Patents
Literature
205 results about "Multi level data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
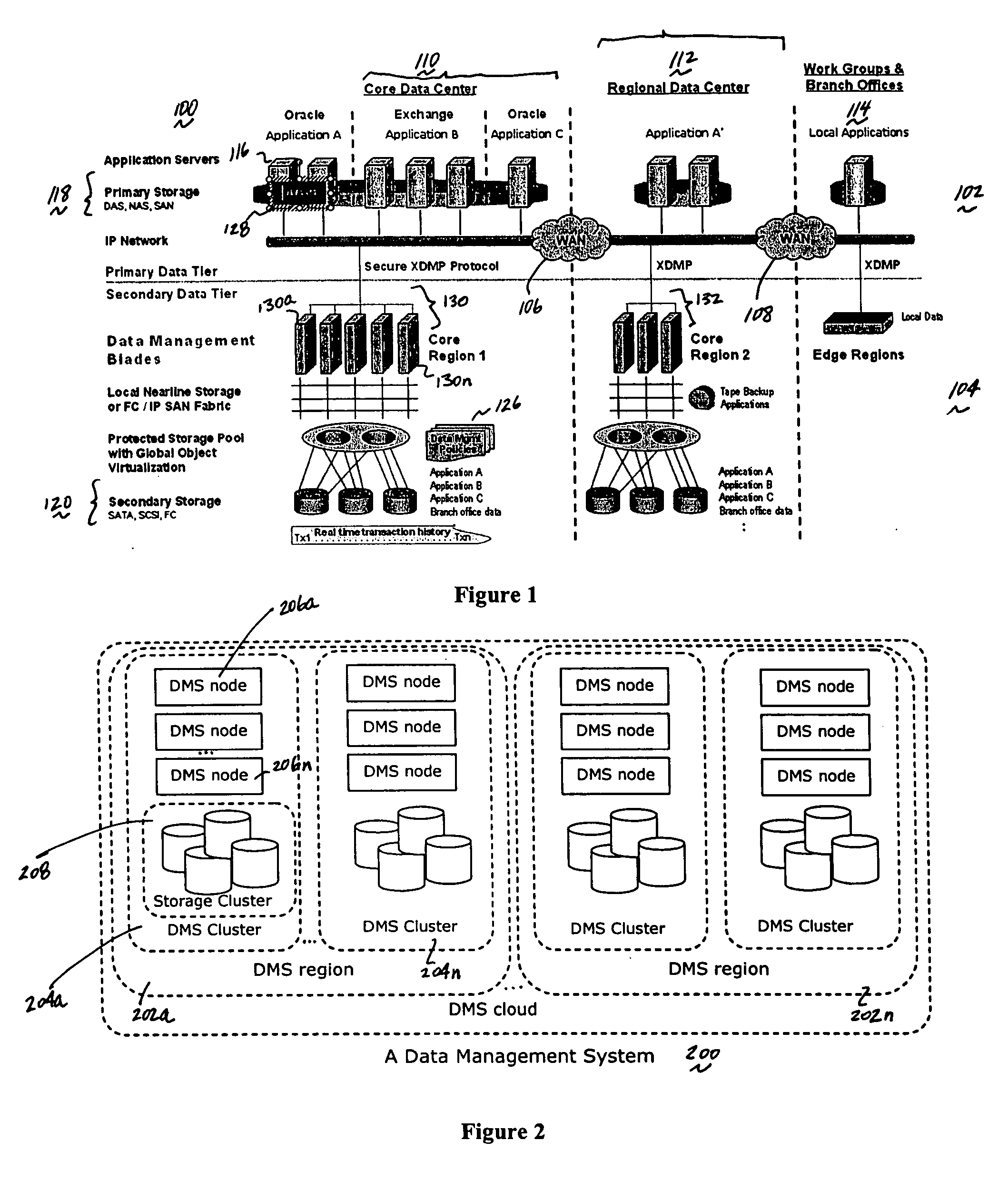
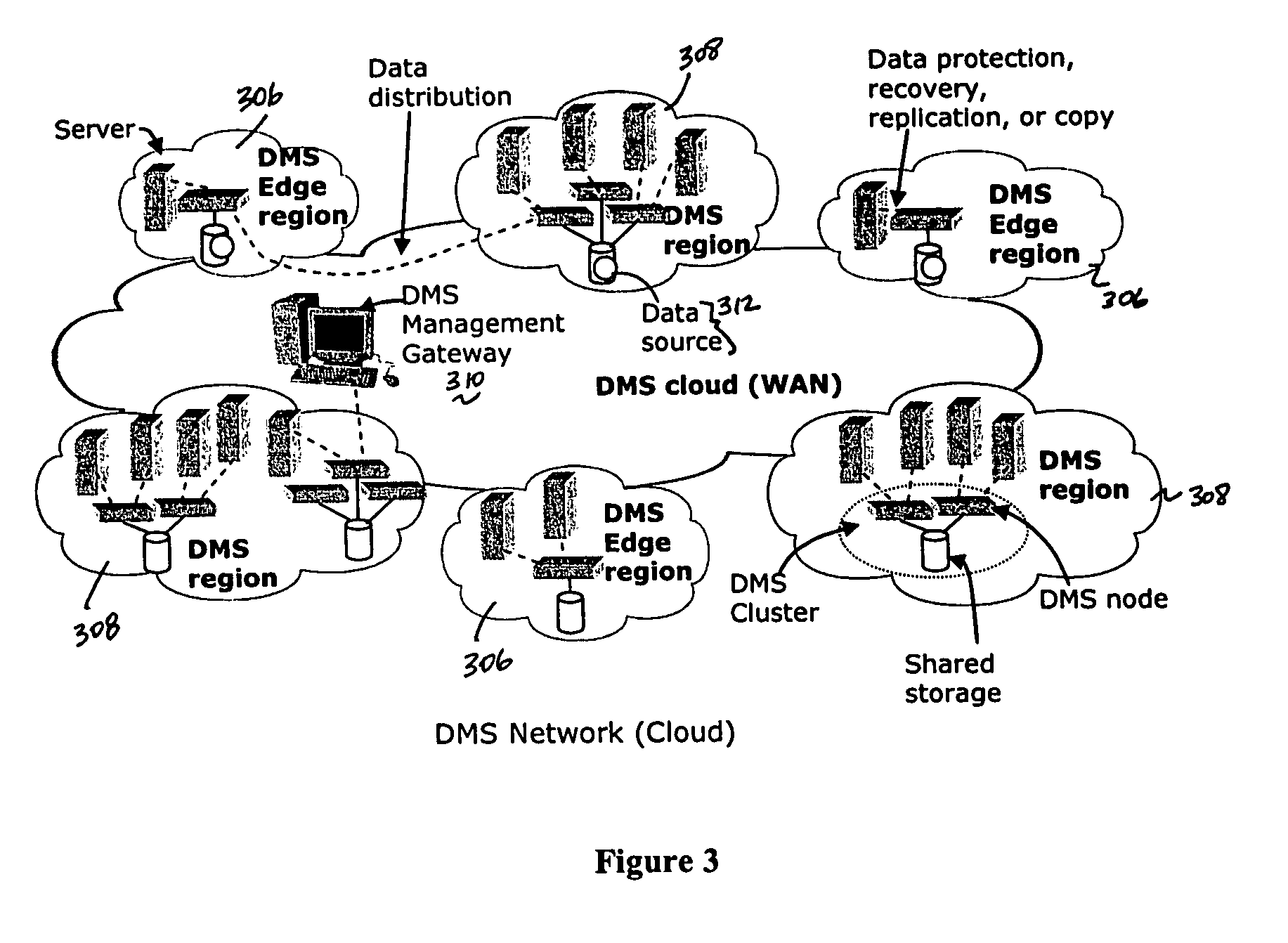
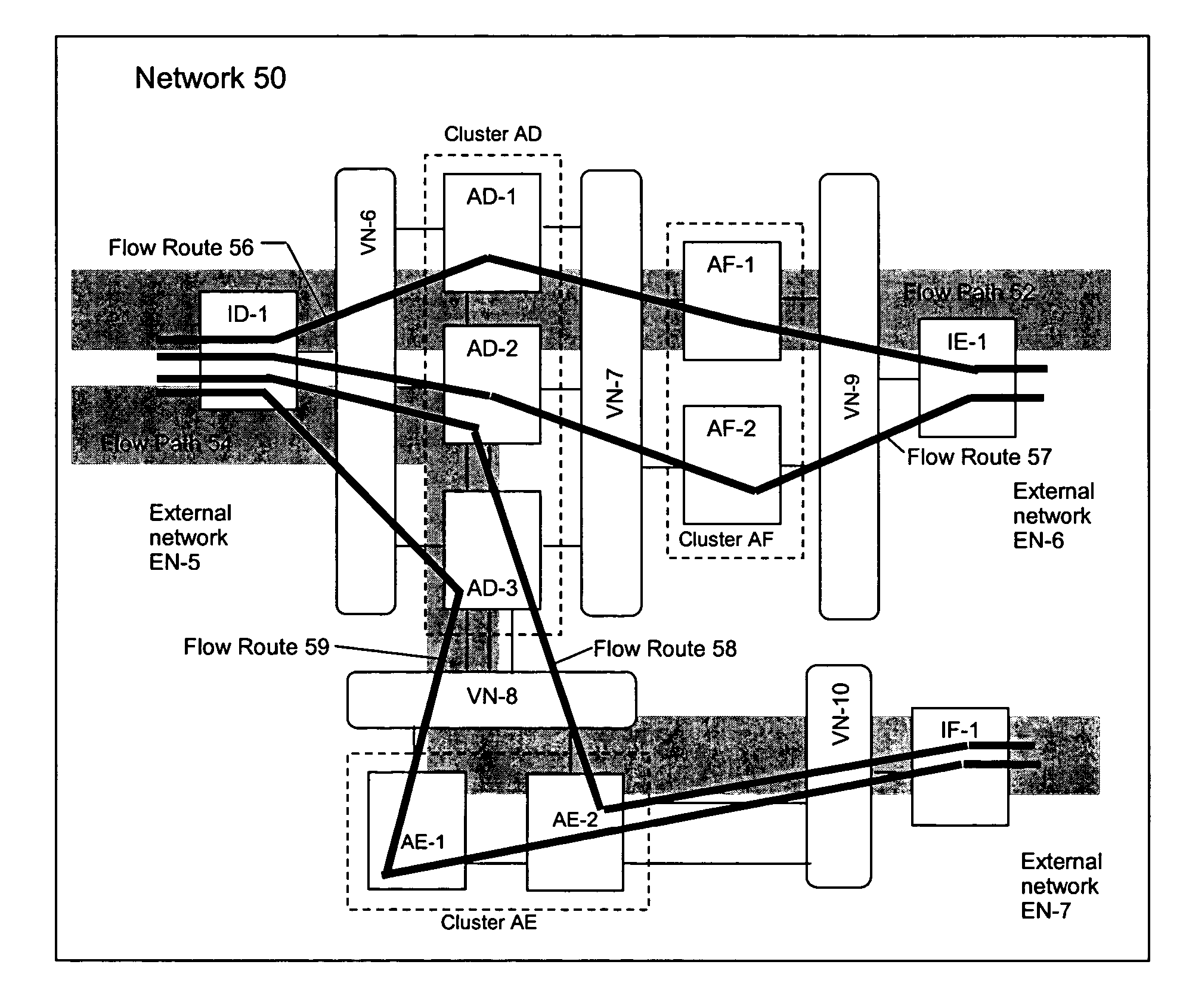
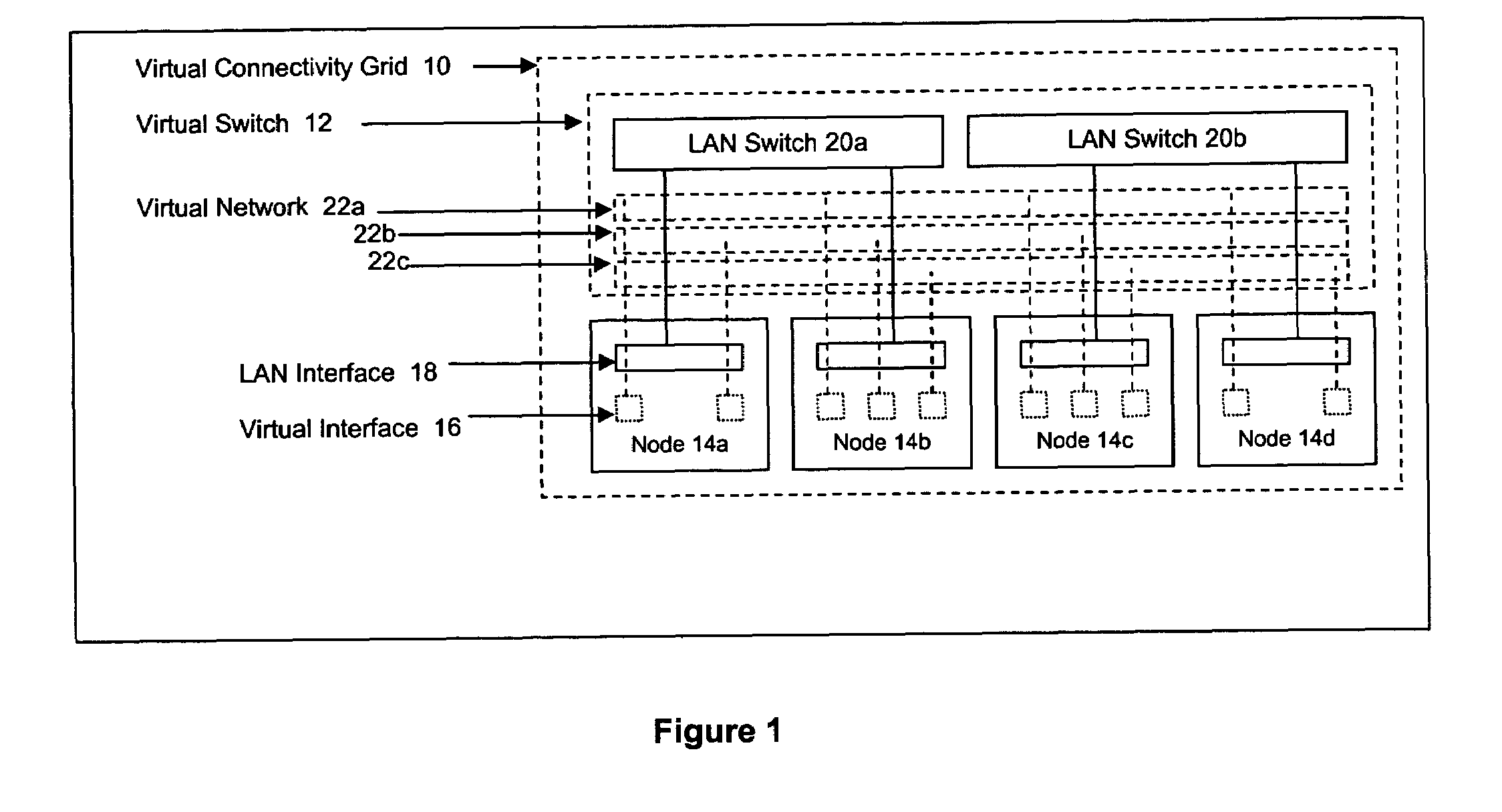
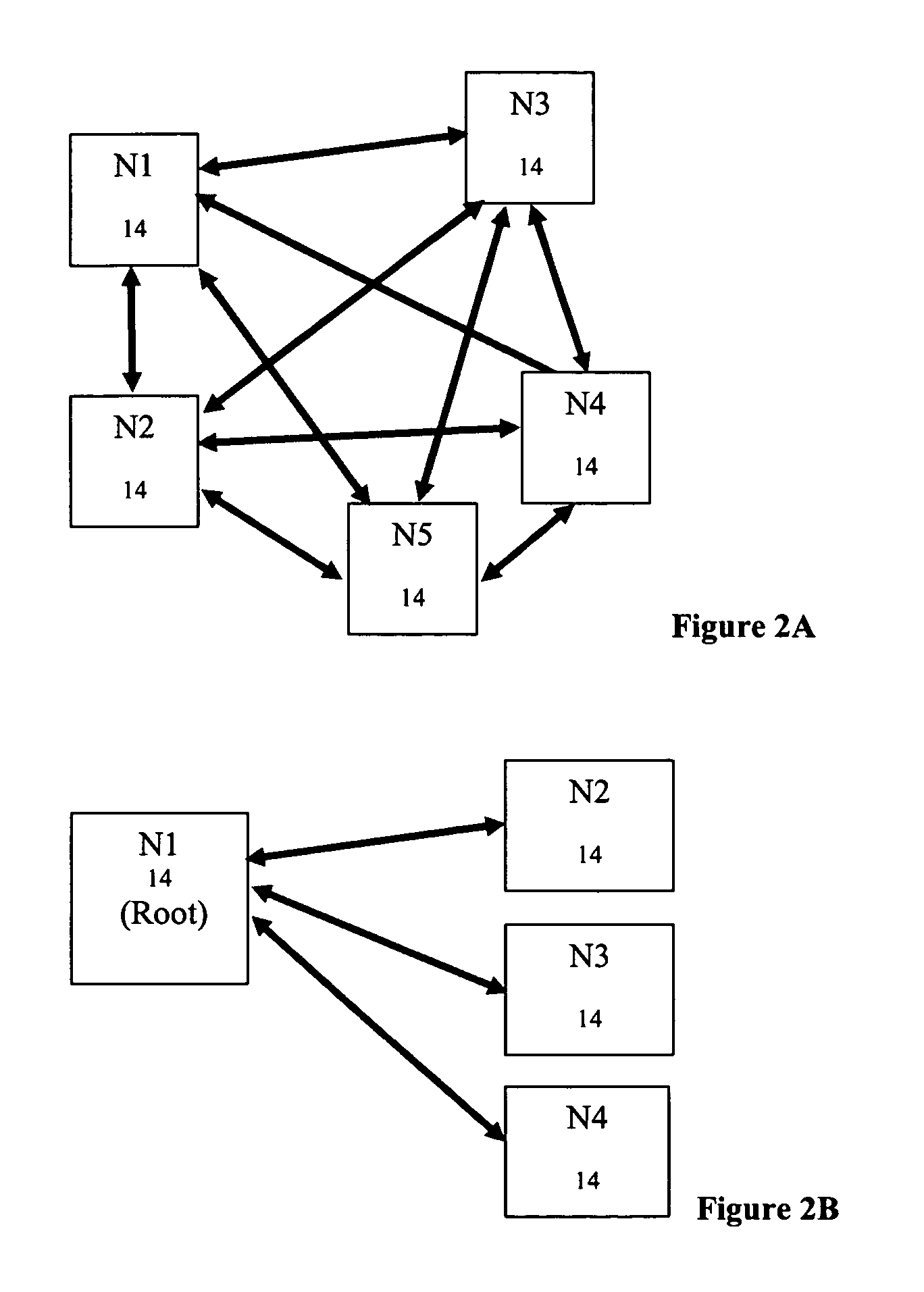
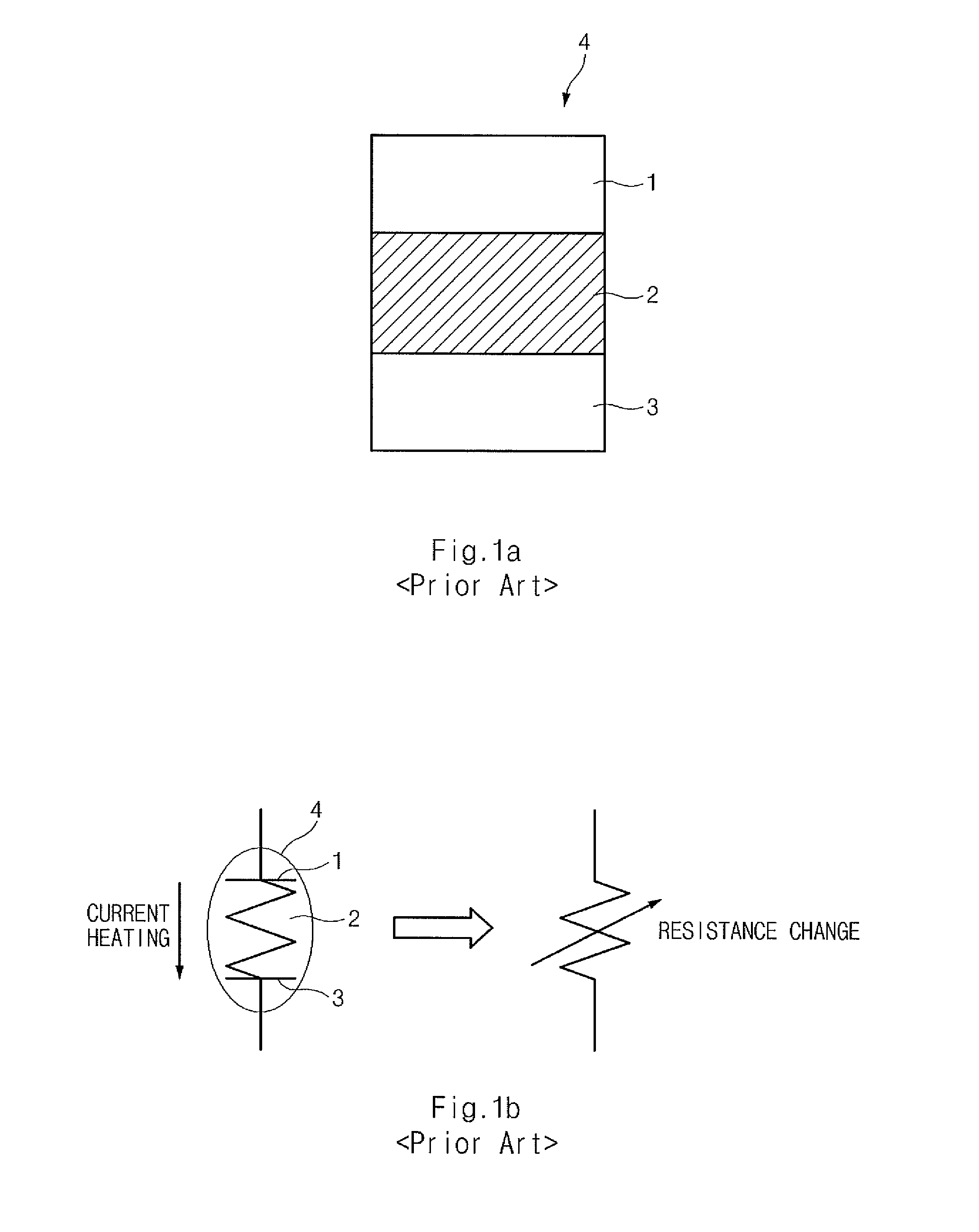
Method and apparatus for achieving dynamic capacity and high availability in multi-stage data networks using adaptive flow-based routing
ActiveUS20050091396A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionSystems managementHigh availability
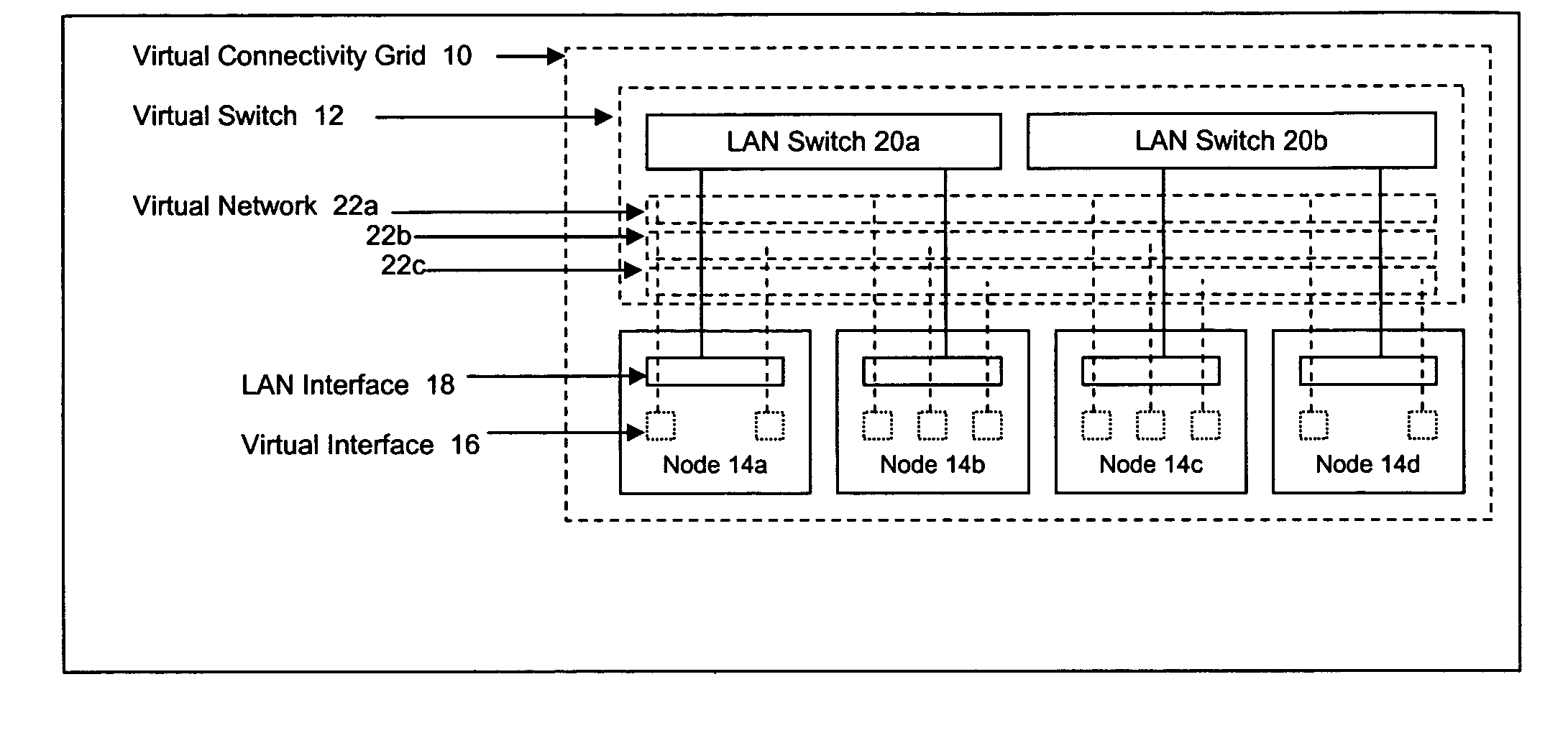
Methods and systems for determining paths for flows within a multi-stage network made up of clusters of processing nodes. The flow paths may be determined without knowledge of whether or not packets of a particular flow will actually traverse specific ones of the clusters within the multi-stage network. In various implementations, the nodes of the multi-stage network may be coupled to one or more physical network switches through respective physical interfaces and a virtual connectivity grid superimposed thereon and configured through the use of a flow routing framework and system management framework to group the nodes into a number of clusters. The nodes of each cluster are configured to perform similar packet processing functions and the clusters are interconnected through virtual networks to which the nodes are communicatively coupled via virtual interfaces overlaid on top of the physical network interfaces.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
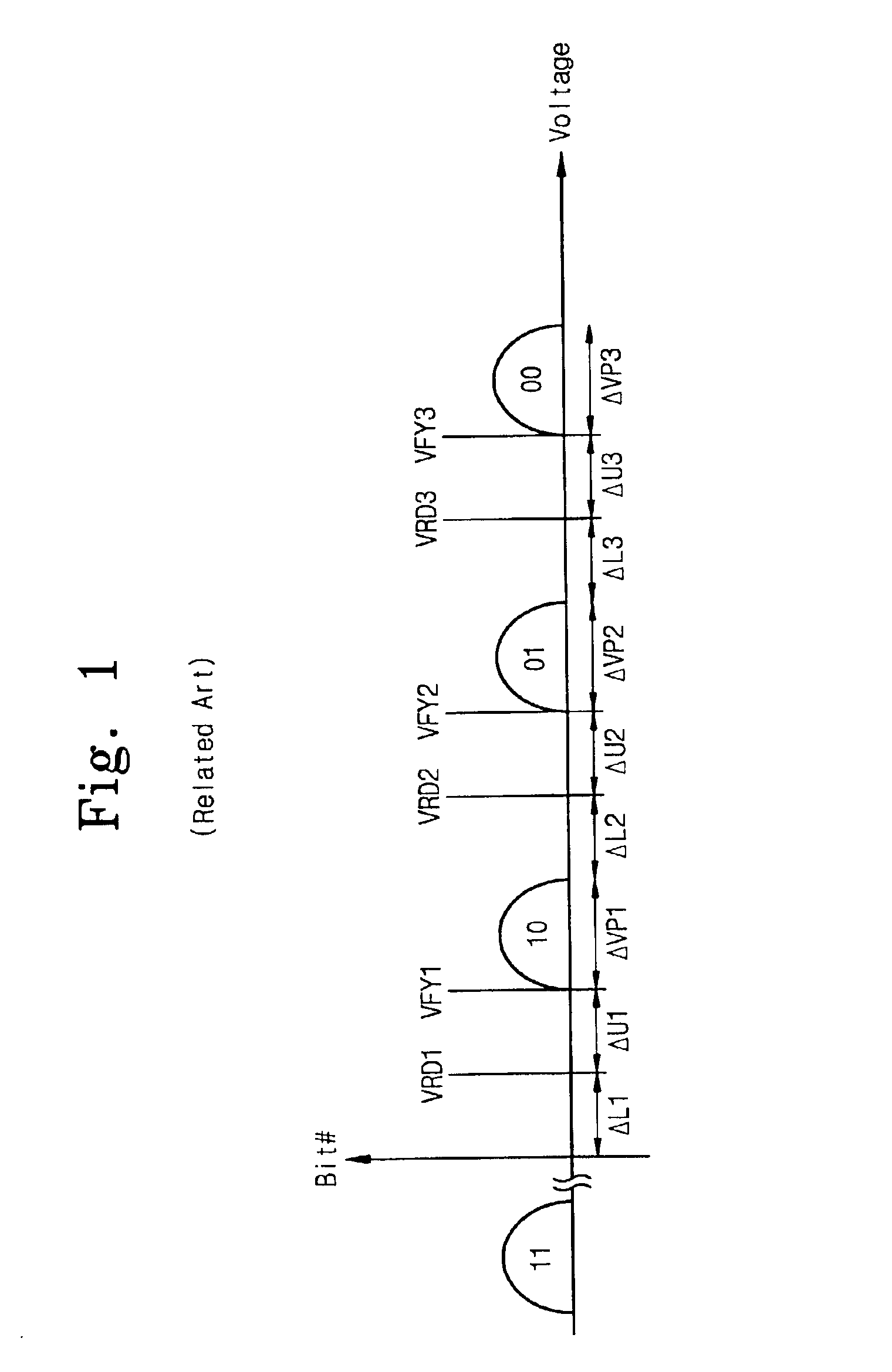
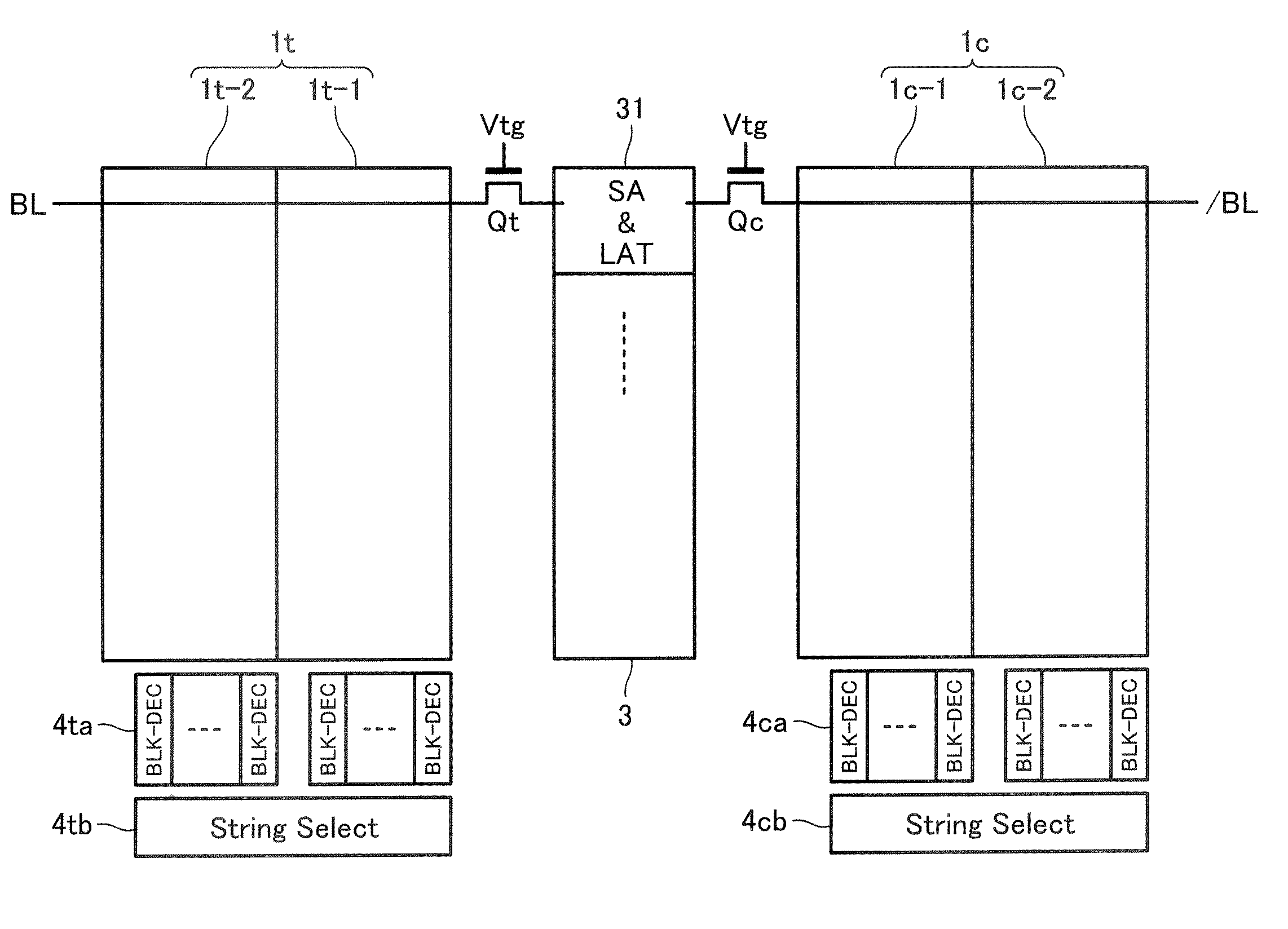
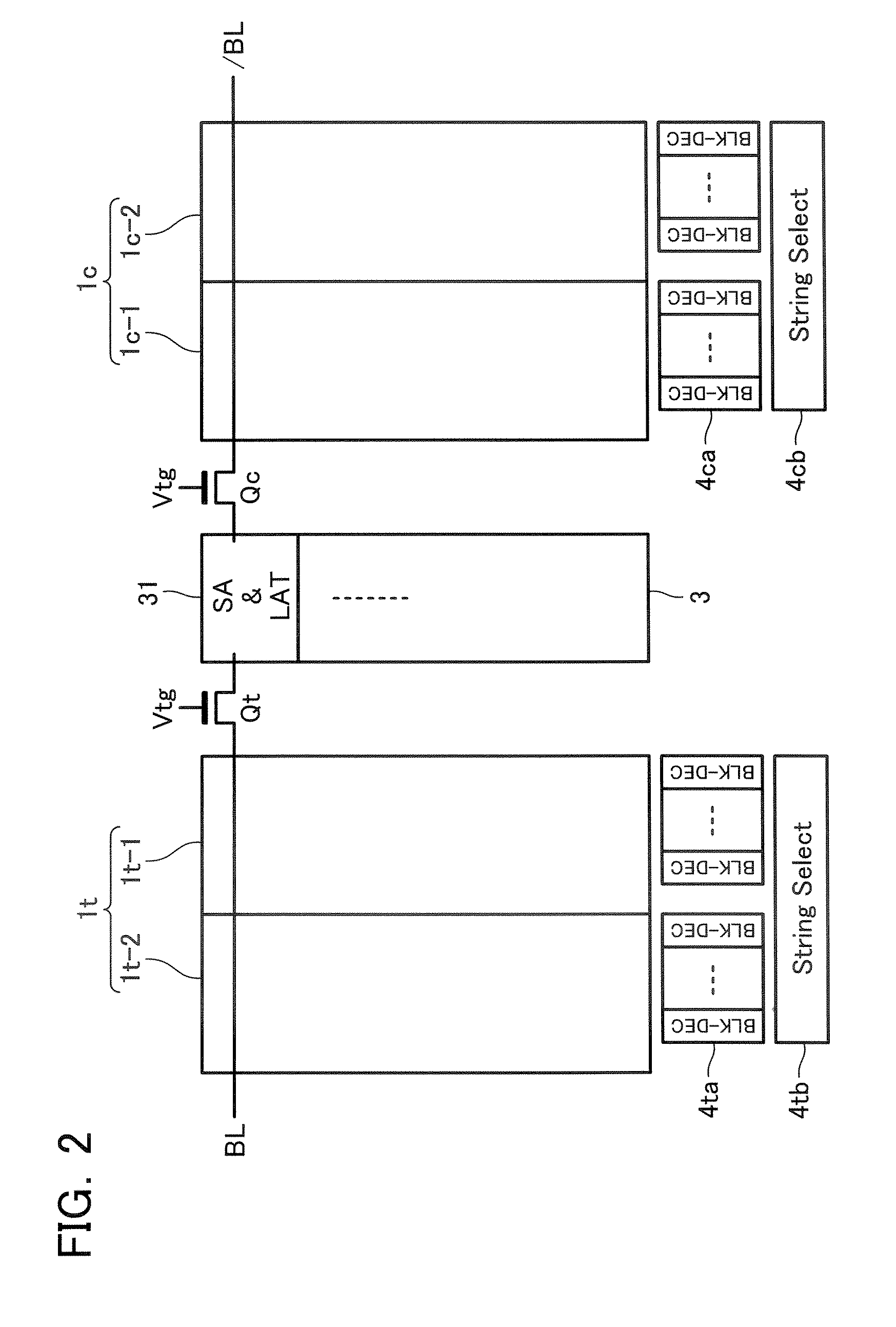
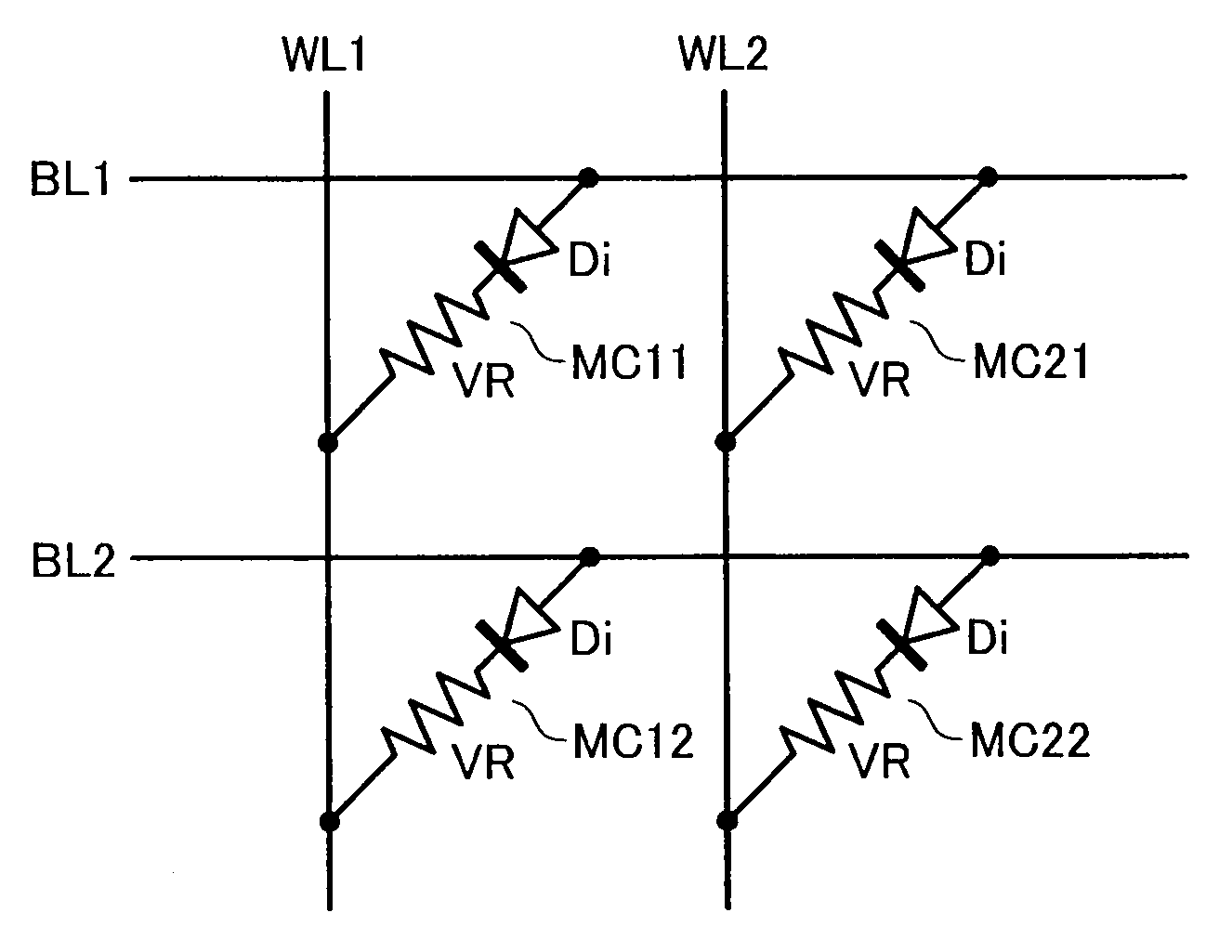
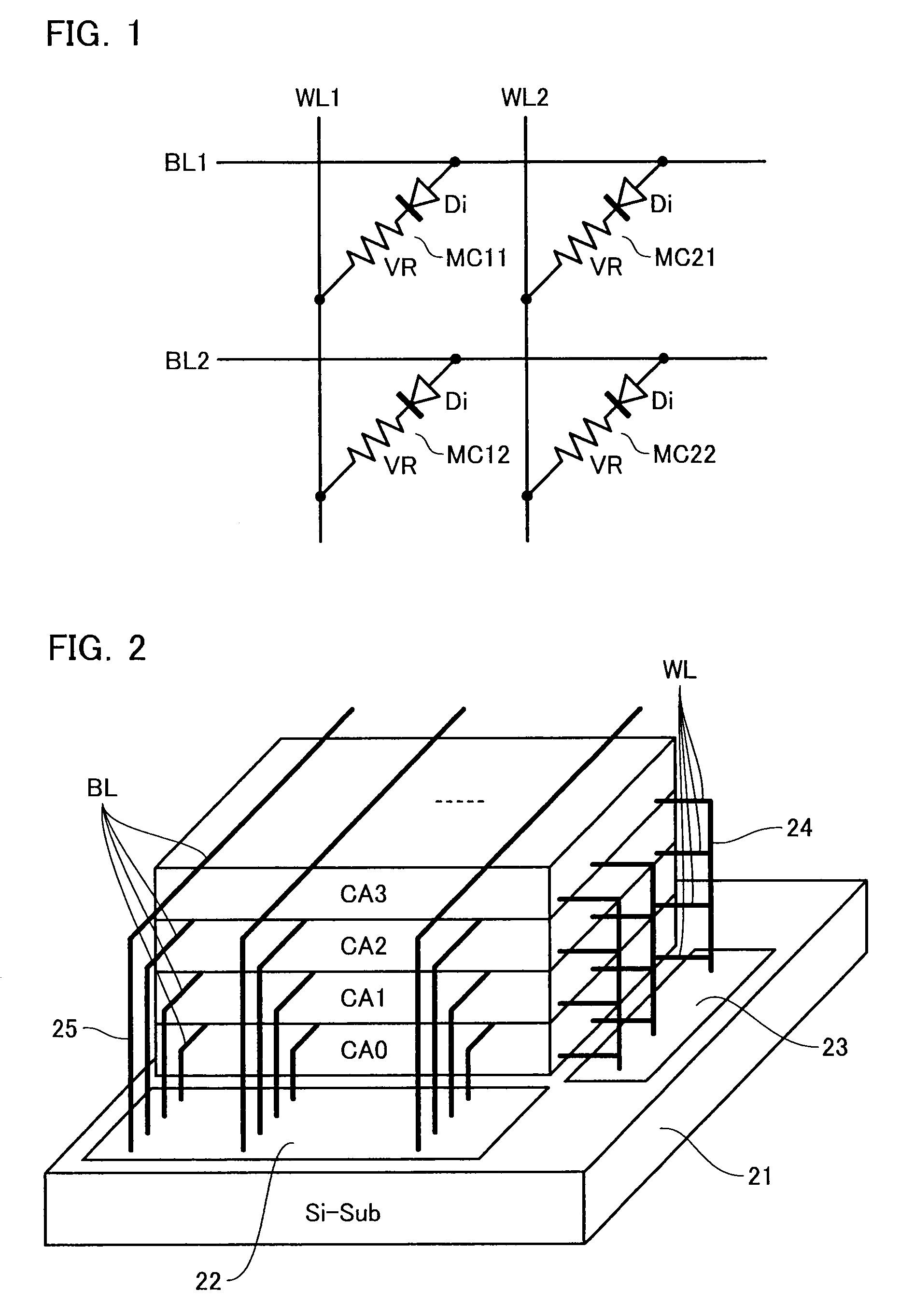
Multi-level flash memory with temperature compensation
InactiveUS6870766B2Reliable functionOperational reliability is increasedRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
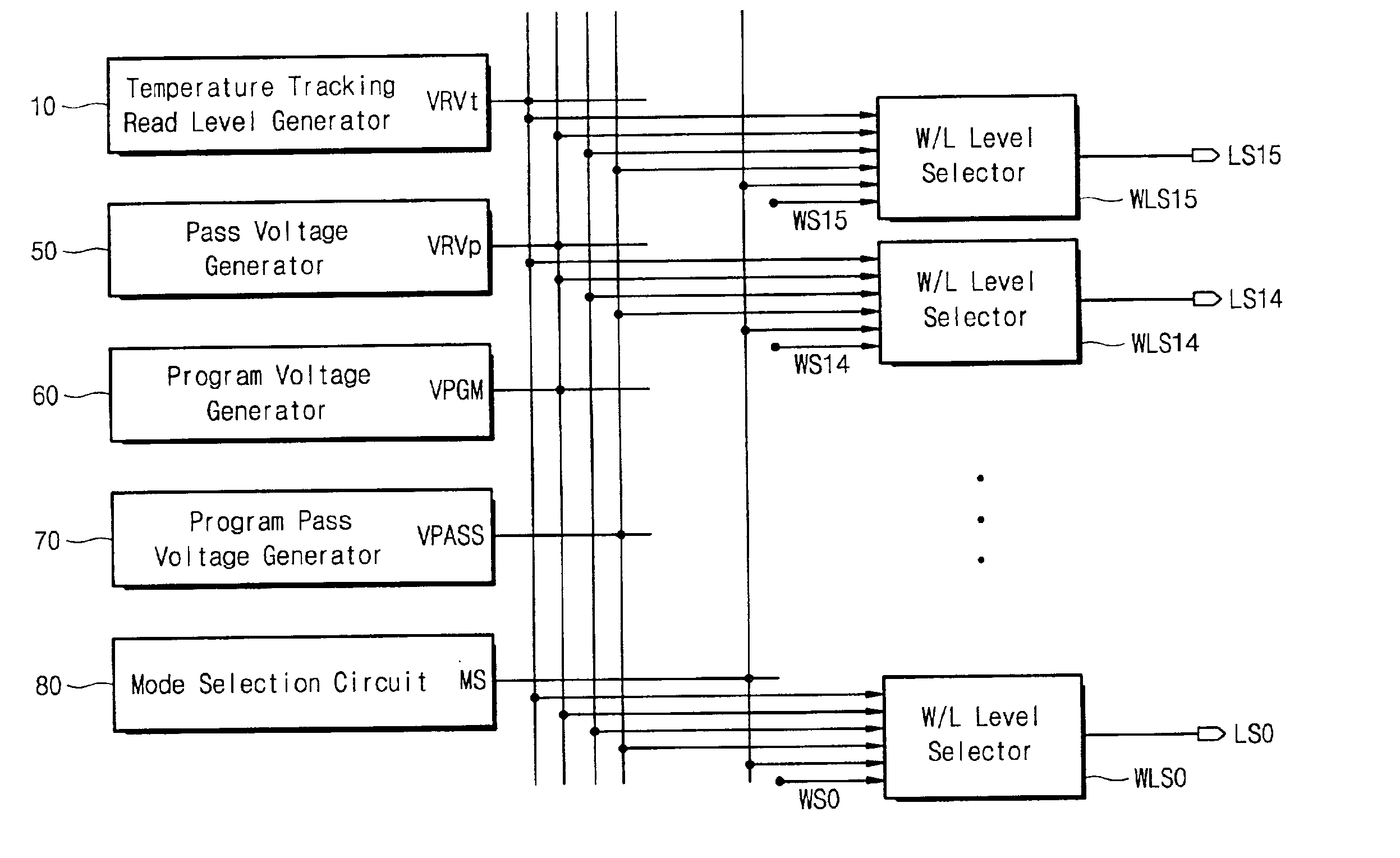
A multi-level semiconductor memory device preferably includes a plurality of wordlines connected to memory cells configured to store multi-level data. A first circuit supplies a temperature-responsive voltage to a selected wordline in order to read a state of a selected memory cell. A second circuit supplies a predetermined voltage to non-selected wordlines. The first circuit preferably includes a semiconductor element that varies its resistance in accordance with temperature. Reliable program-verifying and reading functions are preferably provided despite migration of threshold voltage distribution profiles due to temperature variations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
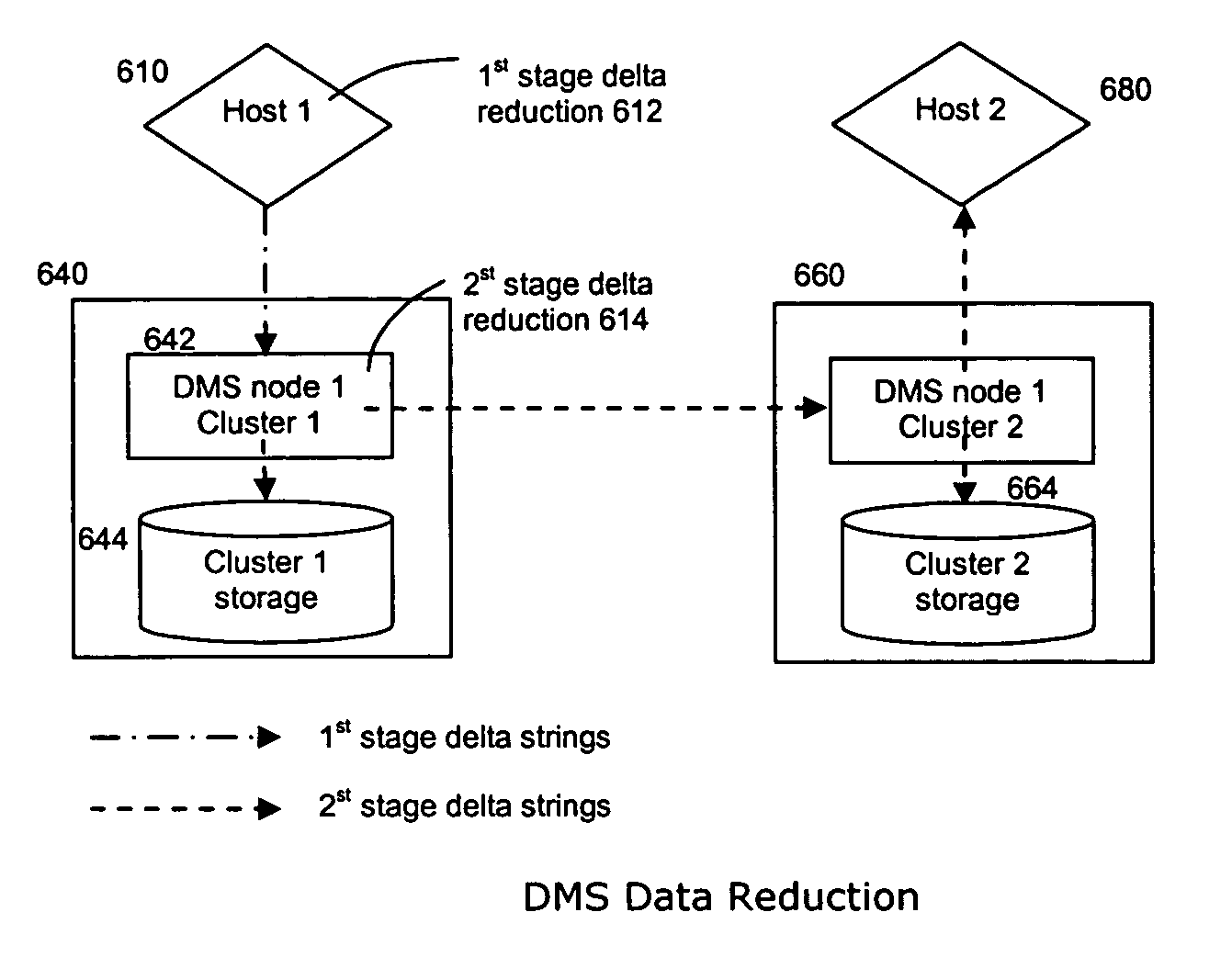
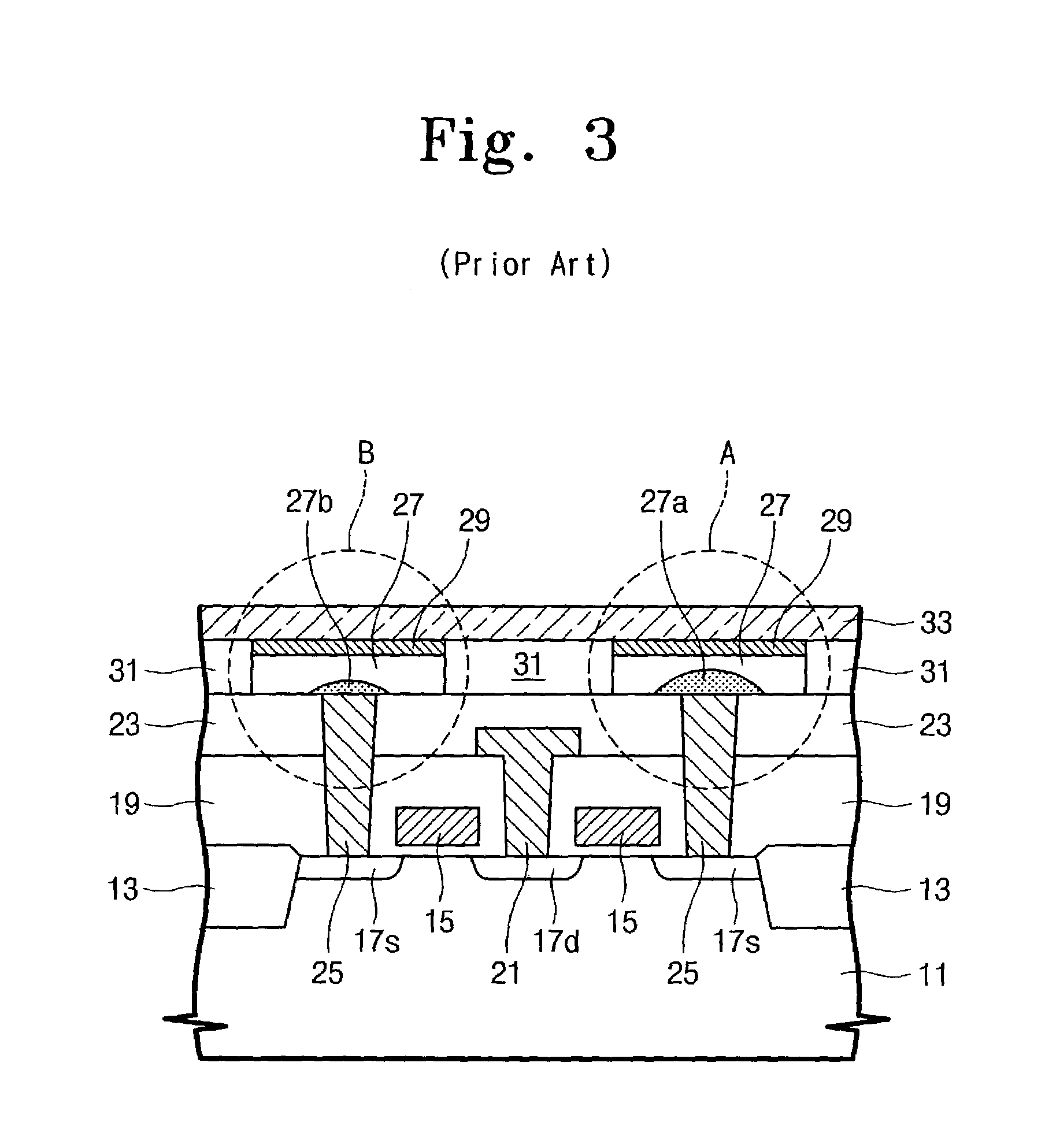
Method and system for data reduction
ActiveUS20060064416A1Efficient transferEfficient storageDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData connectionData stream
A “forward” delta data management technique uses a “sparse” index associated with a delta file to achieve both delta management efficiency and to eliminate read latency while accessing history data. The invention may be implemented advantageously in a data management system that provides real-time data services to data sources associated with a set of application host servers. To facilitate a given data service, a host driver embedded in an application server connects an application and its data to a cluster. The host driver captures real-time data transactions, preferably in the form of an event journal that is provided to the data management system. In particular, the driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. In an illustrative embodiment, a given application aware data stream is processed through a multi-stage data reduction process to produce a compact data representation from which an “any point-in-time” reconstruction of the original data can be made.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Method and apparatus for achieving dynamic capacity and high availability in multi-stage data networks using adaptive flow-based routing
ActiveUS7483374B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionSystems managementHigh availability
Methods and systems for determining paths for flows within a multi-stage network made up of clusters of processing nodes. The flow paths may be determined without knowledge of whether or not packets of a particular flow will actually traverse specific ones of the clusters within the multi-stage network. In various implementations, the nodes of the multi-stage network may be coupled to one or more physical network switches through respective physical interfaces and a virtual connectivity grid superimposed thereon and configured through the use of a flow routing framework and system management framework to group the nodes into a number of clusters. The nodes of each cluster are configured to perform similar packet processing functions and the clusters are interconnected through virtual networks to which the nodes are communicatively coupled via virtual interfaces overlaid on top of the physical network interfaces.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
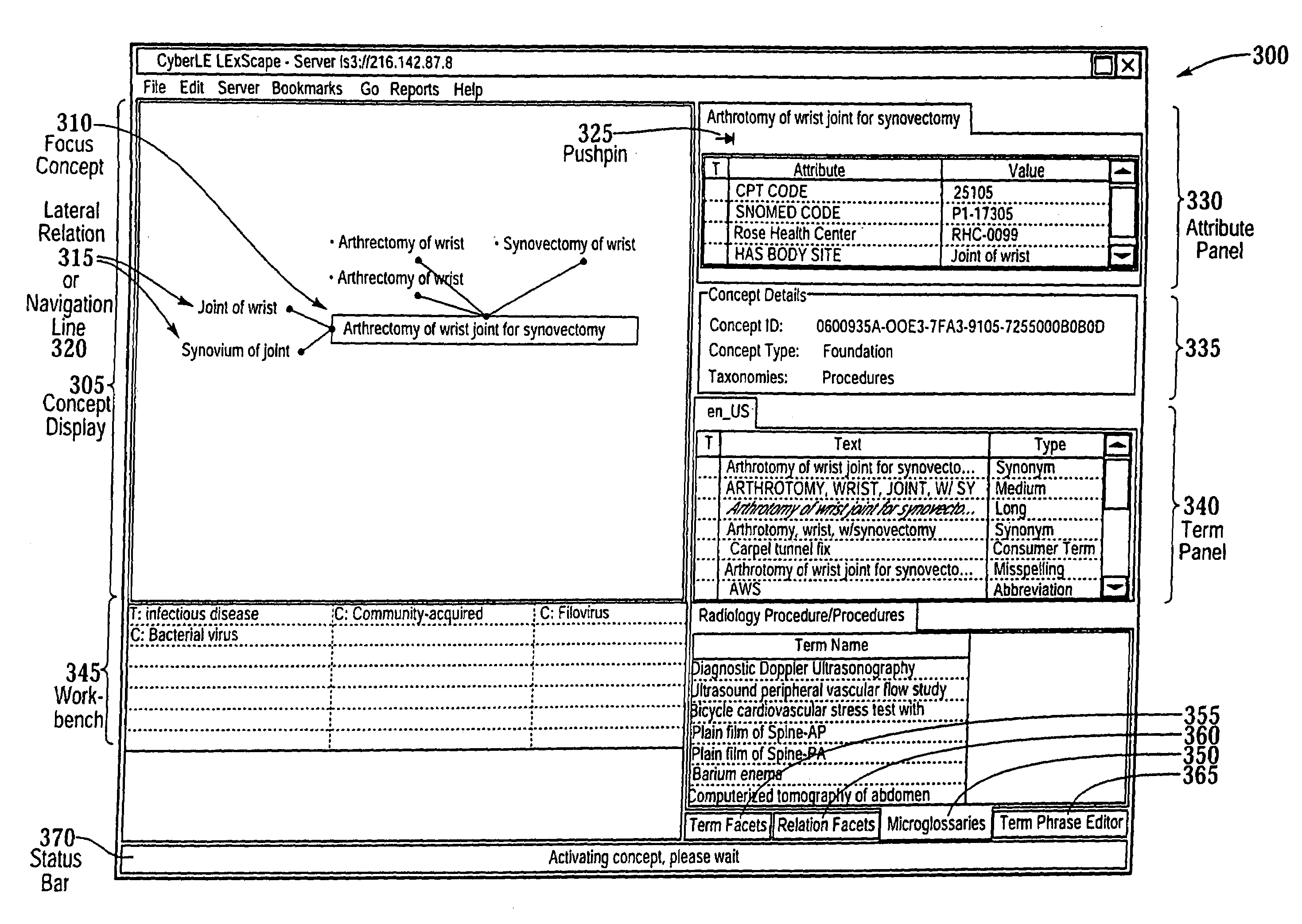
Method and system for interfacing with a multi-level data structure
InactiveUS7120646B2Maintain integrityWide breadthData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsObject storeMulti level data
The present invention provides a method and system for interfacing with a multi-level data structure by selecting a concept object stored in the multi-level data structure, displaying a first image representing the selected concept object, displaying one or more second images generally above the first image, and displaying a first connector connecting each second image to the first image. Whenever the selected concept object has one or more child concept objects, one or more third images are displayed generally below the first image, and a second connector is displayed connecting each third image to the first image. Whenever the selected concept object has one or more lateral concept objects, one or more fourth images are displayed generally on one or both sides of the first image, and a third connector is displayed connecting each fourth image to the first image.
Owner:HEALTH LANGUAGE
Multi-level database compression
InactiveUS20130103655A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGranularityObject store
Embodiments of the invention relate to a multi-level database compression technique to compress table data objects stored in pages. A compact dictionary structure is encoded that represents frequent values of data at any level of granularity. More than one level of compression is provided, wherein input to a finer level of granularity is an output of a coarser level of granularity. Based upon the encoded dictionary structure, a compression technique is applied to a stored page to compress each row on the page. Similarly, a de-compression technique may be applied to decompress the compressed data, utilizing the same dictionary structures at each level of granularity.
Owner:IBM CORP
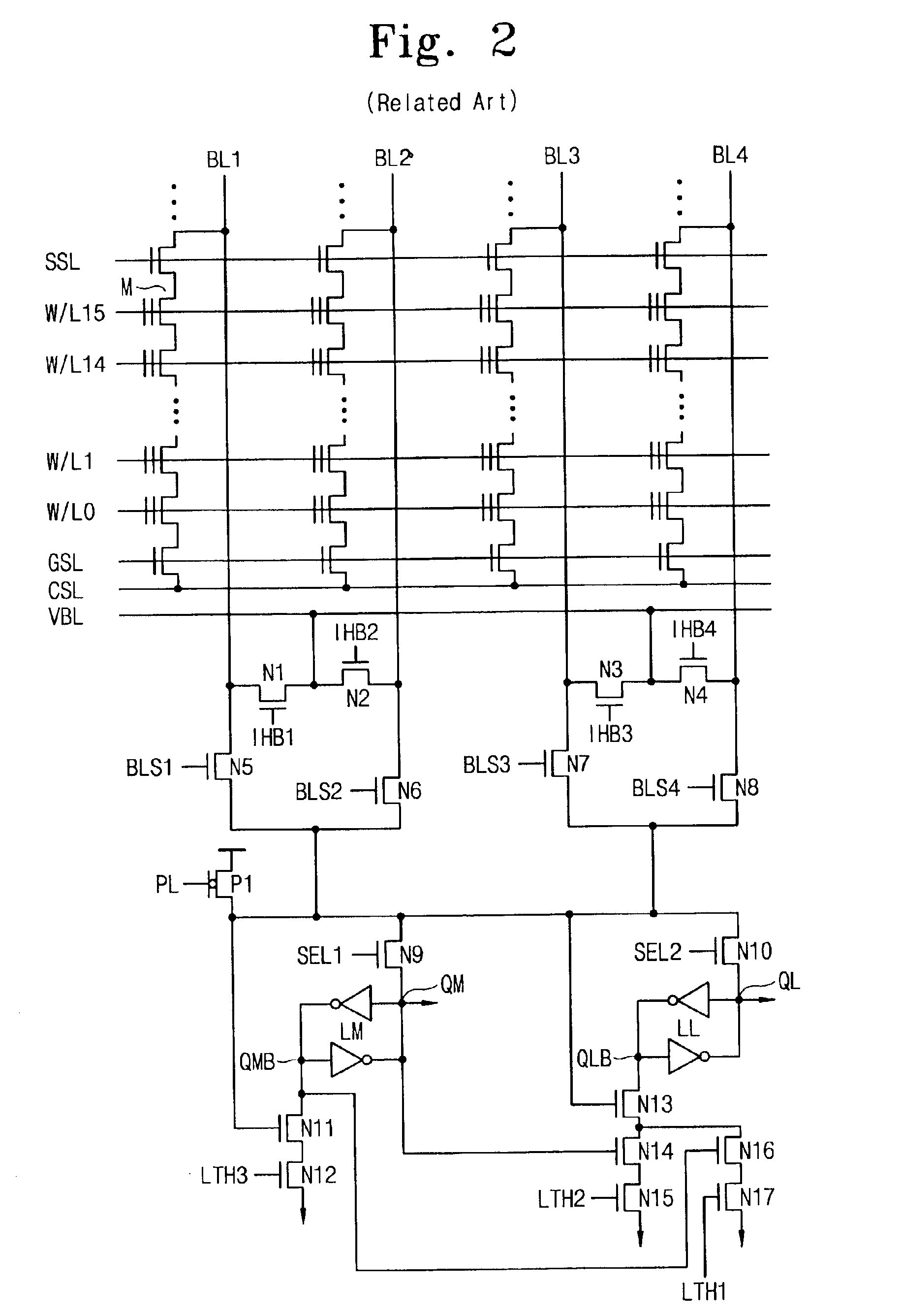
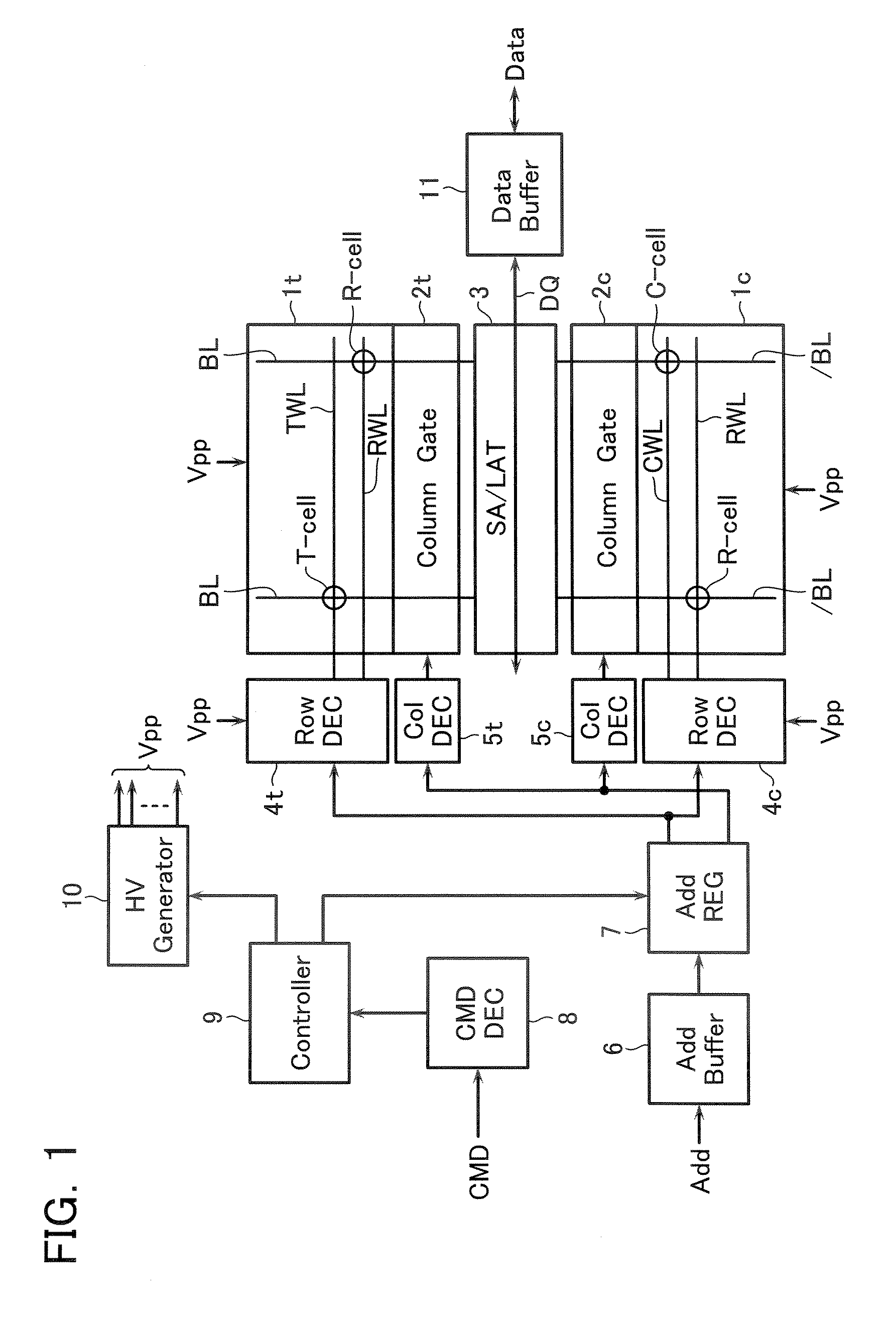
Multi-level nonvolatile semiconductor memory device utilizing a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device for storing binary data
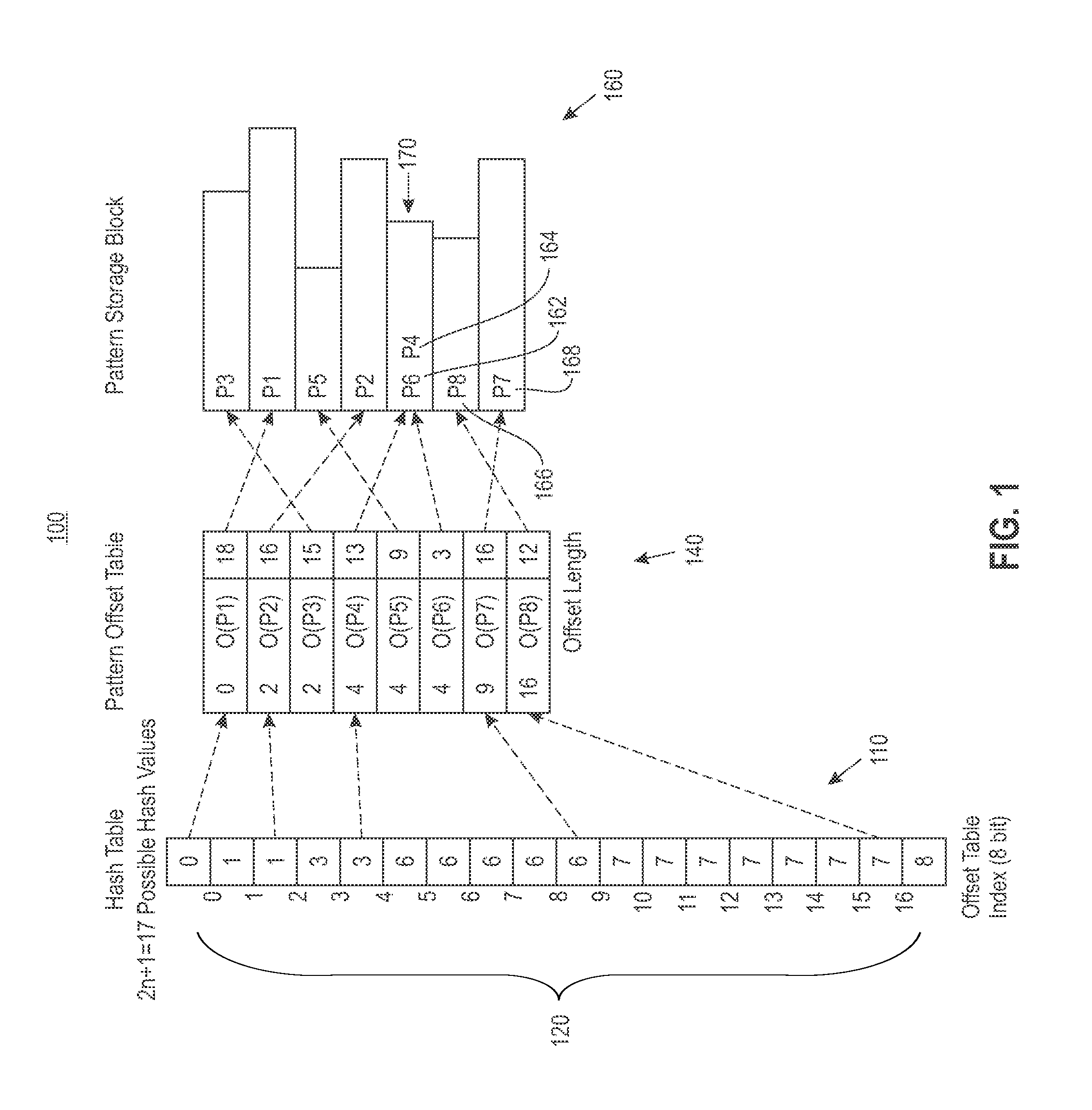
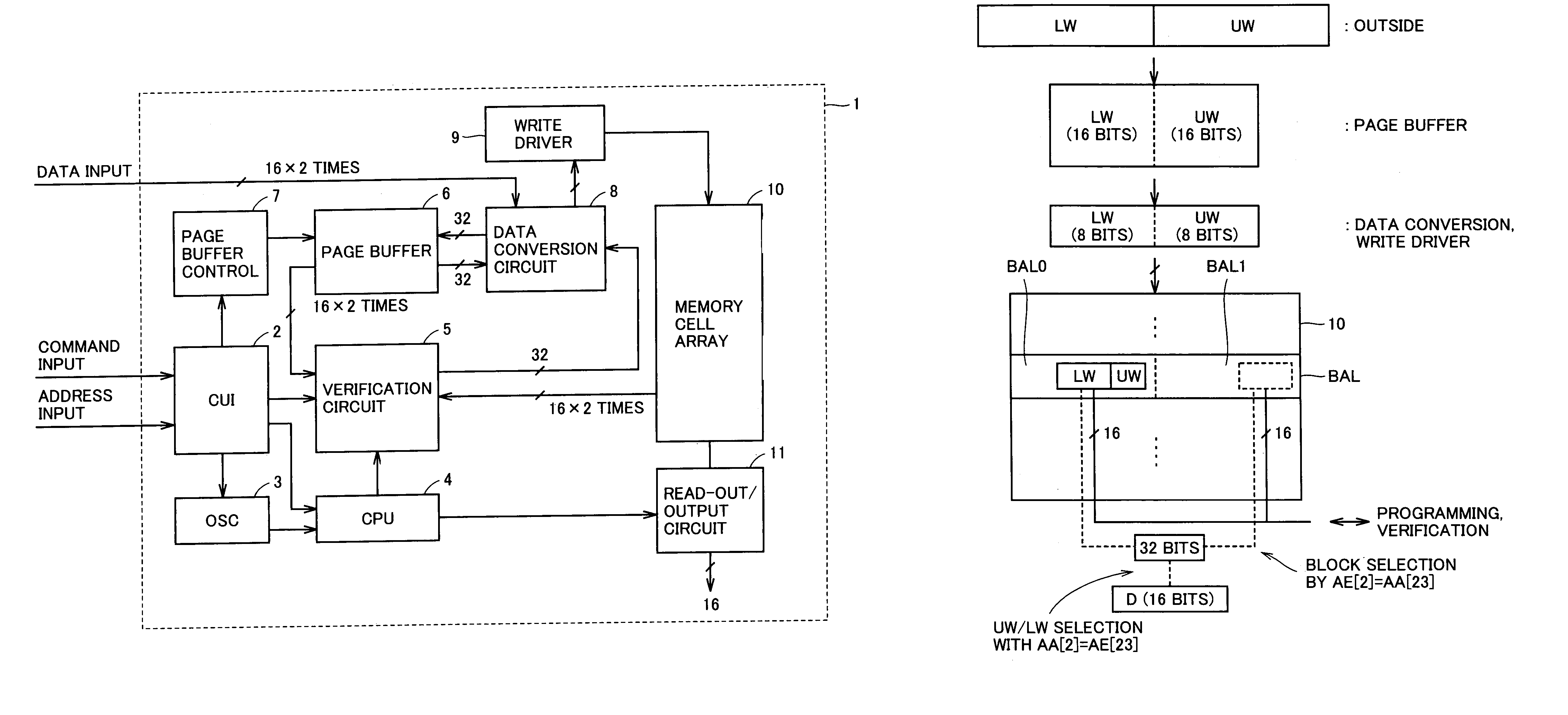
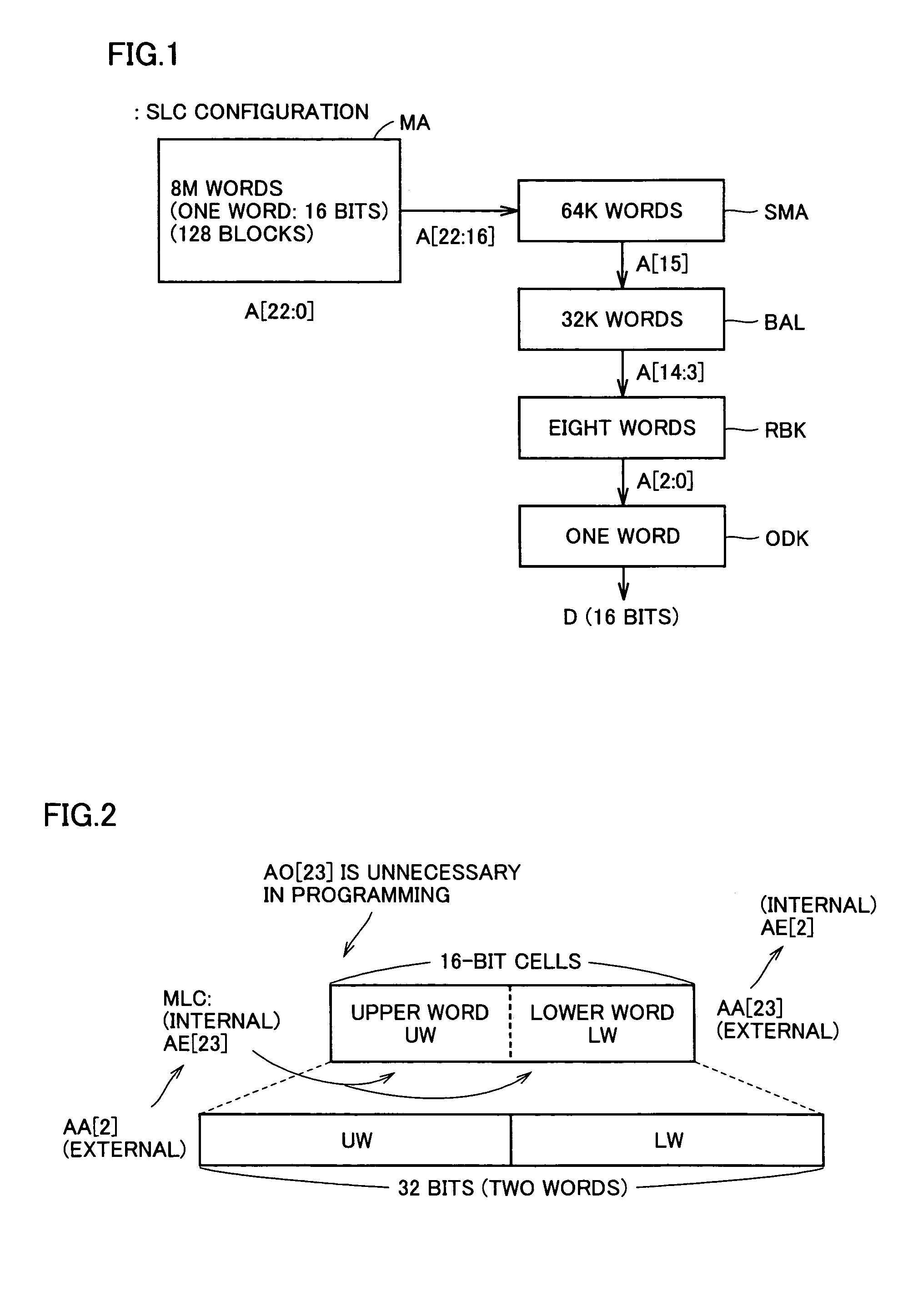
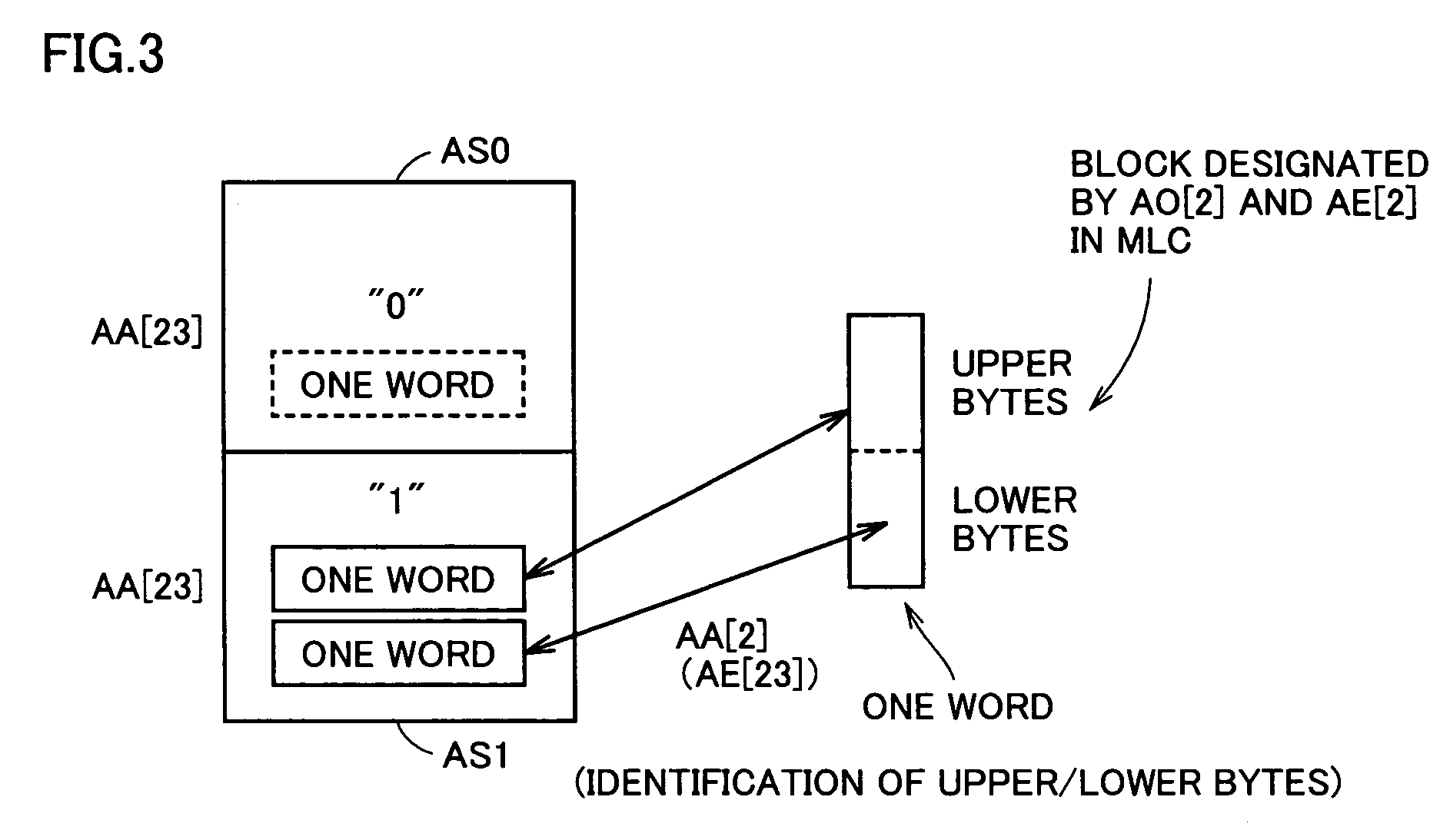
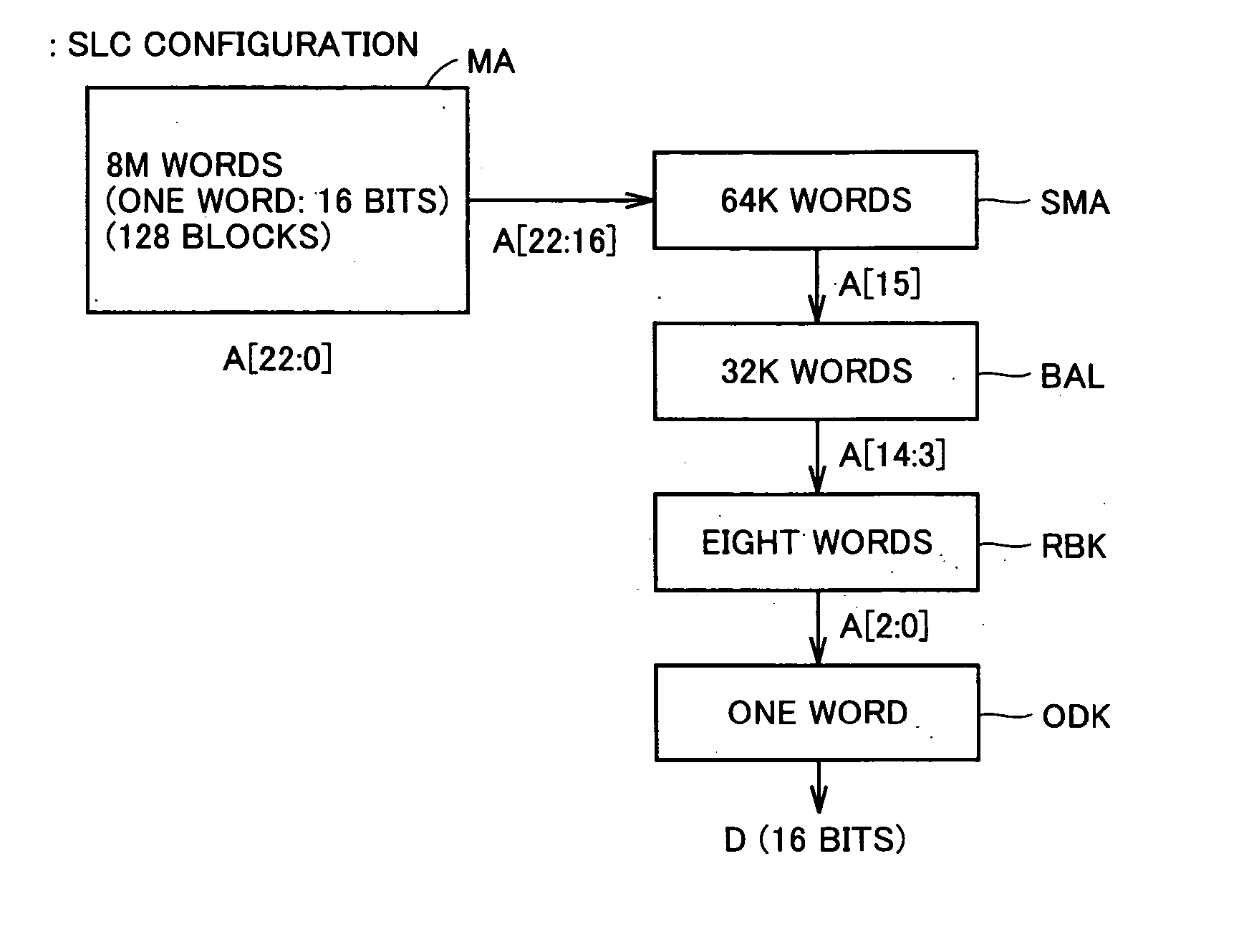
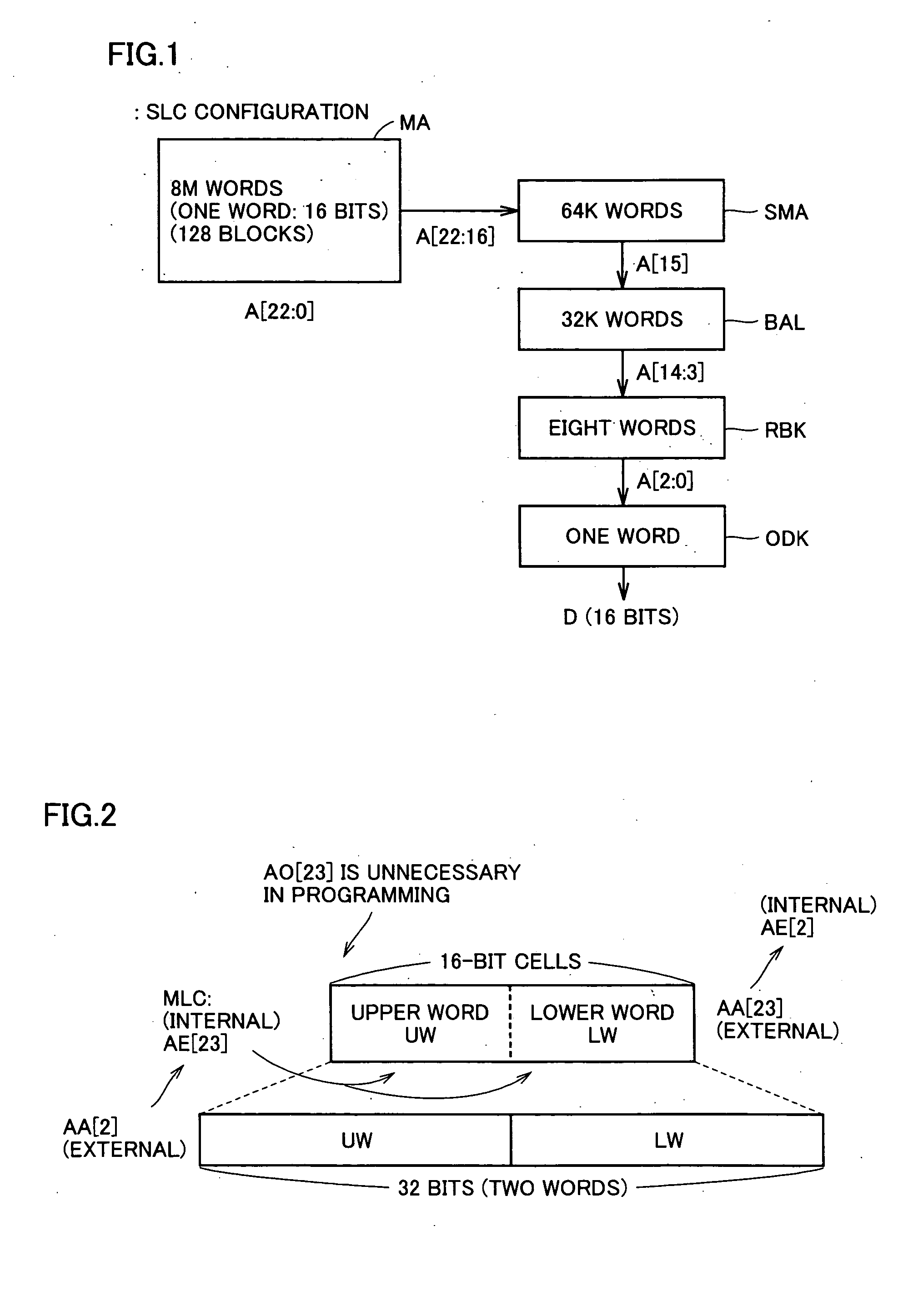
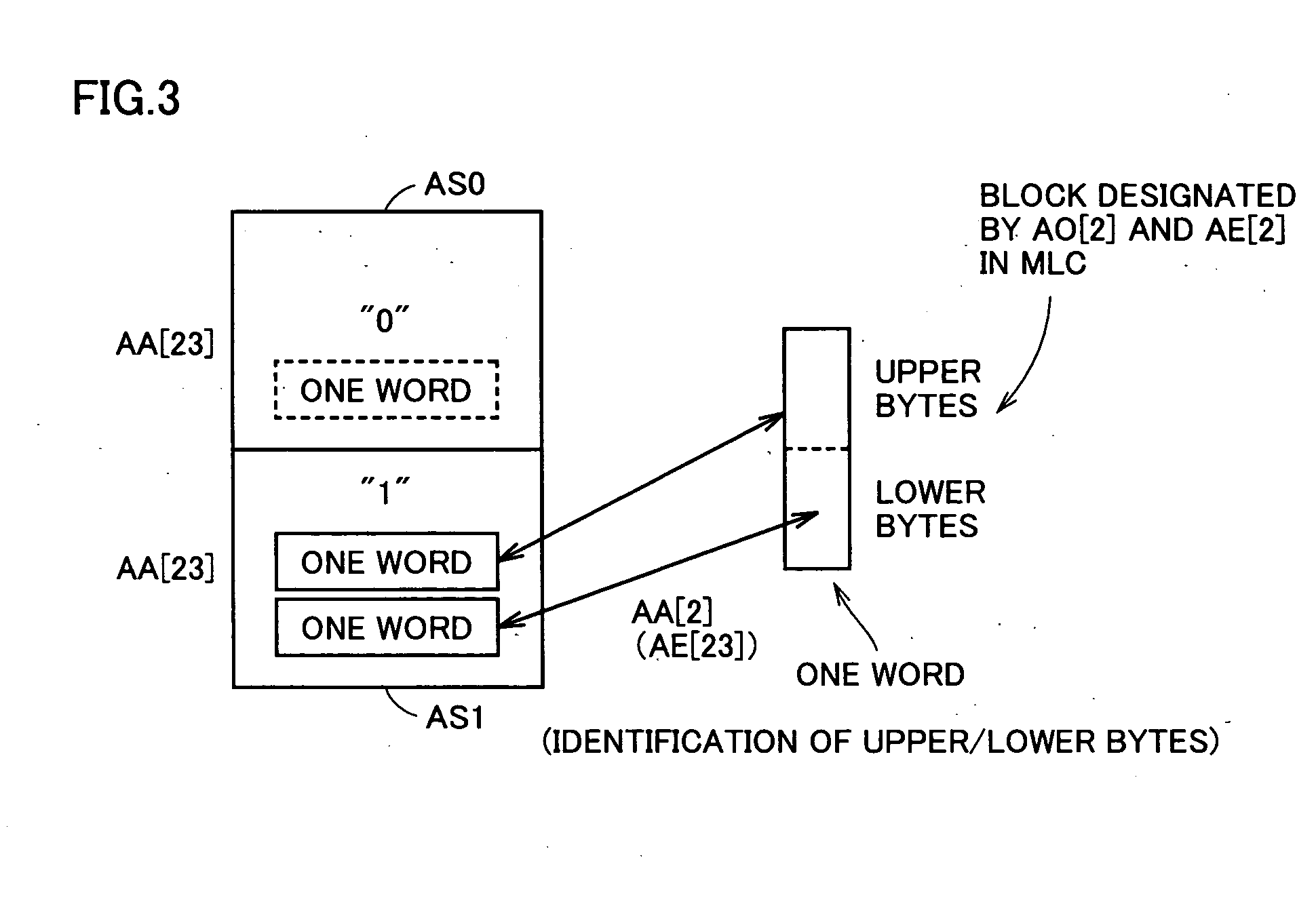
A multi-level semiconductor memory device for storing multi-level data having three or more values is implemented by utilizing a nonvolatile memory device for storing 2-valued data. Identification of successive 16-bit data externally applied is performed with external address bit AA [2], and a storage block is selected with external address bit AA [23]. Upper word data LW and lower word data UW are compressed into byte data of 8 bits, respectively, and stored in a memory cell array.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Non-volatile memory device and sensing method thereof
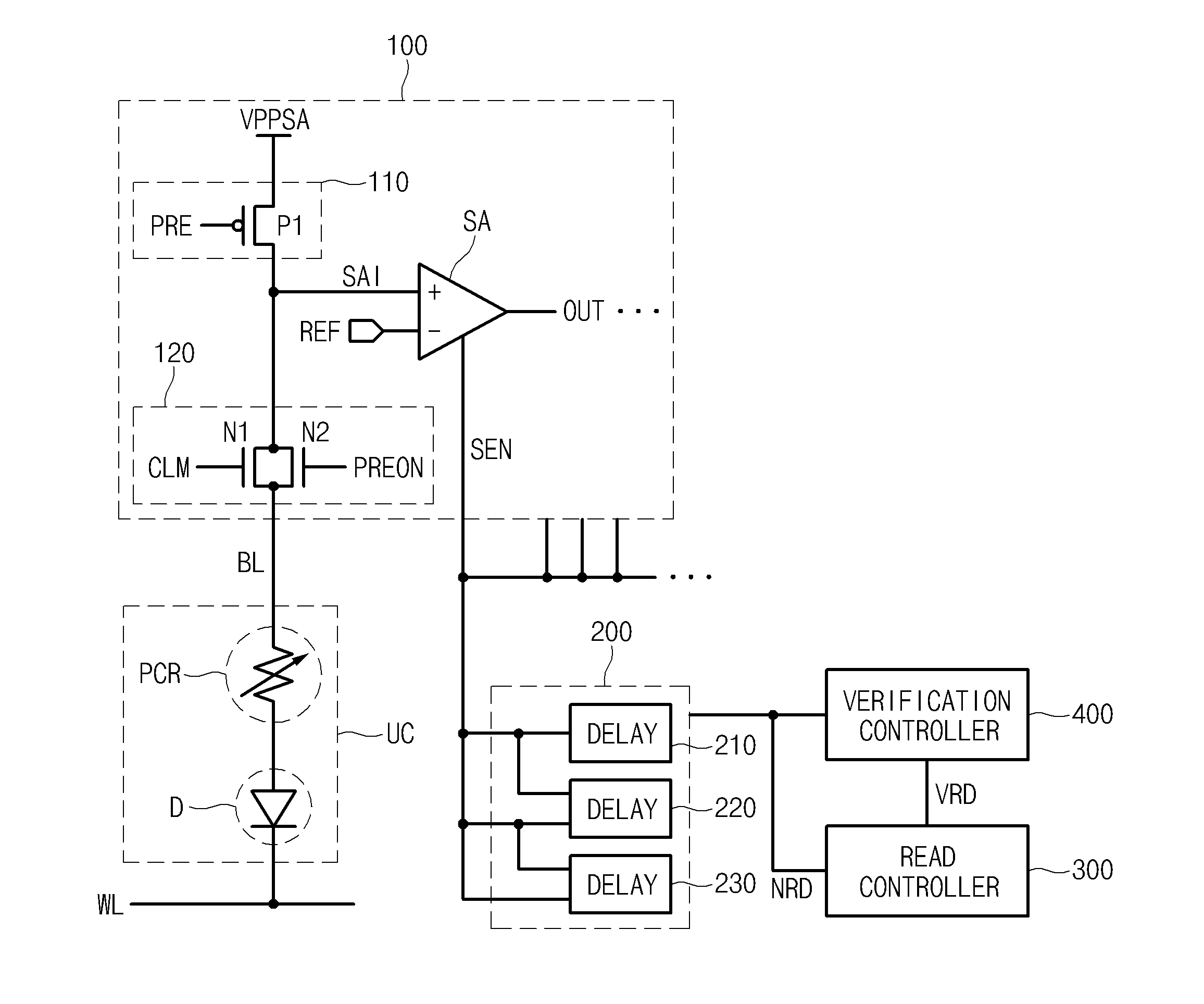
ActiveUS20120287730A1Shorten the timeReduce circuit areaRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceOutput compare
A non-volatile memory device and a sensing method thereof are disclosed, which can sense multi-level data using resistance variation. The non-volatile memory device includes a cell array and a sensing unit. The cell array includes a plurality of unit cells where data is read out or written. The sensing unit compares a sensing voltage corresponding to data stored in the unit cell with a reference voltage, amplifies / outputs the compared result, measures a difference in discharge time where the sensing voltage is discharged in response to a resistance value of the unit cell during an activation period of a sensing enable signal after a bit line is precharged, and senses the data in response to the measured result.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor memory device and data write method thereof
A semiconductor memory device including a memory cell array and a sense amplifier, wherein the memory cell array includes: a plurality of information cells, in each of which either one of multi-level data is written; a first reference cell with the same structure and the same connection state as the information cell, in which a reference data level is written for generating a first reference current; and a second reference cell, which serves for generating a second reference current used for setting the lowest data level of the multi-level data and for setting the reference data level of the first reference cell.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
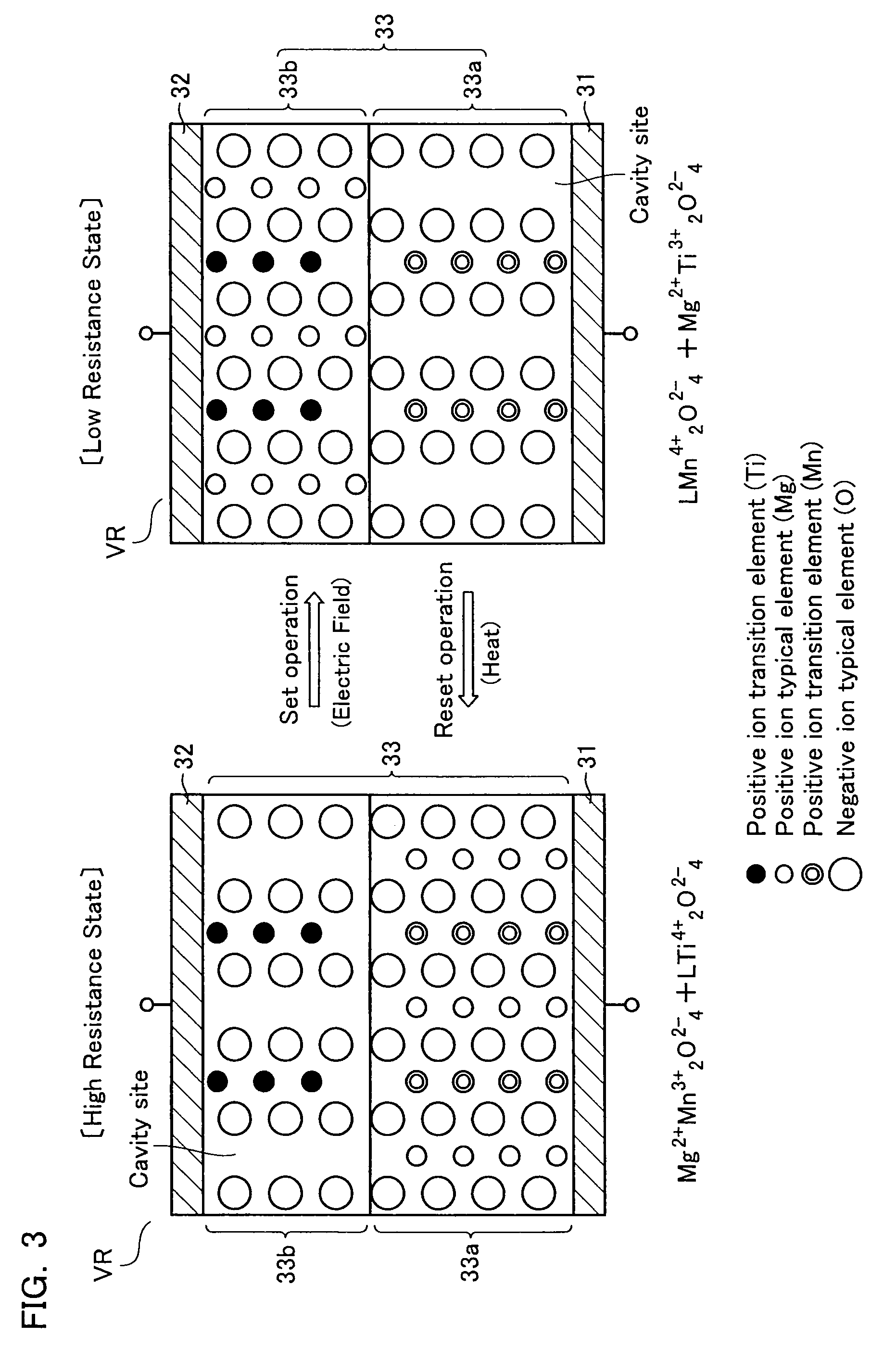
Nonvolatile memory device
ActiveUS6888745B2Increase speedSteady read operationSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesVoltage amplitudeMass storage
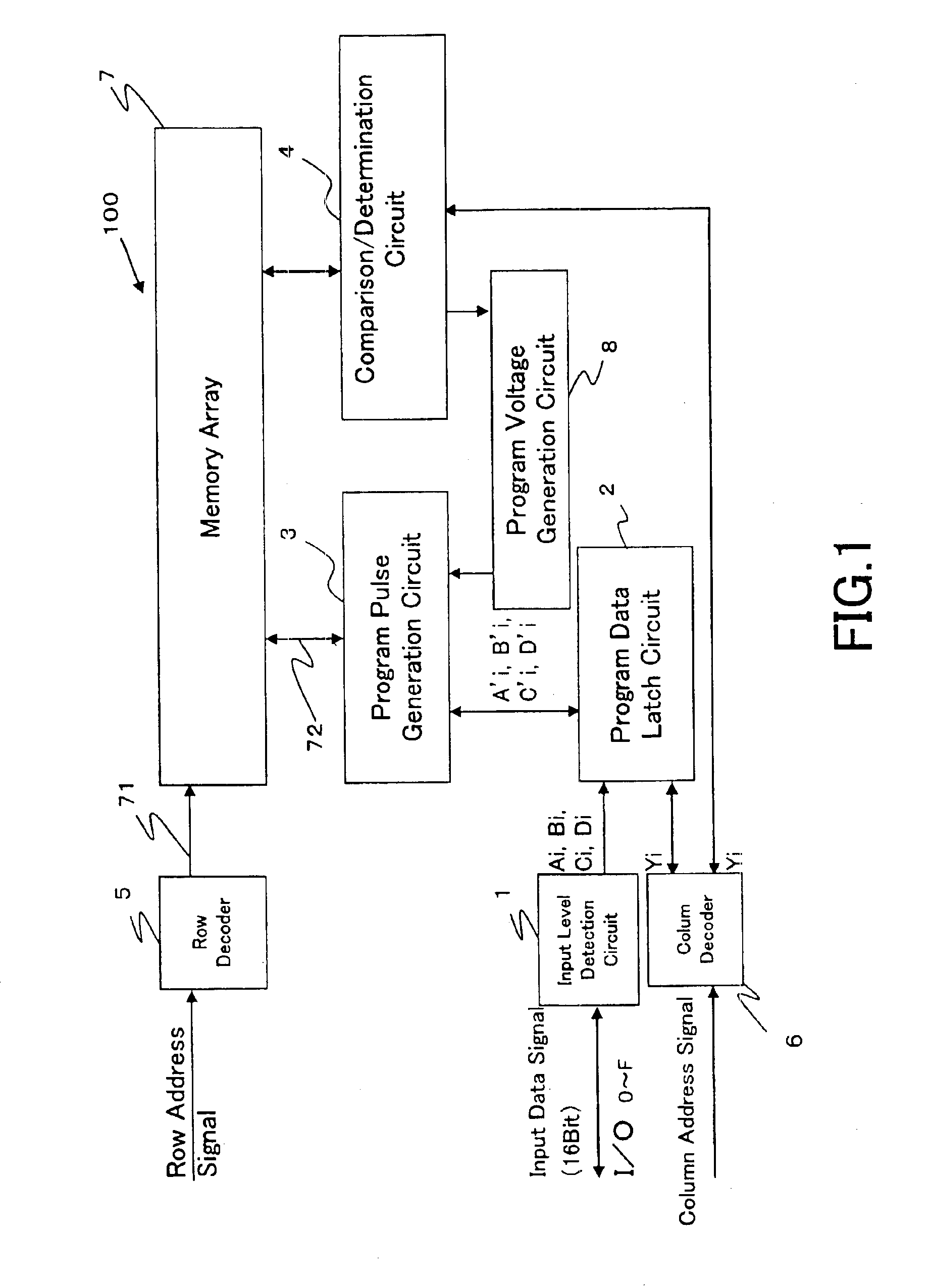
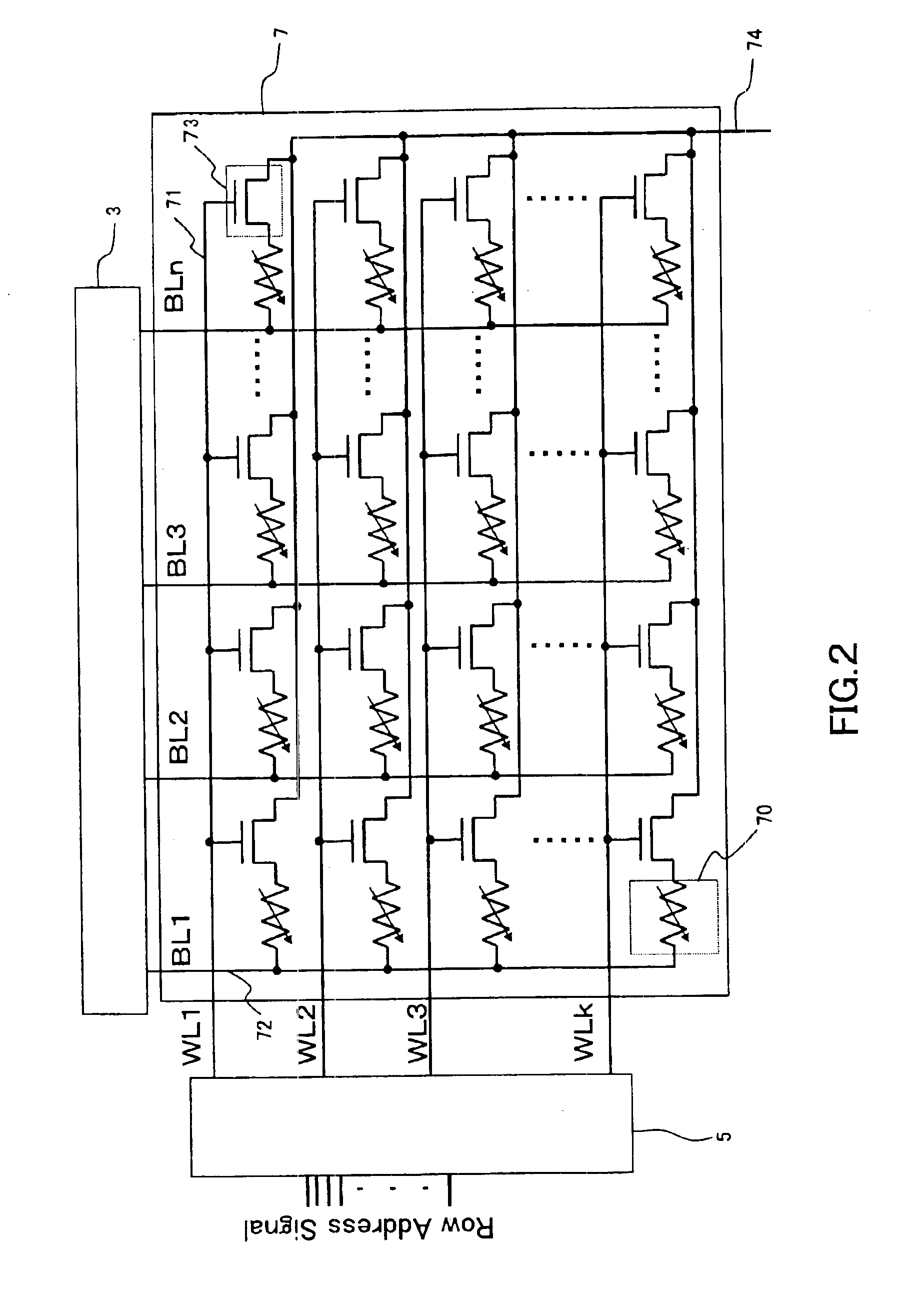
An object of the present invention is to provide a mass-storage nonvolatile memory device capable of performing high speed operation. The nonvolatile memory device comprises a memory array comprising a plurality of memory cells arranged in a matrix, each of the memory cells comprising a variable resistor element formed of a manganese-containing oxide having a perovskite structure in which an electric resistance is varied by application of a voltage pulse and a variation amount of the electric resistance is variable depending on the magnitude of the voltage amplitude; and a program pulse generation circuit that, in order to program 3-level or larger multi-level data corresponding to one erase state and two or more program states into the variable resistor element, is capable of performing generation of program pulses having two or more different voltage amplitudes corresponding to the program states, the generation being separately performed corresponding to program data.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
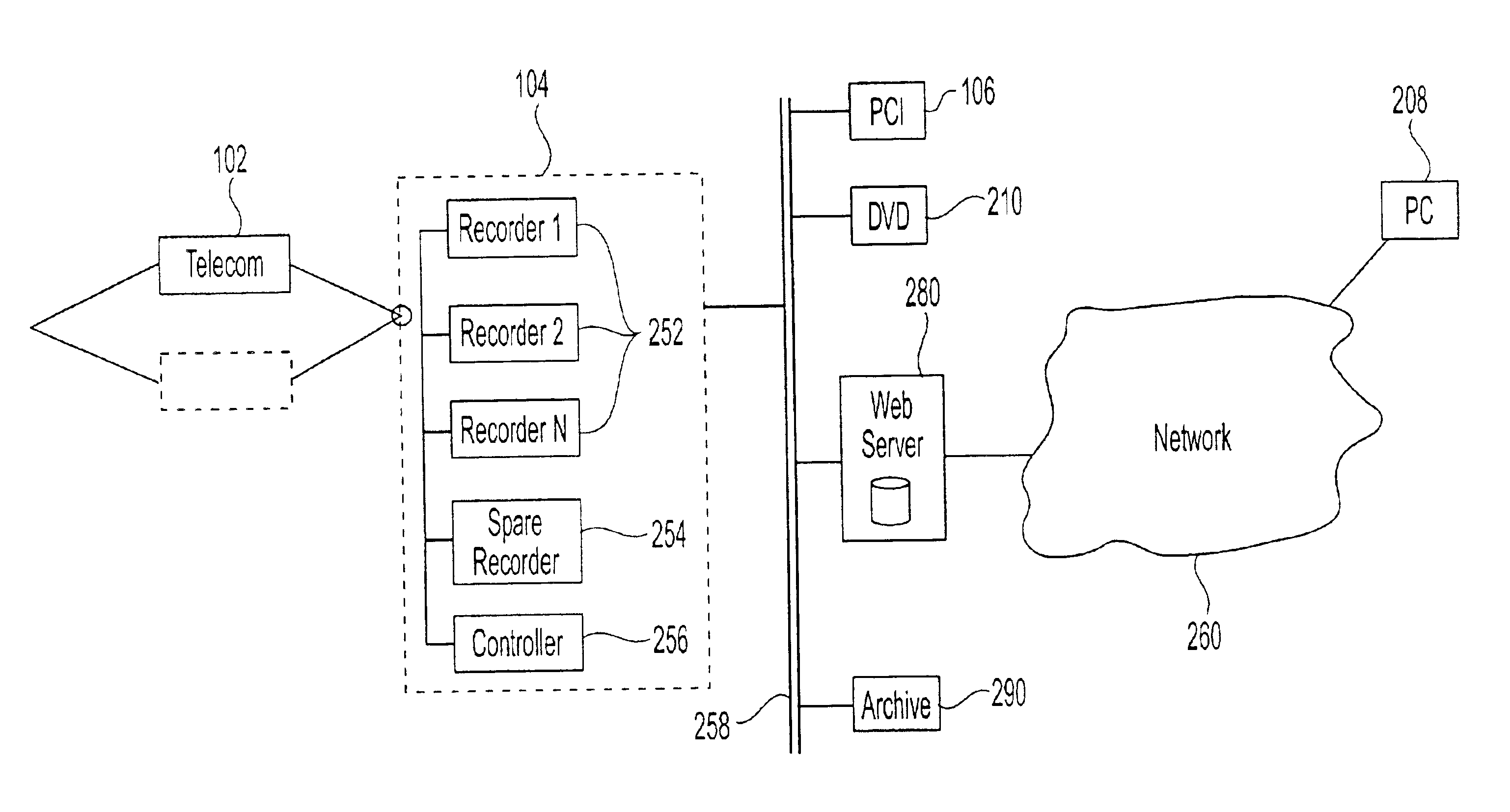
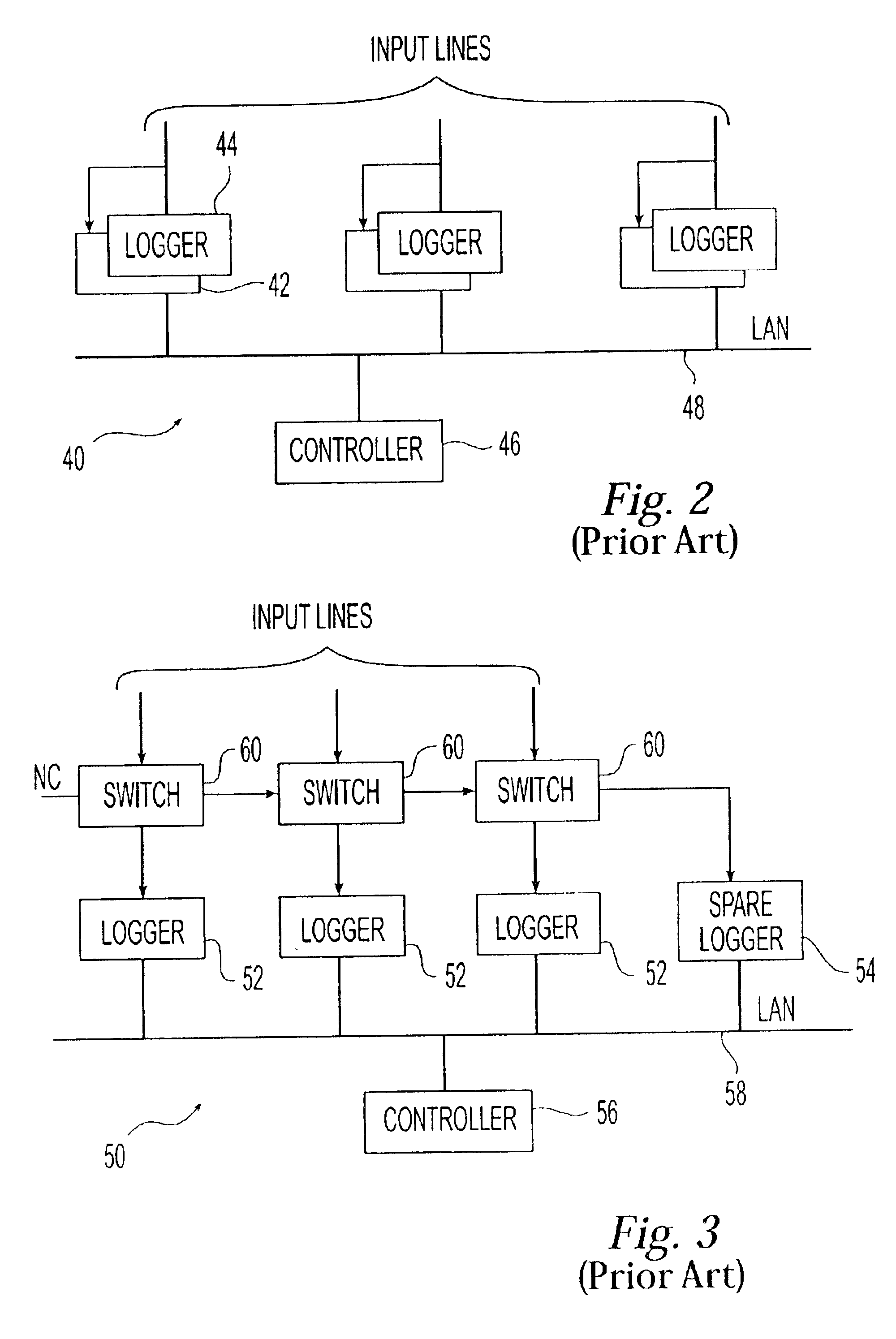
System and method for multi-stage data logging
InactiveUS6870920B2Improve input abilityHigh distribution flexibilityInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersFault toleranceThree stage
A multi-stage data logging system comprising a telecommunications stage for receiving, processing, and compressing data from one or more input channels, a recorder stage for storing said data to a memory device, a distribution stage for retrieving said stored data and distributing said data to one or more output channels, and a plurality of interface paths linking said three stages to one another. Different stages of the system can be located wide distances apart and the interface paths linking the three stages can be automatically switched to achieve fault tolerance of the system.
Owner:NICE SYSTEMS +1
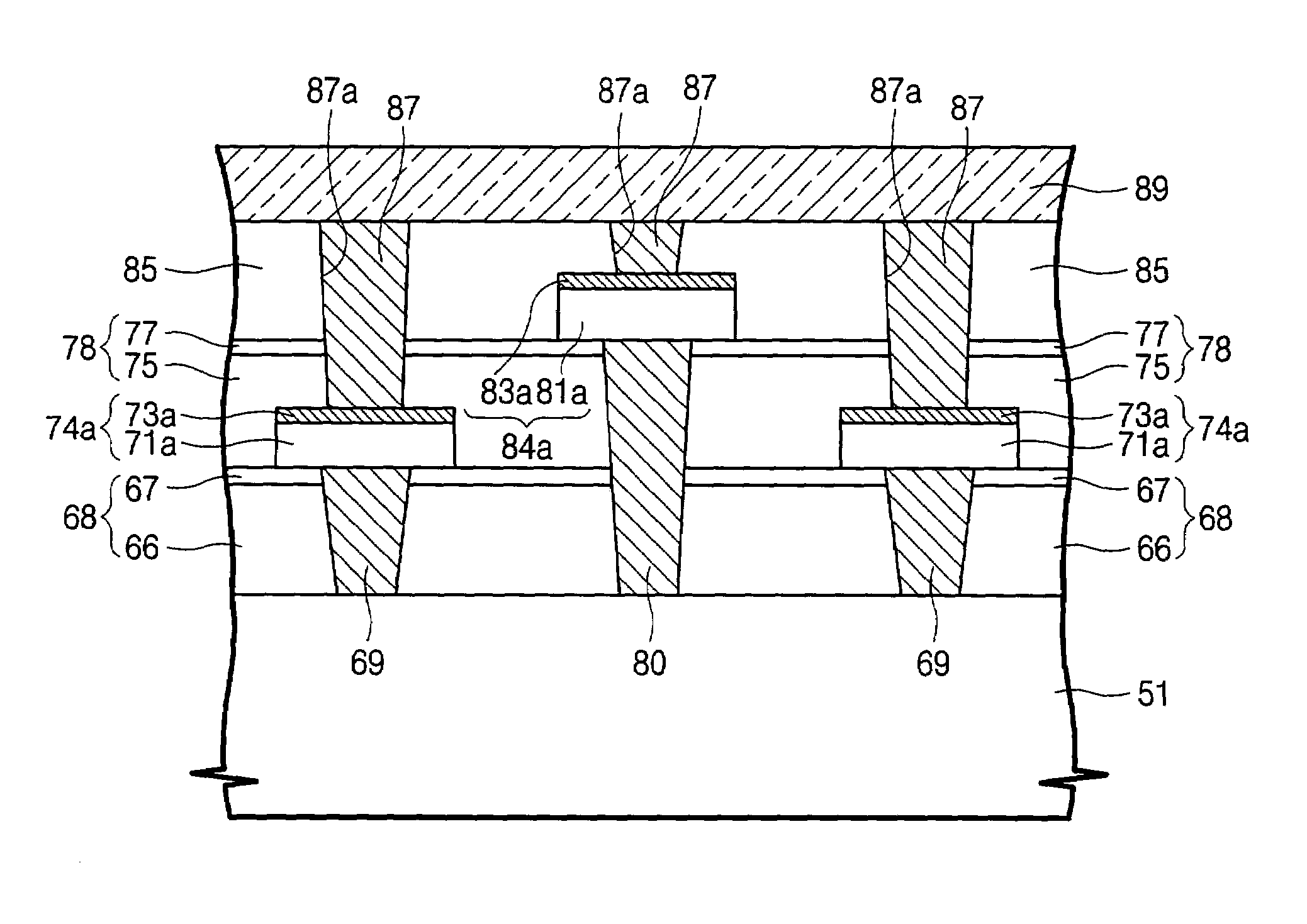
Phase changeable memory devices having multi-level data storage elements and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7037762B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhase-change memoryDielectric layer
A phase changeable memory device includes a lower interlayer dielectric layer on a semiconductor substrate. A plurality of first phase changeable data storage elements is disposed on the lower interlayer dielectric layer. A middle interlayer dielectric layer covers the first phase changeable data storage elements and the lower interlayer dielectric layer. A plurality of second phase changeable data storage elements is disposed on the middle interlayer dielectric layer. The first and second phase changeable data storage elements are arrayed in rows and columns such that respective first phase changeable data storage elements are disposed between respective adjacent second phase changeable data storage elements in the rows and columns. A plate electrode overlies the first and second phase changeable data storage elements and is electrically connected to the first and second phase changeable data storage elements. Related fabrication methods are also disclosed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device
A multi-level semiconductor memory device for storing multi-level data having three or more values is implemented by utilizing a nonvolatile memory device for storing 2-valued data. Identification of successive 16-bit data externally applied is performed with external address bit AA [2], and a storage block is selected with external address bit AA [23]. Upper word data LW and lower word data UW are compressed into byte data of 8 bits; respectively, and stored in a memory cell array.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for programming a semiconductor memory device
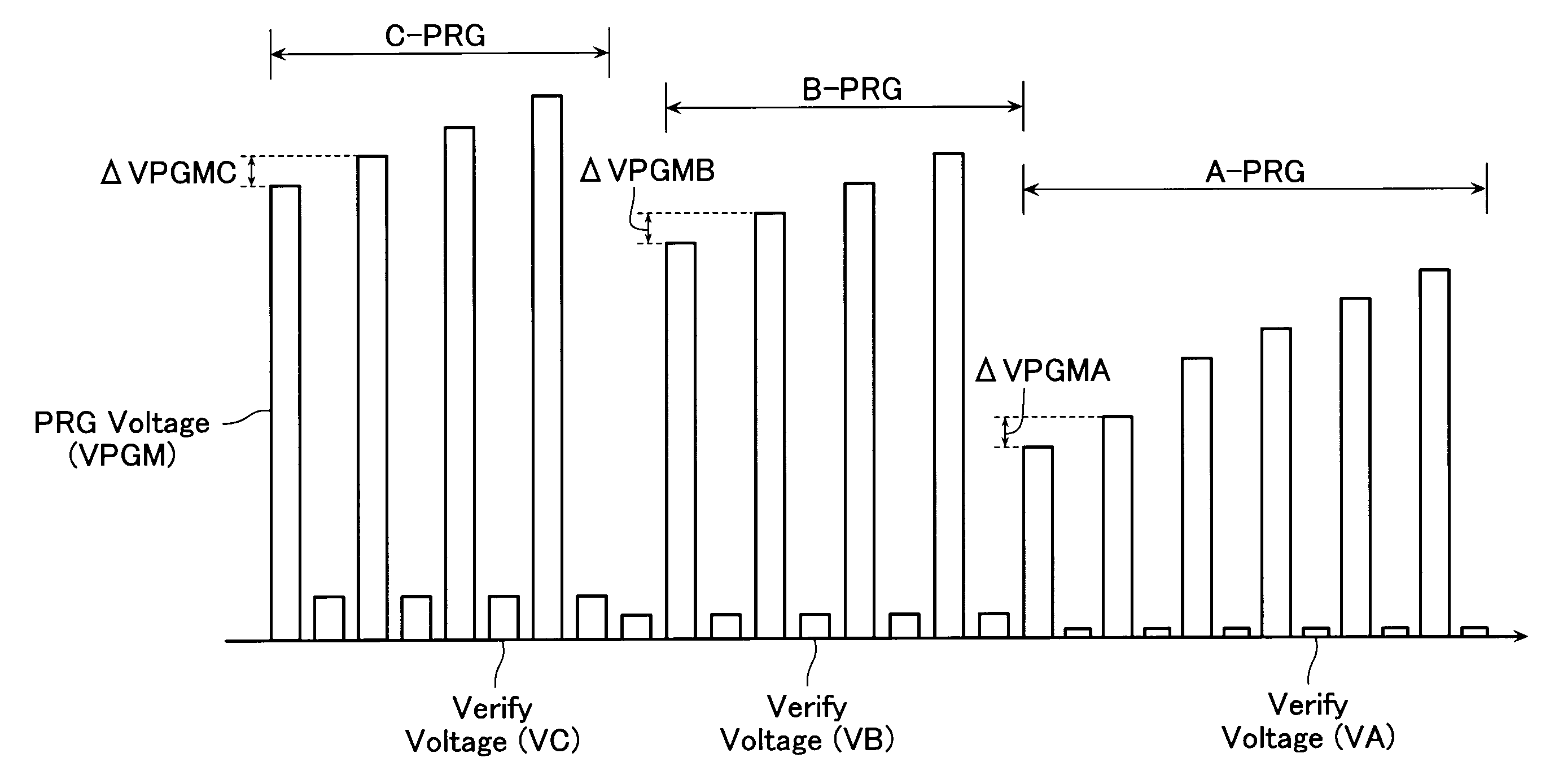
A method for programming a semiconductor memory device including such a program sequence as to program target threshold levels constituting multi-level data into multiple memory cells, which are simultaneously selected, wherein the program sequence is controlled to finish programming the multiple memory cells in order of height of the target threshold levels.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Data recording method of semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20070211530A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesData recordingComputer science
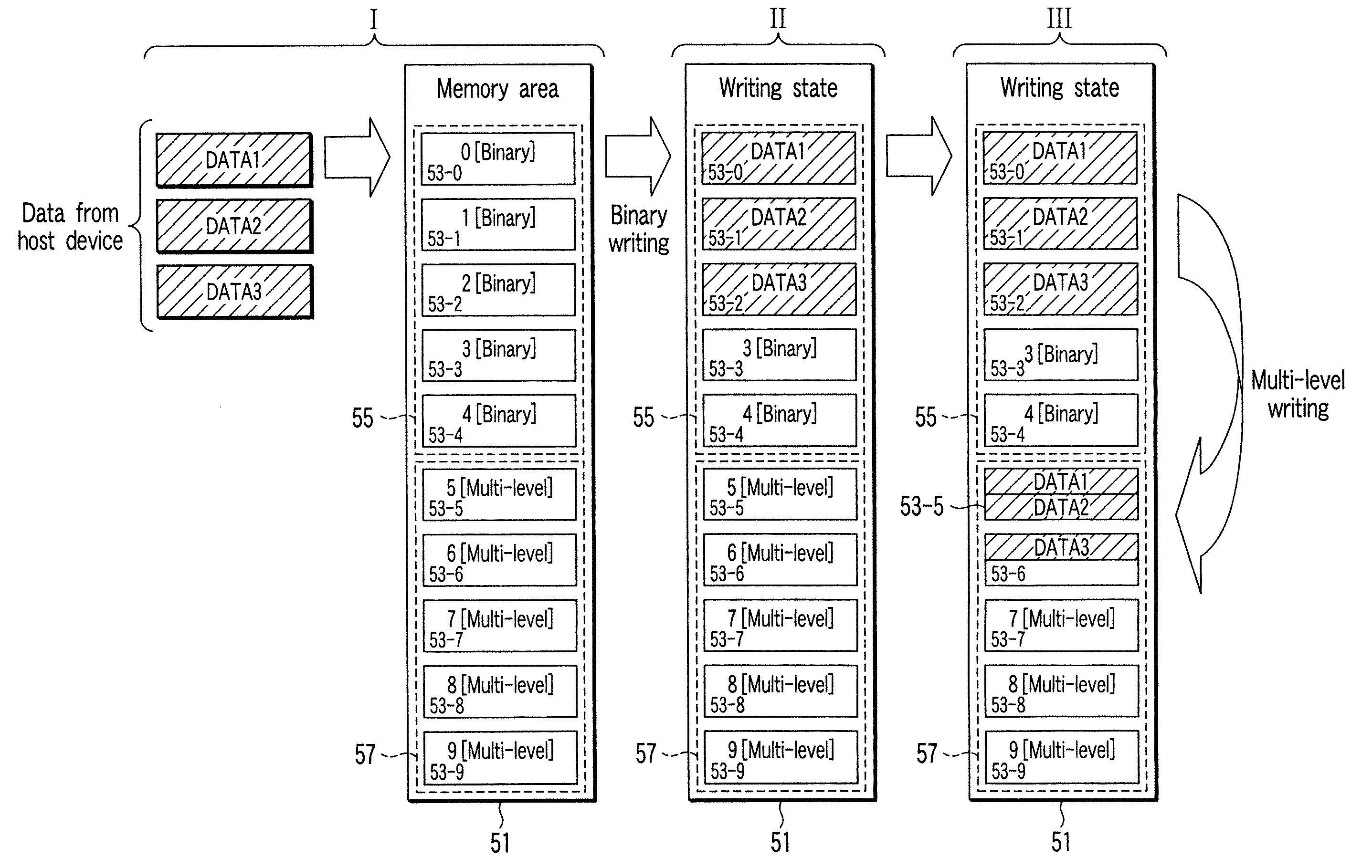
A data recording system of a semiconductor integrated circuit device having a memory area is disclosed. The semiconductor integrated circuit device is equipped with a memory area that includes a binary area and a multi-level area. The semiconductor integrated circuit device records, in the binary area, data transmitted from a host device as binary data. Further, when no access is provided from the host device, the semiconductor integrated circuit device copies, to the multi-level area, the data recorded in the binary area as multi-level data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and system for interfacing with a multi-level data structure
InactiveUS7668737B2Wide breadthMaintain and enhance semantic contentData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsComputer graphics (images)Object store
The present invention provides a method and system for interfacing with a multi-level data structure by selecting a concept object stored in the multi-level data structure, displaying a first image representing the selected concept object, displaying one or more second images generally above the first image, and displaying a first connector connecting each second image to the first image. Whenever the selected concept object has one or more child concept objects, one or more third images are displayed generally below the first image, and a second connector is displayed connecting each third image to the first image. Whenever the selected concept object has one or more lateral concept objects, one or more fourth images are displayed generally on one or both sides of the first image, and a third connector is displayed connecting each fourth image to the first image.
Owner:HEALTH LANGUAGE
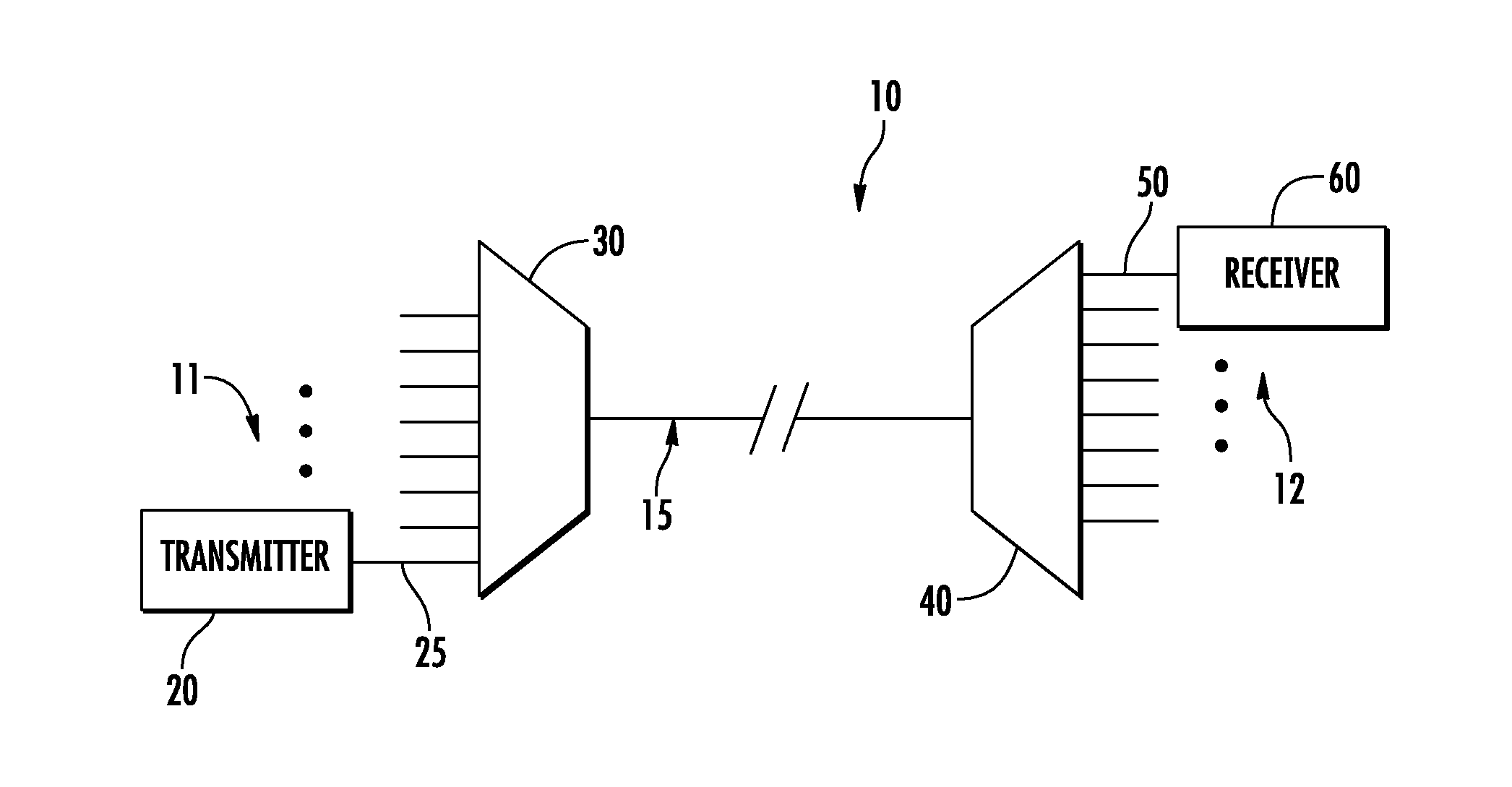
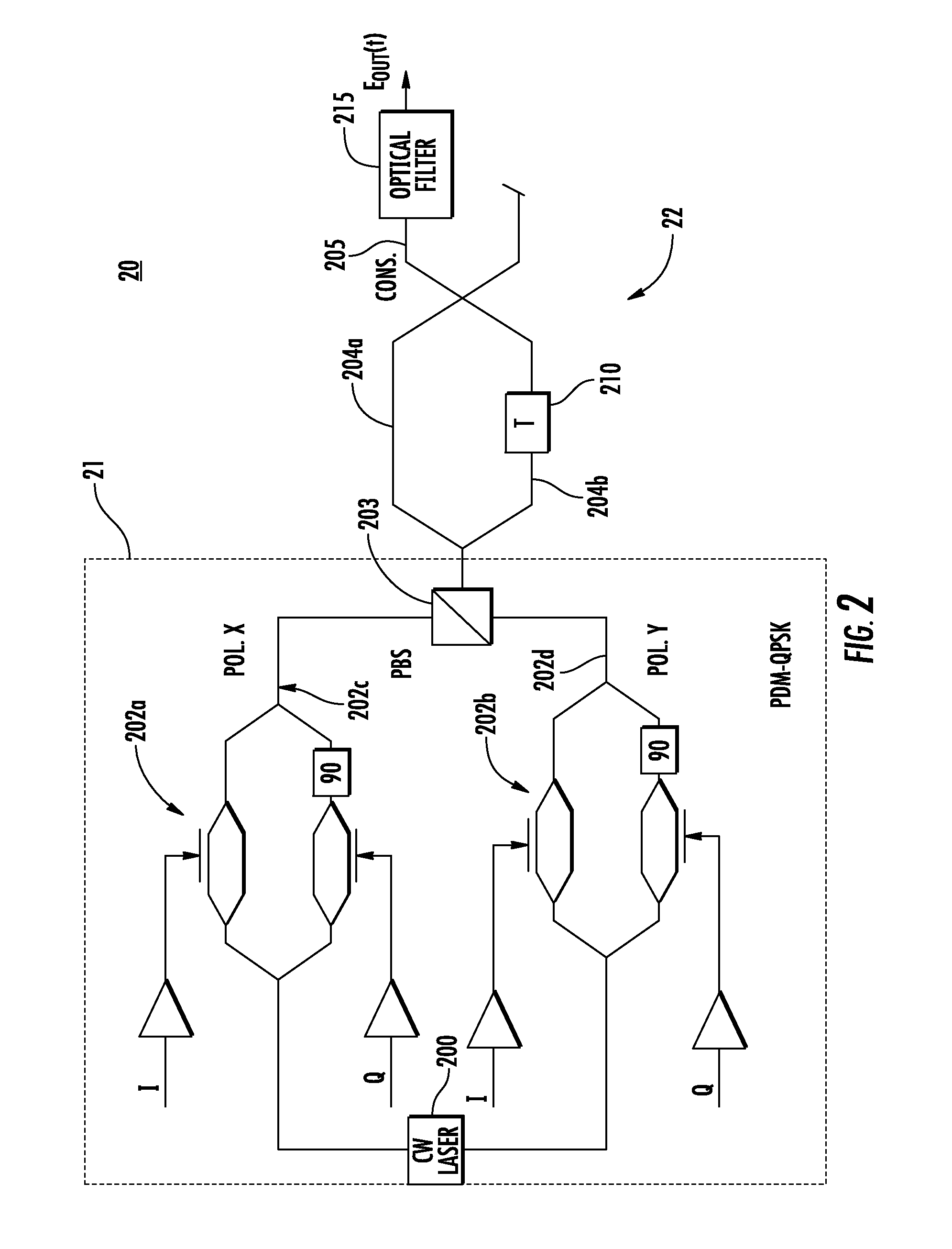
Correlation -control qpsk transmitter
InactiveUS20120093510A1Polarisation multiplex systemsModulated-carrier systemsFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS SUBSEA COMM LLC
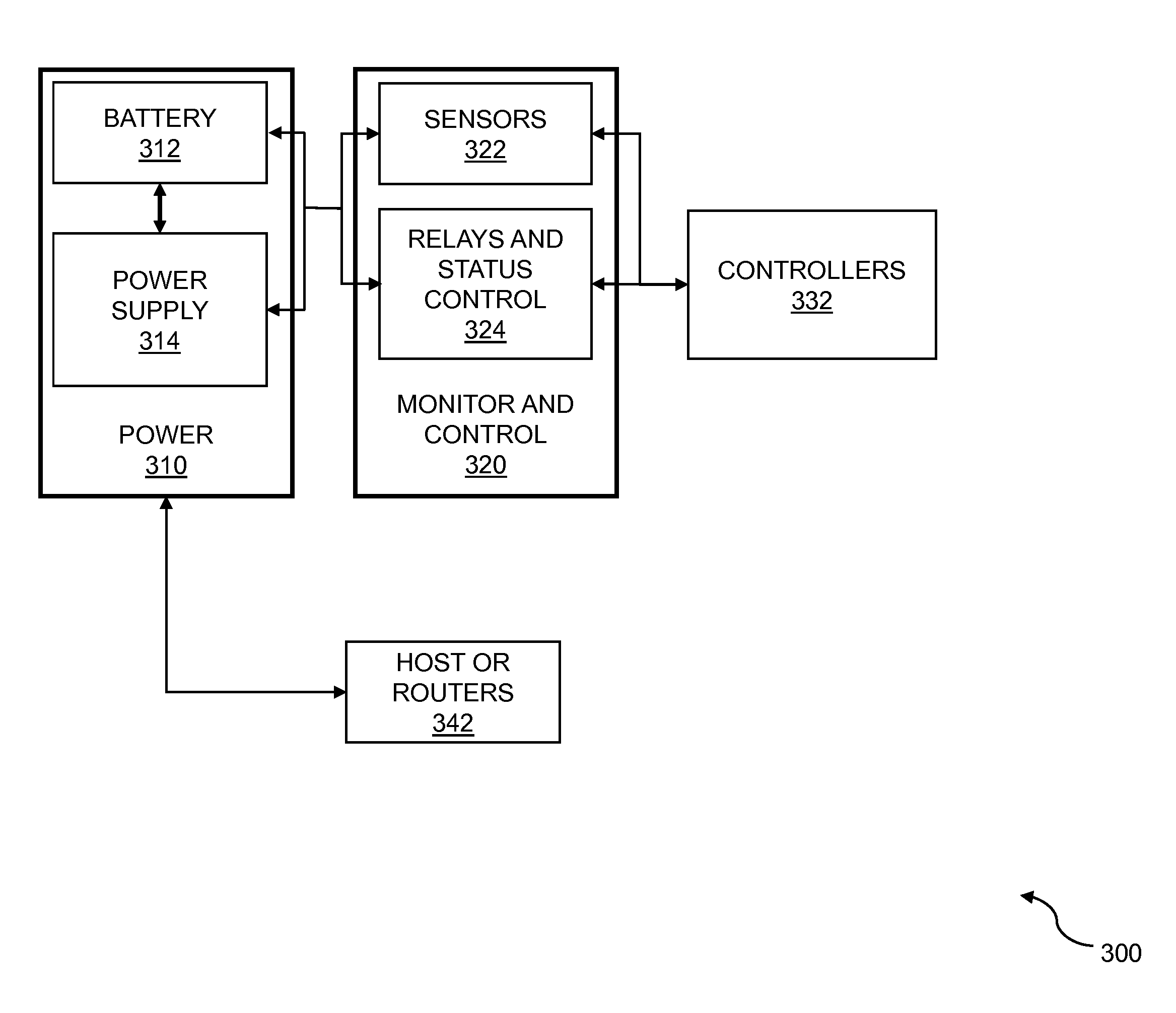
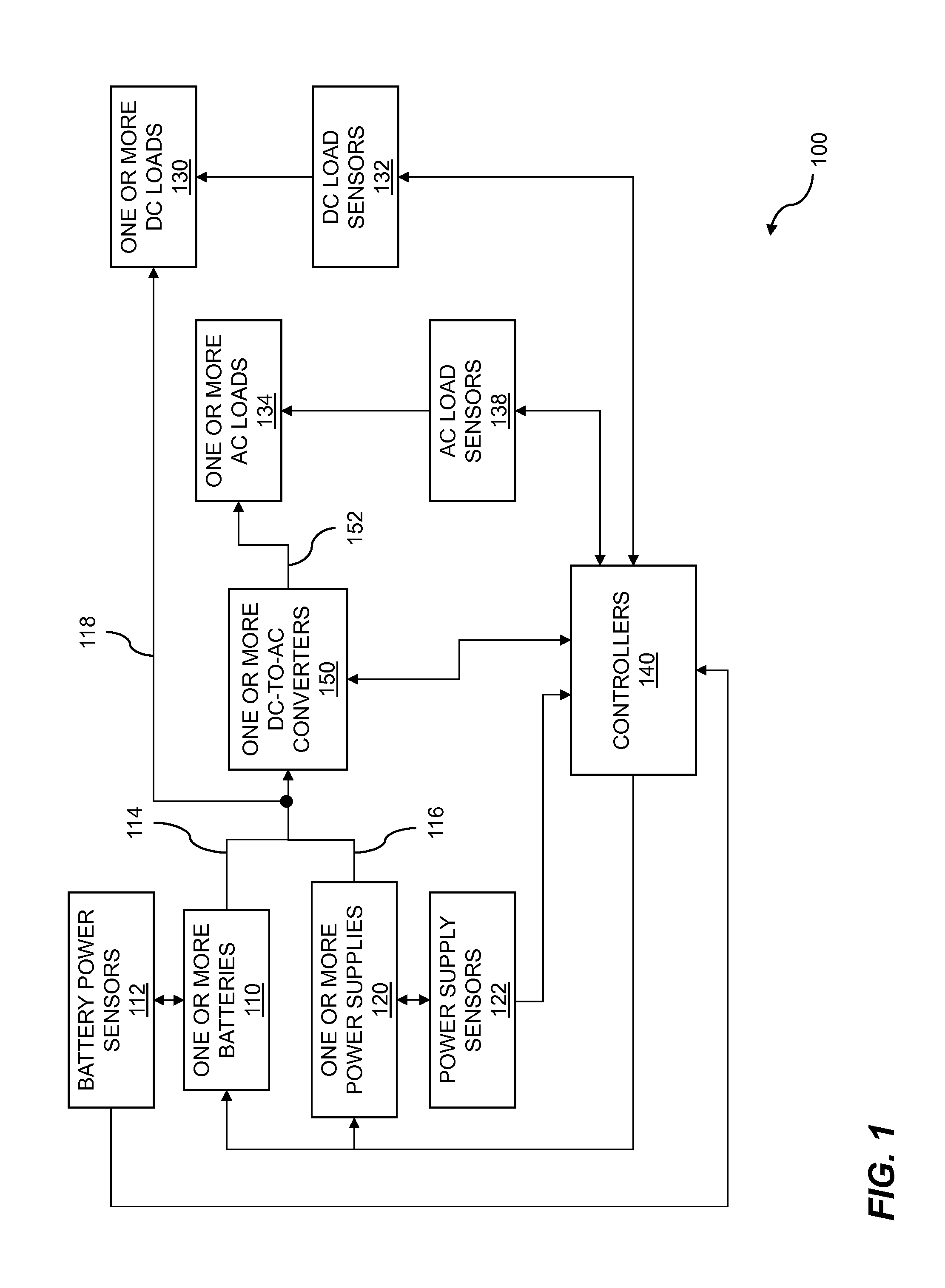
Multi-level data center consolidated power control
ActiveUS20150115711A1Stable and reliable powerPrevent and minimize downtimeSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectric controllersPower flowData center
Multi-level data center consolidated power is disclosed. One or more controllers communicate with one or more power supplies and sensors to adapt to dynamic load requirements and to distribute DC-power efficiently across multiple IT racks. The distributed DC-power includes one or more DC-voltages. Batteries can be temporarily switched into a power supply circuit to supplement the power supply during spikes in power load demand while a controller reconfigures power supplies to meet the new demand. In embodiments, one or more DC-to-AC converters handle legacy power loads. The DC-to-AC converters are modular and are paralleled for redundancy. The AC-power is synchronized for correct power flow control. The one or more controllers communicate with the one or more AC-power supplies to dynamically allocate AC-power from the DC-to-AC converters to the multiple IT racks.
Owner:VIRTUAL POWER SYST
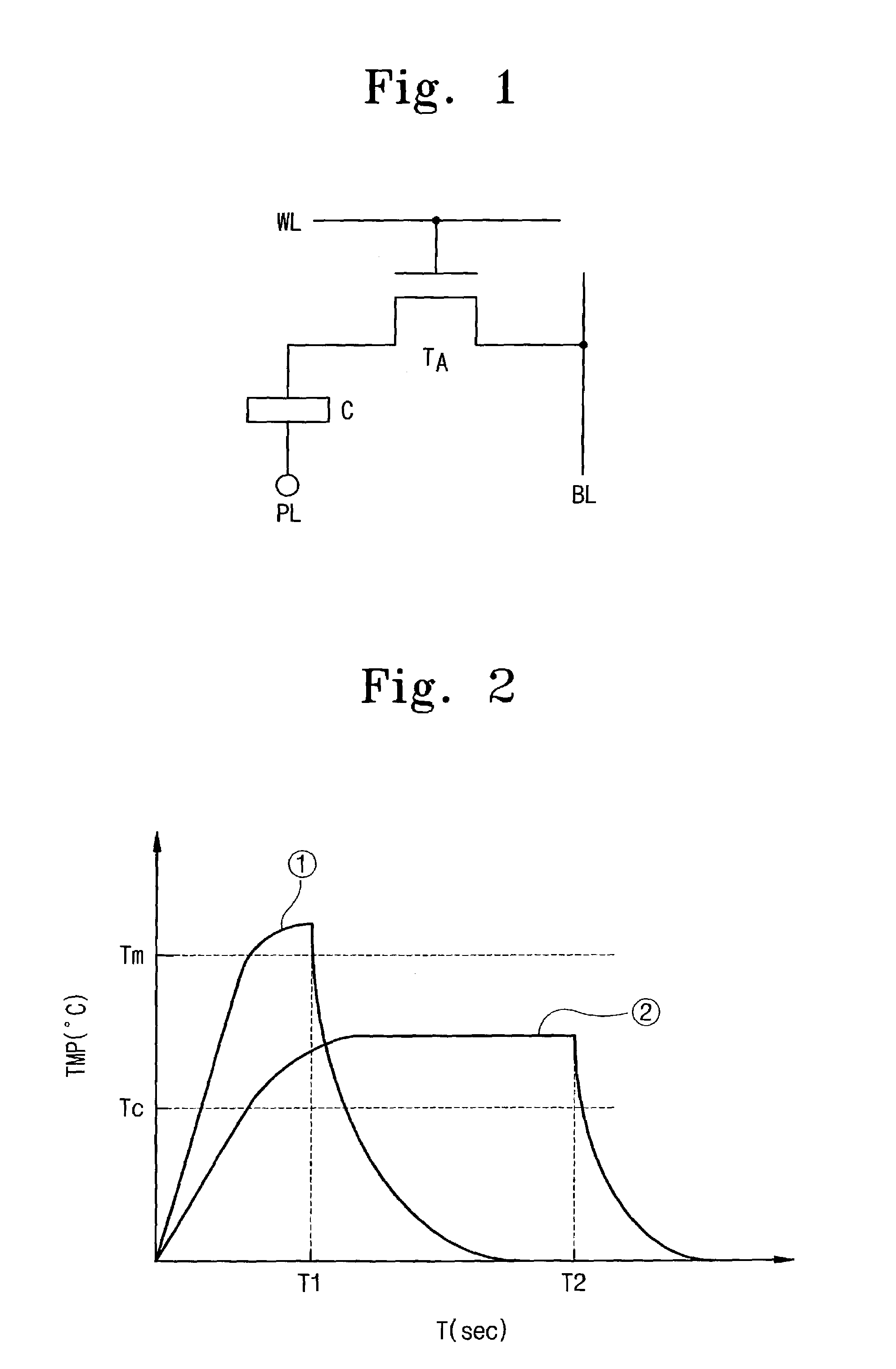
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory having plural data storage portions for a bit line connected to memory cells
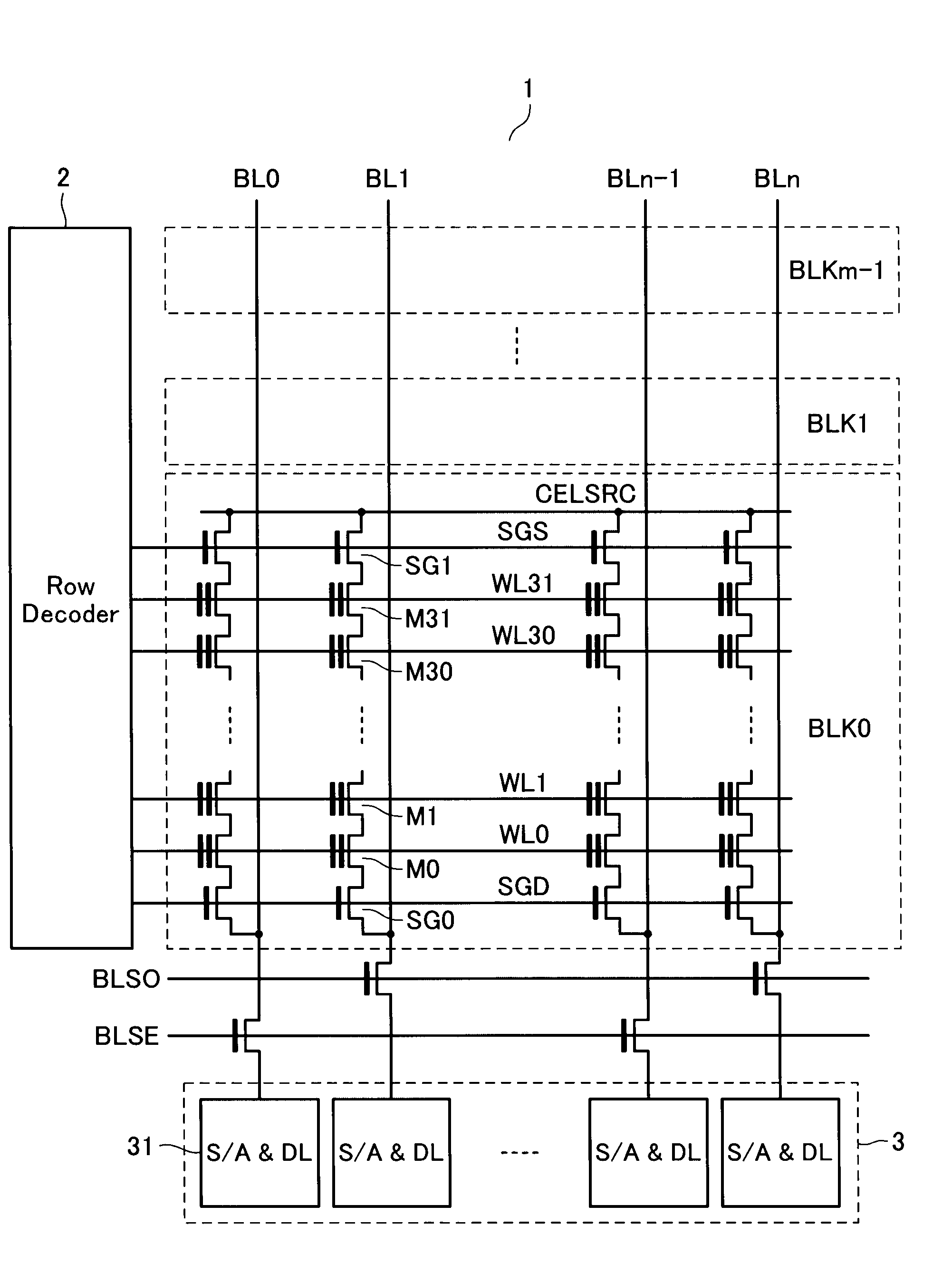
Data having three values or more is stored in a memory cell in a nonvolatile manner. A data circuit has a plurality of storage circuits. One of the plurality of storage circuits is a latch circuit. Another one of the plurality of storage circuits is a capacitor. The latch circuit and the capacitor function to temporarily store program / read data having two bits or more. Data held by the capacitor is refreshed using the latch circuit if data variation due to leakage causes a program. As a result, the data circuit does not become large in size even if multi-level data is used.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device includes: a memory chip configured to be electrically rewritable and store such multi-level data as being defined by n-bits / cell (where n≧2); and a memory controller configured to control read and write of the memory chip, wherein the operation mode of the memory chip is changed from n-bits / cell to m-bits / cell (where m<n) when the number of late-generated defective areas is over a certain threshold value.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Resistance change memory device
A resistance change memory device including memory cells arranged, the memory cell having a stable state with a high resistance value and storing in a non-volatile manner such multi-level data that at least three resistance values, R0, R1 and R2 (R0<R1<R2) are selectively set, wherein resistance gaps ΔR1(=R1−R0) and ΔR2(=R2−R1) are set to satisfy the relationship of ΔR1>ΔR2.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
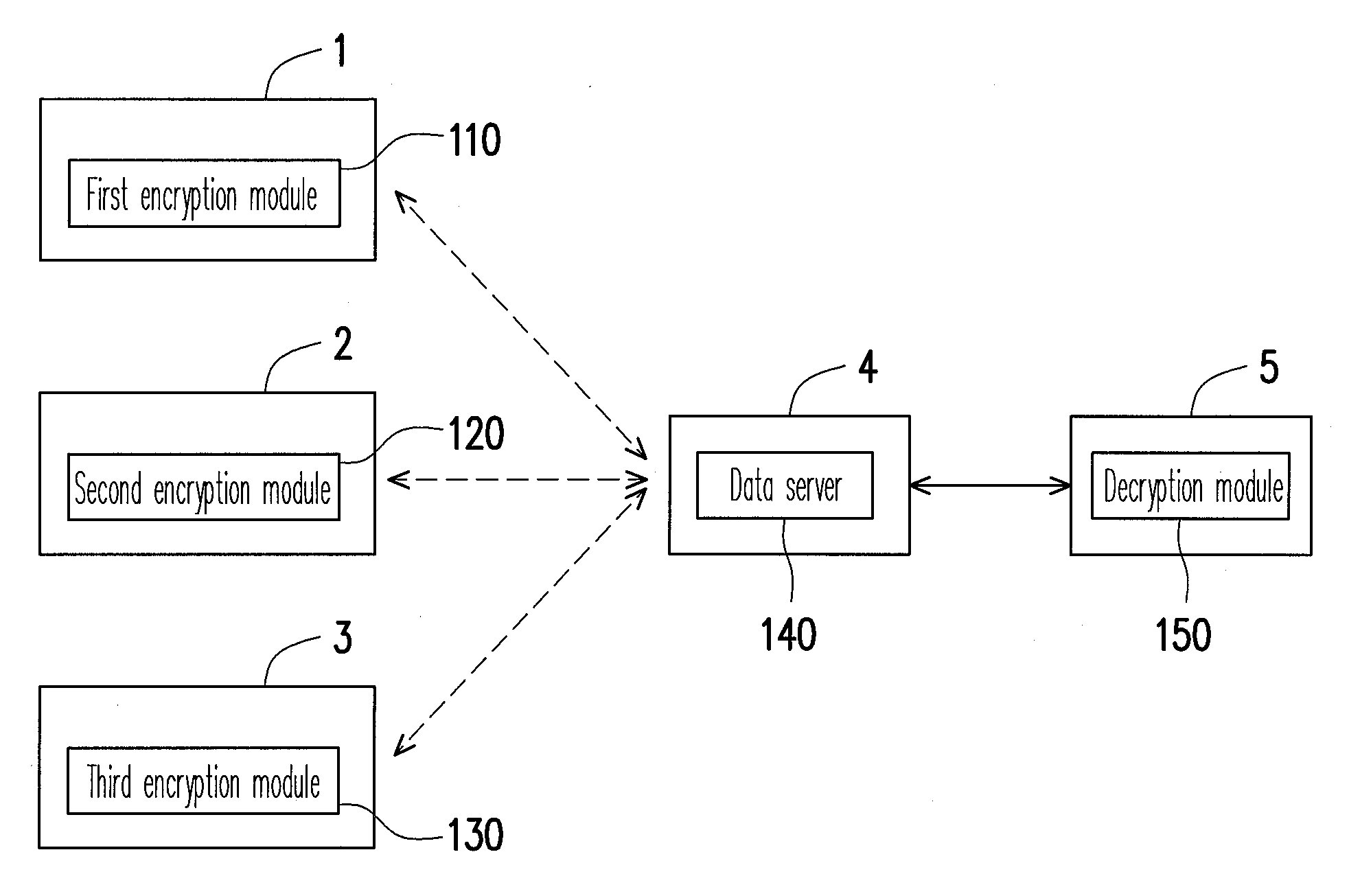
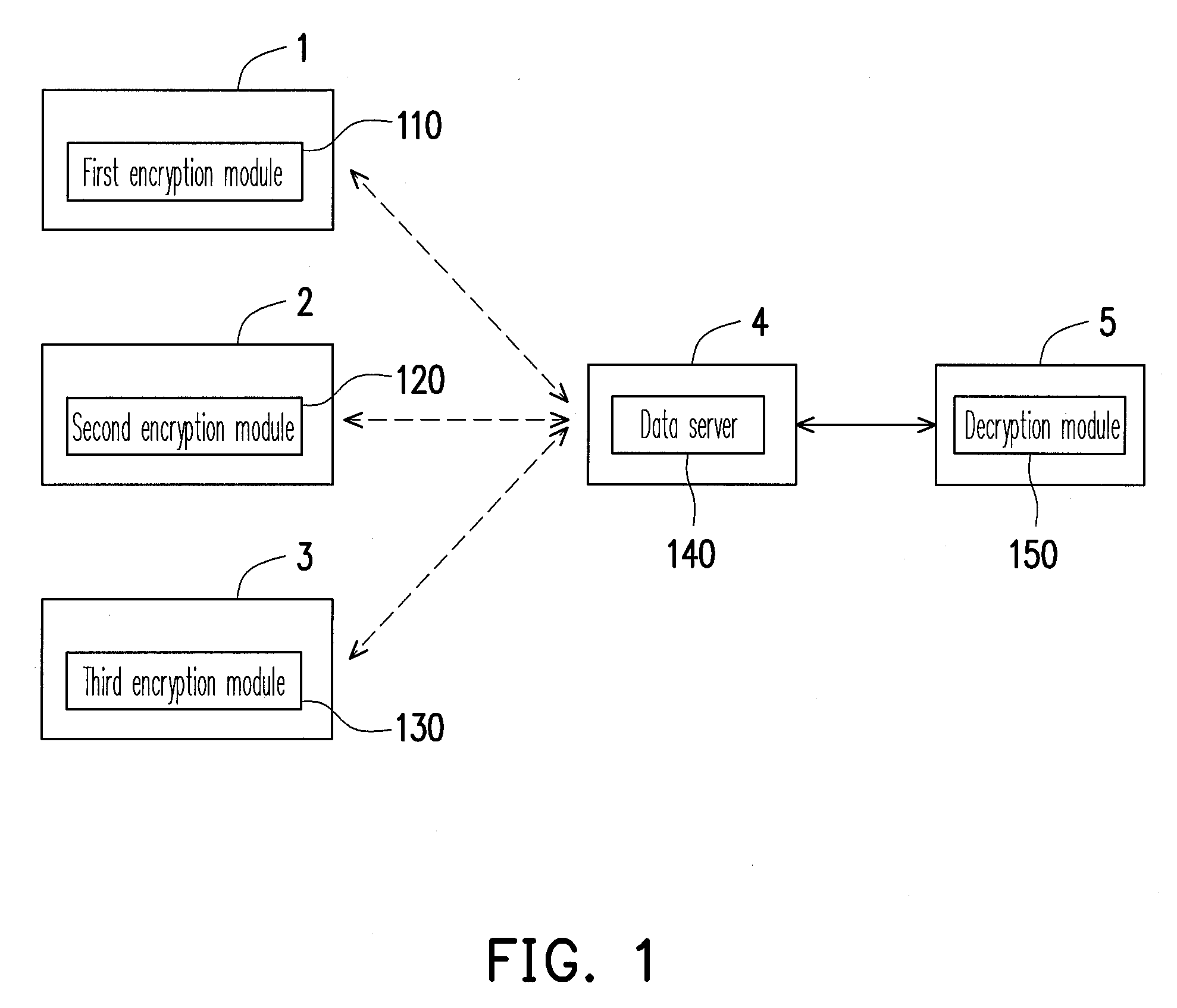
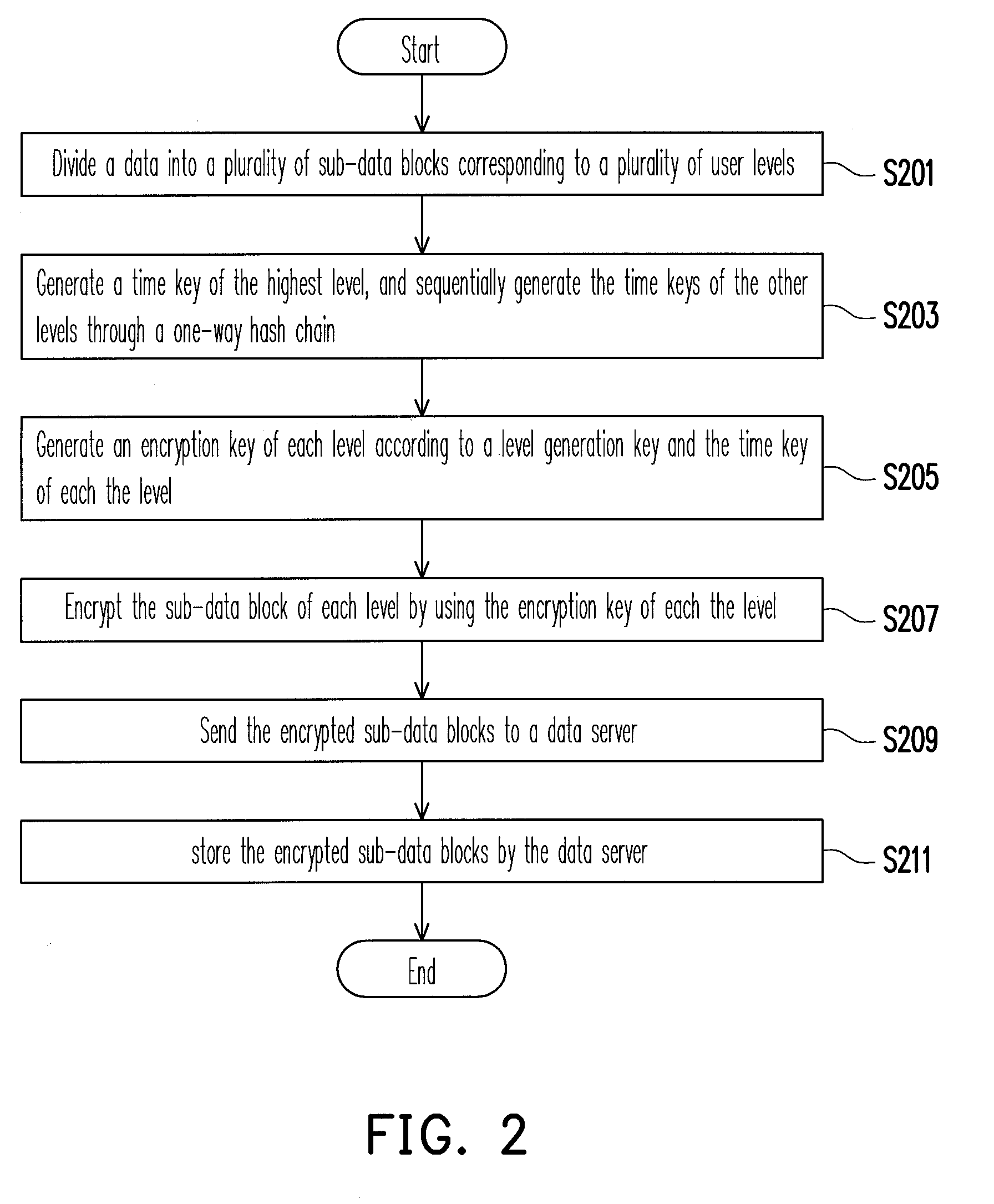
Multi-level data encryption and decryption system and method thereof
ActiveUS20090323937A1Managing accessSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesSecret communicationEncryptionMulti level data
A multi-level data encryption and decryption system and a method thereof are provided. The method includes dividing a data into a plurality of sub-data blocks corresponding to a plurality of user levels. The method also includes generating an encryption key for each level according to a level generation key and a time key of the level and encrypting the sub-data block of each level by using the encryption key of the level, wherein the level generation key and the time key of a lower level are generated based on the same of an upper level, the time key is generated according to a time generation key and a time seed, and the time seed is periodically updated according to different encryption periods. Thereby, the number of keys to be managed by a user is reduced while the read rights of different users are managed with forward and backward data security.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for programming a semiconductor memory device
A method for programming a semiconductor memory device including such a program sequence as to program target threshold levels constituting multi-level data into multiple memory cells, which are simultaneously selected, wherein the program sequence is controlled to finish programming the multiple memory cells in order of height of the target threshold levels.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
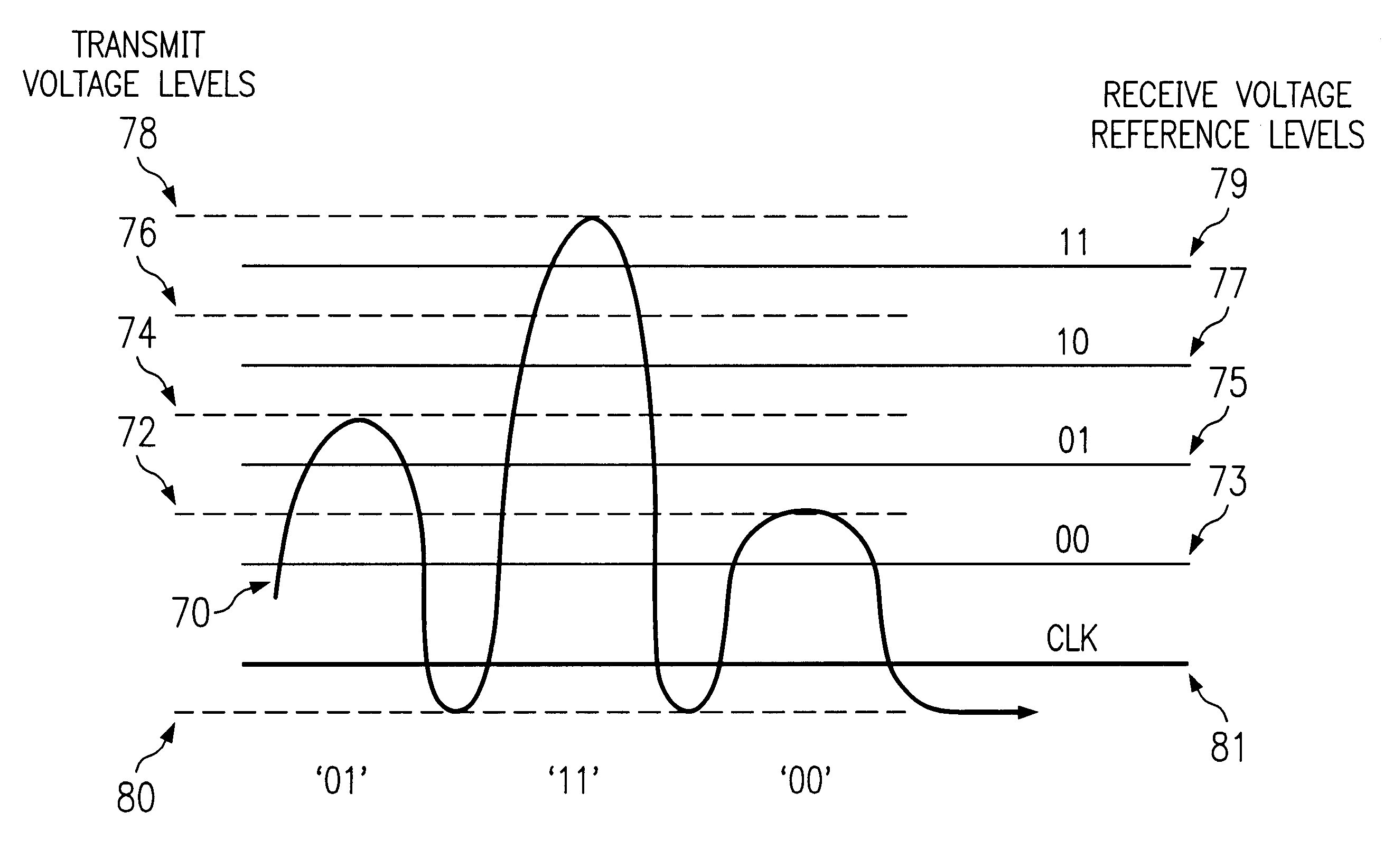
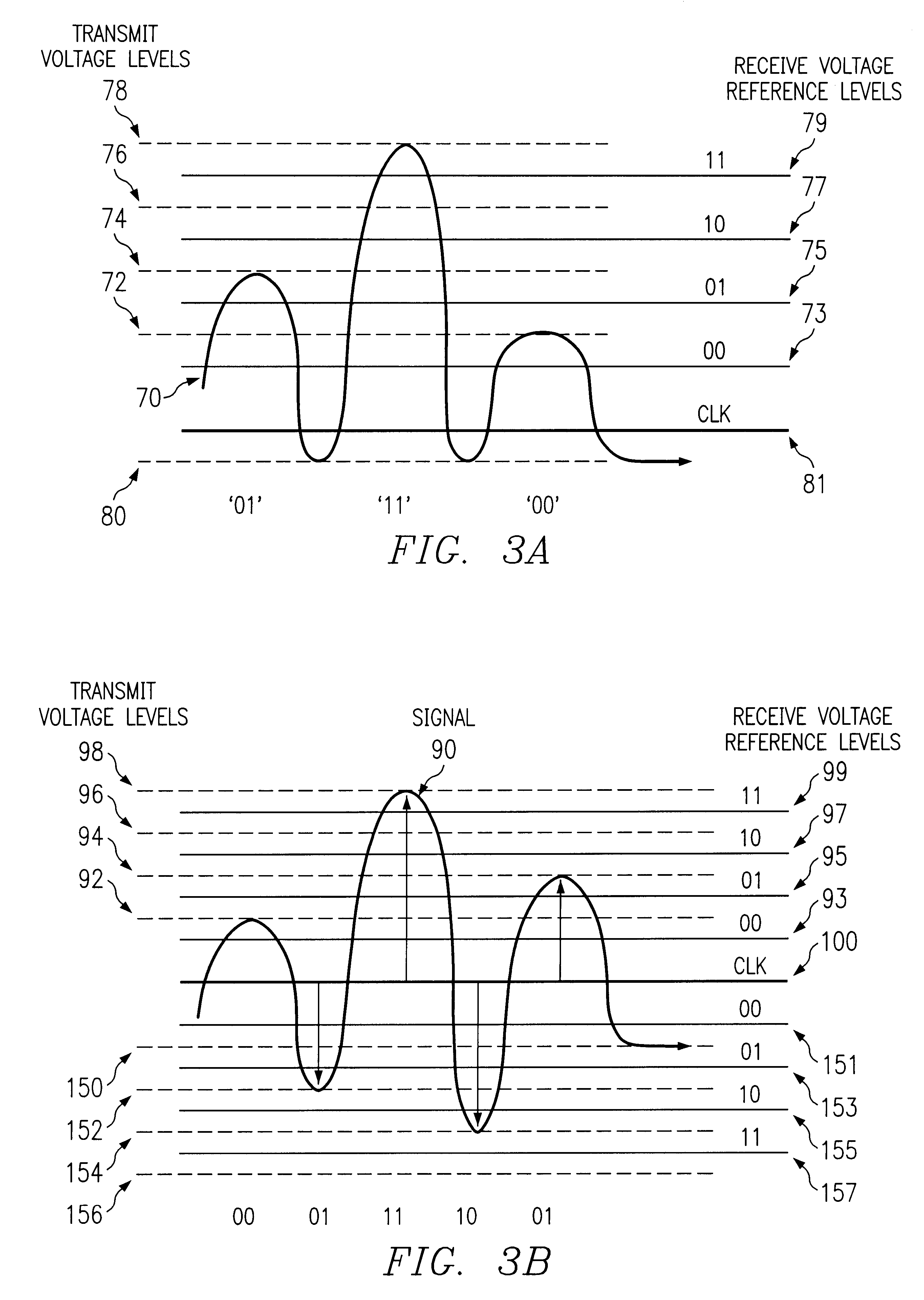
Method and apparatus for utilizing a data processing system for multi-level data communications providing self-clocking
InactiveUS6317469B1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlData processing systemComputer science
A method and apparatus utilizing a data processing system are disclosed for multi-level data communication providing self-clocking. A first digital signal is input which includes a series of digital bits. One of a plurality of output levels is associated with each group of data bits for each of the plurality of the digital bits included within the first digital signal. A particular output level is associated with a clock output level. An output signal is generate which includes a transmission of the output level for each of the groups of digital bits and includes multiple transmissions of the clock output level, where a clock output level is transmitted after each transmission of an output level for each of the groups of digital bits.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
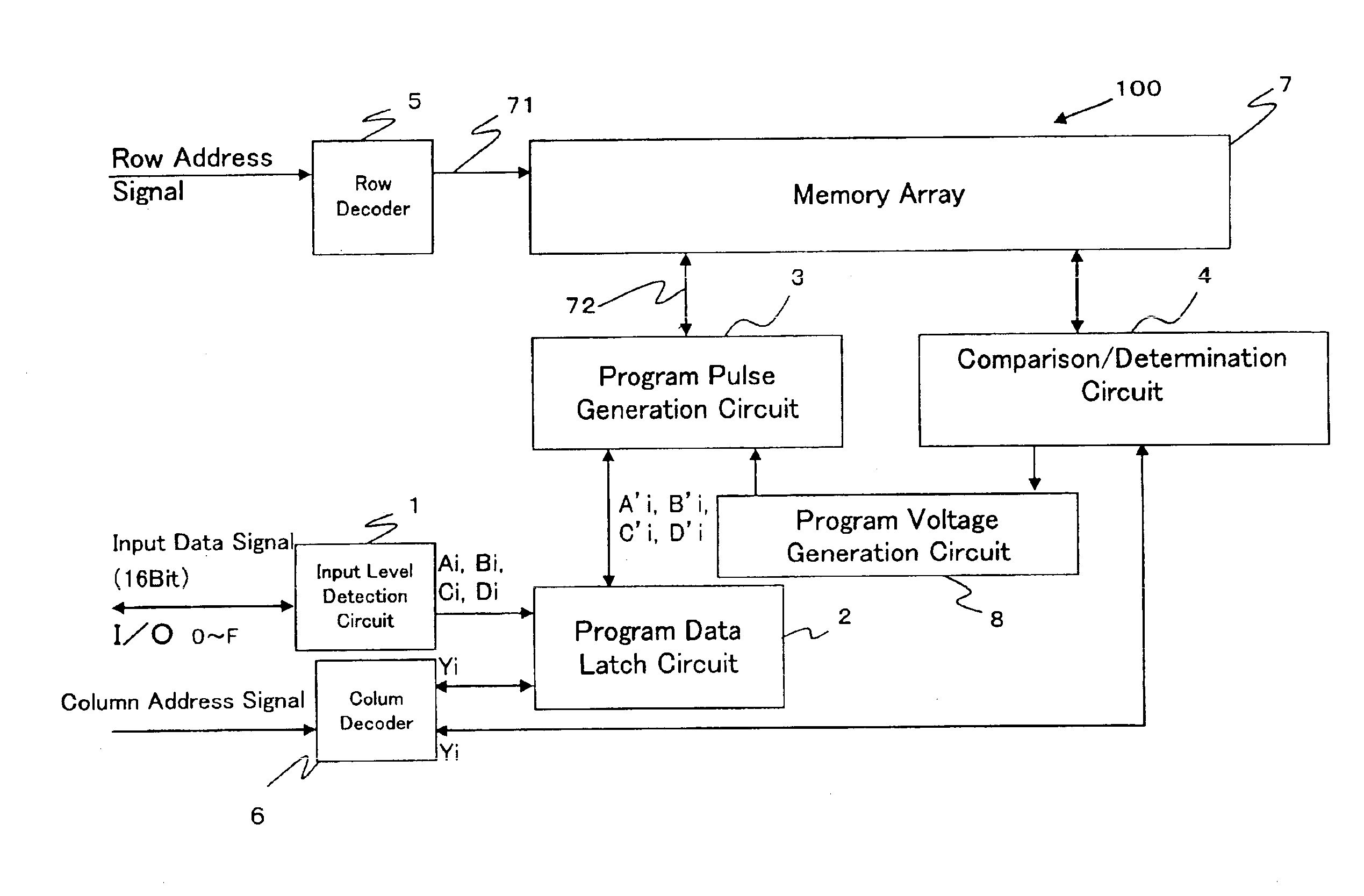
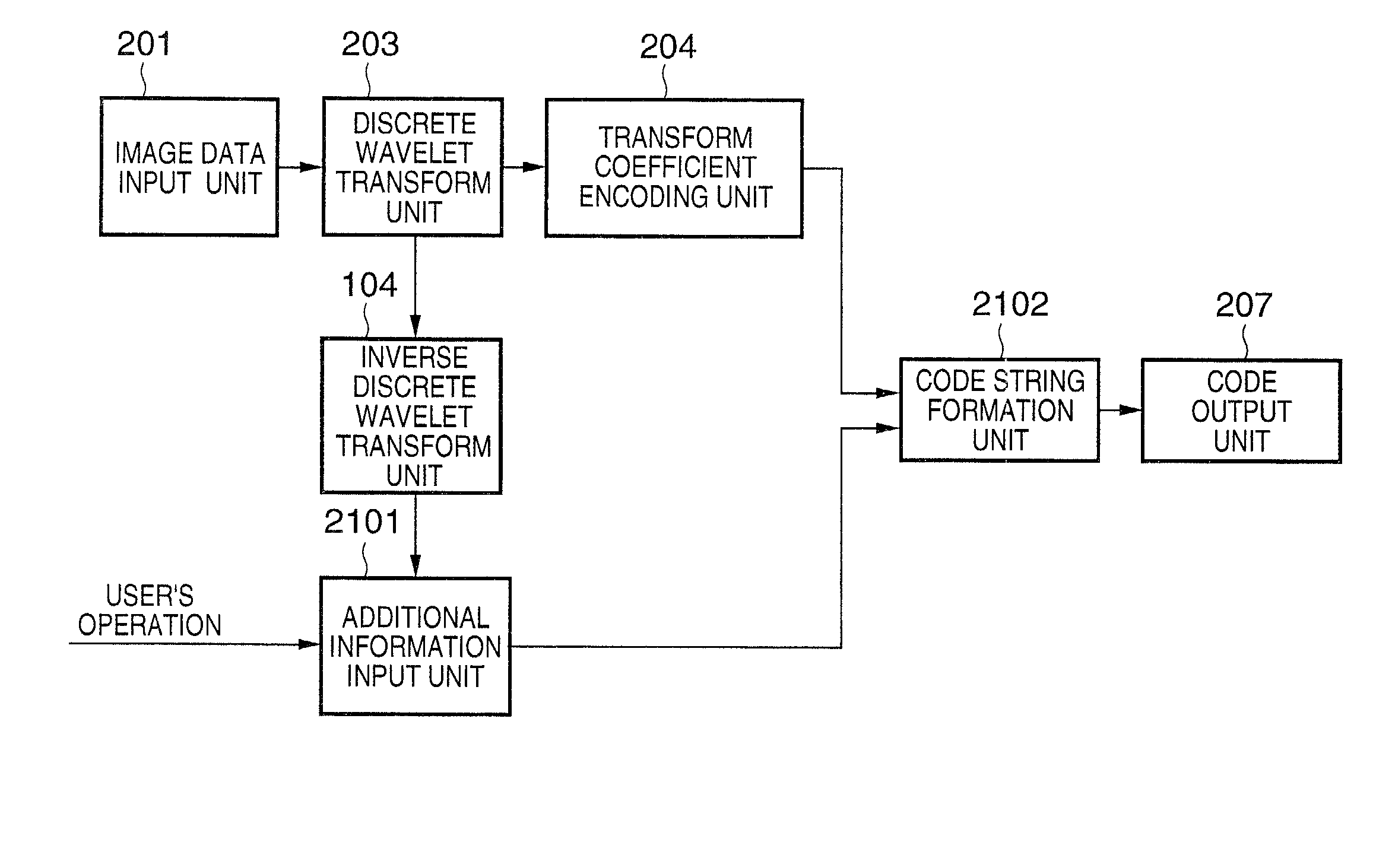
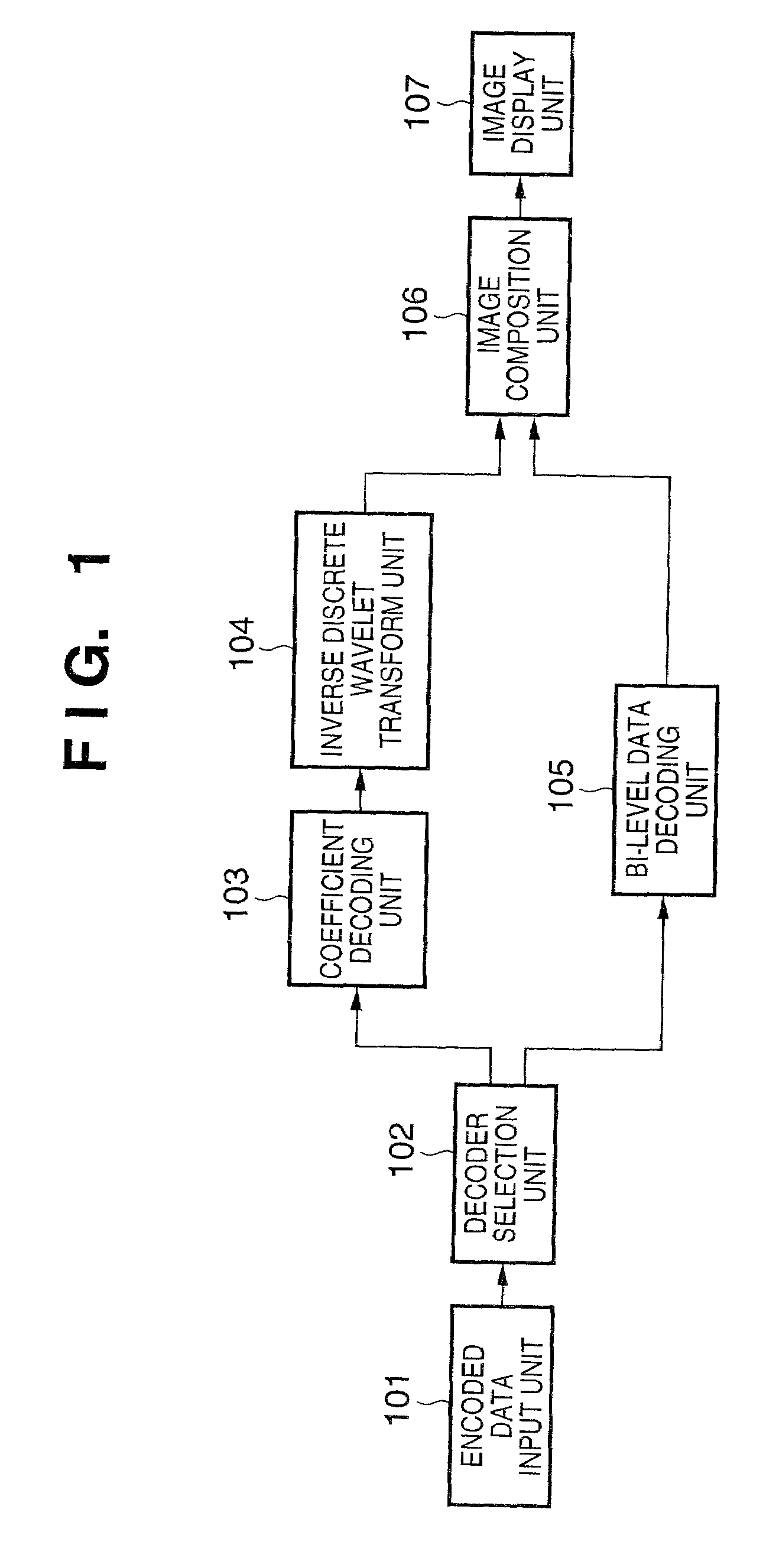
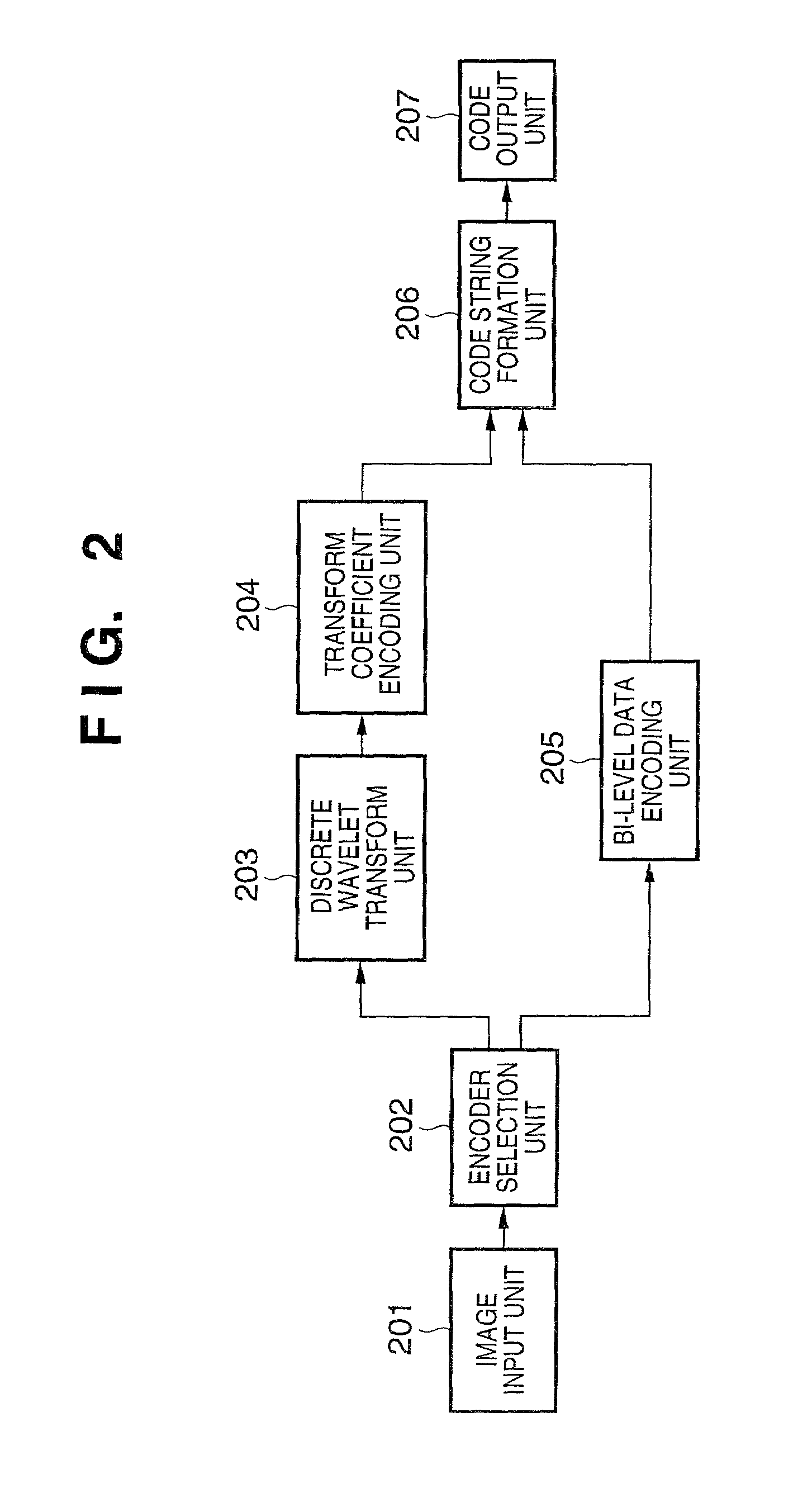
Image processing apparatus and method, program and storage medium
InactiveUS6985630B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
To provide an image processing apparatus and method, a program, and a storage medium which enables, in the case where encoded data is generated by encoding image data including mixed multi-level data and bi-level image data and the encoded data is then decoded, to read bi-level image data from the decoded image in spite of its low resolution. The multi-level image data and bi-level image data are separated and hierarchical encoding is performed on the multi-level image data so as to be decoded with multiple resolutions. Multiple pieces of bi-level data to be superimposed on the decoded image of multiple resolutions are prepared and encoded. The encoded bi-level image data is selected for decoding according to the resolution of the decoded image in the decoding process, and superimposed on the decoded multi-level image.
Owner:CANON KK
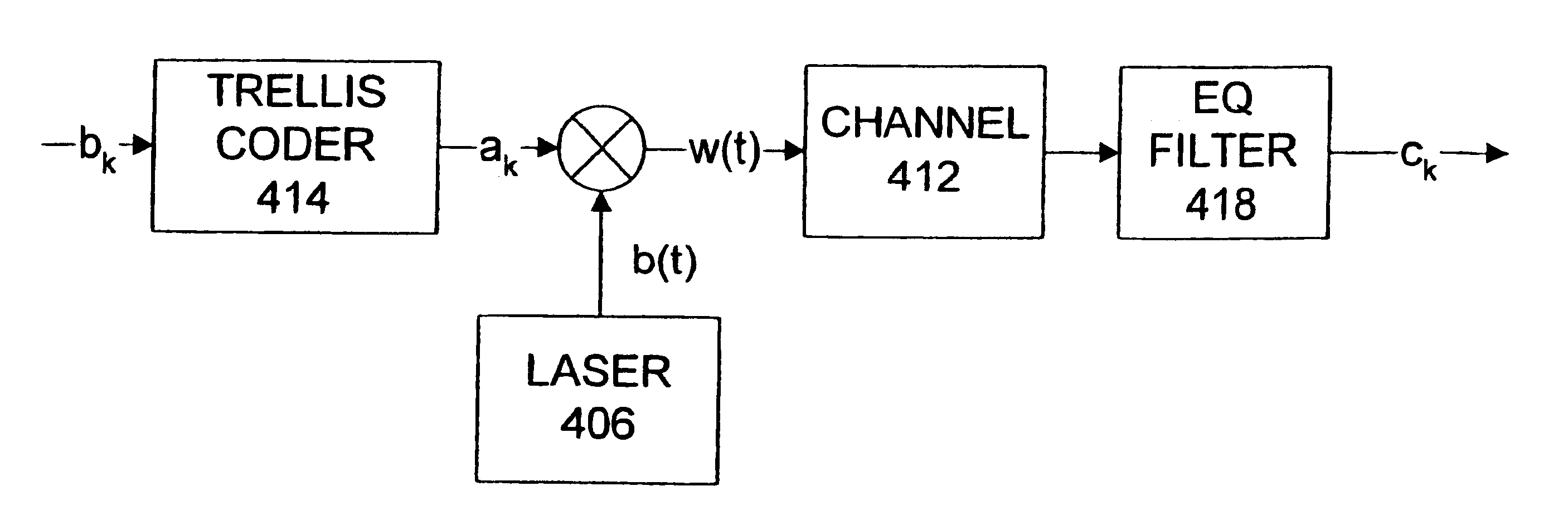
Coding system and method for partial response channels
A system and method for reading data to and writing data from multi-level (M-ary) partial response channels uses a trellis coder to encode an input bit stream sequence into a stream of multi-level data symbols. The data symbols are written to the partial response channel using any of a number of techniques. Preferably, the trellis coder anticipates the modulation transfer function of the partial response channel in encoding the data. Because the partial response channel has its own transfer function, the relationship between the data read from the channel and the actual input data bits is a function not only of the data encoder but also of the partial response channel. Therefore, a decoder specification used to implement the decoder takes into account the effect of the trellis encoder as well as the effect of the partial response channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Phase change data storage device for multi-level recording
An optical data storage device for multi-level recording having: a substrate, and a phase change memory medium supported by the substrate. The phase change memory medium preferably has an alloy with a eutectic crystallization base component and at least one element for enhanced sigma-to-dynamic range. The multi-level data storage device is preferably an optical disk with a single layer of memory material for providing multi-level recording with a sigma-to-dynamic range of less than 2%. The phase change recording alloy is preferably an In:Sb:Te material. Preferably, Sb:Te is present at a ratio at, or near, the eutectic point when combined with 30% or less In. A preferred phase change memory material includes an alloy defined by the formula: Inx(SbnTe100-n)100-x where x is 3-30, and n is 63-82.
Owner:OPTICAL MEMORY STORAGE
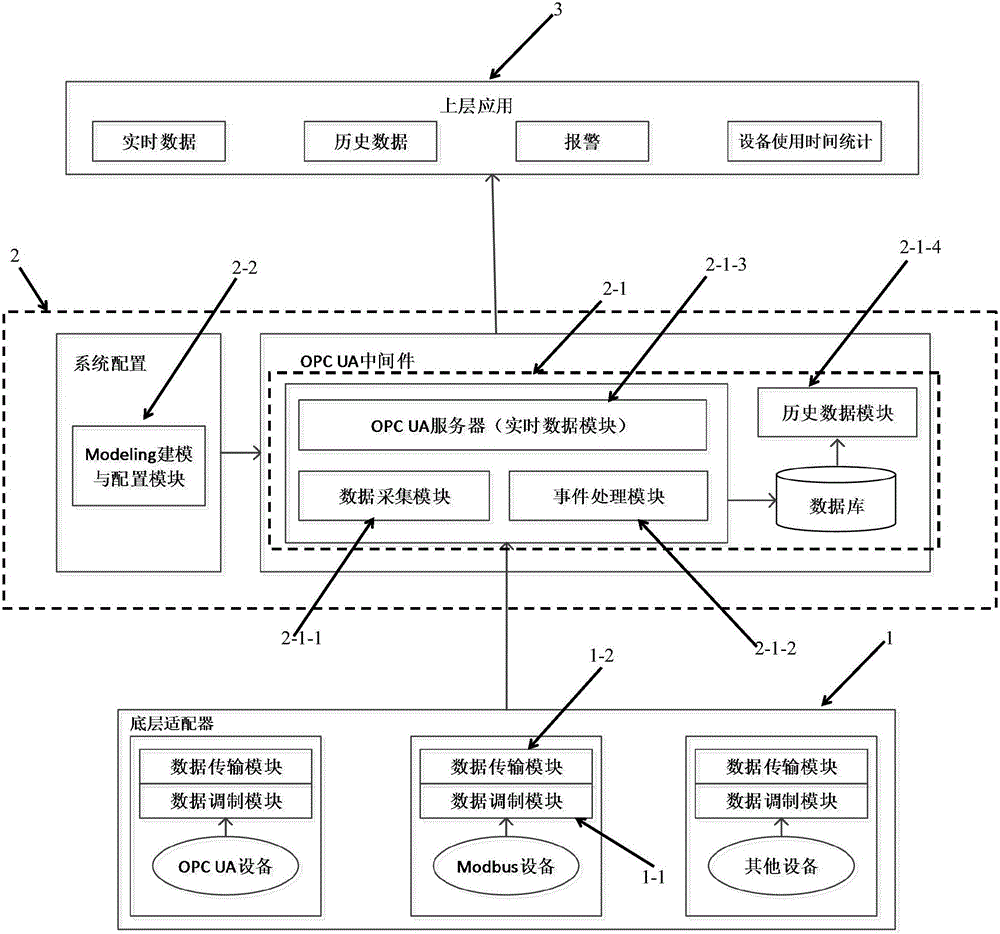
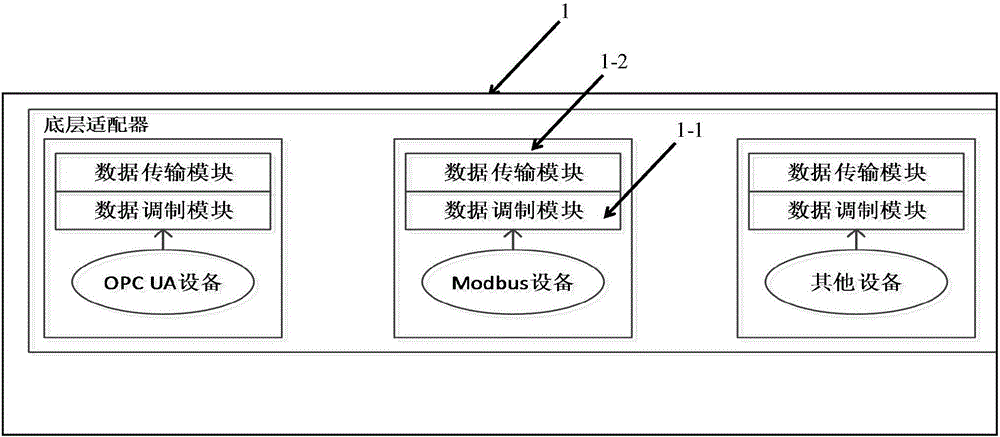
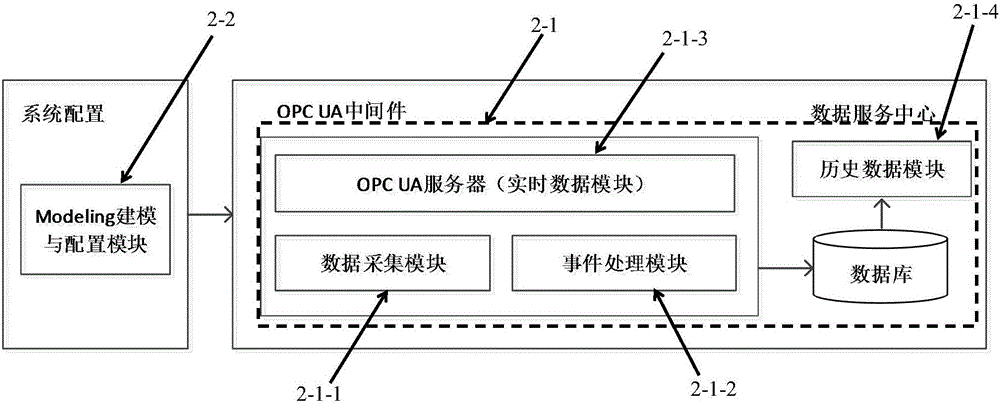
Equipment data collecting system based on OPC UA protocol
ActiveCN106773978AInnovativeMalleableProgramme controlComputer controlAutomatic controlMeasuring instrument
The invention provides an equipment data collecting system based on OPC UA protocol, which can solve multi-level data collection, transmission and monitoring problems of each bottom device, measuring instrument, automatic control system and so on on the industrial site, realize data transparency of complicated bottom automation equipment and improve information integration modes. The equipment data collecting system based on the OPC UA protocol is characterized by comprising a bottom adapter, an OPC UA middleware and an upper application, wherein the bottom adapter comprises a data modulation module and a data transmission module, wherein the data modulation module is used for taking out bottom equipment data value needed by a user, data values of a plurality of communication protocols can be taken out through configuration, and the data transmission module is used for transmitting the data value taken out from the data modulation module to the OPC UA middleware at a configured speed; the OPC UA middleware comprises a data service center and a Modeling and configuring module; and the data service center comprises a data collection module, an even processing module, an OPC UA real-time data server and a history data module.
Owner:武汉集智浩睿技术转移有限公司
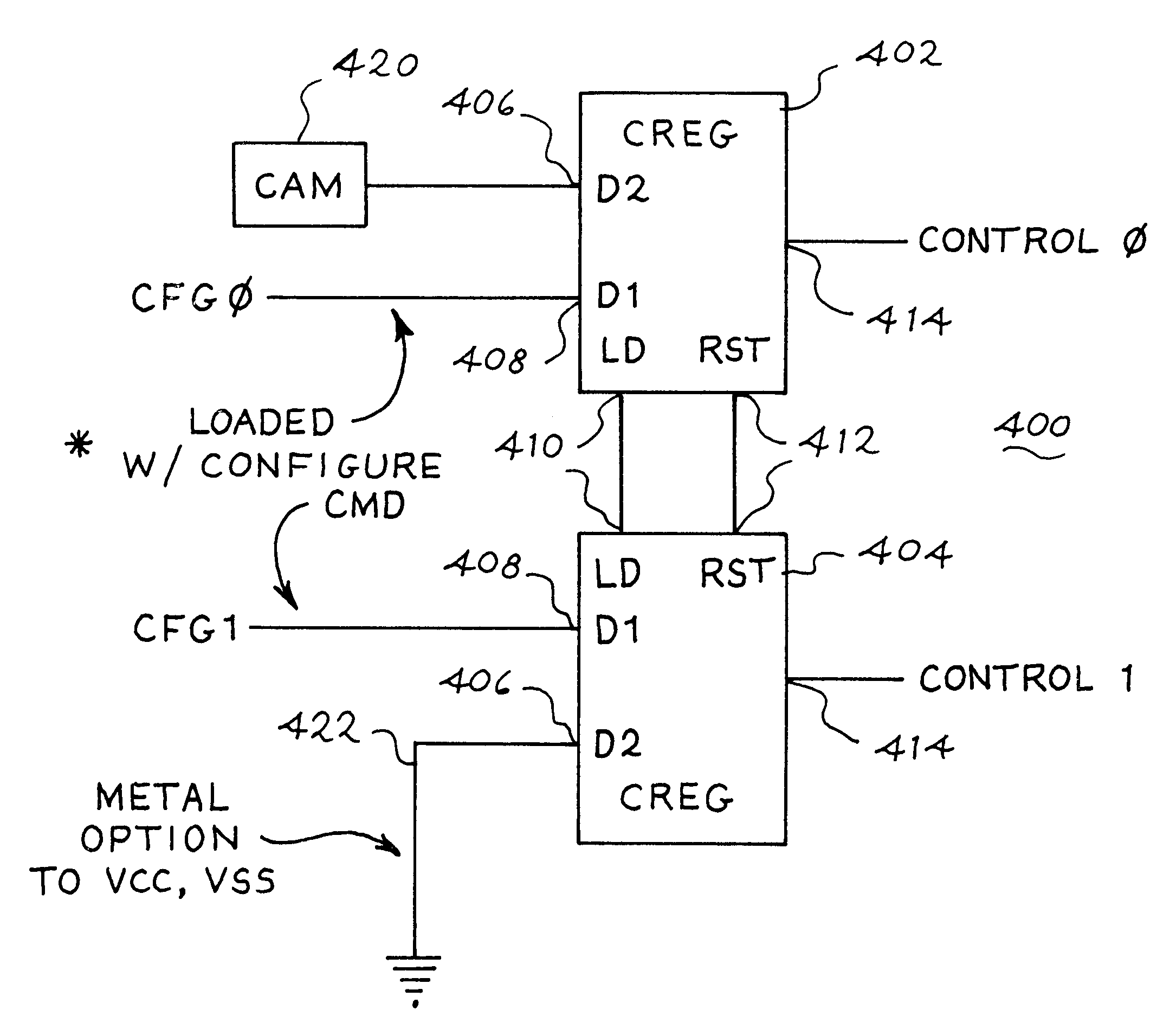
Configure registers and loads to tailor a multi-level cell flash design
A method for testing a multi-level memory includes storing multi-level data in a plurality of memory cells of the multi-level memory and reading from configure registers initial values of a plurality of performance variables. The performance variables set operating parameters of the multi-level memory. The method further includes during a first test phase operating the multi-level memory at the initial values of the plurality of performance variables and reading program values of the plurality of performance variables. During a second test phase, the multi-level memory is operated at the program values of the plurality of performance variables.
Owner:III HLDG 4
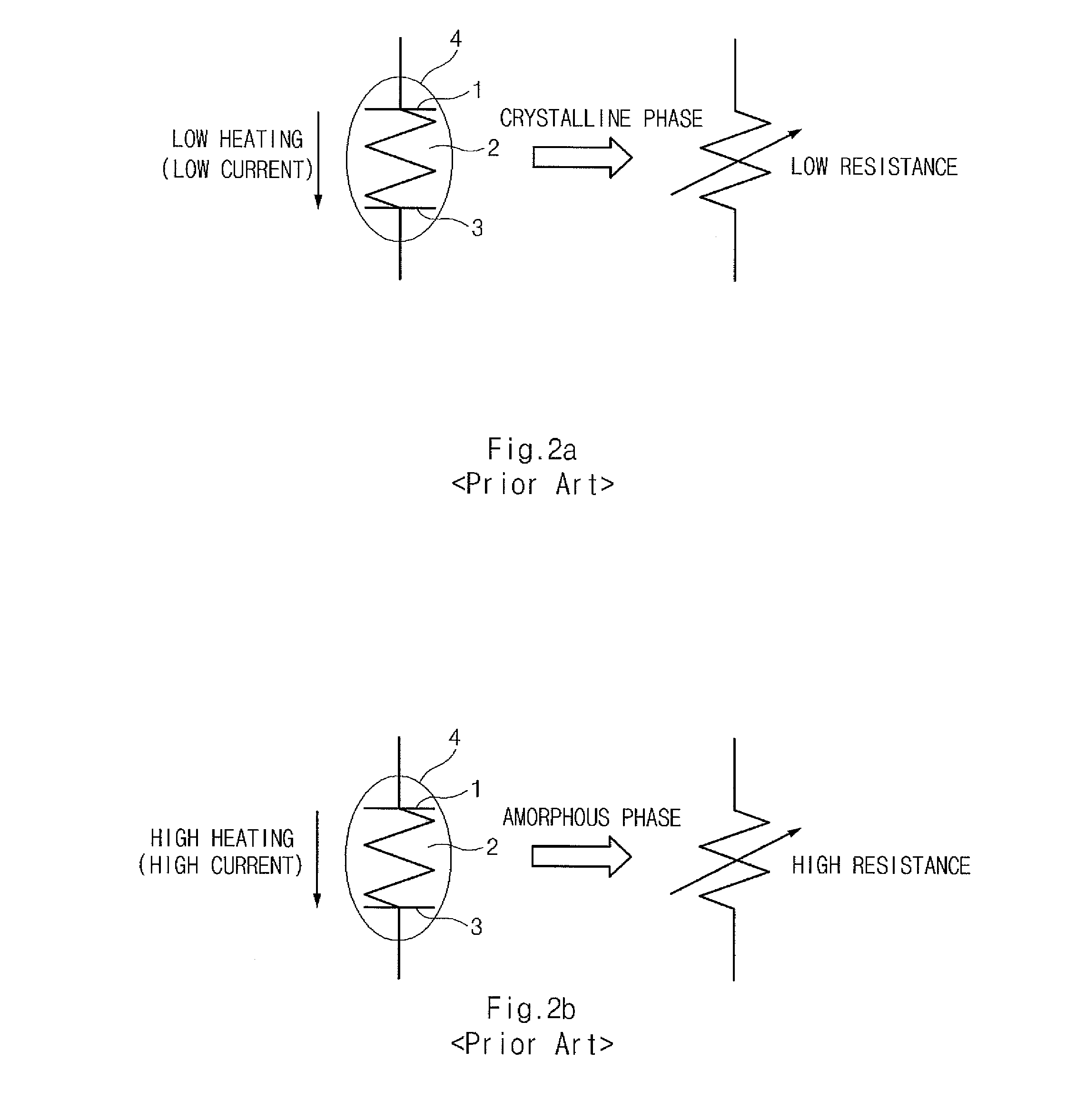
Method for driving multi-level data to a phase change memory device
ActiveUS20090040814A1Reduce in quantityImprove write operation characteristicDigital storageHigh resistancePhase-change memory
A phase change memory device including a phase change resistor senses a crystallization state that is changed according to supplied currents to store data corresponding to the crystallization state. The phase change memory device may receive and store multi-level data. The multi-level data is driven to the phase change memory device by reading cell data of a selected cell. The cell data is compared to multi-level data to be written to the cell. A high resistance reset state is written to the phase change resistor by applying a write voltage that corresponds to a threshold voltage when the cell data is different from the multi-level data. The multi-level data is then written to the phase change resistor by writing and verifying a set state that corresponds to the multi-level data.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com