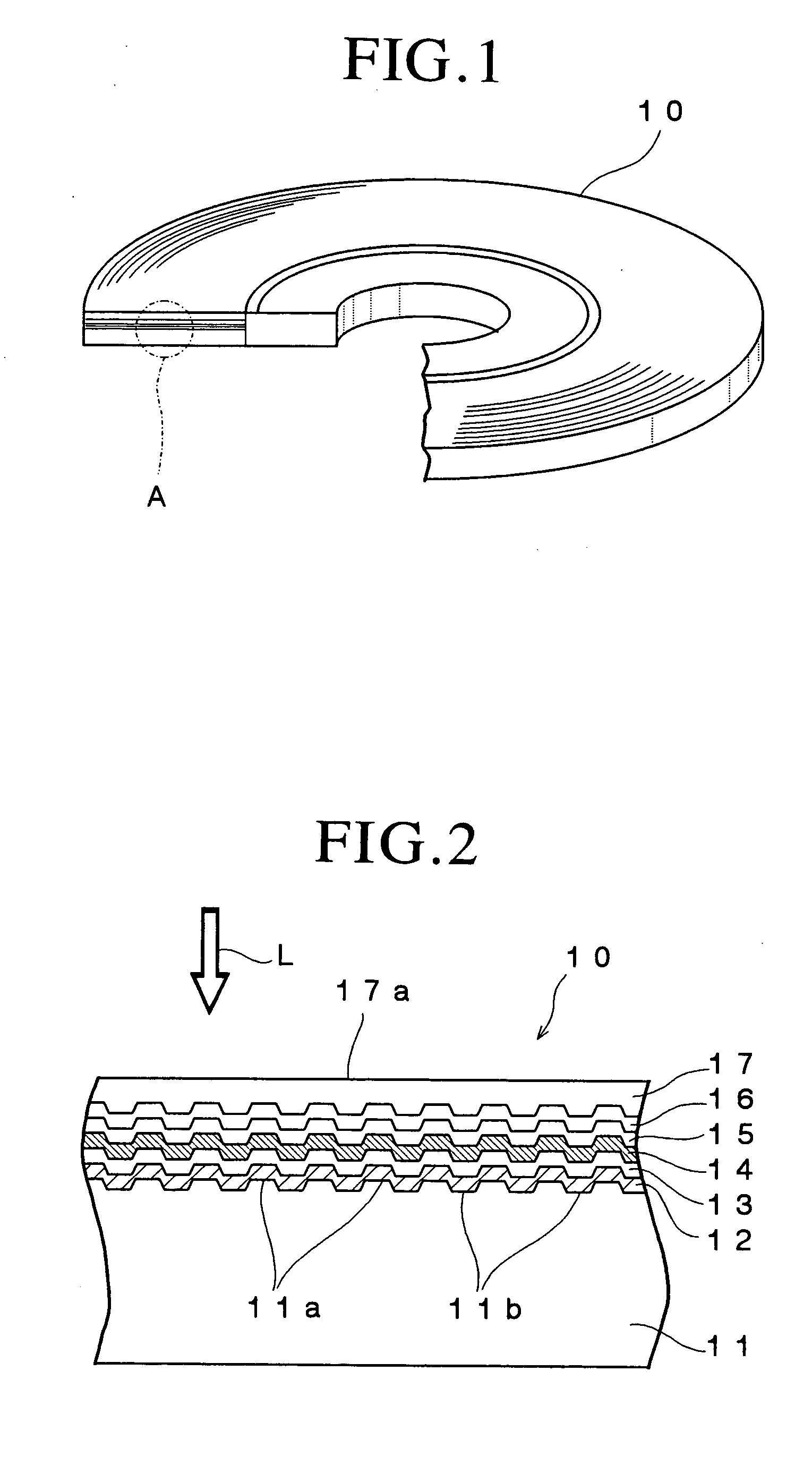
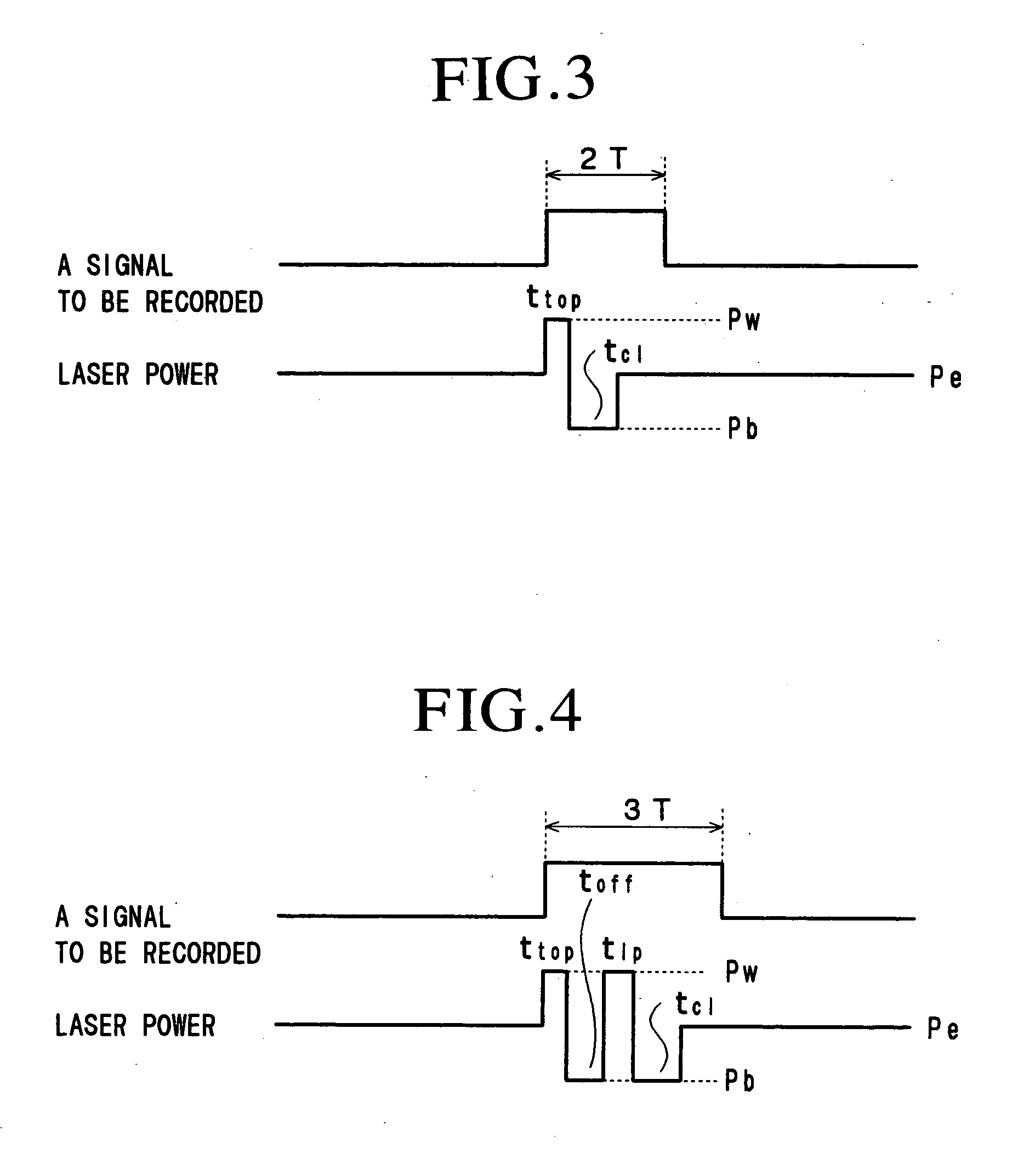
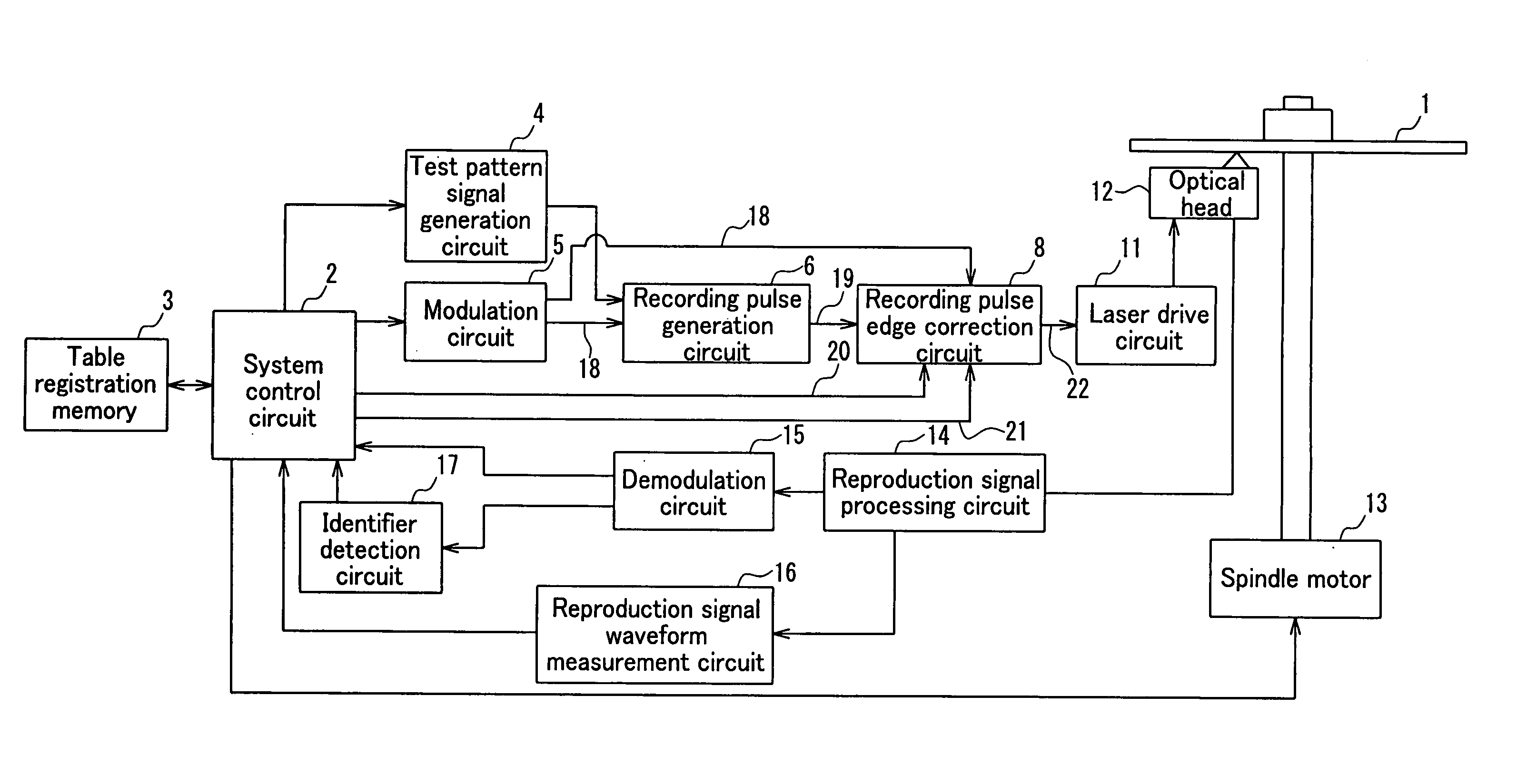
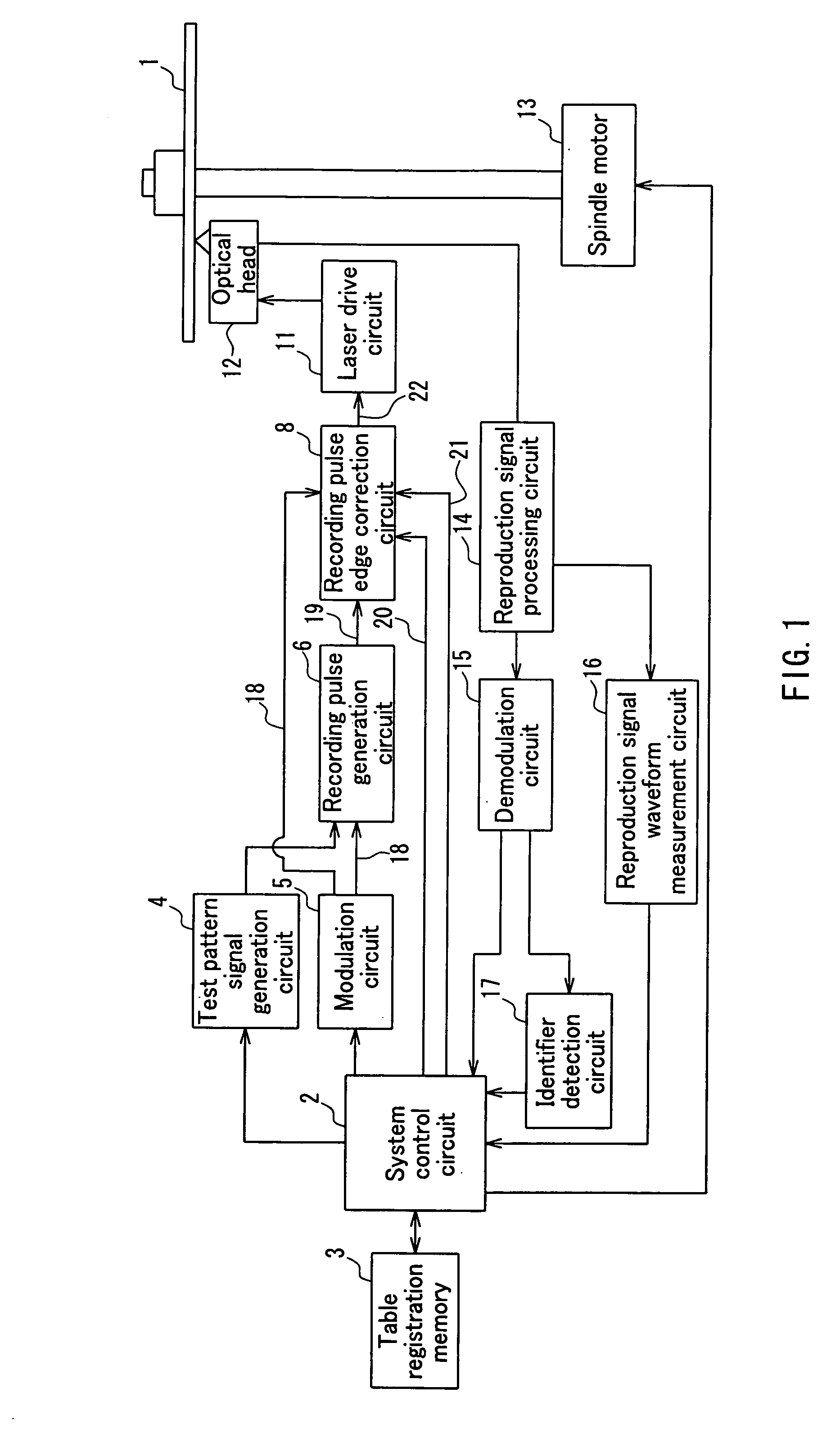
Patents
Literature
770results about "Recording strategies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
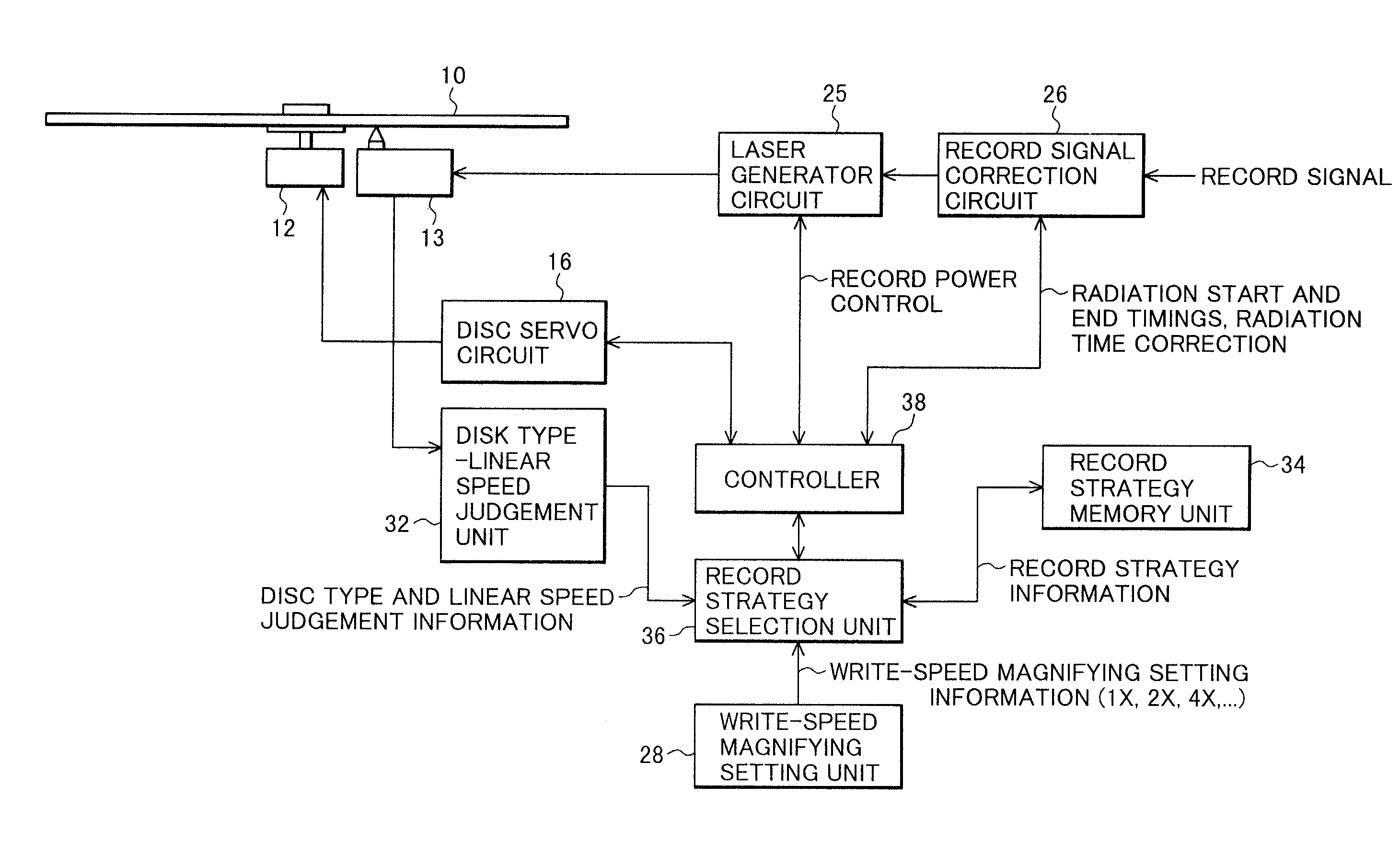
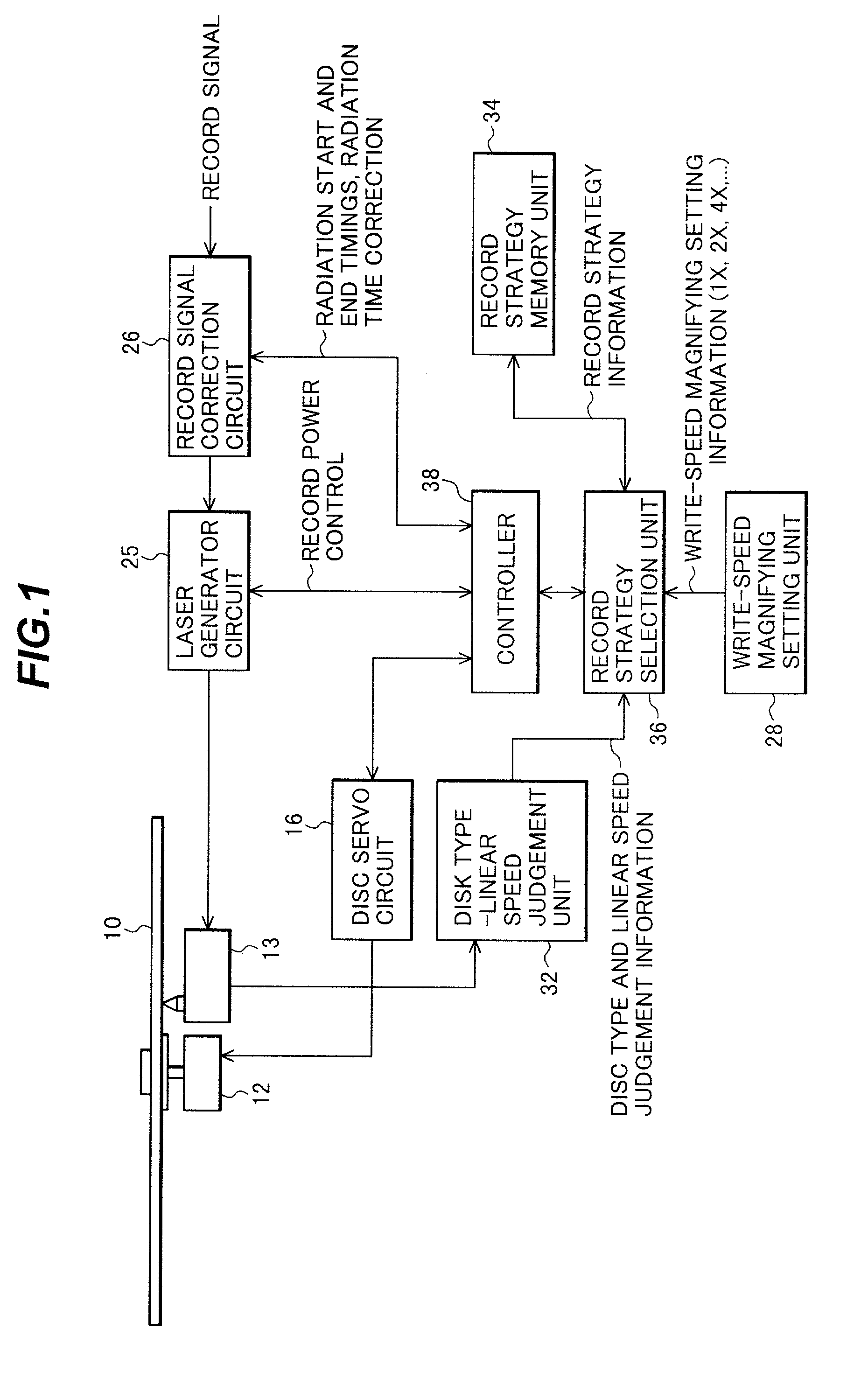
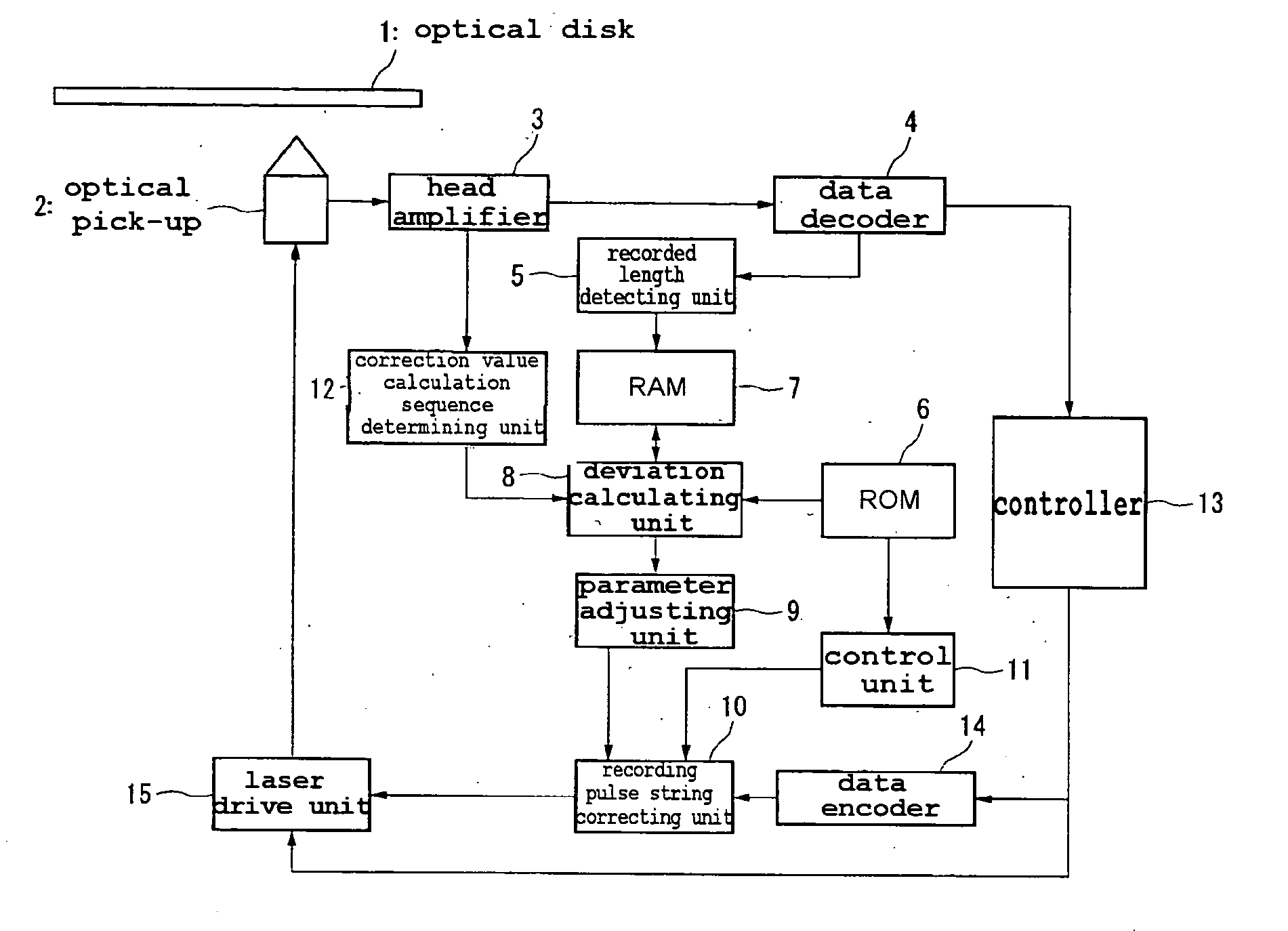
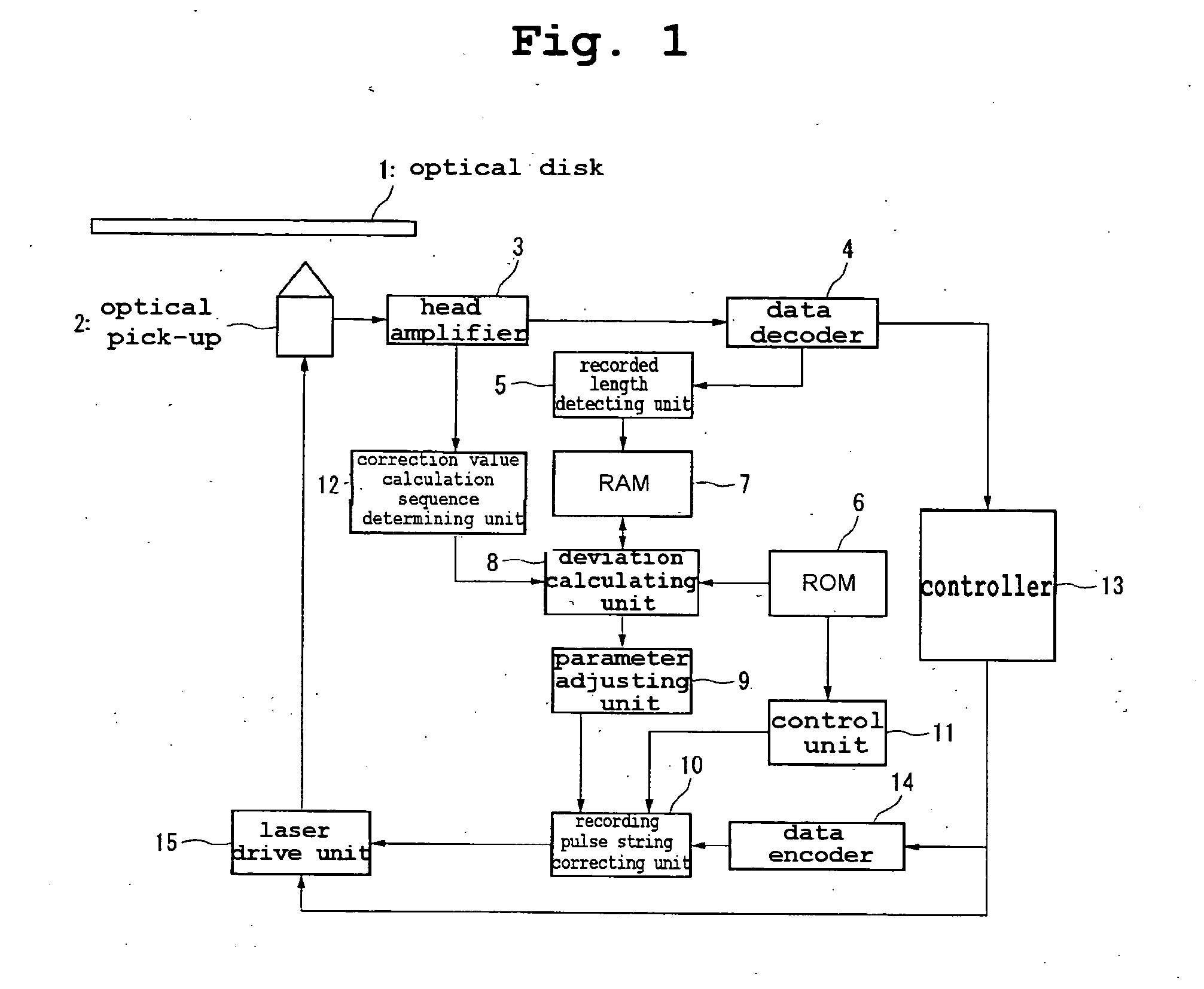
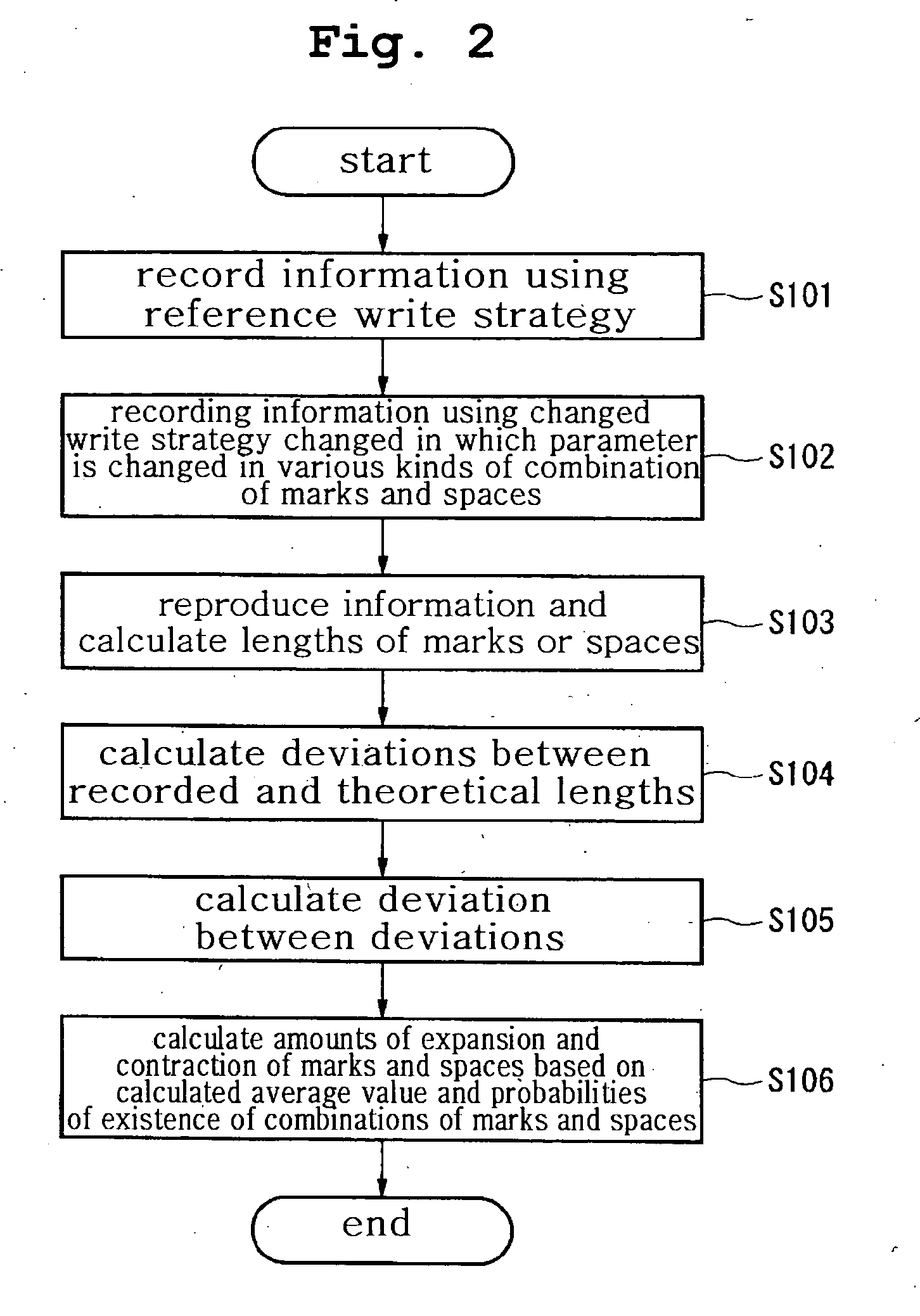
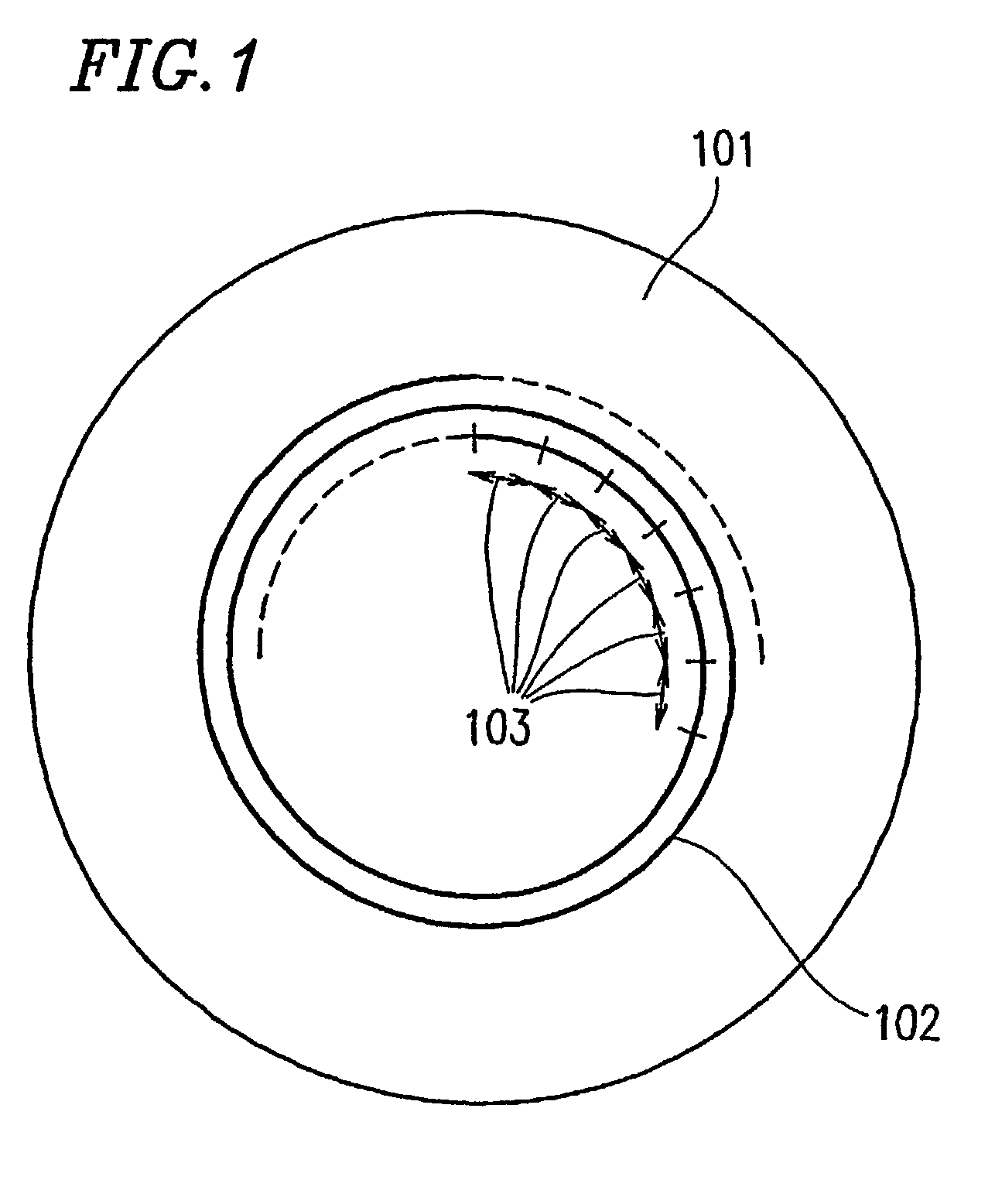
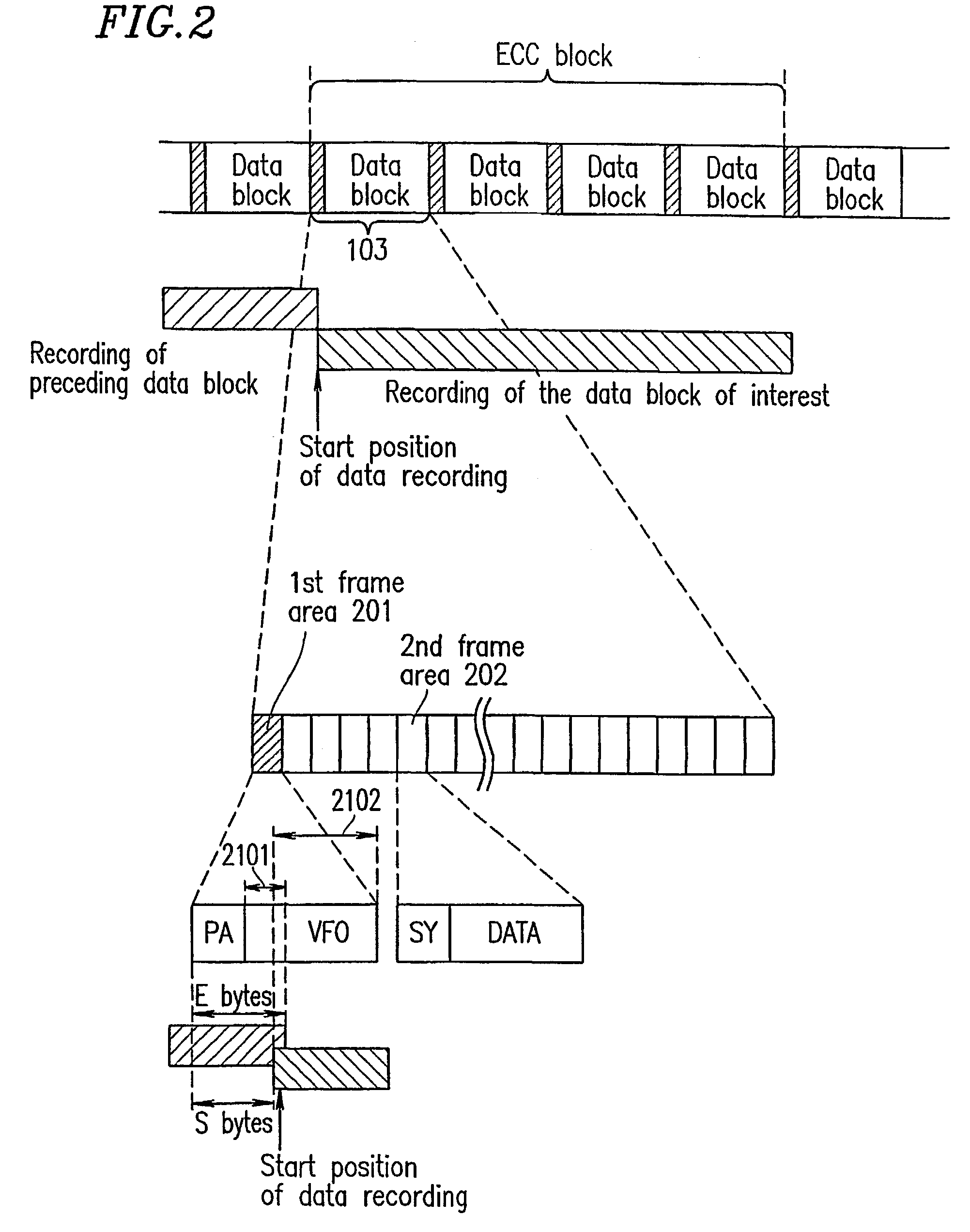
Optical disk recording method, optical disk device and optical disk
ActiveUS20050058047A1Accurate recordEasy to operateRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsFall timeEngineering
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Optical disc, optical disc recording/reproducing apparatus, and optical disc recording/reproducing method
ActiveUS7088667B2Perform recording processingReliable recordRecording strategiesAccessories for auxillary signalsOptical recordingLaser
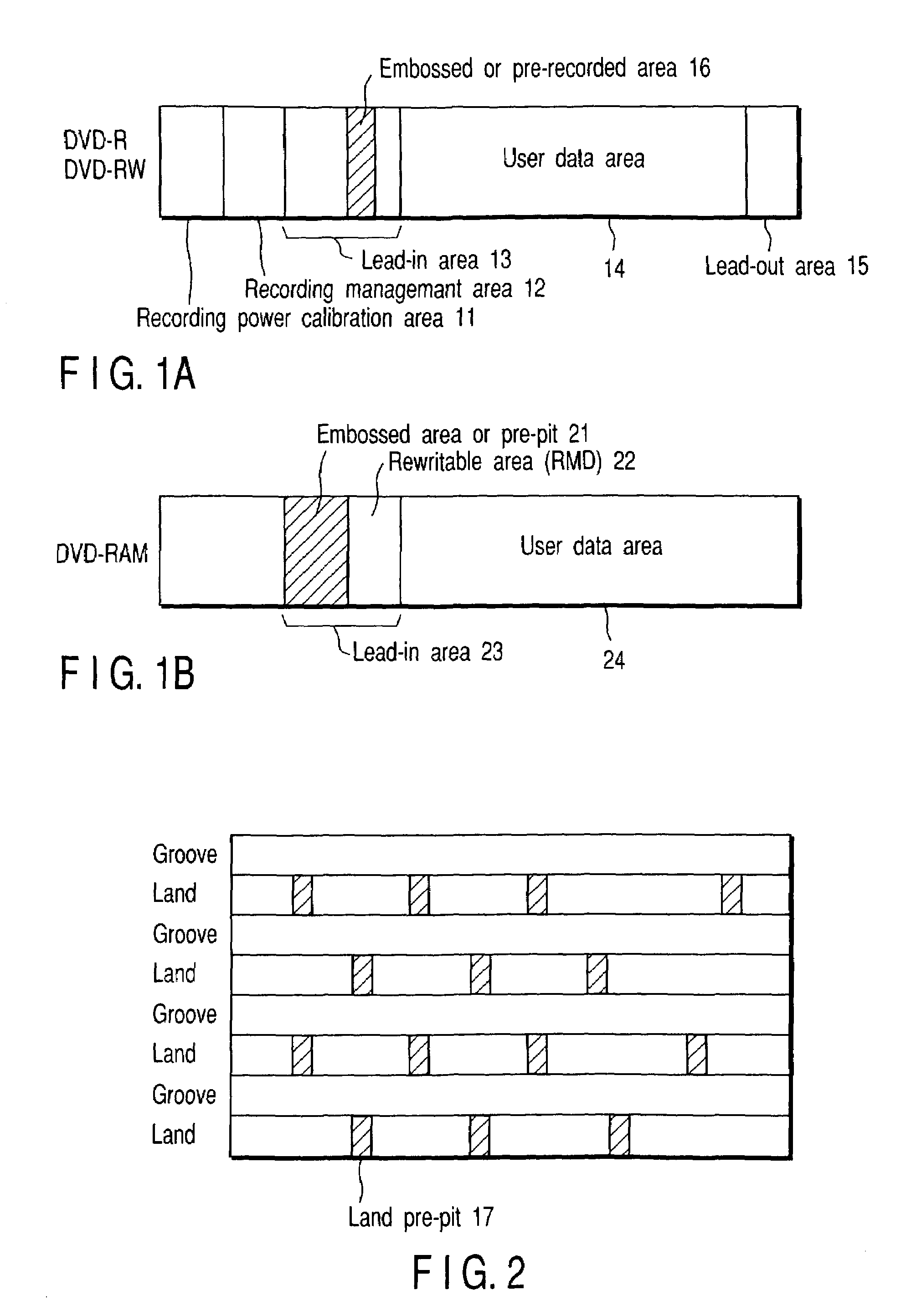
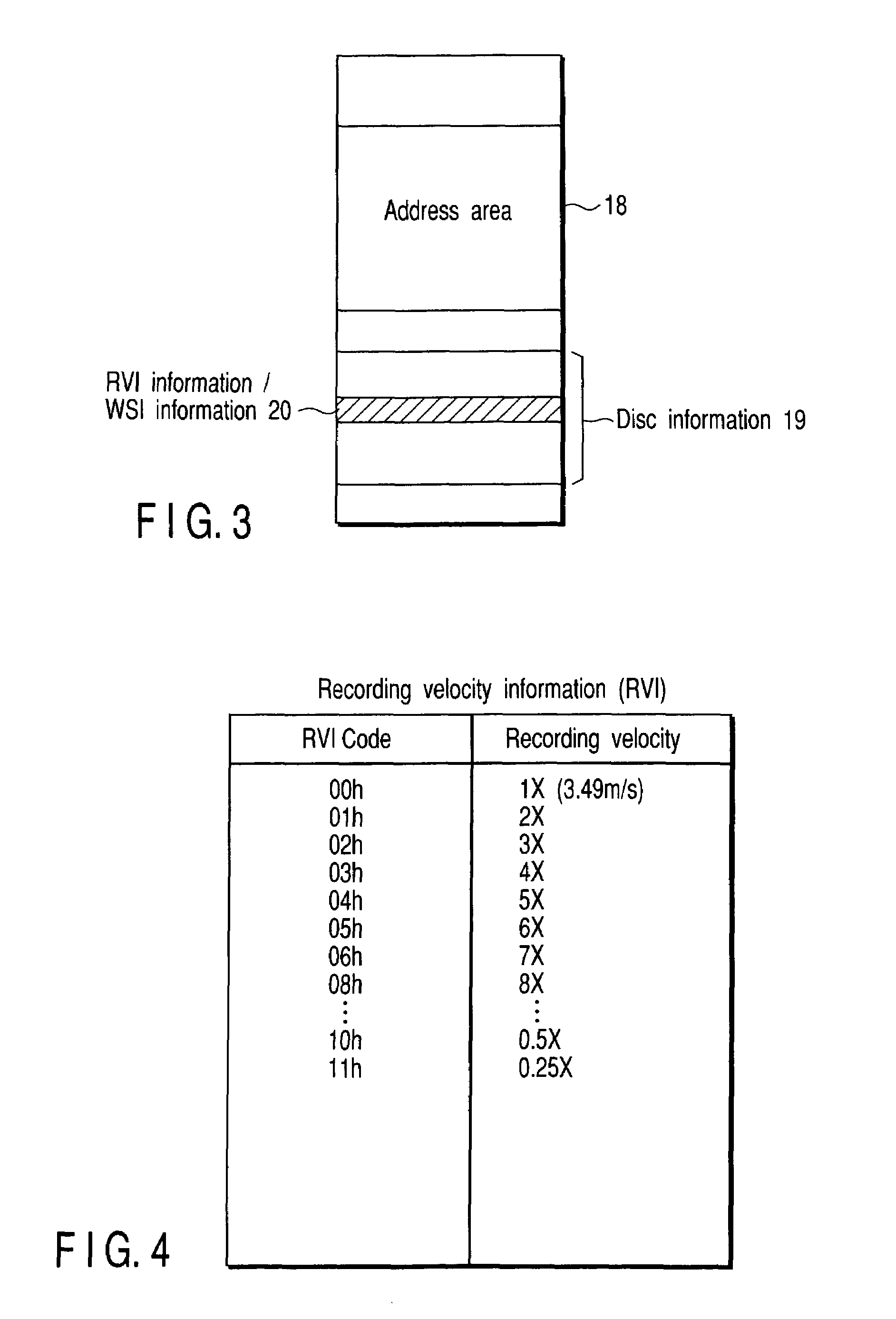
In an optical disc in / from which data is recorded or reproduced by irradiating a storage area on the optical disc with a laser, information containing recording velocity information (RVI) for recording / reproduction, which represents a linear velocity different from the standard linear velocity, and write strategy information (WSI) corresponding to the recording velocity information is stored in a land pre-pit or the like on the optical disc.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
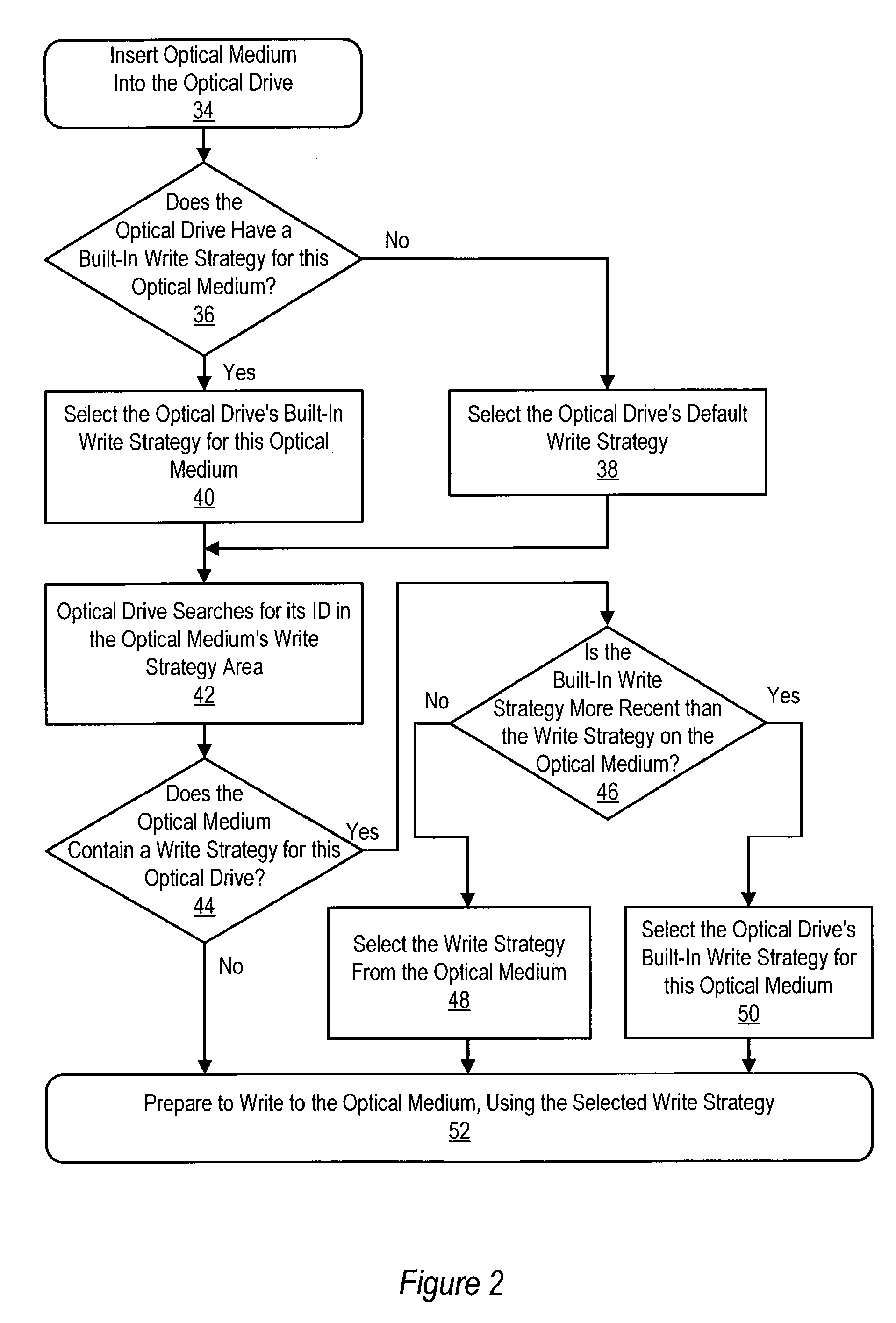
Method and system for optical drive write strategies embedded in an optical medium
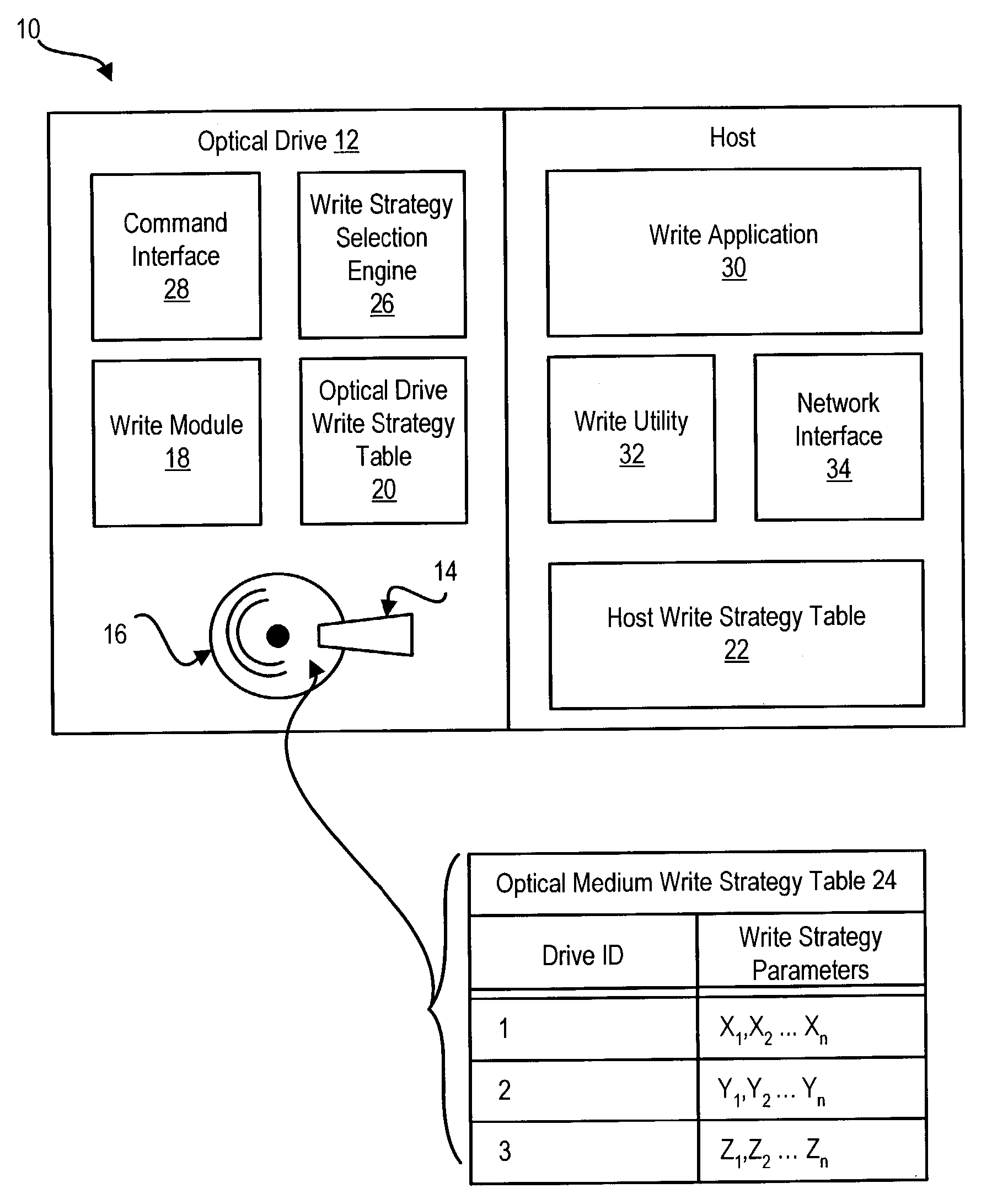
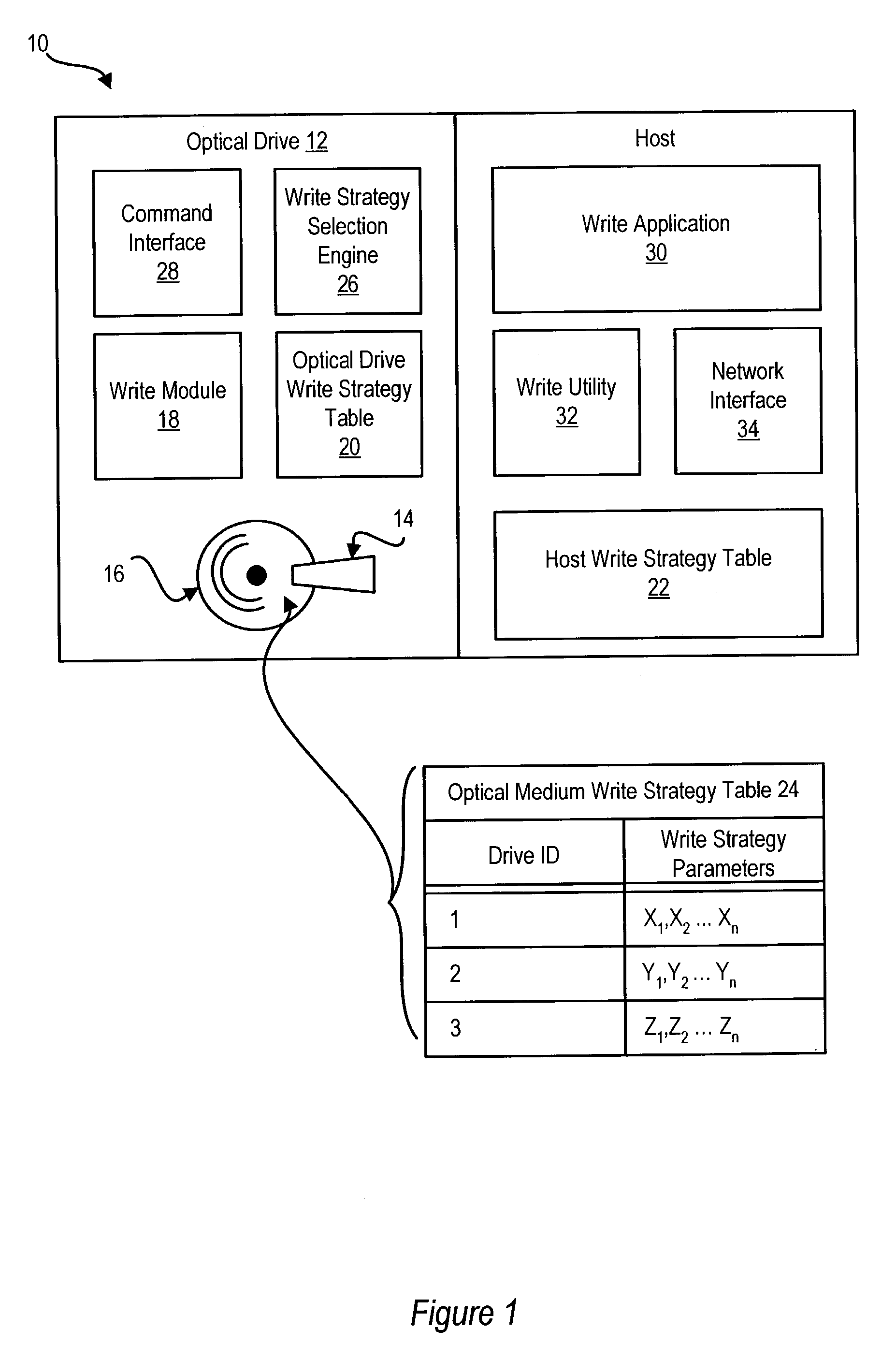
An optical drive writes information to an optical medium by obtaining a write strategy for the optical medium from a write strategy table embedded in the optical medium. A write module in the optical drive reads an optical drive identification code from the optical medium to select a write strategy associated with the optical drive. The write strategy of the embedded write strategy table that is identified for the optical drive is retrieved by the write module to write information to the optical medium with the optical drive using the identified write strategy. In one embodiment, a time stamp of the identified write strategy retrieved from the optical medium is compared with a time stamp of a write strategy already available to the optical drive to select the most recent write strategy for use by the optical drive. The write strategy table is embedded in the optical medium at manufacture of the optical medium, such as by stamping or burning the data into the optical material of the optical medium.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Optical recording medium, method for recording on optical record medium, and apparatus for recording on optical record medium
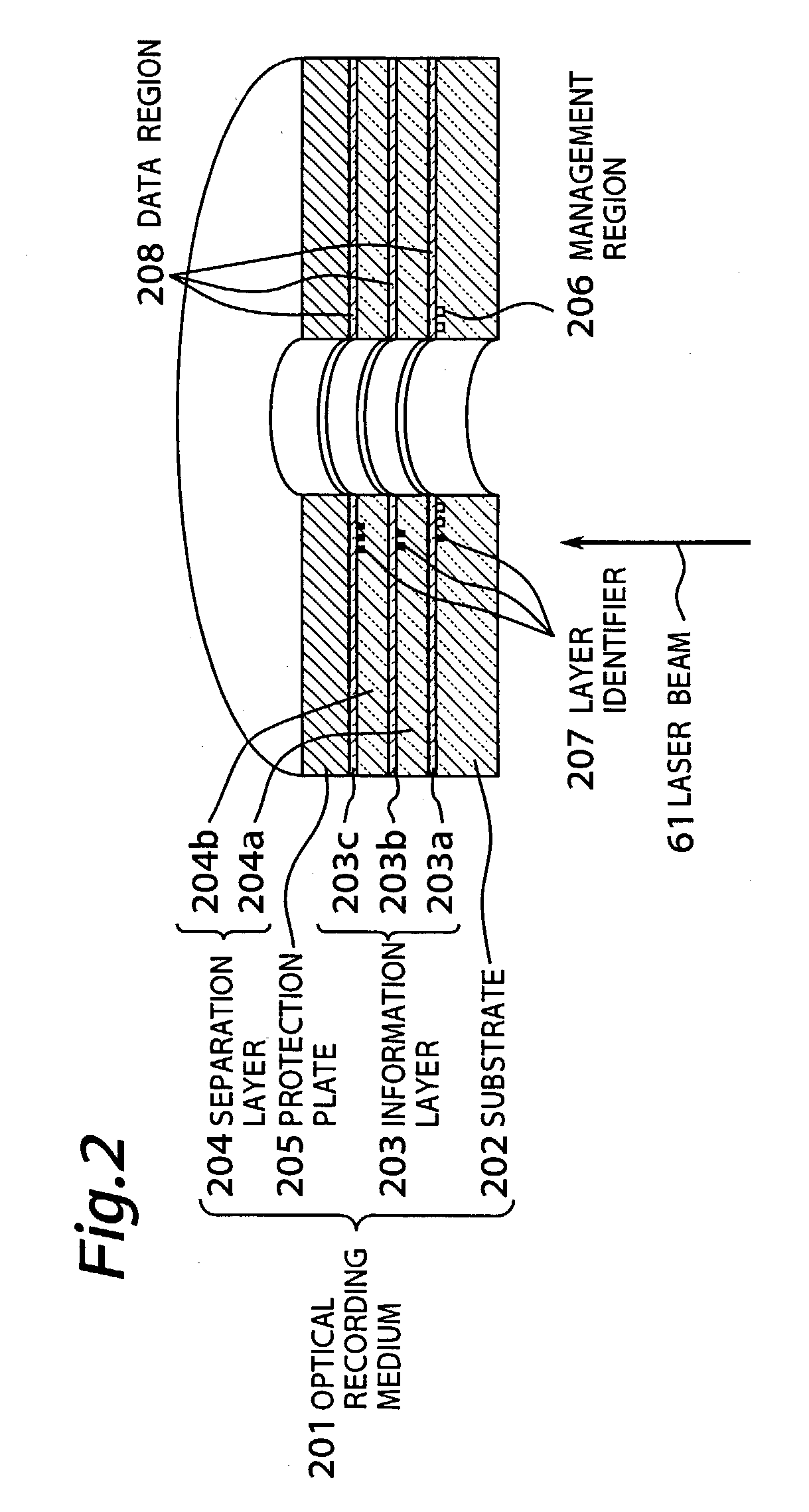
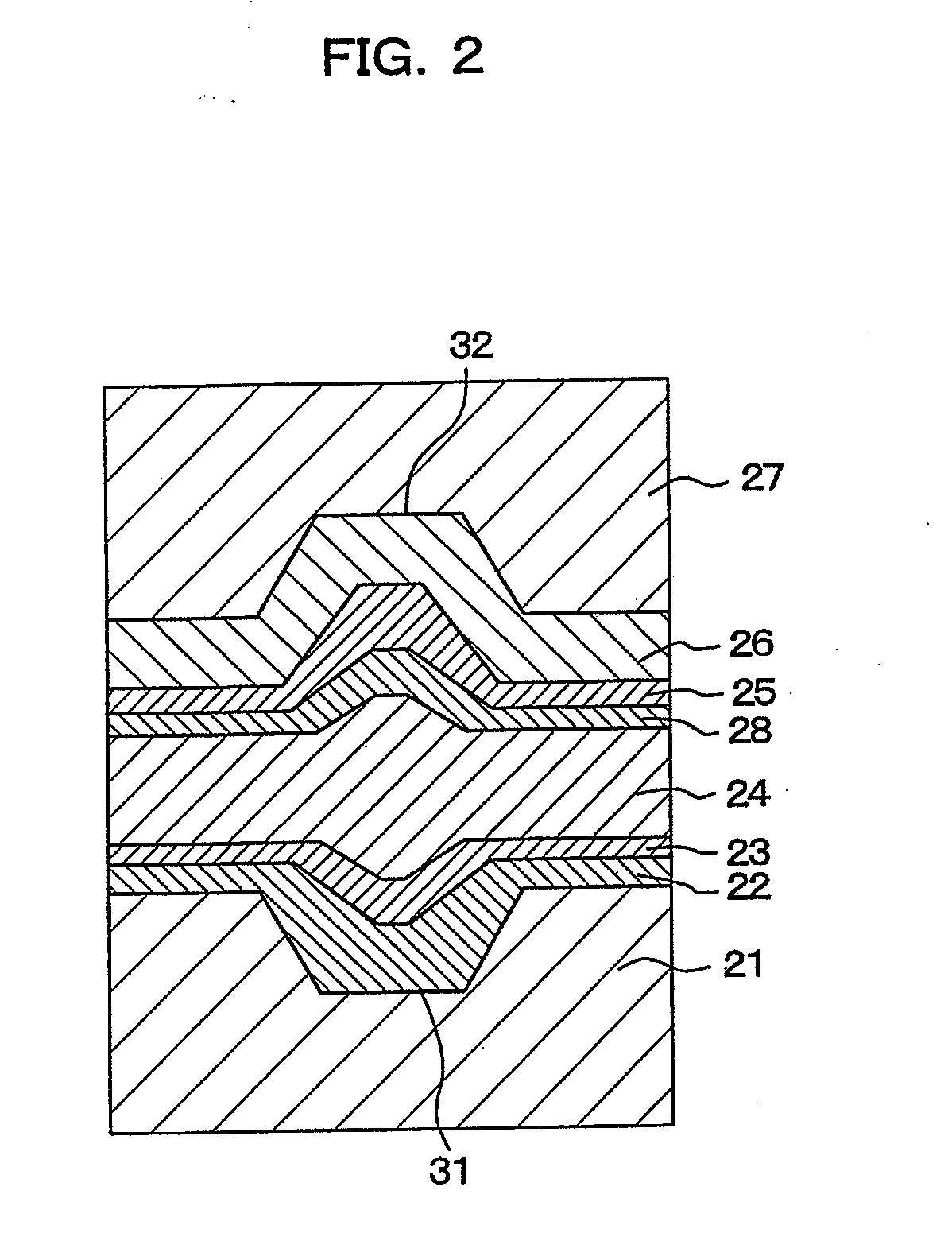
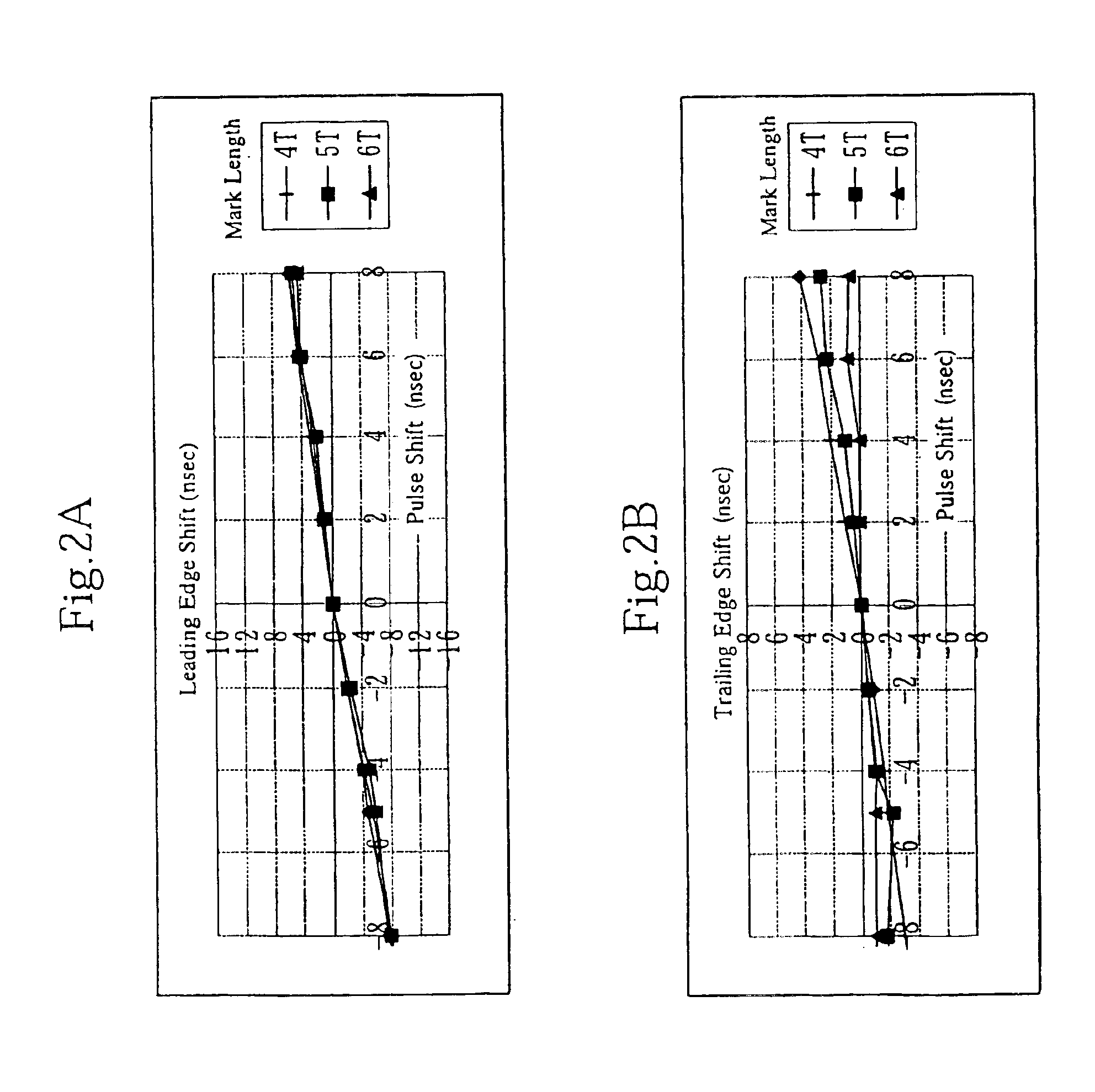
InactiveUS7193948B2Increase capacityReduce signal jitterRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsTrailing edgeElectrical and Electronics engineering
An optical recording medium of the present invention includes a substrate (202), a protection plate (205), and a plurality of information layers (203) sandwiched between the substrate and the protection plate. An information signal is recorded as a length of a mark and a length of a space between two marks. The mark is formed when the information layer is irradiated by light received through the substrate. The information layers have a management region (206) recording a leading edge recording condition and a trailing edge recording condition. The leading edge recording condition is used to change a recording start position for forming a leading edge of the mark. The trailing edge recording condition is used to change a recording end position for forming a trailing edge of the mark. Each of the leading and trailing edge recording condition is depending on which information layer is recorded.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
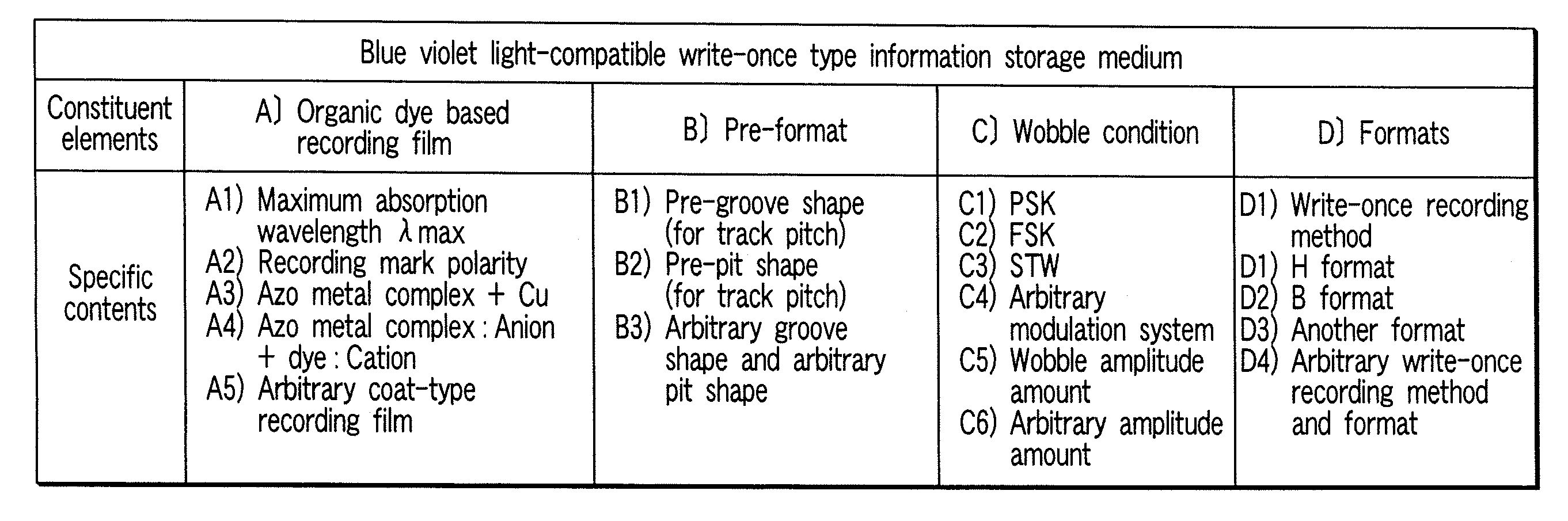
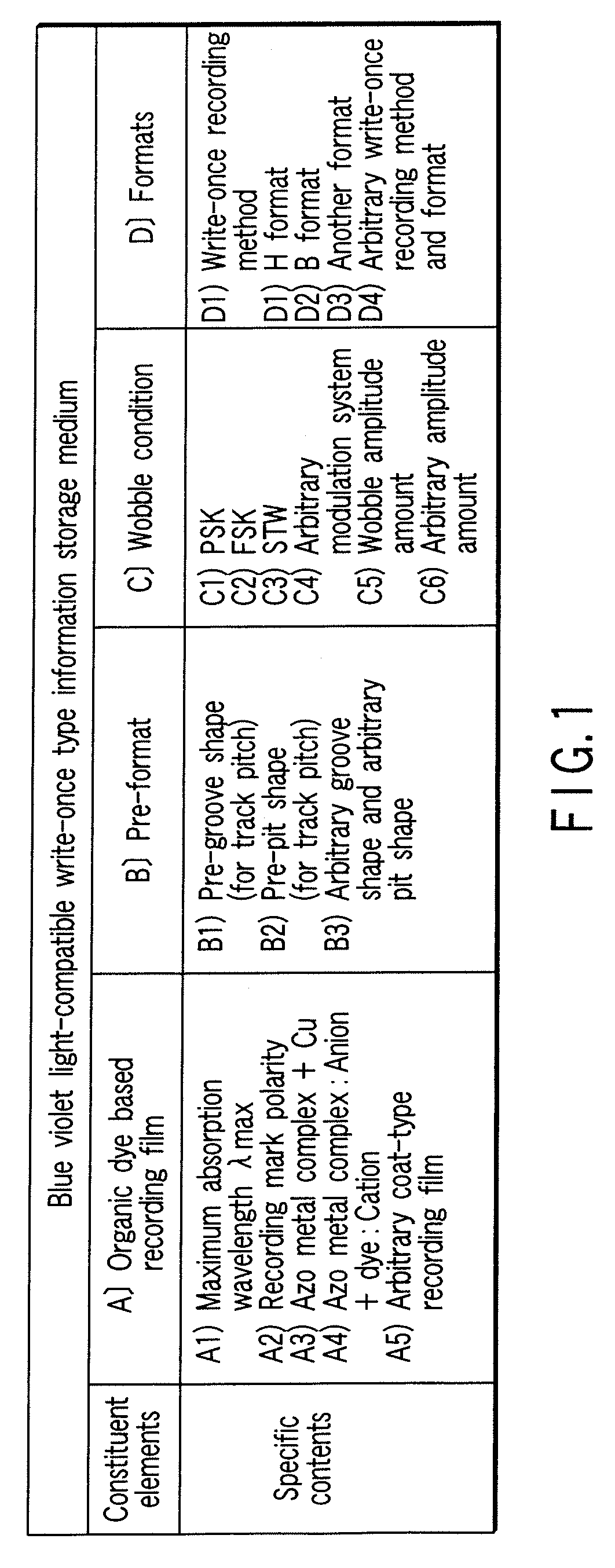
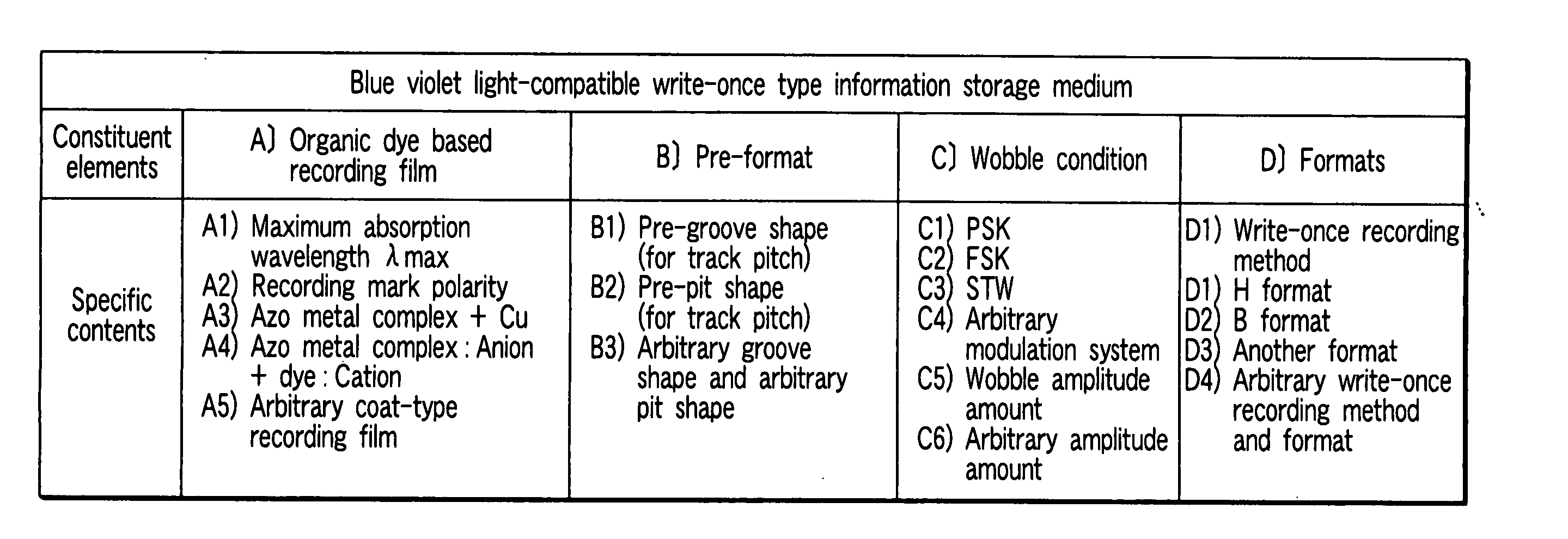
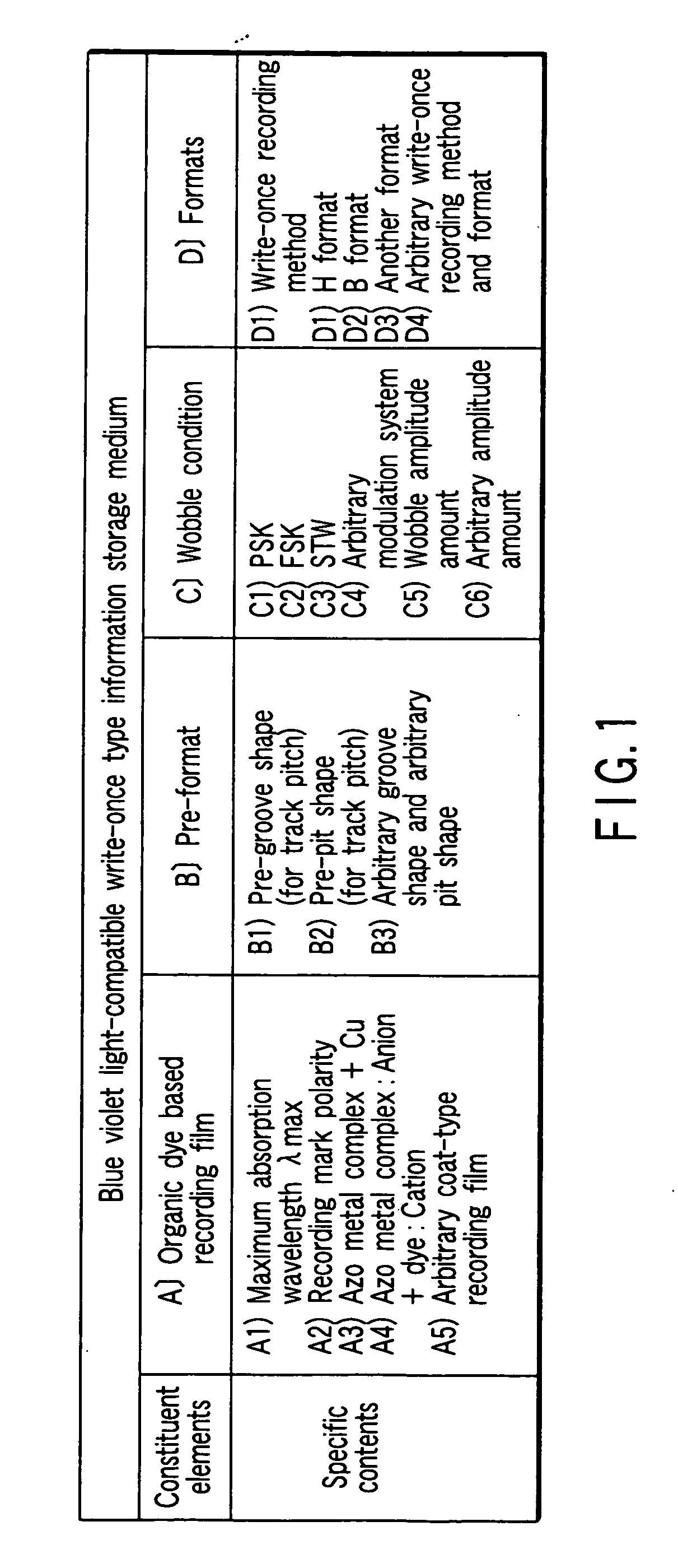
InactiveUS20070098949A1High densityHigh sensitivityRecording strategiesLayered productsOrganic dyeLength wave
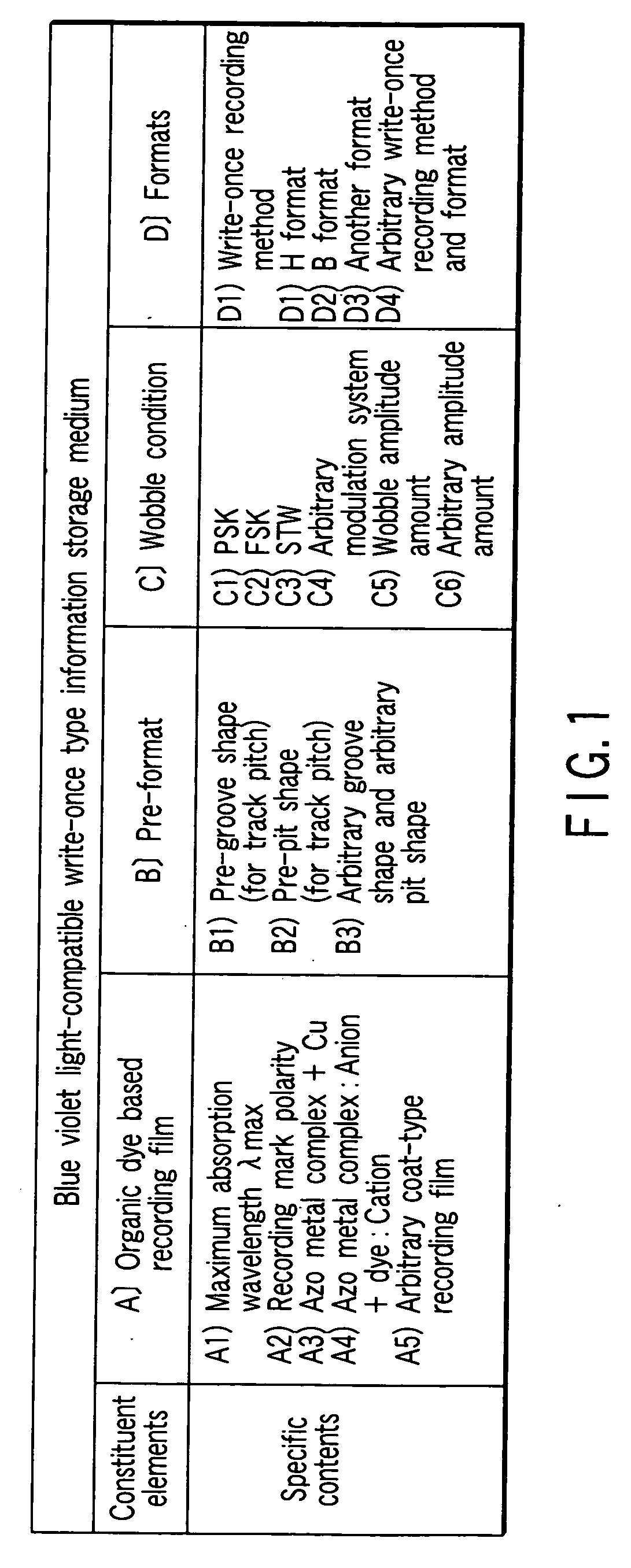
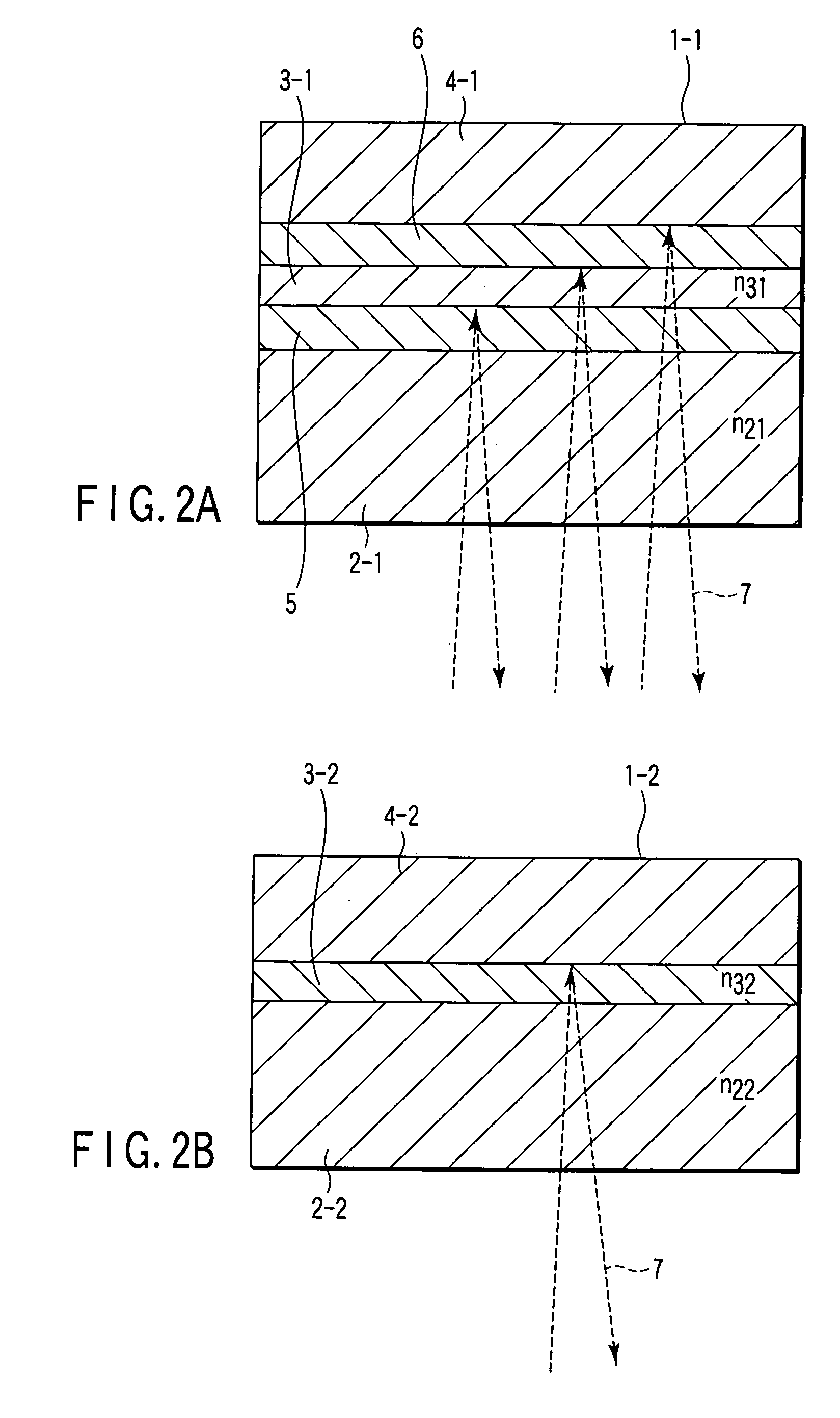
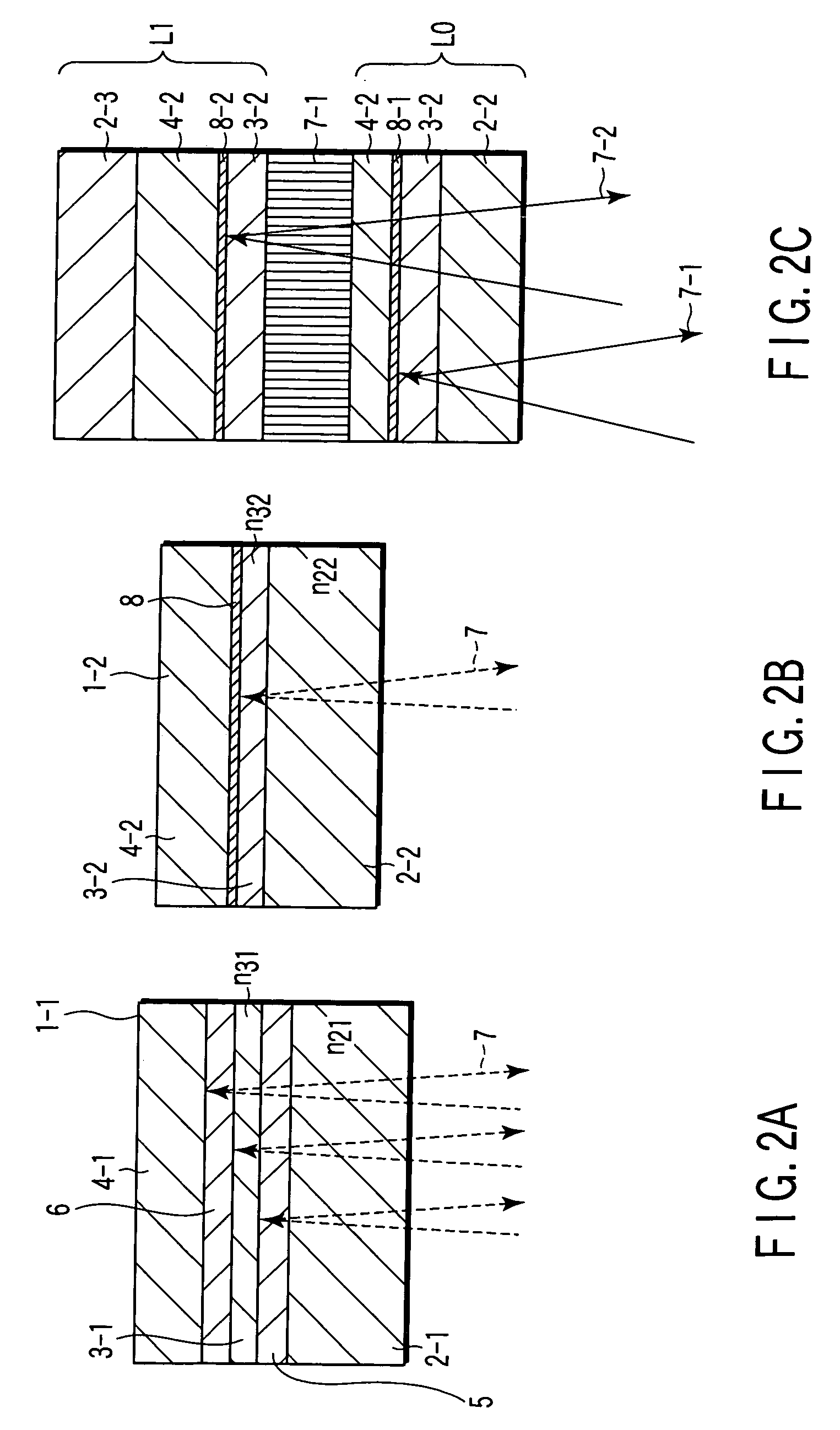
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium comprises an organic dye based recording material having sensitivity at a wavelength of 405 nm and at a recording wavelength in the range of 600 nm to 700 nm, wherein, when absorbance of a maximum absorption wavelength in the vicinity of 405 nm is defined as 1, the absorbance is 5% or more at any wavelength in the range of 600 nm to 700 nm.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS20060233093A1High densityHigh speed recordingRecording strategiesMechanical record carriersOrganic dyeLength wave
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium comprises an organic dye based recording material having sensitivity at a wavelength of 405 nm and at a recording wavelength in the range of 600 nm to 700 nm, wherein, when absorbance of a maximum absorption wavelength in the vicinity of 405 nm is defined as 1, the absorbance is 5% or more at any wavelength in the range of 600 nm to 700 nm.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Information recording method and information recording medium
InactiveUS20050063274A1Enhanced informationRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsHigh densityEngineering
An information recording method allows optical information having a recording mark length smaller than a spot diameter of laser light to be recorded on an optical recording medium having a recording layer, at high density by laser light pulse application. The information recording method has: a power calibration step of determining a recording power for recording a signal having a predetermined signal length in the recording layer using the laser light; and a complementing step of complementing, based on the recording power determined in the power calibration step, a recording power for recording a signal having a signal length equal to or less than ½ of the spot diameter of the laser light in the recording layer using the laser light. In the information recording method, for example, an extremely small mark, such as a 2T signal, can be precisely formed.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION +1
Optical disc recording method and apparatus
InactiveUS6996047B2Improve signal qualityRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLight beamOptoelectronics
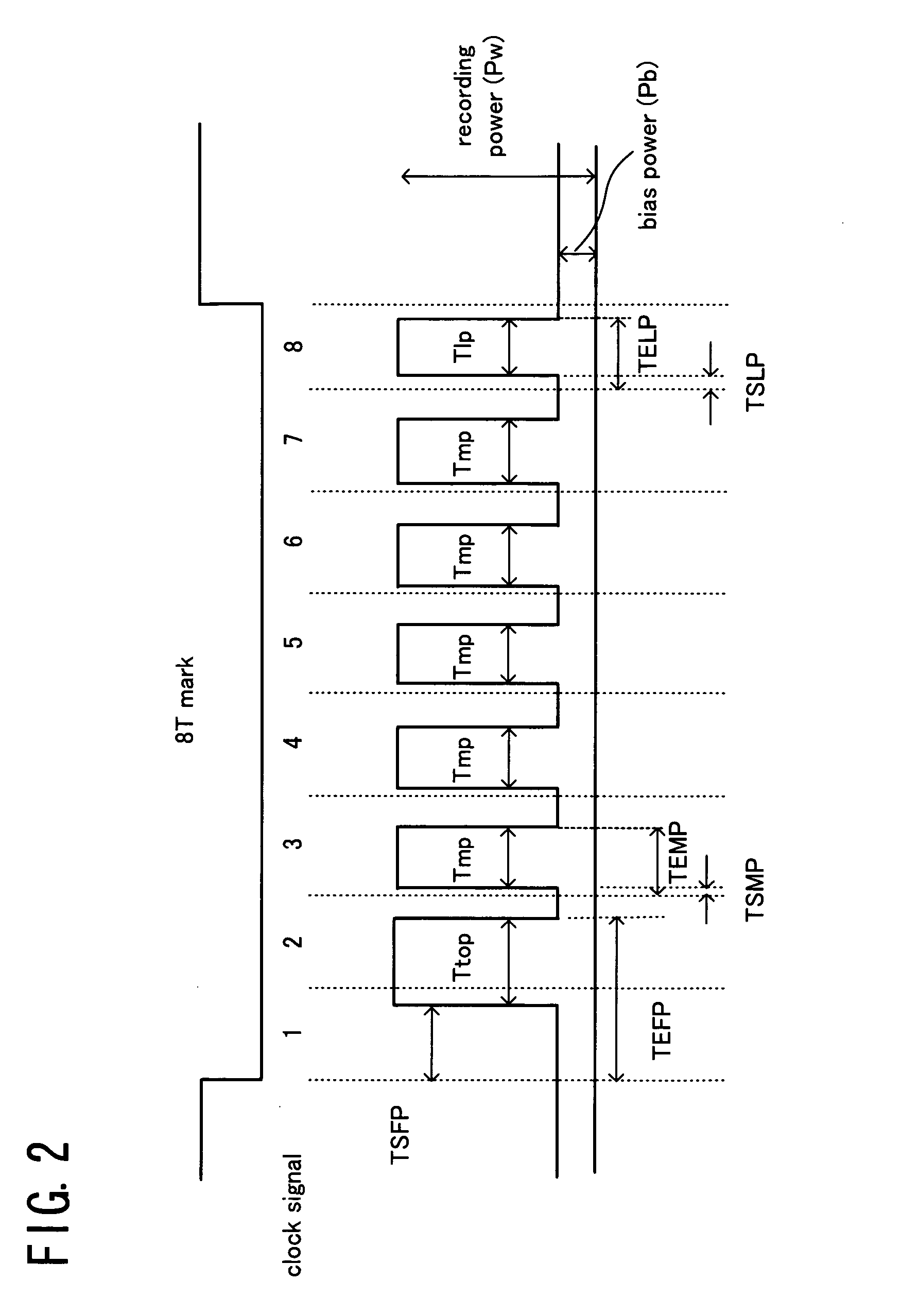
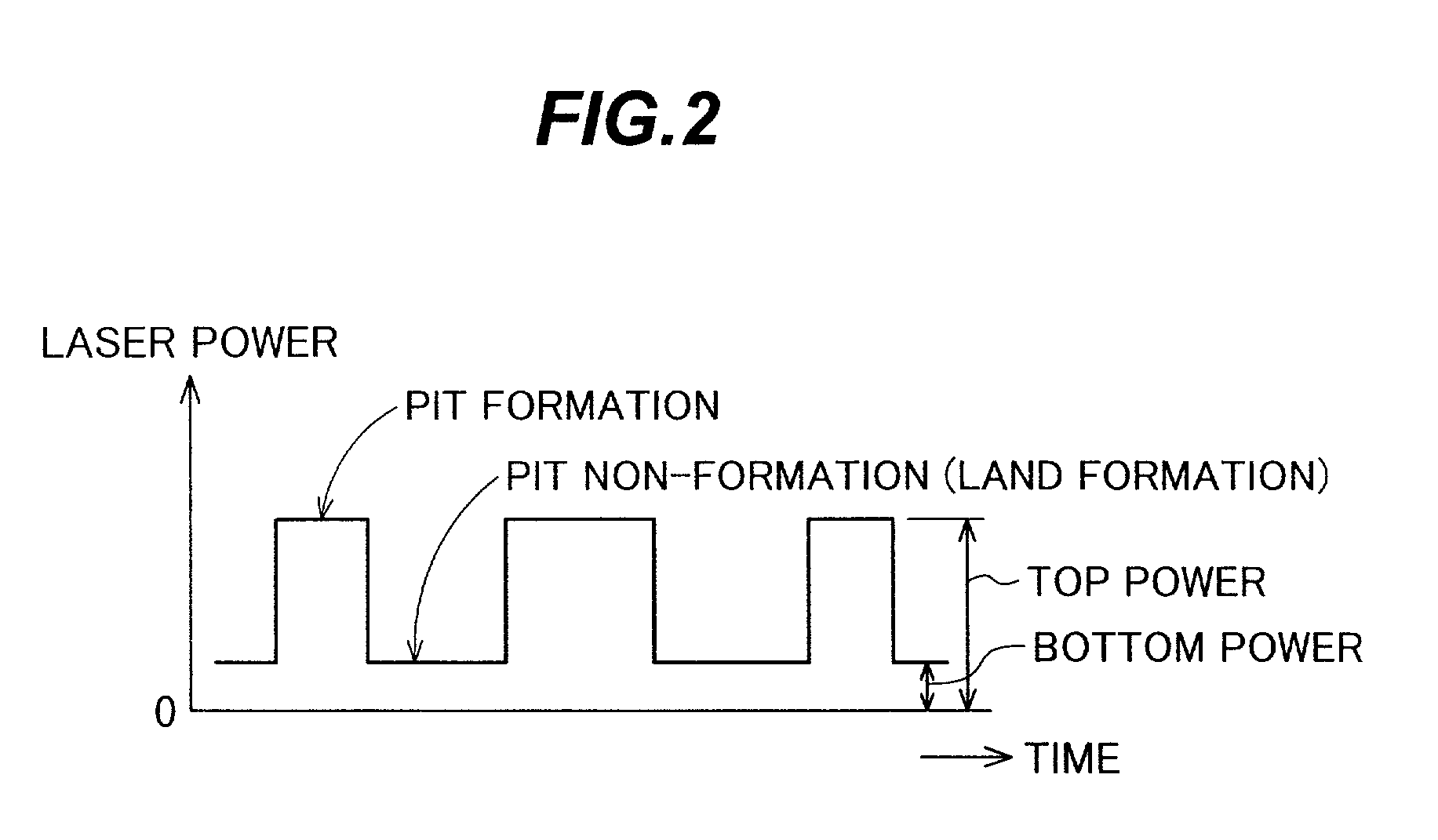
An opical disc recording method, comprises the steps of: a) forming a record signal in accordance with input information; b) generating a recording laser beam modulated with the record signal; c) controlling a laser radiation time at a record power for a 16× or higher write-speed to be (n+K)T for a pit length nT, where n=three to eleven, K is a constant (0≦K≦1.6), and T is a unit time corresponding to a pit length or a land length at a write-speed; and d) radiating the recording laser beam alternately at the recording power for the controlled radiating time to form pits and at a non-recording power to form lands toward a record surface of a recordable optical disc.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Optical disc recording apparatus with realtime updating of strategy
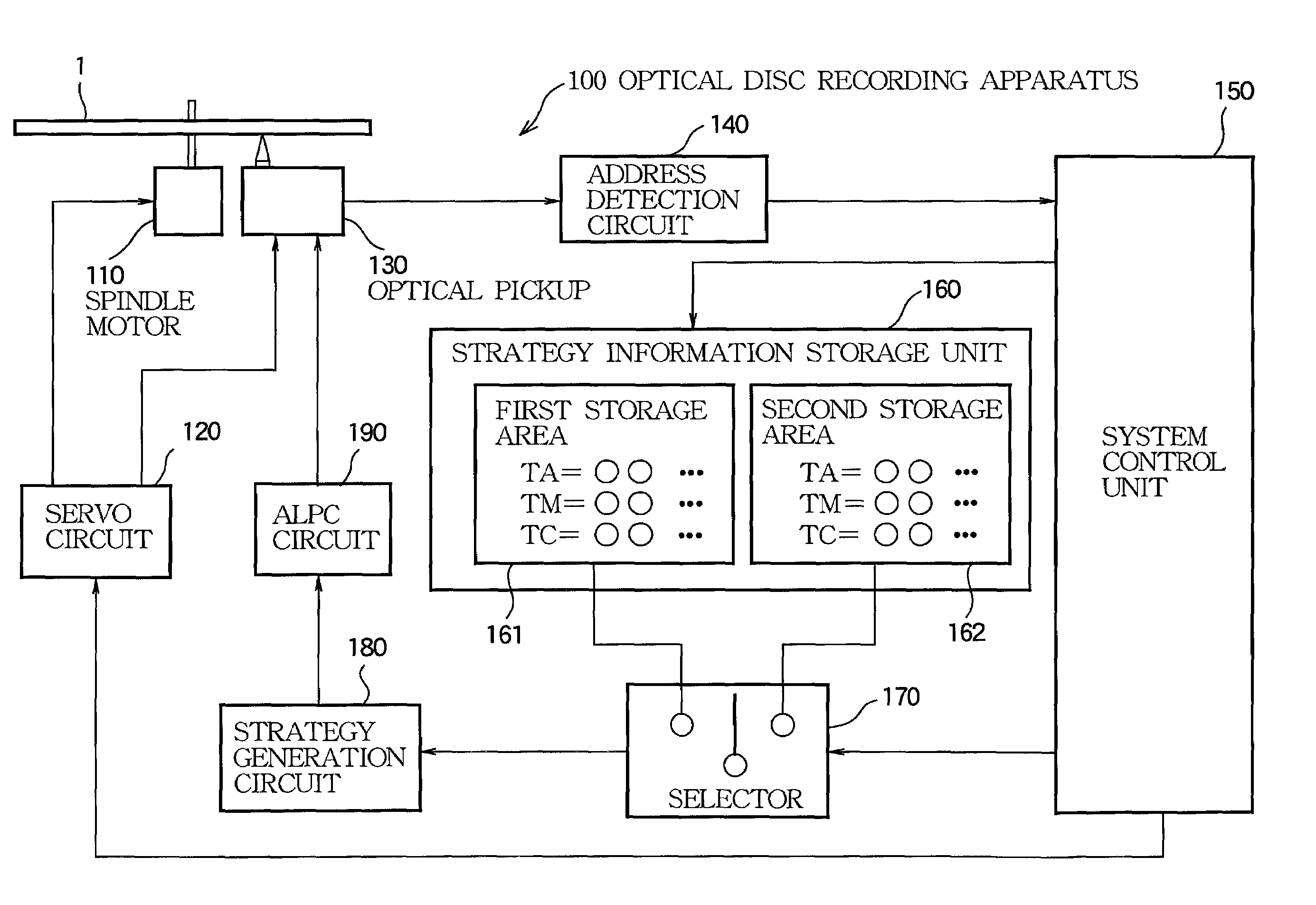
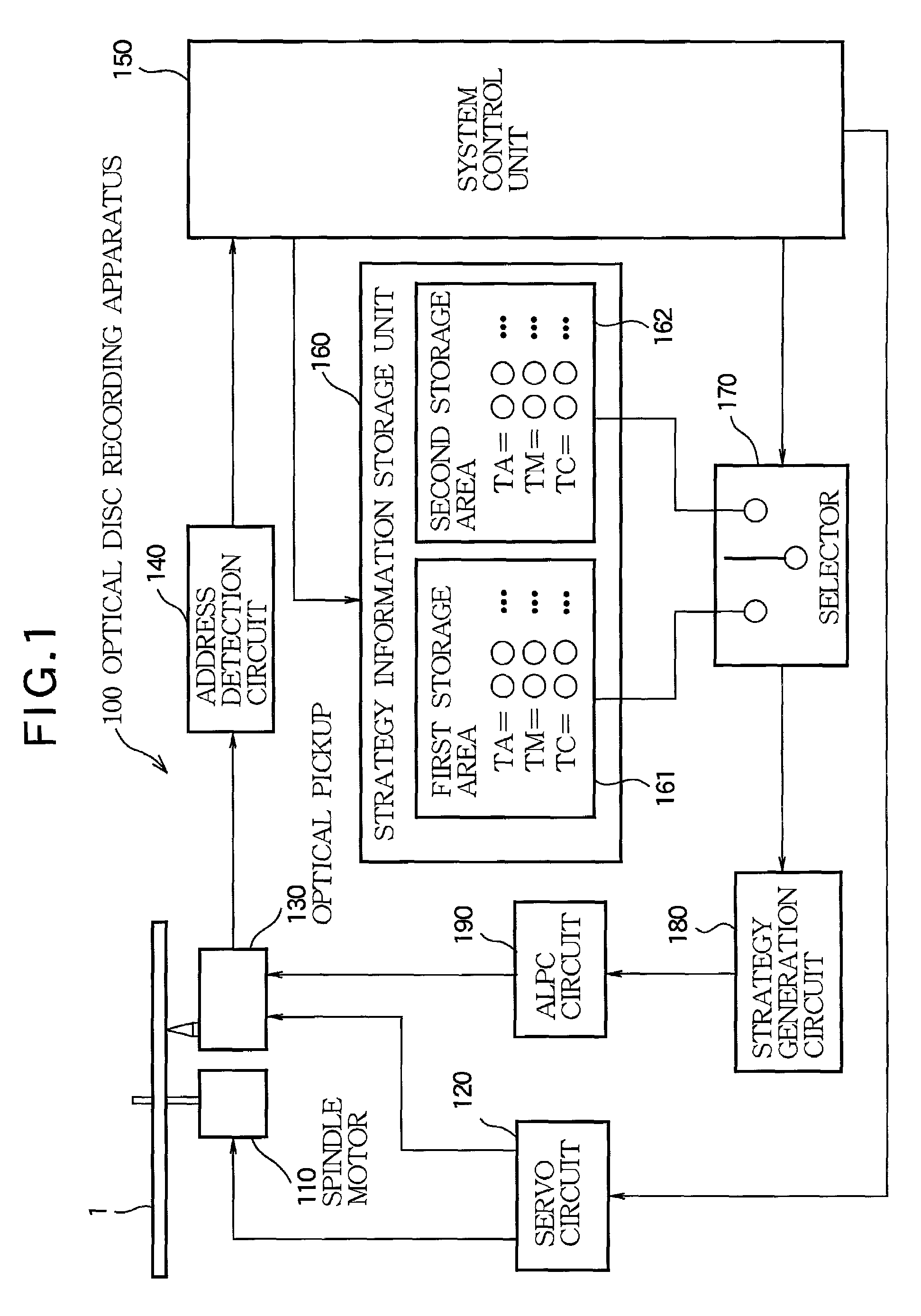
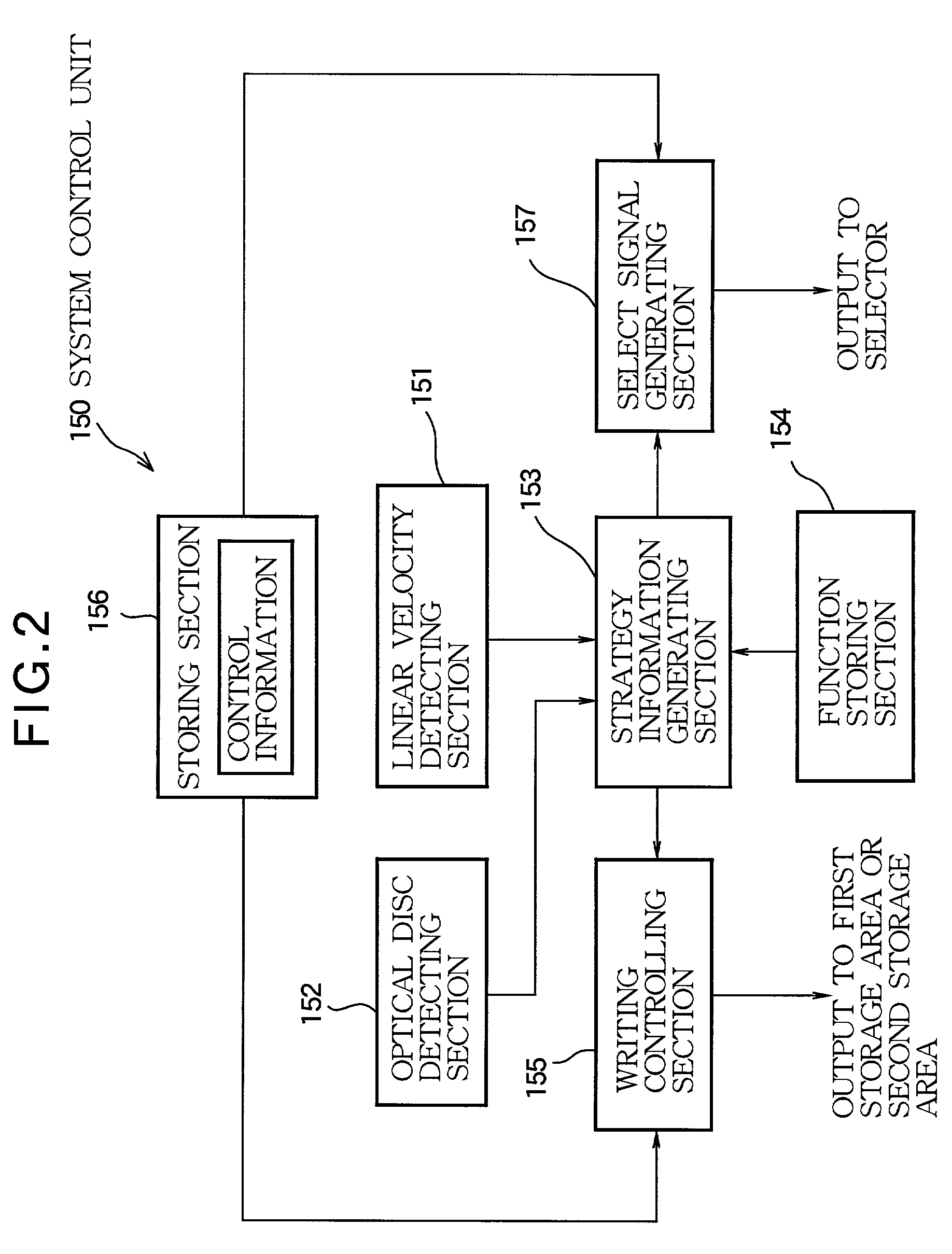
InactiveUS6999393B2Reduce errorsReducing recording errorTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesSignal onPhysics
A disc apparatus is designed for recording a signal on an optical disc by irradiating an optical beam according to a strategy which is stepwise updated by a given step amount. In the disc apparatus, a detector successively detects a linear velocity of the optical disc relative to the optical beam in realtime basis. A strategy generator operates every time the detector detects the linear velocity of the optical disc for successively generating the strategy according to the detected linear velocity. A storage has a plurality of storage areas, each being capable of memorizing the strategy successively generated by the strategy generator. A write controller rewrites one of the storage areas every time the strategy is generated until the strategy is updated by a given step amount and then rewrites another of the storage areas every time the strategy is generated while leaving said one storage area to hold the updated strategy, thereby updating the strategy through the plurality of the storage areas. A read selector selects the storage area holding the updated strategy to read therefrom the updated strategy while allowing the write controller to rewrite another storage area.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Writable optical drive with dynamically variable linear velocity to prevent buffer under-run
InactiveUS6901039B1Extended durationIncrease exposureRecording strategiesFilamentary/web record carriersMicrocontrollerEngineering
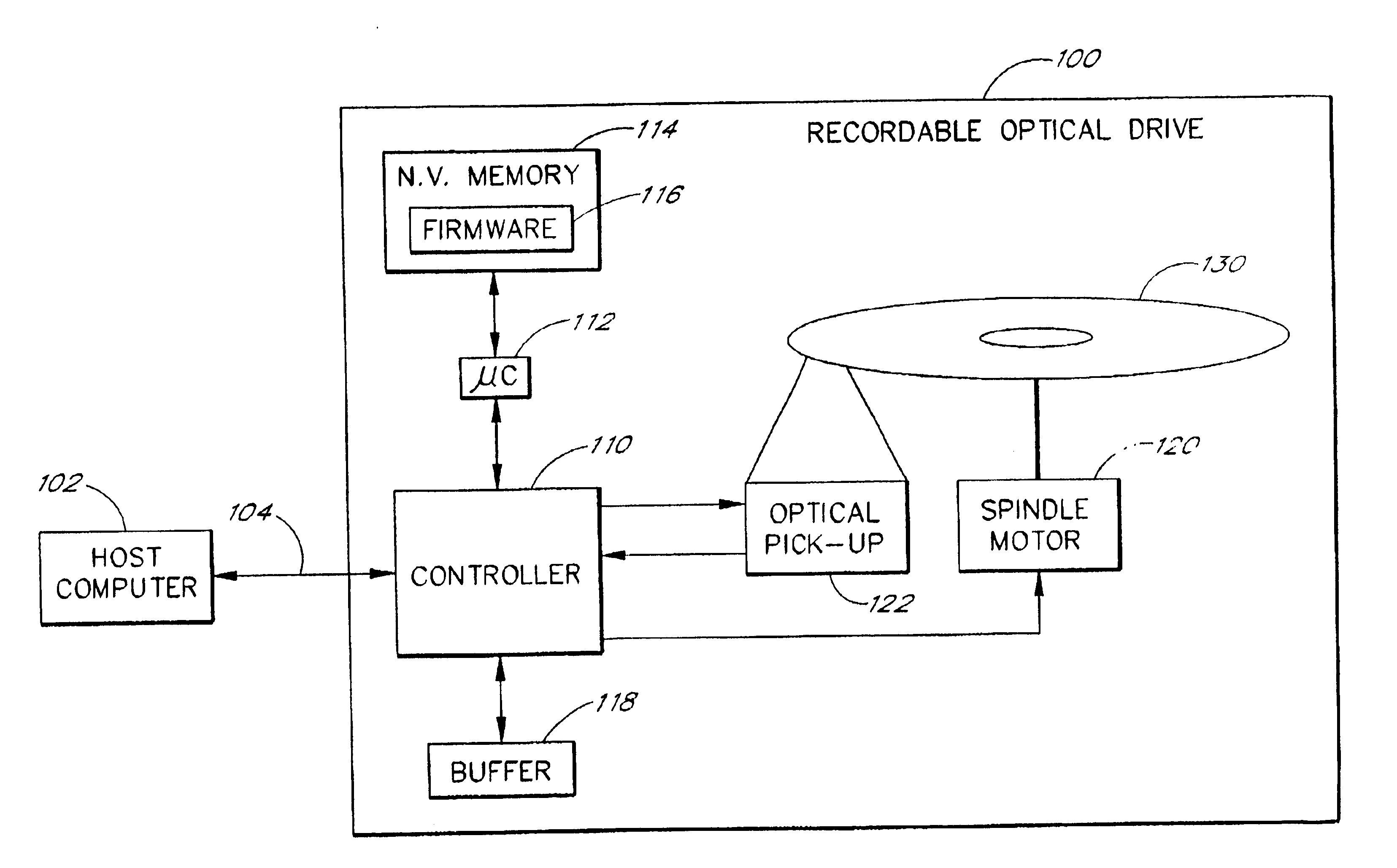
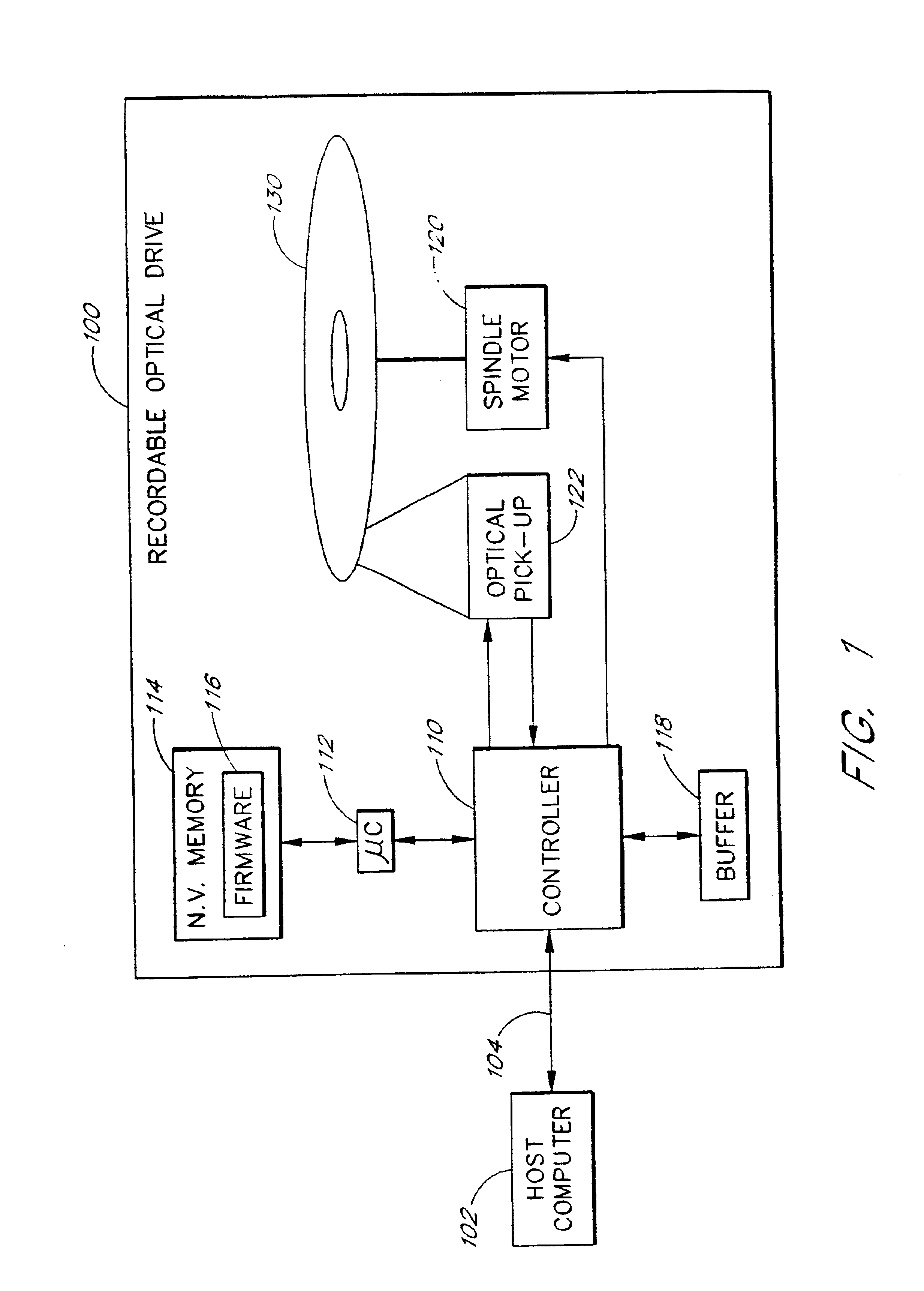
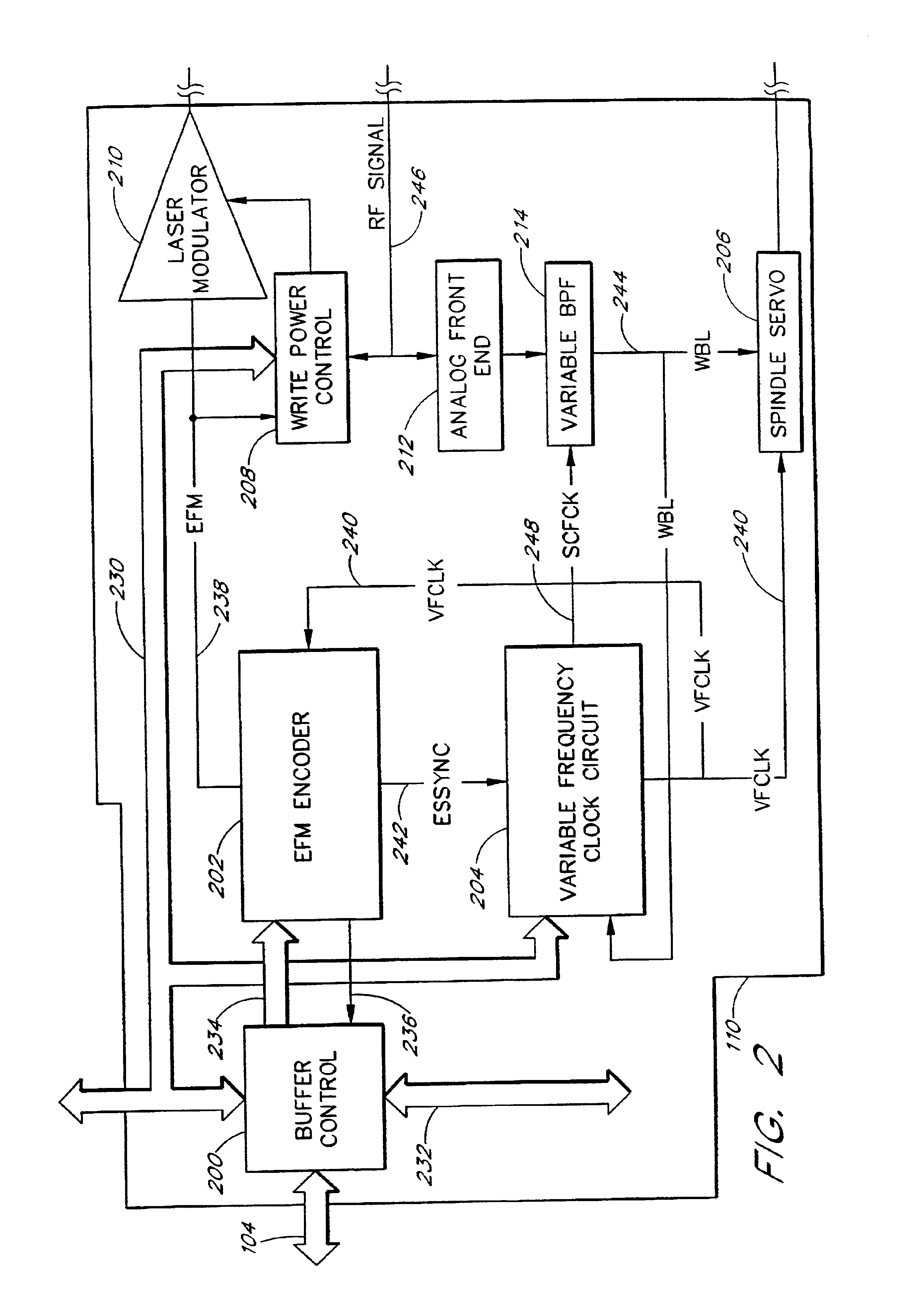
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for dynamically varying a linear velocity of an optical drive during a write operation to an optical disc to reduce the likelihood of a buffer under-run event. By reducing a linear velocity and writing speed while the optical drive writes on the disc, an embodiment of the invention preserves the buffer and reduces a minimum data transfer rate required to sustain writing to the disc for a sustained period of time. The basic components of one embodiment of a CD-RW drive (100) in which the present invention may be implemented include a controller (110), a microcontroller (112), a nonvolatile memory (114), which stores firmware (116) executed by the microcontroller (112), a buffer (118), a spindle motor (120) and an optical pick-up (122).
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS20060210925A1High densityHigh speed recordingRecording strategiesRadiation applicationsSubstrate deformationComputer science
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium using a recording material which has a low to high characteristic that a light reflectivity in a recording mark increases with respect to a non-recording area and which has a recording characteristic in accordance with a principle of recording without substrate deformation, wherein the recording material includes at least an organic metal complex, and wherein the organic metal complex includes a center metal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS20060223004A1High densityHigh speed recordingRecording strategiesLayered productsOrganic dyeLight beam
According to one embodiment, a storage medium comprises a transparent resin substrate on which a groove is formed, a recording layer formed on the groove on the transparent resin substrate, the recording layer using an organic dye material and recording information with a light beam of 620 nm or less in wavelength, a reflection layer formed on the recording layer, and a prevention layer formed between the recording layer and the reflection layer, the prevention layer preventing degradation of characteristics of the reflection layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Recordable optical disc, optical disc recording apparatus, optical disc reproduction apparatus, and method for recording data onto recordable optical disc
InactiveUS7068579B2DataRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsRecordable compact discData recording
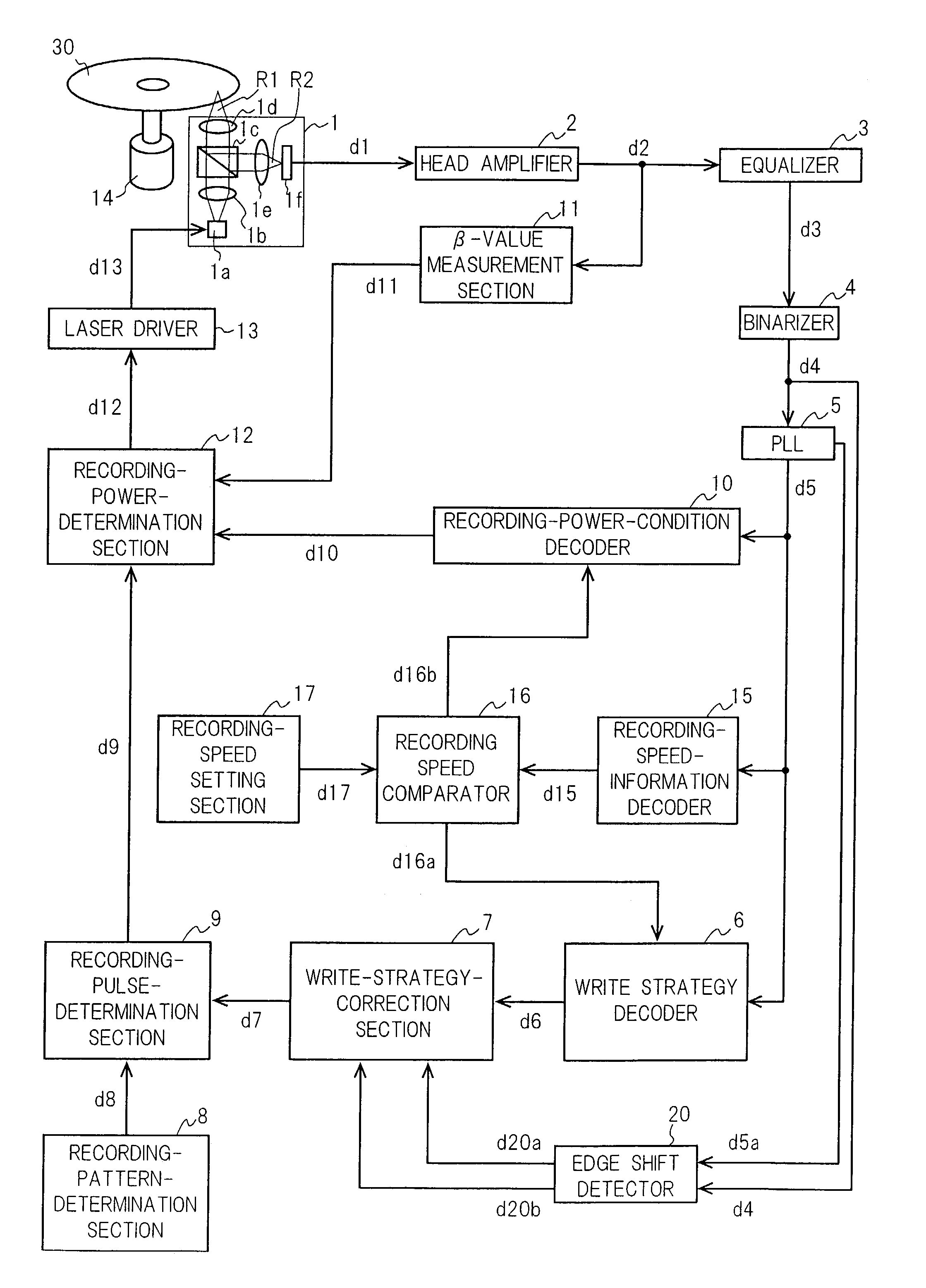
A DVD-R recorder according to the invention detects an item of recording speed information (d15) from a DVD-R (30) on which histories of recording speed information, write strategy, and recording power condition are stored. When the decoded item of recording speed information (d15) agrees with a set item of recording speed information (d17), the recorder detects the write strategy (d6) and the recording power condition (d10) corresponding to the decoded item of recording speed information (d15). A recording-pulse-determination section (9) converts a recording pattern (d8) into a recording pulse (d9) according to the write strategy (d6). A recording-power-determination section (12) performs an OPC based on the recording power condition (d10). The recording power condition (d10) may include information specifying that a recording pulse corresponding to the front edge of a recorded mark has a larger recording power than other recording pulses.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for recording data onto optical recording medium, data recording device, and optical recording medium
ActiveUS20060013111A1High modulationImprove surface smoothnessTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesThree levelLight beam
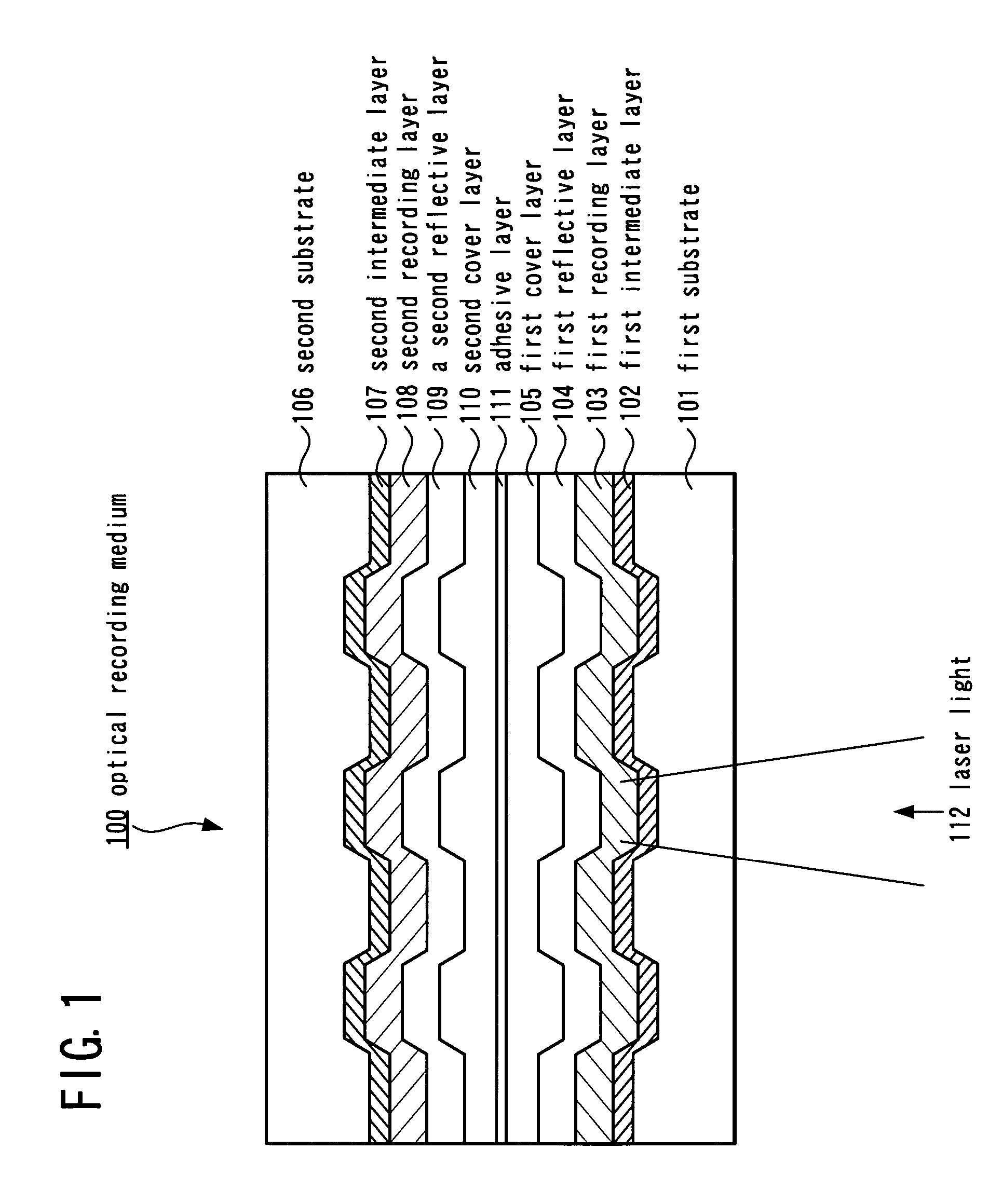
A method for recording data in an optical recording medium which can record data in information recording layers other than an information recording layer farthest from a light incidence plane of an optical recording medium including a plurality of information recording layers in a desired manner and reproduce data from information recording layers other than the information recording layer farthest from the light incidence plane in a desired manner. The method for recording data in an optical recording medium according to the present invention is adapted for recording data in the optical recording medium including a substrate, a protective layer and a plurality of information recording layers between the substrate and the protective layer by projecting a laser beam onto the plurality of information recording layers via a light incidence plane constituted by either the substrate or the protective layer, thereby recording data in the plurality of information recording layers and the method for recording data in an optical recording medium comprises the steps of projecting a laser beam whose power is modulated between at least three levels including a level corresponding to a recording power, a level corresponding to an intermediate power lower than the recording power and a level corresponding to a bottom power lower than the intermediate power onto at least one information recording layer other than an information recording layer farthest from the light incidence plane and forming a recording mark in the at least one information recording layer other than the information recording layer farthest from the light incidence plane, thereby recording data therein.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Recording/reading method for an optical recording medium using an irradiating a laser beam
In an optical recording medium of a single-sided incident type having a plurality of recording layers, recording / reading conditions (for example, tracking polarity, recording pulse strategy, recording recommended power, etc.) can be instantaneously switched according to each of the recording layer, and recording or reading of information can be accurately and surely performed under recording / reading conditions adapted to each recording layer. A control unit reads out layer information from one recording layer of the optical recording medium in which the layer information is recorded in each of the plural layers, on which recording or reading of information can be performed by irradiating a laser beam from one side thereof (layer information reading step), and controls so that recording or reading is performed under recording / reading conditions adapted to a recording layer specified on the basis of the layer information (recording controlling step).
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
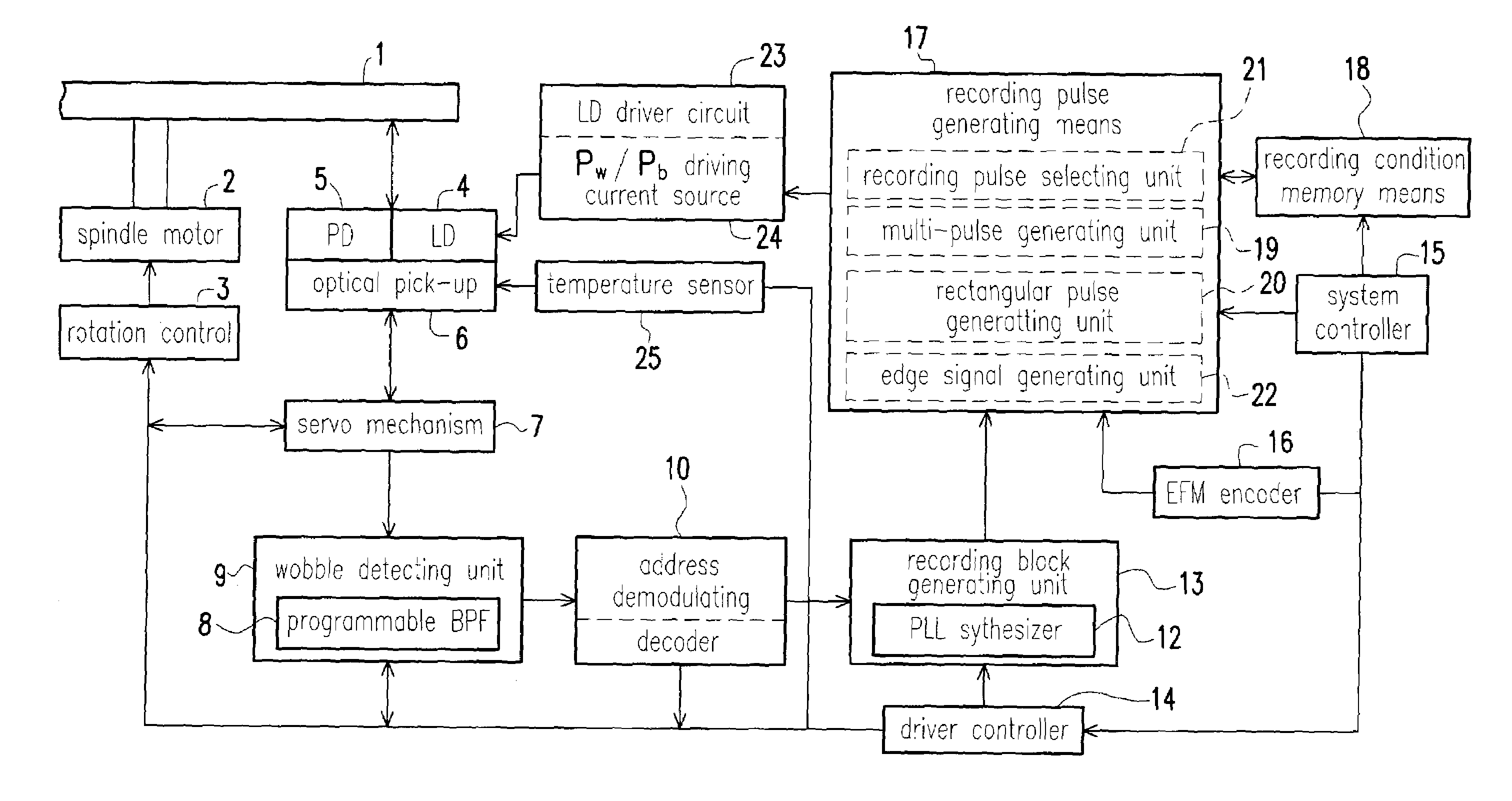
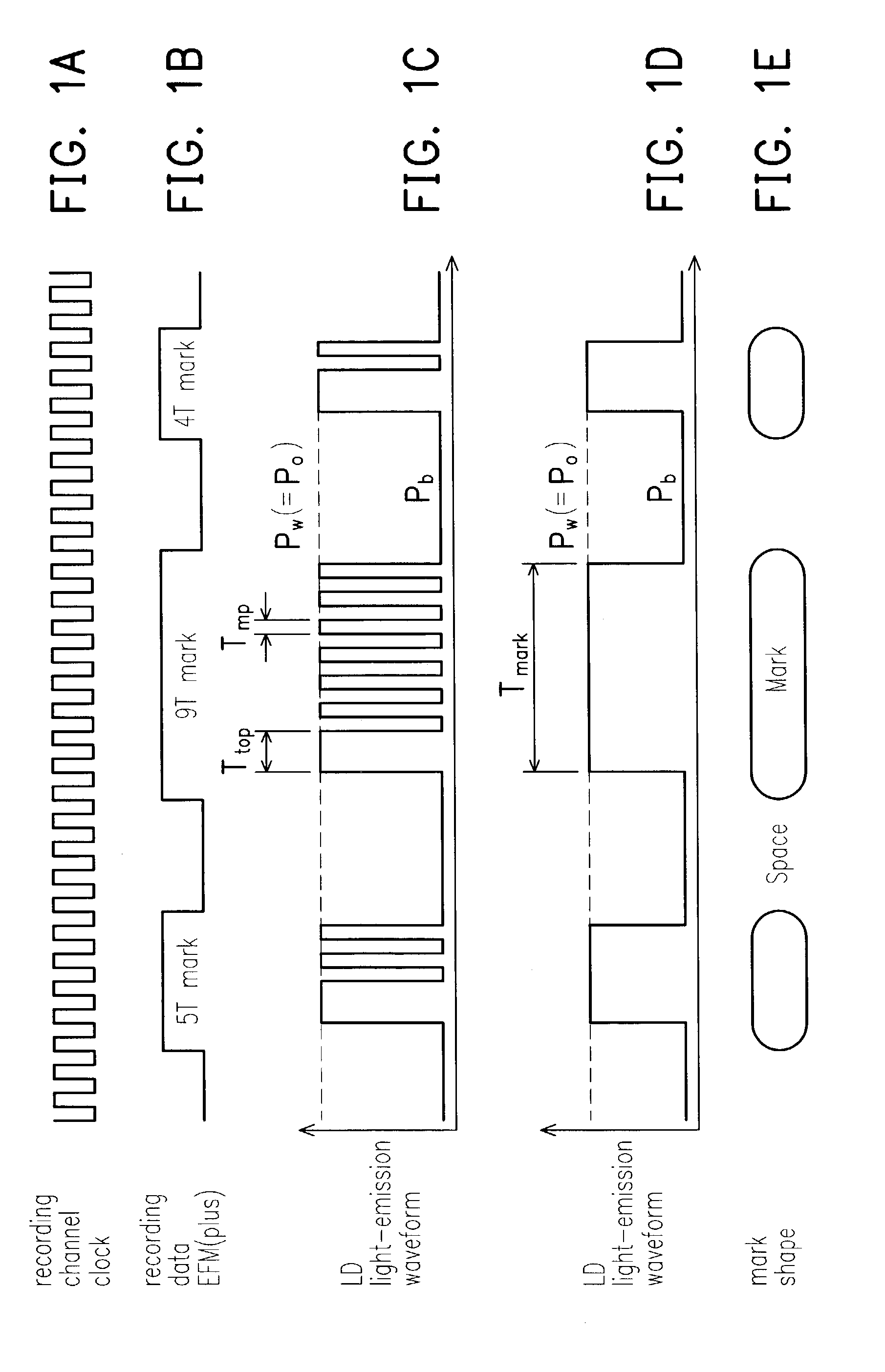
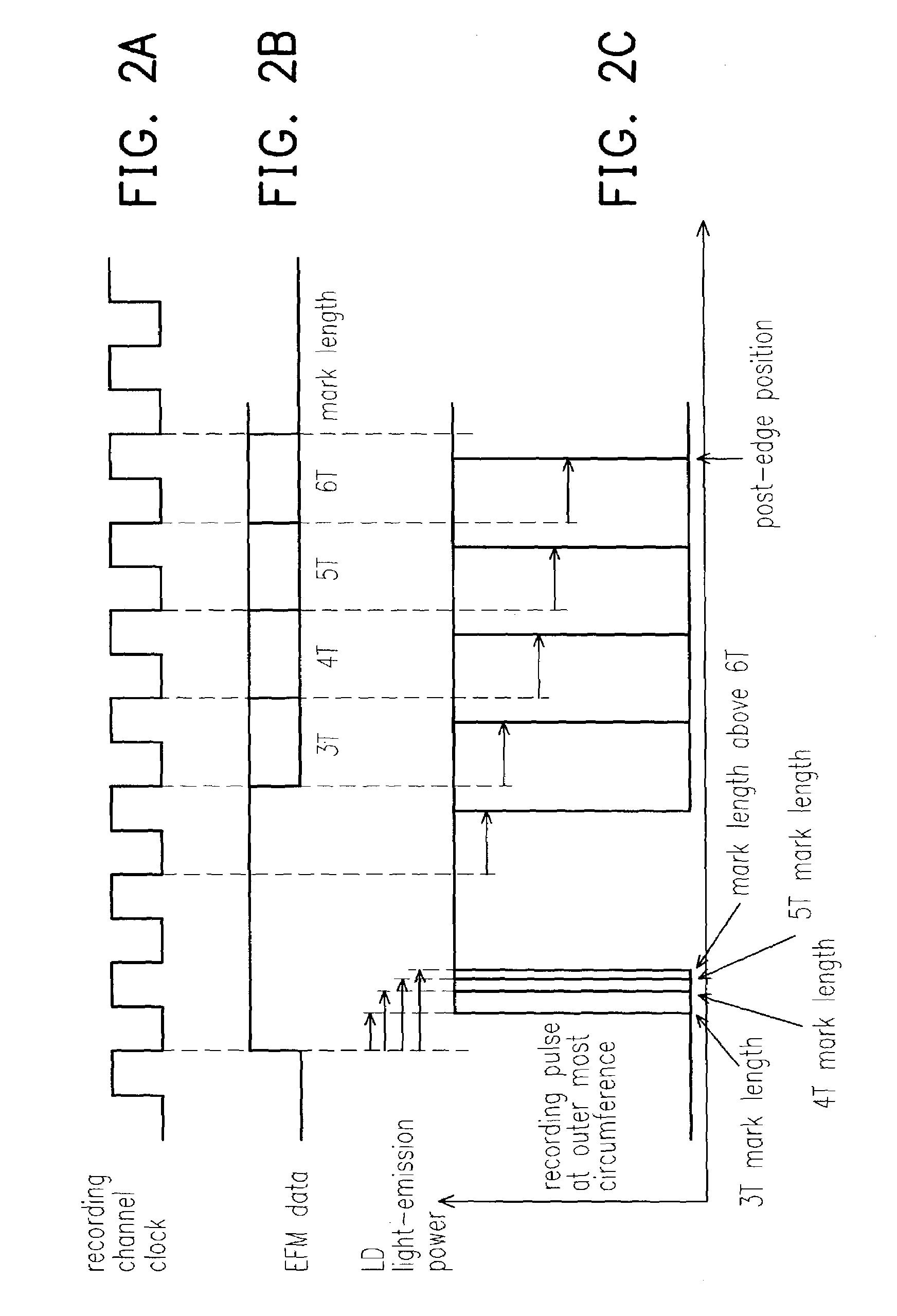
Information recording device
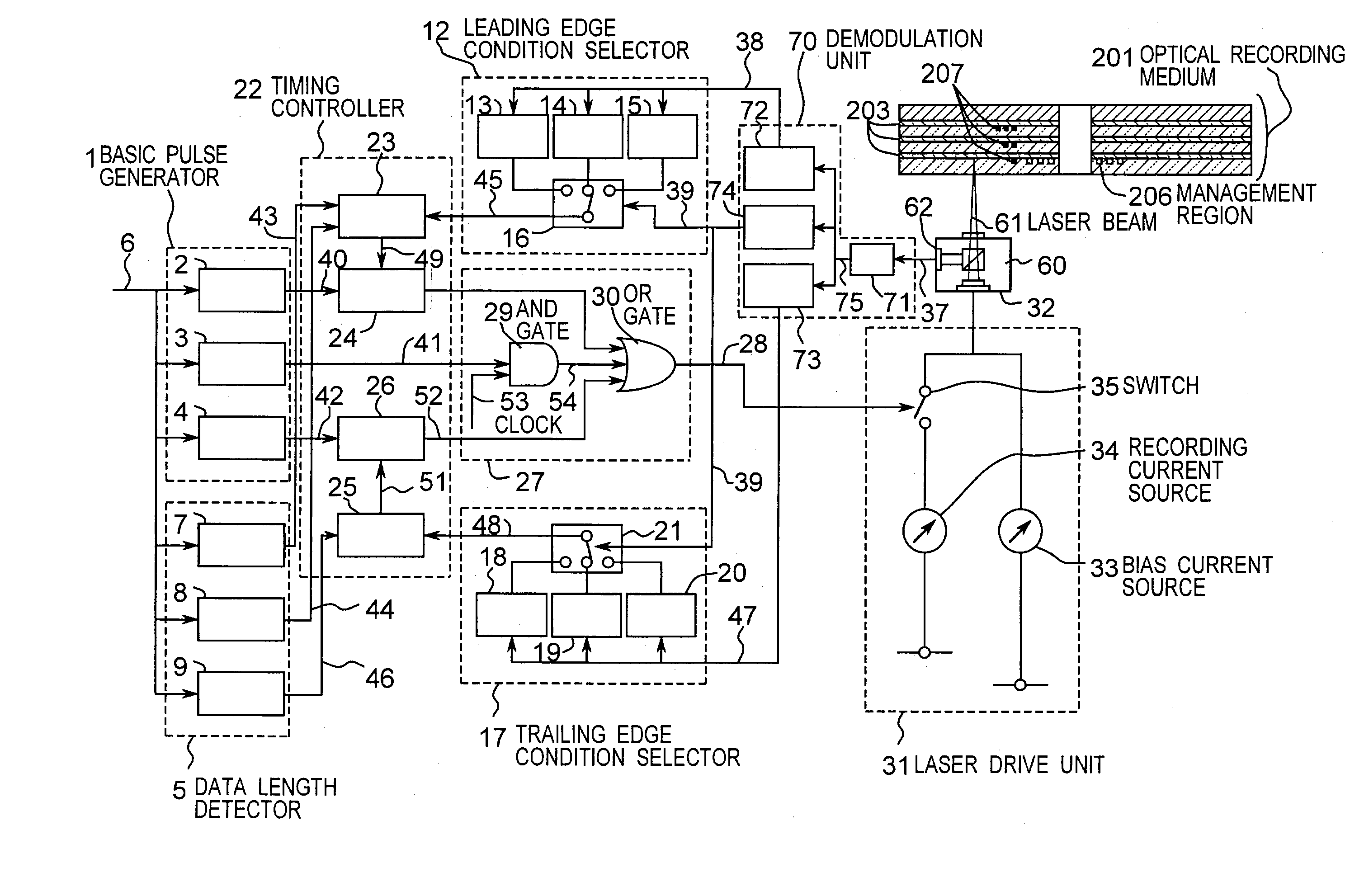
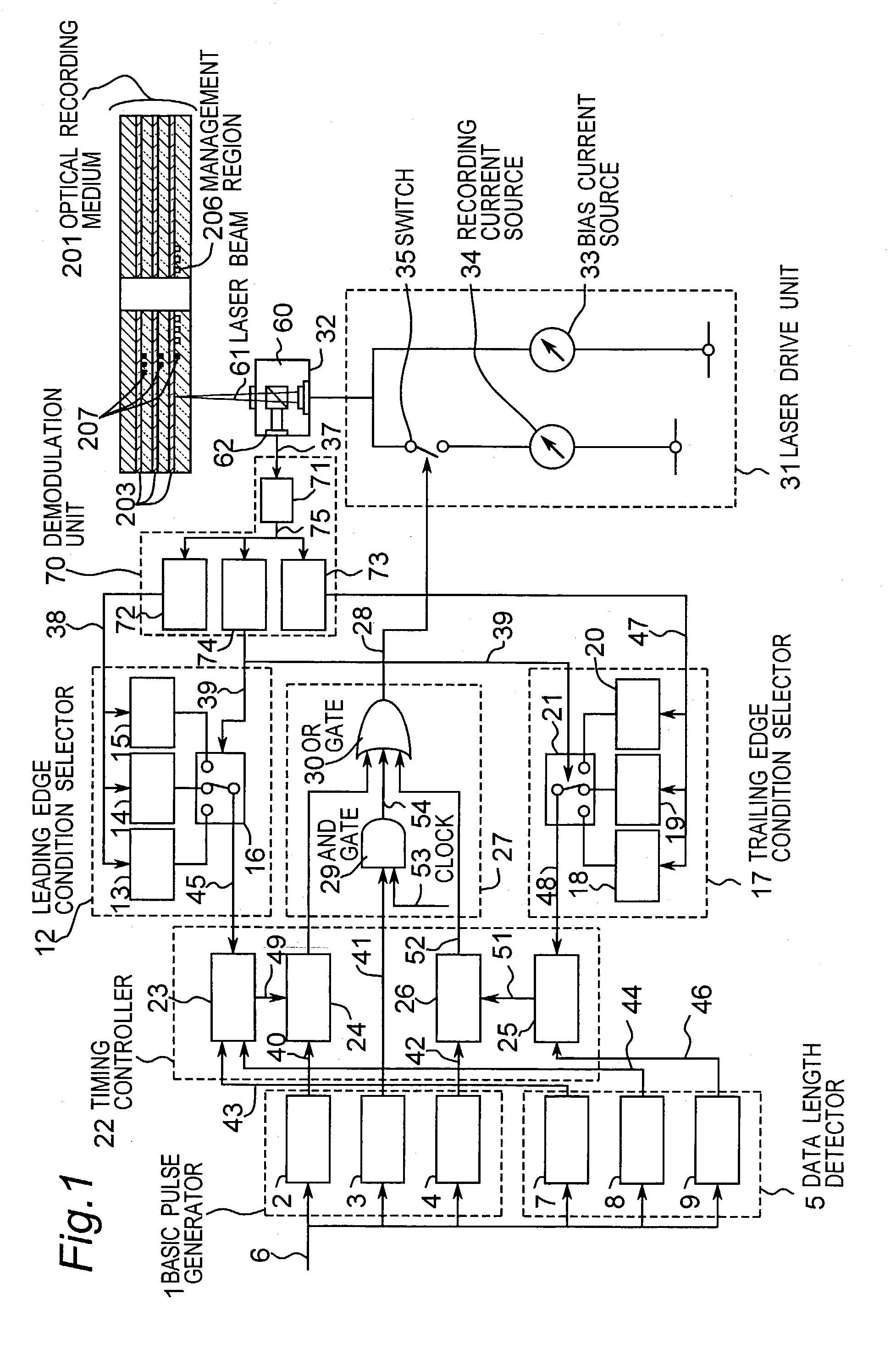
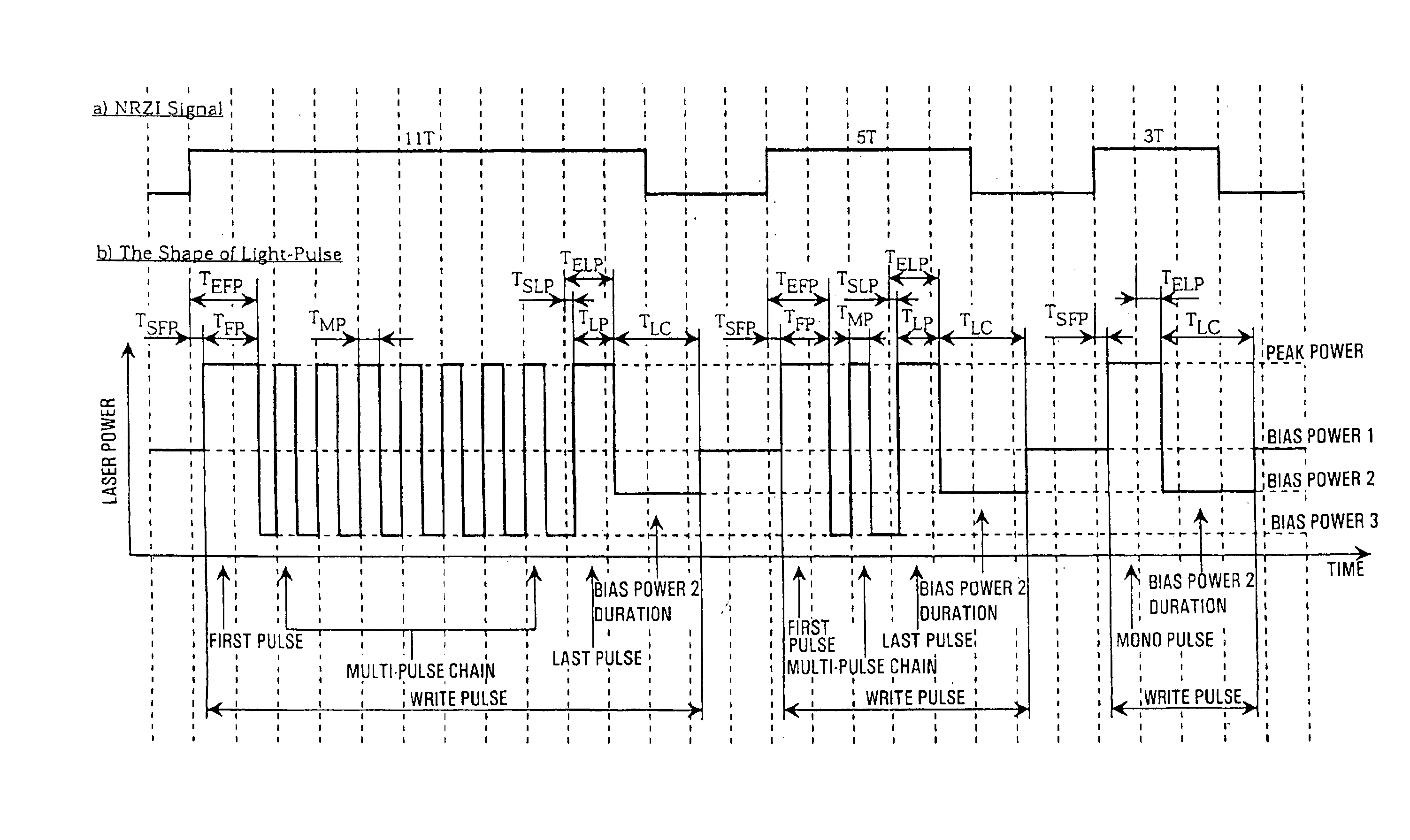
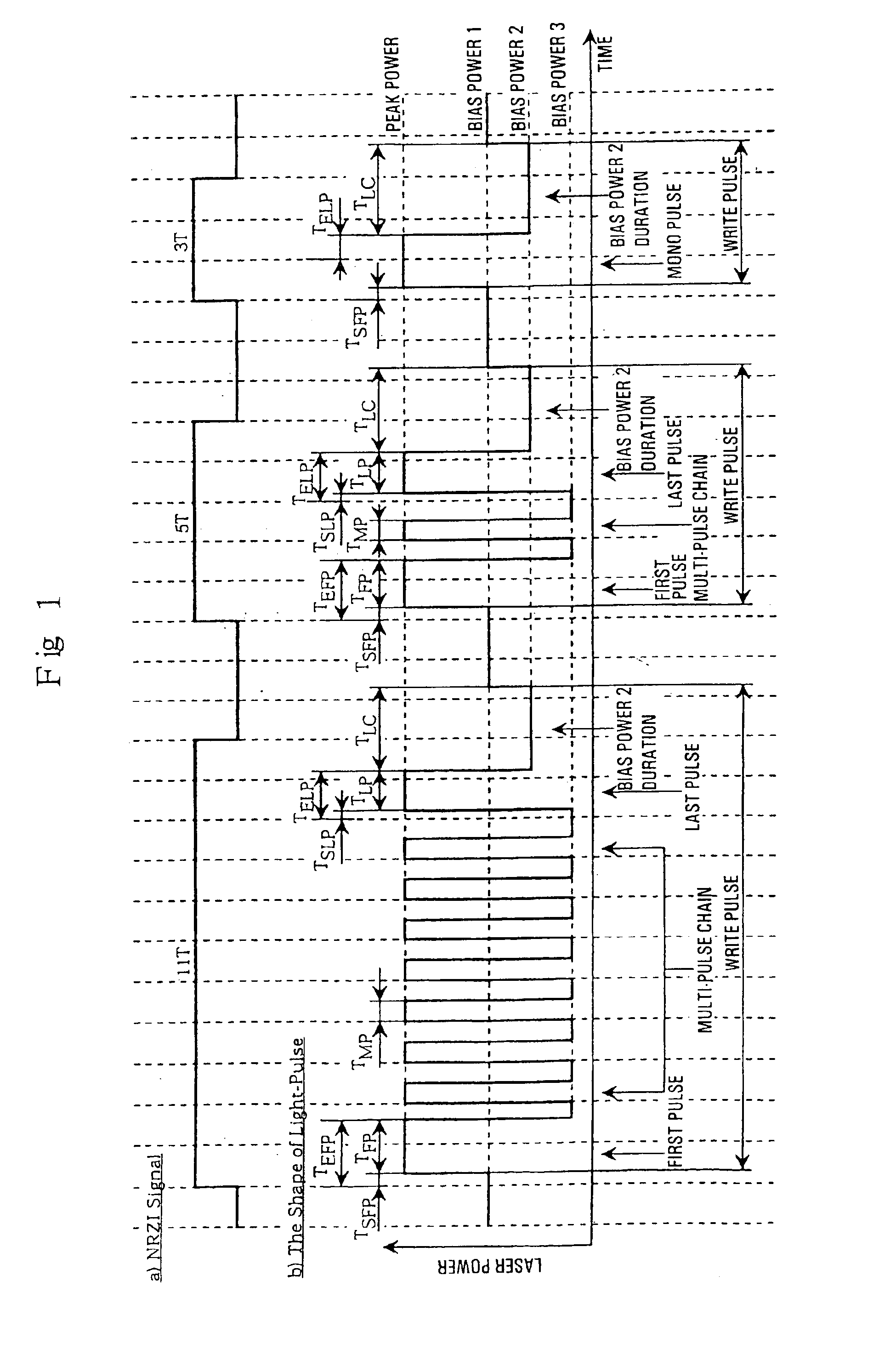
ActiveUS7006419B2Reduction in inabilityQuality improvementRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLaser lightLight emission
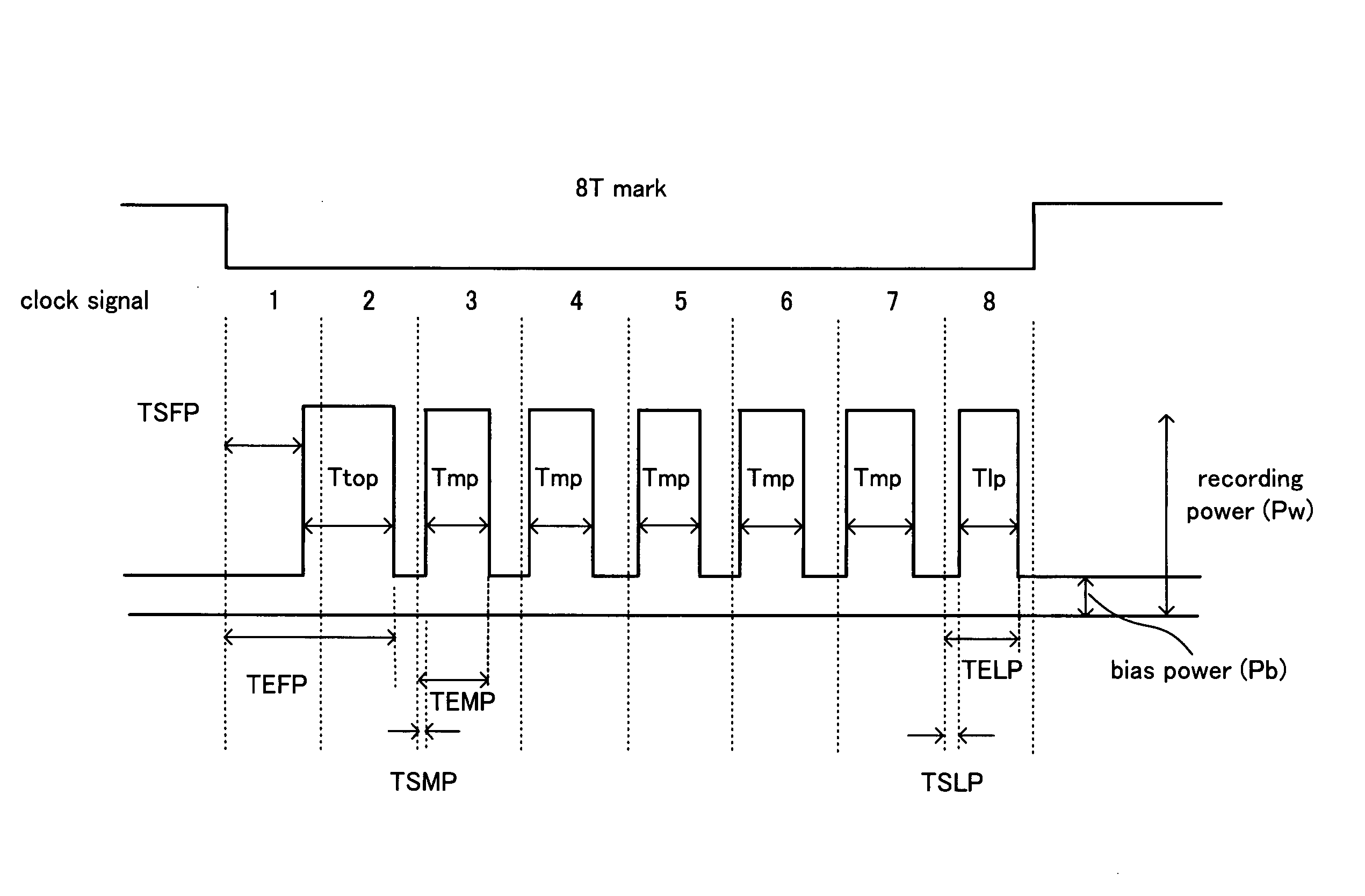
An information recording device comprising at least a recording pulse generating means and a recording pulse selecting means capable of generating various multi-pulses each of which is a combination of a leading heating pulse and a succeeding heating pulse, and rectangular pulses each of which is a single pulse, as a recording pulse, is disclosed. The recording pulse selecting means switches and selects among the multi-pulses and the rectangular pulses according to a recording condition, and then causes a light emission of a laser light source through a light source driving means. Even though in a high recording linear velocity recording condition that is insufficient in power for the recommended multi-pulse recording, a very low recording power can still be used by switching to the rectangular pulse recording, so as to achieve a recording with a much higher recording speed. In addition, good recording marks can be formed without exceeding a maximum allowable recording power.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical disk device and method of recording optical data
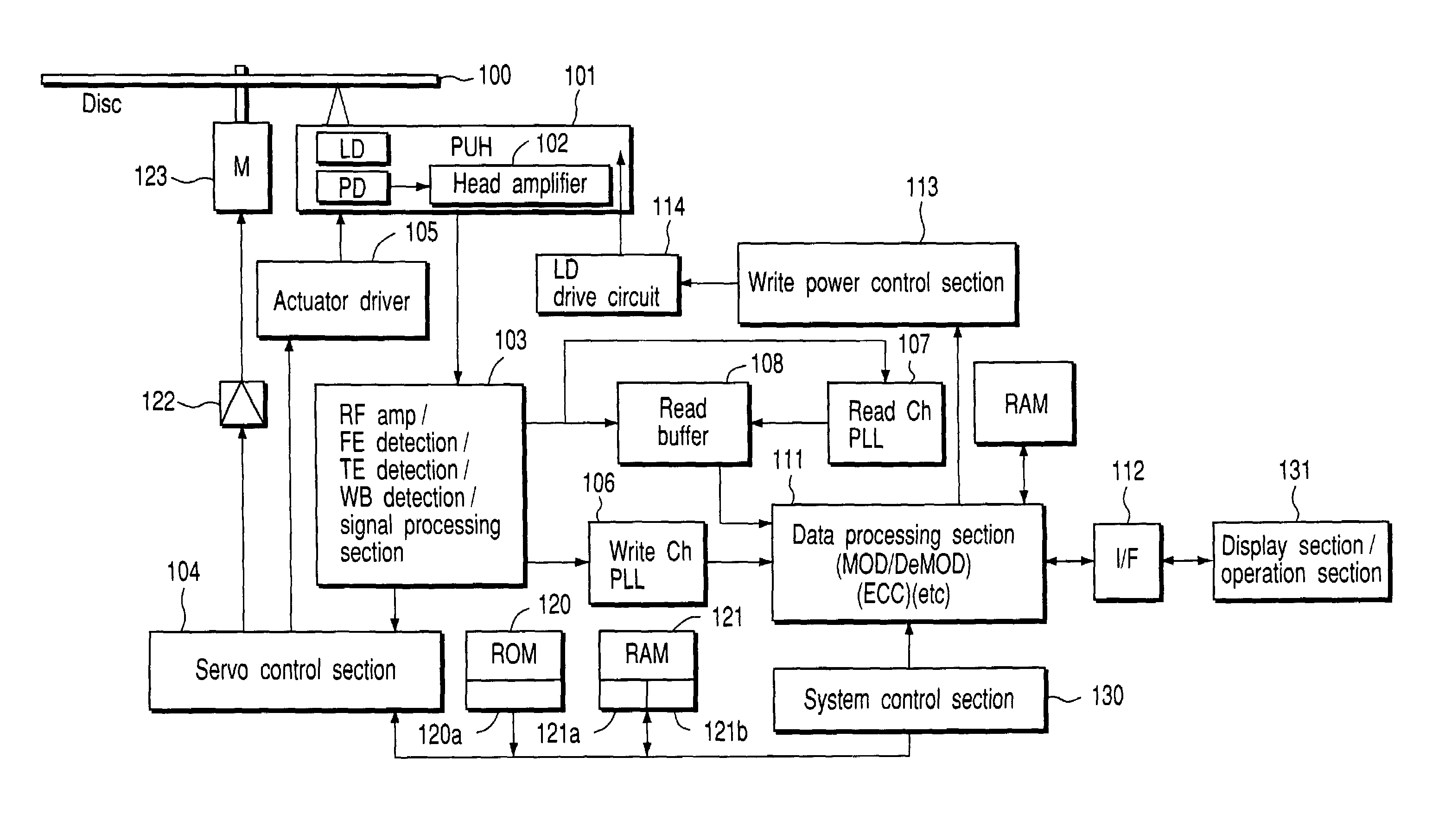
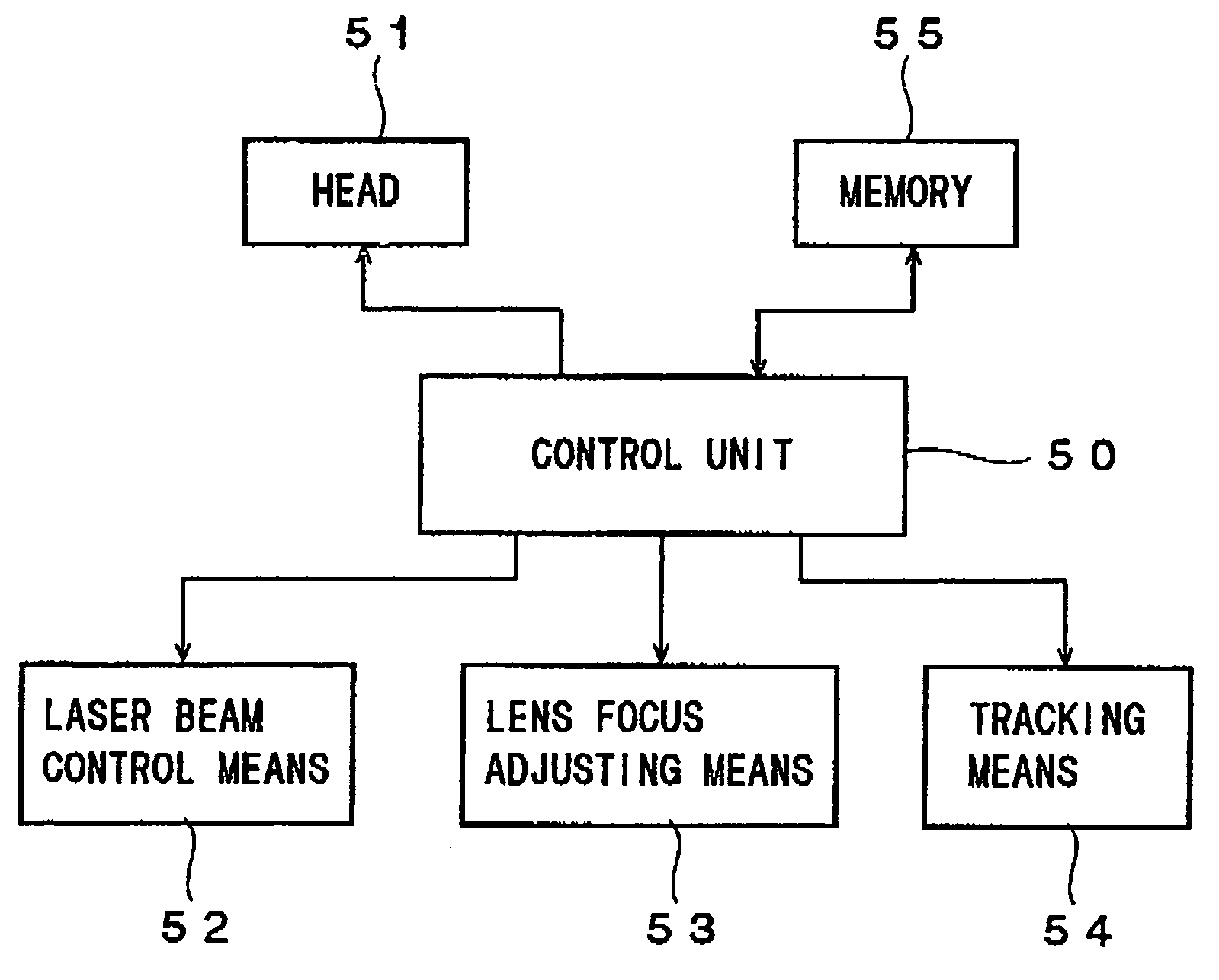
ActiveUS20050099925A1Optimization StrategyQuick SetupTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesOptical recordingComputer science
The present invention relates generally to an optical disk device that records and reproduces information on and from an optical recording medium, such as a compact disk or a digital versatile disk. The optical disk device includes a measurement means and a calculation means.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and device for optical recording onto optical disc medium
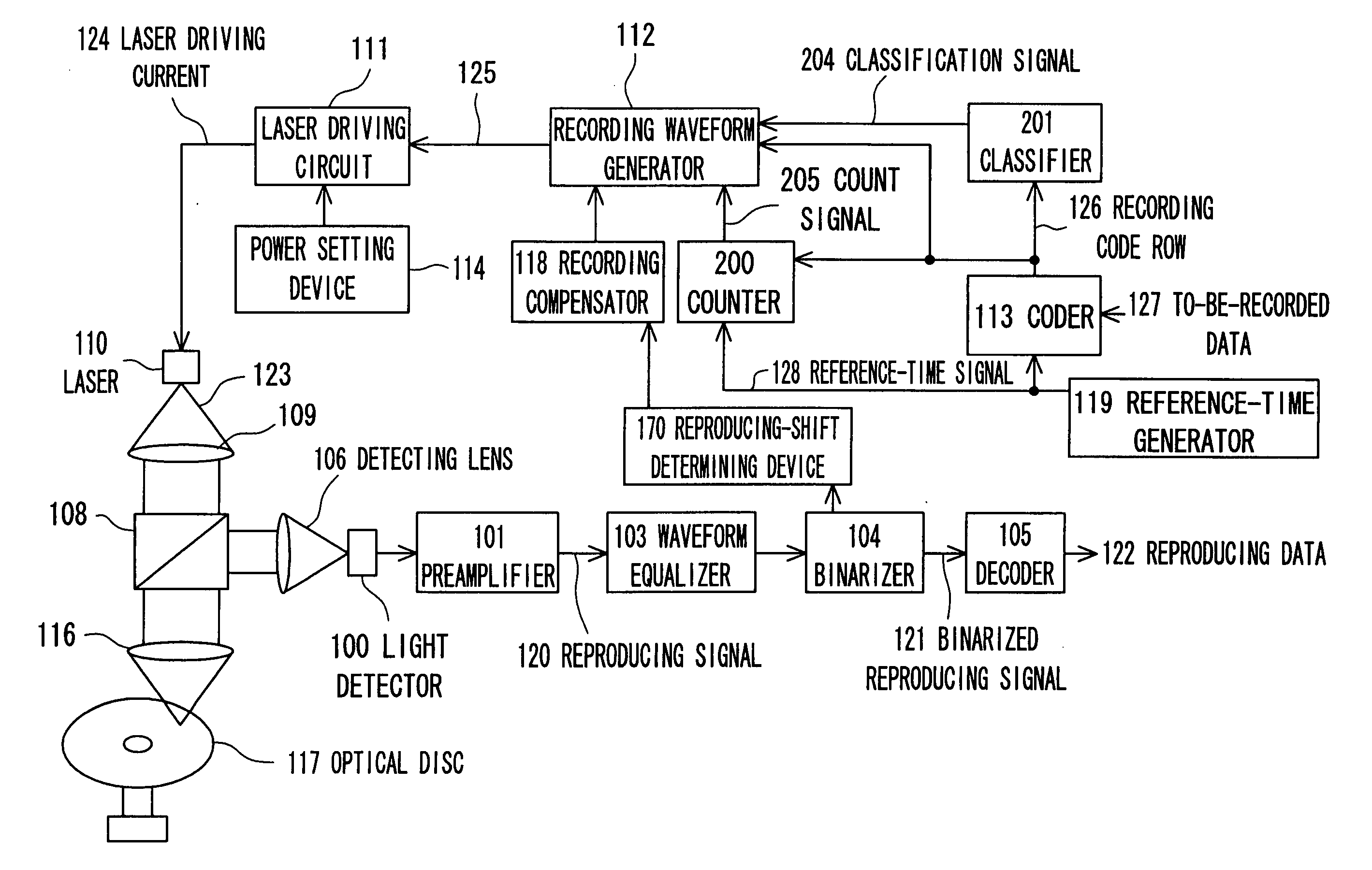
InactiveUS20070165506A1Improve reliabilityEasy to controlRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLaser lightOptical recording
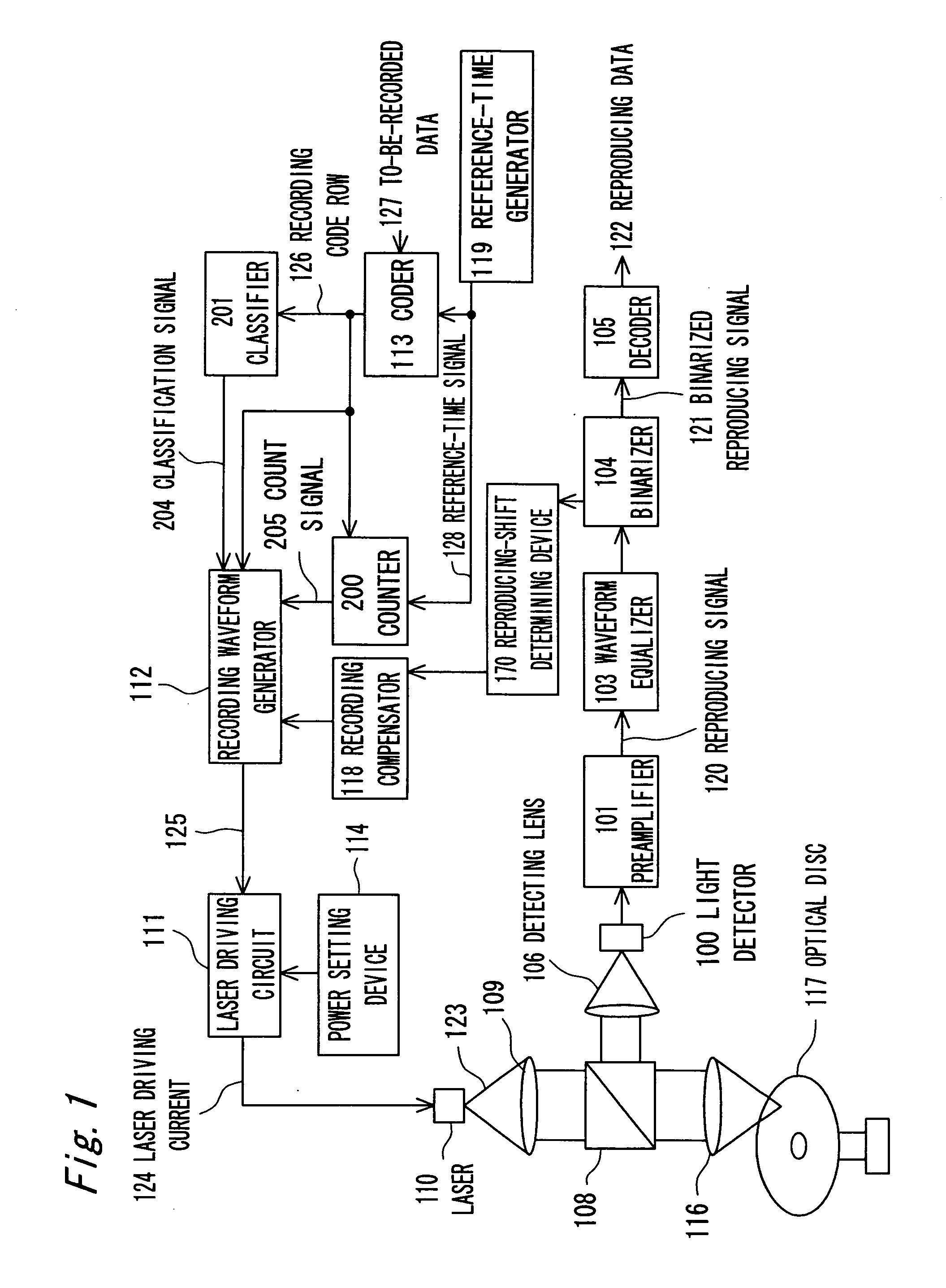
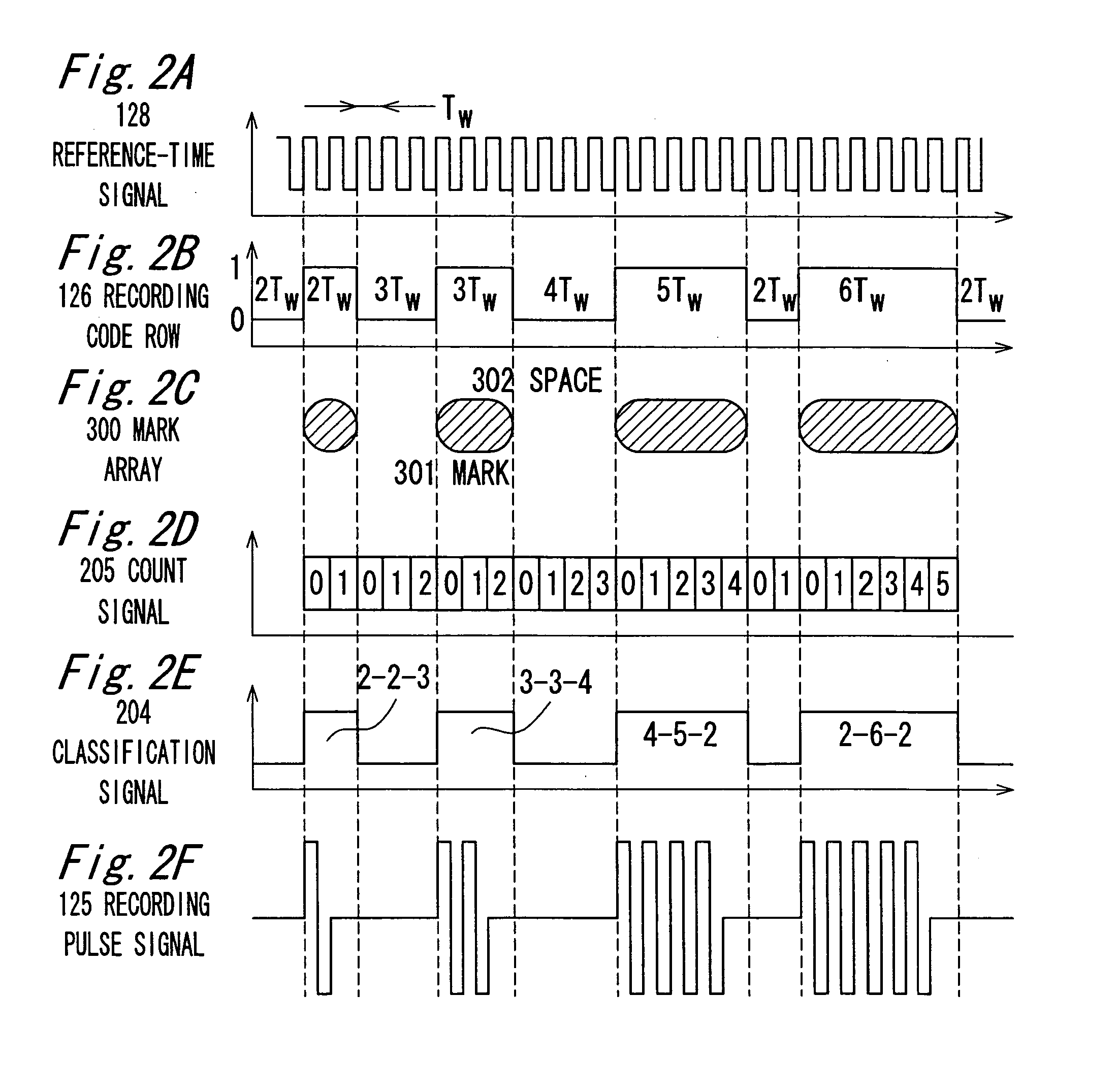
There is provided an optical recording method for directing a recording pulse train to an optical disc medium to form marks thereon and for recording information as information about the edge positions of said marks and the spaces between marks, the recording pulse train having been created by modulating laser light into plural power levels. The method includes: coding to-be-recorded data into coded data consisting of the combination of marks and spaces; classifying said marks within said coded data on the basis of the mark length and the preceding or succeeding space lengths of the marks; shifting the position of the second pulse edge counted from the end portion of the recording pulse train for forming said marks, depending on the result of said classification, to adjust said recording pulse train; and directing said recording pulse train to the optical disc medium to form said marks thereon.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Recording method and optical disk device
InactiveUS20050286390A1Increase speedDeterioration of data can be preventedRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsDVD-RAMOptoelectronics
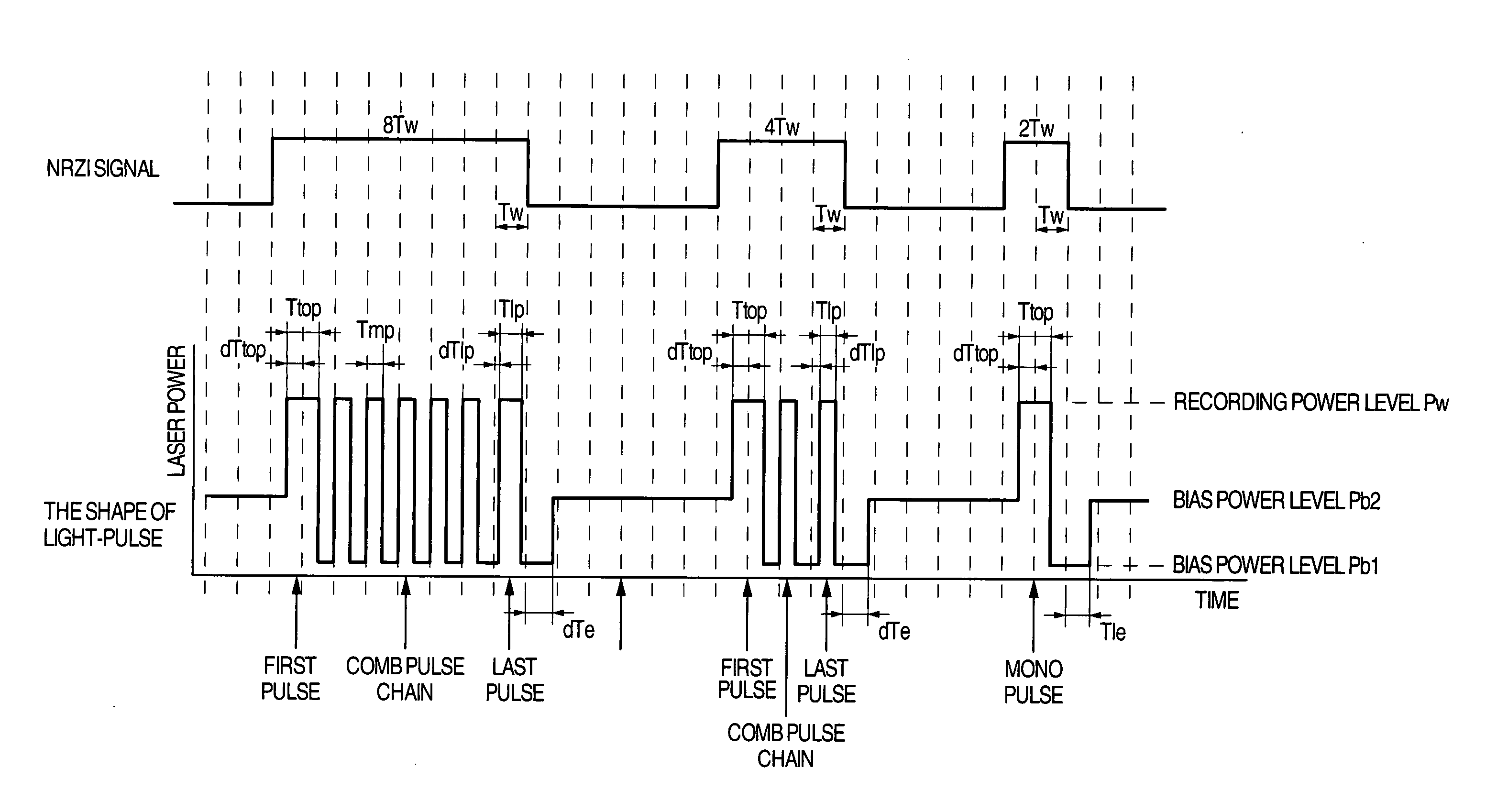
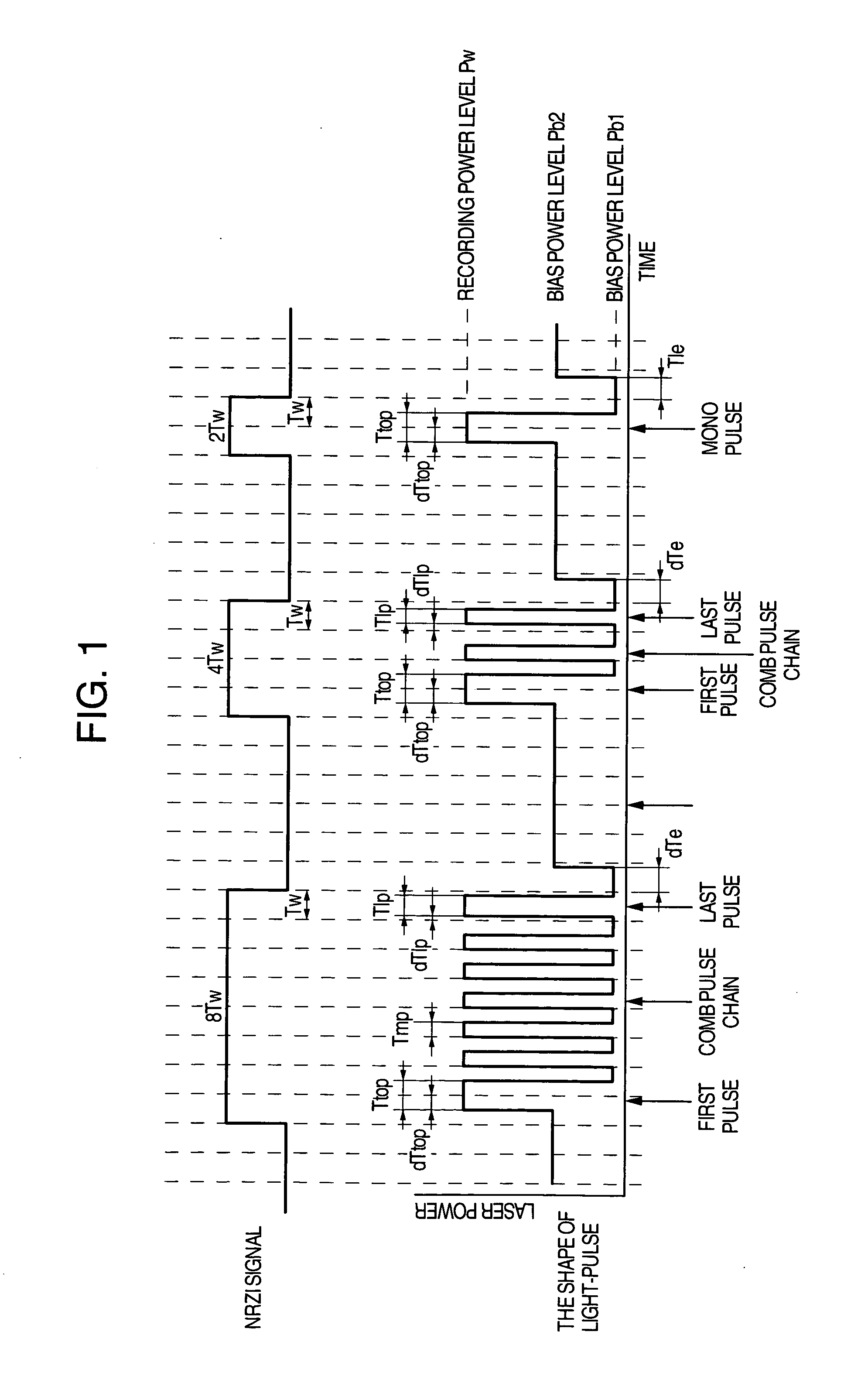
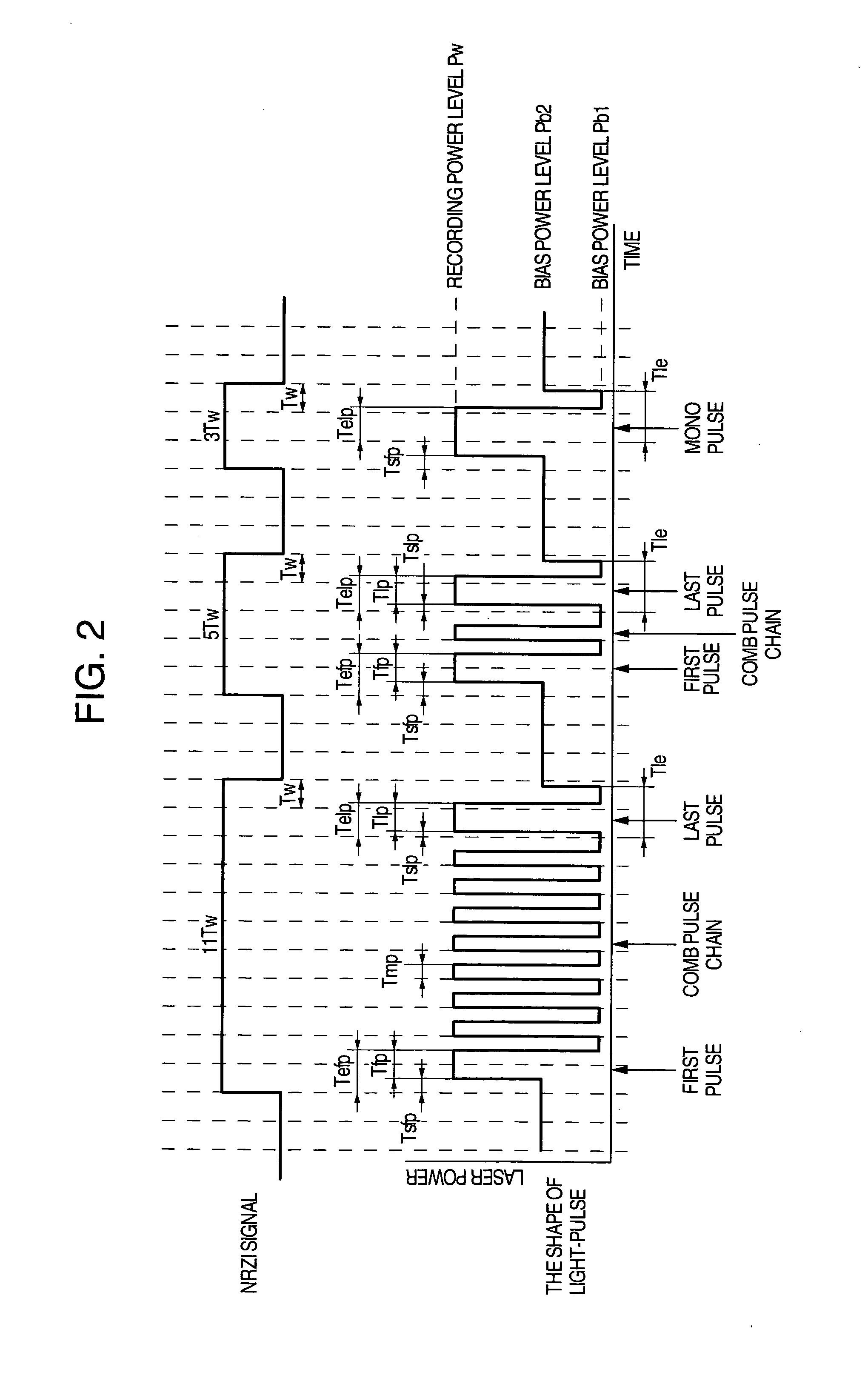
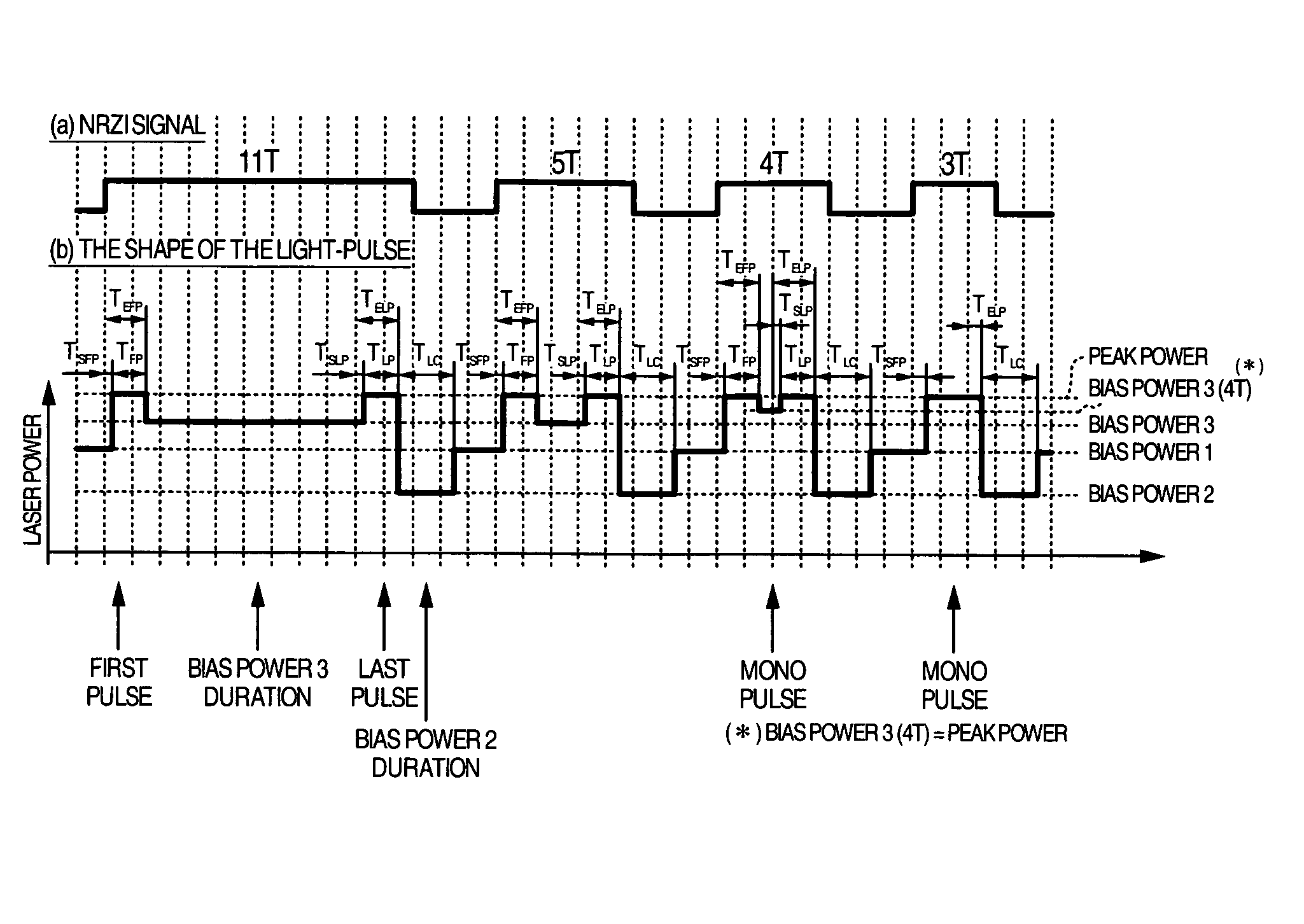
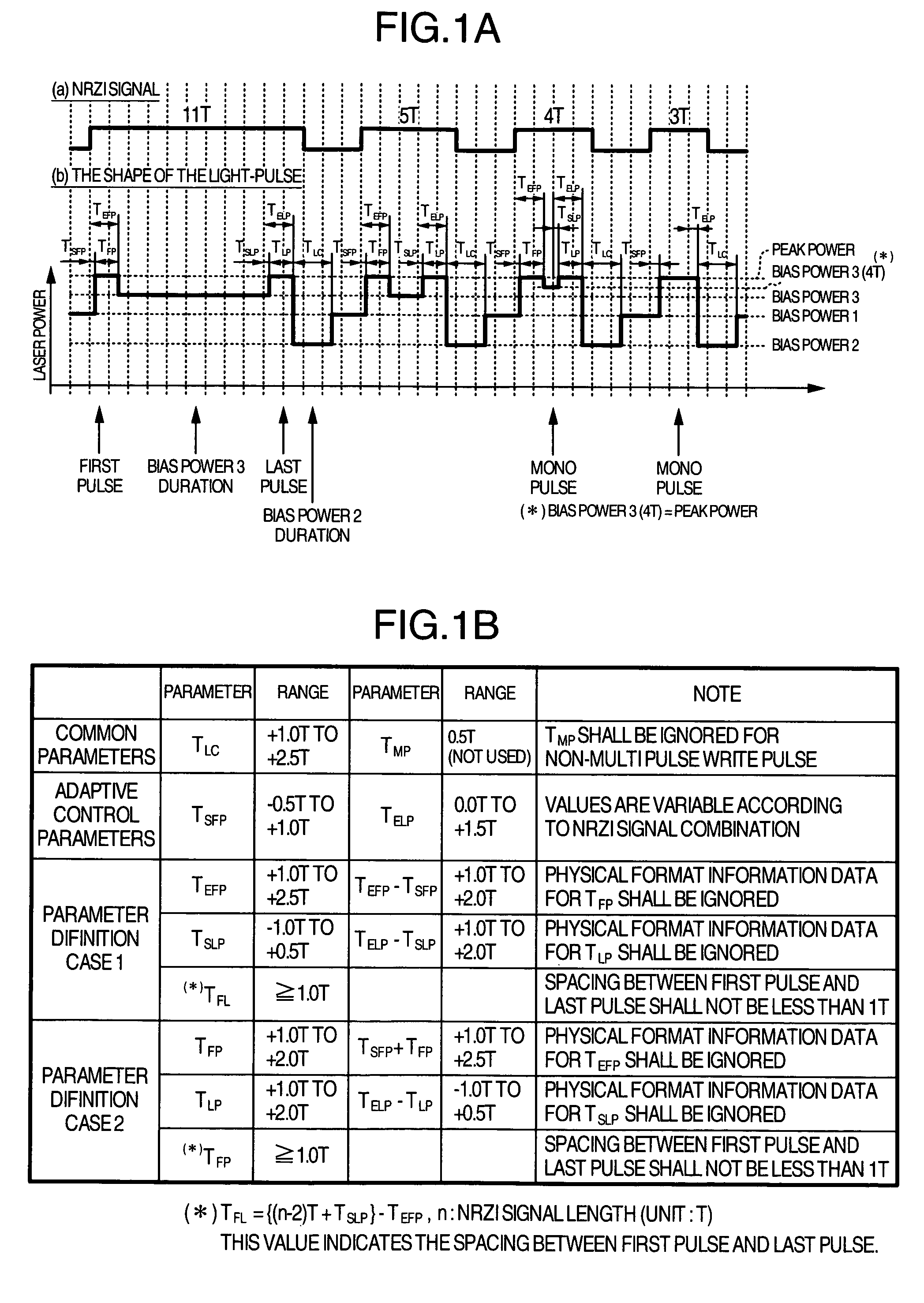
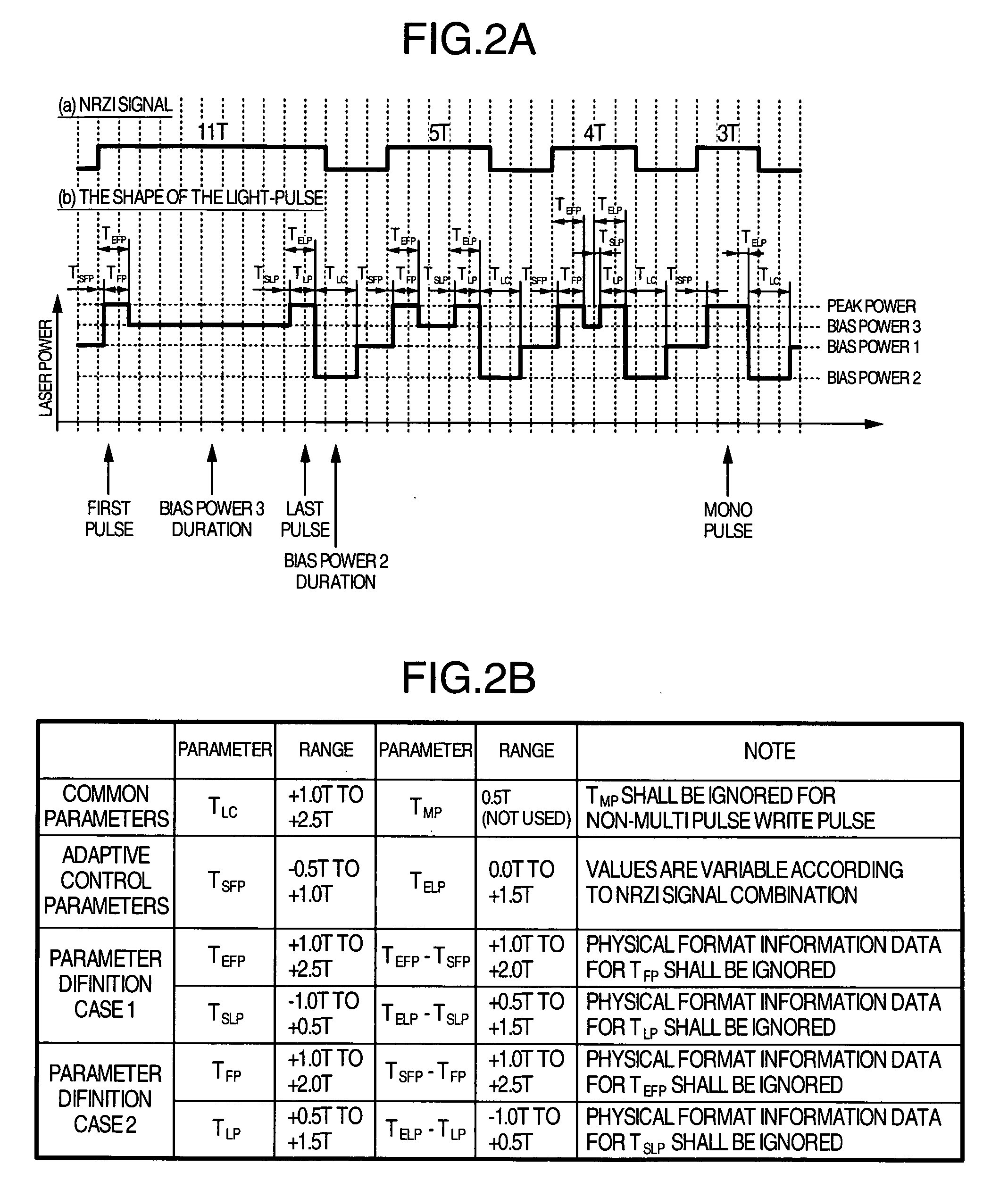
In order that it is realized to put 16× speed DVD-RAM in practice, a recording method coping with CAV (constant angular velocity) and a method for improving S / N ratio are provided and an optical disk device using them is provided. In order that a cutoff phenomenon of pulse in a laser driving circuit may not occur, the shortest pulse width is set at 1 Tw or more where Tw indicates a window width, and a recording pulse in which a 4T mark is recorded with a mono pulse where T indicates a detection window width and the parameter setting range are prescribed. Simultaneously, a reproduction power for 6× speed or more is set at 1.5-2.0 mW, different from a conventional value, and a setup sequence with which deterioration of data in reproducing does not occur is provided. Thereby it becomes possible to put 16× speed DVD-RAM in practice.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP +1
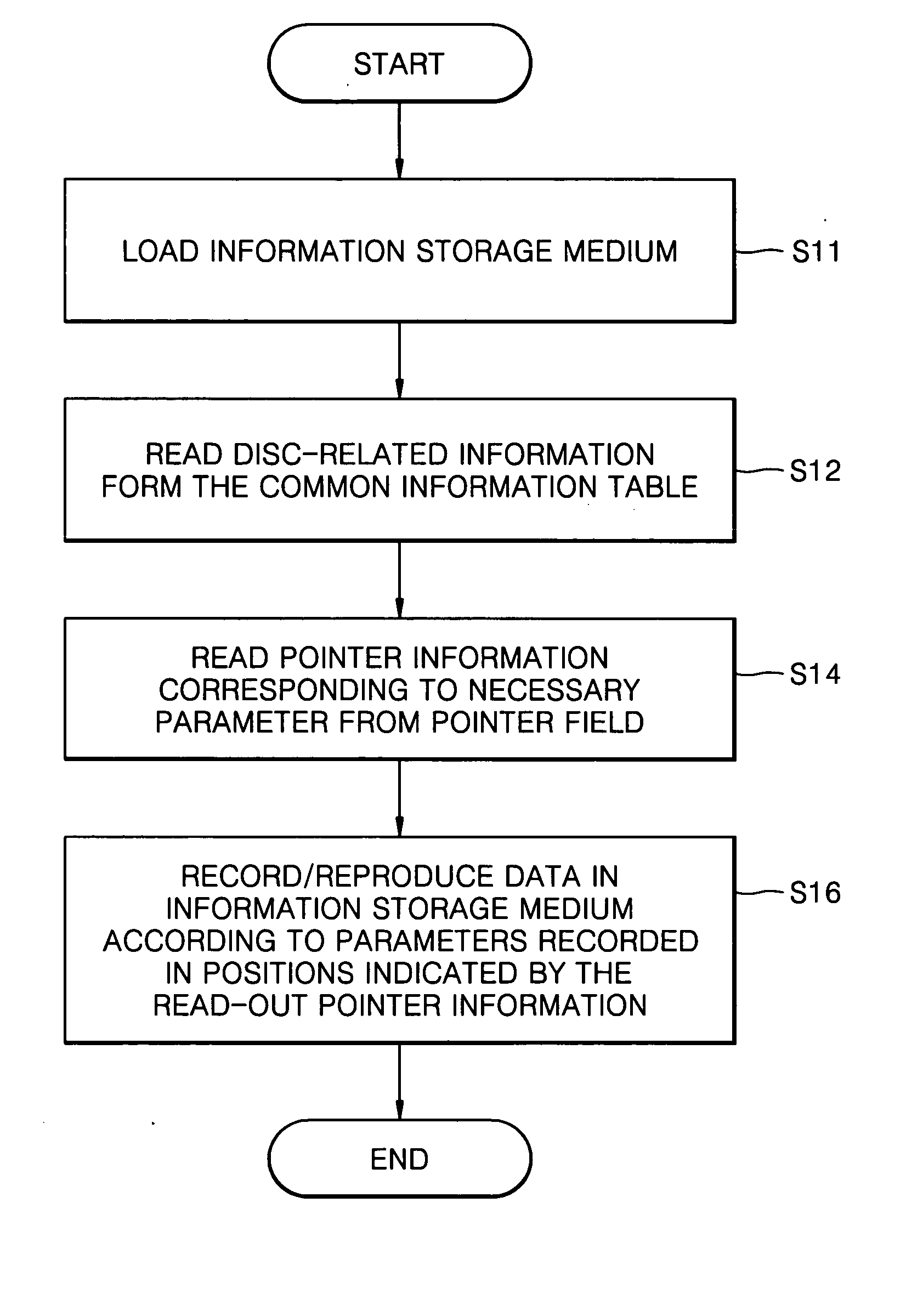
Information storage medium and apparatus of recording and/or reproducing pointing information
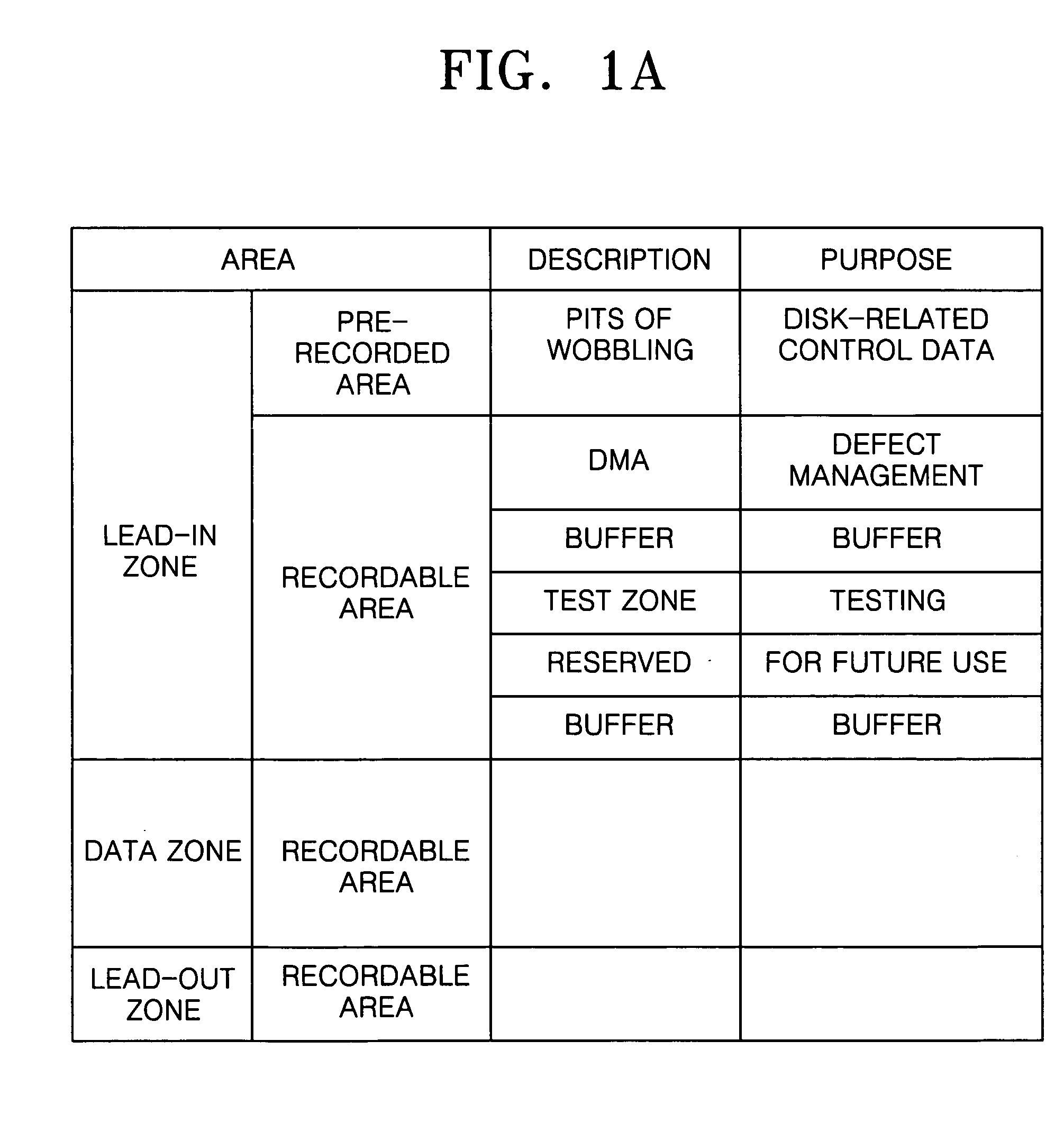
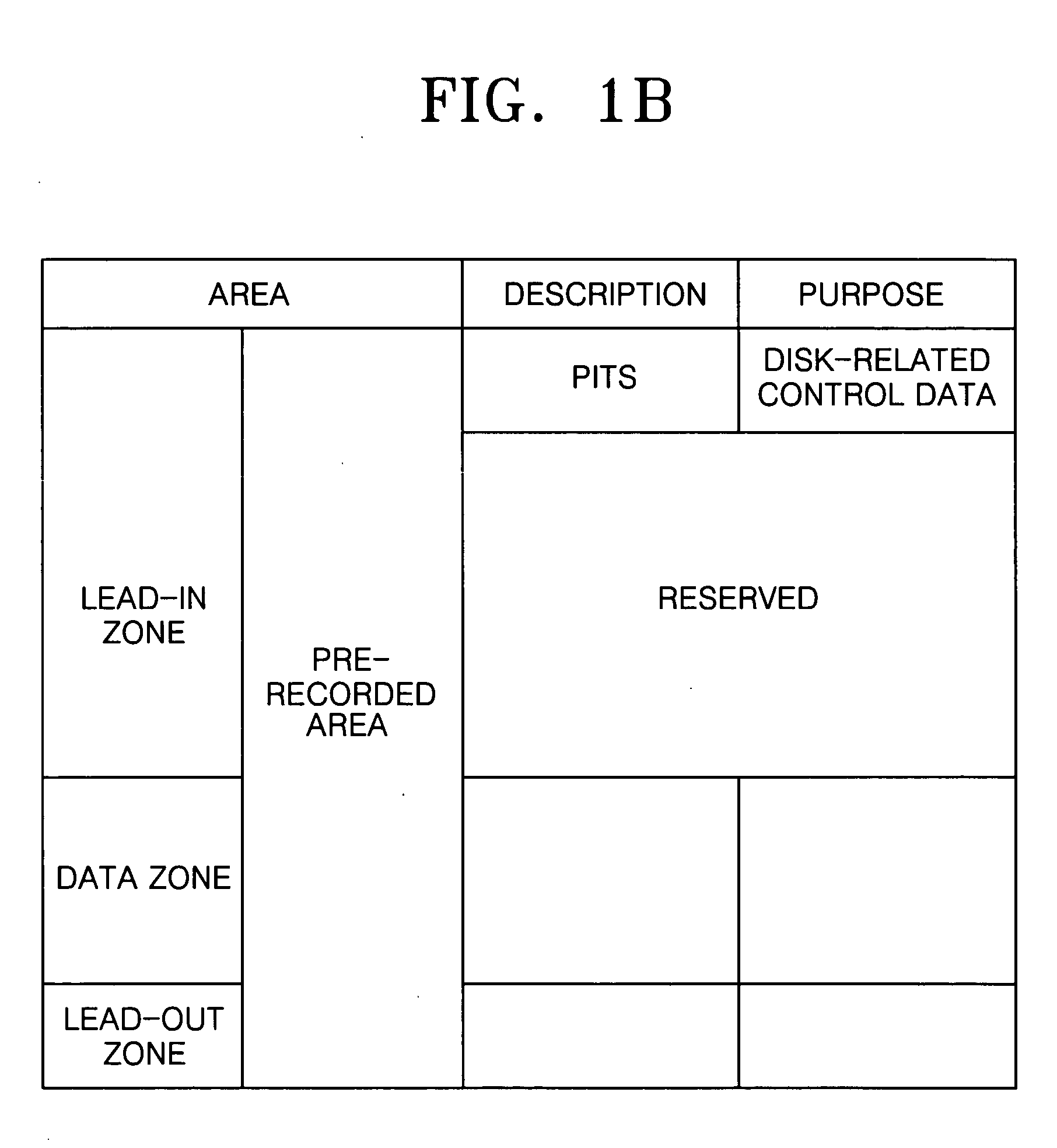
ActiveUS7304938B2Shorten the timeTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesRelevant informationDatabase
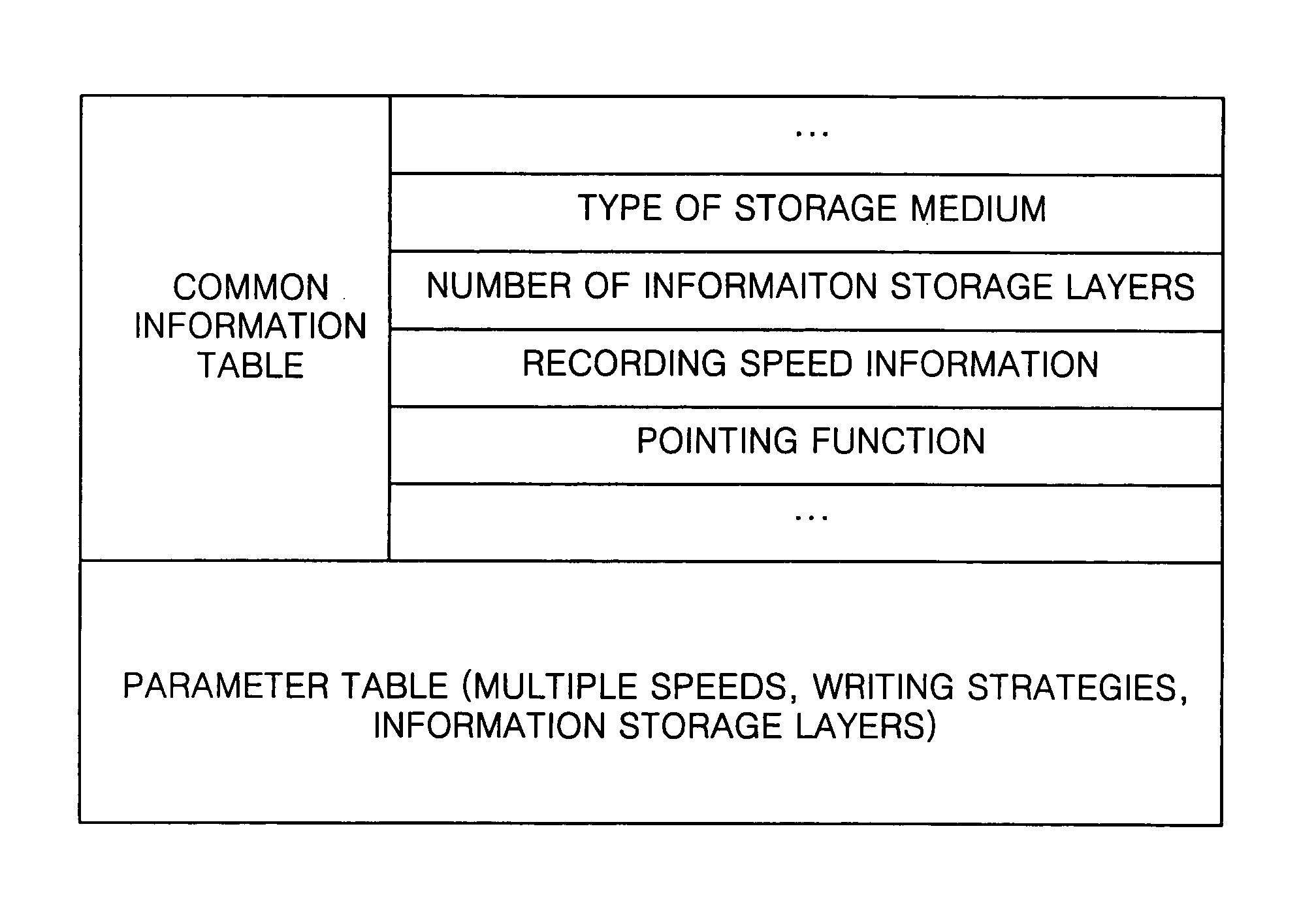
An information storage medium includes areas of disk-related information having disk-related information to record or reproduce data with respect to the information storage medium, wherein the disk-related information includes common disk-related information and changeable parameter information, and the areas of the disk-related information are arranged according to information about the changeable parameter information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical recording medium and method for recording data in the same
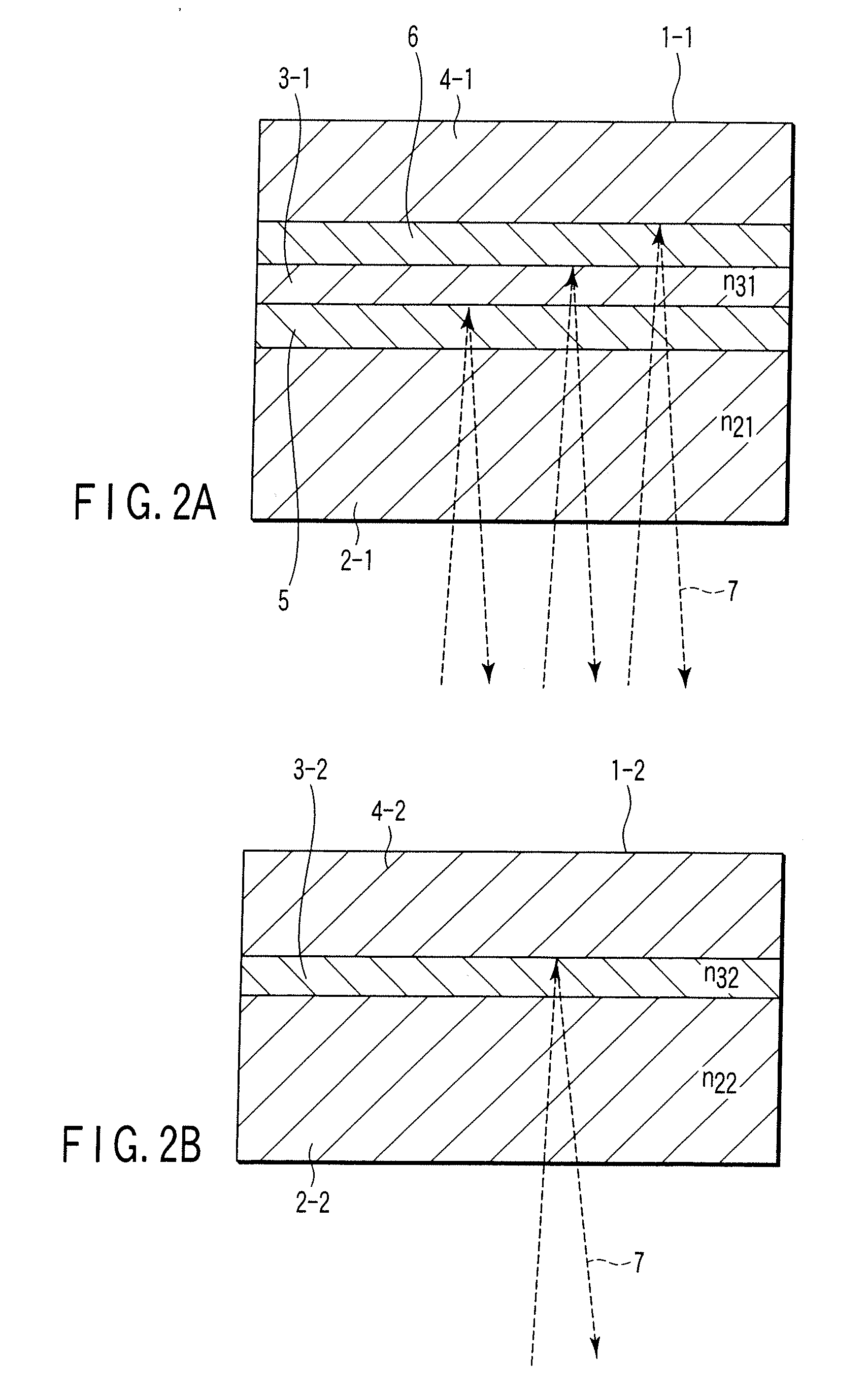
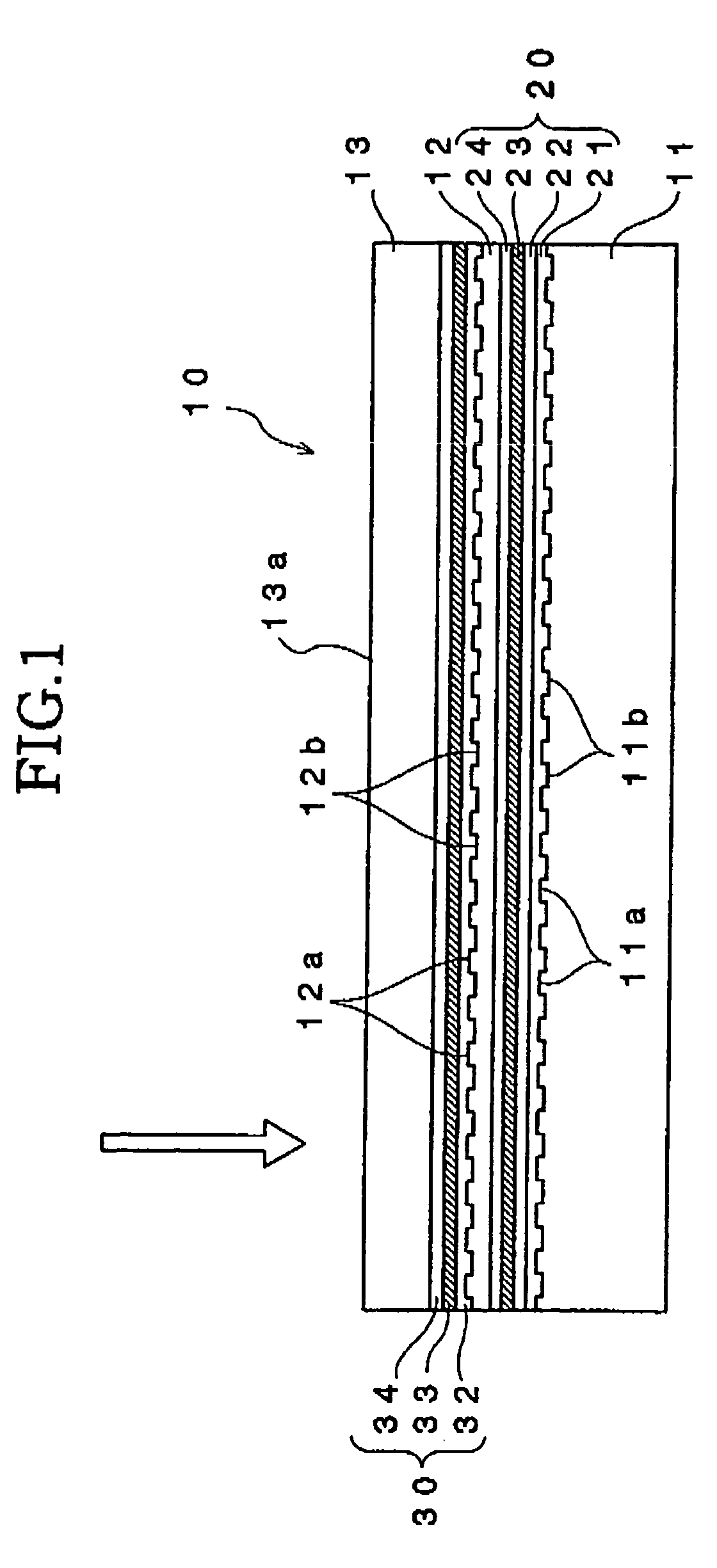
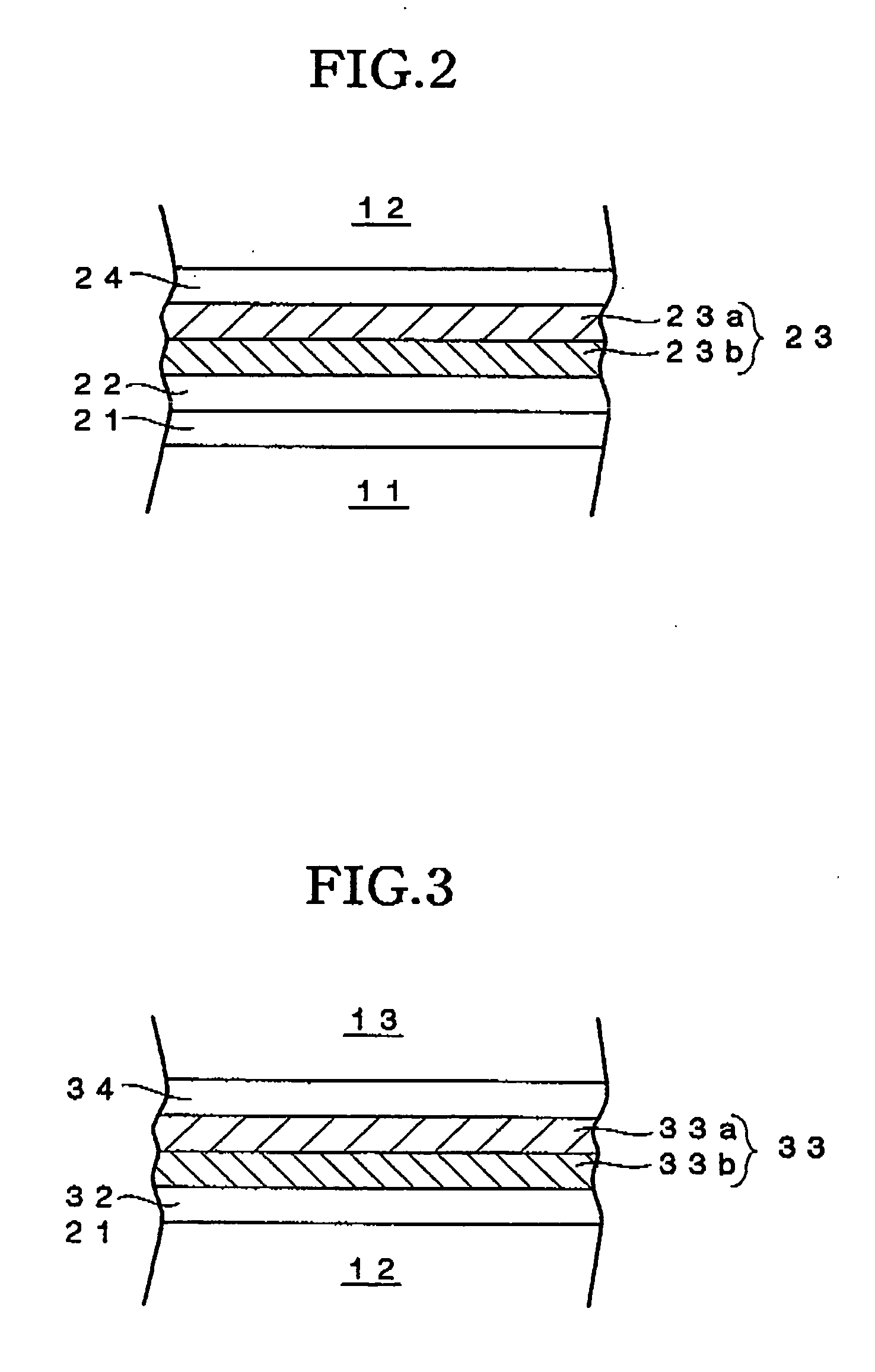
InactiveUS20040038080A1Good signalImprove carrier-to-noise ratioRecording strategiesLayered productsRecording layerOptical recording
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, two recording layers provided on the substrate and two dielectric layers each provided adjacent to one of the recording layers, the optical recording medium being constituted so that when it is irradiated with a laser beam having a wavelength lambda via an objective lens having a numerical aperture NA satisfying lambda / NA<=640 nm from the side opposite from the substrate, a record mark whose reflection coefficient is different from those of other regions of the recording layers is formed in the recording layers and at least a part of a region(s) of the dielectric layers adjacent to the record mark is crystallized to form a crystallized region. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to reproduce a signal having excellent signal characteristics.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical recording medium
An optical recording medium includes a recording layer, a first dielectric layer disposed on the side of a light incidence plane through which the laser beam enters with respect to the recording layer, a second dielectric layer disposed on the side opposite to the light incidence plane with respect to the recording layer, a heat radiation layer disposed on the side of the light incidence plane with respect to the first dielectric layer and a reflective layer disposed on the side opposite to the light incidence plane with respect to the second dielectric layer, the recording layer containing a phase change material represented by an atomic composition formula: SbaTebGecMnd, where a is equal to or larger than 55 and equal to or smaller than 70, c is equal to or larger than 4 and equal to or smaller than 10, d is equal to or larger than 10 and equal to or smaller than 20, a / b is equal to or larger than 2.8 and equal to or smaller than 3.5 and a / d is equal to or larger than 3.0 and equal to or smaller than 6.0, in an amount equal to or more than 95 atomic %. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to simultaneously improve characteristics of recording data therein at a high linear velocity, data reproduction durability and storage reliability.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording method, optical information recording device, and optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20050174906A1Shorten the timeExact reproductionRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsComputer scienceRecording media
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Recording control apparatus, recording and reproduction apparatus, and recording control method
ActiveUS20050078579A1Improve reliabilityTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesAnalog signalComputer science
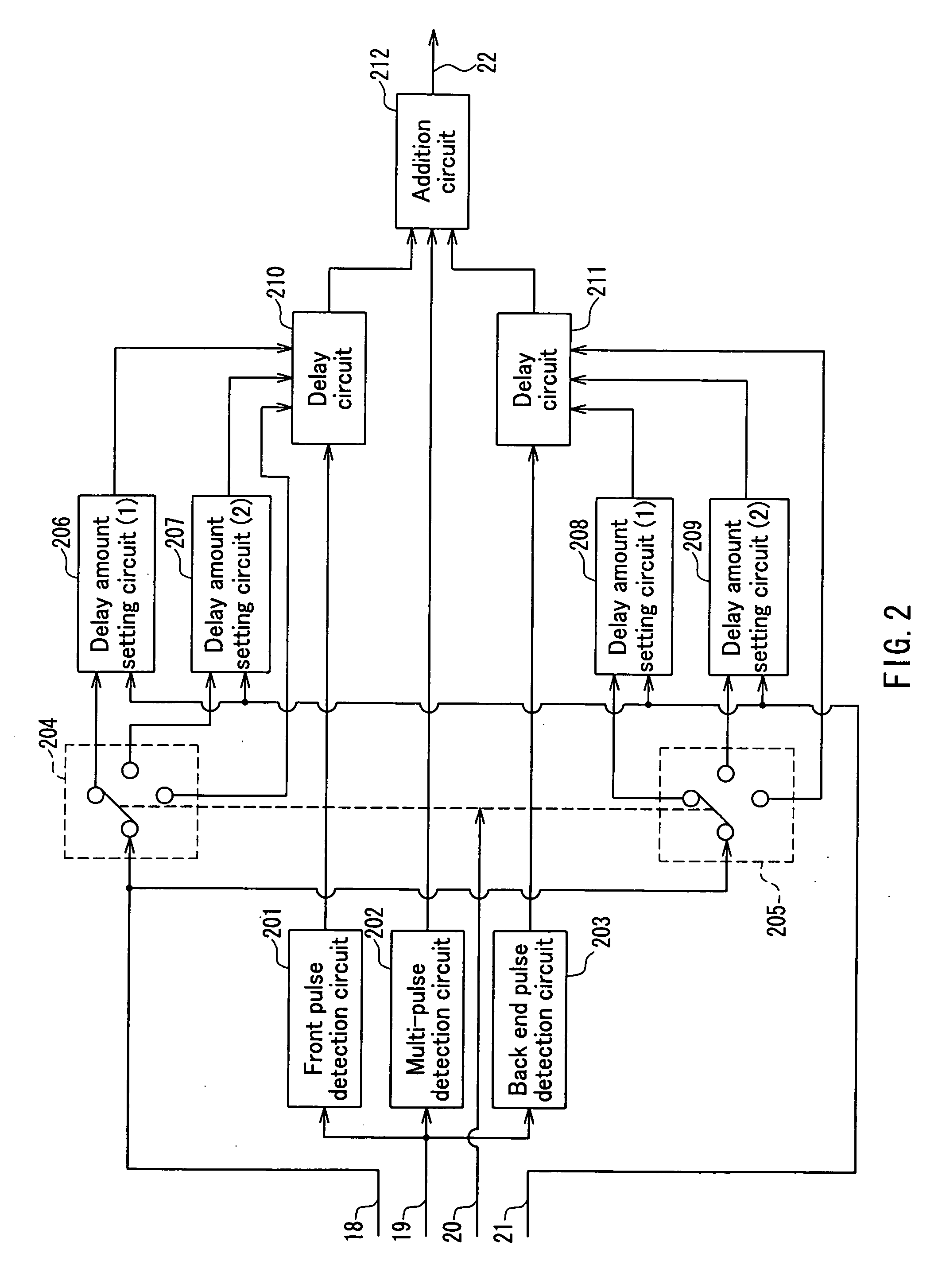
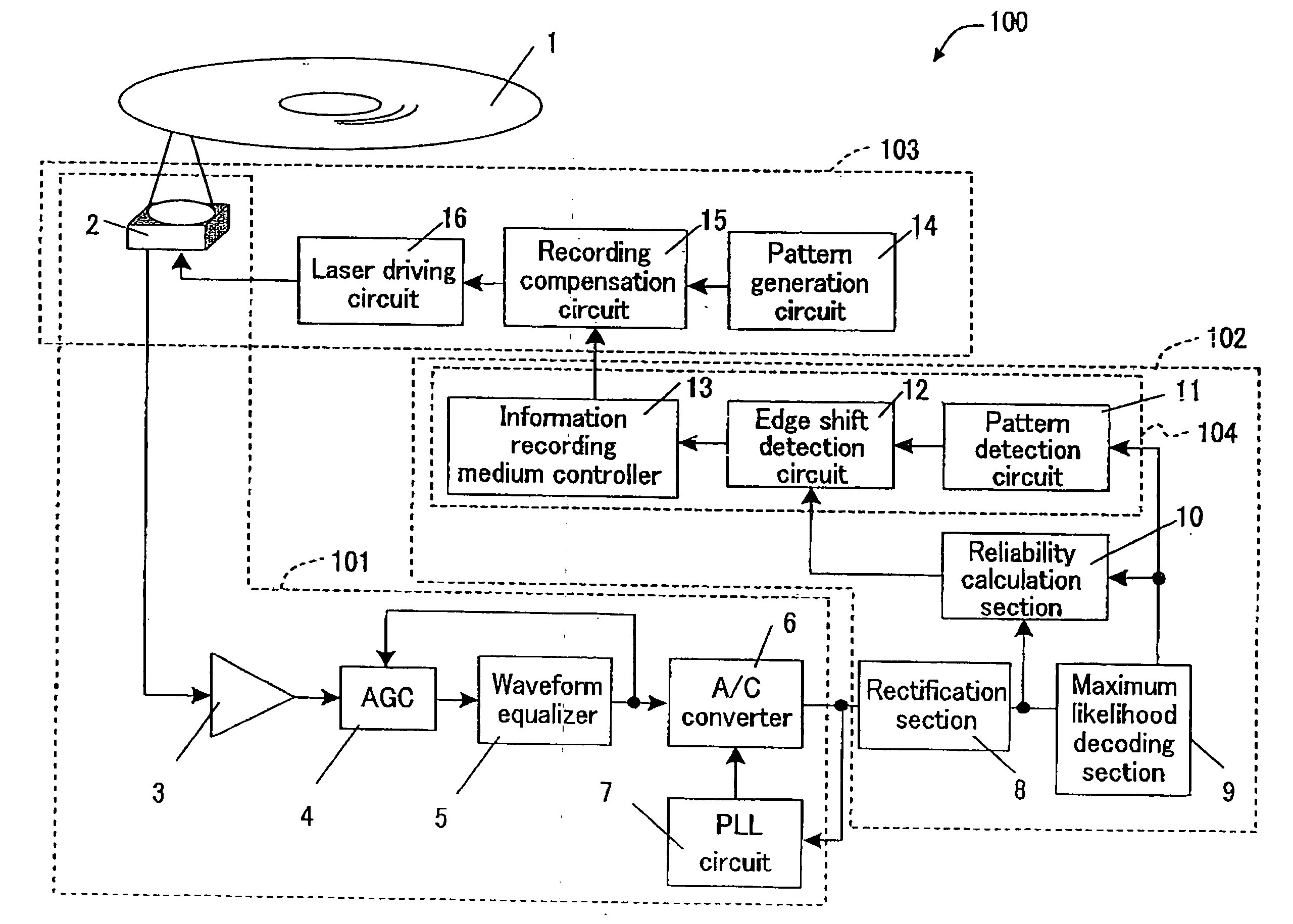
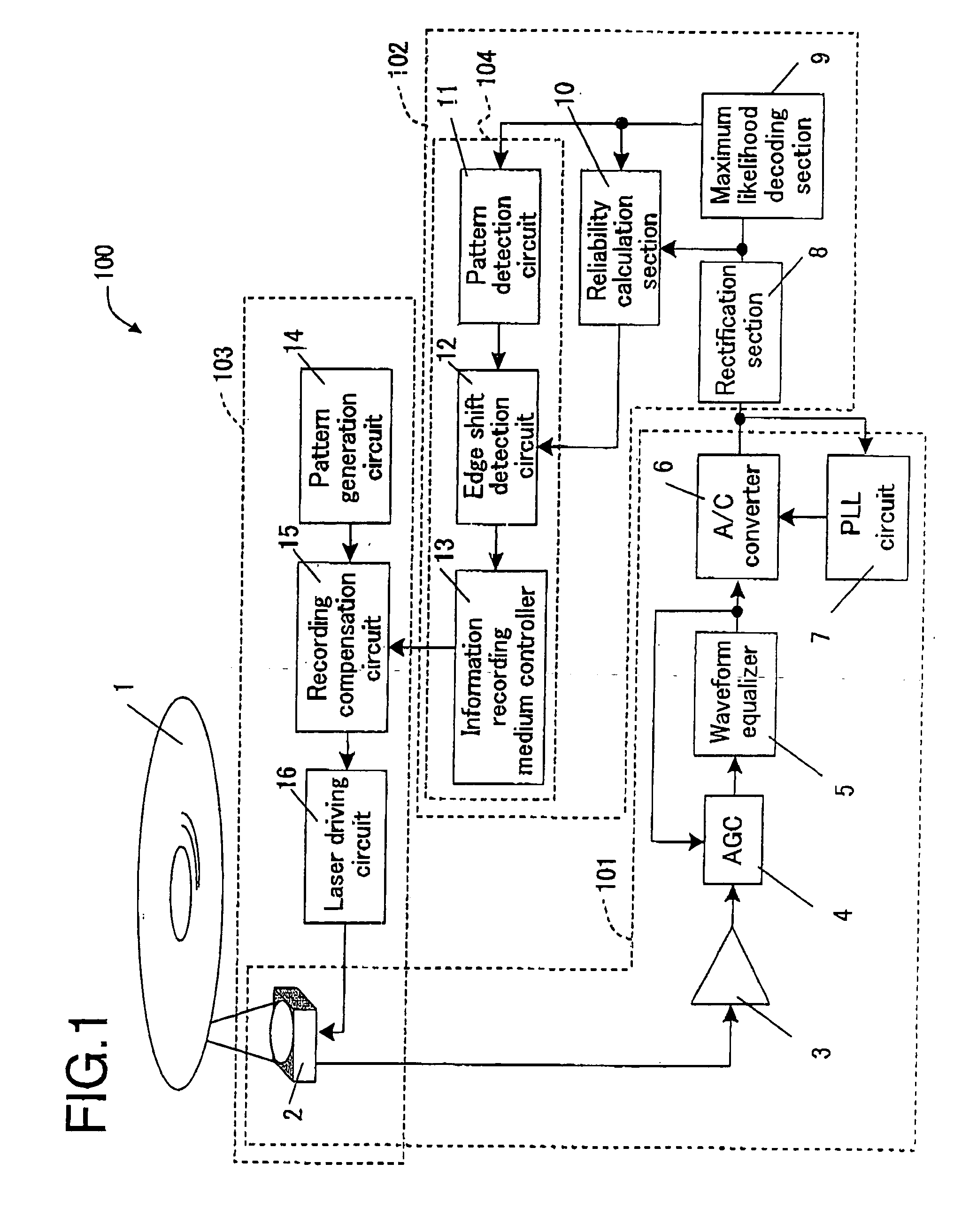
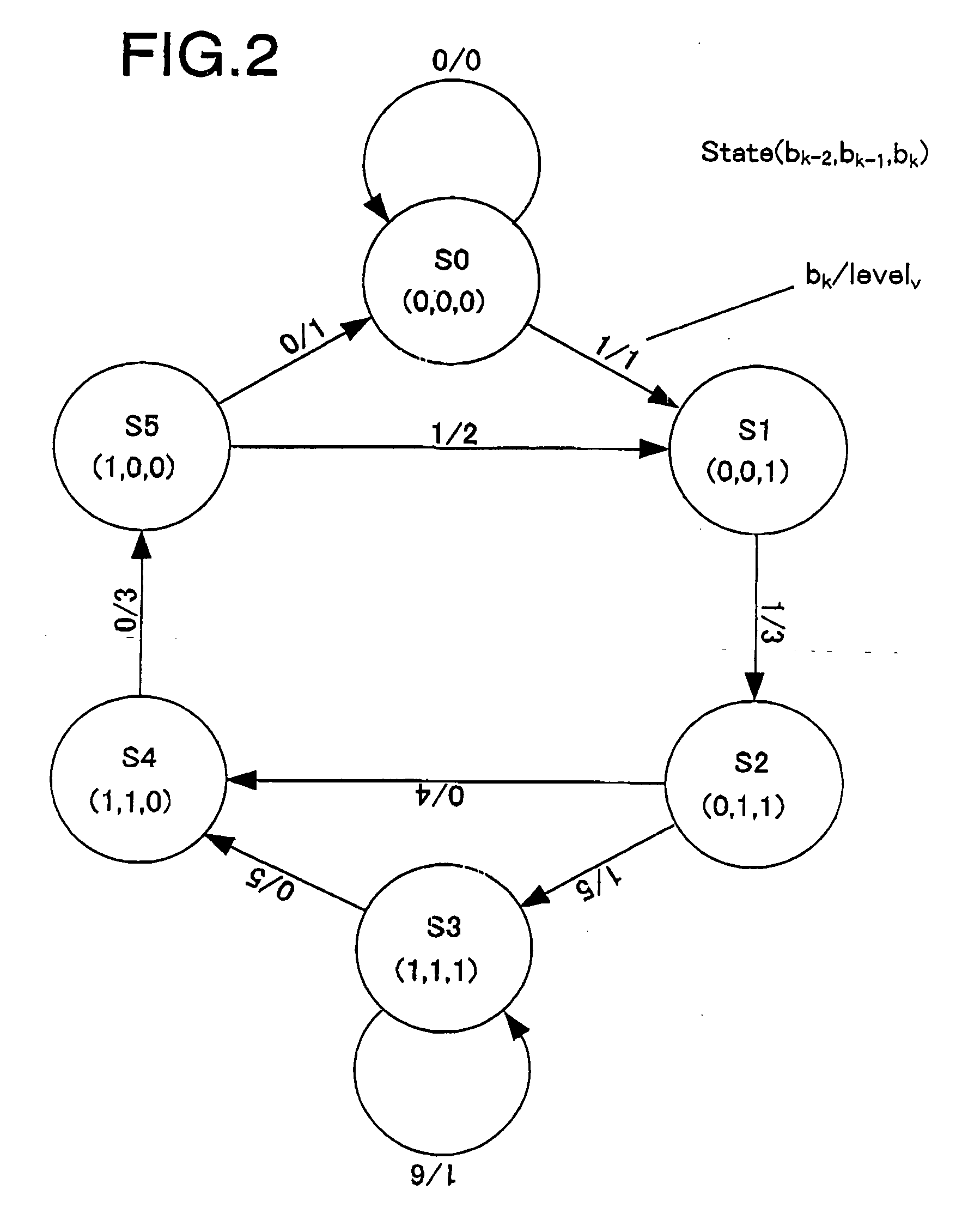
A recording control apparatus includes a waveform rectification section for receiving a digital signal generated from an analog signal representing information reproduced from an information recording medium, and rectifying a waveform of the digital signal; a maximum likelihood decoding section for performing maximum likelihood decoding of the digital signal having the waveform thereof rectified, and generating a binary signal representing a result of the maximum likelihood decoding; a reliability calculation section for calculating a reliability of the result of the maximum likelihood decoding based on the digital signal having the waveform thereof rectified and the binary signal; and an adjusting section for adjusting a shape of a recording signal for recording the information on the information recording medium based on the calculated reliability.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for recording/reproducing data on/from optical disk
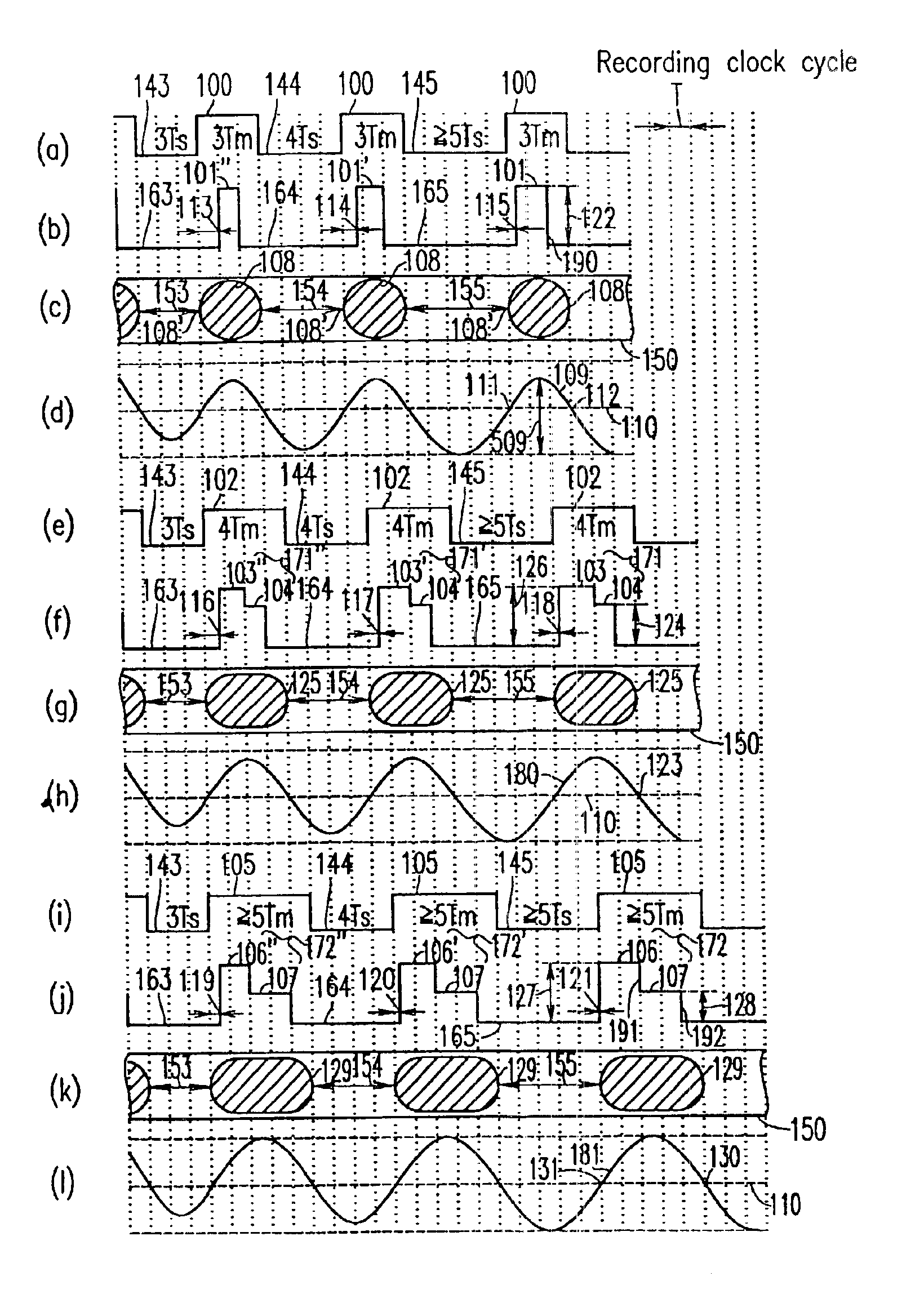
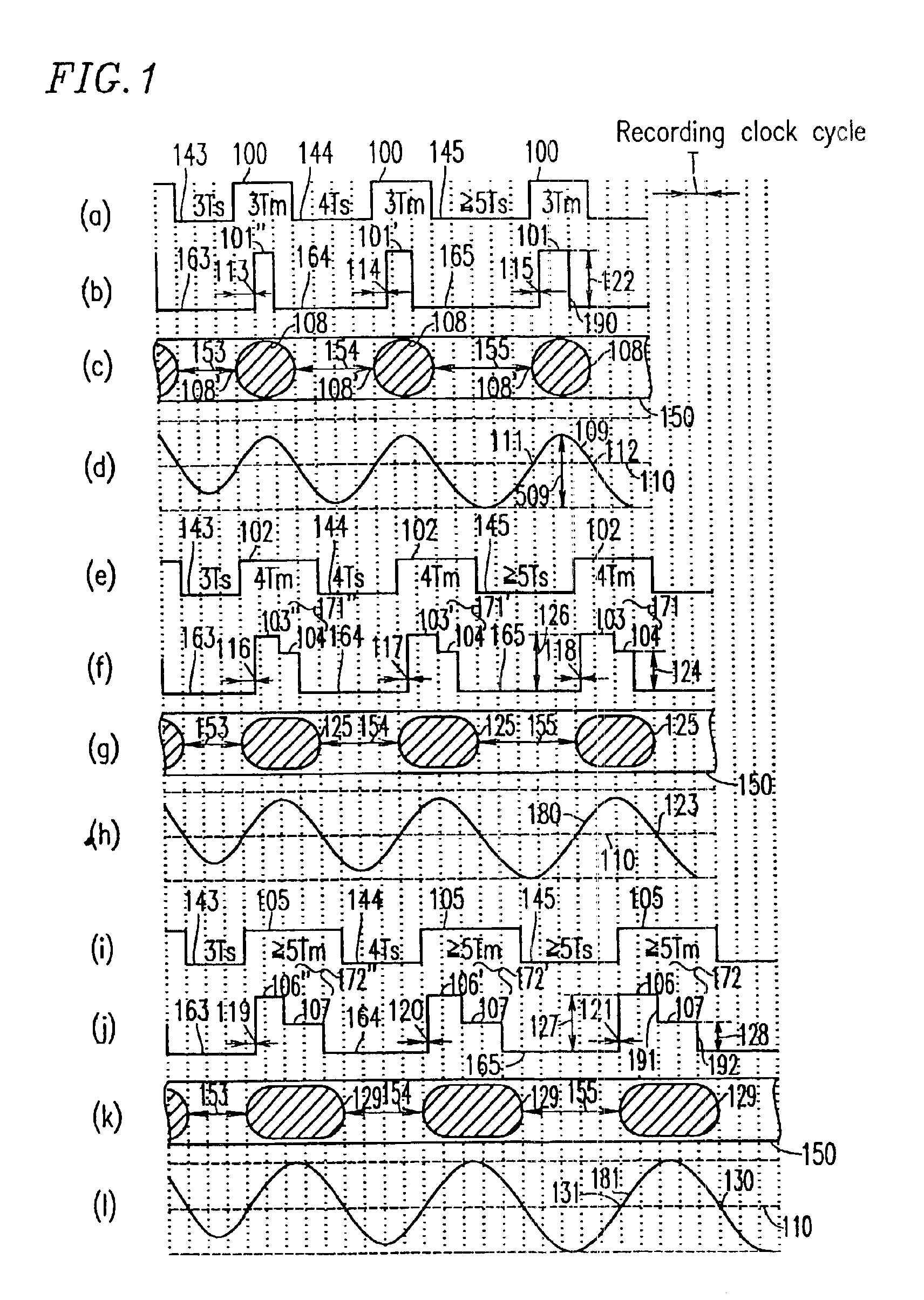
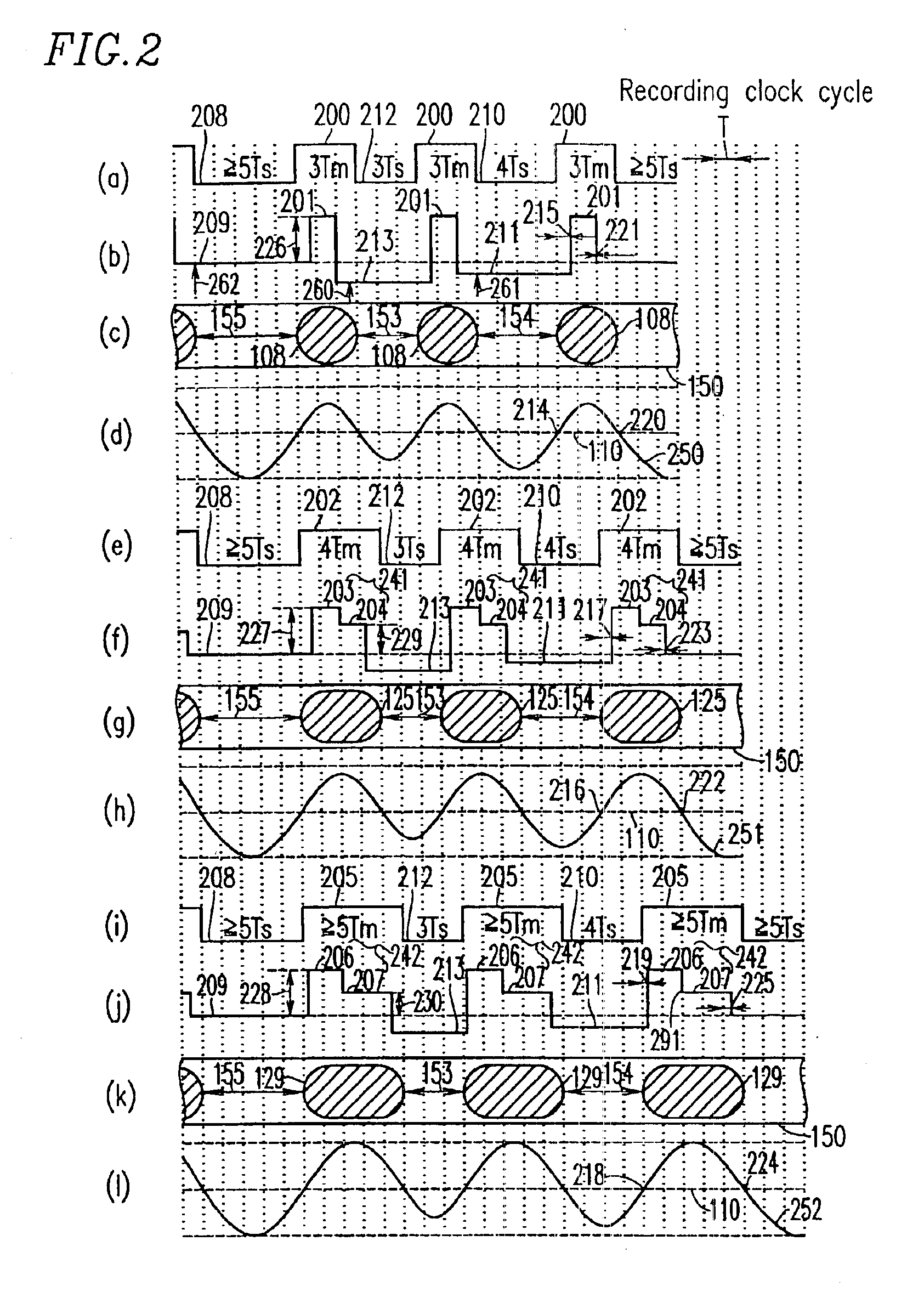
InactiveUS6894965B2Removed positioningMaximising amplitudeTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesEngineeringFront edge
A shortest mark 108 is recorded with a single recording pulse. A long mark 125 is recorded with a two-stage pulse including a first-part pulse and a second-part pulse. In the case where each of positions 115 and 118 of front edges of the recording pulses is determined based on a relationship between a length of a space immediately before a mark and that of the mark itself so as to properly position the front edges of reproduced waveforms of all the mark lengths and each of positions of rear edges of the recording pulses of all the mark lengths is fixed so as to satisfy a prescribed relative relationship with an edge of a recording clock, power 122 of a recording pulse 101 of the shortest mark is determined so as to realize a proper rear edge position 112 of the reproduced waveform of the shortest mark and power 124 of a second-part pulse 104 is determined for each mark length so as to realize a proper rear edge position 123 of the reproduced waveform of the long mark.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Information storage medium and method and apparatus for recording and/or reproducing data
InactiveUS20050030853A1Effectively and rapidly accessedRecording strategiesRecord information storageDatabaseInformation storage
An information storage medium including: a common information table which store information common to plural types of information storage media; at least one parameter table which store parameter information corresponding to a recording characteristic specific to the type of an information storage medium; and a pointer field which stores pointer information indicating a location of the at least one parameter table.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Information recording method, information recording medium and information recording apparatus
InactiveUS6925040B1Avoid distortionIncrease linear densityRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLookup tableComputer science
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for recording data in optical recording medium and an apparatus for recording data in optical recording medium
ActiveUS20050094526A1Reduce jitterTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesTime delaysOptical recording
A method for recording data in an optical recording medium according to present invention is constituted so that data are recorded in an optical recording medium including a light transmission layer and two recording layers by projecting a laser beam whose power is pulse-like modulated between a recording power and a bottom power lower than the recording power onto the optical recording medium from a side of the light transmission layer and forming recording marks having different lengths in the recording layers and that when a recording mark having a longer length than that of the shortest recording mark is to be formed in the recording layers by modulating the power of a laser beam using a single pulse, a time of raising the power of the laser beam to the recording power is delayed relative to a time of raising the power of the laser beam to the recording power when the shortest recording mark is to be formed. In the case of recording data in the optical recording medium in accordance with the thus constituted method for recording data in an optical recording medium, jitter of a reproduced signal obtained by reproducing the recorded data can be markedly reduced.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Recording and reading method and device for dye based write-once DVD medium
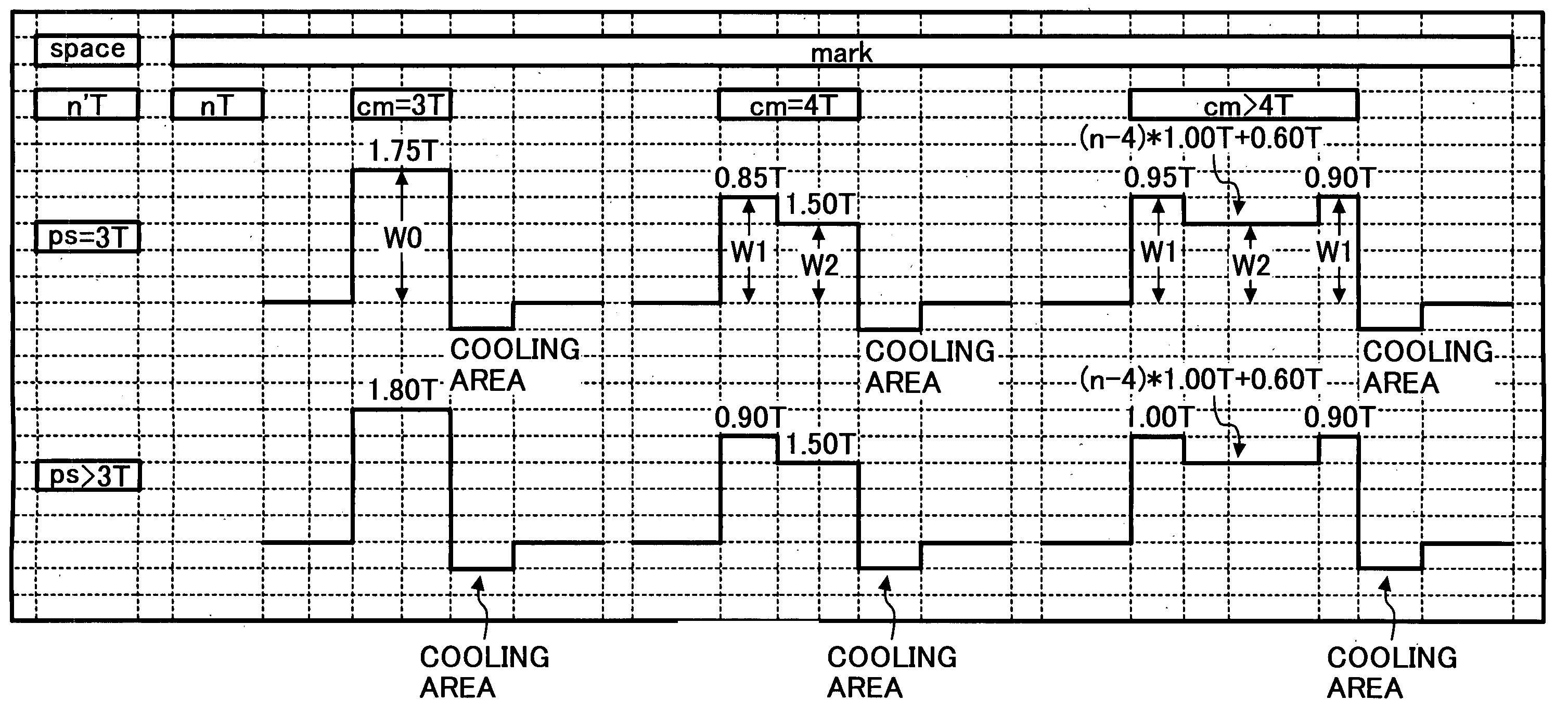
InactiveUS20050169148A1Convenient recordingImprove performanceRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsOrganic dyeRecording layer
A recording method of recording information in a dye-based write-once digital versatile disc (DVD) containing a substrate having a wobbled guide groove and a recording layer containing an organic dye. Recording is performed by irradiating the DVD with three kinds of single light pulses. Each single pulse contains a recording area to record a mark and a cooling area having a light quantity not greater than 0.1 mW for a predetermined time. When the mark having a shortest length is formed, the DVD is irradiated with a first single light pulse. When the mark having a second shortest length is formed, the DVD is irradiated with a second single light pulse. When the mark having a third shortest length or longer is formed, the DVD is irradiated with a third single light pulse.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com