Patents
Literature
245 results about "Light absorption coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
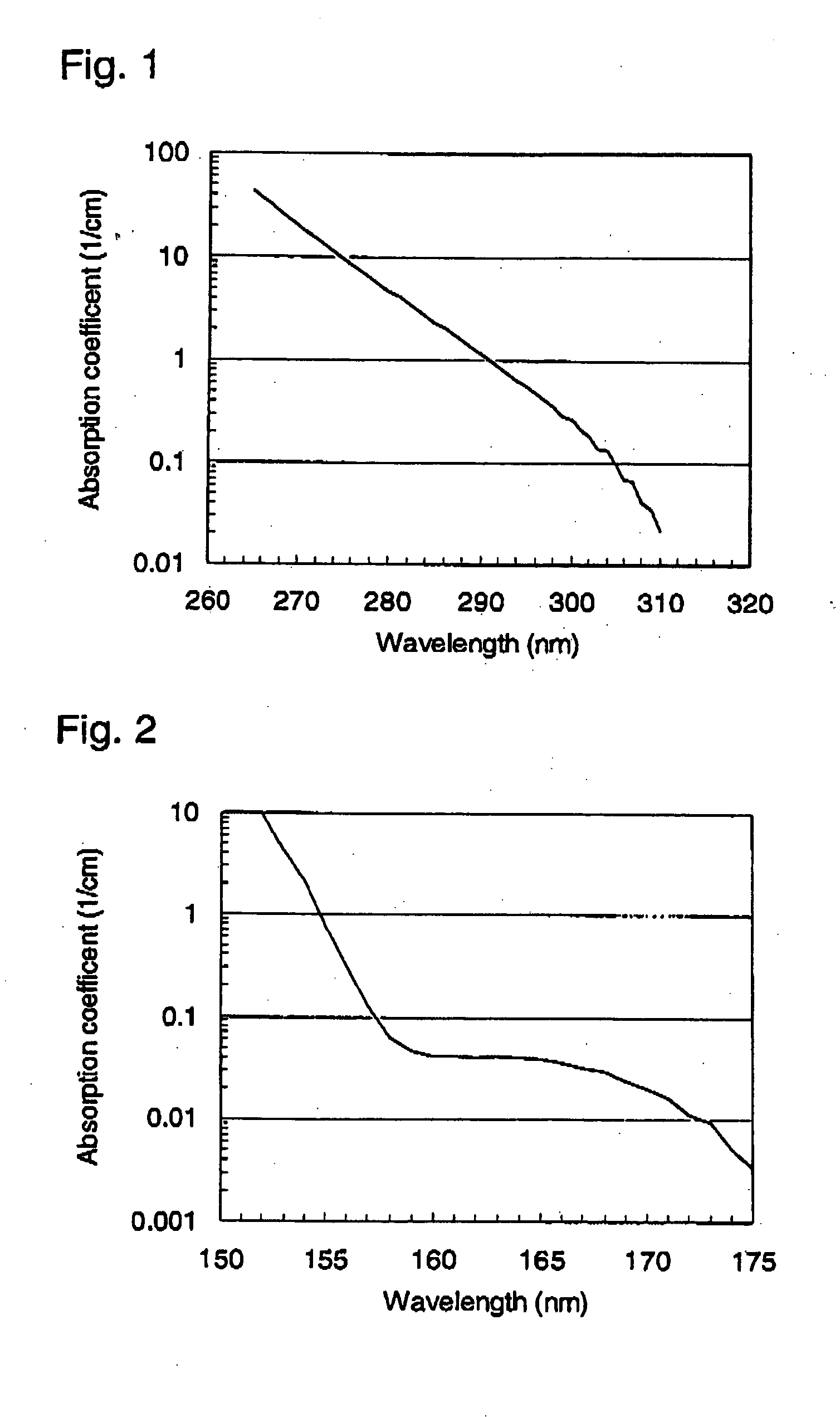
The Absorption Coefficient. The absorption coefficient describes how much light of a given color is absorbed by a material of a given thickness. The absorption coefficient is often represented by the Greek letter alpha. It has units of 1/cm (1/length), because it describes the amount of light absorbed per thickness of material.
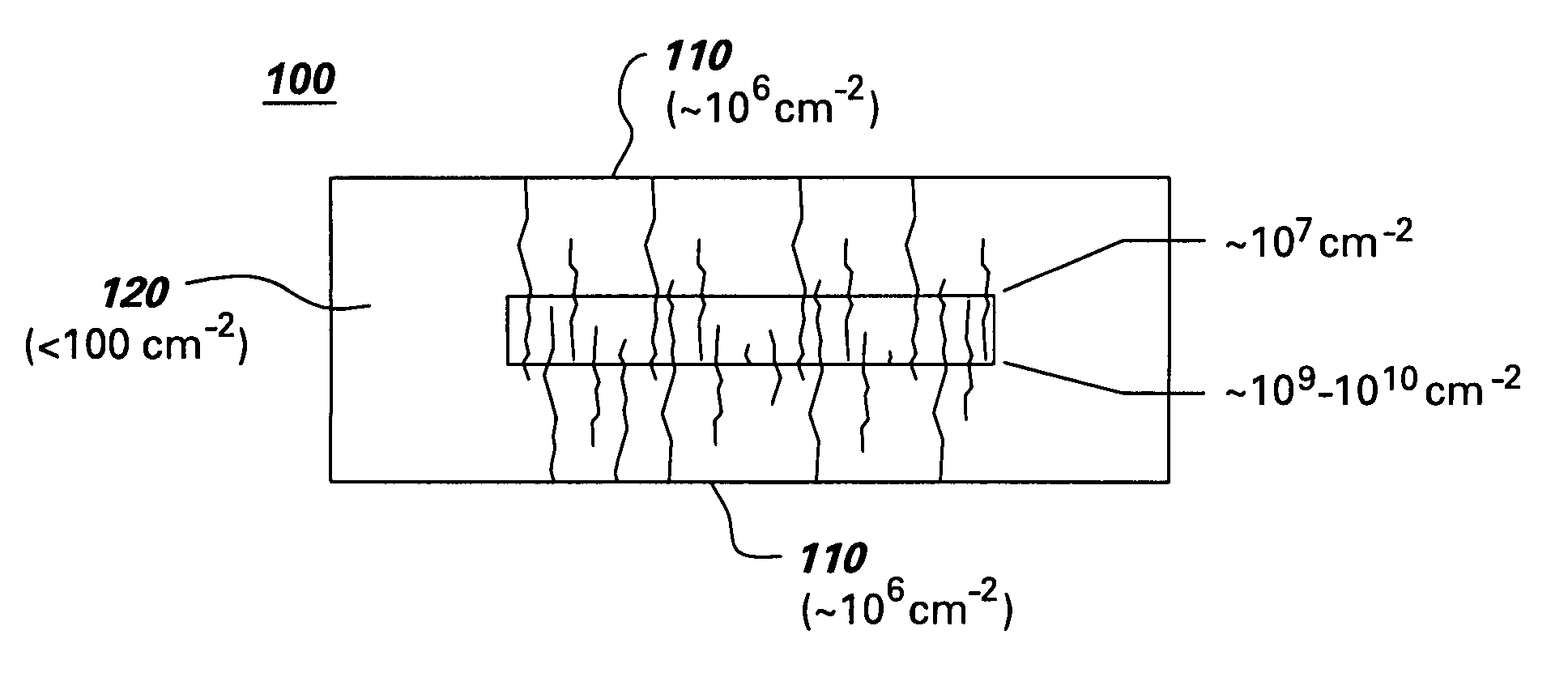
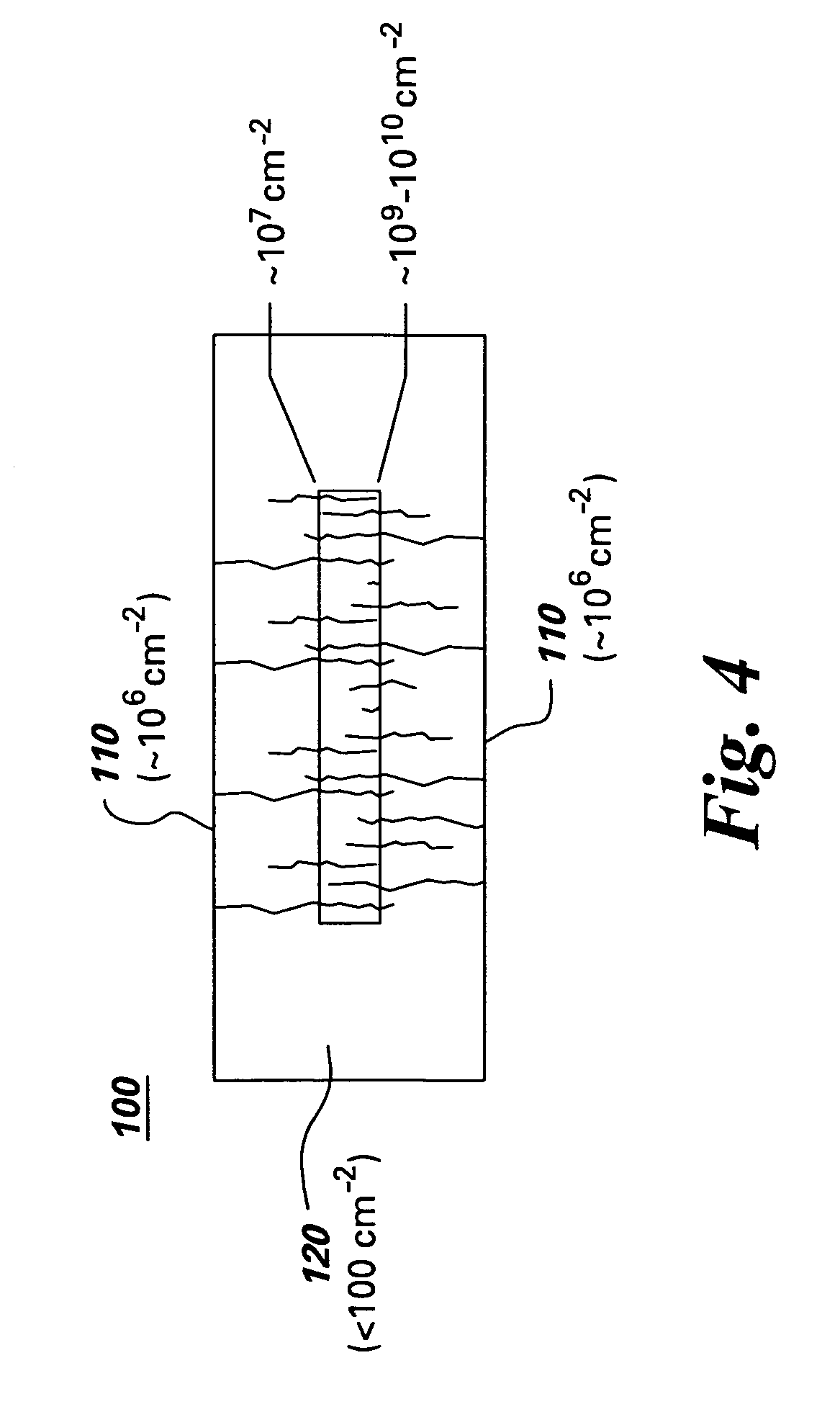
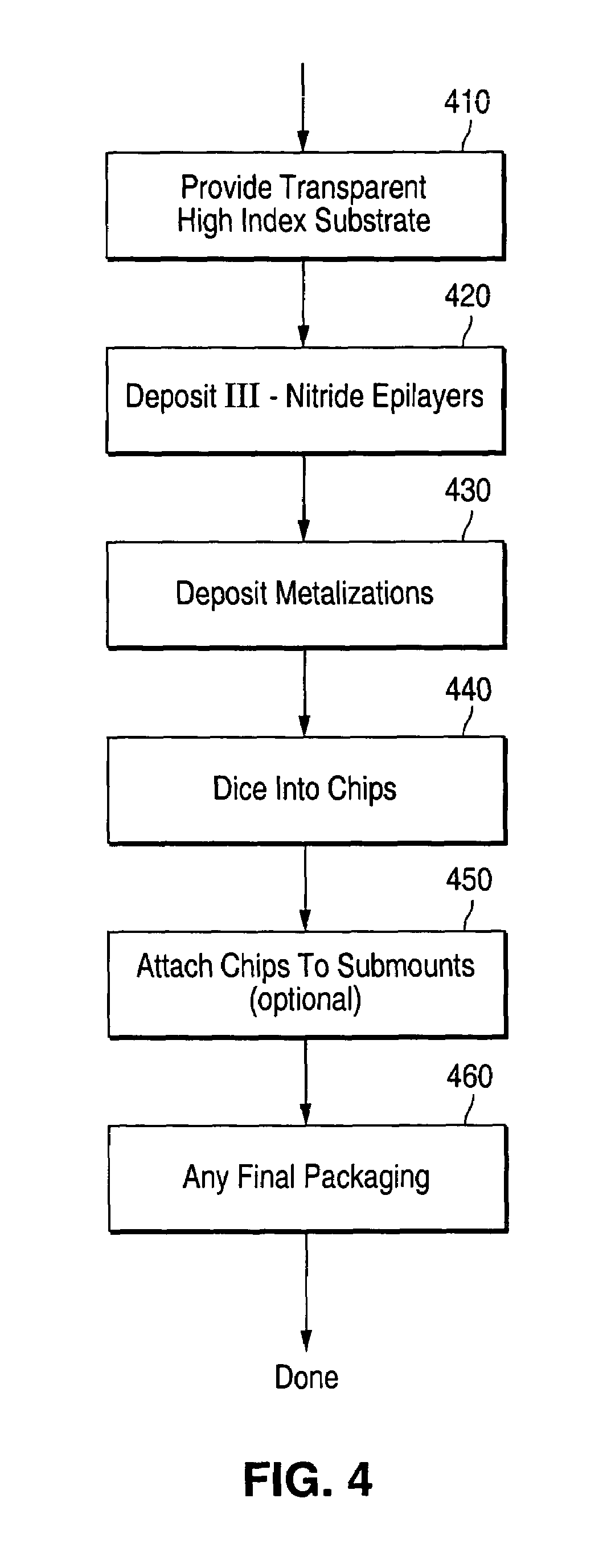
Homoepitaxial gallium-nitride-based light emitting device and method for producing
A light emitting device, such as a light emitting diode or a laser diode. The light emitting device comprises a light emitting semiconductor active region disposed on a substrate. The substrate comprises an optical absorption coefficient below about 100 cm−1 at wavelengths between 700 and 465 nm a GaN single crystal having a dislocation density of less than 104 per cm2 and an optical absorption coefficient below about 100 cm−1 at wavelengths between 700 and 465 nm. A method of making such a light emitting device is also provided.
Owner:SLT TECH +1
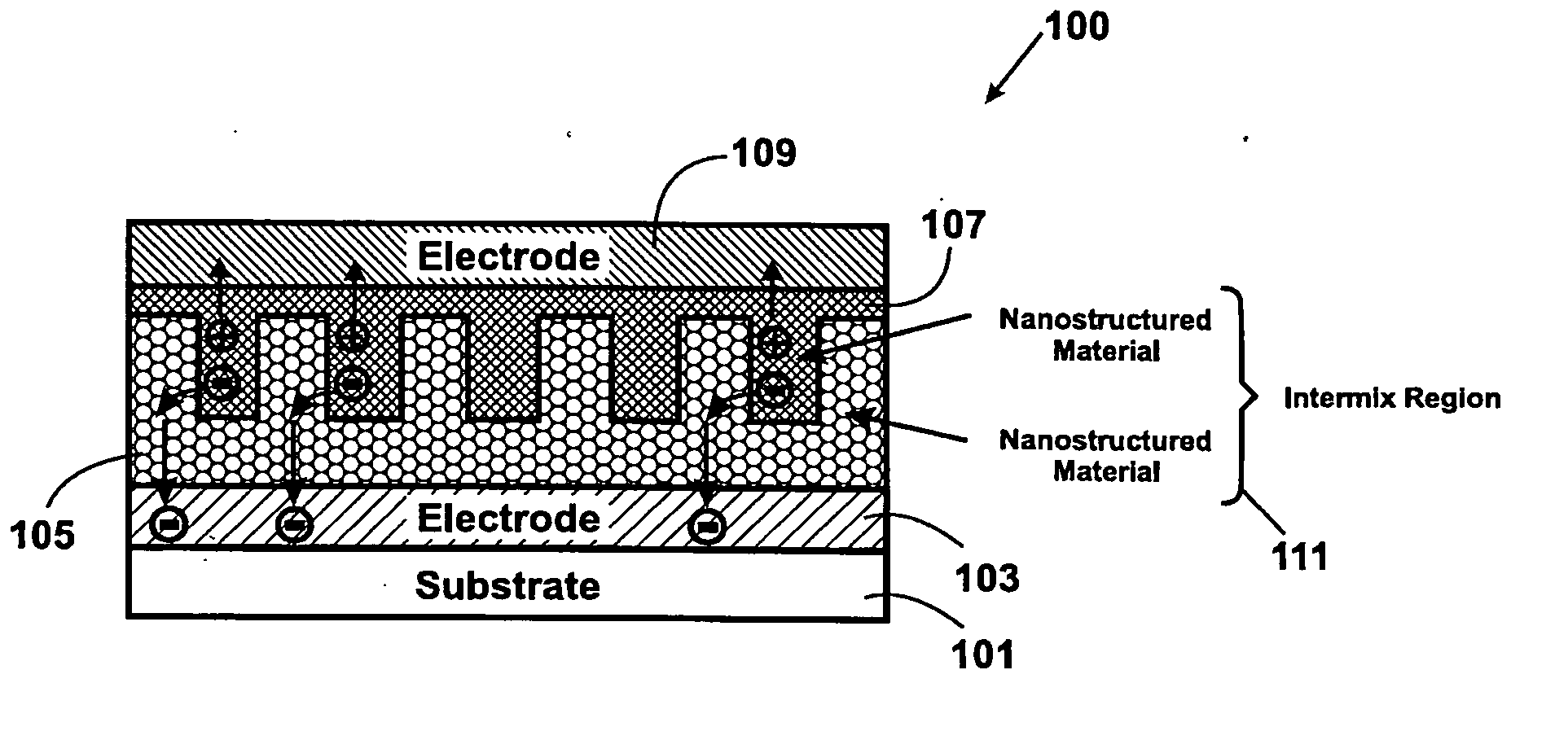
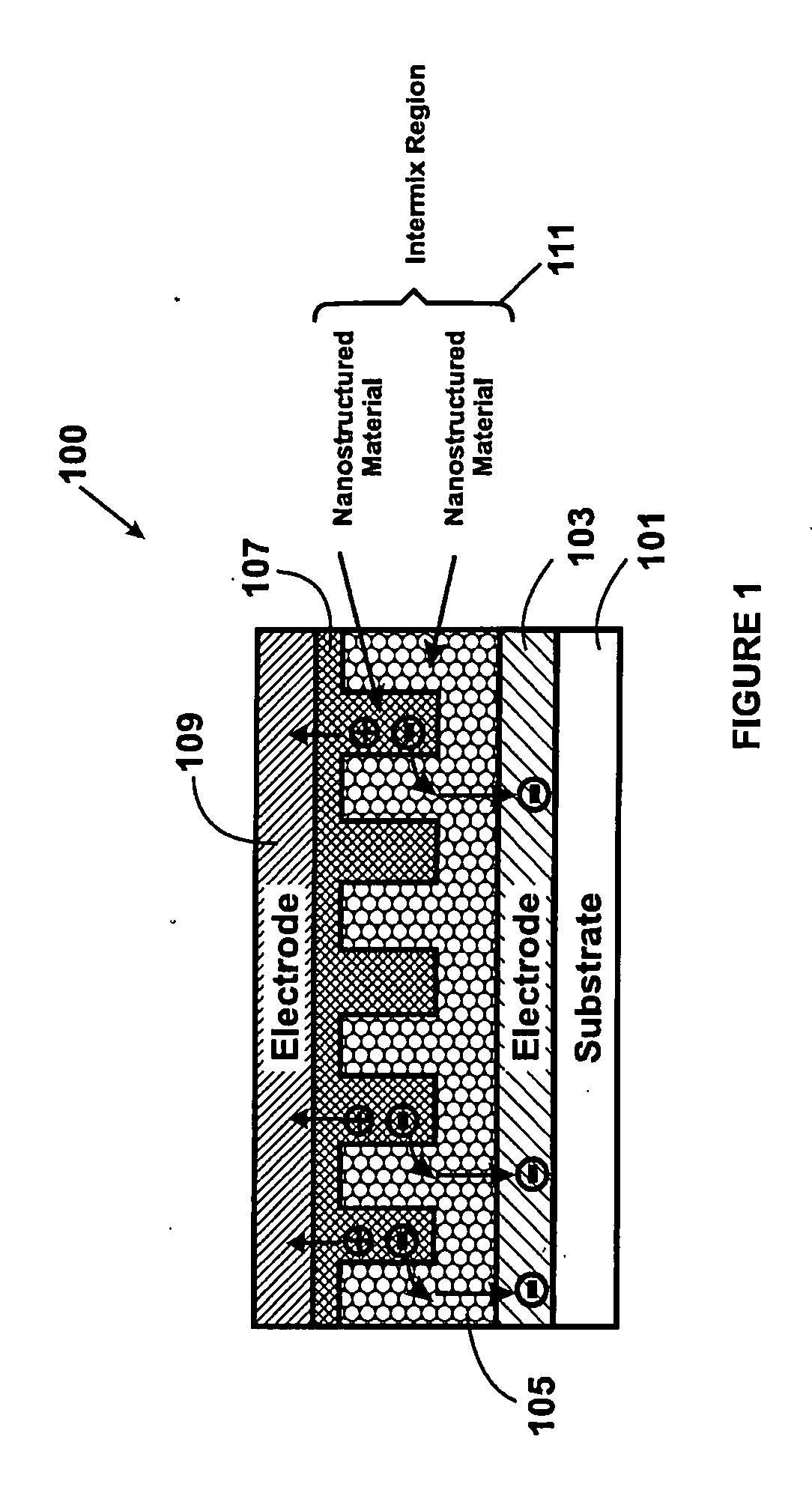
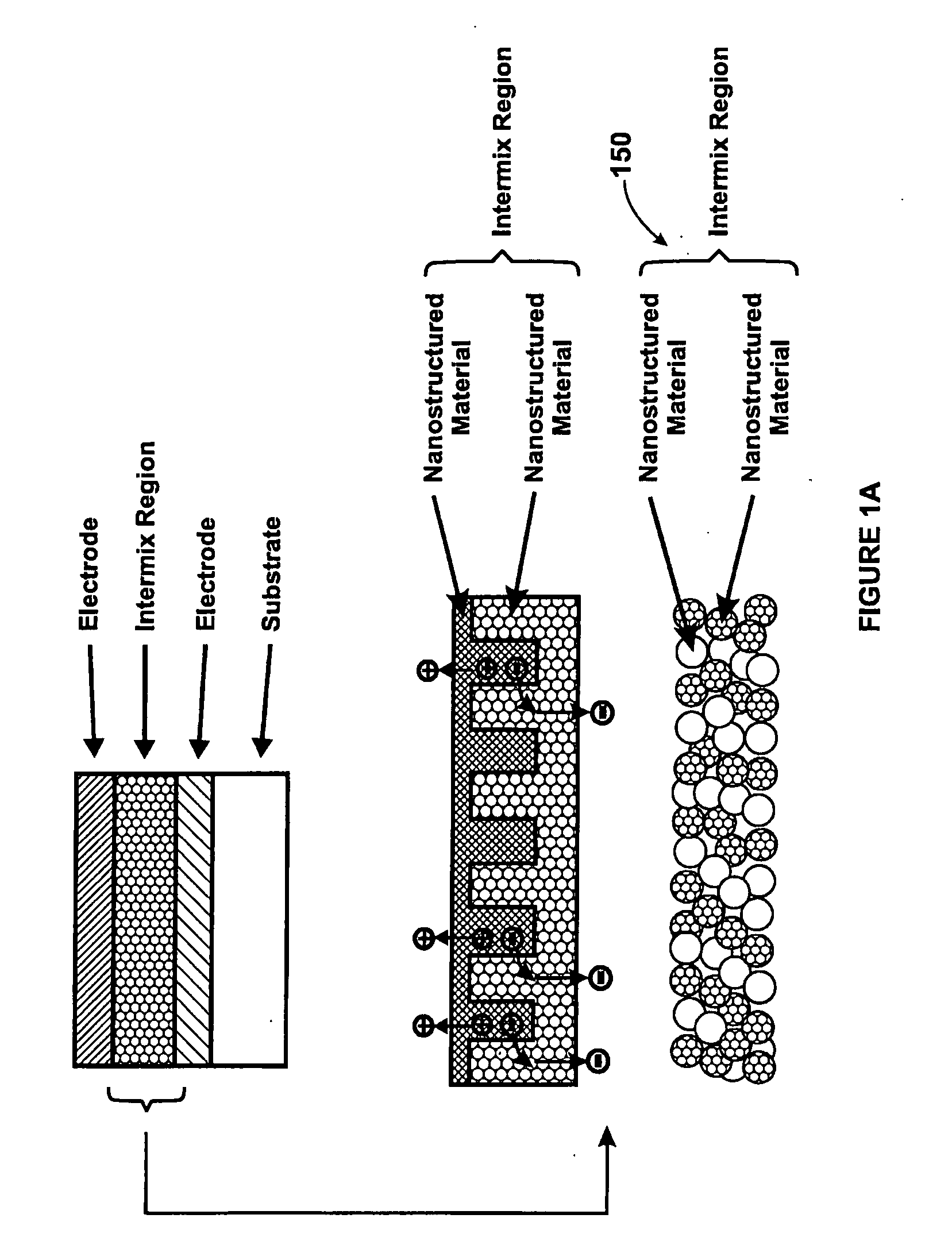
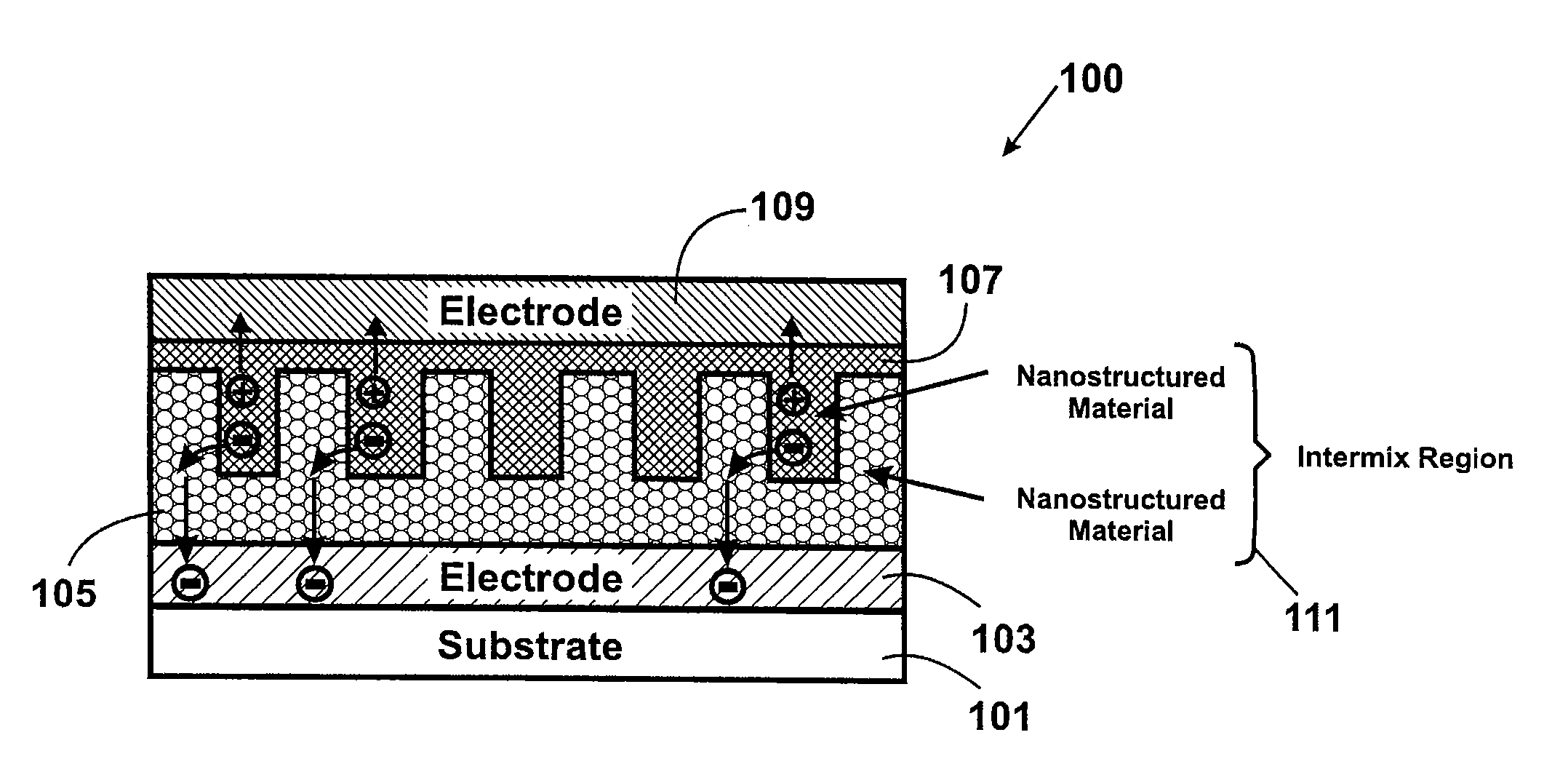
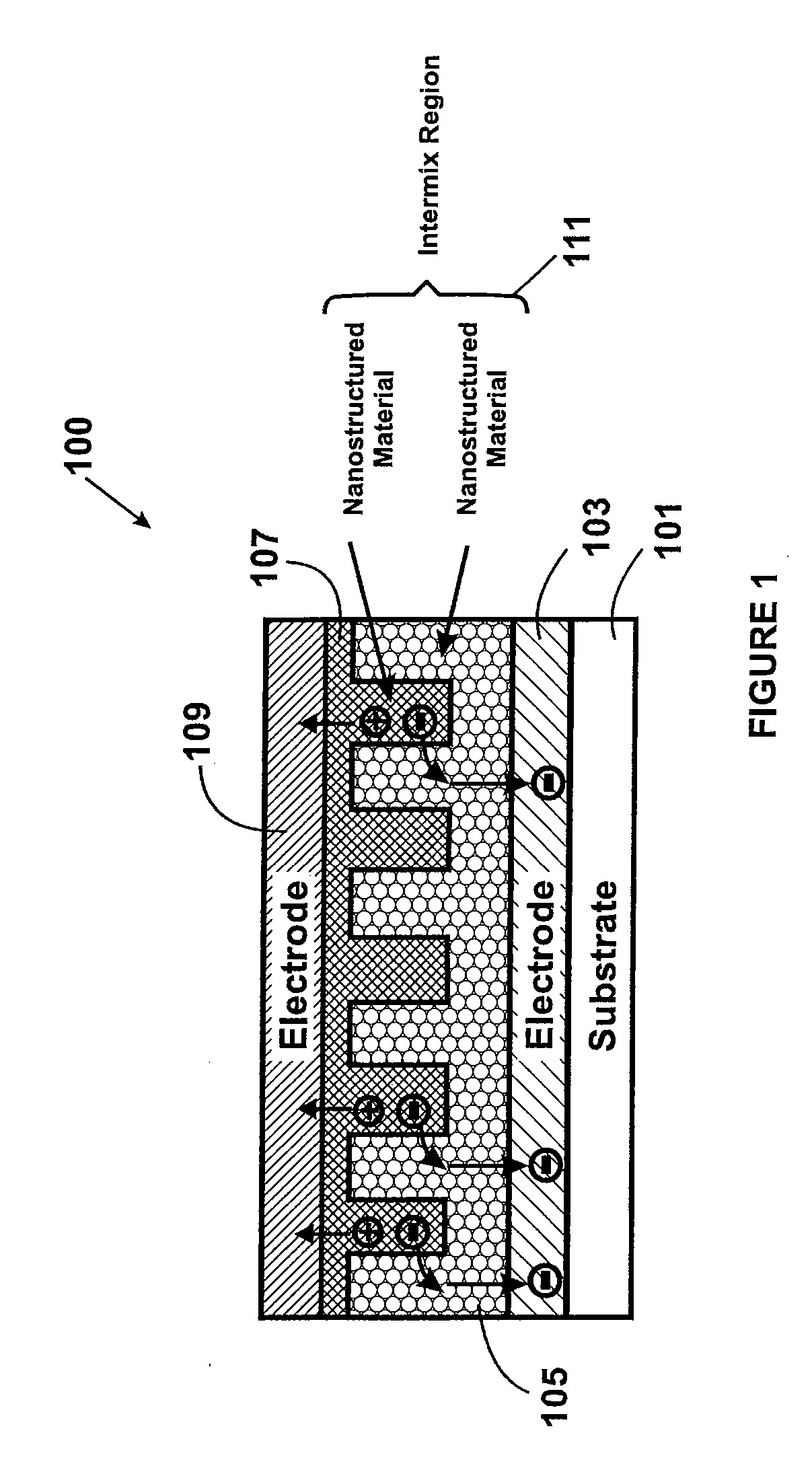
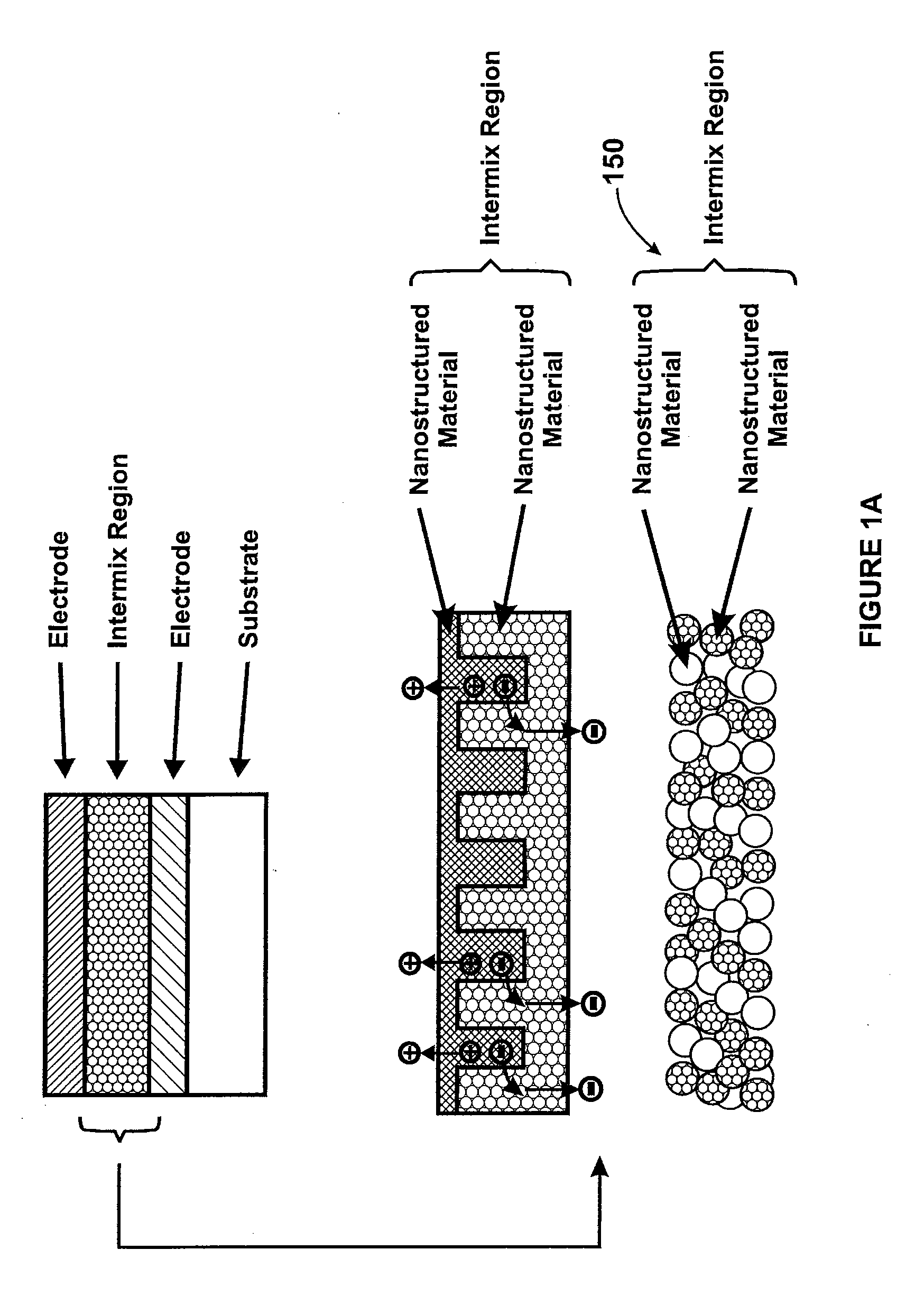
Method and structure for thin film photovoltaic materials using bulk semiconductor materials
ActiveUS20080092953A1Easy to useImprove conversion efficiencyNanoinformaticsPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsCharge carrier
A photovoltaic device and related methods. The device has a structured material positioned between an electron collecting electrode and a hole collecting electrode. An electron transporting / hole blocking material is positioned between the electron collecting electrode and the structured material. In a specific embodiment, negatively charged carriers generated by optical absorption by the structured material are preferentially separated into the electron transporting / hole blocking material. In a specific embodiment, the structured material has an optical absorption coefficient of at least 103 cm−1 for light comprised of wavelengths within the range of about 400 nm to about 700 nm.
Owner:CM MFG
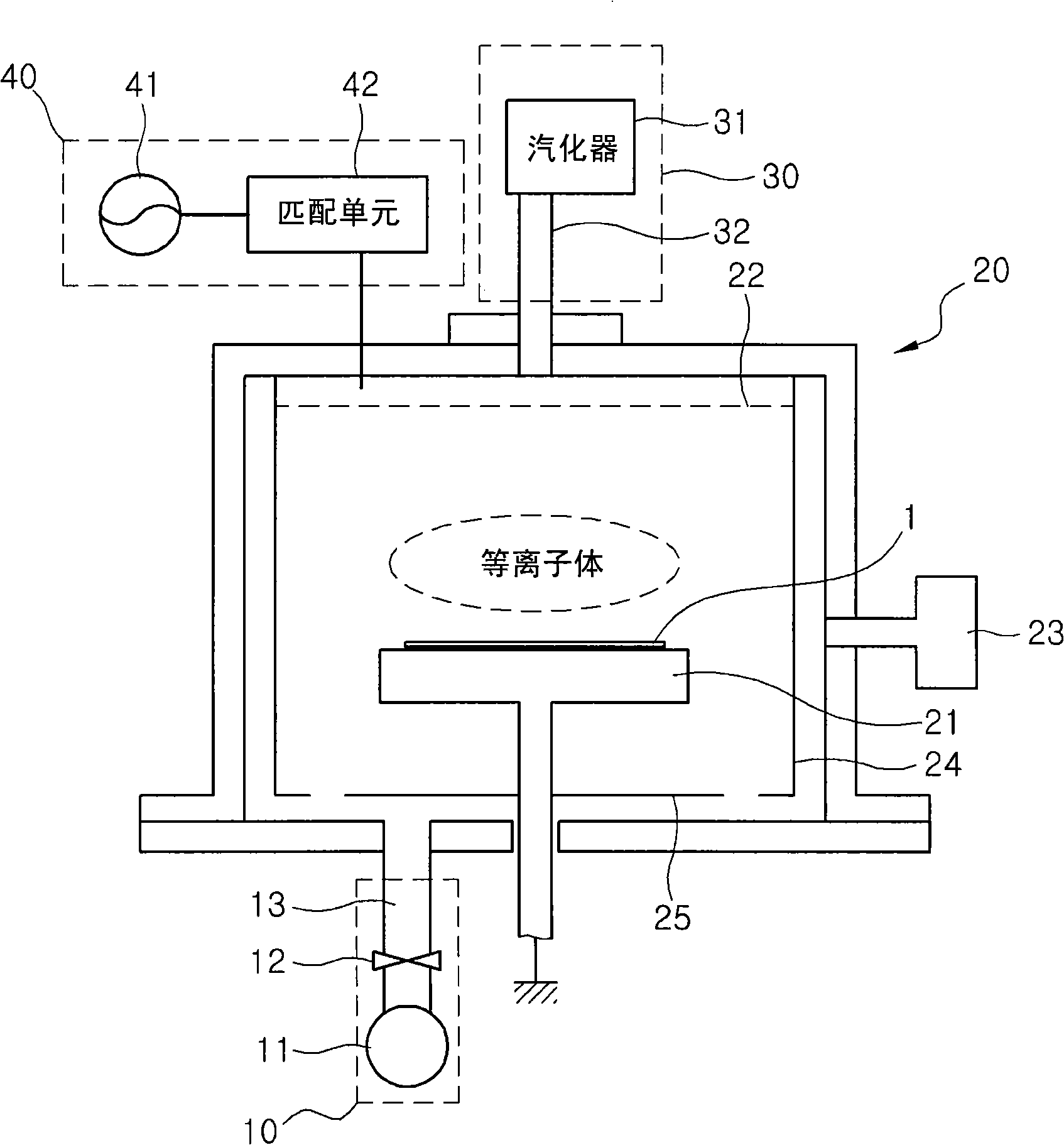
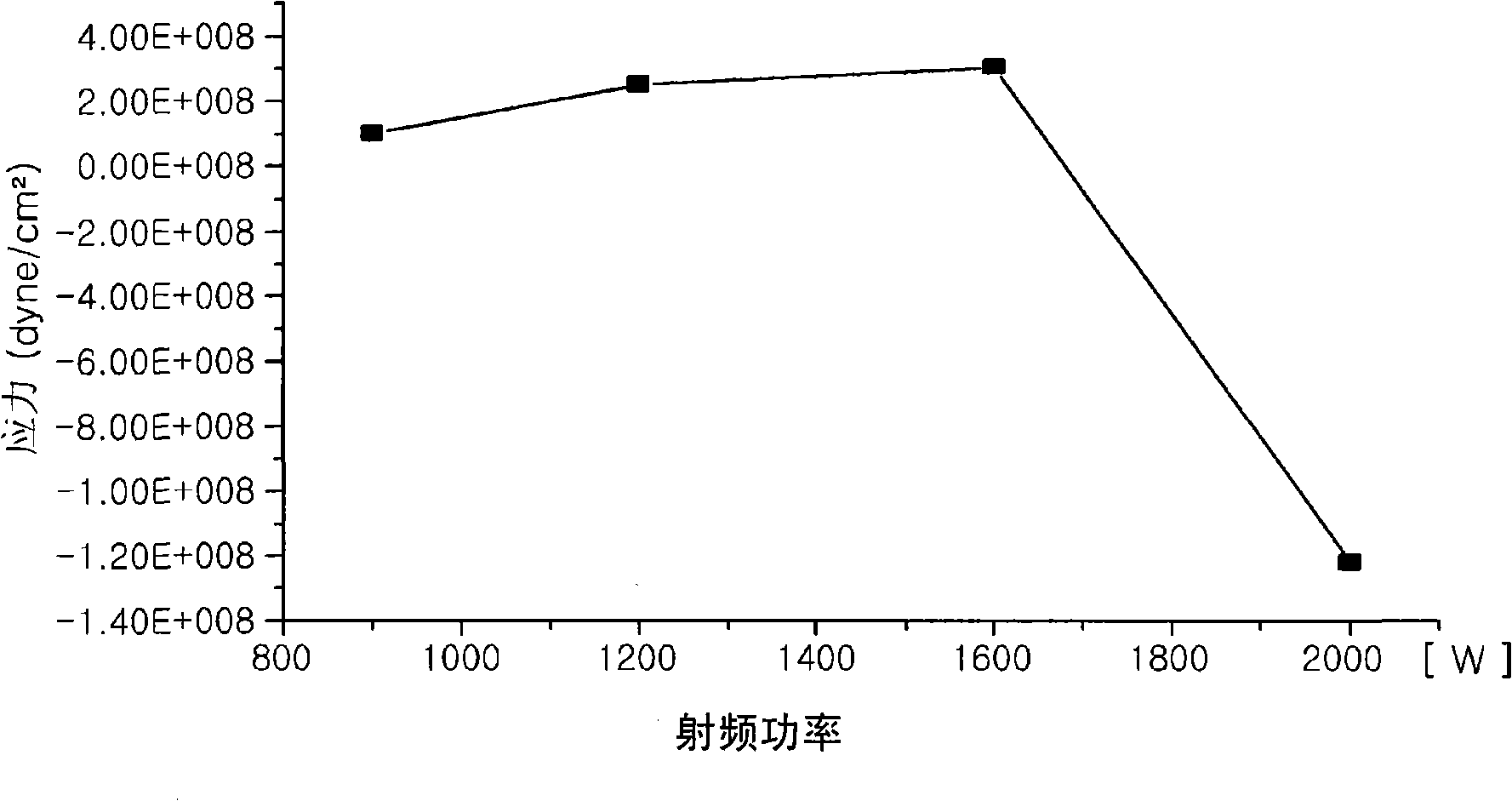
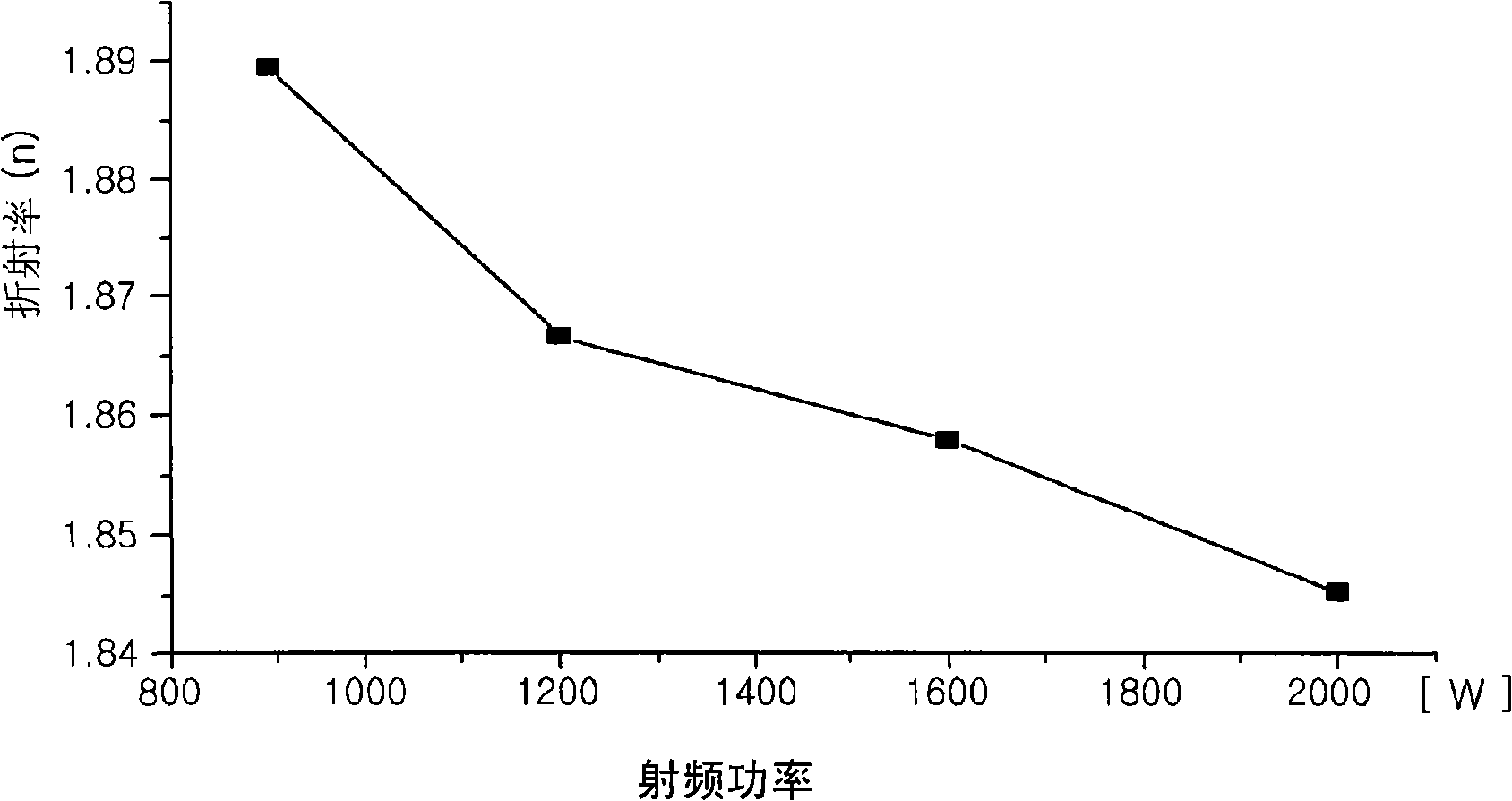
Method of forming amorphous carbon film and method of manufacturing semiconductor device using the same
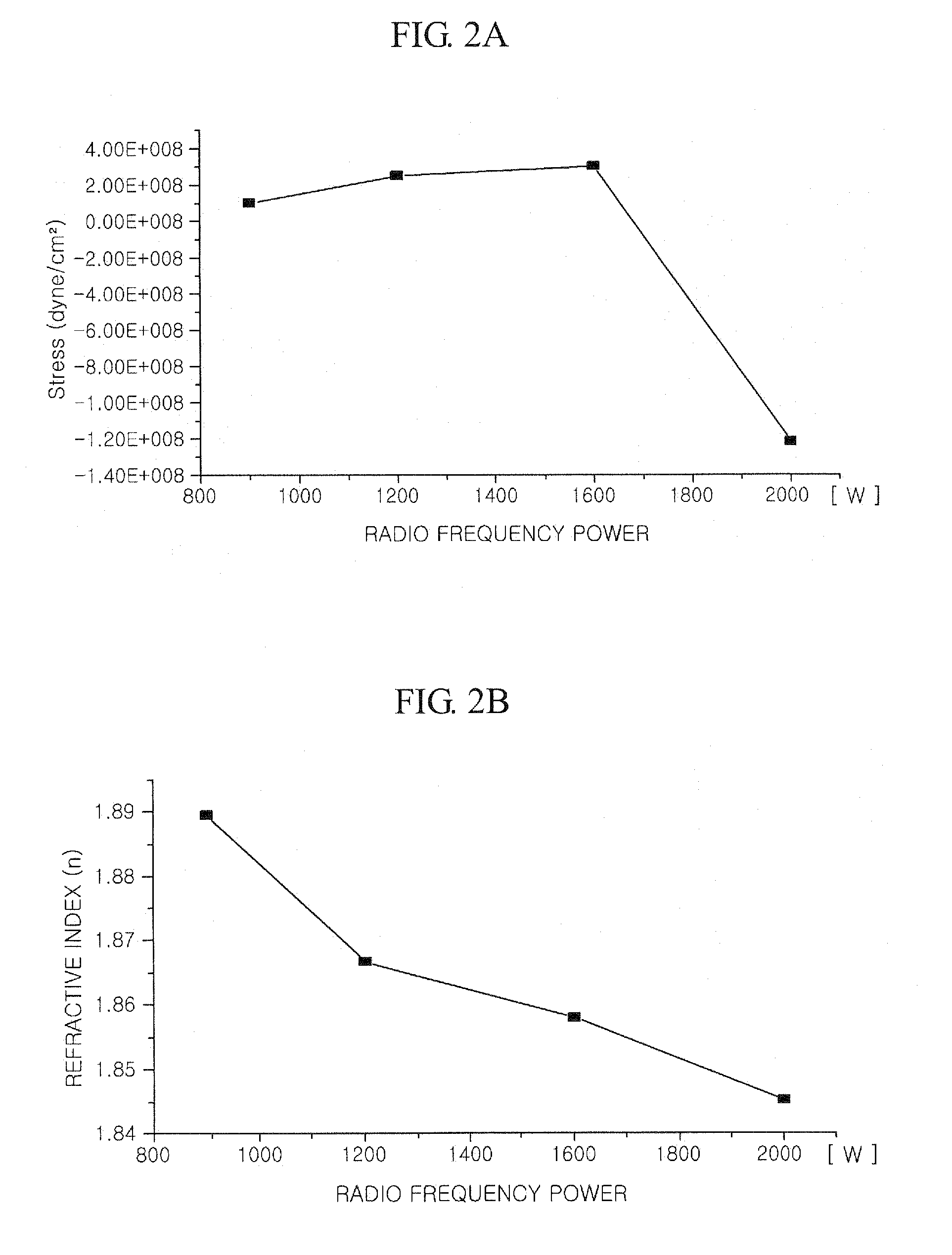
InactiveUS20080293248A1Better controllableLight absorption coefficient is lowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRefractive indexDiffuse reflection
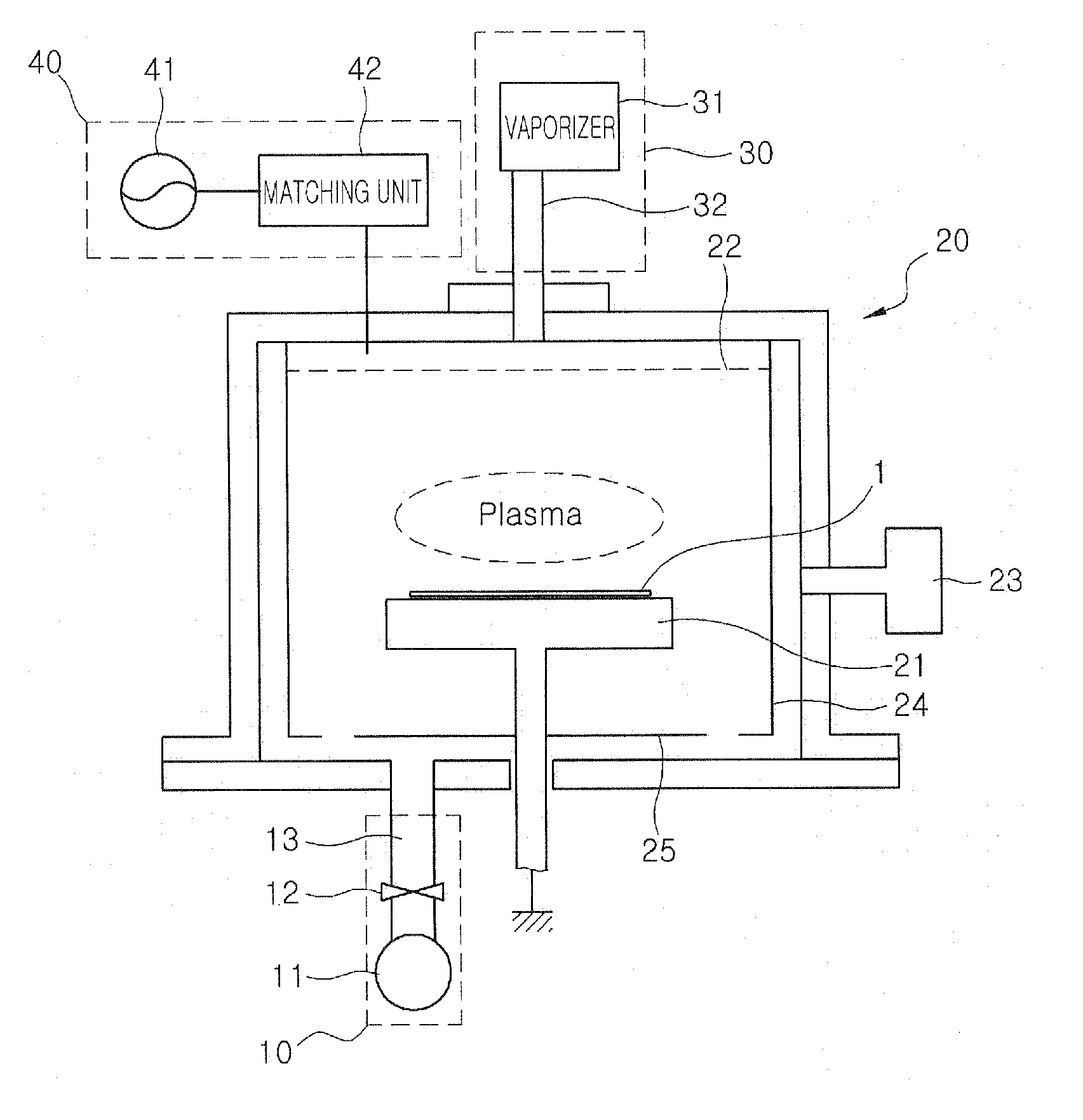
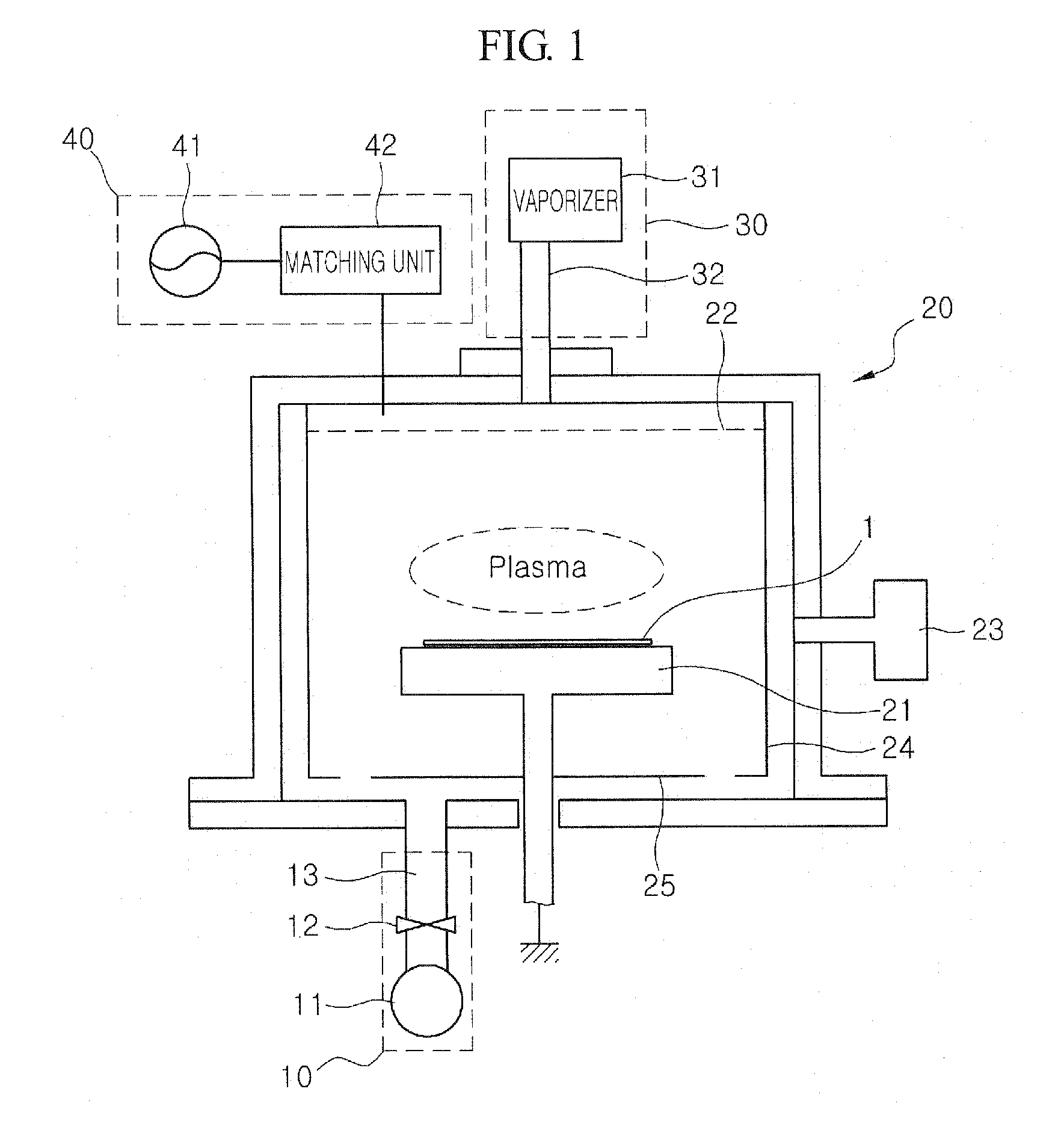
The present invention relates to a method of forming an amorphous carbon film and a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the method. An amorphous carbon film is formed on a substrate by vaporizing a liquid hydrocarbon compound, which has chain structure and one double bond, and supplying the compound to a chamber, and ionizing the compound. The amorphous carbon film is used as a hard mask film.It is possible to easily control characteristics of the amorphous carbon film, such as a deposition rate, an etching selectivity, a refractive index (n), a light absorption coefficient (k) and stress, so as to satisfy user's requirements. In particular, it is possible to lower the refractive index (n) and the light absorption coefficient (k). As a result, it is possible to perform a photolithography process without an antireflection film that prevents the diffuse reflection of a lower material layer.Further, a small amount of reaction by-product is generated during a deposition process, and it is possible to easily remove reaction by-products that are attached on the inner wall of a chamber. For this reason, it is possible to increase a cycle of a process for cleaning a chamber, and to increase parts changing cycles of a chamber. As a result, it is possible to save time and cost.
Owner:TES CO LTD
Method and structure for thin film photovoltaic materials using semiconductor materials
ActiveUS20070264488A1Easy to useImprove conversion efficiencyLayered productsConductive materialSemiconductor materialsCharge carrier
A photovoltaic device and related methods. The device has a nanostructured material positioned between an electron collecting electrode and a hole collecting electrode. An electron transporting / hole blocking material is positioned between the electron collecting electrode and the nanostructured material. In a specific embodiment, negatively charged carriers generated by optical absorption by the nanostructured material are preferentially separated into the electron transporting / hole blocking material. In a specific embodiment, the nanostructured material has an optical absorption coefficient of at least 103 cm−1 for light comprised of wavelengths within the range of about 400 nm to about 700 nm.
Owner:CM MFG
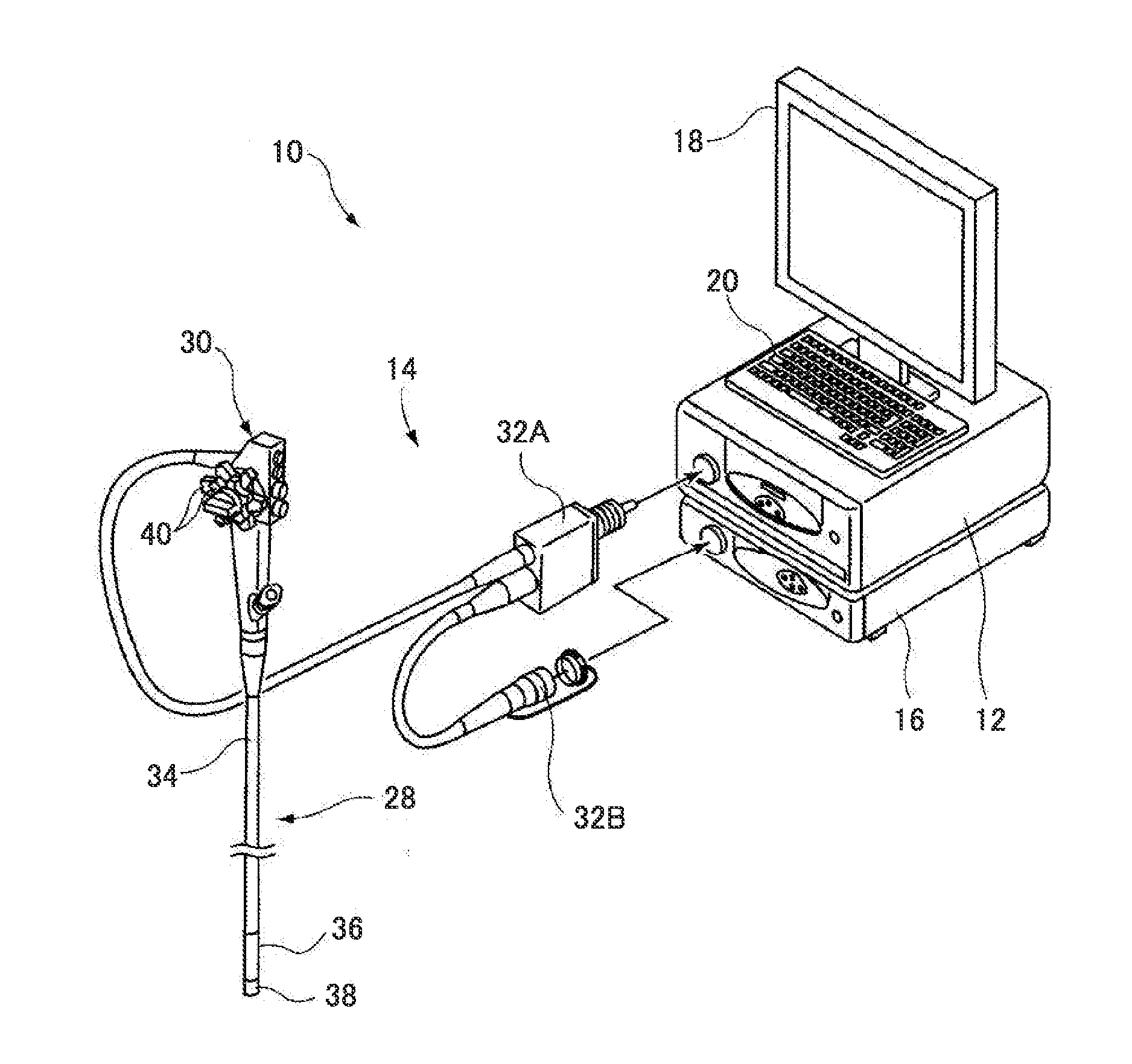
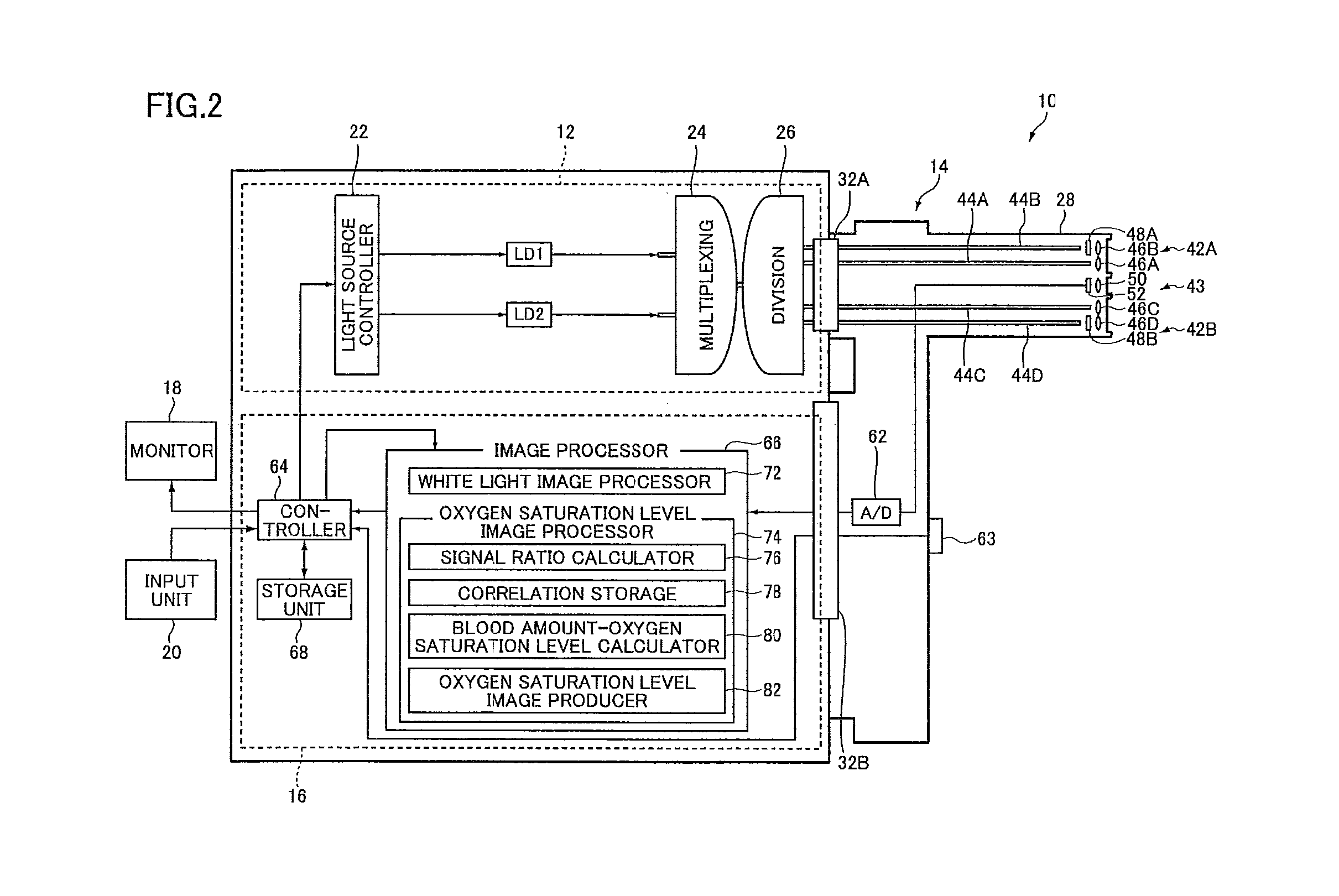
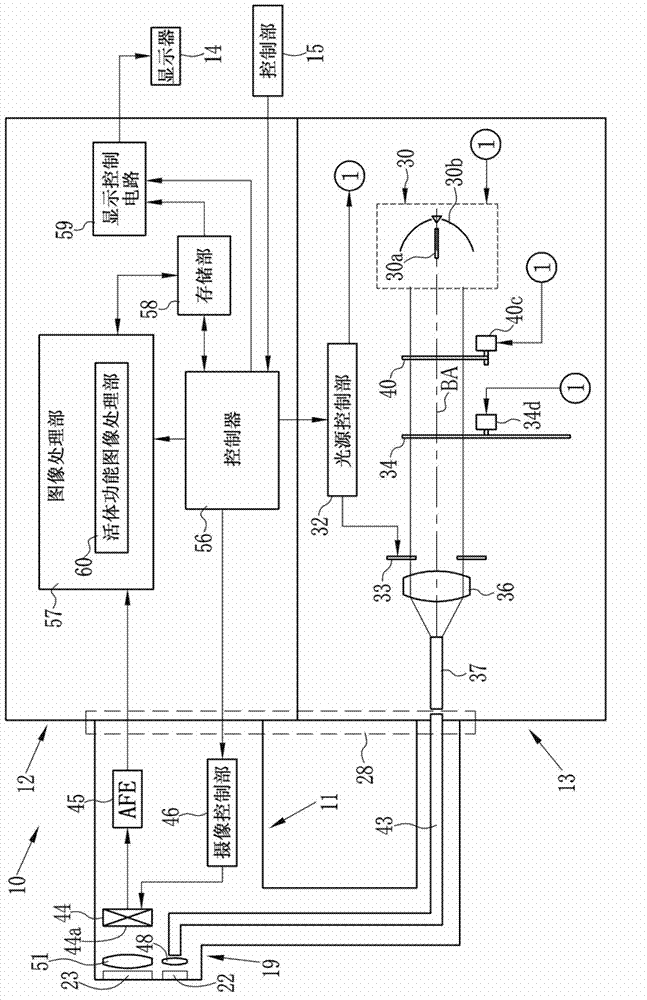
Endoscopic diagnosis system
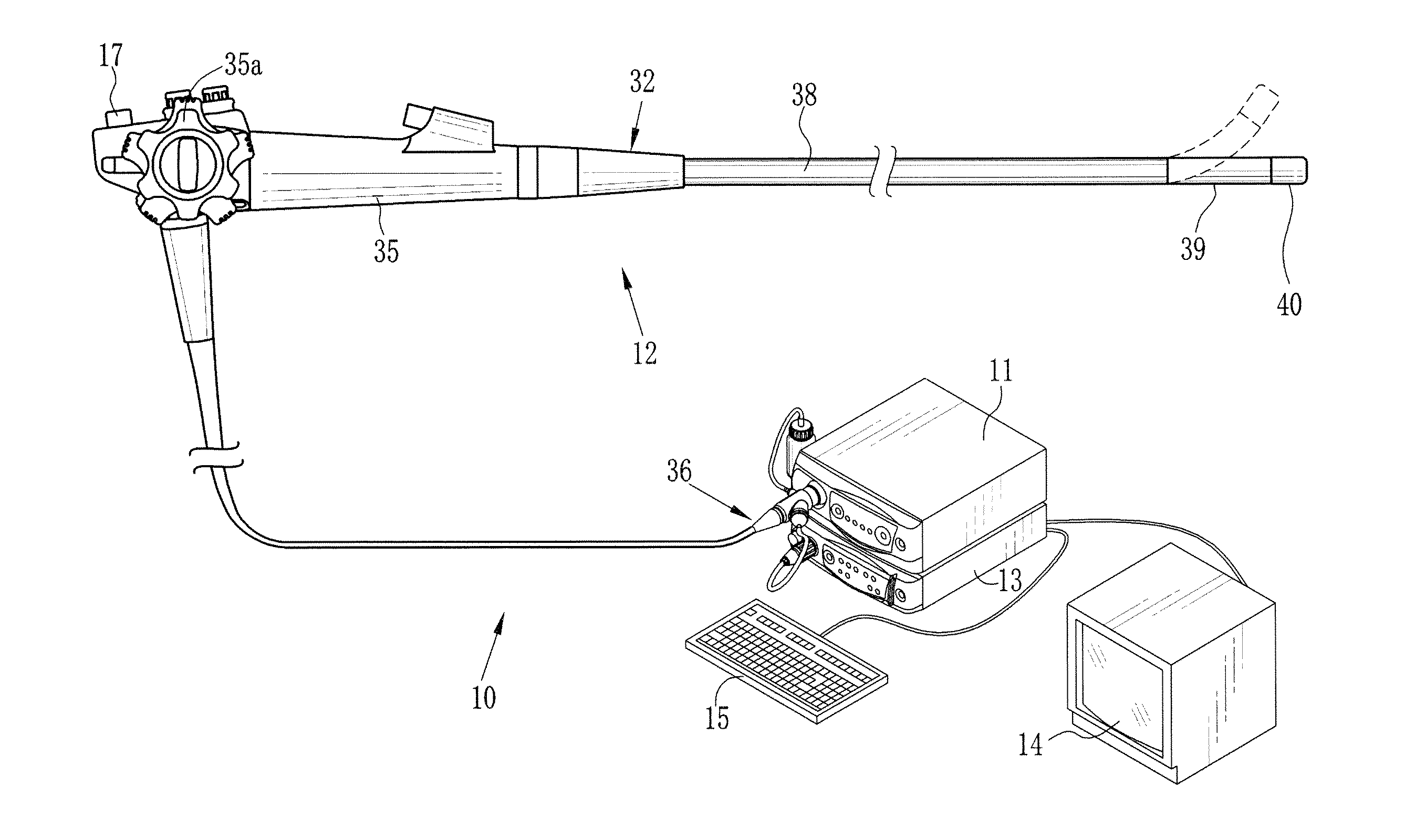
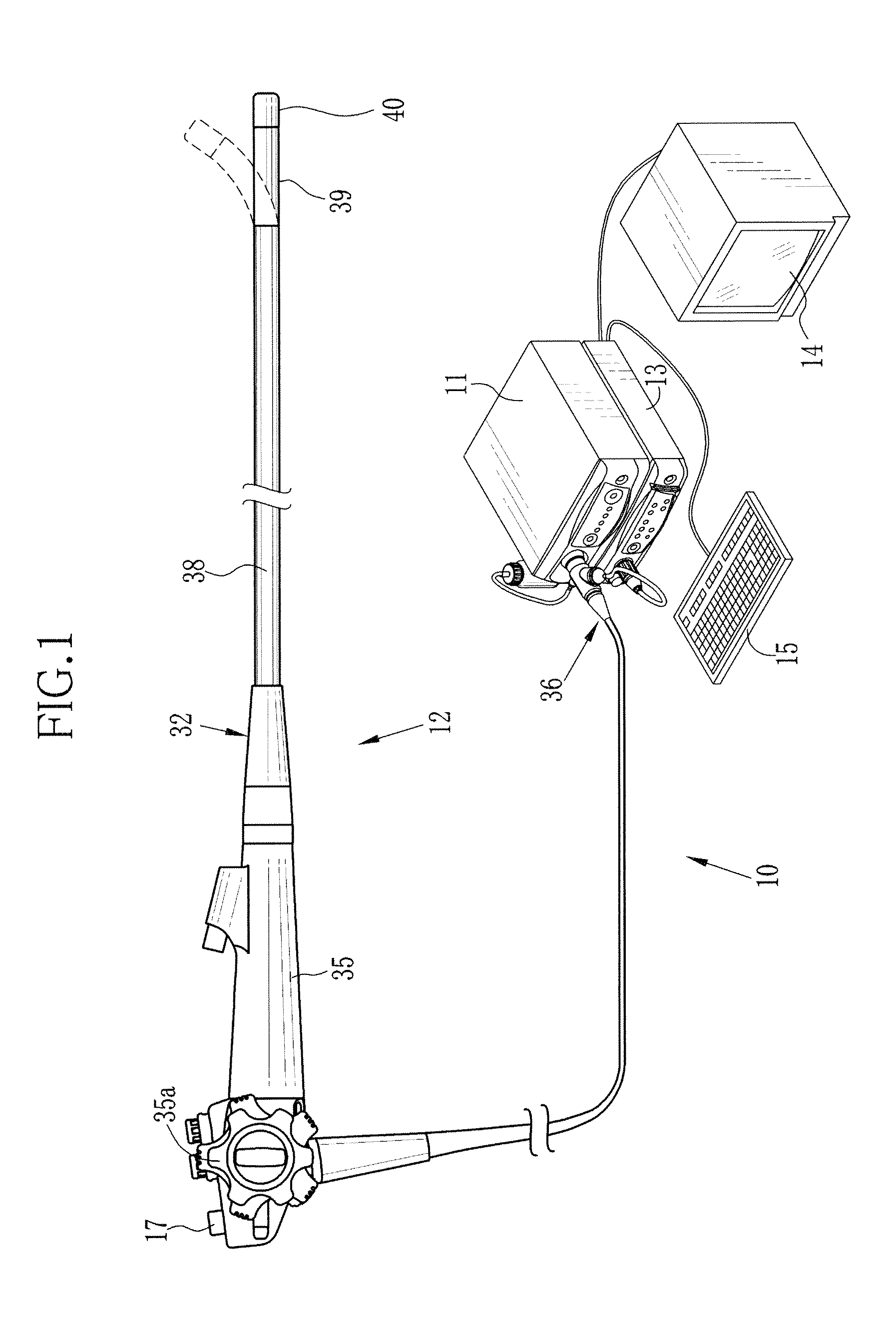
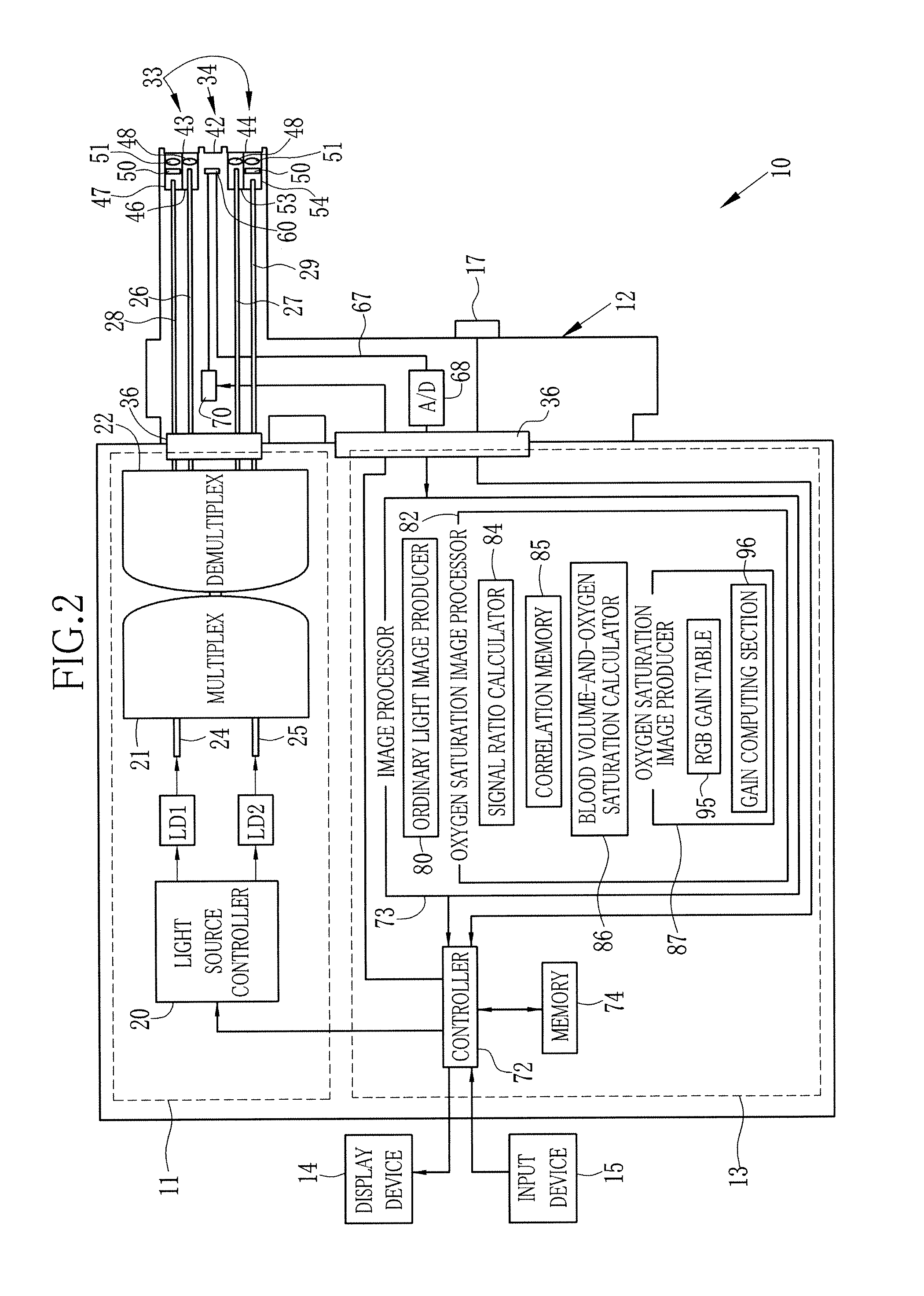
InactiveUS20120116192A1Reducing effect produced by blood vesselAccurate calculationSurgeryEndoscopesDisplay deviceTime signal
An endoscopic diagnosis system accurately calculating the oxygen saturation level considering the effects of the blood vessel depth and the blood amount and displaying an oxygen saturation level distribution in simulated colors includes an endoscope device for illuminating a subject, imaging reflected light, and acquiring image signals corresponding to three or more reflected light having a wavelength range of 460 to 700 nm including a first and a second image signal corresponding to reflected light having two wavelength ranges where the light absorption coefficient changes according to the blood hemoglobin oxygen saturation level and a third image signal corresponding to reflected light having one wavelength range where the light absorption coefficient does not change; a blood amount-oxygen saturation level calculator using the acquired image signals for calculation; and a display for displaying an oxygen saturation level distribution based on the oxygen saturation level information.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
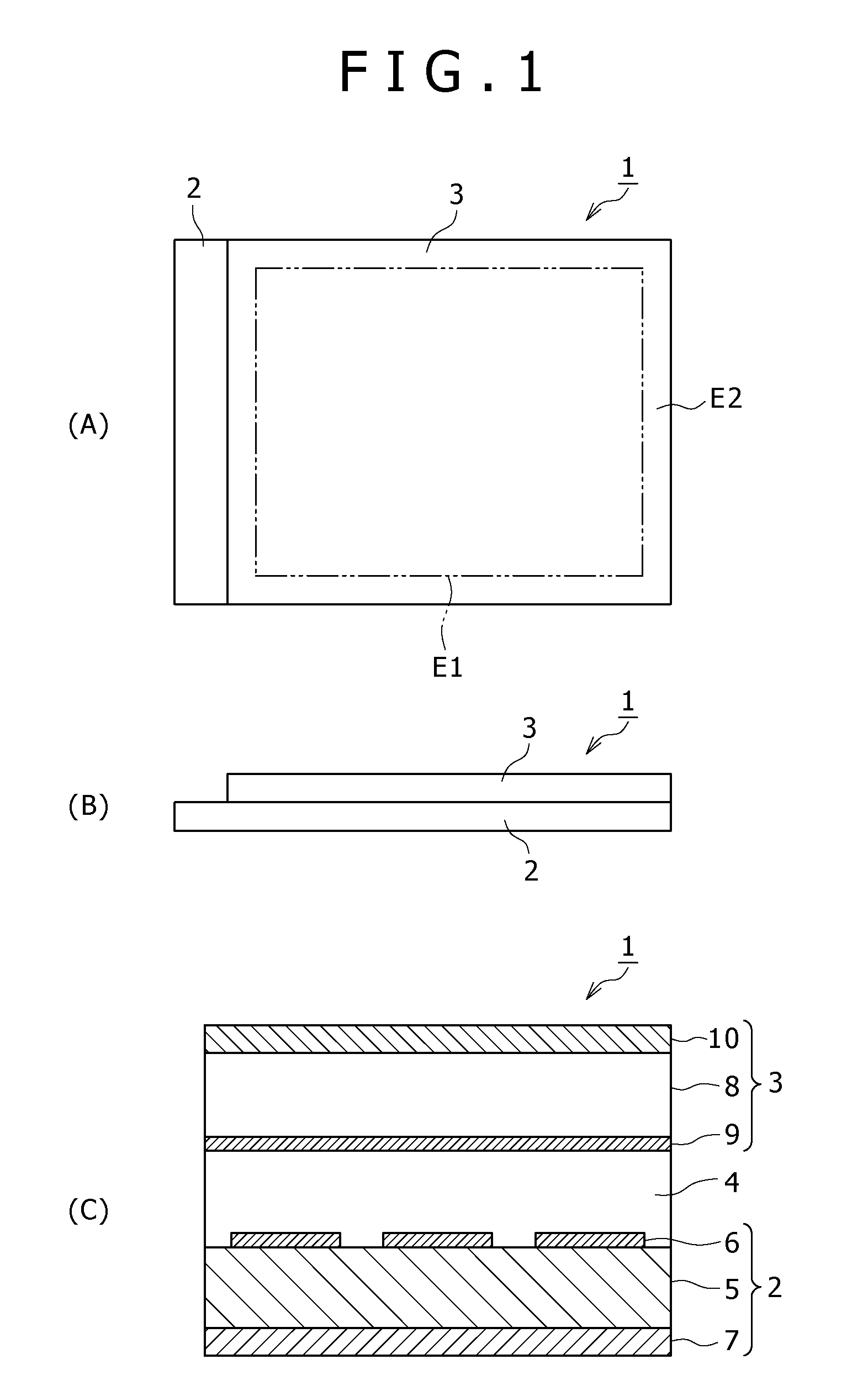
Display and method for manufacturing display
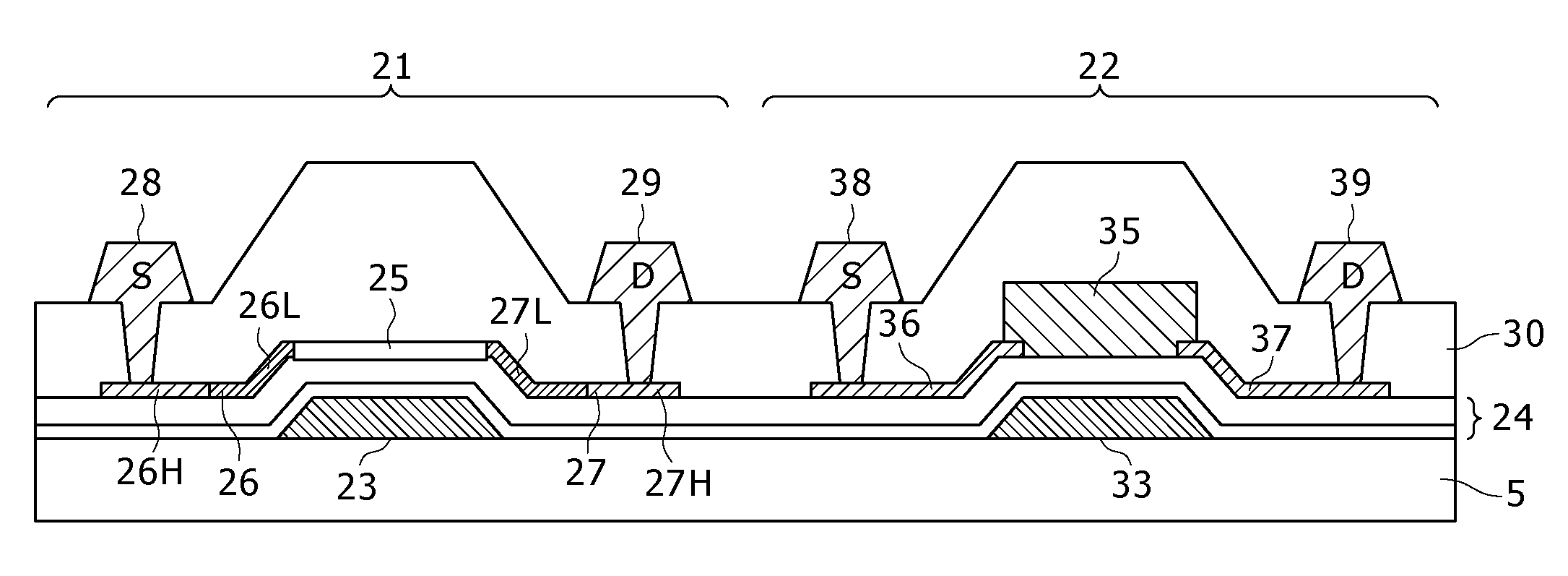
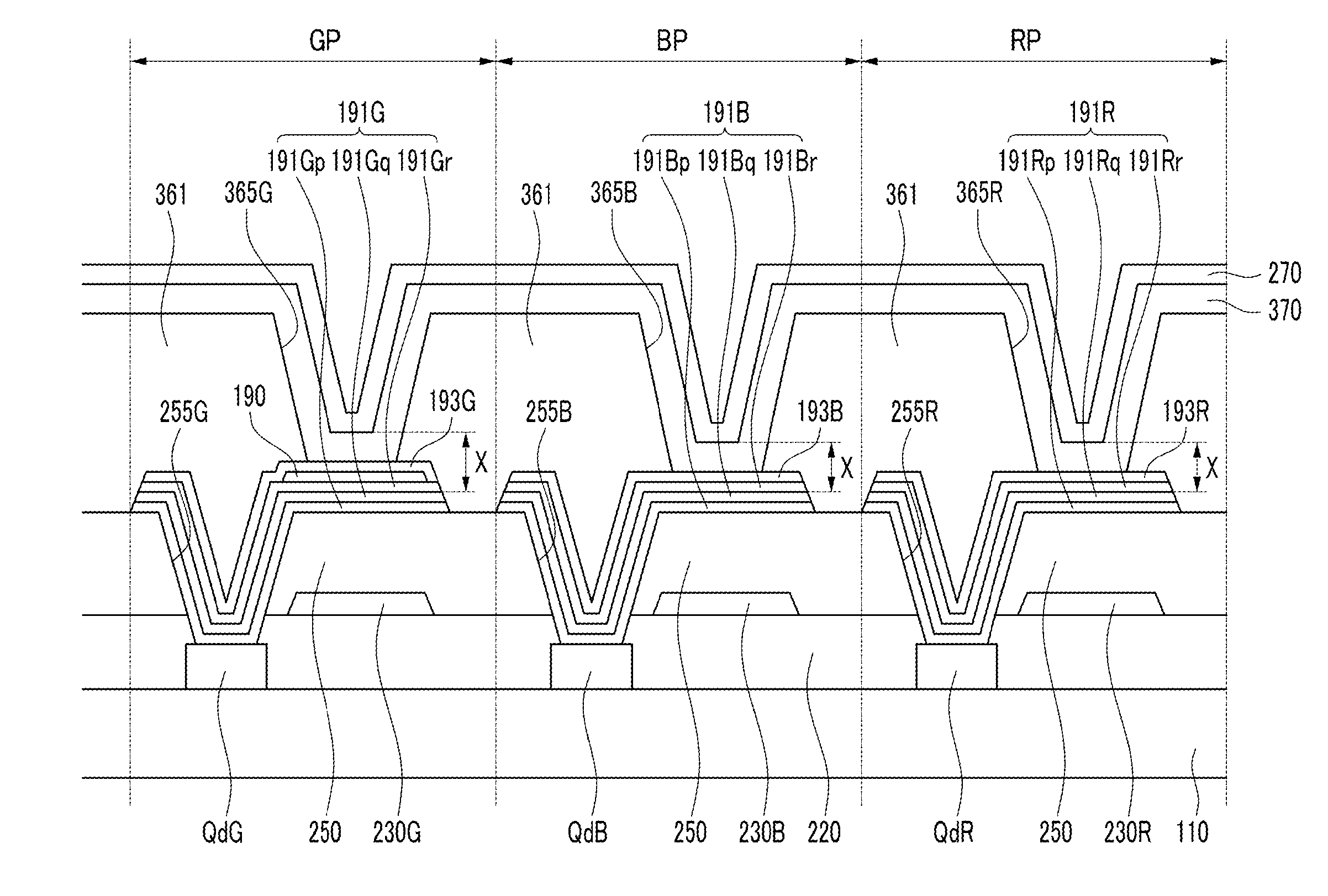
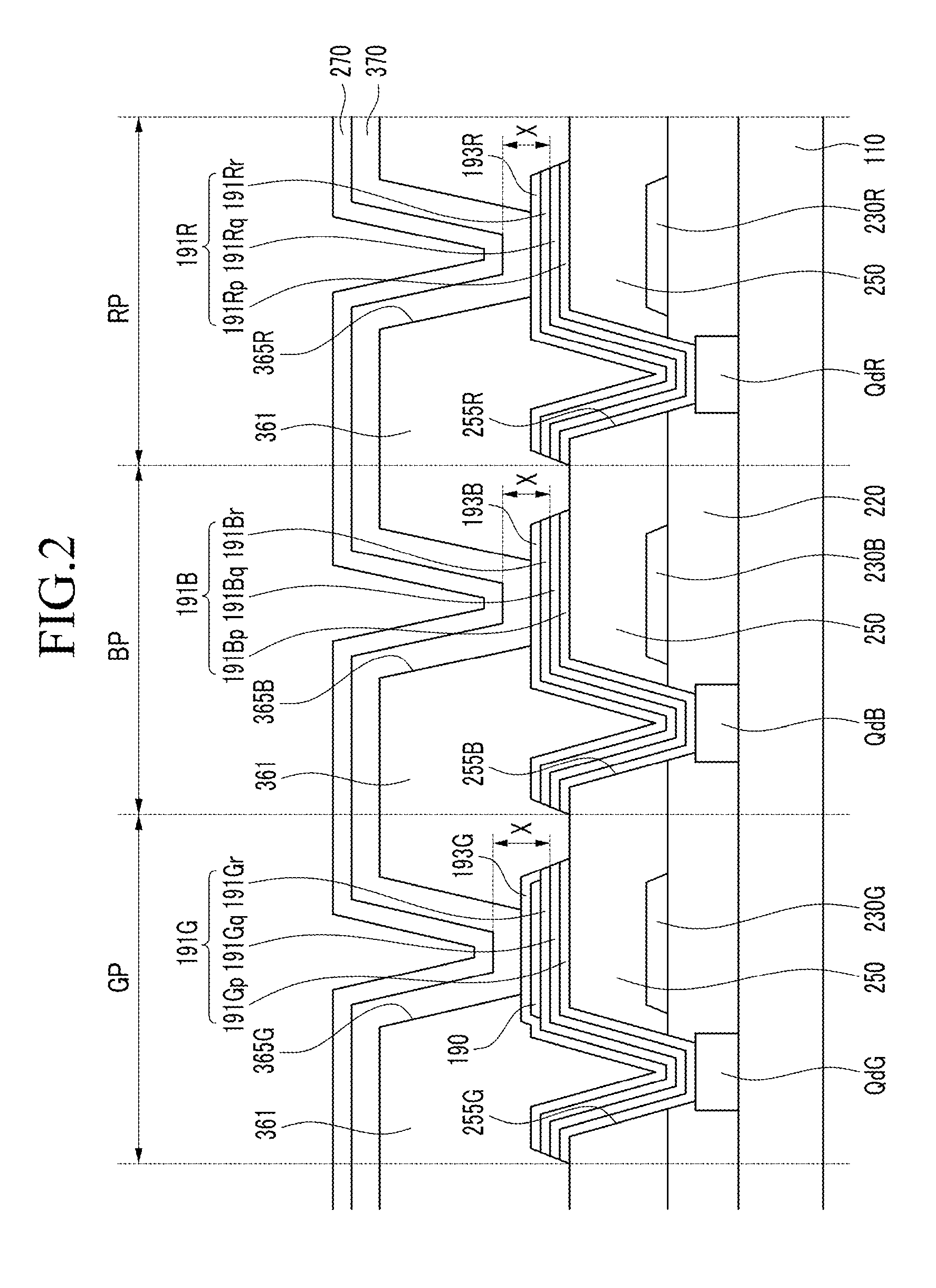
ActiveUS20100171120A1High light sensitivityHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay devicePhotoelectric conversion
In the case of forming switching elements and light sensor elements over the same substrate, an increase in the film thickness of active layers in an attempt to enhance the sensitivity of the light sensor elements would adversely affect the characteristics of the switching elements (TFTs). In a configuration of a display in which a channel layer 25 for constituting thin film transistors to form the switching elements for pixels and a photoelectric conversion layer 35 for constituting the light sensor elements are provided over a gate insulating film 24 on a glass substrate 5 to be provided with a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix pattern, the photoelectric conversion layer 35 is formed to be thicker than the channel layer 25, and / or the photoelectric conversion layer 35 is formed of a material different from the material for the channel layer 25, whereby the light absorption coefficient of the photoelectric conversion layer 35 is made to be higher than that of the channel layer 25.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
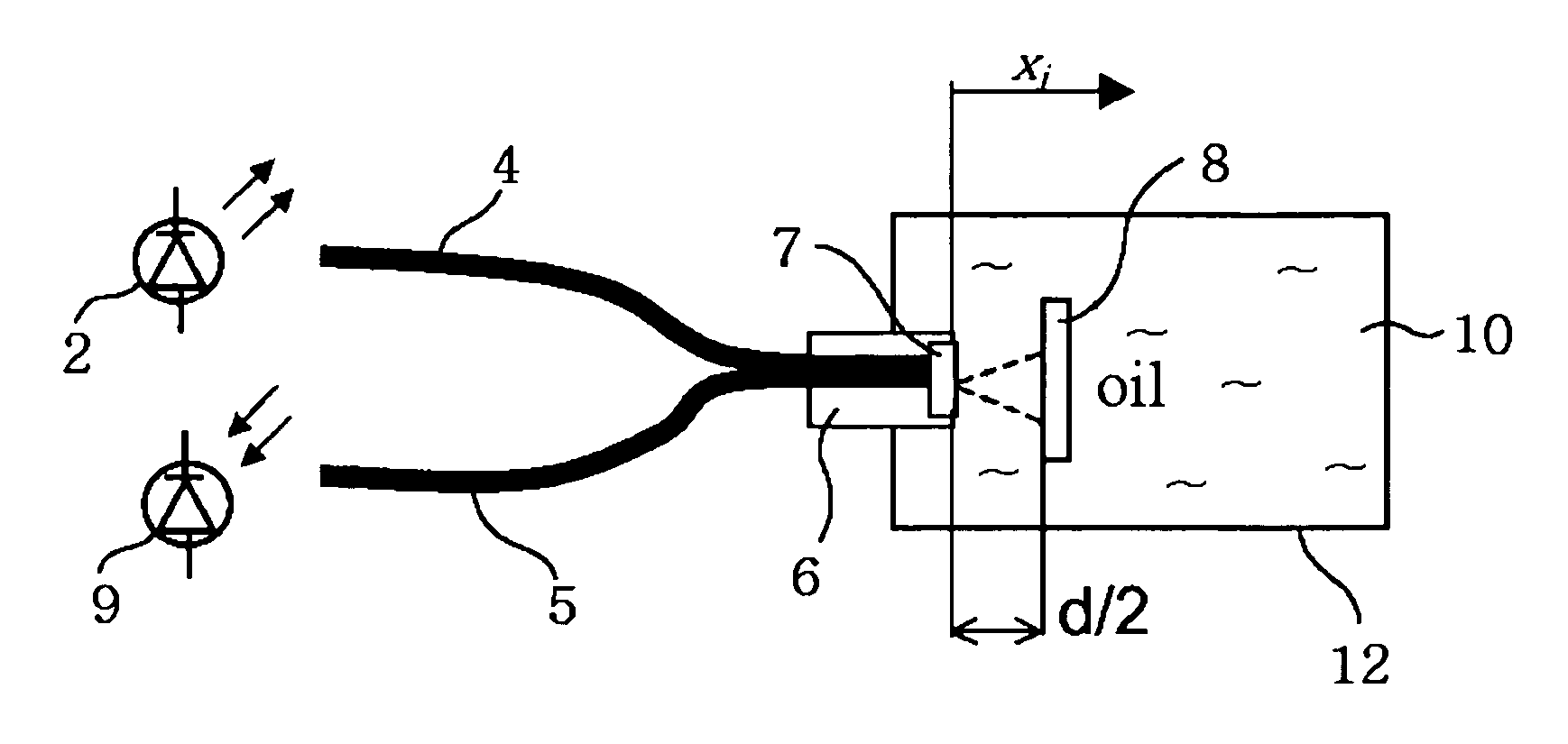
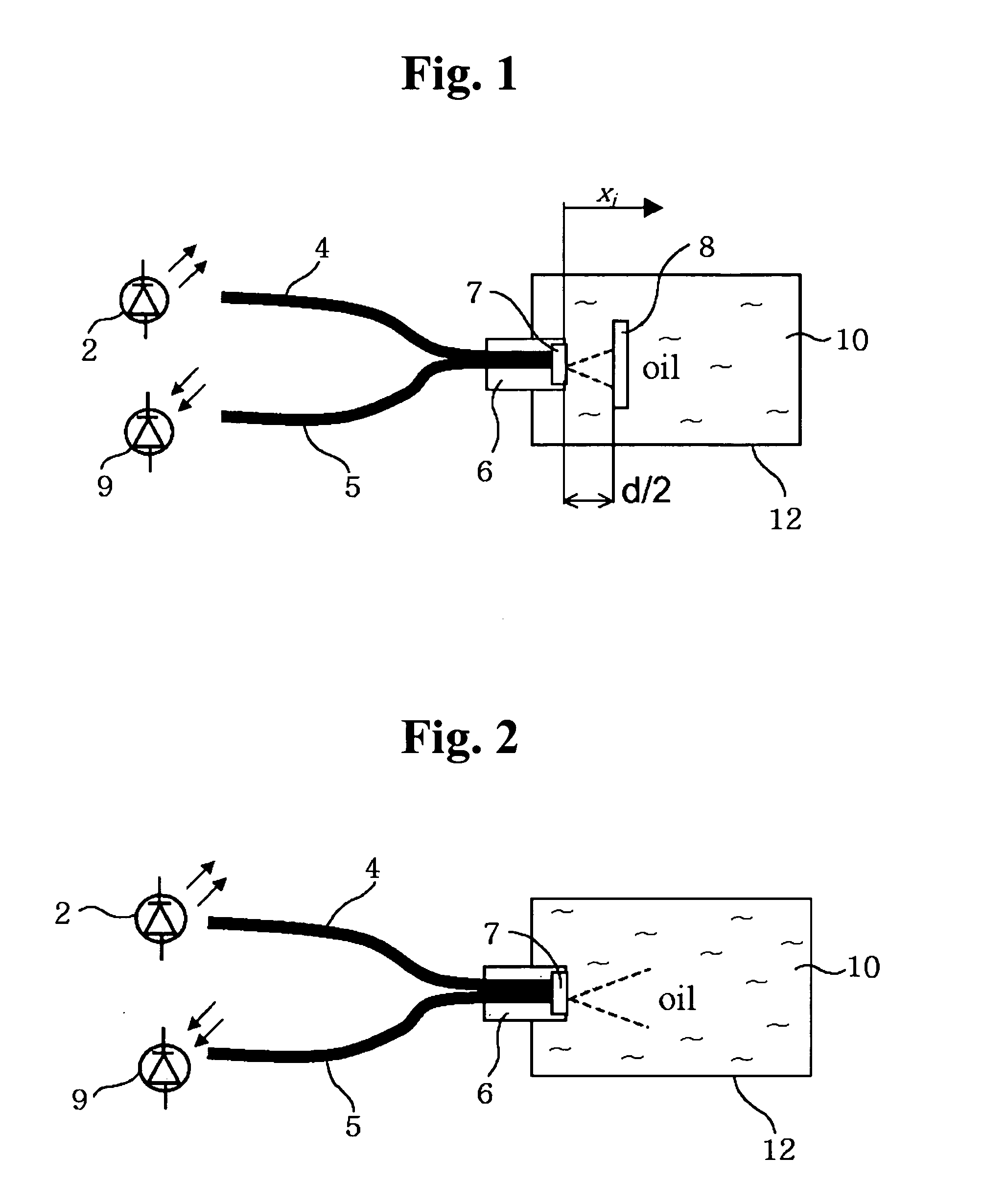
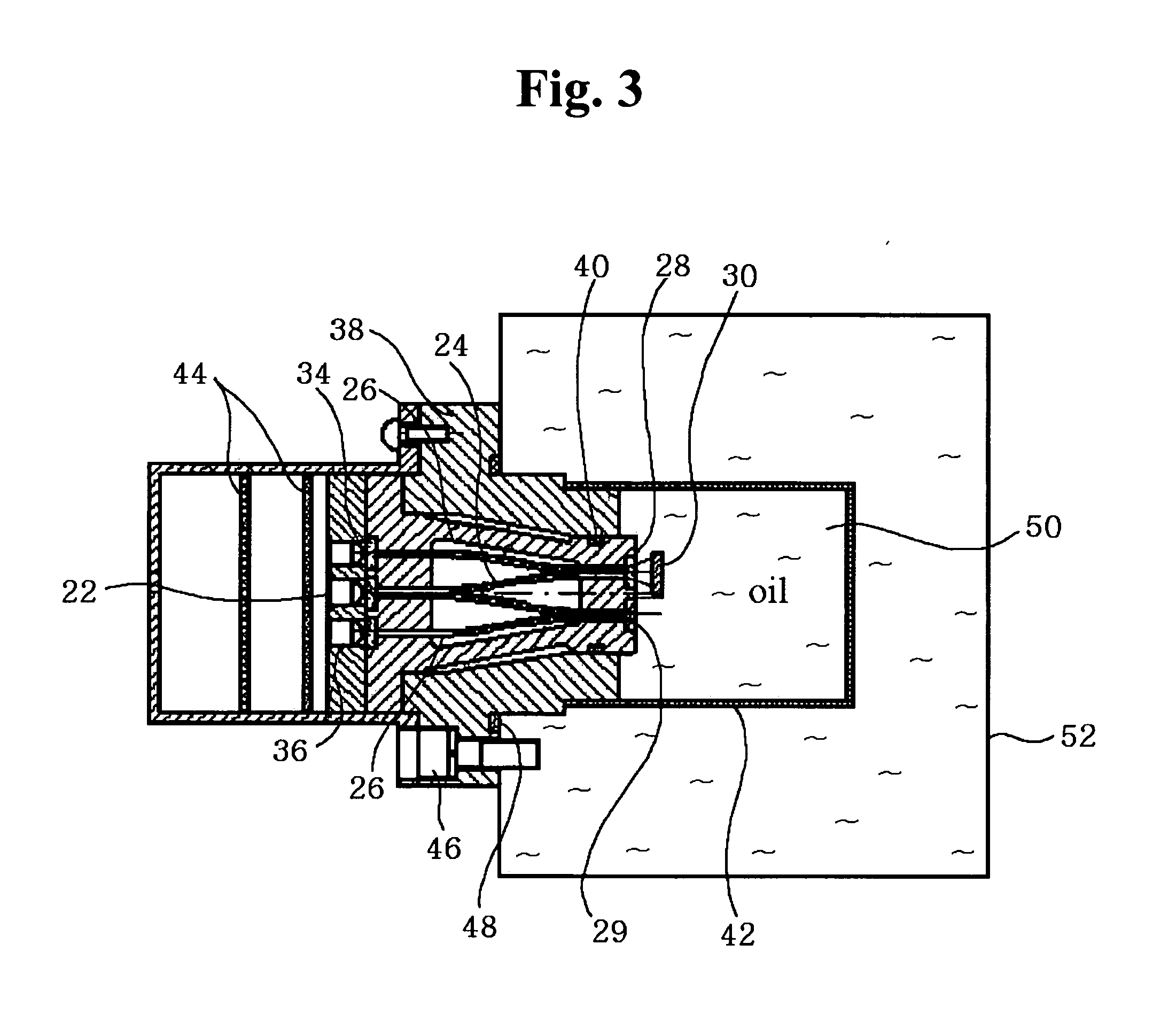
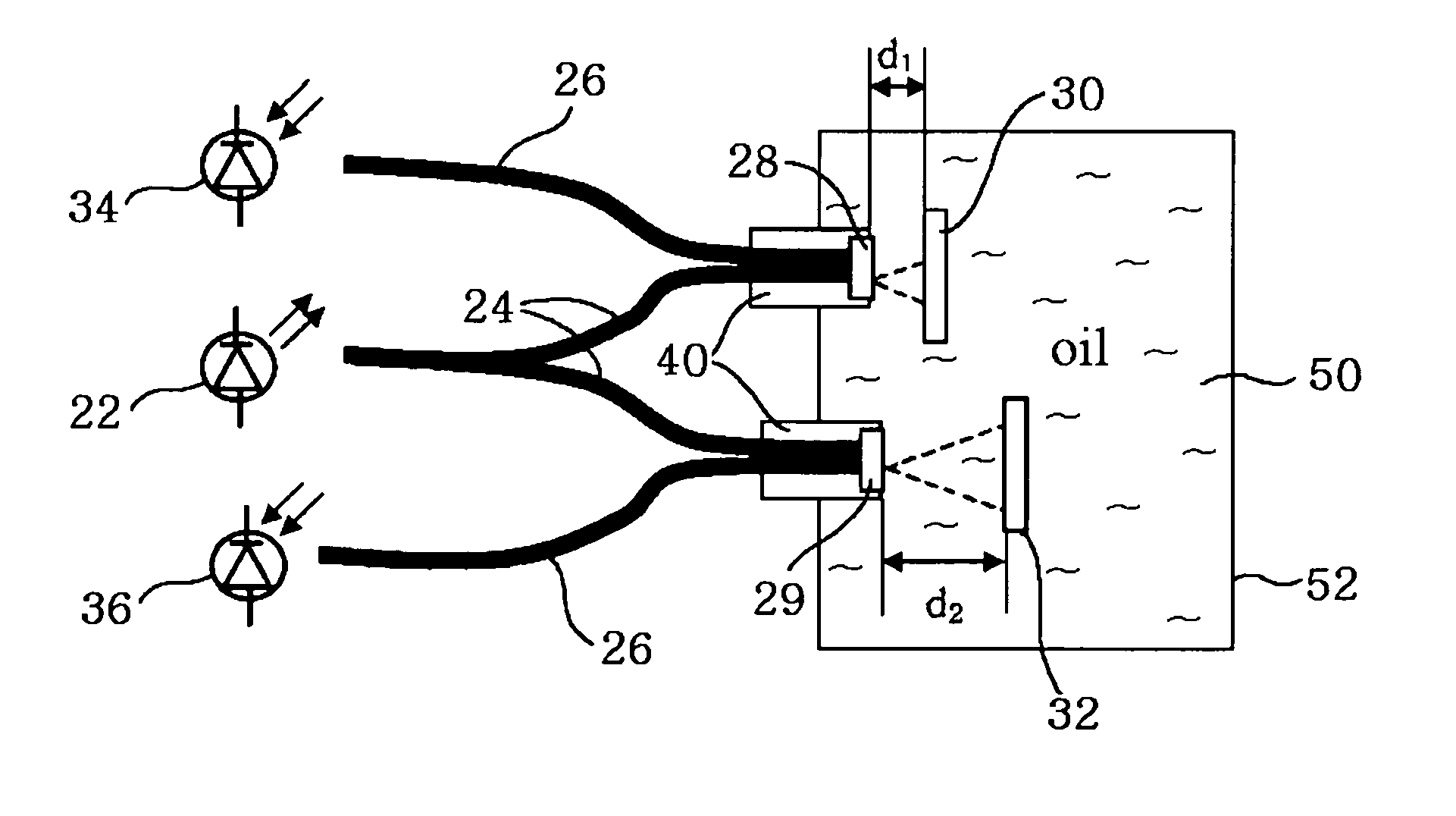
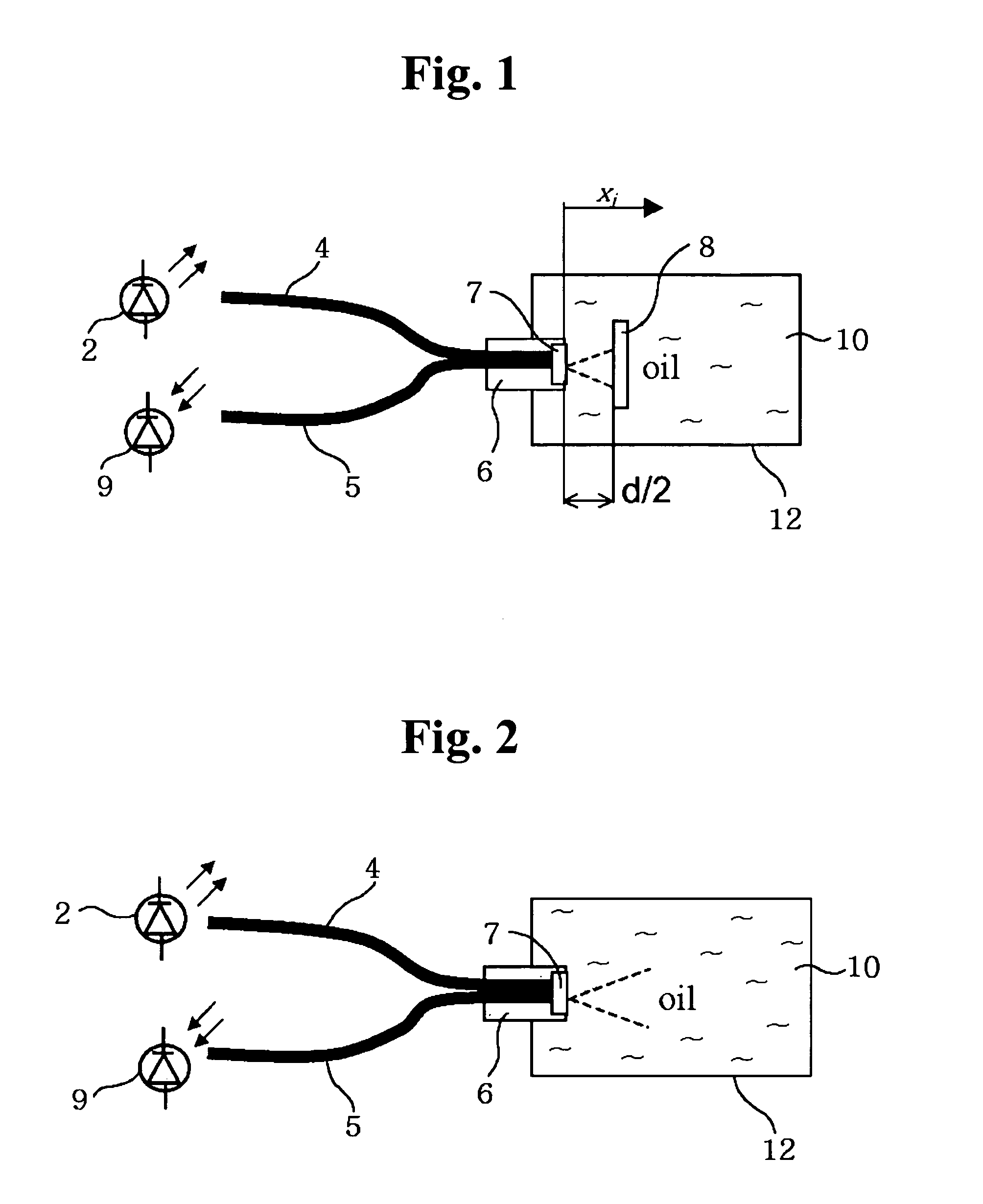
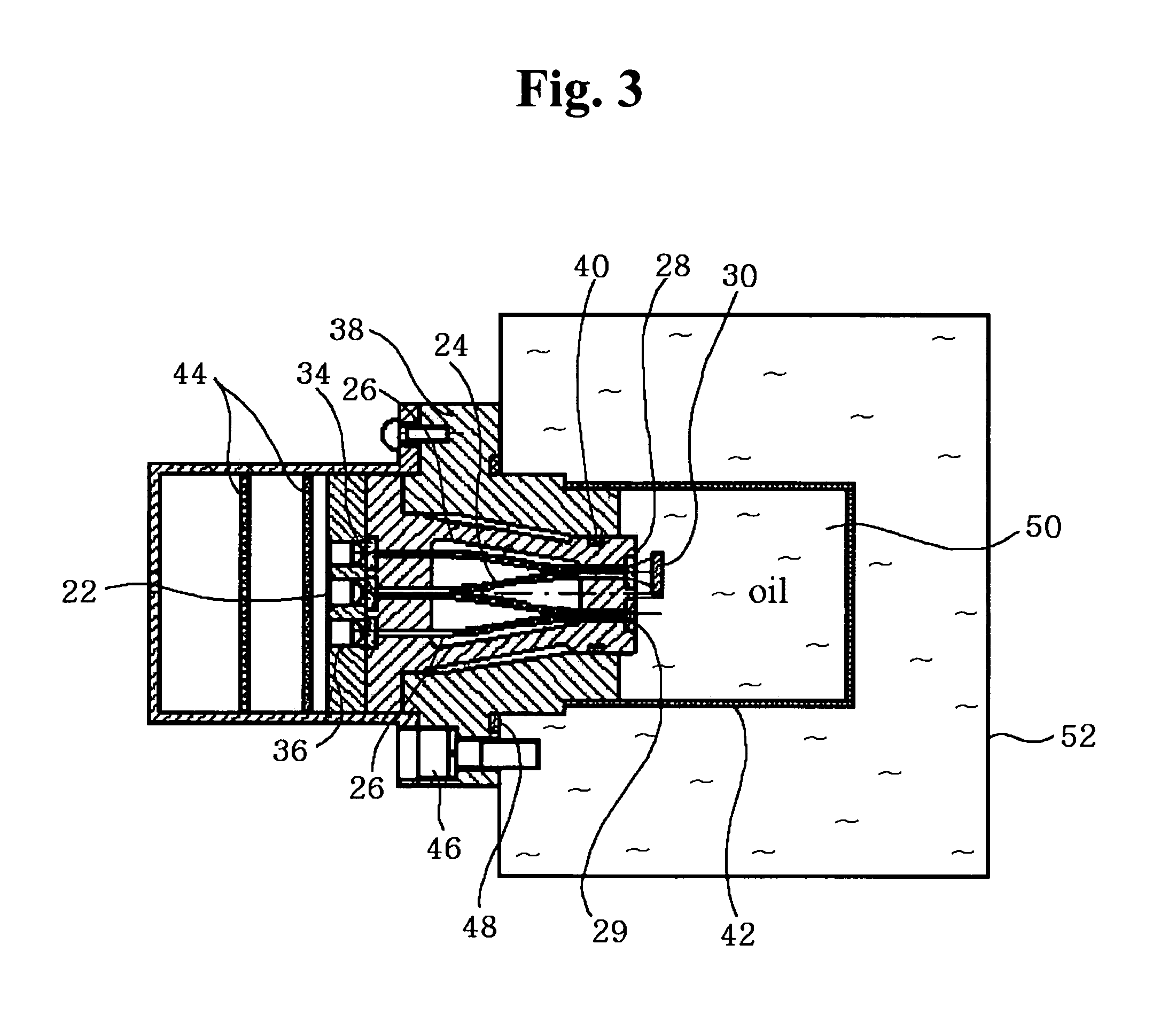
Apparatus for measuring oil oxidation using fluorescent light reflected from oil
An apparatus for measuring oil oxidation is capable of being mounted to mechanical devices for detecting power of fluorescent light reflected from oil in real time as an indication of the oil oxidation. A plurality of first optical fibers are connected to a light-emitting member for introducing the light into oil at different incidence points. A plurality of light-reflecting mirrors are immersed in the oil and disposed opposite to the incidence points. The light-reflecting mirrors are located at different distances from the incidence points. A plurality of second optical fibers are connected to the incidence points, respectively. A plurality of light-receiving members are connected to the second optical fibers for receiving the light and outputting the signals corresponding to the received light. A control portion calculates a fluorescence quantum yield and a light absorption coefficient of the oil based upon the signals from the light-receiving members and compares them with the reference values pre-stored in the control portion to determine the oil oxidation.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Organic light emitting display and fabricating method thereof
ActiveUS20100026178A1Excellent optical propertiesImprove optical efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensFinal product manufactureOptoelectronicsAuxiliary electrode
An organic light emitting display according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes a transistor arranged on an insulating substrate, a pixel electrode connected to the transistor and including a reflective film, an optical path controller arranged on the pixel electrode, an auxiliary electrode arranged on the pixel electrode and the optical path controller, an organic light emitting member arranged on the organic light emitting member, and a common electrode arranged on the organic light emitting member, wherein the optical path controller has a lower light absorption coefficient than the auxiliary electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Endoscope system, processor of endoscope system, and image producing method
ActiveUS20120157768A1Superior and useful for medical diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisTest objectLight absorption coefficient
First illumination light of a first wavelength range, in which light absorption coefficient of blood hemoglobin varies with oxygen saturation thereof, is projected into a test subject body, to capture a first image signal from the first illumination light as reflected from inside the test subject body. Then second illumination light of a second wavelength range different from the first wavelength range is projected into a test subject body, to capture a second image signal from the second illumination light as reflected from inside the test subject body. A subject image of the test subject is produced from the second image signal. Oxygen saturation levels of the test subject are calculated using the first and second image signals. According to the calculated oxygen saturation levels, color properties of the subject image are changed to produce an oxygen saturation image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
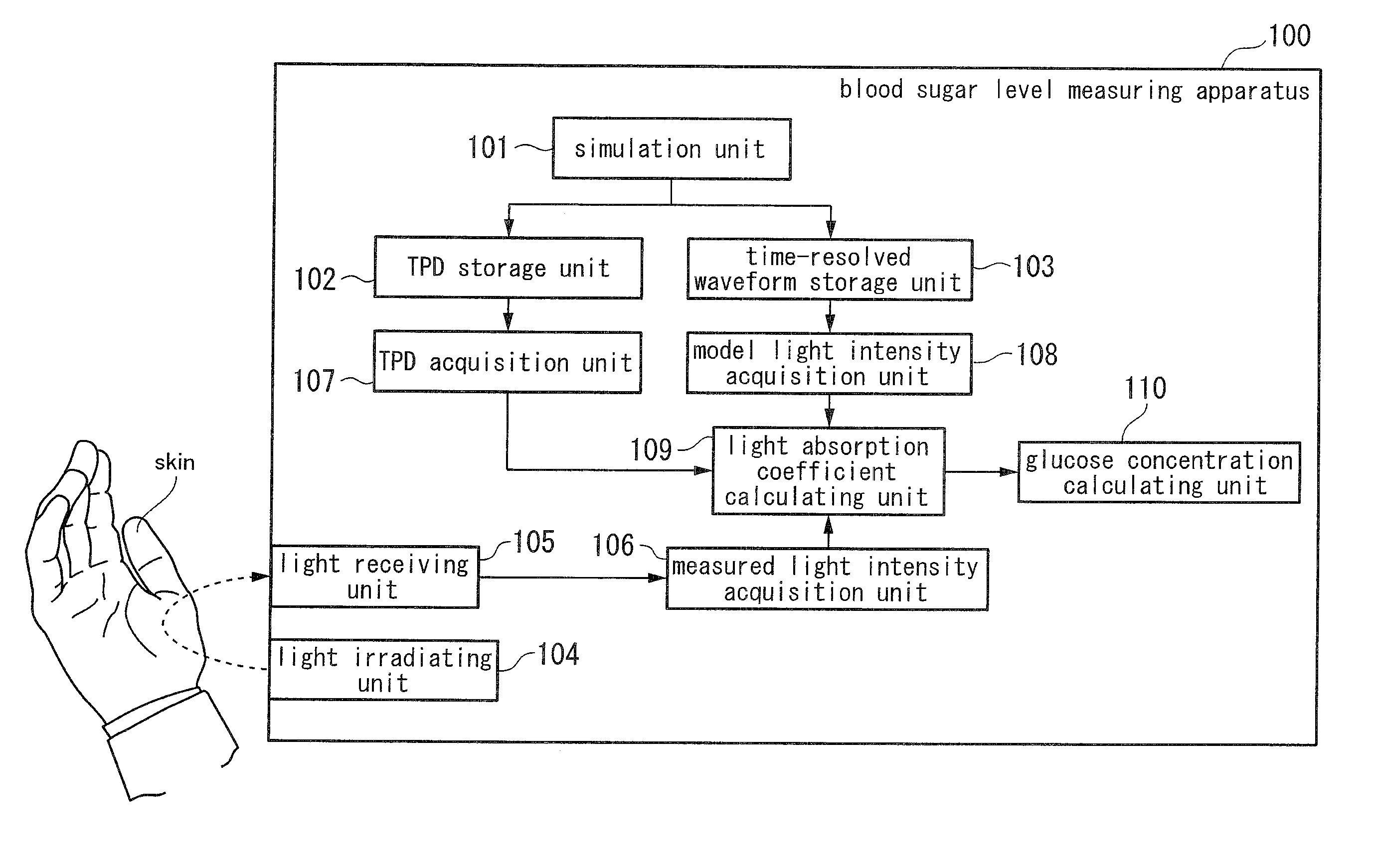
Apparatus for quantifying concentration, method for quantifying concentration, and program for quantifying concentration
InactiveUS20100256920A1Reduce impactImprove accuracyScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPath lengthMedicine
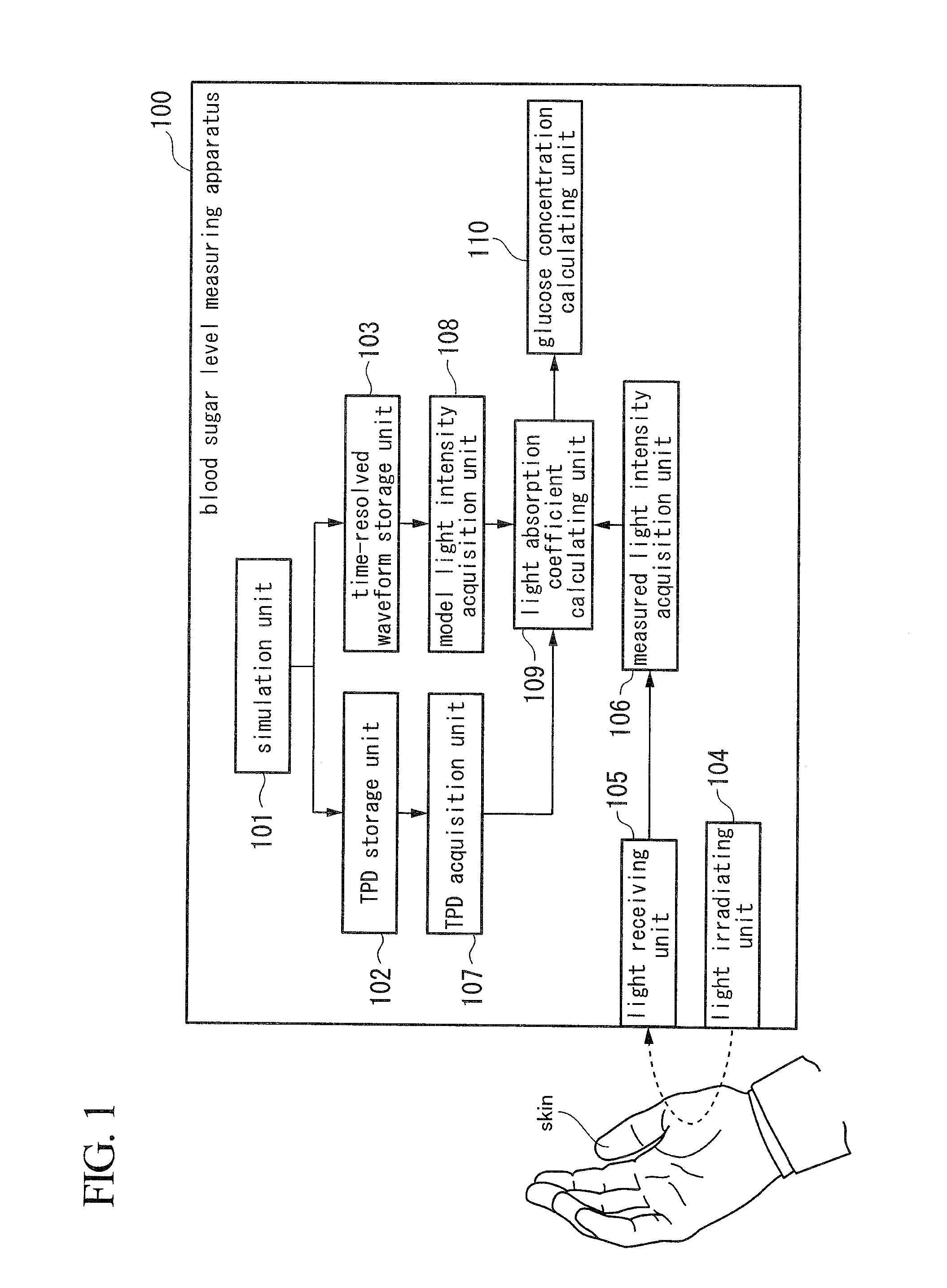
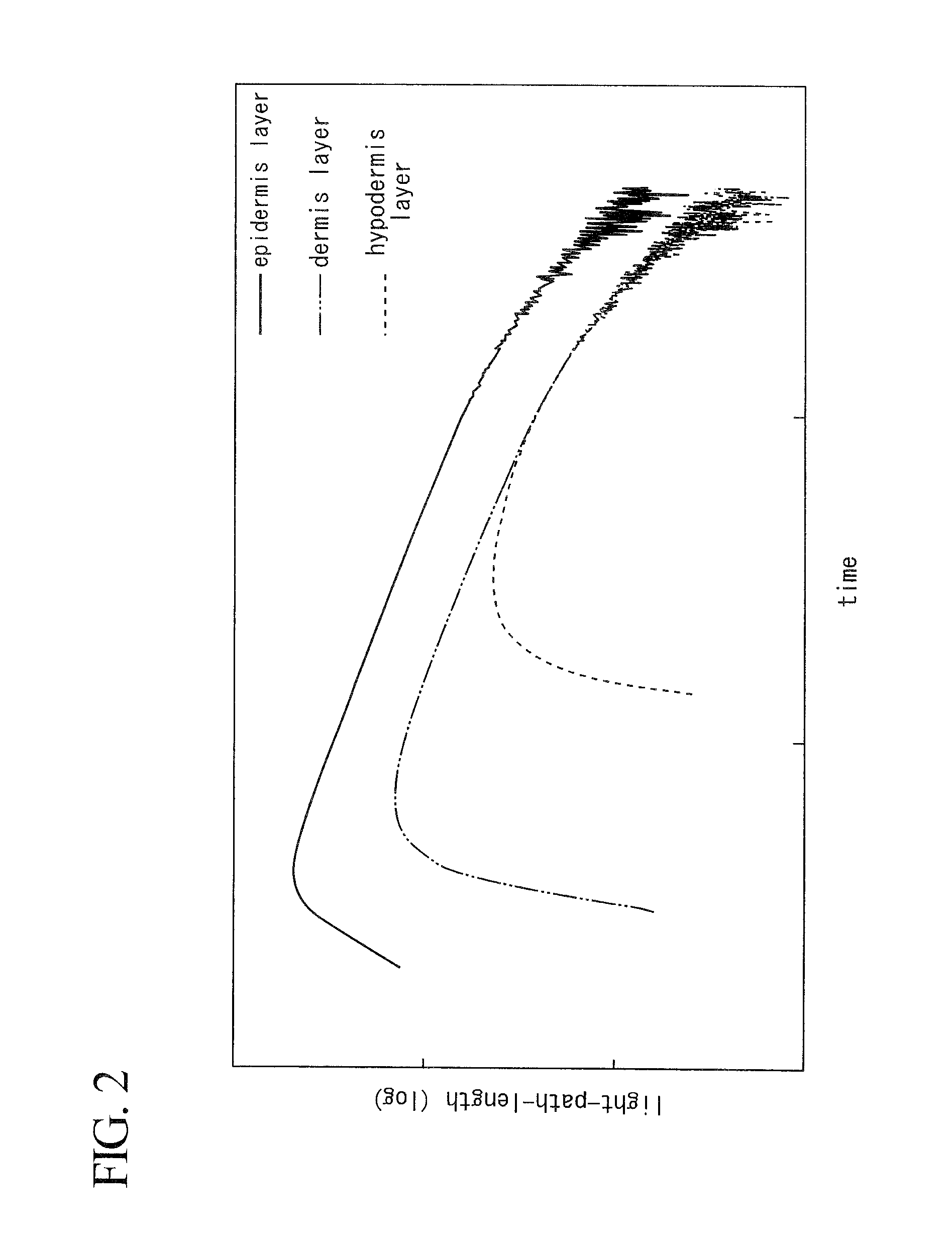
An apparatus for quantifying concentration includes a temporal path-length distribution (TPD) storage unit configured to store a TPD model of a short-time-pulse of light, a time-resolved waveform storage unit configured to store a time-resolved waveform model of the short-time-pulse of light, a light irradiating unit configured to irradiate the short-time-pulse of light, a light receiving unit configured to receive a backscattered light, a measured light intensity acquisition unit configured to acquire a light intensity of the backscattered light, a TPD acquisition unit configured to acquire a TPD, a model light intensity acquisition unit configured to acquire the light intensity of the short-time-pulse of light, a light absorption coefficient calculating unit configured to calculate a light absorption coefficient, and a concentration calculating unit configured to calculate the concentration of a target component.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP +1
Acoustic wave measuring apparatus, acoustic wave imaging apparatus and method for controlling acoustic wave measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20120167693A1Increase signal strengthReduce equipment costsVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic waveLength wave
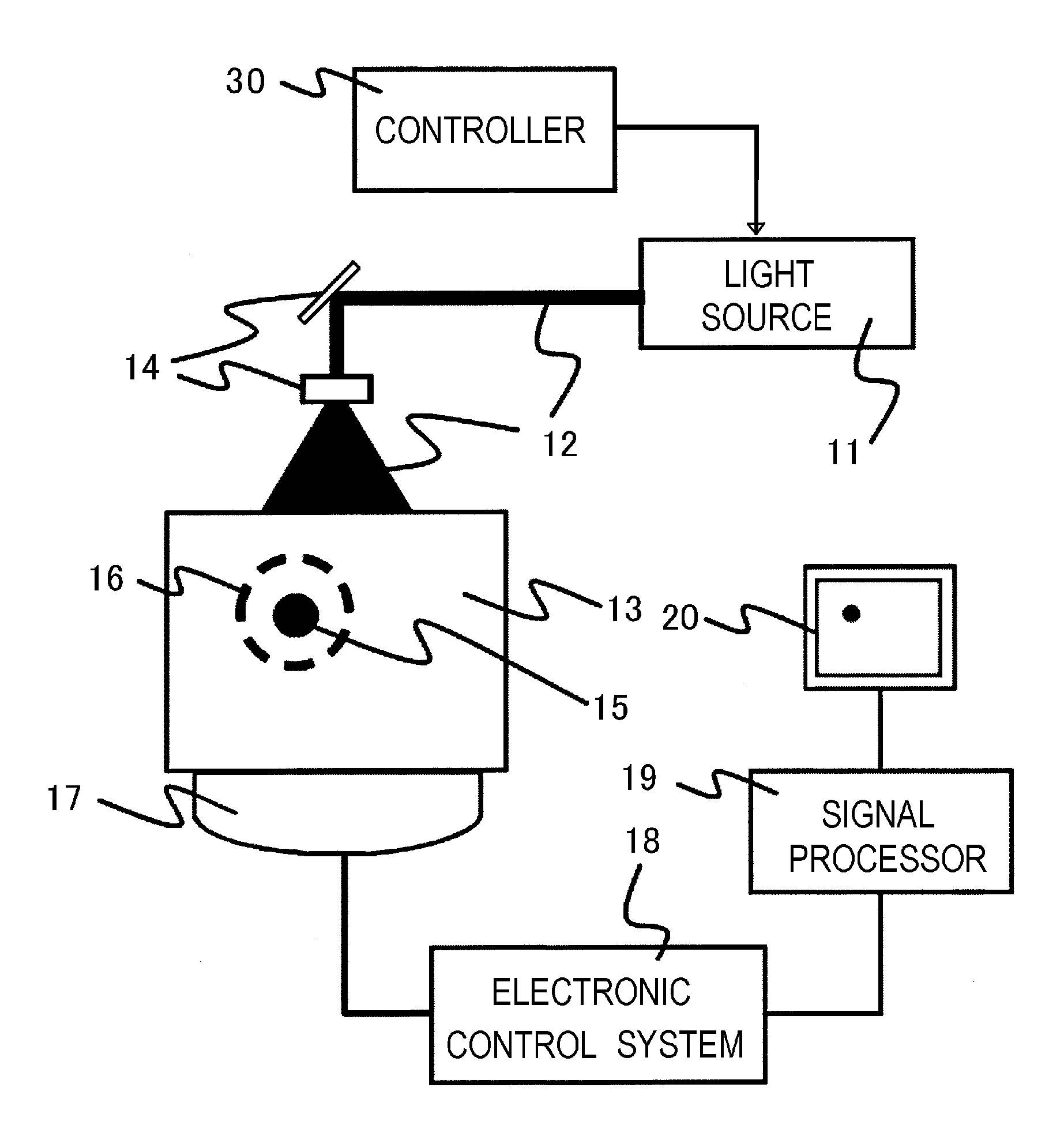
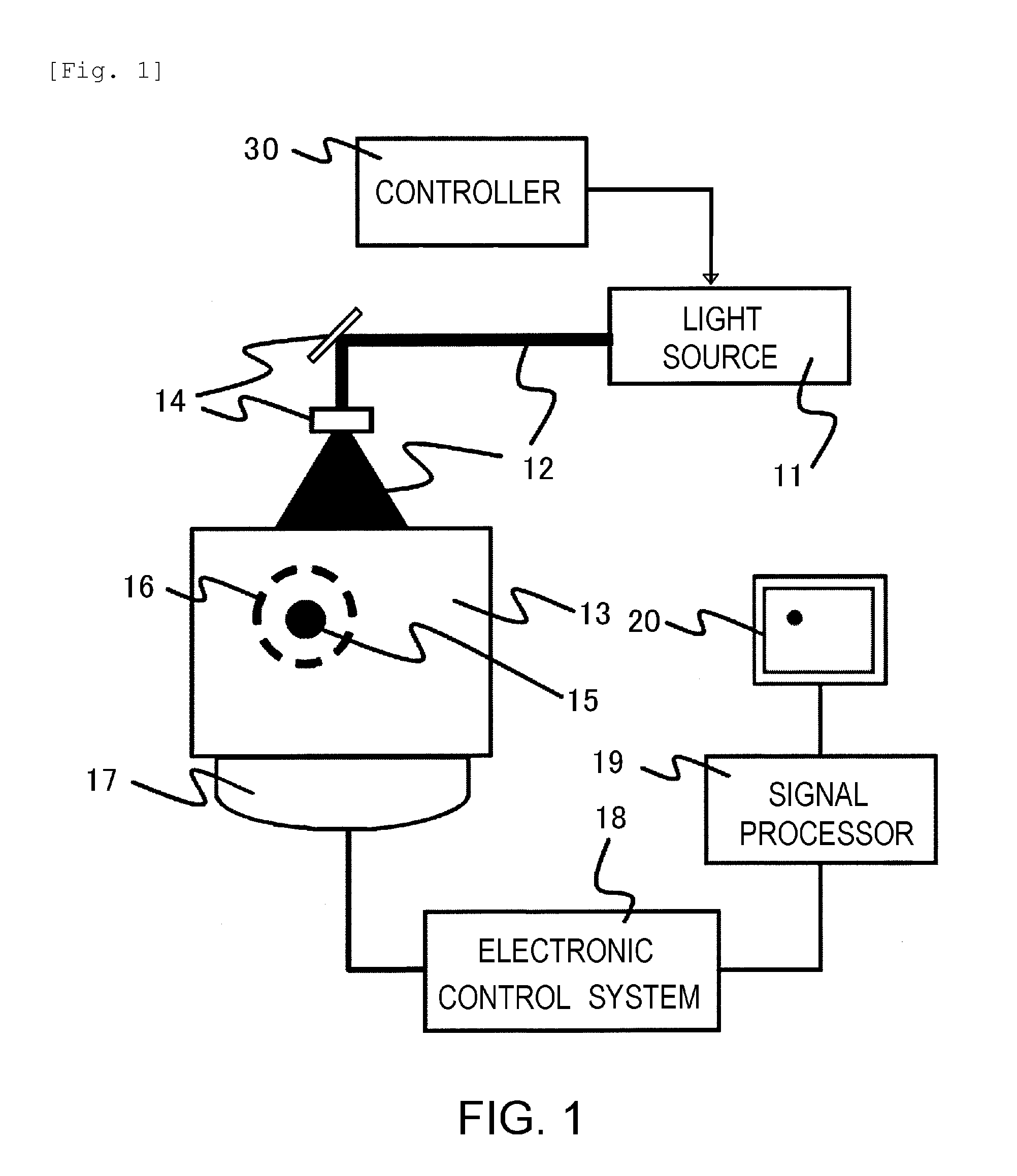
An acoustic wave measuring apparatus includes a light source for radiating a light having a wavelength component in wavelength areas, light filters arranged in a light path from the light source to a subject and each to shut off or transmit the light in one of the wavelength areas, a detector for detecting an acoustic wave generated by the radiation, a controller for generating conditions having different combinations of the wavelength components contained in the light, and a signal processor for calculating an optical absorption coefficient of the subject for the light in each wavelength area based on a pressure of the acoustic wave detected under each of the conditions and a strength of the radiated light for each wavelength area under conditions.
Owner:CANON KK
Colored glass casing
ActiveCN102960081AHigh strengthReduce manufacturing costCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsPortable casingsLength waveUltimate tensile strength
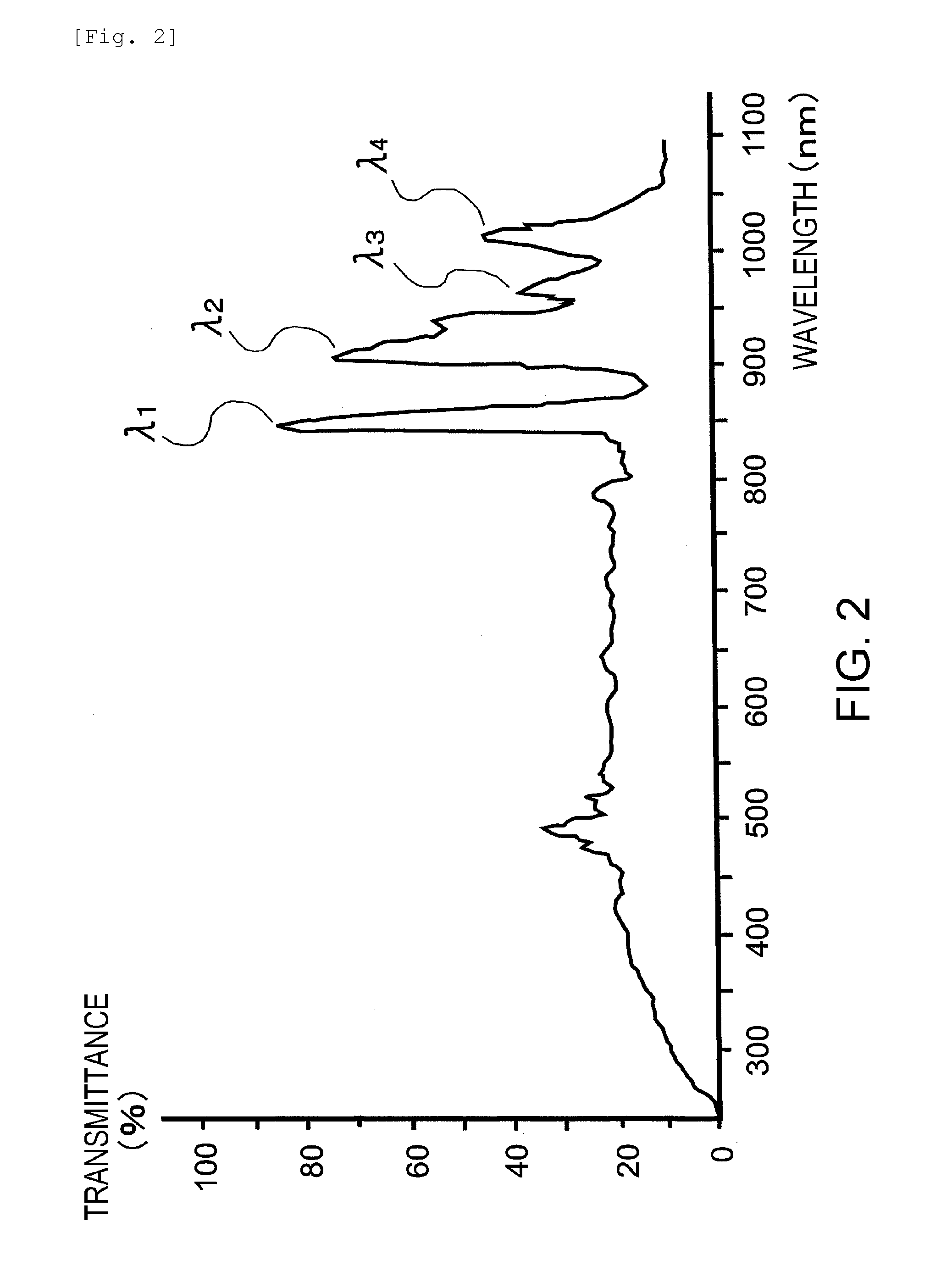
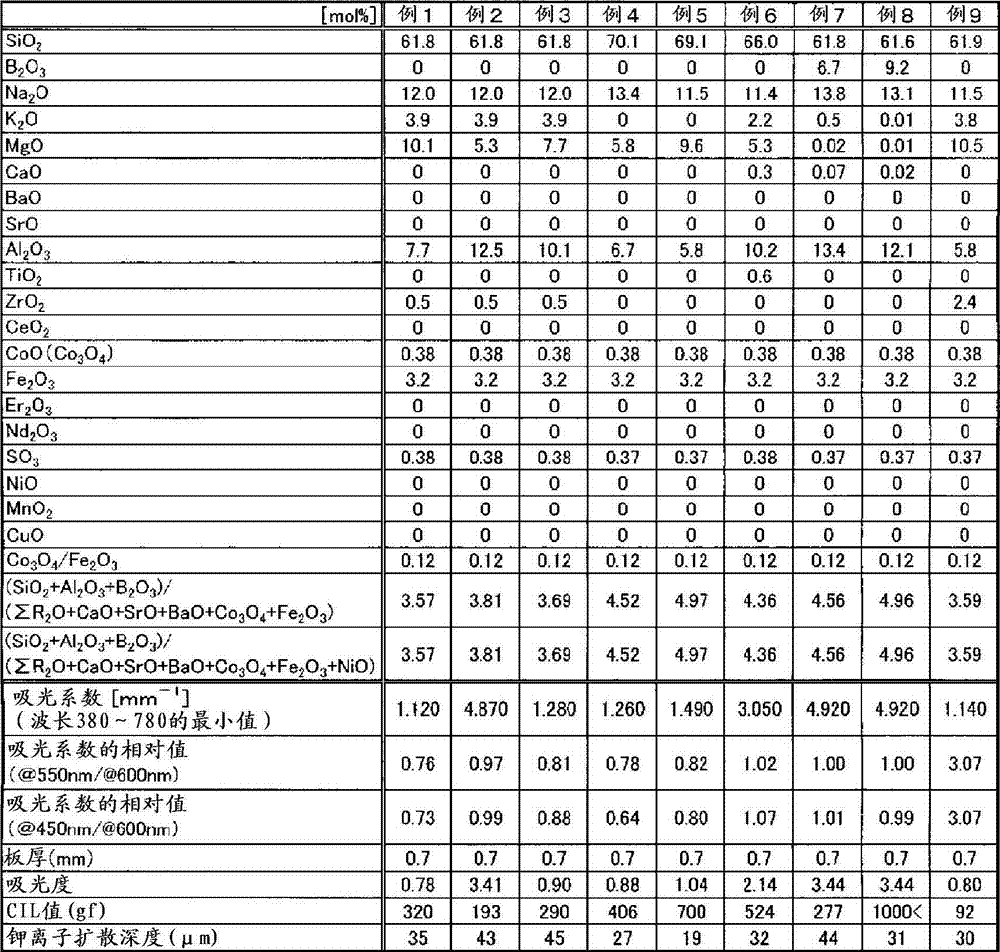
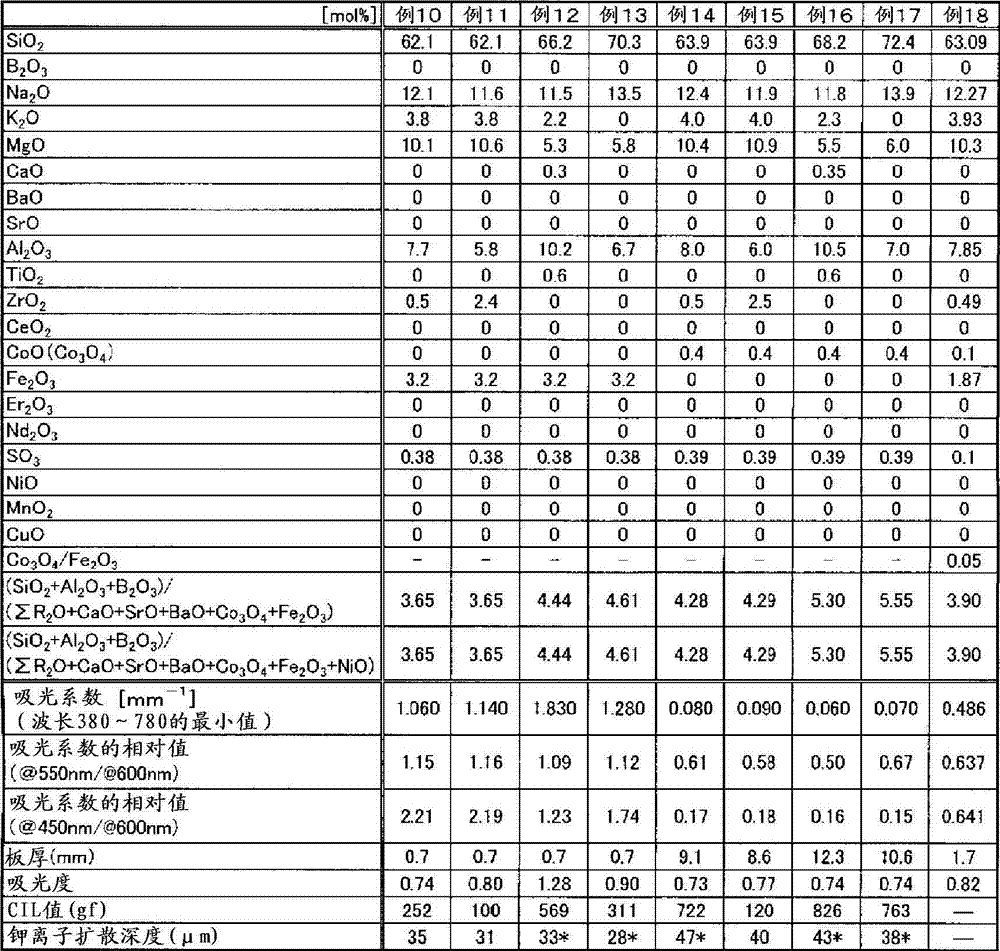
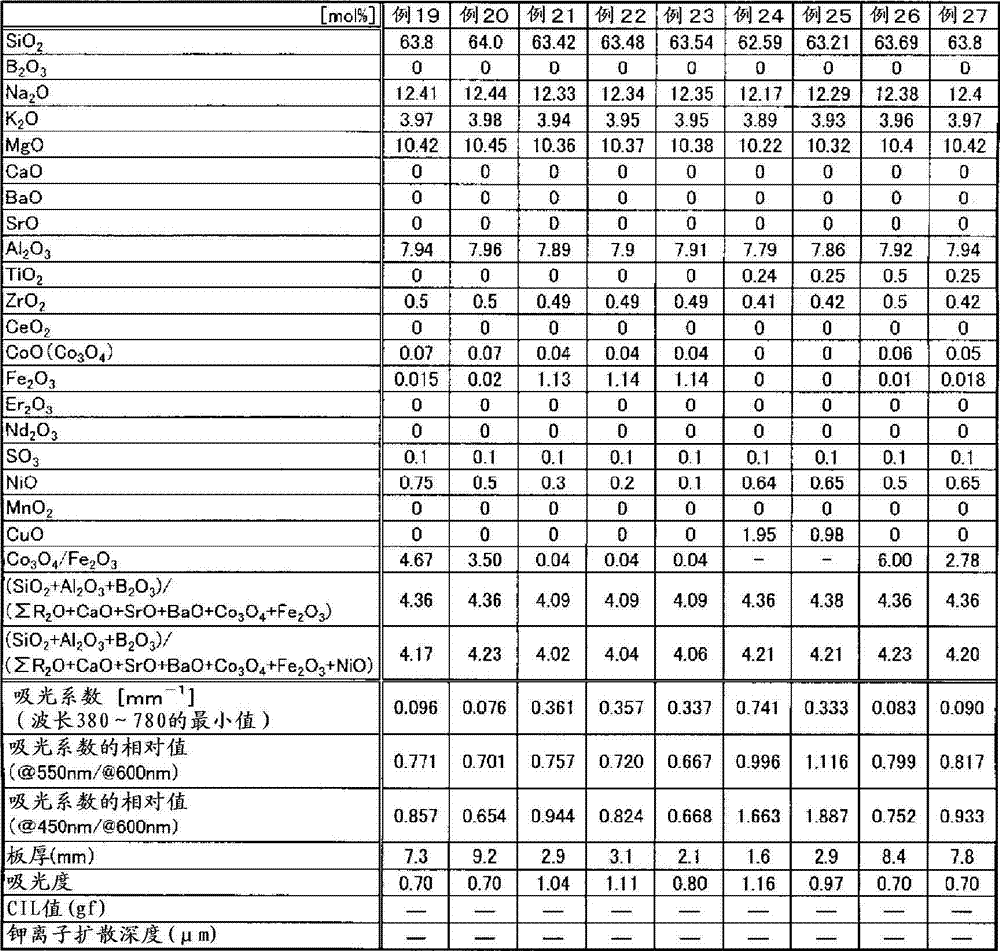
Provided is a colored glass casing having favorable characteristics as a casing of an electronic apparatus, namely having superior production cost, high strength, and light blocking properties. The colored glass casing clads an electronic apparatus, and is configured from a glass having a light absorption at the wavelengths of 380 nm to 780 nm of at least 0.7, preferably a glass having a light absorption coefficient of at least 1 mm-1. To result in the abovementioned glass, preferably 0.1-7% in mole percent on an oxide basis of at least one component selected from the group consisting of the metal oxides of Co, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Cr, V, and Bi is contained as the coloring component in the glass.
Owner:AGC INC
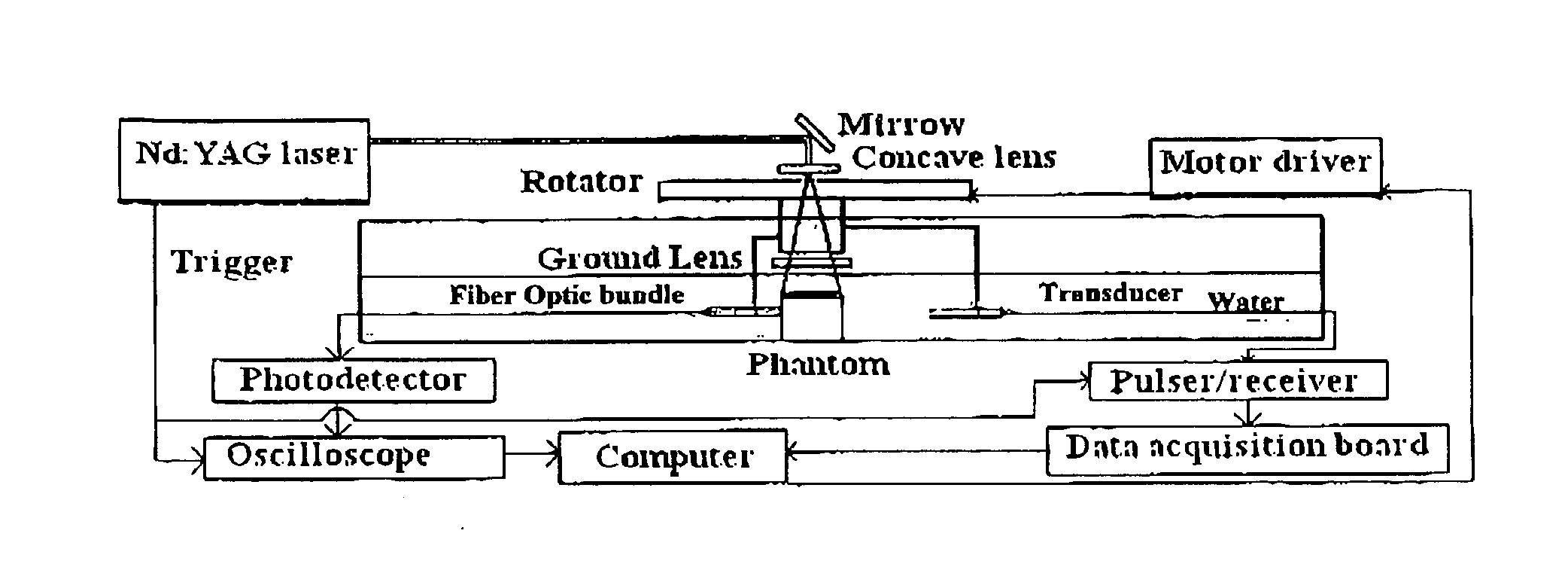
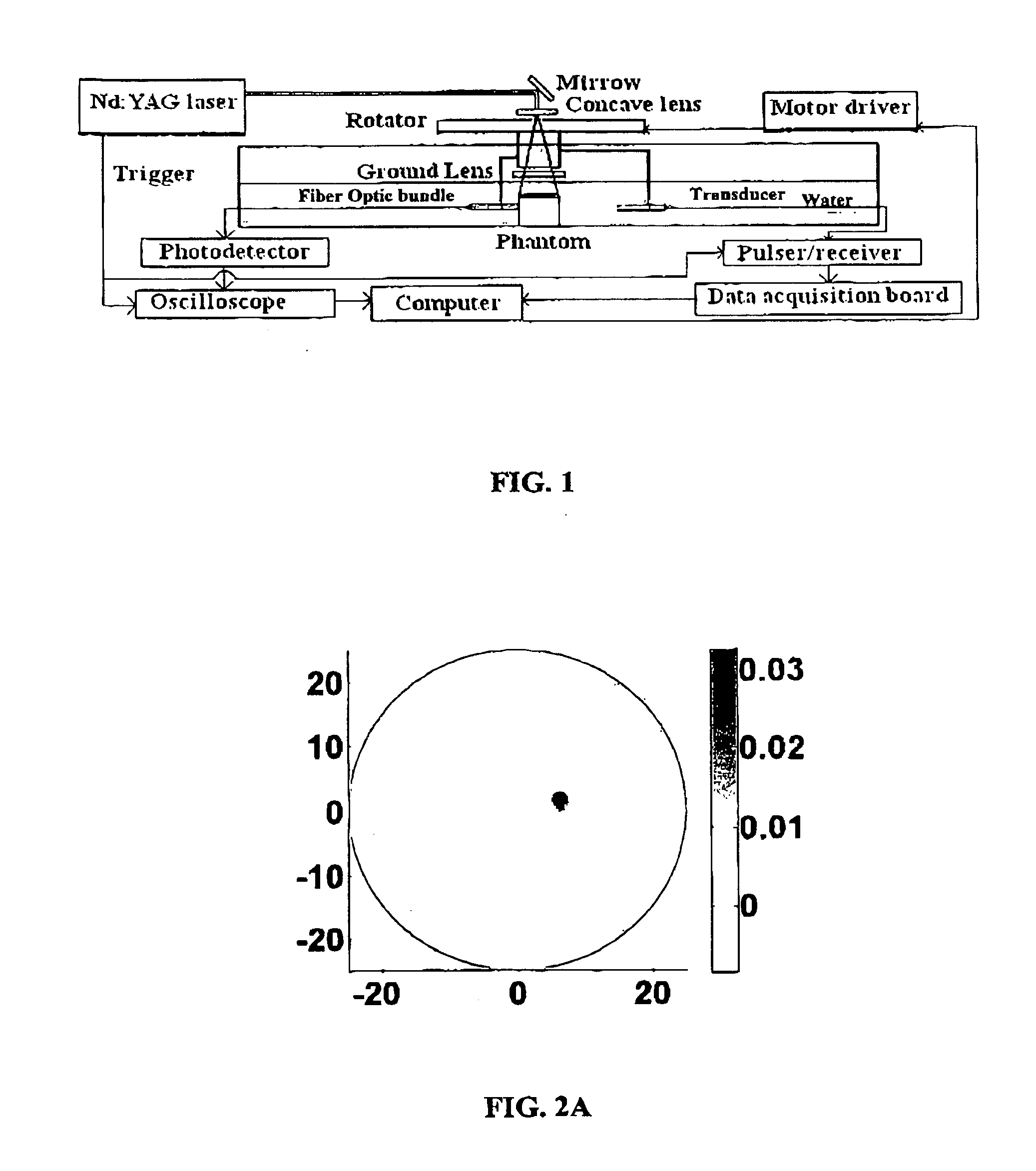
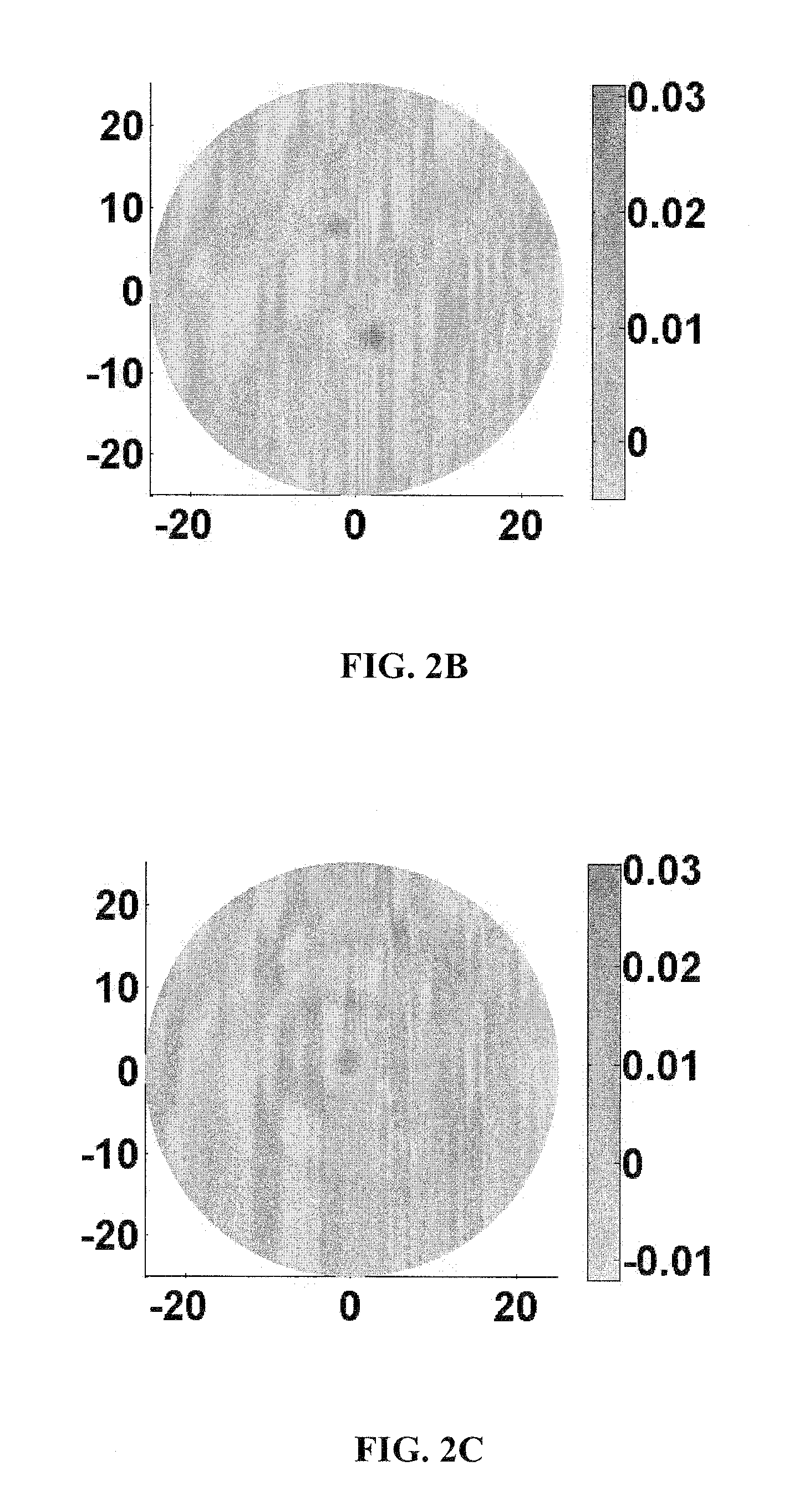
Method and Apparatus for Tomographic Imaging of Absolute Optical Absorption Coefficient in Turbid Media Using Combined Photoacoustic and Diffusing Light Measurements
InactiveUS20100208965A1Careful calibrationEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostics using tomographyWave equationAbsorbed energy
Embodiments of the invention pertain to methods for imaging a light absorption coefficient distribution. Embodiments of the subject method can be implemented without knowing the strength of incident light in advance and without requiring careful calibrations in the non-scattering medium. Embodiments of the method can combine conventional photoacoustic tomography (PAT) with diffusing light measurements coupled with an optimization procedure based on the photon diffusion equation. Images of absorbing targets as small as 0.5 mm in diameter embedded in a 50 mm diameter background medium can be quantitatively recovered. Small targets with various optical contrast levels relative to the background can be detected well. Embodiments of the subject reconstruction method can include first obtaining the map of absorbed optical energy density. Embodiments can obtain the map of absorbed optical energy density through a model-based reconstruction algorithm that is based on a finite element solution to the photoacoustic wave equation in frequency domain subject to the radiation or absorbing boundary conditions (BCs). The distribution of optical fluence can then be obtained. Embodiments can obtain the distribution of optical fluence using the photon diffusion equation based optimization procedure. The distribution of optical absorption coefficient can then be recovered from the distribution of optical fluence and the absorbed energy density.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
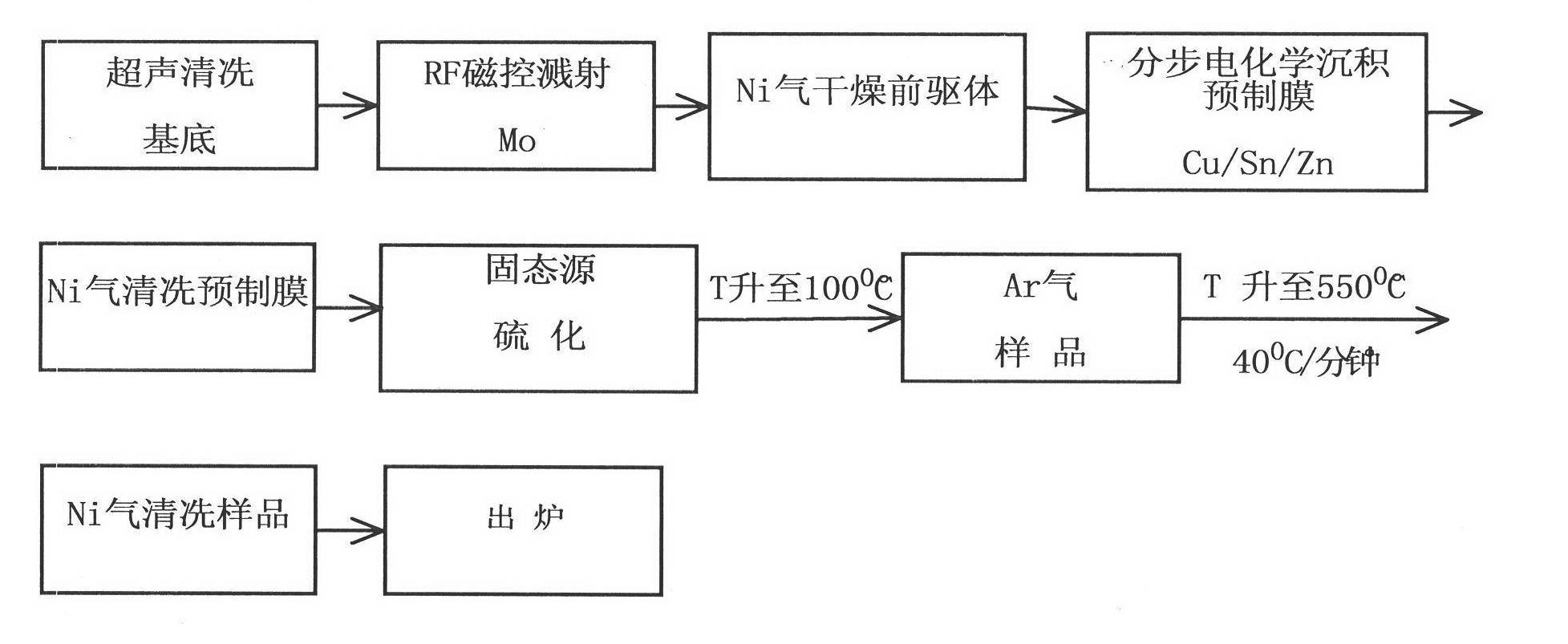
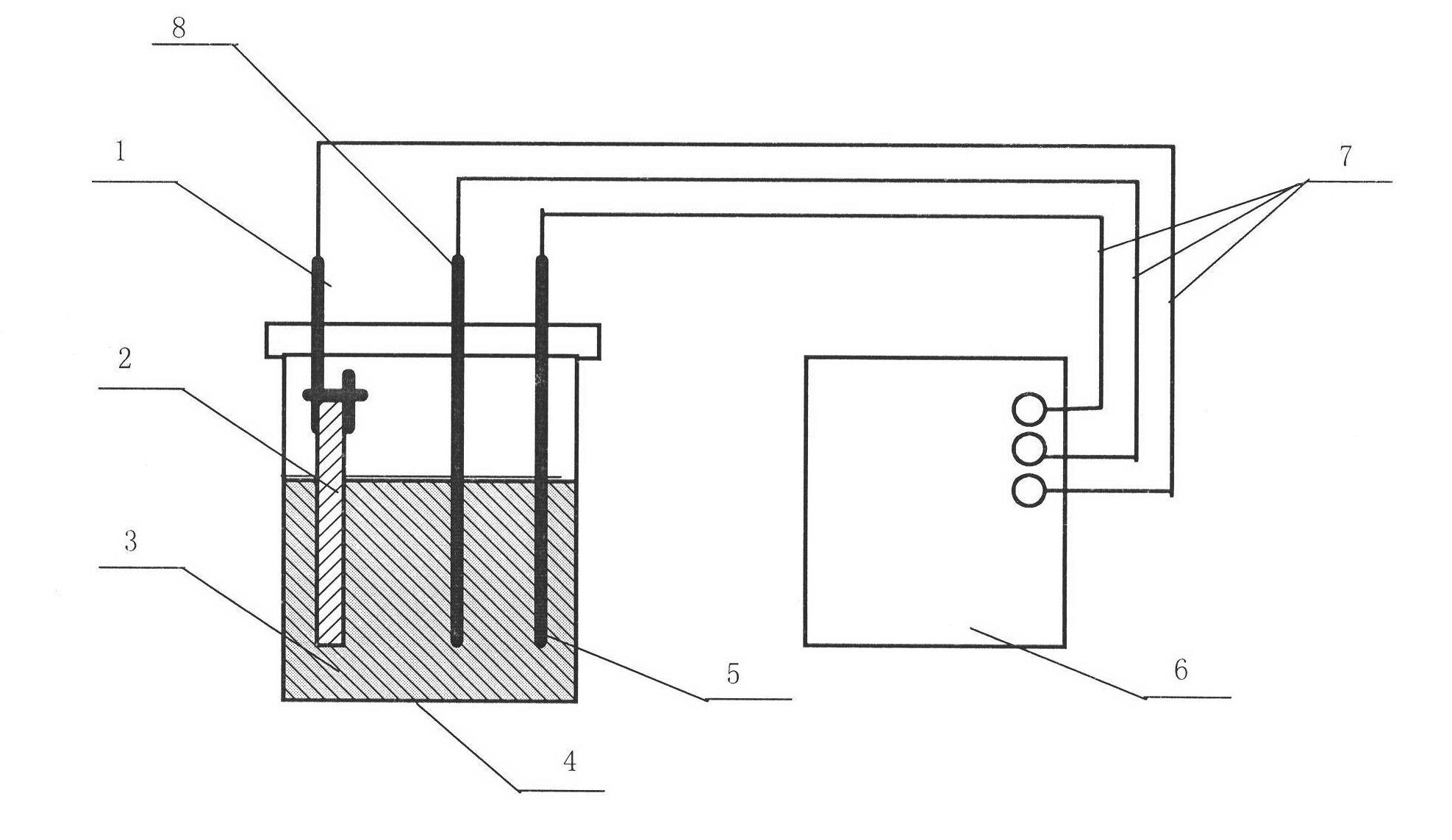
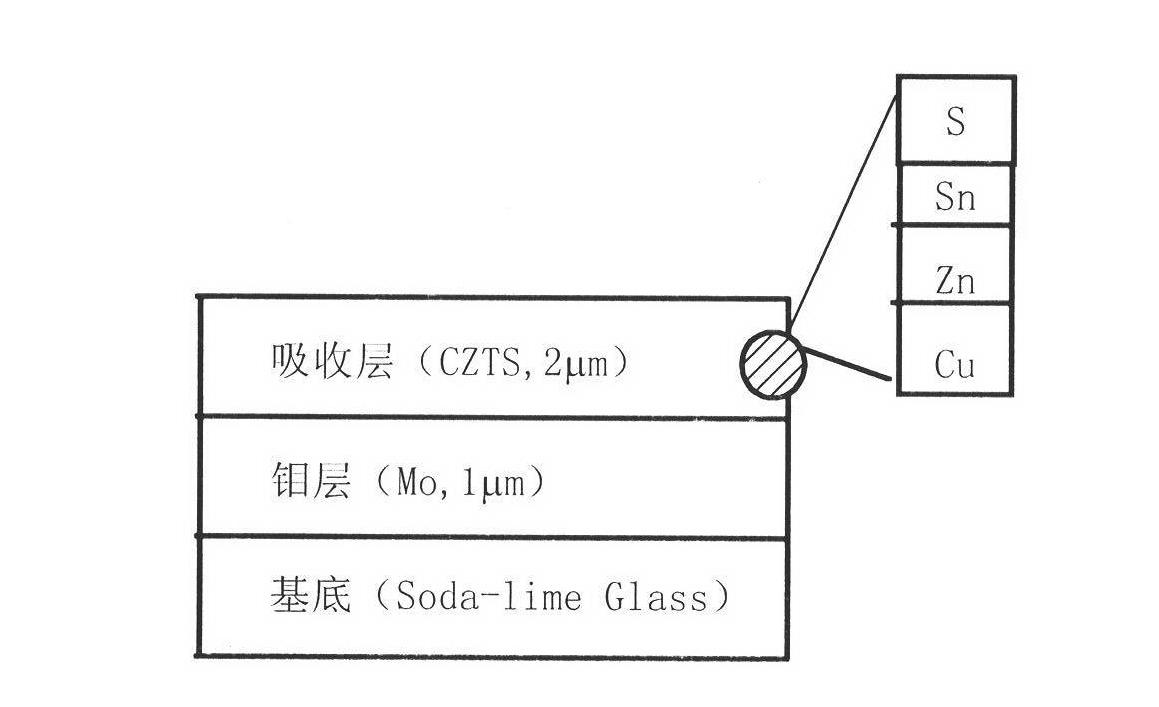
Electrochemical preparation process of Cu2ZnSnS4 film
InactiveCN102492972AEasy to operateAccurate operationElectrolytic inorganic material coatingVacuum evaporation coatingVulcanizationElectrochemistry
The invention relates to an electrochemical preparation process of a Cu2ZnSnS4 film. The electrochemical preparation process is a stepwise electrochemical deposition lamination preparation process. The preparation process comprises the following specific steps of: firstly, sputtering molybdenum (Mo) as a precursor on sodium-lime glass which is used as a substrate by adopting a radio frequency (RF) magnetic control sputtering method; then depositing Cu, Sn and Zn by using an electrochemistry system to stepwise laminate so as to prepare a copper-zinc-tin (CZT) film as a prefabricated film; and finally, putting the metal prefabricated film CZT in a quartz furnace for vulcanization and annealing treatment, so as to obtain a Cu2ZnSnS4 absorption layer film. The absorption layer film is a direct band gap material; the forbidden band width of the absorption layer film is 1.5eV, thus the band gap is the optimal band gap of a uni-junction solar battery; and the light absorption coefficient of the absorption layer film is more than 10<4>cm <-1>.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Compound film solar battery and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104659123ANo pollutionImprove photovoltaic performanceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSpectral responseEngineering
The invention discloses a compound film solar battery and a manufacturing method thereof, belongs to the field of preparation of semiconductor photoelectric materials and film solar batteries, and solves the problems that materials for a compound film solar battery are relatively small in content in the earthcrust, high in price and toxic for human bodies. The compound film solar battery comprises a substrate, a transparent electrode layer, an N-type buffer layer, a P-type absorbing layer and a back electrode layer, wherein the P-type absorbing layer is made of materials such as Sb2Se3, Cu3SbS3 and Cu3SbS4. The manufacturing method comprises steps of depositing the transparent electrode layer, depositing the N-type buffer layer, depositing the P-type buffer layer and depositing the electrode layer, and a step of depositing a hole conduction layer can also be added. Various materials forming the P-type absorbing layer are all selected from elements which are rich in resource and free of toxic component, the environment is not polluted when the compound film solar battery is manufactured and used, the energy gap width of the material of the P-type absorbing layer ranges from about 0.5 ev to 2.5 ev, the spectral response range is relatively wide, and the light absorption coefficient is as high as 10<5> cm<-1>.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN105789347ANarrow detection wavelengthNarrow detection wavelength rangeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCMOSHeterojunction
The invention discloses a GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor and a fabrication method thereof. A collector and an emitter of the transistor both adopt a GeSi material, a light absorption region and a base region both adopt a GeSn material, an emitter region, the base region, the light absorption region and a collector region are sequentially and vertically arranged, and a passivation layer encircles the peripheries of the emitter region, the base region, the light absorption region and the collector region. According to the fabrication method of the transistor, the GeSn material is grown by a low-temperature solid-source molecular beam epitaxial process, and the fabrication method is a standard complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) fabrication method. The GeSn material with a high light absorption coefficient forms heterojunctions in the light absorption region, the GeSi emitter region and the collector region, the light sensitivity and light current during detection of an infrared light signal by the transistor are improved, and the GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor has high light absorption rate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High-visible-light-activity sulfur-modified carbon nitride photocatalyst as well as synthetic method and application of photocatalyst
InactiveCN103920518AIncreased visible light absorption rangeImprove separation efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationLight ActivityModified carbon
The invention relates discloses a high-visible-light-activity sulfur-modified carbon nitride photocatalyst as well as a synthetic method and application of photocatalyst, relating to the technical fields of material preparation and photocatalysis and solving the problem of low activity of an existing graphite-phase carbon nitride catalyst caused by the low visible light absorption coefficient and the large electron hole recombination rate. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: (1) grinding melamine and sublimed sulfur, and uniformly mixing the melamine with the sublimed sulfur so as to obtain mixed powder; (2) filling a combustion boat with the mixed powder obtained in the step (1), putting the combustion boat into a tube furnace, heating the tube furnace from the room temperature to 550-650 DEG C according to a heating rate of 5 DEG C / minute-15 DEG C / minute in the presence of argon, keeping the temperature for 1-4 hours, and cooling the tube furnace to room temperature so as to obtain the sulfur-modified carbon nitride photocatalyst. The sulfur-modified carbon nitride photocatalyst disclosed by the invention can be applied to the fields of producing hydrogen by decomposing water by virtue of visible light and degrading pollutants.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for removing foreign matter from substrate surface
ActiveUS20080092918A1Improve surface roughnessPrevent removalElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingForeign matterCoated surface
To provide a method for removing foreign matters, capable of easily removing inorganic foreign matters strongly attached to the surface of a substrate made of silicon or glass or the surface of an inorganic coating formed on the substrate surface while the increase of the surface roughness is suppressed, and further capable of preventing reattachment of once removed foreign matters to the substrate surface.A method for removing inorganic foreign matters from the surface of a substrate made of silicon or glass or the surface of an inorganic coating formed on the surface of the substrate, which comprises applying a light beam in a wavelength range which makes the light absorption coefficient of at least one of a material of the substrate, a material of the inorganic coating and the inorganic foreign matters be at least 0.01 / cm, to the surface of the substrate or to the surface of the inorganic coating in an application amount of at least 10 J / cm2 in an oxygen- or ozone-containing atmosphere, and exposing the surface of the substrate or the surface of the inorganic coating having a negative surface potential to an acidic solution having a pH≦6.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Photocatalyst material and photocatalyst device
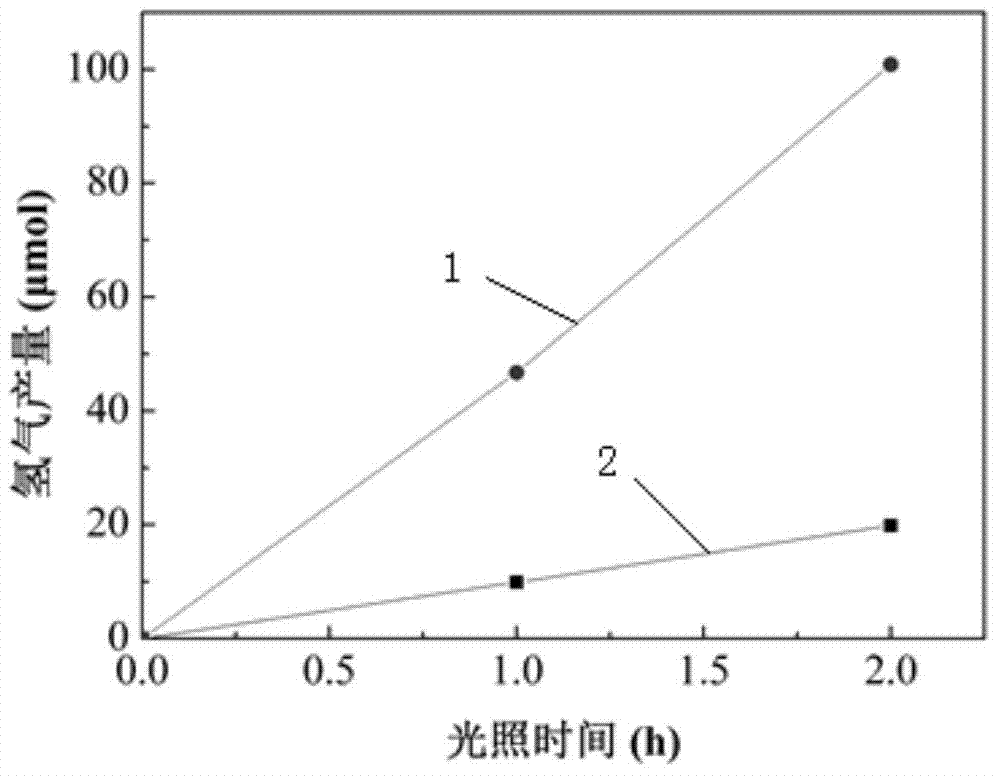
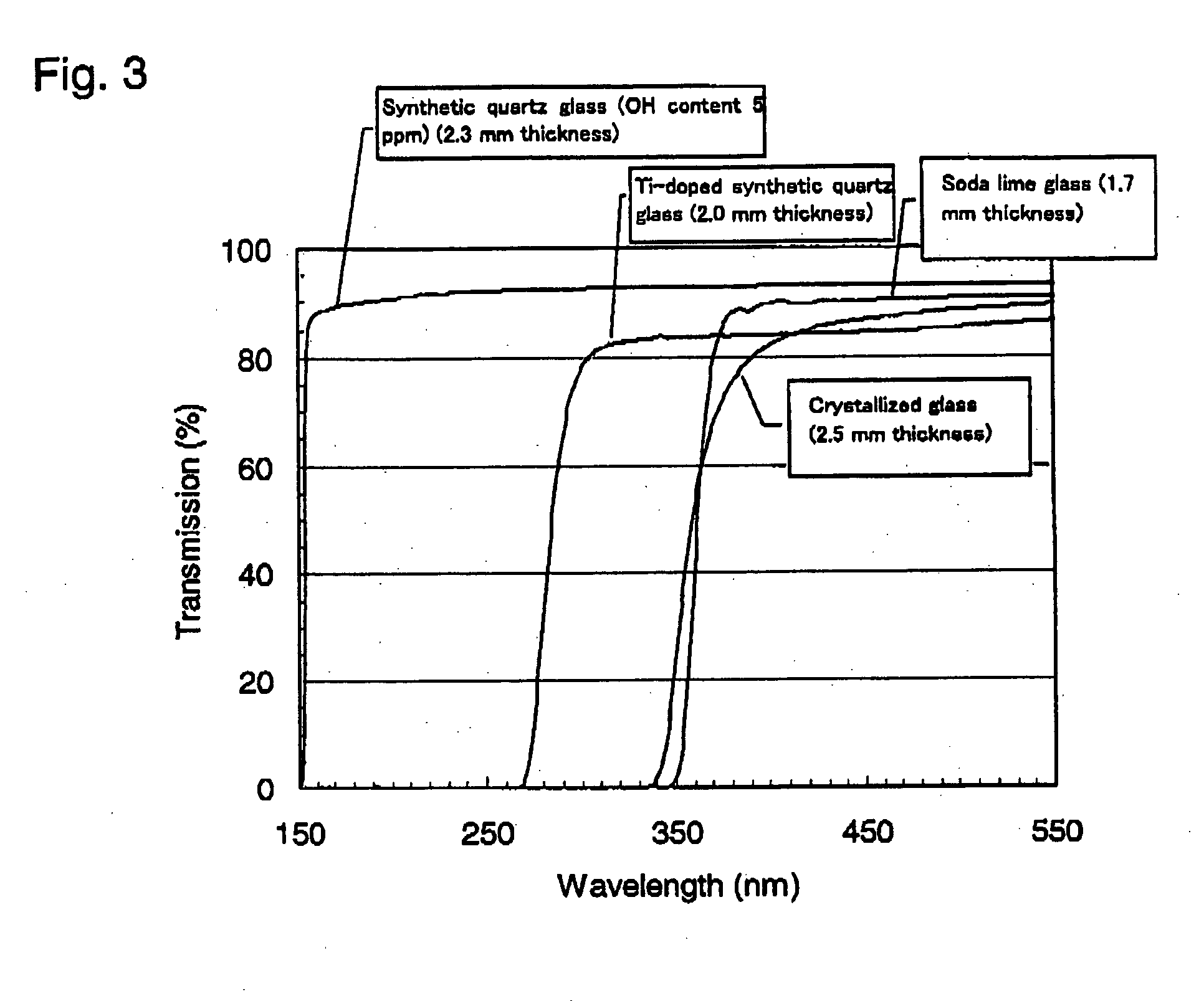
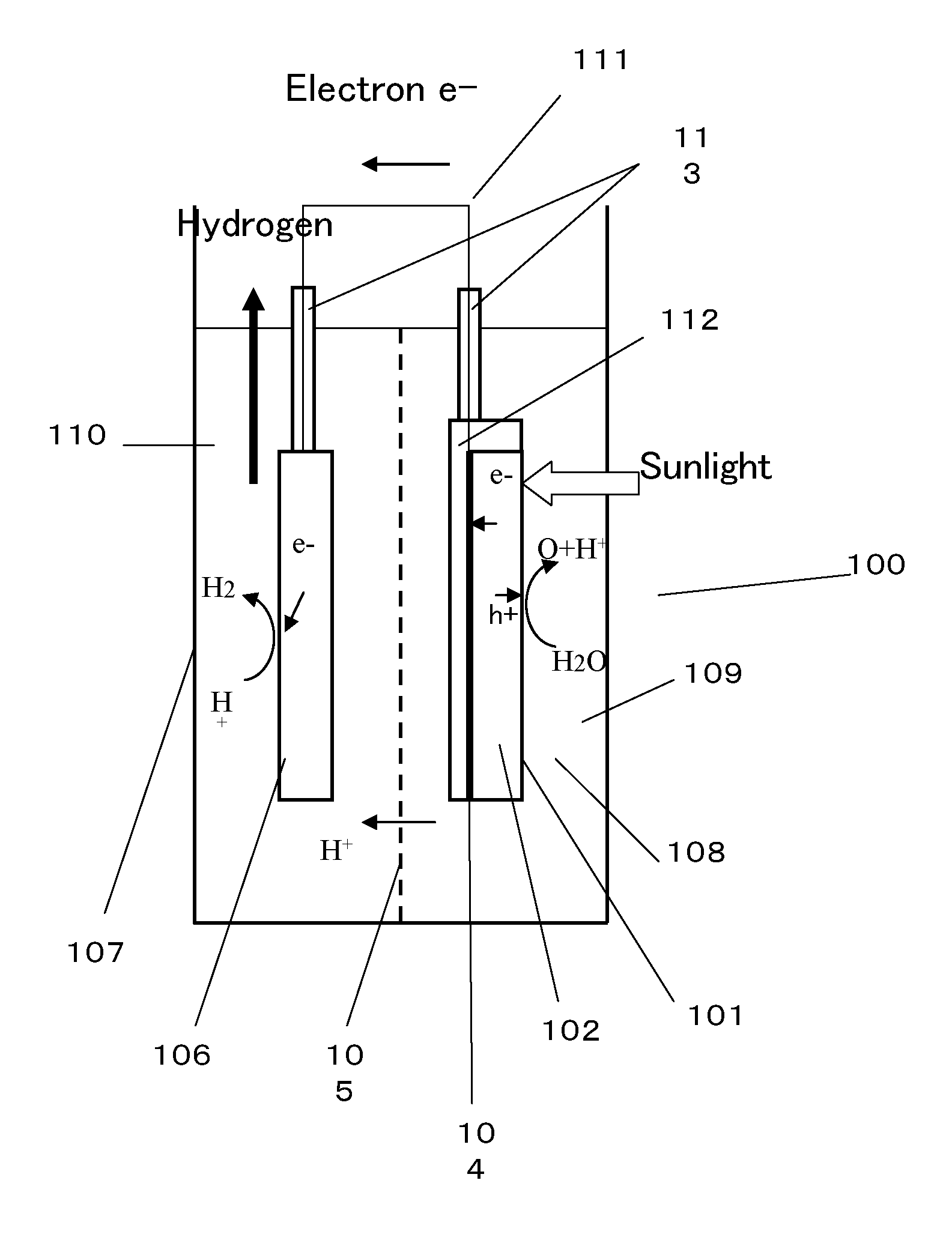
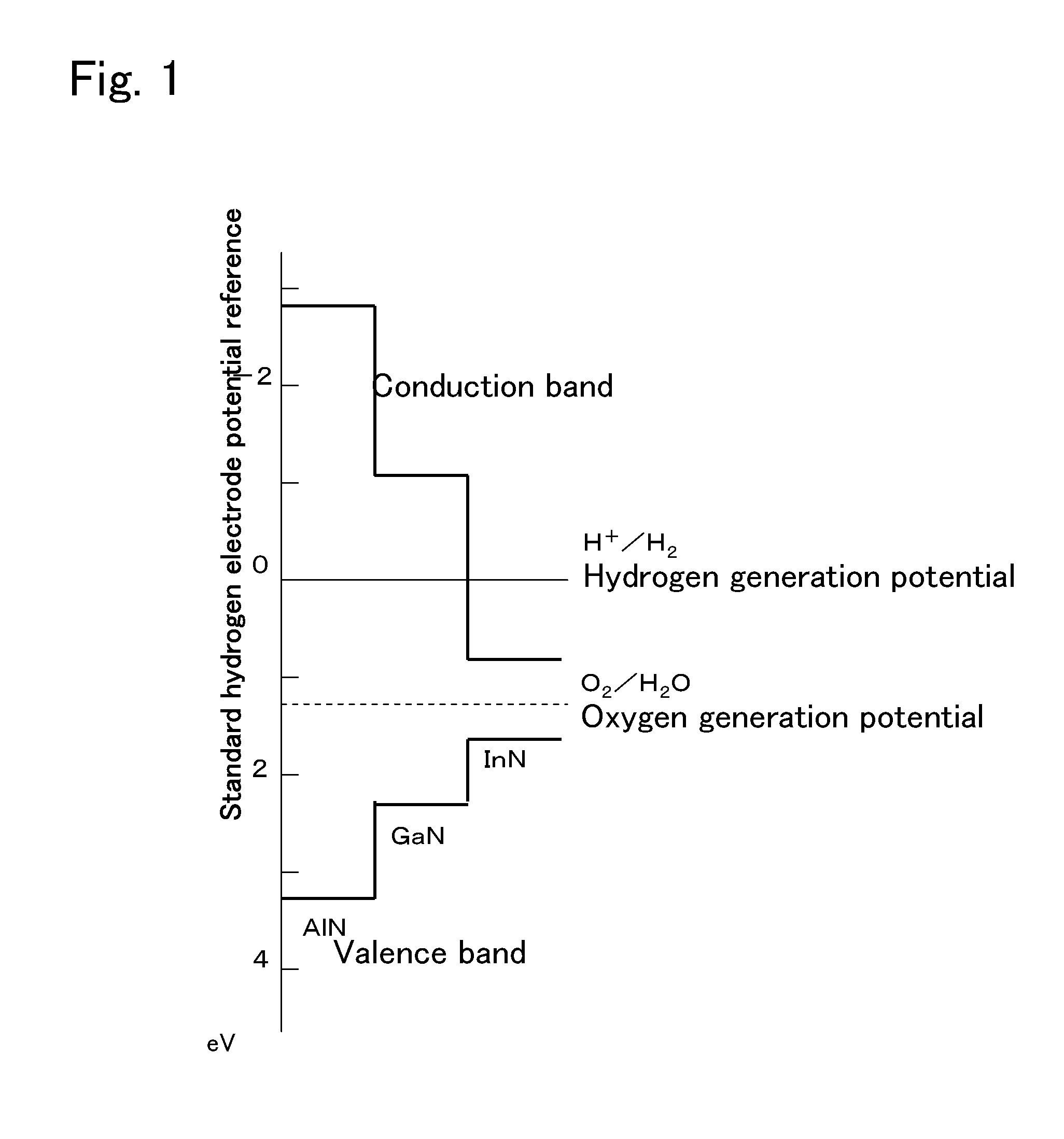
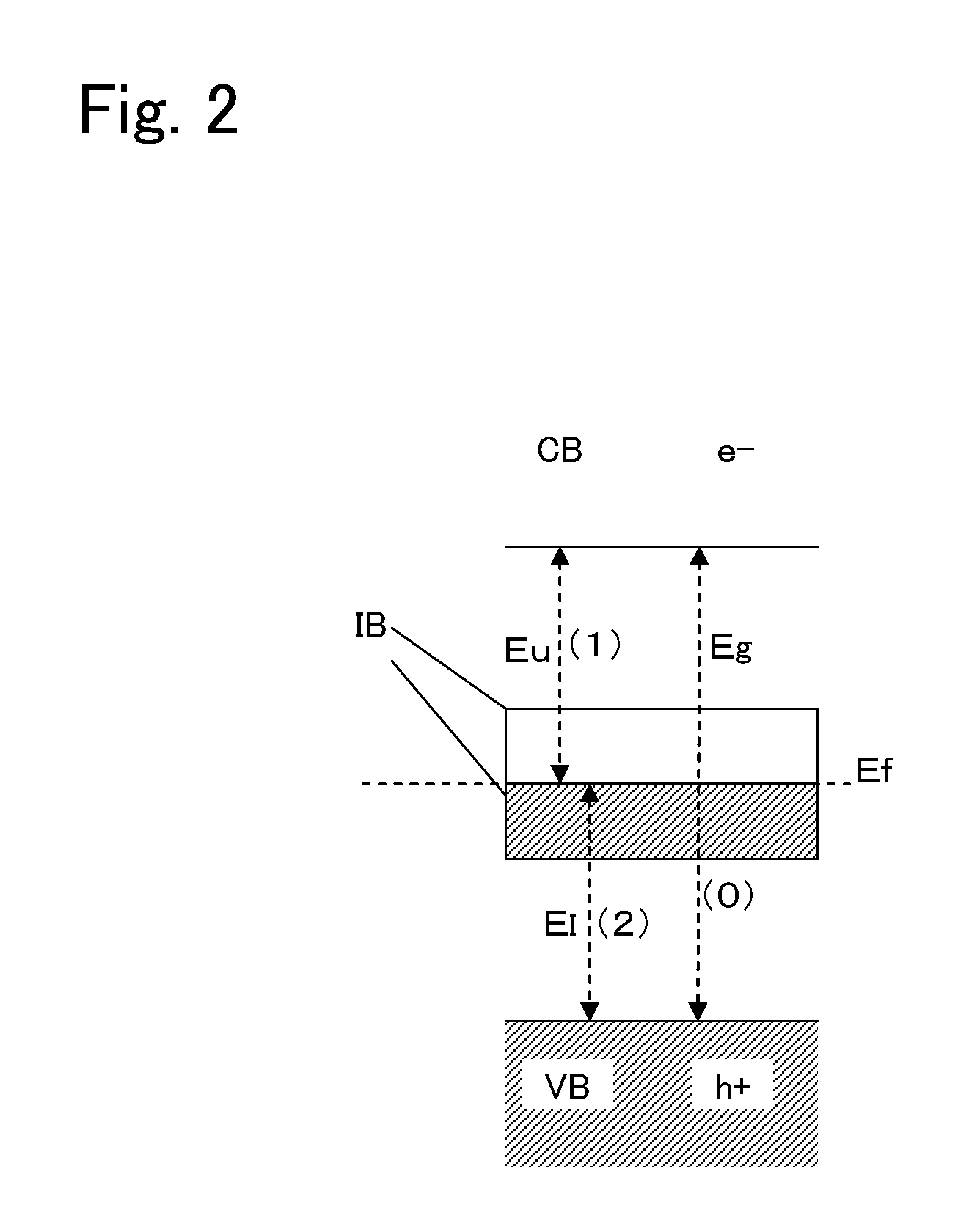
InactiveUS20130105306A1Large light absorption coefficientLittle changeCellsMachining electrodesLight absorption coefficientImpurity
A photocatalyst material and a photocatalyst device capable of generating hydrogen from water by radiation of sunlight at high efficiency. The photocatalyst material according to the present invention includes a nitride-based compound semiconductor obtained by replacement of part of Ga and / or Al by a 3d-transition metal. The nitride-based compound semiconductor has one or more impurity bands. A light absorption coefficient of the nitride-based compound semiconductor is 1,000 cm−1 or more in an entire wavelength region of 1,500 nm or less and 300 nm or more. Further, the photocatalyst material satisfies the following conditions: the energy level of the bottom of the conduction band is more negative than the redox potential of H+ / H2; the energy level of the top of the valence band is more positive than the redox potential of O2 / H2O; and there is no or little degradation of a material even when the material is irradiated with light underwater.
Owner:SAKAI CHEM IND CO LTD +1
Display panel and apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20170141162A1Reduce the amount of lightEnhanced light absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energyFluorescence
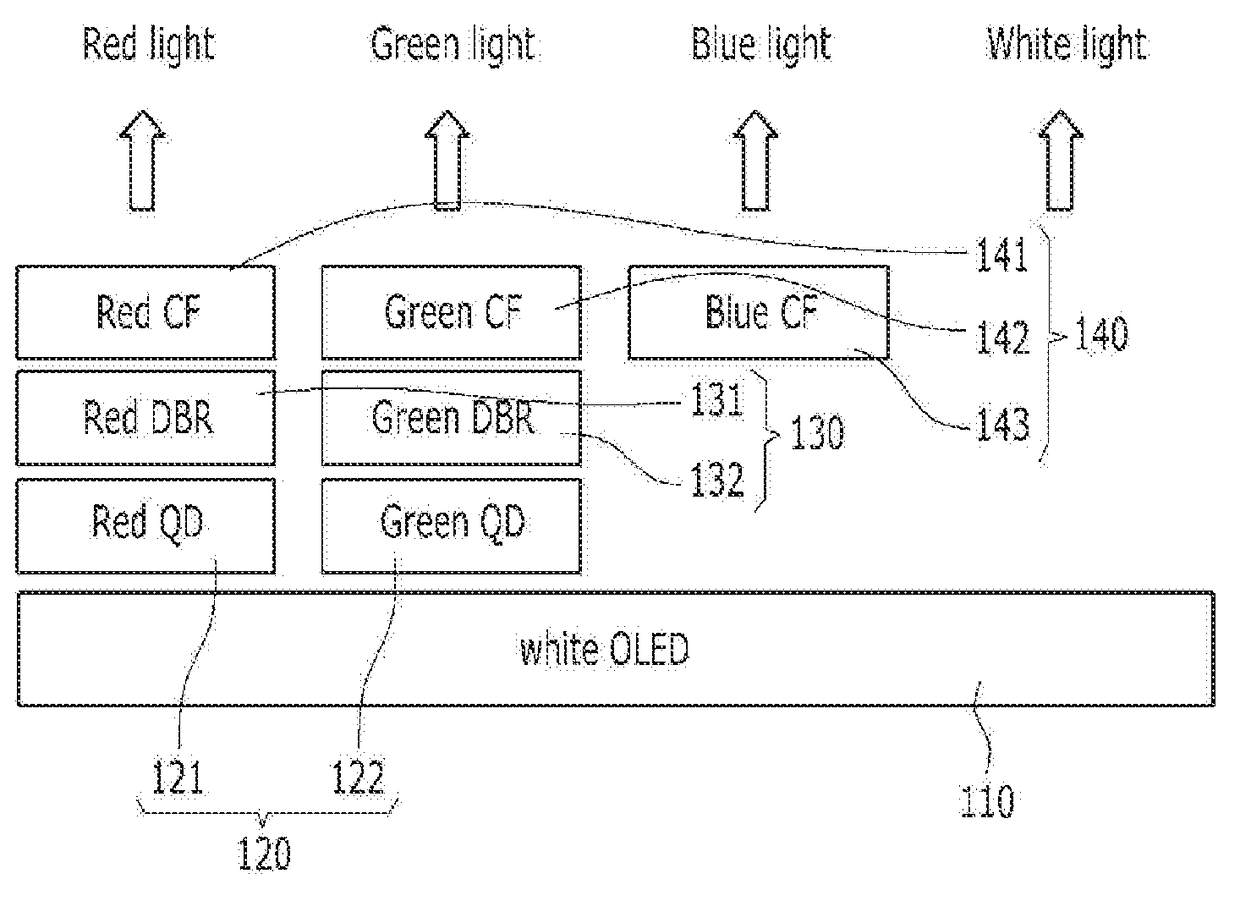
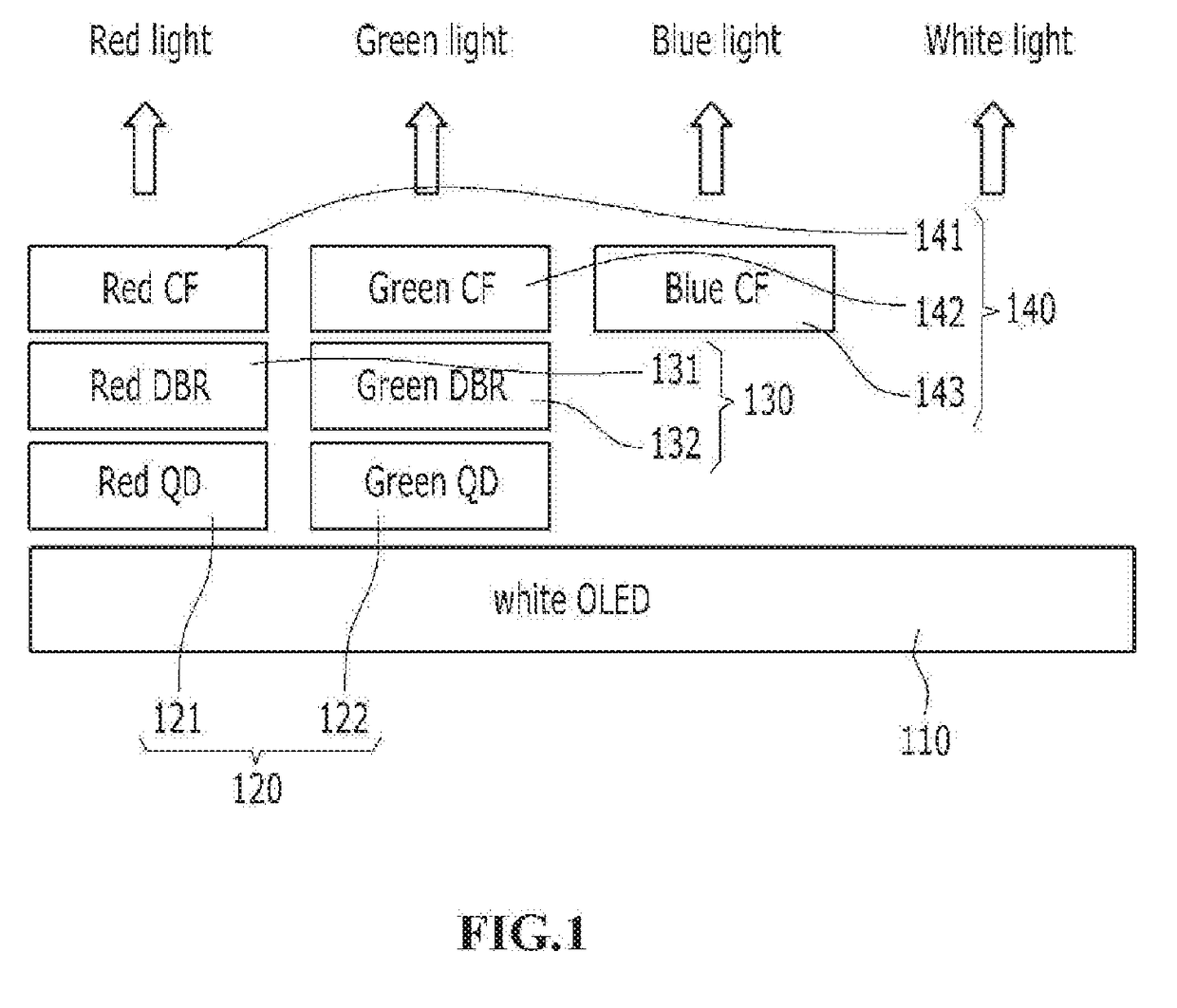
A display panel for simplifying a manufacturing process and having high energy efficiency using an OLED as a light source and also using RGB, QDs, and an LPR layer capable of improving color reproducibility. In an aspect, an LPR layer is interposed between a color filter layer and a fluorescent substance layer so that light is circulated within the fluorescent substance layer again. Accordingly, there is provided a display panel capable of reducing the amount of light absorbed through the color filler by increasing the light absorption coefficient of the fluorescent substance layer and of maximizing energy efficiency by increasing the intensity of light passing through the color filter.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Nanogold colorimetric method for detecting mercury ions
ActiveCN102944557ALow toxicityReduce dosageMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh concentrationMercuric ion
The invention discloses a colorimetric analysis method for simply and rapidly detecting mercury ions in an aqueous solution. According to the method, the characteristic of high light absorption coefficient of nanogold is utilized, the nanogold is used as a chromogenic signal component, and simultaneously mercaptoethylamine is used as a specificity identification component. The colorimetric analysis method has the advantages of being low in cost, simple in operation, convenient and rapid. The modified nanogold is stable, high in resistance to high concentration salt ions, slightly interfered by external factors and suitable for being popularized and applied.
Owner:南京广全环保技术服务有限公司
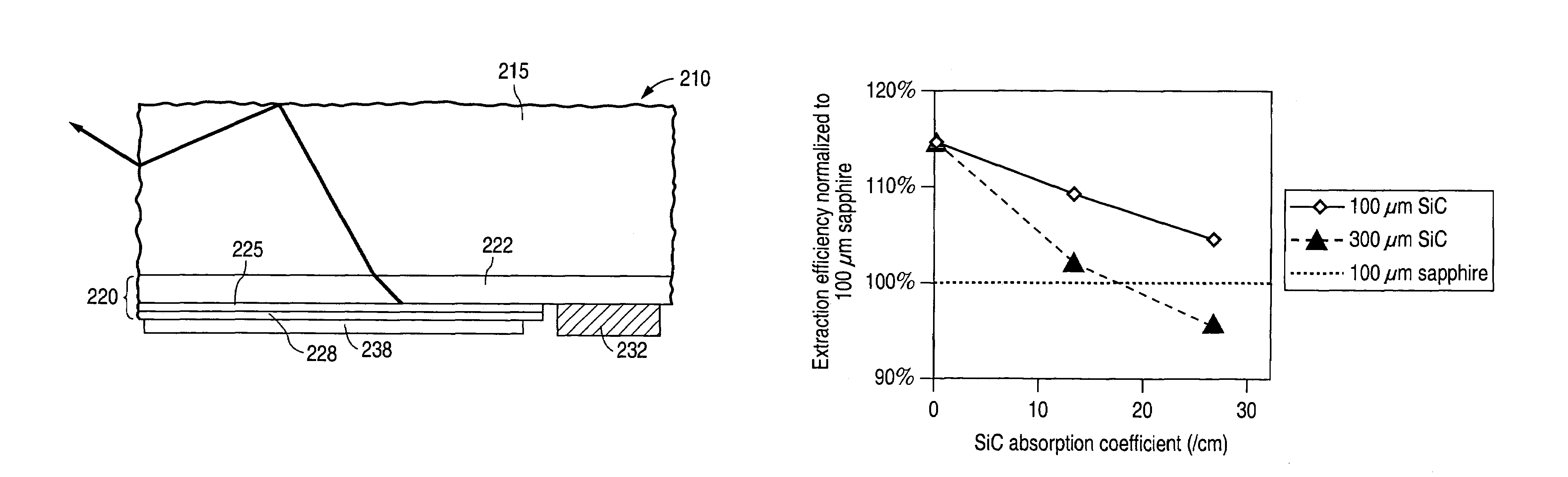
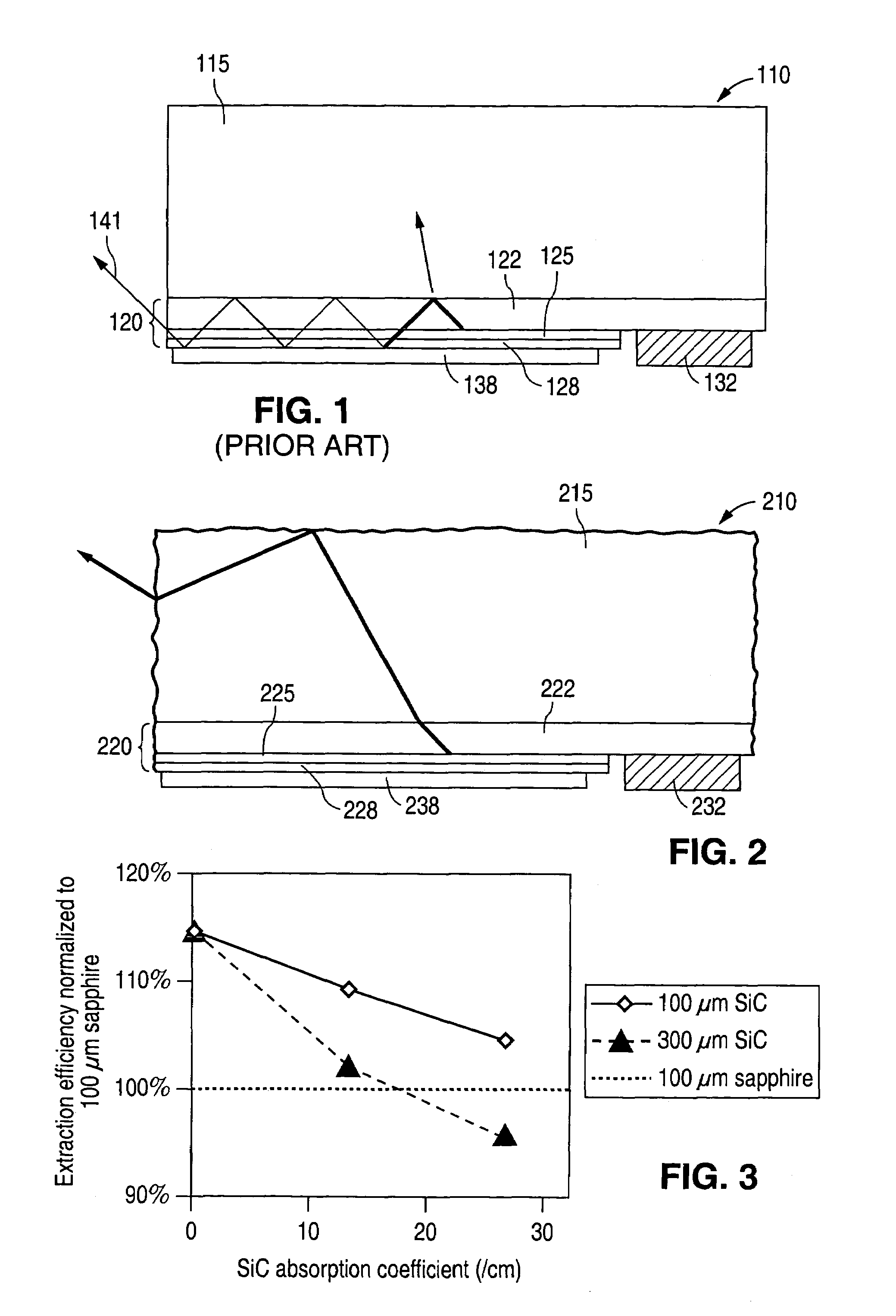
Semiconductor light emitting device and method
InactiveUS7015054B2Reduce thermal resistanceIncreased light generating capabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureRefractive index
A light-emitting device includes: a semiconductor structure formed on one side of a substrate, the semiconductor structure having a plurality of semiconductor layers and an active region within the layers; and first and second conductive electrodes contacting respectively different semiconductor layers of the structure; the substrate comprising a material having a refractive index n>2.0 and light absorption coefficient α, at the emission wavelength of the active region, of α>3 cm−1. In a preferred embodiment, the substrate material has a refractive index n>2.3, and the light absorption coefficient, α, of the substrate material is α<1 cm−1.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Method for forming amorphous carbon film and method for manufacturing semiconductor device using the method
InactiveCN101312126ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingMetallurgyRefractive index
The present invention relates to a method of forming an amorphous carbon film and a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the method. An amorphous carbon film is formed on a substrate by vaporizing a liquid hydrocarbon compound, which has chain structure and one double bond, and supplying the compound to a chamber, and ionizing the compound. The amorphous carbon film is used as a hard mask film. It is possible to easily control characteristics of the amorphous carbon film, such as a deposition rate, an etching selectivity, a refractive index (n), a light absorption coefficient (k) and stress, so as to satisfy user's requirements. In particular, it is possible to lower the refractive index (n) and the light absorption coefficient (k). As a result, it is possible to perform a photolithography process without an antireflection film that prevents the diffuse reflection of a lower material layer. Further, a small amount of reaction by-product is generated during a deposition process, and it is possible to easily remove reaction by-products that are attached on the inner wall of a chamber. For this reason, it is possible to increase a cycle of a process for cleaning a chamber, and to increase parts changing cycles of a chamber. As a result, it is possible to save time and cost.
Owner:TES CO LTD
Apparatus for measuring oil oxidation using fluorescent light reflected from oil
An apparatus for measuring oil oxidation is capable of being mounted to mechanical devices for detecting power of fluorescent light reflected from oil in real time as an indication of the oil oxidation. A plurality of first optical fibers are connected to a light-emitting member for introducing the light into oil at different incidence points. A plurality of light-reflecting mirrors are immersed in the oil and disposed opposite to the incidence points. The light-reflecting mirrors are located at different distances from the incidence points. A plurality of second optical fibers are connected to the incidence points, respectively. A plurality of light-receiving members are connected to the second optical fibers for receiving the light and outputting the signals corresponding to the received light. A control portion calculates a fluorescence quantum yield and a light absorption coefficient of the oil based upon the signals from the light-receiving members and compares them with the reference values pre-stored in the control portion to determine the oil oxidation.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Pellicle and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101414118AGood light transmission performanceGood chemical stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentRoom temperatureAmorphous silicon
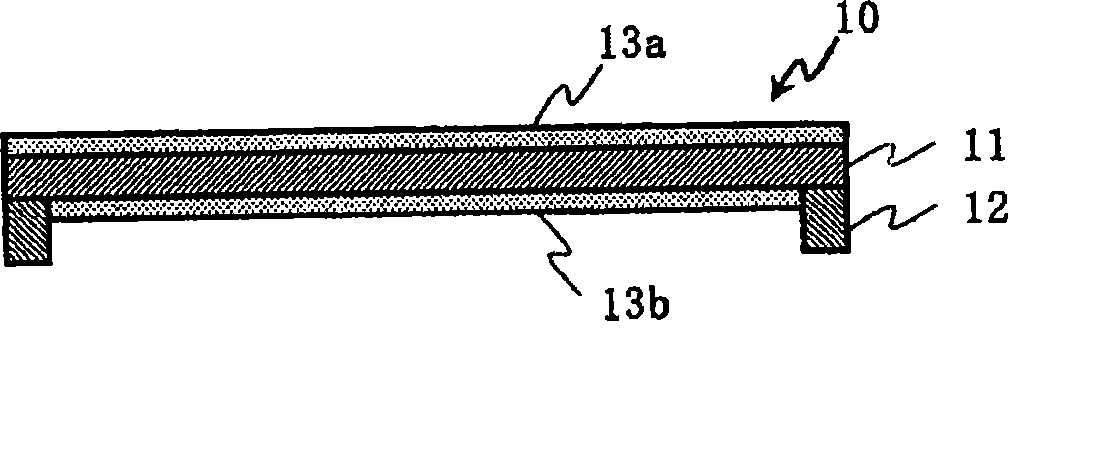
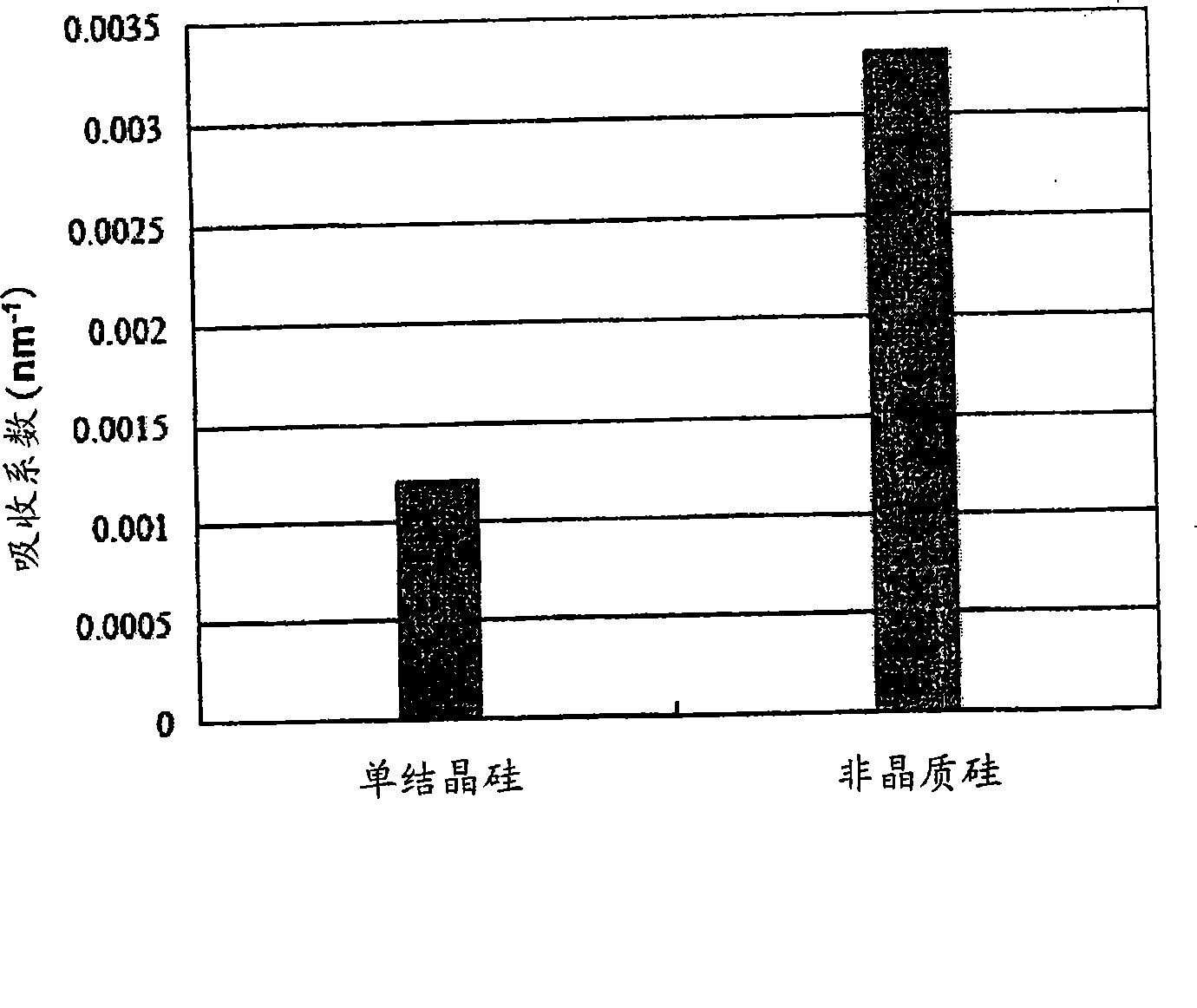
The present invention relates to a pellicle. It is therefore an object of the present invention to provide a pellicle provided with a practical pellicle film for EUV superior in transmittance and chemical stability. A pellicle of the present invention is provided with a silicon crystal film, the absorption coefficient of which is 0.005 / nm or lower with respect to light having a wavelength of 13.5 nm, as a pellicle film. The silicon crystal film is an indirect transition type semiconductor film and, therefore, the optical absorption coefficient thereof is relatively low. In particular, a single-crystal silicon film has a lower absorption coefficient than an amorphous silicon film and a polysilicon film. Thus, it is easy to obtain desired transmissivity required of a pellicle film for EUV from the single-crystal silicon film. Such a pellicle film as described above can be fabricated from an SOI film obtained by thin-filming an SOI substrate (including an SOQ substrate and an SOG substrate). If a pellicle film of the silicon crystal film is made from the SOI film, no excessive stress is subjected in the pellicle film formation process, and the pellicle film is formed under room temperature without causing strains.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
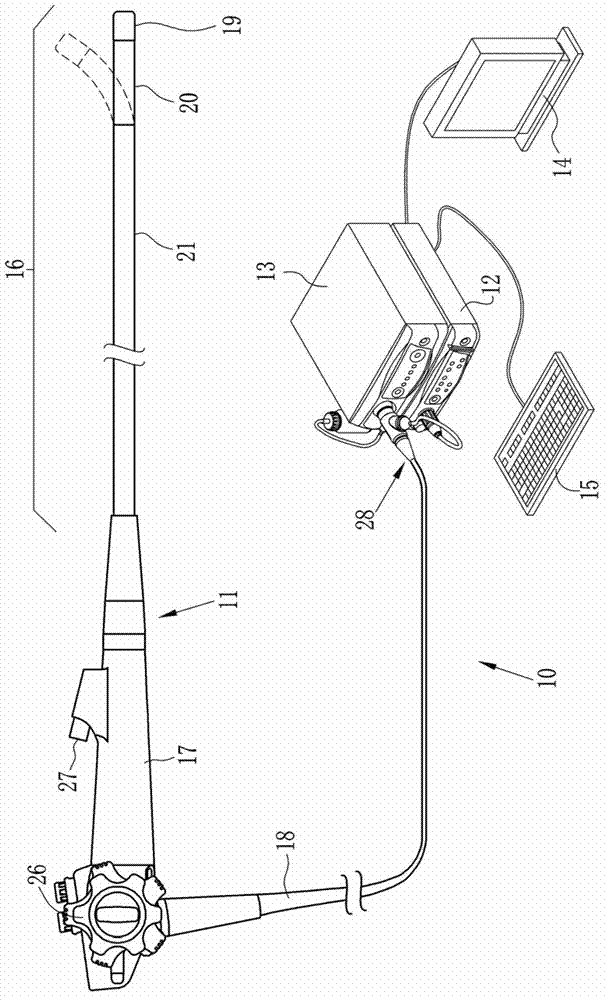
Endoscope system and light source device
ActiveCN103070658AIncrease manufacturing costIncrease brightnessImage enhancementImage analysisLight absorption coefficientMeasurement precision
The present invention provides an endoscope system (10) and a light source device (13). The light source device (13) of the endoscope system (10) is provided with a white light source (30). In the optical path of the light source, a rotating light filter (34) and a bandpass light filter (40). The rotating light filter (34) divides the color of the white color to three colors, namely B, G and R. The bandpass light filter (40) separates narrow-waveband light N from the colors of the white light. The bandpass light filter (40) is a device which is used for generating oxygen saturation measurement light that is used for measuring oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in blood, and has an optical characteristic that two narrow-waveband light N11 and N12 which are used for oxidizing hemoglobin and reducing hemoglobin and have wavebands that the light absorption coefficients are same. Because of the oxygen saturation measurement light is combined with light amount of two narrow-waveband light N11 and N12, the measurement precision or image brightness can be remarkably improved.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Near-infrared spectral tomography reconstruction method based on neural network
InactiveCN108814550AReconstruction from projectionDiagnostics using spectroscopyReconstruction methodLight absorption coefficient
The invention discloses a near-infrared spectral tomography reconstruction method based on a neural network and belongs to the field of medical image processing. In a Boltzmann radiation transmissionequation, a light transmission process is regarded as an absorption and scattering process of photons in a medium, the interaction between light and tissue is determined by absorption coefficients, scattering coefficients and phase functions of reactive scattering distribution, only particle properties of the light are considered in transmission, and the volatility of the light is not considered;therefore, phenomena of polarization and interference correlated with the volatility of the light are not considered, and only the energy transmission of the light is tracked. The reconstruction method based on the BP neural network is used for reconstructing the distribution of the absorption coefficients of the light, and a reconstruction result of the distribution of the absorption coefficientscan be obtained through calculation. By means of the method, not only can the distribution of the absorption coefficients be accurately reconstructed, but also high computational efficiency is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Anode construction for top light emitting organic display and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveCN101459226ASave energySmall ups and downsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal coatingOrganic light emitting device
Disclosed are an anode structure of a top-emitting organic display and a manufacturing process thereof, and relates to a top-emitting organic light-emitting device, in particular to a low resistivity anode structure applied to a top-emitting organic display and a manufacturing process thereof. The anode structure of the top-emitting organic display includes forming an electrode via coating films on a silicon substrate, which is characterized in that four layers of films are coated on the silicon substrate, namely a high purity chromium film layer, a high purity aluminum film layer, a high purity chromium film layer and a high purity aluminum film layer from the silicon substrate layer to the top, besides radio-frequency sputtering process, PVD process is utilized, and pre-heating treatment and metal coating process are performed on the silicon substrate. The novel anode structure has high conductivity and economical property and is easy to be coated, the OLED light emitting efficiency of the novel anode structure is increased to 30% due to the relatively low absorption coefficient of light and higher reflection coefficient of light, and thereby the performance of the novel anode structure is superior to the existing anode structure.
Owner:YUNNAN NORTH OLIGHTEK OPTO ELECTRONICS TECH
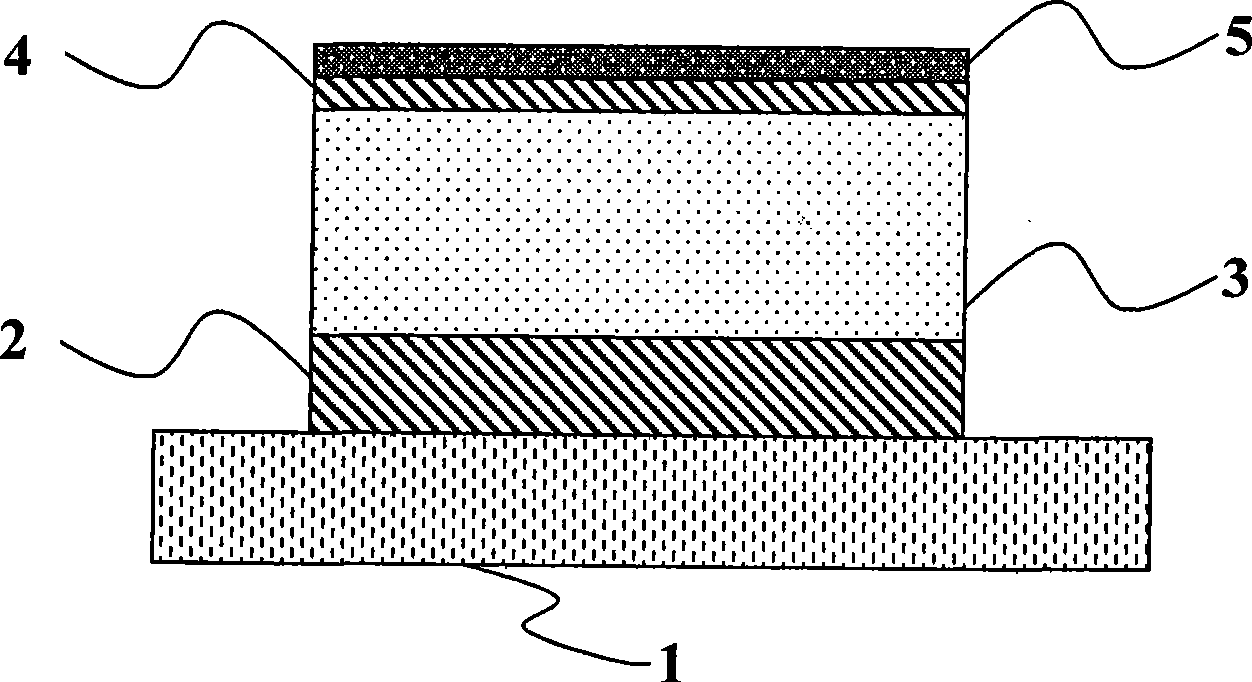
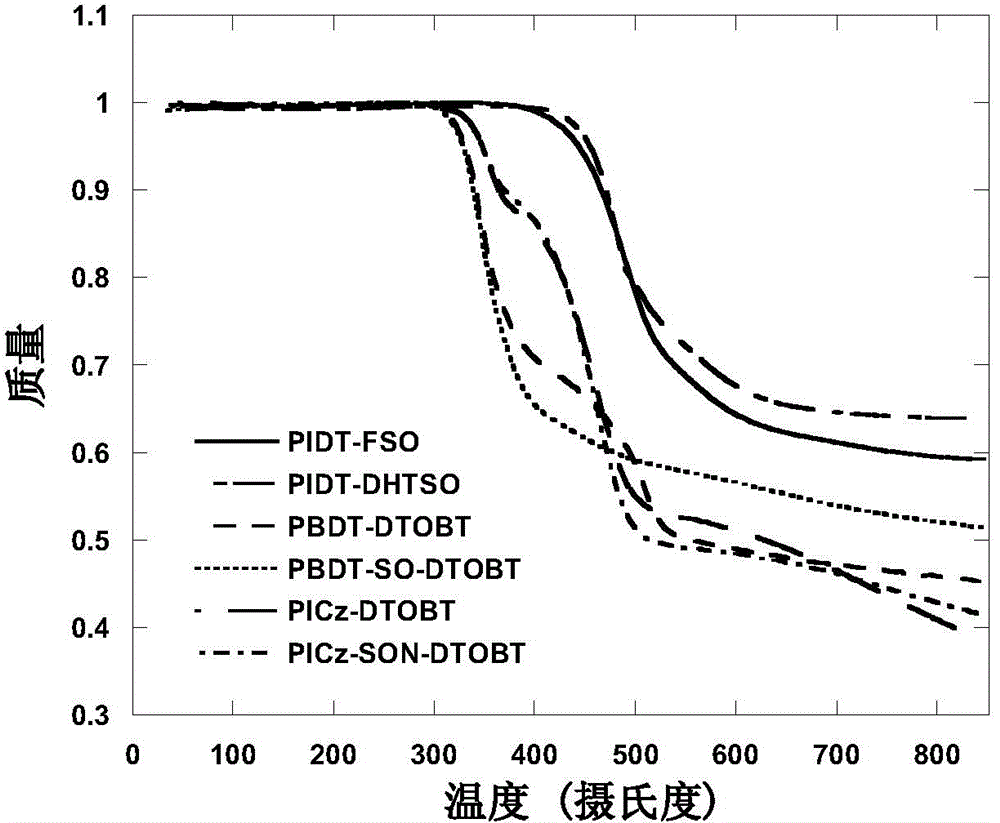
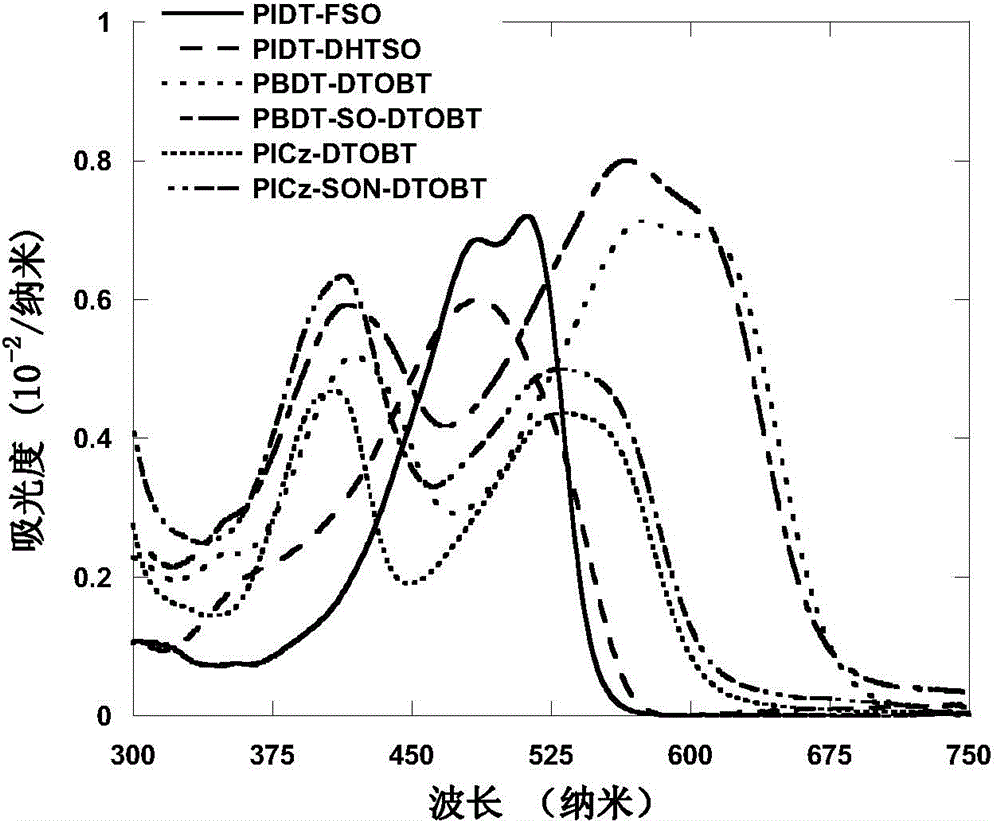
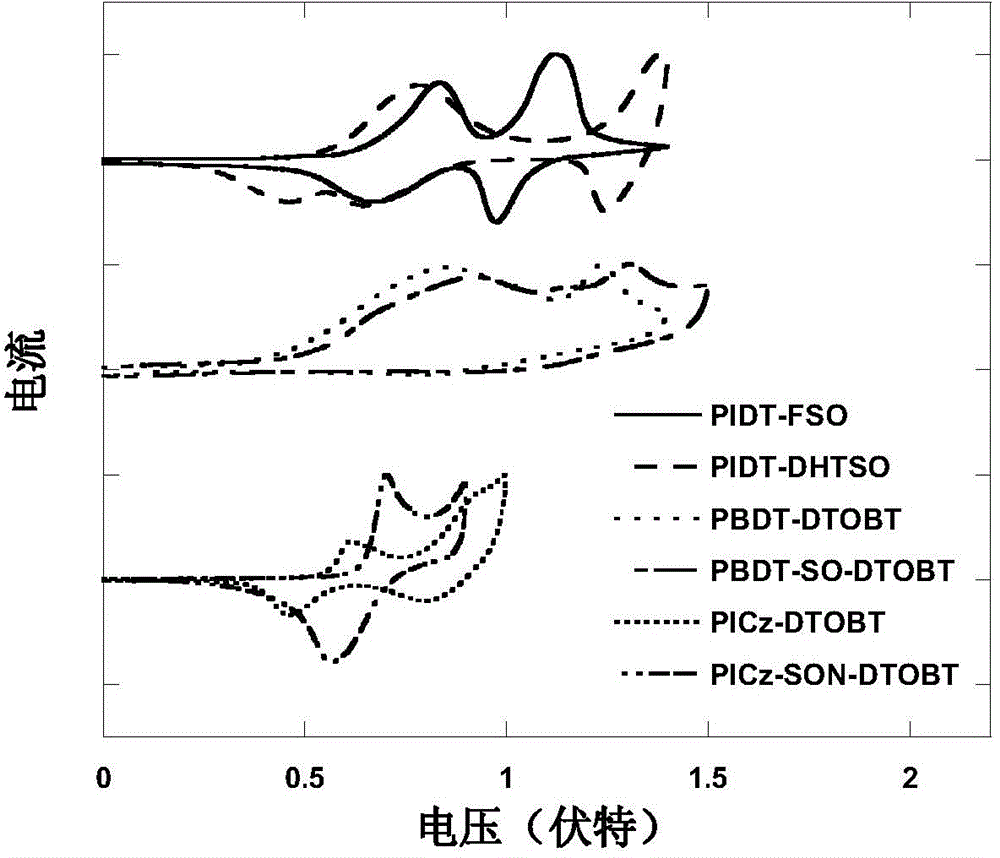
S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene unit-containing electron donor polymer and use thereof
ActiveCN104004165AEasy to synthesizeEasy to purifySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer scienceOrganic field-effect transistor
The invention discloses a S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene unit-containing electron donor polymer and a use thereof. The main chain of the S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene unit-containing electron donor polymer contains a S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene unit. Through Stille and Suzuki polymerization methods, a novel D-A structure conjugated polymer is constructed. The S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene unit has good flatness and high electronegativity. Through the S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene unit, the polymer has a deep HOMO energy level, strong intermolecular interaction, a high light-absorption coefficient, high mobility and high photoelectric response so that the related polymer has wide application prospects in solar cells or organic field effect transistors.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor device manufacturing method, and adhesive film used in semiconductor device manufacturing method
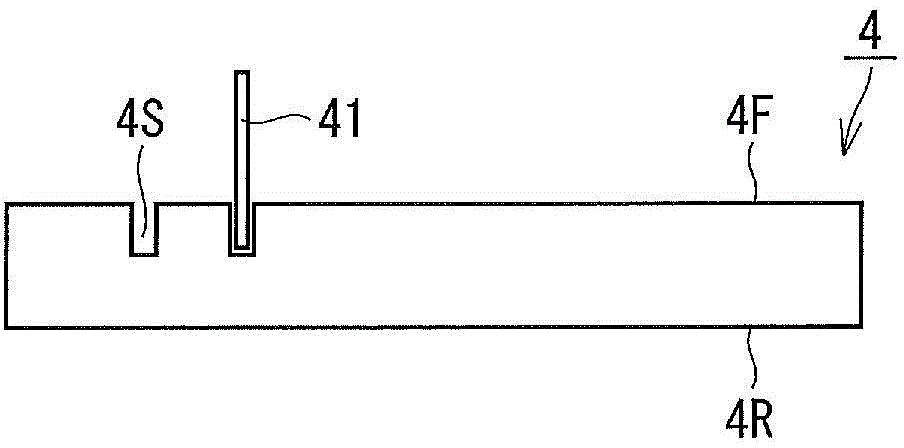
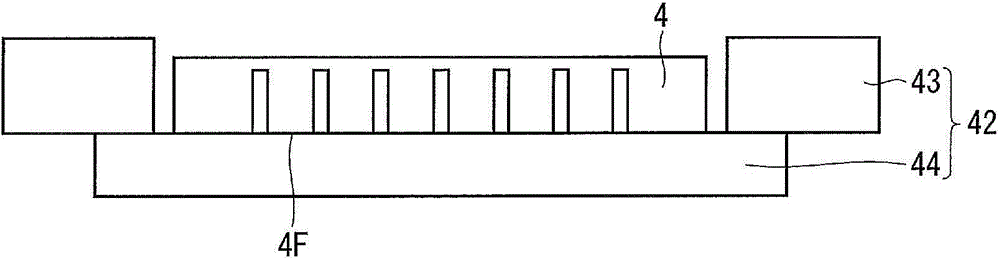
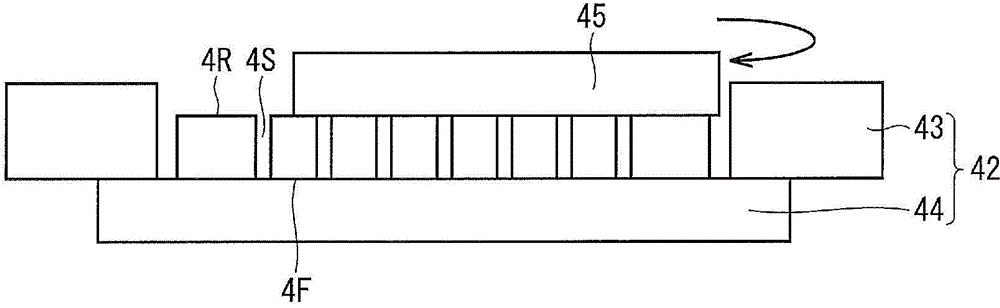
ActiveCN104040697AInhibition of attachmentImprove cut-off reliabilityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesSolid-state devicesEngineeringLength wave
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device manufacturing method, whereby cutting reliability of an adhesive film can be improved and debris contamination due to the adhesive film can be suppressed. Provided is a semiconductor device manufacturing method which is provided with: a step wherein, after forming a groove (4S) on the front surface of a semiconductor wafer (4), a protective adhesive film (44) is adhered, the rear surface of the semiconductor wafer is ground, and the groove is exposed from the rear surface; a step wherein, after adhering the adhesive film on the rear surface of the semiconductor wafer, the protective adhesive film is peeled; and a step wherein a laser beam having a wavelength of 355 nm is radiated along the groove exposed from the adhesive film, and the adhesive film is cut. The adhesive film has (a) a light absorption coefficient of 40 cm-1 or more at a wavelength of 355 nm, (b) a tensile storage elastic modulus of 0.5-20 MPa at 50 DEG C, and (c) a tensile storage elastic modulus of 0.3-7 MPa at 120 DEG C, or a melt viscosity of 2,000 Pa.s or more at 120 DEG C.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com