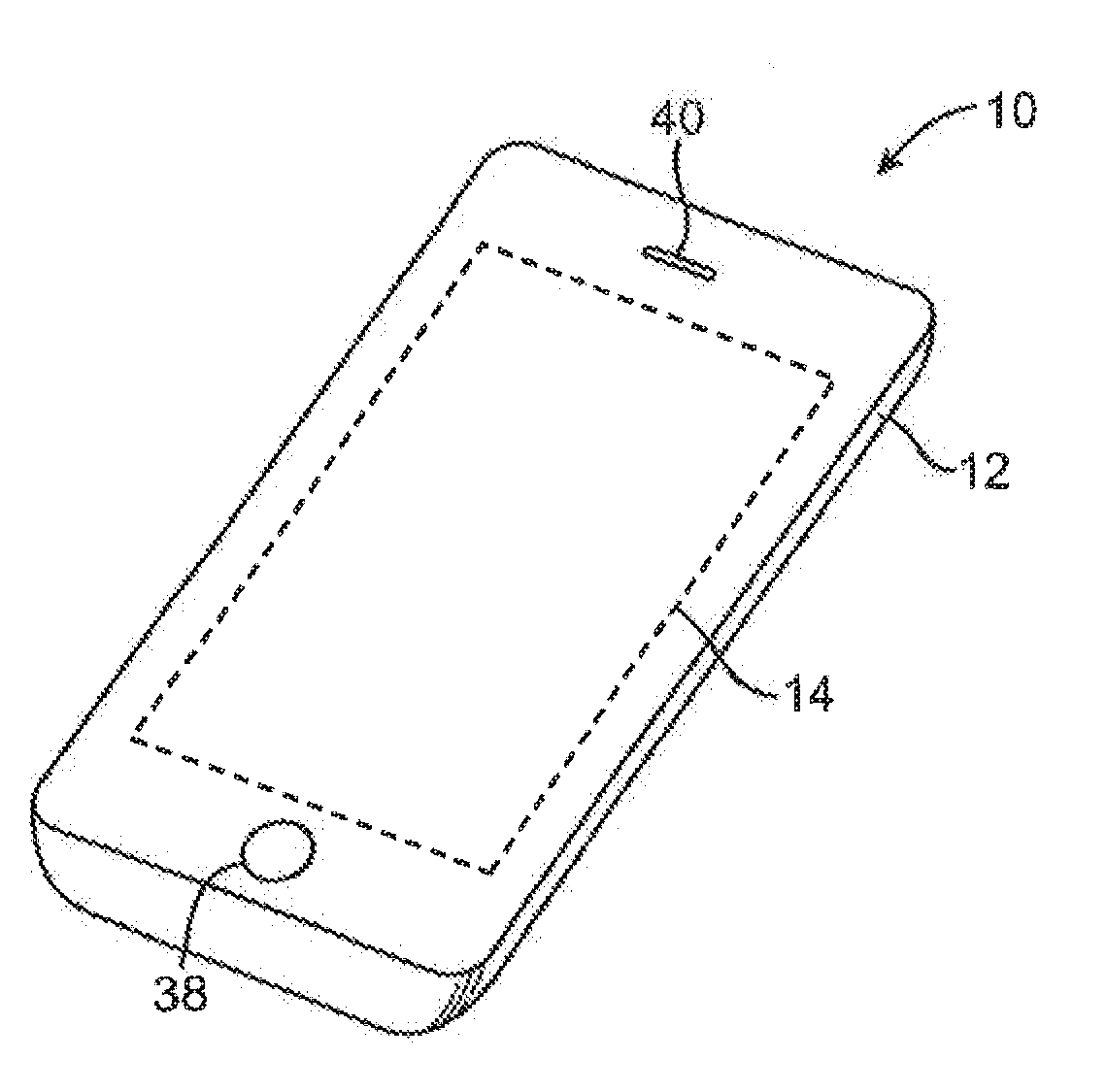
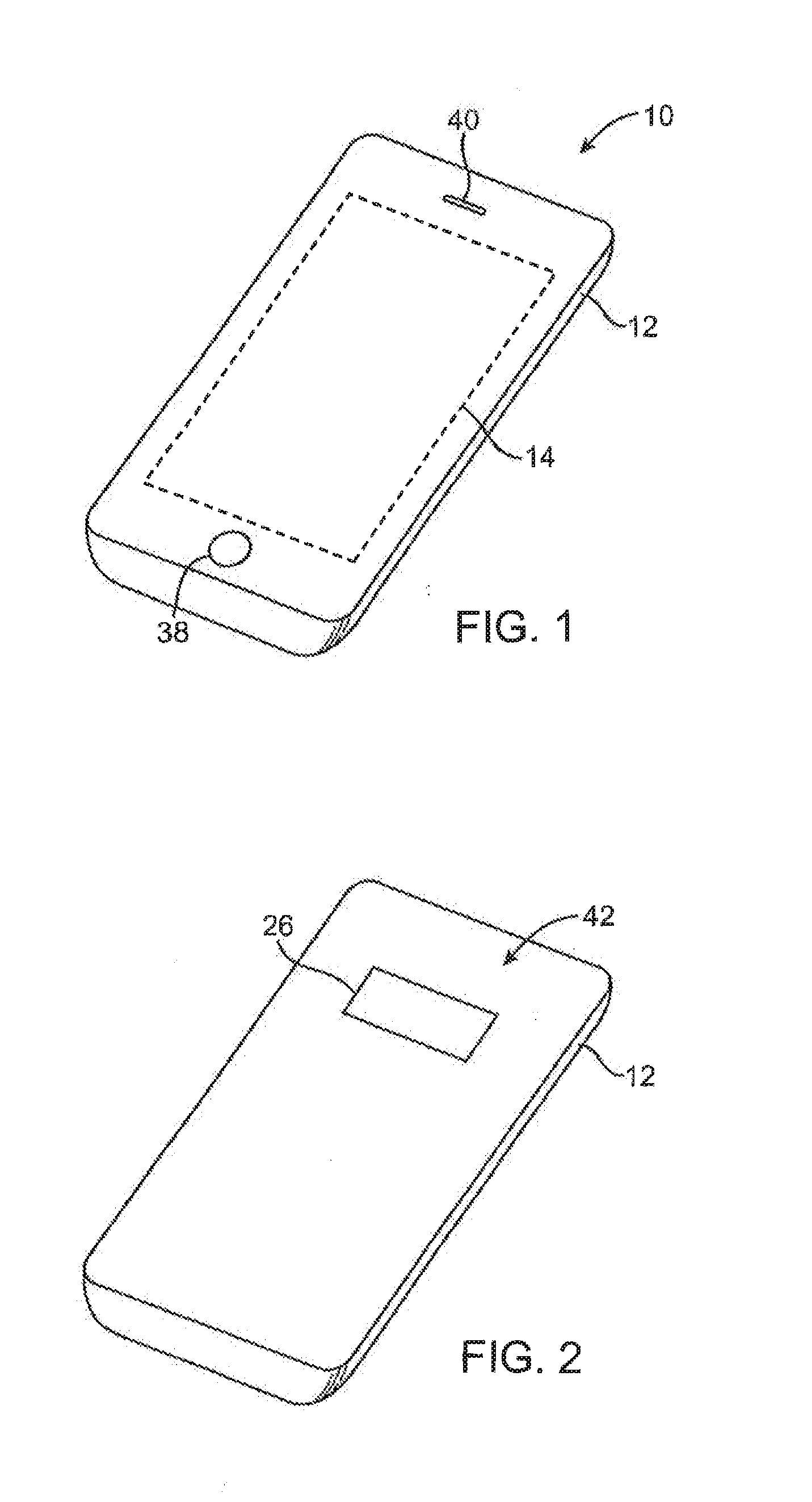
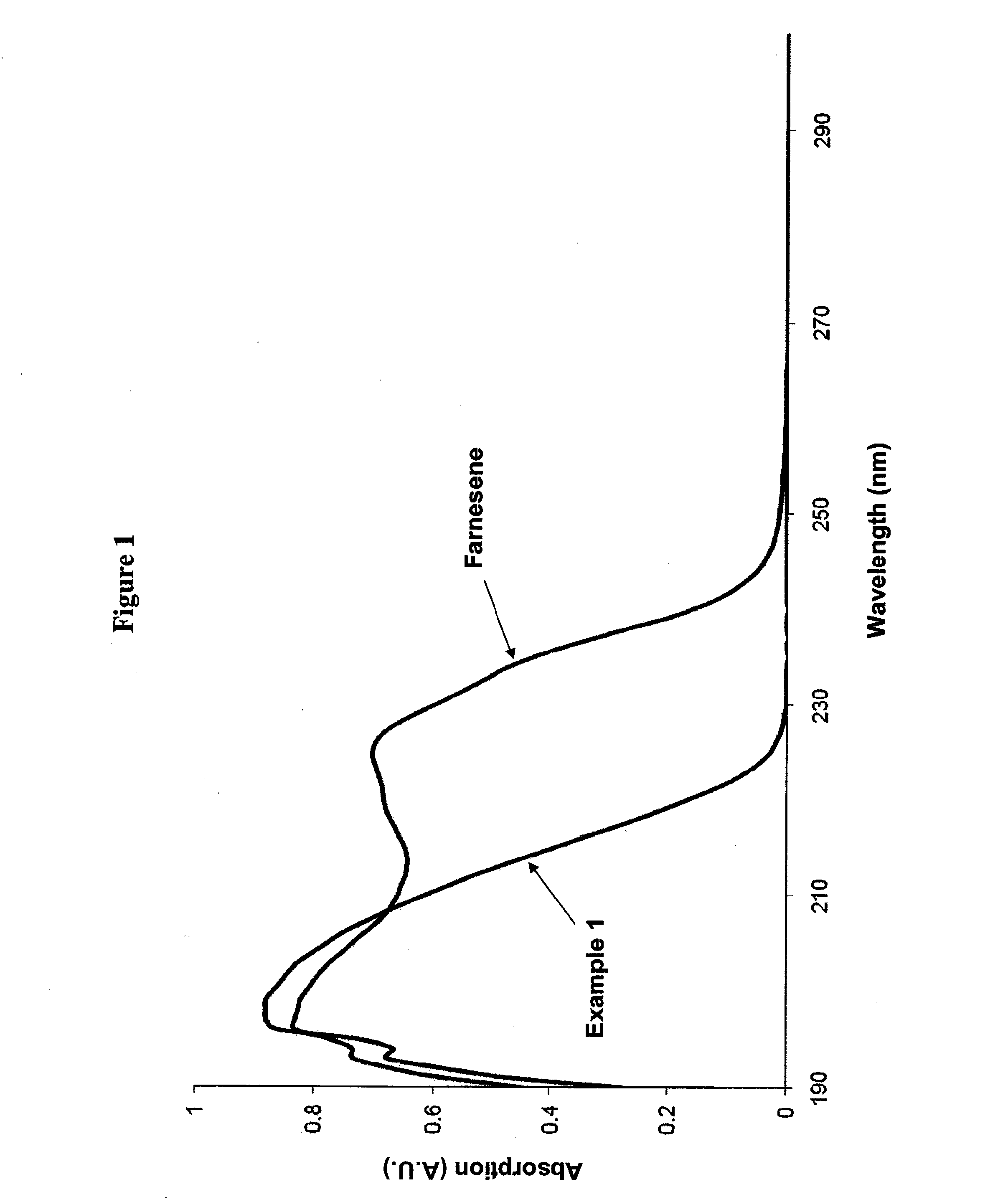
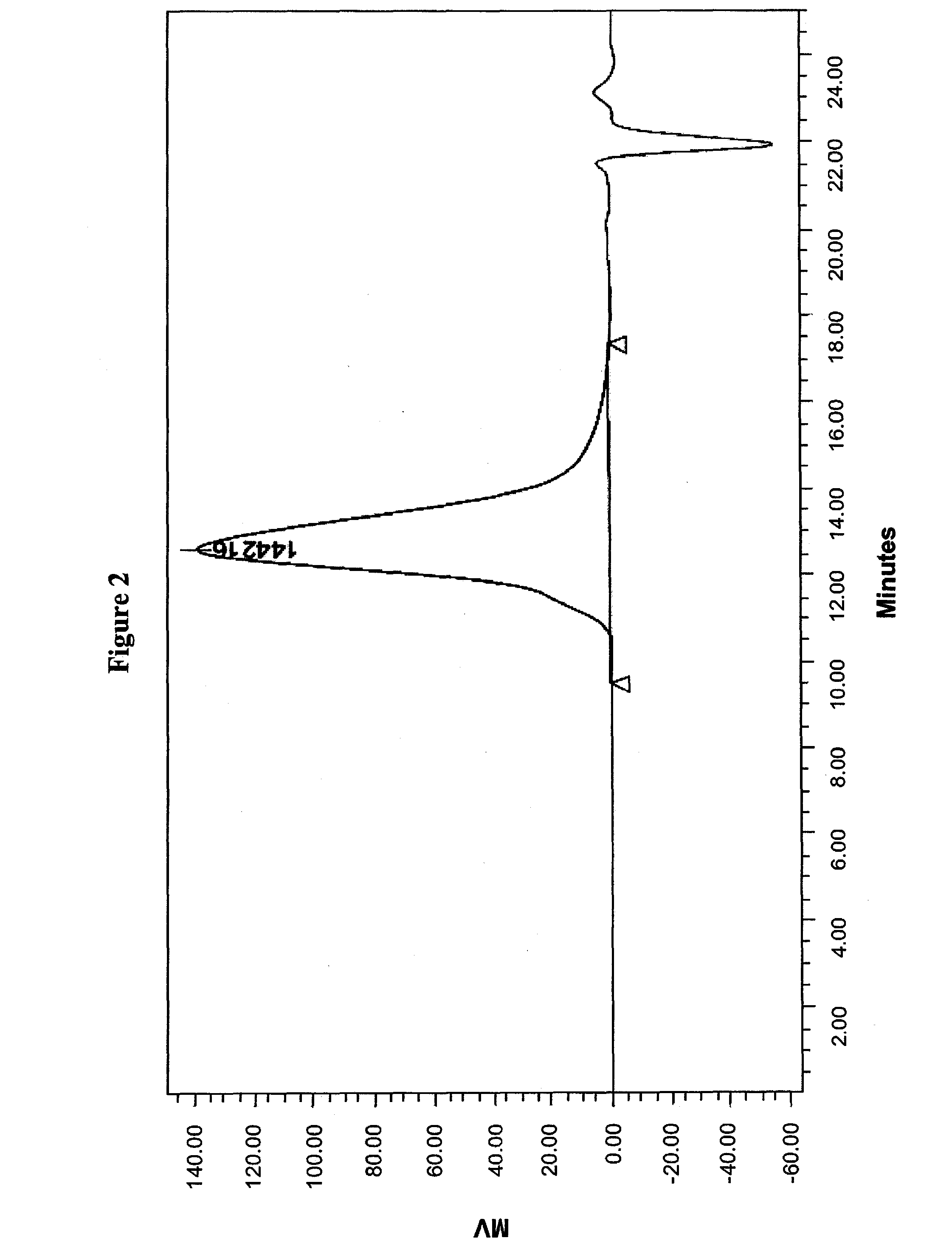
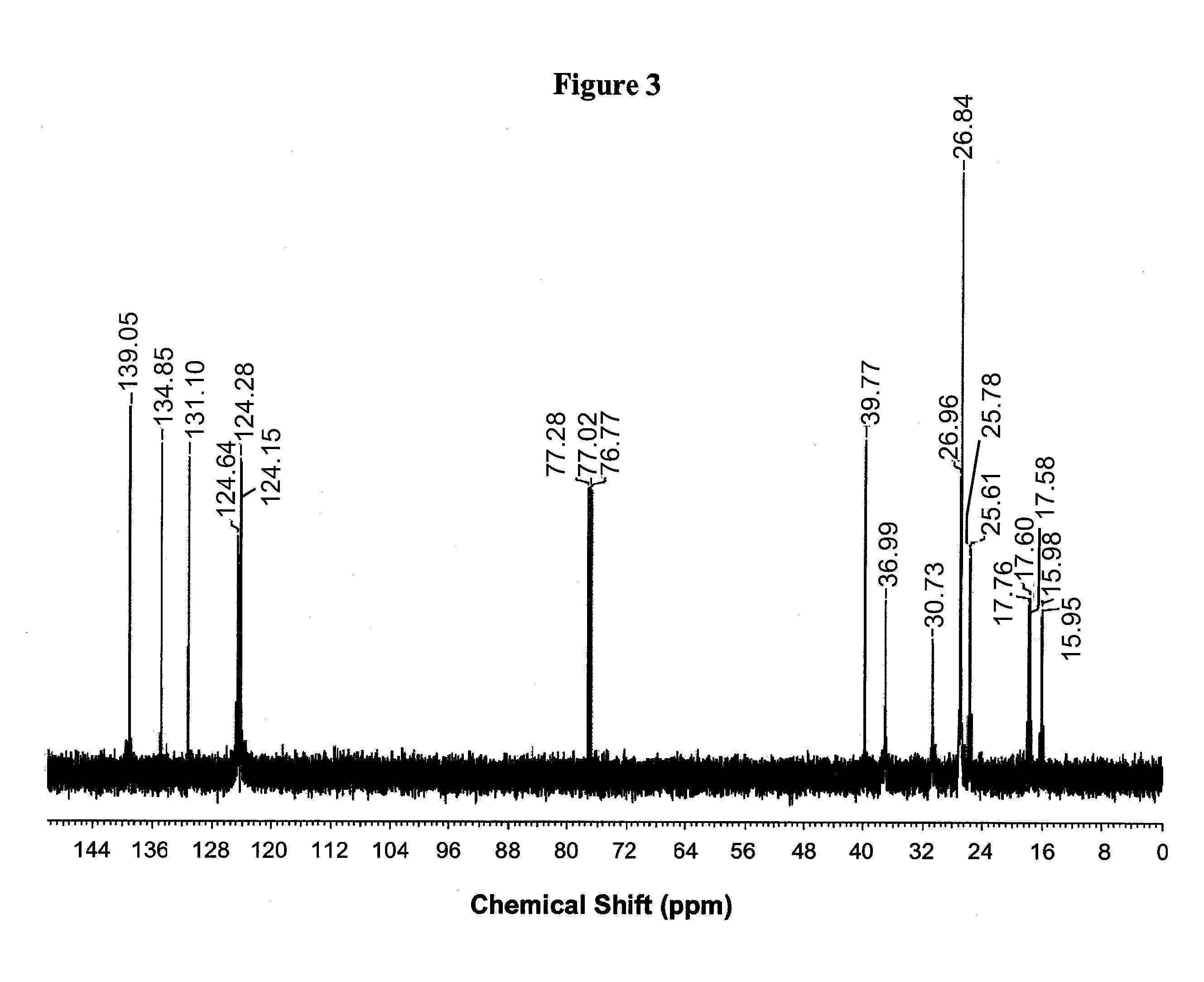
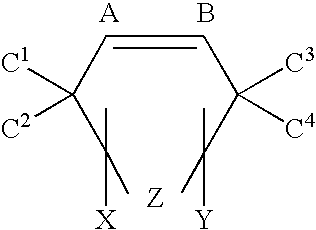
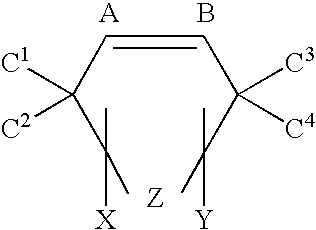
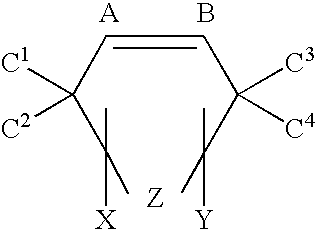
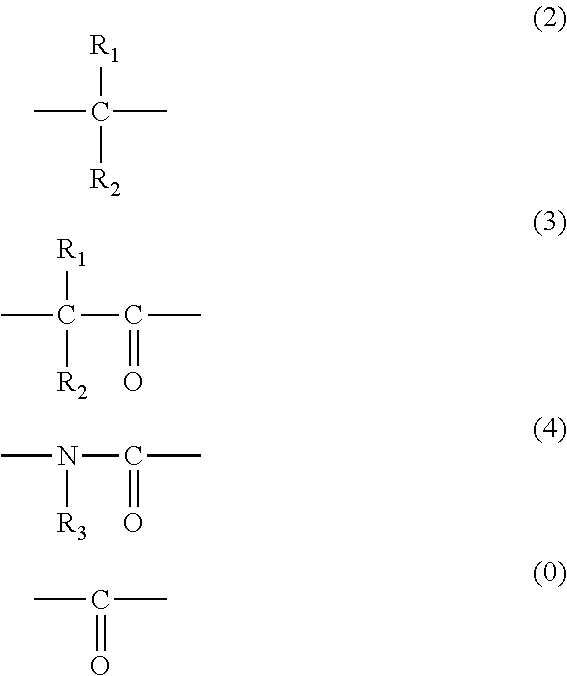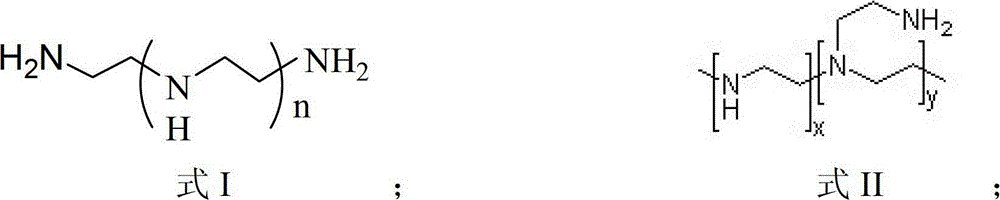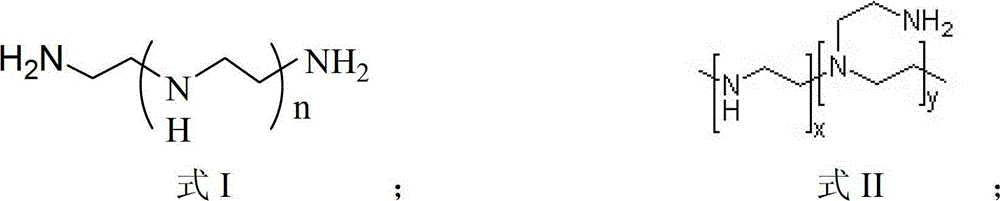Patents
Literature
309 results about "Condensation polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Condensation polymers are any kind of polymers formed through a condensation reaction—where molecules join together—losing small molecules as byproducts such as water or methanol. Condensation polymers are formed by polycondensation, when the polymer is formed by condensation reactions between species of all degrees of polymerization, or by condensative chain polymerization, when the polymer is formed by sequential addition (by condensation reaction) of monomers to an active site in a chain reaction. The main alternative forms of polymerization are chain polymerization and polyaddition, both of which give addition polymers.
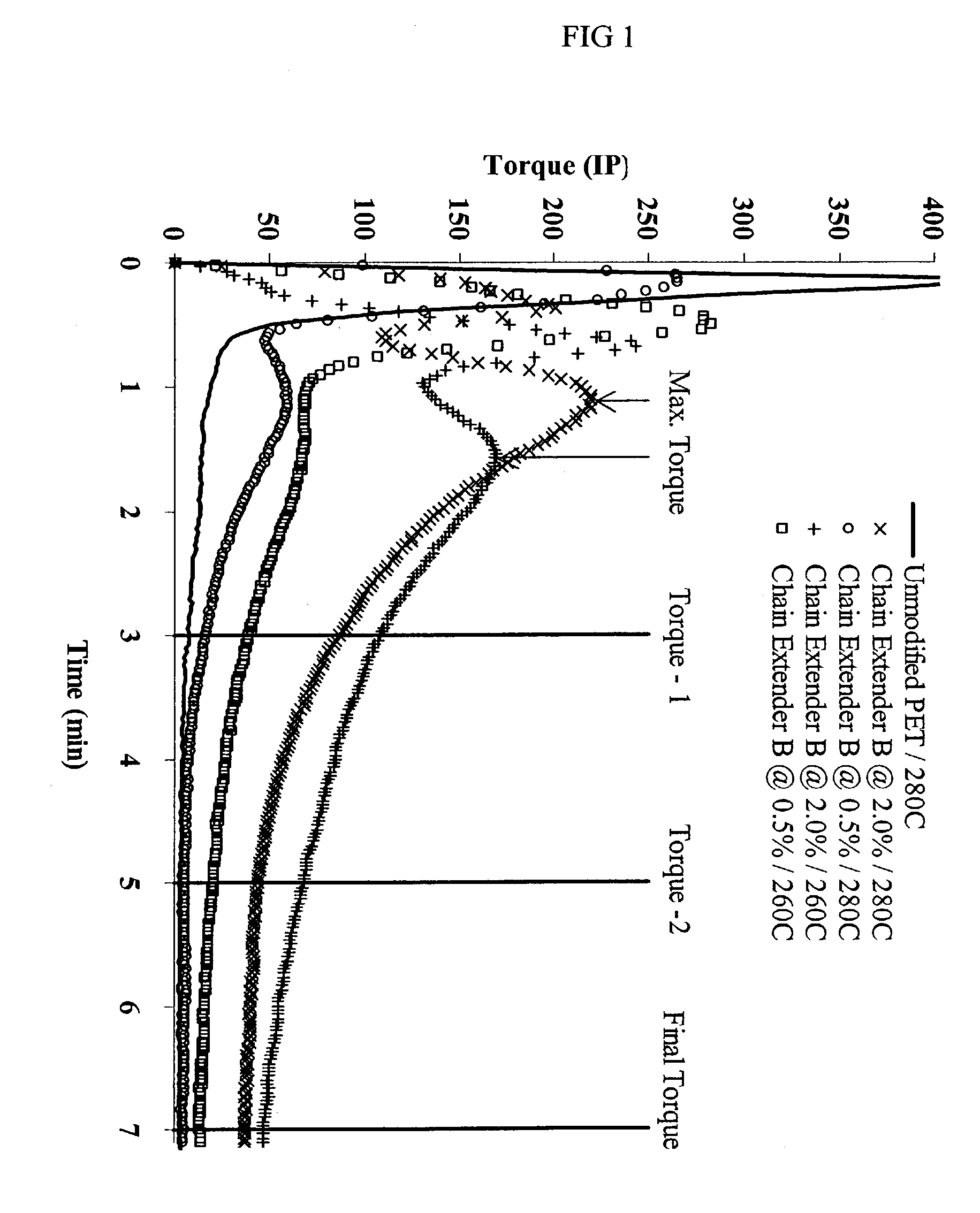
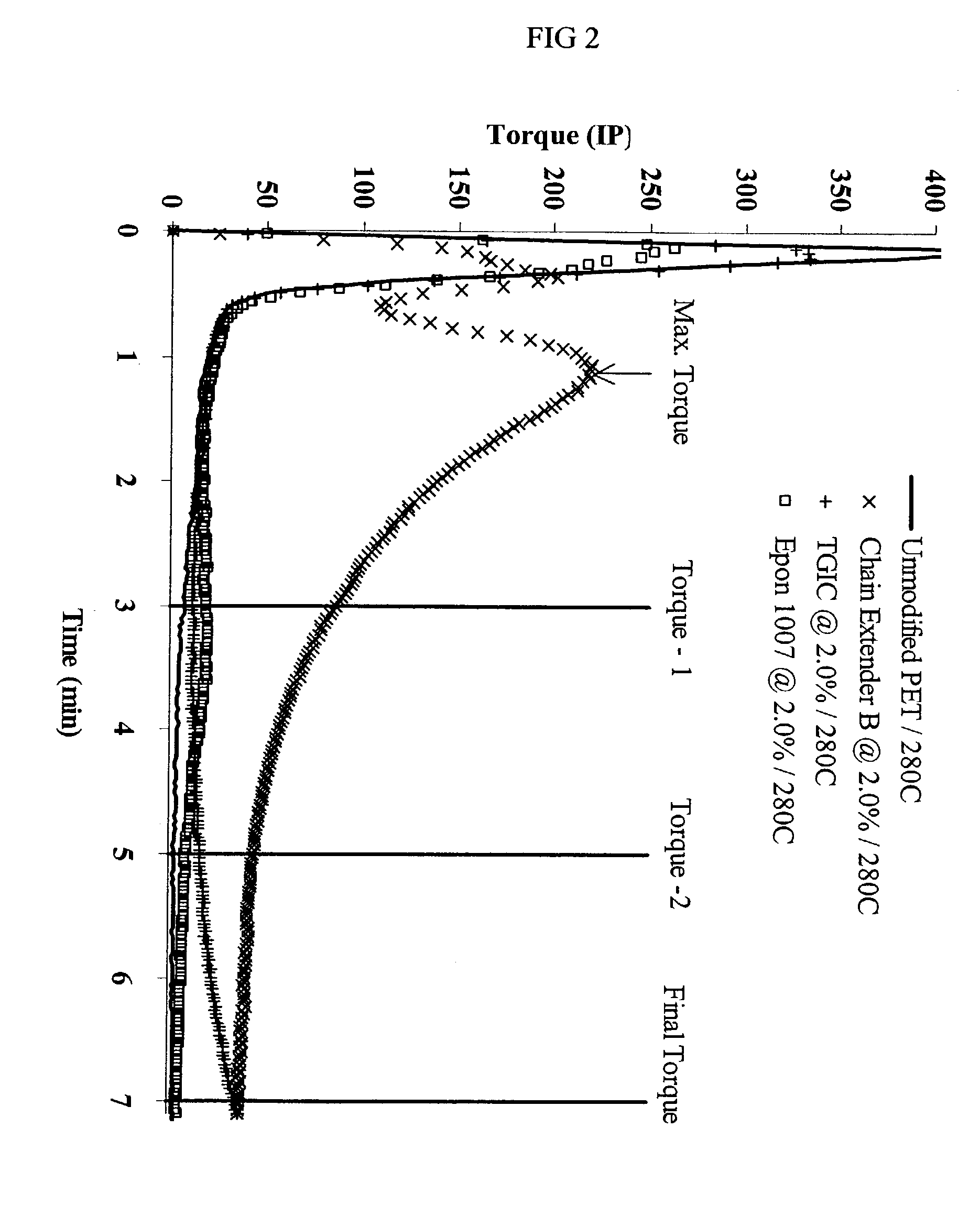
Oligomeric chain extenders for processing, post-processing and recycling of condensation polymers, synthesis, compositions and applications
The invention provides chain extenders made from epoxy-functional (meth)acrylic monomers and styrenic and / or (meth)acrylic monomers. The invention further provides polymeric compositions made from the chain extenders and plastic articles made from the compositions. Finally, the invention provides methods of using the chain extenders to improve the properties of virgin, recycled, and reprocessed condensation polymers.
Owner:BASF CORP +1
Process for making an ink jet ink
A process for making an ink jet ink comprising: a) providing a dispersion containing a pigment, a hydrocarbon carrier, and a polyamine / fatty acid condensation polymer dispersant; b) mixing the pigment dispersion with rigid milling media less than 100 mu m; c) introducing the mixture of step (b) into a mill; d) milling the mixture from step (c) until the pigment particle size is below about 100 nanometers (nm); e) adding to the mixture during or after step d) or f) (below) a stabilizer selected from the group consisting of a polyether polyol; a modified polyester resin; an acrylic polymer; an alkylol ammonium salt of a block copolymer having acidic groups; ethoxylated triethanolamine; a high molecular weight block copolymer having an amine functionality; sorbitan sesquioleate; polyhydroxy stearic acid; butylated polyvinyl pyrrolidone; poly(vinylpyrrolidone / 1-hexadecene); and poly(p-tert-butylstyrene-co-styrene-co-2-sulfoethyl-lithium methacrylate); f) separating the milling media from the mixture milled in step (d); and g) diluting the mixture to obtain an ink jet ink having a pigment concentration suitable for ink jet printers.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Oxygen scavenger block copolymers and compositions
InactiveUS7754798B2Well formedEasy to processOther chemical processesConductive materialThermoplasticPolyester
An oxygen scavenger composition includes a block co-polymer having at least one block including a polyester condensation polymer segment having cycloalkenyl group(s) or functionality directly or indirectly bonded to the polymer chain of said block, and having at least one second block including a polymer segment of a thermoplastic, film forming material. The block copolymer has been found to act as an oxygen scavenger agent under both ambient and refrigerated conditions, to be compatible with conventional film forming packaging materials, and to provide compositions exhibiting low tack which can be readily formed and processed using conventional film forming equipment. A packaging material, such as a film or laminated product suitable for packaging applications, can include the oxygen scavenger composition.
Owner:CRYOVAC ILLC
Process for making an ink jet ink
A process for making an ink jet ink comprising: a) providing a dispersion containing a pigment, a hydrocarbon carrier and a polyamine / fatty acid condensation polymer dispersant; b) mixing the pigment dispersion with rigid milling media less than 100 mu m; c) introducing the mixture of step (b) into a mill; d) milling the mixture from step (c) until the pigment particle size is below about 100 nanometers; e) separating the milling media from the mixture milled in step (d); and f) diluting the mixture from step (e) to obtain an ink jet ink having a pigment concentration suitable for ink jet printers.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Coated ion exchanged substrate and method of forming
ActiveUS7291395B2Promote formationEasy to synthesizeChromatographic cation exchangersLiquid surface applicatorsIon exchangeAminal
A method for making an ion exchange coating (e.g., a chromatographic medium) on a substrate comprising (a) reacting at least a first amine compound comprising amino groups, with at least a first polyfunctional compound, in the presence of a substrate to form a first condensation polymer reaction product, with a first unreacted excess of either at least said first amino group or polyfunctional compound functional moieties, irreversibly attached to the substrate, and (b) reacting at least a second amine compound or at least a second polyfunctional compound with unreacted excess in the first condensation polymer reaction product to form a second condensation polymer reaction product, and repeating the steps to produce the desired coating. A coated ion exchange substrate so made.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
Resist underlayer film-forming composition for EUV lithography containing condensation polymer
ActiveUS20140170567A1Reduce adverse effectsGood, straight-shaped resist patternSynthetic resin layered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistPolymer science
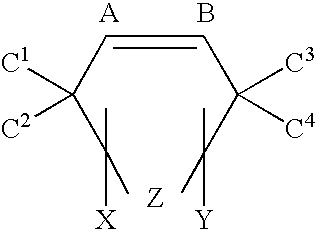
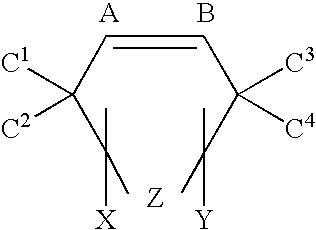
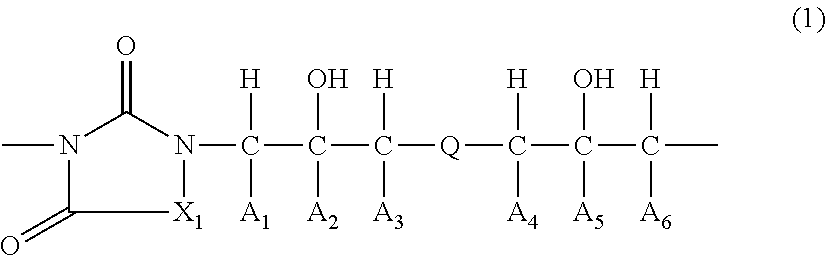
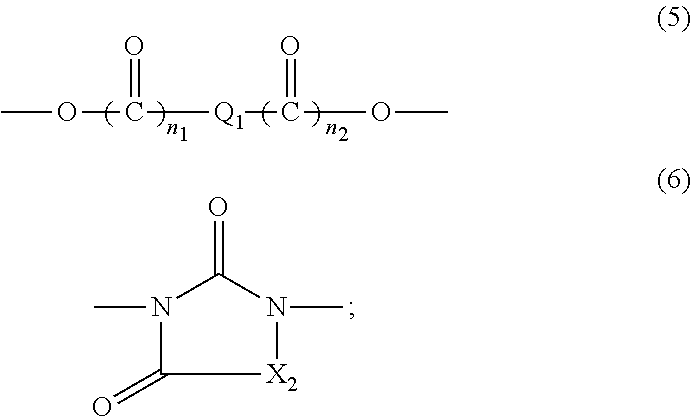
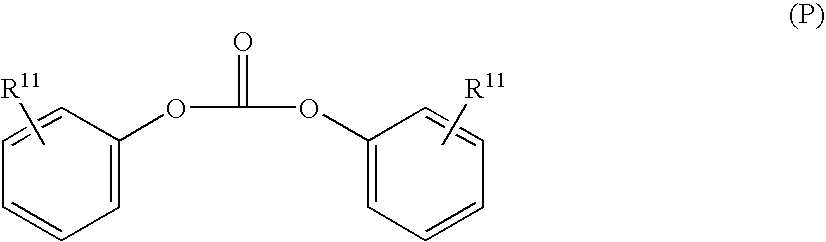
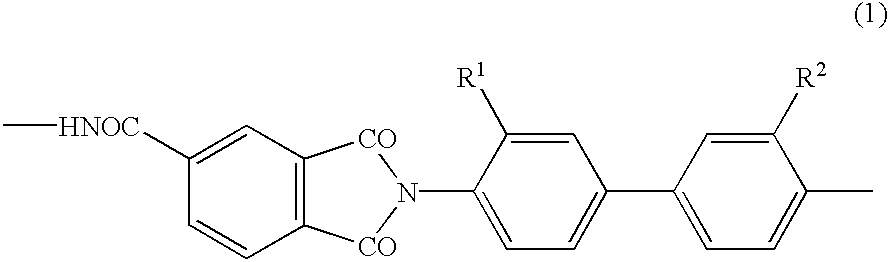
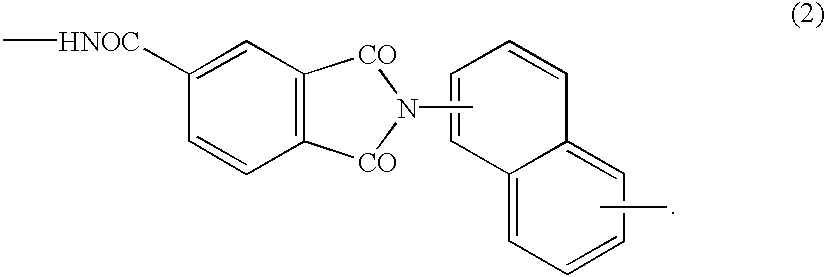
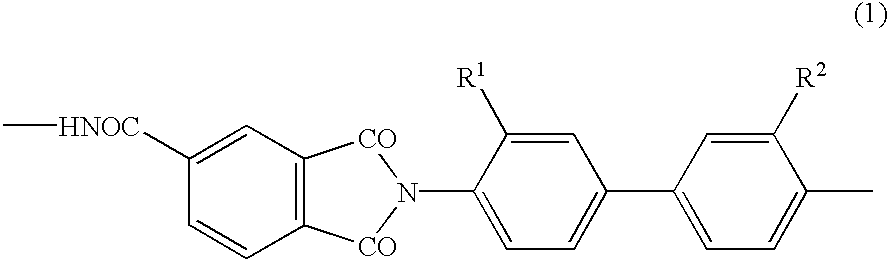
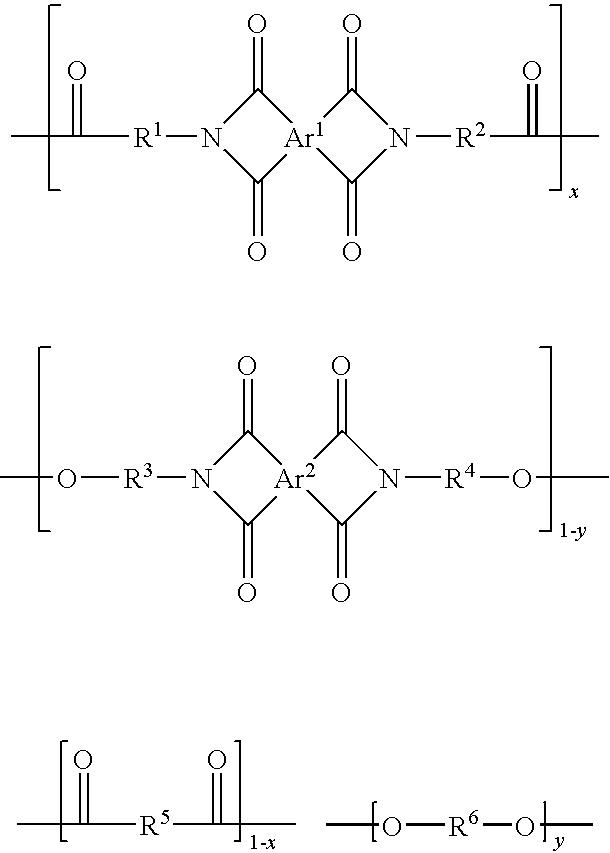
There is provided a resist underlayer film composition for EUV lithography that is used in a device production process using EUV lithography, reduces adverse effects of EUV, and is effective for obtaining a good resist pattern, and to a method for forming a resist pattern that uses the resist underlayer film composition for EUV lithography. A resist underlayer film-forming composition for EUV lithography, including: a polymer having a repeating unit structure of formula (1):[where each of A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, and A6 is a hydrogen atom, a methyl group, or an ethyl group; X1 is formula (2), formula (3), formula (4), or formula (0):Q is formula (5) or formula (6):and a solvent. A resist underlayer film-forming composition for EUV lithography, comprising: the polymer having the repeating unit structure of formula (1); a crosslinkable compound; and a solvent.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Anti-microbial agent delivery system
A delivery system for delivering an anti-microbial agent to a surface in a time release manner. The delivery system includes one or more polymeric particles (e.g., microspheres, core / shell particles, latexes, porogens, cryogenically ground beads, condensation polymer particles, flakes, etc.) and at least anti-microbial agent attached thereto. The anti-microbial agents may or may not be soluble in the polymeric particle or in the monomeric precursor used to make the polymeric particle. The anti-microbial agent can be incorporated into the microsphere using either a post polymerization addition process or an in situ addition process. The delivery system can be fashioned to provide characteristics that are application specific. Examples of such delivery systems include but are not limited to substrates (such as tapes, sheets of material and the like) coated with the releasably loaded polymeric particles, sprayable dispersions or suspensions of these polymeric particles and the like.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Polymer manufacturing process
InactiveUS7157139B2High molecular weightNew technologyLayered productsAnimal housingPolymer scienceAlcohol
A process utilizing PET as a reactive constituent to manufacture other polymers containing the pre-condensed moieties by the rapid transesterification of the condensation polymer with a pre-made modifying polymer containing the desired mix of other monomers. The process involves as a first step the manufacture of a modifying polymer containing the desired mix of acids and alcohols to a specific molecular weight such molecular weight dependent on the desired final level of utilized condensation polymer and the finished molecular weight. The second step of the process involves the rapid buildup of molecular weight and / or polymer uniformity by the rapid transesterification of the condensation polymer with the modifying polymer. The second step can be performed in any suitable vessel including an extrusion line. The process has the advantage of greatly reduced cycle times over other condensation polymer utilization processes such as the recycling of PET into other materials.
Owner:LIGHTHOUSE INT TECH EXCHANGE
Water paint
ActiveCN102757710AFull play hardStrong hardnessAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesEmulsionHardness
The invention discloses water paint. The water paint comprises following components in parts by weight: 70-150 parts of white cement, 5-15 parts of titanium dioxide, 30-70 parts of an urushiol-based emulsifier and 70-110 parts of urushiol formaldehyde condensation polymer emulsion. The water paint, disclosed by the invention, is added with raw lacquer, so that the advantages of the hard, bright, wear-resisting, heat-resisting and corrosion-resisting film formed by the raw lacquer are brought into full play; as the urushiol-based emulsifier is added in a matching manner to emulsify the raw lacquer, so that good compatibility of the raw lacquer can be guaranteed and formation of a compact and rigid interfacial film is facilitated; and as the urushiol-based emulsifier can participate in a film-forming reaction of the raw lacquer, adverse influences from a traditional emulsifier to film coating performances are avoided, and extremely strong hardness is obtained.
Owner:ANHUI JINDUN PAINT
Coated ion exchange substrate and method of forming
ActiveUS20050181224A1Promote formationEasy to synthesizeChromatographic cation exchangersLiquid surface applicatorsPolymer scienceIon exchange
A method for making an ion exchange coating (e.g., a chromatographic medium) on a substrate comprising (a) reacting at least a first amine compound comprising amino groups, with at least a first polyfunctional compound, in the presence of a substrate to form a first condensation polymer reaction product, with a first unreacted excess of either at least said first amino group or polyfunctional compound functional moieties, irreversibly attached to the substrate, and (b) reacting at least a second amine compound or at least a second polyfunctional compound with unreacted excess in the first condensation polymer reaction product to form a second condensation polymer reaction product, and repeating the steps to produce the desired coating. A coated ion exchange substrate so made.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
Carbon nanotube coated with aromatic condensation polymer
InactiveUS20060051579A1Sufficiently dispersedGood dispersibilityMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsPolyesterPolyamide
Coated carbon nanotubes coated with 0.01-100 parts by weight of at least one type of aromatic condensation polymer selected from the group consisting of wholly aromatic polyamides, wholly aromatic polyesters, aromatic polyester carbonates, aromatic polycarbonates, semi-aromatic polyesters and wholly aromatic azoles, with respect to 100 parts by weight of the carbon nanotubes, as well as a process for their production. Aromatic condensation polymer compositions comprising 0.01-100 parts by weight of the coated carbon nanotubes and 100 parts by weight of an aromatic condensation polymer, and molded articles formed using them.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Polymer Manufacturing Process
Embodiments relate to a relatively rapid transesterification process including transesterifying condensation polymers such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), or other polyesters used in commerce, with a modifying monomer mix containing other monomers to manufacture new polymers containing the pre-condensed moieties. The process preferably only involves transesterification as a reaction mechanism. The process preferably produces a rapid buildup of molecular weight and / or polymer uniformity by the high temperature transesterification of the condensation polymer with the modifying monomer mixture. The process can be performed in any suitable vessel including an extrusion line, and it has the advantage of greatly reduced cycle times over currently used condensation polymer utilization processes such as the recycling of PET into other materials.
Owner:ENGINEERED FLOORS LLC
Carbonaceous electrode material for secondary battery
InactiveUS6569570B2Efficient use ofLarge capacityConductive materialCarbon preparation/purificationX-rayPhotochemistry
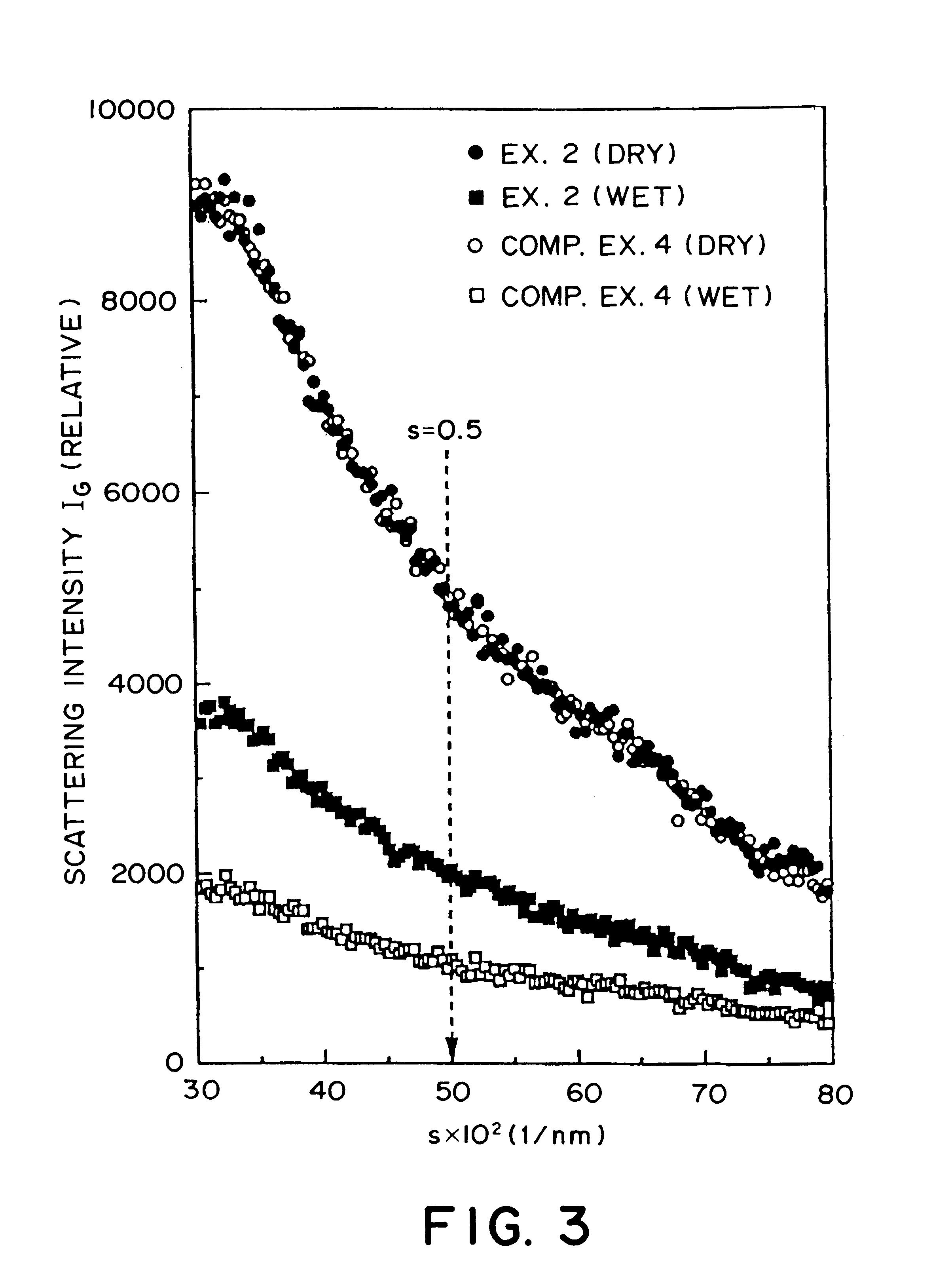
A carbonaceous electrode having improved capacities for doping and dedoping of a cell active substance, such as lithium, and suitable for a non-aqueous secondary battery, is constituted by a carbonaceous material obtained by carbonizing an aromatic condensation polymer formed by condensation of an aromatic compound having a phenolic hydroxy group and an aldehyde. The carbonaceous material is characterized by an atomic ratio H / C between hydrogen atoms and carbon atoms of below 0.1, a carbon dioxide adsorption capacity of at least 10 ml / g, and an X-ray scattering intensity ratio IW / ID of at least 0.25, wherein IW and ID represent scattering intensities as measured in a wet state and a dry state, respectively, at a parameter s=2.sin theta / lambd of 0.5 nm-1, wherein theta denotes a scattering angle and lambd denotes a wavelength of X-rays in X-ray small-angle scattering measurement.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Flexible metal-clad laminate and process for preparing the same
InactiveUS20020160211A1Improve featuresSolve low adhesionInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementPretreated surfacesPolymer scienceMetal foil
Disclosed are a flexible metal-clad laminate comprising a metal foil and a heat-resistant resin film layer formed on one side of the metal foil, the heat-resistant resin film layer comprising a crosslinked condensation polymer and having an N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone-insolule content of at least 1%, and a method for producing the flexible metal-clad laminate comprising the steps of applying a heat-resistant resin solution to a metal foil; predrying the metal foil until the heat-resistant resin layer has an residual solvent content of 10 to 40% by weight; and carrying out solvent removal and heat-treatment while controlling the crosslinking reaction of the resin.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Polymeric additives to improve print quality and permanence attributes in ink-jet inks
One-part and two-part fixatives are provided in conjunction with underprinting or overcoating at least one ink printed on a print medium. The one-part fixative of the present invention comprises a polymer in a vehicle. The polymer is selected from the group consisting of vinyl-based polymers, condensation polymers, and copolymers thereof and the polymer has a glass transition temperature within a range of -50° C. to +100° C., a melting temperature within a range of 30° C. to 150° C., and a molecular weight (weight average basis) within a range of 3,000 to 100,000. The fixative is contained in a separate cartridge from the ink-jet ink print cartridge(s). The two-part fixative of the present invention comprises (1) a reactive monomer or oligomer in a vehicle, the reactive monomer or oligomer selected from the group consisting of iso-cyanates and epoxy-terminated oligomers, and (2) at least one second component selected from the group consisting of polyols, polyvinyl alcohols, and base catalysts. The reactive monomer or oligomer is contained in a separate cartridge from the ink-jet ink print cartridge(s), while the second component(s) is contained in at least one ink-jet ink print cartridge. The reactive monomer or oligomer reacts with the second component(s) on the print medium to form a polymer, which has a glass transition temperature within a range of -20° C. to +50° C. and a melting temperature within a range of 30° C. to 100° C. Enhancement of waterfastness, smearfastness, smudgefastness, and lightfastness is provided by use of the fixative solution of the present invention.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Electrostatically bound hyperbranched anion exchange surface coating prepared via condensation polymerization using ditertiary amine linkers for improved divalent anion selectivity
ActiveUS20120231195A1Easy to separatePoor peak shapeChromatographic cation exchangersIon-exchanger regenerationIon chromatographyIon exchange
The present invention provides a new design for high capacity stationary phases for dianion selective ion chromatography. The stationary phases include one or more layers which are products of condensation polymerization. Multiple components are of use in forming the first polymer layer and the condensation polymer structure, thereby providing a stationary phase that can be engineered to have a desired property such as ion capacity, ion selectivity, and the like. Exemplary condensation polymers are formed by the reaction of at least one polyfunctional compound with at least one compound of complimentary reactivity, e.g., a nucleophilic polyfunctional compound reacting with an electrophilic compound.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
Polyarylene Sulfide Composition for Use in Forming a Laser Direct Structured Substrate
InactiveUS20150175805A1Synthetic resin layered productsRadiating elements structural formsPolymer scienceBiological activation
A polymer composition formed from a polyarylene sulfide matrix that constitutes a majority of the polymer content of the composition is provided. Although polyarylene sulfides are not typically capable of laser activation, particularly at such a high content of the polymer composition, the present inventor has nevertheless discovered that the resulting composition can still be readily activated with one or more conductive elements using a laser direct structuring process. This is accomplished, in part, by dispersing a combination of a condensation polymer and laser activatable additive within the polyarylene sulfide matrix.
Owner:TICONA LLC
Graft copolymers of polyfarnesenes with condensation polymers
Provided herein are graft copolymers of polyfarnesenes with condensation polymers; and methods of making and using the graft copolymers disclosed herein. The graft copolymers are obtained from the reaction of a polycondensation polymer with a modified polyfarnesene obtained from reaction of a polyfarnesene with a modifier in the presence of a grafting initiator. In certain embodiments, the condensation polymers include polyesters, polycarbonates, polyamides, polyethers, phenol-formaldehyde resins, urea-formaldehyde resins, melamine-formaldehyde resins and combinations thereof. In some embodiments, the polyfarnesenes include farnesene homopolymers derived from a farnesene, and farnesene interpolymers derived from a farnesene and at least a vinyl monomer. In certain embodiments, the farnesene is prepared from a sugar by using a microorganism.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Method for preparing an ink jet recording element
InactiveUS6020032AHigh glossImprove image qualityLiquid surface applicatorsDuplicating/marking methodsWater dispersiblePolymer chemistry
A method for making an ink jet recording element comprising simultaneously coating on a support the following layers in order: a) a nonionic, water-dispersible, condensation polymer gloss-enhancing layer; and b) an ink receptive layer for an ink jet image.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Oxygen scavenger block copolymers and compositions
InactiveUS20050048287A1Well formedEasy to processOther chemical processesSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterThermoplastic
An oxygen scavenger composition includes a block co-polymer having at least one block including a polyester condensation polymer segment having cycloalkenyl group(s) or functionality directly or indirectly bonded to the polymer chain of said block, and having at least one second block including a polymer segment of a thermoplastic, film forming material. The block copolymer has been found to act as an oxygen scavenger agent under both ambient and refrigerated conditions, to be compatible with conventional film forming packaging materials, and to provide compositions exhibiting low tack which can be readily formed and processed using conventional film forming equipment. A packaging material, such as a film or laminated product suitable for packaging applications, can include the oxygen scavenger composition.
Owner:CRYOVAC INC
Lithium-ion membrane and the application thereof
InactiveCN101567434AOvercoming the disadvantages of poor securityImprove securitySecondary cellsCell component detailsCombustionOperability
The invention belongs to the field of battery technology, in particular to a lithium-ion battery membrane and the application thereof. The membrane uses polymer as a matrix and comprises uniformly dispersed and flame-resistant inorganic filler, wherein the polymer is a freeradical polymer or a linear condensation polymer, the inorganic filler is alumina, zirconia, silicon oxide and the like. The membrane has good safety performance and high mechanical strength and can prevent gas bulging, combustion and explosion. Compared with other methods, the invention has strong operability, lower cost, good reproducibility, and stable quality and high volume, capacity and density of obtained products, and can be used for lithium-ion batteries.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method of preparing unsaturated polyester resin
The invention discloses a making method of unsaturated polyester resin, which comprises the following steps: 1. preparing dibasic acid and dibasic alcohol with molar rate at 1: (1-1. 2); setting the molar rate of saturated dibasic acid and unsaturated dibasic acid at 1: (0. 5-2. 0); 2. adding the prepared dibasic acid and dibasic alcohol into the reactor to fuse and polymerize; obtaining the condensation polymer; controlling the reacting condition at 170-215 deg. c; making the viscosity of composition in the liquid at 0. 45Pa.s-1. 1Pa.s, acid value at 12-30; stopping reacting; 3. adding phenylethene in the composition; stirring evenly as the product.
Owner:CHANGZHOU TIANMA GROUP CO LTD
Agglomerated ion exchange particle bed and method
ActiveUS20070062854A1Chromatographic cation exchangersIon-exchanger regenerationIon exchangeChromatography column
A liquid chromatography agglomerated bed comprising component A comprising (a) substrate particles and polymer chains (e.g. a condensation polymer) bound to the substrate particles and projecting therefrom, and (b) component B comprising substrate particles having external surfaces of opposite charge to that of the charged polymer chains, components A and B being bound at least in part by electrostatic forces between the component A charged polymer chains and the component B external surfaces to form in composite an agglomerated bed of ion exchange particles packed in a chromatography column.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
Condensation polymerization method for preparing hydroxylated acid condensation polymer
The invention provides a condensation polymerization process for preparing hydroxylated acid condensation polymer, characterized in that hydroxylated acid or hydroxylated acid oligomer are subject to molten condensation polymerization reaction or molten / solid phase condensation polymerization reaction at the presence of ionic liquid catalytic action. The obtained hydroxylated acid condensation polymer contains no metallic elements.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bio-based water-soluble polymer solution, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102911356AMild reaction conditionsShorten the timeProtein adhesivesGlue/gelatin preparationEpoxyPetrochemical
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bio-based water-soluble polymer solution. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: 1) amine is subjected to a first reaction with bio-based dicarboxylic acid to obtain condensation polymers, and then the condensation polymers are dissolved by using water to obtain a water solution of the condensation polymers; and 2) the water solution of the condensation polymers, which is obtained in the step 1), is subjected to a second reaction with epoxy alkyl halide or 1,3-dihalide-2-propanol to obtain the bio-based water-soluble polymer solution. The preparation process of the bio-based water-soluble polymer solution is simple and easy to control, and the product is stable. The preparation method disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the low-cost and solid-content-adjustable bio-based water-soluble polymer solution, so that the problem that the water resistance of protein tackiness agents is poor and curing agents are originated from petrochemical materials are solved; and no formaldehyde is released, the adhesive strength and the water resistance are greatly improved, the preparation is easy, and the use is convenient. The invention further provides the application of the bio-based water-soluble polymer solution. The bio-based water-soluble polymer solution can be used as a curing agent and be applied to the preparation of the protein tackiness agents.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Polymer manufacturing process
InactiveUS20050234213A1High molecular weightNew technologyLayered productsAnimal housingProduction linePolymer science
A process utilizing PET as a reactive constituent to manufacture other polymers containing the pre-condensed moieties by the rapid transesterification of the condensation polymer with a pre-made modifying polymer containing the desired mix of other monomers. The process involves as a first step the manufacture of a modifying polymer containing the desired mix of acids and alcohols to a specific molecular weight such molecular weight dependent on the desired final level of utilized condensation polymer and the finished molecular weight. The second step of the process involves the rapid buildup of molecular weight and / or polymer uniformity by the rapid transesterification of the condensation polymer with the modifying polymer. The second step can be performed in any suitable vessel including an extrusion line. The process has the advantage of greatly reduced cycle times over other condensation polymer utilization processes such as the recycling of PET into other materials.
Owner:LIGHTHOUSE INT TECH EXCHANGE
High capacity ion chromatography stationary phases and method of forming
ActiveUS20110210055A1High resolutionGood choiceIon-exchange process apparatusChromatographic cation exchangersStationary phaseIon chromatography
The present invention provides a new design for high capacity stationary phases for chromatography, for example, ion chromatography. The stationary phases include a first polymer layer in contact with and at least partially coating the substrate of the stationary phase. The first polymer layer serves as a foundation for the attachment, and in various embodiments, the growth and attachment, of a highly hyperbranched polymer structure, typically based on one or more products of condensation polymerization. Multiple components are of use in forming the first polymer layer and the hyperbranched polymer structure, thereby providing a stationary phase that can be engineered to have a desired property such as ion capacity, ion selectivity, and the like. Exemplary condensation polymers are formed by the reaction of at least one polyfunctional compound with at least one compound of complimentary reactivity, e.g., a nucleophilic polyfunctional compound reacting with an electrophilic compound.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
Condensation polymer photoconductive elements
InactiveUS7541124B2Improve the immunityThick and uniformElectrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternElectrical resistance and conductanceCharge carrier
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Cation type water-soluble polymer dispersion
The invention relates to a kind of cation water-soluble macromolecule dispersoid. It includes inorganic salt watery solution, more than one kind of cation addition polymer soluble in the inorganic salt watery solution and more than one kind of water-soluble cation monomer and methylol acrylamide or acrylamide monomer to form water-soluble monomer system. Because the invention uses the compound dispersing agent comprised of cation addition polymer and condensation polymer dispersing agent, it makes the technology effect of cation water-soluble macromolecule dispersoid very remarkable. Compared with the cation addition polymer, the condensation polymer dispersing agent has lower molecular weight and bigger stoichiometic concentration; it's easy to absorb and compactly cover on the surface of particles, and stabilize the dispersed particles by using the repellent effect of its charges; it form microphase separation state between the separated particles and the dissolution state macromolecules, to have the effect of stabilizing the dispersing system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
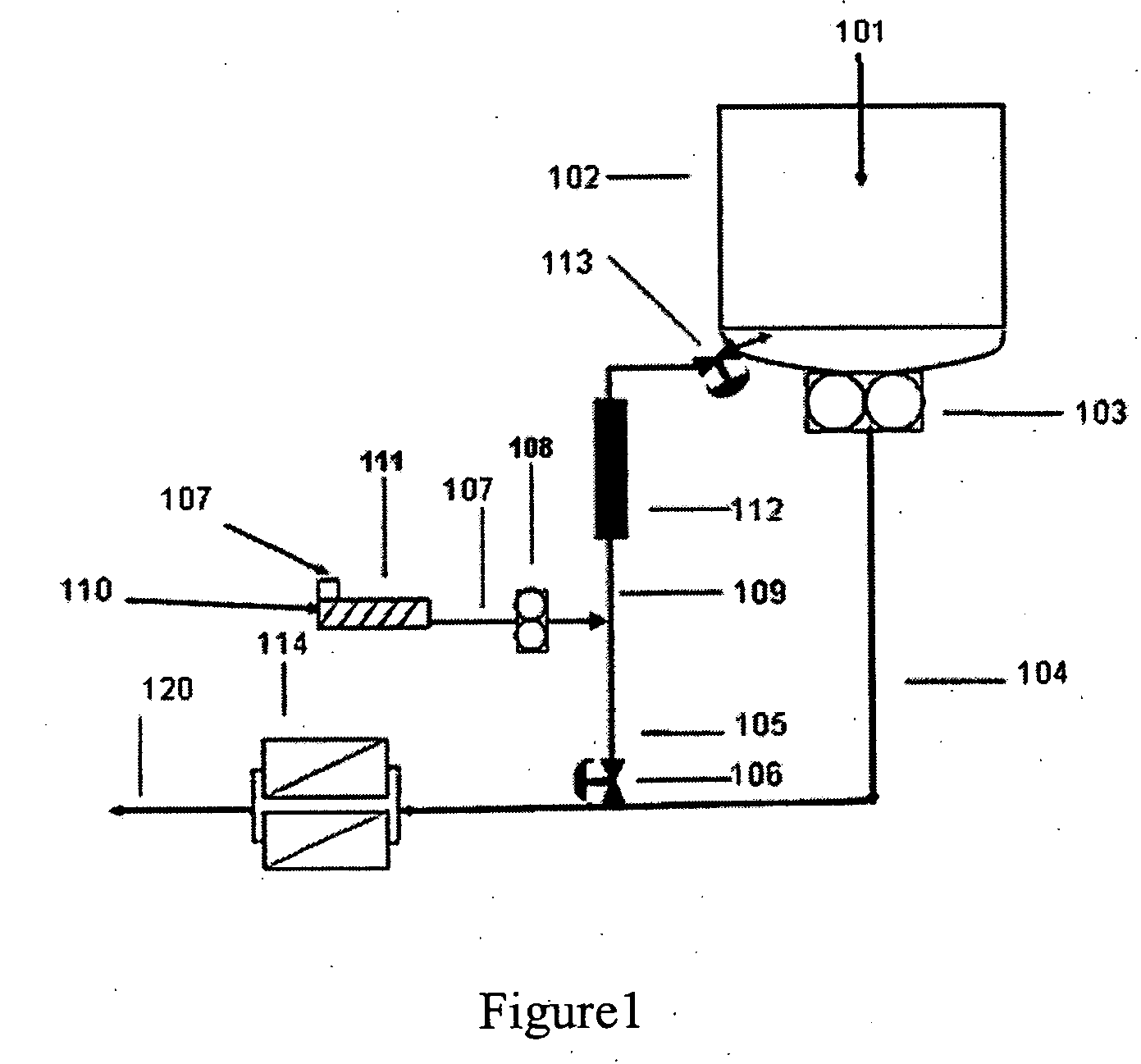
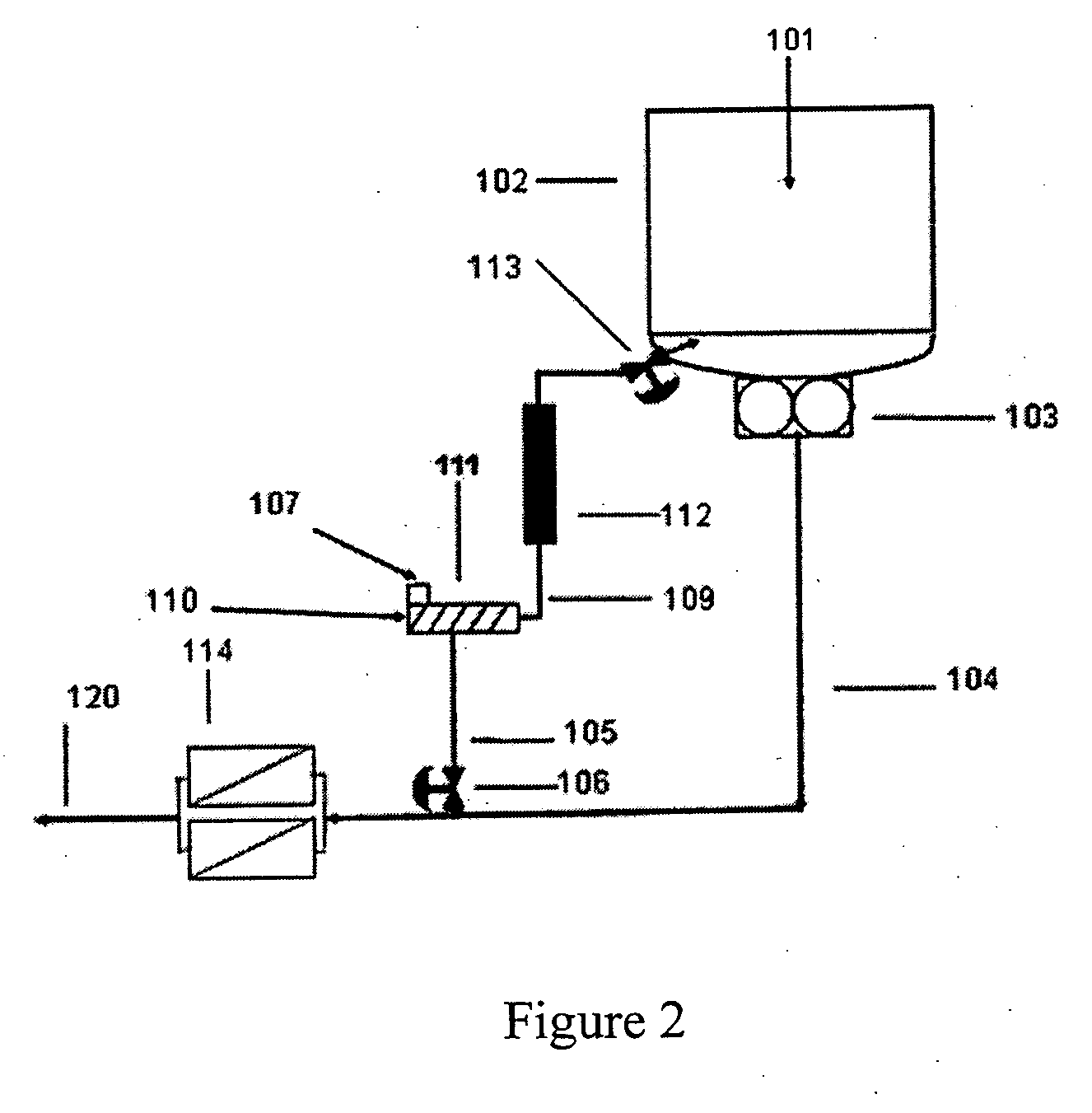
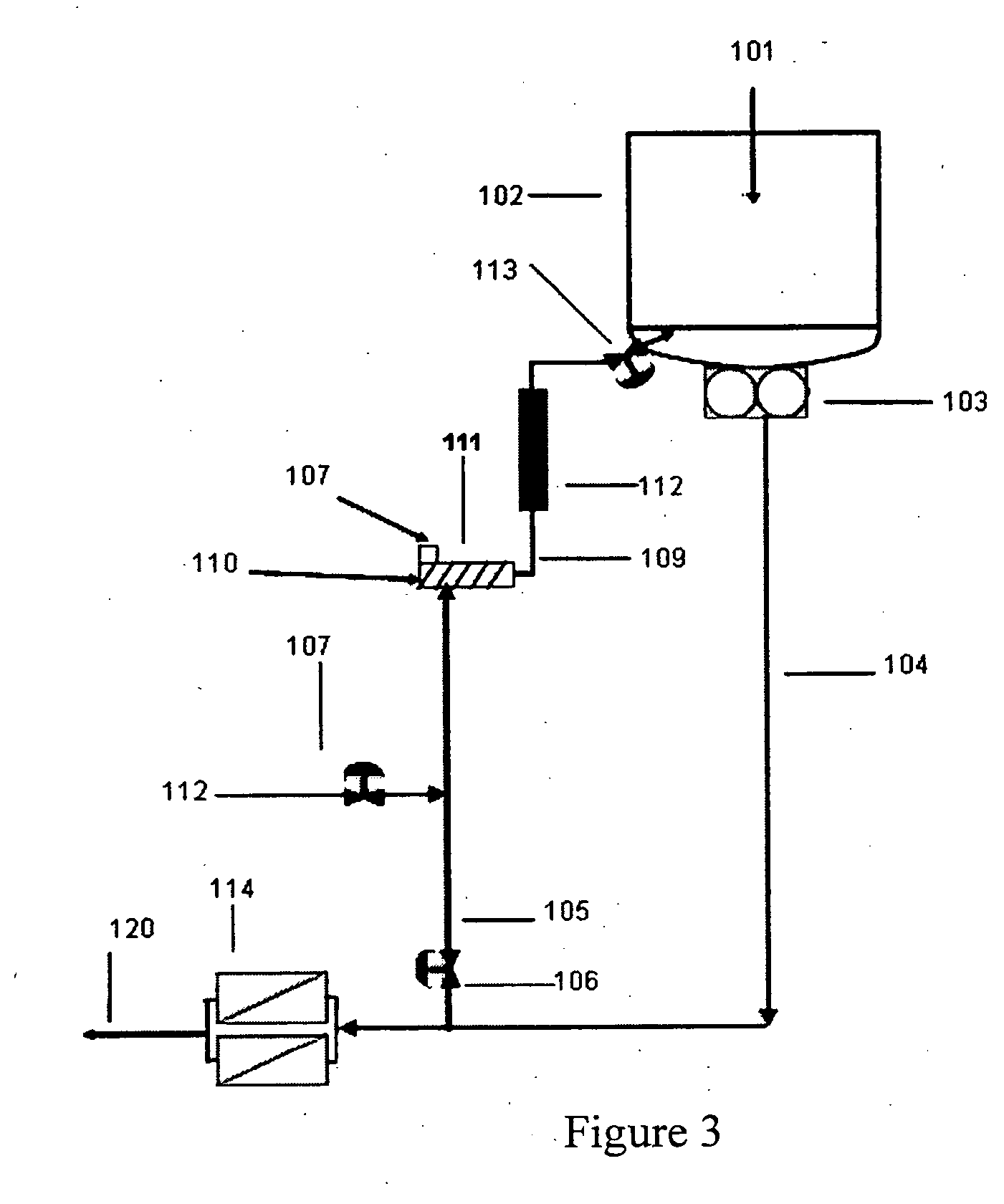
Late addition to effect compositional modifications in condensation polymers
A process for preparing modified polymer by withdrawing a slip stream of polymer melt from the discharge line of a continuous polymerization reactor, admixing in a highly modified polymeric additive into the polymer melt within the slip stream, then introducing the modifier containing slip stream late in the manufacturing process prior to the slip stream withdrawal point. The improved processes of the invention have particular utility for large-scale, continuous reactor where transitions and short production runs are economically prohibitive thereby limiting the product breath. The process is particularly suited for producing a family of copolyesters using a continuous melt phase production process.
Owner:ALPEK POLYESTER SA DE CV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com