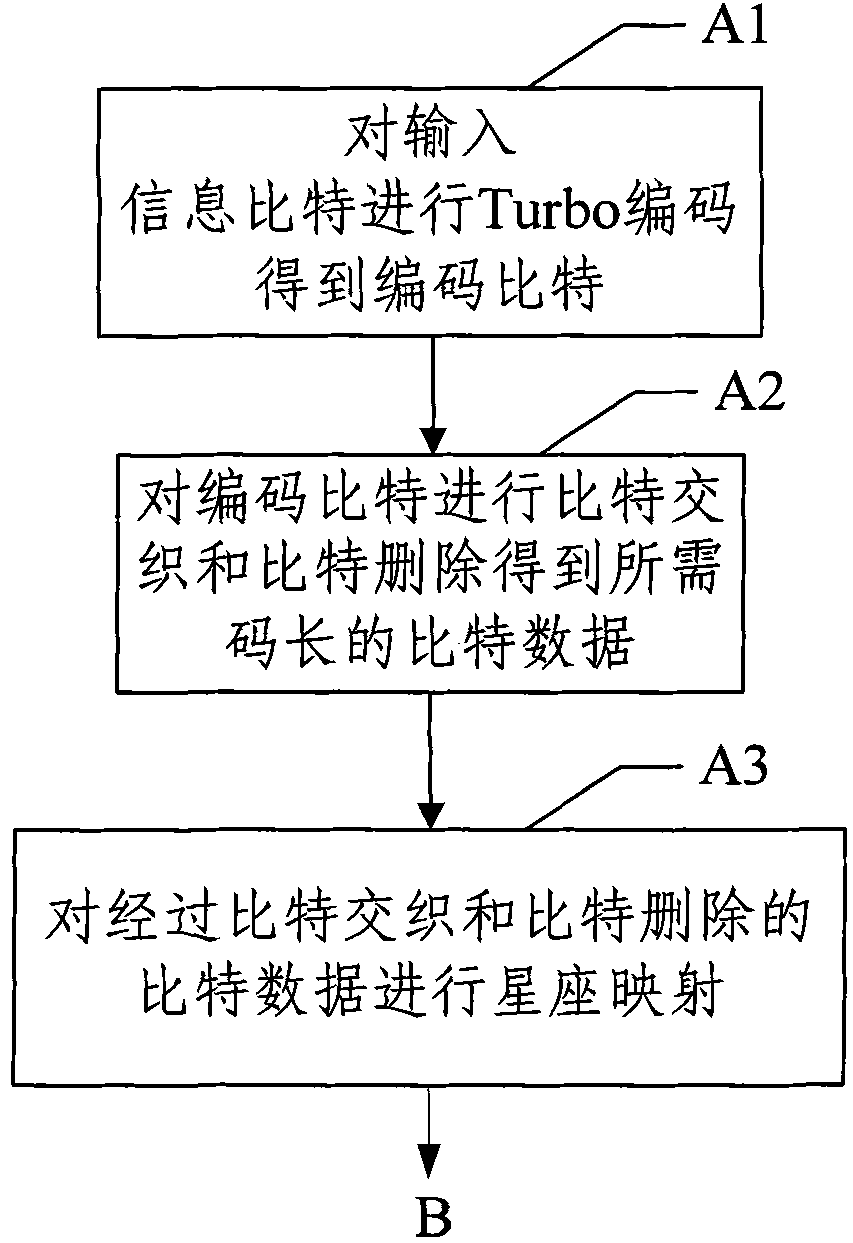
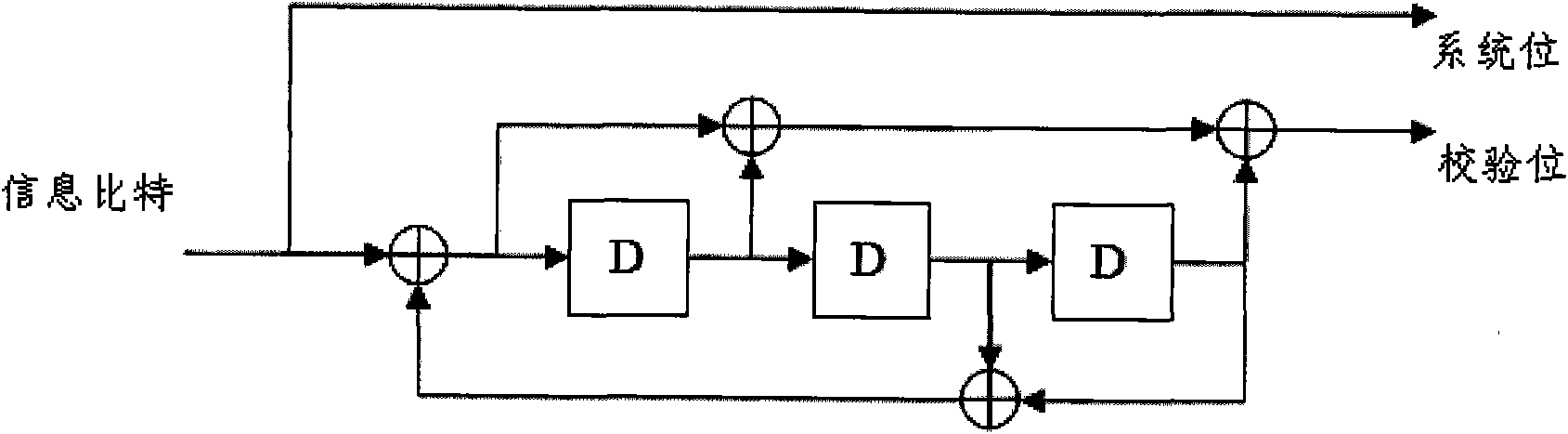
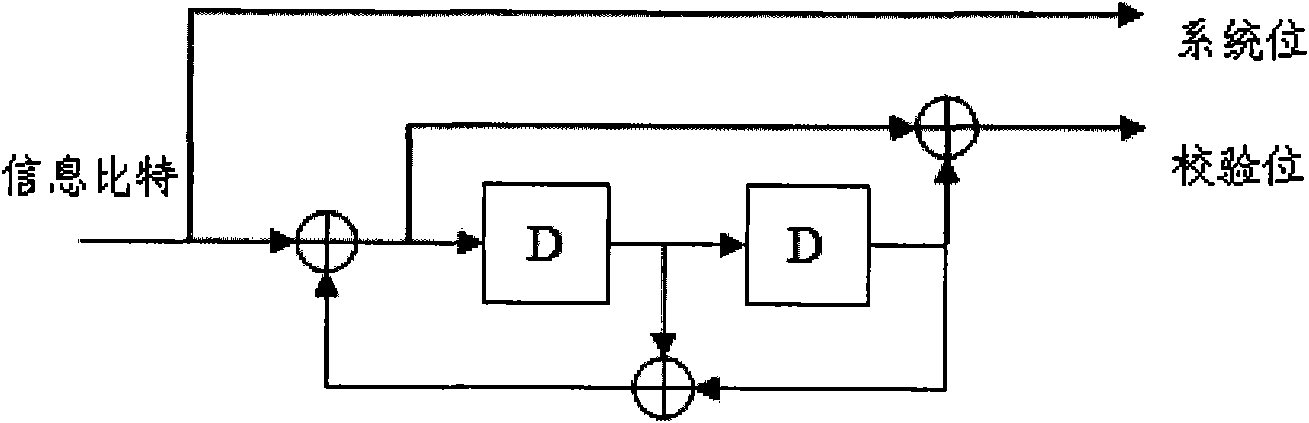
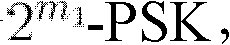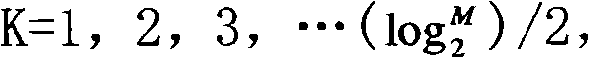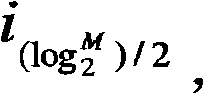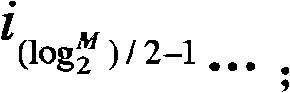Patents
Literature
156 results about "Qam constellations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
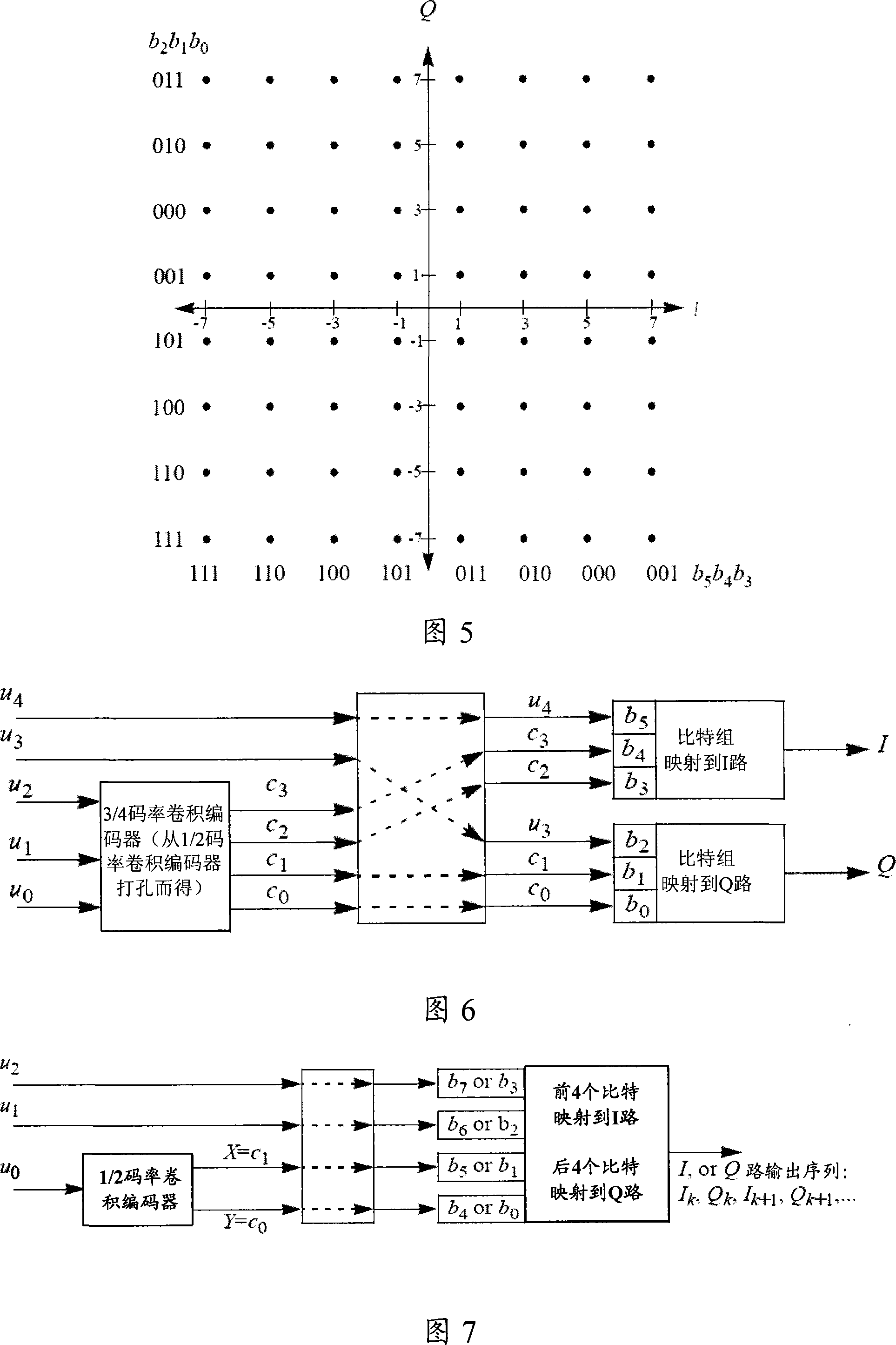
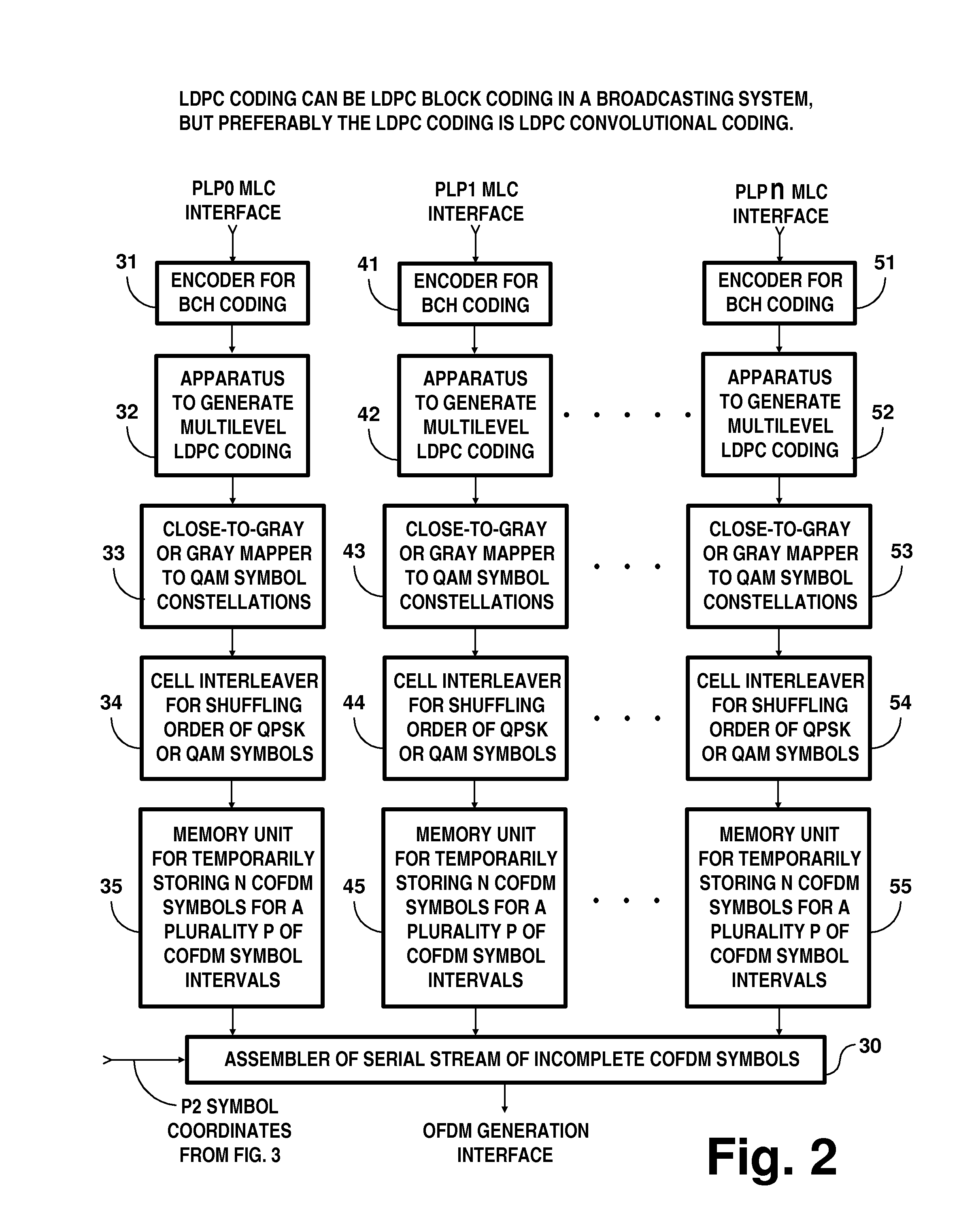
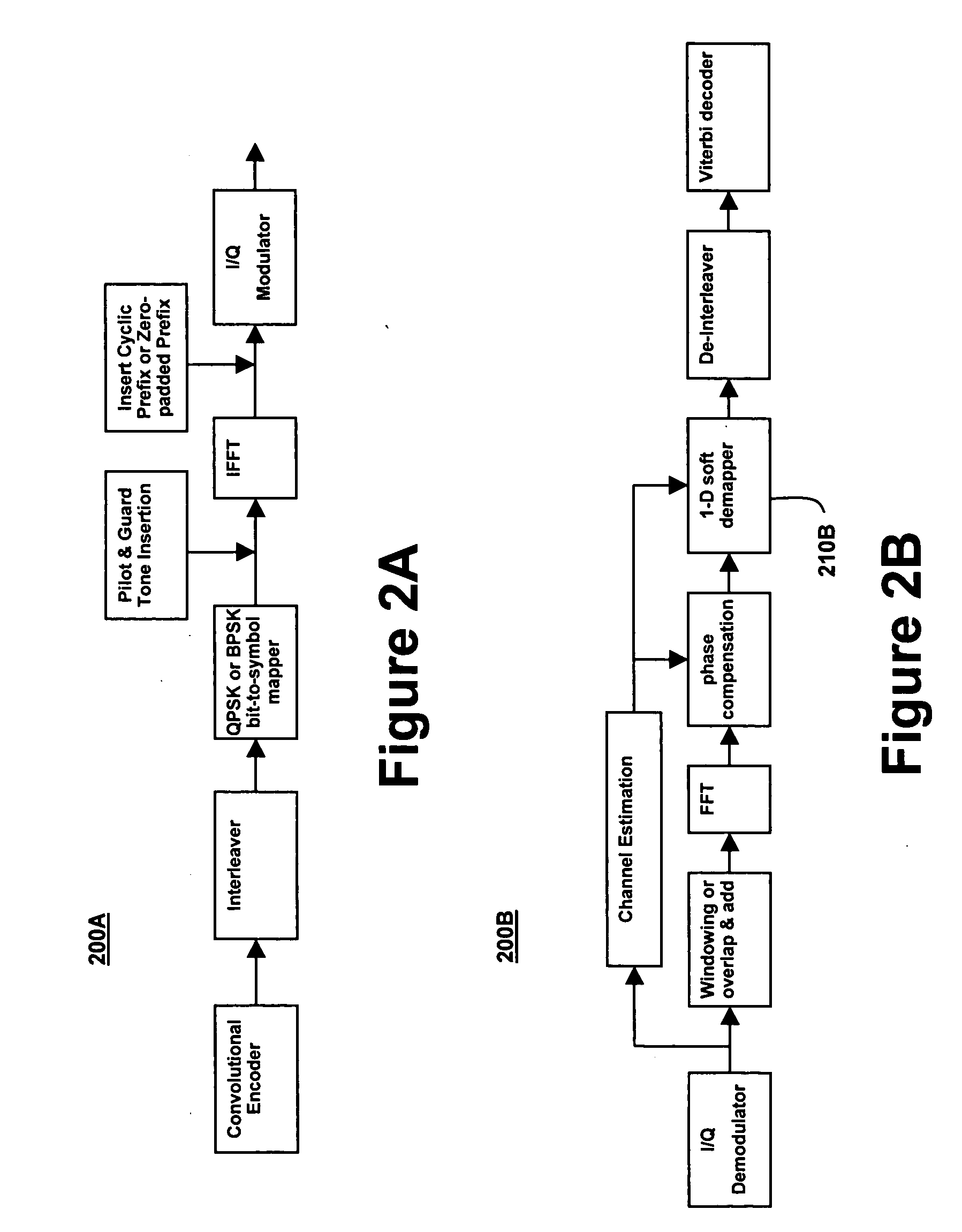
Digital television broadcasting system using coded orthogonal frequency-division modulation and multilevel LDPC convolutional coding
InactiveUS20150358648A1Facilitate parallel independent decodingError preventionError correction/detection using concatenated codesCarrier signalRadio frequency
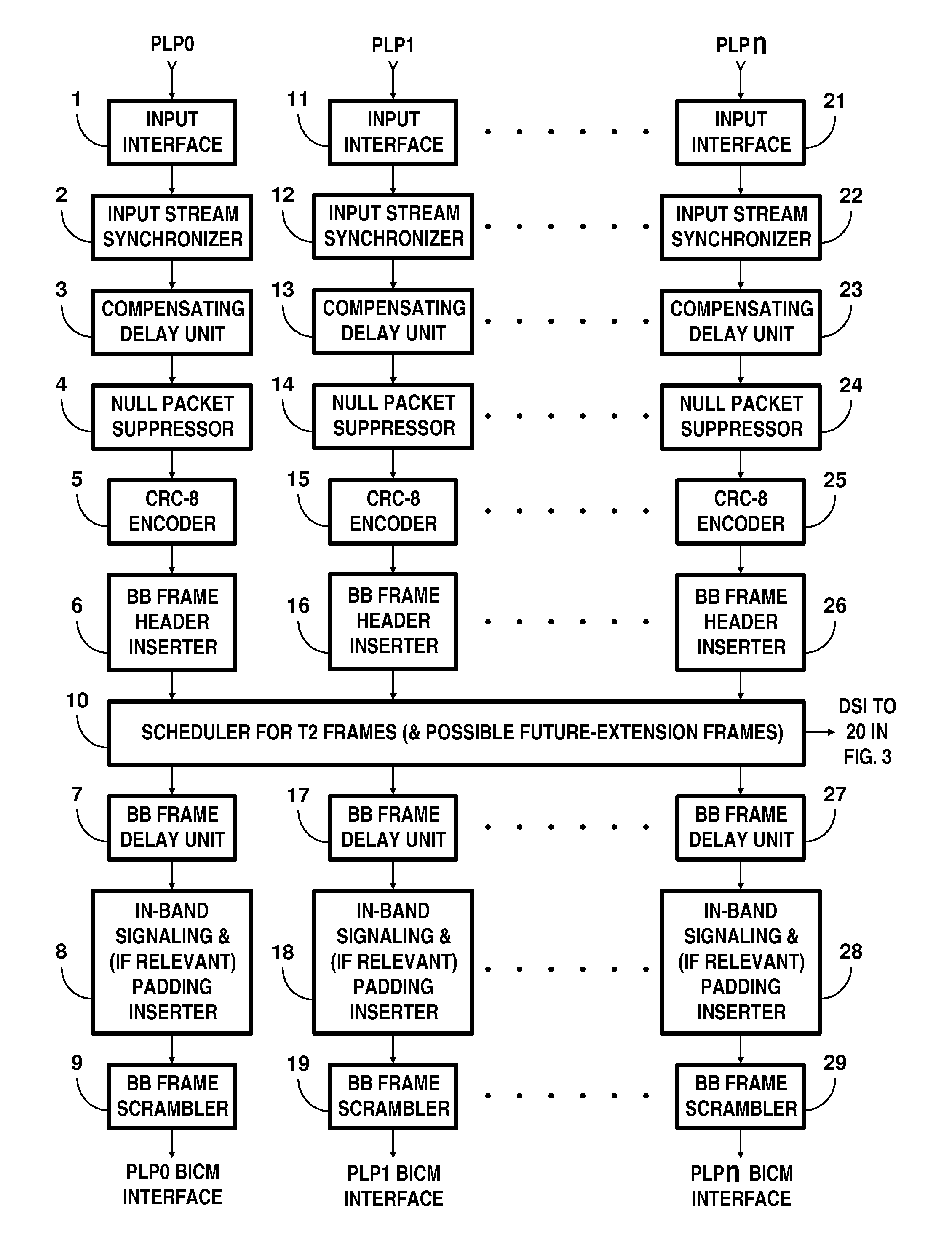
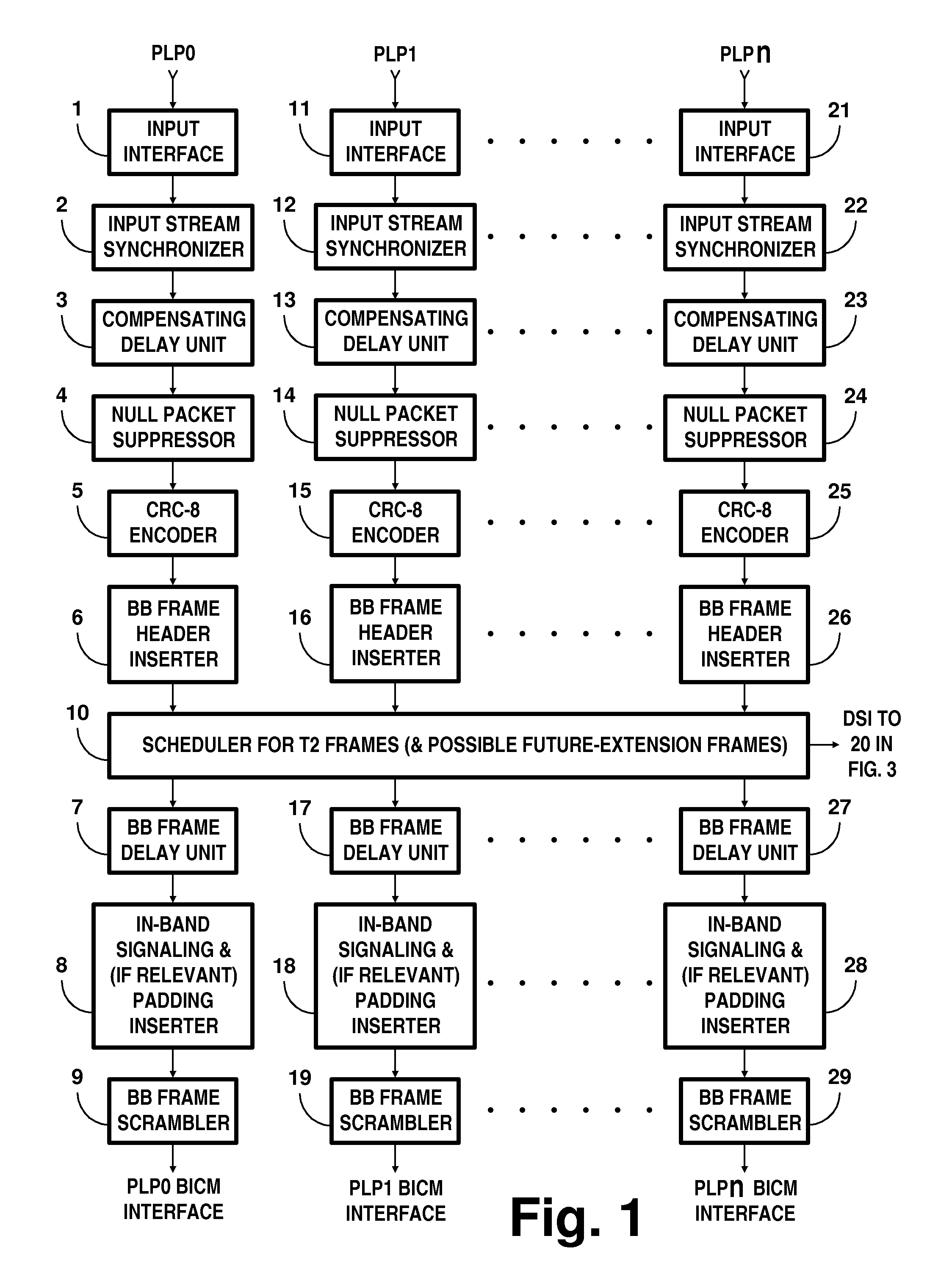
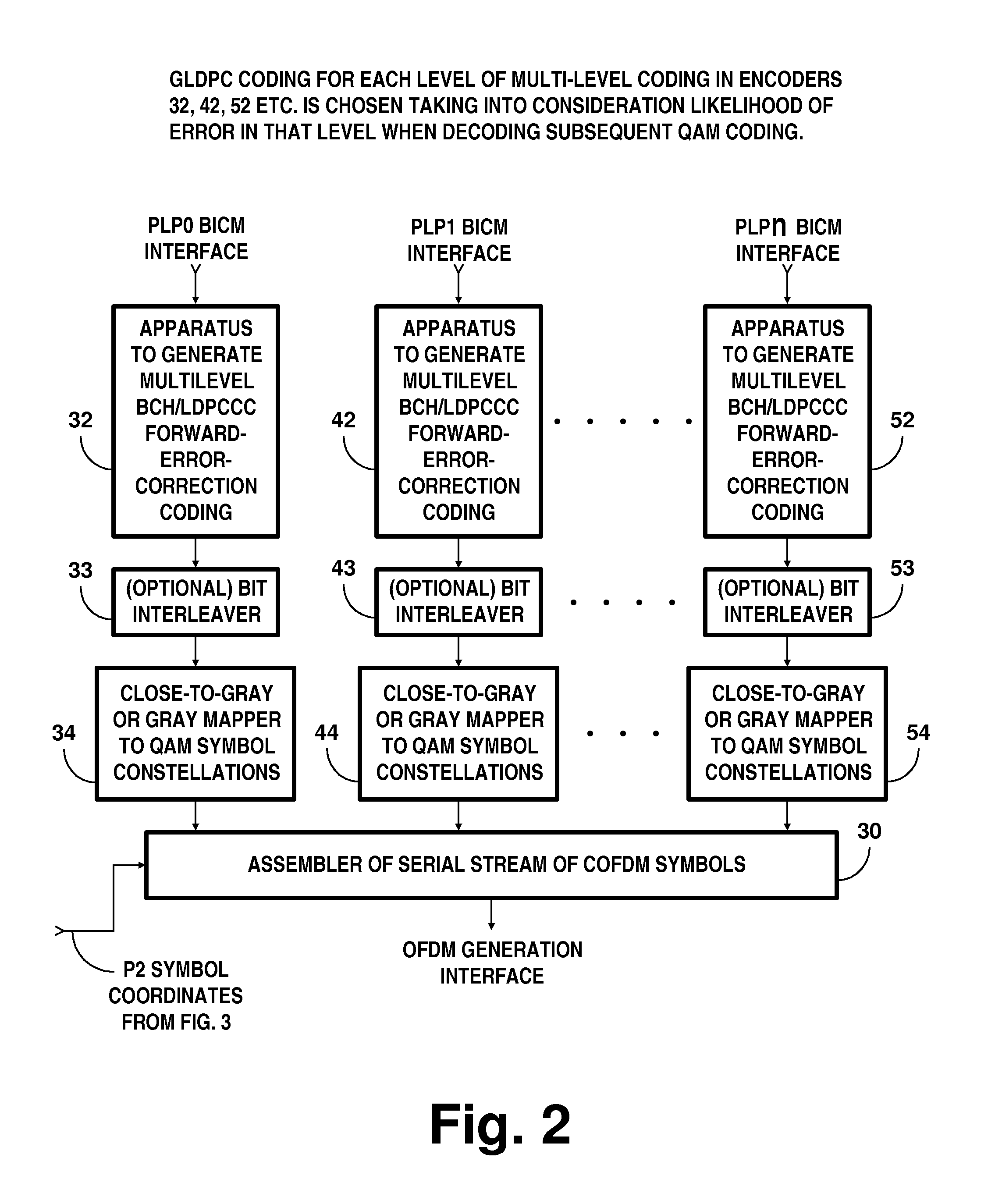
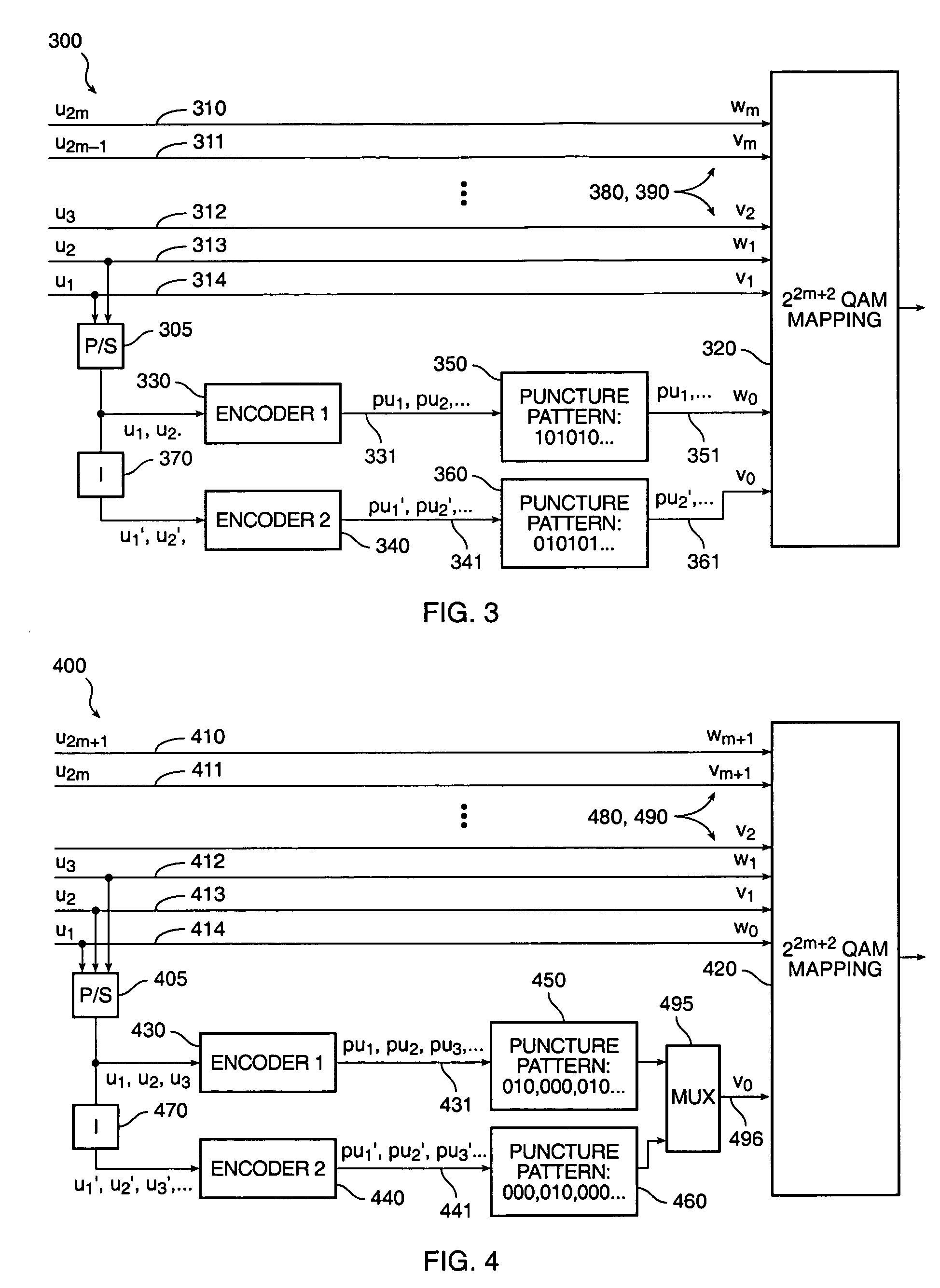
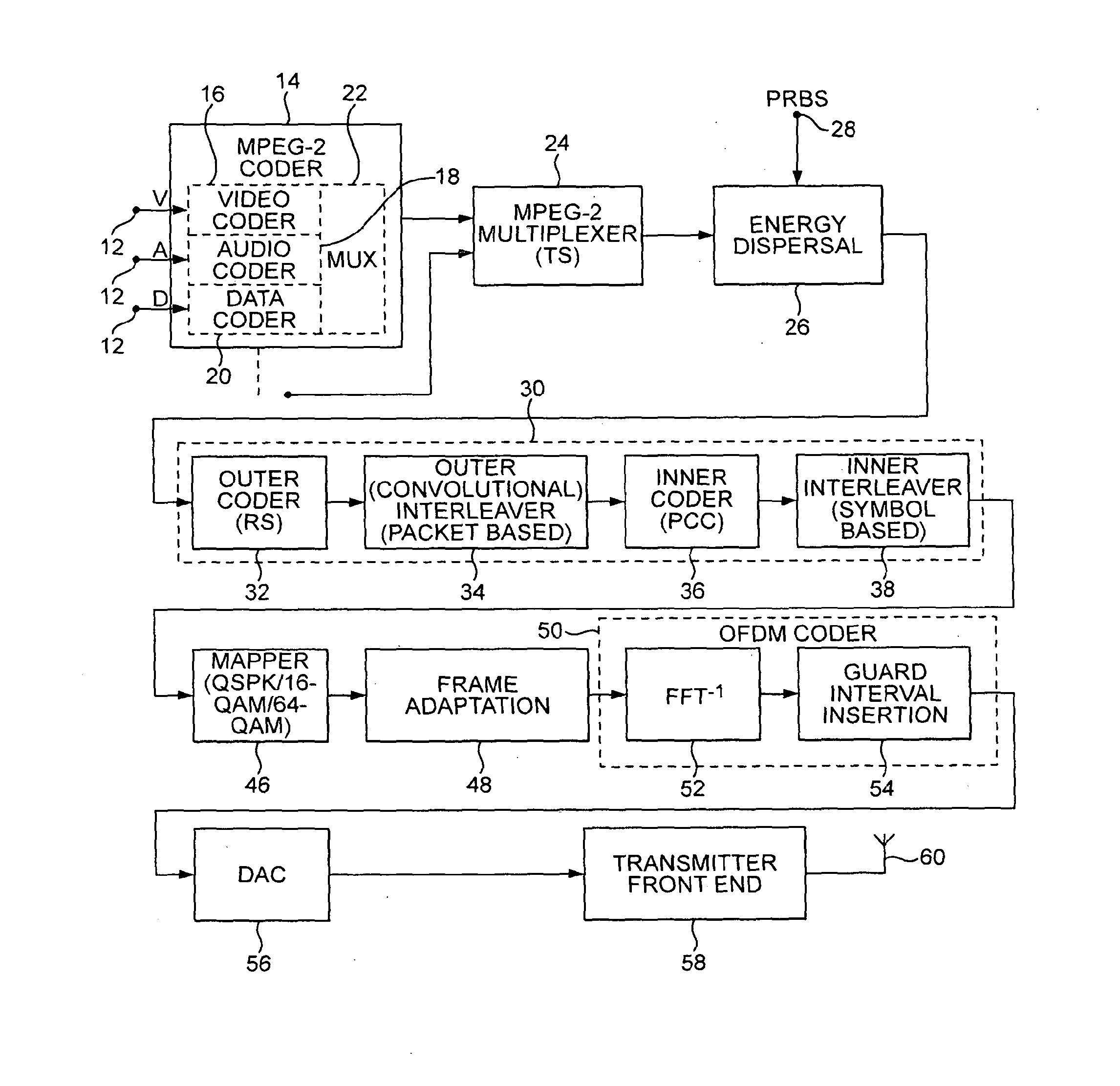
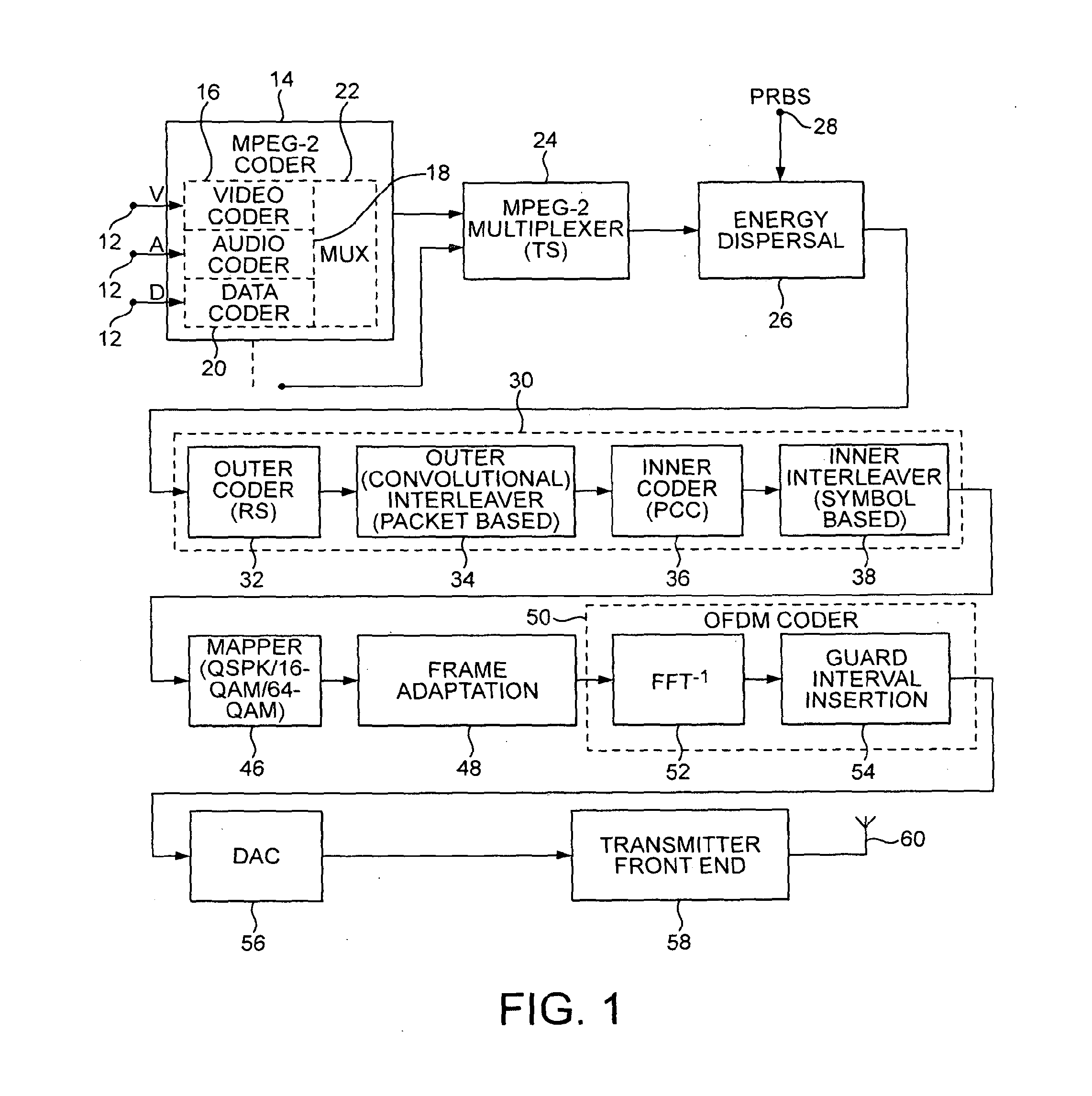
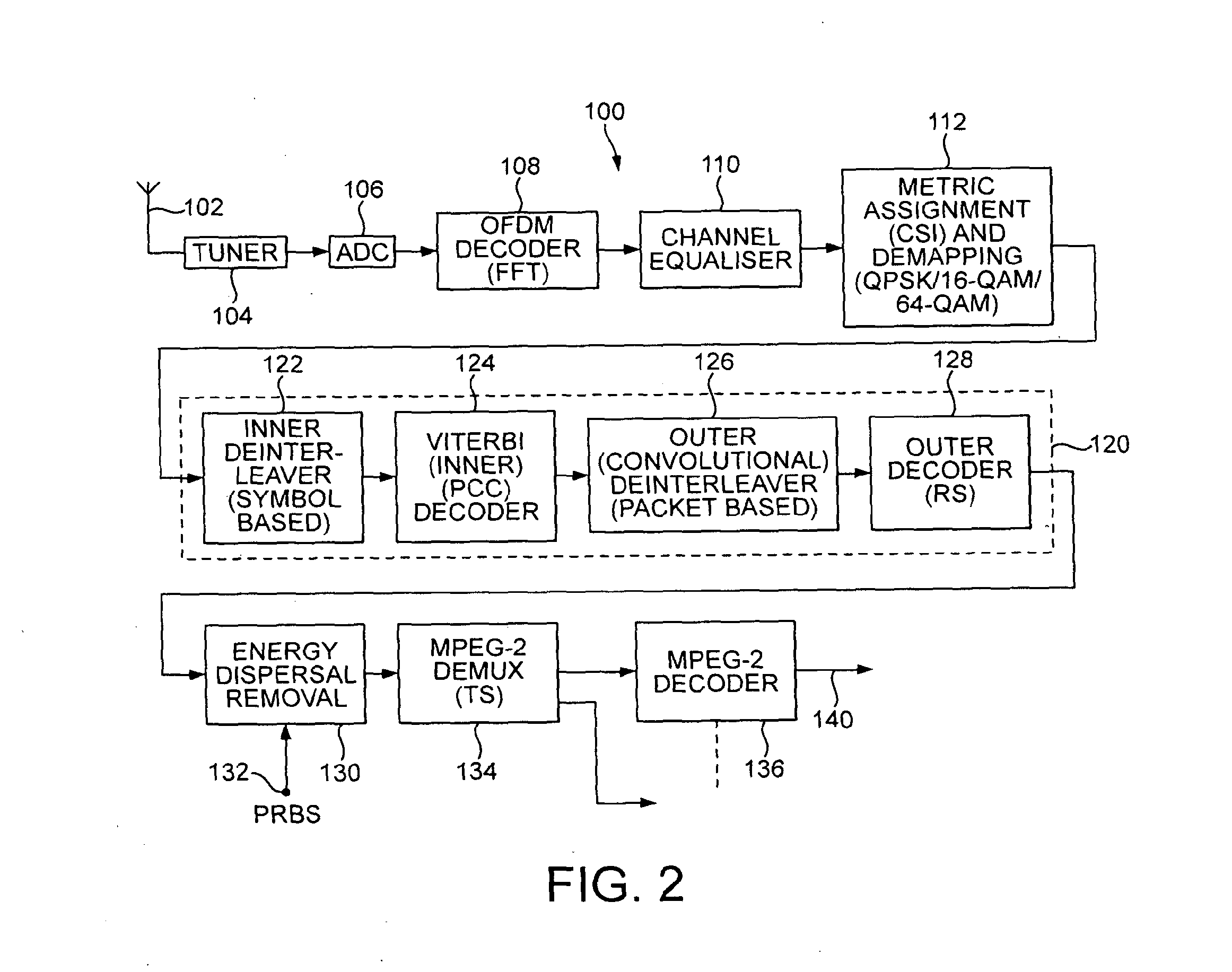
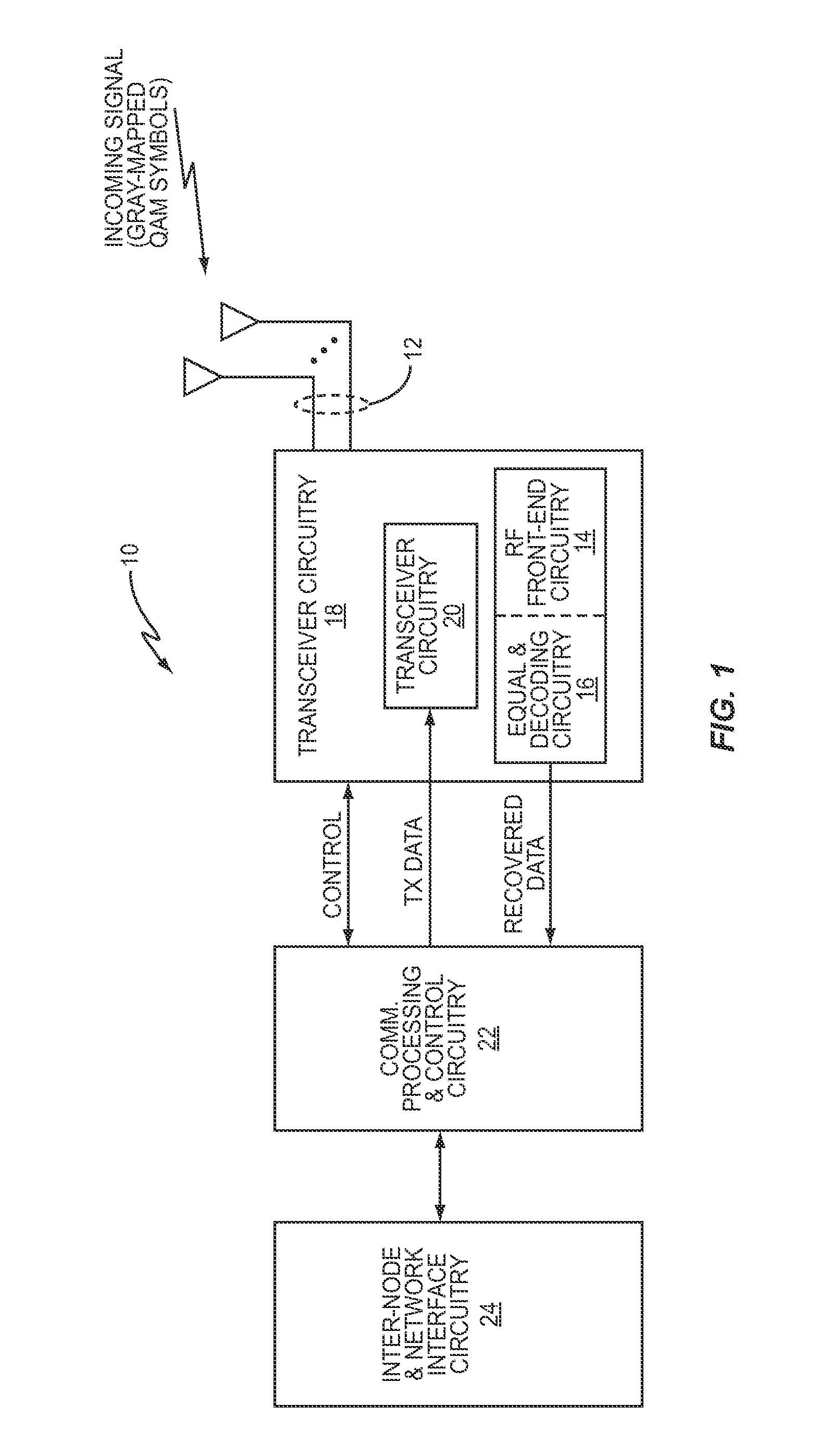
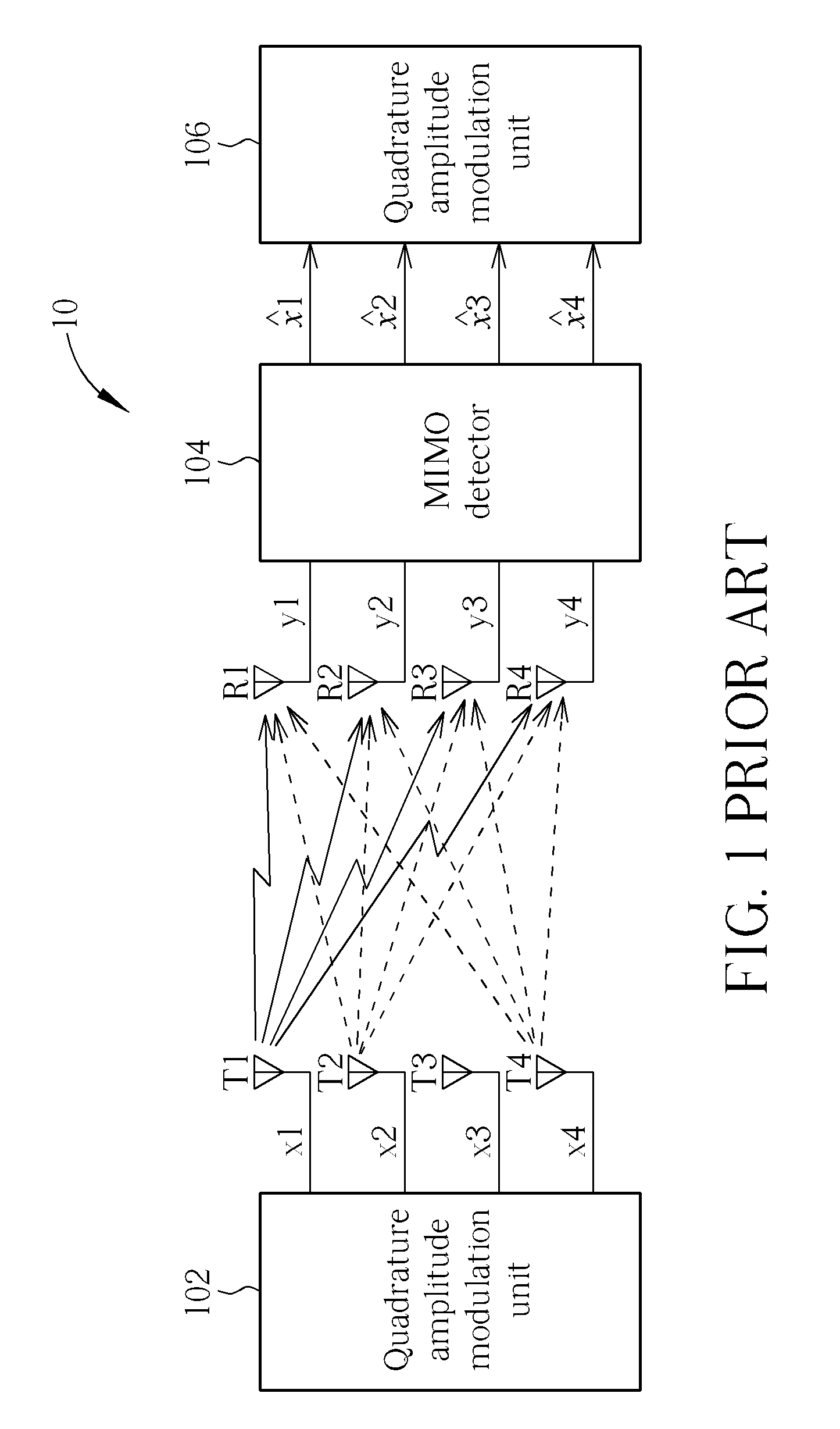
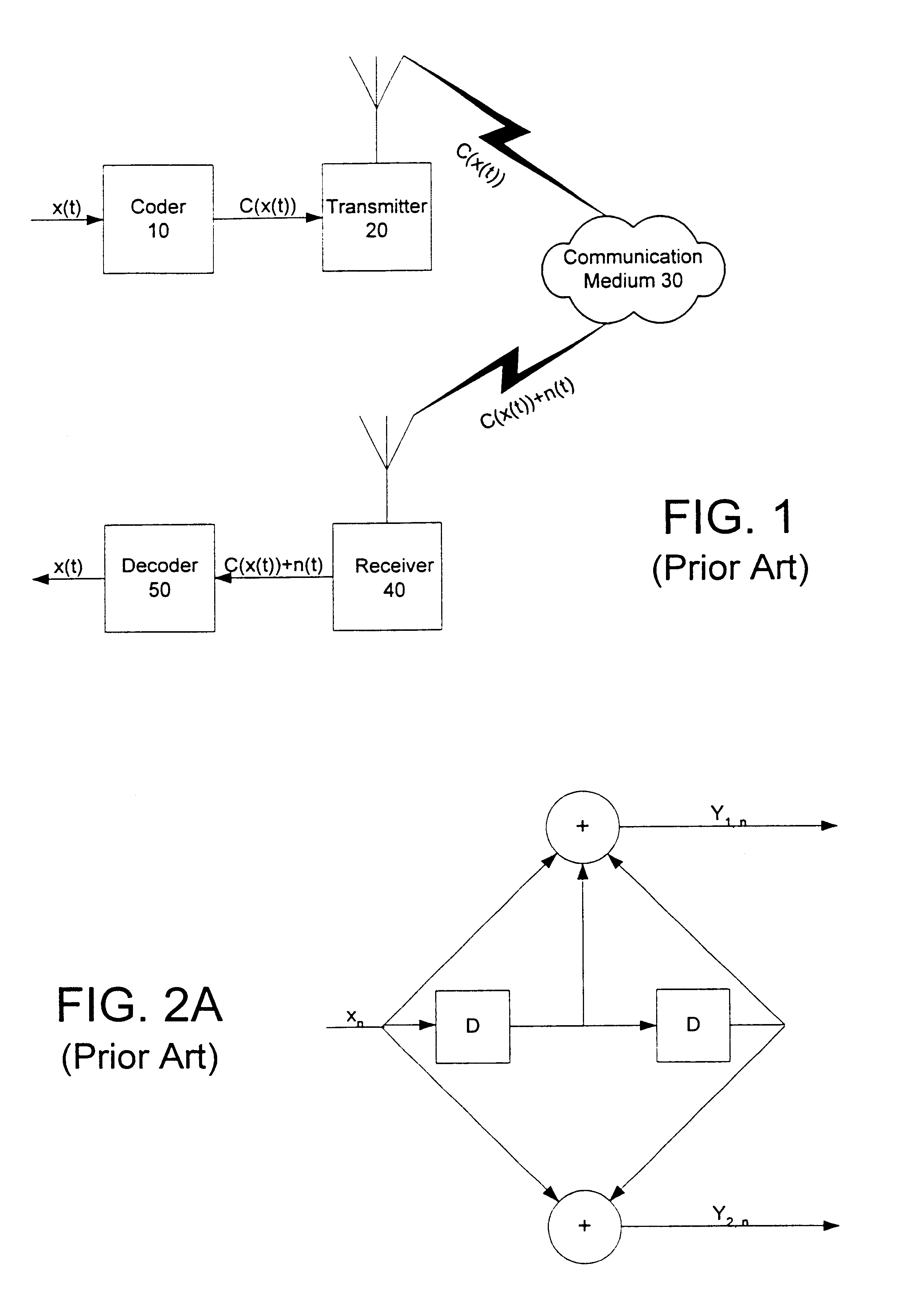
In transmitter apparatus for a digital television (DTV) broadcasting system, internet-protocol (IP) packets of digital television information are subjected to multilevel concatenated Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (BCH) coding and low-density parity-check convolutional coding (LDPCCC) before being bit-interleaved and mapped to quadrature-amplitude-modulation (QAM) constellations. The QAM constellations are used in coded orthogonal frequency-division modulation (COFDM) of plural carrier waves up-converted to a radio-frequency broadcast television channel. In receiver apparatus for the DTV broadcasting system the results of de-mapping QAM constellations recovered from demodulating the COFDM carrier waves are de-interleaved, and the constituent LDPCCC codewords are decoded to recover constituent BCH codewords of the multilevel BCH coding. The constituent BCH codewords are decoded to correct remnant bit errors in them. Then, IP packets of digital television information are reconstituted from the systematic data bits in those BCH codewords.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
Decoding system and method for digital communications
InactiveUS20020051498A1Reduction in uncorrectable errorReduction in packet lossData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesPacket lossDependability
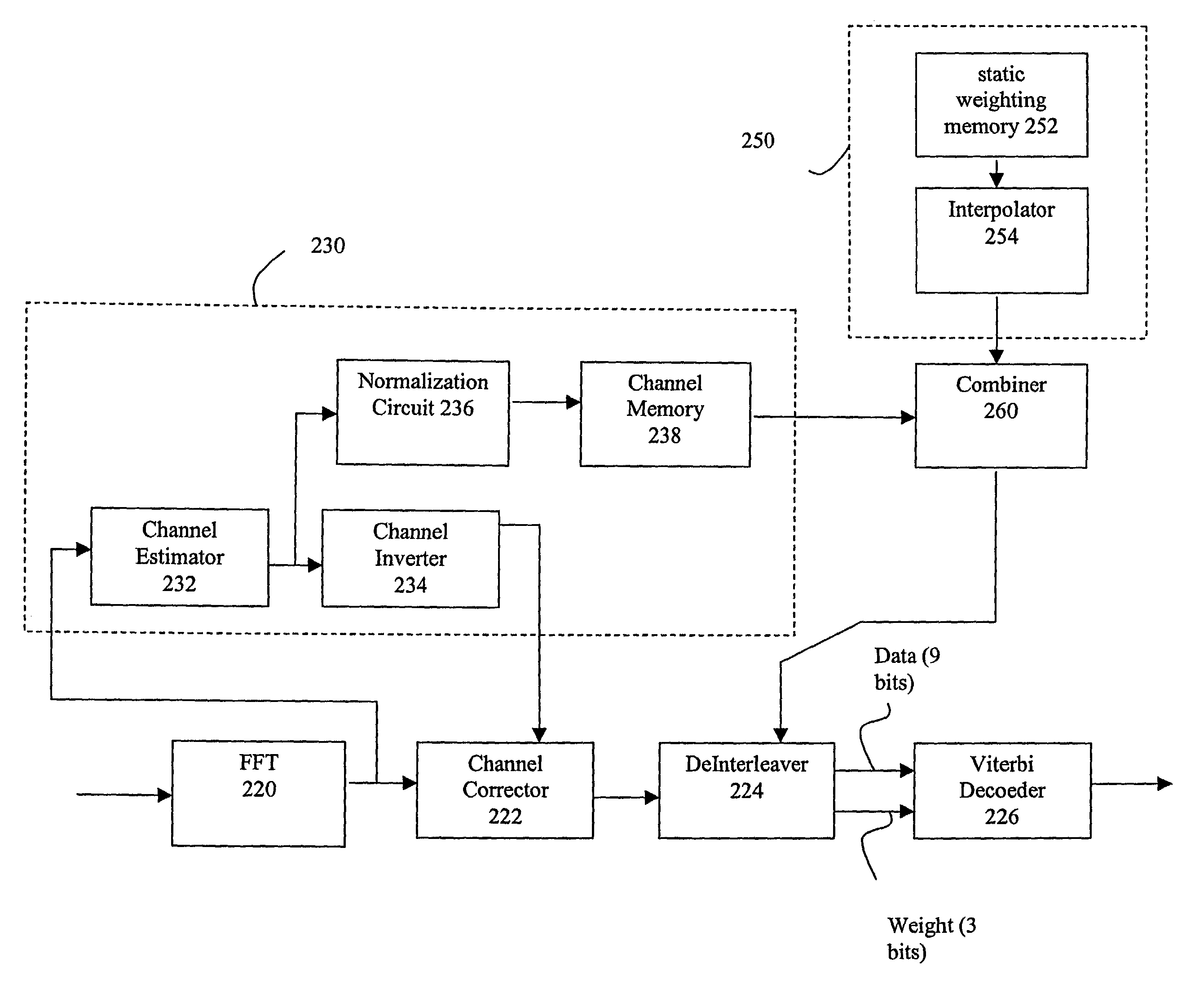
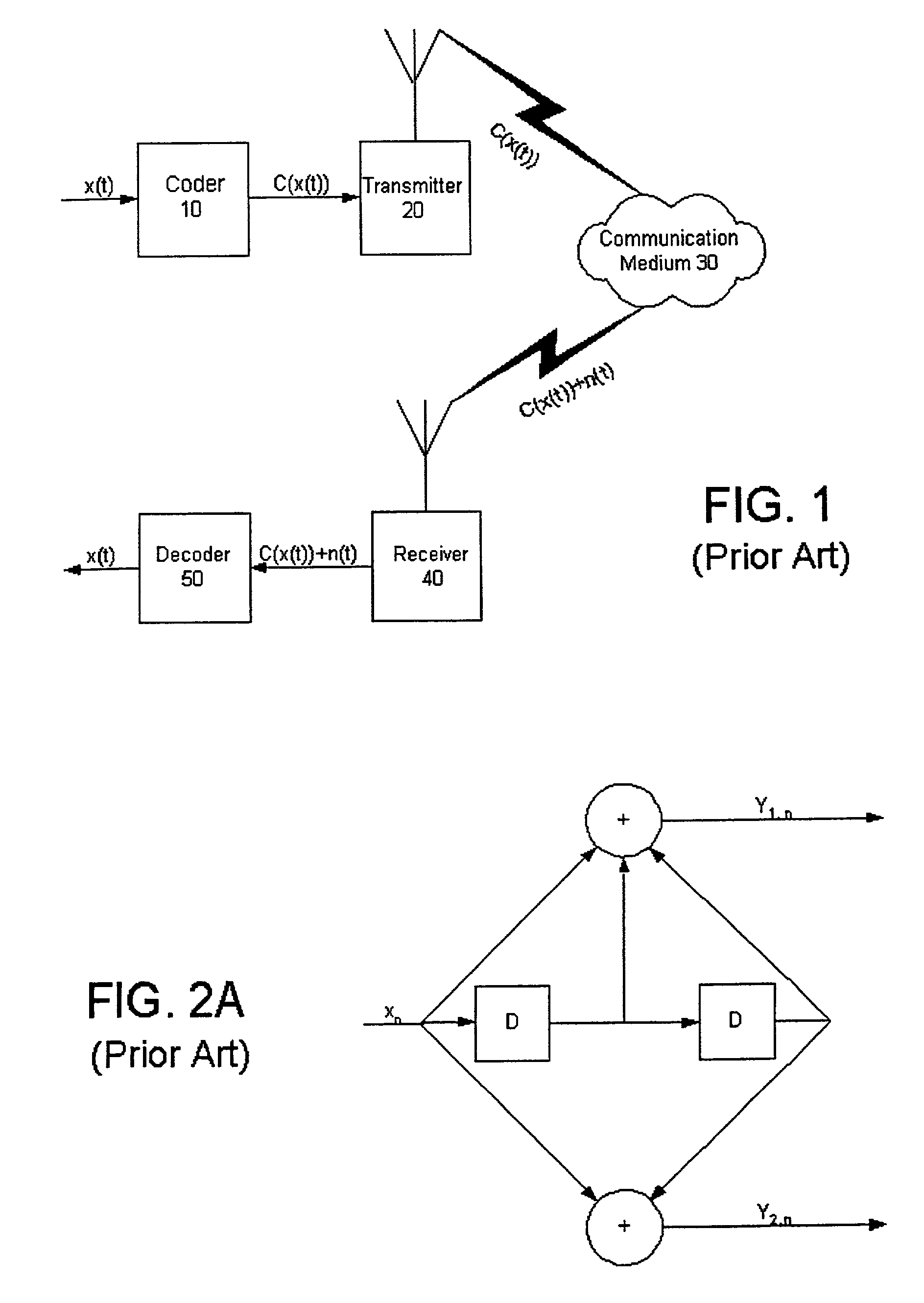
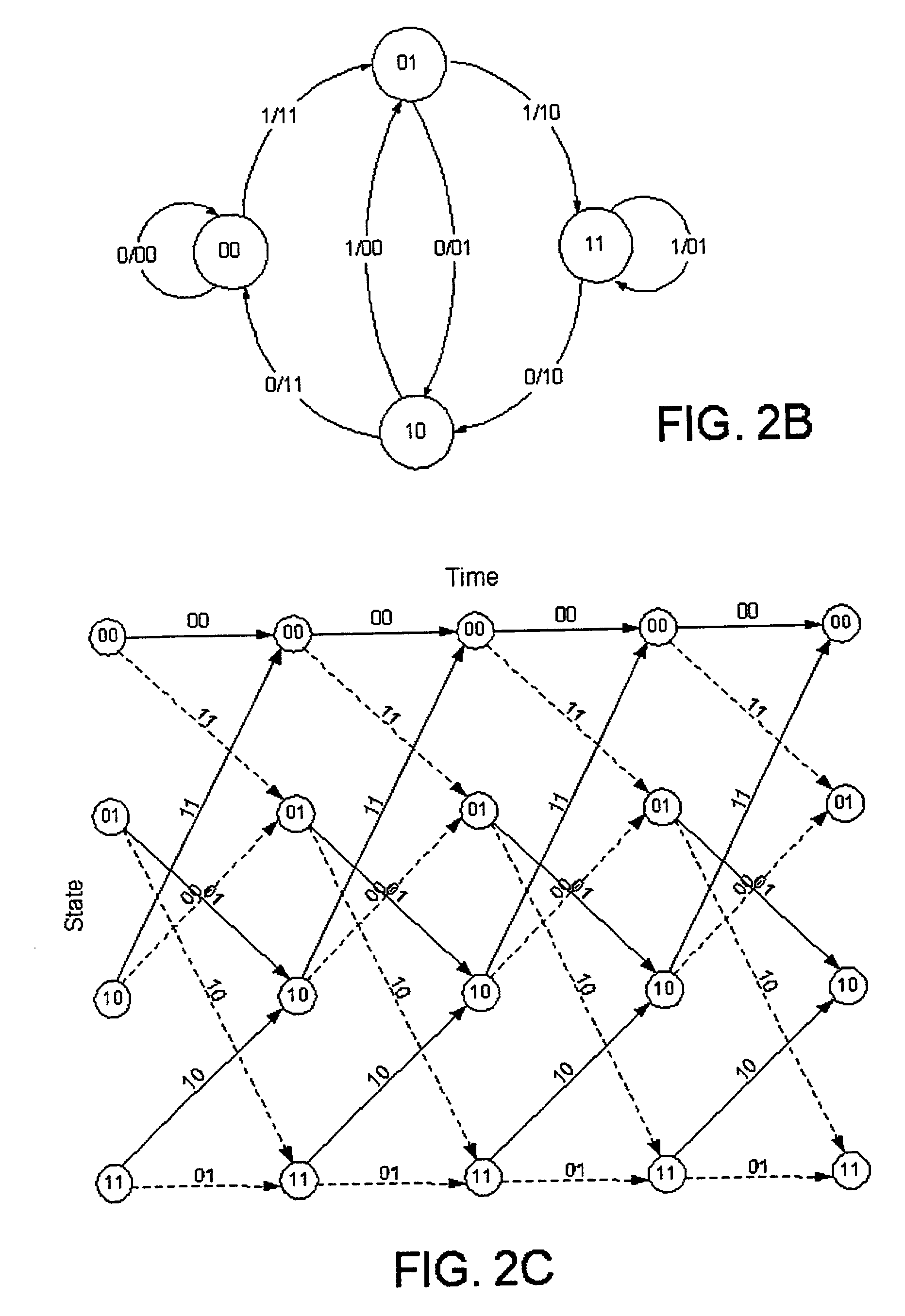
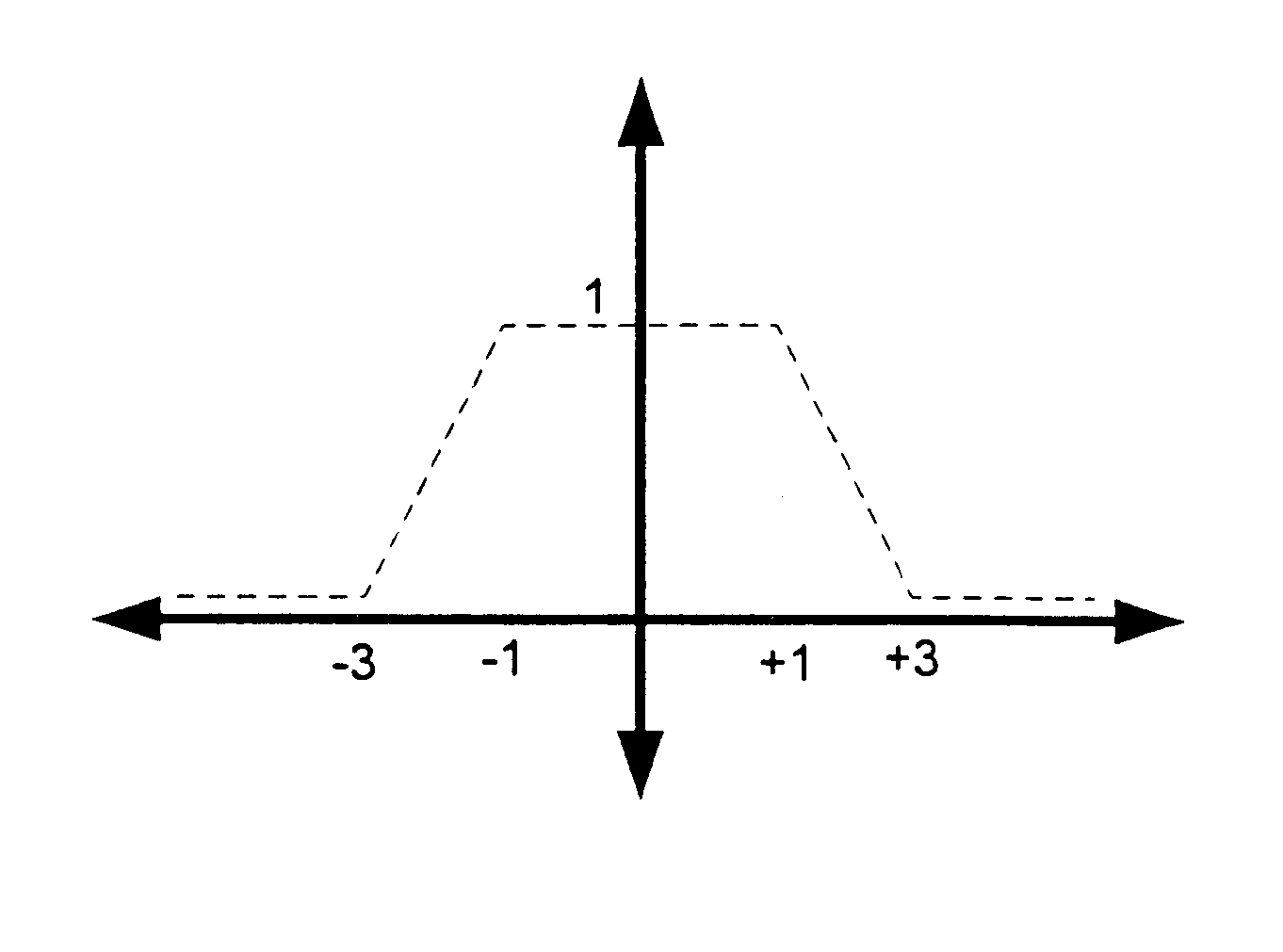
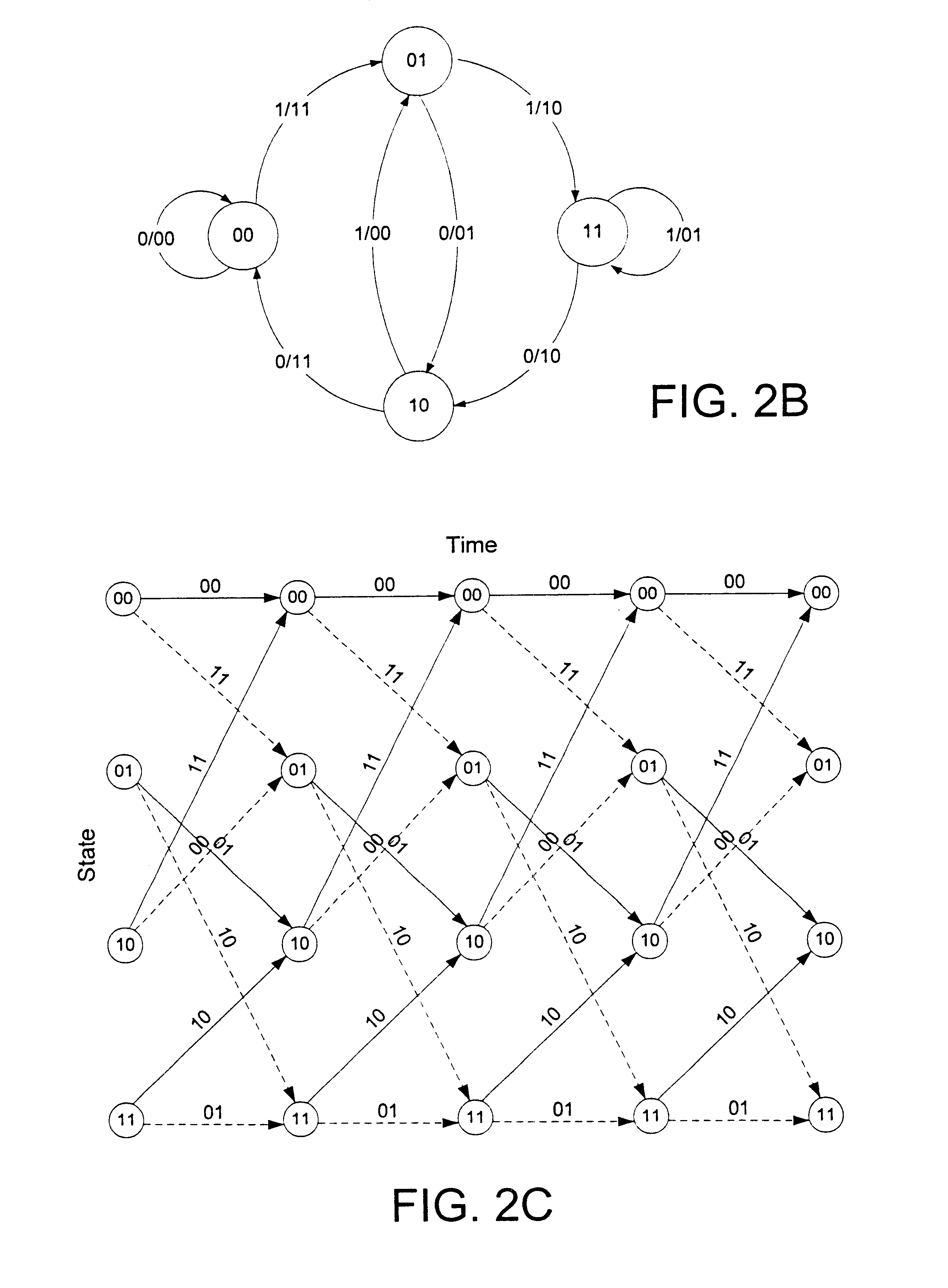
A Viterbi decoding system interprets bits in received QAM constellations as many-valued parameters rather than binary valued parameters. It performs the Viterbi algorithm using these many-valued parameters to provide results superior to hard decision decoding. Rather than applying a hard 0-1 function to the QAM data, the system uses a non-stepped linear or curved transfer function to assign values to the bits. In another aspect, a system differentiates between data bits based on their estimated reliability, giving more emphasis to decoding reliable bits than unreliable bits using any of a variety of techniques. By differentiating between god and bad bits and de-emphasizing or ignoring unreliable bits, the system can provide a significant reduction in uncorrectable errors and packet loss.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
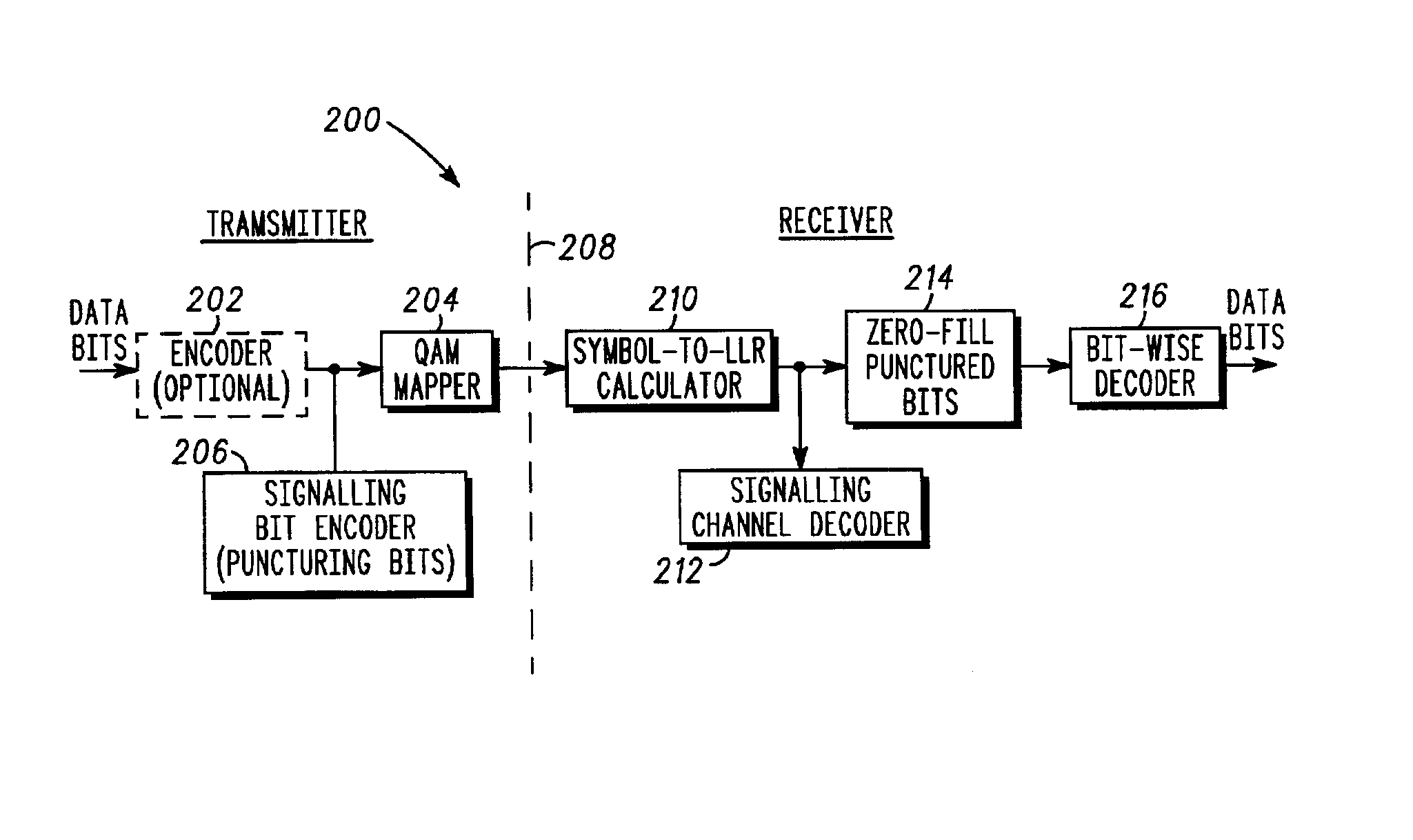
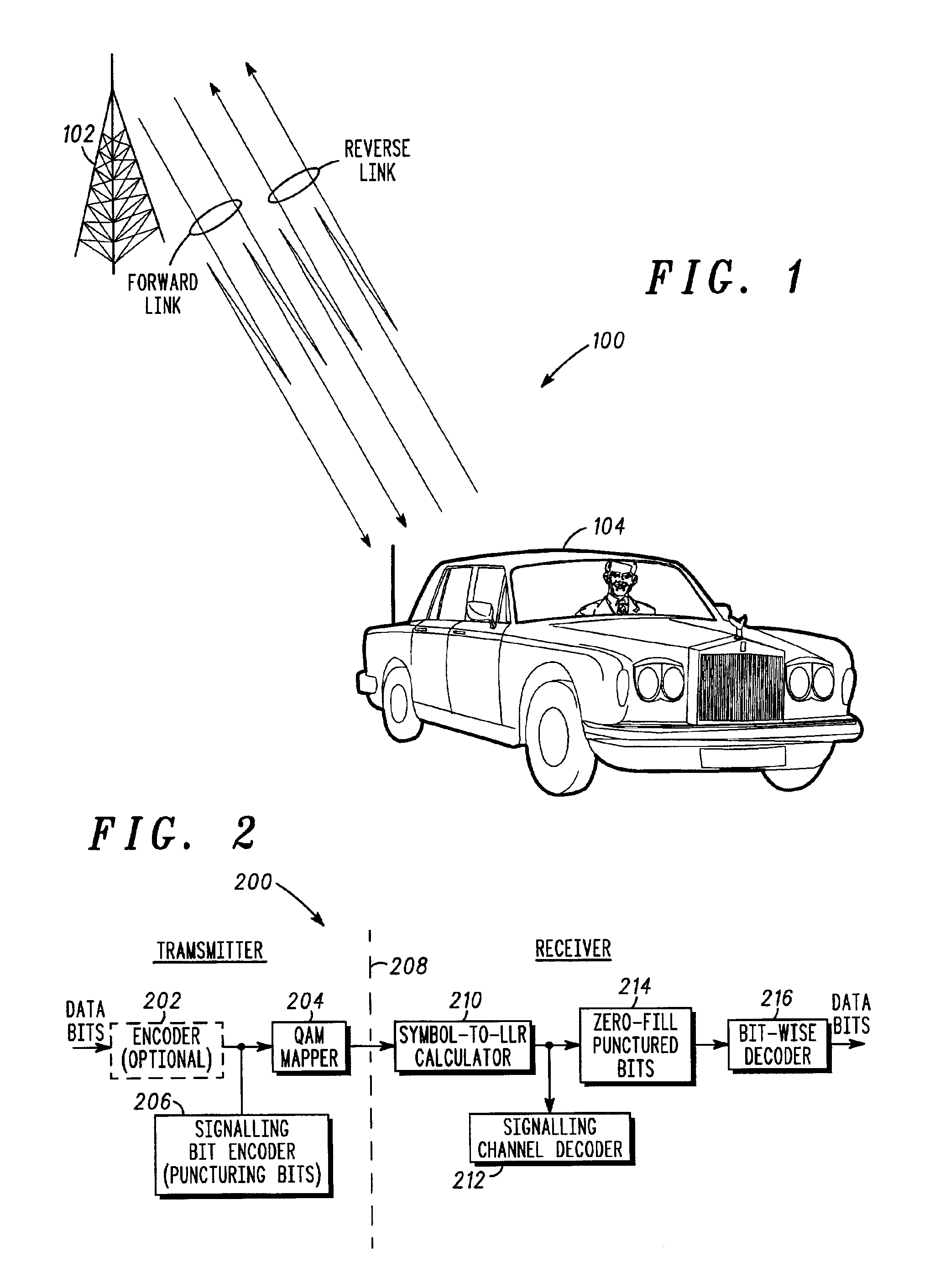
Method and apparatus for adaptive signaling in a QAM communication system
ActiveUS6904097B2Improve reliabilityIncrease the log-likelihood ratio gainsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCommunications systemLog likelihood
A method and apparatus to adaptively puncture bits within QAM modulated data symbols transmitted in a communication system in order to effect a signaling channel. The method and apparatus utilize inherent characteristics of a particular mapping scheme for the QAM constellation to selectively puncture particular bits within a data symbol with signaling information and predetermined binary values to selectively increase the log-likelihood ratio gains of those particular bits punctured with the signaling information. The log-likelihood ratios are used to obtain the signaling information and, thus, increasing the gain of the log-likelihood ratios affords greater reliability for the signaling information without increasing the required system resources.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Flexible multimode QAM modulator
InactiveUS6973141B1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsAngle modulationQam modulationTransmission channel
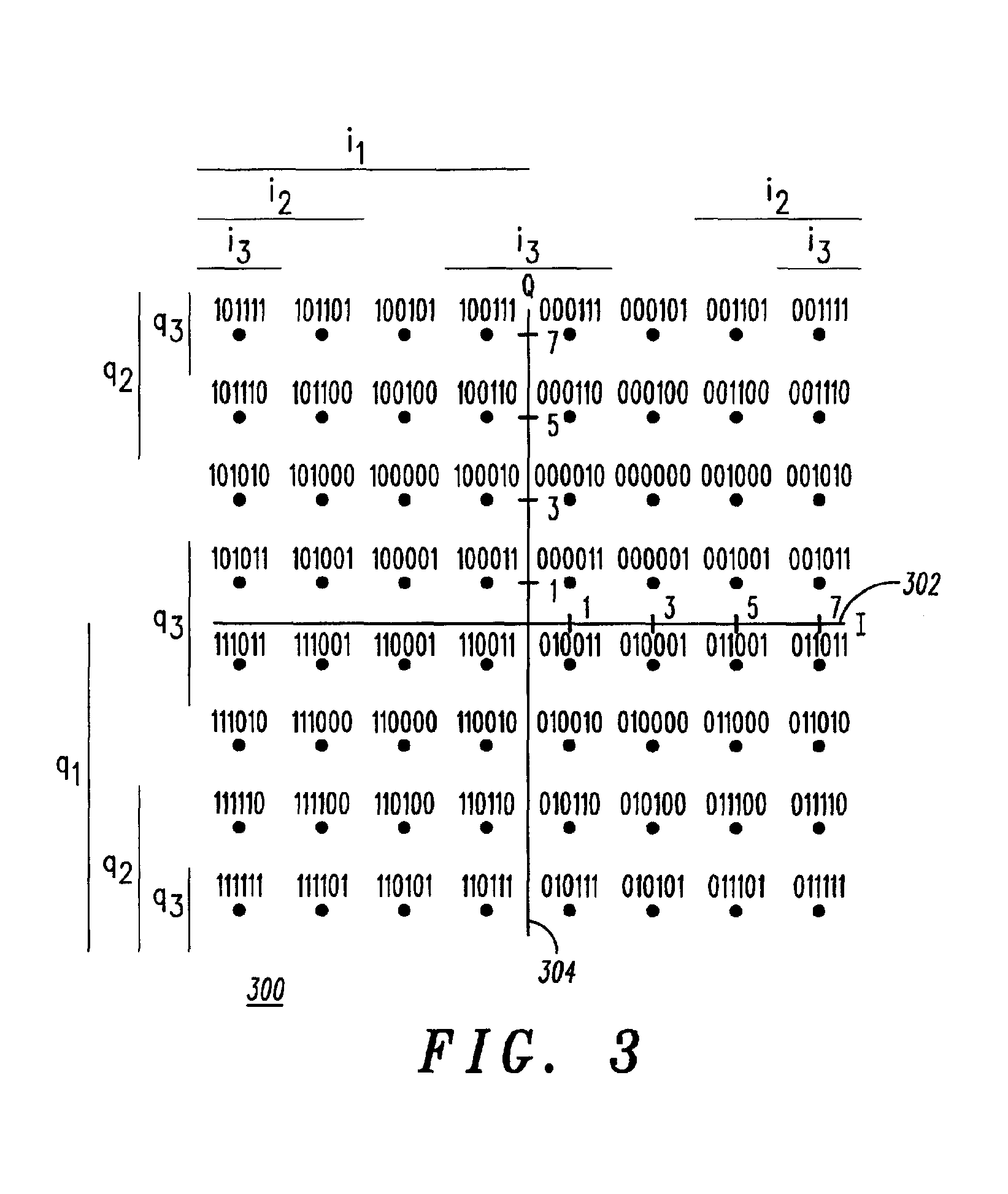
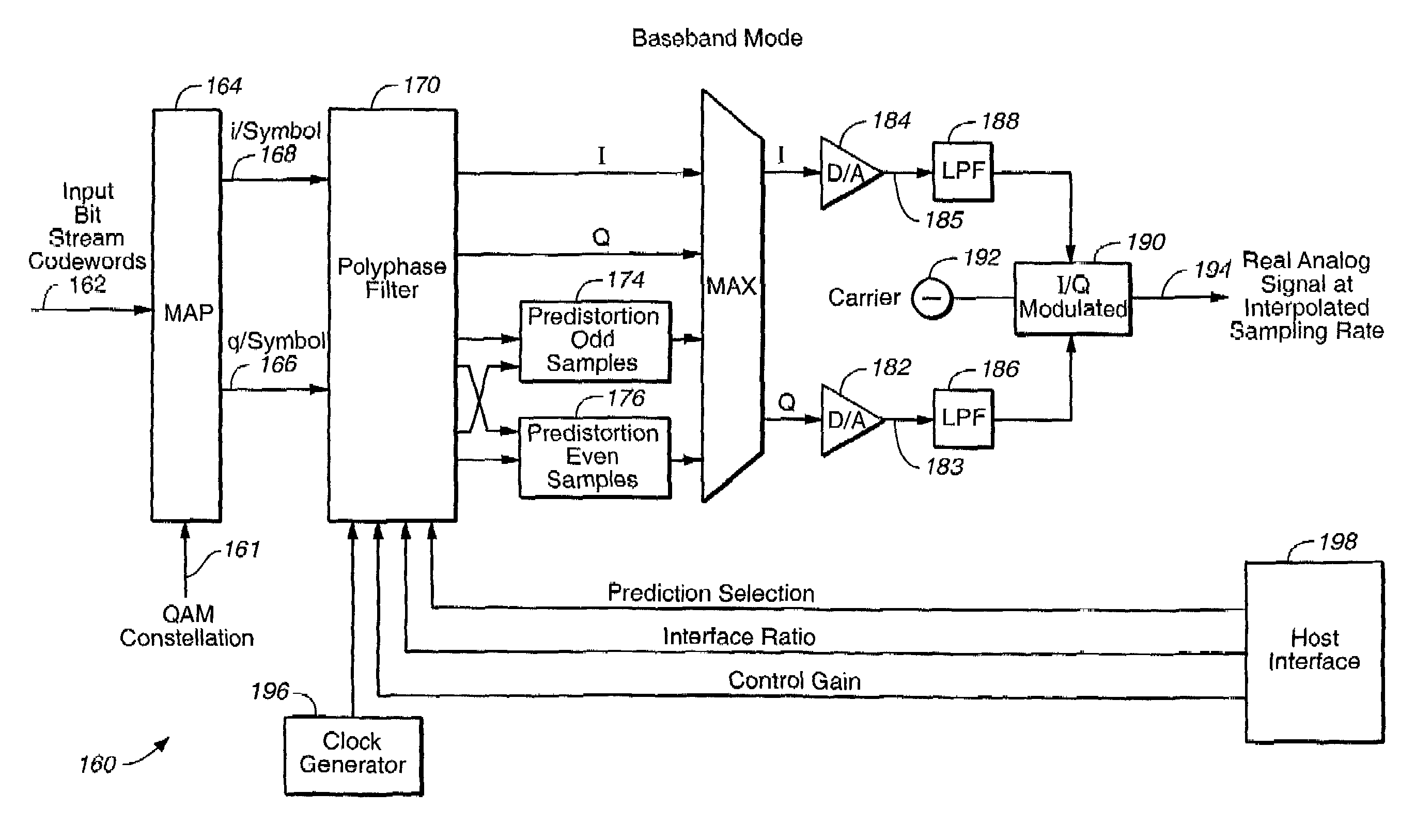
A method of baseband / passband digital modulation for a data transmission system wherein a plurality of data symbols is transmitted over a transmission channel at a symbol rate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) generating a plurality of I and Q components of symbols by mapping an input bit stream comprising a plurality of digital codewords into a QAM constellation; (2) selecting a passband or a baseband mode; and (3) generating an analog output signal in the passband or baseband mode. The step of selecting the passband or the baseband mode depends on the complexity of QAM constellation. If QAM constellation includes less than 64 QAM plant points, the passband mode is selected, and if QAM constellation includes more than 64 QAM plant points, the baseband mode is selected. If the QAM constellation includes less than 64 QAM plant points, initially selecting the passband mode until a D / A conversion speed reaches a maximum passband conversion speed, and until an output symbol rate reaches a maximum passband symbol output rate, and subsequently switching to the baseband mode in order to double the maximum passband conversion speed and to double the maximum passband symbol output rate.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
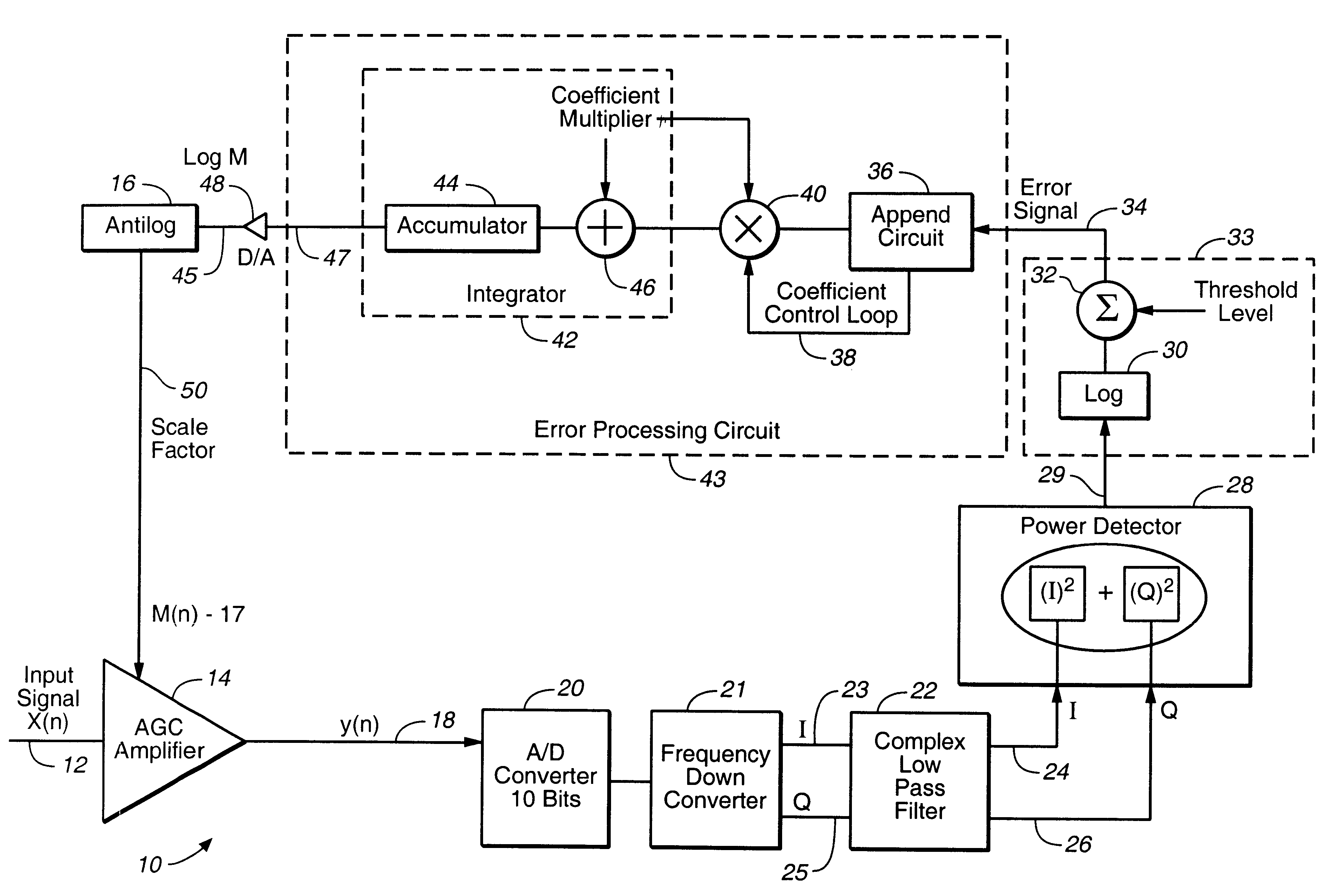
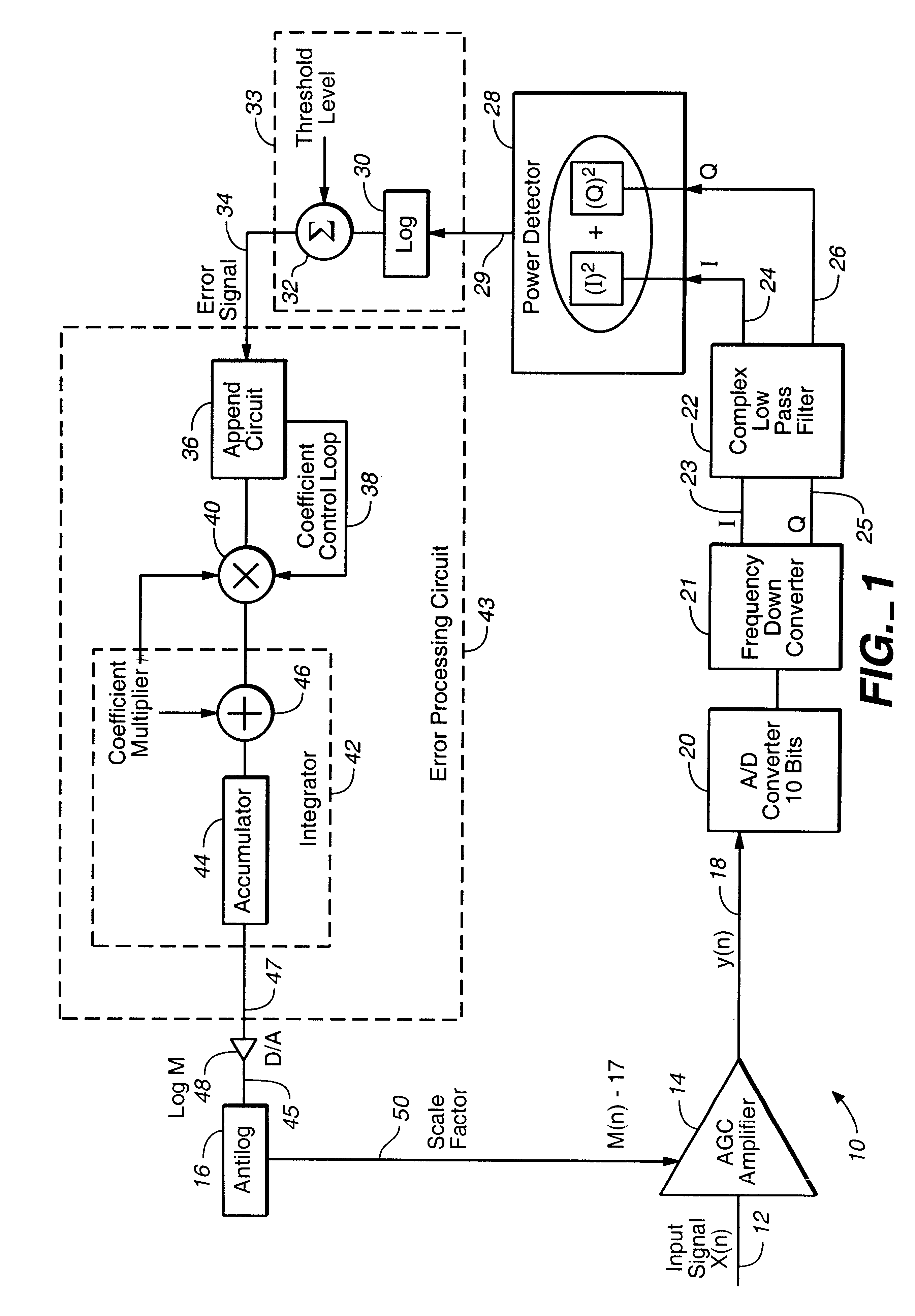
All digital automatic gain control circuit
A digital automatic gain control (AGC) system comprising an AGC amplifier configured to scale an input signal by a scale factor, and configured to generate an analog scaled input signal. An analog-to-digital (A / D) converter is configured to sample and convert the analog scaled input signal into a digital scaled input signal. The frequency down converted digital scaled input signal is processed by a power level detector circuit to detect its power level. The logarithmic comparison circuit (LCC) is configured to compare the detected power level of the digital scaled input signal to a predetermined reference signal and configured to generate a digital error signal. Finally, an error processing circuit is configured to process the digital error signal and configured to determine the scale factor of the AGC circuit. The test results show that for any applicable QAM constellation the AGC circuit of the present invention can control the broadest fades (or decreases) in the power level of the input signal with an accuracy up to 200 dB / per second.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
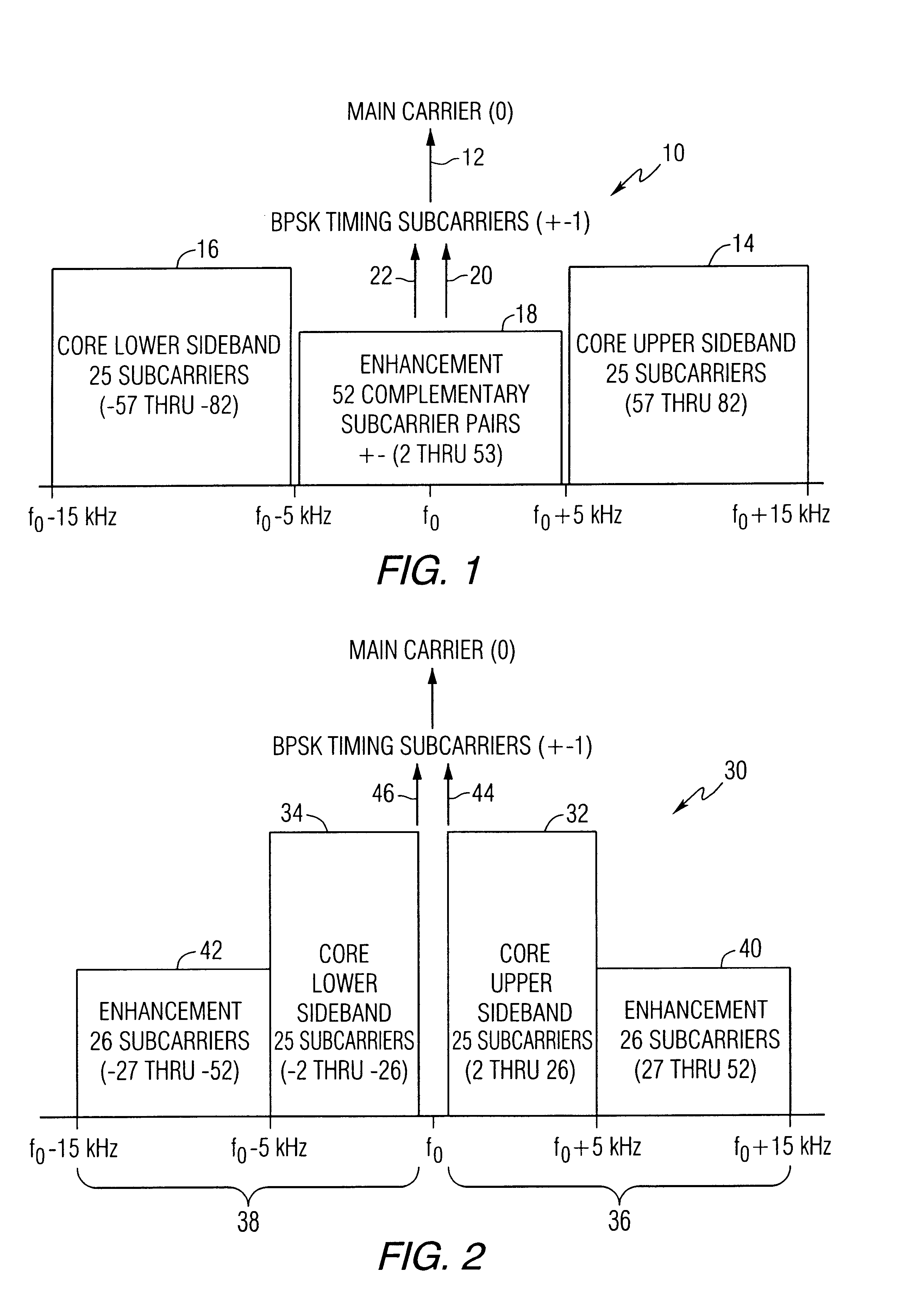
Digital audio broadcasting method and apparatus using complementary pattern-mapped convolutional codes
ActiveUS7043681B2Overcome limitationsError correction/detection using convolutional codesTransmission path divisionIn-phase and quadrature componentsCarrier signal
A method of transmitting digital information comprises the steps of forward error correction encoding a plurality of bits of digital information using complementary pattern-mapped convolutional codes, modulating a plurality of carrier signals with the forward error corrected bits, and transmitting the carrier signals. The modulation can include the step of independently amplitude shift keying in-phase and quadrature components of the QAM constellation using Gray code constellation points corresponding to amplitude levels. Transmitters that transmit signals in accordance with the method and receivers that receive such signals are also included.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
Optical modulator for higher-order modulation
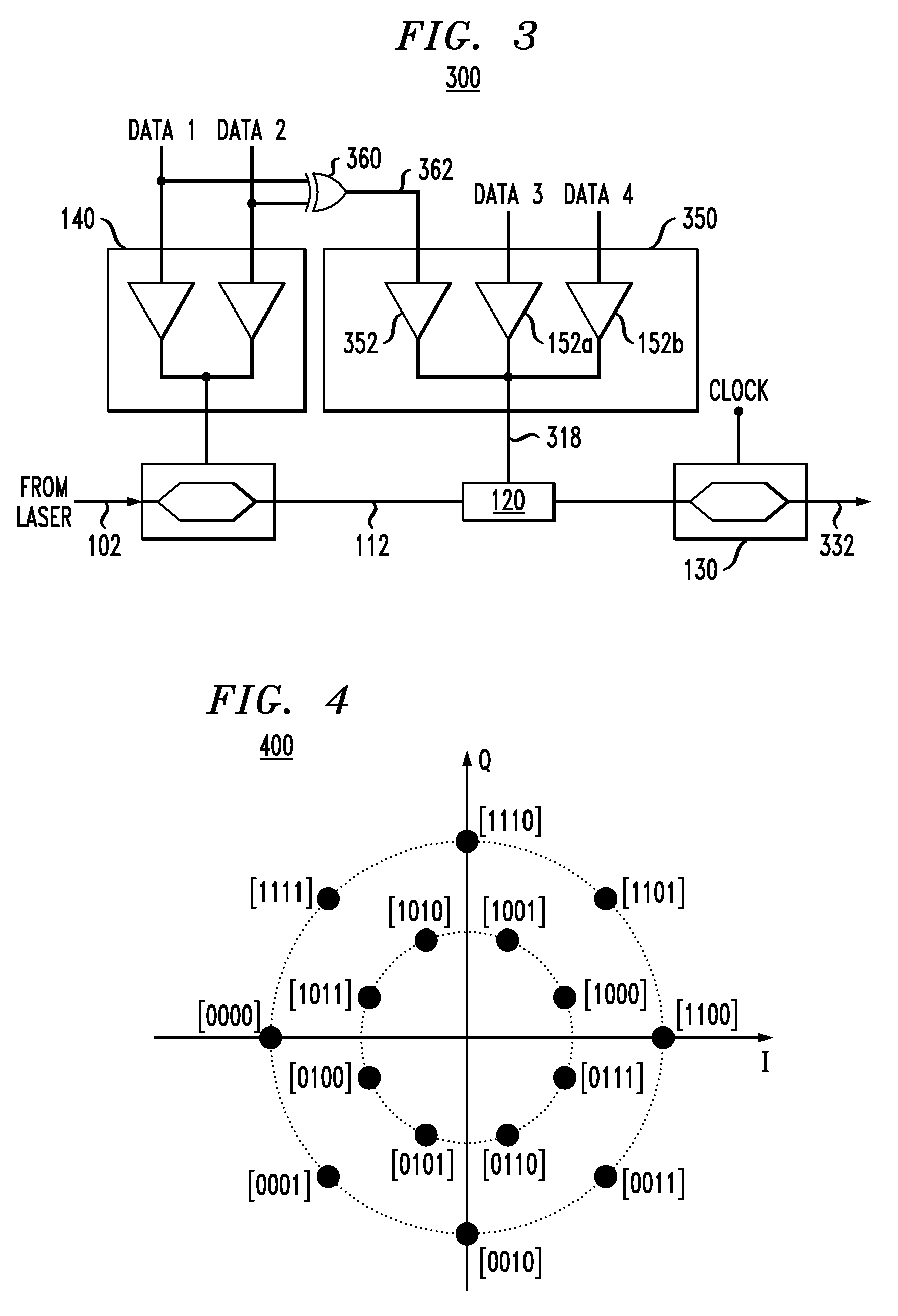
According to one embodiment of the invention, a 16-QAM optical modulator has a Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) coupled to a drive circuit that drives the MZM based on two electrical binary signals. The output of the MZM corresponds to an intermediary constellation consisting of four constellation points arranged on a straight line in the corresponding in-phase / quadrature-phase (I-Q) plane. Two of these constellation points correspond to a zero phase, and the remaining two constellation points correspond to a phase of π radian. The 16-QAM optical modulator further has a phase shifter that modulates the output of the MZM based on two additional electrical binary signals. The resulting optical output signal corresponds to a star 16-QAM constellation, which is produced by incremental rotation of the intermediary constellation.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Constellation mapping method based on absolute phase shift keying (APSK) constellation map, coded modulation method and system
ActiveCN102752261AImprove performanceError preventionMultiple carrier systemsComputer scienceQam constellations
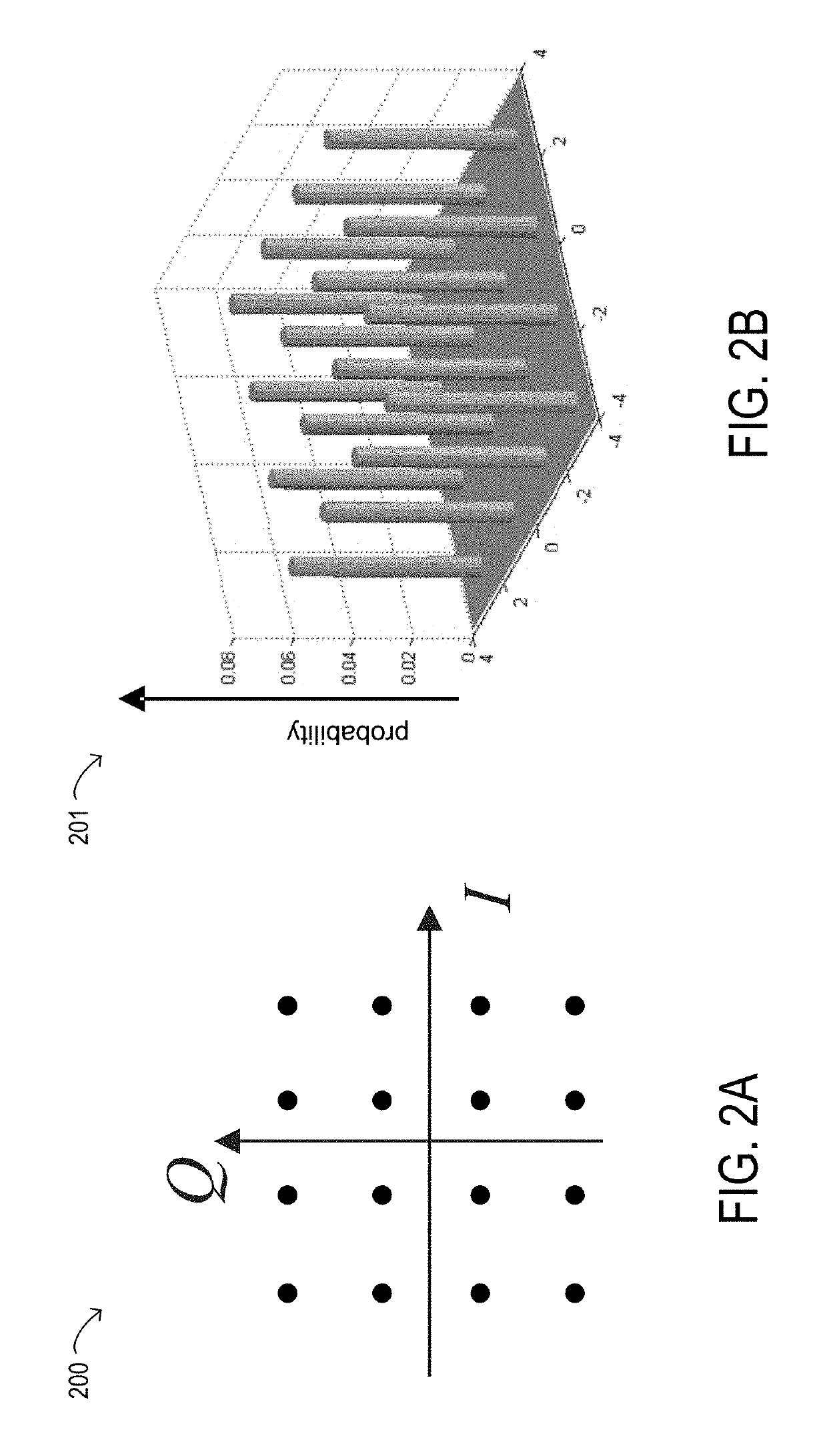
The invention discloses a constellation mapping method based on an absolute phase shift keying (APSK) constellation map. The constellation mapping method is characterized in that the order M of an APSK constellation is equal to 2<m>; the number n1 of points on each ring is equal to a value of powers to 2, namely n1=2<m1>, the number n1=2<m1>-PSK (phase shift keying), the number of rings R=2<m2>, and a set consisting of different ring radiuses is a special 2<m2>-PAM(pulse amplitude modulation ), wherein m1+m2=m; and the phase deflection theta1 of all the rings are the same. The method comprises the following steps of: B1, for a bit vector which is m in length, setting m1 bits to be only related to the phase, and adopting PSK Gray mapping between the m1 bits and the 2<m1>-PSK; and B2, setting the rest m2 bits to be only related to the amplitude, and adopting PAM Gray mapping between the m2 bits and the 2<m2>-PAM. The invention has the advantages that compared with the conventional coded modulation system adopting quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) constellation map mapping, the coded modulation system adopting the APSM constellation map Gray mapping can acquire a considerable error control performance gain regardless of adopting independent demapping or iterative demapping by a receiving end.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
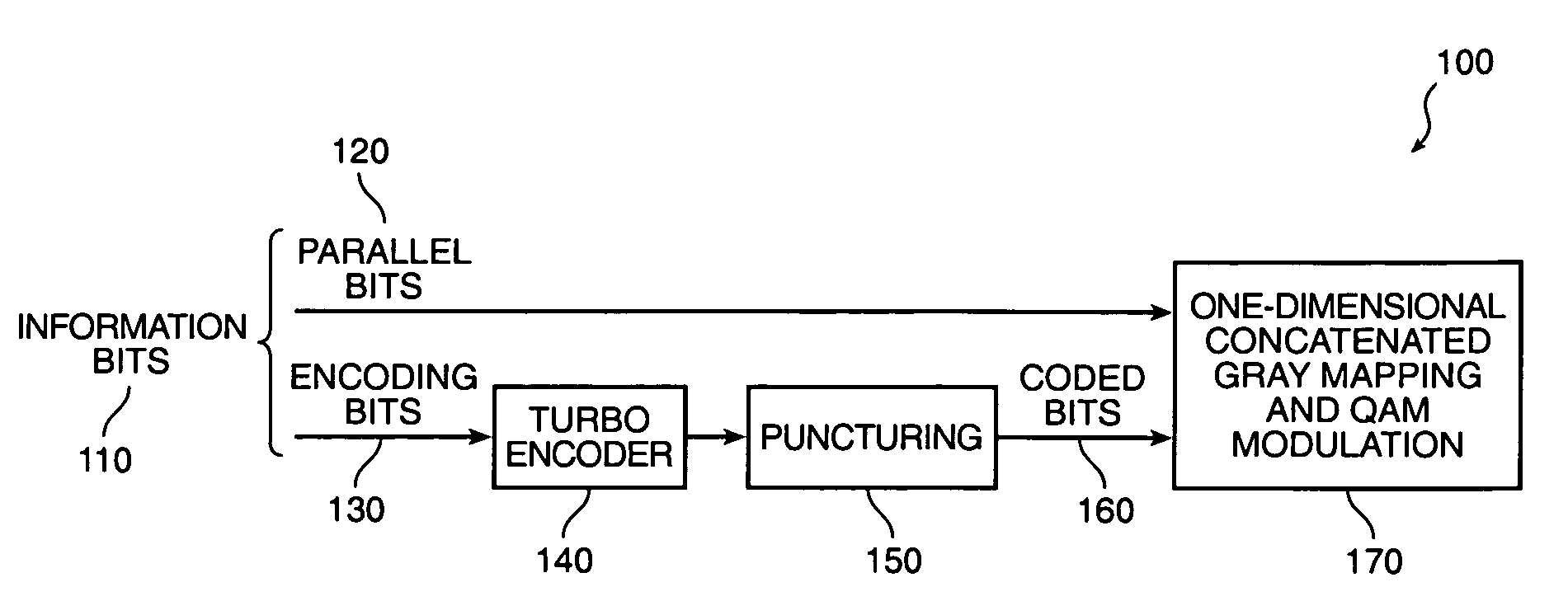
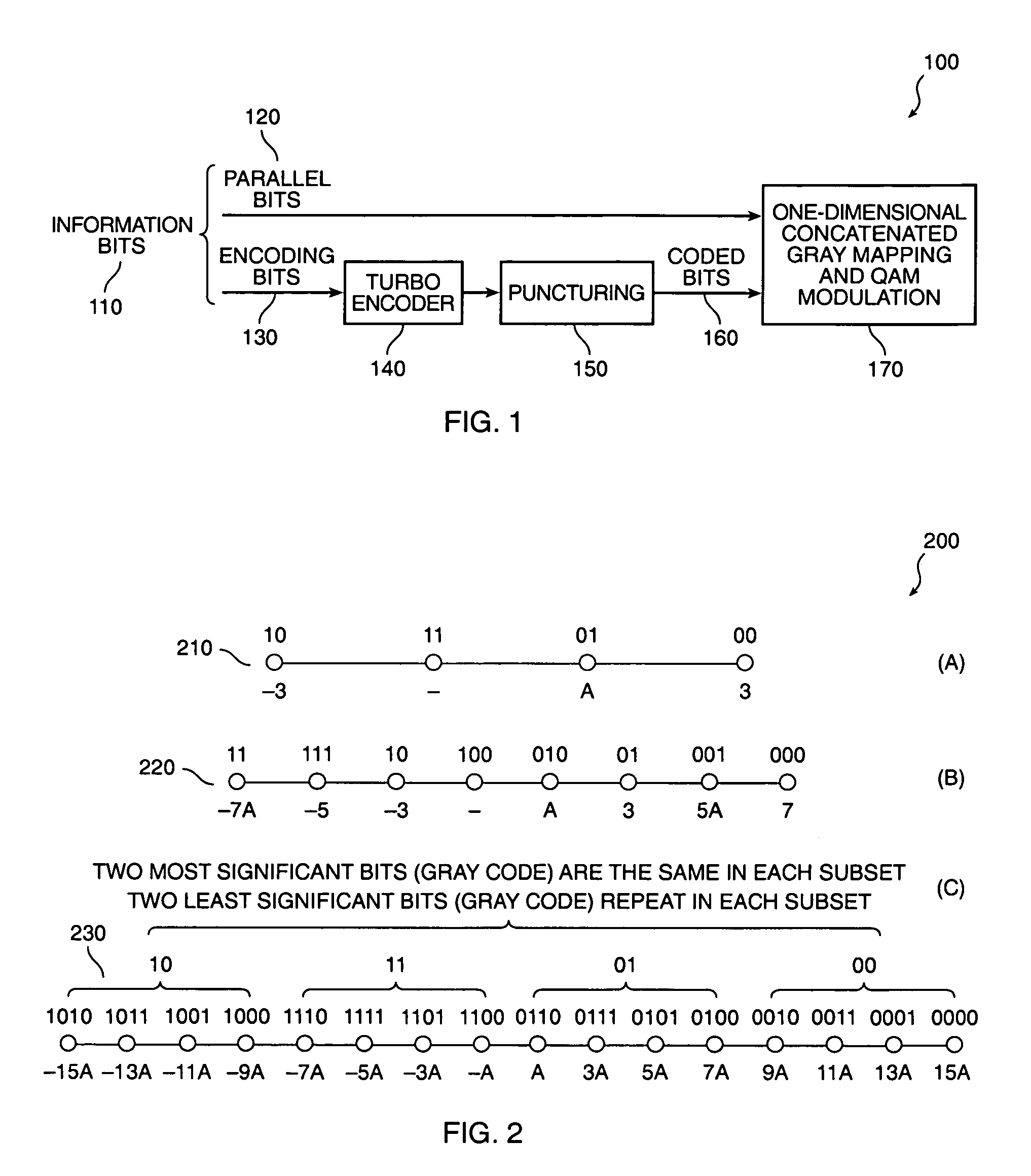
Method and system for turbo encoding in ADSL
ActiveUS7173978B2Multi-frequency code systemsForward error control useAsymmetric digital subscriber lineComputer science
In a coding system for asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) communications, a method of encoding a sequence of information bits is provided comprising the steps of dividing the information bits into encoding bits and parallel bits; encoding the encoding bits to produce encoded bits; mapping the encoded bits and the parallel bits into first and second pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) signals; and generating a quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) signal from these first and second PAM signals. This method overcomes the decoder complexity that would otherwise be required due to the large QAM constellations involved for ADSL communications.
Owner:CIENA
Method And Apparatus For Improved QAM Constellations
InactiveUS20150049844A1Reduce calculationMaximise measureAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsCode conversionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
A method and transmitter and receiver for determining and transmitting or receiving a non-uniform QAM signal comprises selecting a signal to noise ratio for a channel and forward error corrector and then determining positions of constellation points that maximise a measure of channel capacity at the selected signal to noise ratio. The position of one constellation point and another constellation point within the constellation are constrained to be equal to one another prior to determining the positions of the constellation points. In doing so, a so called condensed QAM constellation arrangement may be derived having fewer than conventional number of constellation points for a given QAM scheme. The condensed QAM arrangement has improved performance at certain signal to noise ratios.
Owner:BRITISH BROADCASTING CORP
Data transmitting, receiving method and device
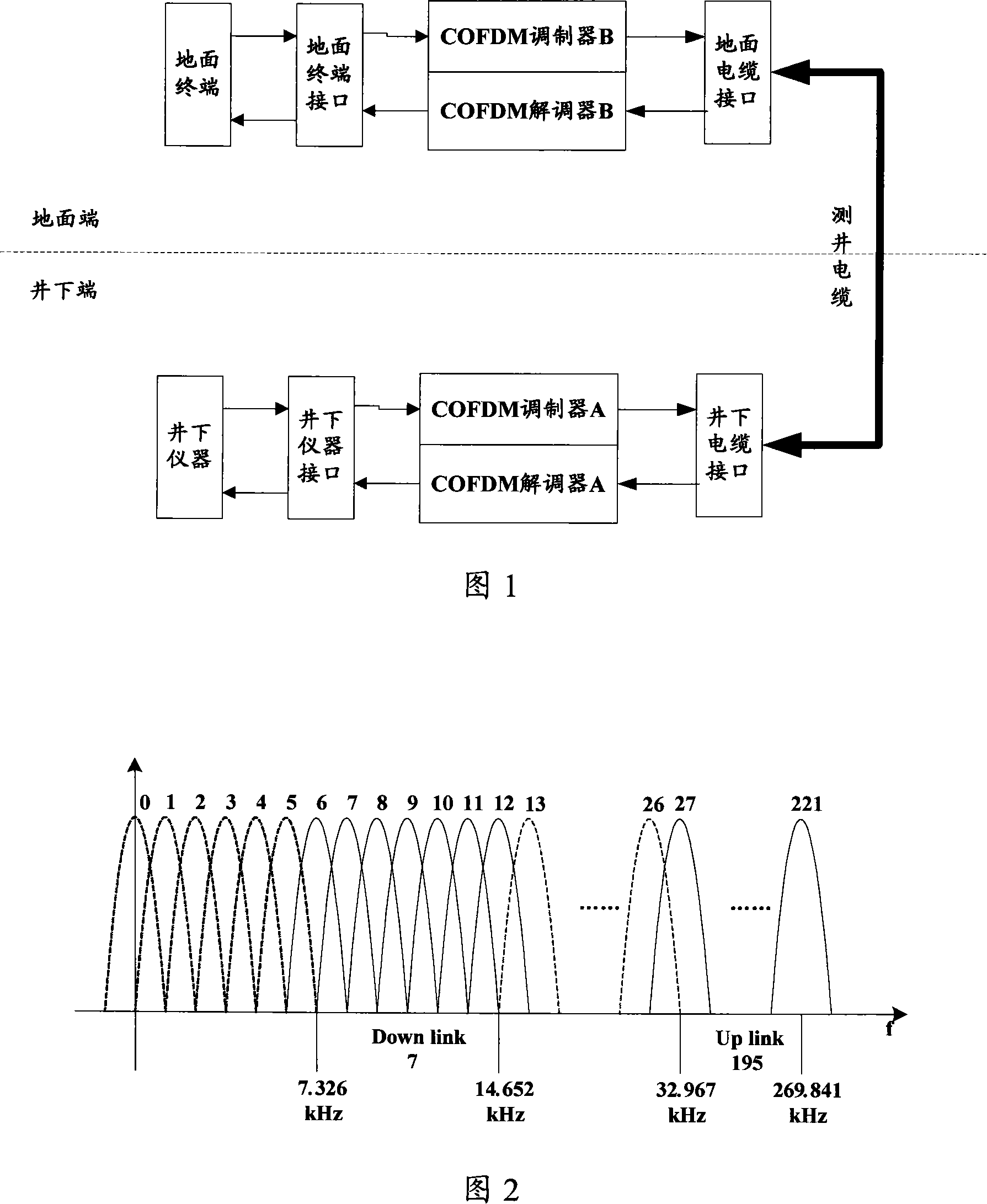
InactiveCN101179356AMeet the transmission requirements of large amounts of dataIncrease data transfer rateError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsCyclic prefixAnalog signal
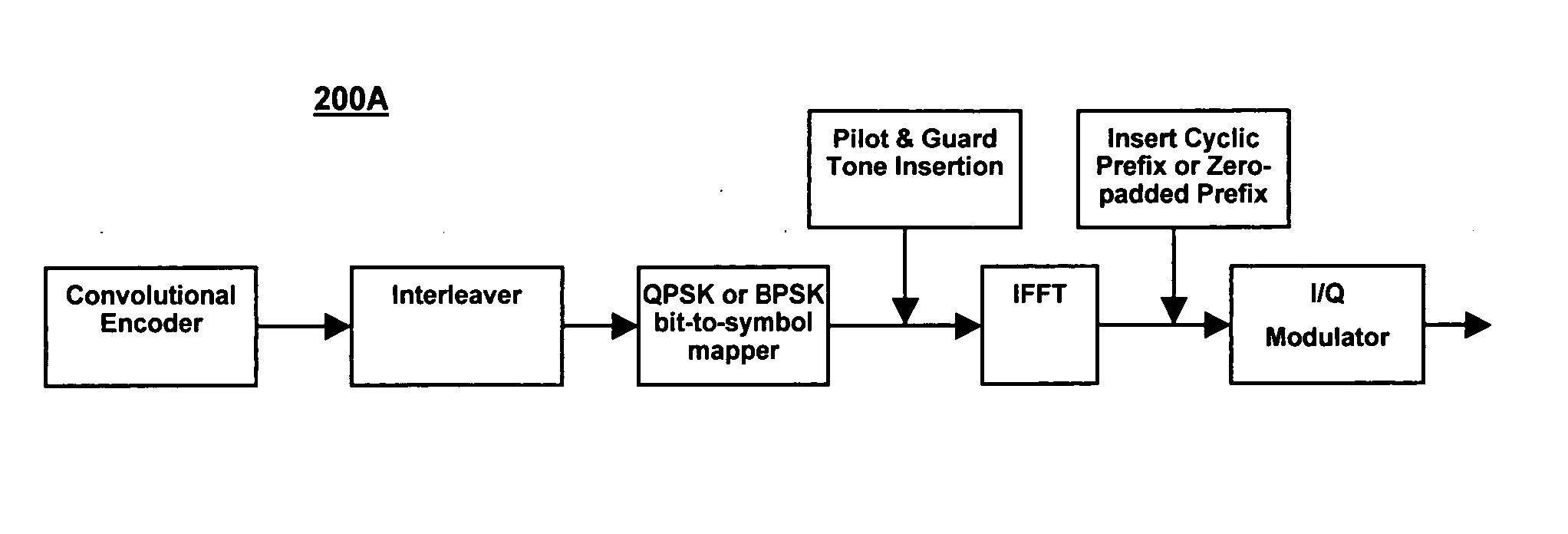
A method and a device for transmitting and receiving data are provided. The method comprises the following steps: A: data to be transmitted are interleaved after being divided, randomized and conducted forward error correction coding on the transmitting terminal. B: QAM maps the interleaved data into corresponding QAM constellation points according to the sub-channel bit and energy distribution parameter. C: after the QAM mapping treatment, the data are generated into frequency field data frame, which are then conducted IFFT transformation and generated into OFDM signals. D: insert cyclic prefix into the OFDM signals, which are then generated into baseband analog signals after digital to analog conversion; the baseband analog signals are transmitted to the receiving terminal in the service sub-channel of the logging cable. By adopting the method and device of the invention, data transmission rate in present logging cable is greatly improved, which in turn meets requirements of the large data amount transmission of under-well instruments.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
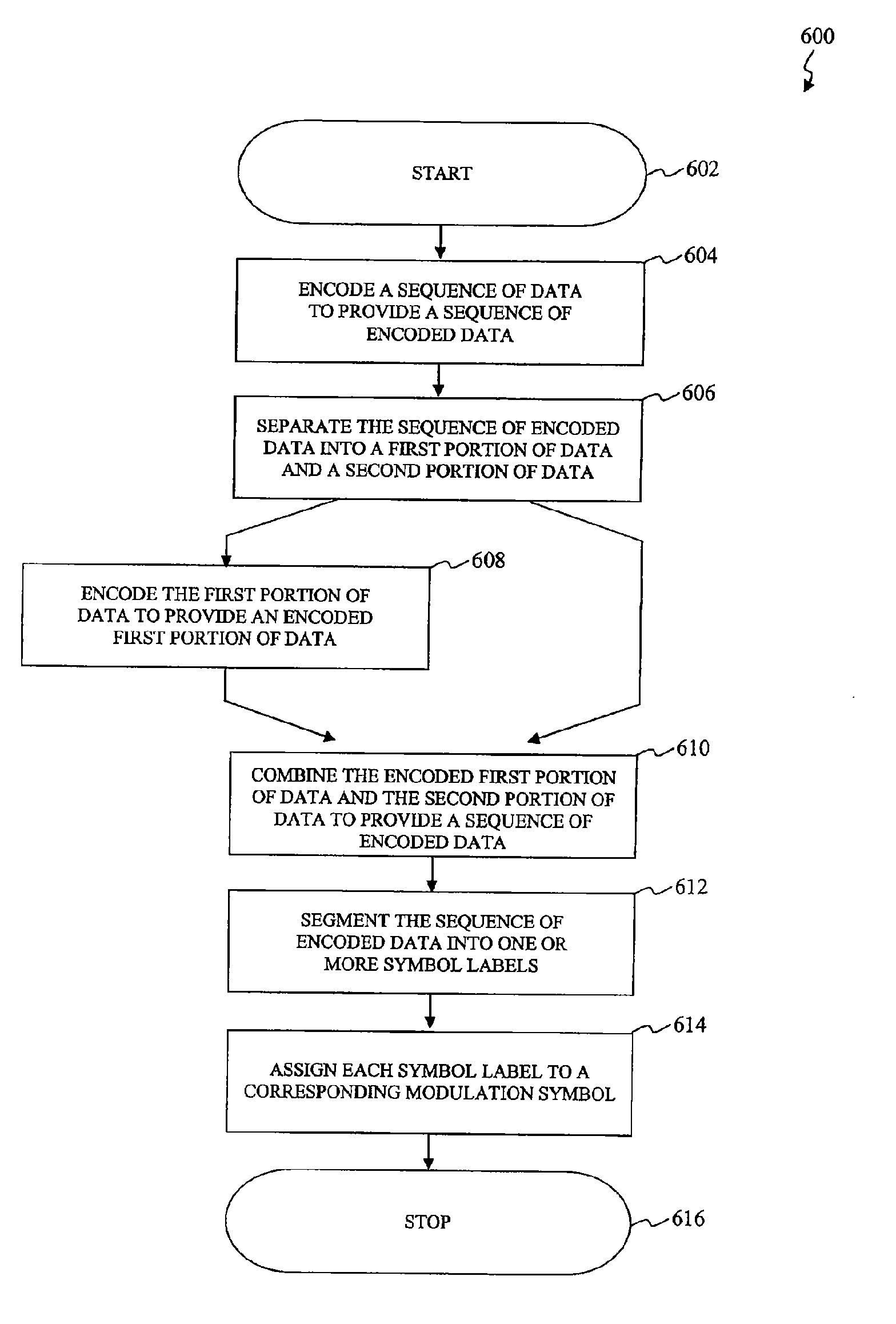
Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) Encoded Higher Order Modulation
InactiveUS20090129484A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionTheoretical computer scienceLow density
A method and apparatus is disclosed to map a sequence of data to Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) constellation symbols. The method and apparatus encodes only a portion of the sequence of data and leaves a remaining portion of the sequence of data unencoded. The encoded portion of the sequence of data and the remaining unencoded portion of the sequence of data are then mapped into modulation symbols of the QAM constellation. The encoded portion of the sequence of data selects subsets of the QAM constellation, and the remaining unencoded portion of the sequence of data determines a specific modulation symbol within each subset of the QAM constellation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
A coding modulation and decoding method and device for grid coding and modulation code
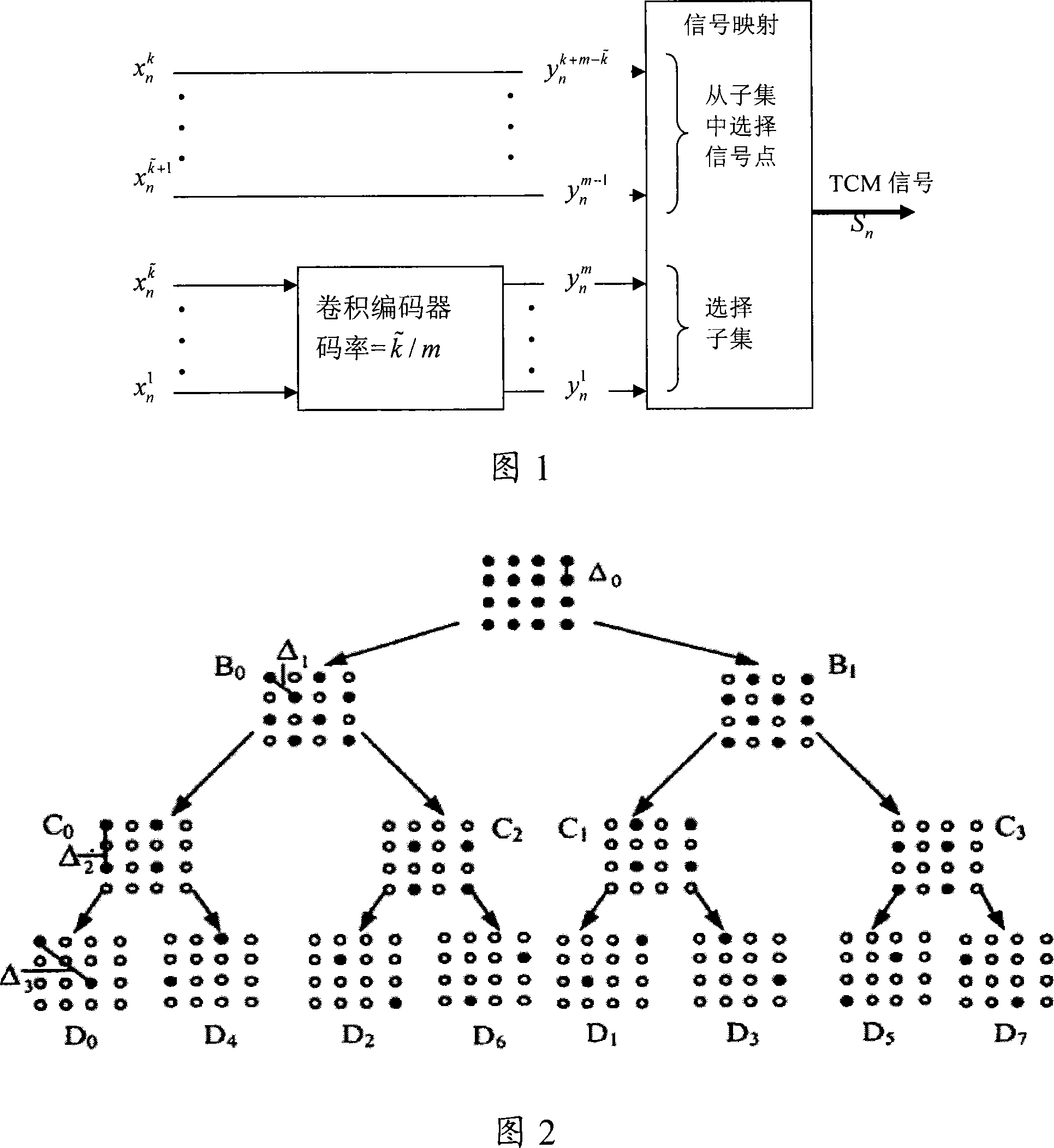
InactiveCN101123439AEvenly mappedThere will be no short Euclidean distanceError correction/detection using trellis codingError correction/detection using multiple codesModulation orderComputer science
The invention discloses a trellis code modulated (TCM) code modulation method, and is to solve the problem of poor entirety of the prior TCM codes. The invention comprises the following steps. Firstly, a square QAM planisphere with the modulation order number larger than 4 is used as a constellation mapping scheme so that after the codes on a way I and a way Q of the constellation mapping scheme are mapped, and bit blocks are arranged repeatedly on a periodic basis on the ways I and Q, and corresponding uncoded bit blocks are different after each repeated arrangement on a periodic basis. Constellation indices including coded bit blocks and uncoded bit blocks are acquired according to original bit message block. Signaling points in the constellation mapping scheme according to the constellation indices are determined as the final emissive TCM signals. As the coded bit blocks are repeatedly arranged on a periodic basis, and corresponding uncoded bit blocks are different from each other, mappings of symbols for parallel paths on the way Q of the constellation mapping scheme are uniform, and the entirety of TCM codes can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
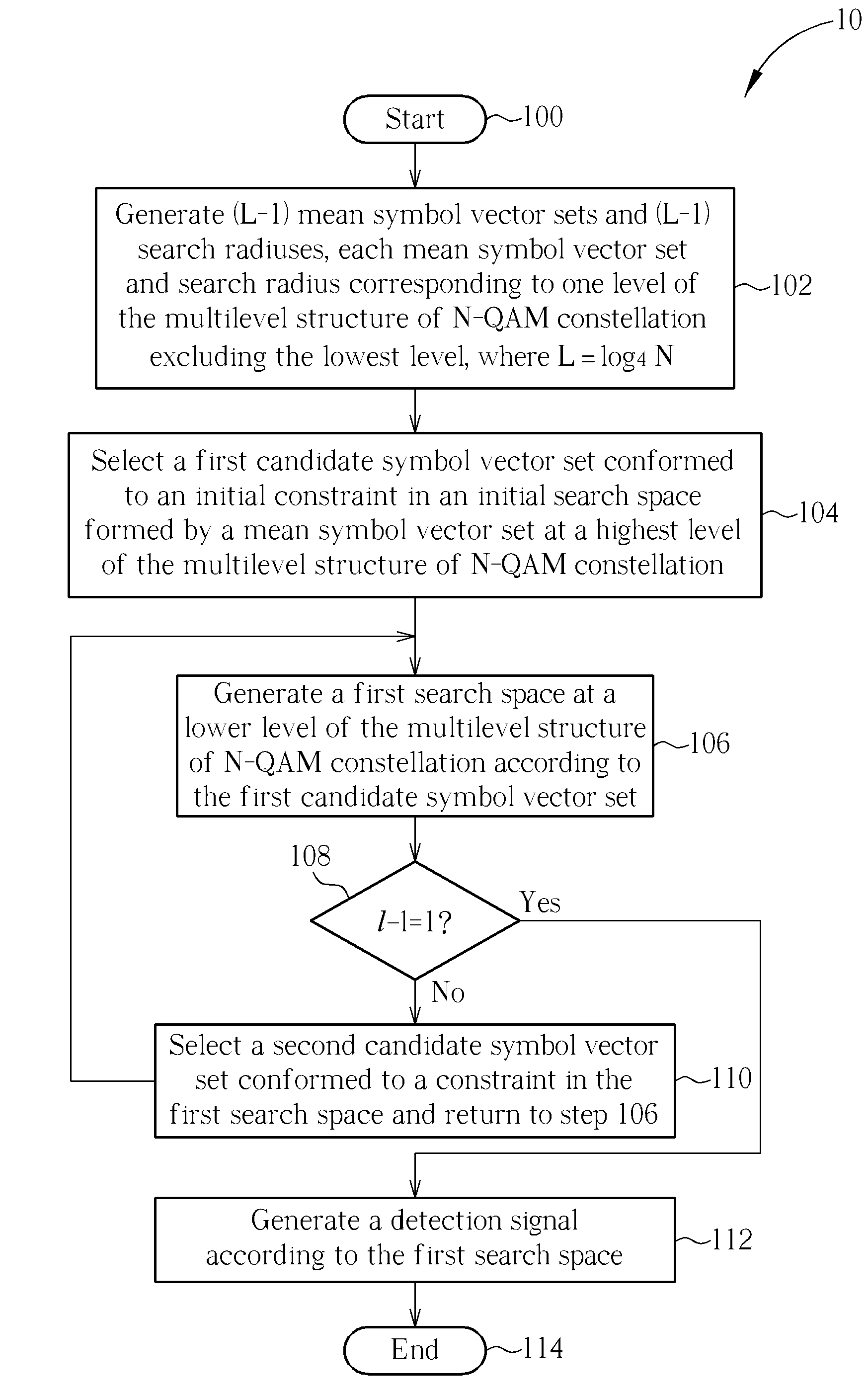
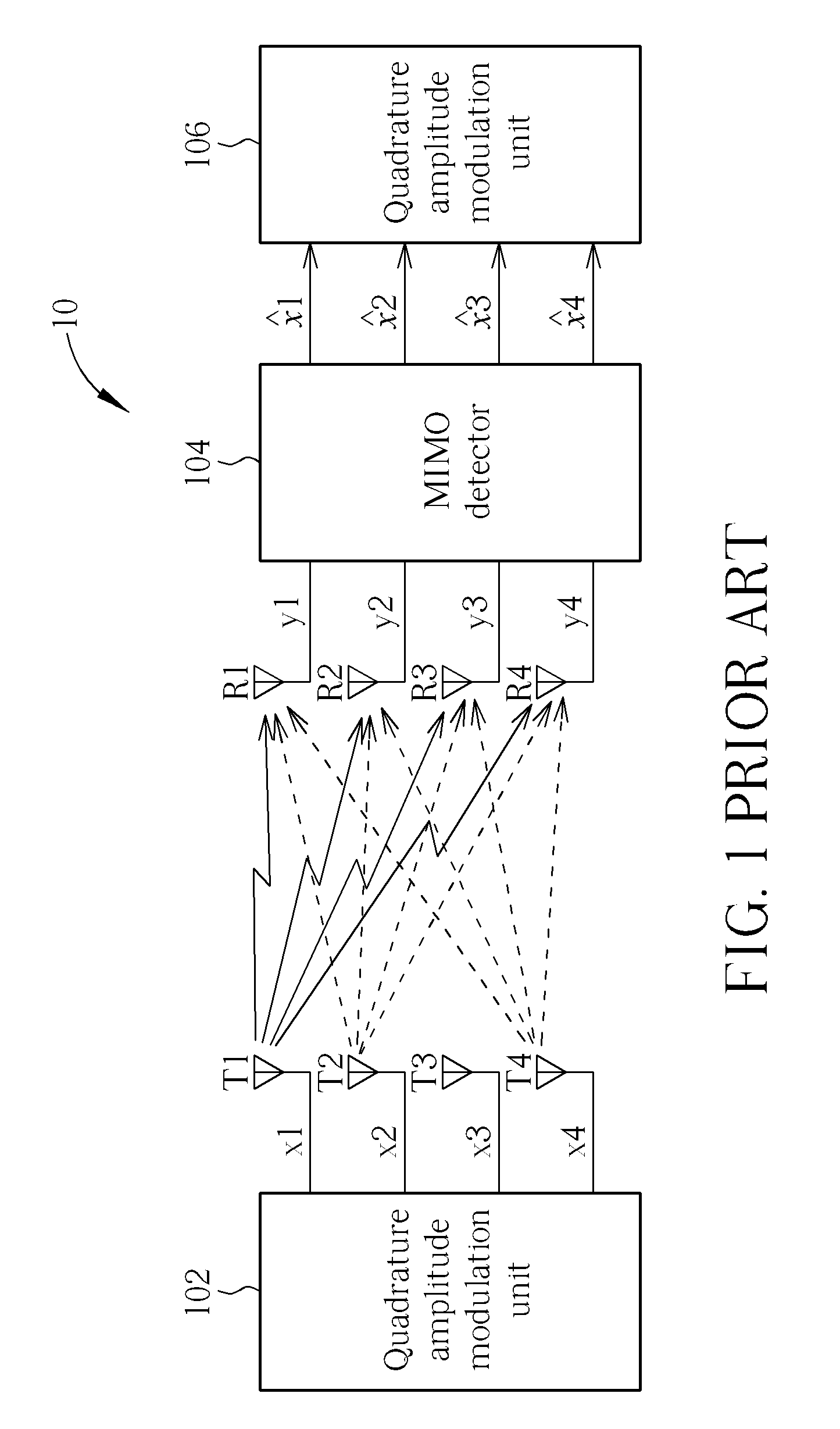
Multilevel Cluster-based MIMO Detection Method and MIMO Detector Thereof
ActiveUS20100054365A1Reduce complexityAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAlgorithmCluster based
A MIMO detection method for a receiver in a MIMO system using N-QAM for modulation, the MIMO detection method including generating a plurality of symbol vector sets and a plurality of search radiuses, selecting a candidate symbol vector set corresponding to a highest level of a multilevel structure of N-QAM constellation, generating a search space corresponding to a lower level of the multilevel structure of N-QAM constellation according to the selected candidate symbol vector set, confirming which level the search space corresponds to, and generating a detection signal according to the search space when the level of the search space is the lowest level of the multilevel structure of the N-QAM constellation.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
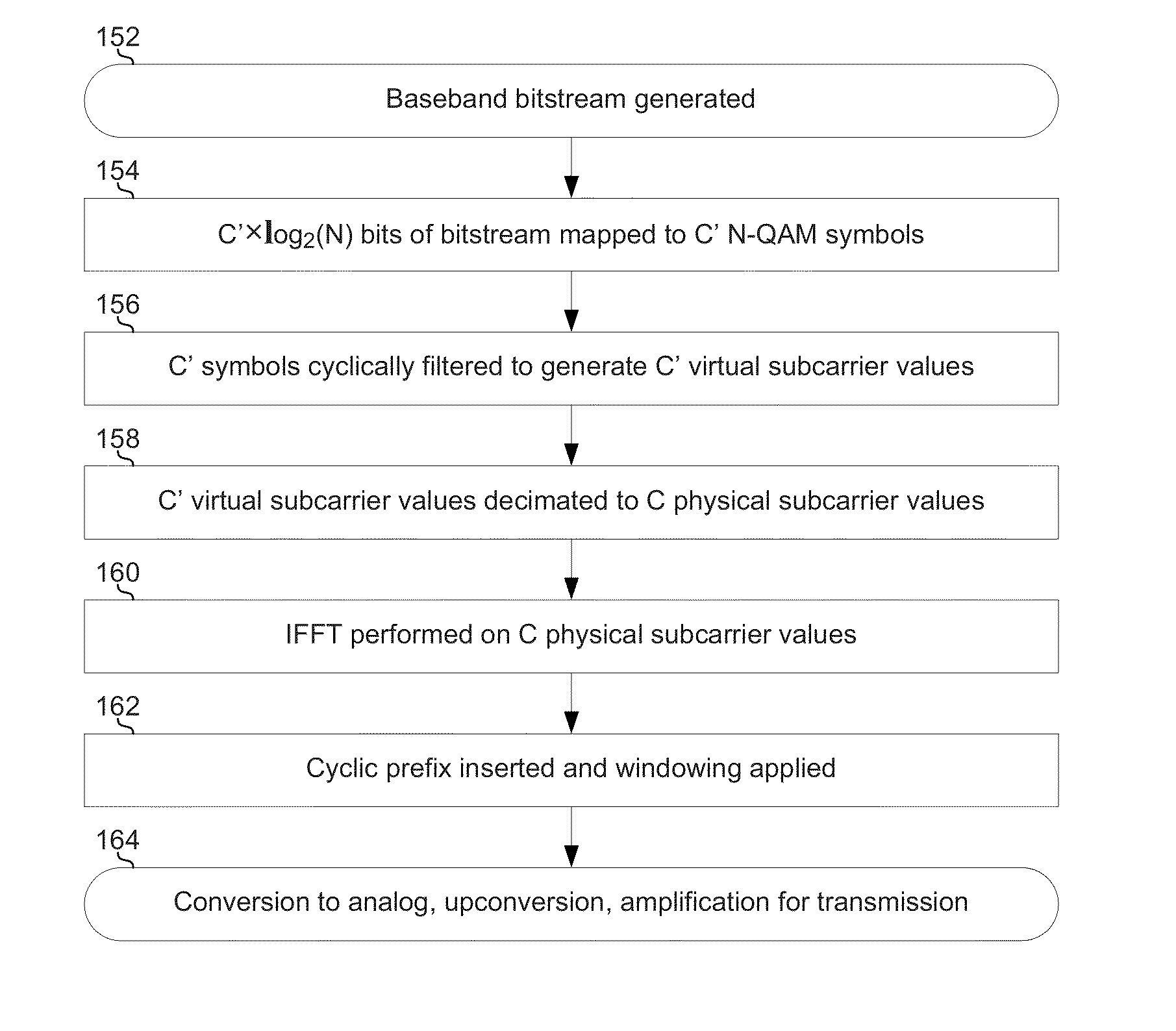
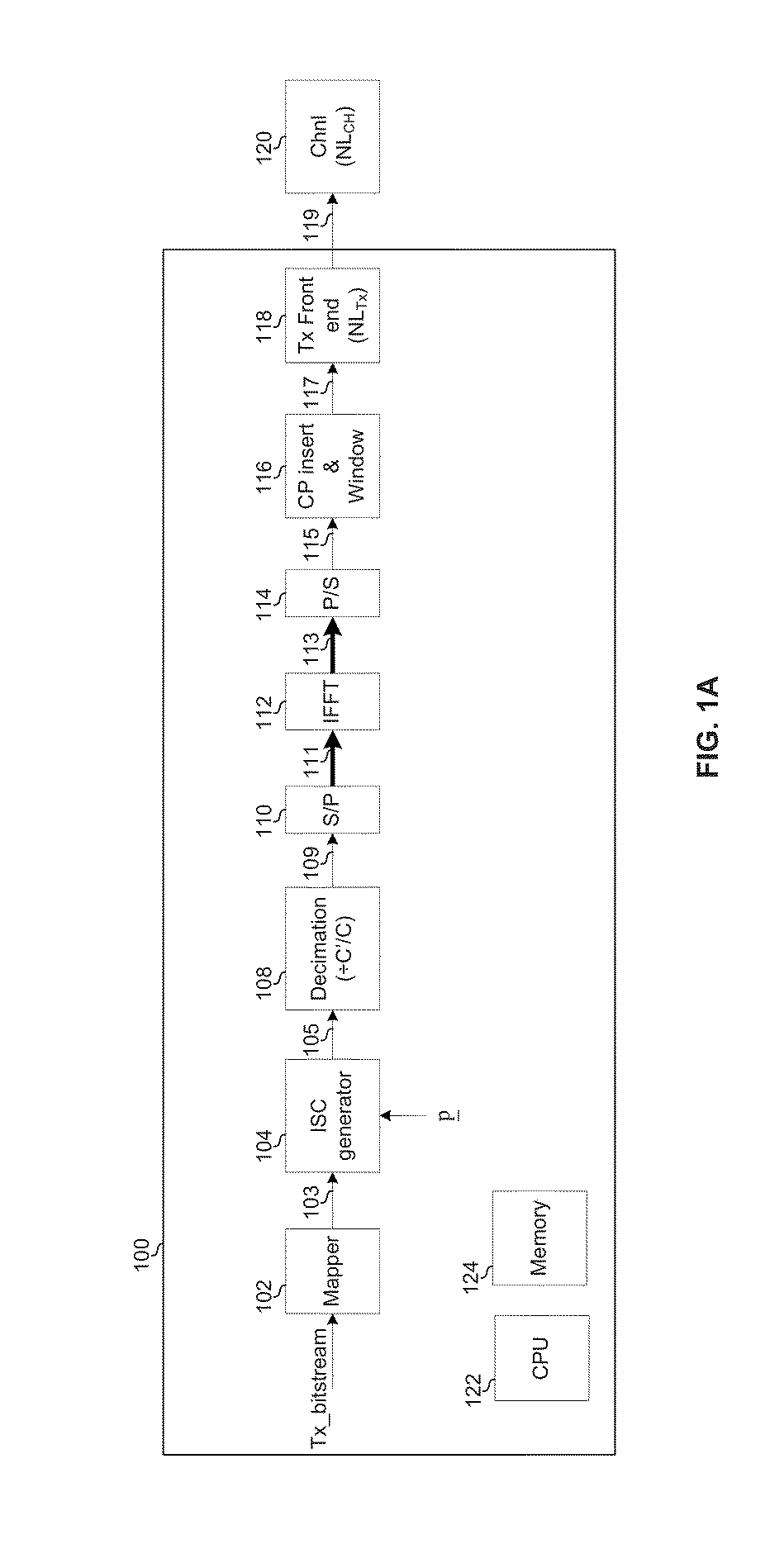
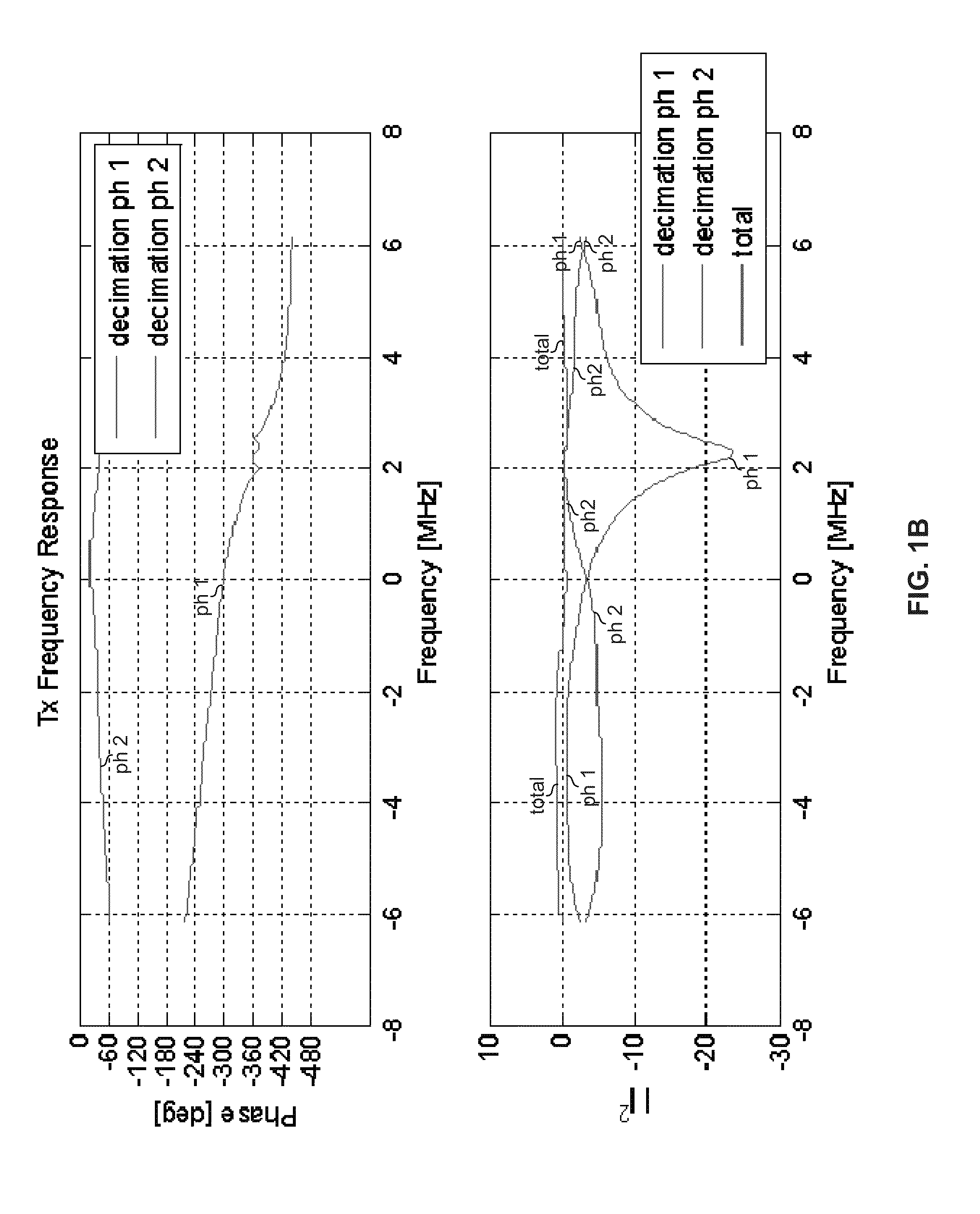
Highly-spectrally-efficient transmission using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing
A transmitter may map, using a selected modulation constellation, each of C′ bit sequences to a respective one of C′ symbols, where C′ is a number greater than one. The transmitter may process the C′ symbols to generate C′ inter-carrier correlated virtual subcarrier values. The transmitter may decimate the C′ virtual subcarrier values down to C physical subcarrier values, C being a number less than C′. The transmitter may transmit the C physical subcarrier values on C orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) subcarriers. The modulation constellation may be an N-QAM constellation, where N is an integer. The processing may comprise filtering the C′ symbols using an array of C′ filter tap coefficients. The filtering may comprise cyclic filtering. The filtering may comprise multiplication by a circulant matrix populated with the C′ filter tap coefficients.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
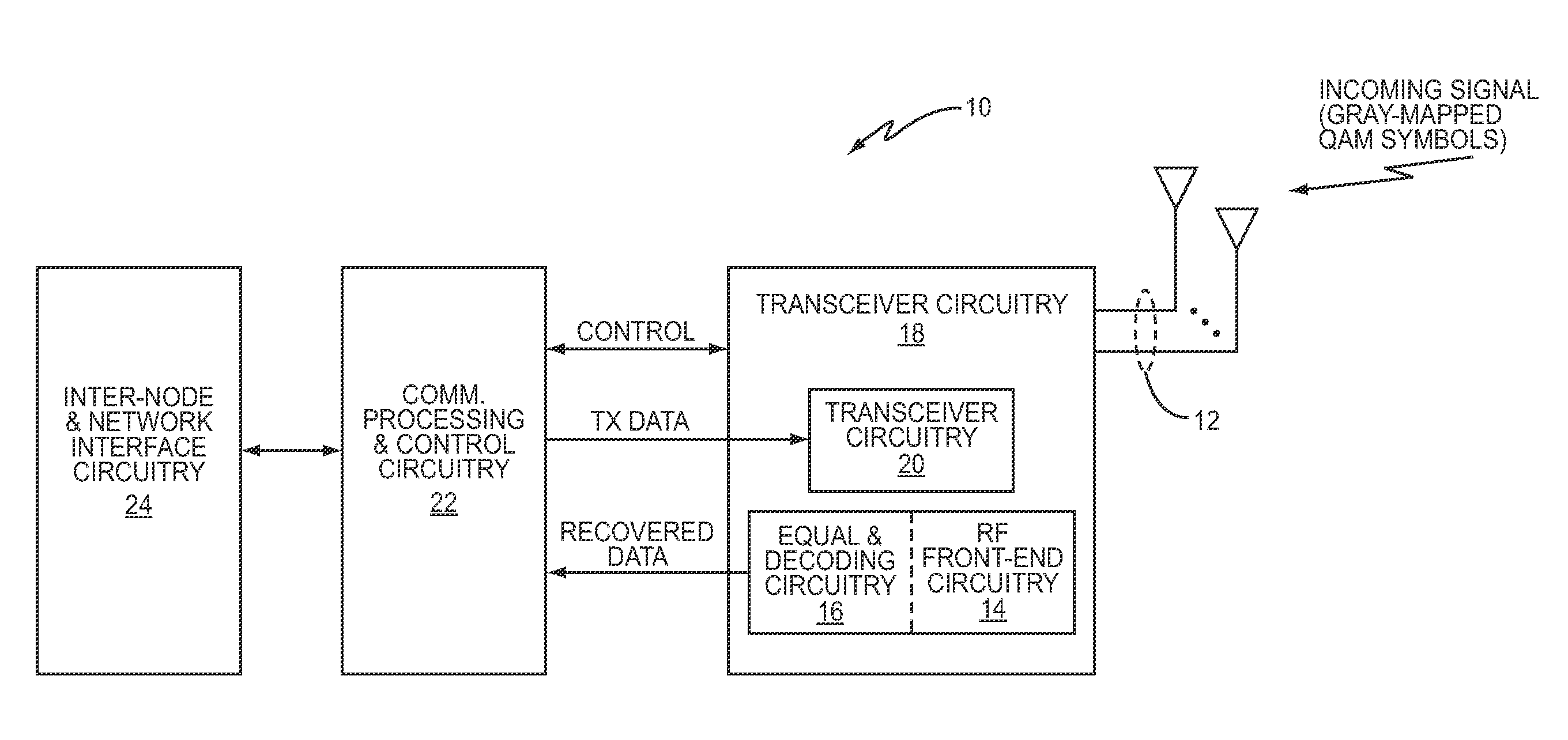
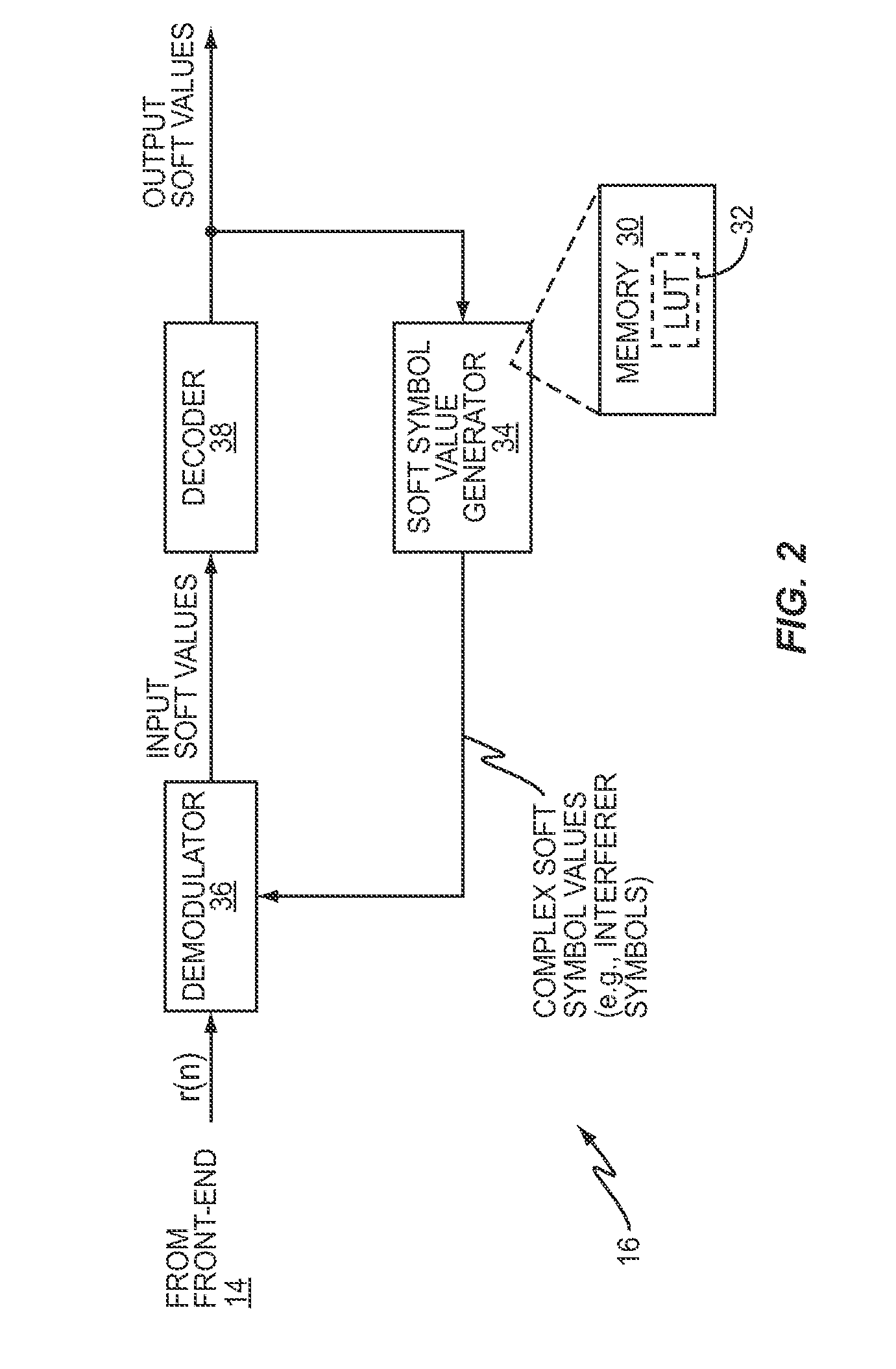
Method and Apparatus for Efficient Soft Modulation for Gray-Mapped QAM Symbols
InactiveUS20110222618A1Simplifies soft modulation calculationSimple processAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationSymbol of a differential operatorGray map
In one aspect, the present invention greatly simplifies soft modulation calculations, in part by exploiting certain properties of Gray-mapped QAM constellations used in modulating symbols of interest. In at least one embodiment, the simplified processing includes performing the soft modulation separately for the real and imaginary parts of each symbol of interest, by using the Gray mapping to decompose each of the real and imaginary parts into binary soft modulations for each bit, and then using a computationally-efficient table lookup to calculate the binary soft modulation. Here, the look-up table comprises pre-computed bit contributions to the complex soft symbol value to be formed for the symbol of interest.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Digital television broadcasting system using coded orthogonal frequency-division modulation with multilevel low-density-parity-check coding
InactiveUS20160087649A1Promote generationReduce in quantityError preventionTransmission path divisionCarrier signalRadio frequency
In transmitter apparatus for a digital television broadcasting system, internet-protocol (IP) packets of digital television information are subjected to multilevel coding (MLC) before being Gray-mapped to quadrature-amplitude-modulation (QAM) constellations. The constituent codes of the MLC comprise respective low-density parity-check (LDPC) inner coding. Preferably, the LDPC inner coding is LDPC convolutional coding. The QAM constellations are used in coded orthogonal frequency-division modulation (COFDM) of plural carrier waves up-converted to a radio-frequency broadcast television channel. In receiver apparatus for the digital television broadcasting system the results of de-mapping QAM constellations recovered from demodulating the COFDM carrier waves are de-interleaved, and the LDPC constituent codes of the MLC are independently decoded in parallel with decoding results time-interleaved to recover the IP packets of digital television information.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
Transmit frequency domain equalizer
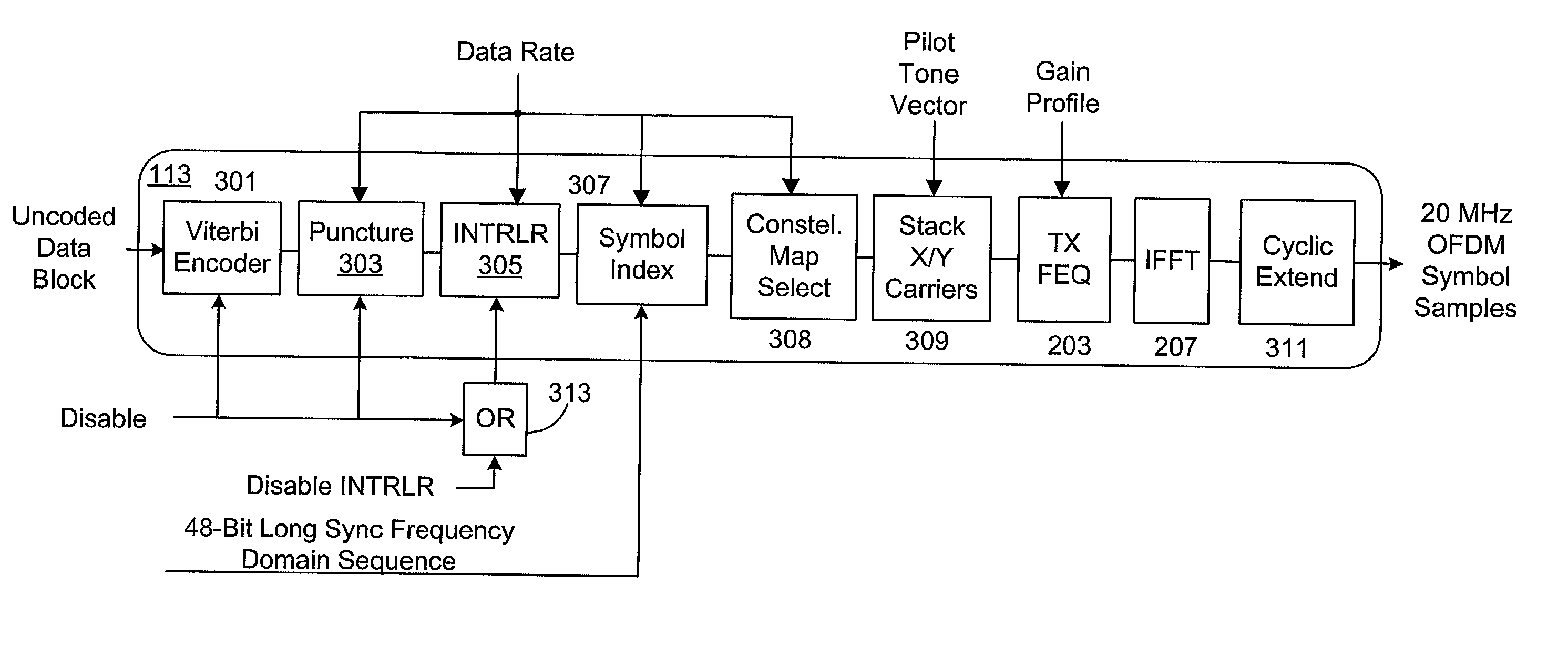
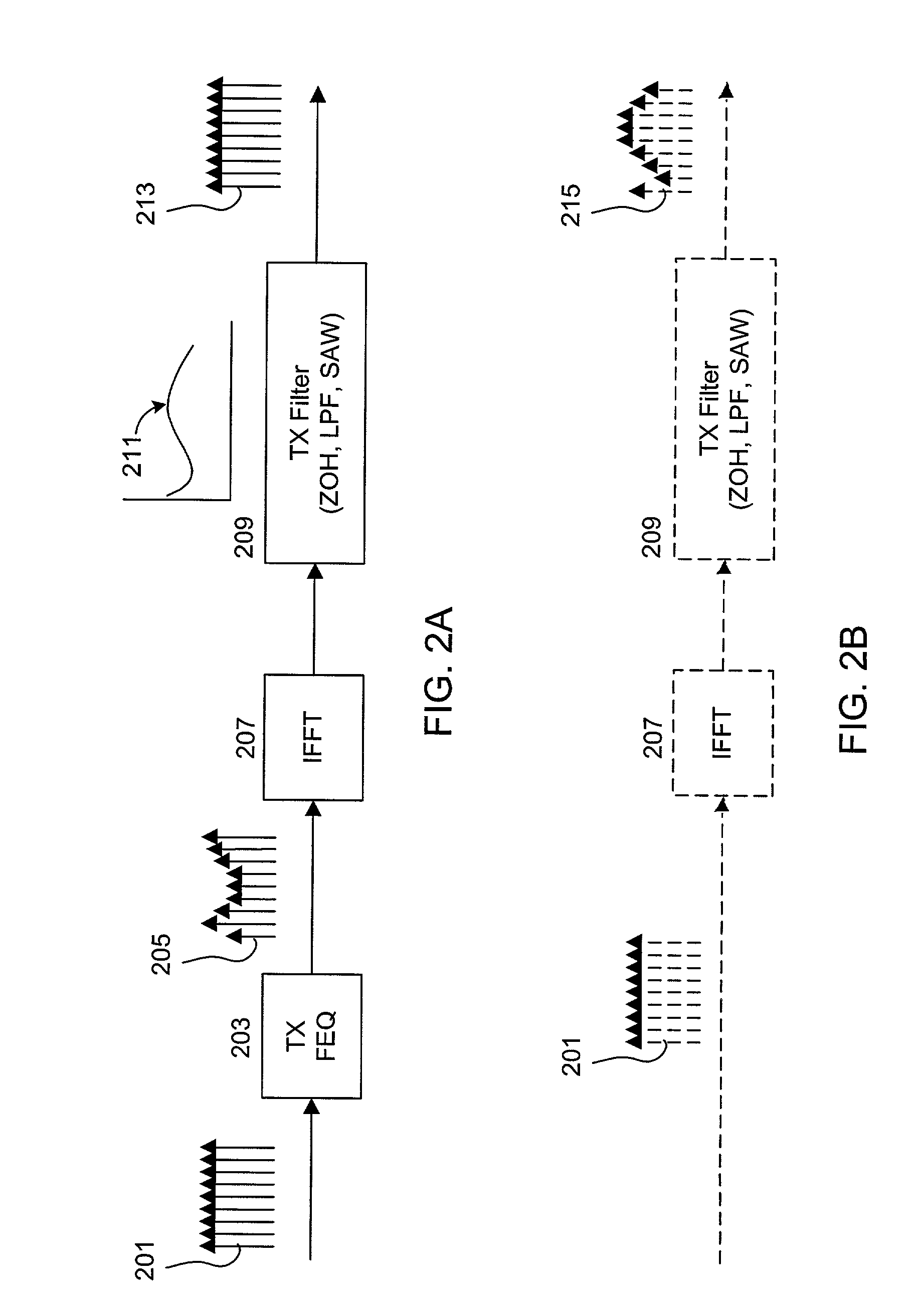
ActiveUS20030103579A1Special service provision for substationMultiple-port networksFrequency spectrumComputer science
A transmit processor that includes a transmit frequency domain equalizer (TX FEQ) that pre-compensates packets in the frequency domain to flatten transmit filter response to improve spectral mask and reduce PER. The TX FEQ taps may be selected so that the average power at output equals the average power applied to the input. The TX FEQ may be designed to yield 64 QAM packets with no quantization distortion at the input of an Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (IFFT) processor. The 64 QAM constellation map points and TX FEQ gain values are selected to avoid exceeding the bit resolution of the IFFT processor. The tones may be bound together into zones to reduce implementation complexity by reducing the number of TX FEQ taps.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Method of hybrid automatic request for retransmission
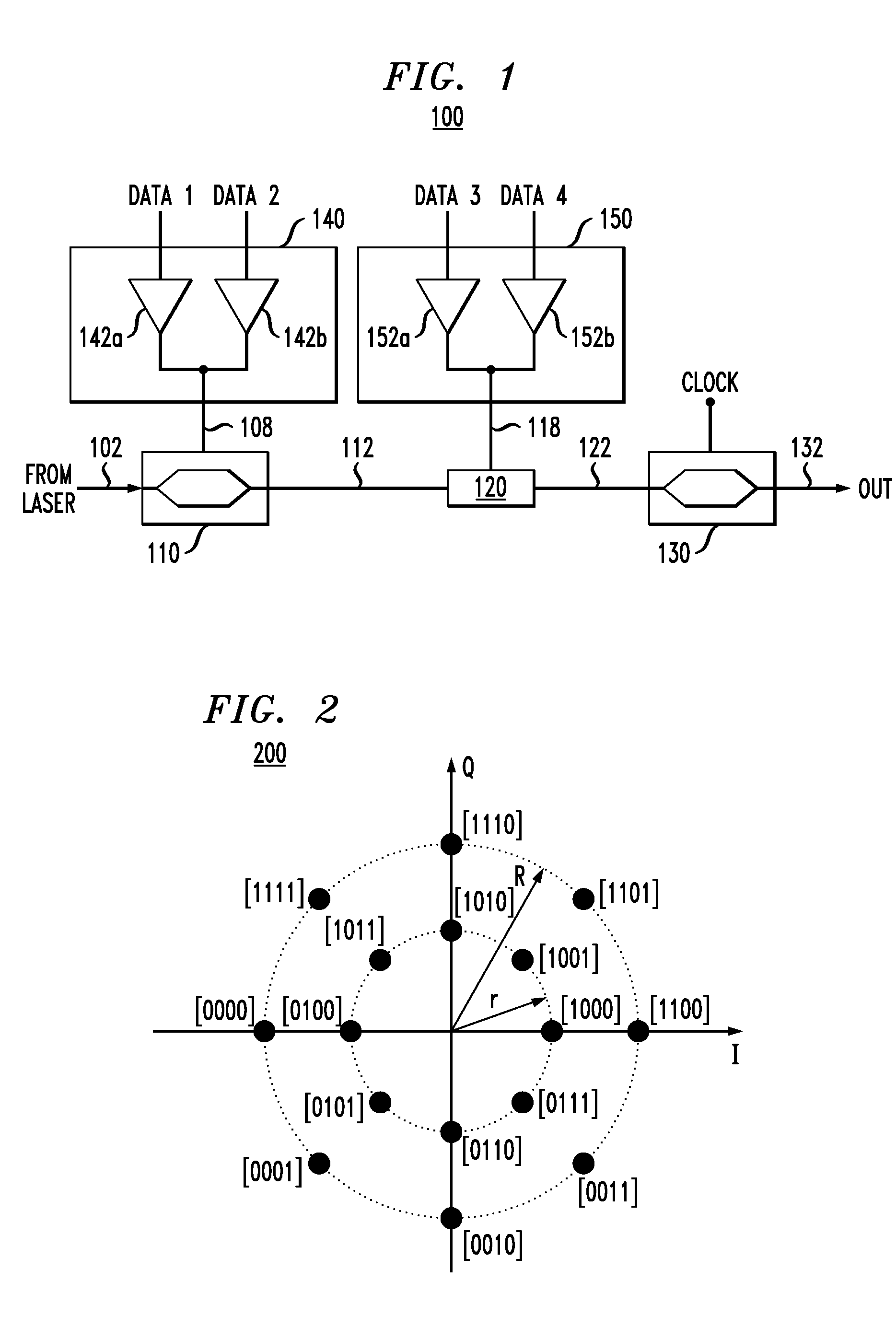
InactiveCN101291200AAverage bit reliabilityImprove decoding performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelComputer scienceConstellation diagram
The invention discloses a method for retransmitting a hybrid automatic request. Four constellation diagrams are defined in the method to form a rearranging HARQ technology based on a 256-QAM constellation diagram. The method comprises the following steps that: a) the first constellation diagram is defined as a standard constellation diagram, and the rearrangement of significance bit for other constellation diagrams based on the first constellation diagram is performed; b) data is mapped to the first constellation diagram to modulate and transmit, after a binary random bit stream generated by an information source is scrambled and coded by a transmitting terminal; c) a receiving terminal passes through an inverse process of step b), decodes and judges the data after modulation, when the data is correct, the data is descrambled and transmitted to an information sink; when the data is incorrect, NACK is transmitted to the transmitting terminal, and the data is mapped to the second constellation diagram, and so on, the data is mapped to the third constellation diagram and the fourth constellation diagram for the modulation and transmission in the third time and the fourth time; when the transmitting terminal receives the NACK for the fourth time, the data is mapped to the first constellation diagram once more for the modulation and the transmission, thereby finishing the circulation.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Multi-carrier-wave IISDPA business trans mission channel code processing method and coding apparatus
ActiveCN1893342AResolving technical issues with control requirementsChannel coding adaptationMulti-frequency code systemsCoding blockPhysical layer
Owner:SHANGHAI ULTIMATE POWER COMM TECH
System & method for spreading on fading channels
InactiveUS20050220203A1Phase-modulated carrier systemsMulti-frequency code systemsRound complexityBpsk modulation
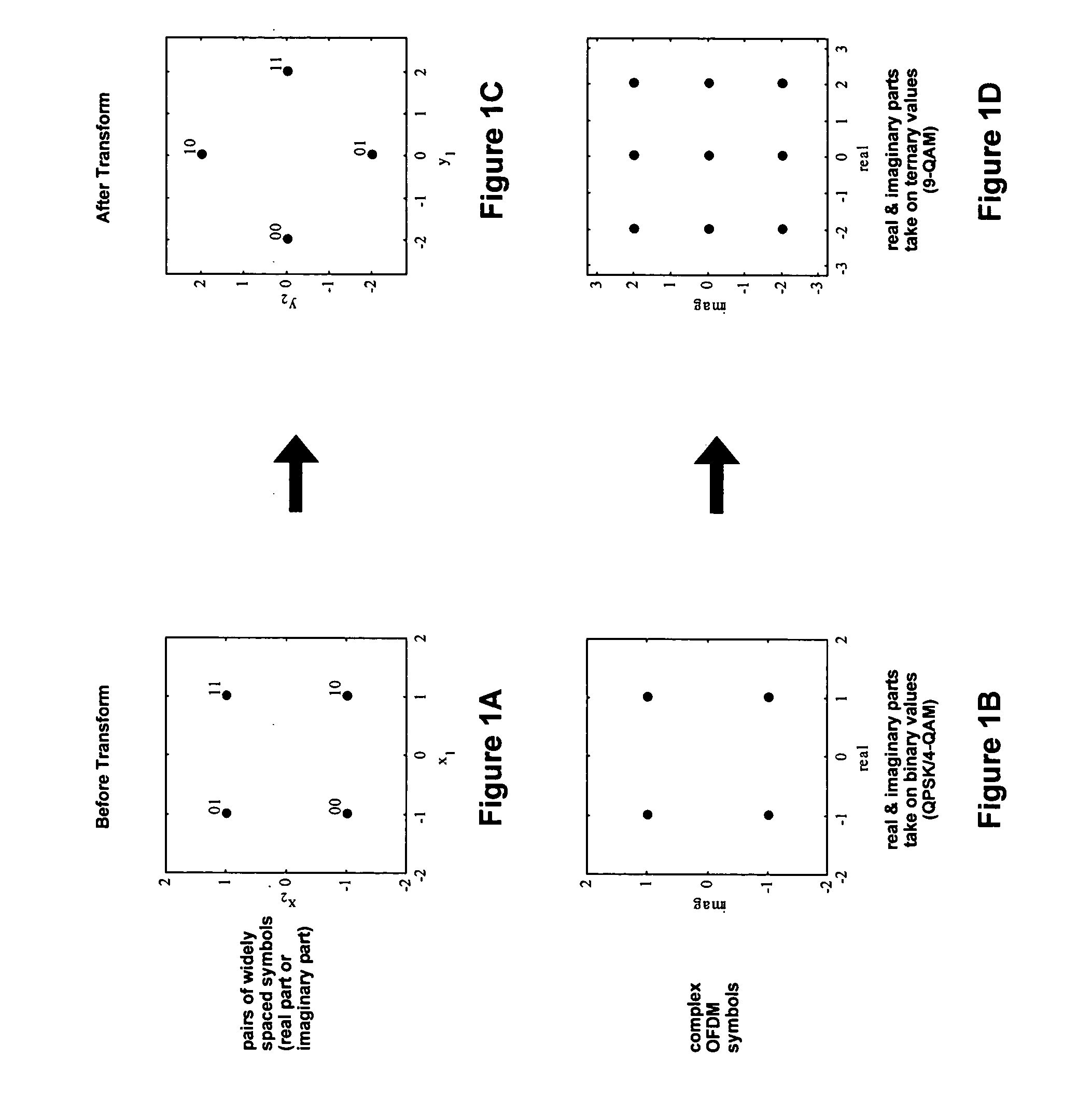
This disclosure describes a simple spreading technique that improves performance for communication over fading channels with QPSK or BPSK modulation. The technique may comprise combining two symbols at the transmitter by applying a 2×2 transform, resulting in a 4-PAM or 16-QAM constellation. The receiver may utilize a 2-dimensional soft de-mapper to provide inputs to a soft-input decoder. This scheme can offer significant performance gains over fading channels with minimal additional complexity. This technique is most beneficial on systems with a weak code or no code at all. One application of this technique is for coded OFDM systems that experience frequency-selective fading. An example of such a system is the MBOA draft specification for UWB wireless communications.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
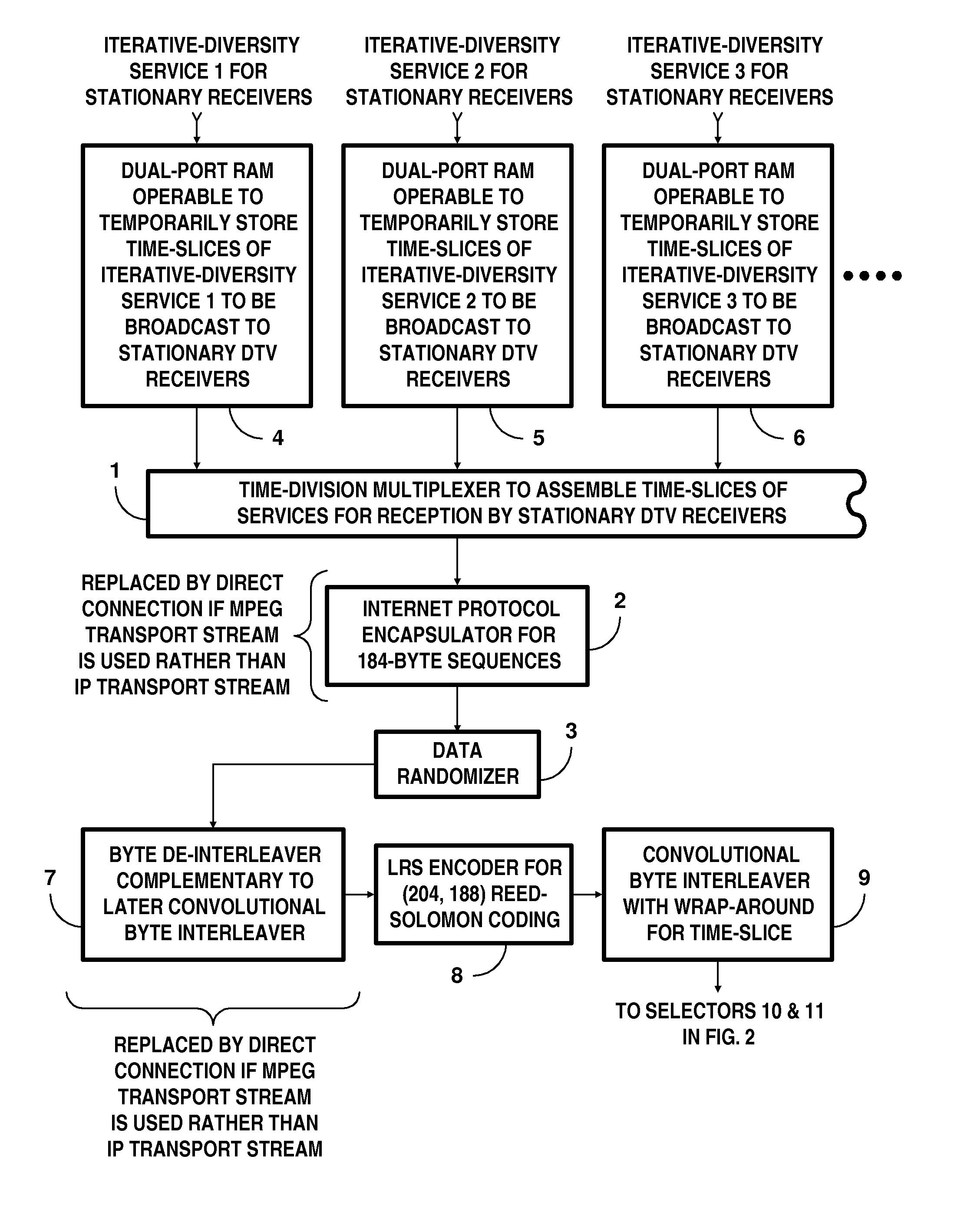
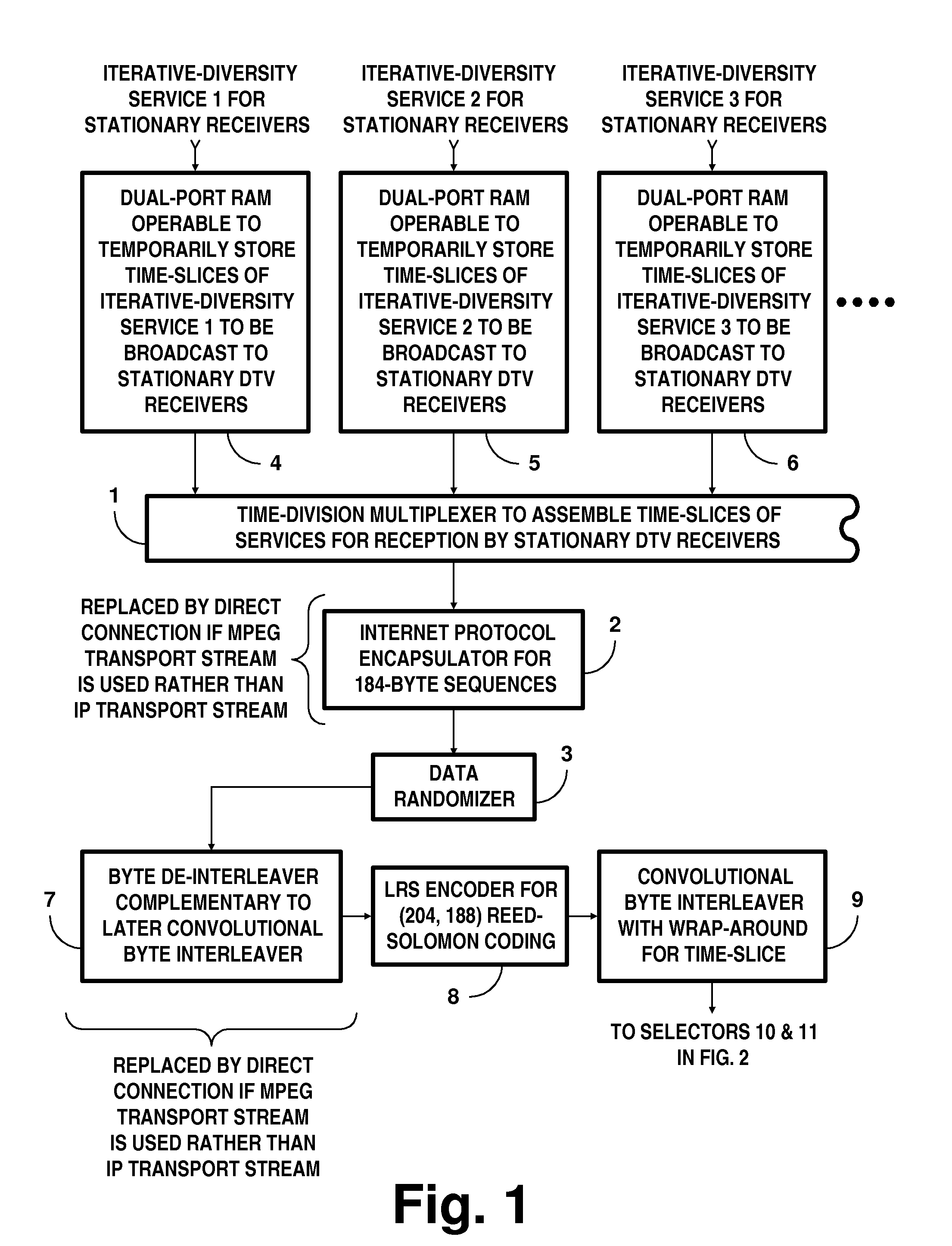
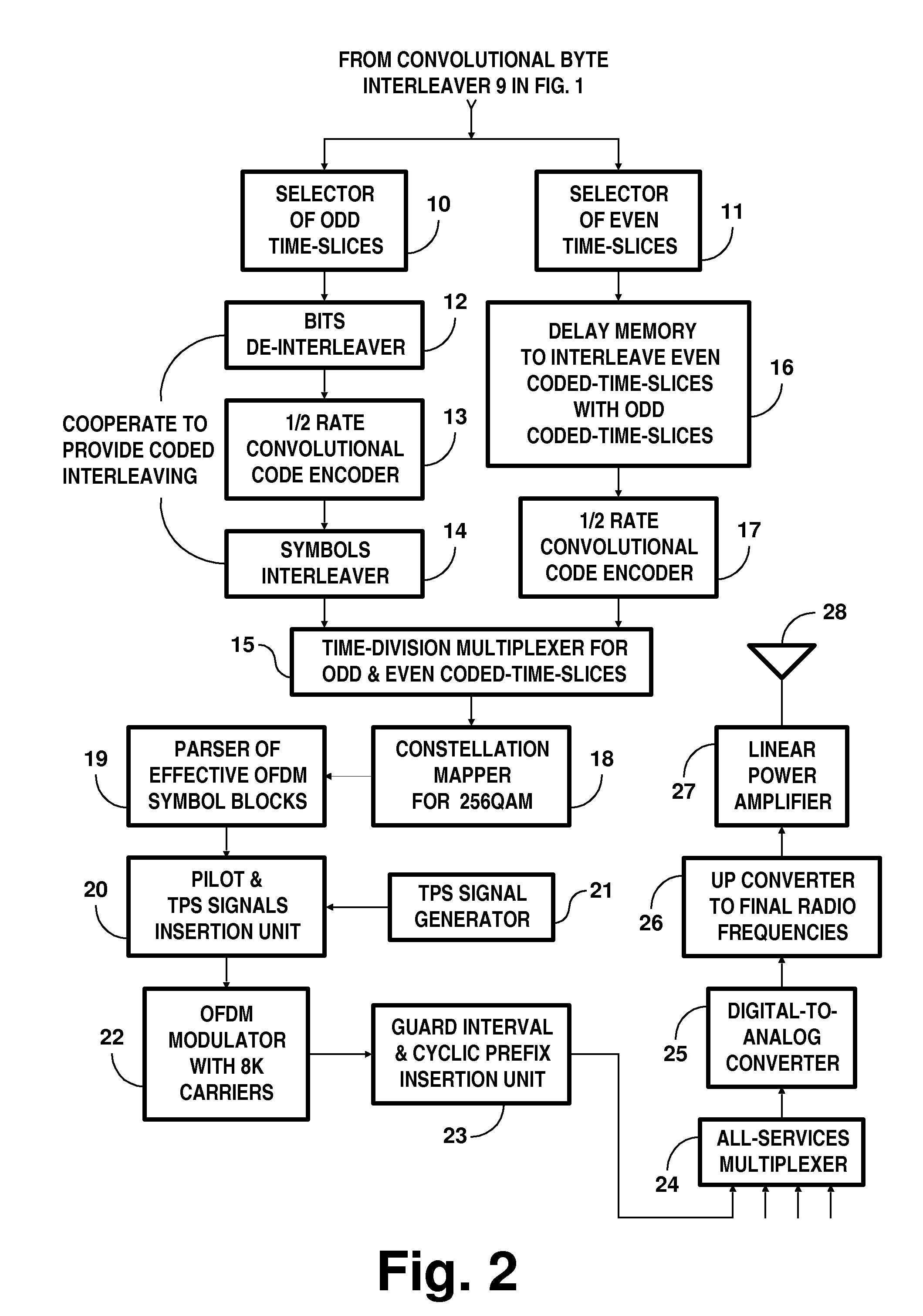
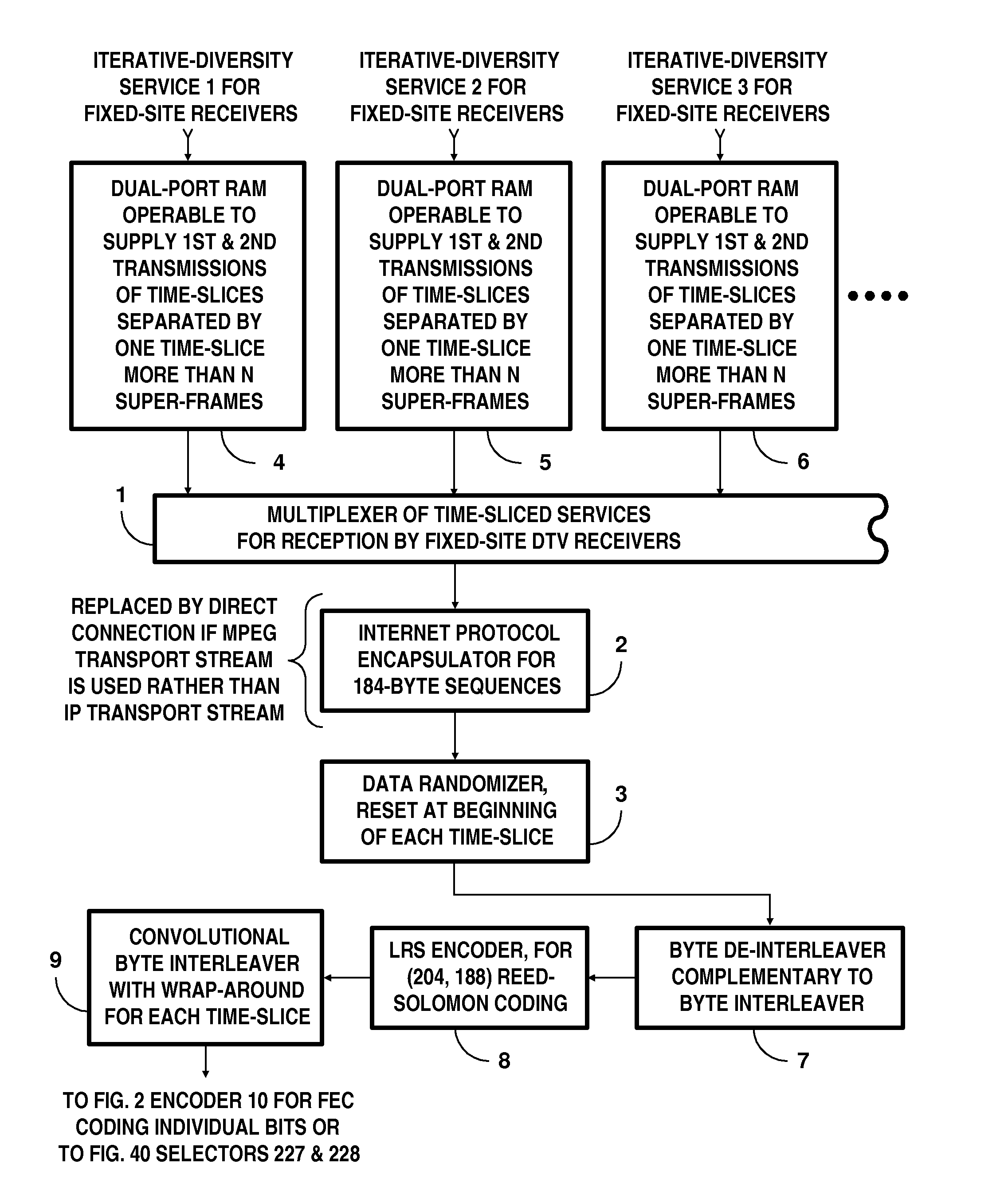
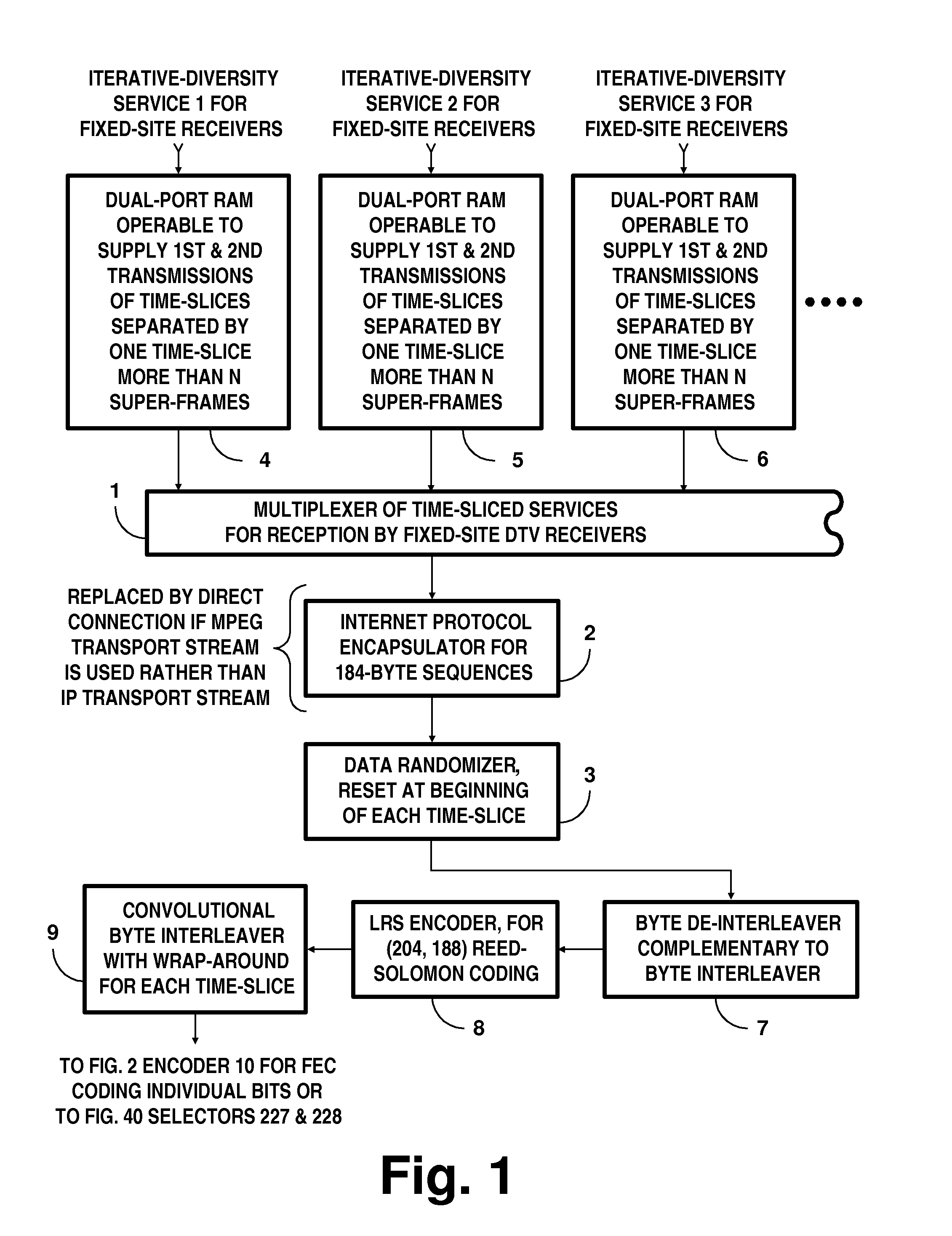
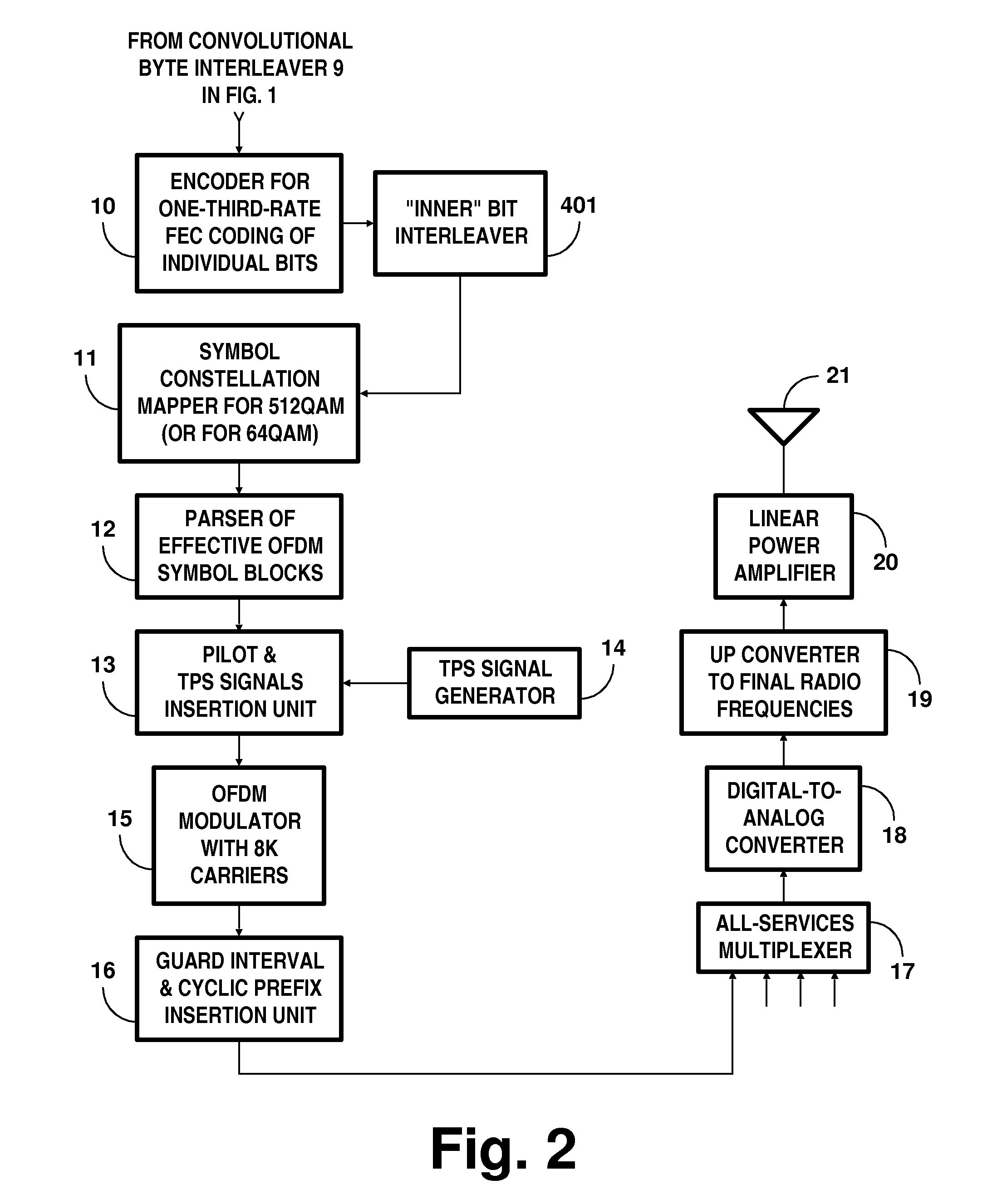
DTV systems employing parallel concatenated coding in COFDM transmissions for iterative diversity reception
InactiveUS20130028269A1Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRandomizationDiversity scheme
A digital television (DTV) system uses parallel concatenated coding (PCC), together with QAM constellations for modulating OFDM carriers. A first encoder responds to bits of randomized data to generate a first component of parallel concatenated coding. A second encoder responds to delayed bits of the randomized data to generate a second component of parallel concatenated coding. A constellation mapper generates QAM symbols responsive to successive time-slices of the first component of the PCC interleaved with successive time-slices of the second component of the PCC. An OFDM modulator generates a COFDM modulating signal responsive to the QAM symbols. In a receiver for the DTV system, the second component of the PCC and delayed first component of the PCC are iteratively decoded. Corresponding soft bits from the second component and delayed first component of the PCC are combined to supply soft randomized data used in that iterative decoding.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
Multilevel cluster-based MIMO detection method and MIMO detector thereof
ActiveUS8665977B2Reduce complexityError preventionAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsAlgorithmCluster based
A MIMO detection method for a receiver in a MIMO system using N-QAM for modulation, the MIMO detection method including generating a plurality of symbol vector sets and a plurality of search radiuses, selecting a candidate symbol vector set corresponding to a highest level of a multilevel structure of N-QAM constellation, generating a search space corresponding to a lower level of the multilevel structure of N-QAM constellation according to the selected candidate symbol vector set, confirming which level the search space corresponds to, and generating a detection signal according to the search space when the level of the search space is the lowest level of the multilevel structure of the N-QAM constellation.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Decoding system and method for digital communications
A Viterbi decoding system interprets bits in received QAM constellations as many-valued parameters rather than binary valued parameters. It performs the Viterbi algorithm using these many-valued parameters to provide results superior to hard decision decoding. Rather than applying a hard 0-1 function to the QAM data, the system uses a non-stepped linear or curved transfer function to assign values to the bits. This results in performance superior to pure hard decision decoding and approaches that of soft decision decoding; moreover, it is applicable in many situations where soft decision decoding cannot be used.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC +1
Highly-Spectrally-Efficient Transmission Using Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
A transmitter may map, using a selected modulation constellation, each of C′ bit sequences to a respective one of C′ symbols, where C′ is a number greater than one. The transmitter may process the C′ symbols to generate C′ inter-carrier correlated virtual subcarrier values. The transmitter may decimate the C′ virtual subcarrier values down to C physical subcarrier values, C being a number less than C′. The transmitter may transmit the C physical subcarrier values on C orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) subcarriers. The modulation constellation may be an N-QAM constellation, where N is an integer. The processing may comprise filtering the C′ symbols using an array of C′ filter tap coefficients. The filtering may comprise cyclic filtering. The filtering may comprise multiplication by a circulant matrix populated with the C′ filter tap coefficients.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Decoding system and method for digital communications
InactiveUS7173972B2Reduction in uncorrectable errors and packet lossData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesPacket lossDependability
A Viterbi decoding system interprets bits in received QAM constellations as many-valued parameters rather than binary valued parameters. It performs the Viterbi algorithm using these many-valued parameters to provide results superior to hard decision decoding. Rather than applying a hard 0-1 function to the QAM data, the system uses a non-stepped linear or curved transfer function to assign values to the bits. In another aspect, a system differentiates between data bits based on their estimated reliability, giving more emphasis to decoding reliable bits than unreliable bits using any of a variety of techniques. By differentiating between god and bad bits and de-emphasizing or ignoring unreliable bits, the system can provide a significant reduction in uncorrectable errors and packet loss.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Encoding modulating method and demodulation modulating method
ActiveCN102316072AImprove transmission performanceImprove performanceError preventionMultiple carrier systemsDecoding methodsTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses an encoding modulating method. In a modulating process, regular constellation mapping or irregular constellation mapping is carried out on bit data, so as to obtain a constellation mapping symbol, wherein the regular constellation mapping means that the mapping from a bit to a symbol is completed by adopting one constellation diagram and one constellation point mapping way, and the irregular constellation mapping means that the mapping from the bit to the symbol is completed by adopting one constellation diagram and more than one constellation point mapping ways. The invention further discloses a demodulation decoding method corresponding to the encoding demodulating method. In the invention, through using regular APSK (amplitude phase shift keying) constellation mapping at a sending end, the shaping loss can be obviously reduced, or by using irregular QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation) constellation mapping, the decoding and the de-mapping are matched more,so as to improve the transmission capability of an encoding modulating system, and through adopting iterative de-mapping at a receiving end, the loss brought by independent de-mapping can be effectively reduced, so as to obviously improve the performance of the encoding modulating system based on the iterative de-mapping.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
COFDM broadcast systems employing turbo coding
InactiveUS20140119458A1Maximizing overall confidence levelImprove trustModulated-carrier systemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDTV receiverCarrier signal
Turbo-coded data are transmitted using quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) of COFDM carrier waves in digital television (DTV) broadcast systems. The QAM symbol constellations map the parity bits of the turbo coded data so as to be de-mapped with higher confidence levels than the data bits, facilitating turbo decoding. A preferred DTV receiver delays the first transmissions of time-slices of a service selected for iterative-diversity reception to concur with second transmissions of those time-slices. The complex coordinates of QAM constellations in the delayed first transmission and the second transmission of the same time-slice are combined by a maximal-ratio QAM combiner after COFDM demodulation, but before de-mapping QAM constellations and turbo decoding. In a less-preferred DTV receiver, QAM constellations in the delayed first transmission of each time-slice and in the second transmission of the same time-slice are de-mapped separately. A maximal-ratio code combiner then combines de-mapping results before turbo decoding.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
Probabilistic constellation shaping using set-partitioned M-QAM
Systems and methods for constellation shaping of M-QAM modulation formats in optical transport networks may receive binary data to be transmitted as an optical signal and partition symbols of an M-QAM constellation in the complex plane into two non-overlapping subsets of symbols, The systems and methods may include assigning respective probabilities to each symbol in the first subset of symbols dependent on a target probability distribution for the first subset, mapping at least a portion of the received binary data to the symbols in the first subset, including generating a respective codeword for each symbol in the first subset, in a first symbol period, providing data representing the respective codewords mapped to the symbols in the first subset to an optical modulator for transmission, and refraining from providing any data representing codewords mapped to the symbols in the second subset to the optical modulator until a second symbol period.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and Apparatus for Multi-Carrier Hsdpa Traffic Transmission Channel Coding
ActiveUS20080317152A1Correction capabilityEfficient processSecret communicationChannel coding adaptationCoding blockComputer hardware
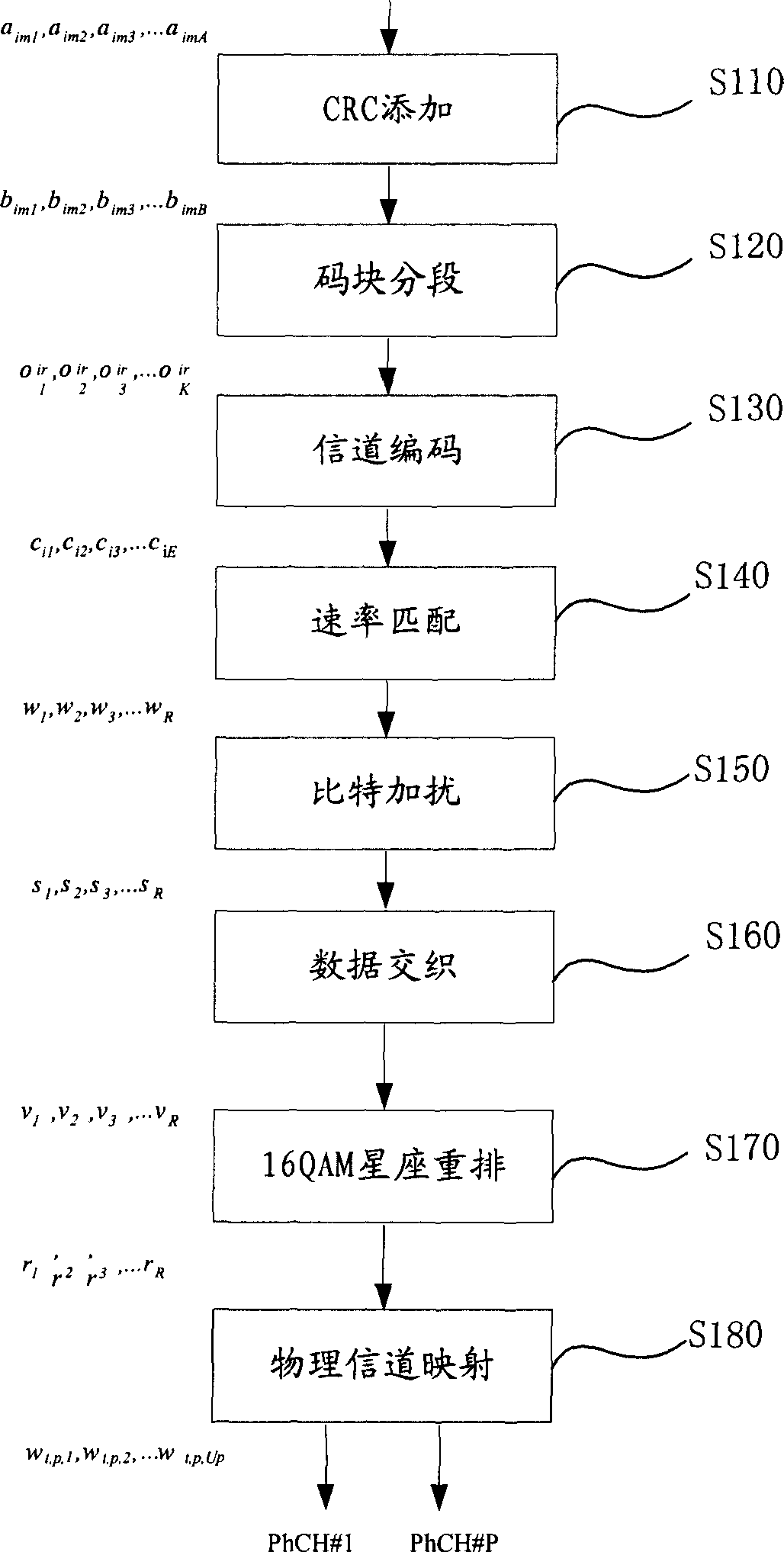
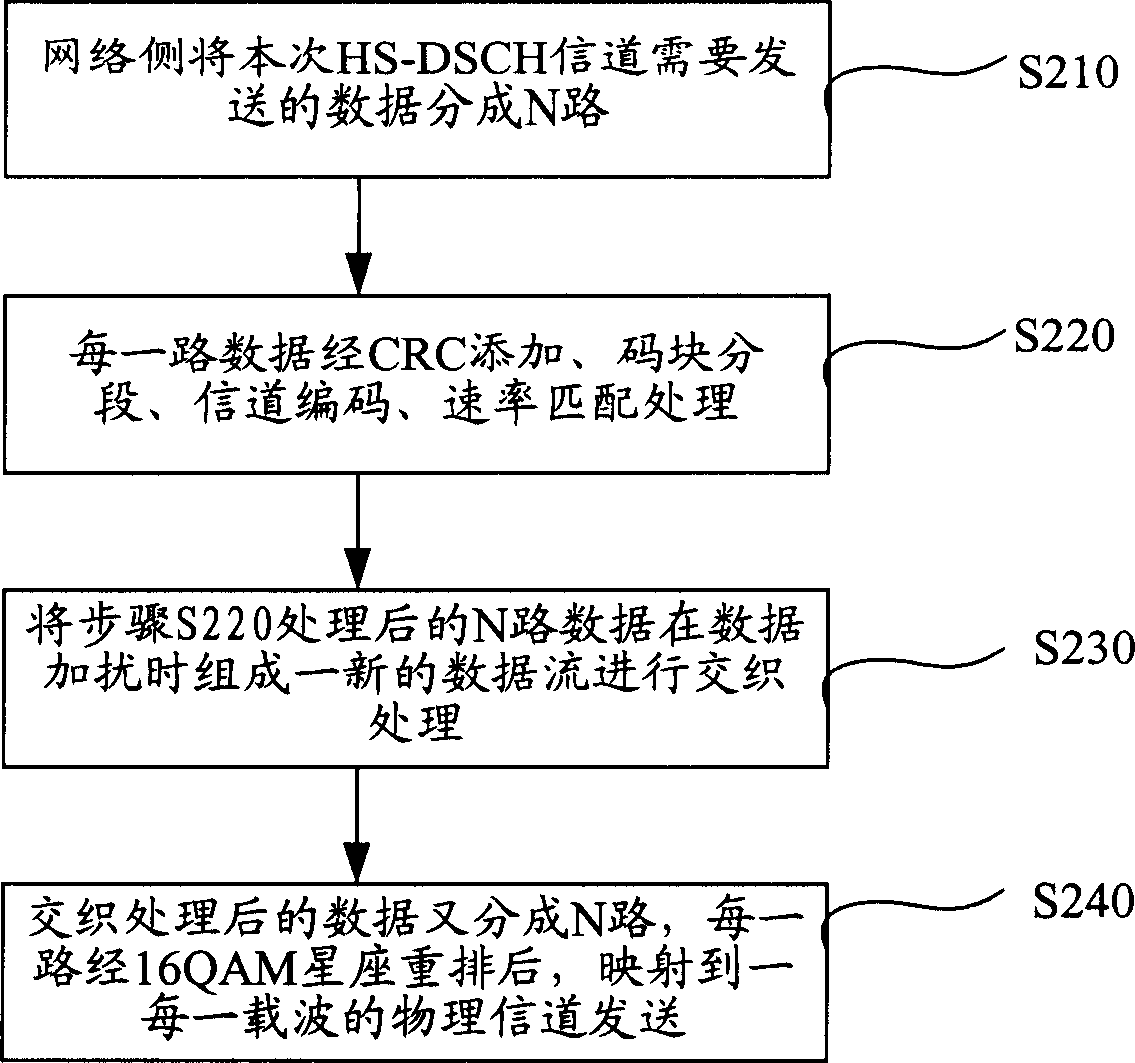
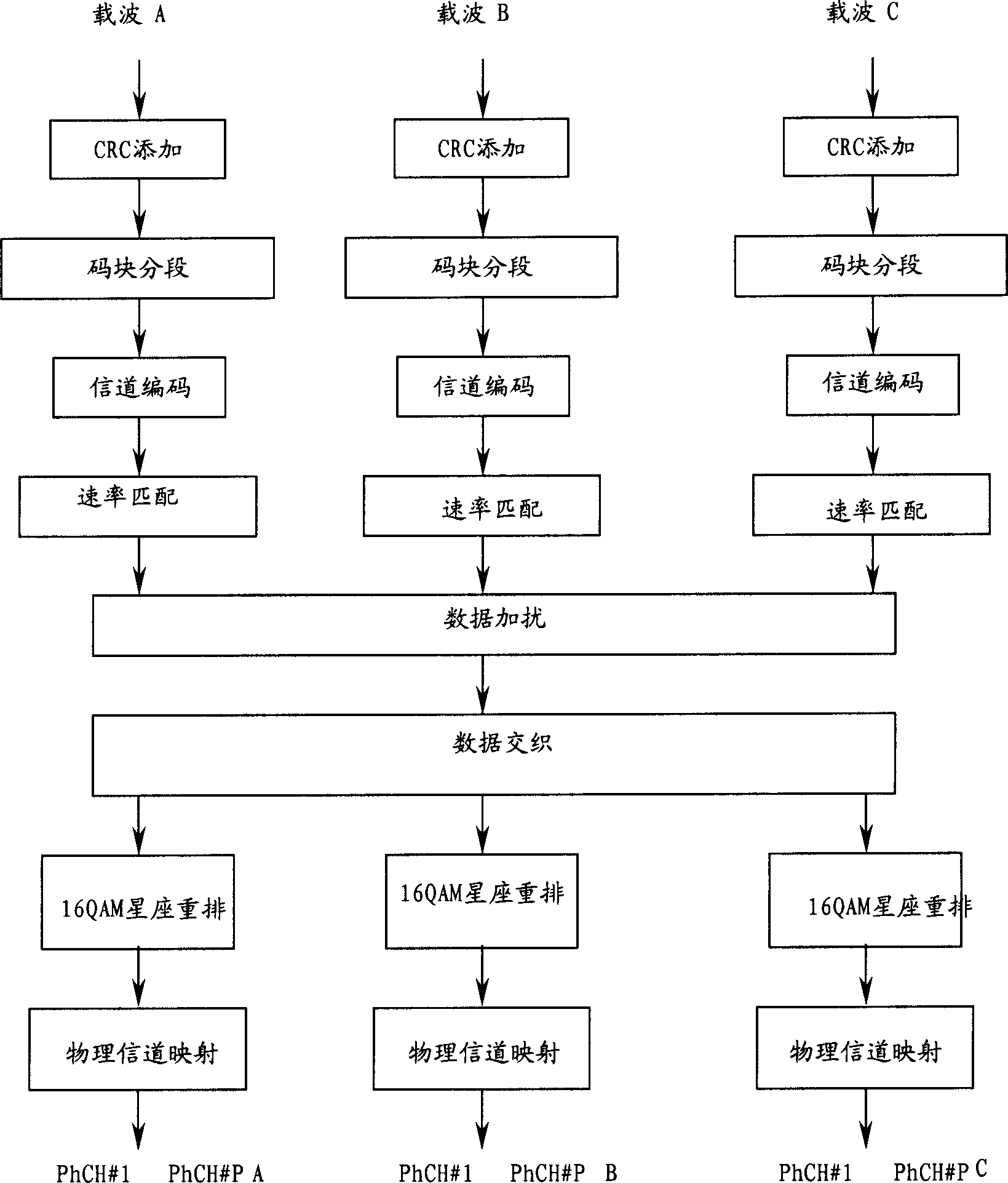
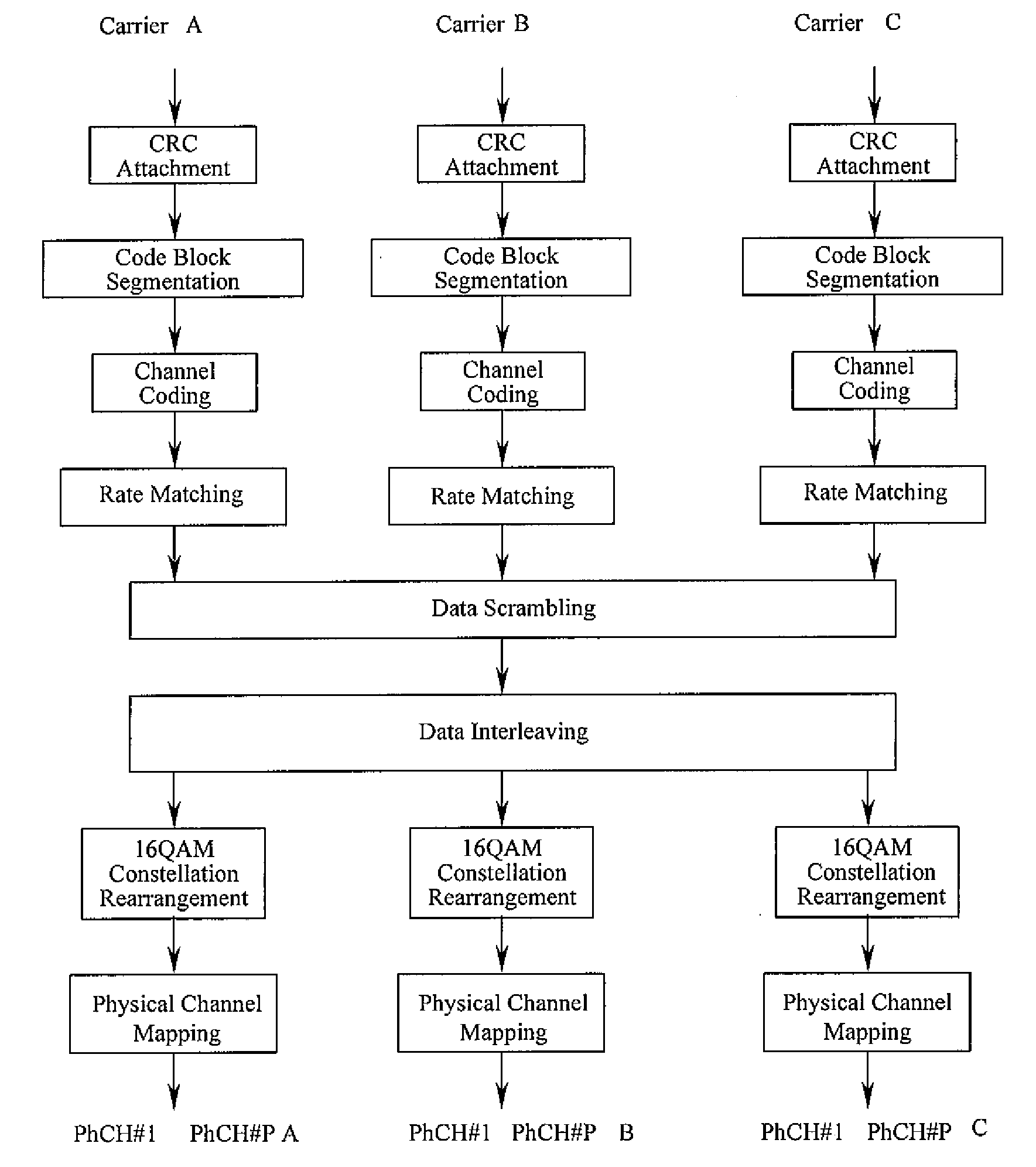
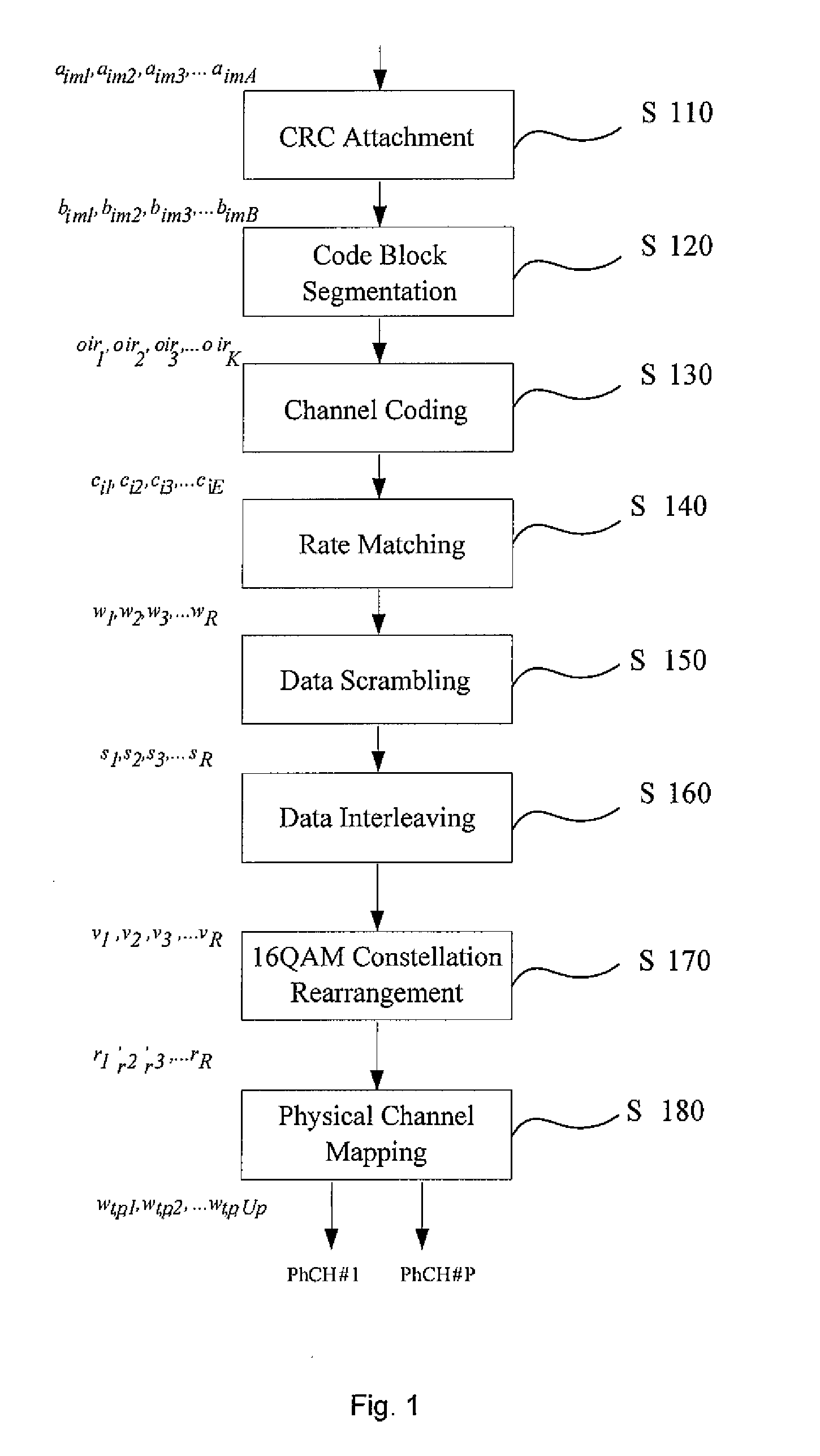
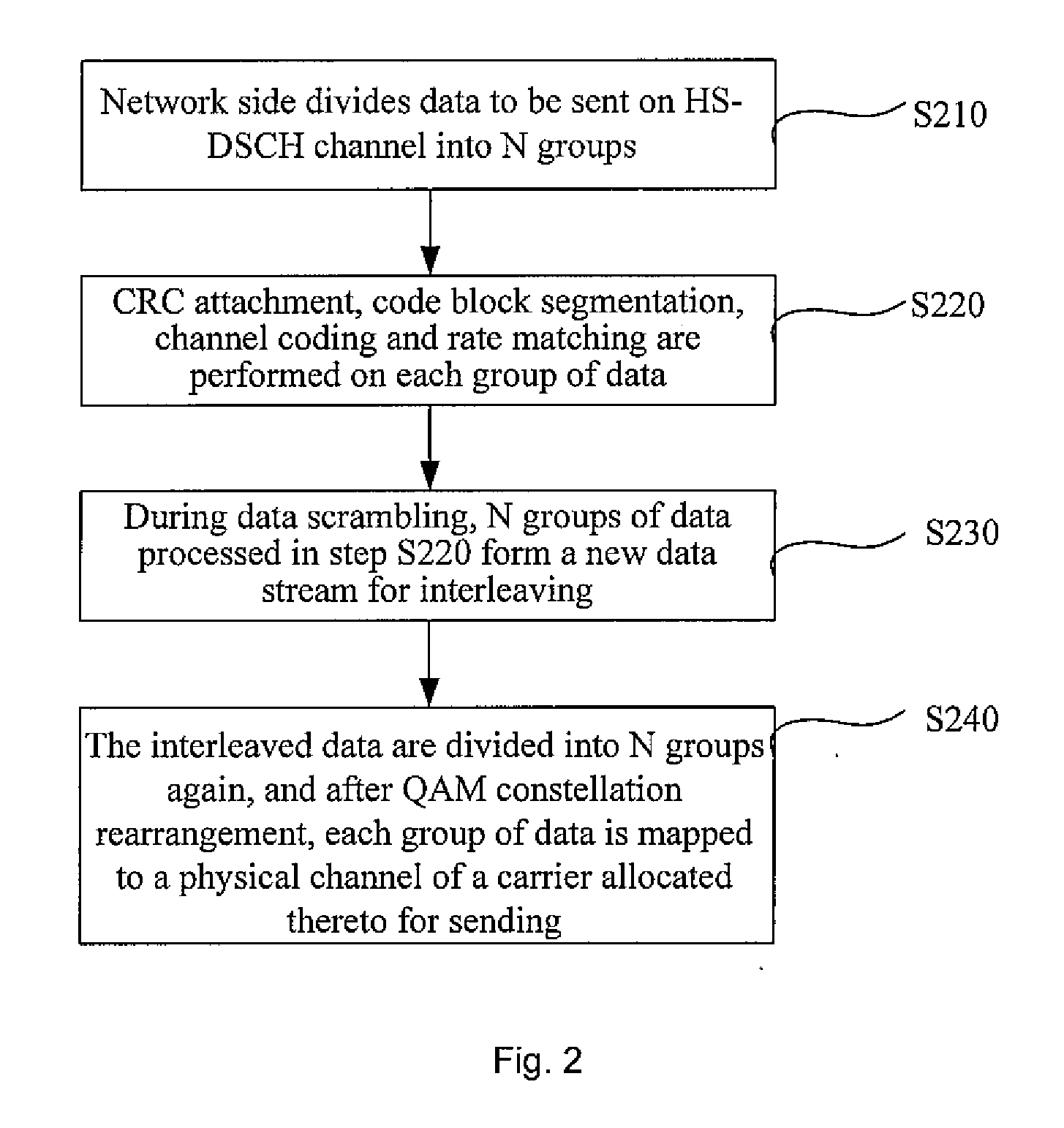
Three channel coding schemes for multi-carrier HSDPA packet data transmission are disclosed. The first scheme includes: dividing data into N groups (S210); performing CRC attachment, code block segmentation, channel coding and rate matching on each group of data respectively (S220); scrambling and interleaving the N groups of data unitedly, and then dividing the data into N groups again to perform QAM constellation rearrangement and then map to physical channels of respective carriers for transmission. The second scheme includes: dividing data to be sent into groups (S510); and sending each group of data via a physical channel of a carrier after coding it according to single-carrier HSDPA (S520). The third scheme includes: sending N carrier channels as a whole to a physical layer to perform processing from CRC attachment to QAM constellation rearrangement (S710); dividing the processed data into groups and mapping them to respective carrier channels for transmission (S720).
Owner:SHANGHAI ULTIMATE POWER COMM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com