Patents
Literature
192 results about "Multilevel data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
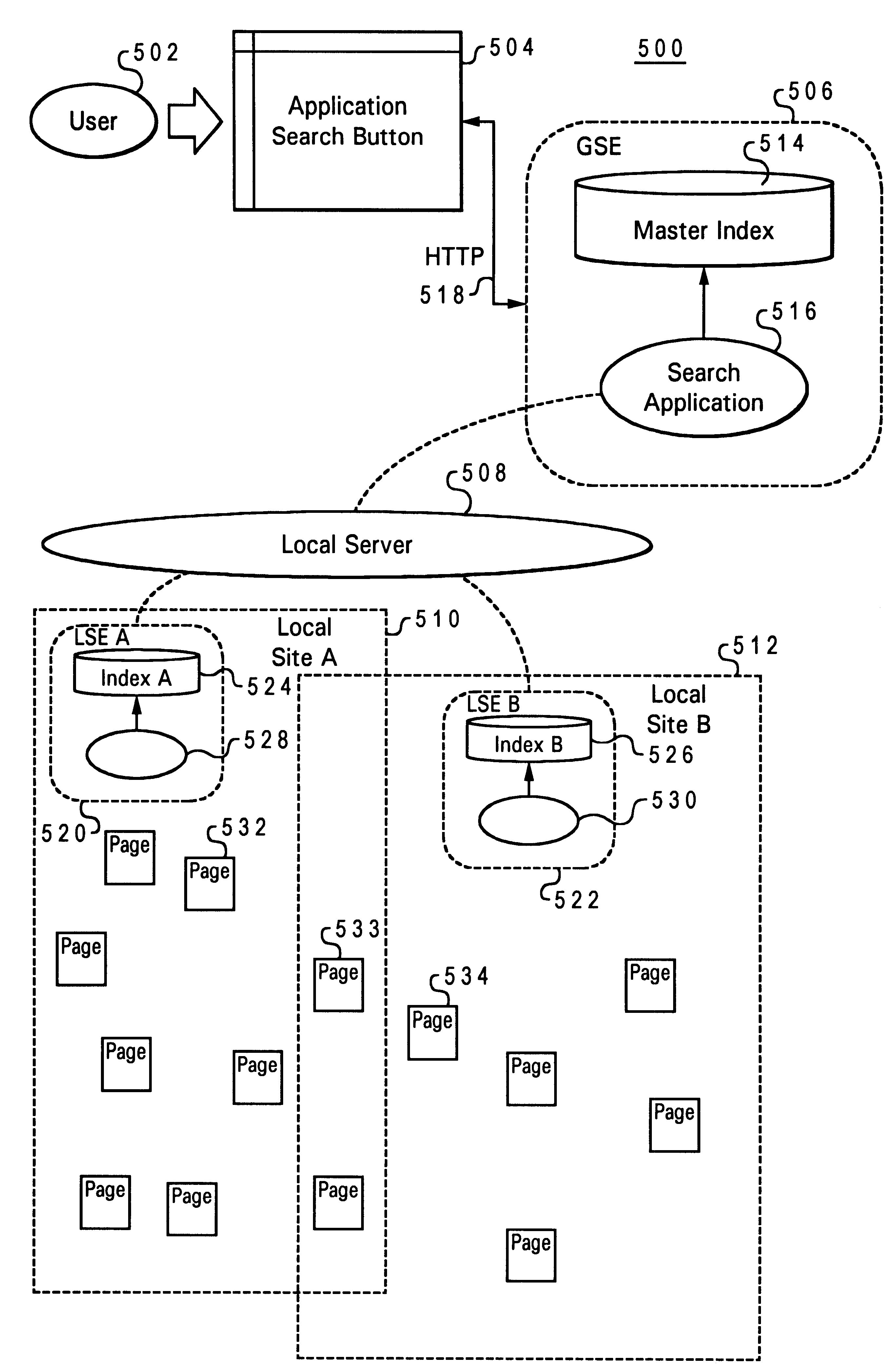
Distributed network search engine
InactiveUS6490575B1Efficient searchImprove search efficiencyData processing applicationsWeb data indexingCentral databaseComputer science
A method and system for facilitating a keyword search request initiated at a client station within a multilevel data network, wherein the multilevel data network includes multiple local sites each containing multiple data pages. Multiple keywords from each of the data pages within the local sites of the multilevel data network are stored locally and indexed such that each of the keywords points to one or more of the data pages in which the keywords are contained. The keywords and their index associations are locally updated. A central database is utilized to compile and index the locally indexed keywords from each of the local sites, such that each of the keywords in the central database points to one or more local sites from which those keywords came in response to a keyword search initiated at the client station.
Owner:IBM CORP
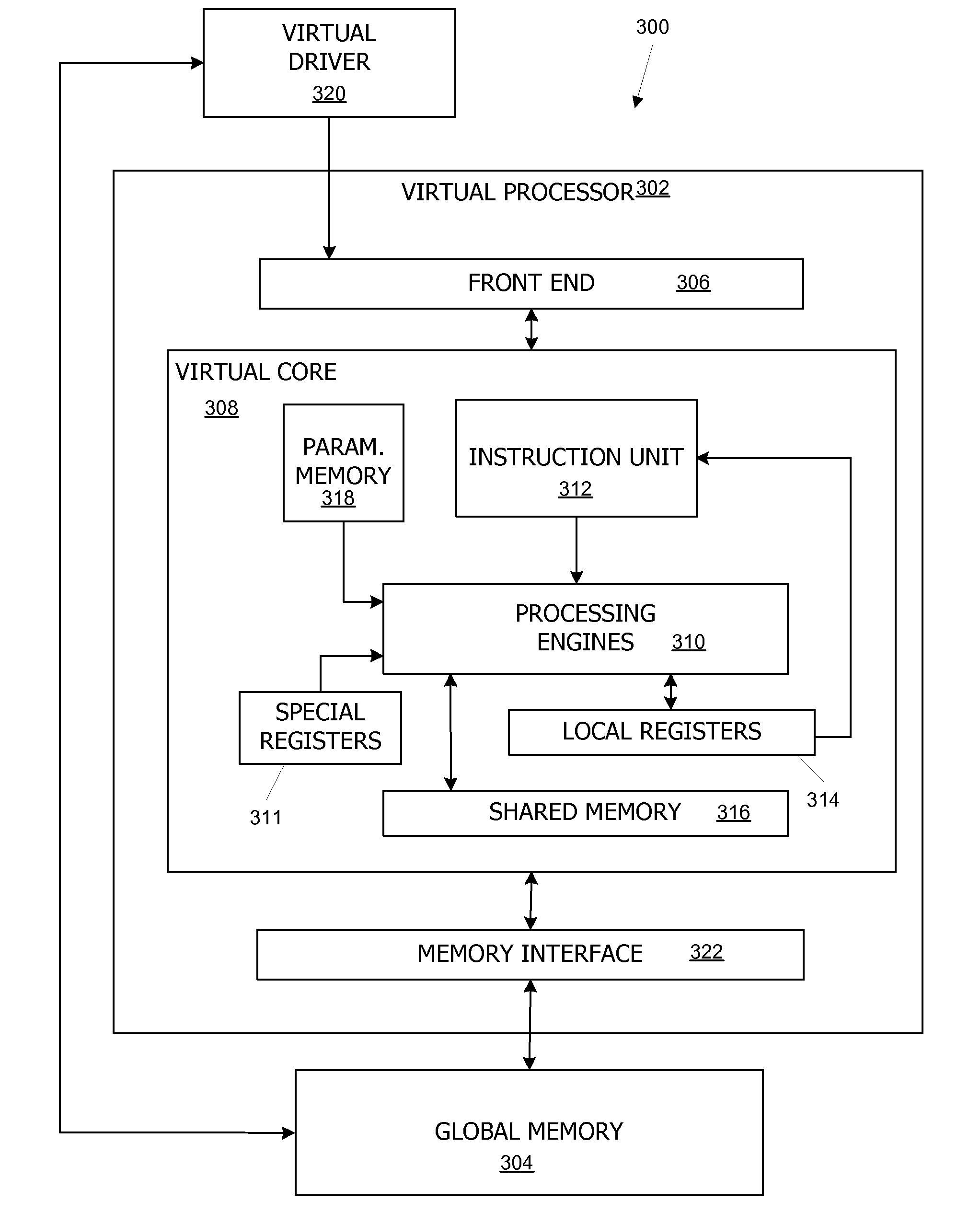
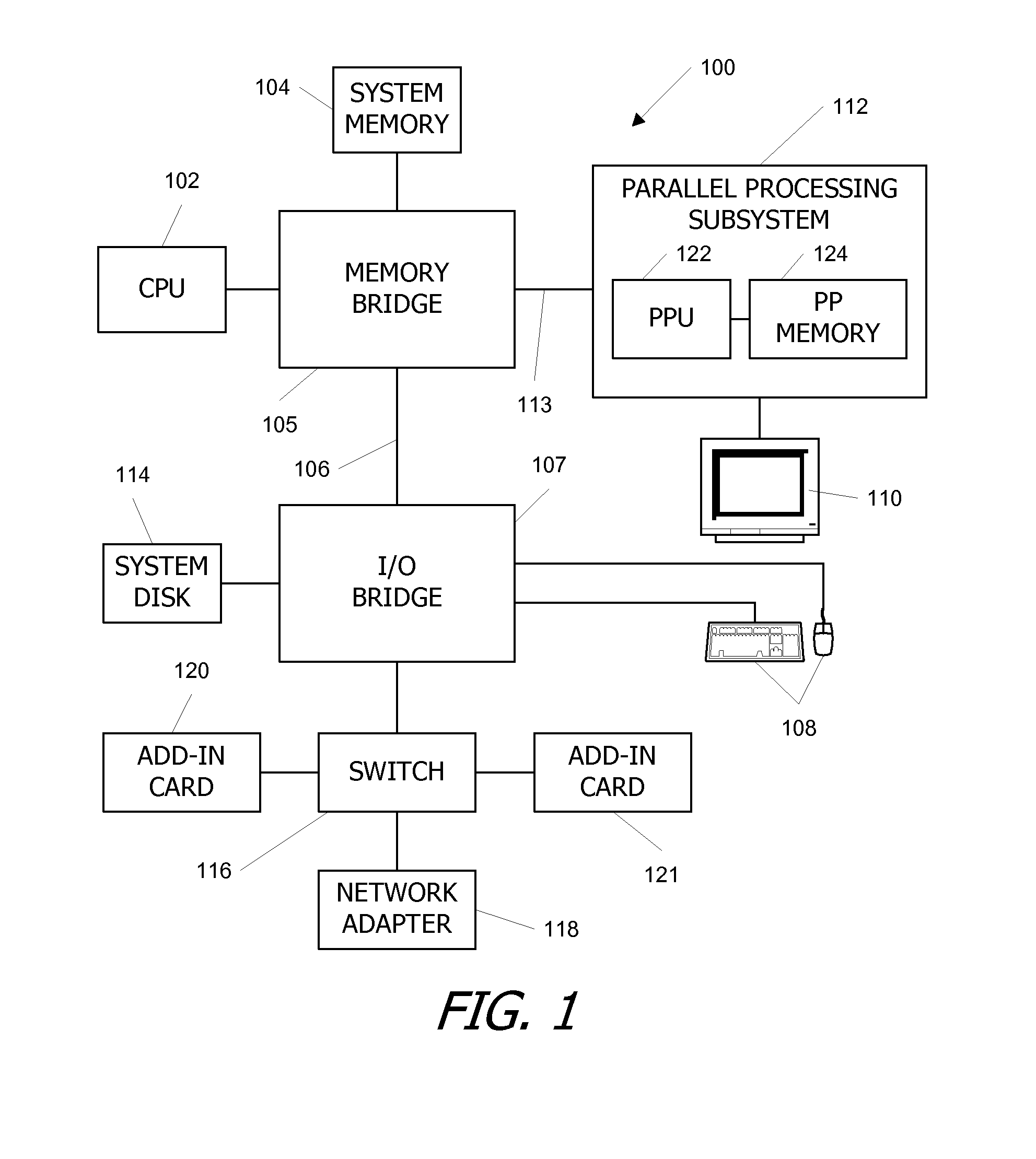
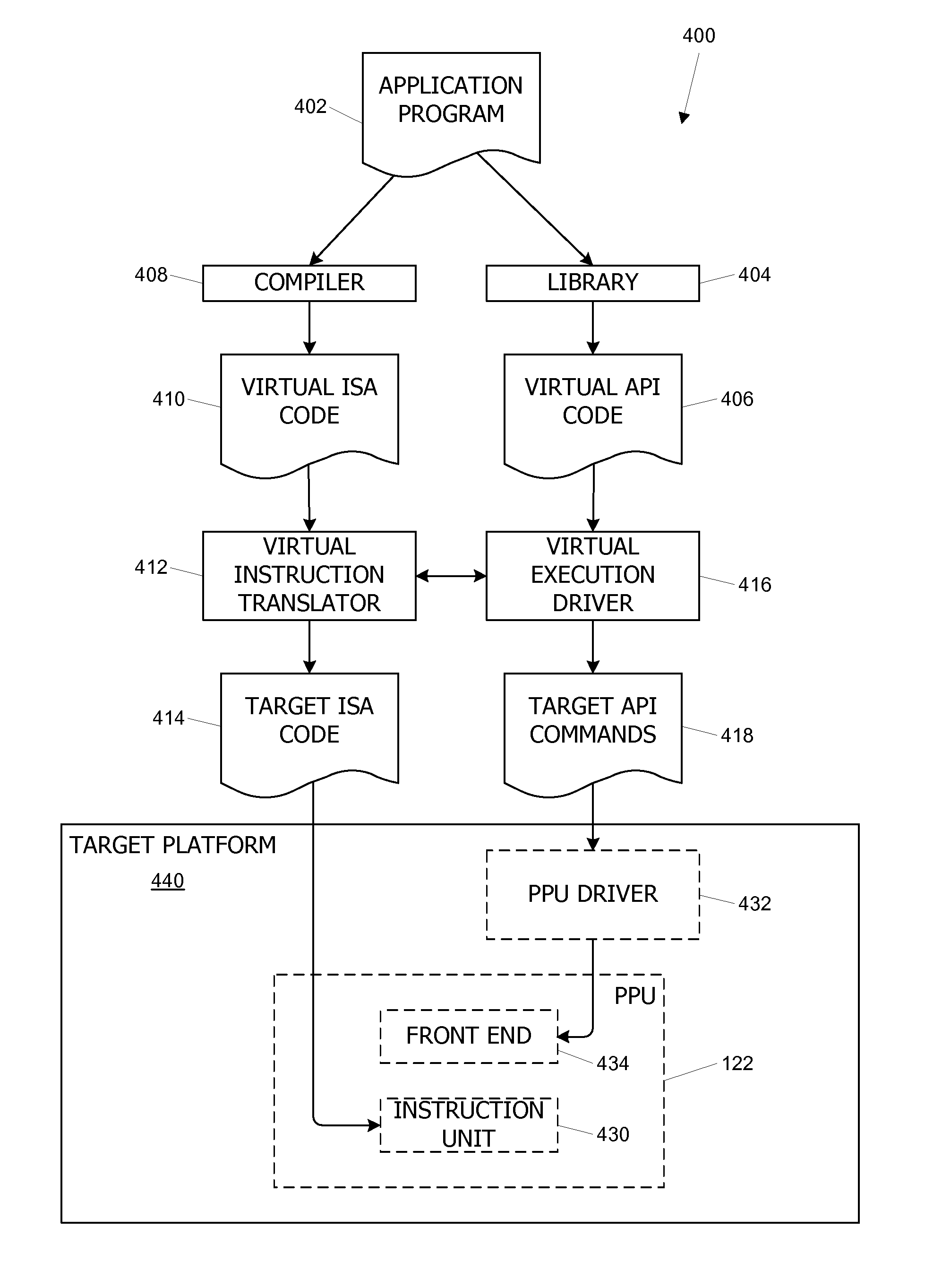
Virtual architecture and instruction set for parallel thread computing
ActiveUS20080184211A1Improve developmentImprove portabilityProgram control using stored programsSoftware engineeringApplication softwareData sharing
A virtual architecture and instruction set support explicit parallel-thread computing. The virtual architecture defines a virtual processor that supports concurrent execution of multiple virtual threads with multiple levels of data sharing and coordination (e.g., synchronization) between different virtual threads, as well as a virtual execution driver that controls the virtual processor. A virtual instruction set architecture for the virtual processor is used to define behavior of a virtual thread and includes instructions related to parallel thread behavior, e.g., data sharing and synchronization. Using the virtual platform, programmers can develop application programs in which virtual threads execute concurrently to process data; virtual translators and drivers adapt the application code to particular hardware on which it is to execute, transparently to the programmer.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
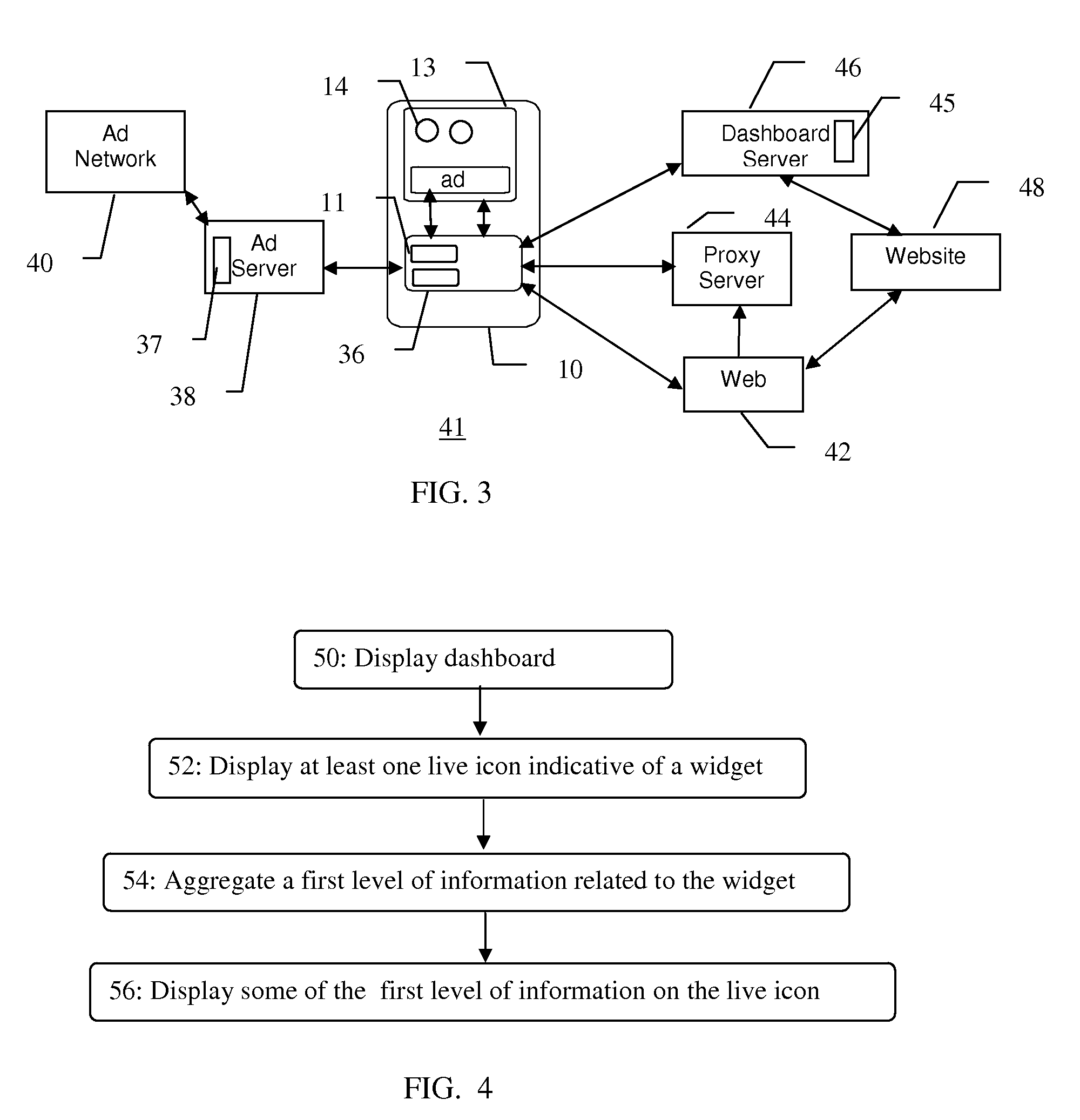
Mobile widget dashboard
The present invention is a method and system for the display of information on a mobile device that overcomes the difficulties such as the small screen size. The information is displayed via widgets having multiple levels of display and interaction. At a first dashboard level the widgets may be represented by live icons that have an information display area capable of displaying a first level of information relevant to said widget while remaining in iconic form. User interaction with the widget may result in multiple levels of data being aggregated and displayed by the widget in multiple levels of screens. The widgets may also display advertising, that may be targeted, in, for instance, a banner.
Owner:DIVAN IND
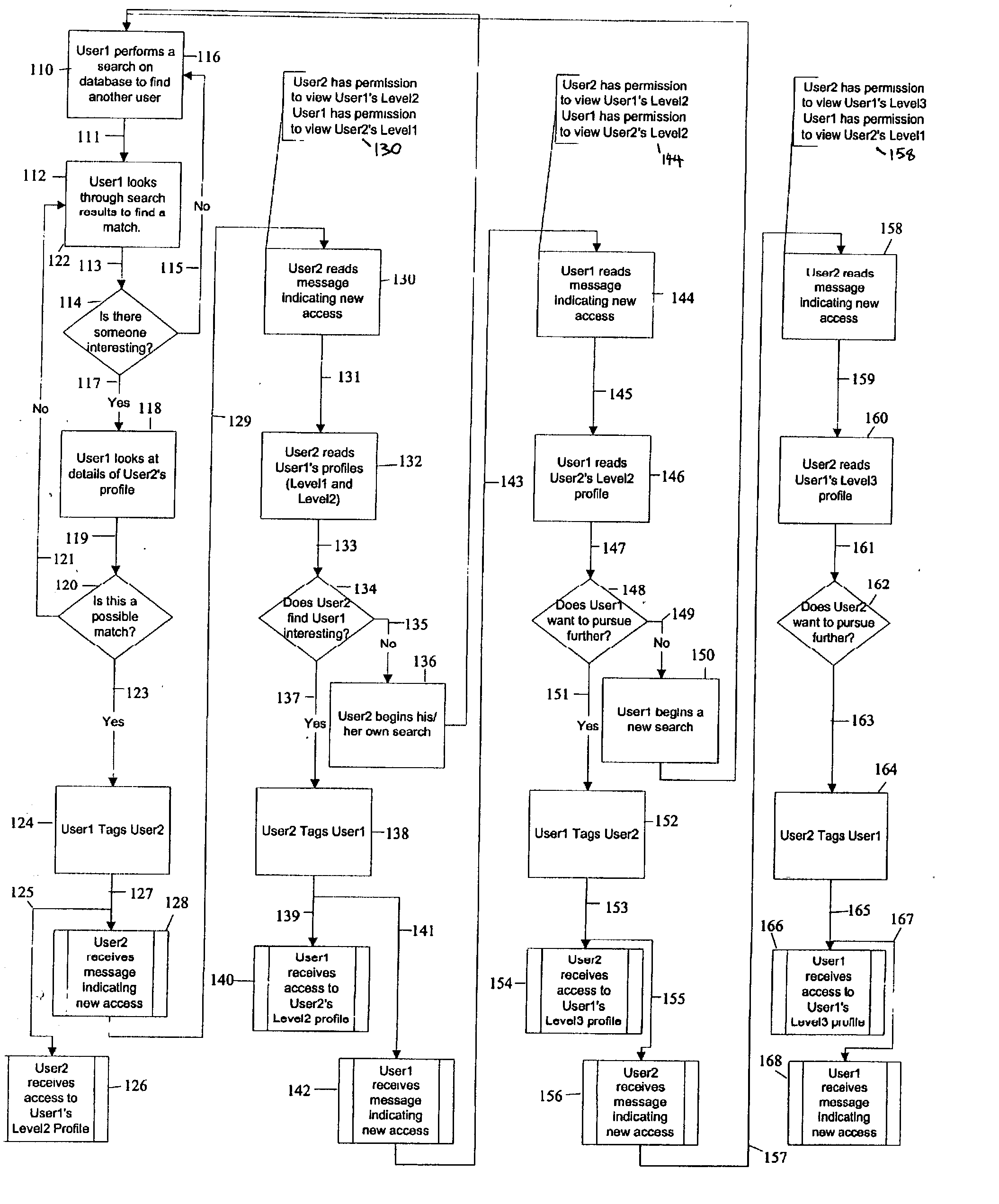
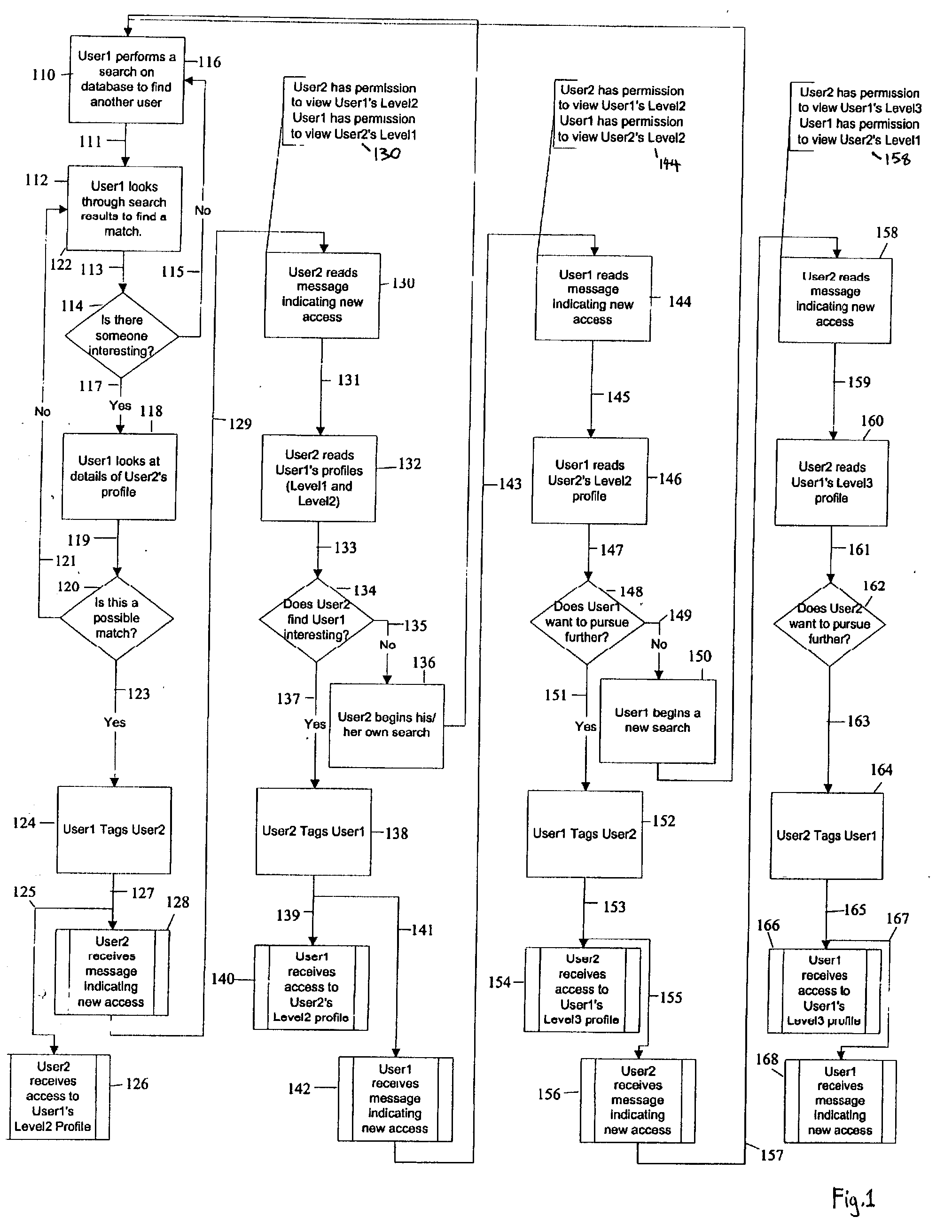
Profile management system
InactiveUS20040093334A1Control over private informationControl the dissemination of private informationDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsBusiness enterpriseNetwork on
Distributed permission based multi level data access system and method allows personal or business profile information dissemination in discrete, staggered and regulated format across a computer network which may be managed by a central server. Permission based requests and grants are administered by users. Sending users may tag recipient users which both sends a message and increments permission access level.
Owner:SCHERER STEPHEN
Virtual architecture and instruction set for parallel thread computing
ActiveUS8321849B2Improve portabilityMore portableProgram control using stored programsSoftware engineeringApplication softwareData sharing
A virtual architecture and instruction set support explicit parallel-thread computing. The virtual architecture defines a virtual processor that supports concurrent execution of multiple virtual threads with multiple levels of data sharing and coordination (e.g., synchronization) between different virtual threads, as well as a virtual execution driver that controls the virtual processor. A virtual instruction set architecture for the virtual processor is used to define behavior of a virtual thread and includes instructions related to parallel thread behavior, e.g., data sharing and synchronization. Using the virtual platform, programmers can develop application programs in which virtual threads execute concurrently to process data; virtual translators and drivers adapt the application code to particular hardware on which it is to execute, transparently to the programmer.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Computation parallelization in software reconfigurable all digital phase lock loop
ActiveUS20090070568A1Easy to reconfigureReduce per cycle current transientPulse automatic controlGeneral purpose stored program computerData stream processingTime-sharing
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
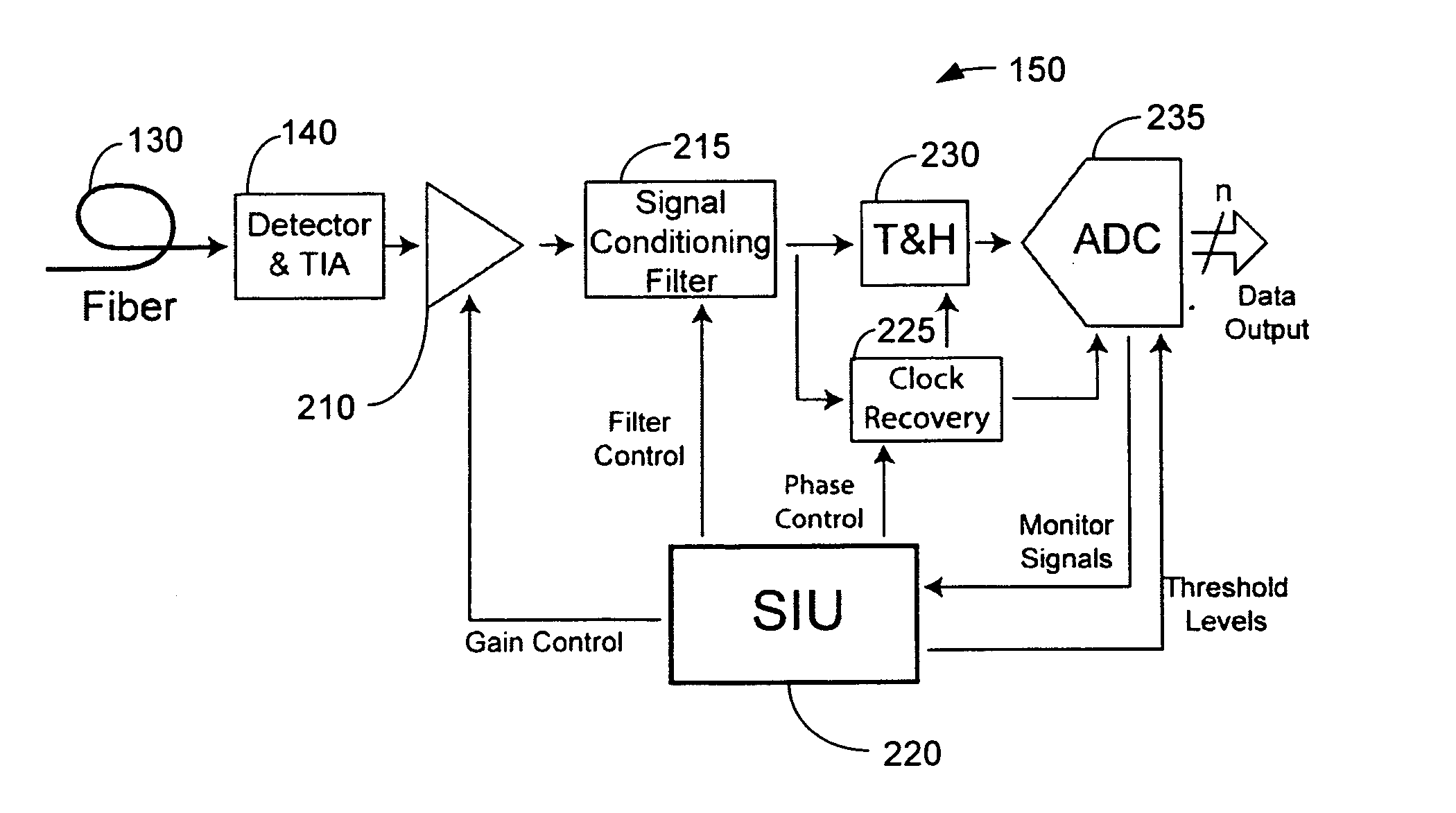
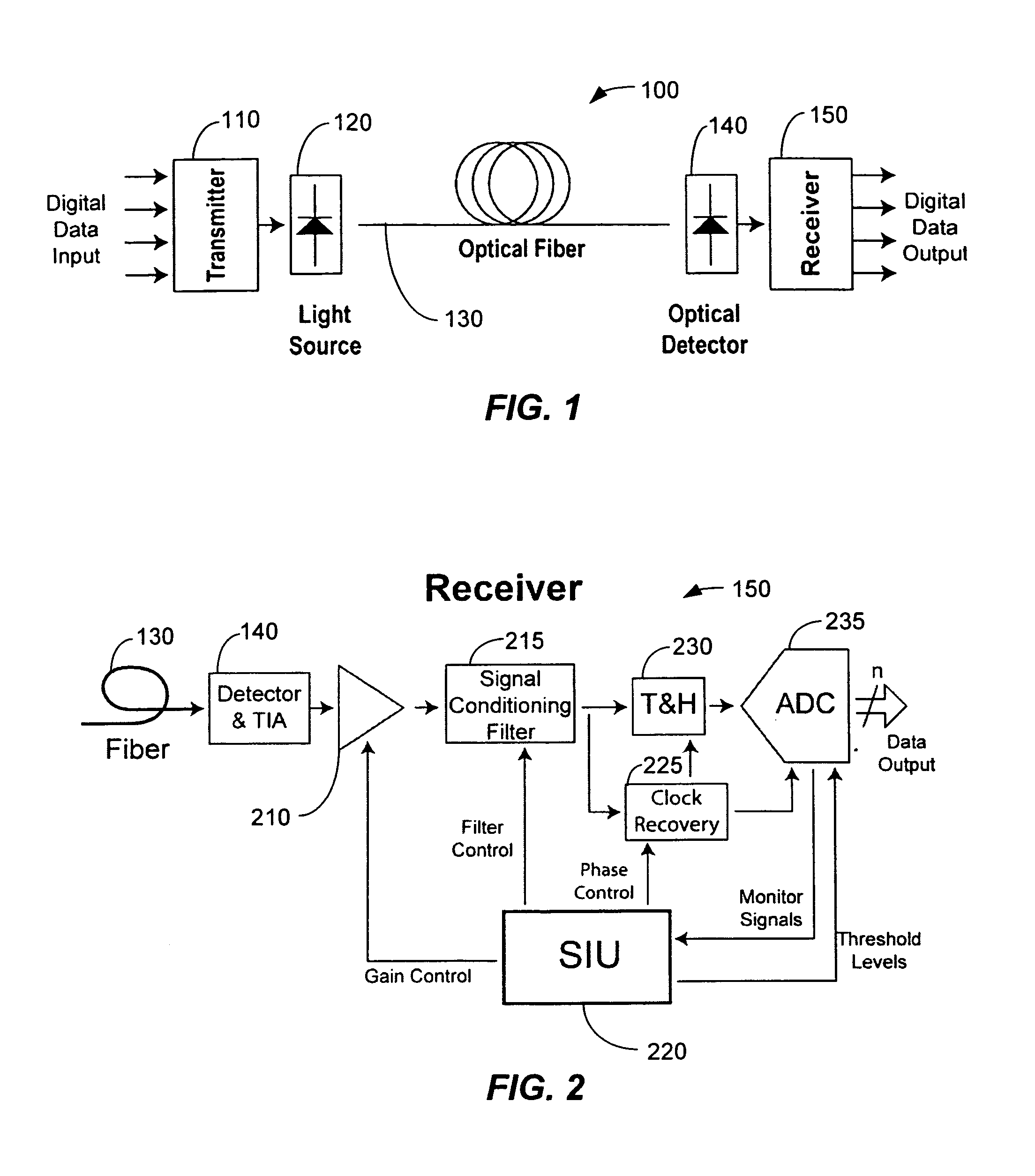
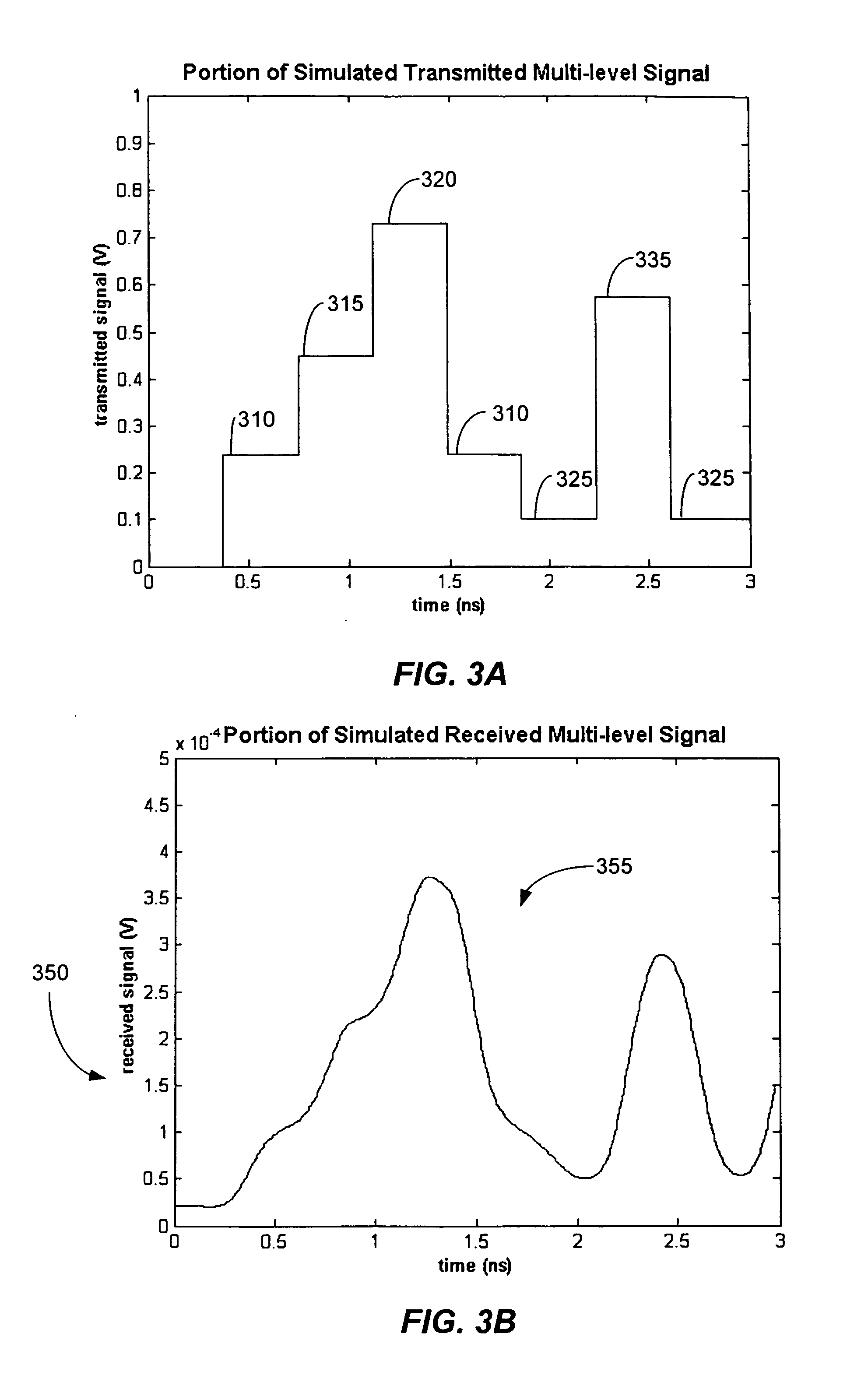
Method and system for decoding multilevel signals
ActiveUS7215721B2Efficient processingMinimizes average error probabilityRepeater/relay circuitsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionNormal densityAutomatic control
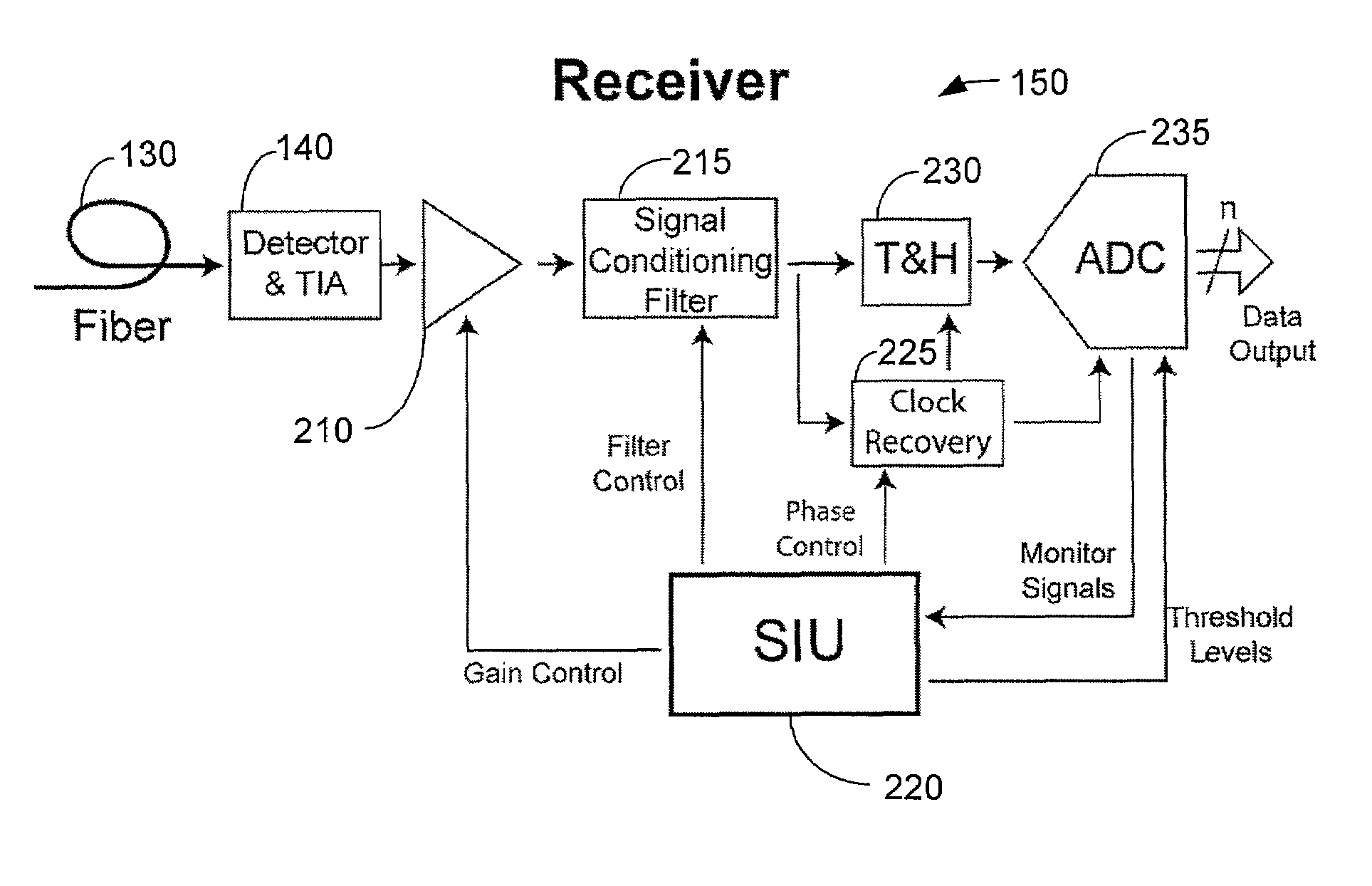
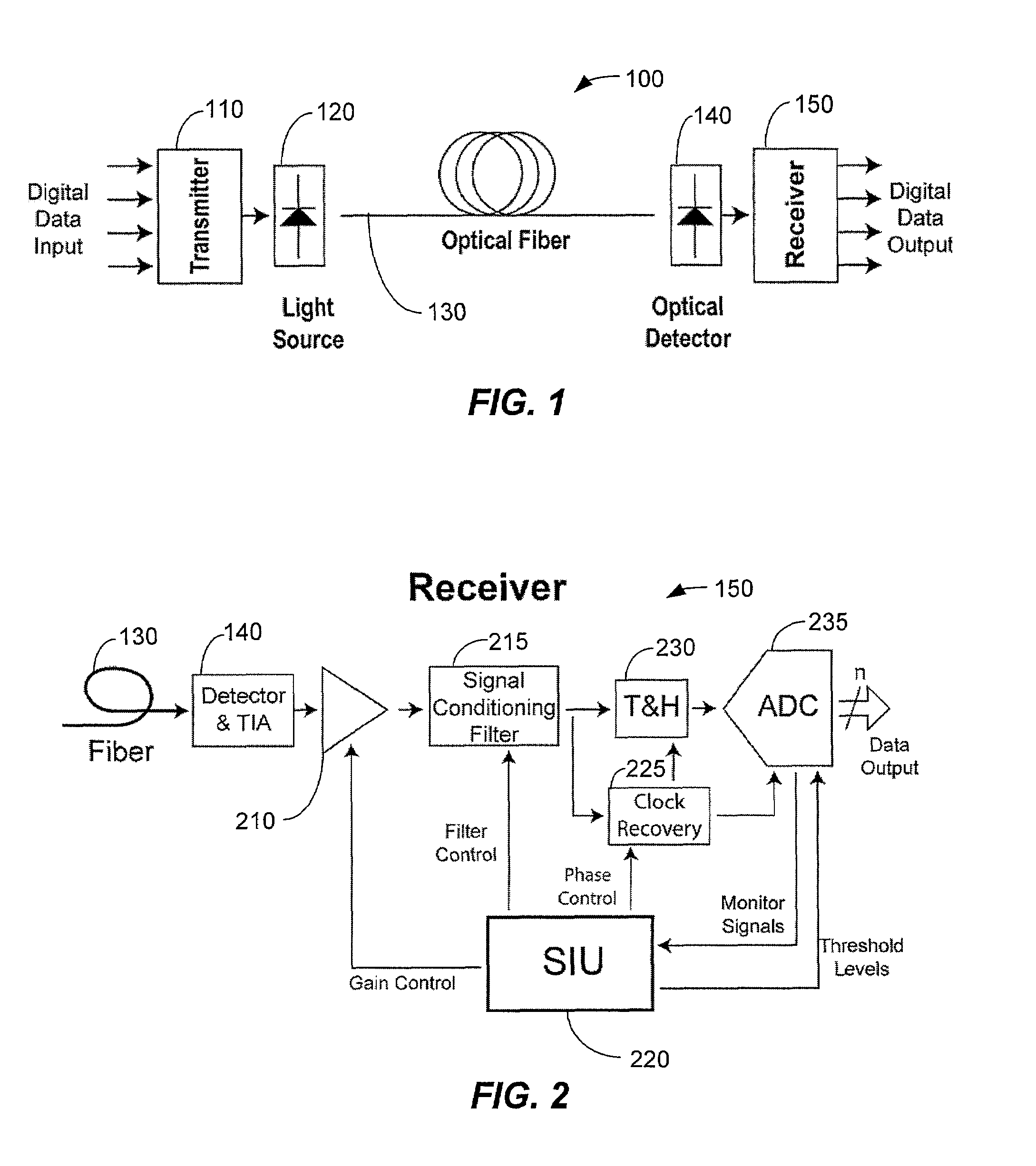
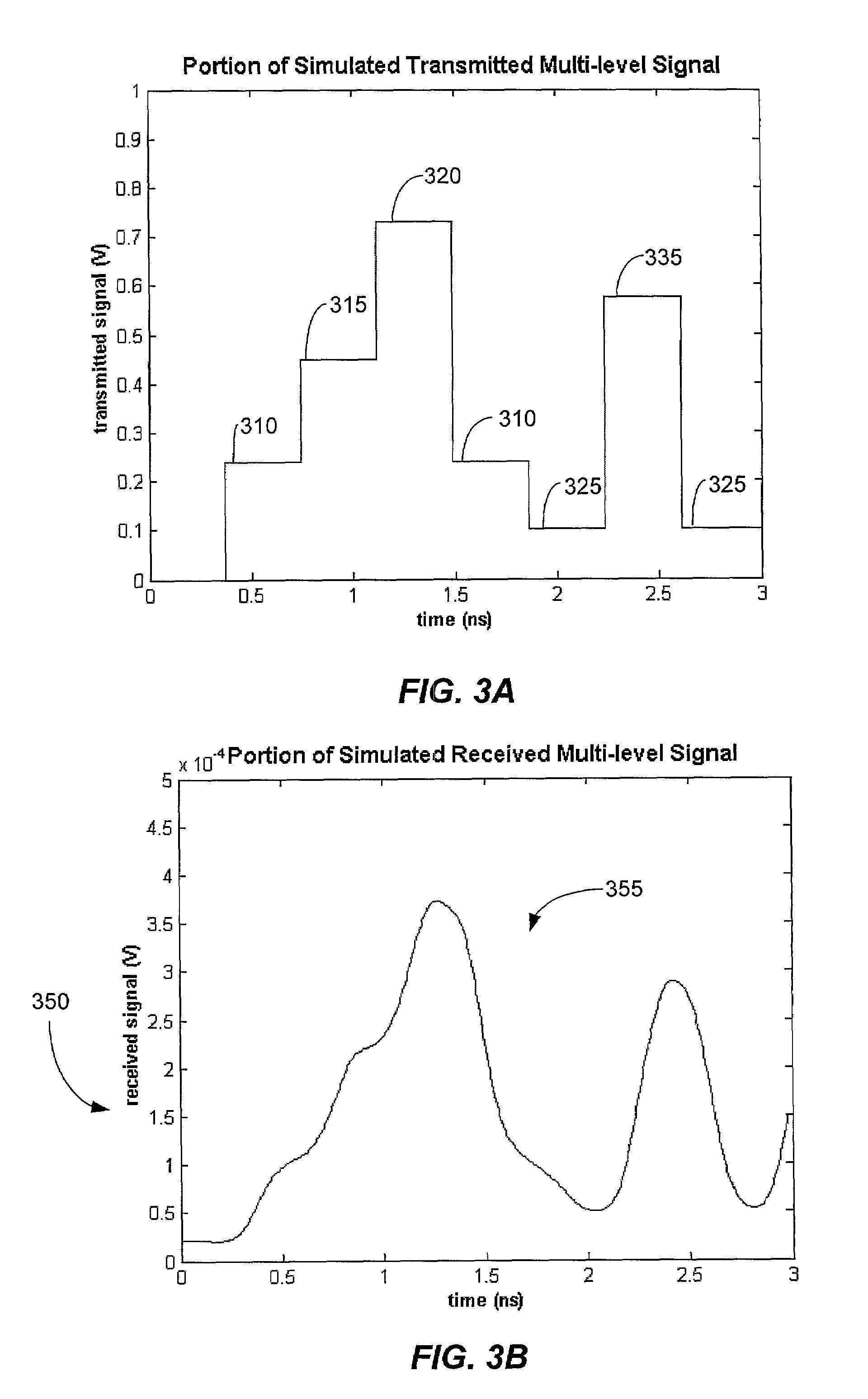
A multilevel optical receiver can comprise a plurality of comparators that generally correspond with the number of levels in a multilevel data stream. Each comparator can be individually controlled and fed a decision threshold in order to decode a multilevel signal. The multilevel optical receiver can generate a statistical characterization of the received symbols in the form of a marginal cumulative distribution function (CDF) or probability density function (pdf). This characterization can be used to produce a set of ε-support estimates from which conditional pdfs are derived for each of the transmission symbols. These conditional pdfs may then be used to determine decision thresholds for decoding the received signal. The conditional pdfs may further be used to continuously estimate the fidelity or error rate of the received signal without the transmission of a testing sequence. The ε-supports may further be used to automatically control the gain on the receiver.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
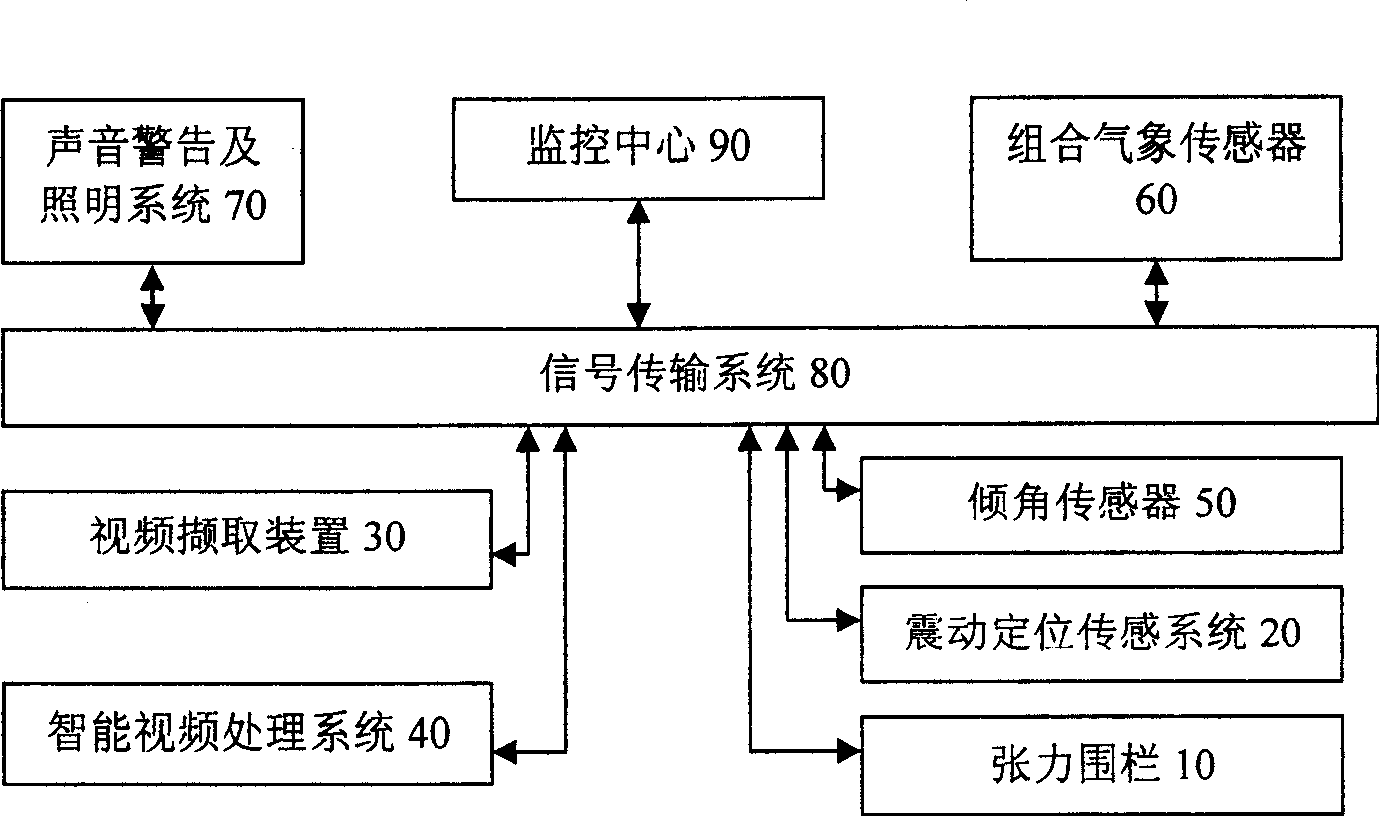
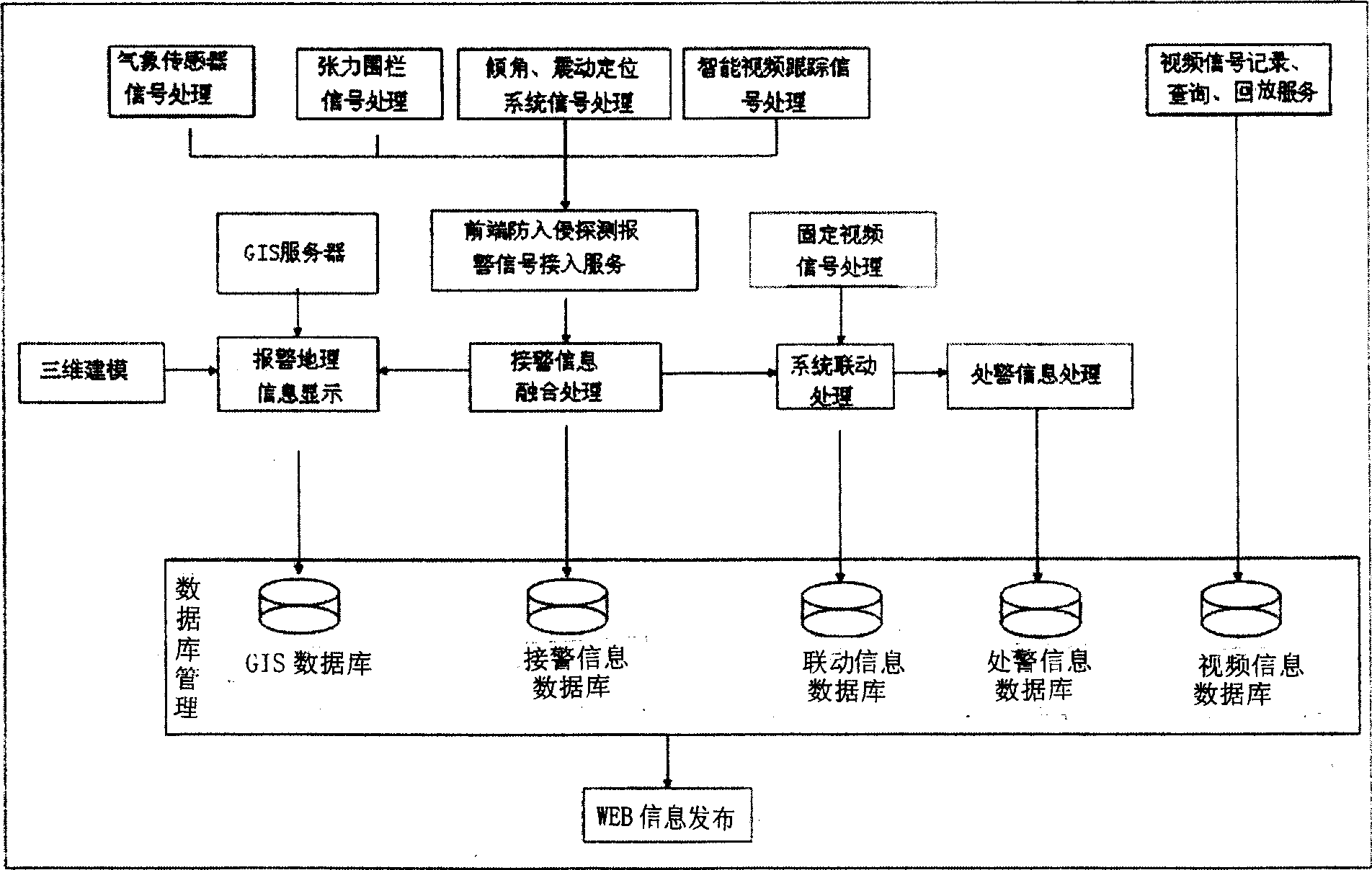
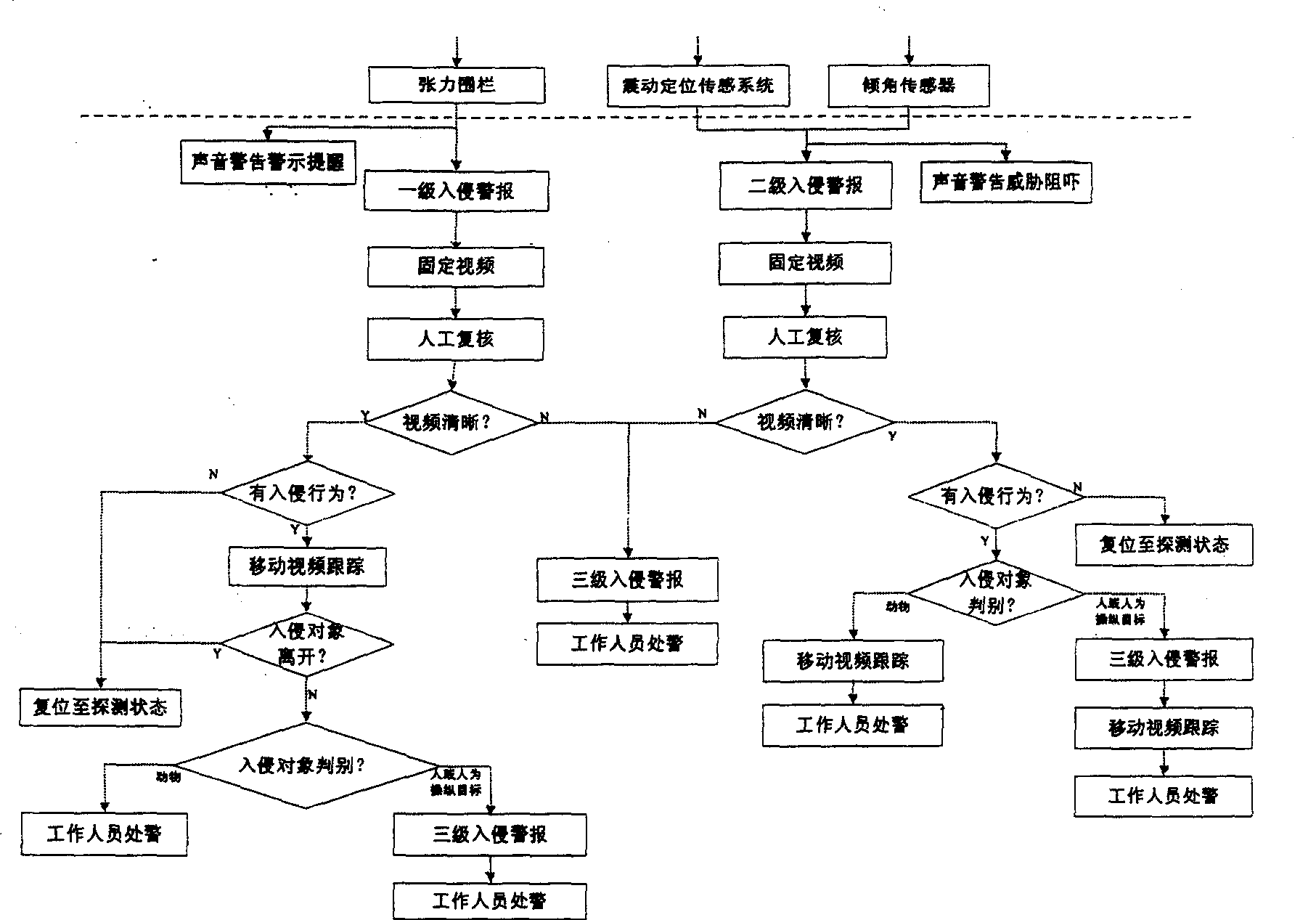
Multi-grade stereo anti-intruding system, apparatus and implementing method based on wireless sensing net
InactiveCN101388130AData switching by path configurationClosed circuit television systemsVideo serverSensing system
The invention relates to a multi-level and stereoscopic boundary anti-intrusion system based on a wireless sensing network, a device and an implementation method thereof, which comprises various sensors, a wireless transmission device, a wireless sensing network node, a video capture device and an intelligent video processing system which are arranged on the boundary to capture and output sensing probing and video signals, a video server which is connected with the video capture device for receiving and storing video signals output by the video capture signals, and a vibration positioning sensing system which is distributed especially aiming at required important defense area. The introducing application of combining a meteorological sensor and a lighting and sound alarm device can roundly and effectively increase the accuracy of system monitoring and alarm in all weather and all days. The invention further provides a stereoscopic level monitoring, an alarm system implementation scheme and a multi-level data fusing alarm scheme, which effectively reduces false alarm rate and false dismissal rate.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
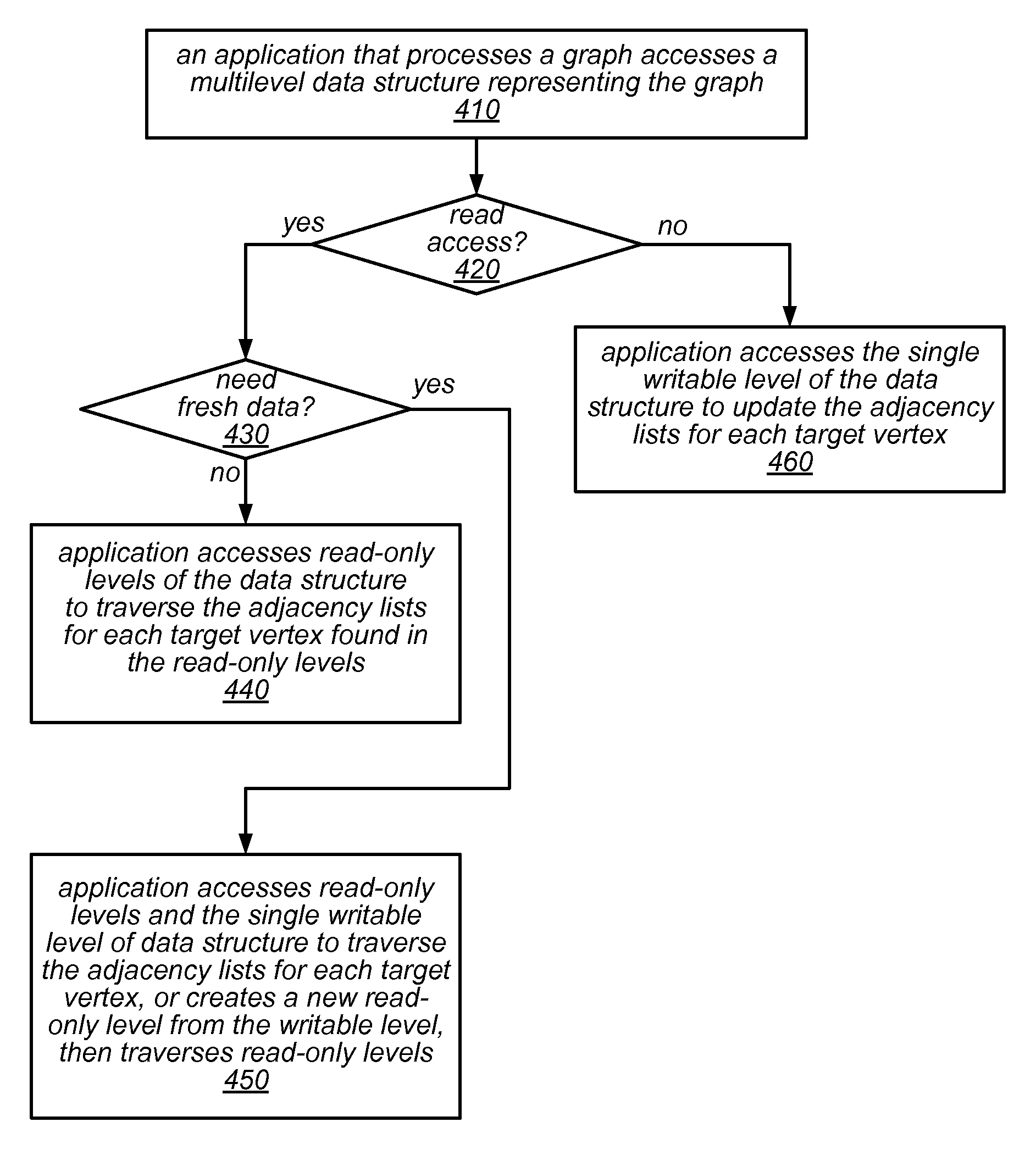
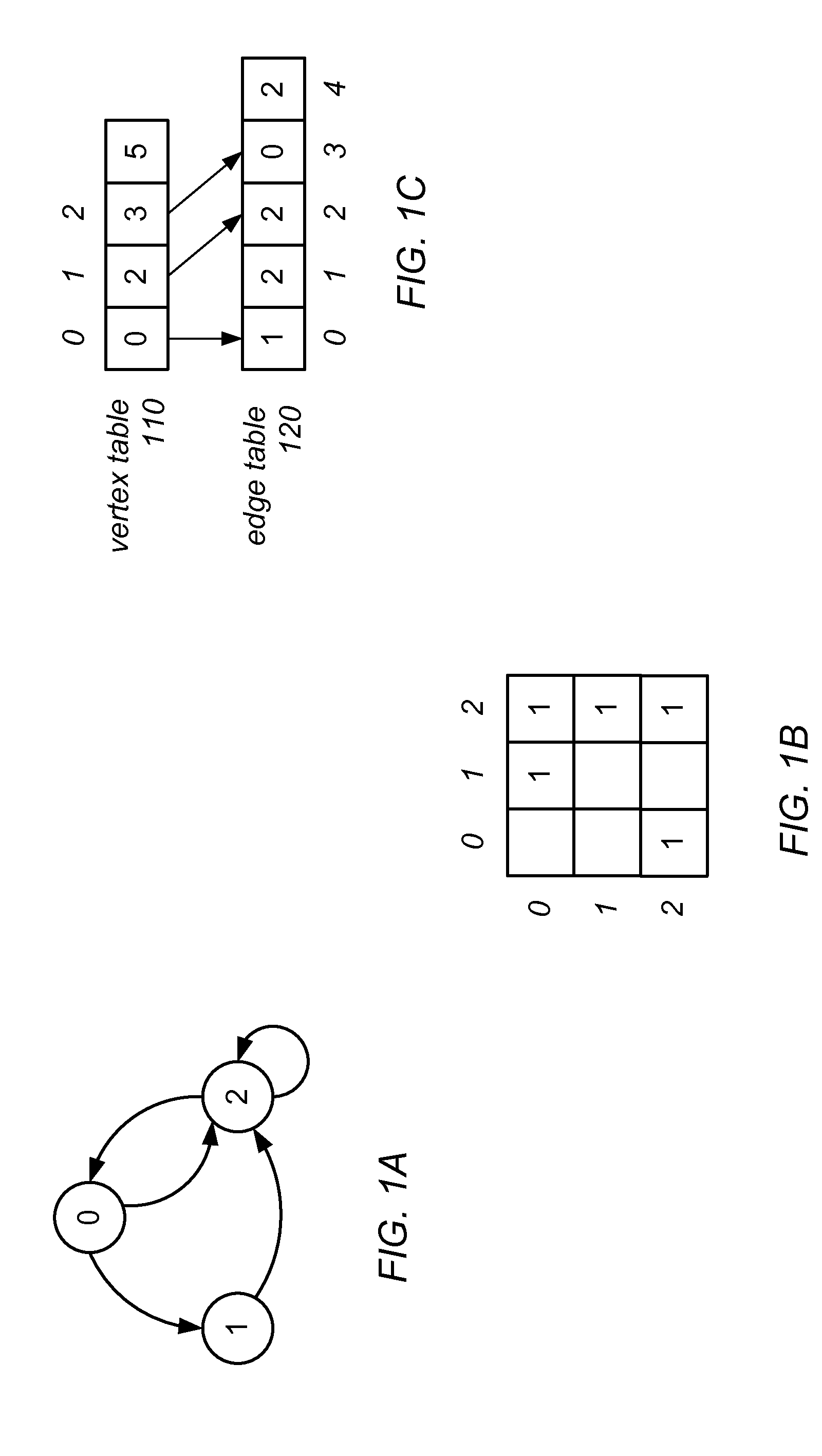
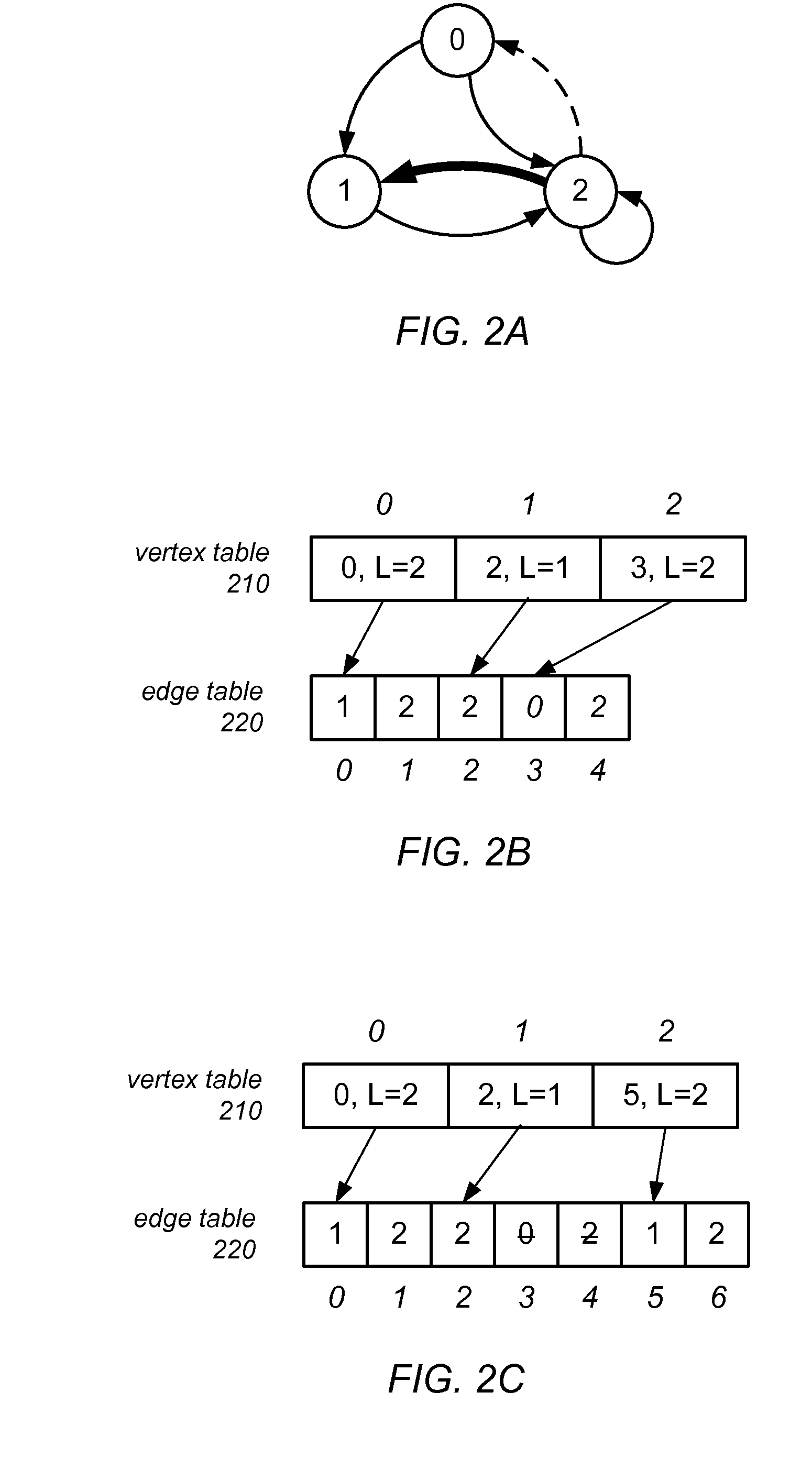
Graph Processing Using a Mutable Multilevel Graph Representation
ActiveUS20160071233A1Improve performanceIncrease spacingDrawing from basic elementsImage memory managementTheoretical computer scienceAdjacency list
A mutable multilevel data structure representing a graph structure may include multiple read-only levels and a single writable level. Each read-only level may include a vertex table (which includes references to edge tables on the same level or a different level containing elements of adjacency lists for some vertices) and an edge table (which includes elements of adjacency lists that changed since the previous read-only level). A hybrid variant may switch between a performance-optimized variant (whose edge tables include complete adjacency lists for vertices whose edge sets were modified) and a space-optimized variant (whose edge tables include only newly added adjacency list elements). The vertex tables and / or the writable level may be implemented using copy-on-write arrays, each including an indirection table and multiple fixed-sized data pages. Computations may be run on the read-only levels or on the writable level and read-only levels.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
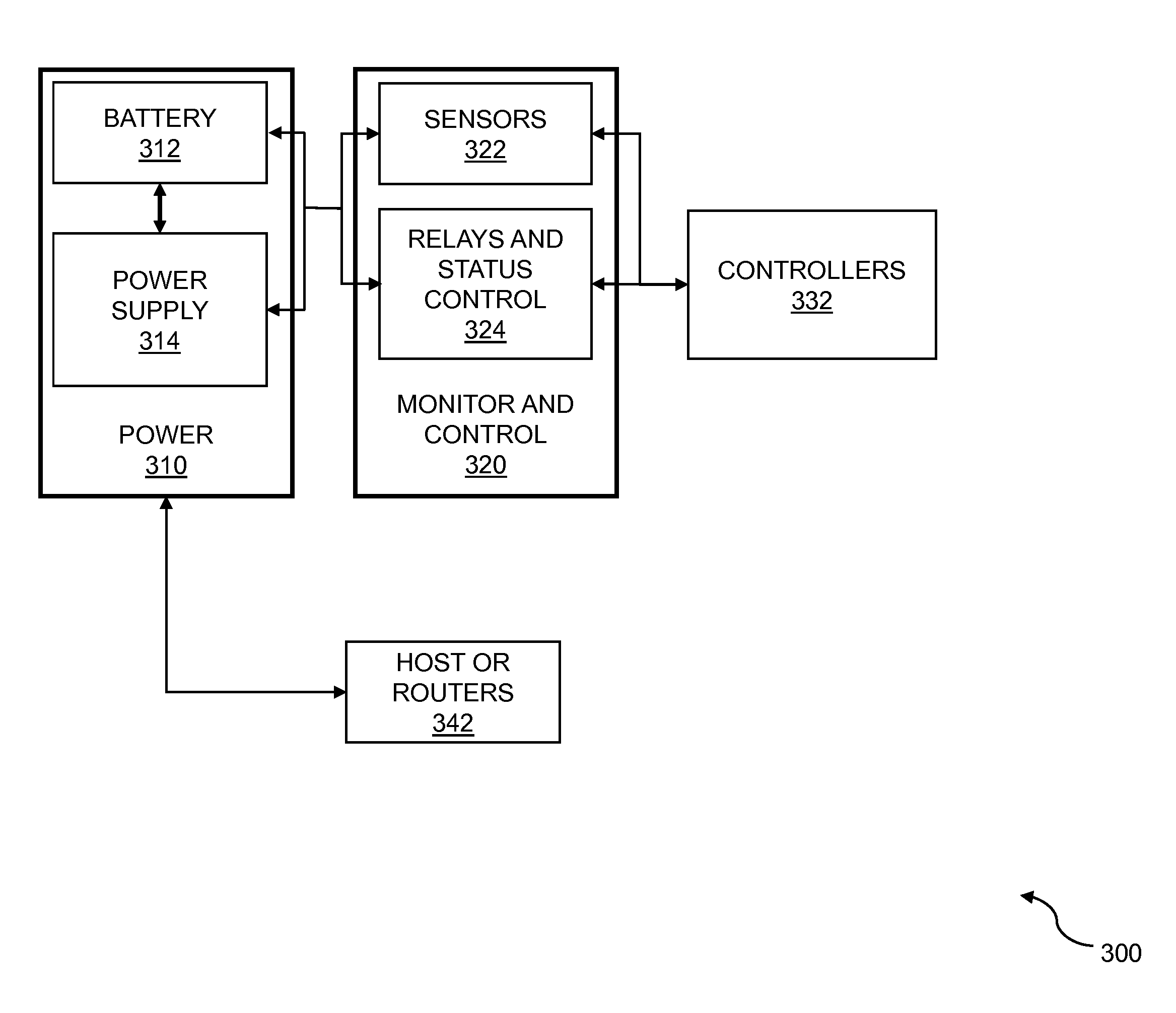
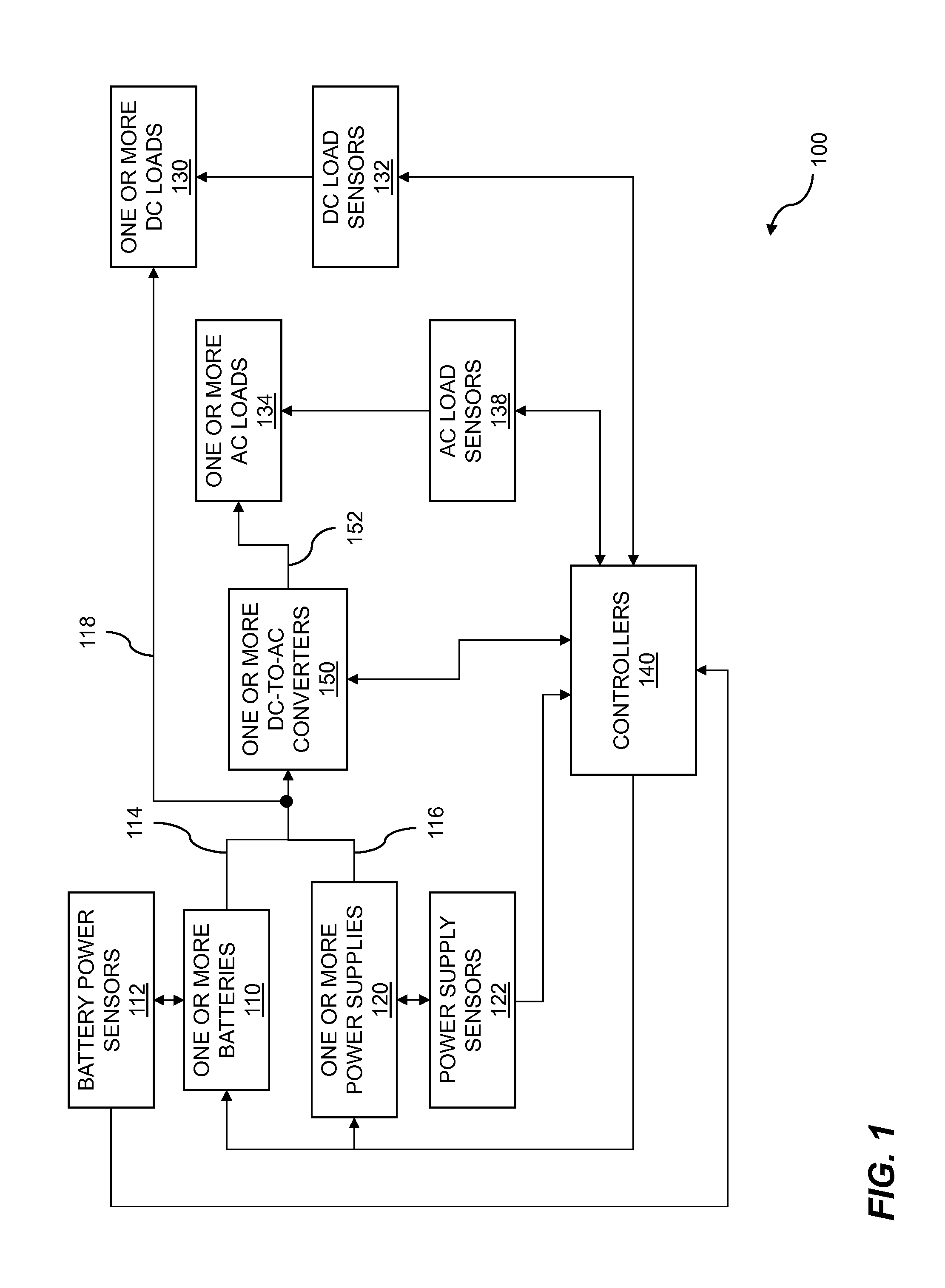
Multi-level data center consolidated power control
ActiveUS20150115711A1Stable and reliable powerPrevent and minimize downtimeSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectric controllersPower flowData center
Multi-level data center consolidated power is disclosed. One or more controllers communicate with one or more power supplies and sensors to adapt to dynamic load requirements and to distribute DC-power efficiently across multiple IT racks. The distributed DC-power includes one or more DC-voltages. Batteries can be temporarily switched into a power supply circuit to supplement the power supply during spikes in power load demand while a controller reconfigures power supplies to meet the new demand. In embodiments, one or more DC-to-AC converters handle legacy power loads. The DC-to-AC converters are modular and are paralleled for redundancy. The AC-power is synchronized for correct power flow control. The one or more controllers communicate with the one or more AC-power supplies to dynamically allocate AC-power from the DC-to-AC converters to the multiple IT racks.
Owner:VIRTUAL POWER SYST
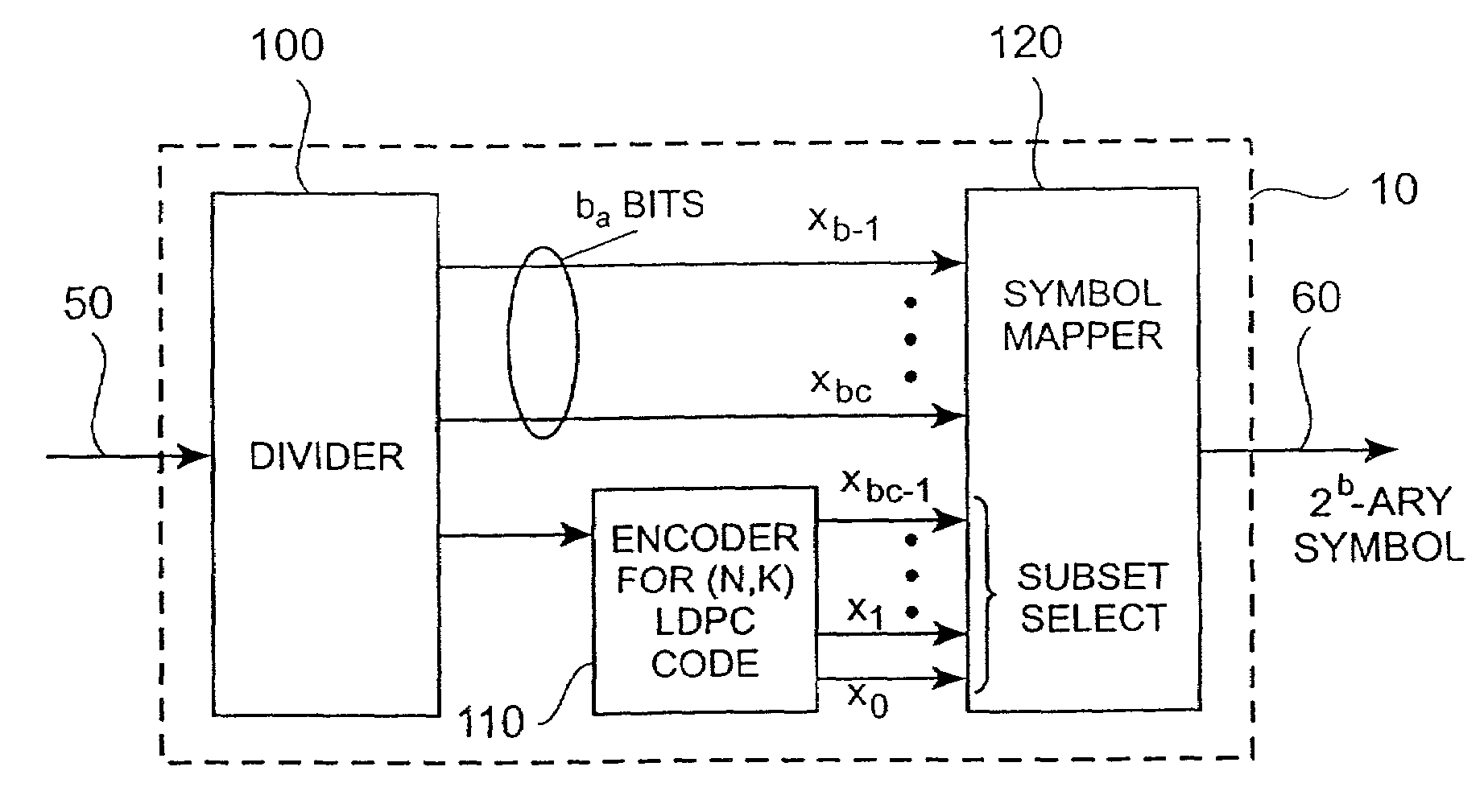
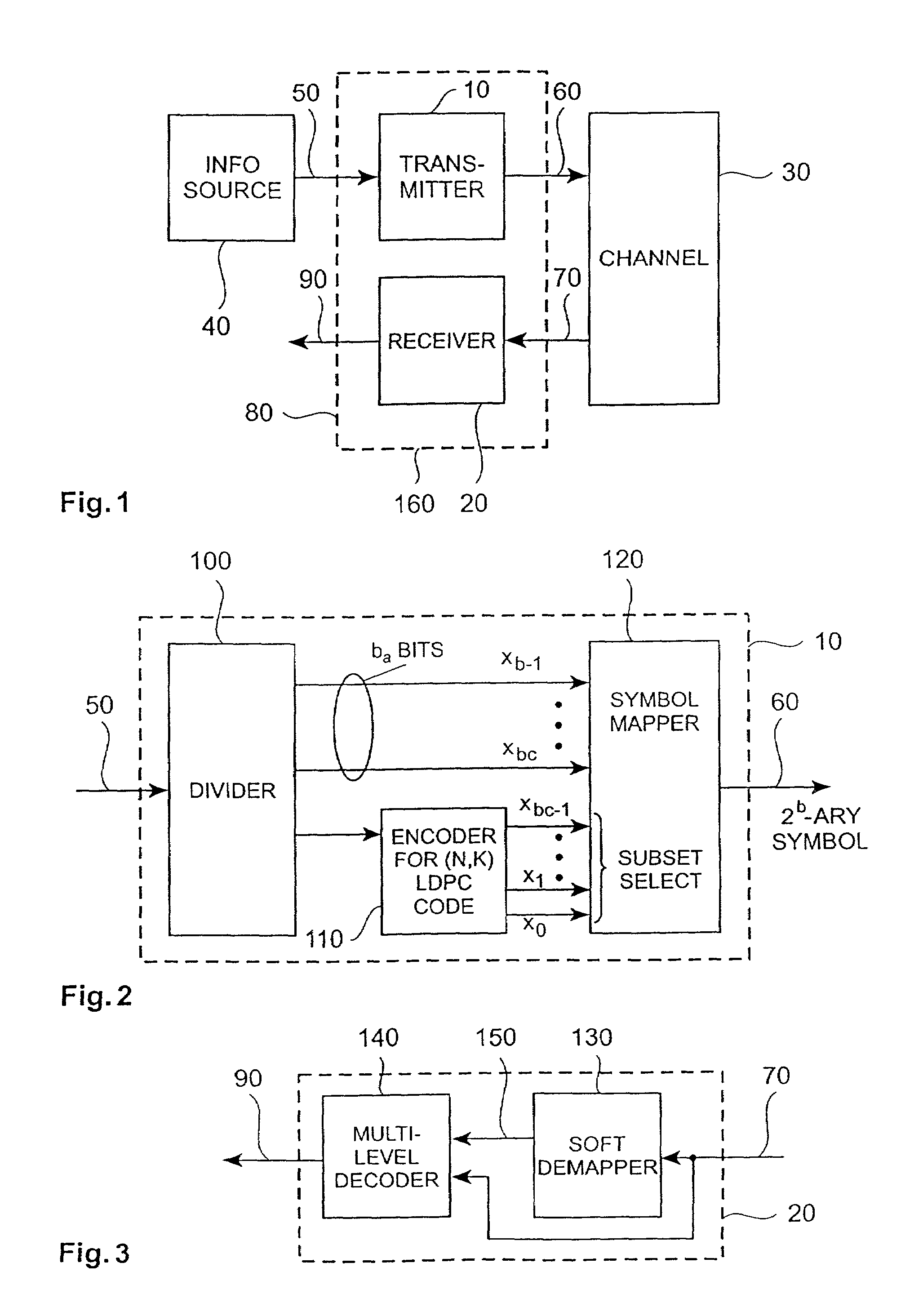
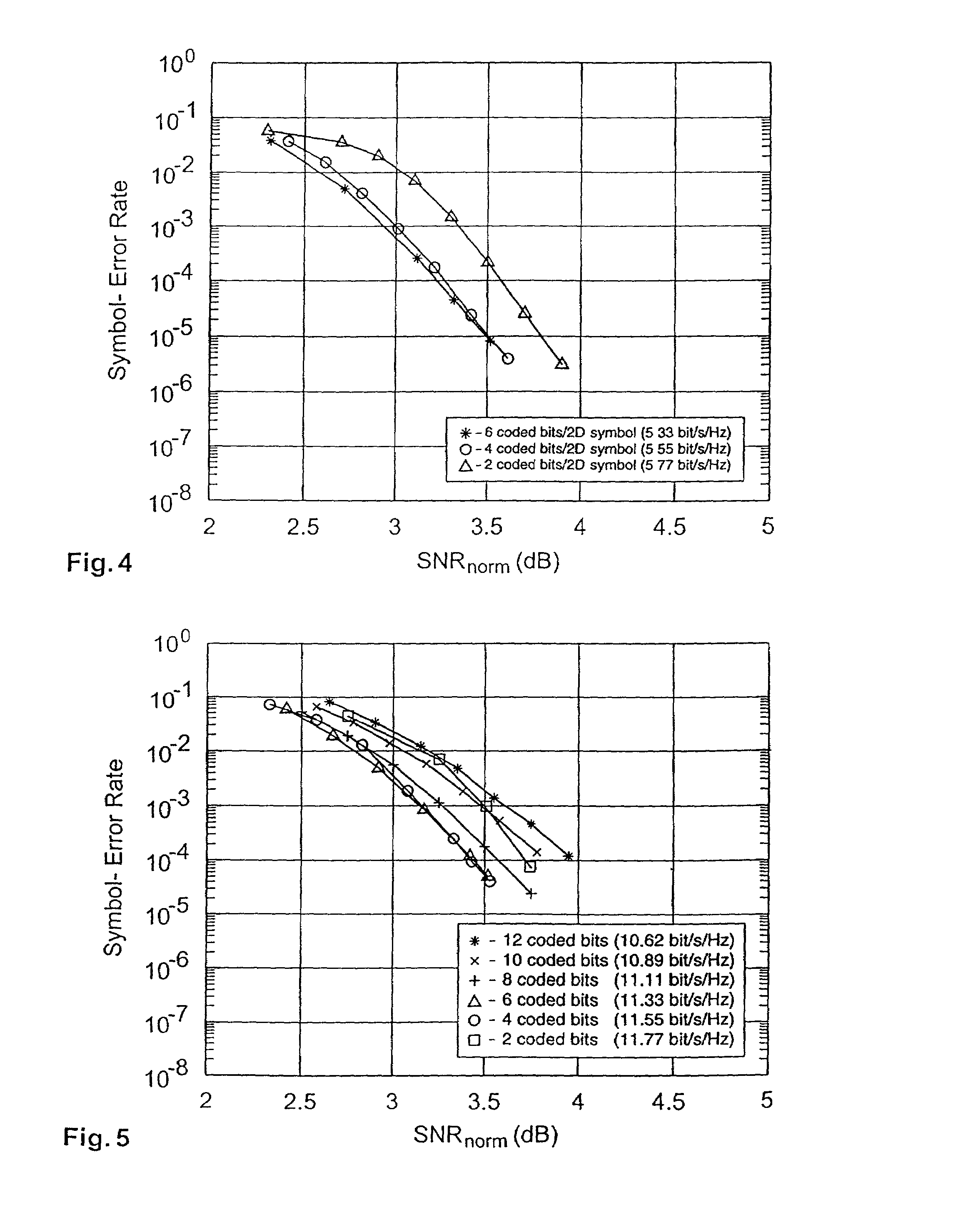
Block coding for multilevel data communication
InactiveUS6985536B2Increase flexibilitySignificant performance gainError preventionSecret communicationBlock codeTheoretical computer science
Methods, apparatus and systems for multilevel data communication comprises dividing a set of information bits to be transmitted into a first group and a second group; encoding the first group to generate a block code, selecting a subset of symbols in a constellation of symbols in dependence on the block code according to a Gray-coded mapping function, selecting a symbol within the subset in dependence on the second group according to a Gray-coded mapping function, and transmitting the selected symbol.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and systems for multilevel data security
InactiveUS20140064479A1Increasing computing and bandwidth resourcePublic key for secure communicationCode conversionComputer hardwareComputer science
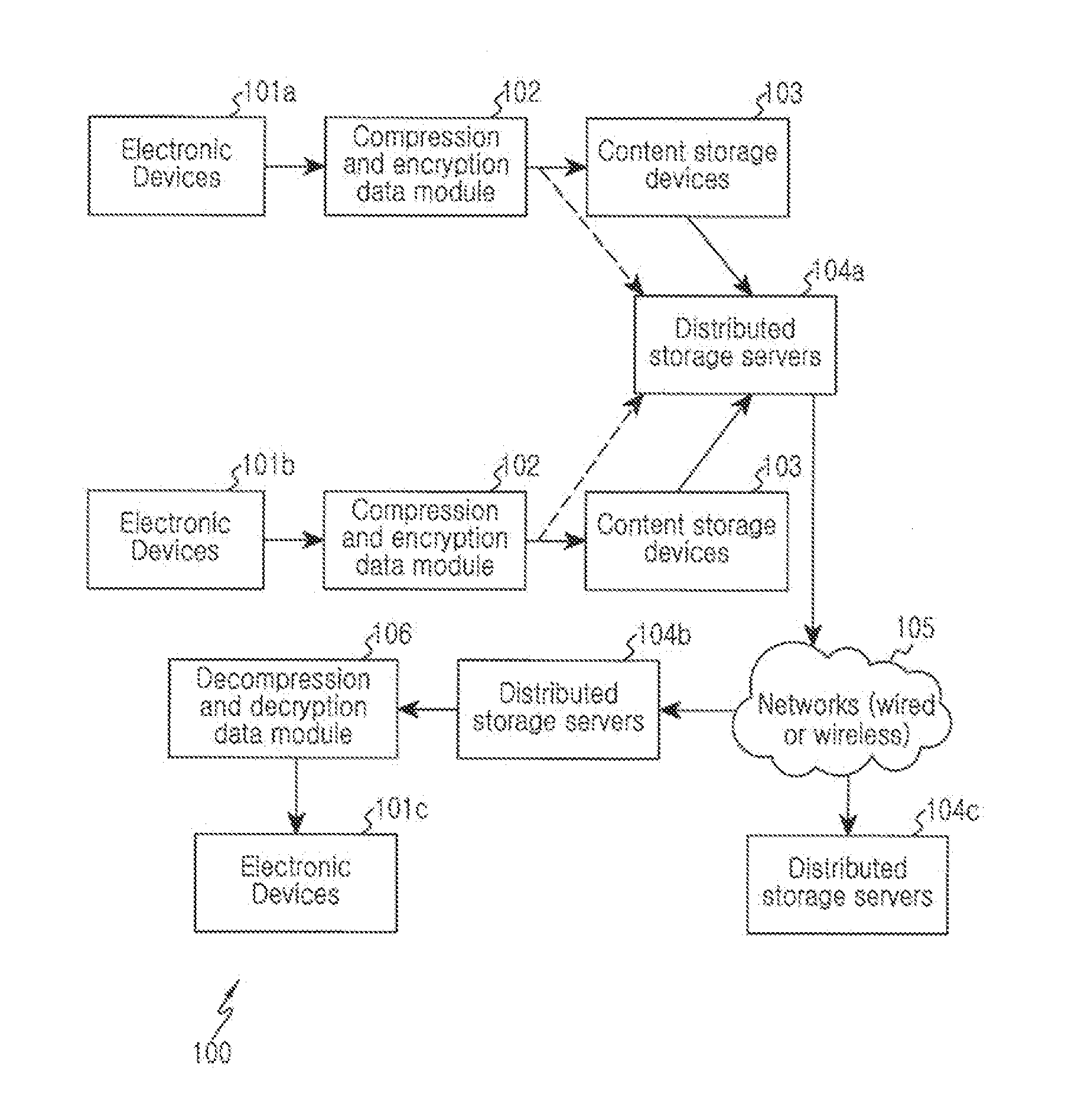
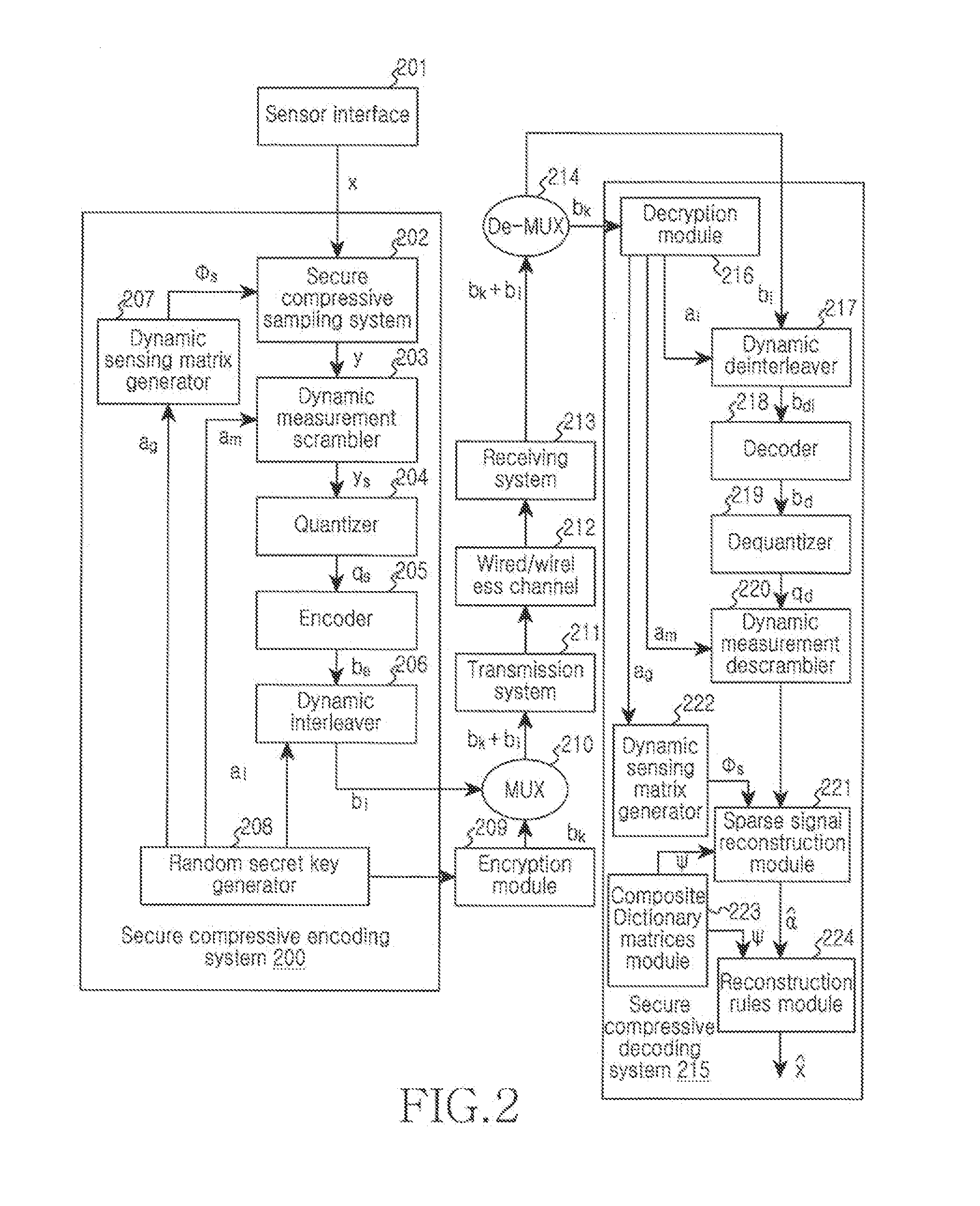
Device and method for multi-level dynamic joint data security and compression are disclosed. The method includes receiving an input signal from a sensor interface, performing encryption on compressive measurement encoded data that is based on the input signal, transmitting the encrypted compressive measurement encoded data through a communication network, performing decryption on the encrypted compressive measurement encoded data after receiving the encrypted compressed measurement encoded data from the communication network to form decrypted compressive measurement decoded data, and reproducing an original signal from the decrypted compressive measurement decoded data that corresponds to the input signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
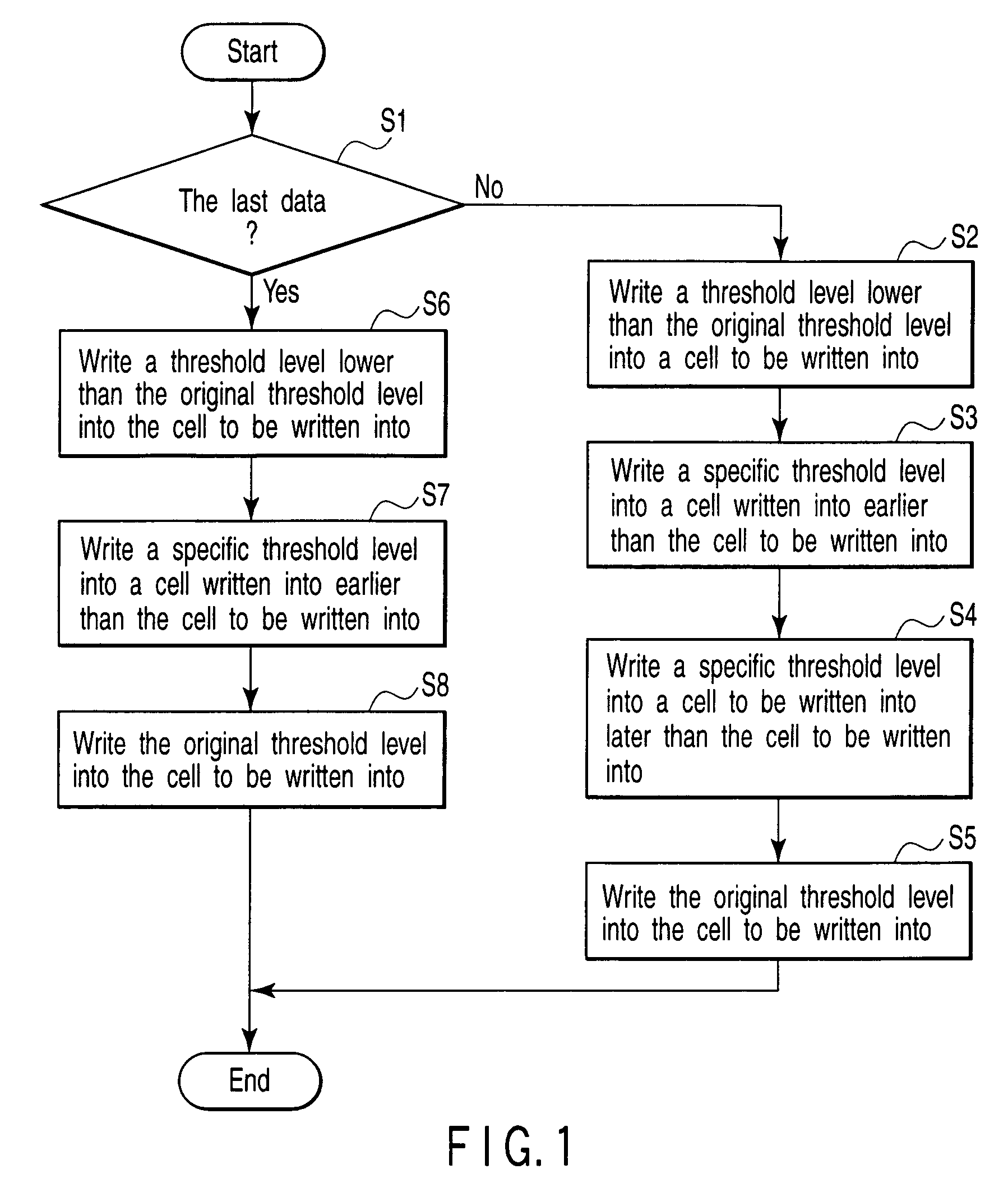
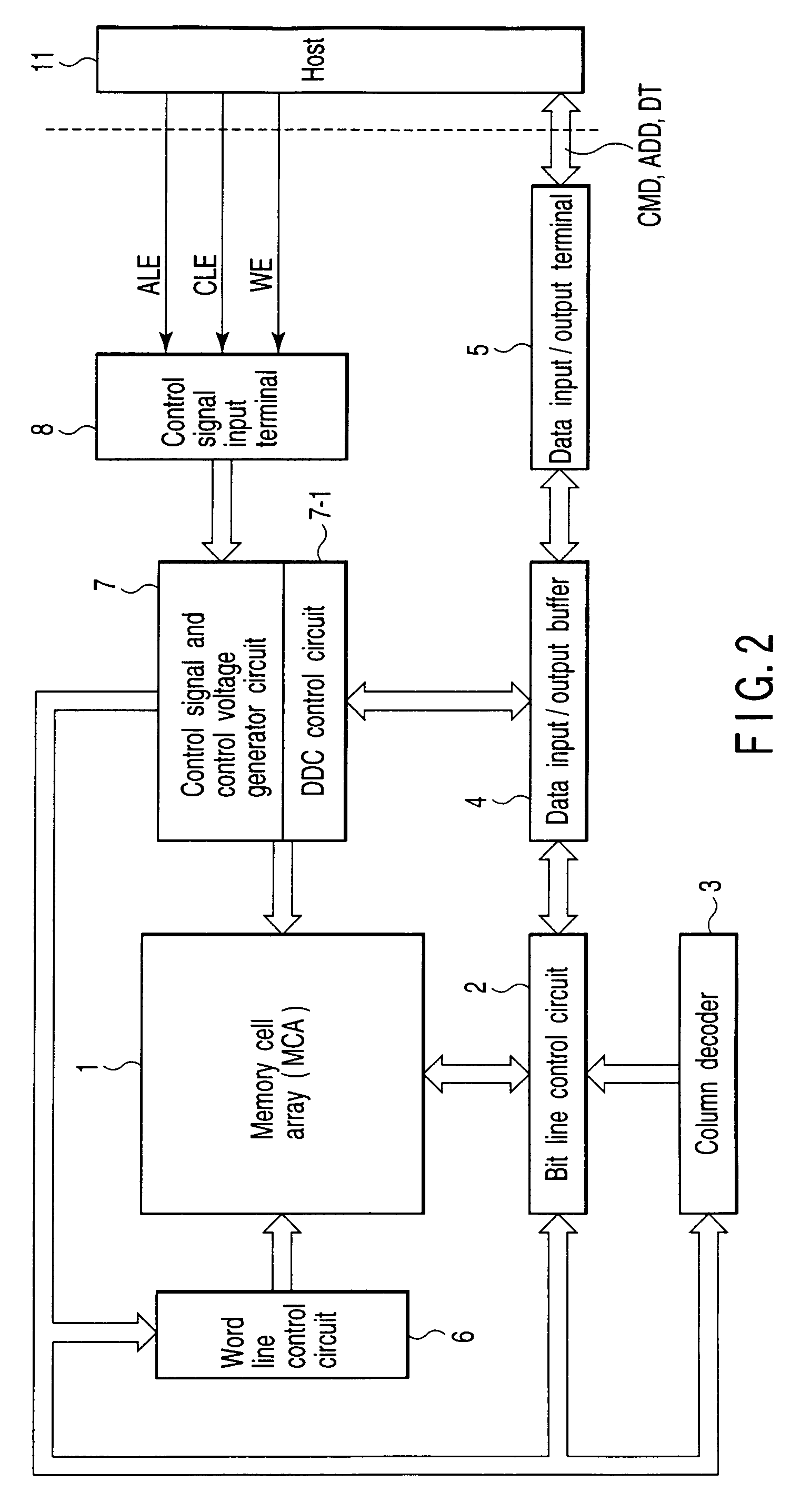
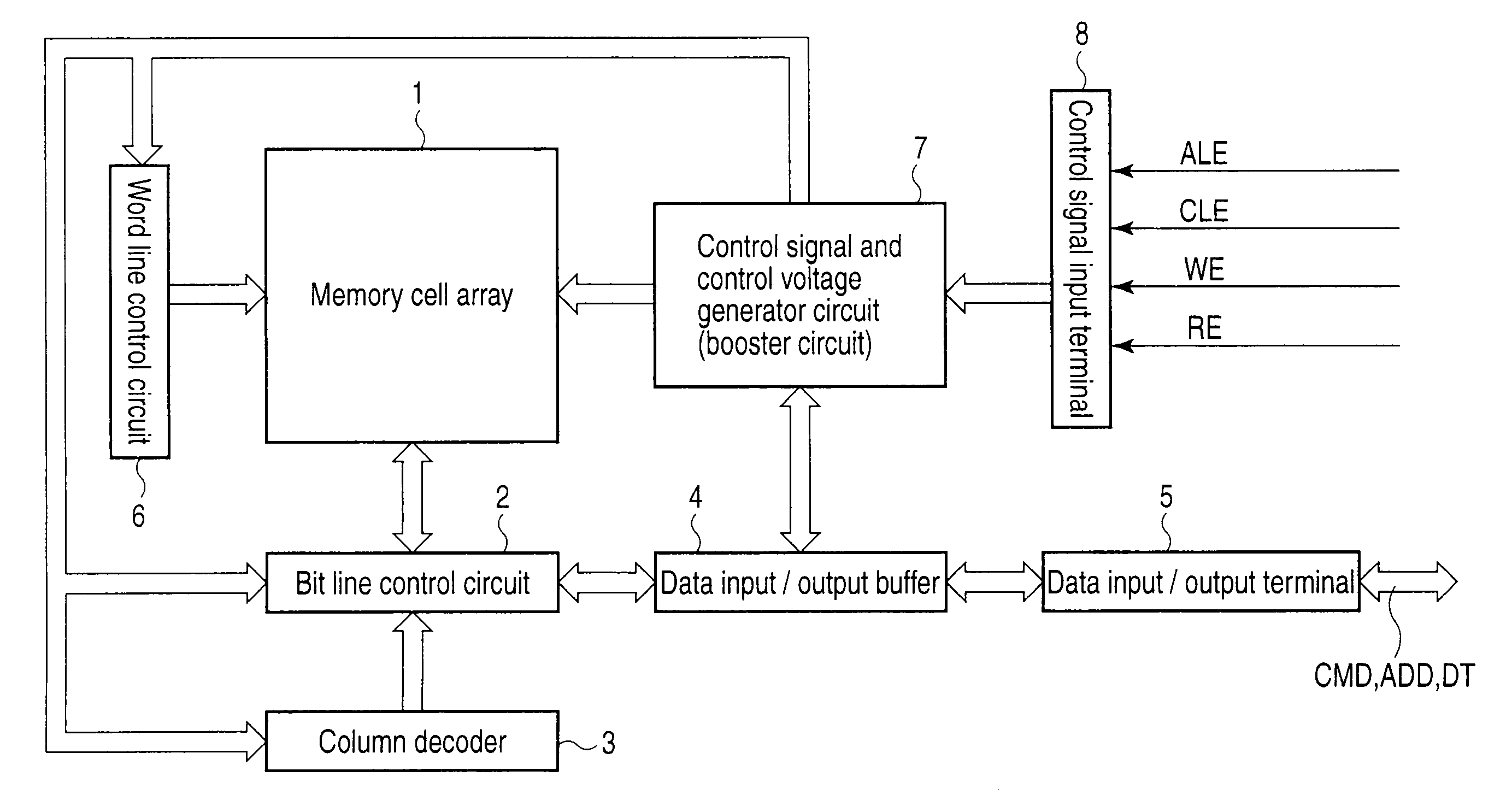
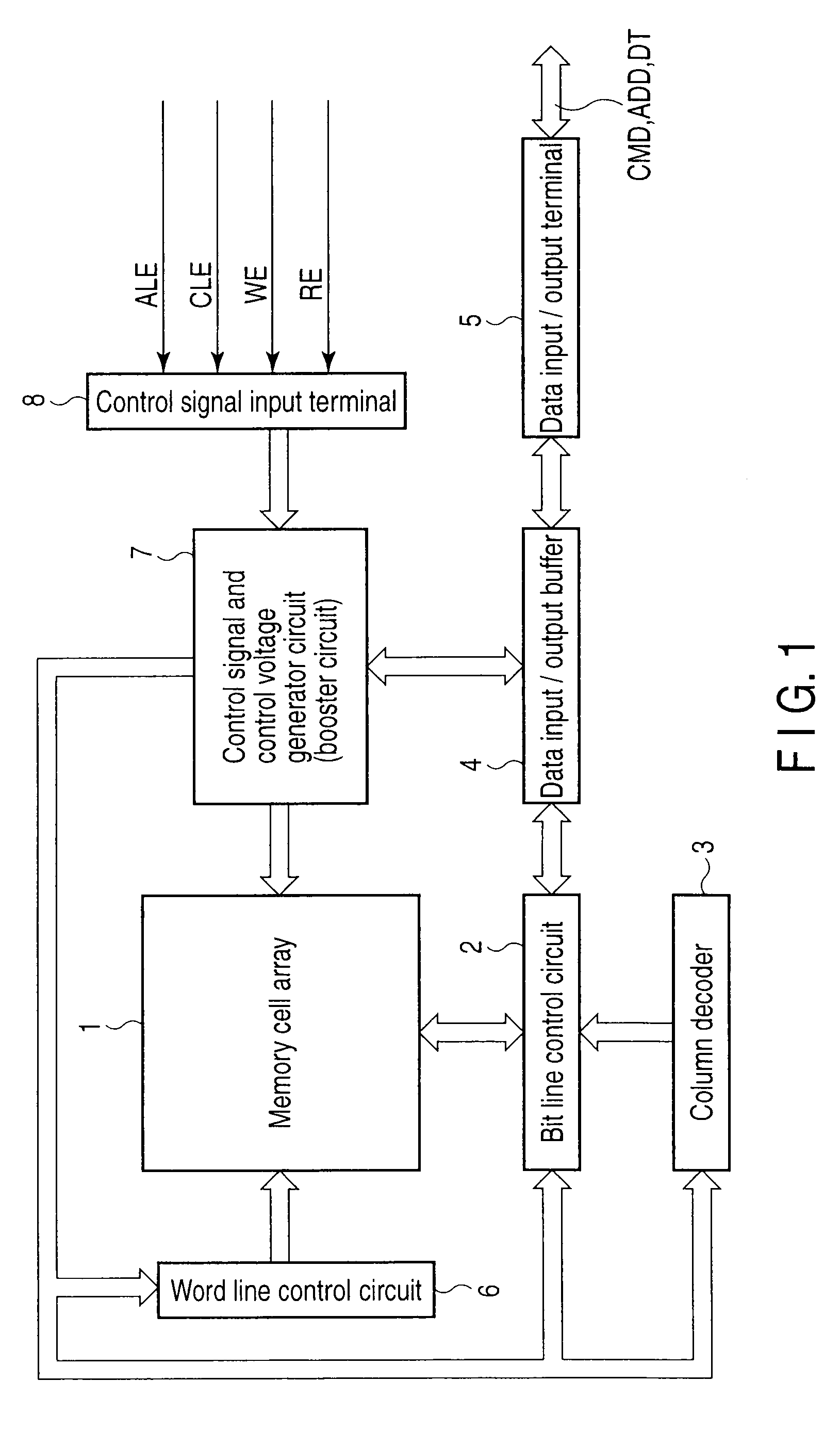
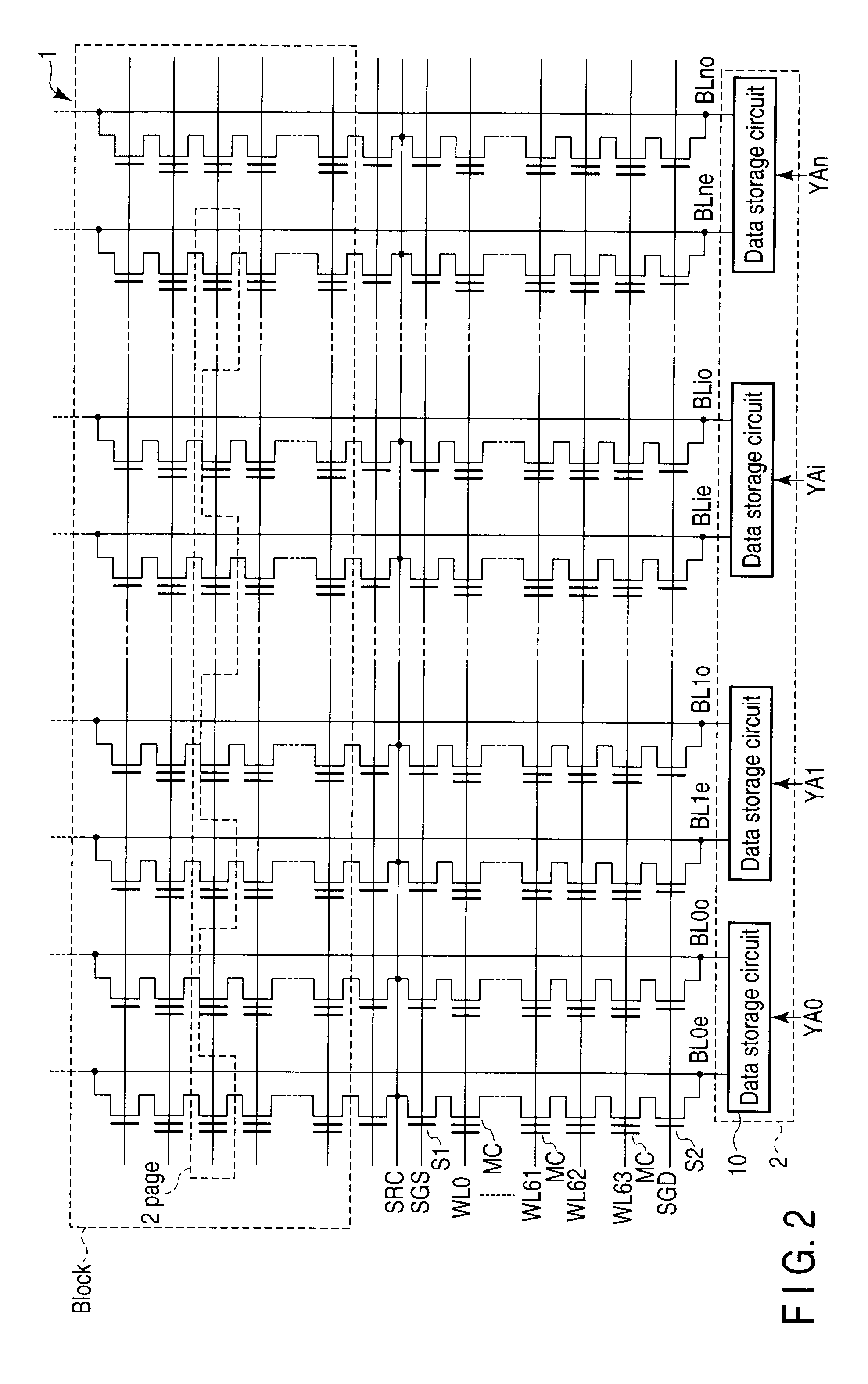
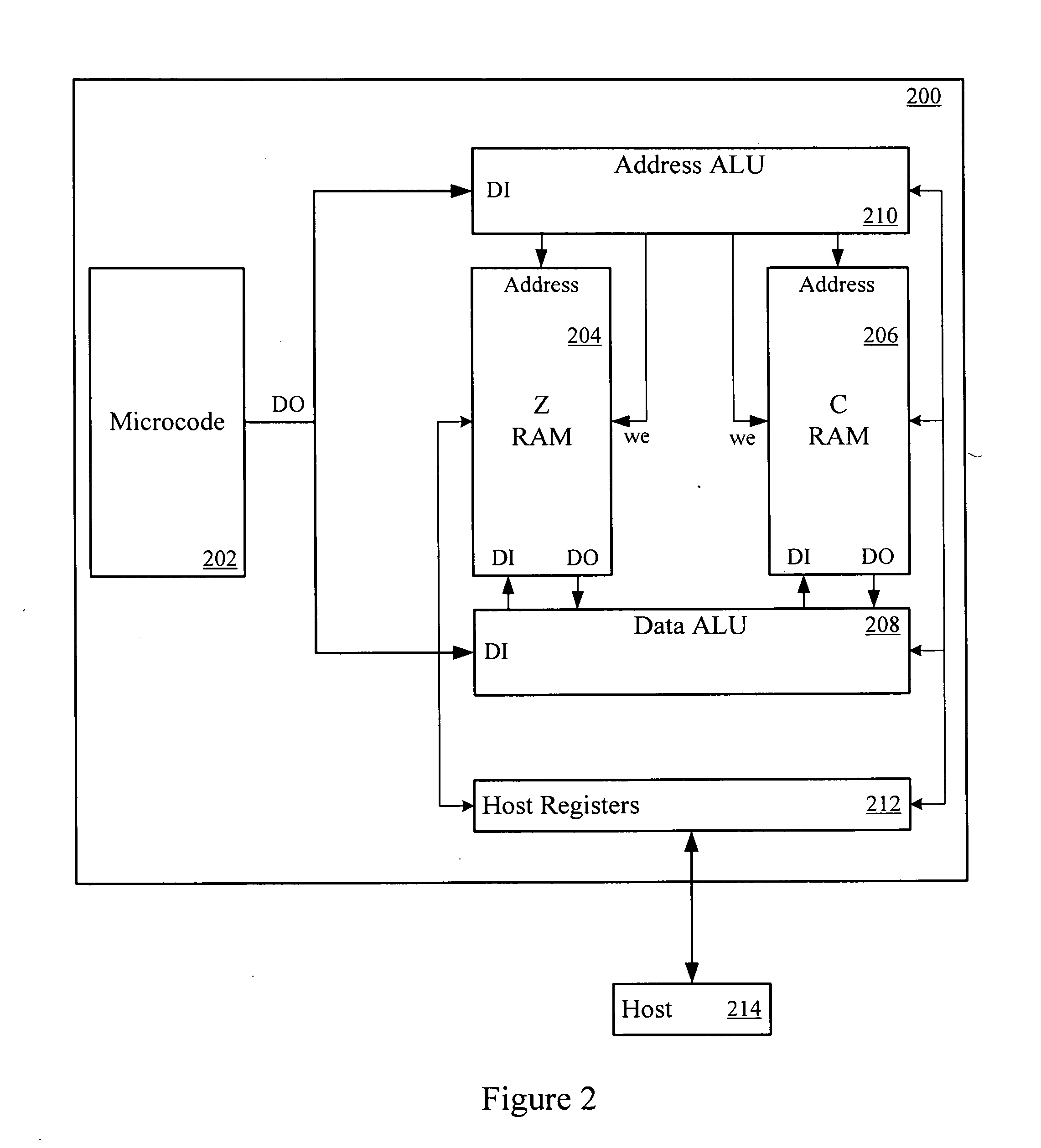
Semiconductor memory device for storing multilevel data
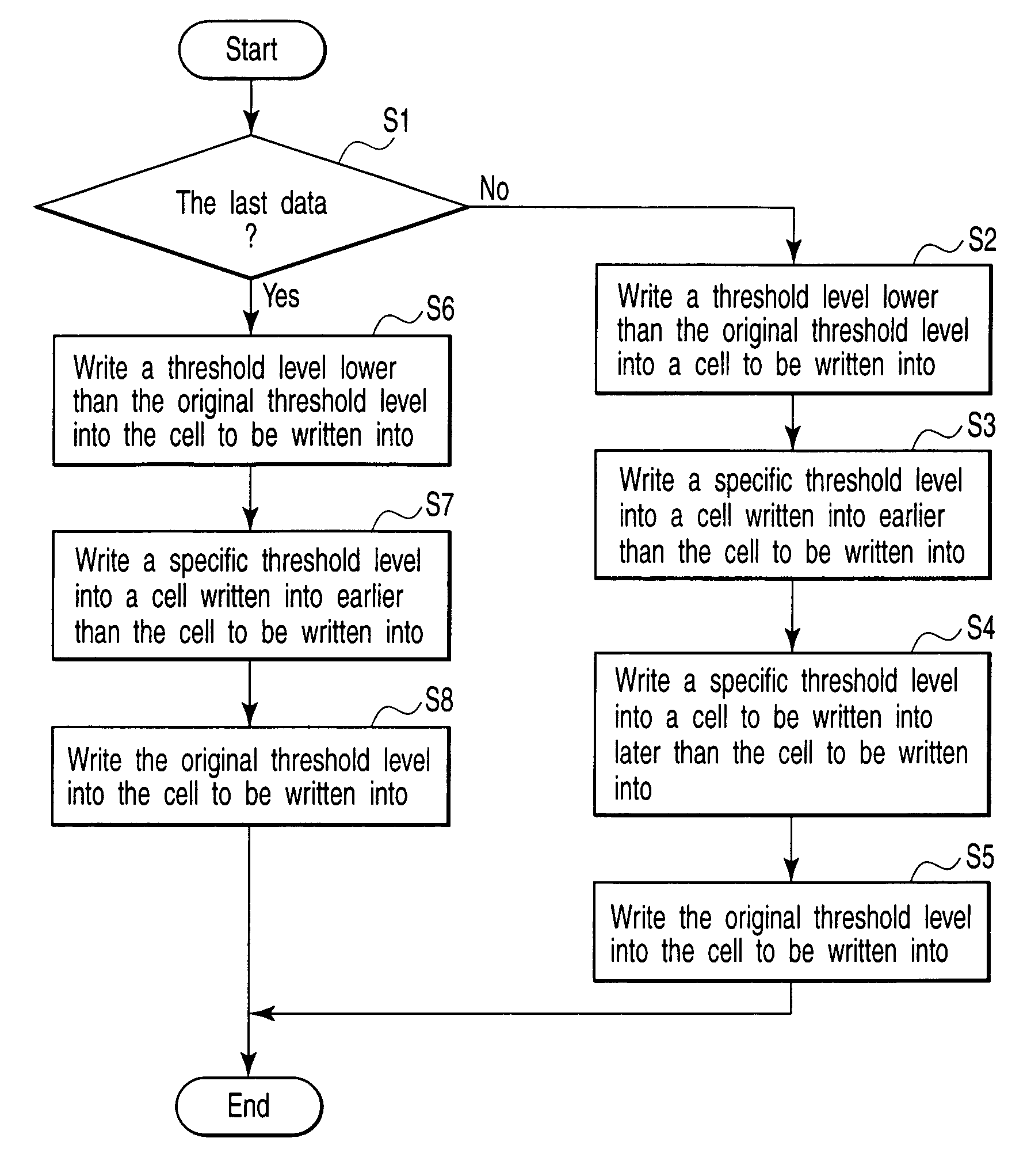
In a memory cell array, a plurality of memory cells are arranged in a matrix. Each of the plurality of memory cells stores one of a plurality of threshold levels. When writing one of the plurality of threshold levels into a first memory cell of the memory cell array, a control circuit writes a threshold level a little lower than the original threshold level. When not writing a second memory cell adjacent to the first memory cell consecutively, the control circuit writes the original threshold level into the first memory cell.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Method and system for decoding multilevel signals
InactiveUS20070171998A1Efficient processingMinimizes average error probabilityDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationData streamNormal density
A multilevel optical receiver can comprise a plurality of comparators that generally correspond with the number of levels in a multilevel data stream. Each comparator can be individually controlled and fed a decision threshold in order to decode a multilevel signal. The multilevel optical receiver can generate a statistical characterization of the received symbols in the form of a marginal cumulative distribution function (CDF) or probability density function (pdf). This characterization can be used to produce a set of ε-support estimates from which conditional pdfs are derived for each of the transmission symbols. These conditional pdfs may then be used to determine decision thresholds for decoding the received signal. The conditional pdfs may further be used to continuously estimate the fidelity or error rate of the received signal without the transmission of a testing sequence. The ε-supports may further be used to automatically control the gain on the receiver.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
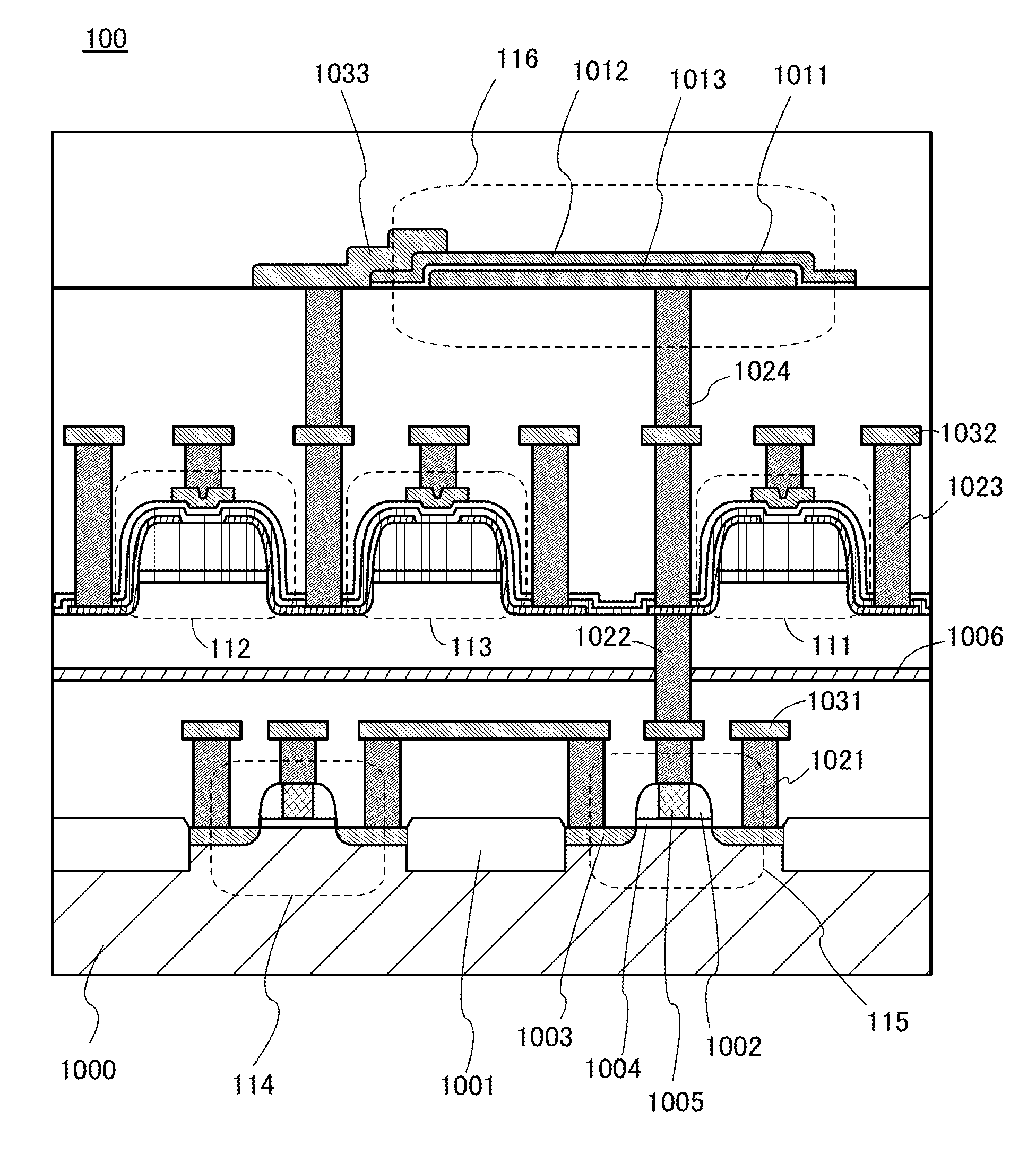
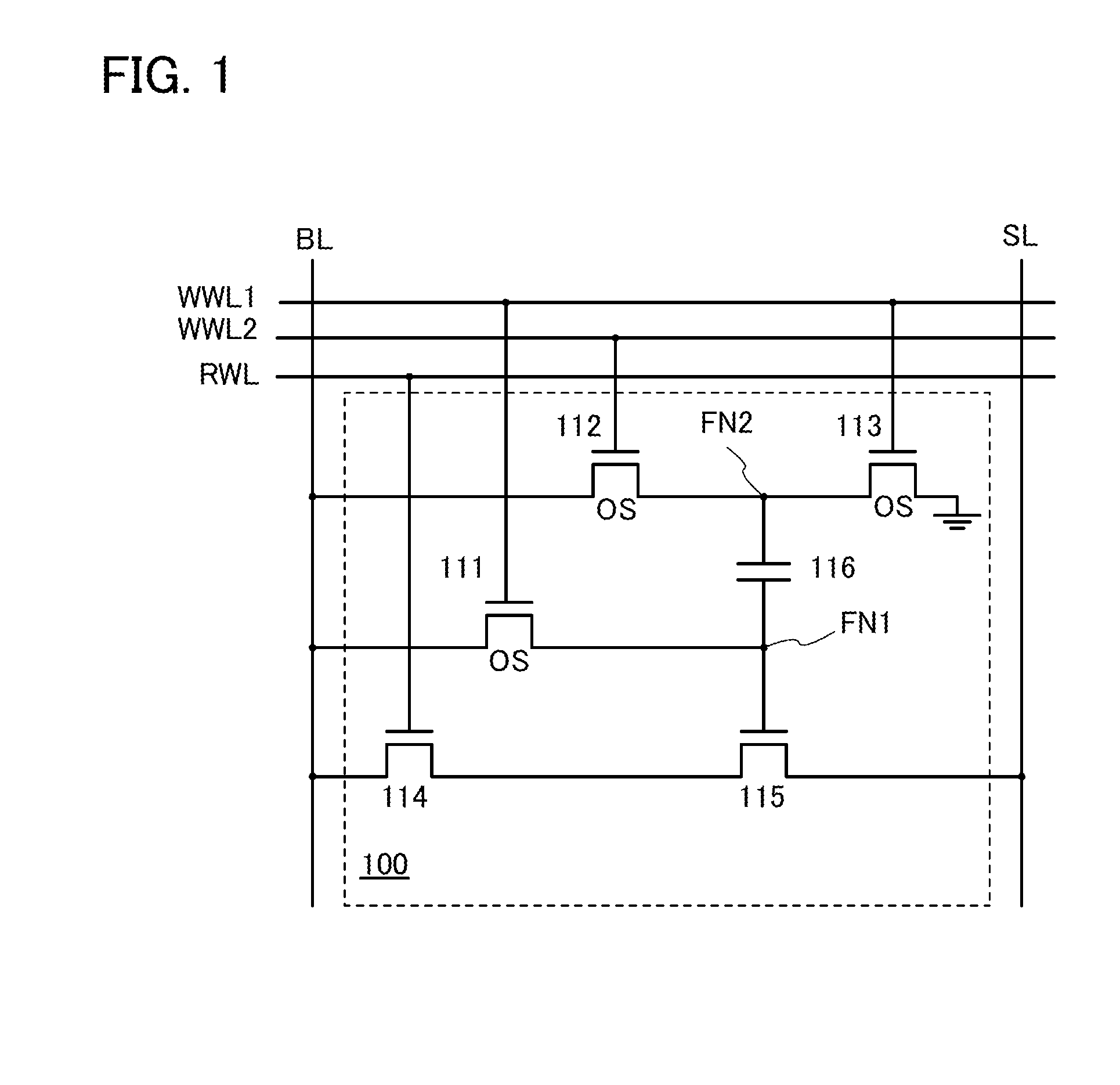
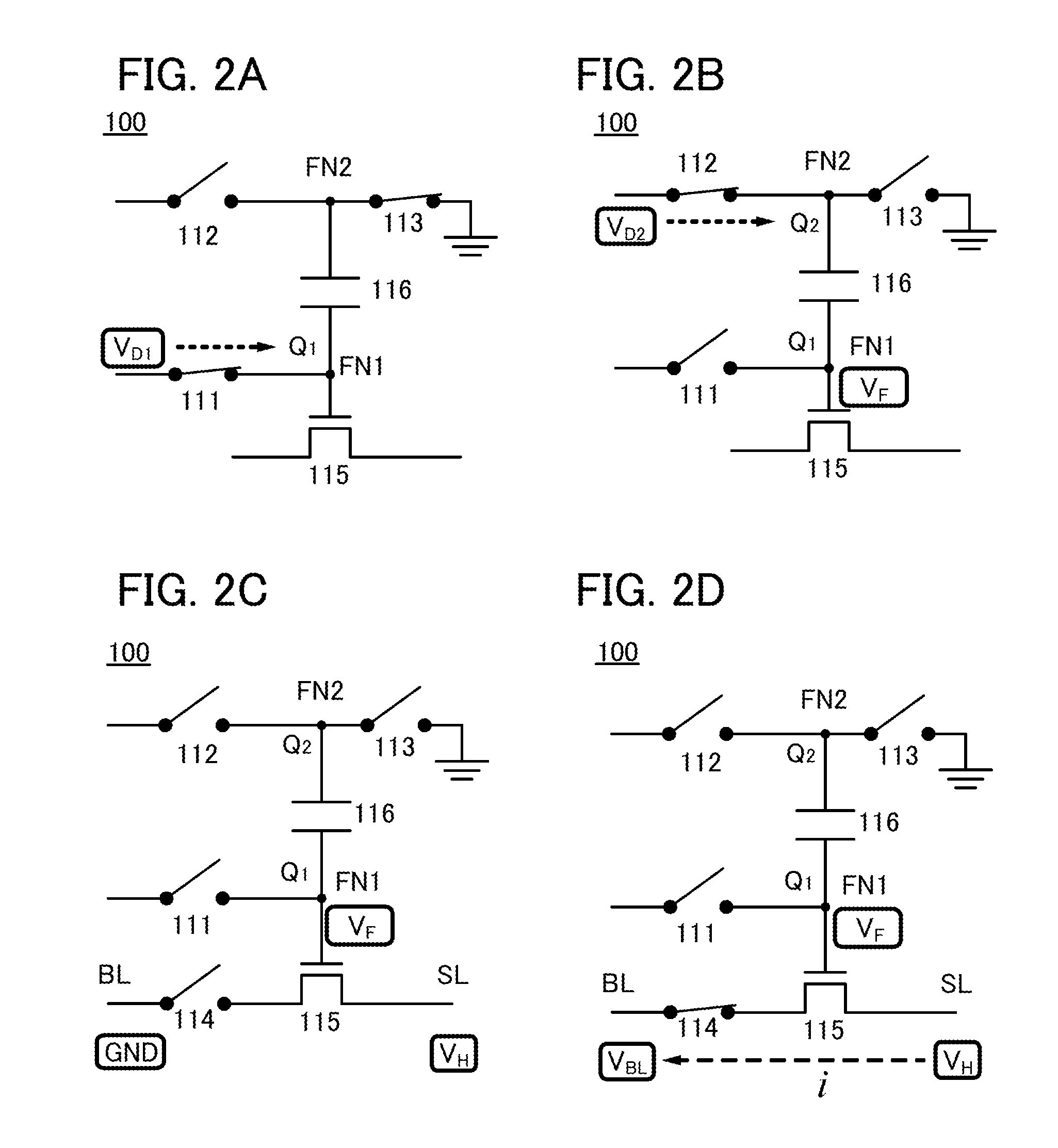
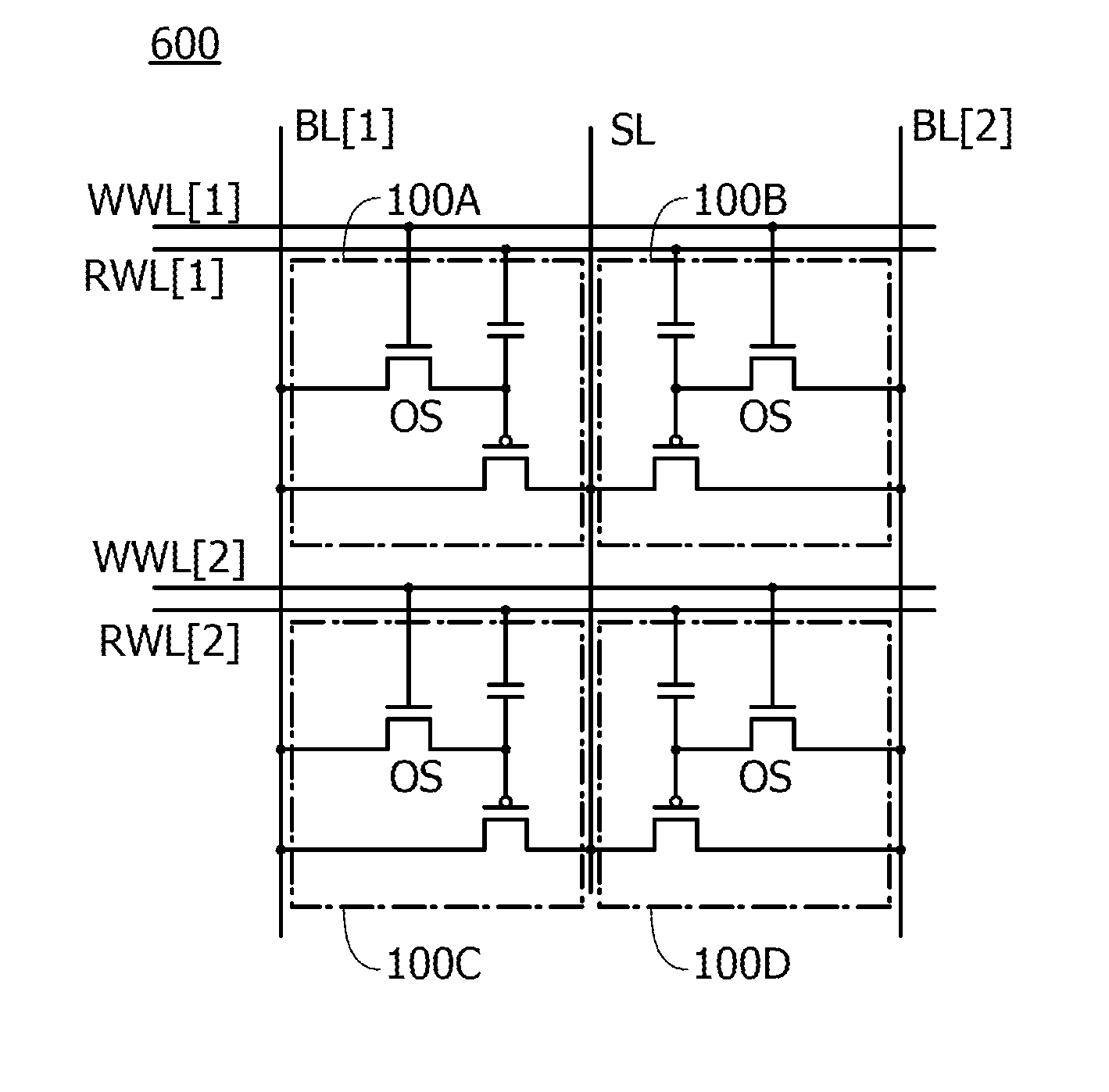
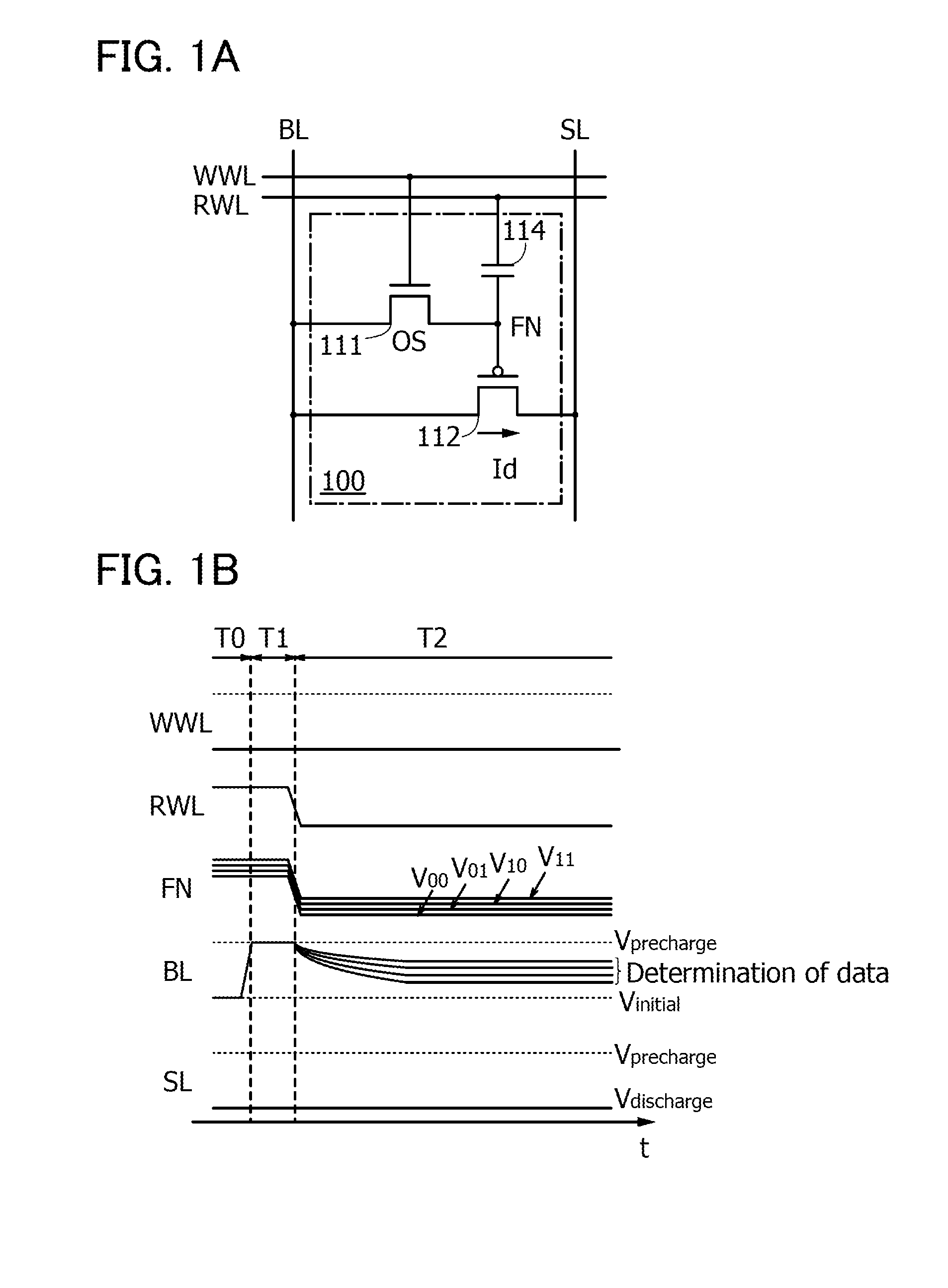
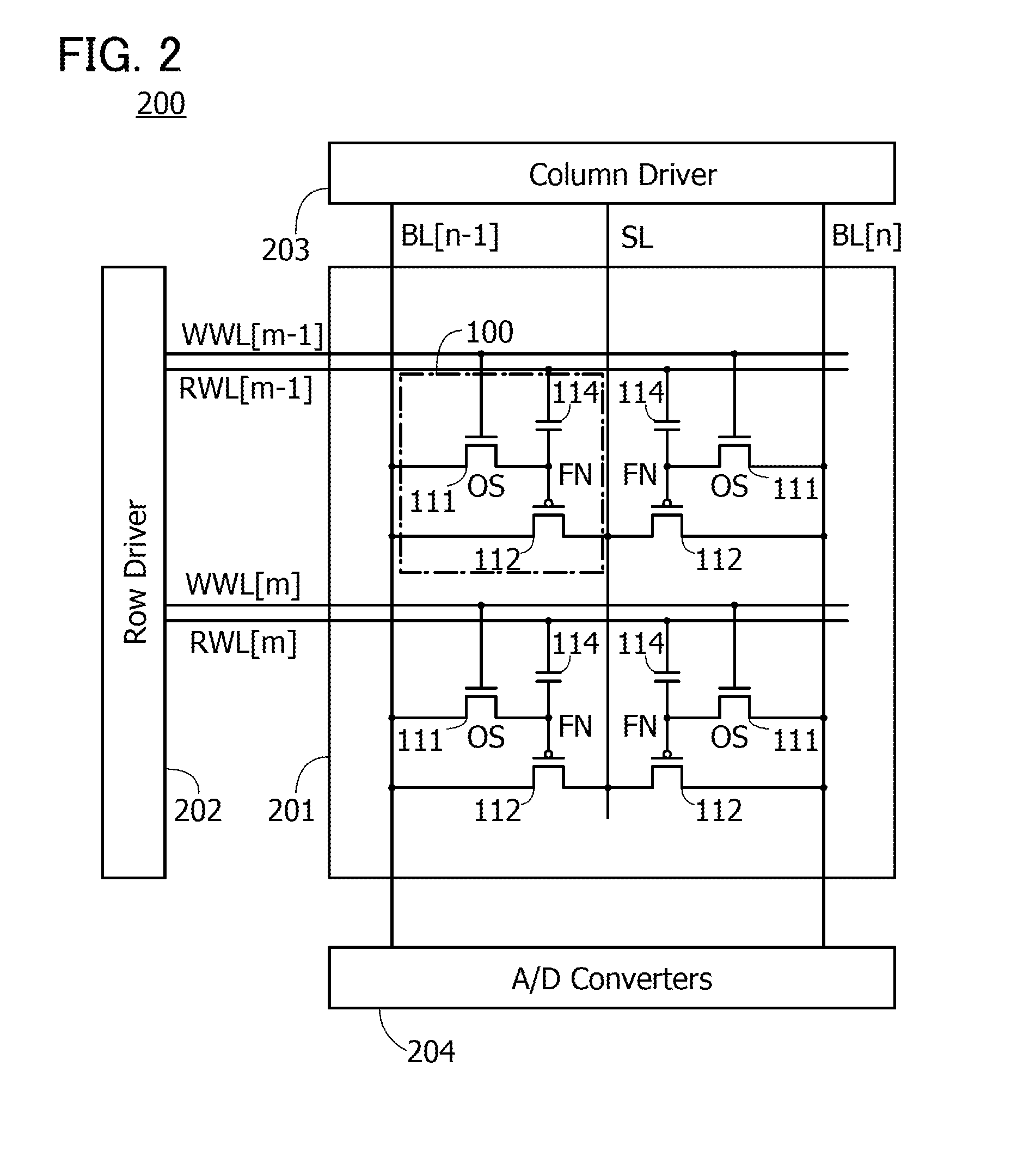
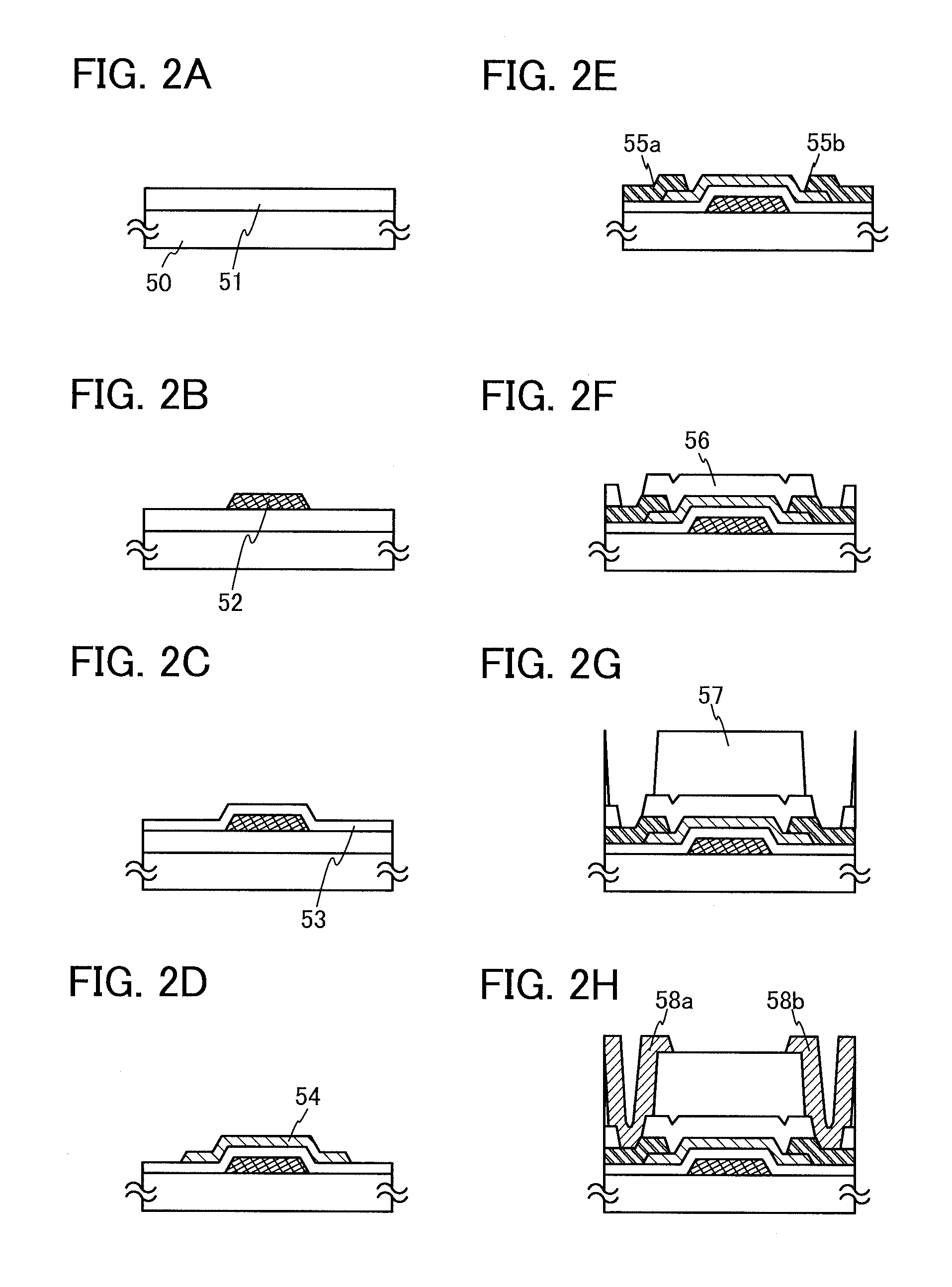
Semiconductor device and method for driving the same
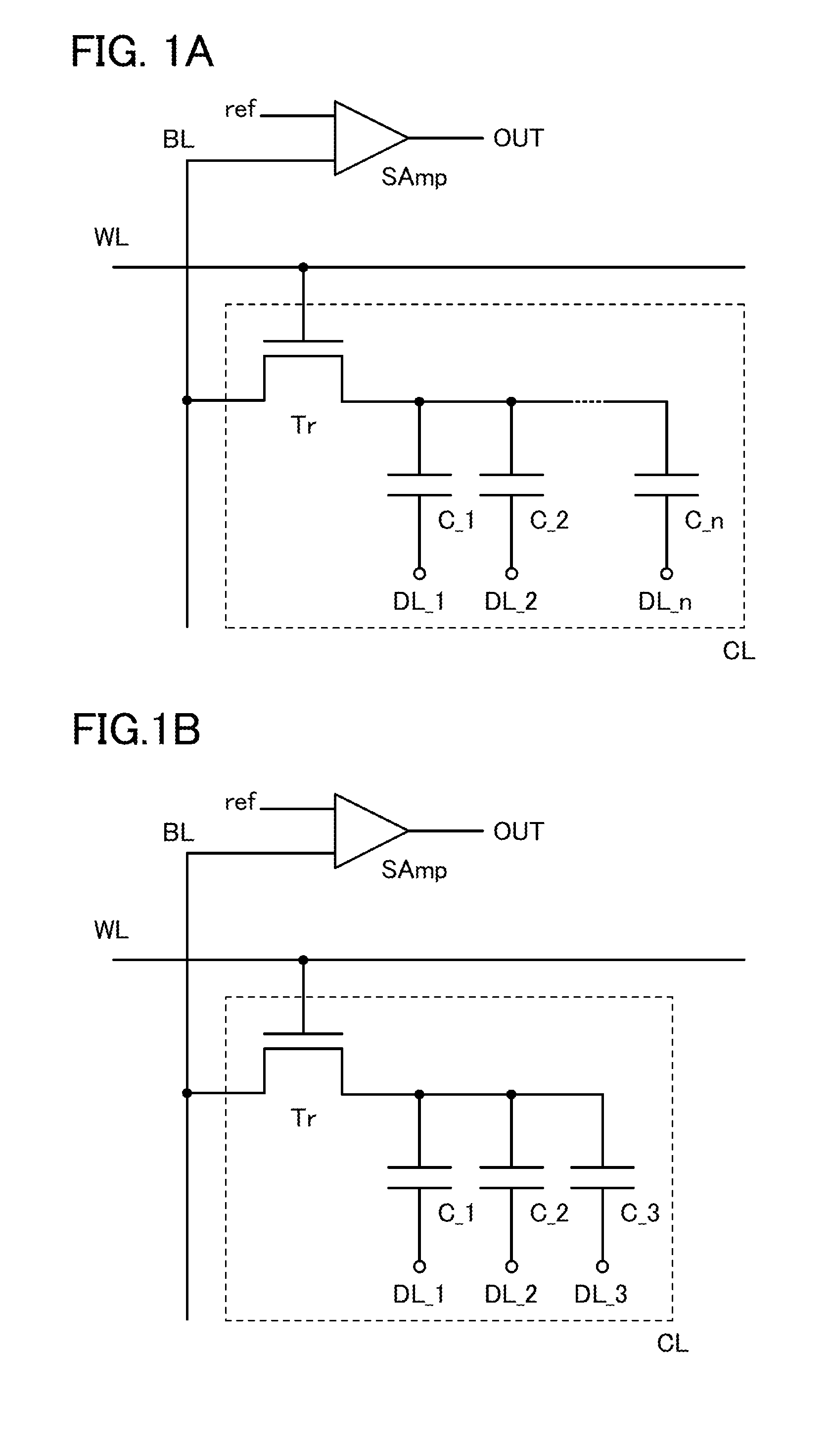
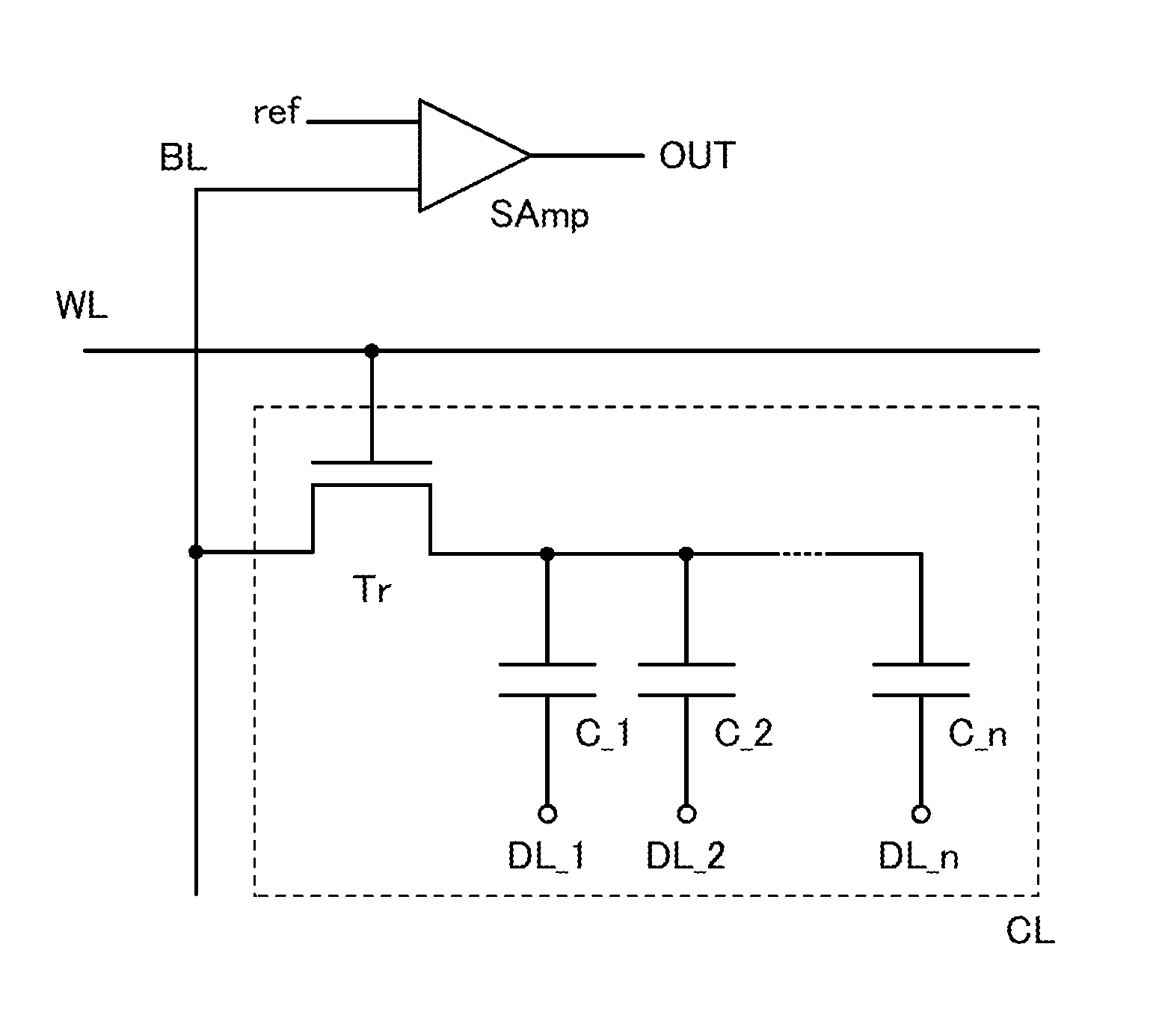
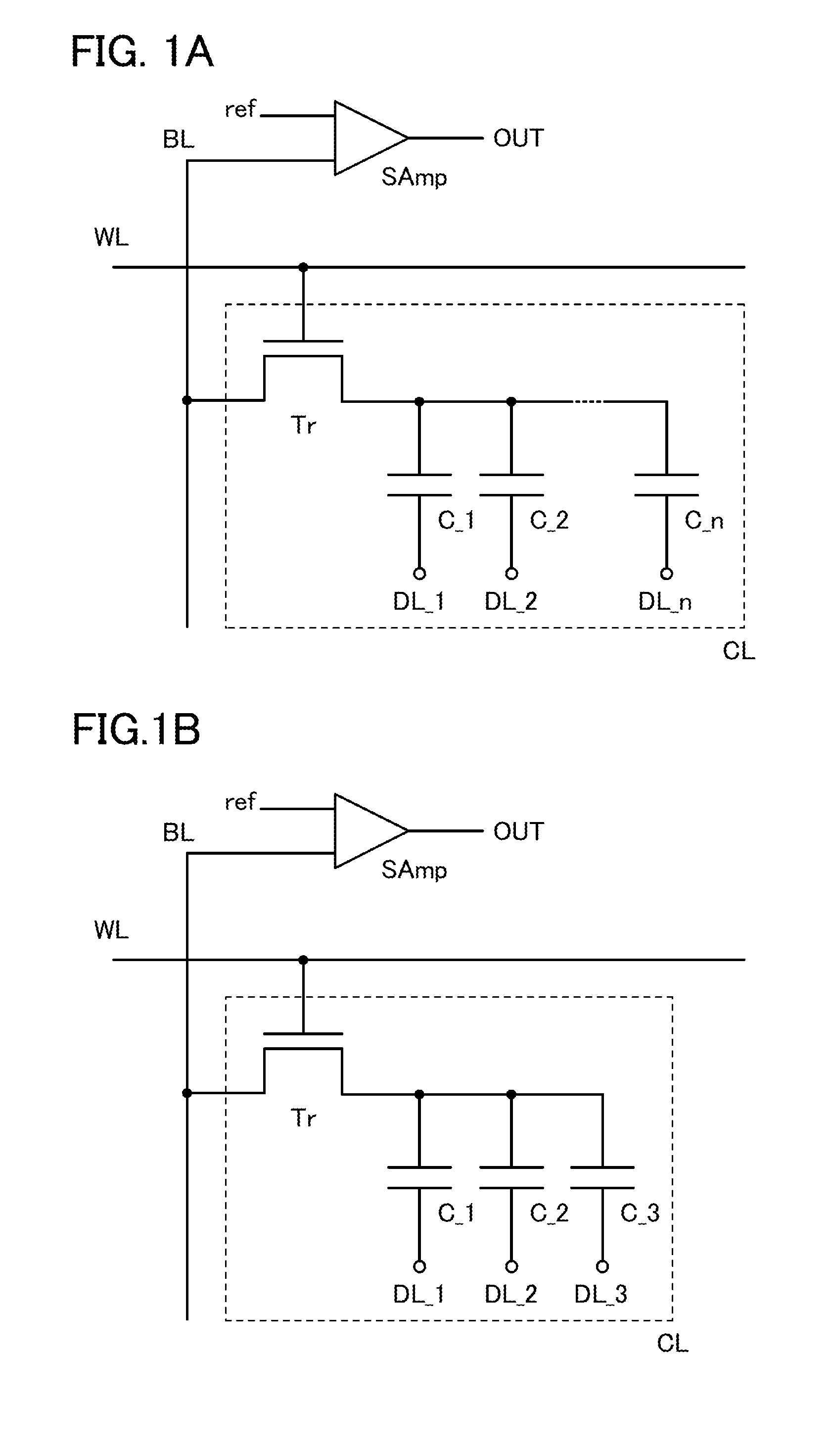
A novel semiconductor device where multilevel data can be written and read. The semiconductor device includes first to fifth transistors, a capacitor, a bit line, and a power supply line. Write operation is performed in such a manner that first data is supplied to a gate of the fifth transistor through the first transistor; the first transistor is turned off; second data is supplied to a second electrode of the capacitor through the second transistor to convert the first data into third data; and the second electrode of the capacitor are made electrically floating. The second electrode of the capacitor is initialized to GND through the third transistor. Read operation is performed by charging or discharging the bit line through the fourth transistor and the fifth transistor. The first to third transistors are preferably oxide semiconductor transistors.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device with advanced multi-page program operation
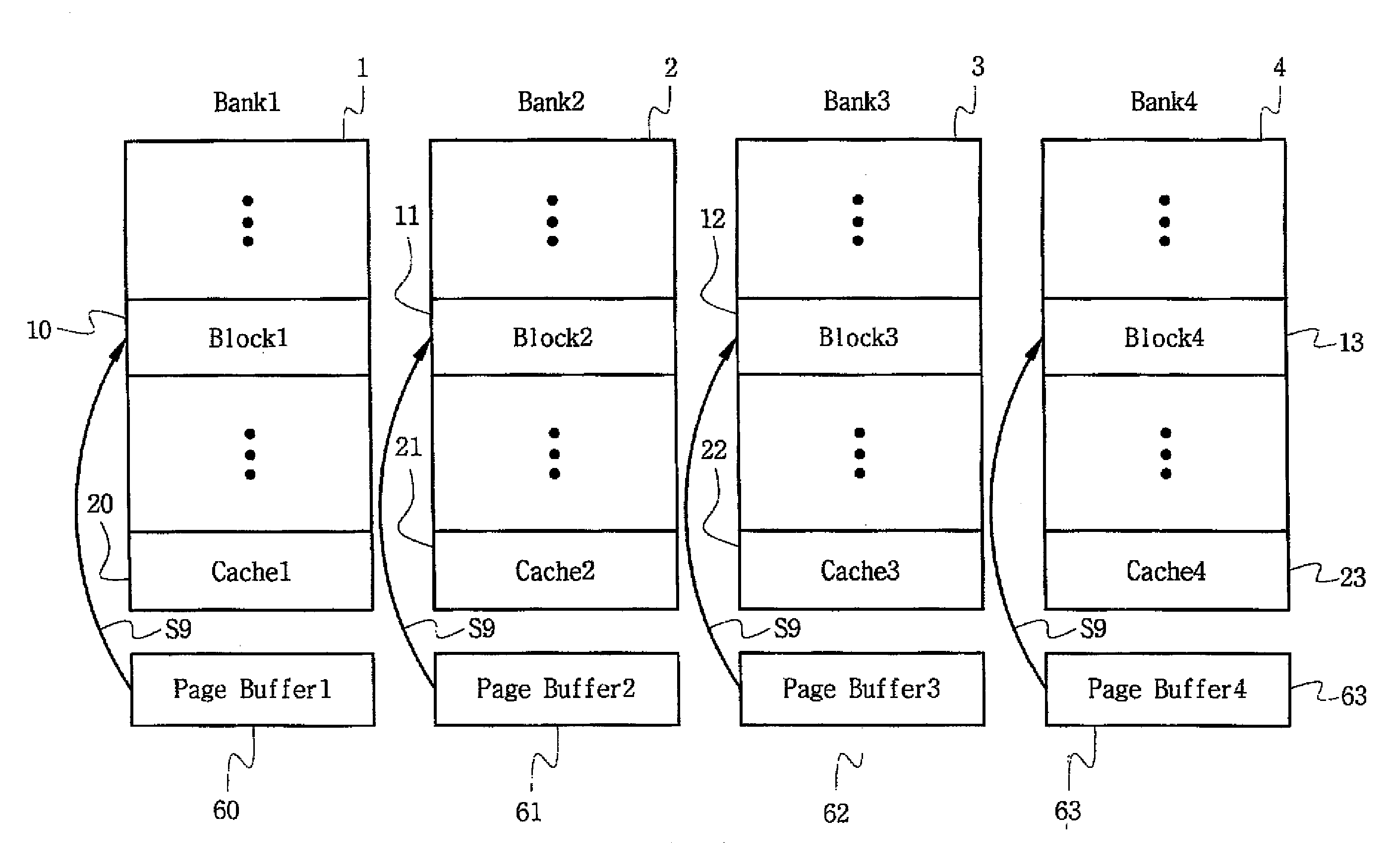
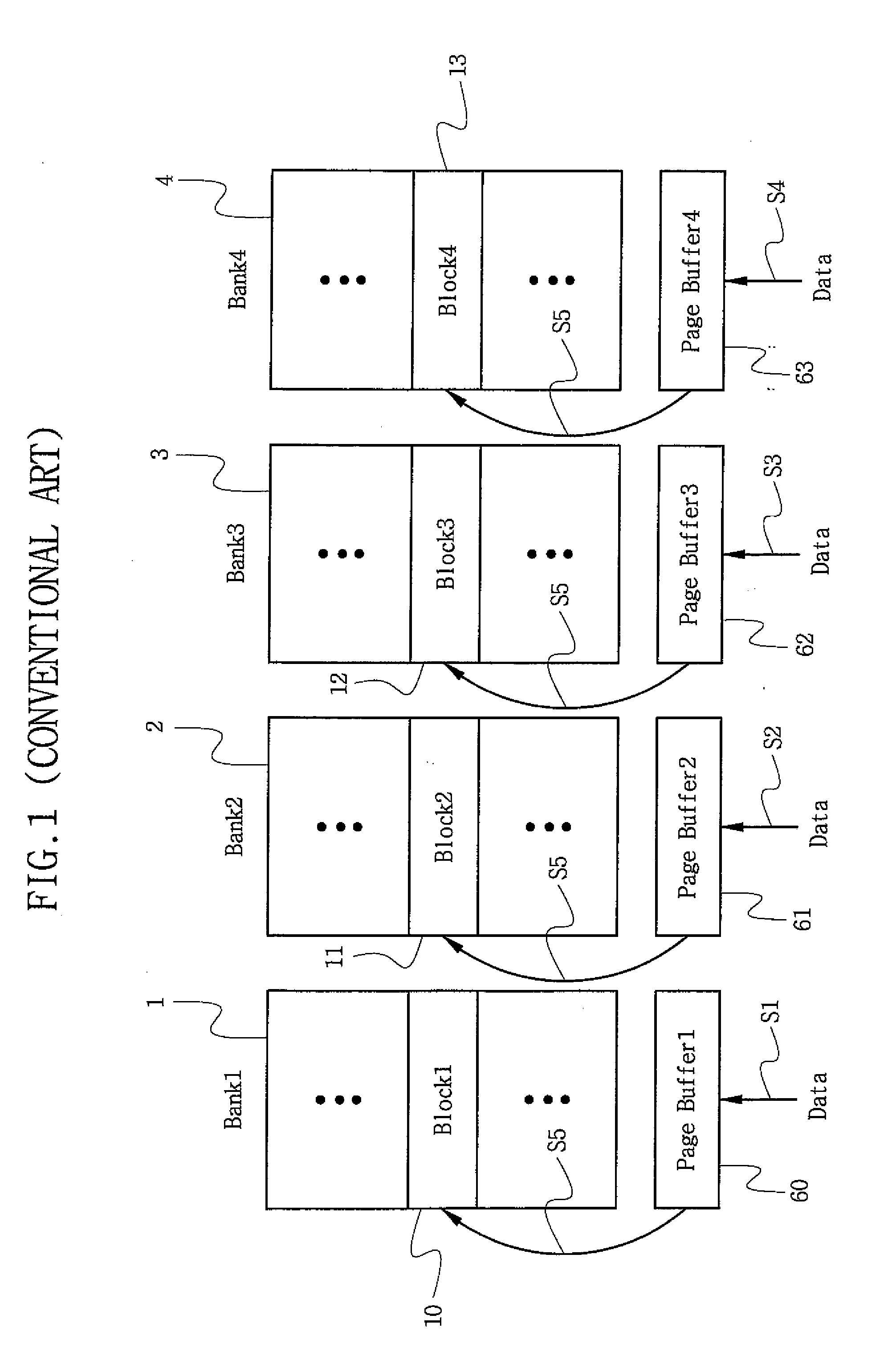
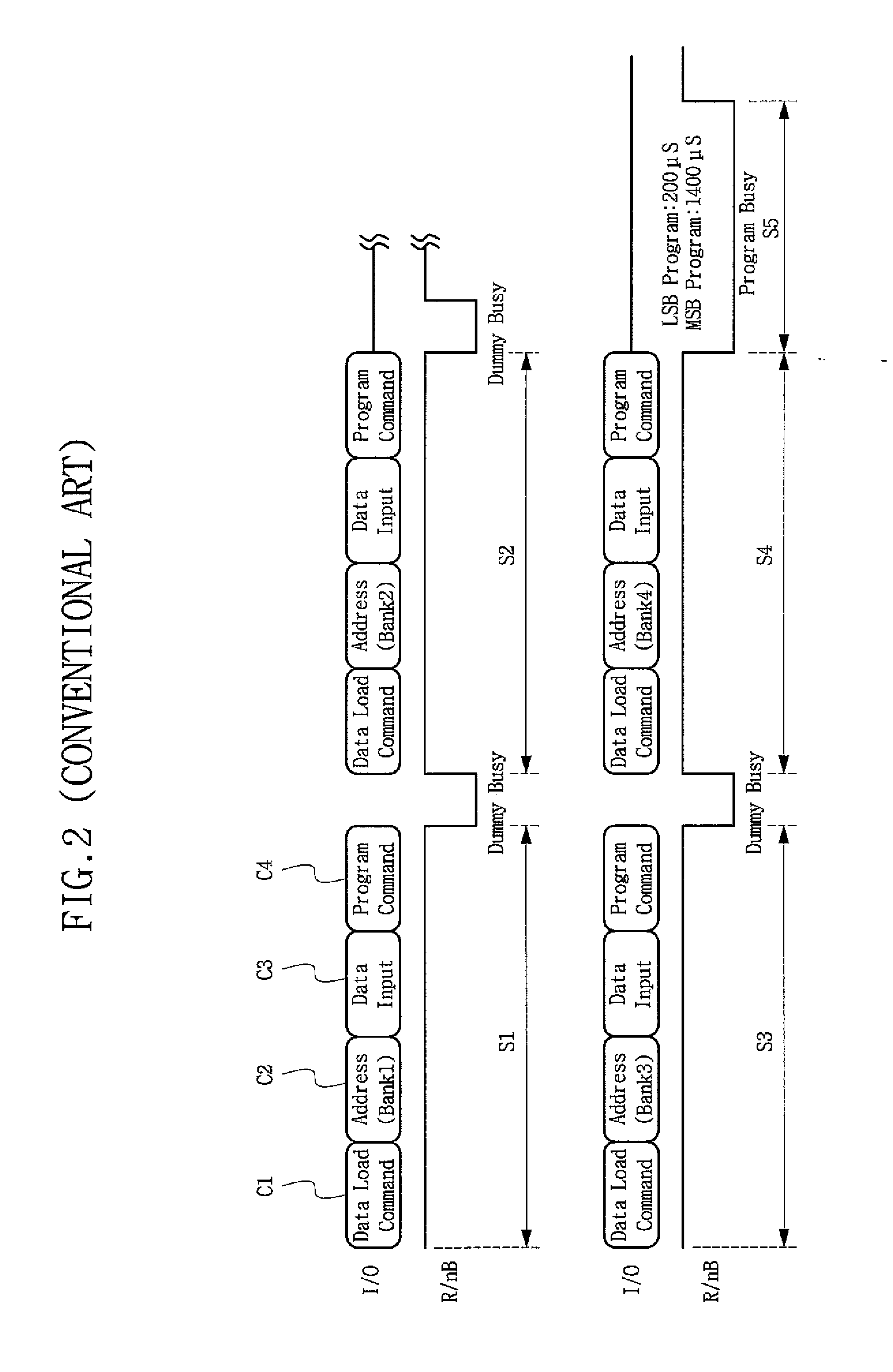
ActiveUS20080189478A1Shorten programming timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory bankData store
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device for an efficient program of multilevel data includes a memory cell array having a plurality of banks and a cache block corresponding to each of the plurality of banks. The cache block has a predetermined data storage capacity. A page buffer is included which corresponds to each of the plurality of banks. A programming circuit programs all of the plurality of banks except a last of said banks with page data. The page data is loaded through each page buffer and programmed into each cache block such that when page data for the last bank is loaded into the page buffer, the loaded page data and the page data programmed into the respective cache blocks are programmed into respective corresponding banks. Accordingly, the time taken in programming can be reduced without increasing a unit of program in a multilevel flash memory, thereby improving performance in a multilevel program of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
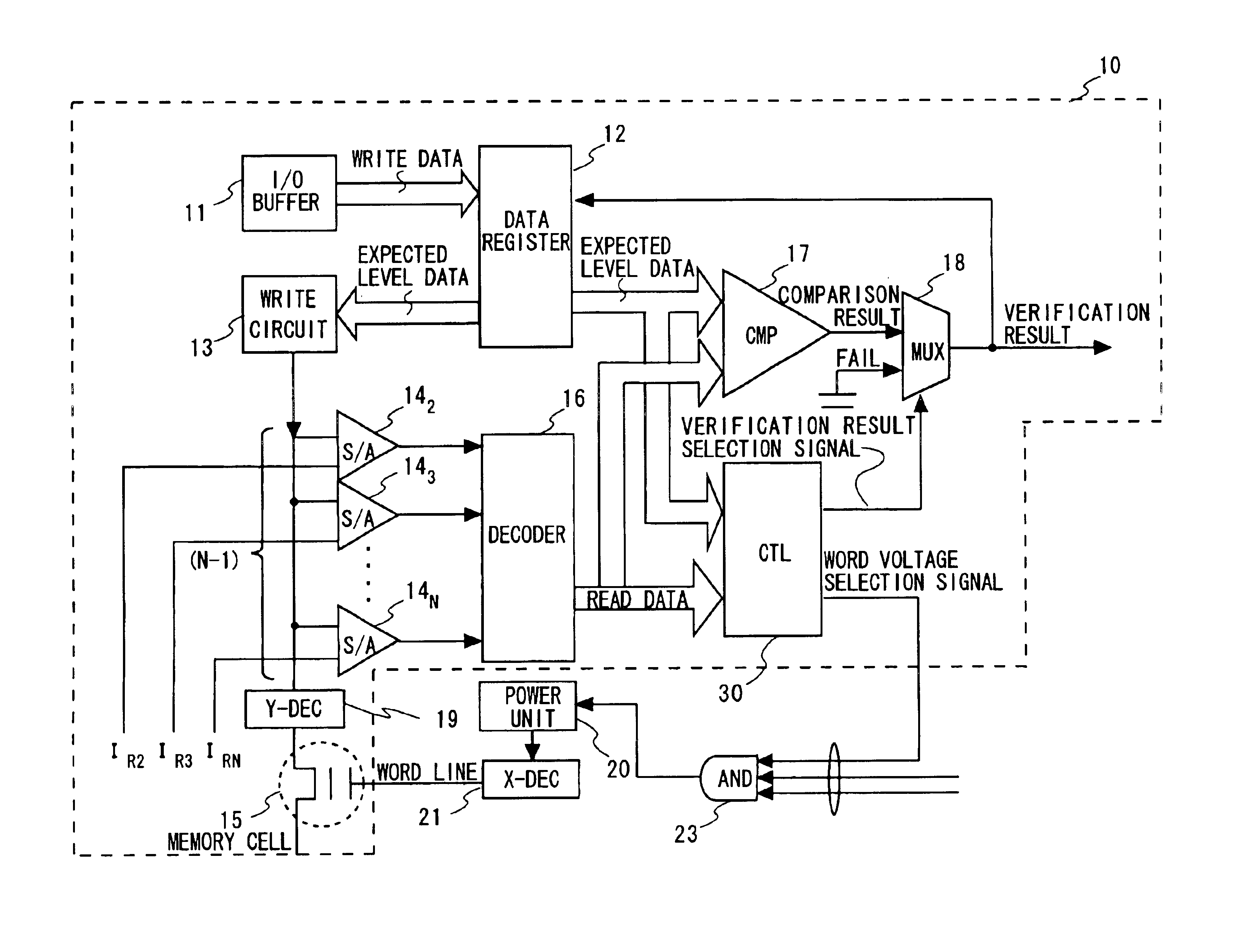
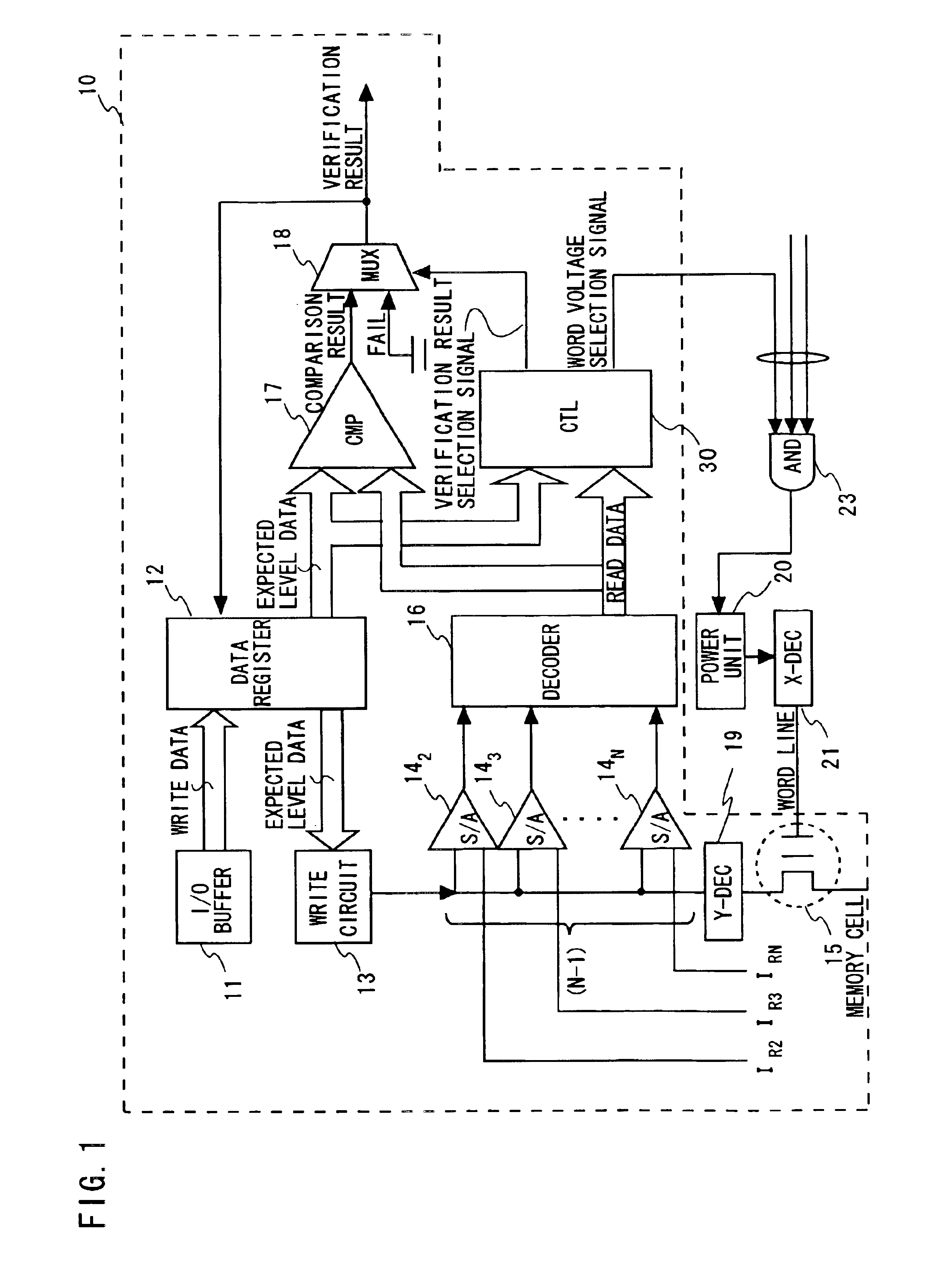
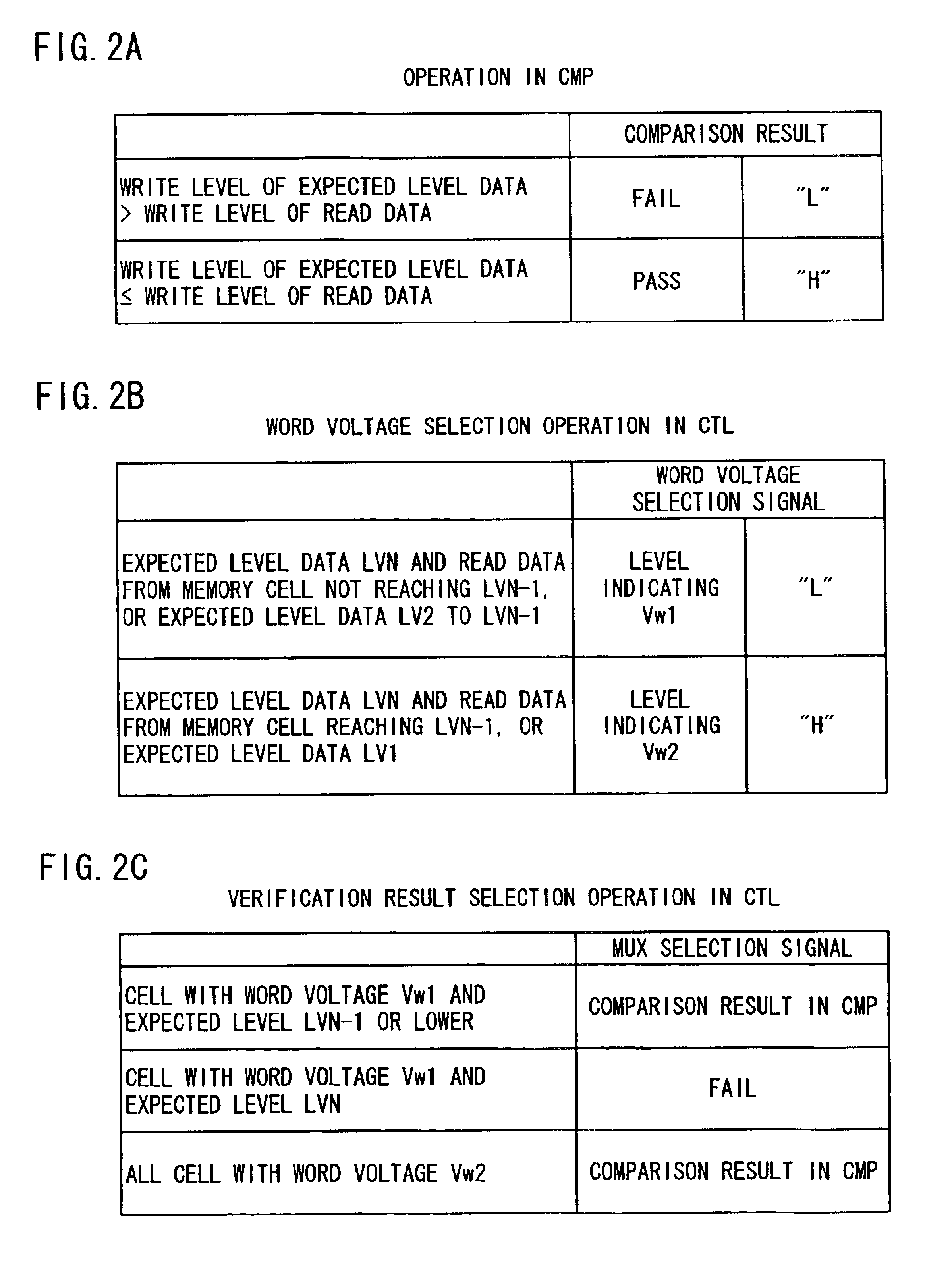
ActiveUS6937522B2Large possible marginPreventing indeterminate sensingRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierComputer architecture
In writing N level of multilevel data to nonvolatile semiconductor memory by repeating a verification process, a verification result of a memory cell where the Nth threshold level which is the highest level is to be written as an expected level is invalidated until completion of writing to a memory cell where the (N−1)th and lower level is to be written. The verification result of the memory cell where the Nth level is to be written is validated after reaching the (N−1)th write level. A reference current supplied to a sense amplifier corresponding to the Nth level is set at at least a level allowing no indeterminate sensing of a sense amplifier. In verification of the Nth level data, a word line voltage supplied for verify-reading is raised from VW 1 to VW 2.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
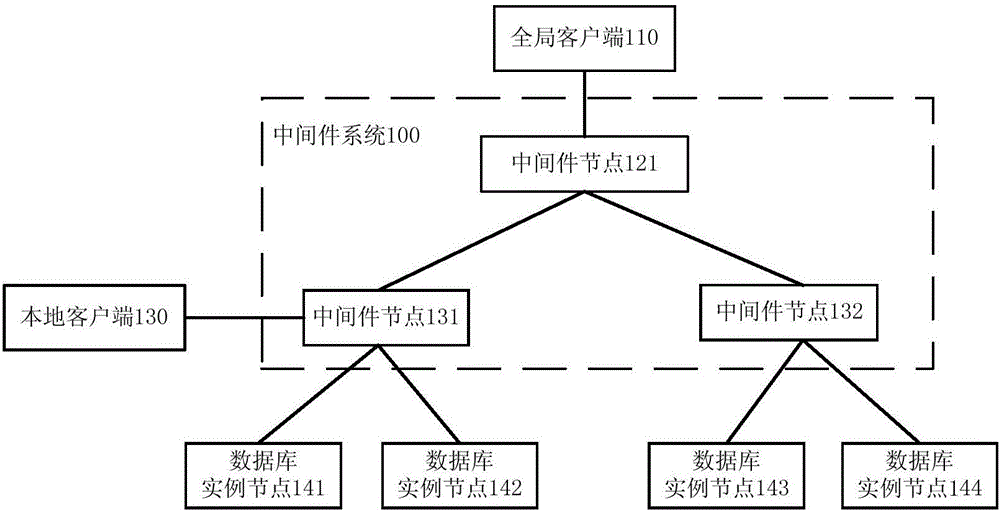
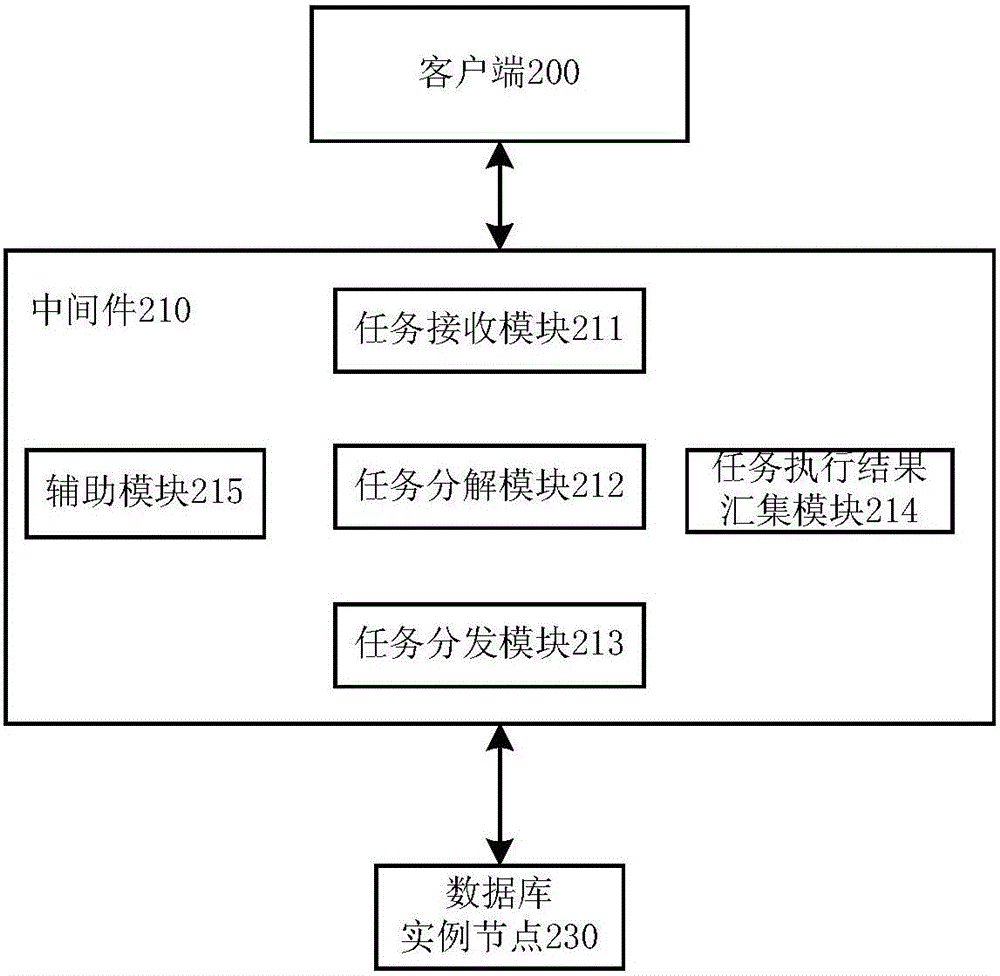
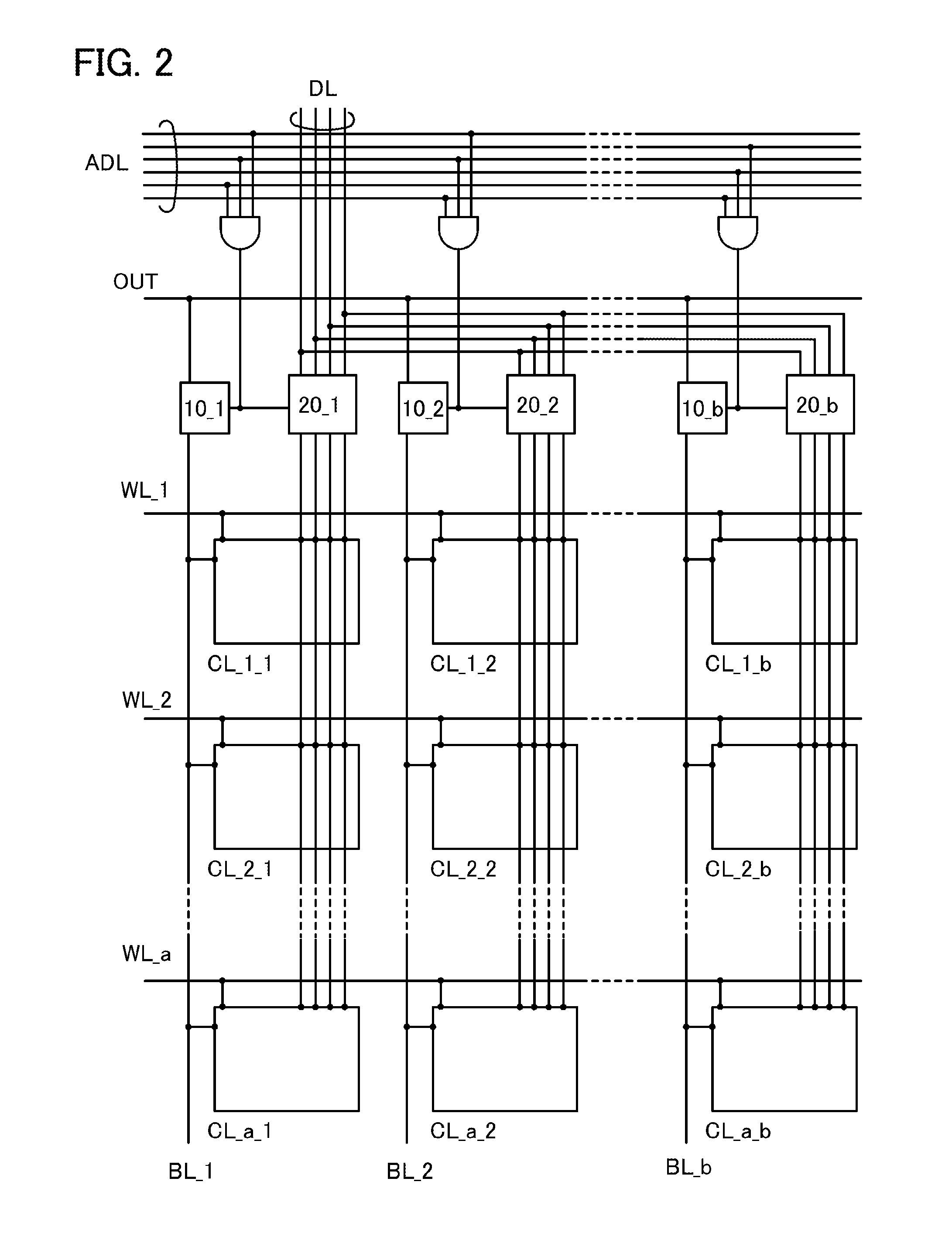
Middleware used for multilevel database and multilevel database system
InactiveCN106599043ARealize cross-domain deploymentLighten processing tasksInterprogram communicationDatabase distribution/replicationDecompositionData center
The invention discloses middleware used for a multilevel database and a multilevel database system. The middleware comprises a task receiving module, a task decomposition module, a task distribution module, and a task execution result statistics module. The task receiving module is used for receiving a task request from a previous node, wherein the previous node is a client or other middleware. The task decomposition module queries a next node executing a sub-task and correspondingly forwards the next node, wherein the next node is a database instance or other middleware. The task execution result statistics module is used for collecting an executive result of the task request from the next node and feeding back the executive result to the previous node. According to the middleware technology, the multilevel database system can be deployed in a cross-domain manner, so that the big data processing capability can be improved and the data management needs of numerous multilevel multi-data centers are met.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120051119A1Constant potentialAccurate dataTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
An object is to provide a semiconductor device which includes a memory cell capable of holding accurate data even when the data is multilevel data. The semiconductor device includes a memory cell holding data in a node to which one of a source and a drain of a transistor whose channel region is formed from an oxide semiconductor. Note that the value of off-state current (leakage current) of the transistor is extremely small. Thus, after being set to have a predetermined value, the potential of the node can be kept constant or substantially constant by turning the transistor off. In this manner, accurate data can be stored in the memory cell.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
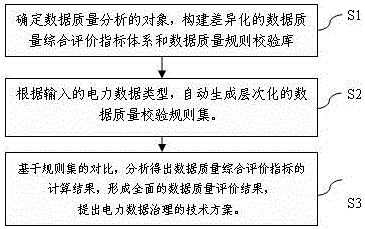
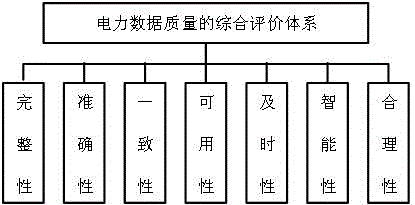
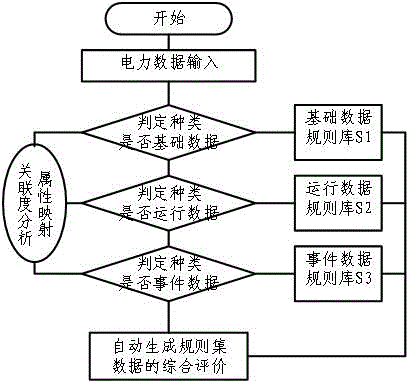
Method suitable for power data quality assessment and rule check
InactiveCN106649840AData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsElectric power systemPower equipment
The invention discloses a method suitable for power data quality assessment and rule check. The method comprises the steps of establishing a differential data quality comprehensive evaluation index system and a data quality rule check library for a device object of a specific region in a power system and for data describing a basic feature, a running feature and an event process of a power device; and automatically generating a multilevel data check rule set based on the rule check library according to to-be-checked power data, thereby realizing automated data monitoring and check. According to the method, the power data quality comprehensive evaluation index system and the data quality rule check library are established and the multilevel power data rule set is automatically generated, so that the features of differential power data are comprehensively assessed and comprehensively evaluated; and the method is of important significance for realizing data quality management control and forming a technical scheme and a long-term mechanism of data management.
Owner:国网江西省电力有限公司经济技术研究院 +1
Method for driving semiconductor device and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140269099A1Novel structureSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPower semiconductor deviceTime switching
To read multilevel data from a memory cell having a transistor using silicon and a transistor using an oxide semiconductor, without switching a signal for reading the multilevel data in accordance with the number of the levels of the multilevel data. The potential of the bit line is precharged, the electrical charge of the bit line is discharged via a transistor for writing data, and the potential of the bit line which is changed by the discharging is read as multilevel data. With such a structure, the potential corresponding to data held in a gate of the transistor can be read by only one-time switching of a signal for reading data.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
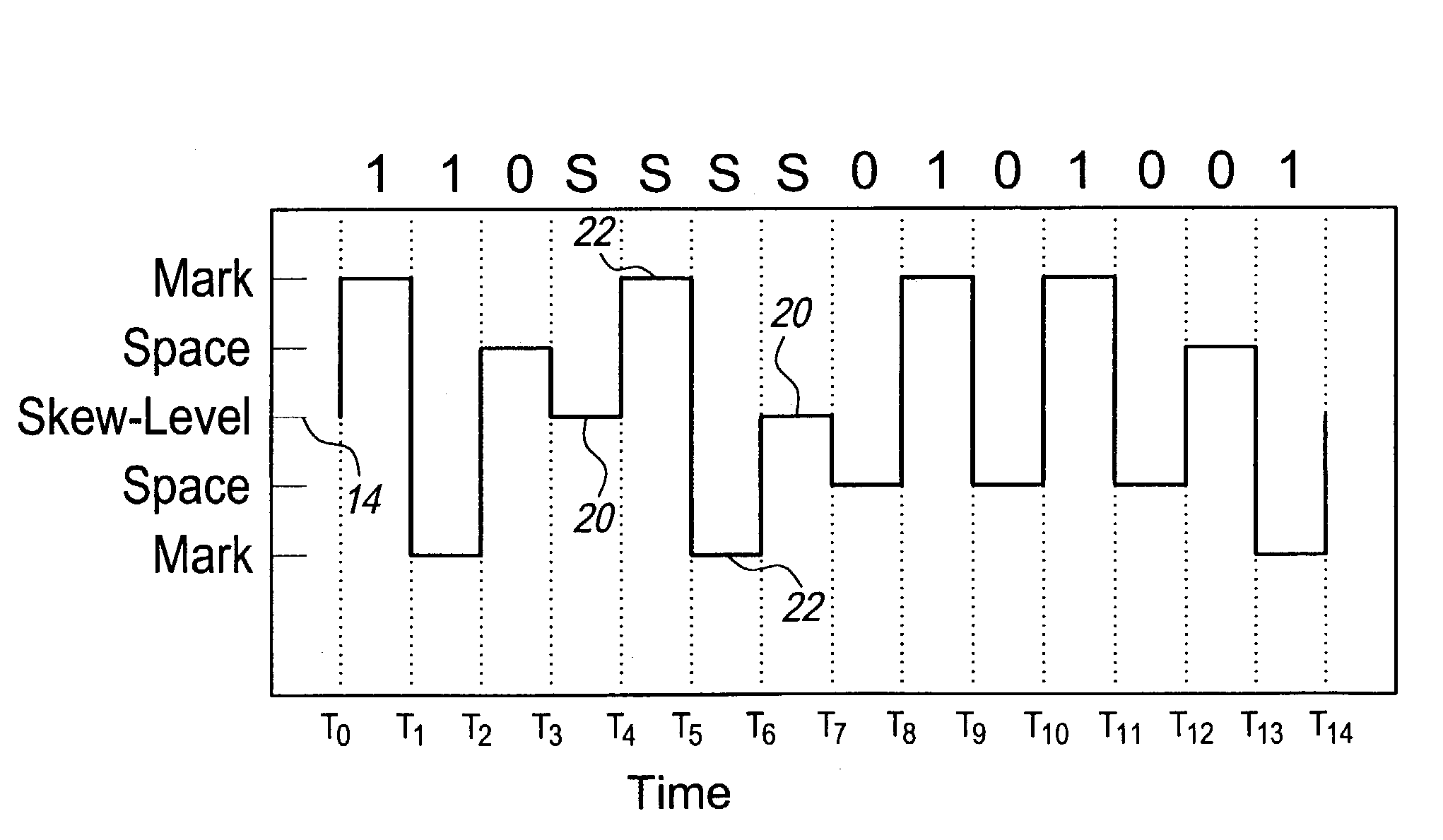
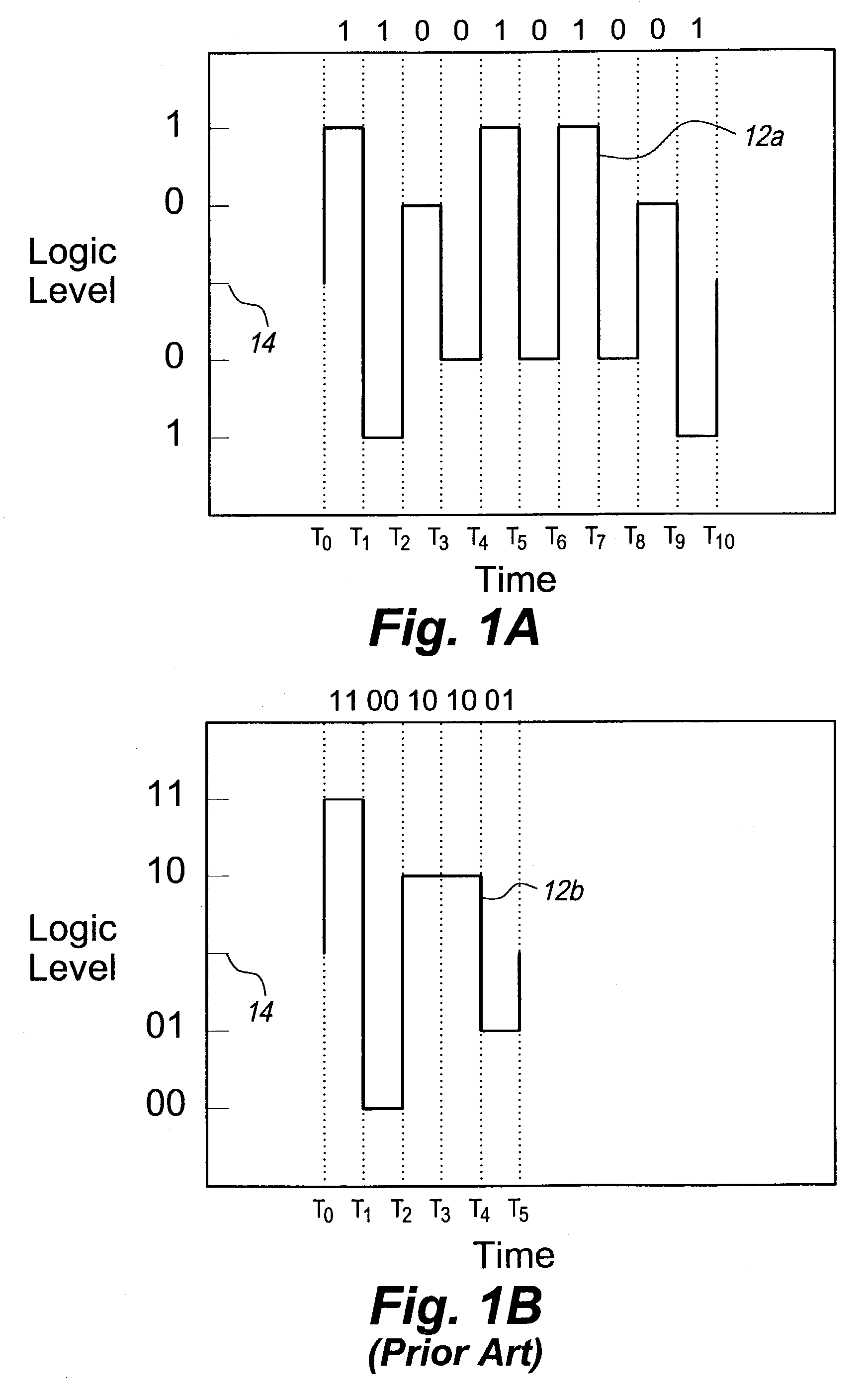
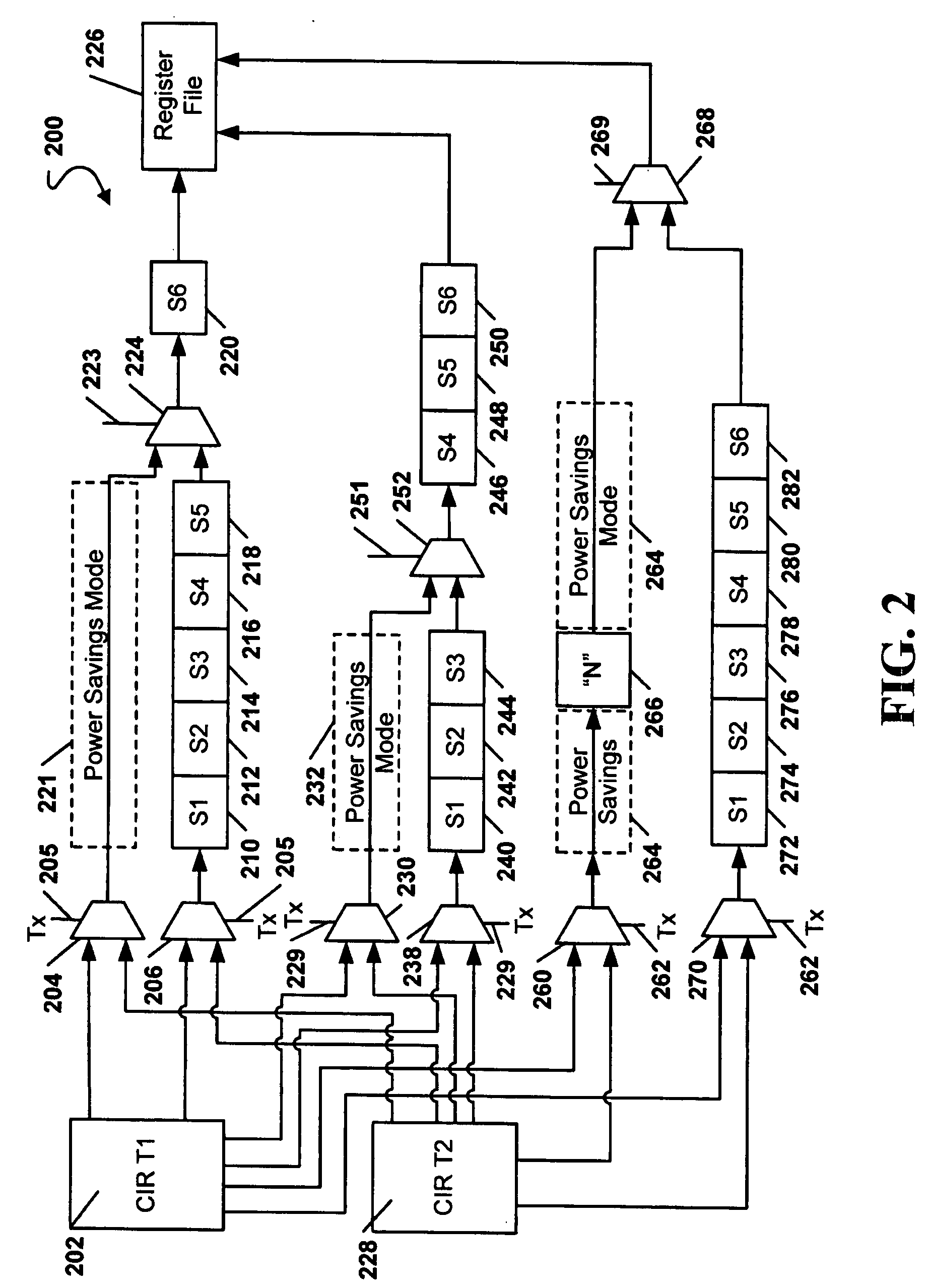
Multilevel data encoding and modulation technique
ActiveUS7221711B2Improve discriminationImprove anti-interference abilityPulse conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsHarmonicPeak value
The multilevel data encoding and modulation technique uses a pair of complementary logic sets. In its most basic form, the sets are binary sets each containing a line level for a logical one and a line level for a logical zero for a total of four logic levels. The encoding technique requires a polar change in the line level after every bit. An optional fifth level may be used in order to skew the frequency or to enable automatic gain control circuitry to ensure consistent level discrimination. The encoding technique may be used in a bipolar device, or a bias level may be applied to the signal for unipolar transmission. The encoding technique involves inverting the polarity of alternating bits, filtering out all odd harmonics, transmitting and receiving the waveform, and decoding the demodulated waveform by comparing the absolute value of the half-cycle peak-to-peak voltage gain to a predetermined table.
Owner:INFON8UM INC
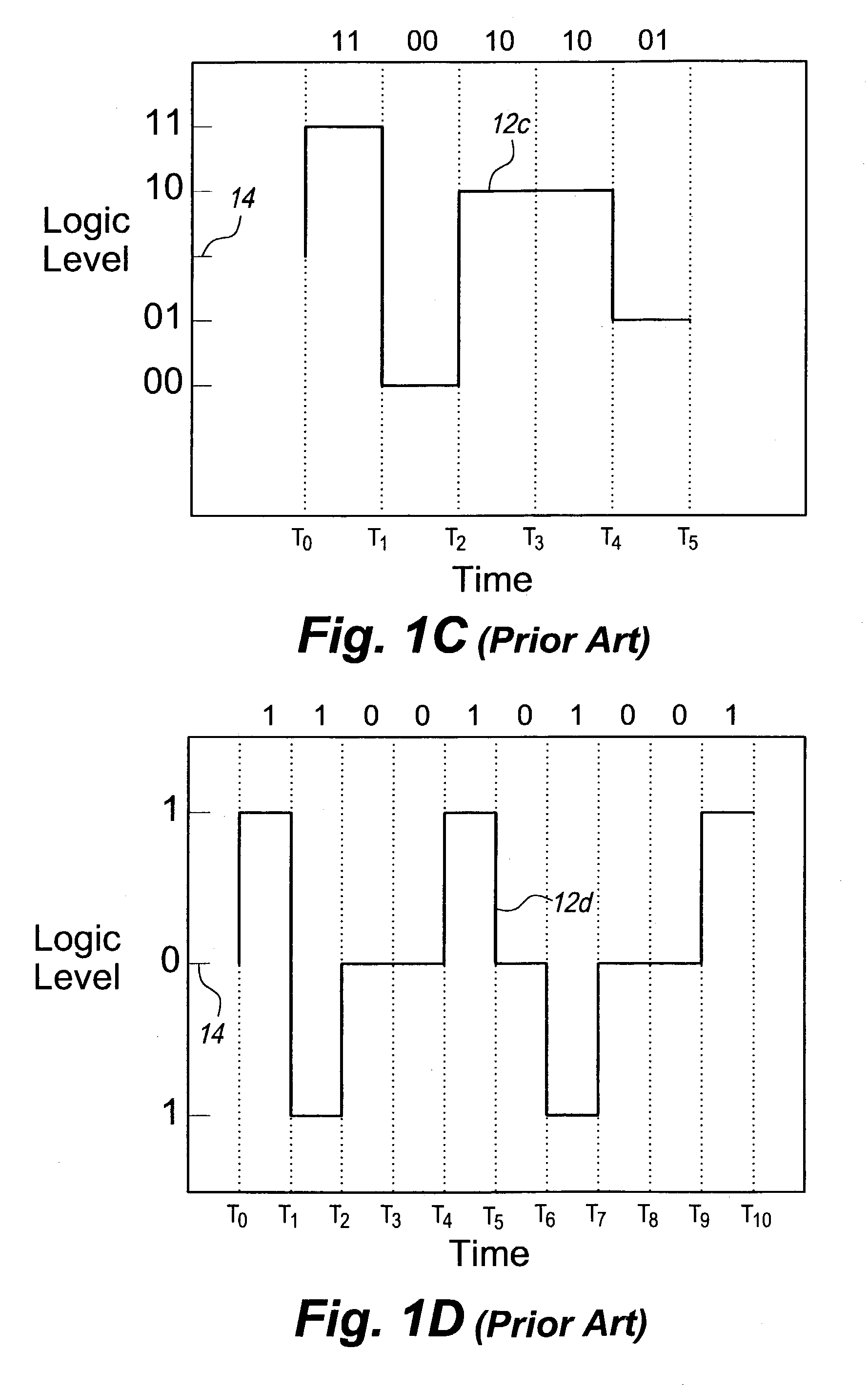
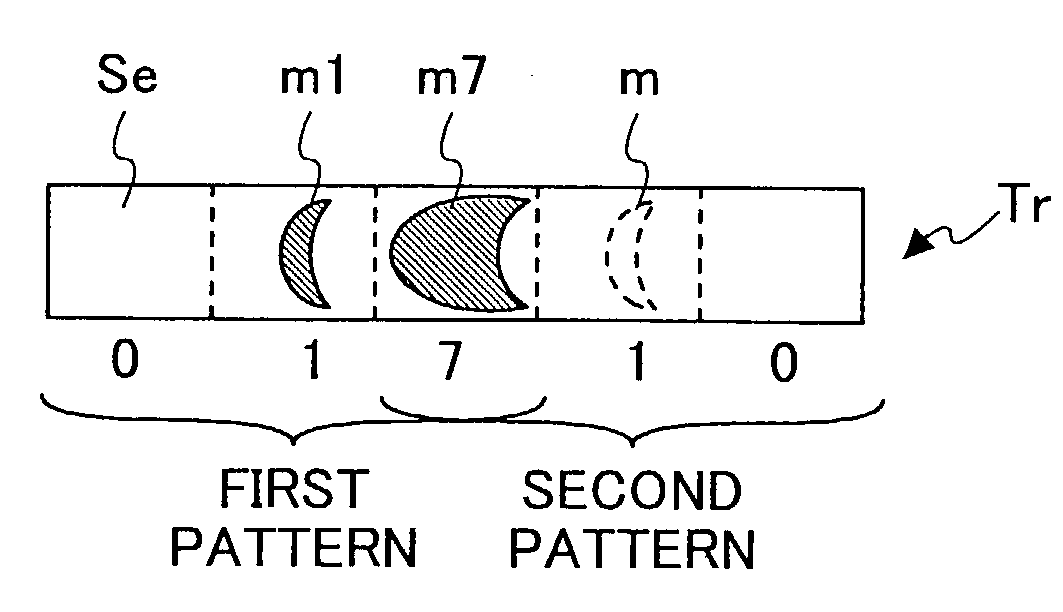
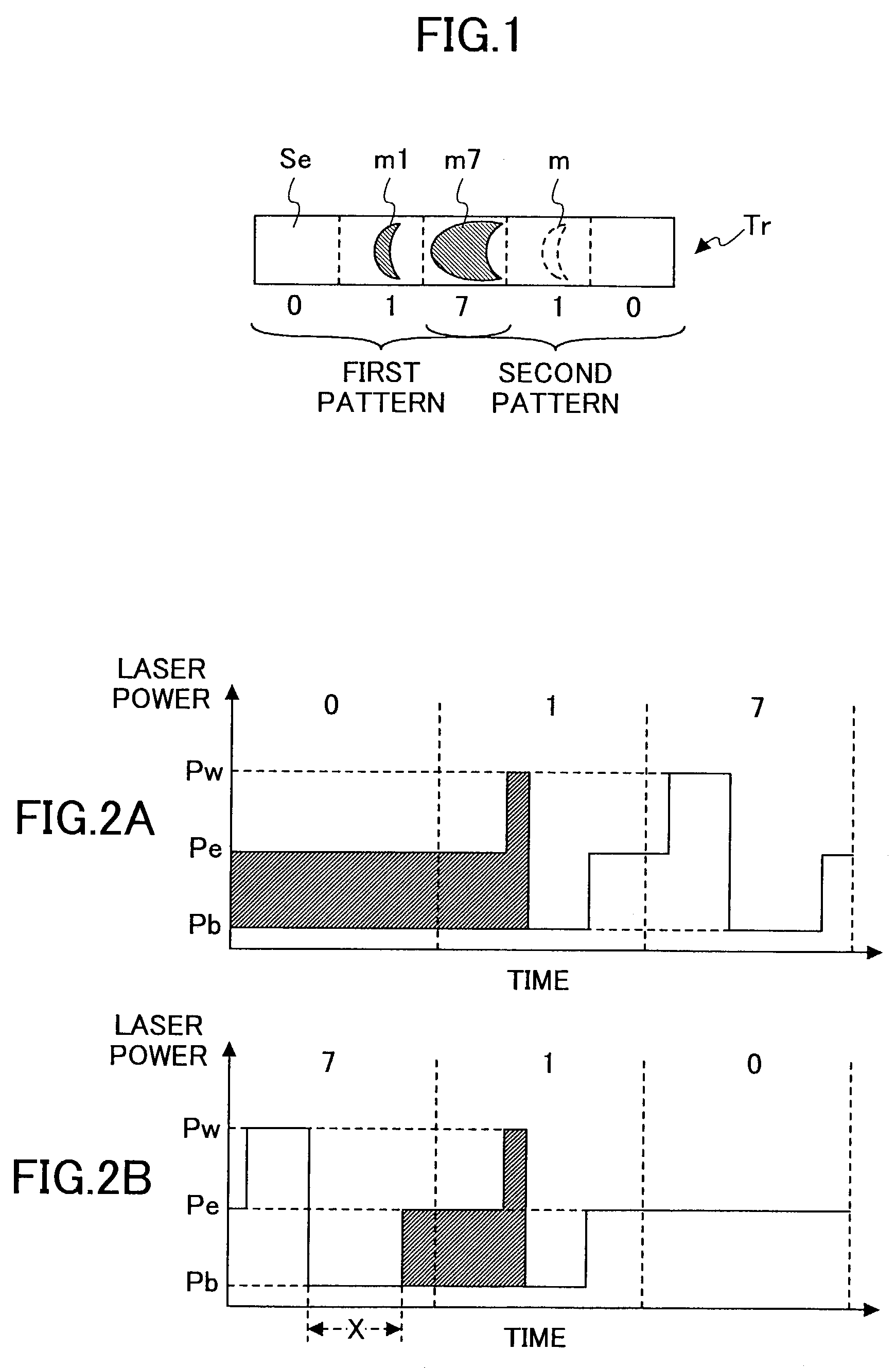
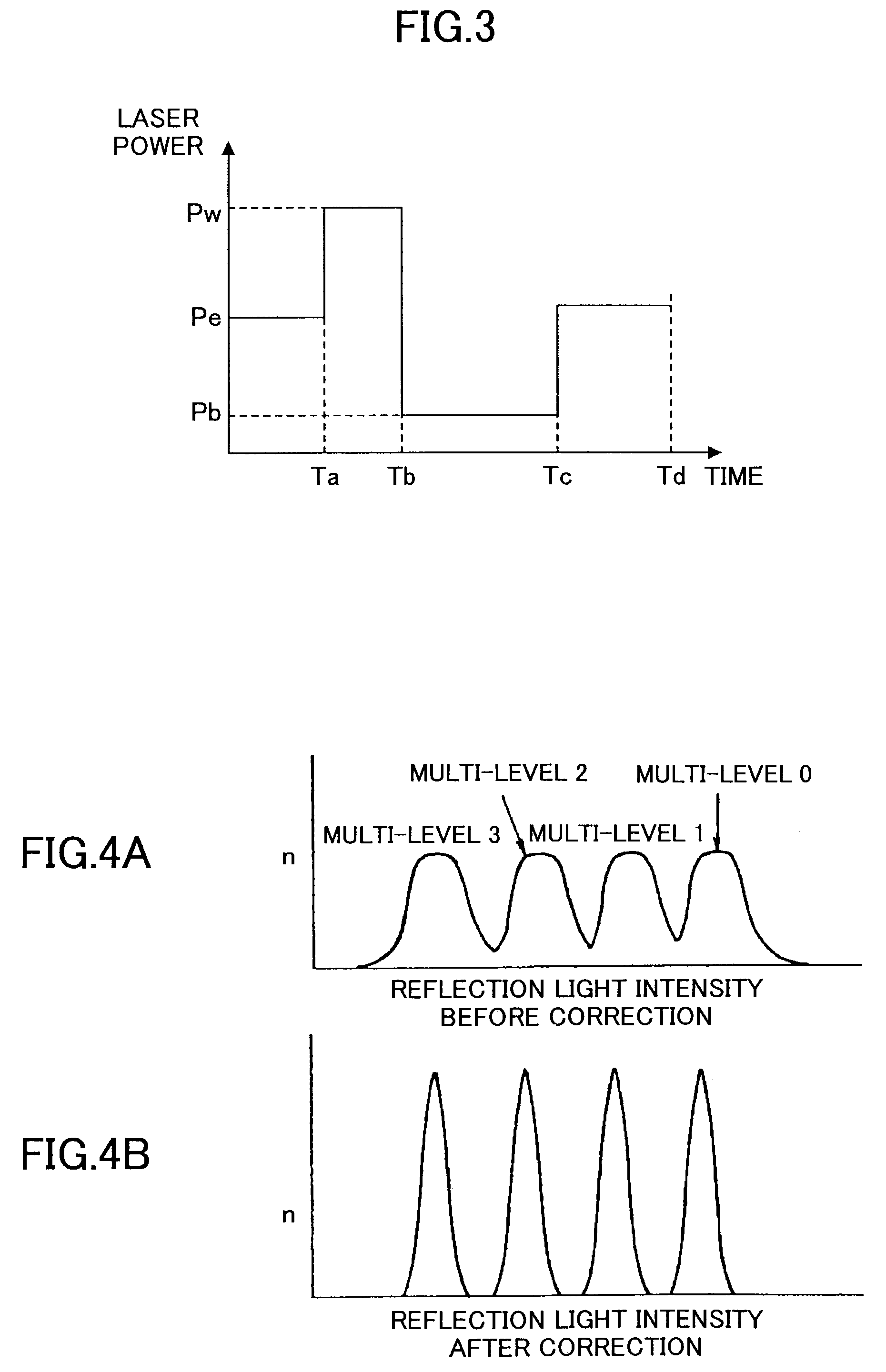
Multi-level information recording apparatus, multi-level information recording method, multi-level information recording medium and multi-level information recording-reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS7126897B2Improve accuracyReduce errorsTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesRecording densityComputer science
A multi-level information recording-reproducing apparatus can accurately determine multi-level information even if recording density is increased. A multi-level information recording-reproducing apparatus radiates a laser beam to an information recording medium by switching a radiation energy level of the laser beam in a multi-level fashion and records a recorded mark in the information recording medium. The multi-level information recording-reproducing apparatus reproduces a multi-level data sequence recorded as a test pattern in the information recording medium, sets a reproduction signal level of a recorded mark based on an immediately-before cell located immediately before a cell to be reproduced, and corrects the radiation energy level of the laser beam so that the reproduction signal level can have a separate distribution from a distribution of another reproduction signal level.
Owner:RICOH KK
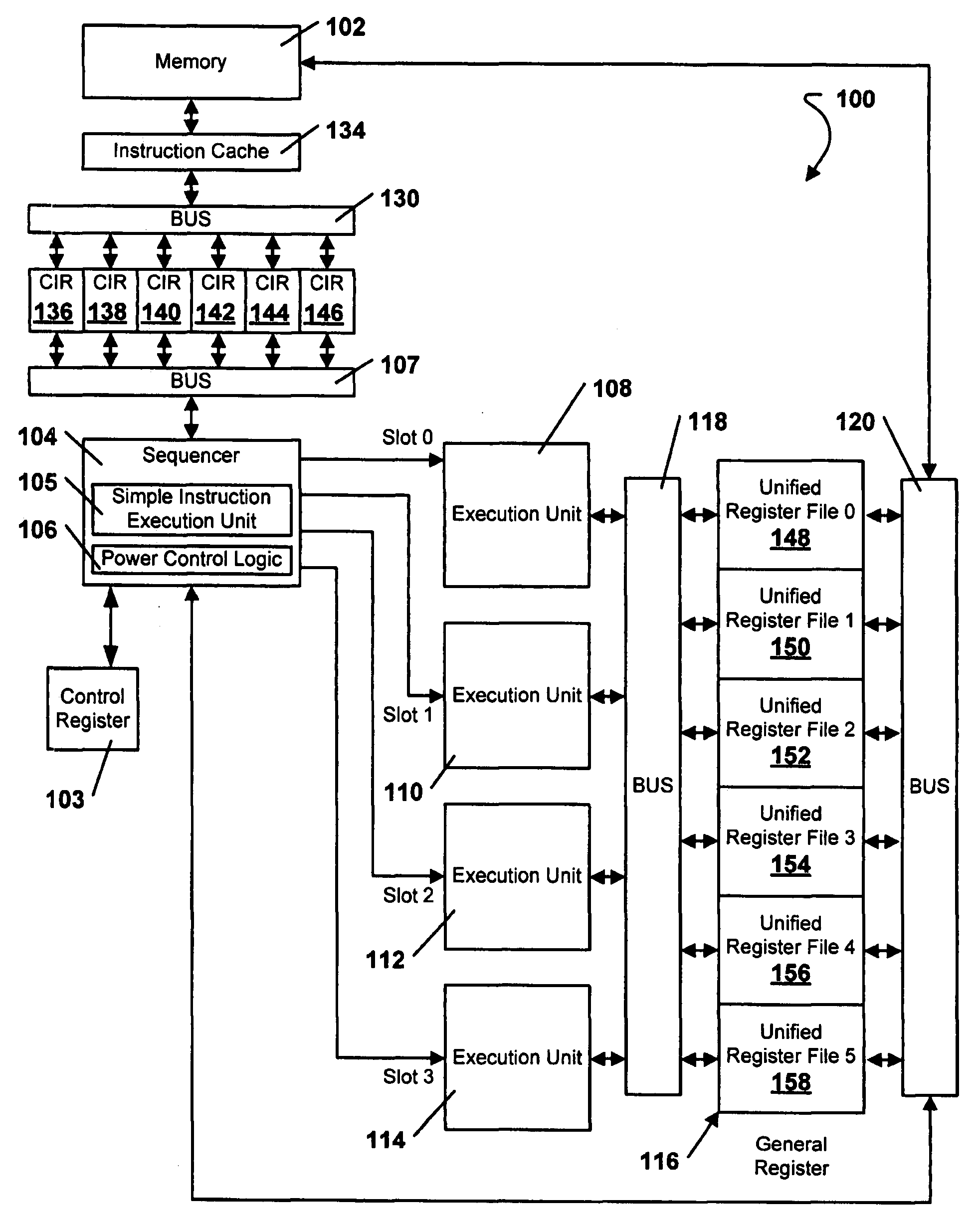
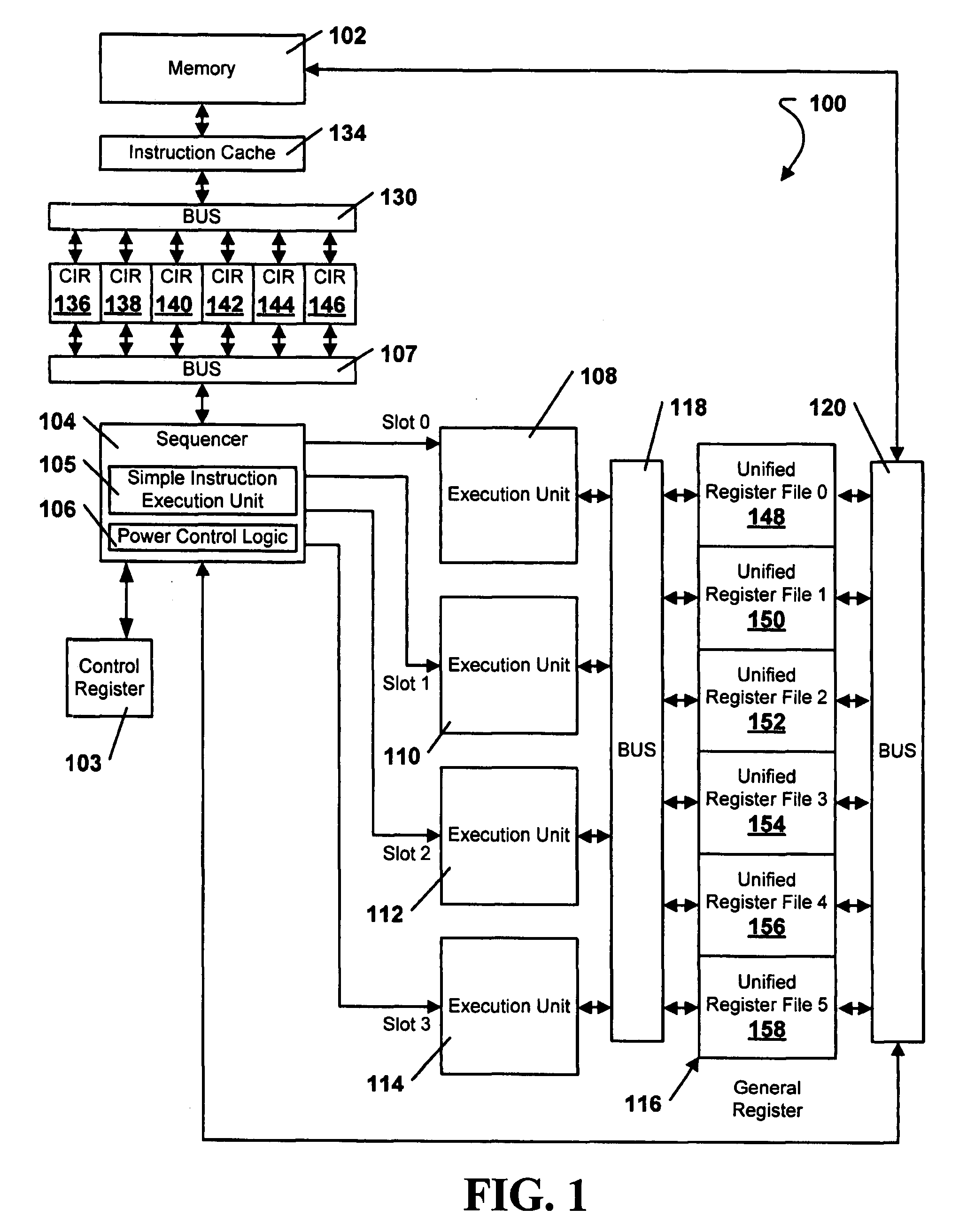
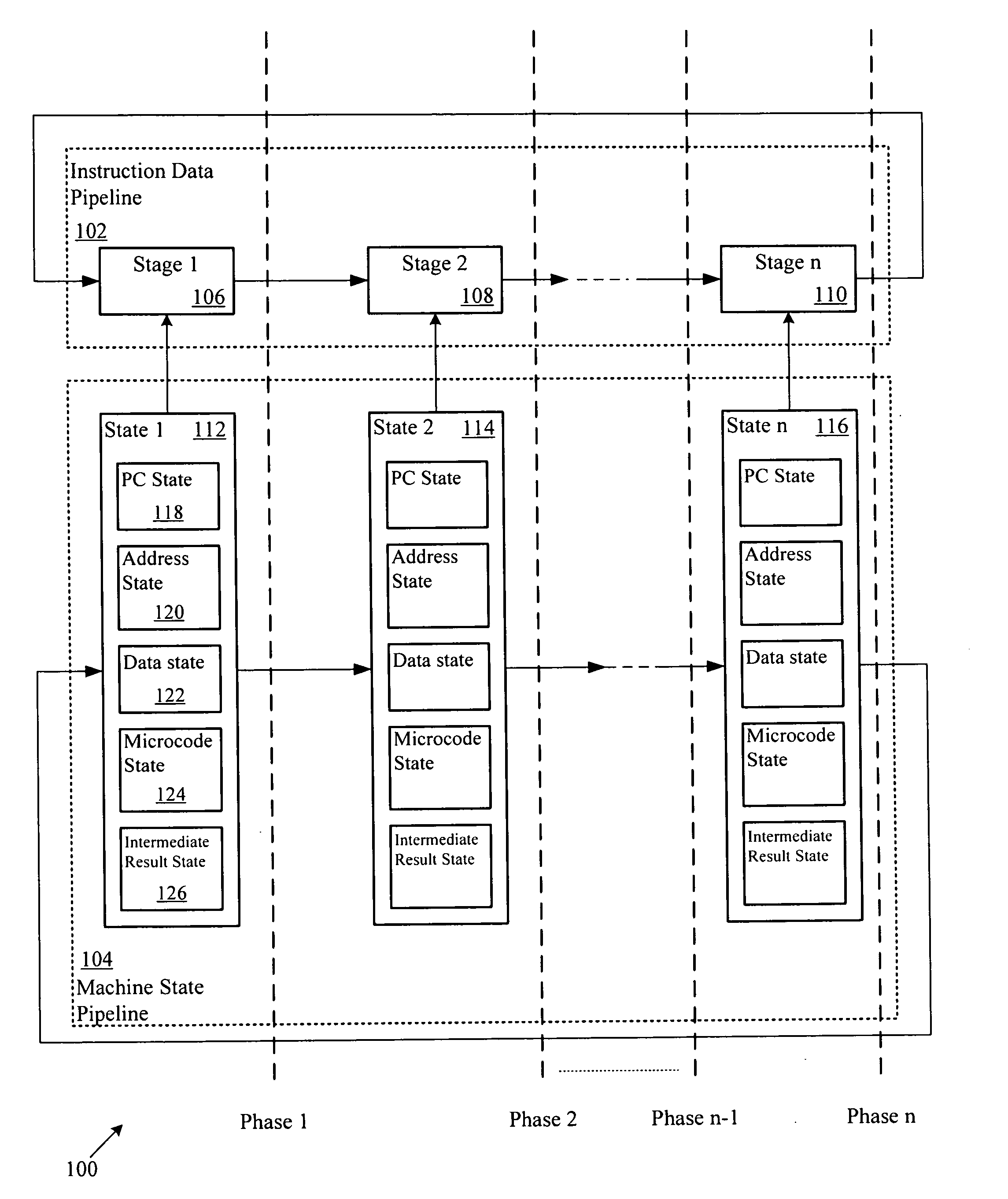
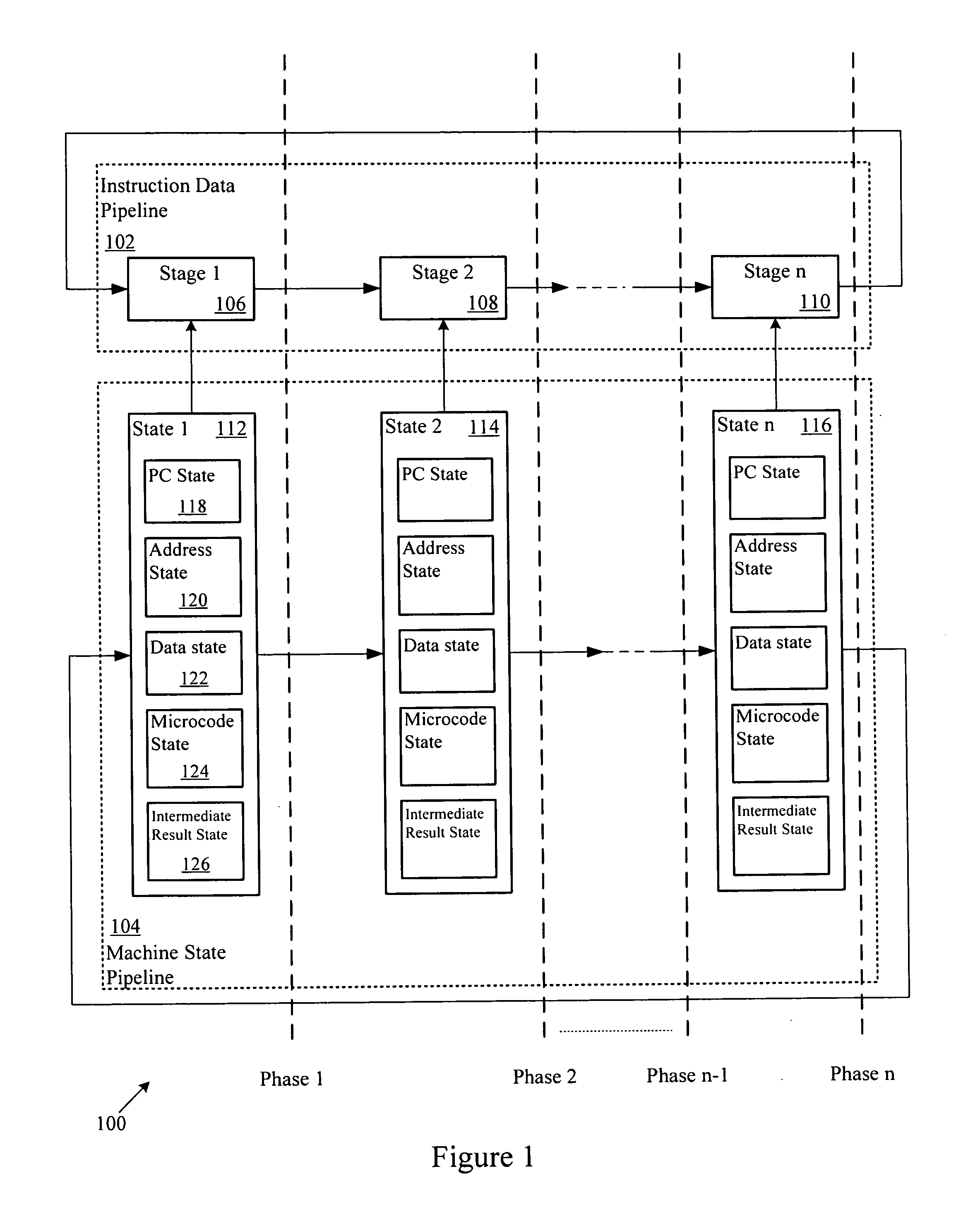
System and Method of Executing Instructions in a Multi-Stage Data Processing Pipeline
InactiveUS20090070602A1Extend battery lifeVolume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsParallel computingControl logic
A device is disclosed that includes an instruction execution pipeline having multiple stages for executing an instruction. The device also includes a control logic circuit coupled to the instruction execution pipeline. The control logic circuit is adapted to skip at least one stage of the instruction execution pipeline during execution of the instruction. The control logic circuit is also adapted to execute at least one non-skipped stage during execution of the decoded instruction.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
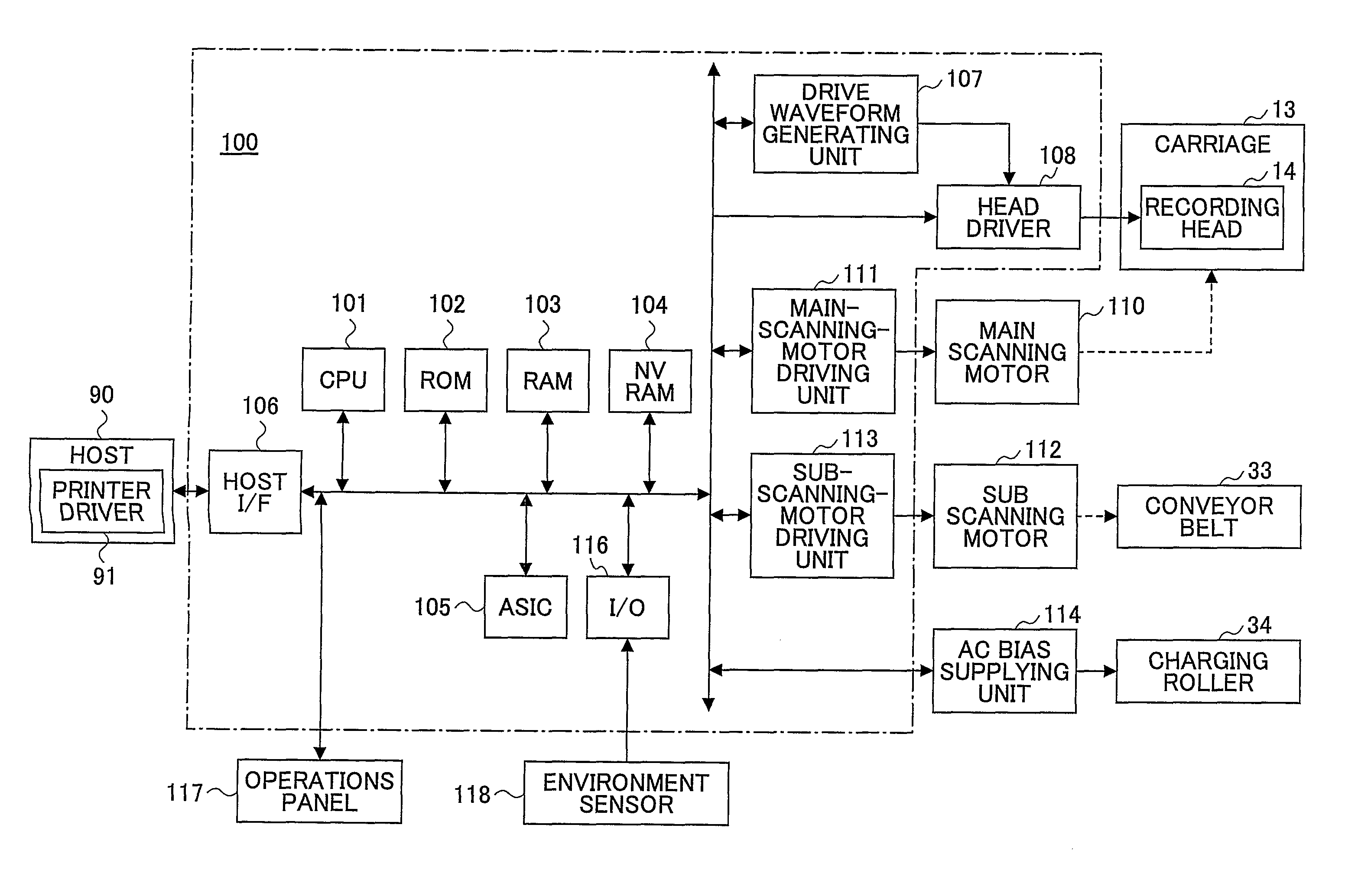
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, image forming system, and storage medium
InactiveUS20110090276A1Small droplet sizeSolve or reduce one or more problemsOther printing apparatusPictoral communicationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing method includes converting multilevel data of an image into a dot pattern using a multilevel error diffusion process. The conversion includes determining a pixel corresponding to an abnormal nozzle based on abnormal nozzle information provided for each of droplet sizes supported by nozzles of an image forming apparatus; preventing jetting of a droplet onto the determined pixel; distributing a quantization error of the determined pixel calculated in the multilevel error diffusion process to neighboring pixels; and if extra-large droplets with a droplet size greater than the droplet size of a full-size droplet capable of filling a pixel are to be formed in the neighboring pixels as a result of distributing the quantization error, removing one or more of the extra-large droplets or reducing the droplet size of one or more of the extra-large droplets.
Owner:RICOH KK
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS8582349B2Constant potentialAccurate dataSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesNODALPower semiconductor device
An object is to provide a semiconductor device which includes a memory cell capable of holding accurate data even when the data is multilevel data. The semiconductor device includes a memory cell holding data in a node to which one of a source and a drain of a transistor whose channel region is formed from an oxide semiconductor. Note that the value of off-state current (leakage current) of the transistor is extremely small. Thus, after being set to have a predetermined value, the potential of the node can be kept constant or substantially constant by turning the transistor off. In this manner, accurate data can be stored in the memory cell.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device and semiconductor memory system storing multilevel data
A first memory cell stores data of k bits in one cell. A second memory cell stores data of h bits (h<k) in one cell. Data of i bits (i<=k) is stored in the first memory cell, and data of h bits (h<i) generated from the i-bit data is stored in the second memory cell.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Interleaved hardware multithreading processor architecture
ActiveUS20080016321A1Complicated processAvoid instructionConditional code generationGeneral purpose stored program computerParallel computingData treatment
An architecture for a digital signal processor alleviates the difficulties and complexities normally associated with writing and optimizing programs to avoid stalls during which one instruction awaits the result of a prior instruction. The architecture coordinates the processing of data for multiple instructions through a multiple stage data pipeline. As a result, the architecture not only supports simultaneous execution of multiple programs, but also permits each program to execute without delays caused by inter-relationships between instructions within the program.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
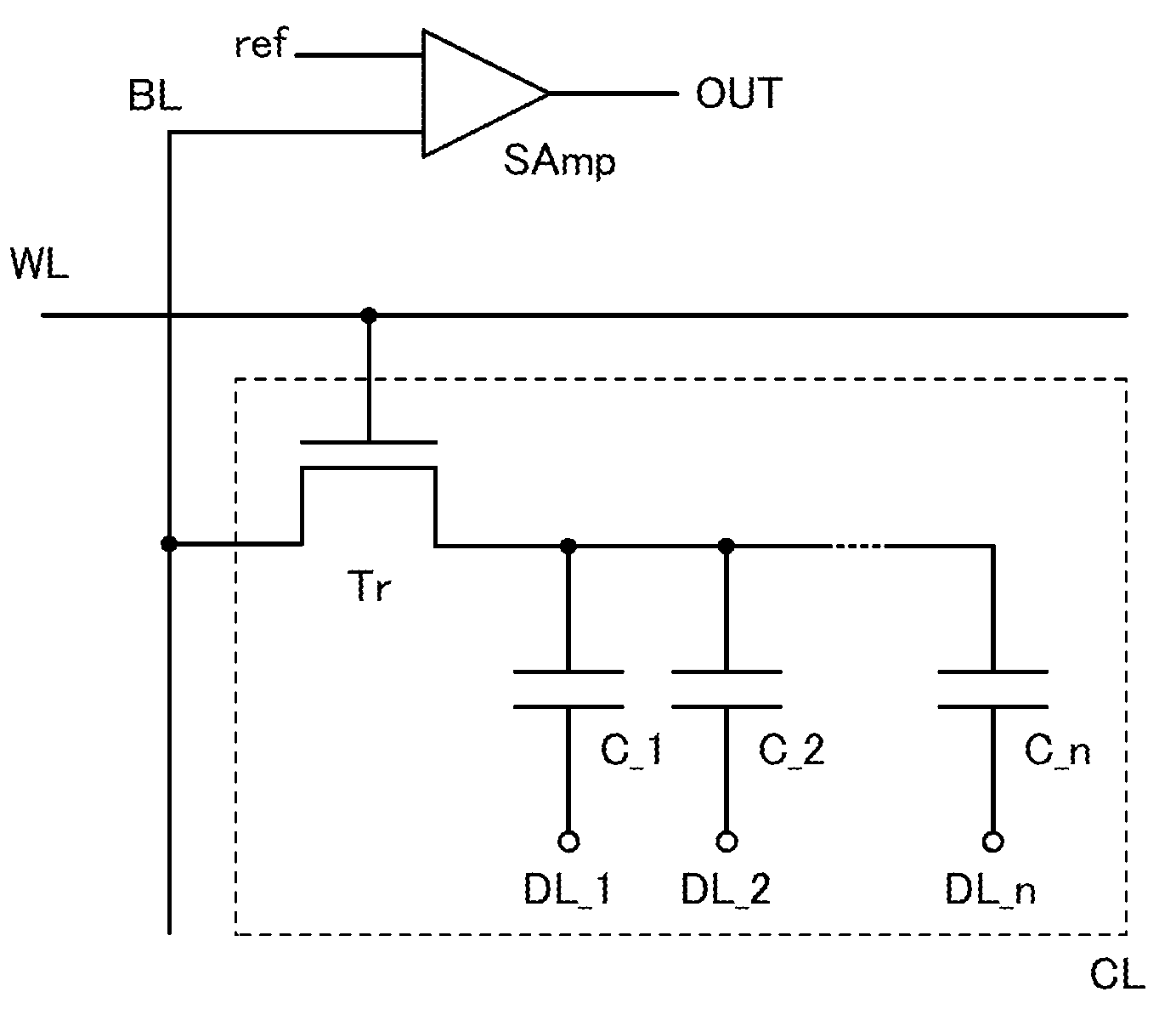
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20120127781A1More memory capacityIncrease storage capacityTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceRetention period
To increase a storage capacity of a memory module per unit area, and to provide a memory module with low power consumption, a transistor formed using an oxide semiconductor film, a silicon carbide film, a gallium nitride film, or the like, which is highly purified and has a wide band gap of 2.5 eV or higher is used for a DRAM, so that a retention period of potentials in a capacitor can be extended. Further, a memory cell has n capacitors with different capacitances and the n capacitors are each connected to a corresponding one of n data lines, so that a variety of the storage capacitances can be obtained and multilevel data can be stored. The capacitors may be stacked for reducing the area of the memory cell.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS8854865B2Solve the large power consumptionReduce the refresh rateTransistorSolid-state devicesRetention periodCapacitance
To increase a storage capacity of a memory module per unit area, and to provide a memory module with low power consumption, a transistor formed using an oxide semiconductor film, a silicon carbide film, a gallium nitride film, or the like, which is highly purified and has a wide band gap of 2.5 eV or higher is used for a DRAM, so that a retention period of potentials in a capacitor can be extended. Further, a memory cell has n capacitors with different capacitances and the n capacitors are each connected to a corresponding one of n data lines, so that a variety of the storage capacitances can be obtained and multilevel data can be stored. The capacitors may be stacked for reducing the area of the memory cell.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com