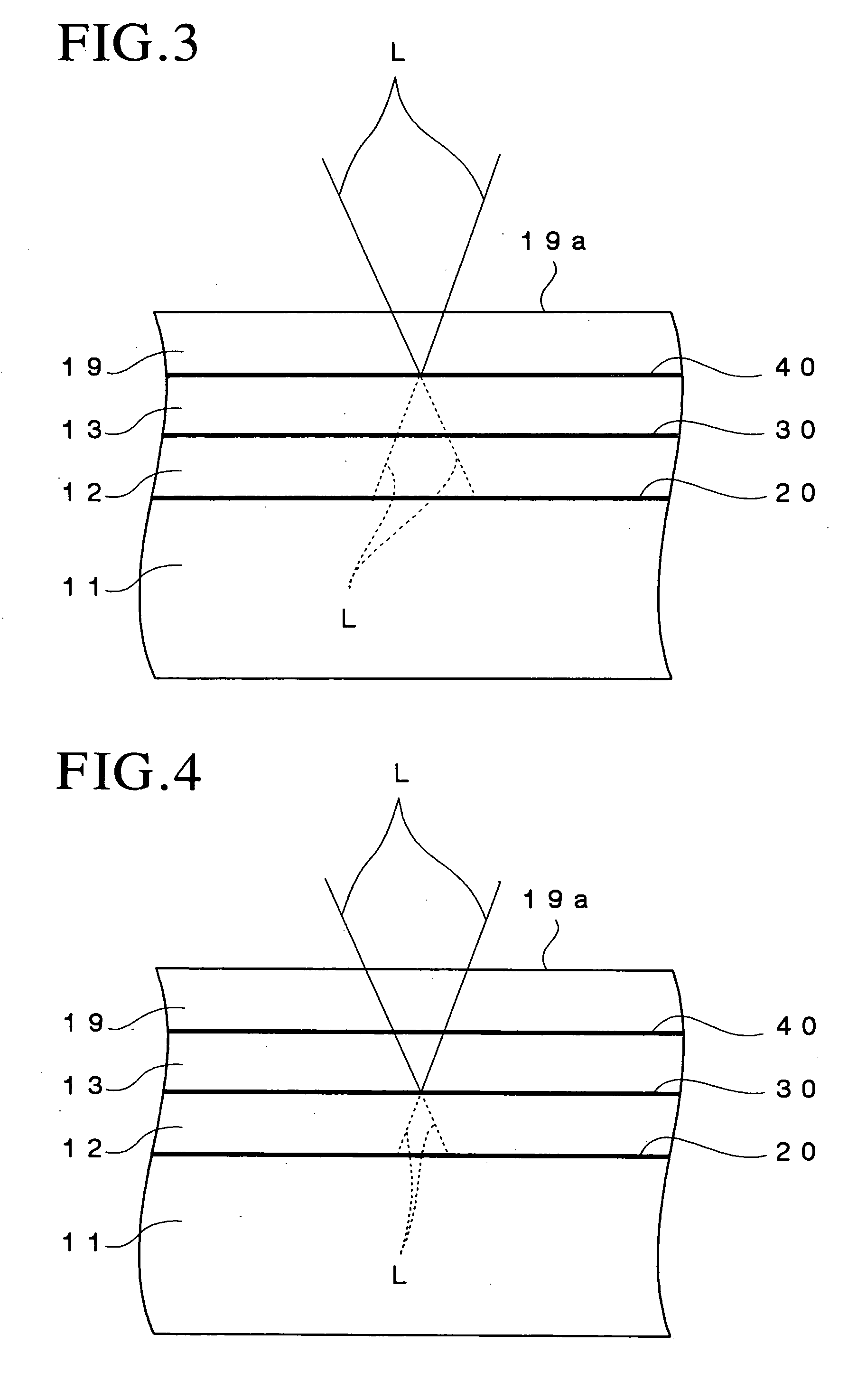
Patents
Literature
3668results about "Optical record carrier manufacture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical disk, optical disk recording and reproducing apparatus, method for recording, reproducing and deleting data on optical disk, and information processing system
InactiveUS6938162B1Prevent unjust digital copyingImprove reliabilityAccessories for auxillary signalsAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useInformation processingHandling system
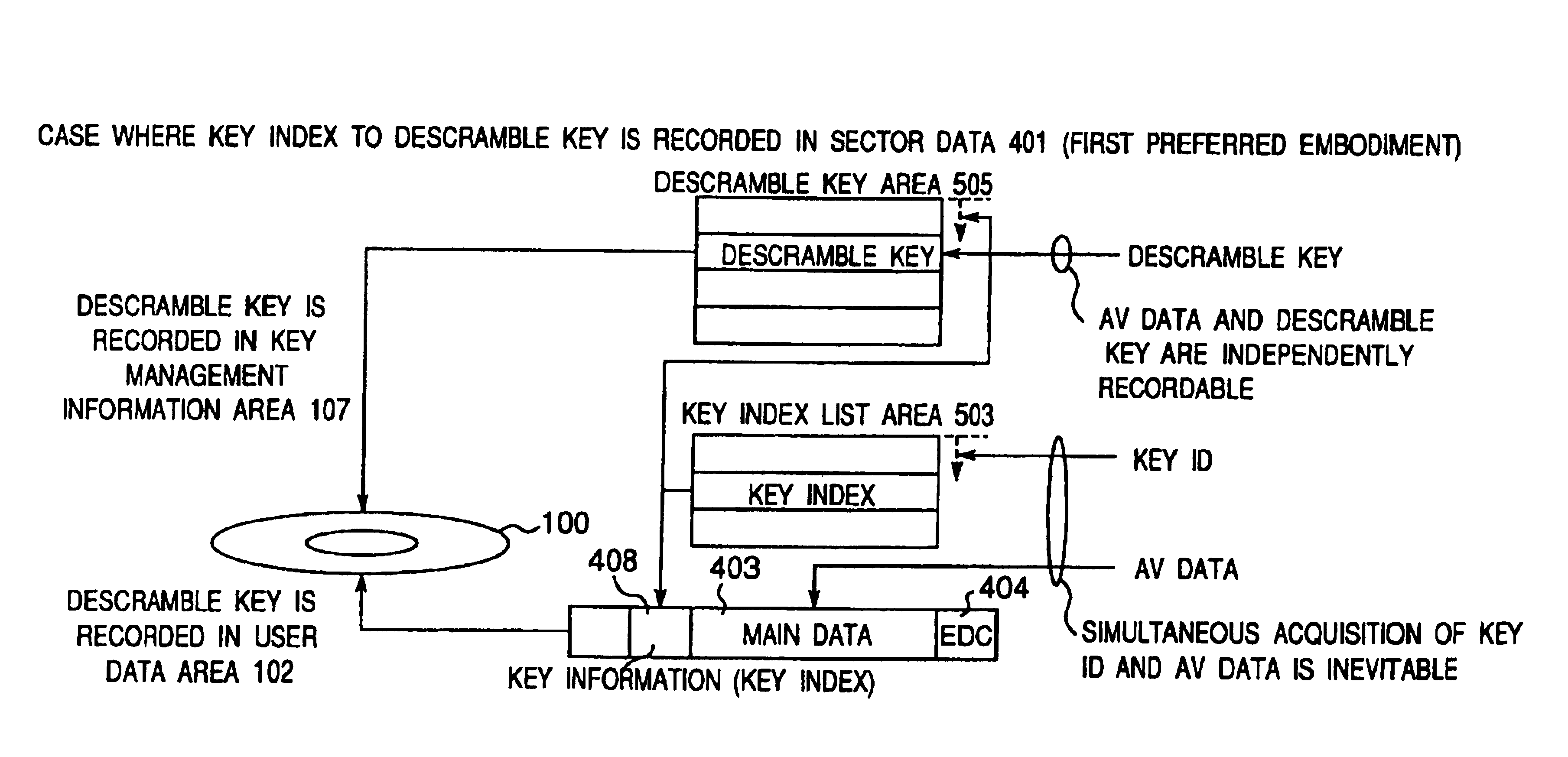
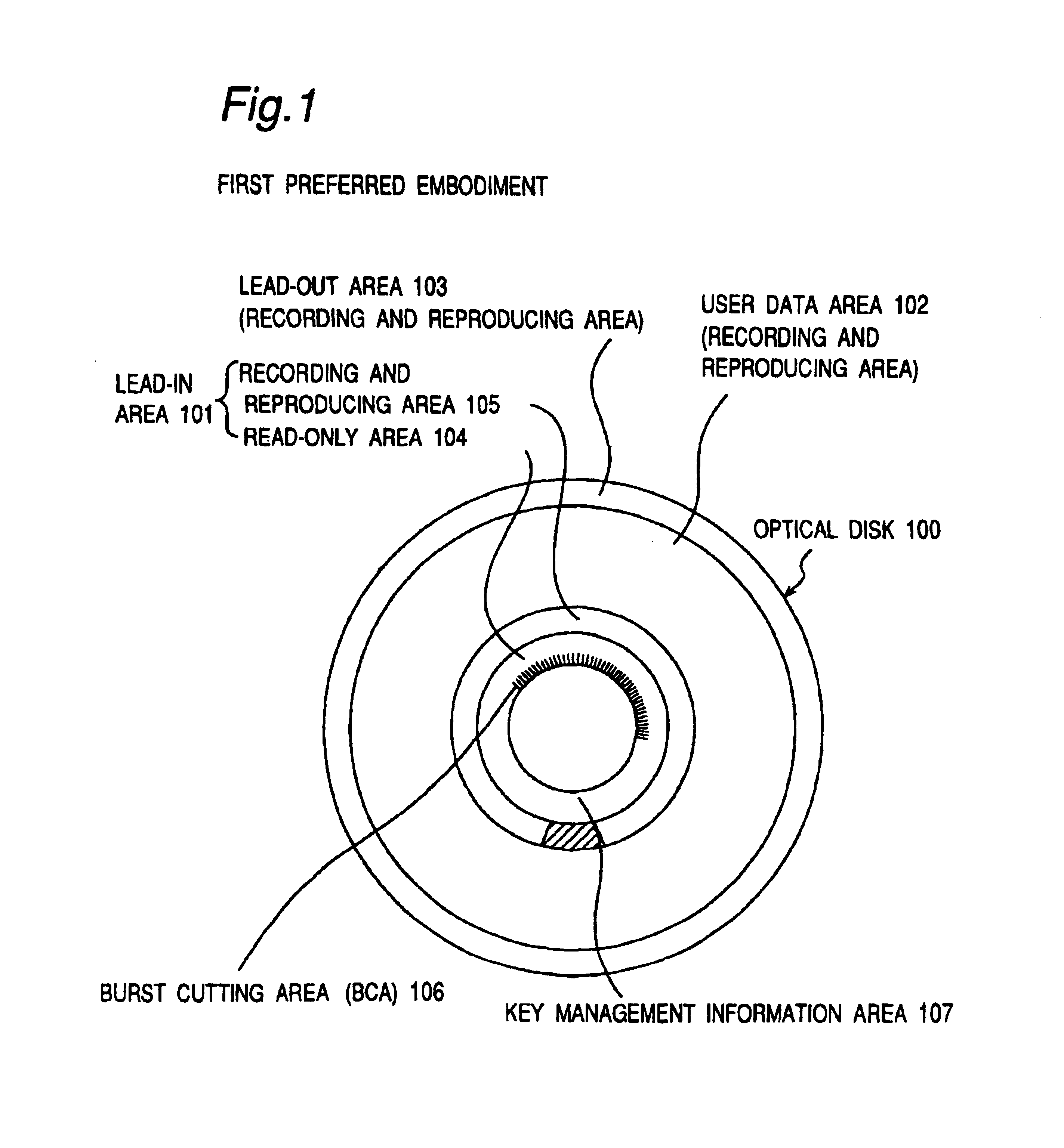
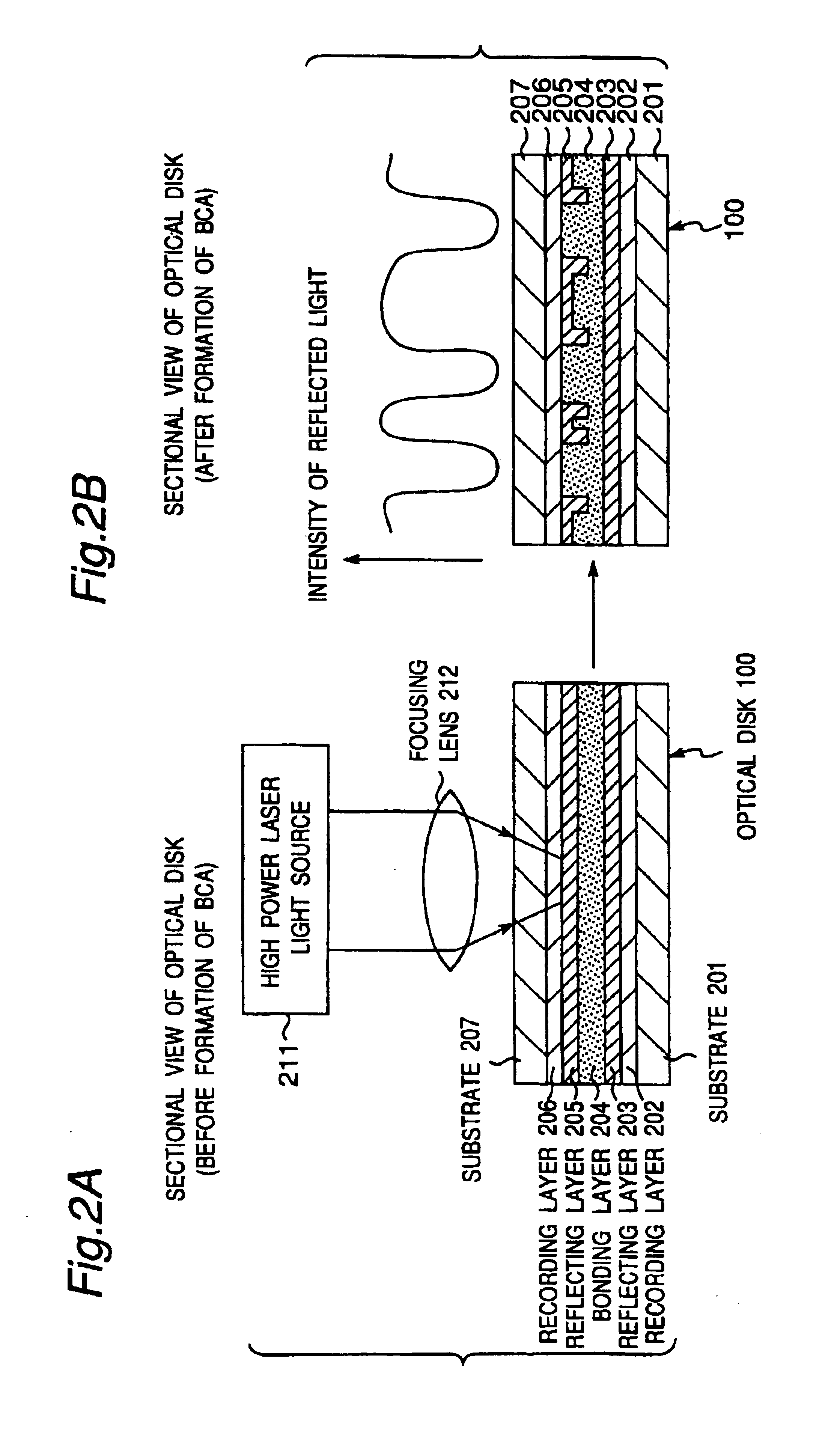
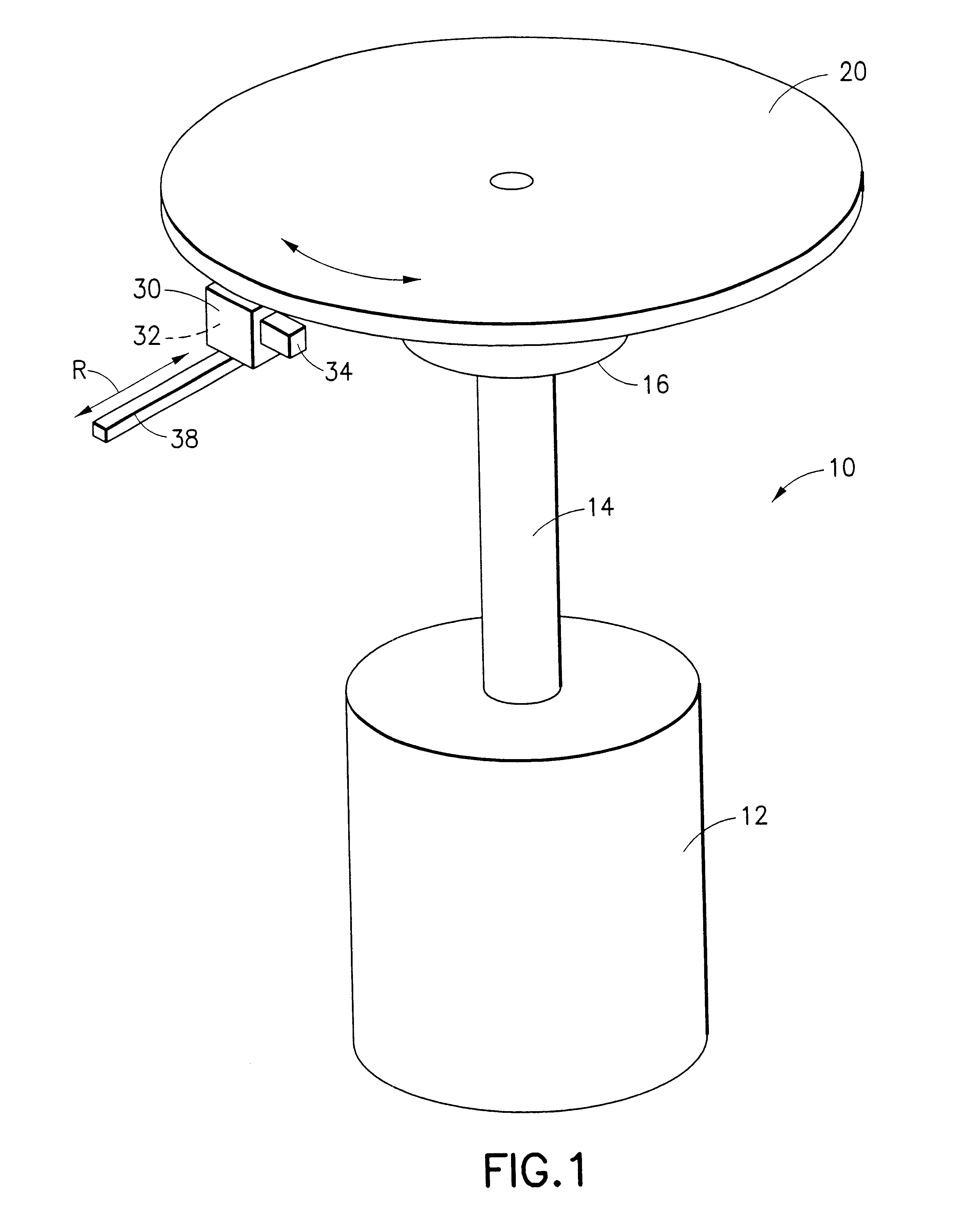
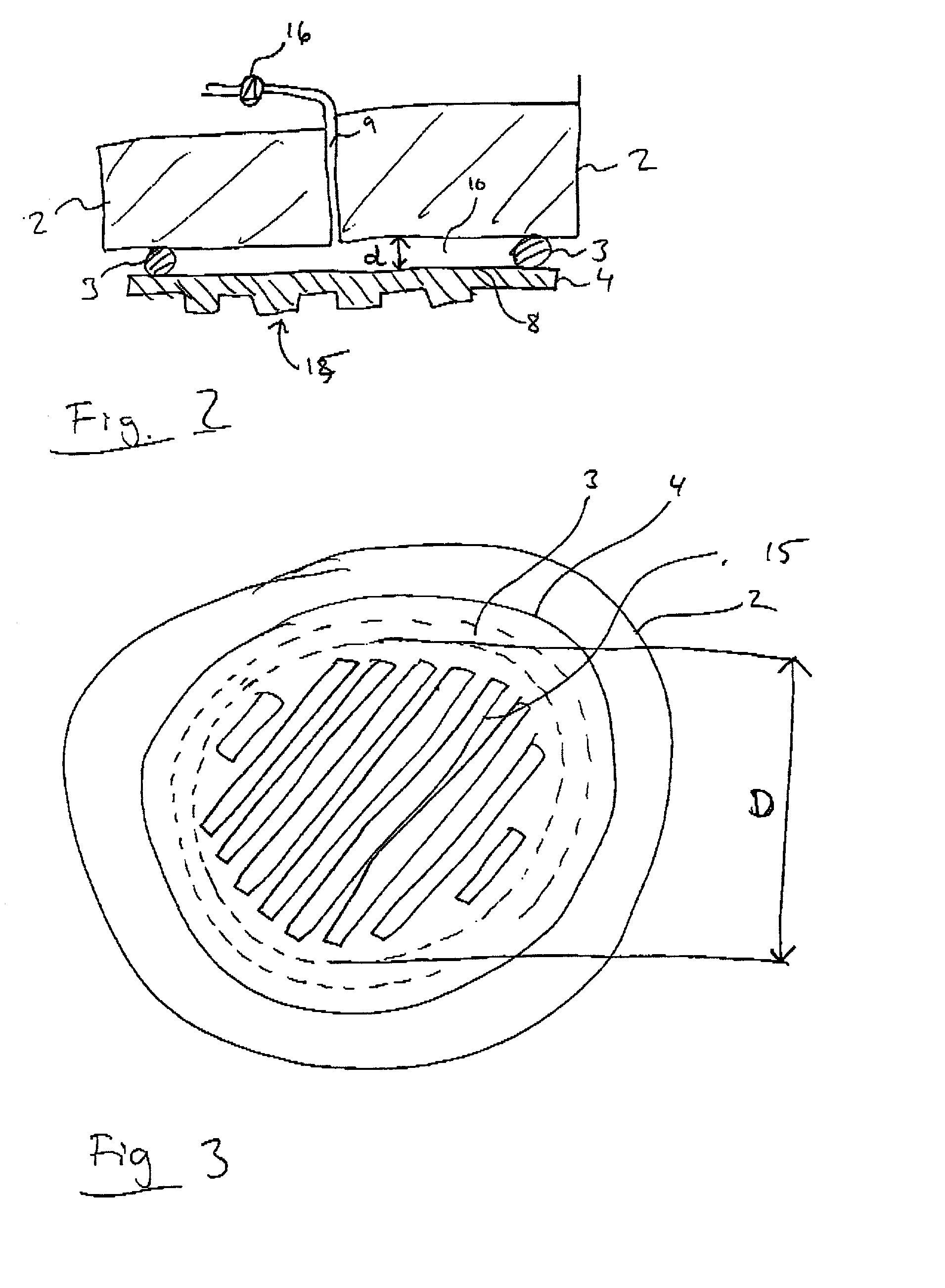
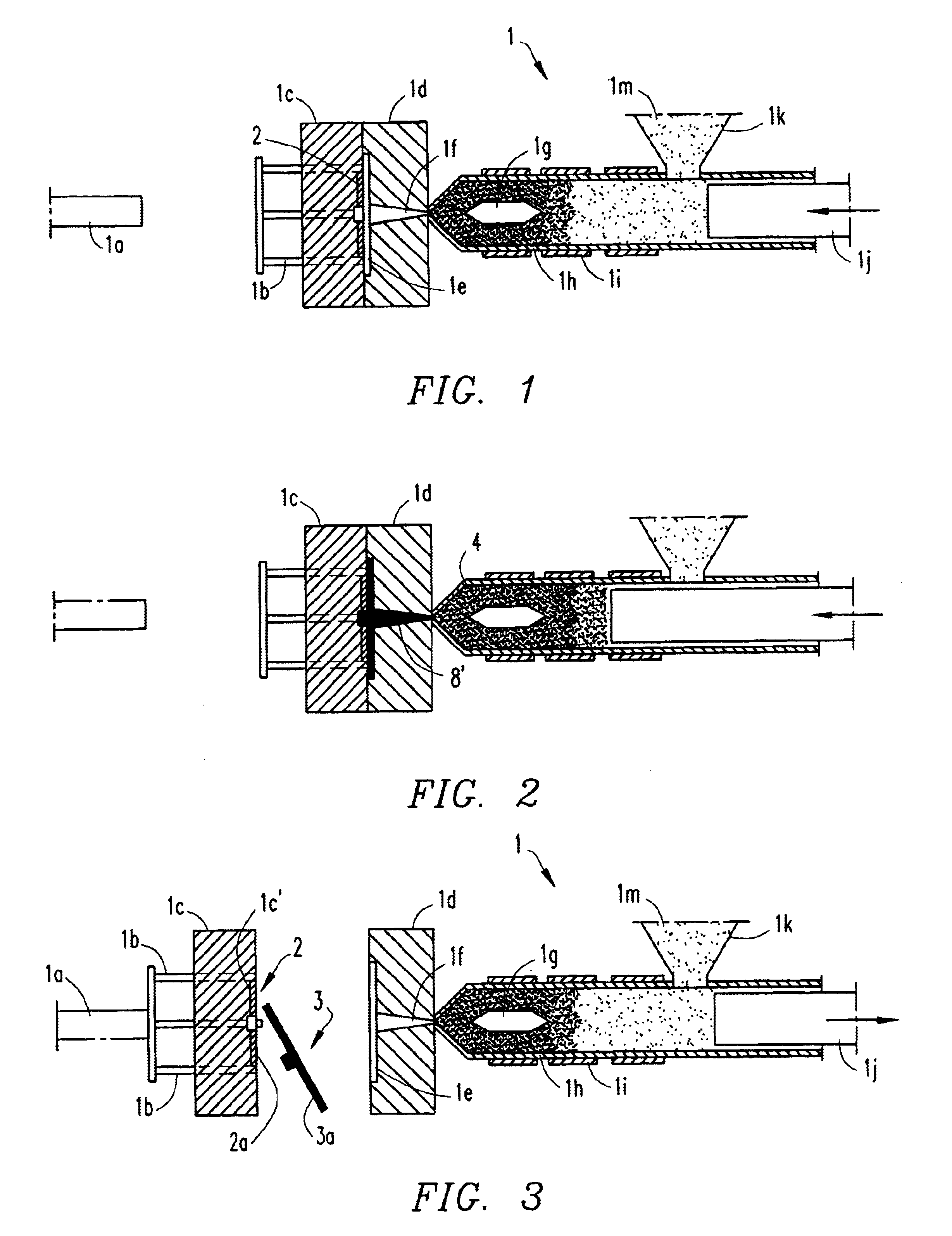
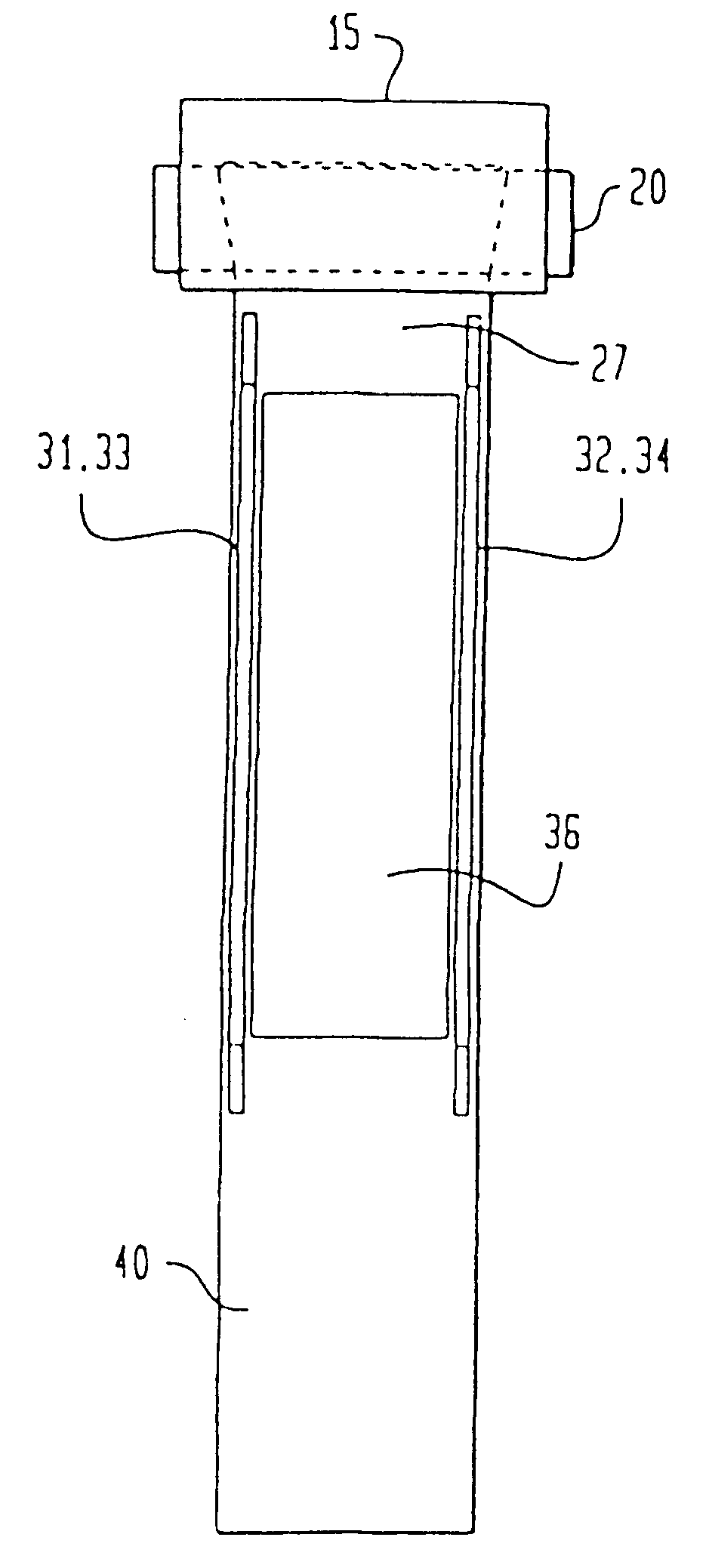
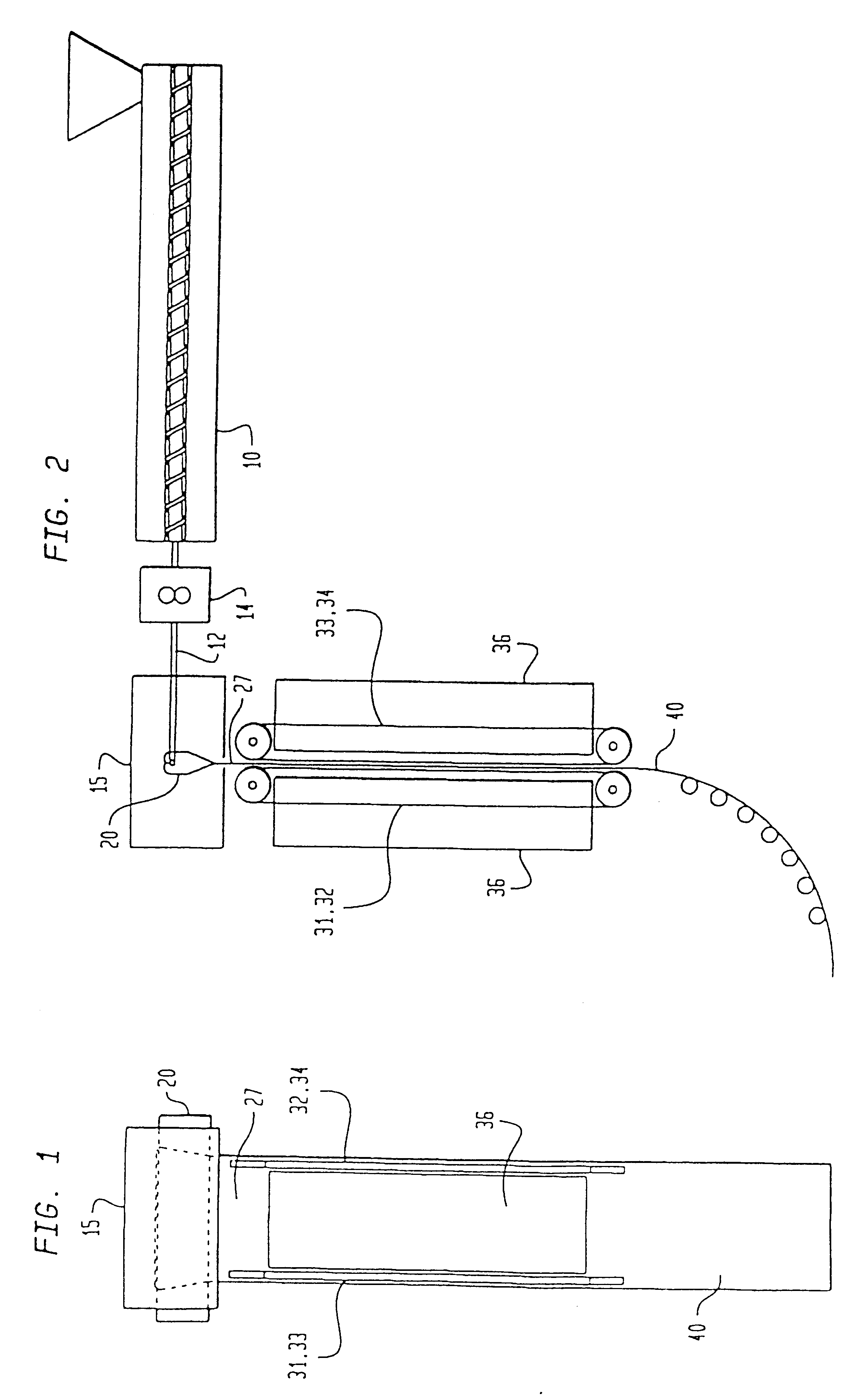
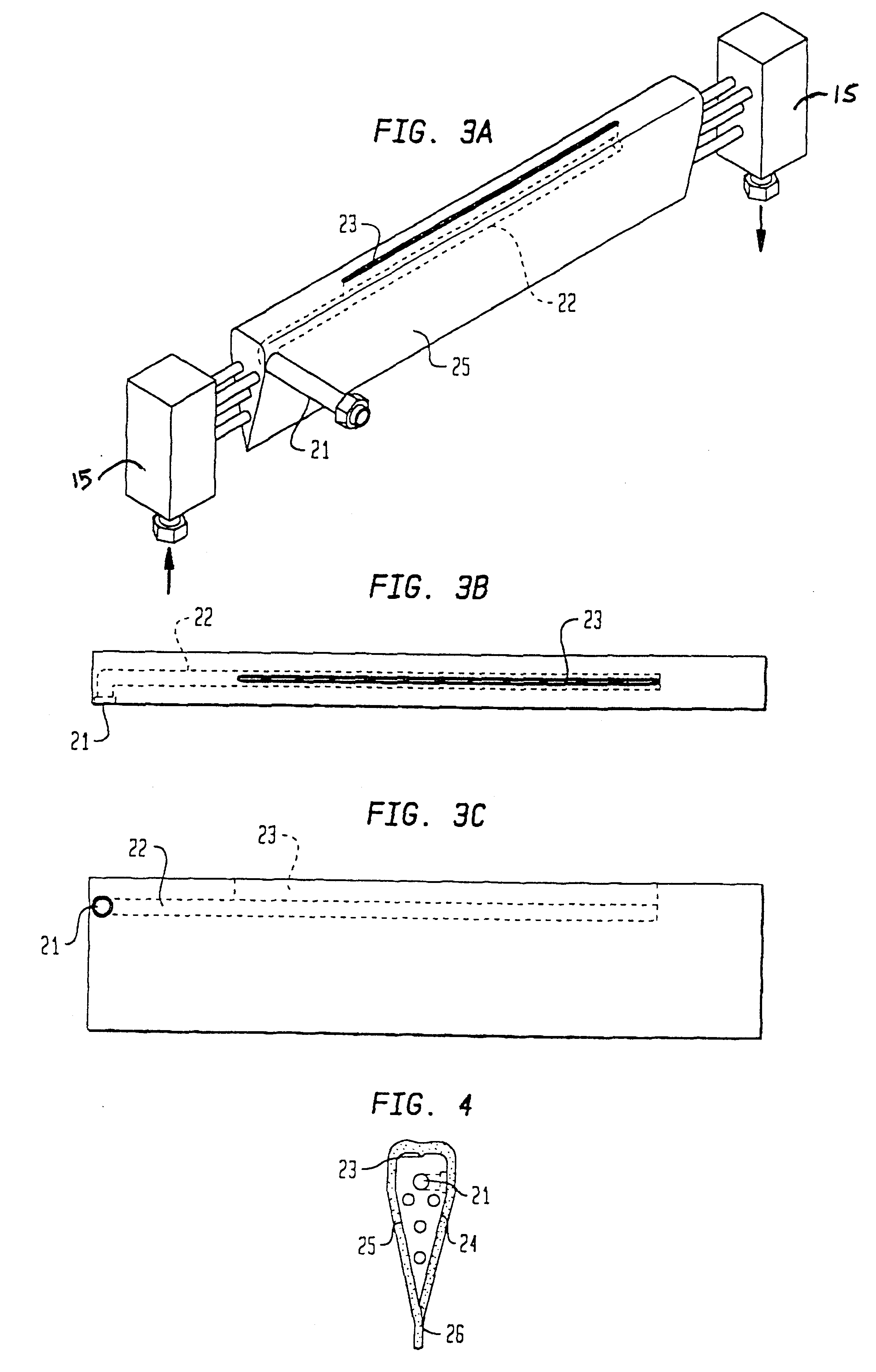
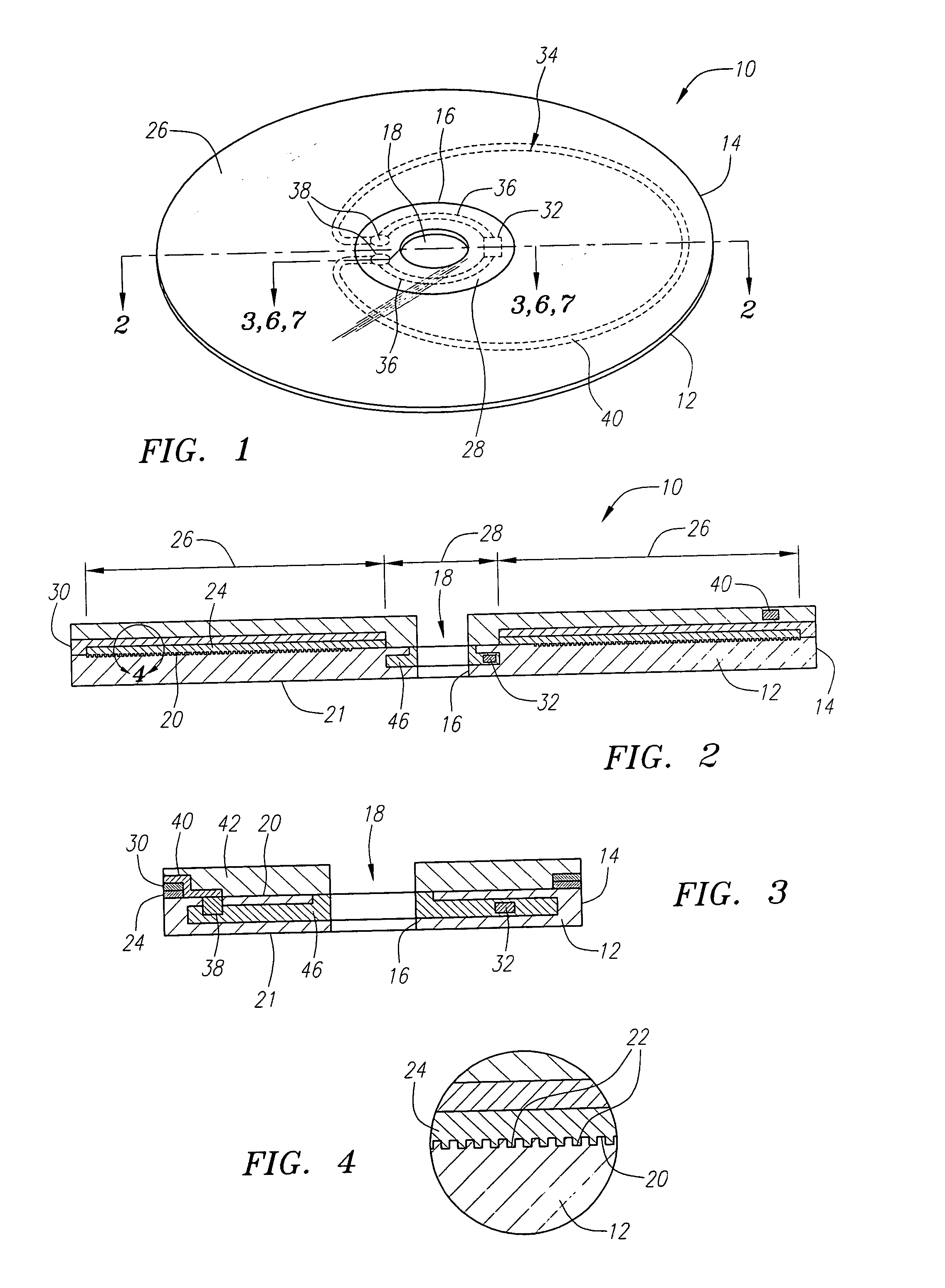
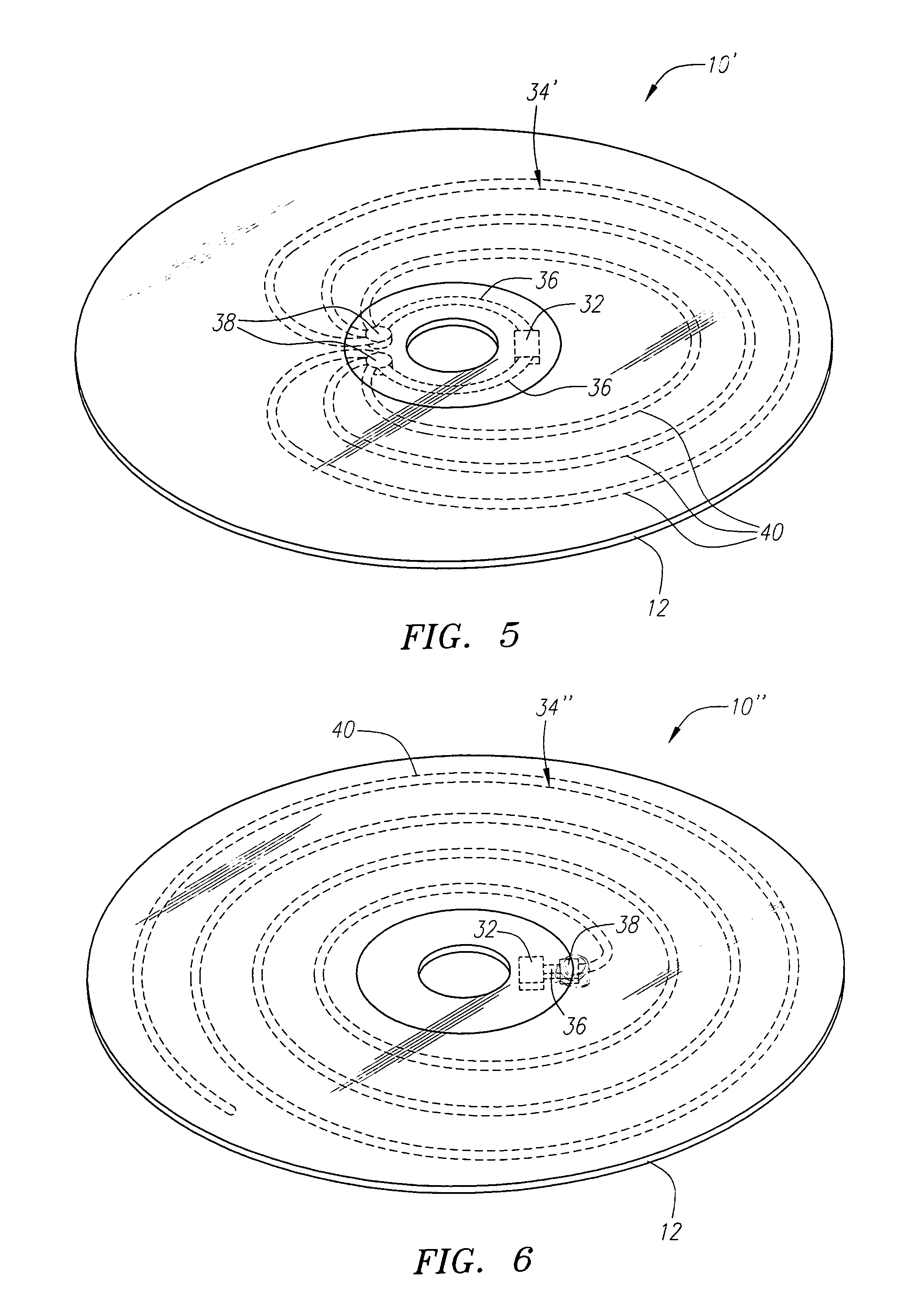
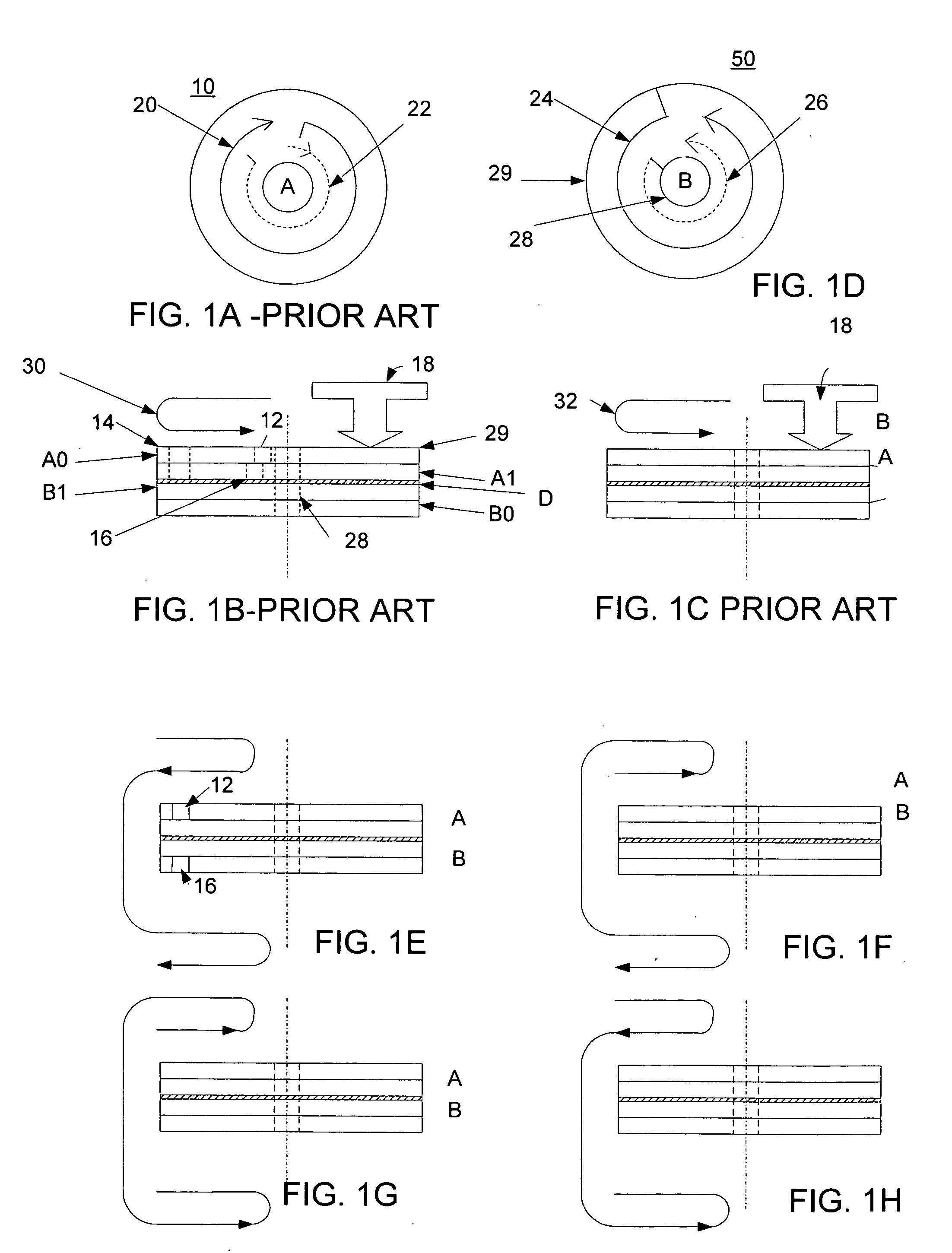
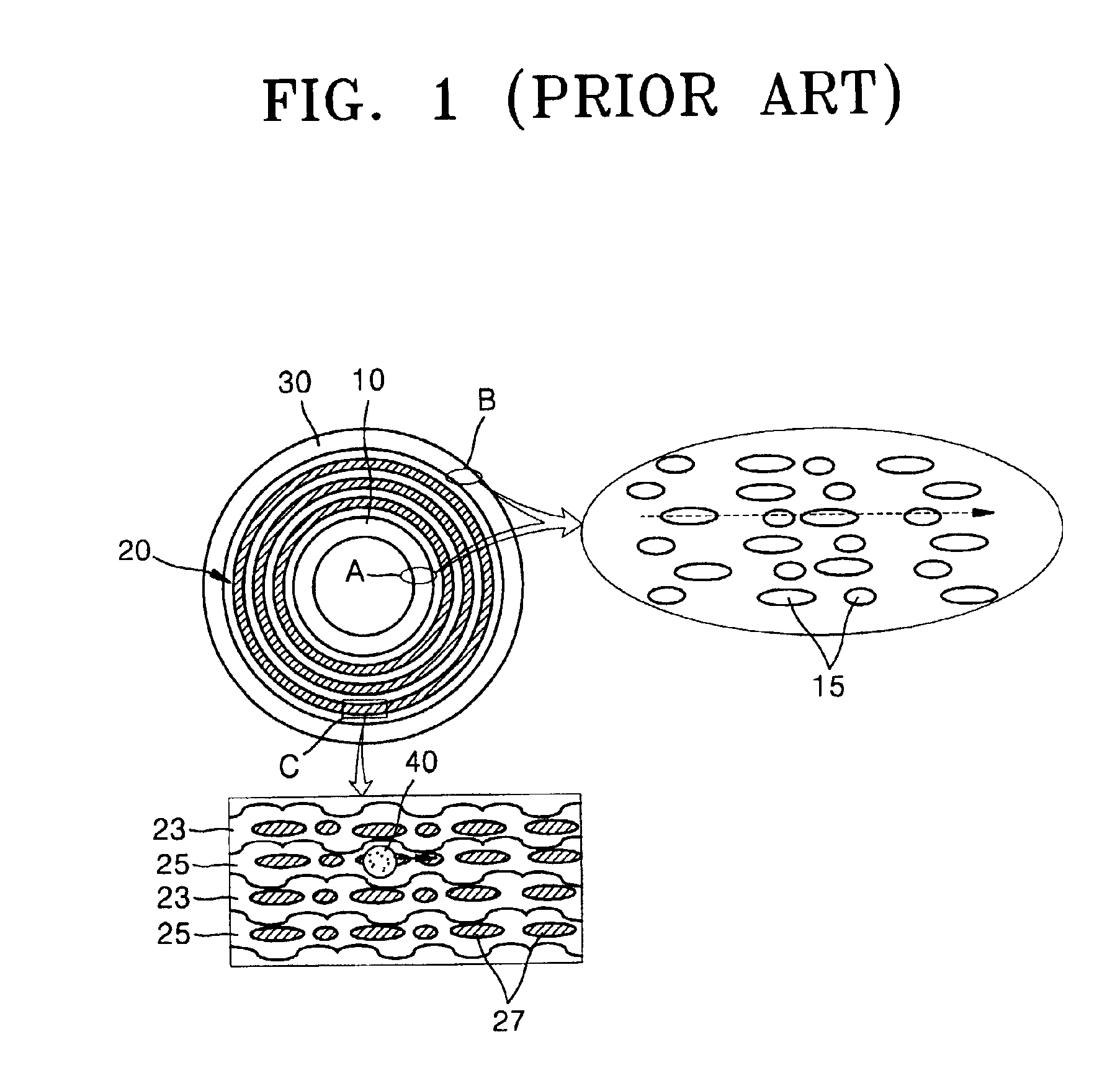
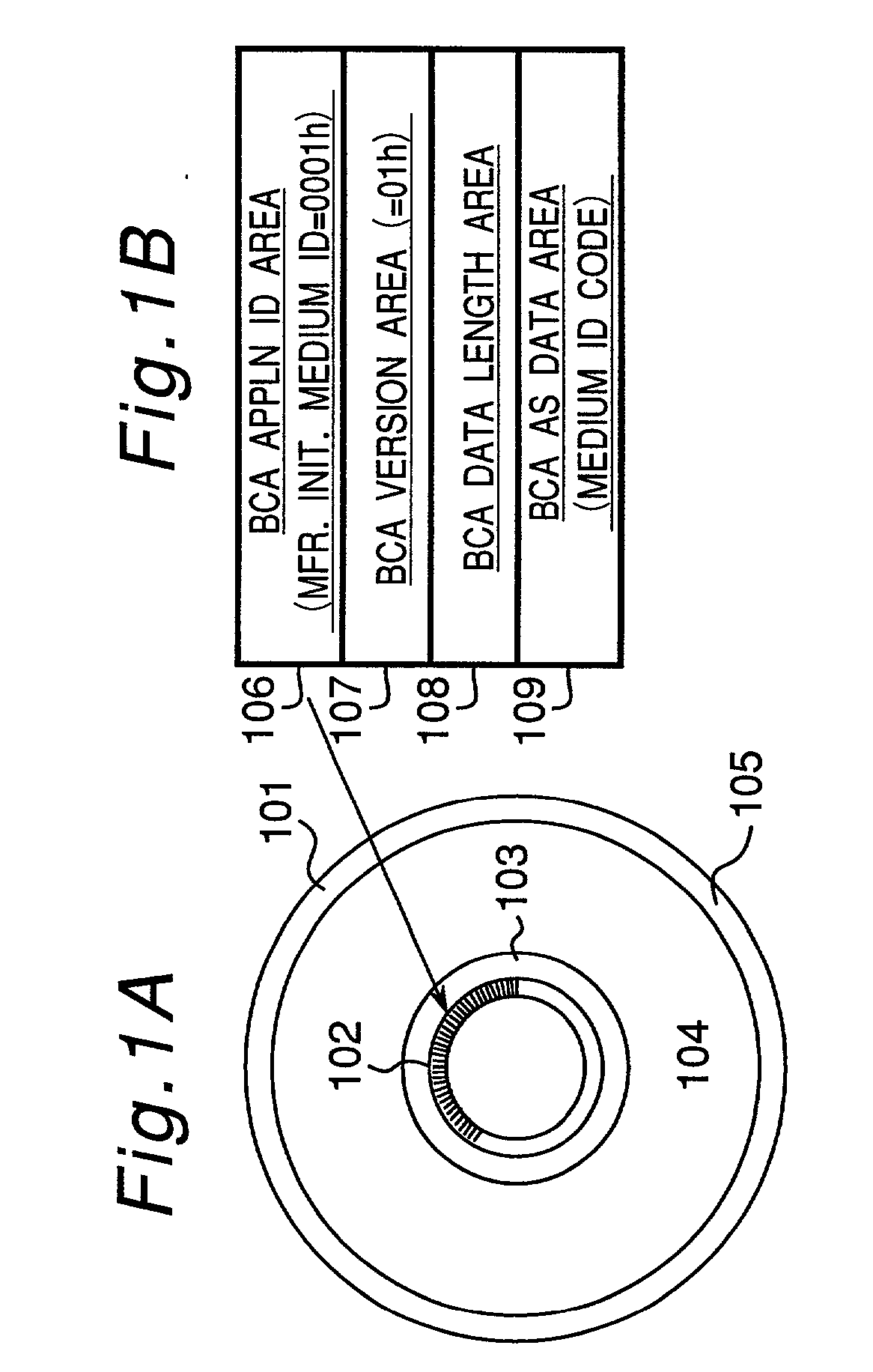
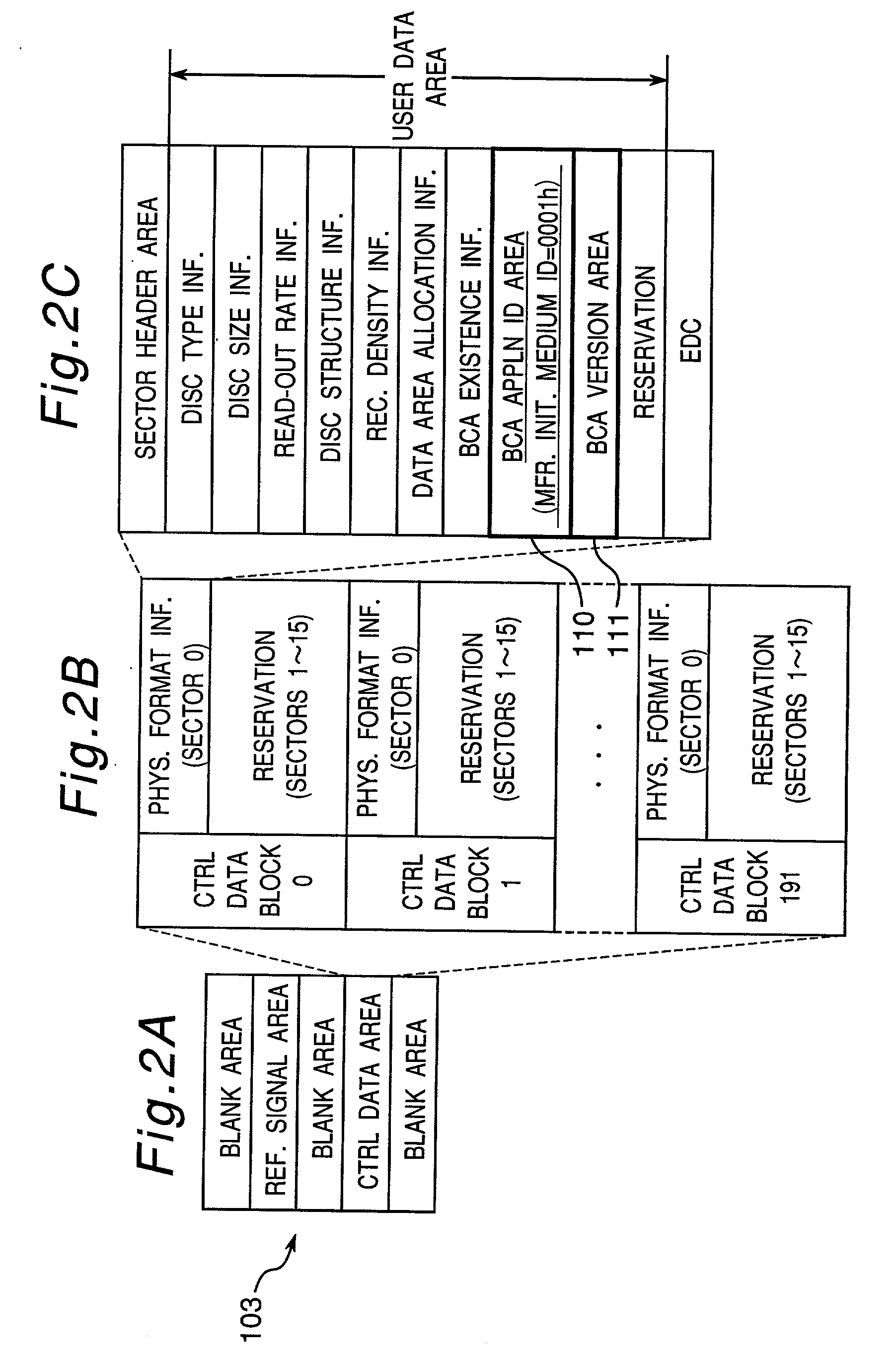
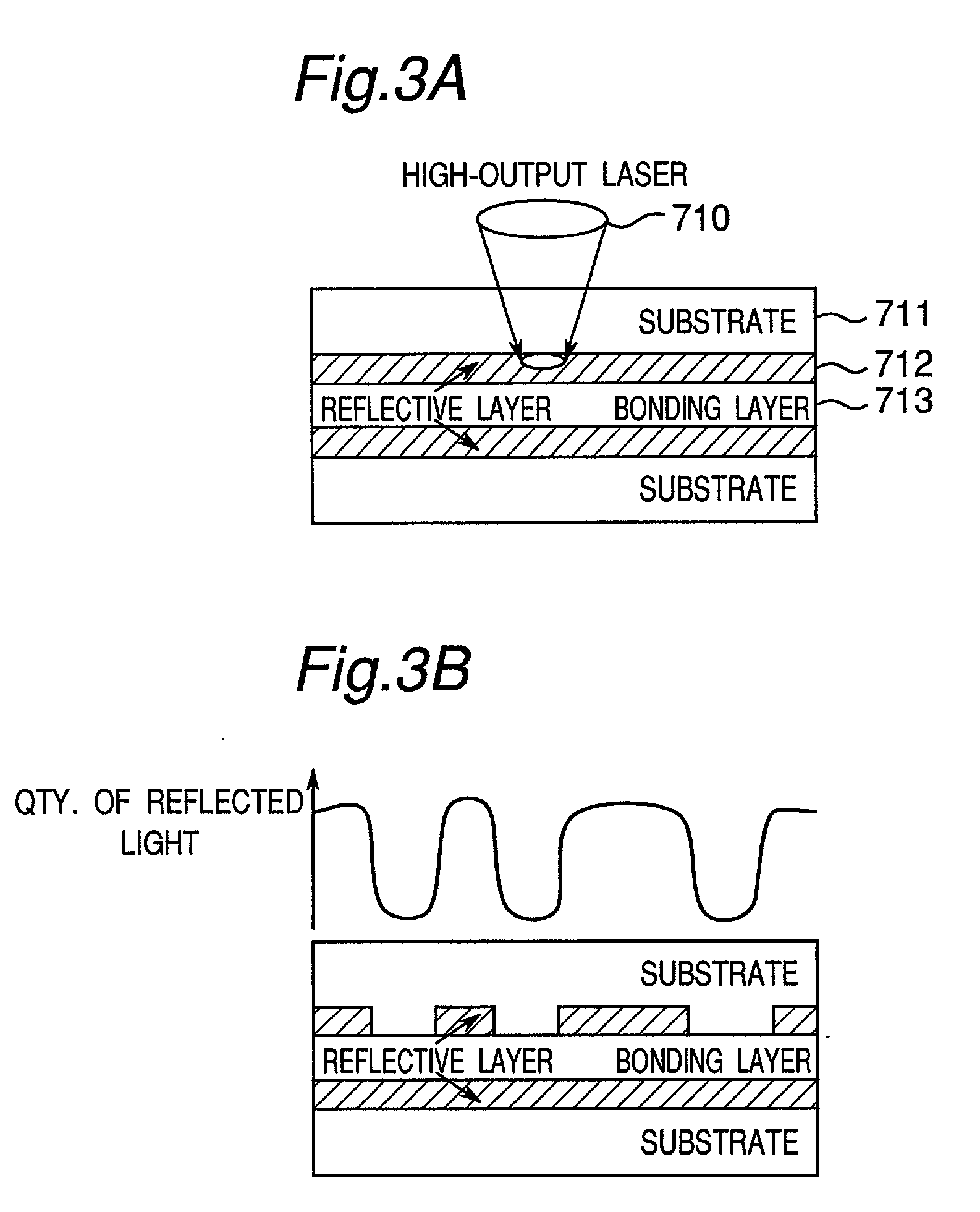
A recording type optical disk on which data is recordable includes a data recording and reproducing area for recording data therein and reproducing data therefrom, and a read-only disk identification information area for recording disk identification information for identifying the optical disk therein. In the optical disk, the disk identification information is formed by removing a reflection film that is formed on the optical disk in a strip shape. The disk identification information includes an inherent disk identifier for each optical disk, and the data recording and reproducing area includes an area for recording encrypted data therein. The encrypted data is encrypted by using information including the disk identification information for identifying the optical disk as a key.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS6338933B1Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationAtmospheric air
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Optical articles comprising isosorbide polyesters and method for making same
InactiveUS6126992AHigh light transmittanceEasy to copySynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesPolyesterPolymer science
An optical article made of a transparent polymer which includes terephthaloyl moieties, optionally, other aromatic diacid moieties; ethylene glycol moieties; isosorbide moieties; and, optionally, one or more other diol moieties, wherein the polymer has an inherent viscosity of at least about 0.35 dL / g as measured on a 1% solution (weight / volume) in o-chlorophenol at 25 DEG C.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Imprint method and device
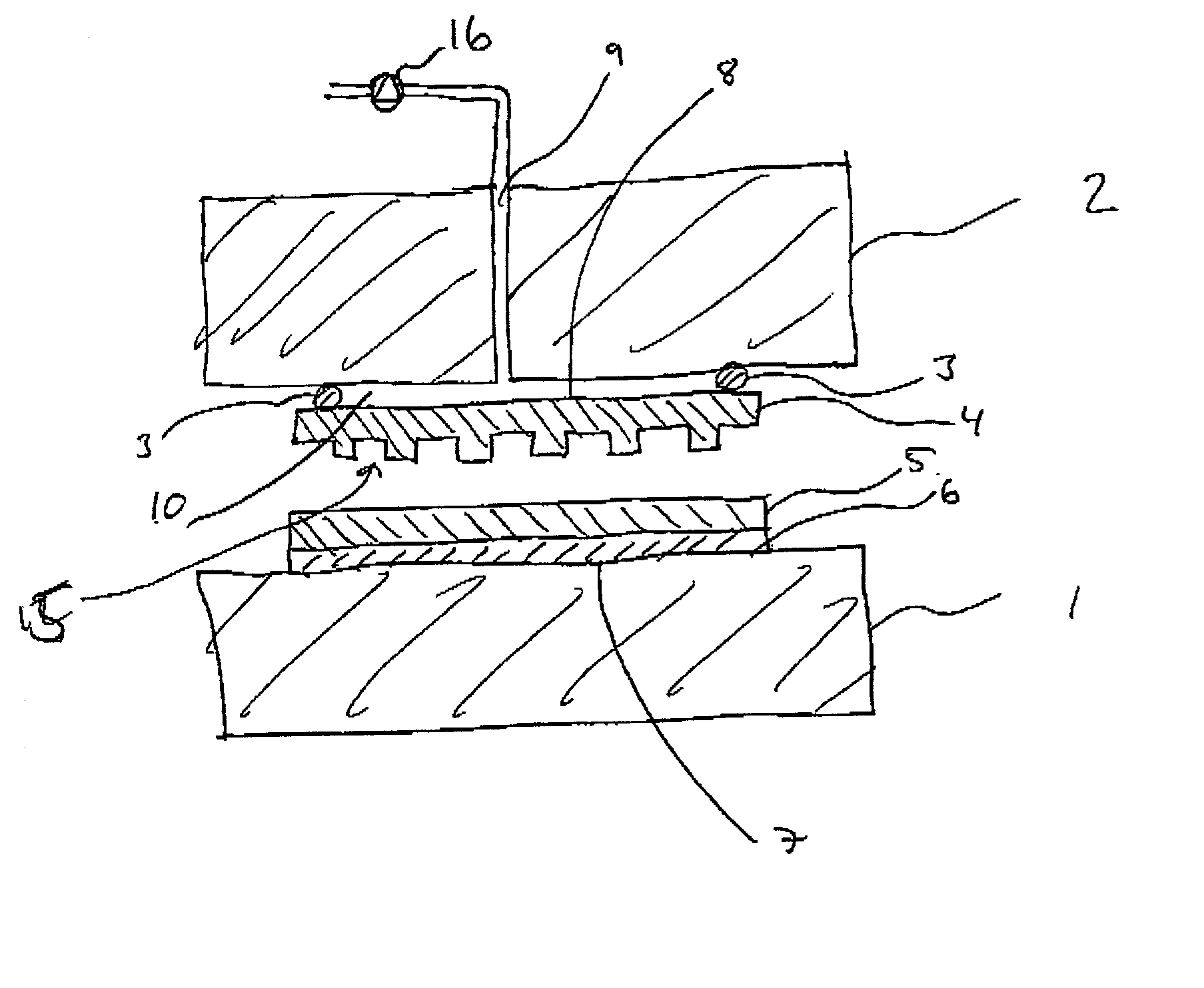
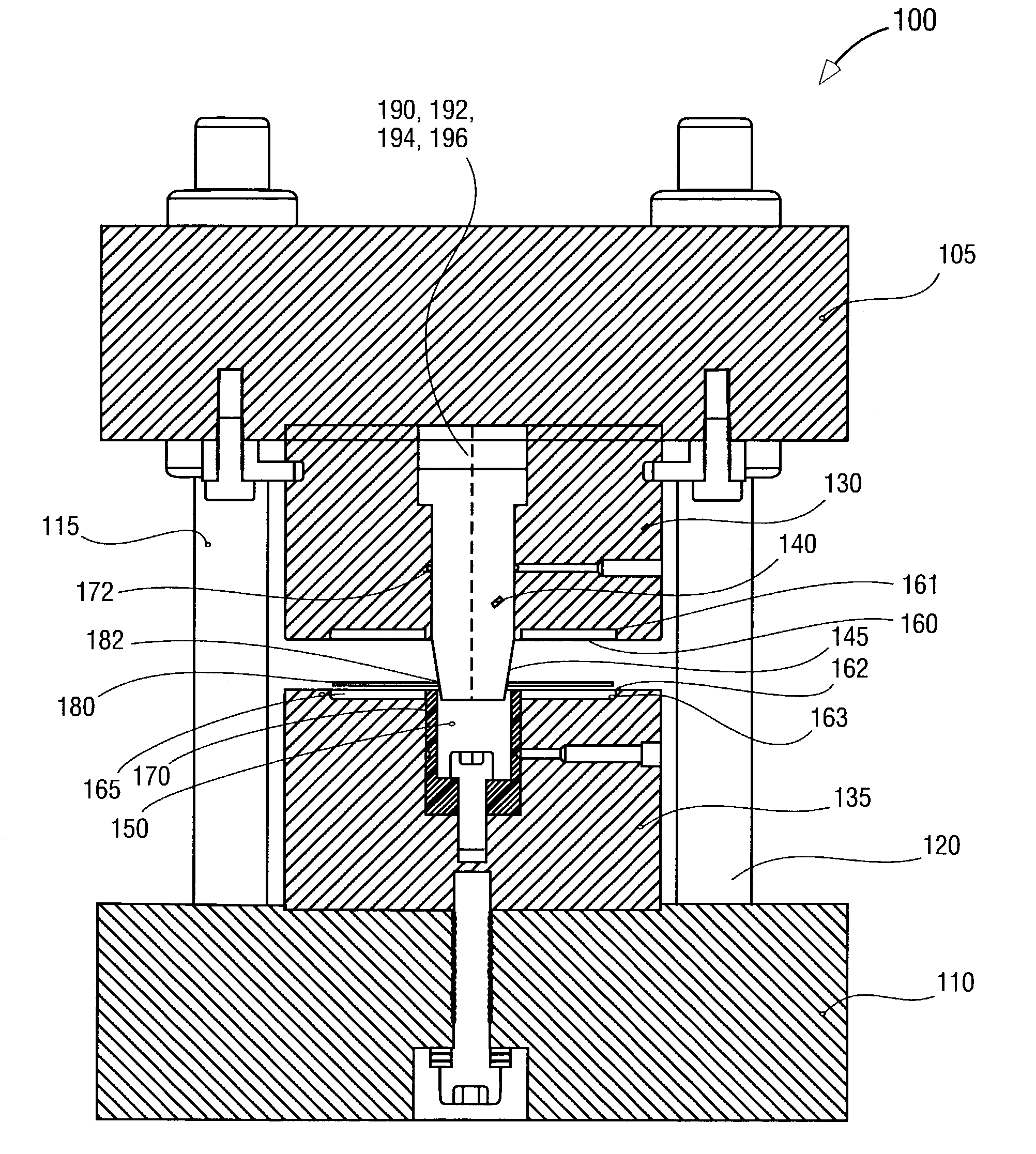
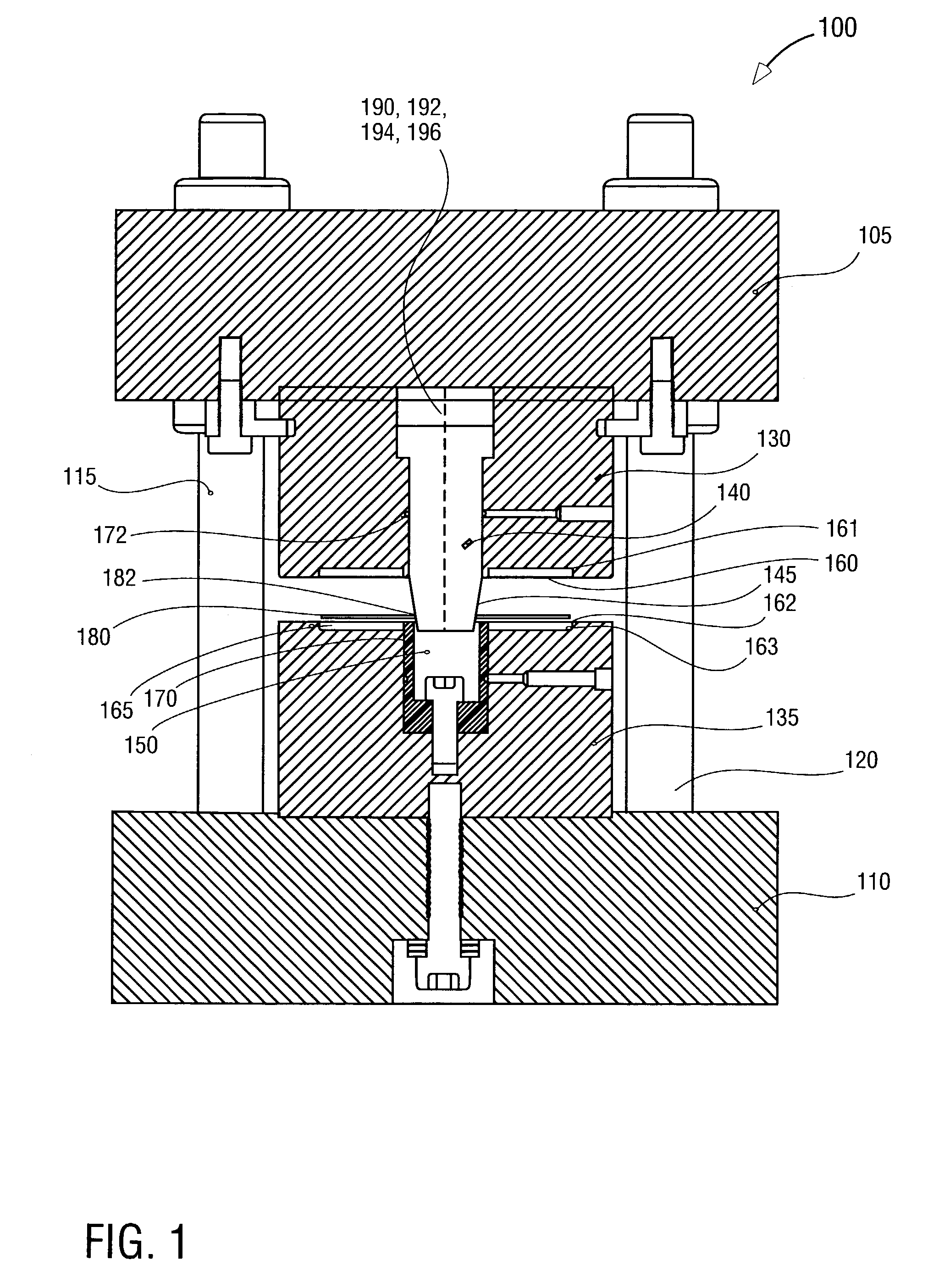
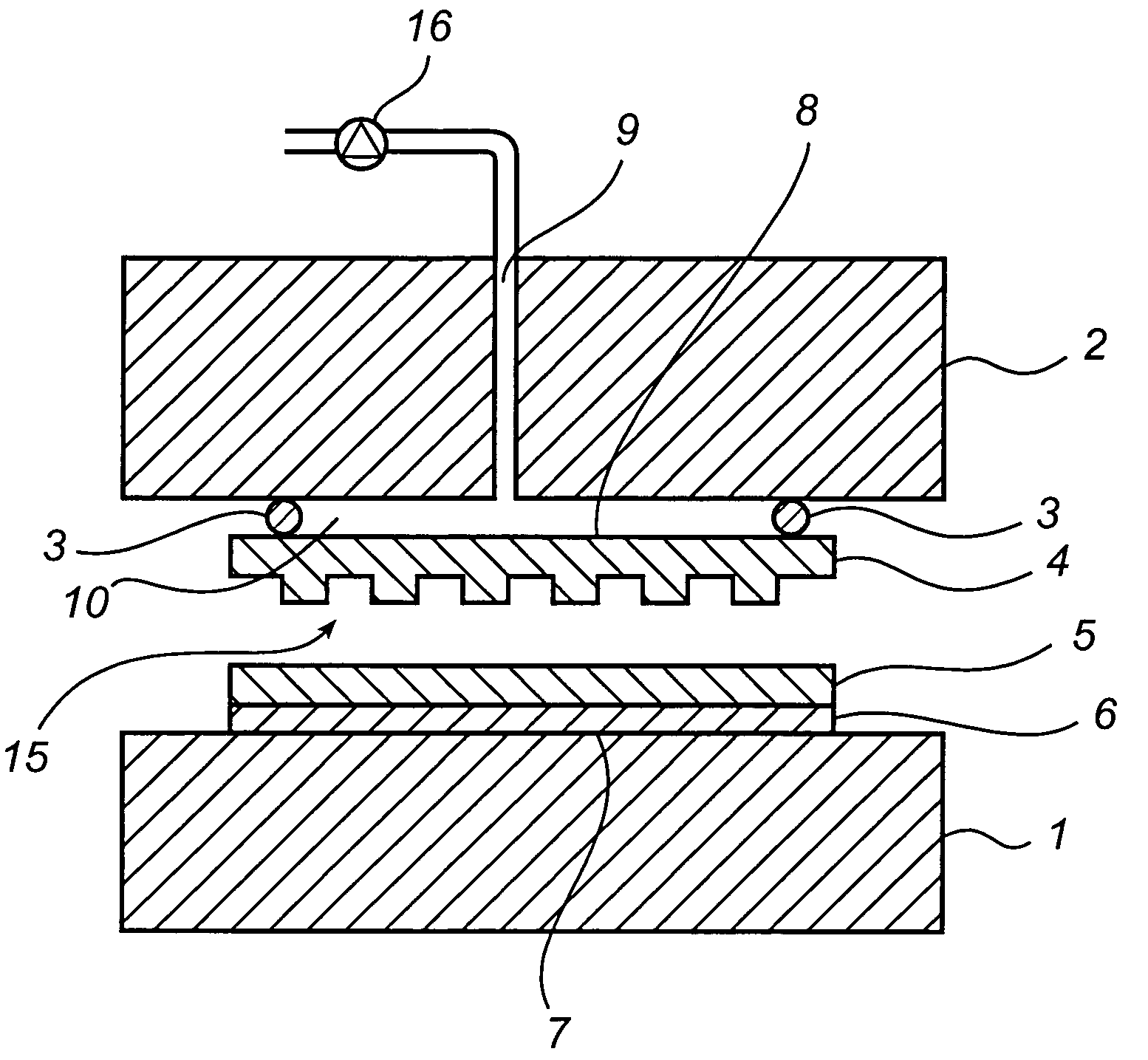
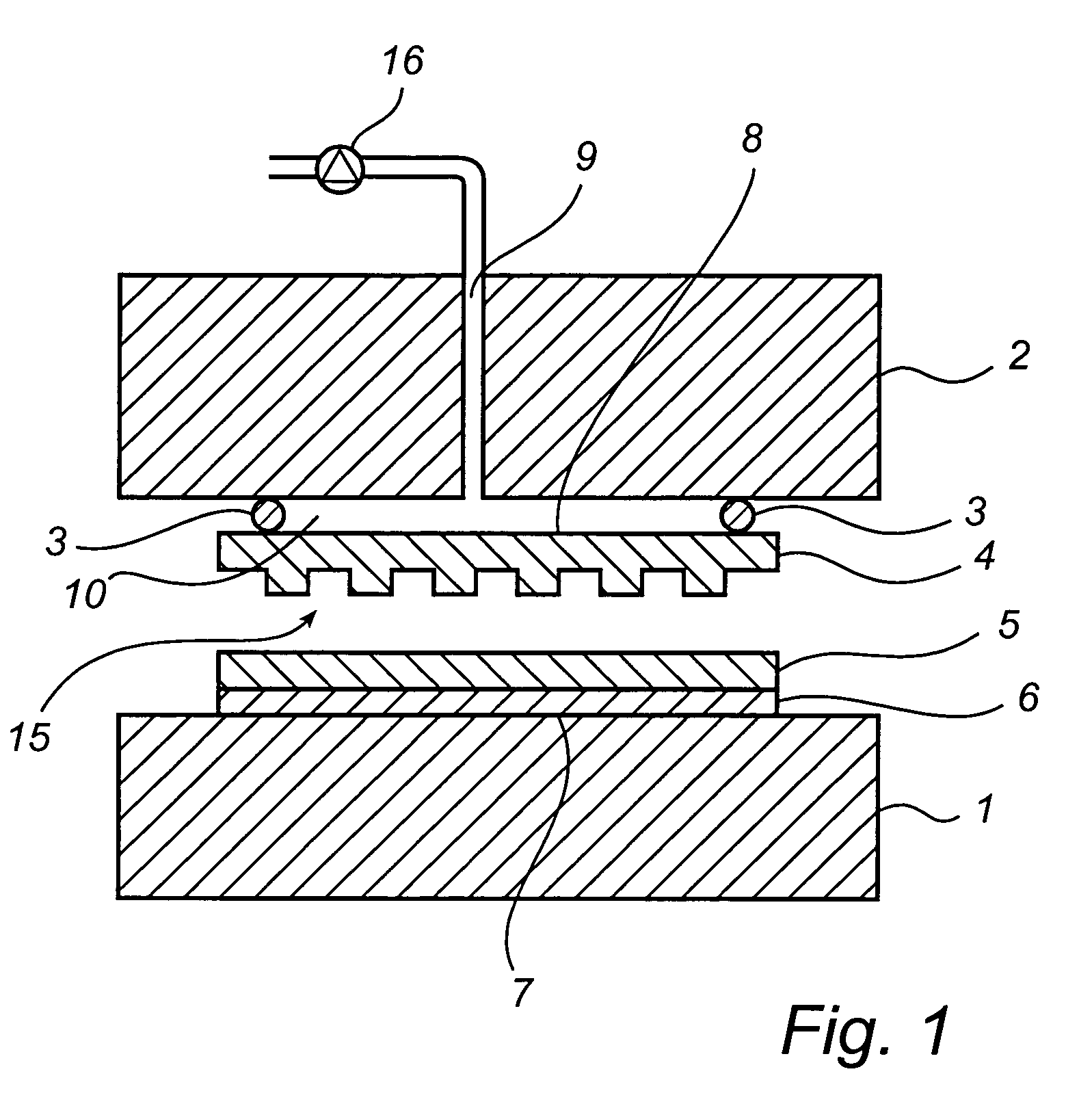
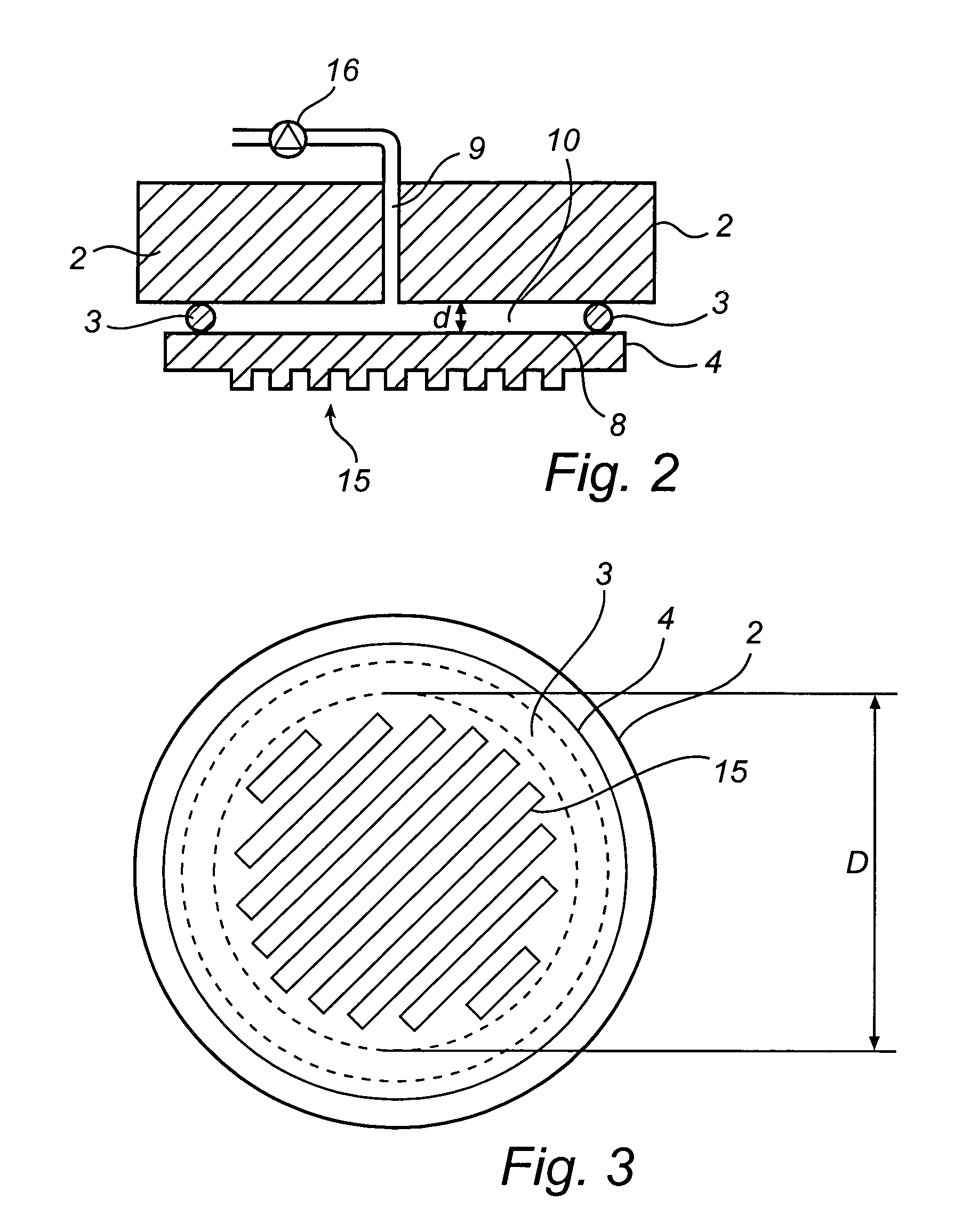
An imprint process comprises the step of aligning a substrate, supported on a first support member, with a template, supported on a second support member. The substrate has at least one essentially plane surface provided with a moldable film. The template has at least one essentially plane surface provided with a relief pattern. The relief pattern is adapted to interact with the moldable film. The process further comprises the step of arranging a sealing gasket between the template and the second support member, such that a pressure cavity is defined by the second support member, the template and the sealing gasket. The process also comprises the step of applying a static gas pressure to the pressure cavity, in order to provide a pressure between the template and the substrate. The pressure is sufficient to form a pattern in the moldable film. An imprint device is also disclosed.
Owner:OBDUCAT AB SE
Information recording medium which indicates information according to the wobbling of a track and information recording and reproducing apparatus
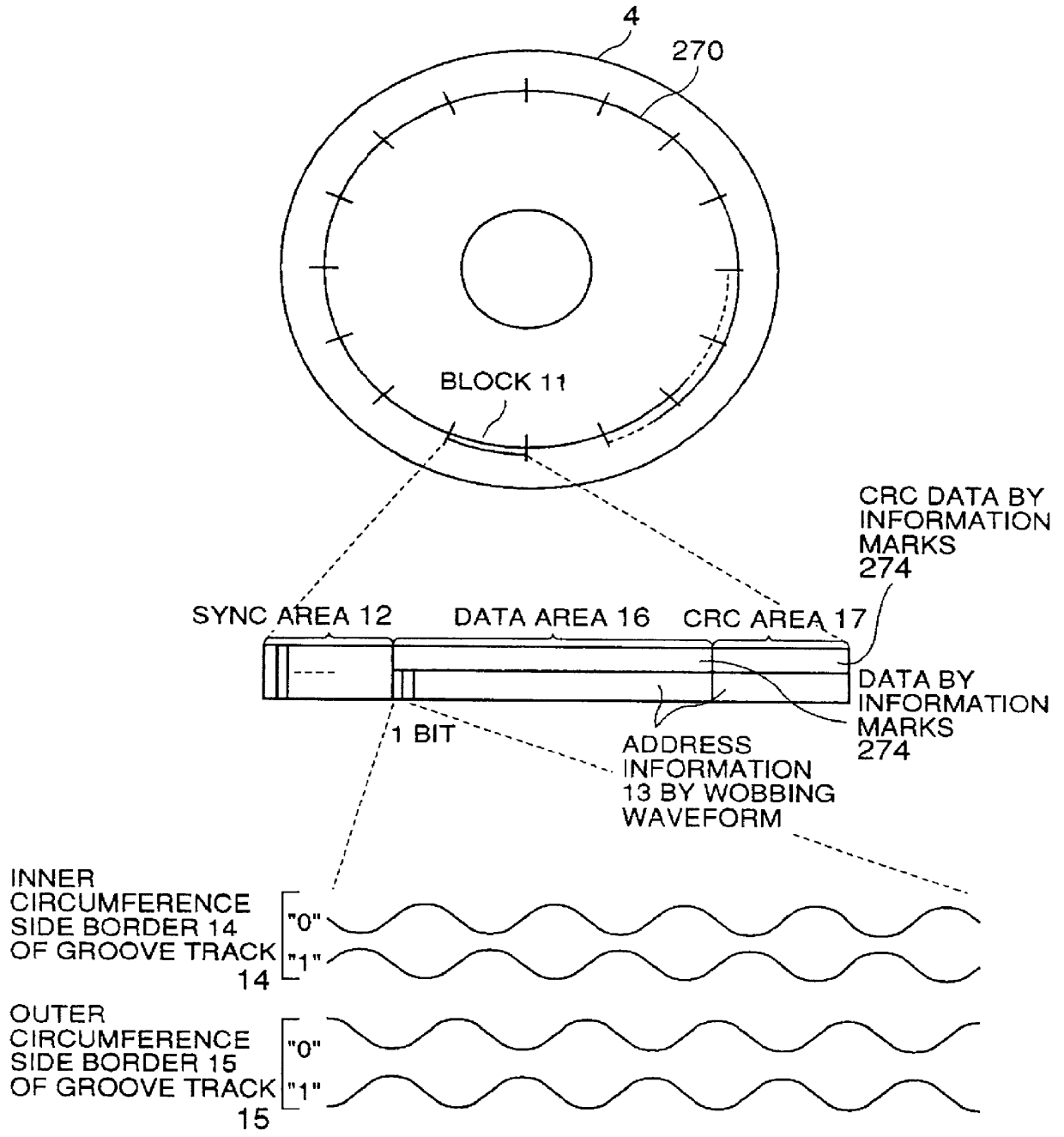
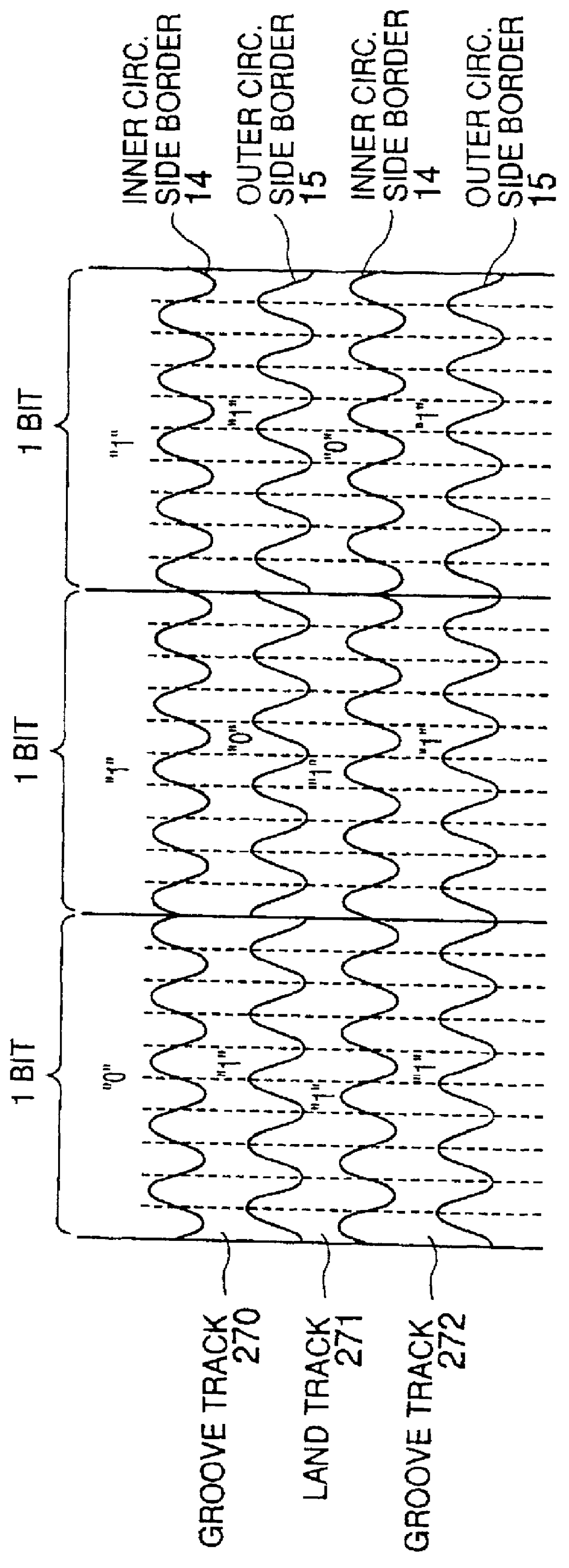
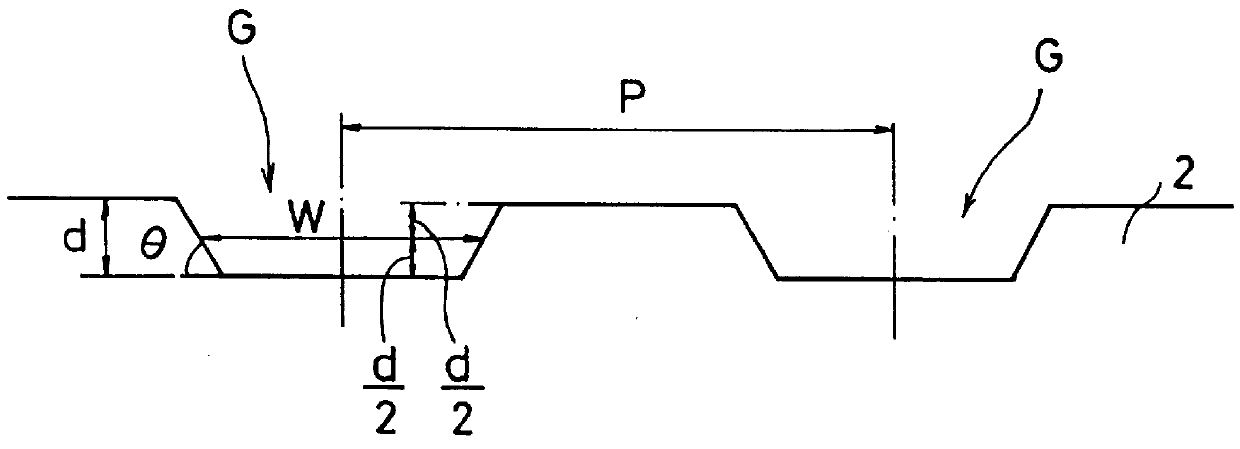
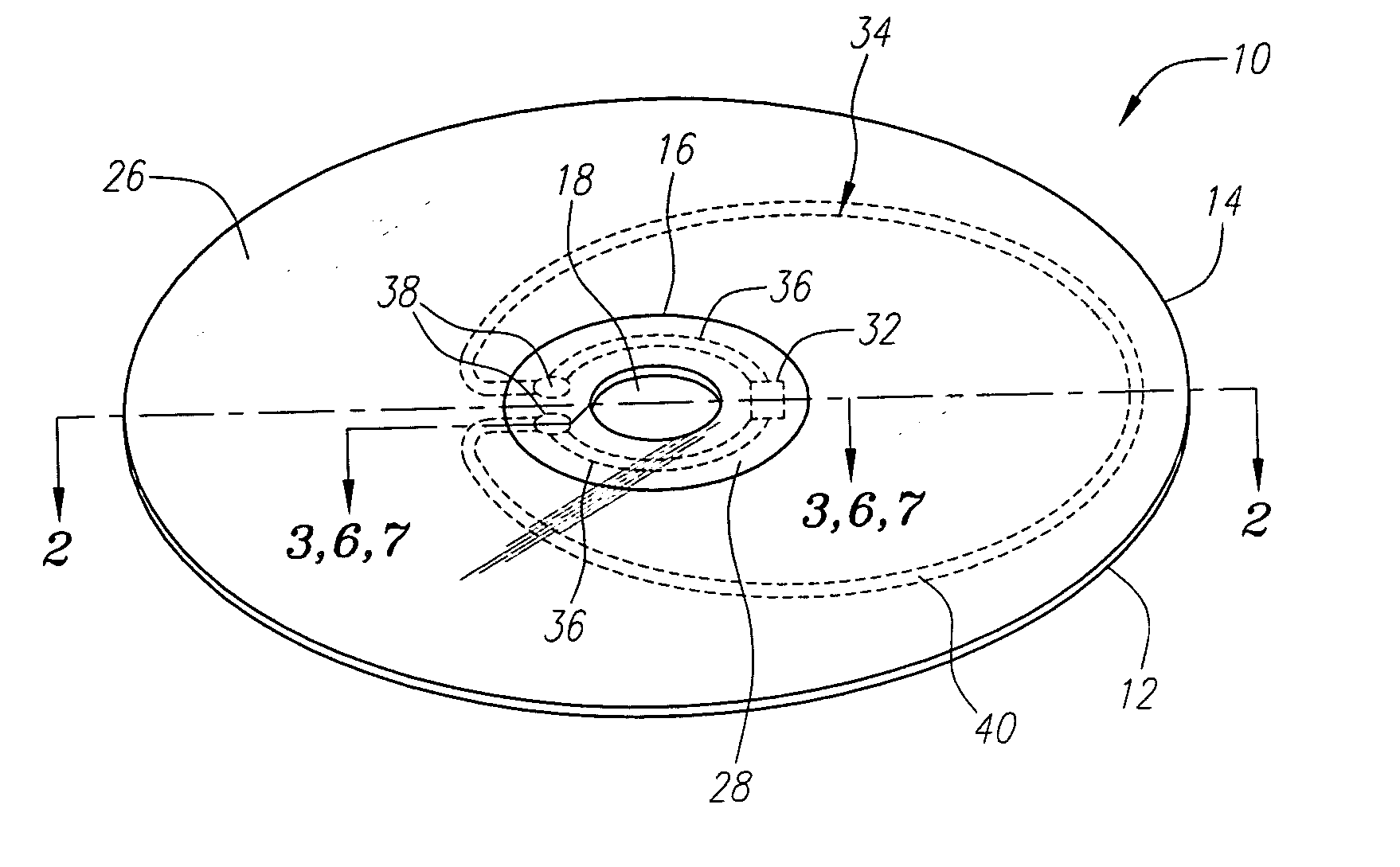
An optical disk comprising a substrate 4, and a plurality of tracks 269 to 273 formed on the substrate 4, wherein the plurality of tracks 269 to 273 include groove tracks 270, 272 consisting of a plurality of grooves mutually space apart by a fixed space, and land tracks 269, 271, 273 consisting of areas between the groove tracks, wherein the borders 14, 15 between the groove tracks and the land tracks represent information using the waveforms from their wobbling patterns, wherein the period of the wobbling waveforms of the borders 14, 15 are constant on each border, but the wobbling waveforms of the opposite portions of the borders across the track are shifted in phase by a predetermined phase difference.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Multi-layered information recording medium with spare defect management areas
ActiveUS7123556B2Shorten the timeEfficient managementInput/output to record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareRecording layer
A multi-layered information recording medium comprising a plurality of recording layers, a user data area for recording user data, provided in at least two of the plurality of recording layers, and a defect list storing area for storing a defect list. When at least one defective area is detected in the user data area, the defect list is used to manage the at least one defective area.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Matrix and method of producing said matrix
The invention relates to a matrix suitable for use in the replication of a plastic element having a positive microstructure, comprising a first wear-resistant layer that is supported by a carrier element, wherein the matrix comprises a heating means for supplying electrical heat energy through the wear-resistant layer or carrier element. The invention further relates to a plastic element producing machine and a method for the manufacture of a plastic element having a surface with a positive microstructure.
Owner:GYROS
Disk alignment apparatus and method for patterned media production
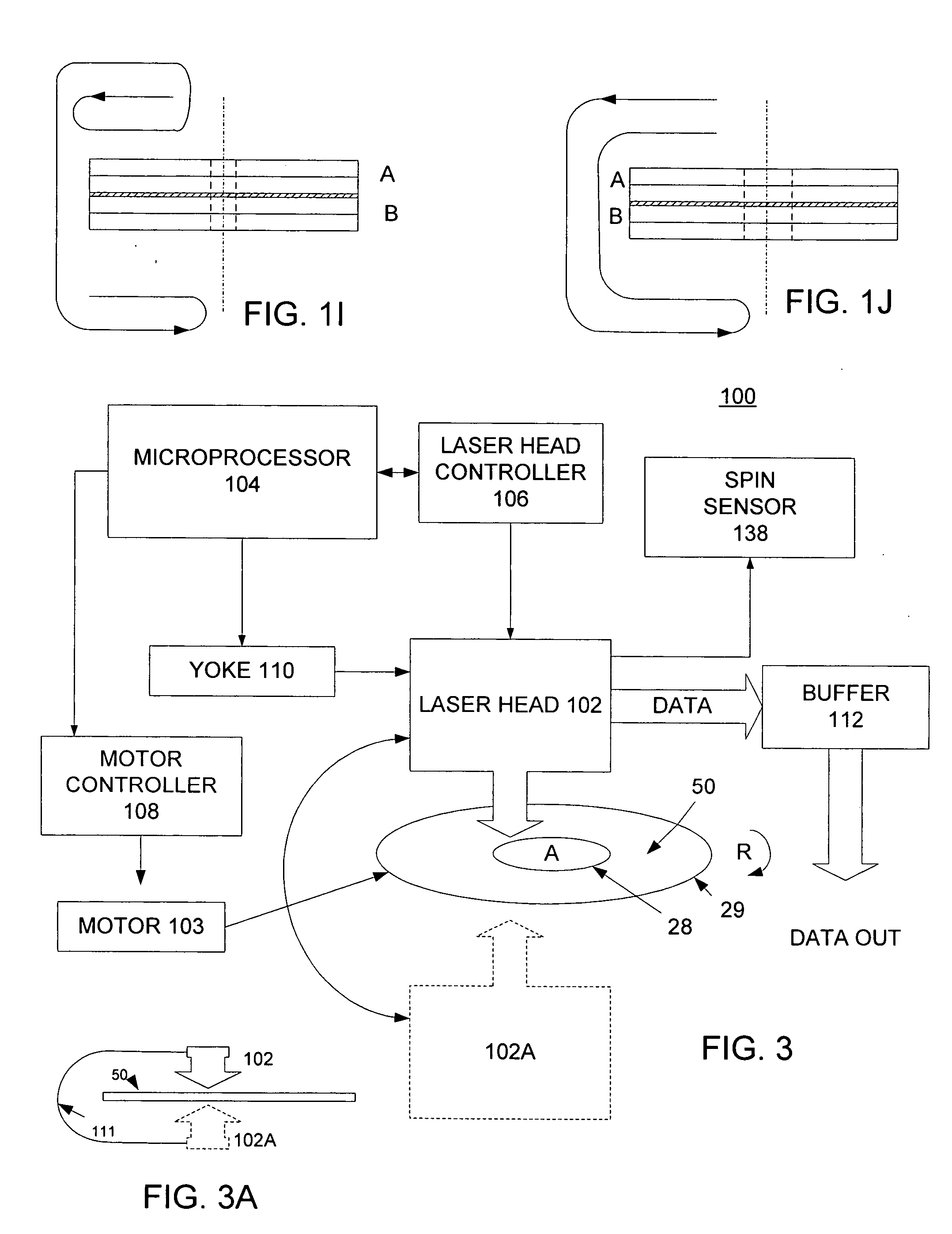
An apparatus and method for aligning a disk with an imprinting surface are described. In one embodiment, the apparatus has a die which includes an air-bearing mandrel having a tapered nose to engage an ID of the disk, a circular imprinting surface having a centerline concentric with the air-bearing mandrel, and an air-bearing cavity to position the disk. The axial movement of the top die towards the bottom die guides the ID of the disk into coincident alignment with the centerline of the top die.
Owner:WD MEDIA
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS6544616B2Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicMagnetic materials for record carriersVacuum evaporation coatingMetal alloyManganese
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective coating layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include zinc, aluminum, zinc plus aluminum, manganese, germanium, and copper plus manganese. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Optical recording medium and method for recording optical information
The present invention provides an optical recording medium which incorporates an inorganic based recording layer which has a high reflectance, sufficient for reproduction compatibility on devices such as CD-ROM drives, as well as a high degree of modulation between the state prior to recording and that after recording, as well as an information recording method therefor. Accordingly, an optical recording medium comprises a substrate (2) which is substantially transparent with respect to a recording light beam and a reproduction light beam, a first recording layer (3) which is layered on top of the substrate (2) and which incorporates as the main constituent a metal which has a low melting point and a high reflectance, and a second recording layer (4) which is layered on top of the first recording layer (3) and which will, due to heat generated from irradiation of a light beam through the substrate (2), either mix, or alternatively react, with the first recording layer (3) to form an alloy of low reflectance as well as forming irregularities or pitting in the surface, thereby enabling the recording of information. Due to the heat generated from irradiation of a recording light beam through the substrate (2) the first recording layer (3) and the second recording layer (4) are either mixed, or alternatively reacted to form an alloy as well as forming irregularities or pitting in the surface, thereby recording information.
Owner:KAO CORP
Optimized media grain packing fraction for bit patterned magnetic recording media
InactiveUS20050157597A1Optimizes optical coupling efficiencyOptimizes medium grain packing fractionCombination recordingNanoinformaticsEngineeringOptical coupling
A bit patterned magnetic recording medium for use in HAMR, which is optimized for optical coupling efficiencies and improved magnetic read-back coupling. The medium comprises bit-patterned magnetic recording elements, each corresponding to a magnetic data bit, and each comprising a cluster of discrete and separated magnetic grains. The desired packing fraction may be obtained by defining the number of grains within a bit, while bit-patterning provides efficient optical transmission. The grains have an effective packing fraction that enhances magnetic read-back signals, and the bits are distributed in a pattern having a packing fraction that enhances the optical coupling efficiency. The bits and / or the grains may be substantially thermally and optically isolated.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Novel optical storage materials based on narrowband optical properties
InactiveUS20050136333A1Photomechanical apparatusRecord information storageHolographic storageOptical property
Holographic storage media including a substrate and a dye material capable of undergoing a photo-induced change are disclosed. Data may be written into the holographic storage media using light of one wavelength and read using light of a different wavelength.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
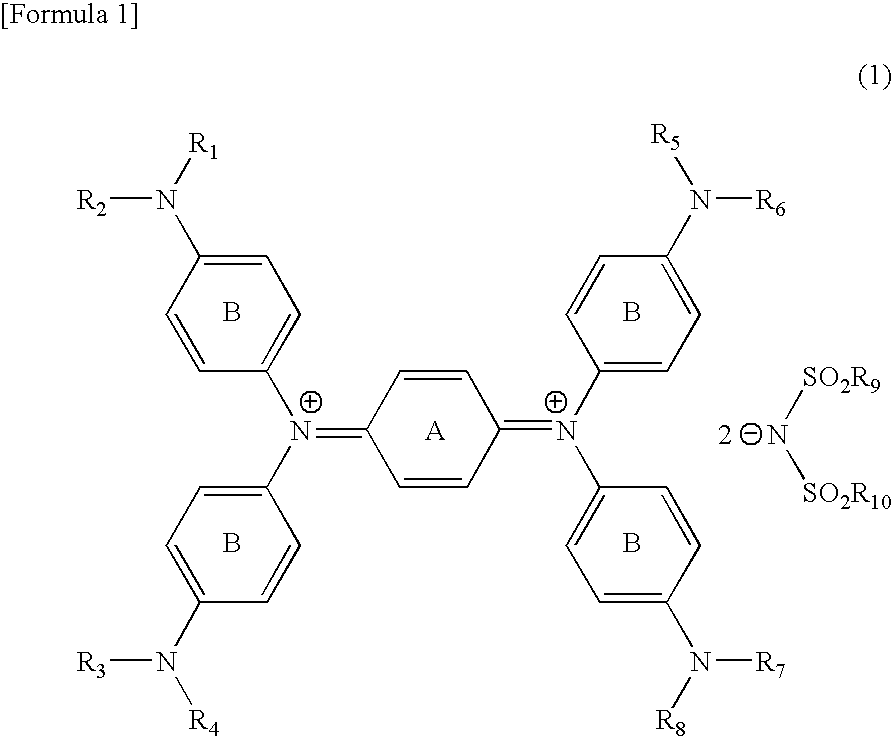
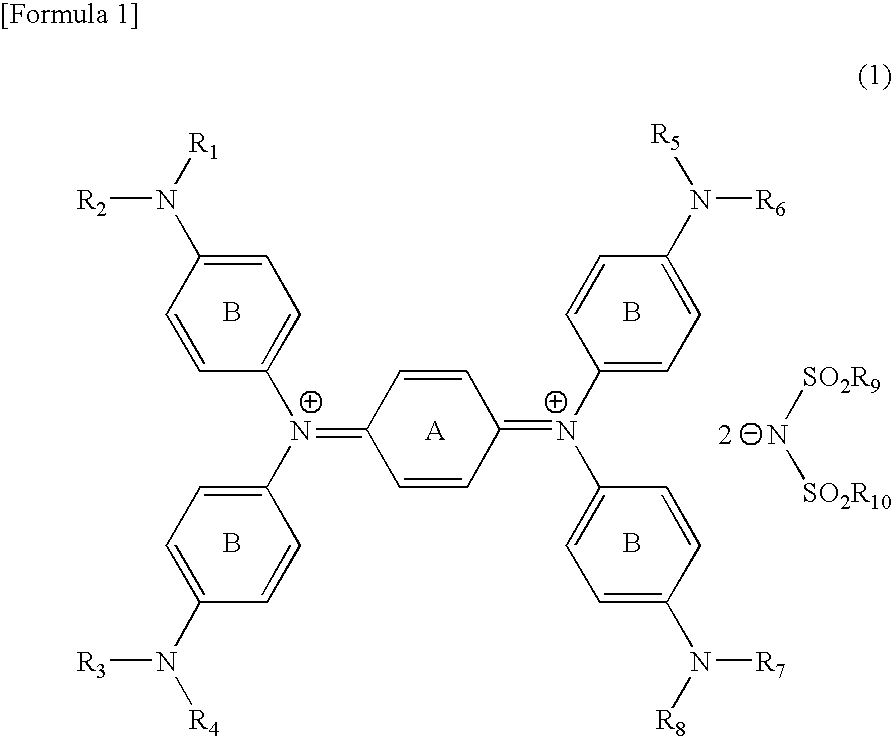
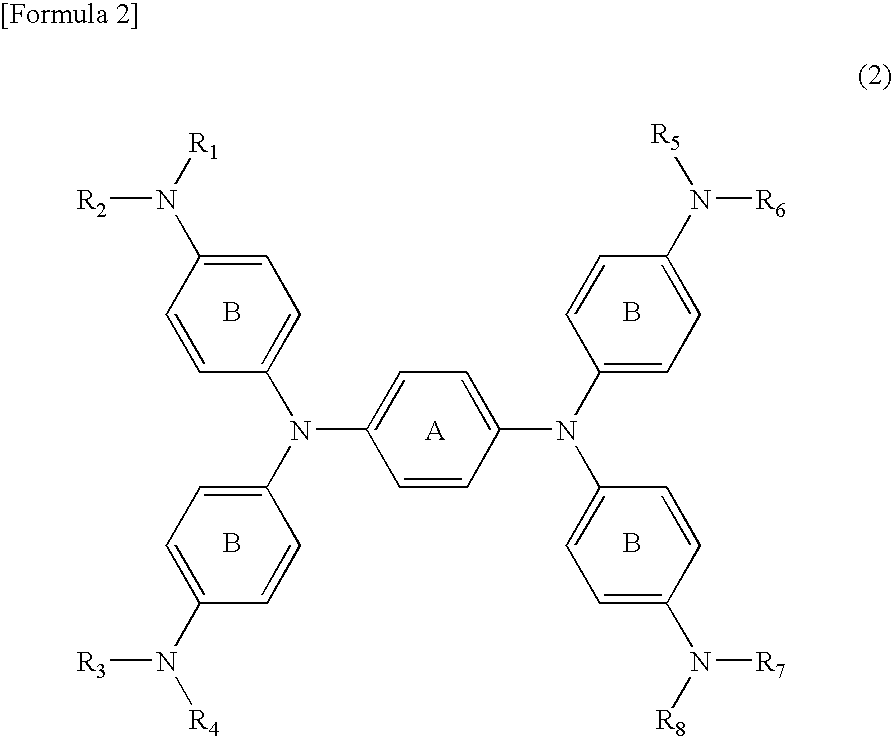
Diimmonium compound and use thereof
InactiveUS20050148786A1High visible light transmittanceHigh light transmittanceOrganic chemistryPhotomechanical apparatusInfraredAmmonium compounds
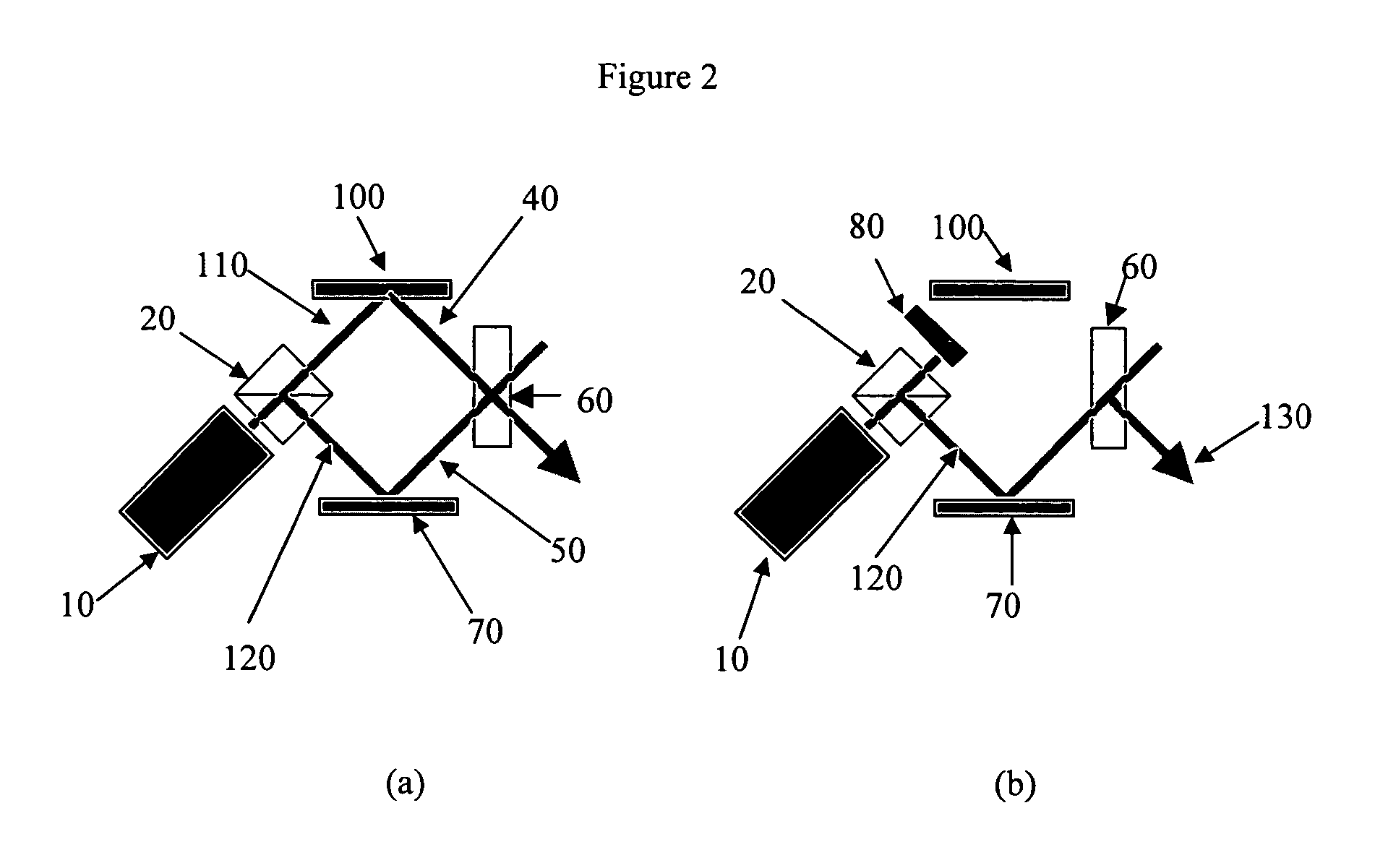
To provide a near-IR absorption compound free from antimony or arsenic and excellent in stability, especially, in heat resistance, light fastness, and moisture-and-heat resistance and also an IR absorption filter, an optical information recording medium, and a resin composition excellent in durability by using the near-IR absorption compound. The near-IR absorption compound is a diimmonium compound having the following structure and the resin composition contains the diimmonium compound: (wherein R1 to R8 independently denote hydrogen atom or an optionally substituted aliphatic hydrocarbon group; R9 and R10 independently denote an aliphatic hydrocarbon group optionally containing a halogen atom; and rings A and B may further have substituent groups.).
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Process and apparatus for forming plastic sheet
InactiveUS6183829B1Avoid mistakesLow birefringenceRecord carriersPhotosensitive materialsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
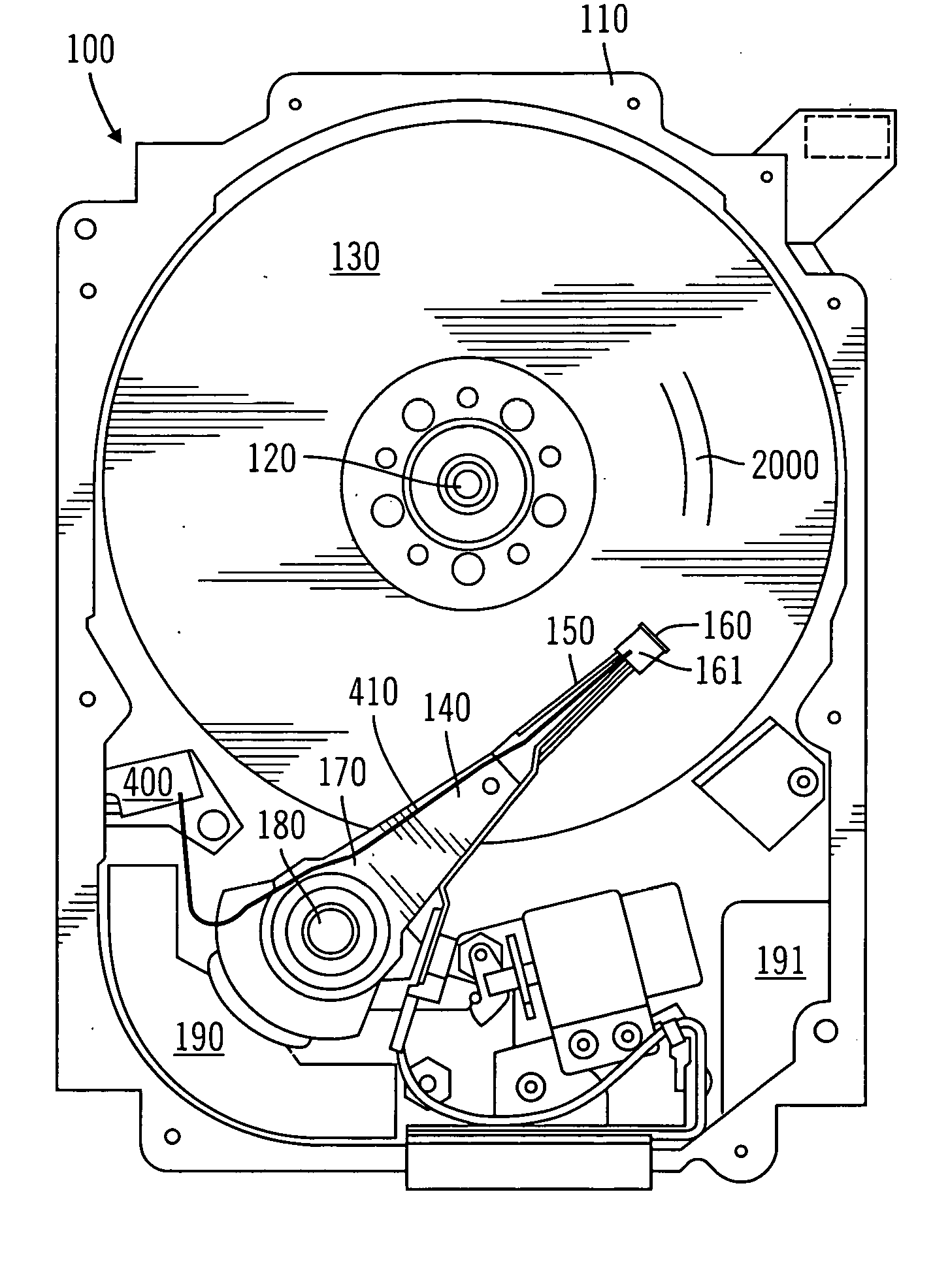
Optical disk and method of integrating a high gain RFID antenna
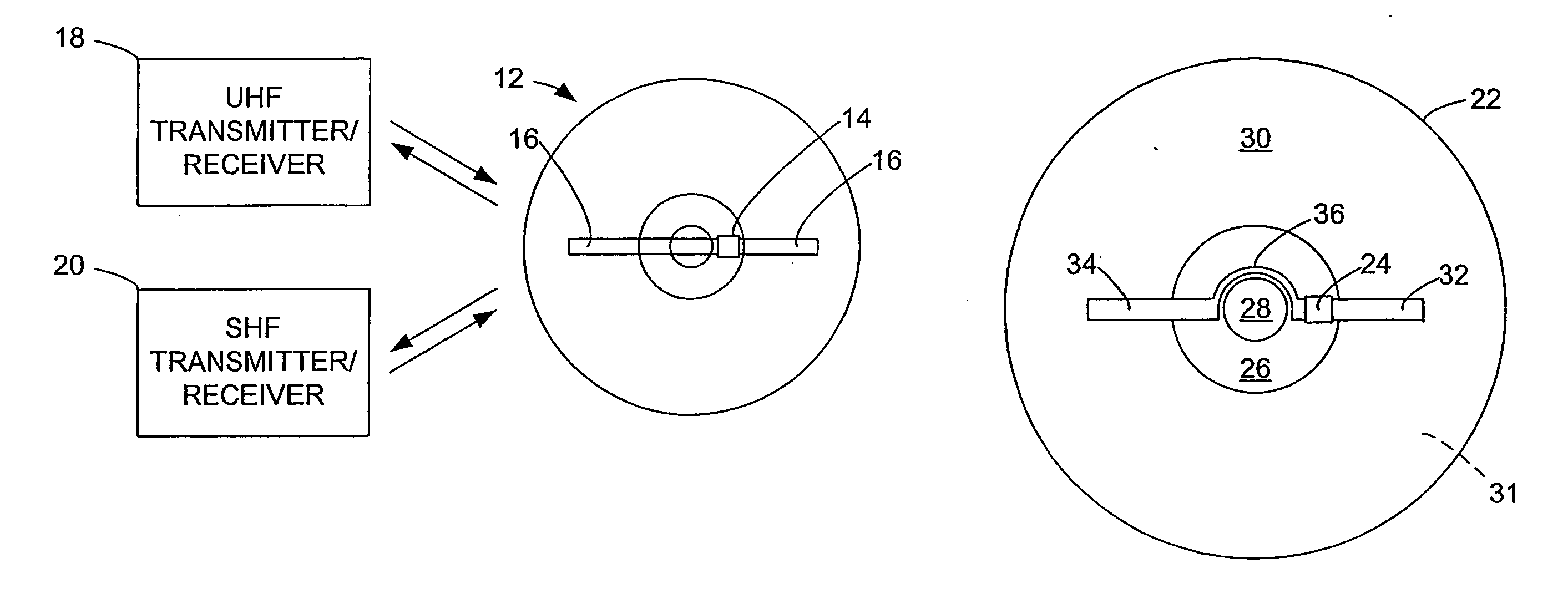
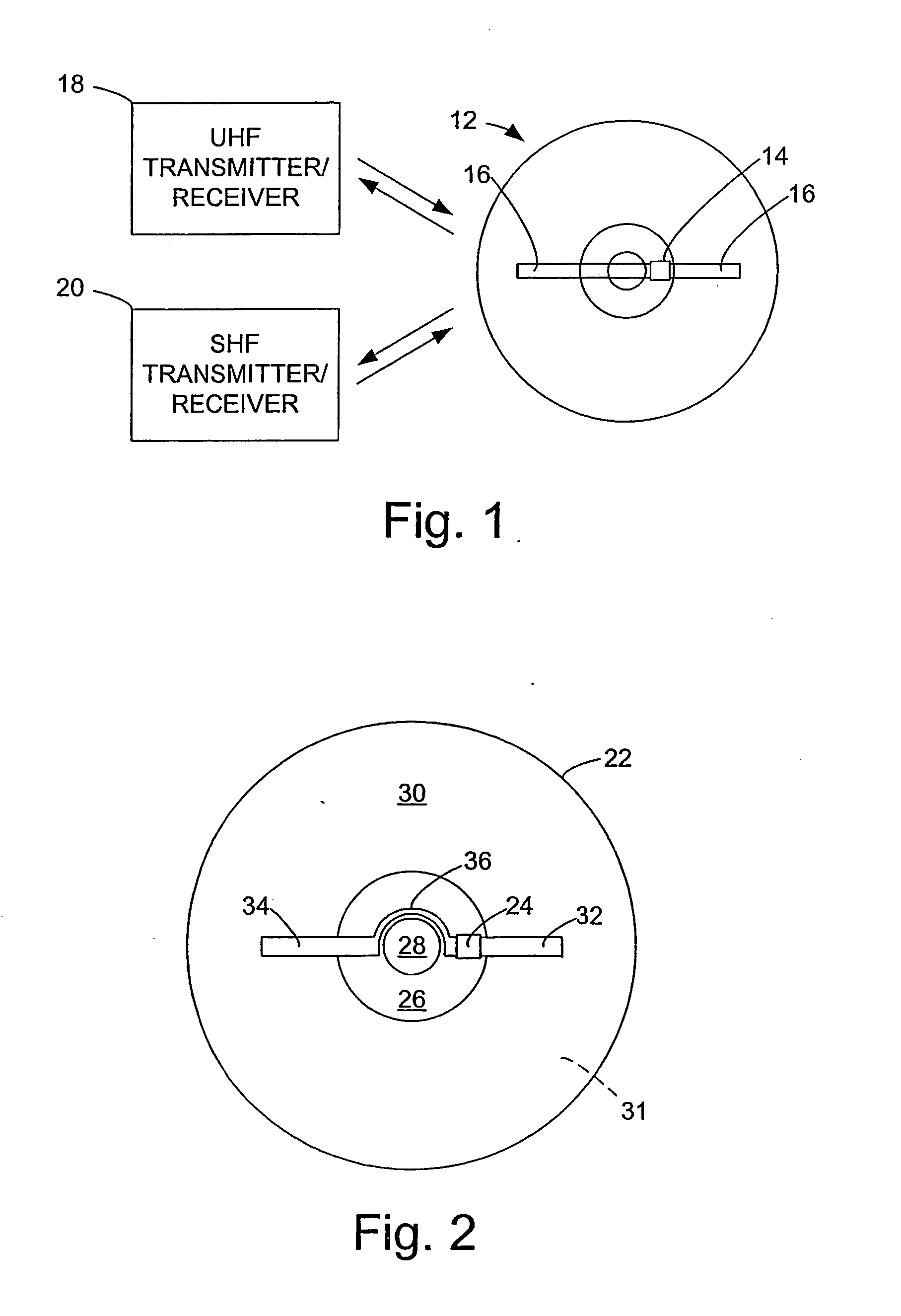
InactiveUS20060071795A1Easy to mergePrevent tamperingMechanical record carriersRecord information storageRadio frequency signalEngineering
An optical disk comprises a disk substrate having a hub and an annular optical metallicized data region extending radially outward from the hub. The optical disk further comprises a radio frequency identification (RFID) transponder affixed to the disk substrate, e.g., within the non-data containing hub region. The optical disk further comprises at least one linear antenna element coupled to the transponder, e.g., via pole lead(s), and extending within the data region. The antenna element(s) can be applied to the disk substrate as a patterned antenna layer over a metallicized data region, and can be electrically isolated from the data region. A method and system of identifying an optical disk is provided. A radio frequency (RF) signal can be transmitted to the optical disk at a range of at least five feet, and preferably at a range of at least ten feet. An RF signal with an identification code (e.g., a unique number) can be received from the optical disk in response to the transmitted RF signal. The activating RF signal can be transmitted by, and the identification RF signal can be received by, e.g., a handheld RF reader or an RF reader that is affixed to a building. The identification code can then be processed for many purposes, such as identifying the optical disk as a non-counterfeited optical disk, calculating a royalty, or tracking the location of the optical disk.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Extended range RFID system
InactiveUS20060028344A1Increase rangeAntenna supports/mountingsMechanical record carriersExtended coverageEngineering
A radio frequency identification (RFID) system for discs such as CDs, DVDs or minidiscs includes a special RFID transponder and antenna configuration. The discs normally include an outer metallized annular zone where information is stored, a central hole, and an inner annular zone between the hole and the outer annular zone. The transponder may be located in the inner annular zone, with antenna elements coupled to the transponder extending in opposite directions part way across the outer annular zone. Multilayer labels with a recess for the transponder chip, and antenna elements formed by conductive material may be employed to apply the RFID assembly to the discs. A monopole or dipole mode of antenna operation, prominently involving the metallized disc layer, results from the antenna configuration, and serves to more than double the range of the system.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS20020034603A1Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicMagnetic materials for record carriersVacuum evaporation coatingManganeseHigh reflectivity
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective coating layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include zinc, aluminum, zinc plus aluminum, manganese, germanium, and copper plus manganese. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
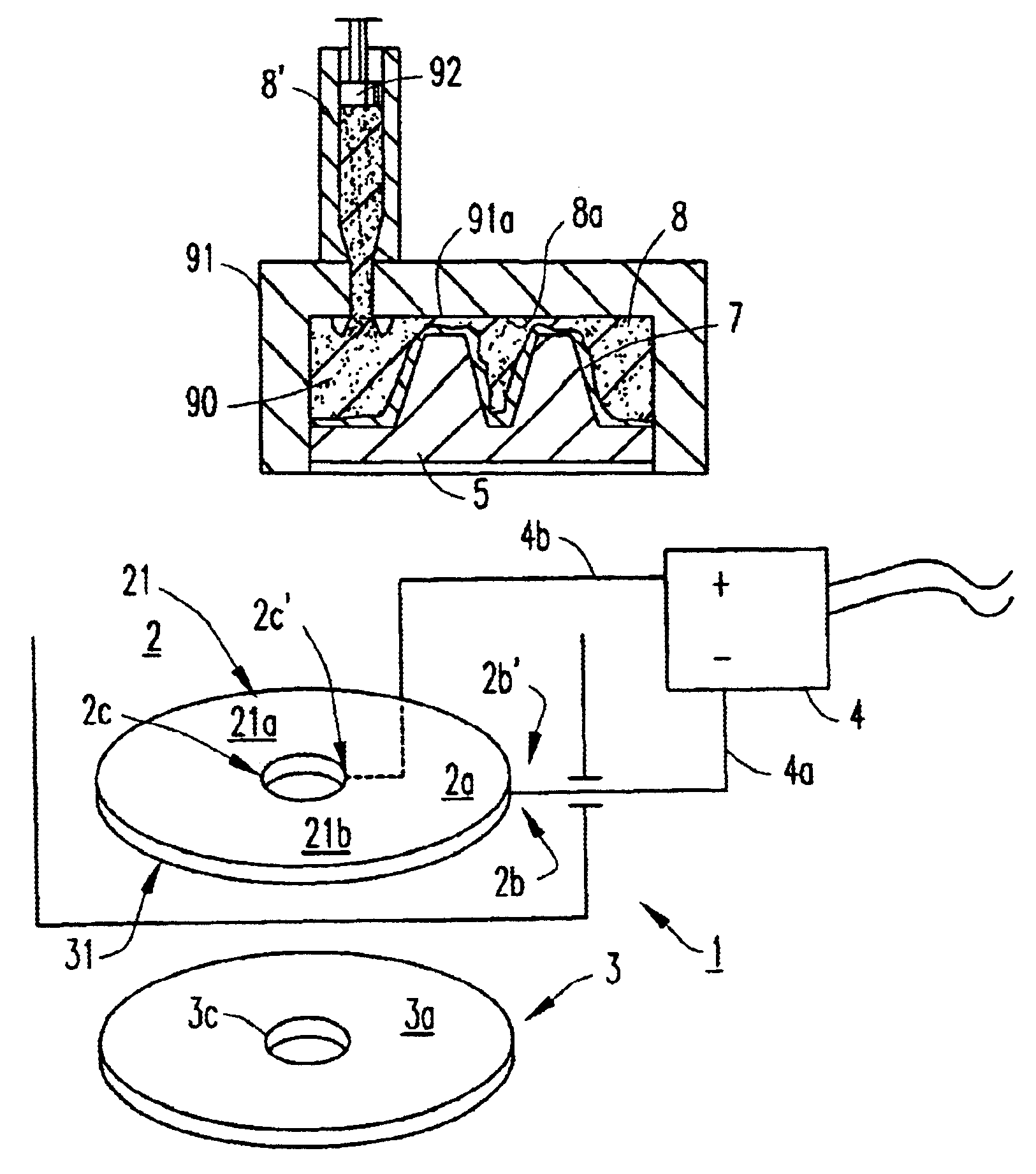
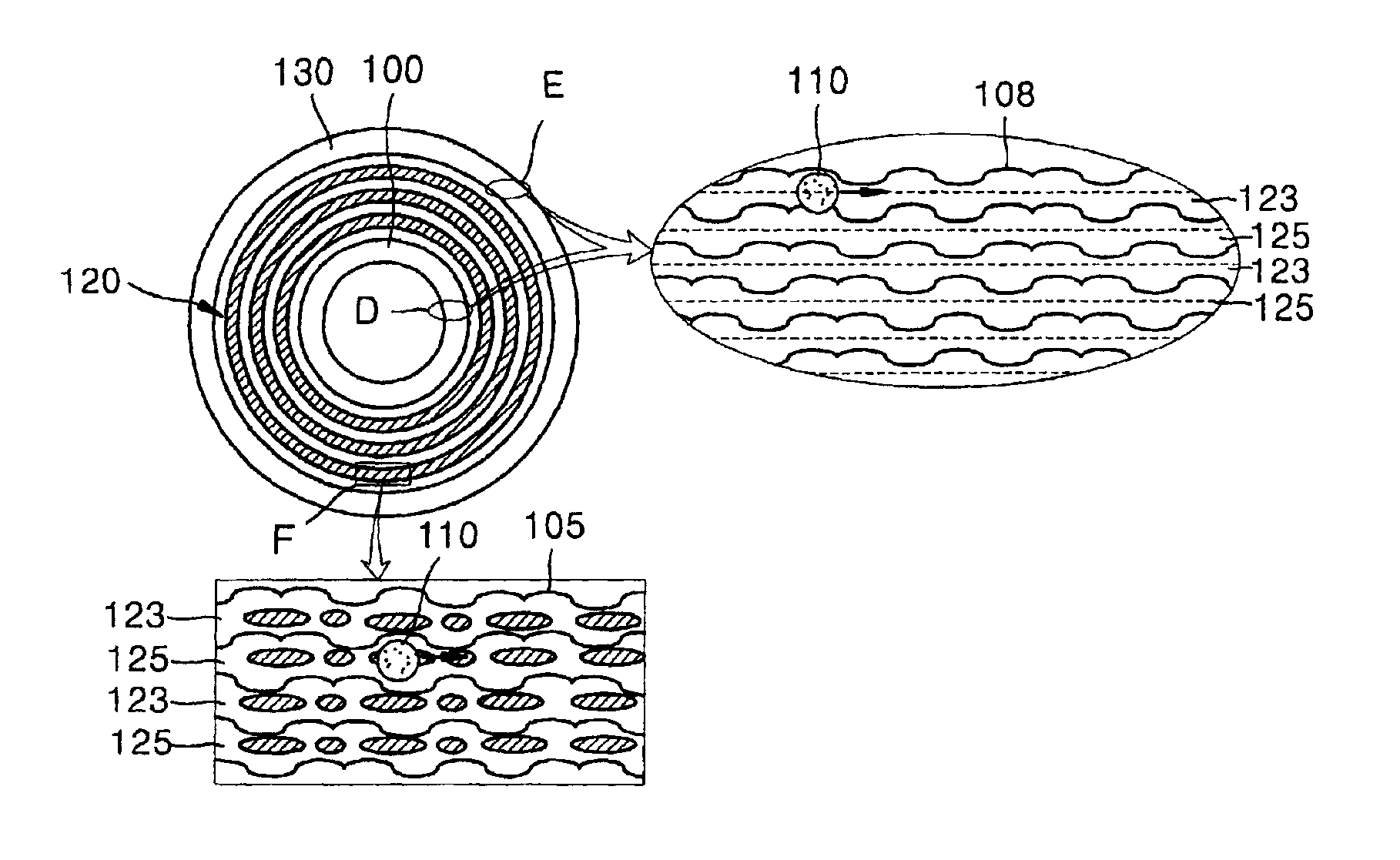
Information recording mediums, supporter used in the mediums, manufacture methods of the supporter, manufacturing apparatus of the supporter and stampers for producing the mediums
InactiveUS6254966B1Magnetic materials for record carriersLayered productsHigh densityManufactured apparatus
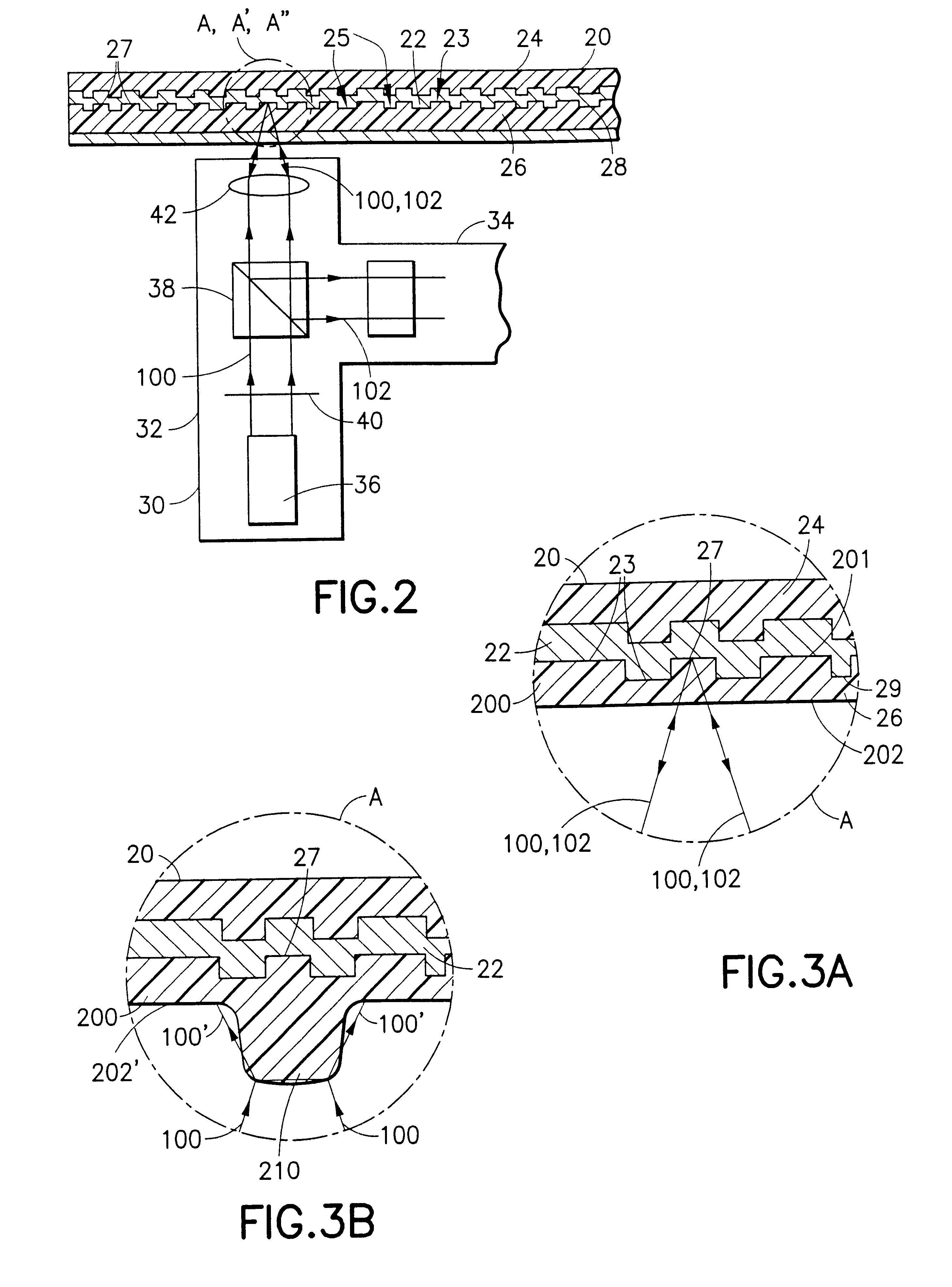
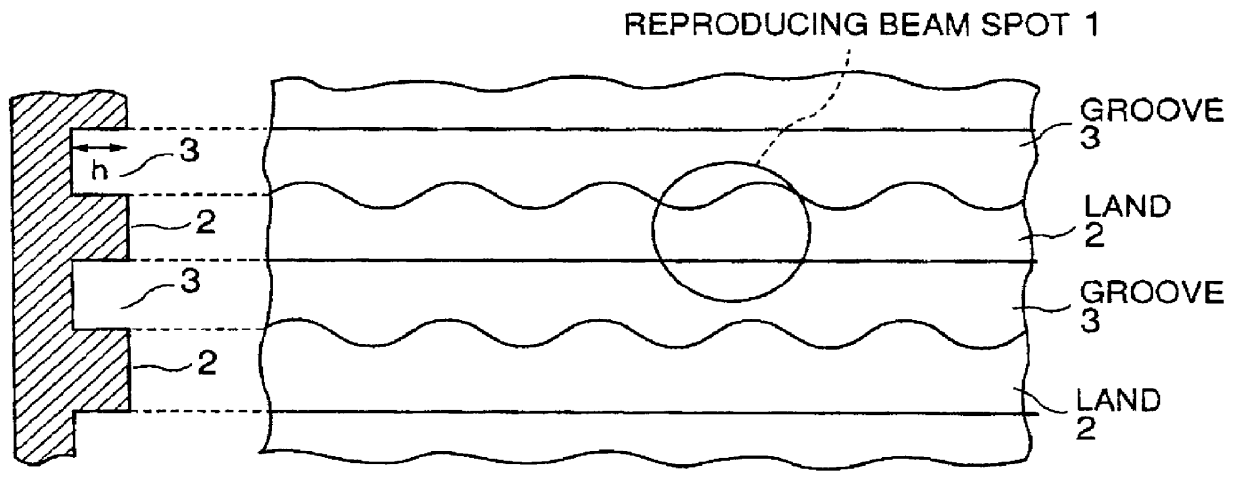
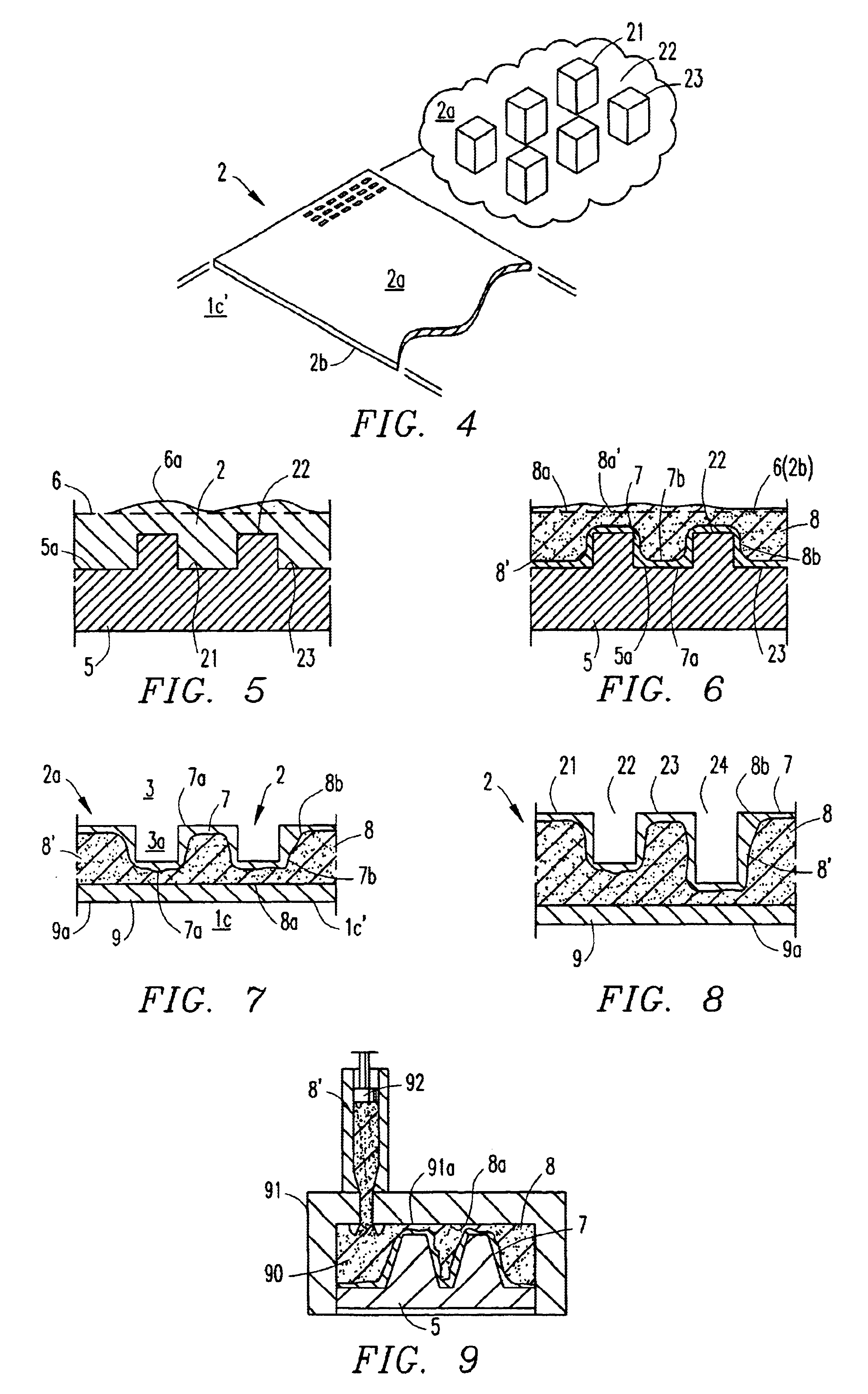
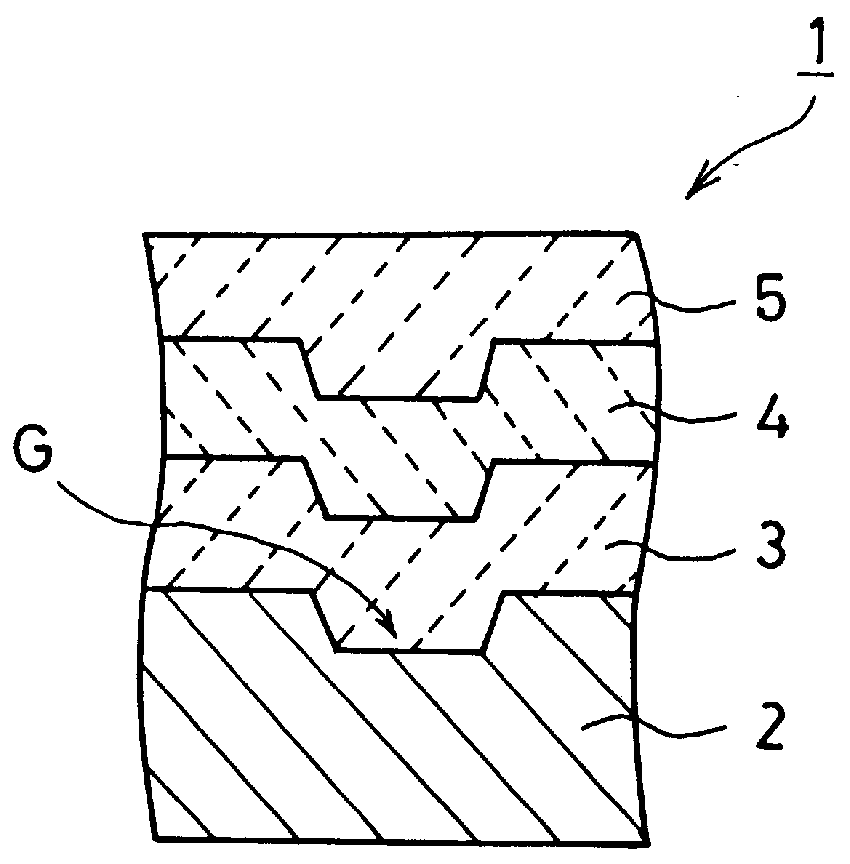
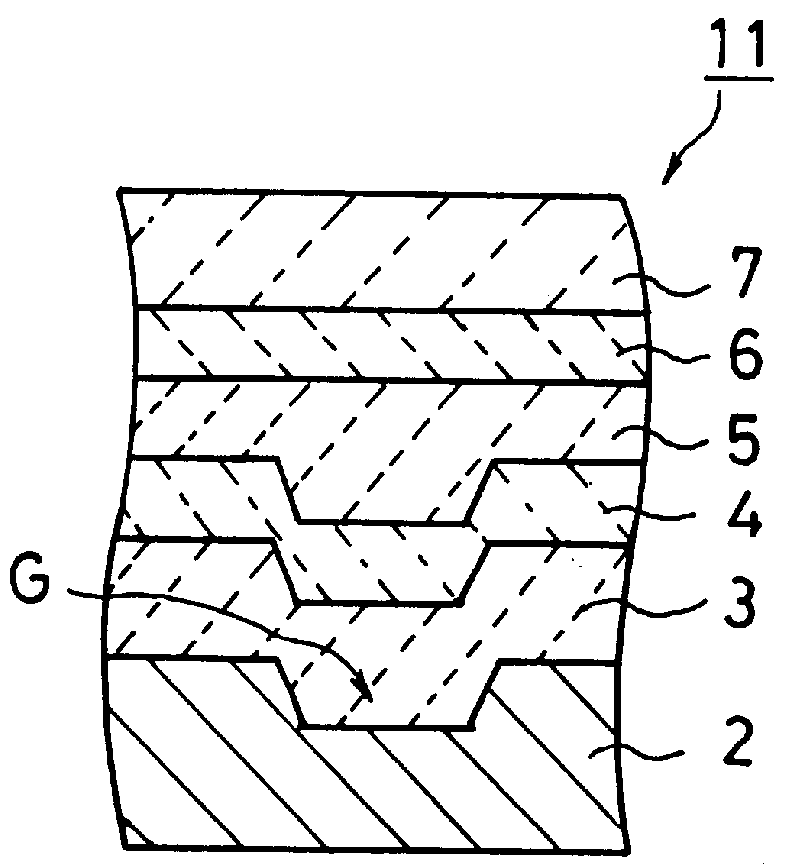
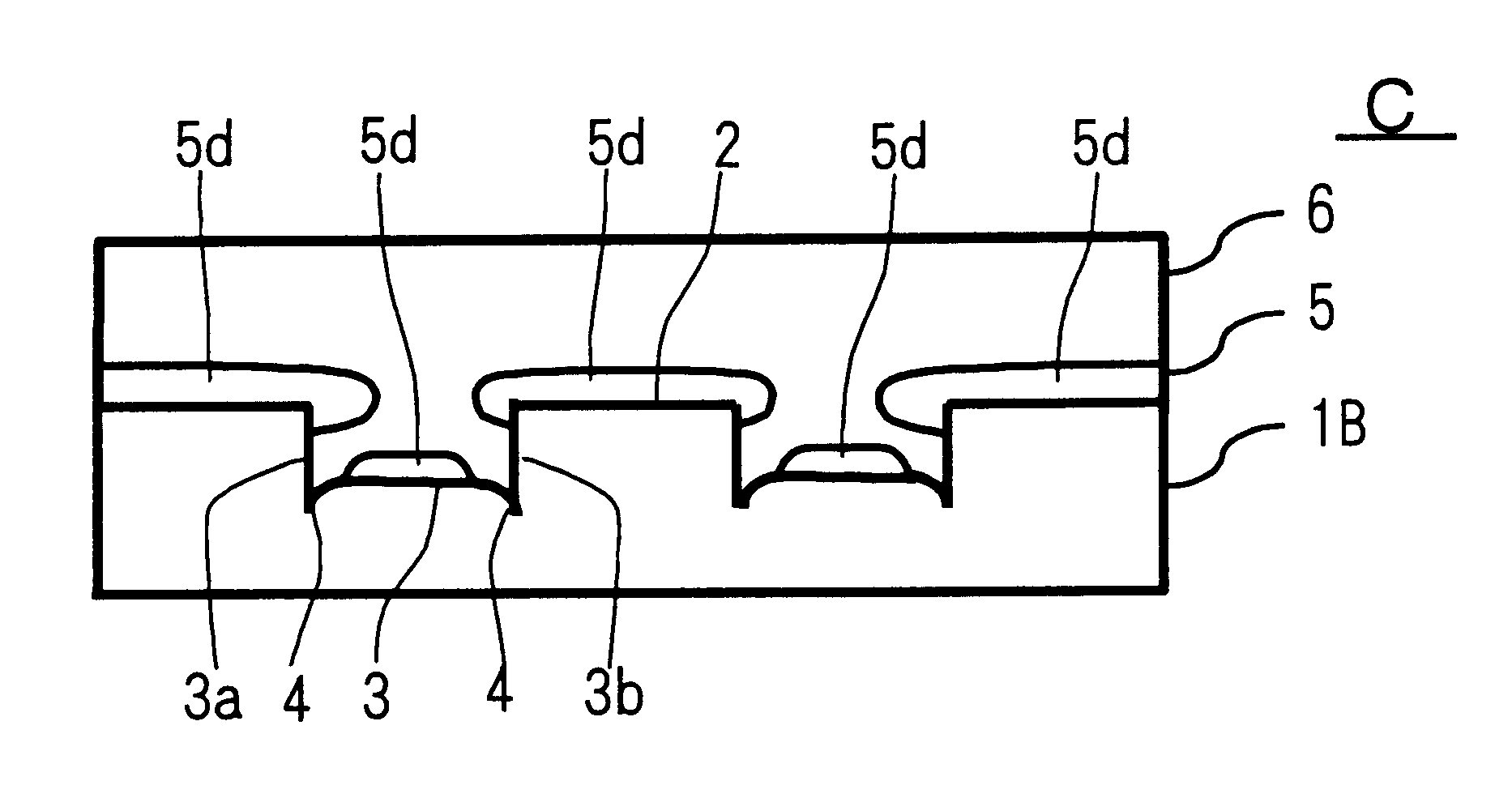
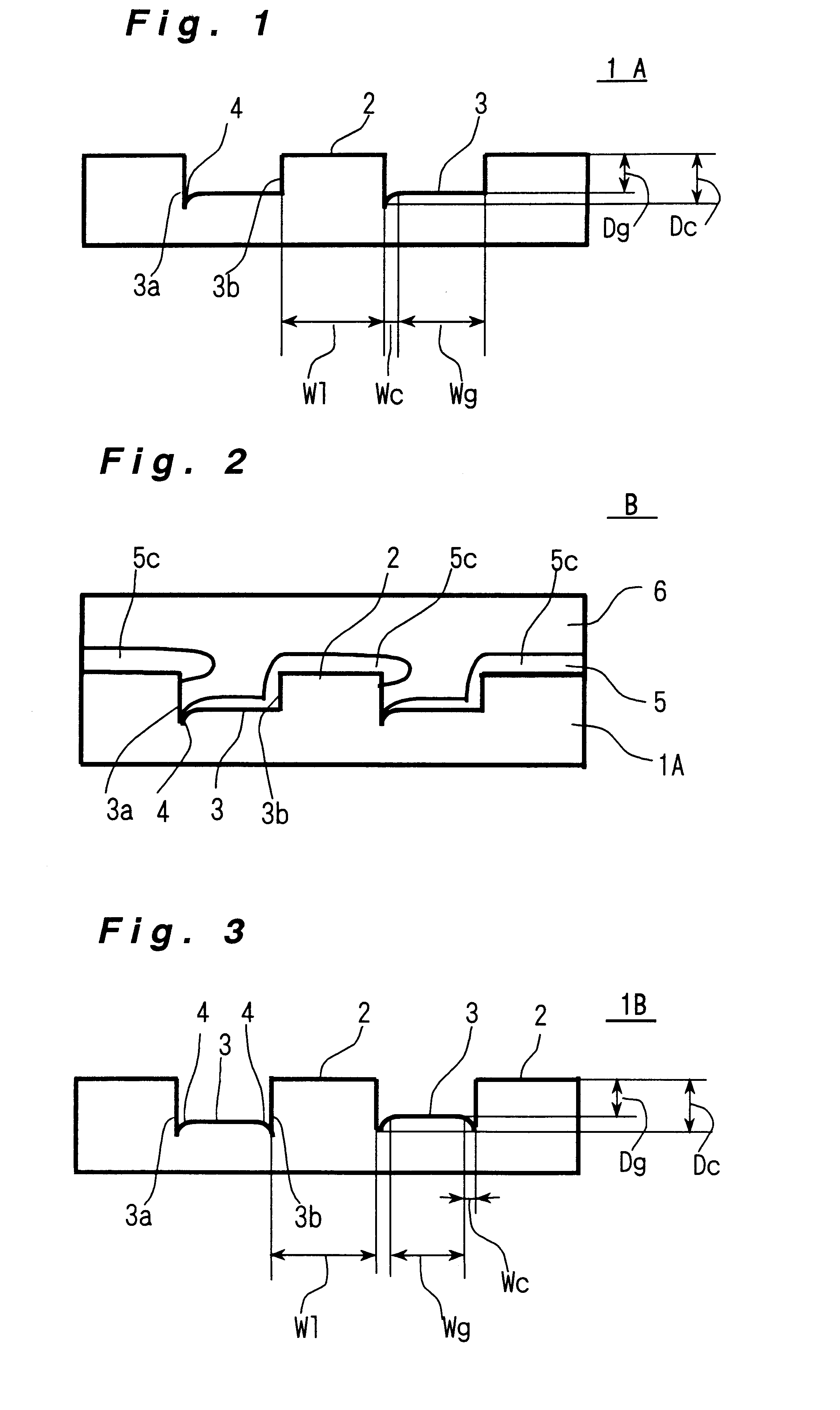
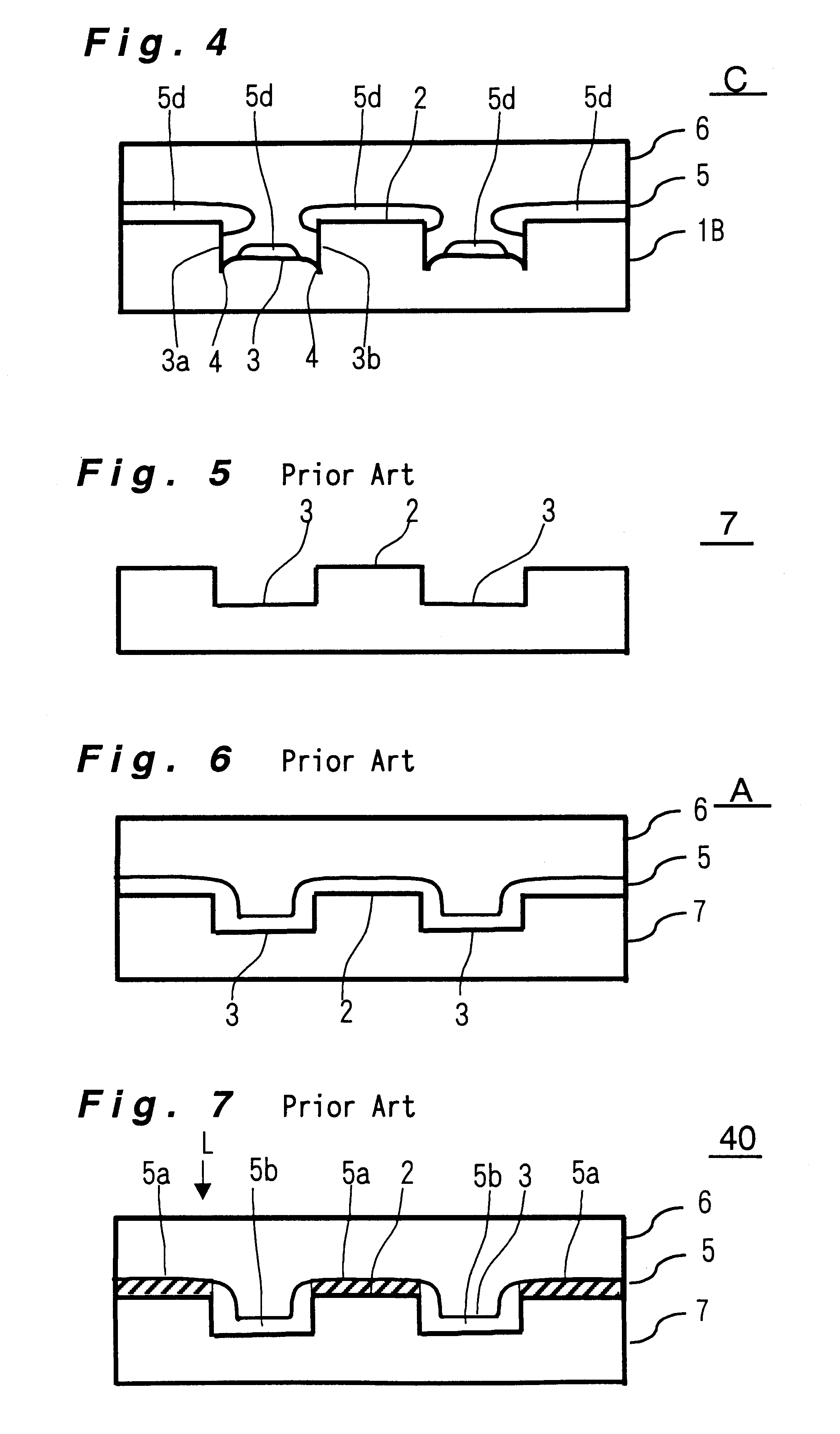
An information recording medium and a supporter used for the information recording medium capable of recording a land / groove recording by using a high density recording technique such as a super-resolution, resulting in a high density recording. An information recording medium B has a supporter 1A, on which a recording layer 5 is formed. On the supporter 1A, lands 2 and groove 3 are alternately formed as a minute track pattern. A crevice 4 having a depth Dc larger than a depth Dg of the respective grooves 3 is formed in the respective grooves 3 at one end of the respective grooves 3 in a width direction of the respective grooves.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Double-sided optical disc
A double-sided optical disc, is formed with data tracks on each layer. The tracks on one side follow one spiral while the tracks on the other side follow a second spiral, the two spirals being oriented in opposite directions as viewed from the respective sides, and therefore being mirror images of each other. This allows data to be read by a player seamlessly from both sides of the disc without changing the direction of rotation of the disc.
Owner:WARNER HOME VIDEO
Optical information recording medium, producing method thereof and method of recording/erasing/reproducing information
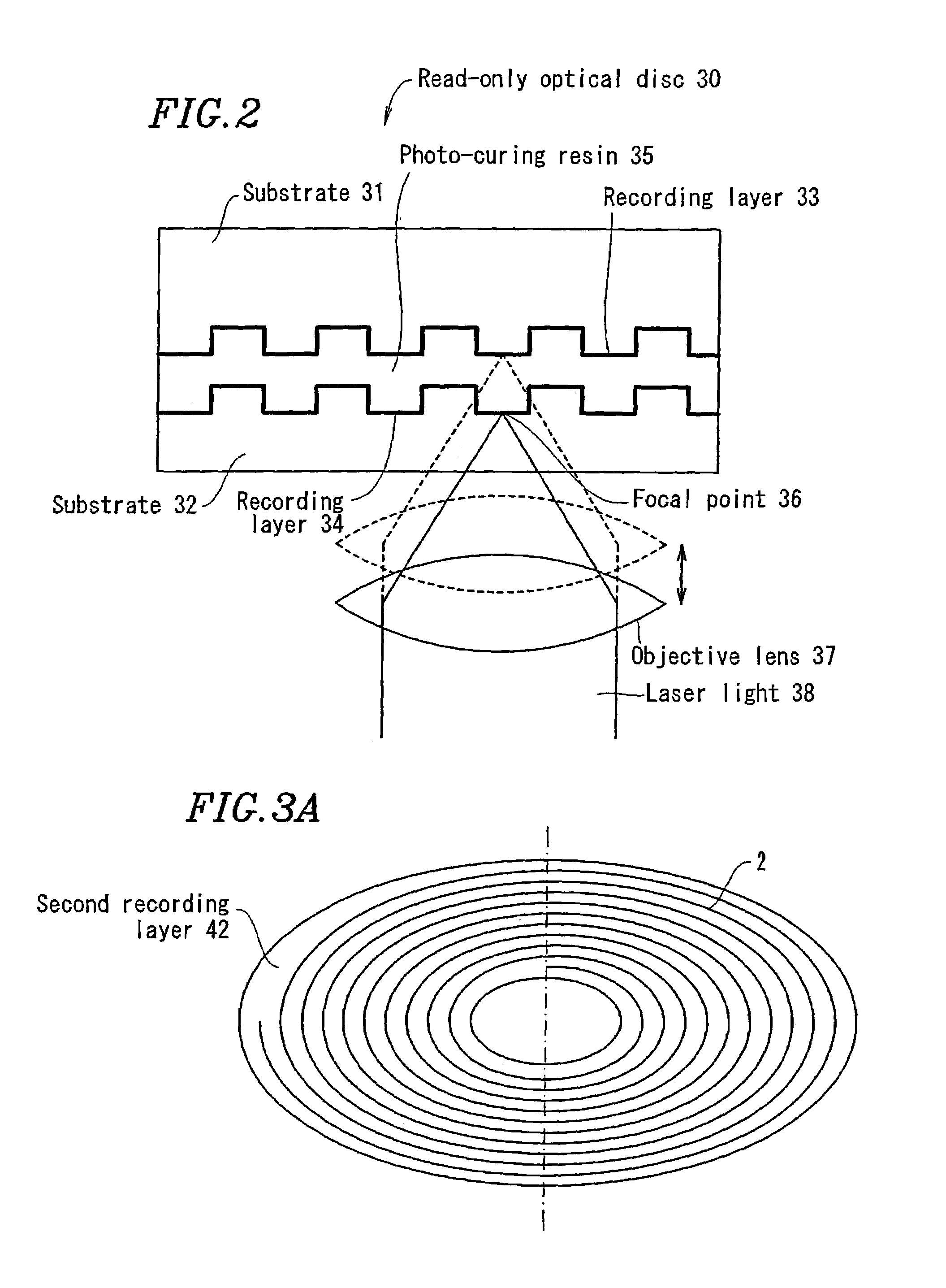
In a phase-change recording medium, a recording medium is provided with a barrier layer including Ge-N, Ge-N-O between a recording layer and a dielectric protective layer in order to prevent a chemical reaction and an atom diffusion between the recording layer and the dielectric protective layer. A barrier material can be also applied to the protective layer itself. Thereby, it is possible to considerably suppress a reduction of a reflectivity and a reduction of a signal amplitude due to the repeat of recording and erasing, such reductions being observed in a conventional phase-change optical information recording medium, and thereby the number of overwriting times can be increased.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Carrier card capable of storing information data in CD or DVD formats
InactiveUS6542444B1Easy to manufactureEasy to installCombination recordingOther printing matterSemiconductor chipComputer science
A data carrier and a method of making the data carrier. The data carrier includes a plastic body, at least one metal layer arranged in or on the plastic body for carrying information encoded in one of CD and DVD format, a semiconductor chip arranged in the plastic body, a communication device for connecting the semiconductor chip with an external apparatus, and a mechanism for balancing an unbalance caused by the semiconductor chip. The method includes providing a matrix carrying the encoded information in a relief, the matrix including at least one projection, casting a first part of the plastic body against the matrix, forming the metal layer on a side of the first part of the plastic body disposed adjacent the matrix, forming at least one recess in the plastic body with the projection, and coating the metal layer with a second part of the plastic body, wherein the recess in the plastic body is capable of receiving the semiconductor chip.
Owner:OMD INT
Imprint method and device
InactiveUS7144539B2Eliminate disadvantagesConfectioneryNanoinformaticsShell moldingMembrane interaction
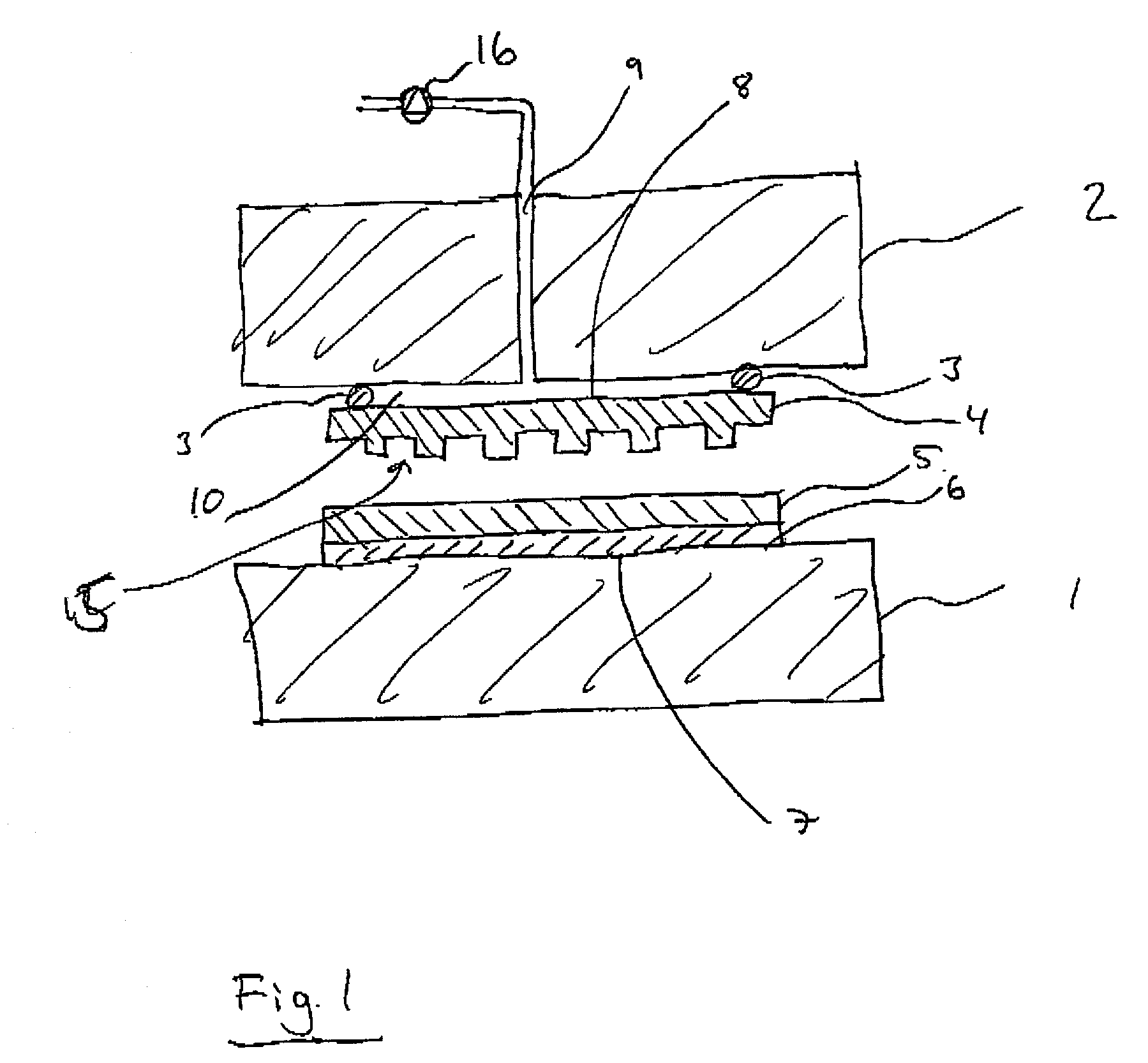
An imprint process comprises the step of aligning a substrate, supported on a first support member, with a template, supported on a second support member. The substrate has at least one essentially plane surface provided with a moldable film. The template has at least one essentially plane surface provided with a relief pattern. The relief pattern is adapted to interact with the moldable film. The process further comprises the step of arranging a sealing gasket between the template and the second support member, such that a pressure cavity is defined by the second support member, the template and the sealing gasket. The process also comprises the step of applying a static gas pressure to the pressure cavity, in order to provide a pressure between the template and the substrate. The pressure is sufficient to form a pattern in the moldable film. An imprint device is also disclosed.
Owner:OBDUCAT AB SE
Optical disc having uniform structure
InactiveUS7065015B2Increase productionReduce manufacturing costFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
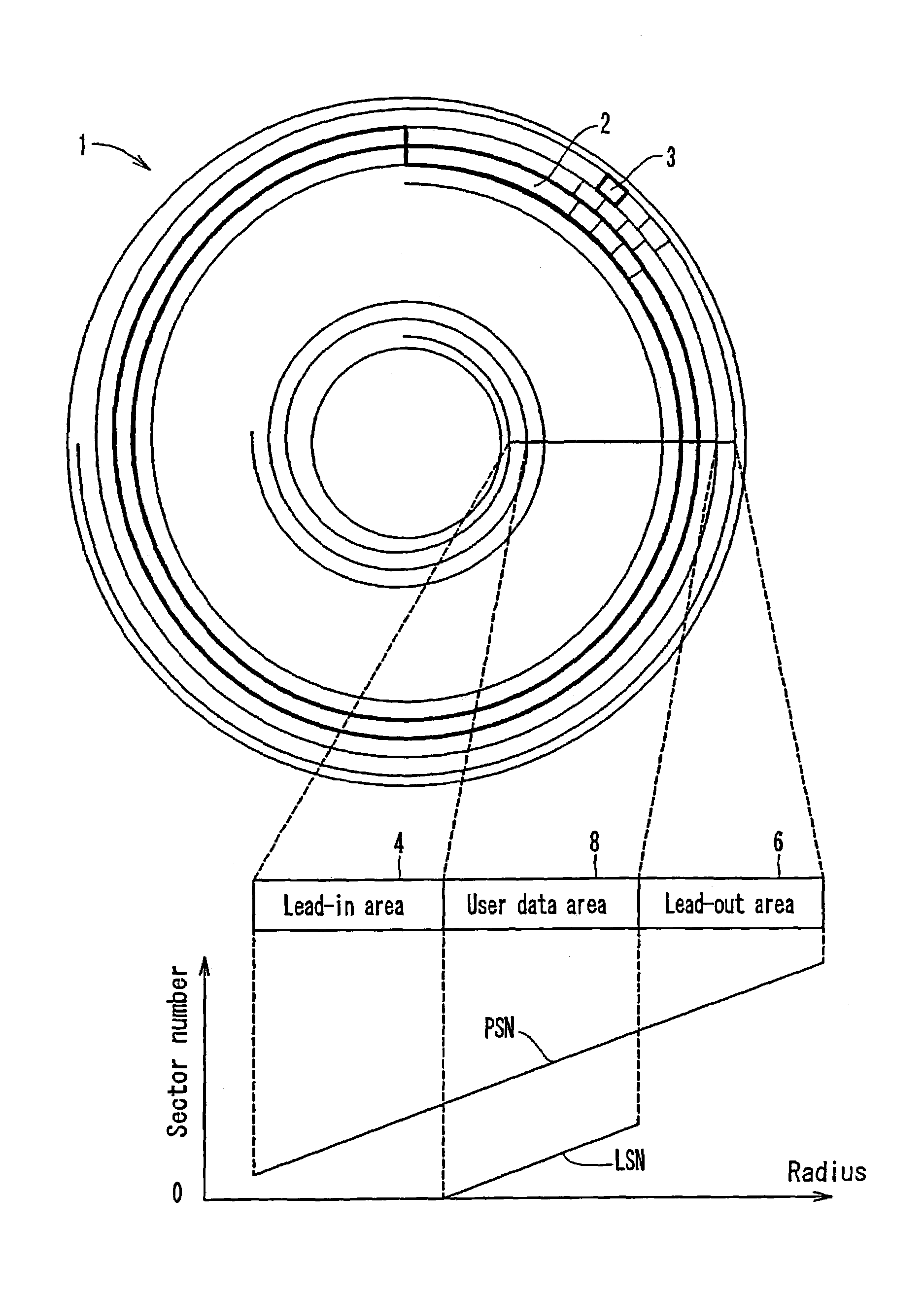
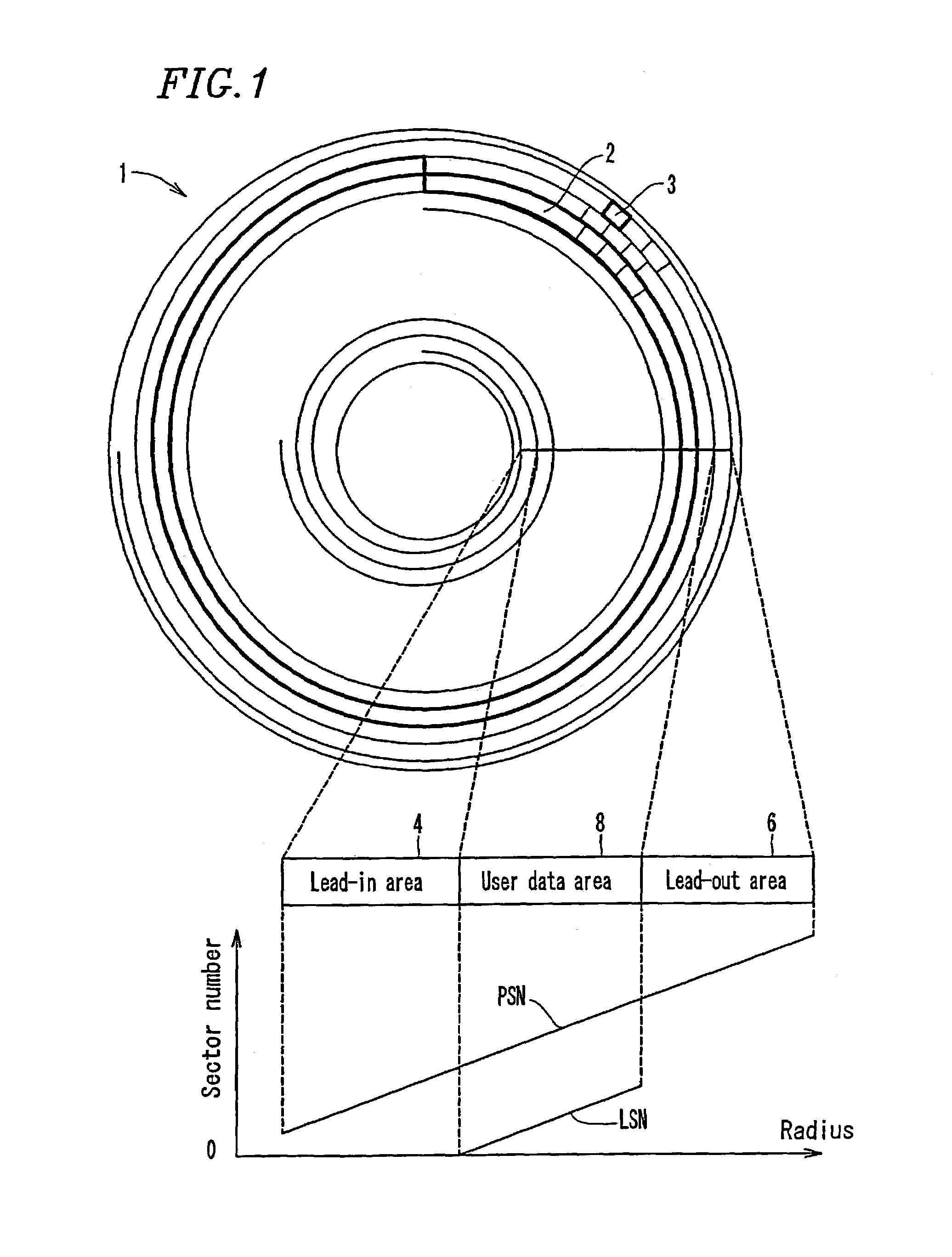
An optical disc is manufactured under a uniform condition by forming grooves and lands on the entire surface of the disc. The optical disc is configured to obtain a reliable reproduction signal, and the grooves and lands are formed on a lead-in area, a user data area and a lead-out area of the optical disc. Since the same manufacturing condition can be adopted in mastering discs, the yield can be enhanced and the manufacturing cost can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical phase-change disc
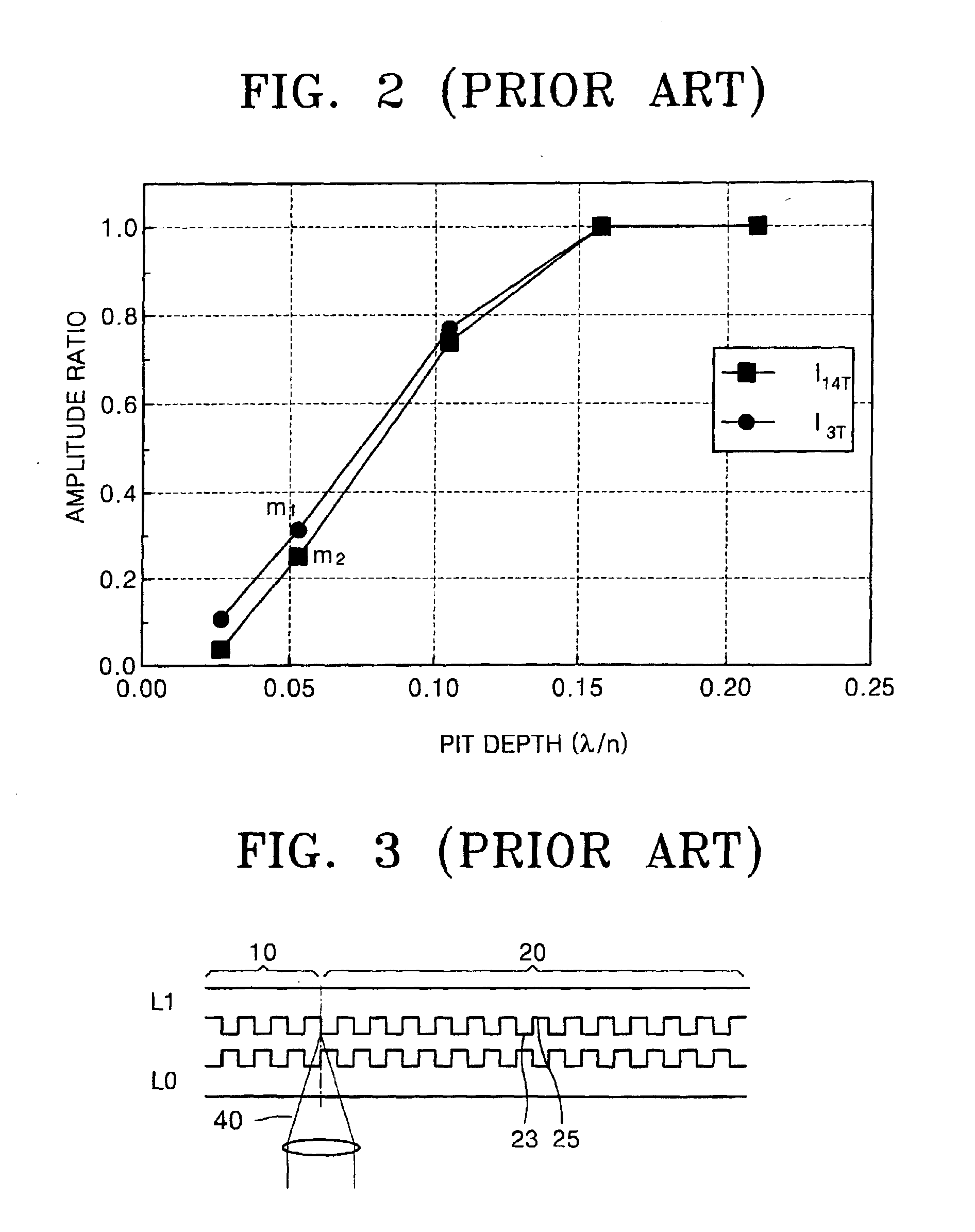
An optical phase-change disc comprises a substrate having thereon a spiral groove or concentric grooves for guiding a focused light beam, and a layer structure including a recording layer and protective layers sandwiching therebetween the recording layer. The groove has wobble for recording ATIP (absolute time information) or ADIP (address information). The following relationship between the groove width GW, beam diameter R0 and wobble amplitude aw: 0.25< / =GW / R0< / =0.45 or 0.65< / =GW / R0; and 0.03< / =aw / GW< / =0.08 hold for preventing distortion of the groove caused by repeated overwriting operation to improve reliability of the optical disc.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
Limited use DVD-video disc
InactiveUS20030081521A1Efficient interfaceCombination recordingAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useOptical propertyTime segment
A limited-use Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) includes a storage layer for storing content data and control key data. At least one mark of photosensitive dye is disposed on the disc exterior to the storage layer and over at least a portion of the control key data. In one embodiment, the mark is initially transparent to allow a DVD player to read the control key data. The mark changes from clear to become opaque when it is exposed to DVD reader laser light for a cumulative period of time. This change in the optical property of the mark and the configuration of the control key data prevents further reading of the content data after predetermined reading and playback usage of at least some of the content data is permitted. In another embodiment, the mark is initially opaque to initially prevent the successful reading of the control key data, and permanently changes to transparent when exposed to DVD reader laser light for a cumulative period of time.
Owner:NOW SHOWING ENTERTAINMENT
Method of recording or reproducing data on or from high density multi-layer recording medium using variable light intensity
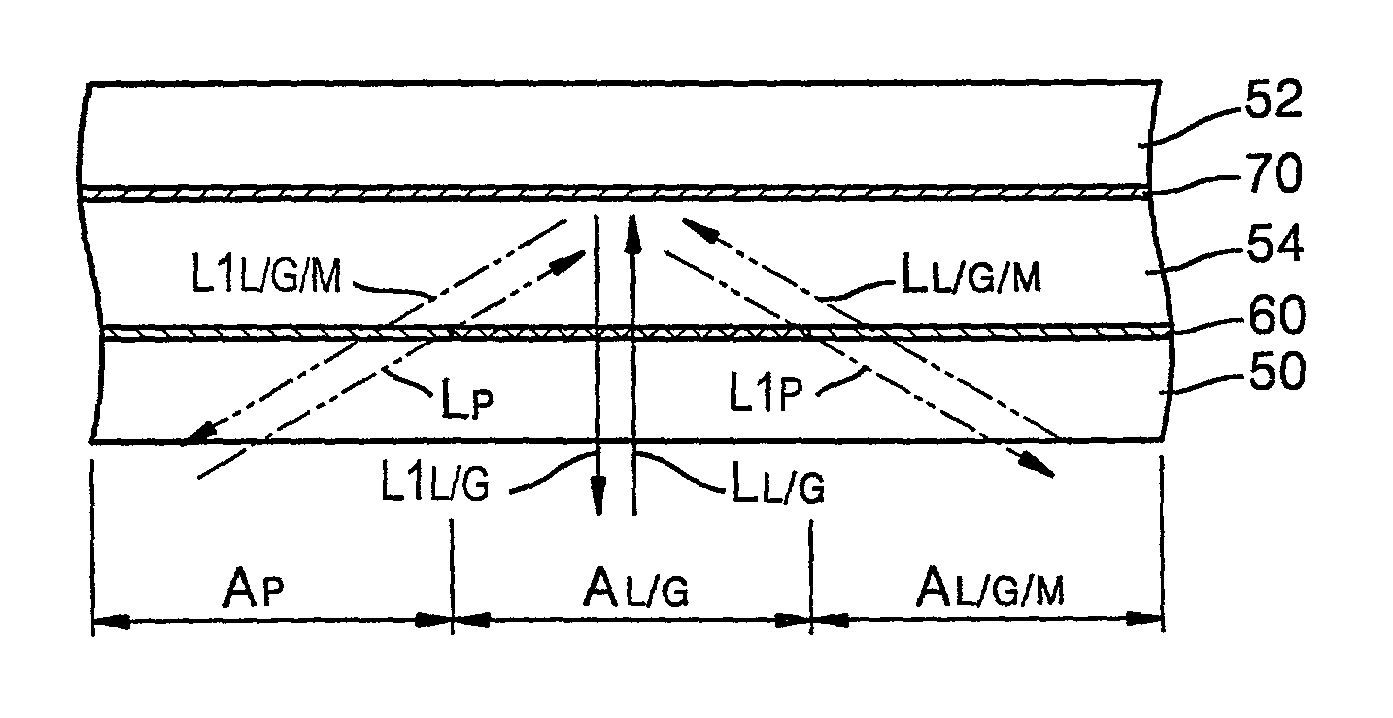
InactiveUS7009927B2Diminishing of dataDiminishing of surfaceOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageHigh densityData recording
A high-density optical recording medium and method of recording data on the optical recording medium. The optical recording medium includes a plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces having reflectances for light passing through a pit area, a land / groove area, and a land / groove area on which data are recorded, of a data recording / reproducing surface included between a light source for emitting light and a recording / reproducing surface selected from the plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces, the reflectances satisfy the expressions r1≧r2≧r3 and {(r1−r3) / r3}≦0.2, where r1, r2 and r3 are the reflectances of the pit area, the land / groove area and the land groove area on which data are recorded, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for making a stamper for patterning CDs and DVDs
InactiveUS20050167867A1Good resistance stabilityUnnecessary to performRecord carriersConfectioneryResistCompact Disc manufacturing
A method for forming a stamper used in the manufacture of CDs, DVDs, and other types of optical disks comprises forming a substrate by rolling. A layer of material is deposited (e.g. by plating) onto the substrate. Thereafter, a resist layer is formed on the layer of material and patterned. Because the substrate is formed by rolling, it is relatively inexpensive to form the substrate to a desired thickness. Because the layer of material is formed by deposition (e.g. plating), it is relatively inexpensive to ensure that the layer has a very smooth surface (i.e. without necessitating a great deal of polishing).
Owner:WD MEDIA
Optical recording medium
ActiveUS20040139459A1Avoid it happening againMechanical record carriersRecord information storageInter layerOptical recording
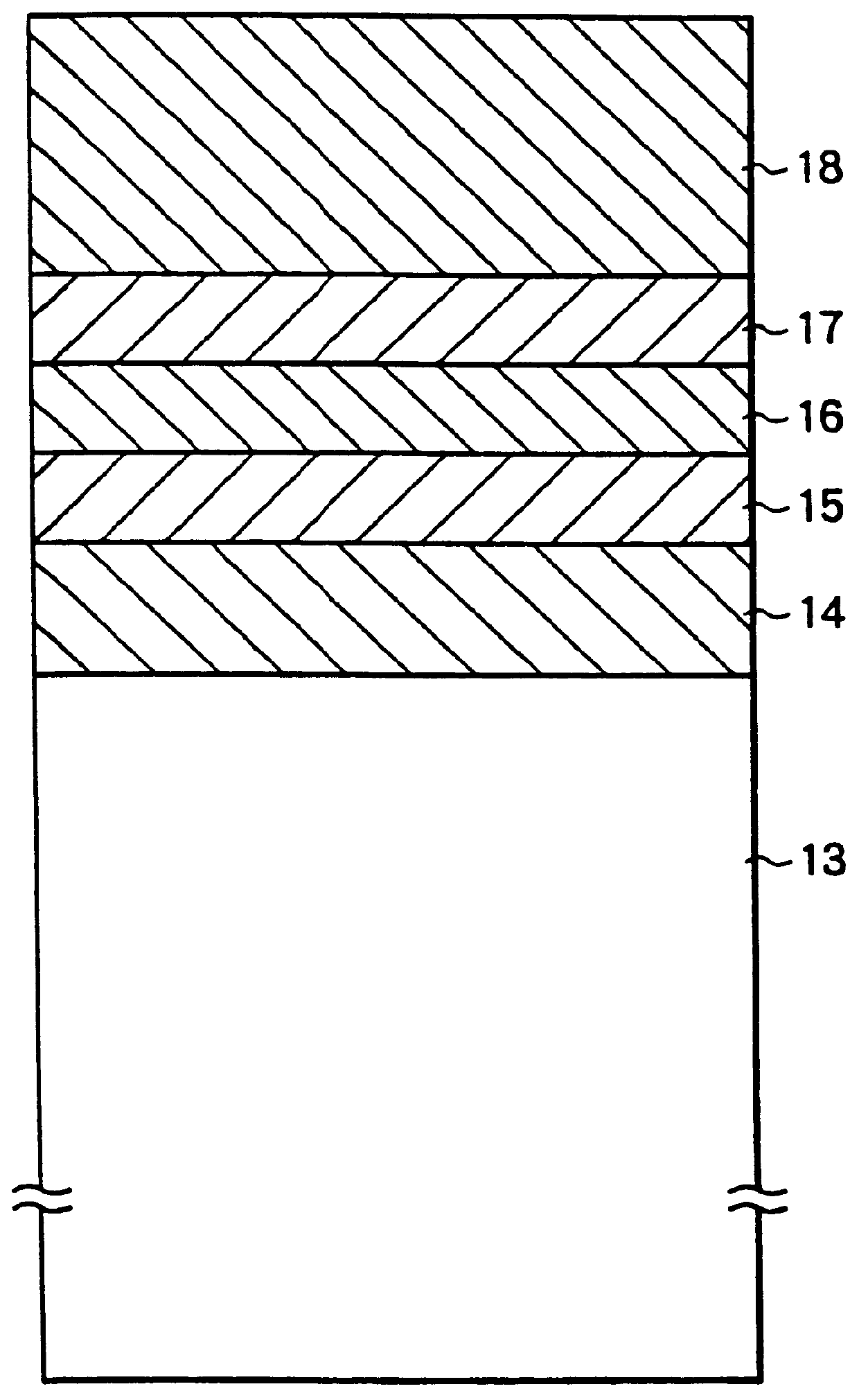
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a protective layer, three or more information recording layers formed between the substrate and the protective layer and transparent intermediate layers each formed between neighboring information recording layers and capable of recording data in the three or more information recording layers and reproducing data recorded in the three or more information recording layers by projecting a laser beam onto the three or more information recording layers via a light incidence plane constituted by the surface of either the substrate or the protective layer, wherein neighboring transparent intermediate layers facing each other across an information recording layer have different thicknesses. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to reduce interlayer cross-talk.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method and apparatus for making a stamper for patterning CDs and DVDs
InactiveUS20050151283A1Reduced and no sacrifice in data storage densityHuge savingsRecord carriersOptical articlesResistCompact Disc manufacturing
A method for forming a stamper used in the manufacture of CDs, DVDs, and other types of optical disks comprises forming a substrate by rolling. A layer of material is deposited (e.g. by plating) onto the substrate. Thereafter, a resist layer is formed on the layer of material and patterned. Because the substrate is formed by rolling, it is relatively inexpensive to form the substrate to a desired thickness. Because the layer of material is formed by deposition (e.g. plating), it is relatively inexpensive to ensure that the layer has a very smooth surface (i.e. without necessitating a great deal of polishing).
Owner:WD MEDIA
Information recording disc and information reproducing system
InactiveUS20010007545A1Method securityAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useRecord information storageControl dataApplication specific
An information recording disc having a burst cutting area (BCA) for recording control information for a reproducing apparatus by removing a reflective layer of the disc in a striped shape and a data recording area for recording user data, wherein the burst cutting area includes at least one BCA control information area and the BCA control information area comprises: an application identifier area for identifying applications of control data; a data length area for indicating data length of the control data; and an application specific data area for recording the control data, and an information reproducing drive for reproducing data from the information recording disc.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com