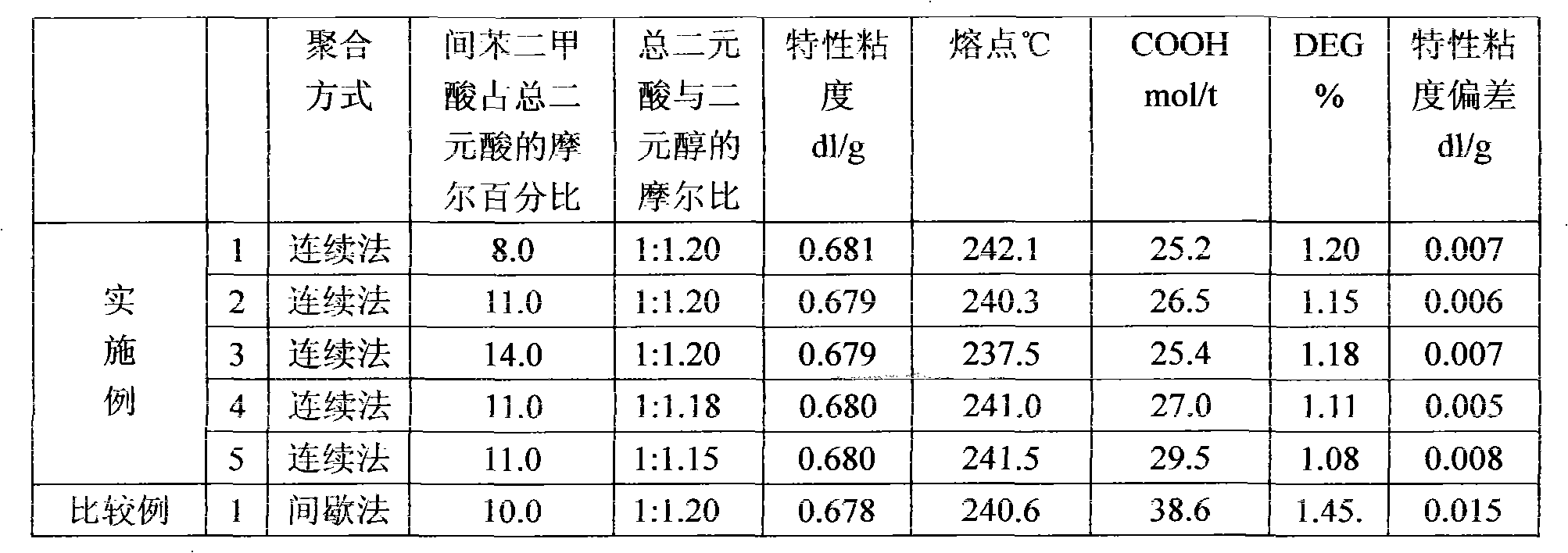
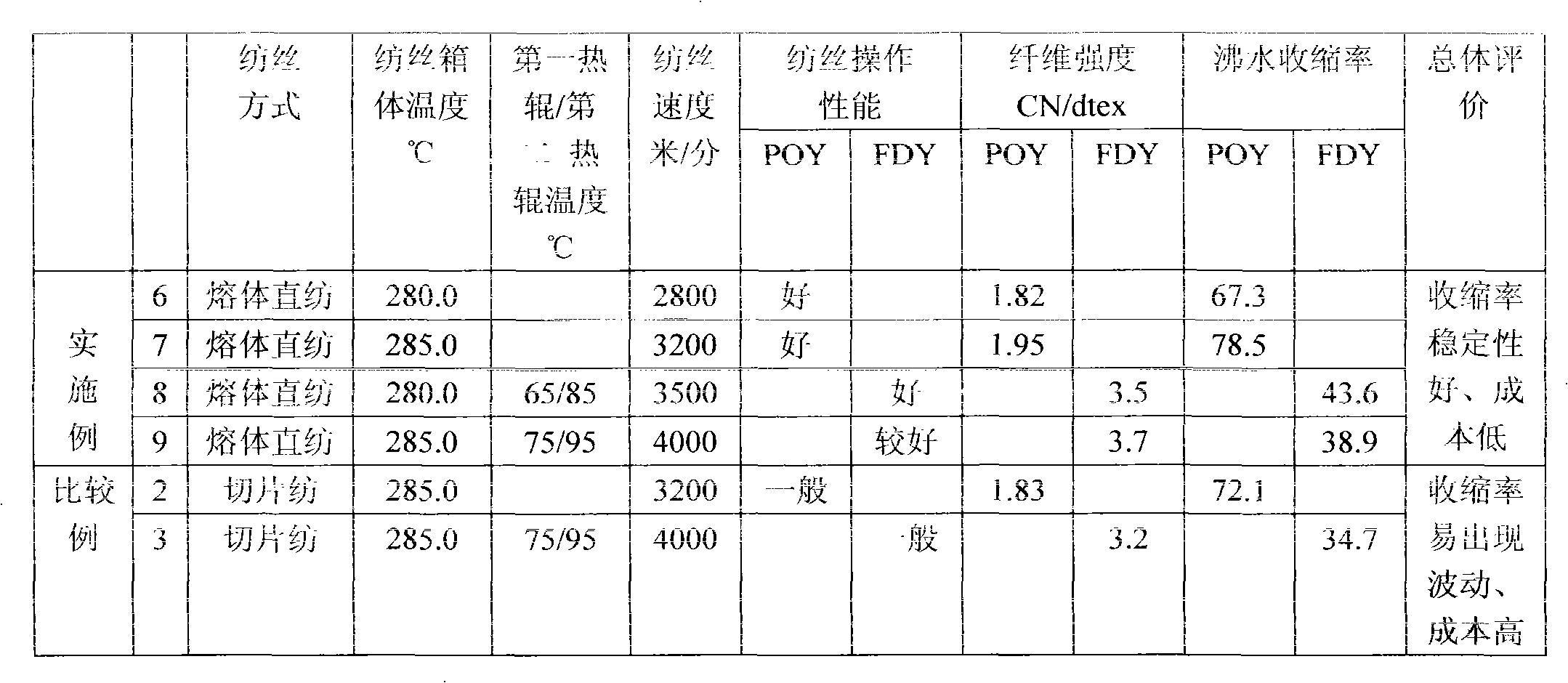
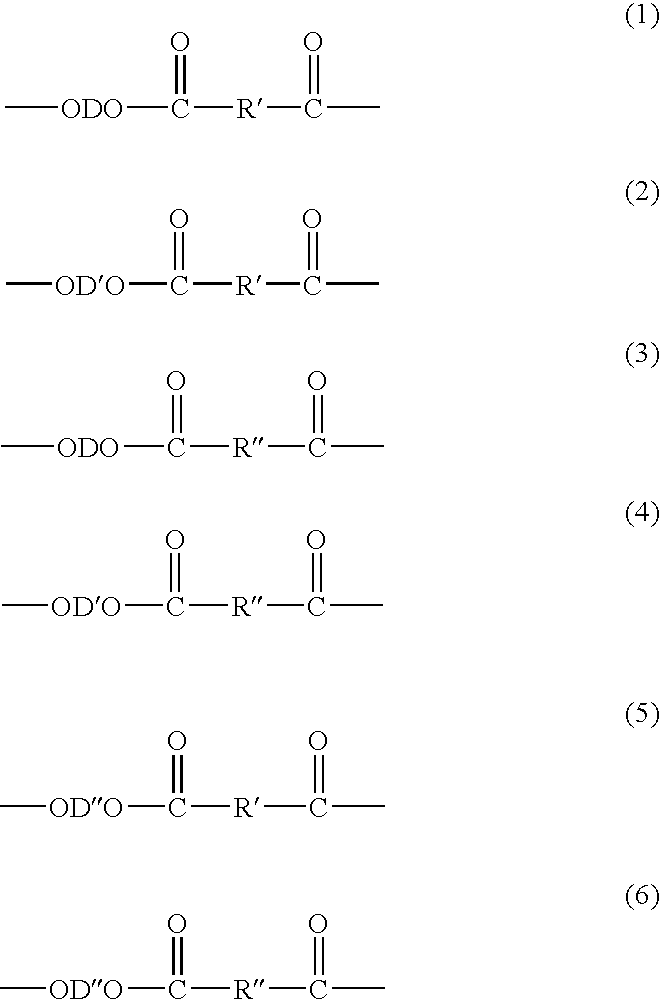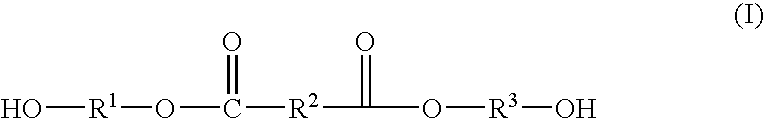Patents
Literature
2388 results about "Isophthalic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
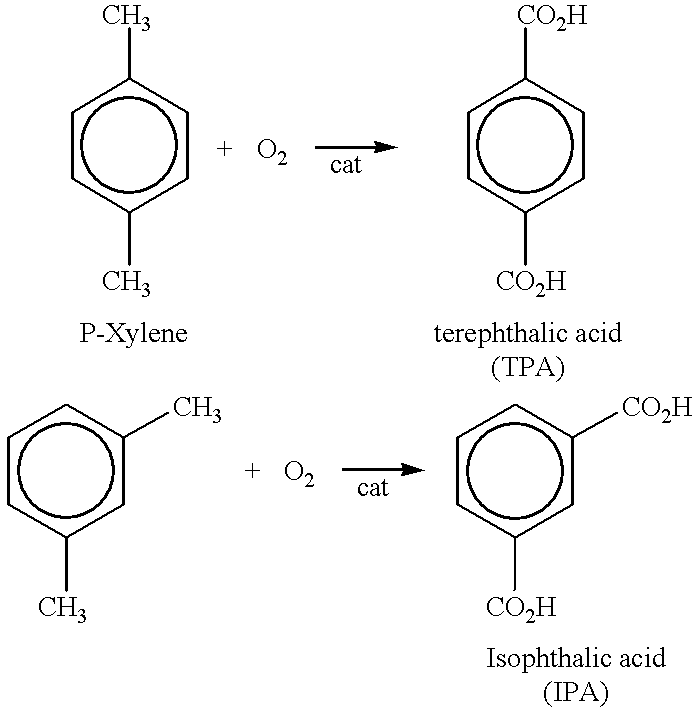
Isophthalic acid is an organic compound with the formula C₆H₄(CO₂H)₂. This colorless solid is an isomer of phthalic acid and terephthalic acid. The main industrial uses of purified isophthalic acid (PIA) are for the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) resin and for the production of unsaturated polyester resin (UPR) and other types of coating resins.
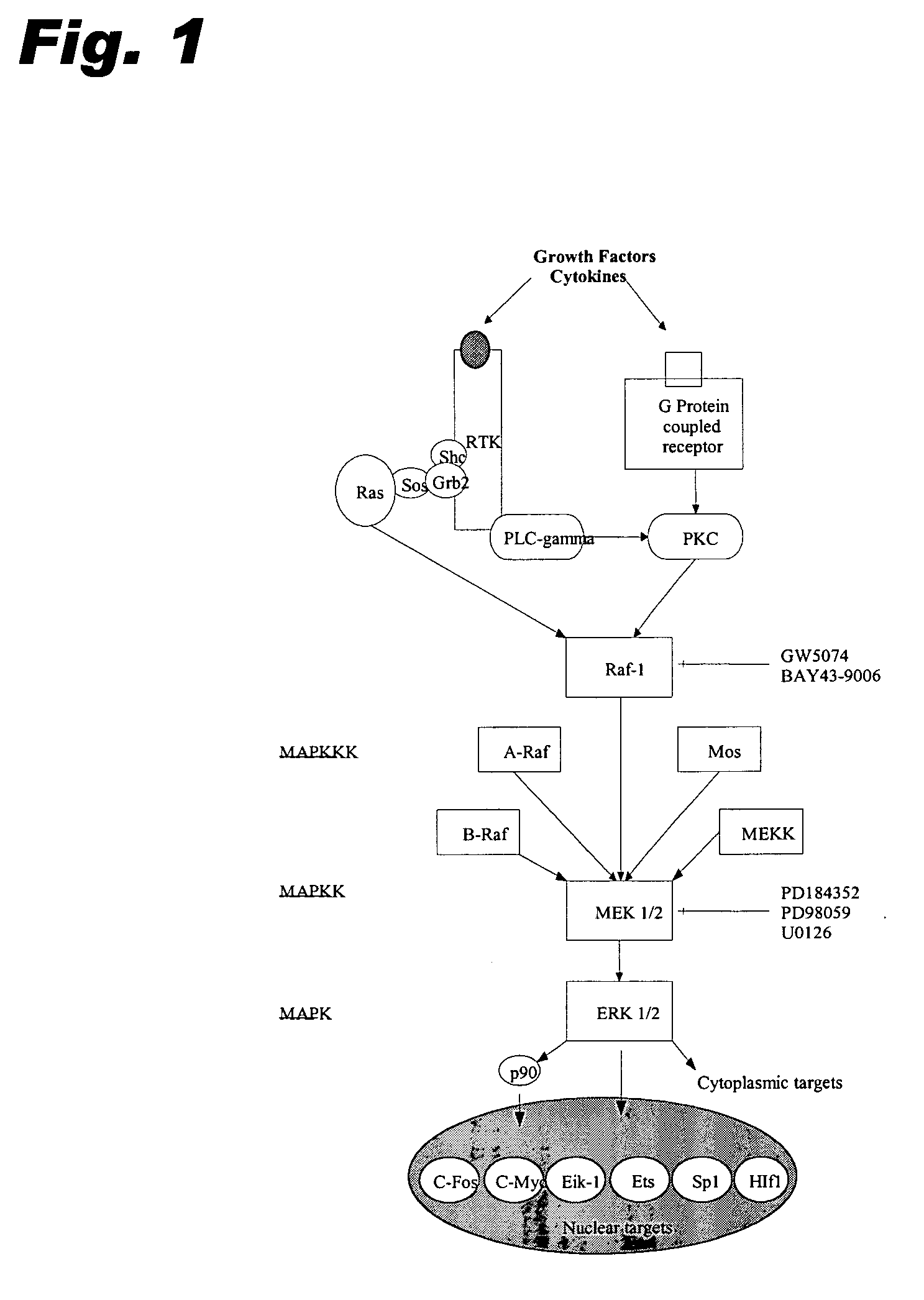
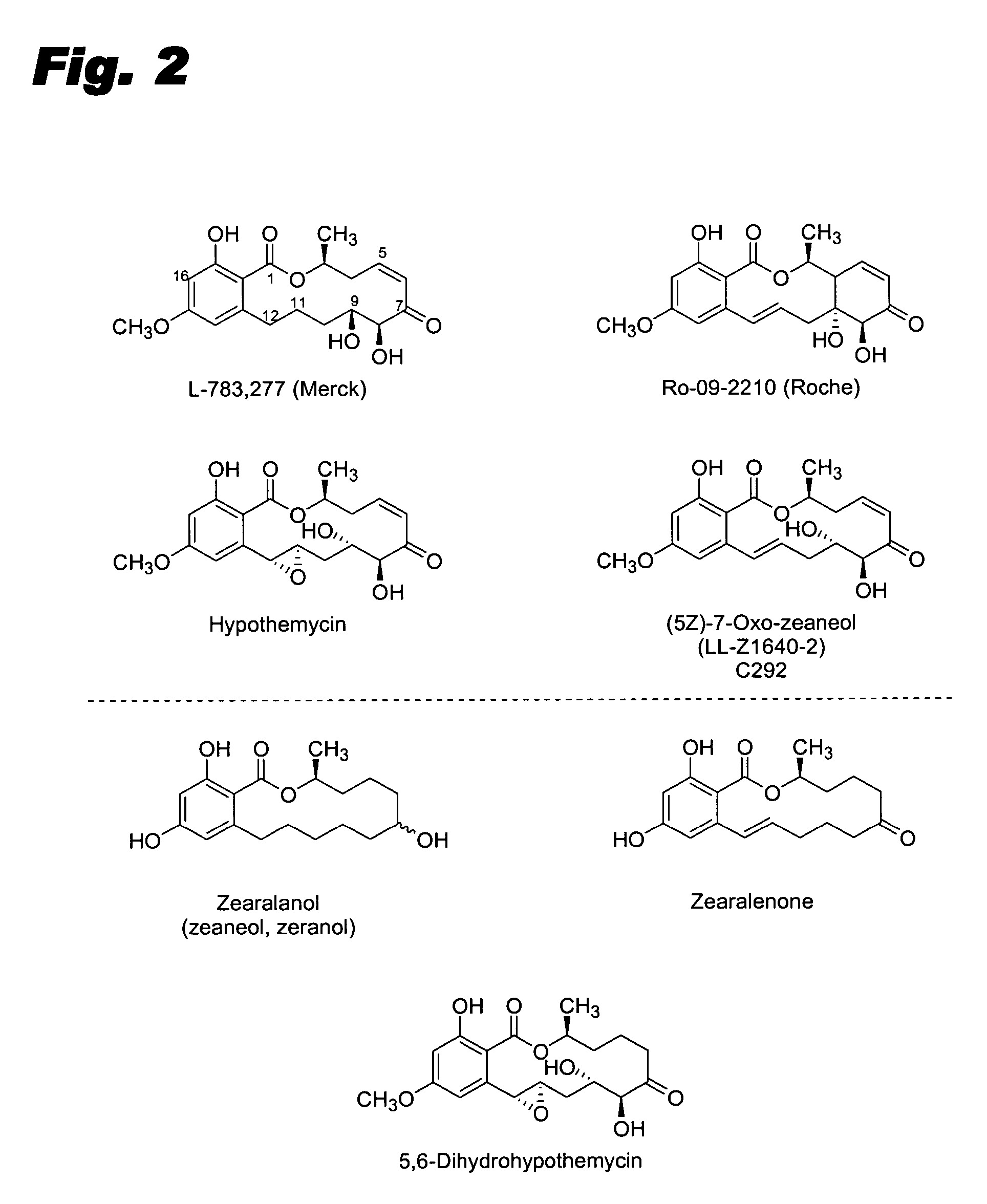
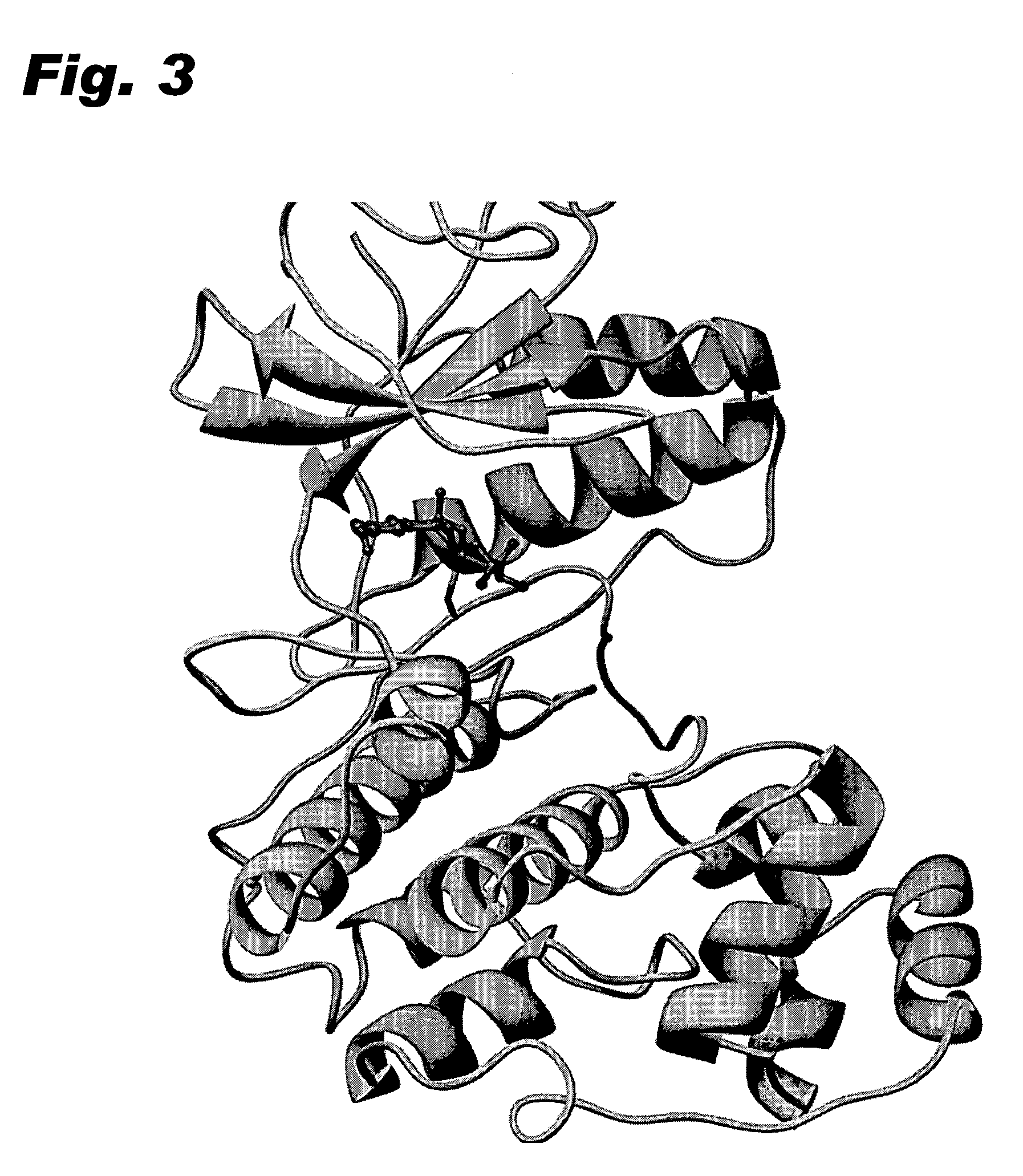
Specific kinase inhibitors
Resorcylic acid lactones having a C5-C6 cis double bond and a ketone at C7 and other compounds capable of Michael adduct formation are potent and stable inhibitors of a subset of protein kinases having a specific cysteine residue in the ATP binding site.
Owner:KOSAN BIOSCI
Articles derived from compositions containing modified polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) random copolymers derived from polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
ActiveUS20070275242A1Useful performance propertyPlastic recyclingSpecial tyresPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
Compositions of matter including articles derived from (a) from 5 to 99.99 wt % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate and (2) contains a at least one residue derived from polyethylene terephthalate selected from the group consisting of antimony, germanium, diethylene glycol groups, isophthalic acid groups, cis isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, trans isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, sodium benzoate, alkali salts, napthalane dicarboxylic acids, 1,3-propane diols, cobalt, cobalt-containing compounds, and combinations thereof, and (b) from 0.01 to 95 wt. % of a member selected from the group consisting of (1) fillers, (2) a carboxy reactive component, (3) polyethyelene terephthalate, (4) a component including a polycarbonate and an impact modifier. The articles may be derived from various conversion processes, e.g., injection molding processes, extrusion processes, thermoforming processes, melt-blown process.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Novel copolyester compositions with improved impact strength at low temperatures
This invention relates to a polyester composition comprising: (i) diacid residues comprising at least 80 mole percent, based on the total moles of diacid residues, of one or more residues of: terephthalic acid, naphthalenedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid, or isophthalic acid; and (ii) diol residues comprising from about 25 to about 70 mole percent, based on the total moles of diol residues, of the residues of 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol, and from about 75 to about 30 mole percent, based on the total moles of diol residues, of the residues of 1,3-propanediol. This invention has surprising improved impact strength at low temperatures.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Flexible, super durable powder coating composition
InactiveUS20060079650A1Good weather resistanceImprove mechanical propertiesPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPowdery paintsPolyesterPolymer science
Powder coatings having good impact resistance and weatherability characteristics are produced with an isophthalic acid-based polyester and an isocyanate-based curing agent.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
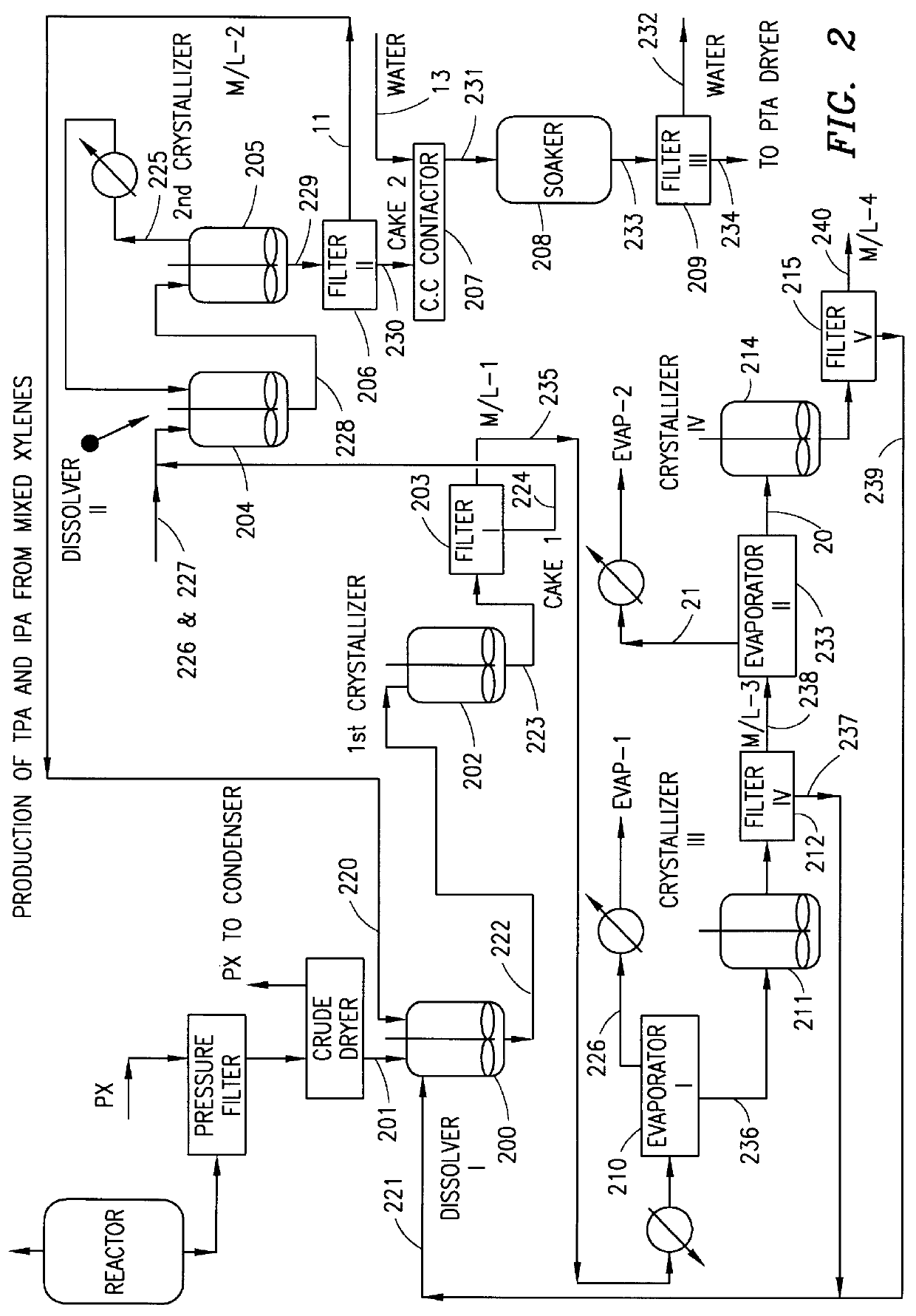
Method and apparatus for preparing purified terephthalic acid and isophthalic acid from mixed xylenes
InactiveUS6054610AReduce pressureReduce the temperatureOrganic compound preparationChemical industryIsophthalic acidXylene
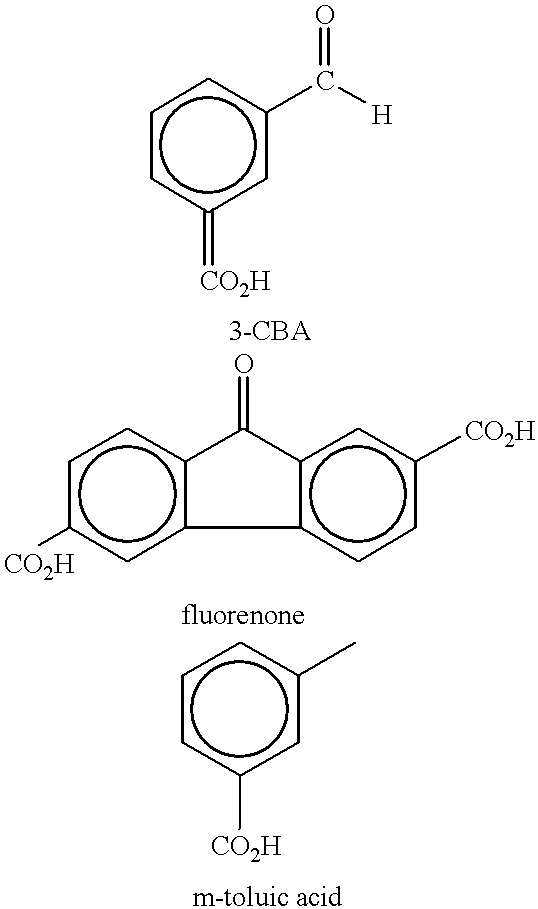
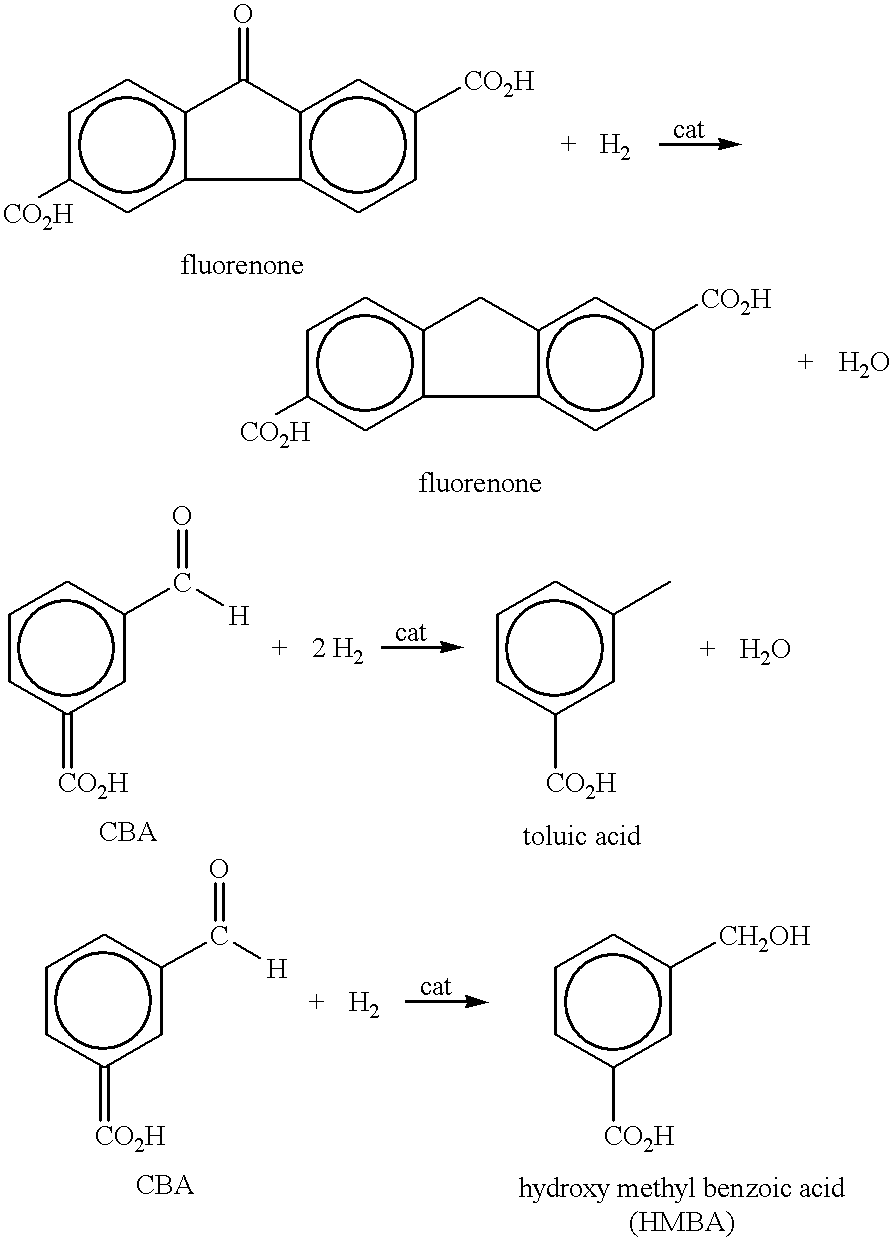
A method and apparatus for preparing purified terephthalic acid and, optionally, isophthalic acid from mixed xylenes. The method of the present invention purifies the oxidation reactor effluent containing a mixture of terephthalic acid and isophthalic acid as well as minor amounts of 4-carboxybenzaldehyde (4-CBA), 3-carboxybenzaldehyde (3-CBA), and toluic acid isomers, to produce purified terephthalic acid and, optionally, purified isophthalic acid in an integrated process.
Owner:GTC TECHNOLOGY INC
Method for preparing polyester filament capable being dyed by continuous condensed direct-spinning cation dye
InactiveCN101070642AReasonable workmanshipShort processMelt spinning methodsMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentFiberEther
A method for making a continuous polycondensation direct spinning cationic dye and tinctable polyester filament, it pertains to chemical art. Refining terephthalic acid and Glycol Monomer are raw materials, also including the preparation continuous polycondensation cationic dye and can-be-stained polyester and direct spinning dye tinctable polyester filament. In the present continuous polyester device, first beat the refining terephthalic acid and Glycol, then add Benzene PTA acid Glycol ester-5-Sodium and Ether-agent and stabilizer to get cationic dye tinctable polycondensation melt, then through pipeline, after measure, extrude, draw, wind to obtain cationic dye tinctable polyester pre-orientation silk or cationic dye can-be-stained polyester all-orientation silk. The invention has a short and less process, reasonable art. The quality of product is stable. And the fiber gained has high intensity, small deviation, and is dyed well-distributed, and has a better spinning quality. It can decrease production cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHEM FIBER UNITED GROUP
Luminescent solar collector
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Polyester coil coating
A coil coating composition producing a coil coating with excellent properties at a lower peak metal temperature includes (a) a first, branched polyester prepared by condensation of a polyol component consisting essentially of a flexibilizing diol, 2-methyl-1,3-propanediol, and a polyol having at least three hydroxyl groups and an acid component consisting essentially of isophthalic acid; (b) a second, essentially linear polyester prepared by condensation of a polyol component consisting essentially of a flexibilizing diol and 2-methyl-1,3-propanediol and an acid component consisting essentially of isophthalic acid; and (c) a crosslinking agent.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Method of Making Polybutylene Terephthalate and Compositions and Articles Comprising the Same
A process for making modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymers from a polyethylene terephthalate component includes reacting an oligomeric diol component selected from the group consisting of bis(hydroxybutyl)terephthalate, bis(hydroxybutyl)isophthalate, hydroxybutyl-hydroxyethyl terephthalate, and combinations thereof to a reactor; (i) a polyethylene terephthalate component selected from the group consisting of polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene terephthalate copolymers with (ii) a diol component selected from the group consisting of 1,4-butanediol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and combinations thereof, in the reactor under conditions sufficient to depolymerize the polyethylene terephthalate component into a first molten mixture; combining the first molten mixture is combined with 1,4-butanediol under conditions to form a second molten mixture; and placing the second molten mixture under conditions sufficient to produce the modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymers. Also described are compositions and articles made from the process.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Method for preparing continuous polymerization directly-spun high-shrinkage polyester filaments
InactiveCN101787583AShrinkage stableShort processSpinning head liquid feederMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentYarnFiber
The invention discloses a method for preparing continuous polymerization directly-spun high-shrinkage polyester filaments, which comprises a process for preparing continuous polymerization modified copolyester melt and a process for preparing directly-spun cation-dyeable high-shrinkage polyester filaments. In the process for preparing the continuous polymerization modified copolyester melt, purified terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid and glycol monomers are taken as raw materials to prepare the modified copolyester melt; and the copolyester melt directly passes through a melt conveying piping equipment, and is metered, extruded, blown to be cooled, drawn for heat shaping, and wound to prepare one of high-shrinkage polyester preoriented yarns and high-shrinkage polyester drawn yarns. The method has the advantages of short flow, less working procedures, reasonable process, stable melt quality, and good spinning performance; and the prepared high-shrinkage fibers have good shrinkage stability and even dyeing, and the production cost is reduced obviously.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV +1
Transparent polyamide molding materials having improved transparency, resistance to chemicals and high permanent fatigue strength
ActiveUS6943231B2High transparencyHigh permanent fatigue strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionFramesPolyamideCarboxylic acid
Transparent polyamide molding materials are provided which are characterized in that they have a melting enthalpy between 0 and 12 J / g and the polyamides are constituted of100 mole-% of a diamine mixture having 10-70 mole-% of PACM [bis-(4-amino-cyclohexyl)-methane] with less than 50 wt.-% of trans,trans-isomer and 90-30 mole-% of MACM [bis-(4-amino-3-methyl-cyclohexyl)-methane], wherein, optionally, 0-10 mole-% can be replaced by other aliphatic diamines having 6 to 12 C atoms, cycloaliphatic, alkyl-substituted cycloaliphatic, branched aliphatic diamines or multiamines having 3 to 12 amino groups or mixtures thereof, and100 mole-% of long-chain aliphatic dicarboxylic acids having 8 to 14 C atoms or mixtures of these dicarboxylic acids, wherein 0-10 mole-% can be replaced by other aromatic or cycloaliphatic dicarboxylic acids having 8 to 16 C atoms, which are especially selected from the group consisting of isophthalic acid, terephthalic acid, naphthalenedicarboxylic acid, cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid or mixtures thereof, andwherein, optionally, 0-10 mole-% of the other long-chain aliphatic diamines and 0-10 mole-% of the other long-chain aliphatic dicarboxylic acids can be added as 0-20 mole-% of ω-aminocarboxylic acids having 6 to 12 C atoms or lactams having 6 to 12 C atoms.Further, methods for producing the polyamide moulding materials and methods for producing and further treating moulded articles from the polyamide moulding materials are provided. Especially, the present invention relates to glasses and lenses which are obtainable from the polyamide moulding materials.
Owner:EMS CHEM AG
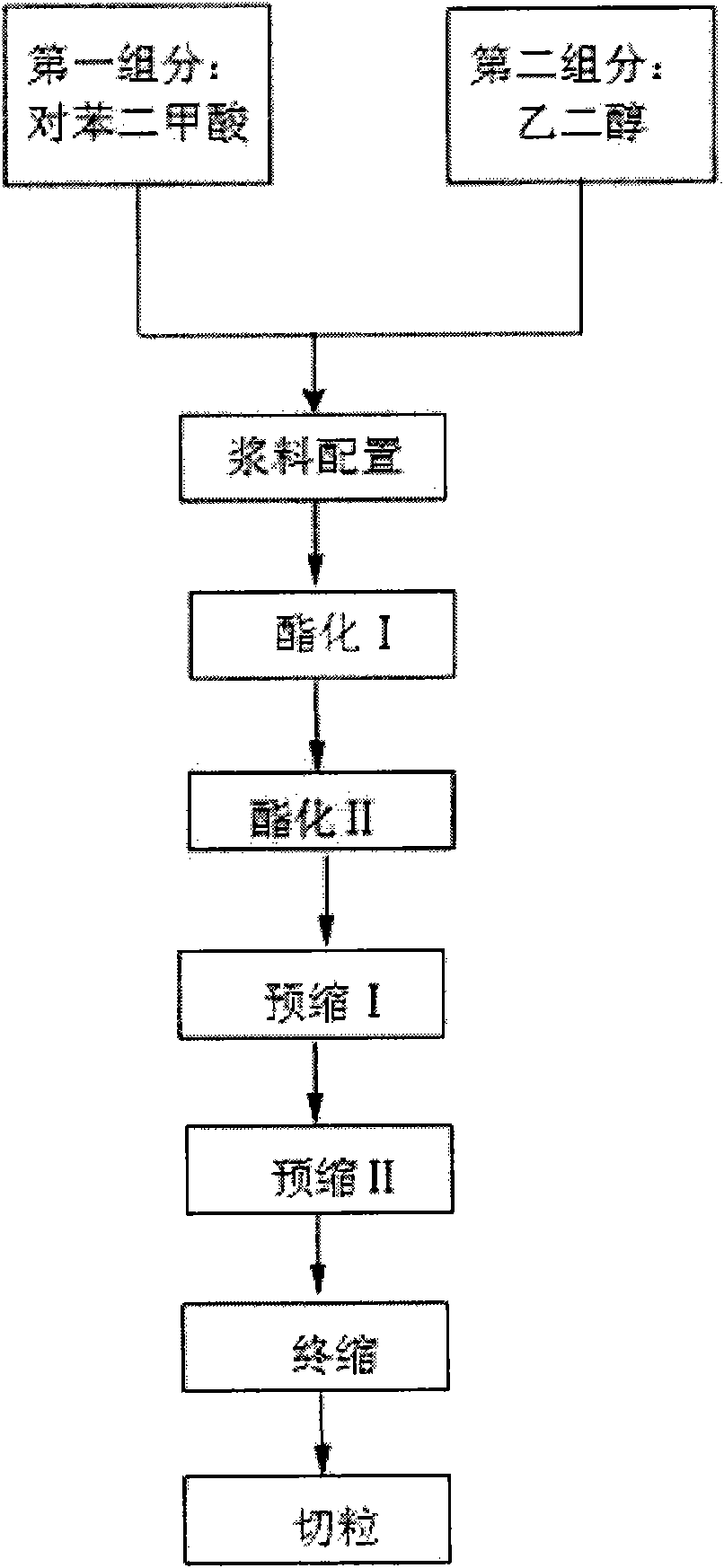
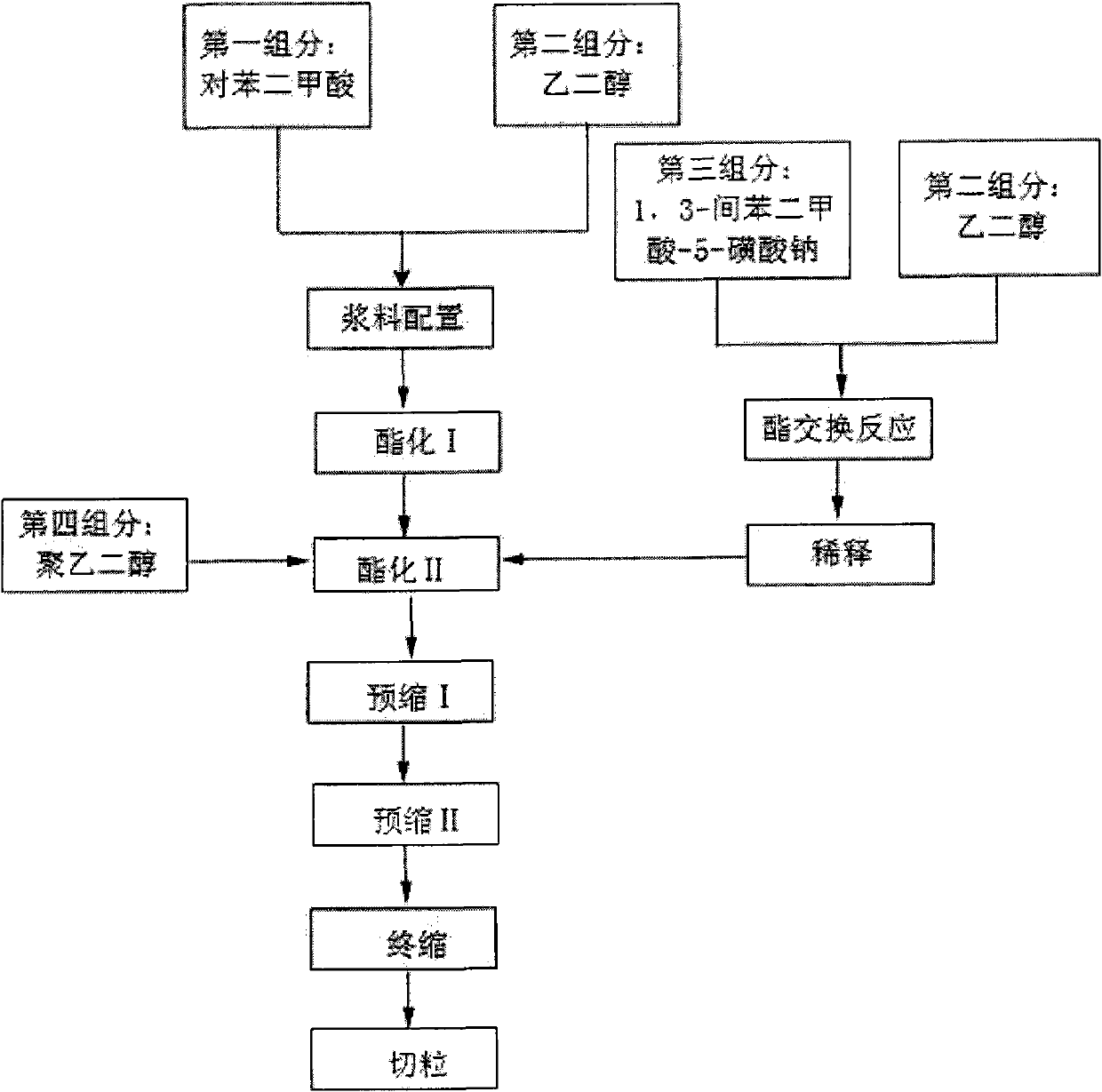
Preparation method of polyol copolyester
InactiveCN102086261AIncrease the chances of participating in a responseAchieve mass ratioDyeing processSlurryPhotochemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of polyol copolyester. The preparation method comprises the following steps of carrying out slurry preparation, esterifying I, esterifying II, pre-condensing I, pre-condensing II, final condensing and pelletizing on terephthalic acid and glycol. The preparation method also comprises: carrying out ester exchange reaction on 1,3-isophthalic acid-5-sodium sulfonate and another polyol; diluting with the glycol, and then performing the esterifying II. In the preparation method, 1,3-isophthalic acid-5-sodium sulfonate and another polyol react in advance, thereby increasing the reaction probability of another polyol and ensuring that another poyol can reach the required mole ratio in a finished product. The preparation method is mainly applied to production of dye modified polyester by using various dihydric alcohols at normal temperature and normal pressure. The modified polyester is dyed by mainly using anode pigment, the used dye chromatograph is more than that of common polyester, dye-uptake rate can reach above 99%, colour fastness reaches 4-5 grade of European standard, and the color is more flamboyance and beautiful. When filament yarns are subjected to spinning, full-package rate is up to 95%-100%.
Owner:SHANGHAI DEFULUN CHEM FIBER
Method of purifying aromatic dicarboxylic acids
InactiveUS6265608B1MinimizationReduce usageOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPalladium catalystCarboxylic acid
An aromatic dicarboxylic acid is purified by oxidizing m-xylene or p-xylene to produce crude isophthalic acid or crude terephthalic acid, respectively. The products of the oxidizing step are hydrogenated in the presence of a palladium catalyst. Carbon monoxide is introduced during the hydrogenation step. The palladium catalyst is provided on a carbon substrate. The products of the oxidizing step are dissolved in a solvent, which may be water, prior to the hydrogenation step. The products of the oxidizing step may be dissolved at an elevated temperature, above the normal boiling point of the solvent. The oxidation step produces isophthalic acid, 3-carboxybenzaldehyde and fluorenones in the case of oxidizing m-xylene and produces terephthalic acid, 4-carboxybenzaldehyde and fluorenones in the case of oxidizing p-xylene. It may be helpful to monitor the disappearance of 3-carboxybenzaldehyde in the case of oxidizing m-xylene and 4-carboxybenzaldehyde in the case of oxidizing pxylene, and reducing the amount of carbon monoxide when the rate of disappearance is below a predetermined minimum. After the hydrogenation step, the isophthalic acid or terephthalic acid may be crystallized. The carbon monoxide may be maintained at a concentration of 100 to 500 ppm based on added hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Other aromatic dicarboxylic acids may also purified by this procedure.
Owner:GRUPO PETROTEMEX DE C V
Heat-shrinkable multilayer film
A polyamide resin-based heat-shrinkable multilayer film is caused to satisfy various properties required of a packaging material, especially a food packaging material, at high levels, and particularly exhibit a highest level of heat-shrinkability. The multilayer film comprises at least three layers including an outer surface layer (a) which comprises a polyester resin or a polyolefin resin; an intermediate layer (b) which comprises a mixture of 85-60 wt. % of an aliphatic polyamide resin, and 15-40 wt. % of an aromatic copolyamide resin which is a copolymer of aliphatic diamine / isophthalic acid and aliphatic diamine / terephthalic acid, and an inner surface layer (c) which essentially comprises a copolymer of ethylene and alpha-olefin having a density below 0.915. The heat-shrinkable multilayer film has been biaxially stretched and then heat-treated to have hot-water shrinkabilities at 80° C. of at least 30% in each of longitudinal / transverse directions and at least 35% in at least one of longitudinal / transverse directions.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Aqueous acrylic acid-modified alkyd resin and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103554379AImprove water resistanceImprove aging resistanceCoatingsBenzoic acidPolymer science
The invention discloses aqueous acrylic acid-modified alkyd resin and a preparation method thereof. Basic alkyd resin of the aqueous acrylic acid-modified alkyd resin is prepared from an unsaturated fatty acid, benzoic acid, trimethylolpropane, pentaerythritol, maleic anhydride, isophthalic acid, ethylene glycol monobutyl ether and butanol. The aqueous acrylic acid-modified alkyd resin is prepared by adding styrene, methyl methacrylate, butyl acrylate, acrylic acid, a silane coupling agent, benzoyl peroxide, tert-butyl hydroperoxide, ethylene glycol monobutyl ether and a mixing neutralizer into the basic alkyd resin. According to the aqueous acrylic acid-modified alkyd resin and the preparation method thereof, the advantages of alkyd resin and acrylic resin are integrated, and a product has high gloss retention, color retention and weather resistance; a production process is simple, the raw materials are readily available, and the production cost is low; a paint production process is simple, water is used as a diluting agent, and safety and convenience in construction are ensured.
Owner:西北永新涂料有限公司
Low-melting-point copolyester and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101338023AIncrease exerciseLow melting pointMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
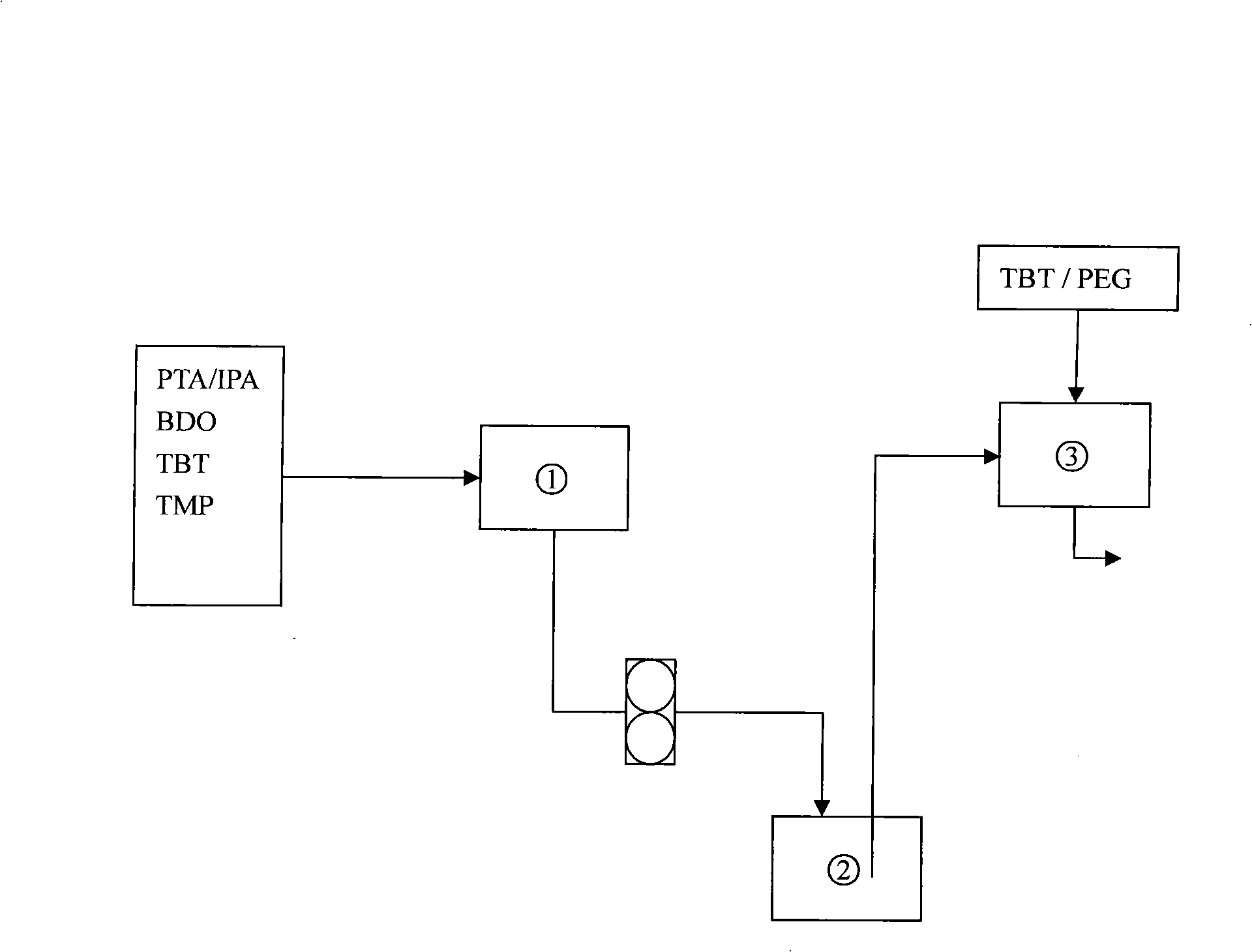
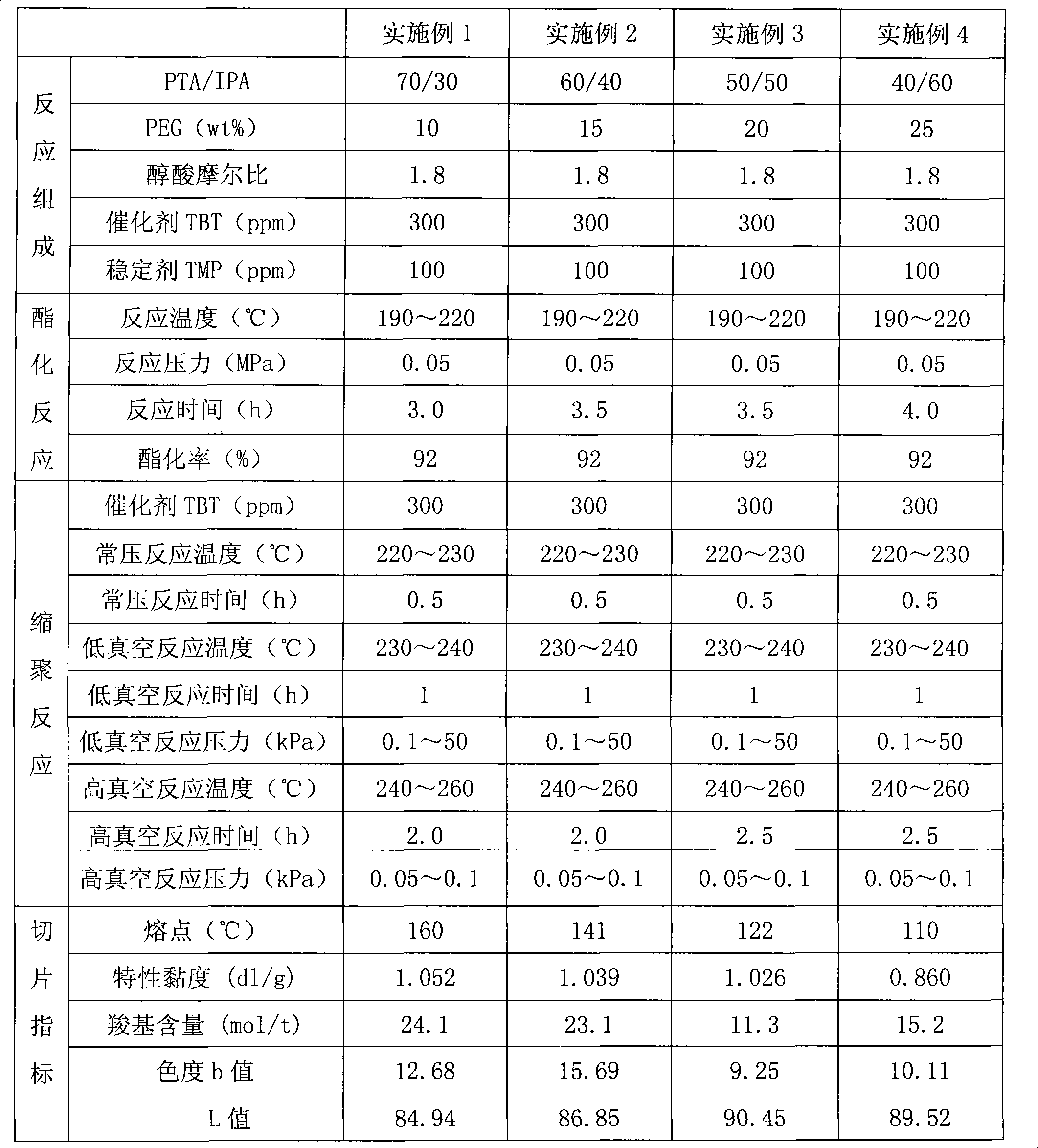
The invention relates to low melting point copolyester and a preparation method thereof. The low melting point copolyester is made from the following monomers followed by the esterification reaction and the polycondensation reaction: (a) terephthalic acid (PTA) and isophthalic acid (IPA), (b) 1, 4- butanediol (BDO) and (c) polyethylene glycol 600 to 6000 (PEG); wherein, in the a component, the feeding mass ratio of the terephthalic acid and the isophthalic acid is between 80 to 20 : 20 to 80; in the c component, the feeding weight ratio of polyethylene glycol is 1 to 30 percent based on the a; the molar ratio of the a and the b is 1:1.5 to 2.3. The preparation method comprises an esterifcation stage and a polycondensation stage. The copolyester has the characteristics of low melting point, good crystallization property, high intrinsic viscosity and difficult adhesion of particles, and is suitable for spinning the filament, the staple fibers and the non-woven fabrics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Thermoplastic composition, method of making, and articles formed therefrom
A thermoplastic composition comprises a polyester-polycarbonate polymer comprising isophthalate-terephthalate-resorcinol ester units and carbonate units, and a poly(alkylene ester) comprising ethylene terephthalate units, 1,4-cyclohexyldimethylene terephthalate units, or a combination of ethylene terephthalate units and 1,4-cyclohexyldimethylene terephthalate units, wherein the sum of the mole percentage values of isophthalate-terephthalate-resorcinol ester units in the polyester-polycarbonate polymer, and of the mole percentage values of 1,4-cyclohexanedimethylene terephthalate units in the poly(alkylene ester) polymer, is a value greater than 40. In other embodiments, polycarbonate may be included. Also disclosed is a method for forming the thermoplastic compositions, and articles prepared therefrom.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Polyester compositions and laminates and processes for producing biaxially stretched polyester bottles
InactiveUS6485804B1Increase crystallization rateMaintain good propertiesBottlesSynthetic resin layered productsCarboxylic acidDicarboxylic acid
The novel polyester (first polyester [A]) of the invention comprises dicarboxylic acid constituent units derived from at least one dicarboxylic acid selected from terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid and naphthalenedicarboxylic acid and diol constituent units derived from diols comprising ethylene glycol and a polyalkylene glycol having a C2-C10 alkylene chain, wherein the proportion of constituent units derived from the polyalkylene glycol is 0.001 to 10% by weight based on the diol constituent units. The polyester [A] has an excellent crystallization rate, is suitably used, singly or as compositions together with another polyester [B] and / or other polymers, for production of molded products such as films, sheets, laminates, preforms and bottles, which have excellent thermal, gas barrier and transparency properties.
Owner:MITSUI PETROCHEMICAL INDUSTRIES LTD
Articles derived from compositions containing modified polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) random copolymers derived from polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
Compositions of matter including articles derived from (a) from 5 to 99.99 wt % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate and (2) contains a at least one residue derived from polyethylene terephthalate selected from the group consisting of antimony, germanium, diethylene glycol groups, isophthalic acid groups, cis isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, trans isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, sodium benzoate, alkali salts, napthalane dicarboxylic acids, 1,3-propane diols, cobalt, cobalt-containing compounds, and combinations thereof, and (b) from 0.01 to 95 wt. % of a member selected from the group consisting of (1) fillers, (2) a carboxy reactive component, (3) polyethyelene terephthalate, (4) a component including a polycarbonate and an impact modifier. The articles may be derived from various conversion processes, e.g., injection molding processes, extrusion processes, thermoforming processes, melt-blown process.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
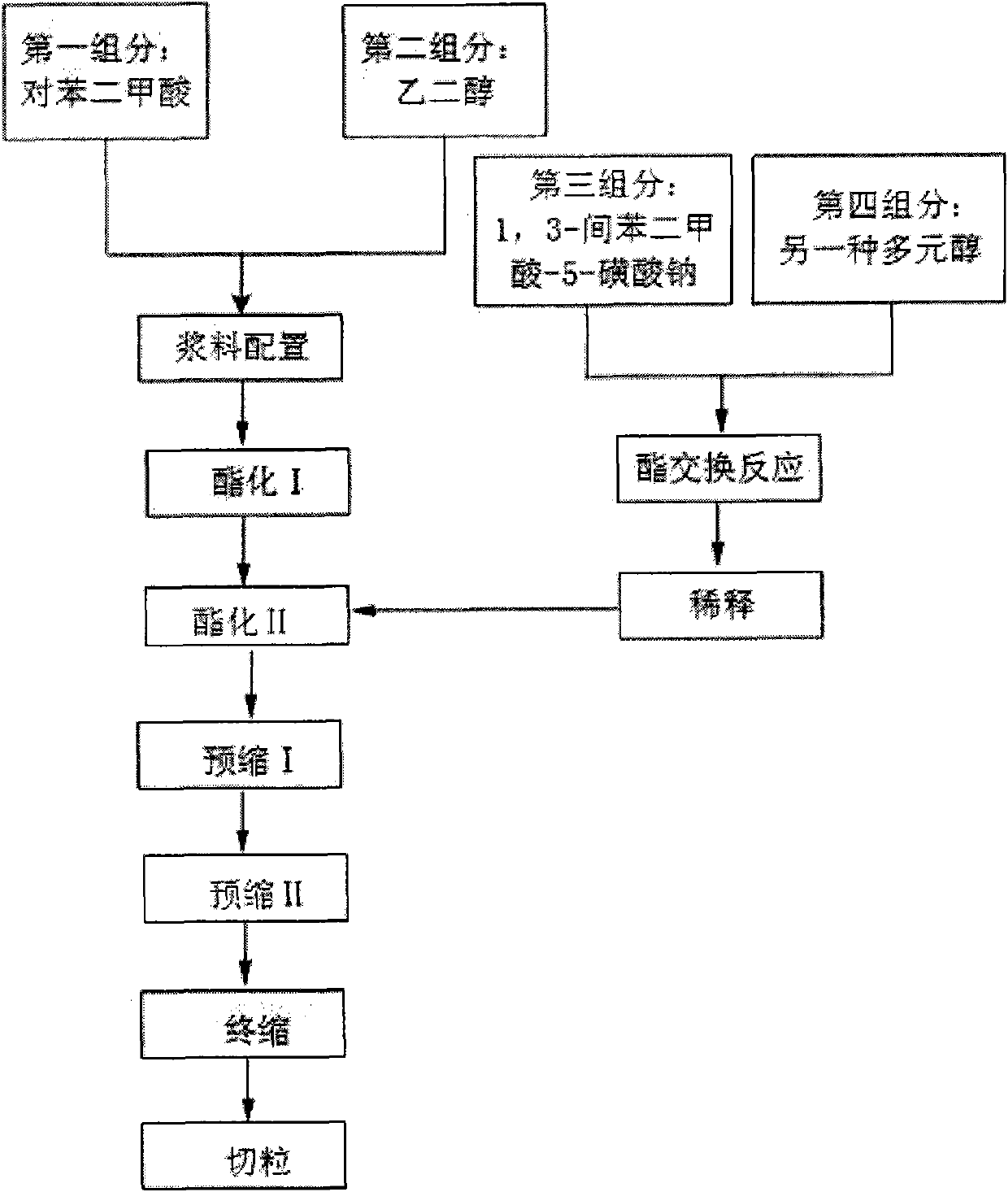
Process for preparing water-soluble copolyester
The water soluble copolyester is prepared with polytetrahydrofuran in number average molecular weight of 350-20000 as the fourth component, and metaphthalate-5-sodium sulfonate, metaphthalate dihydroxyethyl-5-sodium sulfonate, metaphthalate dimethyl-5-potassium sulfonate, or other metaphthalate type sulfonate as the third component, and through polycondensation in PTA or DMT path. Compared with the copolyester with polyglycol and other aliphatic flexible compound as the fourth component, the present invention is water soluble and has better crystallizing performance. The product produces no adhesion during drying, and may be blended with conventional polyester slice to obtain POY sea island cotton with flexible elastic process to raise the spinnability and processibility of sea island fiber.
Owner:SINOPEC YIZHENG CHEM FIBER
Paint for H grade polyurethane enamelled wire with good saline water needle performace capable of directing welding at low temp.
InactiveCN1597815AImprove heat resistanceQuality improvementPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsLacquerSolvent
The invention relates to an H-grade wire coating enamel that has good salt water pinhole performance and can be directly welded at low temperature, containing hydroxyl component, sealed isocyanate component and solvent, where its hydroxyl component has an acid value less than 2, a hydroxyl value of 150-300, and number-average molecular weight of 1500-5000, and as synthesized, the raw materials has at least m-phthalic acid, p-phthalic acid, adilic acid, glycerin and a kind of dibasic alcohol in the weight ratio of 1 to (0.2-2) to (0.2-0.5) to (0.5-3) to (0.5-1.5); and its sealed isocyanate component is partially added of MDI by mixed polyalcohol that at least has a dibasic alcohol and a tribasic alcohol; in the paint base, the equivalent ratio of isocyanate base to OH is (0.9-1.2) : 1, and it reaches H-grade and has good salt water pinhole property of paint film, tin daubing temperature less than or equal to 375 deg.C.
Owner:CNOOC CHANGZHOU PAINT & COATINGS IND RES INST
Method for preparing water-soluble sulfo-copolyester
The invention discloses a method for preparing water-soluble sulfo-copolyester used in textile slurry. The method comprises the following steps of: performing esterification reaction or transesterification on dibasic acid / ester at least containing isophthalic acid, sulfo-dibasic acid or ester and terephthalic acid and dibasic alcohol at least containing ethanediol to obtain polycondensation prepolymer; and performing polycondensation under reduced pressure to obtain a product, wherein the molar ratio of the dibasic acid to the dibasic alcohol is 1:1.3-1:1.8; the materials are put at one time; and the polycondensation prepolymer is obtained in one step. The method has the advantages of not using expensive polyethylene glycol materials, adopting a lower molar ratio of the dibasic acid to the dibasic alcohol, putting the materials at one time, reducing cost, along with simple process. The product has high water solubility and higher glass-transition temperature, is suitable for storage, and has good effect in slurry.
Owner:苏州瀚海化学有限公司
Fast-flow high temperature resistant nylon composite material
ActiveCN101200591AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove heat resistanceHeat resistanceMechanical property
The present invention provides composite material used for preparing fast flowing high-temperature resistant nylon, which comprises the following components: 20 to 84.9 weight portions of high-temperature resistant nylon resin and 0.1 to 10 weight portions of flowing modifier, wherein, the high-temperature resistant nylon resin is selected from the semi-aromatic nylon with the self melting point between 290 DEG C to 330 DEG C; the semi-aromatic nylon is obtained by the copolymerization of terephthalic acid or isophthalic acid, the diamine with 4 to 12 carbon atoms and the aliphatic nylon with 6 to 24 carbon atoms. The fast flowing high-temperature resistant nylon of the present invention has good heat resistance and fluidity and good chemical performance, exact formability and size stability and is mainly used for the production of thin-wall product in the electronic appliance field.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
Plasticizing and modifying method for polylactic acid
The invention provides a toughening modification method of polylactic acid. The polylactic acid and toughening modifier are mixed according to the proportion and are dried to lead the moisture content percentage to be lower than 50 ppm, then a melting extrusion method is adopted to mould the polylactic acid and the toughening modifier into a product, wherein, the toughening modifier is copolyester with melting point in 125 to 200 DEG C, in particular is the copolyester obtained by adopting isophthalic acid, hexanediamine, 1,4-butanediol, etc. as third monomers to modify PET. When blending, the quantity of the copolyester accounts for 1 to 20 Wt percent of the quantity of the polylactic acid, the melting extrusion processing temperature is 180 to 240 DEG C, and the breaking elongation of the obtained injection molding spline is improved by 10 to 300 percent. The invention greatly makes up for the disadvantage of deficient toughness of PLA, so as to lead the processing property to be improved greatly.
Owner:中国石化仪征化纤股份有限公司
Process for controlled polymerization of a mixed polymer
InactiveUS7297721B2Reduce the degree of polymerizationReduce usageProductsReagentsPolymer scienceMonoethylene Glycol
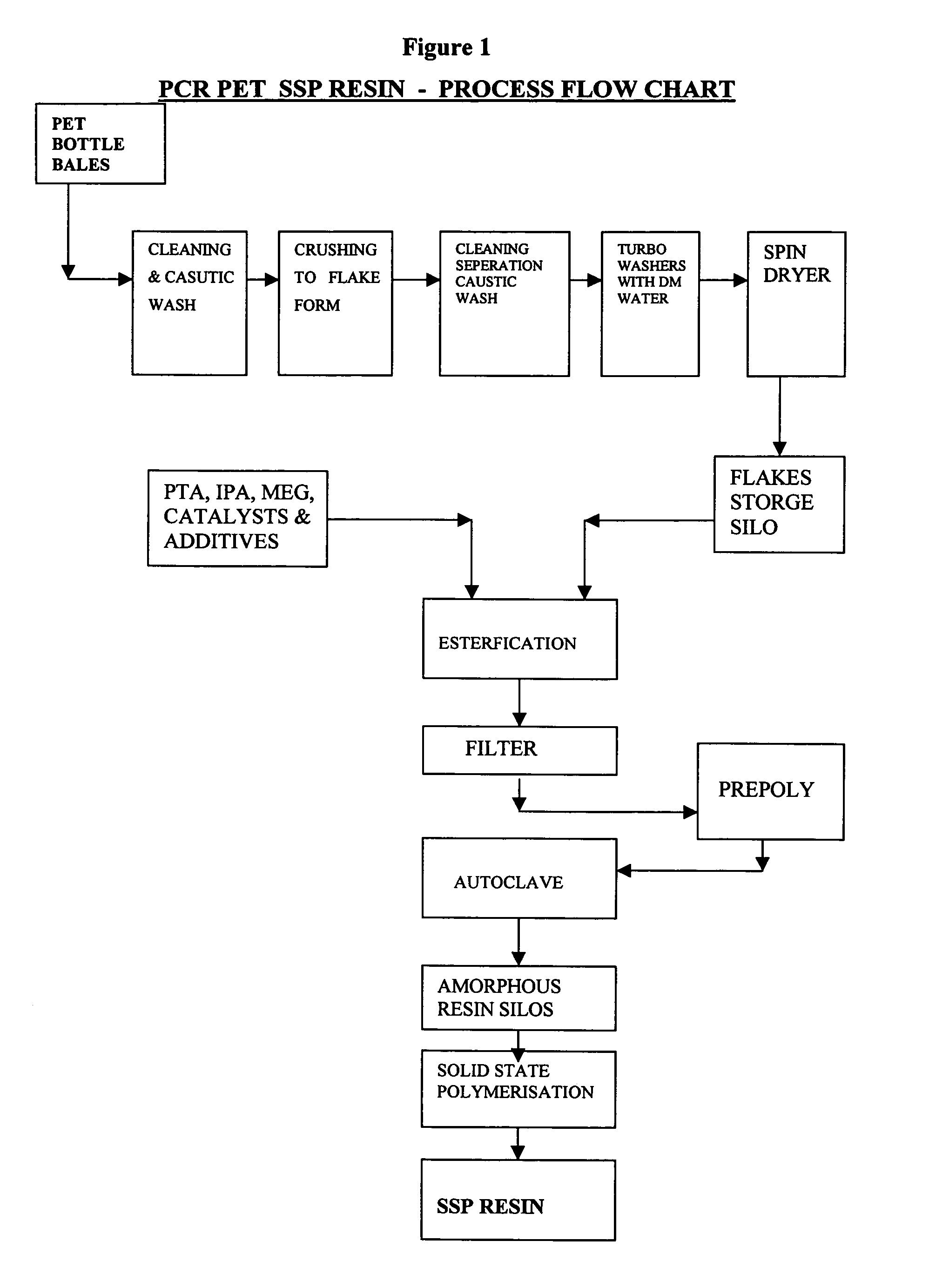
The present invention provides a process for the preparation of high molecular weight crystalline Polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) using up to 50% of Post consumer recycled PET flakes along with Pure Terephthalic Acid (PTA), Isophthalic Acid (IPA) and Mono Ethylene Glycol (MEG) as a virgin raw material, in the presence of a combination of catalysts and additives to obtain an intermediate prepolymer heel having a low degree of polymerization further subjecting to autoclaving to yield an amorphous melt and followed by solid state polymerization.
Owner:FUTURA POLYESTERS LTD
Filament low-melting-point polyester fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106757518AImprove fitImprove stabilityFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsPolymer sciencePolyethylene terephthalate
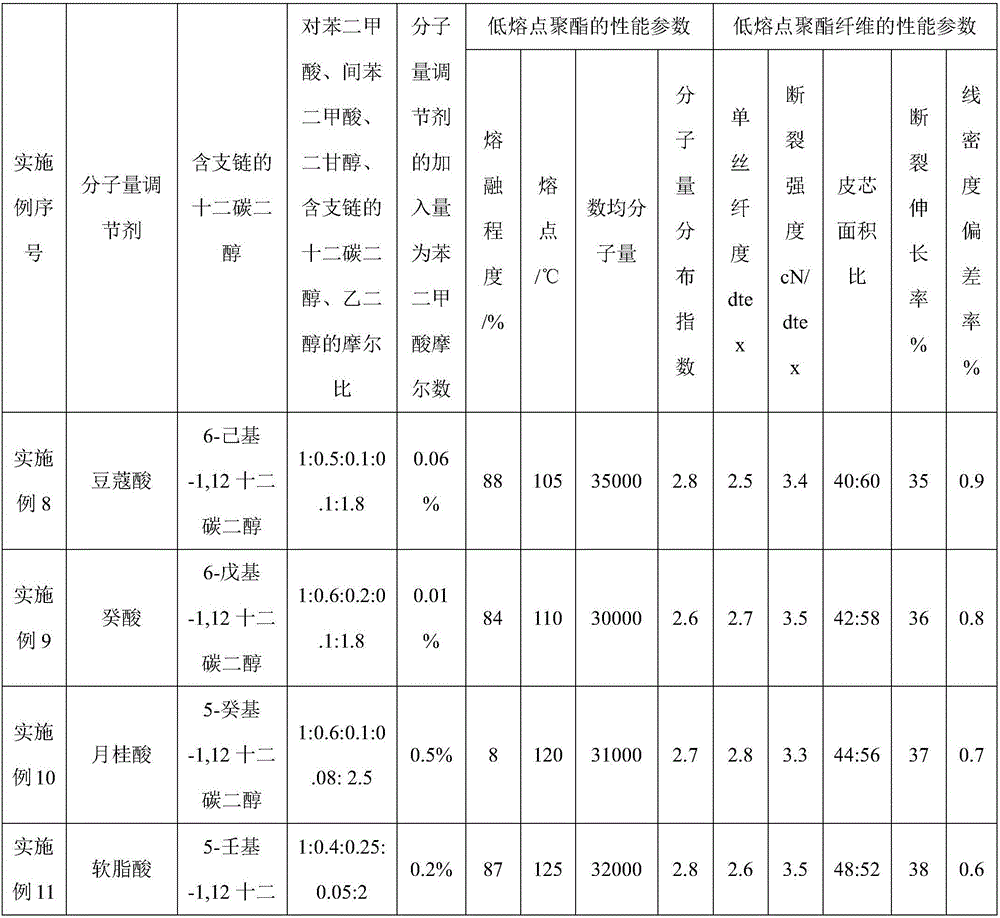
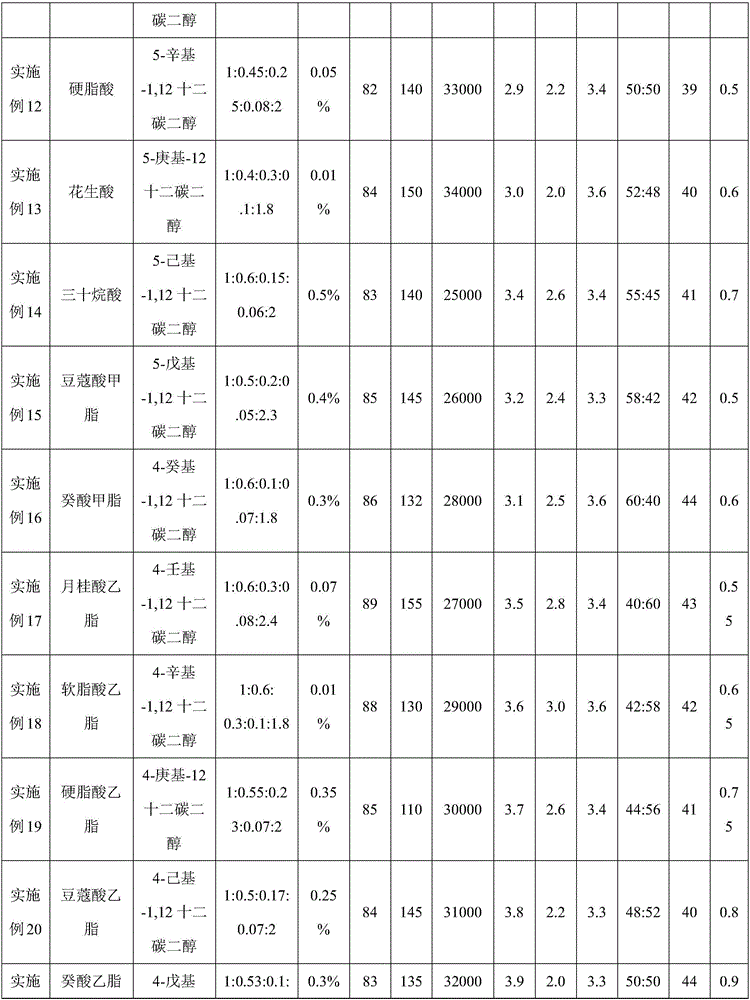
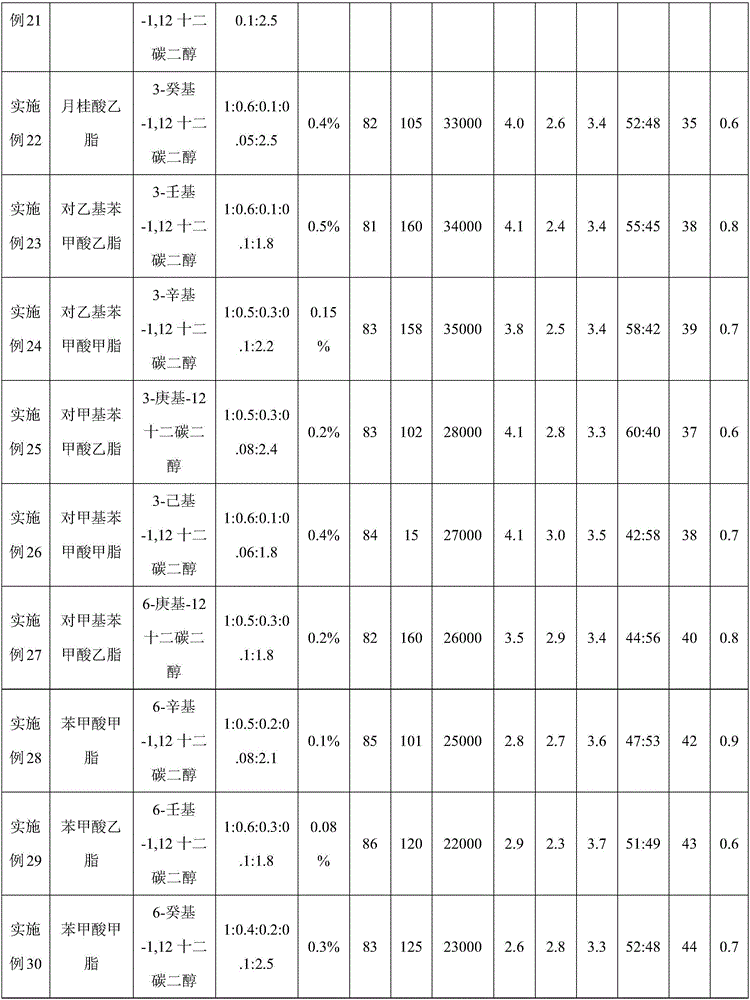
The invention relates to a filament low-melting-point polyester fiber and a preparation method thereof. The filament low-melting-point polyester fiber is in a skin-core structure, a skin layer is made of low-melting-point polyester; a core layer is made of PET (polyethylene terephthalate); the low-melting-point polyester consists of a terephthalic acid chain segment, an isophthalic acid chain segment, an ethylene glycol chain segment, a diethylene glycol chain segment, a molecular weight modifier chain segment and a 1, 12-Dodecanediol chain segment containing branched chains; a molecular weight modifier corresponding to the molecular weight modifier chain segment is specifically a monoacid series or a diacid series; the preparation method of the filament low-melting-point polyester fiber comprises the following steps: polymerization of the low-melting-point polyester and skin-core composite spinning, so as to obtain the filament low-melting-point polyester fiber. The prepared filament low-melting-point polyester fiber has the advantages that the initial melting point is reduced, the melting speed is increased, the polyester fiber is immediately melted at the corresponding temperature, and the melting effect is good.
Owner:扬州富威尔复合材料有限公司
Microbial production of terephthalic acid and isophthalic acid
This invention relates to a biocatalytic process to produce terephthalic acid and isophthalic acid from p-xylene and m-xylene, respectively. Terephthalic acid has been prepared by oxidizing p-xylene with bacteria belonging to the genus Burkholderia. Conversion of p-xylene into terephthalic acid is accomplished by a single bacterial strain that produces all of the requisite enzymes. In addition, this invention relates to the preparation of isophthalic acid from a mixture of m- and p-xylene.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for forming coated film and intermediate coating material
InactiveUS6863929B2Easy to separateSmall sizeElectric shock equipmentsPretreated surfacesPolyolAlcohol
A method for forming a coated film comprising the steps of sequentially applying an intermediate coating material, a base coating material and a clear coating material on a substrate on which an electrodeposition coated film has been formed; and simultaneously curing the applied three layers by baking, wherein the intermediate coating material comprises: (a) 40 to 56% by weight of an urethane modified polyester resin, the urethane modified polyester resin being obtainable by polyaddition of: a hydroxyl group containing polyester resin which is obtainable by polycondensation of an acid ingredient including not less than 80% by mole of isophthalic acid with a polyhydric alcohol ingredient, with an aliphatic diisocyanate compound; (b) 10 to 30% by weight of a melamine resin; (c) 15 to 30% by weight of a blocked isocyanate compound; (d) 4 to 15% by weight of a nonaqueous dispersion resin having core-shell structure; and (e) 0.4 to 2 parts by weight of a flake-like pigment. The resulting layered coated film is superior in aesthetic appearance and chipping resistance even formed in the three-coating and one-baking method.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP +1
Preparation method of polyester resin for mixing type powdery coating
InactiveCN1962717AReduce melt viscosityUniform molecular weightPowdery paintsPolyester coatingsPolymer sciencePolymer resin
Owner:GUANGZHOU QINGTIAN INDAL
Polyamide resin, composition containing polyamide resin, and molded articles of polyamide resin and composition
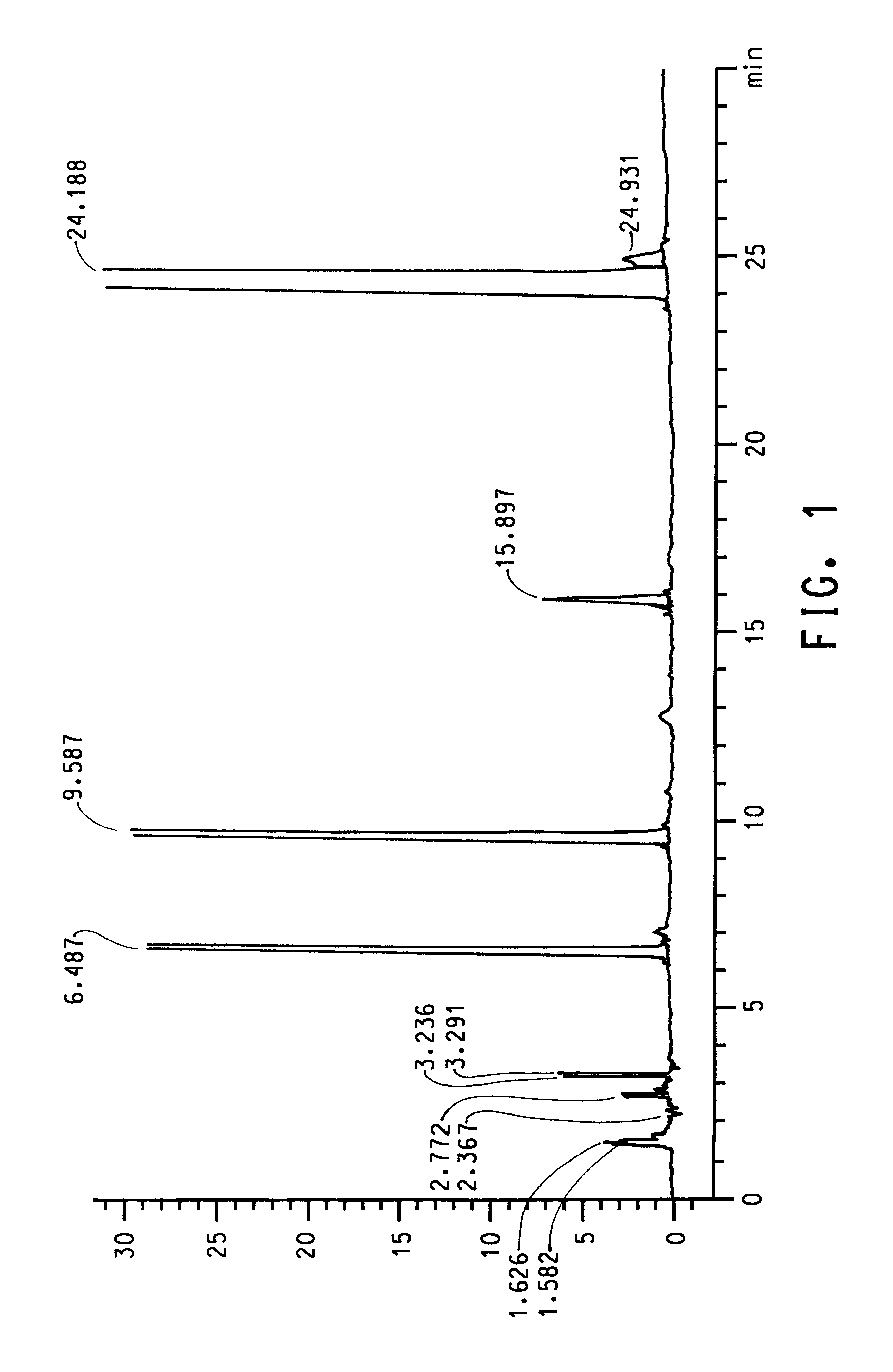
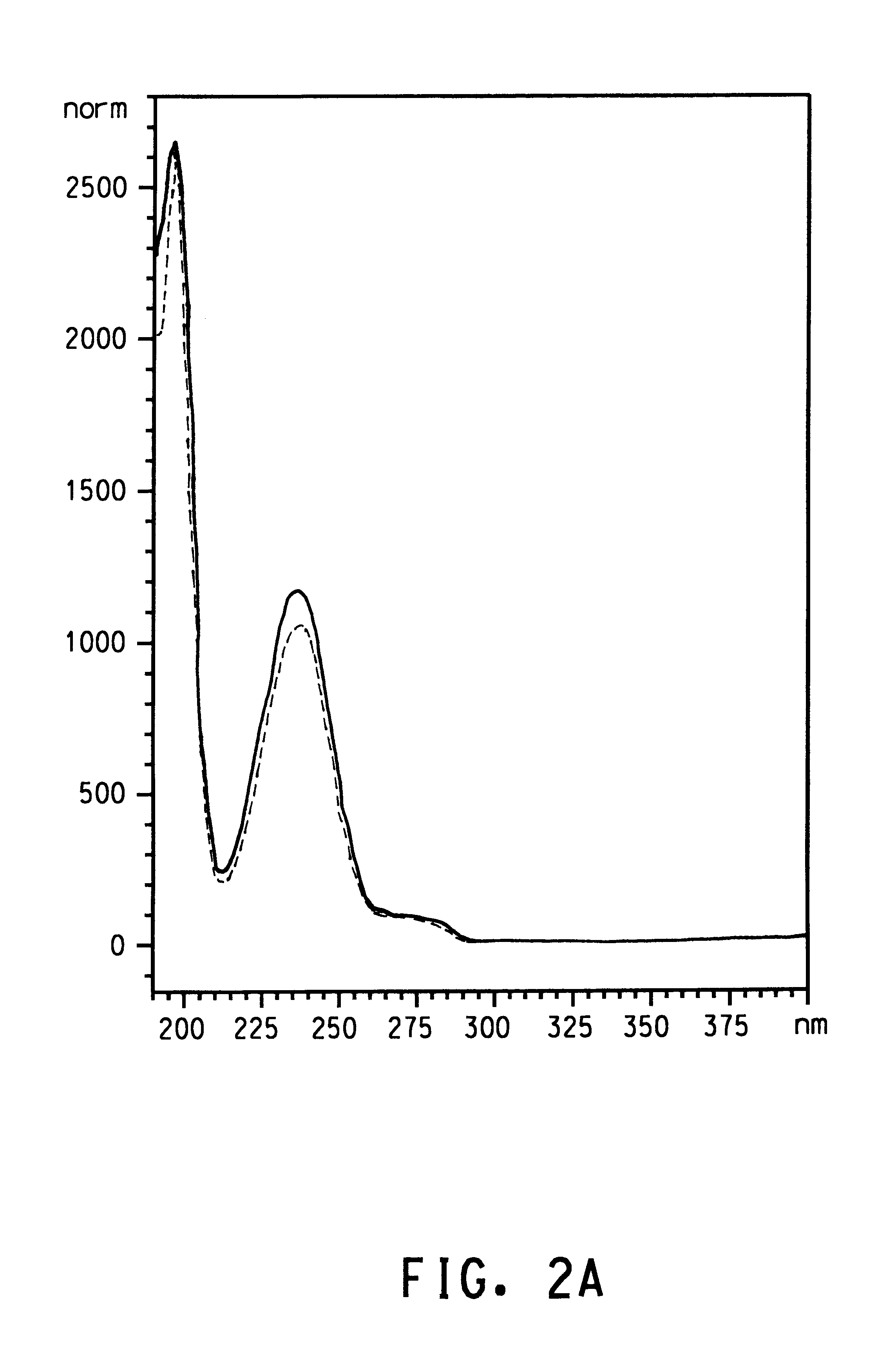
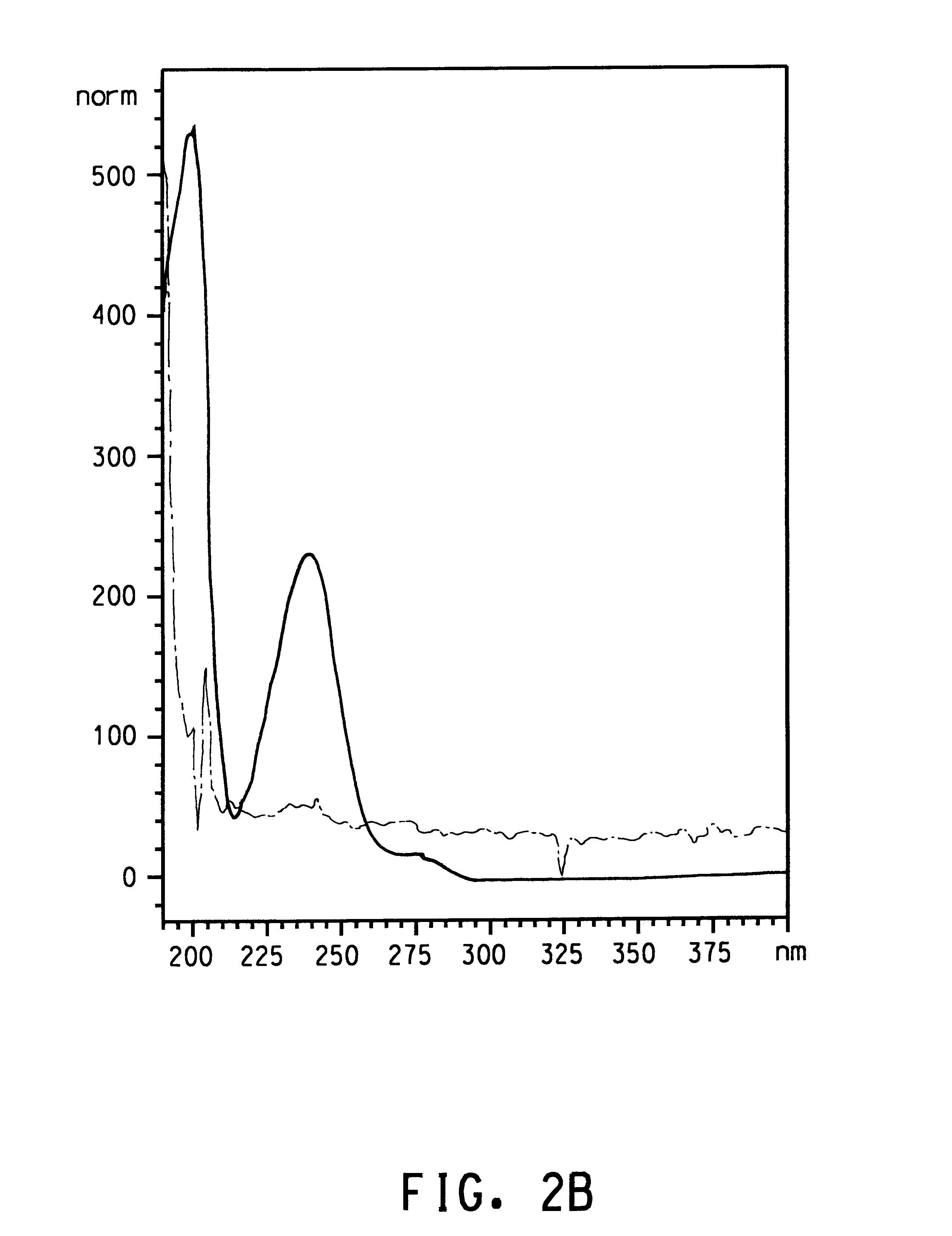
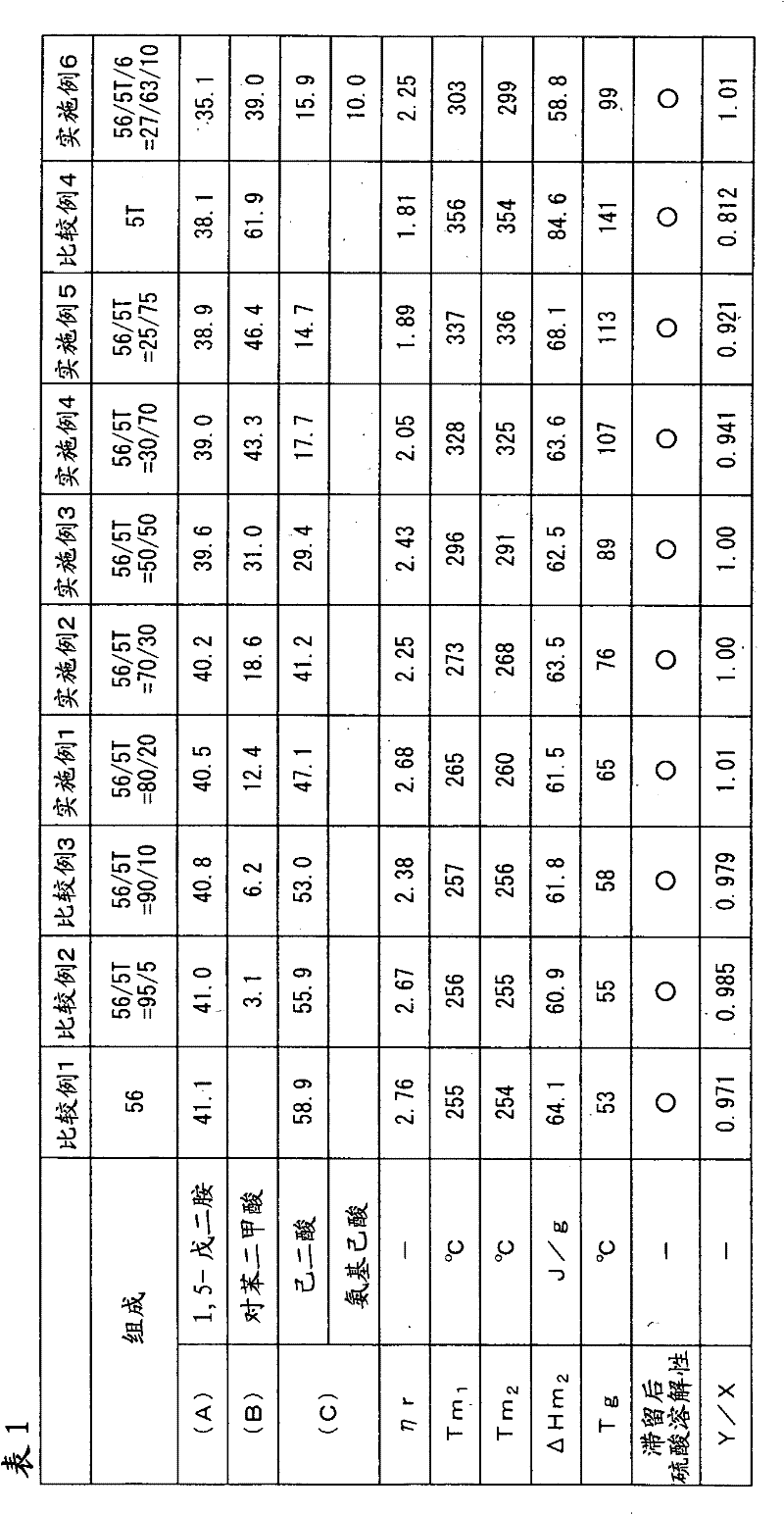
InactiveCN102131845AImprove heat resistanceExcellent melt retention stabilityLaurolactamPolymer science
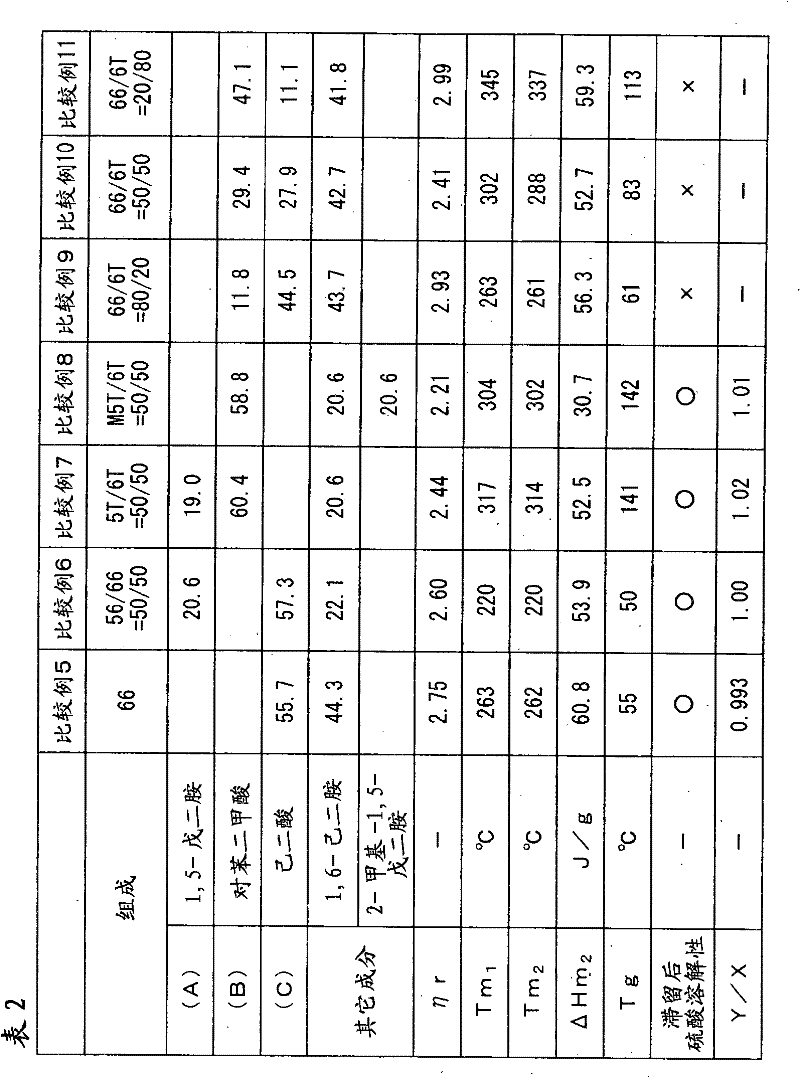
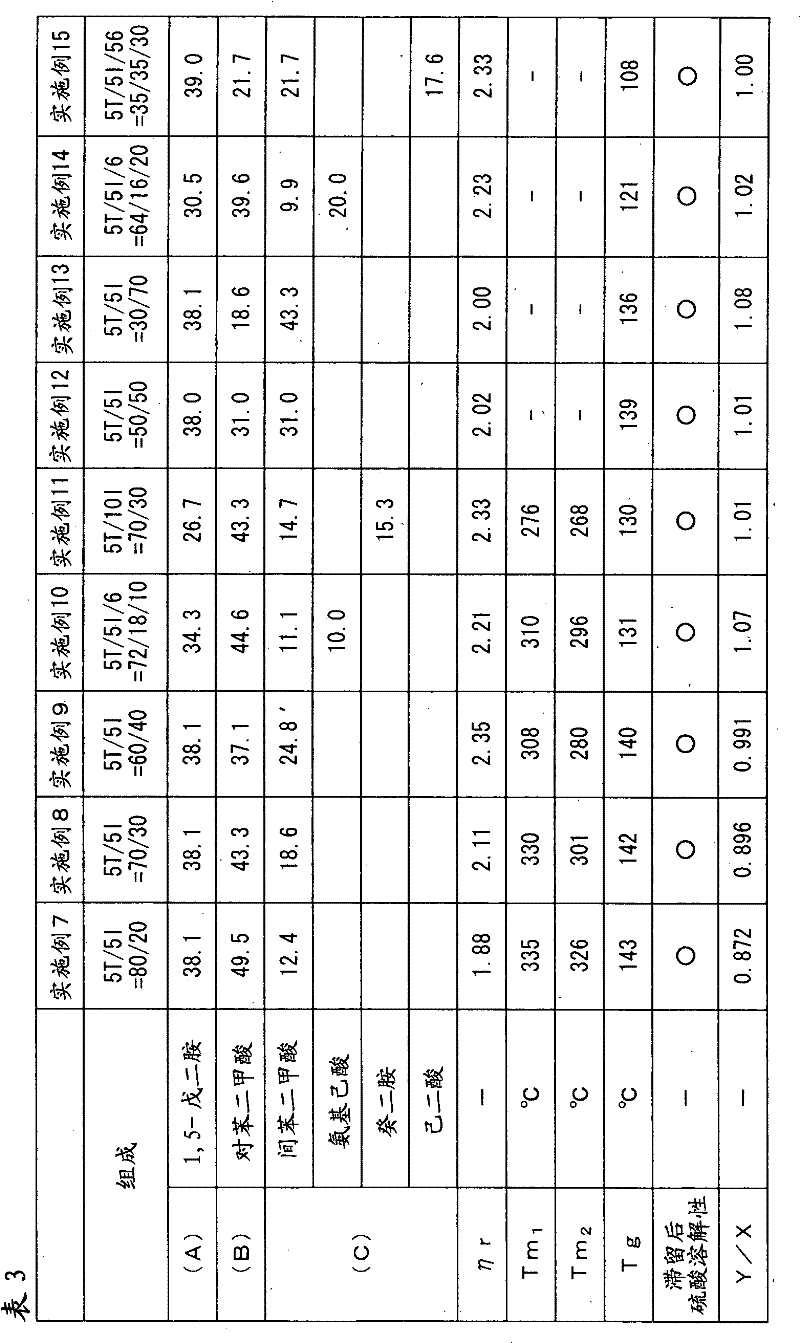
Disclosed is a polyamide resin which is produced by the polycondensation of (A) pentamethylenediamine, (B) terephthalic acid and / or a derivative thereof, and (C) at least one compound selected from adipic acid, azelaic acid, sebacic acid, undecanedioic acid, dodecanedioic acid, isophthalic acid, 1,9-diaminononane, 1,10-diaminodecane, 1,11-diaminoundecane, 1,12-diaminododecane, caprolactam, undecalactam, laurolactam, aminocaproic acid, 11-aminoundecanoic acid, 12-aminododecanoic acid, and derivatives of these compounds. In the polyamide resin, the ratio of a repeating unit derived from the component (C) is 10 to 50 wt% (inclusive) relative to the total weight of the polymer. A solution of the polyamide resin in 98% sulfuric acid, which contains the polyamide resin at a concentration of 0.01 g / ml, has a relative viscosity of 1.5 to 4.5 at 25 DEG C.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com