Patents
Literature
82results about "Erasing involving phase-change media" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical information recording medium, producing method thereof and method of recording/erasing/reproducing information
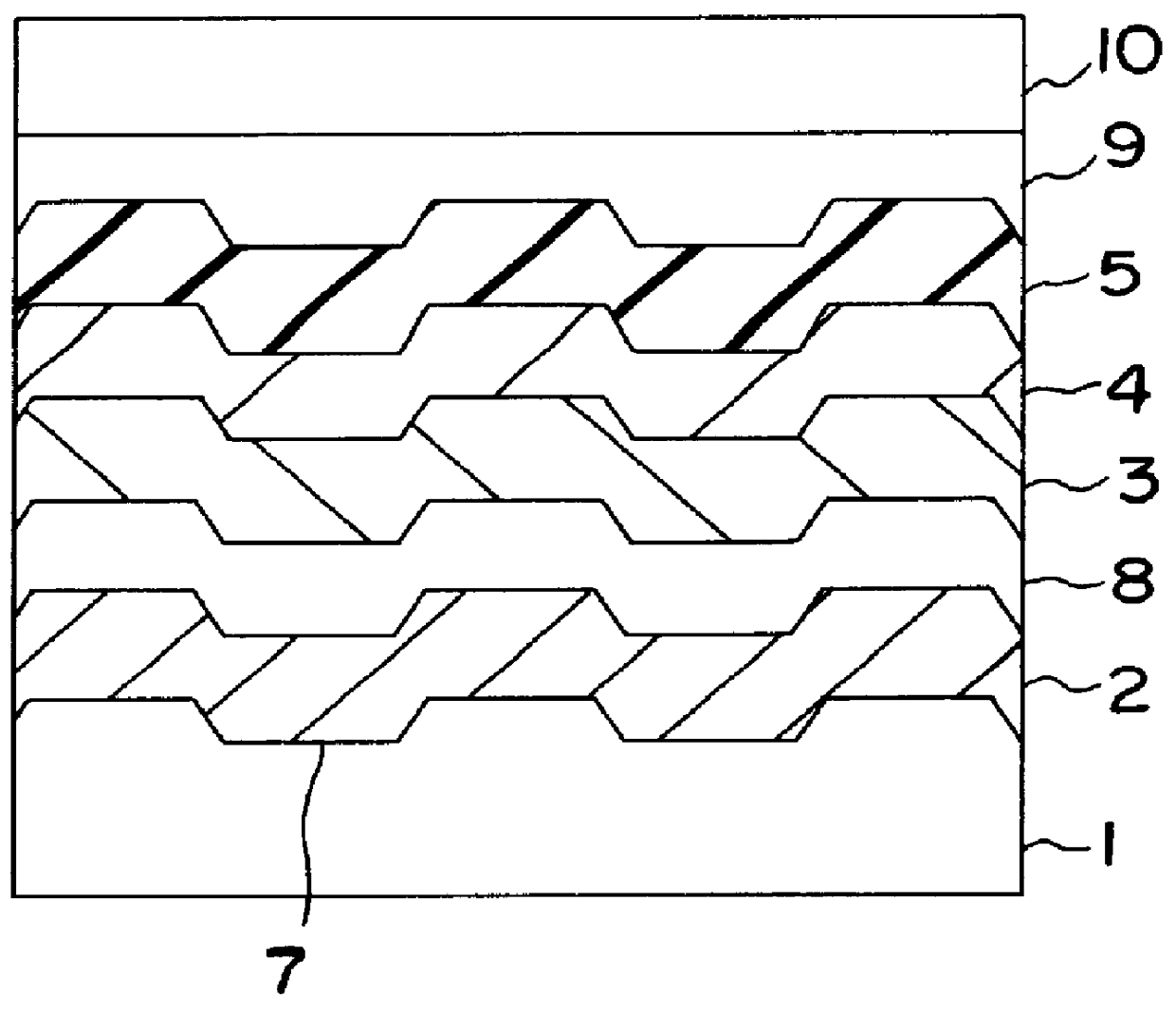
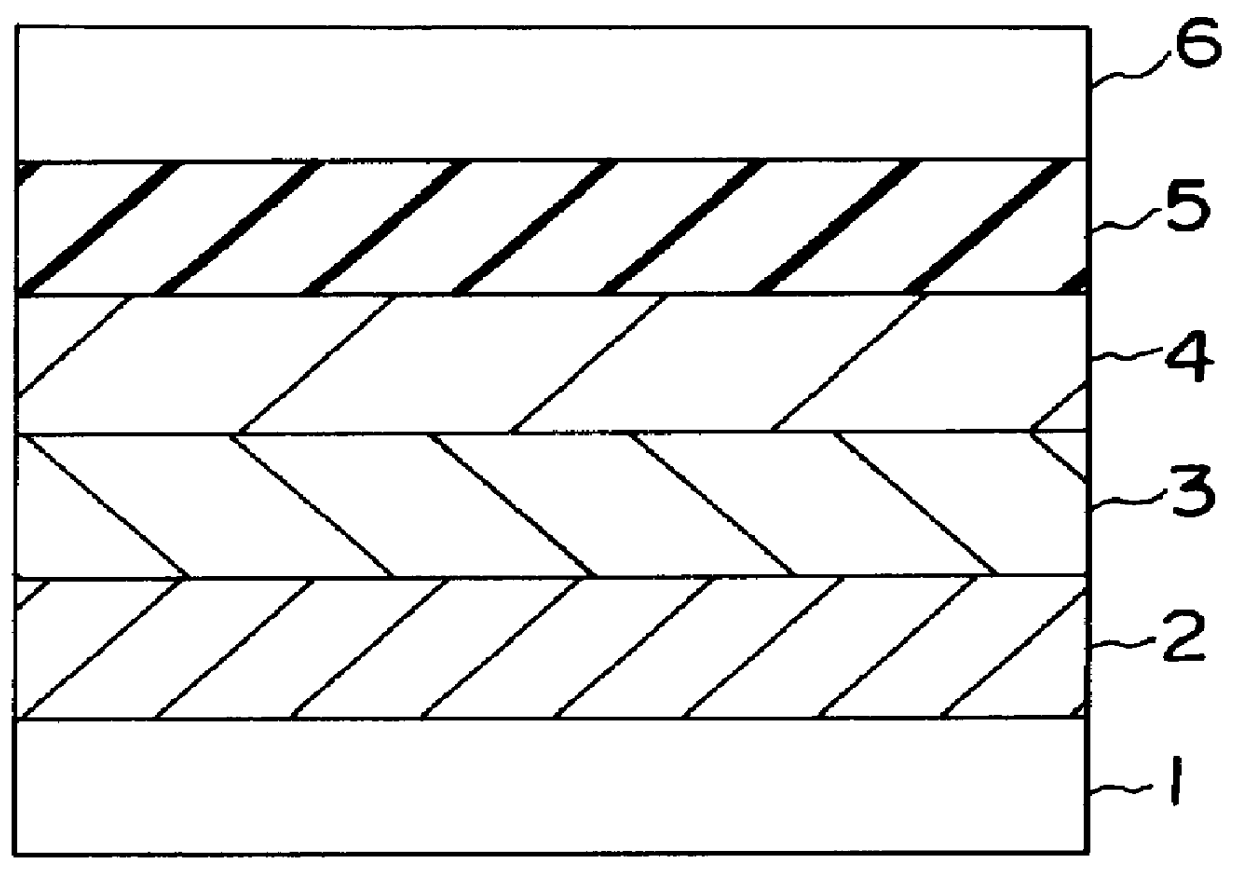
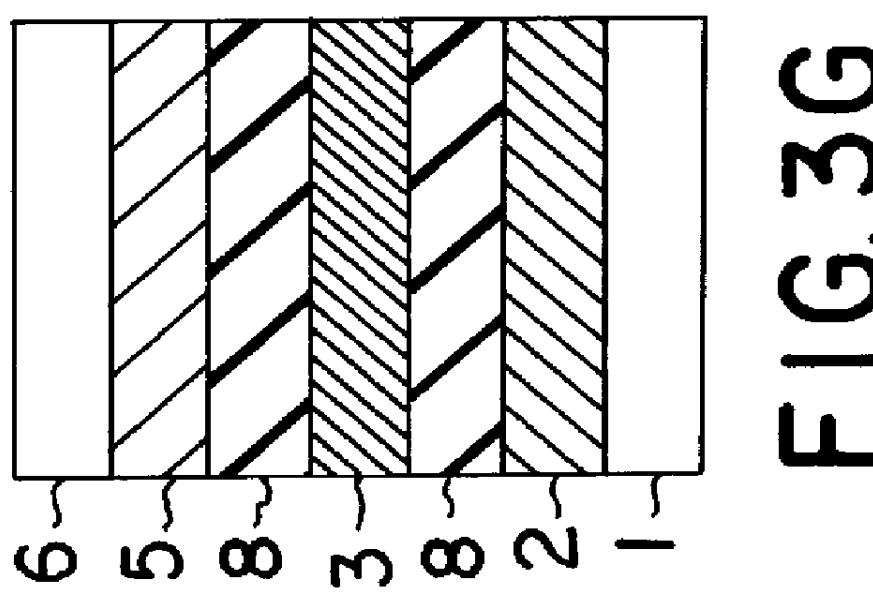
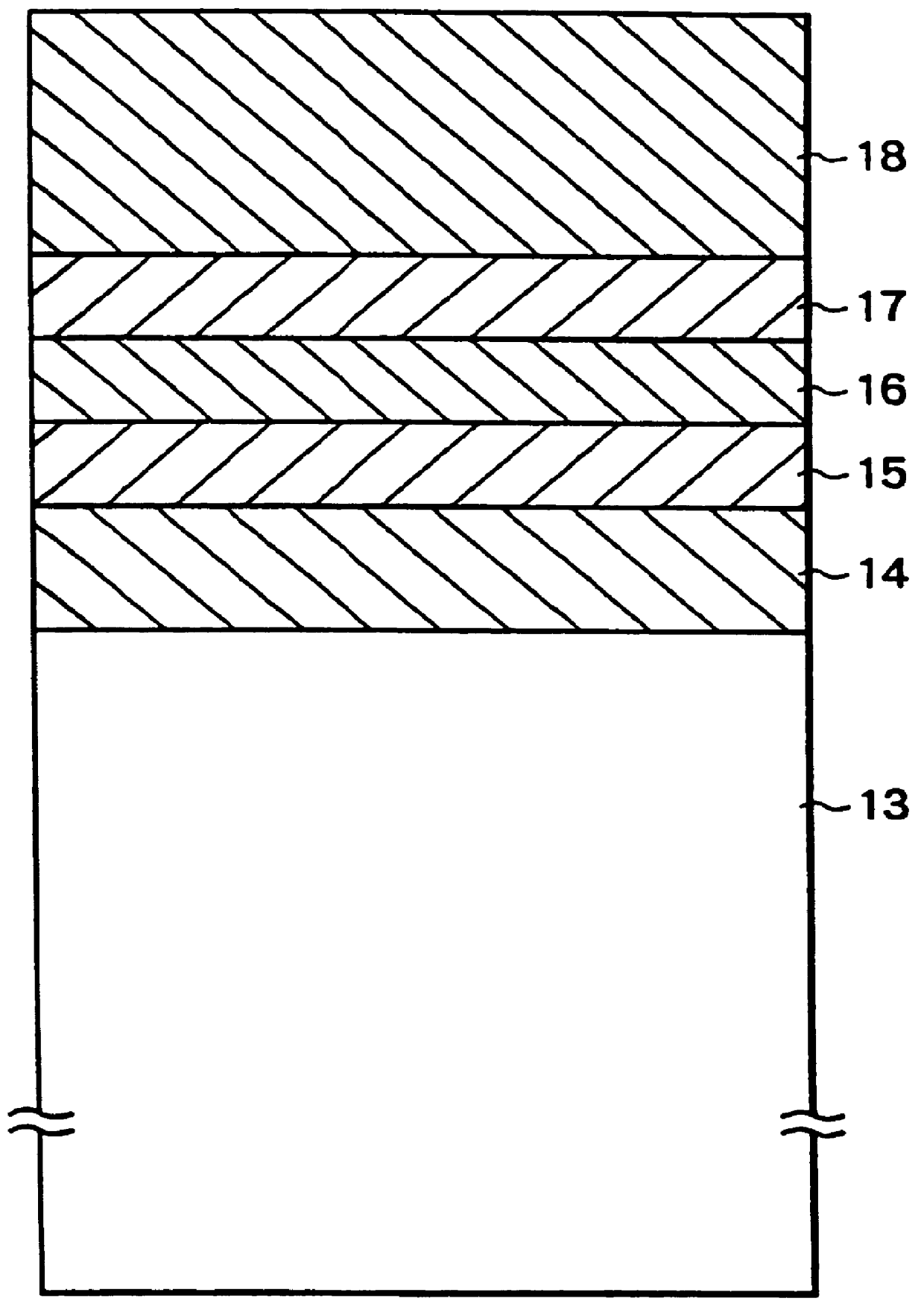
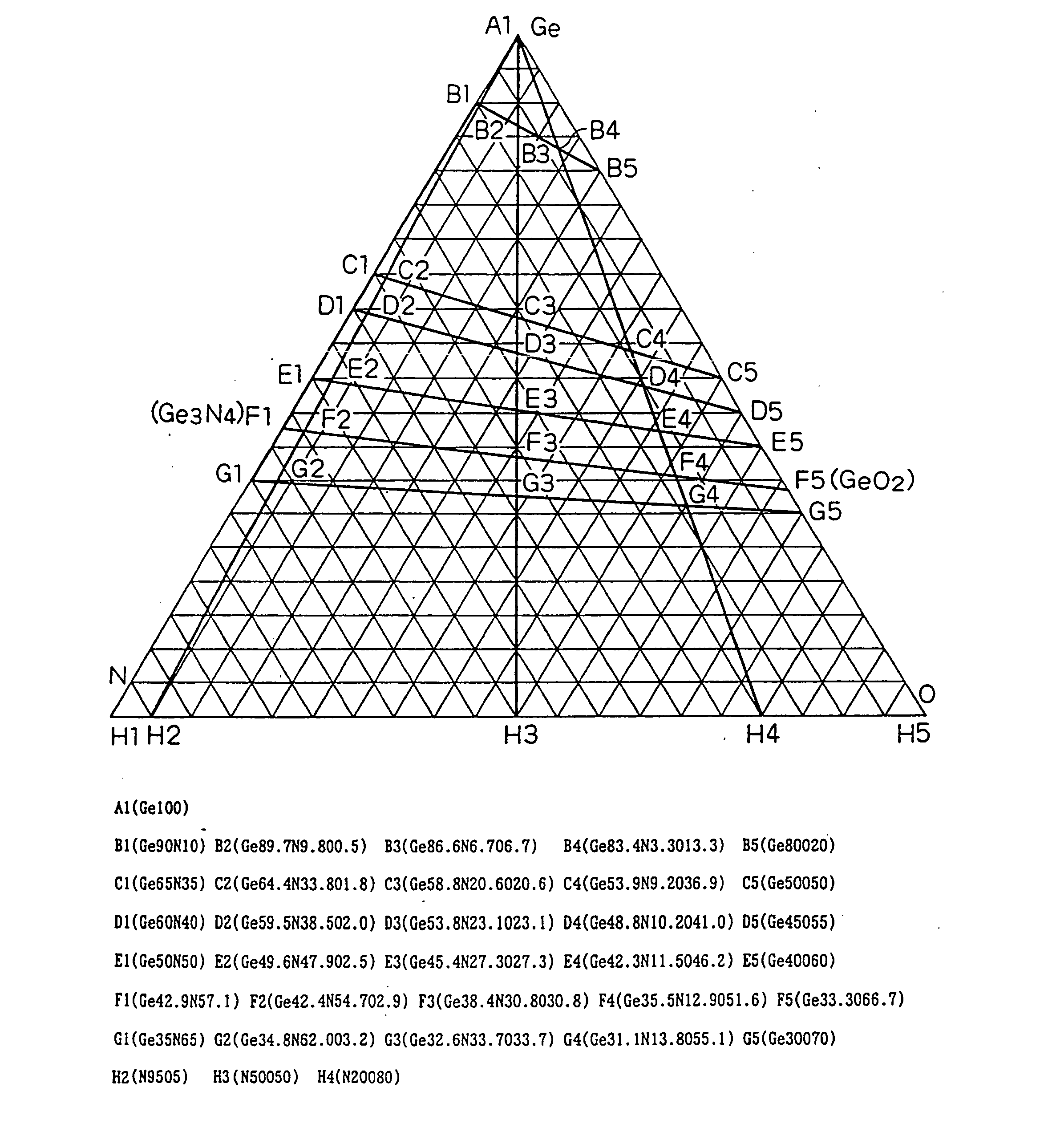
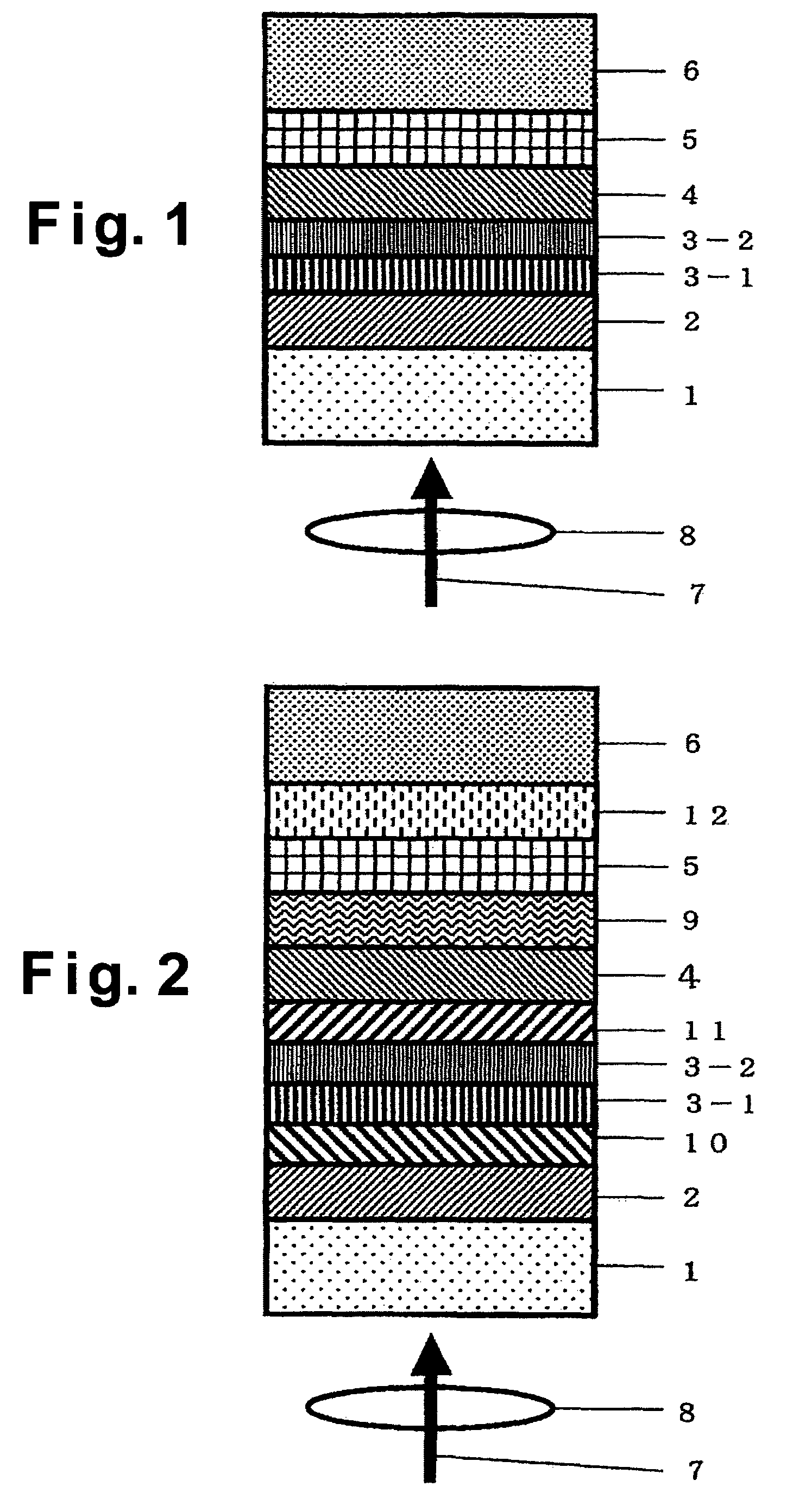
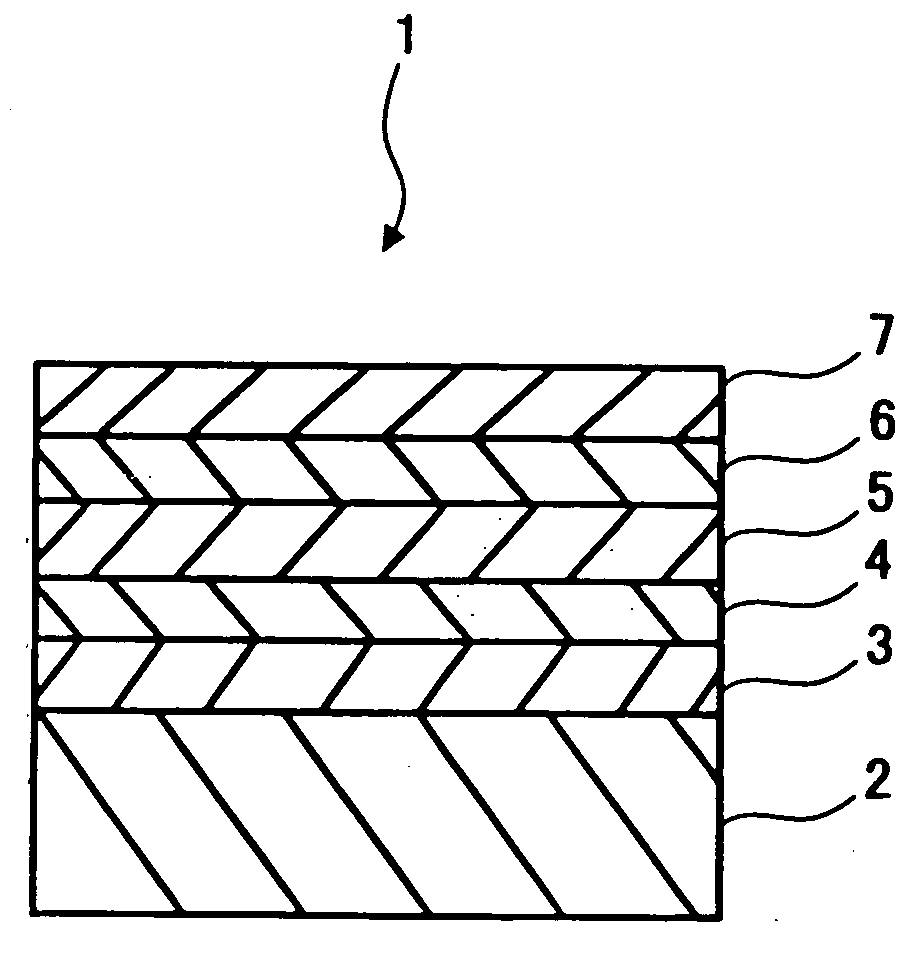
In a phase-change recording medium, a recording medium is provided with a barrier layer including Ge-N, Ge-N-O between a recording layer and a dielectric protective layer in order to prevent a chemical reaction and an atom diffusion between the recording layer and the dielectric protective layer. A barrier material can be also applied to the protective layer itself. Thereby, it is possible to considerably suppress a reduction of a reflectivity and a reduction of a signal amplitude due to the repeat of recording and erasing, such reductions being observed in a conventional phase-change optical information recording medium, and thereby the number of overwriting times can be increased.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical phase-change disc
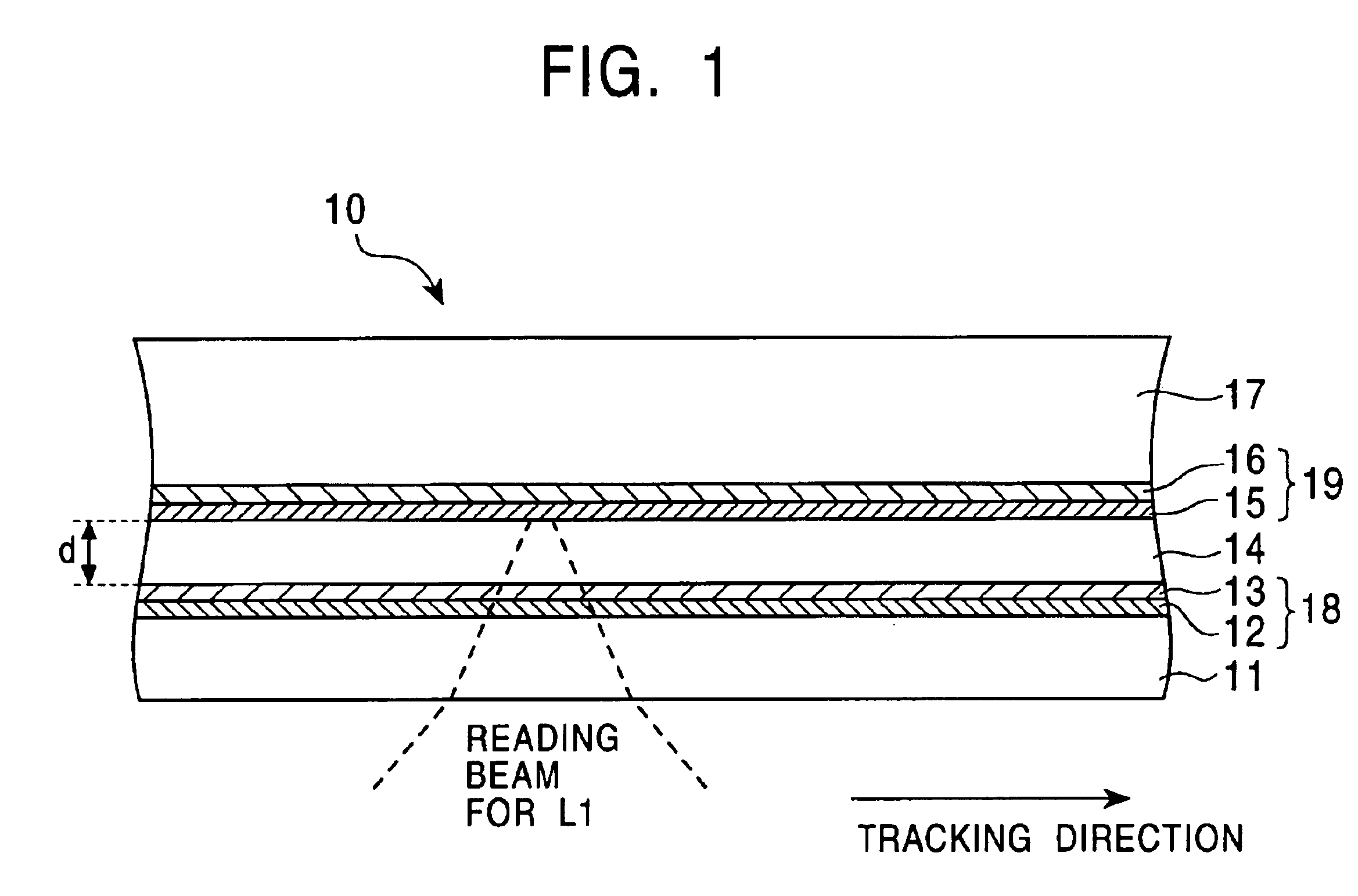
An optical phase-change disc comprises a substrate having thereon a spiral groove or concentric grooves for guiding a focused light beam, and a layer structure including a recording layer and protective layers sandwiching therebetween the recording layer. The groove has wobble for recording ATIP (absolute time information) or ADIP (address information). The following relationship between the groove width GW, beam diameter R0 and wobble amplitude aw: 0.25< / =GW / R0< / =0.45 or 0.65< / =GW / R0; and 0.03< / =aw / GW< / =0.08 hold for preventing distortion of the groove caused by repeated overwriting operation to improve reliability of the optical disc.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
Optical phase-change disc having a grooved substrate, with the groove having specific wobbled and non-wobbled regions
An optical phase-change disc comprises a substrate having thereon a spiral groove or concentric grooves for guiding a focused light beam, and a layer structure including a recording layer and protective layers sandwiching therebetween the recording layer. The groove has wobble for recording ATIP (absolute time information) or ADIP (address information). The following relationship between the groove width GW, beam diameter R0 and wobble amplitude aw: 0.25< / =GW / R0< / =0.45 or 0.65< / =GW / R0; and 0.03< / =aw / GW< / =0.08 hold for preventing distortion of the groove caused by repeated overwriting operation to improve reliability of the optical disc.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
Optical recording medium and method for its initialization
InactiveUS20030008235A1Reduce laser powerRadiation applicationsLayered productsLight beamRecording layer
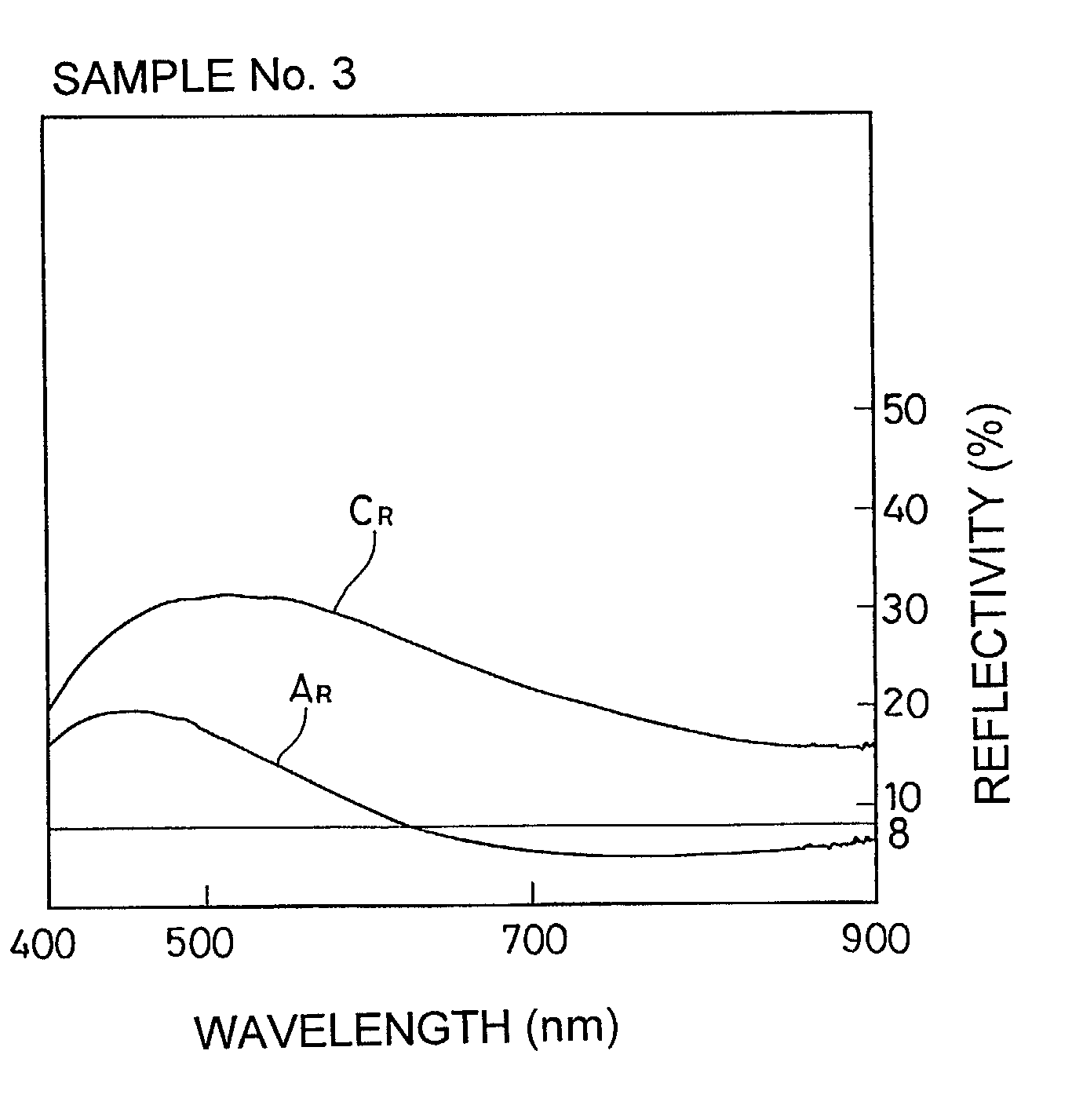
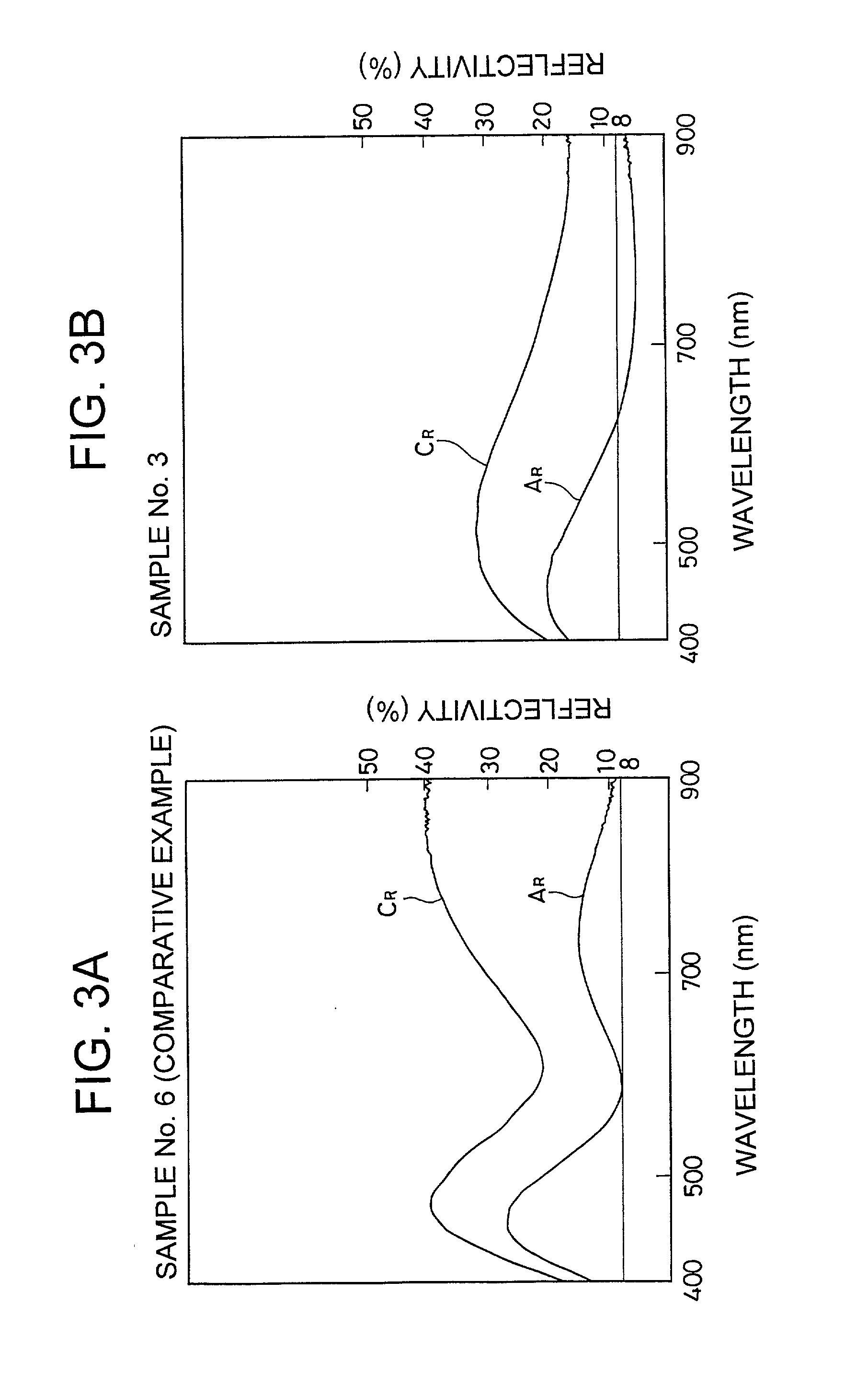
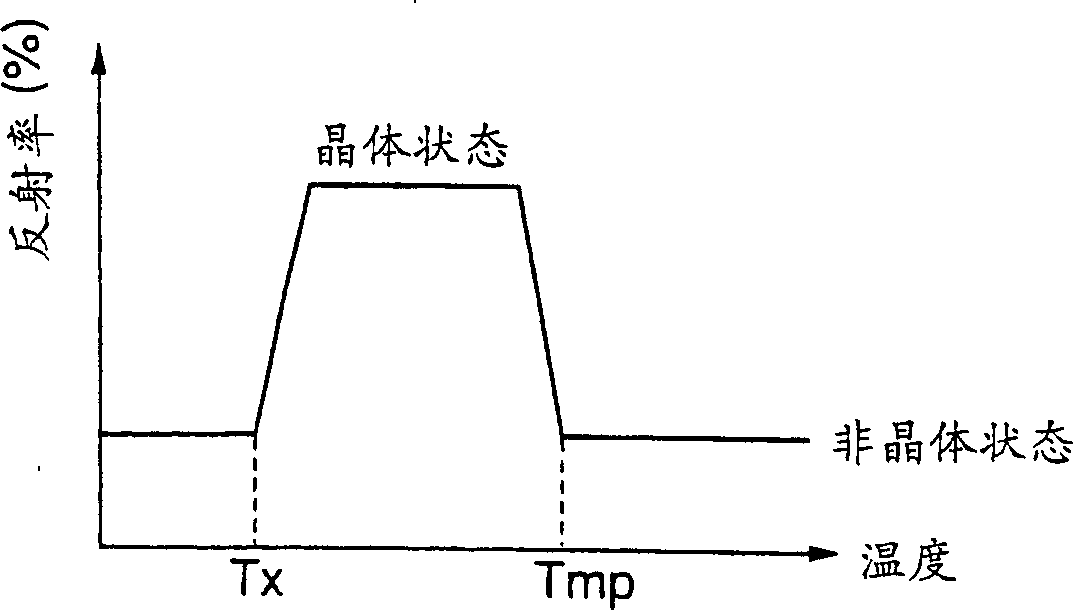
A phase change optical recording medium is provided wherein the power of the laser beam per unit area required in the initialization is reduced. The optical recording medium has a phase change recording layer satisfying the relations: A.sub.I.ltoreq.8.0%, and C.sub.I / A.sub.I.gtoreq.3.0 when the medium is initialized with a light beam having a wavelength .lambda..sub.I, and said recording layer exhibits a reflectivity A.sub.I in amorphous region and a reflectivity C.sub.I in crystalline region at said wavelength .lambda..sub.I.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium and optical recording method
InactiveUS6996052B1Reduce jitterCombination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersRecord statusHigh density
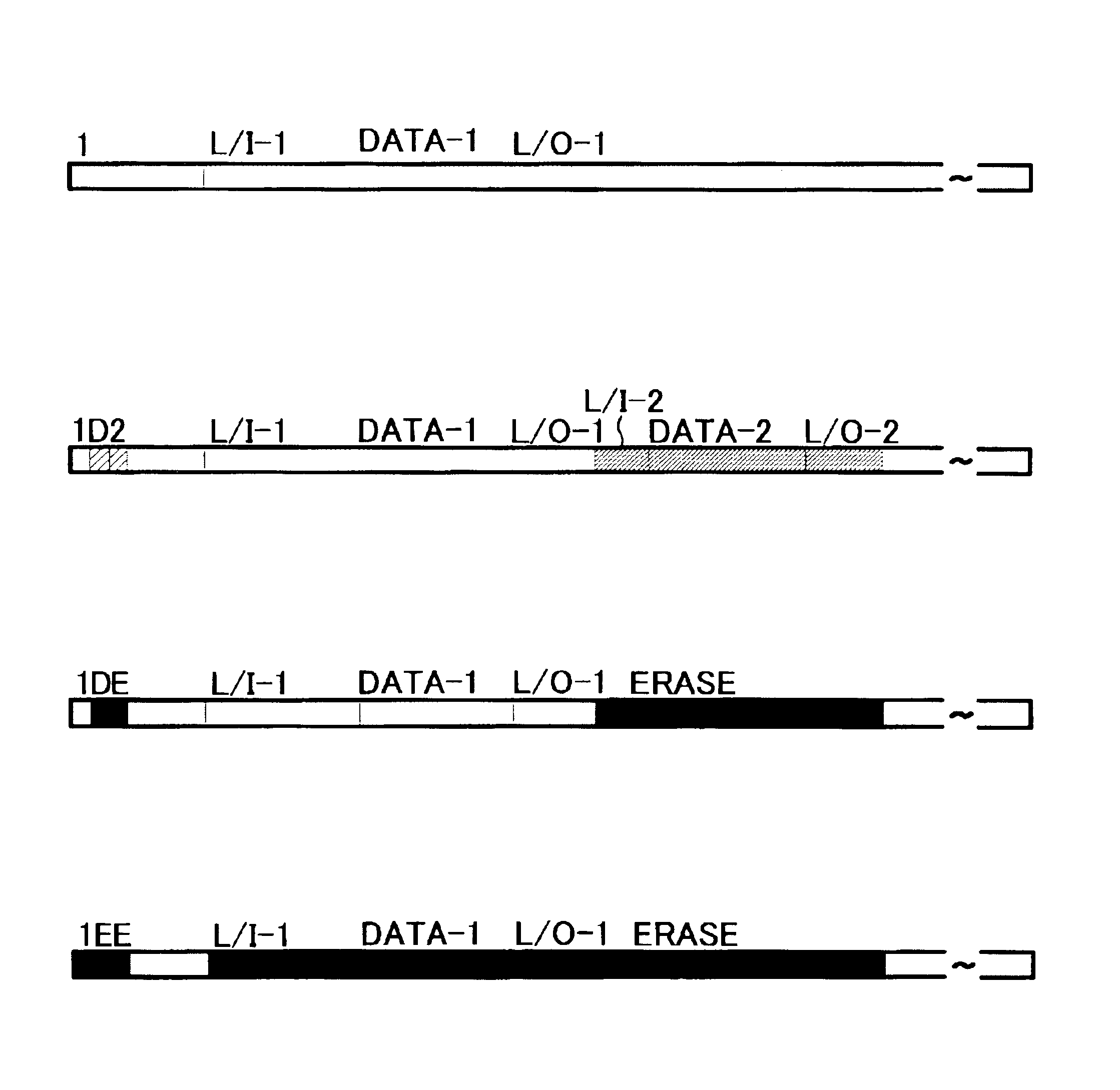
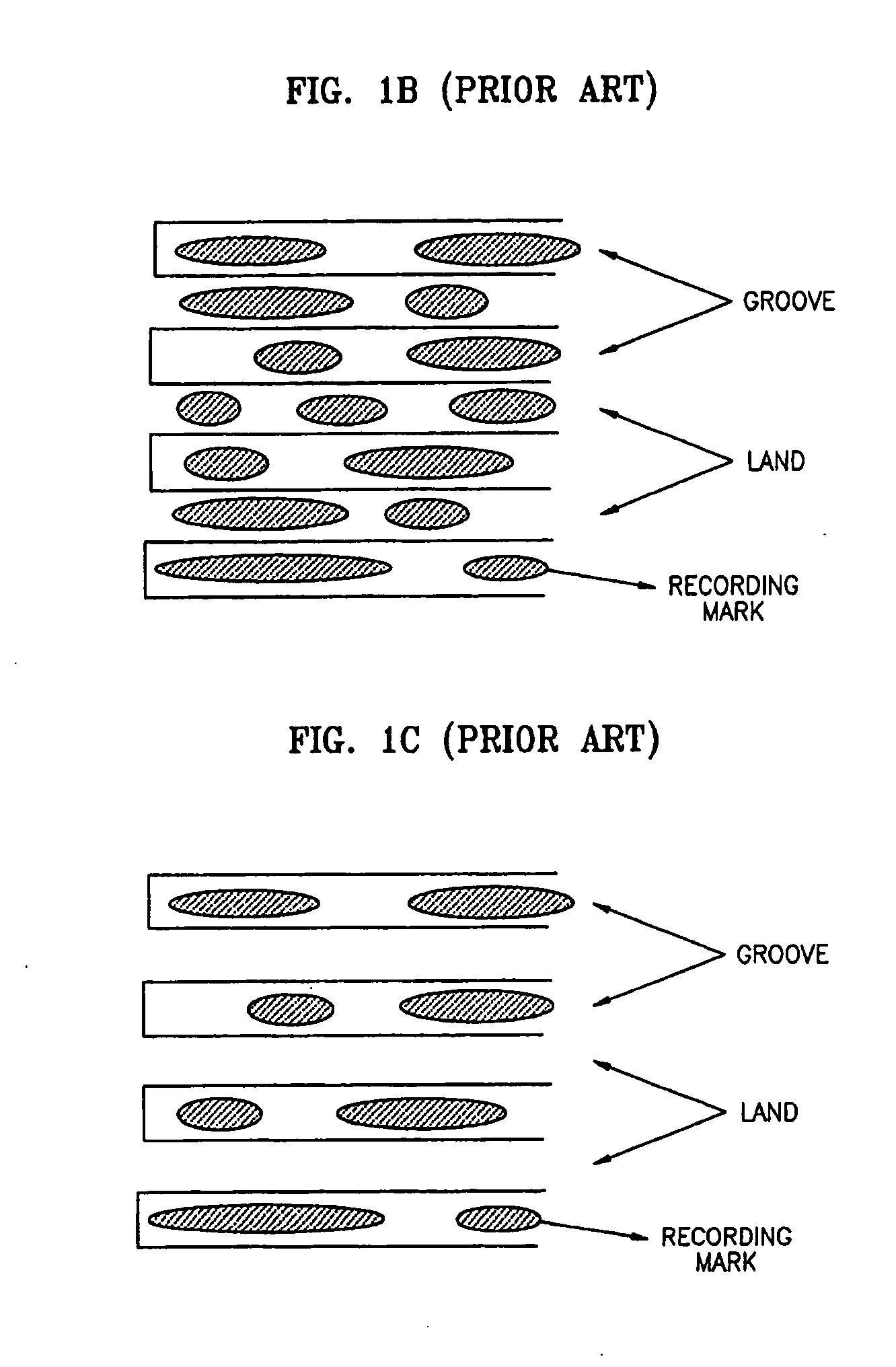
An optical information recording medium for recording information by a plurality of record mark lengths, wherein the shortest mark length is at most 0.5 μm, and a crystal state is an unrecorded or erased state and an amorphous state is a recorded state, wherein the erasing is carried out by recrystallization which substantially proceeds by crystal growth from an interface between the amorphous portion or a melt portion and a peripheral crystal portion; and an optical recording method suitable therefore. The medium of the present invention has characteristics that overwriting can be made at a high speed, the jitter of mark edge is small, mark length modulation recording can be made at a high density, and the formed mark is excellent in the stability with the lapse of time.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
Multilayer optical recording medium and recording method and apparatus for the same
A recording method of a multilayer recording medium includes a first initializing step of initializing a lower recording layer based on a first initializing condition and a second initializing step of initializing an upper recording layer on the basis of a second initializing condition different from the first initializing condition. The second initializing condition is determined so that a transmittance of the recording layer after execution of the second initializing step is approximately equal to a transmittance of the recording layer after a predetermined data signal is recorded on an upper recording layer.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Rewritable optical recording medium, recording method on the same, and optical disc recording/retrieving apparatus
InactiveUS20040190407A1Filamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesRecord statusRewritable compact disc
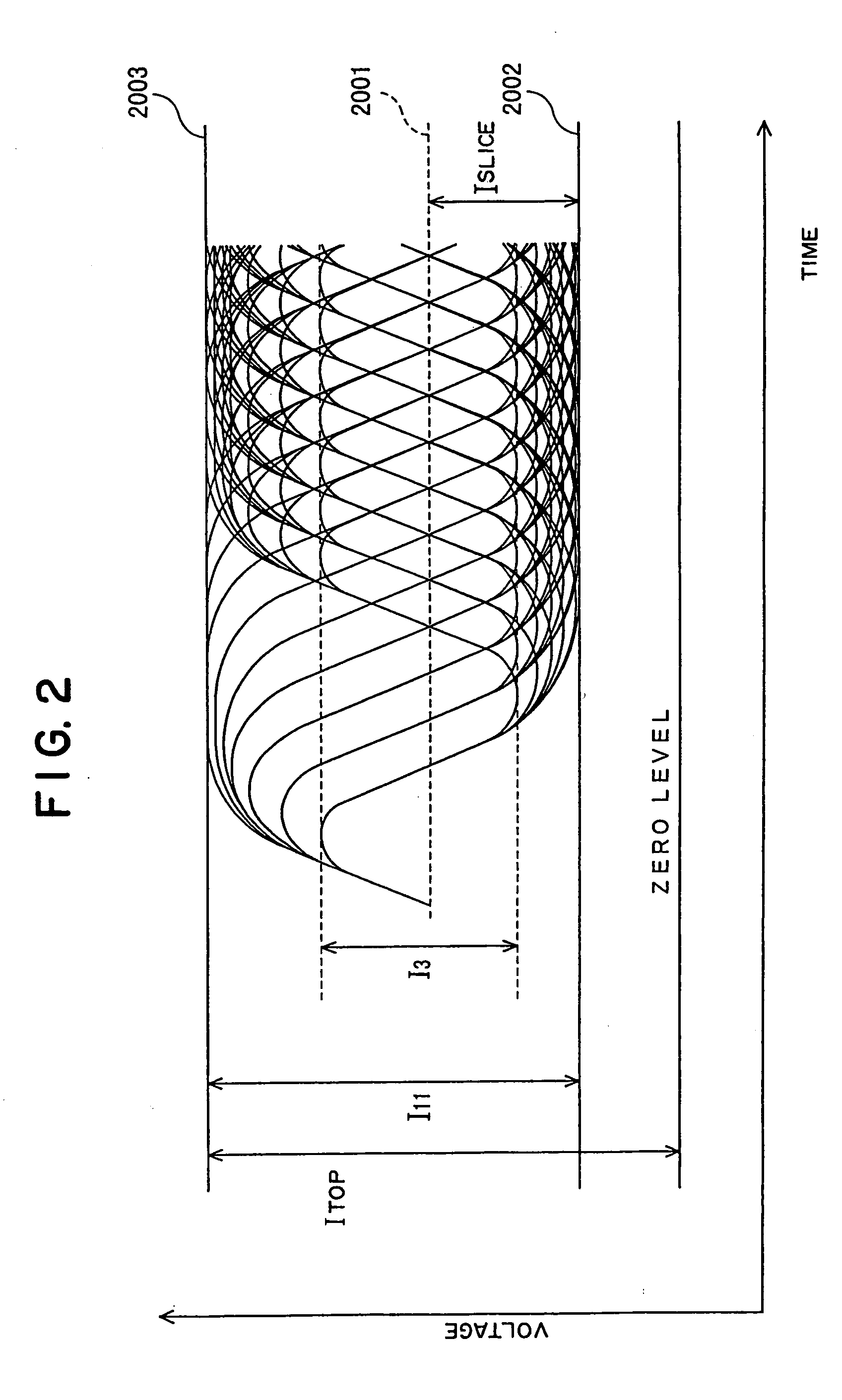
In a rewritable compact disc having a wobble groove on a substrate, crystal and amorphous states of a phase-change recording layer are an unrecorded / erased state and a recorded state, respectively. When the recording layer is exposed to recording light, amorphous marks assuming the recorded state are formed. At any of 2-, 4- and 8-times velocities with respect to a reference velocity (1-times velocity) whose linear velocity is 1.2-1.4 m / s, modulation m11 of a recorded signal when the recording light of approximately 780 nm in wavelength irradiates the recording layer via an optical system with NA=0.5 or 0.55 is 60-80%. A topmost level Rtop of reflectivity of the eye pattern of the recorded signal during retrieving at the 1-times velocity is 15-25%, and a jitter of the individual length of marks and inter-mark spaces during retrieving at 1-times velocity is 35 ns or less. Recording at 8-times or higher velocities is thereby realized without any risk of impairing the read-compatibility with the conventional CD-RW specifications at least at 4-times velocity.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
Optical information recording medium, producing method thereof and method of recording/erasing/reproducing information
InactiveUS20050089799A1Good weather resistanceImprove featuresRadiation applicationsOptical overwritingWeather resistanceOptoelectronics
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Heater and memory cell, memory device and recording head including the heater
InactiveUS20100103721A1NanoinformaticsOhmic-resistance heating detailsElectrical polarityEngineering
A heater includes at least two leads, and a heating element which is formed between the at least two leads, a material of the heating element being different from a material of the at least two leads such that a location of a hot spot in the heater is controllable based on a polarity of current in the heater.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Optical recording medium
InactiveUS6300039B1Required erasing timeImprove featuresRadiation applicationsLayered productsShortest distanceRecording layer
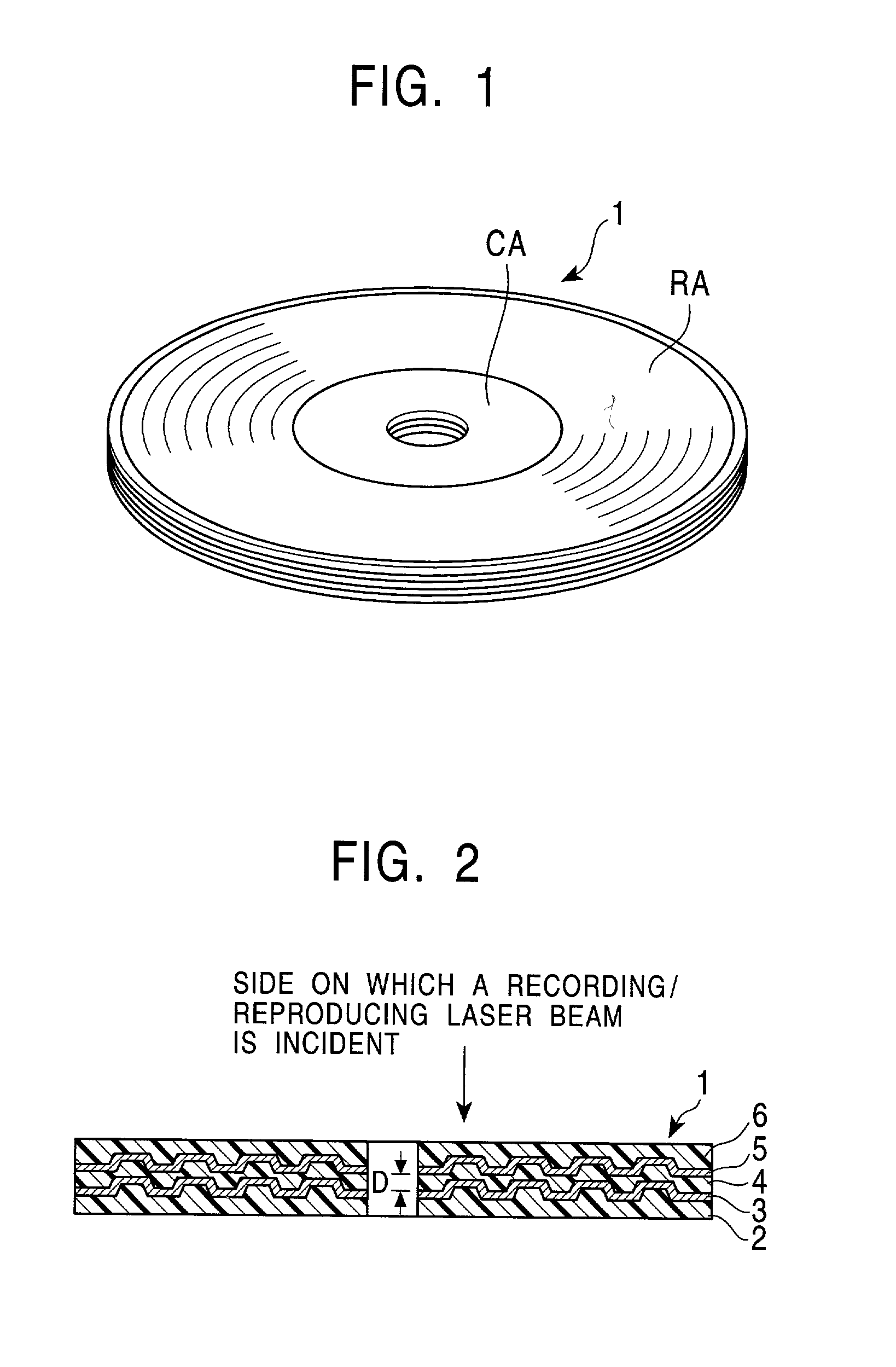
Phase-change type rewritable optical recording media, such as optical discs, optical cards, and optical tapes, where recorded data can be erased or overwritten and where data can be recorded with high speed and high density by applying a light beam can include an optical recording medium is one that includes a laminate member, which in various embodiments contains a transparent substrate, a first dielectric layer, a recording layer, a second dielectric layer, a light absorbing layer, and / or a reflecting layer. In various embodiments of the invention, the shortest distance between recorded marks in the recording direction along the track is less than lambd / NA, with lambd and NA denoting the wavelength of the light used and the numerical aperture of the objective lens of the optical head, respectively.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
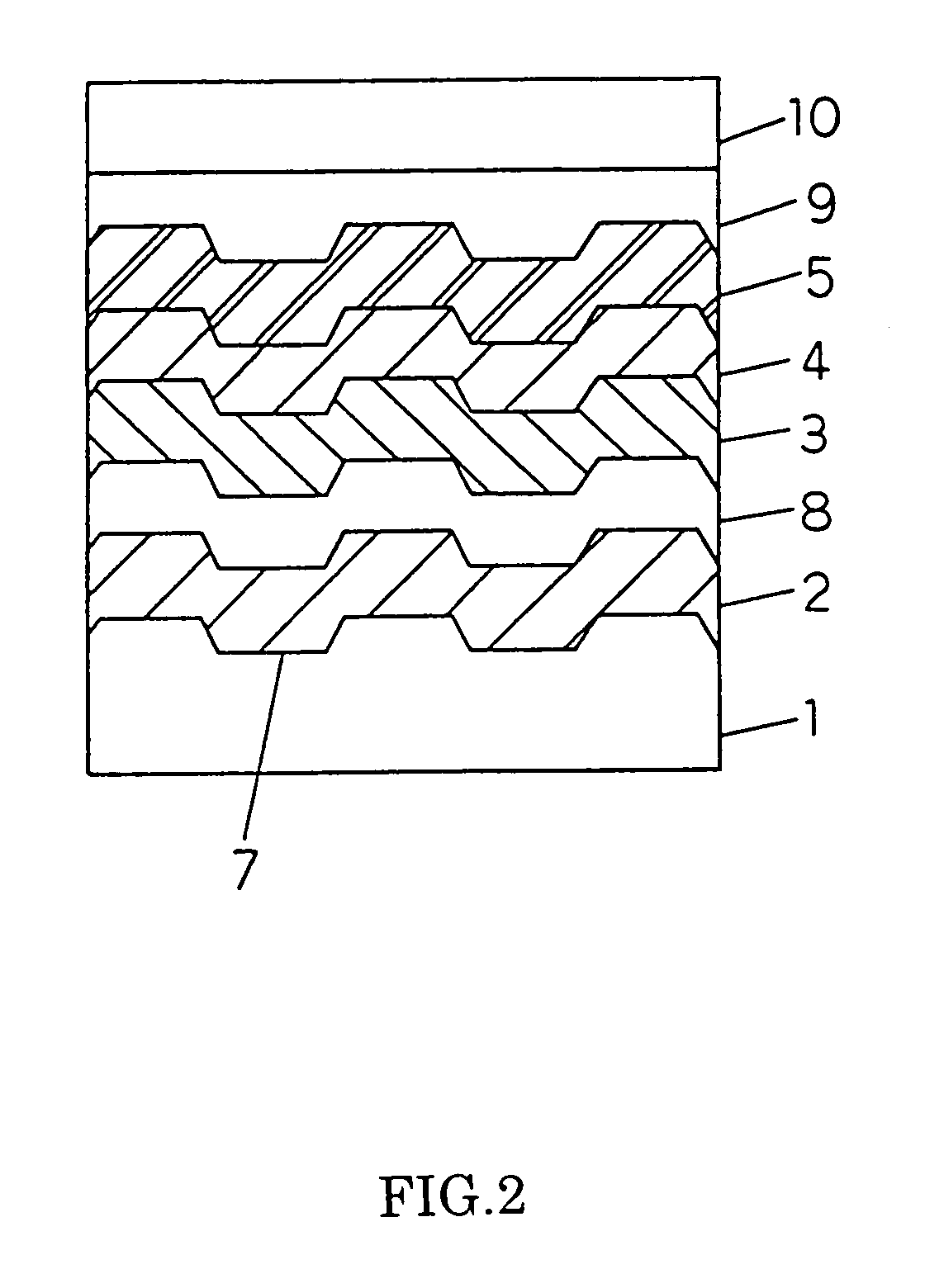
Optical recording medium
There is provided an optical recording medium capable of preventing cross erase and increasing its recording density. The optical recording medium includes: a reflecting film; a first transparent film provided on the reflecting film; a first semitransparent film provided on the first transparent film; a second transparent film provided on the first semitransparent film; a recording film provided on the second transparent film, the recording film being capable of reversibly changing an atomic arrangement; and a third transparent film provided on the recording film. The first semitransparent film has a complex refractive index of n-k satisfying relationships of 0<n<1 and 1<k, and a product of a thickness d (nm) of the first semitransparent film and an extinction coefficient k of the complex refractive index is dxk<=44.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical information recording medium, producing method thereof and method of recording/erasing/reproducing information
InactiveUS7037413B1Improve cycle performanceImprove performanceRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingWeather resistanceRecording layer
The present invention provides an optical information medium having excellent weather resistance and repeating characteristics. The optical information medium has a barrier layer between a protective layer and a recording layer. The barrier layer includes GeN or GeON, and at least one element selected from the group consisting of Al, B, Ba, Bi, C, Ca, Ce, Cr, Dy, Eu, Ga, H, In, K, La, Mn, N, Nb, Ni, Pb, Pd, S, Si, Sb, Sn, Ta, Te, Ti, V, W, Yb, Zn and Zr.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical recording medium
There is provided an optical recording medium capable of preventing cross erase and increasing its recording density. The optical recording medium includes: a reflecting film; a first transparent film provided on the reflecting film; a first semitransparent film provided on the first transparent film; a second transparent film provided on the first semitransparent film; a recording film provided on the second transparent film, the recording film being capable of reversibly changing an atomic arrangement; and a third transparent film provided on the recording film. The first semitransparent film has a complex refractive index of n-k satisfying relationships of 0<n<1 and 1<k, and a product of a thickness d (nm) of the first semitransparent film and an extinction coefficient k of the complex refractive index is dxk<=44.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for recording and reproducing signal on and from optical information recording medium
InactiveUS7729218B2Accurate decisionFilamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesSignal onEngineering
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP
Optical information recording medium, and manufacturing method, recording method, and recording apparatus thereof
InactiveUS7431973B2Good recording and reproduction characteristicHigh densityLayered productsOptical beam sourcesPhysical chemistryThin membrane
A recording medium has at least a recording layer on a transparent substrate. The recording layer has at least a first phase-changeable film and a second phase-changeable film in that order, starting on the side closest to the transparent substrate. The first phase-changeable film and the second phase-changeable film each contains at least 10 atom % and no more than 50 atom % germanium and at least 45 atom % and no more than 60 atom % tellurium. Also at least one of the phase-changeable films contains bismuth.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical recording/ reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20050185546A1Little calculation errorPrevent deterioration of overwriting characteristicTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersDriving currentControl signal
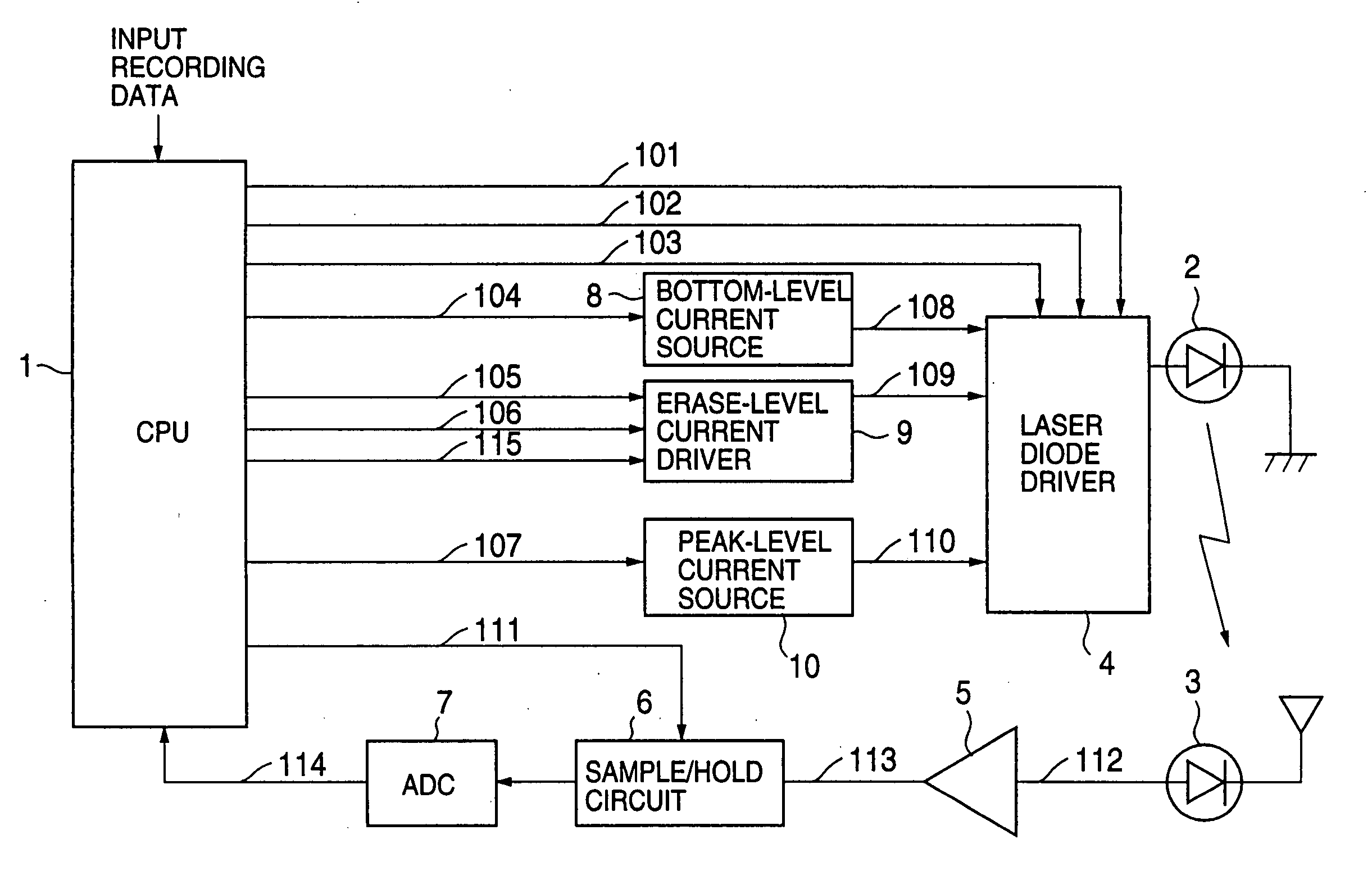
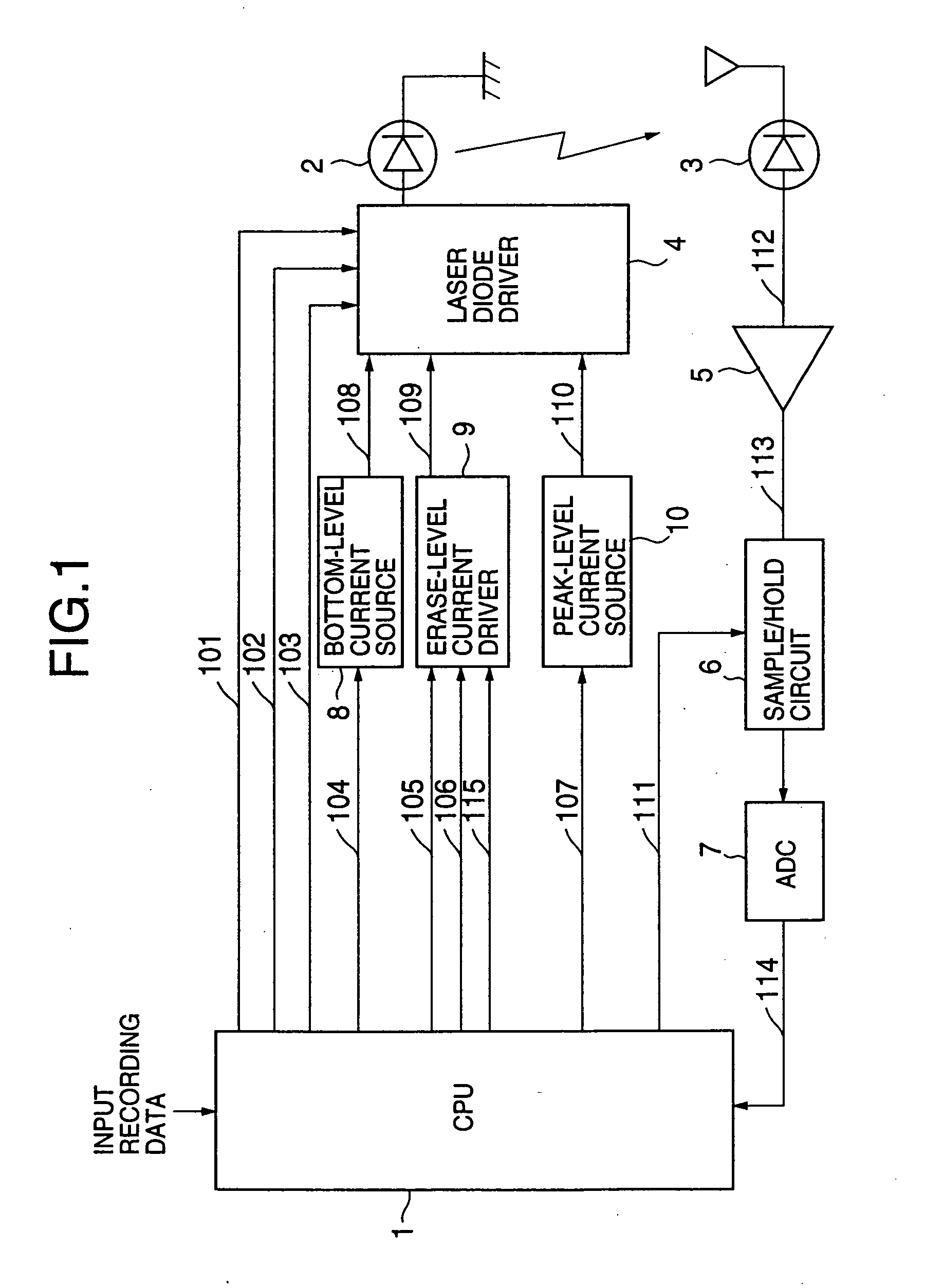
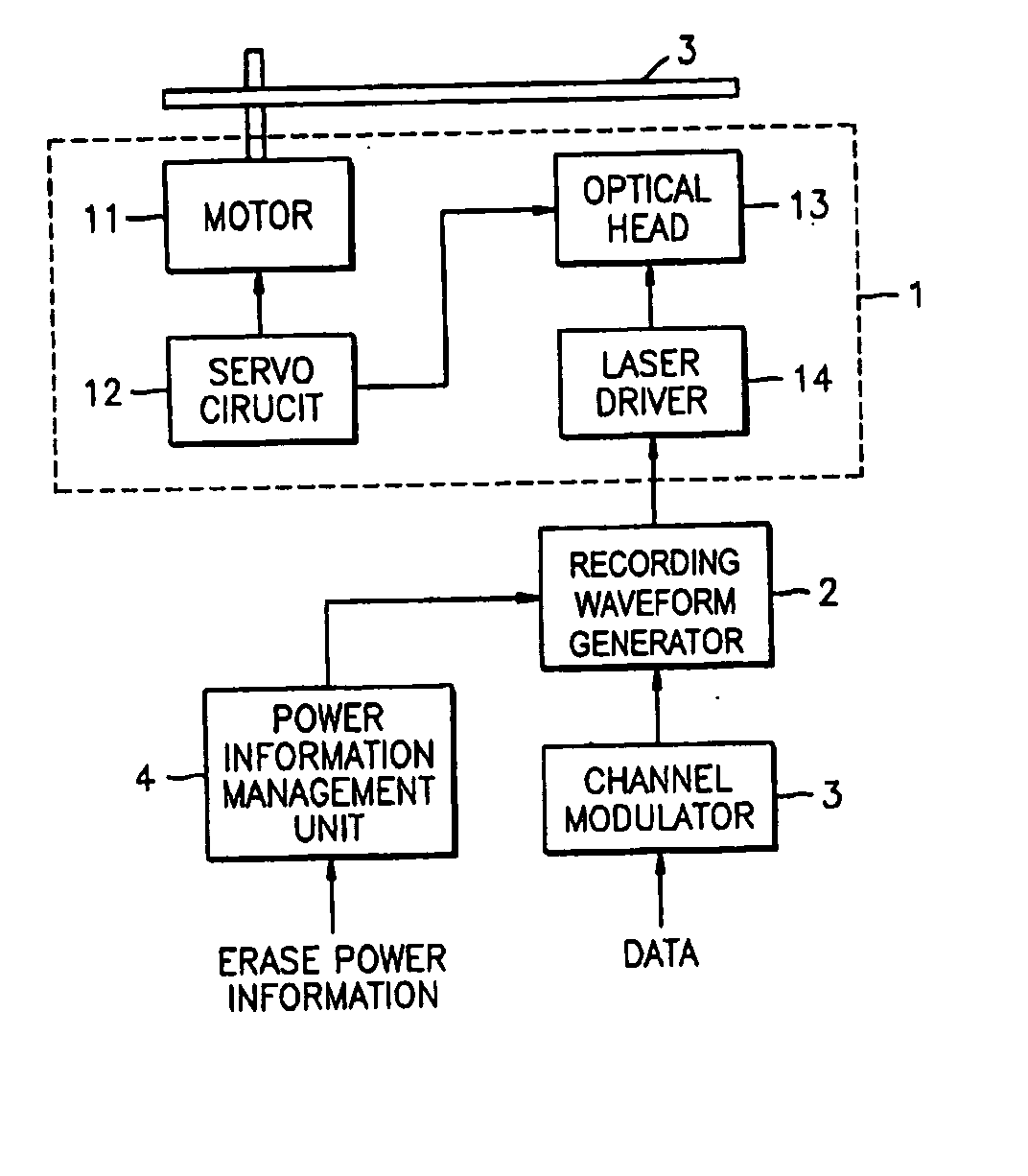
In an optical recording / reproducing apparatus of the present invention, a semiconductor laser driver supplies a selected one of a plurality of drive currents, including at least a first-level drive current and a second-level drive current, to a semiconductor laser to control the emission of a laser beam by the laser. A current driver selectively outputs one of a plurality of increment currents to the laser driver in response to control signals, the plurality of increment currents including a first increment current supplied to the laser driver during an automatic power control process and a second increment current supplied to the laser driver during a special power setting process. A detection unit detects a first power sample signal, at a first sampling point of a laser driving current waveform, from the laser beam emitted when the first increment current is supplied to the laser driver, and detects a second power sample signal, at a second sampling point of the waveform, from the laser beam emitted when the second increment current is supplied to the laser driver. A calculation unit calculates a derivative efficiency of the laser based on the first and second power sample signals detected by the detection unit, so that the drive currents of the laser driver, supplied to the laser, are controlled based on the calculated derivative efficiency.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method and apparatus for recording and reproducing signal on and from optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20070070846A1Accurate decisionFilamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesSignal onEngineering
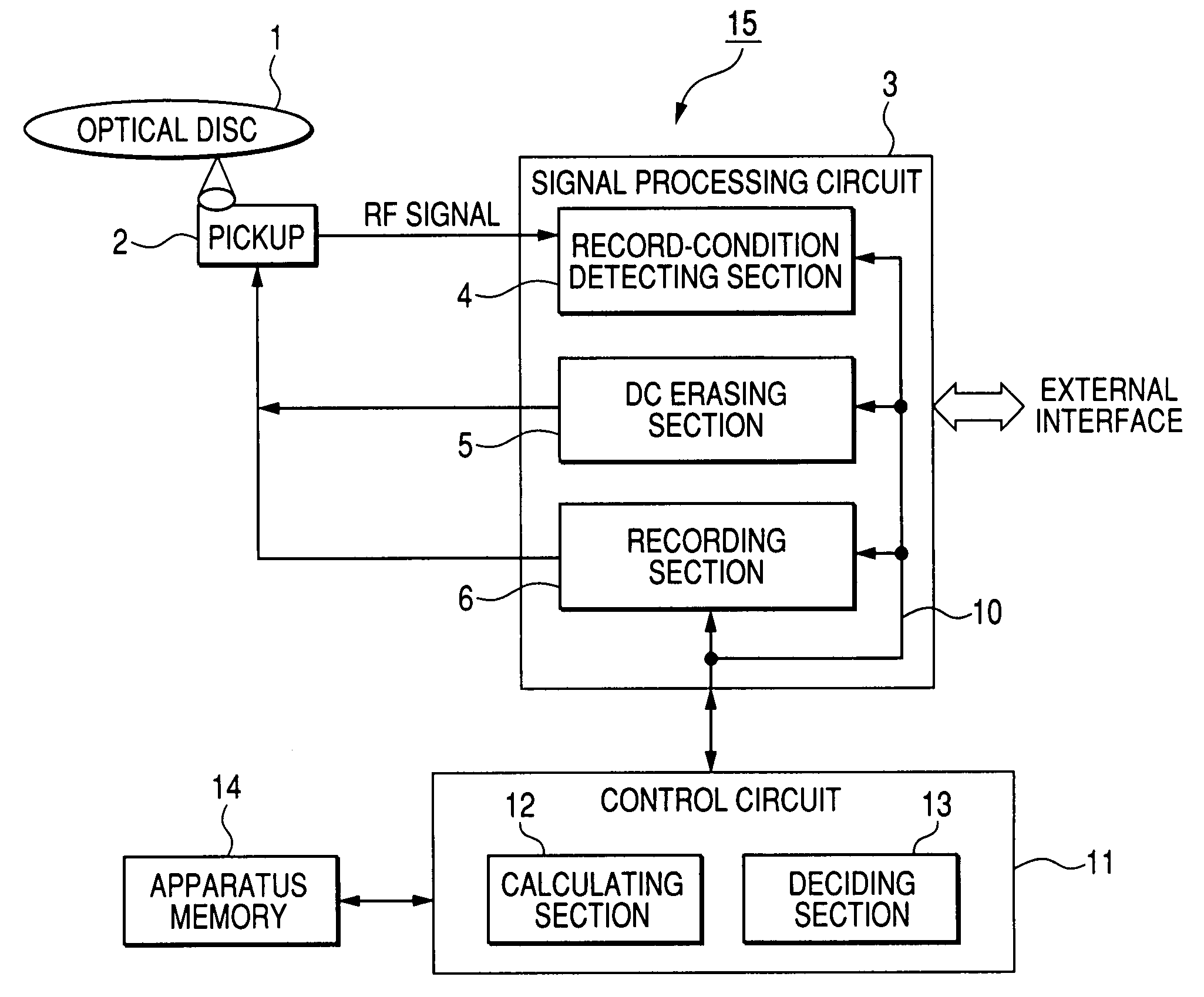
Test signals are recorded on a prescribed area in an optical disc. The prescribed area is scanned by a laser beam while the power of the laser beam is changed among different DC erasing values. The different DC erasing values are assigned to the recorded test signals, respectively. The recorded test signals are reproduced from the prescribed area to obtain reproduced signals. Parameter values of the respective reproduced signals are detected. The detected parameter values correspond to the different DC erasing values, respectively. Among the detected parameter values, a detected parameter value is decided which matches a target. One corresponding to the decided parameter value is selected from the different DC erasing values. A prescribed coefficient and the selected DC erasing value are multiplied to calculate an optimum level of an erasing power of the laser beam.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Multilayer optical disk and method of initializing the same
InactiveUS20020018428A1Reduce variationQuantity minimizationMechanical record carriersRecord information storageInter layerLight beam
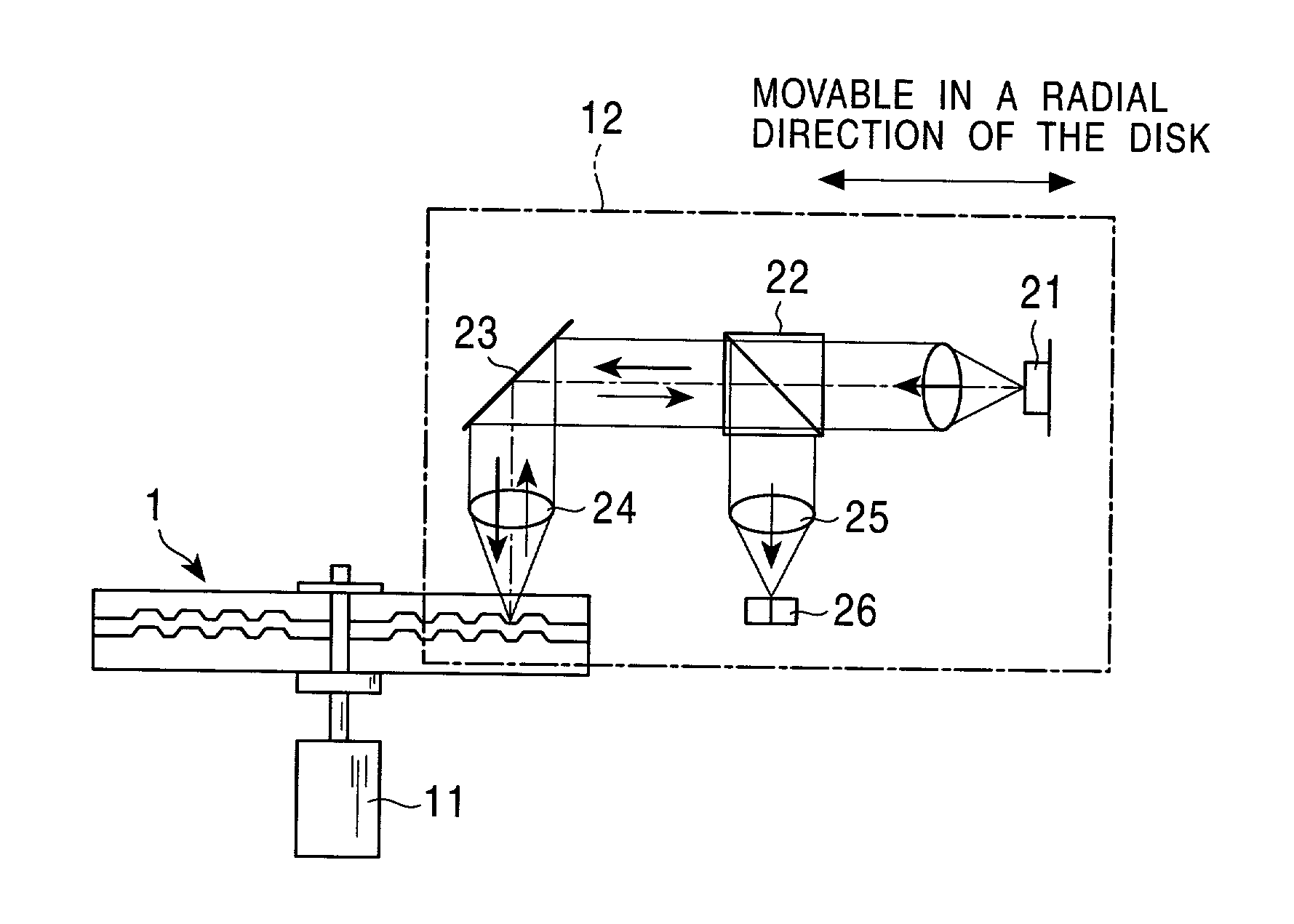
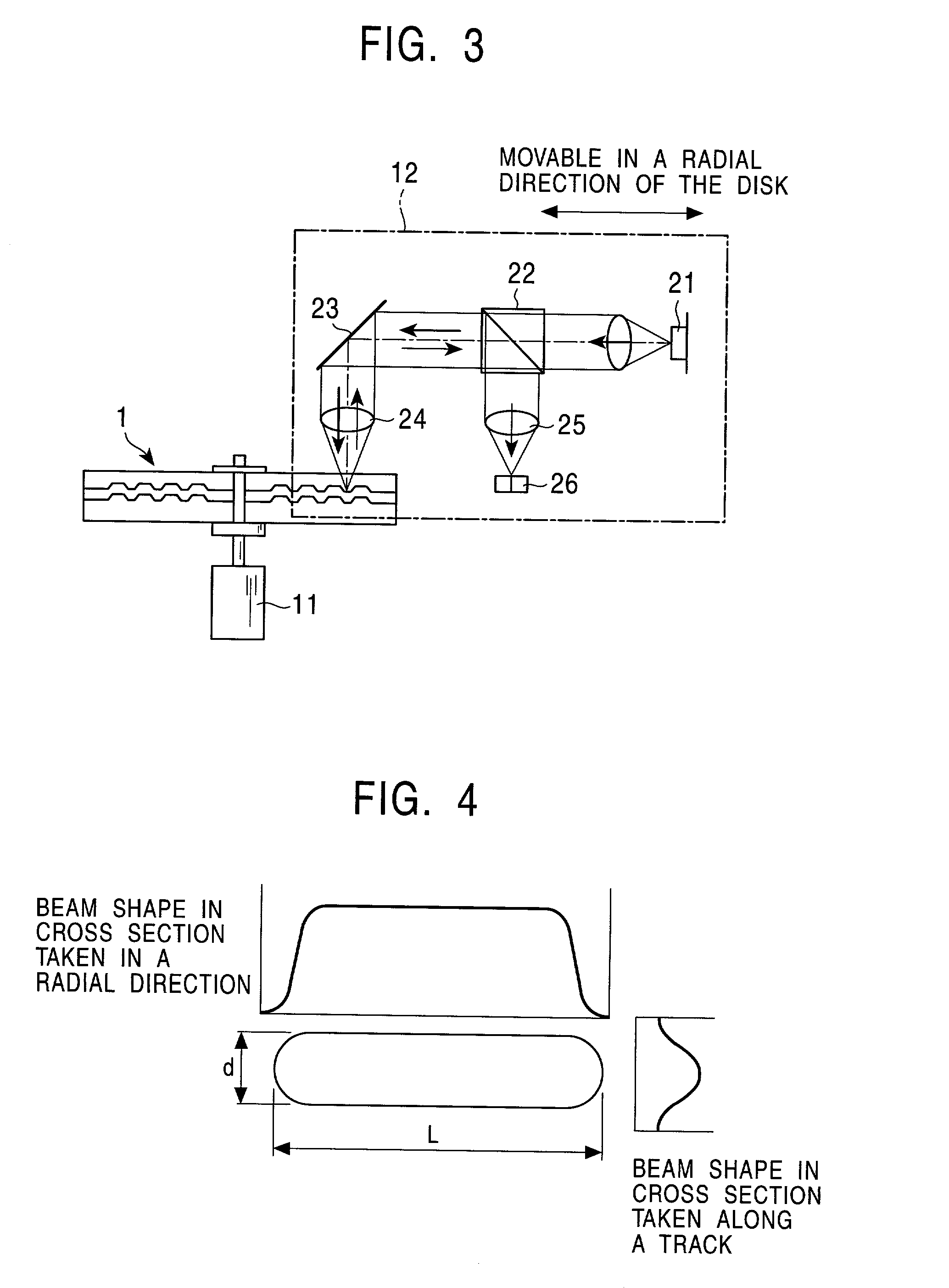
Initialization nonuniformity due to interference of light which occurs during an initialization process is reduced without causing degradation in the characteristic of signals recorded / reproduced on / from respective recording layers. A multilayer optical disk comprising at least a first information recording layer and a second information recording layer formed, on a substrate, into a multilayer structure with an intermediate layer disposed therebetween is illuminated with initializing light from the side of the first information recording layer to initialize the first information recording layer formed of a phase-change material serving as a recording material. The illumination with the initializing light is performed such that the numerical aperture NA of an objective lens used for illumination with the illuminating light, the longitudinal length L of the beam size of the initializing light, the thickness D of the intermediate layer, and the ratio R1 of the amount of light striking the first information recording layer after passing through the first information recording layer and being reflected by the second information recording layer to the amount of light incident on the first information recording layer satisfy the following relation for a wavelength lambdi of the initializing light: LxR1<=25[1-exp(-0.0004xNA4xD2)].
Owner:SONY CORP
Phase change optical information recording medium
InactiveUS6956810B2Easy to controlImprove protectionCarrier editingFilamentary/web record carriersRecording layerPhase change
A phase change optical information recording medium including: a substrate; and a recording layer which is located overlying the substrate and in which marks are to be formed to store information, wherein the substrate includes plural sessions including a first session in which pits are formed and which includes a RAM region including a groove and a wobble signal, and a program memory area in which pits are formed and which includes position information of the first session and does not include disc ID information of the phase change optical information recording medium.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical disk apparatus and method for recording data by utilizing an overwrite technique or a two-path write technique
InactiveUS6888781B2Error rateExcellent characteristicsRecording verificationOptical beam sourcesClock rateData access
There are provided an optical disk, a magneto-optical disk, a disk apparatus therefor, and a data recording method which can provide improved recording / reproducing characteristics and record durability without linear velocity dependency even if the data access speed is increased by increasing the channel clock frequency. In a disk device for recording data on an optical disk by using a phase change recording scheme, erasing means for erasing data on the optical disk, and recording means for recording other data on the optical disk after the data is erased are provided.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information Recording Medium
InactiveUS20070206463A1Know informationTimely controlInformation arrangementFilamentary/web record carriersOptical propertyLaser beams
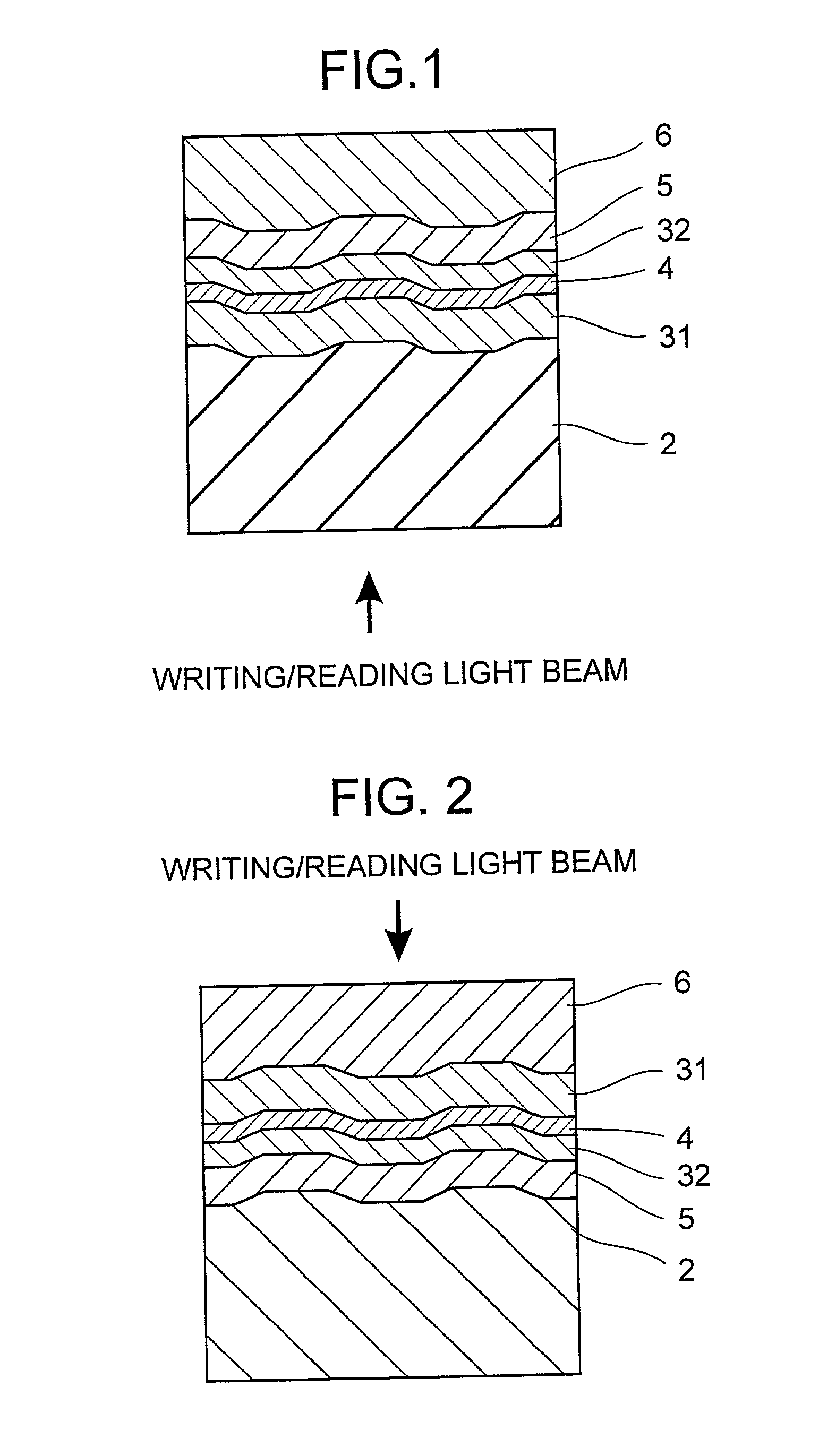
An information recoding medium having a substrate (32) and a recoding layer (30) whose optical property is changed by being irradiated by a laser beam to display or erase a visible display pattern.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Phase-change optical information recording medium and information recording and reading method using the recording medium
InactiveUS20050007938A1High-density recordingHigh refractive indexRecord carriersInformation arrangementAmorphous phaseLength wave
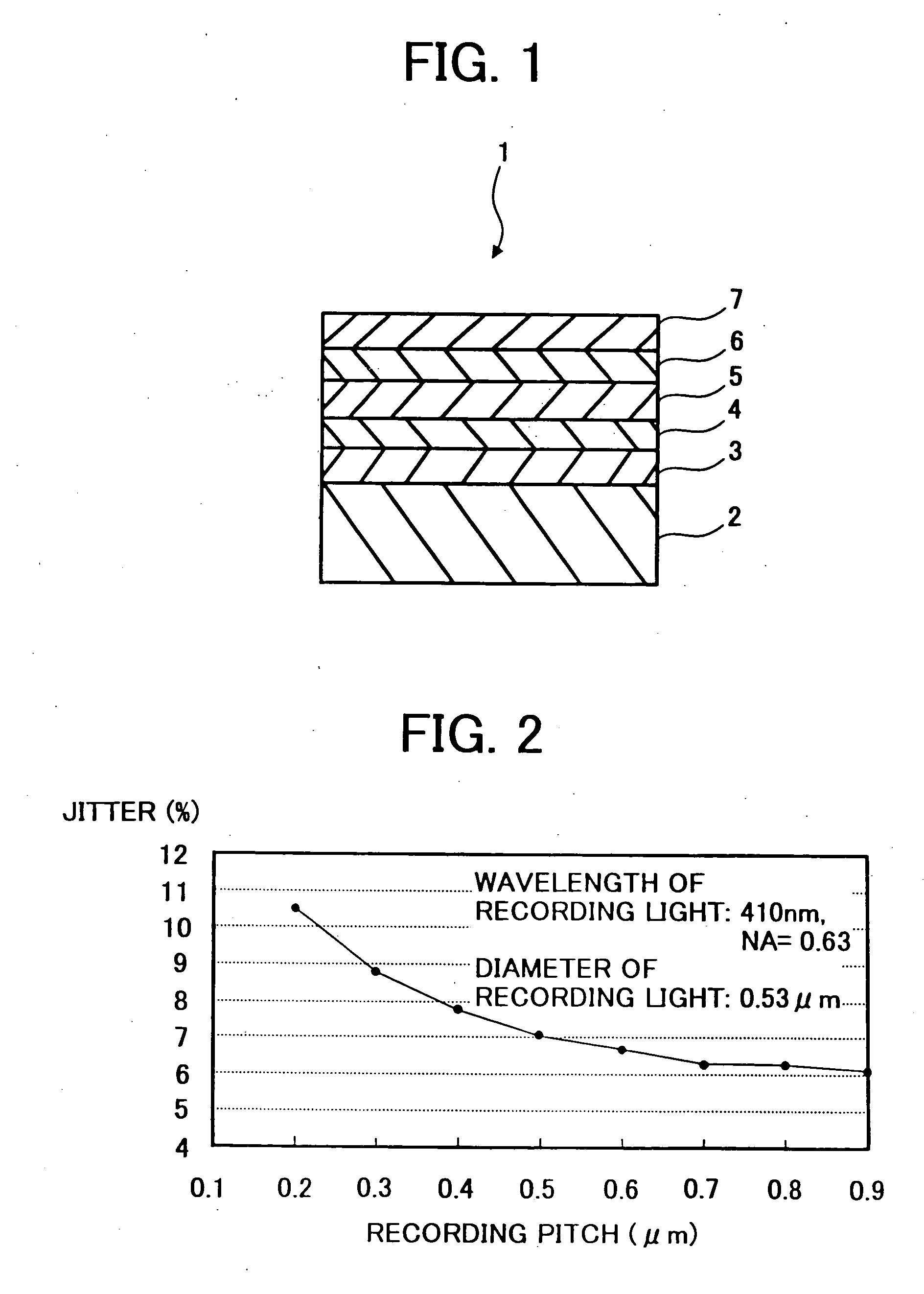
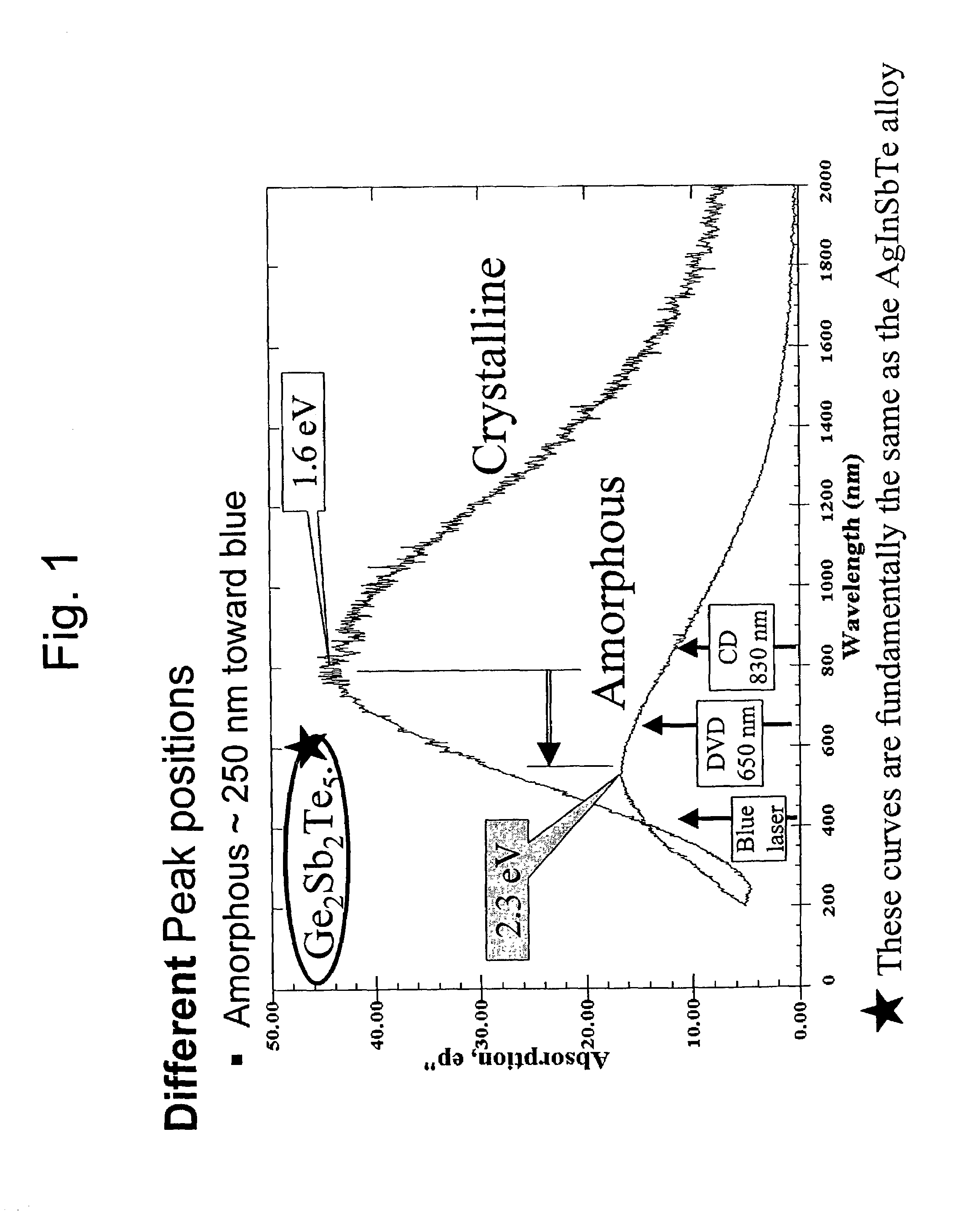
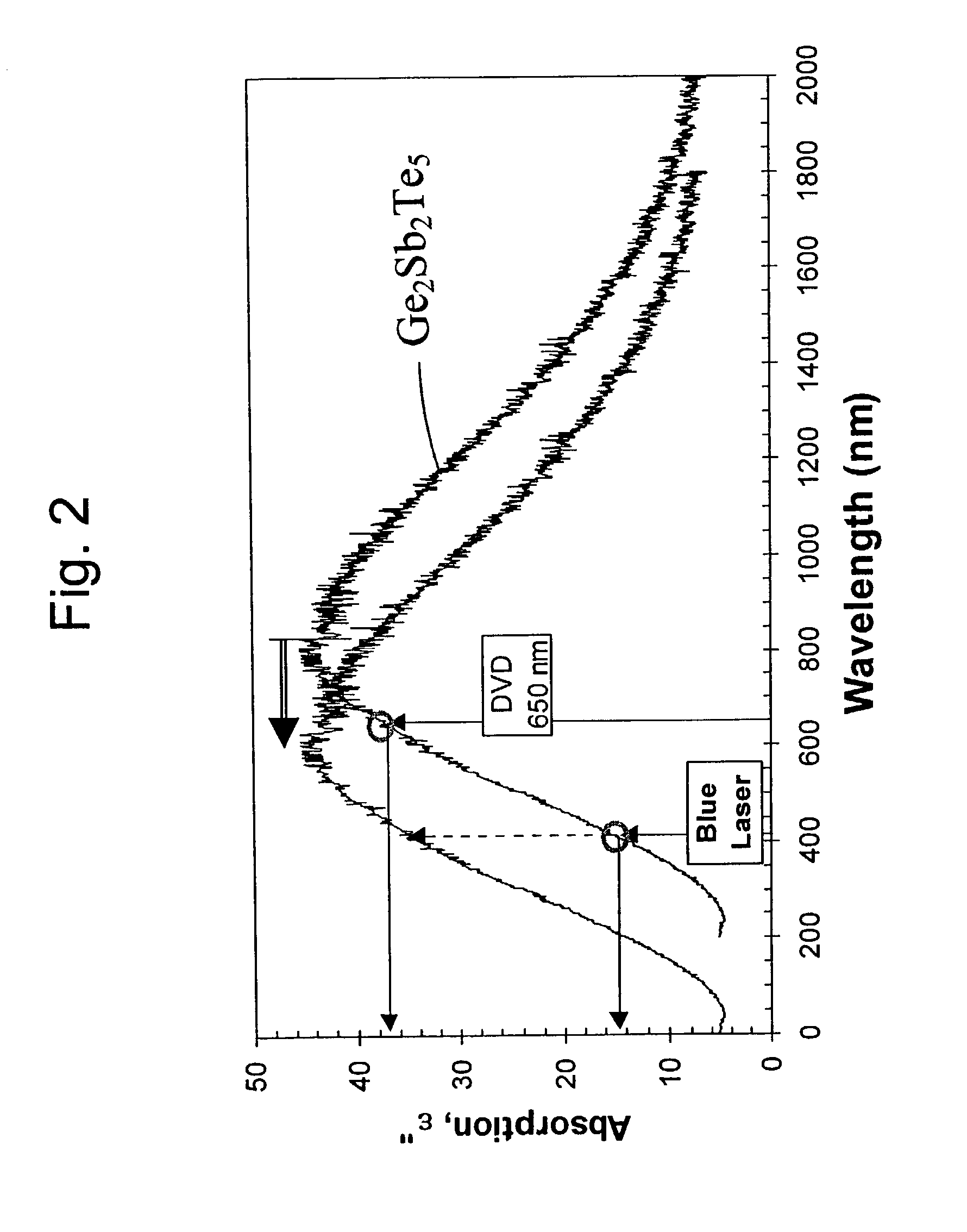
A phase-change optical information recording medium in which information can be recorded, erased, and read includes a substrate and a recording layer overlying the substrate. The recording layer achieves a crystal phase and an amorphous phase. The absorptance Ac of the recording layer in the crystal phase against light having a wavelength of from 370 nm to 450 nm is lower than the absorptance Aa of the recording layer in the amorphous phase against the light. Information is recorded on the recording medium with a recording wavelength of from 370 nm to 450 nm at a recording pitch of 0.3 μm to 0.52 μm.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical information recording medium, and manufacturing method, recording method, and recording apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20050202203A1Easy to recordGood reproduction characteristicLayered productsOptical beam sourcesTe elementRecording layer
A recording medium is provided that has at least a recording layer on a transparent substrate. The recording layer has at least a first phase-changeable film and a second phase-changeable film in that order, starting on the side closest to the transparent substrate. The first phase-changeable film and the second phase-changeable film each contains at least 10 atom % and no more than 50 atom % germanium and at least 45 atom % and no more than 60 atom % tellurium. Also at least one of the phase-changeable films contains bismuth.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical information recording medium and optical recording method
InactiveUS20050175808A1Reduce jitterTelevision system detailsLayered productsRecord statusHigh density
An optical information recording medium for recording information by a plurality of record mark lengths, wherein the shortest mark length is at most 0.5 μm, and a crystal state is an unrecorded or erased state and an amorphous state is a recorded state, wherein the erasing is carried out by recrystallization which substantially proceeds by crystal growth from an interface between the amorphous portion or a melt portion and a peripheral crystal portion; and an optical recording method suitable therefore. The medium of the present invention has characteristics that overwriting can be made at a high speed, the jitter of mark edge is small, mark length modulation recording can be made at a high density, and the formed mark is excellent in the stability with the lapse of time.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for recording data on optical recording medium
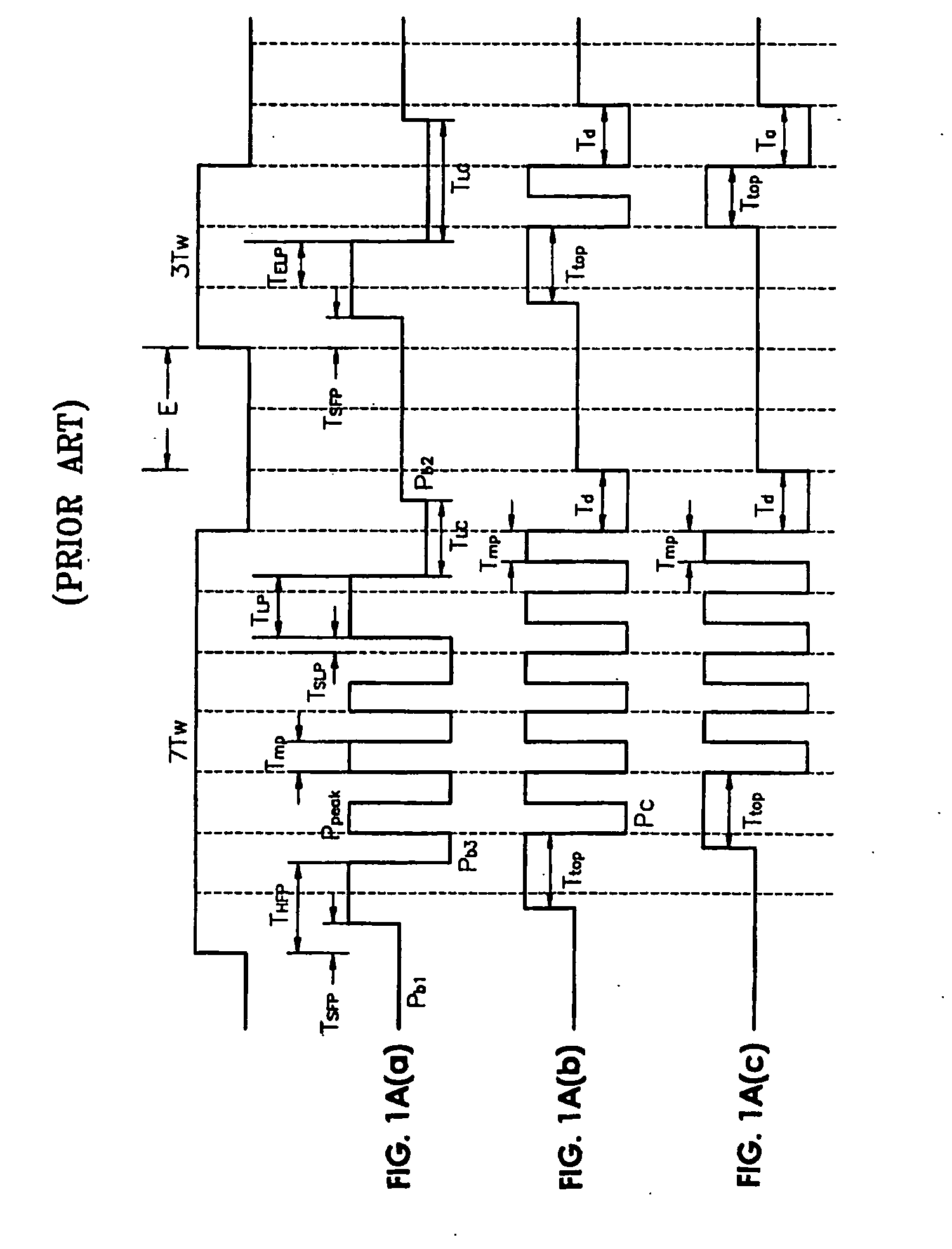
InactiveUS20060245328A1Prevent degradationPreventing leading and trailing edges of a mark from being distortedCombination recordingRecording strategiesOptical recordingComputer science
A method and apparatus to record data on an optical recording medium include generating a recording waveform having an erase pattern comprising a multi-pulse having a high level which is higher than an erase power level and a low level which is lower than the erase power level. A power level of a leading one of the multi-pulse of the erase pattern and a power level between an end of the erase pattern and a start point of a leading pulse of a recording pattern are controlled to be the low level and the high level, respectively, the high level and the high level, respectively, the high level and the low level, respectively, or the low level and the low level, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Heater and memory cell, memory device and recording head including the heater
A heater includes at least two leads, and a heating element which is formed between the at least two leads, a material of the heating element being different from a material of the at least two leads such that a location of a hot spot in the heater is controllable based on a polarity of current in the heater.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Information recording method and apparatus with suppressed mark edge jitters
InactiveUS20050088943A1High densityHigh-density recordingTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersElectric forcePower modulation
A method for recording information is disclosed in which an information recording medium is irradiated with a recording energy beam power-modulated into at least a record power level and a record-ready power level lower than the record power level. When forming a mark portion of a predetermined length, the radiation energy of the energy beam is increased as compared with when forming a mark portion of a different length before or after the first pulse of an energy beam pulse train including at least a pulse for forming the mark portion. Also, only in the case where the energy beam is modulated by the power lower in power level than the record-ready power level after the last pulse of the energy beam pulse train including at least one pulse for forming a mark portion and the mark portion is followed by a space portion of a predetermined length, the particular radiation energy of low power level is reduced as compared with when the mark portion is followed by a space potion of a different length. The radiation energy is increased and / or decreased.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Apparatus and method for recording data in optical recording medium
InactiveUS20050174912A1Improve recording qualityReduce manufacturing costTelevision system detailsOptical beam sourcesAmplitude controlData recording
An optical data recording method for recording data in a phase-change optical recording medium using a sequence of one or more short pulses is provided. In this method, a temperature is detected at a prescribed spot around the optical recording medium. The amplitude of the short pulses is controlled in response to the detected temperature. Then, data are recorded in the optical recording medium using the sequence of amplitude-controlled short pulses.
Owner:RICOH KK
Increased data storage in optical data storage and retrieval systems using blue lasers and/or plasmon lenses
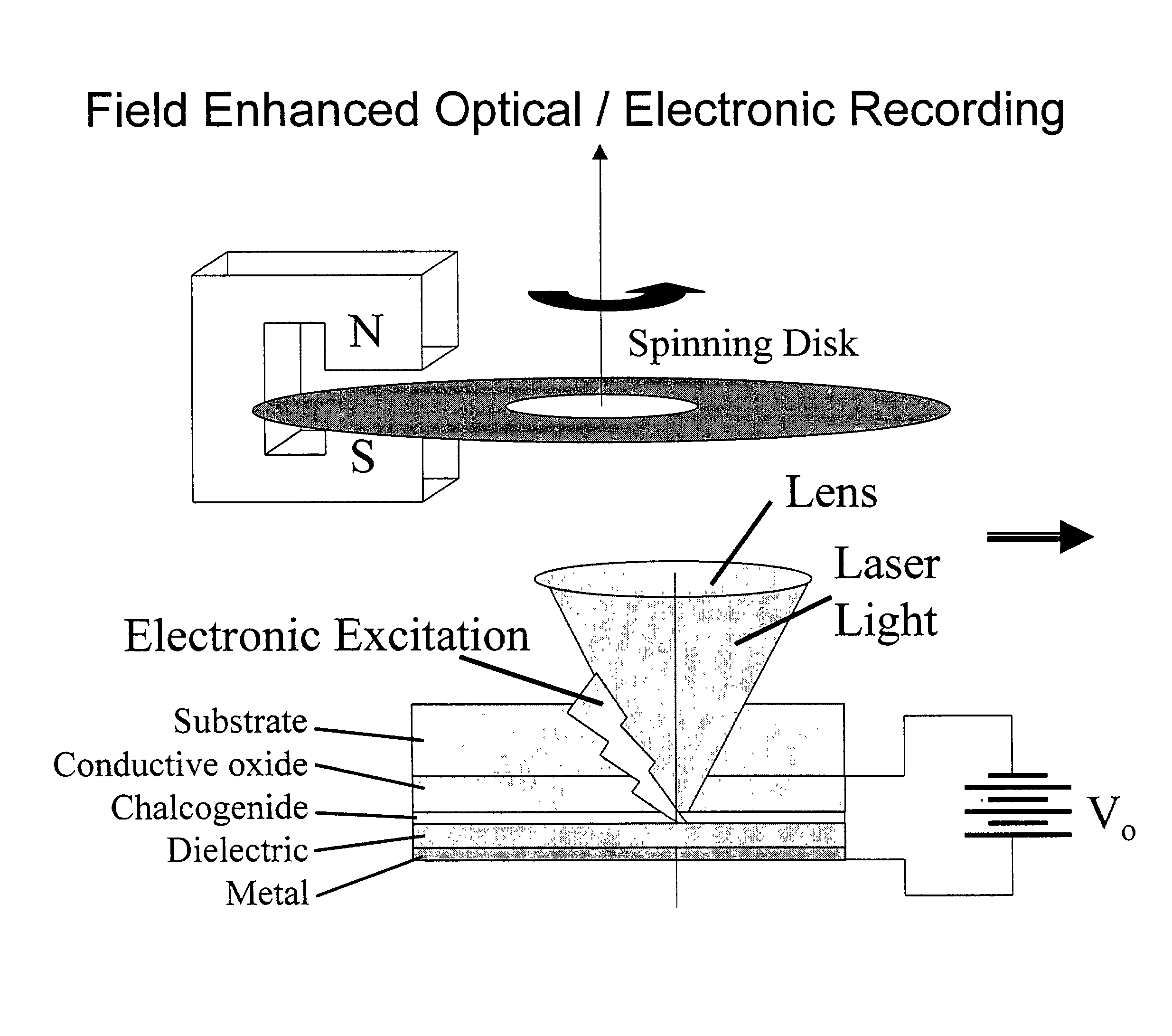
InactiveUS7113474B2Improve recordImprove erase efficiencyRecording by optical meansNanoinformaticsPhase-change memoryPlasmonic coupling
An optical recording medium includes a crystallizing layer for enhancing the crystallization of a phase change memory layer, an energy storage layer for aiding the state transformations of a phase change memory layer, and / or a modifying element for increasing absorption and contrast at short wavelengths. An optical data storage and retrieval system containing same. Also a light-plasmon coupling lens including an optically transparent substrate having a light incident surface and a light-plasmon coupling surface opposite the light incident surface. The light-plasmon coupling surface including at least a set of circular concentric peaks / valleys which form a Fourier sinusoidal pattern in the radial direction of the circular concentric peaks / valleys. A conformal layer of metal is deposited on the light-plasmon coupling surface of the substrate and has aperture at the center of thereof through which plasmons are transmitted.
Owner:OPTICAL MEMORY STORAGE
Optical data recording and reproducing apparatus and method and optical storage medium
InactiveCN1140897COptical beam sourcesAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsLight beamOptical storage
A first laser beam and a second laser beam are selectively generated. The first or the second laser beam is irradiated on an optical storage medium having a recording layer on which main data has been recorded. The main data includes data to be reproduced and reproduction management data. The laser beam selection is made according to the reproduction management data. The first laser beam has a first laser power capable of carrying the main data without erasing when reflected from the optical storage medium. On the other hand, the second laser beam has a second laser power capable of erasing the main data from the optical storage medium while carrying the main data when reflected from the optical storage medium. The data to be reproduced and carried by the first or the second laser beam is then reproduced.
Owner:VICTOR CO OF JAPAN LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com