Filament low-melting-point polyester fiber and preparation method thereof
A low-melting point polyester and filament technology, applied in fiber processing, rayon manufacturing, fiber chemical characteristics, etc., can solve the problem of large market demand for low-melting point polyester, late start of low-melting point fiber development, and impact on low-melting point polyester Use and other problems to achieve the effect of easy melting speed, widening molecular weight distribution, and good coating adhesion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
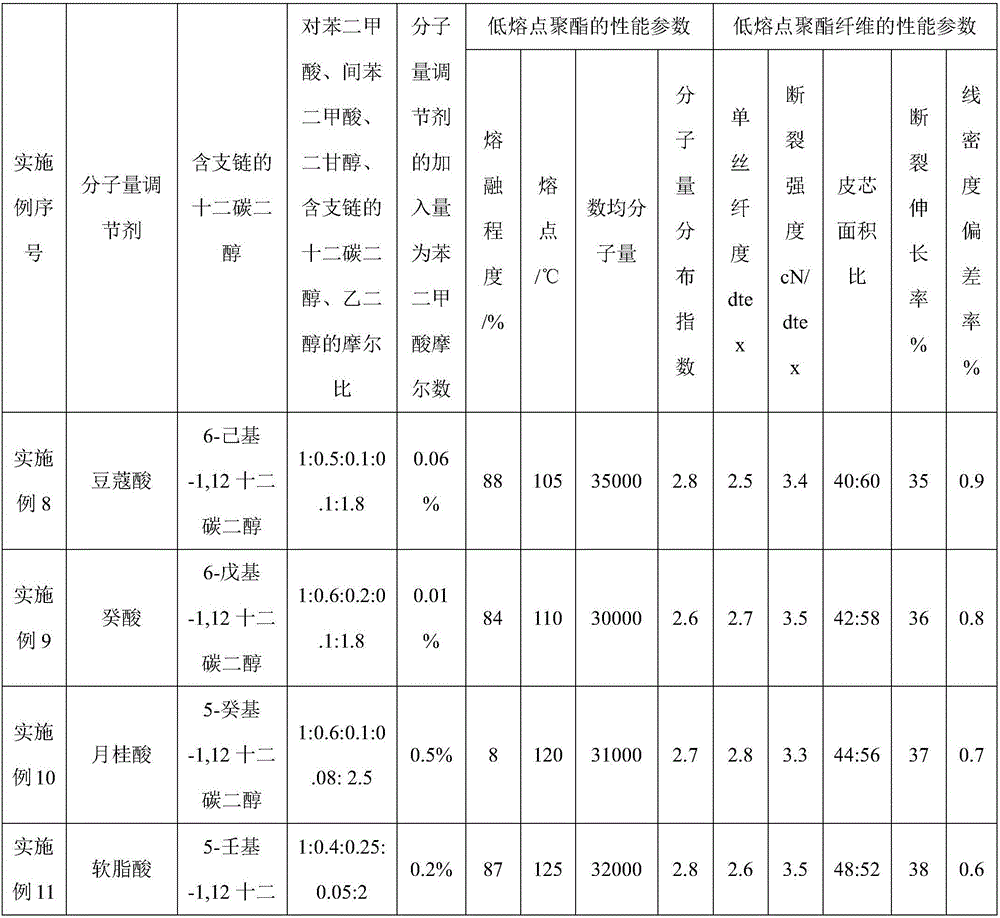
Embodiment 1
[0050] A preparation method of filament low melting point polyester fiber:
[0051] a) low melting point polyester polymerization;
[0052] (1) Esterification reaction;
[0053] After preparing terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid, ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, benzoic acid and 2-pentyl-1,12 dodecanediol into slurry, carry out esterification reaction, under nitrogen atmosphere Pressurized reaction, the pressurized pressure is normal pressure, the temperature is 230 ° C, when the distilled amount of water in the esterification reaction reaches more than 90% of the theoretical value, it is the end point of the esterification reaction, and the esterification product is obtained; wherein, p-benzene The molar ratio of dicarboxylic acid, isophthalic acid, diethylene glycol, branched dodecyl glycol, and ethylene glycol is 1:0.4:0.1:0.05:1.8; the amount of benzoic acid added is the number of moles of phthalic acid 0.01%.
[0054] (2) polycondensation reaction;
[0055] Then, ...
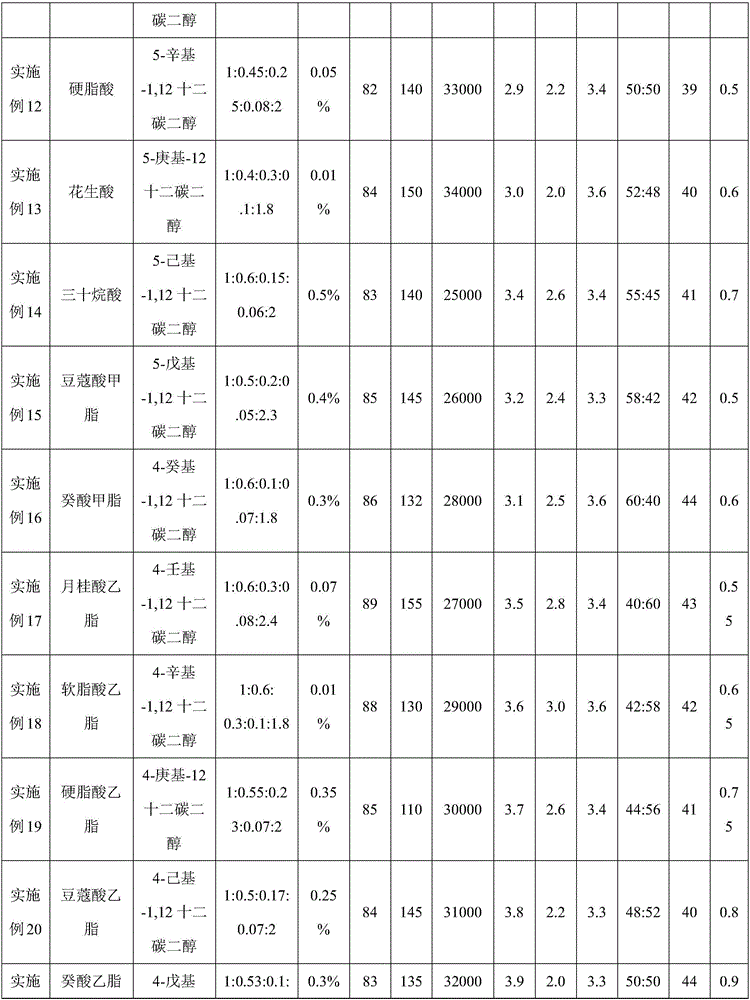
Embodiment 2
[0068] A preparation method of filament low melting point polyester fiber:
[0069] a) low melting point polyester polymerization;
[0070] (1) Esterification reaction;
[0071] After preparing terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid, ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, p-toluic acid and 2-hexyl-1,12 dodecanediol into a slurry, carry out esterification reaction, in nitrogen Pressurized reaction under the atmosphere, the pressurized pressure is 0.3MPa, the temperature is 250 ° C, when the distilled amount of water in the esterification reaction reaches more than 90% of the theoretical value, it is the end point of the esterification reaction, and the esterification product is obtained; wherein, The molar ratio of terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid, diethylene glycol, 2-hexyl-1,12 dodecanediol, and ethylene glycol is 1:0.6:0.3:0.1:2.5; p-toluic acid The addition amount is 0.5% of the moles of phthalic acid.
[0072] (2) polycondensation reaction;
[0073] Then, under the action...
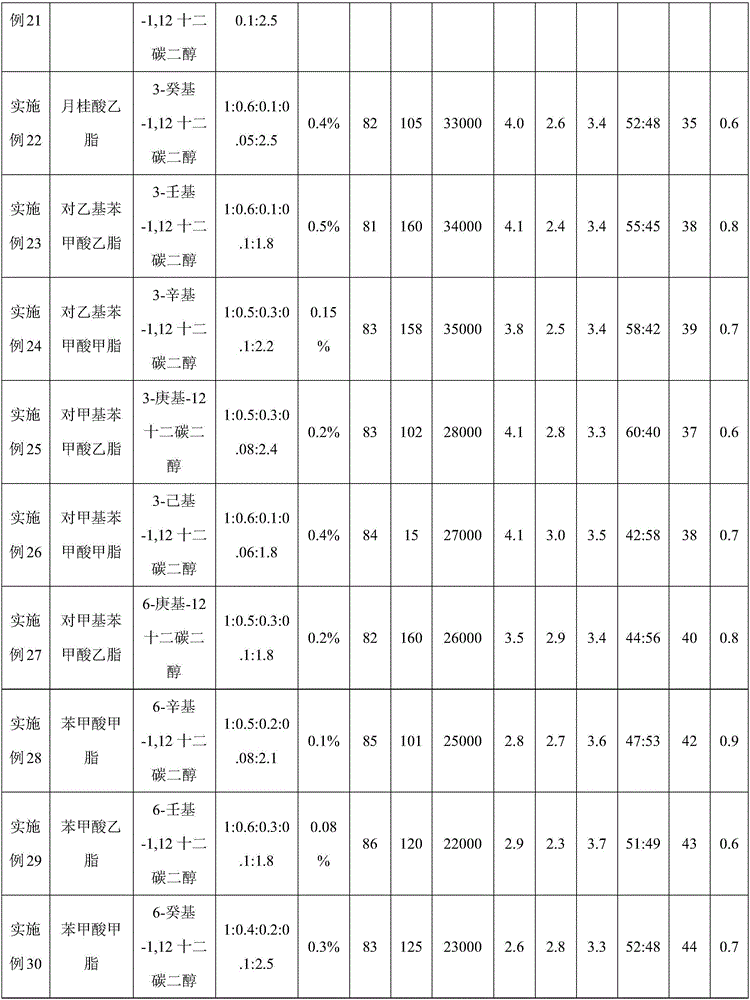
Embodiment 3
[0086] A preparation method of filament low melting point polyester fiber:
[0087] a) low melting point polyester polymerization;
[0088] (1) Esterification reaction;
[0089] After preparing terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid, ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, p-ethylbenzoic acid and 2-heptyl-12 dodecanediol into a slurry, carry out esterification reaction, in a nitrogen atmosphere Under pressurized reaction, the pressurized pressure is 0.1MPa, and the temperature is 240°C. When the distilled amount of water in the esterification reaction reaches more than 90% of the theoretical value, it is the end point of the esterification reaction, and the esterification product is obtained; wherein, for The molar ratio of phthalic acid, isophthalic acid, diethylene glycol, 2-heptyl-12 dodecanediol, and ethylene glycol is 1:0.5:0.2:0.07:2; the amount of p-ethylbenzoic acid added 0.1% of the moles of phthalic acid.
[0090] (2) polycondensation reaction;
[0091] Then, under the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com