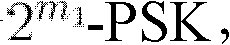Constellation mapping method based on absolute phase shift keying (APSK) constellation map, coded modulation method and system
A technology of constellation mapping, coding and modulation, applied in the field of digital information transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] APSK constellation diagram design method with Gray mapping, the key lies in the parameter m 1 and m 2 (m 1 and m 2 Both are positive integers) and the determination of the radius, where, for a Gray map of 2 m - APSK constellation diagram, with m 1 +m 2 = m, m, m 1 and m 2 are positive integers, so m 1 and m 2There are a total of m-1 combinations. The optimal parameters should make the CM-AMI and BICM-AMI corresponding to APSK constraints as large as possible. In addition, in this embodiment, the radius of the lth ring is preferably In traditional constellation diagram design, the minimum Euclidean distance d between constellation points is always desired min maximization, unfortunately this is not guaranteed to have a large BICM-AMI. In the present invention, a larger BICM-AMI corresponds to a larger harmonic mean Euclidean square distance and:
[0096] 1 d ¯ 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0105] This embodiment provides a coding, modulation, demodulation and decoding method using gray-mapped APSK constellation diagrams, wherein the receiving end uses an independent demapping algorithm. Such as Figure 7 As shown, the encoding modulation and demodulation decoding method comprises steps:
[0106] sender:
[0107] S201. The information bits to be transmitted {s k} Carry out FEC encoding on the finite field;
[0108] S202. Encoding the above FEC bits {s k} for bit interleaving to get interleaved bits {b k};
[0109] S203. Interleave bits {b k} After gray-mapped APSK constellation mapping, the constellation mapping symbol {x} is obtained and sent to the channel;
[0110] Receiving end:
[0111] S204. Perform constellation demapping on the received signal {y} to obtain the demapped log likelihood ratio LLR soft information;
[0112] S205. Deinterleaving the log likelihood ratio above to obtain {L k} and sent to the decoder;
[0113] S206. Based on {L k}, ...
Embodiment 3
[0133] This embodiment provides a coding, modulation, demodulation and decoding method using gray-mapped APSK constellation diagrams, wherein the receiving end uses an iterative demapping algorithm. Such as Figure 12 As shown, the encoding modulation and demodulation decoding method comprises steps:
[0134] sender:
[0135] S301. The information bits to be transmitted {s k} Carry out FEC encoding on the finite field;
[0136] S302. Encoding the above FEC bits {s k} for bit interleaving to get interleaved bits {b k};
[0137] S303. Interleave bits {b k} After gray-mapped APSK constellation mapping, the constellation mapping symbol {x} is obtained and sent to the channel;
[0138] Receiving end:
[0139] S304. Based on the prior information fed back in step S307, perform constellation demapping on the received signal {y}, and obtain the demapped log likelihood ratio LLR soft information;
[0140] S305. Deinterleaving the log likelihood ratio above to obtain {L k} and s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com