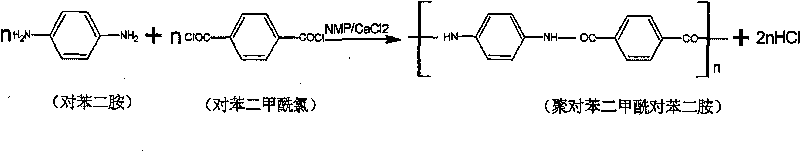
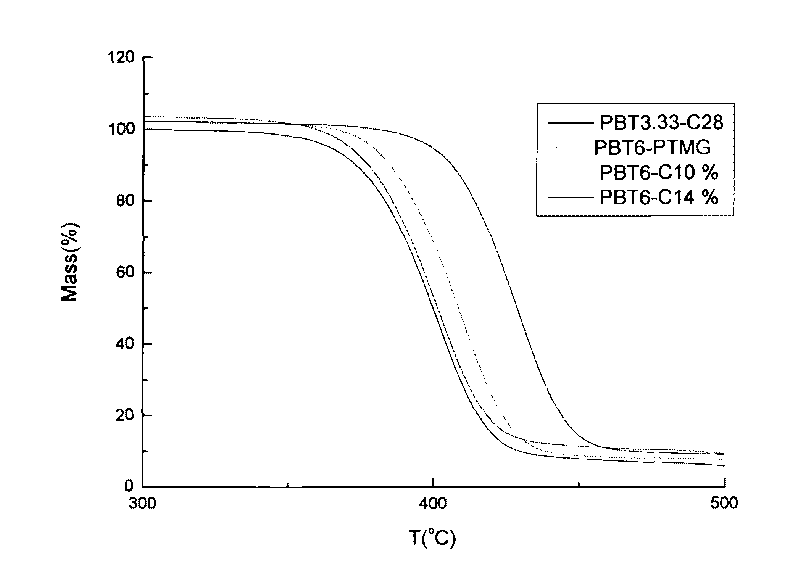
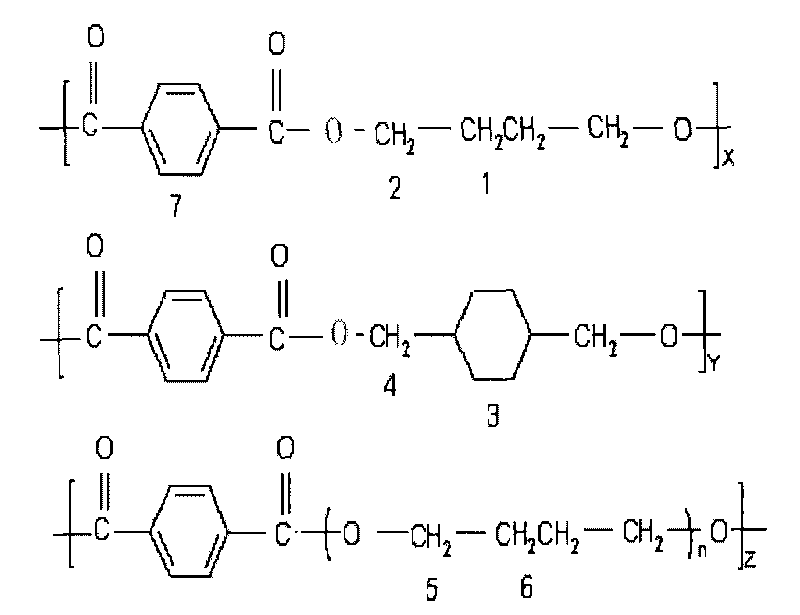
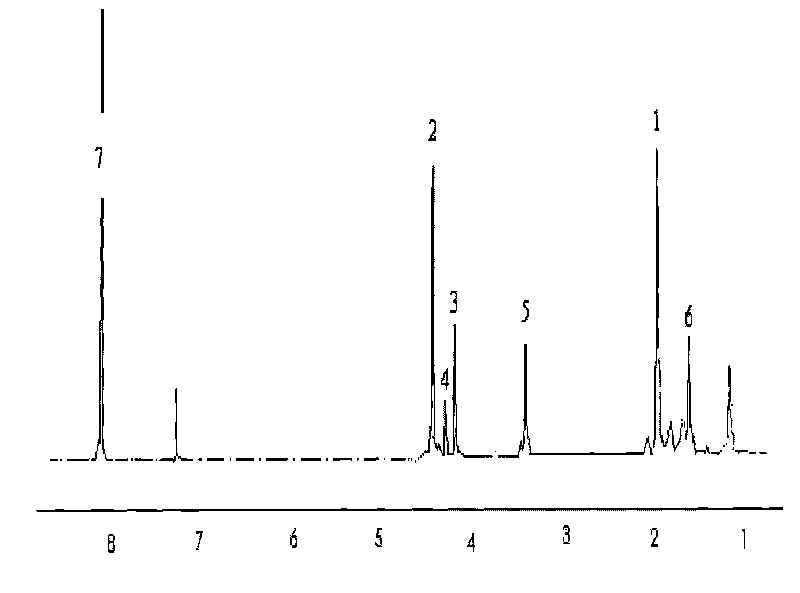
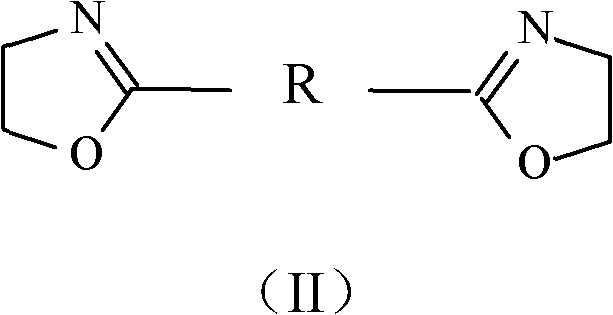
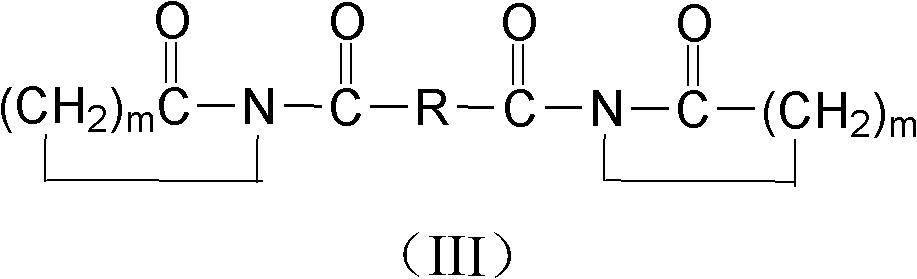
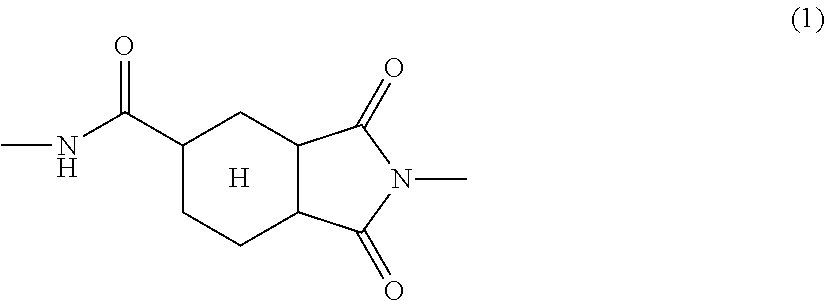
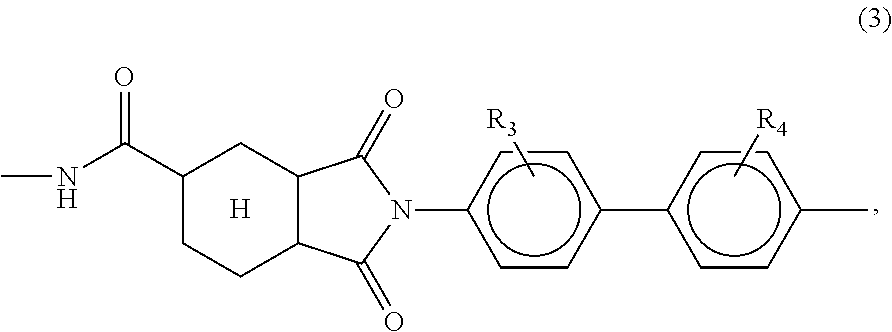
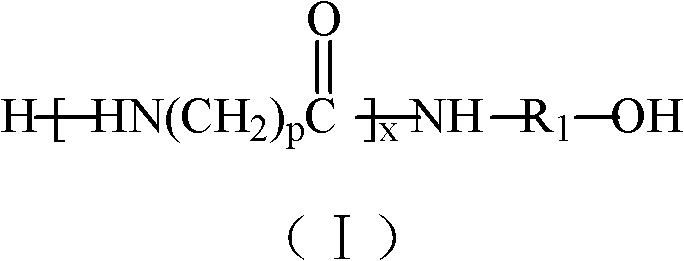Patents
Literature
293 results about "Inherent viscosity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inherent viscosity is the ratio of the natural logarithm of the relative viscosity to the mass concentration of the polymer. Inherent viscosity is defined as ηᵢₙₕ=lnηᵣₑₗ/c where c is the mass concentration of the polymer (g/dL) and ηᵣₑₗ is the relative viscosity, which is defined as ηᵣₑₗ=η/ηₛ where η is the viscosity of the solution and ηₛ is the viscosity of the solvent. The unit of inherent viscosity is dL/g.
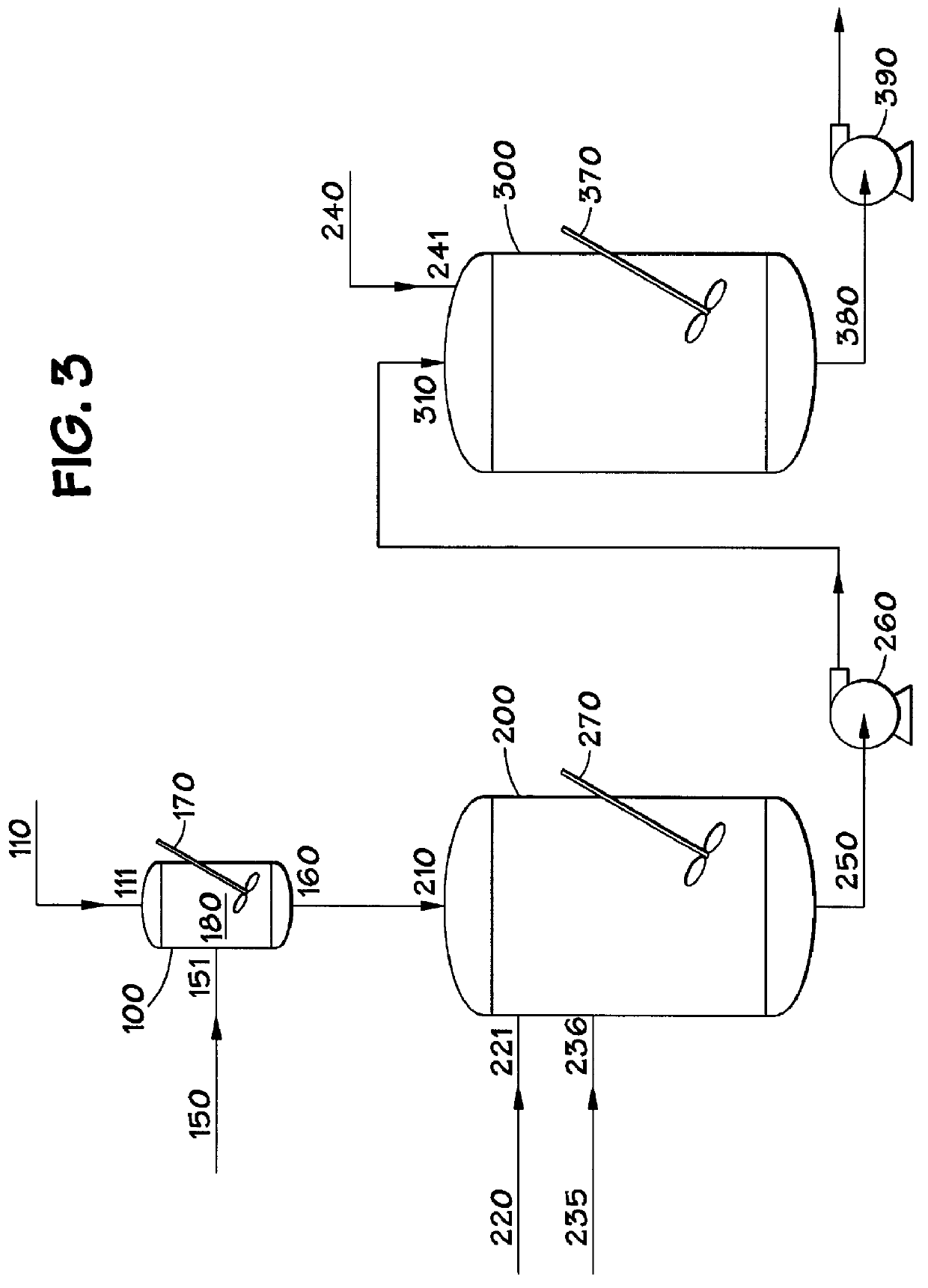
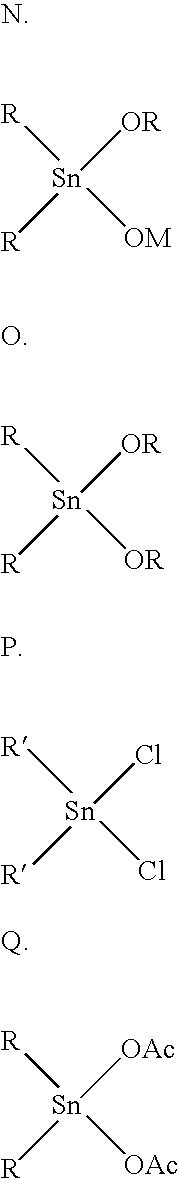
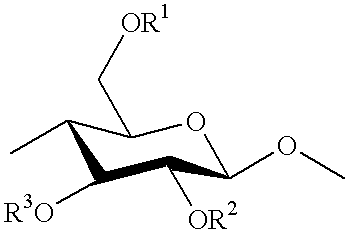
Isosorbide containing polyesters and methods for making same
InactiveUS6063464AHigher inherent viscosityInherent viscosityBottlesSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterDiol
A polyester polymer and method for making the polyester, wherein the polyester is prepared by (1) combining in a reactor a monomer containing a diacid moiety; a monomer comprising a diol moiety; and a monomer containing an isosorbide moiety; with a condensation catalyst suitable for condensing aromatic diacids and diols; and (2) heating the monomers and catalyst to polymerize the monomers to yield a polyester having an inherent viscosity of at least about 0.15 dL / g.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Sheets formed from polyesters including isosorbide
InactiveUS6025061AImprove low temperature impact strengthIncrease the maximum use temperatureLayered productsAnimal housingPolyesterInherent viscosity
A sheet made of a polyester which includes monomer units of terephthaloyl moieties, ethylene glycol moieties and isosorbide moieties is described. The polyester has an inherent viscosity of at least about 0.35 dL / g when measured as a 1% (weight / volume) solution of said polyester in o-chlorophenol at a temperature of 25 DEG C. The present invention also relates to a method of making the polyester sheet described above and a method of thermoforming the sheet into articles.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Optical articles comprising isosorbide polyesters and method for making same
InactiveUS6126992AHigh light transmittanceEasy to copySynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesPolyesterPolymer science
An optical article made of a transparent polymer which includes terephthaloyl moieties, optionally, other aromatic diacid moieties; ethylene glycol moieties; isosorbide moieties; and, optionally, one or more other diol moieties, wherein the polymer has an inherent viscosity of at least about 0.35 dL / g as measured on a 1% solution (weight / volume) in o-chlorophenol at 25 DEG C.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Polyesters including isosorbide as a comonomer blended with other thermoplastic polymers
A polymer blend including a polyester and another thermoplastic polymer. The polyester includes terephthaloyl moieties and, optionally, other aromatic diacid moieties; and ethylene glycol moieties; optionally diethylene glycol moieties; isosorbide moieties; and, optionally one or more other diol moieties. The polyester has an inherent viscosity of at least about 0.35 dL / g.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Polyester compositions for calendering
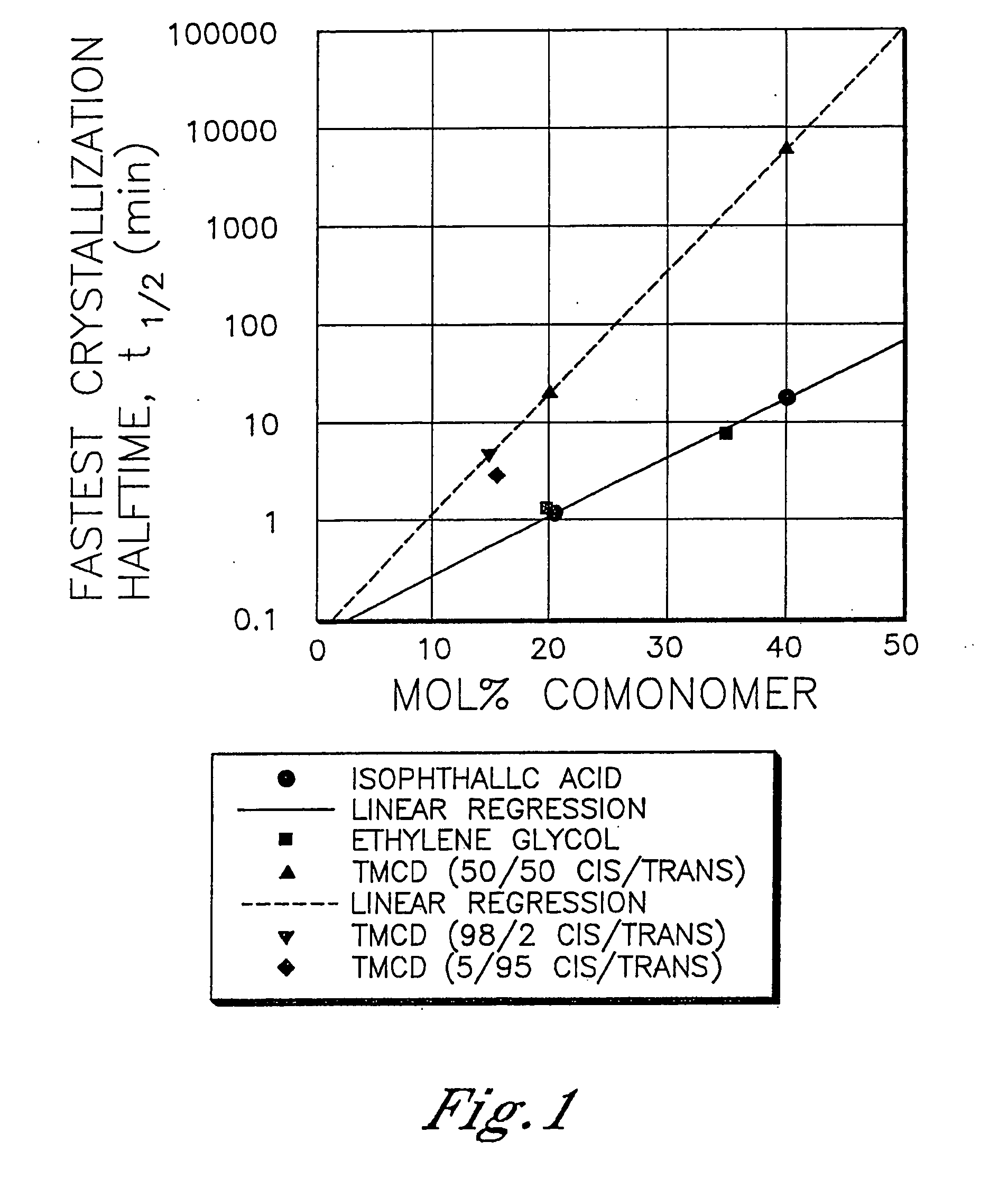
Polyester compositions that provide a higher throughput in calendering processes may be prepared from a polyester having crystallization half time of at least 5 minutes, an inherent viscosity of about 0.55 to about 0.75 dL / g, a branching monomer, and a release additive. The polyester compositions show a combination of excellent melt strength with good shear response that permits higher calendering line speeds before melt fracture occurs. Also disclosed are processes for film or sheet by calendering the above compositions and the film or sheet produced therefrom. The polyester compositions, film, or sheet also may include plasticizers and / or flame retardants to increase their flexibility and enable their use in commercial applications requiring flame resistance. The film and sheet have excellent appearance and can be used in a wide range of decorative and packaging applications.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
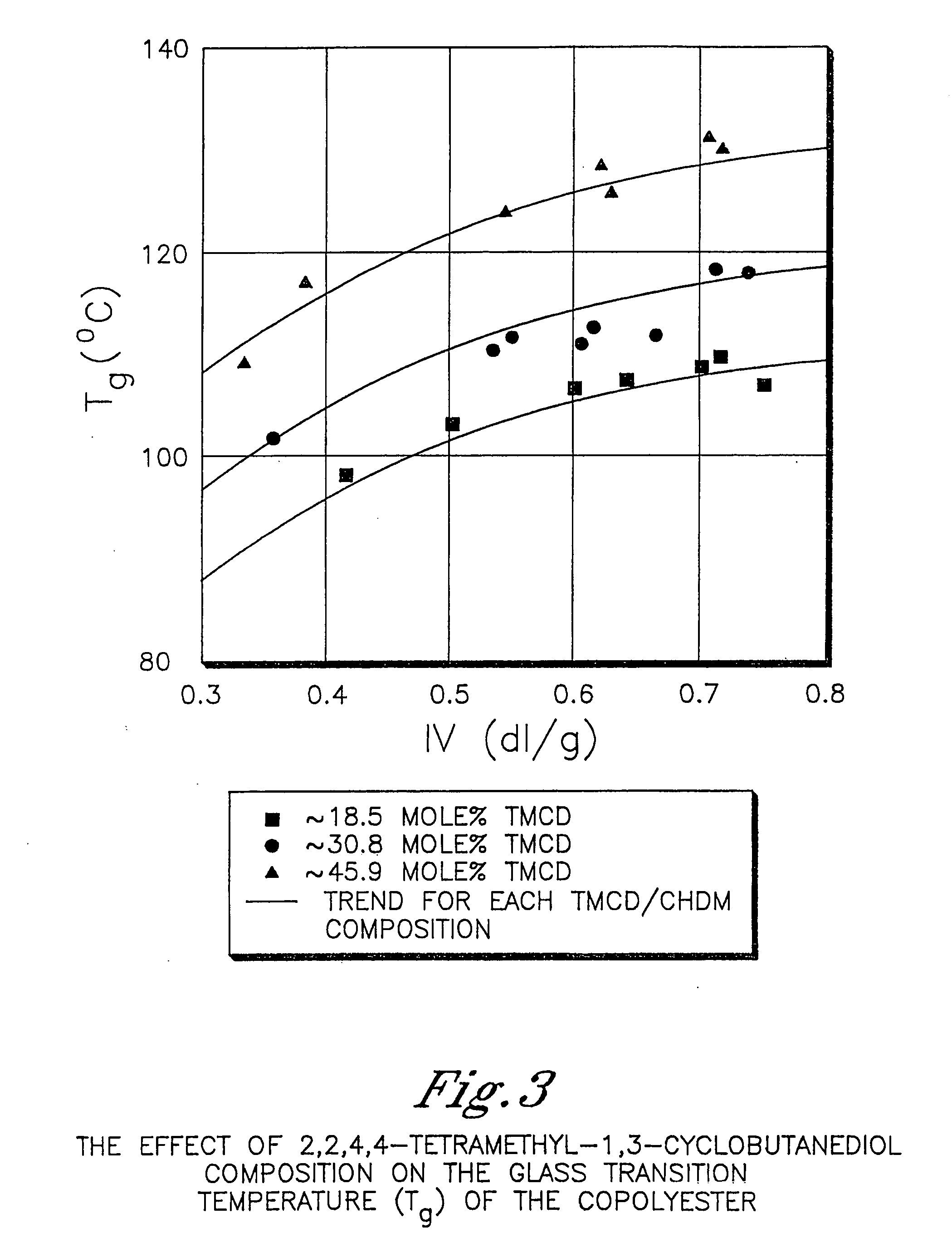
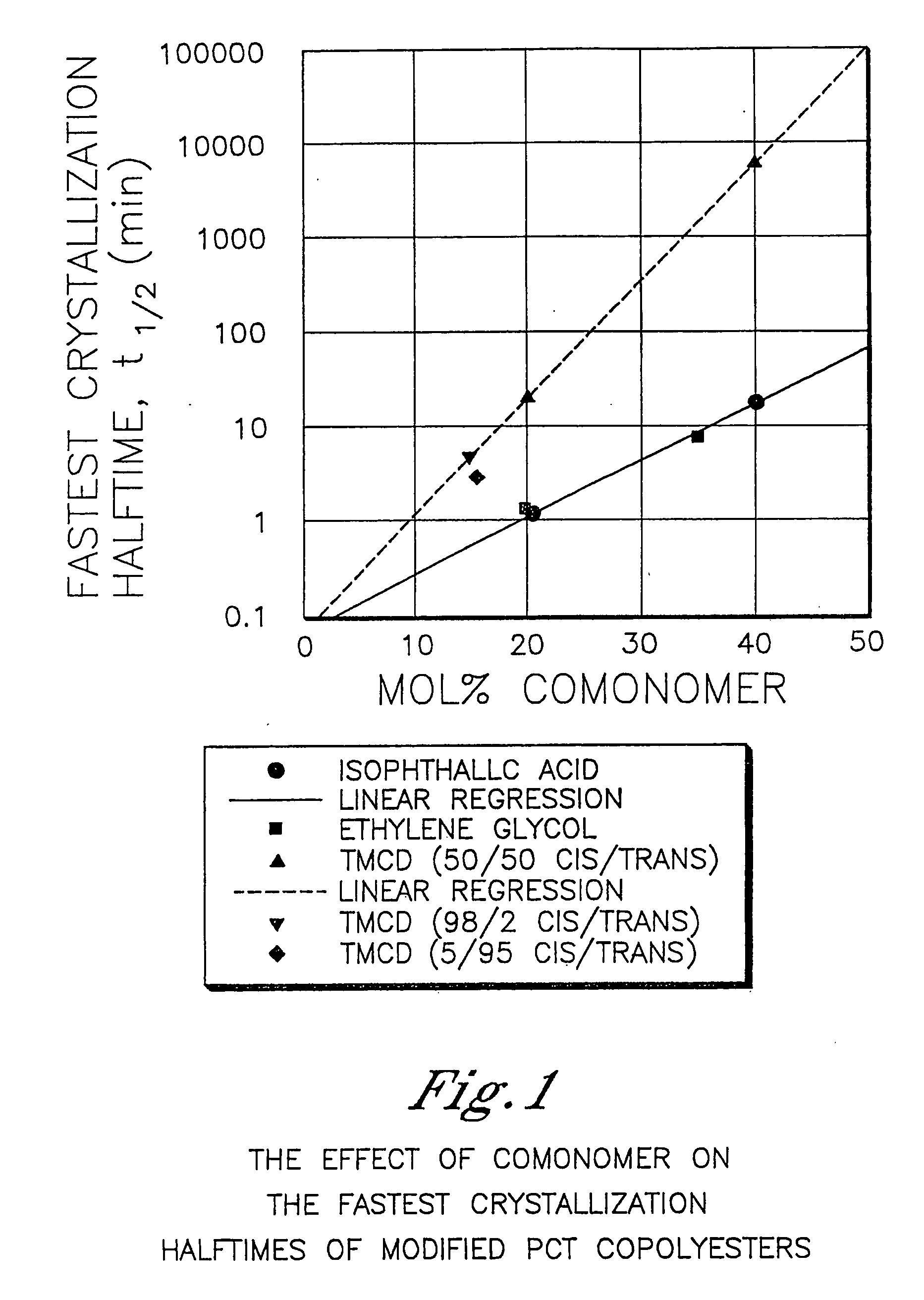
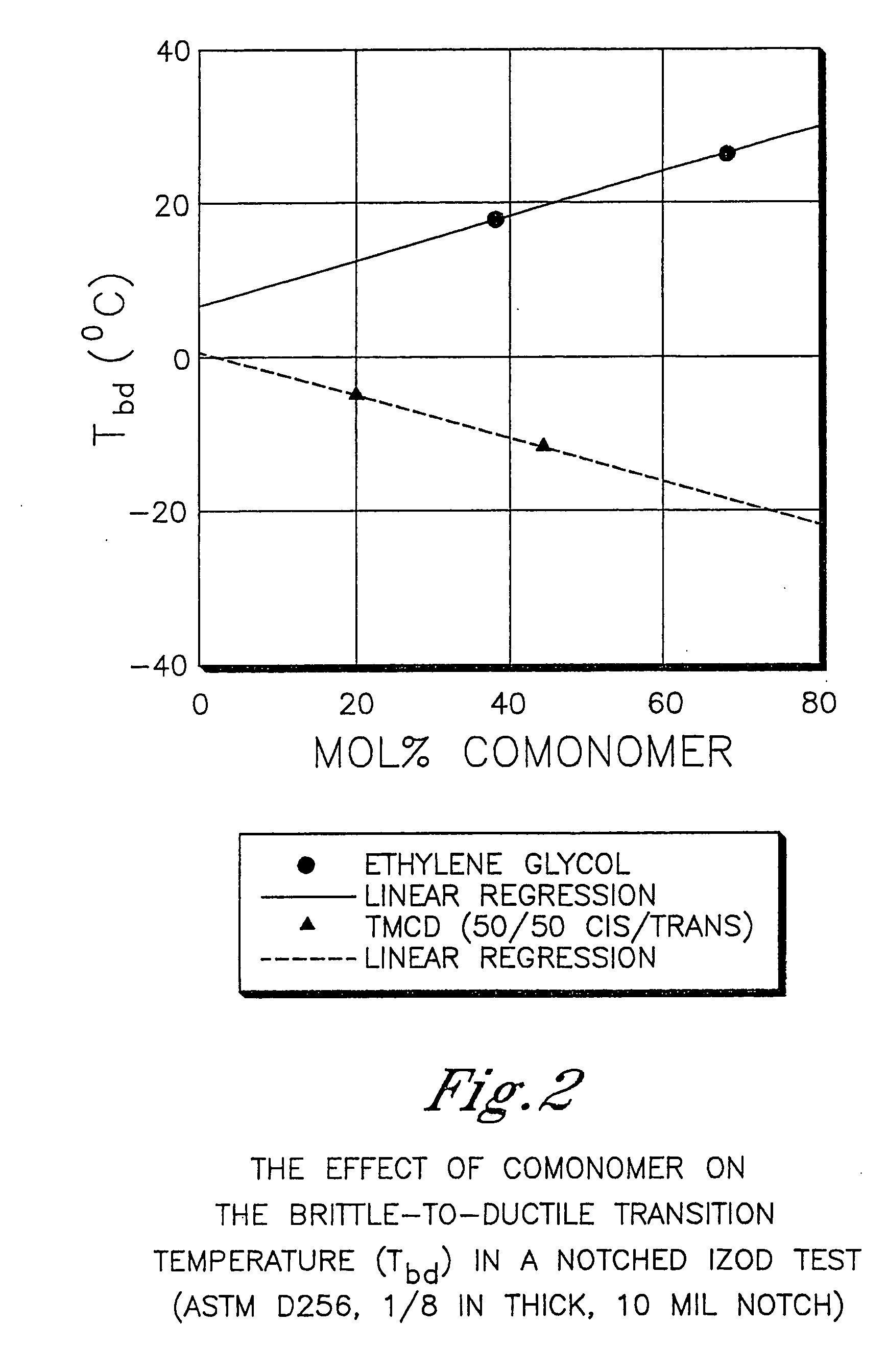
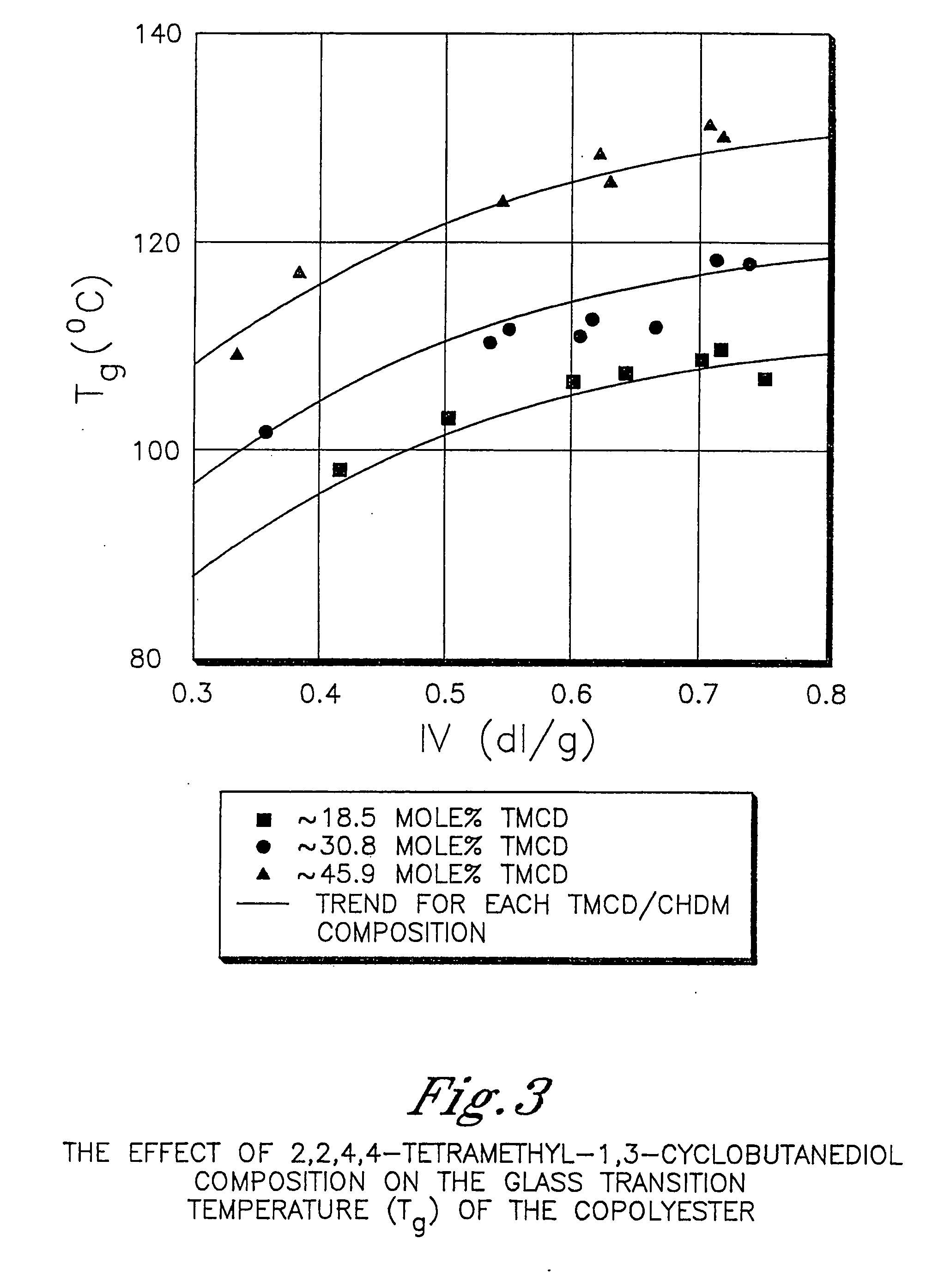
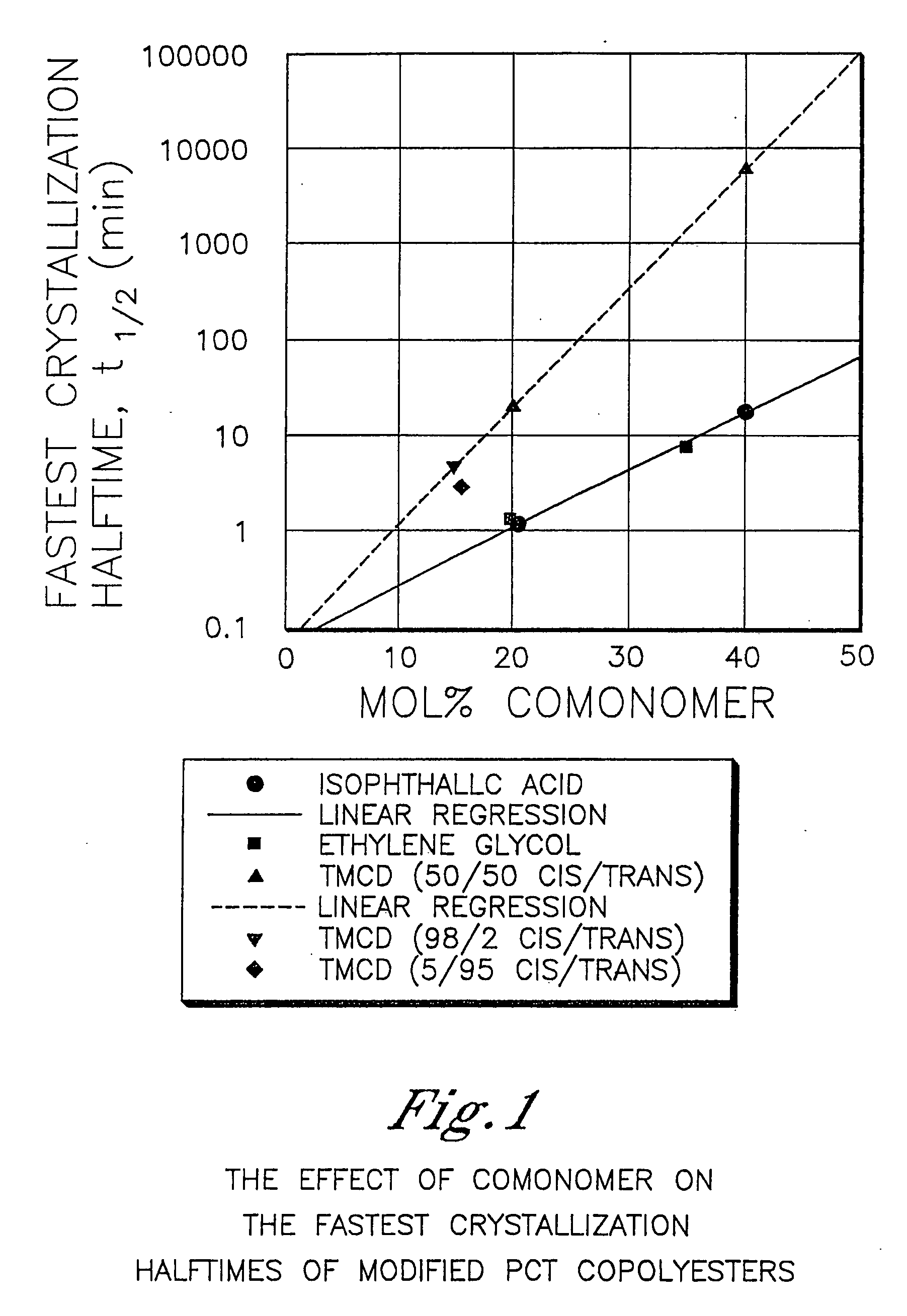
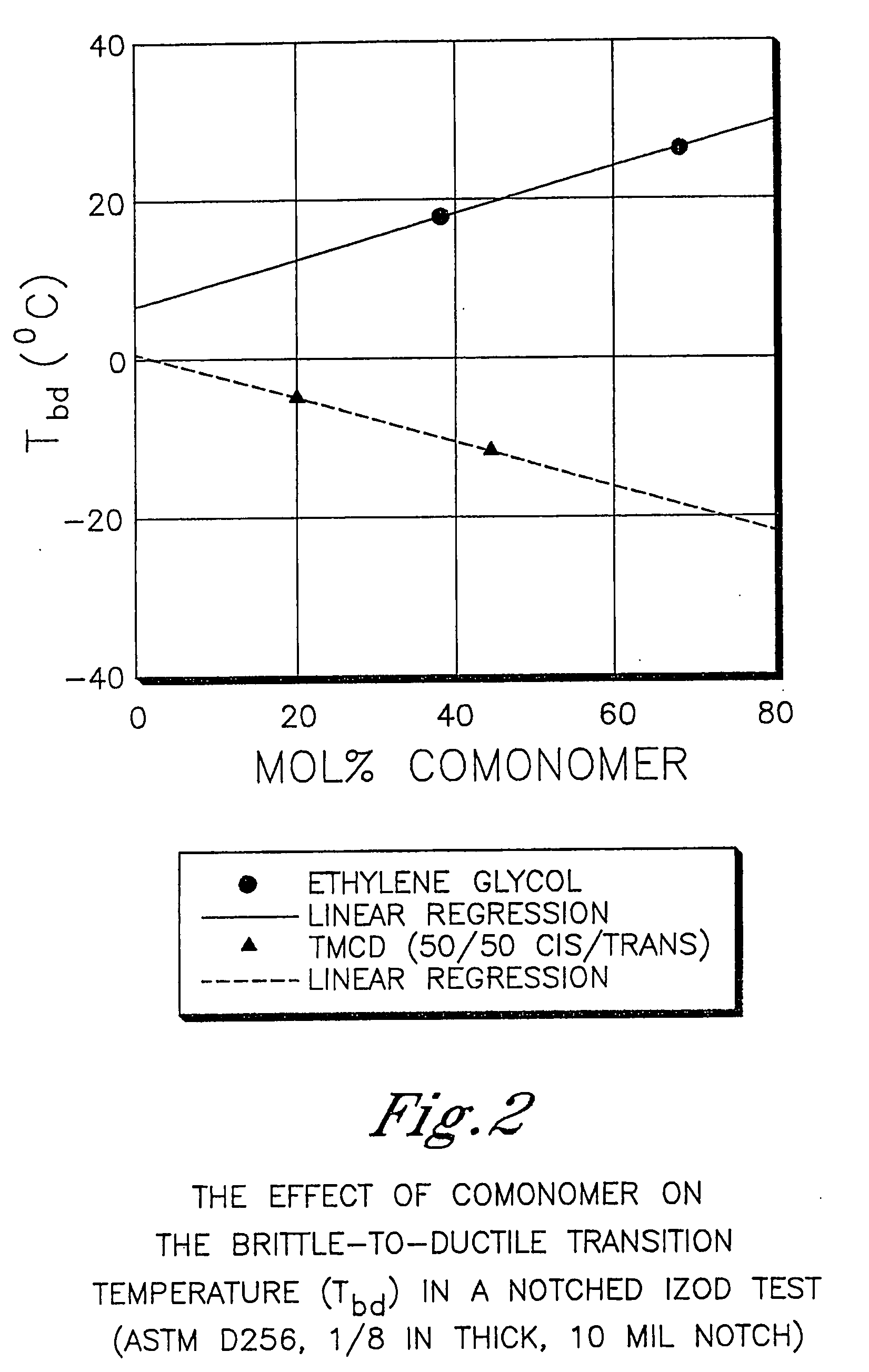
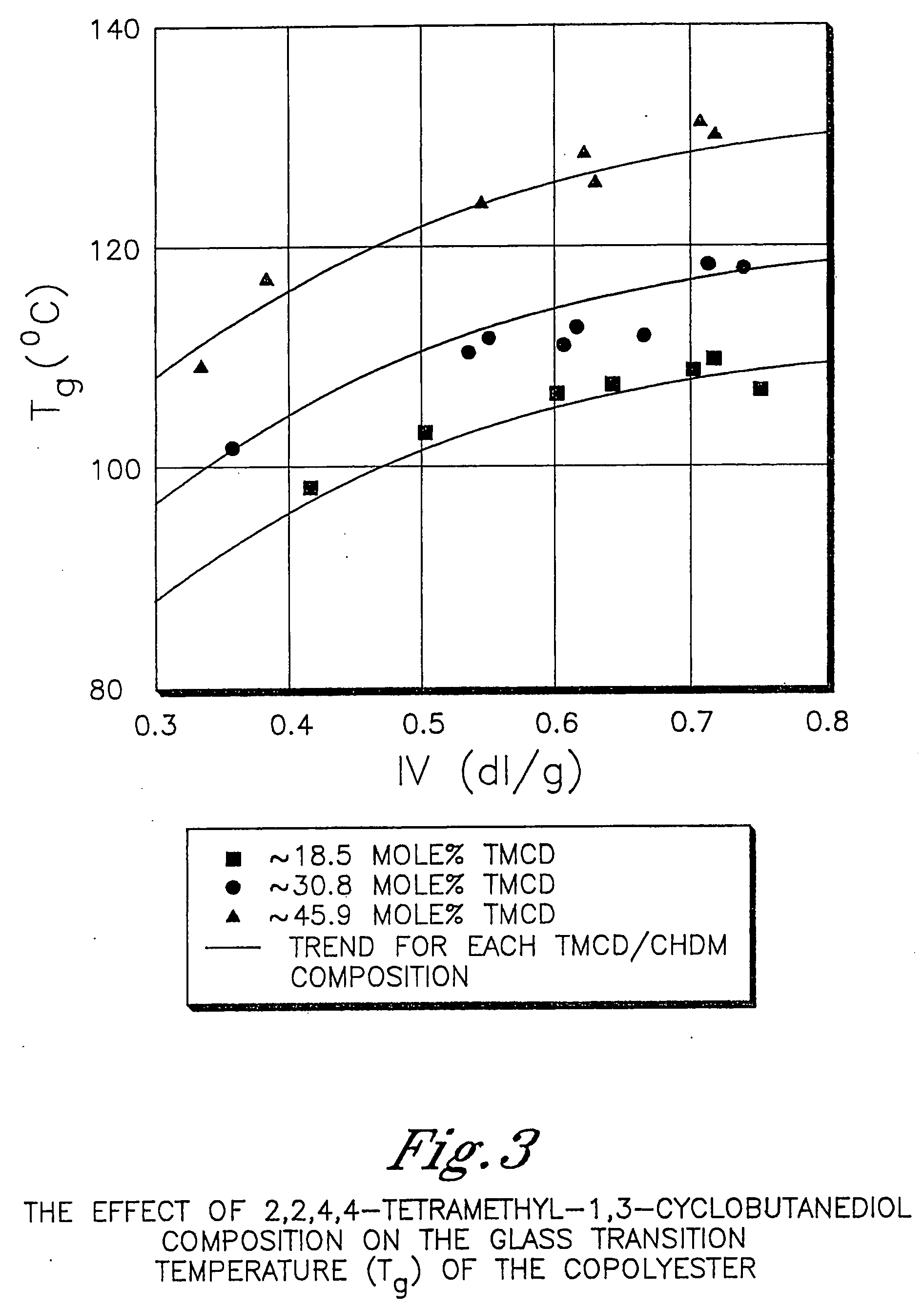
Polyester compositions containing cyclobutanediol having a certain combination of inherent viscosity and high glass transition temperature and articles made therefrom
Described are polyester compositions comprising at least one polyester which comprises terephthalic acid residues, 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol, and cyclohexanedimethanol, wherein the inherent viscosity and the Tg of the polyester provides for certain polyester properties. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles such as fibers, films, bottles or sheets.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Polyester compositions containing cyclobutanediol having a certain combination of inherent viscosity and high glass transition temperature and articles made therefrom
ActiveUS20060287482A1Good chemical resistanceHigh impact strengthDialysis systemsDialysisFiberPolymer science
Described are polyester compositions comprising at least one polyester which comprises terephthalic acid residues, 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol, and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol, wherein the inherent viscosity and the Tg of the polyester provides for certain polyester properties. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles such as fibers, films, bottles or sheets.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Polyester compositions containing cyclobutanediol having a certain combination of inherent viscosity and moderate glass transition temperature and articles made therefrom
ActiveUS20060293495A1Easy to optimizeHigh impact strengthDialysis systemsDialysisFiberCyclohexanedimethanol
Described are polyesters comprising (a) a dicarboxylic acid component comprising terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles such as fibers, films, bottles or sheets.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Film(s) and/or sheet(s) comprising polyester compositions which comprise cyclobutanediol and have a certain combination of inherent viscosity and moderate glass transition temperature
ActiveUS20060293494A1Improve bindingIncrease temperatureDialysis systemsDialysisCyclohexanedimethanolCarboxylic acid
Described are film(s) and / or sheet(s) comprising polyesters comprising (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic residues; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Semi-aromatic polyamide and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to semi-aromatic polyamide and a preparation method thereof. The semi-aromatic polyamide is prepared by: adding aromatic dicarboxylic acids and the fatty diamine with 4-14 carbon atoms to an organic solvent to undergo neutralization reaction to prepare high-purification salt; pre-polymerizing by taking the high-purification salt as the raw material with the existence of water; preparing the semi-aromatic polyamide by the further tackification reaction of the prepolymer. By using high-purification salt, the preparation method can accurately control the molar ratio of dicarboxylic acids and diamine, and avoid the loss of the diamine. By purifying monomers in the salifying process, the preparation method also improves the quality of the semi-aromatic polyamide and obtains the semi-aromatic polyamide with high inherent viscosity, high crystallinity, high melting point and good mechanical performance.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Certain polyester compositions which comprise cyclohexanedimethanol, moderate cyclobutanediol, cyclohexanedimethanol, and high trans cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid
InactiveUS20070232779A1Good chemical resistanceLess reactiveSynthetic resin layered productsOptical articlesPolyesterCyclohexanedimethanol
Described as one aspect of the invention are polyester compositions A polyester composition comprising at least one polyester which comprises:(A) a dicarboxylic acid component comprising:i) 70 to 100 mole % of cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues or an ester thereof comprising:(a) 80 to 99 mole % trans-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues or an ester thereof; and(b) 1 to 20 mole % cis-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues or an ester thereof;ii) 0 to 30 mole % of aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues, other than cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues, having up to 16 carbon atoms or esters thereof, other than cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues; andiii) 0 to 10 mole % of aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues having up to 20 carbon atoms; and(B) a glycol component comprising:i) 5 to 35 mole % of 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; andii) 65 to 95 mole % of 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues, 1,3-cyclohexanedimethanol residues, 1,2-cyclohexanedimethanol residues or esters thereof or mixtures thereof,wherein the total mole % of said dicarboxylic acid component is equal to 100 mole %;the total mole % of said glycol component is equal to 100 mole %;wherein the inherent viscosity of said polyester is from 0.35 to 1.2 dL / g as determined in 60 / 40 (wt / wt) phenol / tetrachloroethane at a concentration of 0.5 g / 100 ml at 25° C.; and wherein said polyester has a Tg of from 66 to 120° C. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters
InactiveUS7687143B2Reduces blocking and fusionLayered productsConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsPolymer scienceWater dispersible
Disclosed are multicomponent fibers derived from a blend of a sulfopolyester with a water non-dispersible polymer wherein the as-spun denier is less than about 6 and wherein the water dispersible sulfopolyester exhibits a melt viscosity of less than 12,000 poise measured at 240° C. at a strain rate of 1 rad / sec, wherein the sulfopolyester comprising less than about 25 mole % of residues of at least one sulfomonomer, based on the total moles of diacid or diol residues, and wherein said poly(ethylene) terephthalate has an inherent viscosity of less than 0.55 dL / g. The multicomponent fiber is capable of being drawn at a relatively high fiber speed, particularly at least about 2000 m / min, and may be used to produce microdenier fibers. Fibrous articles may be produced from the multicomponent fibers and microdenier fibers. Also disclosed is a process for multicomponent fibers, nonwoven fabrics, and microdenier webs.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters
InactiveUS20070259177A1Layered productsConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsPolymer scienceWater dispersible
Disclosed are multicomponent fibers derived from a blend of a sulfopolyester with a water non-dispersible polymer wherein the as-spun denier is less than about 6 and wherein the water dispersible sulfopolyester exhibits a melt viscosity of less than 12,000 poise measured at 240° C. at a strain rate of 1 rad / sec, wherein the sulfopolyester comprising less than about 25 mole % of residues of at least one sulfomonomer, based on the total moles of diacid or diol residues, and wherein said poly(ethylene) terephthalate has an inherent viscosity of less than 0.55 dL / g. The multicomponent fiber is capable of being drawn at a relatively high fiber speed, particularly at least about 2000 m / min, and may be used to produce microdenier fibers. Fibrous articles may be produced from the multicomponent fibers and microdenier fibers. Also disclosed is a process for multicomponent fibers, nonwoven fabrics, and microdenier webs.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Methods for forming amorphous ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin drag reducing agents
InactiveUS6015779AReduce frictional energy lossHigh molecular weightOther chemical processesLiquid organic insulatorsHalohydrocarbonAlpha-olefin
A composition including polyalphaolefins that function as drag reducing agents and a process for the preparation of polyalphaolefins that function as drag reducing agents are disclosed. The process includes contacting alpha olefin monomers with a catalyst system, which includes a catalyst and an activator (co-catalyst) in a reactant mixture. The catalyst is a transition metal catalyst, preferably titanium trichloride, and the co-catalyst may include an alkylaluminoxane, alone or in combination, with a dialkylaluminum halide or a halohydrocarbon. The polymerization of the alpha olefin monomers produces a non-crystalline, ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin having an inherent viscosity of at least 10 dL / g. The addition of the alkylaluminoxane during the polymerization process provides for a non-crystalline, ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin and a more uniform molecular weight distribution of the resulting polyalphaolefin, thereby creating a drag reducing agent superior to known drag reducing agents. A process for forming a drag reducing agent comprising a non-crystalline, ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin having an inherent viscosity of about at least 10 dL / g and a process for reducing drag in a conduit are also disclosed.
Owner:MPOWER SPECIALTY CHEM
High strength fibers of L-lactide copolymers epsi-caprolactone and trimethylene carbonate and absorbable medical constructs thereof
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably epsi-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 25%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.4 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Surgical sutures made of mono- or multifilament yarns of the present copolymers will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
Parallel composite elastic fiber and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN101851812ALow costElastic Elongation GuaranteedFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsExtensibilityPolytetramethylene terephthalate
The invention discloses parallel composite elastic fiber and a manufacture method thereof. The parallel composite elastic fiber is obtained through false twisting process after parallel composite spinning of valox and polyethylene glycol terephthalate according to a weight ratio of 70 / 30 to 30 / 70, wherein the inherent viscosity of the valox is between 0.45 to 0.60 dl / g, and the difference of the inherent viscosity of the valox and the inherent viscosity of the polyethylene glycol terephthalate is between 0.40 and 1.05 dl / g. The elastic extensibility of the elastic fiber of the invention is between 130 and 220 percent, and the elastic recovery rate is higher than 85 percent.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Polyester compositions which comprise cyclobutanediol ethylene glycol, titanium, and phosphorus with improved color and manufacturing processes therefor
Described as one aspect of the invention are polyester compositions comprising at least one polyester which comprises: (a) a dicarboxylic acid component comprising: (i) about 90 to about 100 mole % of terephthalic acid residues; (ii) about 0 to about 10 mole % of aromatic and / or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues having up to 20 carbon atoms; and (b) a glycol component comprising: (i) about 1 to less than 90 mole % 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and (ii) about 0 to about 89 mole % cyclohexanedimethanol residues; (iii) greater than 10 mole % ethylene glycol residues, and (iv) less than about 2 mole % of a modifying glycol having from 3 to 16 carbon atoms; (c) titanium atoms and phosphorus atoms, wherein the total mole % of the dicarboxylic acid component is 100 mole %, and wherein the total mole % of the glycol component is 100 mole %; and wherein the inherent viscosity of the polyester is from 0.50 to 1.2 dL / g as determined in 60 / 40 (wt / wt) phenol / tetrachloroethane at a concentration of 0.25 g / 50 ml at 25° C. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
High strength fibers of l-lactide copolymers, epsilon-caprolactone, and trimethylene carbonate and absorbable medical constructs thereof
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably ε-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 20%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.1 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Surgical sutures made of mono- or multifilament yams of the present copolymers will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
Polyphenylene terephthalamide fibre and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101724935AHigh overall process efficiencyLow efficiencyWet spinning methodsMonocomponent polyamides artificial filamentPolymer scienceAramid
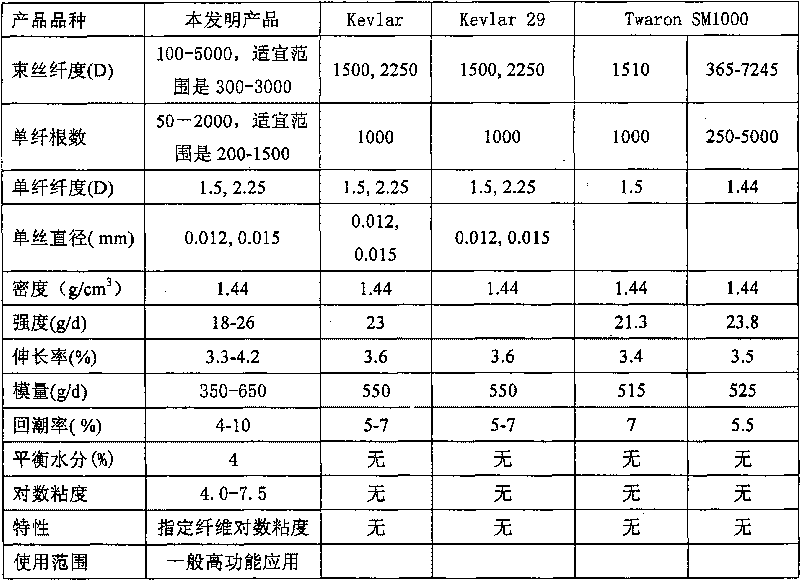
The invention discloses a polyphenylene terephthalamide fibre and a preparation method thereof. For the polyphenylene terephthalamide fibre (PPTA) which has with high performance and is prepared by the dry-jet wet spinning method, a polyphenylene terephthalamide fibre (PPTA) polymer which has the inherent viscosity of 4.5-8.0dL / g and is obtained by adopting the low-temperature solution polycondensation method is used as the start point, and the polyphenylene terephthalamide fibre is adaptive to the industrial large-scale production. The inherent viscosity of the fibre is reduced by 0.5dL / g than the inherent viscosity of the polymer. The polyphenylene terephthalamide fibre (PPTA) with high performance comprises the specific indexes as follows: a synnema titer is 300-3000 denier, an intensity is 18-26g / denier, an elongation rate is 3.2-3.8percent, a modulus is 350-650 g / denier, a water ratio is 3-10 percent and an inherent viscosity is 4-7.5dL / g. The physical property of the fibre is superior to the traditional aramid fibre II fibre. The invention discloses the inherent viscosity with the purpose of specifically showing the material of polyphenylene terephthalamide with higher molecular weight.
Owner:中蓝晨光化工有限公司
Phosphorus containing compounds for reducing acetaldehyde in polyesters polymers
InactiveUS20070066794A1High intrinsic viscosityLow in acetaldehydeOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsTobacco devicesPolyesterPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
Polyesters whose polycondensation is catalyzed by titanium-containing catalysts and which are susceptible to acetaldehyde formation during polycondensation or subsequent molding operations are prepared with low finished acetaldehyde content and reduced acetaldehyde generation by adding an ammonium or amine salt of an oxyphosphorus-acid. Polyesters, especially polyethylene terephthalate, may be produced with high inherent viscosity in reduced processing time, without the necessity of further polymerization in the solid state.
Owner:GRUPO PETROTEMEX DE C V
Certain polyester compositions which comprise cyclobutanediol, cyclohexanedimethanol, and high trans-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid
InactiveUS20070232778A1Easily or more expensively stabilizedLess expensivePolyesterTetrachloroethane
Described as one aspect of the invention are polyester compositions comprising at least one polyester which comprises:(A) a dicarboxylic acid component comprising:i) 70 to 100 mole % of cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues or an ester thereof comprising:(a) 70 to 98 mole % trans-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues or an ester thereof; and(b) 2 to 30 mole % cis-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues or an ester thereof;ii) 0 to 30 mole % of aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues, other than cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues, having up to 16 carbon atoms or esters thereof, other than cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues,; andiii) 0 to 10 mole % of aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues having up to 20 carbon atoms; and(B) a glycol component comprising:i) 1 to 99 mole % of 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; andii) 1 to 99 mole % of 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues, 1,3-cyclohexanedimethanol residues, 1,2-cyclohexanedimethanol residues or esters thereof or mixtures thereof,wherein the total mole % of said dicarboxylic acid component is equal to 100 mole %;the total mole % of said glycol component is equal to 100 mole %;wherein the inherent viscosity of said polyester is from 0.35 to 1.2 dL / g as determined in 60 / 40 (wt / wt) phenol / tetrachloroethane at a concentration of 0.5 g / 100 ml at 25° C.; and wherein said polyester has a Tg of from 60 to 155° C. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Polyester compositions which comprise cyclobutanediol, cyclohexanedimethanol, and ethylene glycol and manufacturing processes therefor
Described as one aspect of the invention are polyester compositions comprising at least one polyester which comprises: (a) a dicarboxylic acid component comprising: (i) about 90 to about 100 mole % of terephthalic acid residues; (ii) about 0 to about 10 mole % of aromatic and / or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues having up to 20 carbon atoms; and (b) a glycol component comprising: (i) about 20 to about 40 mole % 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and (ii) about 20 to about 40 mole % cyclohexanedimethanol residues; (iii) ethylene glycol residues, and (iv) less than about 2 mole % of a modifying glycol having from 3 to 16 carbon atoms; wherein the total mole % of the dicarboxylic acid component is 100 mole %, and wherein the total mole % of the glycol component is 100 mole %; and wherein the inherent viscosity of the polyester is from 0.50 to 1.2 dL / g as determined in 60 / 40 (wt / wt) phenol / tetrachloroethane at a concentration of 0.25 g / 50 ml at 25° C. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Coated, slow-absorbing textile constructs for sutures and tissue engineering
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably epsi-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 20%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.1 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Disclosed are coated surgical constructs including sutures made of multifilament yarns of the present copolymers and coated with nitrogenous copolyesters which will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
Cellulose acetate film for use in liquid crystal displays
A liquid crystal device having a plurality of pixel electrodes for transmitting light, a first panel having an activation portion for selectively activating the plurality of pixel electrodes, an orientation layer formed on the activation portion, a light shielding pattern formed on the orientation layer, a second panel having a second orientation layer, a liquid crystal formed between the first and second panels, a polarizing plate or a color filter and a protective film on at least one of the aforementioned surfaces wherein the protective layer includes a cellulose ester selected from the group consisting of cellulose acetate, cellulose formate, cellulose propionate, cellulose butyrate, ethyl cellulose, methyl cellulose and benzyl cellulose having an inherent viscosity of from about 1.0 to less than 2.0 dl / g.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Molding of Thermoplastic Polyesters
InactiveUS20070224377A1Improve clarityIncrease flexibilityLayered productsBottlesPolyesterPolymer science
Disclosed are processes for rotational molding of thermoplastic polyesters and for hollow articles produced therefrom. The thermoplastic polyesters have a crystallization half time of at least 10 minutes and an inherent viscosity of 0.55 to 0.70 dL / g. Additional thermoplastic polymers may be used to produce multilayered articles.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Cellulose ester blends
This invention relates to a blend comprising(a) about 2% to about 98% by weight of at least one ester of cellulose comprising an alkanoyl chain having from about 1 to about 10 carbon atoms, and having at a D.S. of about 2.3 to about 3.0, and an inherent viscosity of about 0.2 to about 3.0 deciliters / gram as measured at a temperature of 25° C. for a 0.5 g sample in 100 ml of a 60 / 40 parts by weight solution of phenol / tetrachloroethane, and(b) about 98% to about 2% by weight of at least one ester of cellulose comprising an alkanoyl chain having from about 1 to about 10 carbon atoms, and having a D.S. of about 1.5 to about 2.2, and an inherent viscosity of about 0.2 to about 3.0 deciliters / gram as measured at a temperature of 25° C. for a 0.5 g sample in 100 ml of a 60 / 40 parts by weight solution of phenol / tetrachloroethane, said percentages being based on the weight of component (a) plus component (b).
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Thermoplastic block copolyether ester elastomer and preparation method thereof
This invention relates to a thermoplastic block copolyether ester elastomer and a preparation method thereof, wherein the aromatic dicarboxylic acid and mixing divalent alcohol are reacted at 180-265 DEG C in the mol ratio of 1: 1.2-2.2; the titanium compound, the mixture of titanium compound and zinc compound or the mixture of titanium compound and magnesium compound is used as catalyst; the copolyether ester contains 15-90ppm of titanium element, 10-200ppm of zinc or magnesium, and 300-4000ppm of antioxidant; the obtained matter is reacted under pressure lower than 150Pa to distil out 1,4-butanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol; the final temperature of the reaction is at 260-290 DEG C; in terms of total weight of the copolyether ester, the content of the hard segment is 50-92wt%; the inherent viscosity is 0.65-1.85dl / g; the melting point is at 160-220 degrees centigrade; the elongation at break is 500-1400% and the thermal decomposition temperature is 360 to 450 DEG C.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Preparation method of aliphatic polyester amide containing short polyamide segment
The invention discloses a preparation method of aliphatic polyester amide containing a short polyamide segment, which comprises the following steps: polymerizing cyclic lactam or amino acid with alkamine to prepare a polyamide oligomer; carrying out melt polycondensation on the polyamide oligomer, aliphatic dibasic acids and diatomic alcohols to prepare a polyester amide prepolymer with a carboxyl-terminated and hydroxyl-terminated structure; and carrying out chain extension on the polyester amide prepolymer by using diacyl dilactam or carbonyl dilactam and dioxazoline chain extender to prepare the biodegradable polyester amide containing a short polyamide segment, of which the inherent viscosity is 0.37-0.74 dL / g. The invention has the characteristics of simple method, mild conditions, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Bioswellable, crystalline, amphiphilic, block/graft polymers and applications thereof
Absorbable, essentially non-absorbable, and non-absorbable crystalline, amphiphilic, block / graft copolymeric compositions exhibit an inherent viscosity of at least 0.5 dL / g, a heat of fusion of at least 10 J / g and undergo swelling in the biological environment due to a water up-take of at least 10 percent of original dry mass. These compositions are designed for use in swellable surgical sutures, coatings of medical devices, and carriers for the delivery of bioactive agents.
Owner:POLY MED
Polyamideimide resin, as well as a colorless and transparent flexible metal-clad laminate and circuit board obtained therefrom
ActiveUS20100018756A1Excellent heat resistance and flexibilitySufficient colorless and transparent propertySynthetic resin layered productsTransparent dielectricsHeat resistancePolyamide-imide
[Object] To provide a flexible metal-clad laminate having excellent heat resistance, flexibility and low thermal expansion together with sufficient colorless transparency and a flexible printed circuit board using the same.[Constitution] A colorless and transparent flexible metal-clad laminate where metal foil is directly laminated or is laminated via an adhesive layer on at least one side of the polyamideimide resin layer in which cyclohexane tricarboxylic acid anhydride is a main monomer, characterized in that said polyamideimide resin has an inherent viscosity of 0.8 dl / g or more and 2.5 dl / g or less.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com