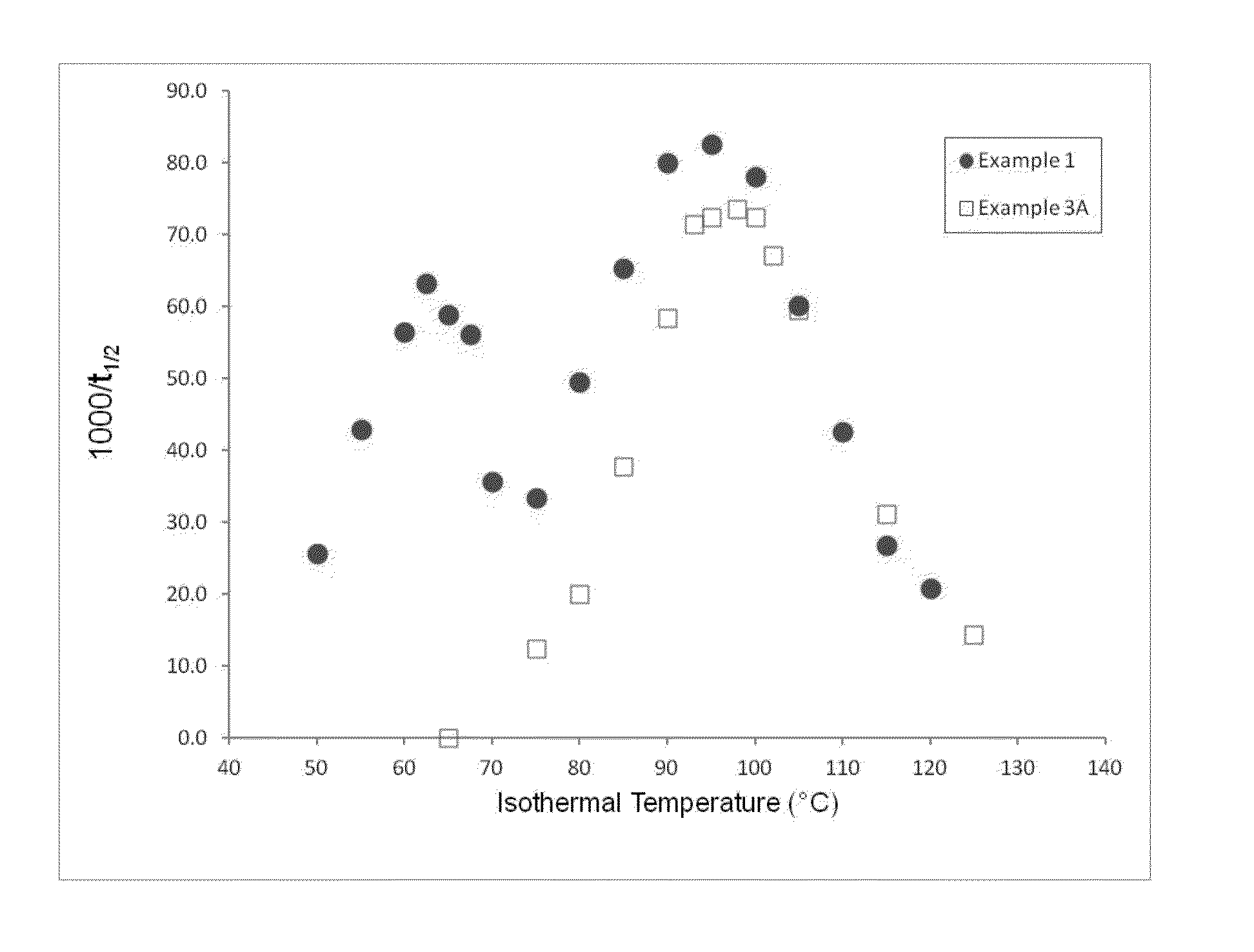
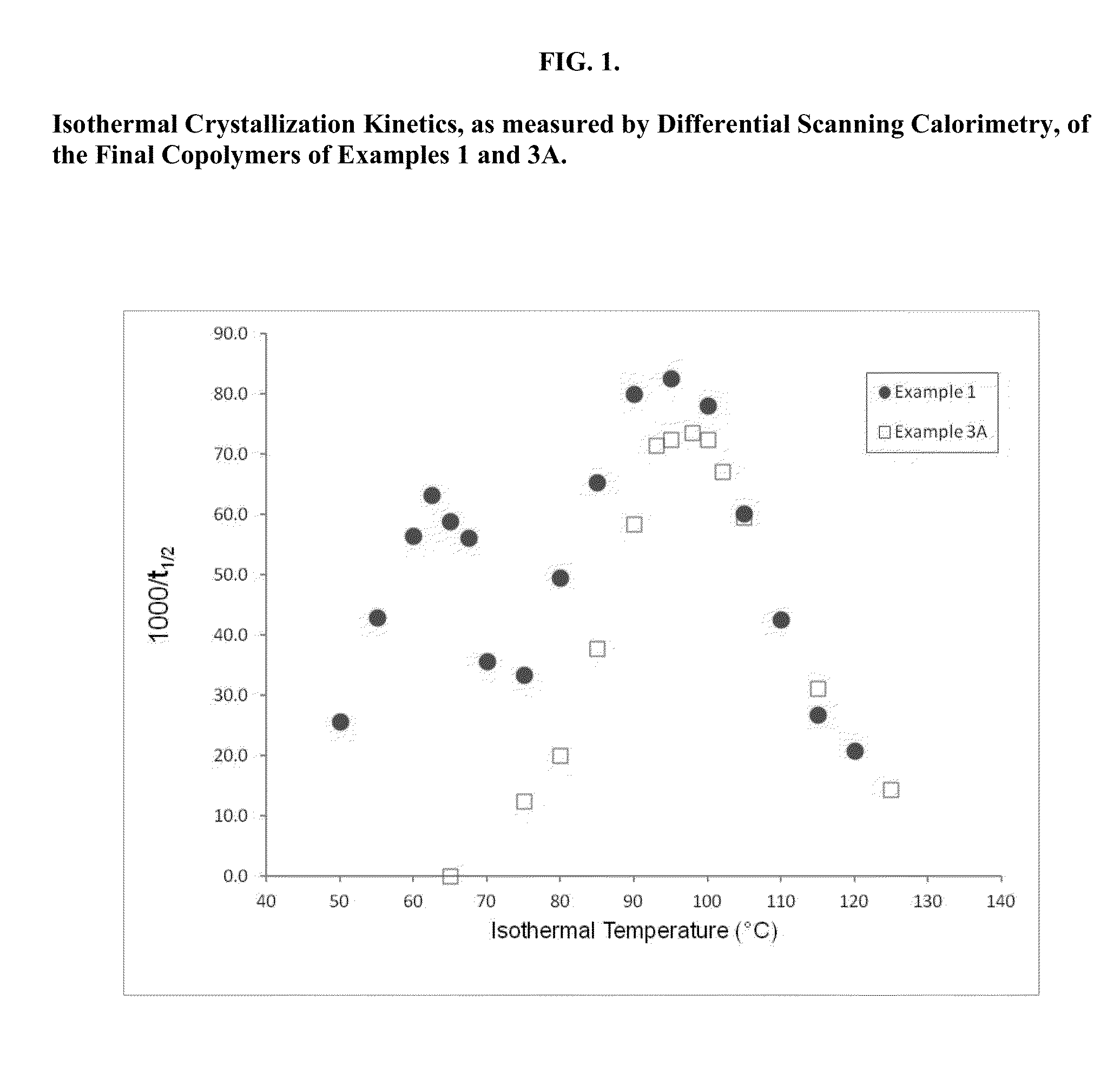
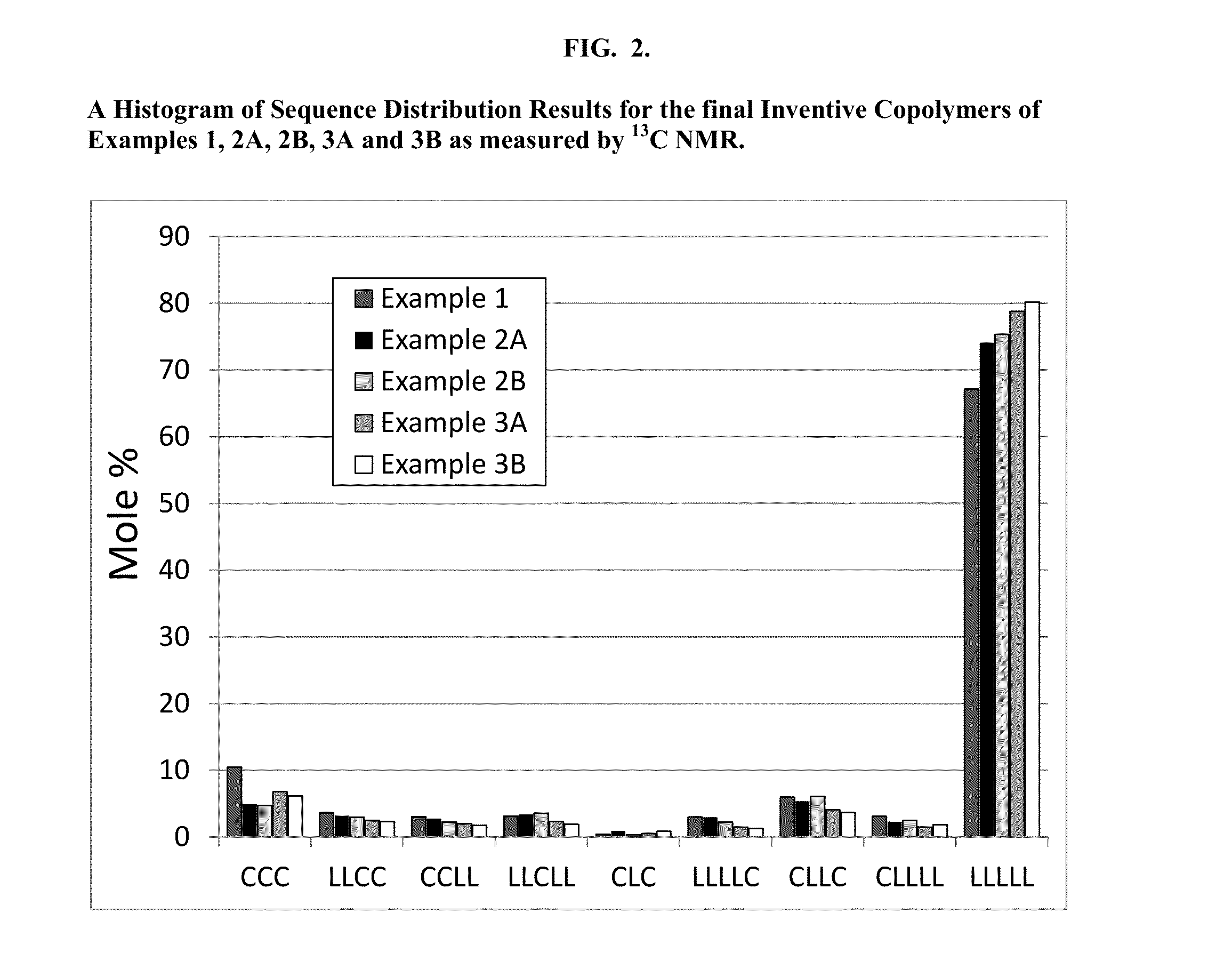
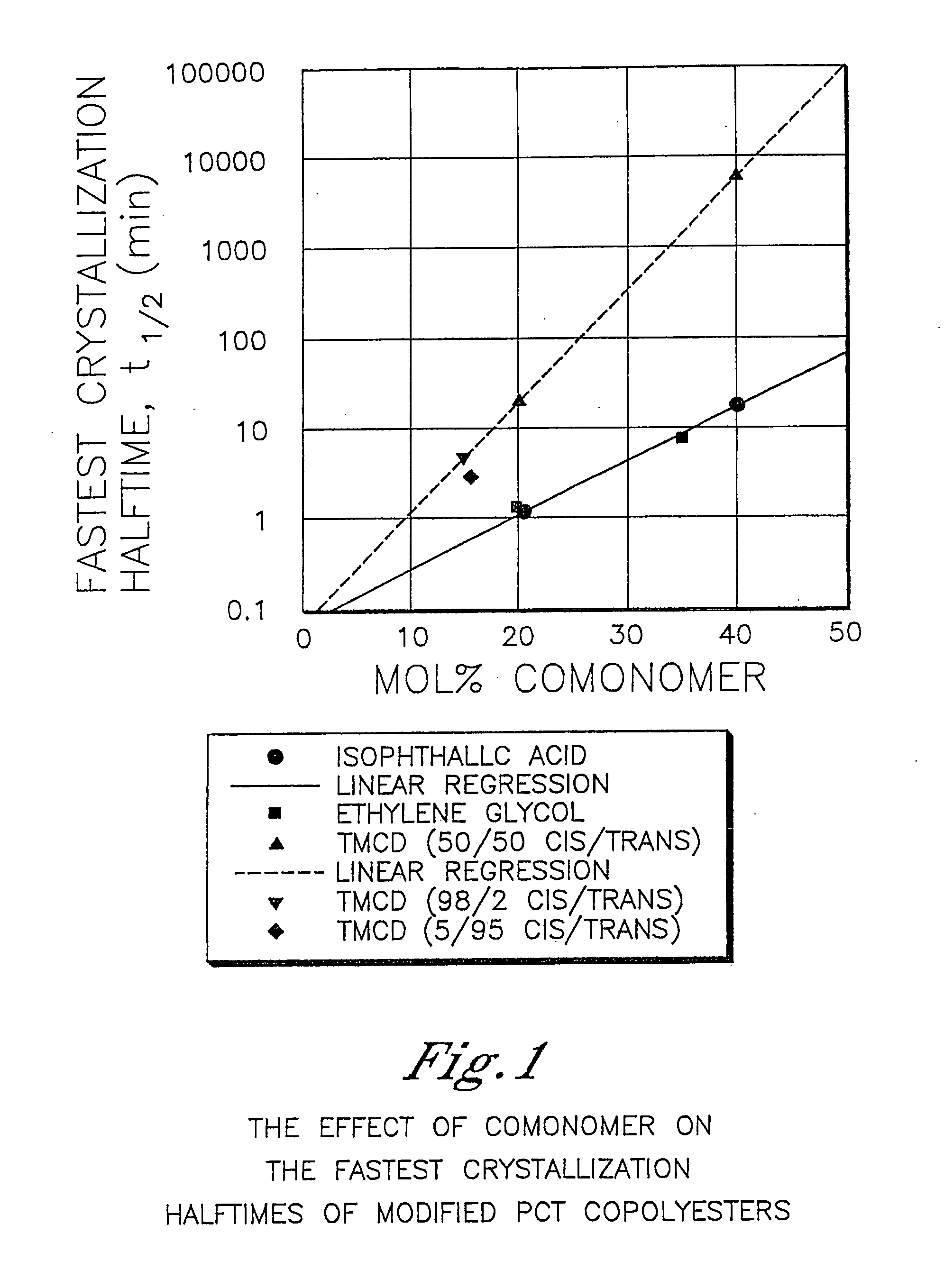
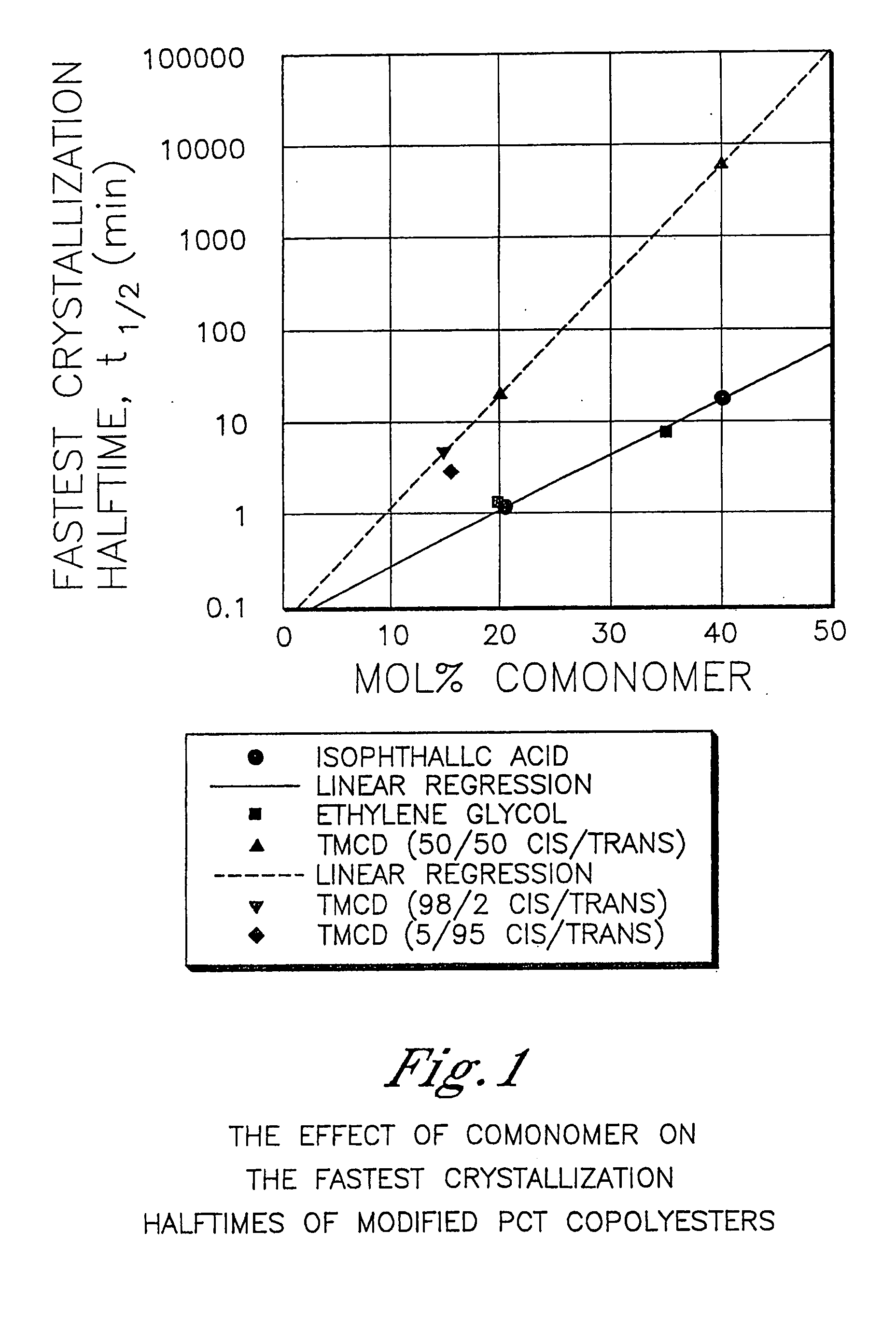
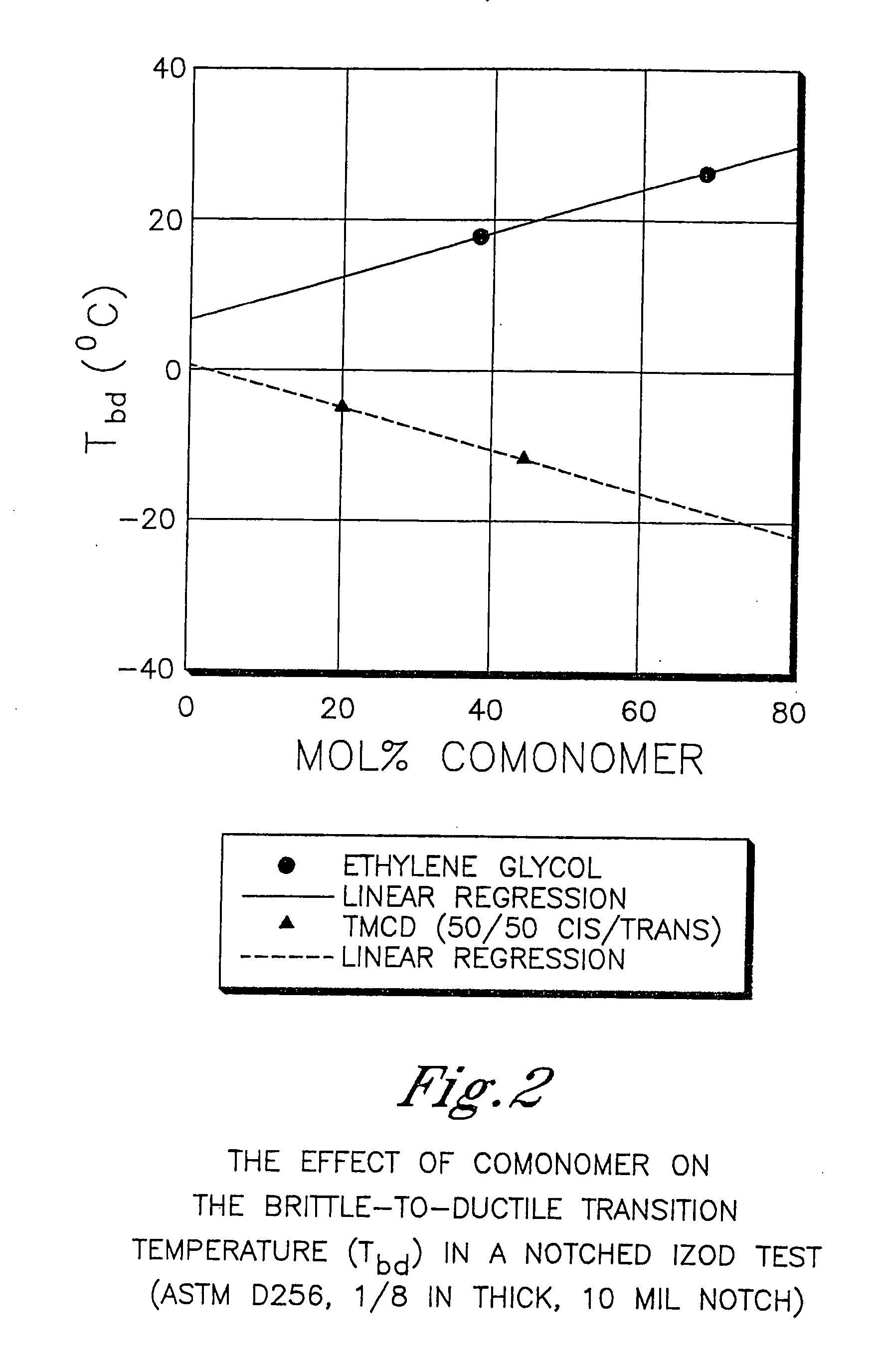
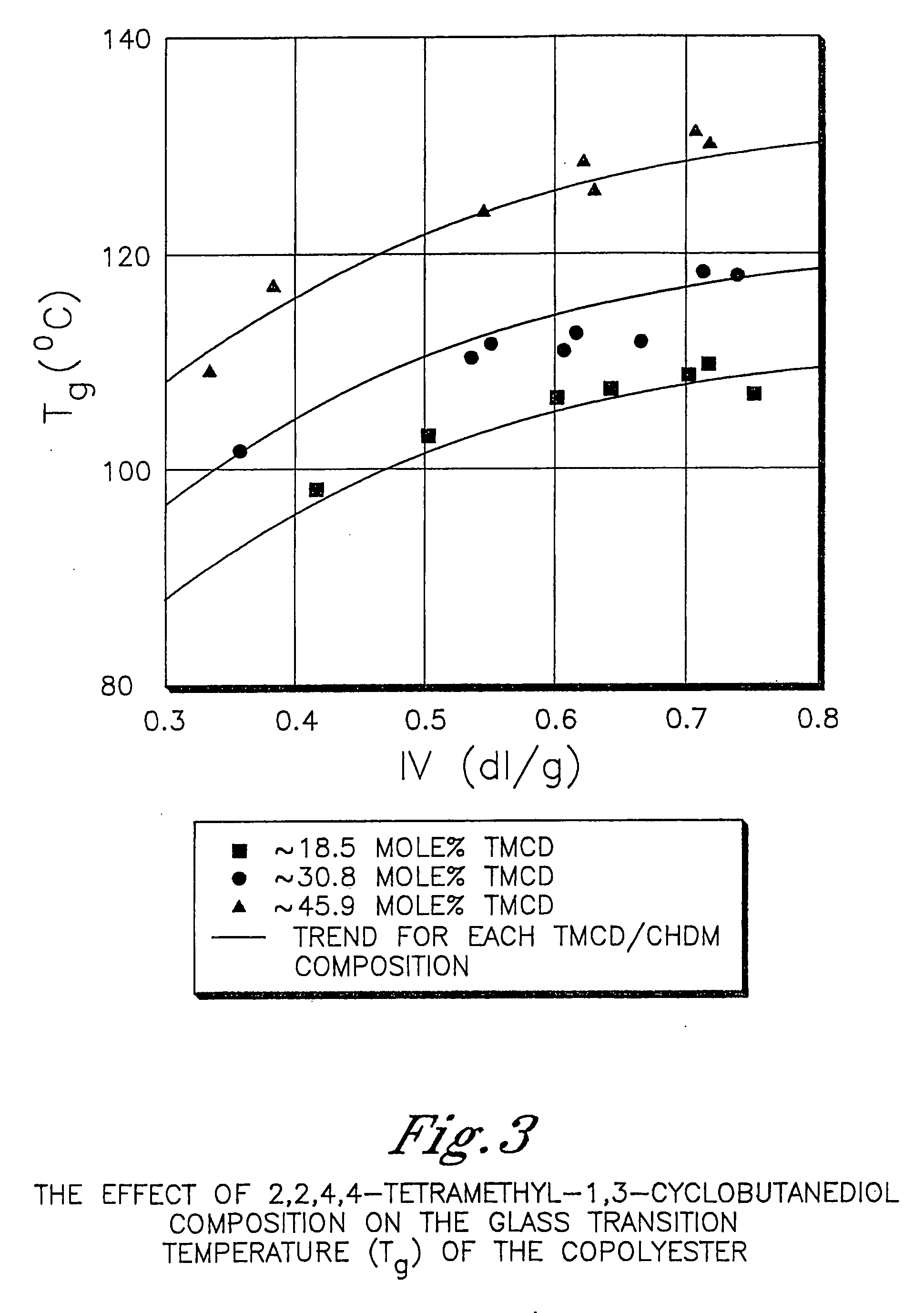
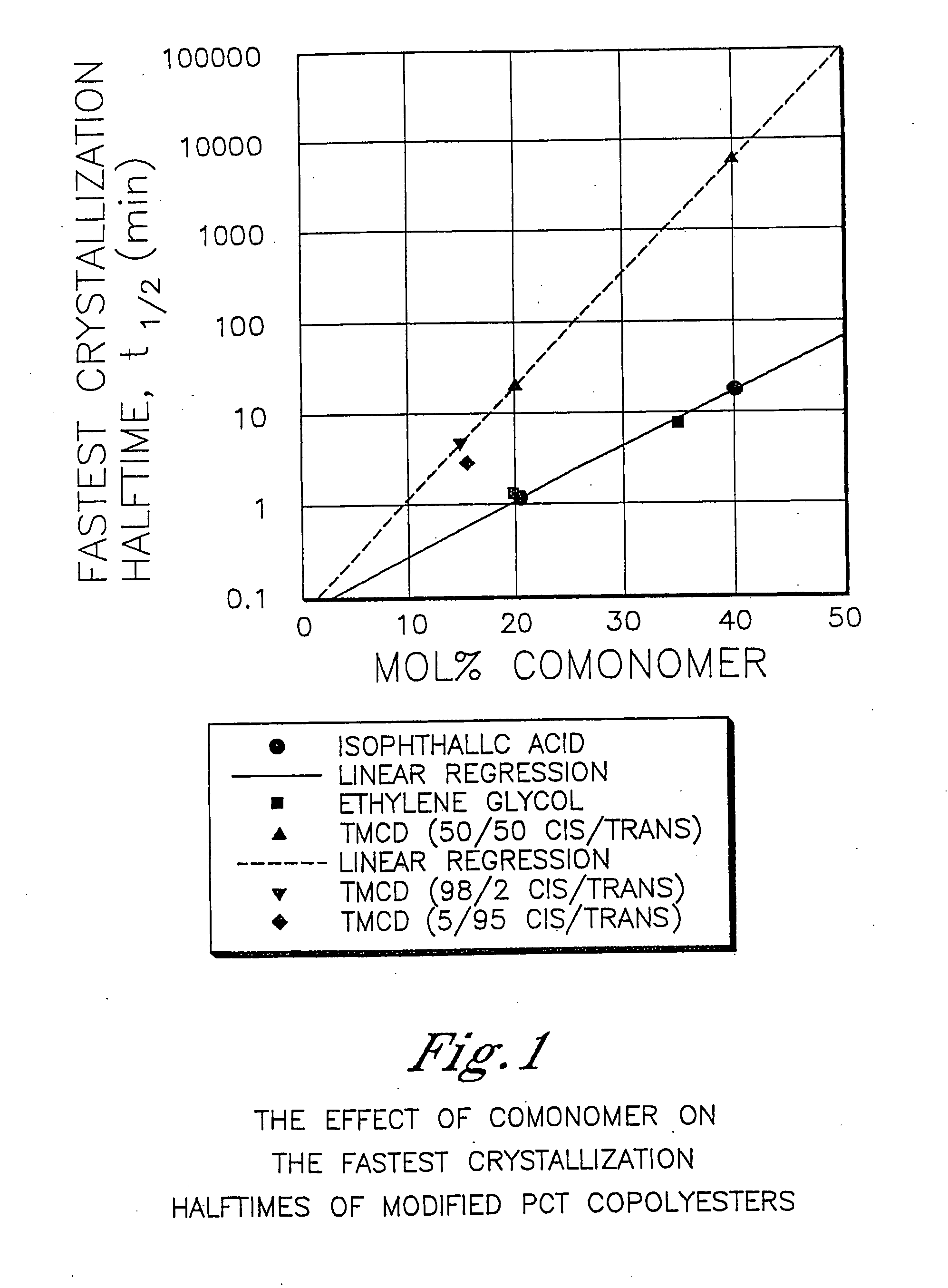
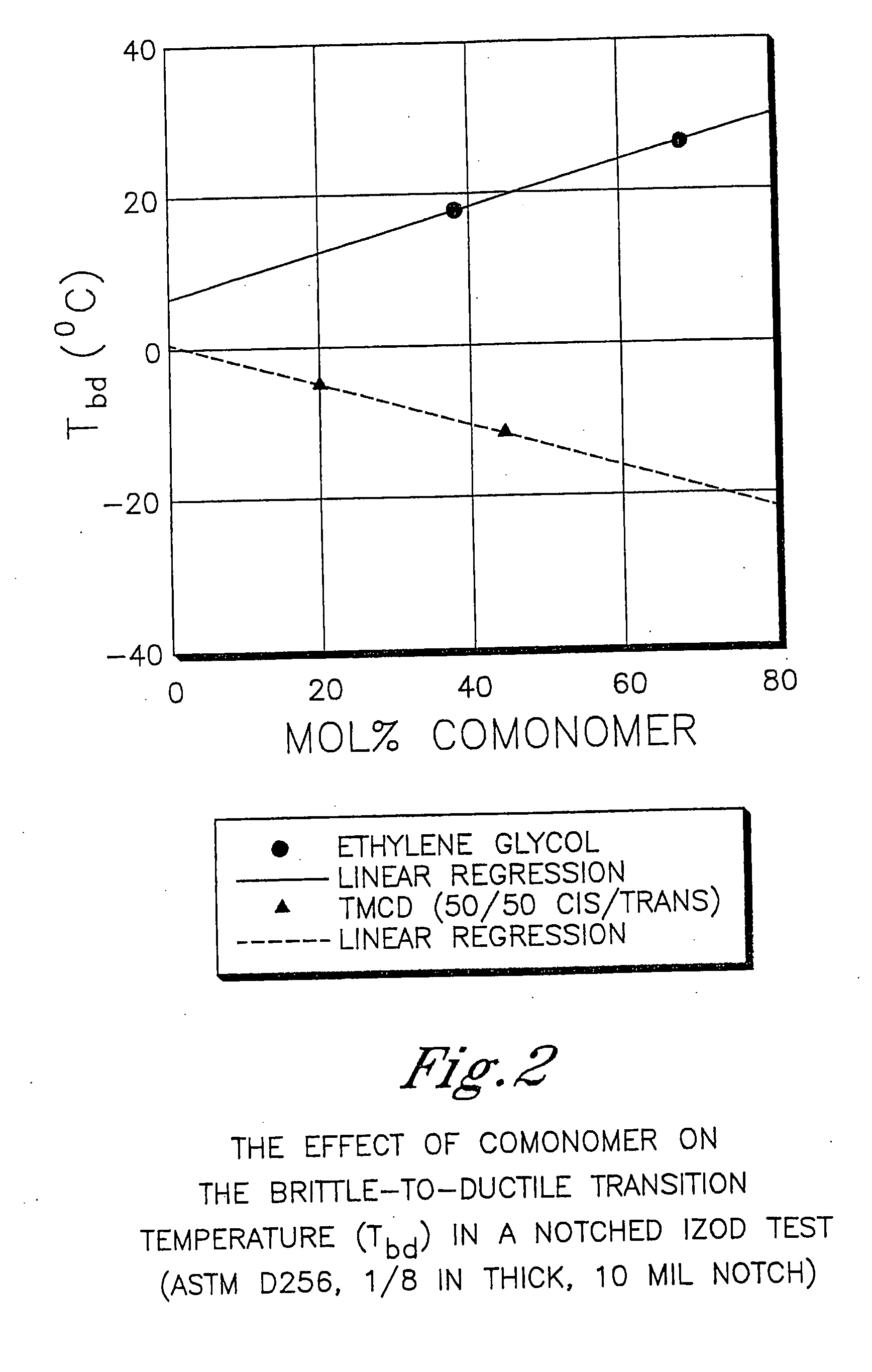
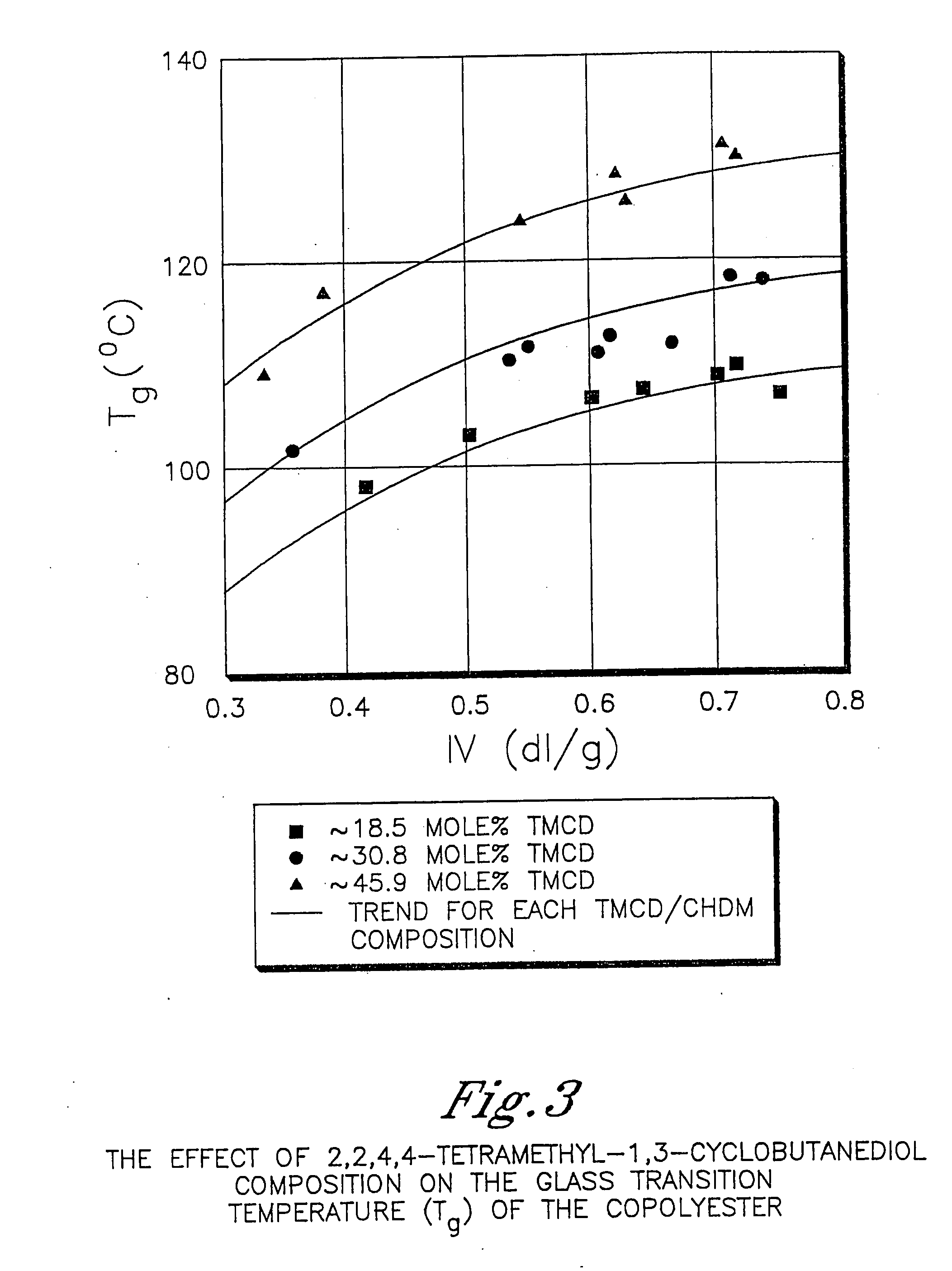
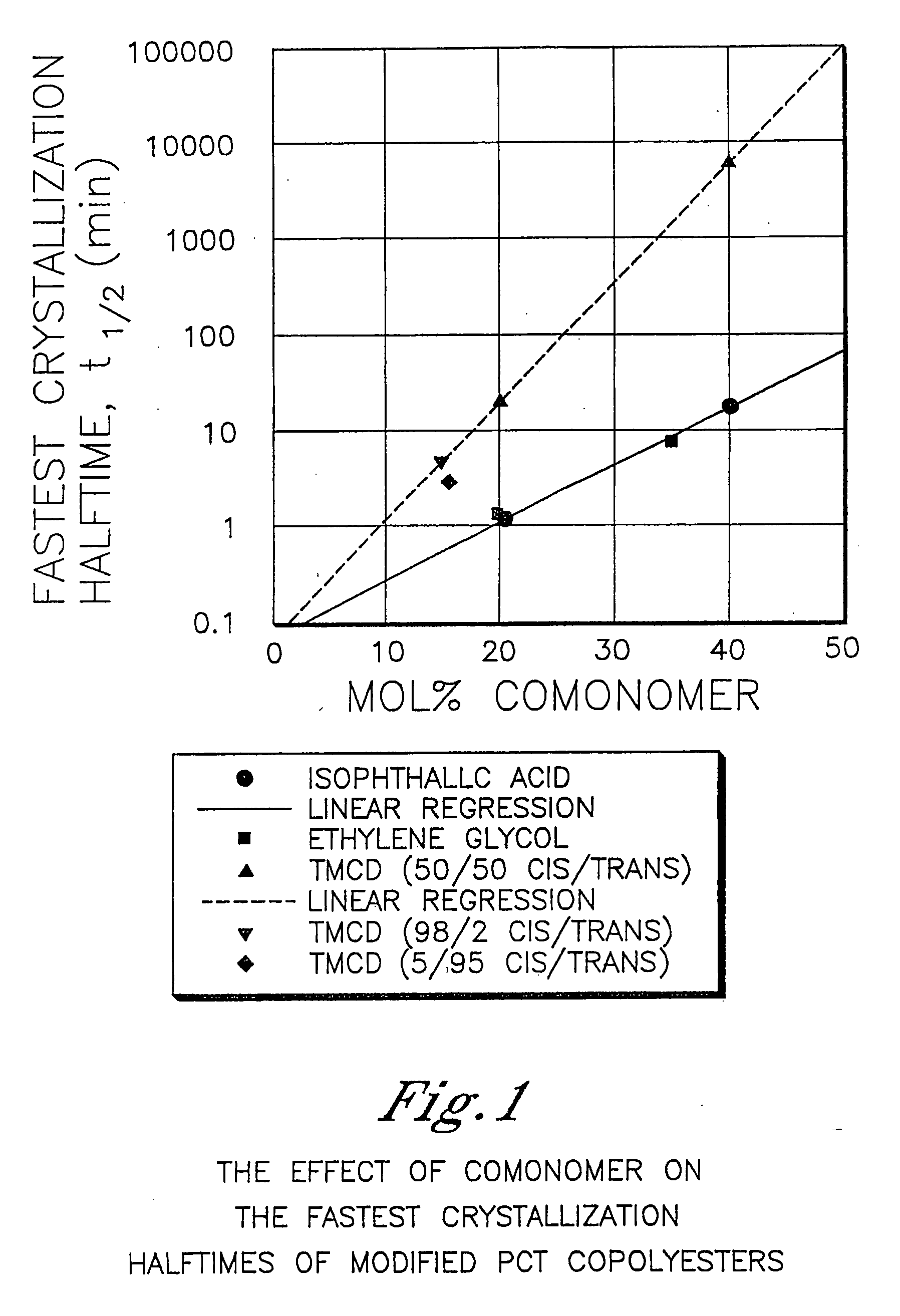
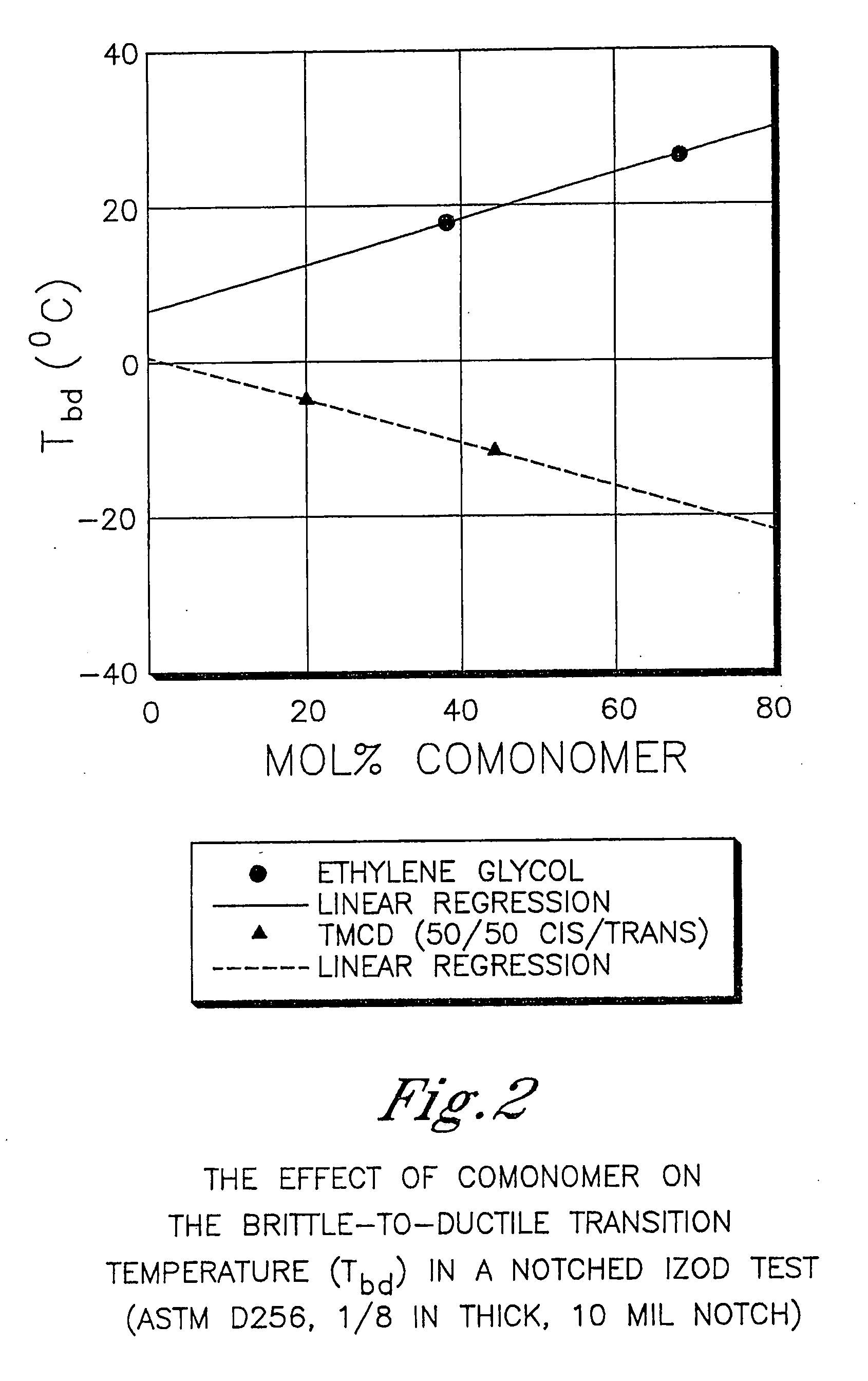
Patents
Literature
48results about How to "Inherent viscosity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polyesters including isosorbide as a comonomer blended with other thermoplastic polymers
A polymer blend including a polyester and another thermoplastic polymer. The polyester includes terephthaloyl moieties and, optionally, other aromatic diacid moieties; and ethylene glycol moieties; optionally diethylene glycol moieties; isosorbide moieties; and, optionally one or more other diol moieties. The polyester has an inherent viscosity of at least about 0.35 dL / g.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Polyester compositions for calendering
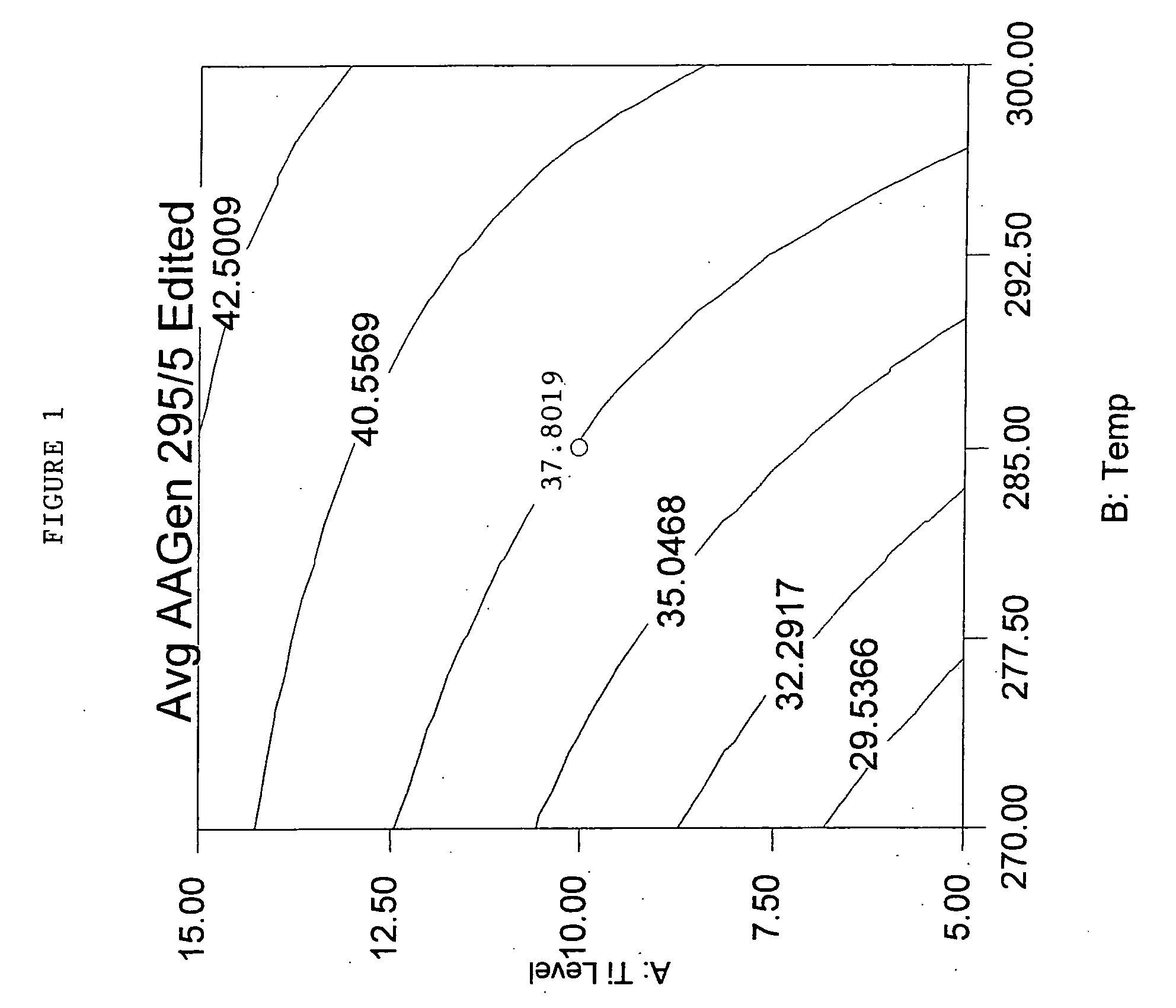
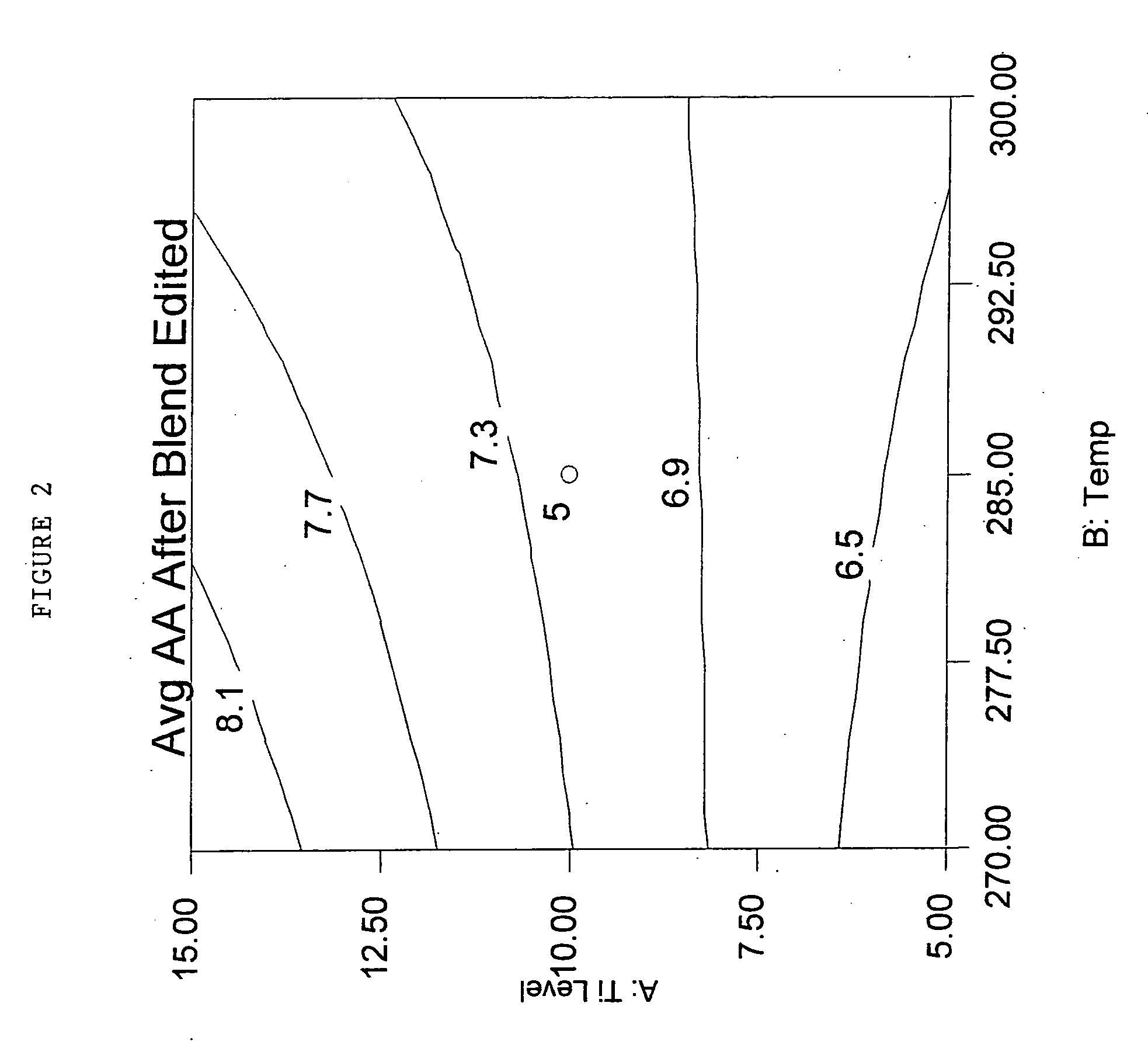
Polyester compositions that provide a higher throughput in calendering processes may be prepared from a polyester having crystallization half time of at least 5 minutes, an inherent viscosity of about 0.55 to about 0.75 dL / g, a branching monomer, and a release additive. The polyester compositions show a combination of excellent melt strength with good shear response that permits higher calendering line speeds before melt fracture occurs. Also disclosed are processes for film or sheet by calendering the above compositions and the film or sheet produced therefrom. The polyester compositions, film, or sheet also may include plasticizers and / or flame retardants to increase their flexibility and enable their use in commercial applications requiring flame resistance. The film and sheet have excellent appearance and can be used in a wide range of decorative and packaging applications.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Polyester fiber and methods for making same
InactiveUS6063495AGood useImproved strength and elasticity and abrasion resistanceMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentCeramic shaping apparatusPolyesterChemistry
A polyester fiber made from a polymer having ethylene glycol moieties, isosorbide moieties and terepthaloyl moieties, and the method of making the fiber is described. The polyester fiber is used to form articles suitable for commercial, especially textile, and industrial uses, and has an inherent viscosity of at least 0.35 dL / g when measured as a 1% (weight / volume) solution of the polyester in o-chlorophenol at a temperature of 25 DEG C.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Polyesters including isosorbide as a comonomer blended with other thermoplastic polymers
A polymer blend including a polyester and another thermoplastic polymer. The polyester includes terephthaloyl moieties and, optionally, other aromatic diacid moieties; and ethylene glycol moieties; optionally diethylene glycol moieties; isosorbide moieties; and, optionally one or more other diol moieties. The polyester has an inherent viscosity of at least about 0.35 dL / g.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Polyester-polycarbonate blends for diffuser sheets with improved luminance
InactiveUS20060270773A1Inherent viscosityIncrease temperatureSpecial tyresOptical light guidesPolyesterParticulates
Disclosed is a composition for a diffuser sheet or film with improved luminance or brightness. The composition comprises about 80 to about 99.8 percent by weight of a miscible blend of a polycarbonate with a polyester, and about 0.2 to about 20 percent by weight of a particulate light diffusing component, and about 10 to about 1000 ppm of a brightness enhancing agent. Also disclosed is a process for the preparation of a diffuser film or sheet from this composition. Diffuser films and sheets prepared from this composition are useful for bulk light diffusers for backlight displays.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Process to produce polyesters which incorporate isosorbide
The present invention provides a process to produce isosorbide-containing polyesters. The process allows for higher isosorbide incorporation than previously found while maintaining high polymeric molecular weights.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
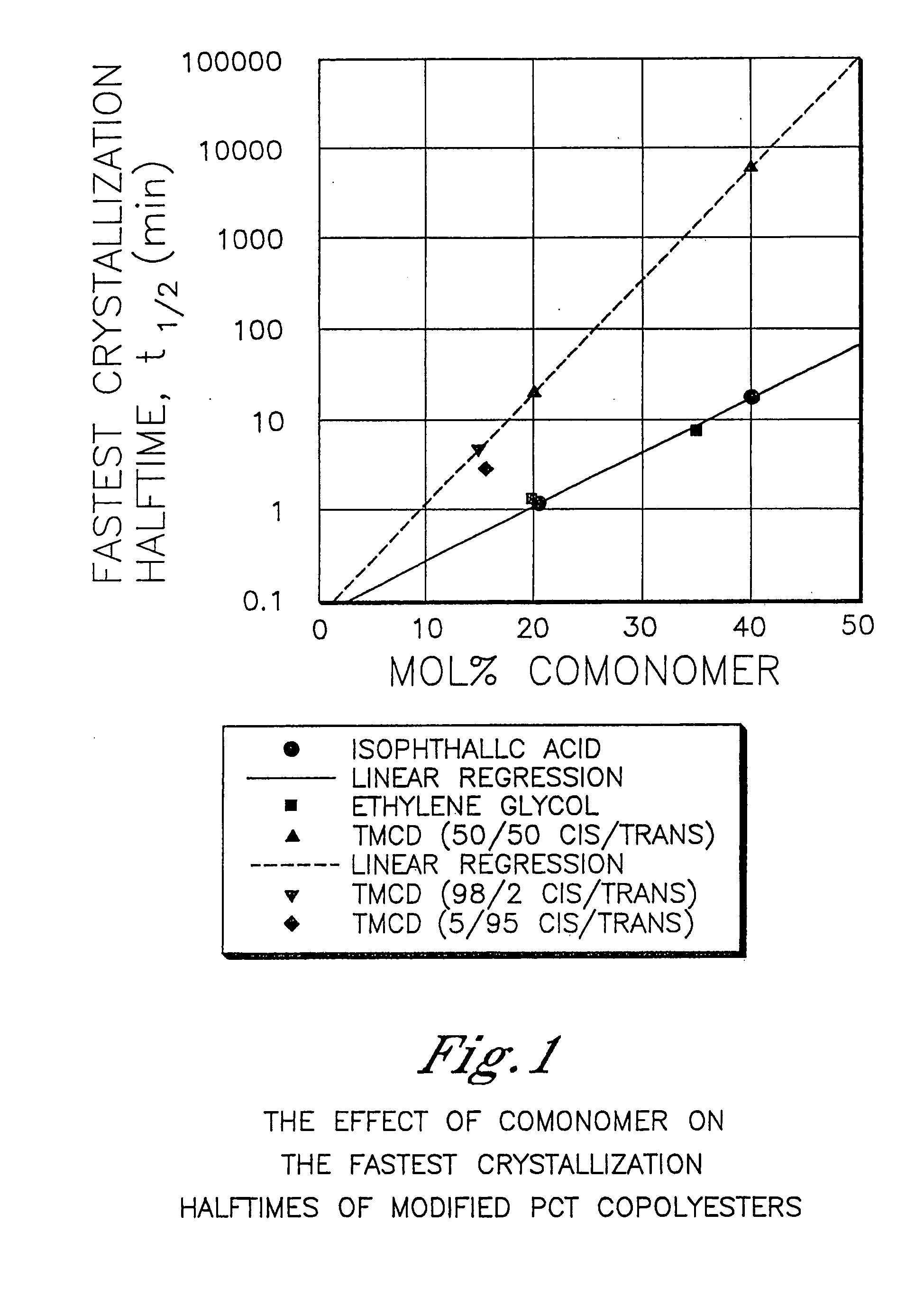
Certain polyester compositions which comprise cyclohexanedimethanol, moderate cyclobutanediol, cyclohexanedimethanol, and high trans cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid
InactiveUS20070232779A1Good chemical resistanceLess reactiveSynthetic resin layered productsOptical articlesPolyesterCyclohexanedimethanol
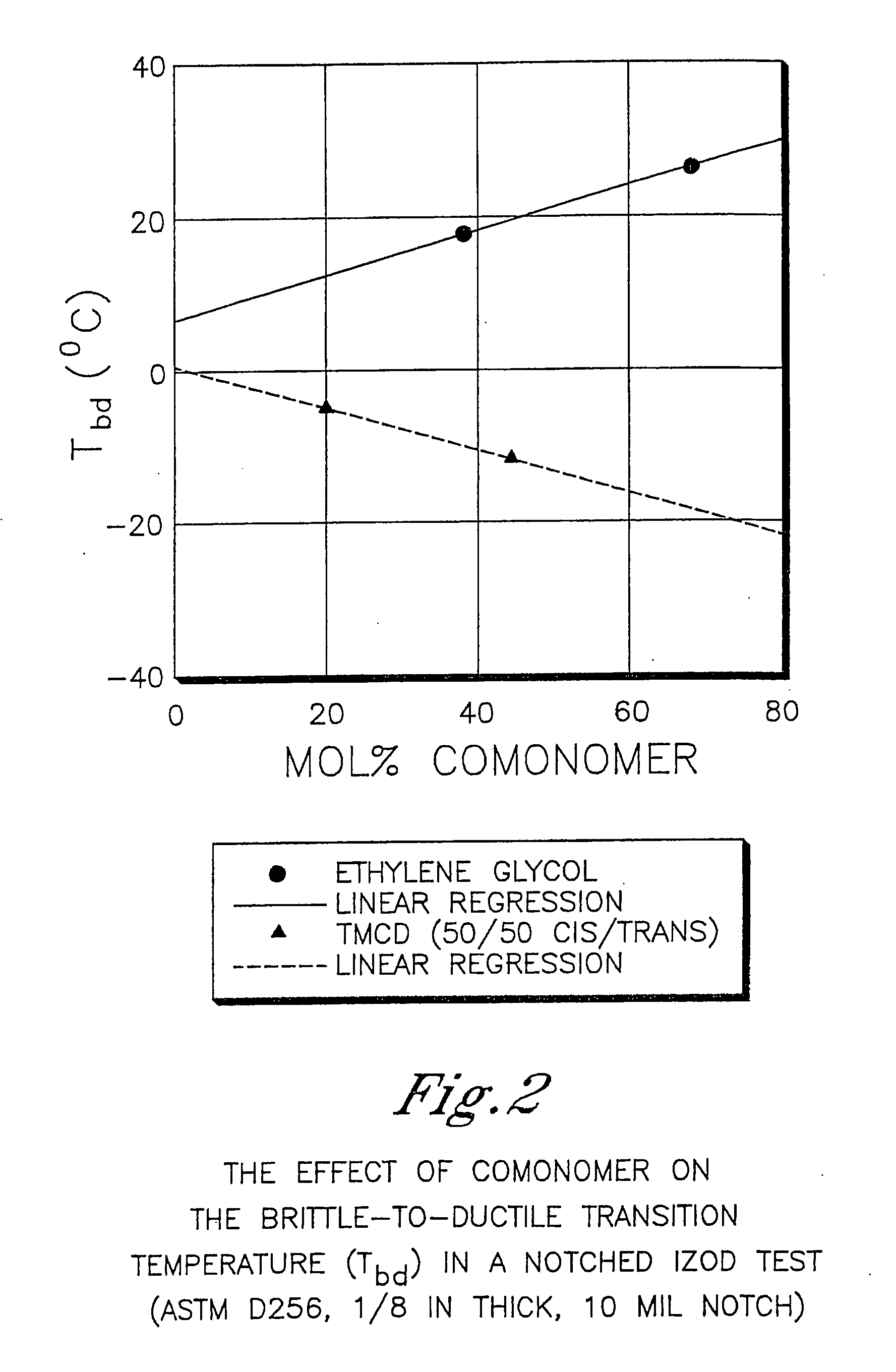
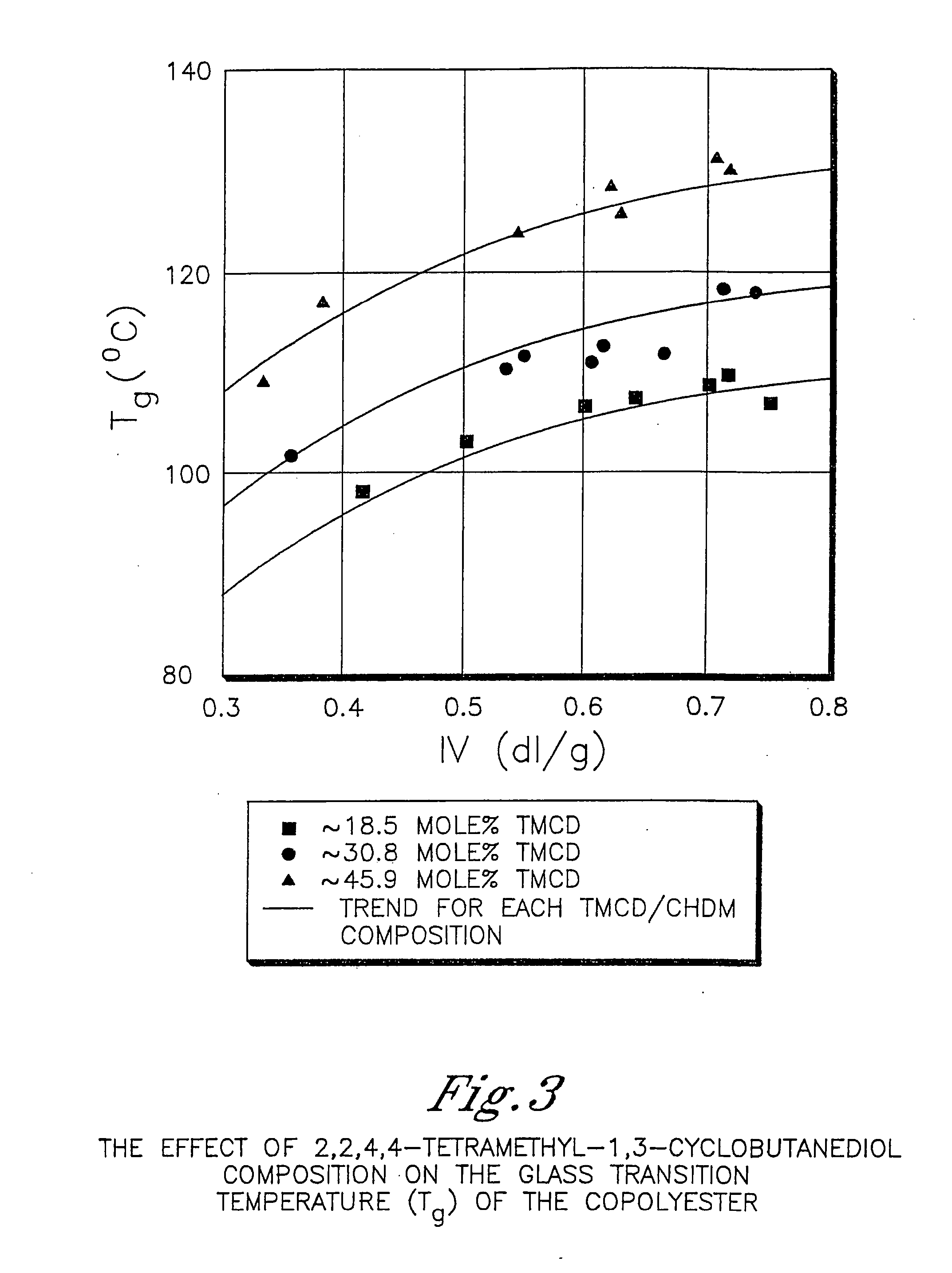
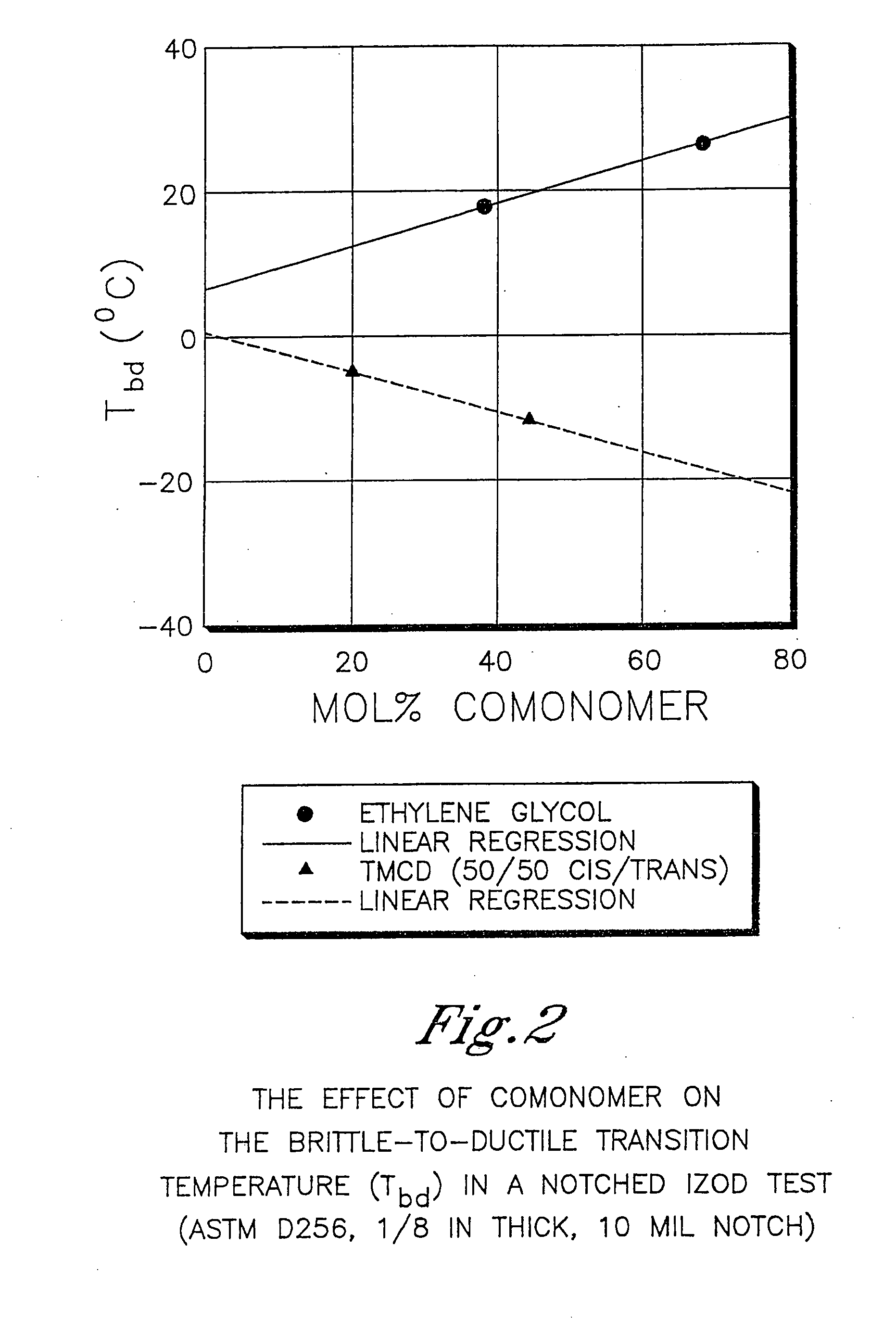
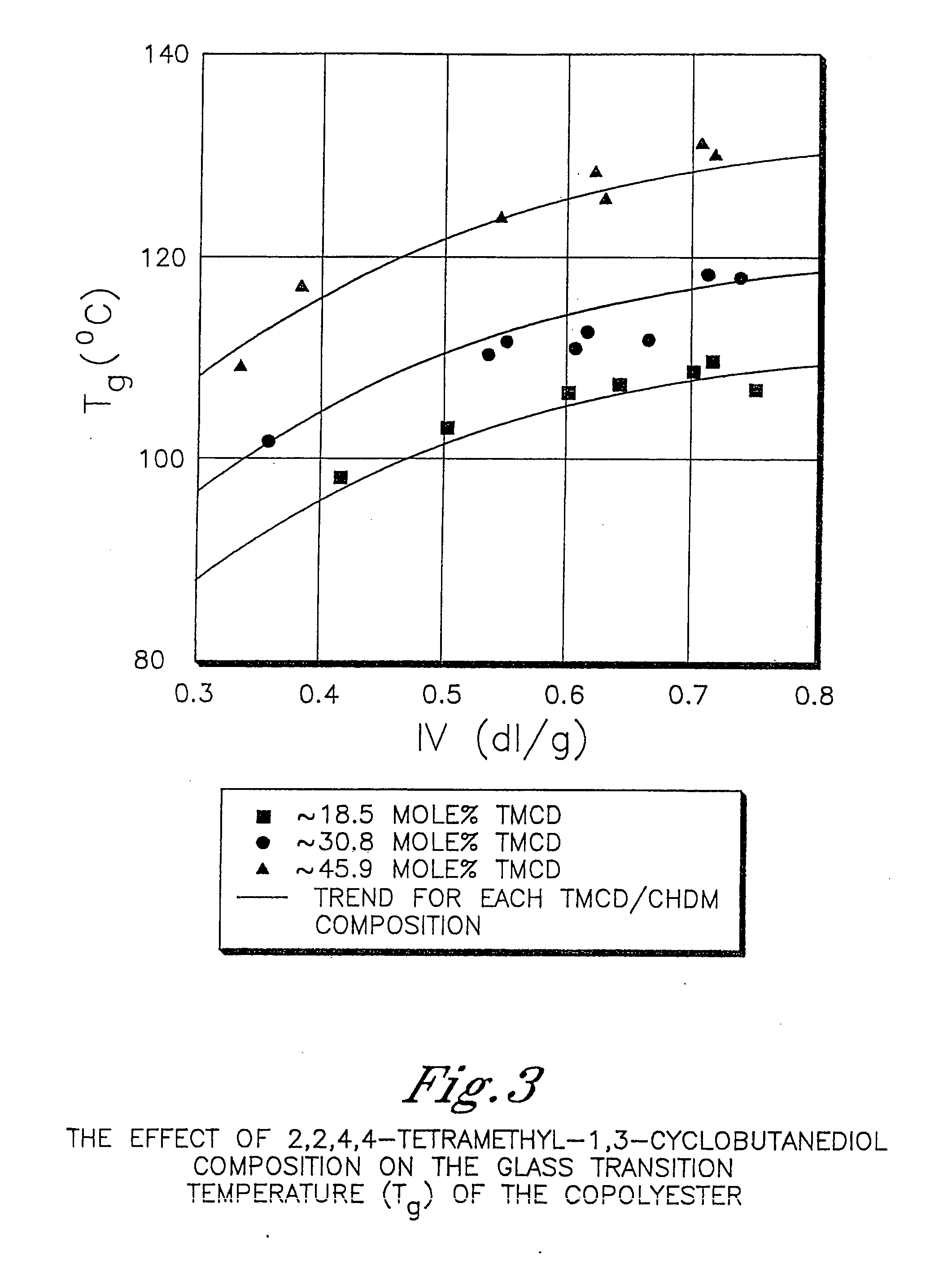
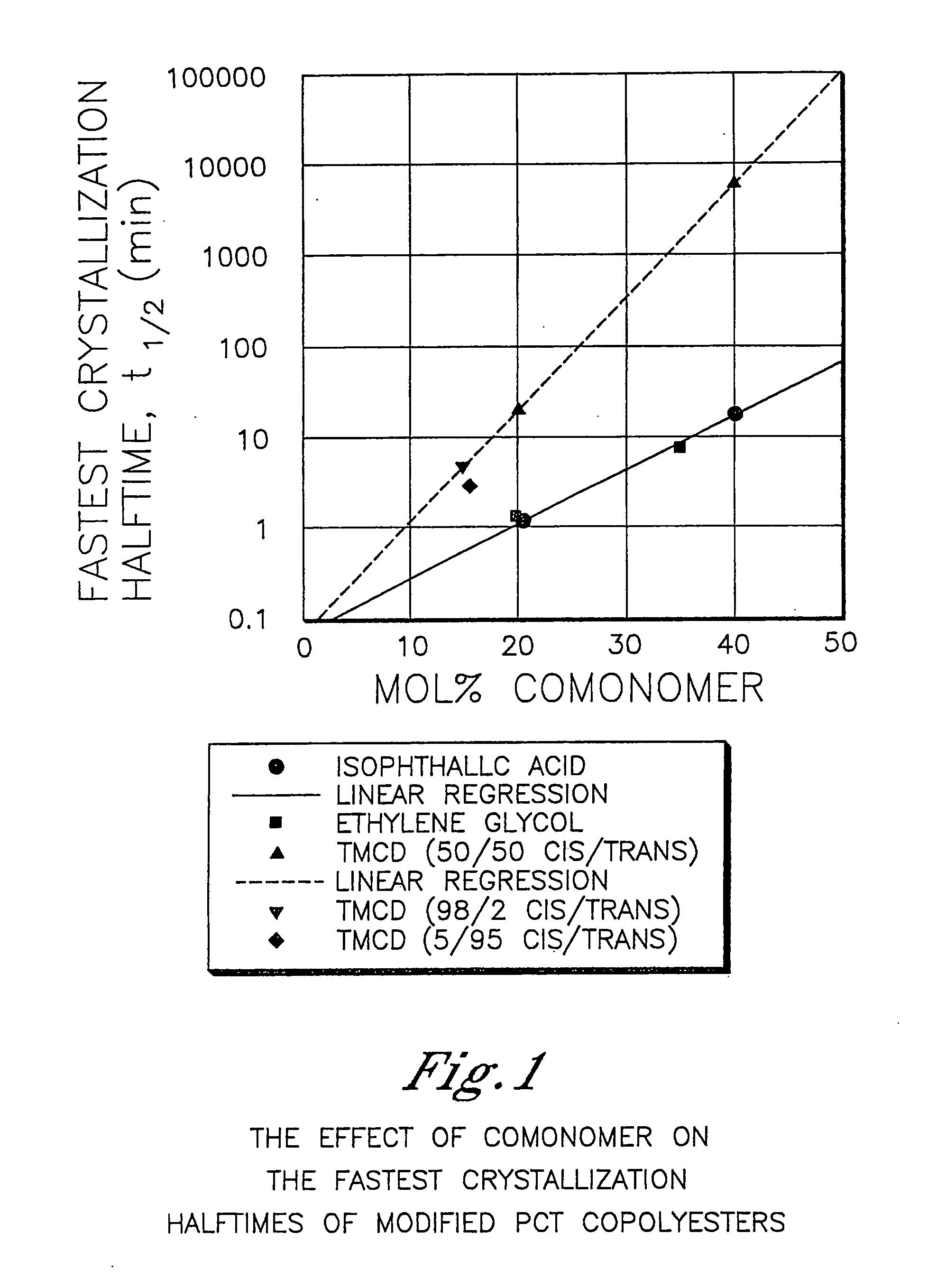
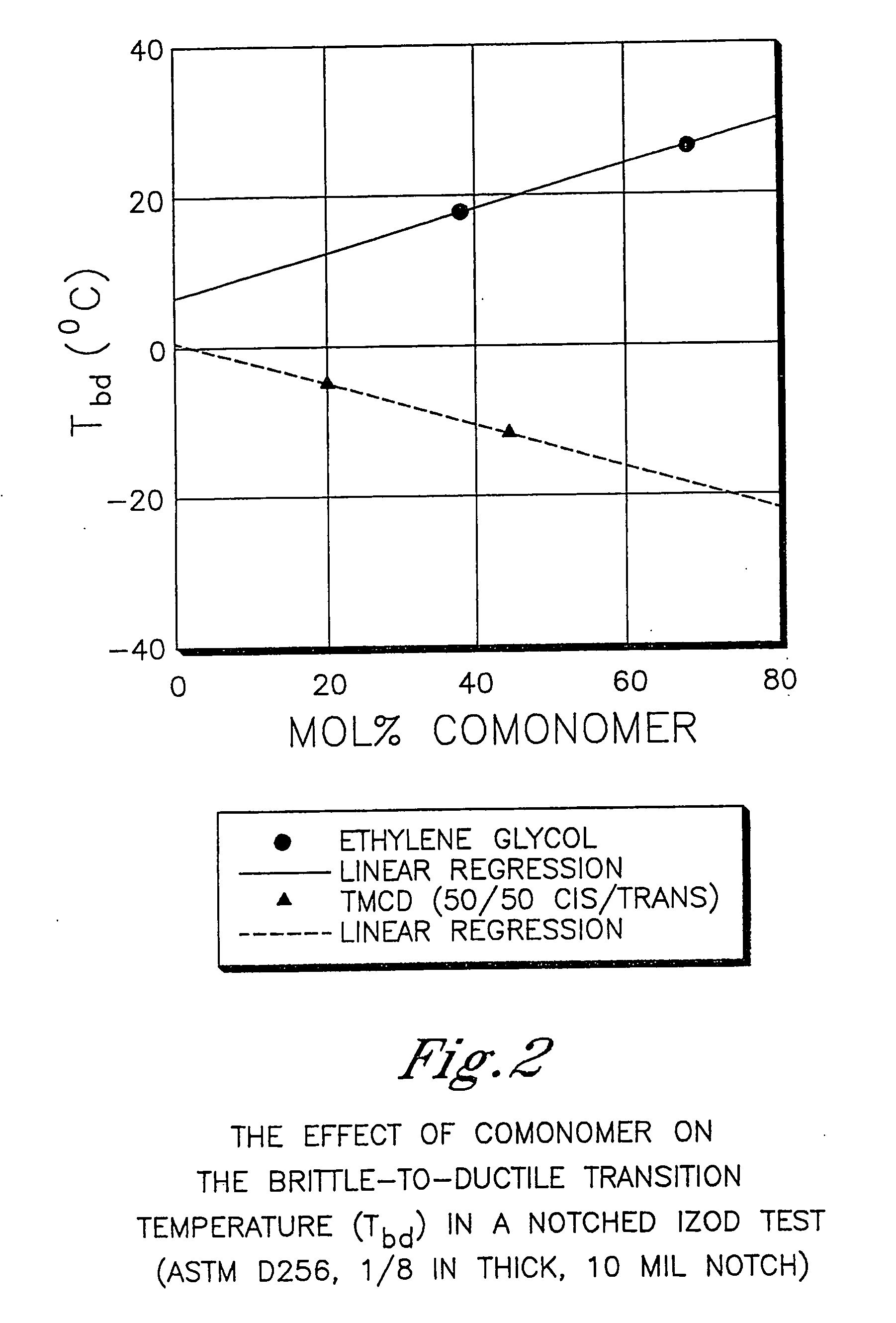
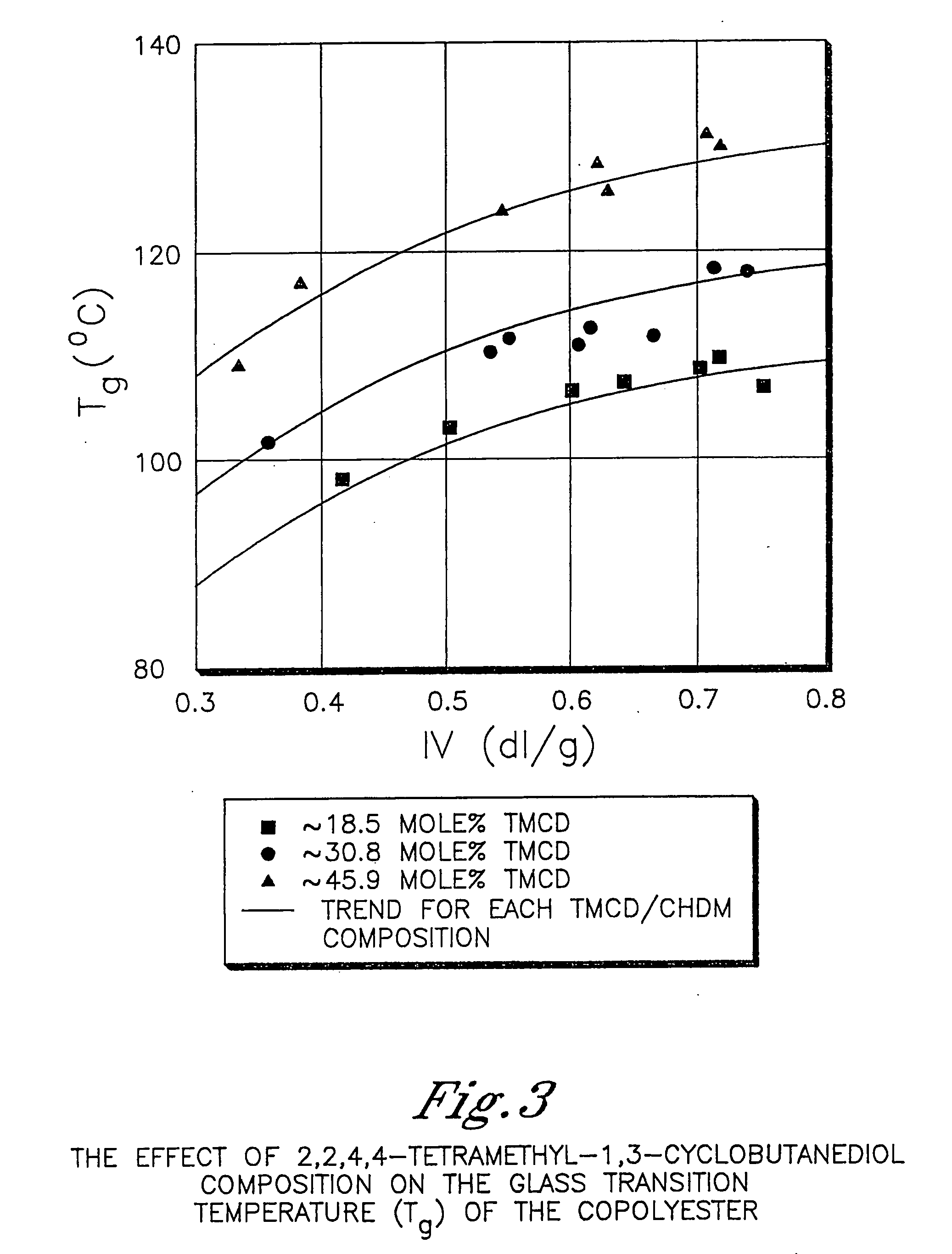
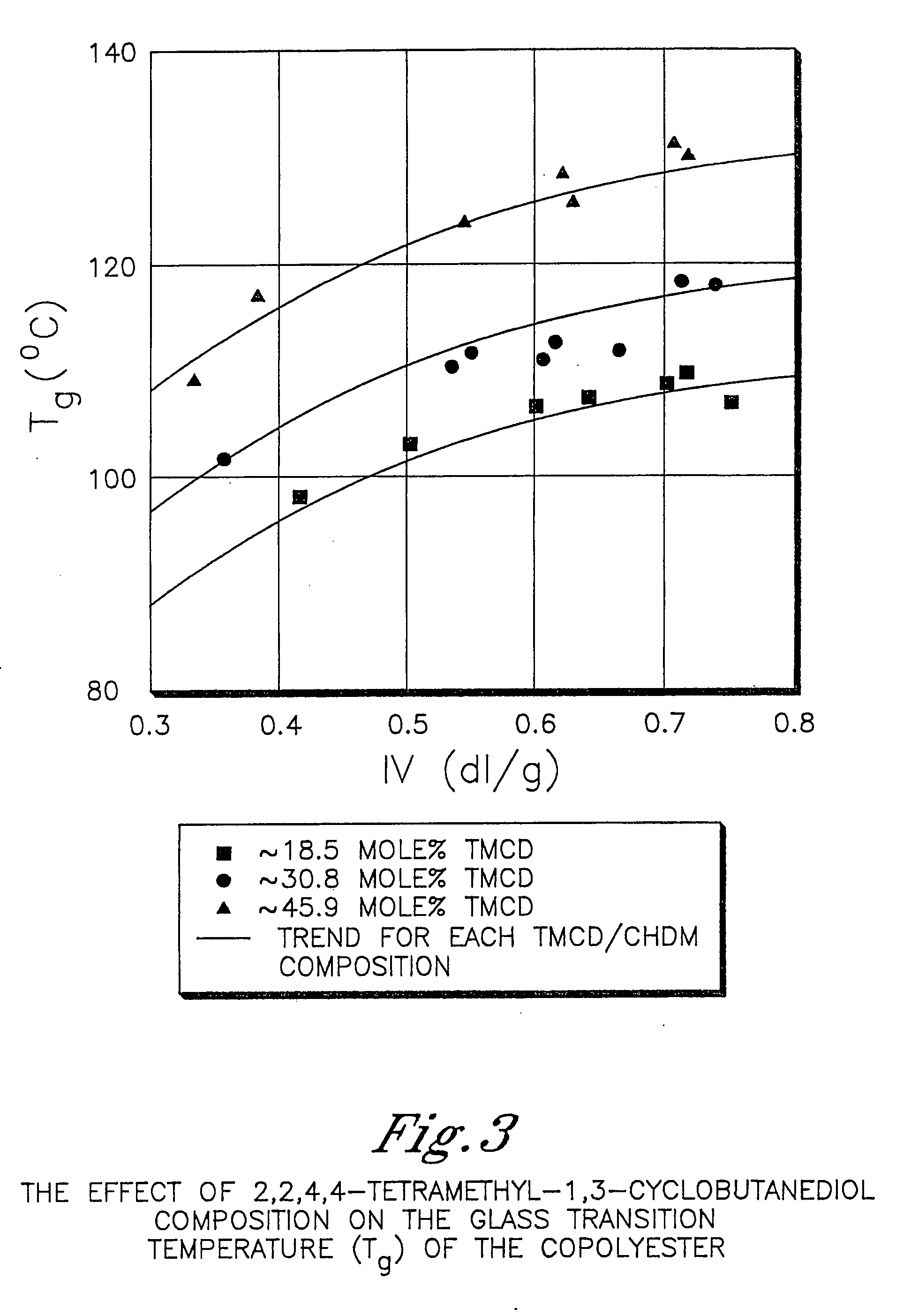
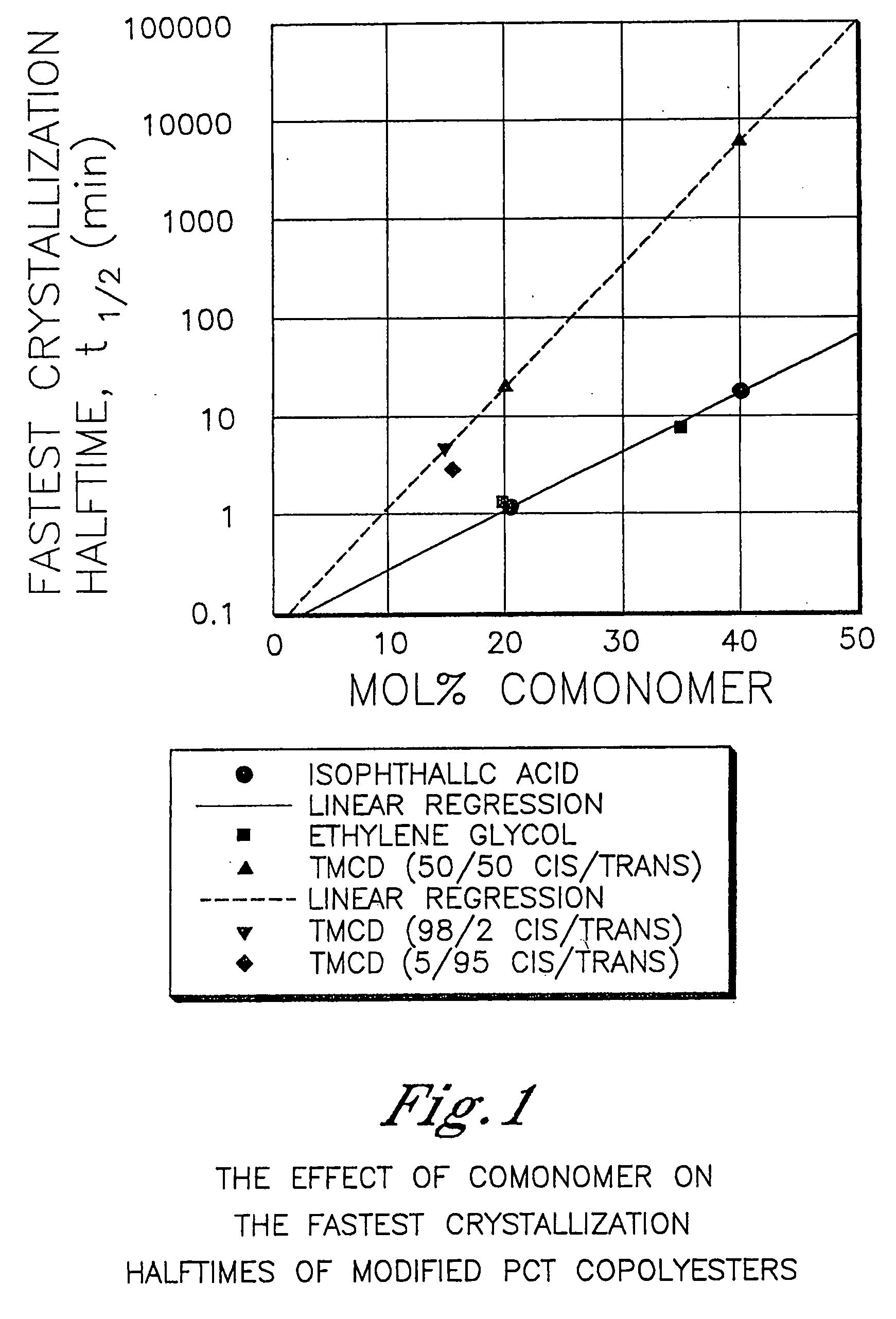
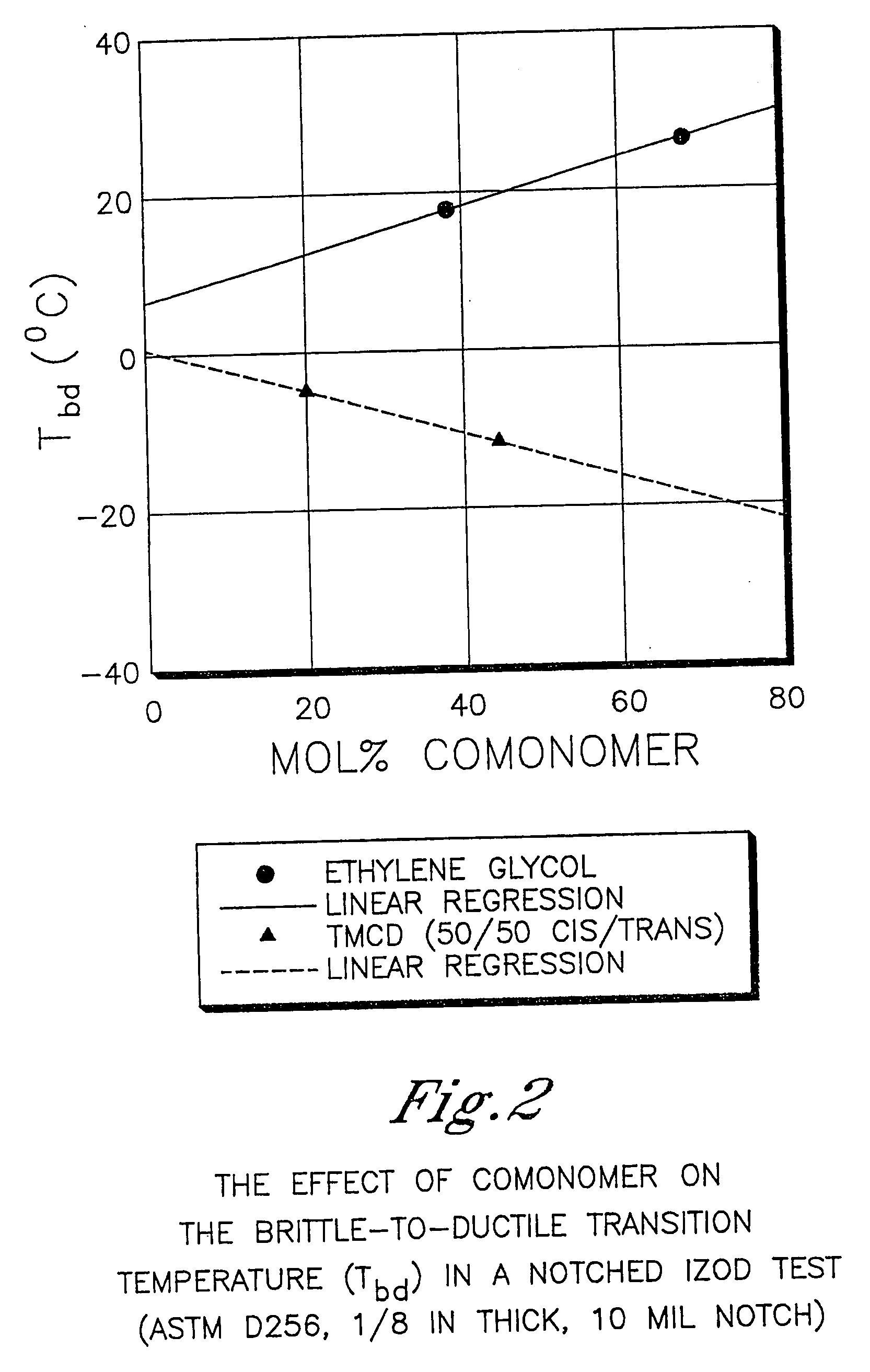
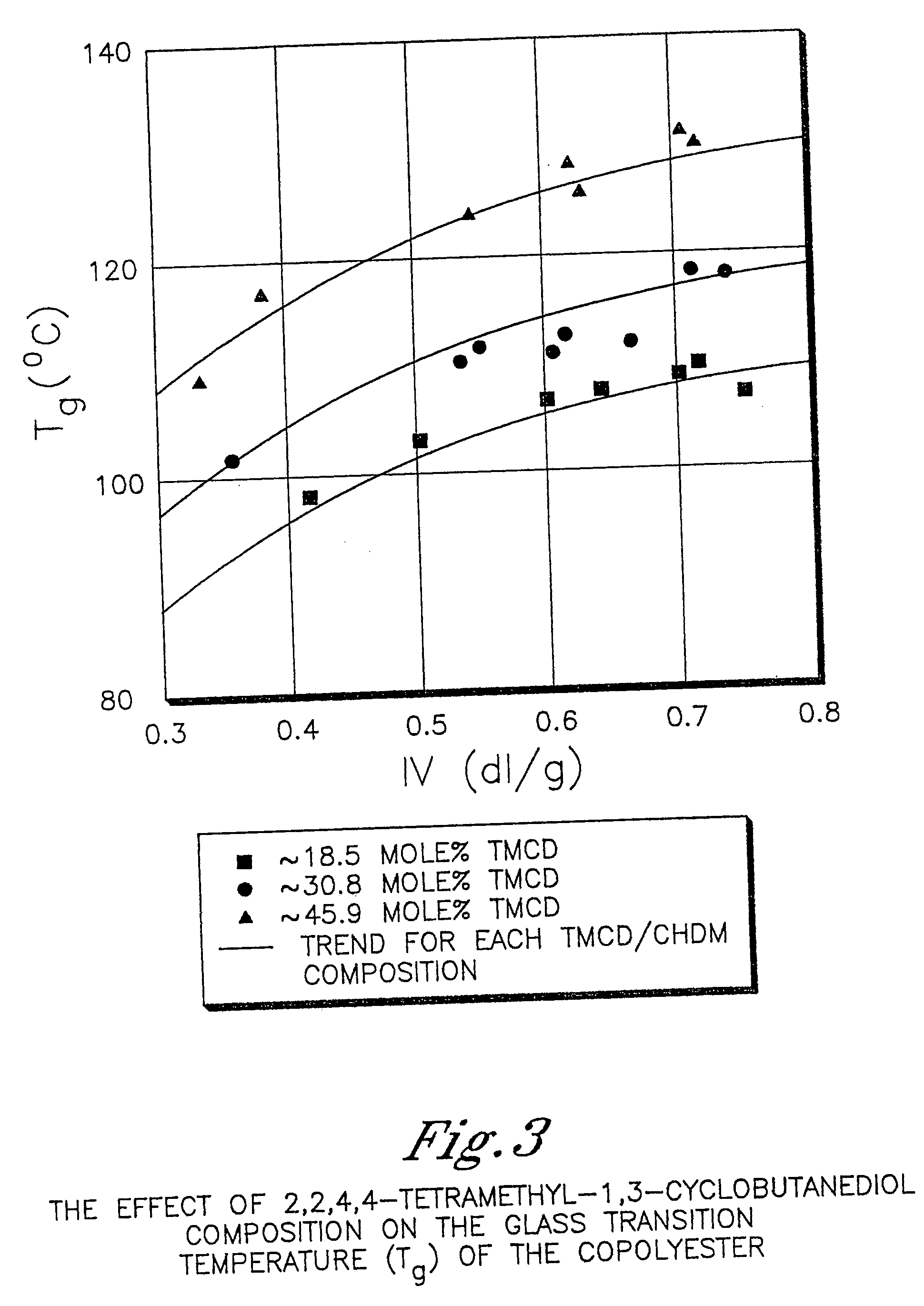
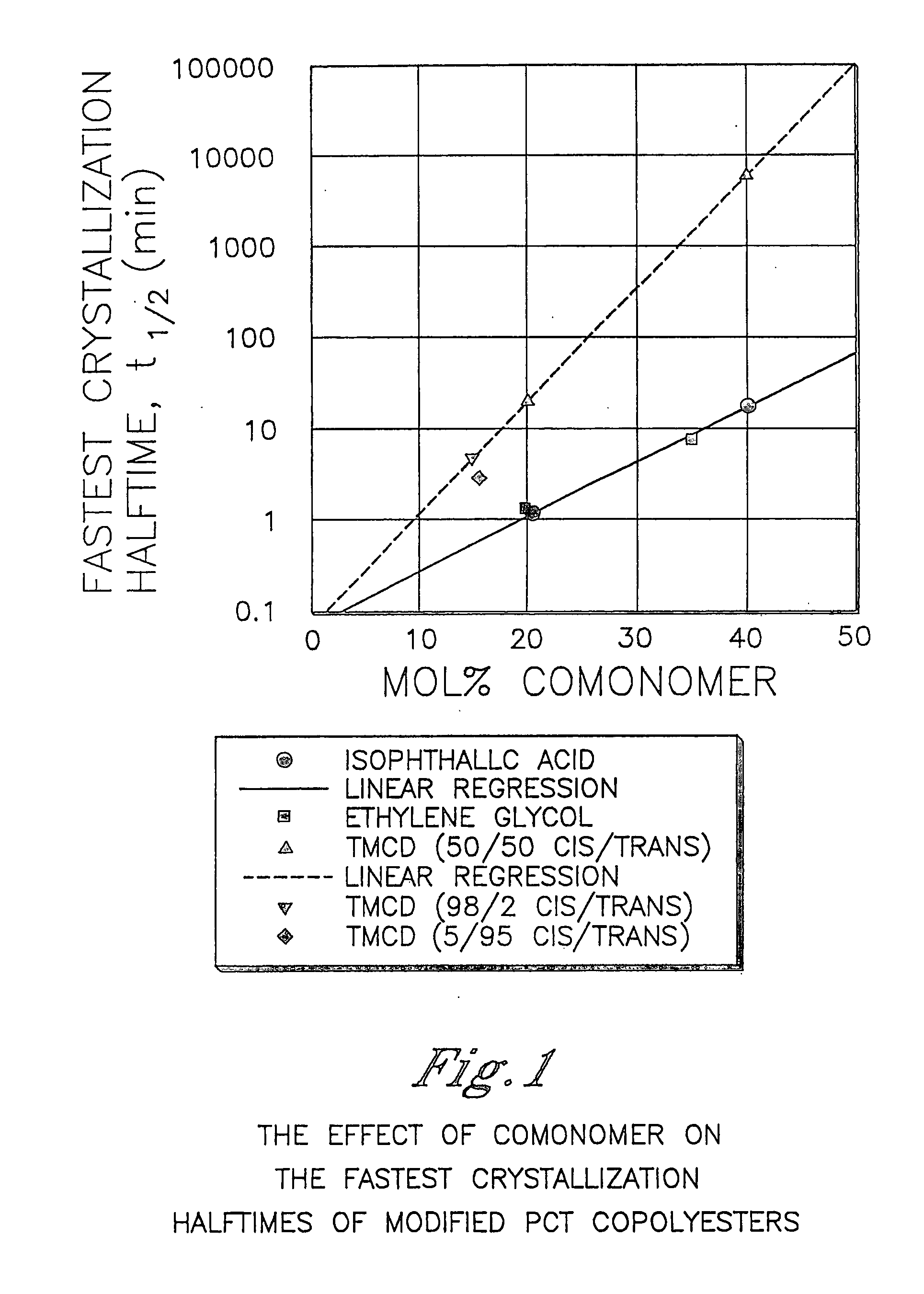
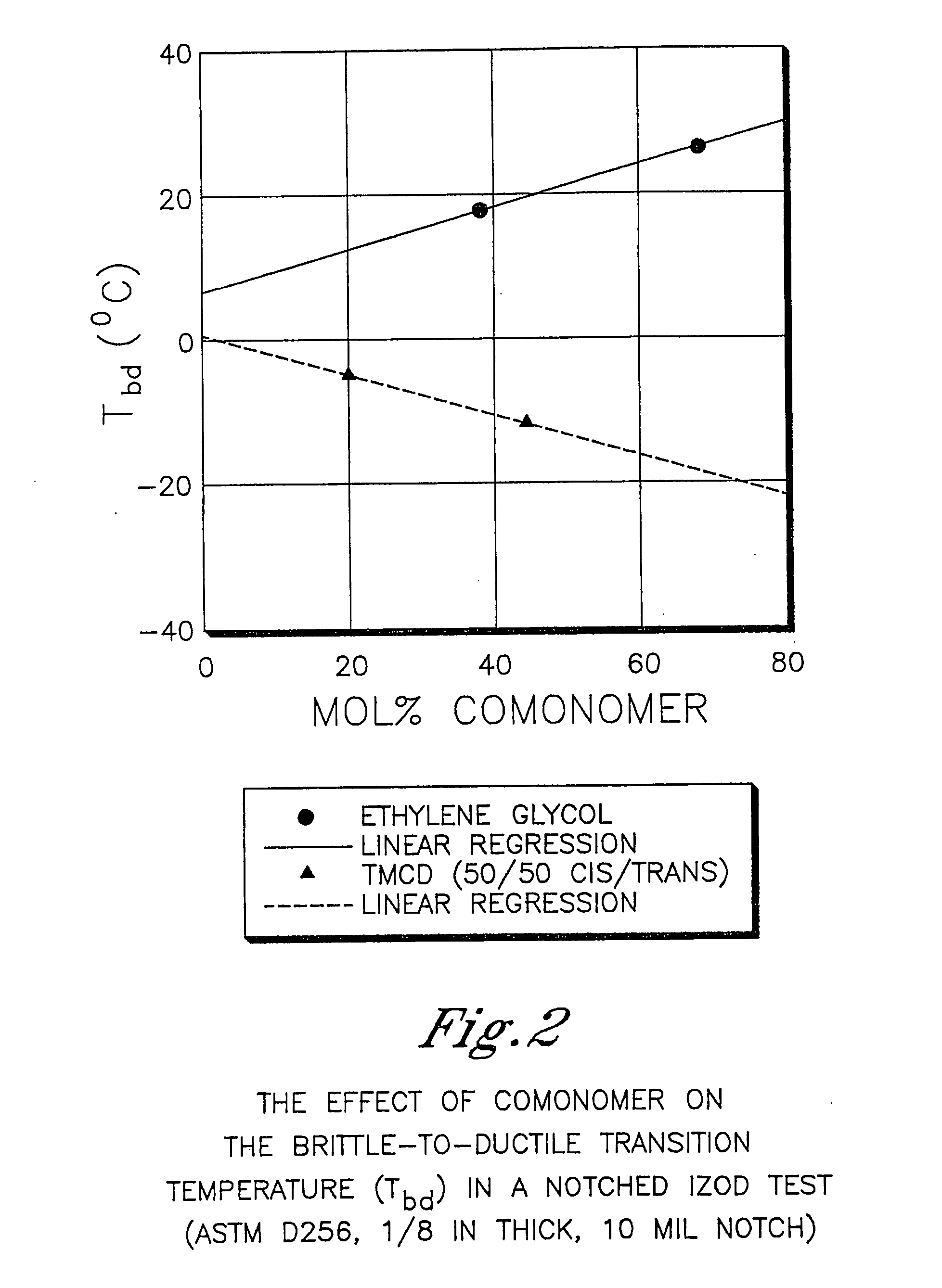
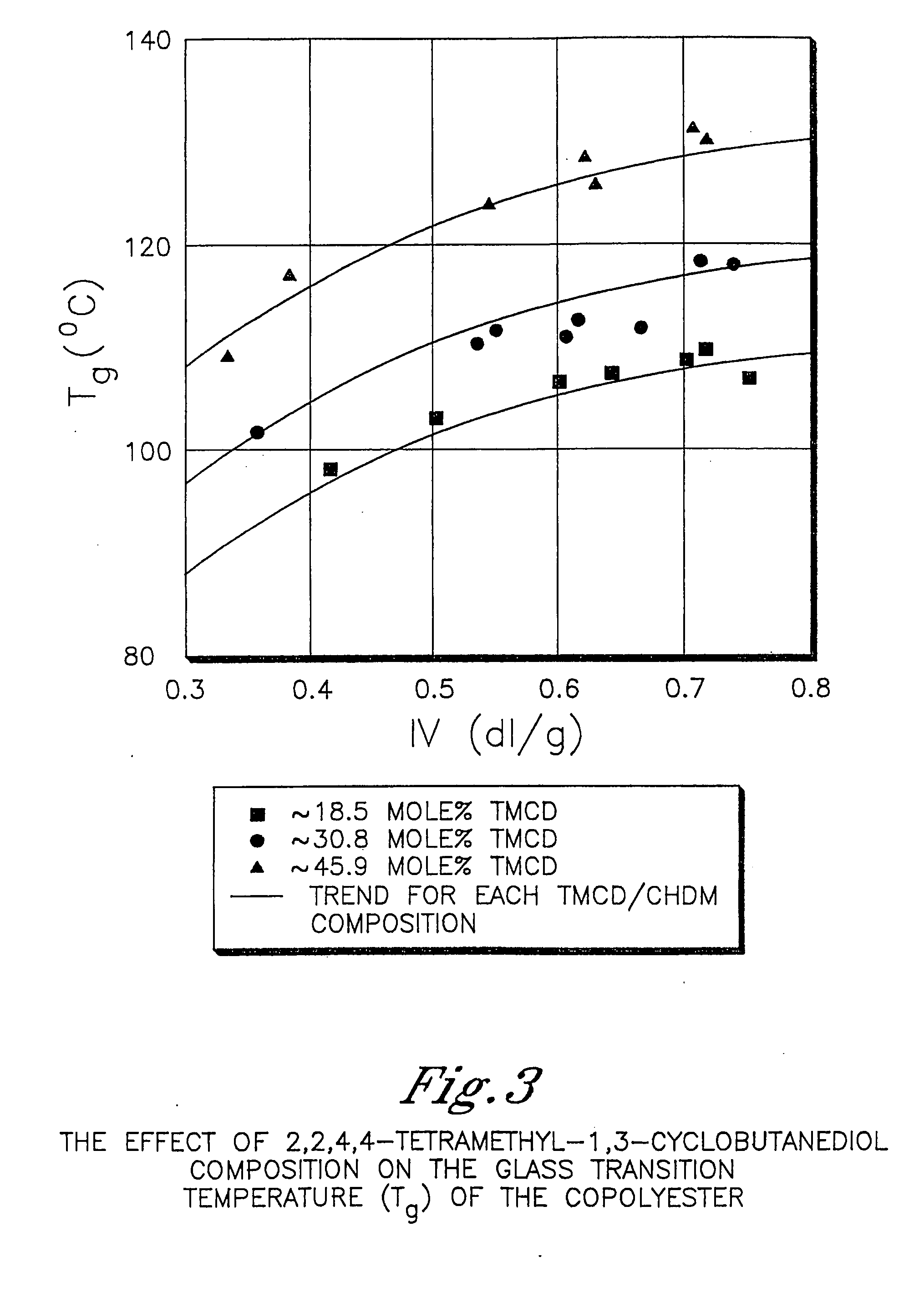
Described as one aspect of the invention are polyester compositions A polyester composition comprising at least one polyester which comprises:(A) a dicarboxylic acid component comprising:i) 70 to 100 mole % of cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues or an ester thereof comprising:(a) 80 to 99 mole % trans-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues or an ester thereof; and(b) 1 to 20 mole % cis-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues or an ester thereof;ii) 0 to 30 mole % of aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues, other than cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues, having up to 16 carbon atoms or esters thereof, other than cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid residues; andiii) 0 to 10 mole % of aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues having up to 20 carbon atoms; and(B) a glycol component comprising:i) 5 to 35 mole % of 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; andii) 65 to 95 mole % of 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues, 1,3-cyclohexanedimethanol residues, 1,2-cyclohexanedimethanol residues or esters thereof or mixtures thereof,wherein the total mole % of said dicarboxylic acid component is equal to 100 mole %;the total mole % of said glycol component is equal to 100 mole %;wherein the inherent viscosity of said polyester is from 0.35 to 1.2 dL / g as determined in 60 / 40 (wt / wt) phenol / tetrachloroethane at a concentration of 0.5 g / 100 ml at 25° C.; and wherein said polyester has a Tg of from 66 to 120° C. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Methods for forming amorphous ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin drag reducing agents
InactiveUS6015779AReduce frictional energy lossHigh molecular weightOther chemical processesLiquid organic insulatorsHalohydrocarbonAlpha-olefin
A composition including polyalphaolefins that function as drag reducing agents and a process for the preparation of polyalphaolefins that function as drag reducing agents are disclosed. The process includes contacting alpha olefin monomers with a catalyst system, which includes a catalyst and an activator (co-catalyst) in a reactant mixture. The catalyst is a transition metal catalyst, preferably titanium trichloride, and the co-catalyst may include an alkylaluminoxane, alone or in combination, with a dialkylaluminum halide or a halohydrocarbon. The polymerization of the alpha olefin monomers produces a non-crystalline, ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin having an inherent viscosity of at least 10 dL / g. The addition of the alkylaluminoxane during the polymerization process provides for a non-crystalline, ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin and a more uniform molecular weight distribution of the resulting polyalphaolefin, thereby creating a drag reducing agent superior to known drag reducing agents. A process for forming a drag reducing agent comprising a non-crystalline, ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin having an inherent viscosity of about at least 10 dL / g and a process for reducing drag in a conduit are also disclosed.
Owner:MPOWER SPECIALTY CHEM
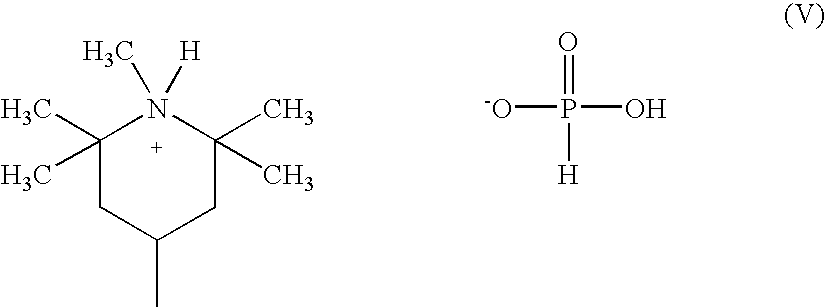
Phosphorus containing compounds for reducing acetaldehyde in polyesters polymers
InactiveUS20070066794A1High intrinsic viscosityLow in acetaldehydeOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsTobacco devicesPolyesterPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
Polyesters whose polycondensation is catalyzed by titanium-containing catalysts and which are susceptible to acetaldehyde formation during polycondensation or subsequent molding operations are prepared with low finished acetaldehyde content and reduced acetaldehyde generation by adding an ammonium or amine salt of an oxyphosphorus-acid. Polyesters, especially polyethylene terephthalate, may be produced with high inherent viscosity in reduced processing time, without the necessity of further polymerization in the solid state.
Owner:GRUPO PETROTEMEX DE C V
Opththalmic devices comprising polyester compositions formed from 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol
InactiveUS20060287484A1Inherent viscosity and/or glass transition temperatureInherent temperatureDialysis systemsDialysisDicarboxylic acid2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol
Described are ophthalmic products comprising polyester compositions comprising polyesters which comprise (a) a dicarboxylicacid component having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues or ester residues thereof; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Methods for forming amorphous ultra-high molecular weight polyolefins for use as drag reducing agents
InactiveUS6730750B2Low costReduce polymerizationHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalystsPolyolefinLiquid hydrocarbons
The present invention is directed to improved drag reducing agents and methods of forming improved drag reducing agents comprising the steps of isomerizing olefin monomers to form isomerized olefin monomers, polymerizing the isomerized olefin monomers in the presence of at least one catalyst to form a polyolefin drag reducing agent having unexpectedly superior drag reduction properties when combined with liquid hydrocarbons, such as viscous crude oil. Therefore, the drag reducing agents of the present invention may be introduced into conduits, such as pipelines, to increase the flow of the hydrocarbons through the conduit.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Polyester compositions for calendering
Polyester compositions that provide a higher throughput in calendering processes may be prepared from a polyester having crystallization half time of at least 5 minutes, an inherent viscosity of about 0.55 to about 0.75 dL / g, a branching monomer, and a release additive. The polyester compositions show a combination of excellent melt strength with good shear response that permits higher calendering line speeds before melt fracture occurs. Also disclosed are processes for film or sheet by calendering the above compositions and the film or sheet produced therefrom. The polyester compositions, film, or sheet also may include plasticizers and / or flame retardants to increase their flexibility and enable their use in commercial applications requiring flame resistance. The film and sheet have excellent appearance and can be used in a wide range of decorative and packaging applications.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Non-lead jacket for non-metallic sheathed electrical cable
ActiveUS7485810B2Easy to pullReduce frictionPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesElectrical conductorPlasticizer
A jacket for an electrical conductor, which jacket includes from about 40% to about 50% by weight of a polyvinyl chloride resin and from about 0.1% to about 0.5% by weight of an unsaturated primary amide derived from erucic acid. The jacket may also include from about 20% to about 35% by weight of a filler; from about 20% to about 30% by weight of a phthalate-based plasticizer; and from about 0.5% to about 5% by weight of a lead-free heat-stabilizing system. Methods for manufacturing a lead-free NM jacket are also provided.
Owner:SOUTHWIRE CO LLC
Polyester compositions containing low amounts of cyclobutanediol and articles made therefrom
InactiveUS20100096589A1Increase temperatureHigh viscosityLiquid crystal compositionsPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsDicarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
Described as one aspect of the invention are polyesters containing (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having from 70 to 100 mole % of terephthalic acid residues and up to 30 mole % of aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues; and (b) a glycol component having from 11 to 25 mole % of 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues, and 75 to 89 mole % of cyclohexanedimethanol residues; wherein the total mole % of the dicarboxylic acid component is 100 mole %, and the total mole % of the glycol component is 100 mole %. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Semi-aromatic polyamide and a method for preparation with low wastewater discharge
The present invention relates to a semi-aromatic polyamide and a method for preparing it with low wastewater discharge. The semi-aromatic polyamide for the present invention is obtained by introducing aromatic dicarboxylic acid, aliphatic diamine containing 4˜14 carbon atoms and the wastewater generated during the previous prepolymerization into an autoclave for prepolymerization reaction and then further polymerizing the prepolymer. In this preparation method, the wastewater generated during polymerization is recycled, thus greatly reducing the wastewater discharge; the raw materials in the wastewater are effectively recycled, thus improving the utilization rate of raw materials; meanwhile, the diamine in the wastewater compensates that lost along with water discharge during prepolymerization, thus ensuring the Mole ratio balance between dicarboxylic acid monomer and diamine monomer.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Methods for forming amorphous ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin drag reducing agents using a halohydrocarbon
InactiveUS6162773AGood drag reduction effectInherent viscosityOther chemical processesLiquid organic insulatorsHalohydrocarbonAluminoxane
A composition including polyalphaolefins that function as drag reducing agents and a process for the preparation of polyalphaolefins that function as drag reducing agents are disclosed. The process includes contacting alpha olefin monomers with a catalyst system, which includes a catalyst and an activator (co-catalyst) in a reactant mixture. The catalyst is a transition metal catalyst, preferably titanium trichloride, and the co-catalyst may include an alkylaluminoxane, alone or in combination, with a dialkylaluminum halide or a halohydrocarbon. The polymerization of the alpha olefin monomers produces a non-crystalline, ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin having an inherent viscosity of at least 10 dL / g. The addition of the alkylaluminoxane during the polymerization process provides for a non-crystalline, ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin and a more uniform molecular weight distribution of the resulting polyalphaolefin, thereby creating a drag reducing agent superior to known drag reducing agents. A process for forming a drag reducing agent comprising a non-crystalline, ultra-high molecular weight polyalphaolefin having an inherent viscosity of about at least 10 dL / g and a process for reducing drag in a conduit are also disclosed.
Owner:MPOWER SPECIALTY CHEM
Polyester compositions containing low amounts of cyclobutanediol and articles made therefrom
ActiveUS20060287481A1High glass transition temperatureHigh viscosityDialysis systemsDialysisDicarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
Described as one aspect of the invention are polyesters containing (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having from 70 to 100 mole % of terephthalic acid residues and up to 30 mole % of aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues; and (b) a glycol component having from 11 to 25 mole % of 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues, and 75 to 89 mole % of 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues; wherein the total mole % of the dicarboxylic acid component is 100 mole %, and the total mole % of the glycol component is 100 mole %. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Segmented, Semicrystalline Poly(Lactide-co-epsilon-Caprolactone) Absorbable Copolymers
Novel semi-crystalline, segmented copolymers of lactide and epsilon-caprolactone exhibiting long term absorption characteristics are disclosed. The novel polymer compositions are useful for long term absorbable meshes, surgical sutures, especially monofilament sutures, and other medical devices.
Owner:ETHICON INC
LCD films comprising polyester compositions formed from 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol
InactiveUS20070010649A1Inherent temperatureInherent viscosityDialysis systemsDialysisDicarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
Described are LCD films or sheets comprising polyester compositions comprising polyesters which comprise (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues or ester residues thereof; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Retort containers comprising polyester compositions formed from 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol
InactiveUS20060286327A1Inherent glass transition temperatureInherent viscosityBottlesDialysis systemsDicarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
Described are retort food containers comprising polyester compositions comprising polyesters which comprise (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues or ester residues thereof; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:CRAWFORD EMMETT DUDLEY +4
Blood therapy containers comprising polyester compositions formed from 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol
ActiveUS20060286322A1Inherent viscosity and glass transition temperatureHigh impact strengthBottlesDialysis systemsChemistryPolyester
Described are blood therapy containers comprising polyester compositions comprising polyesters which comprise (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues or ester residues thereof; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Sterilization containers comprising polyester compositions formed from 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol
InactiveUS20060286330A1Inherent glass transition temperatureInherent viscosityBottlesDialysis systemsDicarboxylic acid2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol
Described are infant-care sterilization containers comprising polyester compositions comprising polyesters which comprise (a) a dicarboxylicacidcomponent having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues or ester residues thereof; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Method for preparing butadiene/isoprene copolymers and resulting copolymers
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation random copolymers of butadiene and isoprene, essentially consisting of reacting a catalytic system in the presence of butadiene and isoprene and using, as catalytic system, a system based on at least:—a conjugated diene monomer,—an organic phosphoric acid salt of one or more rare earth metals,—an alkylating agent consisting of an alkylaluminium of the formula AlR3 or HAlR2, and—a halogen donor consisting of an alkylaluminium halide, said salt being in suspension in at least one inert, saturated and aliphatic or alicyclic hydrocarbon solvent, which is included in said catalytic system, and the “alkylating agent:rare earth salt” molar ratio falls within a range of from 1 to 8, and performing the copolymerisation reaction in an inert hydrocarbon polymerisation solvent or without solvent. These copolymers are in particular such that the butadiene and isoprene units which they comprise each have an elevated content of cis-1,4 linkages.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
Intravenous components comprising polyester compositions formed from 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol
ActiveUS20060287495A1Inherent temperatureInherent viscosityDialysis systemsDialysisDicarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
Described are intravenous components comprising polyester compositions comprising polyesters which comprise (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues or ester residues thereof; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Greenhouses comprising polyester compositions formed from 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol and 1,4- cyclohexanedimethanol
InactiveUS20060287477A1Inherent viscosity and glass transition temperatureHigh impact strengthDialysis systemsDialysisDicarboxylic acid2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol
Described are greenhouses comprising polyester compositions comprising polyesters which comprise (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues or ester residues thereof; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
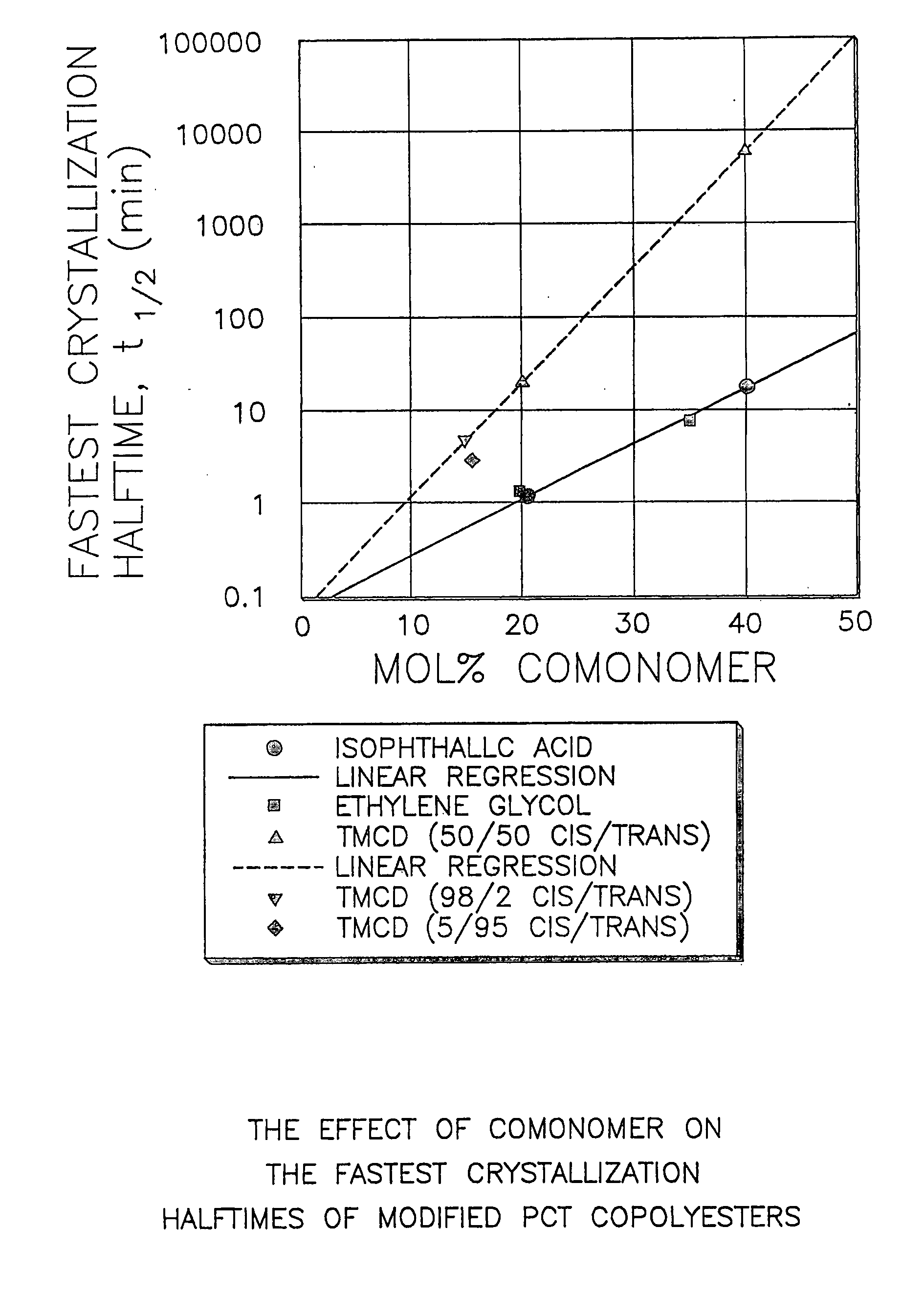
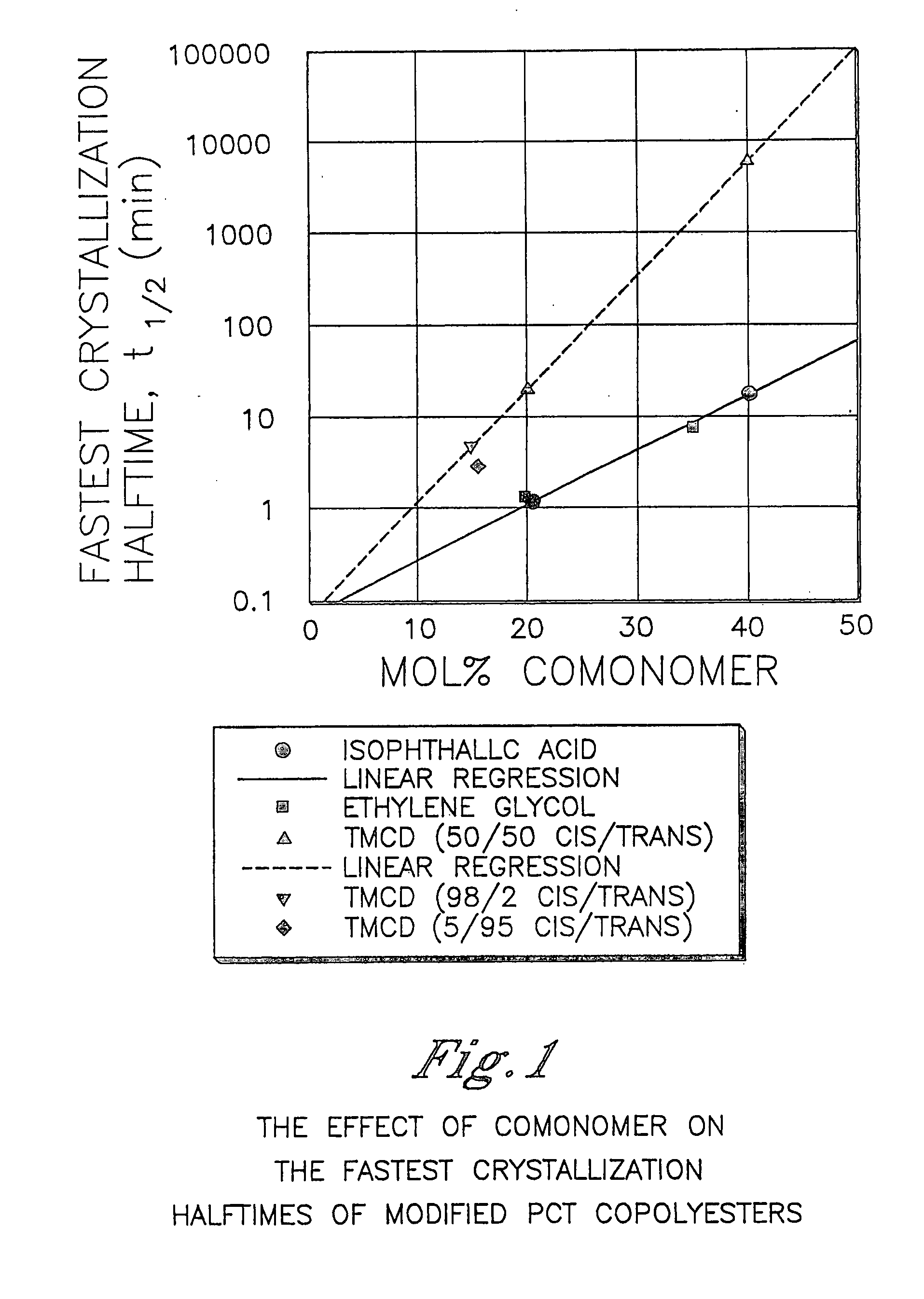
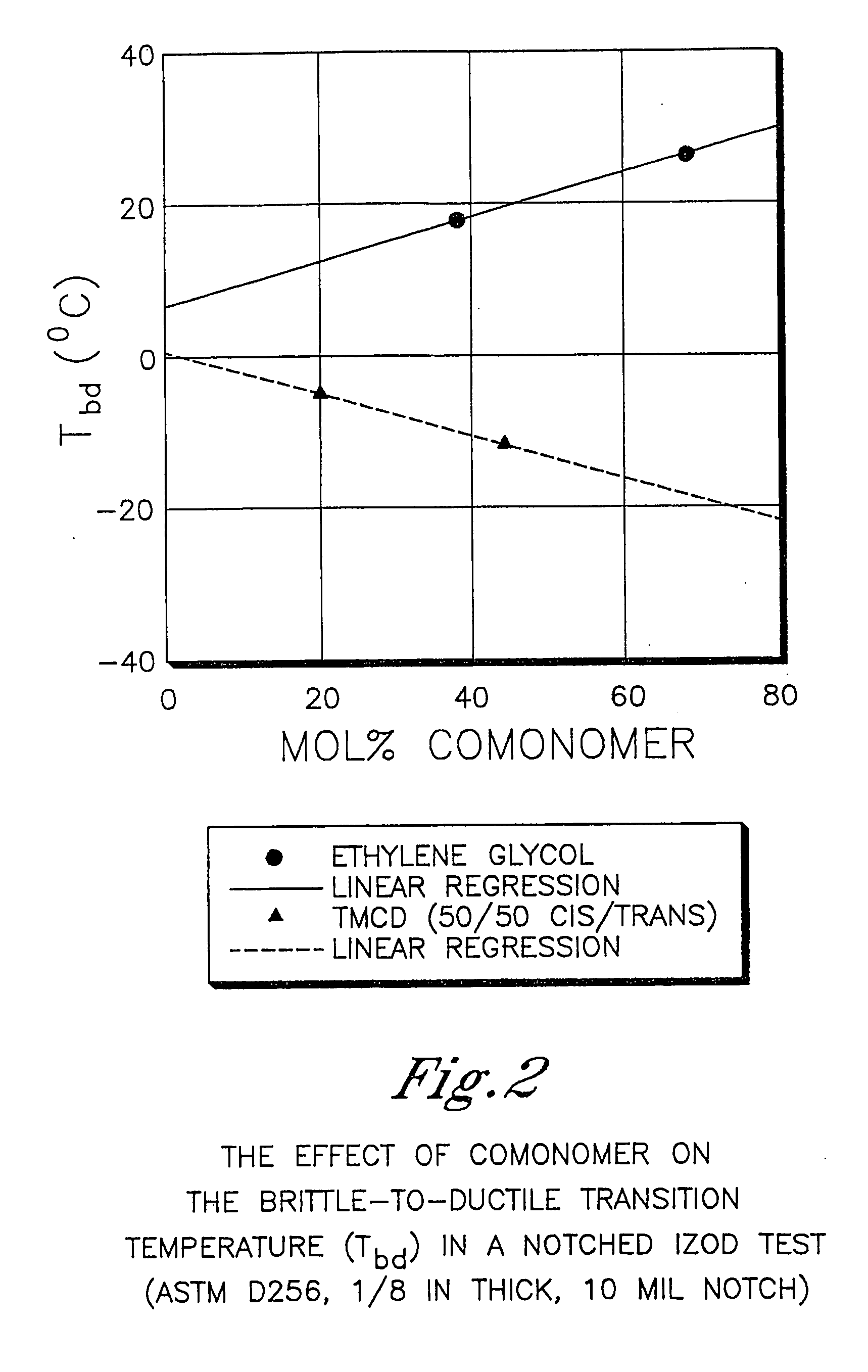
Polyester compositions which comprise cyclobutanediol having certain cis/trans ratios
ActiveUS20060287489A1Good chemical resistanceHigh strength stabilityDialysis systemsDialysisCarboxylic acidDicarboxylic acid
Described are polyester compositions comprising (a) a dicarboxylic acid component comprising terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues, wherein said 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol contains certain cis to trans ratios; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Polyurethane thickeners for aqueous systems
InactiveUS7189772B2Easy to handleEasy to to meterOther chemical processesFilm/foil adhesivesHydrogenOrganic solvent
The invention provides for thickeners for inks and coating materials, comprising polyurethanes, water, viscosity regulators, and, if desired, organic solvents, wherein said viscosity regulators comprise compounds of the general formula (I)R1—O—(SO)a—(EO)b—(PO)c—(BO)d-(DTO)e—R2in whichR1 and R2 independently of one another are one of the radicals from the group consisting of hydrogen, an aliphatic or cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon radical which optionally is substituted and / or contains multiple bonds and / or contains heteroatoms, an aromatic radical which optionally is substituted and / or contains heteroatoms, an acyl radical, a carboxyacyl radical, and a carboxyalkyl radical,a=1 to 5,b=3 to 30,c=0 to 5,d=0 to 5, ande=0 to 5where (a+c+d+e)<=b.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Vending machines comprising polyester compositions formed from 2,2,4,4,-tetramethyl-1,3,-cyclobutanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol
InactiveUS20060287476A1Inherent glass transition temperatureInherent viscosityDialysis systemsDialysisCyclohexanedimethanolCarboxylic acid
Described are vending machine display panels comprising polyester compositions comprising polyesters which comprise (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues or ester residues thereof; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Outdoor shelters comprising polyester compositions formed from 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol
InactiveUS20060287480A1Inherent temperatureInherent viscosityDialysis systemsDialysisCarboxylic acidDicarboxylic acid
Described are outdoor shelters comprising polyester compositions comprising polyesters which comprise (a) a dicarboxylic acid component having terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues or ester residues thereof; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Additives To Increase Degradation Rate Of A Biodegradable Scaffolding And Methods Of Forming Same
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com