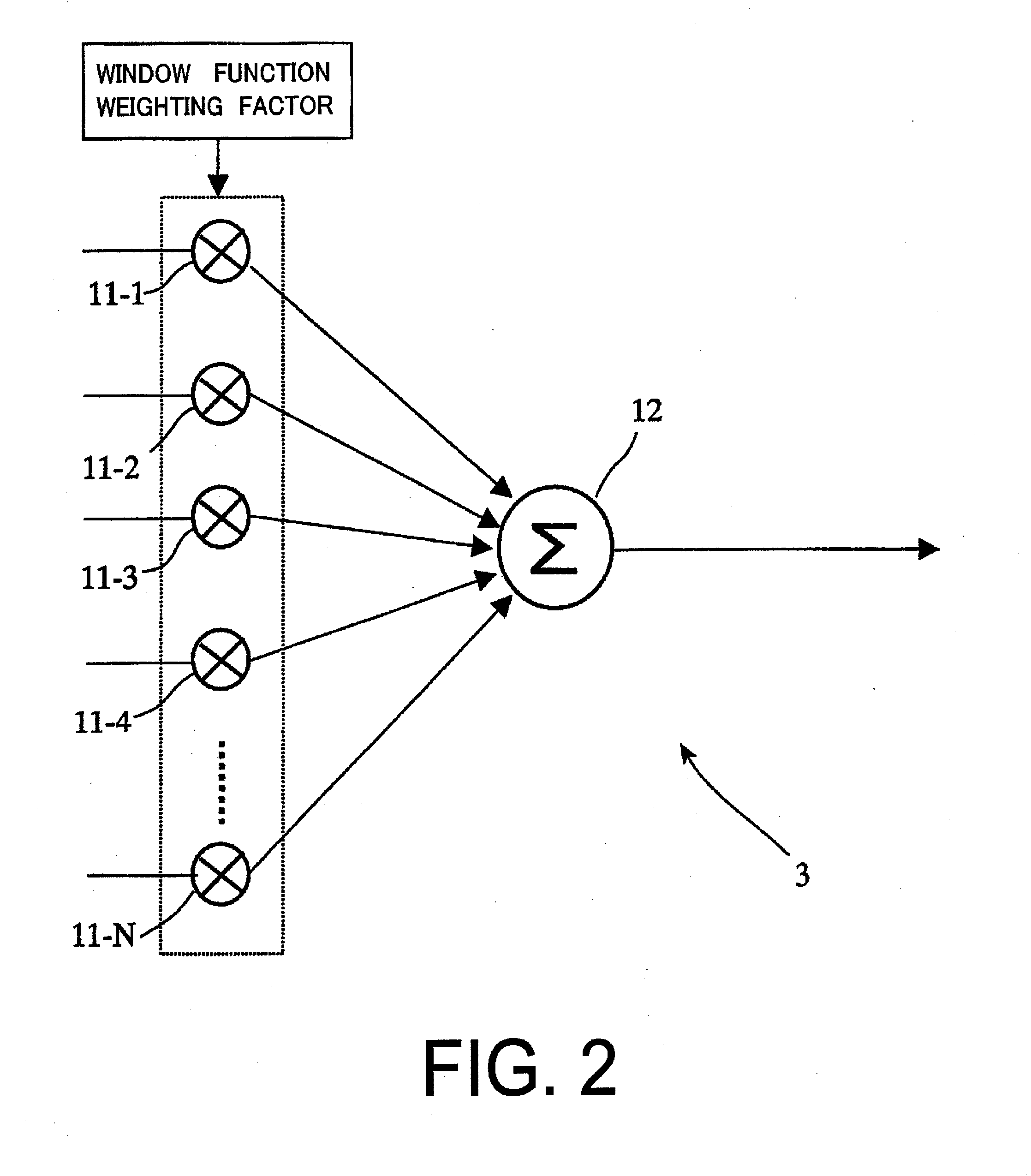
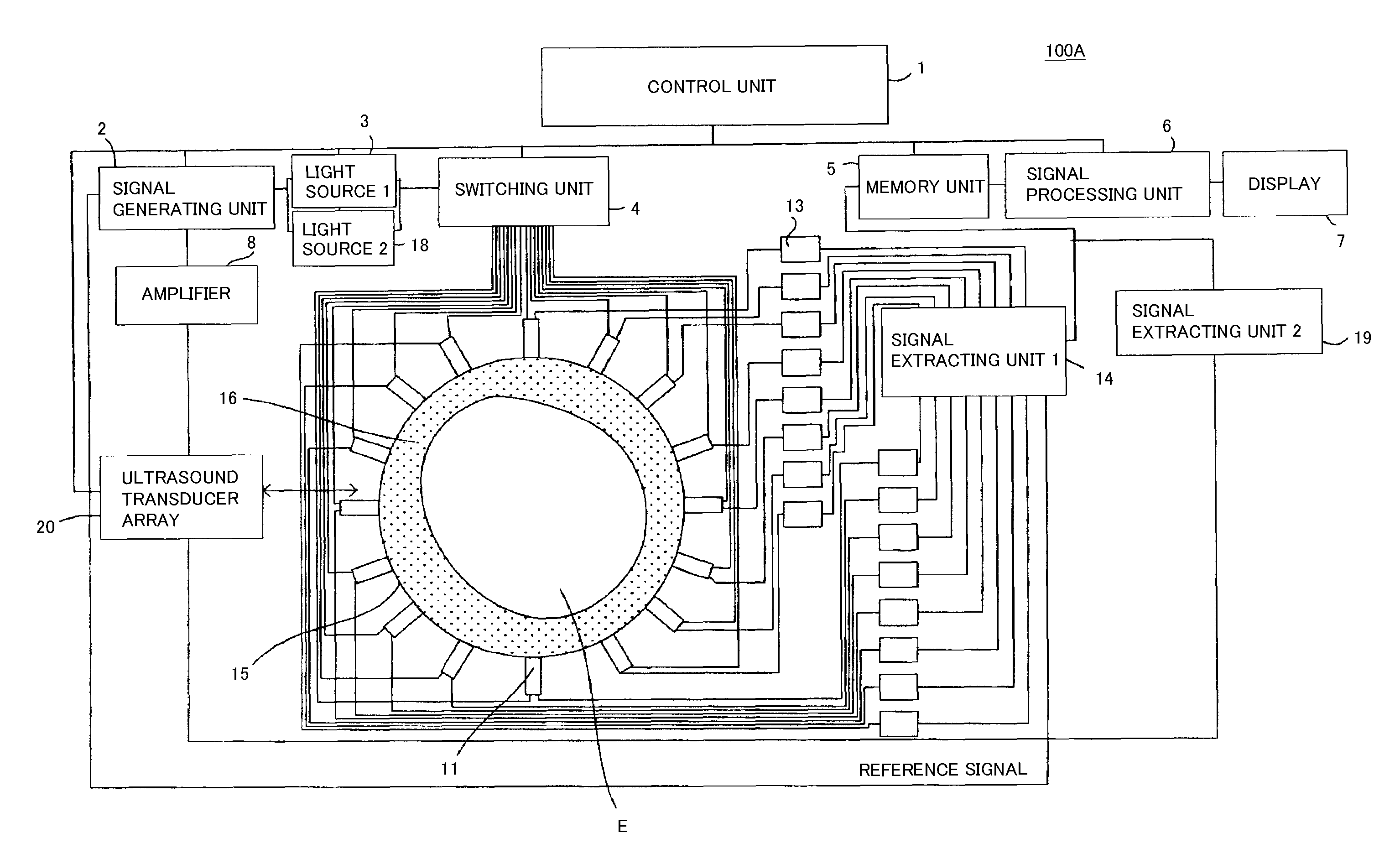
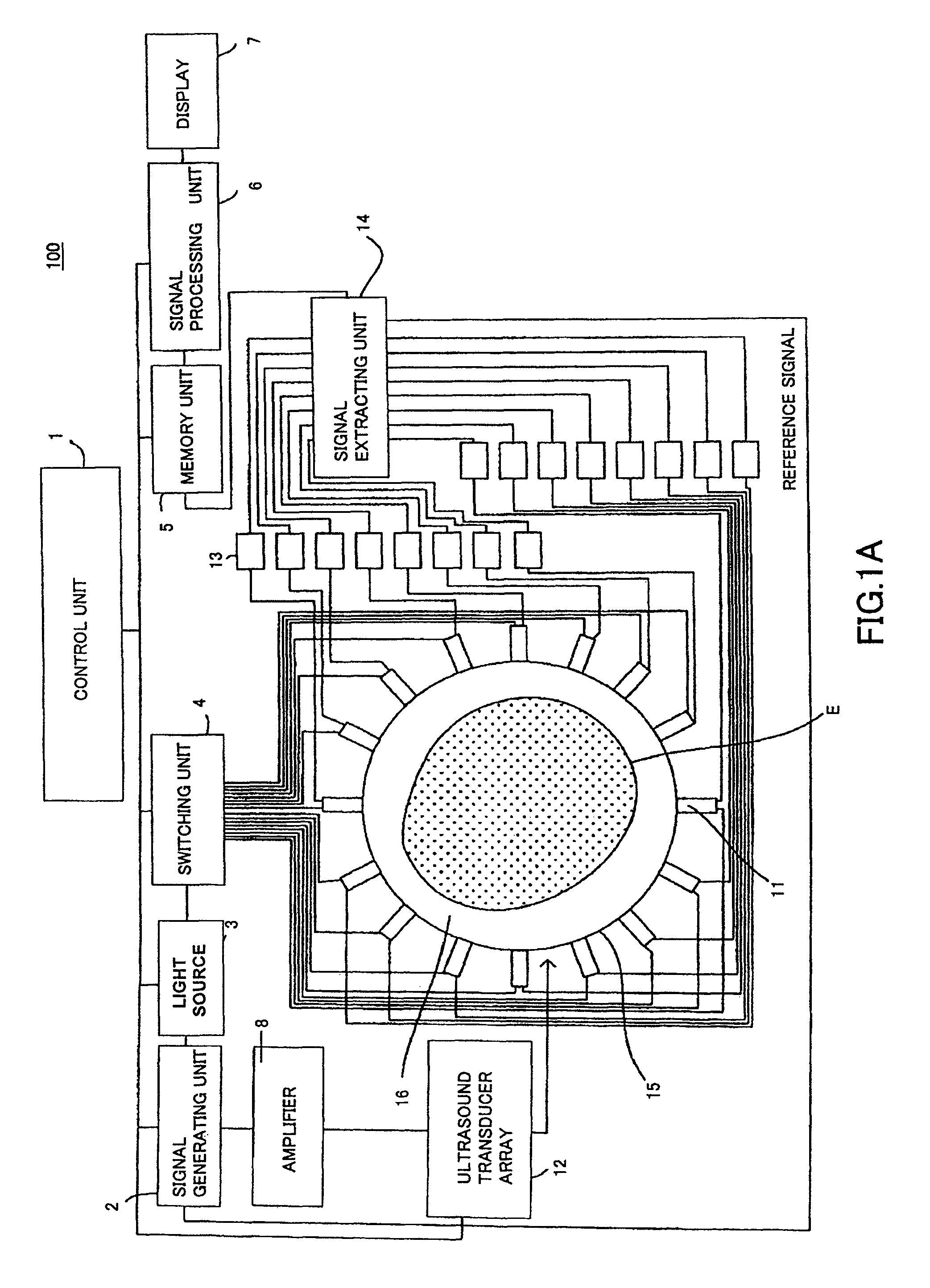
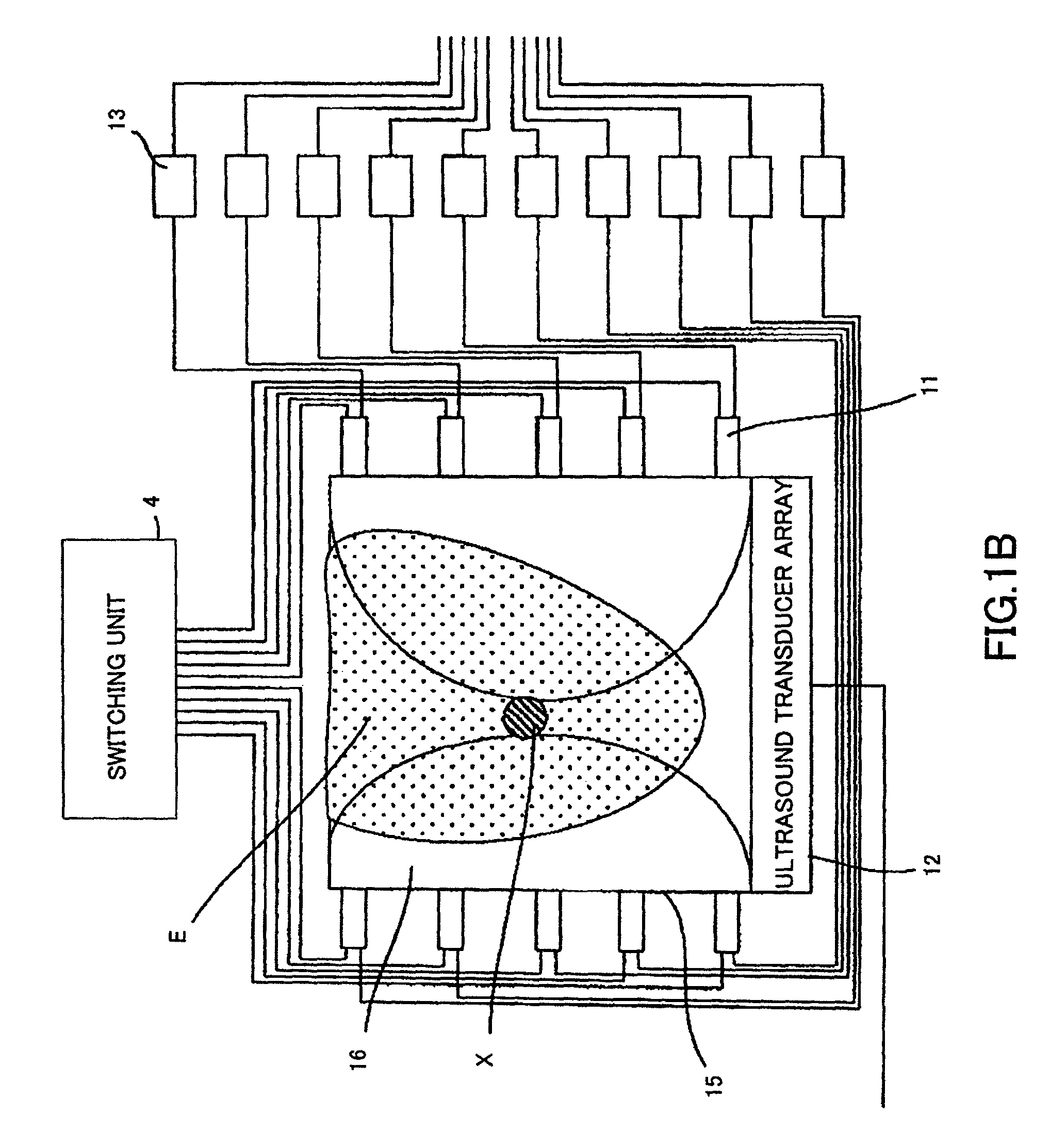
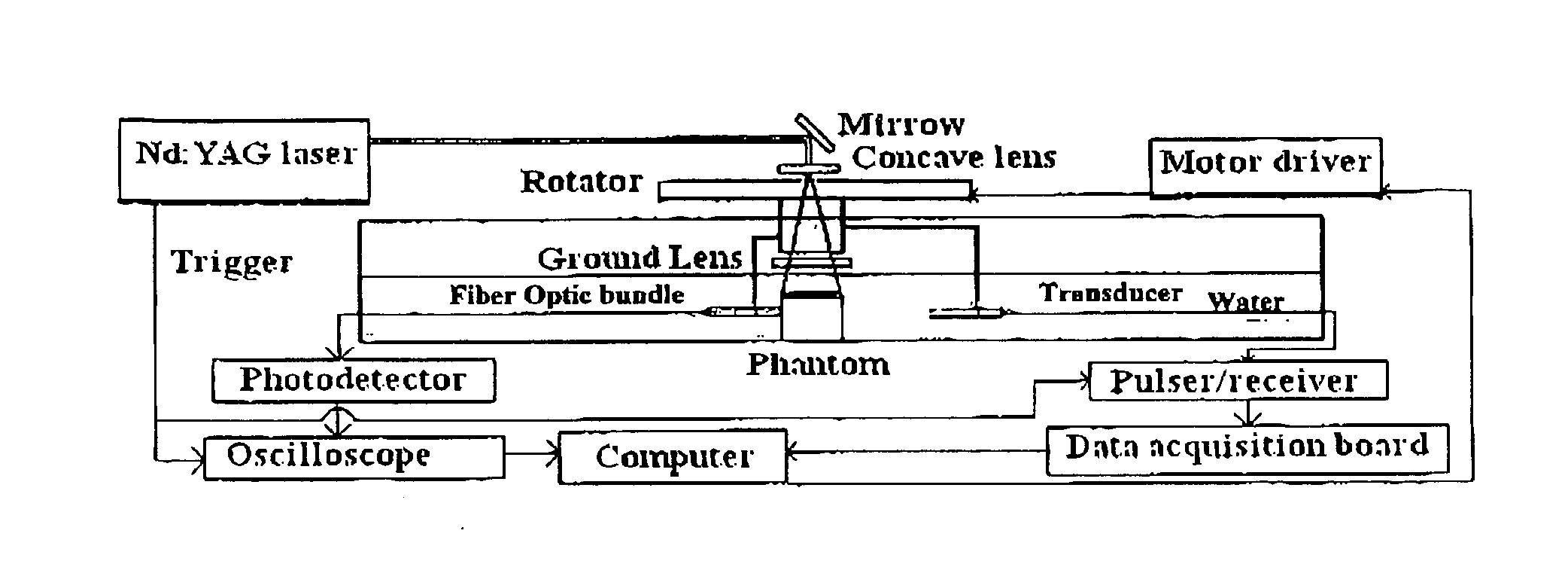
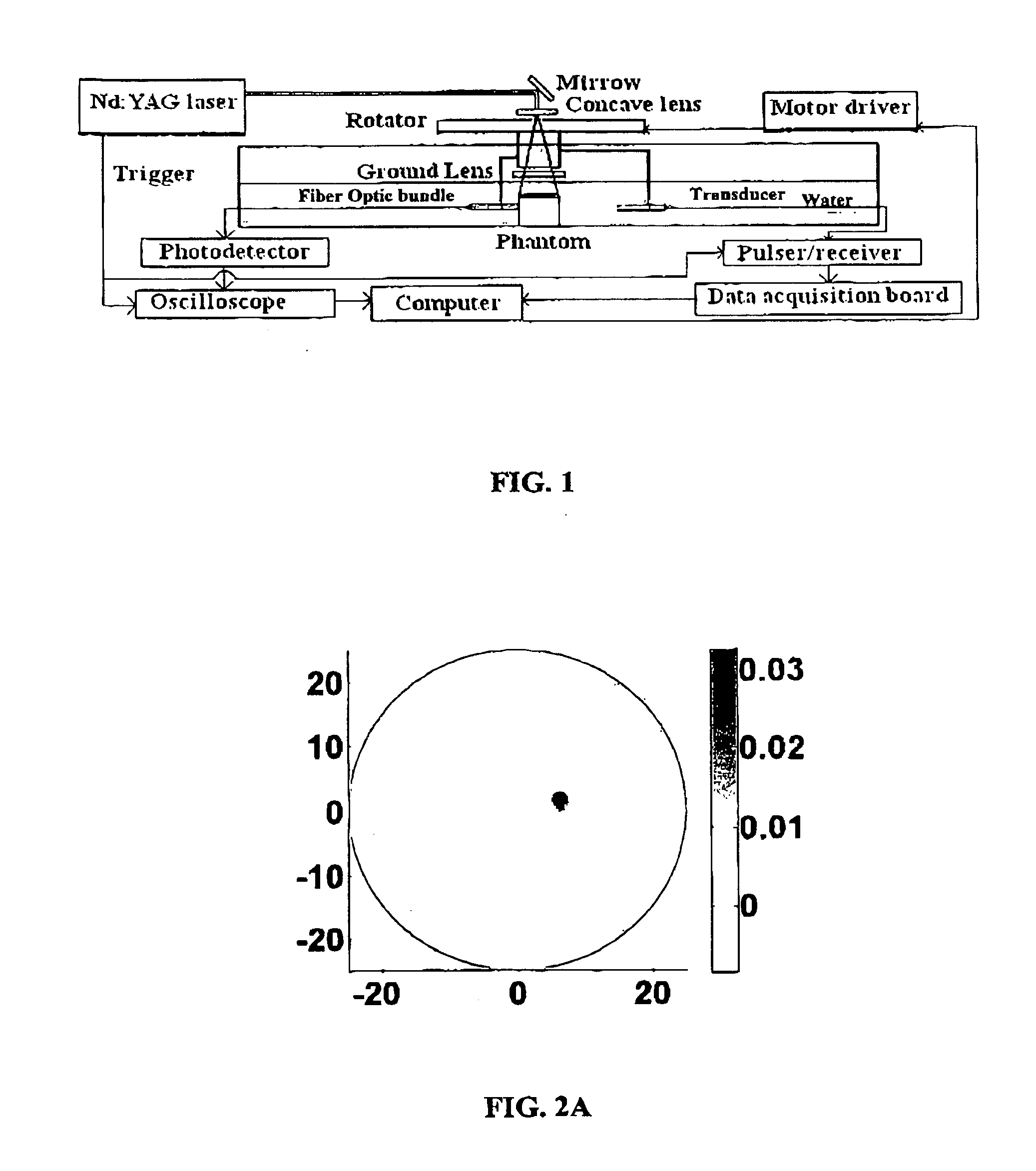
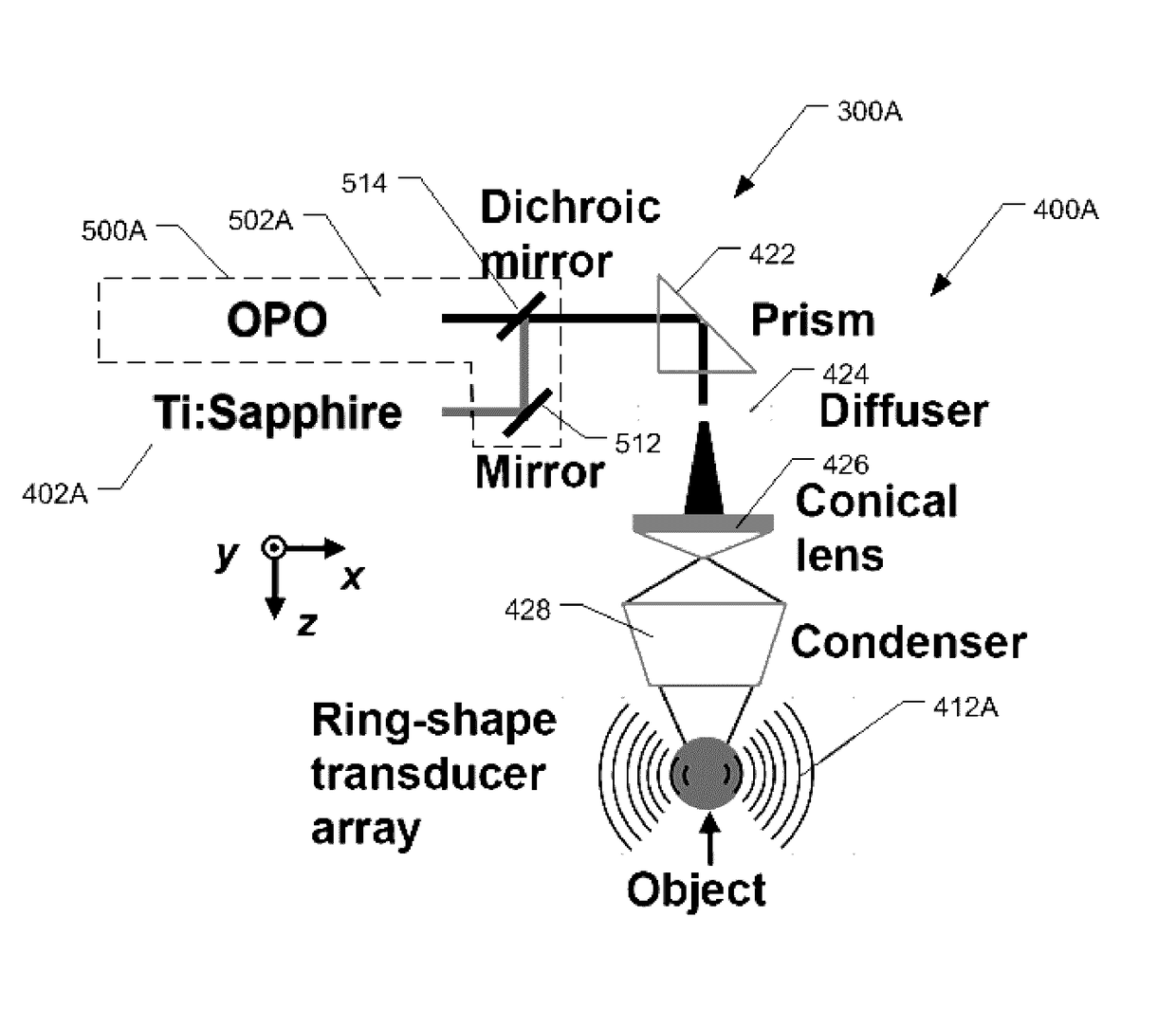
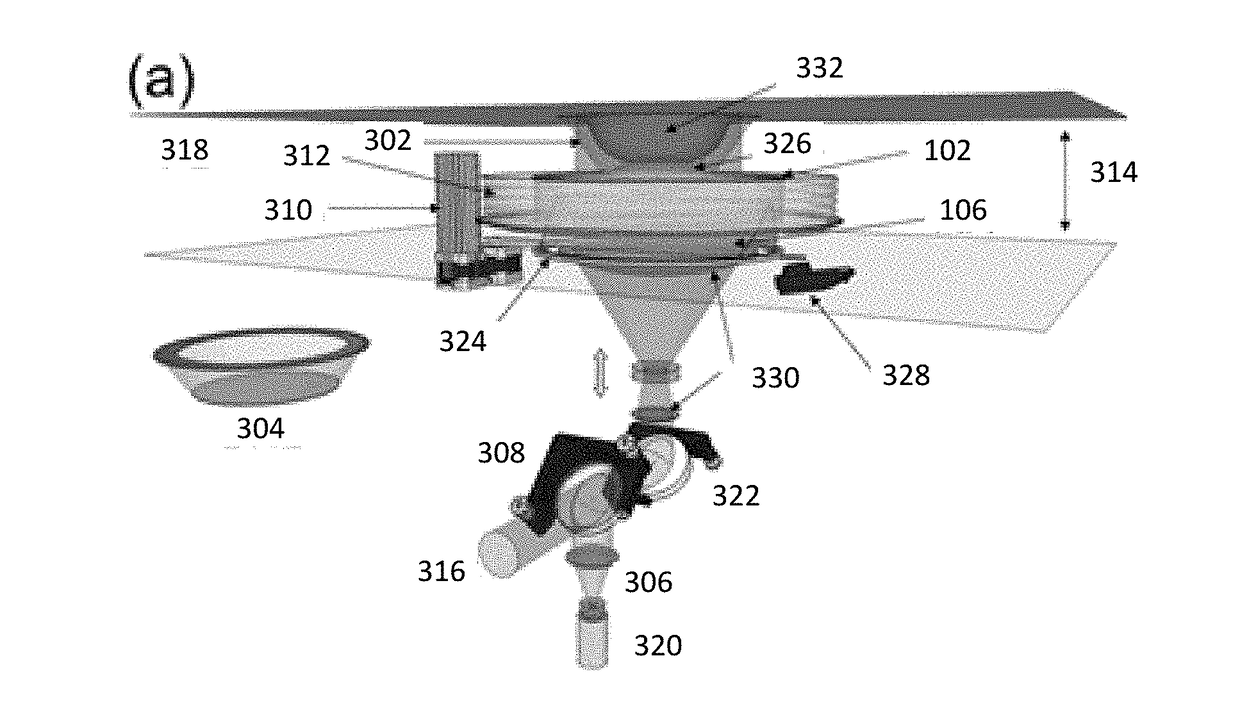
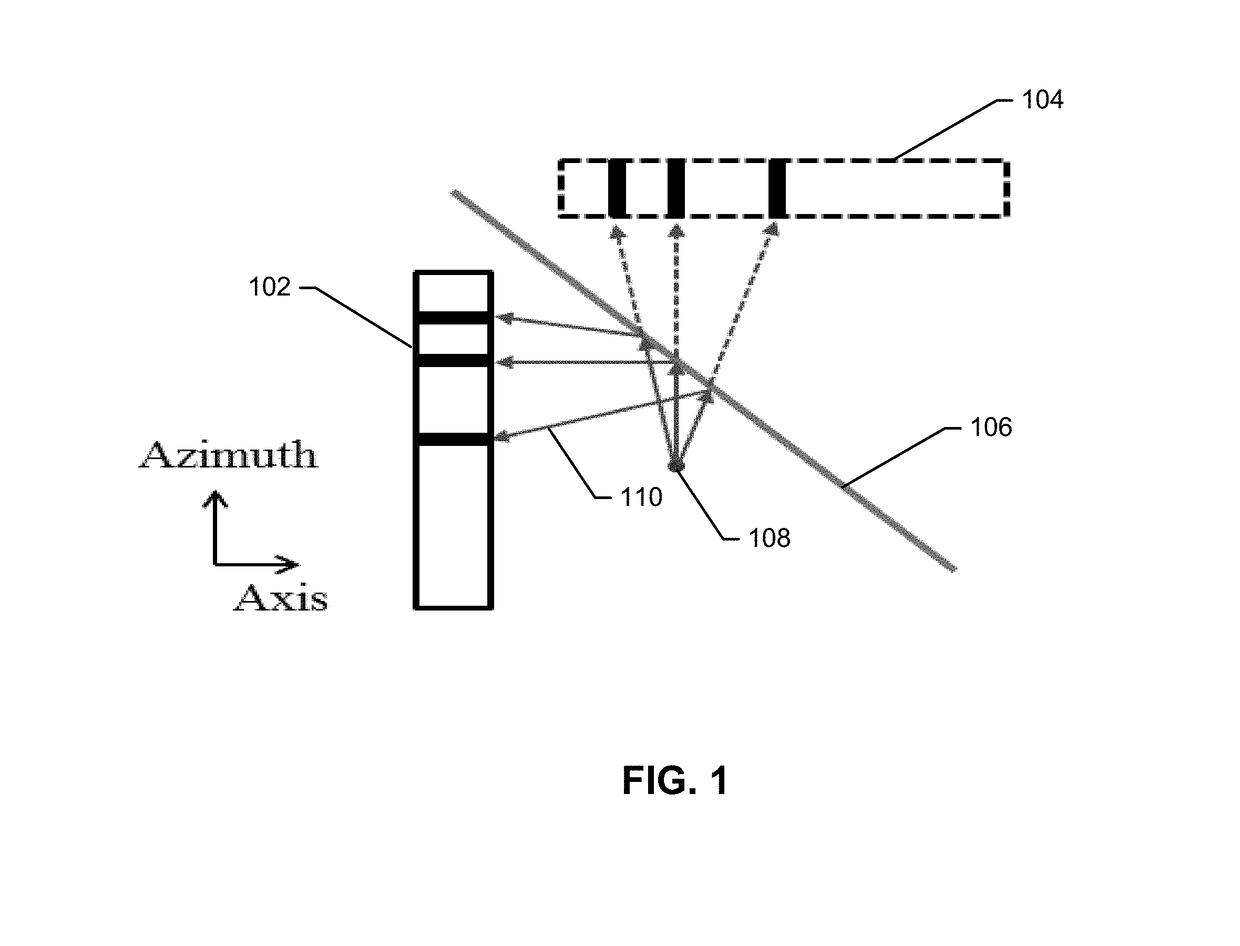
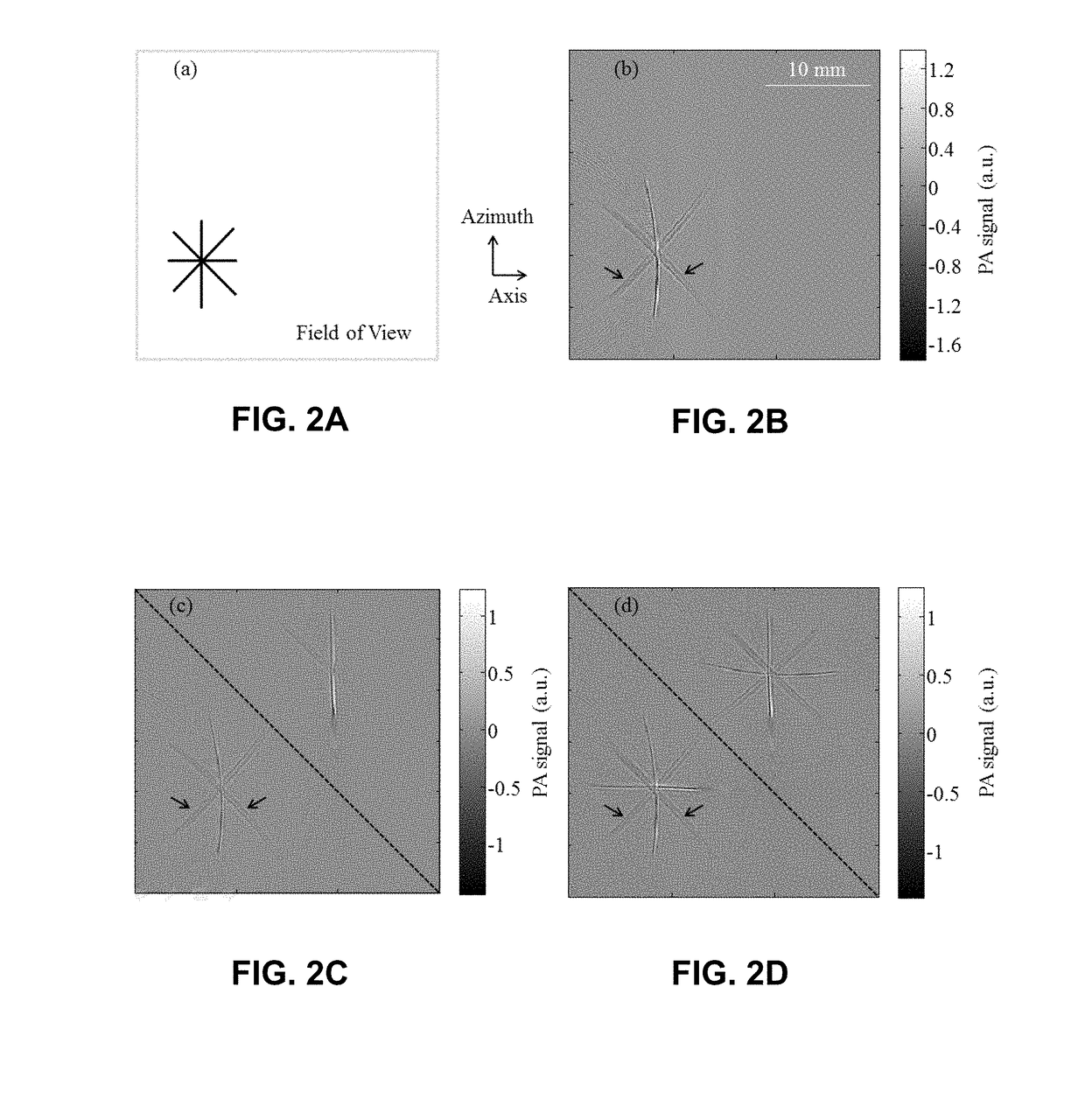
Patents
Literature
95 results about "Photoacoustic tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
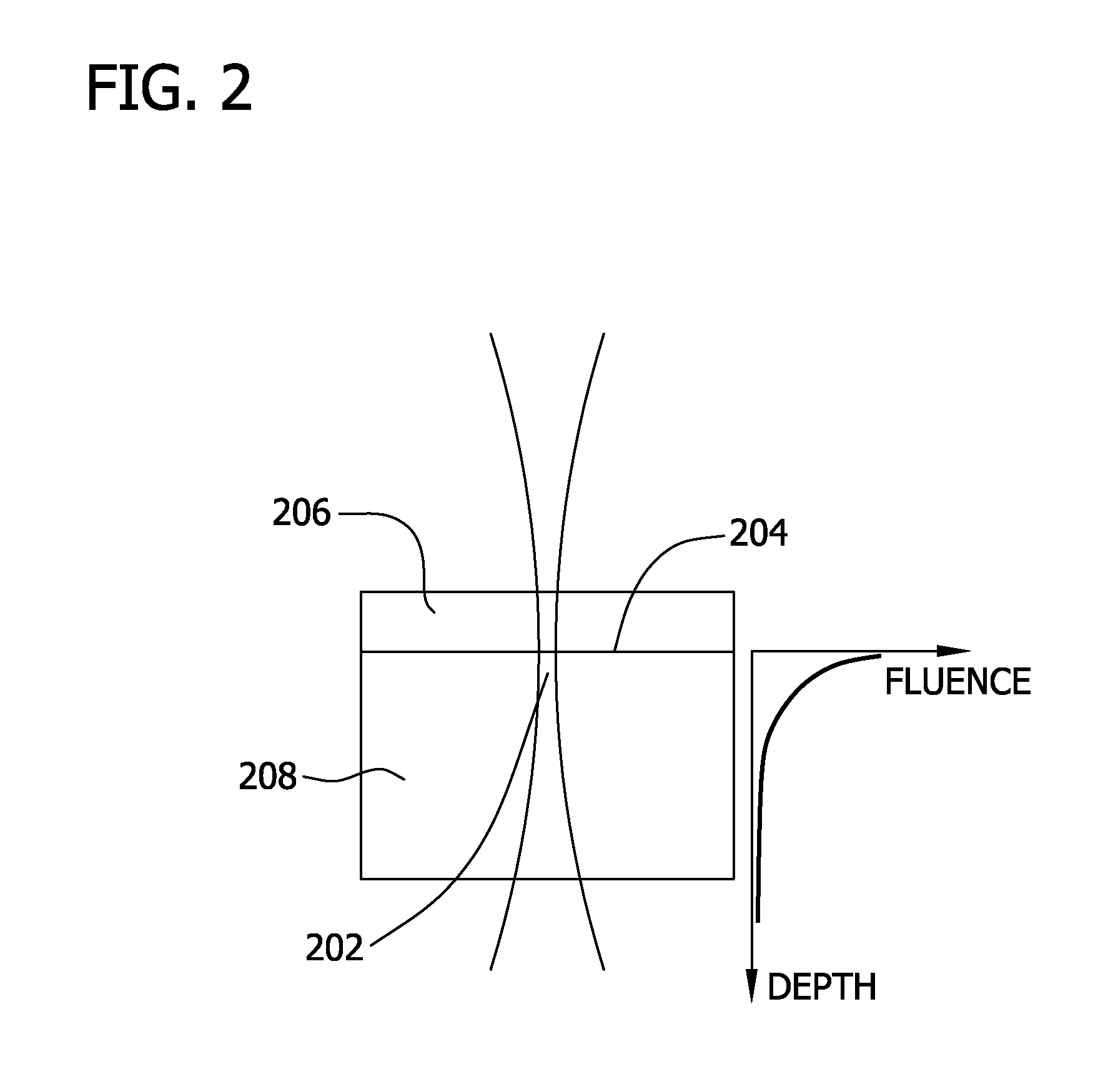
Photoacoustic tomography, or Photoacoustic computed tomography, is a materials analysis technique based on the reconstruction of an internal photoacoustic source distribution from measurements acquired by scanning ultrasound detectors over a surface that encloses the source under study.
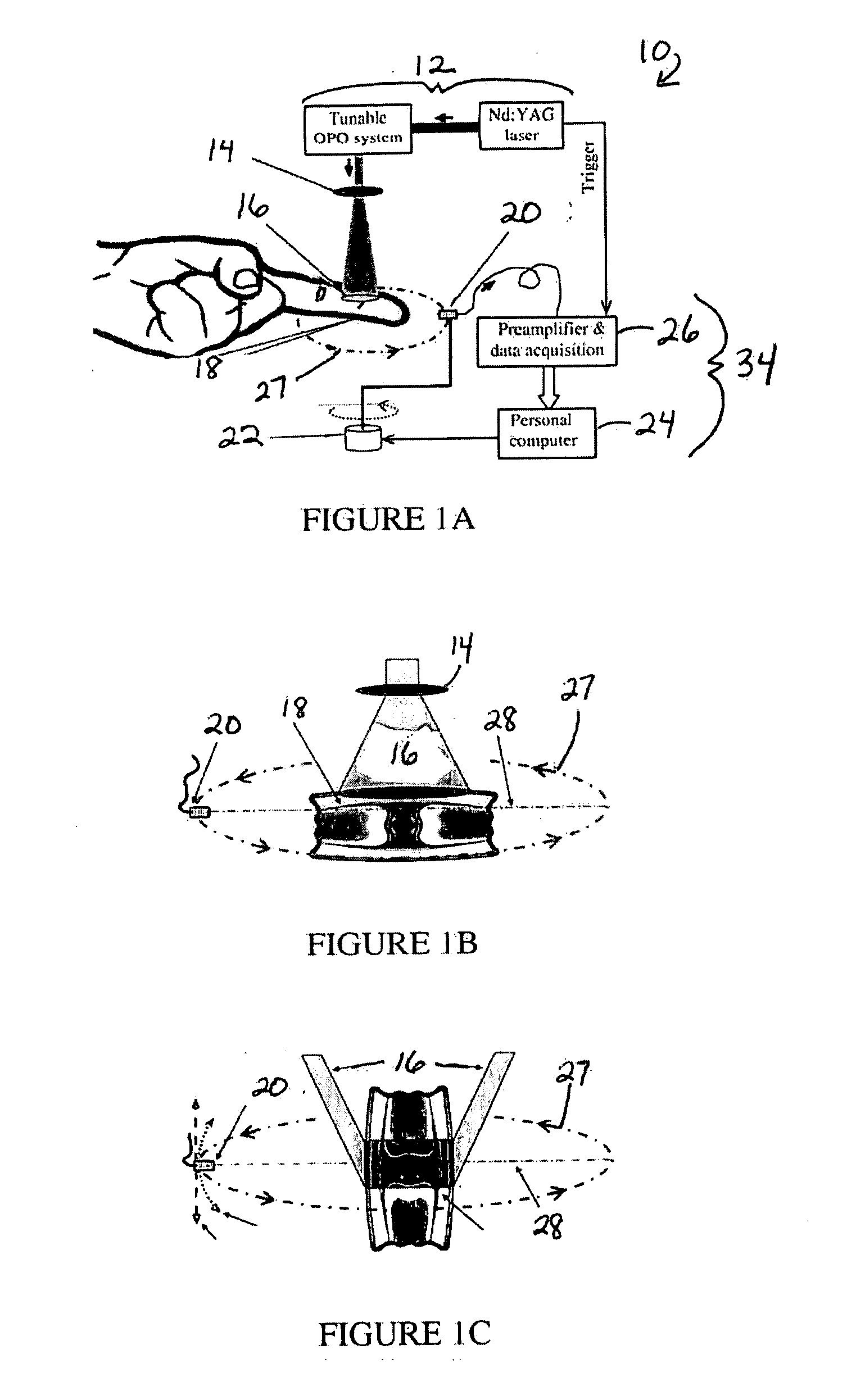
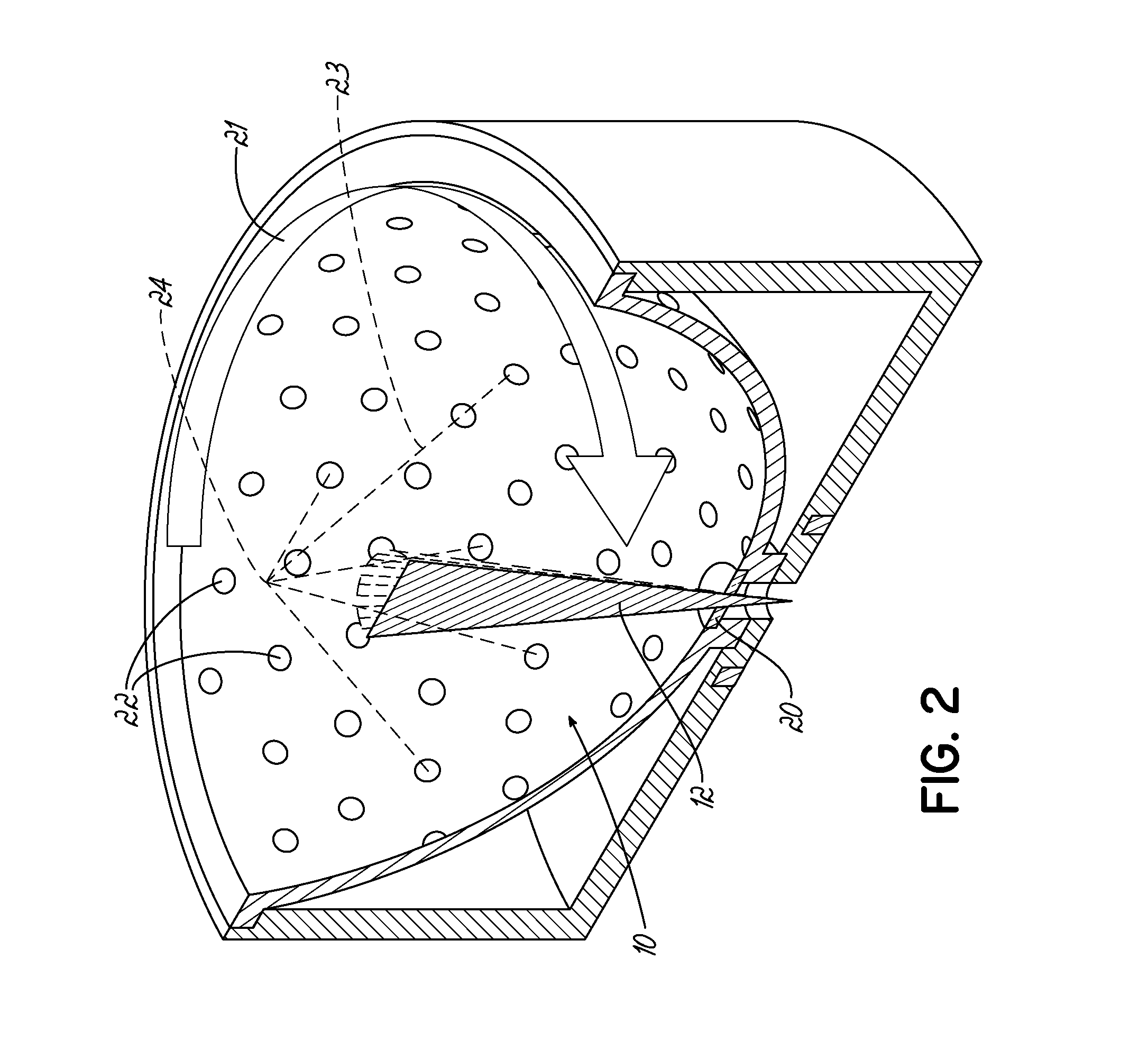
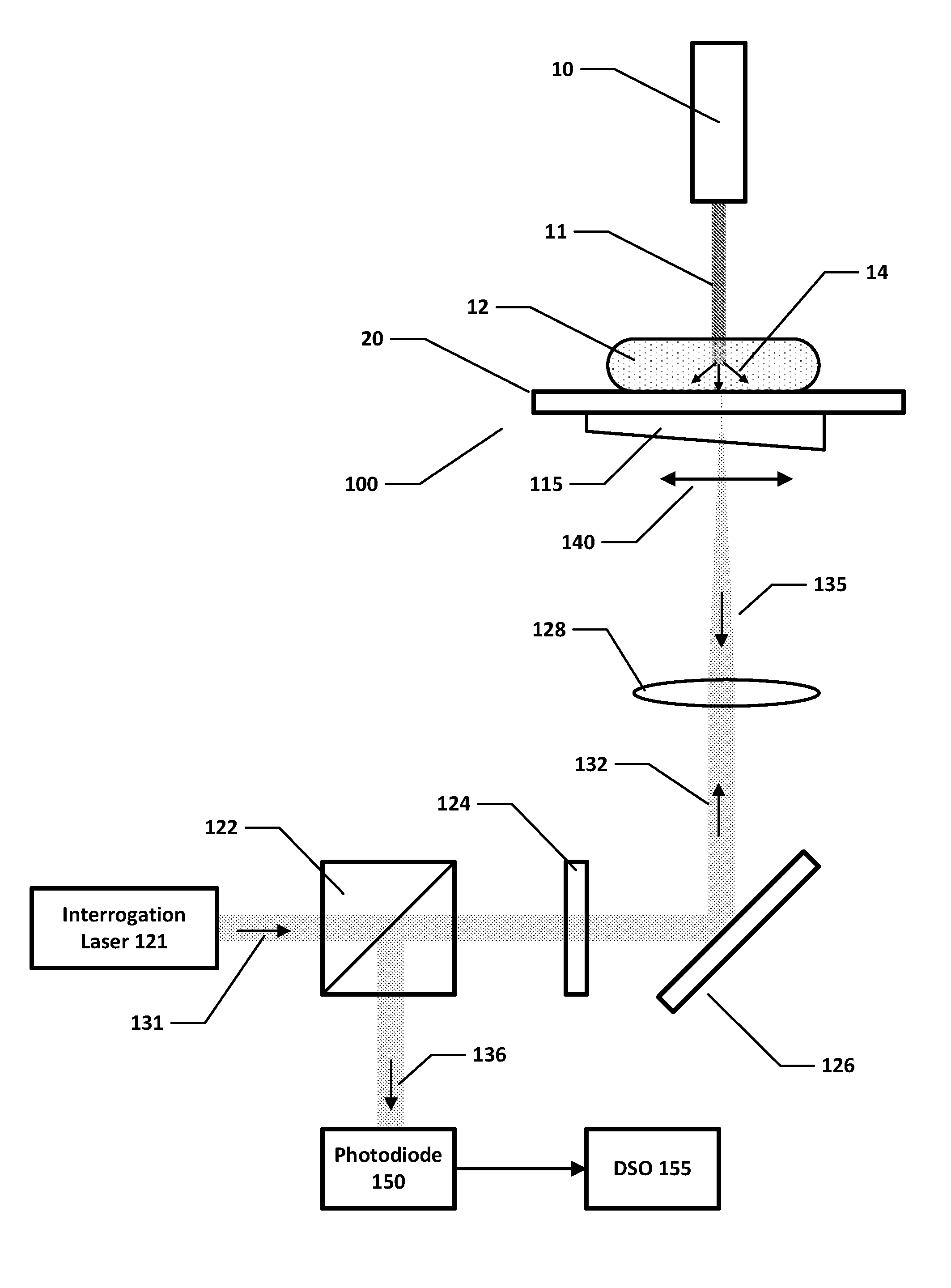
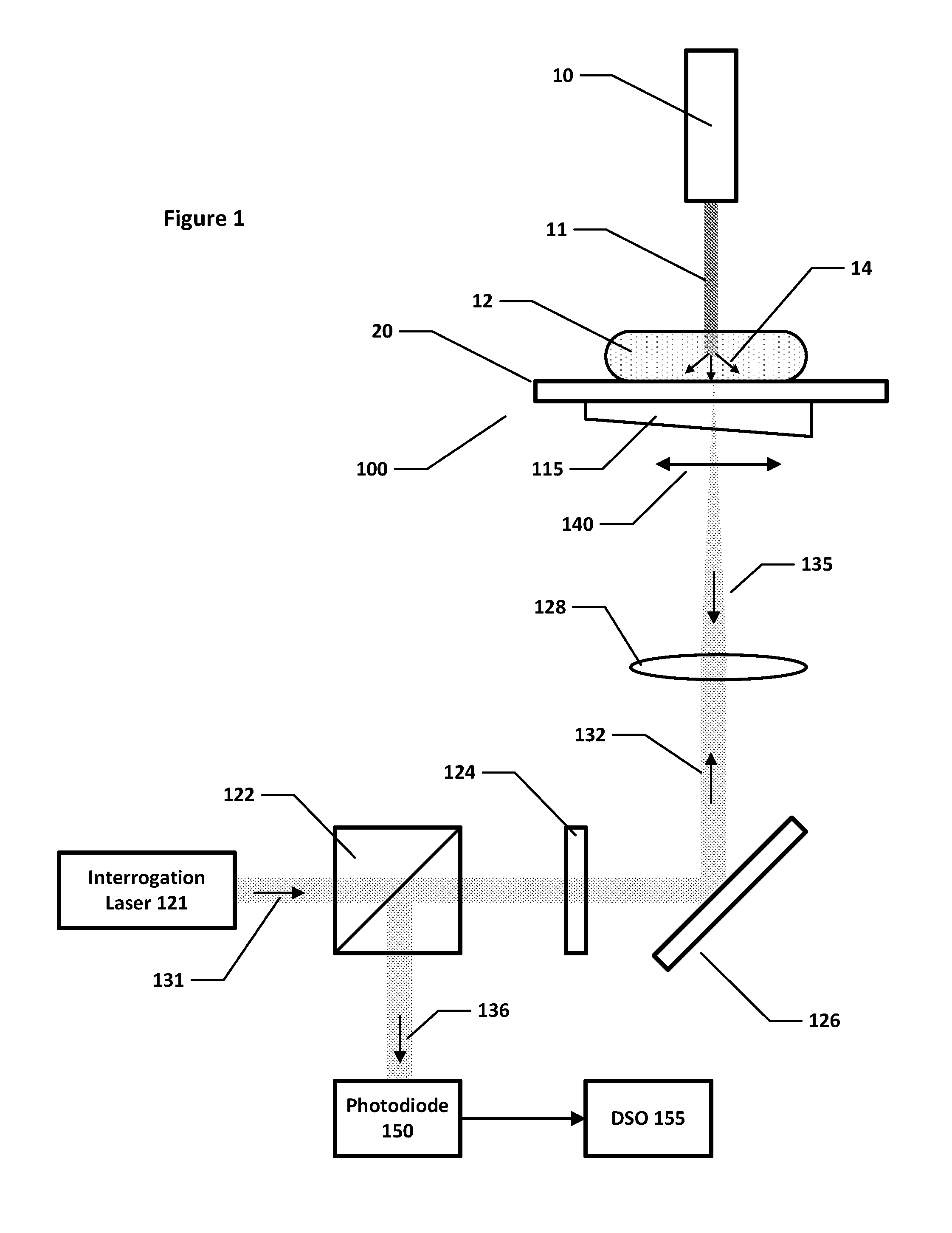
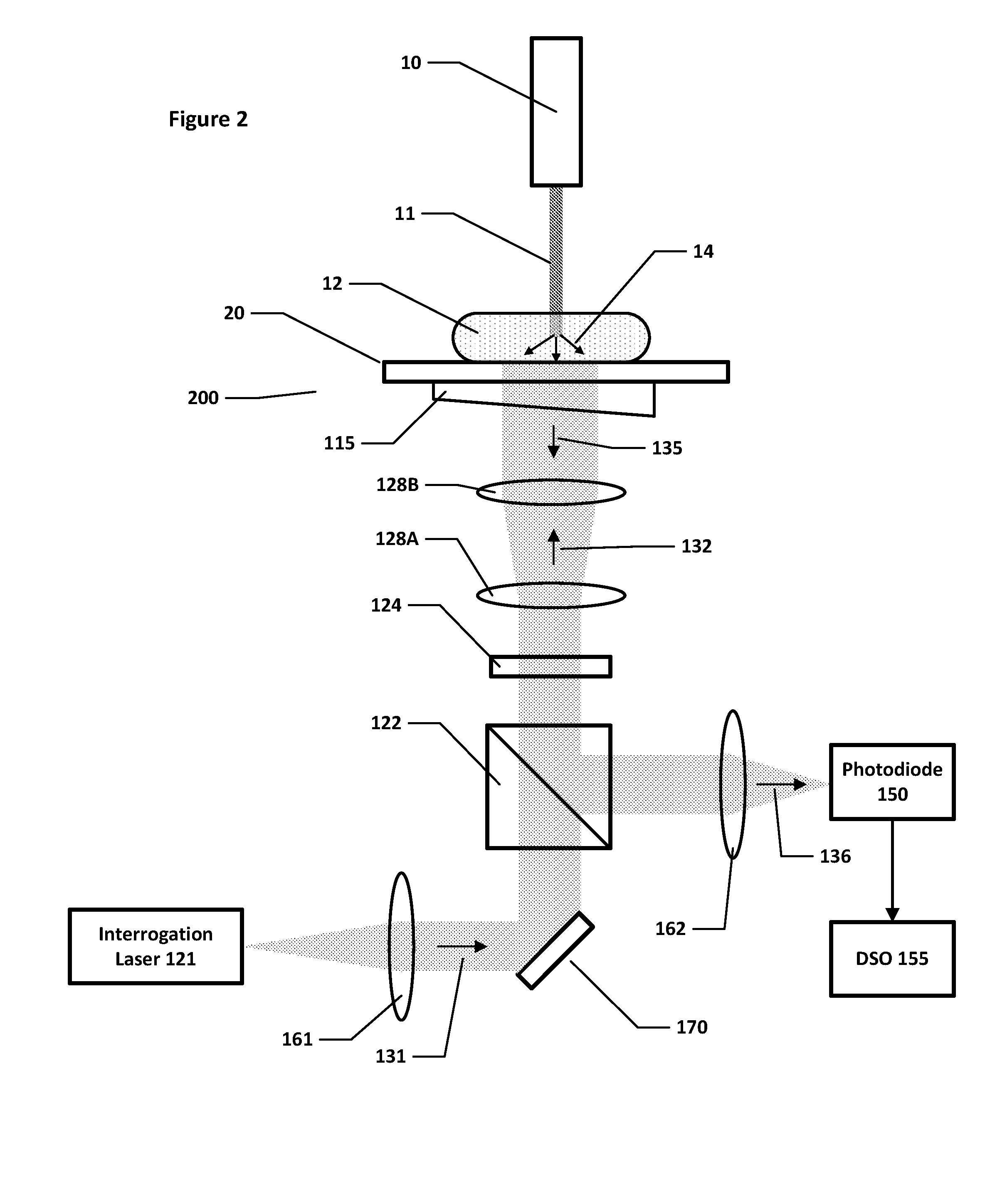
Method, system and apparatus for dark-field reflection-mode photoacoustic tomography
InactiveUS20060184042A1Enhance the imageMinimize interferenceCatheterDiagnostics using tomographyUltrasonic sensorAcoustic wave
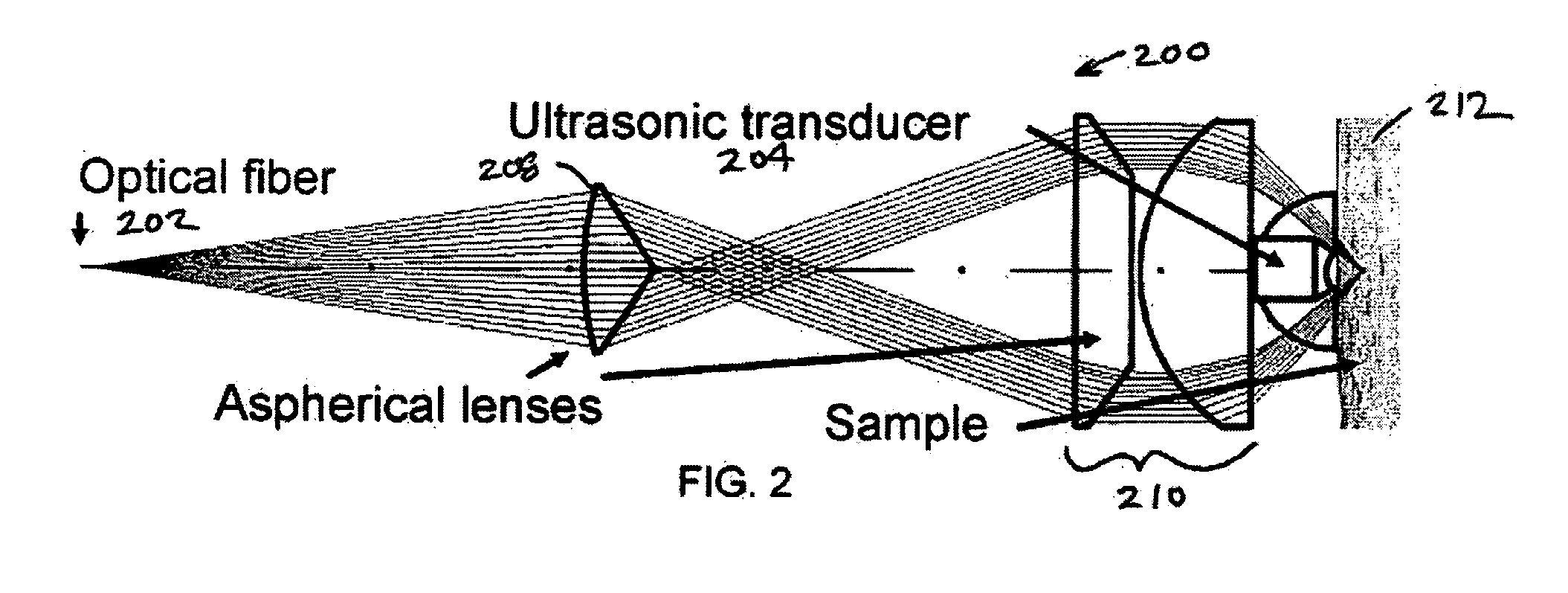
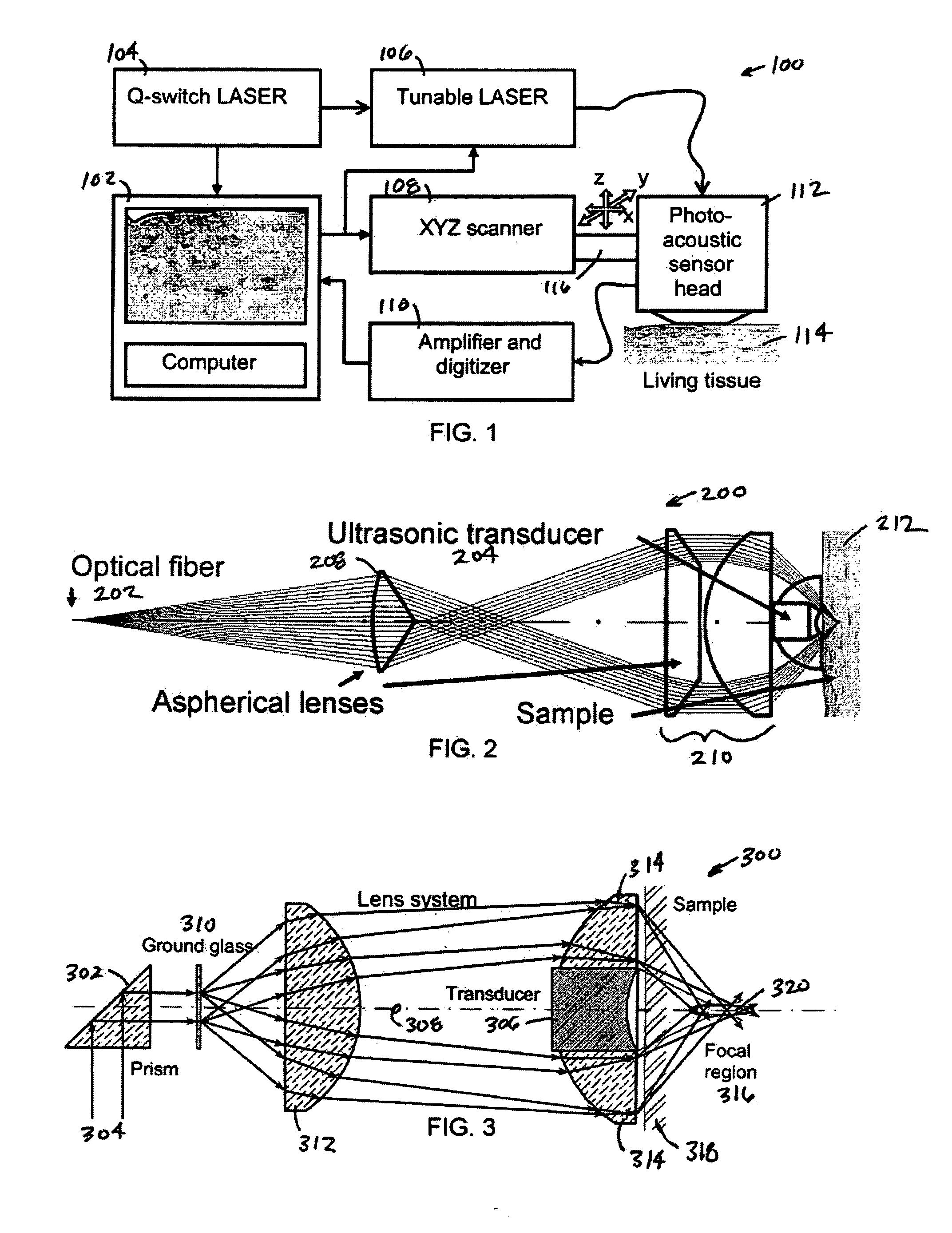
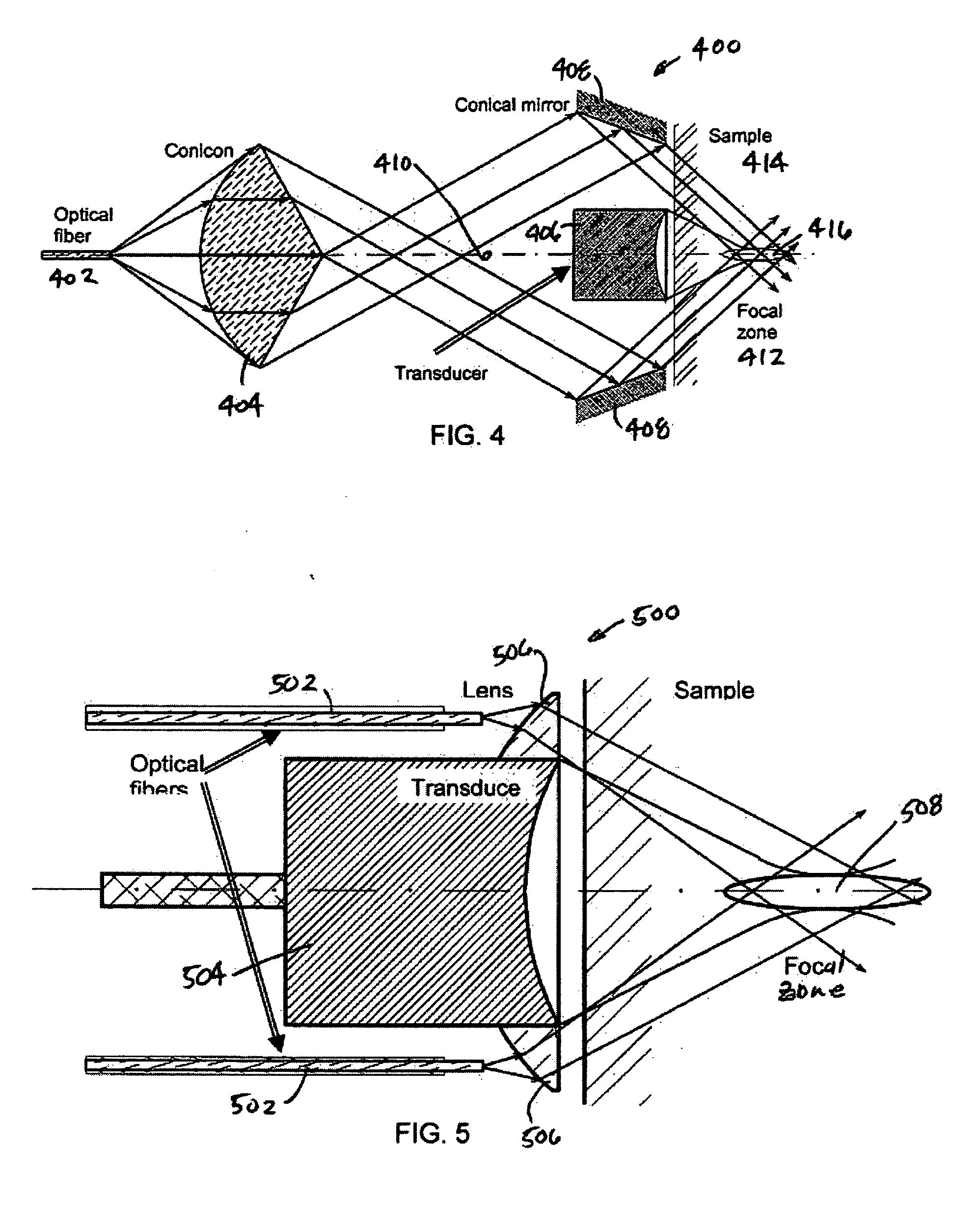
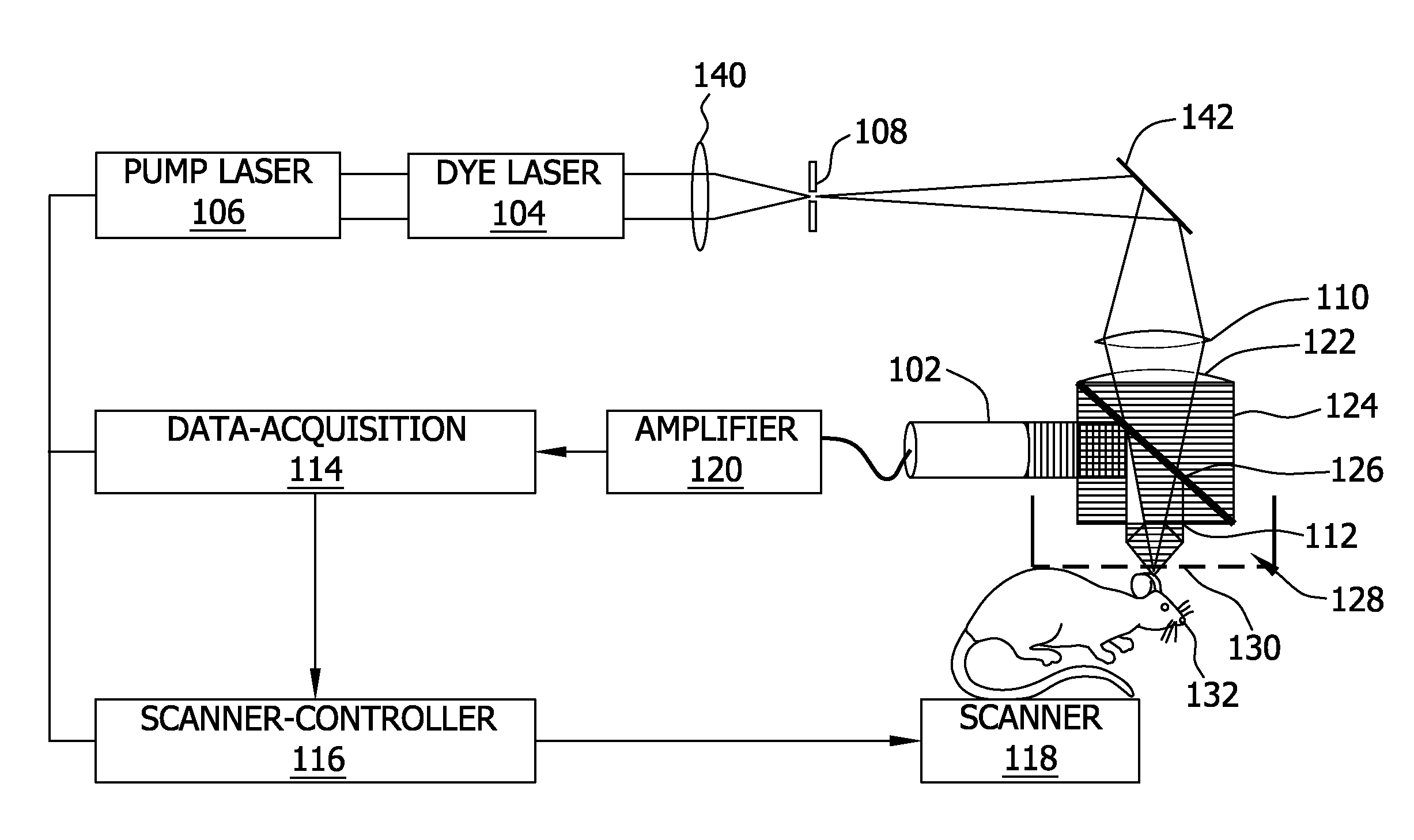
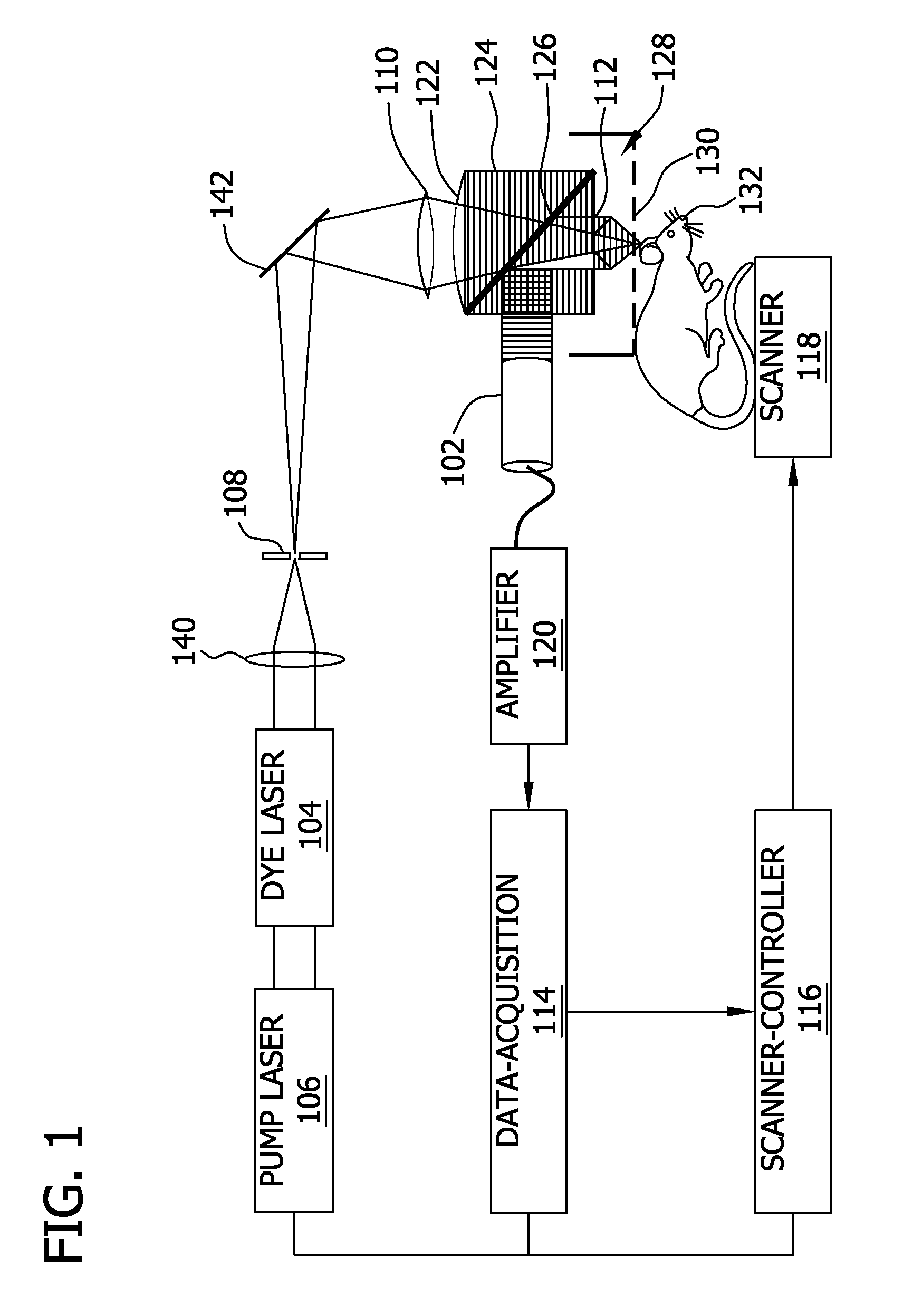
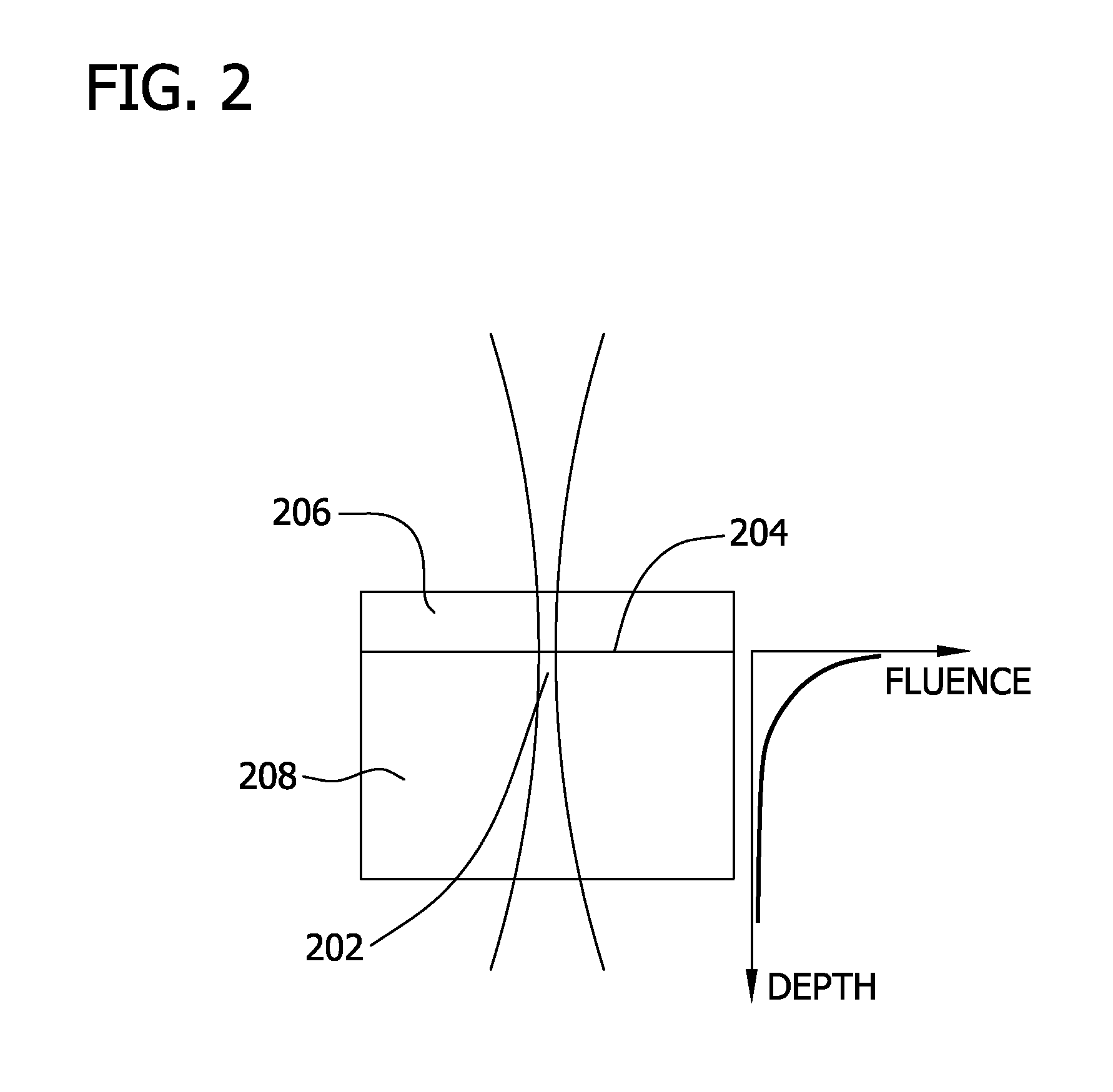
The present invention provides a method, system and apparatus for reflection-mode microscopic photoacoustic imaging using dark-field illumination that can be used to characterize a target within a tissue by focusing one or more laser pulses onto a surface of the tissue so as to penetrate the tissue and illuminate the target, receiving acoustic or pressure waves induced in the target by the one or more laser pulses using one or more ultrasonic transducers that are focused on the target and recording the received acoustic or pressure waves so that a characterization of the target can be obtained. The target characterization may include an image, a composition or a structure of the target. The one or more laser pulses are focused with an optical assembly of lenses and / or mirrors that expands and then converges the one or more laser pulses towards the focal point of the ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
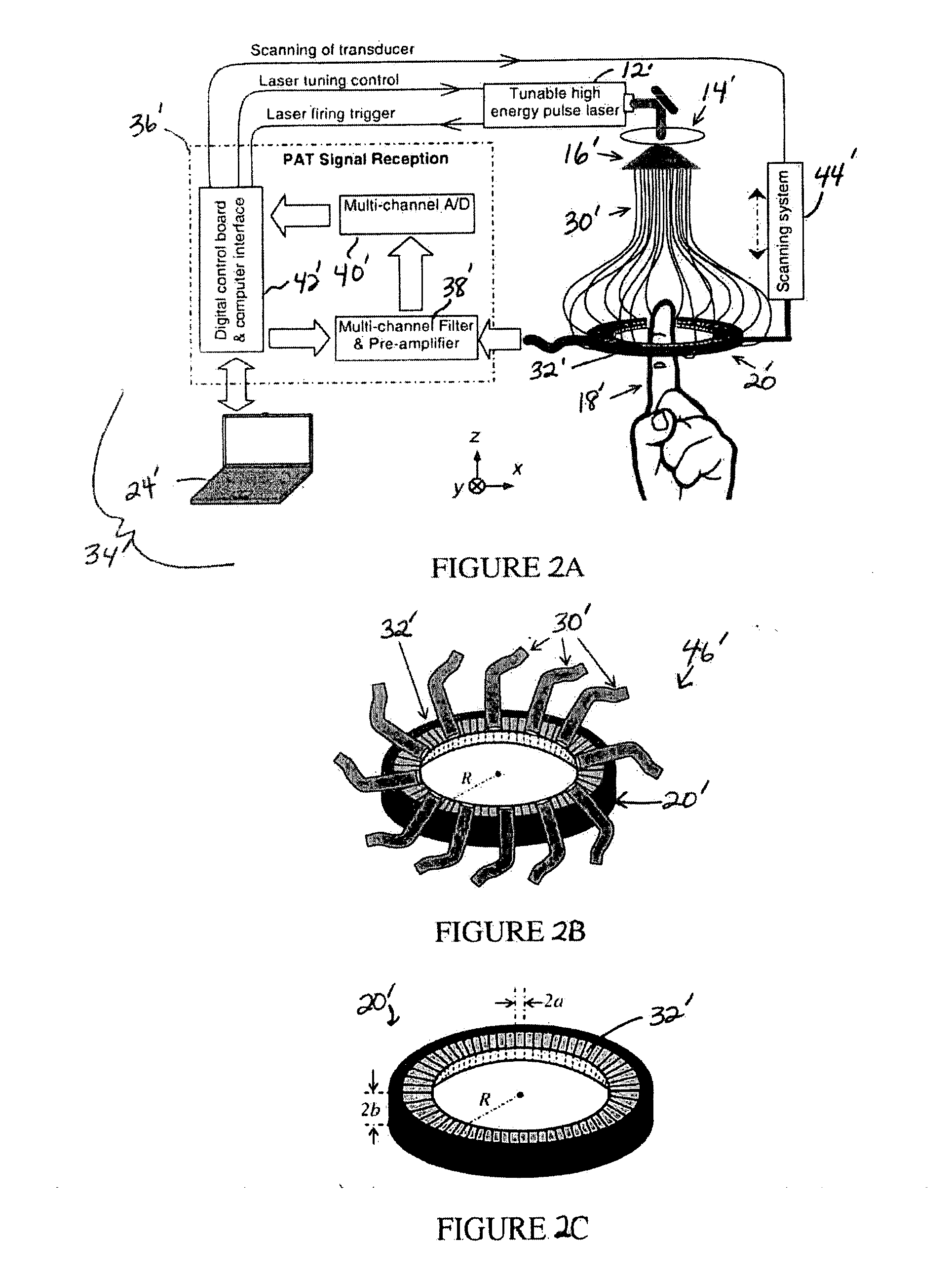
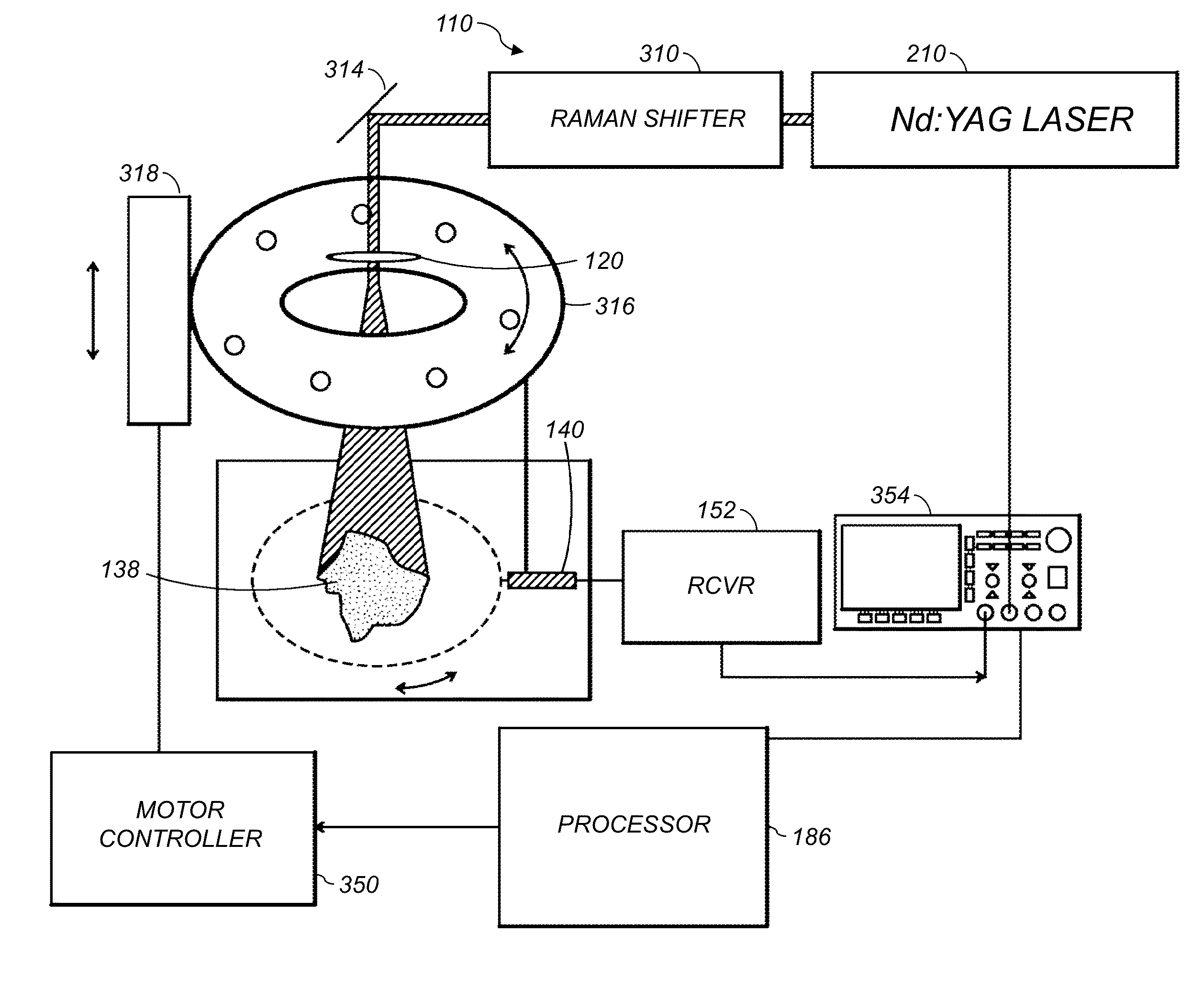
System and method for photoacoustic tomography of joints
InactiveUS20080173093A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansUltrasonic sensorControl system
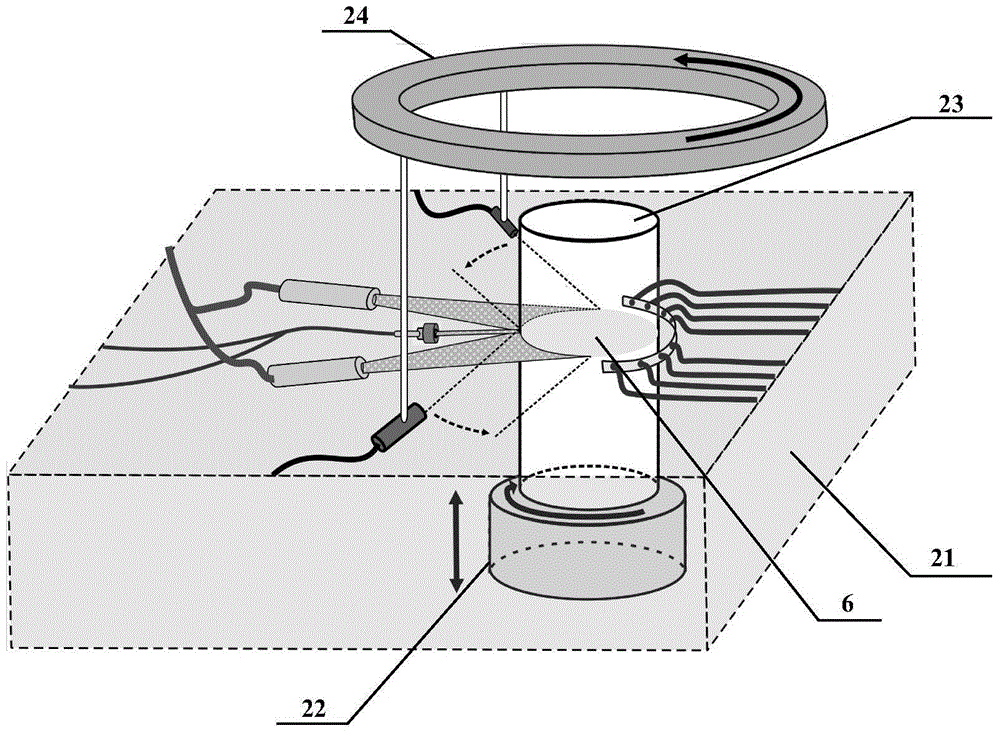
A system and method for photoacoustic tomography of a sample, such as a mammalian joint, includes a light source configured to deliver light to the sample, an ultrasonic transducer disposed adjacent to the sample for receiving photoacoustic signals generated due to optical absorption of the light by the sample, a motor operably connected to at least one of the sample and the ultrasonic transducer for varying a position of the sample and the ultrasonic transducer with respect to one another along a scanning path, and a control system in communication with the light source, the ultrasonic transducer, and the motor for reconstructing photoacoustic images of the sample from the received photoacoustic signals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Photoacoustic Tomography of Breast Tissue Using Hemispherical Array and Planar Scanning
InactiveUS20130217995A1Reduce physical sizeHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using tomographySensorsSensor arrayMedicine
Photoacoustic imaging is enhanced by scanning (61) the sensor array (10) used in photoacoustic imaging laterally relative to the tissue being imaged, gathering multiple tissue images (70, 71, 72, 73) at multiple relative lateral positions, and generating a photoacoustic image (80) of the tissue by combining the images taken at multiple relative lateral positions.
Owner:OPTOSONICS
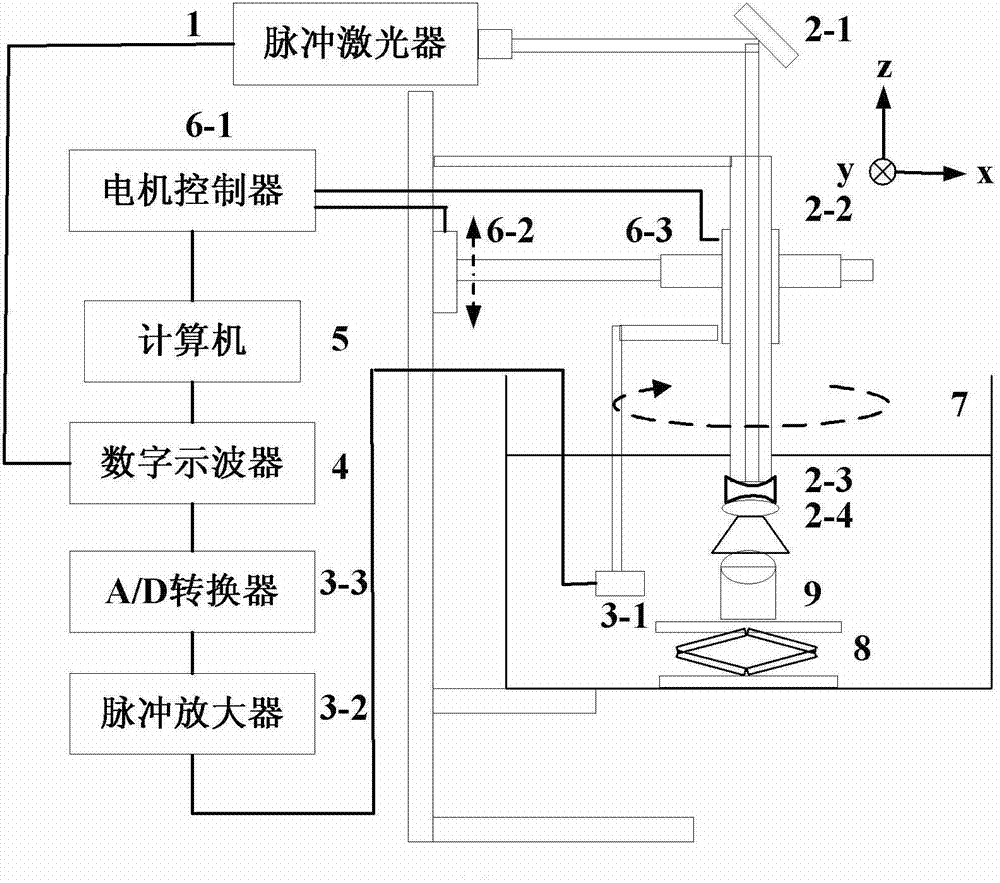
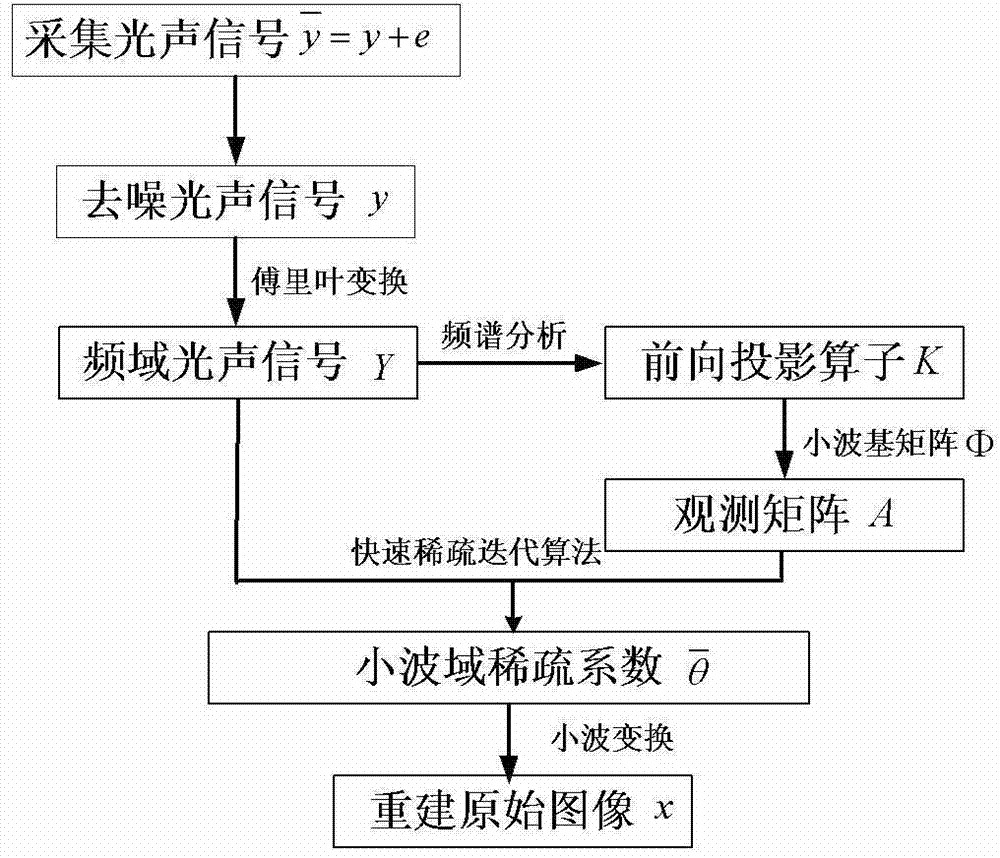
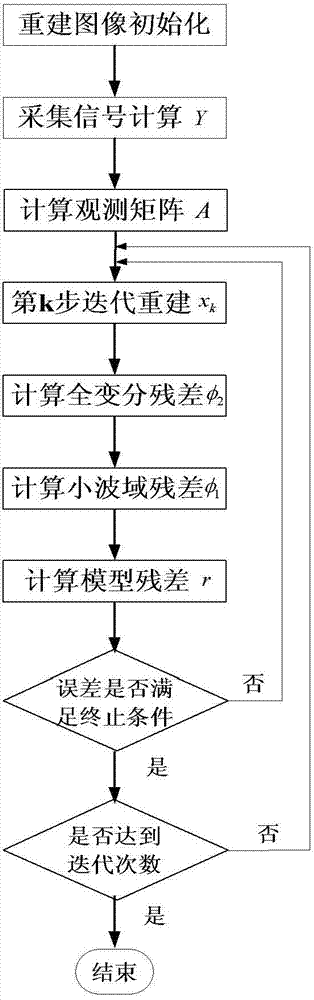
Photoacoustic tomography device and method based on limited-angle scanning
ActiveCN102727259AImprove reliabilityReduce hardware costsTomographyThinning algorithmDigital signal
The invention relates to the technical field of photoacoustic imaging and discloses a rapid photoacoustic tomography device and a rapid photoacoustic tomography method based on limited-angle scanning. The method comprises the following steps of: transmitting pulse laser into an imaging sample to generate a photoacoustic signal, acquiring the photoacoustic signal at a limited position on an arc through an ultrasonic detector unit, amplifying the signal through a signal amplifier, converting the photoacoustic signal into an electric signal through an analog / digital (A / D) converter, and finally transmitting the electric signal to an oscilloscope to finish digital signal acquisition; inputting the photoacoustic signal of the imaging sample into a computer, performing filtering and Fourier transform processing on the photoacoustic signal through the computer, extracting the frequency domain information of the photoacoustic signal according to experiment conditions, establishing a forward projection operator and a measurement matrix, and performing reconstruction imaging on the signal based on a quick thinning algorithm through the computer. The method and the device have the advantages of short signal acquisition time, high reconstruction speed, convenience in operation, high adaptability, high expansibility and the like.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photoacoustic and fluorescence dual-mode integrated tomography imaging system and imaging method
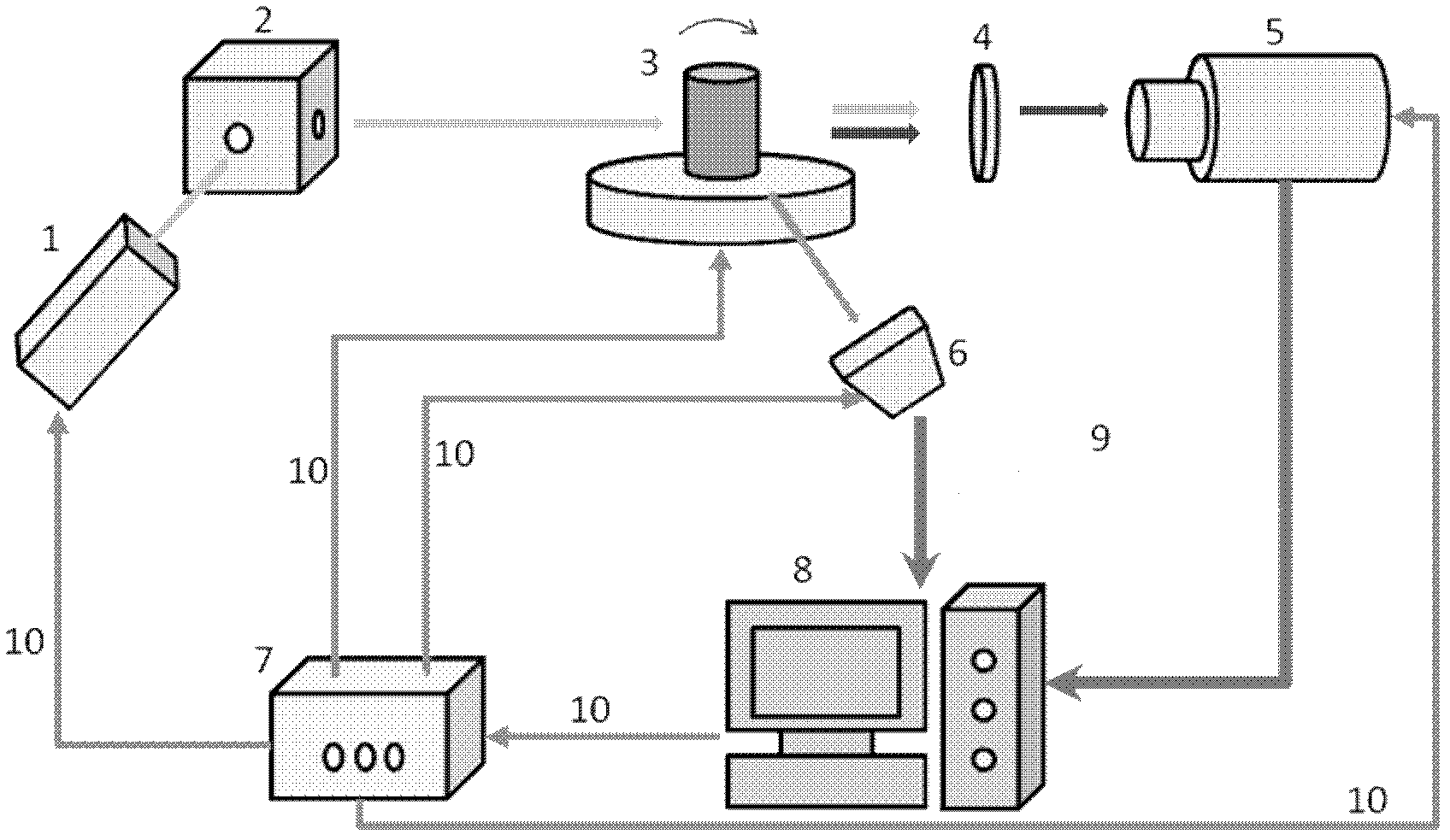
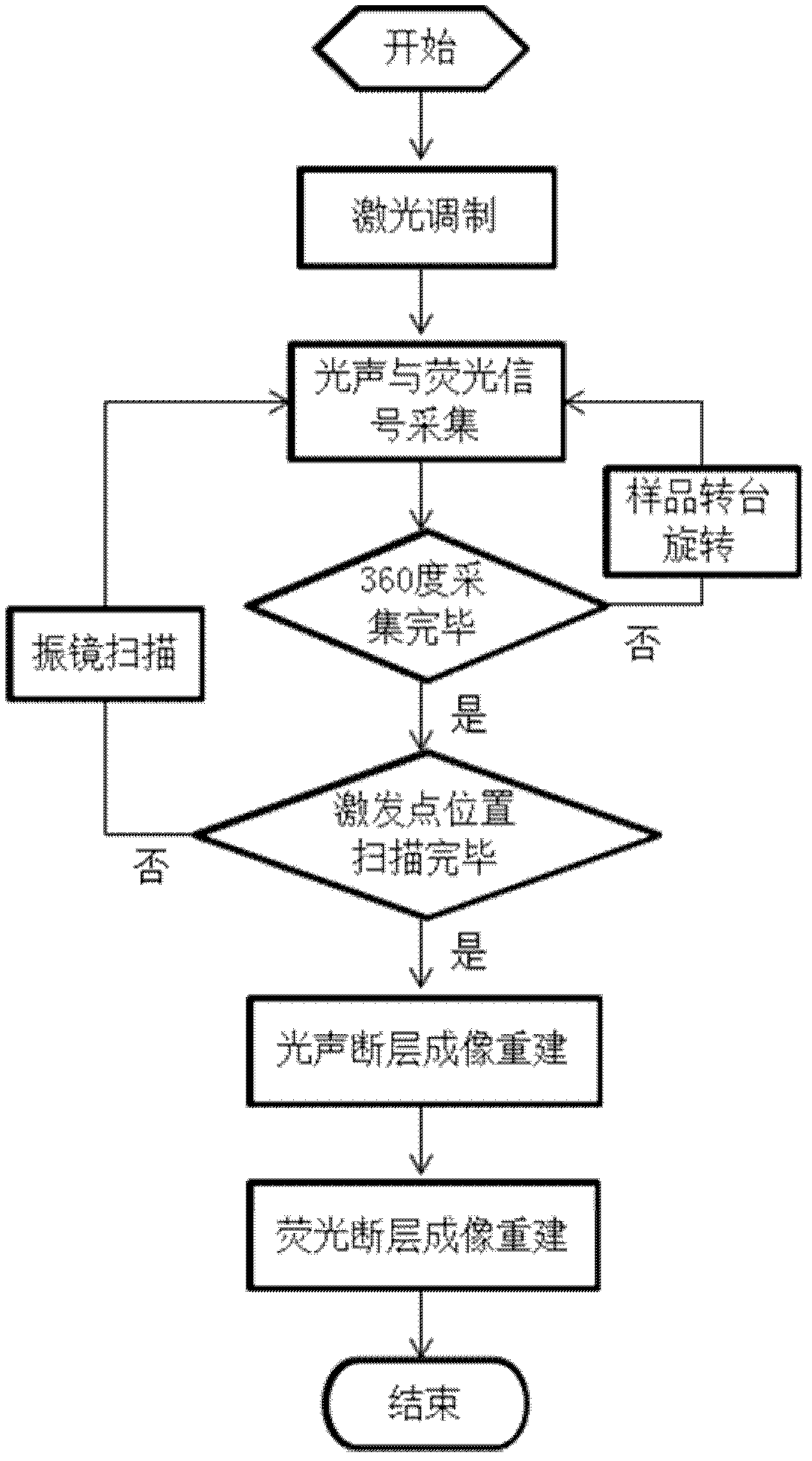
InactiveCN102499645ALow costReduce volumeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsDual modeFluorophore
The invention discloses a photoacoustic and fluorescence dual-mode integrated tomography imaging system and a photoacoustic and fluorescence dual-mode integrated tomography imaging method. The system comprises a modulation laser light source (1), a vibrating mirror (2), a sample rotary table (3), a filtering wheel (4), a gating intensified charge-coupled device (ICCD) camera (5), a photoacoustic detection acquisition module (6), a system control module (7), a computer (8), a data bus (9) and a control bus (10), wherein the vibrating mirror, the sample rotary table, the filtering wheel and the gating ICCD camera are positioned on the same straight line with the direction of lasers; the ultrasound transduction array normal direction of the photoacoustic detection acquisition module is perpendicular to the straight line to form a crossed vertical detection mode. According to the imaging method, light absorption distribution formed by photoacoustic tomography imaging is used as prior information for the reestablishment of fluorescence tomography imaging, and the positions of fluorophores, fluorescent yield and fluorescence lifetime parameters are reestablished by an iterative method. By the photoacoustic and fluorescence dual-mode integrated tomography imaging system and the photoacoustic and fluorescence dual-mode integrated tomography imaging method, the imaging complexity can be reduced, the cost of hardware can be saved, and the flexibility of the system and the reestablishing accuracy of the fluorescence tomography imaging can be improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
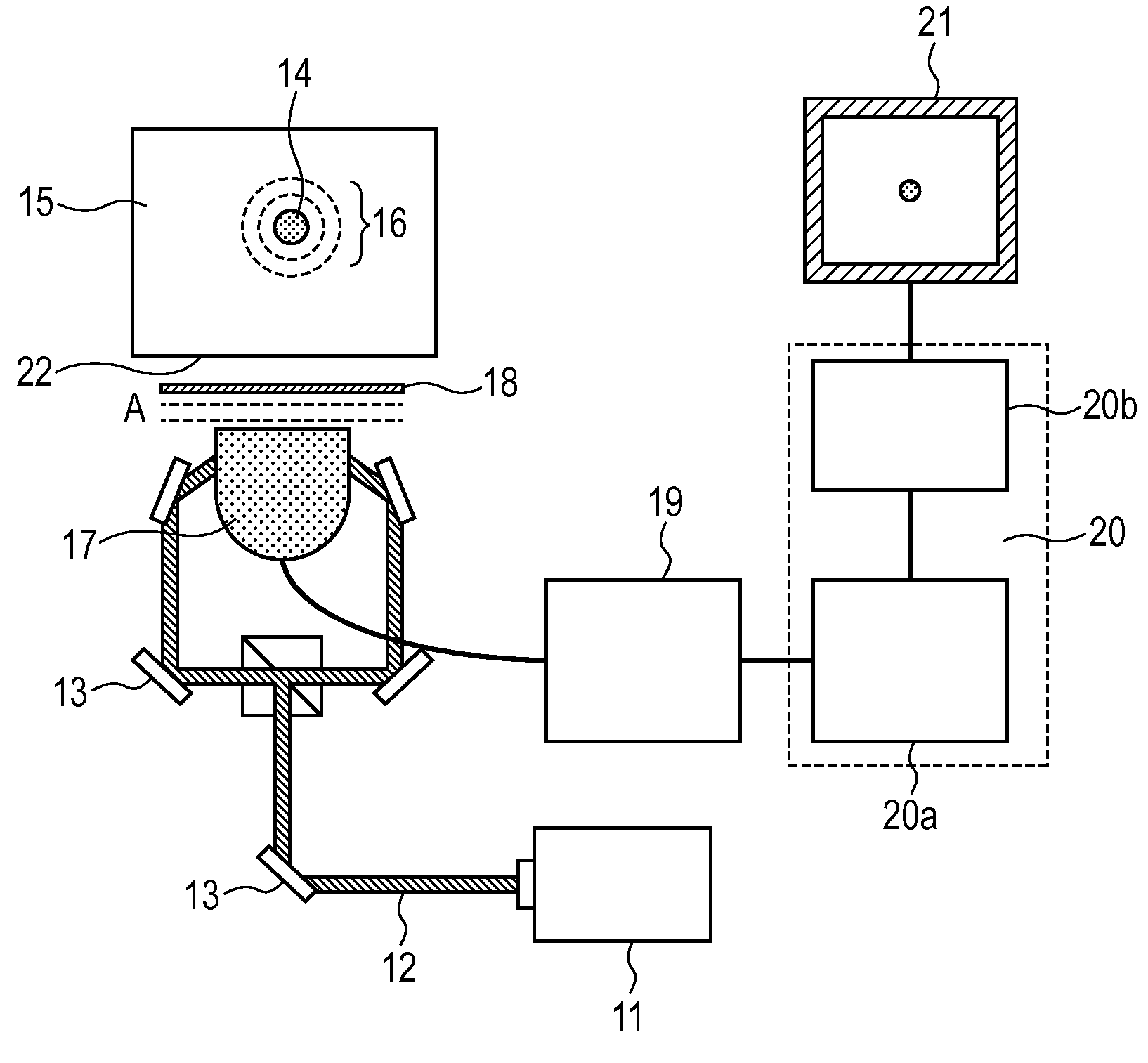
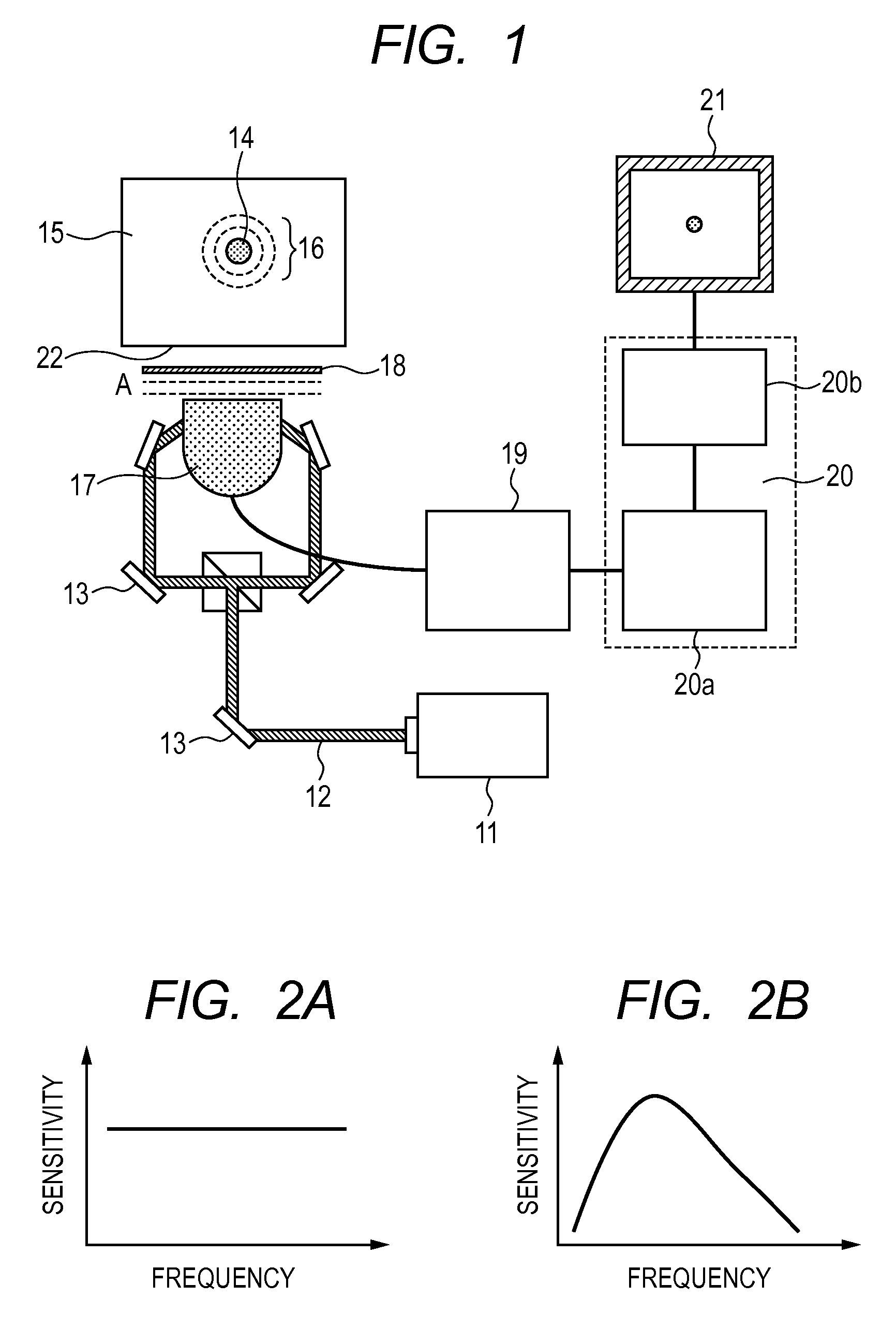
Measurement method and measurement apparatus
InactiveUS20090066949A1Easy to measureHigh resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical tomographyPhotoacoustic tomography
A measurement method of measuring a spectroscopic characteristic inside of a scattering medium includesa first step of measuring the spectroscopic characteristic of the scattering medium by using diffuse optical tomography by irradiating light into the scattering medium, a second step of measuring the spectroscopic characteristic of the scattering medium by using acousto-optical tomography or photo acoustic tomography by irradiating light into the scattering medium, and a third step of making an assumption of a distribution of the spectroscopic characteristic inside of the scattering medium and of changing the assumption such that a difference between a predicted value of the spectroscopic characteristic derived from the assumption and a measured value obtained in the first step can fall upon a permissible range. The third step uses data obtained in the second step for at least one of the parameter: an initial value, a constraint condition, or a boundary condition.
Owner:CANON KK
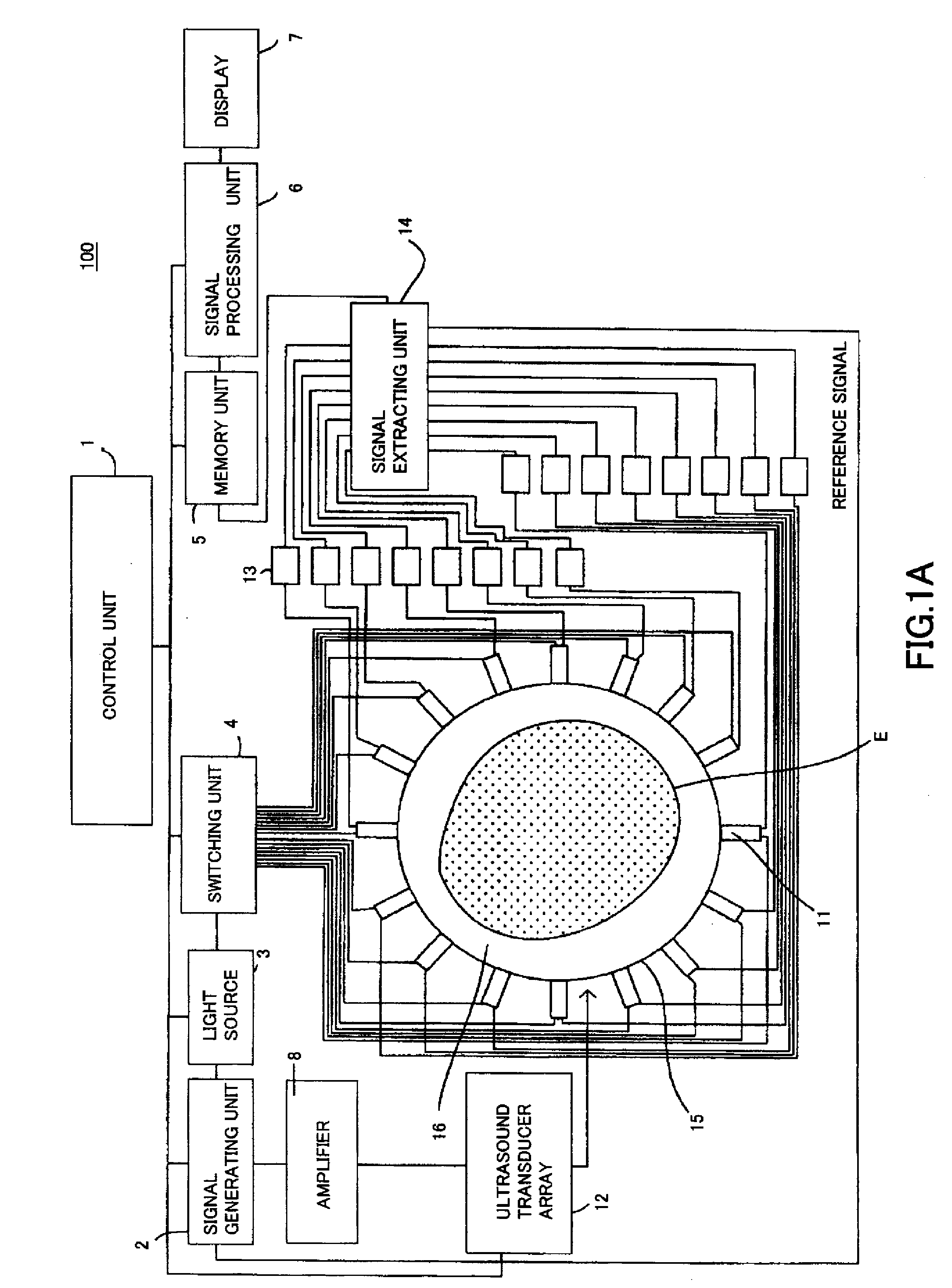
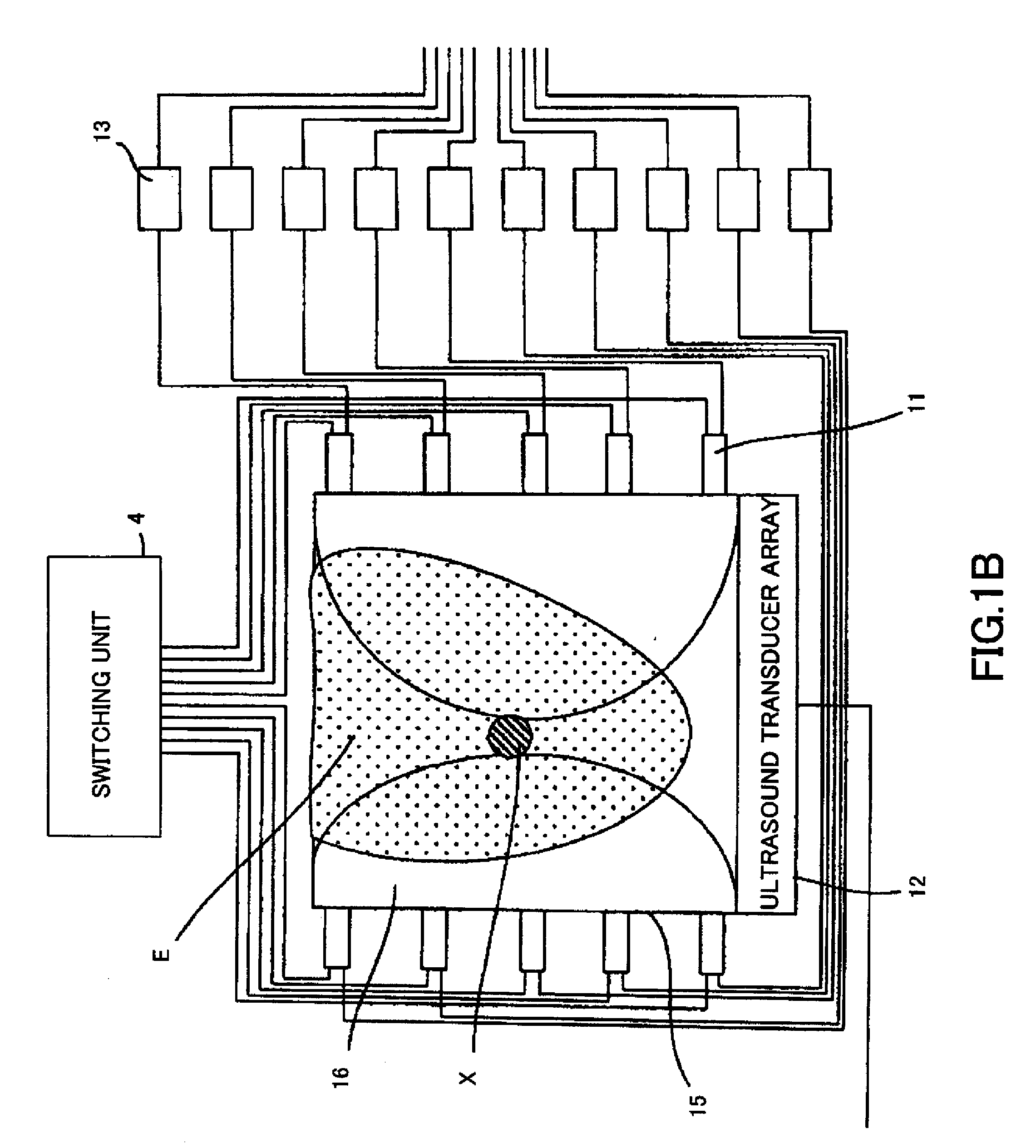
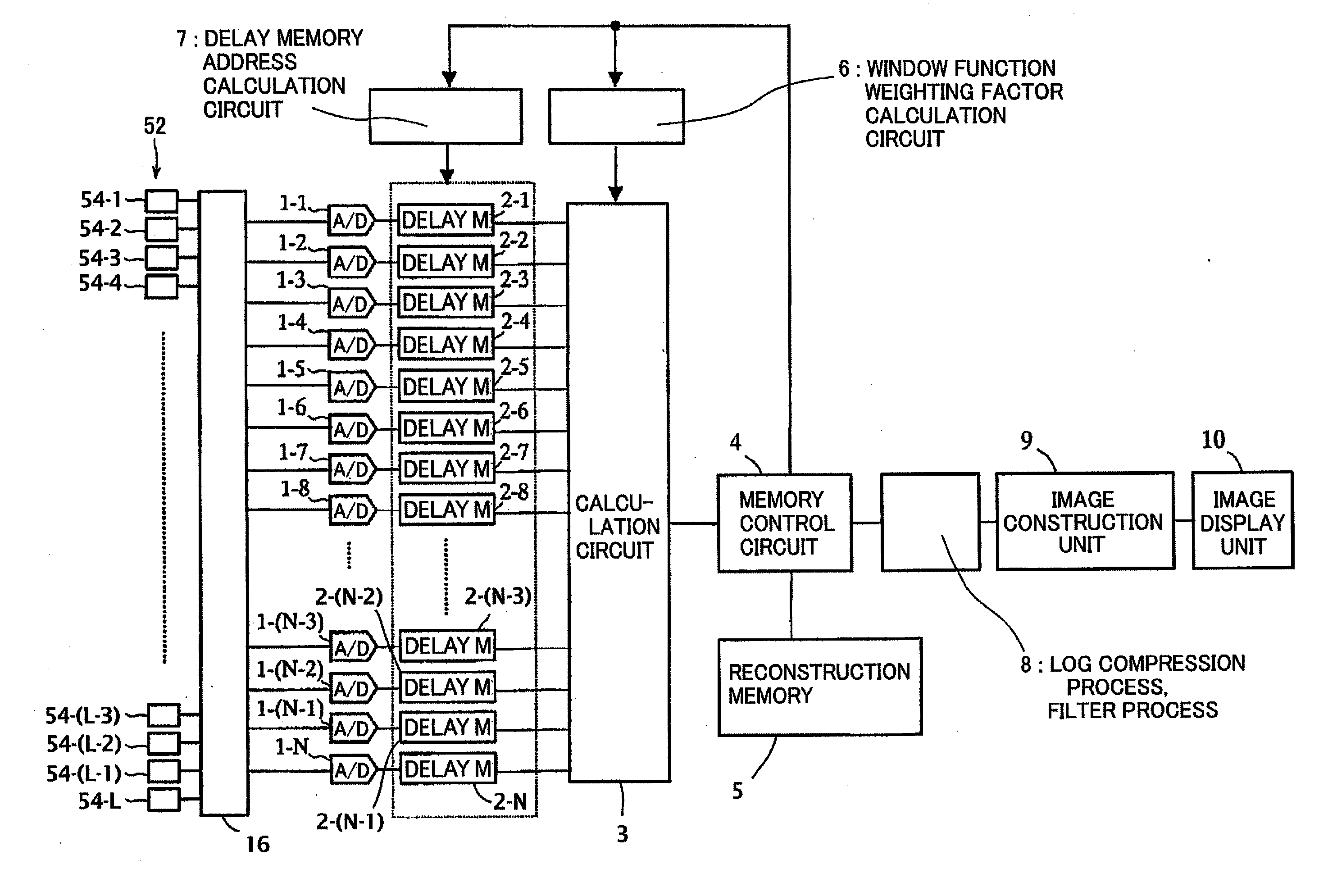
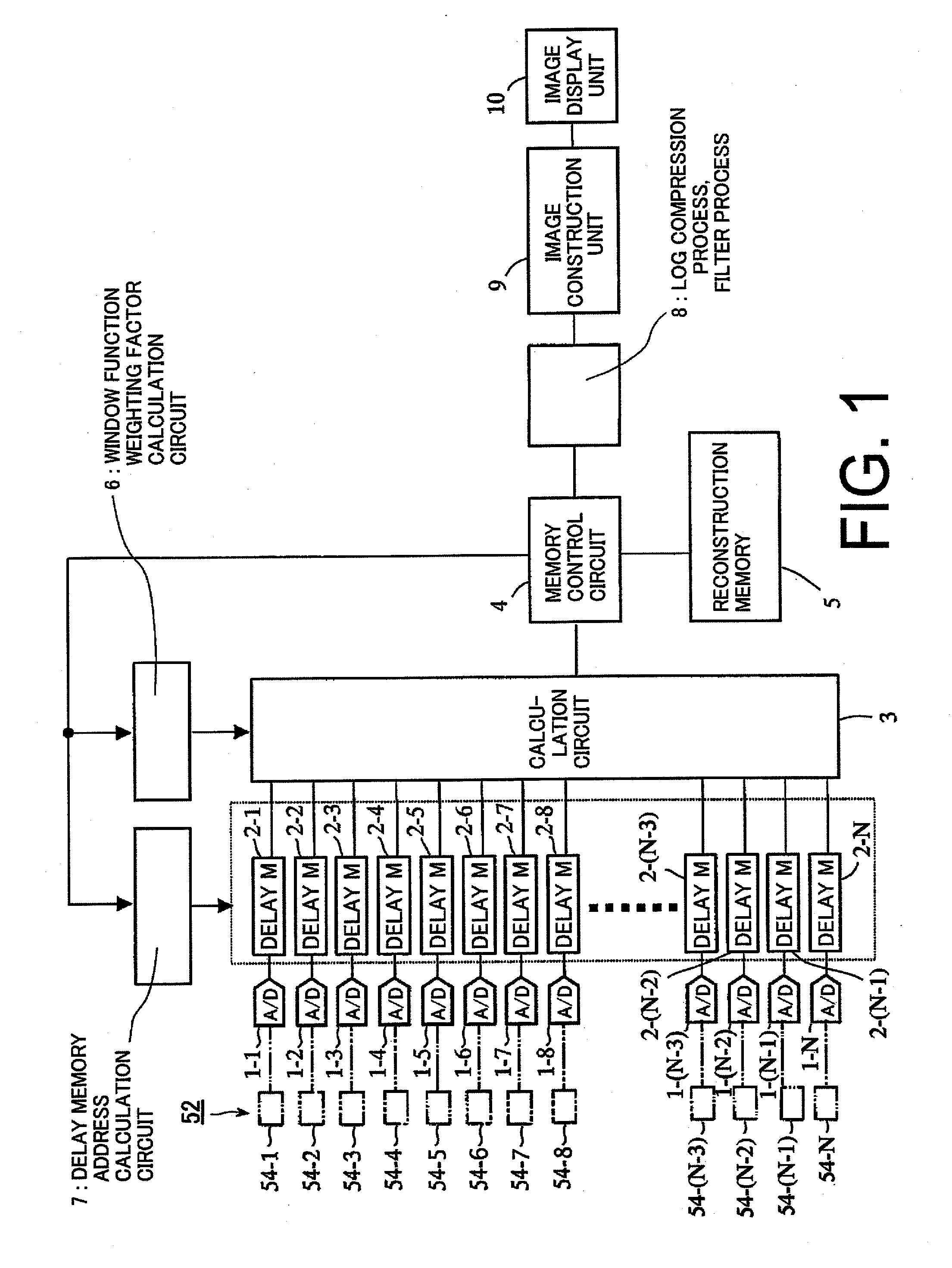
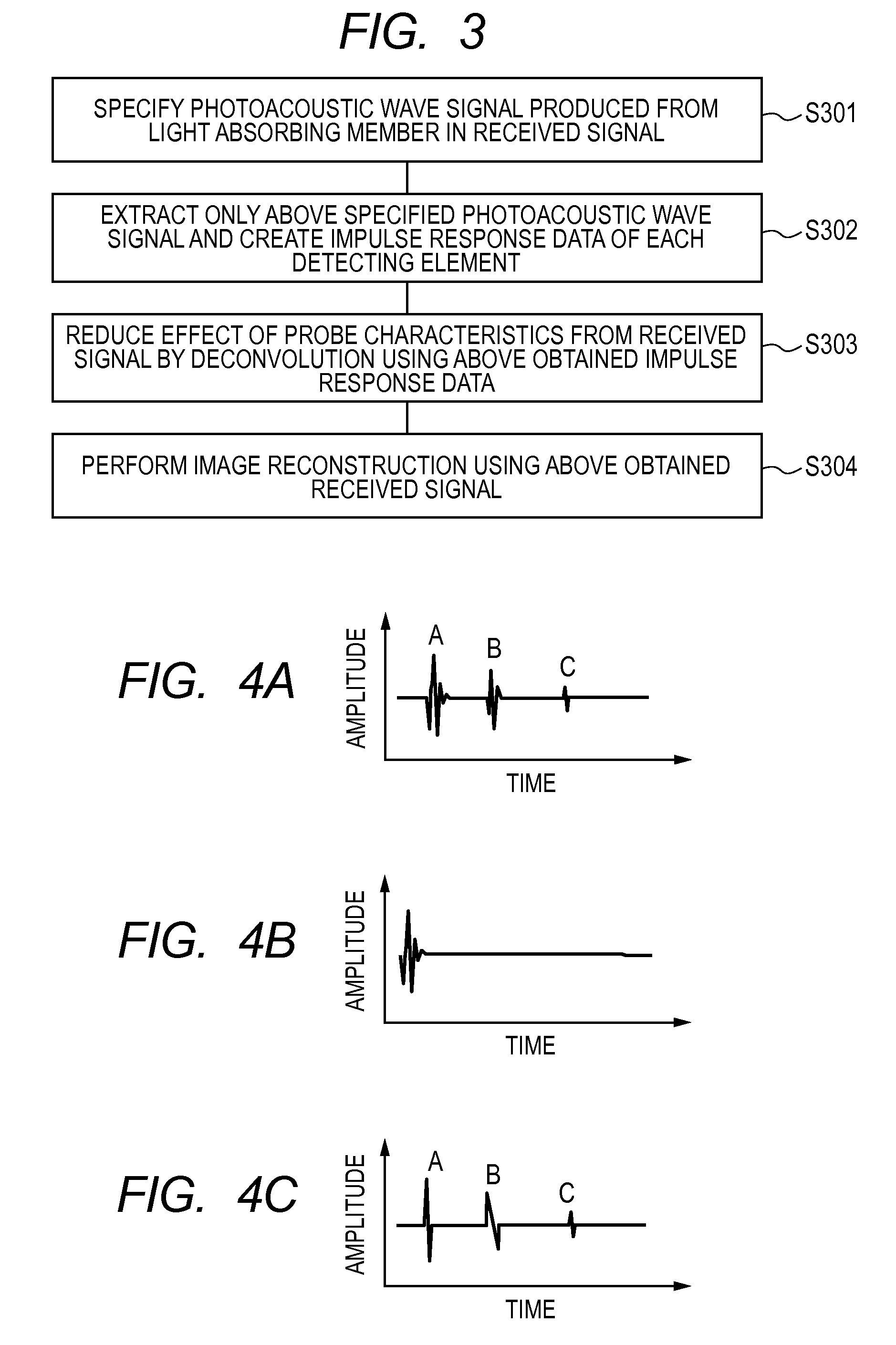
Received data processing apparatus of photoacoustic tomography
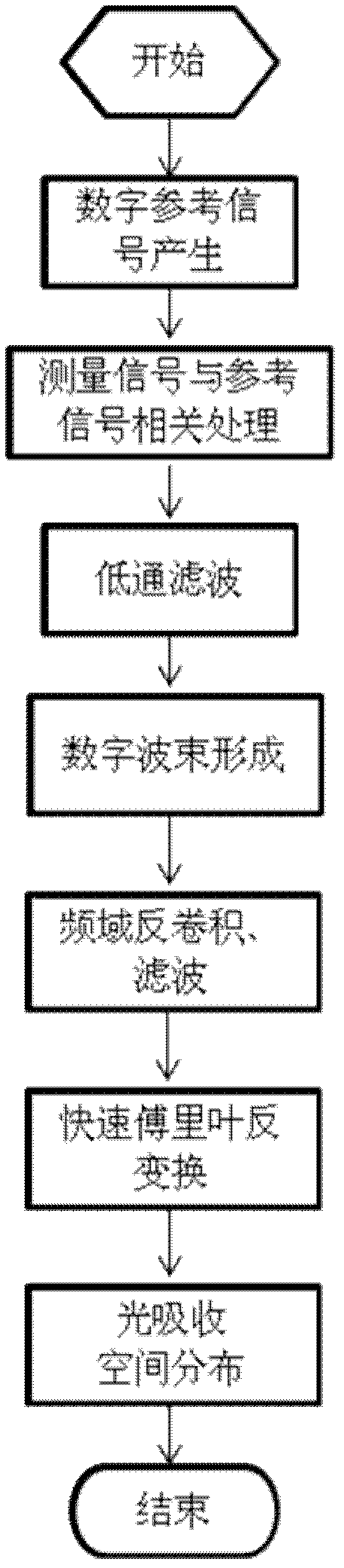
ActiveUS20110128816A1Increase in sizeIncrease equipment costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using tomographyDelay and sumAcoustic wave
There is provided a received data processing apparatus of photoacoustic tomography including a minimum constitution unit data composition unit that sequentially reads receiving digital signals from first storage units and composes minimum constitution unit data of the acoustic wave of the minimum constitution units by performing a delay-and-sum process; a second storage unit that stores the minimum constitution unit data of the entire region of the specimen; an image construction unit that constructs an image of the specimen based on the minimum constitution unit data stored in the second storage unit; and a control unit that sequentially stores the minimum constitution unit data calculated by the minimum constitution unit data composition unit in the second storage unit and reads the stored minimum constitution unit data of the entire region of the specimen to transmit the minimum constitution unit data to the image construction unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Measurement method and measurement apparatus
InactiveUS7898649B2Easy to measureHigh resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMeasurement deviceOptical tomography
A measurement method of measuring a spectroscopic characteristic inside of a scattering medium includesa first step of measuring the spectroscopic characteristic of the scattering medium by using diffuse optical tomography by irradiating light into the scattering medium, a second step of measuring the spectroscopic characteristic of the scattering medium by using acousto-optical tomography or photo acoustic tomography by irradiating light into the scattering medium, and a third step of making an assumption of a distribution of the spectroscopic characteristic inside of the scattering medium and of changing the assumption such that a difference between a predicted value of the spectroscopic characteristic derived from the assumption and a measured value obtained in the first step can fall upon a permissible range. The third step uses data obtained in the second step for at least one of the parameter: an initial value, a constraint condition, or a boundary condition.
Owner:CANON KK
Measurement apparatus
InactiveUS8326567B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInflated body pressure measurementMeasurement devicePhotoacoustic tomography
Owner:CANON KK
Quantitative optoacoustic tomography with enhanced contrast
InactiveUS20070238958A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyOptoacoustic imaging
Provided herein is an optoacoustic imaging system configured to produce images of one or more objects in a body using at least a maximum angular amplitude probability algorithm to reconstruct the optoacoustic images of the body. In addition the optoacoustic imaging system may be configured to produce 3D maps from the reconstructed optoacoustic images of the body. Also, provided is a method for diagnosing a pathophysiological condition characterized by abnormal optical properties of tissues in a body from maps so produced.
Owner:SENO MEDICAL INSTR
Quantification of optical absorption coefficients using acoustic spectra in photoacoustic tomography
ActiveUS20130199299A1Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFluorescenceOptical absorption coefficient
Accurately quantifying optical absorption coefficient using acoustic spectra of photoacoustic signals. Optical absorption is closely associated with many physiological parameters, such as the concentration and oxygen saturation of hemoglobin, and it can be used to quantify the concentrations of non-fluorescent molecules. A sample is illuminated by, for example, a pulsed laser and following the absorption of optical energy, a photoacoustic pressure is generated via thermo-elastic expansion. The acoustic waves then propagate and are detected by a transducer. The optical absorption coefficient of the sample is quantified from spectra of the measured photoacoustic signals. Factors, such as system bandwidth and acoustic attenuation, may affect the quantification but are canceled by dividing the acoustic spectra measured at multiple optical wavelengths.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method and device for biological tissue photoacoustic tomography
InactiveCN1433739AStrong penetrating powerRadiation damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsFrequency spectrumData acquisition
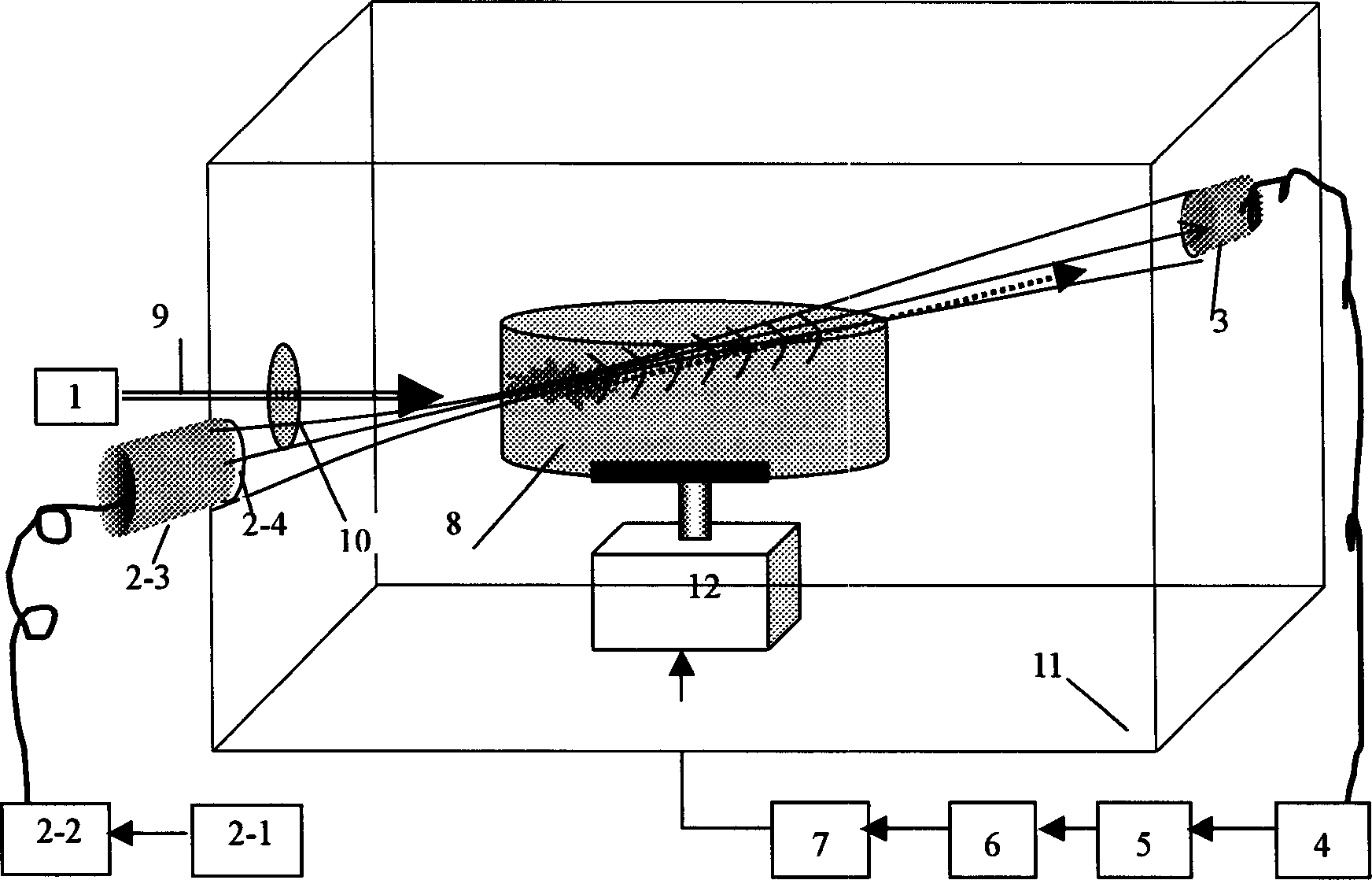
The biological tissue photoacoustic tomography method includes the following steps: (1). making pulse laser come into the biological tissue to produce photoacoustic signal; (2). making a beam of detection focus ultrasonic wave come into the photoacoustic zone, and interacting with photoacoustic signal to form superposition of the above-mentioned two signal; (3). receiving and measuring the superimposed signal; (4) making frequency spectrum separation by using computer, extracting and storing photoacoustic signal; and (5). making filtering and integration treatment of the photoacoustic signal,and utilizing the leaner projection algorithm to implement tissue chromatographic imaging. Said equipment includes laser, ultrasonic wave generator component, acoustic sgnal measuring component, signal amplifier, data collecting card, three-D electric rotating platform and computer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and Apparatus for Tomographic Imaging of Absolute Optical Absorption Coefficient in Turbid Media Using Combined Photoacoustic and Diffusing Light Measurements
InactiveUS20100208965A1Careful calibrationEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostics using tomographyWave equationAbsorbed energy
Embodiments of the invention pertain to methods for imaging a light absorption coefficient distribution. Embodiments of the subject method can be implemented without knowing the strength of incident light in advance and without requiring careful calibrations in the non-scattering medium. Embodiments of the method can combine conventional photoacoustic tomography (PAT) with diffusing light measurements coupled with an optimization procedure based on the photon diffusion equation. Images of absorbing targets as small as 0.5 mm in diameter embedded in a 50 mm diameter background medium can be quantitatively recovered. Small targets with various optical contrast levels relative to the background can be detected well. Embodiments of the subject reconstruction method can include first obtaining the map of absorbed optical energy density. Embodiments can obtain the map of absorbed optical energy density through a model-based reconstruction algorithm that is based on a finite element solution to the photoacoustic wave equation in frequency domain subject to the radiation or absorbing boundary conditions (BCs). The distribution of optical fluence can then be obtained. Embodiments can obtain the distribution of optical fluence using the photon diffusion equation based optimization procedure. The distribution of optical absorption coefficient can then be recovered from the distribution of optical fluence and the absorbed energy density.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
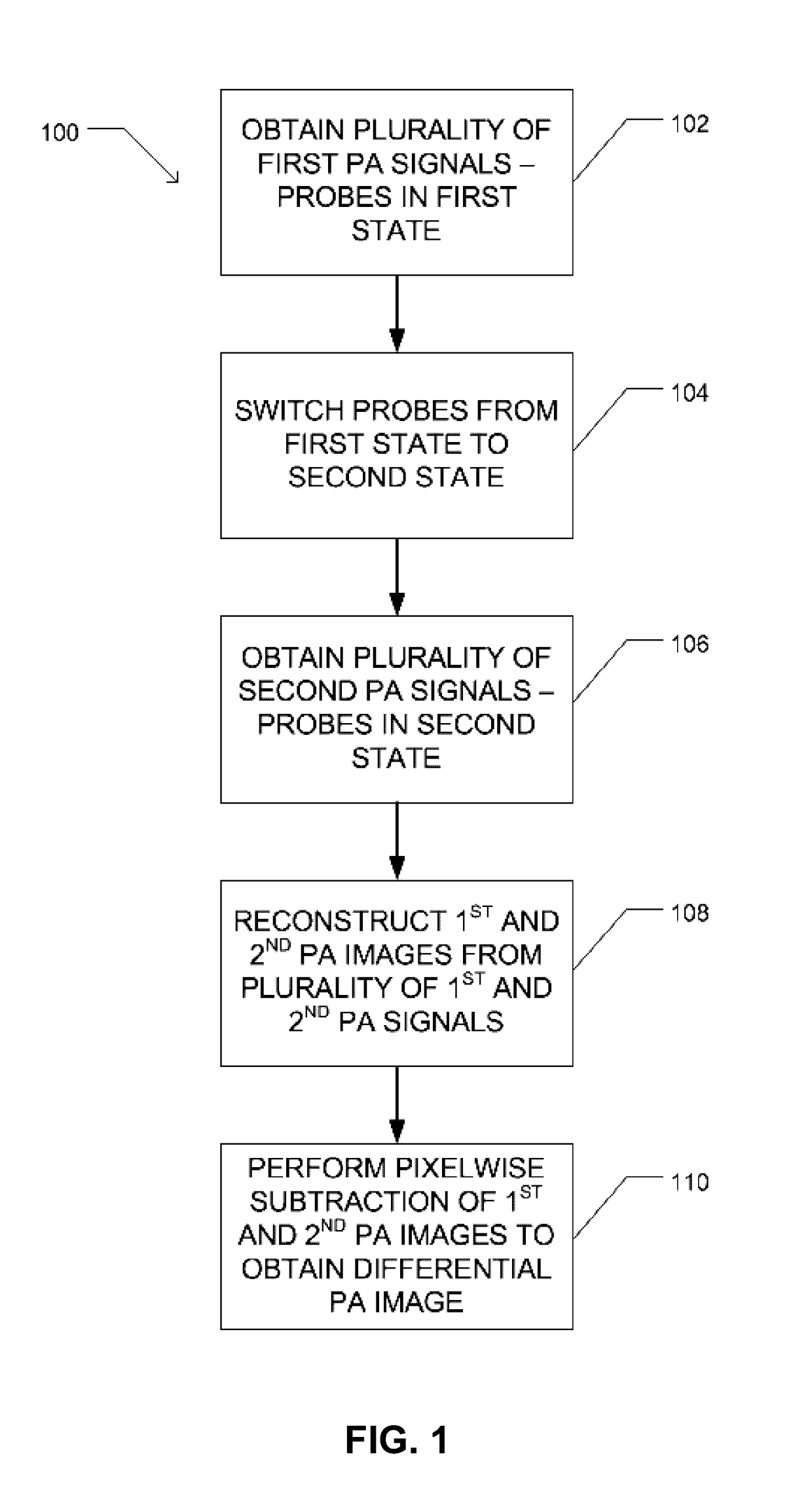
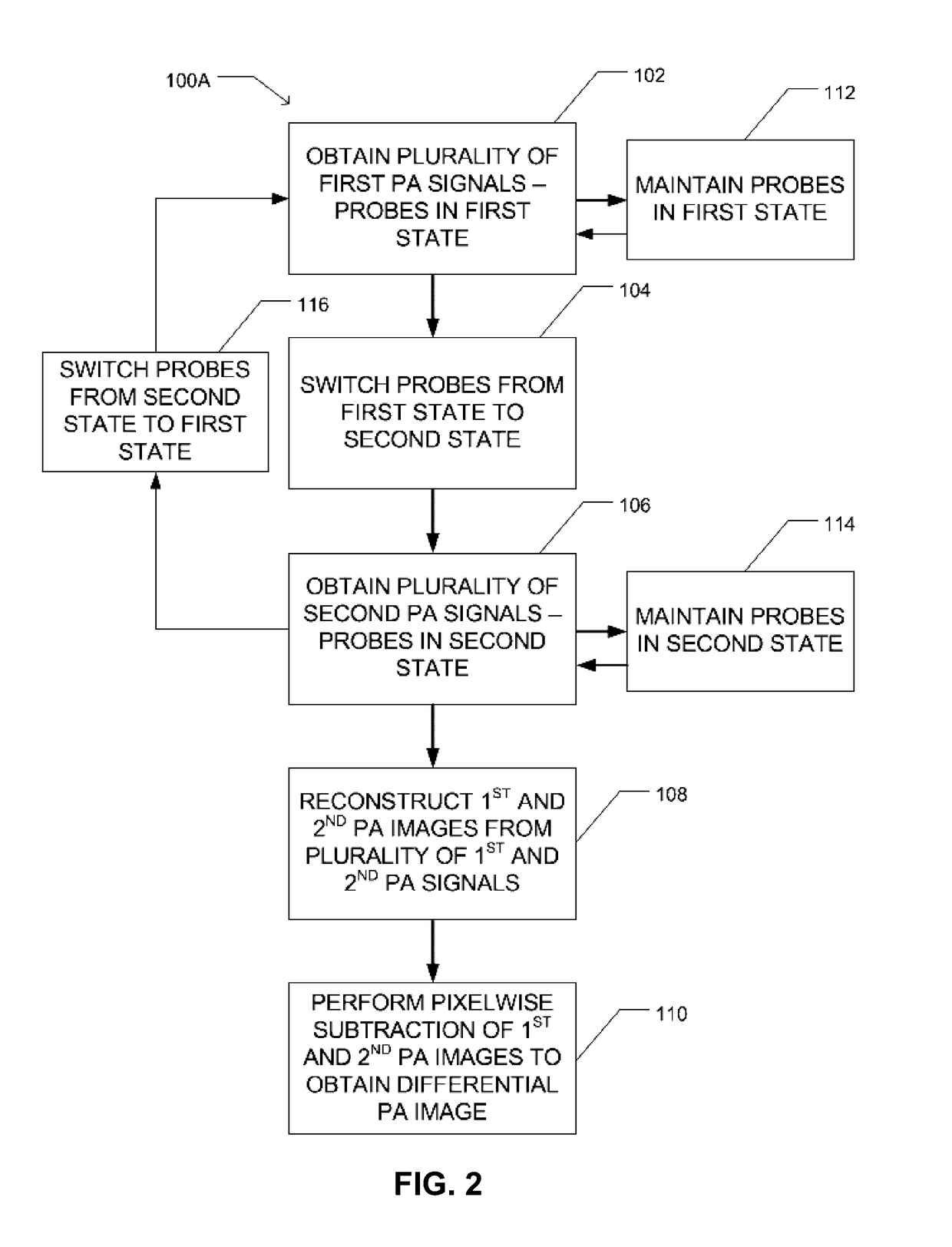
Reversibly switchable photoacoustic imaging systems and methods
InactiveUS20170065182A1Medical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringImage resolutionPhotoacoustic tomography
Reversibly switchable photoacoustic tomography (RS-PAT), a photoacoustic technique with enhanced sensitivity and resolution, is disclosed. RS-PAT utilizes a subtractive process for the formation of a photoacoustic image of a region containing a plurality of switchable photoacoustic probes. In various aspects, the photoacoustic detection in RS-PAT imaging occurs minimally twice: a first image obtained when the photoacoustic probe is in active (absorbing or ON) state and a second image obtained when the photoacoustic probe is in an inactive (less-absorbing or OFF) state. Subtraction of the second image from the first image is used to obtain the RS-PAT image.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV +1
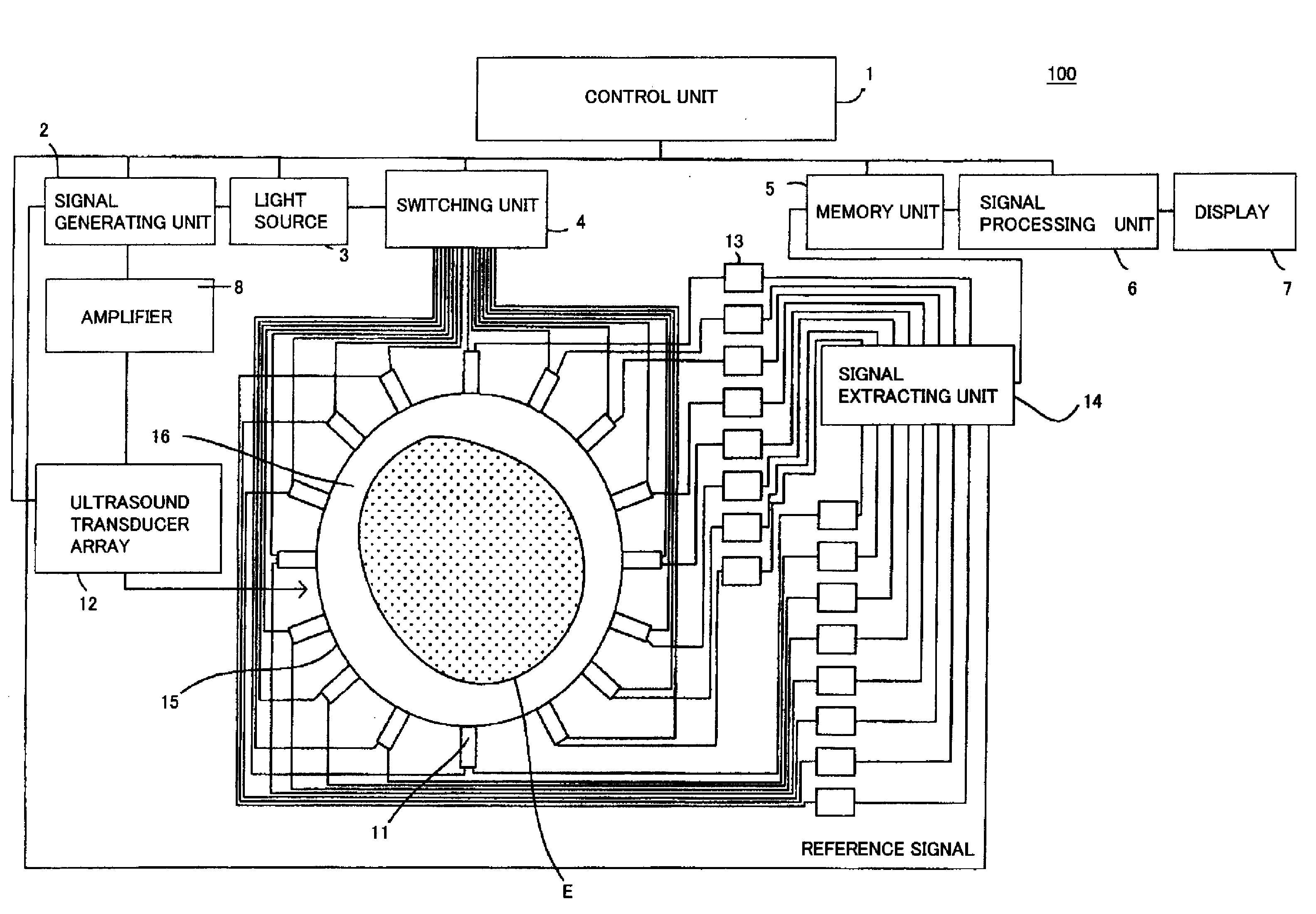
Subject information acquiring device and subject information acquiring method
InactiveUS20130245420A1Reduce image quality degradationDiagnostic signal processingSensorsInformation gainAcoustic wave
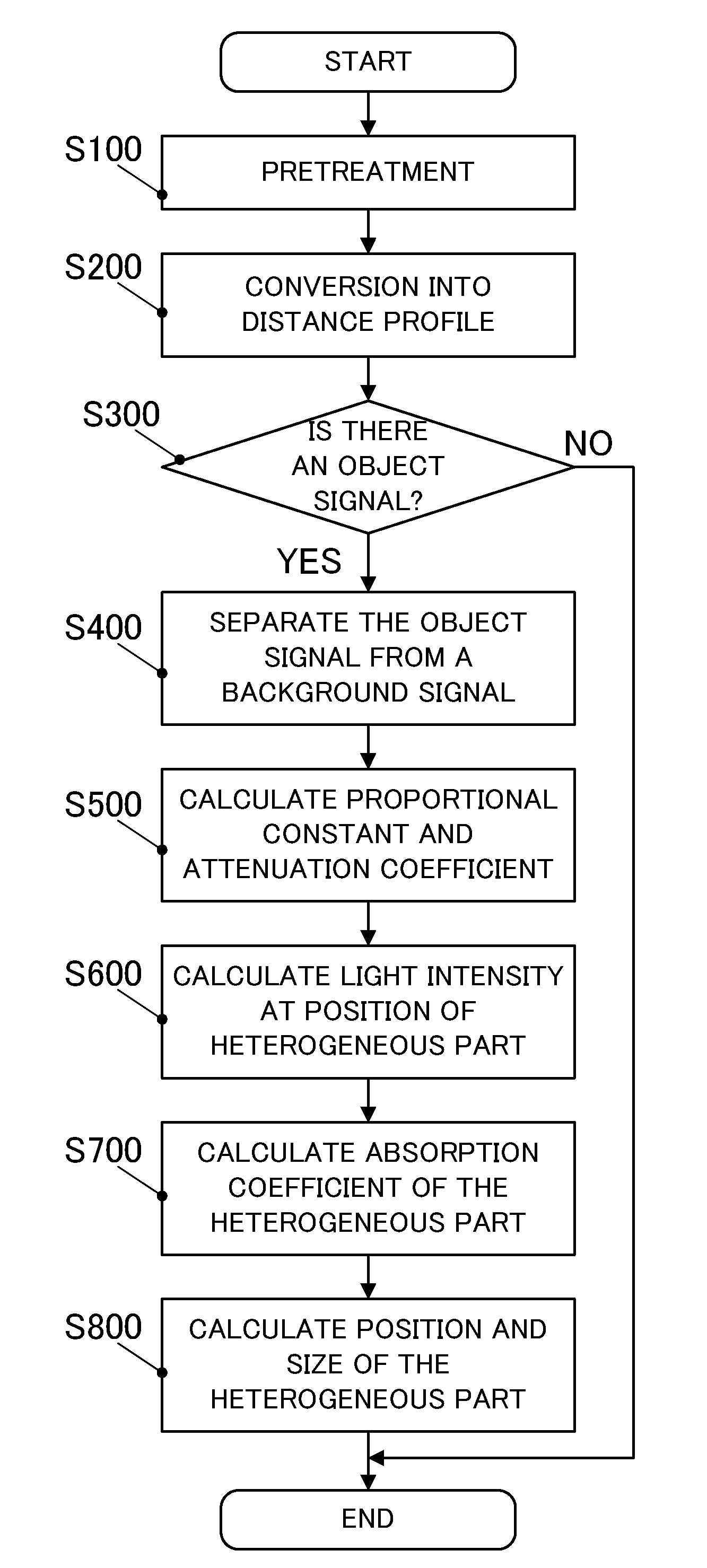
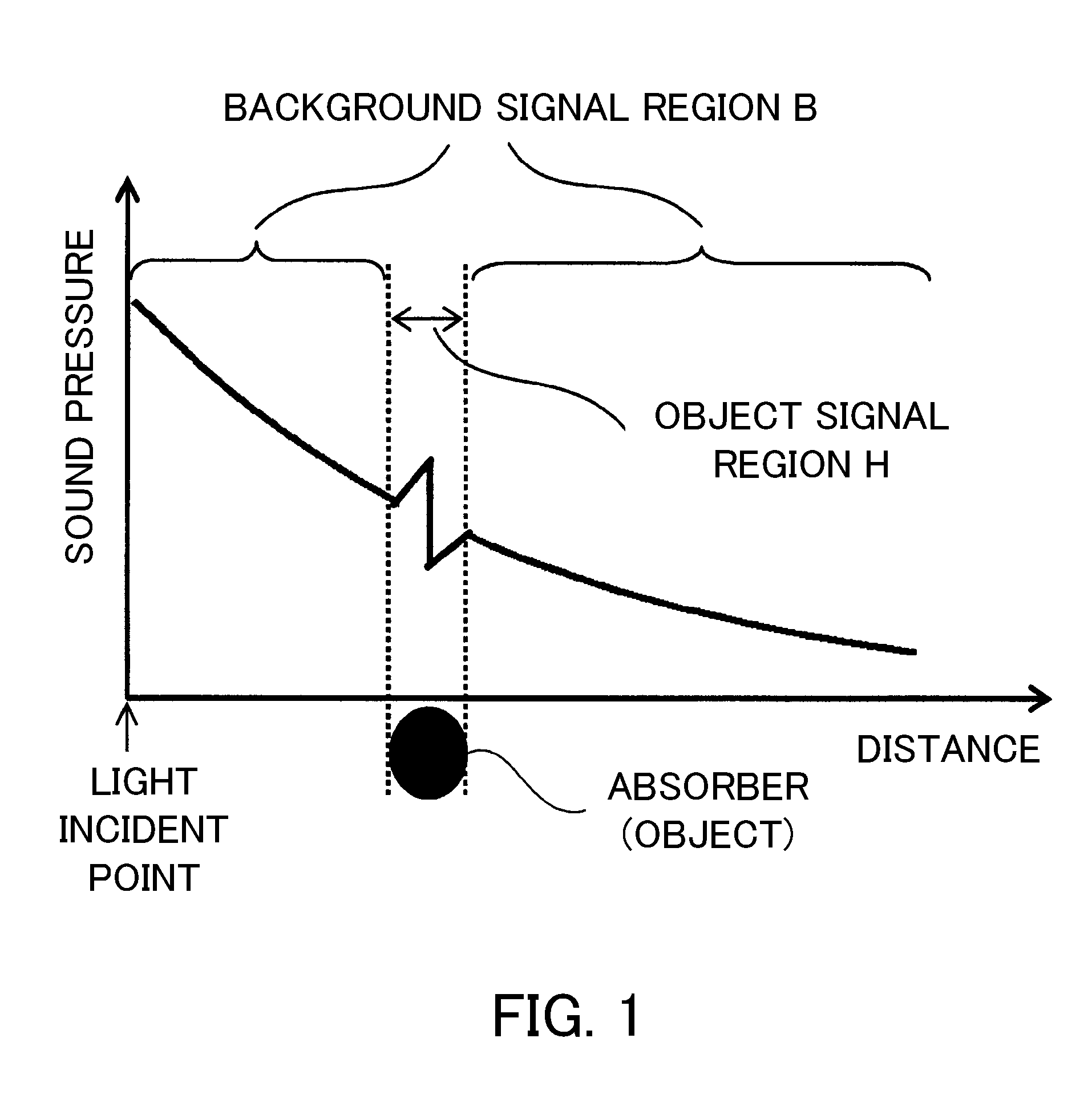
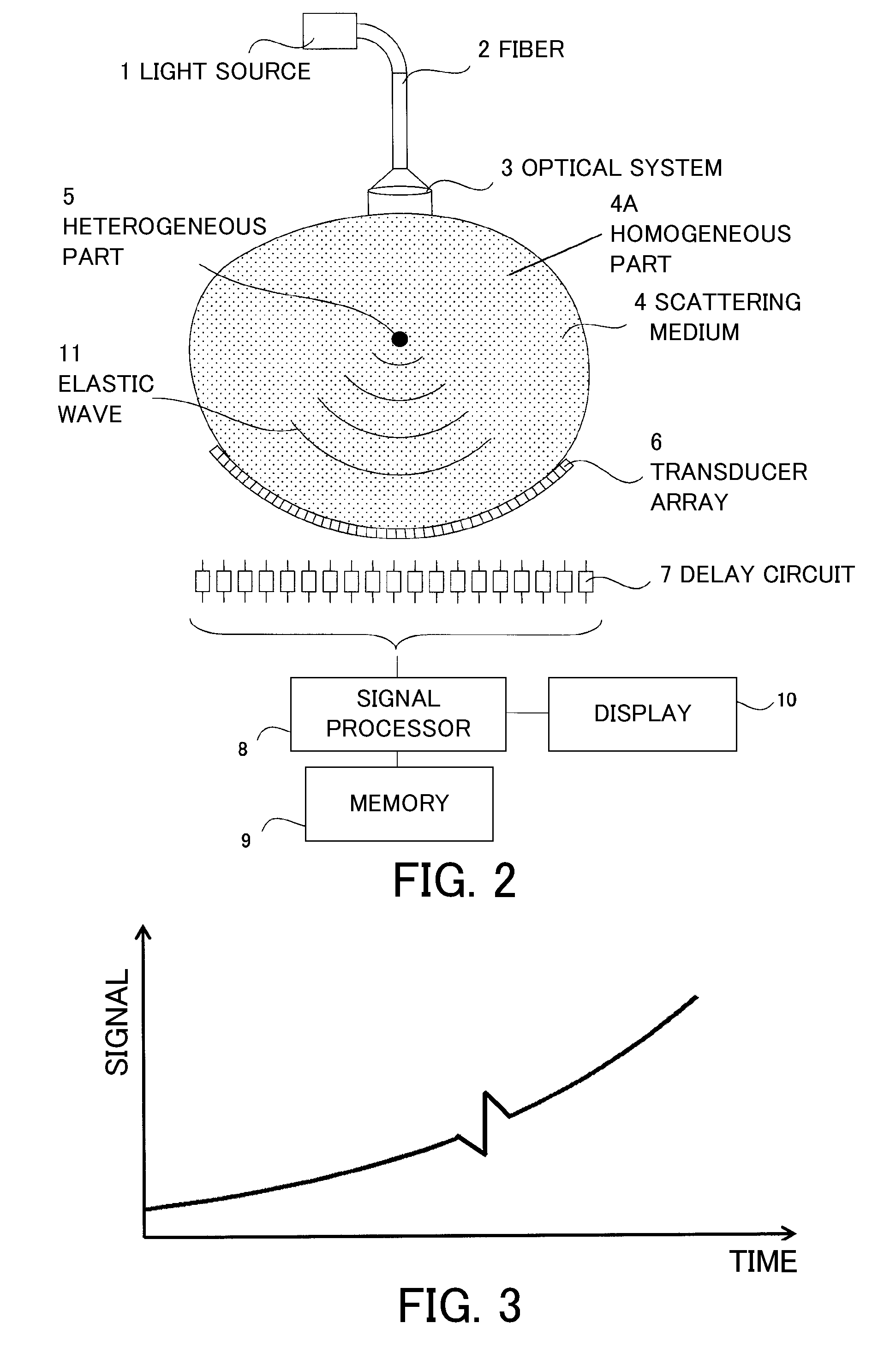
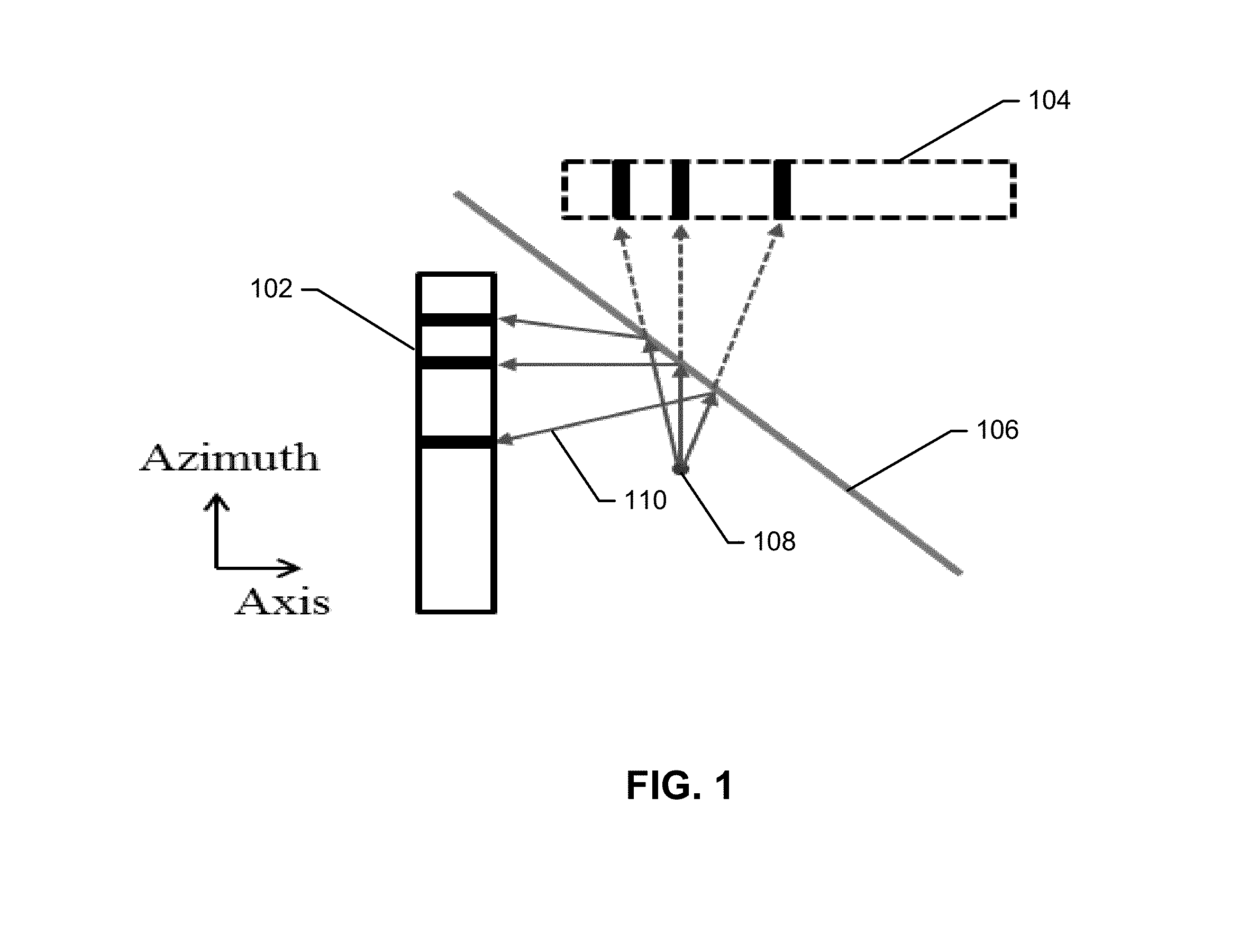
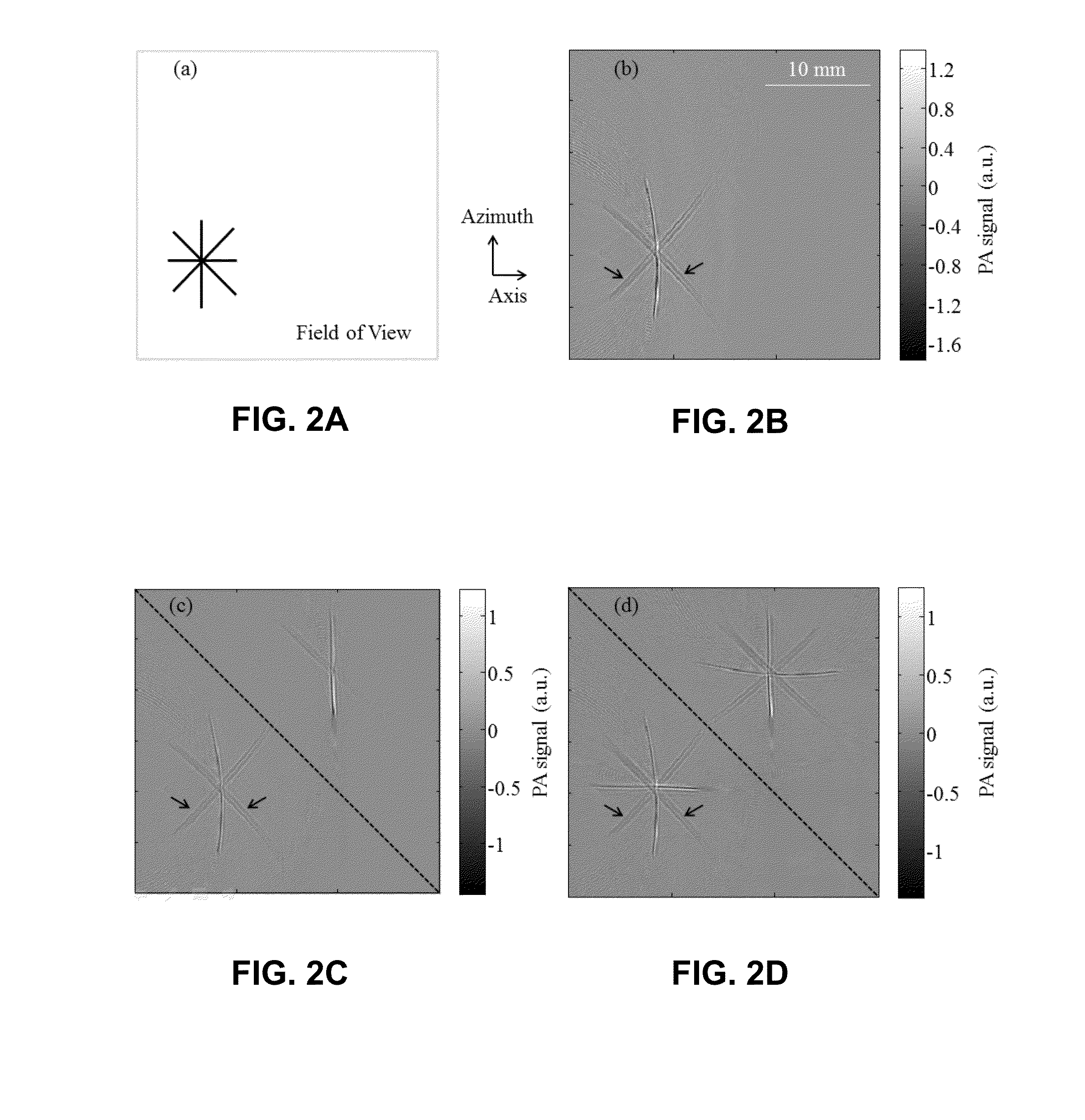
A subject information acquiring device which has: an light absorbing member provided outside a subject; a light source radiating pulsed light on the subject and the light absorbing member; a detector detecting an acoustic wave produced from the subject and the light absorbing member by means of the pulsed light; and a signal processing unit acquiring subject information using a detection signal, and the signal processing unit calculates a second detection signal by specifying a signal resulting from an acoustic wave produced from the light absorbing member in a first detection signal, acquiring impulse response data using the specified signal, and deconvoluting the first detection signal using the impulse response data, and acquires the subject information using the second detection signal, can reduce image deterioration due to probe characteristics even when an impulse response of a probe is not measured in advance in a photoacoustic tomography.
Owner:CANON KK
Photoacoustic computed tomography with an acoustic reflector
ActiveUS20160262628A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAcoustic sensorsSonificationComputing tomography
Systems and methods for improving limited-view photoacoustic tomography using an acoustic reflector are described. In particular, an acoustic reflector and ultrasonic transducer array are integrated to provide a virtual array that enhances the field of view of the ultrasonic transducer array, thereby improving the quality of photoacoustic tomography images obtained using the systems and methods described herein.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
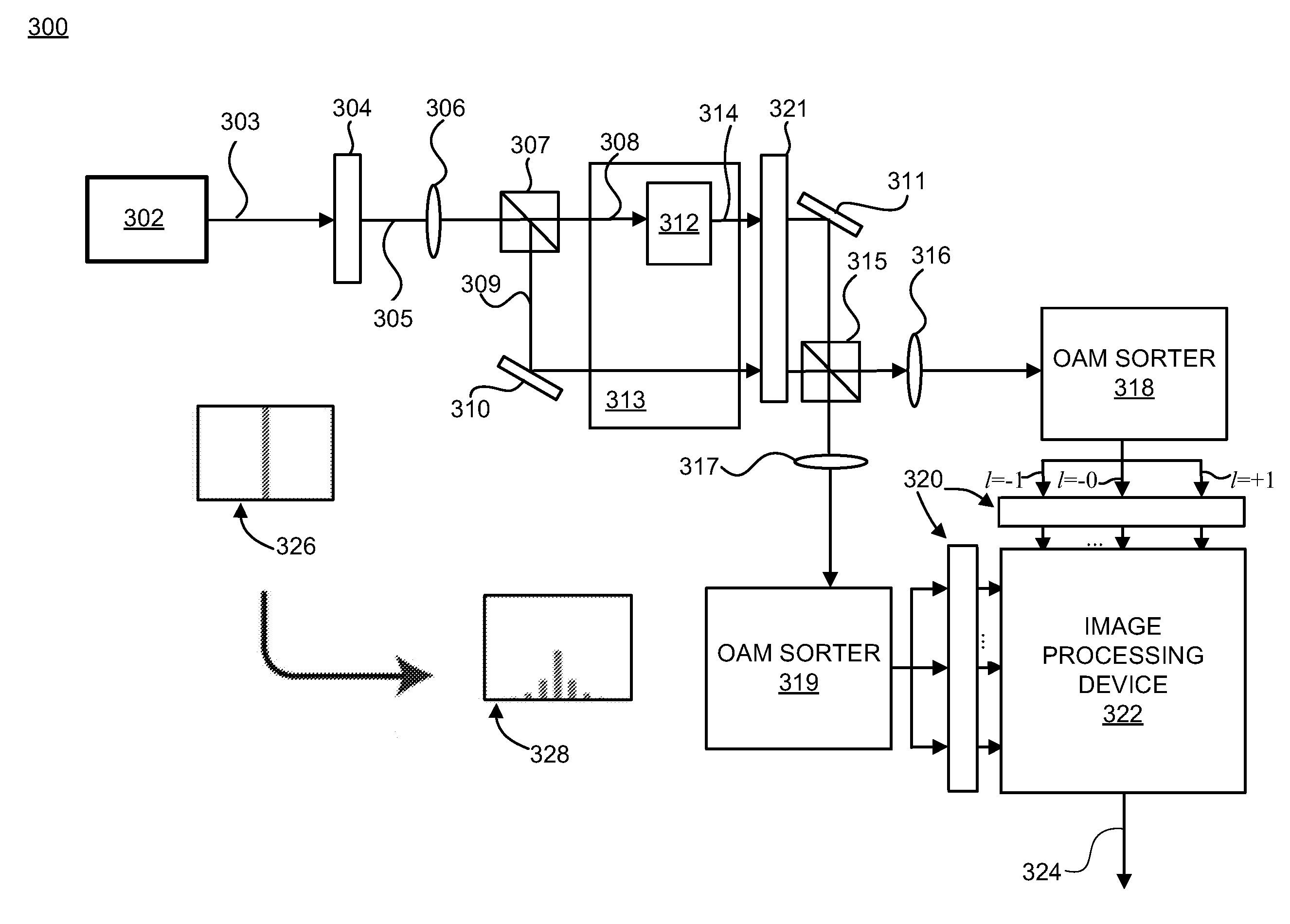
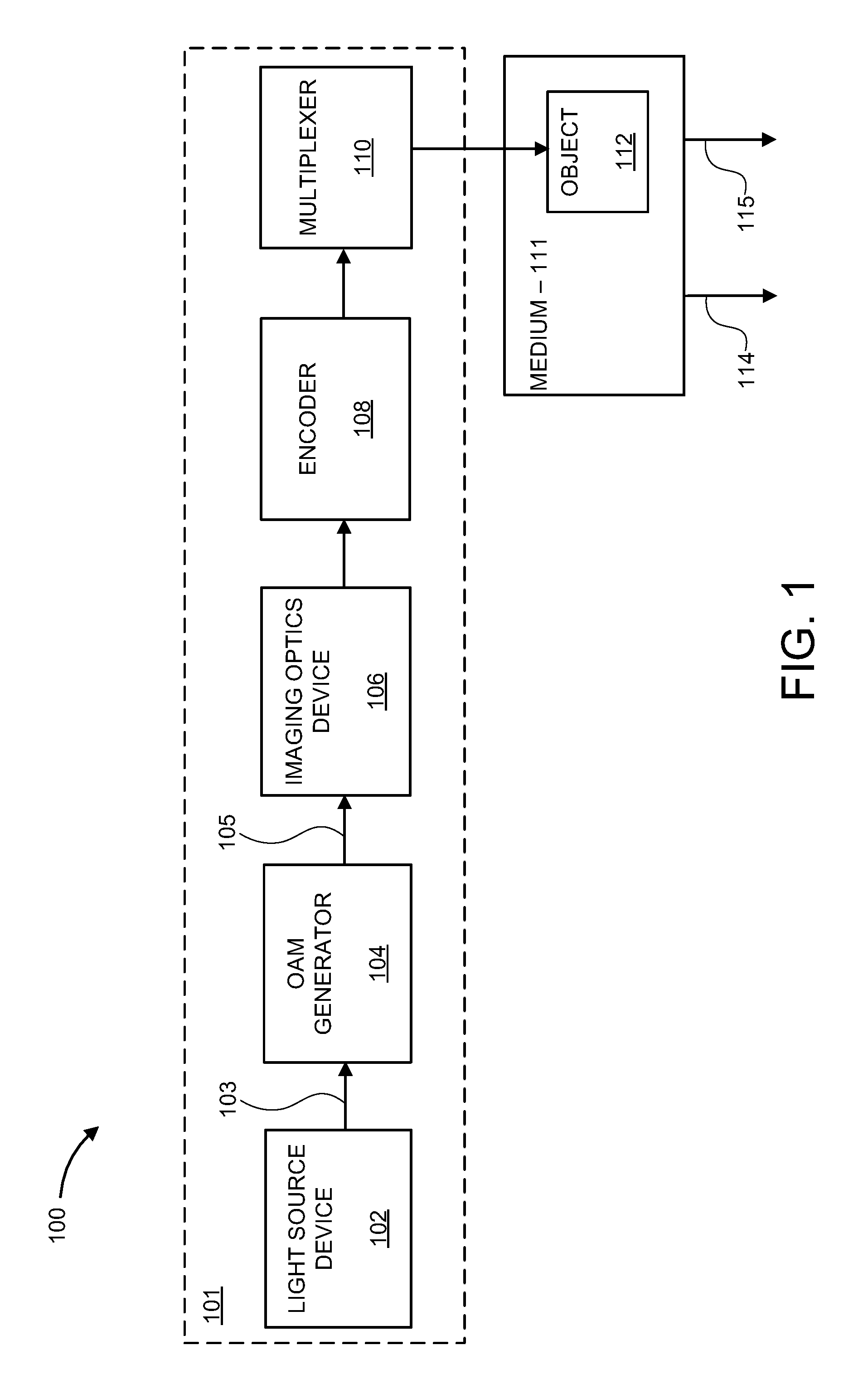
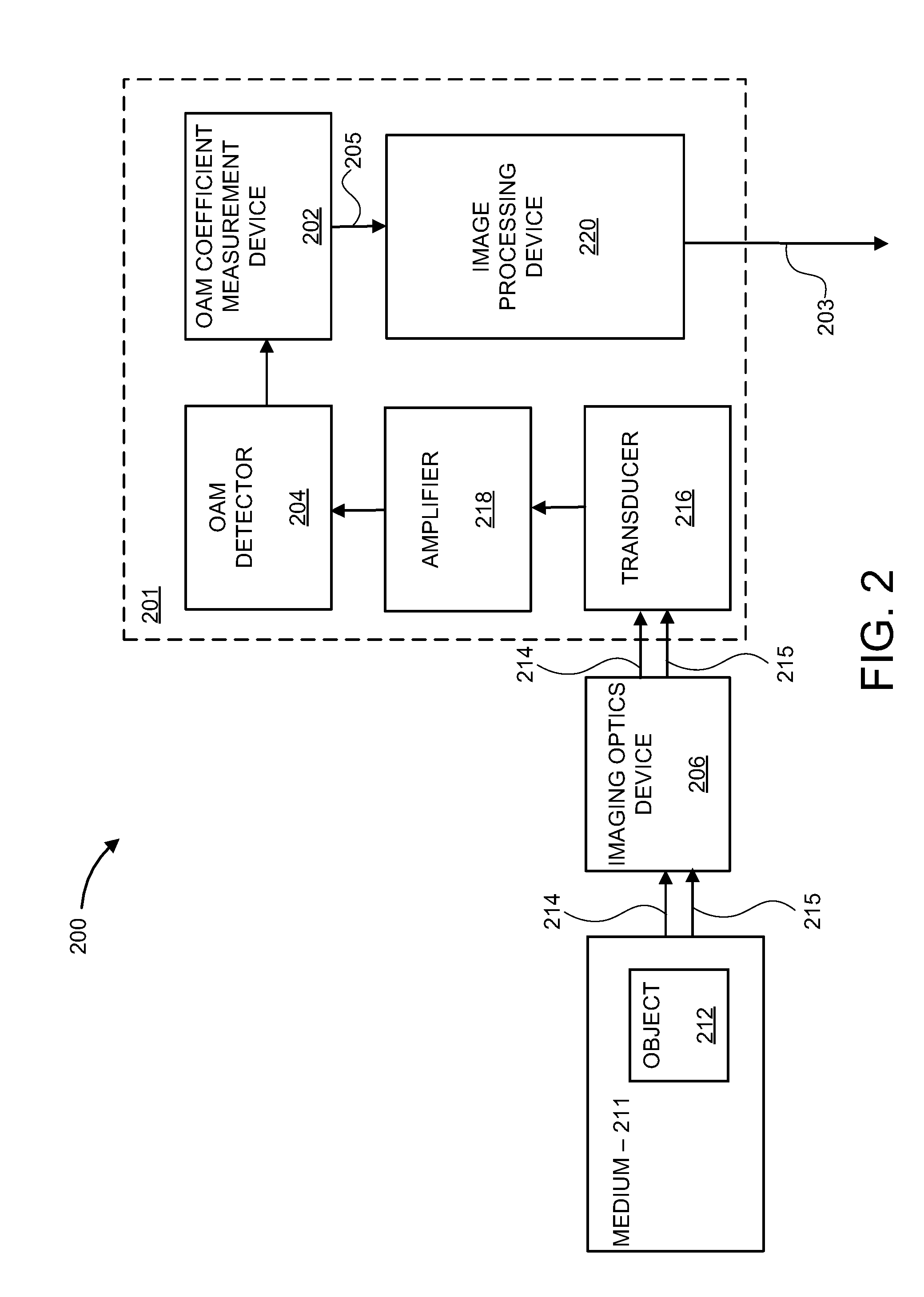
Method and apparatus for photoacoustic tomography using optical orbital angular momentum (OAM)
ActiveUS20160198954A1High resolutionMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringObject basedLight beam
A method and system for remote sensing. The method includes applying an orbital angular momentum (OAM) mode on a light beam to generate an OAM light beam having an optical OAM spectrum, exposing a target object to the OAM light beam such that the target object absorbs energy of the OAM light beam to generate ultrasonic emissions, the ultrasonic emissions having a reflected OAM spectrum associated with the target object, and generating a high resolution image of the target object based on the reflected OAM spectrum.
Owner:NEC CORP
Double-focusing ultrasonic probe and sparse array photoacoustic tomography imaging system
ActiveCN105595964ALow costImprove image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic signal processingSonificationData acquisition
The invention relates to a double-focusing ultrasonic probe and sparse array photoacoustic tomography imaging system. Each probe comprises a concave detection face. The numerical value hole diameter of each concave detection face in the first direction is larger than that of the concave detection face in the second direction. A signal receiving angle of each concave detection face in the first direction is larger than that of the concave detection face in the second direction. The focused region length of each concave detection face in the second direction is larger than that of the concave detection face in the first direction. The first direction is perpendicular to the second direction. Each probe has a large signal receiving angle on an imaging fracture surface, and therefore the quality of an image reconstructed by a compressed sensing image reconstructing method under a low sampling rate can be improved. Meanwhile, an annular probe array can be formed in a sparse distribution mode, and cost of the imaging system can be reduced. Data acquisition amount needed by image reconstruction can be reduced, and therefore data acquisition speed and imaging speed are increased.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
System and method for diffused optical tomography and photoacoustic tomography combined measurement
InactiveCN104873175AQuality improvementMake up for spatial resolutionDiagnostic signal processingComputerised tomographsOptical tomographyAutomatic control
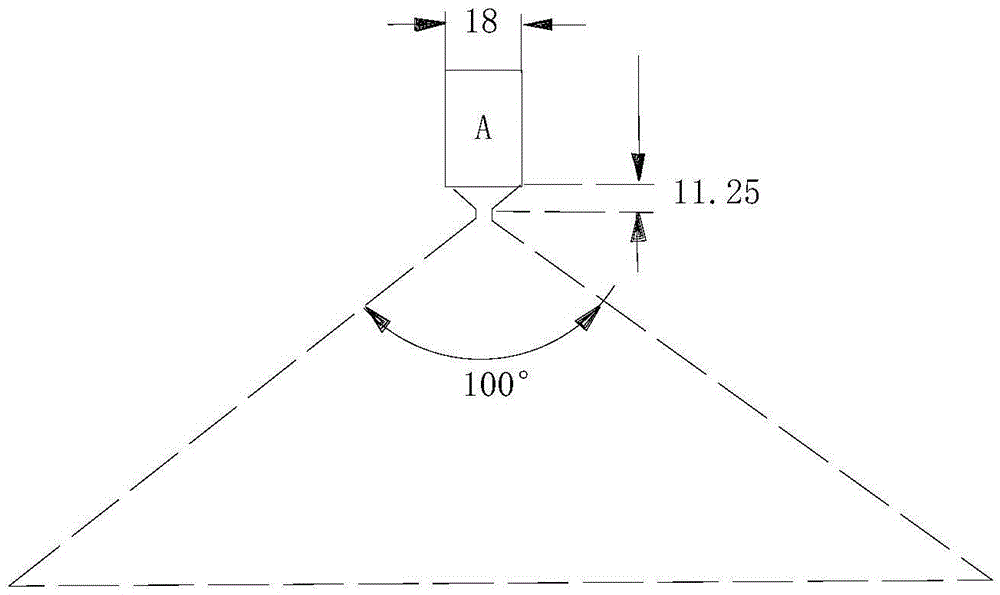
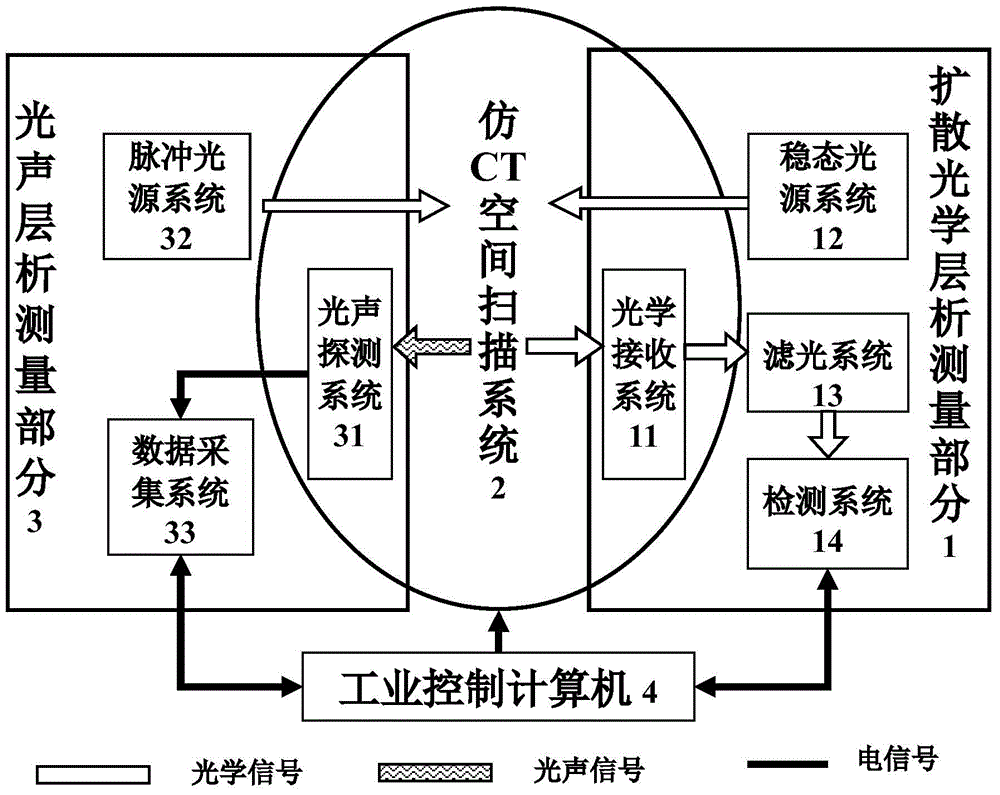
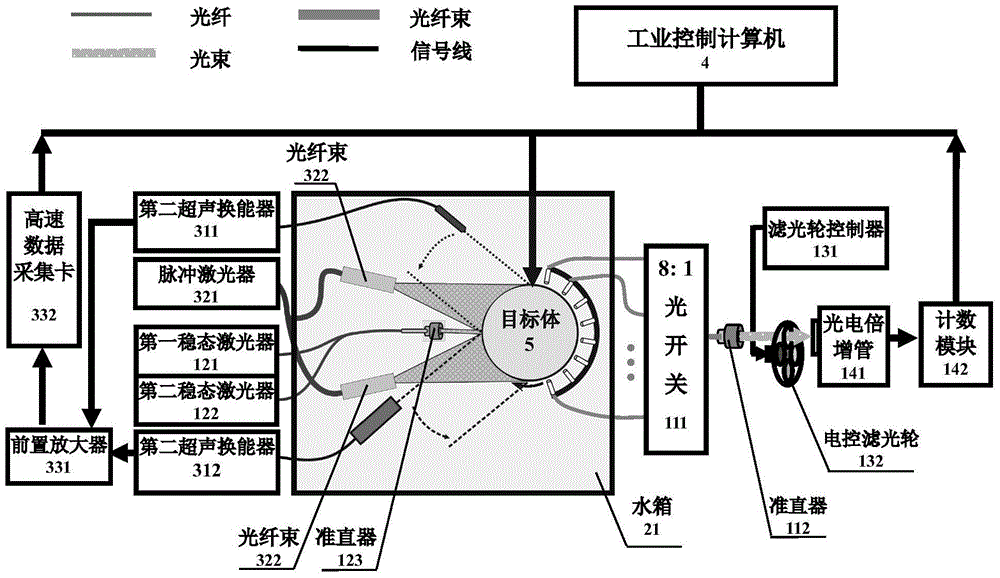
The invention discloses a system and method for diffused optical tomography and photoacoustic tomography combined measurement. The system comprises a diffused optical tomography measurement part (1), an imitating CT space scanning system (2), a photoacoustic tomography measurement part (3) and an industrial control computer (4), wherein the diffused optical tomography measurement part (1) and the photoacoustic tomography measurement part (3) are jointly connected with the imitating CT space scanning system (2) to form an integrated multi-mode measurement system, and system automatic control software of the industrial control computer (4) is used for achieving automatic detection and data collection of a diffused optical signal and a photoacoustic signal. Compared with the prior art, by means of the system and method for the diffused optical tomography and photoacoustic tomography combined measurement, the defects of an existing single-mode imaging technique are overcome, the defect that for the prior art, the spatial resolution and the quantitative feature cannot be achieved simultaneously is overcome, the imaging method can achieve the spatial resolution of the photoacoustic tomography technique and the quantitative precision of the diffused optical tomography technique, and therefore the high-quality optical parameter imaging function is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Quantification of optical absorption coefficients using acoustic spectra in photoacoustic tomography
ActiveUS9086365B2Vibration measurement in solidsMedical imagingFluorescenceOptical absorption coefficient
Accurately quantifying optical absorption coefficient using acoustic spectra of photoacoustic signals. Optical absorption is closely associated with many physiological parameters, such as the concentration and oxygen saturation of hemoglobin, and it can be used to quantify the concentrations of non-fluorescent molecules. A sample is illuminated by, for example, a pulsed laser and following the absorption of optical energy, a photoacoustic pressure is generated via thermo-elastic expansion. The acoustic waves then propagate and are detected by a transducer. The optical absorption coefficient of the sample is quantified from spectra of the measured photoacoustic signals. Factors, such as system bandwidth and acoustic attenuation, may affect the quantification but are canceled by dividing the acoustic spectra measured at multiple optical wavelengths.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Apparatus and method for performing photoacoustic tomography
InactiveUS20160095520A1Reduce the numberFast imagingMedical imagingMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLight beamElectromagnetic radiation
A method and apparatus are provided for performing photoacoustic tomography with respect to a sample that receives a pulse of excitation electromagnetic radiation and generates an acoustic field in response to said pulse. One embodiment provides an apparatus comprising an acoustically sensitive surface, wherein the acoustic field generated in response to said pulse is incident upon said acoustically sensitive surface to form a signal. The apparatus further comprises a source for directing an interrogation beam of electromagnetic radiation onto said acoustically sensitive surface so as to be modulated by the signal; means for applying a sensitivity pattern to the interrogation beam; and a read-out system for receiving the interrogation beam from the acoustically sensitive surface and for determining a value representing a spatial integral of the signal across the acoustically sensitive surface, wherein said spatial integral is weighted by the applied sensitivity pattern. The apparatus is configured to apply a sequence of sensitivity patterns to the interrogation beam and to determine a respective sequence of values for said weighted spatial integral for generating a photoacoustic image.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
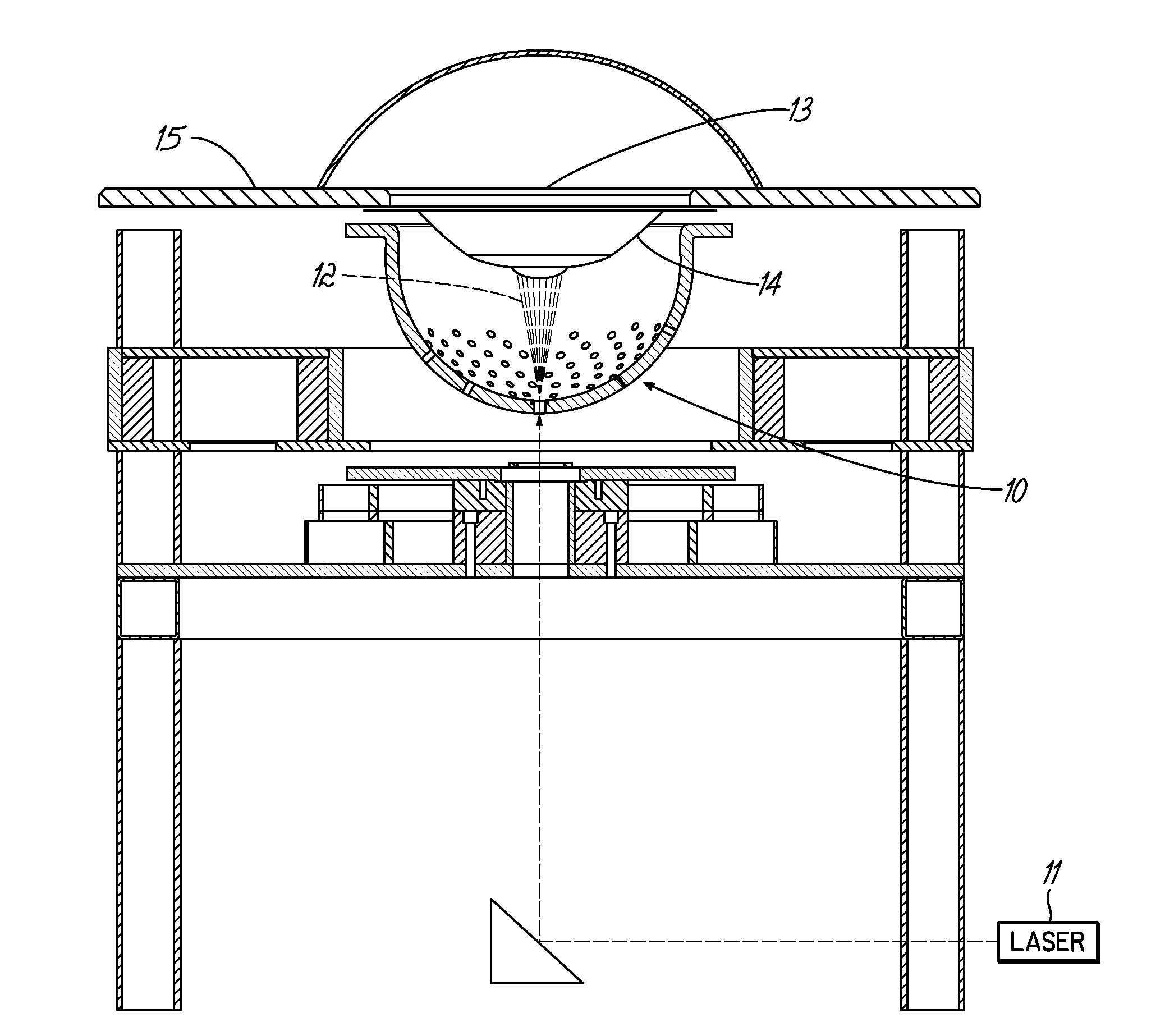
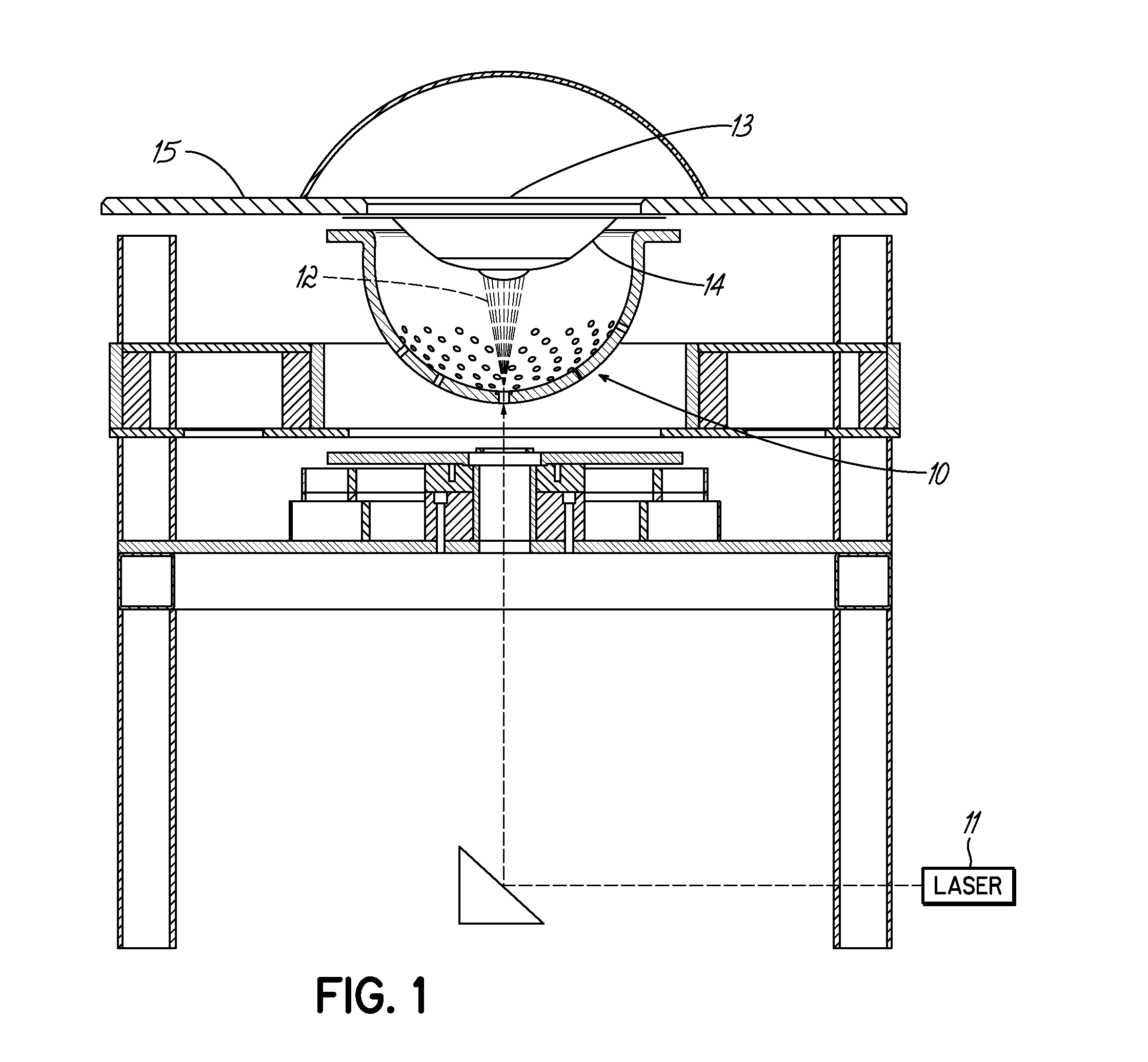
Tri-modal breast imaging system and imaging method thereof
InactiveCN104825180ASuitable for detectionSuitable for therapeuticOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTreatment effect
The invention discloses a tri-modal breast imaging system and an imaging method thereof.A testing system of the tri-modal breast imaging system comprises a frame, first, second and third lifting platforms, a pressing plate, a transparent plate, an X-ray source, an X-ray detector, an ultrasonic array, a laser, a data collection card, a computer, a refractive divergence component and a motion platform or a transfer platform. By means of integration among three modals including photoacoustic tomography, X-ray breast imaging and ultrasonic imaging, one piece of imaging equipment is adopted for tri-modal breast imaging without changing positions of tissue to be tested. The three modals differ in imaging contrast sources and complement with one another in terms of information. Therefore, non-invasive imaging among the structure, physiological and pathological features and the metabolic function of mammary tissue is carried out after images are filtered, projected and fused so that position and size of a tumor can be accurately determined. The tri-modal breast imaging system is particularly suitable for early detection and continuous monitoring of treatment effect of a breast cancer.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Photoacoustic tomography system combined with acoustical transmission reflector and imaging method thereof
InactiveCN102824185ASmall attenuationReduce lossRadiation diagnosticsLow-density polyethyleneStructure function
The invention discloses a photoacoustic tomography system combined with an acoustical transmission reflector and an imaging method of the photoacoustic tomography system combined with the acoustical transmission reflector. The photoacoustic tomography system comprises a laser light source, a conscope body, the acoustical transmission reflector, an animal platform, a water tank, a detector and a computer. The acoustical transmission reflector is utilized, and a metal-coated LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) material is adopted as the material of the acoustical transmission reflector, so that acoustic impedance similar to that of water is obtained, and further, remarkable ultrasonic reflection is not generated at a water-medium interface; and the material is thin, so that attenuation of ultrasonic waves in the material is lower, loss of the acoustical transmission reflector on the ultrasonic waves is very small, and the transmission of the ultrasonic waves is more convenient. Further, the conscope body is combined with an inverted cone-shaped acoustical transmission reflector, light is focused in a horizontal plane and irradiated onto an animal body to form 360-degree horizontal and uniform irradiation on the animal body, and a uniform and stable light field can be formed in the animal body, so that a reconstructed image can more accurately reflect physiological structure function information in the animal body when the detector is used for detection.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
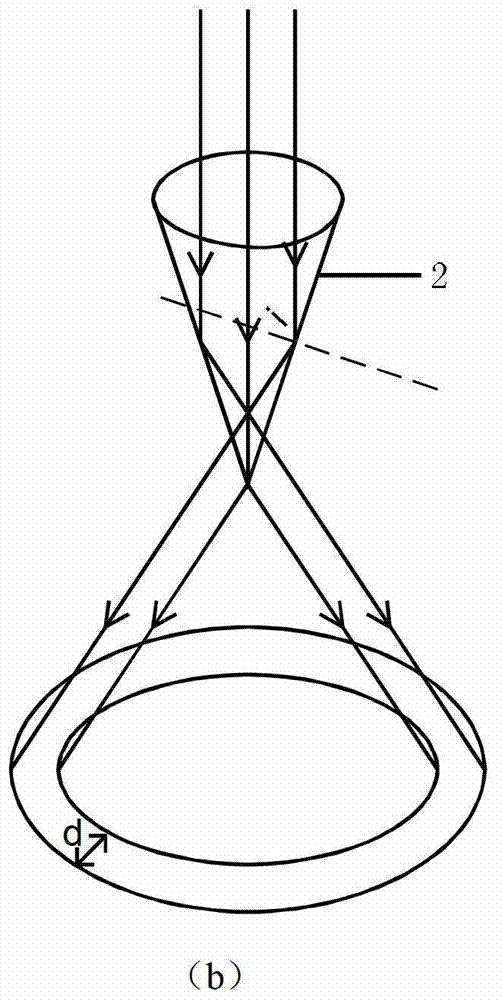
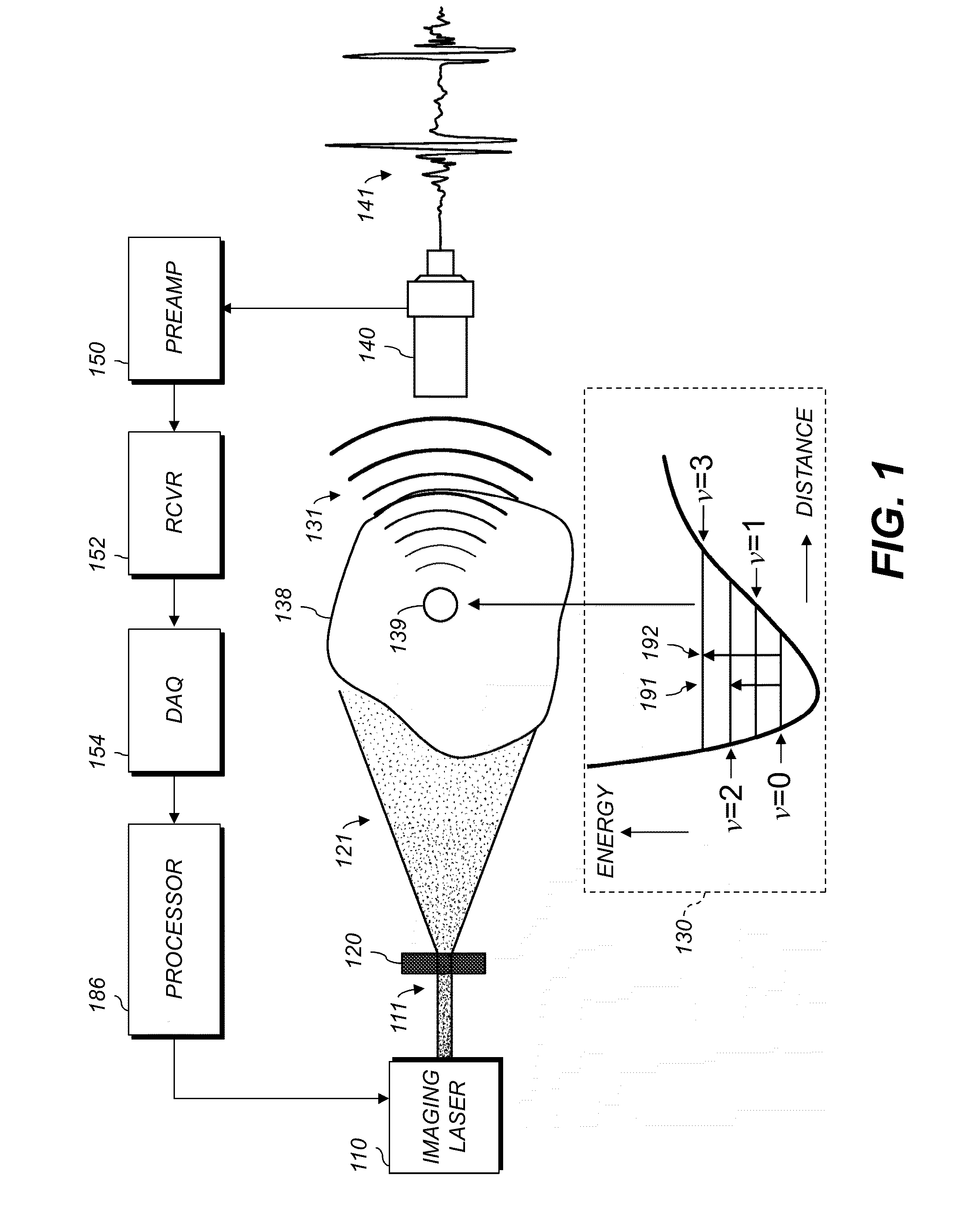
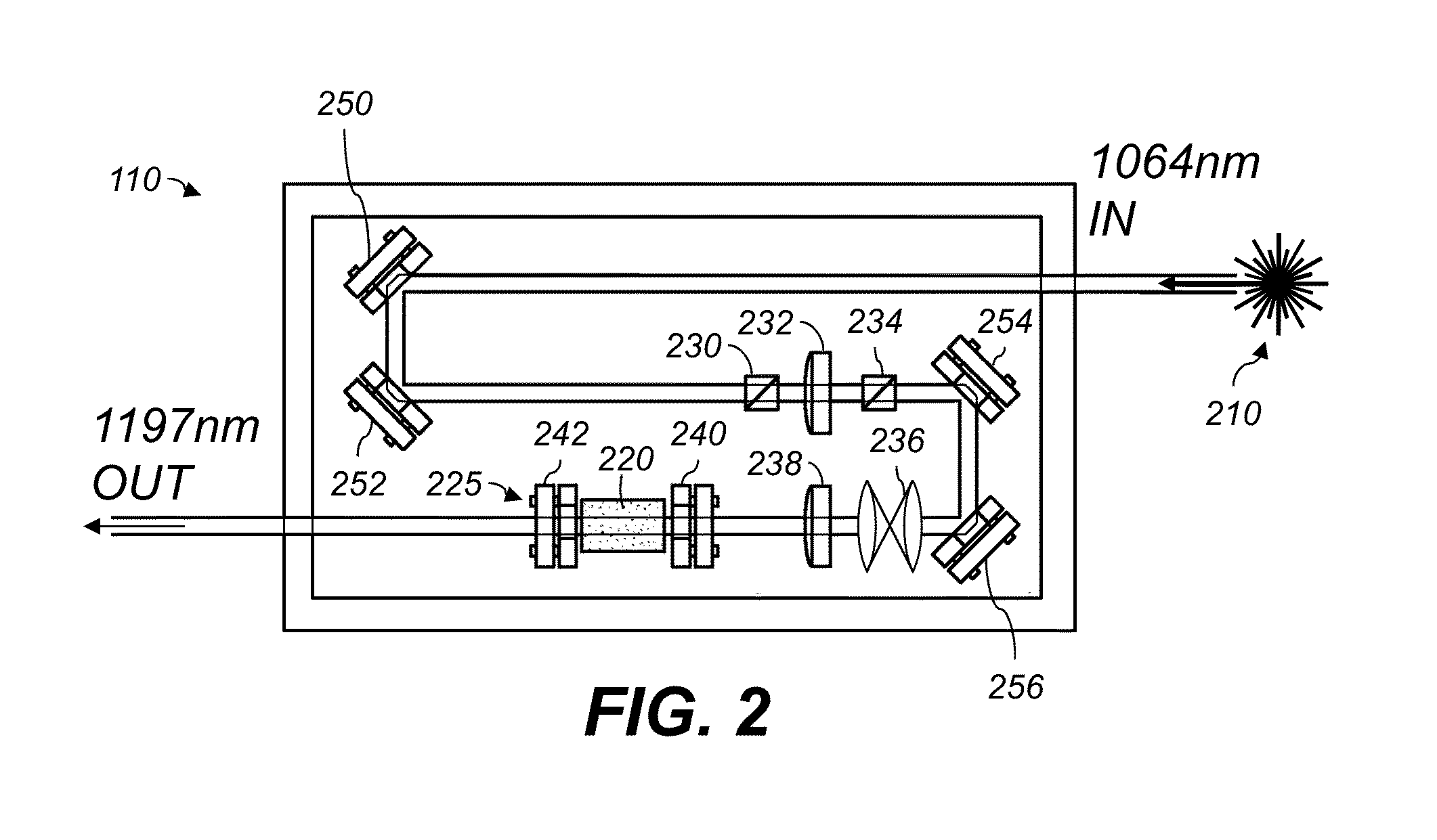
Vibrational photoacoustic tomography using raman laser
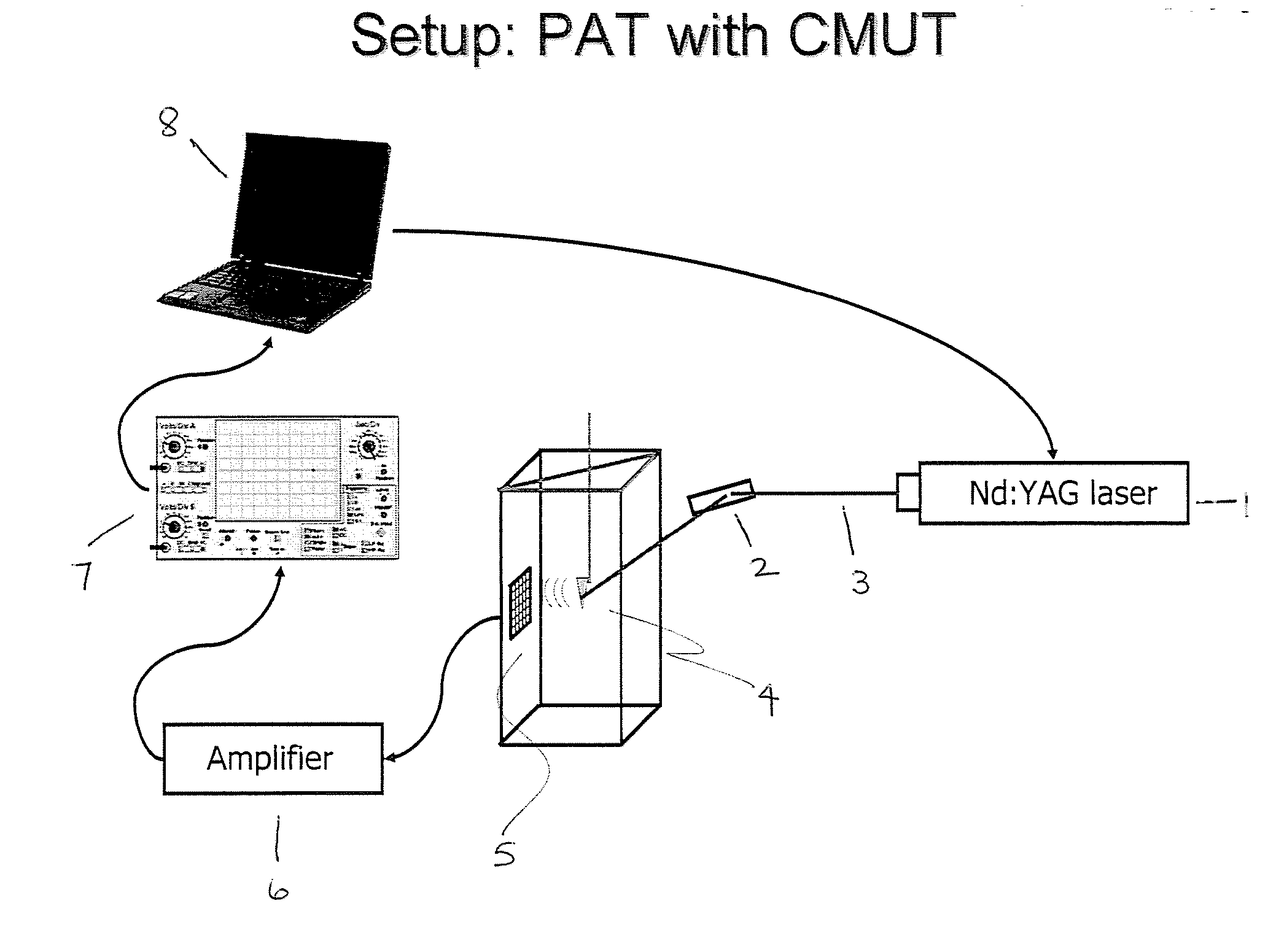
ActiveUS20140200434A1Improved laserIncrease contrastDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUltrasonic sensorPhotoacoustic tomography
A method of noninvasively imaging tissue within a body includes irradiating the tissue using an imaging laser including a Raman-based laser tuner, the radiation including a plurality of laser pulses, each having energy greater than 100 mJ; receiving an acoustic signal generated by vibrational energy in the tissue, wherein the vibrational energy is a result of selective overtone excitation of molecules in the tissue by the radiation; and automatically converting the acoustic signal to an image representative of the tissue using a processor. An imaging system includes an imaging laser configured to irradiate tissue with a plurality of laser pulses using a Raman-based laser tuner. An ultrasonic transducer receives an acoustic signal generated by vibrational energy in the tissue due to overtone excitation by the radiation. A processor is configured to automatically produce an image representative of the tissue using the received acoustic signal.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Photoacoustic imaging agent
InactiveUS20100196278A1Large output signalMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsColour centreIn vivo
A molecular probe marked with a color center material is used as a photoacoustic imaging agent to obtain an acoustic signal of practically adequate intensity using weak near-infrared light, which has good in vivo penetration depth but has small excitation energy, and is within the maximum permissible exposure, in photoacoustic tomography (PAT) diagnosis of a living body.
Owner:CANON KK
Display data obtaining apparatus and display data obtaining method
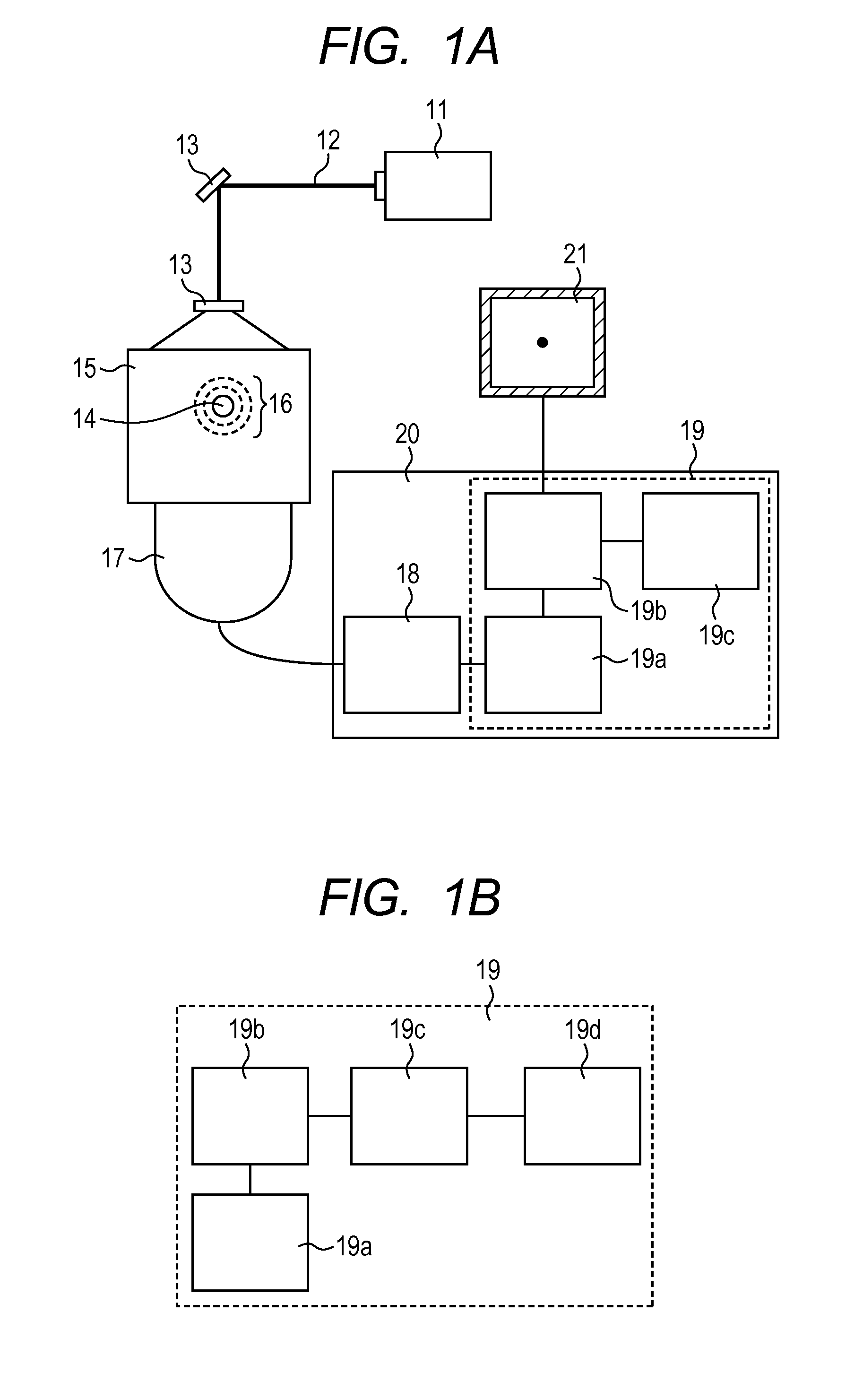
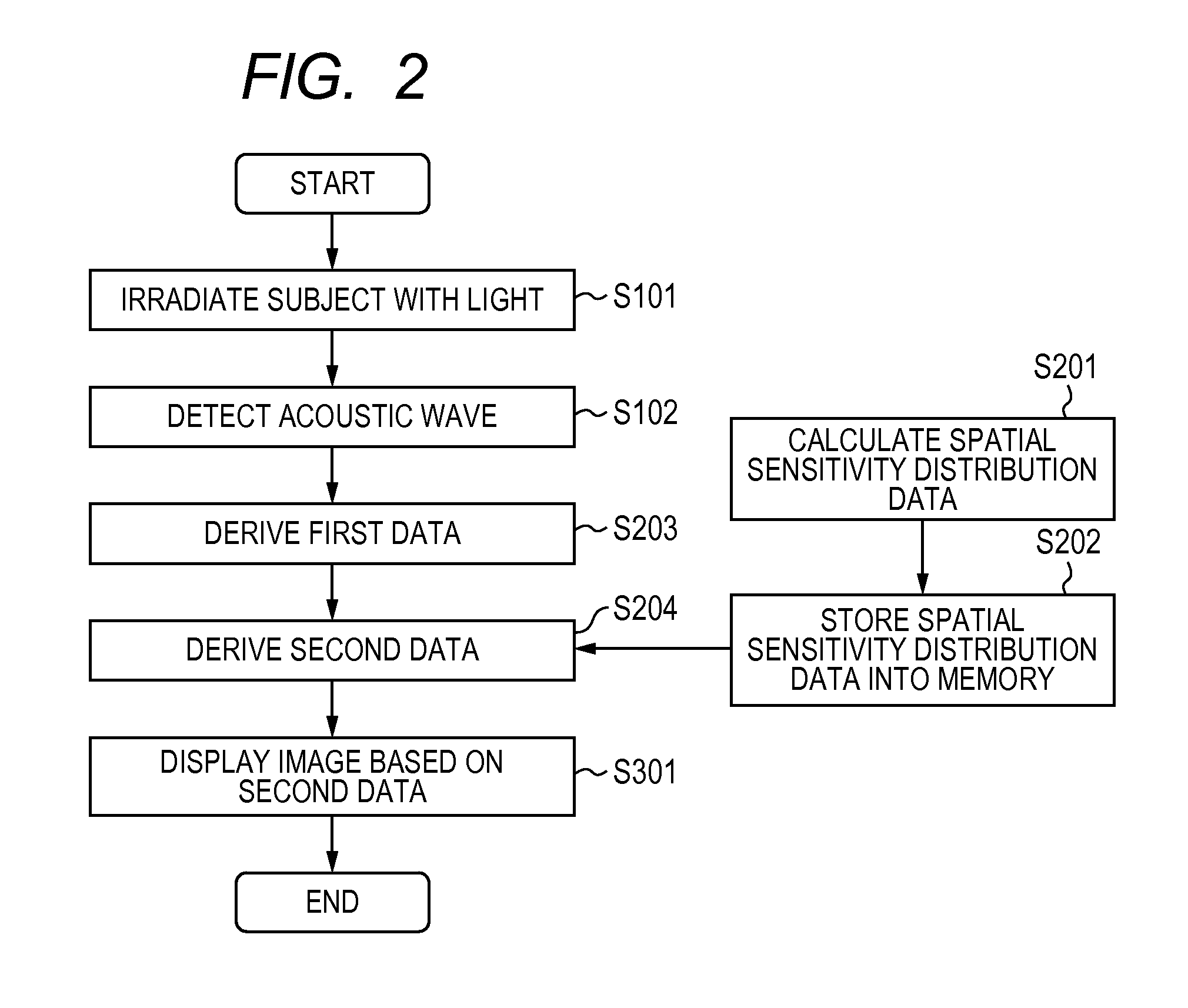
ActiveUS20110261056A1Reduce volatilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDrawing from basic elementsAcoustic waveSensitivity distribution
Provided is a display data obtaining apparatus capable of, in photoacoustic tomography, reducing a fluctuation in sensitivity which depends on location for image reconstruction even in a limited measurement condition in which a photoacoustic wave generated in the entire subject cannot be obtained in a sufficient range. The display data obtaining apparatus includes: an acoustic wave detecting unit for detecting an acoustic wave generated from a subject irradiated with pulsed light to obtain a signal; a first data deriving unit for deriving first data exhibiting an optical characteristic distribution of the subject based on the obtained signal obtained by the acoustic wave detecting unit; a memory for storing spatial sensitivity distribution data specific to the display data obtaining apparatus; and a second data deriving unit for deriving second data exhibiting the optical characteristic distribution of the subject using the first data and the spatial sensitivity distribution data.
Owner:CANON KK
Preparation method and application of transferrin modified hollow mesoporous copper sulfide/artesunate nanoparticles
ActiveCN105126113ASmall toxicityThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsSide effectTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of transferrin modified hollow mesoporous copper sulfide / artesunate nanoparticles and effectively and simultaneously achieves targeting, photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy, photoacoustic tomography, drug therapy and DMR (diffusion molecular retention) effect to realize integration of diagnosis and treatment. The method includes: synthesizing hollow mesoporous copper sulfide nanoparticles, loading artesunate in copper sulfide in a hollow mesoporous structure, and modifying with transferrin through electrostatic adherence to obtain the transferrin modified hollow mesoporous copper sulfide / artesunate nanoparticles. The synthesis process is simple, anti-cancer drugs are sent to cancerous parts by means of peri-cancerous injection, and accordingly treatment effects can be further improved, and toxic and side effects on normal tissues and cells are reduced. A function of infrared photothermal therapy is realized while photodynamic therapy and photoacoustic tomography can be carried out, and accordingly integration of photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy, chemotherapy, tumor diagnosis and comprehensive therapy is realized. The transferrin modified hollow mesoporous copper sulfide / artesunate nanoparticles realize a great innovation of drugs for tumor treatment.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Photoacoustic contrast agents for molecular imaging
InactiveUS20080181851A1Facilitating the photoacoustic detectionEfficient absorberUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsOrganic baseLipid composition
Compositions of photoacoustic tomography (PAT) contrast agents, and methods of achieving contrast enhancement and amplification of photo-induced acoustic signal for in vivo photoacoustic imaging of animals and human subjects are provided. Contrast agents of interest are organic-based agents, which may be targeted or non-targeted, e.g. protein-based and / or lipid-based molecules, in combination with an inorganic core, e.g. a metal or silicon core, herein referred to as a composite PAT contrast agent. Preferred agents absorb in the near IR spectrum, e.g. from around about 650 nm to around about 800 nm, for example from about 720 to about 790 nm. In some embodiments of the invention, the organic component is a lipid composition, which optionally comprises one or more targeting moieties. In some embodiments the inorganic core is gold or another noble metal, e.g. silver, platinum, etc.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
A photoacoustic tomography method and system
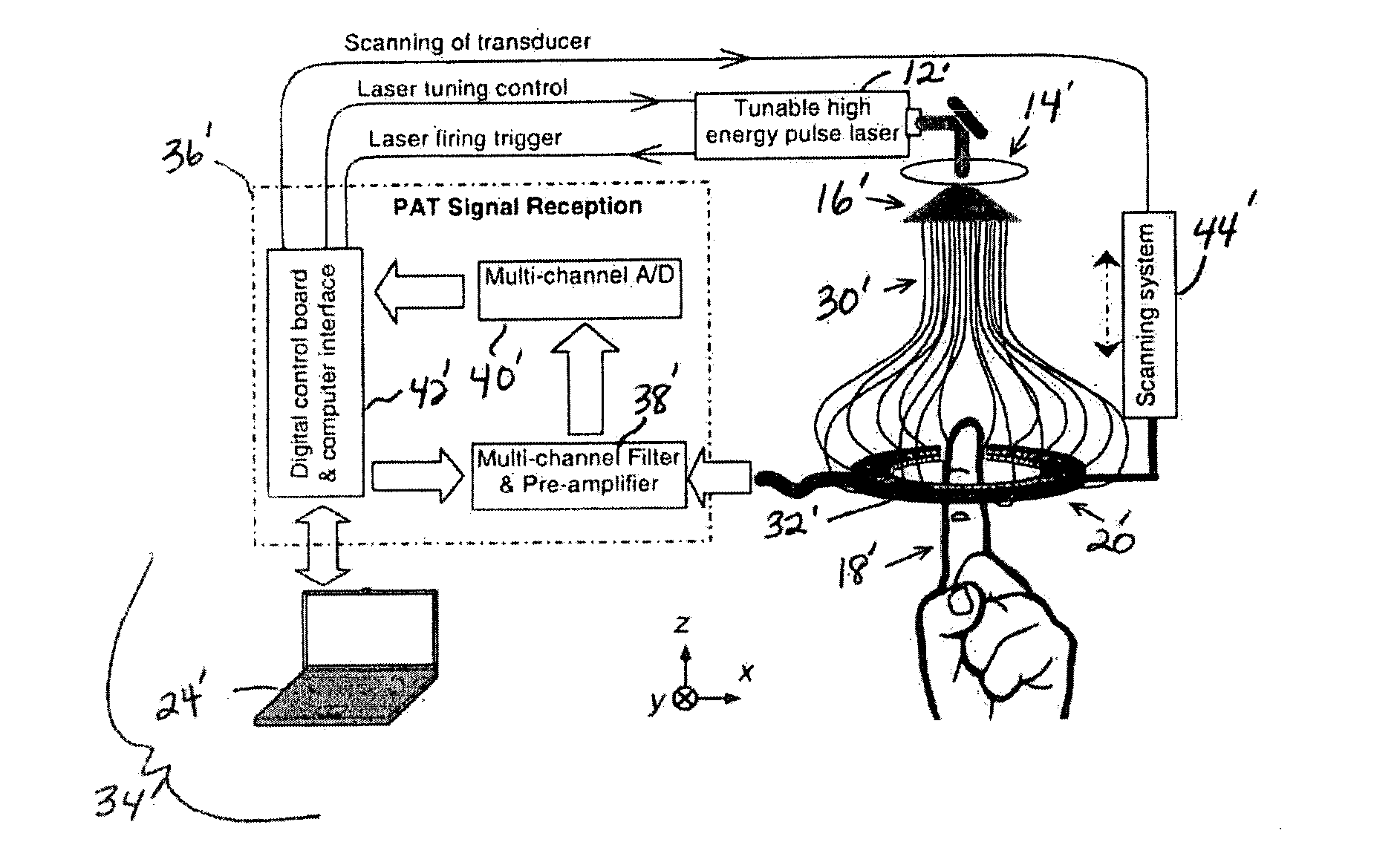
A method of calibrating a PAI system (401-413) is described. The method includes a signal processing unit (404) determining optical fluence at voxels within arteries of a human or animal, and interpolating from these measurements to provide a fluence map with a fluence value for all voxels of interest. The system (404) stores the fluence map for subsequent use in making PAI measurements. The arterial optical fluence may be determined on the basis that the arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is the same throughout the arterial part of the circulation system.
Owner:THE NAT UNIV OF IRELAND GALWAY
Photoacoustic computed tomography with an acoustic reflector
ActiveUS20170367586A9Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAcoustic sensorsComputing tomographyVirtual array
Systems and methods for improving limited-view photoacoustic tomography using an acoustic reflector are described. In particular, an acoustic reflector and ultrasonic transducer array are integrated to provide a virtual array that enhances the field of view of the ultrasonic transducer array, thereby improving the quality of photoacoustic tomography images obtained using the systems and methods described herein.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com