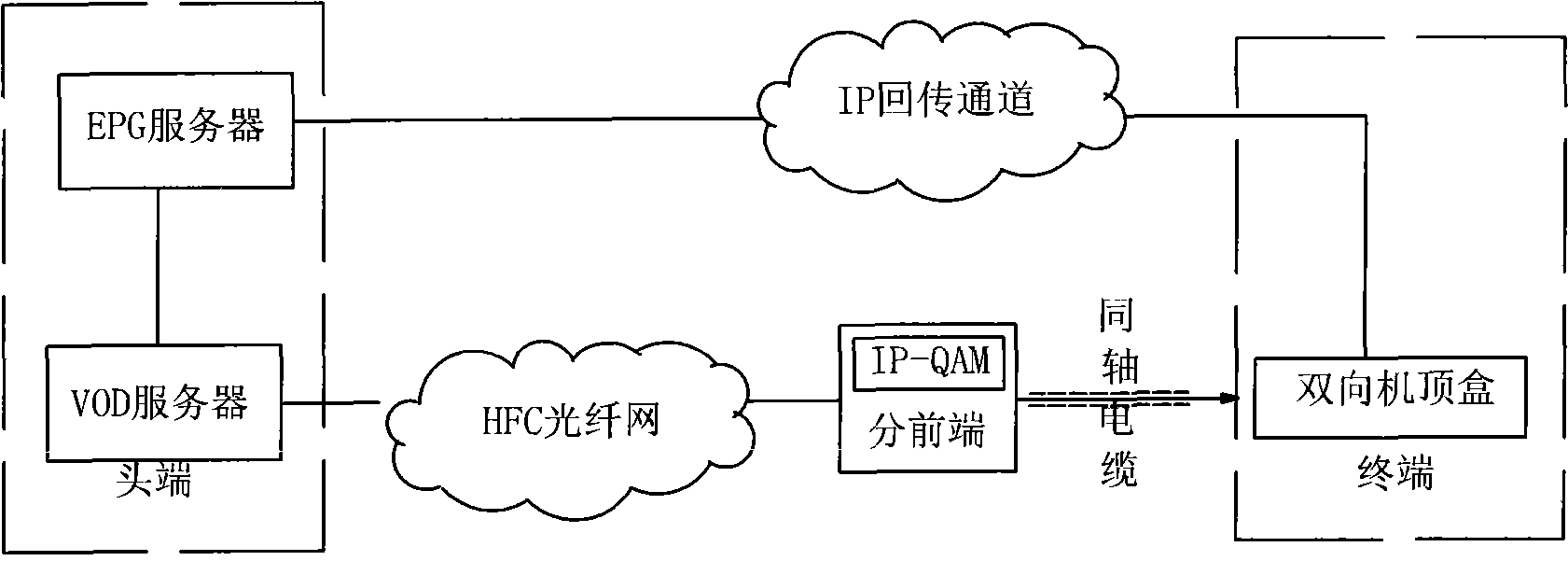
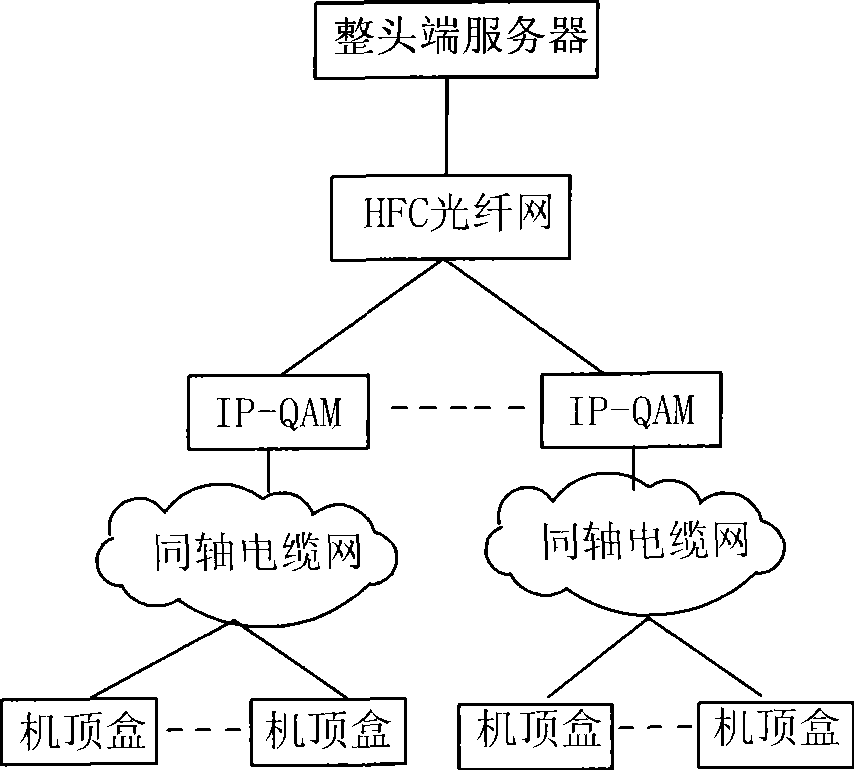
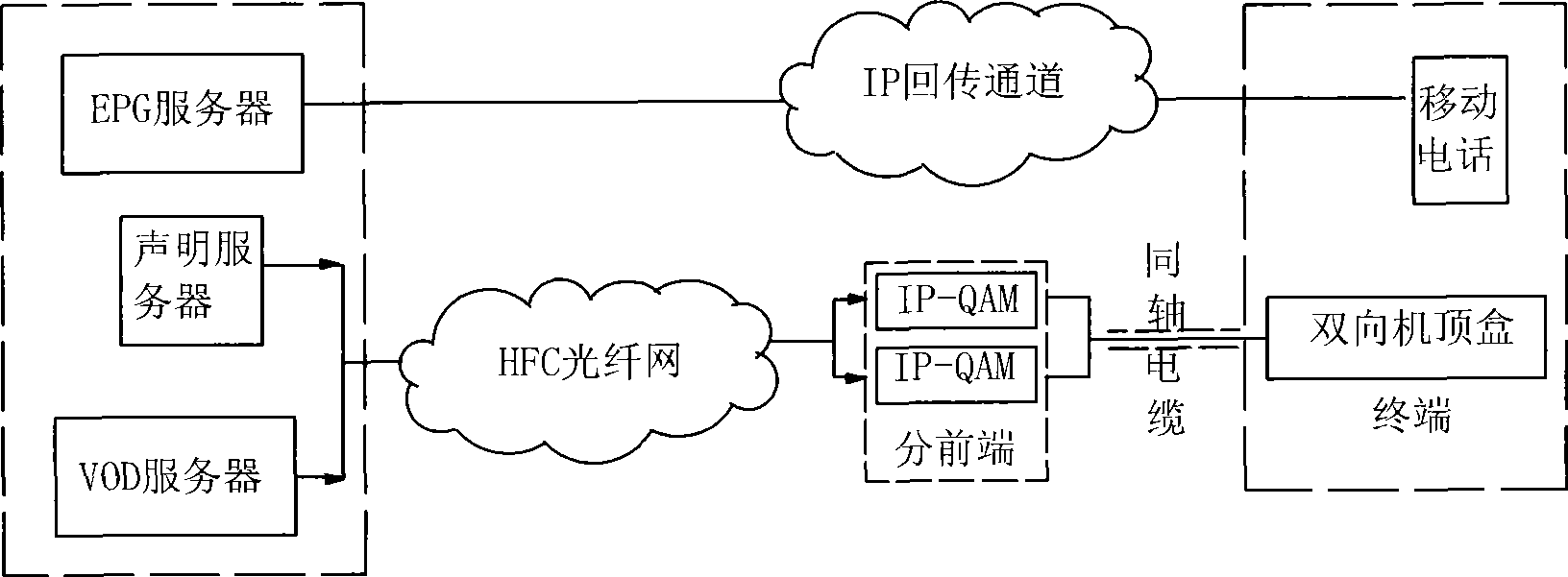
Method for requesting unidirectional wired TV set-top box video back-transmitted by using mobile communication network
InactiveCN101510994AGuaranteed to receiveReceived guaranteeTwo-way working systemsElectrical cable transmission adaptationRadio frequency signalVideo on demand
The invention provides a uni-directional set-top cable box video-on-demand method making use of the passback of mobile communication network, which is that users use mobile communication network for visiting EPG server and examining the list of programs; a request for ordering programs is proposed; video-on-demand server sends the program stream to the IP-QAM equipment of users; IP-QAM modulates the program stream to the radio-frequency signal; and the program stream is received by the set box of the users for the playback. The video-on-demand method needs no double action transformation of cable, and extra computer network to realize the fast video-on-demand service.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
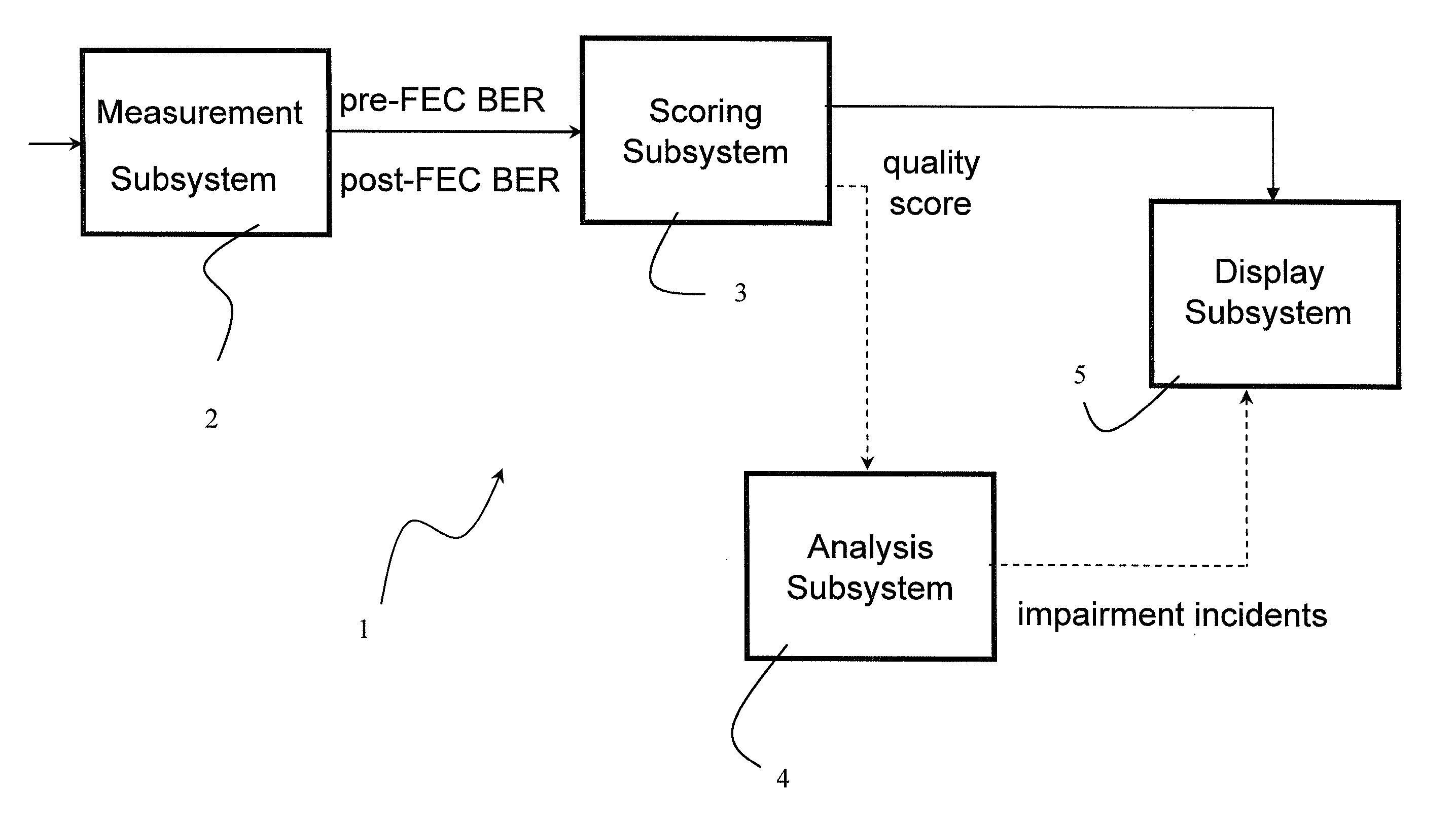
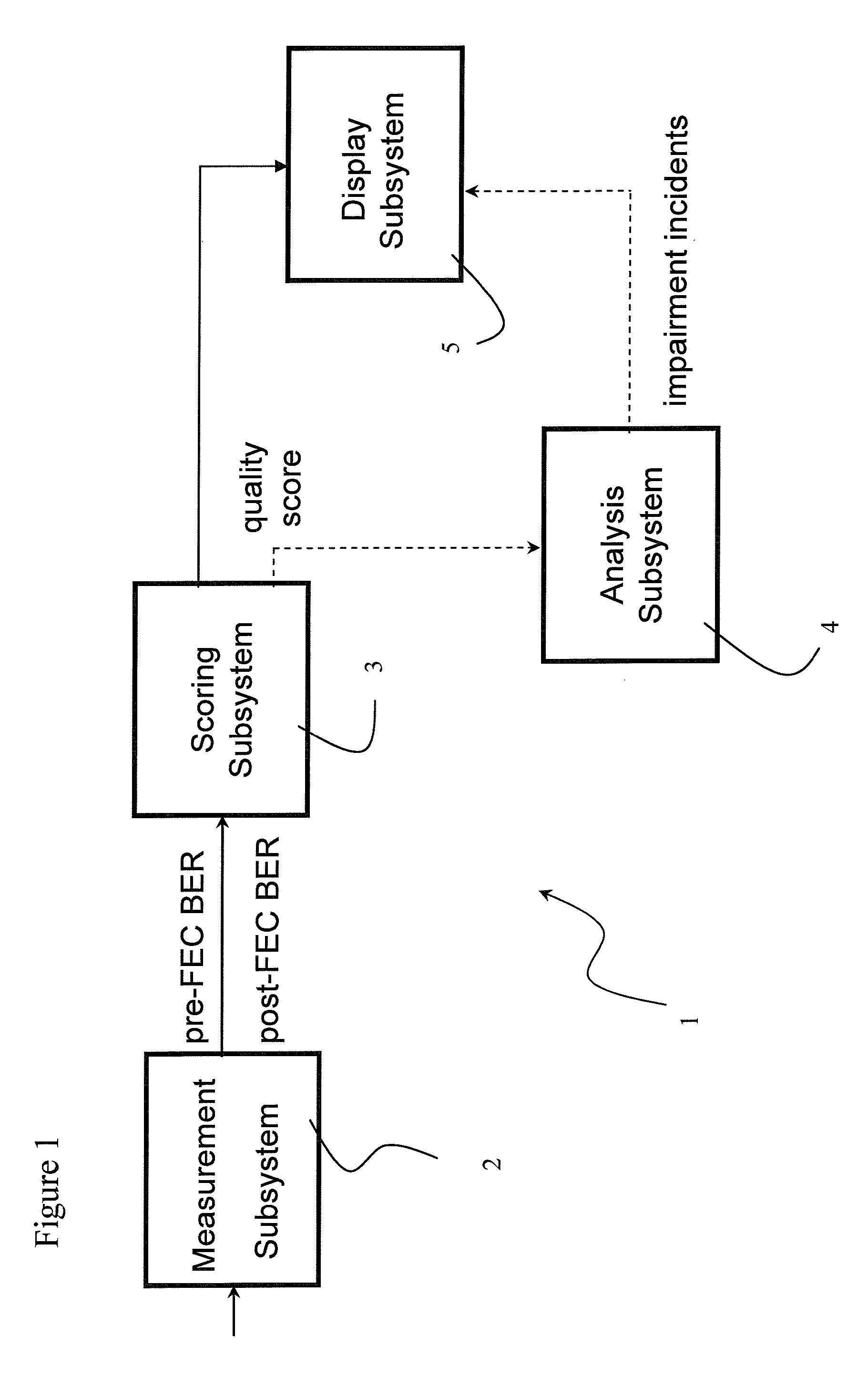
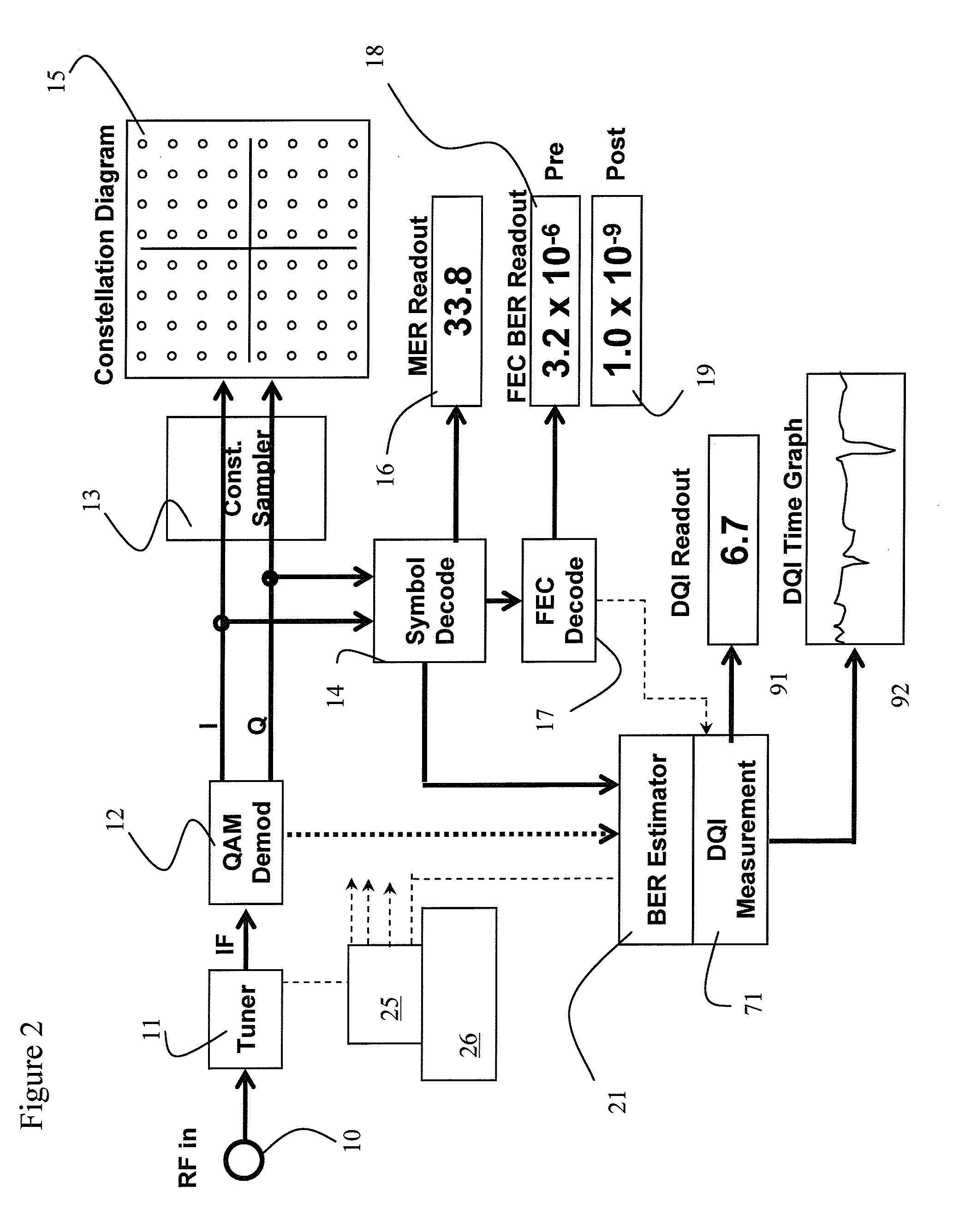
Digital quality index for QAM digital signals
ActiveUS7792183B2Receivers monitoringLine-transmission monitoring/testingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Forward error correction
The present invention relates to a system for calculating a digital quality index (DQI), which provides a rating on a predetermined scale, indicative of the impairments in a received quadrature amplitude modulated (QAM) signal in a CATV cable system. The DQI system utilizes bit error rates prior to and after forward error correction to calculate the DQI value. To increase the calculation rate, the bit error rates can be estimated using voltage errors, signal to noise ratios and / or average corner error metrics.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Secure orthogonal frequency multiplexed optical communications
InactiveUS20110170690A1Improve securityMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsDigital signal processingOptical communication
The invention provides a system and method for secure communication that involve encoding and transmitting an optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) signal. Each subcarrier of an optical carrier in OFDM transmission is modulated with data individually, and a variety of data format are used, such as QPSK, OOK, QAM, etc. The data format of each subcarrier may change in time according to a predetermined pattern. An optical receiver uncovers the data transmitted via an optical link. It is based on a coherent optical receiver and a digital signal processing (DSP) unit. A key to the data mapping and change is transmitted via the same optical link or by a separate channel. In one embodiment, the key is transmitted using quantum encryption technique. Besides subcarrier modulation encoding, the system may provide additional layers of security: optical carrier frequency hopping and polarization scrambling.
Owner:CELIGHT
A transmission system and method of the mobile digital multimedia broadcast signals
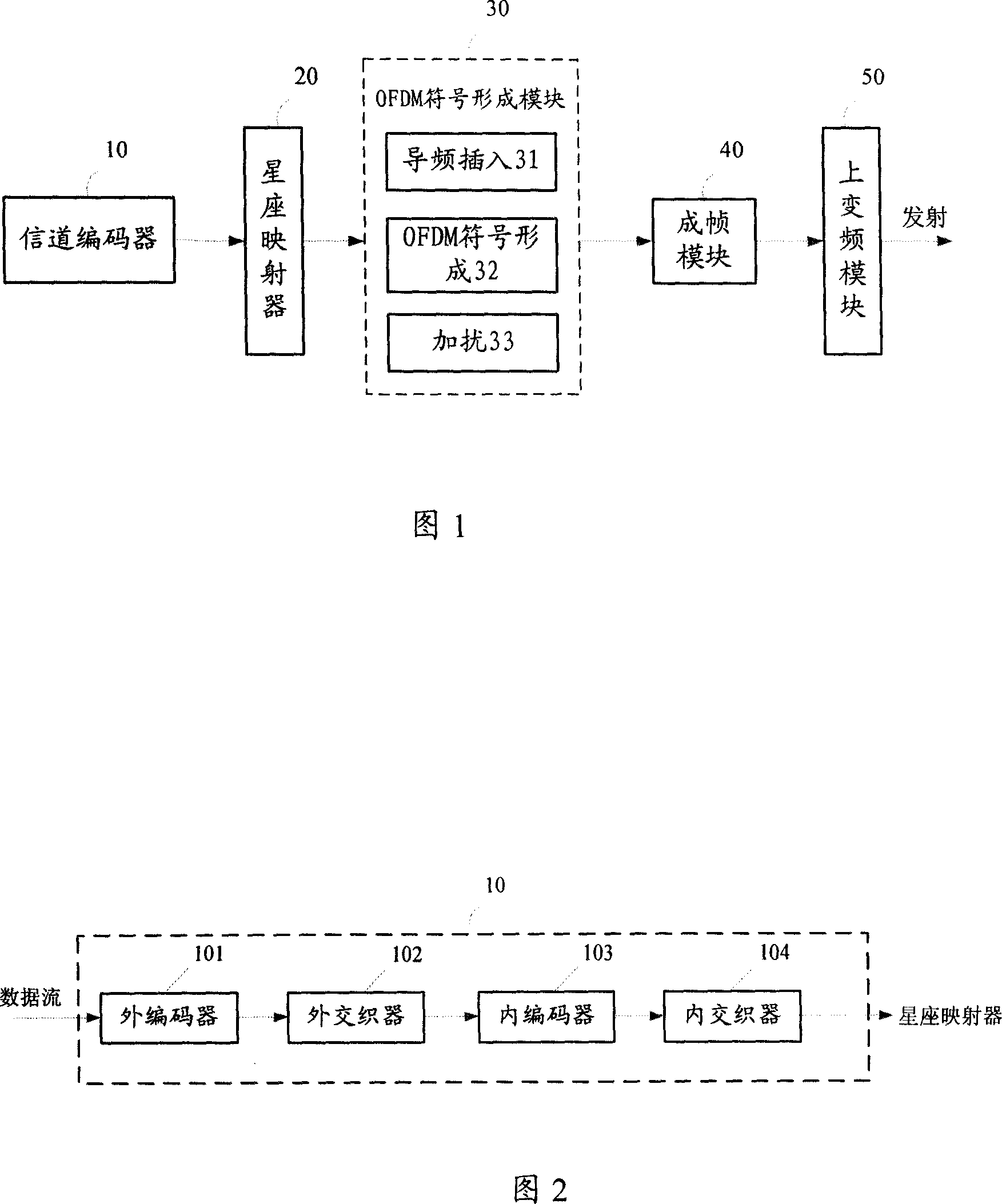
InactiveCN101018223AImprove estimation performanceGood estimateMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexData streamUp conversion
The disclosed transmission system for mobile digital multimedia broadcast signal comprises: a channel coder to receive, code and interlace data flow to transform it into bit flow; a constellation mapper to map the bit flow into QAM, BPSK or QPSK signal flow; an OFDM signal forming module to insert the continual and discrete pilot frequency into last signal flow and load on the service sub-carrier to form OFDM signal; a framing module to add beacon into the OFDM signal and form transmission frame; and an up-conversion module to generate RF signal for transmission. It also discloses corresponding transmission and allocation method.
Owner:INNOFIDEI TECHNOLOGIES INC
Combined modulation recognition method based on clustering and support vector machine
InactiveCN102497343AImprove recognition rateImprove modulation recognition ratePhase-modulated carrier systemsMultiple carrier systemsPattern recognitionCluster algorithm
The invention provides a combined modulation recognition method based on clustering and a support vector machine in order to overcome the shortcoming of low modulation recognition rate of a clustering algorithm with a low signal to noise ratio. According to the method, a characteristic parameter of a modulation signal is extracted by using the clustering algorithm according to a phase shift keying / quadrature amplitude modulation (PSK / QAM) mode based on a constellation diagram; and a modulation mode for a signal is recognized through the support vector machine, so that the modulation recognition rate of a system is increased. The method comprises the following steps of: aiming at the PSK / QAM mode based on the constellation diagram, reconstructing the constellation diagram of a receiving signal by using the clustering algorithm; and obtaining an effective function value, which can reflect an outstanding difference of modulation types under different clustering central numbers, as the characteristic parameter input into the support vector machine by constructing an effectiveness evaluation function. In order to overcome the shortcoming that two common algorithms of one to multiple and one to one have high calculation complexity when the support vector machine recognizes multiple types, the support vector machine is trained by adopting a hierarchical algorithm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
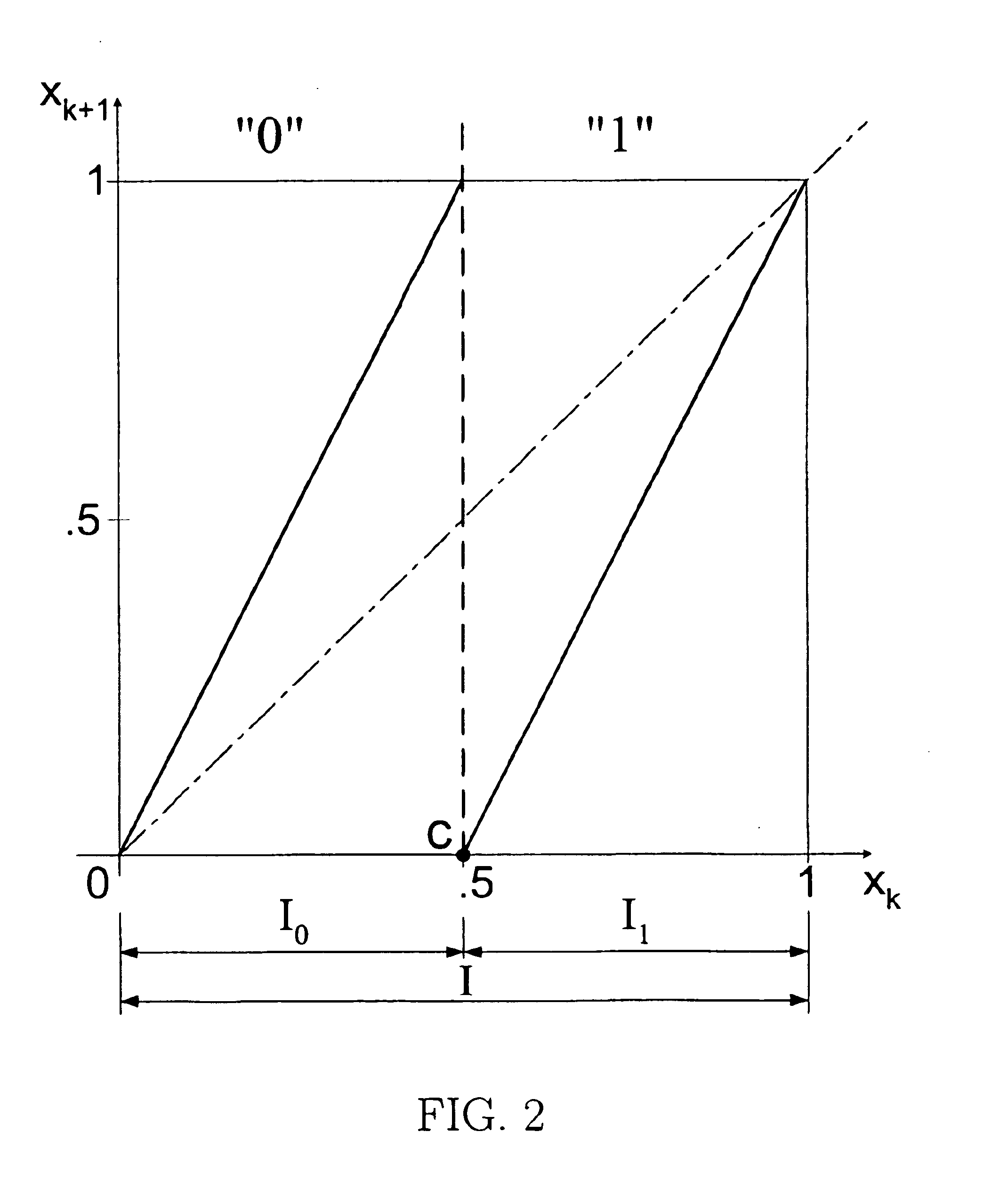
Pseudo-chaotic communication method exploiting symbolic dynamics
InactiveUS6882689B2Receiver scalabilityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationShift registerData signal
A pseudo-chaotic coding / modulation method. The coding method exploits symbolic dynamics of a chaotic map at the transmitter to encode data. The encoding synthesizes the chaotic map based upon the data to be transmitted. In a preferred embodiment, pseudo-chaotic iterates are generated from a digital implementation of a Bernoulli shift map. The output of the shift map is translated by a mapping, preferably implemented by a digital signal processor, to allow transitions between states in a transmitted signal to differ, and the translated map is used to drive a modulator (for example PPM, FSK, PSK, QAM, etc.). In the specific case of pulse-position modulation (PPM) the translated map is used to modulate pulse train positions within a periodic synchronization frame. The preferred embodiment uses a shift register to implement an approximation of the Bernoulli shift map acting as a form of convolutional code with a number of states equal to the symbolic states defined on the chaotic map. A receiver may use fewer states and still decode the data signal, allowing receiver scalability.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
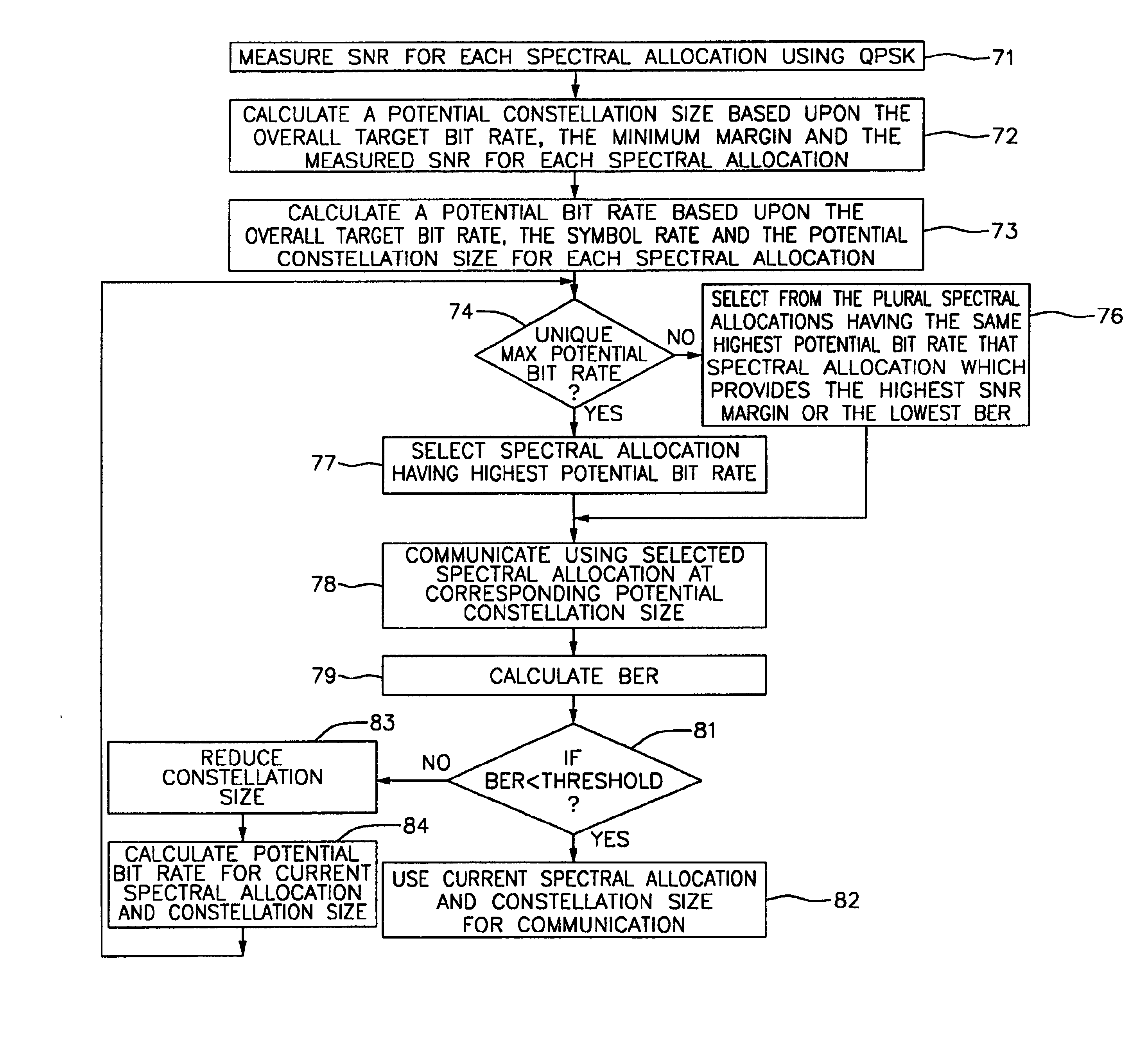
DSL rate adaptation
InactiveUS6904082B2Minimizes high-frequency contentIncrease distortion and noiseTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationConstellationRate adaptation
A method for enhancing the bit rate and / or margin at which quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) communication is performed includes the steps of varying a spectral allocation and constellation size with which communication is performed, so as to define a combination of spectral allocation and constellation size at which the bit rate and / or margin are enhanced. The spectral allocation can be varied by varying a stop frequency thereof, while maintaining a substantially constant start frequency, so as to mitigate undesirable high frequency content of the bandwidth. Alternatively, both start and stop frequencies may be varied.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
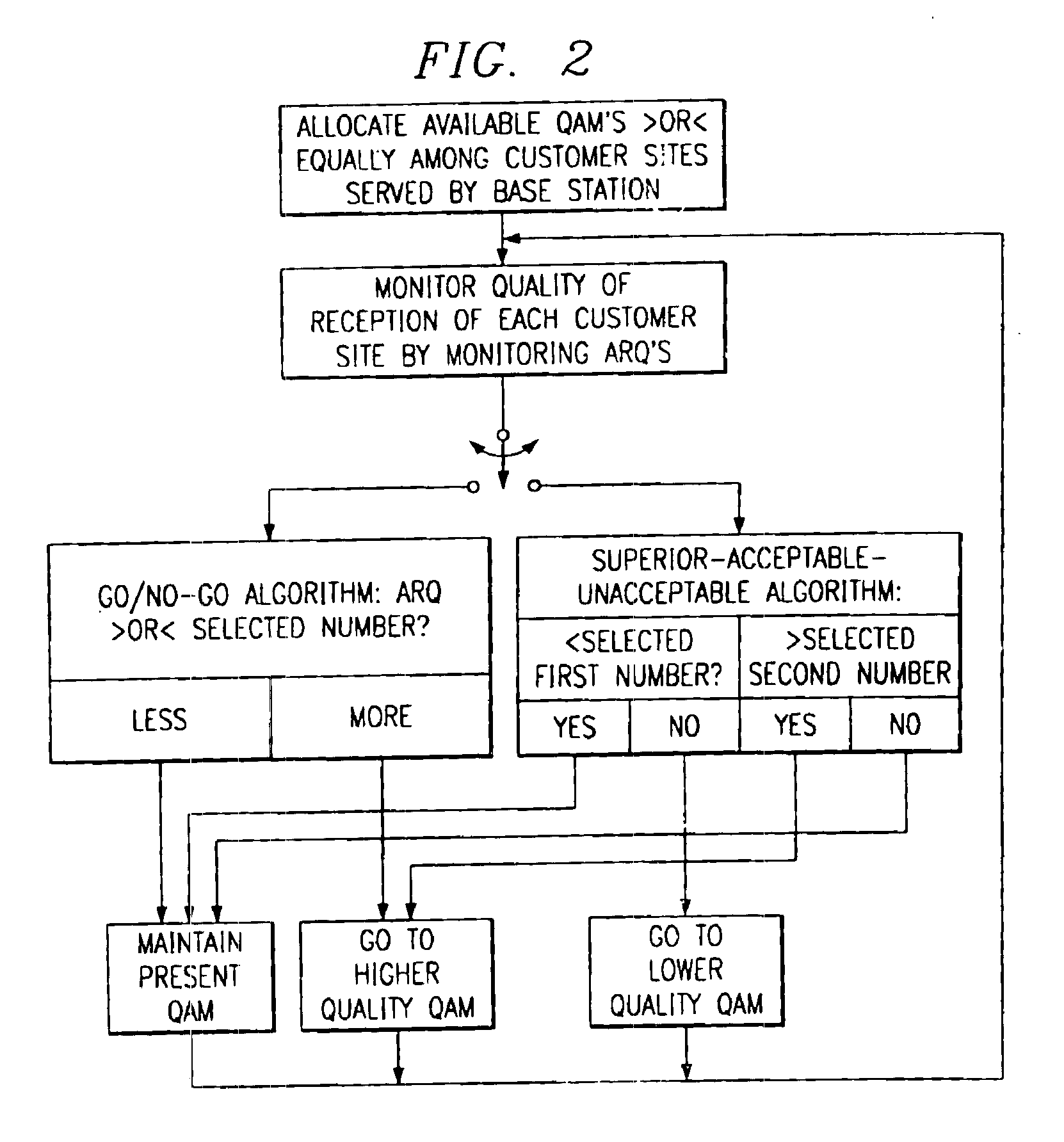
Method of and apparatus for implementing adaptive downstream modulation in a fixed wireless communication system
InactiveUS6898418B2Delay in transmission timeLess susceptible to degradationError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorSignal qualityCommunications system
Available quadrature amplitude modulation (“QAM”) carriers transmittable by a base station to customer sites are substantially equally divided among the sites according to the expected quality of reception. ARQ transmissions from the sites are monitored as a measure of the quality of signals received by the sites. If the quality of received signals is unacceptable, the affected site is re-assigned to a higher quality QAM. In addition, if the quality of received signals is too high, the affected site is re-assigned to a lower quality QAM.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
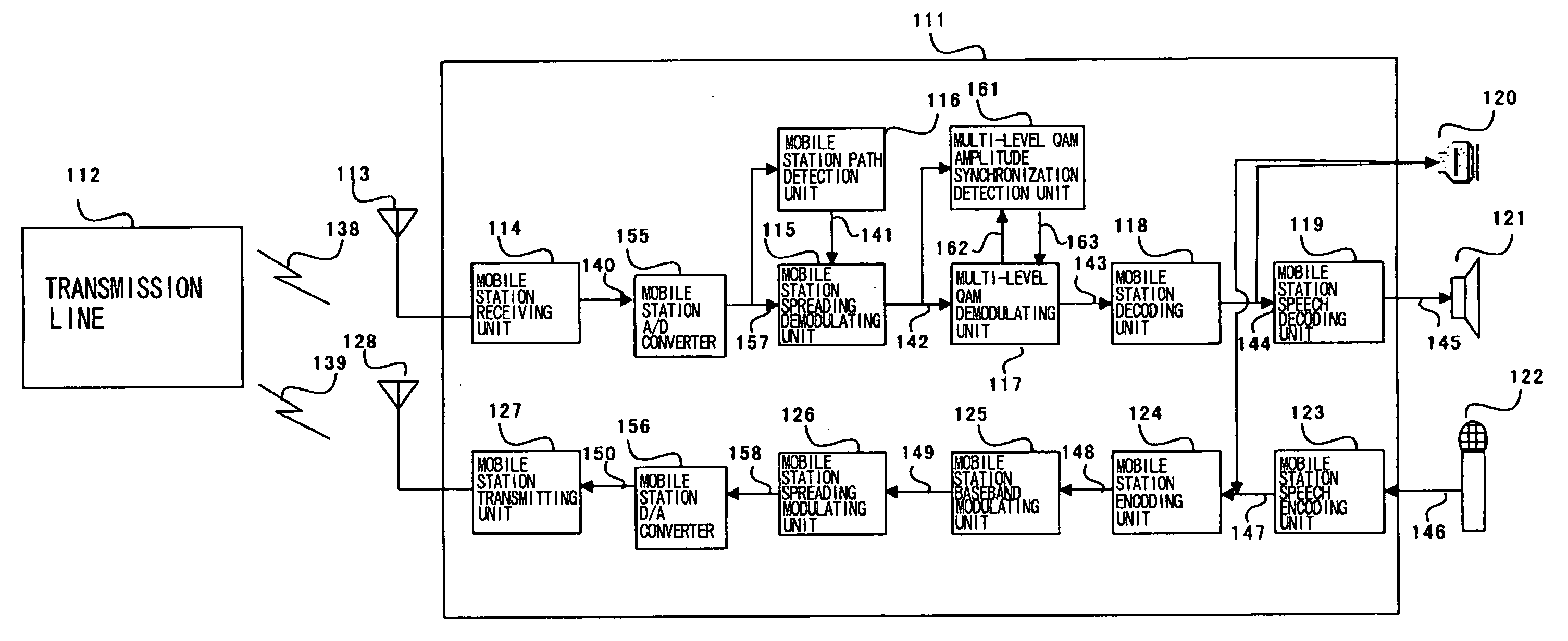
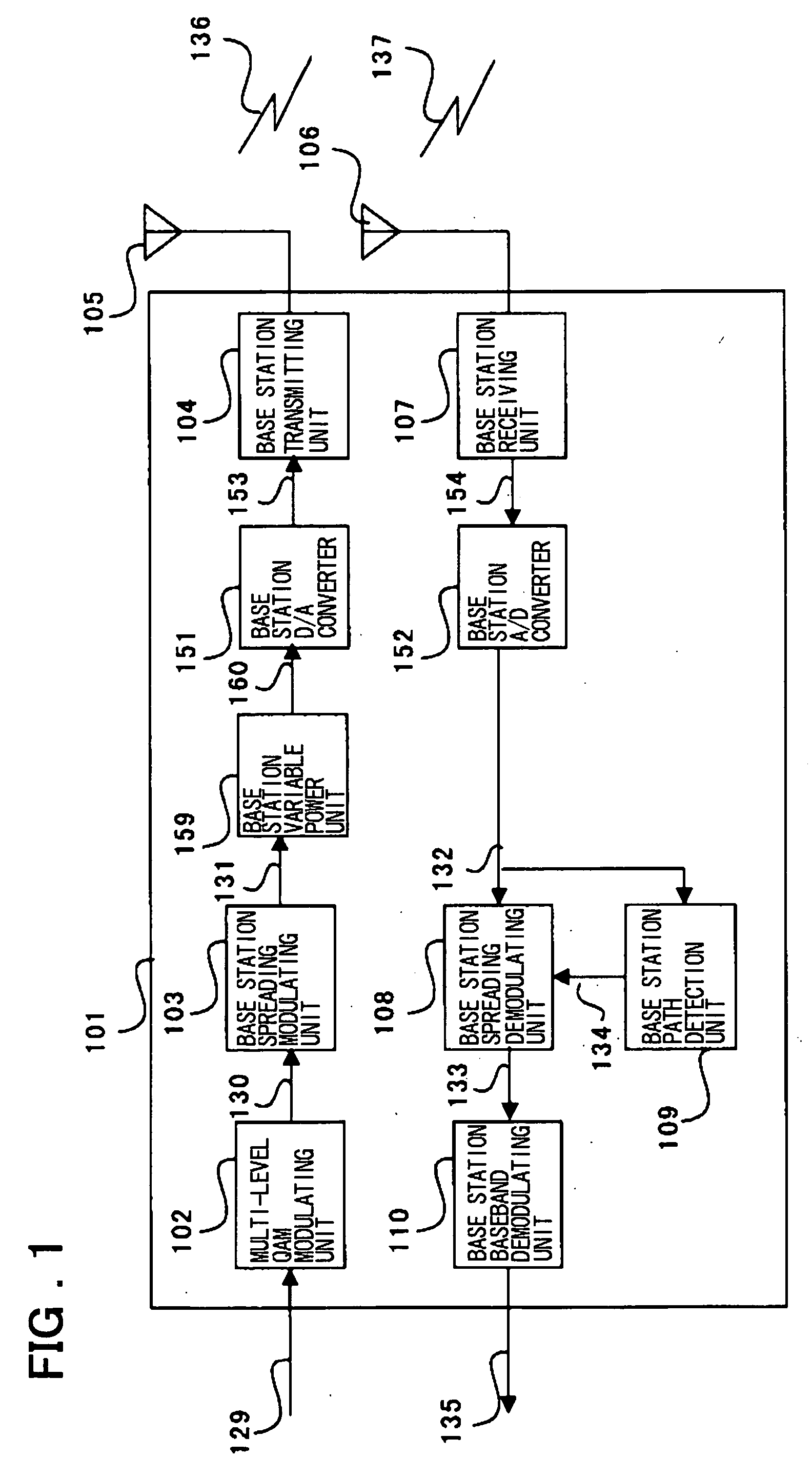
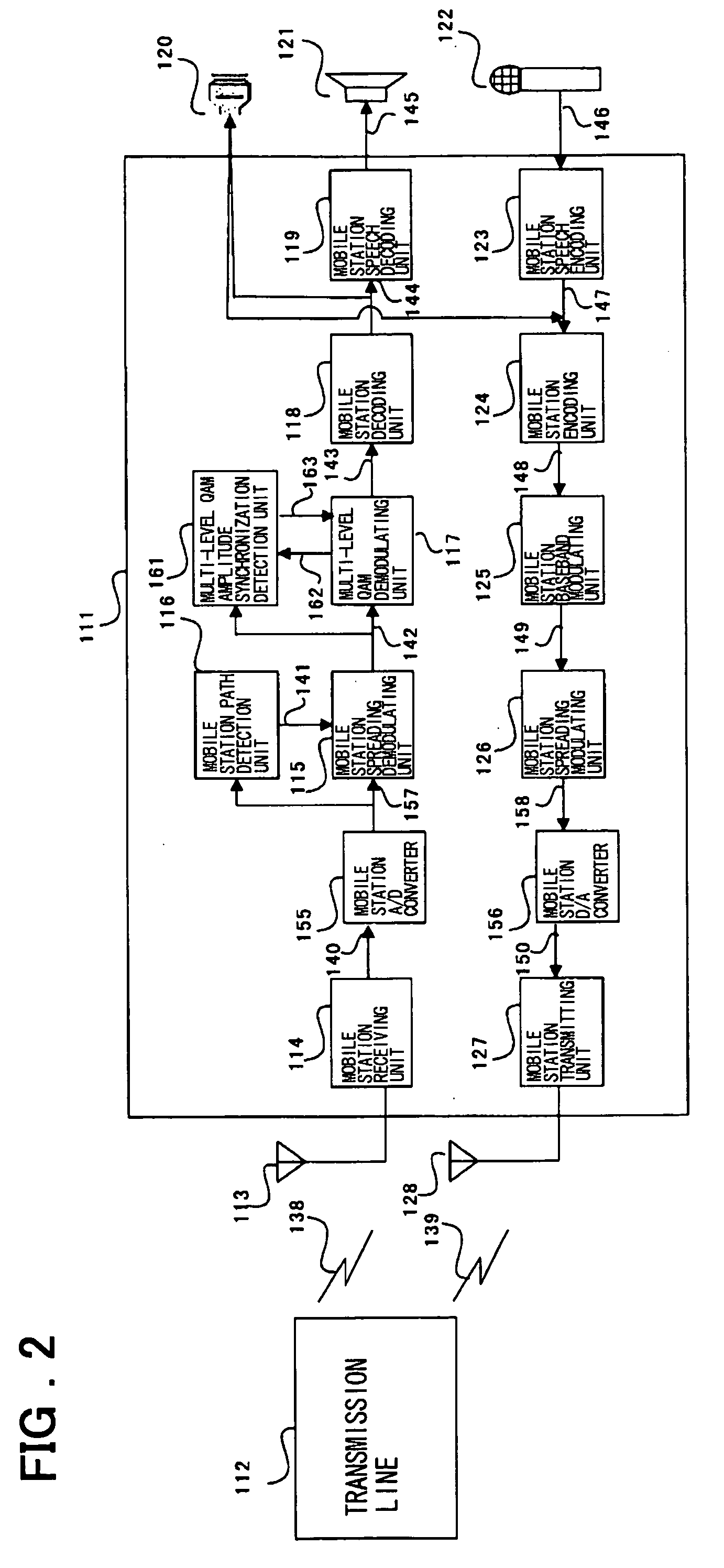
Wireless apparatus employing multi-level QAM and method for estimating threshold value
InactiveUS20040114692A1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionTransmission monitoringTelecommunicationsEngineering
An wireless terminal includes a demodulating unit which comprises an FV (fading vector) estimating unit for receiving a CPICH spread / demodulated signal to output an FV signal with a reduced noise ratio; a phase synchronization unit for multiplying a PDSCH spread / demodulated signal with a complex conjugate of the FV signal to correct the phase offset of the PDSCH I and Q signals to send the resulting PDSCH I and Q signals to a multi-level QAM amplitude synchronization detection unit and to an amplitude demodulating unit; a first-quadrant transformation unit for collecting the second to fourth quadrant signals of the phase-synchronized PDSCH I and Q signals; and a threshold value detecting unit for calculating a multi-level QAM threshold value from the first quadrant signals and the FV signals to send the threshold signal to an amplitude demodulating unit. The amplitude demodulating unit effects amplitude demodulation to output multi-level QAM demodulated signals. The threshold value detecting unit previously assumes a plural number of probabilities as to which of the levels received data belongs to and, using a plural number of the data, raises the precision of the assumed data. The threshold value is estimated, using the frequencies and differences of the respective levels, from the assumed plural threshold values.
Owner:NEC CORP
Probabilistic Shaping for Arbitrary Modulation Formats
ActiveUS20190109752A1Improve data transfer performanceError preventionElectromagnetic receiversOptical data transmissionComputer science
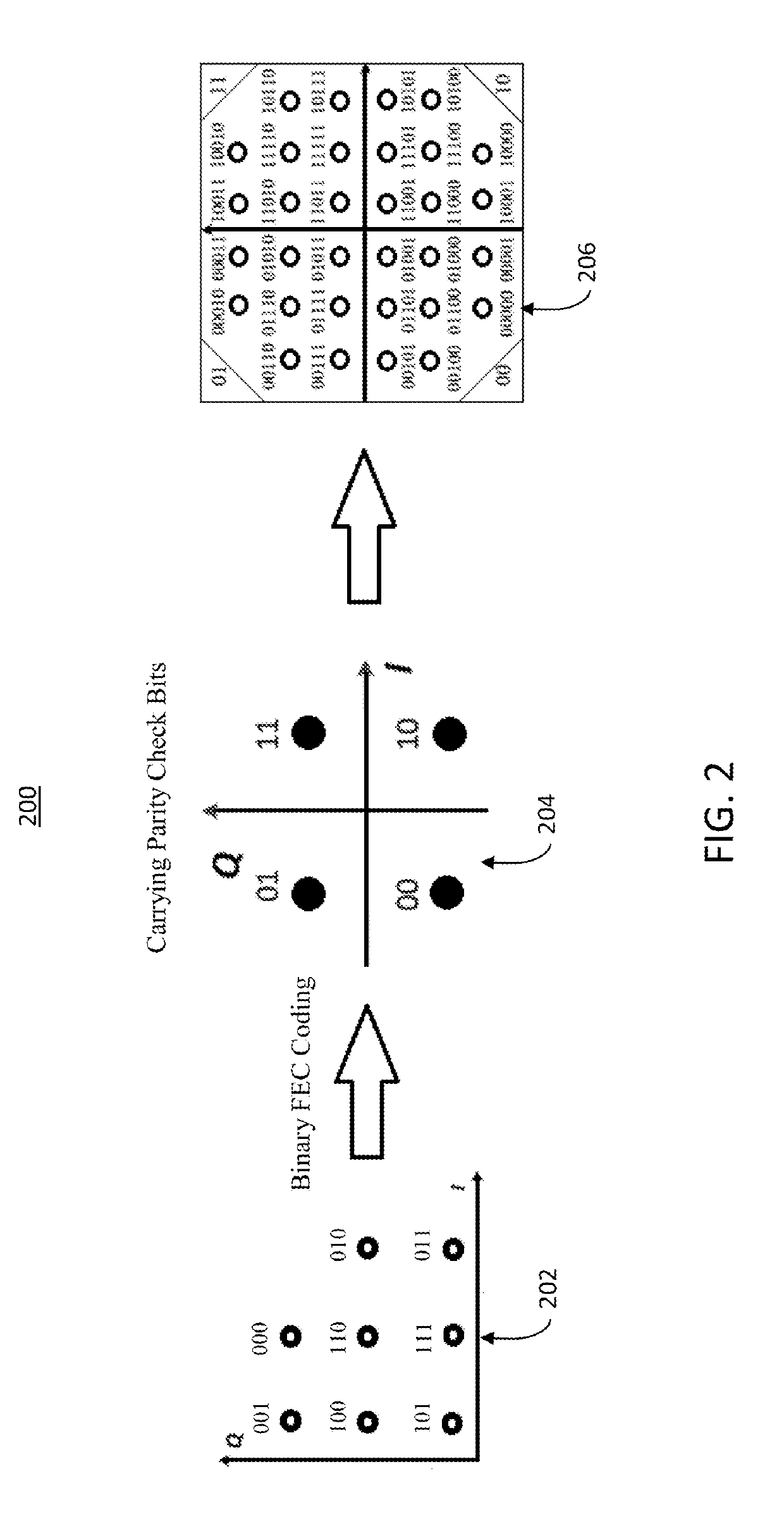
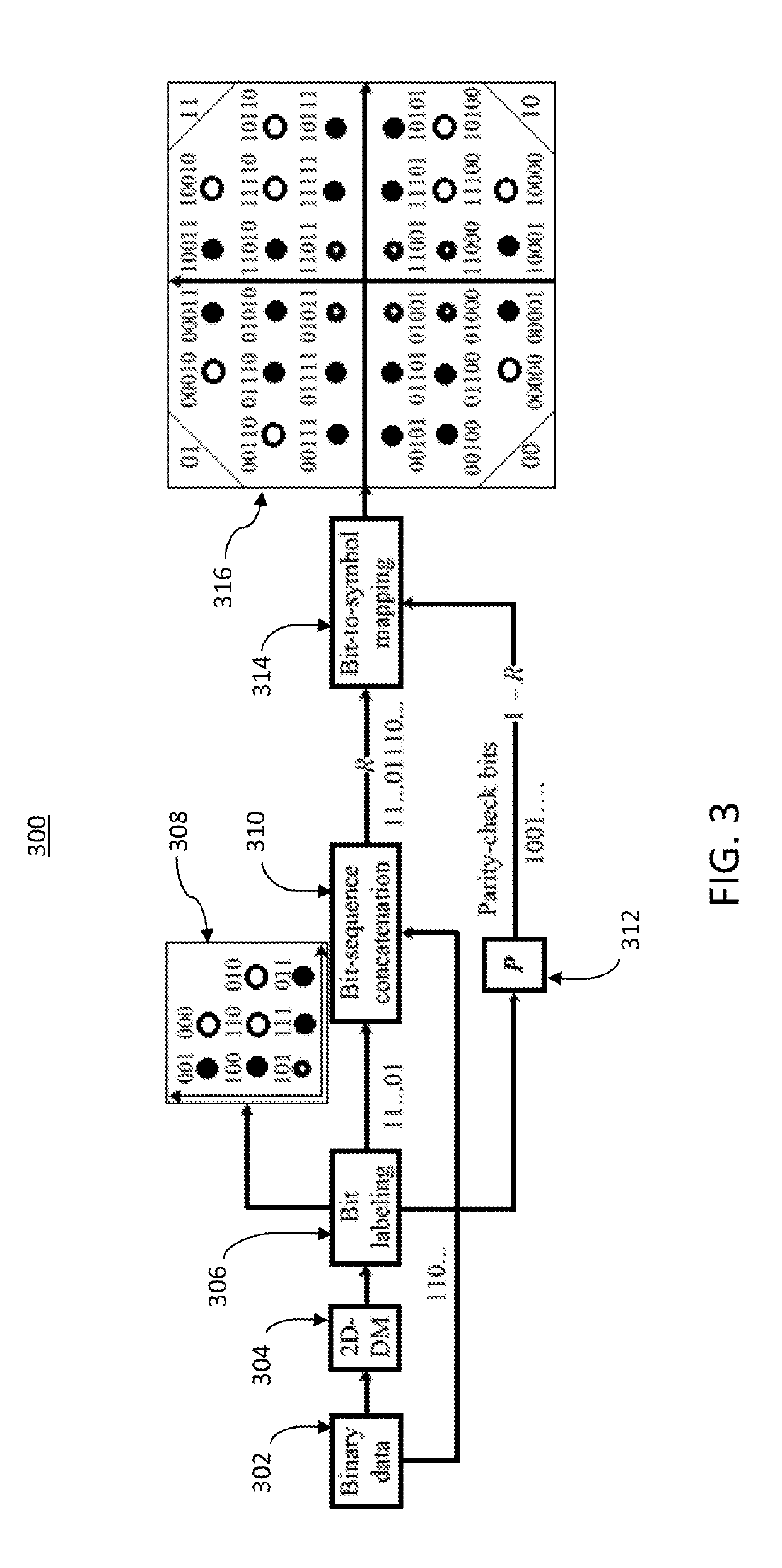
Systems and methods for optical data transport, including controlling data transport across an optical transmission medium by generating two-dimensional (2D) distribution matchers (DMs) based on probabilistic fold shaping (PFS) and arbitrary probabilistic shaping (APS). The 2D PFS-based DM is can encode any N-fold rotationally symmetrical Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) format by applying the 2D PFS-based DM only to symbols in one quadrant based on a target entropy. A fold index yield uniform distribution is determined, and is utilized to carry generated uniform distributed parity check bits across the optical transmission medium. The 2D APS-based DM can encode any arbitrary modulation formats by encoding uniform binary data to generate non-uniform target symbols, and generating a probability distribution for the target symbols by indirectly applying the 2D APS-based DM based on a target probability distribution and a detected code rate of generated FEC code.
Owner:NEC CORP
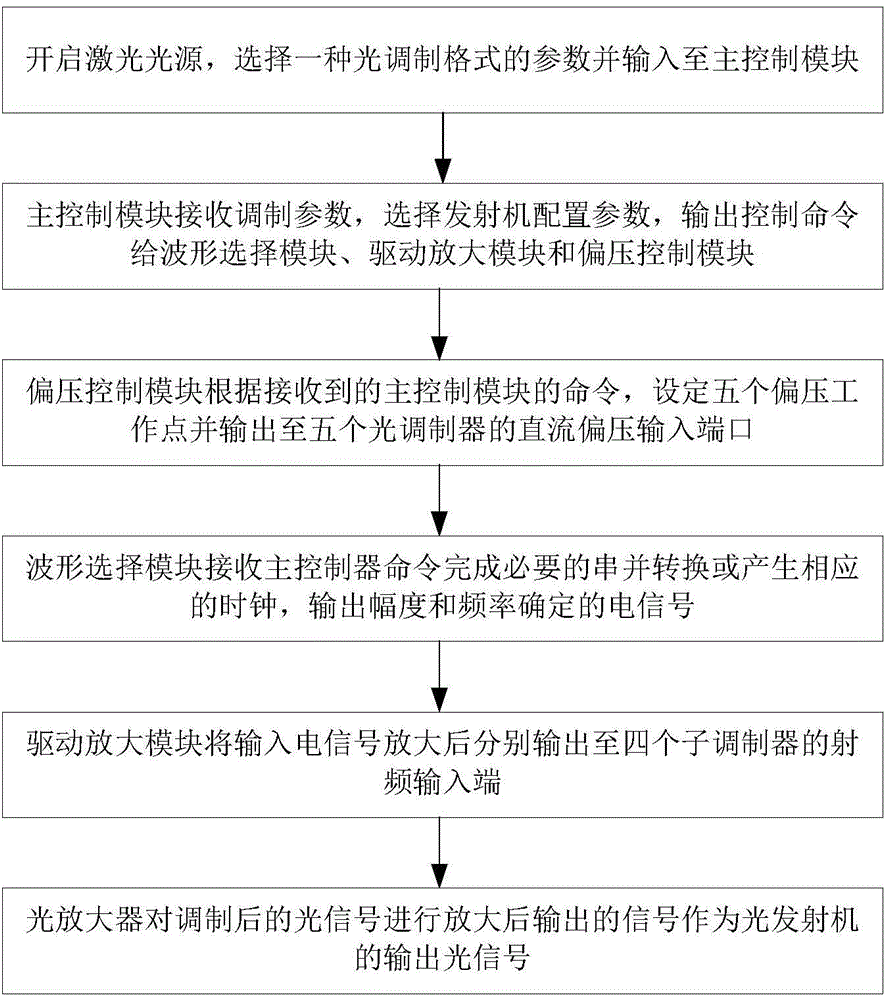
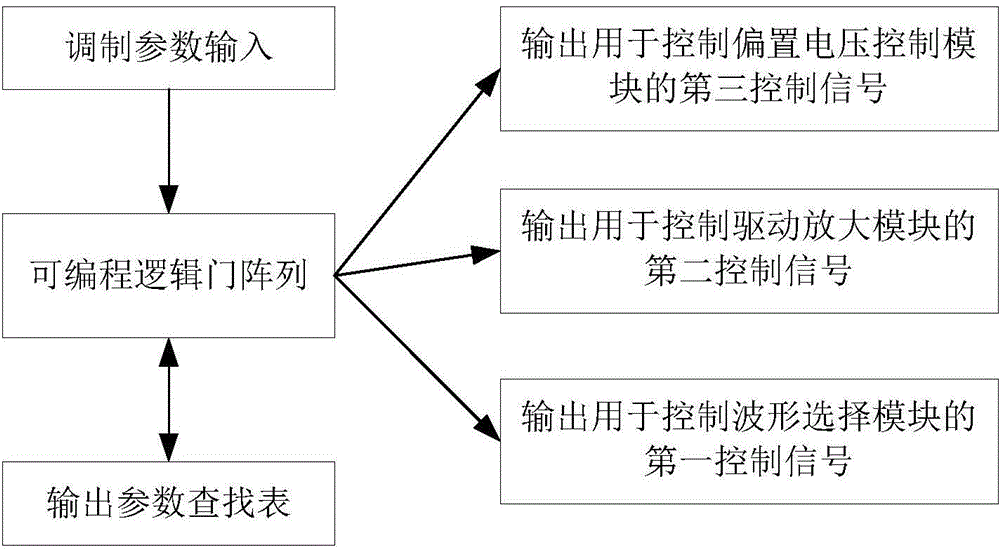
Optical transmitter supporting multiple modulation formats and control method
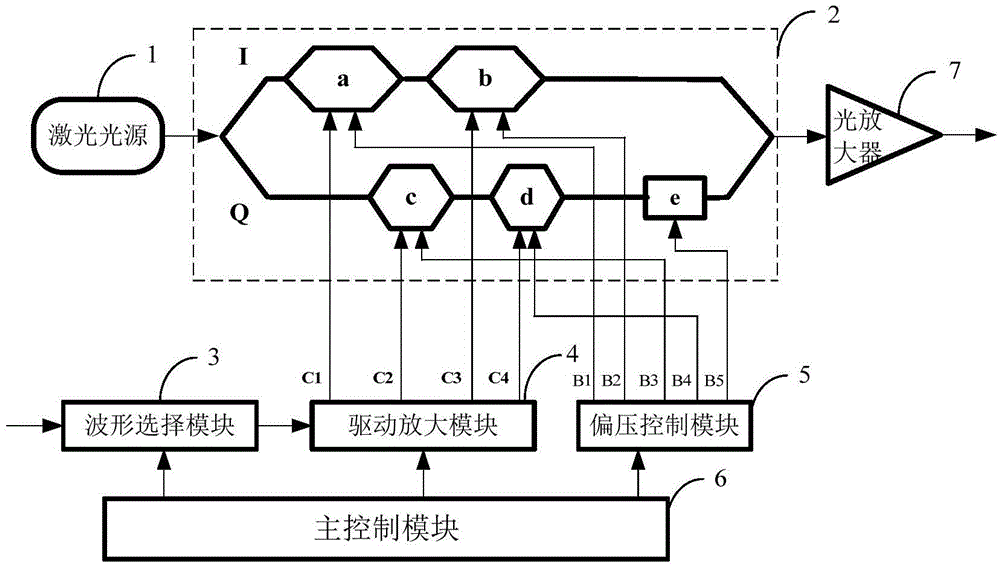
ActiveCN104467978AReduce complexitySimple configurationElectromagnetic transmittersComputer moduleEngineering
The invention discloses an optical transmitter supporting multiple modulation formats and a control method. The optical transmitter comprises a laser source, two parallel optical modulators, a waveform selection module, a drive amplification module, a bias control module, a master control module and an optical amplifier. The master control module is connected with the waveform selection module, the drive amplification module and the bias control module and transmits control information. The waveform selection module conducts series-parallel conversion on data to be modulated according to input modulation parameters and generates clock signals, drive amplification is conducted on the clock signals, and then the clock signals are then loaded to the optical modulator. The bias control module selects a proper bias working point according to the specified modulation format. The modulated optical signals are amplified by the optical amplifier and then are used as output of the transmitter. The optical transmitter can flexibly support multiple modulation formats only by utilizing binary data, switching between multiple modulation formats such as NRZ-2PSK, RZ-2PSK with the duty ratio of 50%, NRZ-QPSK, CSRZ-QPSK and 16 QAM is achieved, and the optical transmitter is suitable for high-speed and flexible optical fiber communication systems and networks in the future.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
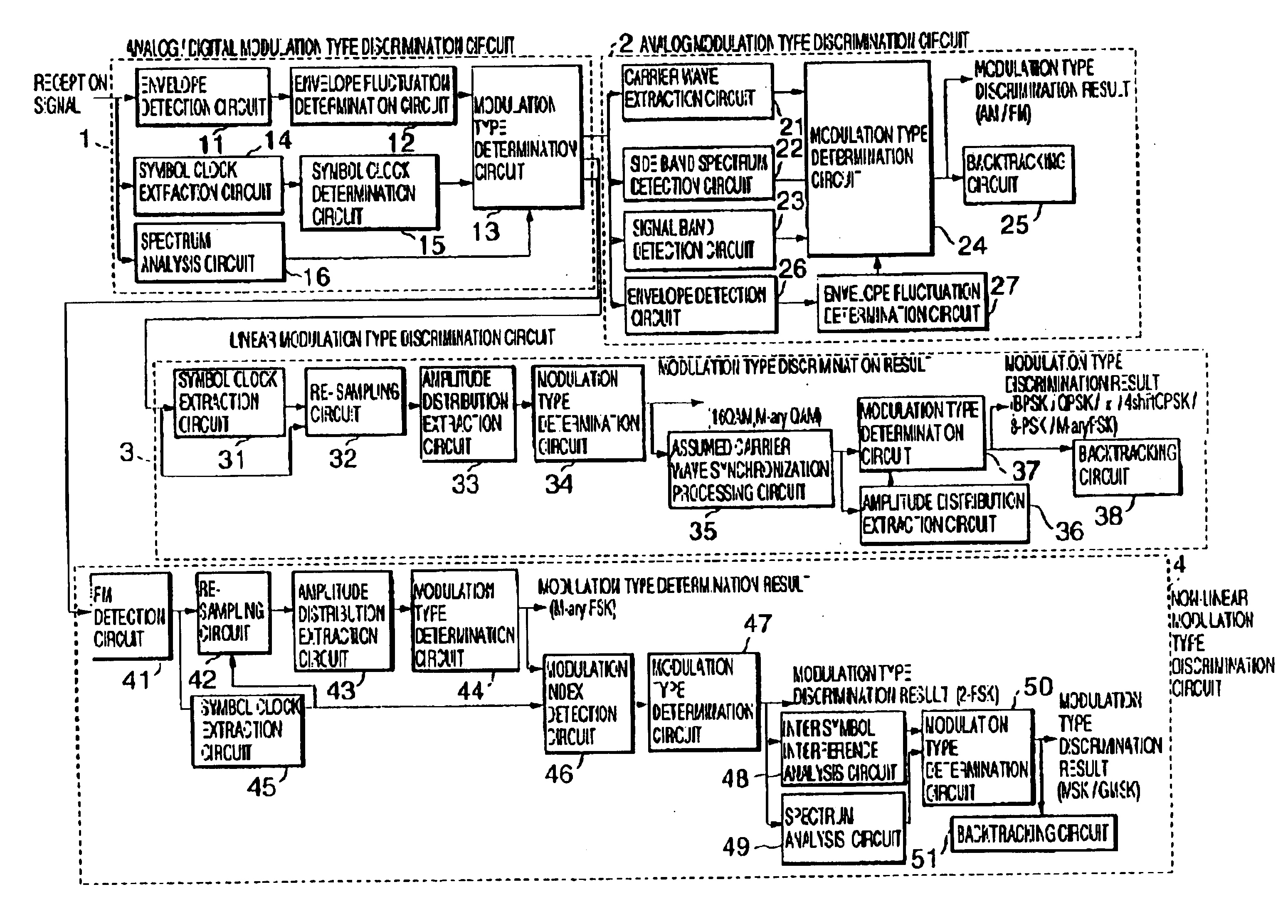
Automatic modulation type discrimination apparatus and automatic modulation type discrimination method capable of discriminating plural kinds of modulation types
InactiveUS6934342B1Possible to performImprove reliabilitySimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationModulation type identificationNonlinear modulationLinear modulation
A analog / digital modulation type discrimination circuit 1 discriminates whether a reception signal is an analog modulation type, a linear modulation type or a non-linear modulation type by digital modulation type. In case where the reception signal is discriminated to be the analog modulation type, an analog modulation type discrimination circuit 2 discriminates whether it is an AM signal or an FM signal among the analog modulation type. In case where the reception signal is discriminated to be the linear modulation type by digital modulation type, a linear modulation type discrimination circuit 3 discriminates whether it is a BPSK signal, a QPSK signal, a π / 4-shift QPSK signal, an 8-PSK signal, an M-ary PSK signal of multi-level exceeding 8-levels, a 16 QAM signal or a n M-ary QAM signal of multi-level exceeding 16-levels among the linear modulation type by digital modulation type. In case where the reception signal is discriminated to be the non-linear modulation type by the digital modulation type a non-linear modulation type discrimination circuit 4 discriminates whether it is an M-ary FSK signal, a 2-FSK signal, an MSK signal or a GMSK signal among the non-linear modulation type by the digital modulation type.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication method and system based on probabilistic shaping mapping
ActiveCN108631879AQuality improvementHigh sensitivityElectromagnetic transmissionMultiple carrier systemsFiberFrequency spectrum
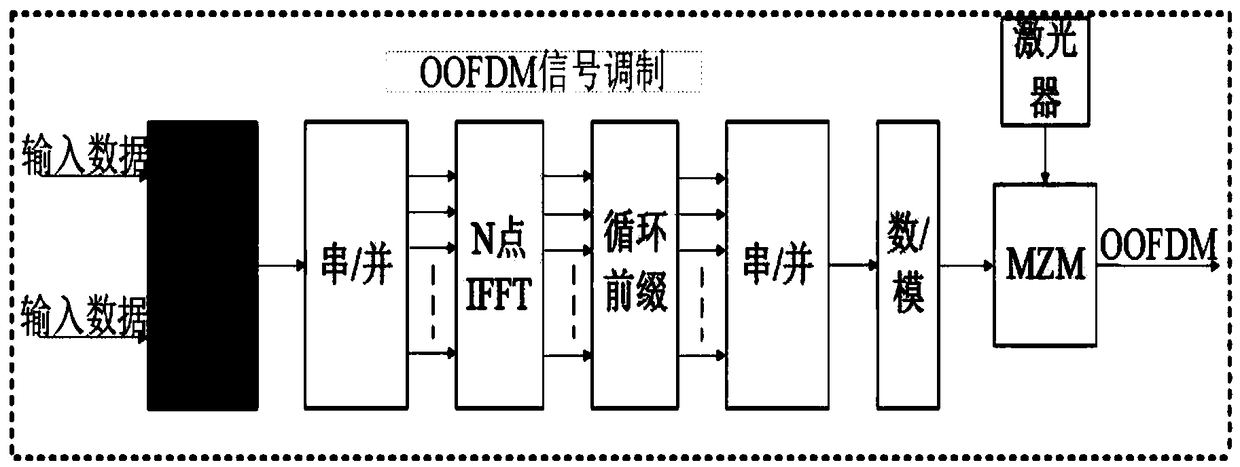
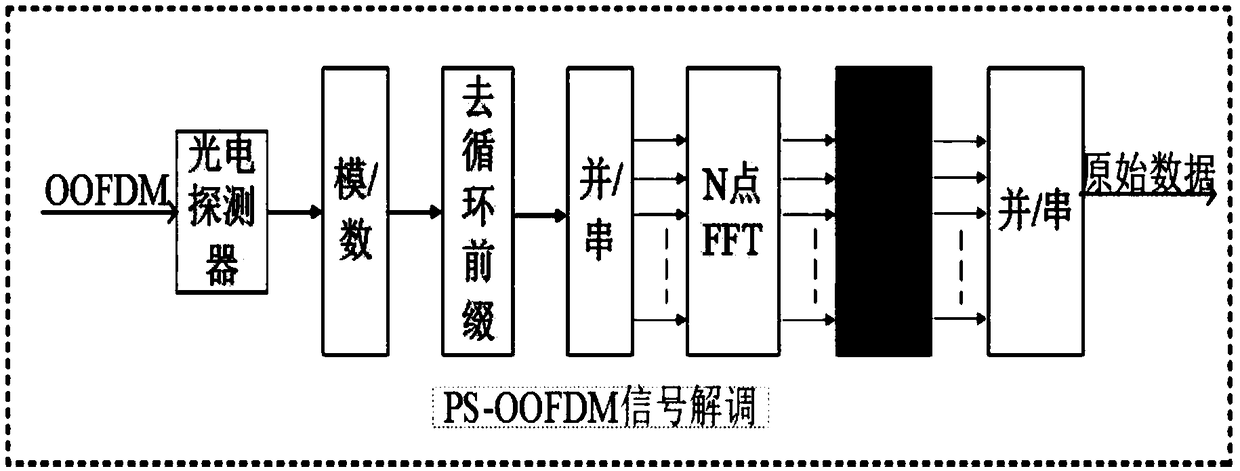
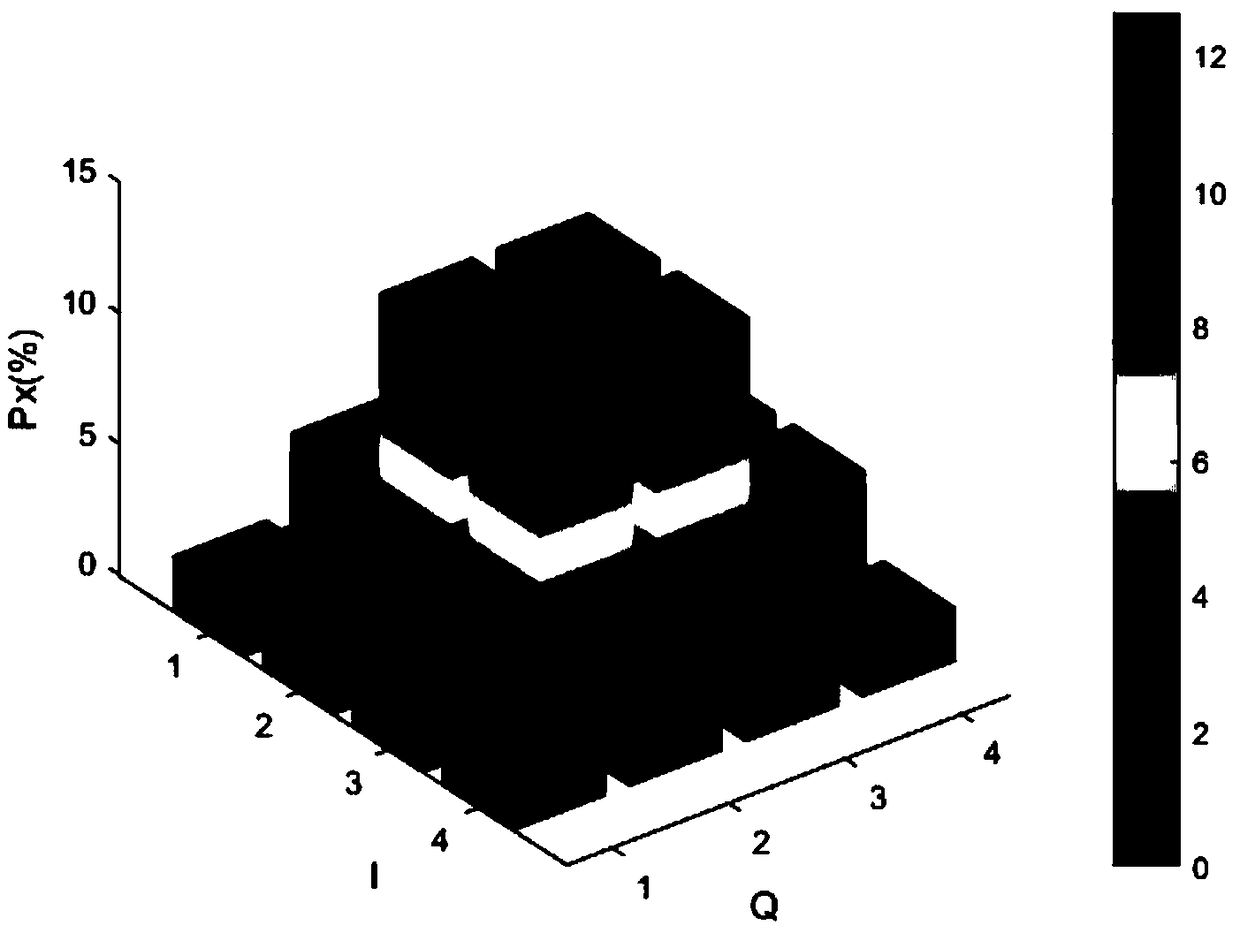
The invention relates to an optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication method and a system thereof based on probabilistic shaping mapping, wherein the method comprises: generating a pseudo random binary bit stream PBRS signal; modulating the PRBS signal to obtain a PS-QAM complex signal; performing serial / parallel conversion, inverse fast Fourier transform and parallel / serialconversion on the PS-QAM complex signal to obtain a baseband OFDM signal, and obtaining an OFDM baseband signal with a cyclic prefix; modulating the OFDM baseband signal onto an optical carrier afterdigital / analog conversion to obtain a PS-OOFDM signal, and transmitting the signal to the optical fiber; converting the PS-OOFDM signal on the optical fiber into an analog OFDM electrical signal; performing analog / digital conversion on the analog OFDM electrical signal to obtain a digital OFDM signal, removing the cyclic prefix, and performing the inverse fast Fourier transform after parallel / serial conversion to obtain the PS-QAM complex signal; separating the real part and the imaginary part of the PS-QAM complex signal, and restoring the corresponding PBRS signal by de-mapping. The invention is capable of achieving shaping gain and improving the spectral efficiency of fiber communication.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
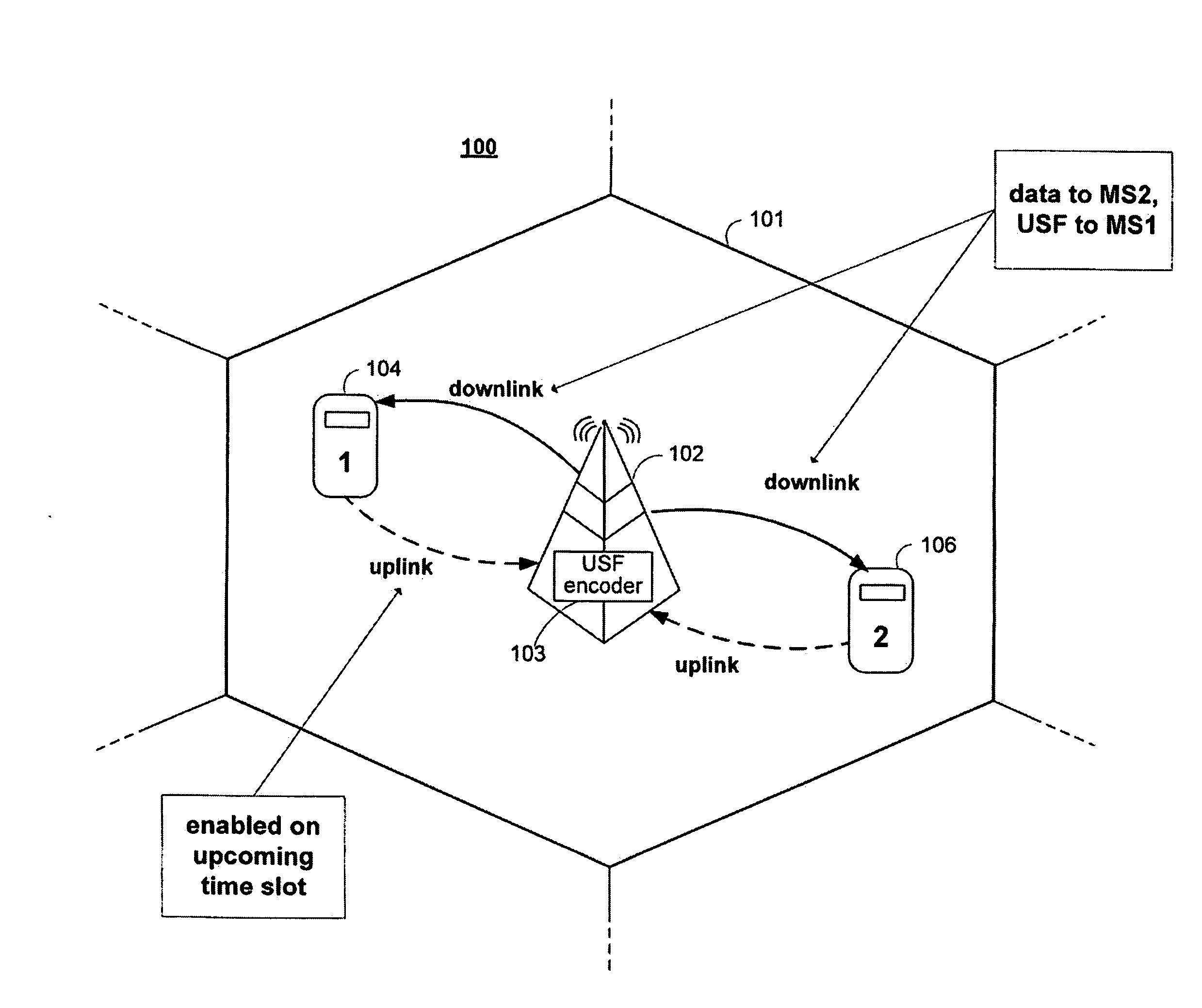
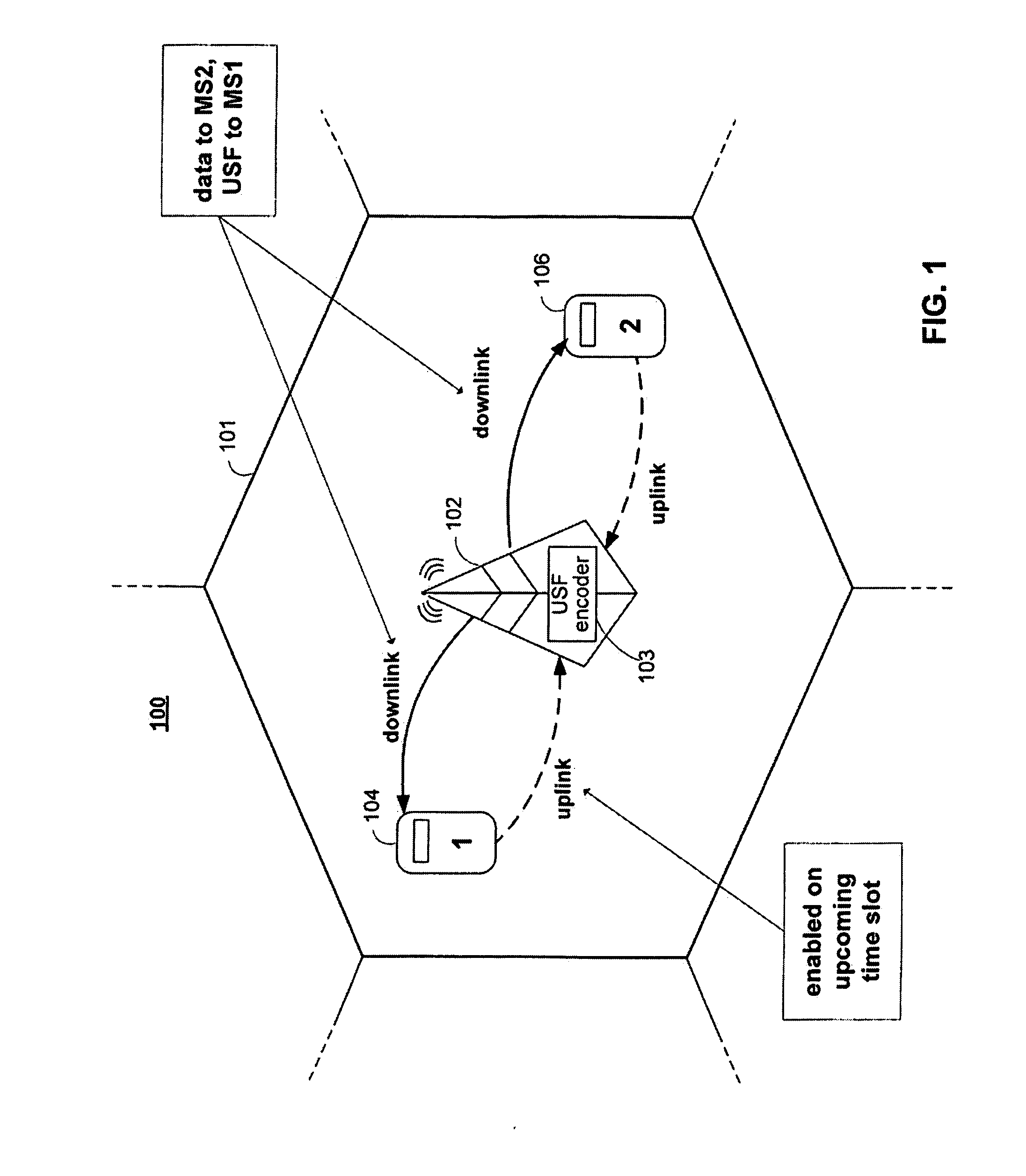
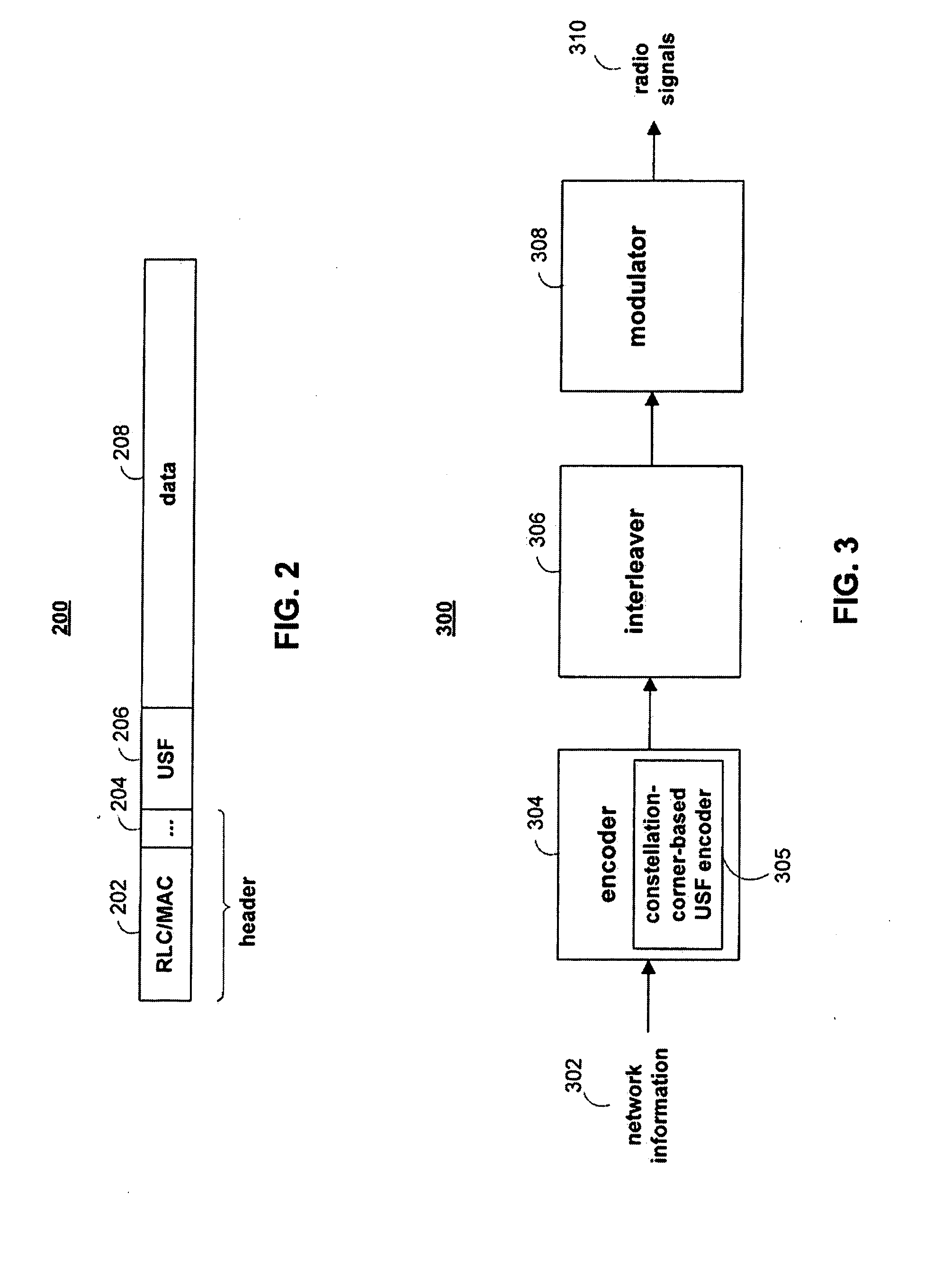
Usf coding
ActiveUS20080311918A1Improve noiseEasy to distinguishRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsForward error control useModulation codingMobile station
Systems and methods are provided for transmitting and receiving an uplink state flag (USF) in a cellular network. A base station may transmit the USF to plurality of mobile stations that share the same frequency channel, and each mobile station can use the USF to determine whether that mobile station can transmit data in an upcoming uplink time period. The base station can encode the USF bits into a plurality of encoded USF symbols, where the encoded USF symbols may be selected from corner signal points in a QAM signal constellation set or from signal points adjacent to the corners of a QAM signal constellation set. The base station can interleave the encoded USF symbols and modulate the encoded USF symbols for transmission using the signal constellation set. A mobile station that can communication with the base station can include a corresponding receiver, de-interleaver, and decoder.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
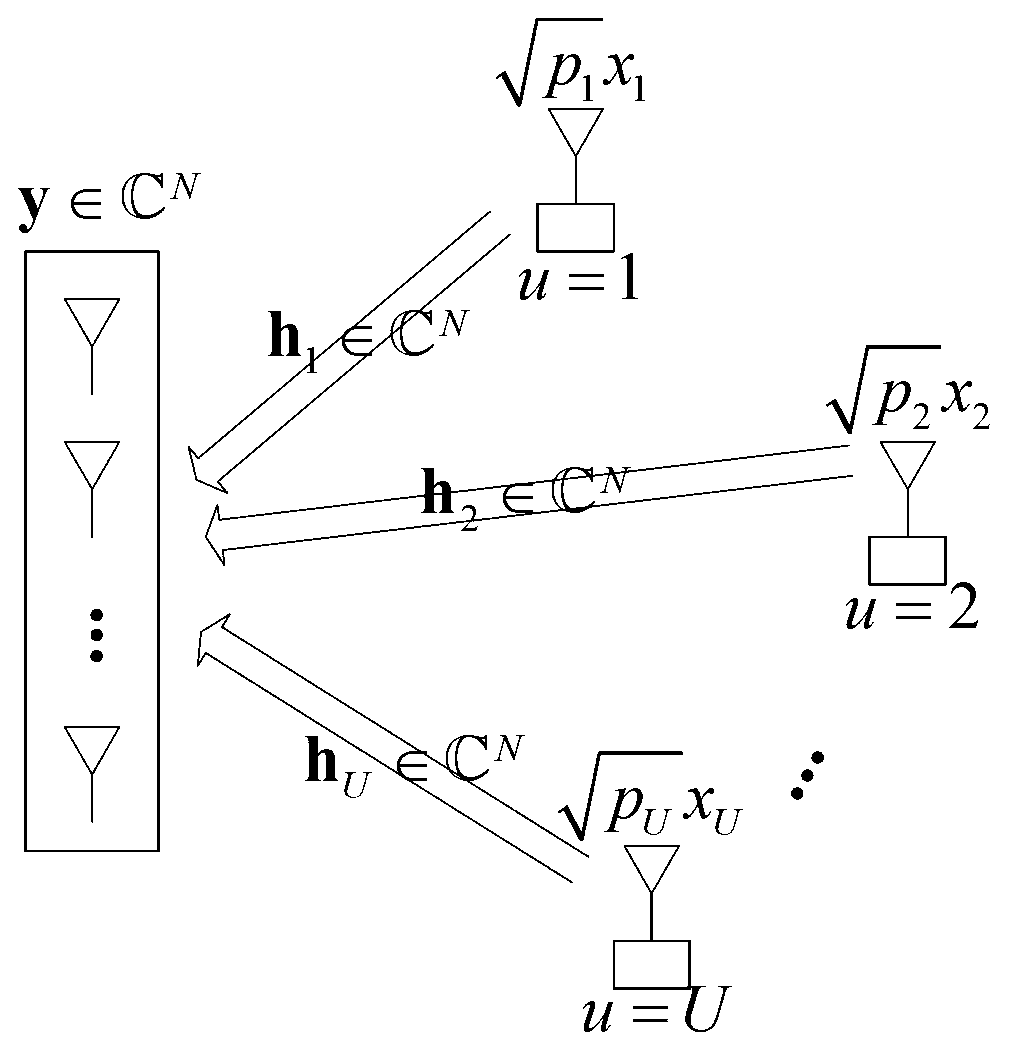
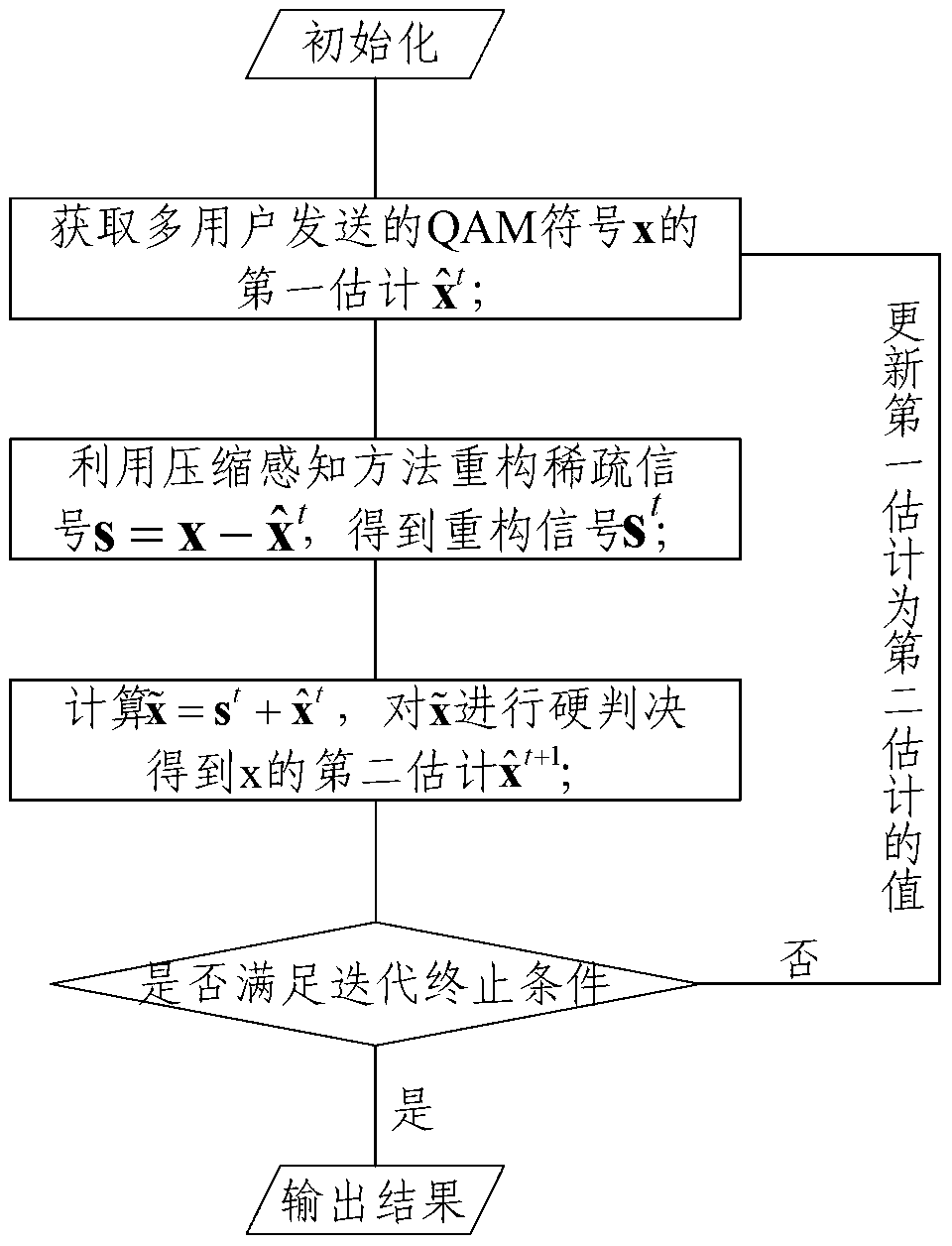
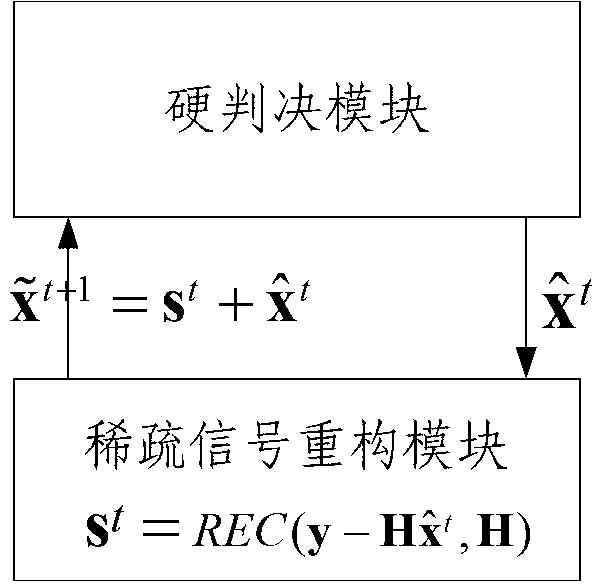
Multiple input multiple output (MIMO) uplink multi-user signal detection method, detection device and receiving system
InactiveCN103297111AReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMessage passingMultiple input
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, in particular to a large-scale multiple input multiple output (MIMO) uplink multi-user signal detection method and detection device and an MIMO receiving system. The large-scale MIMO uplink multi-user signal detection method comprises the steps of utilizing matched filtering to obtain an initial first estimation of a quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) symbol sent by a user; after offsetting influence of the current user signal first estimation from an MIMO detection equation, utilizing a compressed sensing method to reconstruct sparse signals; performing a hard decision on signals obtained after the first estimation and the reconstructed signals are added so as to obtain a second estimation, and utilizing the second estimation to update the current first estimation; enabling the process to be subjected to iteration until iteration end conditions are met; adopting an approximate message passing algorithm to serve as a compressed sensing signal reconstructing algorithm, and simultaneously setting to-be-reconstructed signal prior probability distribution to be Bernoulli-uniform distribution. The large-scale MIMO uplink multi-user signal detection method has the advantages of being low in complexity and being easily achieved on a current hardware device and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Linearized optical digital-to-analog modulator
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Encoding modulating method and demodulation modulating method
ActiveCN102316072AImprove transmission performanceImprove performanceError preventionMultiple carrier systemsDecoding methodsTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses an encoding modulating method. In a modulating process, regular constellation mapping or irregular constellation mapping is carried out on bit data, so as to obtain a constellation mapping symbol, wherein the regular constellation mapping means that the mapping from a bit to a symbol is completed by adopting one constellation diagram and one constellation point mapping way, and the irregular constellation mapping means that the mapping from the bit to the symbol is completed by adopting one constellation diagram and more than one constellation point mapping ways. The invention further discloses a demodulation decoding method corresponding to the encoding demodulating method. In the invention, through using regular APSK (amplitude phase shift keying) constellation mapping at a sending end, the shaping loss can be obviously reduced, or by using irregular QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation) constellation mapping, the decoding and the de-mapping are matched more,so as to improve the transmission capability of an encoding modulating system, and through adopting iterative de-mapping at a receiving end, the loss brought by independent de-mapping can be effectively reduced, so as to obviously improve the performance of the encoding modulating system based on the iterative de-mapping.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Optical transmitter and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20140029956A1The signal is stable and reliableStable and reliable modulated lightwave signalElectromagnetic transmittersNon-linear opticsOperating pointEngineering
Since it is difficult to emit a stable and reliable modulated lightwave signal by means of IQ modulators used for QAM format, a method for controlling an optical transmitter according to an exemplary aspect of the invention includes the steps of (a) keeping an optical amplitude of a continuous wave light output from the optical transmitter constant, (b) making operating point values in optical modulation converge to predetermined values during step (a), and (c) modulating the continuous wave light with multiple amplitudes and phase levels around the operating point values converged in step (b).
Owner:NEC CORP
Demodulation of 16-QAM, DCM data symbols using two hybrid-QPSK constellations
InactiveUS20080240299A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsSymbol of a differential operatorLog likelihood
In one embodiment, a demapper uses two hybrid-QPSK constellations to demap pairs of equalized data symbols recovered from 16-QAM, DCM OFDM symbols, wherein the equalized data symbols in a pair correspond to the same four-bit group. A first hybrid-QPSK constellation is generated by combining the real components of both 16-QAM mapping constellations onto one coordinate plane. The demapper generates a first set of two decision variables by combining the real components of each equalized data symbol in a pair to correspond to the first hybrid-QPSK coordinate plane. A log-likelihood ratio is then calculated for both decision variables in the set to determine likelihood estimates for the first and second bits of the four-bit group. This process is repeated for the imaginary components of each corresponding pair of equalized data symbols to generate likelihood estimates for the third and fourth bits of the four-bit group.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
QAM receiver and method for constellations having at least sixteen symbols
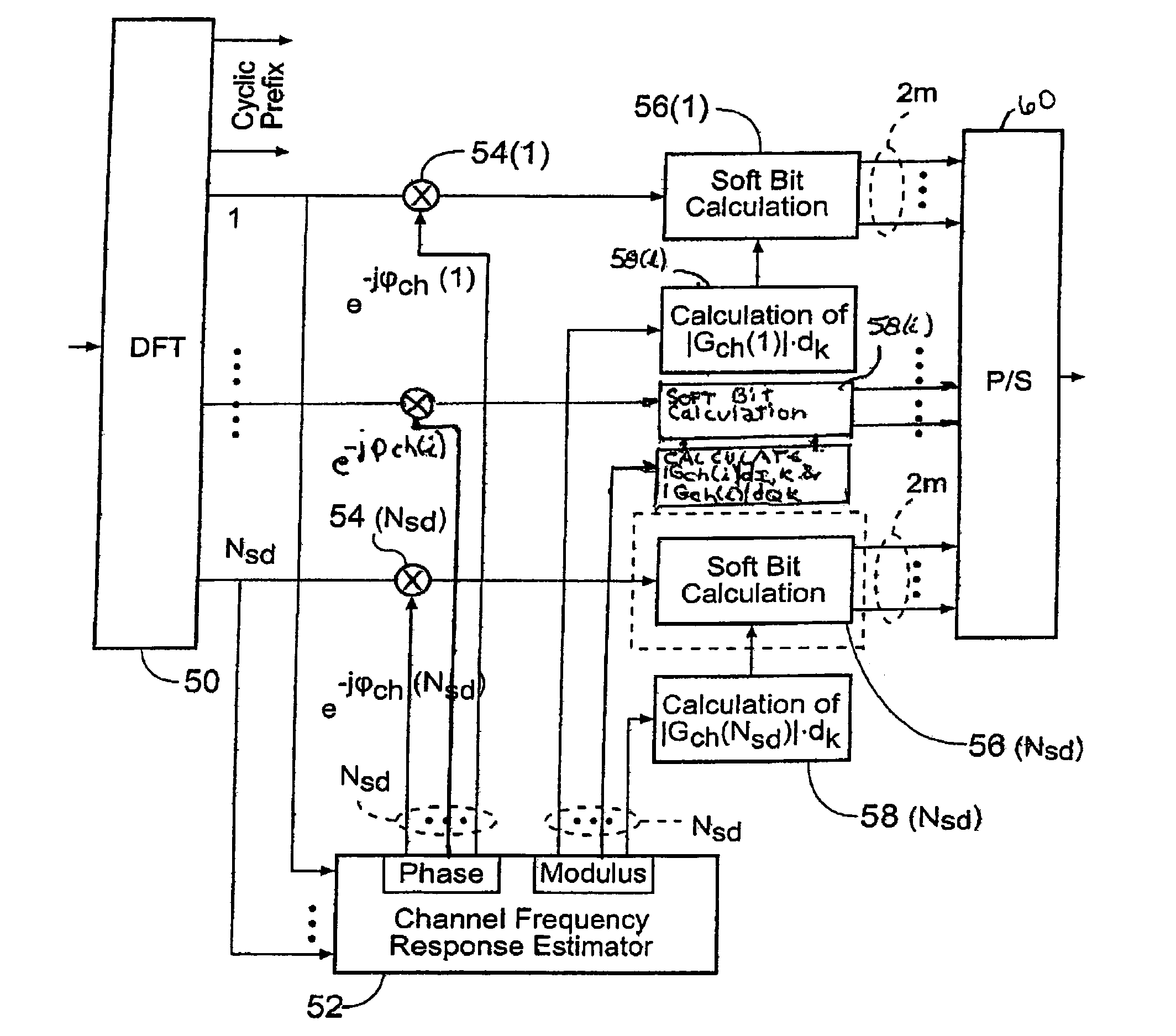
InactiveUS7653153B2Reduce in quantityReducing computational taskError preventionOther decoding techniquesEngineeringChannel frequency response
A QAM receiver for constellations having at least 16 symbols converts its received QAM signal into outputs including indications of the received symbols. A channel frequency response estimator responsive to outputs of the converter derives indications of estimates of effects of a link to the receiver on the phase and amplitude of the received signals. A processor responsive to outputs of the converter and the estimator (1) equalises the phases of the converter outputs, (2) scales the amplitude estimates by amounts determined by the amplitude associated with the separation of boundaries between symbols in the constellation, and (3) combines the phase equalised converter outputs and the scaled amplitude estimates to derive likely bit values of the received symbols.
Owner:MEIZU TECH CO LTD
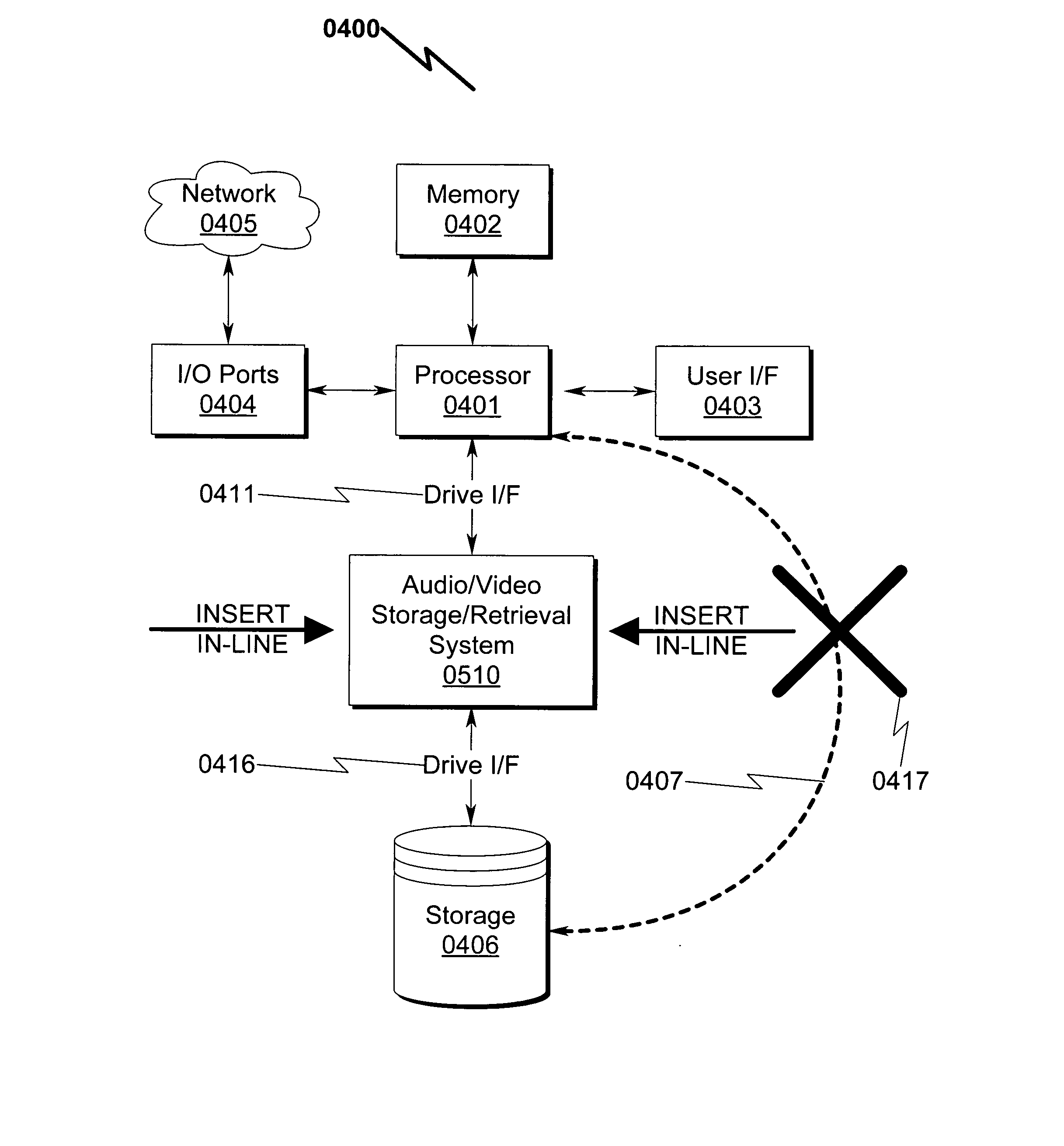
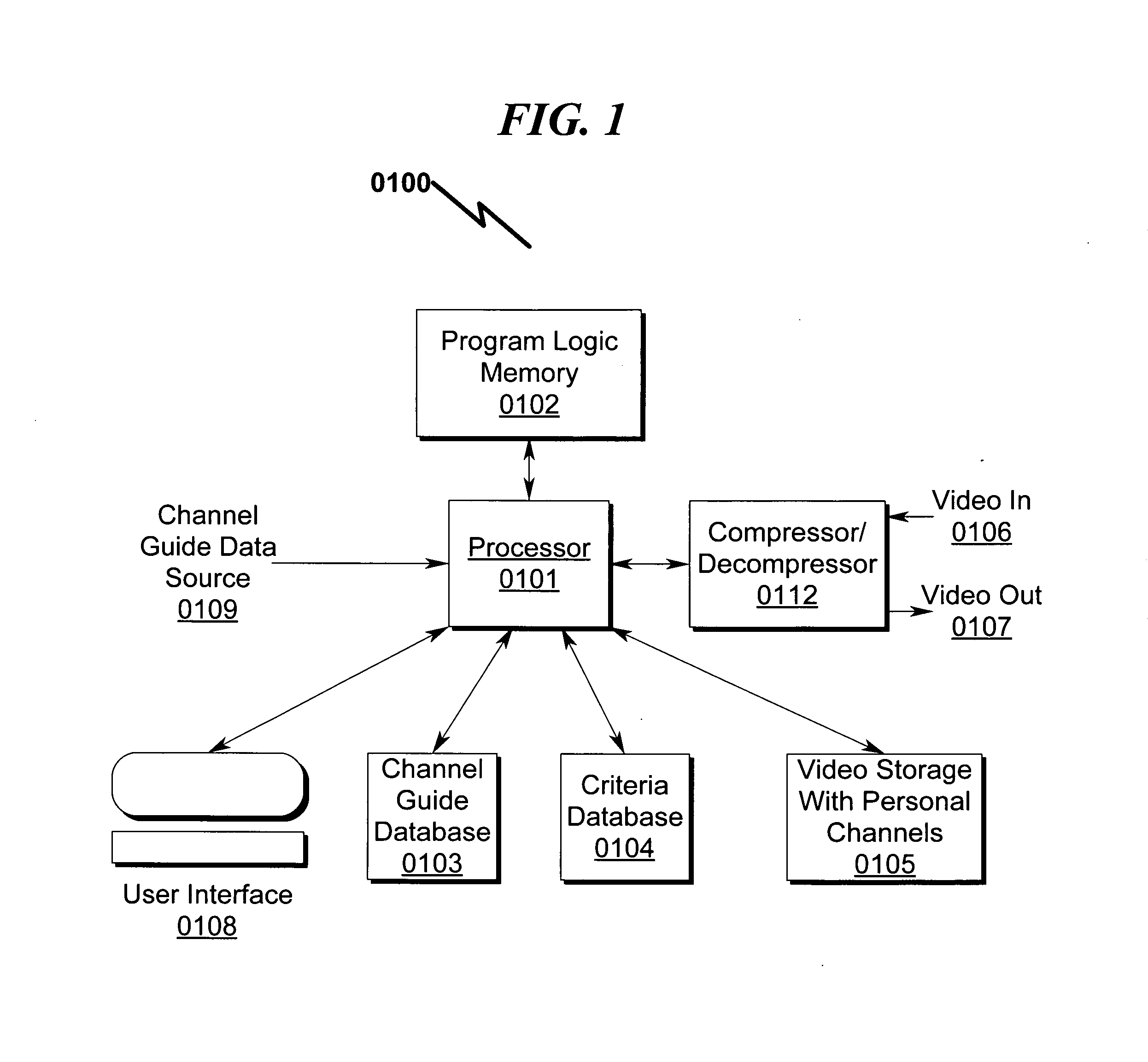
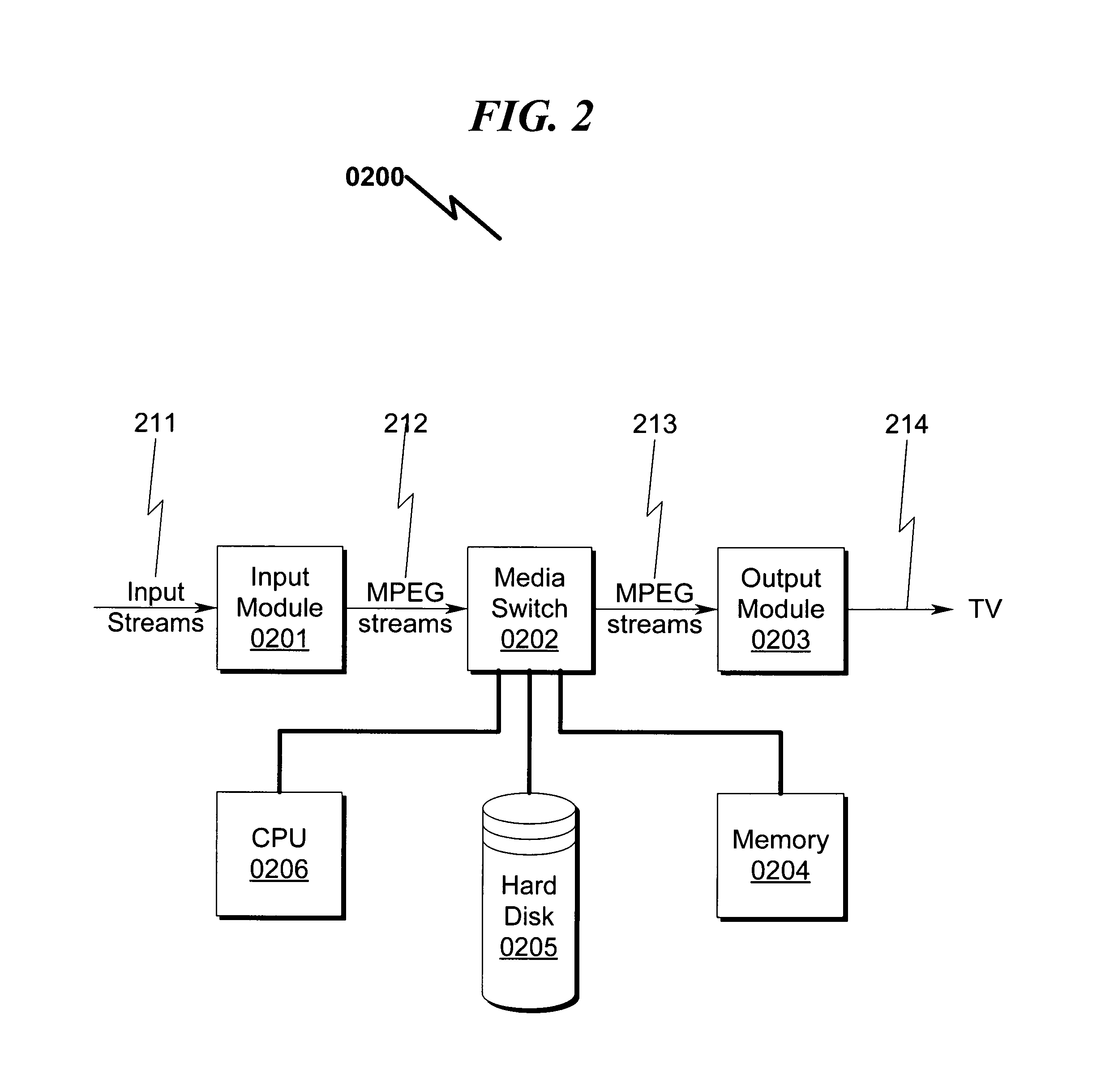
Audio/video storage/retrieval system and method
ActiveUS20130081098A1Inexpensive and extensible storageAlleviates CPUTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVideo storageComputerized system
An audio / video storage / retrieval system and method that permits efficient and cost-effective simultaneous recording of multi-channel A / V information from a variety of sources is disclosed. The system / method may be broadly described as generally incorporating baseband conversion of source RF modulated A / V information followed by analog-to-digital conversion and storage on a storage device utilizing a dual port interface that incorporates an additional computer access port to permit transparent storage access by a computer system. Retrieval of stored A / V programming from the storage device via the dual port interface permits the stored A / V data to be converted to analog and RF modulated for presentation to an A / V presentation device. Additional A / V source and / or target selectors may be incorporated into the system / method to permit recording a plethora of A / V sources such as raw A / V signaling, OTA broadcasts, clear / encrypted cable QAM broadcasts, cable set top boxes (STBs), and the like.
Owner:KLUGHART KEVIN MARK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com