Patents
Literature
208results about How to "Improve bandwidth efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
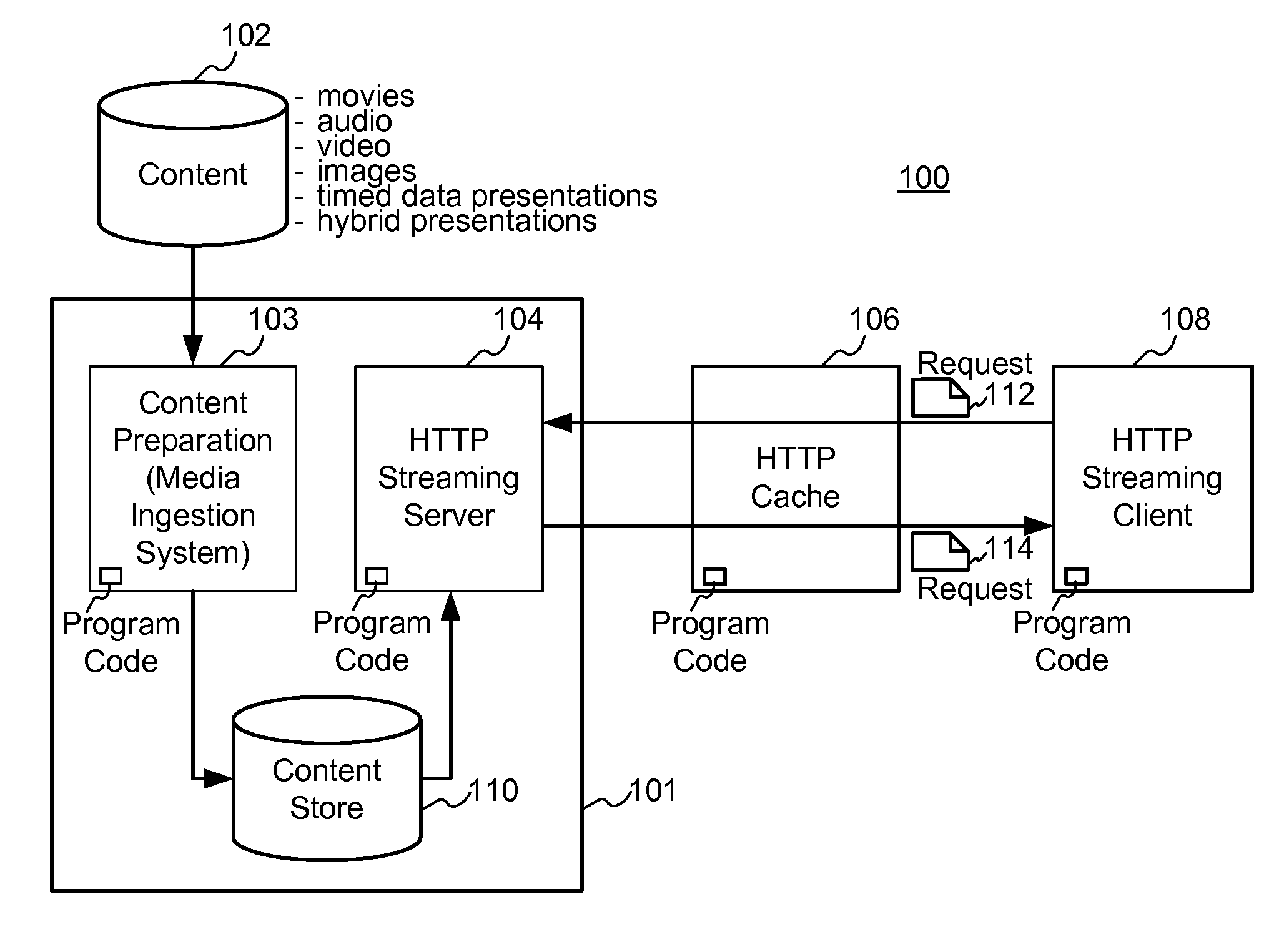
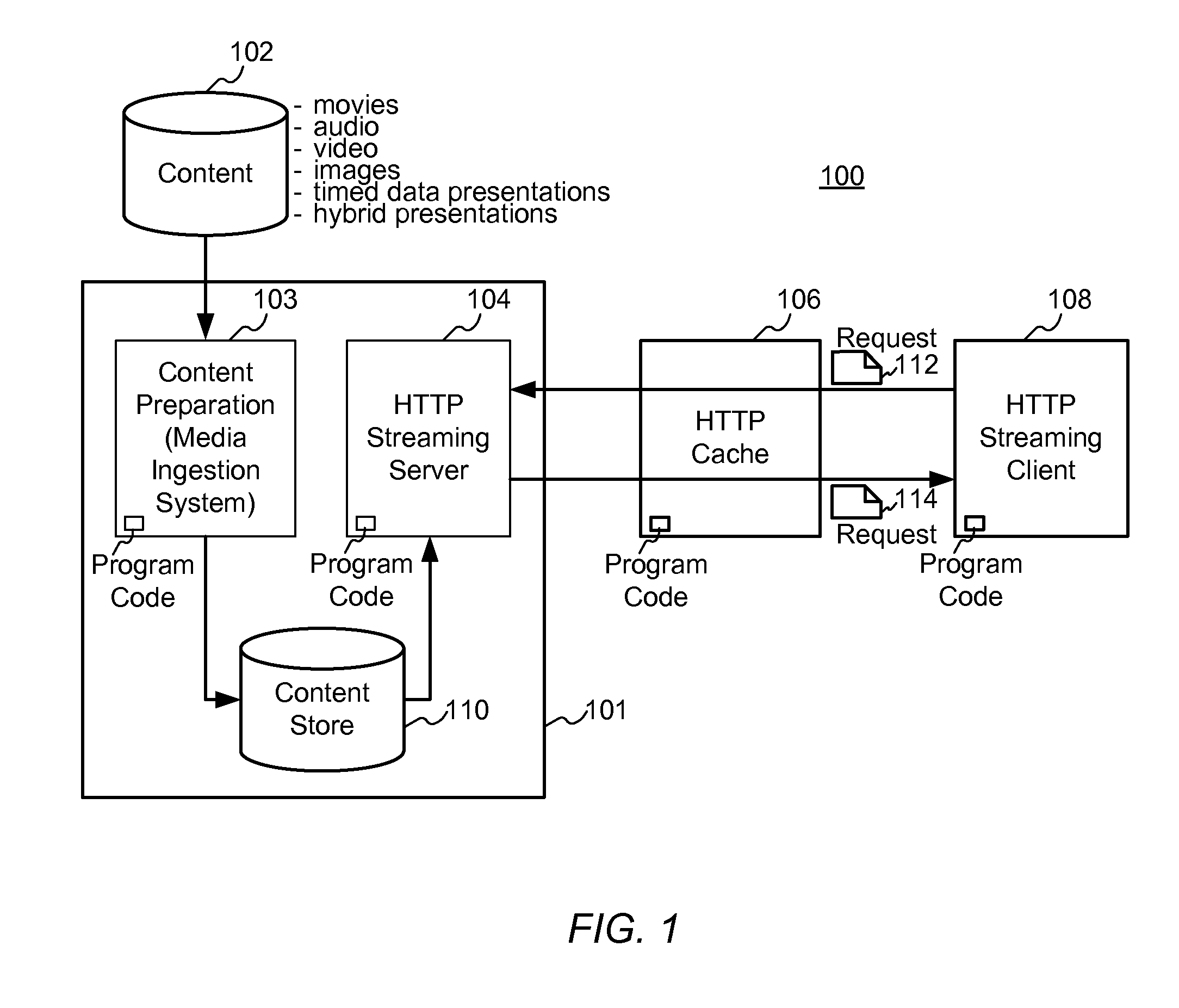
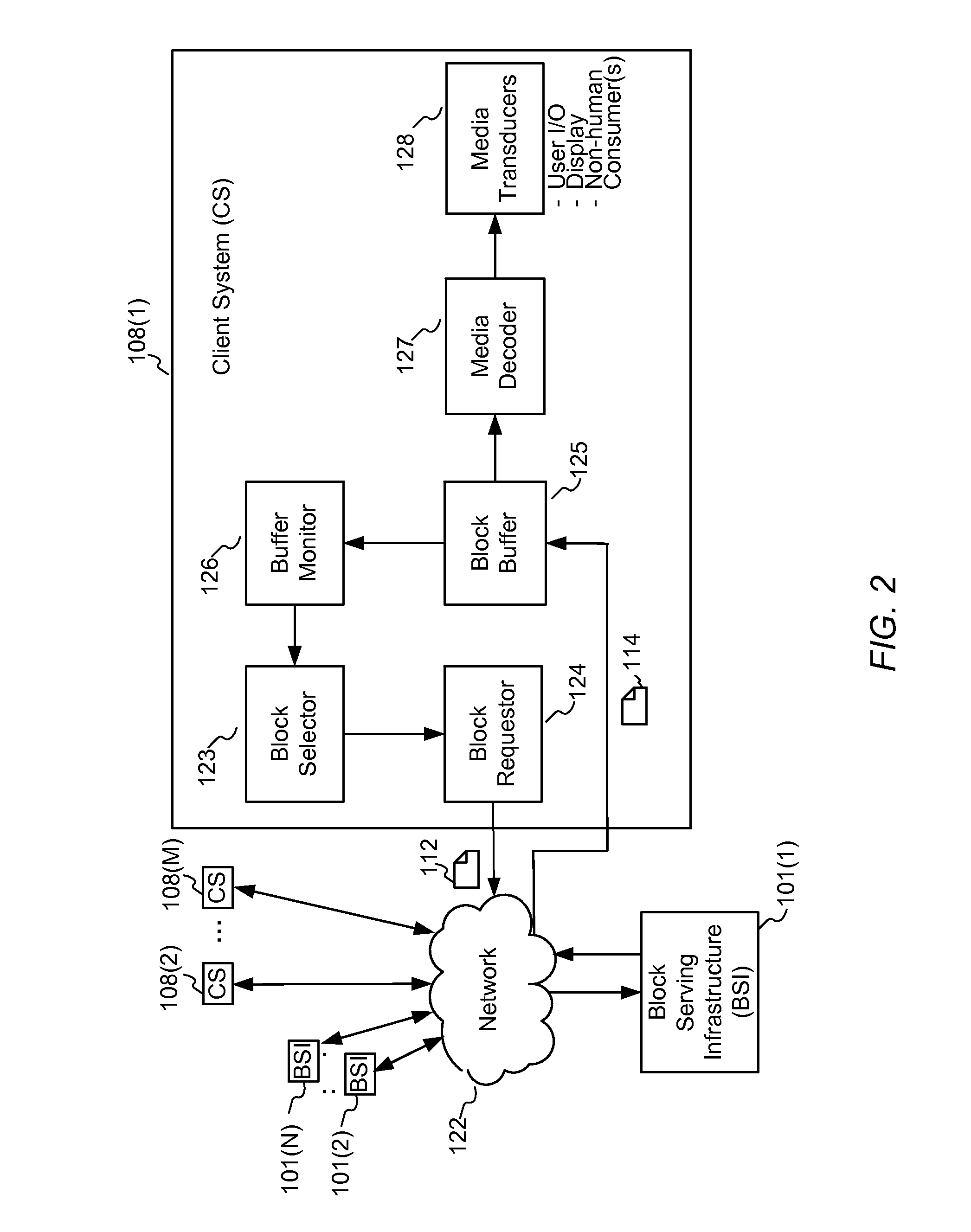
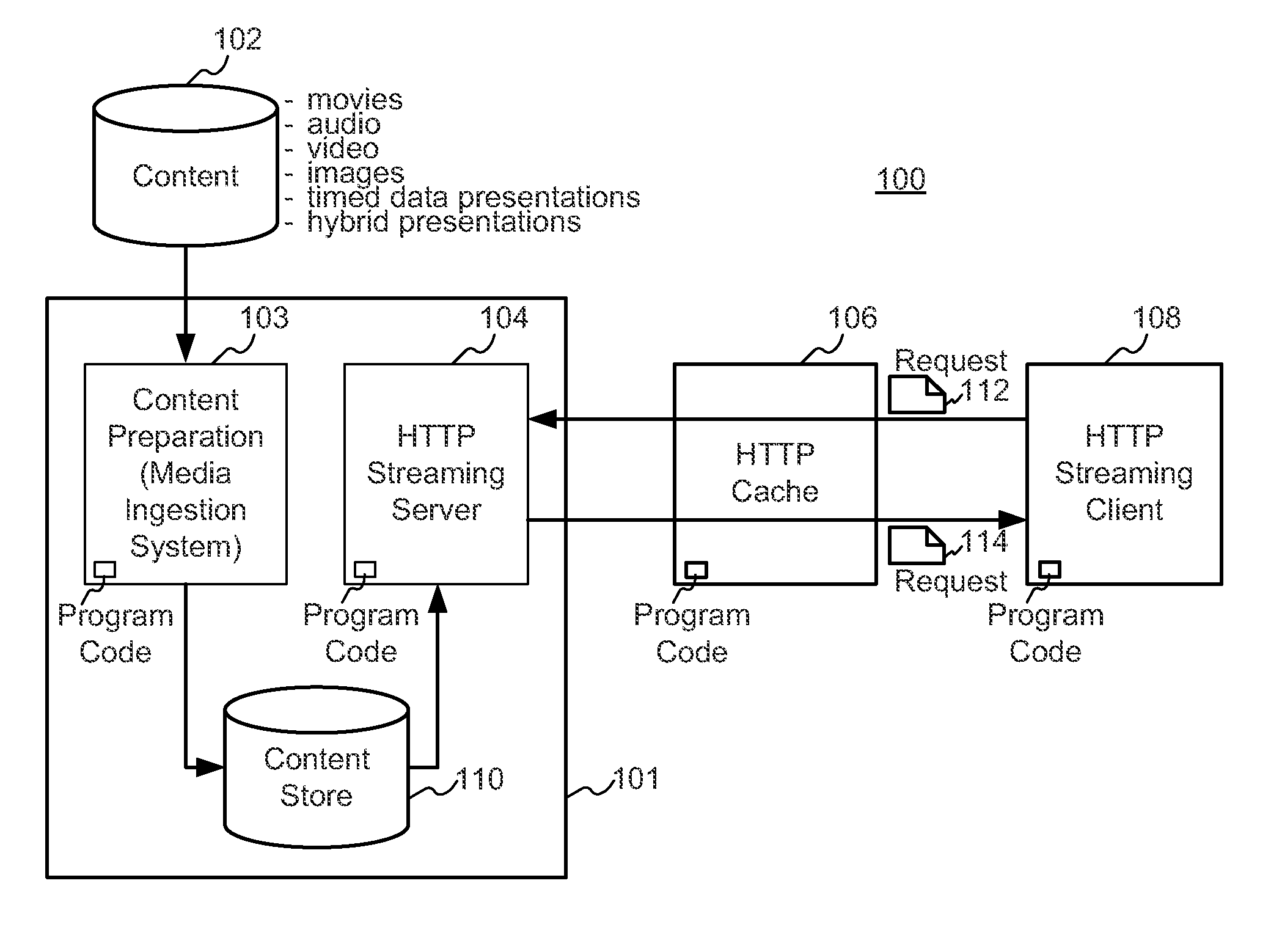
Enhanced block-request streaming system for handling low-latency streaming
ActiveUS20130007223A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyImprove user experienceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTransport systemLatency (engineering)
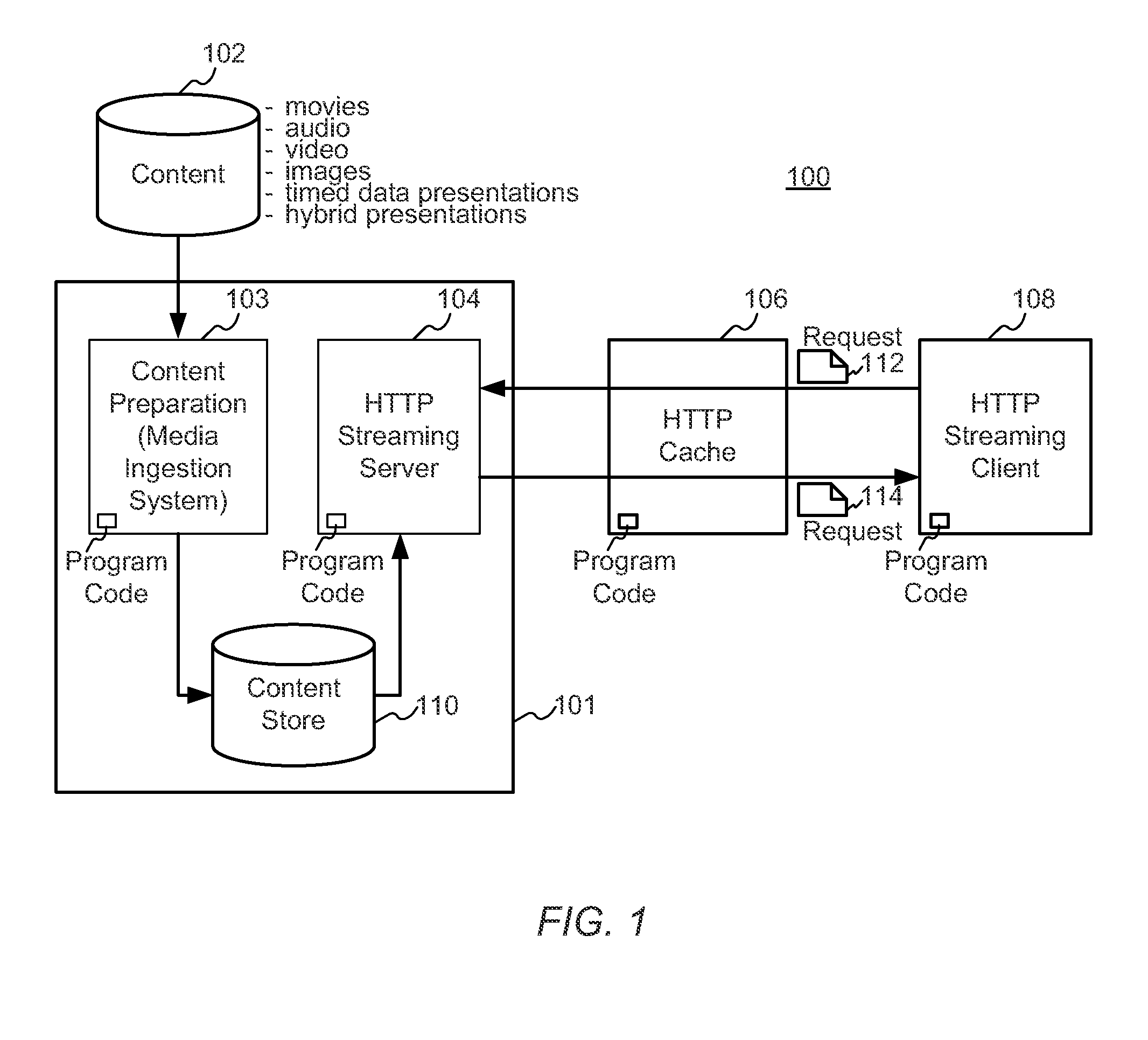
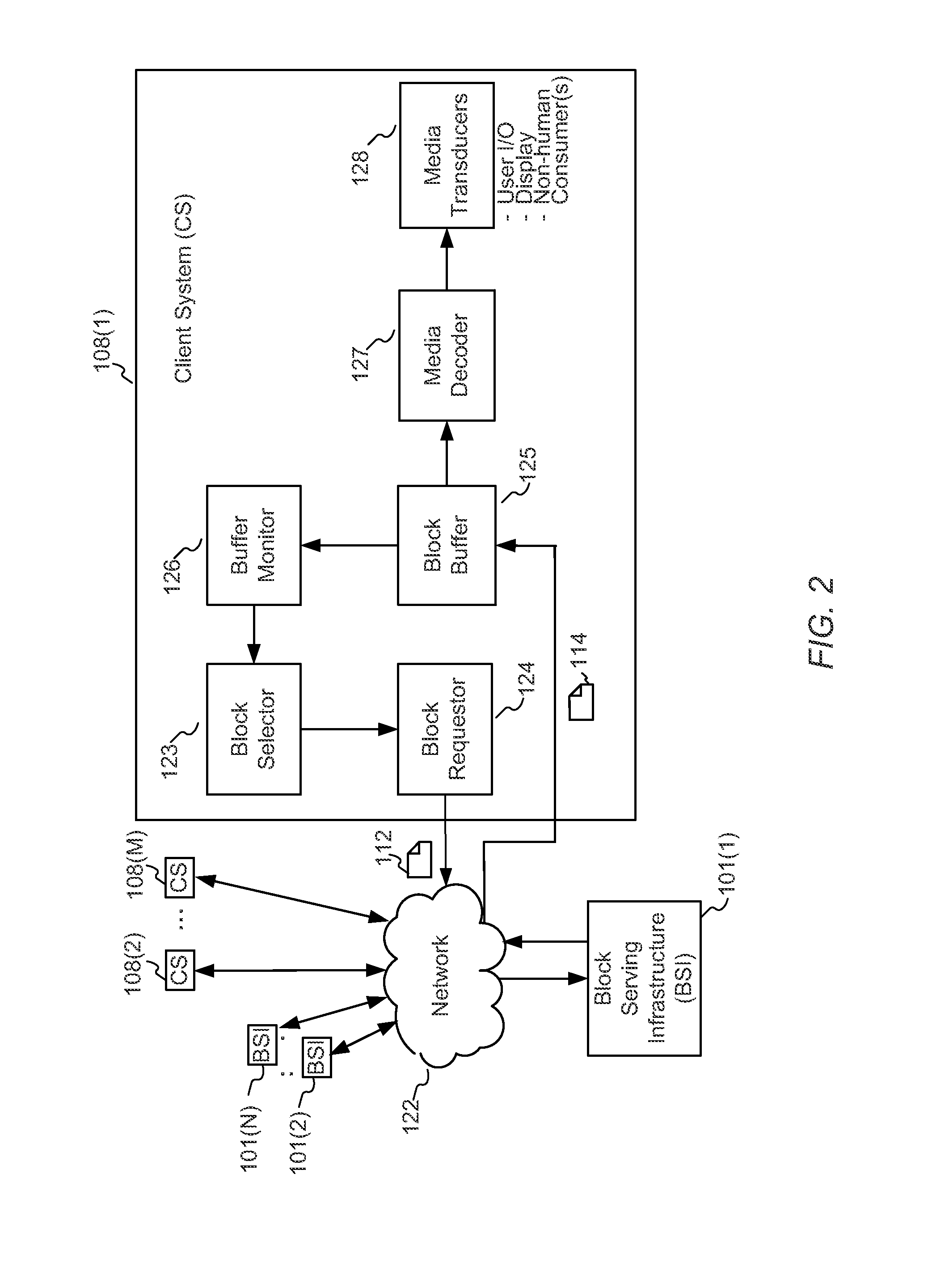
A block-request streaming system provides for low-latency streaming of a media presentation. A plurality of media segments are generated according to an encoding protocol. Each media segment includes a random access point. A plurality of media fragments are encoded according to the same protocol. The media segments are aggregated from a plurality of media fragments.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Enhanced block-request streaming system using signaling or block creation
ActiveUS20110238789A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyImprove user experiencePulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransport systemPoint placement
A block-request streaming system provides for improvements in the user experience and bandwidth efficiency of such systems, typically using an ingestion system that generates data in a form to be served by a conventional file server (HTTP, FTP, or the like), wherein the ingestion system intakes content and prepares it as files or data elements to be served by the file server. The system might include controlling the sequence, timing and construction of block requests, time based indexing, variable block sizing, optimal block partitioning, control of random access point placement, including across multiple presentation versions, dynamically updating presentation data, and / or efficiently presenting live content and time shifting.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system to increase the throughput of a communications system that uses an electrical power distribution system as a communications pathway
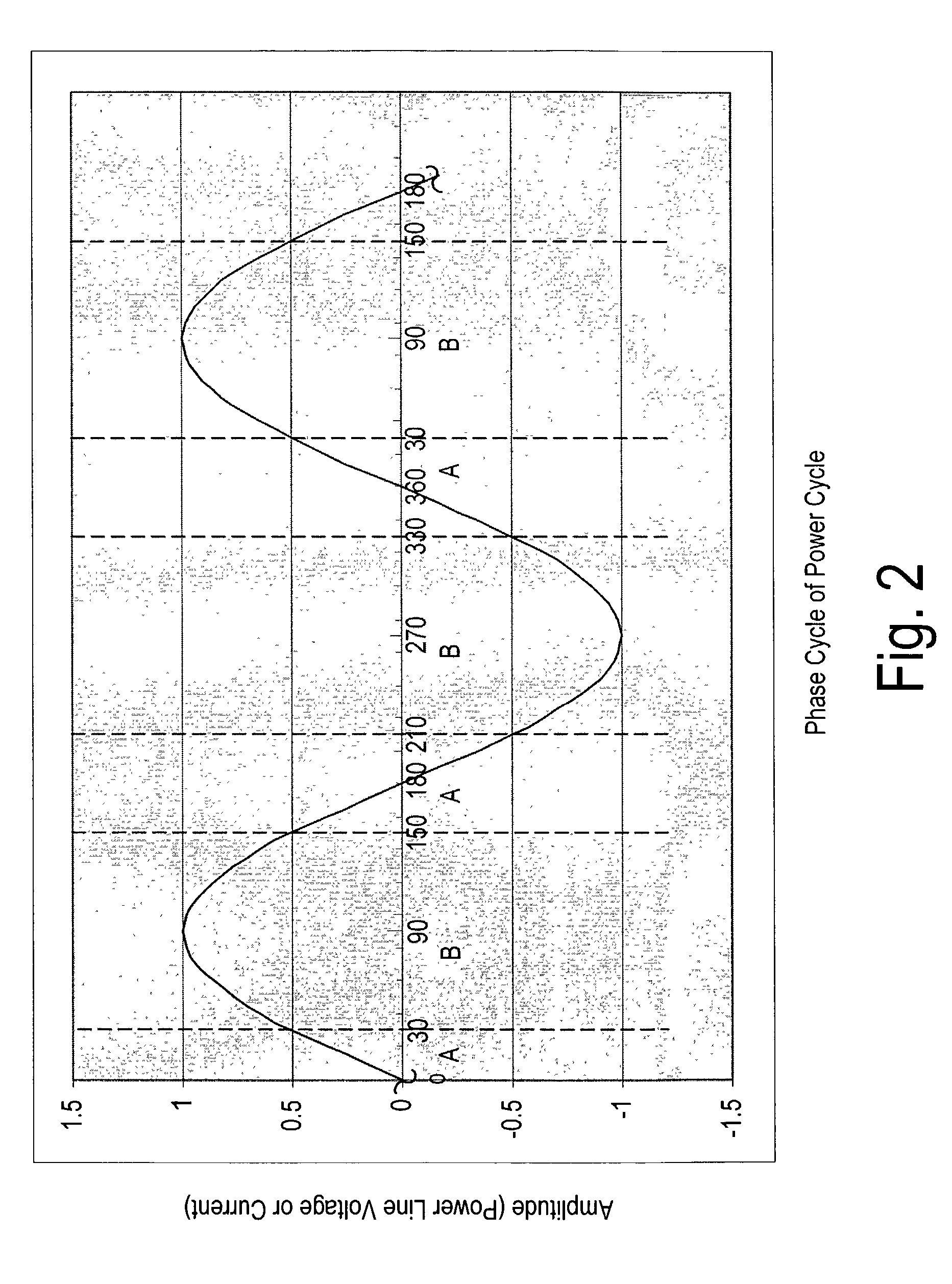
InactiveUS7307357B2High bandwidth efficiencyError correction overheadSystems with measurements/testing channelsPower distribution line transmissionDistribution systemEngineering
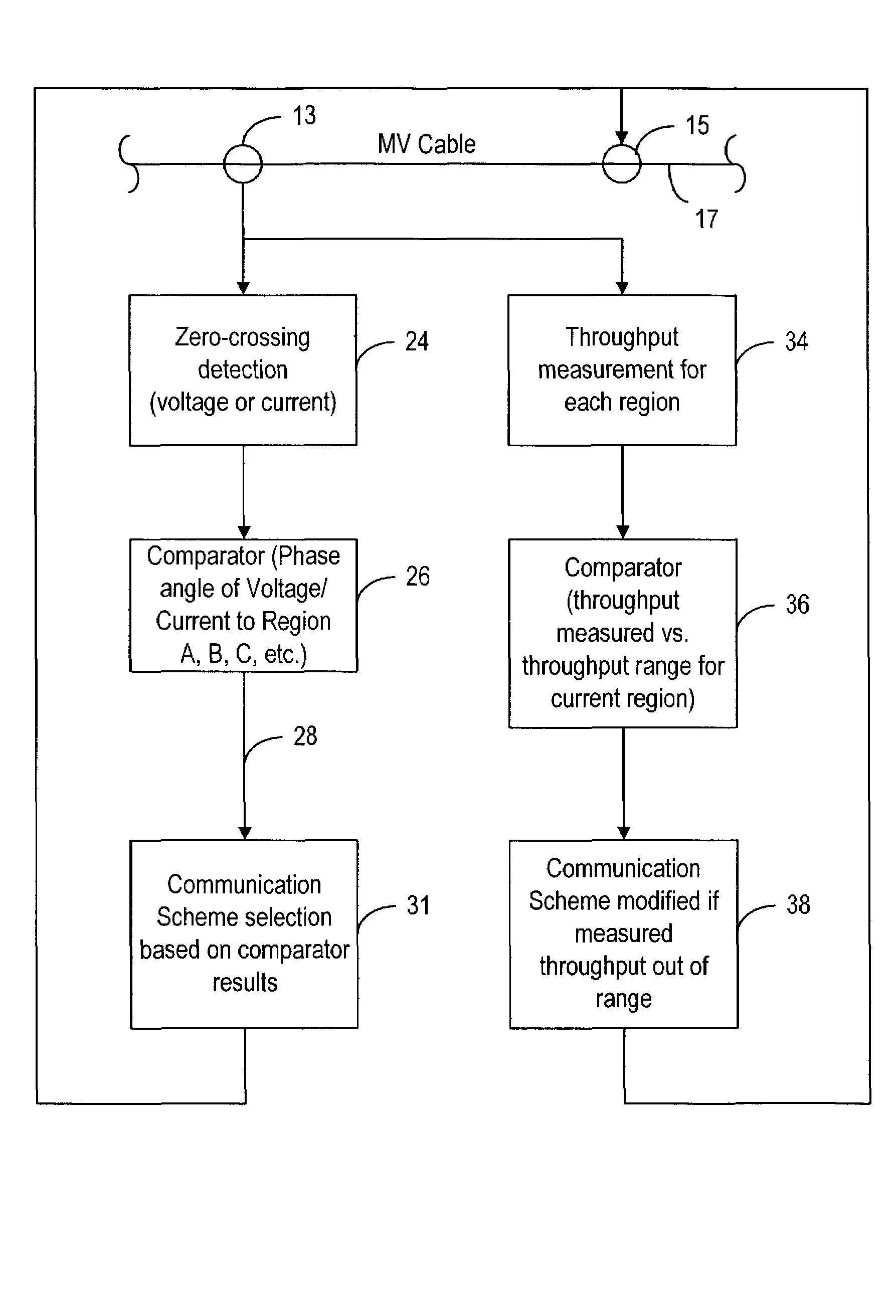
A method and system to increase the throughput of a communications system that uses an electrical power distribution system as a communications pathway, determines the phase of the power distribution power cycle and compares this determined phase to predetermined regions of the power cycle. If the power cycle is within a predetermined region, a particular communication scheme is used for transmitting and receiving information. The power cycle can have two or more predetermined regions. Optionally, the throughput for any or all regions can be determined so as to provide for modification of the associated communication scheme if the throughput is determined to be outside some predetermined range.
Owner:AMPERION
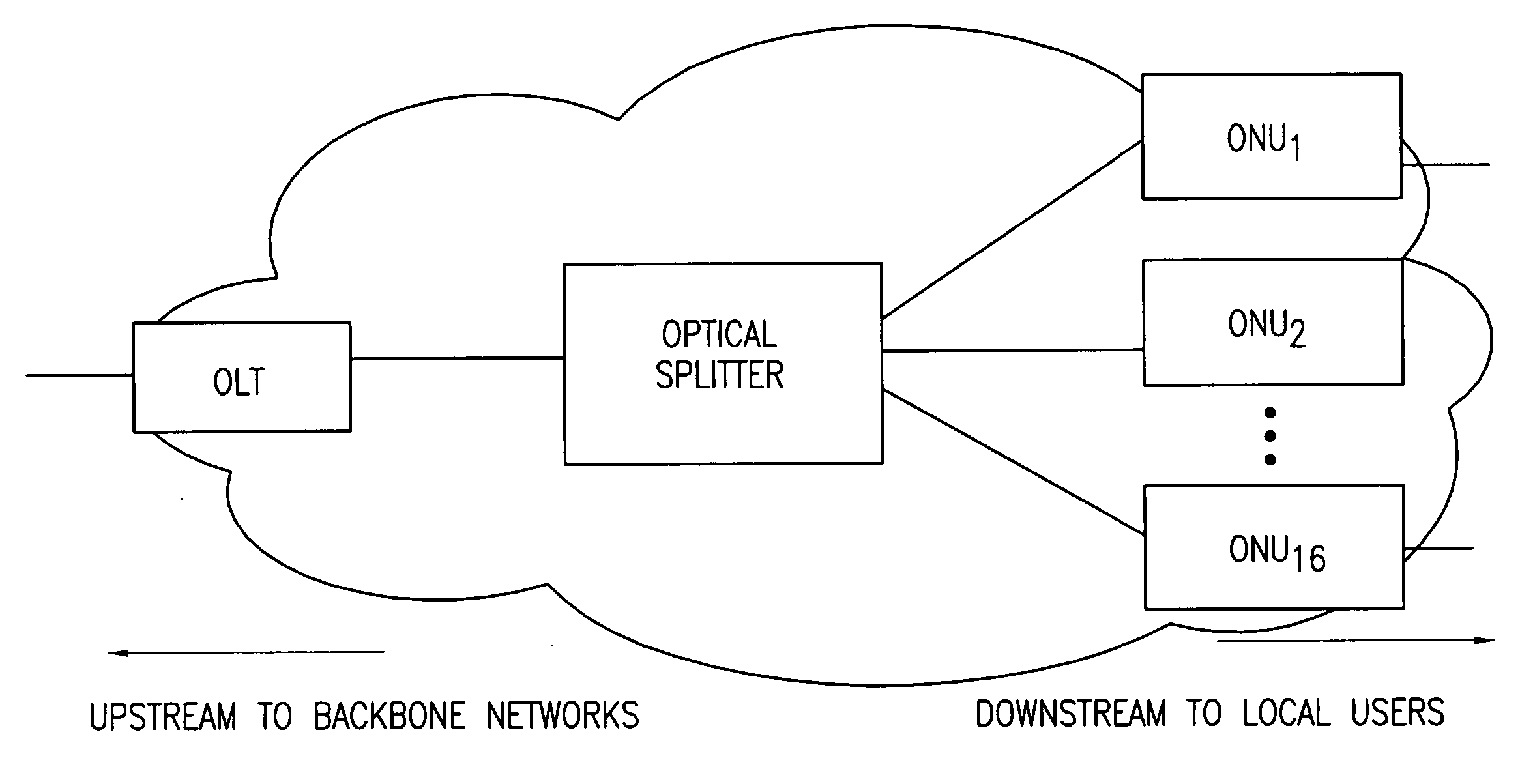
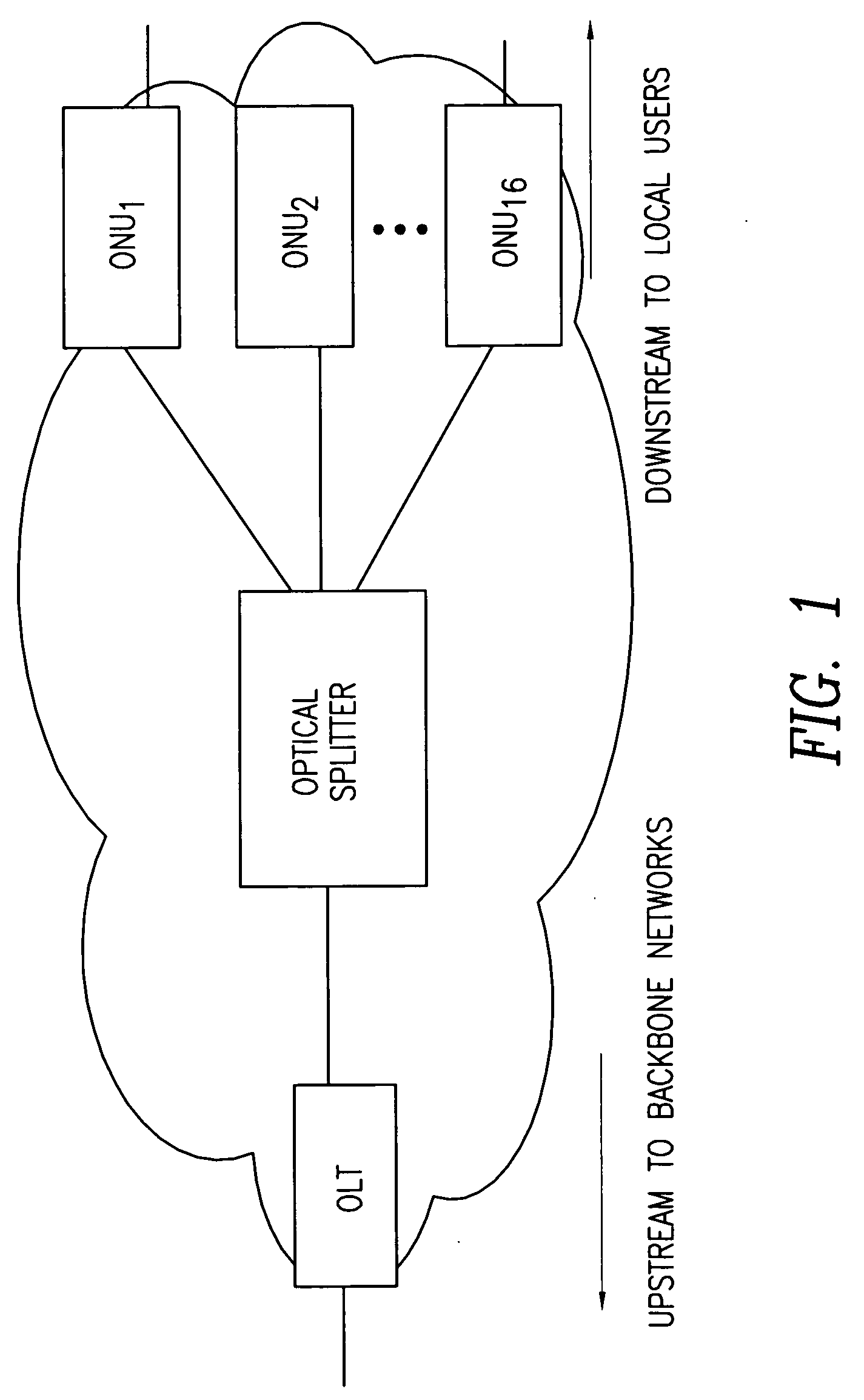
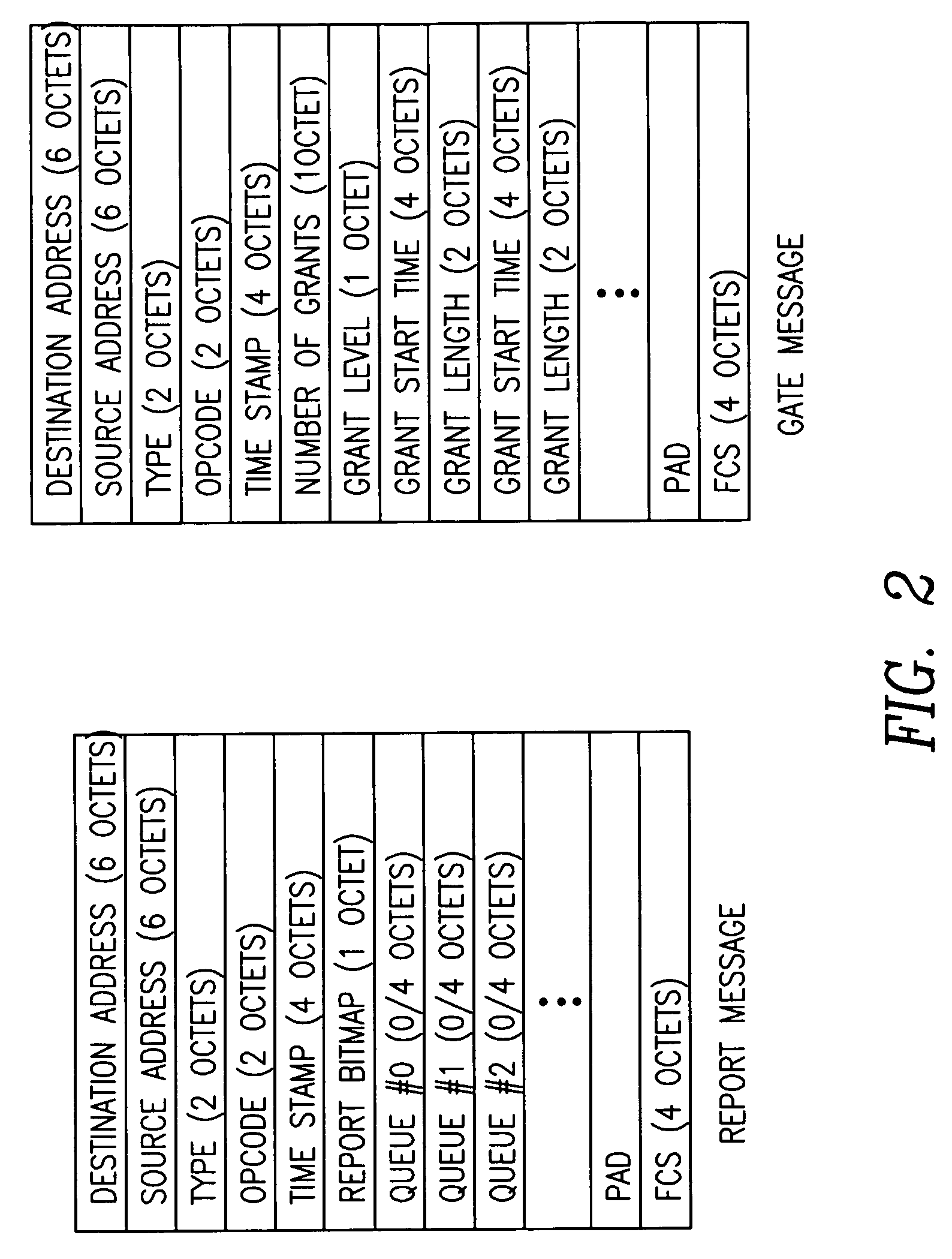
Dynamic bandwidth allocation and service differentiation for broadband passive optical networks
InactiveUS20060268704A1Effective bandwidthSpace complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionService-level agreementTraffic prediction
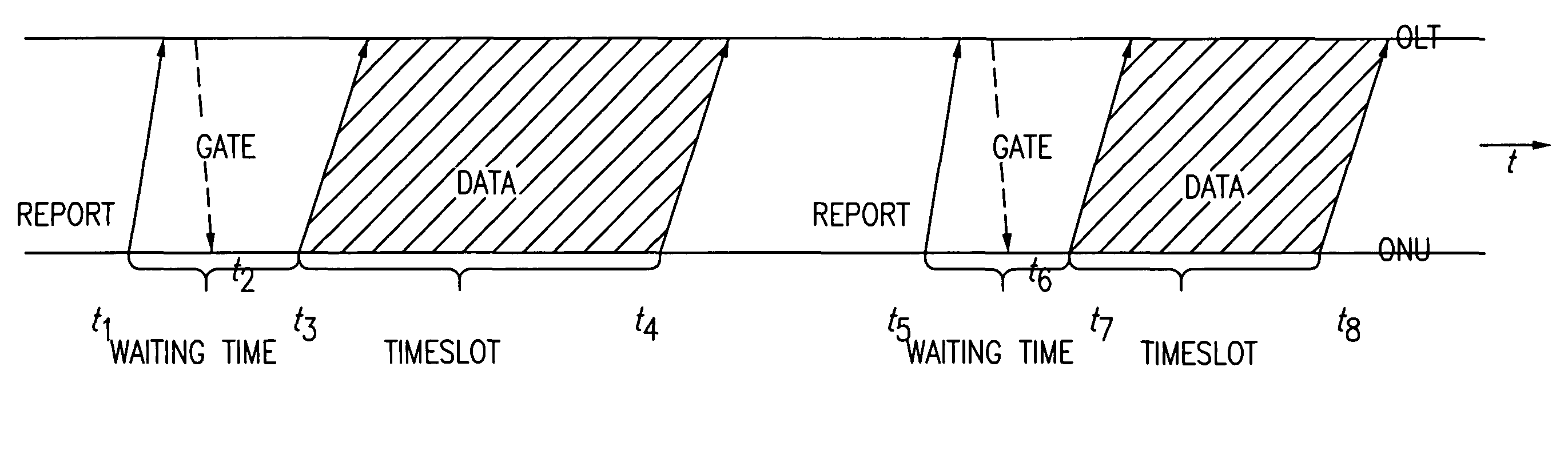
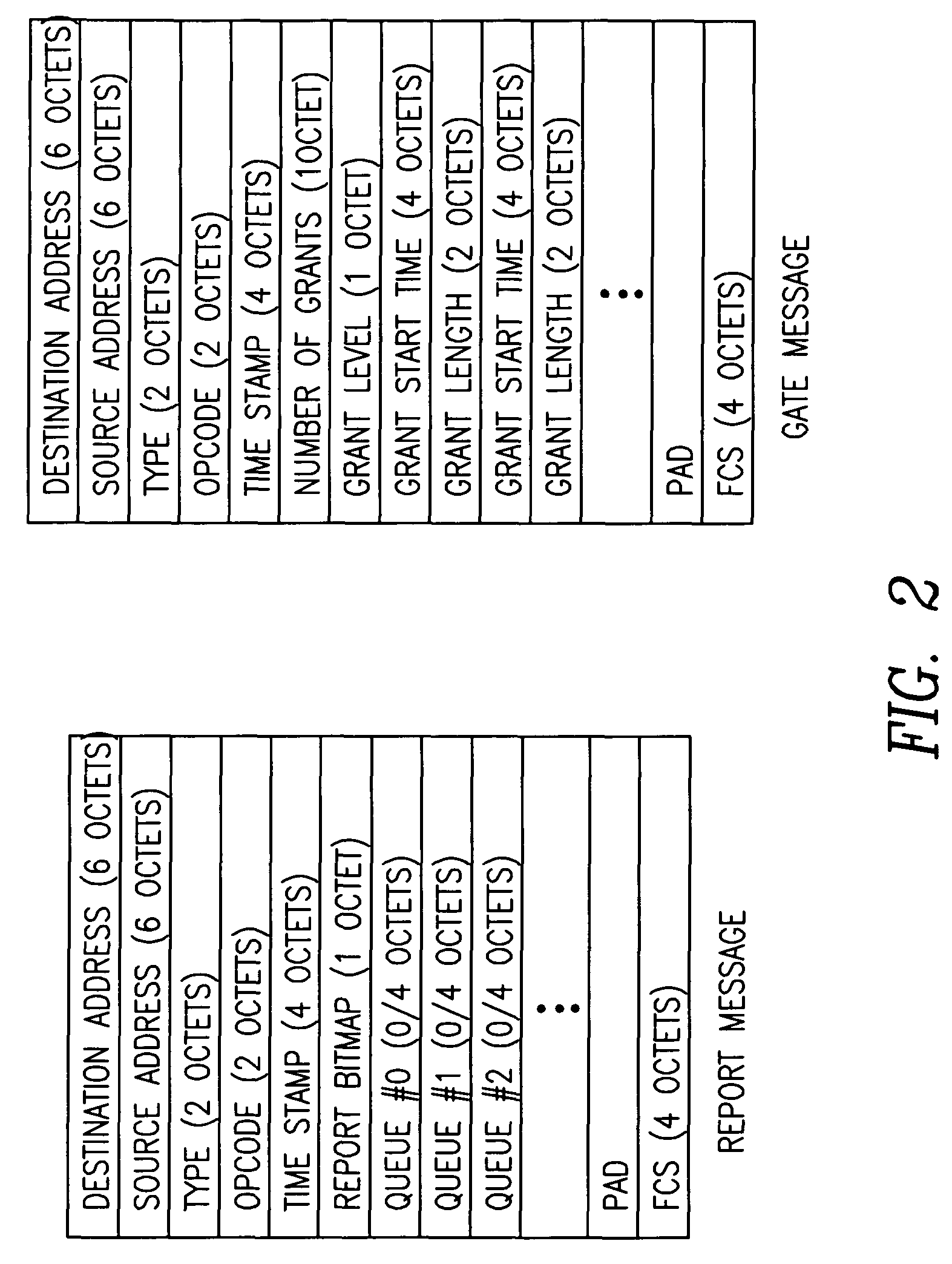
A dynamic upstream bandwidth allocation scheme is disclosed, i.e., limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP), to improve the bandwidth efficiency of upstream transmission over PONs. LSTP adopts the PON MAC control messages, and dynamically allocates bandwidth according to the on-line traffic load. The ONU bandwidth requirement includes the already buffered data and a prediction of the incoming data, thus reducing the frame delay and alleviating the data loss. ONUs are served by the OLT in a fixed order in LSTP to facilitate the traffic prediction. Each optical network unit (ONU) classifies its local traffic into three classes with descending priorities: expedited forwarding (EF), assured forwarding (AF), and best effort (BE). Data with higher priority replace data with lower priority when the buffer is full. In order to alleviate uncontrolled delay and unfair drop of the lower priority data, the priority-based scheduling is employed to deliver the buffered data in a particular transmission timeslot. The bandwidth allocation incorporates the service level agreements (SLAs) and the on-line traffic dynamics. The basic limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP) scheme is extended to serve the classified network traffic.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Apparatus and method for constructing and packaging printed antenna devices
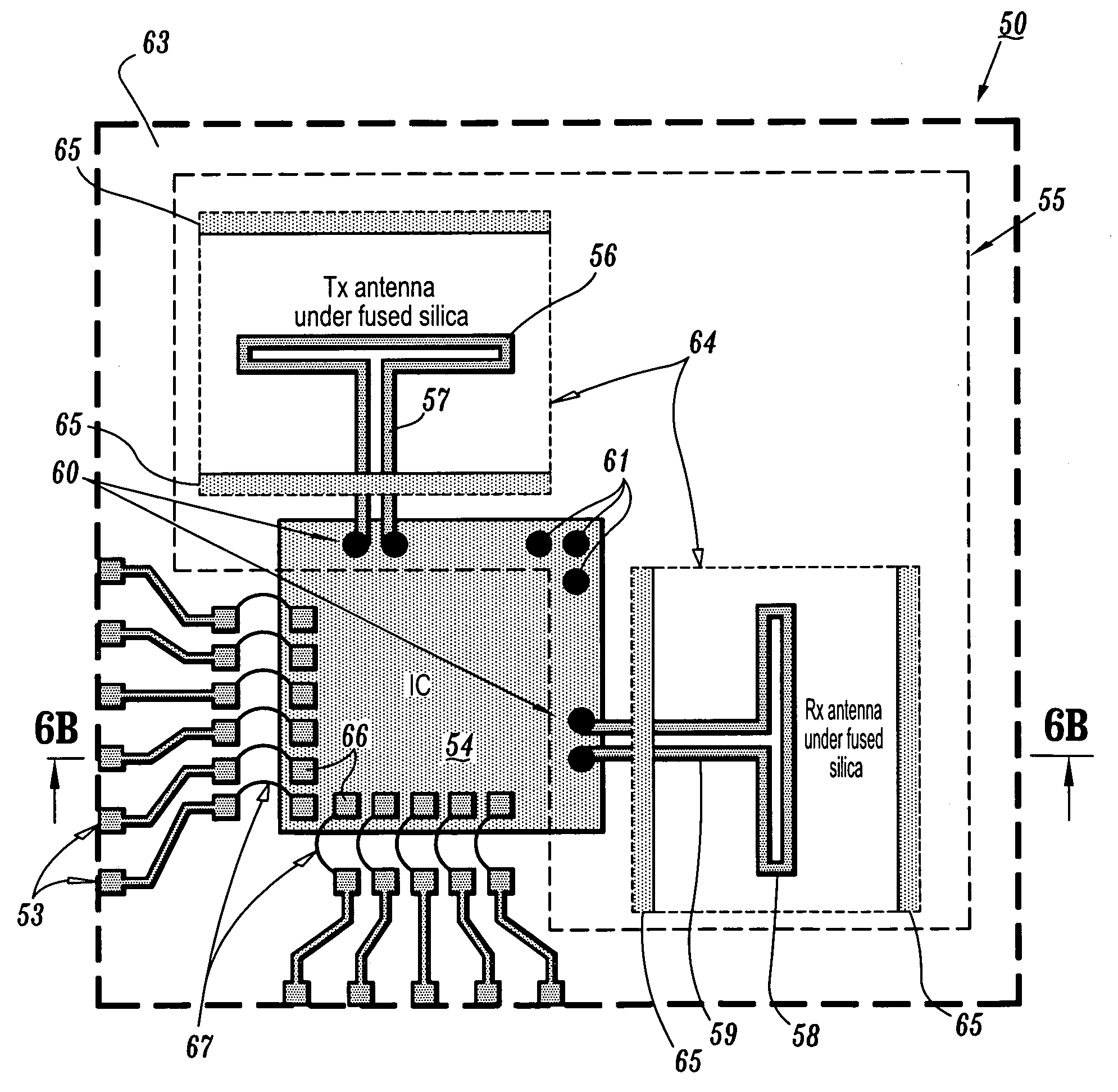
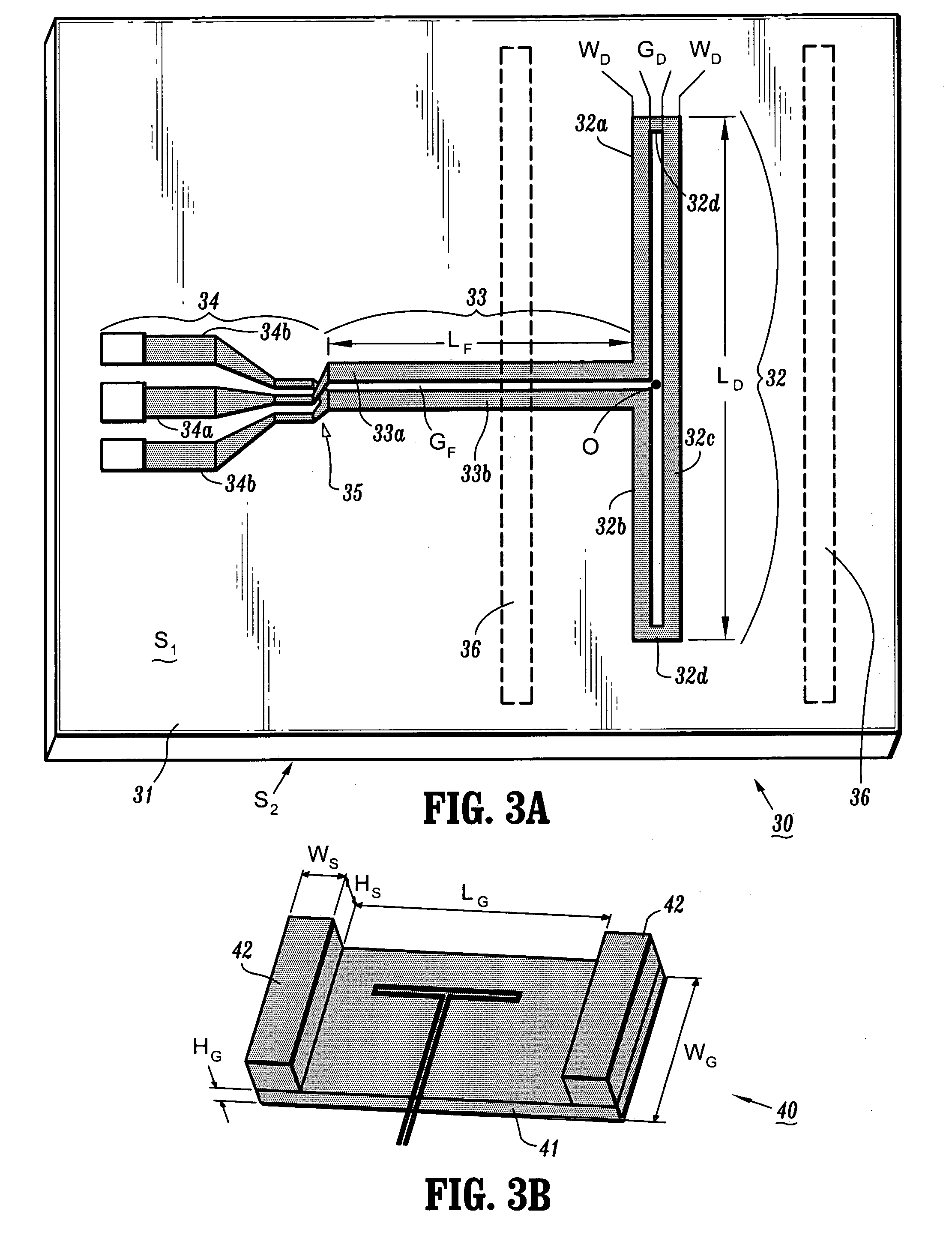
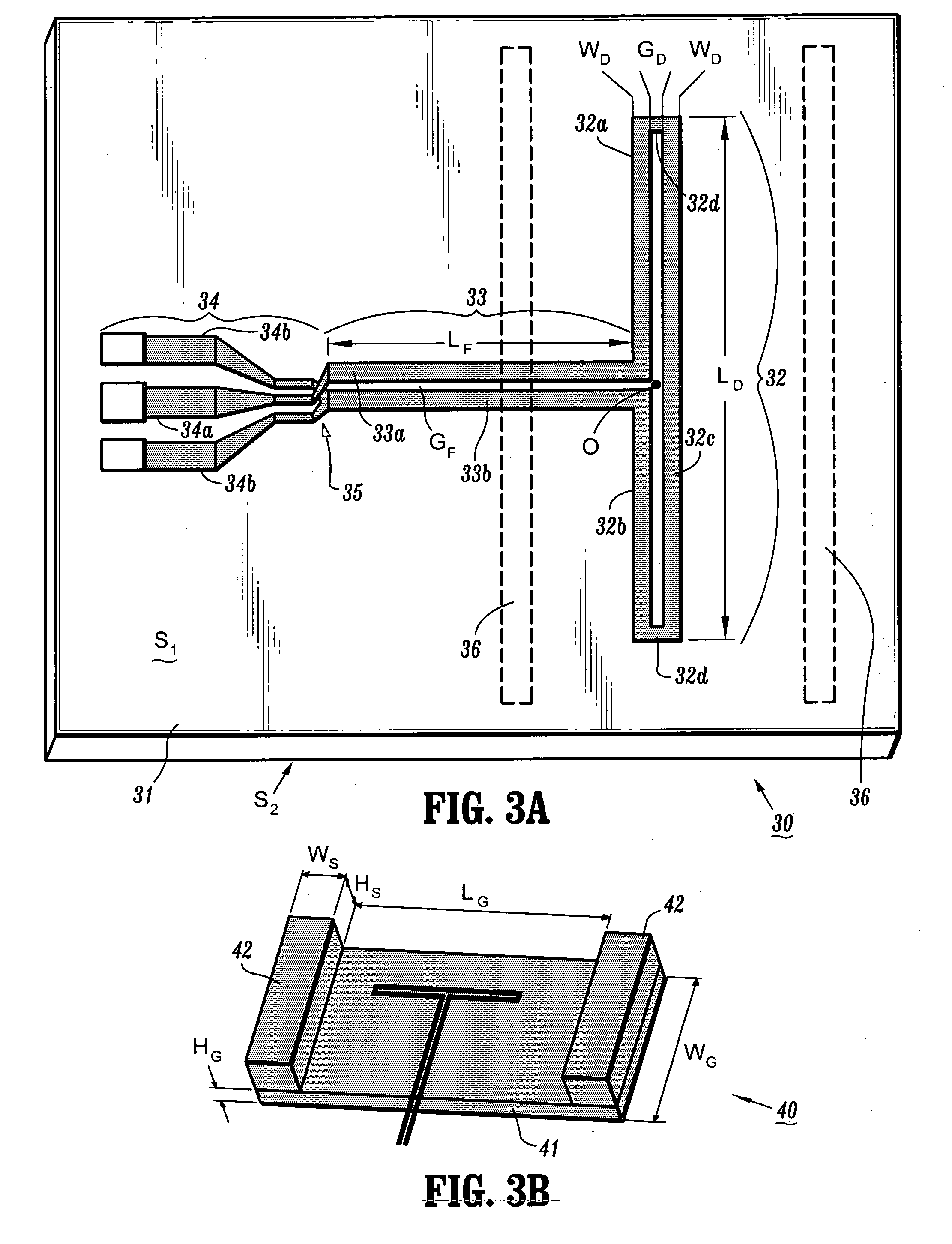
ActiveUS7119745B2Improve bandwidth efficiencySimple designSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverHigh bandwidth
Printed antenna devices are provided, which can operate at RF and microwave frequencies, for example, while simultaneously providing antenna performance characteristics such as high gain / directivity / radiation efficiency, high bandwidth, hemispherical radiation patterns, impedance, etc., that render the antennas suitable for voice communication, data communication or radar applications, for example. Further, apparatus are provided for integrally packaging such printed antenna devices with IC (integrated circuit) chips (e.g., transceiver) to construct IC packages for, e.g., wireless communications applications.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
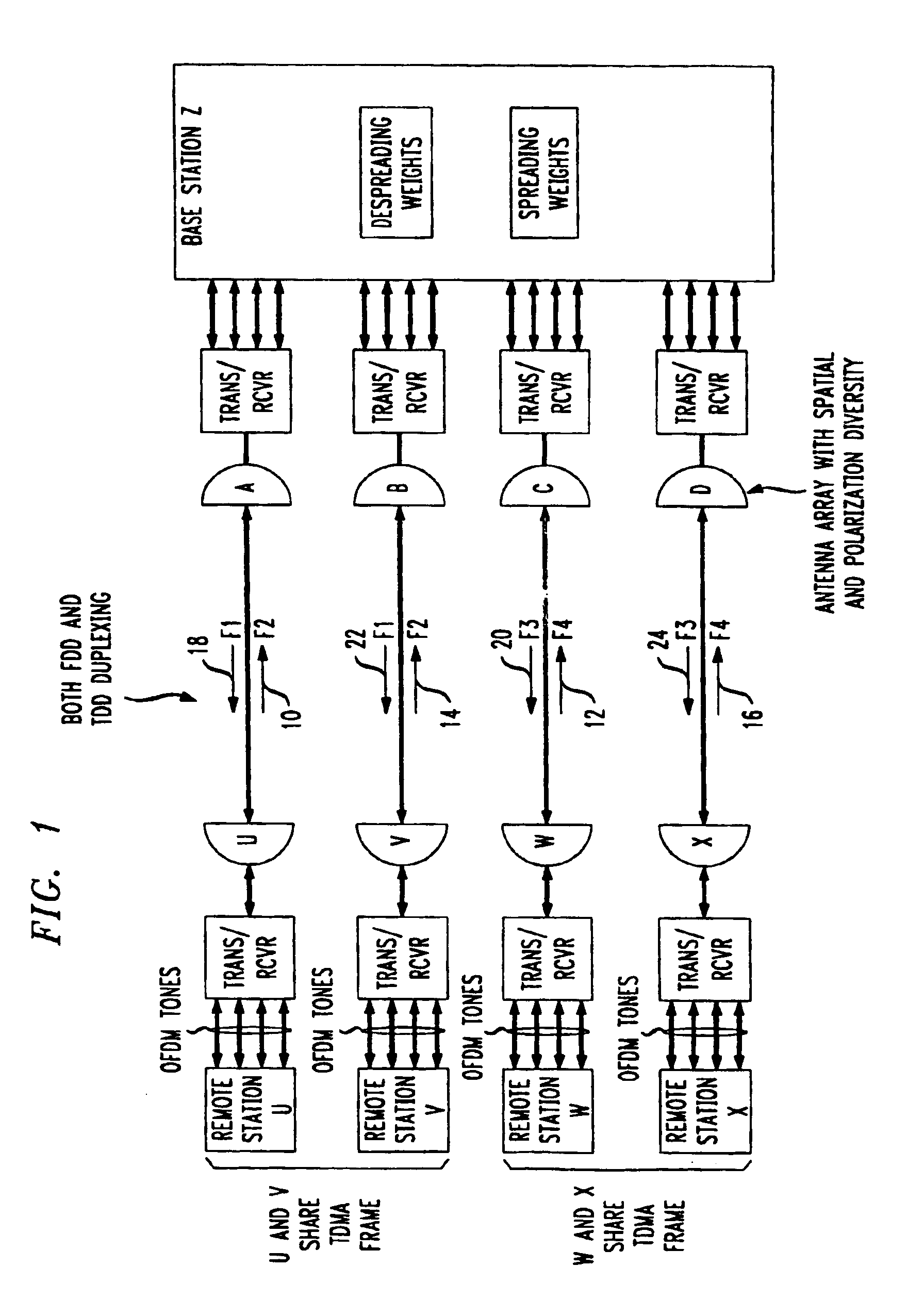
Method for frequency division duplex communications
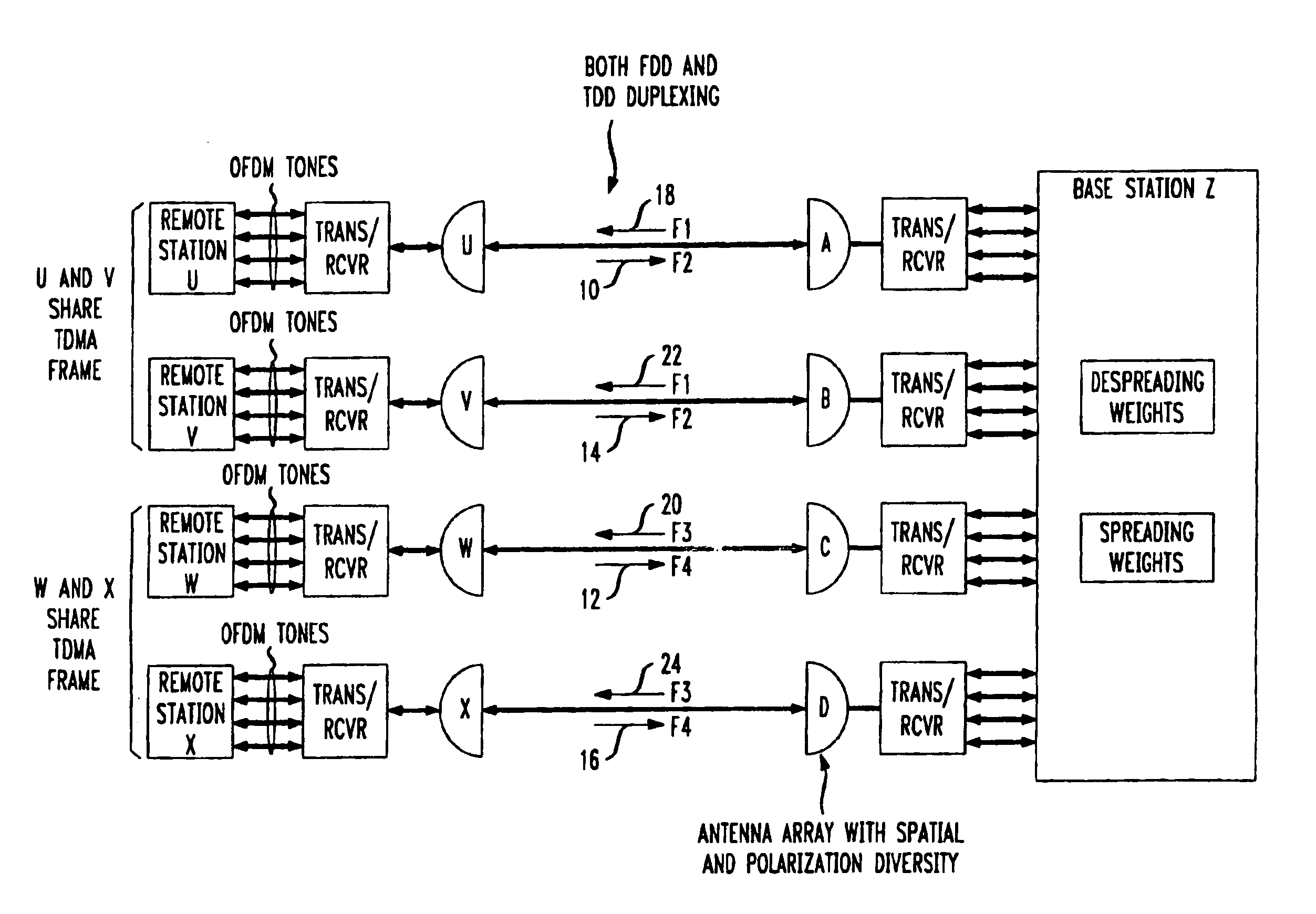
InactiveUS6853629B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyQuality improvementSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsPolarization diversity
The high quality PCS communications are enabled in environments where adjacent PCS service bands operate with out-of-band harmonics that would otherwise interfere with the system's operation. The highly bandwidth-efficient communications method combines a form of time division duplex (TDD), frequency division duplex (FDD), time division multiple access (TDMA), orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), spatial diversity, and polarization diversity in various unique combinations. The method provides excellent fade resistance. The method enables changing a user's available bandwidth on demand by assigning additional TDMA slots during the user's session.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Apparatus and method for constructing and packaging printed antenna devices
ActiveUS20060001572A1Reduce radiationImproved radiation patternSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsHigh bandwidthTransceiver
Printed antenna devices are provided, which can operate at RF and microwave frequencies, for example, while simultaneously providing antenna performance characteristics such as high gain / directivity / radiation efficiency, high bandwidth, hemispherical radiation patterns, impedance, etc., that render the antennas suitable for voice communication, data communication or radar applications, for example. Further, apparatus are provided for integrally packaging such printed antenna devices with IC (integrated circuit) chips (e.g., transceiver) to construct IC packages for, e.g., wireless communications applications.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for packet grooming and aggregation
InactiveUS7492714B1Improve bandwidth efficiencyEfficient forwardingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiplexingEdge node
A method and apparatus for building a packet grooming and aggregation engine is disclosed. The grooming and aggregation engine can be applied to the network for providing flexible aggregation and service multiplexing functions. A method and apparatus achieves the intended function that is easy to implement and easy for the network operator to manage, yet provides enough flexibility to mix and match various services at the edge node of the network. One specific embodiment of the patent is an Ethernet over SONET mapping system where user traffic is aggregated and groomed into SONET transport virtual concatenation channels.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Multi-carrier spread spectrum device using cyclic shift orthogonal keying, transmitter, receiver, and communication system thereof
ActiveUS20090059882A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyIncrease bit transmission rateSecret communicationRadio transmissionBase codeCommunications system
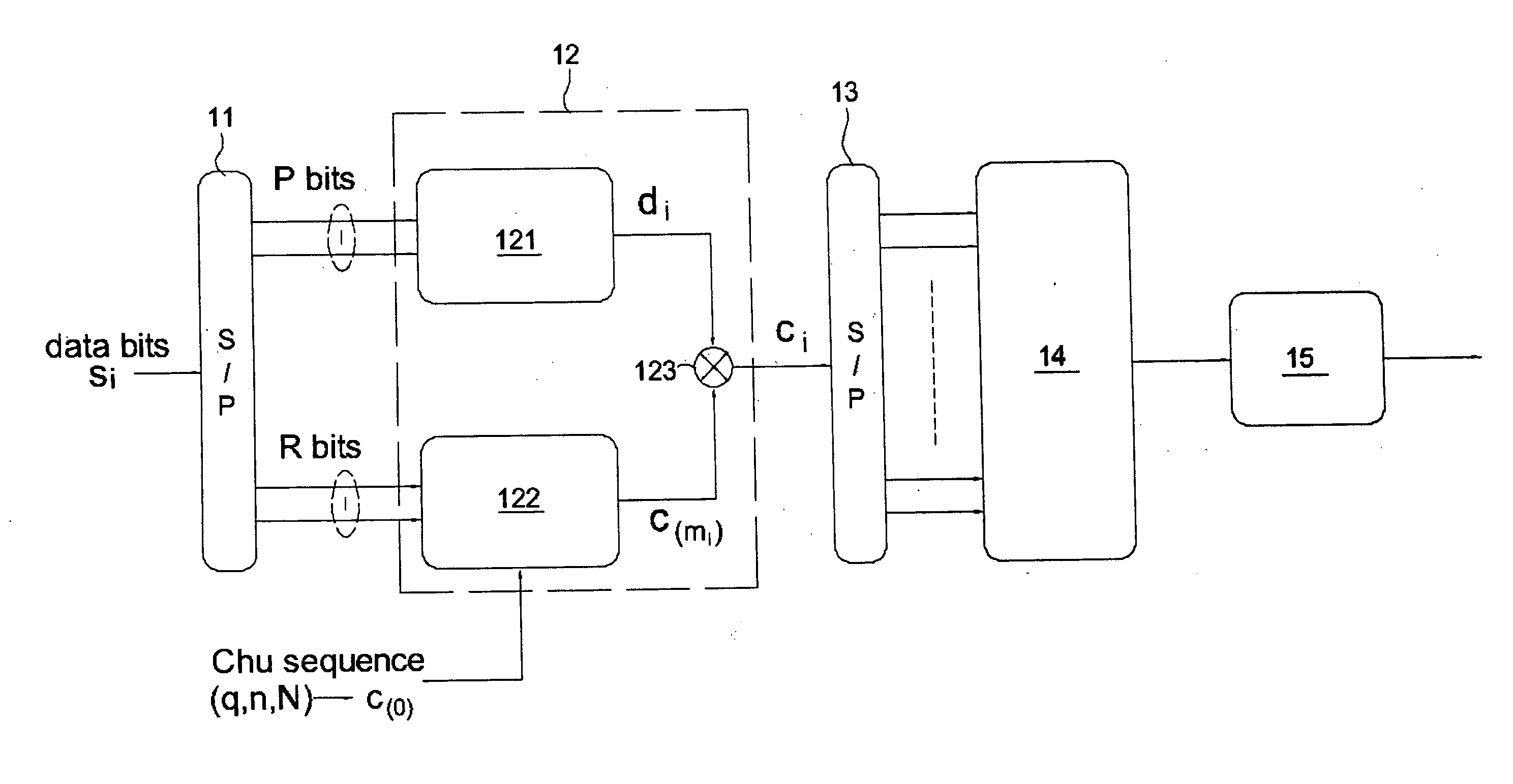
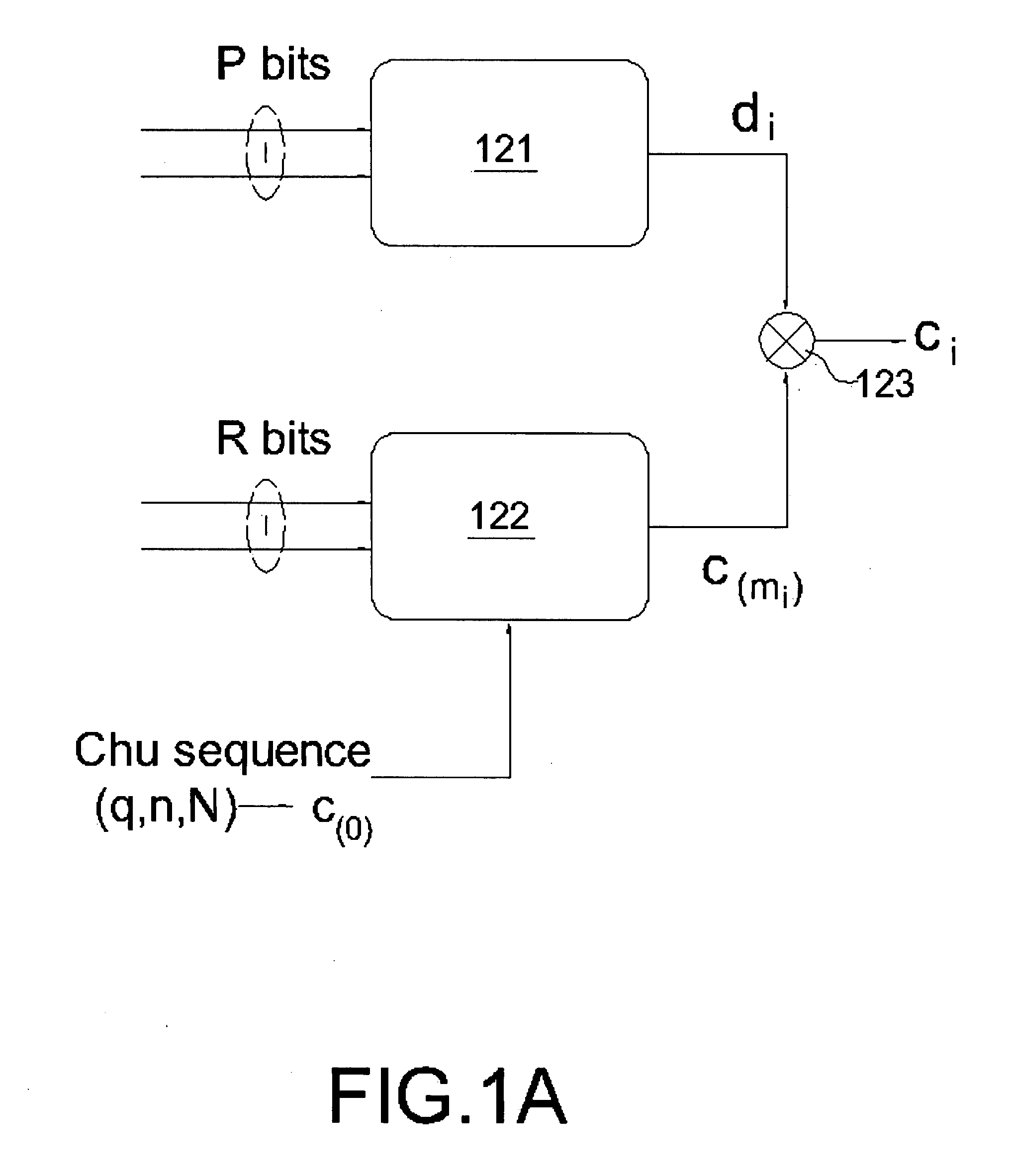
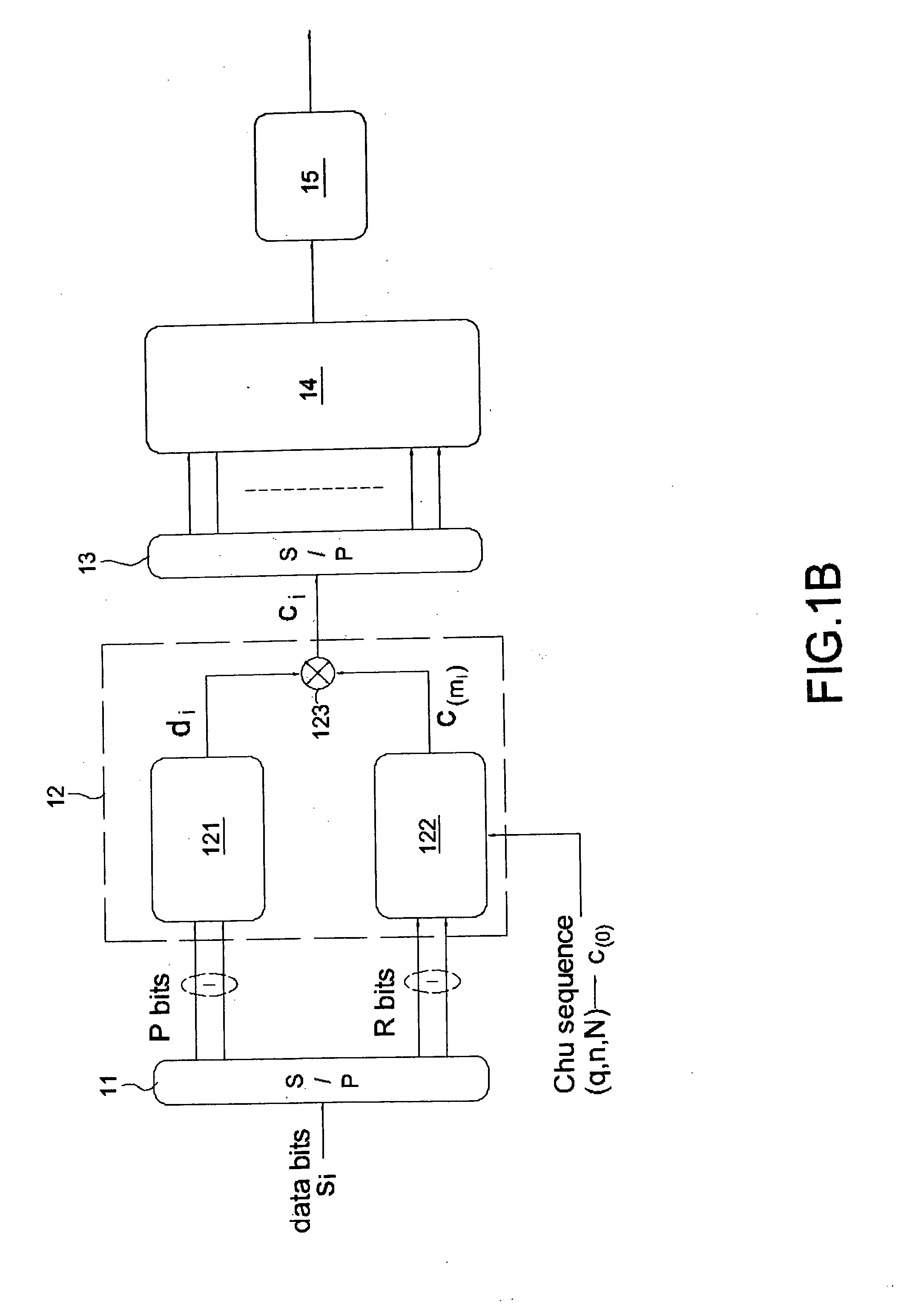
A multi-carrier spread spectrum device using cyclic shift orthogonal keying includes: a modulation unit for receiving a first part of data bits and transforming the first part of data bits to a modulation symbol di by modulation; a cyclic-shift unit for receiving a base code c(0) and a second part of data bits, and performing a cyclic-shift to the base code c(0) in accordance with the second part of data bits to generate a CSOK symbol c(m<sub2>i< / sub2>); and a multiplier for multiplying the modulation symbol di by the CSOK symbol c(m<sub2>i< / sub2>) to generate a spread spectrum signal ci.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
Packet communications system and method
InactiveUS7012922B1Improve efficiencyImprove bandwidth efficiencyTime-division multiplexNetwork connectionsDigital subscriber lineTraffic capacity
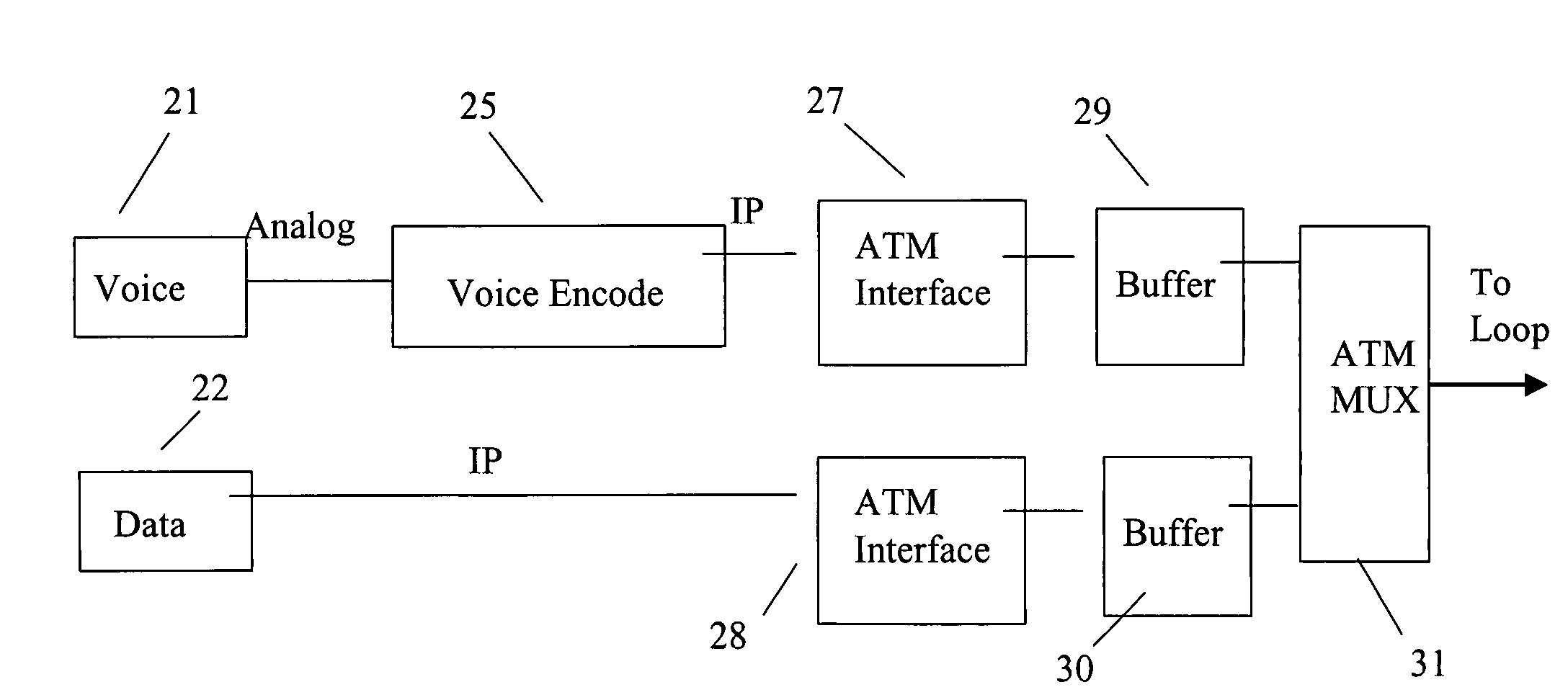
A digital subscriber line (DSL) arrangement provides data and voice over IP (VoIP) services over a subscriber loop. Instead of conventional multiplexing at the IP layer, two separate IP packet streams are provided, one stream carrying delay insensitive data traffic and the other transporting delay sensitive traffic, in particular, packetised voice. The system segments each IP stream (i.e. those carrying voice and data) separately to produce two ATM streams which are then multiplexed using an ATM multiplexer. This reduces the delays to voice traffic resulting from queuing behind long data packets.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
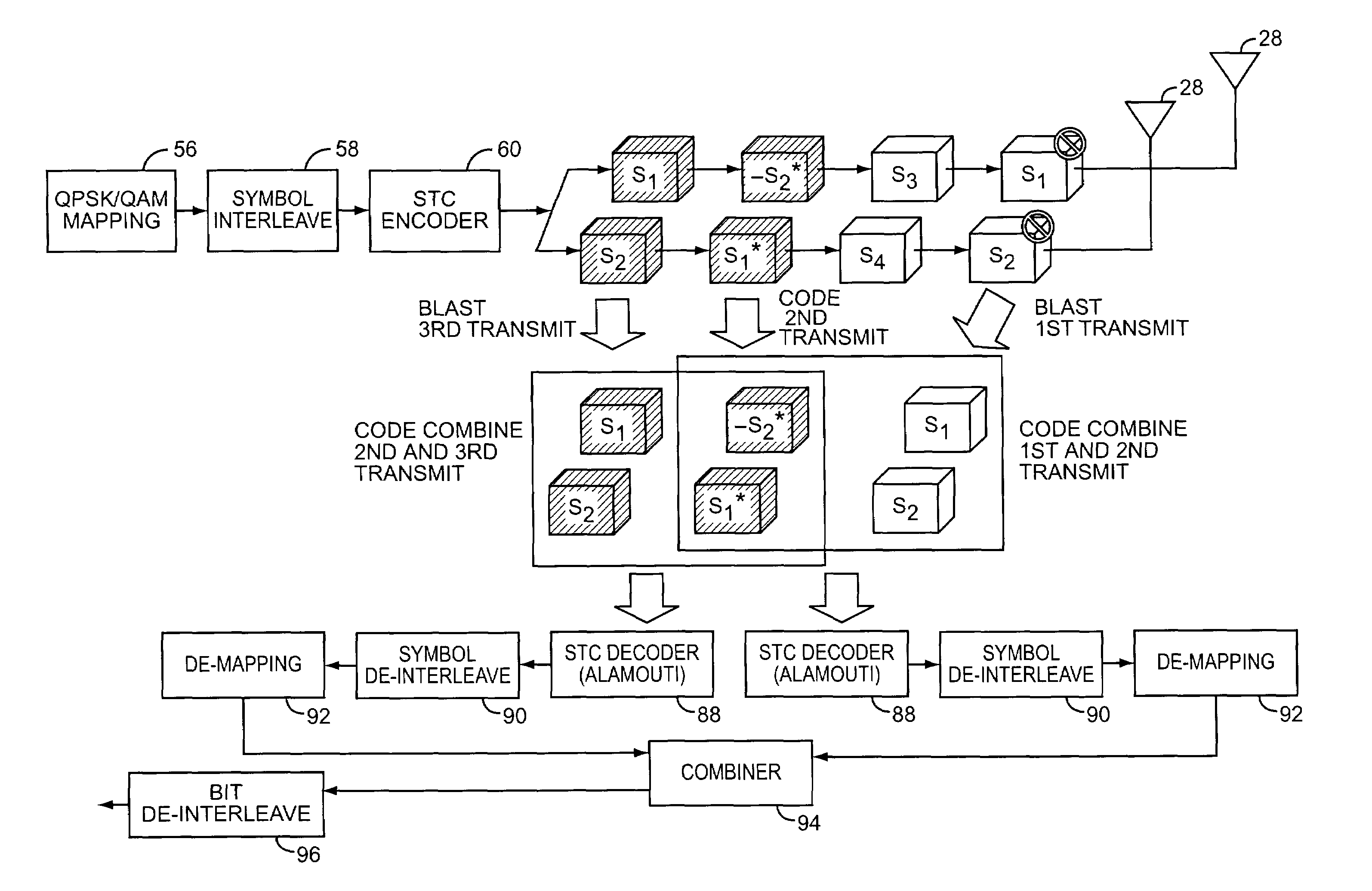
Incremental redundancy with space-time codes
ActiveUS7397864B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyDecreasing bandwidth efficiencyError prevention/detection by using return channelModulated-carrier systemsHigh bandwidthDiversity scheme
The present invention relates to space-time coding techniques capable of providing incremental redundancy in wireless communication environments incorporating spatial and temporal diversity. In general, a transmitter sends packets, via blocks of symbols, to a receiver with high bandwidth efficiency and only in the event that the receiver does not correctly receive a data packet does the transmitter send additional symbols to assist with the decoding of the incorrectly received packet. A hybrid ARQ feedback mechanism is used such that the receiver can inform the transmitter whether the packets were correctly or incorrectly received. From the feedback, the transmitter can determine whether to send new symbols or initiate incremental redundancy. By combining the received words corresponding to the redundant symbols and those of the original packet transmission, additional diversity, coding gain, signal energy, or a combination thereof are provided to the receiver and are used to correctly decode the transmitted data.
Owner:APPLE INC
Collaboration partner selection and pre-coding collaboration communication method in cellular communication system
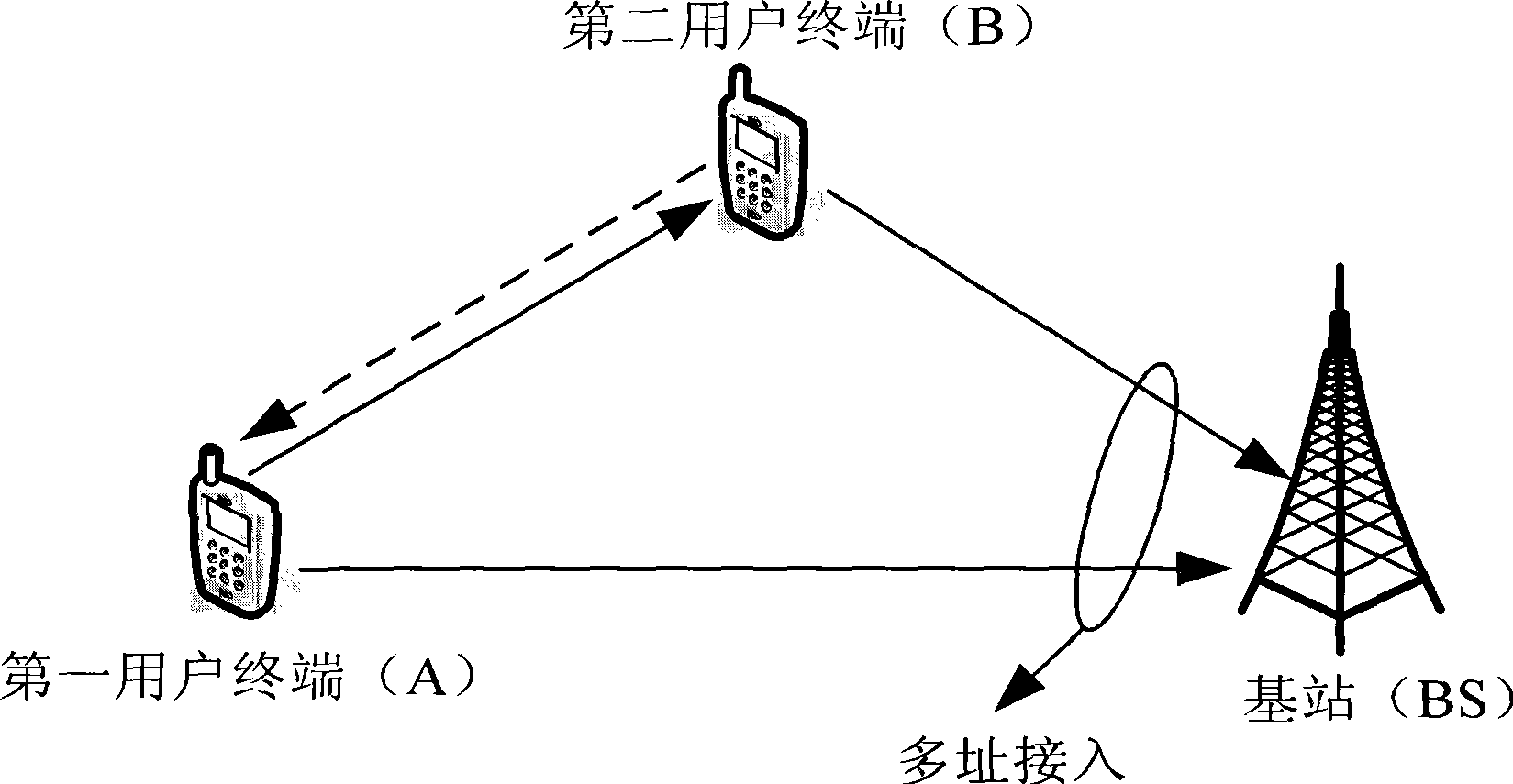
InactiveCN101399583AReduce complexityImprove transmission reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityAssess restrictionCellular communication systemsData transmission
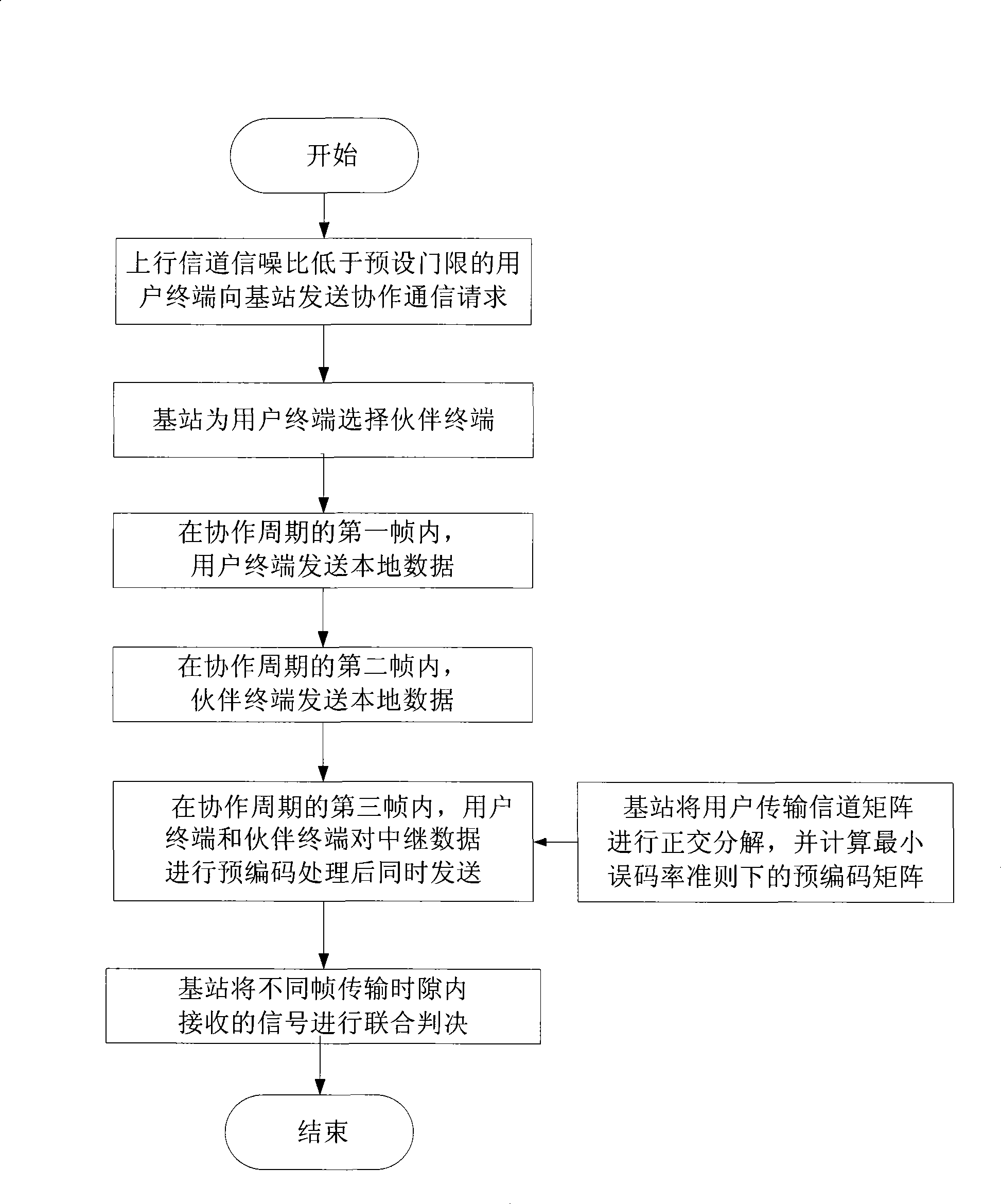
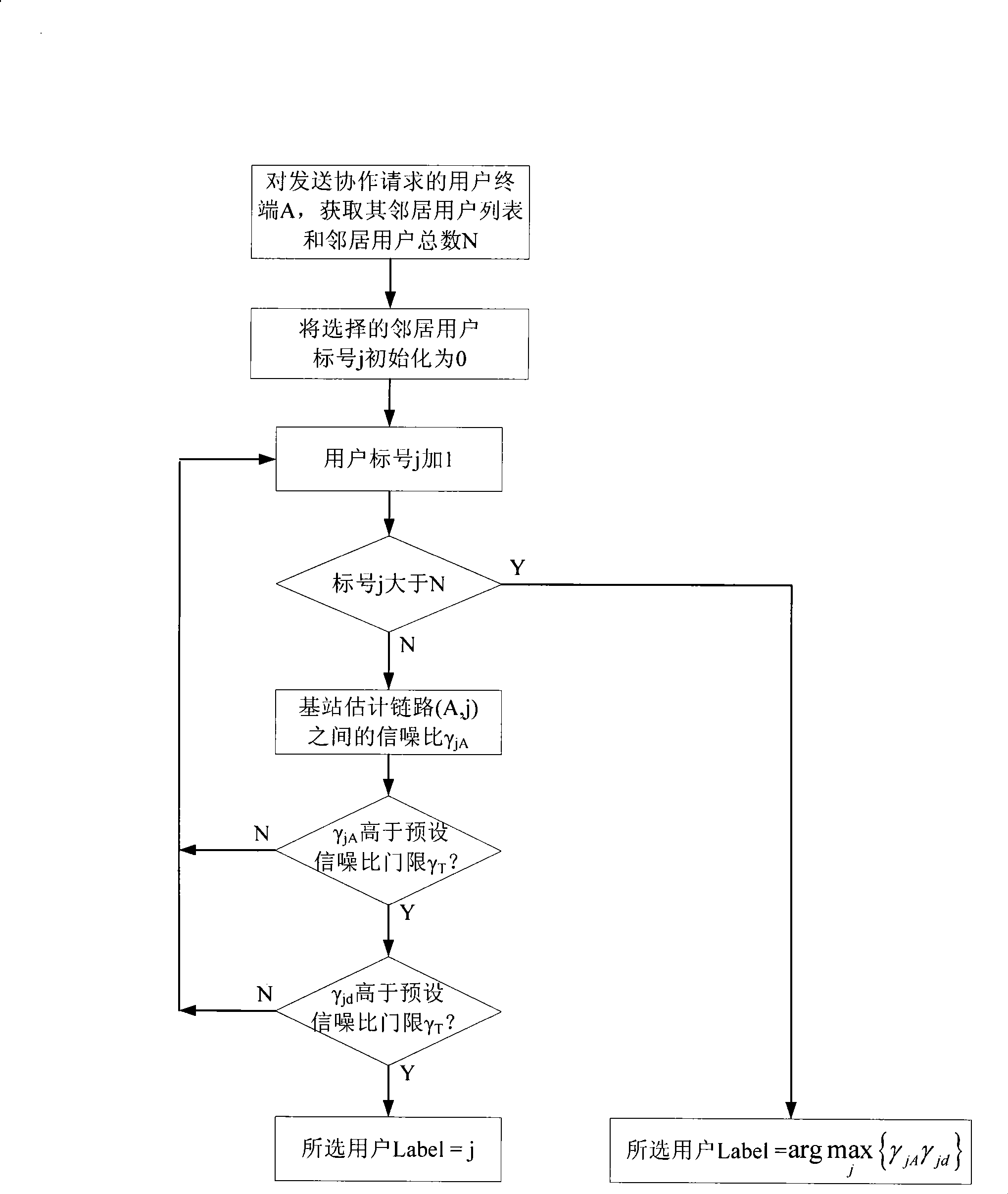
The invention discloses a method for cooperation partner selection and precoding cooperative communications in a cellular communication system. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a user terminal with bad uplink channel quality sends a cooperative communication request to a base station; (2) the base station selects a partner terminal for the user terminal; (3) in a first frame of a cooperation period, the user terminal sends local data to the base station, and the base station and the partner terminal receive the data simultaneously; (4) in a second frame of the cooperation period, the partner terminal sends the local data to the base station, and the base station and the user terminal receive the data simultaneously; (5) in a third frame of the cooperation period, the user terminal and the partner terminal preprocess the relay data by a precoding matrix which is fed back by the base station, and send the relay data to the base station simultaneously; and (6) the base station judges the signals received in the transmission time slots of different frames in a combination way to obtain an estimated value of the sent signal. The method has the advantages of low complexity and high utilization rate of the system resources, and is used for the reliable data transmission in the cellular communication system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Transport network and method
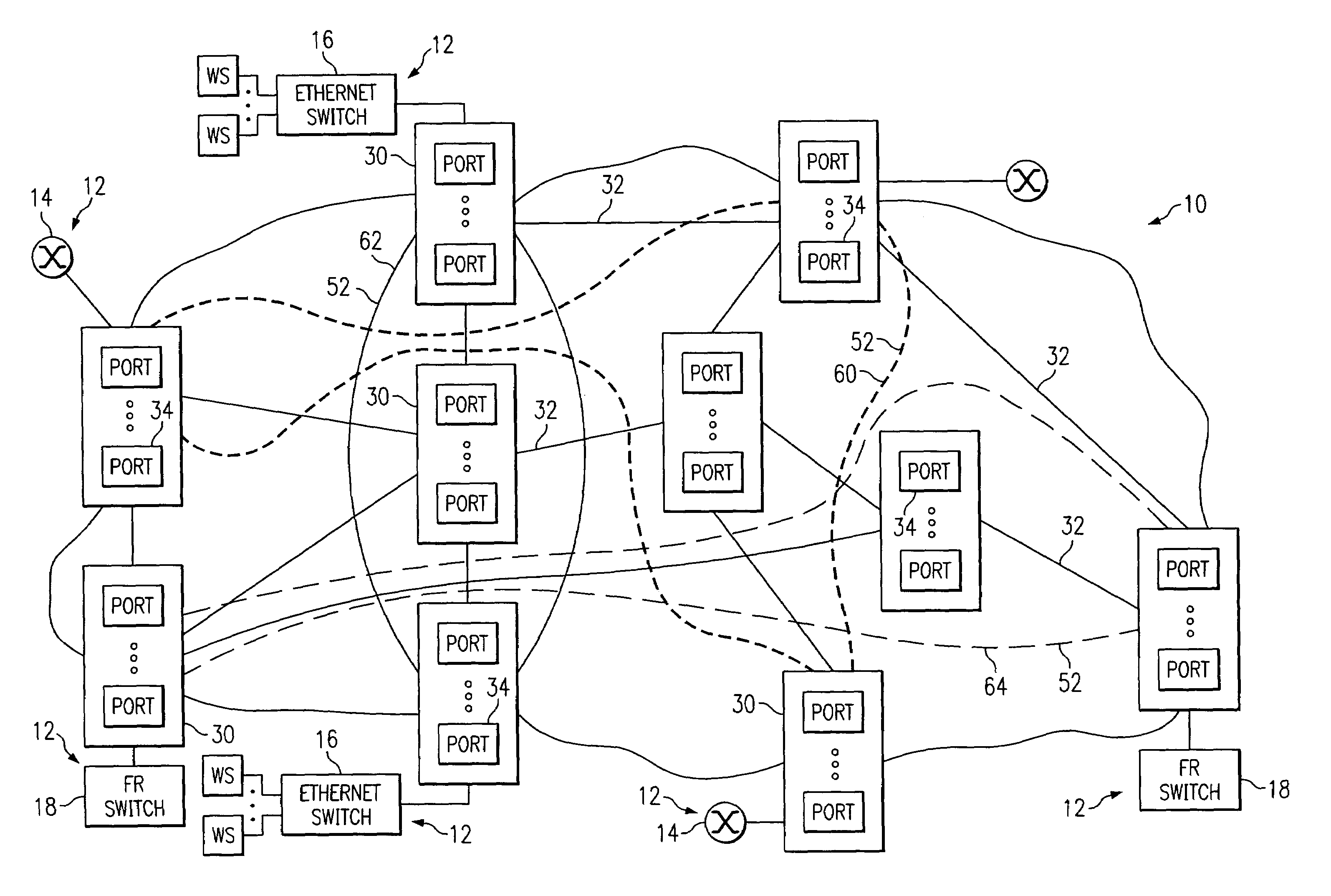
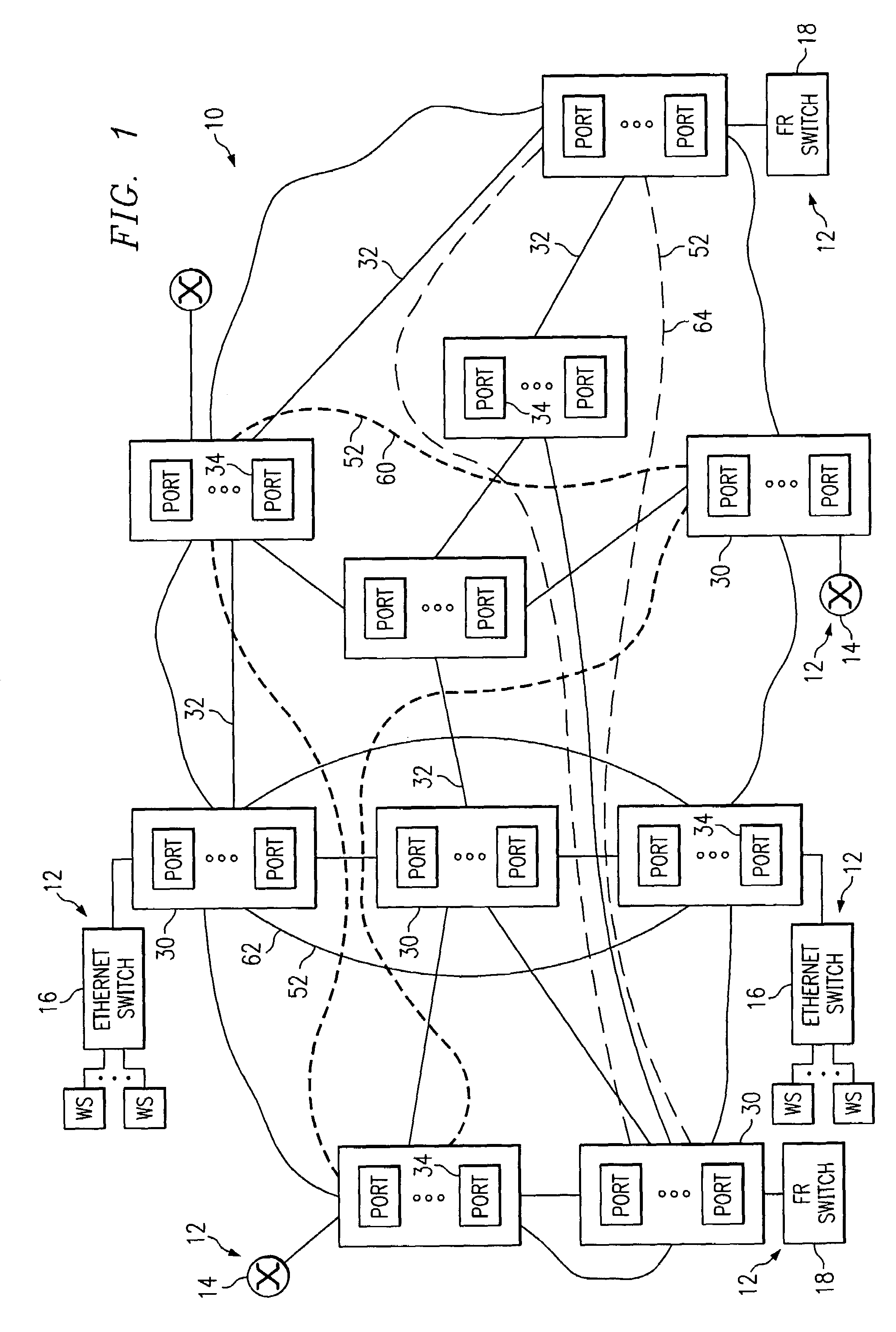
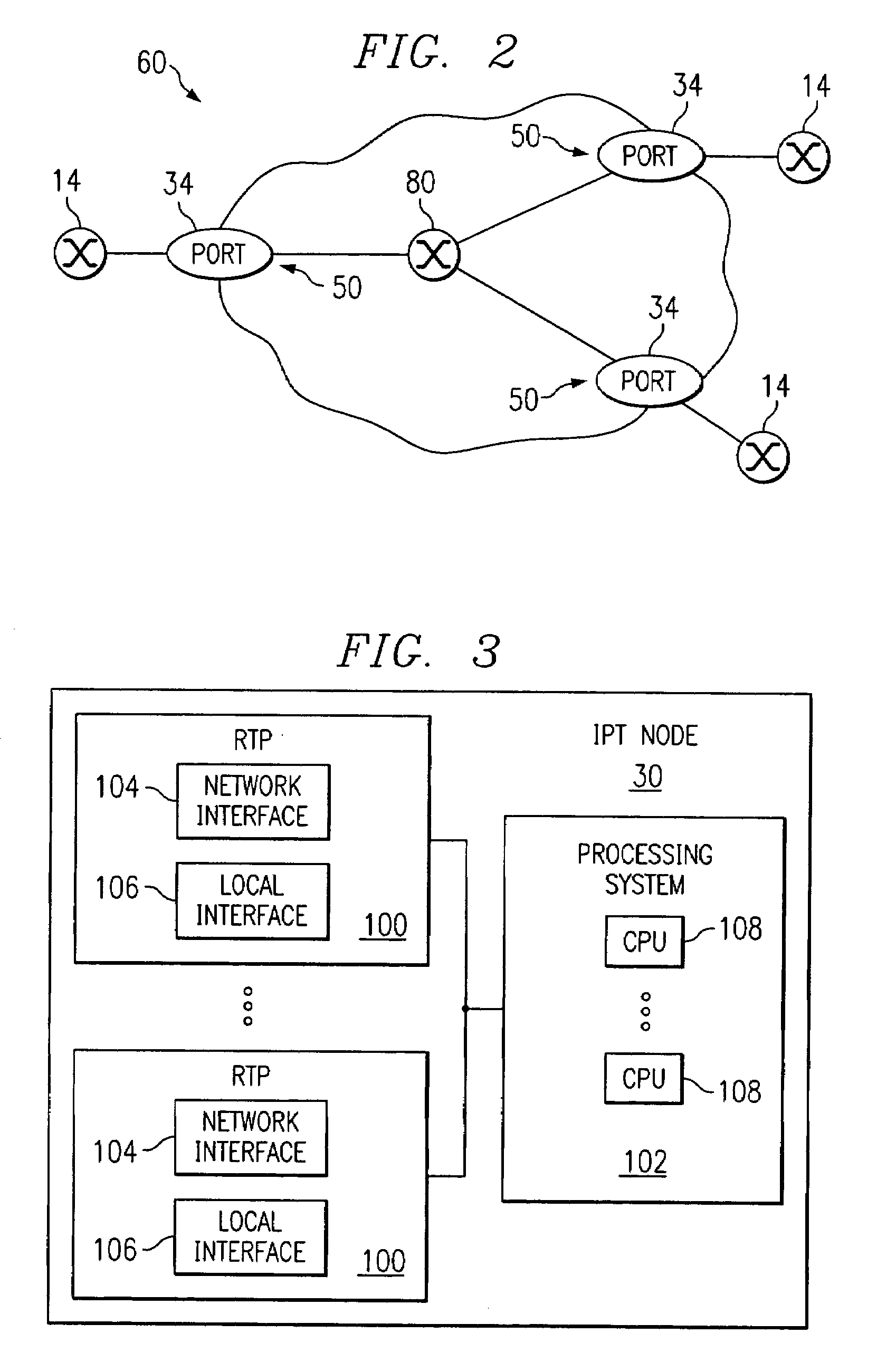
InactiveUS7133403B1Improved external representationEasy to optimizeData switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionSingle elementEngineering
A transport network includes a flexible topology for internally defining transport elements. The transport elements each include a port group having a plurality of geographically distributed ports from the transport network. Point-to-multipoint connectivity is defined between the ports in a port group. An identifier represents the port group as a single element to internal and / or external elements for protocol exchanges.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
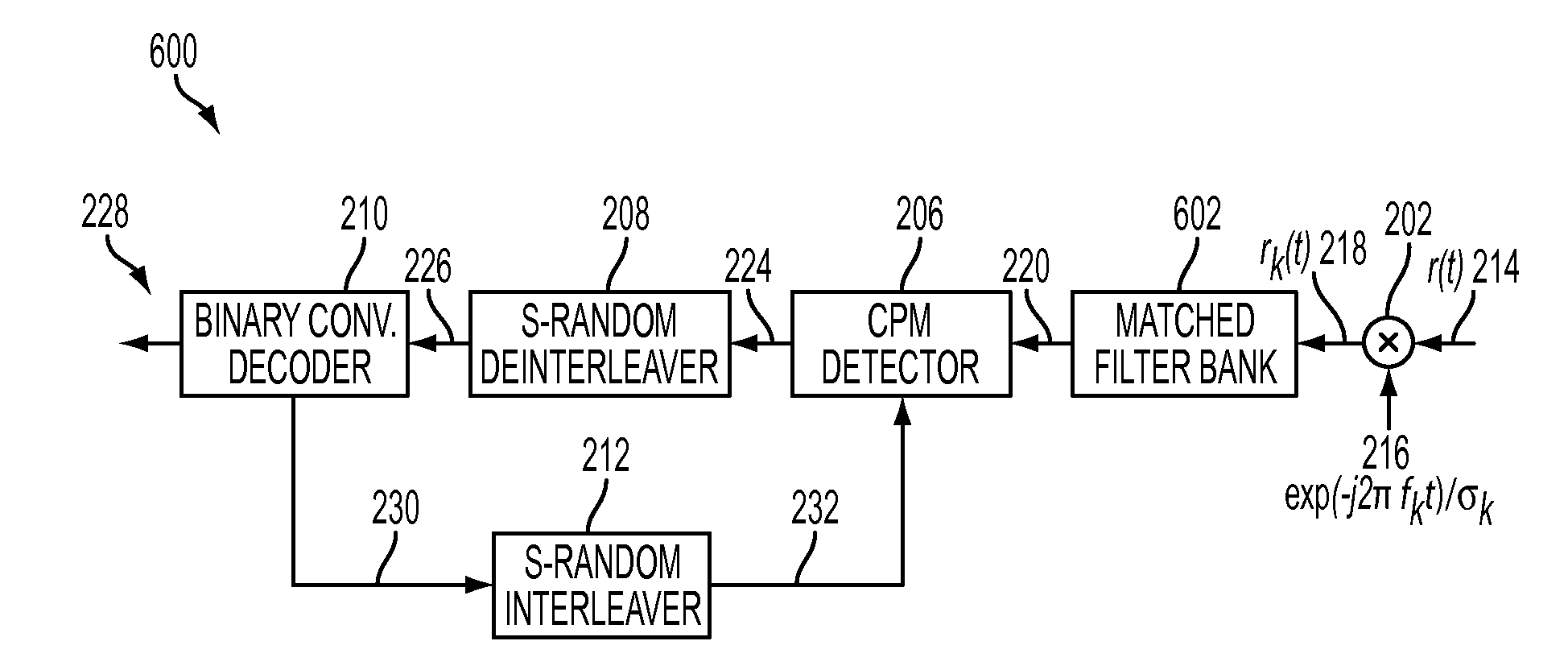
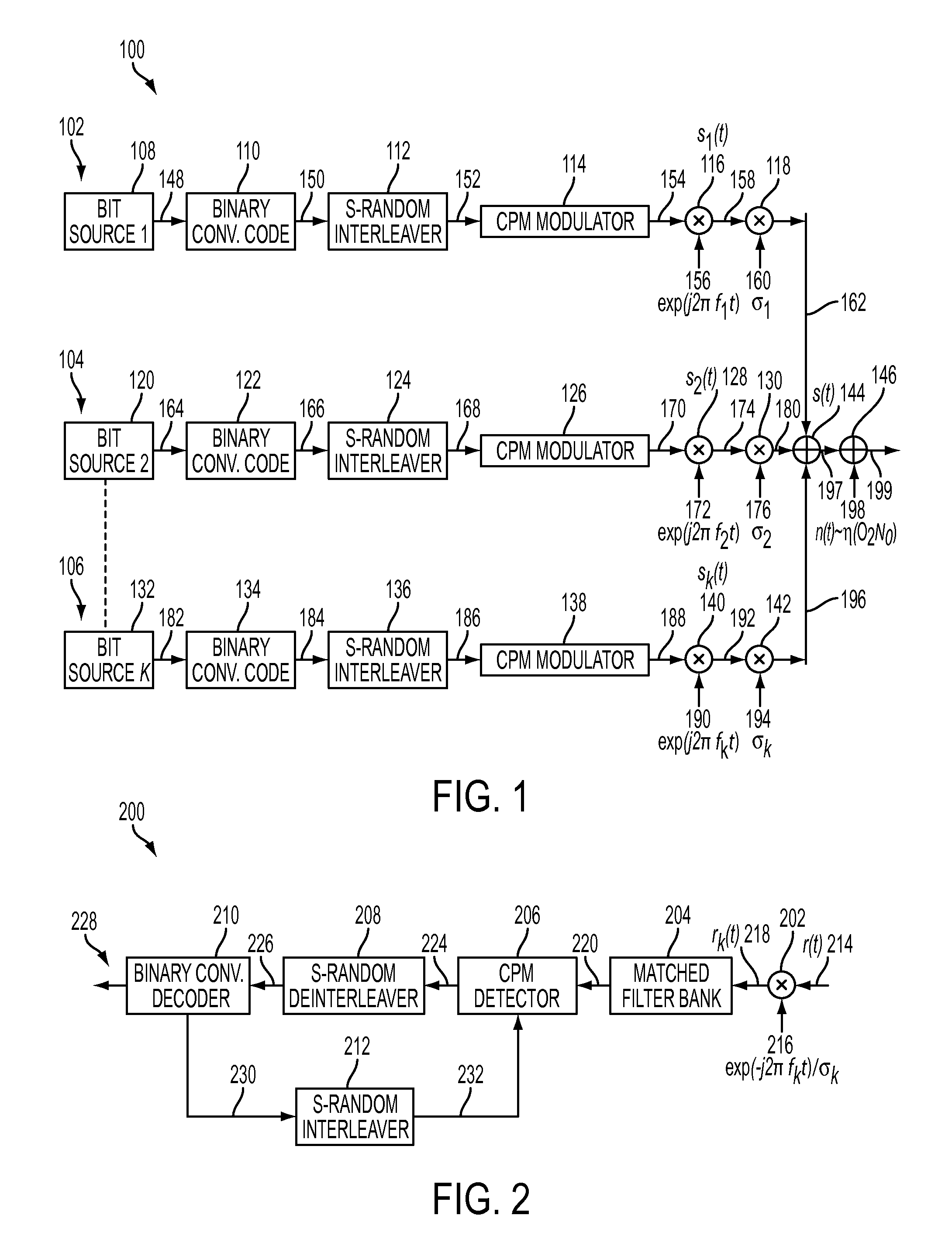
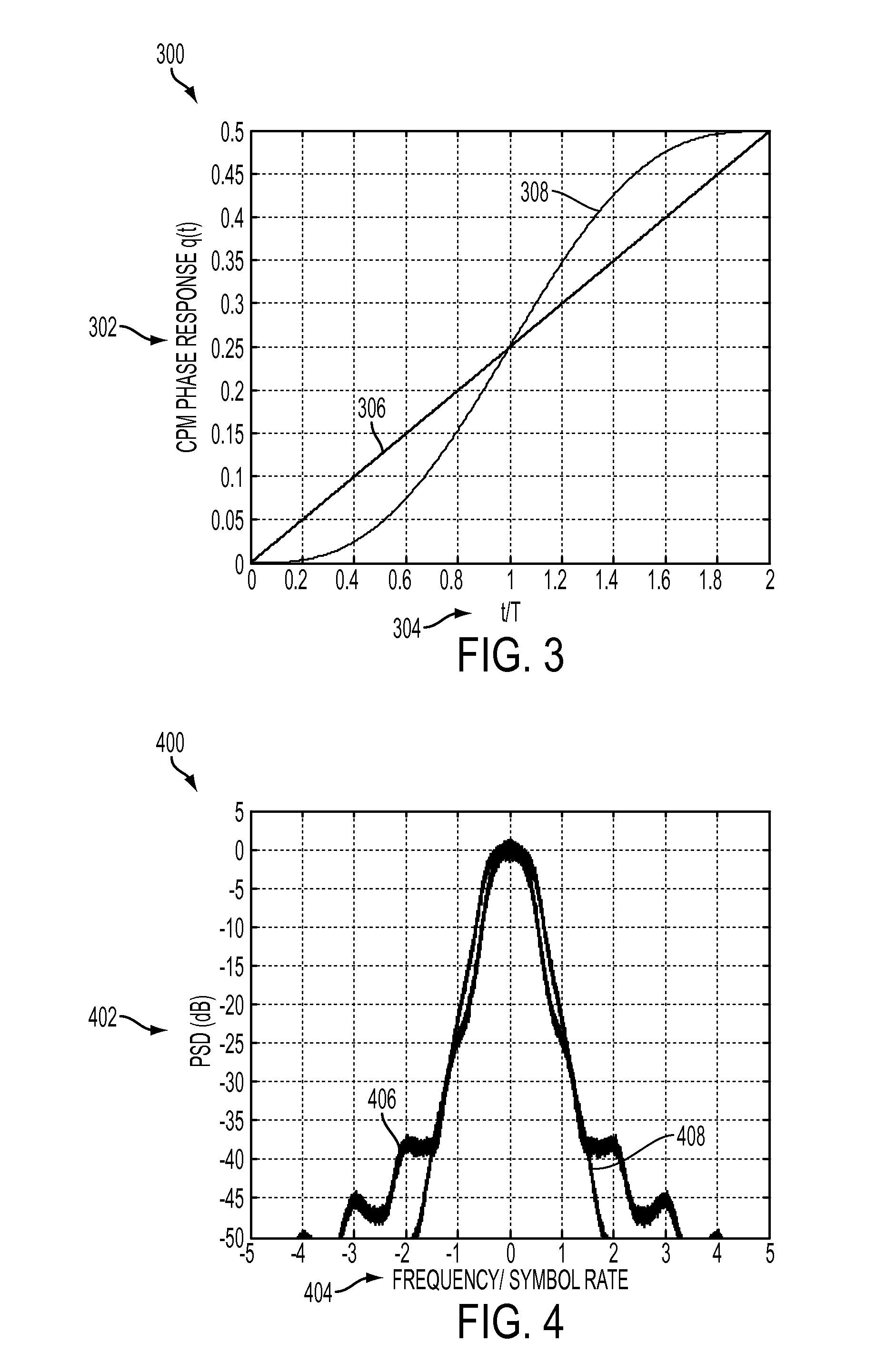
Phase pulse system and method for bandwidth and energy efficient continuous phase modulation
ActiveUS20110275338A1Improve performanceImprove bandwidth efficiencyError preventionAngle modulation detailsSide lobePulse shaping
A new pulse shape for CPM is introduced which is obtained by a linear combination of well-known RC and REC pulse shapes. The new pulse shape addresses the tradeoff between the width of the PSD main lobe and the rate of decay of the side lobe to improve the coded performance of multi-carrier systems affected by ACI. Also, a methodology is proposed to design and evaluate the performance of the new pulse shape for multi-carrier, coded systems based on the modulation constrained capacity. Furthermore, a binary convolutional code and the CPM modulator are concatenated using an S-random bit interleaver to lower the error floor. Finally, Laurent representation of the new pulse shape is suggested such that by retaining only the principal pulses at the receiver, complexity of the receiver can be reduced.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
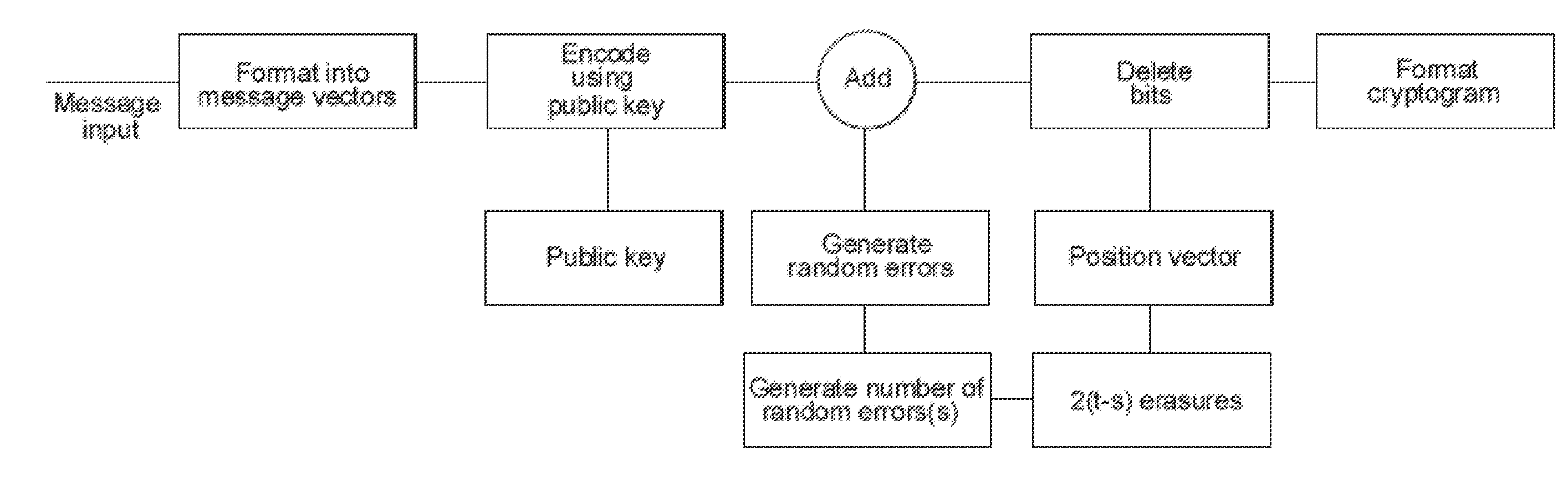
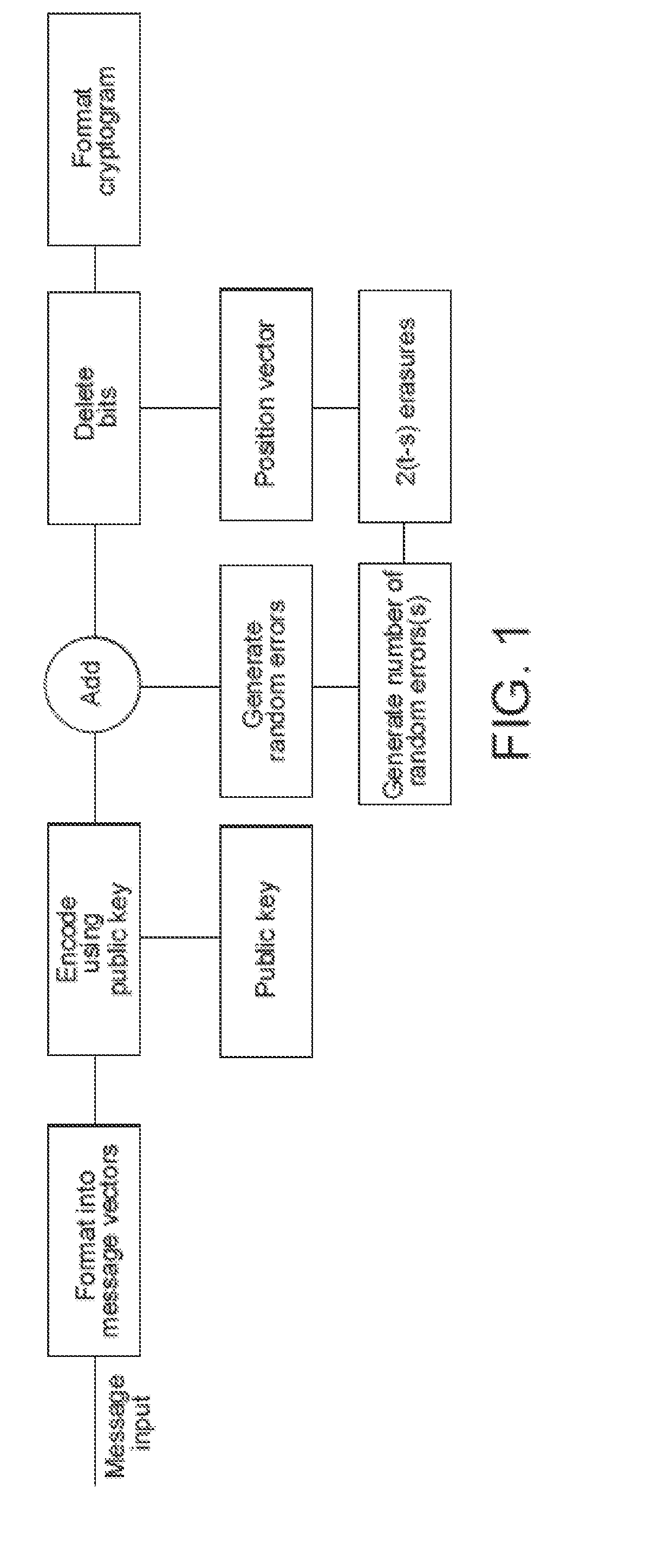
Methods, systems and apparatus for public key encryption using error correcting codes
InactiveUS20150163060A1Improve securityEasy to broadcastKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareTrade offs
This invention provides improved security of the McEliece Public Key encryption system adding features which make full use of random number generation for given message and cryptogram parameters. Different embodiments of the invention are described which enable the level of security to be traded-off against cryptogram size and complexity. Message vectors are encoded with a scrambled generator matrix, using matrix multiplication to form codeword vectors. Shortened corrupted codewords are generated by corrupting each codeword vector and omitting a predefined number of bits, whereby a cryptogram is formed from the shortened corrupted codewords. Measures are included to defeat attacks based on information set decoding. A number of different applications are given.
Owner:PQ SOLUTIONS LTD
Apparatus and method for transmitting data using adaptive modulation and coding in mobile communication system having a relay station
InactiveUS20070155338A1Improve bandwidth efficiencySite diversityActive radio relay systemsHigh bandwidthEngineering
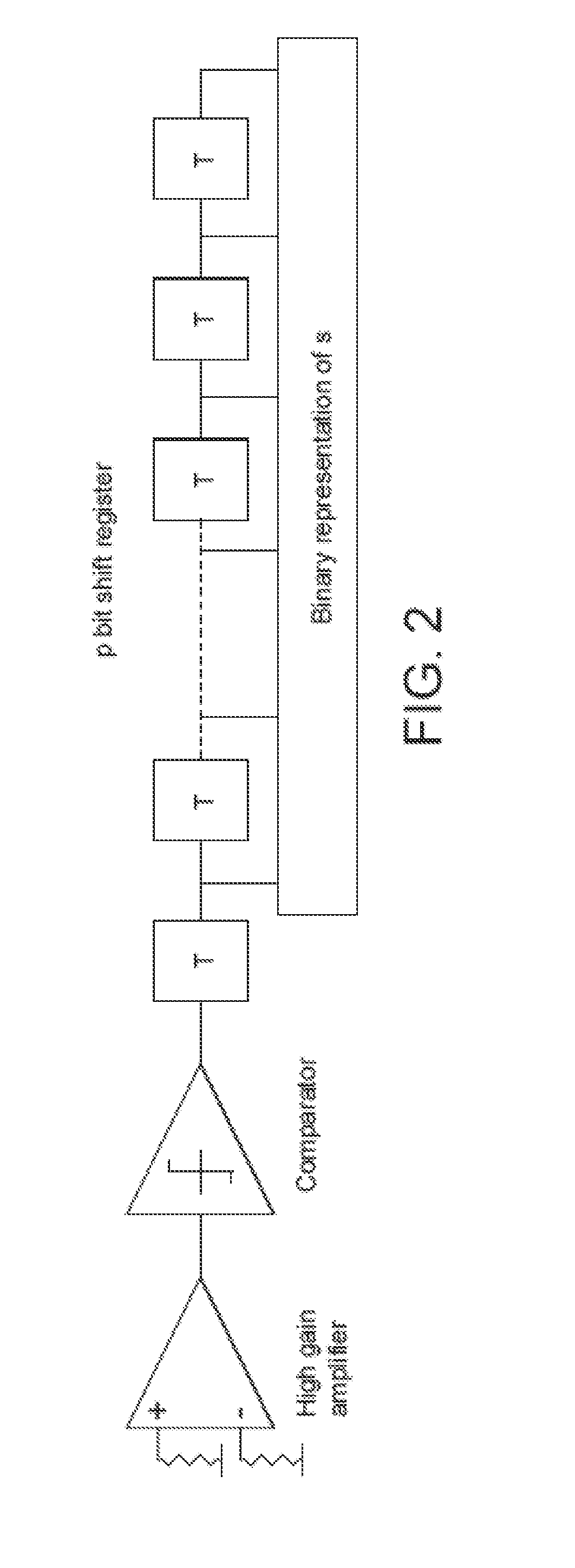
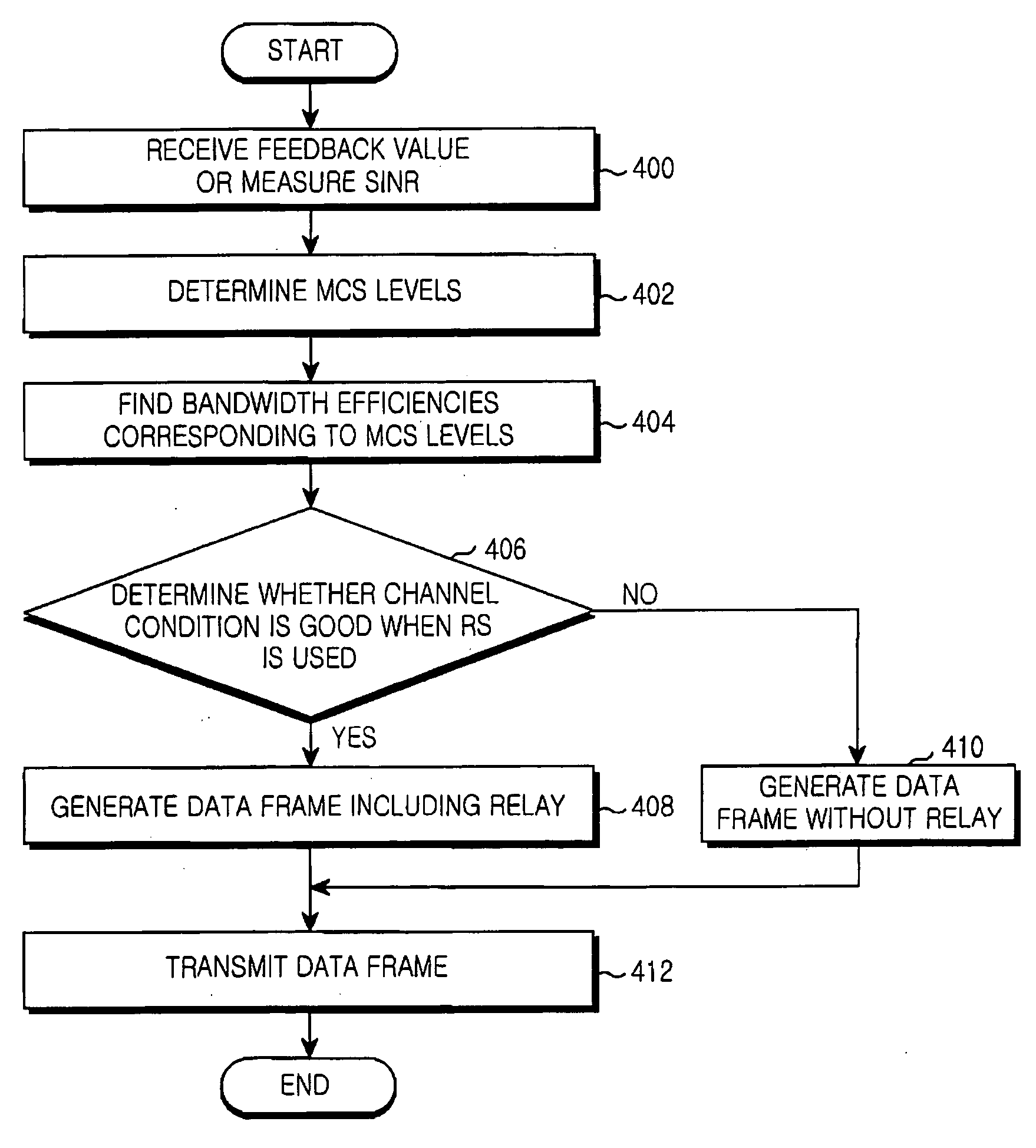
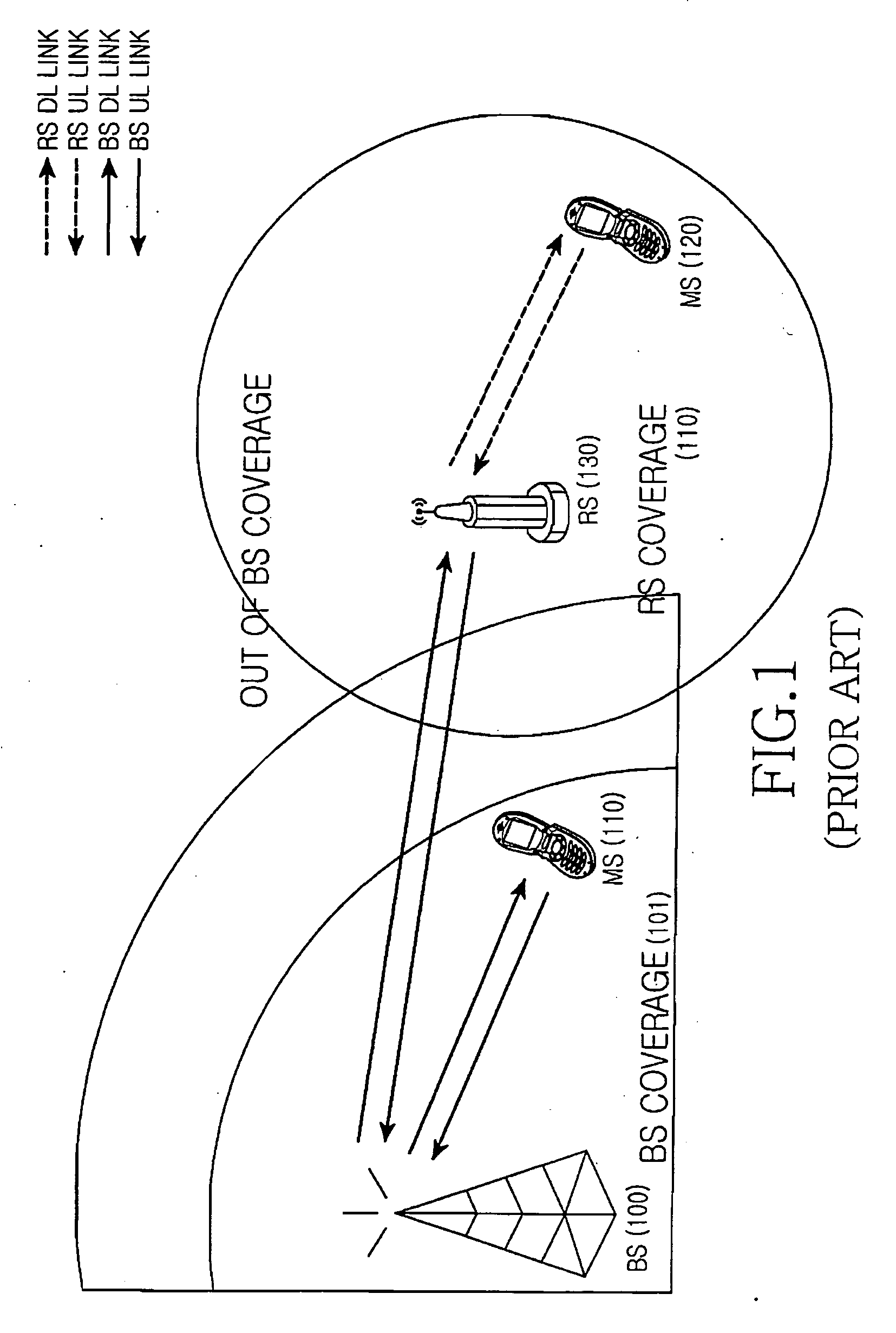
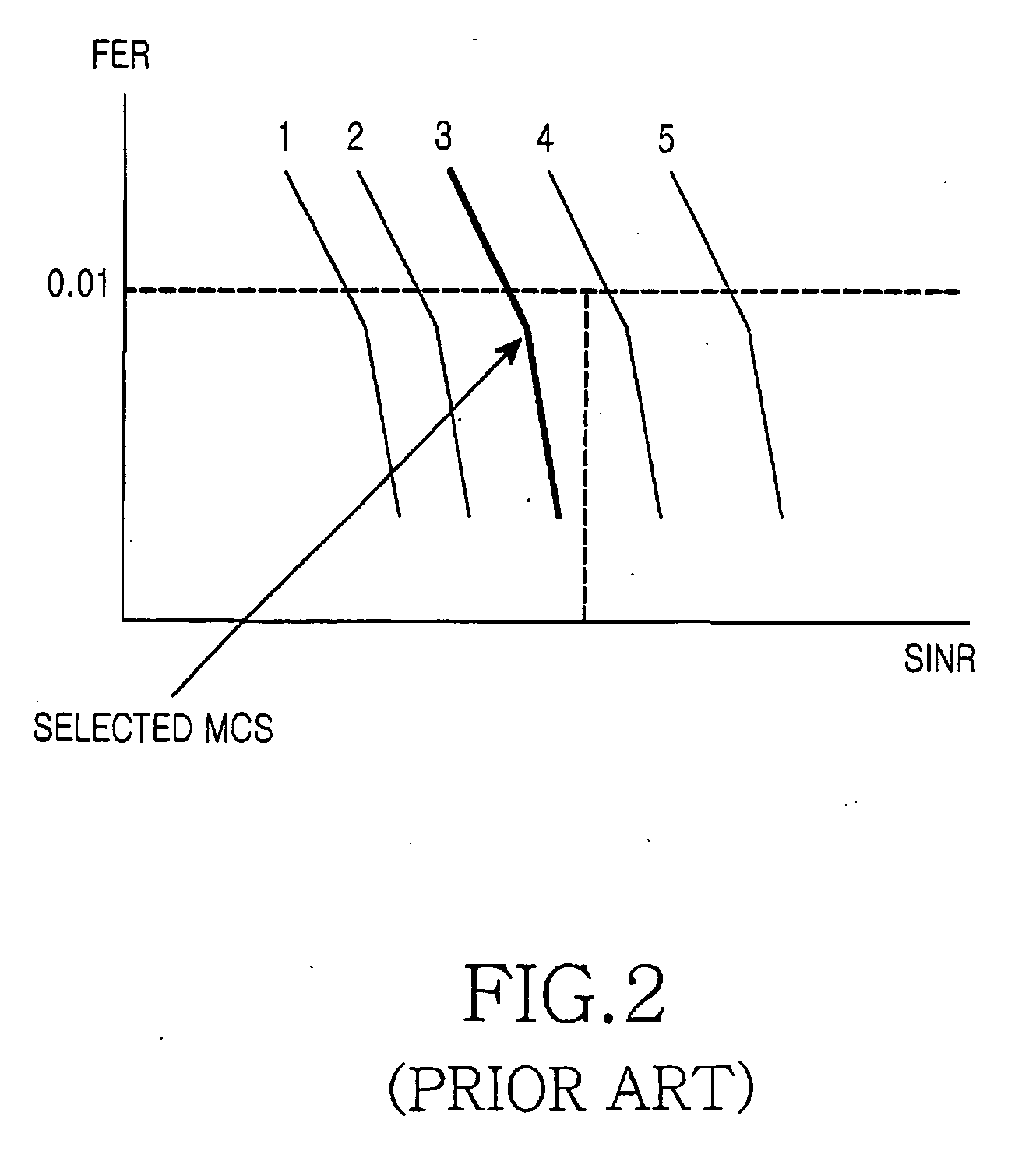
Provided are an apparatus and method for transmitting data using an Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC) scheme in a mobile communication system with a Relay Station (RS). A relay indicator value is received indicating a strength of a downlink signal transmitted to a destination through a relay path including the RS and a direct indicator value indicating a strength of an downlink signal directly transmitted to the destination via a direct path without passing through the RS. Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS) levels are determined using the relay and direct indicator values for both the relay and direct paths. Bandwidth efficiencies are found in correspondence with the MCS levels and are compared depending on whether the relay path or the direct path is used. A path resulting in a higher bandwidth efficiency is selected to generate a data frame having a structure corresponding to the selected path. The data frame is transmitted to the destination or the RS.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dynamic bandwidth allocation and service differentiation for broadband passive optical networks
InactiveUS7808913B2Effective bandwidthSpace complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionService-level agreementTraffic prediction
A dynamic upstream bandwidth allocation scheme is disclosed, i.e., limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP), to improve the bandwidth efficiency of upstream transmission over PONs. LSTP adopts the PON MAC control messages, and dynamically allocates bandwidth according to the on-line traffic load. The ONU bandwidth requirement includes the already buffered data and a prediction of the incoming data, thus reducing the frame delay and alleviating the data loss. ONUs are served by the OLT in a fixed order in LSTP to facilitate the traffic prediction. Each optical network unit (ONU) classifies its local traffic into three classes with descending priorities: expedited forwarding (EF), assured forwarding (AF), and best effort (BE). Data with higher priority replace data with lower priority when the buffer is full. In order to alleviate uncontrolled delay and unfair drop of the lower priority data, the priority-based scheduling is employed to deliver the buffered data in a particular transmission timeslot. The bandwidth allocation incorporates the service level agreements (SLAs) and the on-line traffic dynamics. The basic limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP) scheme is extended to serve the classified network traffic.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
System and method for reducing adjacent channel interference (ACI) in a multicarrier modulation system
InactiveUS6934246B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyReasonable power sensitivity lossError preventionTime-division multiplexAdjacent-channel interferenceFrequency spectrum
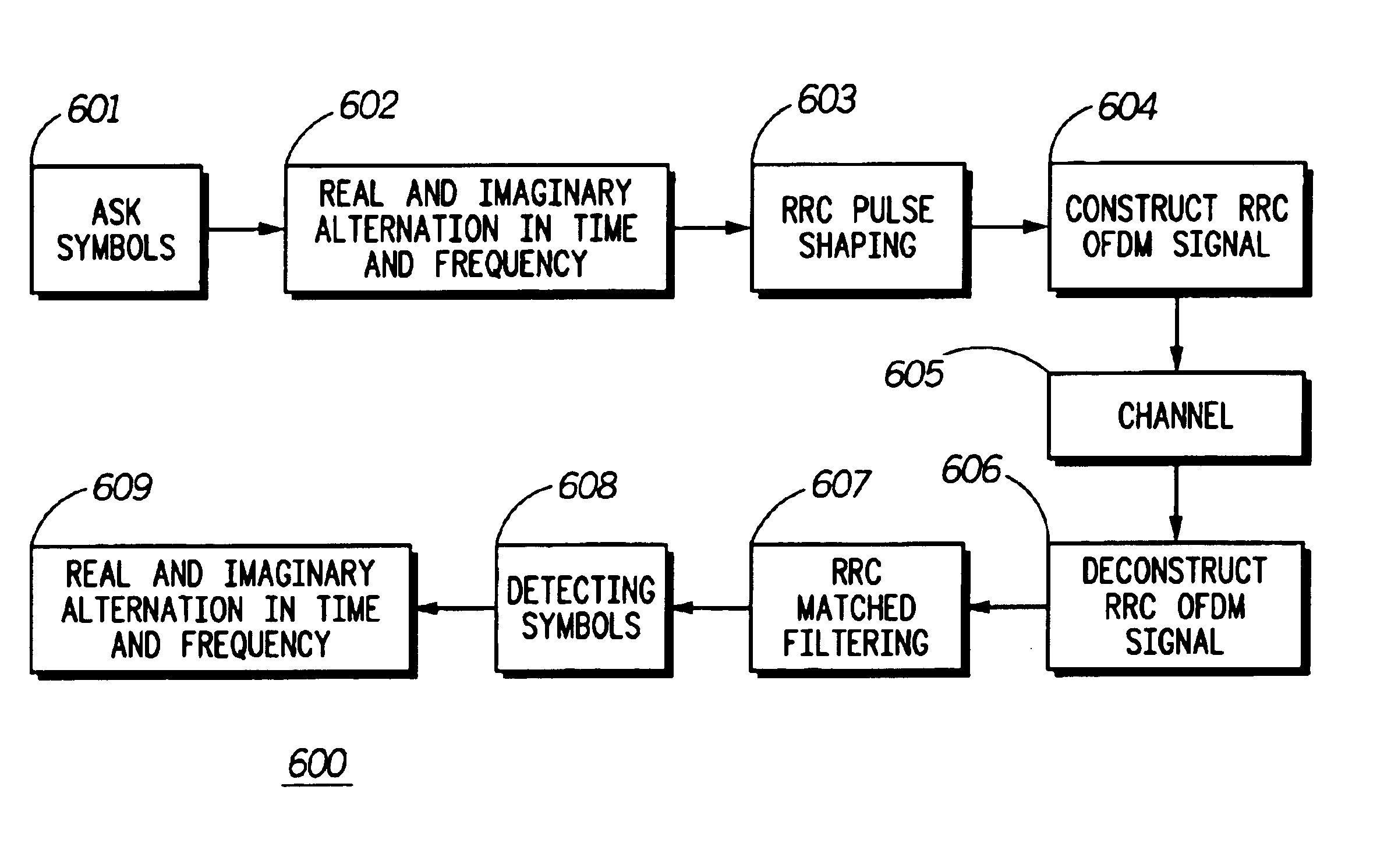
An improved multicarrier modulation system and method, which has the advantages of both isotropic orthogonal transfer algorithm orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (IOTA OFDM) and scalable advanced modulation (SAM), is introduced. The invention is root raised cosine (RRC) OFDM using the most spectrally efficient RRC filter without sacrificing the compact subchannel spacing of OFDM. The invention further provides an adjacent channel interference (ACI) suppression scheme and a modified RRC for better suppressing ACI of RRC OFDM. The ACI suppression scheme can also be applied to SAM with the modified RRC and to IOTA OFDM with a modified IOTA. The invention greatly improves a major problem of conventional OFDM namely ACI due to the use of a wide subchannel filter. Thus, the invention allows OFDM to meet even the strictest ACI requirements, which was not possible by using a conventional raised cosine windowing method.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
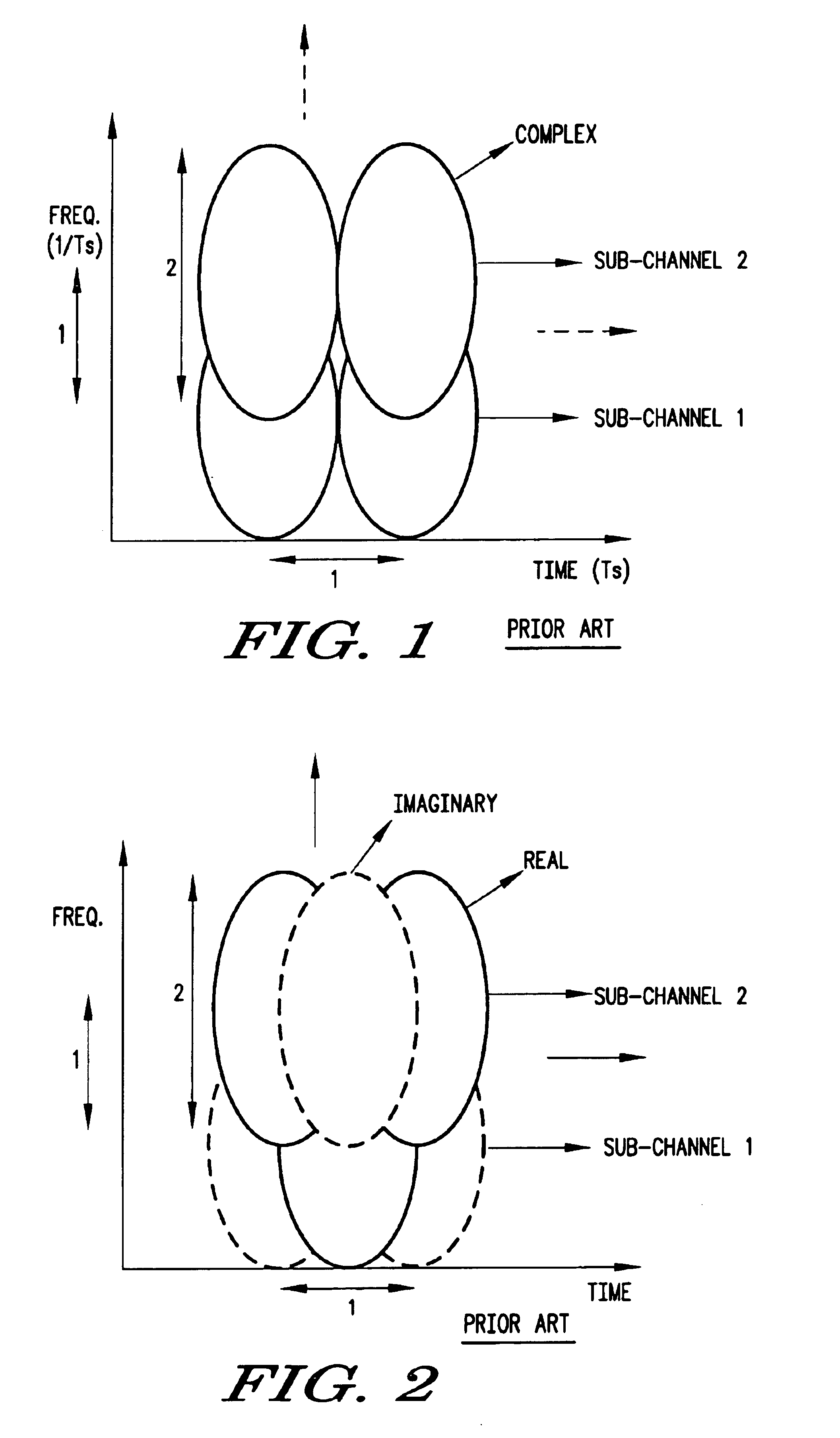
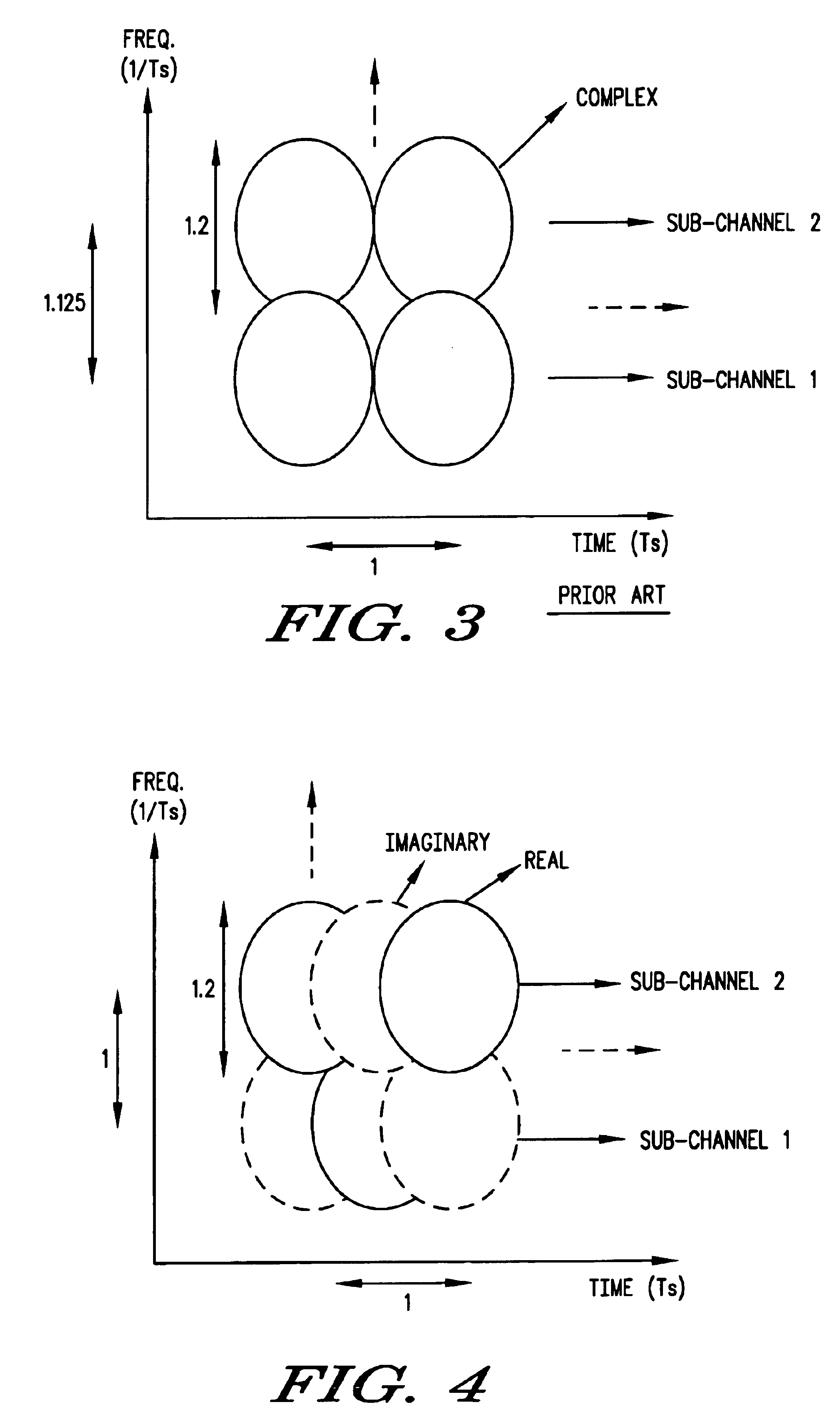
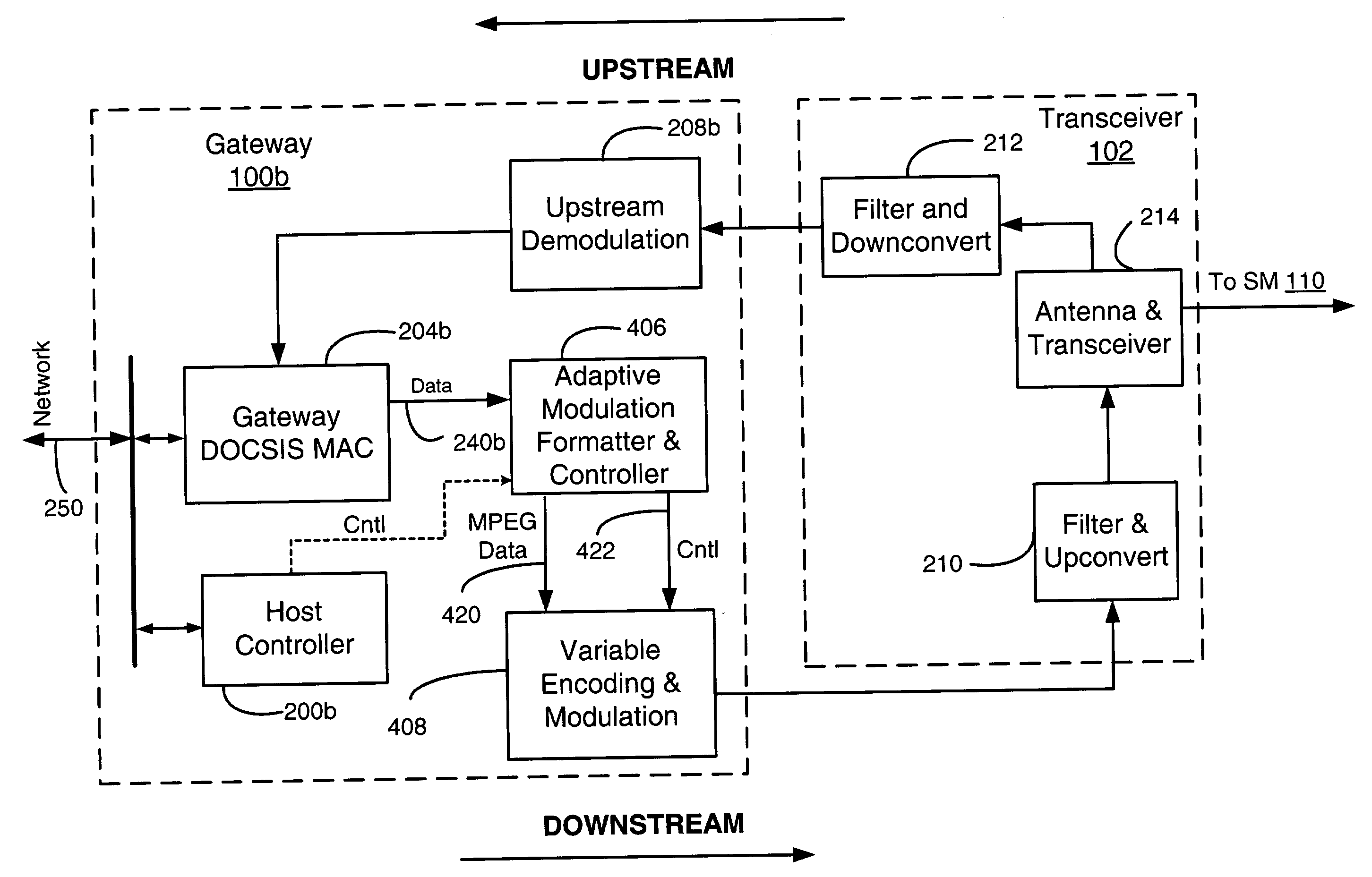
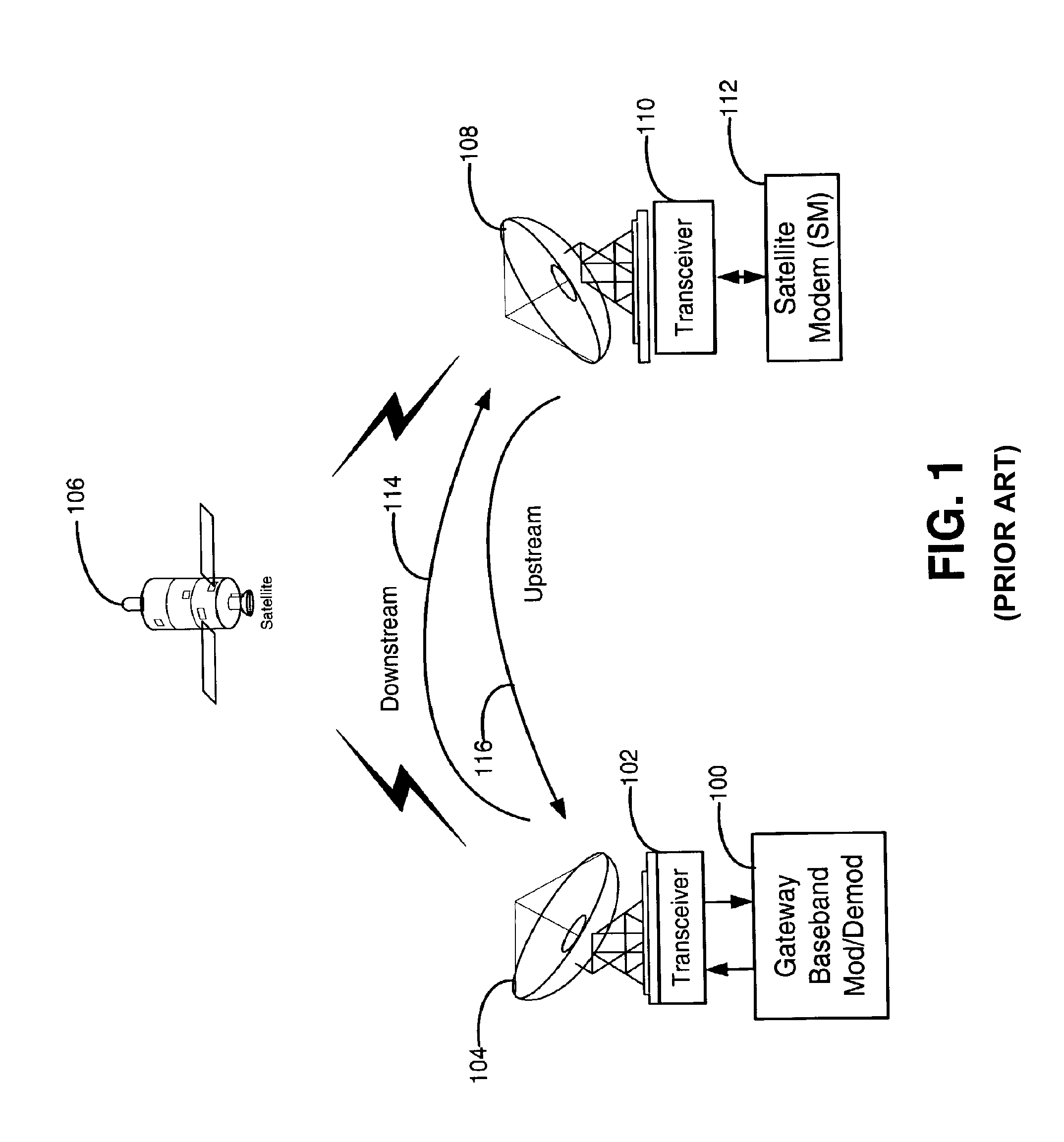
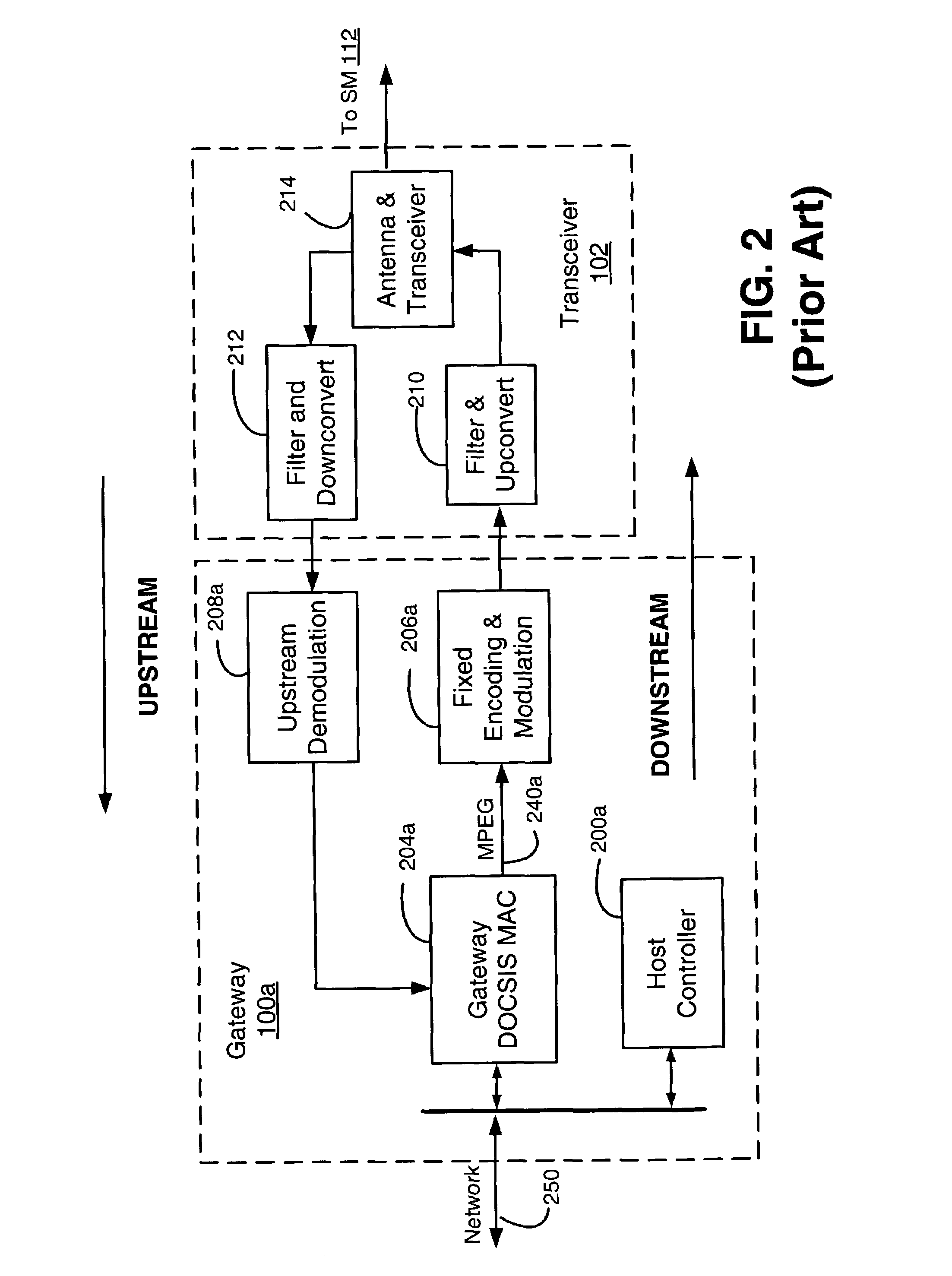
Downstream time domain based adaptive modulation for DOCSIS based applications
InactiveUS7508785B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove bandwidth efficiencyBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexTime domainSignal quality
In a DOCSIS based satellite gateway data is transmitted over a single downstream channel, at different throughput rates. Data destined for each subscriber / receiver is assigned a throughput rate depending upon the downstream signal quality of that subscriber / receiver. To accomplish this, the downstream DOCSIS MAC data is parsed to extract DOCSIS packets. The DOCSIS packets are then loaded into packet queues based on an identifier within such packets such as the MAC destination address or SID. Each of the queues represents a bandwidth efficiency or throughput rate that can be currently tolerated by specific subscribers based on the current signal quality being experienced at the subscriber location. A PHY-MAP describing the downstream data structure to be transmitted and inserted into the downstream data. Data is extracted from the packet queues in queue blocks as defined by the PHY-MAP. The queue blocks are modulated with transmission parameters appropriate for each queue block and transmitted to the DOCSIS based satellite modems. The satellite modems extract the PHY-MAP from the downstream data and use the information contained in it to demodulate and decode the queue for which they have sufficient downstream signal quality. Satellite modems measure and transmit downstream signal quality to the satellite gateway to be used to assigned traffic to the appropriate queues.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
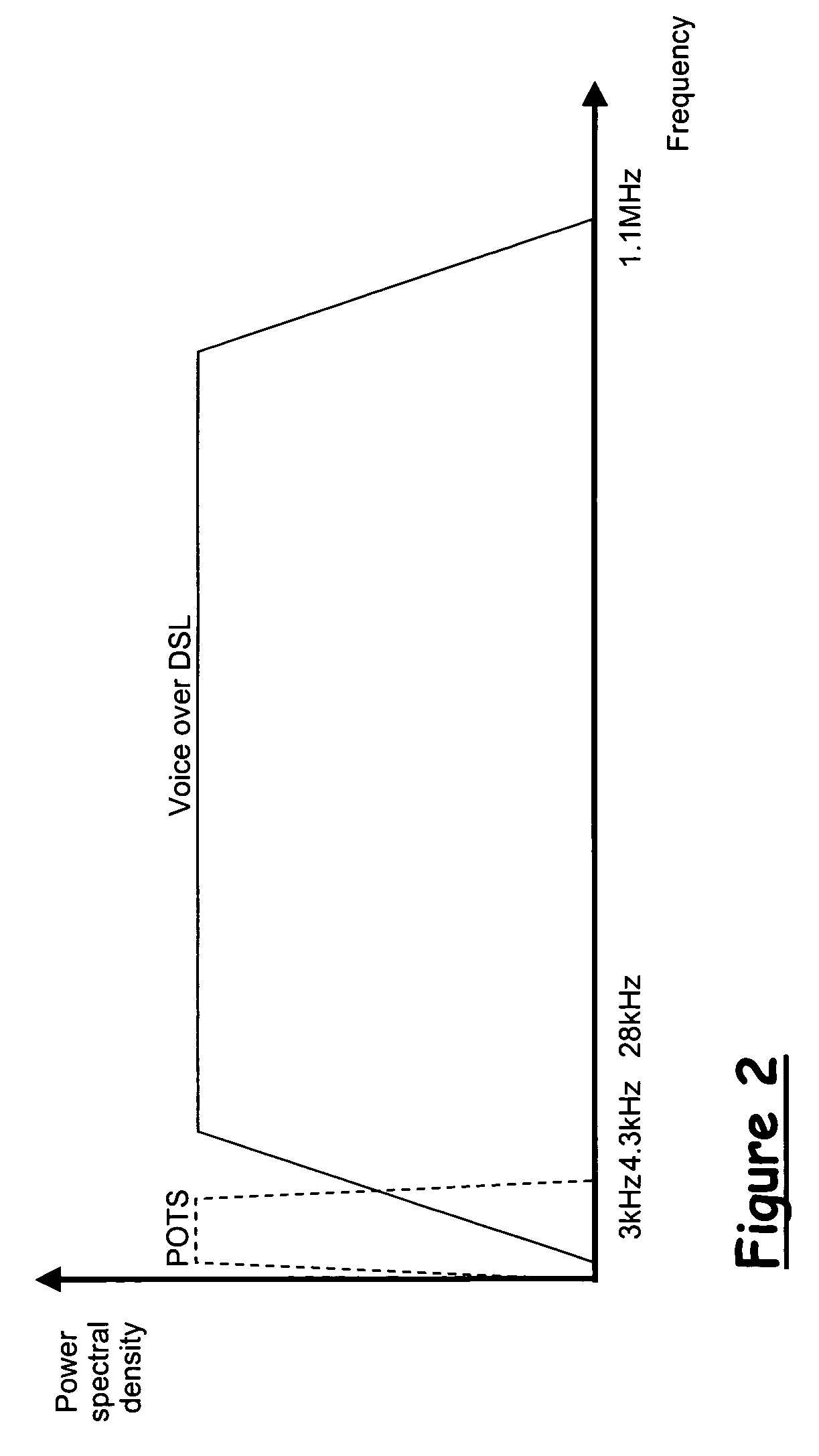
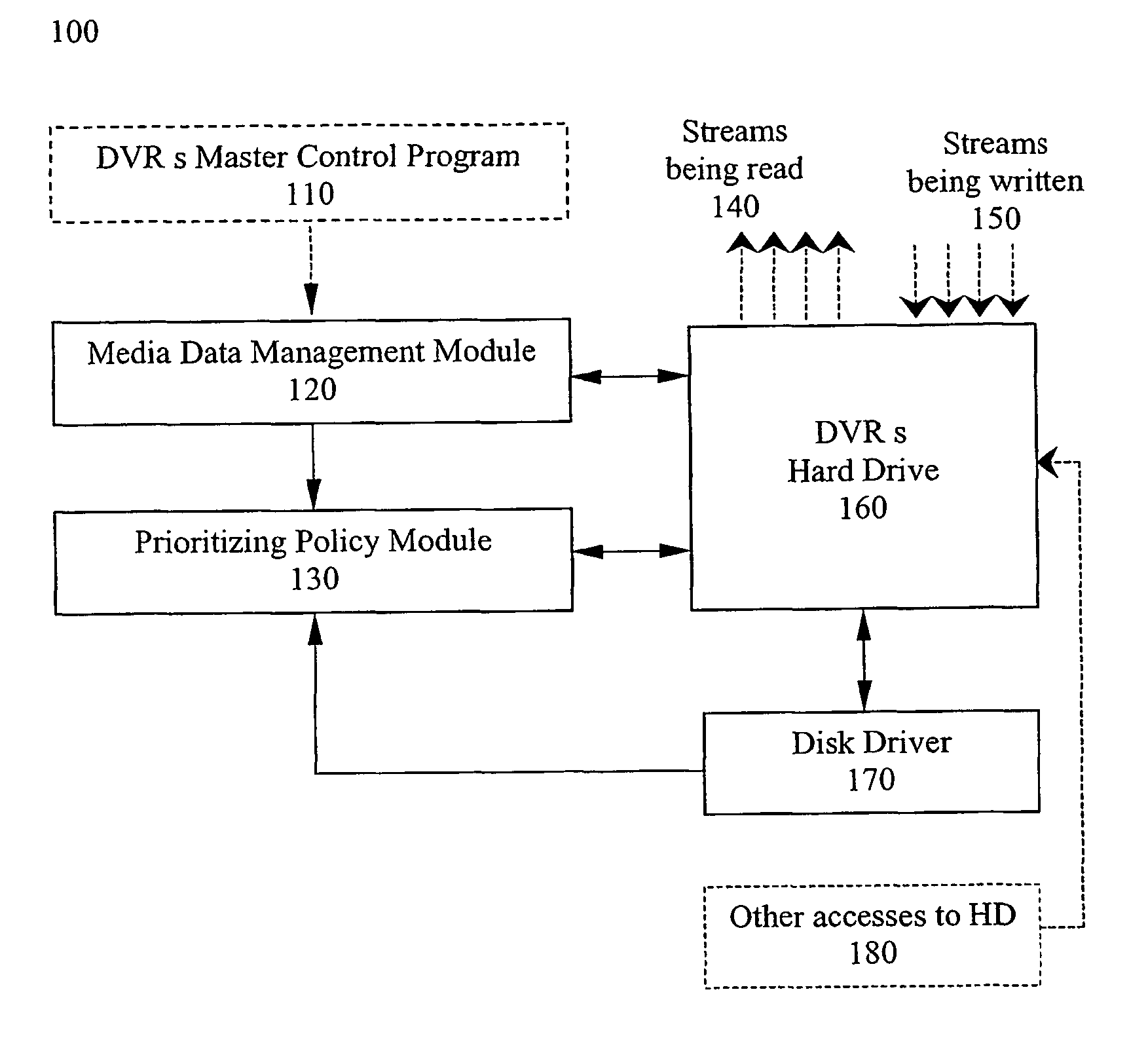
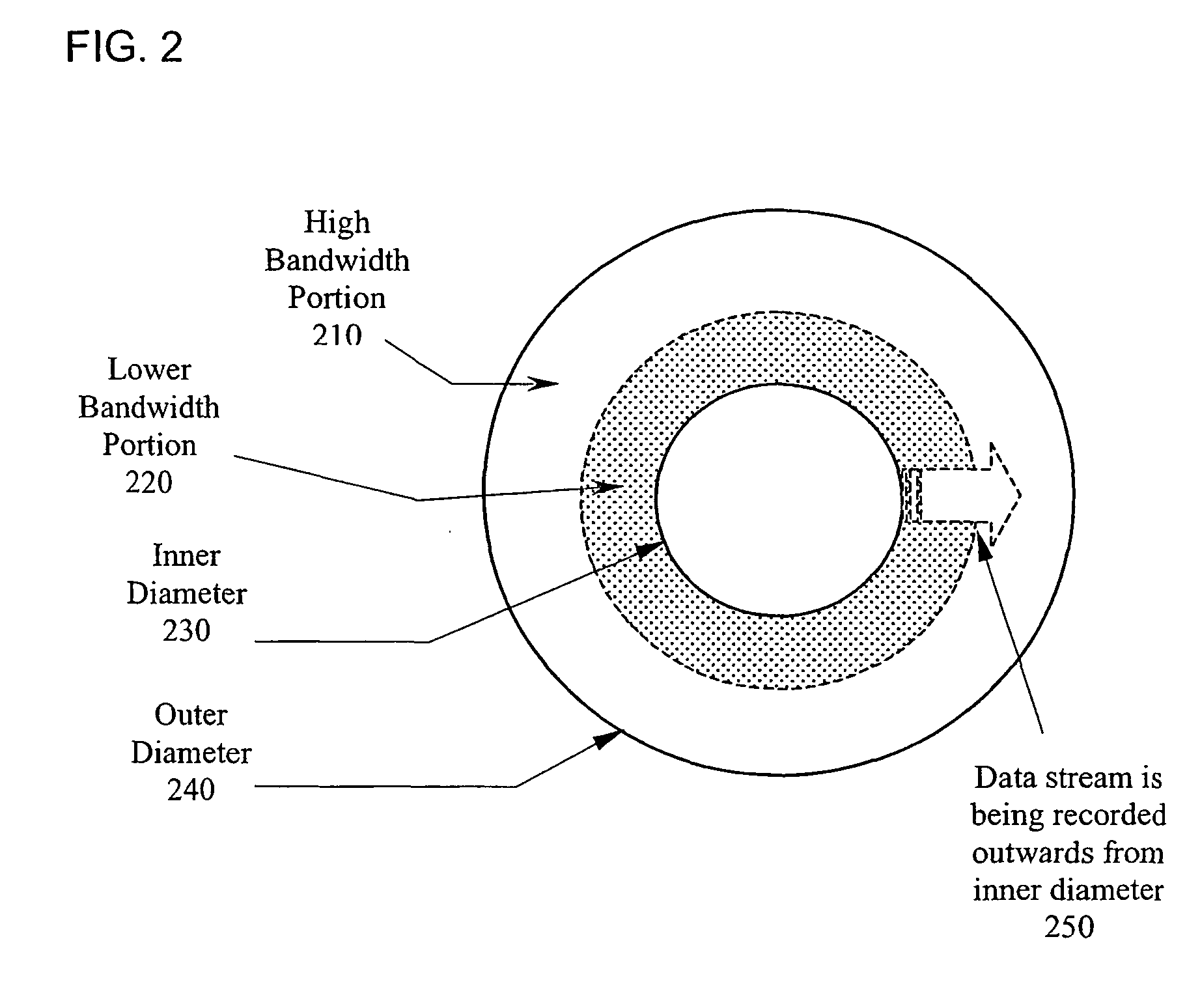
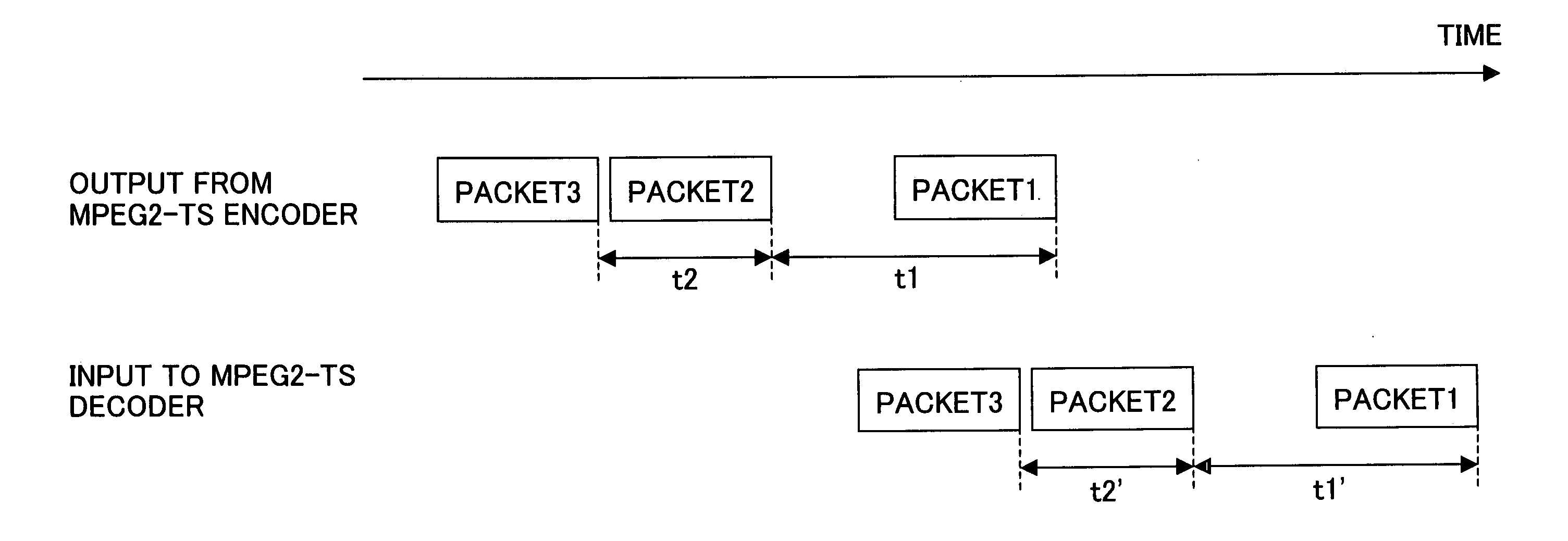
Method for improving bandwidth efficiency
InactiveUS6965730B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh bandwidthHard disc drive
A method for dynamically managing a digital recording system's bandwidth requirements, provides prioritized accesses to the recording system's hard drive according to a pre-defined policy which gives the first priority to the data streams being written to the disk, the second priority to the data streams being read from the disk, and the third priority to other accesses to the disk. The recording system's bandwidth efficiency may also be improved by optimizing allocation of the disk's storage space which is partitioned into lower bandwidth portions and higher bandwidth portions, where lower bandwidth data streams are stored in lower bandwidth portions and higher bandwidth data streams are stored in higher bandwidth portions.
Owner:TIVO SOLUTIONS INC
Multi transform OFDM systems and methods with low peak to average power ratio signals
InactiveUS20140362934A1Low peak to average power ratioImprove bandwidth efficiencyAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationHigh bandwidthOfdm transmitter
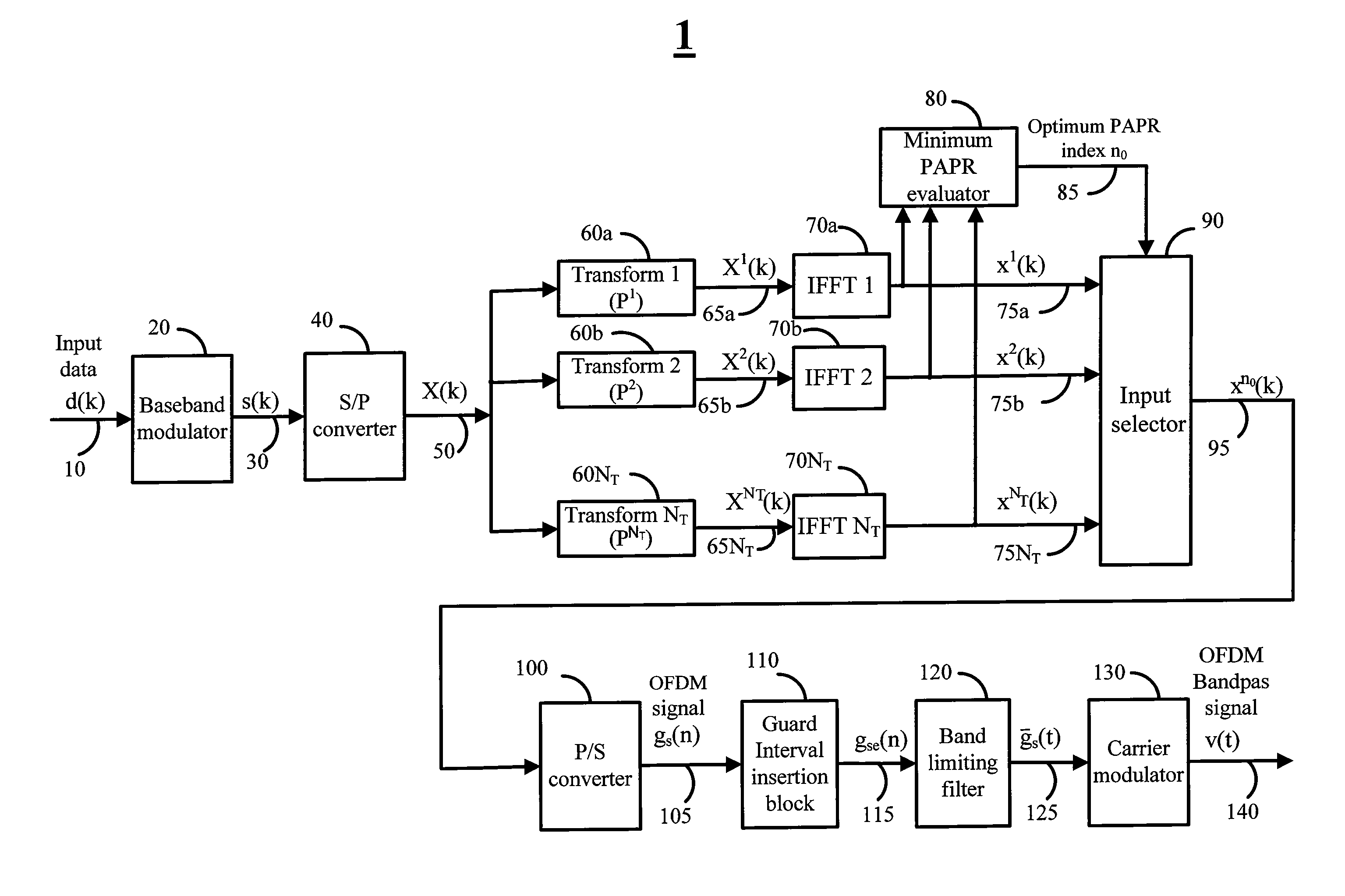
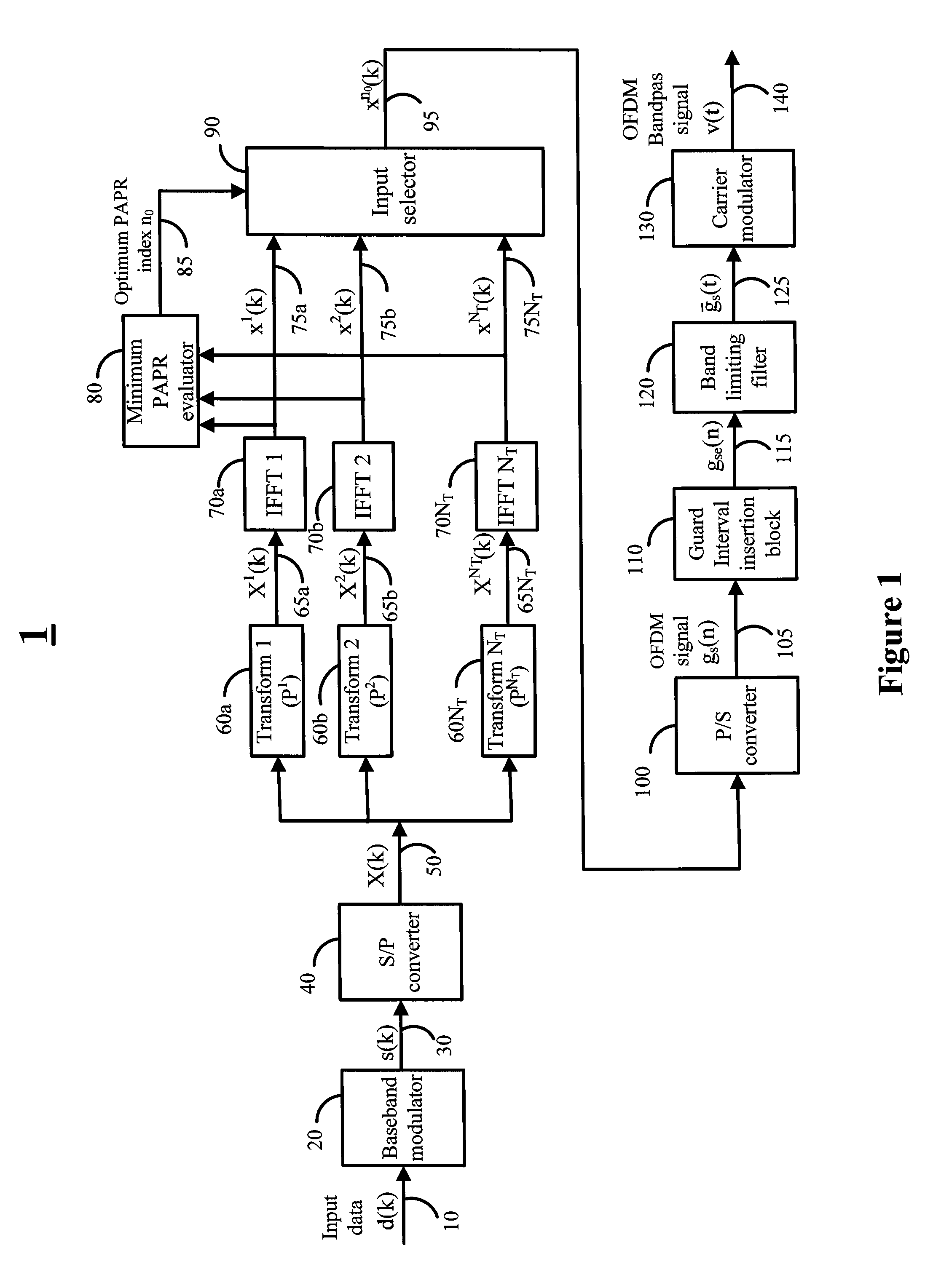
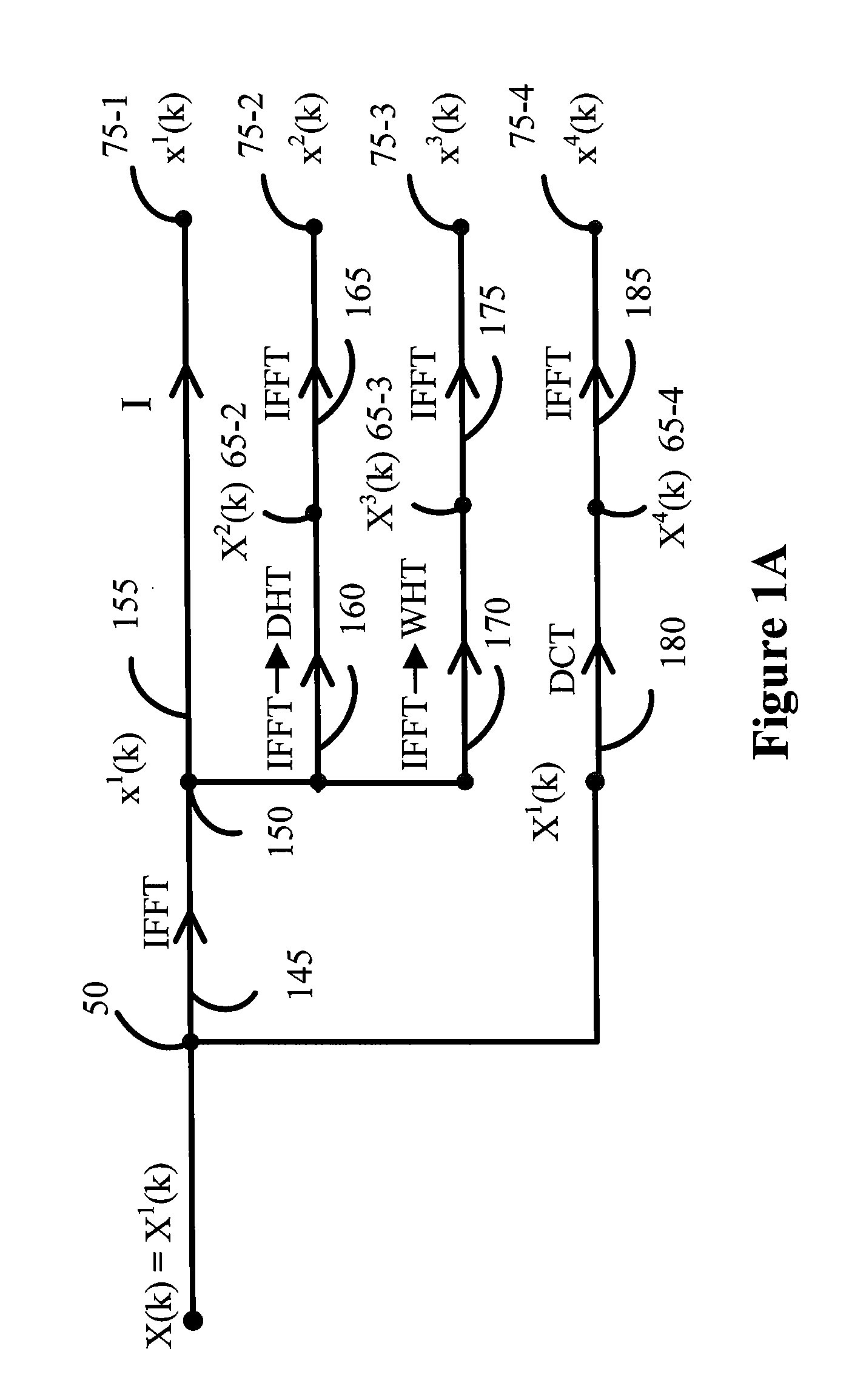
Various embodiments of the invention are directed to methods and systems for multi transform OFDM transmitter and receivers with low peak to average power ratio (PAPR) signals, that have high bandwidth efficiency and are computational efficient. For example, various embodiments of the transmitter may utilize an architecture comprised of a baseband modulator, a serial to parallel converter, a bank of multiplicity NT orthonormal transforms unit, a bank of multiplicity NT inverse Fourier transforms unit, a dummy symbols generator, and a minimum PAPR evaluation unit for finding the optimum transform index n0. Various embodiments of the receiver may comprise of a transform index detection unit for the detection of the transform index imbedded in the OFDM signal.
Owner:KUMAR RAJENDRA
Method and apparatus for signal transmission and reception
InactiveUS20050141603A1Minimal costMinimal complexitySecret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksModem deviceCarrier signal
A method and modem for communicating serial input data over a transmission link. Serial input data is partitioned into parallel data elements prior to rotation by an invertible linear mapping. Resulting frames of parallel signal elements sequentially modulate a carrier, which is then transmitted over the link. After receipt of the modulated carrier from the link, the signal is demodulated and assembled into frames of parallel signal elements which are de-rotated by an inverse linear mapping. Thresholding the result of the inverse mapping recovers the parallel data elements, which are then re-assembled into serial output data. The linear mapping employs: 1) commuting rotation matrices for convolutionally rotating data vectors into signal vectors and vice-versa; 2) filter bank polyphase rotation matrices; or 3) computationally efficient multi-rate wavelet filter banks. Transmitter pre-emphasis places most of the information in lower baseband frequencies; complimentary de-emphasis occurs in the receiver. Logarithmic amplification of the baseband signal prior to carrier modulation improves modulation gain and transmit channel noise attenuation. Coefficients of the rotation matrix of the receiver are adaptively equalized to correct for transmission path distortion. FM double-side band is employed in systems requiring minimized cost and complexity. FM single-side band is employed in systems in which bandwidth reduction is desirable. AM is also employable.
Owner:INTRATECH
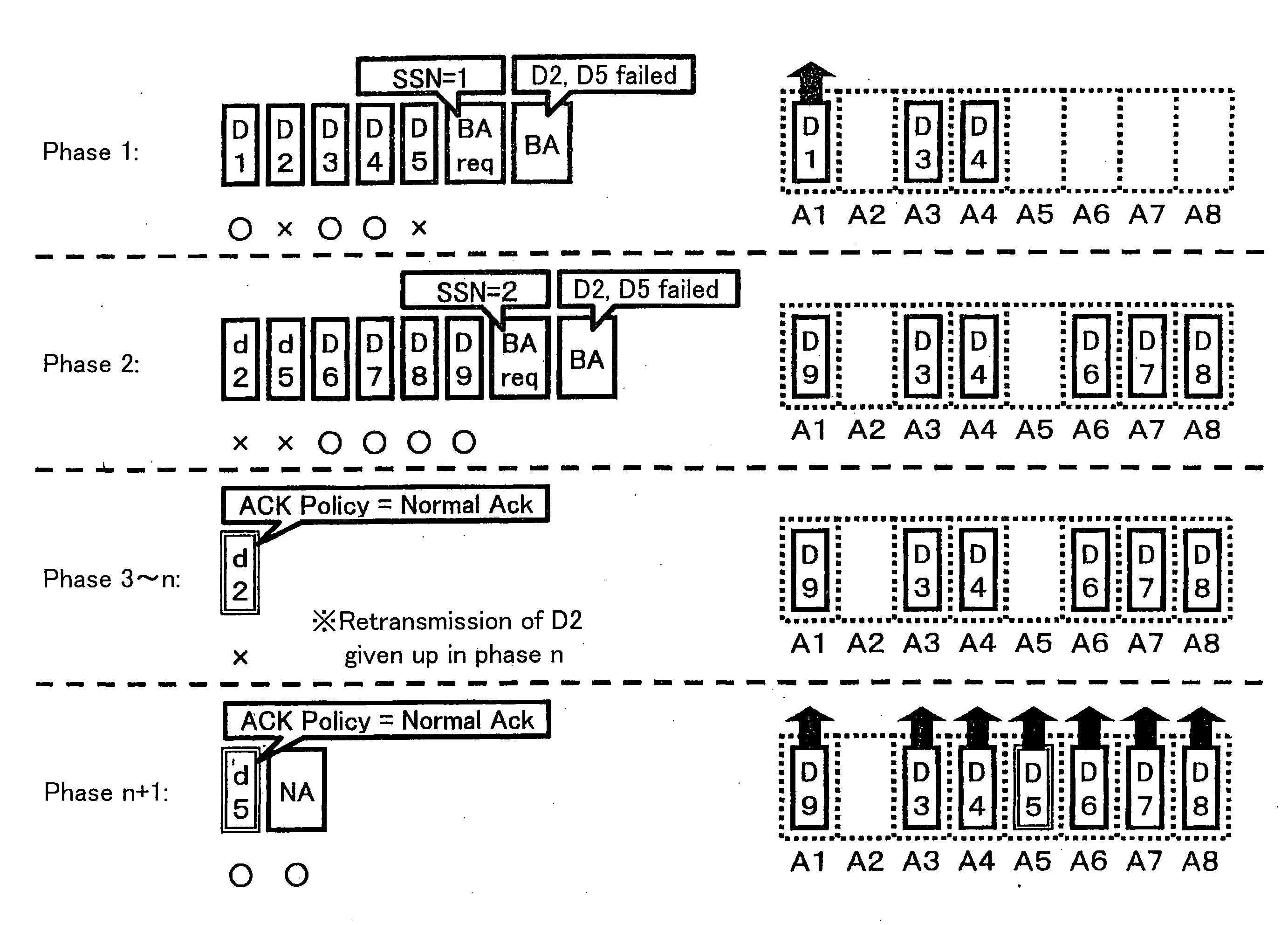
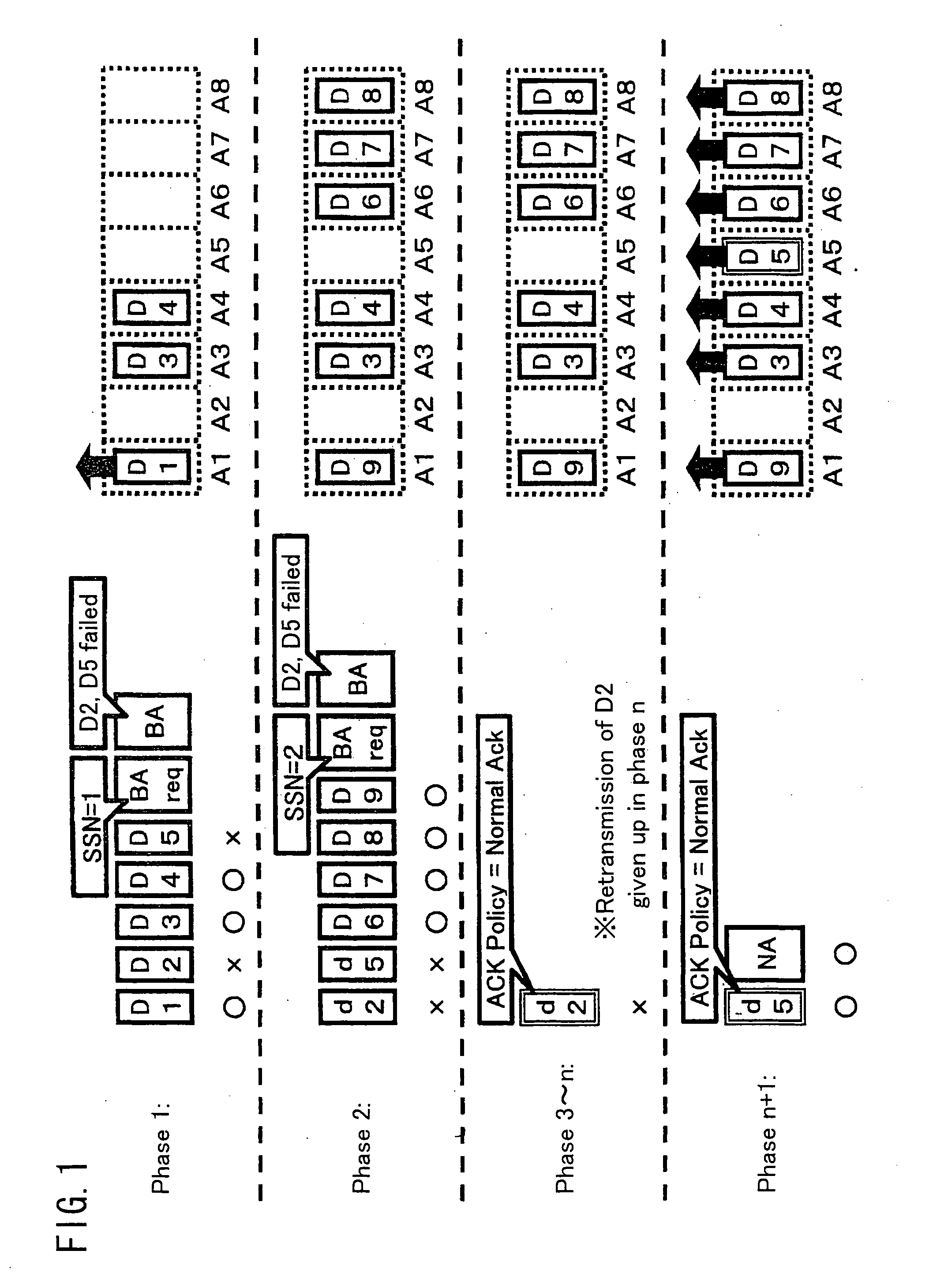
Transmitting station, receiving station, communications method, communications program, computer-readable storage medium containing the program
ActiveUS20070162813A1Effective bandwidthEfficiently usError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsTransmission order
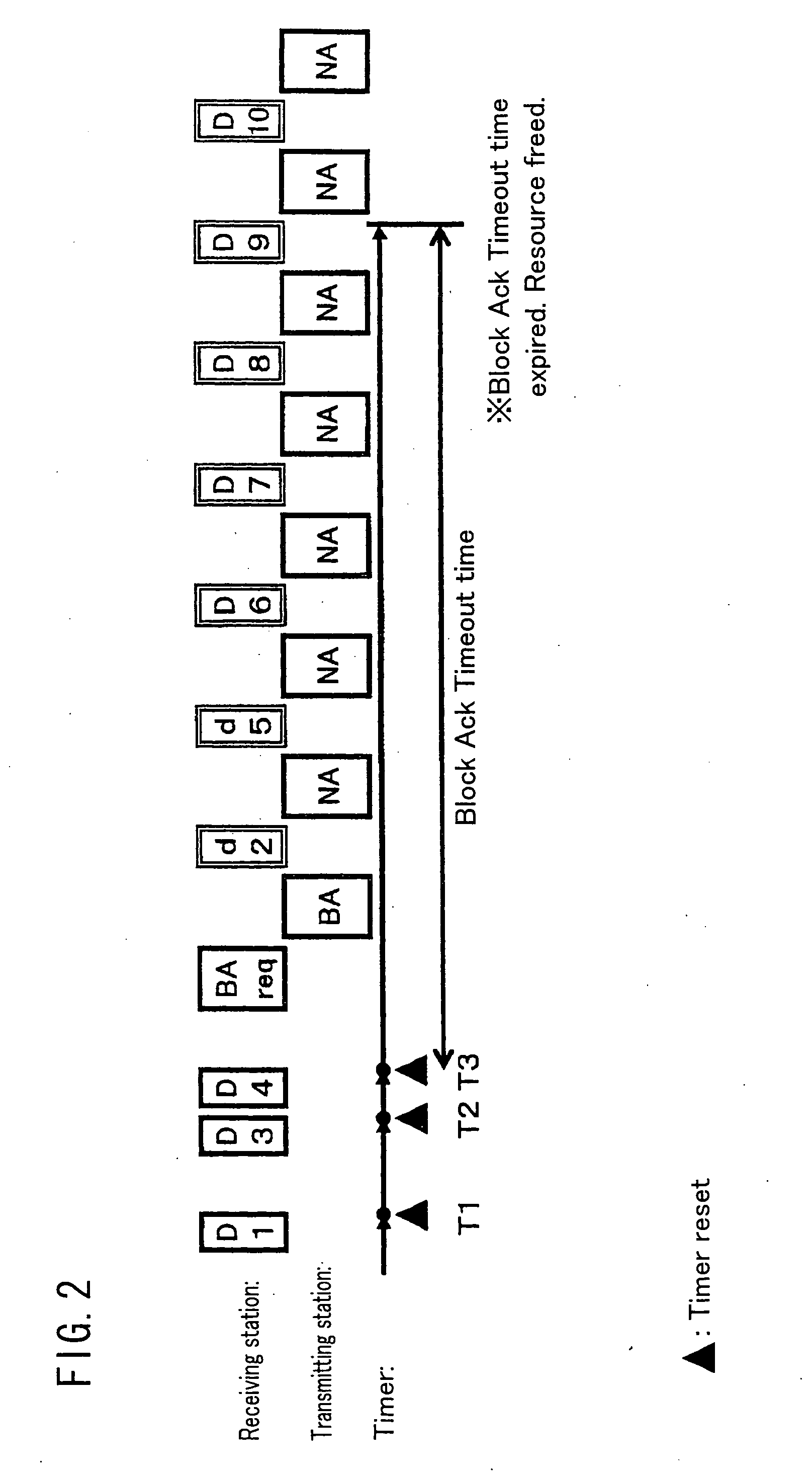
The current Draft IEEE 802.11e standard specifies two types of schemes for obtaining an acknowledgement from a receiving station: BlockAck and NormalAck. The current specifications allow temporary use of NormalAck while transmitting data frames in a BlockAck scheme. The specifications however does not explicitly describe the data frames that are allowed to be transmitted using NormalAck. Should these data frames follow the same rules as in BlockAck schemes, and if the transmitting station has dynamically switched between these two types of schemes, the receiving station can know only with extended delays that unreceived data frames are no longer valid. Therefore, the passing of subsequent, successfully received data frames from the receiving station to an upper layer may be significantly delayed, which is a problem. Another problem occurs if a BlockAck scheme timeout is determined in accordance with the rules in the current draft: the resource being used for BlockAck, which should be released, may not be released forever. The present invention addresses these problems by making suitable changes to the transmission sequence of data that is allowed to be transmitted by NormalAck while transmitting data by BlockAck and the determination process for a BlockAck scheme timeout.
Owner:SHARP KK
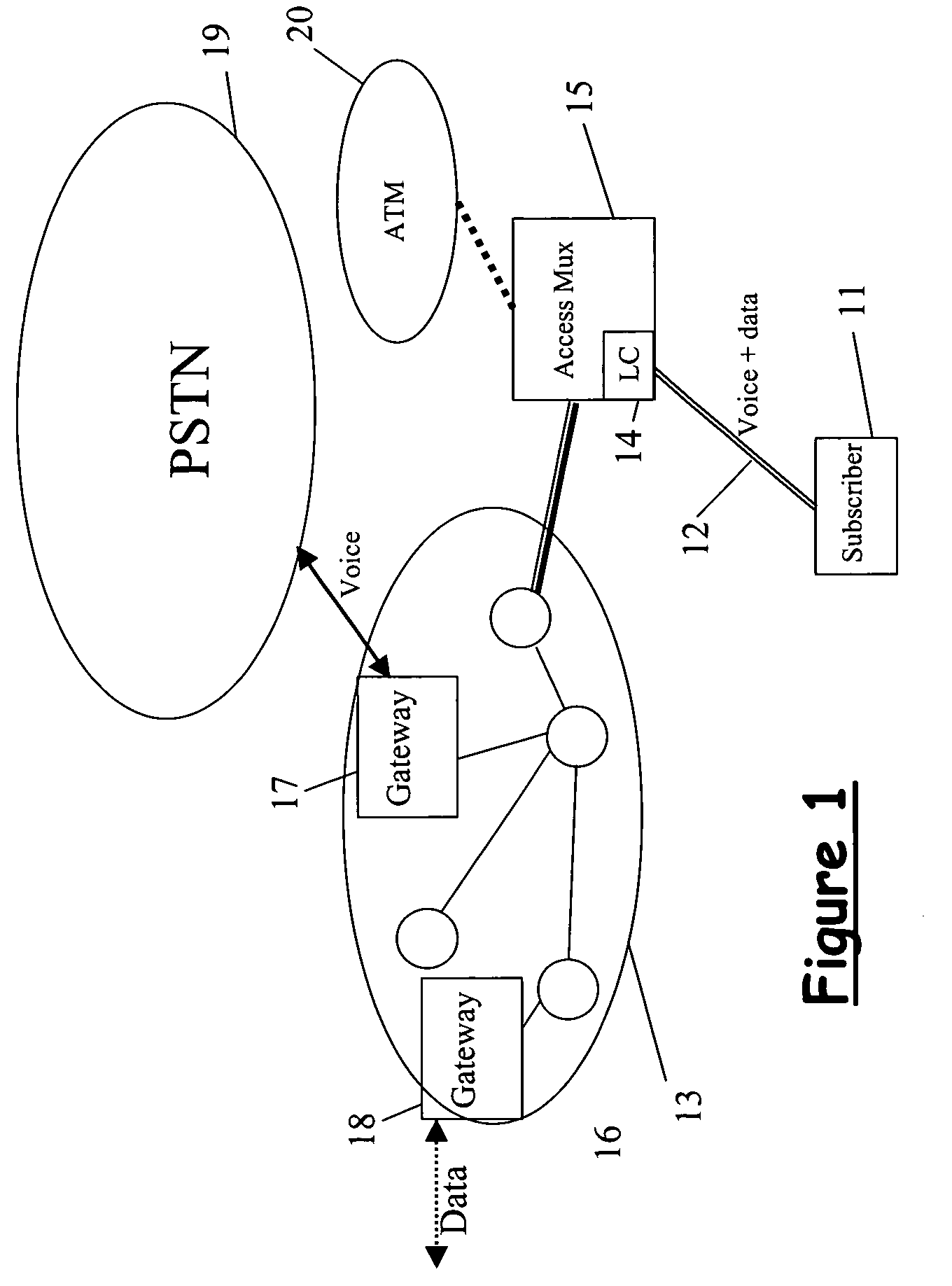
Method of providing multi-media communications over a DSL access network
InactiveUS20060159129A1Facilitate communicationHigh bandwidthFrequency-division multiplex detailsData switching by path configurationMultiplexingAccess network
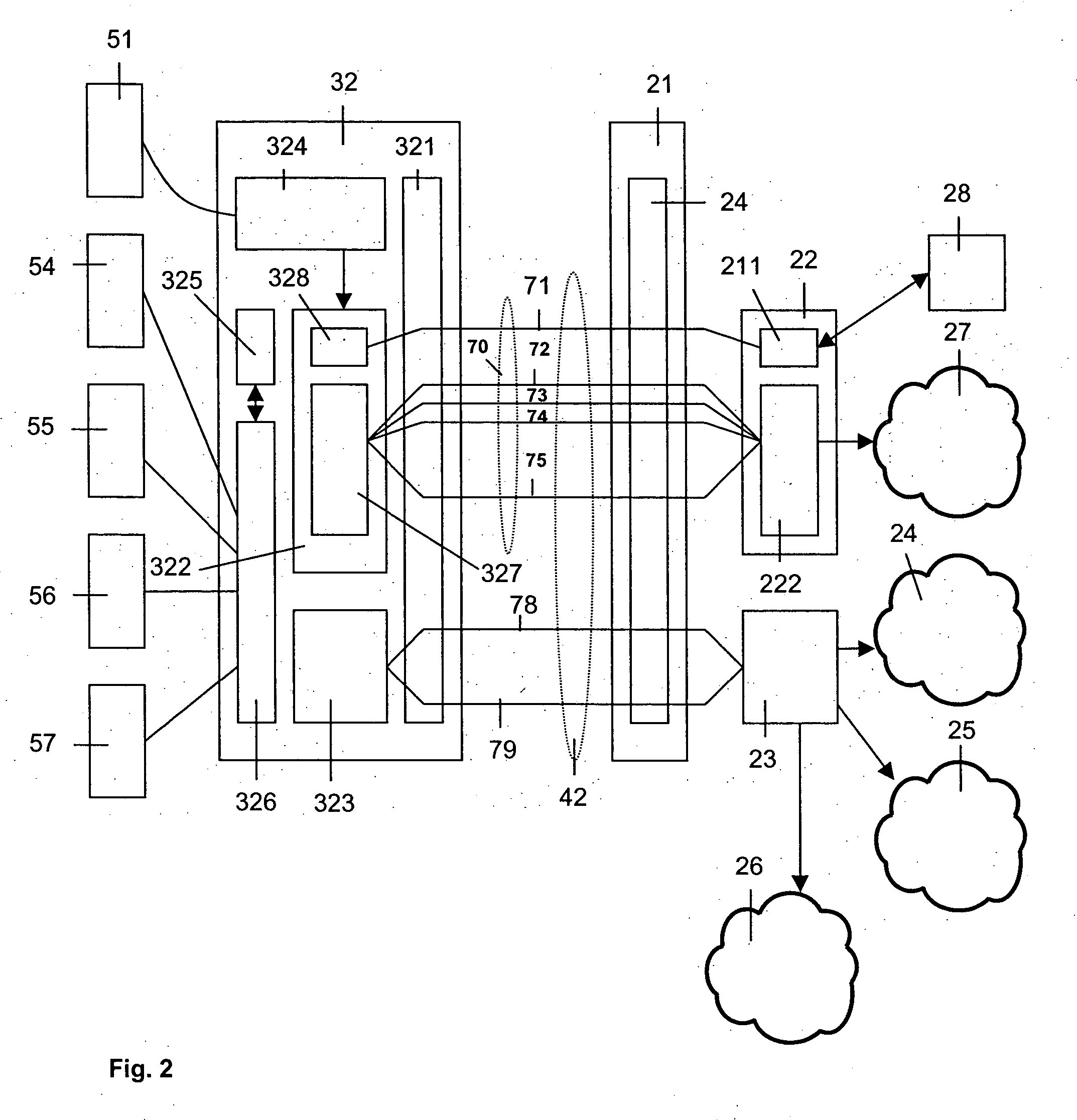
The invention concerns a method of providing voice and / or multi-media communication over a DSL access network as well as a DSL access multiplexer (21) and at least one integrated access device (32). The DSL access multiplexer (21) and the integrated access device (32) are connected via a subscriber line (42). A voice / multi-media session is established via the DSL access network, wherein data of the voice / multi-media sessions are transported in form of IP packets by using a real time protocol. An AAL2 circuit (72 to 75) is allocated to the voice / multi-media session. The headers of the packets of the voice / multi-media session are compressed and AAL2 circuits (72 to 75) allocated to voice / multi-media sessions are used as underlying tunnel layer. The header compressed packet of the voice / multi-media session are multiplexed into the allocated AAL2 circuits (72 to 75) and the header compressed packets are transported via the allocated AAL2 circuits (72 to 75) between the integrated access device (32) and the DSL access multiplexer (21) through the DSL access network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
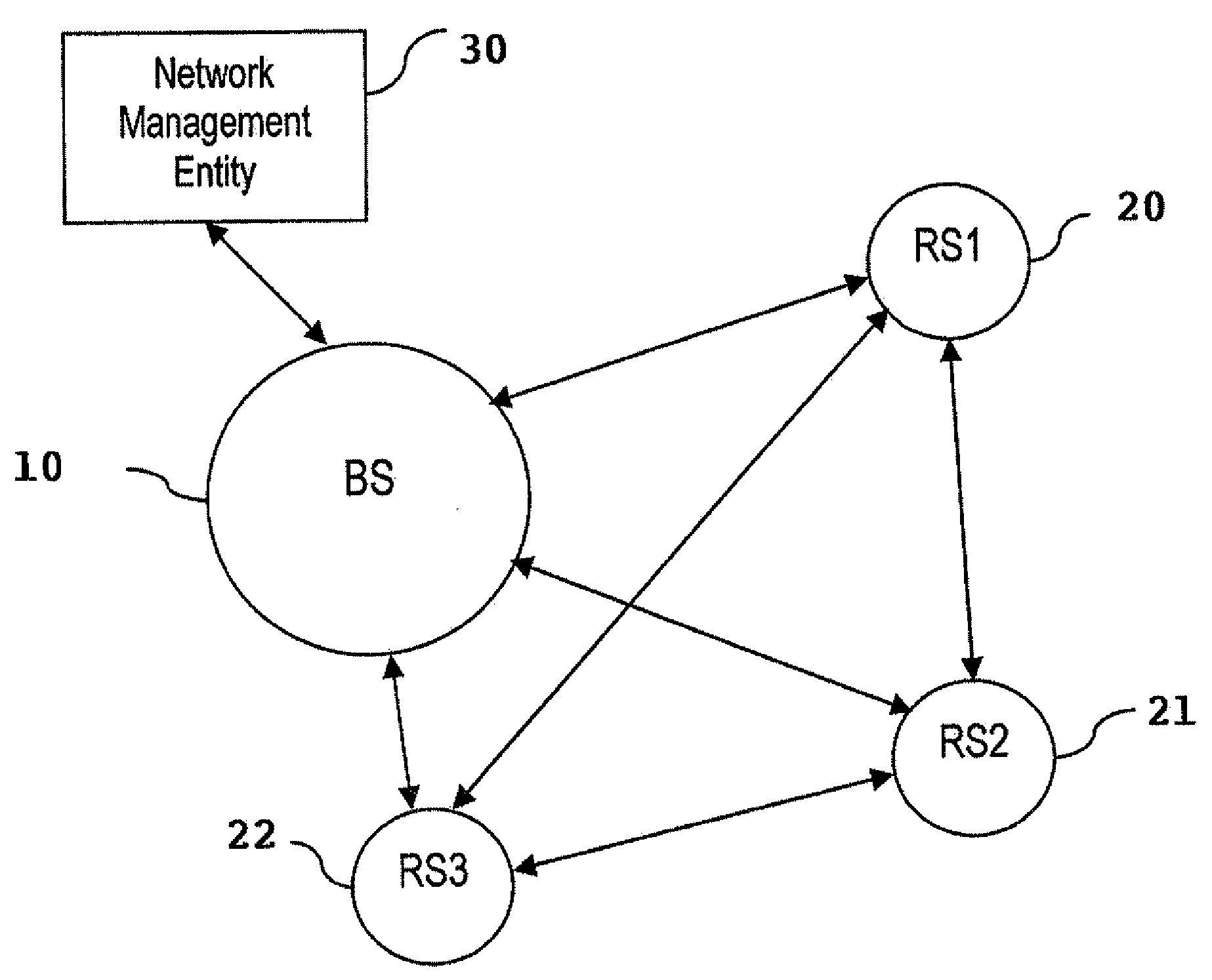
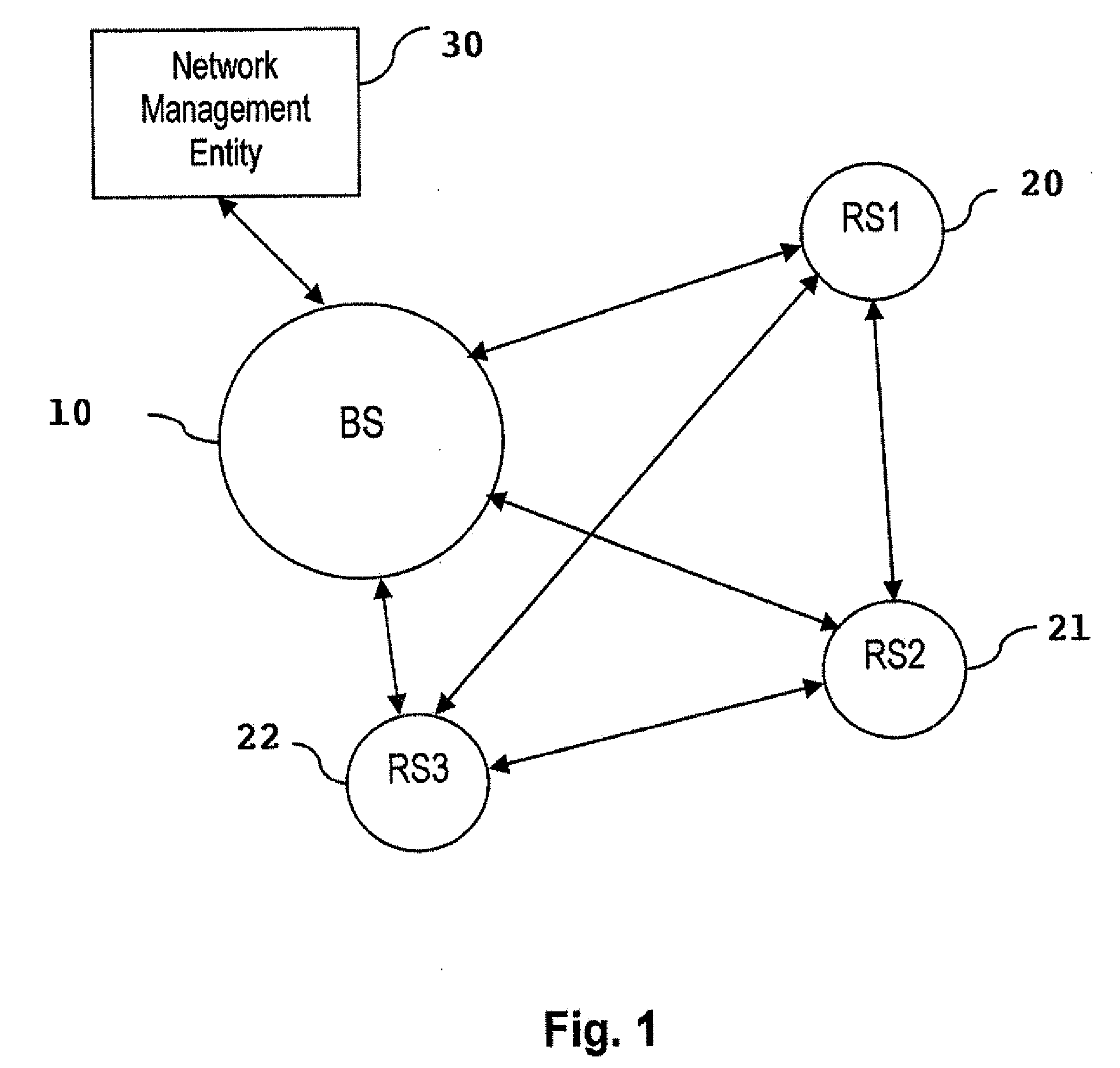
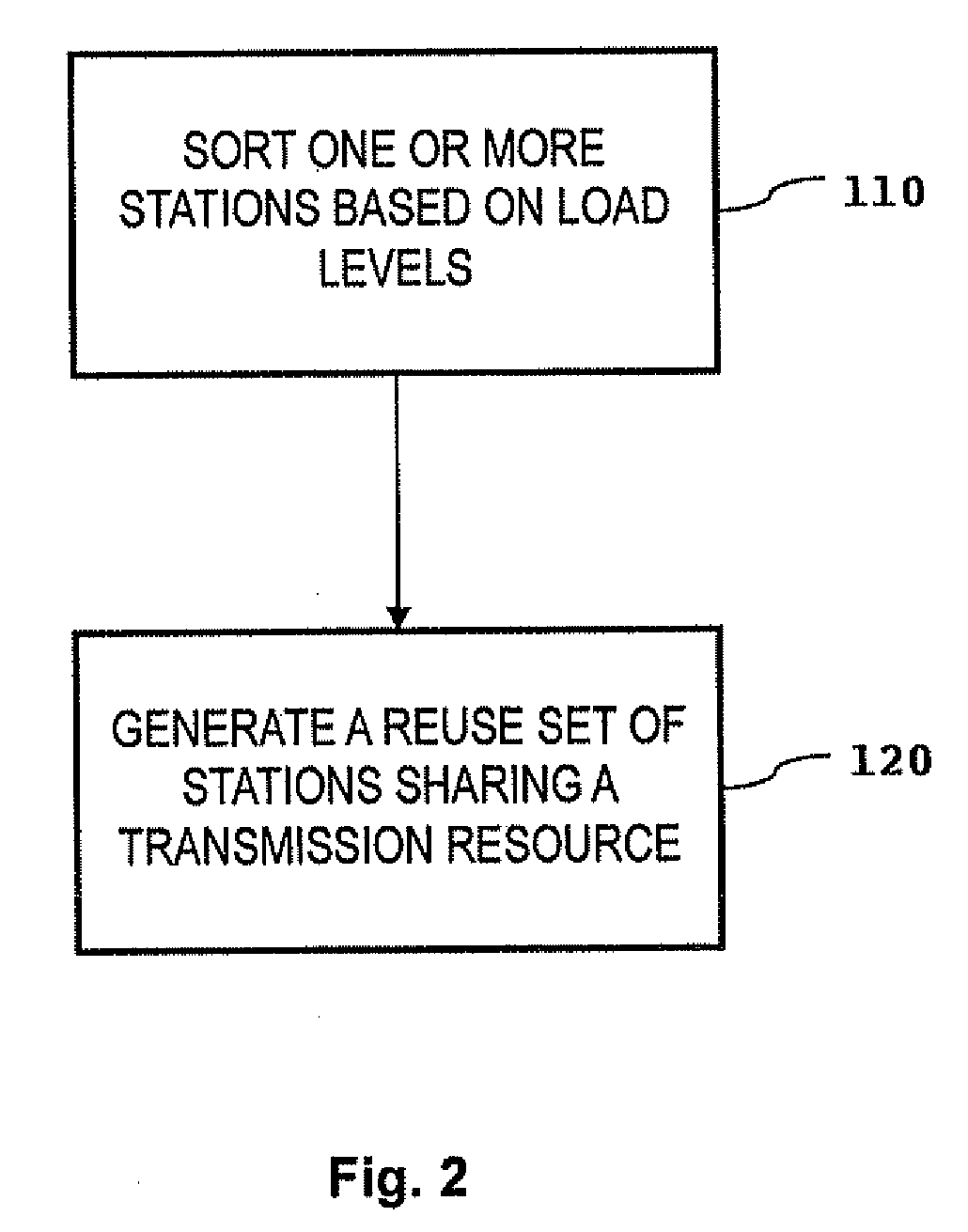
Reuse pattern network scheduling using load levels
InactiveUS20080171551A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsEngineering
One or more stations are sorted based on respective load levels, and a reuse pattern is generated, based on the sorted load levels and mapped interference levels, including one or more reuse sets of stations capable of sharing a transmission resource. The stations within each reuse set are listed in order based on their respective load levels, and an additional station is added to a reuse set, as long as the cumulative transmission level within the reuse set is below a threshold interference level and the additional station is not already listed in another reuse set. A network schedule is updated based on the reuse pattern to increase bandwidth efficiency in the network.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
End to End Multicast
ActiveUS20140095924A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyData switching networksRedundant hardware error correctionSource encodingComputer network
IP multicast enabled devices, systems and methods for use on an end-to-end IP multicast-enabled network are disclosed. An IP multicast system, device and method operable on the network includes an IP multicast-engine, and storage for storing instruction sets to instruct the engine to send messages according to a select multicast application. A plurality of devices become members of an IP multicast group such that sending a message to a single multicast address can provide for the concurrent control of, and the delivery of the multicast message to, the devices of the group. Error conditions in a multicast source may be handled by preserving the multicast session resources, and reassigning a multicast source address from a faulty source encoding device to an alternate device.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
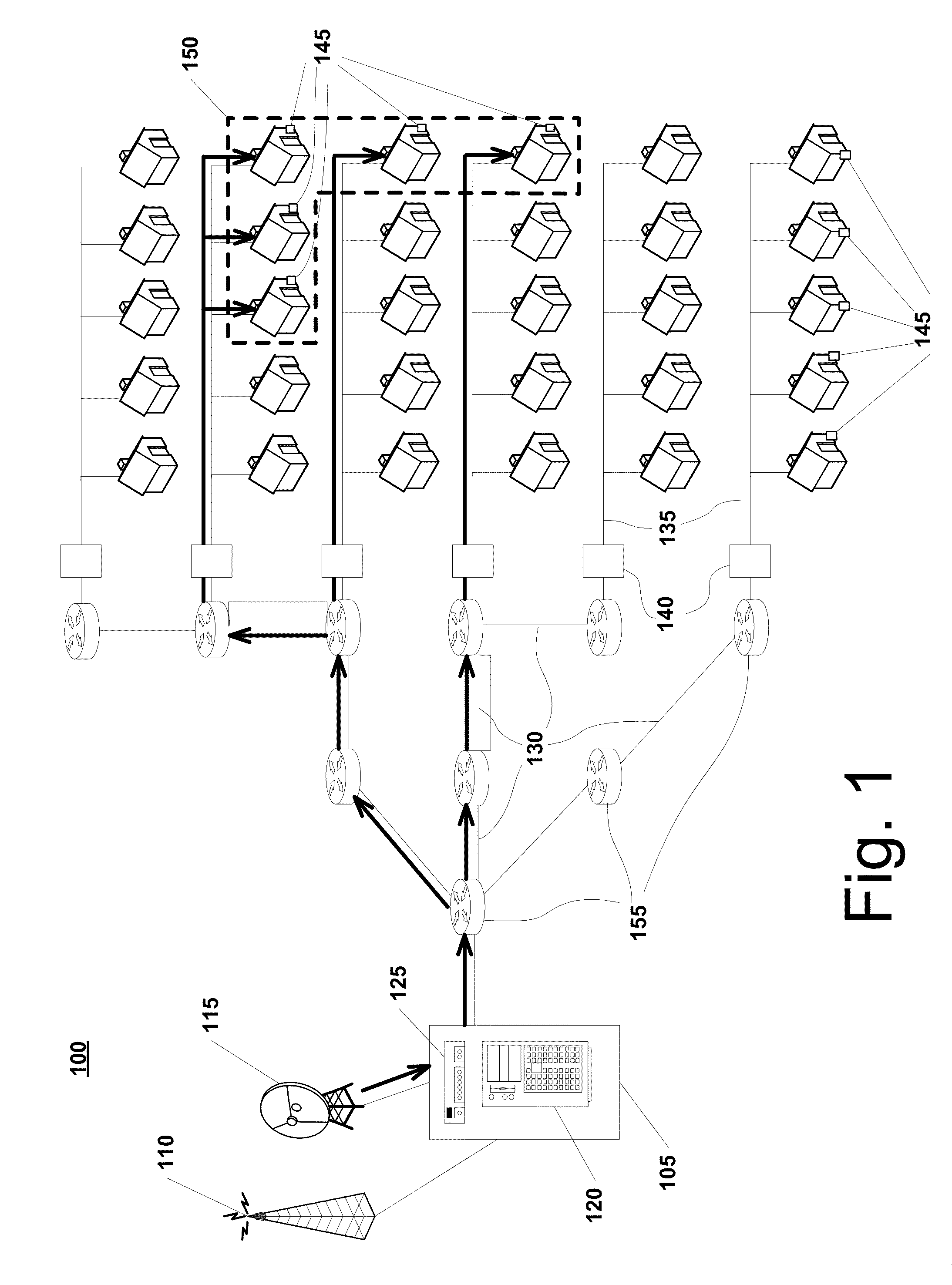
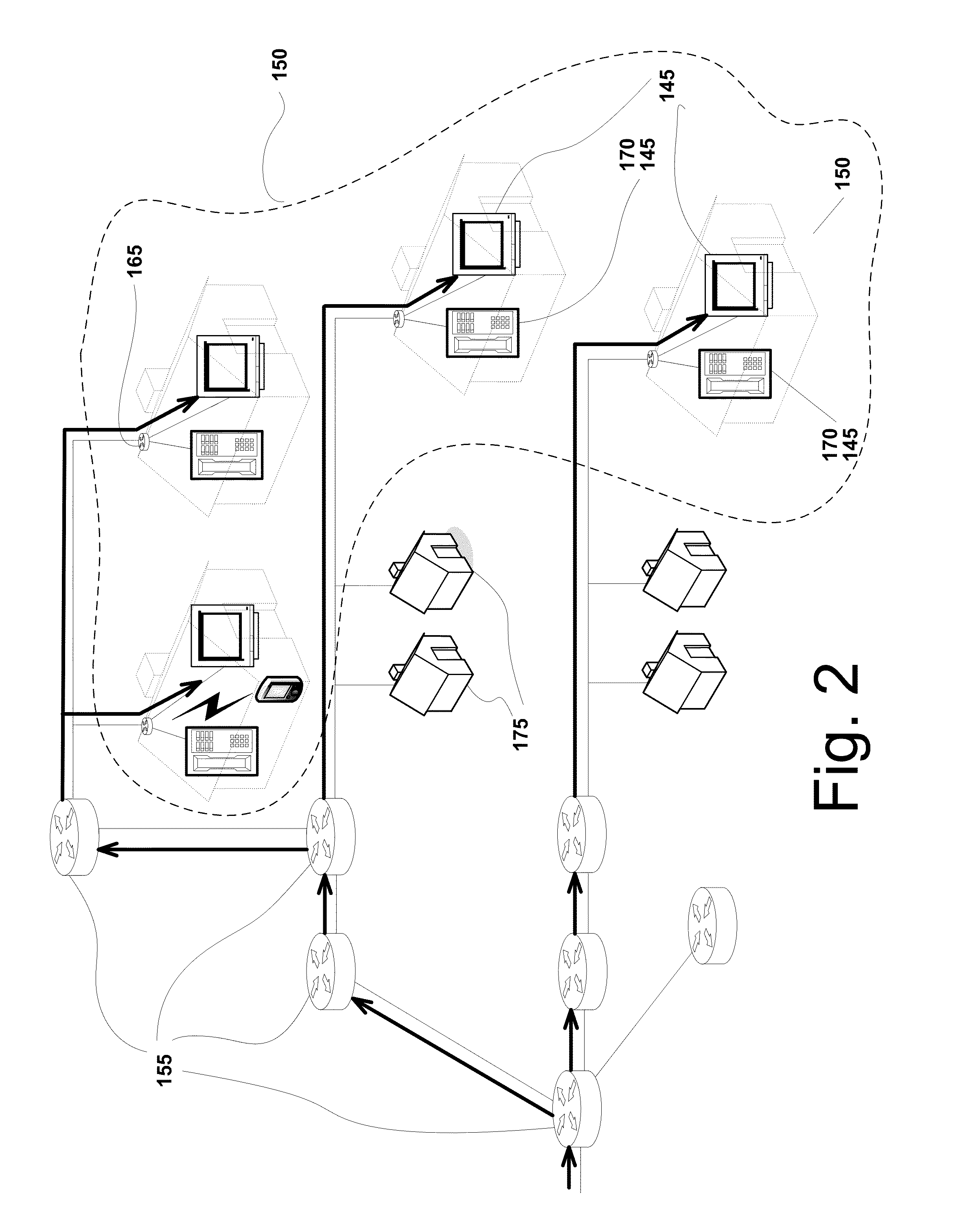
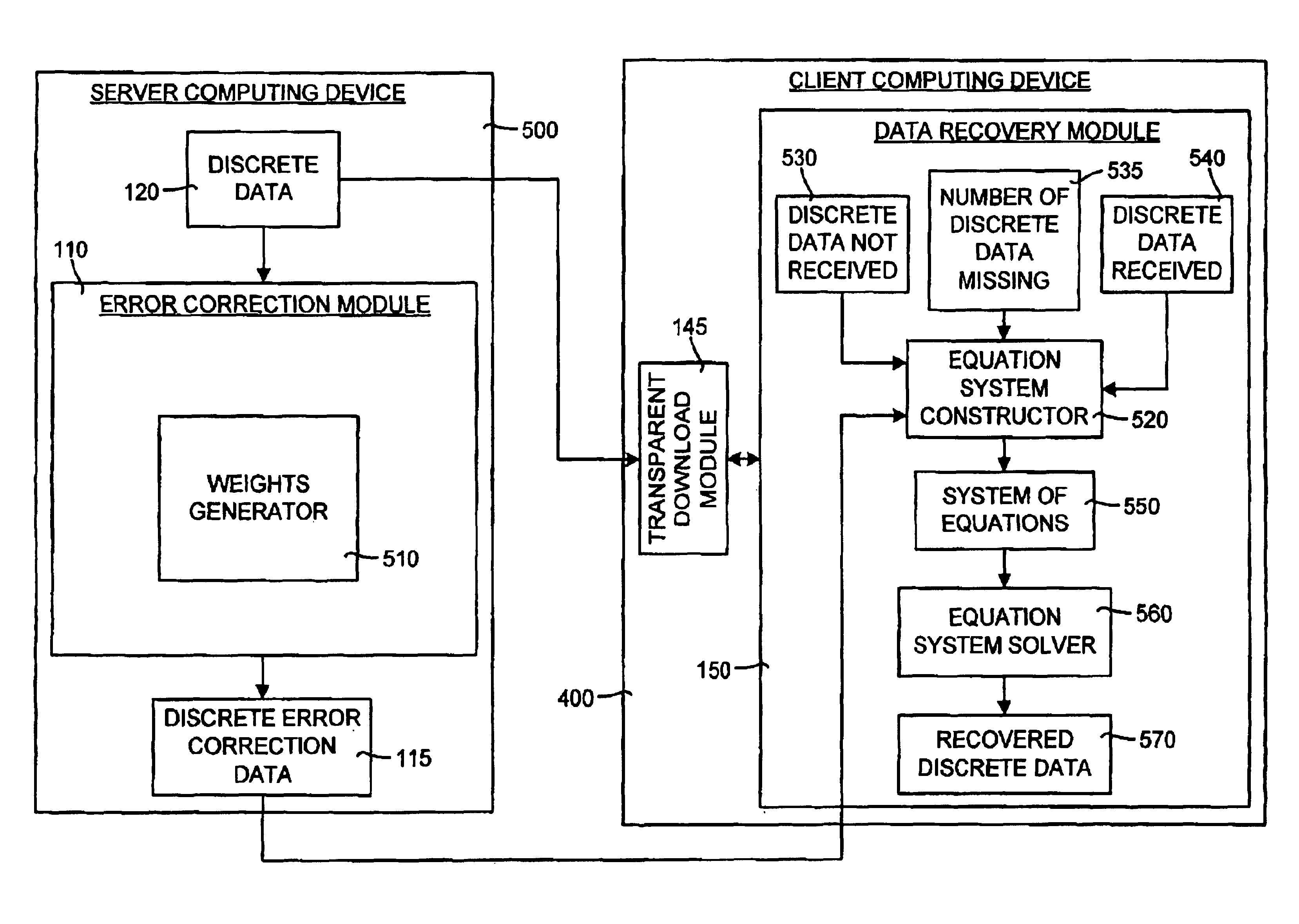
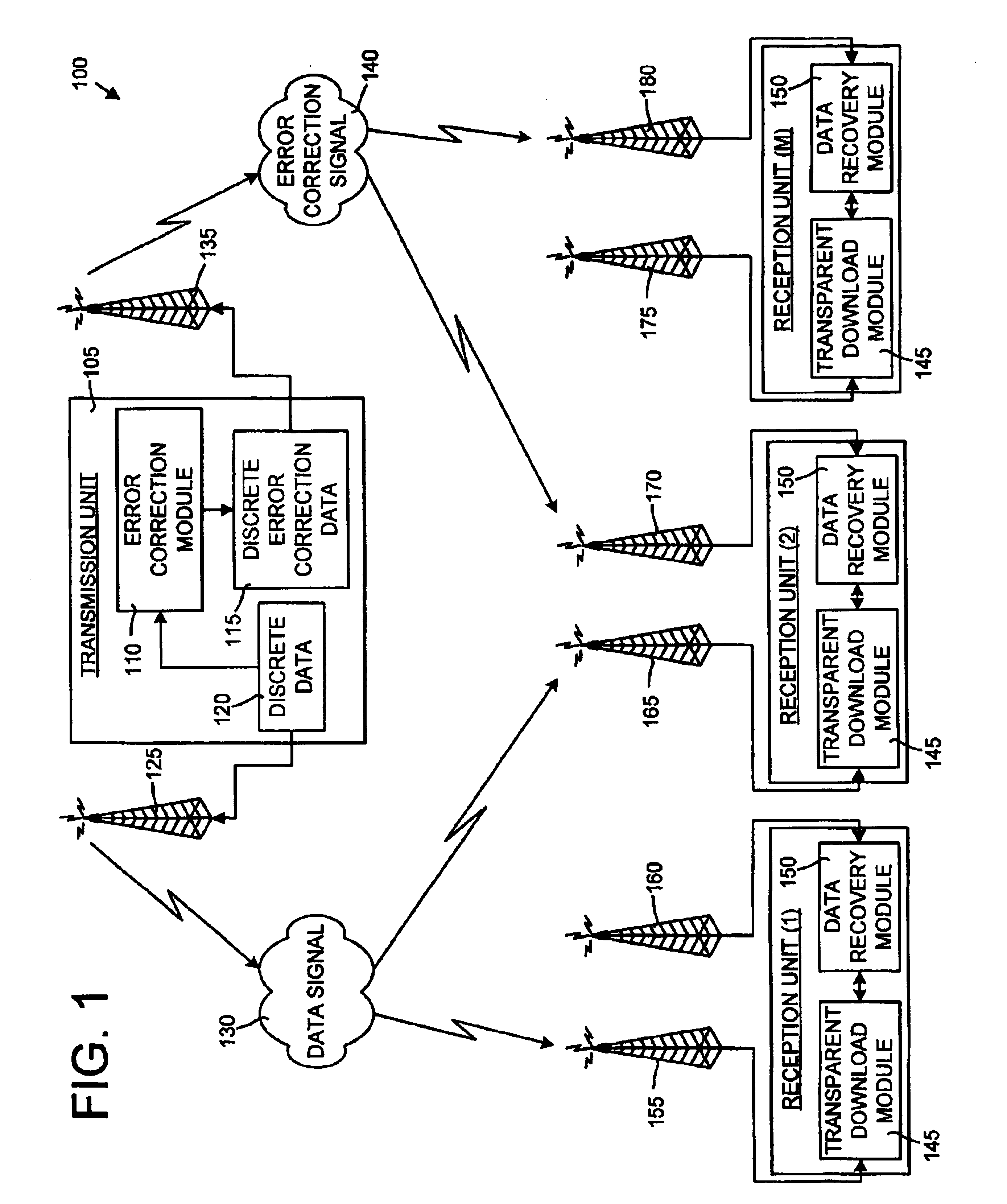
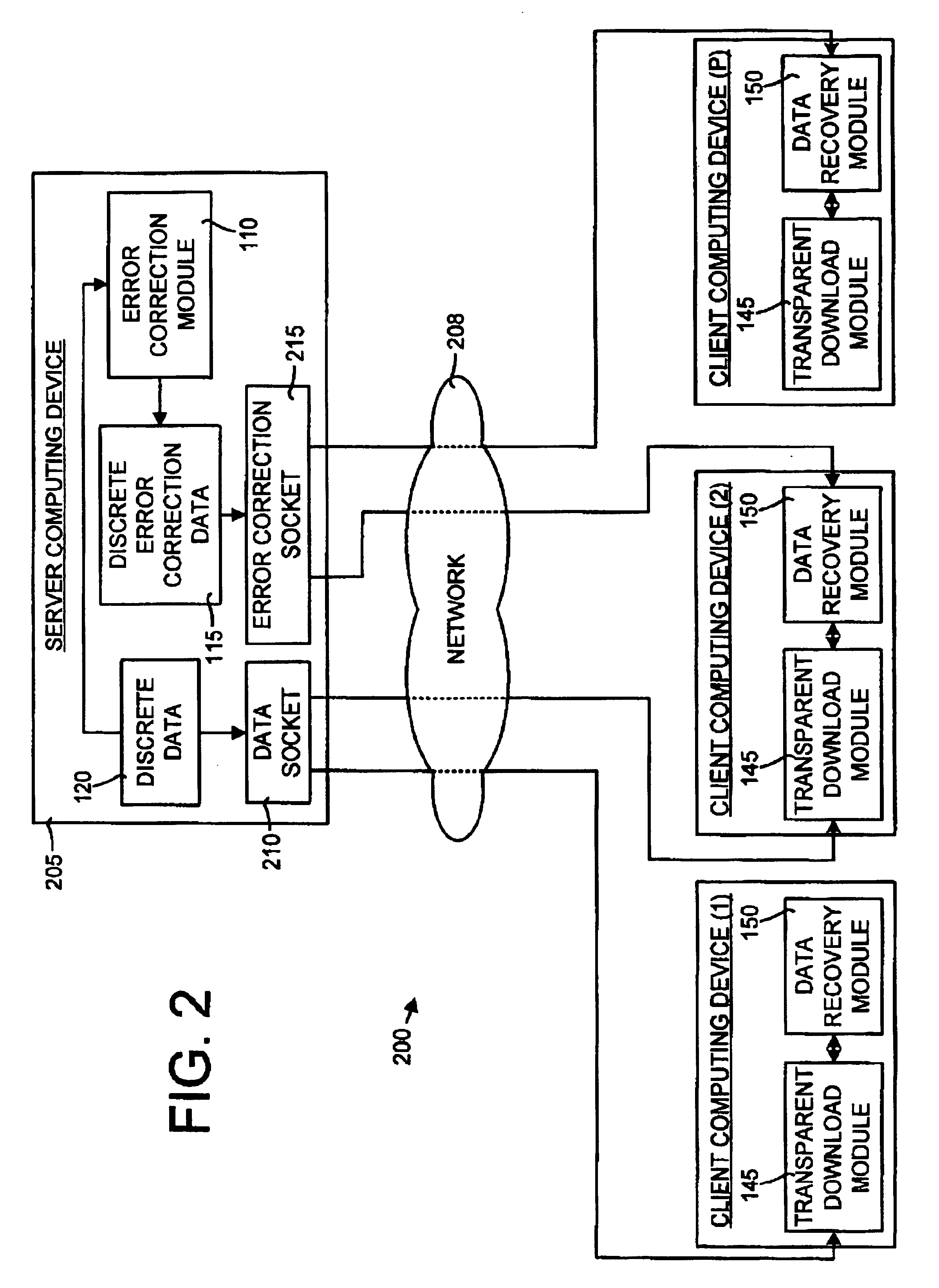
System and method for transparent electronic data transfer using error correction to facilitate bandwidth-efficient data recovery
InactiveUS6948104B2Promote recoveryAvoid contentionError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsTraffic capacityMissing data
The invention disclosed herein includes a system and method for electronically transferring data through a communications connection in a transparent manner such that the data transfer does not interfere with other traffic sharing the connection. The invention transfers data using bandwidth of the connection that other traffic are not using. If other traffic desires to use the bandwidth currently being used by the invention, the invention relinquishes the bandwidth to the other traffic and retreats to avoid bandwidth contention. Although a retreat may cause gaps in the data transferred, a key aspect of the invention is that any missing data due to these gaps is recovered easily and in a bandwidth-efficient way using novel error correction and recovery.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multilevel data encoding and modulation technique
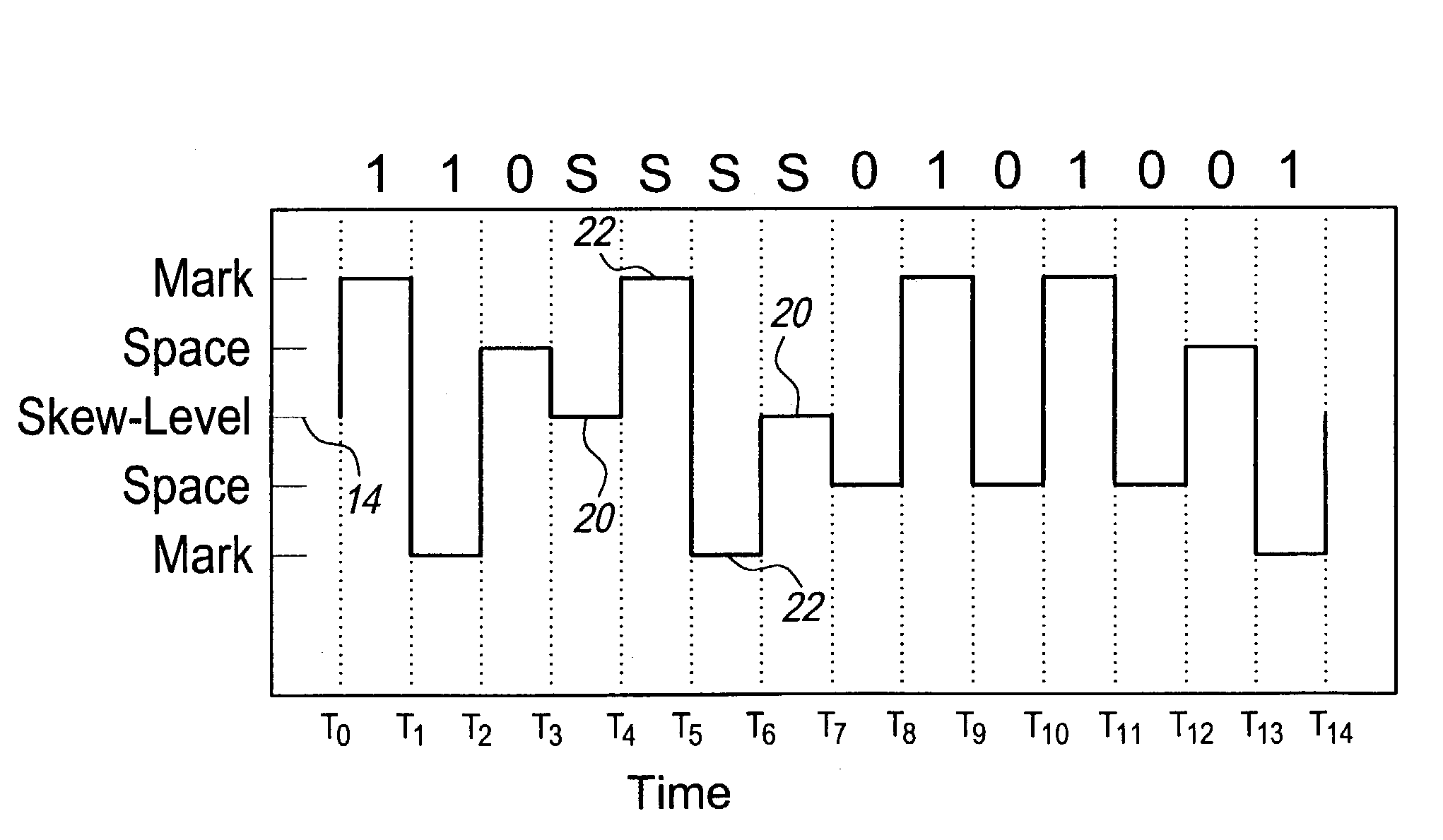
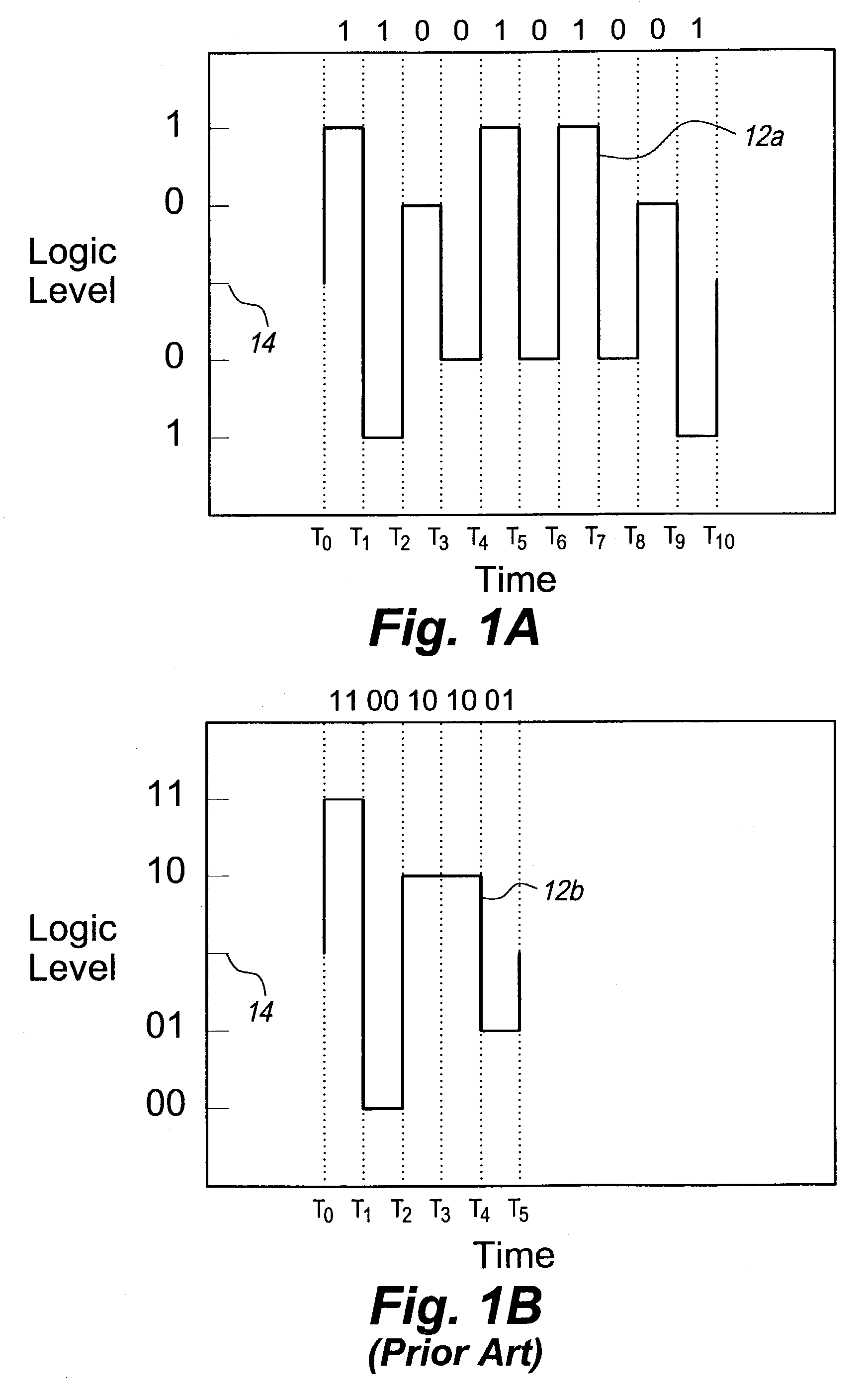
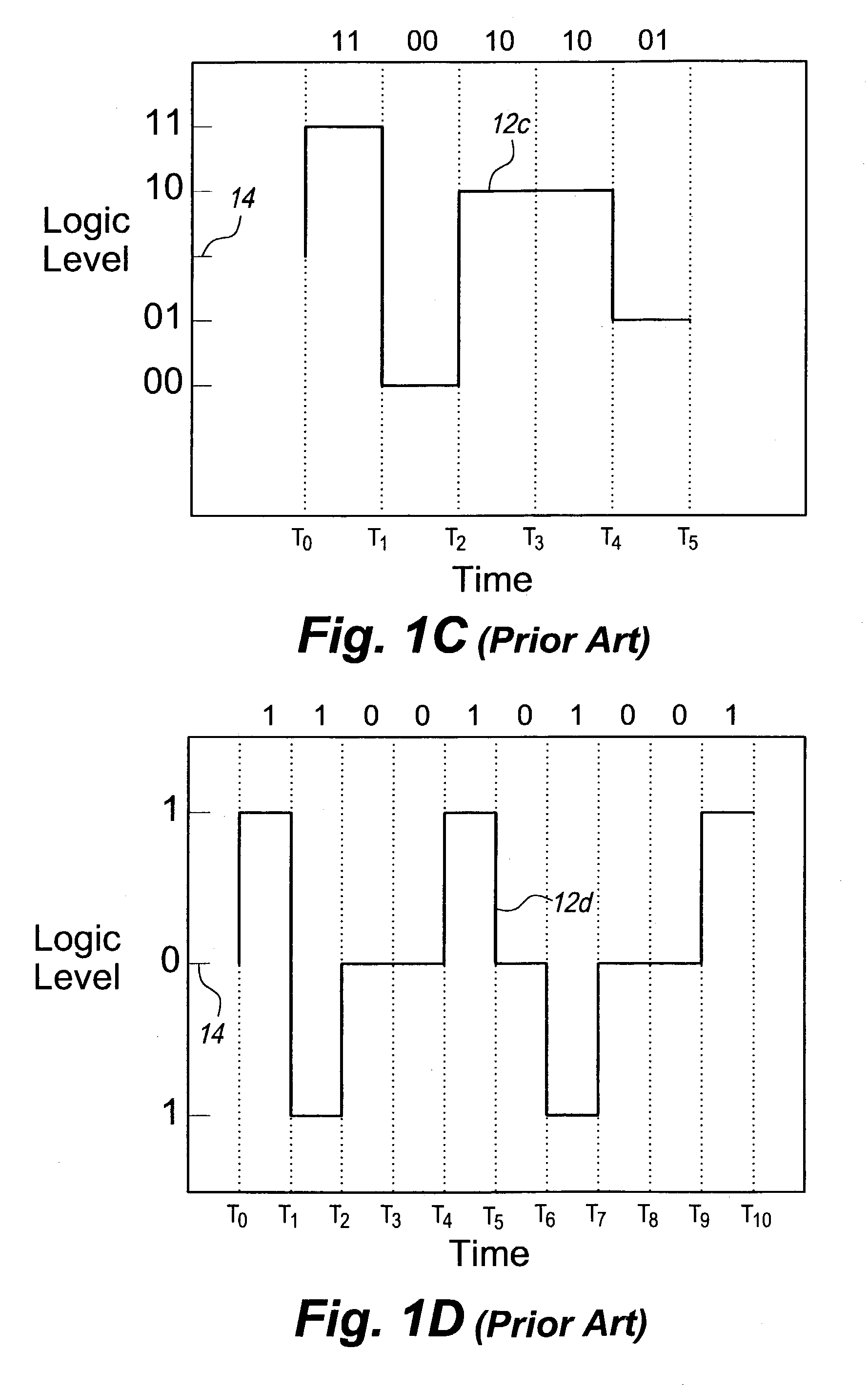
ActiveUS7221711B2Improve discriminationImprove anti-interference abilityPulse conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsHarmonicPeak value
The multilevel data encoding and modulation technique uses a pair of complementary logic sets. In its most basic form, the sets are binary sets each containing a line level for a logical one and a line level for a logical zero for a total of four logic levels. The encoding technique requires a polar change in the line level after every bit. An optional fifth level may be used in order to skew the frequency or to enable automatic gain control circuitry to ensure consistent level discrimination. The encoding technique may be used in a bipolar device, or a bias level may be applied to the signal for unipolar transmission. The encoding technique involves inverting the polarity of alternating bits, filtering out all odd harmonics, transmitting and receiving the waveform, and decoding the demodulated waveform by comparing the absolute value of the half-cycle peak-to-peak voltage gain to a predetermined table.
Owner:INFON8UM INC
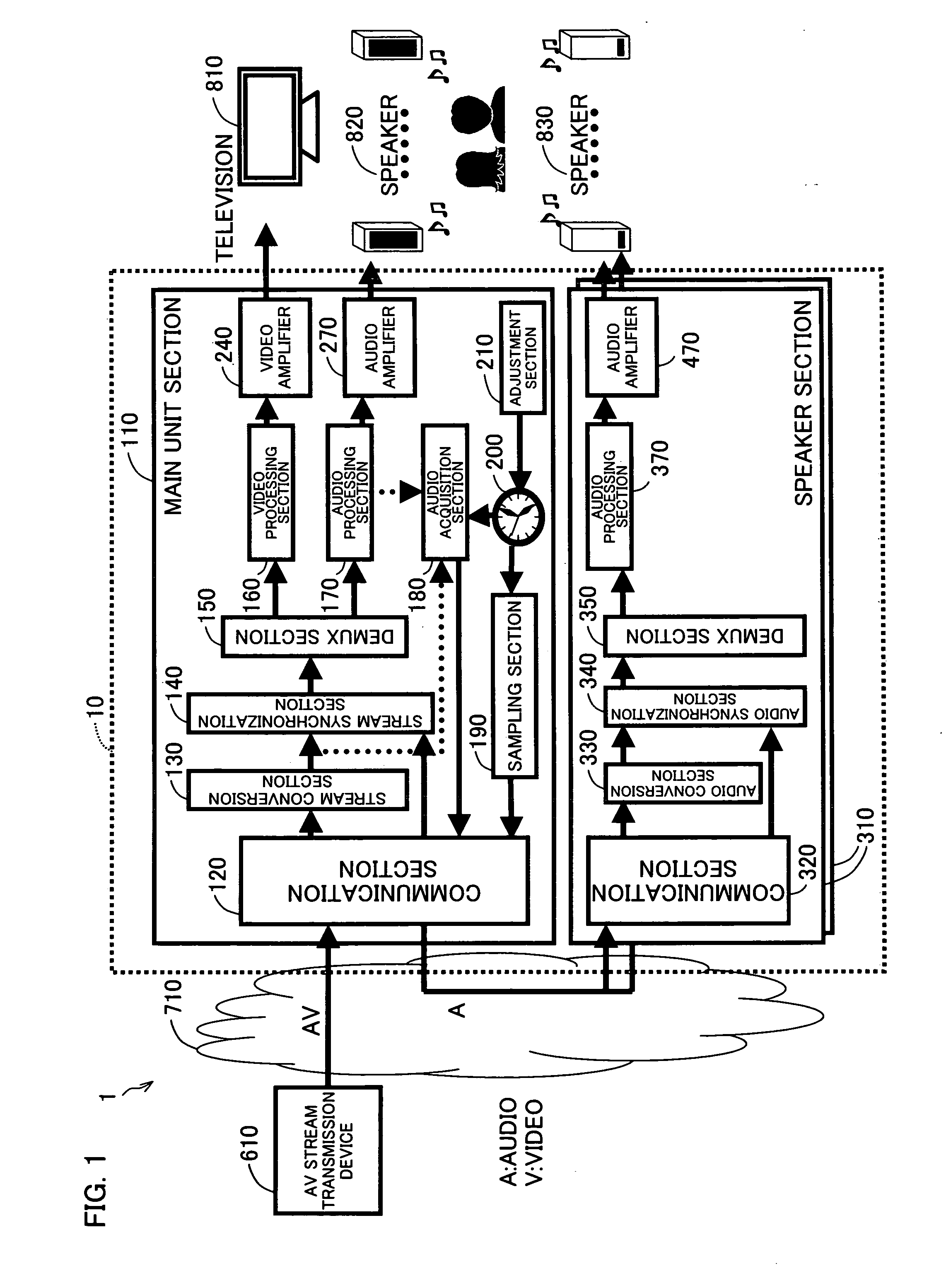
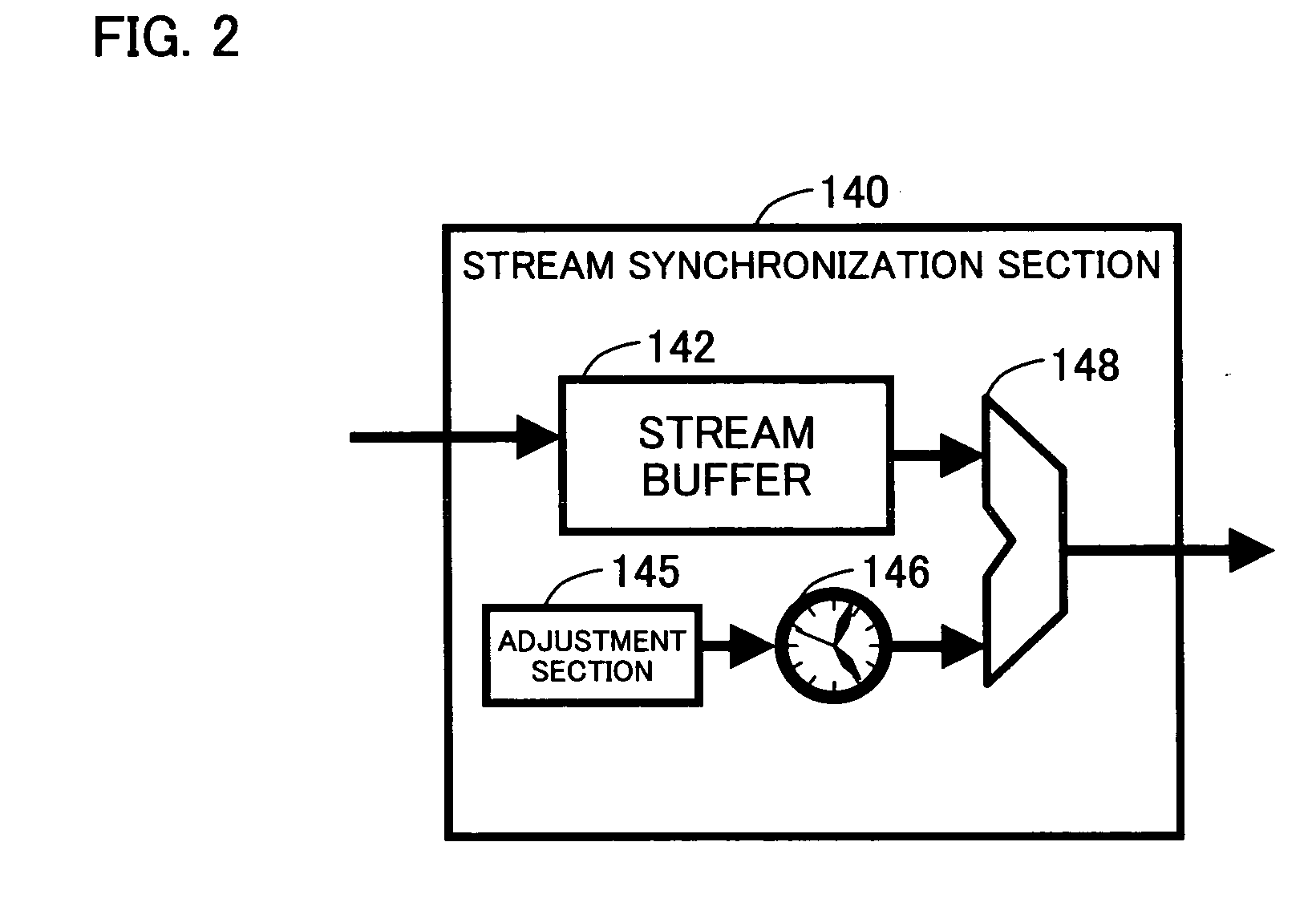
Audio/video processing main unit and control method thereof, audio processing terminal device and control method thereof, audio processing main unit, audio/video processing system, audio/video processing main unit control program, audio processing terminal device control program, and storage medium in which the program is stored
InactiveUS20070110110A1Improve bandwidth efficiencySpeech analysisTime-division multiplexVideo processingTerminal equipment
A home theater includes a main unit section and at least one speaker section. The main unit section includes a communication section which receives an AV stream from an AV stream transmission device and via a communication network, a demux section which separates the AV stream into a video stream and an audio stream, a video processing means which processes the video stream so as to generate a video signal, an audio processing section which processes the audio stream so as to generate an audio signal, and an audio acquisition section which acquires an audio stream which includes at least a part of the audio of the AV stream. The communication section transmits the audio stream acquired by the audio acquisition section to the speaker section, via the communication network.
Owner:SHARP KK
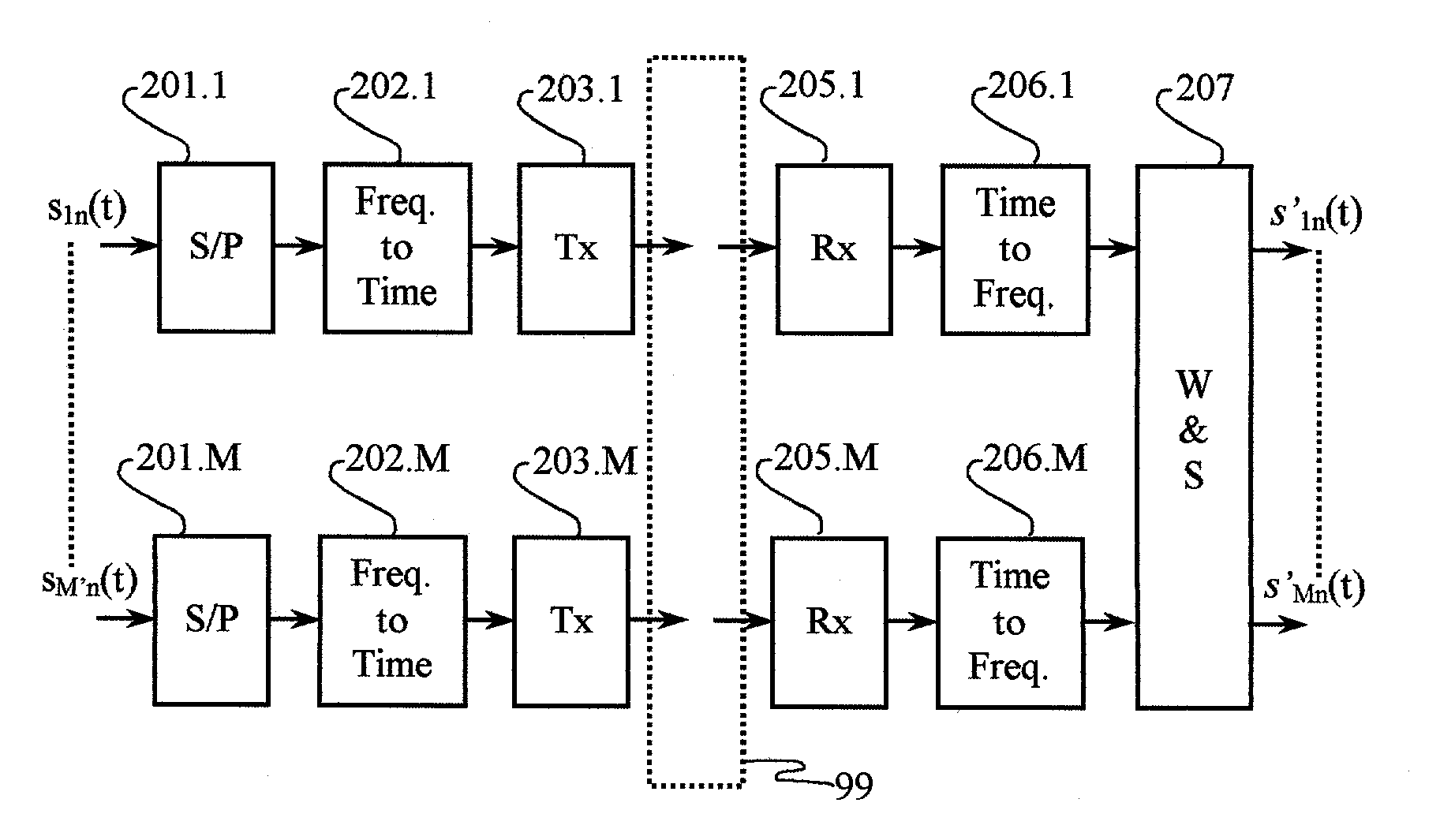
Cancellation systems for multicarrier transceiver arrays
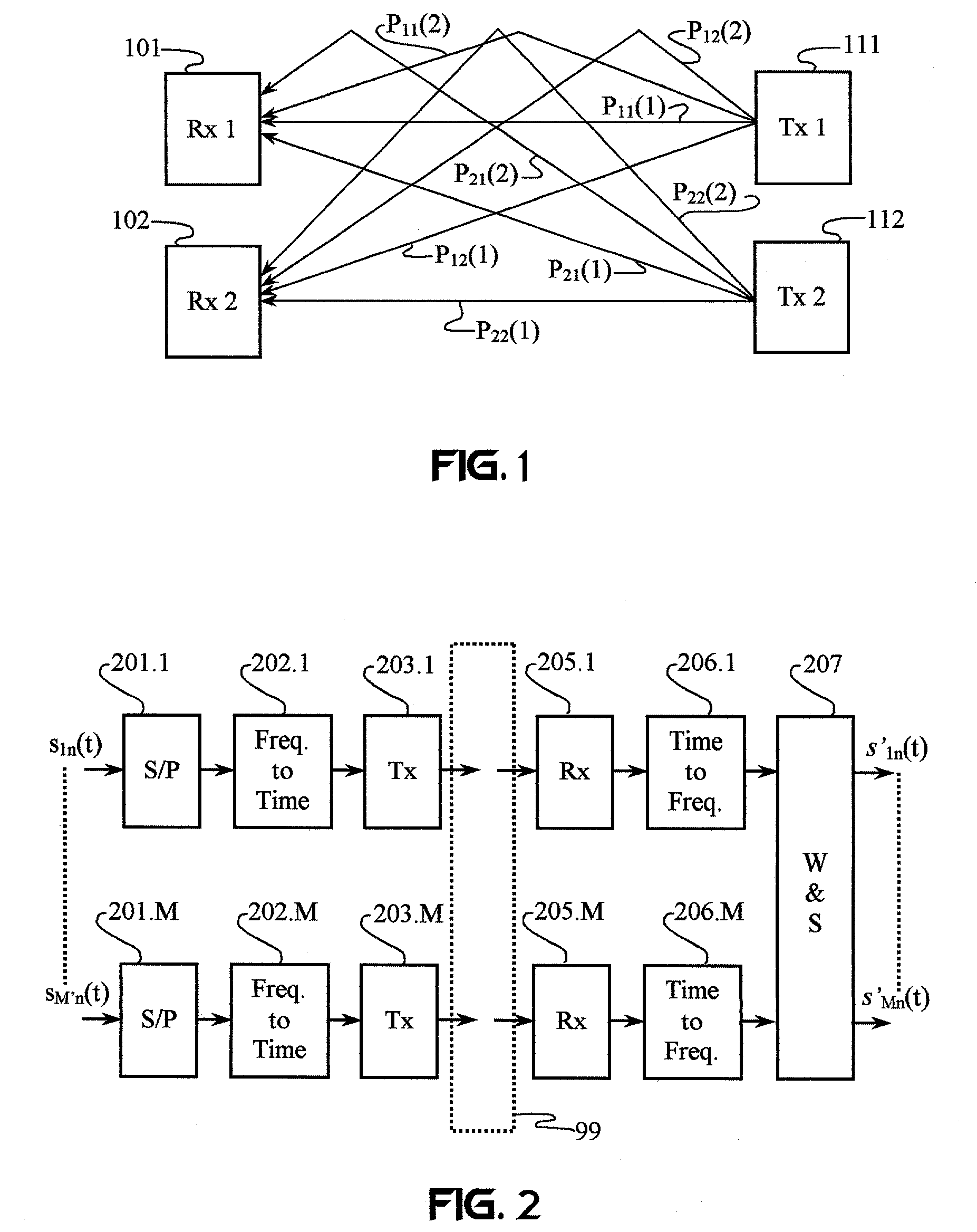
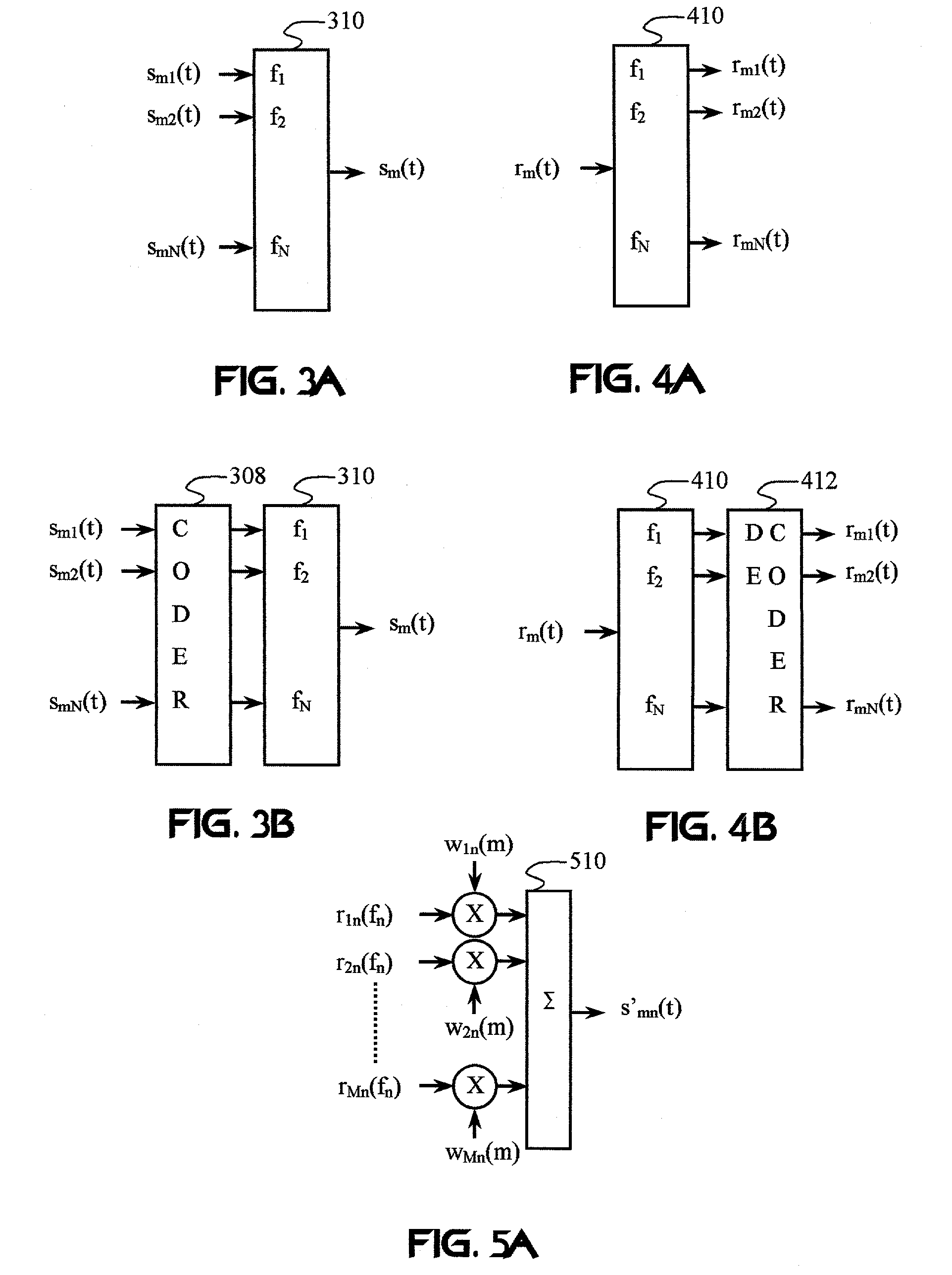
InactiveUS7092352B2Improve bindingImprove bandwidth efficiencyMagnetic measurementsError preventionTransceiverTime division multiple access
Frequency-dependent cancellation separates a plurality of interfering signals received by a plurality of receivers. Received wideband single-carrier signals or multicarrier signals are separated into a plurality of narrowband subcarriers. Sub-carrier frequencies and frequency-band characteristics may be selected with respect to channel characteristics (e.g., coherence bandwidth, interference, etc.). A cancellation circuit provides complex weights to the sub-carrier components. Weighted components associated with each sub-carrier frequency are combined to separate a plurality of interfering signals. Optionally, a plurality of the separated subcarriers may be combined to reconstruct at least one transmitted single-carrier signal from a plurality of frequency components. Combining may include decoding, such as to reconstruct a coded sequence of data symbols transmitted via direct-sequence coding, code division multiple access (CDMA), multicarrier CDMA, carrier interferometry (CI), CI coding, or coded orthogonal frequency division multiplexing.
Owner:S AQUA SEMICONDUCTOR LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com