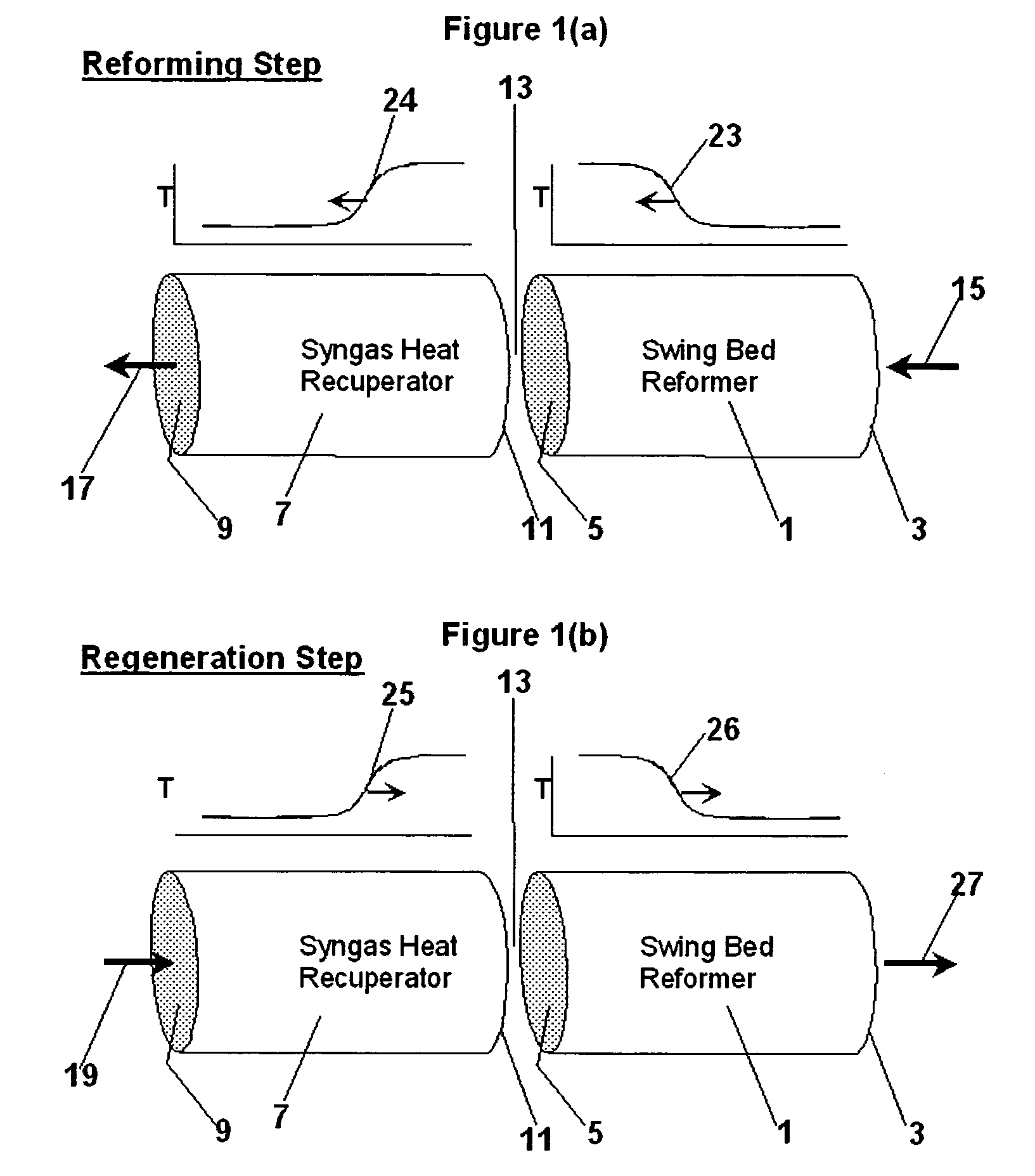
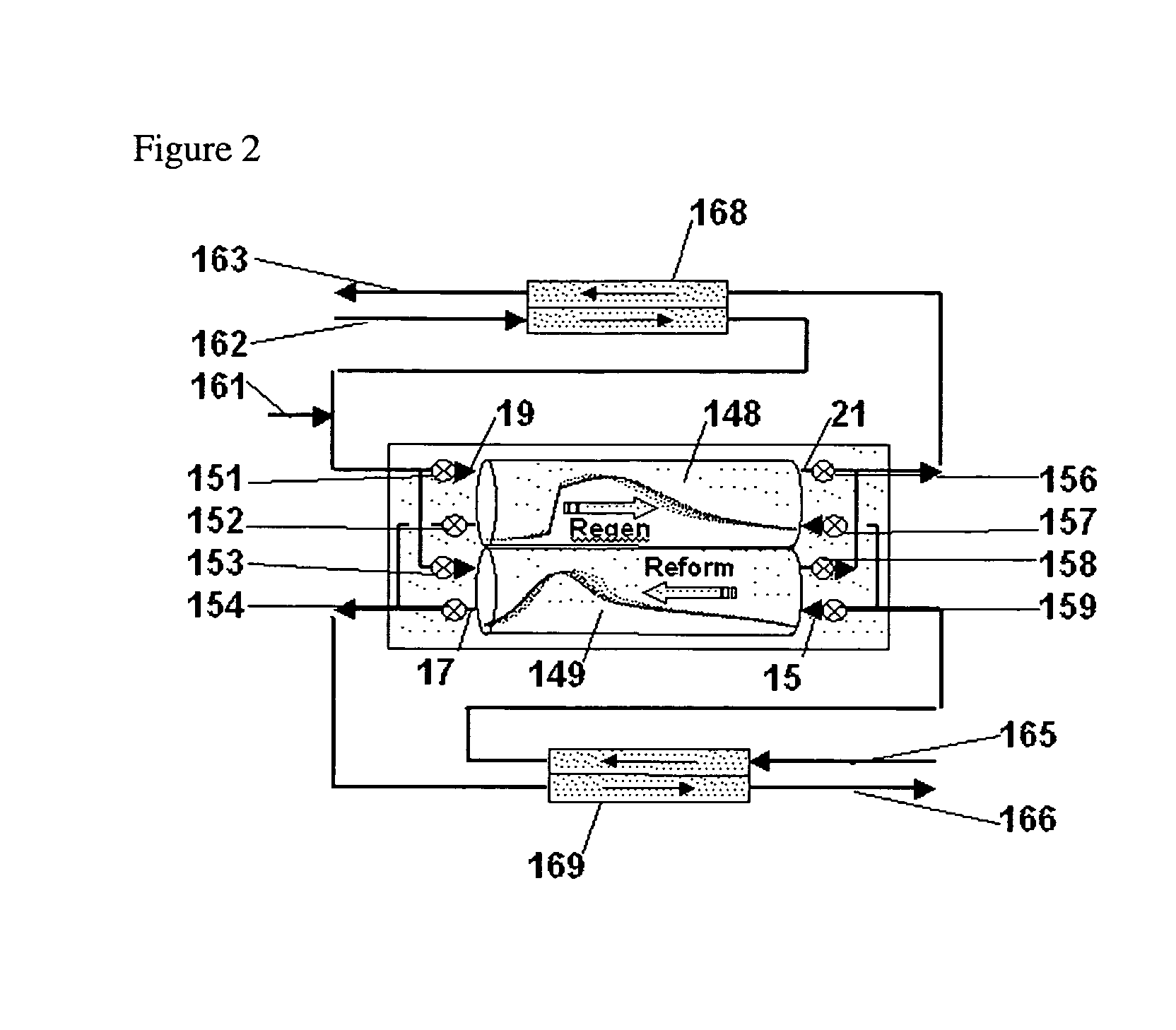
Patents
Literature
1688 results about "Liquid hydrocarbons" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and compositions for forming permeable cement sand screens in well bores
Methods and compositions for forming permeable cement sand screens in well bores are provided. The compositions are basically comprised of a hydraulic cement, an acid soluble particulate solid, a liquid hydrocarbon solvent soluble particulate solid, a particulate cross-linked gel containing an internal breaker which after time causes the gel to break into a liquid, water present in an amount sufficient to form a slurry, a gas present in an amount sufficient to form a foam and a mixture of foaming and foamed stabilizing surfactants.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Modified polyethylene compositions
The present invention relates to a composition comprising more than 25 weight % (based on the weight of the composition) of one or more ethylene polymers having an Mw of 20,000 g / mole or more and at least 0.1 weight % of a liquid hydrocarbon modifier where the modifier has: 1) a viscosity index of 120 or more, and 2) an kinematic viscosity of 3 to 3000 cSt at 100° C., and 3) a pour point of −10° C. or less, and 4) a flash point of 200° C. or more; and wherein the modifier contains less than 5 weight % of functional groups selected from hydroxide, aryls, substituted aryls, halogens, alkoxys, carboxylates, esters, acrylates, oxygen, nitrogen, and carboxyl, based upon the weight of the modifier.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for the continuous production of aligned carbon nanotubes
ActiveUS7160531B1Improve flow characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsMetal catalystPorous medium
Novel methods and apparati for continuous production of aligned carbon nanotubes are disclosed. In one aspect, the method comprises dispersion of a metal catalyst in a liquid hydrocarbon to form a feed solution, and volatilizing the feed solution in a reactor through which a substrate is continuously passed to allow growth of nanotubes thereon. In another aspect, the apparatus comprises a reactor, a tube-within-a-tube injector, and a conveyor belt for passing a substrate through the reactor. The present invention further discloses a method for restricting the external diameter of carbon nanotubes produced thereby comprising passing the feed solution through injector tubing of a specified diameter, followed by passing the feed solution through an inert, porous medium. The method and apparati of this invention provide a means for producing aligned carbon nanotubes of a particular external diameter which is suitable for large scale production in an industrial setting.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Methods and compositions for forming permeable cement sand screens in well bores
Methods and compositions for forming permeable cement sand screens in well bores are provided. The compositions are basically comprised of a hydraulic cement, an acid soluble particulate solid, a liquid hydrocarbon solvent soluble particulate solid, a particulate cross-linked gel containing an internal breaker which after time causes the gel to break into a liquid, water present in an amount sufficient to form a slurry, a gas present in an amount sufficient to form a foam and a mixture of foaming and foamed stabilizing surfactants.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method of forming amorphous carbon film and method of manufacturing semiconductor device using the same
InactiveUS20080293248A1Better controllableLight absorption coefficient is lowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRefractive indexDiffuse reflection
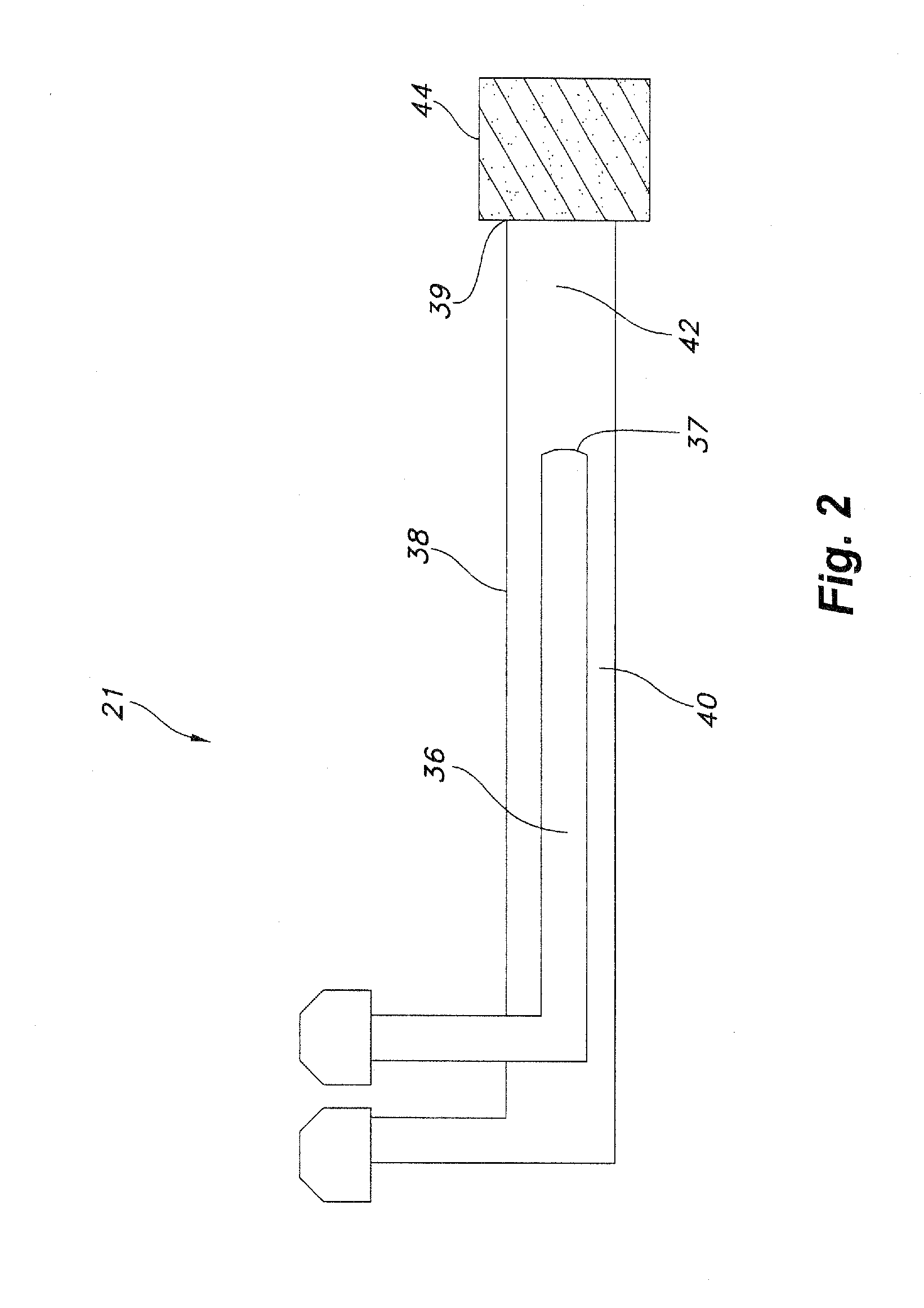
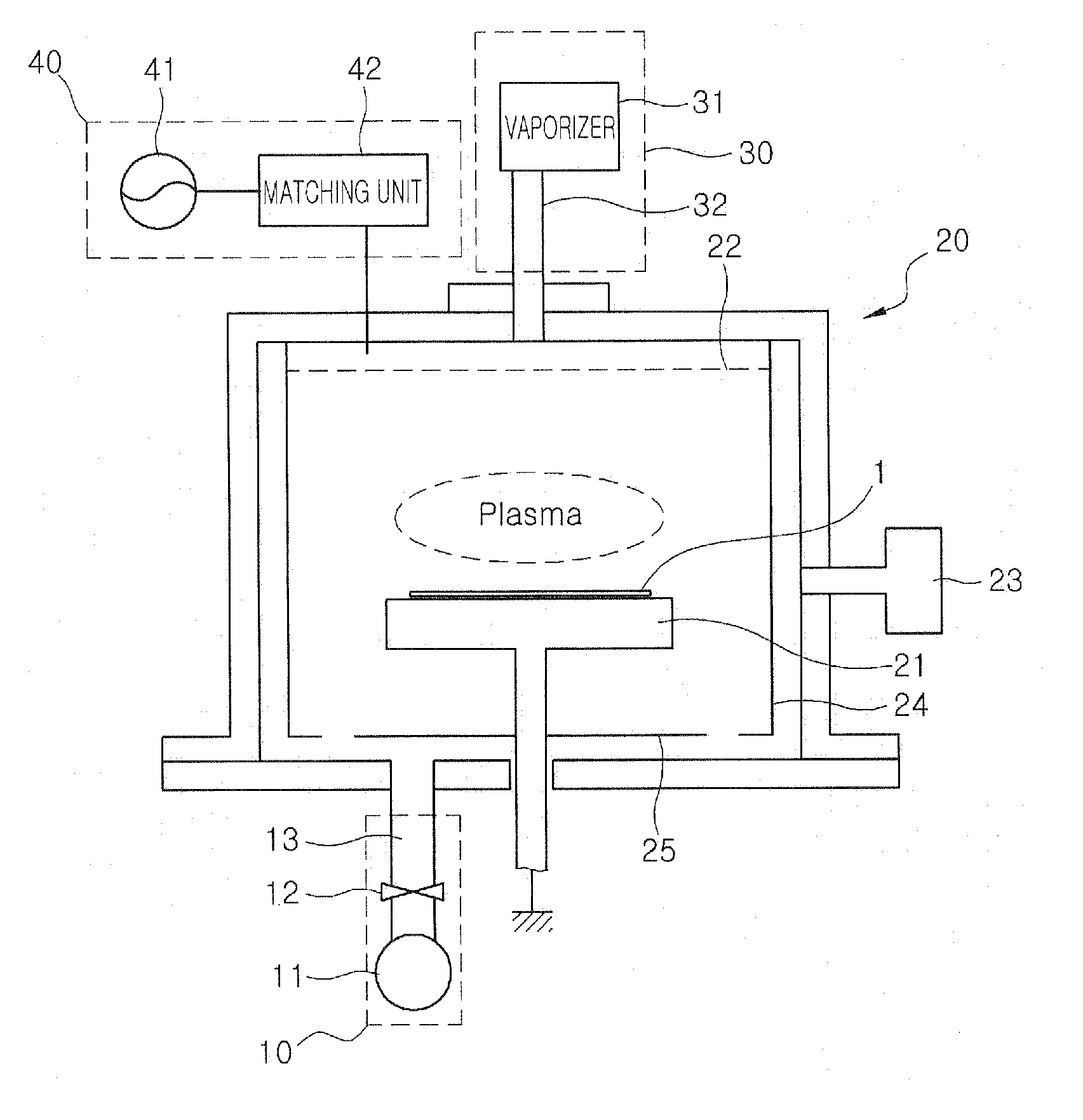
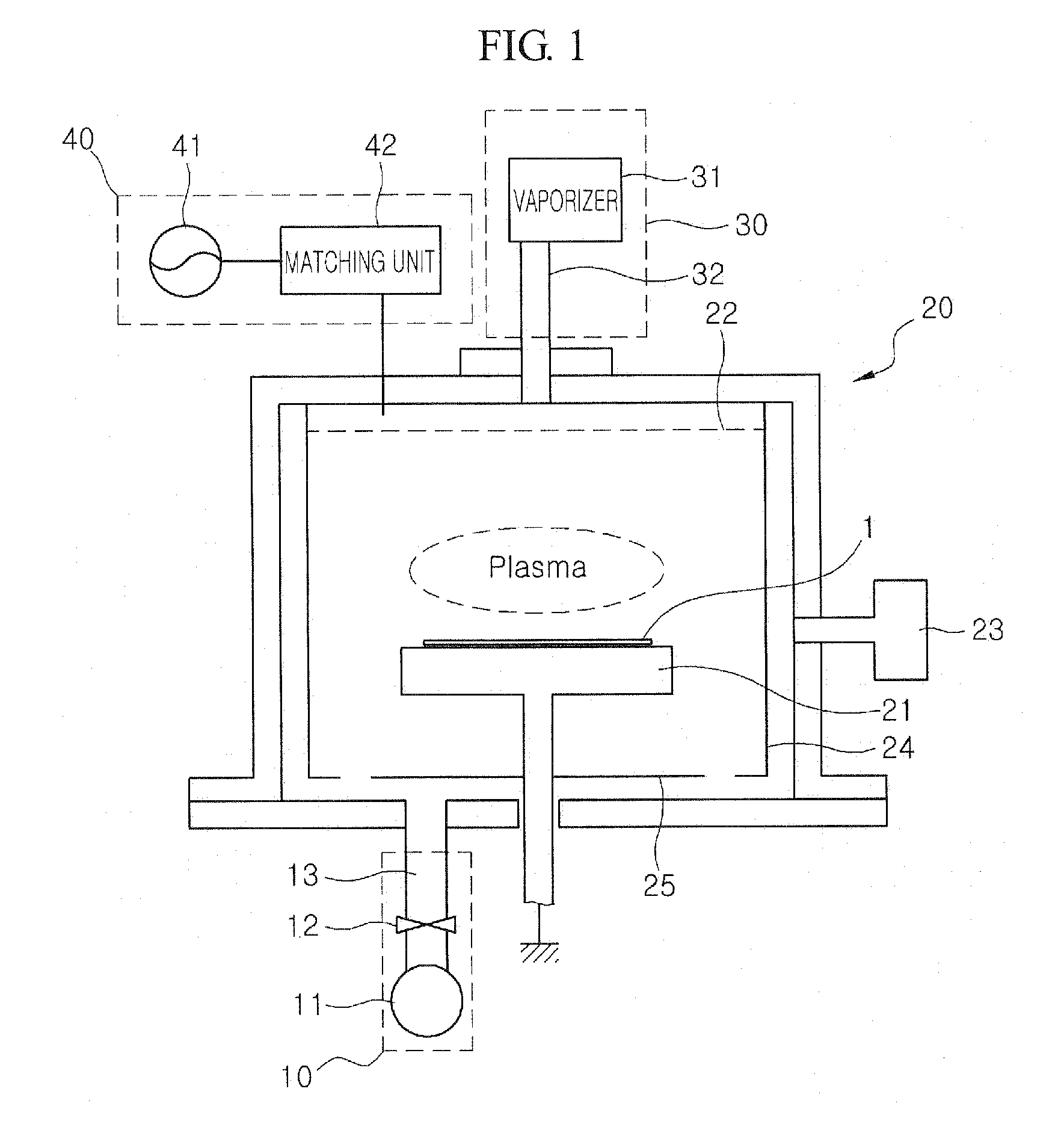
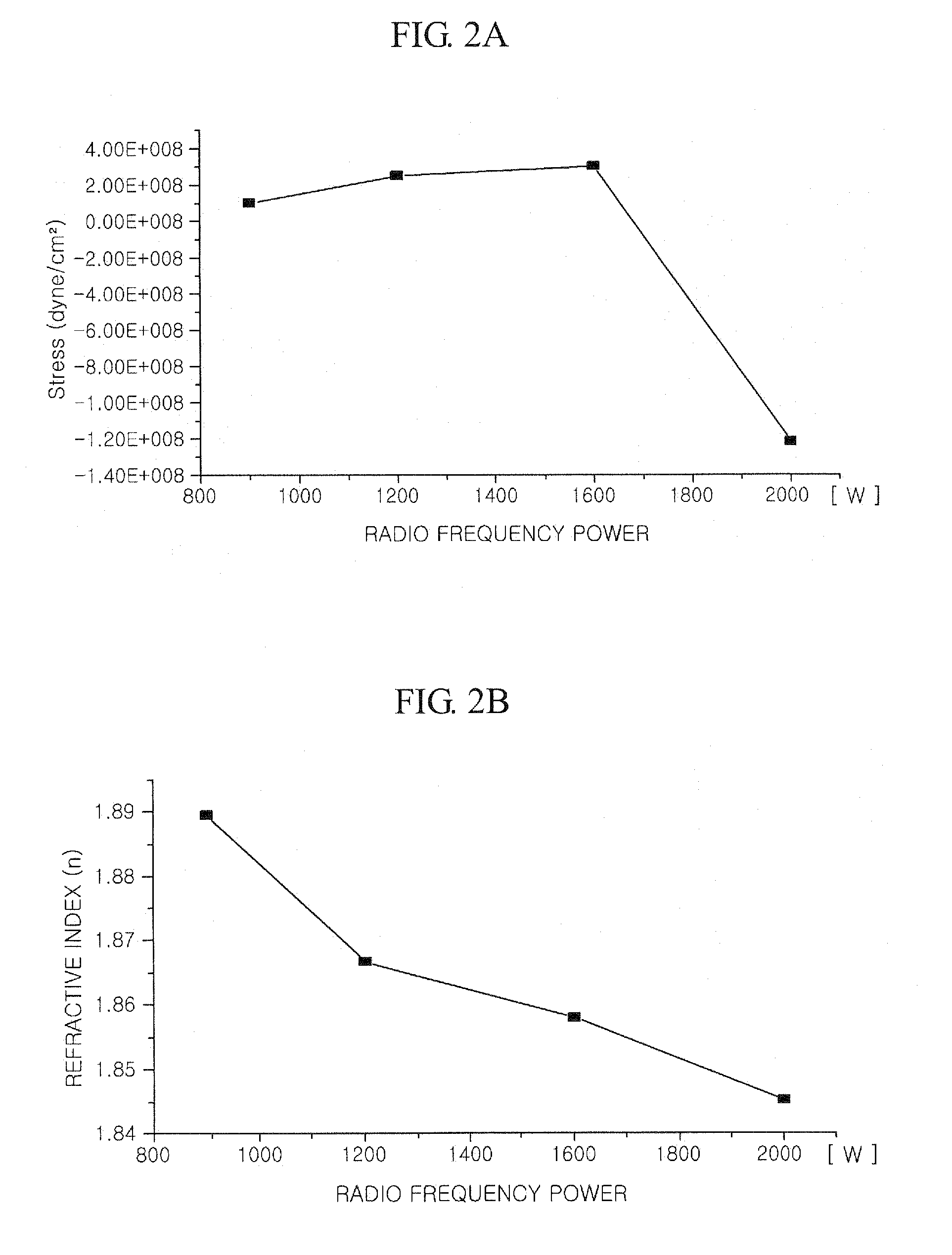
The present invention relates to a method of forming an amorphous carbon film and a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the method. An amorphous carbon film is formed on a substrate by vaporizing a liquid hydrocarbon compound, which has chain structure and one double bond, and supplying the compound to a chamber, and ionizing the compound. The amorphous carbon film is used as a hard mask film.It is possible to easily control characteristics of the amorphous carbon film, such as a deposition rate, an etching selectivity, a refractive index (n), a light absorption coefficient (k) and stress, so as to satisfy user's requirements. In particular, it is possible to lower the refractive index (n) and the light absorption coefficient (k). As a result, it is possible to perform a photolithography process without an antireflection film that prevents the diffuse reflection of a lower material layer.Further, a small amount of reaction by-product is generated during a deposition process, and it is possible to easily remove reaction by-products that are attached on the inner wall of a chamber. For this reason, it is possible to increase a cycle of a process for cleaning a chamber, and to increase parts changing cycles of a chamber. As a result, it is possible to save time and cost.
Owner:TES CO LTD
Method of hydraulic fracturing to reduce unwanted water production
ActiveUS20050016732A1Reduce conductivityFluid removalDrilling compositionGeomorphologyWater production
A method of hydraulically fracturing a hydrocarbon-bearing subterranean formation ensures that the conductivity of water inflow below the productive zone of the subterranean formation is reduced. The method consists of two principal steps. In the first step, a fracture in and below the productive zone of the formation is initiated by introducing into the subterranean formation a fluid, free of a proppant, such as salt water, fresh water, brine, liquid hydrocarbon, and / or nitrogen or other gases. The proppant-free fluid may further be weighted. In the second step, a proppant laden slurry is introduced into the subterranean formation which contains a relatively lightweight density proppant. Either the fluid density of the proppant-free fluid is greater than the fluid density of the proppant laden slurry or the viscosity of the proppant-free fluid is greater than the viscosity of the proppant laden slurry. The method limits undesirable fracture height growth in the hydrocarbon-bearing subterranean formation during the fracturing.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
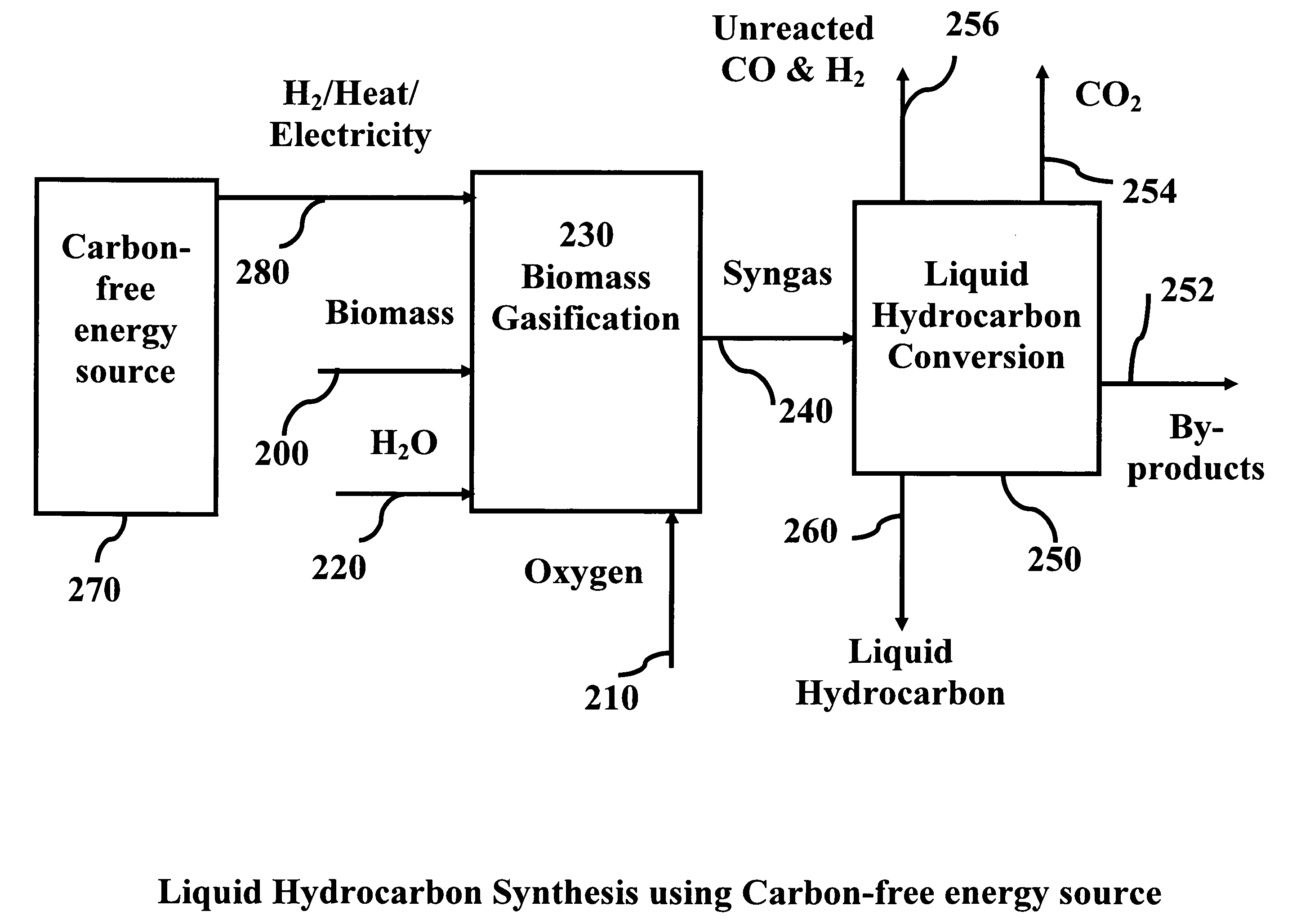
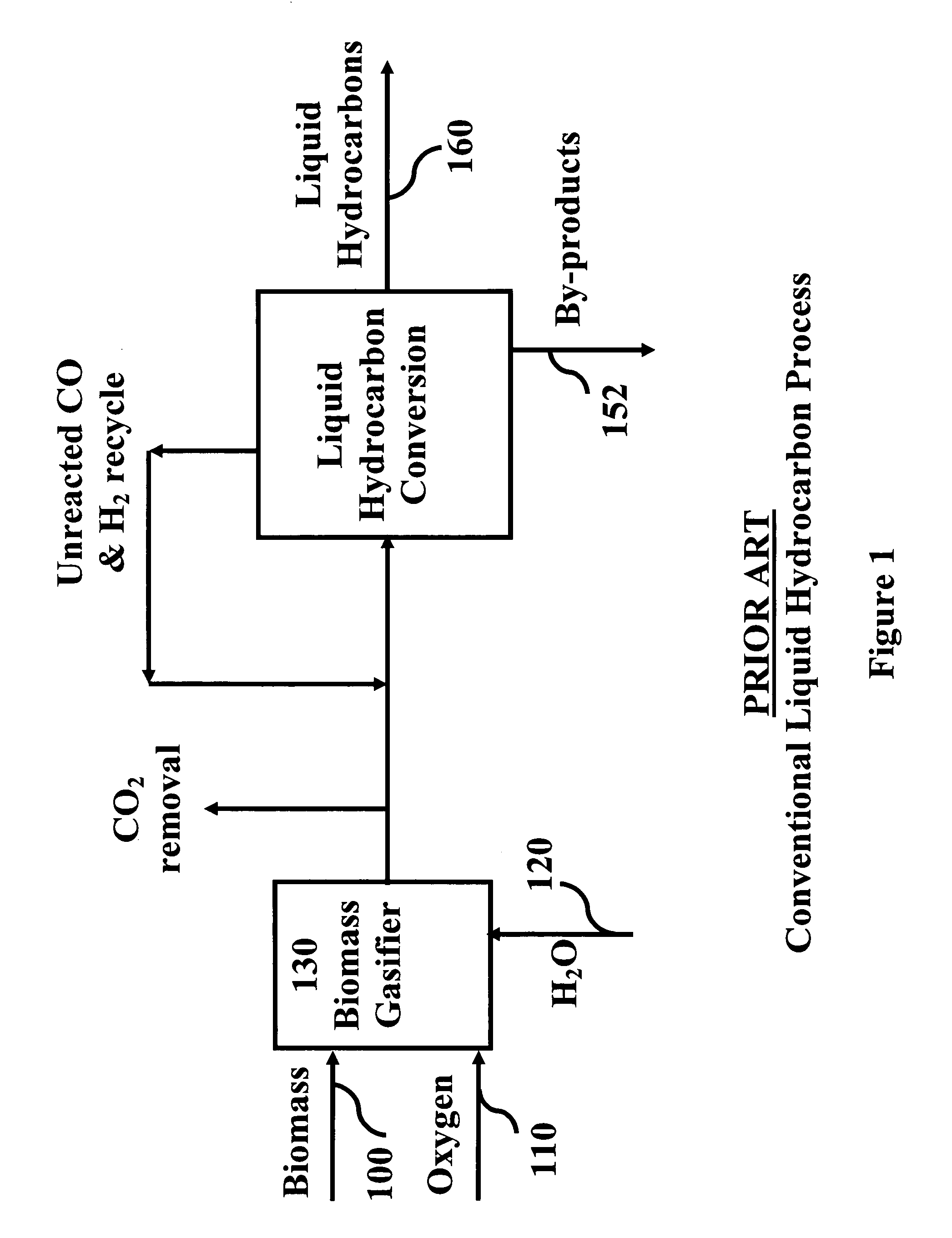
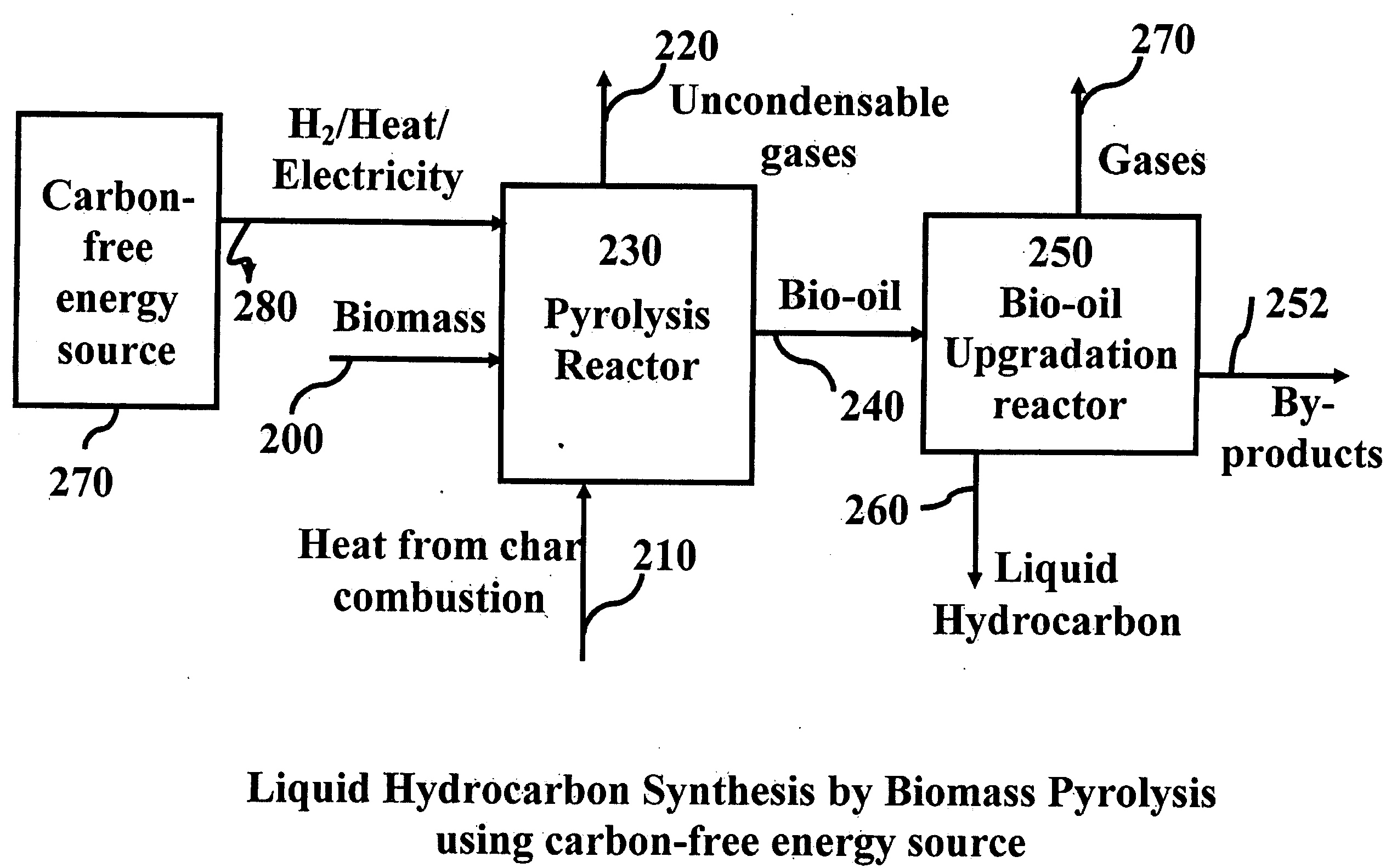
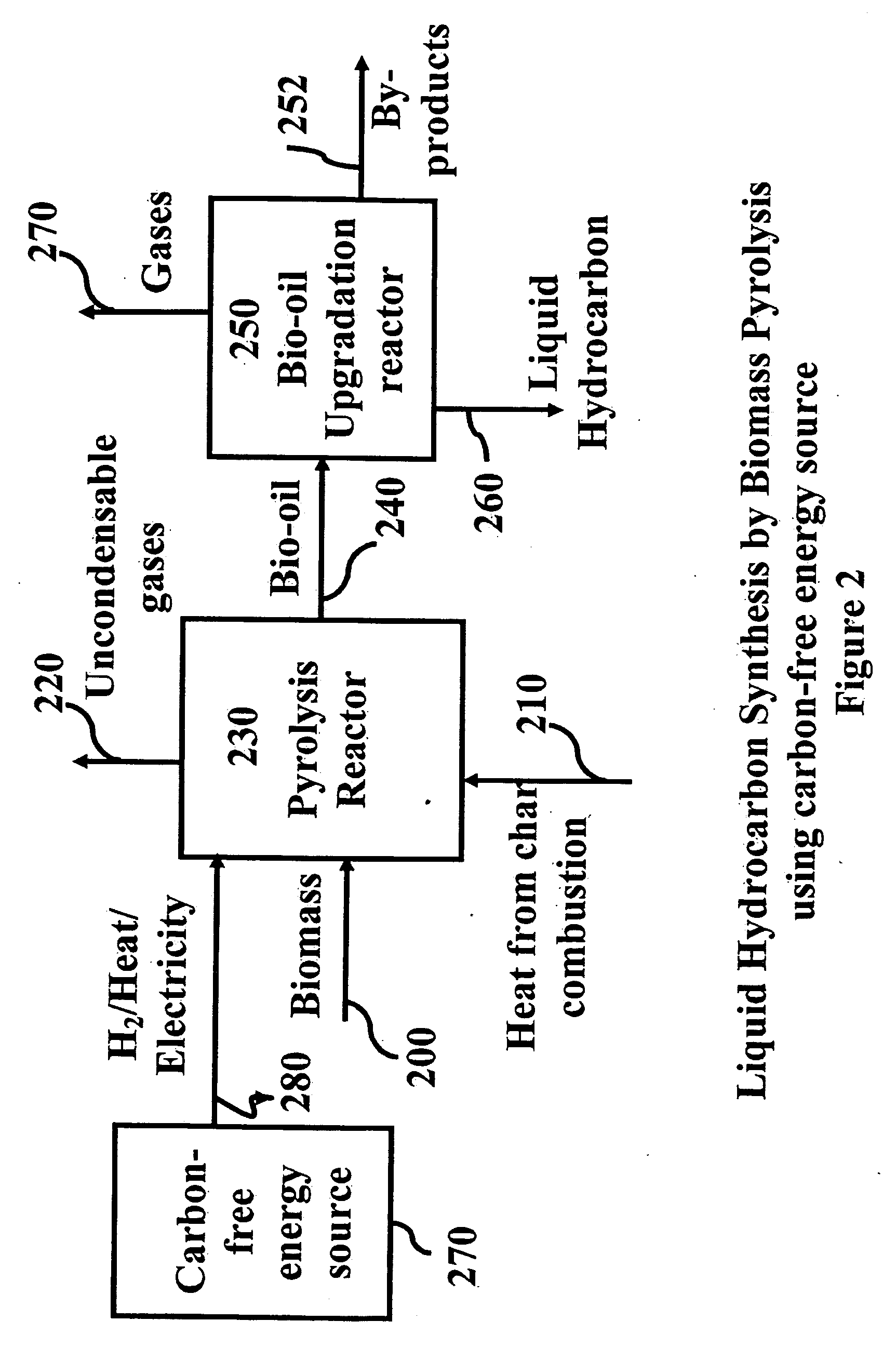
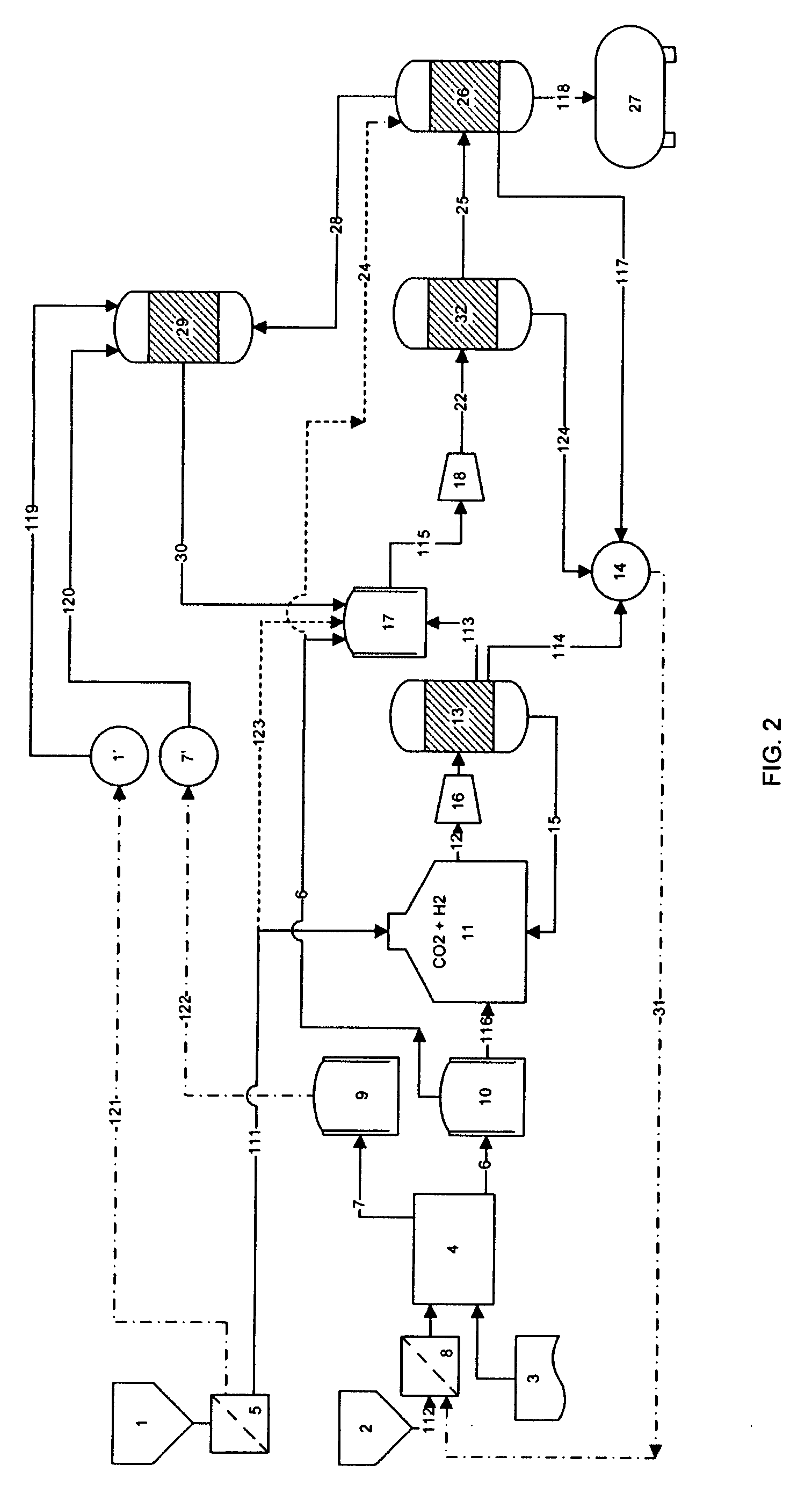
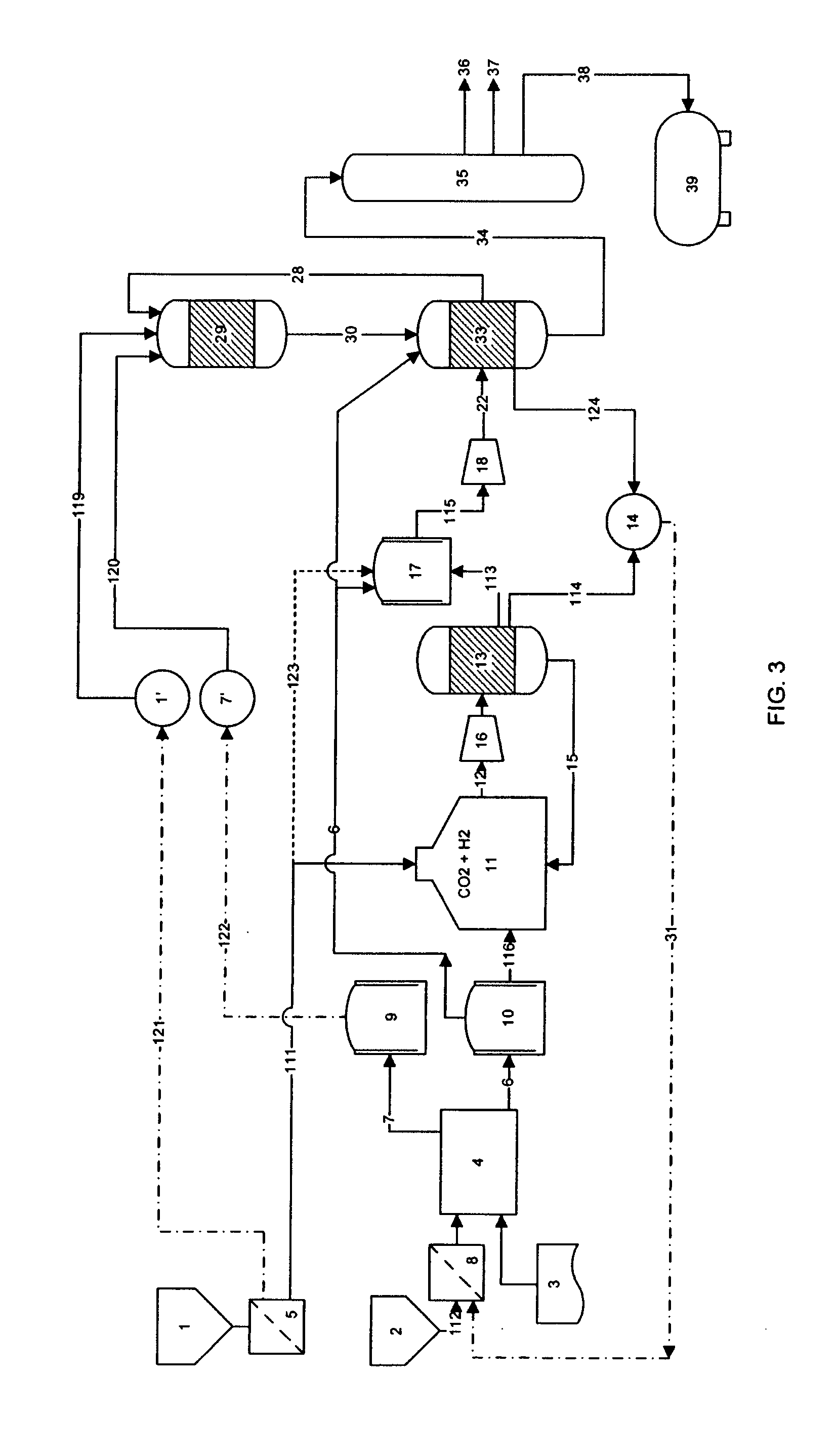
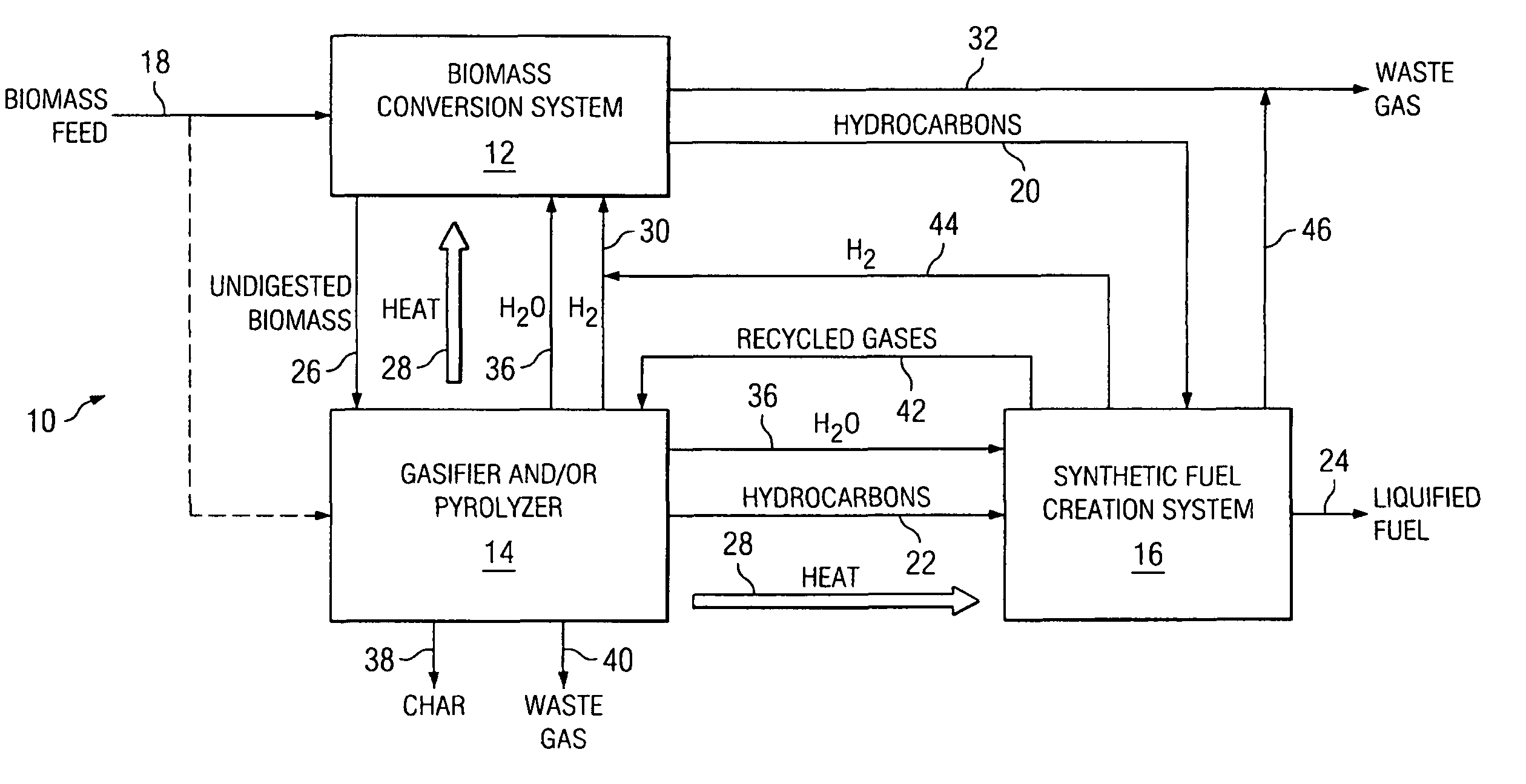
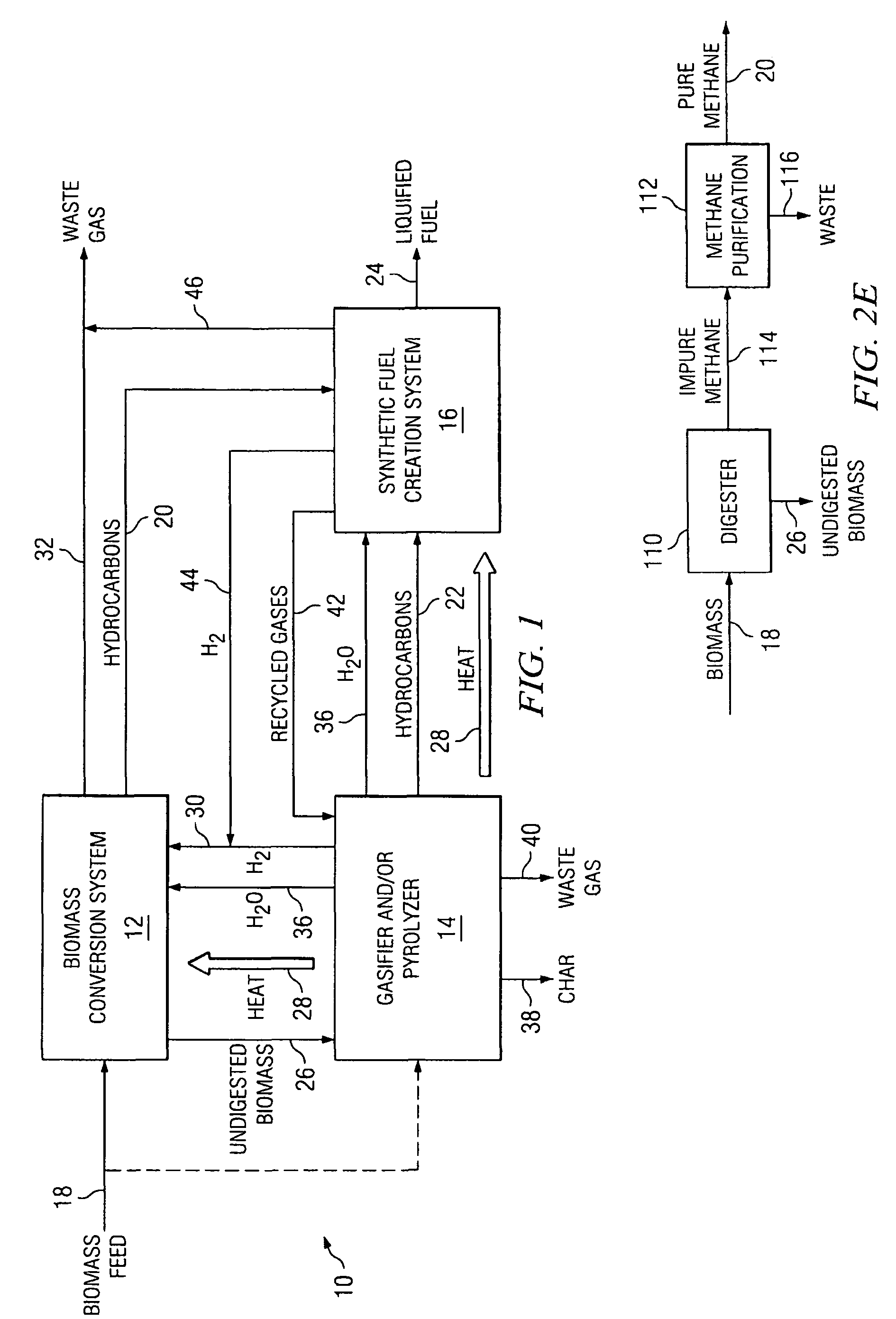
System and process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbon
ActiveUS20080115415A1Improve carbon efficiencyReduce area requirementsMuffle furnacesCarbon compoundsOxygenElectrolysis of water
Production of synthetic liquid hydrocarbon fuel from carbon containing moieties such as biomass, coal, methane, naphtha as a carbon source and hydrogen from a carbon-free energy source is disclosed. The biomass can be fed to a gasifier along with hydrogen, oxygen, steam and recycled carbon dioxide. The synthesis gas from the gasifier exhaust is sent to a liquid hydrocarbon conversion reactor to form liquid hydrocarbon molecules. Unreacted CO & H2 can be recycled to the gasifier along with CO2 from the liquid hydrocarbon conversion reactor system. Hydrogen can be obtained from electrolysis of water, thermo-chemical cycles or directly by using energy from carbon-free energy sources.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Gelled hydrocarbon compositions and methods for use thereof
InactiveUS6849581B1Improve stabilityAvoid stabilityOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsOrganic baseOrganic fluid
Gelled organic compositions and methods for using same. The gelled compositions may be liquid organic fluids, such as gelled liquid hydrocarbons, formed from a mixture of an organic-base fluid, a carboxylic acid, and one or more metal source compounds, such as a metal salt of carboxylic acid. The gelled compositions may be used in variety of applications including, but not limited to, oil field, pipeline and processing facility applications.
Owner:BJ SERVICES LLC +1
Process for the production of synthesis gas with conversion of CO2 into hydrogen
ActiveUS7846979B2Useful thermal recovery on the gasification effluentCombustible gas chemical modificationProductsSteam reformingPartial oxidation
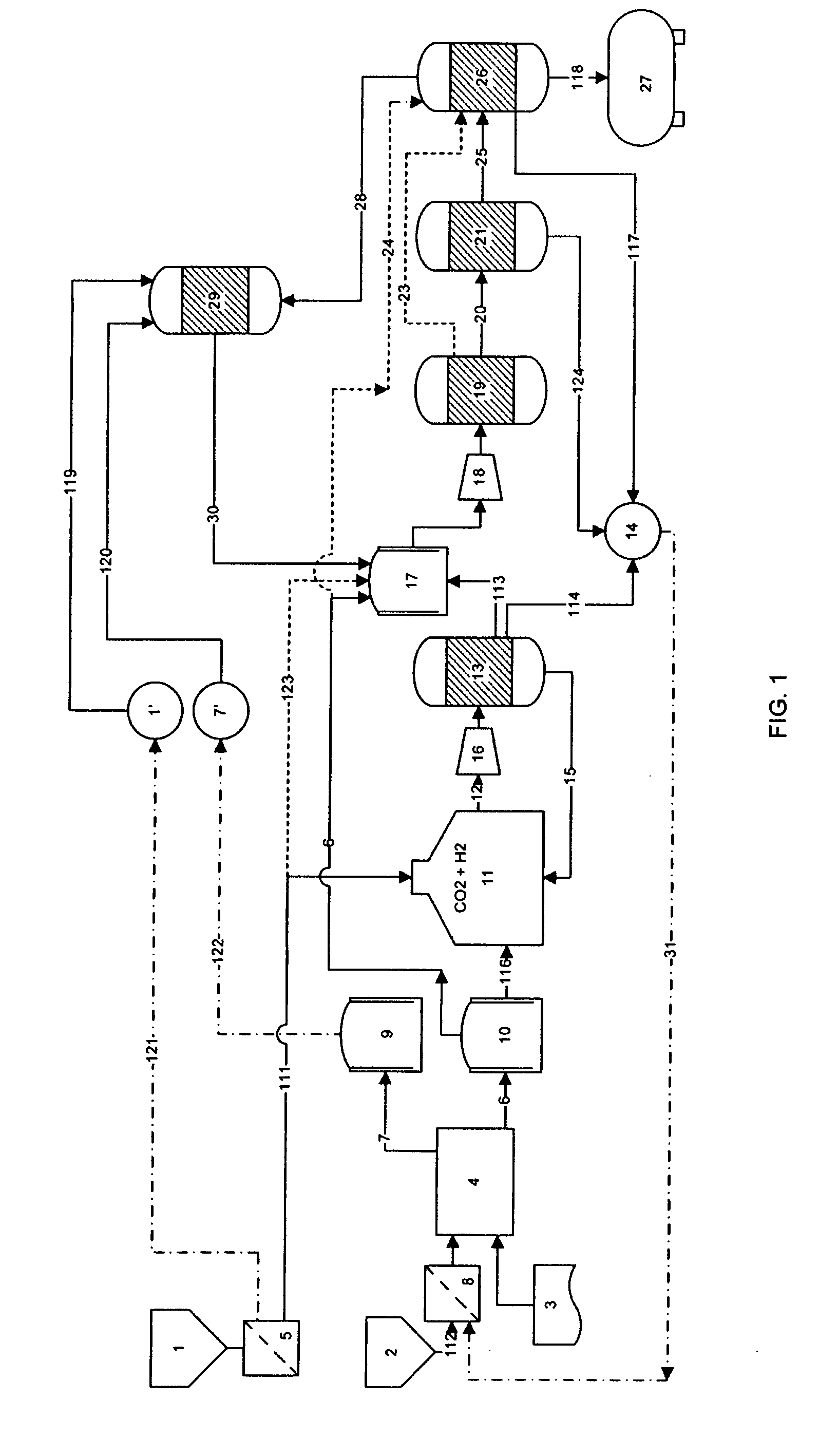
Process for the production of liquid hydrocarbons from a feedstock that comprises at least one elementary feedstock from the group of biomass, coal, lignite, petroleum residues, methane, and natural gas, comprising: at least one stage a) for gasification of the feedstock by partial oxidation and / or steam reforming to produce a synthesis gas SG; a stage b) for separating CO2 from SG and a portion of the effluent of the subsequent stage c); the mixing of a portion of the CO2 that is separated with a gas of an H2 / CO ratio of more than 3; a stage c) for partial conversion with hydrogen, thermal or thermocatalytic, of the CO2 that is present in said first mixture according to the reaction: CO2+H2→CO+H2O in a specific reaction zone that is separated from said gasification zone or zones; a stage d) for Fisher-Tropsch synthesis on a synthesis gas that comprises at least a portion of SG and at least a portion of the CO that is produced by the conversion of CO2 into hydrogen.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
System and method for extraction of hydrocarbons by in-situ radio frequency heating of carbon bearing geological formations
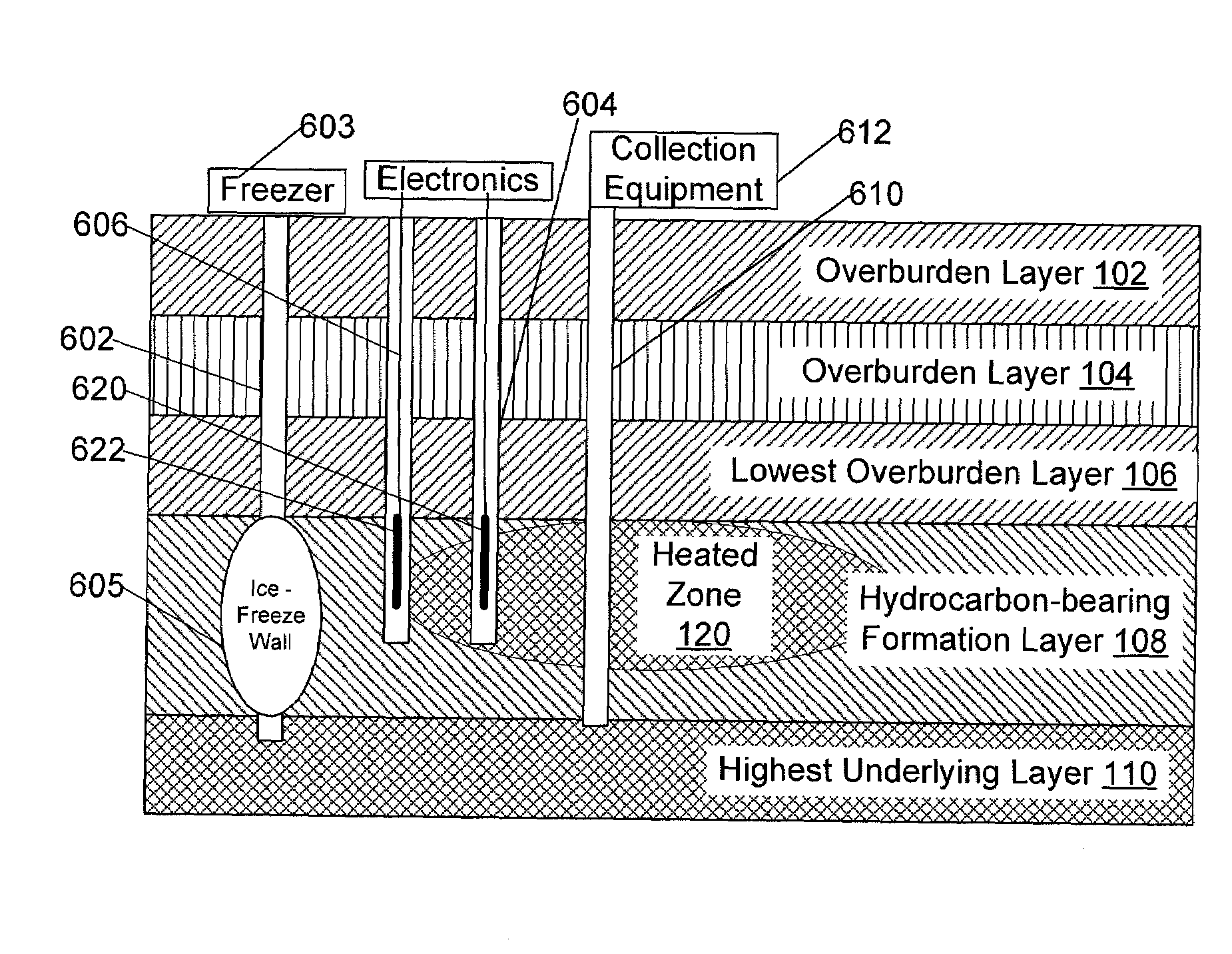
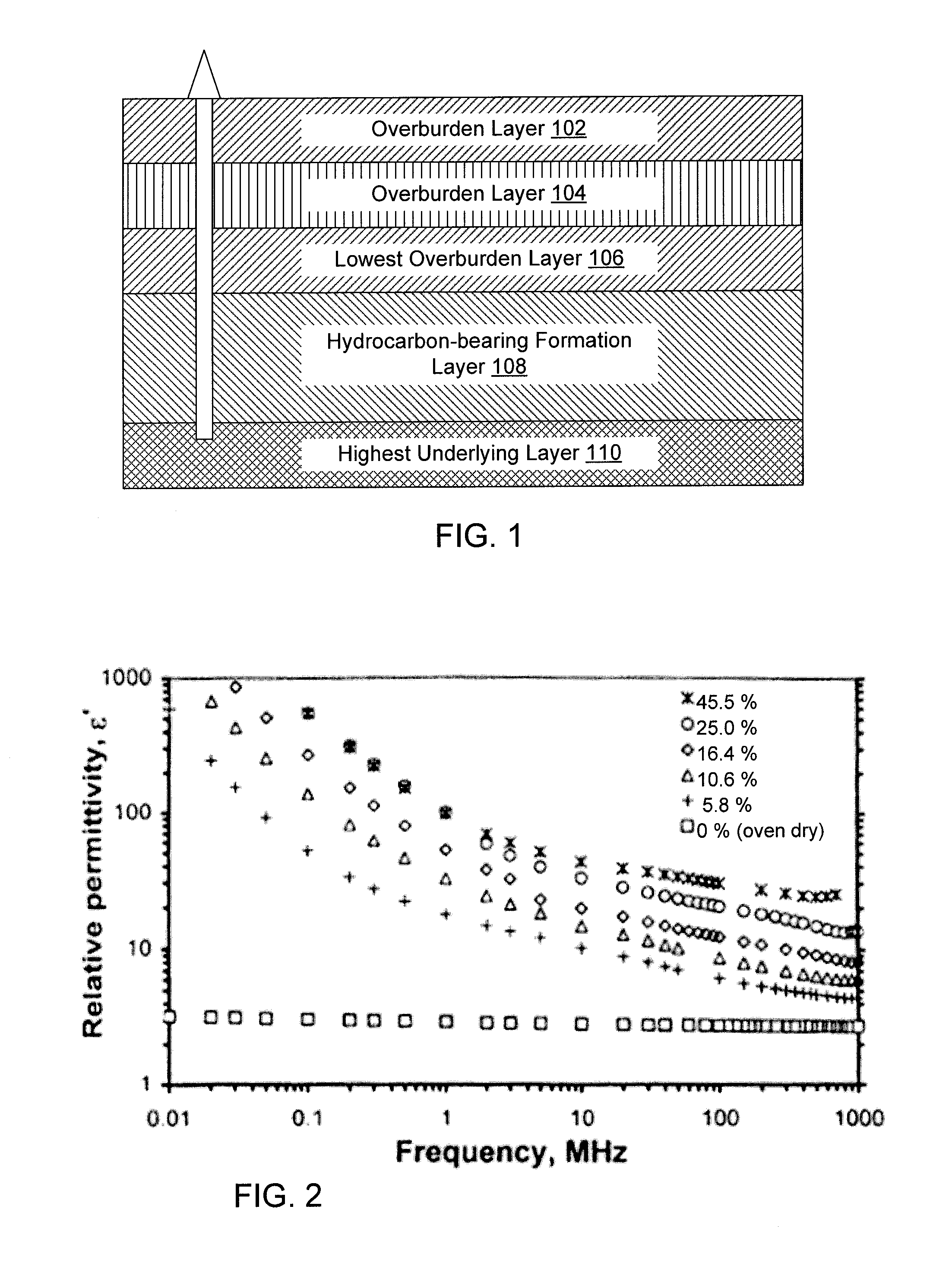
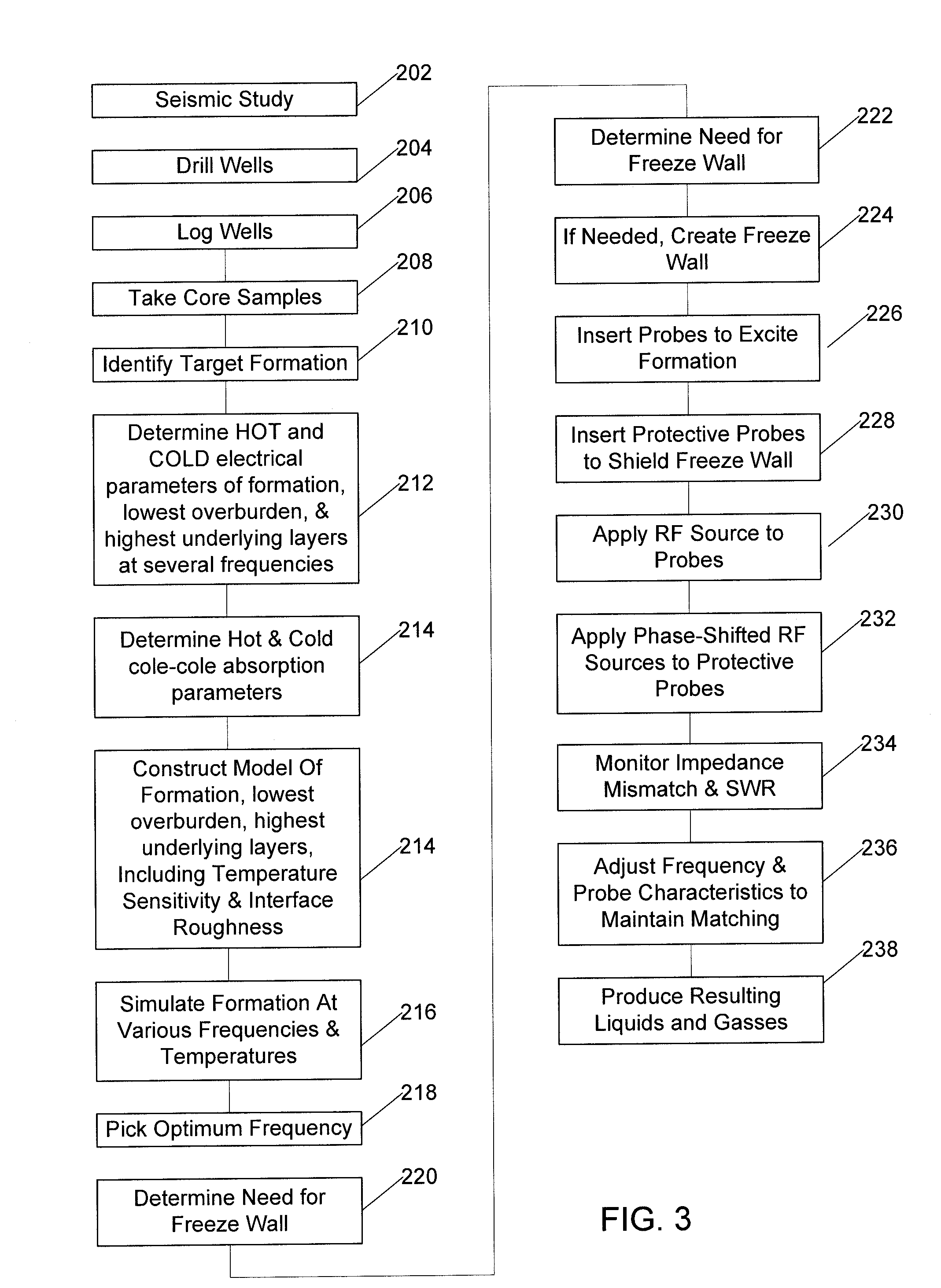
A method of producing liquid hydrocarbons from a hydrocarbon-bearing rock in situ in a geological formation begins with exploring the formation by drilling a plurality of boreholes into the formation and taking core samples of the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and at least one overburden layer. Electrical parameters of the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and the overburden layer are determined, as well as a roughness of a boundary between the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and the at least one overburden layer. These electrical parameters are used to construct a computer model of a portion of the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and at least one overburden layer, the computer model based upon modeling the formation as a rough-walled waveguide. This computer model is used to simulate propagation of radio frequency energy within the hydrocarbon-bearing rock, including simulation of radio frequency wave confinement within the hydrocarbon-bearing rock, at several frequencies and temperatures. A frequency for retorting is selected based upon simulation results. Radio frequency couplers are installed into at least one borehole in the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and driven with radio frequency energy to heat the hydrocarbon-bearing rock. As the rock heats, it releases carbon compounds and these are collected.
Owner:PAO HSUEH YUAN
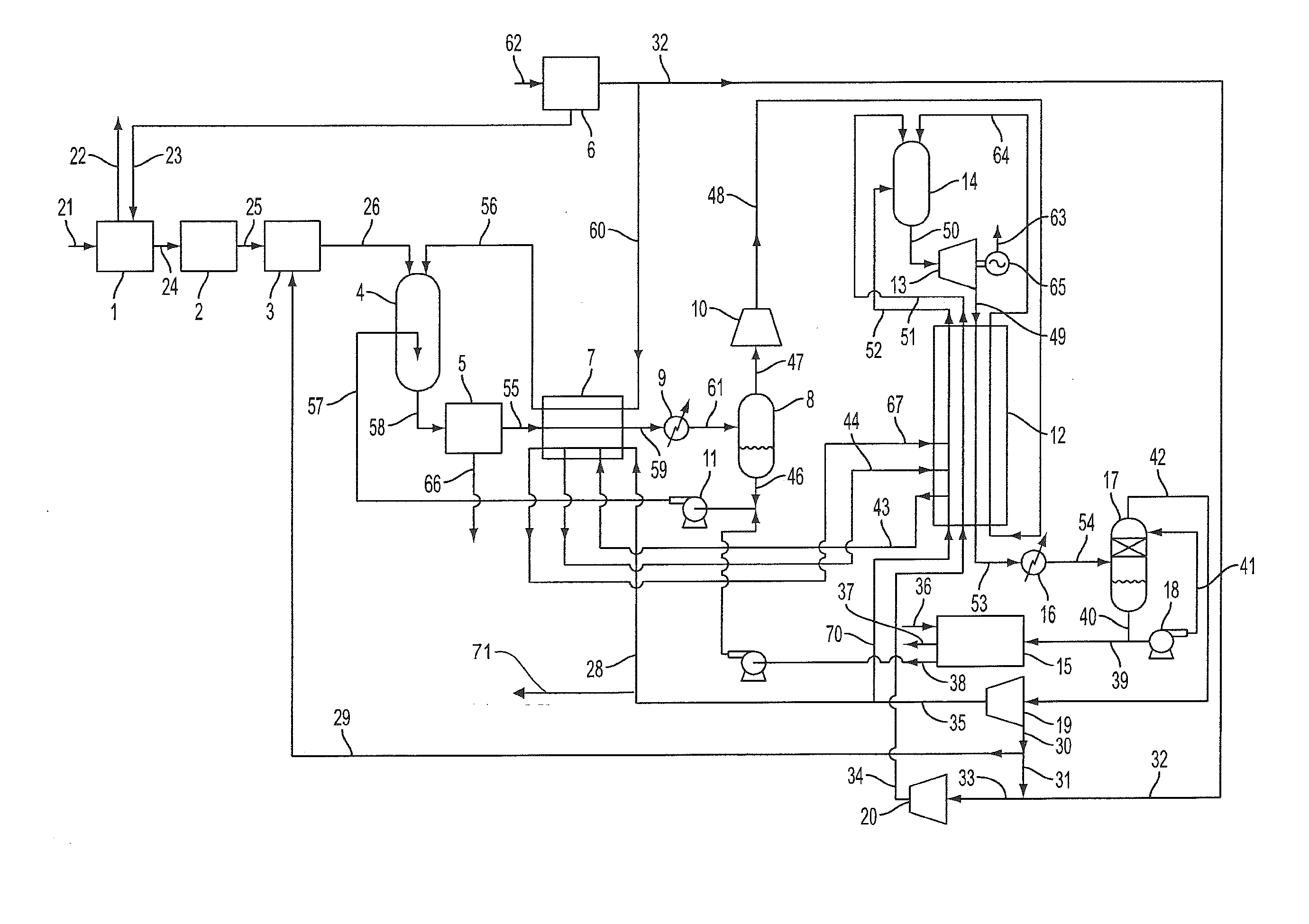
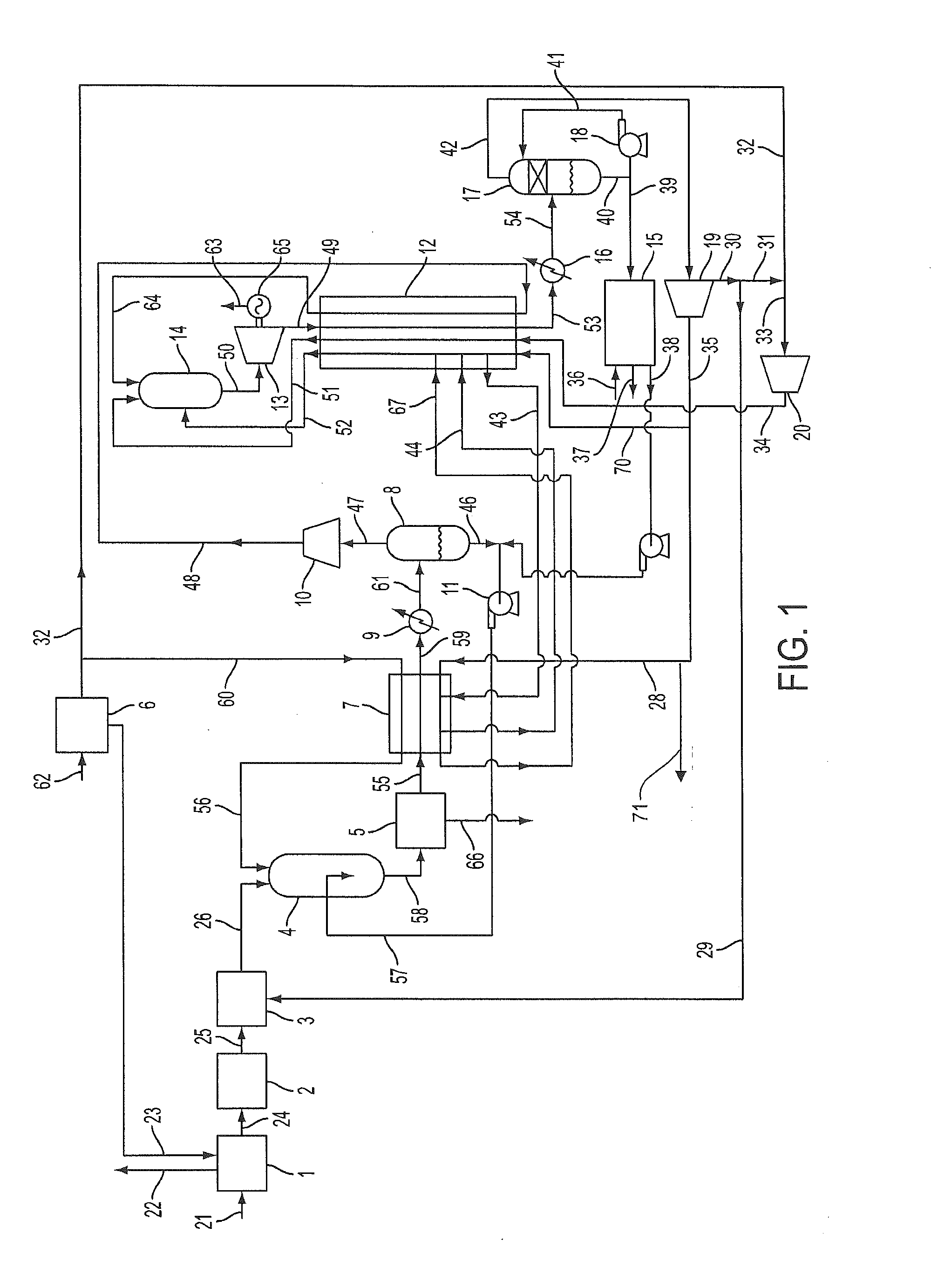
Partial oxidation reaction with closed cycle quench
ActiveUS8776532B2Prevent metal dustingReaction is slowSolidificationLiquefactionPartial oxidationCombustor
The present disclosure relates to a power production system that is adapted to achieve high efficiency power production with complete carbon capture when using a solid or liquid hydrocarbon or carbonaceous fuel. More particularly, the solid or liquid fuel first is partially oxidized in a partial oxidation reactor. The resulting partially oxidized stream that comprises a fuel gas is quenched, filtered, cooled, and then directed to a combustor of a power production system as the combustion fuel. The partially oxidized stream is combined with a compressed recycle CO2 stream and oxygen. The combustion stream is expanded across a turbine to produce power and passed through a recuperator heat exchanger. The expanded and cooled exhaust stream is scrubbed to provide the recycle CO2 stream, which is compressed and passed through the recuperator heat exchanger and the POX heat exchanger in a manner useful to provide increased efficiency to the combined systems.
Owner:8 RIVERS CAPTTAL LLC
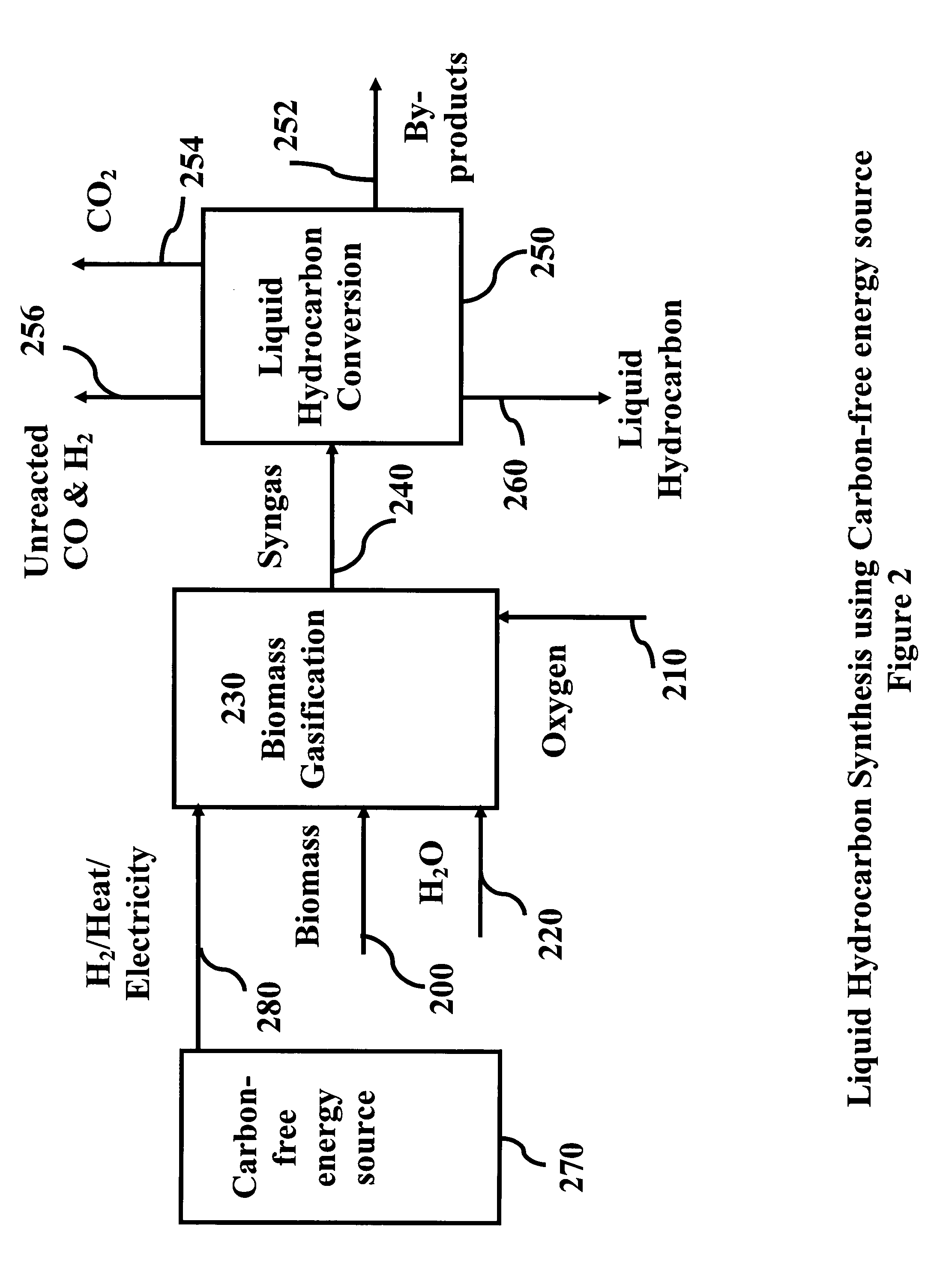
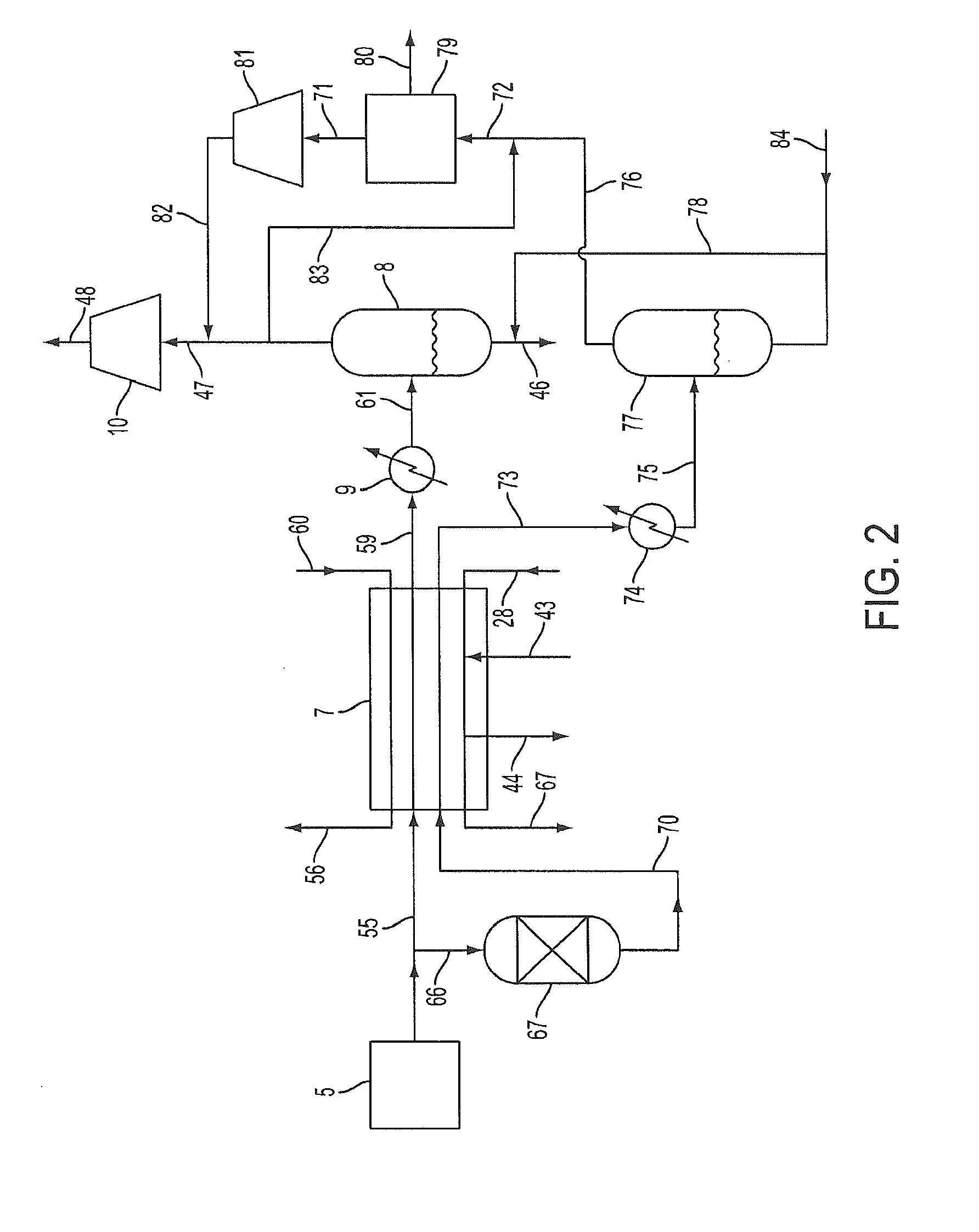
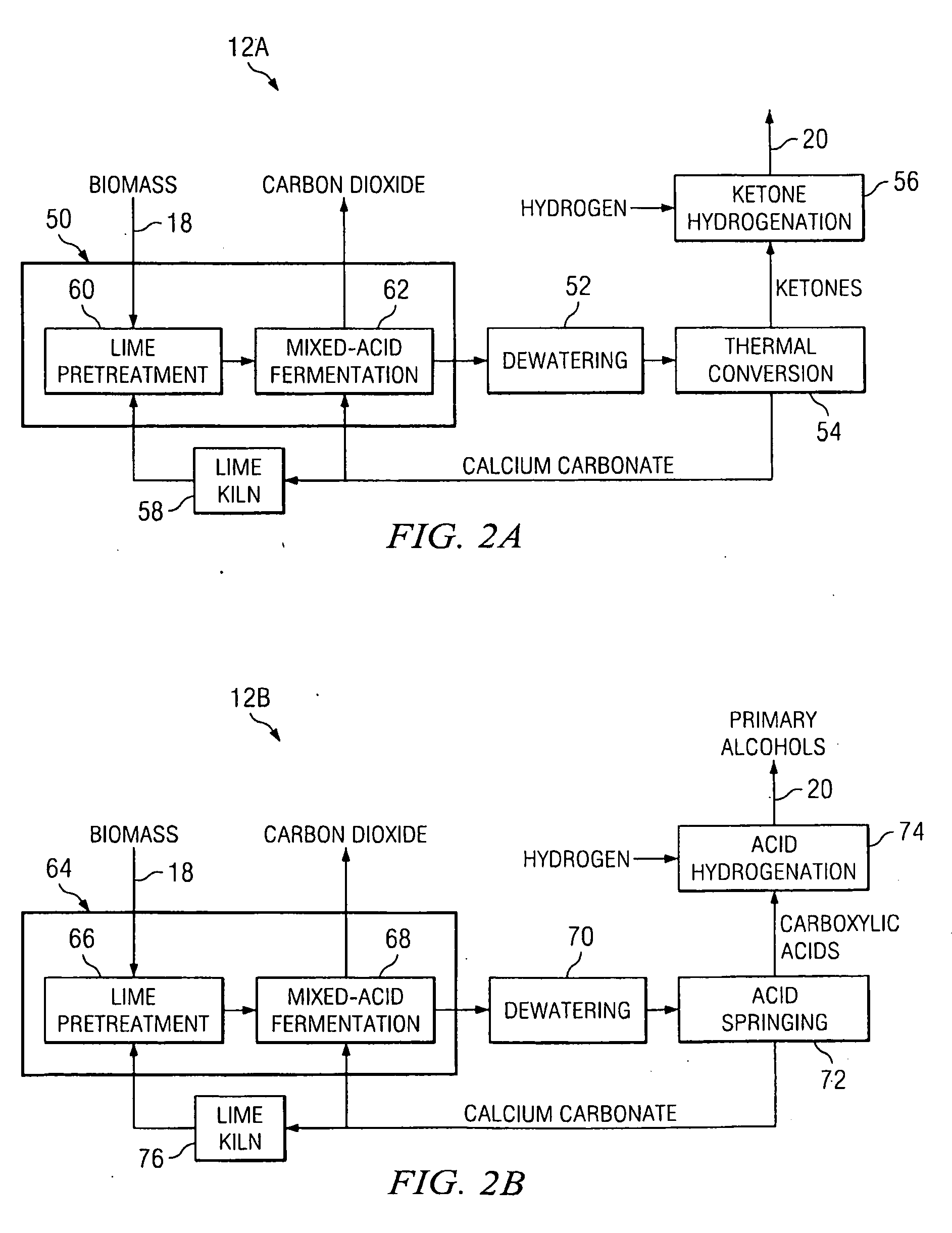
Novel process for producing liquid hydrocarbon by pyrolysis of biomass in presence of hydrogen from a carbon-free energy source
ActiveUS20090082604A1Process stabilityIncrease energy contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlkaneHydrogen
In at least one embodiment of the present invention, a method for producing liquid hydrocarbons from biomass is provided. The method comprises pyrolizing the biomass with hydrogen (H2) to form bio-oil. The bio-oil comprises alkanes, alkenes, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, aromatics, hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof. The H2 is formed from a carbon-free energy source.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Internal combustion engine system
InactiveUS20070028861A1Easy to operateInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHomogeneous charge compression ignitionAlcohol
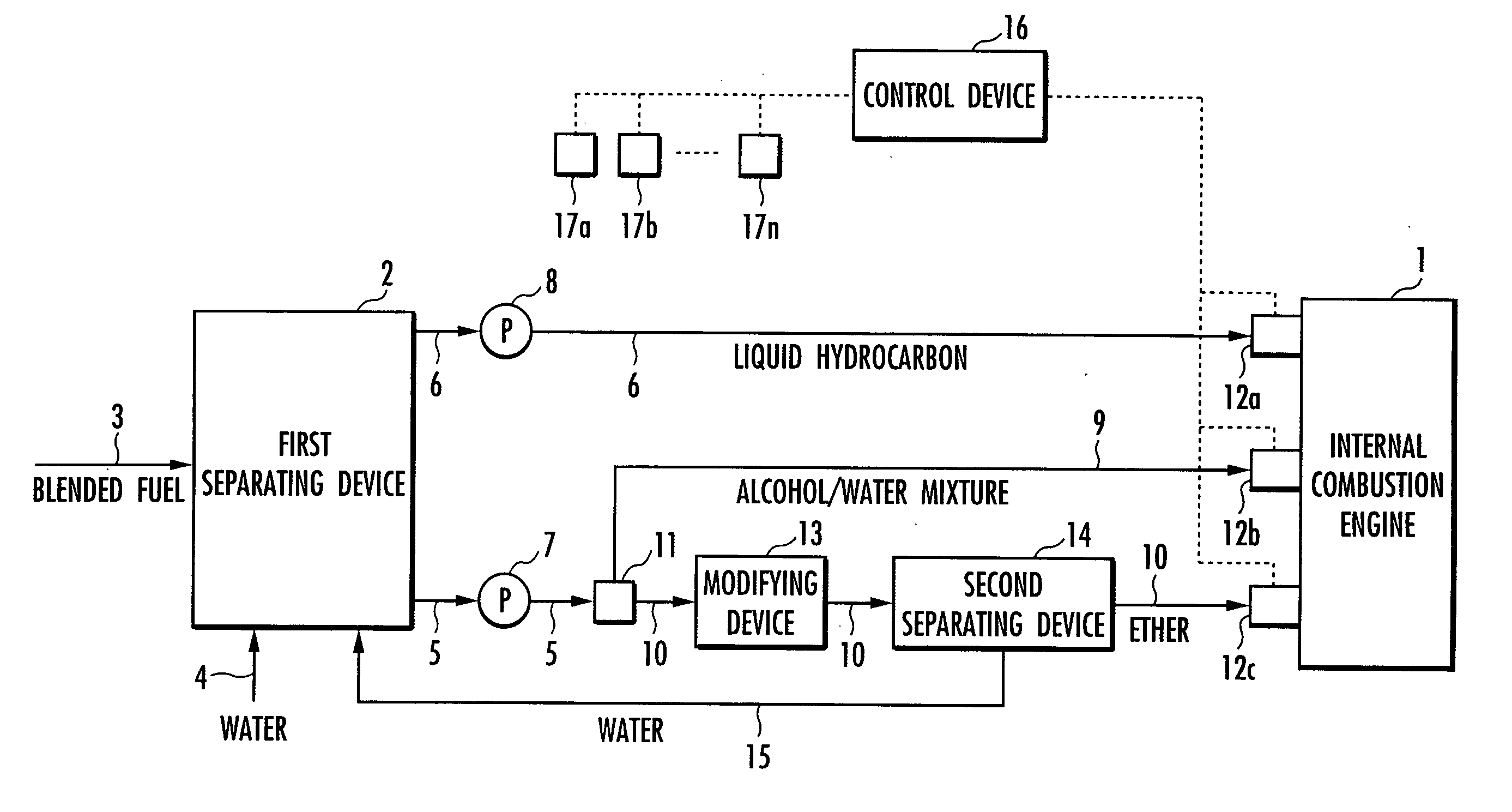
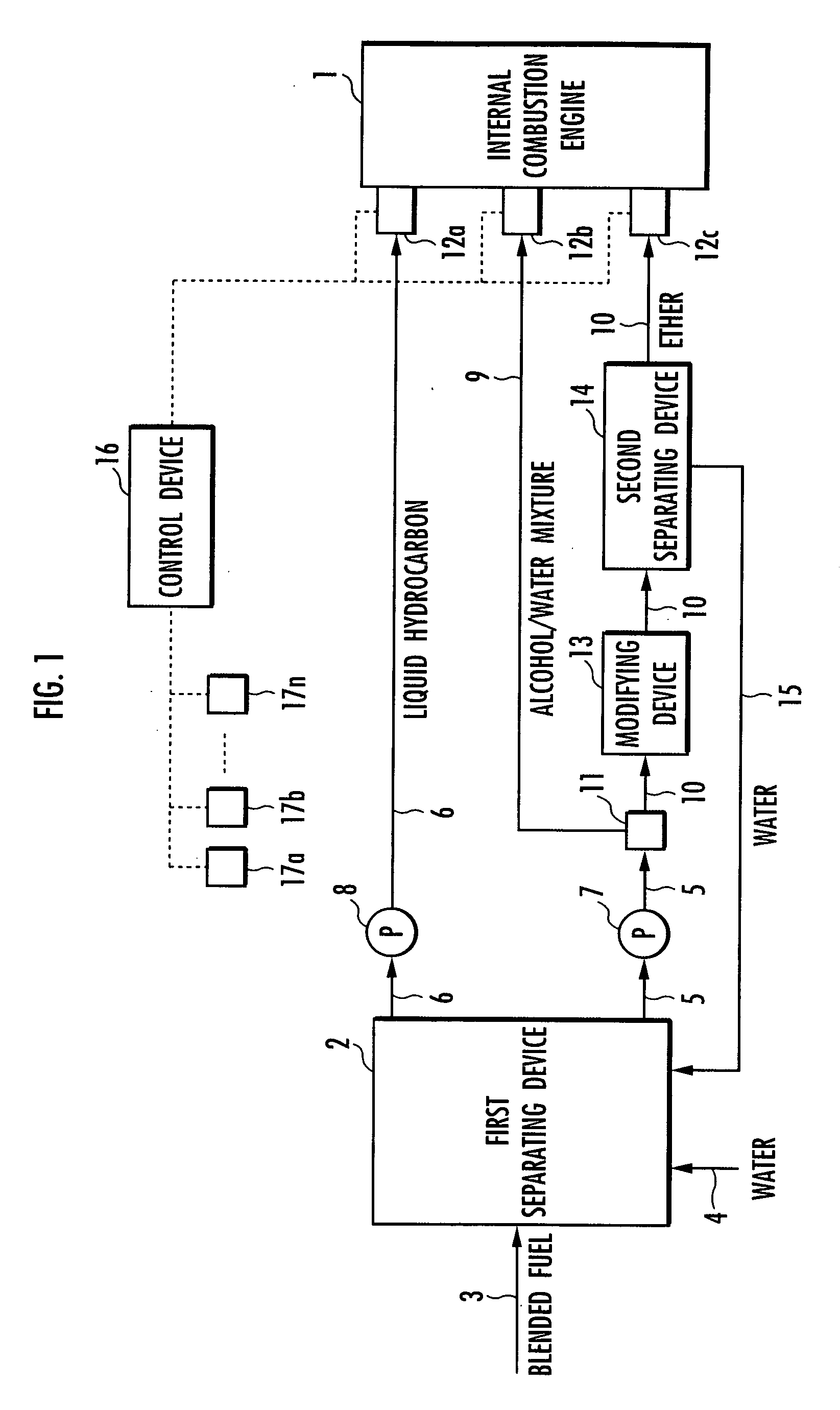
The invention provides an internal combustion engine system that uses a blended fuel consisting of hydrocarbon and alcohol, and can efficiently operate relative to a wide range of required load. The internal combustion engine system includes: an internal combustion engine 1; a first separating means 2 for separating the blended fuel into an alcohol / water mixture 21 and liquid hydrocarbon 22; a reforming means 13 for reforming the alcohol / water mixture to an ether / water mixture; a second separating means 14 for separating the ether / water mixture into the ether and the water; and control means 16 that controls the ratios of the liquid hydrocarbon 22, the alcohol / water mixture 21, and the ether. The internal combustion engine 1 is a homogeneous charge compression ignition internal combustion engine. The internal combustion engine system further includes: a first injector 12a that supplies the liquid hydrocarbon 22; a second injector 12b that supplies the alcohol / water mixture 21; and a third injector 12c that supplies the ether. The control means 16 increases the alcohol / water mixture 21 with increasing required load, and increases the ether with decreasing required load.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Process for producing liquid fuel from carbon dioxide and water
ActiveUS20070244208A1Combustible gas chemical modificationOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationHydrocotyle bowlesioidesLiquid fuel
A process for producing high octane fuel from carbon dioxide and water is disclosed. The feedstock for the production line is industrial carbon dioxide and water, which may be of lower quality. The end product can be high octane gasoline, high cetane diesel or other liquid hydrocarbon mixtures suitable for driving conventional combustion engines or hydrocarbons suitable for further industrial processing or commercial use. Products, such as dimethyl ether or methanol may also be withdrawn from the production line. The process is emission free and reprocesses all hydrocarbons not suitable for liquid fuel to form high octane products. The heat generated by exothermic reactions in the process is fully utilizes as is the heat produced in the reprocessing of hydrocarbons not suitable for liquid fuel.
Owner:CRI EHF
Hydrocarbon-Producing Catalyst, Process for Producing the Same, and Process for Producing Hydrocarbons Using the Catalyst
InactiveUS20080064769A1Increase probabilityStably and smoothly promoteHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesOrganic compound preparationRutheniumLiquid hydrocarbons
An object of the present invention is to provide a catalyst which, in the FT process, exhibits a high chain growth probability, and a high catalytic activity, can stably and smoothly promote the reaction, exhibits a high productivity of C5+, and can efficiently produce liquid hydrocarbons, and a process therefor.The invention relates to a hydrocarbon-producing catalyst obtainable by supporting a ruthenium compound on a support composed of a manganese oxide and an aluminum oxide, and which satisfies at least one of characteristics (1) and (2): (1) the catalyst being treated with an aqueous alkaline solution and subsequently subjected to calcination treatment in the air at 150 to 500° C., (2) the aluminum oxide being an aluminum oxide wherein pore volume formed by pores having a pore diameter of 8 nm or more accounts for 50% or more of total pore volume.
Owner:JAPAN OIL GAS & METALS NAT CORP +1
Integrated processes and systems for conversion of methane to multiple higher hydrocarbon products
Integrated systems are provided for the production of higher hydrocarbon compositions, for example liquid hydrocarbon compositions, from methane using an oxidative coupling of methane system to convert methane to ethylene, followed by conversion of ethylene to selectable higher hydrocarbon products. Integrated systems and processes are provided that process methane through to these higher hydrocarbon products.
Owner:LUMMUS TECH LLC
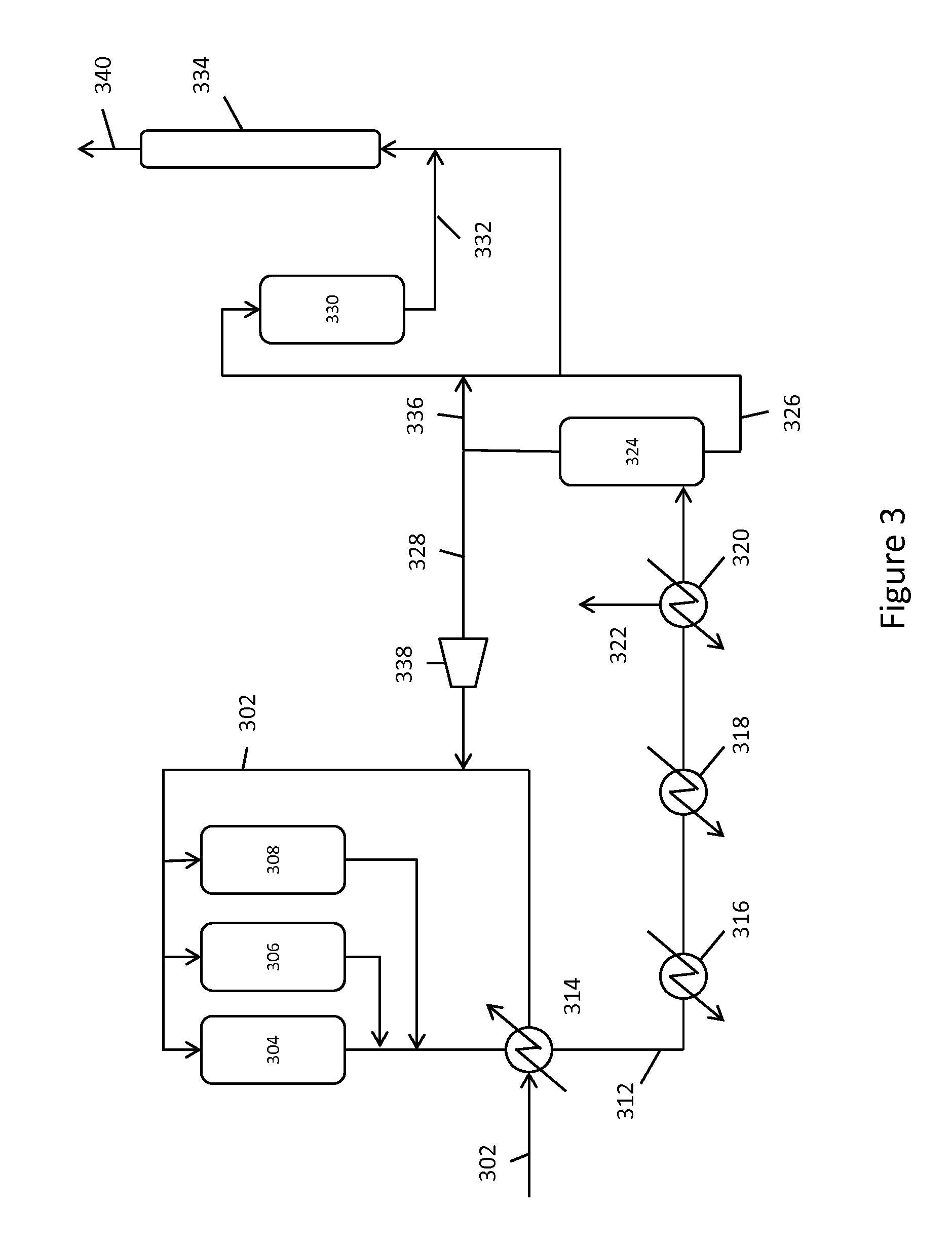
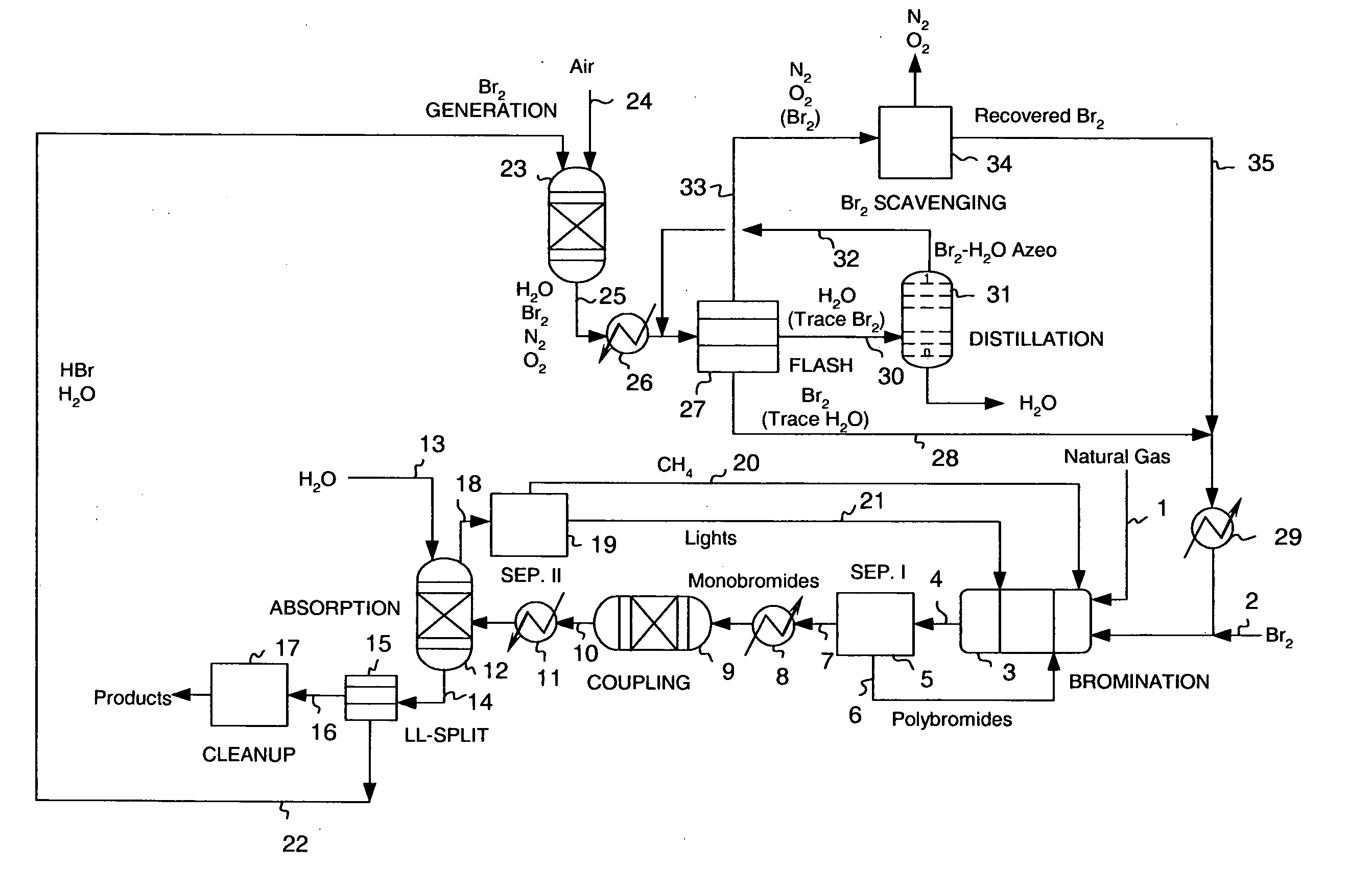
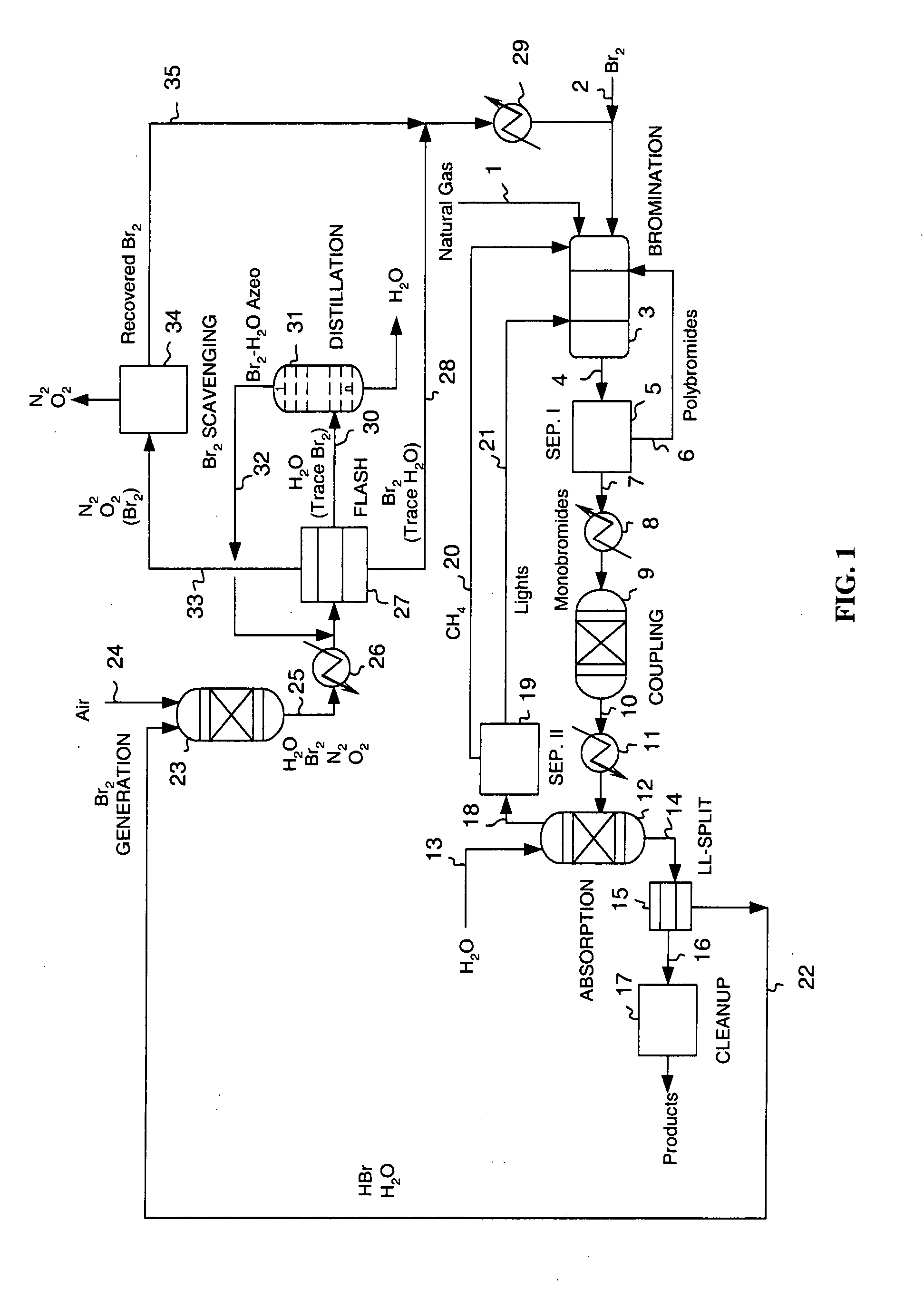
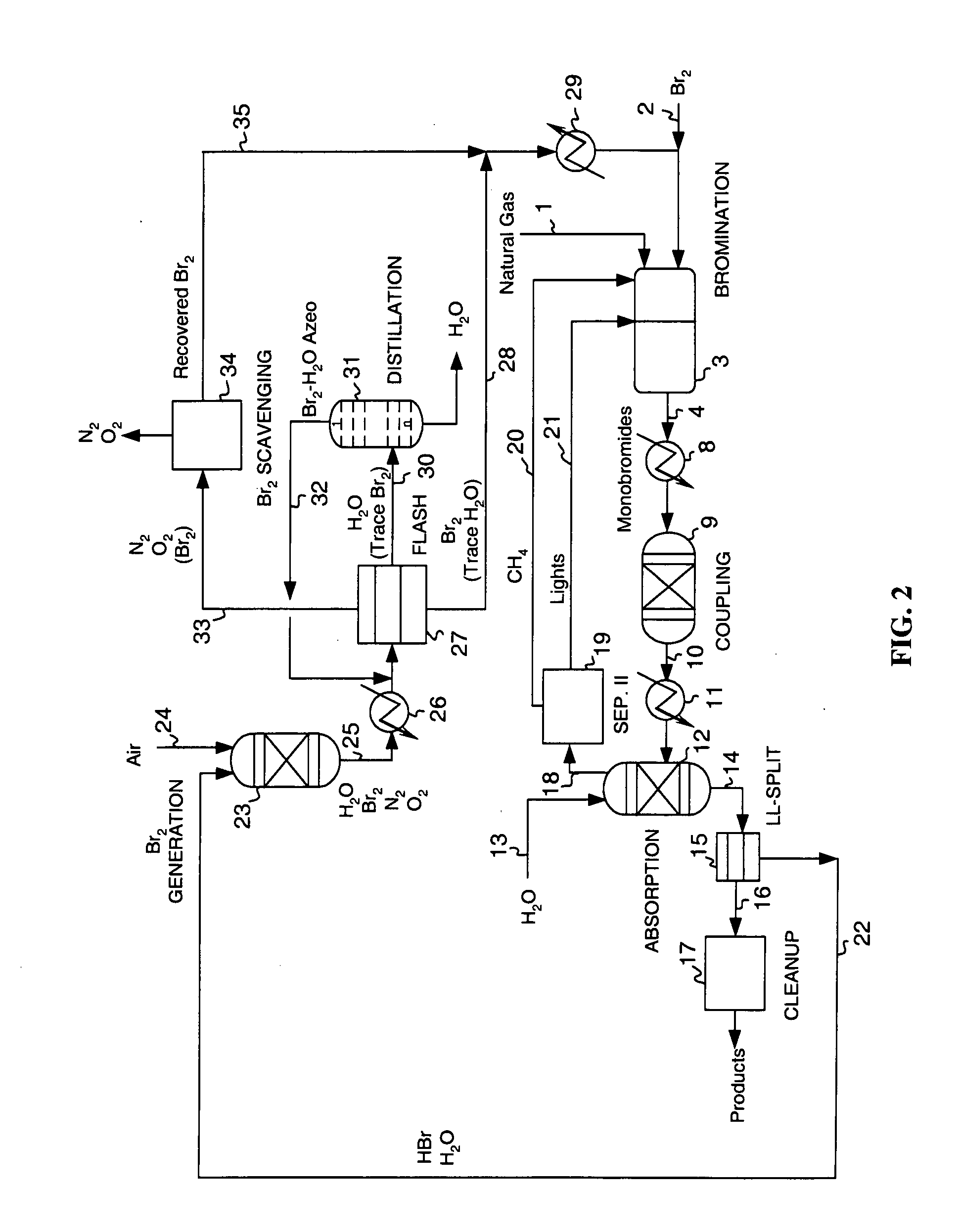
Continuous process for converting natural gas to liquid hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20070238909A1Easily toleratedContinuous regenerationMolecular sieve catalystLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryAlkaneOxygen
An improved continuous process for converting methane, natural gas, or other hydrocarbon feedstocks into one or more higher hydrocarbons or olefins by continuously cycling through the steps of alkane halogenation, product formation (carbon-carbon coupling), product separation, and regeneration of halogen is provided. Preferably, the halogen is continually recovered by reacting hydrobromic acid with air or oxygen. The invention provides an efficient route to aromatic compounds, aliphatic compounds, mixtures of aliphatic and aromatic compounds, olefins, gasoline grade materials, and other useful products.
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
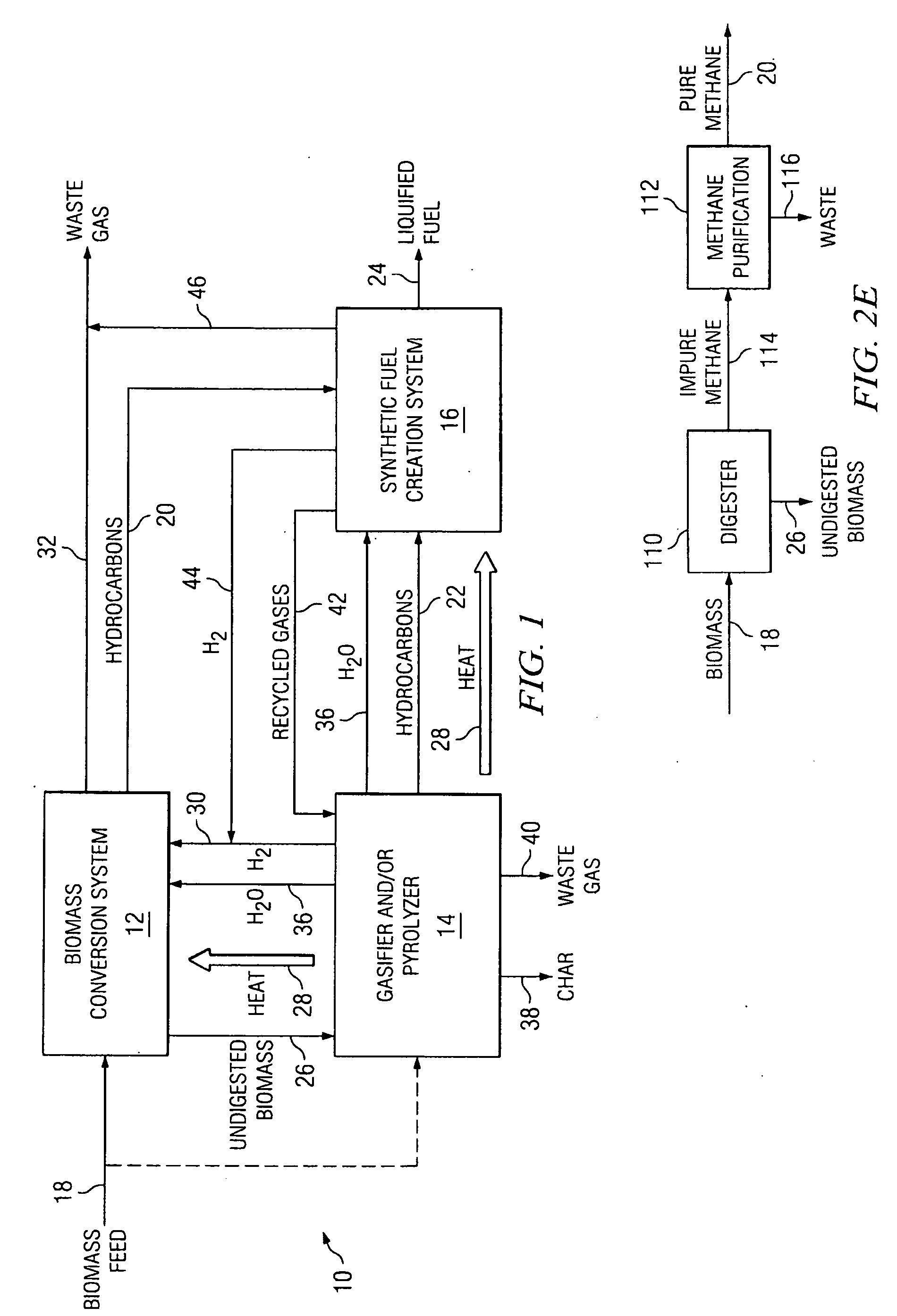
Integrated Biofuel Production System
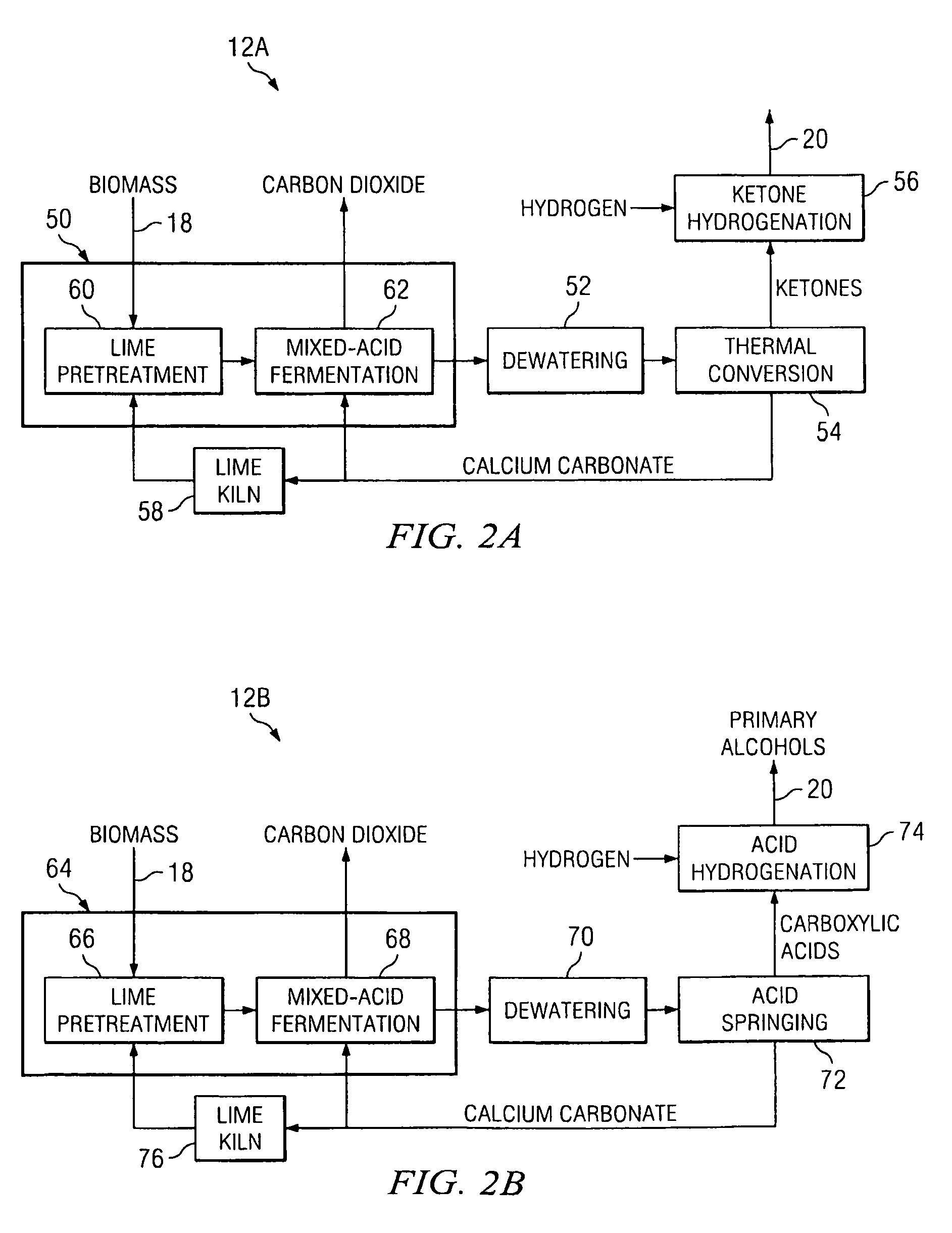
InactiveUS20090239279A1Increase energy densityImprove conversion efficiencyWaste based fuelSedimentation separationThermal energyResidual biomass
According to an embodiment, a biomass conversion subsystem produces methane and / or alcohol and residual biomass. A pyrolysis or a gasification subsystem is used to produce thermal energy and / or process gasses. The thermal energy may be stored thermal energy in the form of a pyrolysis oil. A fuel conversion subsystem produces liquid hydrocarbon fuels from the methane and / or alcohol using thermal energy and / or process gasses produced by the gasification or pyrolysis subsystem. Because the biomass production system integrates the residual products from biomass conversion and the residual thermal energy from pyrolysis or gasification, the overall efficiency of the integrated biomass production system is greatly enhanced.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
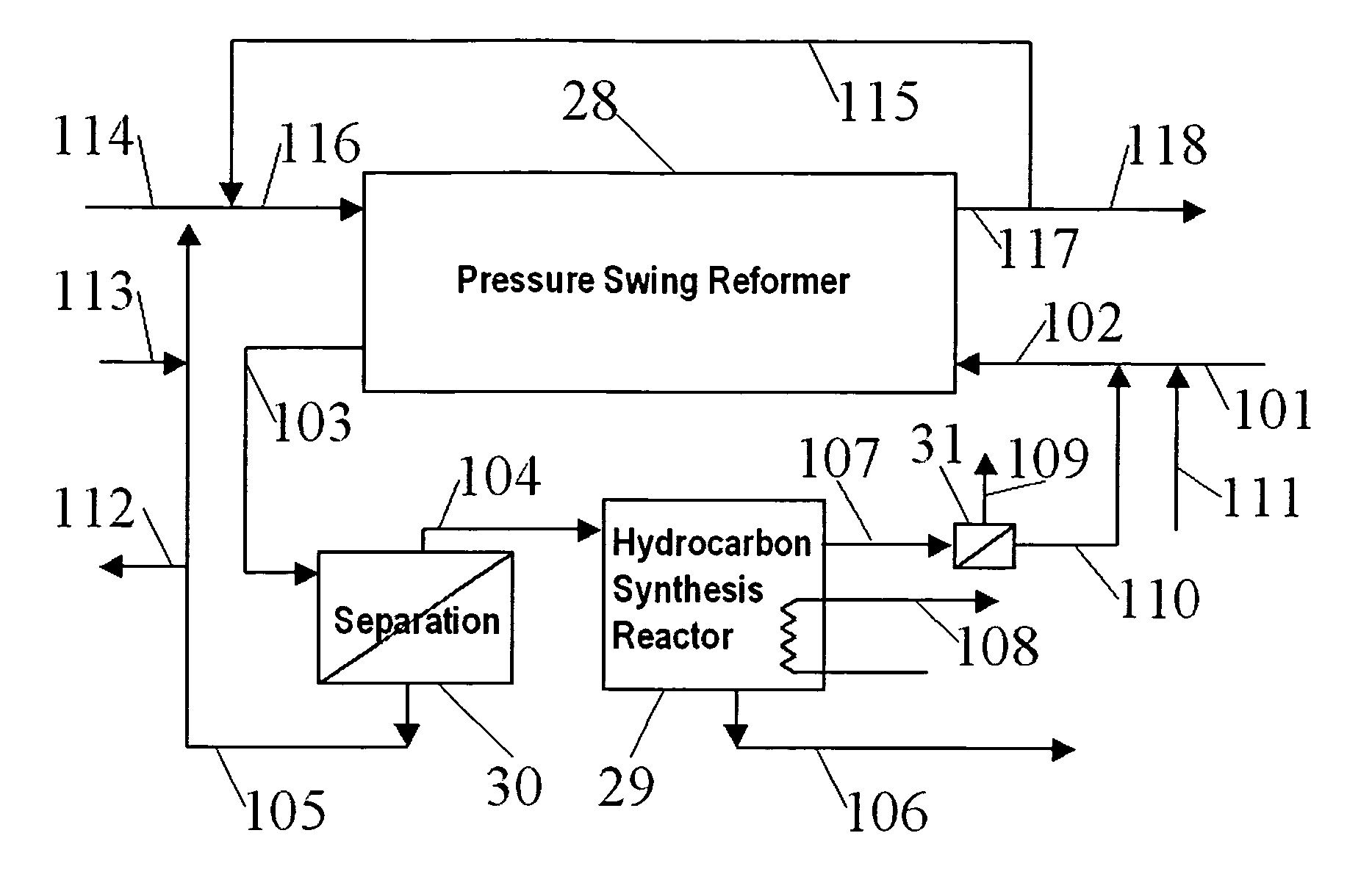
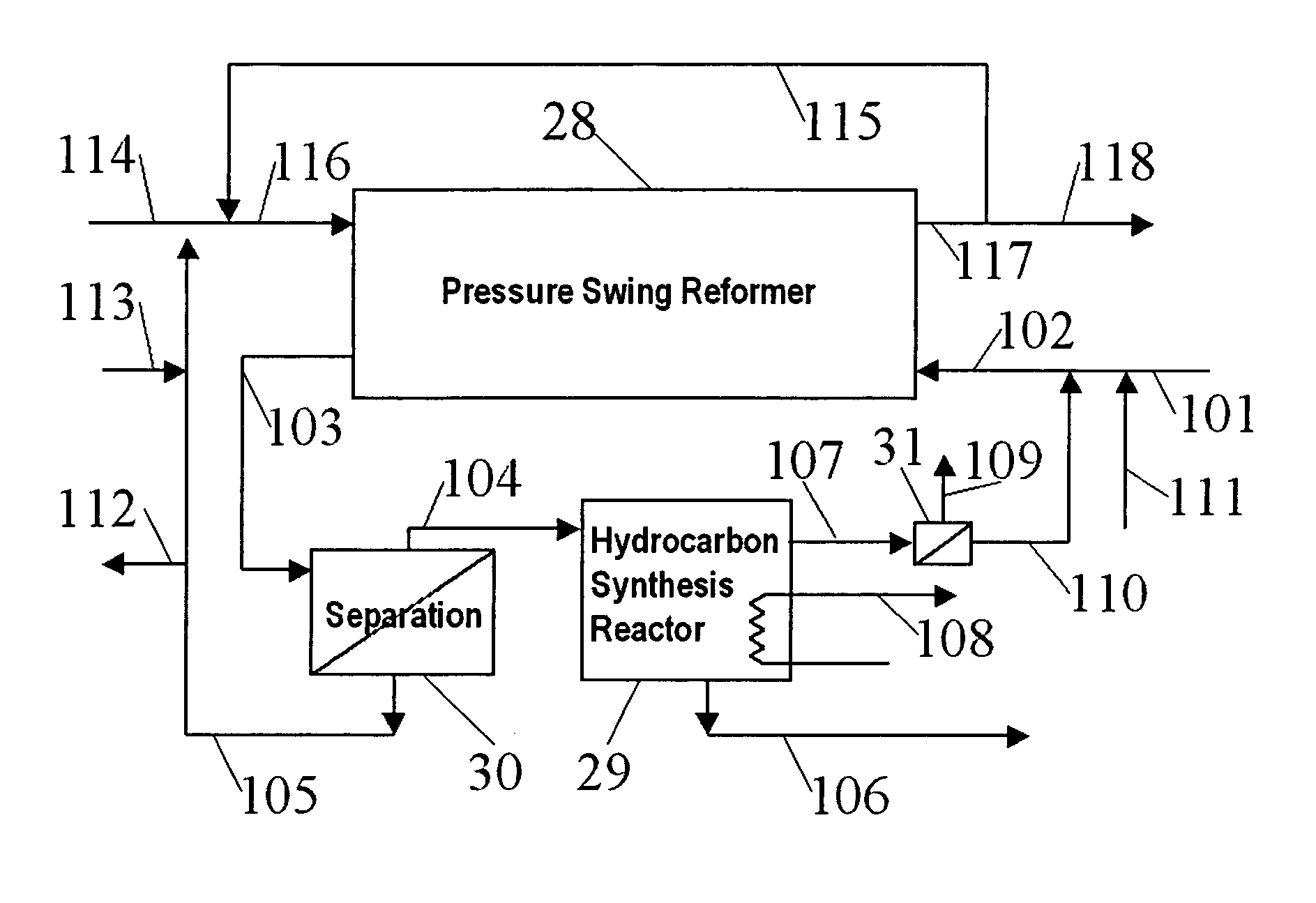
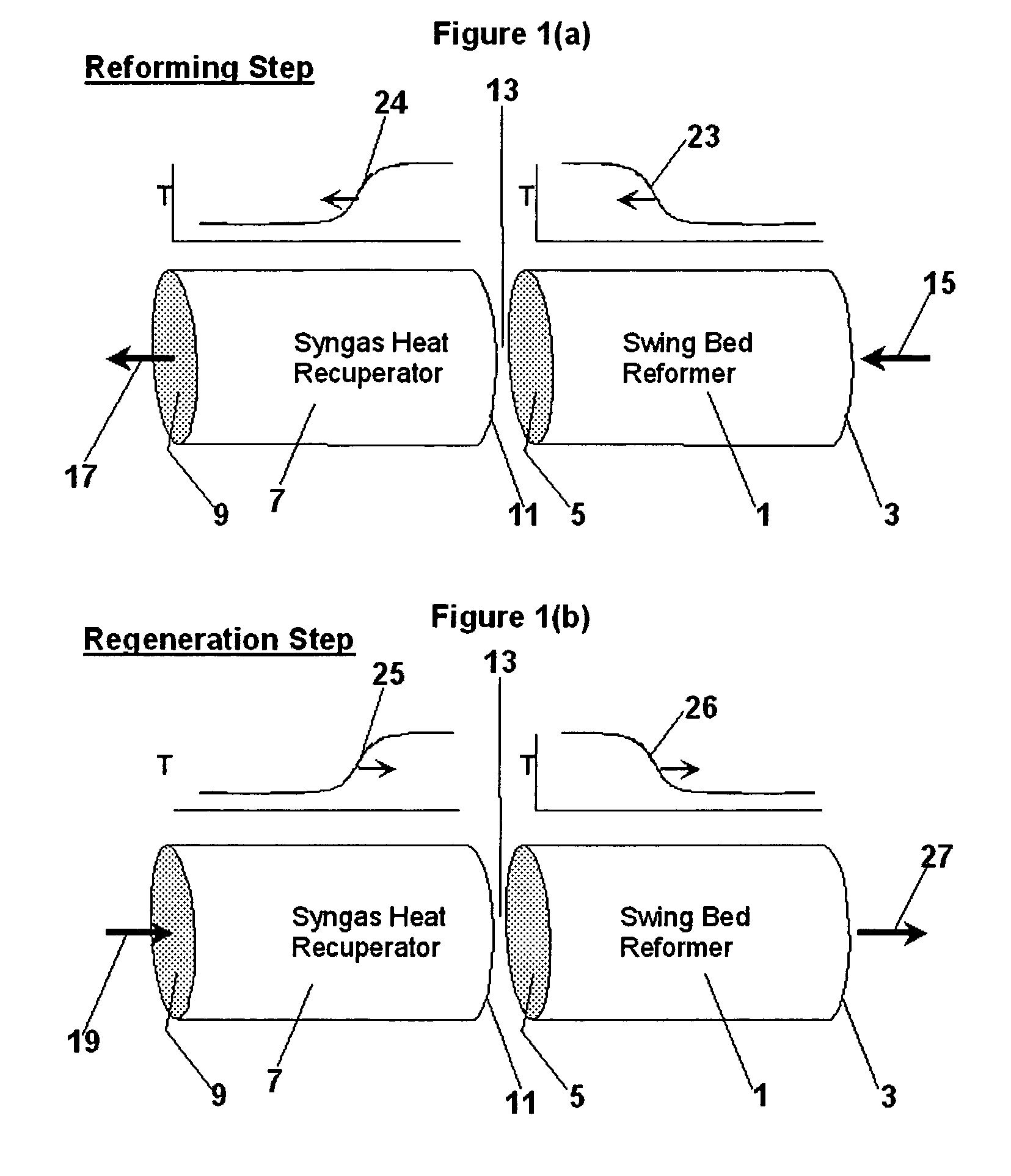
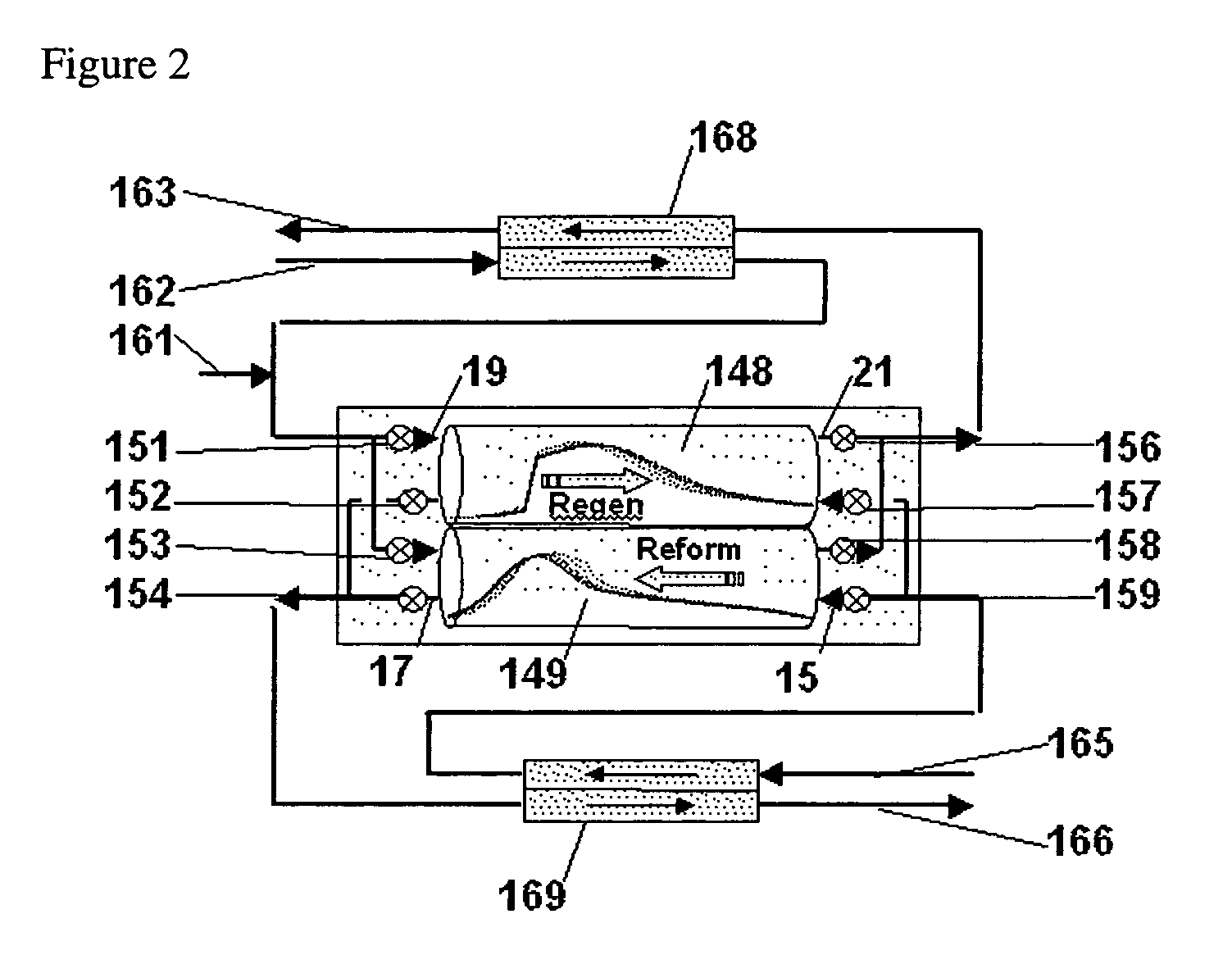
Hydrocarbon synthesis process using pressure swing reforming
ActiveUS7045553B2Material efficiencyAccelerates synthesis processOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationHydrogenLiquid productSyngas
The invention provides a method for producing liquid hydrocarbons by first generating in a pressure swing reformer a synthesis gas stream having a mole ratio of H2:CO greater than 2:1. Then, a portion of the hydrogen is separated to produce a synthesis gas stream having a mole ratio of H2:CO of about 2:1 which steam is then introduced into a hydrocarbon synthesis reactor for conversion to liquid products.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
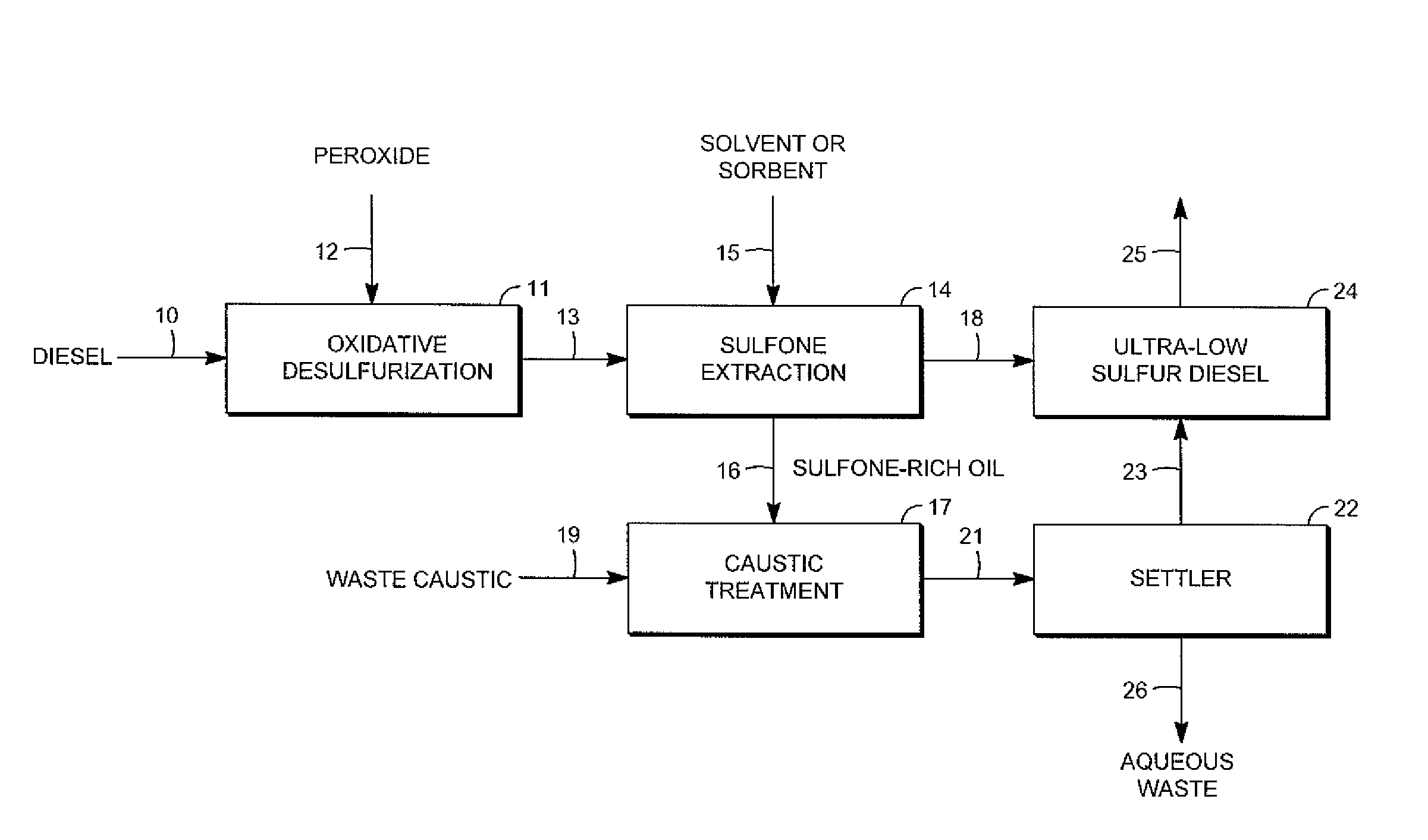
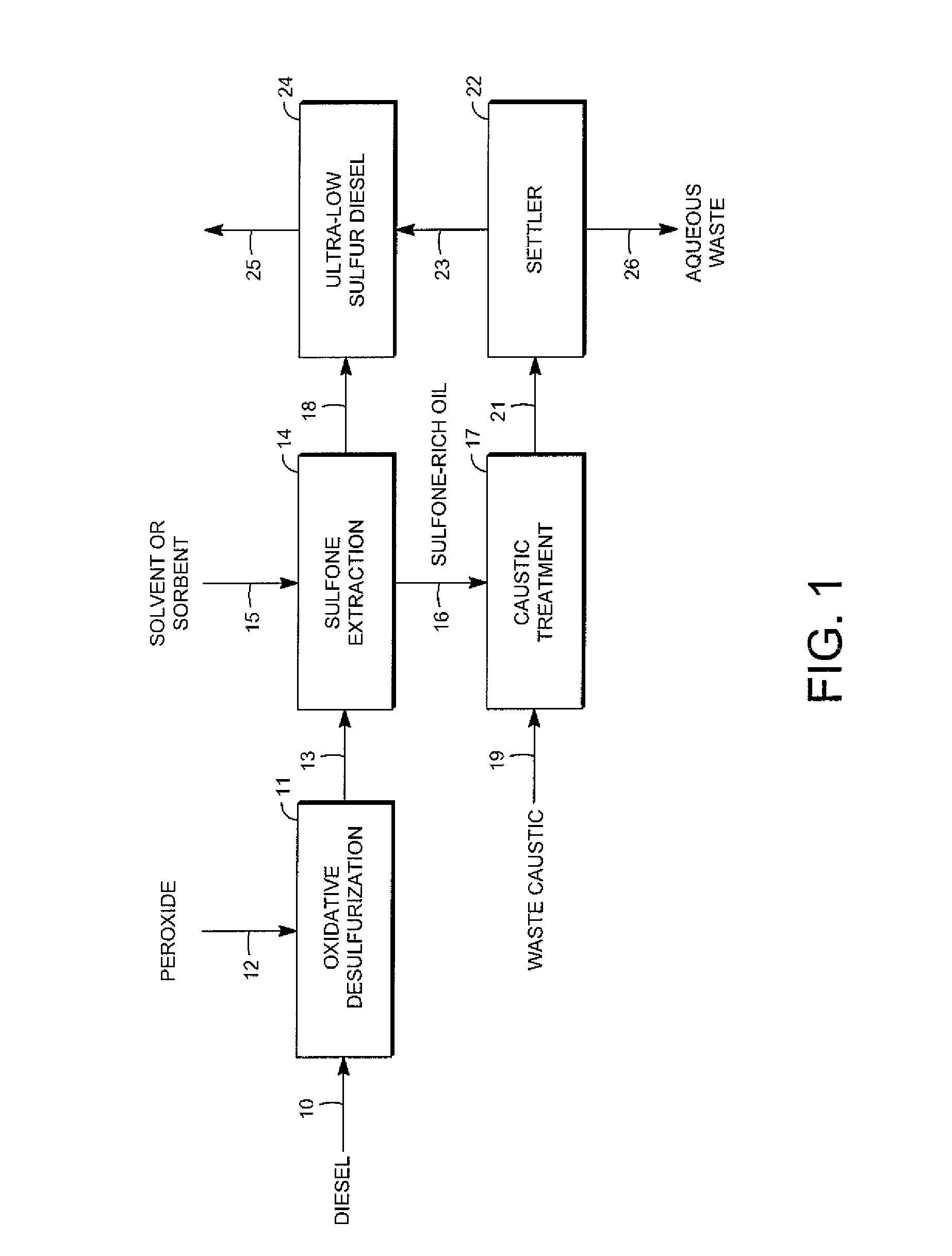
Removal of sulfur-containing compounds from liquid hydrocarbon streams
InactiveUS20090065399A1Easy to separateEasy extractionRefining with oxygen compoundsTreatment with plural serial refining stagesLiquid hydrocarbonsImproved method
An improved method for desulfurizing a fuel stream such as a diesel stream is disclosed which includes generation of a sulfone oil, the desulfurization of the sulfone oil and the recycling of the resulting biphenyl-rich stream and ultra-low sulfur diesel streams. The method includes combining a thiophene-rich diesel stream with an oxidant to oxidize the thiophenes to sulfones to provide a sulfone-rich diesel stream. Sulfone oil is extracted from the sulfone-rich diesel stream to provide sulfone oil and a first low-sulfur diesel stream The low-sulfur diesel stream is recycled. The sulfone-rich oil stream is combined with an aqueous oxidant-containing stream, such as caustic stream, which oxidizes the sulfones to biphenyls and forms sulfite to provide a second low-sulfur diesel stream
Owner:UOP LLC
Reduced-emission gasification and oxidation of hydrocarbon materials for liquid fuel production
InactiveUS8038746B2Reduce system sizeHigh heat transfer rateHydrogenGas modification by gas mixingLiquid hydrocarbonsLiquid fuel
Owner:CLARK STEVE L
Hydrocarbon synthesis process using pressure swing reforming
ActiveUS7053128B2HydrogenOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationLiquid productHydrogen
The invention provides a method for producing liquid hydrocarbons by first generating in a pressure swing reformer a synthesis gas stream having a mole ratio of H2:CO greater than 2:1. Then, a portion of the hydrogen is separated to produce a synthesis gas stream having a mole ratio of H2:CO of about 2:1 which steam is then introduced into a hydrocarbon synthesis reactor for conversion to liquid products.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Synthetic fuel production methods and apparatuses
InactiveUS20080098654A1Promote conversionReduce the amount requiredMuffle furnacesRetortsLiquid hydrocarbonsLiquid fuel
Carbon-containing tail gases and pollutants in a coal-to-liquid hydrocarbon production process, or other liquid fuel production process, may be reacted to produce additional synthesis gas which may be used to produce liquid fuels and hydrocarbons or which may be recycled within the liquid fuel production process to improve conversion of carbon to liquid fuels or hydrocarbons.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
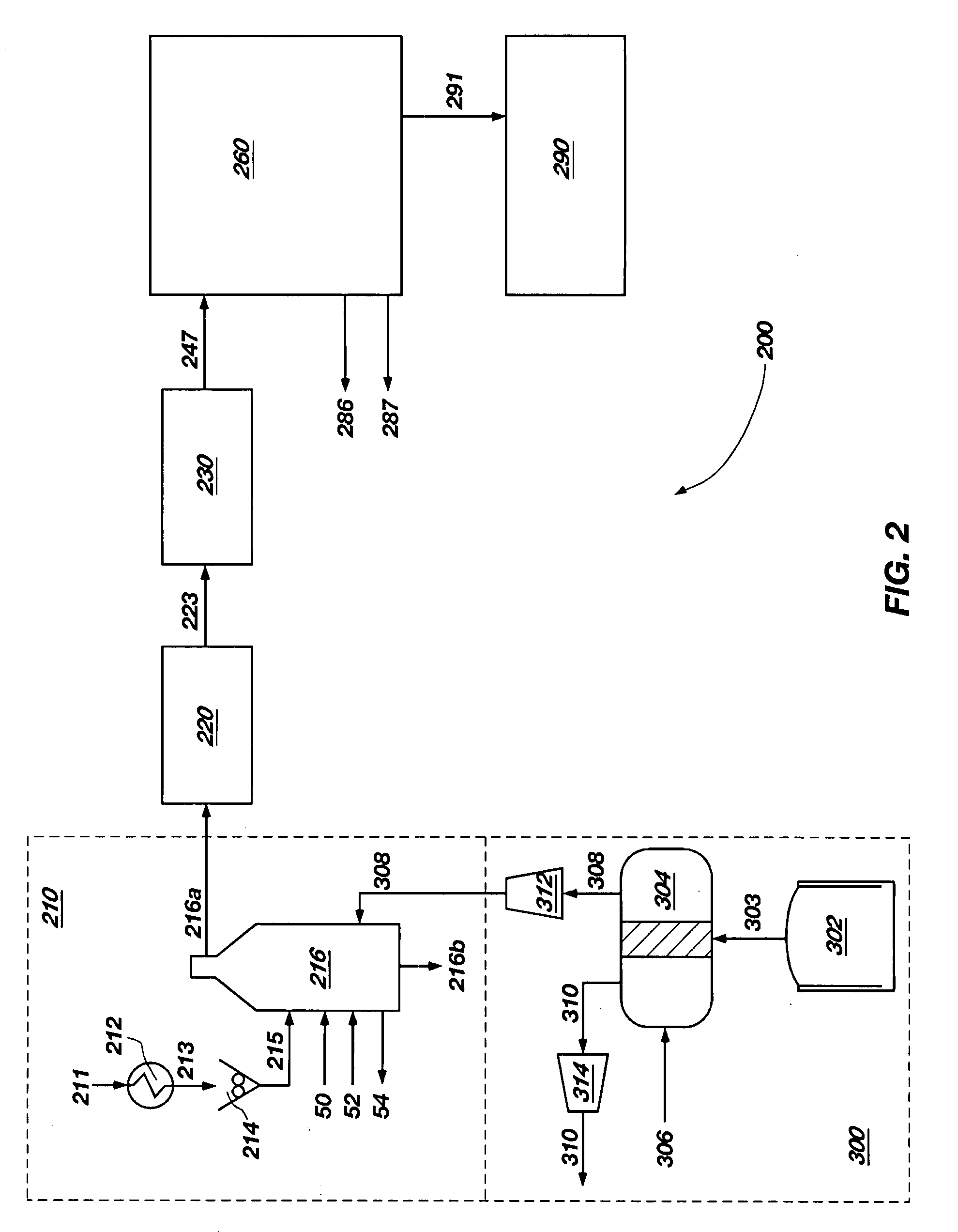
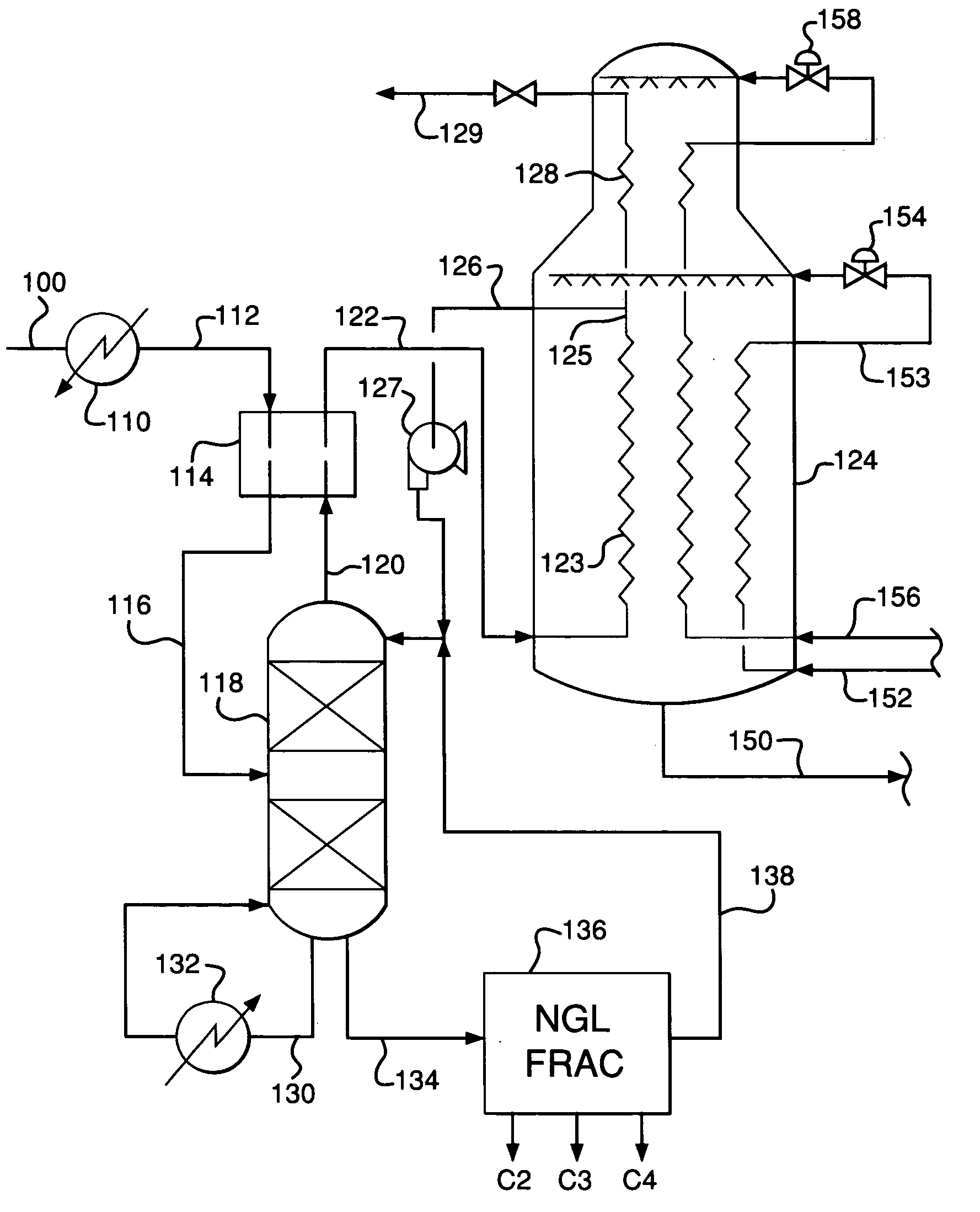
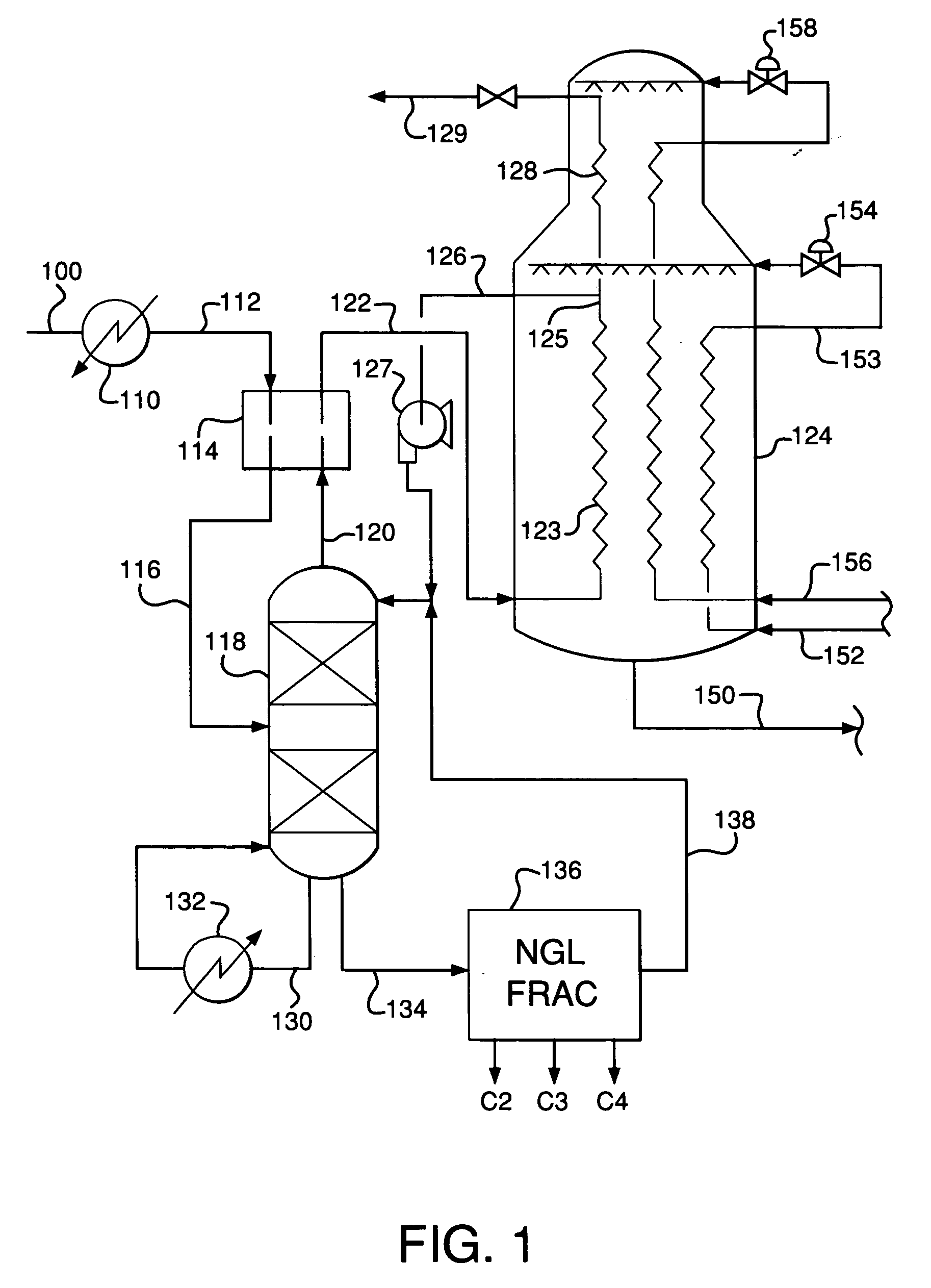
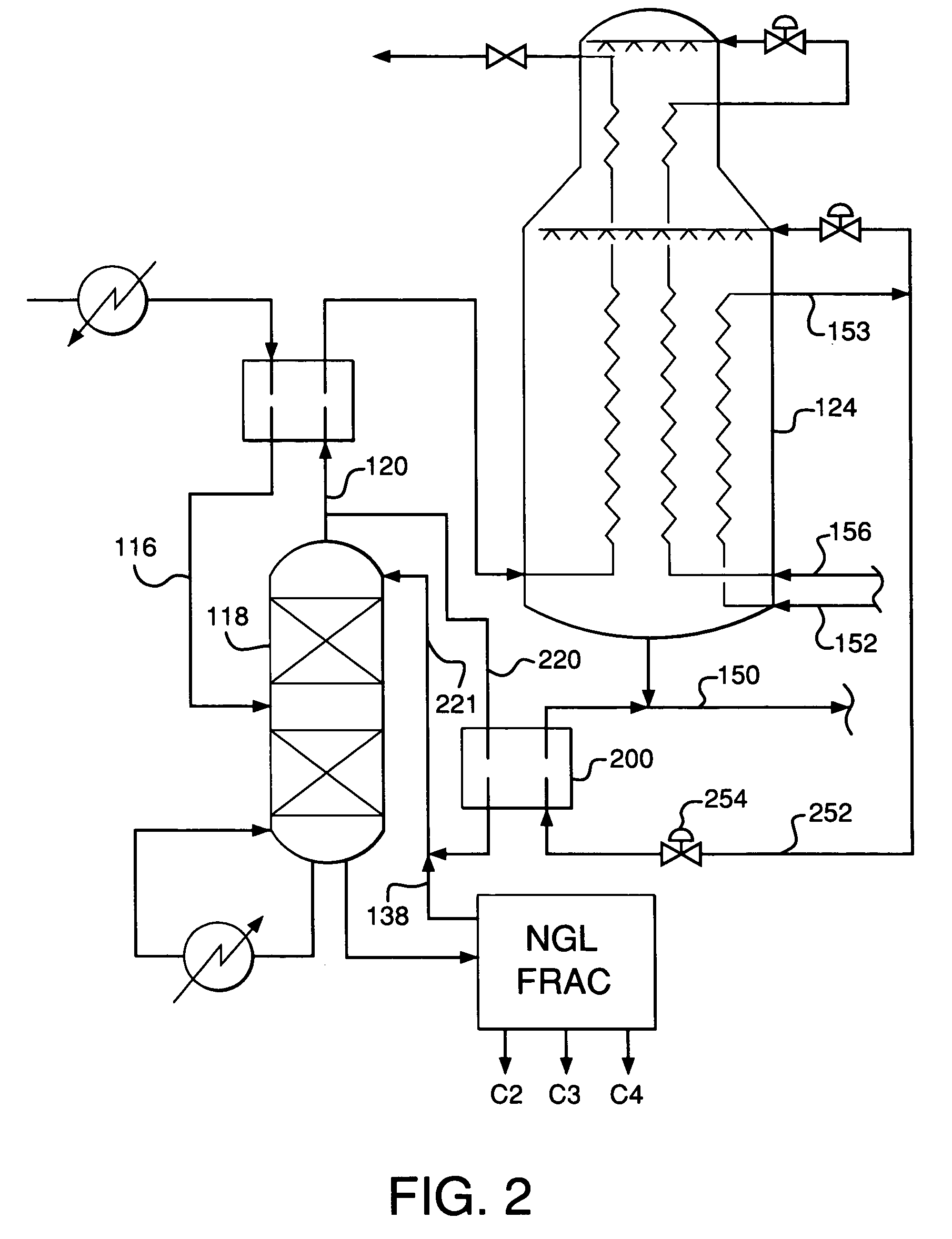
Integrated NGL recovery in the production of liquefied natural gas
Process for the liquefaction of natural gas and the recovery of components heavier than methane wherein natural gas is cooled and separated in a first distillation column into an overhead vapor enriched in methane and a bottoms stream enriched in components heavier than methane, wherein the first distillation column utilizes a liquefied methane-containing reflux stream. This reflux stream may be provided by a condensed portion of the overhead vapor or a portion of totally condensed overhead vapor that is subsequently warmed. The bottoms stream may be separated in one or more additional distillation columns to provide one or more product streams, any of which are partially or totally withdrawn as recovered hydrocarbons. A stream of unrecovered liquid hydrocarbons may be combined with either the condensed portion of the overhead vapor or a portion of totally condensed overhead vapor that is subsequently warmed.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method of hydraulic fracturing to reduce unwanted water production
ActiveUS7207386B2Limit undesirable height growthFluid removalDrilling compositionSaline waterGeomorphology
A method of hydraulically fracturing a hydrocarbon-bearing subterranean formation ensures that the conductivity of water inflow below the productive zone of the subterranean formation is reduced. The method consists of two principal steps. In the first step, a fracture in and below the productive zone of the formation is initiated by introducing into the subterranean formation a fluid, free of a proppant, such as salt water, fresh water, brine, liquid hydrocarbon, and / or nitrogen or other gases. The proppant-free fluid may further be weighted. In the second step, a proppant laden slurry is introduced into the subterranean formation which contains a relatively lightweight density proppant. Either the fluid density of the proppant-free fluid is greater than the fluid density of the proppant laden slurry or the viscosity of the proppant-free fluid is greater than the viscosity of the proppant laden slurry. The method limits undesirable fracture height growth in the hydrocarbon-bearing subterranean formation during the fracturing.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
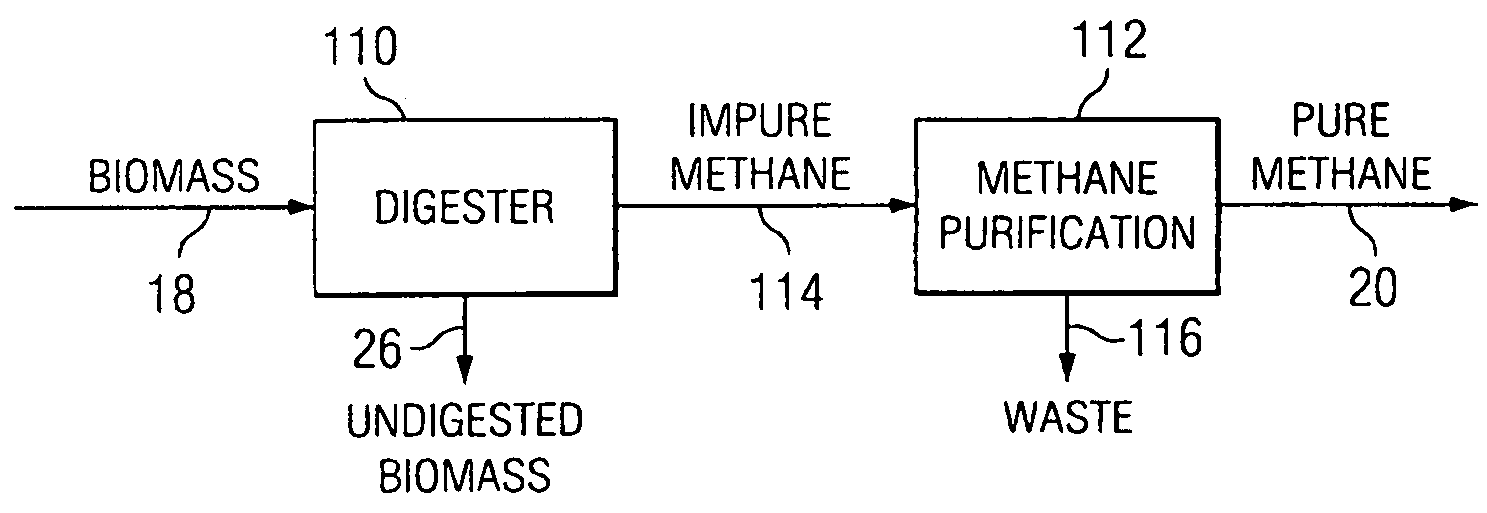
Integrated biofuel production system
InactiveUS8153850B2Improve efficiencyIncrease energy densityGas production bioreactorsWaste based fuelThermal energySystem integration
According to an embodiment, a biomass conversion subsystem produces methane and / or alcohol and residual biomass. A pyrolysis or a gasification subsystem is used to produce thermal energy and / or process gasses. The thermal energy may be stored thermal energy in the form of a pyrolysis oil. A fuel conversion subsystem produces liquid hydrocarbon fuels from the methane and / or alcohol using thermal energy and / or process gasses produced by the gasification or pyrolysis subsystem. Because the biomass production system integrates the residual products from biomass conversion and the residual thermal energy from pyrolysis or gasification, the overall efficiency of the integrated biomass production system is greatly enhanced.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Partial oxidation reaction with closed cycle quench
ActiveUS20130205746A1Prevent metal dustingReaction is slowSolidificationLiquefactionPartial oxidationCombustor
The present disclosure relates to a power production system that is adapted to achieve high efficiency power production with complete carbon capture when using a solid or liquid hydrocarbon or carbonaceous fuel. More particularly, the solid or liquid fuel first is partially oxidized in a partial oxidation reactor. The resulting partially oxidized stream that comprises a fuel gas is quenched, filtered, cooled, and then directed to a combustor of a power production system as the combustion fuel. The partially oxidized stream is combined with a compressed recycle CO2 stream and oxygen. The combustion stream is expanded across a turbine to produce power and passed through a recuperator heat exchanger. The expanded and cooled exhaust stream is scrubbed to provide the recycle CO2 stream, which is compressed and passed through the recuperator heat exchanger and the POX heat exchanger in a manner useful to provide increased efficiency to the combined systems.
Owner:8 RIVERS CAPTTAL LLC
Process and System for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbon fuels
ActiveUS7420004B2High volumetric and gravimetric energy densityExcellent resistance to thermal oxidation processLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionOxygen compounds purification/separationOcean thermal energy conversionElectric power
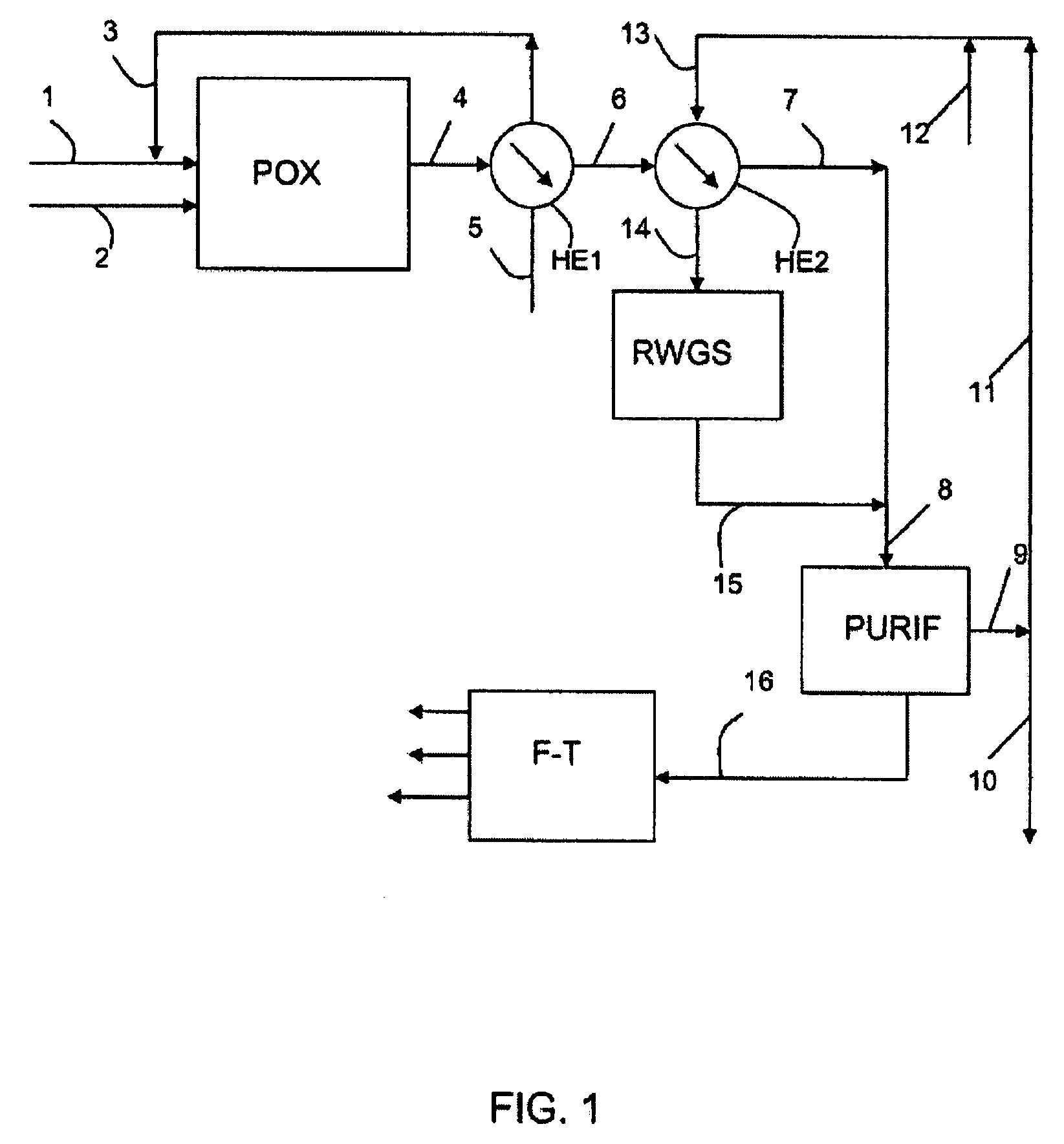
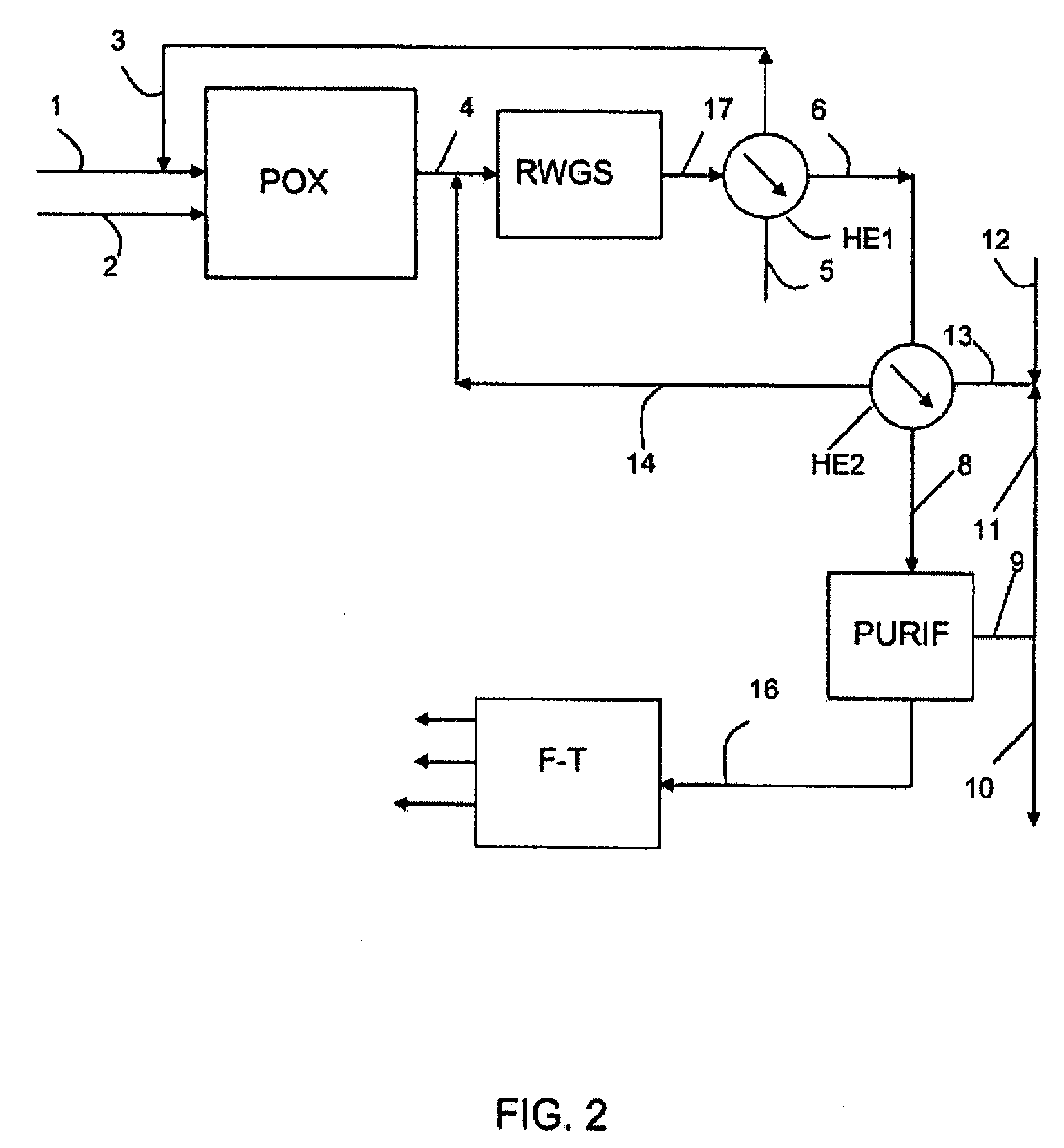
A process for producing synthetic hydrocarbons that reacts carbon dioxide, obtained from seawater of air, and hydrogen obtained from water, with a catalyst in a chemical process such as reverse water gas shift combined with Fischer Tropsch synthesis. The hydrogen is produced by nuclear reactor electricity, nuclear waste heat conversion, ocean thermal energy conversion, or any other source that is fossil fuel-free, such as wind or wave energy. The process can be either land based or sea based.
Owner:NAVY U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
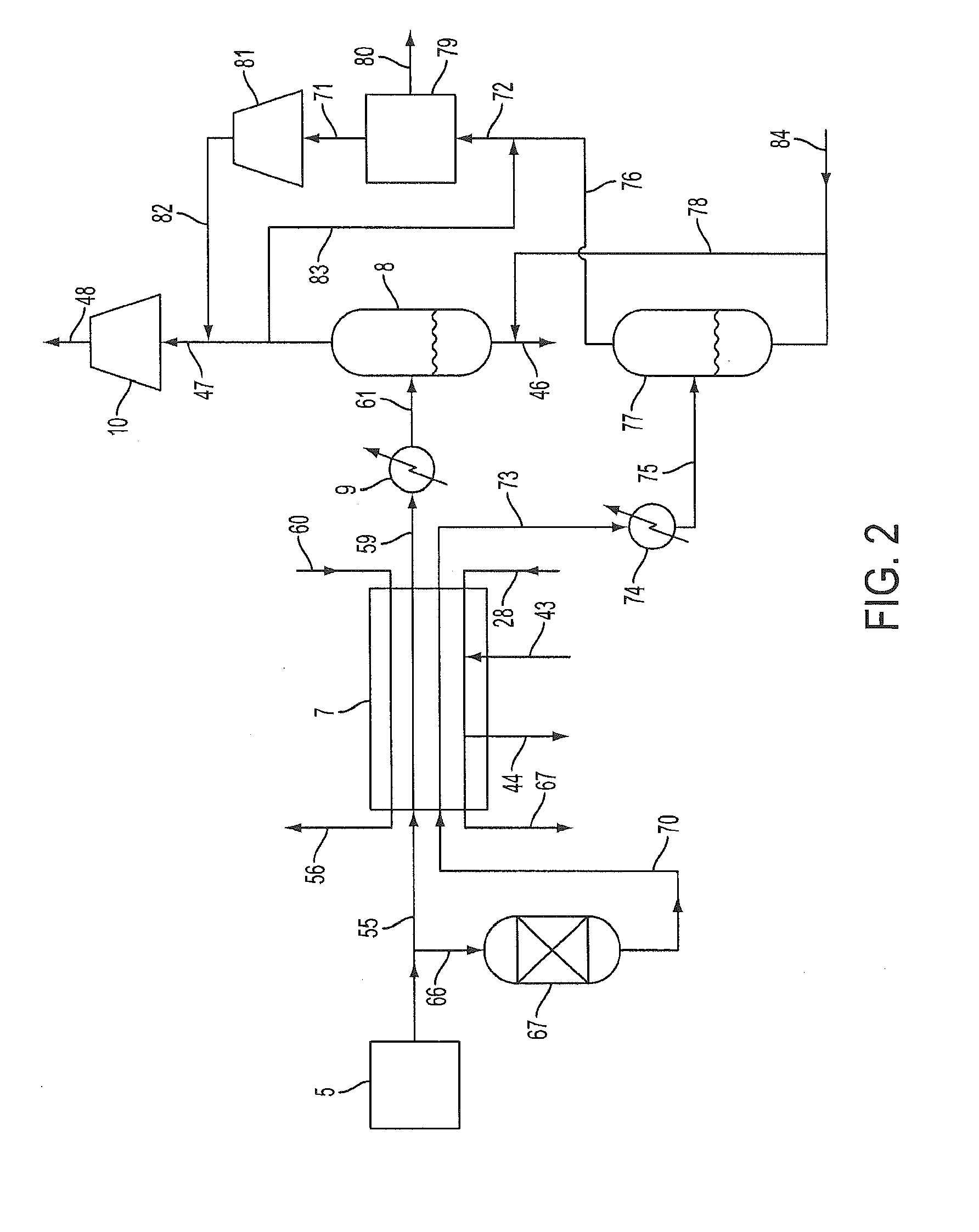
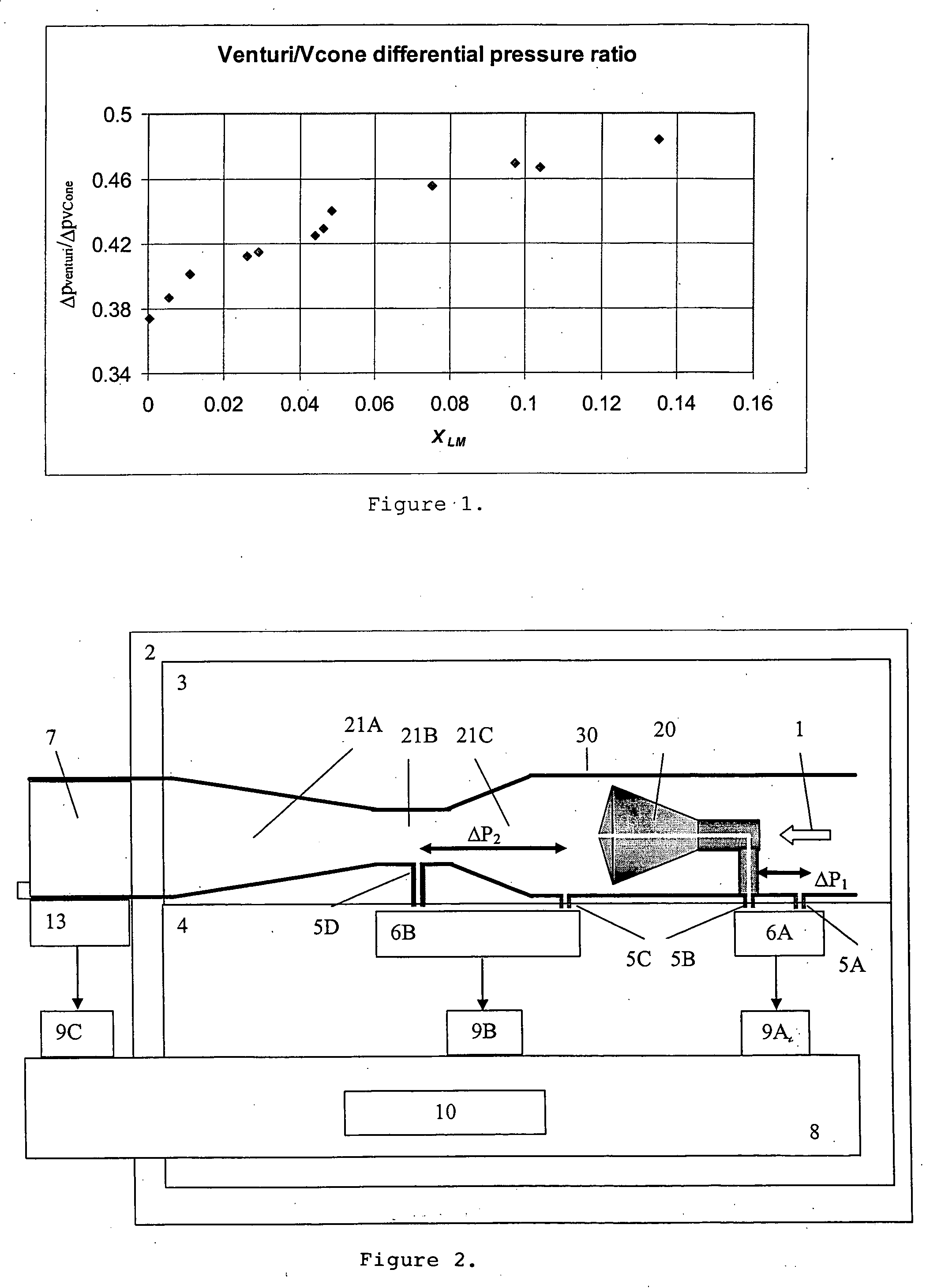
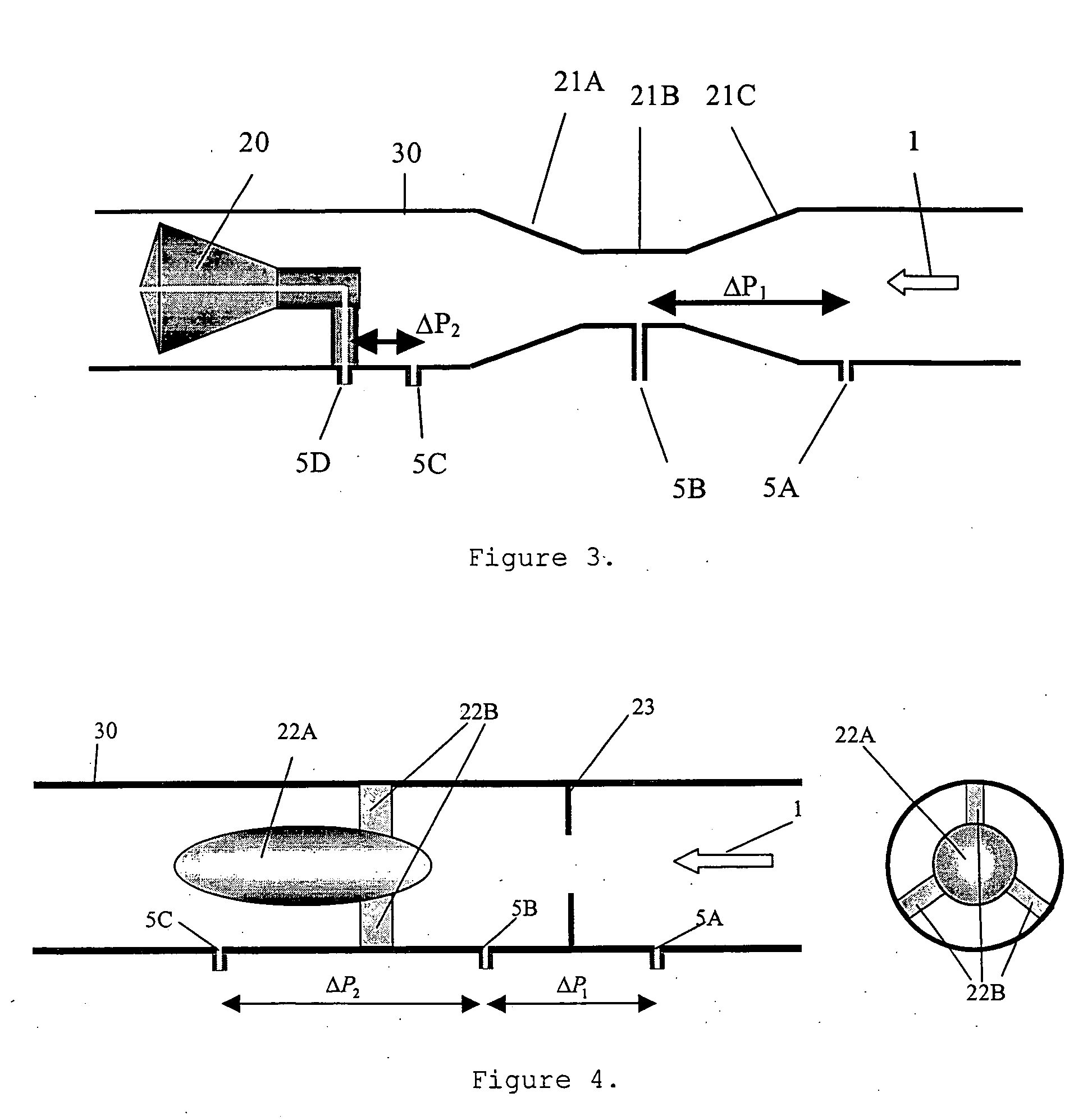
Flow meter
ActiveUS20050188771A1Specific gravity by measuring pressure differencesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLiquid stateDifferential pressure
A flow meter obtains the individual flow rates of gas, liquid hydrocarbons, and water in a predominantly gas-containing flowing fluid mixture. The flow meter comprises a water content meter (7) provides a signal representing a measure of the water content of said fluid. It also comprises a double differential pressure generating (3) and measuring (4) structure, denoted a DDP-unit (2), that provides two measurement signals (6A and 6B) representing two independent values of differential pressure (DP) in said fluid (1). In addition to the above, the meter also comprises a signal processing unit (8) having inputs (9A-C) for receiving the measurement signals and the water content signal, and a calculation module (10) which calculates values representing the volumetric flow rates of said gas, liquid hydrocarbons and water in said fluid.
Owner:ROXAR FLOW MEASUREMENT
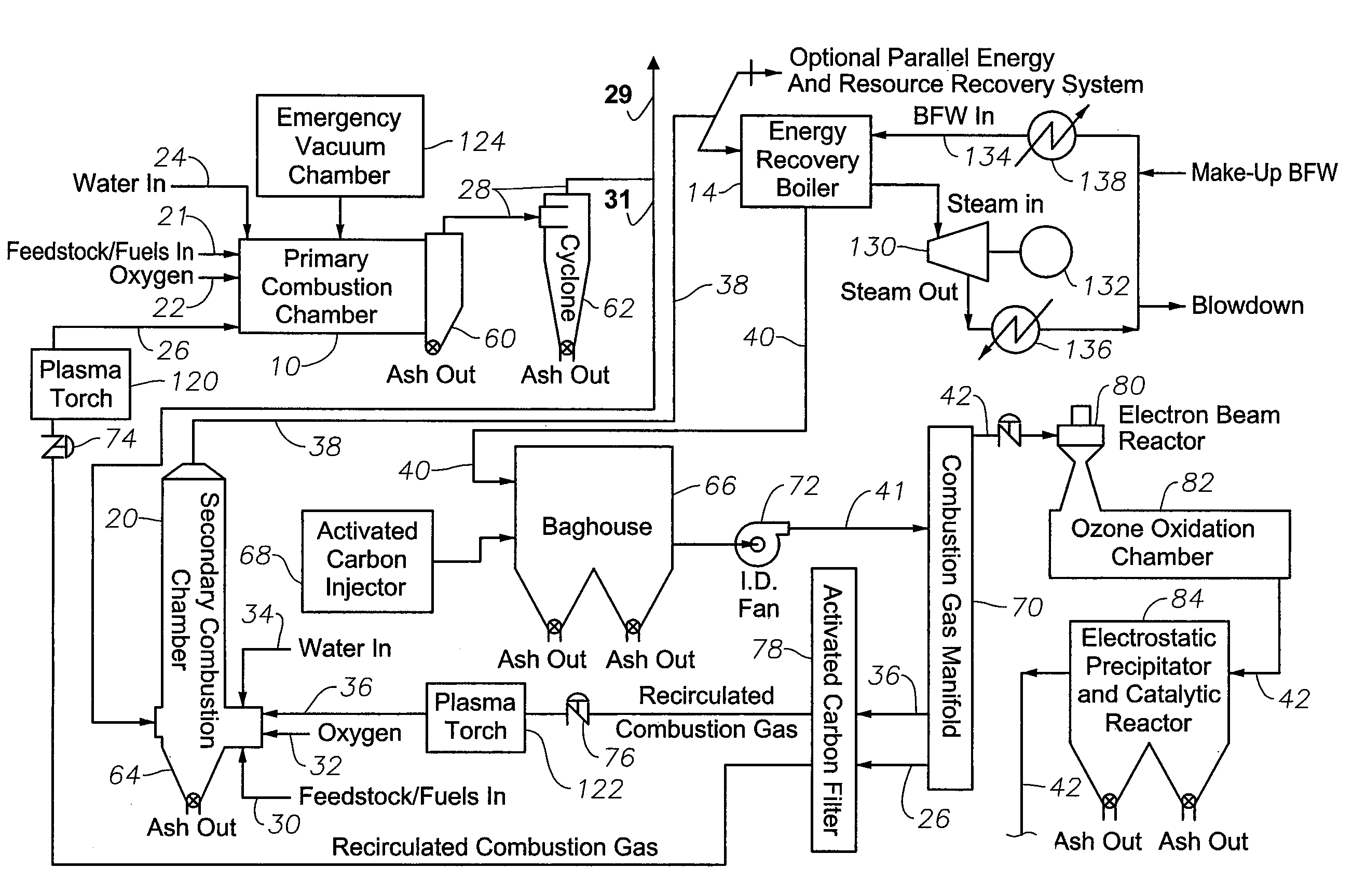
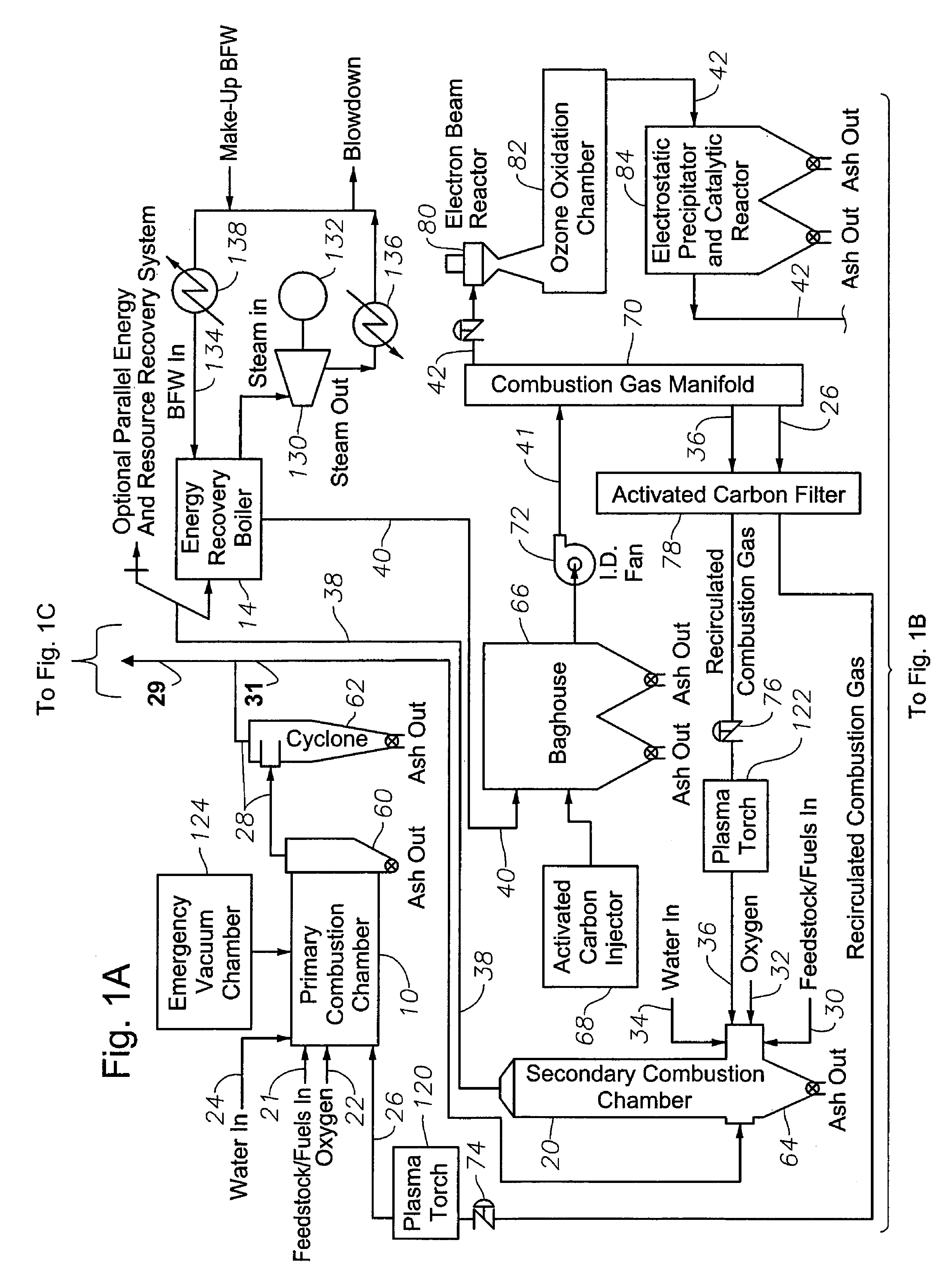
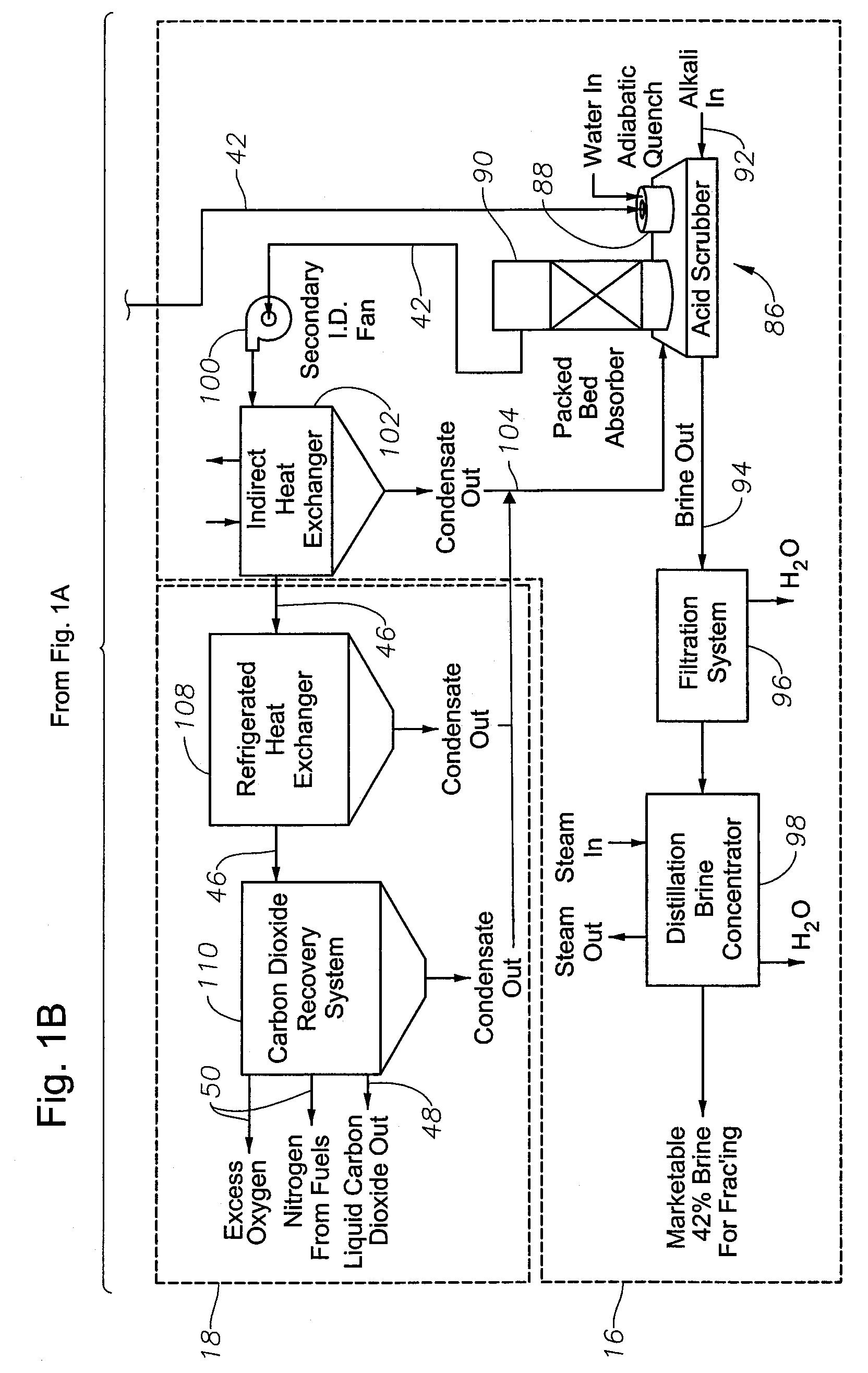
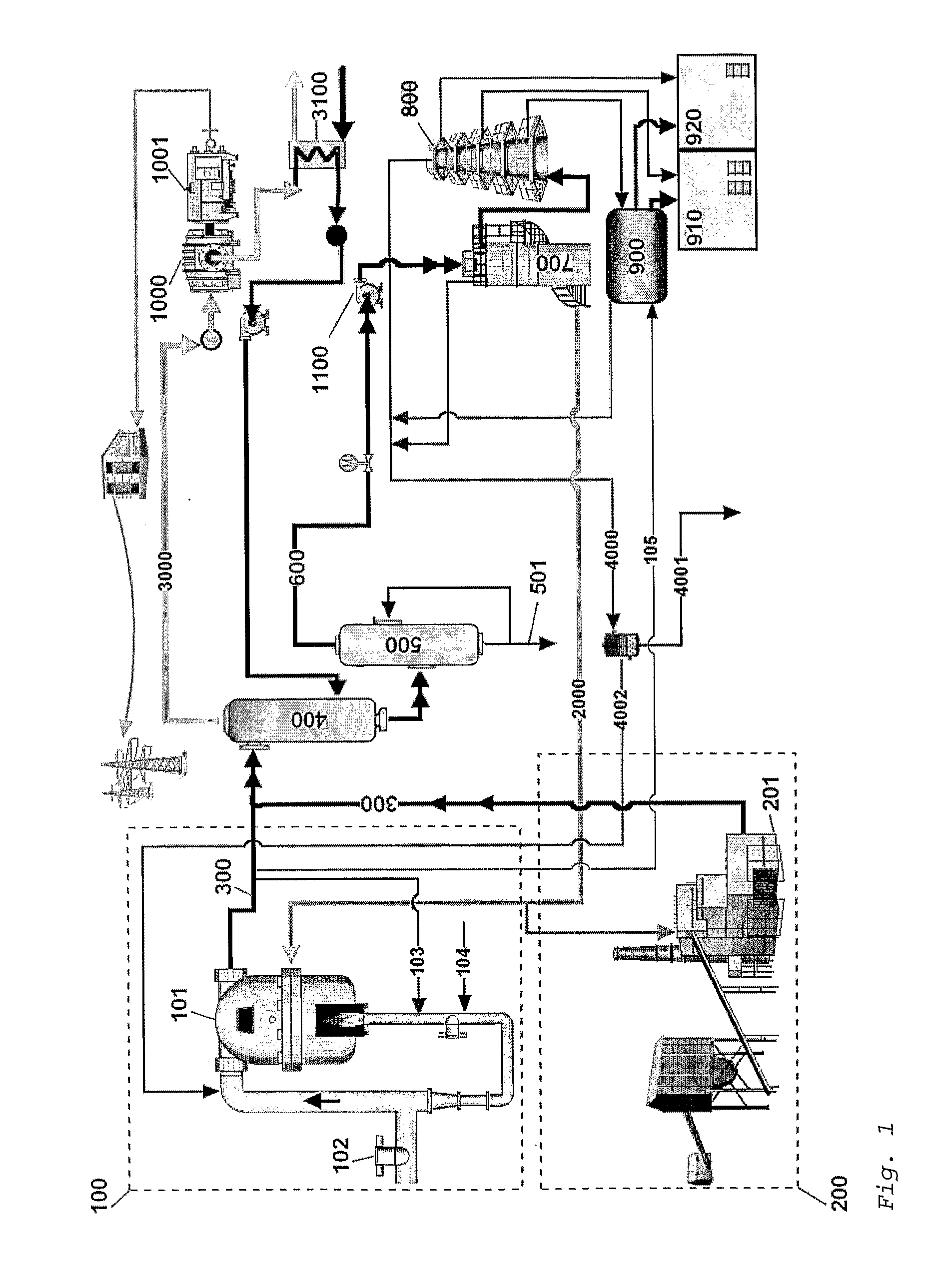
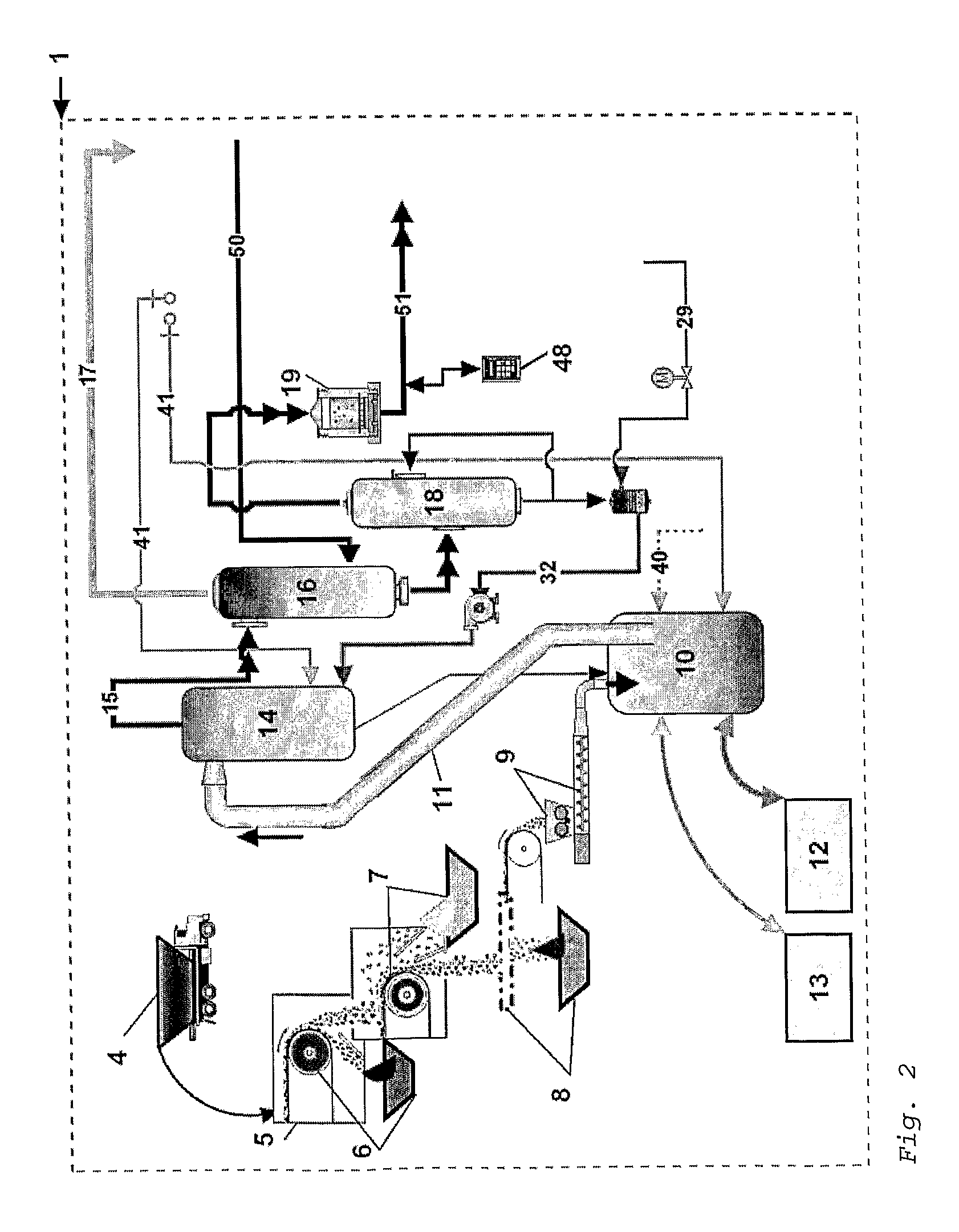
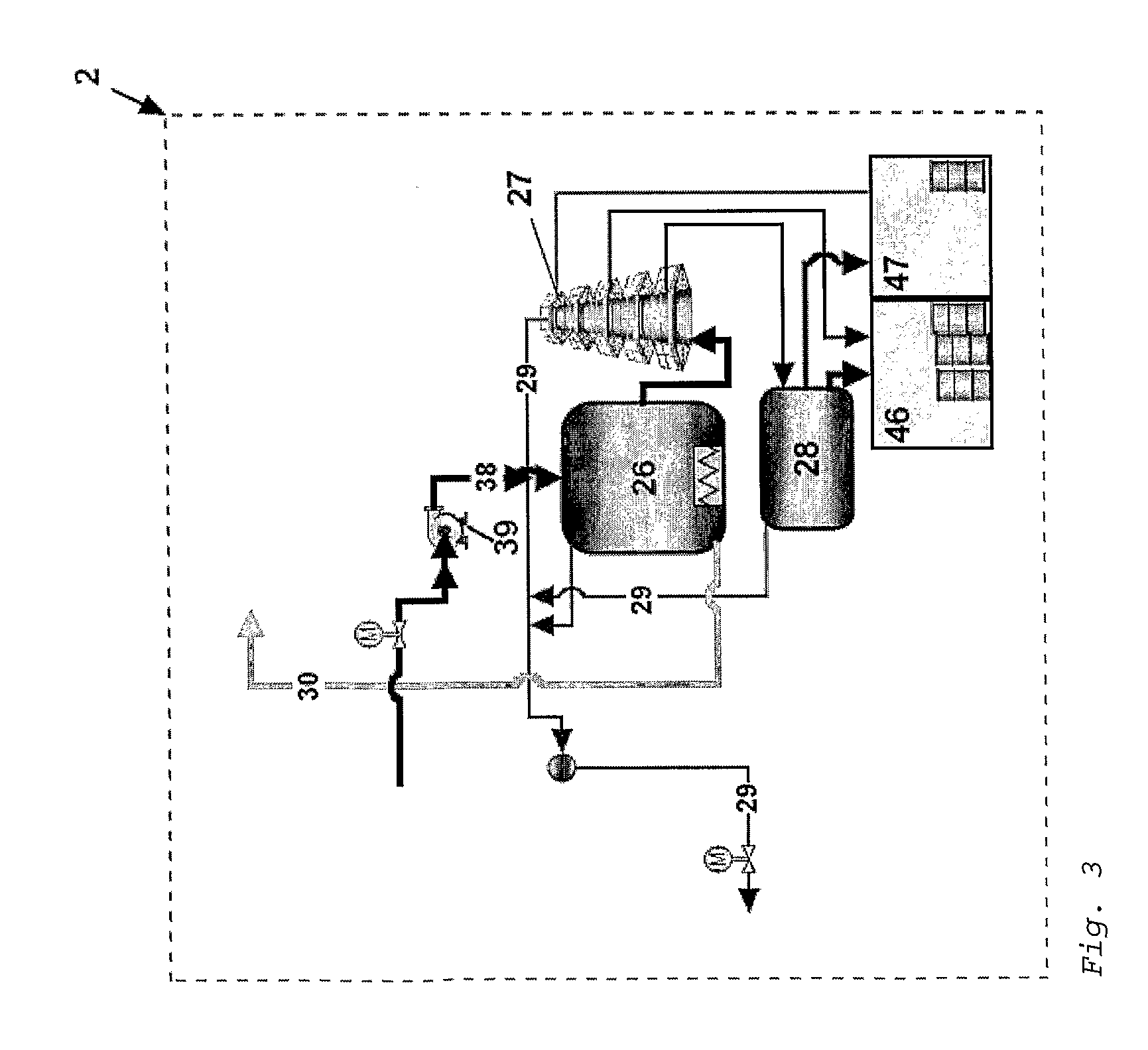
Waste to liquid hydrocarbon refinery system
InactiveUS20110158858A1Eliminate concernsReduce dependenceDirect heating destructive distillationCombustible gas catalytic treatmentLiquid wasteCogeneration
A Waste to Liquid Hydrocarbon Refinery System that transforms any municipal solid wastes and hazardous industrial wastes, Biomass or any carbon containing feedstock into synthetic hydrocarbon, particularly, but not exclusively, diesel and gasoline and / or electricity and co-generated heat, comprising three major subsystems: i) the Pyro-Electric Thermal Converter (PETC) (10) and Plasma Arc (PA) waste and biomass gasification subsystem (1); ii) the hydrocarbon synthesis subsystem (2); and iii) the electricity generation and heat co-generation subsystem (3).
Owner:ALVES RAMALHO GOMES MARIO LUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com