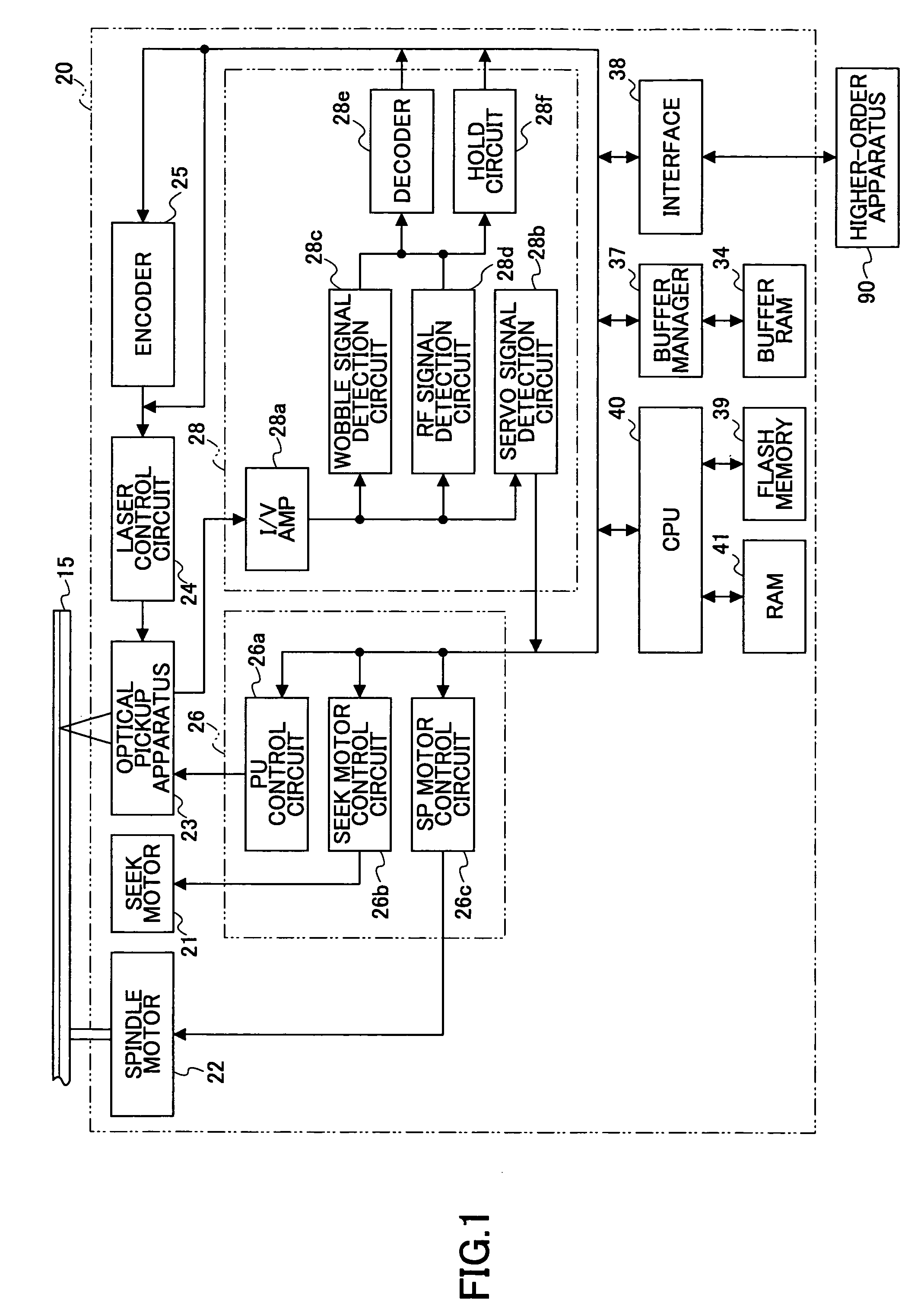
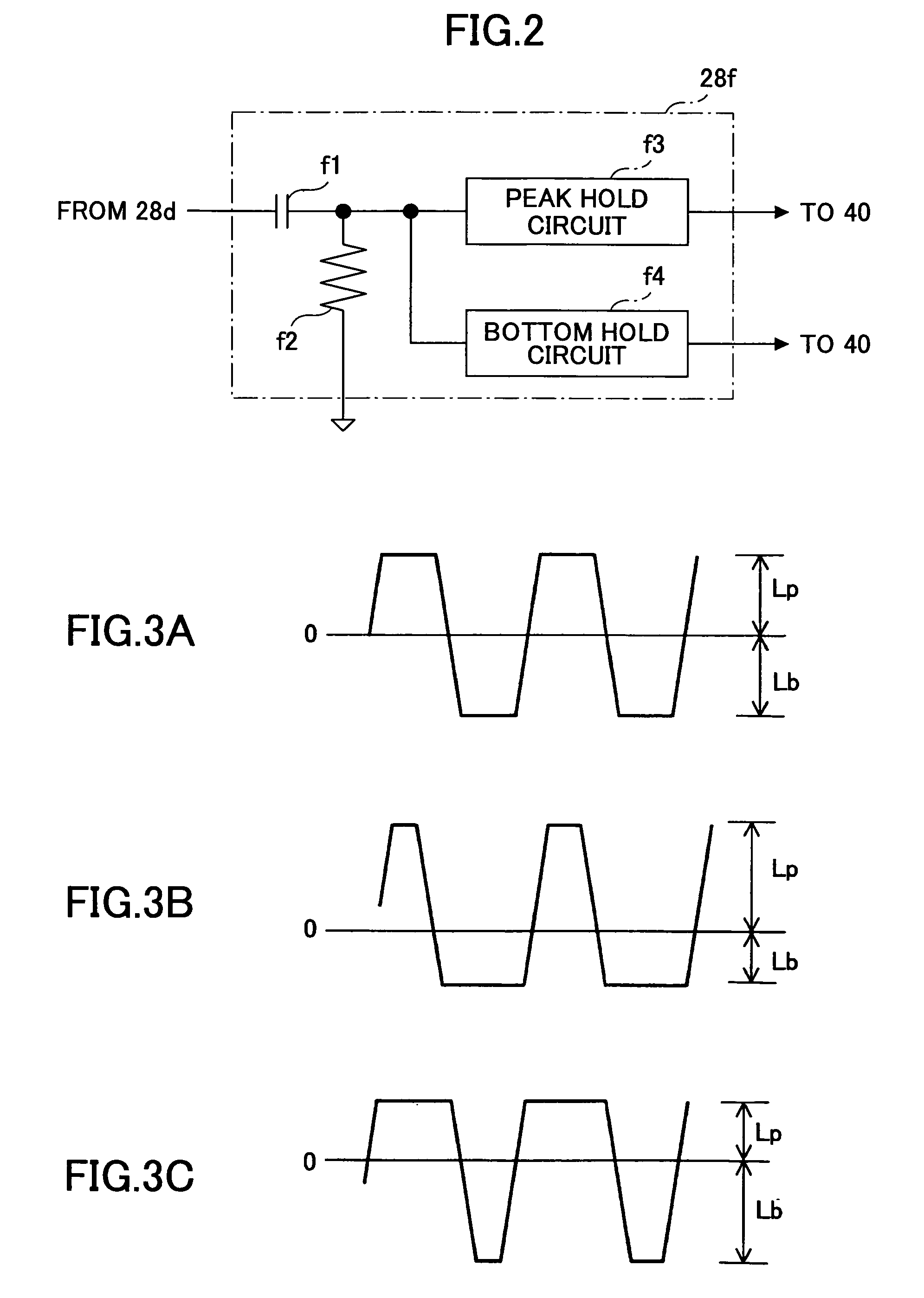
Patents
Literature
592results about "Optical overwriting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical information recording medium, producing method thereof and method of recording/erasing/reproducing information
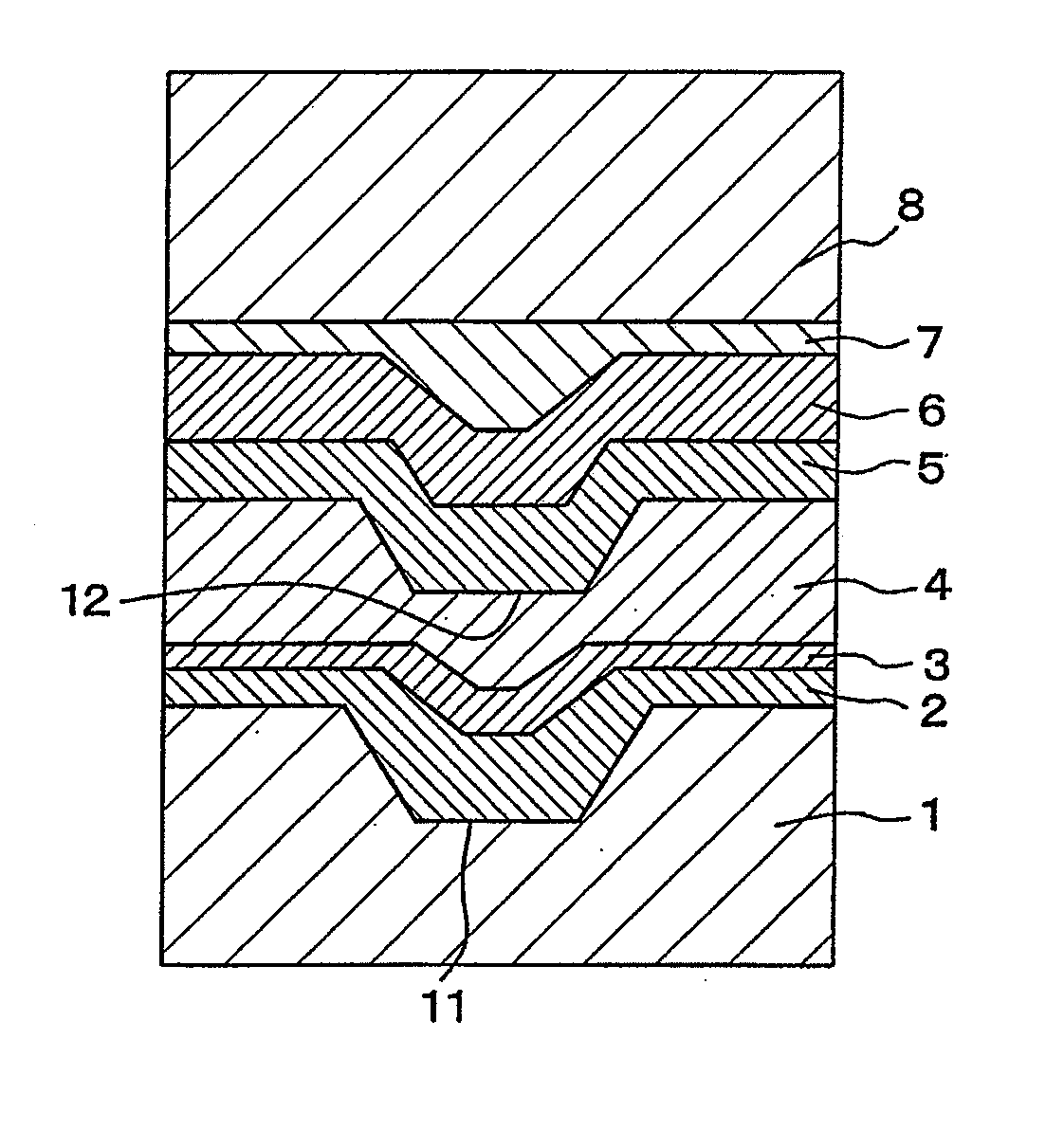
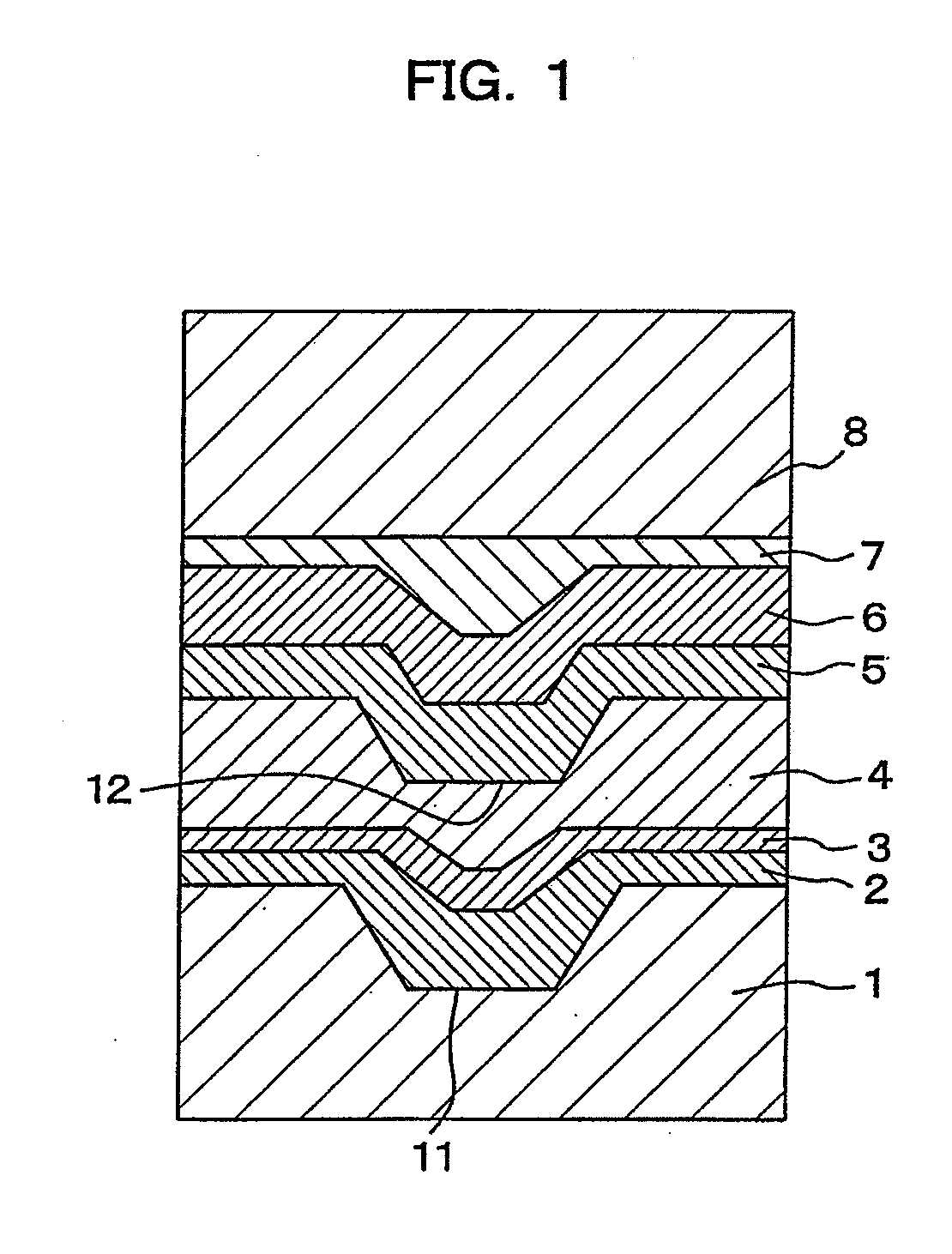
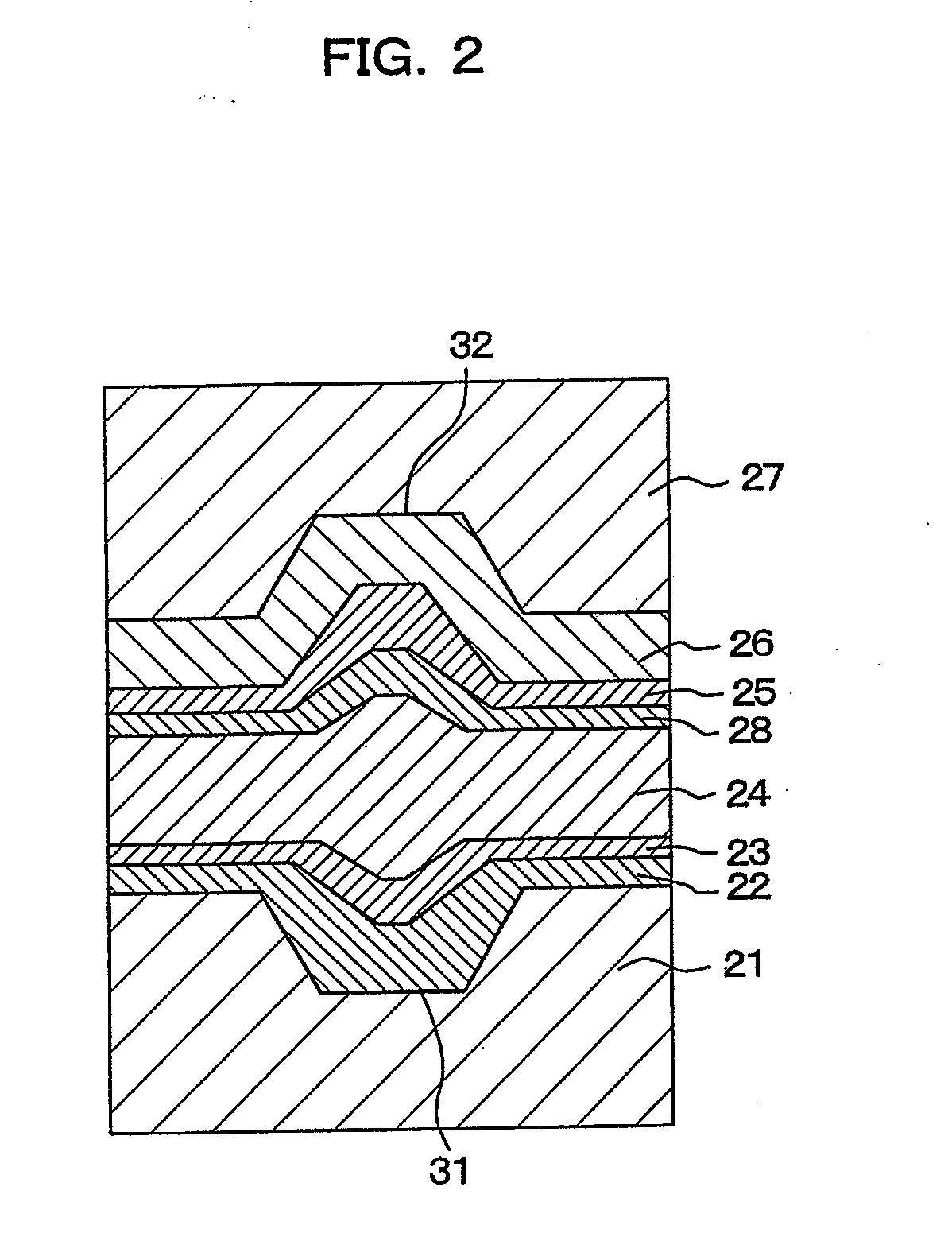
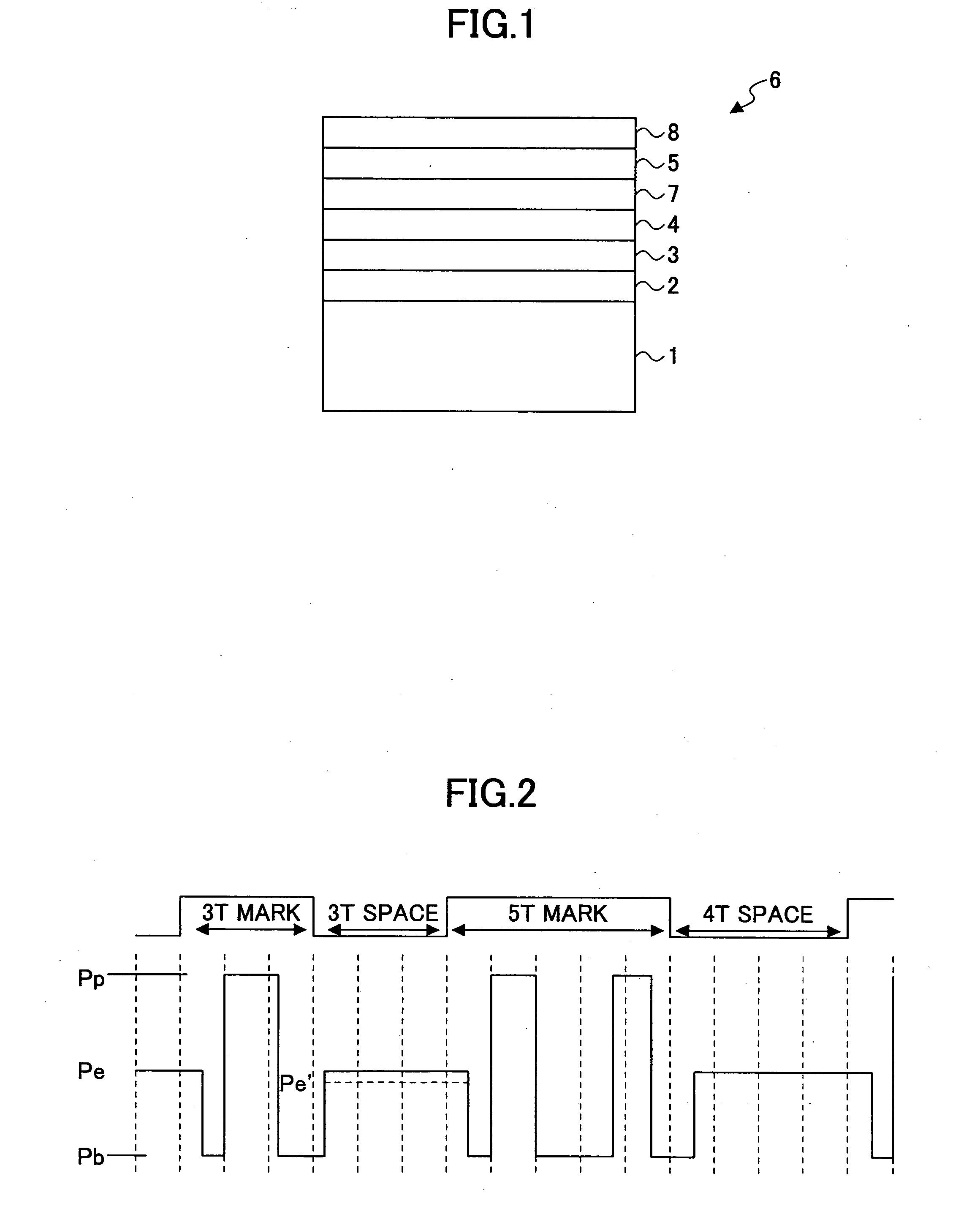
In a phase-change recording medium, a recording medium is provided with a barrier layer including Ge-N, Ge-N-O between a recording layer and a dielectric protective layer in order to prevent a chemical reaction and an atom diffusion between the recording layer and the dielectric protective layer. A barrier material can be also applied to the protective layer itself. Thereby, it is possible to considerably suppress a reduction of a reflectivity and a reduction of a signal amplitude due to the repeat of recording and erasing, such reductions being observed in a conventional phase-change optical information recording medium, and thereby the number of overwriting times can be increased.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
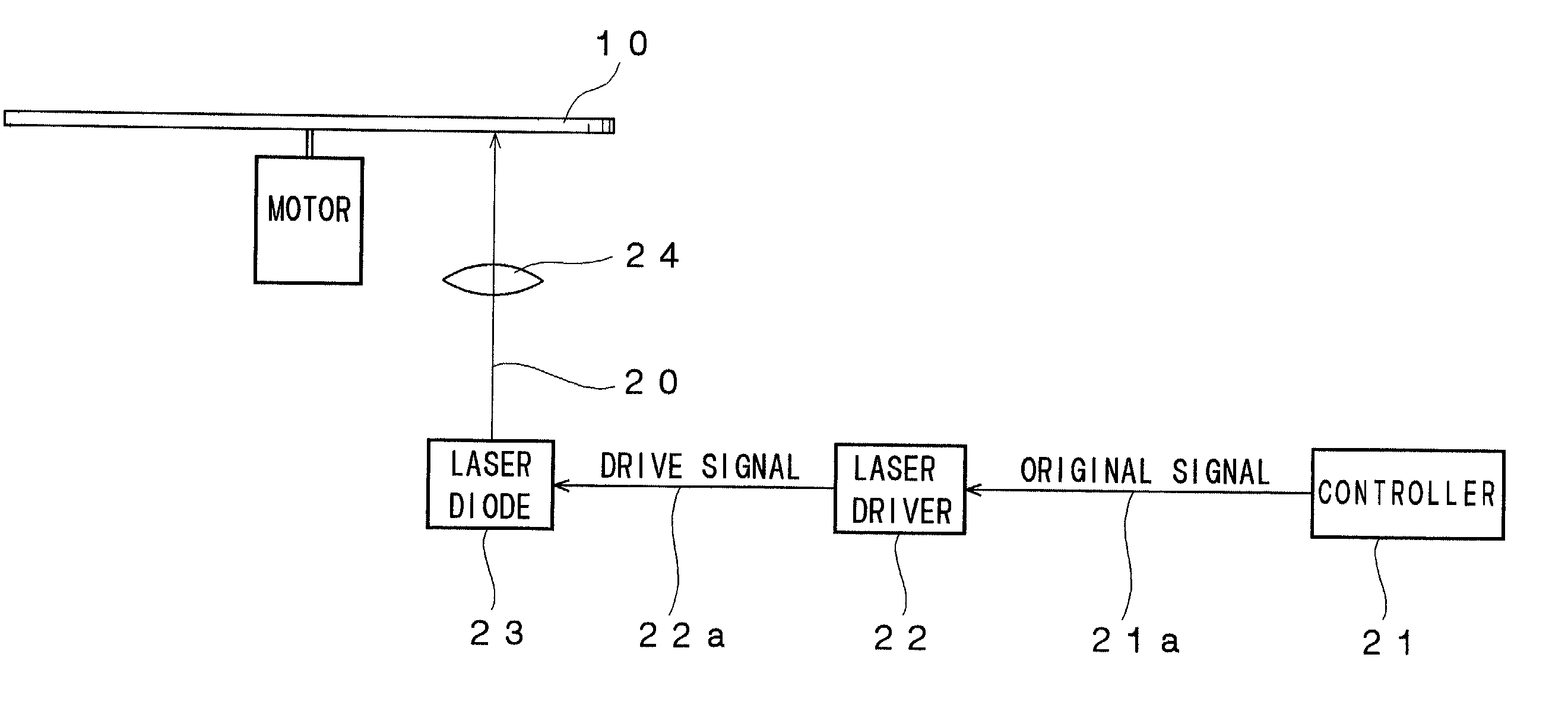
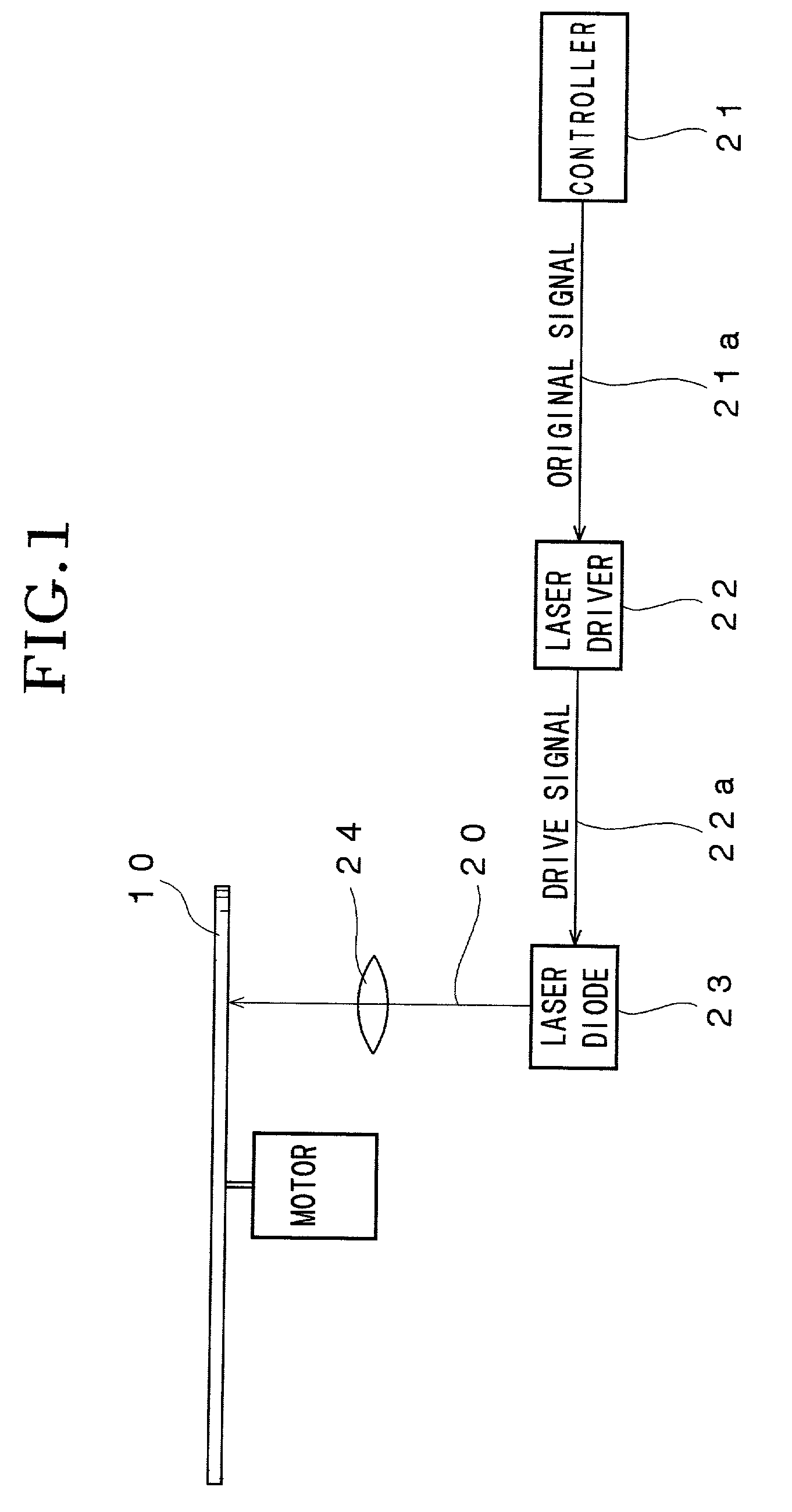
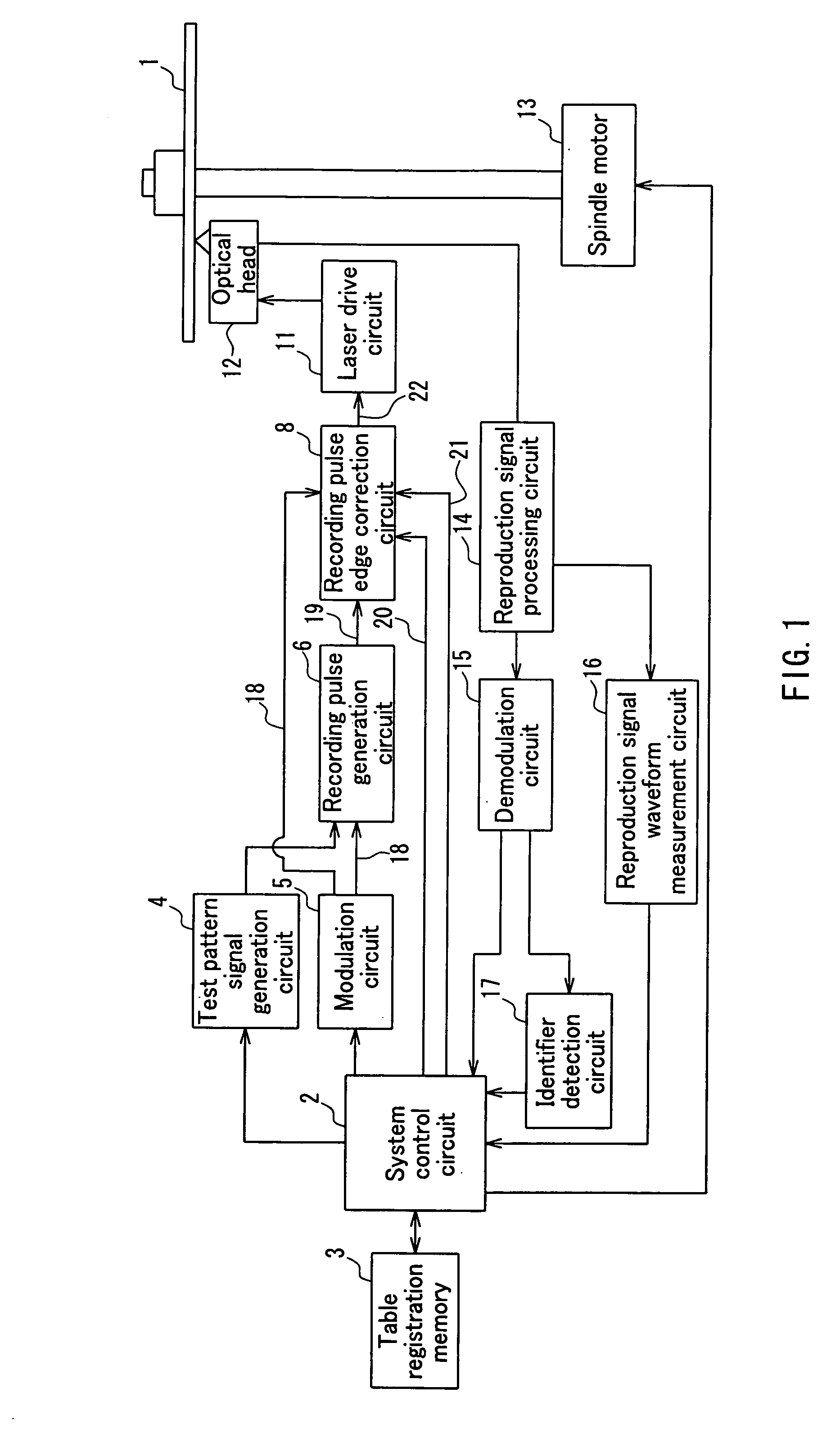
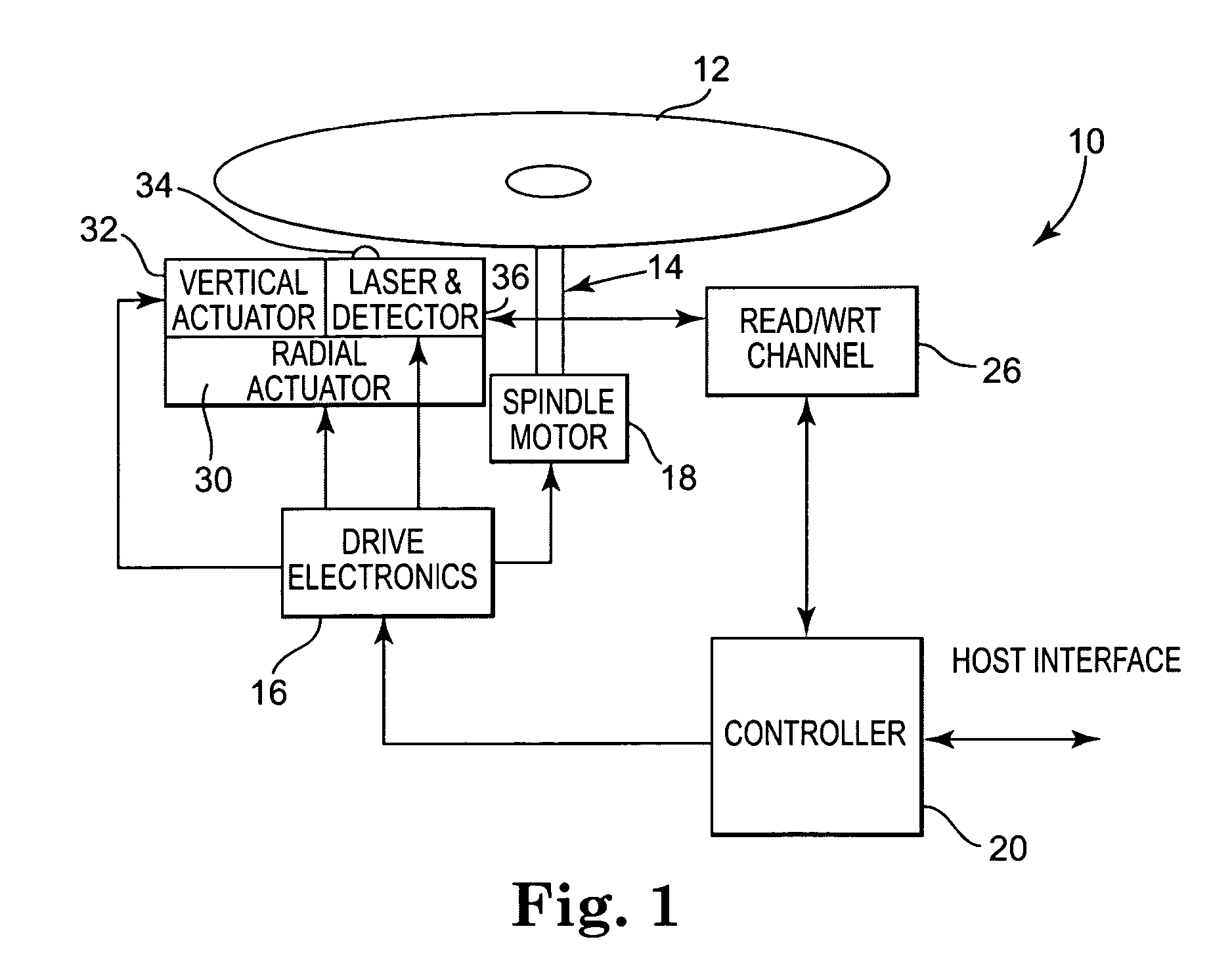
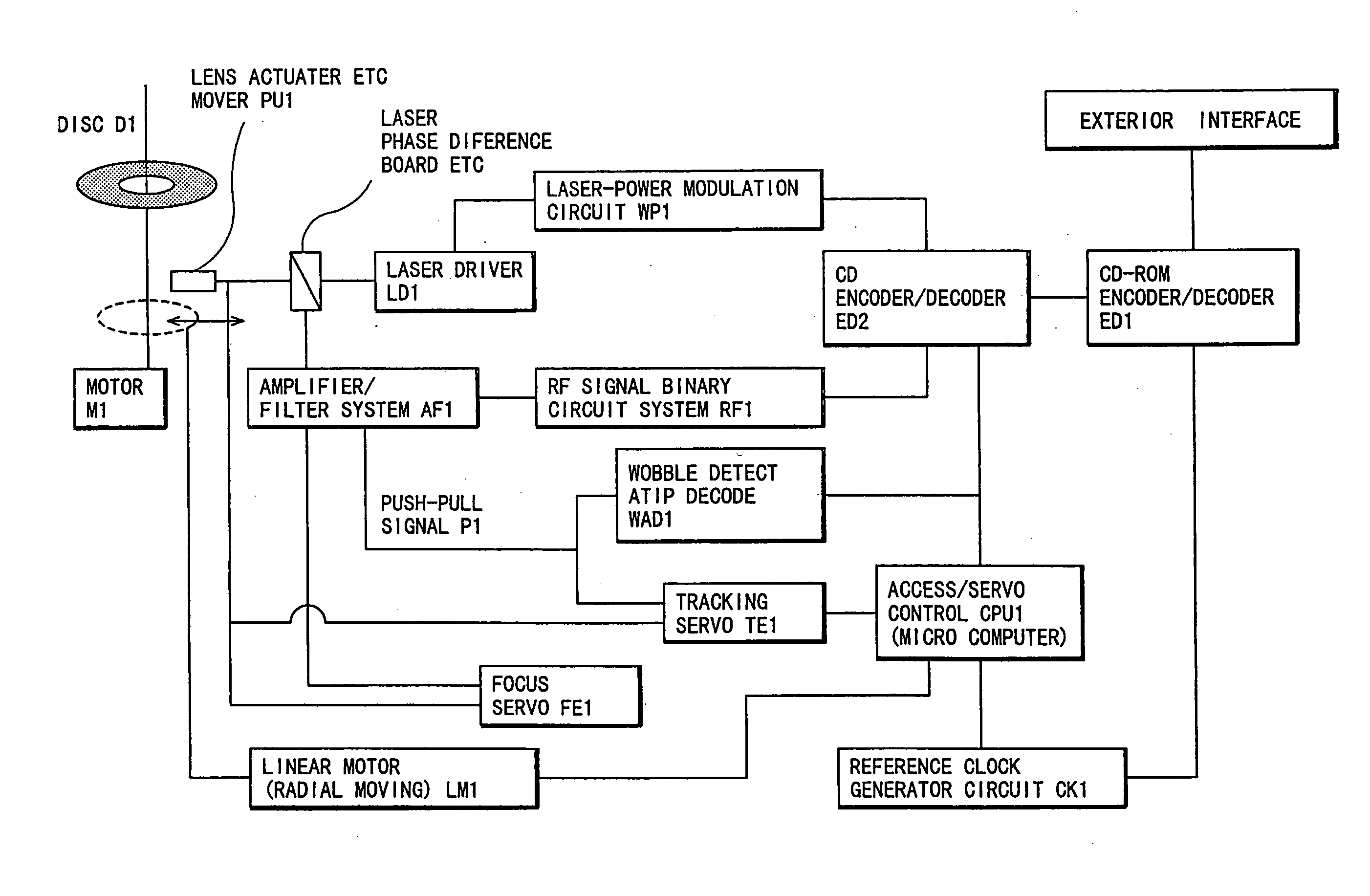
Optical disk recording method, optical disk device and optical disk
ActiveUS20050058047A1Accurate recordEasy to operateRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsFall timeEngineering
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Optical phase-change disc
An optical phase-change disc comprises a substrate having thereon a spiral groove or concentric grooves for guiding a focused light beam, and a layer structure including a recording layer and protective layers sandwiching therebetween the recording layer. The groove has wobble for recording ATIP (absolute time information) or ADIP (address information). The following relationship between the groove width GW, beam diameter R0 and wobble amplitude aw: 0.25< / =GW / R0< / =0.45 or 0.65< / =GW / R0; and 0.03< / =aw / GW< / =0.08 hold for preventing distortion of the groove caused by repeated overwriting operation to improve reliability of the optical disc.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
Optical disc, optical disc recording/reproducing apparatus, and optical disc recording/reproducing method
ActiveUS7088667B2Perform recording processingReliable recordRecording strategiesAccessories for auxillary signalsOptical recordingLaser
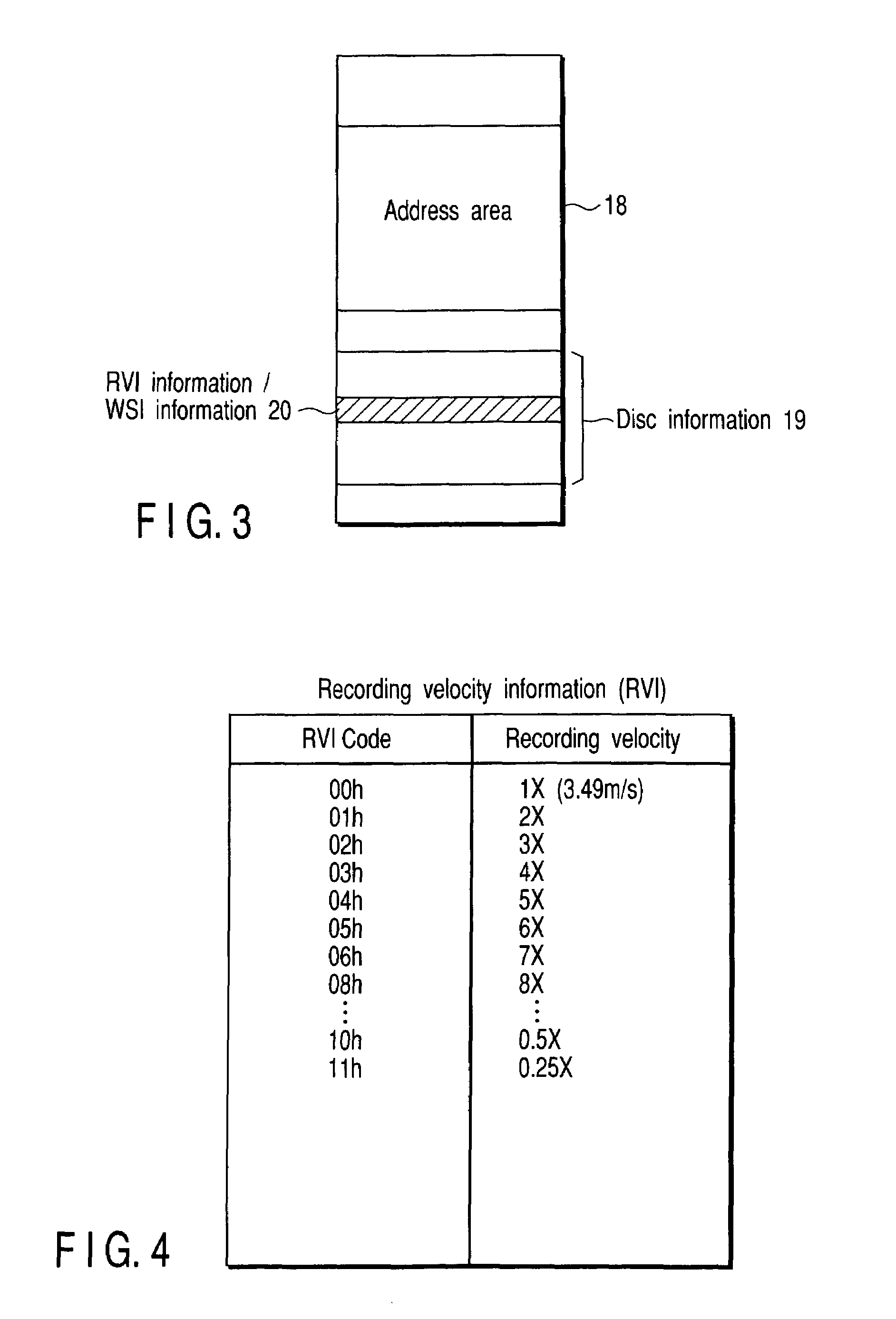
In an optical disc in / from which data is recorded or reproduced by irradiating a storage area on the optical disc with a laser, information containing recording velocity information (RVI) for recording / reproduction, which represents a linear velocity different from the standard linear velocity, and write strategy information (WSI) corresponding to the recording velocity information is stored in a land pre-pit or the like on the optical disc.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method of recording and reproducing information and apparatus for recording and reproducing information using the method
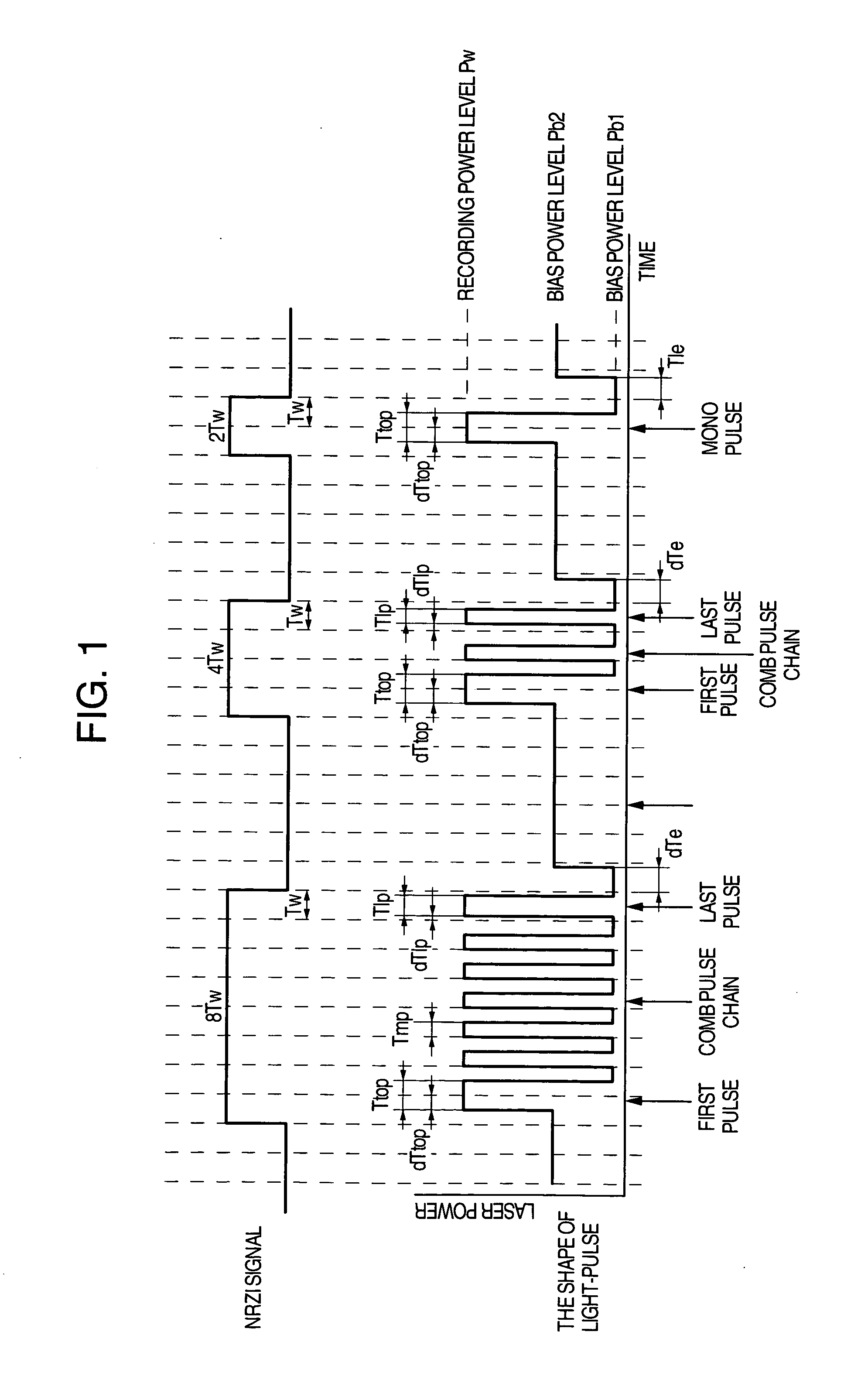
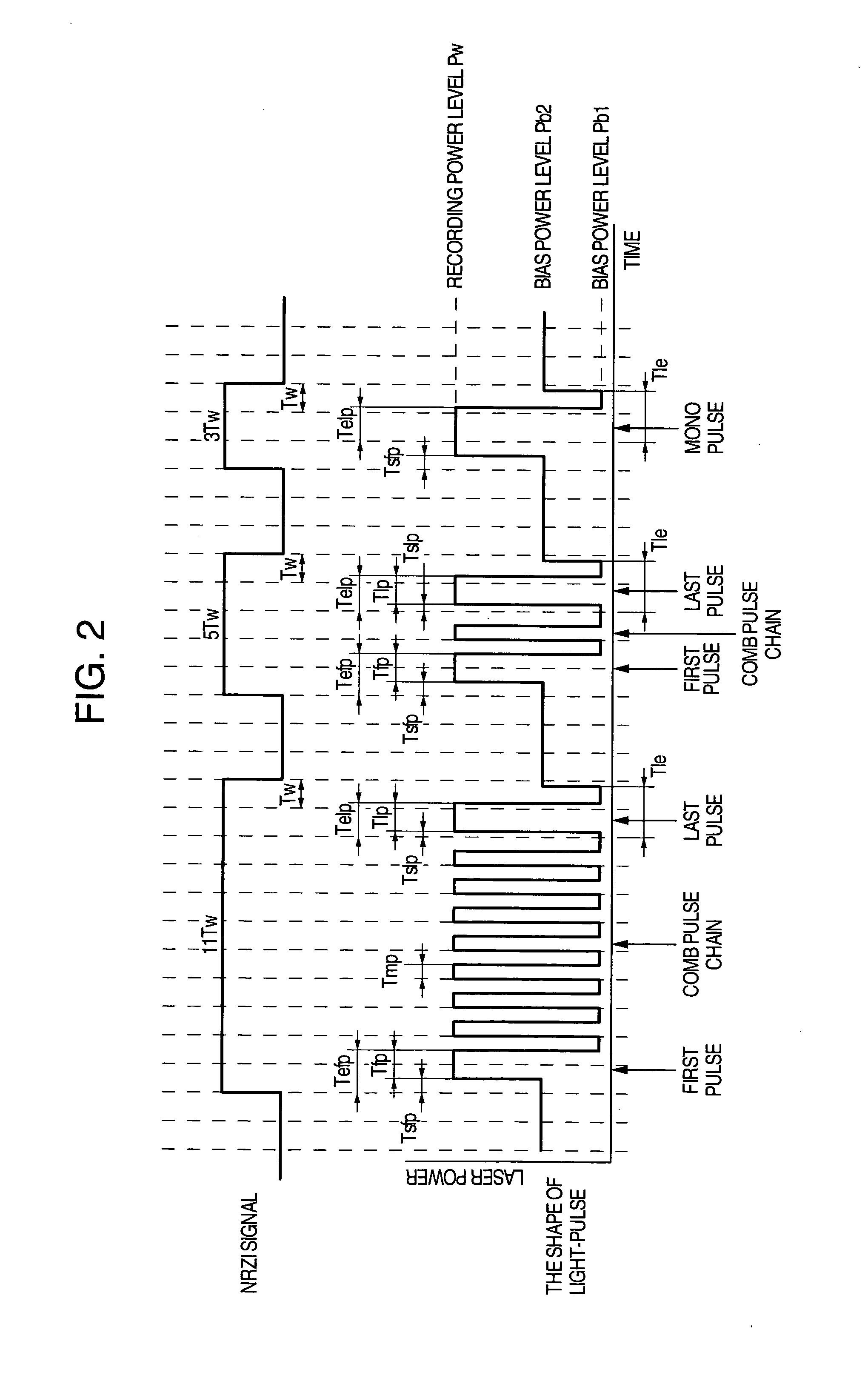
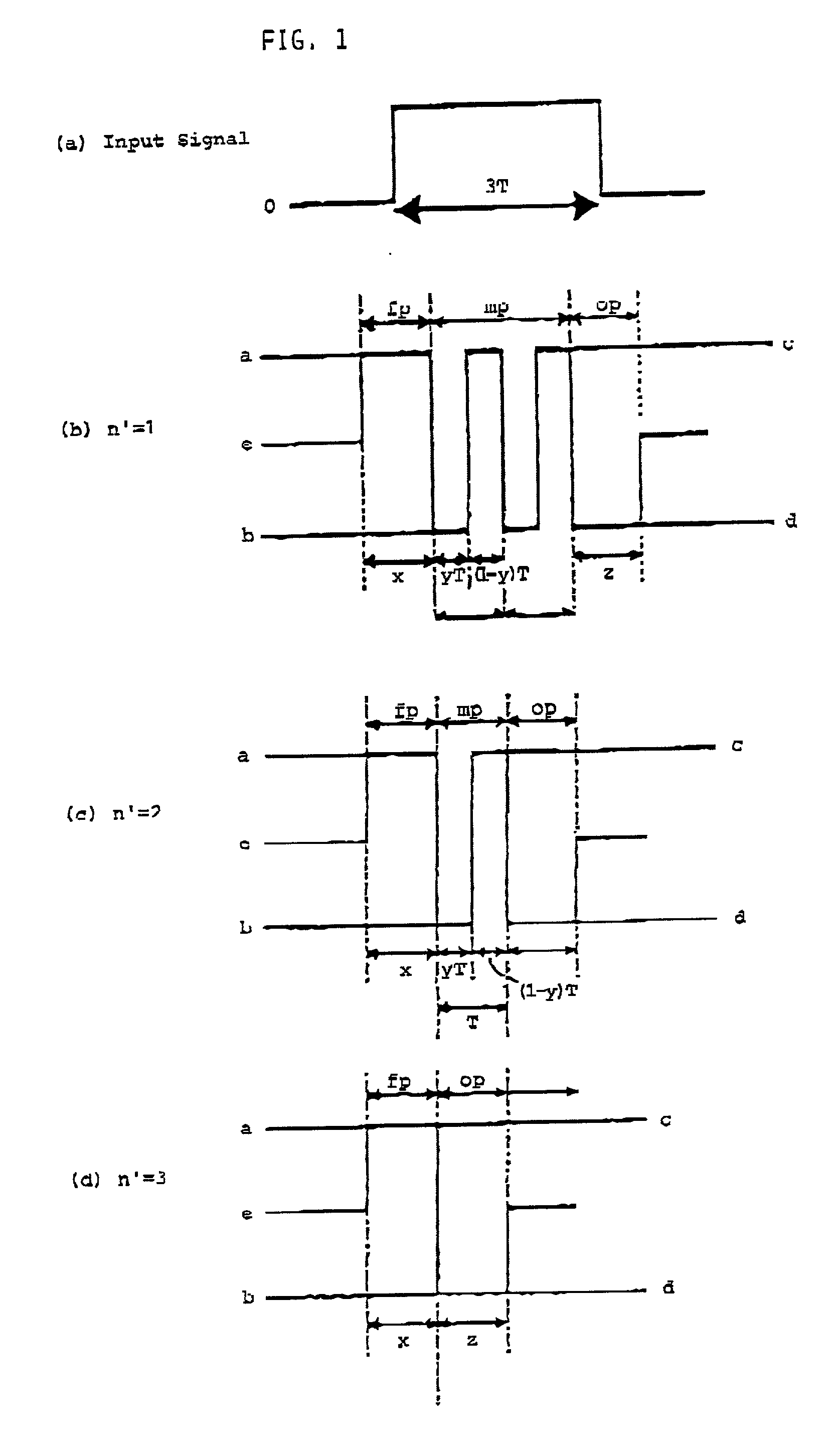
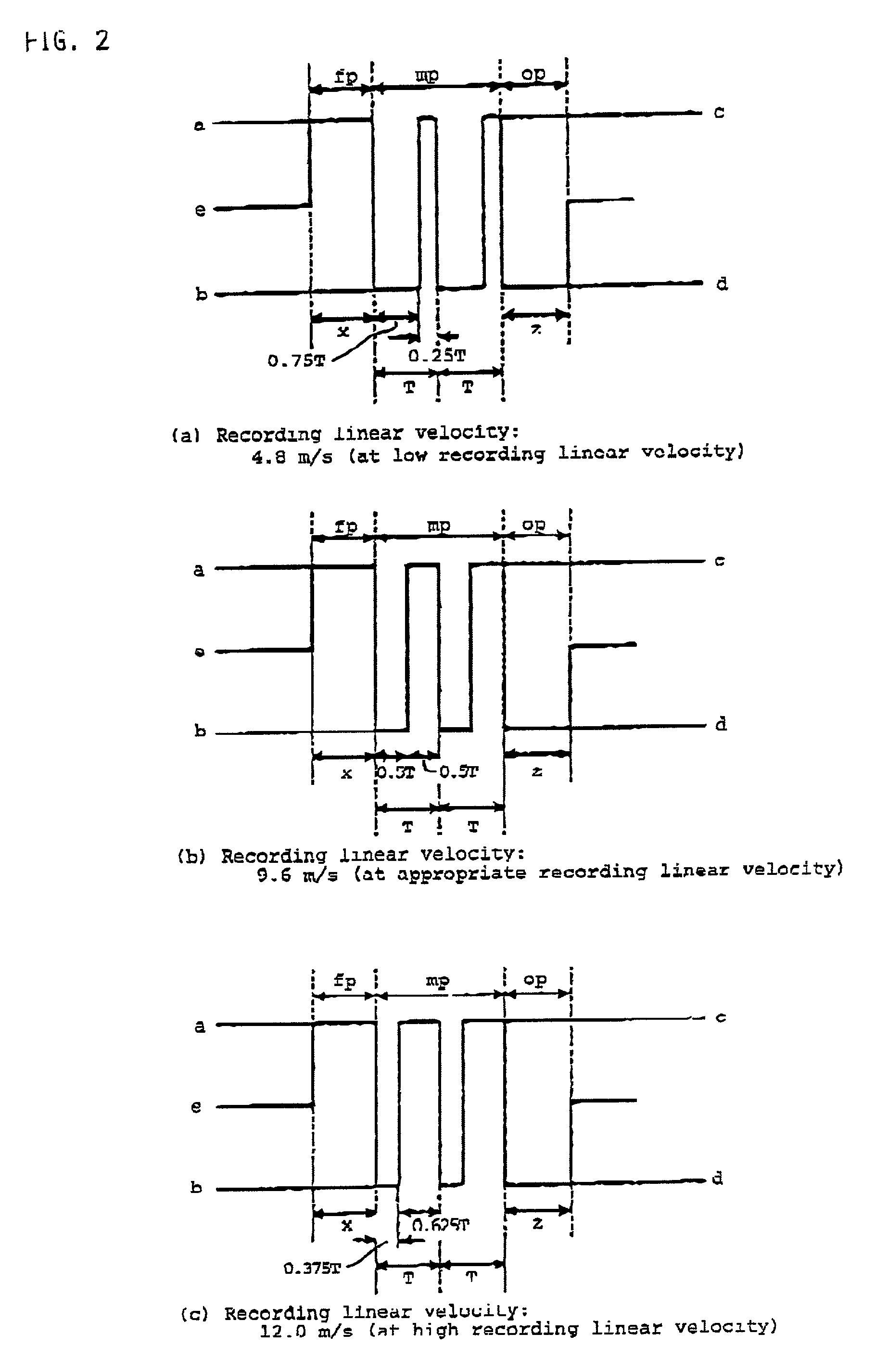
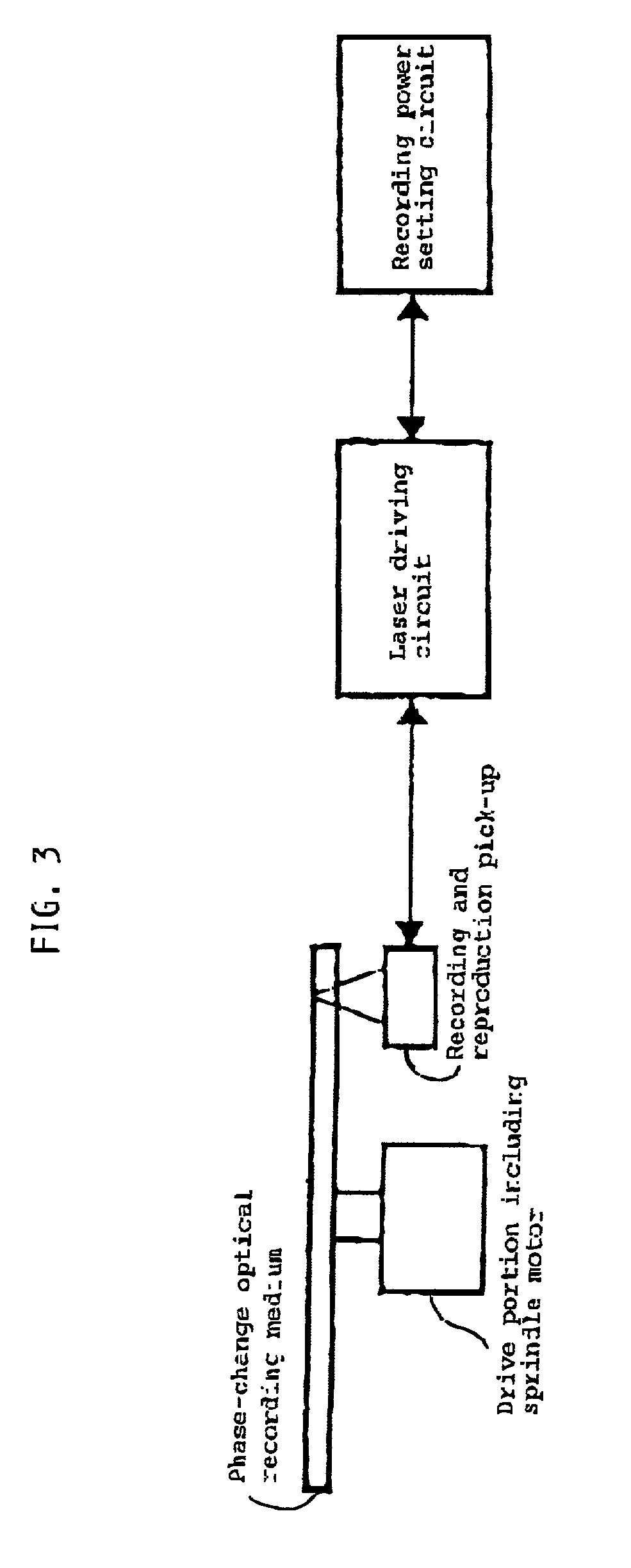
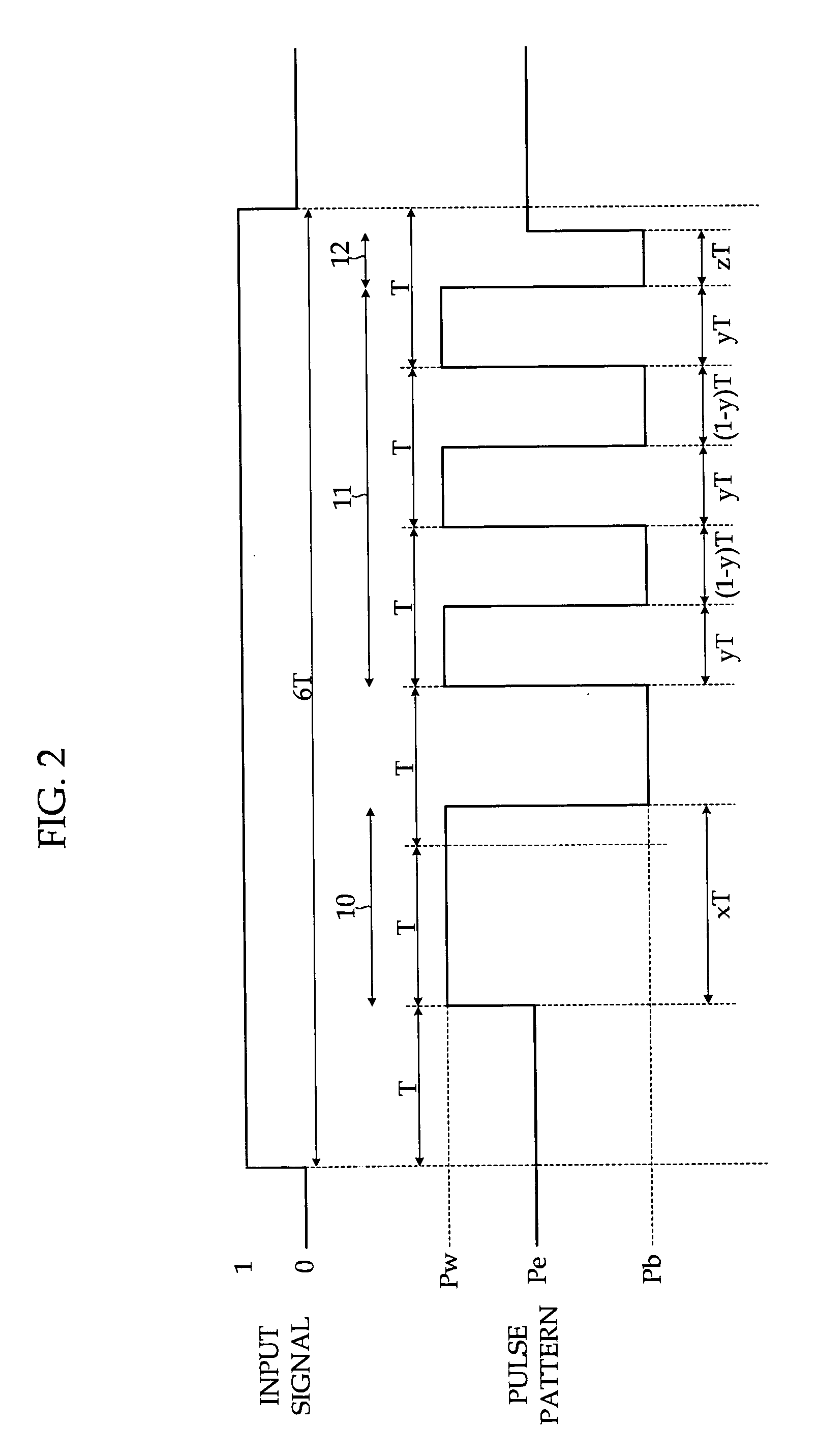
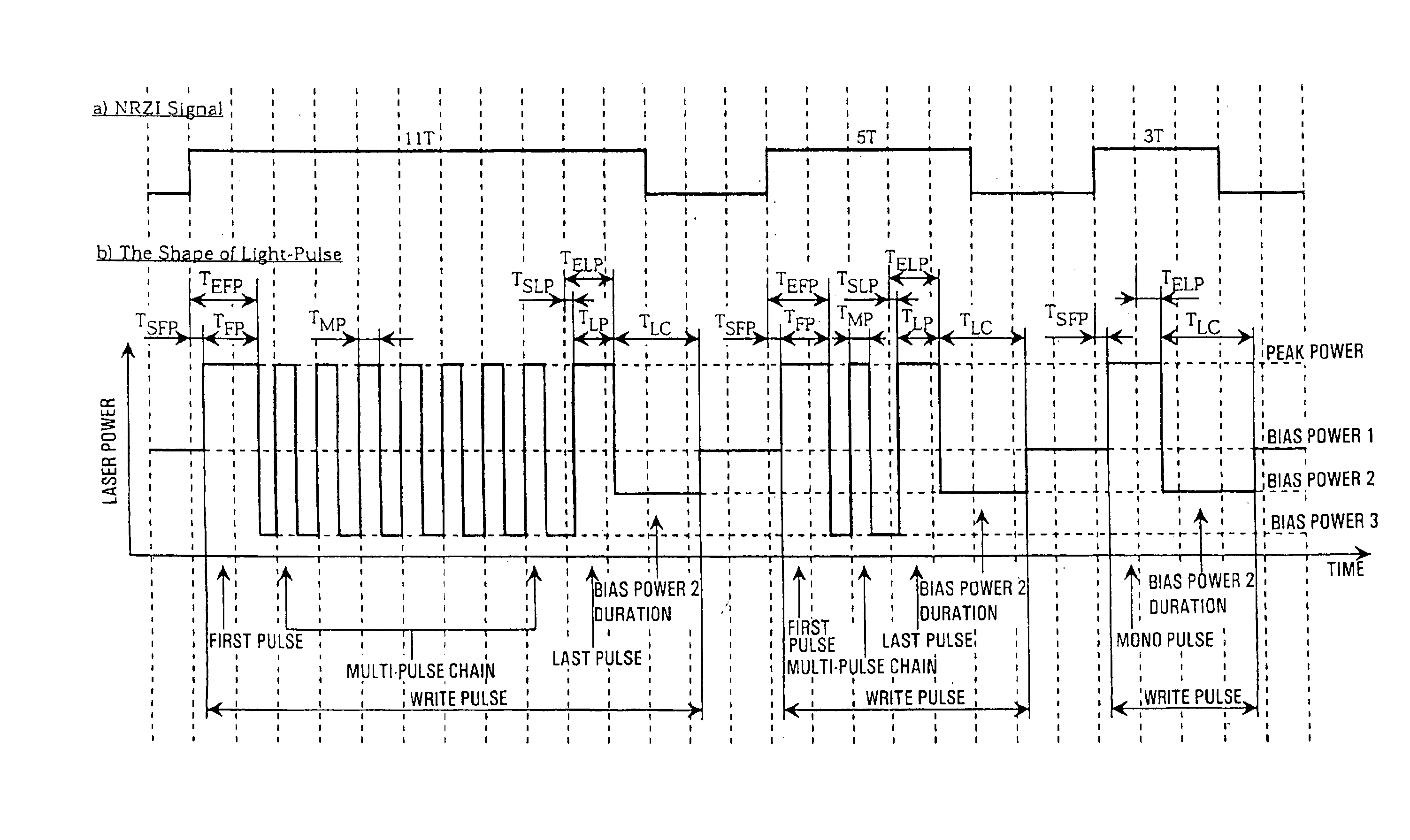
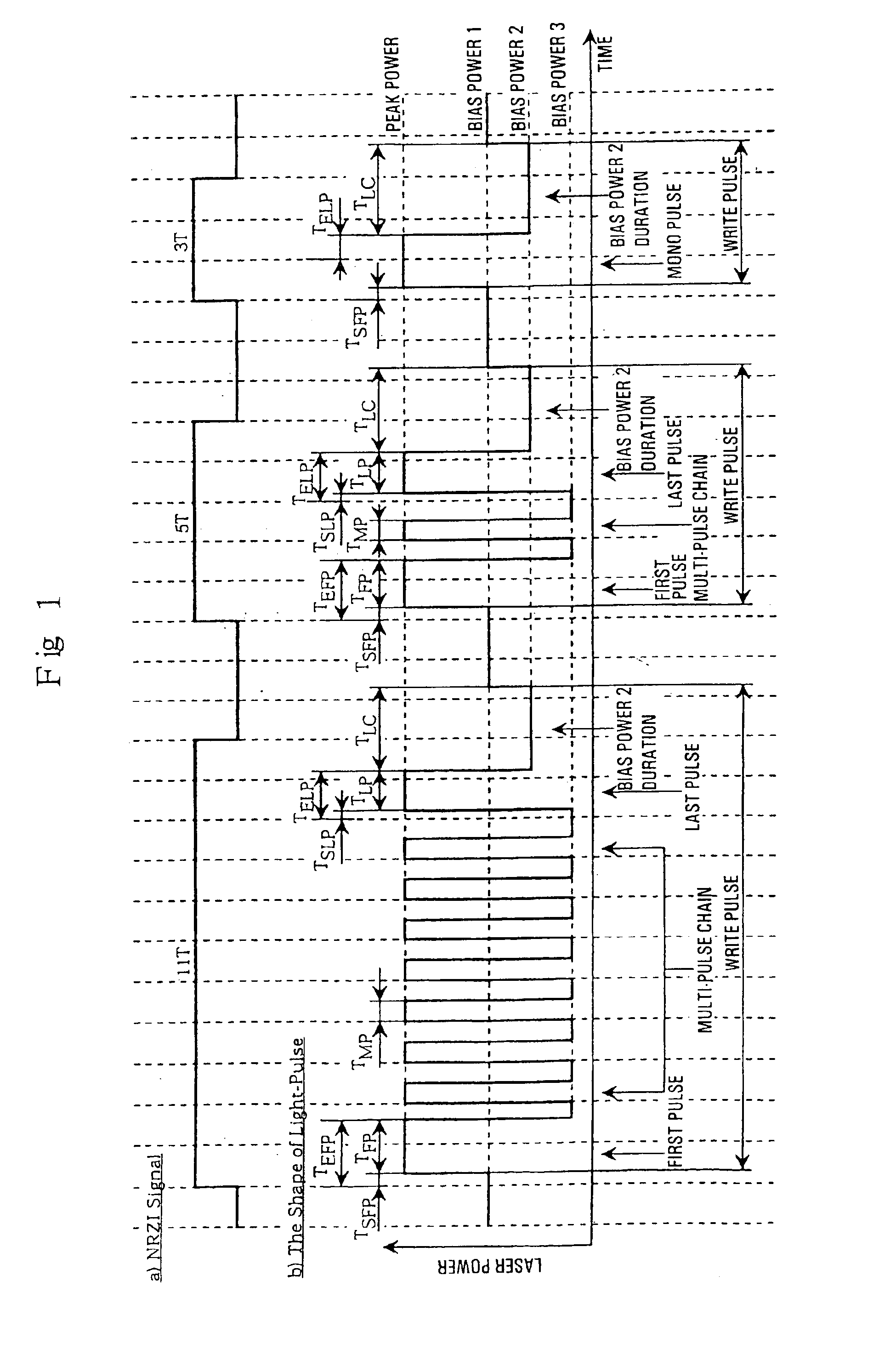
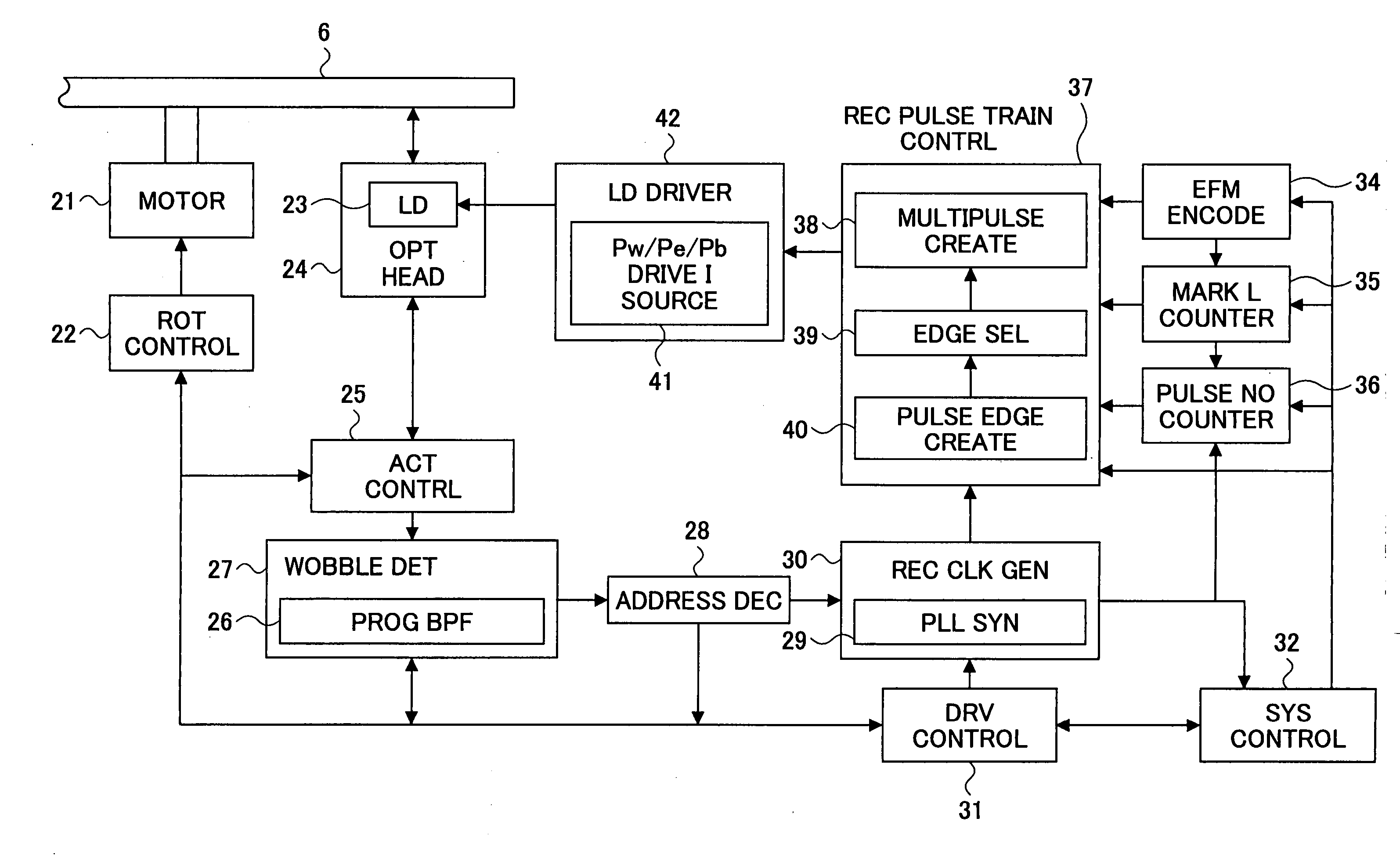
A method of recording and reproducing information in a phase-change optical recording medium by irradiation of an electromagnetic wave for recording, reproducing and / or rewriting information is proposed, wherein when information is recorded in the phase-change optical recording medium by modulating an input signal and conducting pulse width modulation recording, a recording pulse string for recording and rewriting is a continuous electromagnetic wave, and a recording pulse string for input signal, is an electromagnetic wave pulse string having a front-pulse portion fp, a multi-pulse portion mp with a total pulse duration period T and a duty ratio y, and an off-pulse portion op, wherein the duty ratio y is decreased as a recording linear velocity for the phase-change change optical recording medium is increased, whereby multi-speed recording or CAV (constant angular velocity) recording is carried out. An information recording and reproducing apparatus, using the above method, is also proposed.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical phase-change disc having a grooved substrate, with the groove having specific wobbled and non-wobbled regions
An optical phase-change disc comprises a substrate having thereon a spiral groove or concentric grooves for guiding a focused light beam, and a layer structure including a recording layer and protective layers sandwiching therebetween the recording layer. The groove has wobble for recording ATIP (absolute time information) or ADIP (address information). The following relationship between the groove width GW, beam diameter R0 and wobble amplitude aw: 0.25< / =GW / R0< / =0.45 or 0.65< / =GW / R0; and 0.03< / =aw / GW< / =0.08 hold for preventing distortion of the groove caused by repeated overwriting operation to improve reliability of the optical disc.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
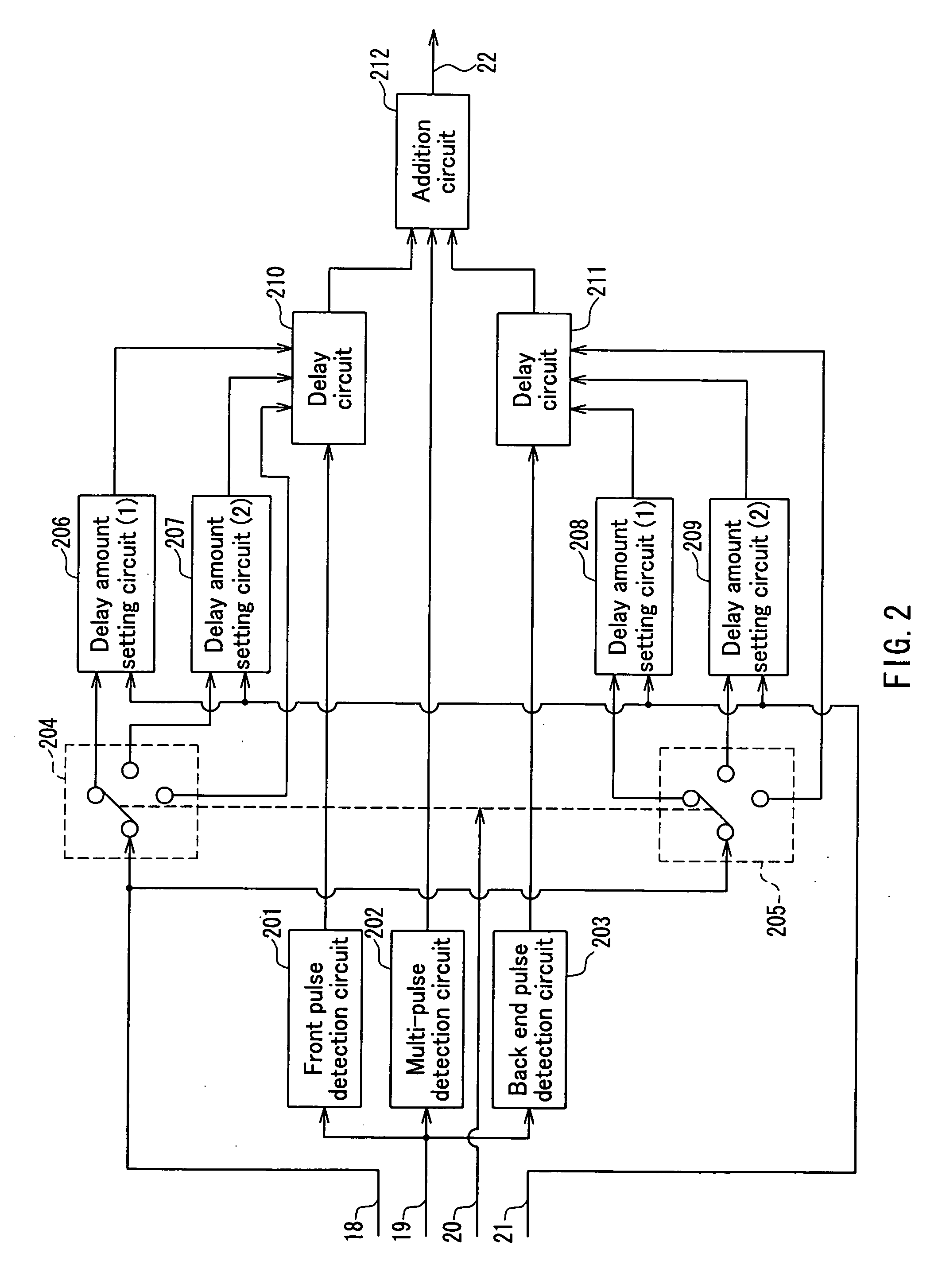
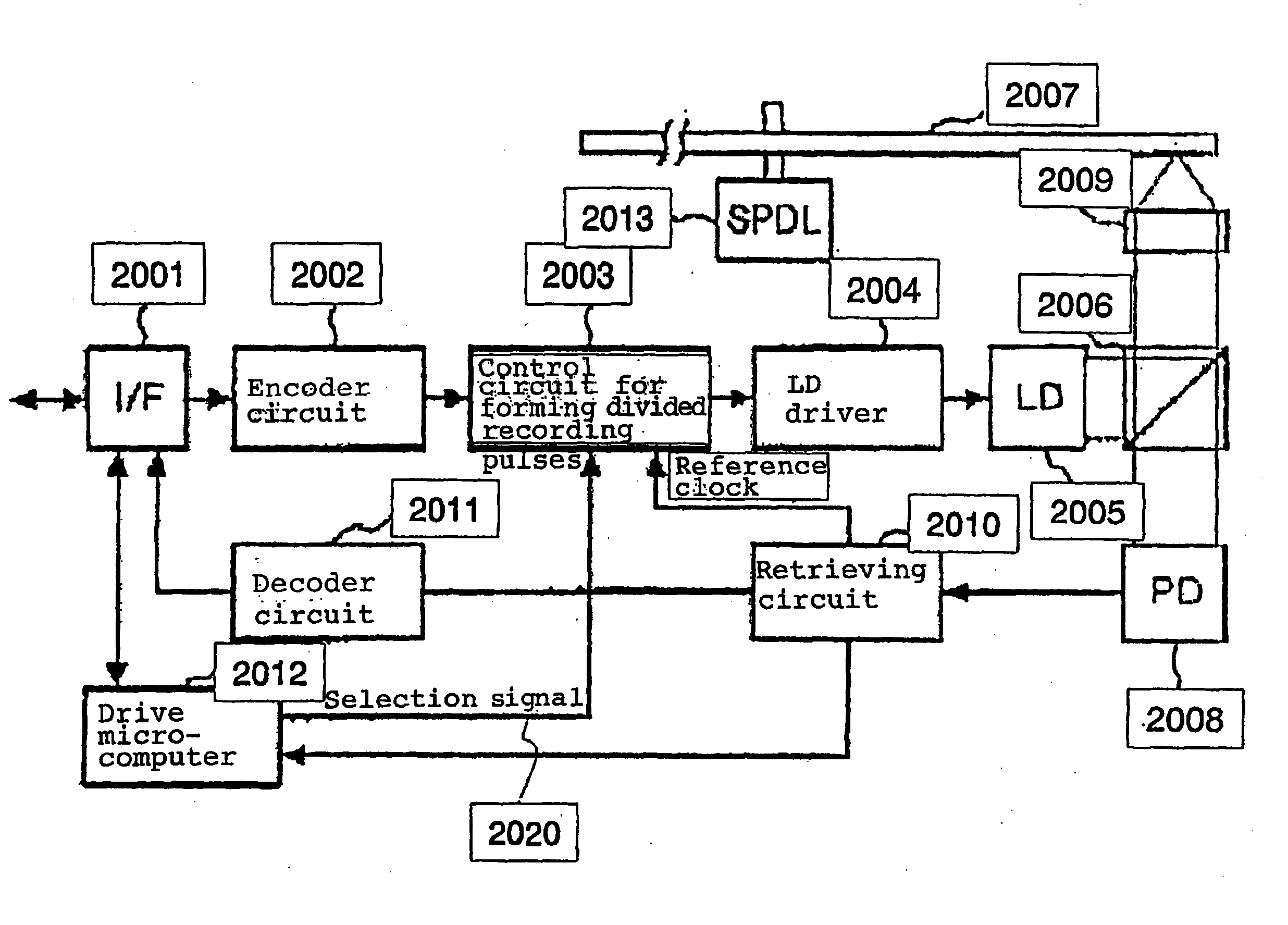
Device and method for recording data to optical disk using recording pulse with corrected edge position
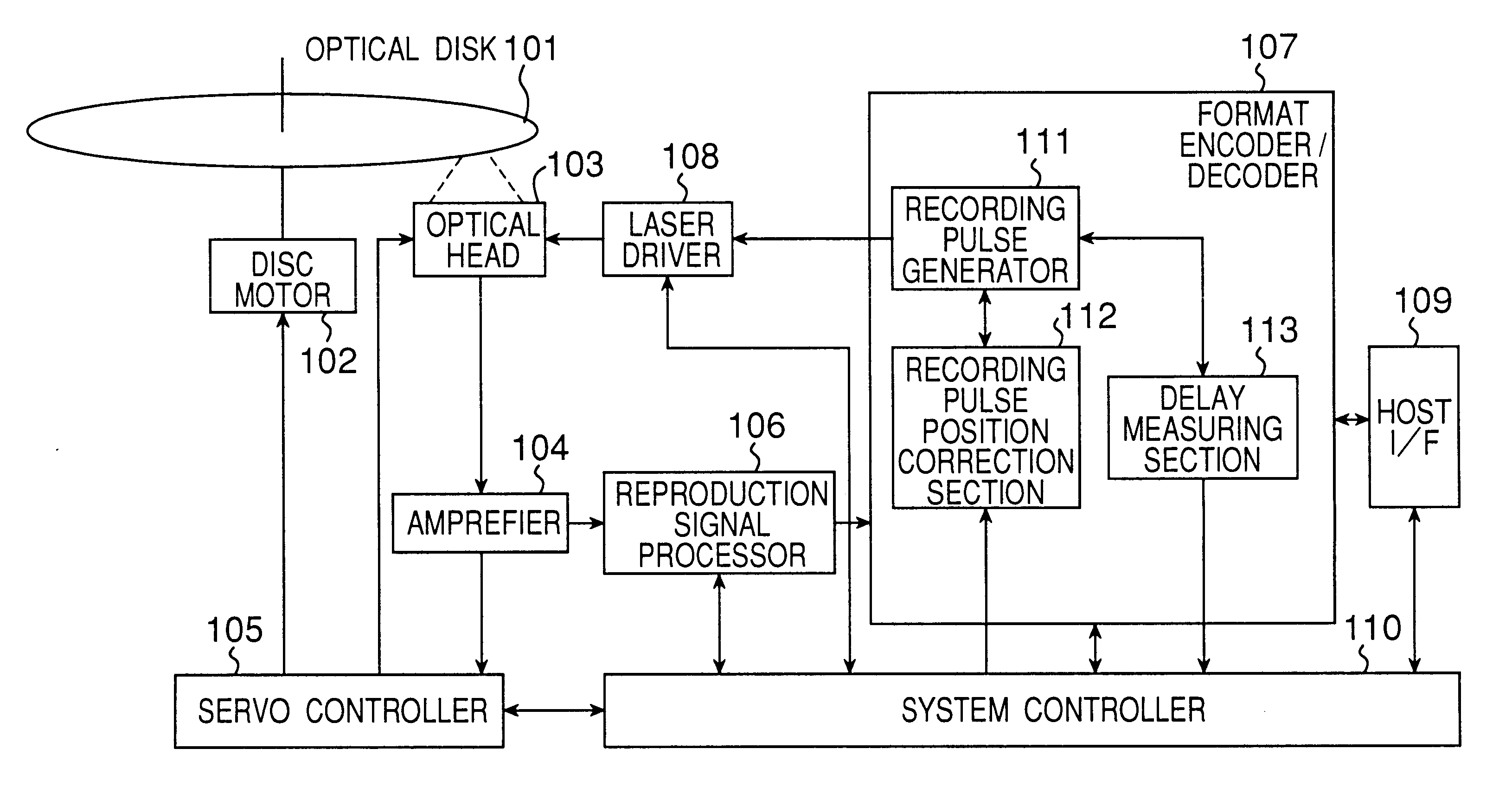
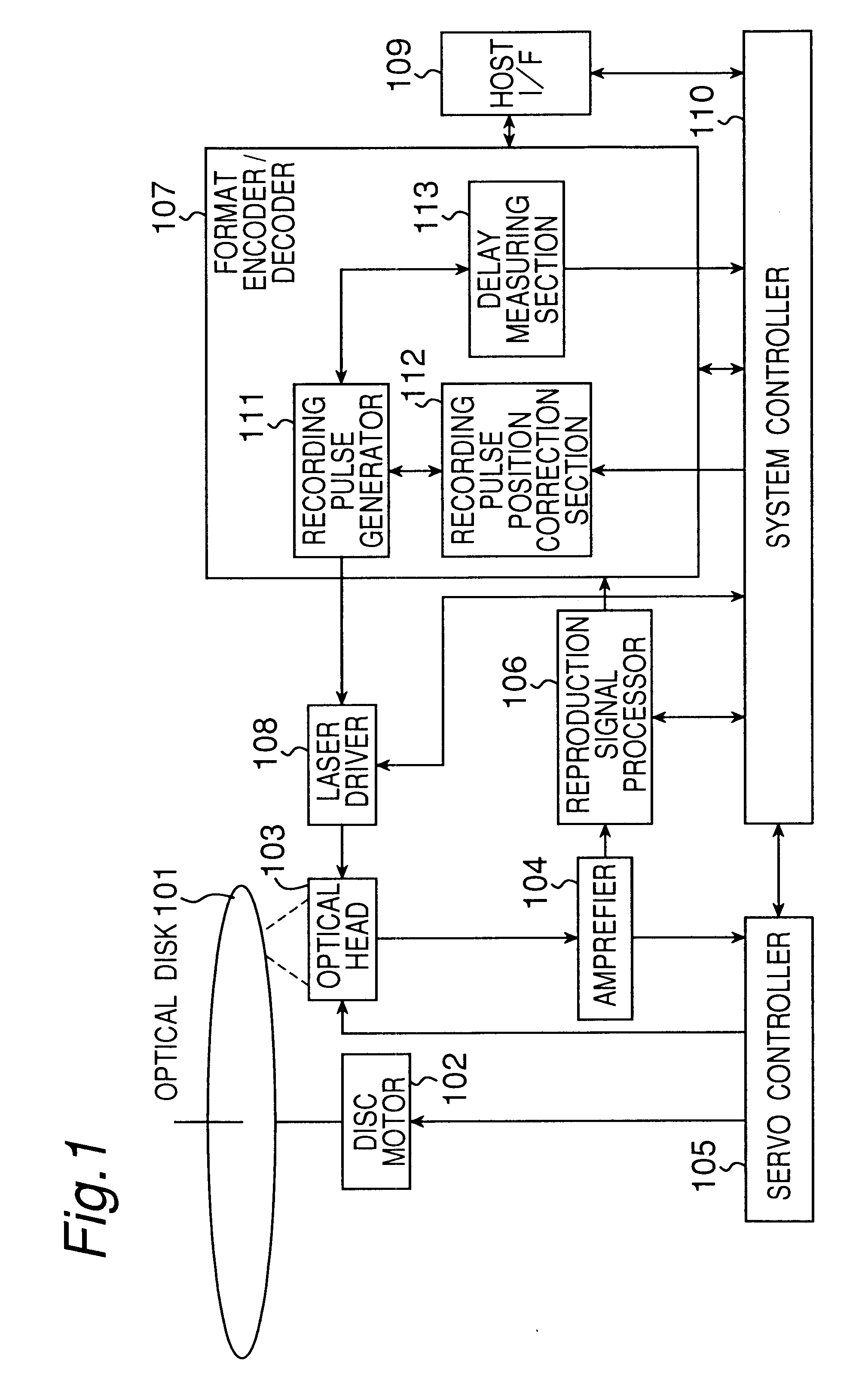
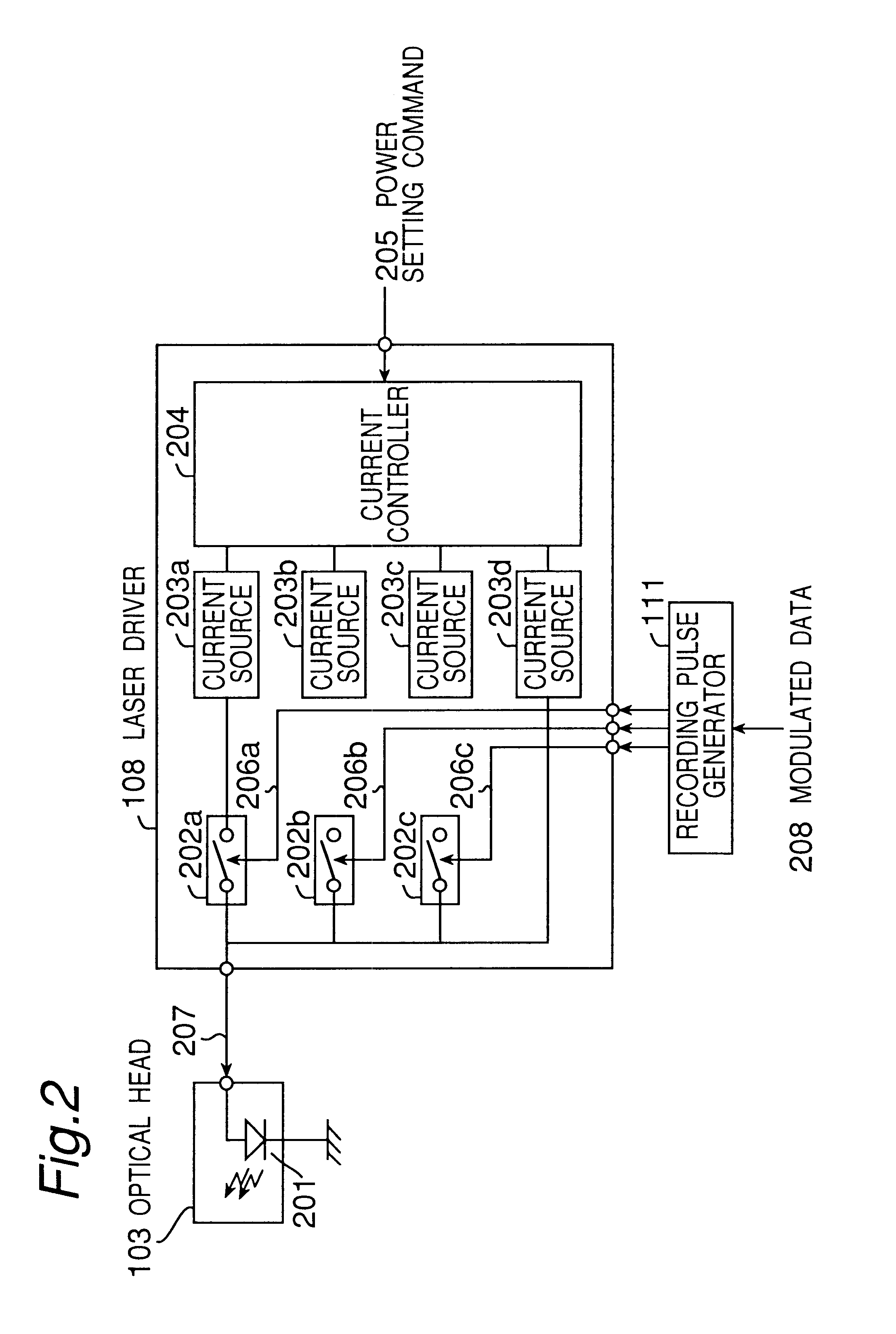
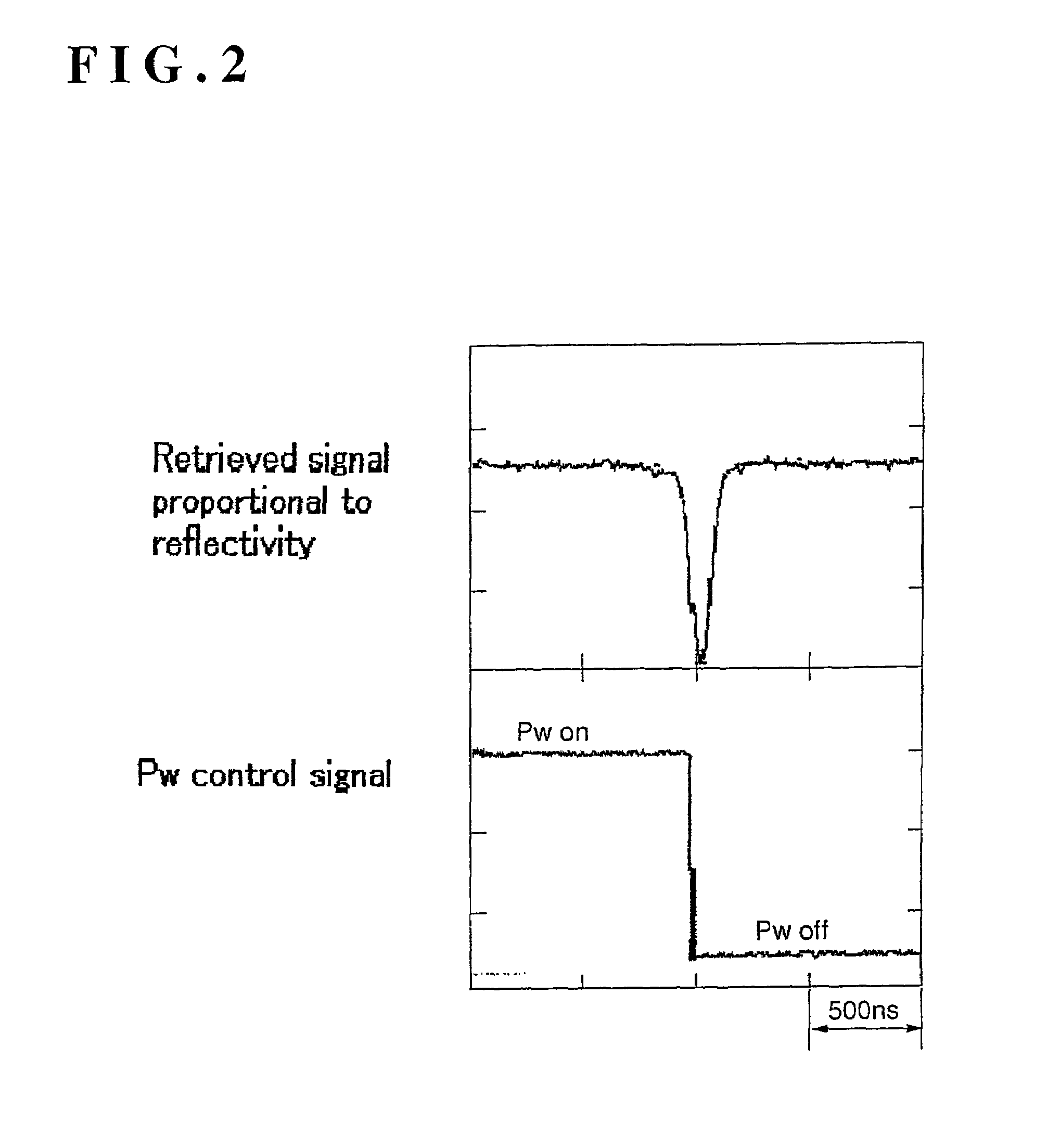
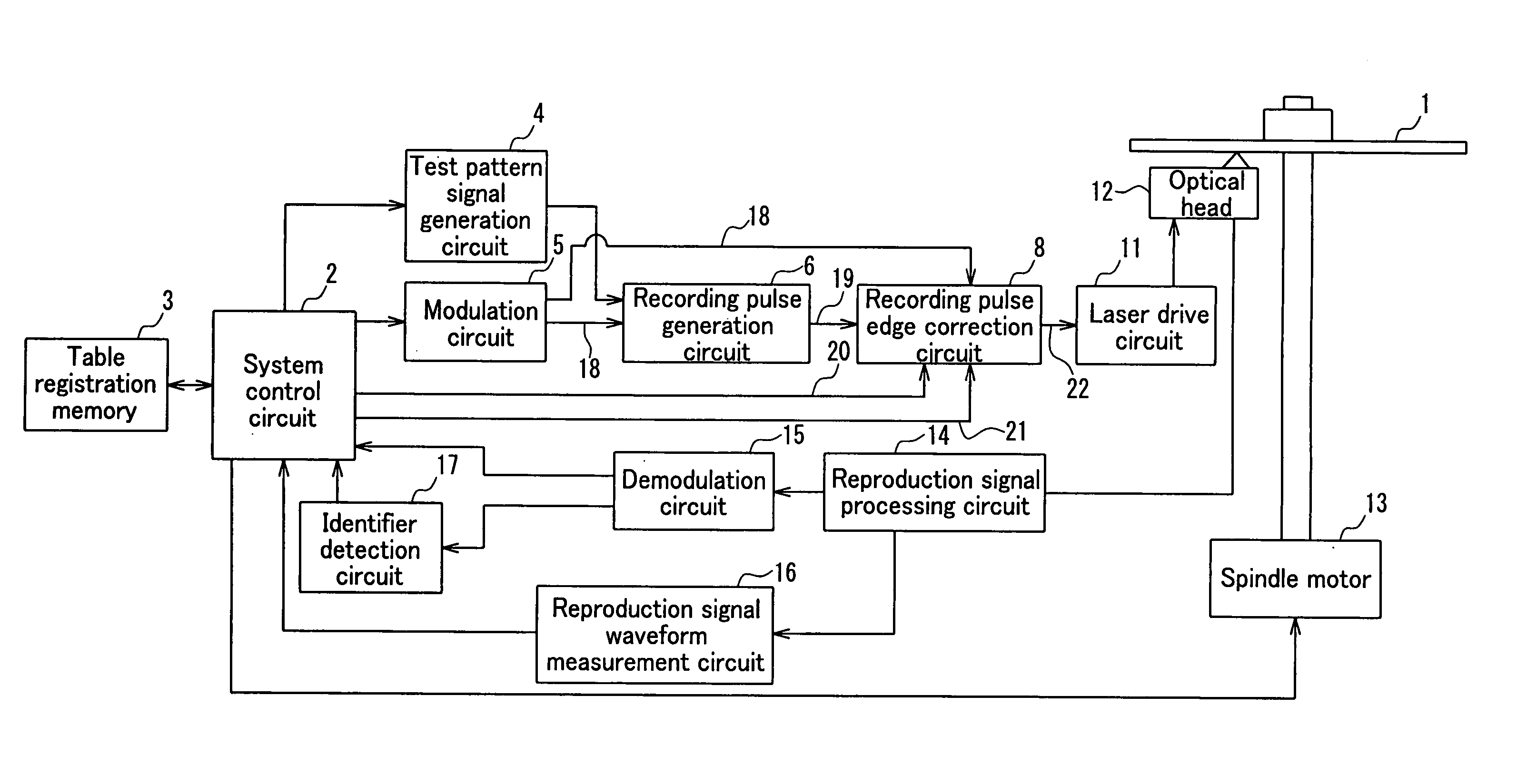
The present invention provides a device and method for an optical disc such as a DVD which can keep proper edge position of a recording pulse to record data of high quality without depending on a fluctuation in a supply voltage and a fluctuation in a temperature. The optical disc device according to the present invention comprises a laser driver for driving a laser to record data on an optical disc, a recording pulse generator for generating a recording pulse signal by using a predetermined delay circuit, to control the switching of the laser power of the laser driver, a delay amount measuring section for measuring the delay amount of a delay circuit in the recording pulse generator, and a recording pulse position correction section for correcting the predetermined edge position of the recording pulse based on the result of the measurement.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
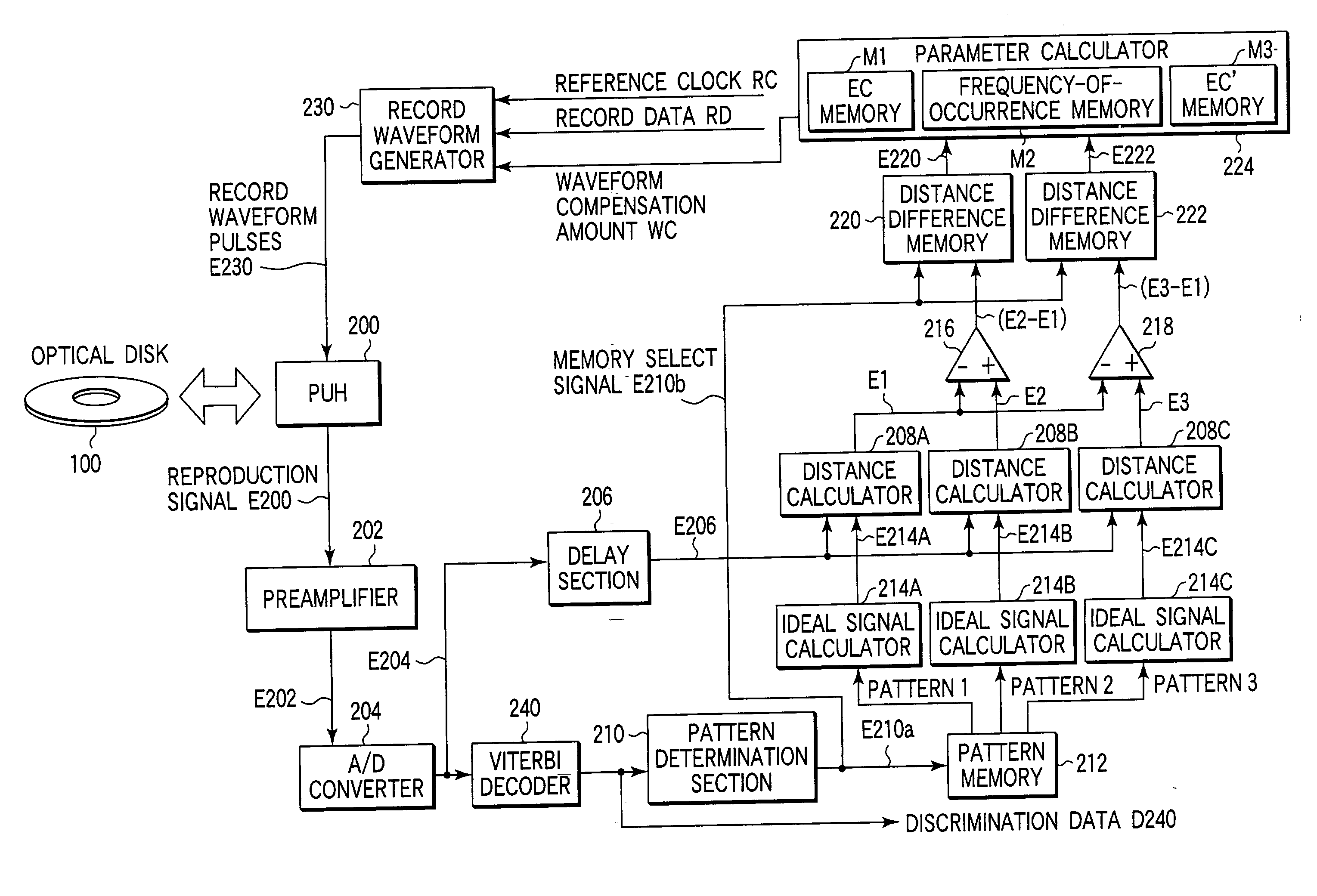
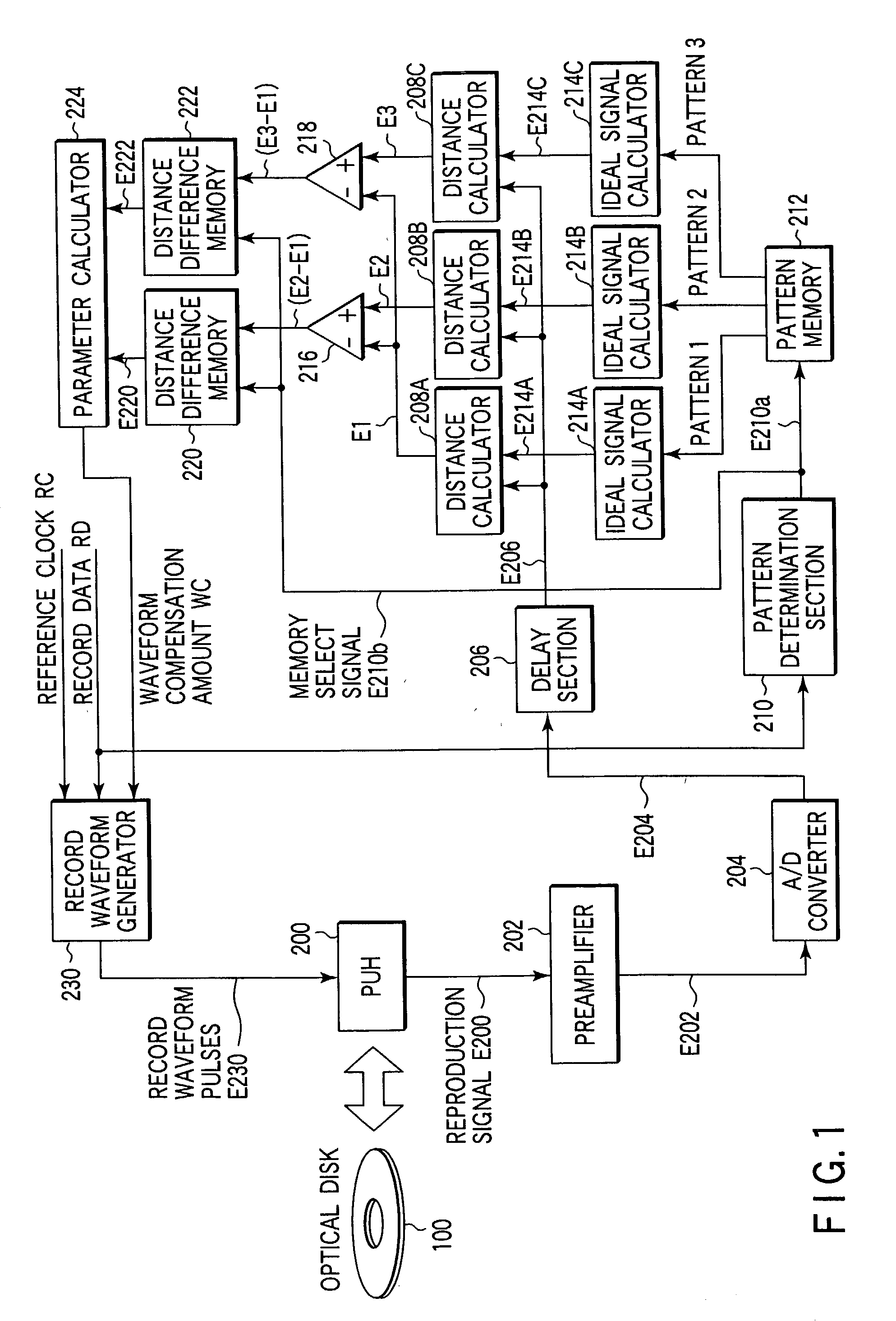
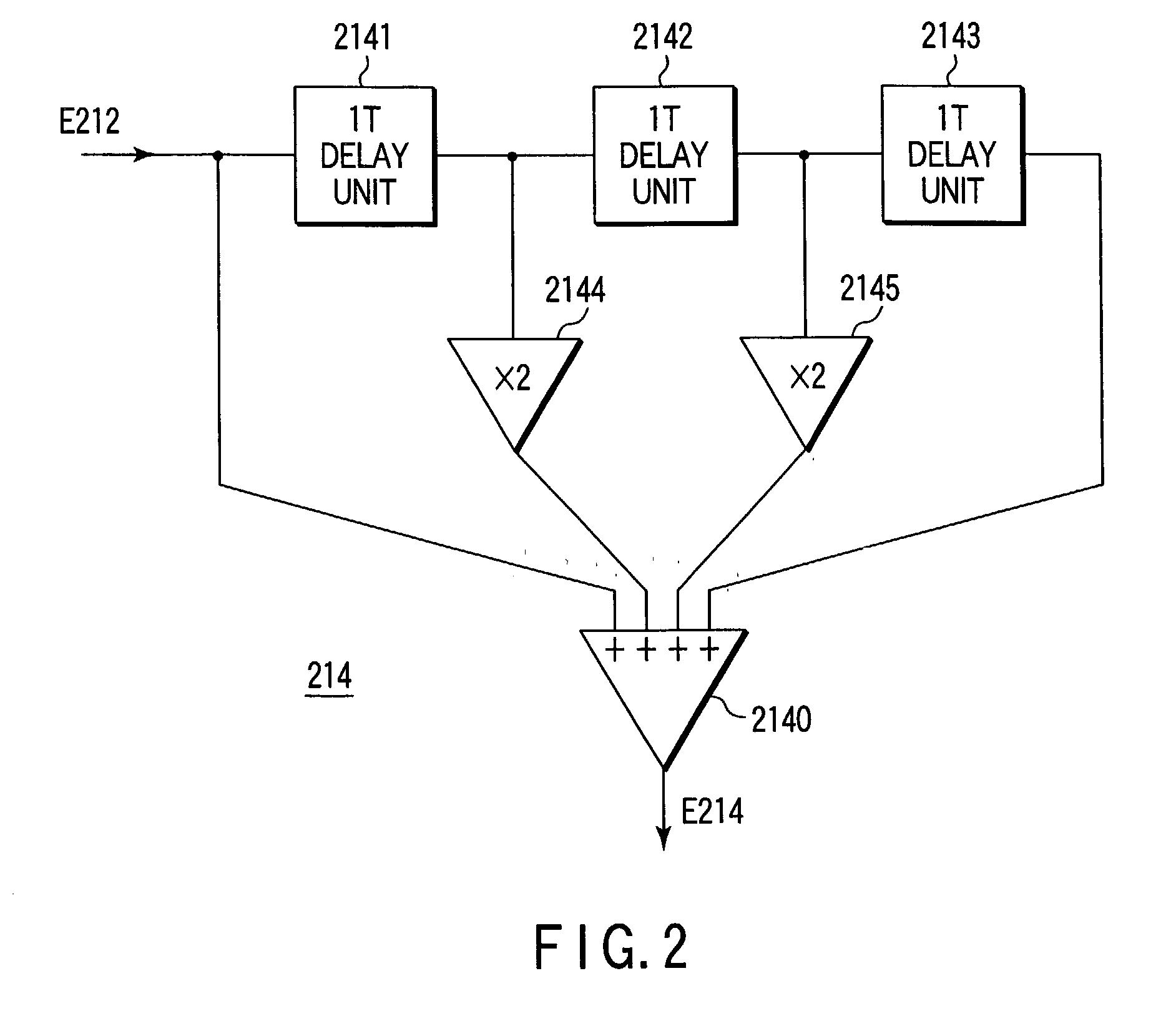
Signal quality evaluation method, information recording/reproducing system, and recording compensation method
InactiveUS20030090980A1Television system detailsData representation error detection/correctionSignal qualityComputer science
Signal quality evaluation is performed using a predetermined reproduction signal, a first pattern corresponding to a signal waveform pattern of the reproduction signal, and a given pattern corresponding to the signal waveform pattern of the reproduction signal and being different from the first pattern.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Recording/reading method for an optical recording medium using an irradiating a laser beam
In an optical recording medium of a single-sided incident type having a plurality of recording layers, recording / reading conditions (for example, tracking polarity, recording pulse strategy, recording recommended power, etc.) can be instantaneously switched according to each of the recording layer, and recording or reading of information can be accurately and surely performed under recording / reading conditions adapted to each recording layer. A control unit reads out layer information from one recording layer of the optical recording medium in which the layer information is recorded in each of the plural layers, on which recording or reading of information can be performed by irradiating a laser beam from one side thereof (layer information reading step), and controls so that recording or reading is performed under recording / reading conditions adapted to a recording layer specified on the basis of the layer information (recording controlling step).
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
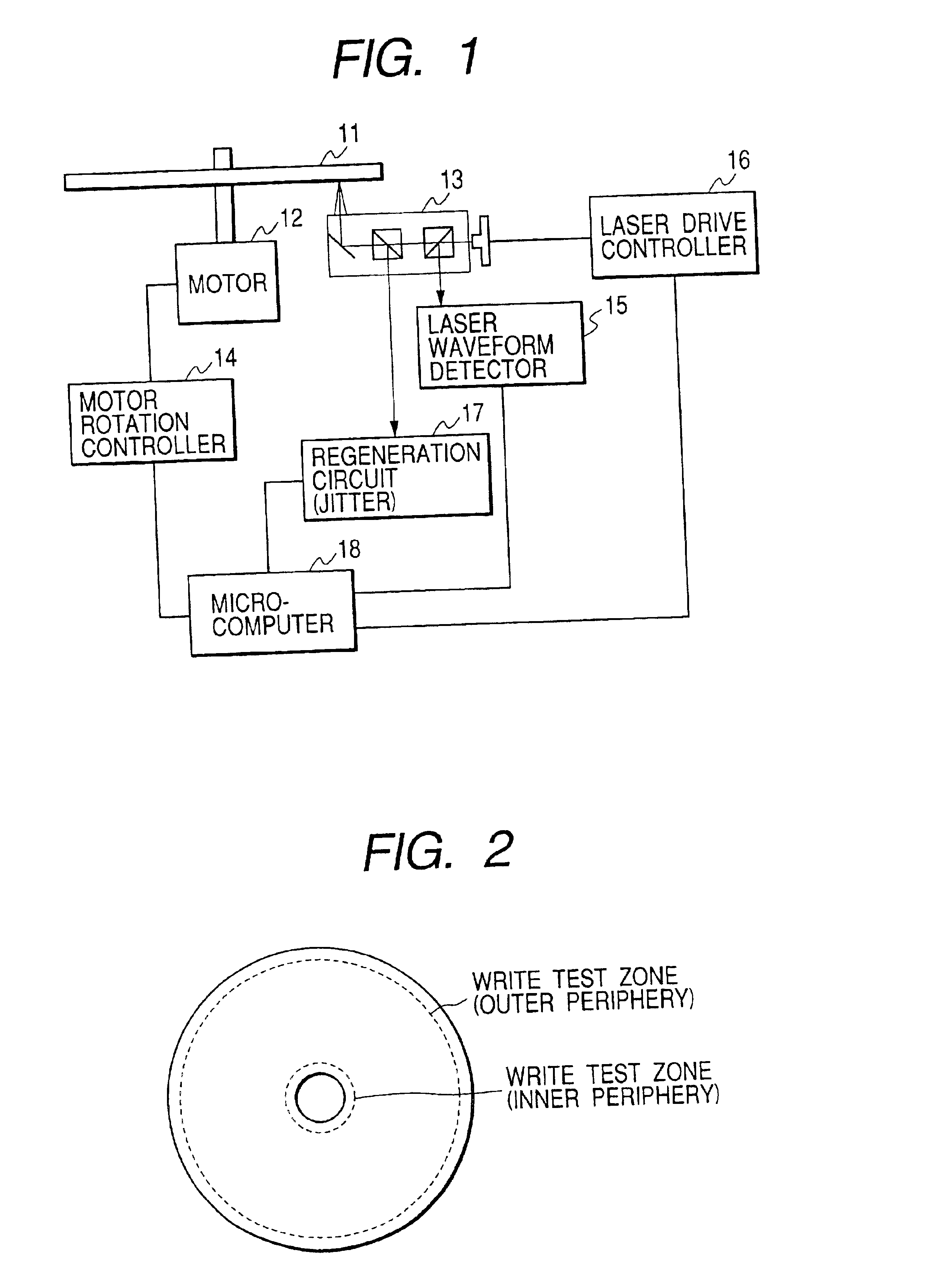
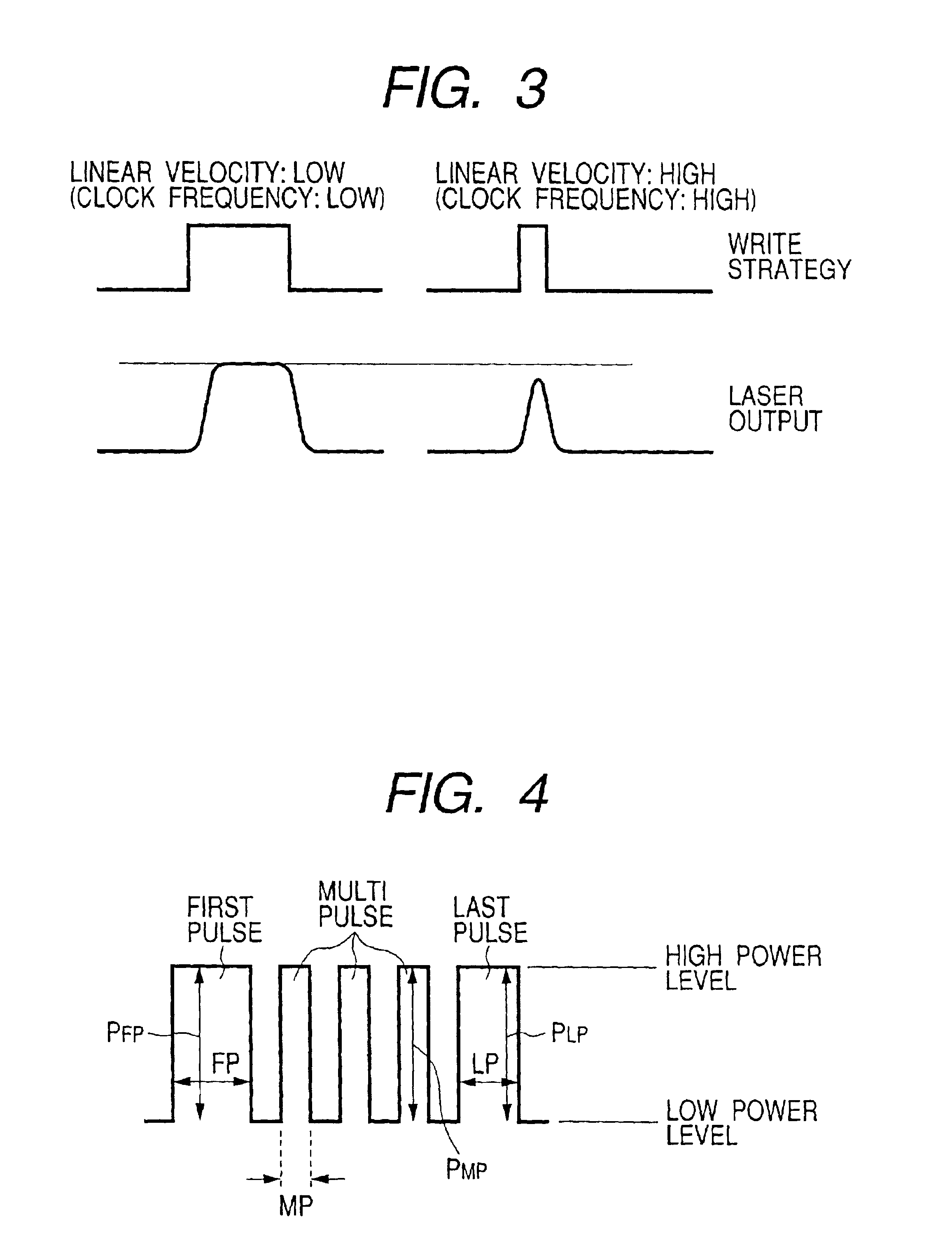
Information recording method and optical disc apparatus
InactiveUS6842412B2Great jitterPrecise mark-edge recordingCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsPhysicsJitter
Good jitter is retained and recorded even when a linear velocity is variable. A recording parameter suitable for each of the linear velocities is obtained by performing test writings for an outer periphery zone of a disc at different linear velocities, and based on a correlation between each of the linear velocities and a recording parameter suitable for each of the linear velocities, a recording parameter corresponding to a linear velocity on an area onto which information is to be recorded is obtained.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Optical information recording medium, method for determining recording condition, optical information recording apparatus, and information processing apparatus
InactiveUS20040052176A1Prolong lifeImproving compatibility and matchingTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareInformation processing
The present invention is directed to an optical information recording medium on which parameters of a plurality of multipulse pattern each having a different applied liner velocity ranges and information regarding recordable liner velocities capable of recording with each of the multipulse patterns are pre-formatted as recording conditional information. The present invention is also directed to an optical information recording apparatus capable of reading pre-formatted information from the optical information recording medium, comparing the pre-formatted information and the specification of the apparatus and selecting an optimum recording condition from the result of comparing. The present invention further relates to a method for determining a recording condition using the optical information recording medium and / or the optical information recording apparatus, and an information processing apparatus disposing the optical information recording apparatus therein.
Owner:RICOH KK
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS7018696B2Sufficient chemicalSufficient thermalLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingManganeseHigh reflectivity
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective coating layer of optical discs. Elements that can be added to silver to produce useful silver alloys include zinc, aluminum, copper, manganese, germanium, yttrium, bismuth, scandium, and cobalt. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Optical recording medium and optical recording medium recording device
InactiveUS20060098559A1Difficult to forgeEffective protectionOptical overwritingRecord information storageOptical recordingData recording
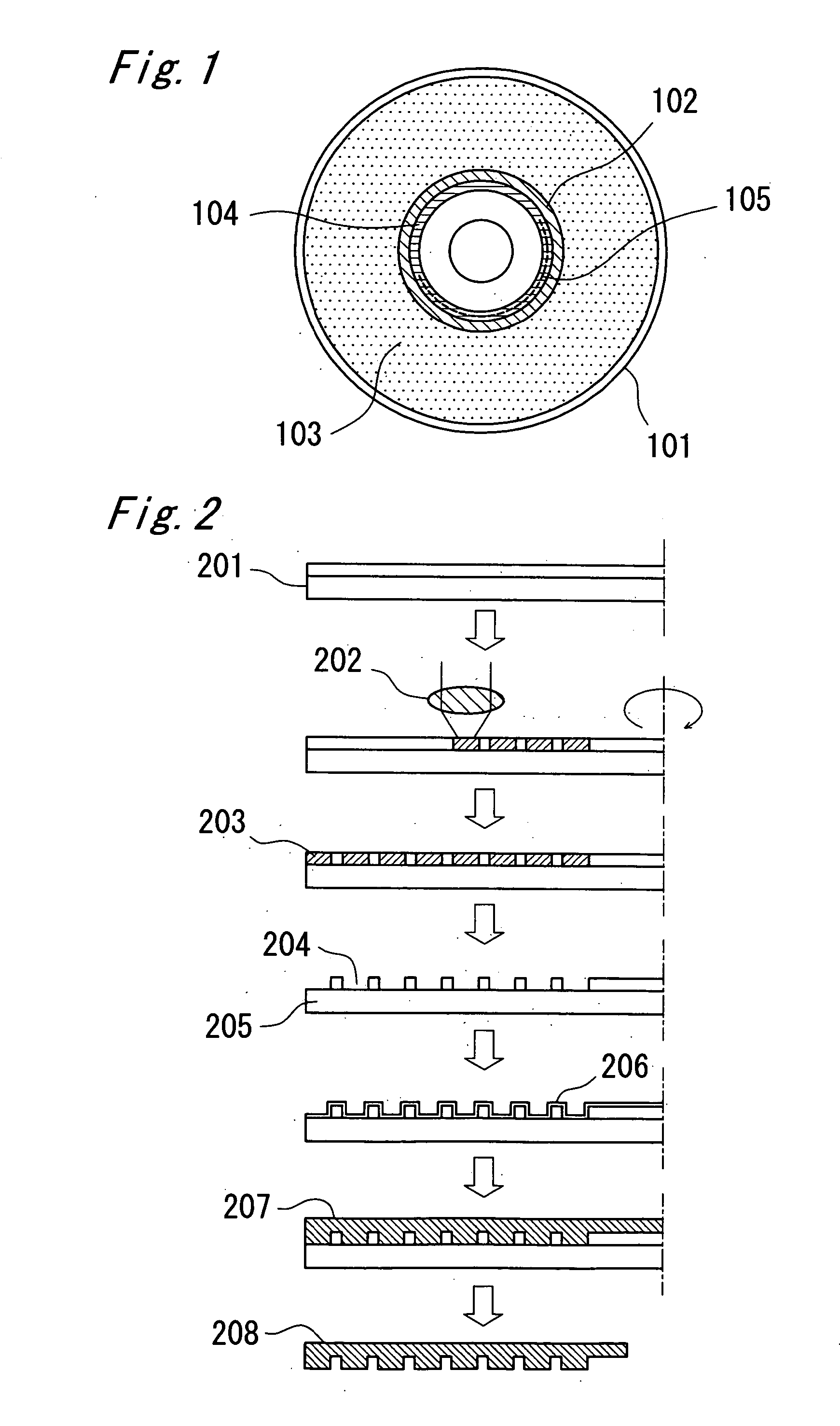
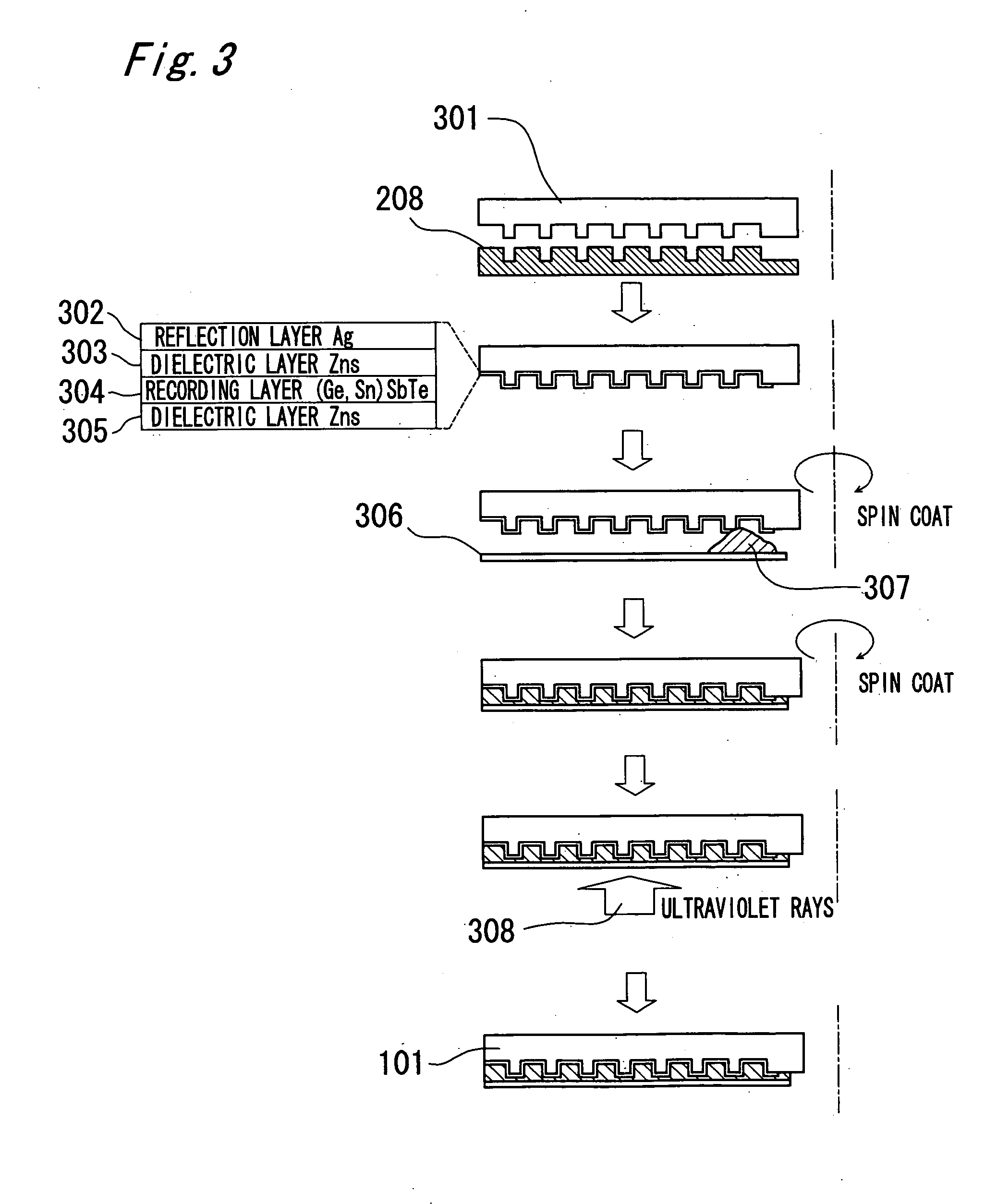
An optical recording medium such as DVD has a data recording area (103) in which data can be rewritten and a write-once area (104) in which data can be written only once and not be erased. A medium specific ID (105) which is specific to an optical recording medium is recorded in the write-once area (104). In the data recording area (103), a reflectance ratio of a part where the data is recorded is different from a reflectance ratio in a part where the data is not recorded. A reflectance ratio of a recording pit formed in the write-once area (104) is higher than the higher one of the reflectance ratios in the part where the data is recorded and in the part where the data is not recorded in the data recording area (103). Data recoding in the write-once area (104) is performed by irradiating to the write-once area (104) a laser beam with heat amount of three to 25 times heat amount necessary for recording rewritable data in the data recording area (103).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
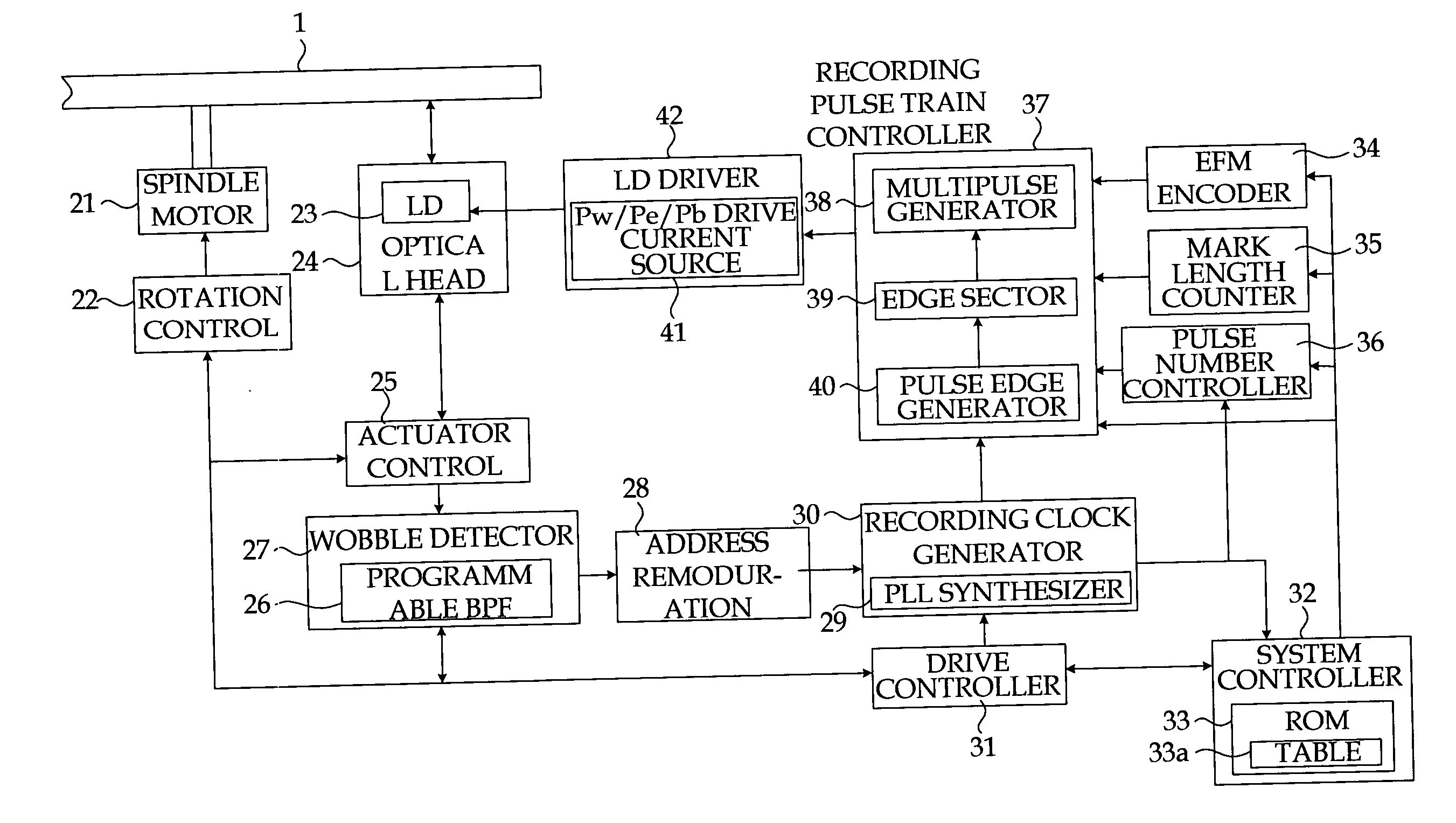
Method and device for optical recording onto optical disc medium
InactiveUS20070165506A1Improve reliabilityEasy to controlRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLaser lightOptical recording
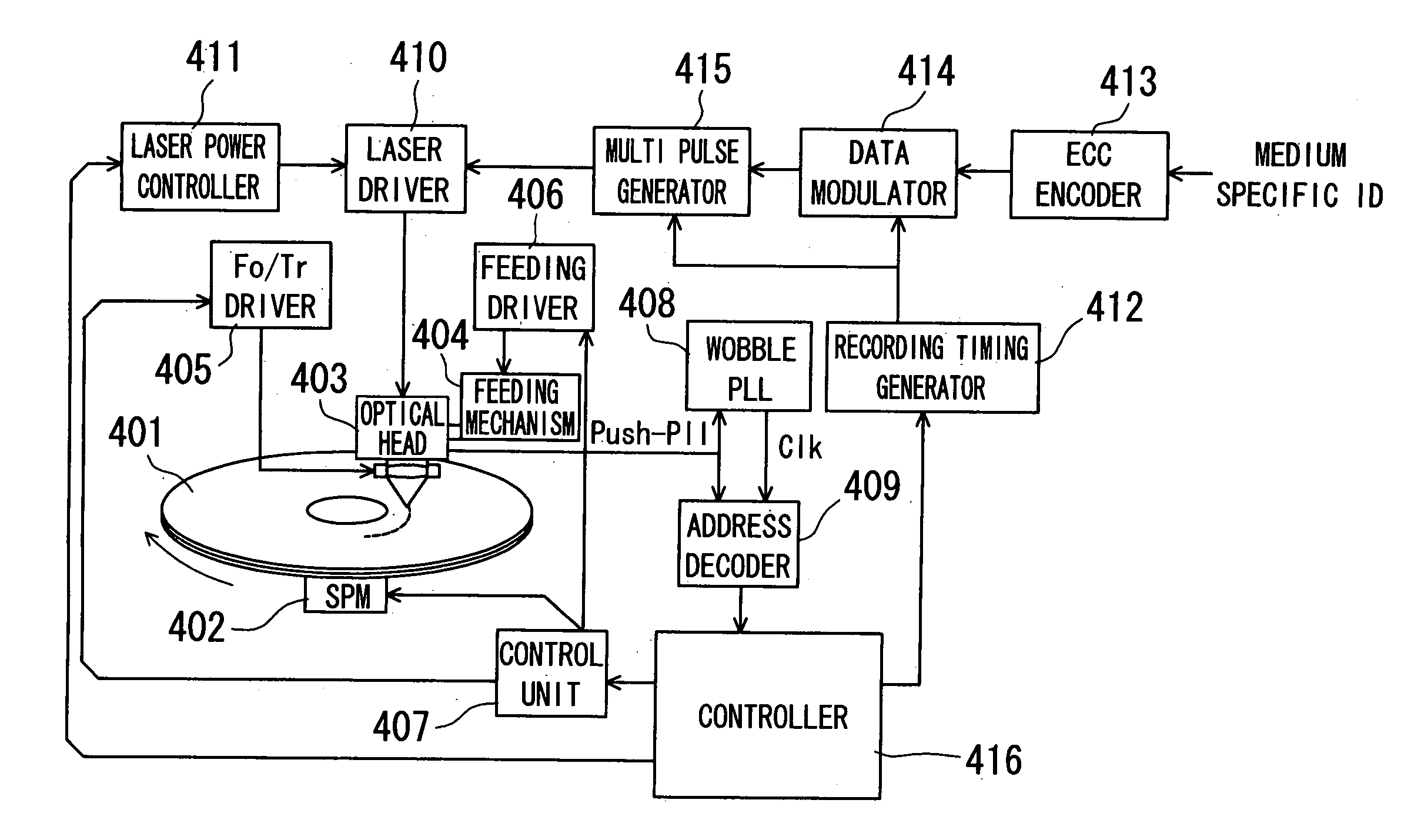
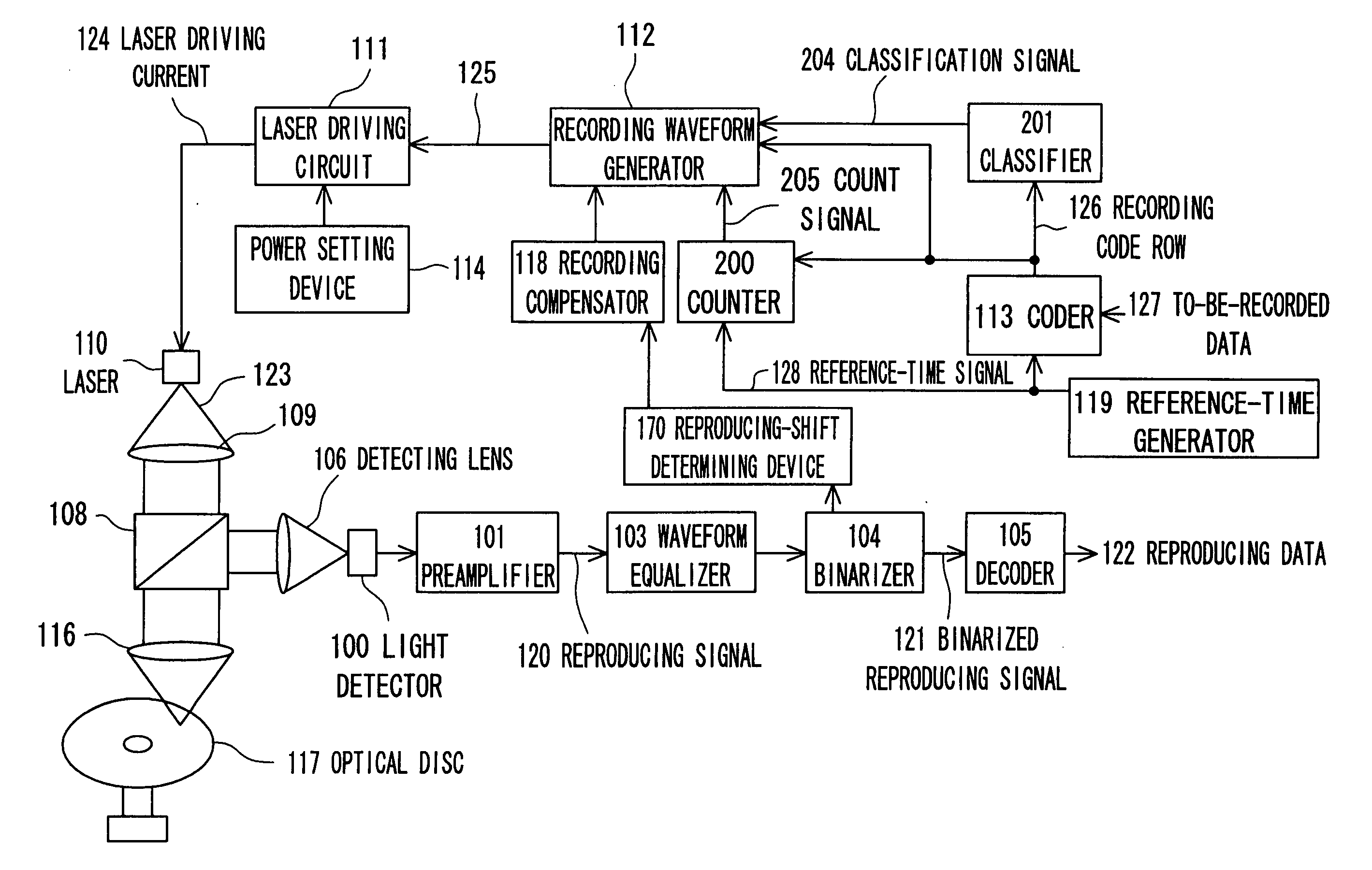
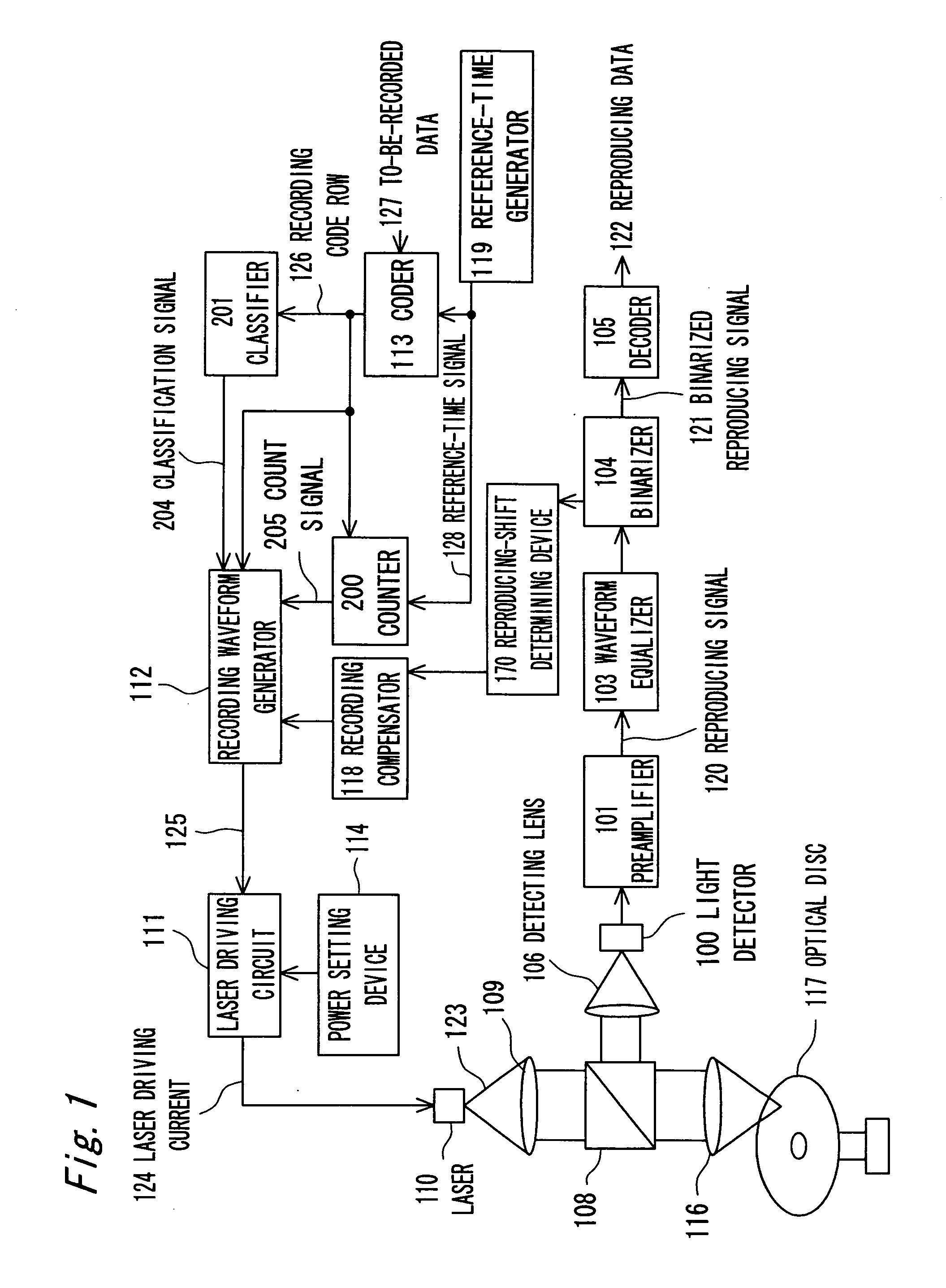
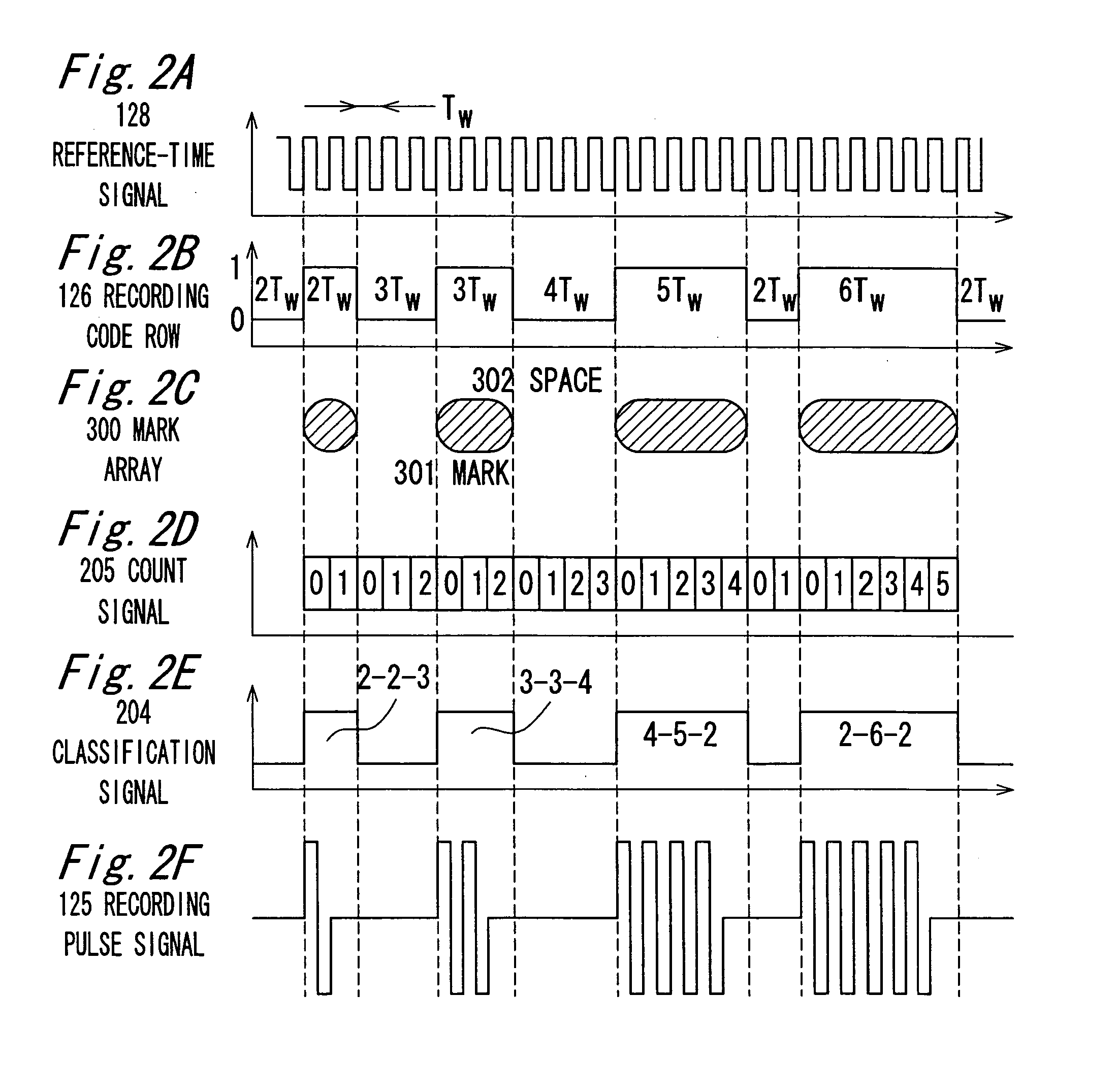
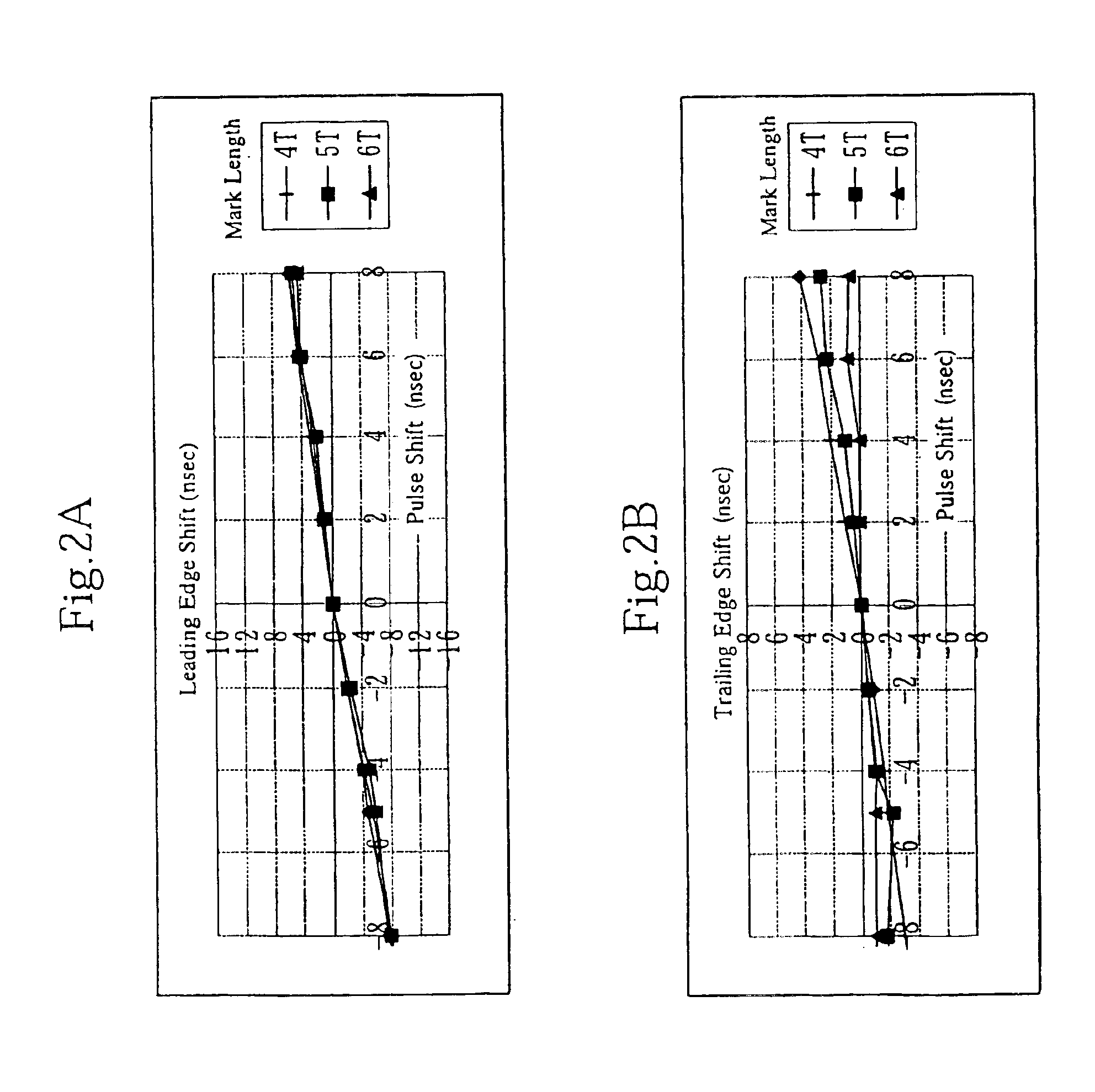
There is provided an optical recording method for directing a recording pulse train to an optical disc medium to form marks thereon and for recording information as information about the edge positions of said marks and the spaces between marks, the recording pulse train having been created by modulating laser light into plural power levels. The method includes: coding to-be-recorded data into coded data consisting of the combination of marks and spaces; classifying said marks within said coded data on the basis of the mark length and the preceding or succeeding space lengths of the marks; shifting the position of the second pulse edge counted from the end portion of the recording pulse train for forming said marks, depending on the result of said classification, to adjust said recording pulse train; and directing said recording pulse train to the optical disc medium to form said marks thereon.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Information storage medium and apparatus of recording and/or reproducing pointing information
ActiveUS7304938B2Shorten the timeTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesRelevant informationDatabase
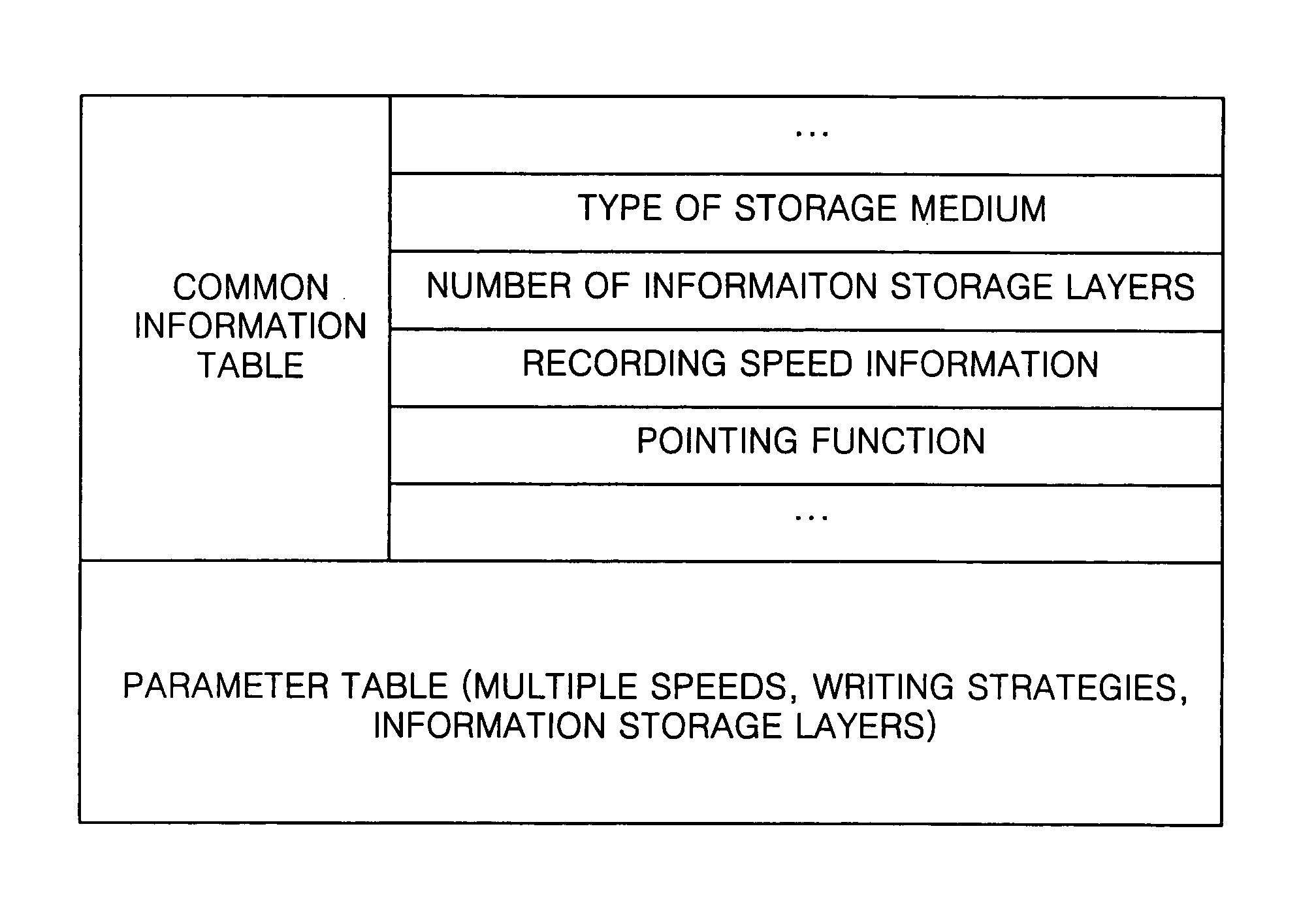
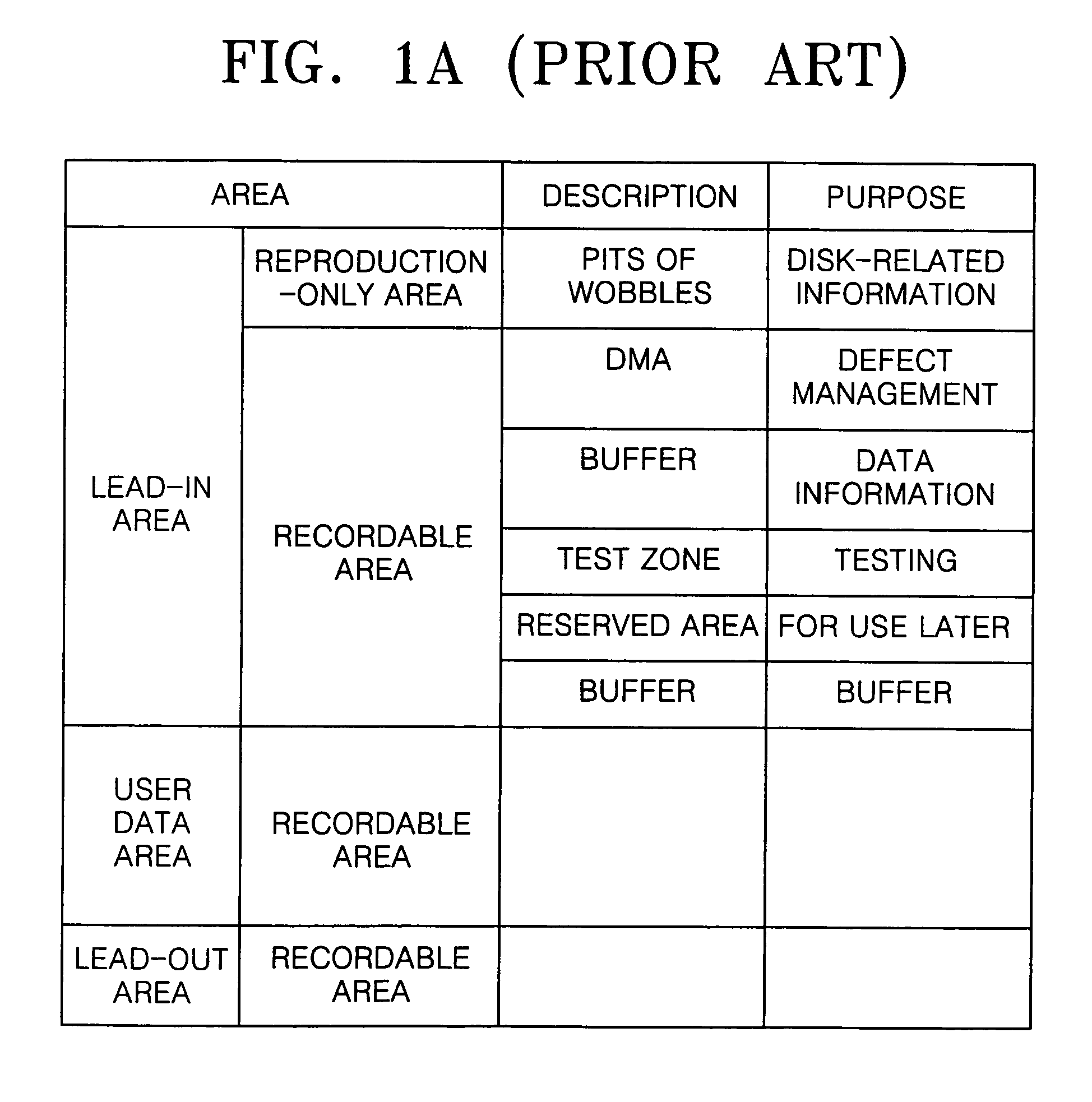
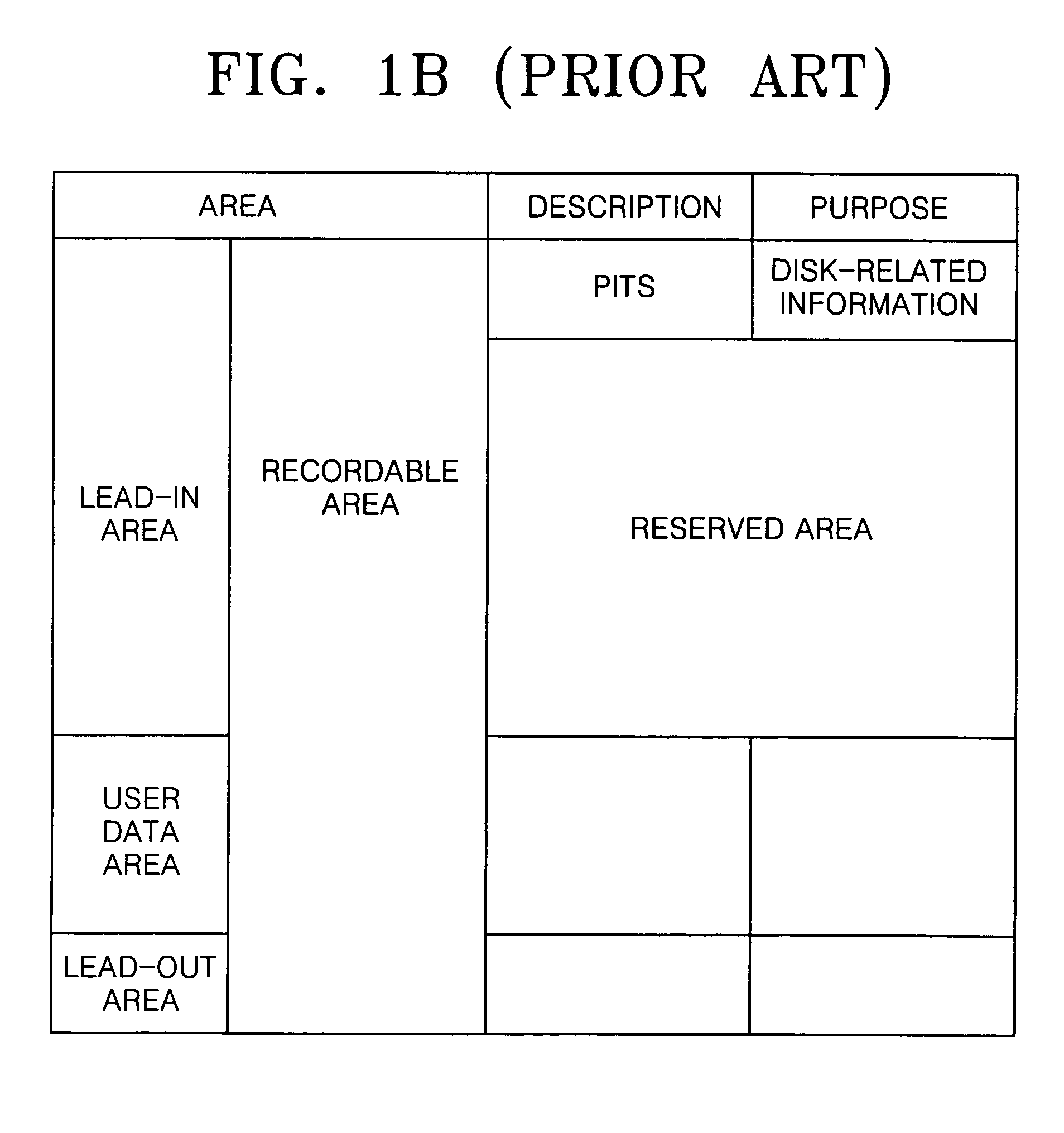
An information storage medium includes areas of disk-related information having disk-related information to record or reproduce data with respect to the information storage medium, wherein the disk-related information includes common disk-related information and changeable parameter information, and the areas of the disk-related information are arranged according to information about the changeable parameter information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical information recording medium and optical recording method
InactiveUS6996052B1Reduce jitterCombination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersRecord statusHigh density
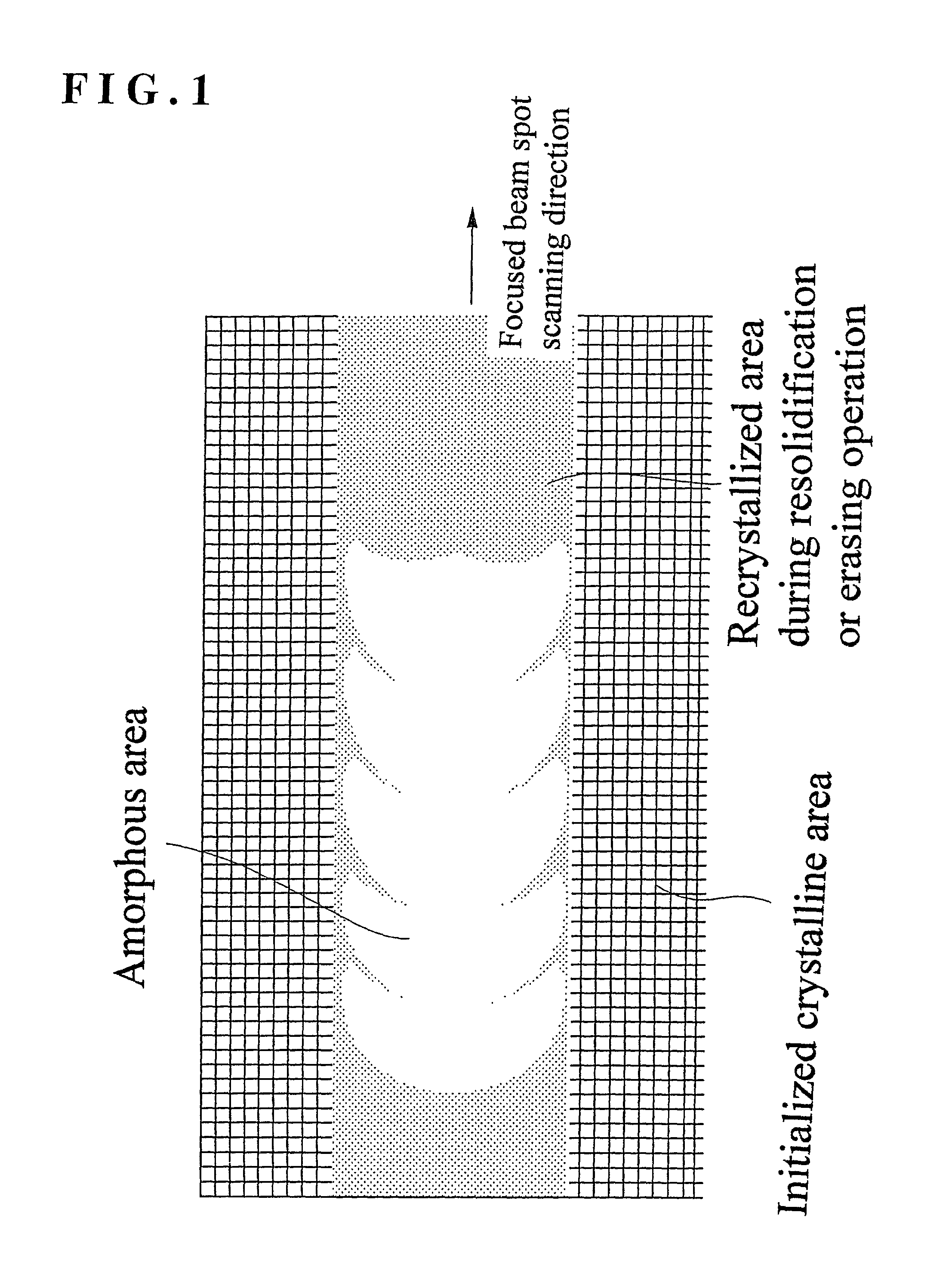
An optical information recording medium for recording information by a plurality of record mark lengths, wherein the shortest mark length is at most 0.5 μm, and a crystal state is an unrecorded or erased state and an amorphous state is a recorded state, wherein the erasing is carried out by recrystallization which substantially proceeds by crystal growth from an interface between the amorphous portion or a melt portion and a peripheral crystal portion; and an optical recording method suitable therefore. The medium of the present invention has characteristics that overwriting can be made at a high speed, the jitter of mark edge is small, mark length modulation recording can be made at a high density, and the formed mark is excellent in the stability with the lapse of time.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
Optical recording method
InactiveUS20030063540A1Accurately achieve desired write waveformTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersLight beamOptical recording
An optical recording method that performs recording by irradiating optical recording media with laser beam modulated in intensity based on a write waveform is provided. The write waveform has a plurality of write pulse blocks for forming write marks, and each write pulse block has at least one type of upward pulse. In the event that the width of said upward pulse is so narrow that the laser beam intensity corresponding to the peak intensity of that upward pulse cannot be obtained, the peak intensity of that upward pulse is increased so that, in said laser beam, the beam intensity it should have or a value close thereto is obtained. Thereby, good recording and playback characteristics can be obtained even when recording at a high transfer rate.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording method, optical information recording device, and optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20050174906A1Shorten the timeExact reproductionRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsComputer scienceRecording media
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
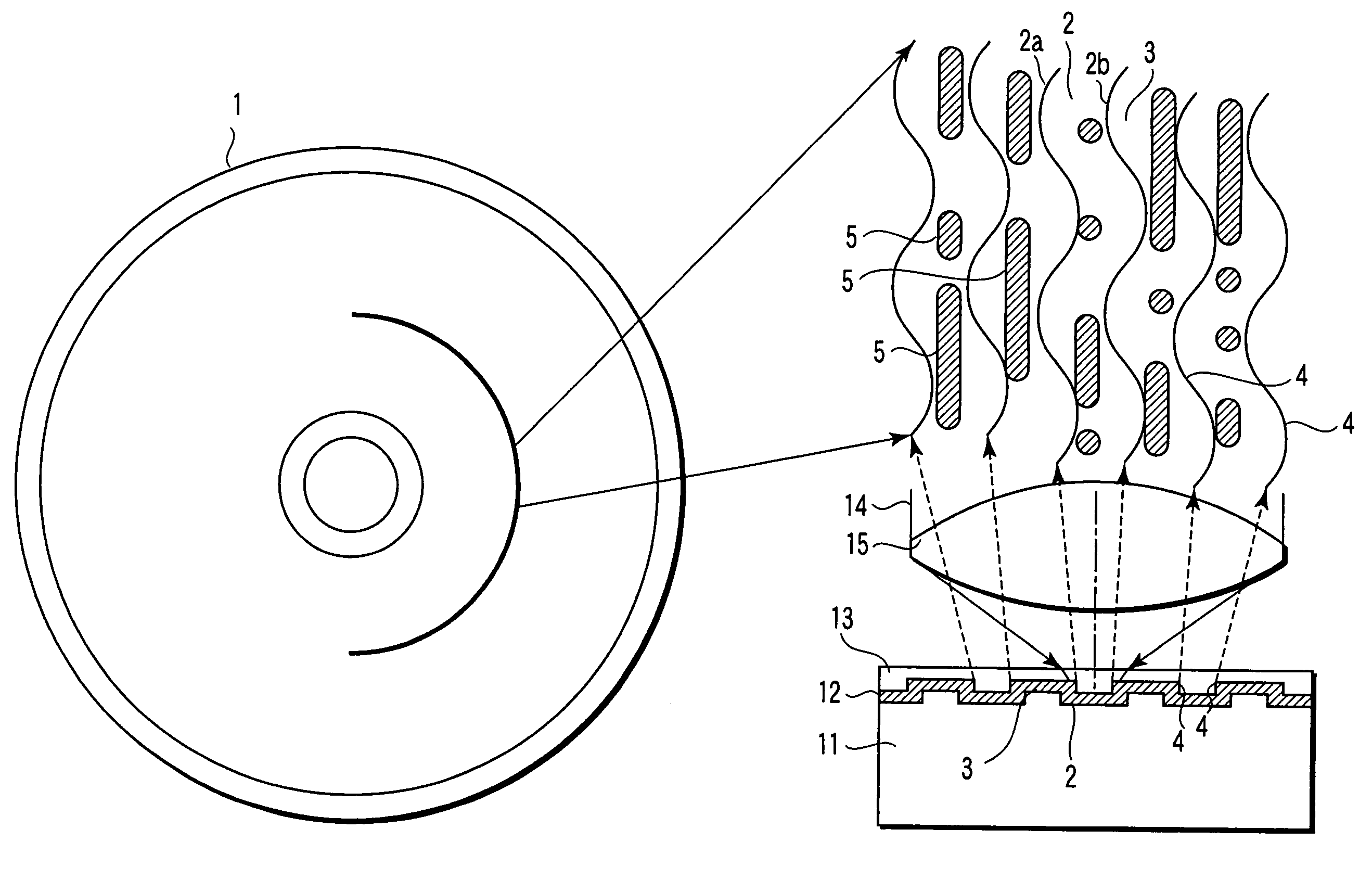
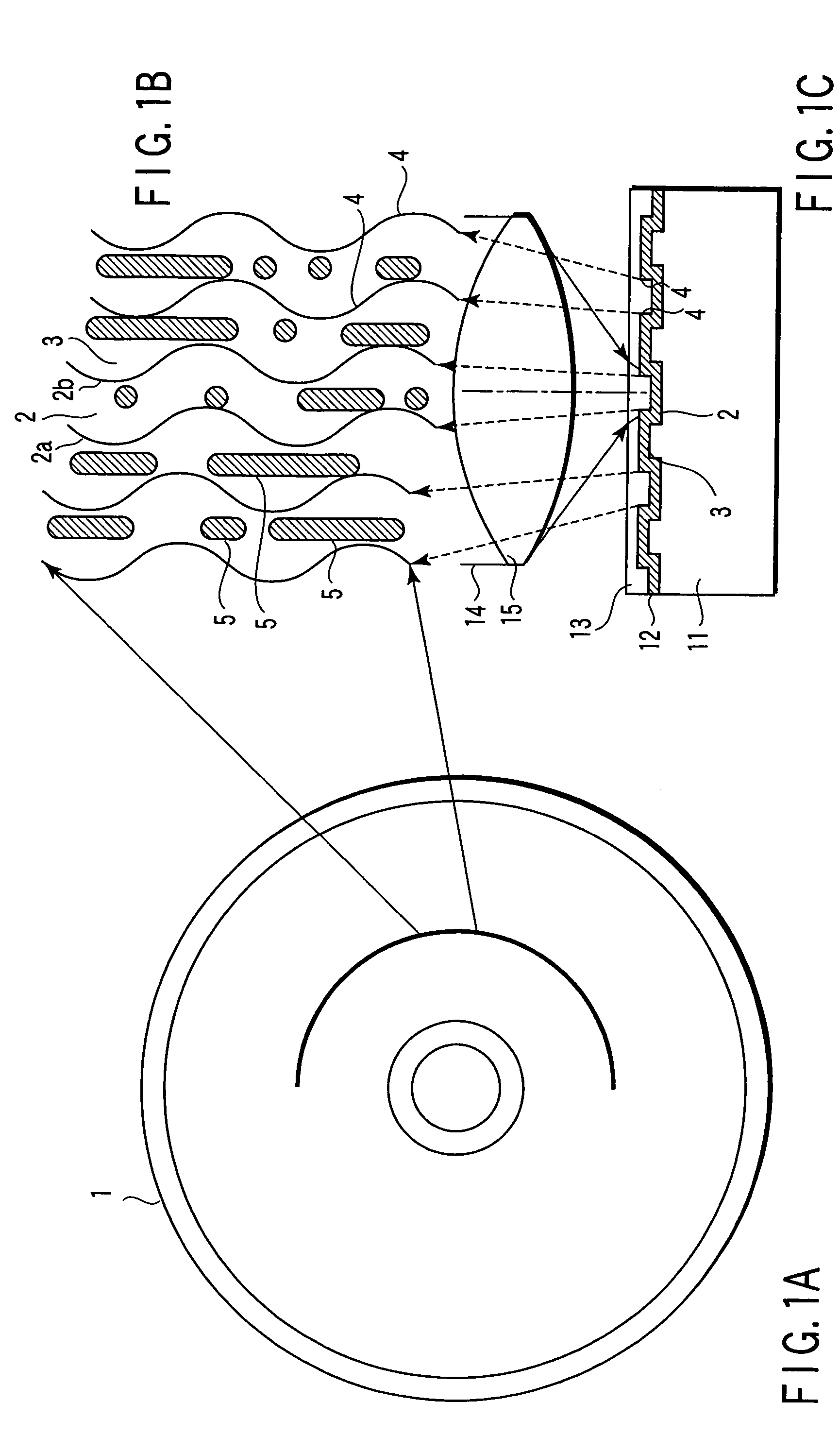
Information recording medium and information recording/ reproducing device and method
InactiveUS20050122890A1Increase recording capacityIncrease capacityRecord information storageDigital recordingEngineeringRecording media
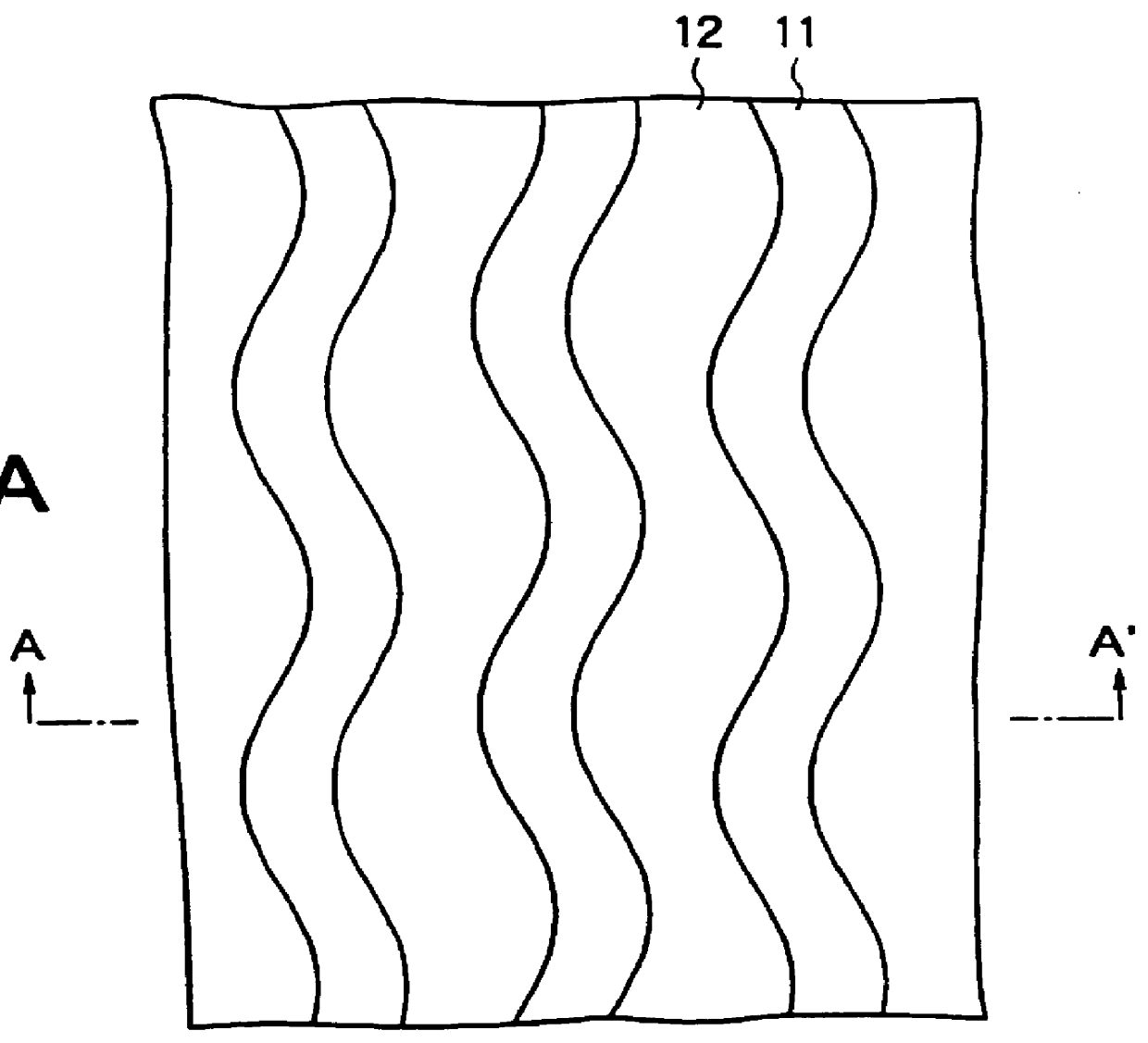
An information storage medium (1) has tracks in which information is recorded. The tracks are formed as a groove section (2) and a land section (3). The groove section (2) has a synchronous structure in which wobbles (2a) and (2b) formed on both walls of the groove section (2) are not displaced from each other in the circumferential direction of the medium, and the land section (3) has an asynchronous structure in which wobbles formed on both sides of the land section (3) are displaced from each other. A good signal is reproduced from each of the groove and land sections.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for recording/reproducing data on/from optical disk
InactiveUS6894965B2Removed positioningMaximising amplitudeTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesEngineeringFront edge
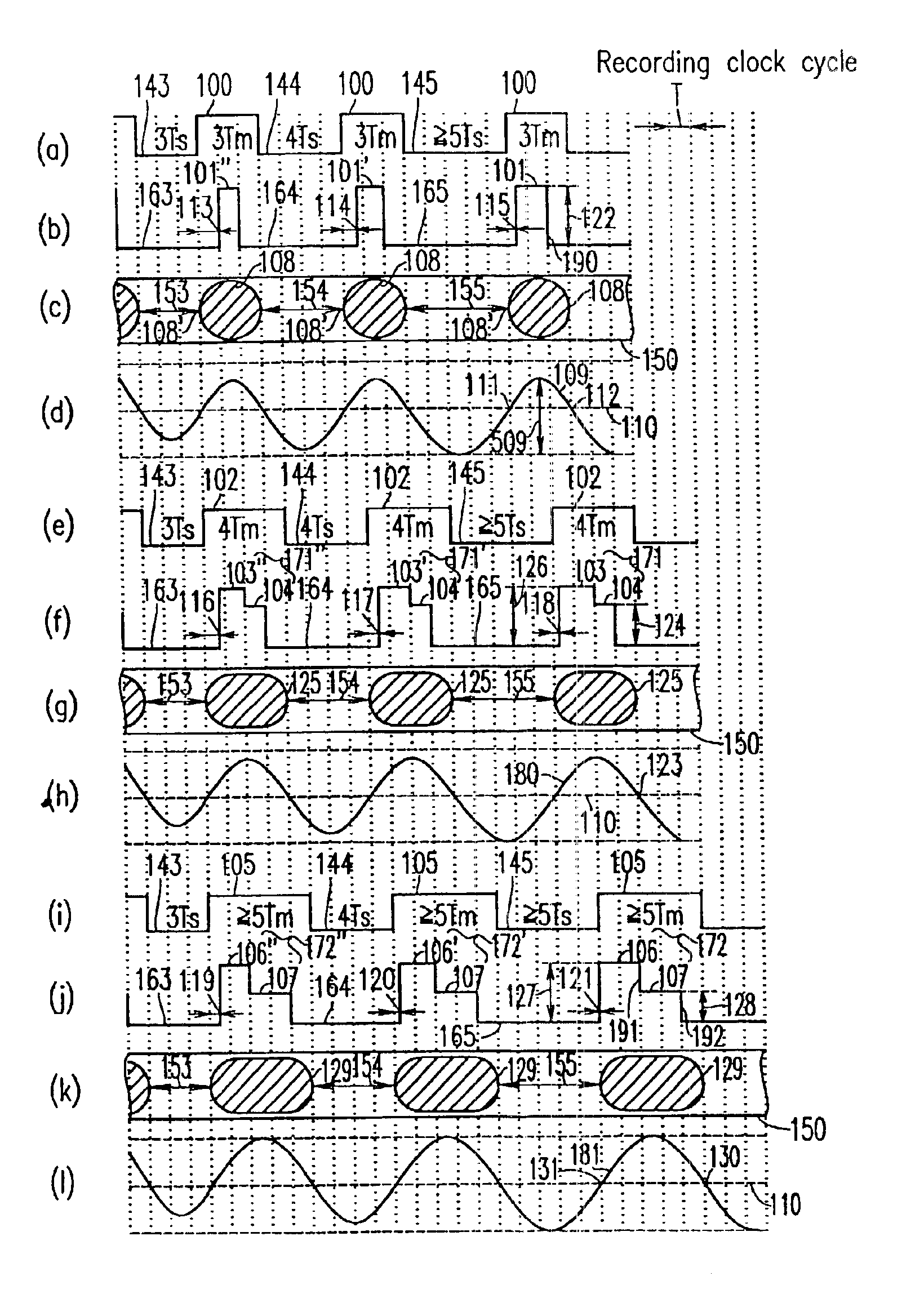
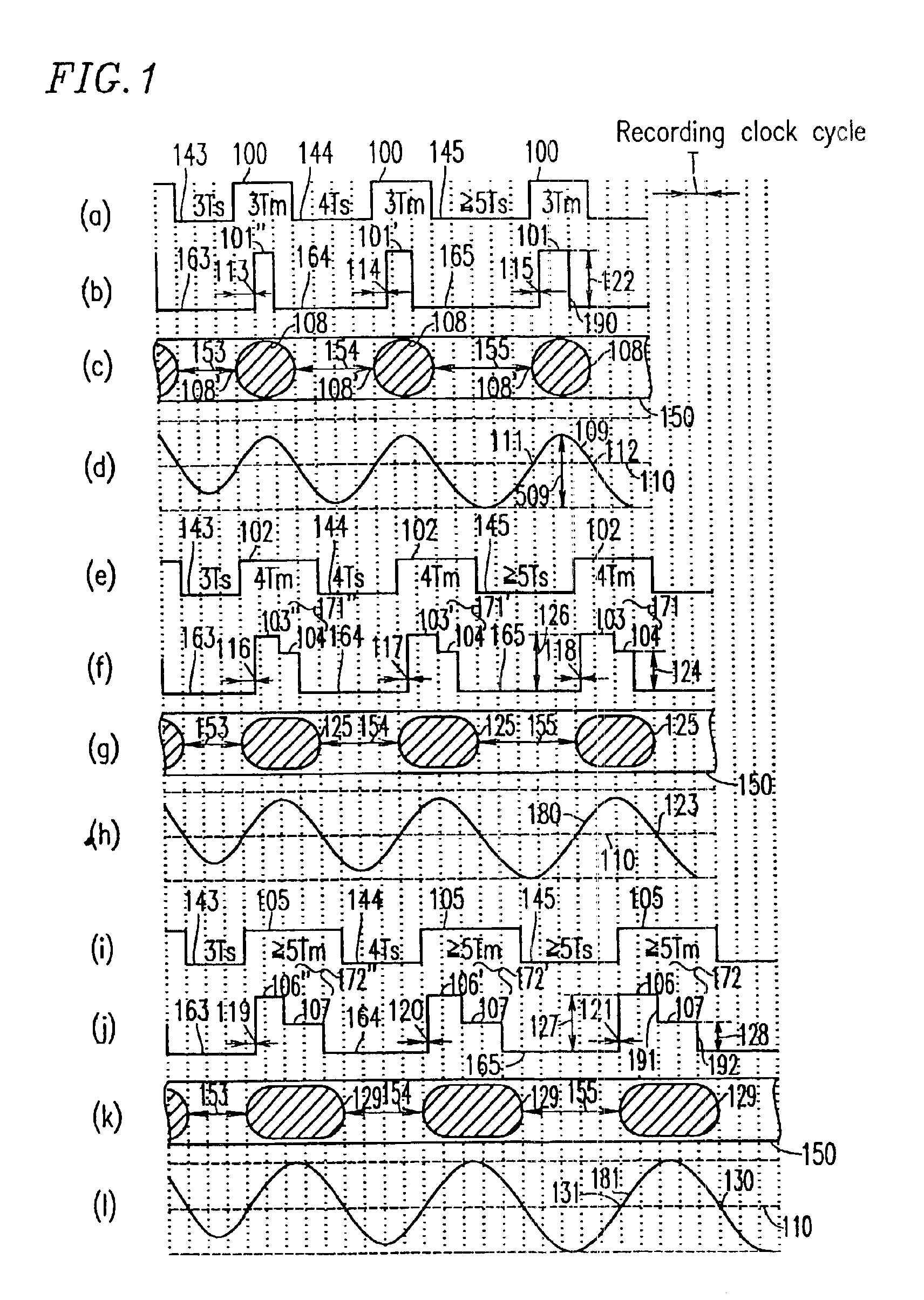
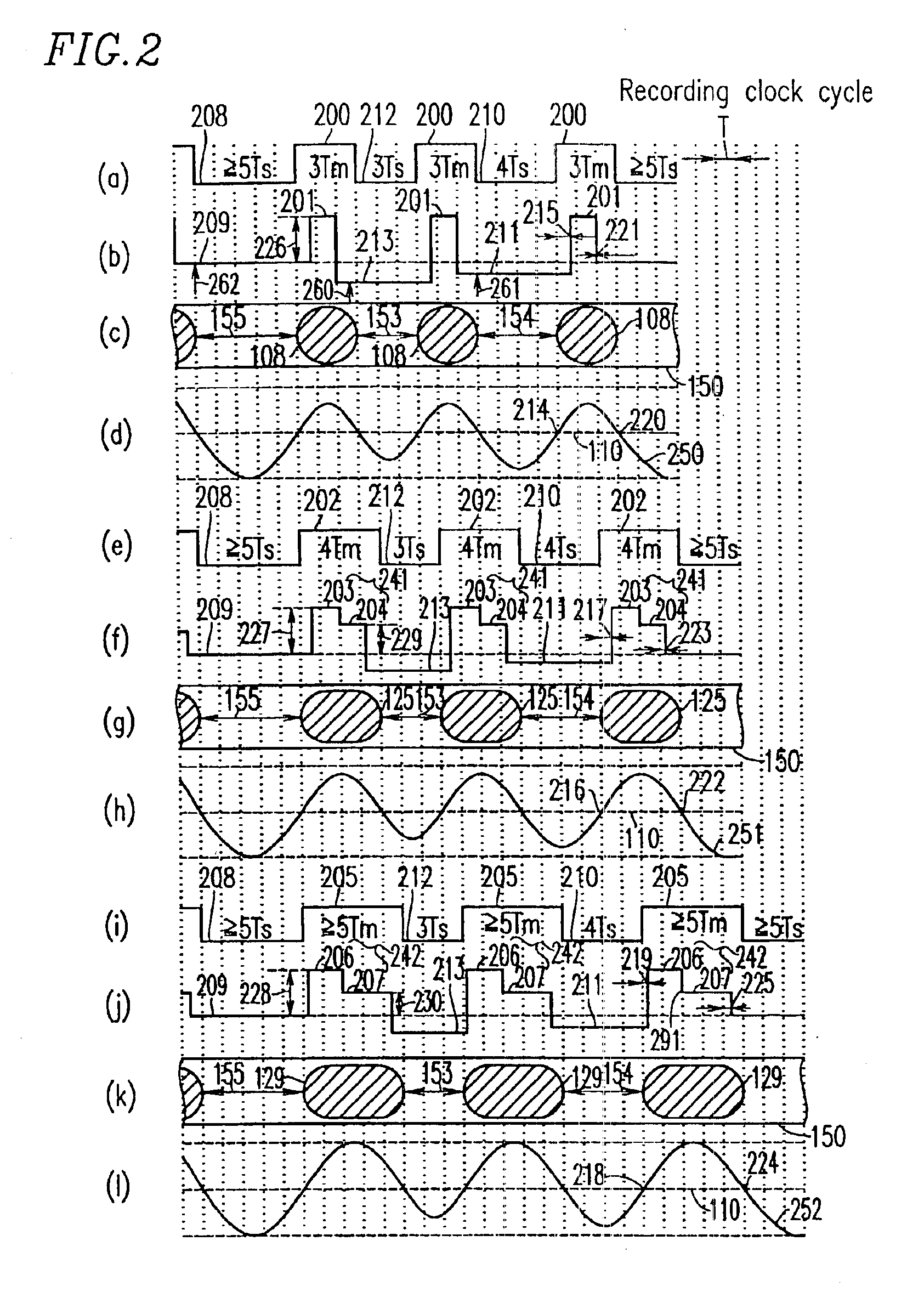
A shortest mark 108 is recorded with a single recording pulse. A long mark 125 is recorded with a two-stage pulse including a first-part pulse and a second-part pulse. In the case where each of positions 115 and 118 of front edges of the recording pulses is determined based on a relationship between a length of a space immediately before a mark and that of the mark itself so as to properly position the front edges of reproduced waveforms of all the mark lengths and each of positions of rear edges of the recording pulses of all the mark lengths is fixed so as to satisfy a prescribed relative relationship with an edge of a recording clock, power 122 of a recording pulse 101 of the shortest mark is determined so as to realize a proper rear edge position 112 of the reproduced waveform of the shortest mark and power 124 of a second-part pulse 104 is determined for each mark length so as to realize a proper rear edge position 123 of the reproduced waveform of the long mark.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Information recording method, information recording medium and information recording apparatus
InactiveUS6925040B1Avoid distortionIncrease linear densityRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLookup tableComputer science
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
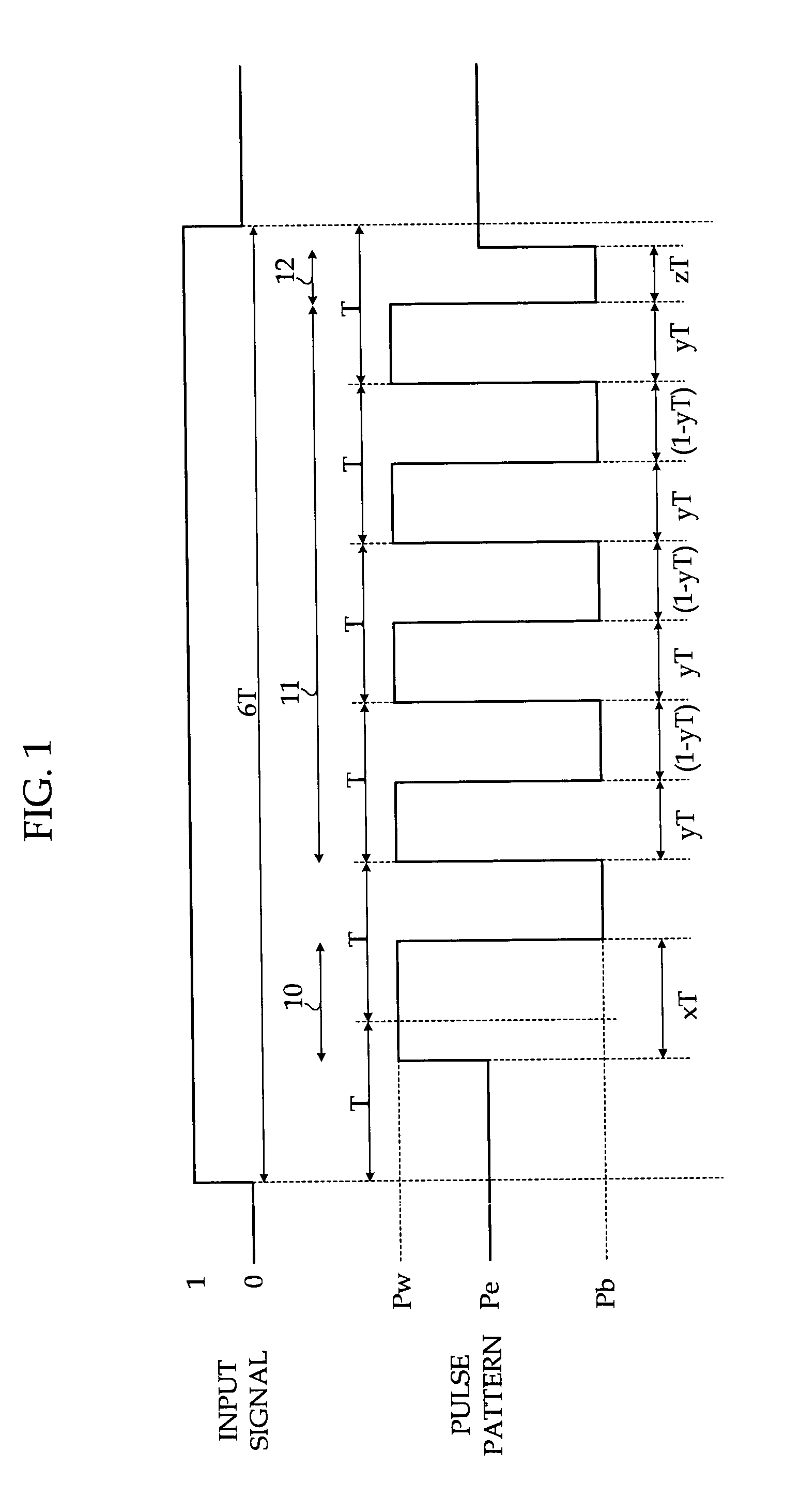
Recording method for phase-change recording medium
InactiveUS20020167879A1Television system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersPhoto irradiationOptical recording
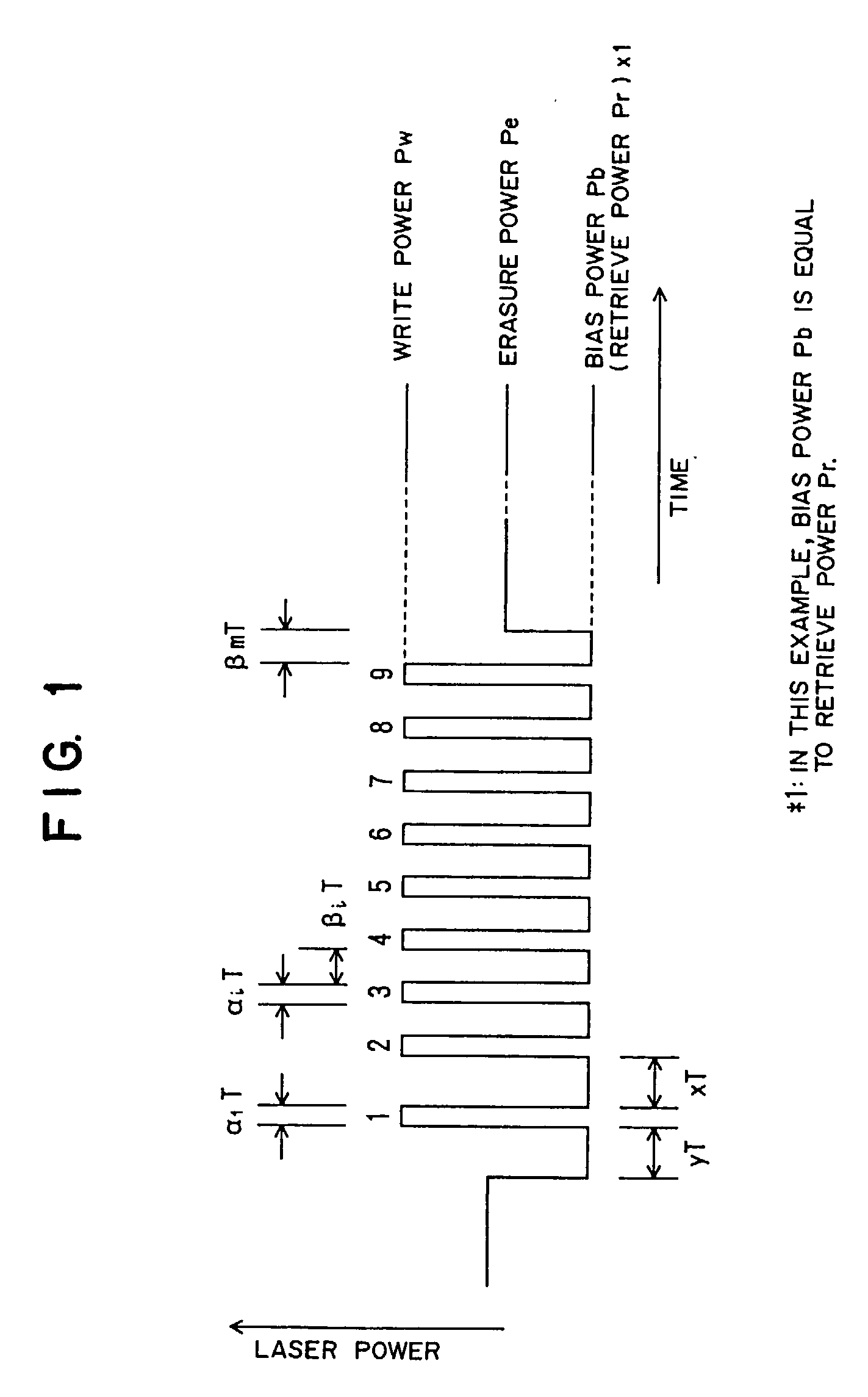
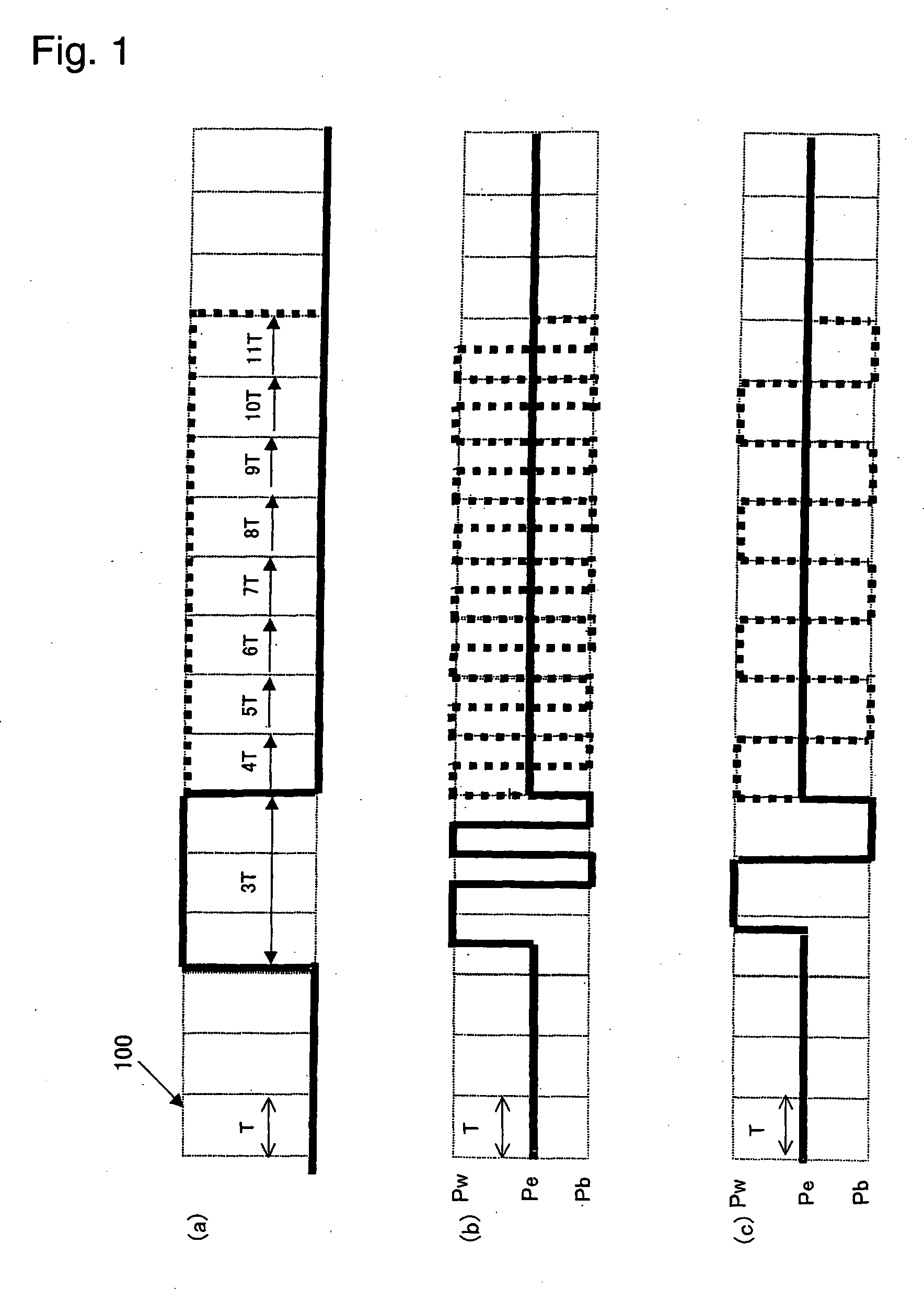
In a recording method for a rewritable optical recording medium, immediately before a prospective leading pulse that is a time section where recording light of write power Pw irradiates a phase-change recording layer for the first time as a front low-power energy irradiating step, light of bias power Pb irradiates the phase-change recording layer for a first set time length yT as a preceding low-power energy irradiation step. And immediately after the leading pulse, the light of bias power Pb irradiates the phase-change recording layer for a set time length xT as a succeeding low-power energy irradiation step. The relation between x and y satisfies: 0.95 <=x+0.7*y<=2.5. The high-power energybeam irradiates the recording medium in such a manner that a period of irradiation for pulses subsequent to the leading pulse is in a range of from 0.5T to 2.5T. The result is that it is possible to facilitate forming / erasing amorphous marks even in a phase-change recording medium devoid of a reflective layer, without any risk of narrowing the range of effective crystallization speeds.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
Method for recording data against ATE and storage medium therefor
InactiveUS20050180267A1Minimize impactCombination recordingTelevision system detailsComputer scienceCalculated data
A method of recording data capable of preventing an adjacent track erase is provided. The method includes accumulating and computing the number of times the data is recorded in sectors of at least one track, determining whether the accumulated number of times exceeds a predetermined number of times, and rewriting the data, which is recorded in adjacent tracks to the at least one track, in the adjacent tracks, if the accumulated number of times exceeds the predetermined number of times. If the number of times exceeds a predetermined number, the data is rewritten in regions adjacent to the specific region, thereby minimizing the influence of the ATE.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical recording method, optical recording medium, optical recording medium recording device, optical recording device, optical disk, optica disk recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS20060140094A1Relatively low linear speedRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsEngineeringIrradiation laser
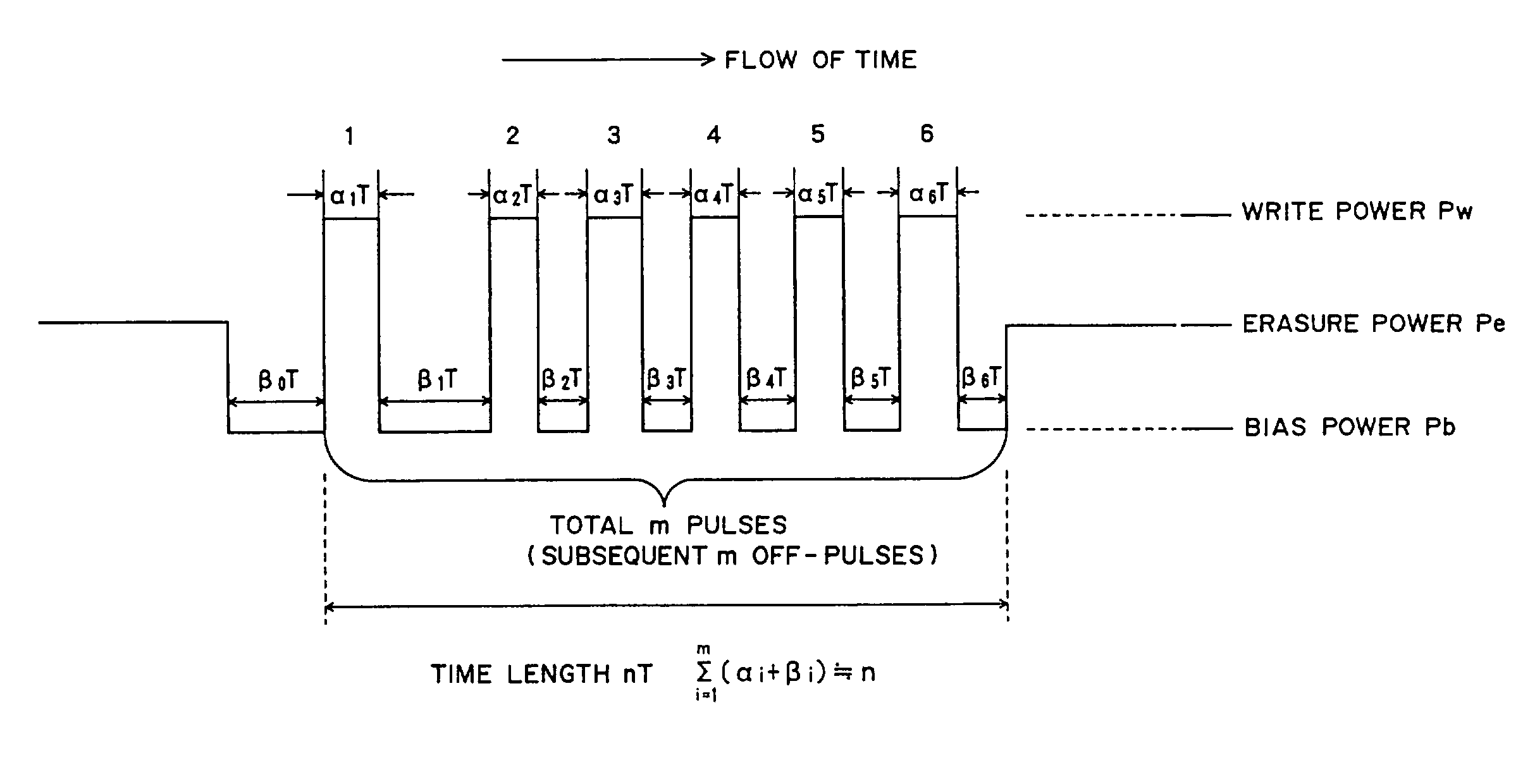
A mark having a length nT (n being an integer equal to or greater than 3 and T being a clock period) is formed by modulating irradiation laser power with three values of recording power Pw, erase power Pe, and bias power Pb (Pw>Pe>Pb). Constant strength periods (At) of the recording power Pw are set as AtT, A1T, . . . and AmT and constant strength periods (Bt) of the bias power Pb are set as BtT, B1T, . . . BmT, and CT (C=−1 to 3). The application of laser is divided into pulses in order of AtT, BtT, A1T, B1T, . . . , AmT, BmT, and CT (m=(n−k) / 2, k=3 (if n is an odd number), or k=4 (if n is an even number)). (Here, the constant strength period of the recording power Pw for n=3, n=4, n≧5 (odd number), and n≧6 (even number) is set as At3, At4, Atod, and Atev, the constant strength period of the bias power Pb for n=3, n=4, n≧5 (odd number), and n≧6 (even number) is set as Bt3, Bt4, Btod, and Btev, and then, At3+Bt3=Atod+Btod=Am+Bm=2T and At4+Bt4=Atev+Btev=3T).
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Optical recording method
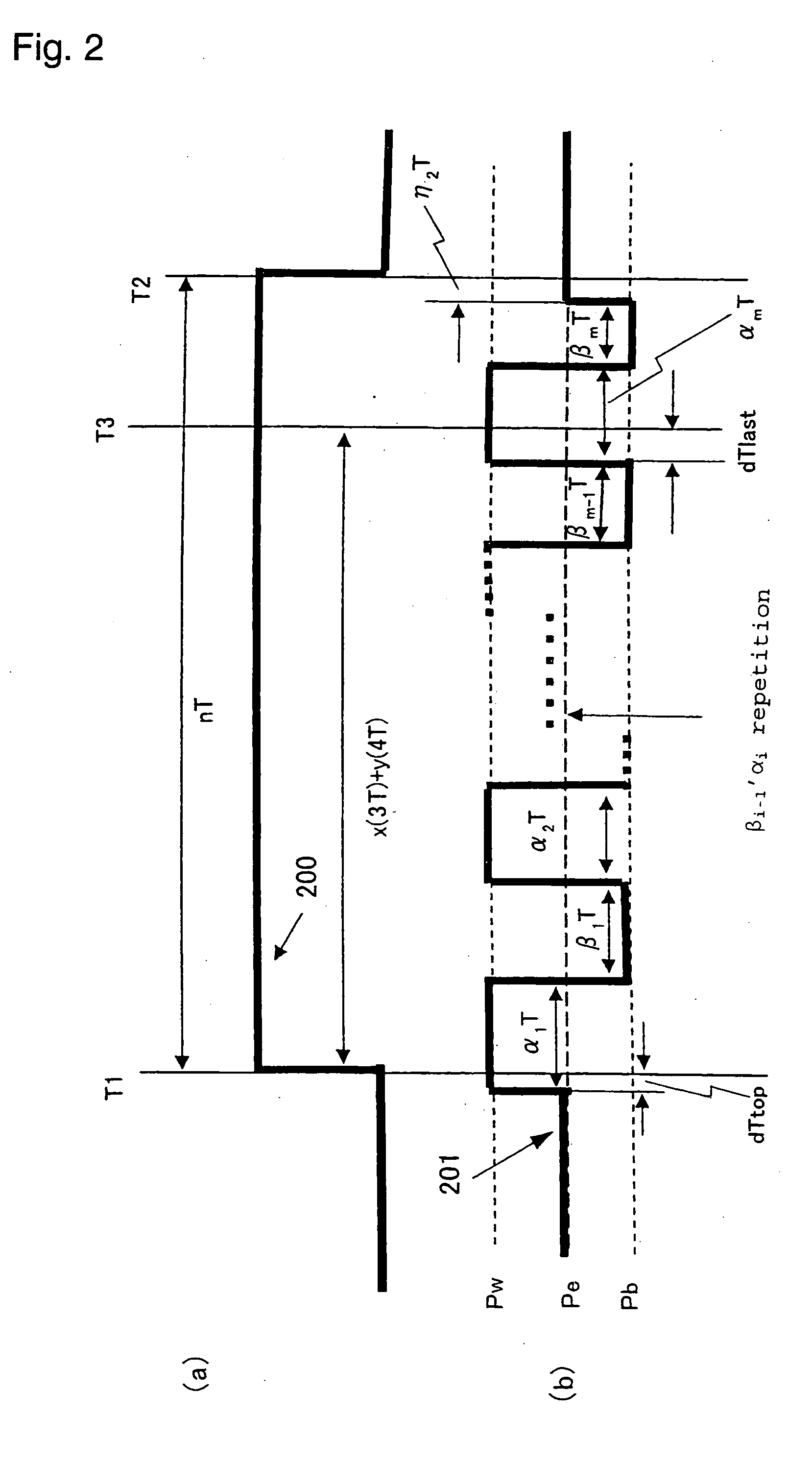
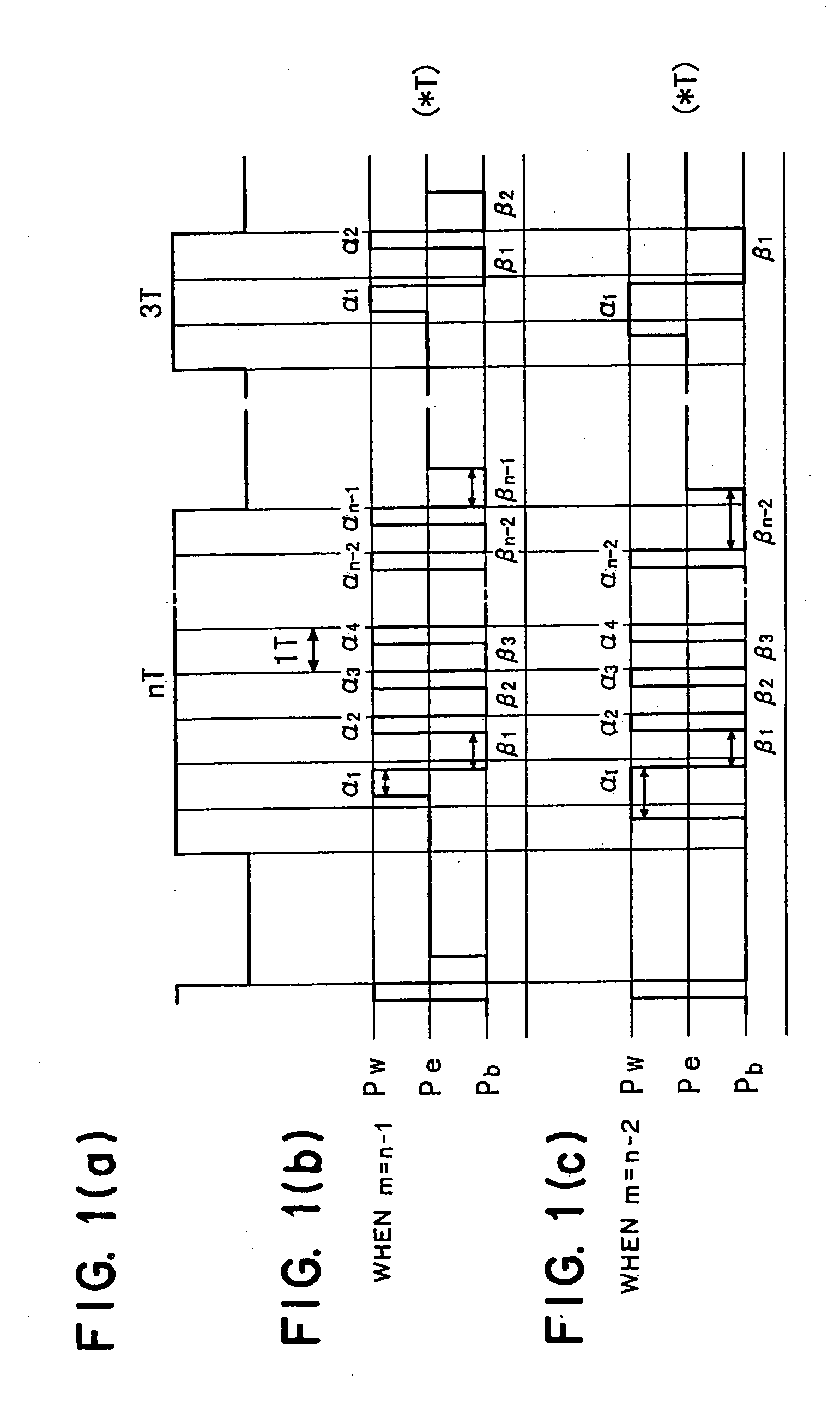
ActiveUS20060062125A1Improve data transfer rateTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersClock rateOptical recording
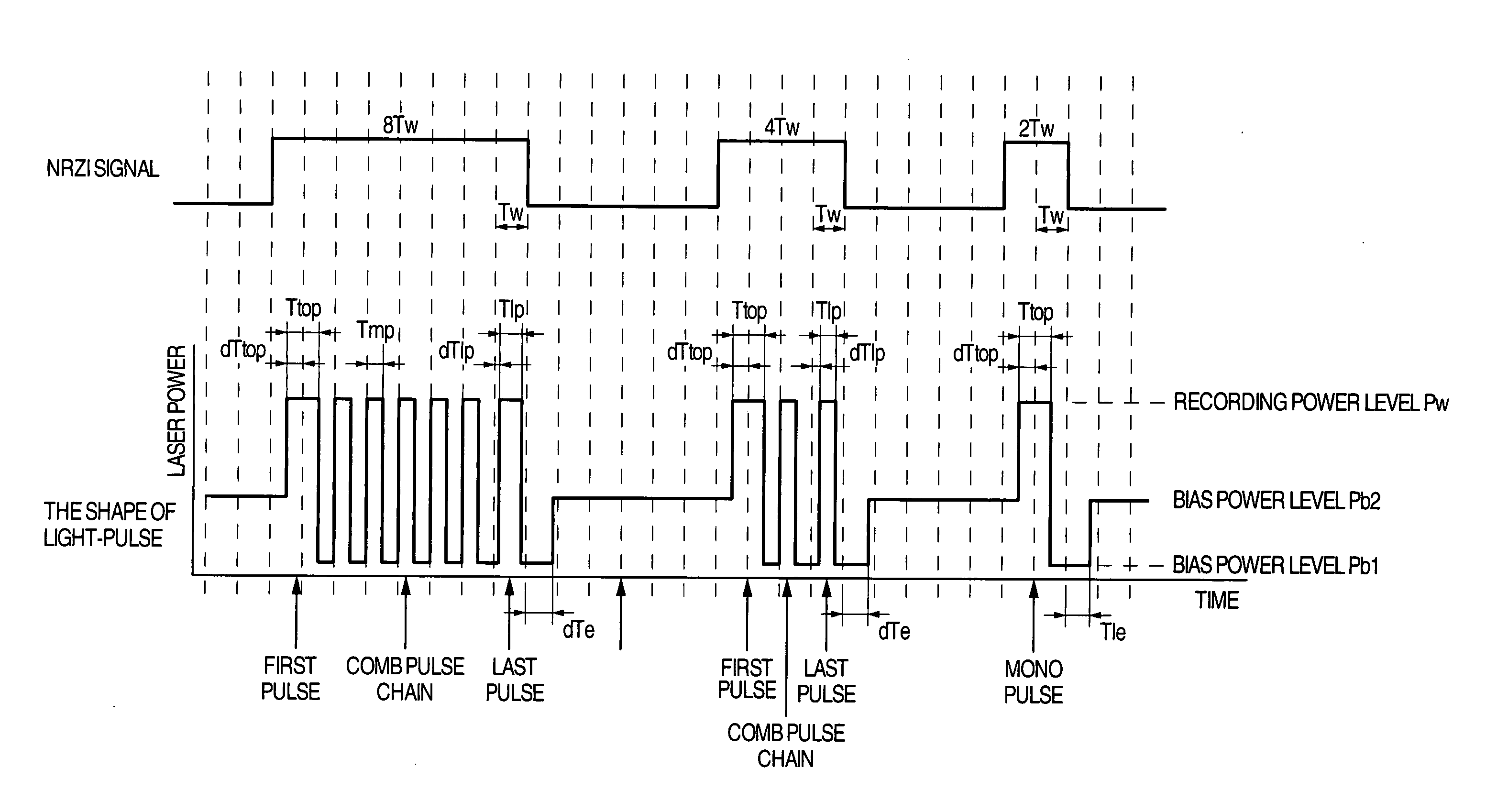
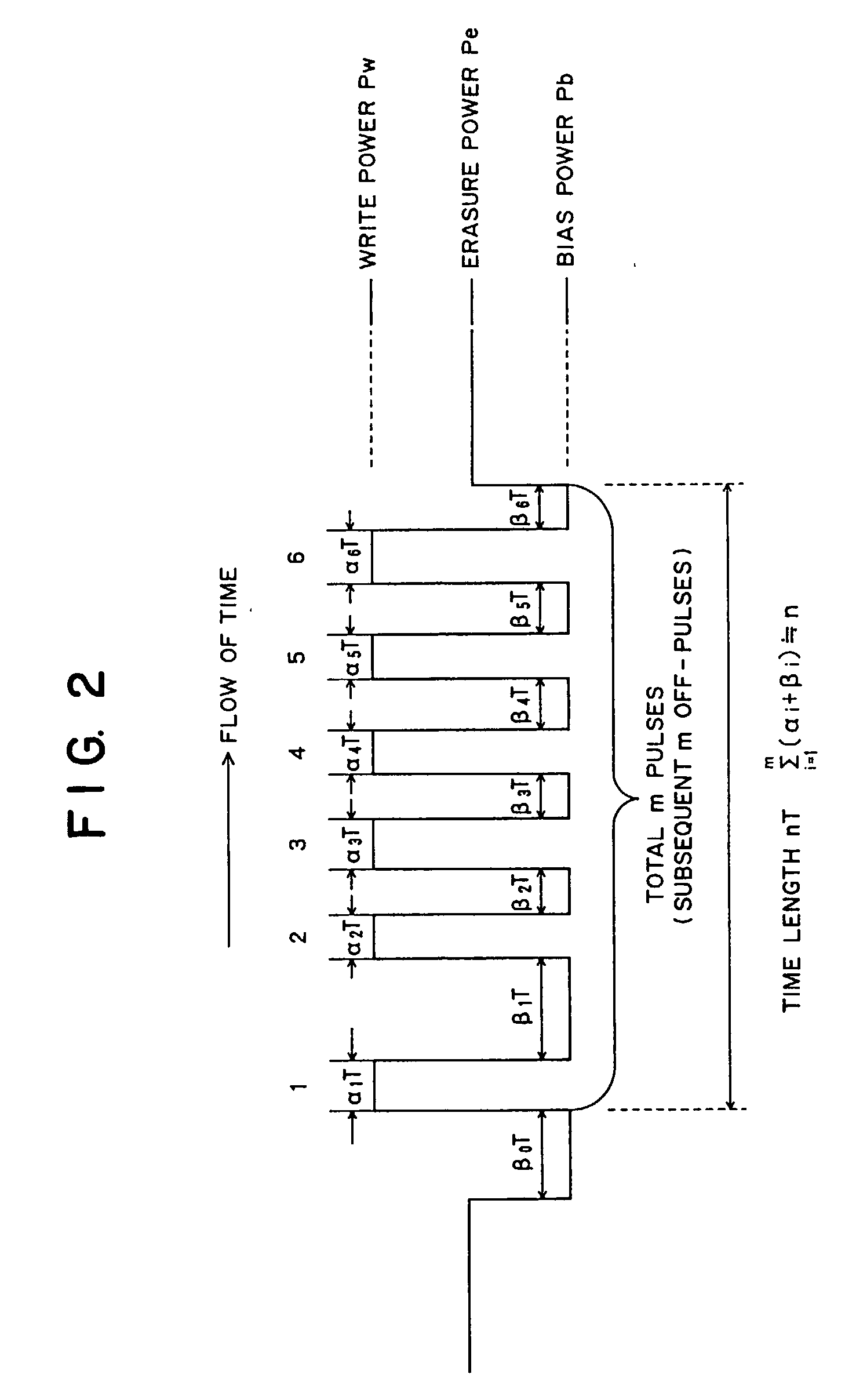
To provide an optical recording method to be used for recording at a high data transfer rate where the reference clock frequency is at least about 200 MHz and a linear velocity is about 40 m / sec. When recording mark length-modulated information is to be recorded on a recording medium by applying a recording laser beam locally to the recording medium, in order to form one record mark length of nT, m pieces of recording pulses αiT (1≦i≦m) and m pieces of off-pulses βiT (1≦i≦m), represented by: α1T, β1T, α2T, β2T, . . . , α1T, β1T, . . . , αmT, βmT (where m is a natural number representing a pulse dividing number, αi (1≦i≦m) is a real number of larger than 0, βi (1≦i≦m-1) is a real number of larger than 0, and βm is a real number of at least 0), are used, and a recording laser beam having a writing power Pwi is applied within a time of αiT (1≦i≦m), a recording laser beam having a bias power Pbi of Pbi<Pwi and Pbi<Pwi+1, is applied within a time of βiT (1≦i≦m-1), the front recording pulse α1T will rise as deviated for a time of dTtop from the front position of the record mark having a length of nT, with respect to at least two record marks, the pulse dividing number m is at least 2, and with respect to all record marks with m being at least 2, 2.5≦n / m, in a case where plural different record mark lengths are to be respectively formed by the same pulse dividing number m, α1 and / or αm is changed to form such record mark lengths having different lengths respectively, provided that when the α1 is changed, dTtop and / or β1 is also changed, and when the αm is changed, βm-1 and / or βm is also changed.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
Optical disk shred operation with detection
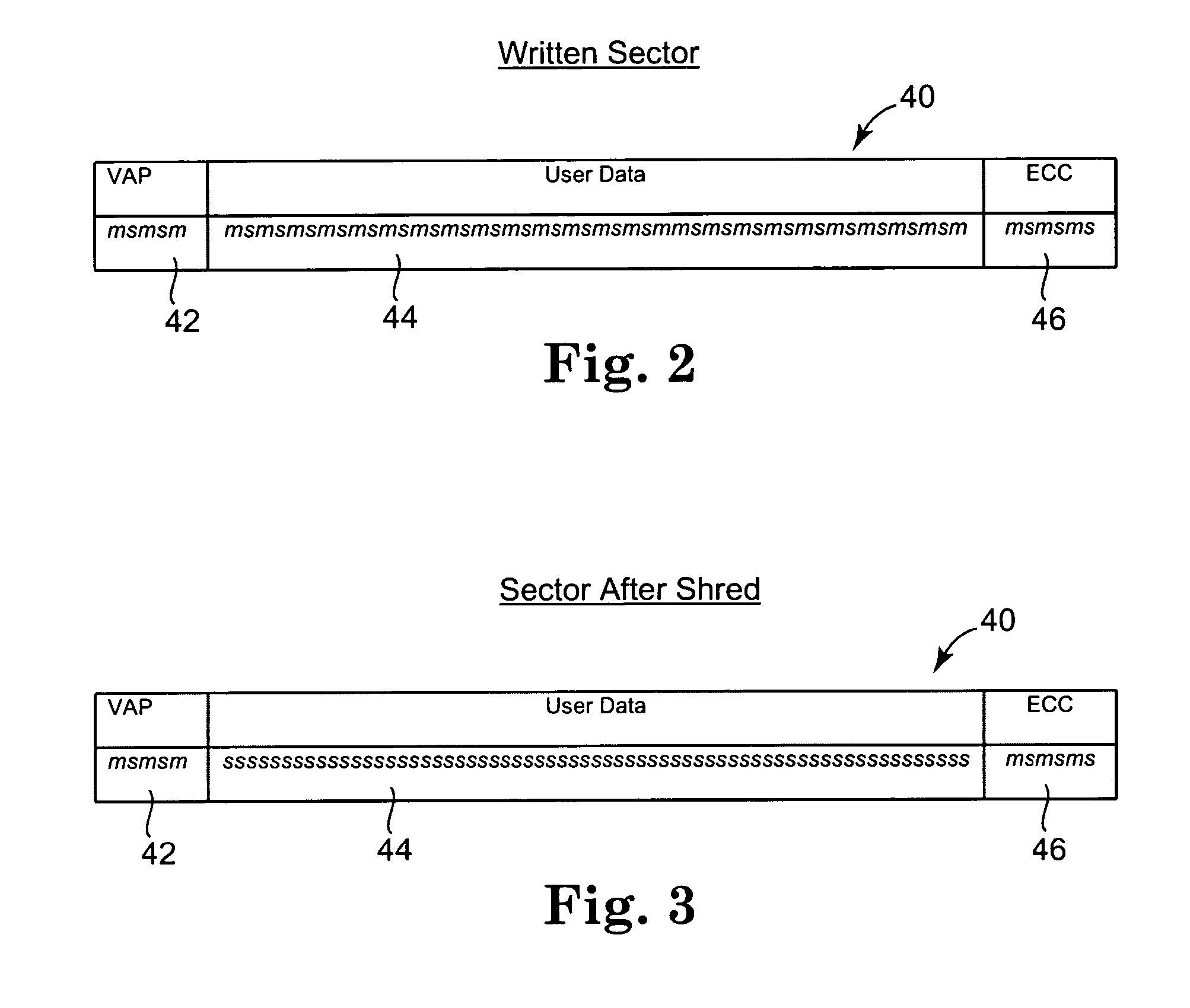
InactiveUS20070047395A1Easy to identifyCarry-out quicklyMultilayered discsRecording verificationConfusionData store
Data protection and security is provided by incorporating a data shredding operation which renders data previously stored on storage media unrecoverable. In the shredding operation of the present invention, certain overhead portions of a data storage sector remain unchanged, while the data area is overwritten with a predetermined pattern. By maintaining the overhead portions of the sectors (addressing, verify and protect, error correction codes, etc.) the sectors can be easily identified as being previously shredded, thus not providing a source of possible confusion to the data storage device. Further, the data becomes unrecoverable as it has been overwritten by the predetermined pattern, which thus eliminates all previously existing transitions which contained the encoded data.
Owner:PLASMON LMS
Optical information recording method and optical information recording apparatus
InactiveUS20050105438A1Increase speedQuality improvementTelevision system detailsMechanical recordingOptical powerLight beam
Optical information recording is achieved at high speed such as sixthfold to eightfold speed of DVD while suppressing jitter by a high-speed recording strategy such as a 2T period strategy, by once reducing the optical power of the optical beam used for optical recording, when starting recording of an amorphous mark pattern after the step of forming a crystalline space region but before the step of irradiating the optical beam with a peak power level for the mark formation, such that the optical power of the optical beam is reduced below the erasing optical power used for forming the crystalline space region.
Owner:RICOH KK
Apparatus and method for laser power control
InactiveUS20050083828A1Constant power levelTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersLow-pass filterPhotodiode
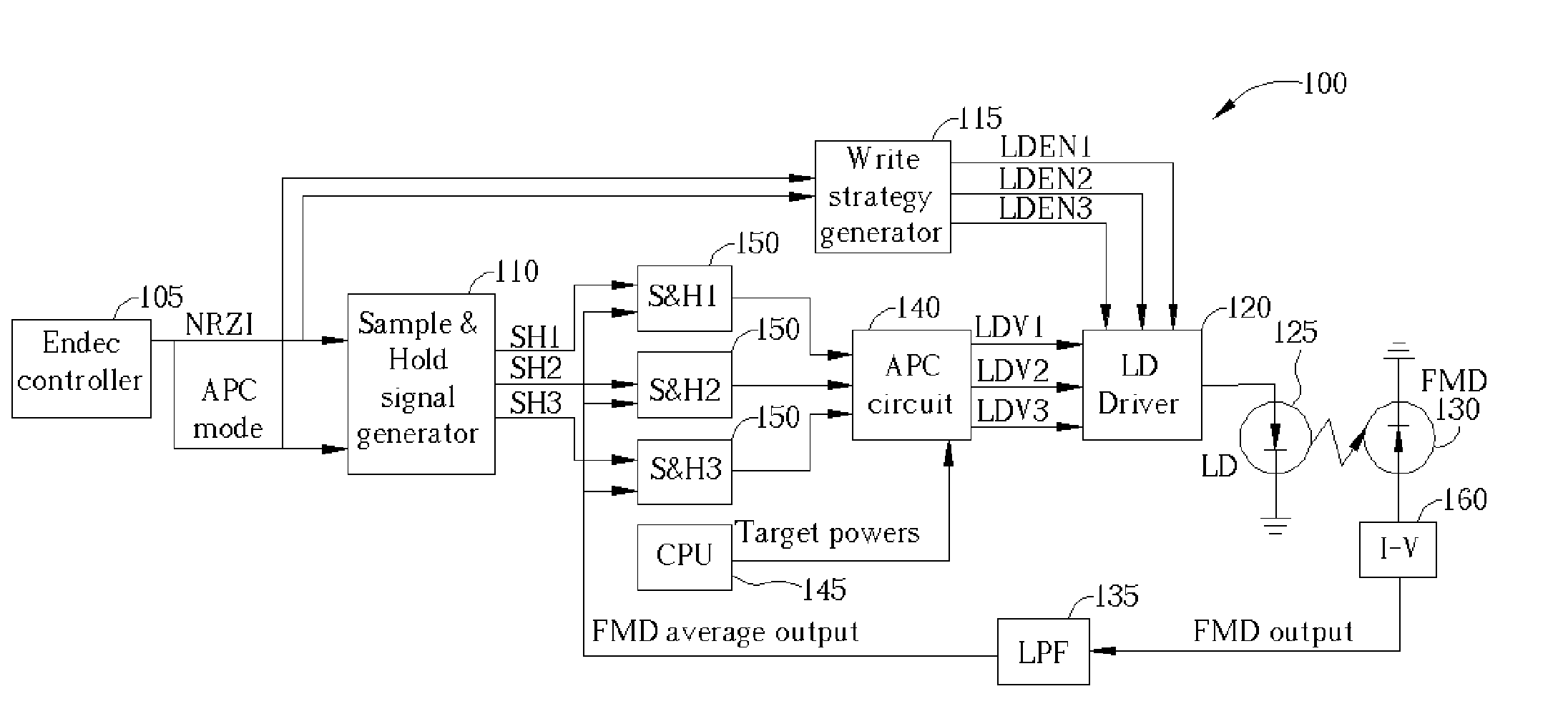
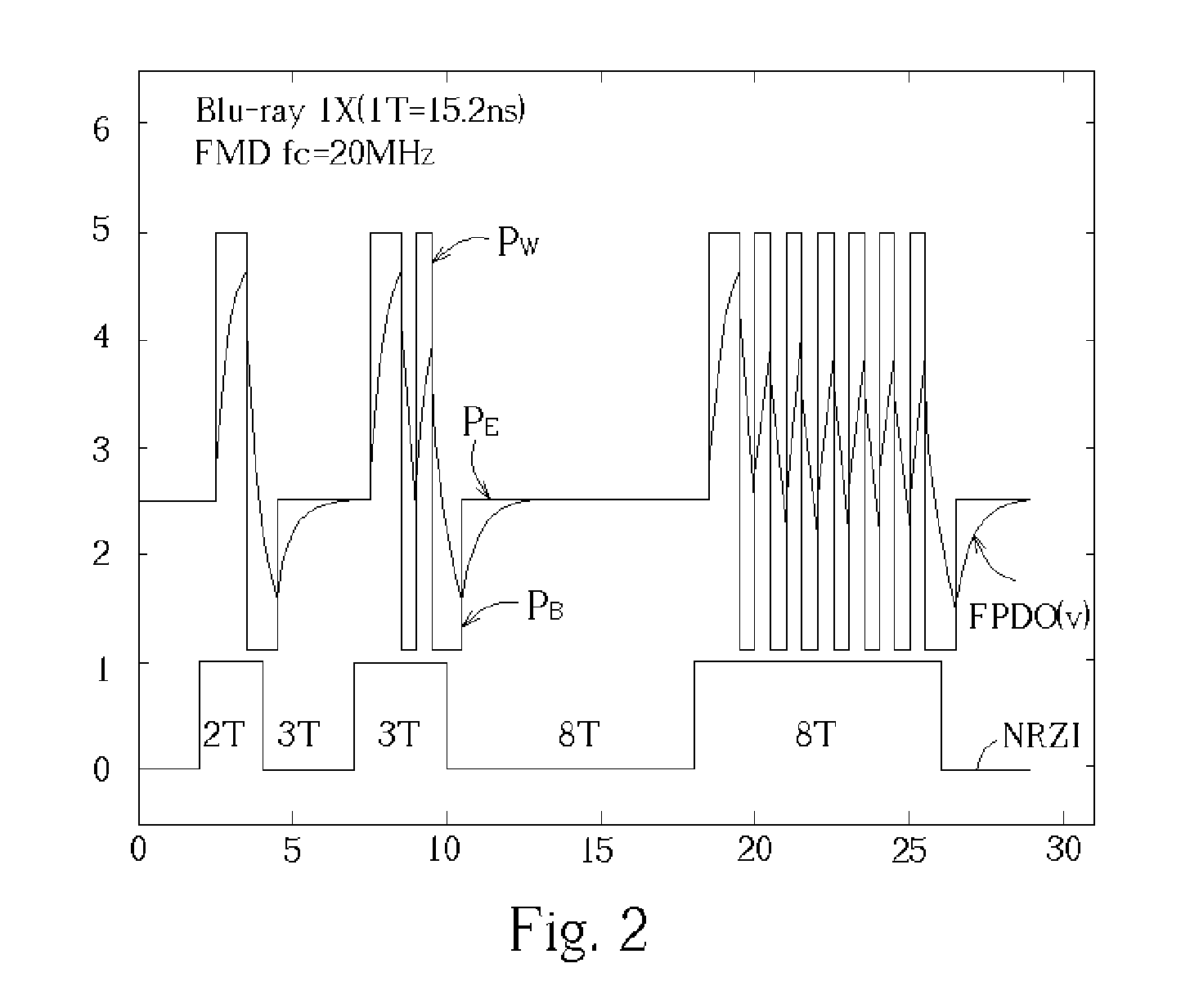
A high-speed optical disc recording apparatus includes a laser diode for generating multi-pulse light pulses and a photodiode outputting a measured power of the light pulses. An NRZI pattern encoder generates a predetermined power control pattern causing a write strategy generator to generate write strategy to a laser diode driver such that the laser diode outputs a multi-pulse having a fixed-duty ratio with two power levels. The measured power is averaged with a low-pass filter, is sampled and held, and is calibrated according to the fixed-duty ratio. The calibrated held average output of the measured power of the light pulses is compared with predetermined present levels to control the laser diode driver output voltage.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Rewritable optical recording medium, recording method on the same, and optical disc recording/retrieving apparatus
InactiveUS20040190407A1Filamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesRecord statusRewritable compact disc
In a rewritable compact disc having a wobble groove on a substrate, crystal and amorphous states of a phase-change recording layer are an unrecorded / erased state and a recorded state, respectively. When the recording layer is exposed to recording light, amorphous marks assuming the recorded state are formed. At any of 2-, 4- and 8-times velocities with respect to a reference velocity (1-times velocity) whose linear velocity is 1.2-1.4 m / s, modulation m11 of a recorded signal when the recording light of approximately 780 nm in wavelength irradiates the recording layer via an optical system with NA=0.5 or 0.55 is 60-80%. A topmost level Rtop of reflectivity of the eye pattern of the recorded signal during retrieving at the 1-times velocity is 15-25%, and a jitter of the individual length of marks and inter-mark spaces during retrieving at 1-times velocity is 35 ns or less. Recording at 8-times or higher velocities is thereby realized without any risk of impairing the read-compatibility with the conventional CD-RW specifications at least at 4-times velocity.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
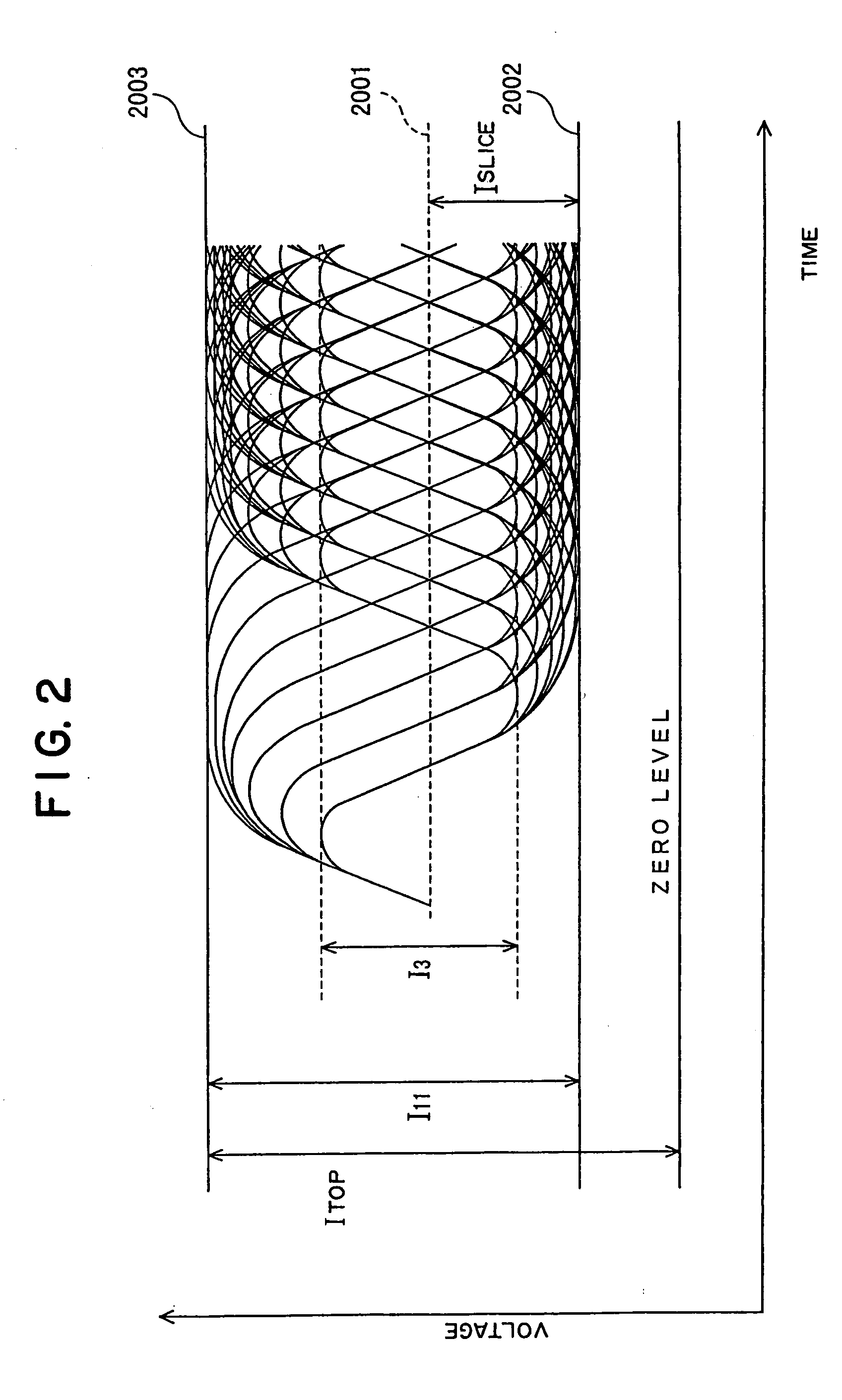
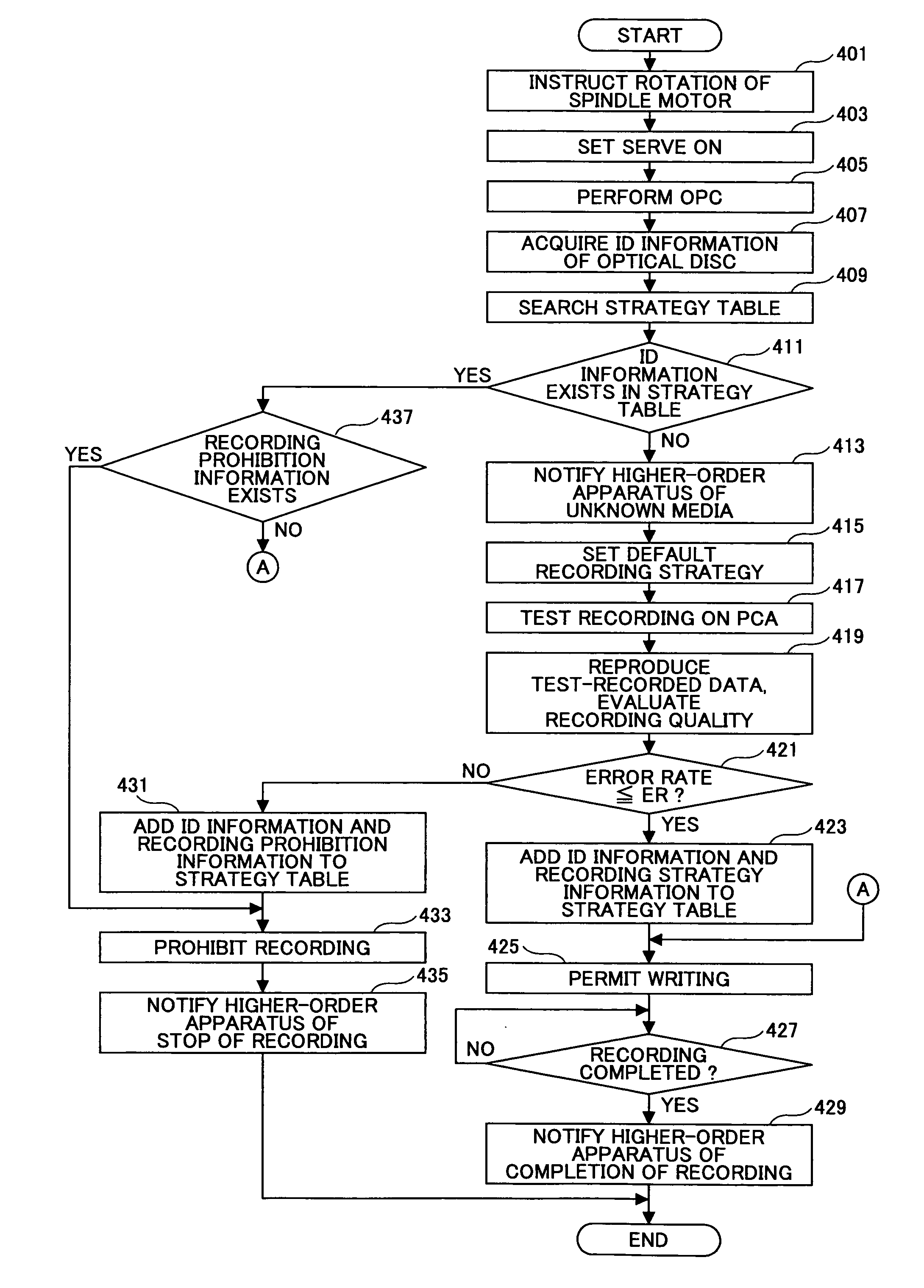
Evaluation method, recording method, program and recording medium, and optical disk apparatus
InactiveUS20050185537A1Eliminate the problemQuality improvementRecording strategiesFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareOptical recording
An optical recording apparatus can maintain an excellent recording quality. A recording quality is evaluated when recording information on an optical disc Test recording is performed on a predetermined test area, when recording strategy information corresponding to the optical disc is unknown, based on default recording strategy information. The recording quality is evaluated by reproducing data recorded on the test area.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com