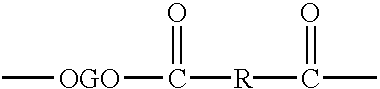
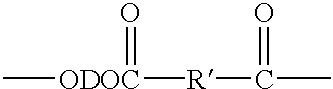
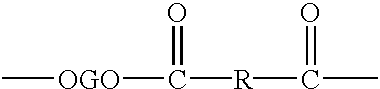
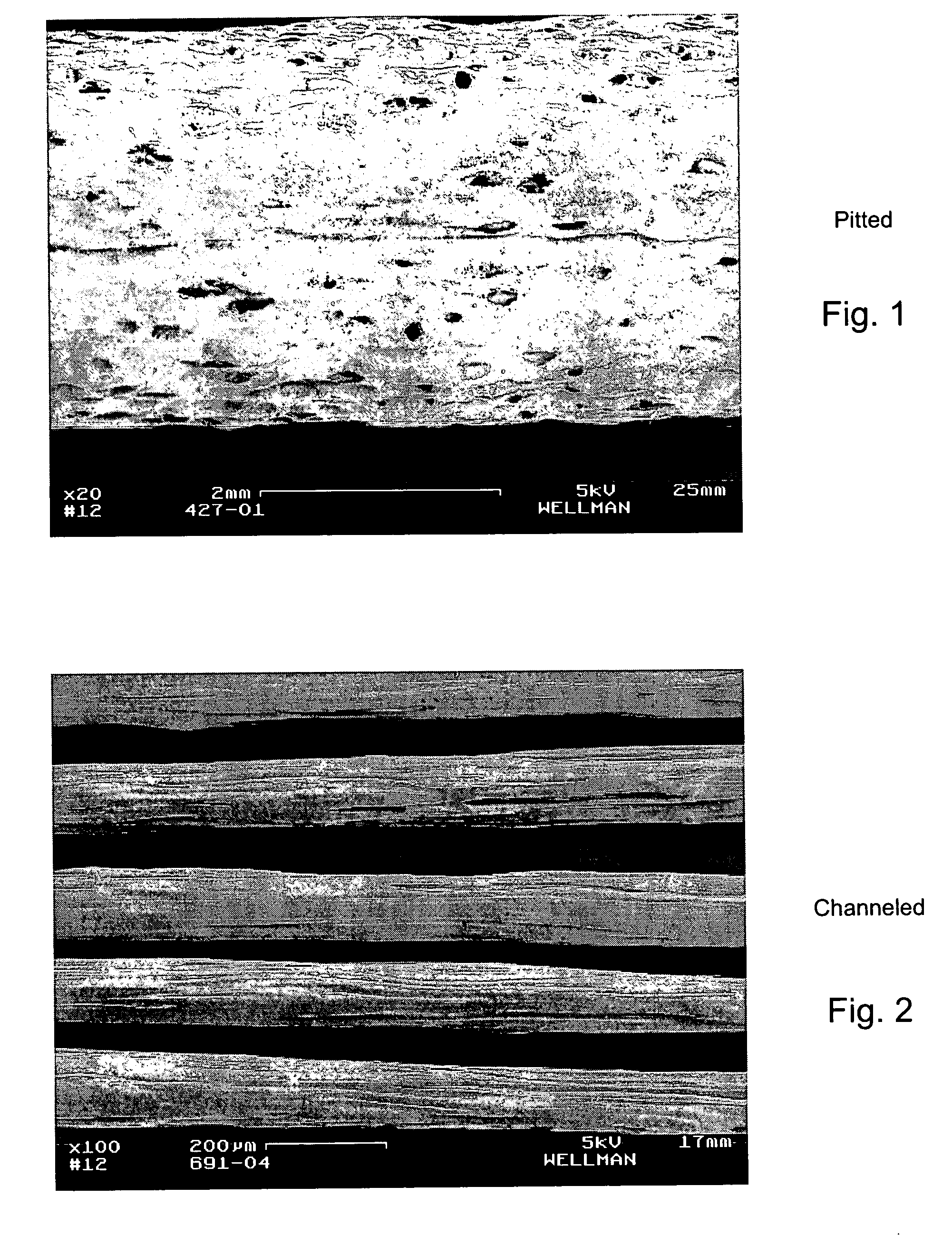
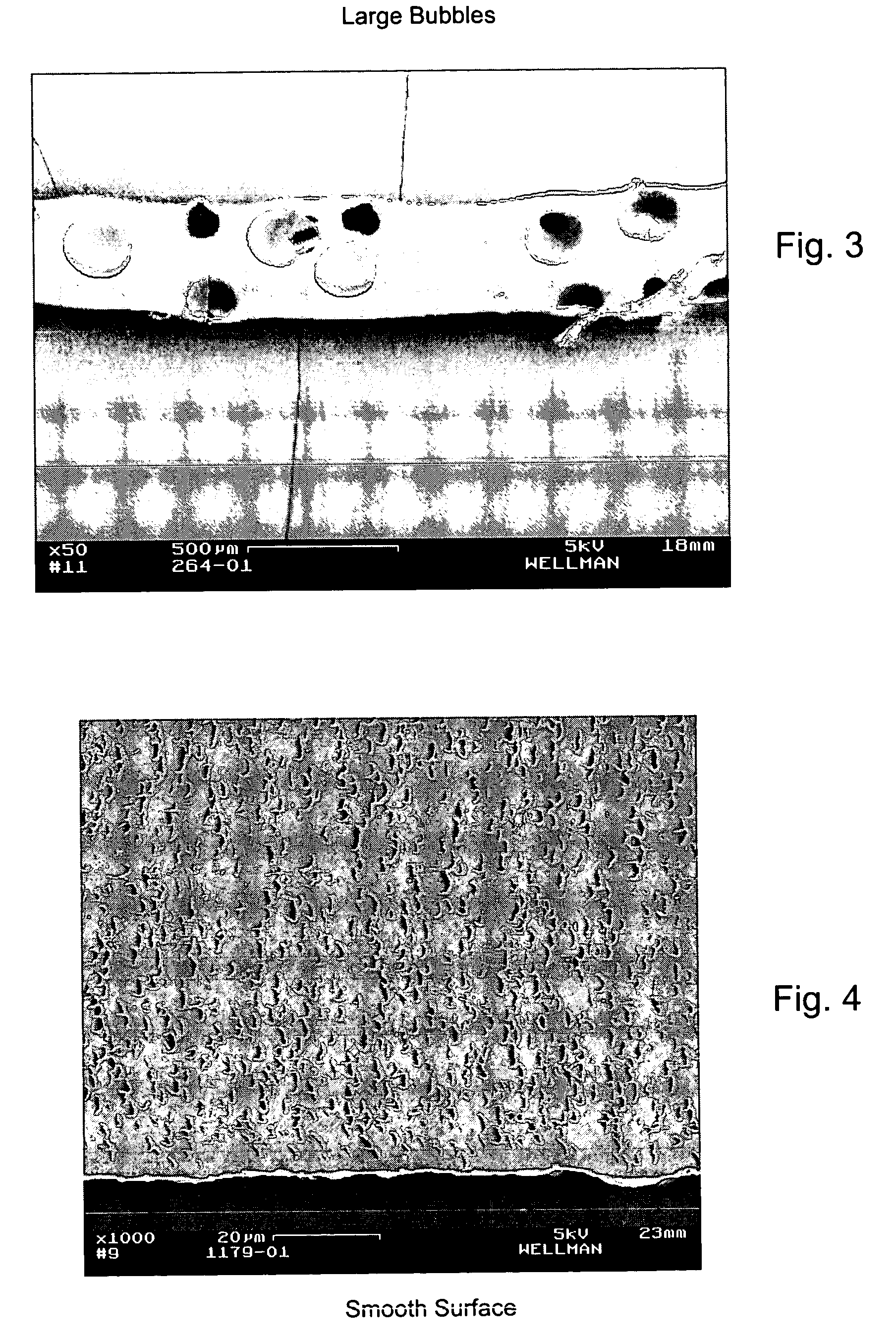
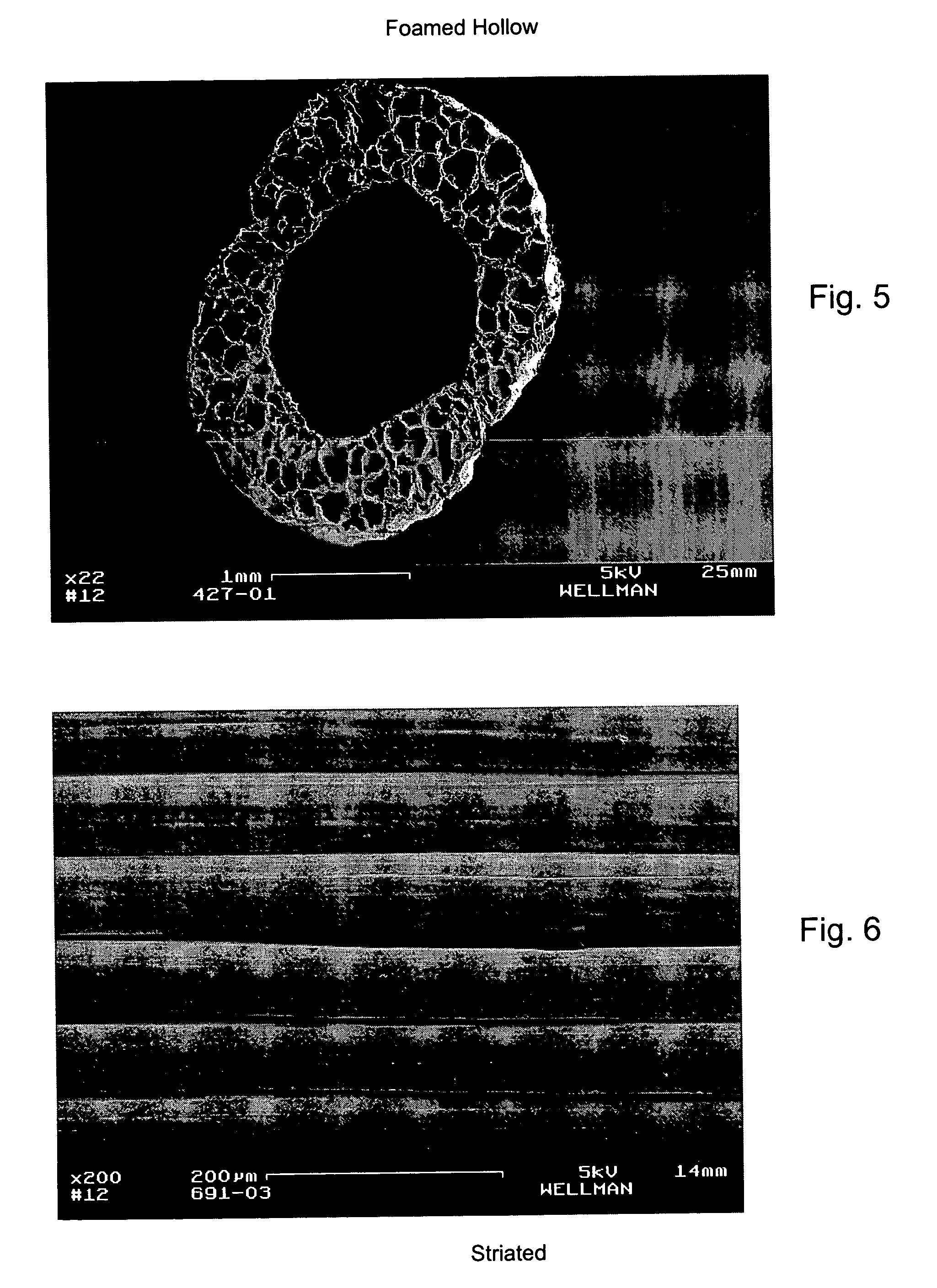
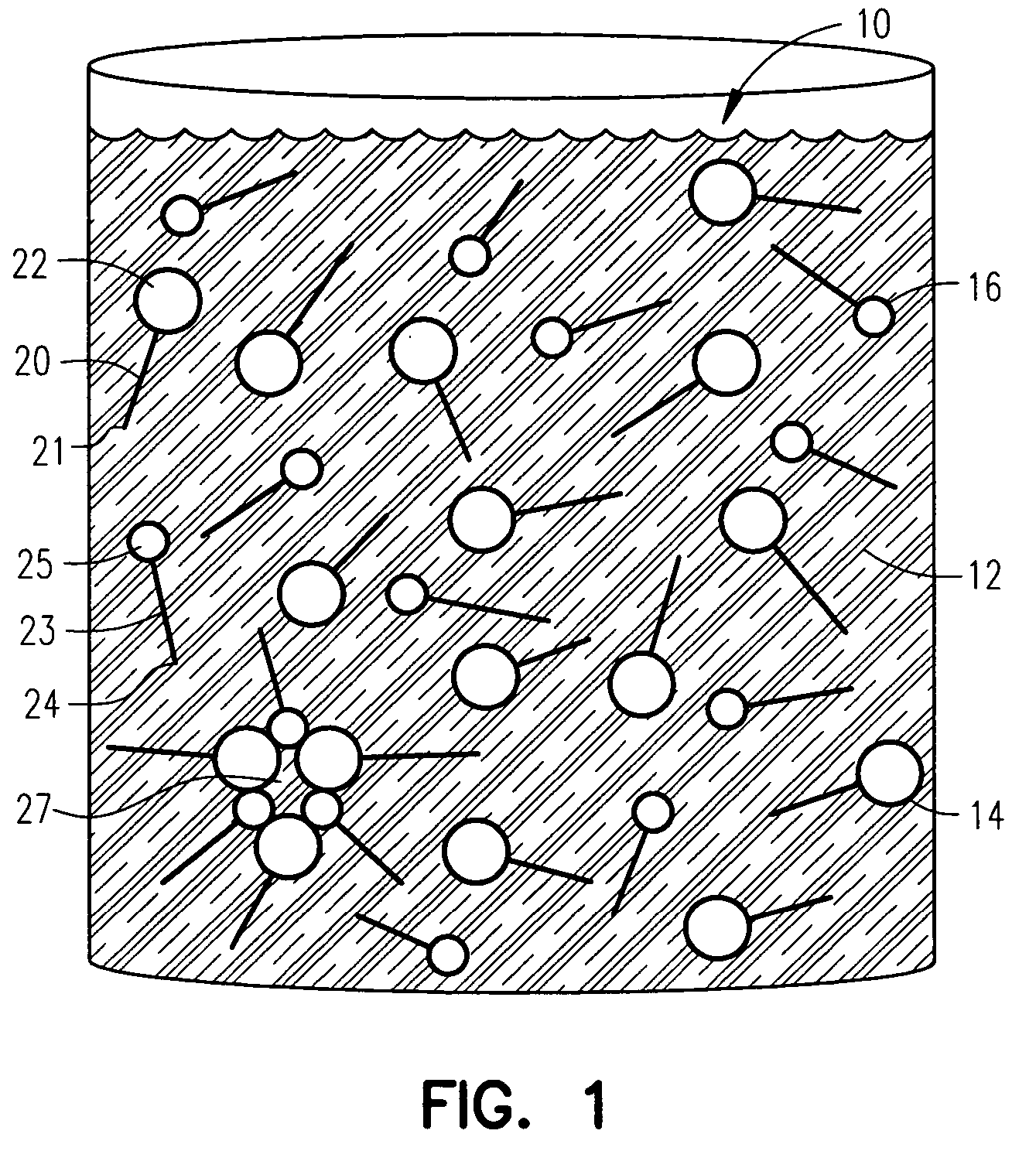
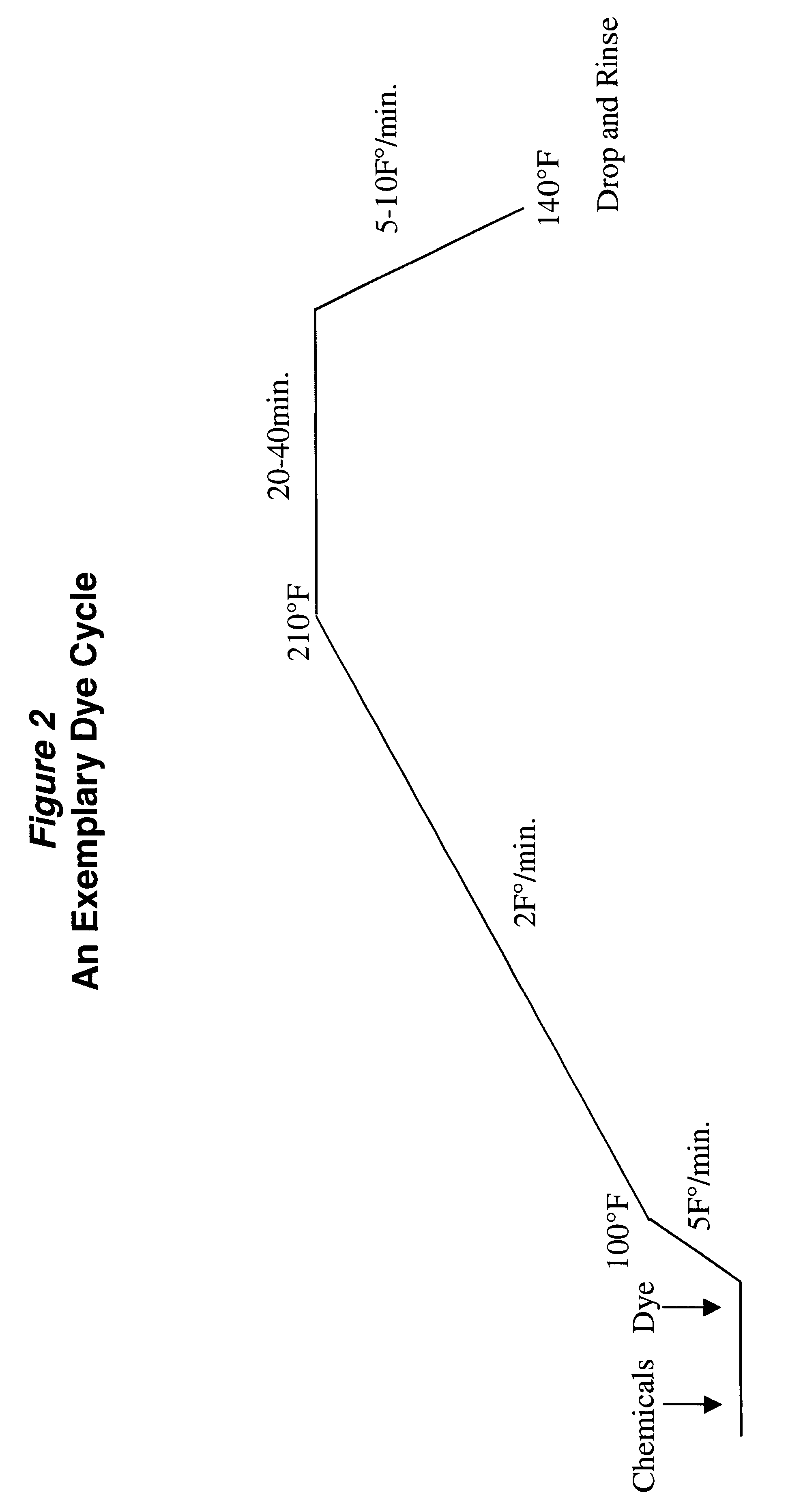
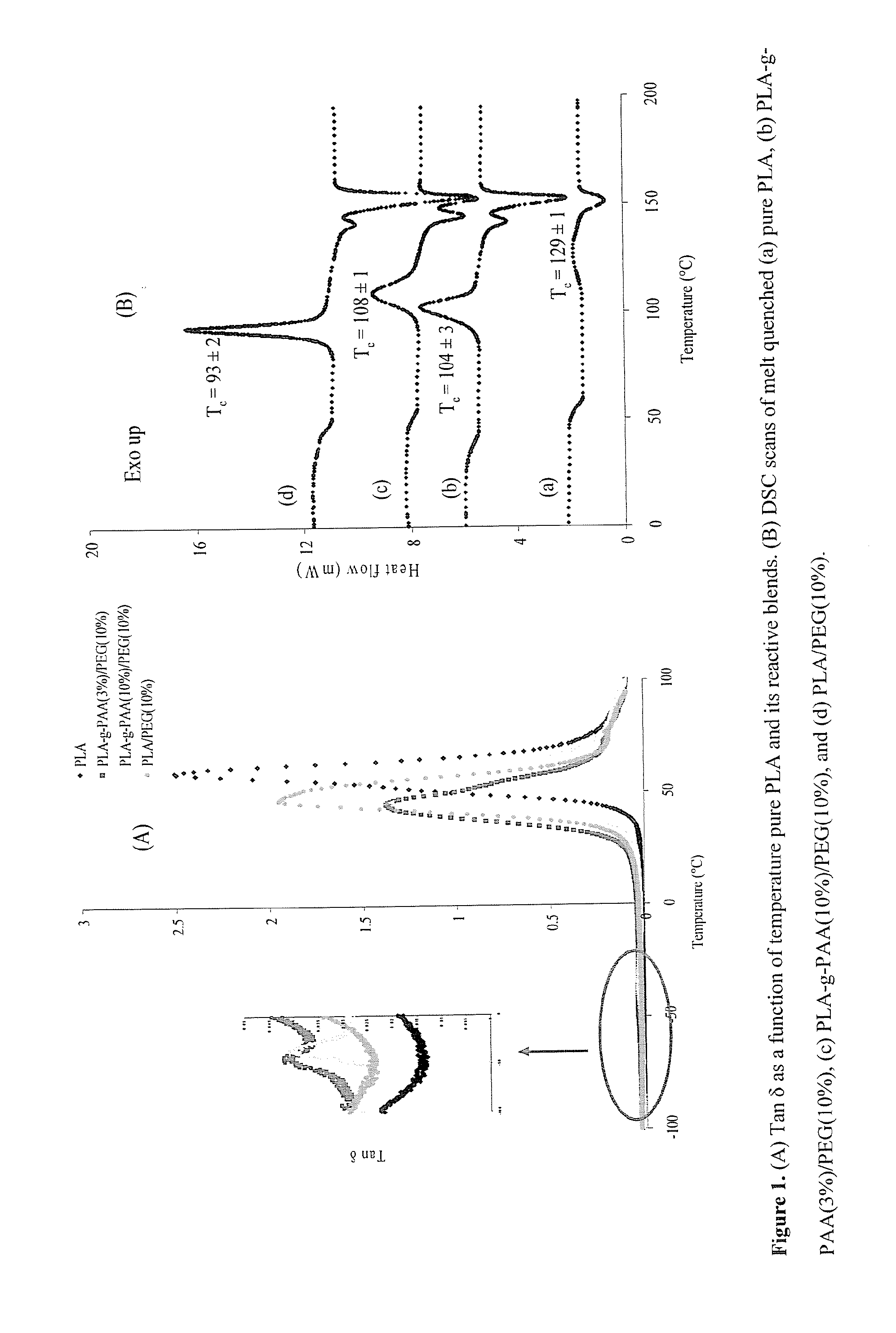
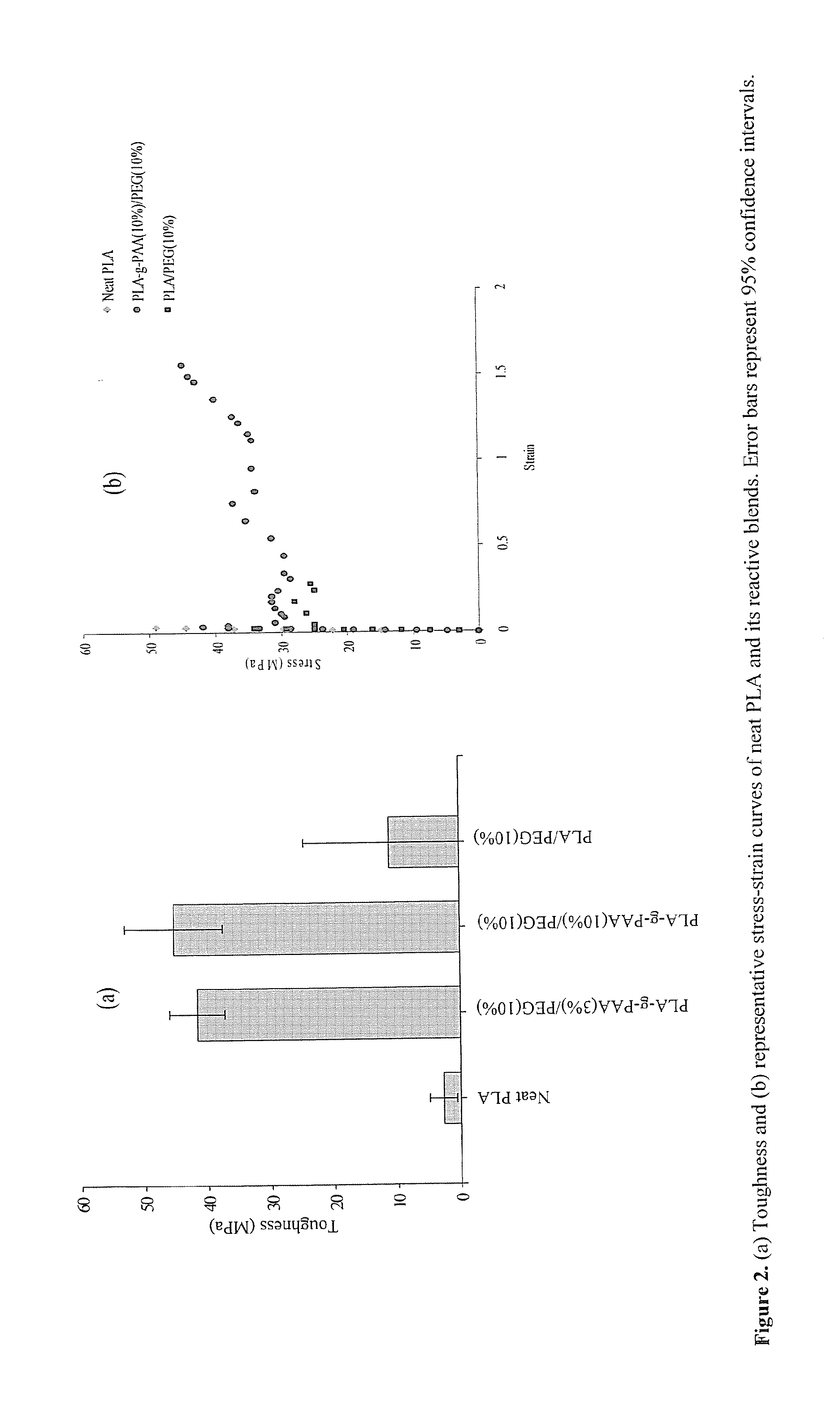
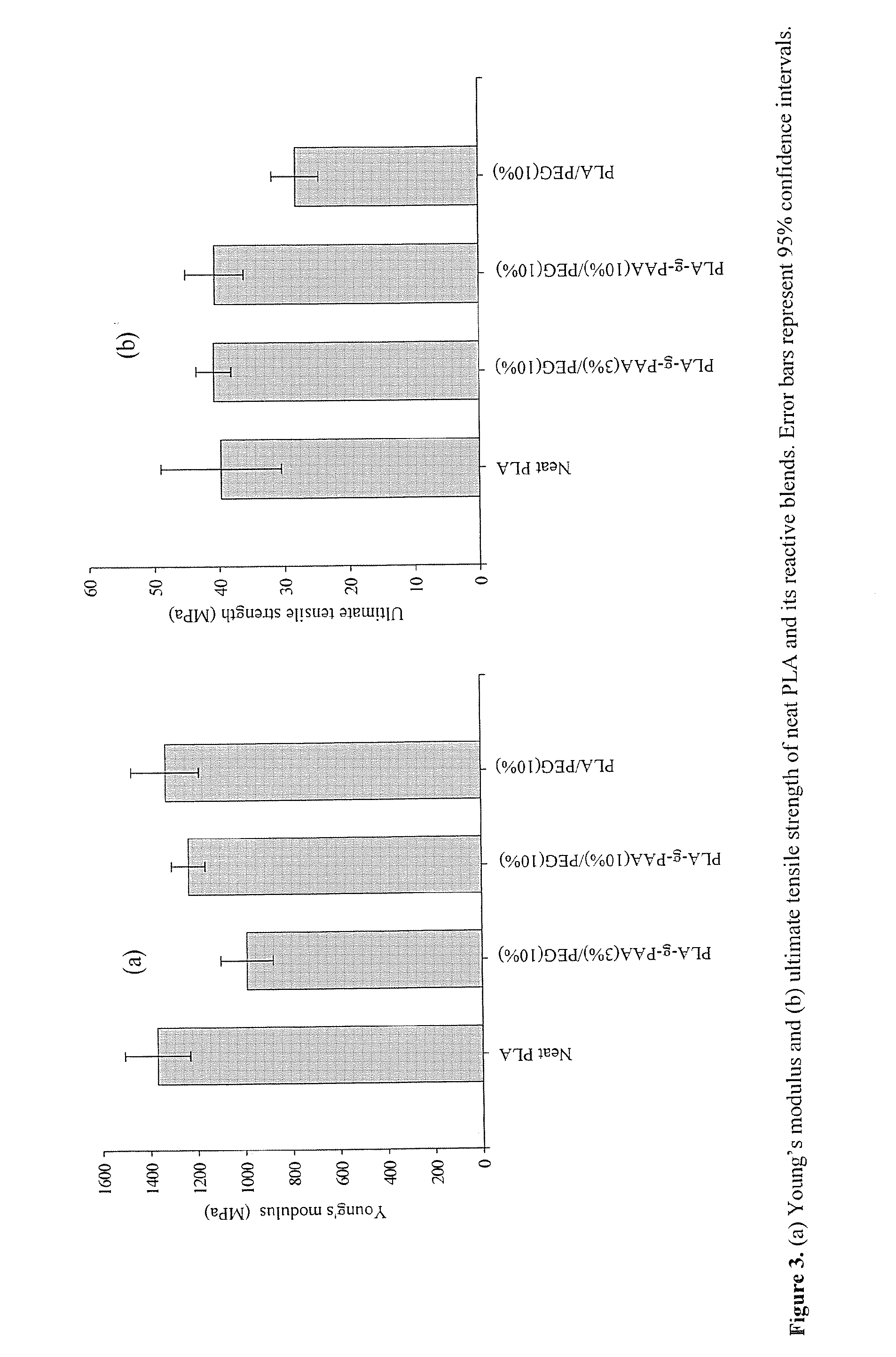
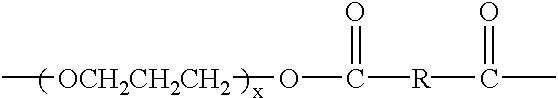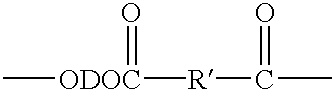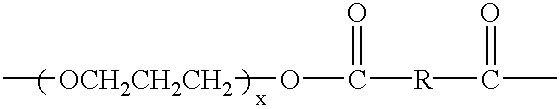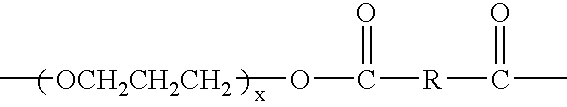Patents
Literature
88results about "Monocomponent polyetheresters artificial filament" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polyether ester elastomer comprising polytrimethylene ether ester soft segment and tetramethylene ester hard segment
A polyether ester elastomer comprising about 90-about 60 weight % polytrimethylene ether ester soft segment and about 10-about 40 weight % tetramethylene ester hard segment, and use thereof in fibers and other shaped articles. The fibers have excellent physical properties, including superior strength and stretch recovery.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
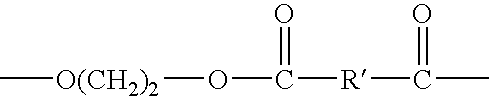
Polyether ester elastomer comprising polytrimethylene ether ester soft segment and trimethylene ester hard segment
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
Microfiber supported nanofiber membrane
A nanofiber membrane is formed on a microfiber membrane. The nanofiber membrane may be electro sprayed directly onto the microfiber membrane and becomes integrated with the microfiber membrane to form a filter. The microfiber membrane provides structural integrity to for the nanofiber membrane, and an additional microfiber membrane may be added to sandwich the nanofiber membrane.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Sulfonated copolyetherester compositions from hydroxyalkanoic acids and shaped articles produced therefrom
InactiveUS7193029B2Optimized balance of physical propertyOptimized balanceWrappers shrinkageMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentEtherDicarboxylic acid
The present invention provides certain sulfonated copolyetherester compositions containing hydroxyalkanoic acids and processes for producing such sulfonated aromatic copolyetheresters. The invention further provides shaped articles, preferably in the shape of films, coatings and laminates, having improved thermal properties, wherein the shaped articles are produced from the certain sulfonated copolyetherester compositions. Some of these materials are also biocompostable. The sulfonated copolyetheresters are produced from a mixture of an aromatic dicarboxylic acid component, hydroxyalkanoic acid component, a sulfonate component, a poly(alkylene ether) glycol component, a glycol component, an optional other glycol component, an optional branching agent, and an optional color reducing agent.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Sulfonated copolyetherester compositions from hydroxyalkanoic acids and shaped articles produced therefrom
InactiveUS20060009610A1Optimized balance of physical propertyOptimized balanceWrappers shrinkageMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentEtherDicarboxylic acid
The present invention provides certain sulfonated copolyetherester compositions containing hydroxyalkanoic acids and processes for producing such sulfonated aromatic copolyetheresters. The invention further provides shaped articles, preferably in the shape of films, coatings and laminates, having improved thermal properties, wherein the shaped articles are produced from the certain sulfonated copolyetherester compositions. Some of these materials are also biocompostable. The sulfonated copolyetheresters are produced from a mixture of an aromatic dicarboxylic acid component, hydroxyalkanoic acid component, a sulfonate component, a poly(alkylene ether) glycol component, a glycol component, an optional other glycol component, an optional branching agent, and an optional color reducing agent.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
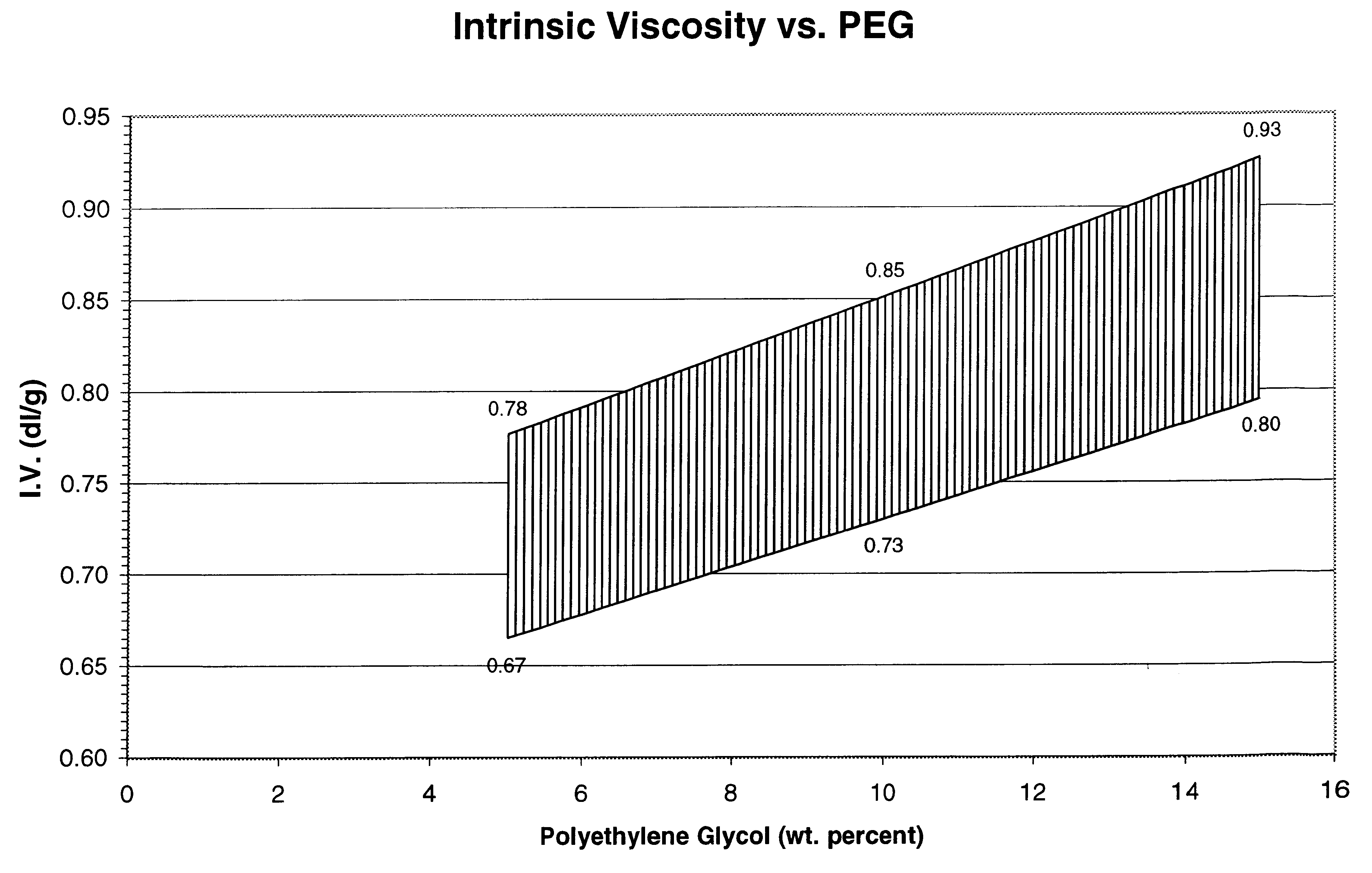
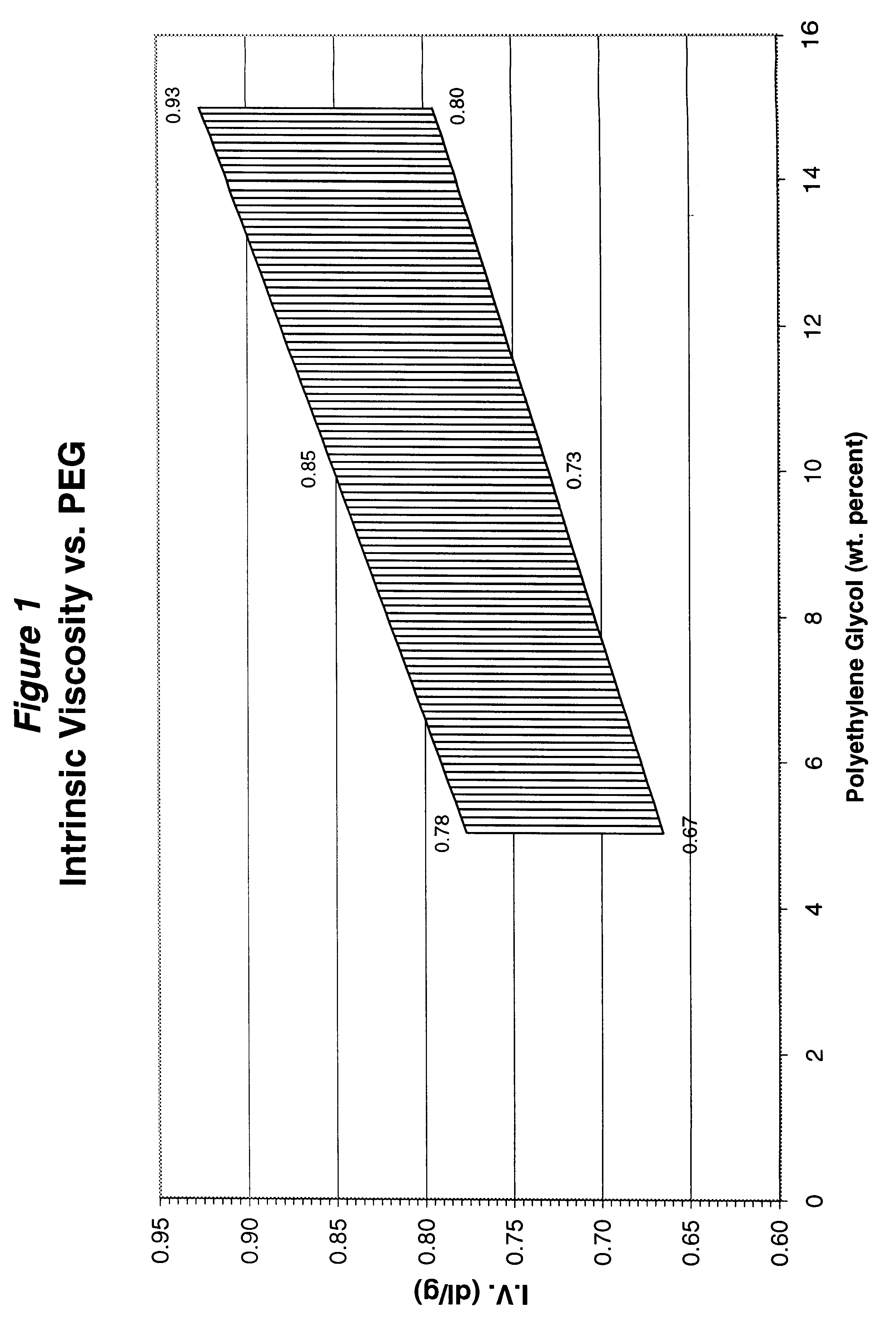
Polyethylene glycol modified polyester fibers and method for making the same
InactiveUS6623853B2Easy to dyeEnhance dye uptakeMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentAnimal housingYarnFiber
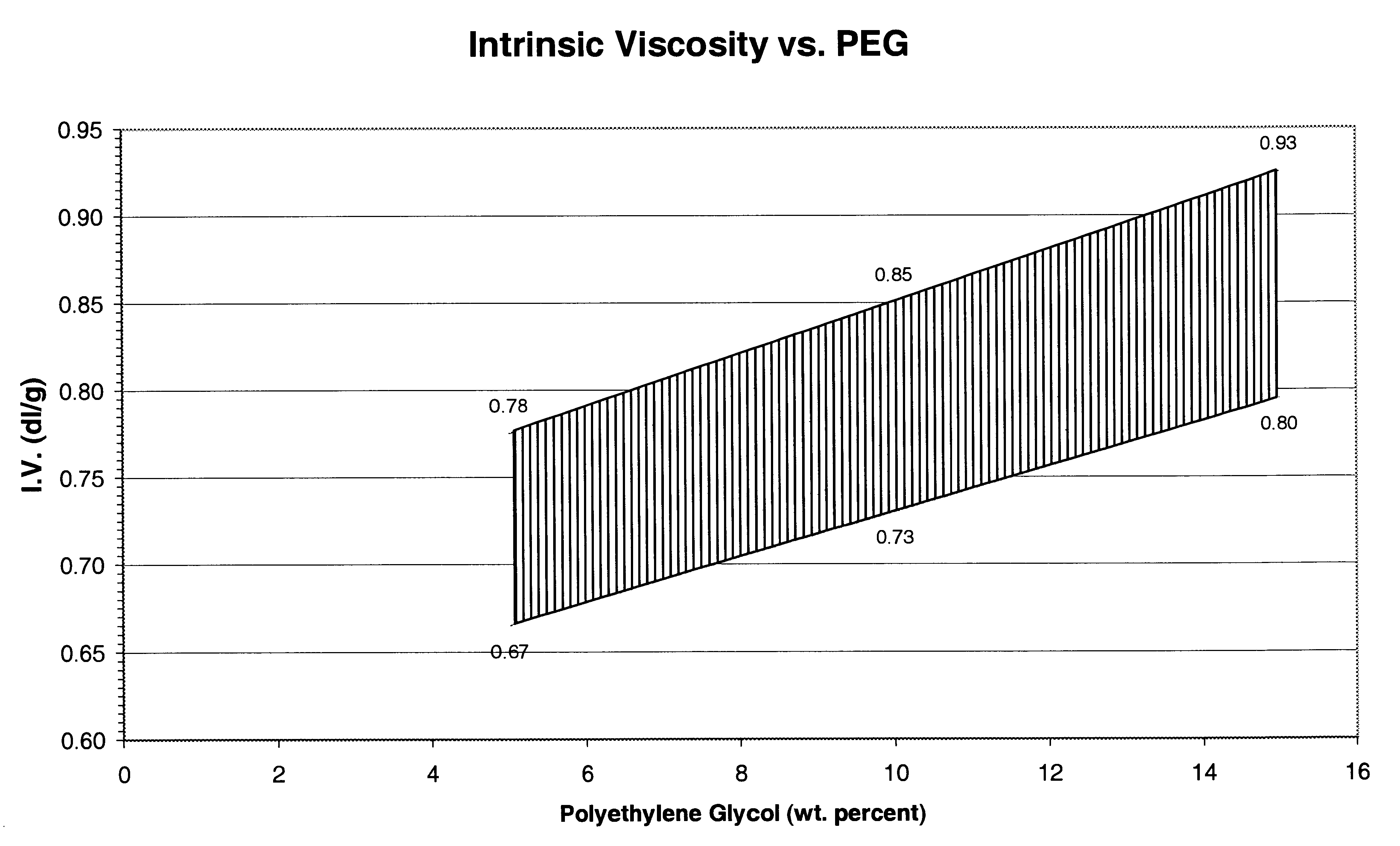
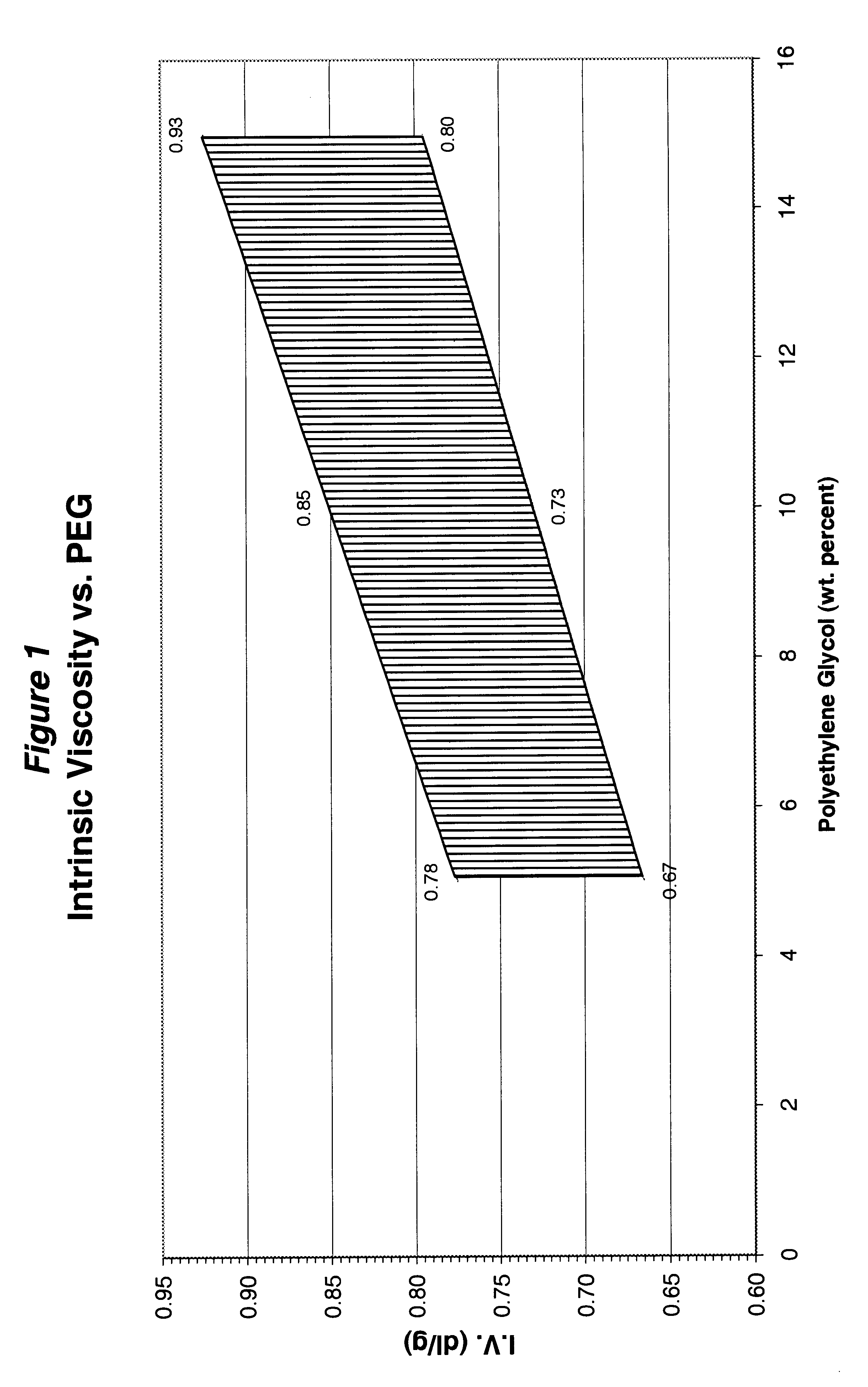
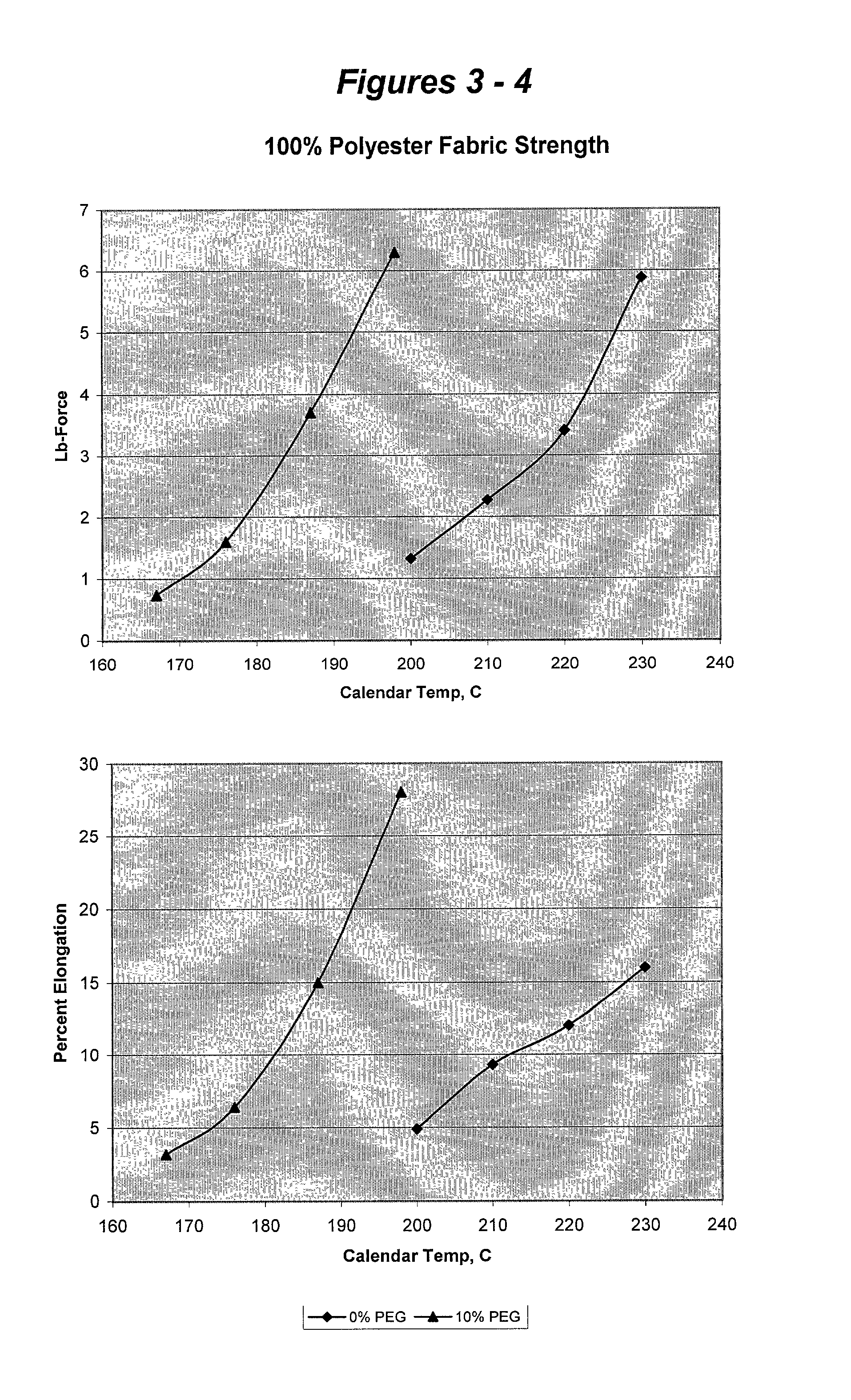
Disclosed is a method of copolymerizing polyethylene glycol (PEG) and branching agent into polyethylene terephthalate (PET) to achieve a polyethylene glycol-modified polyester composition that can be spun into filaments. Fabrics made from fibers formed from the copolyester composition possess wicking, dyeability, and tactility properties that are superior to those of fabrics formed from conventional polyethylene terephthalate fibers of the same yarn and fabric construction. Also disclosed are polyethylene glycol modified copolyester compositions, fibers, yarns, and fabrics.
Owner:FIBER IND INC
Low density light weight filament and fiber
InactiveUS20050221075A1Increase elasticityLow fiber densityNatural cellulose pulp/paperHollow filament manufactureFiberPolyester
A lightweight, low density fiber is disclosed along with a method of manufacture. The fiber includes a polyester copolymer for providing a greater elasticity than a corresponding monomer-based polyester, more than fifty percent functional void fraction in the form of foam-forming cells for reducing the density of the fiber as compared to a solid fiber, at least five void cells per axial cross section for increasing the structural integrity of the fiber as compared to less uniform foams, and submicron-sized particles of a fluorocarbon polymer, present in an amount less than 10 percent by weight.
Owner:FIBER IND INC
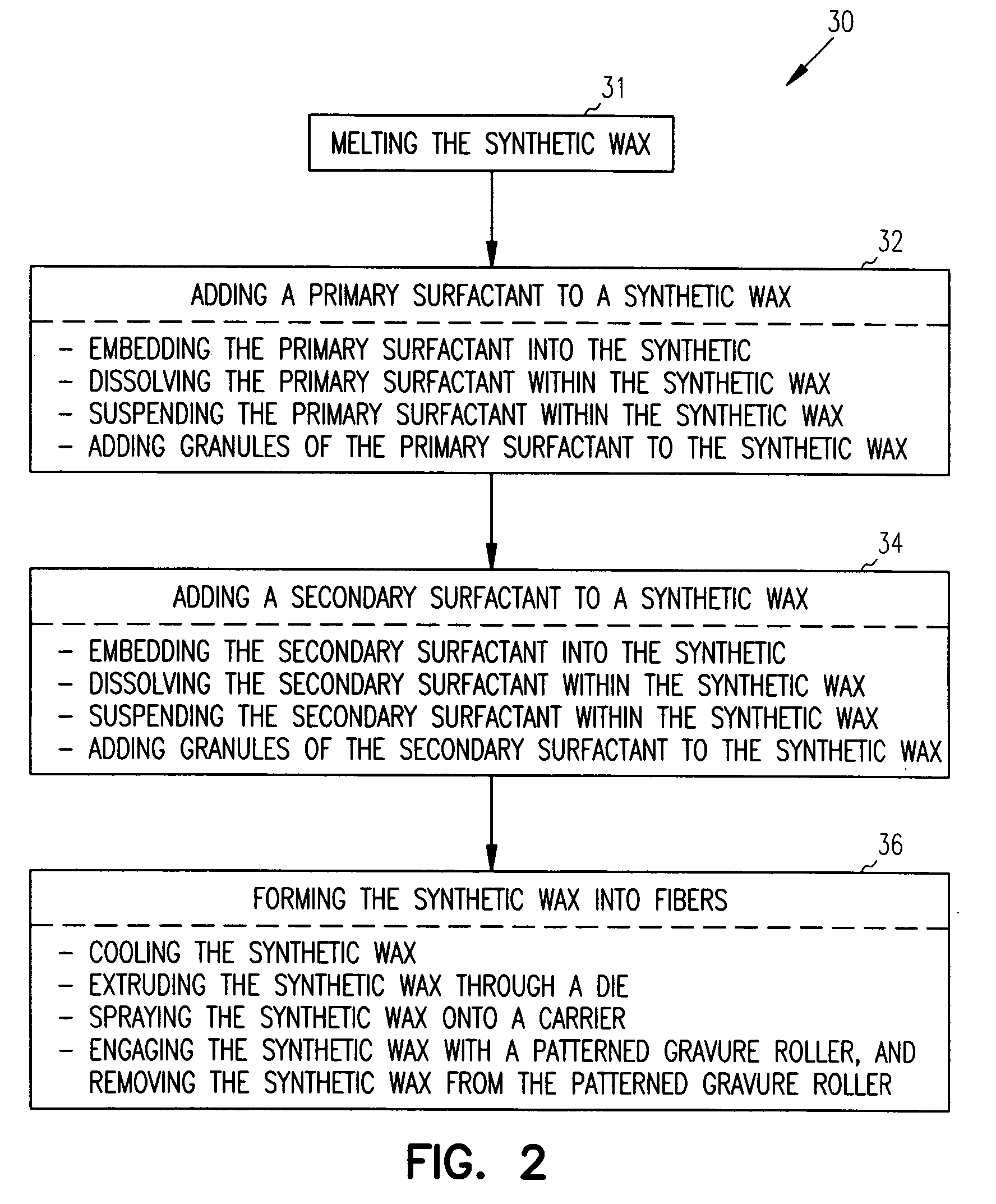
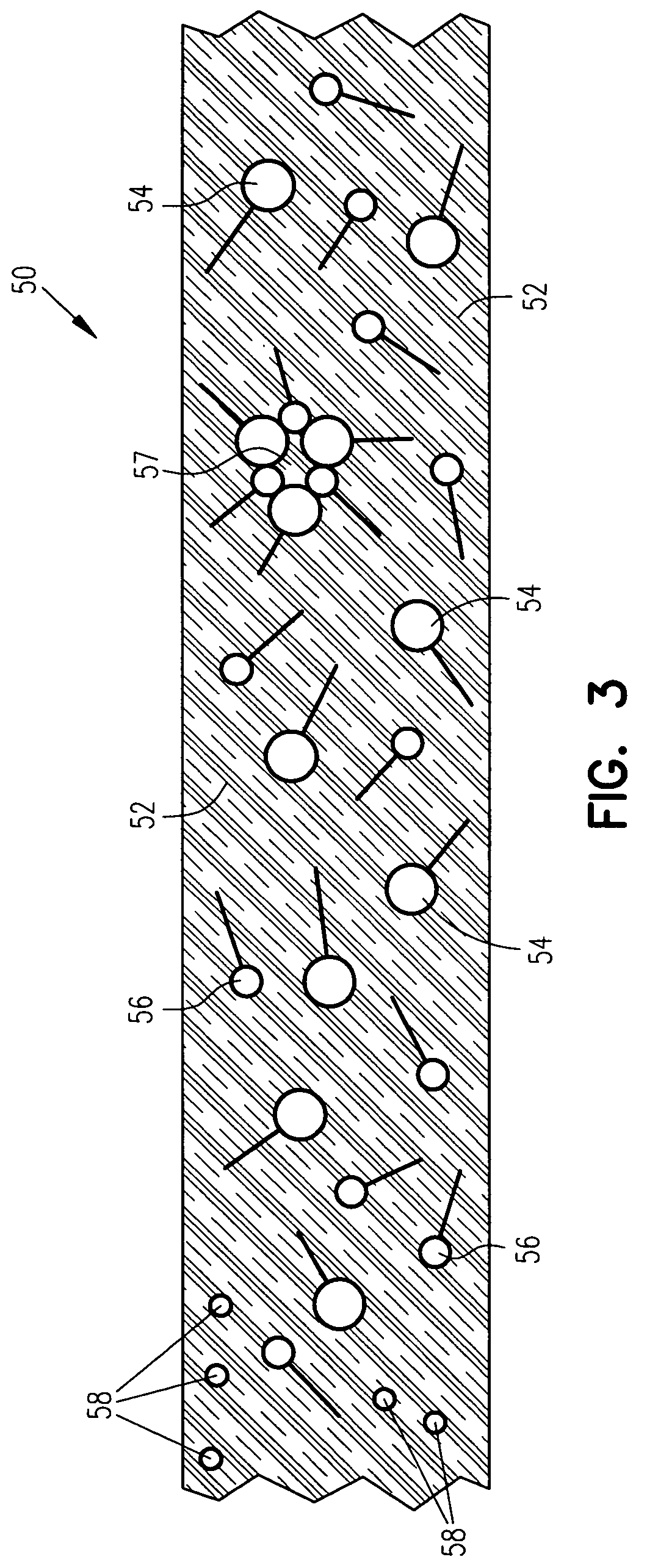
Fibrous matrix of synthetic detergents
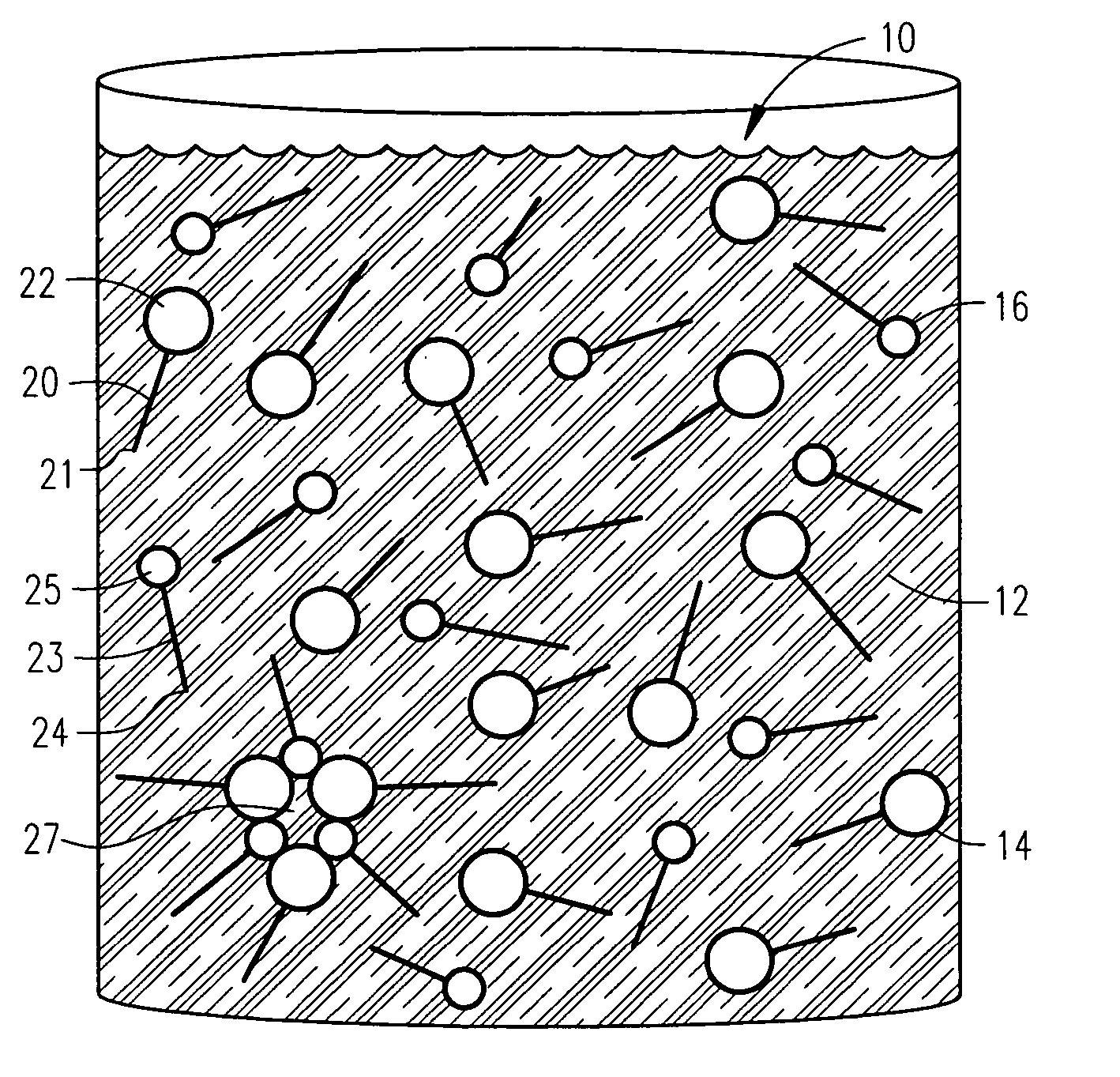
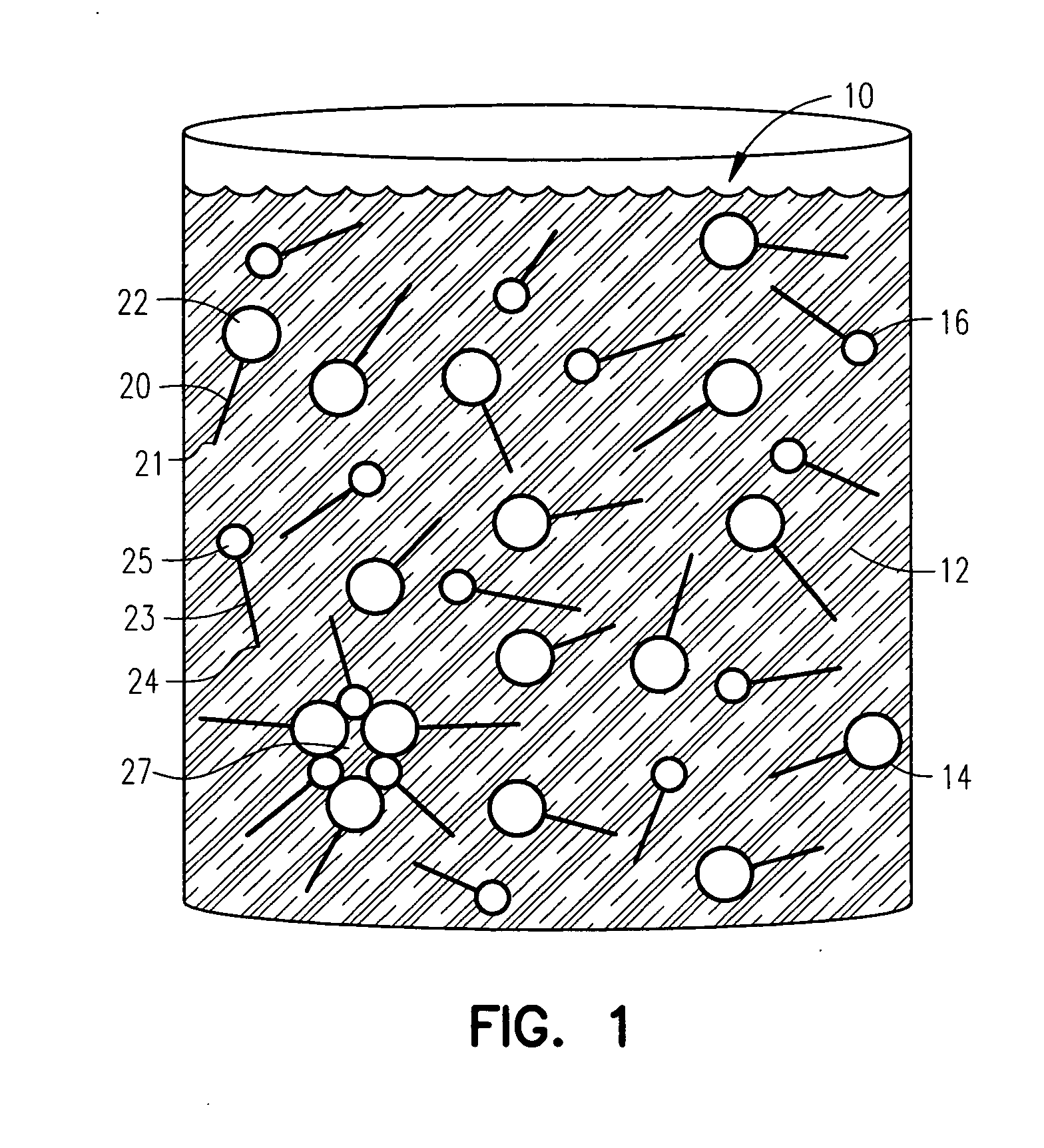
ActiveUS7226899B2Convenient and cost-effective methodInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsFiberWax
The present invention relates to a fibrous matrix of synthetic detergents. The fibrous matrix includes fibers formed of a synthetic wax and a primary surfactant embedded in the fibers. The fibrous matrix further includes a secondary surfactant embedded in the fibers.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Inorganic-organic hybrid micro-/nanofibers
InactiveUS20070112115A1Material nanotechnologyMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentElectrospinningMelt blowing
Inorganic-organic hybrid micro- / nanofibers having a cross-sectional area not exceeding 140μ2 include micro- / nanoparticulate inorganic components dispersed in an organic, absorbable or non-absorbable polymeric matrix at a weight concentration of at least about 4 percent by weight and are produced by electrostatic spinning or melt-blowing.
Owner:POLY MED
Polyethylene glycol modified polyester fibers and method for making the same
InactiveUS6291066B1Easy to dyeImprove dyeing effectProtective fabricsMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentFiberYarn
Disclosed is a method of copolymerizing polyethylene glycol (PEG) and branching agent into polyethylene terephthalate (PET) to achieve a polyethylene glycol-modified polyester composition that can be spun into filaments. Fabrics made from fibers formed from the copolyester composition possess wicking, drying, stretching, abrasion-resistance, flame-retardancy, static-dissipation, dyeability, and tactility properties that are superior to those of fabrics formed from conventional polyethylene terephthalate fibers of the same yarn and fabric construction. Also disclosed are polyethylene glycol modified copolyester compositions, fibers, yarns, and fabrics.
Owner:FIBER IND INC
Copolymer including polylactic acid, acrylic acid and polyethylene glycol and processes for making the same
InactiveUS20110245420A1Improve toughnessSlow degradation rate and hydrophilicityMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
The present invention relates to polymer compositions having a polylactic acid backbone with improved toughness, modulus and / or strength. The present invention further relates to films and articles including the polymer compositions and methods of making the polymer compositions.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for forming fibers of synthetic detergents
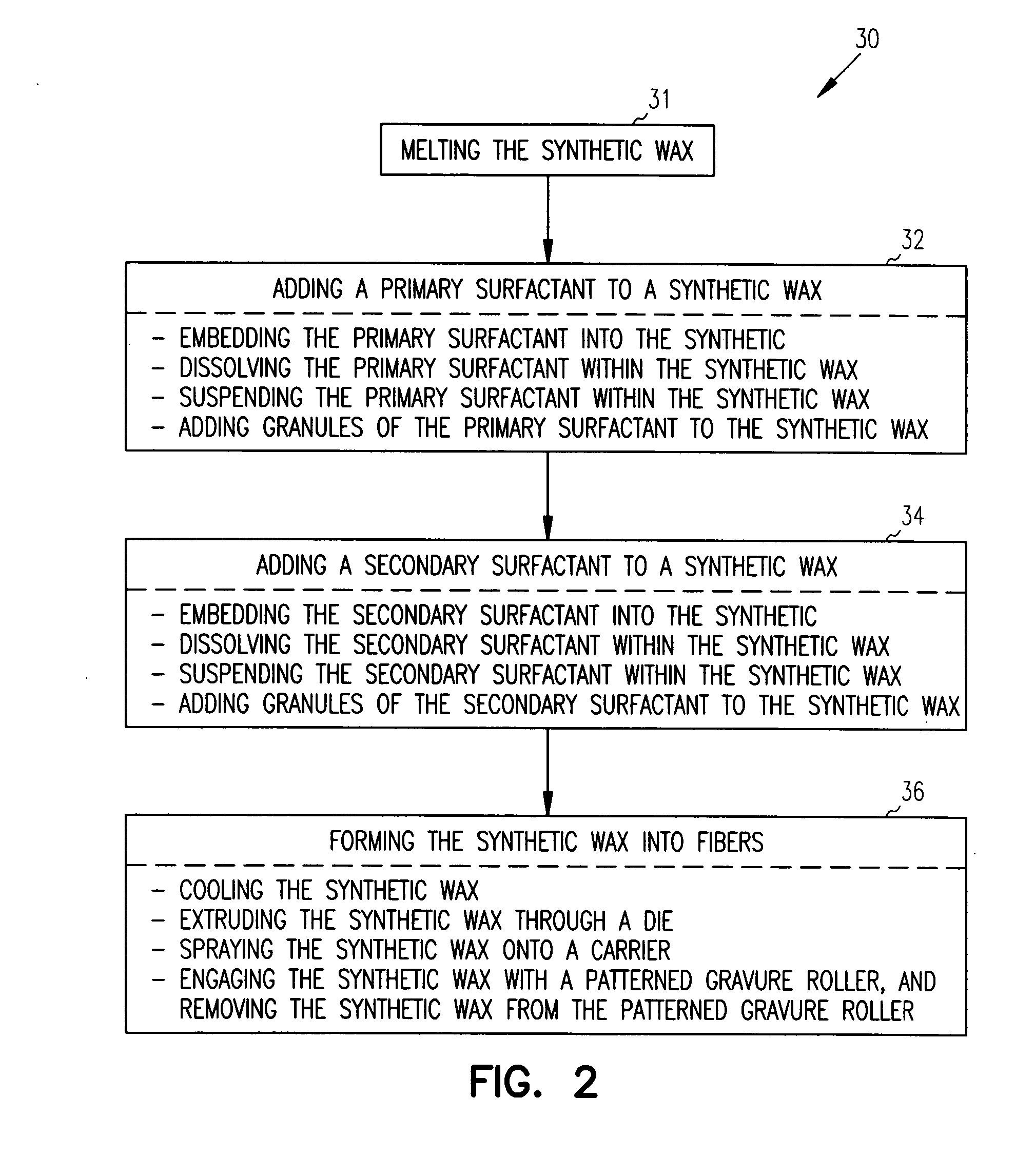
ActiveUS20050137115A1Convenient and cost-effective methodInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsWaxSynthetic Detergents
The present invention relates to a composition for forming fibers of synthetic detergents. The composition includes a synthetic wax, a primary surfactant added to the synthetic wax, and a secondary surfactant added to the synthetic wax. The present invention also relates to a method for developing fibers of synthetic detergents. The method includes adding a primary surfactant to a synthetic wax; adding a secondary surfactant to the synthetic wax; and forming the synthetic wax into fibers. In another form, the present invention relates to a fiber that includes a synthetic wax, a primary surfactant embedded in the synthetic wax, and a secondary surfactant embedded in the synthetic wax. The present invention also relates to a fibrous matrix of synthetic detergents. The fibrous matrix includes fibers formed of a synthetic wax and a primary surfactant embedded in the fibers. The fibrous matrix further includes a secondary surfactant embedded in the fibers.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Microfiber supported nanofiber membrane
A nanofiber membrane is formed on a microfiber membrane. The nanofiber membrane may be electro sprayed directly onto the microfiber membrane and becomes integrated with the microfiber membrane to form a filter. The microfiber membrane provides structural integrity to for the nanofiber membrane, and an additional microfiber membrane may be added to sandwich the nanofiber membrane.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Polyether ester elastic fiber and fabric, clothes made by using the same
InactiveUS20060177655A1Good hygroscopicityImprove comfortMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentWoven fabricsPolytetramethylene terephthalateFiber
A polyether ester elastic fiber comprising a polyether ester elastomer containing polybutylene terephthalate as a hard segment and polyoxyethylene glycol as a soft segment and copolymerized with a specific metal organic sulfonate, having a coefficient of moisture absorption of not less than 5% at 35° C. and at a RH of 95% and a coefficient of water absorption extension of not less than 10%. The above-mentioned polyether ester elastic fiber has a good moisture-absorbing property, and is reversibly largely expanded or contracted by the absorption or release of water. Therefore, a fabric giving excellent comfortableness can be obtained from said elastic fibers, and can be recycled.
Owner:TEJIN FIBERS LTD
Rebound elasticity being improved polyether ester elastic fiber
An elastic polyether ester fibre with improved resiliency is prepared from binary carboxylic acid, and two or more kinds of polyalkyleneether diol, whose number average molecular weight of 1000-4000, and mixing with composite deoxidizing agent (0.05-2%). Its advantages are high toughness and strength, and high resistance to fatigue, wearning, oil and chlorine.
Owner:上海中纺物产发展有限公司
Polyether ester elastomer comprising polytrimethylene ether ester soft segment and trimethylene ester hard segment
A polyether ester elastomer comprising about 90-about 60 weight % polytrimethylene ether ester soft segment and about 10-about 40 weight % trimethylene ester hard segment, and use thereof in fibers and other shaped articles. The fibers have excellent physical properties, including superior strength and stretch recovery.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
Polyethylene glycol modified polyester fibers
InactiveUS6509091B2Easy to dyeImprove dyeing effectMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentDyeing processFiberPolymer science
Disclosed is a polyethylene glycol modified copolyester fiber that has exceptional moisture management characteristics and that can be formed into exceptionally comfortable fabrics. The copolyester fiber includes polyethylene terephthalate in an amount sufficient for the copolyester fiber to possess dimensional stability properties substantially similar to those of conventional, unmodified polyethylene terephthalate fibers, polyethylene glycol in an amount sufficient for the copolyester fiber to possess wicking properties that are superior to those of conventional, unmodified polyethylene terephthalate fibers, and chain branching agent in an amount less than about 0.0014 mole-equivalent branches per mole of standardized polymer.
Owner:FIBER IND INC
Polyethylene glycol modified polyester fibers
InactiveUS20020019508A1Easy to dyeImprove dyeing effectMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentDyeing processFiberPolyethylene terephthalate
Disclosed is a polyethylene glycol modified copolyester fiber that has exceptional moisture management characteristics and that can be formed into exceptionally comfortable fabrics. The copolyester fiber includes polyethylene terephthalate in an amount sufficient for the copolyester fiber to possess dimensional stability properties substantially similar to those of conventional, unmodified polyethylene terephthalate fibers, polyethylene glycol in an amount sufficient for the copolyester fiber to possess wicking properties that are superior to those of conventional, unmodified polyethylene terephthalate fibers, and chain branching agent in an amount less than about 0.0014 mole-equivalent branches per mole of standardized polymer.
Owner:FIBER IND INC
Polyether ester elastomer composition
InactiveUS20080103217A1Fast crystallizationEffectively utilize the polymerOther chemical processesMixing methodsElastomerFiber
Disclosed are polyether ester elastomer compositions having polytrimethylene ether ester soft segments and polyethylene ester hard segments and containing a nucleating agent. Shaped articles can be made from these compositions, particularly molded articles, films and fibers.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Normal pressure cation dyeable polyester, textile product made from the same, and process for production of the same
ActiveCN1831028AImprove qualityWill not embrittleMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentPolyesterFiber
The present invention provides one kind of normal pressure dyeable polyester and its preparation process, and the polyester may be used in producing fiber product with stable quality and high light resistance no matter water color shade is. The present invention features that the polyester has main repetition units of ethylene terephthalate, and contains metal sulfonate containing isophthalic acid component in 2.0-3.0 mol% of the acid components, polyalkylene glycol of average molecular weight 150-600 in 1.5-4.0 wt% of polyester, diglycol in 4.5-6.5 mol% of the diol components and terminal carboxyl group concentration of 20-30 equivalent / ton.
Owner:SEIREN CO LTD
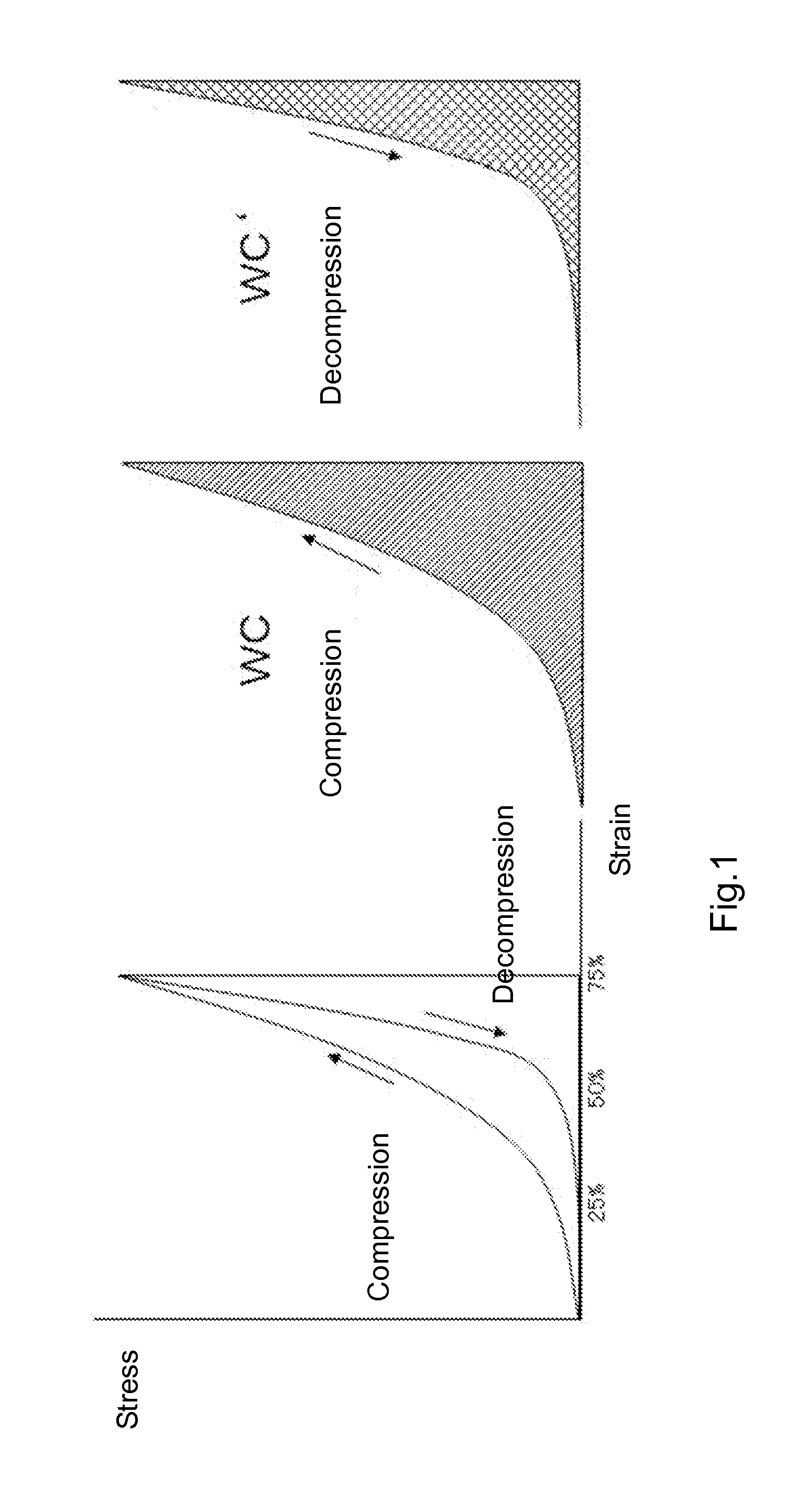
Fibrous Network Structure Having Excellent Compression Durability
InactiveUS20160010250A1Excellent repeated compression durabilityLow repeated compression residual strainMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterMolten state
The present invention provides a network structure having excellent repeated compression durability, the network structure having a low repeated compression residual strain and a high hardness retention after repeated compression.A network structure comprising a three-dimensional random loop bonded structure obtained by forming random loops with curling treatment of a continuous linear structure including a polyester-based thermoplastic elastomer and having a fineness of not less than 100 dtex and not more than 60000 dtex, and by making each loop mutually contact in a molten state, wherein the network structure has an apparent density of 0.005 g / cm3 to 0.20 g / cm3, a 50%-constant displacement repeated compression residual strain of not more than 15%, and a 50%-compression hardness retention of not less than 85% after 50%-constant displacement repeated compression.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Normal-pressure cation-dyeable polyester, textile product made from the same, and production method for the same
InactiveUS20090131628A1Quality improvementEfficient productionMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentSulfonatePolyester
A normal-pressure cation-dyeable polyester is provided which contains an isophthalic acid component having a metal sulfonate group in a predetermined proportion based on the total of acid components present in the polyester, and contains a polyalkylene glycol having an average molecular weight of 150 to 600 in a predetermined proportion based on the polyester, wherein the proportion of diethylene glycol based on the total of glycol components and a terminal carboxyl group concentration are each set within a predetermined range. The polyester is stable in quality and excellent in dark- and pale-color light fastness when used for textile products.
Owner:KB SEIREN LTD
Nonwoven fabrics formed from polyethylene glycol modified polyester fibers and method for making the same
InactiveUS20010039160A1Easy to dyeImprove dyeing effectEngine sealsProtective fabricsPolyesterPolyethylene terephthalate
Disclosed is a nonwoven fabric that is formed of polyethylene glycol modified copolyester staple fibers. The copolyester staple fibers include polyethylene terephthalate in amount sufficient for the copolyester staple fibers to possess dimensional stability properties substantially similar to those of conventional, unmodified polyethylene terephthalate fibers, polyethylene glycol in an amount sufficient for the copolyester staple fibers to possess wicking characteristics that are superior to those of conventional, unmodified polyethylene terephthalate fibers, and chain branching agent in an amount less than about 0.0014 mole-equivalent branches per mole of standardized polymer. Also disclosed are methods for making such nonwoven fabrics.
Owner:FIBER IND INC
Bio-based degradable polyester fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107936237AImprove hydrophilicityPromote degradationMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentArtificial filament heat treatmentPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a bio-based degradable polyester fiber and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes: adopting bio-based diol and bio-based binary acid as the raw materials, adopting melt polycondensation, carrying out esterification reaction, segmented pre-polycondensation reaction and final polycondensation reaction successively to obtain bio-based degradable polyester, and then conducting melt spinning forming to obtain the bio-based degradable polyester fiber. Specifically, the segmented pre-polycondensation reaction falls into first pre-polycondensation reaction and second pre-polycondensation reaction, wherein polyethylene glycol is added in the first pre-polycondensation reaction process, and a monomer with a polyhydroxyl structure is added in the secondpre-polycondensation reaction process. The final product has a moisture regain of greater than or equal to 2.0% and a surface contact angle of less than or equal to 60 degrees. The preparation methodprovided by the invention has a simple process, effectively reduces the duration of polycondensation reaction, lowers energy consumption and material consumption, and has good economic benefits. Theproduct prepared by the method provided b the invention has the advantages of good degradability, good fiber mechanical strength and high quality, and has great application prospects.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
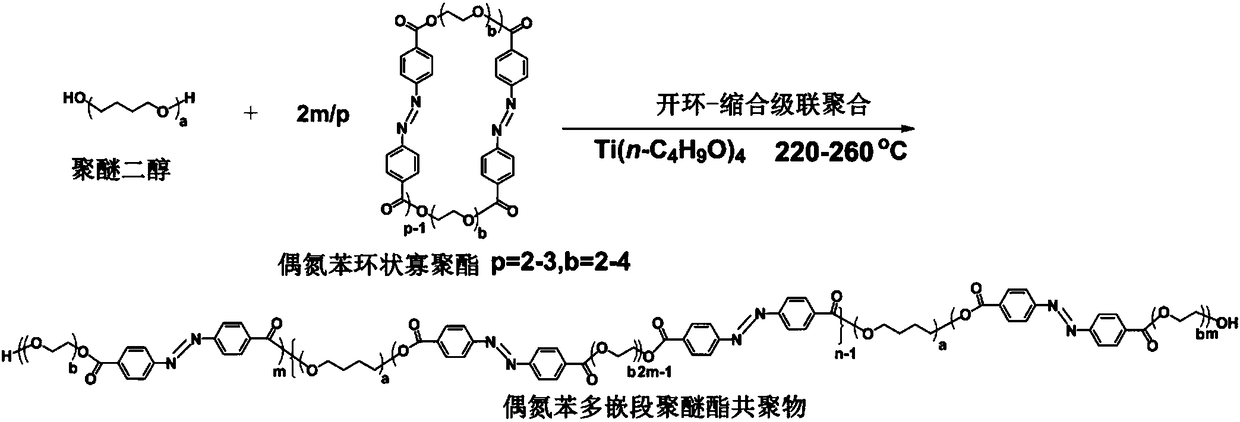
Azobenzene polyether ester multi-block copolymer elastomer with photo-induced deformation performance and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108395527AGood photodeformation performanceMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentElastomerFiber
The invention discloses azobenzene polyether ester multi-block copolymer elastomer with photo-induced deformation performance and a preparation method for high-strength super-tough fibers of the azobenzene polyether ester multi-bock copolymer elastomer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adopting an open loop-condensation cascade polymerization method, leading an azobenzene group into a main chain of polyether ester multi-block copolymer, and combining photo-induced deformation performance of azobenzene with good elasticity of the polyether ester multi-block copolymer, thereby obtaining high-molecular-weight azobenzene polyether ester multi-block copolymer elastomer with photo-induced deformation performance, and fusion-spinning to prepare high-strength super-tough fibers with good mechanical properties.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Inorganic-organic melt-extruded hybrid yarns and fibrous composite medical devices thereof
ActiveUS20080183208A1Suture equipmentsMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentYarnThermoplastic
Composite fibrous constructs are made of combinations of inorganic-organic hybrid monofilament or multifilament yarns containing at least 6 weight percent of inorganic micro- / nanoparticles and organic monofilament or multifilament yarn with typical examples of the hybrid yarn matrix made of absorbable or non-absorbable thermoplastic polymers and final constructs being in the form of knitted or woven meshes and braided ligatures intended to perform under specific mechanically, biologically, and / or radiologically related functions.
Owner:POLY MED
Method for preparing nano TiO2 polyester ether elastic fiber
InactiveCN101100768AIncrease elasticityUniform elastic recoveryMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentMelt spinning methodsPolyesterNanoparticles dispersion
The invention relates to nanometer TiO2 polyether ester elastic fiber manufacturing method. It includes the following steps: preparing nanometer TiO2 / 1, 4-butanediol system that replacing the nanometer TiO2 by 1,4-butanediol as dispersion medium and vacuum pumping at 70-80 deg.C; preparing polyether ester elastic body that using dimethyl terephthalate, polytetrahydrofuran ether glycol, 1, 4-butanediol as material, adding 0.1-2.0% mass fraction nanometer TiO2, vacuum pumping at 50-100 deg.C, ester interchange reacting at 180-200 deg.C, condensation polymer reacting for 3-4h at 230-250 deg.C under 80Pa; melt spinning. This technology is simple. In addition, the prepared fiber has even nanometer particle disperse, good elastic recovery, low cost, suits for industrialization production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparing method for ordinary-pressure positive-ion dyeable polyester fiber
ActiveCN107541803ALess impuritiesReduce pressure riseMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentMelt spinning methodsPressure risePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a preparing method for an ordinary-pressure positive-ion dyeable polyester fiber. The preparing method includes the steps that dimethyl isophthalate-5-sodium benzenesulfonate,ethylene glycol, a catalyst and an anti-ether agent are mixed to be subjected to an ester exchange reaction, the reaction is end, then ethylene glycol and sodium ethylene glycol are added, modulationis carried out, then terephthalic acid, ethylene glycol and a catalyst are mixed, and the mixture is subjected to an esterification reaction; the modulated product after the ester exchange reaction is end and polyethylene glycol are added into an esterification reaction system reaching the end point of the esterification reaction, condensation polymerization is carried out, and spinning melt is obtained; the spinning melt is measured, extruded, cooled, subjected to oil applying, stretched, subjected to heat setting and wound, and the ordinary-pressure positive-ion dyeable polyester fiber is prepared. According to preparing method, generation of impurities in the polyester-fiber production process is reduced, pressure rising of a spinning assembly and a filter is reduced accordingly, the service cycle of the polyester fiber is prolonged, the continuity and the safety of the whole production process are guaranteed, and the preparing method has the good economic value and popularizationvalue.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGKE ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Inorganic-organic melt-extruded hybrid yarns and fibrous composite medical devices thereof
ActiveUS7632765B2Suture equipmentsMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentYarnThermoplastic
Composite fibrous constructs are made of combinations of inorganic-organic hybrid monofilament or multifilament yarns containing at least 6 weight percent of inorganic micro- / nanoparticles and organic monofilament or multifilament yarn with typical examples of the hybrid yarn matrix made of absorbable or non-absorbable thermoplastic polymers and final constructs being in the form of knitted or woven meshes and braided ligatures intended to perform under specific mechanically, biologically, and / or radiologically related functions.
Owner:POLY MED
Preparation method of heat-sensitive copolyester fiber
ActiveCN108660537AReduce consumptionReduce self-condensation side reactionsMonocomponent polyetheresters artificial filamentMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
The invention relates to a preparation method of a heat-sensitive copolyester fiber. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing terephthalic acid, aliphatic diol I, a guide and a titanium-silicon-cobalt composite catalyst uniformly, then subjecting the mixture to an esterification reaction, a pre-polycondensation reaction and a final polycondensation in sequence to obtain heat-sensitive copolyester, and then preparing the heat-sensitive copolyester fiber by melt direct spinning; the aliphatic diol I is propylene glycol or butylene glycol; the guide is an ester compound generated by a reaction between dibasic acid and aliphatic diol II; the molar ratio of the terephthalic acid to the aliphatic diol I is 1:(1.05-1.10); the titanium-silicon-cobalt composite catalyst is formed by compounding a titanium-silicon composite catalyst and a cobalt catalyst; the titanium-silicon composite catalyst is obtained by loading a titanium-based catalyst with a silicon-based catalyst; and polysiloxane and a copolymerization component are added during the final polycondensation reaction. The preparation method provide by the invention is few in side reactions and high in reaction rate; an obtained product is concentrated in molecular weight distribution and good in quality; and the fiber is prepared with the melt direct spinning.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com