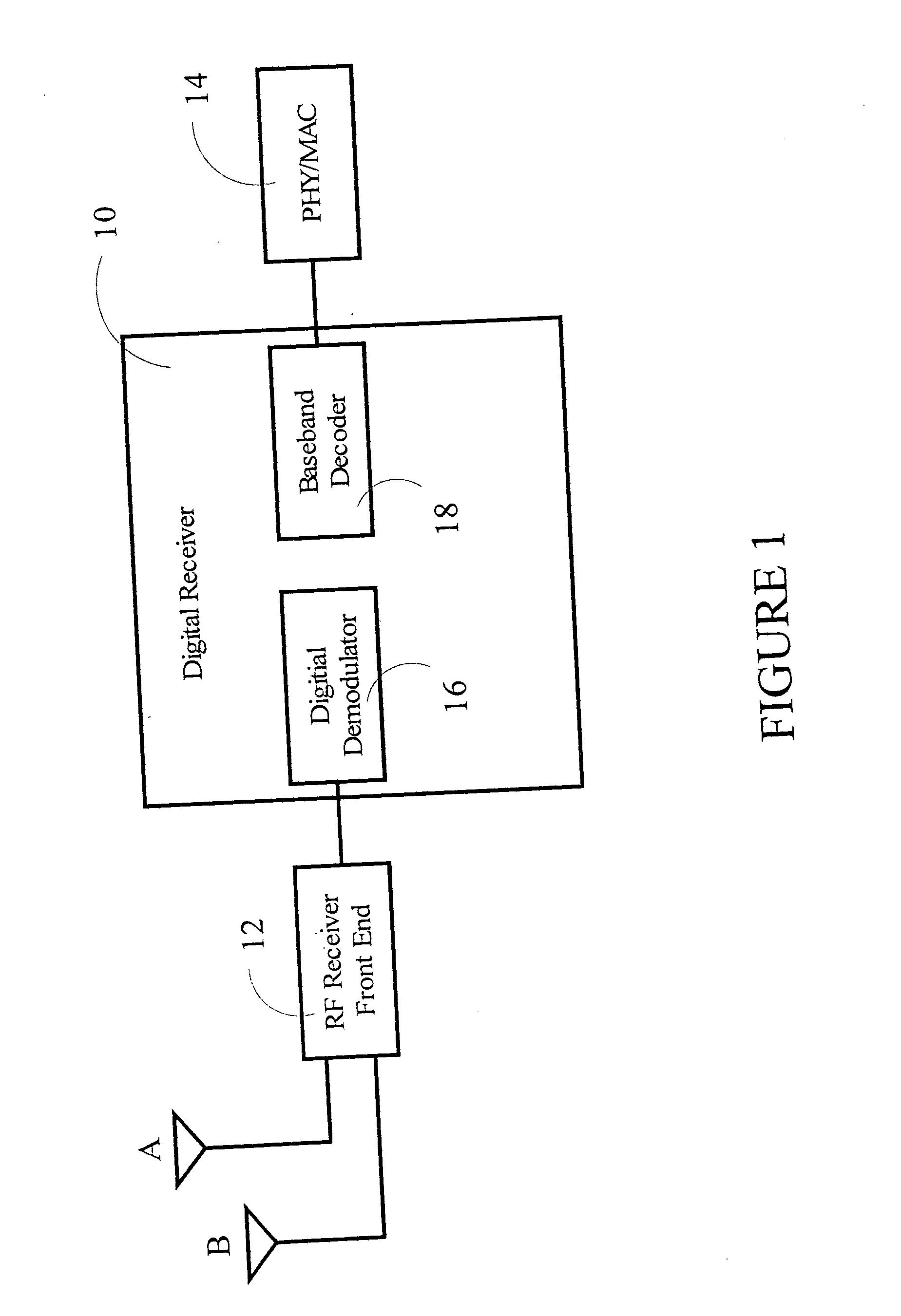
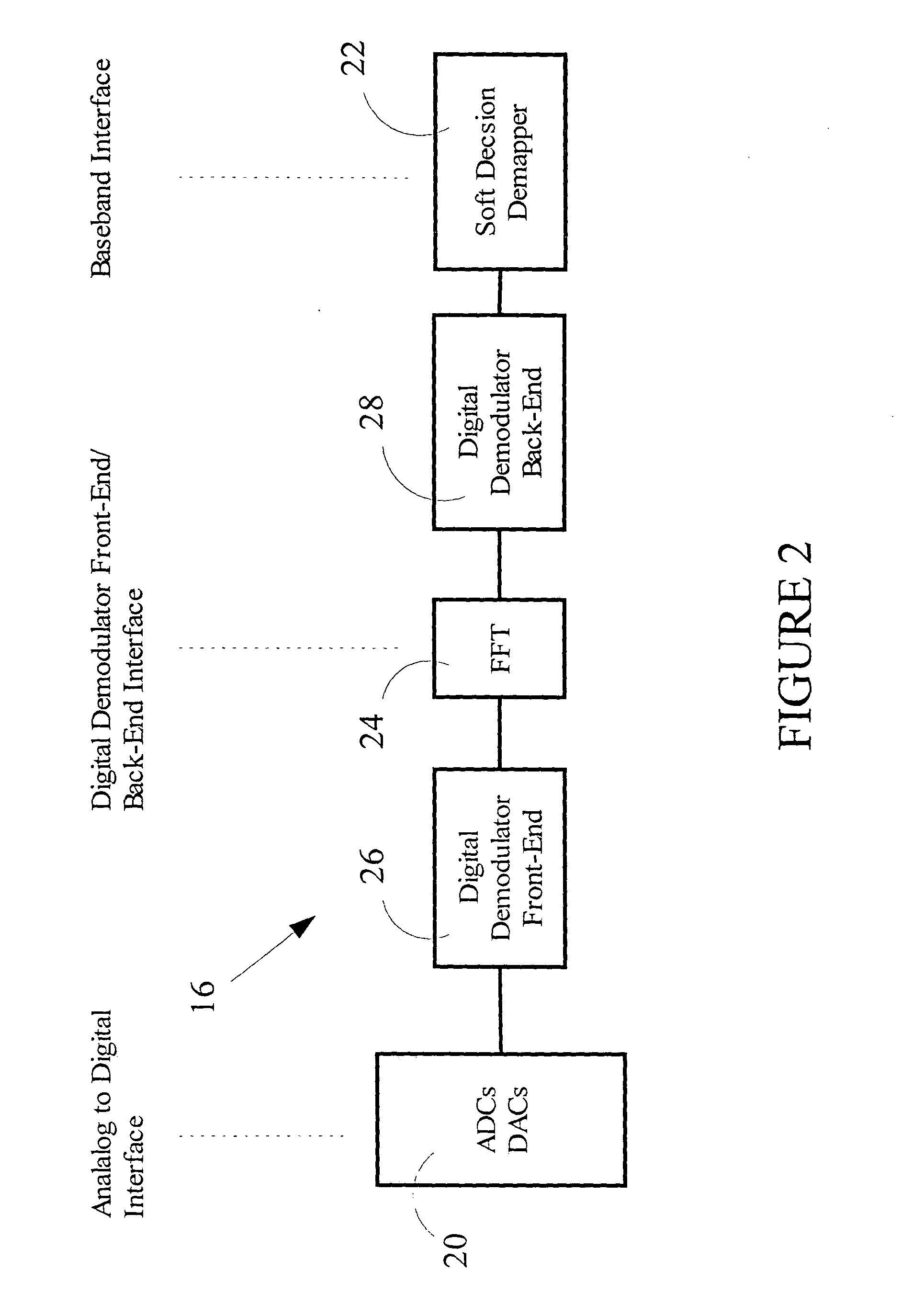
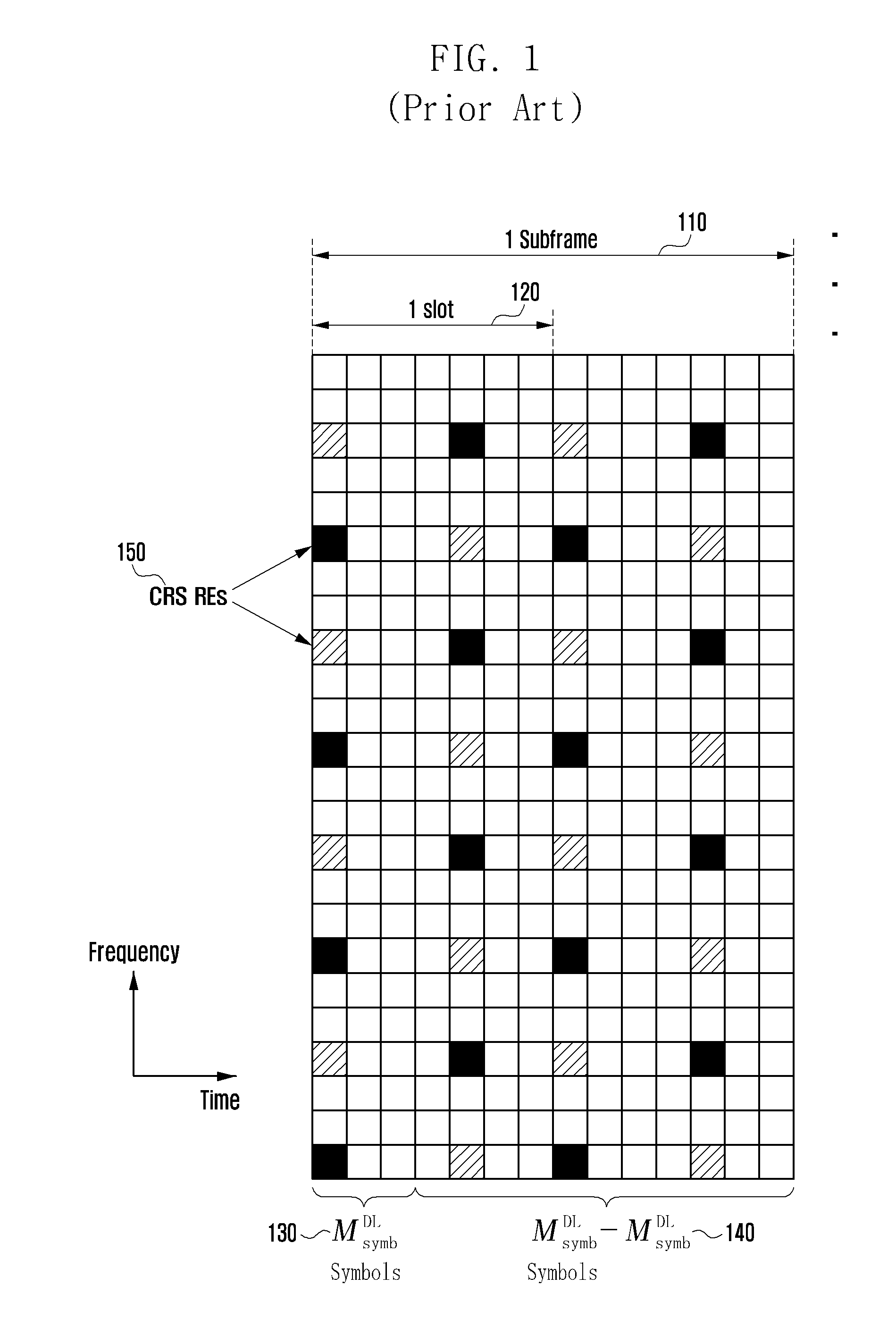
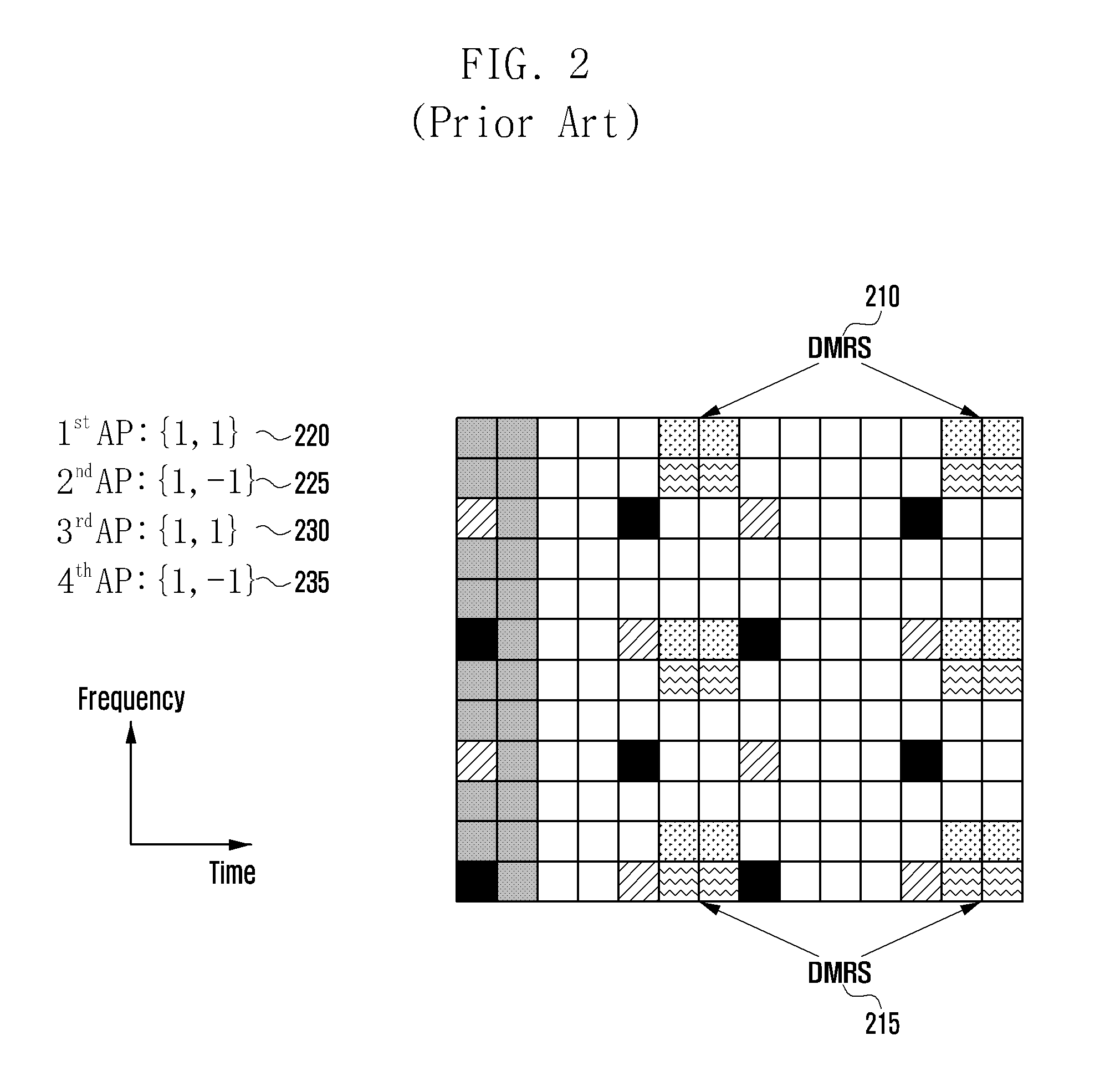
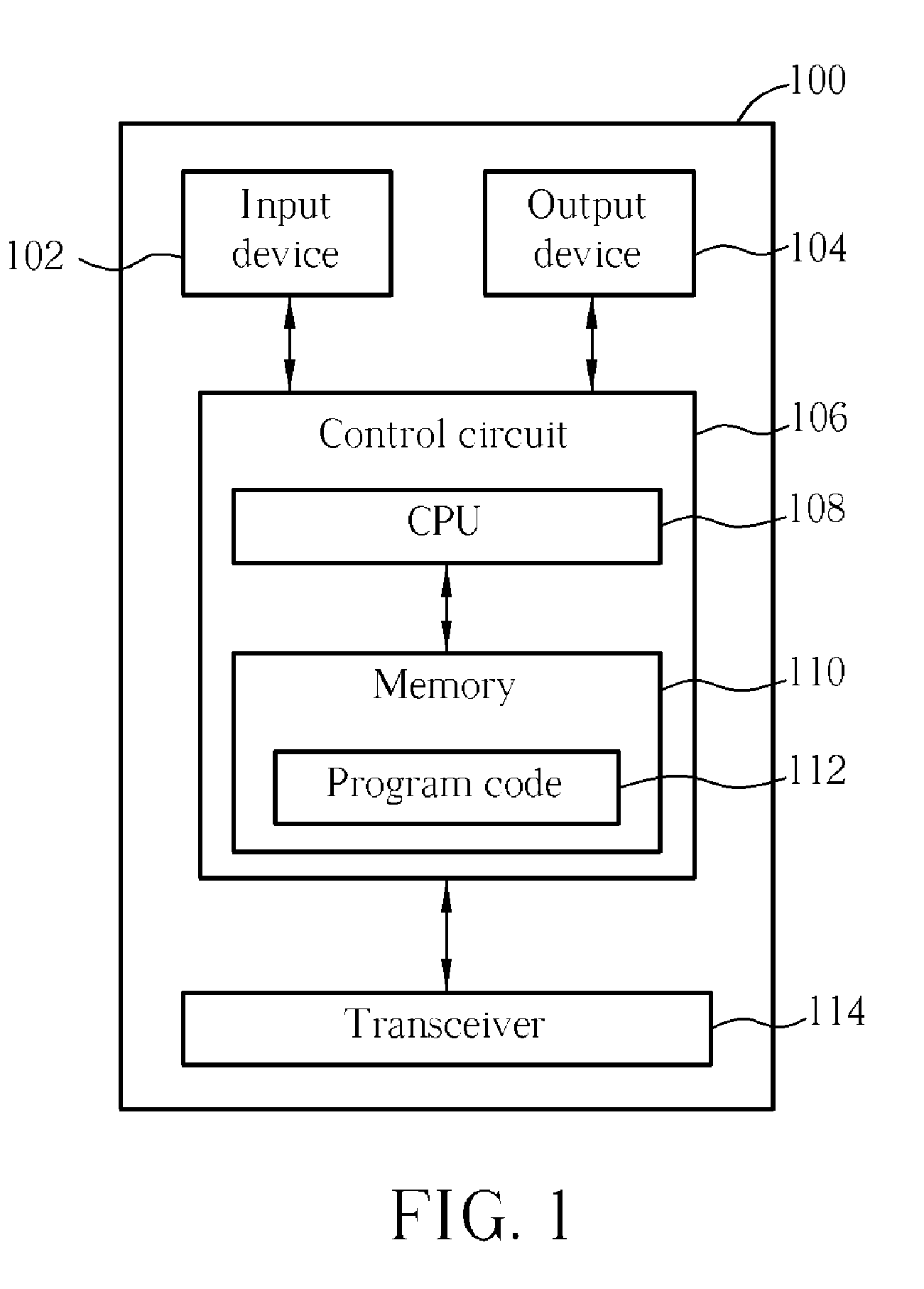
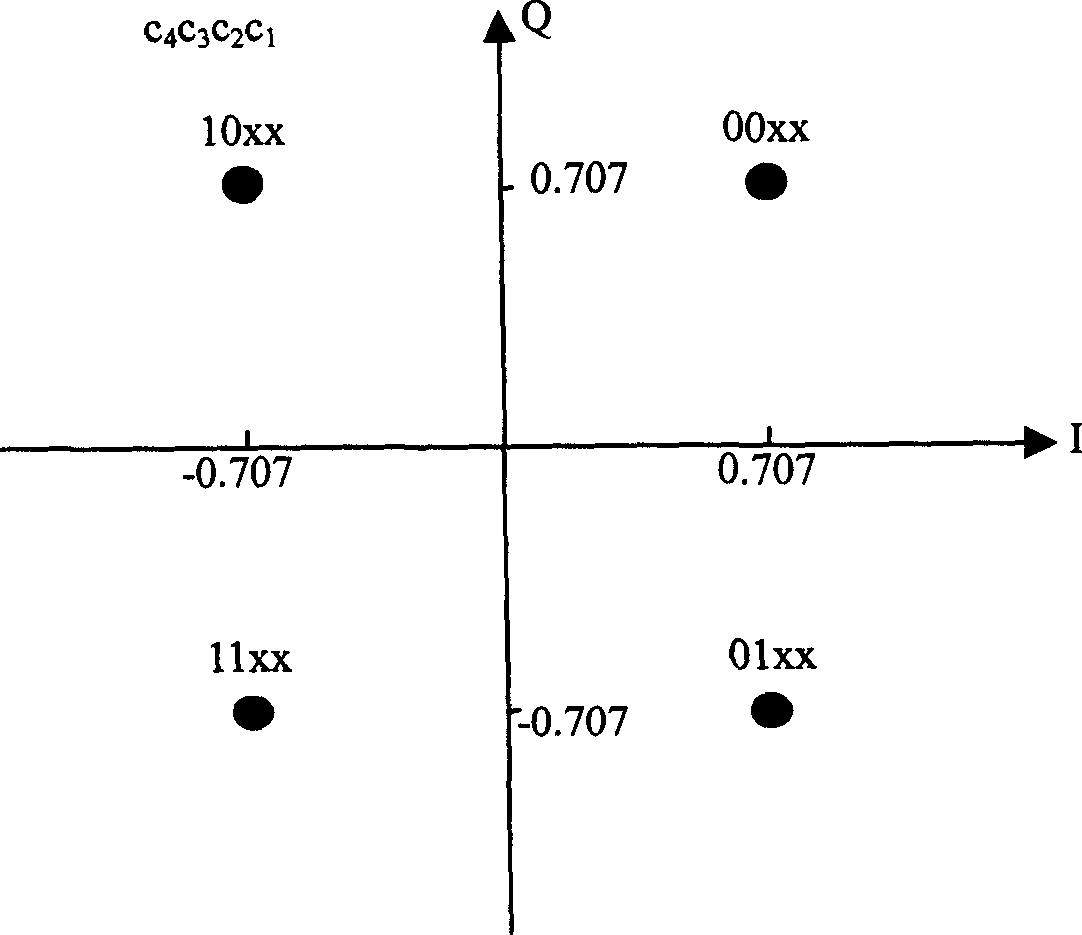
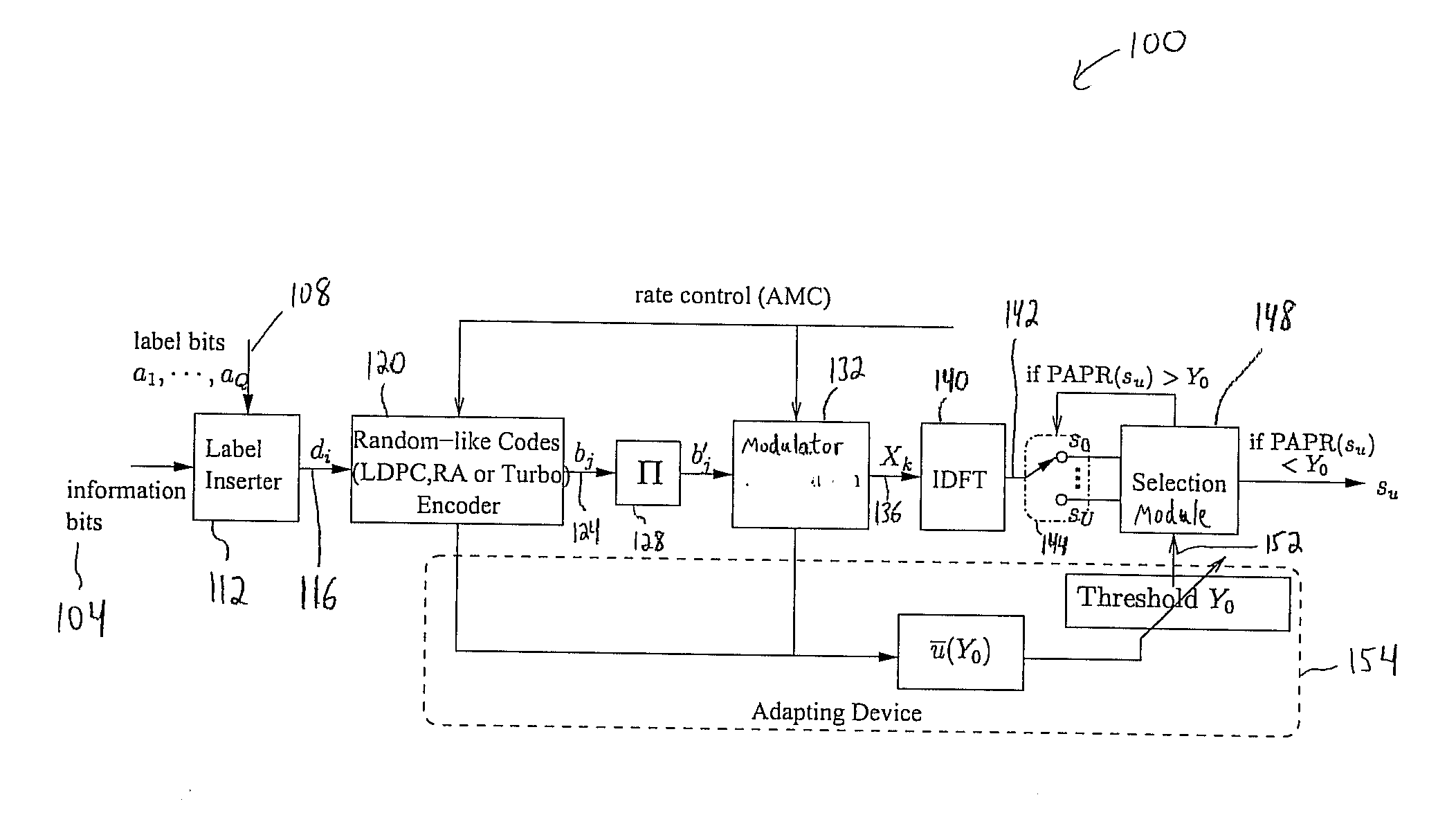
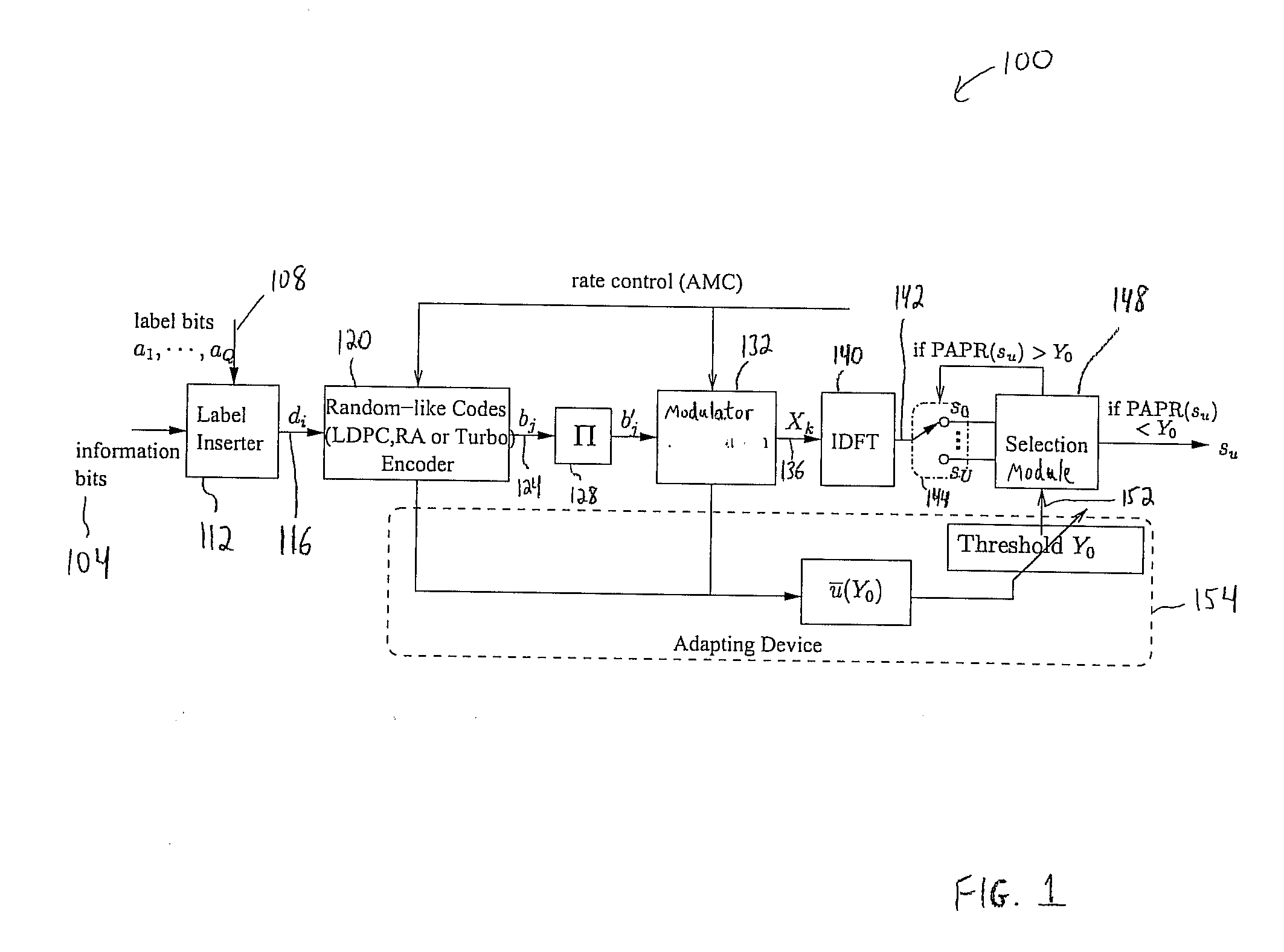
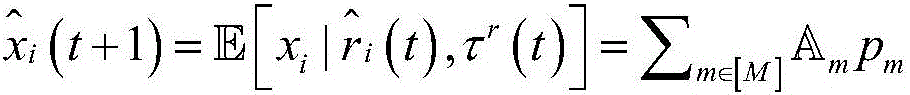Patents
Literature
772 results about "Quadrature amplitude modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing (modulating) the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying (ASK) digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation (AM) analog modulation scheme. The two carrier waves of the same frequency are out of phase with each other by 90°, a condition known as orthogonality or quadrature. The transmitted signal is created by adding the two carrier waves together. At the receiver, the two waves can be coherently separated (demodulated) because of their orthogonality property. Another key property is that the modulations are low-frequency/low-bandwidth waveforms compared to the carrier frequency, which is known as the narrowband assumption.
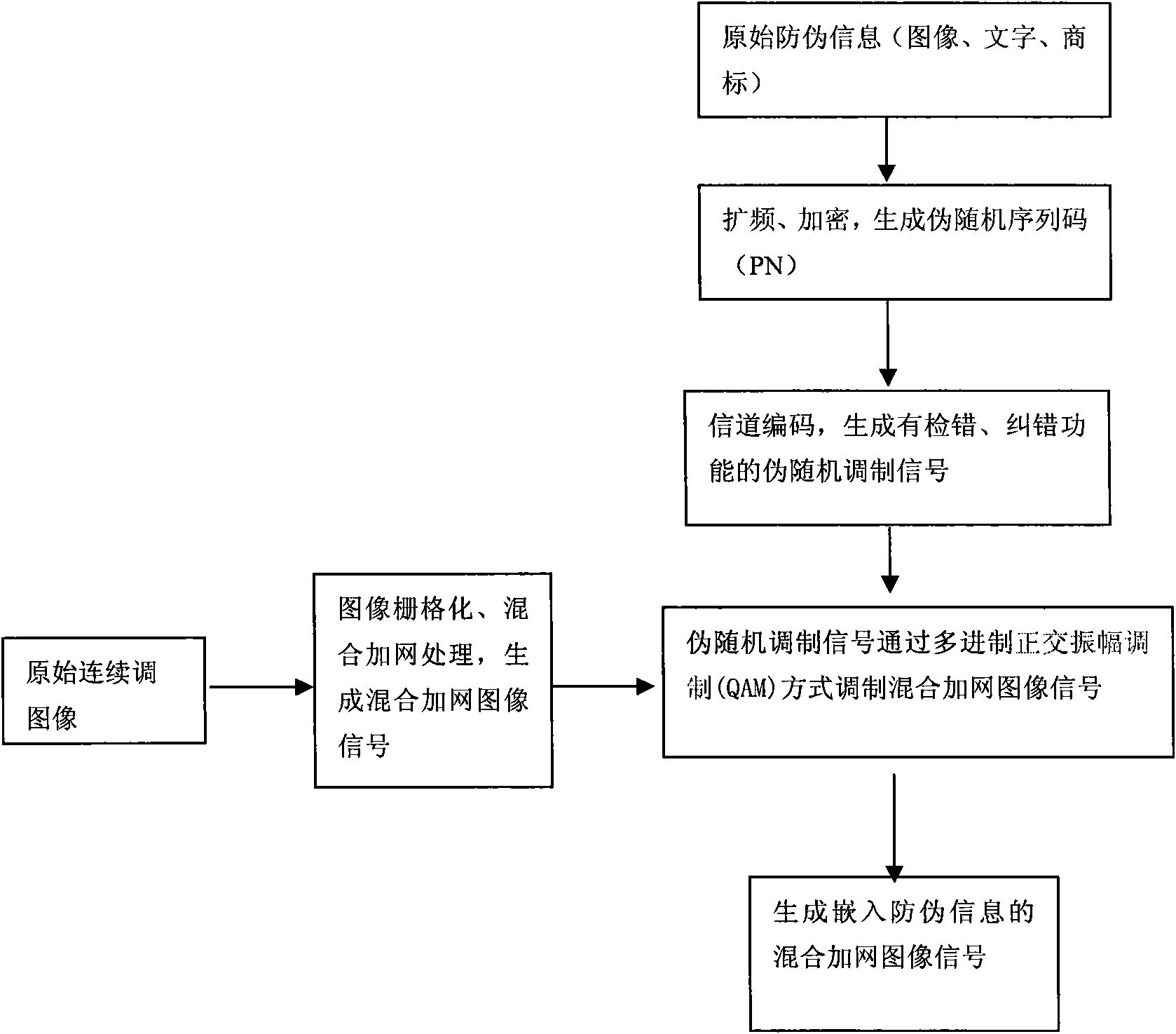
Presswork encryption security printing technology based on multi-system quadrature amplitude modulation
InactiveCN101777134ACombating Illegal CopyingStrong anti-counterfeiting abilityVisual presentationElectronic documentSecurity printing
The invention discloses a presswork encryption security printing technology based on multi-system quadrature amplitude modulation. By adopting the security printing technology, a paseudorandom modulating signal can be generated from anti-counterfeiting information through spread spectrum, encryption and channel coding, the anti-counterfeiting information can be embedded into a whole page through a multi-system quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) mode, and the anti-counterfeiting information can be identified from any fragment in presswork identification. The invention has very strong smash-resistance, can effectively resist piracy behaviour based on cameras, scanners, electronic documents and the like, and can be widely applied to the field of presswork anti-counterfeit.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
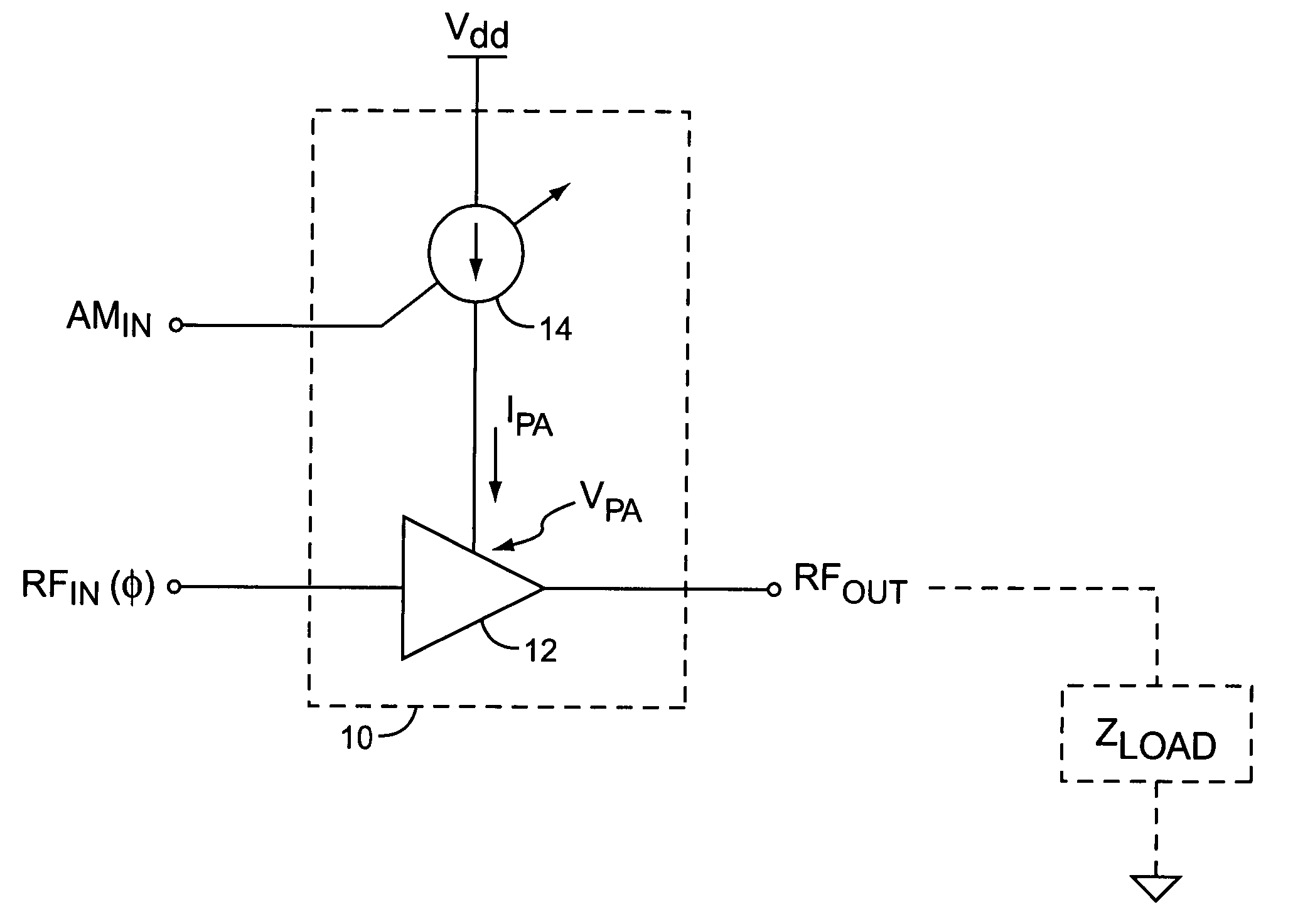
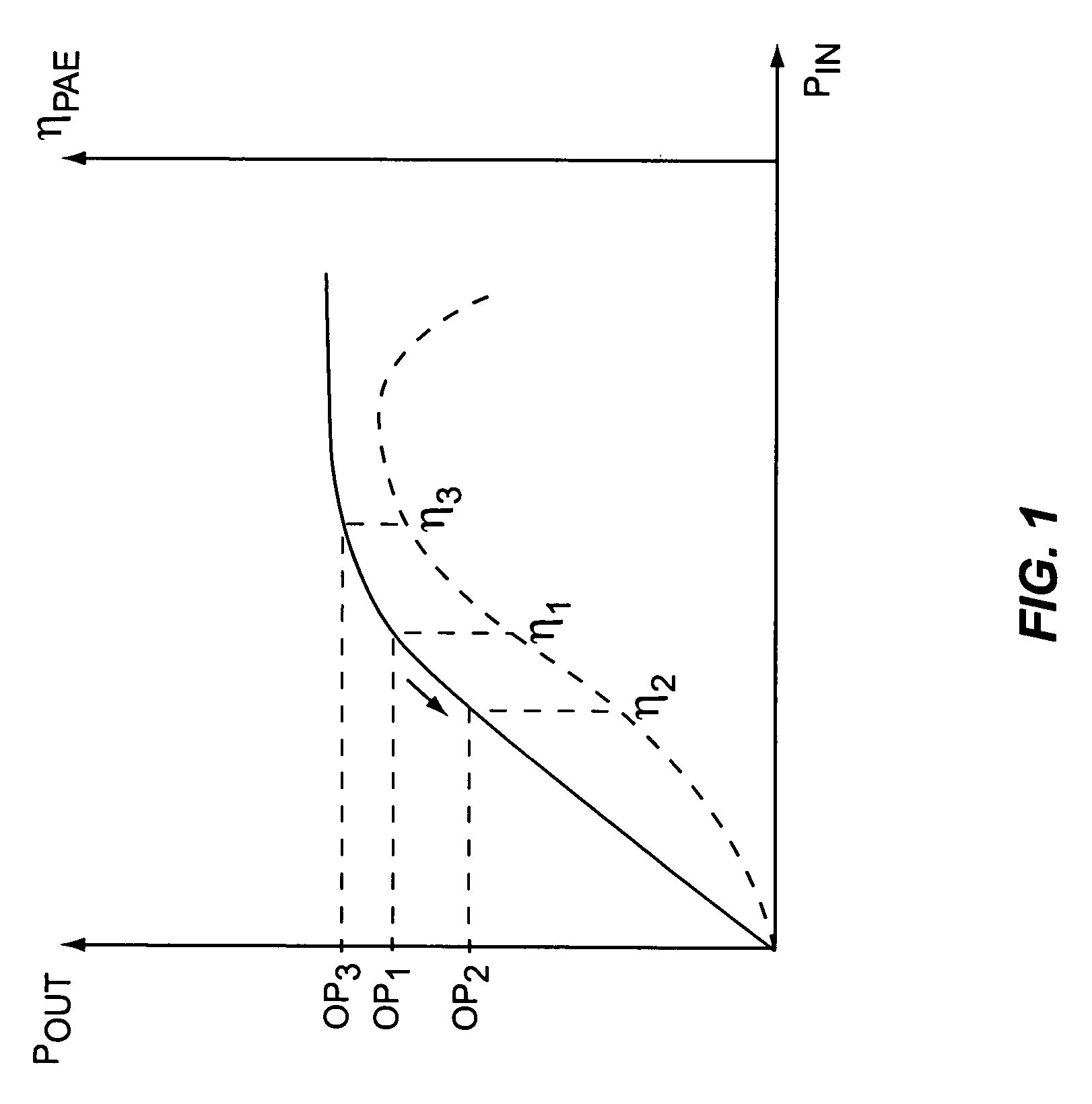
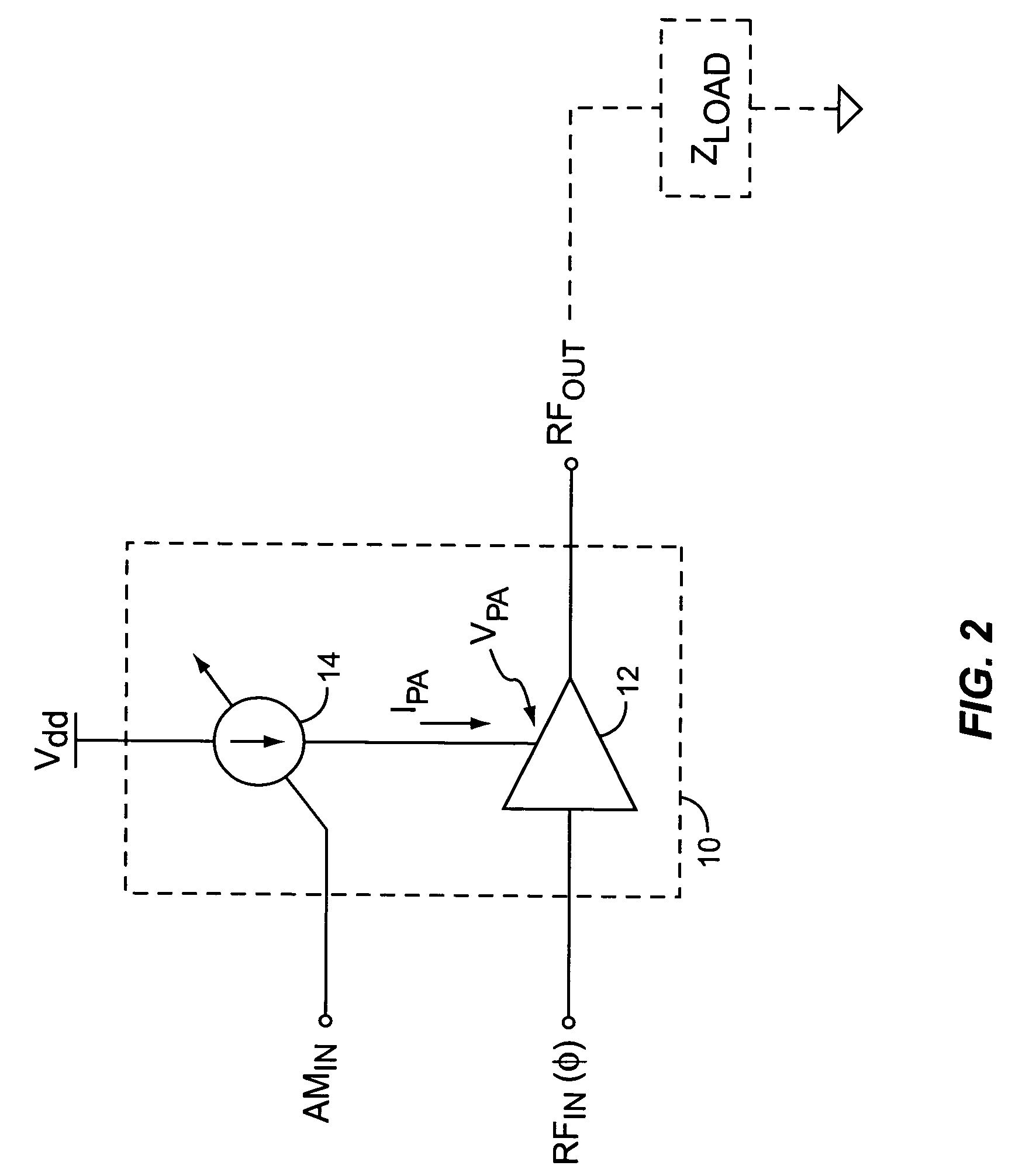
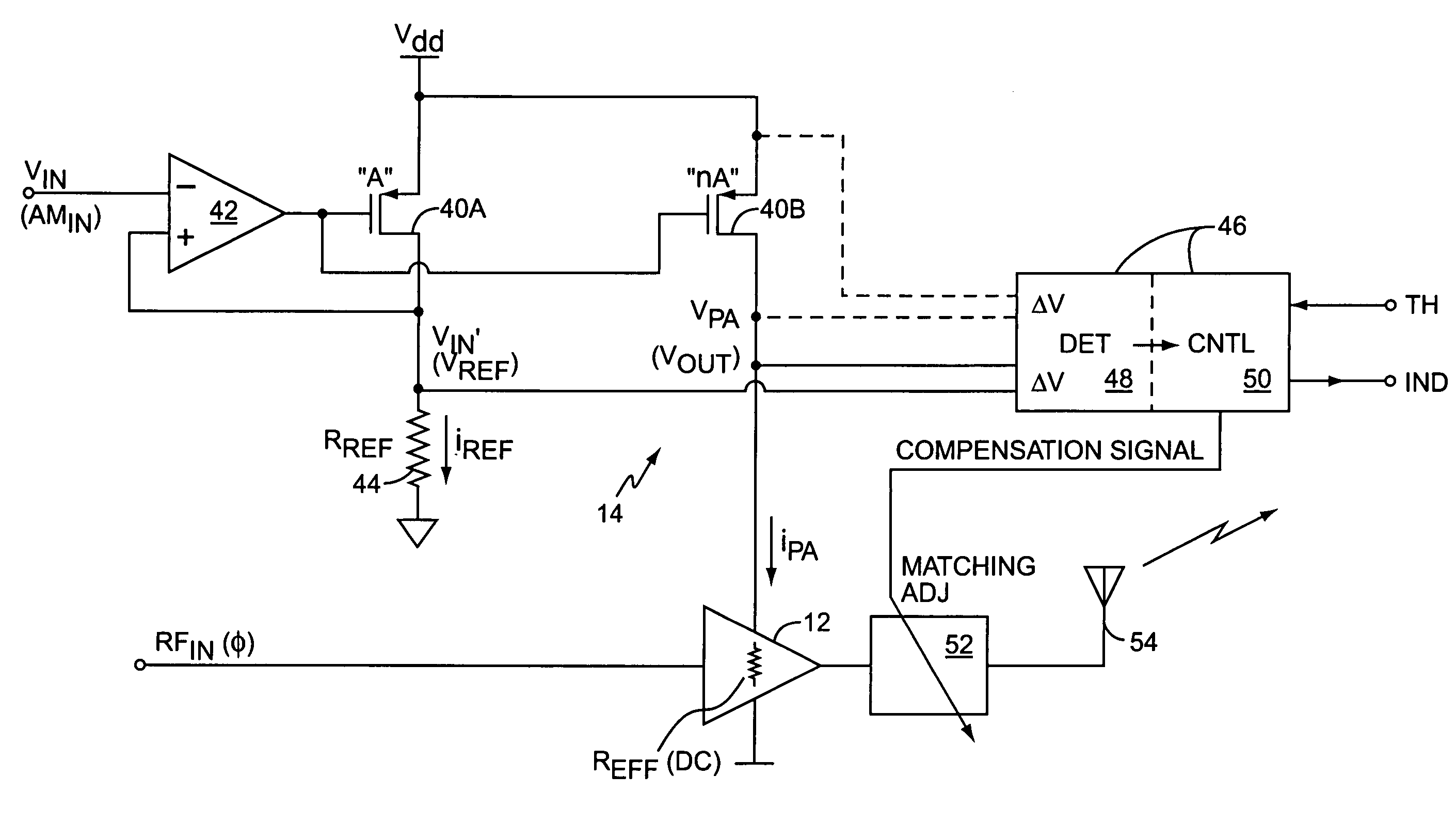
System and method for current-mode amplitude modulation
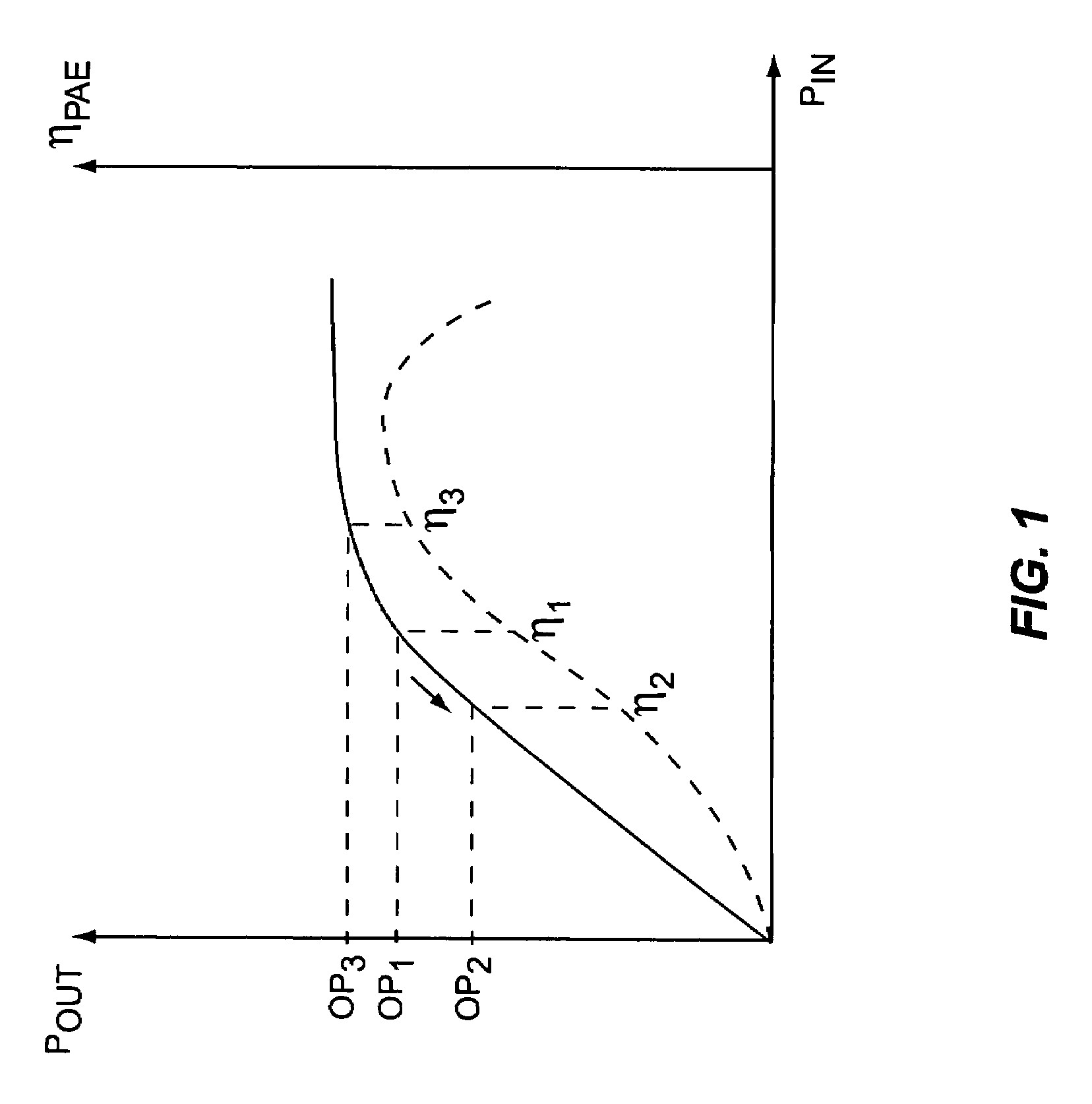
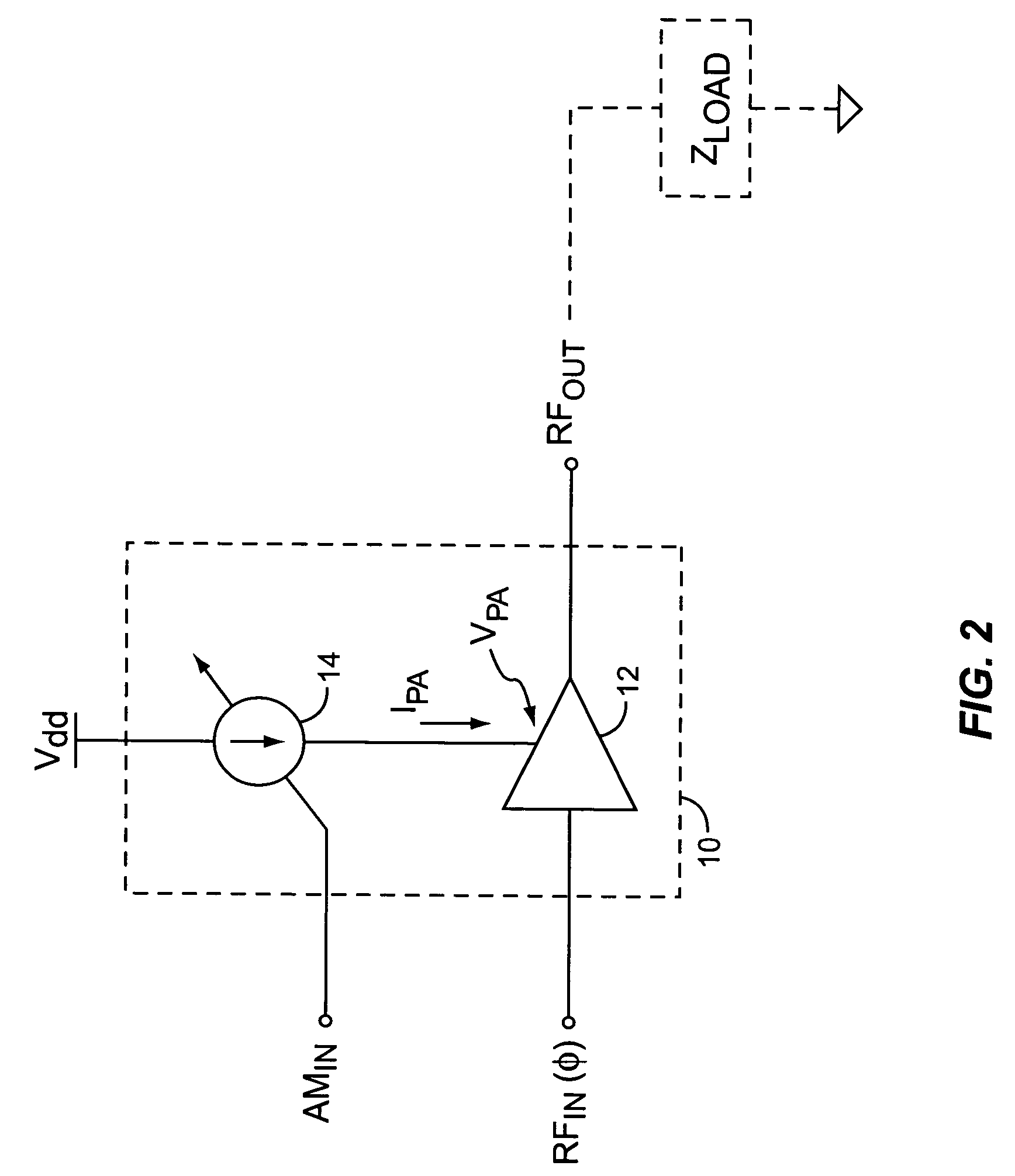
InactiveUS20050032488A1Efficient and linear amplificationHighly linear envelope modulationSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAntenna impedanceAudio power amplifier
An amplifier circuit includes a power amplifier biased for saturated mode operation, and a controllable current source to provide supply current to the power amplifier. The controllable current source effects desired amplitude modulation of the output signal from the power amplifier by modulating the supply current it provides responsive to an amplitude information signal. In one or more embodiments, the current source includes a circuit that is configured to adjust one or more transmitter operating parameters responsive to detecting changes in the effective DC resistance of the power amplifier. For example, the circuit may generate a compensation signal that reduces the effective DC resistance responsive to detecting that the effective DC resistance has undesirably increased. By way of non-limiting examples, such compensation may be effected by changing a current mirror, an amplifier-to-antenna impedance matching, an amplifier bias or device size, or imposing some form of transmit signal back-off.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
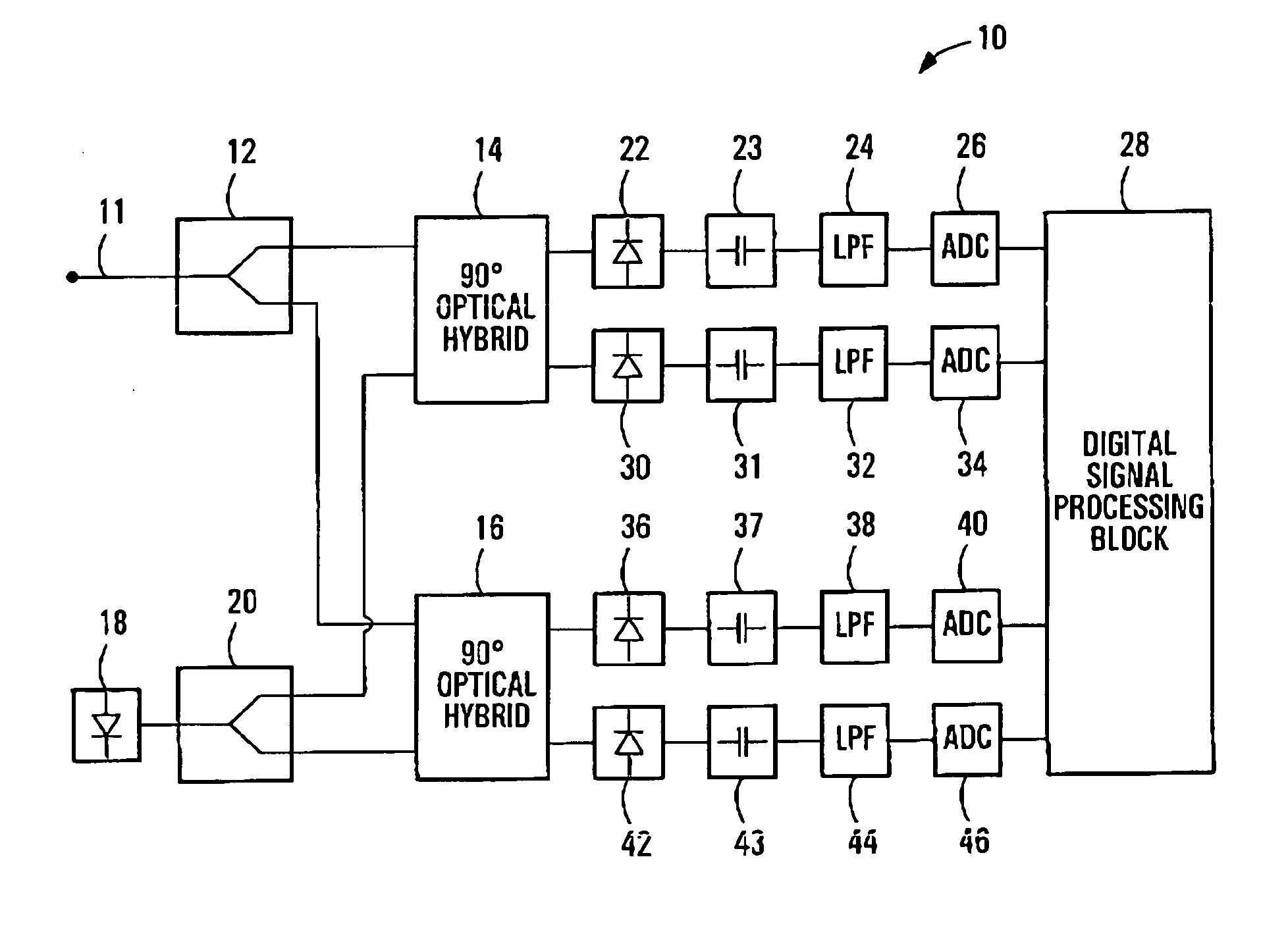
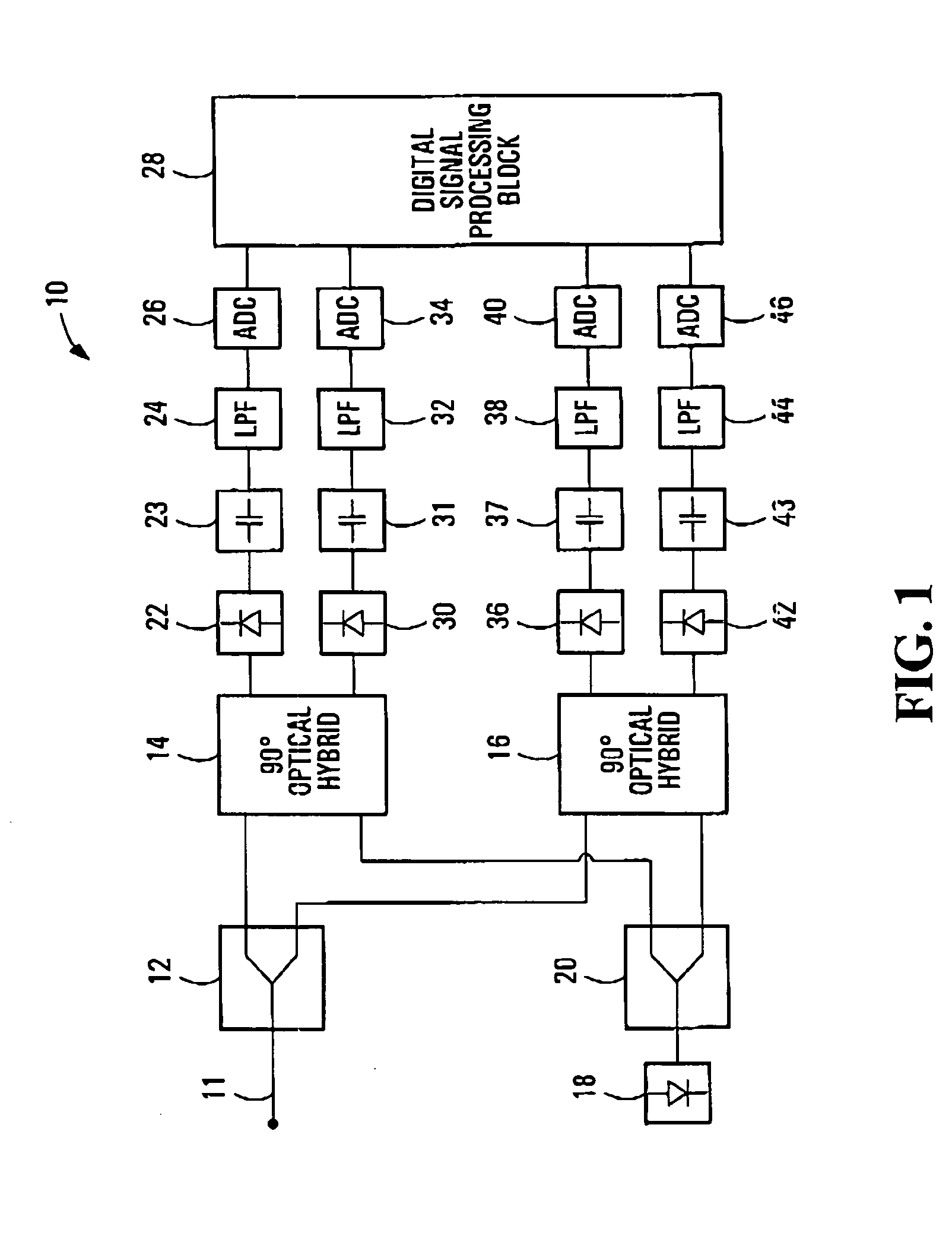
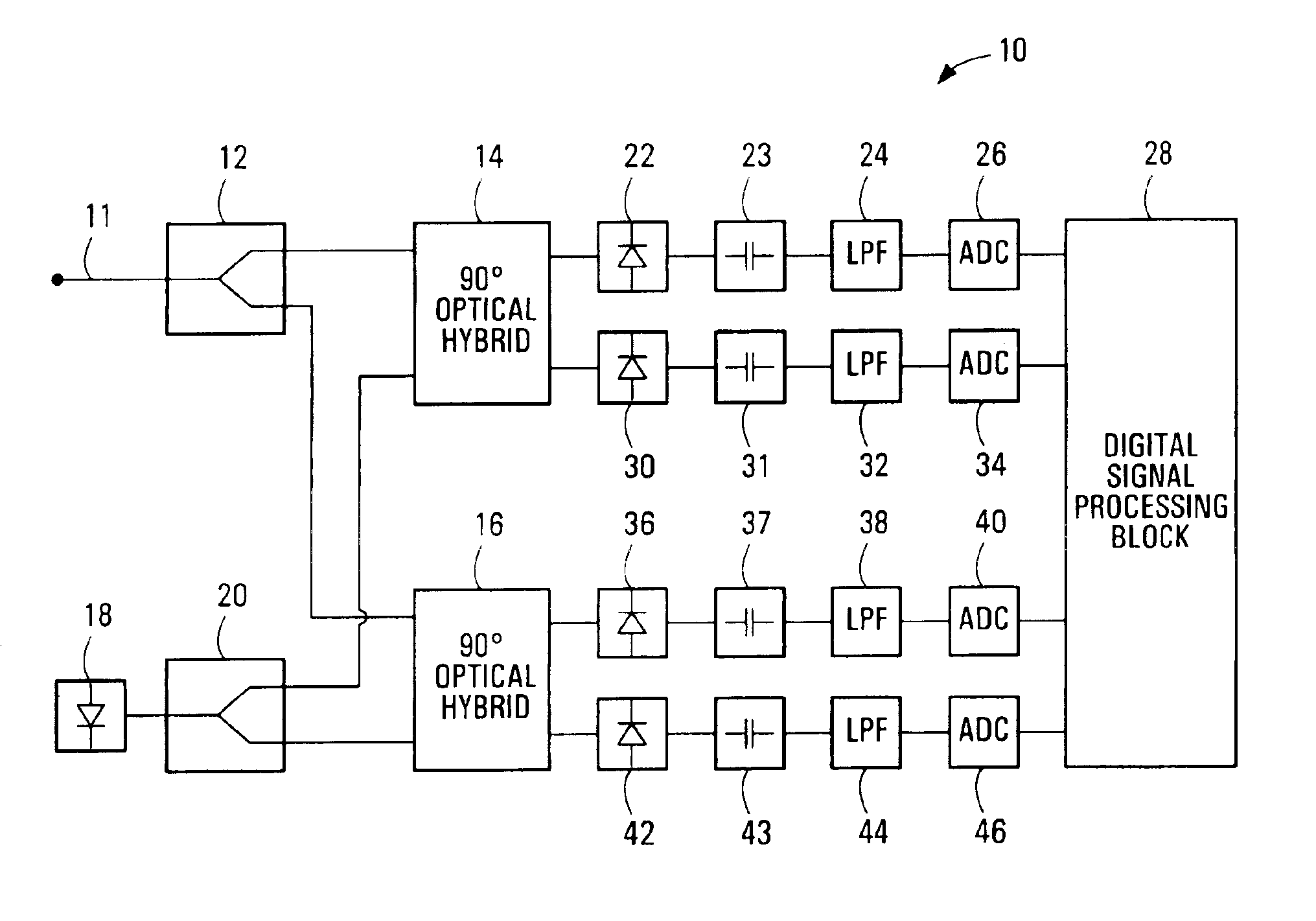
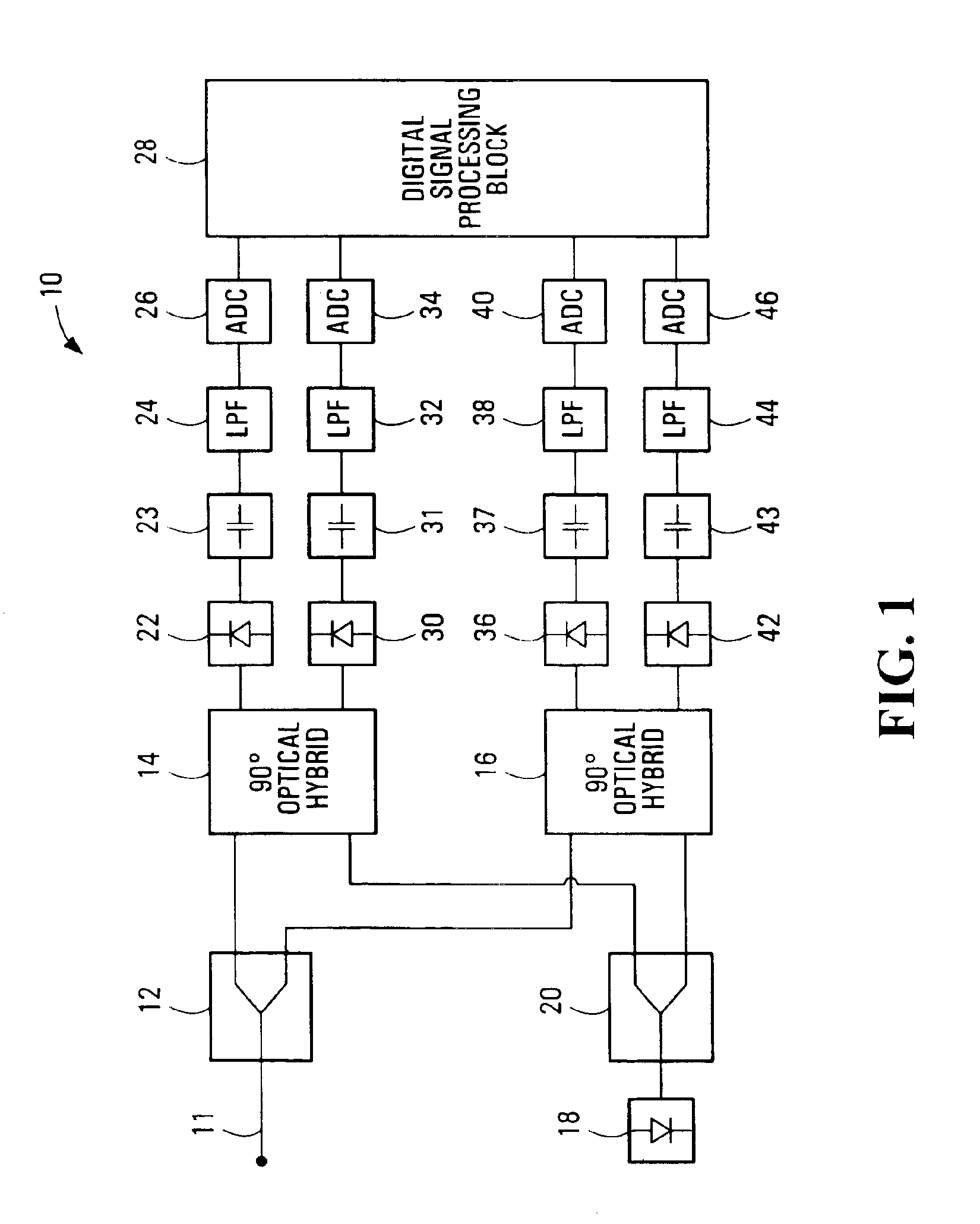
Equalization strategy for dual-polarization optical transport system
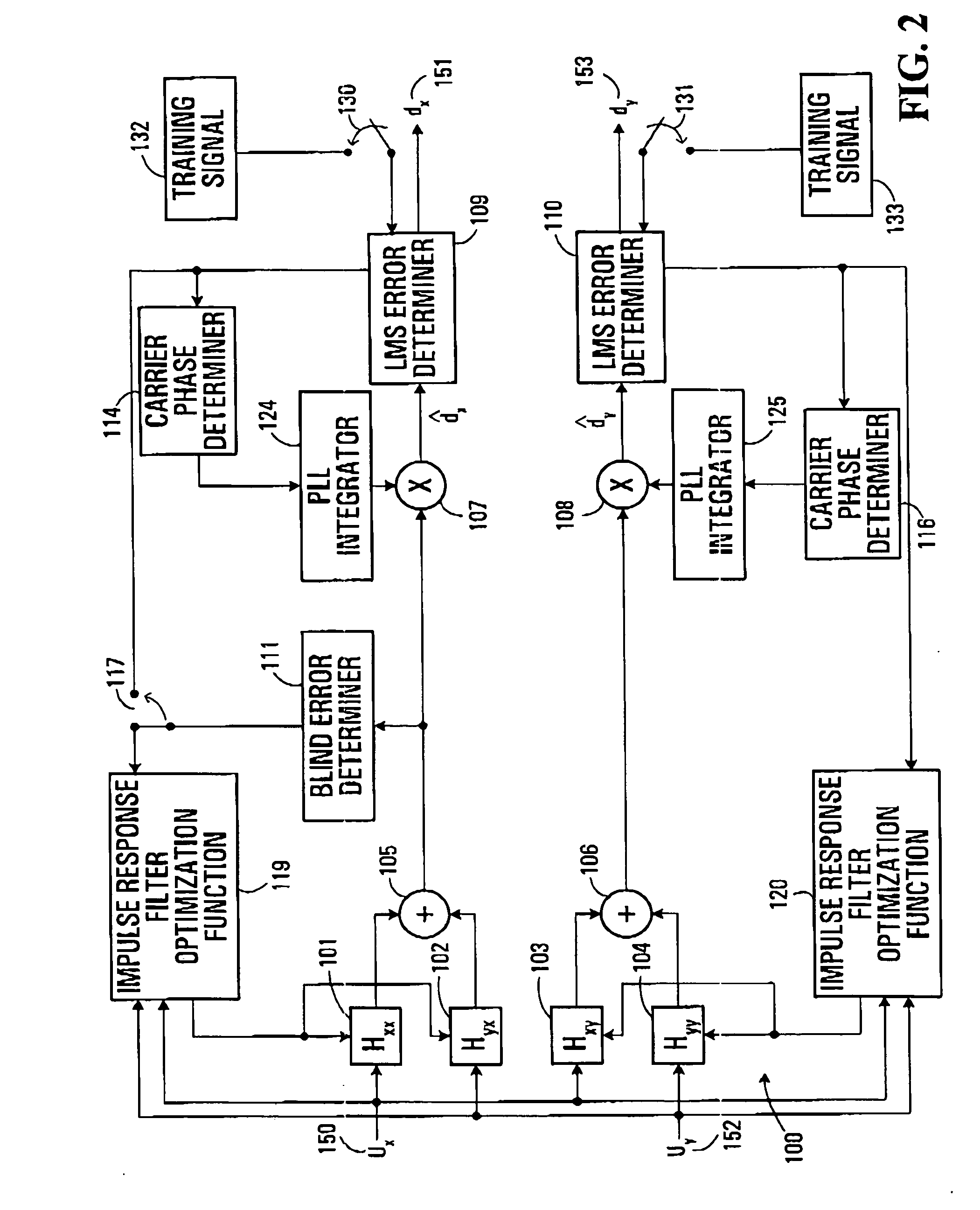
ActiveUS20050196176A1Avoid convergencePrevent degradationMultiple-port networksError preventionDigital signal processingSelf recovery
A method is provided for an equalization strategy for compensating channel distortions in a dual-polarization optical transport system wherein the received signal includes a complex signal of a first transmitted polarization component and a complex signal of a second transmitted polarization component. In a first step, a blind self-recovery mode used a blind adaptation algorithm in calculating and modifying multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of only the complex signal of the first transmitted polarization component. By recovering only a single polarization component in the first step the degenerate case of recovering only a single transmitted signal at both polarization component outputs of an equalizer is prevented. In a second step, equalization is performed in a training mode for calculating and modifying the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. In a third step, equalization is performed in a data directed mode for continuing to calculate and modify the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to ensure continued recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. The method is suited for a digital signal processing implementation in a coherent receiver when a modulation scheme used on a transmitted signal is quadriphase-shift keying (QPSK). In other embodiments, the method can be used with modulation schemes such as binary PSK, M-ary PSK where M>4, or Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM).
Owner:CIENA
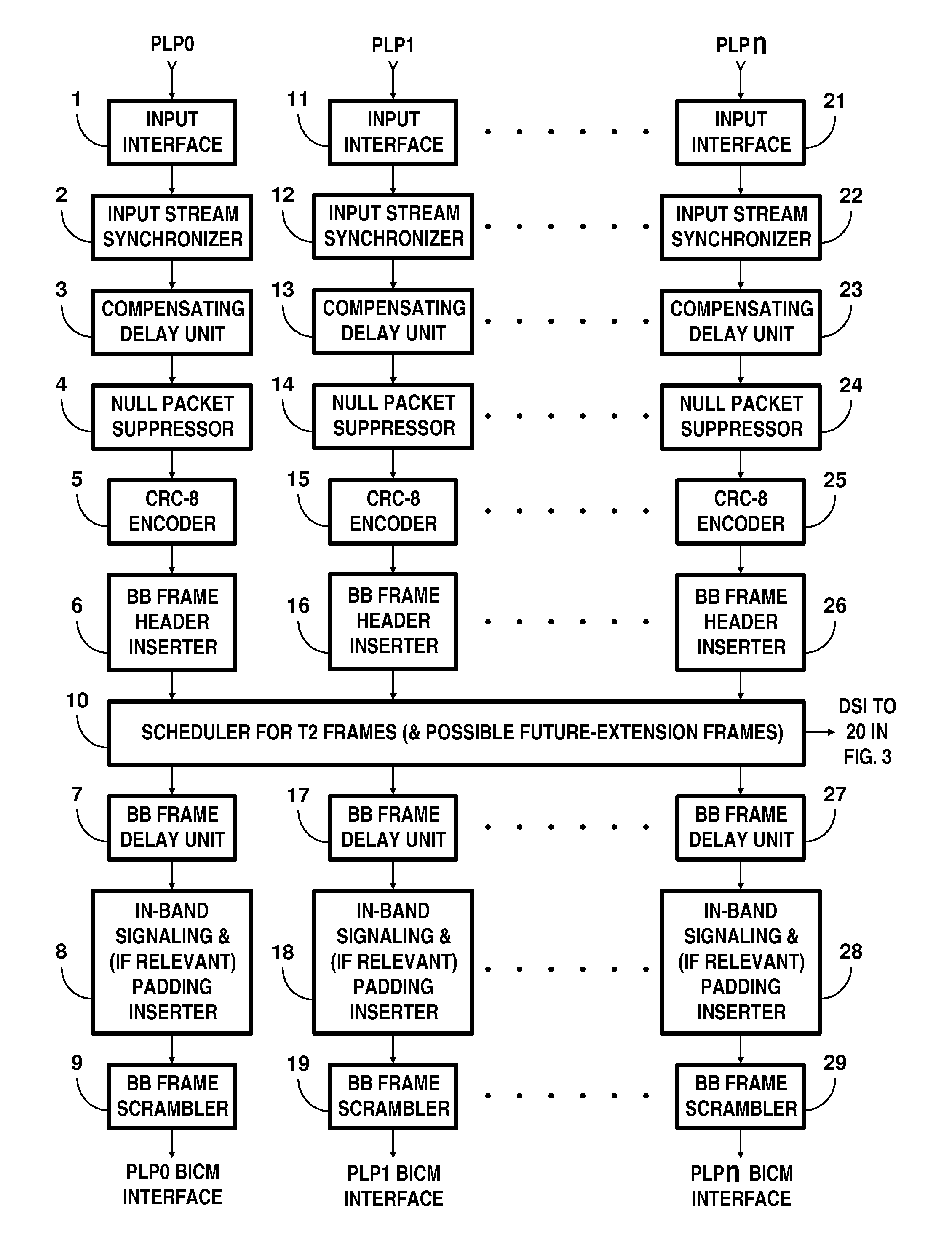
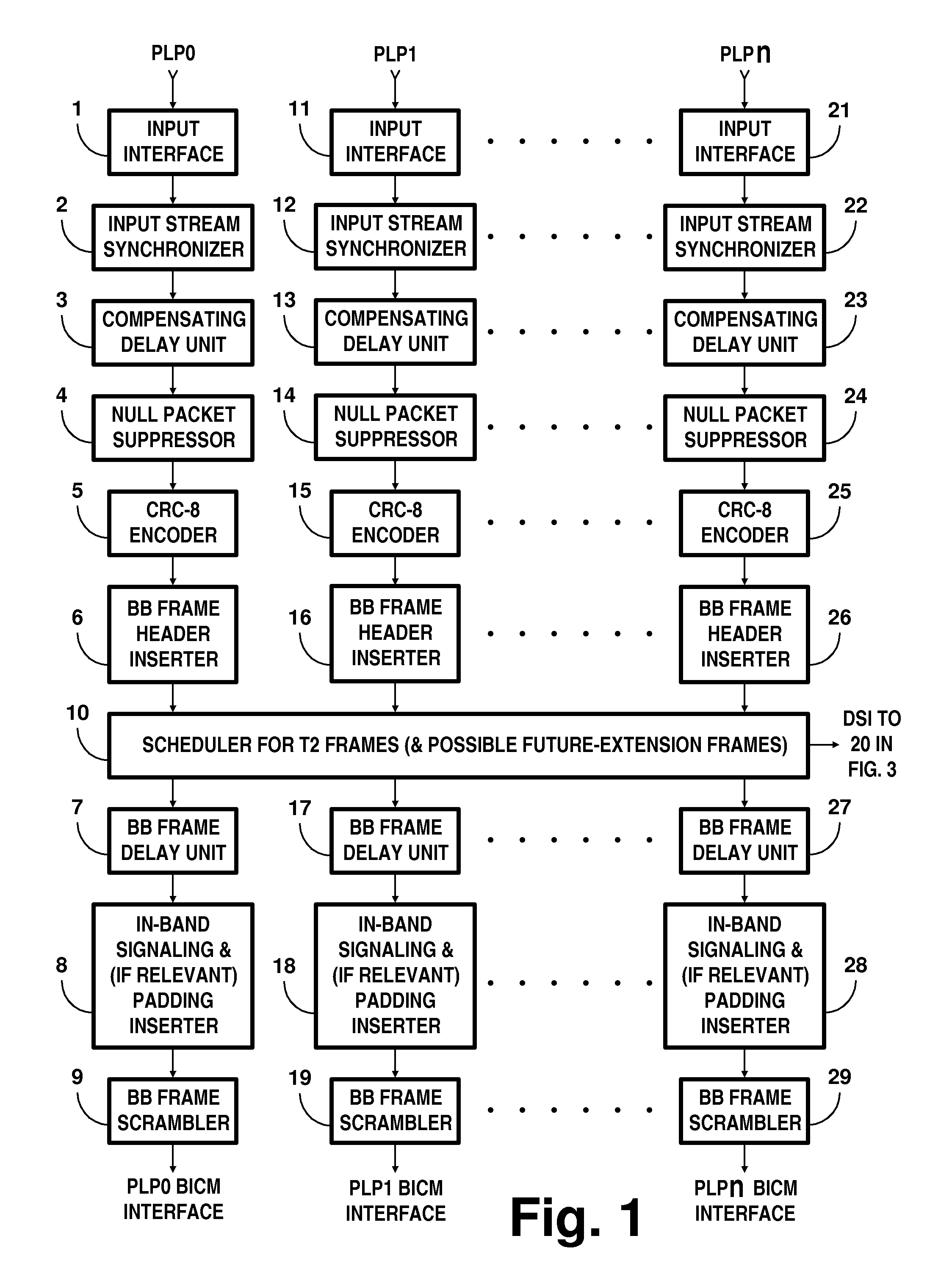
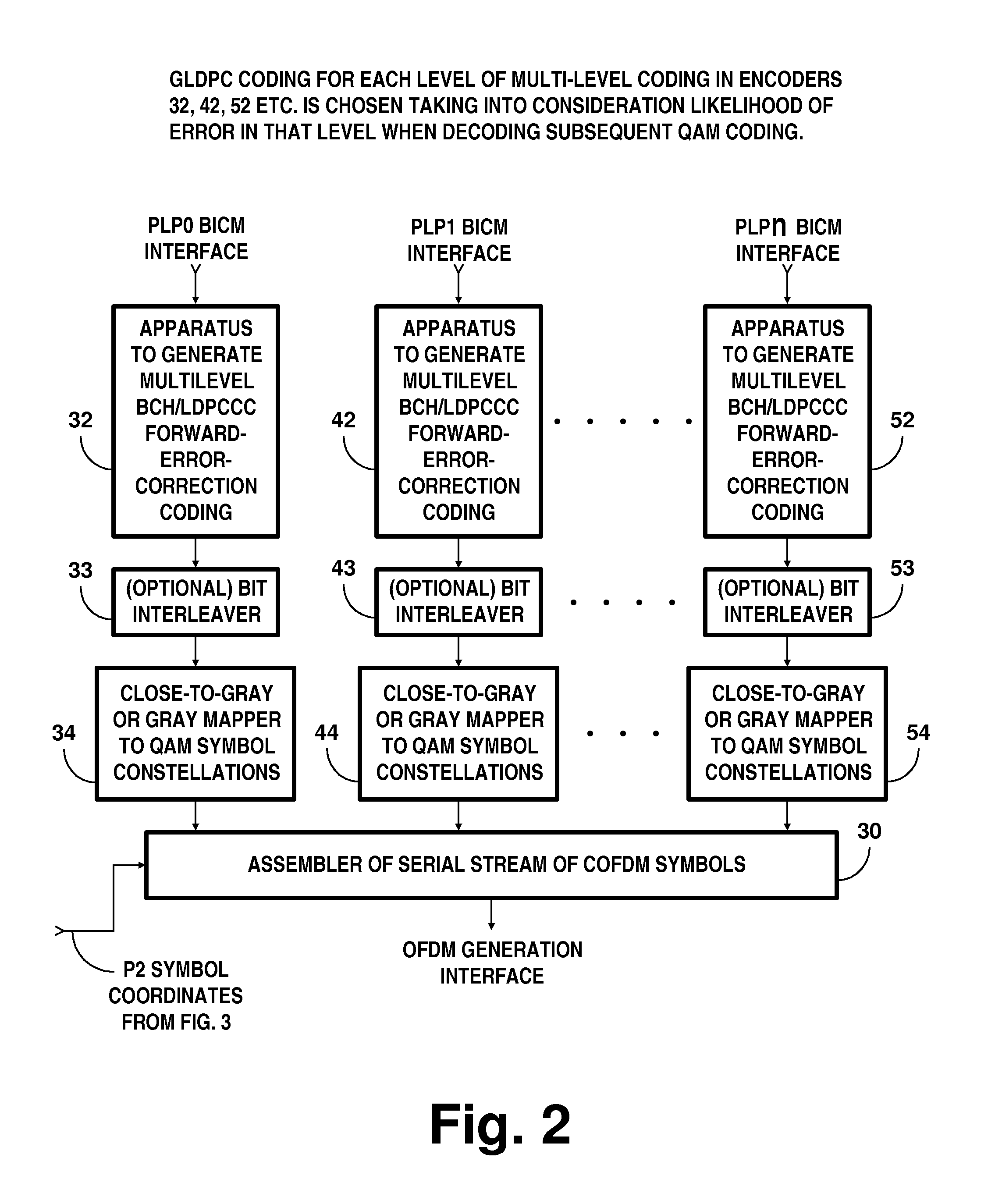
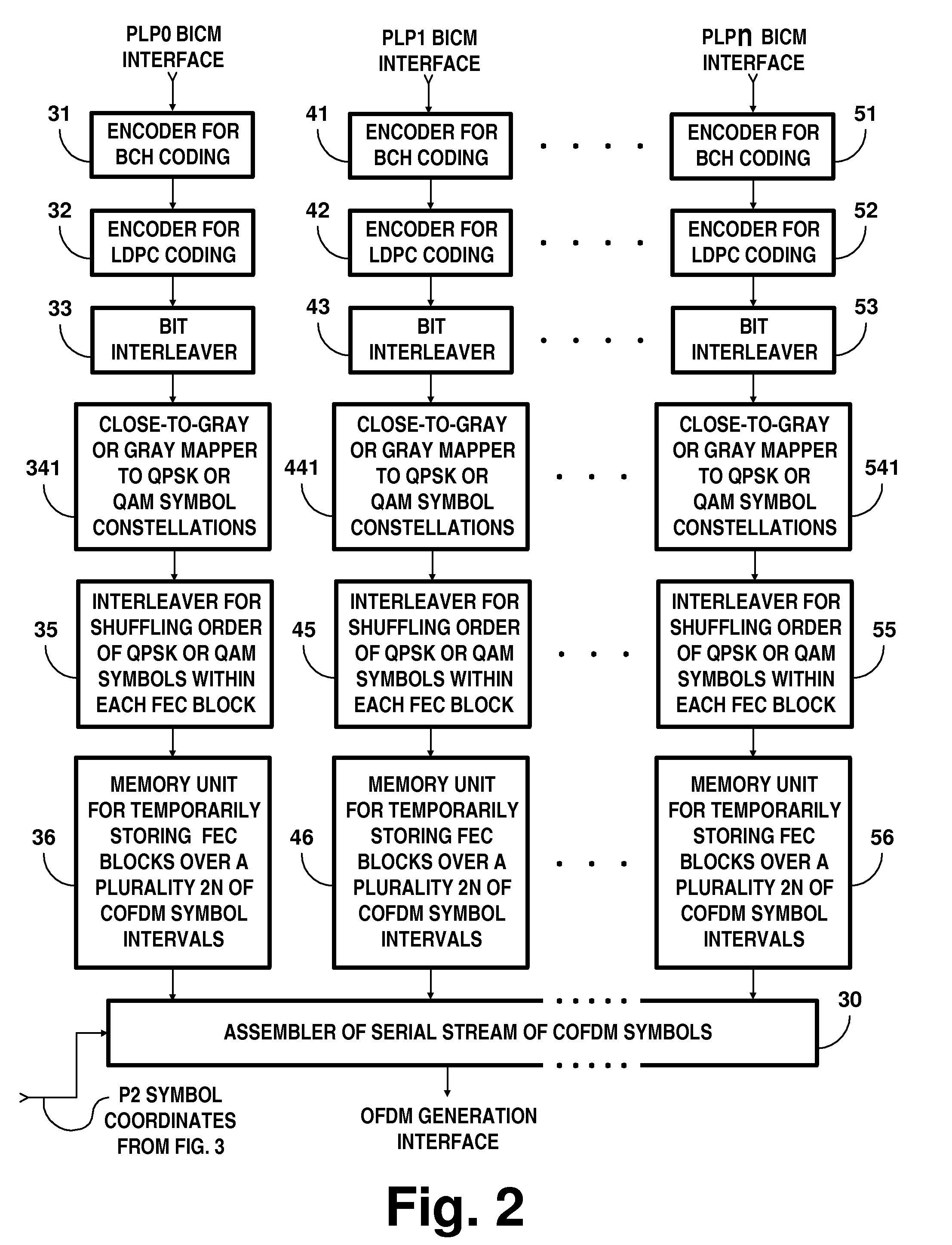
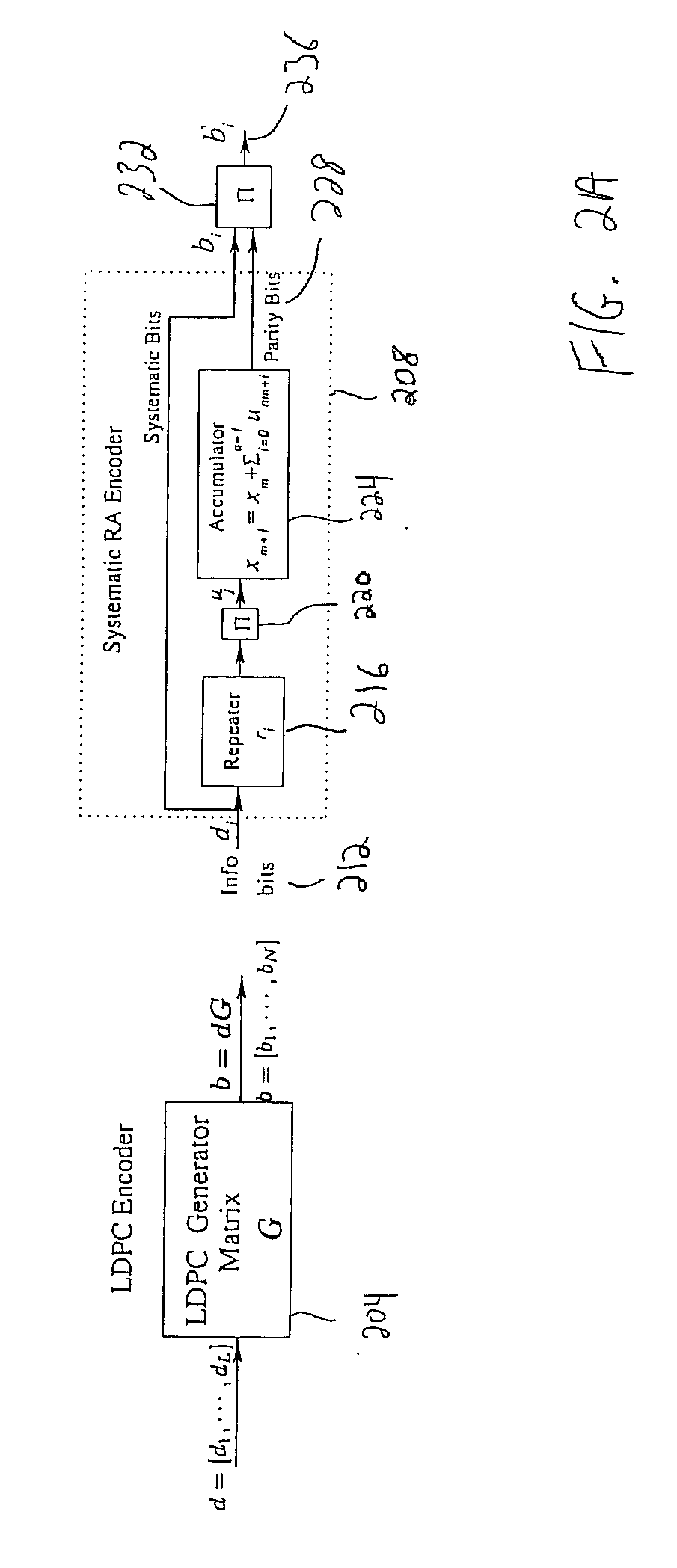
Digital television broadcasting system using coded orthogonal frequency-division modulation and multilevel LDPC convolutional coding
InactiveUS20150358648A1Facilitate parallel independent decodingError preventionError correction/detection using concatenated codesCarrier signalRadio frequency
In transmitter apparatus for a digital television (DTV) broadcasting system, internet-protocol (IP) packets of digital television information are subjected to multilevel concatenated Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (BCH) coding and low-density parity-check convolutional coding (LDPCCC) before being bit-interleaved and mapped to quadrature-amplitude-modulation (QAM) constellations. The QAM constellations are used in coded orthogonal frequency-division modulation (COFDM) of plural carrier waves up-converted to a radio-frequency broadcast television channel. In receiver apparatus for the DTV broadcasting system the results of de-mapping QAM constellations recovered from demodulating the COFDM carrier waves are de-interleaved, and the constituent LDPCCC codewords are decoded to recover constituent BCH codewords of the multilevel BCH coding. The constituent BCH codewords are decoded to correct remnant bit errors in them. Then, IP packets of digital television information are reconstituted from the systematic data bits in those BCH codewords.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
FMOD transceivers including continuous and burst operated TDMA, FDMA, spread spectrum CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA
InactiveUS6928101B2Improve performanceLow costAsymmetric modulation circuitsPhase-modulated carrier systemsModem deviceFrequency spectrum
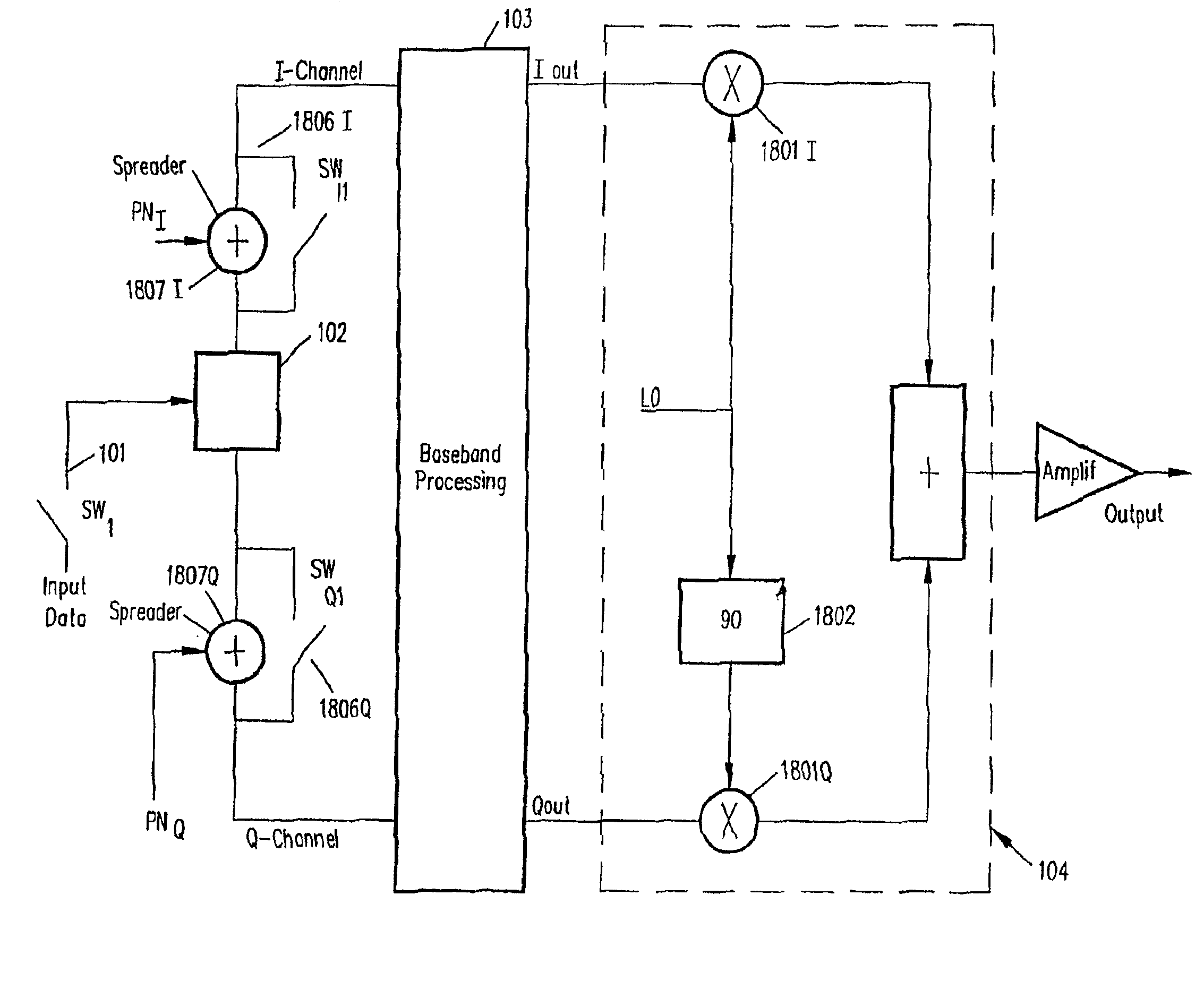
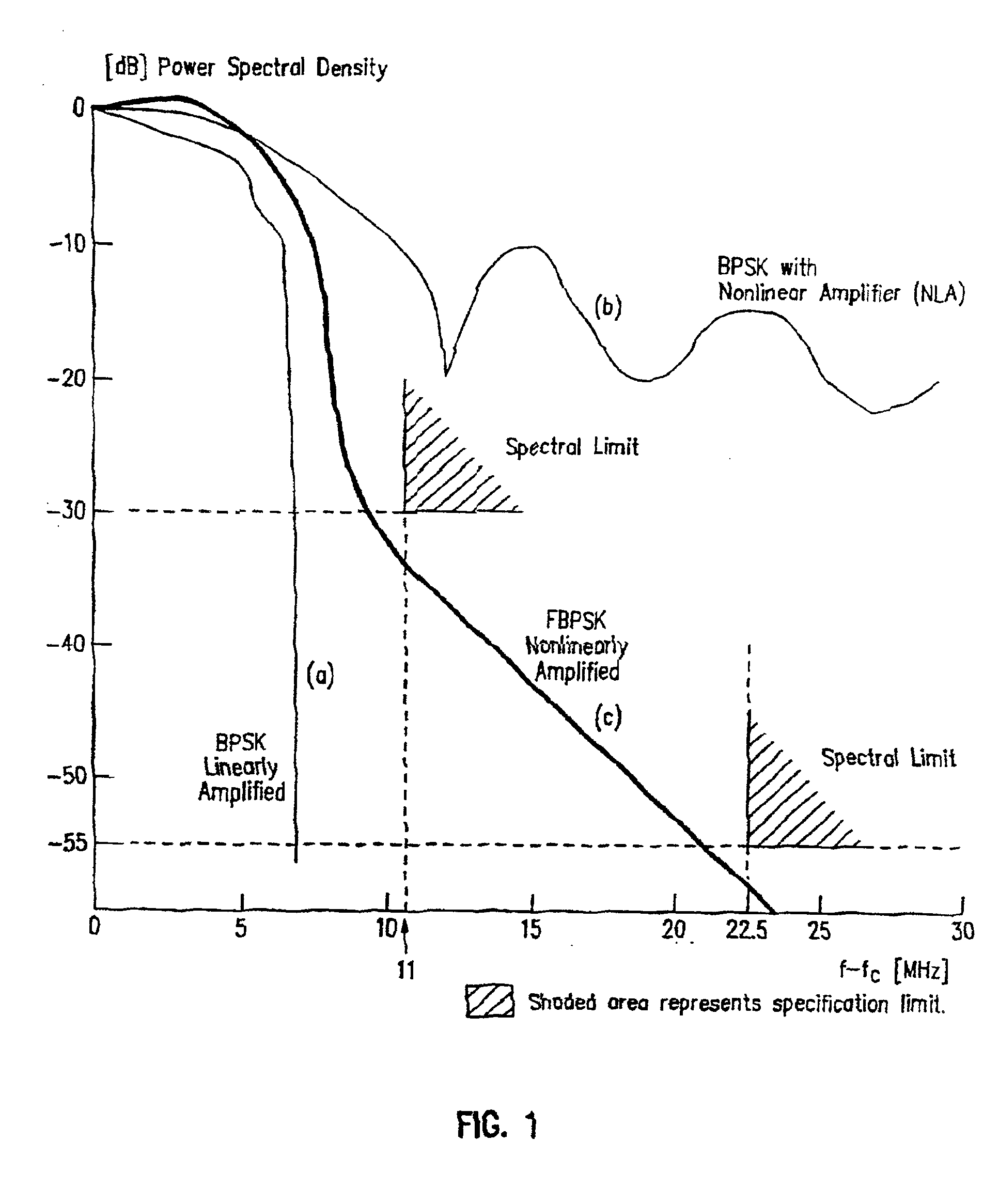
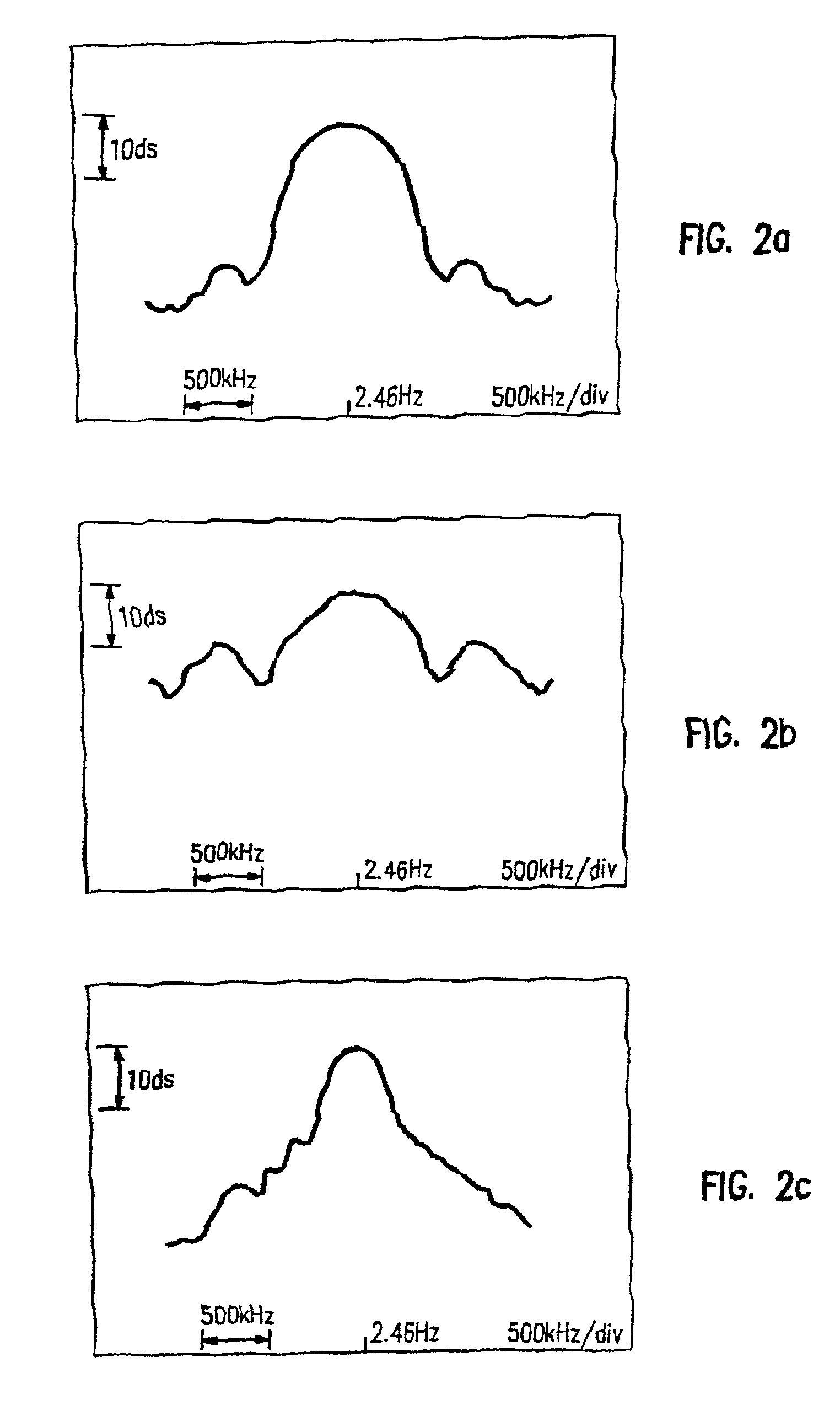
Binary and Quadrature Feher's Modulation (F-Modulation, or FMOD) Transmitter-Receiver systems and circuits exhibit reduced envelope fluctuation and peak radiation, and increased efficiency. A subclass of these systems has a constant envelope. They advantageously provide lower power operation with improved performance including robust BER performance, and compatibility with both linearly and nonlinearly amplified narrow spectrum, and without disadvantages of conventional BPSK, DBPSK QPSK and pi / 4-QPSK. Feher's BPSK (FBPSK) is an improved efficiency transmitter which is compatible with conventional BPSK receivers. FBPSK modems are based on using quadrature structure where Q-channel data is inserted in quadrature with I-channel data for certain applications. The Q-channel data may be “offset” from the I-channel data by an amount selectable between zero and a specified time. Further improvement in the spectrum is attained using correlation between I and Q channels. FBPSK modem is shown to meet the IEEE 802.11 specified spectral direct sequence spread spectrum mask (−30 dB point) for wireless LAN, and leads to an output power gain of 6.5 dB over conventional BPSK modems. The cross-coupled quadrature FMOD structure is also suitable for continuous mode and for burst operated TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA Frequency Modulation Quadrature AM (QAM), QPSK and offset QPSK, as well as pi / 4-shifted QPSK modems / processors. Reduced modulation index Gaussian FSK (GFSK), multilevel FM and cross-coupled Quadrature Amplitude Modulated (QAM) transmitters and combinations of these modulations and corresponding coherent demodulators are disclosed. Controlled rise and fall time descriptions of burst operated systems are included.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Featureless coherent chaotic amplitude modulation
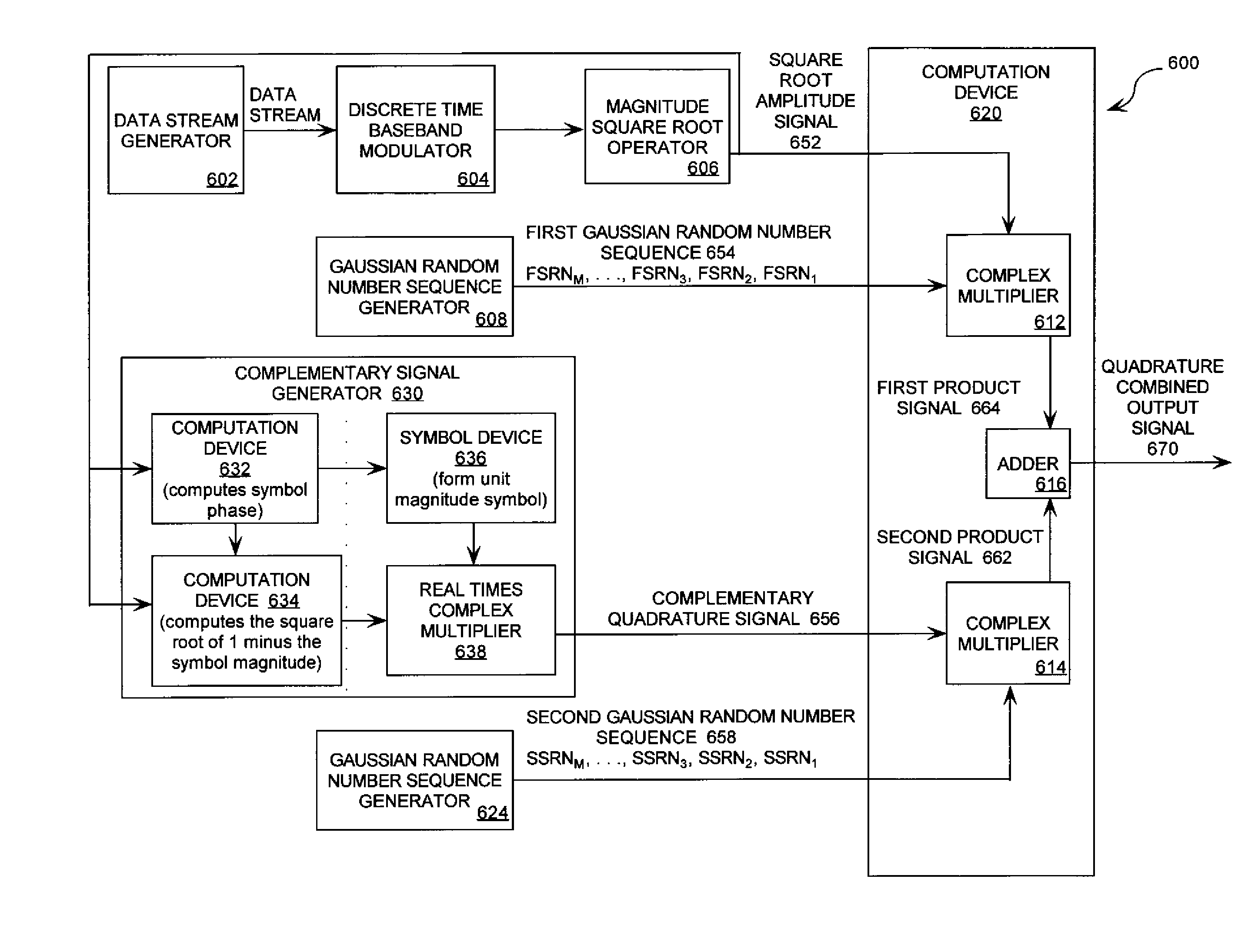
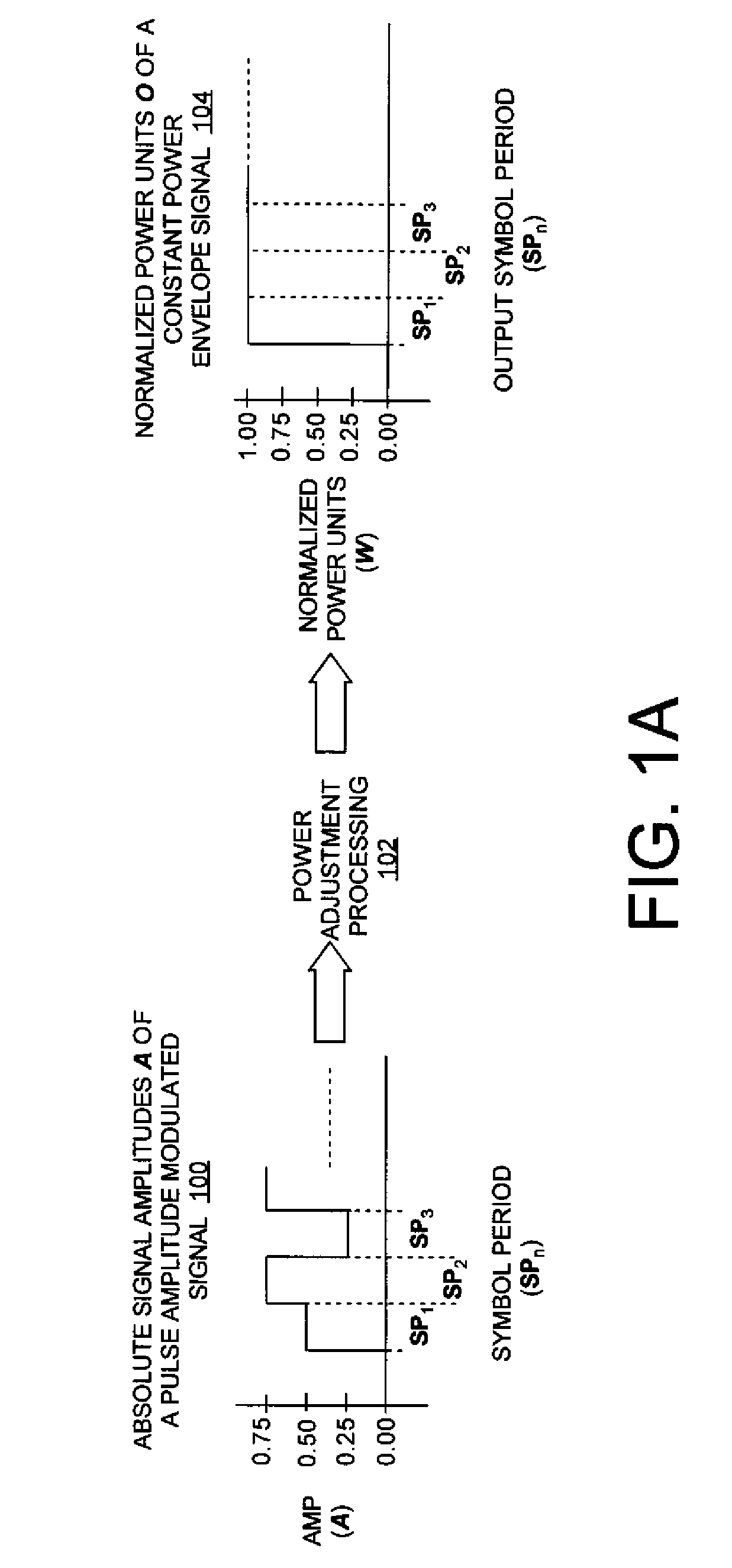
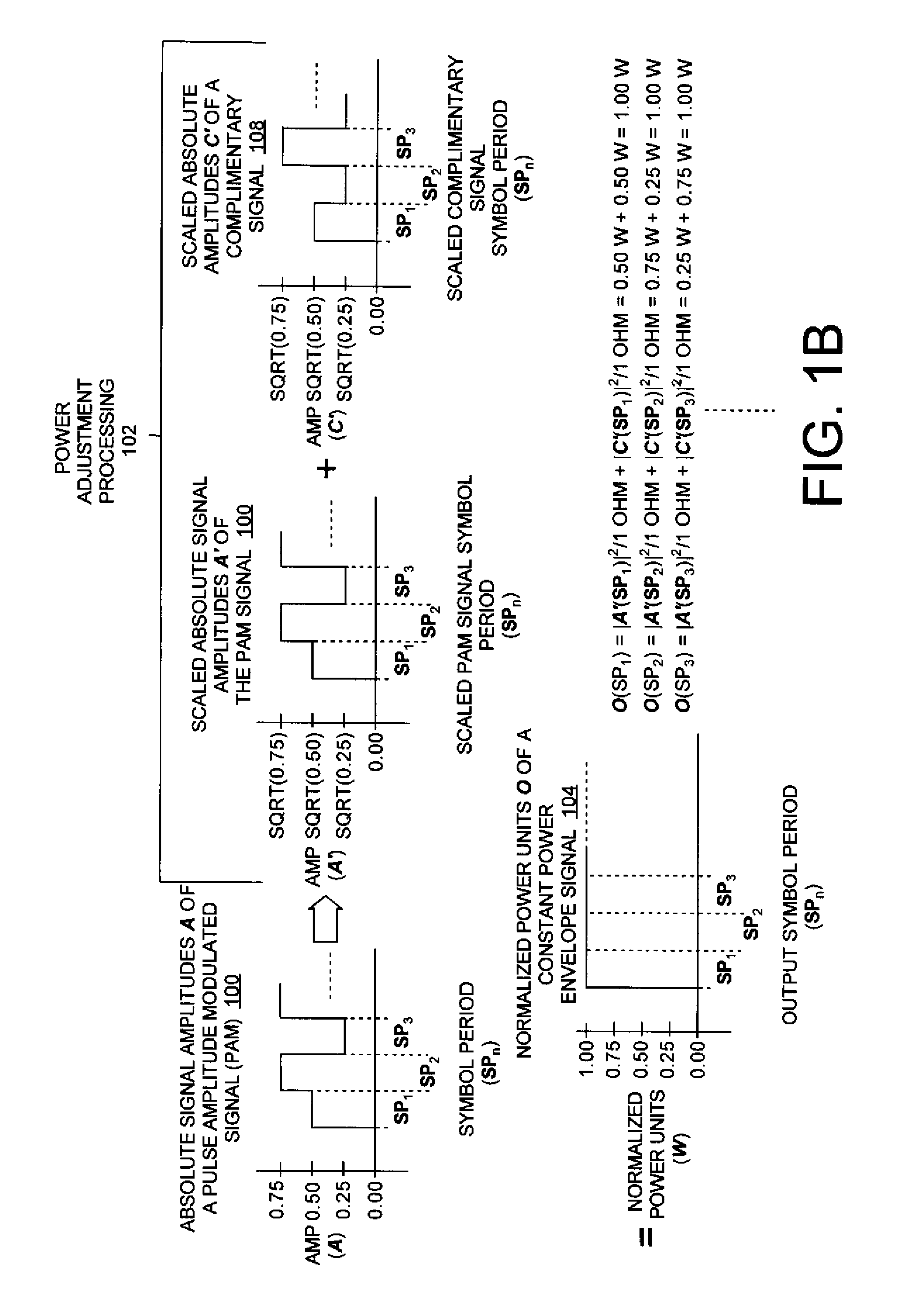
ActiveUS20090310650A1Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsConstant powerPulse-code modulation
Systems (400, 500, 600) and methods (300) for generating a chaotic amplitude modulated signal absent of cyclostationary features by preserving a constant variance. The methods involve: generating a PAM signal including pulse amplitude modulation having a periodically changing amplitude; generating a first part of a constant power envelope signal (FPCPES) by dividing the PAM signal by a square root of a magnitude of the PAM signal; generating a second part of the constant power envelope signal (SPCPES) having a magnitude equal to a square root of one minus the magnitude of the PAM signal; and generating first and second spreading sequences (FSS and SSS). The methods also involve combining the FPCPES with the FSS to generate a first product signal (FPS) and combining the SPCPES with the SSS to generate a second product signal (SPS). A constant power envelope signal is generated using the FPS and SPS.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Apparatus for adaptable/variable type modulation and demodulation in digital tx/rx system
InactiveUS20110167317A1Improve transfer rateImproved channel efficiencyJoint error correctionMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsQuadrature amplitude modulationSelf adaptive
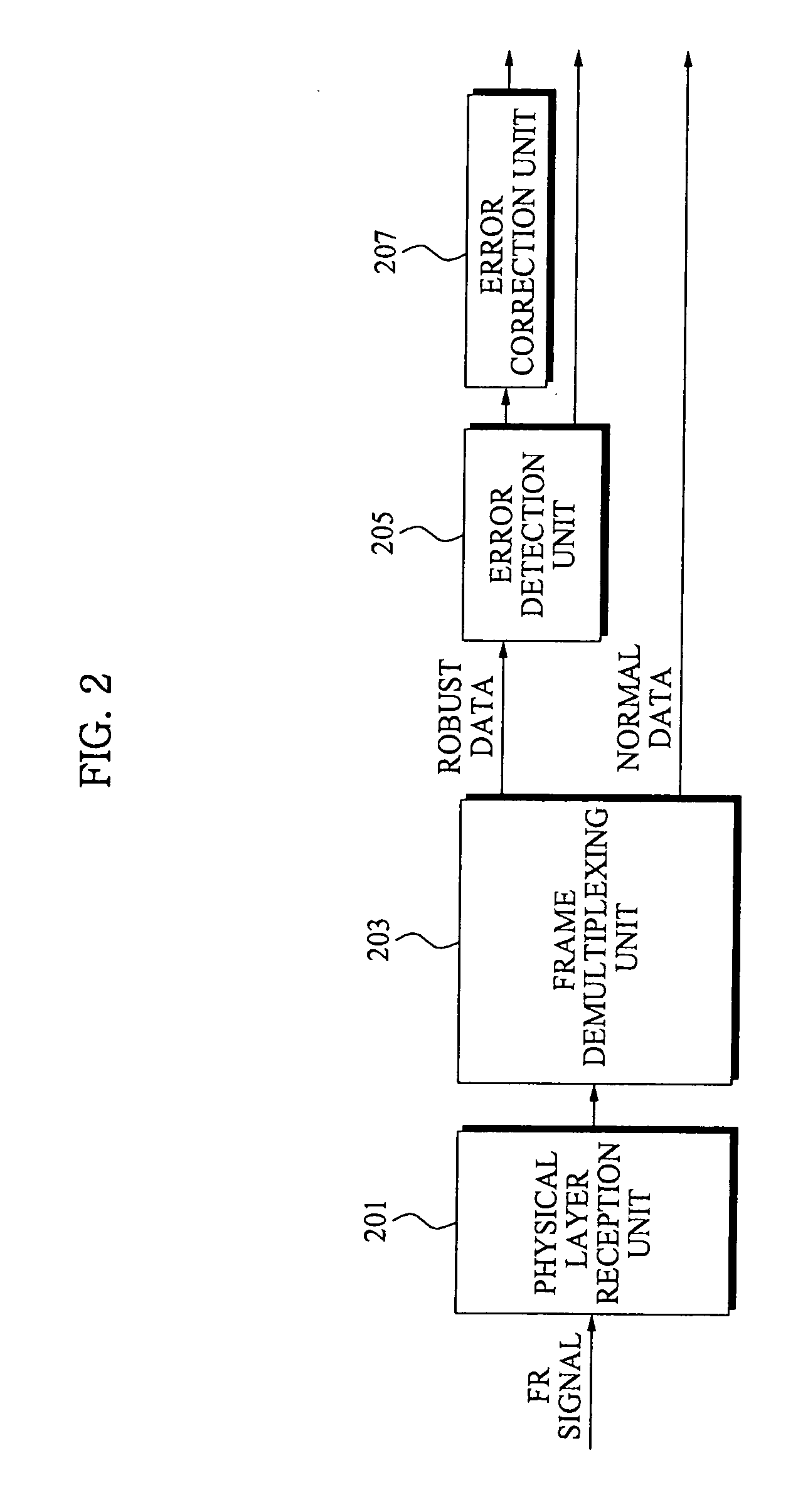
Disclosed is an adaptable / variable type modulation / demodulation apparatus. A physical layer transmission apparatus for adaptable / variable type modulation, the transmission apparatus including a classification unit to classify a bit stream according to a standard that is determined in advance after receiving the bit stream, an uncoded bit group unit to group the bit stream not to be LDPC-coded by a predetermined number of bits, an LDPC encoder to perform LDPC-coding of the bit stream, a coded bit group unit to group the coded bit stream by the predetermined number of bits, a quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) unit to select a symbol coset using the coded bit groups; and a convolutional interleaver to perform convolutional interleaving of the symbol.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
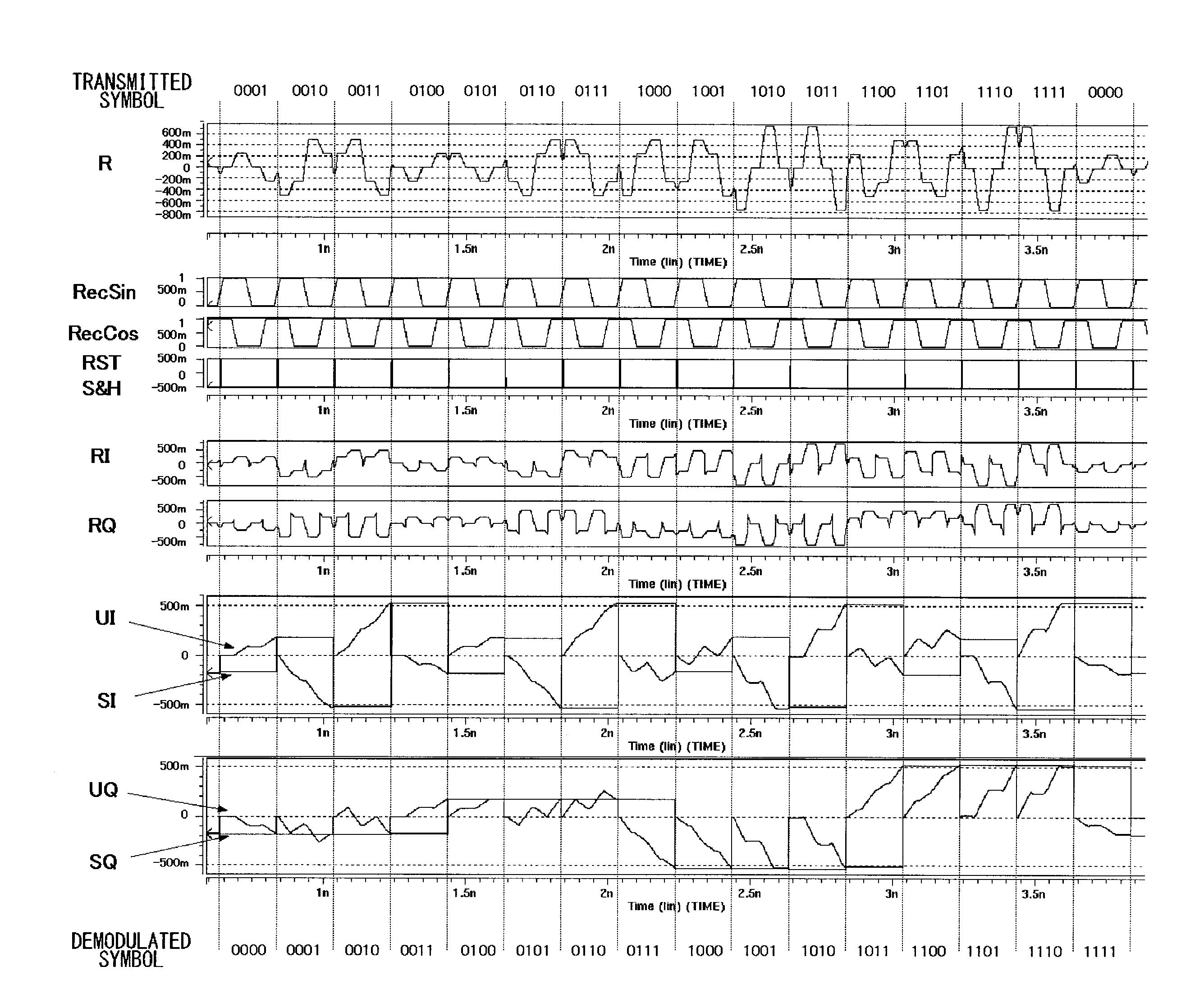
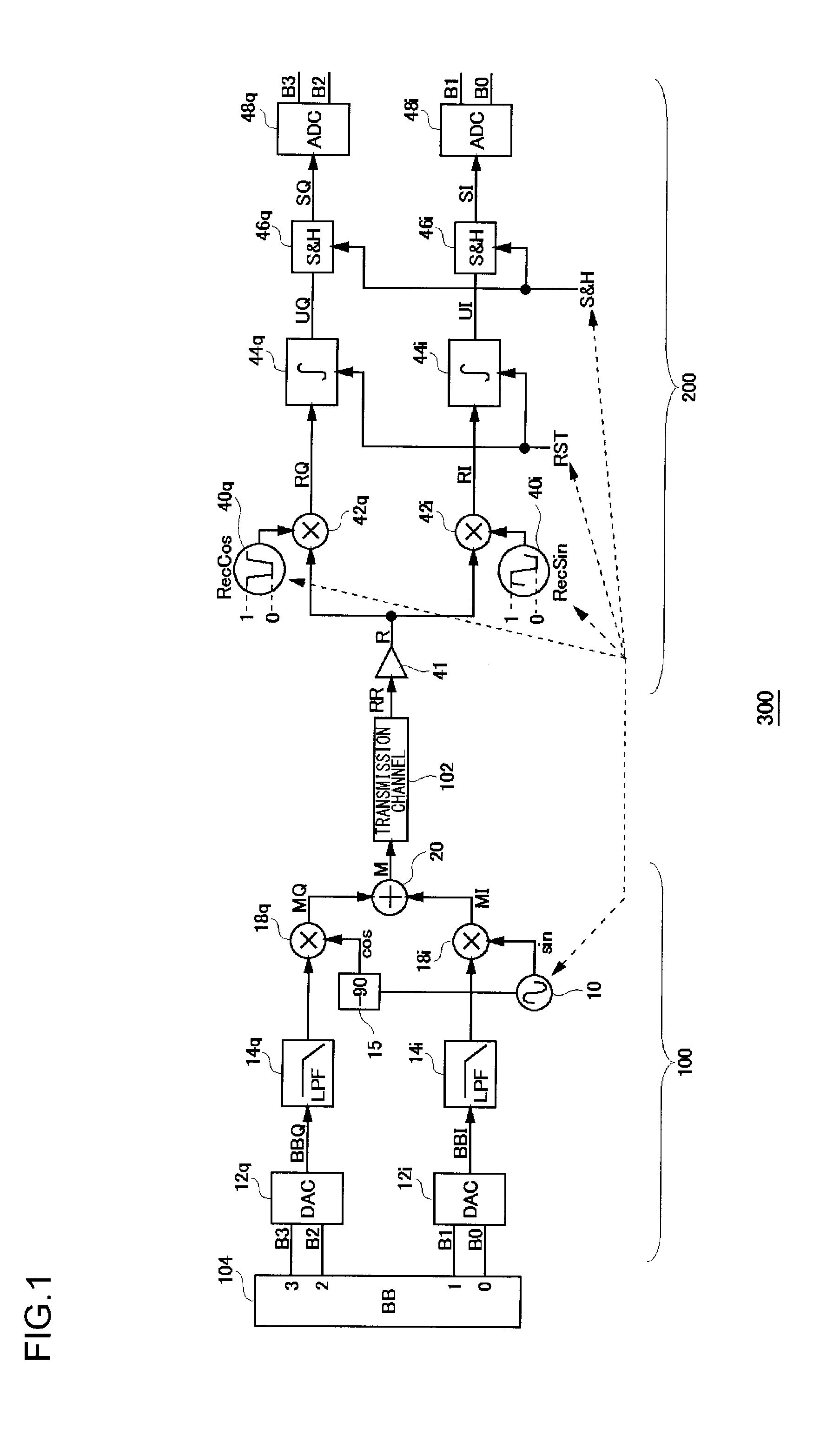
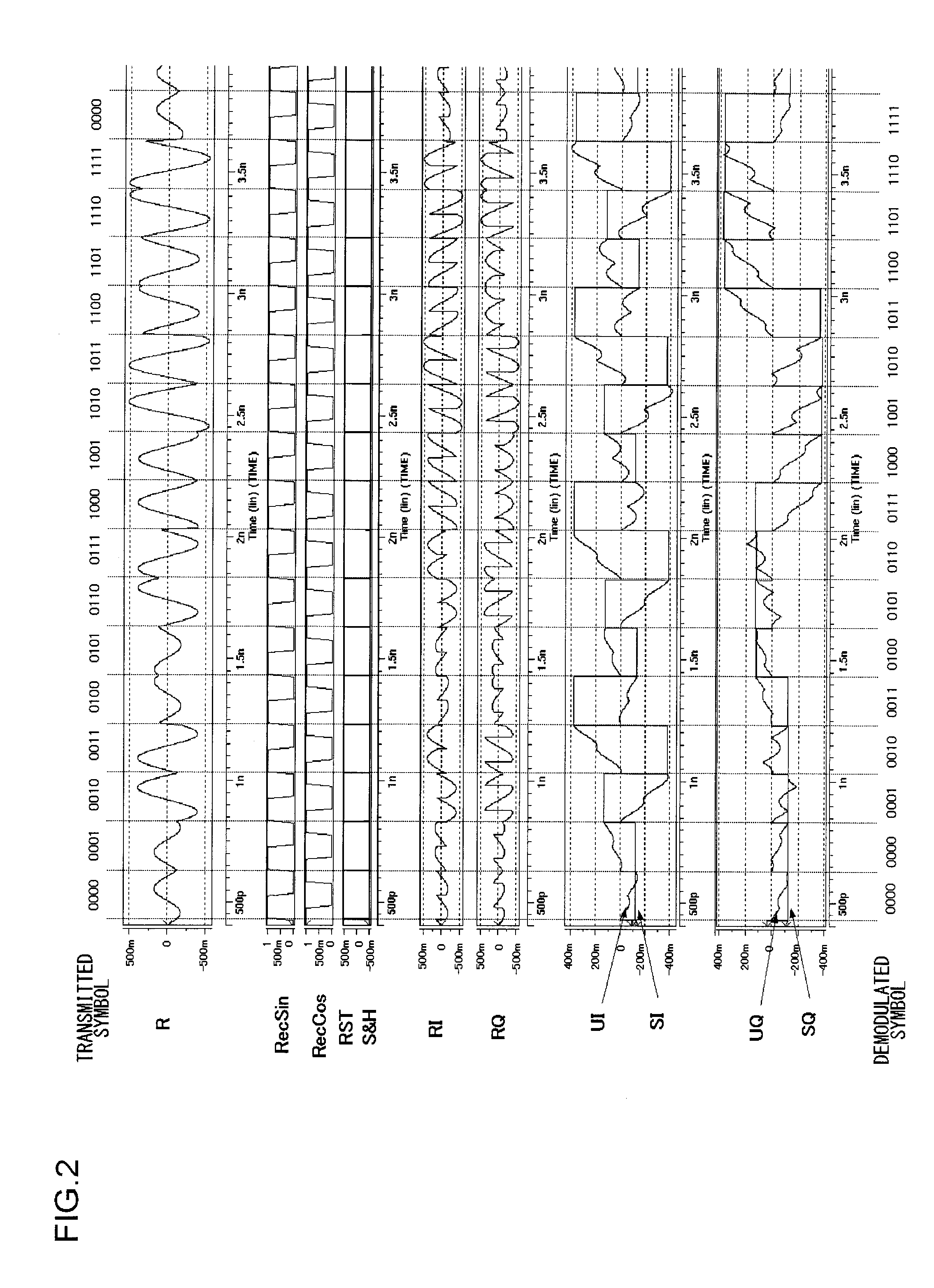
Quadrature amplitude demodulator and demodulation method
InactiveUS20110018626A1Readily implement dataModulation transferencePhase-modulated carrier systemsIntegratorFrequency mixer
A quadrature amplitude demodulator demodulates a modulated signal on which quadrature amplitude modulation is performed. Oscillators generate an in-phase carrier signal having a rectangular wave, a trapezoidal wave or a waveform similar to these, and a quadrature carrier signal, the phase of which is shifted by ¼ cycle relative to the in-phase signal. First and second mixers respectively perform mixing of the modulated signal with the in-phase signal and the quadrature carrier signal. First and second integrators respectively integrate output signals of the first and the second mixers, for a predetermined period in accordance with the cycle of the in-phase carrier signal and the quadrature carrier signal. First and second A / D converters respectively convert outputs of the first and the second integrators into digital values.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
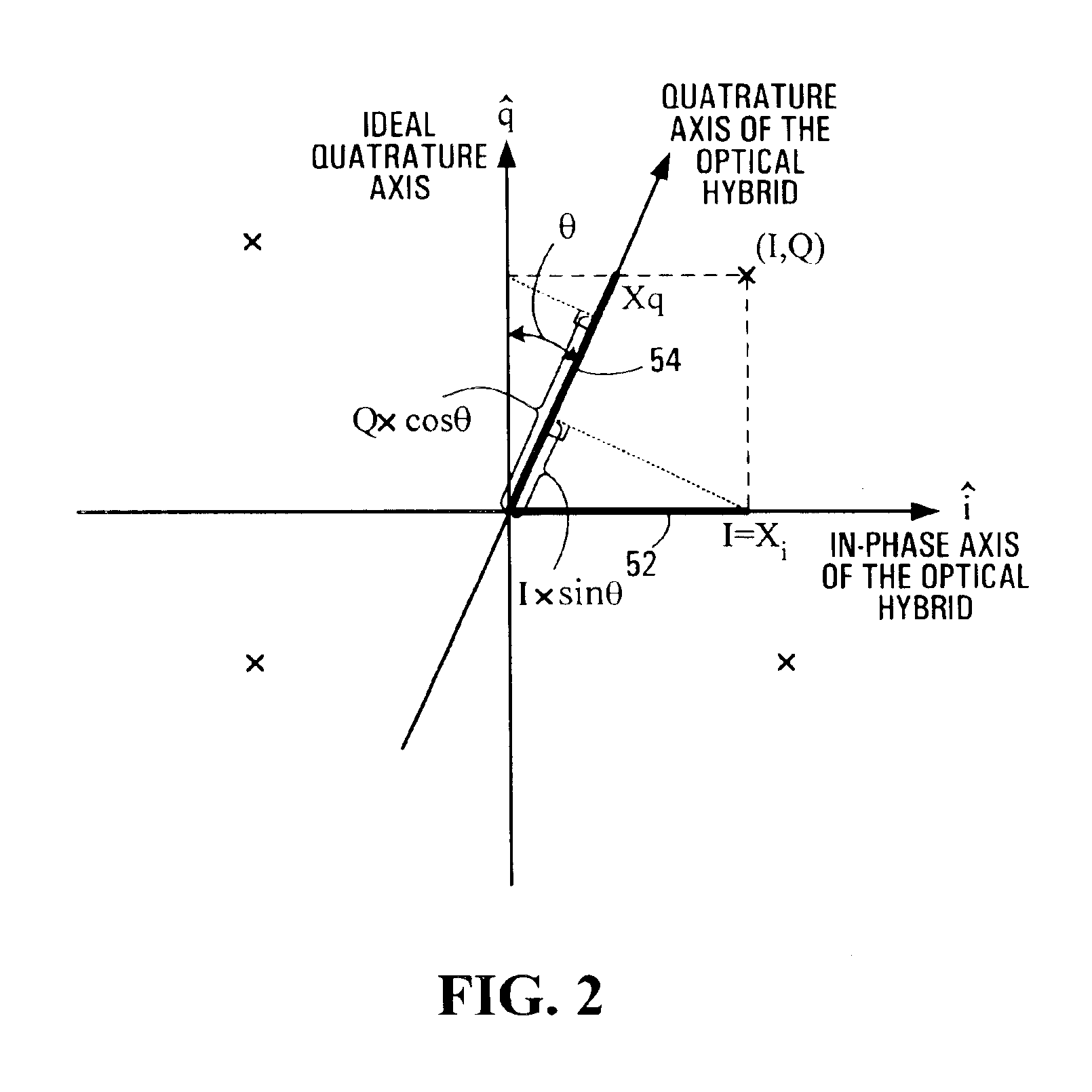
Method for quadrature phase angle correction in a coherent receiver of a dual-polarization optical transport system
ActiveUS6917031B1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesDigital signal processingTransport system
A method is provided for correcting a quadrature angle error that exists in the coherent receiver hardware of a dual-polarization optical transport system. The receiver hardware that causes the quadrature angle error is a 90 degree optical hybrid mixing device. The method involves generating an estimate of the quadrature angle error and compensating for the quadrature angle error by multiplying the first and second detected baseband signals by coefficients that are a function of the estimate of the quadrature angle error. The method is robust to severe channel distortion encountered within an optical fiber transmission channel as well as temperature effects and ageing of the 90 degree optical hybrid. The method is suited for a digital signal processing implementation in the coherent receiver when a modulation scheme used on a transmitted signal is quadriphase-shift keying (QPSK). In other embodiments, the method can be used to correct for quadrature angle error in modulation schemes such as binary PSK, M-ary PSK where M>4, or Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM). The method can be implemented by an application-specific integrated circuit(ASIC).
Owner:CIENA
Method for amplitude insensitive packet detection
ActiveUS20050058227A1High outputEasy to detectAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPhase correlationComputer science
The invention relates generally to the field of wireless communications and more particularly to a method of and device for detecting the presence of a received data packet in a digital receiver. The present invention proposes a simplified method of correlation by removing dependency on the amplitude fluctuations while at the same time maintaining phase relevancy. The key advancement involves mapping the complex quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) preamble to a quantized phase shift keying (PSK) constellation before application to a matched complex correlator. The proposed process essentially “amplitude normalizes” the input signal without the use or complexity associated with a divider. This simplified normalization scheme makes the packet detection algorithm robust against amplitude variations in the input signal, while still allowing for good correlation output. In applications where interference is superimposed on the I / Q input signals, the invention improves the detection capability over automatic gain control (AGC) normalization methods.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
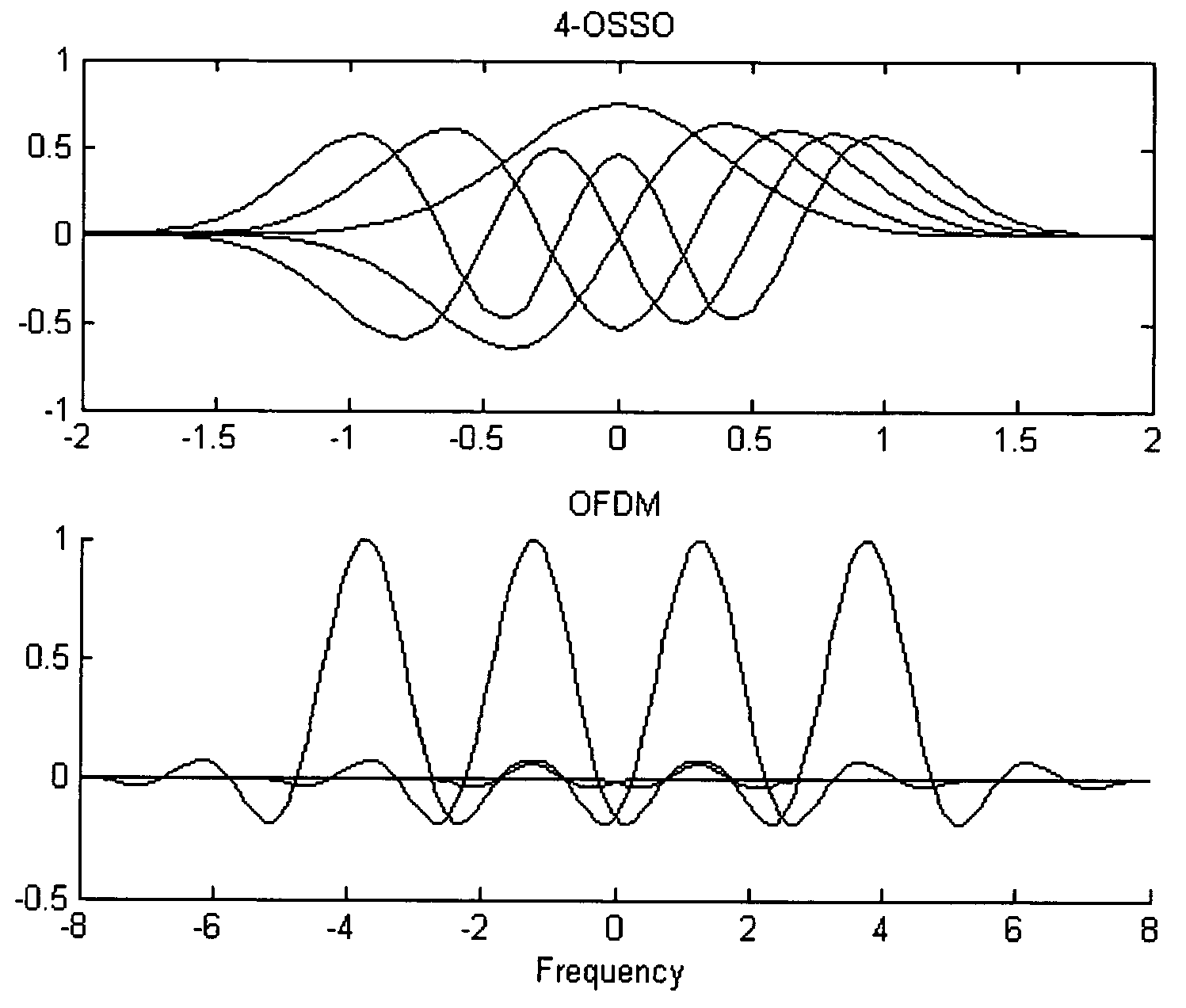
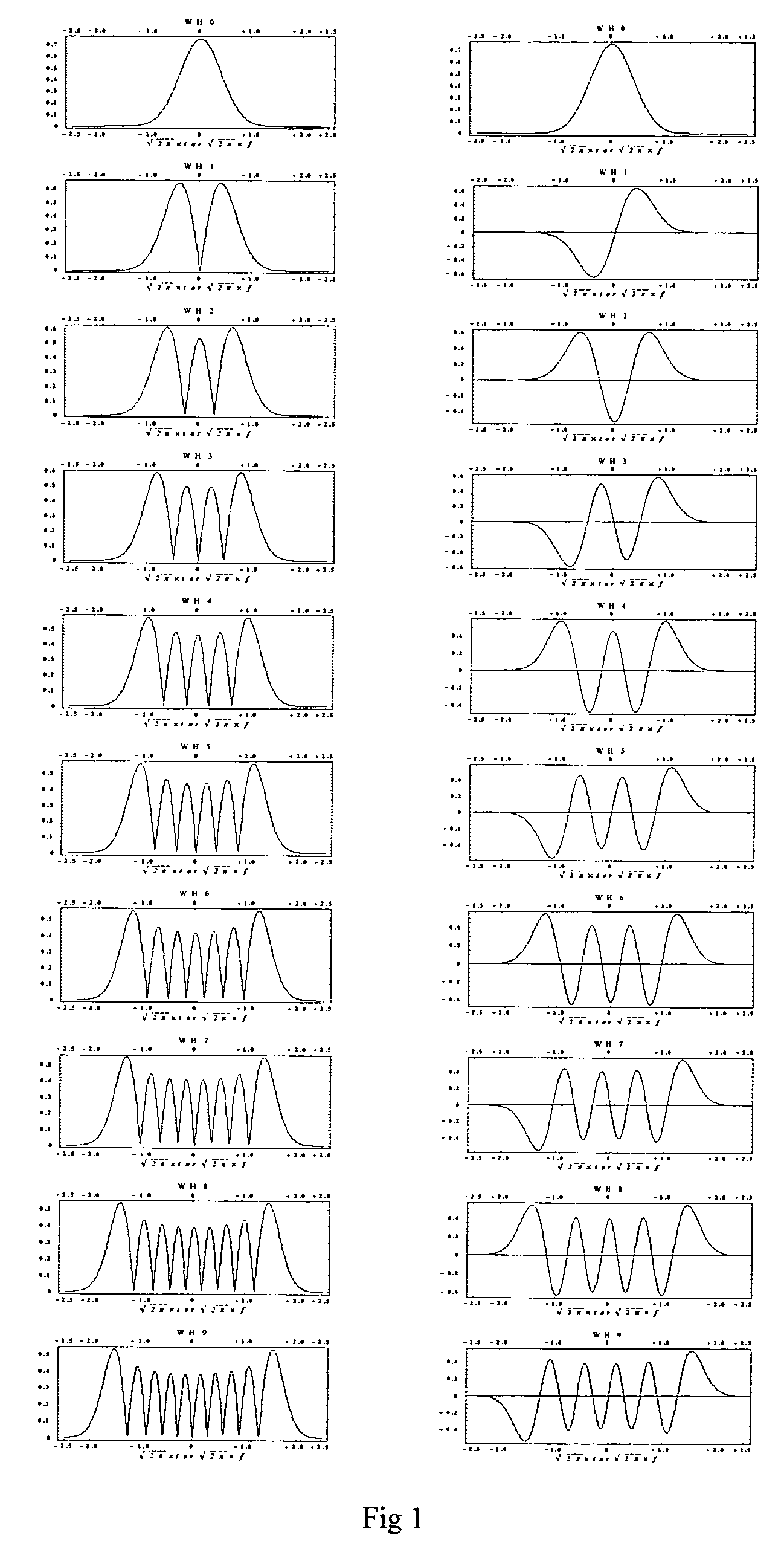
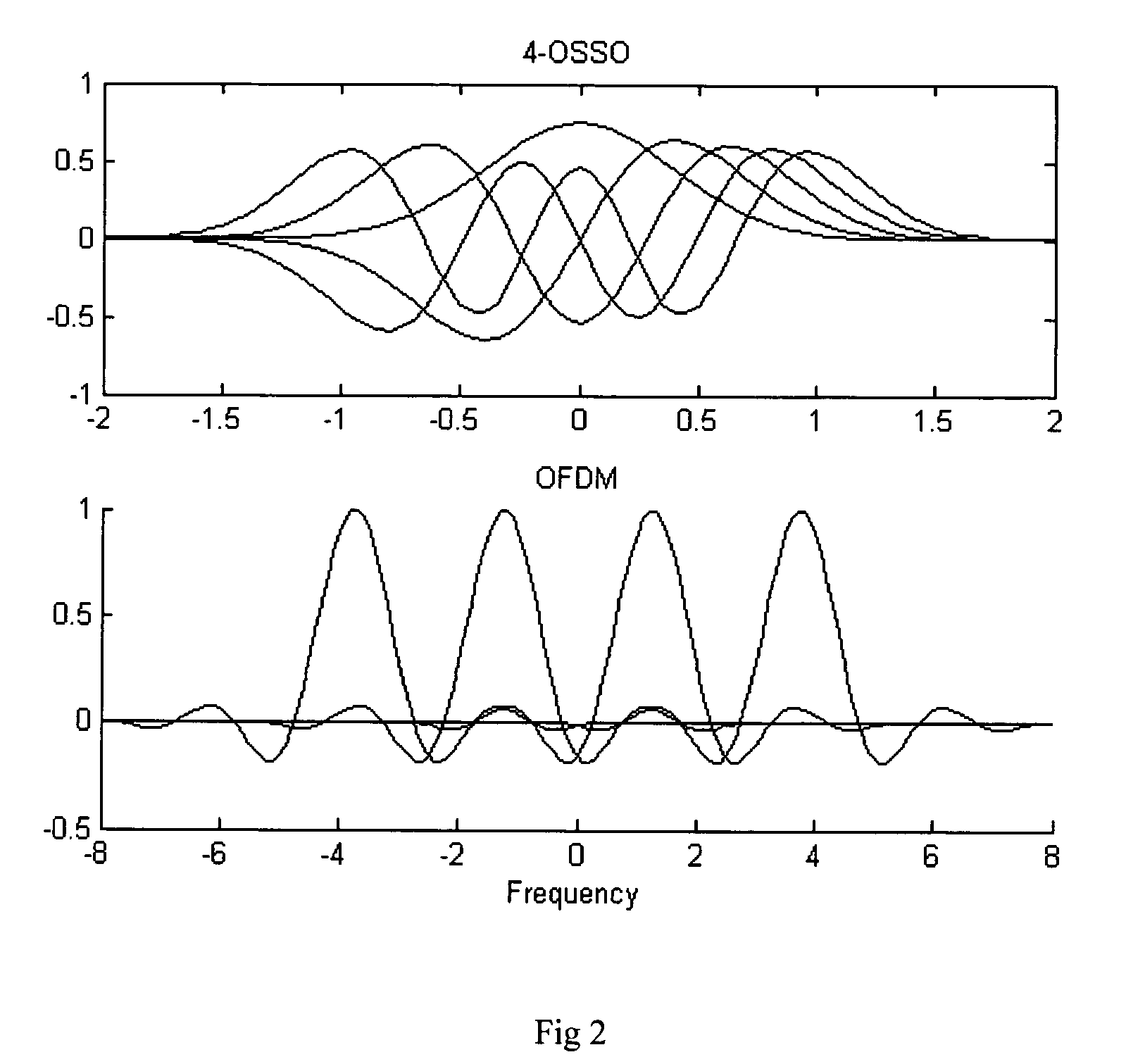
Method and system of orthogonal signal spectrum overlay (OSSO) for communications
InactiveUS7577165B1Improve bandwidth efficiencyIncreasing physical bandwidthTransmission path divisionTime-division multiplexMultiplexingComplete data
A method and system for increasing the effective communications channel bandwidth beyond that of the constrained physical bandwidth of a given channel by orthogonal signal spectrum overlay (OSSO) comprising: decomposing the time-bandwidth product (TBP) of a given symbol in a data stream transmitted through a given bandwidth, expanding the TBP in terms of overlaid orthogonal signals such as Weber-Hermite (WH) functions that constitute the eigensignals of the symbol. The complete data stream is multiplexed to produce a plurality of data channels, each of which is encoded on an orthogonal signal by quadrature amplitude modulation. The overlay of these signals constitutes the OSSO symbol. The OSSO symbols are transmitted in quadrature format (I and Q) and are the result of the addition of orthogonal signals, each of which constitutes a separate overlaid communication channel, occupying the same physical bandwidth.
Owner:BARRETT TERENCE W
Method and apparatus for sending channel quality indication
ActiveCN102624501AImprove throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelMultiple carrier systemsCurrent channelQam modulation
The invention provides a method for sending channel quality indication. The method comprises that: channel quality indication supporting a 256 quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) mode is newly increased; and user equipment receives a pilot signal sent by a base station, carries out channel measurement according to the pilot signal and feedbacks current channel quality indication to the base station. Besides, provided is an apparatus for sending channel quality indication. According to the invention, a 256 QAM modulation mode is supported and the system throughput is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
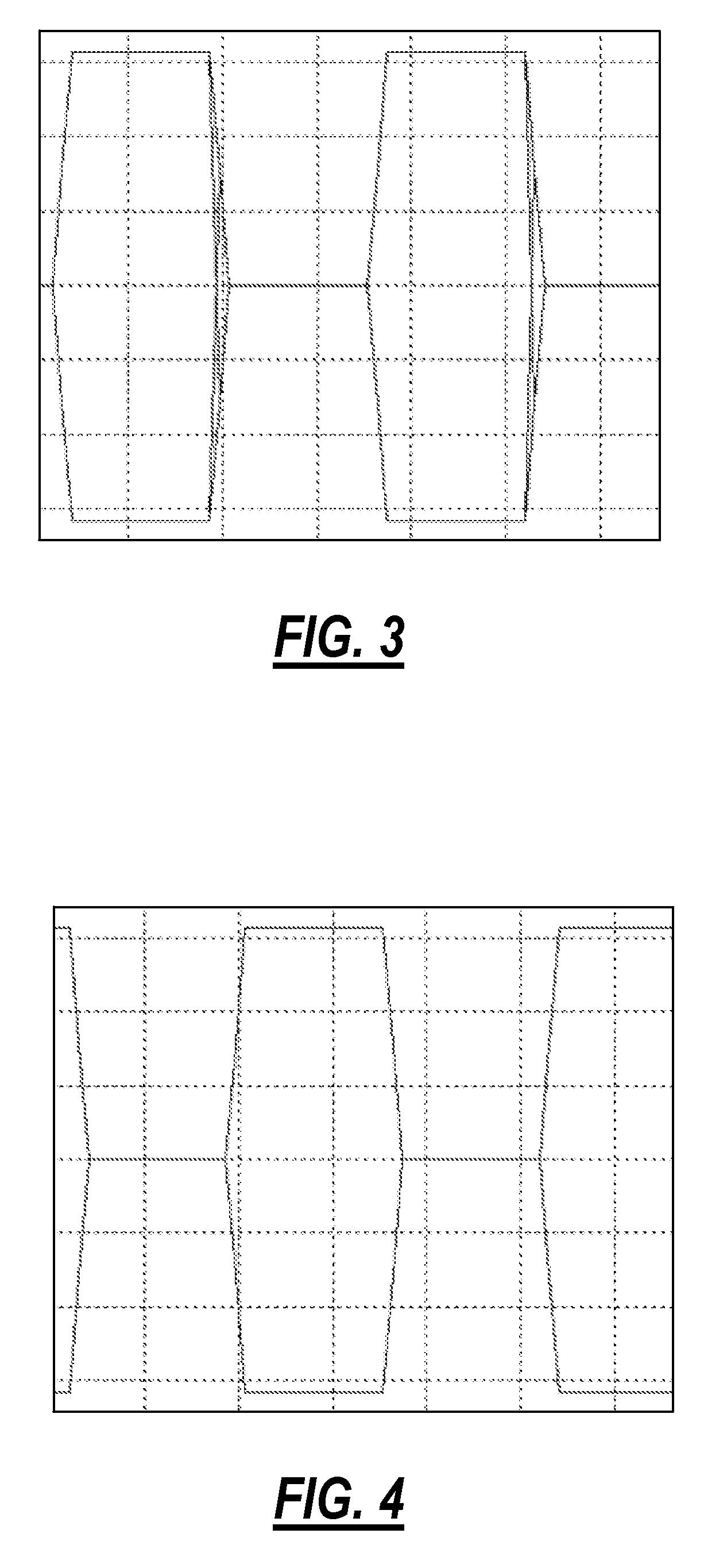
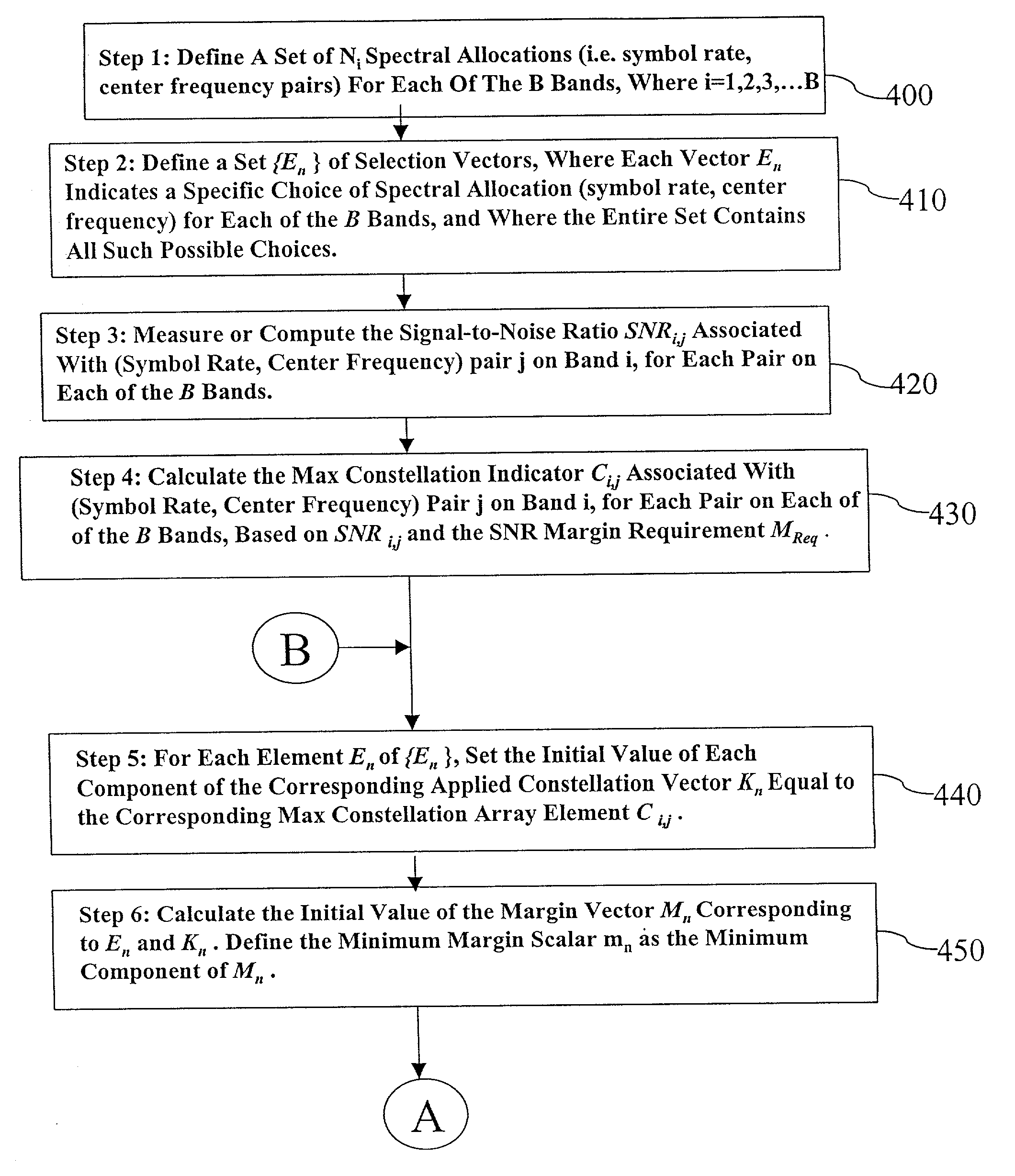
Rate adaptation and parameter optimization for multi-band single carrier transmission
InactiveUS20050276343A1Transmission path divisionCriteria allocationMulti bandTelecommunications link
A method for enhancing the bit rate and / or margin at which quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) communication is performed over multiple bands of a communication link includes the steps of varying a spectral allocation and constellation size with which communication is performed, so as to define a combination of spectral allocation and constellation size at which the bit rate and / or margin are enhanced. The rate adaptation method identifies the spectral allocation and constellation size to use on each of the multiple bands that results in a total bit rate greater than or equal to the target bit rate, subject to specified constraints on SNR margin and / or BER limits. If more than one parameter set has this property, the rate adaptation method may for example select the spectral allocation and constellation size combination that maximizes the minimum SNR margin across the multiple bands.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Reference signal design and association for physical downlink control channels
A method and apparatus for designing a Reference Signal (RS) used by a User Equipment (UE) to obtain respective channel estimates for demodulating respective Physical Downlink Control CHannels (PDCCHs), for determining at a UE a number of resource blocks to include for a reception of a Physical Downlink Shared CHannel (PDSCH), for determining at a UE a RS antenna port in order to enable spatial multiplexing of Enhanced PDCCH (EPDCCH) transmissions to different UEs, and for supporting Quadrature Amplitude Modulation 16 (QAM16) modulation, in addition to Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) modulation, for EPDCCH transmissions without increasing a number of decoding operations at a UE are provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
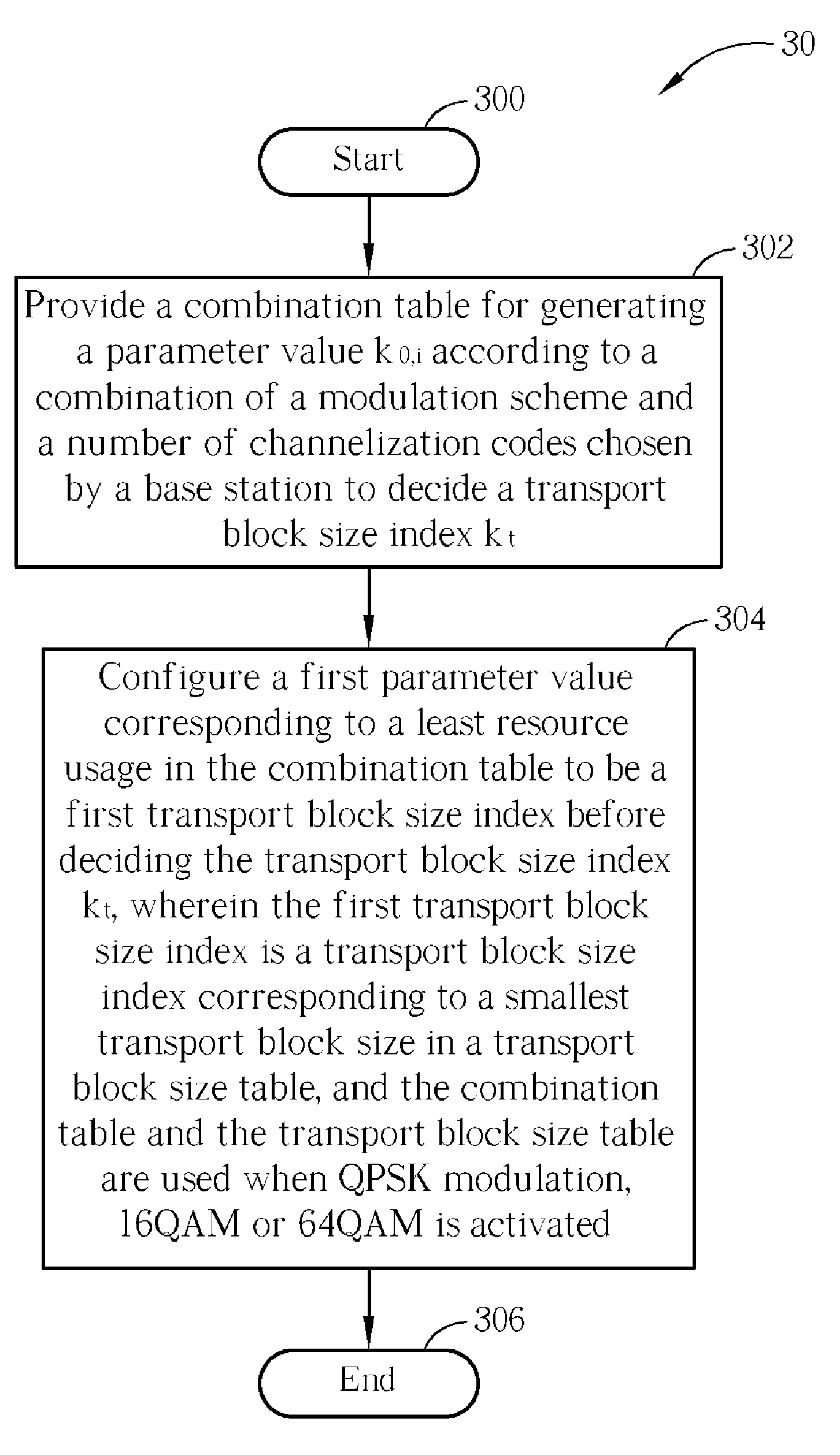
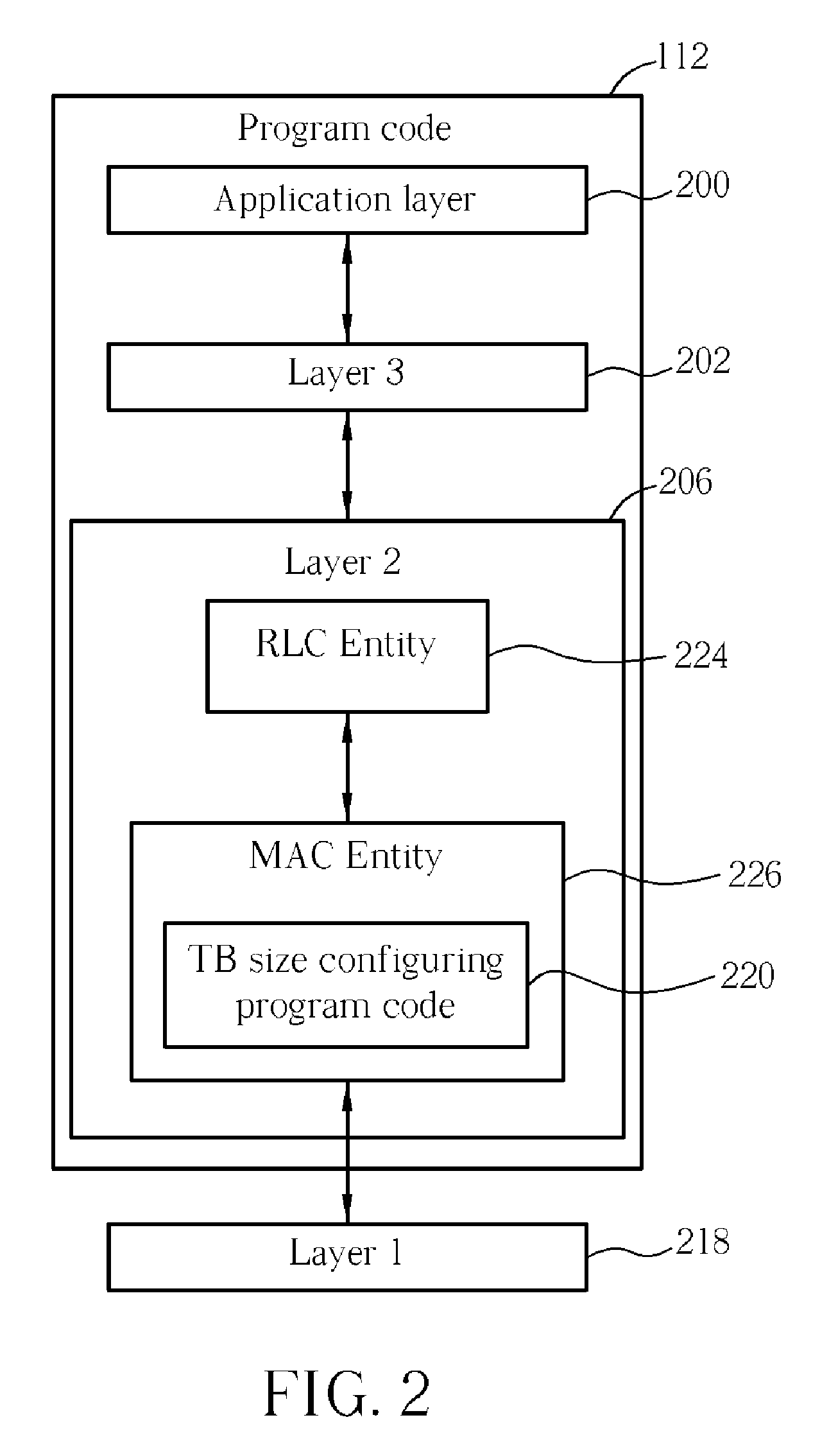
Method and Apparatus for Configuring a Transport Block Size in a Wireless Communications System
ActiveUS20080225784A1Multiplex communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemUser equipment
A method of setting a transport block size for a user equipment in a wireless communications system includes providing a combination table for being looked up to generate a parameter value according to a combination of a modulation scheme and a number of channelization codes indicated by a base station, so as to decide a transport block size index, and configuring a first parameter value corresponding to a least resource usage in the combination table as a first transport block size index before deciding the transport block size index. The first transport block size index is a transport block size index corresponding to a smallest transport block size in a transport block size table, and the combination table and the transport block size table are used when quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) modulation, 16 quadrature amplitude modulation (16 QAM) or 64 quadrature amplitude modulation (64 QAM) is activated.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SONIC
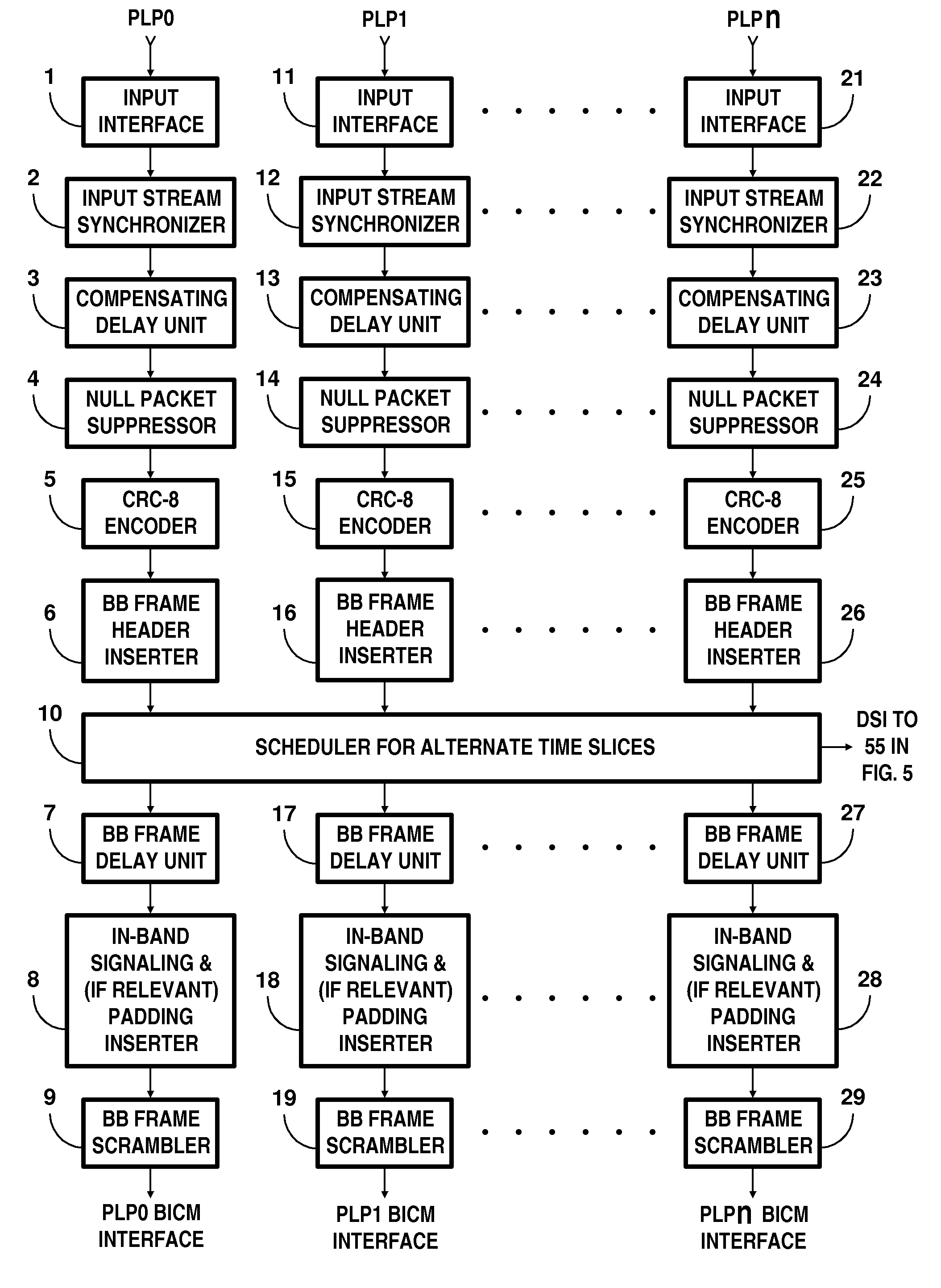
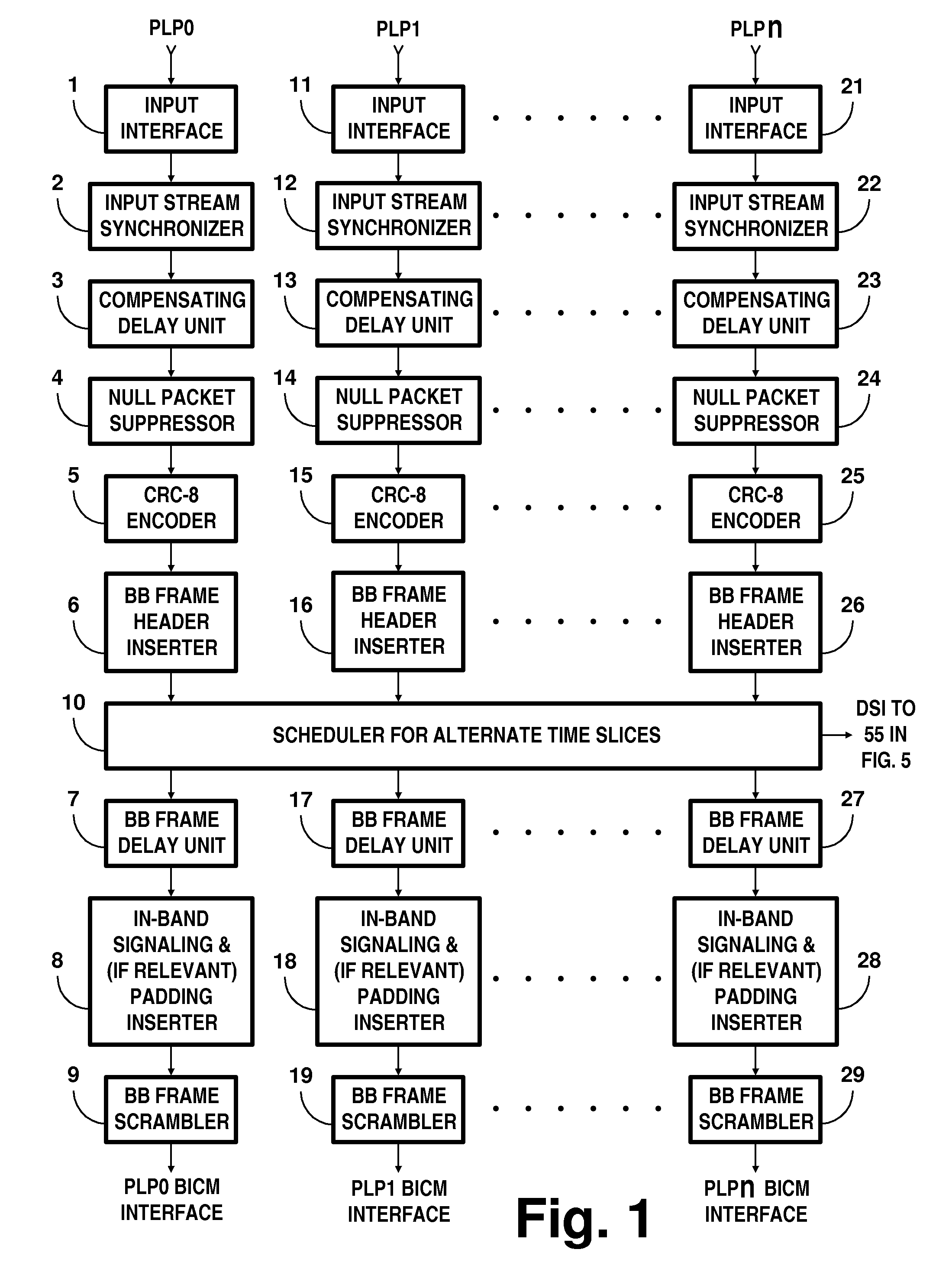
COFDM broadcasting with single-time retransmission of COFDM symbols
InactiveUS20140161209A1Facilitate transmissionPolarisation/directional diversityEqualisersLow-density parity-check codeRadio frequency
Transmitter apparatus to broadcast coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexed (COFDM) radio-frequency carriers conveying digital television (DTV) signals encoded using Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (BCH) coding concatenated with subsequent low-density parity-check coding (LPDC) transmits the same coded DTV signals twice some time apart. The coded DTV signals are mapped to quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) of the COFDM carriers. Preferably, the circular Fourier transforms of COFDM symbols in the earlier transmissions are rotated one half revolution respective to the circular Fourier transforms of corresponding COFDM symbols in the later transmissions. Receiver apparatus combines the earlier and later transmissions of twice-transmitted COFDM signals as part of iterative procedures for de-mapping QAM and decoding the concatenated BCH-LDPC coding of the DTV signals.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
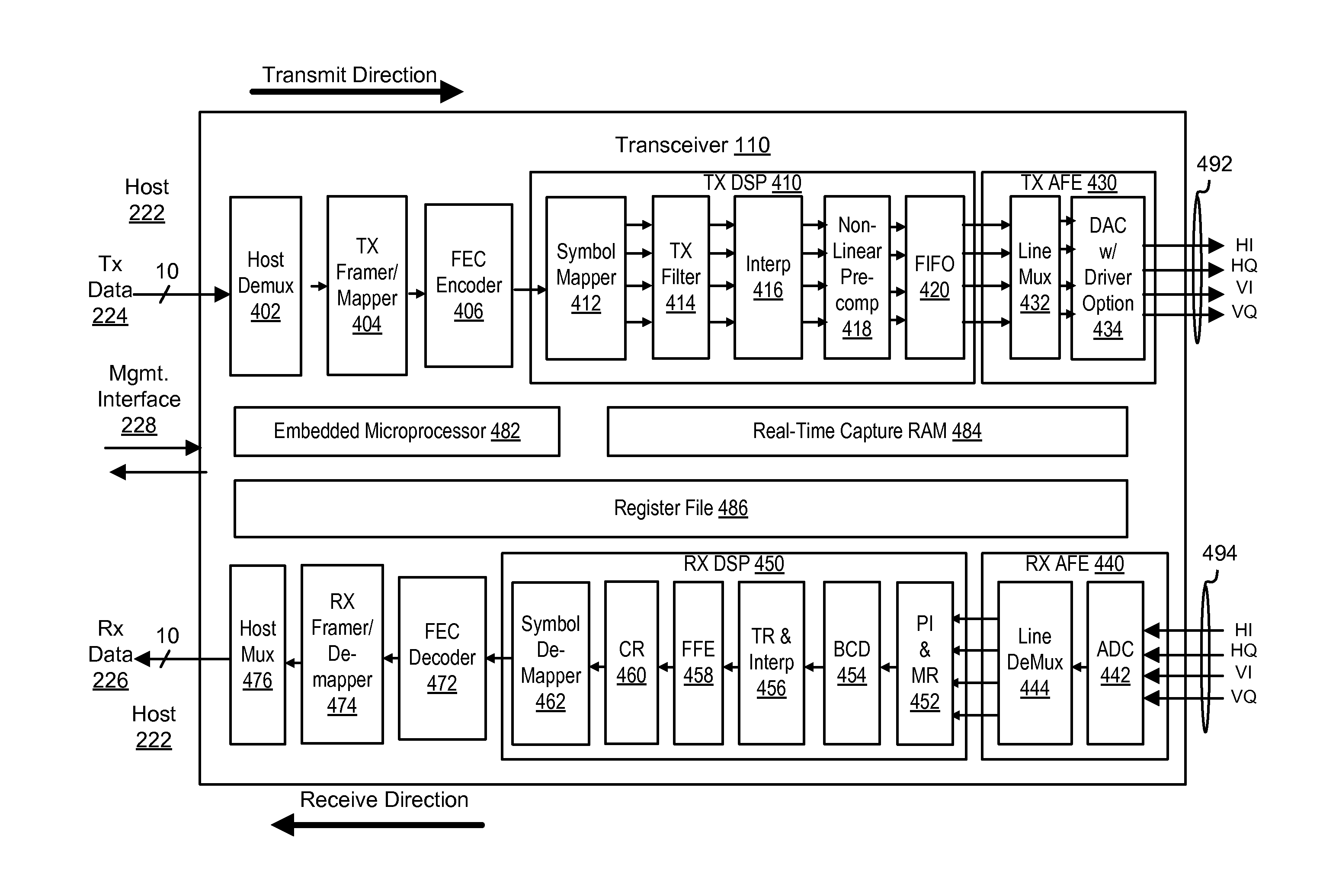
Coherent optical transceiver with programmable application modes
ActiveUS9071364B1Distortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersIndium phosphideQuadrature modulation
An optical communication system provides coherent optical transmission for metro applications. Relative to conventional solutions, the optical communication system can be implemented with reduced cost and can operate with reduced power consumption, while maintaining high data rate performance (e.g., 100 G). Furthermore, a programmable transceiver enables compatibility with a range of different types of optical networks having varying performance and power tradeoffs. In one embodiment, the optical communication system uses 100 Gb / s dual-polarization 16-point quadrature amplitude modulation (DP-16QAM) with non-linear pre-compensation of Indium Phosphide (InP) optics for low power consumption.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
System and method for current-mode amplitude modulation
InactiveUS7333778B2Efficient and linear amplificationEasy to operateSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAntenna impedanceAudio power amplifier
An amplifier circuit includes a power amplifier biased for saturated mode operation, and a controllable current source to provide supply current to the power amplifier. The controllable current source effects desired amplitude modulation of the output signal from the power amplifier by modulating the supply current it provides responsive to an amplitude information signal. In one or more embodiments, the current source includes a circuit that is configured to adjust one or more transmitter operating parameters responsive to detecting changes in the effective DC resistance of the power amplifier. For example, the circuit may generate a compensation signal that reduces the effective DC resistance responsive to detecting that the effective DC resistance has undesirably increased. By way of non-limiting examples, such compensation may be effected by changing a current mirror, an amplifier-to-antenna impedance matching, an amplifier bias or device size, or imposing some form of transmit signal back-off.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
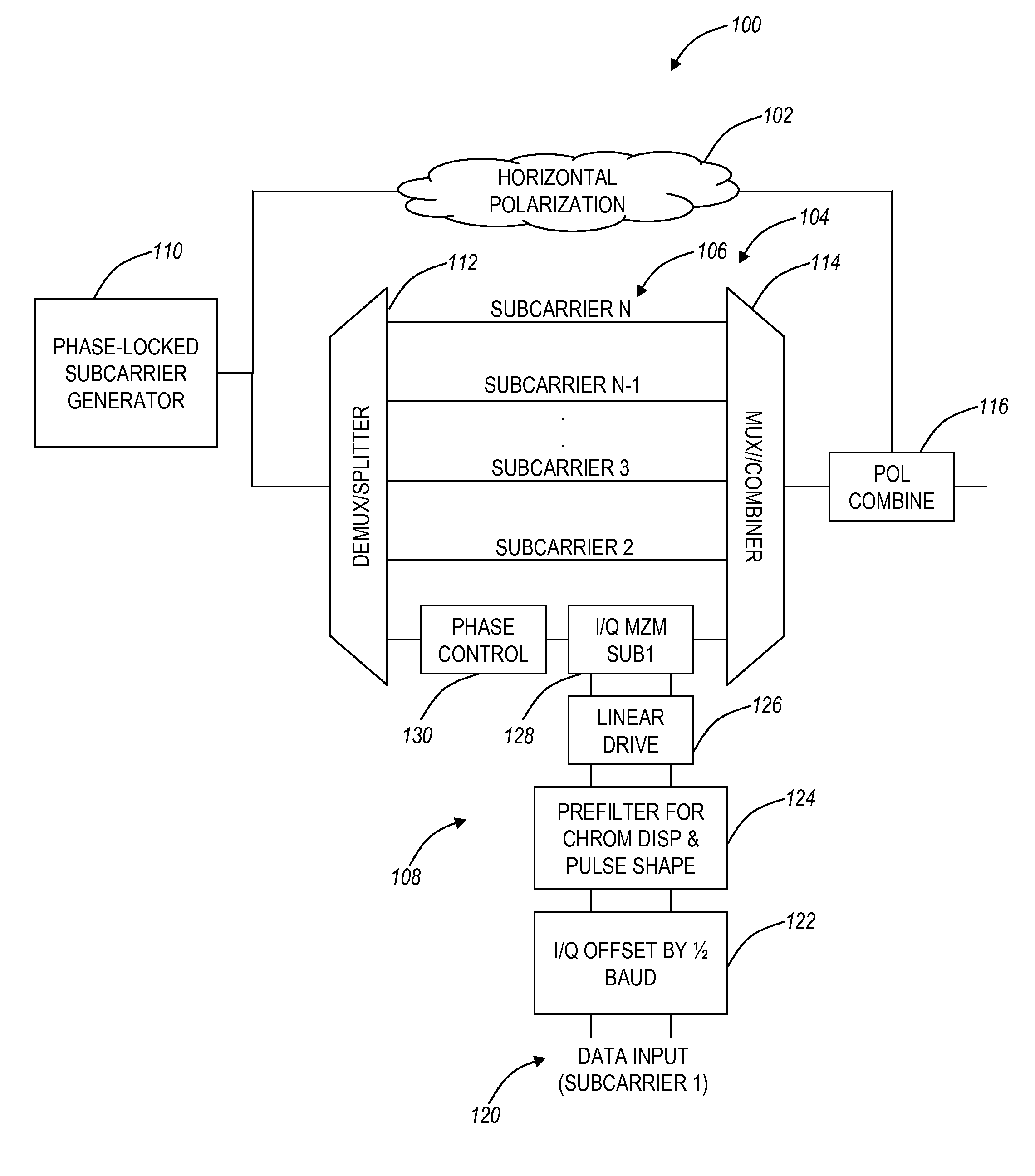
Multi-channel optical transceiver with offset quadrature amplitude modulation
The present disclosure provides a multi-carrier optical transmitter, receiver, transceiver, and associated methods utilizing offset quadrature amplitude modulation thereby achieving significant increases in spectral efficiency, with negligible sensitivity penalties. In an exemplary embodiment, an optical transmitter includes circuitry configured to generate a plurality of optical subcarriers, a plurality of data signals for each of the plurality of subcarriers, and a plurality of modulator circuits for each of the plurality of subcarriers, wherein each of the plurality of modulator circuits includes circuitry configured to offset an in-phase component from a quadrature component of one of the plurality data signals by one-half baud period.
Owner:CIENA
Rate adaptation and parameter optimization for multi-band single carrier transmission
A method for enhancing the bit rate and / or margin at which quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) communication is performed over multiple bands of a communication link includes the steps of varying a spectral allocation and constellation size with which communication is performed, so as to define a combination of spectral allocation and constellation size at which the bit rate and / or margin are enhanced. The rate adaptation method identifies the spectral allocation and constellation size to use on each of the multiple bands that results in a total bit rate greater than or equal to the target bit rate, subject to specified constraints on SNR margin and / or BER limits. If more than one parameter set has this property, the rate adaptation method may for example select the spectral allocation and constellation size combination that maximizes the minimum SNR margin across the multiple bands.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method of and apparatus for reducing papr in filter-bank multi-carrier system
InactiveUS20140192925A1Optimum Peak-to-Average Power RatioReduce ratio of average powerAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsLine-faulsts/interference reductionNonlinear distortionFourier transform on finite groups
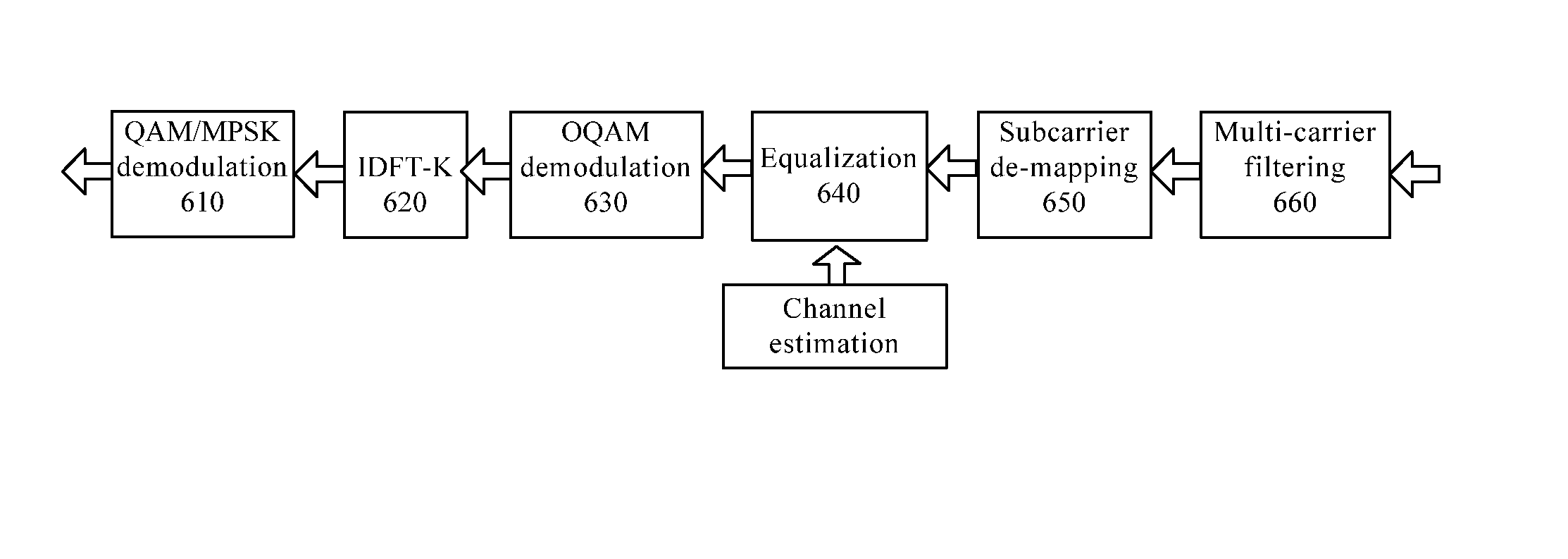
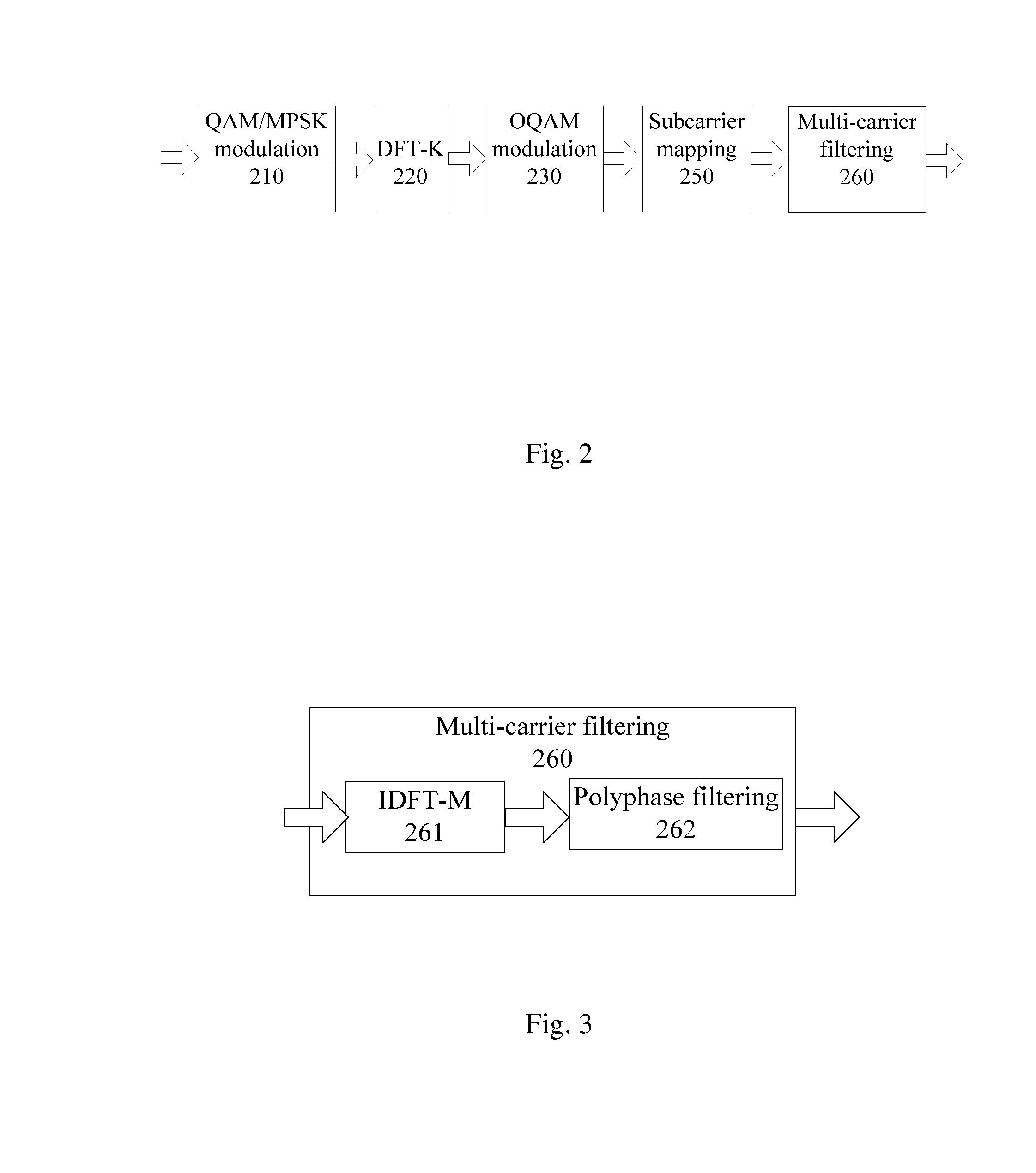
The invention relates to a method of reducing Peak-to-Average. Power Ratio in a transmitting device of a filter-hank multi-carrier system, which includes the steps of: performing constellation modulation (210) on data to be transmitted; performing K-point Discrete Fourier Transform (220) on a vector composed of K constellation symbols resulting from the constellation modulation: and performing Offset-Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (230) on a data vector resulting from the Discrete Fourier Transform, wherein the parameter K represents the number of subcarriers allocated for transmission of the data to be transmitted. With the solution proposed by the invention. PAPR of a signal can be significantly reduced without adding a large number of operations to thereby improve the efficiency of a power amplification circuit, to improve effective transmission, power and to alleviate nonlinear distortion of the signal during a power amplification.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Uniform and ununiform modulated constellation mapping based nonisoprotective mixed automatic retransmission inquiry method
InactiveCN1490972AHigh error protectionImprove performanceUnequal/adaptive error protectionMultiple carrier systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
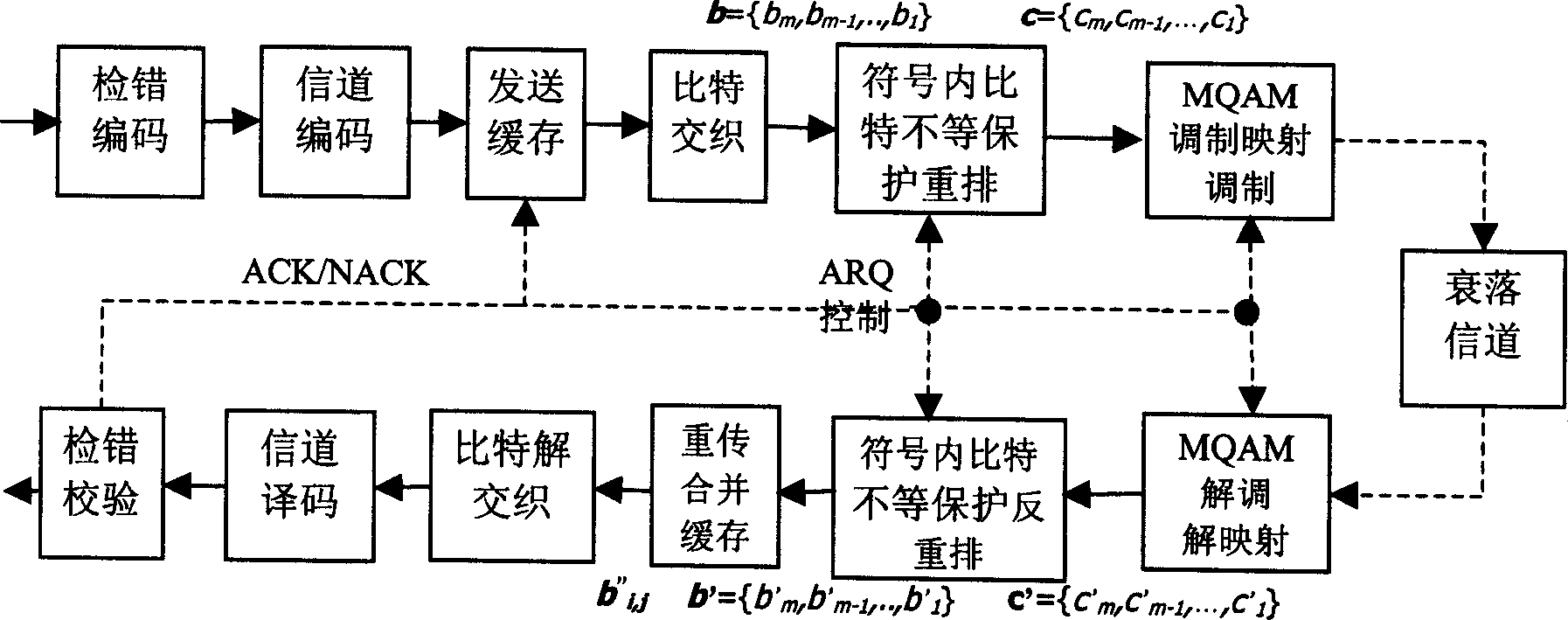
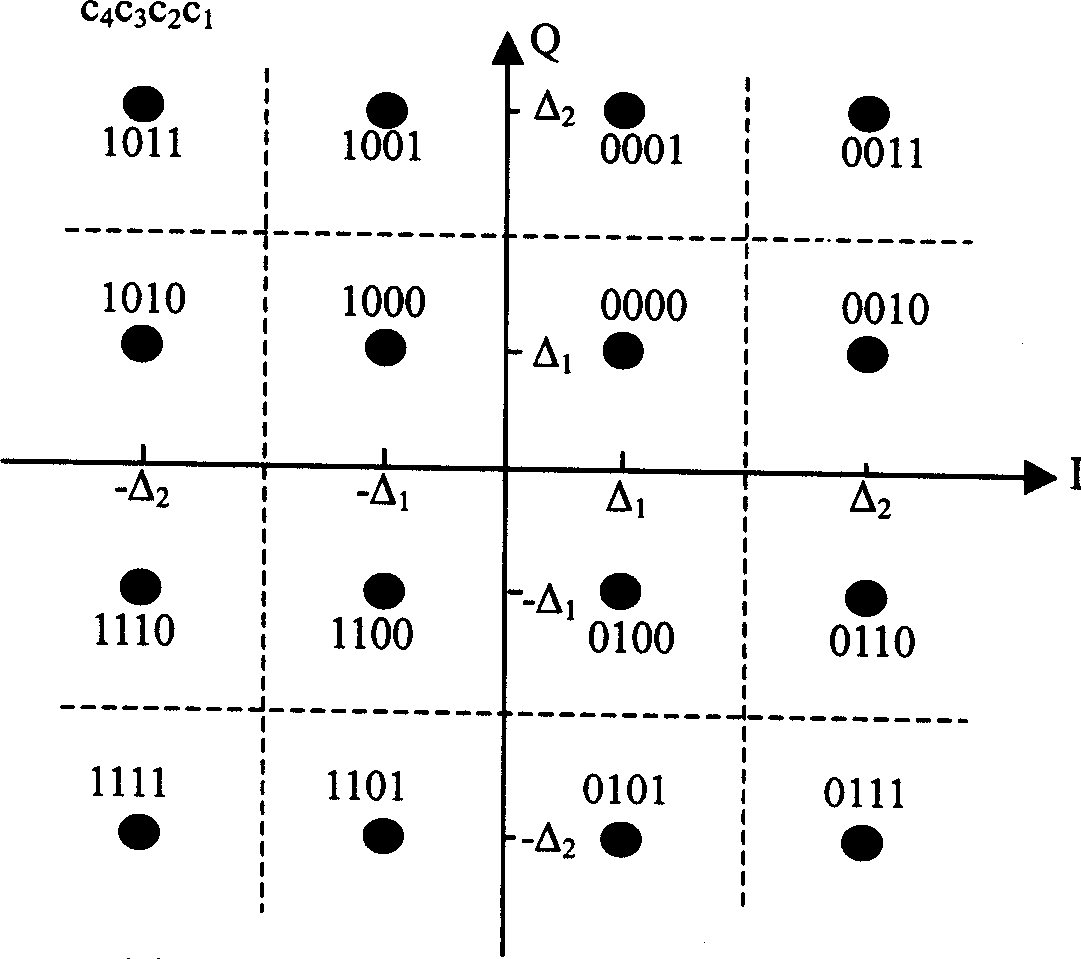
A unequal protection hybrid automatic retransfer request method based on equality and un-equality constellation diagram mapping, it is used in MQAM communication system with which the stage numbers is M and M=2, the modulation mapping of sending end and the resolving mapping of receiving end adopt constellation diagrams that have same distribution, in the first transmission and anterior m / 2-1 time retransmission, adopts equality constellation diagram, at the m / 2 time and the latter retransmission adopts un-equality constellation diagram, provides higher error protection for two most significant bit in the modification symbol; the bits un-equality protection in the modification symbol of sending end reset; uses m / 2 reset and opposite reset rules, at different retransmission time adopts circularly in turn, achieves alternative protecting the bits in modulation symbol; the bits in modulation symbol of receiving end reset oppositely. Reset oppositely the bits according to the reset rules of sending end, recover it into bits sequence soft value before sending end bits resetting. It promotes the signals S / N of combining soft value after demodulating and resolving mapping at receiving end, reduces efficiently grouping retransmission time, makes the output of system maximum.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Constellation mapping method based on absolute phase shift keying (APSK) constellation map, coded modulation method and system
ActiveCN102752261AImprove performanceError preventionMultiple carrier systemsComputer scienceQam constellations
The invention discloses a constellation mapping method based on an absolute phase shift keying (APSK) constellation map. The constellation mapping method is characterized in that the order M of an APSK constellation is equal to 2<m>; the number n1 of points on each ring is equal to a value of powers to 2, namely n1=2<m1>, the number n1=2<m1>-PSK (phase shift keying), the number of rings R=2<m2>, and a set consisting of different ring radiuses is a special 2<m2>-PAM(pulse amplitude modulation ), wherein m1+m2=m; and the phase deflection theta1 of all the rings are the same. The method comprises the following steps of: B1, for a bit vector which is m in length, setting m1 bits to be only related to the phase, and adopting PSK Gray mapping between the m1 bits and the 2<m1>-PSK; and B2, setting the rest m2 bits to be only related to the amplitude, and adopting PAM Gray mapping between the m2 bits and the 2<m2>-PAM. The invention has the advantages that compared with the conventional coded modulation system adopting quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) constellation map mapping, the coded modulation system adopting the APSM constellation map Gray mapping can acquire a considerable error control performance gain regardless of adopting independent demapping or iterative demapping by a receiving end.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Peak-to-Average Power Ratio Reduction with Threshold Limited Selection for Coded OFDM Systems
InactiveUS20070098094A1Reduce ratio of average powerError preventionSecret communicationInverse discrete fourier transformEngineering
Disclosed is a coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) system and method for reducing a peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). The system and method include a modulator configured to modulate (e.g., using quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)) coded bits into symbols. The system and method also include an inverse discrete fourier transform (IDFT) module to perform an IDFT on the symbols to produce an OFDM signal. The system and method measure the PAPR of the OFDM signal and transmit the signal to a receiver if the PAPR of the signal is less than a threshold PAPR.
Owner:NEC CORP
Anti-terrorism communications systems and devices
InactiveUS20050273330A1Simplify the communication processFast transferSubstation equipmentSpeech recognitionEngineeringElectric power
An array of electromagnetic implements which, singly or in combination, enable audio, analog or digital communications over short or long distances using low power and a narrow (audio) bandwidth of 3 KHz or less, preferably 1 KHz or less. These electromagnetic implements maintain or restore emergency communications during terrorist and related disasters when commercial power is unavailable and traditional communications infrastructures and systems have failed. Conveyance of data is accomplished by computer generated voice transmission or by variously engineered tone transmissions, with or without quadrature amplitude modulation, forward error correction, and / or vocabulary encoding, among other features. Receipt of the data may be controlled by automated prioritization and transcription as well as manual or automated display on a computer screen.
Owner:JOHNSON RICHARD G
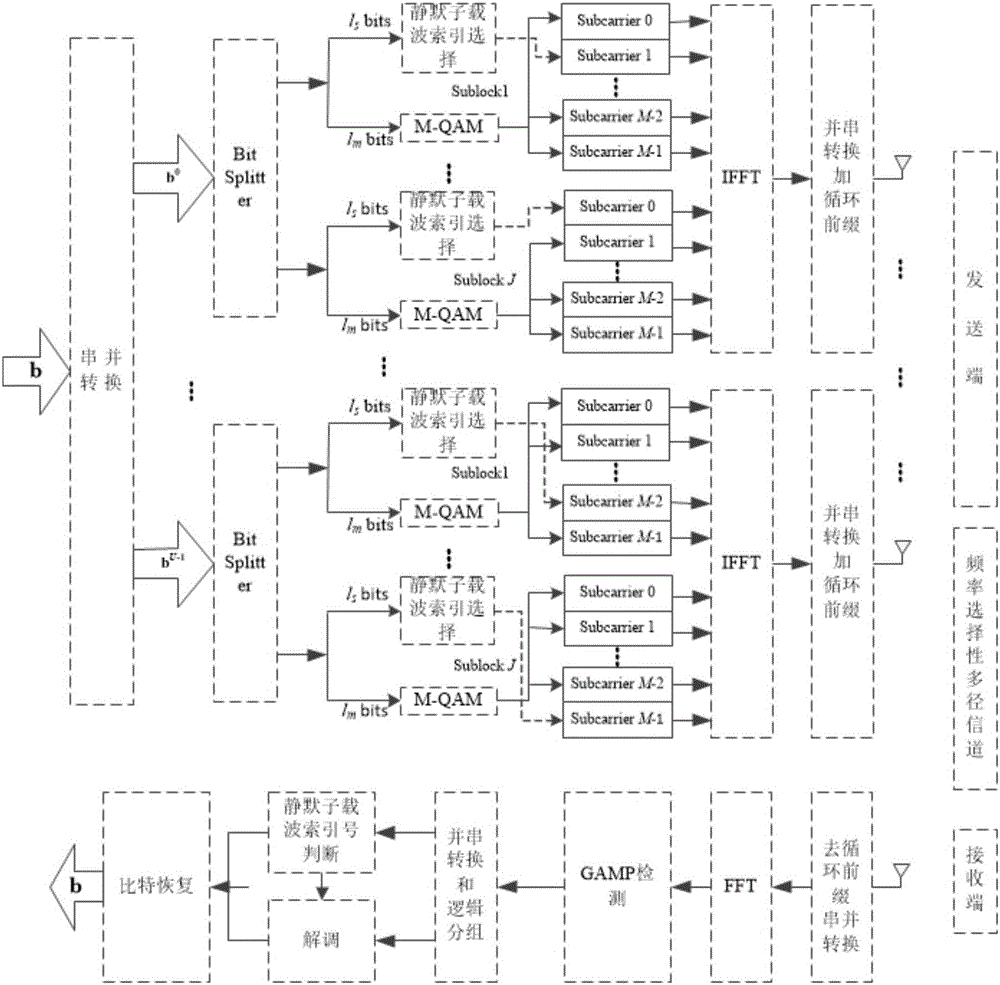
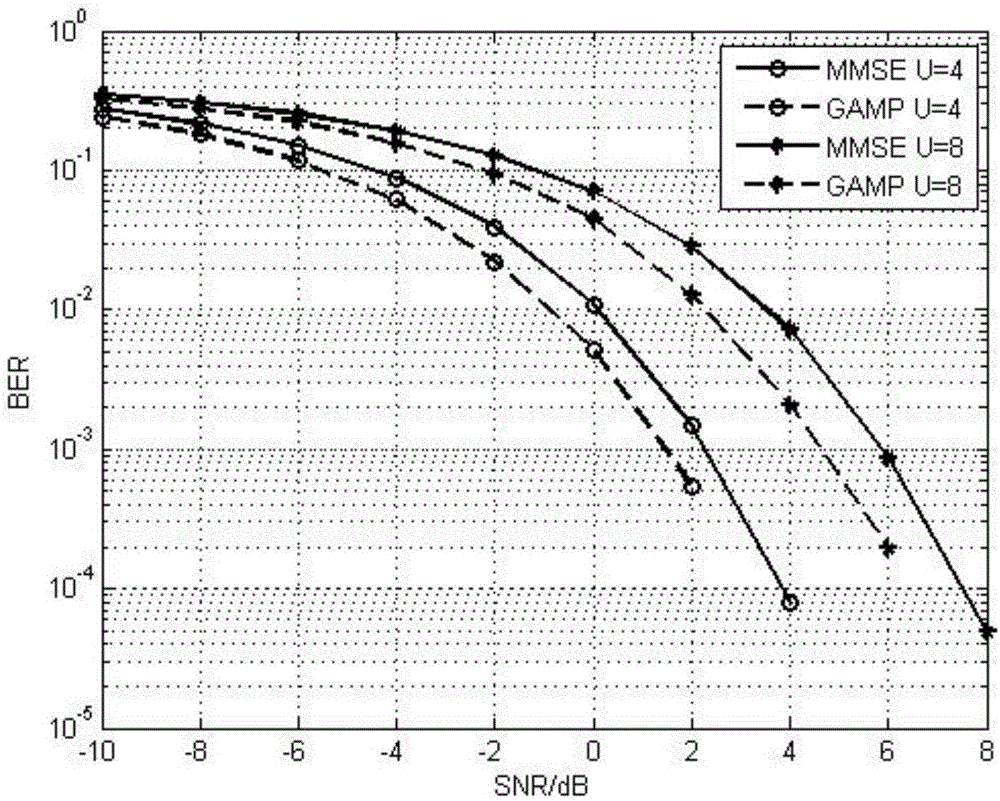
Multi-user sub-carrier index modulation orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (SIM-OFDM) transmission method
InactiveCN106453190AImprove spectral efficiencyImprove energy efficiencySpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsChannel state informationFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses a multi-user sub-carrier index modulation orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (SIM-OFDM) transmission method. At a sending end, logic blocking of sub-carriers is carried out by adoption of an orthogonal amplitude modulation order M at first; then, information bits of all users are also grouped correspondingly; each group is divided into two parts again; one part selects one sub-carrier in each block to enable the sub-carrier to be silent; the other part modulates the residual activated sub-carriers in each sub-block; due to inverse fast Fourier transform, parallel-serial conversion and addition of a cyclic prefix, an SIM-OFDM symbol is formed and sent; at a receiving end, logic grouping, which is the same as that at the sending end, of a detection signal output by a GAMP detector is carried out by adoption of a multi-user iterative detection method based on a generalized approximate message transferring algorithm under non-ideal channel state information; a symbol having the minimum power in each group is judged, so that the positions of silent sub-carriers are identified; index bits are recovered; and residual symbols are demodulated, so that digital modulation bits are obtained. By means of the multi-user sub-carrier index modulation orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (SIM-OFDM) transmission method disclosed by the invention, the energy efficiency and the BER performance are improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
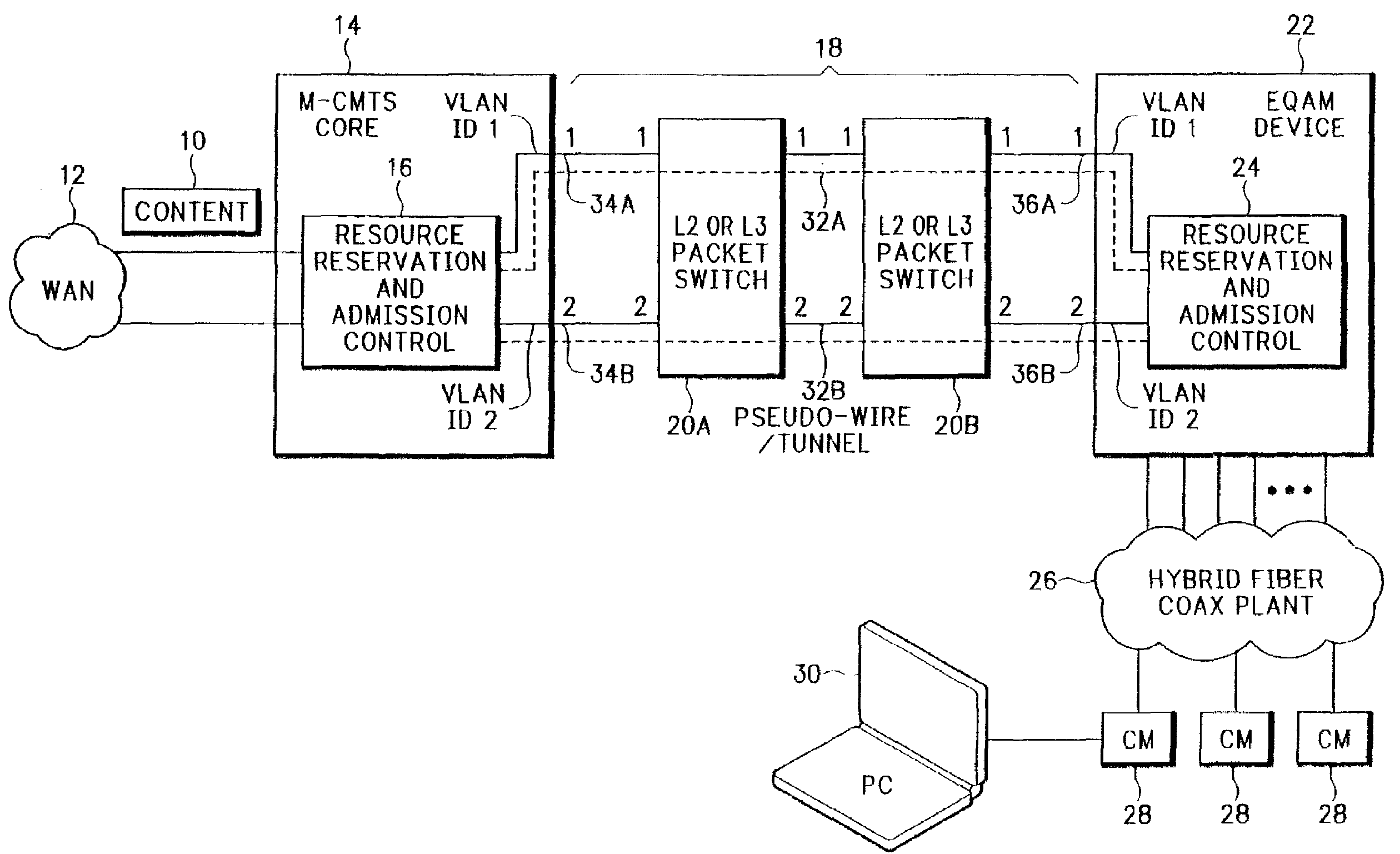
Resource reservation and admission control for IP network
ActiveUS7701951B2Error preventionTransmission systemsModem deviceNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Resource reservation and admission control for IP network
ActiveUS20070206607A1Effective distributionReadily apparentBroadband local area networksModem devicePseudo-wire
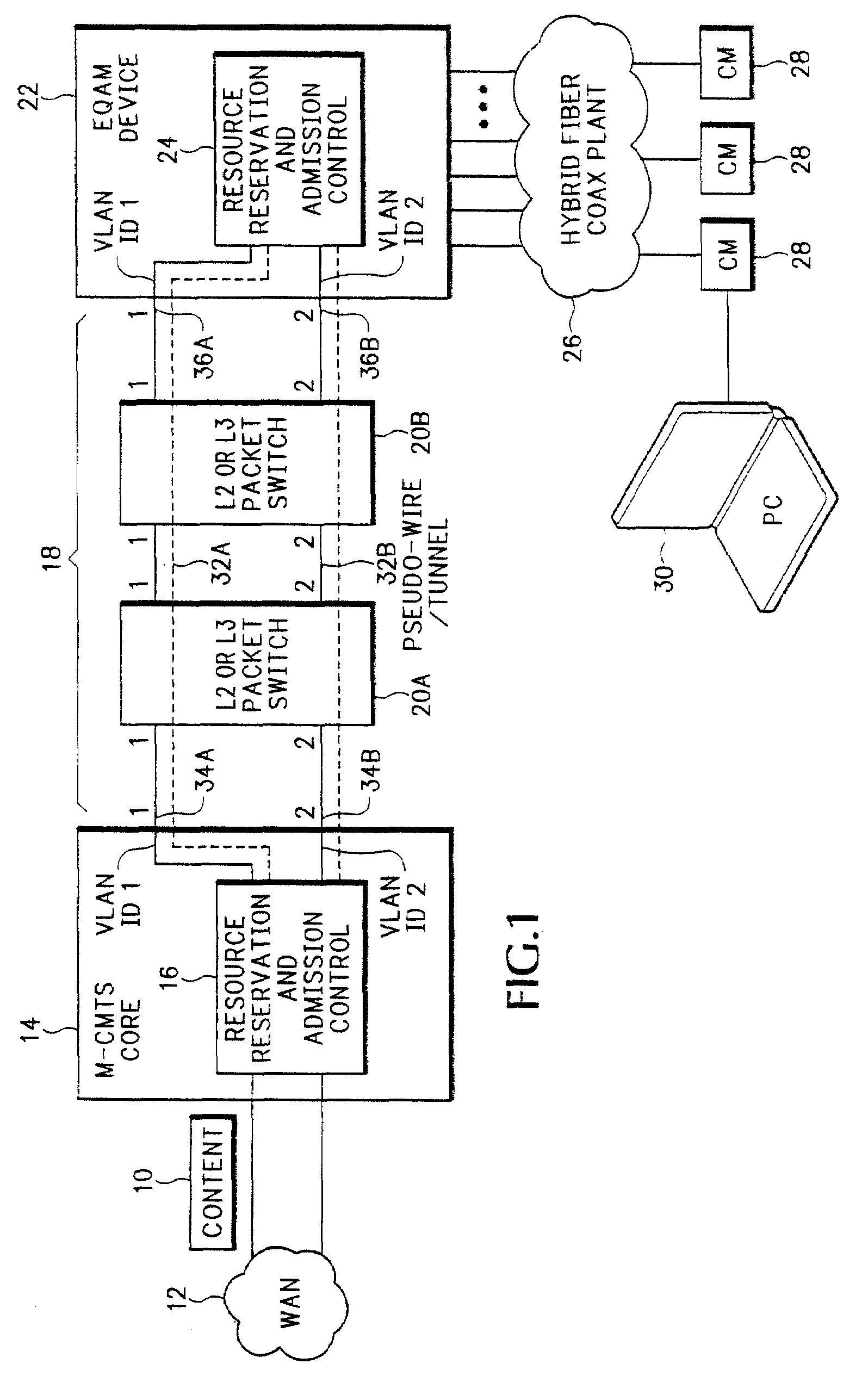
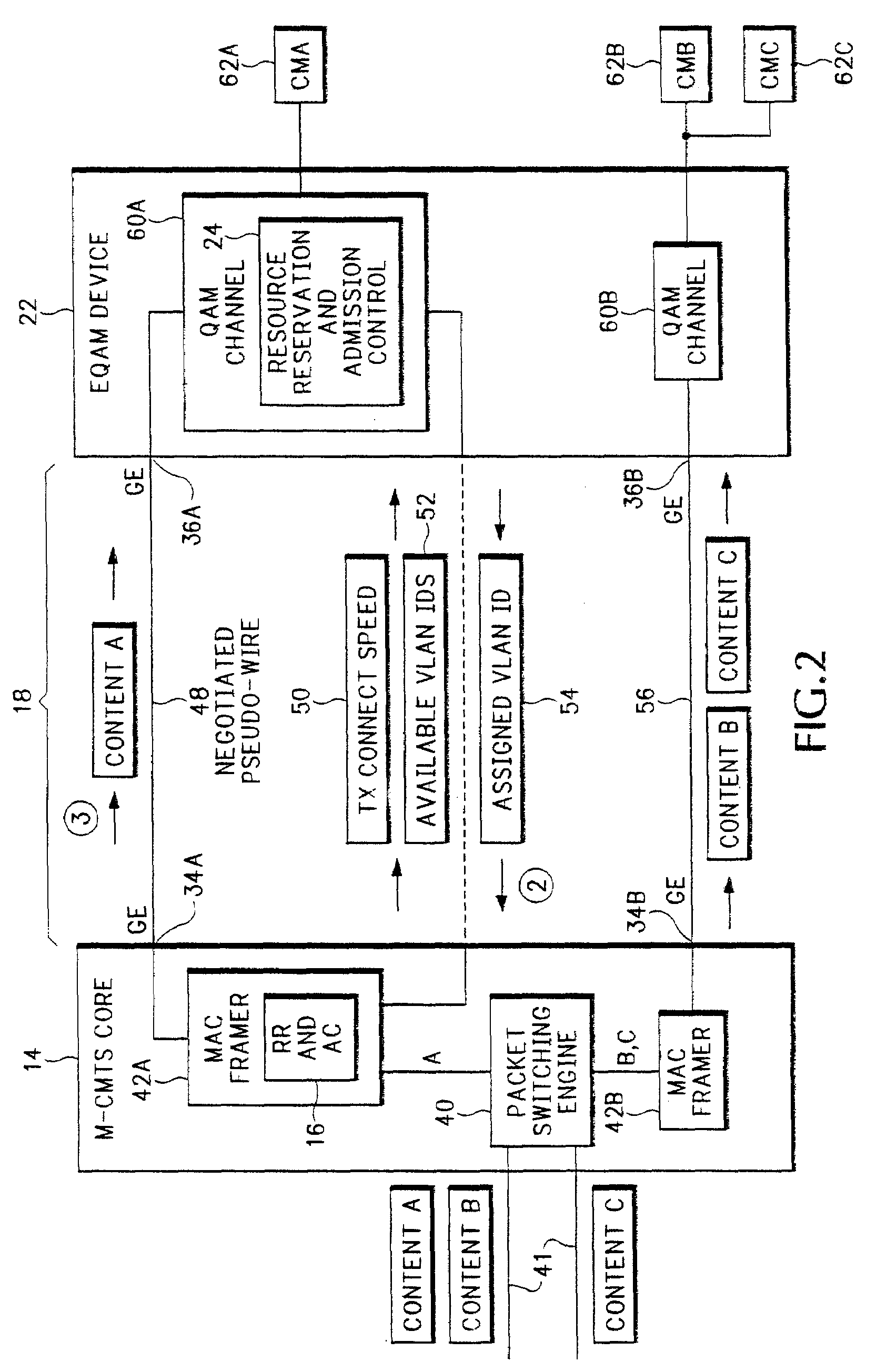
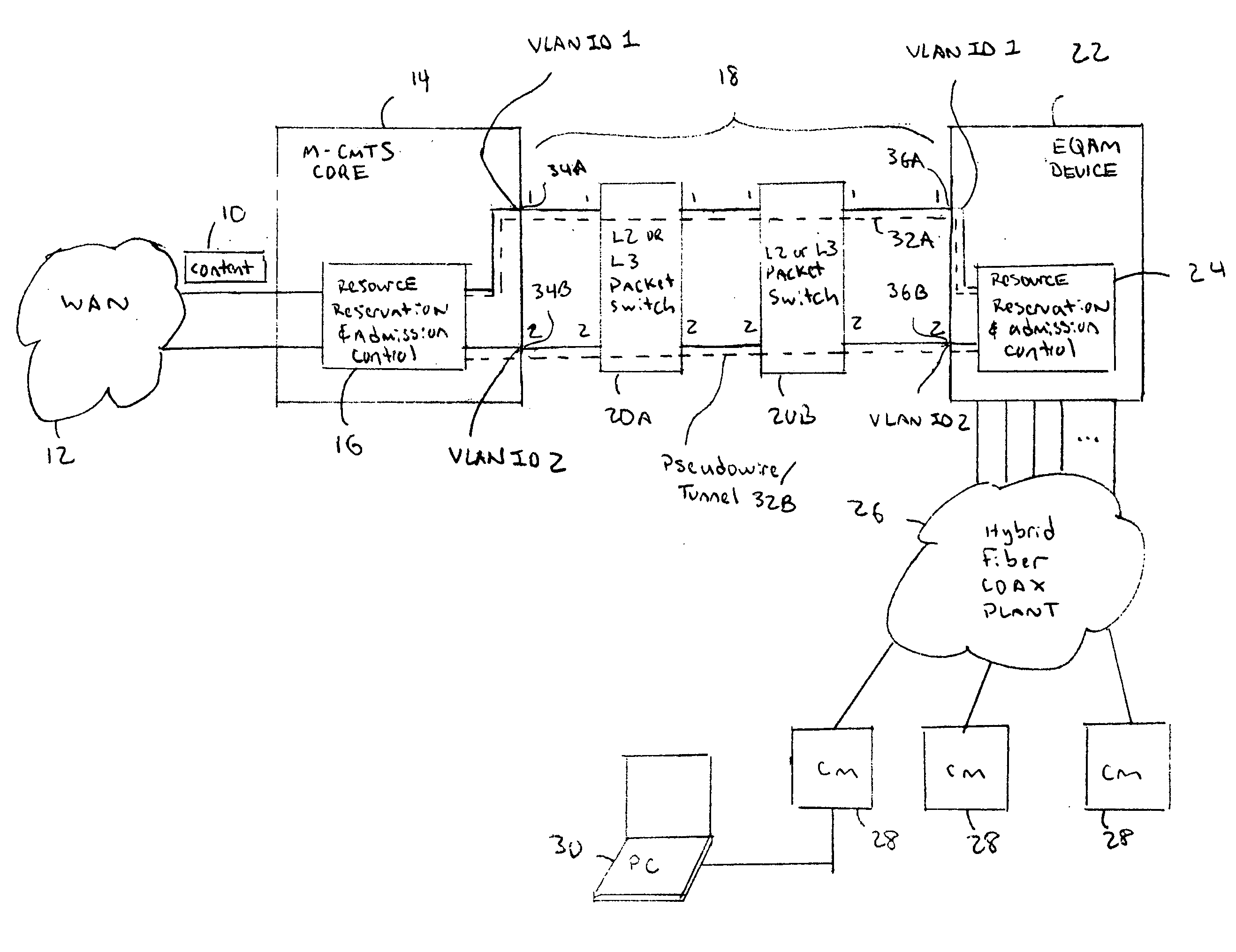
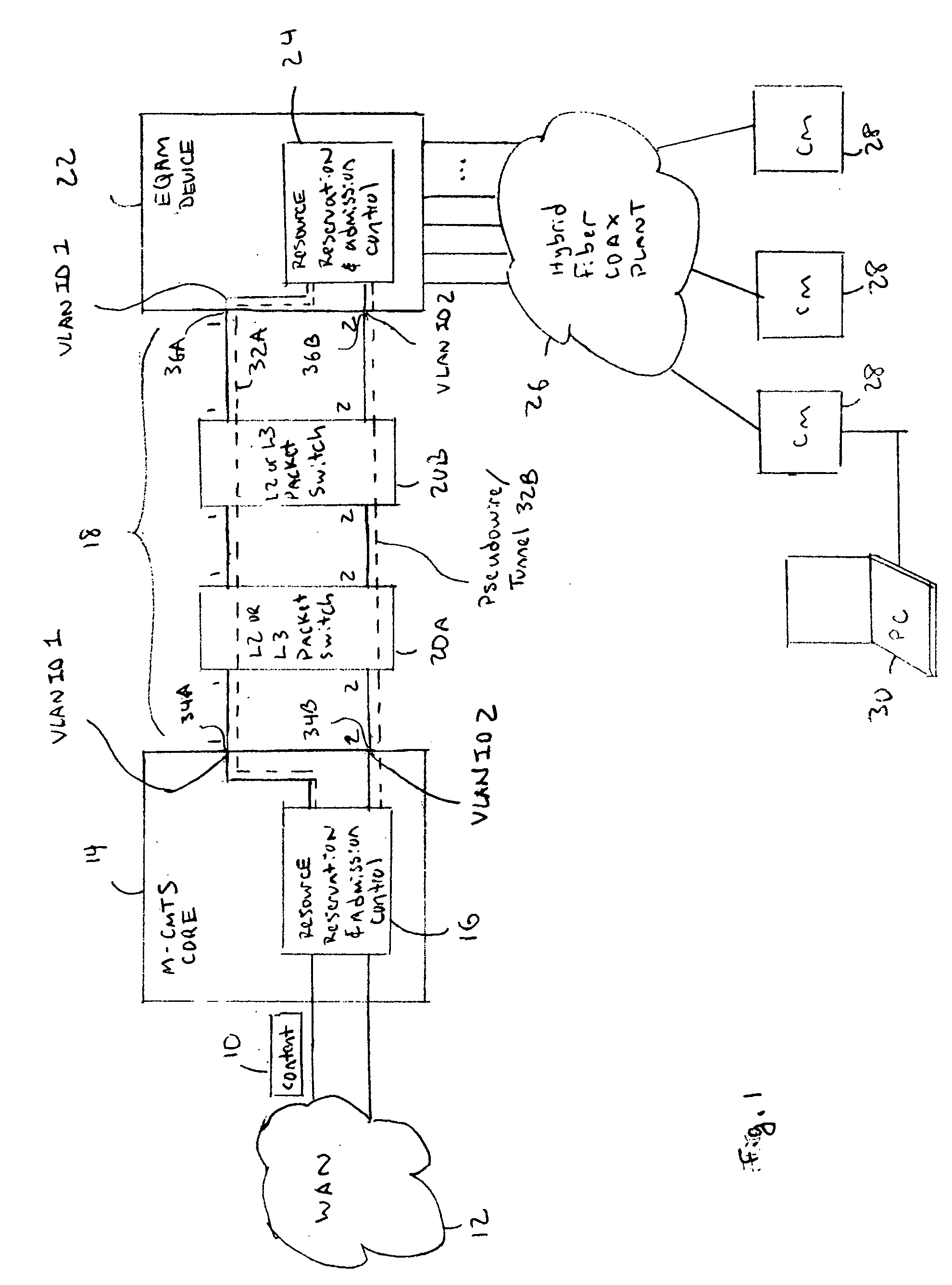
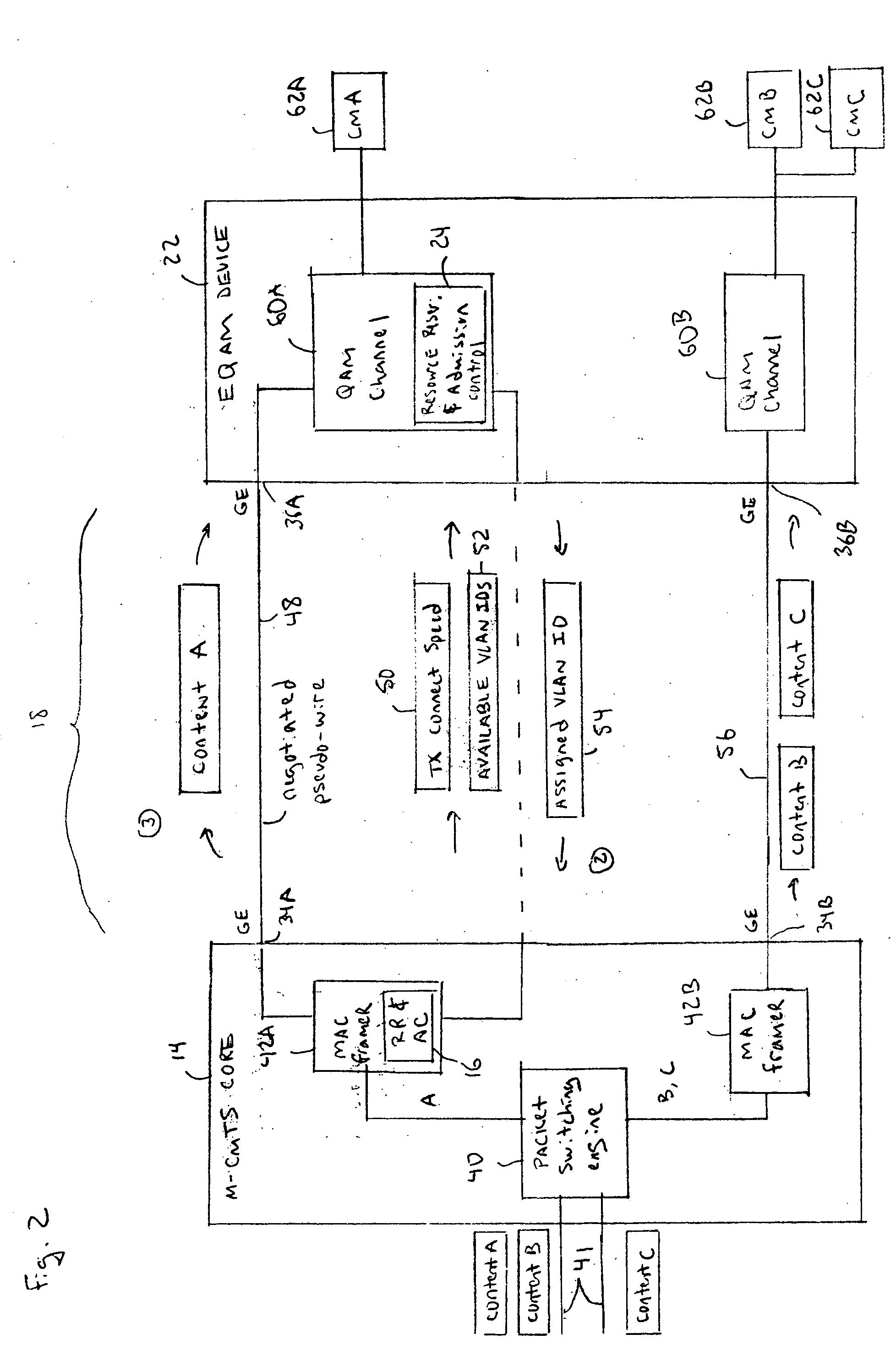
A resource reservation and admission control scheme uses pseudowires to reserve bandwidth over a layer-2 and / or layer-3 network. The pseudowires are associated with ports on different network processing devices. During a resource reservation and admission control session, the physical links used by the pseudowire are selected and reserved to more effectively allocate network bandwidth. The negotiated pseudowire is then used to transport content for a communication session over the network. In one example application, the resource reservation and admission control scheme is used during a Downstream External PHY Interface (DEPI) session for pseudowires established between a Modular Cable Modem Termination System (M-CMTS) Core and an Edge Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Interface (EQAM) device. However, the reservation protocol can be used in any application that needs to reserve bandwidth over an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for turbo encoding in ADSL
ActiveUS7173978B2Multi-frequency code systemsForward error control useAsymmetric digital subscriber lineComputer science
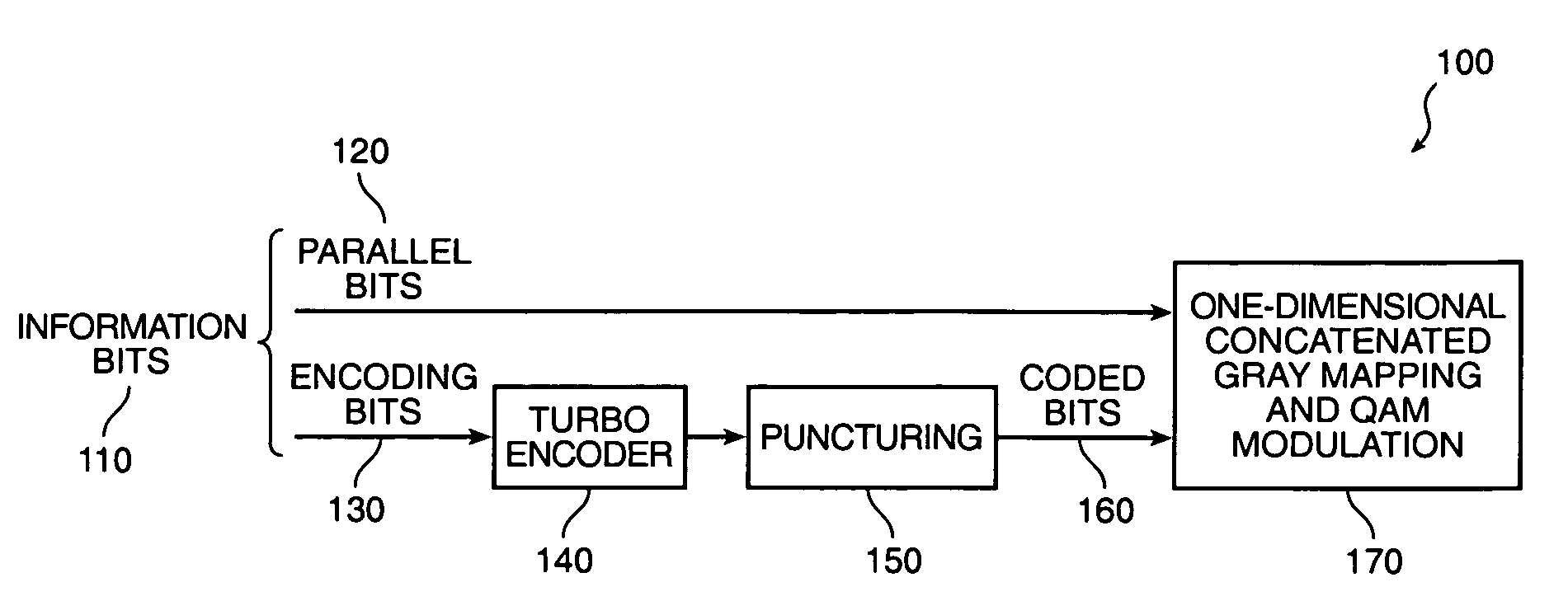
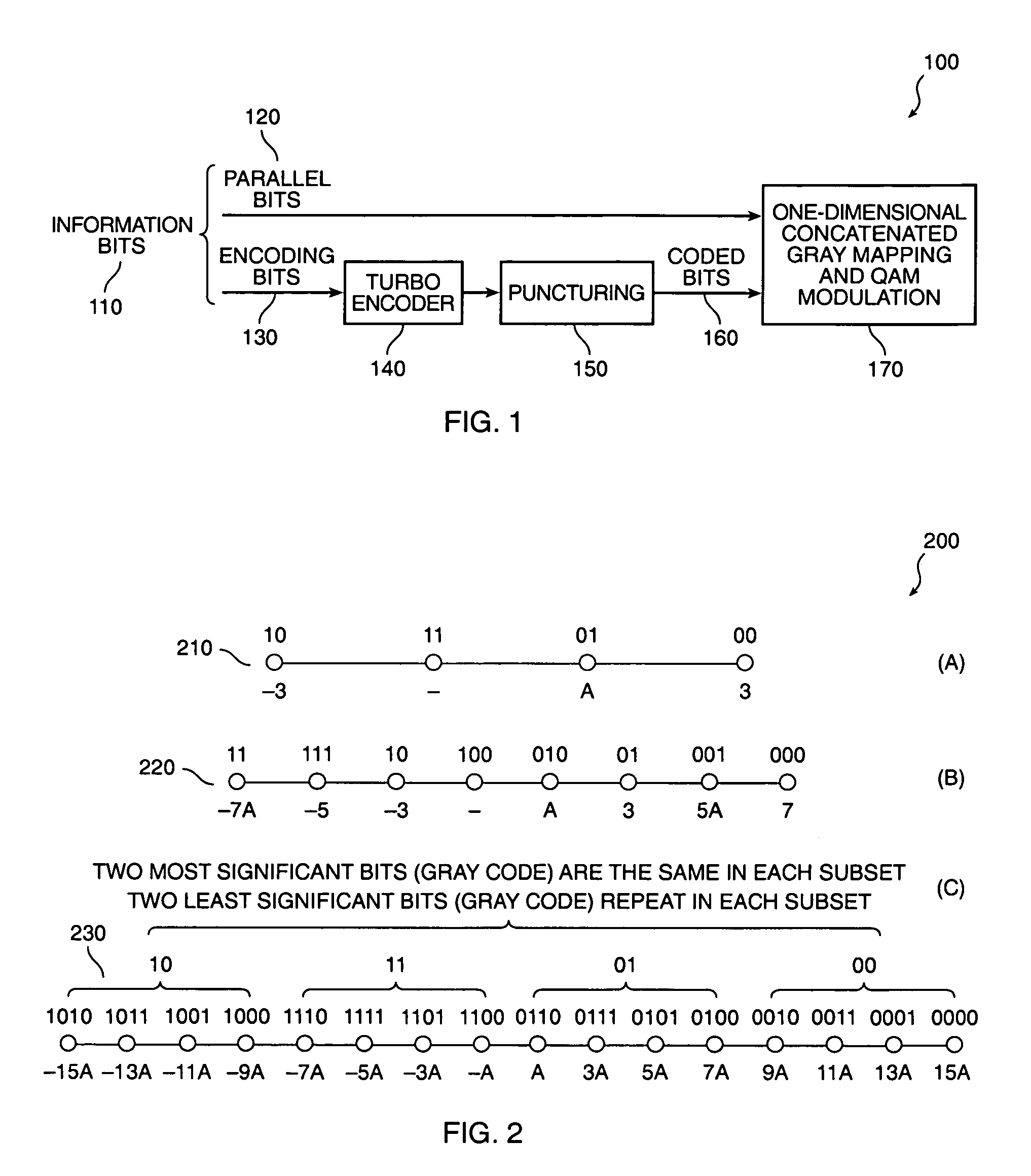
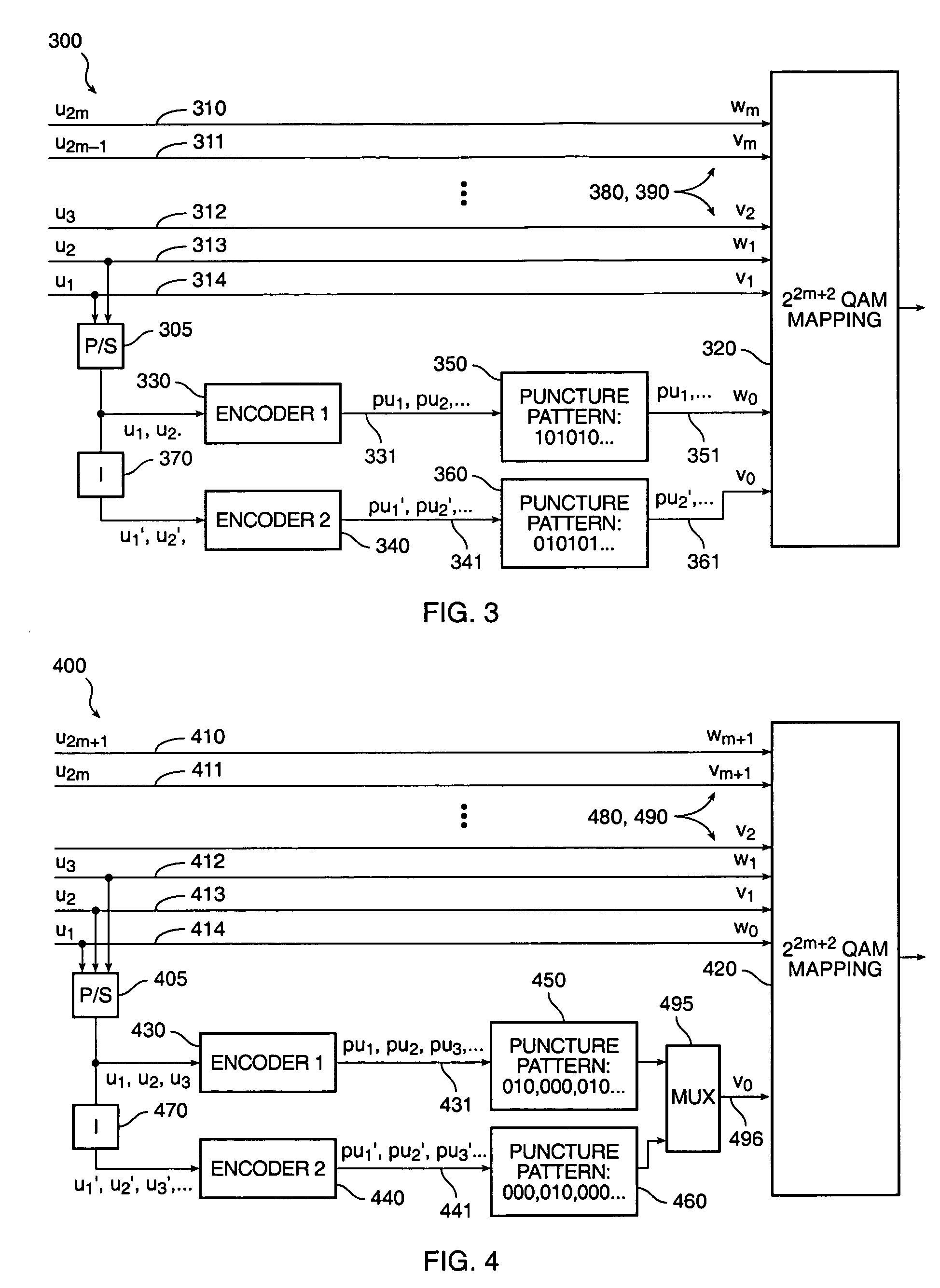
In a coding system for asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) communications, a method of encoding a sequence of information bits is provided comprising the steps of dividing the information bits into encoding bits and parallel bits; encoding the encoding bits to produce encoded bits; mapping the encoded bits and the parallel bits into first and second pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) signals; and generating a quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) signal from these first and second PAM signals. This method overcomes the decoder complexity that would otherwise be required due to the large QAM constellations involved for ADSL communications.
Owner:CIENA
Integral wired-wireless optical fiber asymmetric full-duplex access method and system
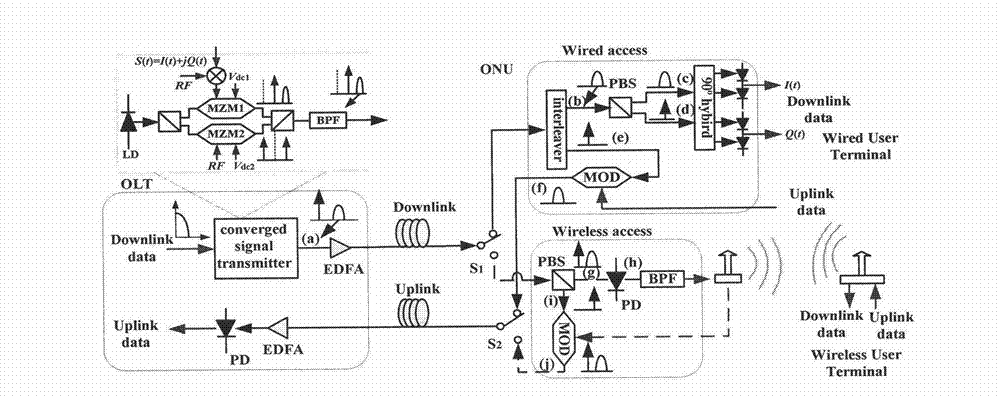
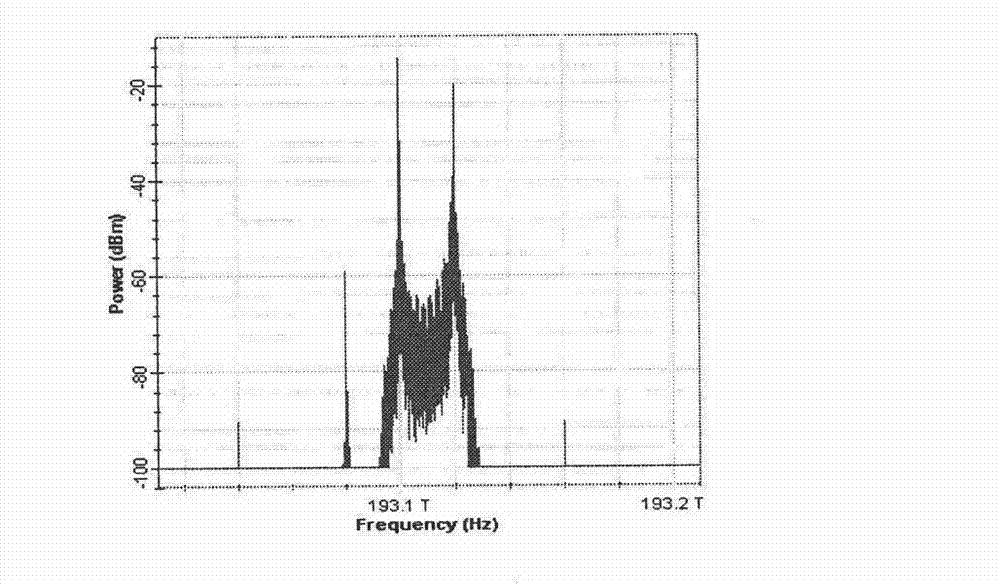
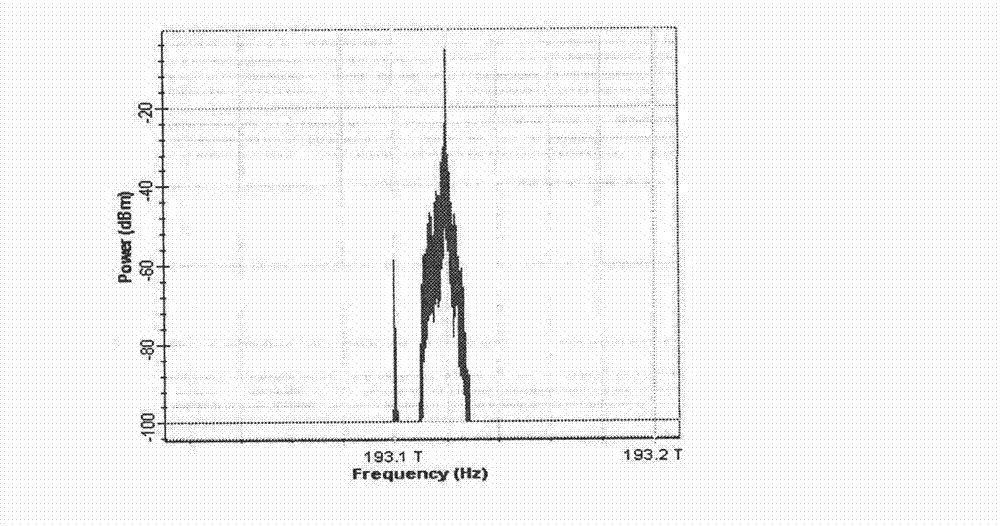
InactiveCN103051385AEnable selective accessImprove transfer data rateRadio-over-fibreLow speedOptical polarization
The invention discloses an integral wired-wireless optical fiber asymmetric full-duplex access method and system. A light with the frequency being f0 is divided into two beams; one beam is modulated by a high-speed QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) millimeter-wave signal single side band with the frequency being fRF to generate a light carrier OLO1 (Optical Line Output 1) and a signal side band BBD with same polarization; and the other beam is inhibited and modulated by a local oscillator carrier with the frequency being fRF to generate an OLO2 with the same frequency as the BBD, after the OLO2 is orthogonal and combined with the OLO1, excess optical frequency components are filtered, and a downward infusion optical signal is generated. The infusion optical signal is transmitted to a base station through optical fiber, and can provide wired or wireless access. When the base station is accessed in a wired manner, a wavelength interpolation device separates the OLO2, the BBD from the OLO1, the OLO2 is subjected to coherent demodulation so as to obtain a downlink baseband signal, and the OLO1 carries an uplink low-speed signal and is back to a central station through the optical fiber; and when the base station is wirelessly accessed, a polarization beam splitter separates the OLO1, the BBD and the OLO2, the OLO1 is an optical millimeter-wave signal and is converted to electrical millimeter-wave through a photoelectric detector, and the OLO2 carries an uplink low-speed millimeter-wave signal and is back to the central station through the optical fiber, so that wired or wireless asymmetric full-duplex access is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com