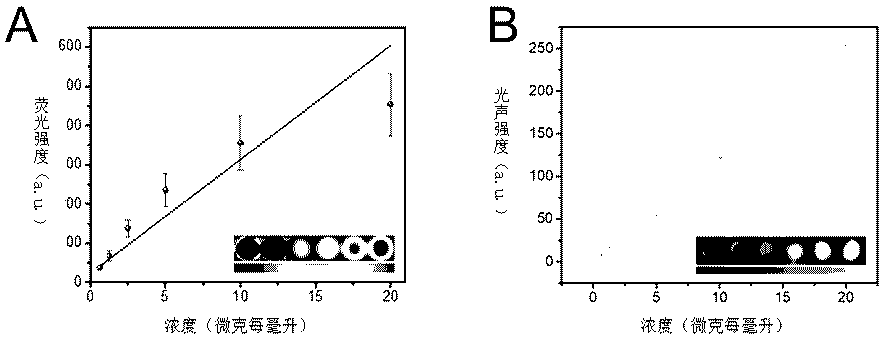
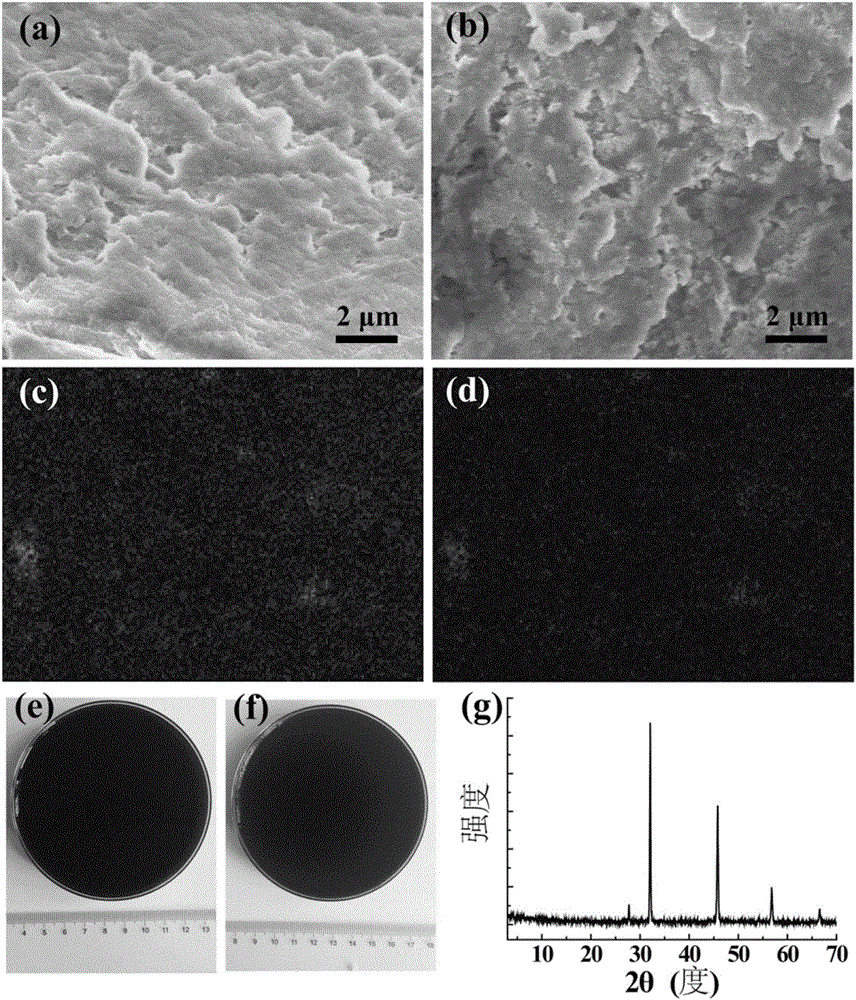
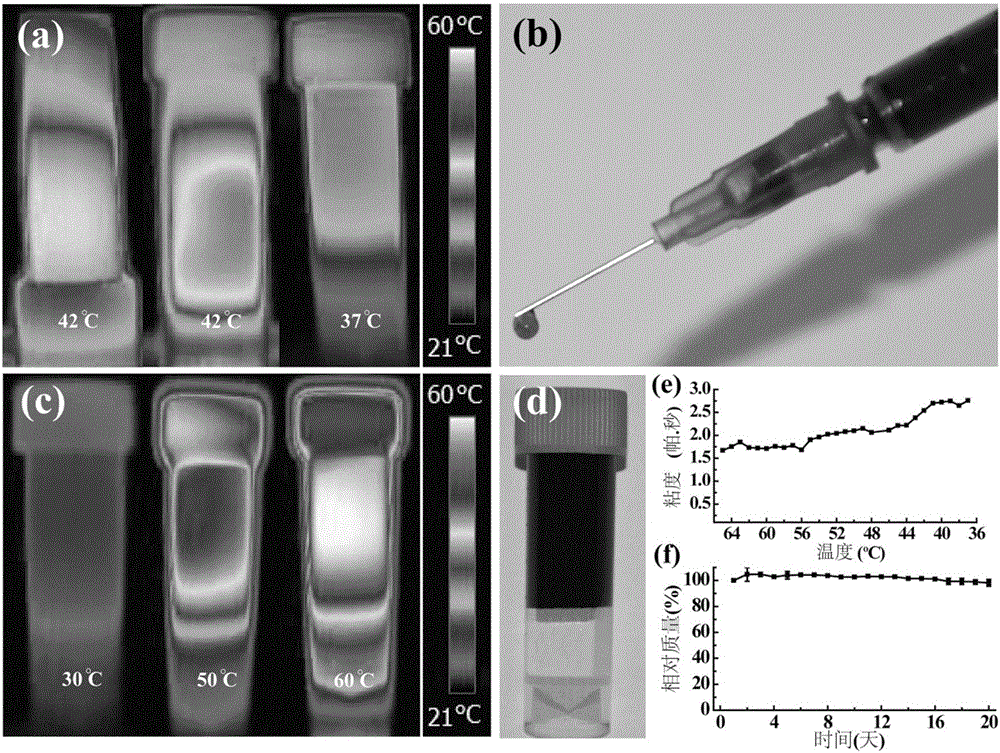
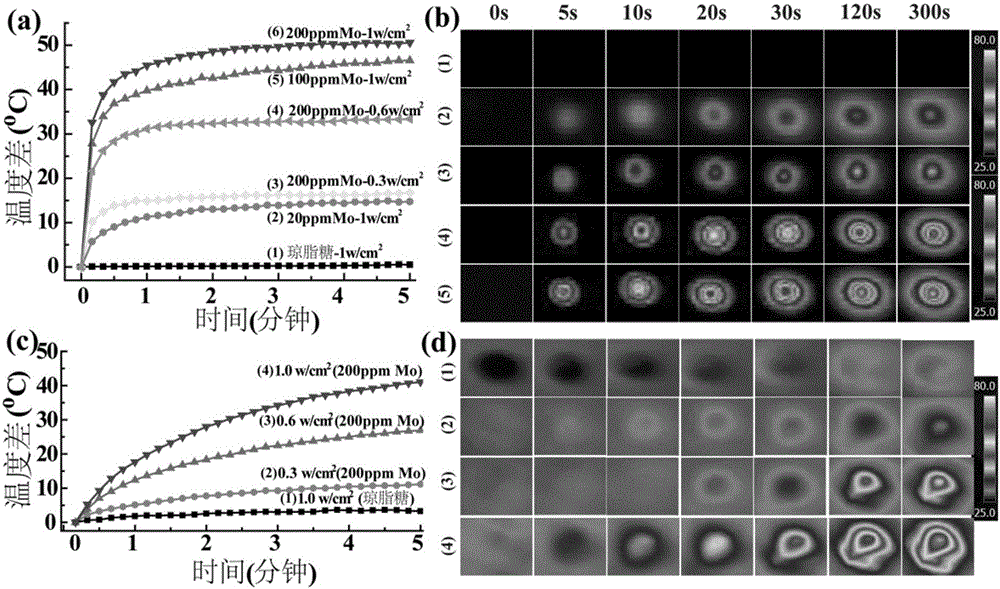
Patents
Literature
368 results about "Optoacoustic imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optoacoustic imaging is an imaging technology based on the photoacoustic effect, and can be used for obtaining images of structures in turbid environments. The optoacoustic technique combines the accuracy of spectroscopy with the depth resolution of ultrasound.
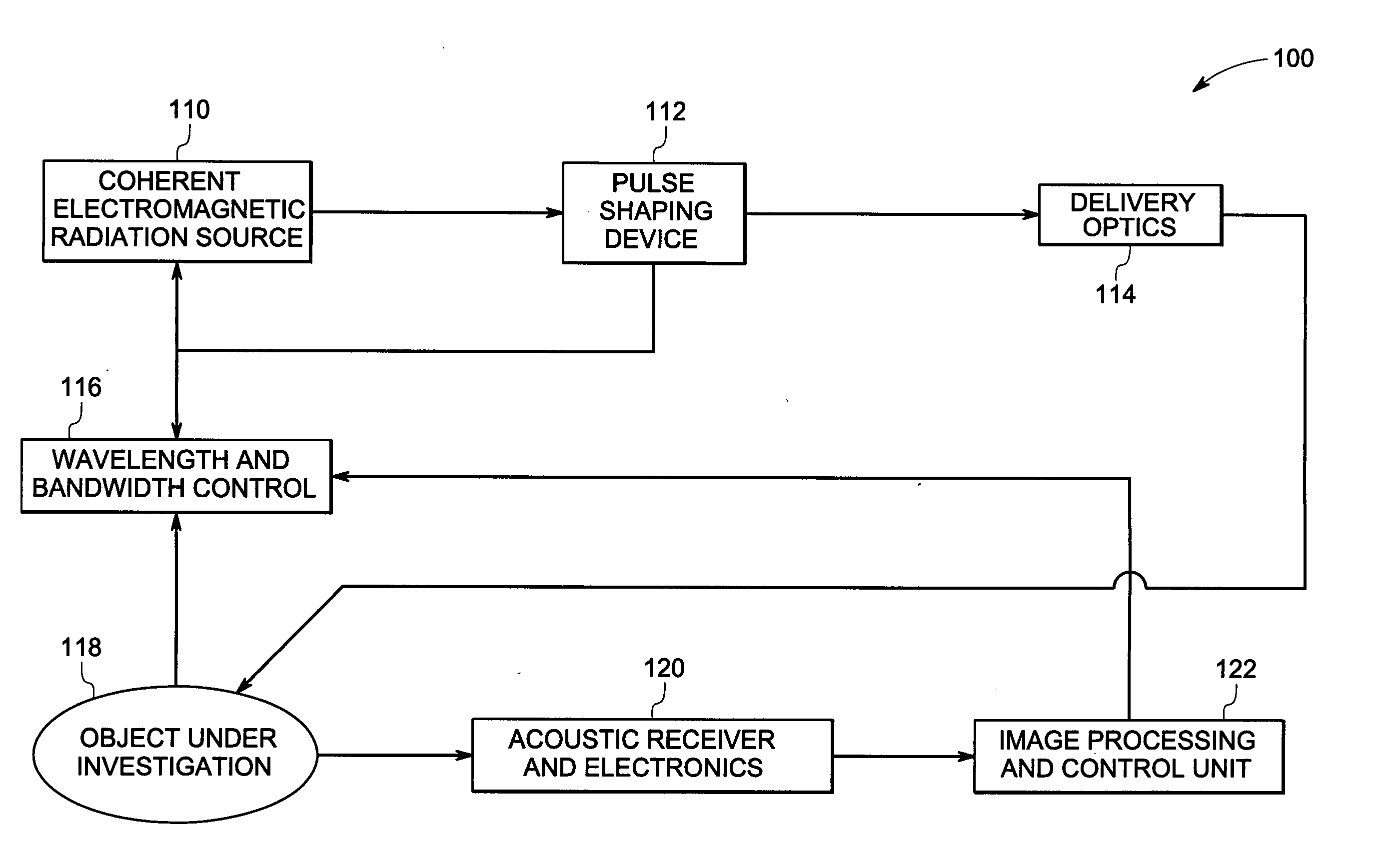
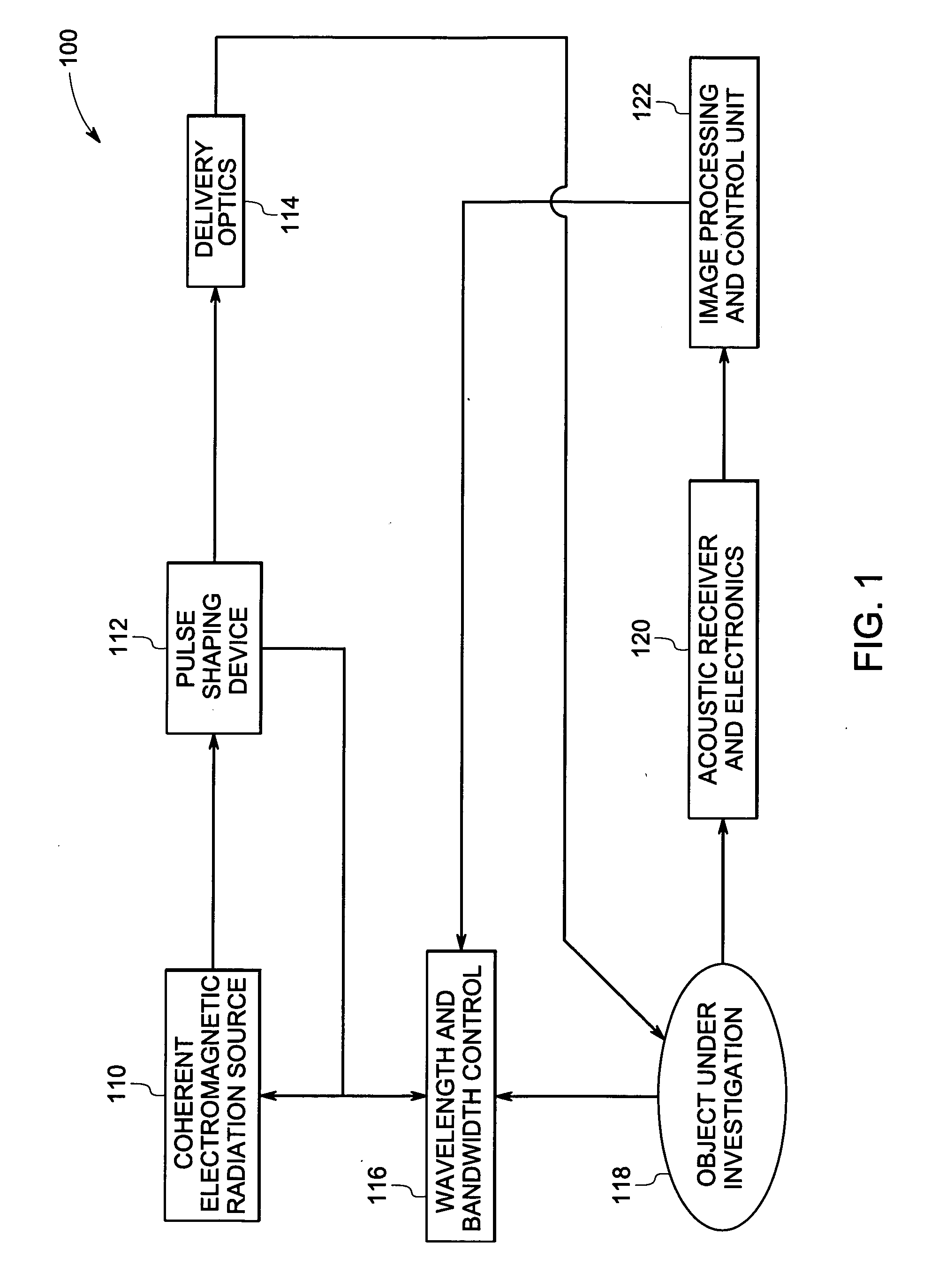
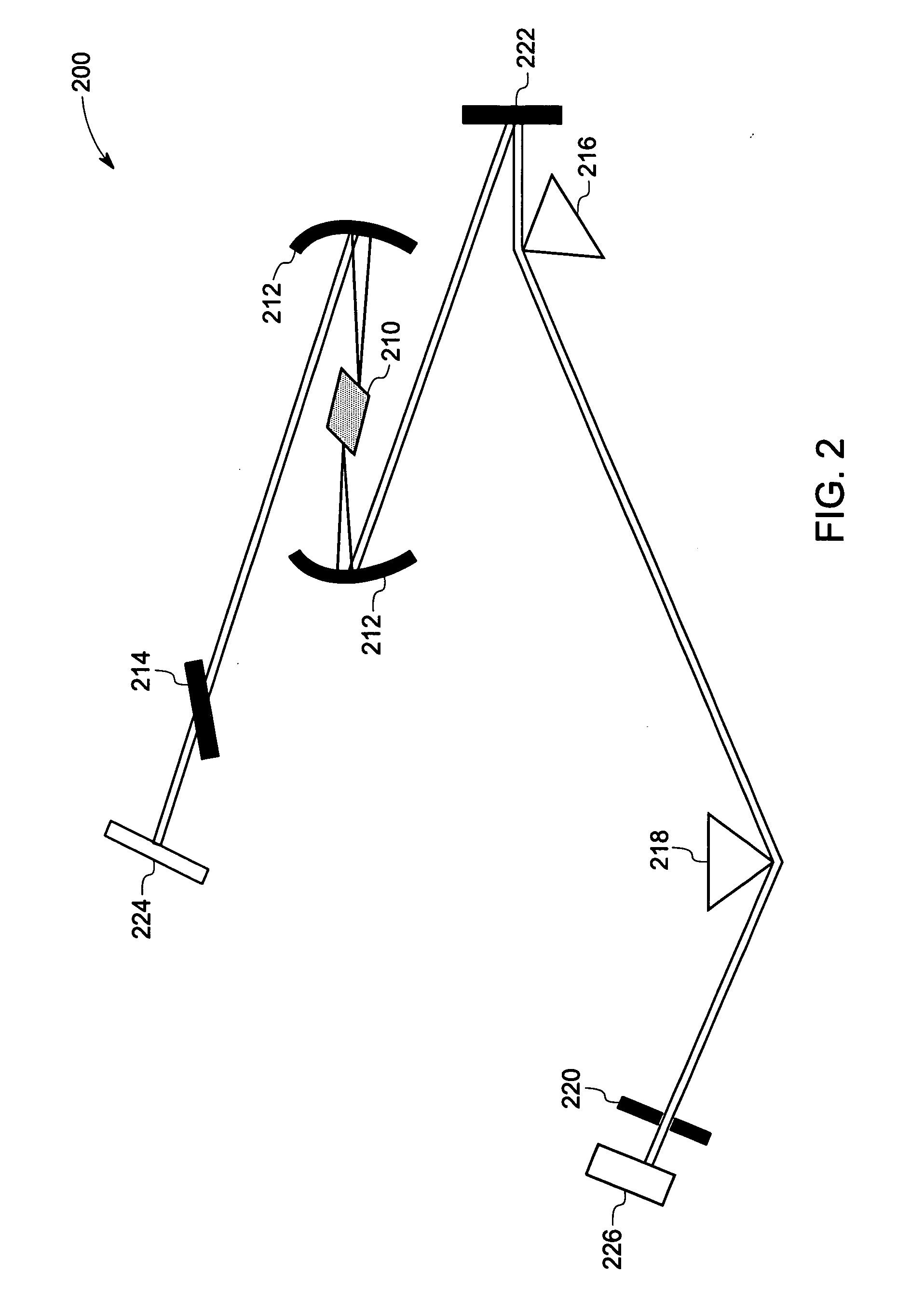
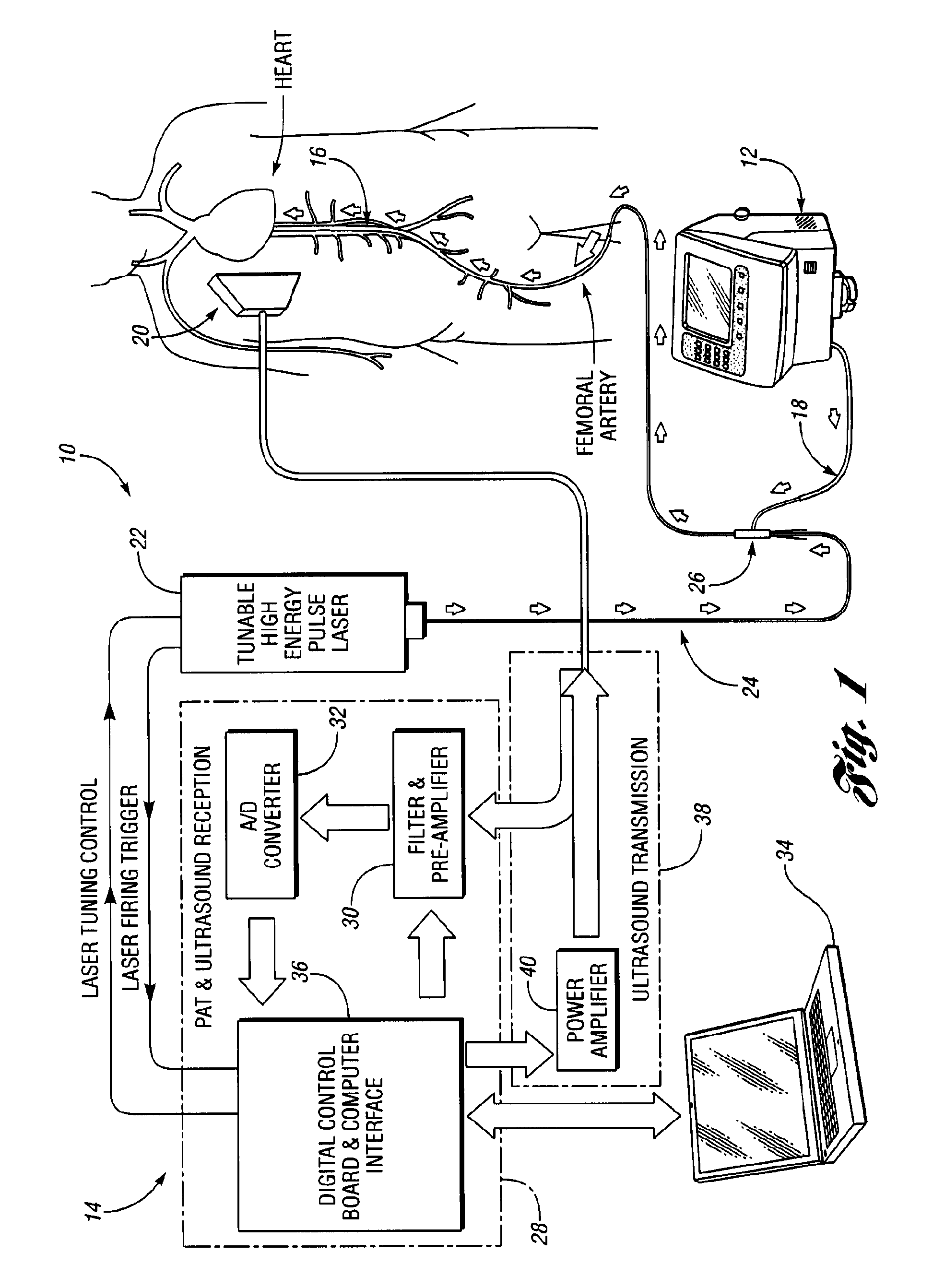
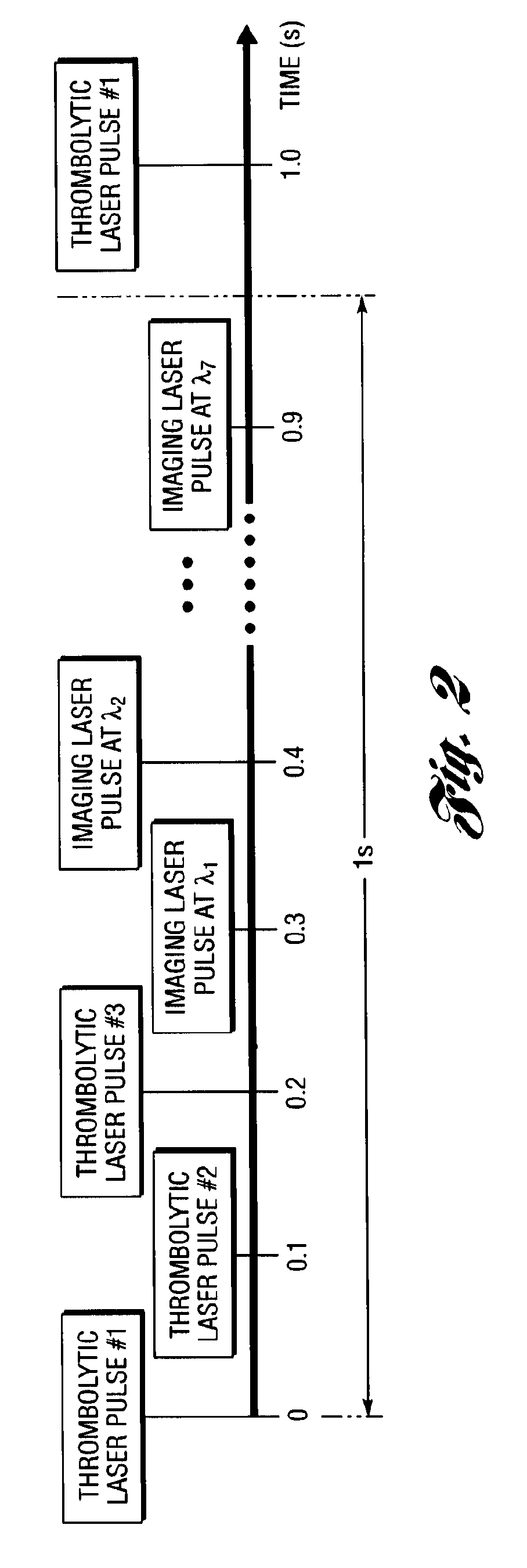
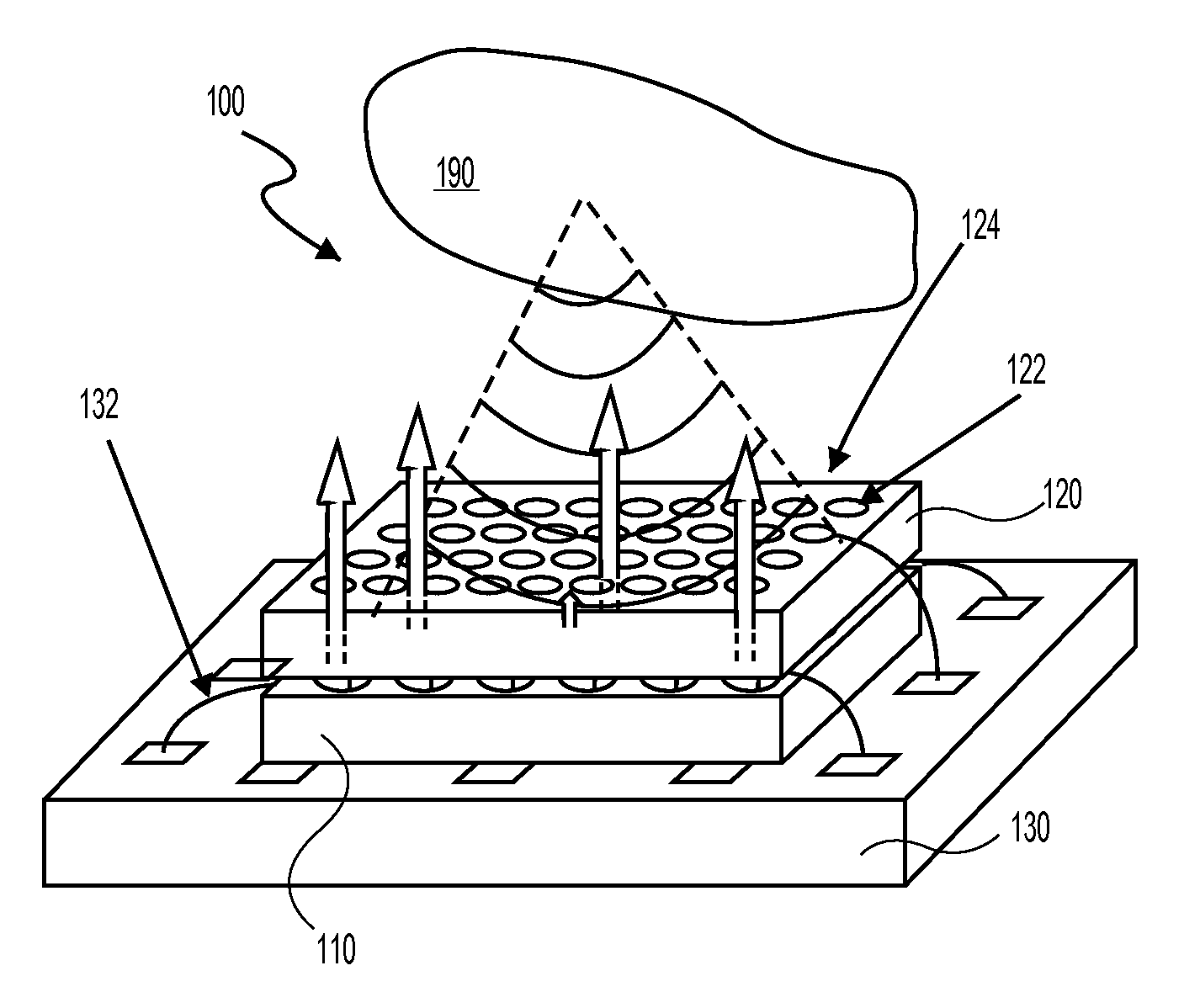
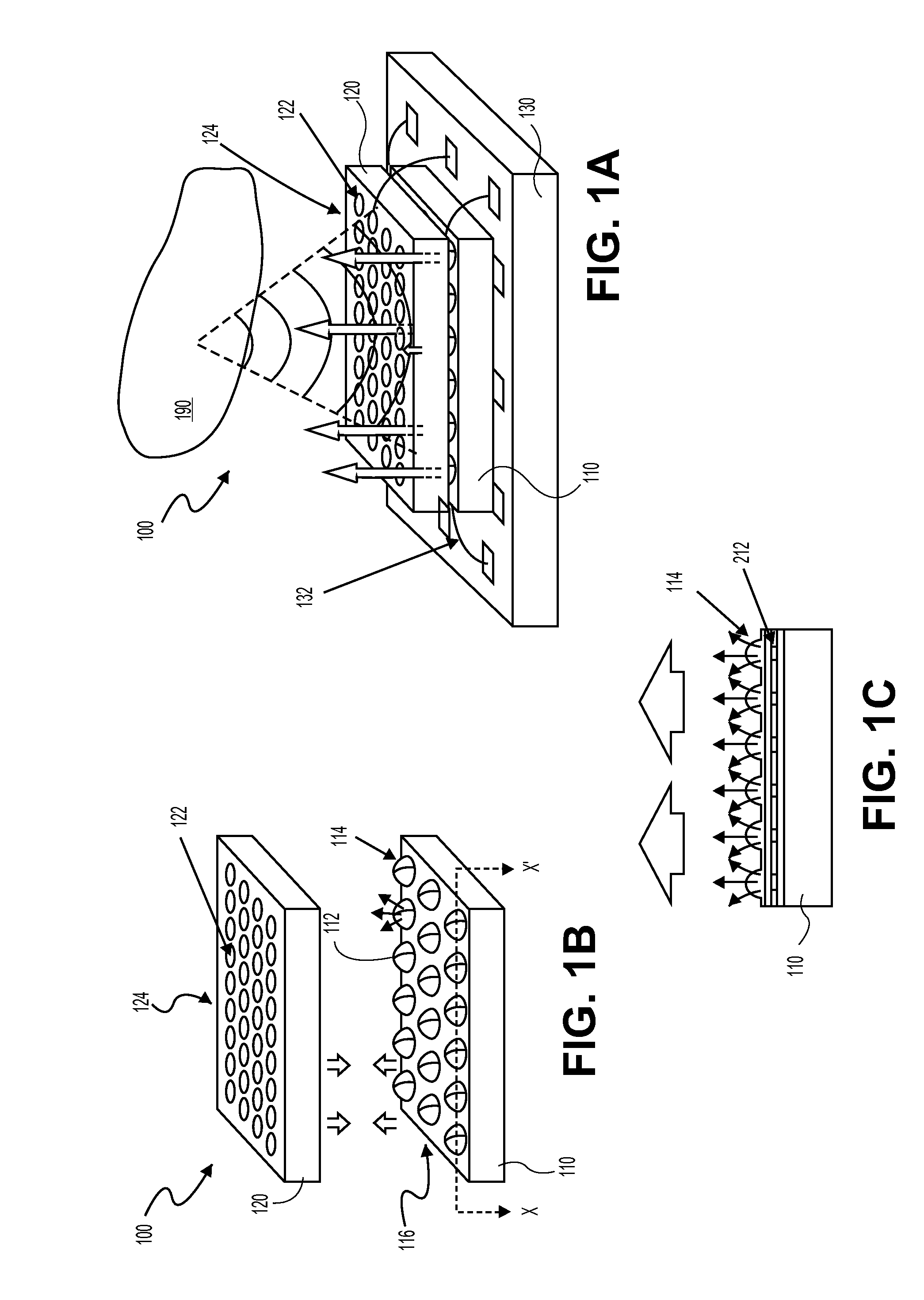
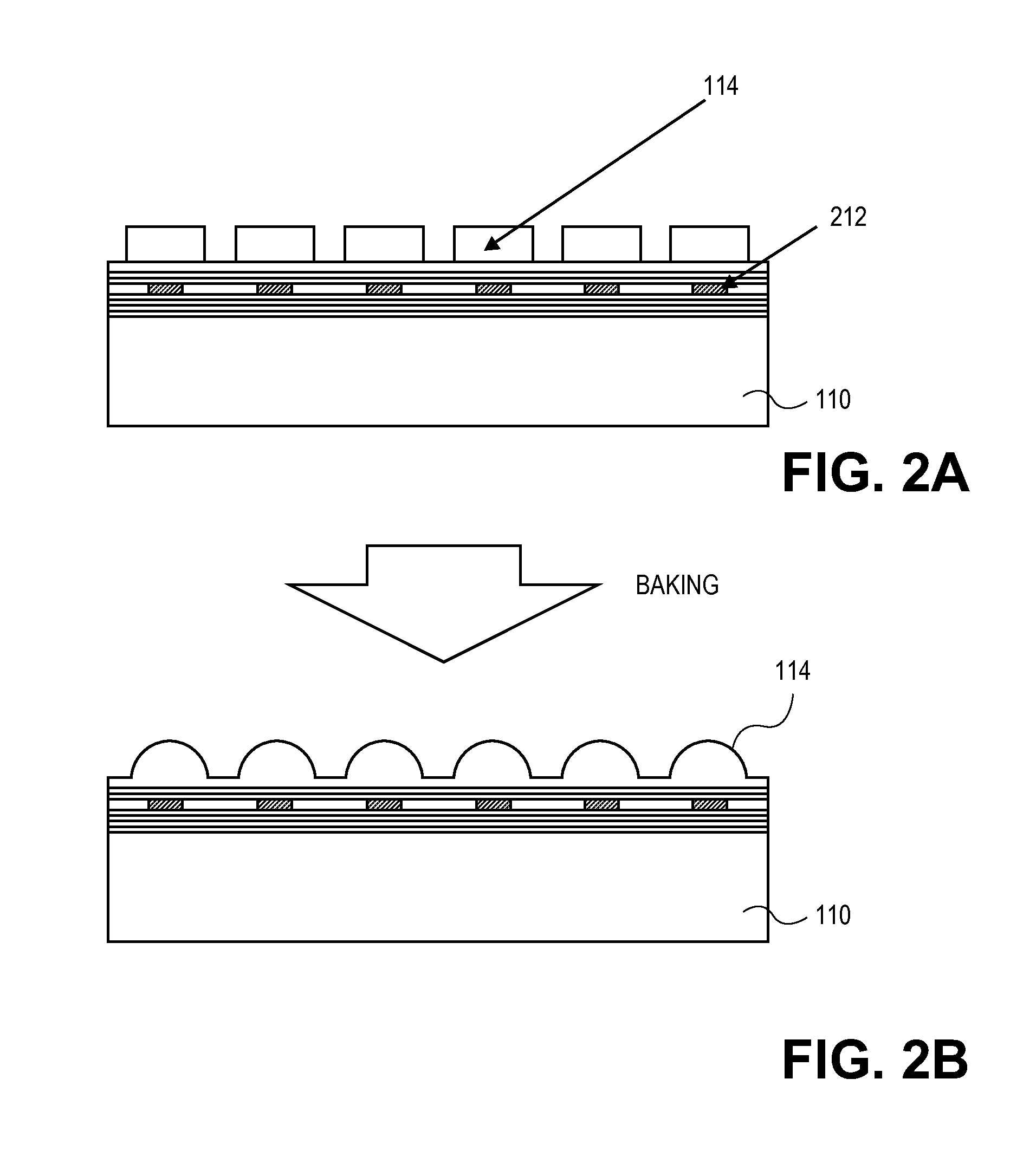
System and method for optoacoustic imaging
InactiveUS20070015992A1Scattering properties measurementsDiagnostics using tomographyPulse shaperElectromagnetic radiation
A system and method are described for optoacoustic imaging a structural or compositional characteristic of an biological object using a coherent, broad range frequency tunable, electromagnetic radiation source and a pulse shaper to generate a sequence of electromagnetic radiation excitation signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
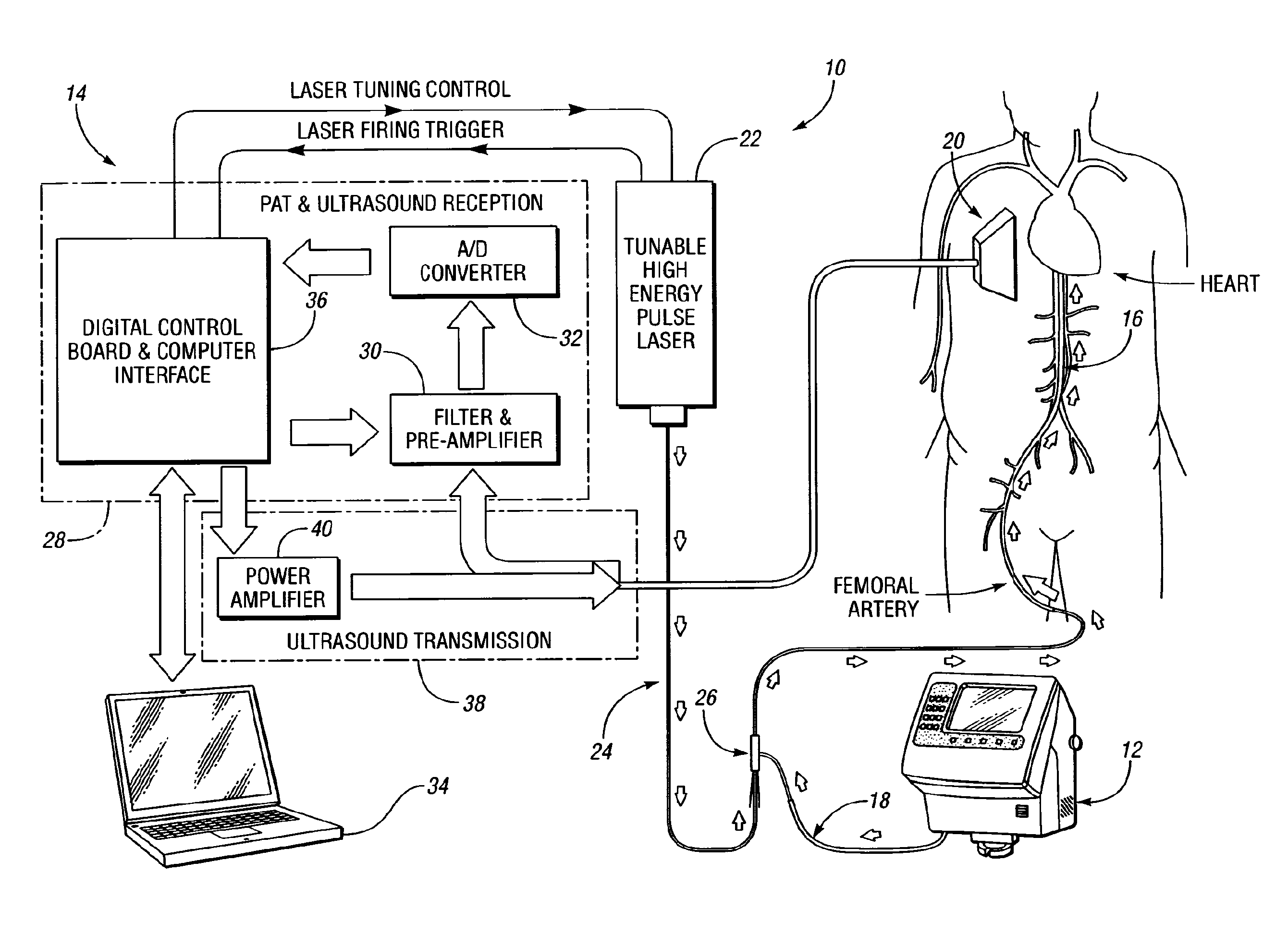
System and method for photoacoustic imaging and monitoring of laser therapy
InactiveUS20090227997A1Control damageEasy to controlUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterTherapy controlTomographic image
A system and method for monitoring laser therapy of a target tissue include a therapeutic control unit having a first light source configured to deliver light to the target tissue for therapy, an ultrasonic transducer for receiving photoacoustic signals generated due to optical absorption of light energy by the target tissue, and a monitoring control unit in communication with the ultrasonic transducer for reconstructing photoacoustic tomographic images from the received photoacoustic signals to provide an optical energy deposition map of the target tissue. A second light source utilized for imaging may also be provided.
Owner:THE RGT OF THE UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Low-cost device for c-scan photoacoustic imaging
ActiveUS20100016717A1Small sizeLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsSensor arraySonification
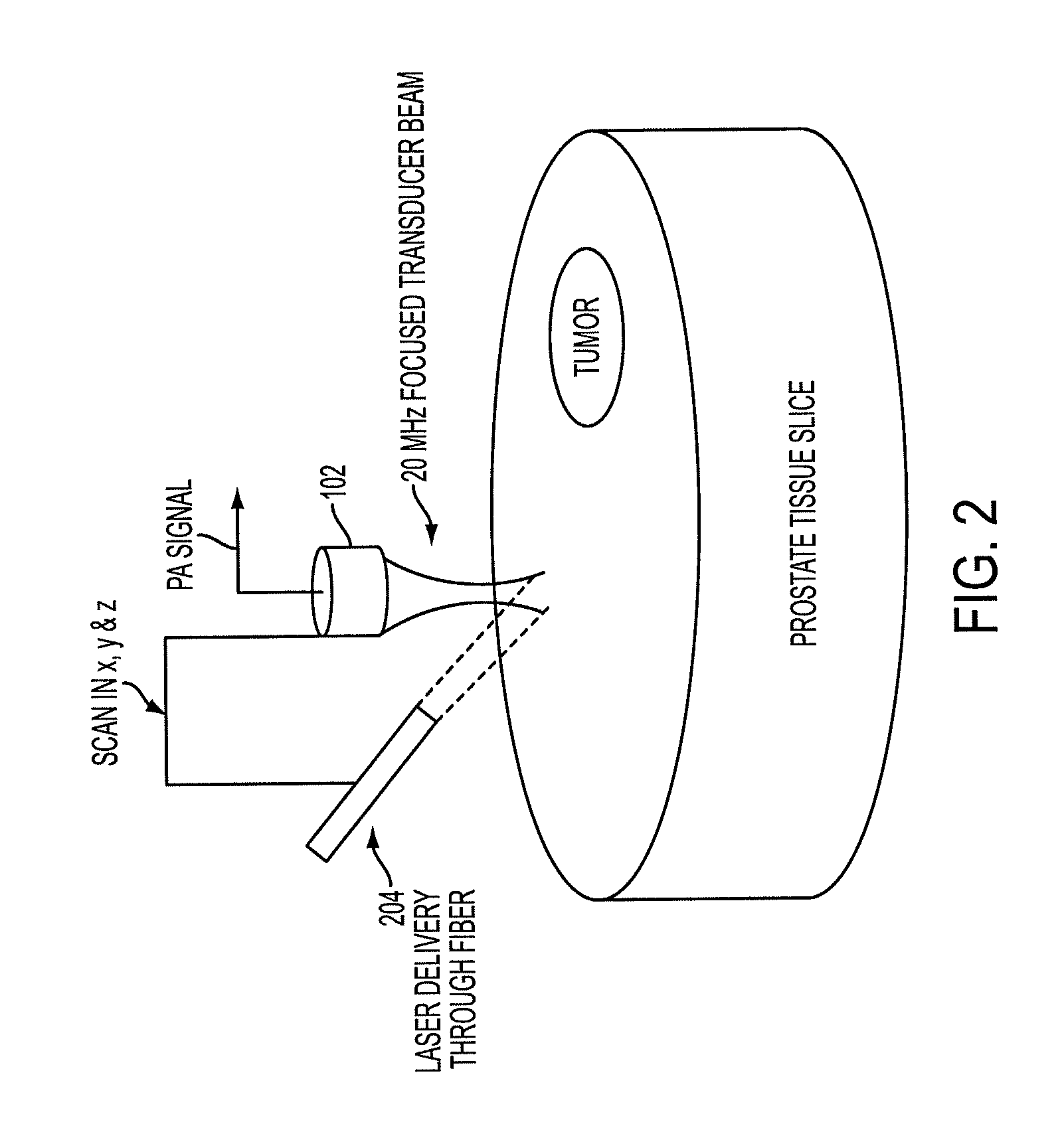
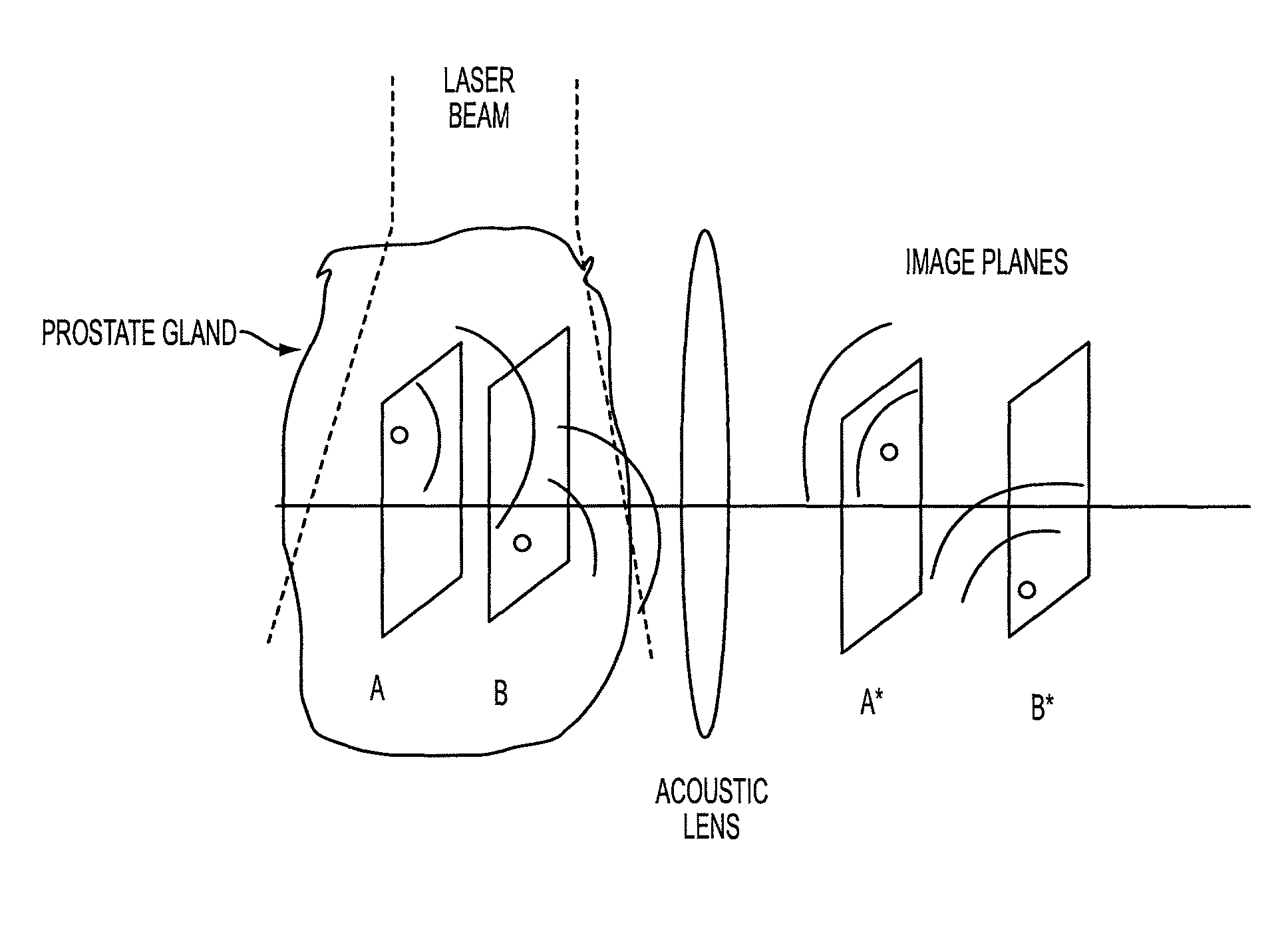
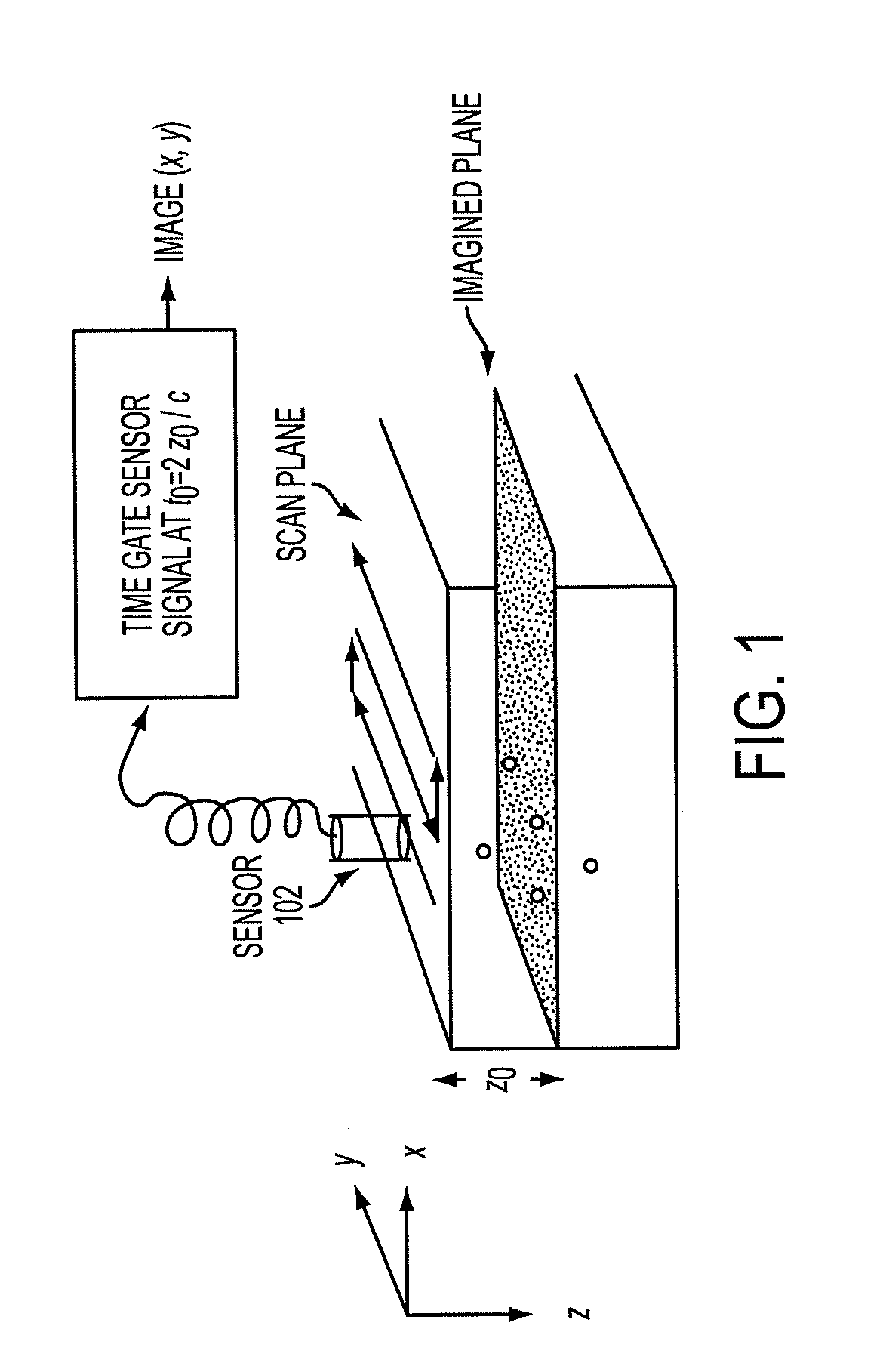
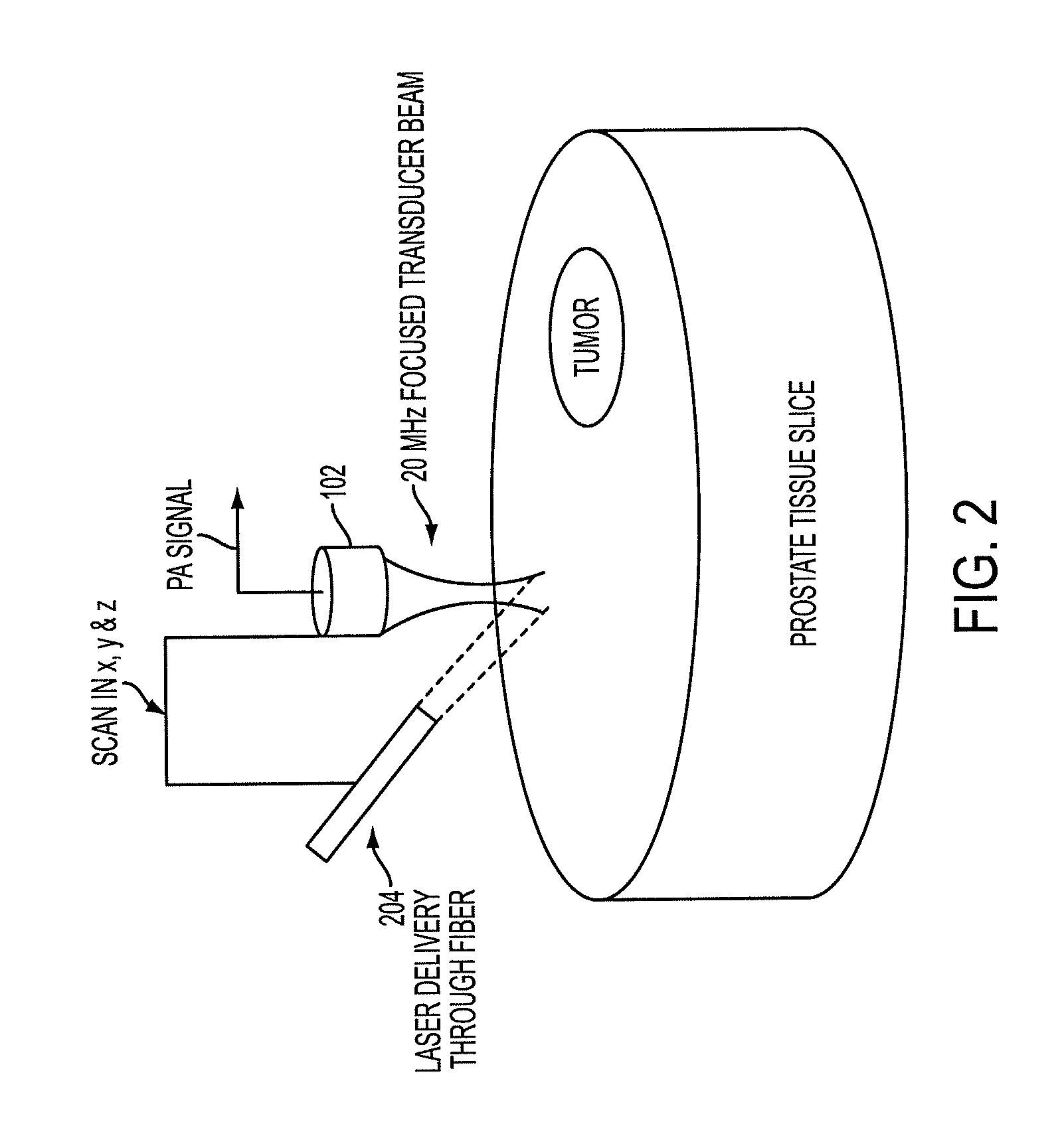
The prostate gland or other region of interest is stimulated with laser light, resulting in ultrasound waves (photoacoustic effect) which are focused by an acoustic lens and captured by a specific 1- or 2D sensor array and subsequently displayed as a C-scan on a computer screen. The amplitude of the ultrasound waves generated by laser stimulation is proportional to the optical absorption of the tissue element at that spatial location. Variability in tissue absorption results in C-scan image contrast. The photoacoustic imaging is combined with an ultrasound C-scan image produced with a plane ultrasound wave applied to the region of interest.
Owner:ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Photoacoustic imaging devices and methods of imaging
ActiveUS20100268058A1Improve image contrastFast processingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterFiberUltrasonic sensor
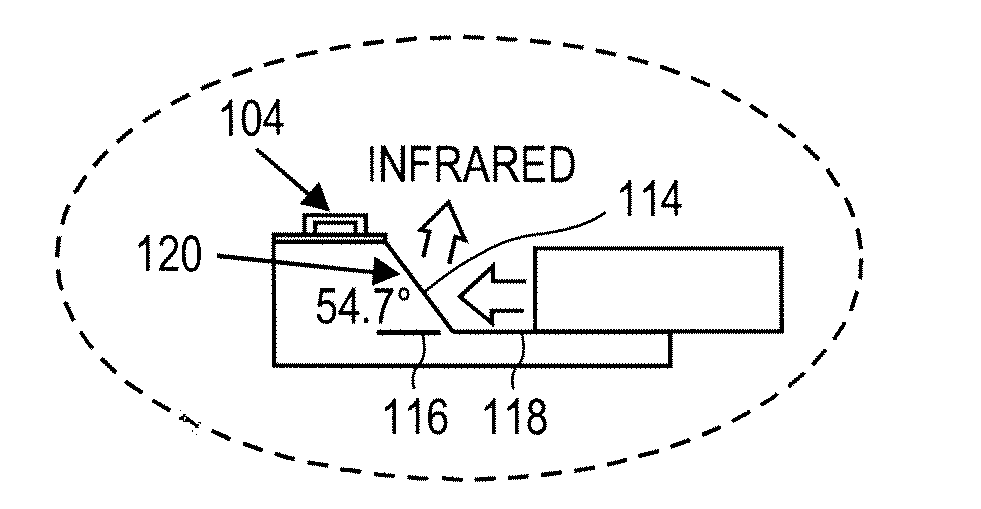
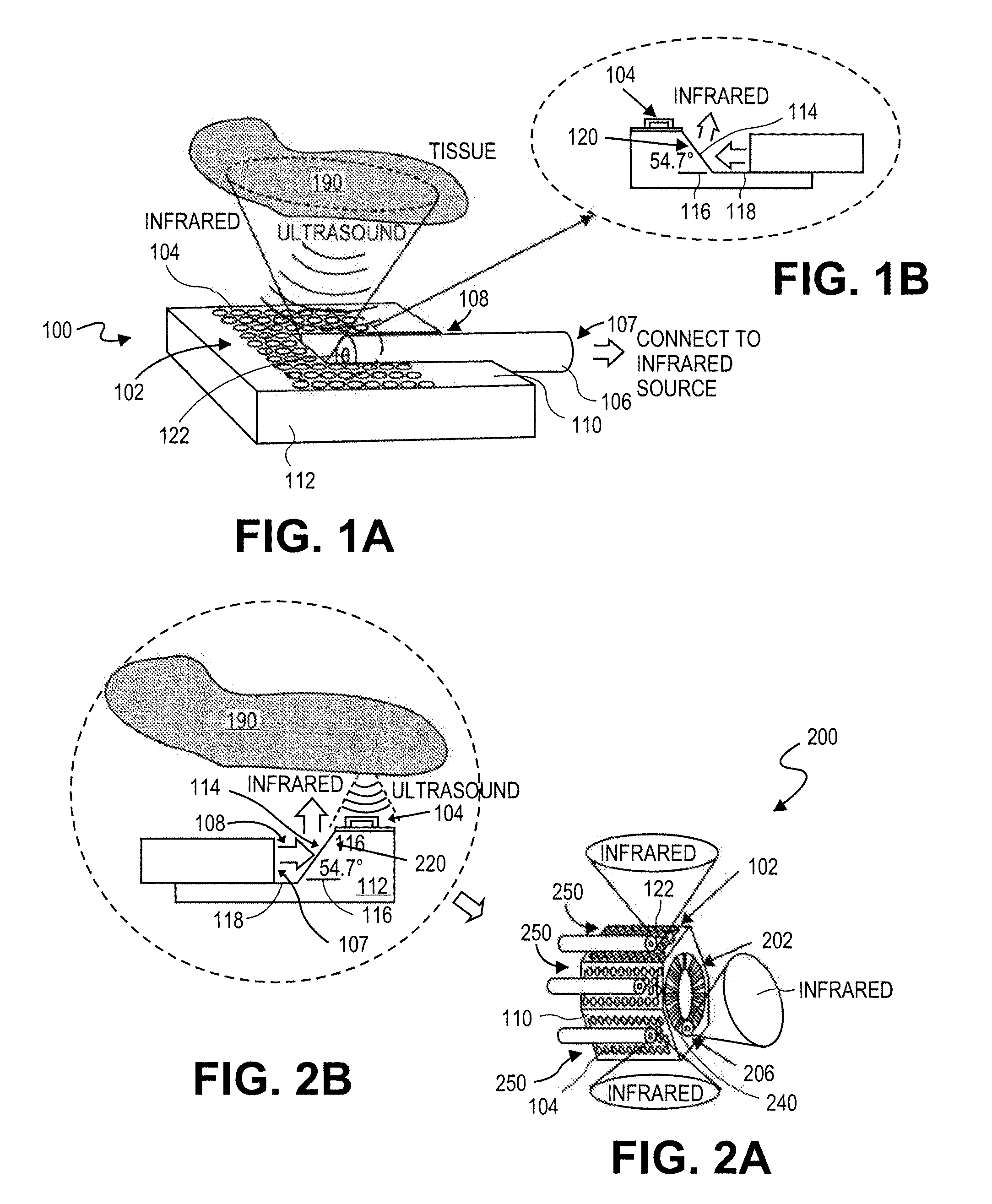
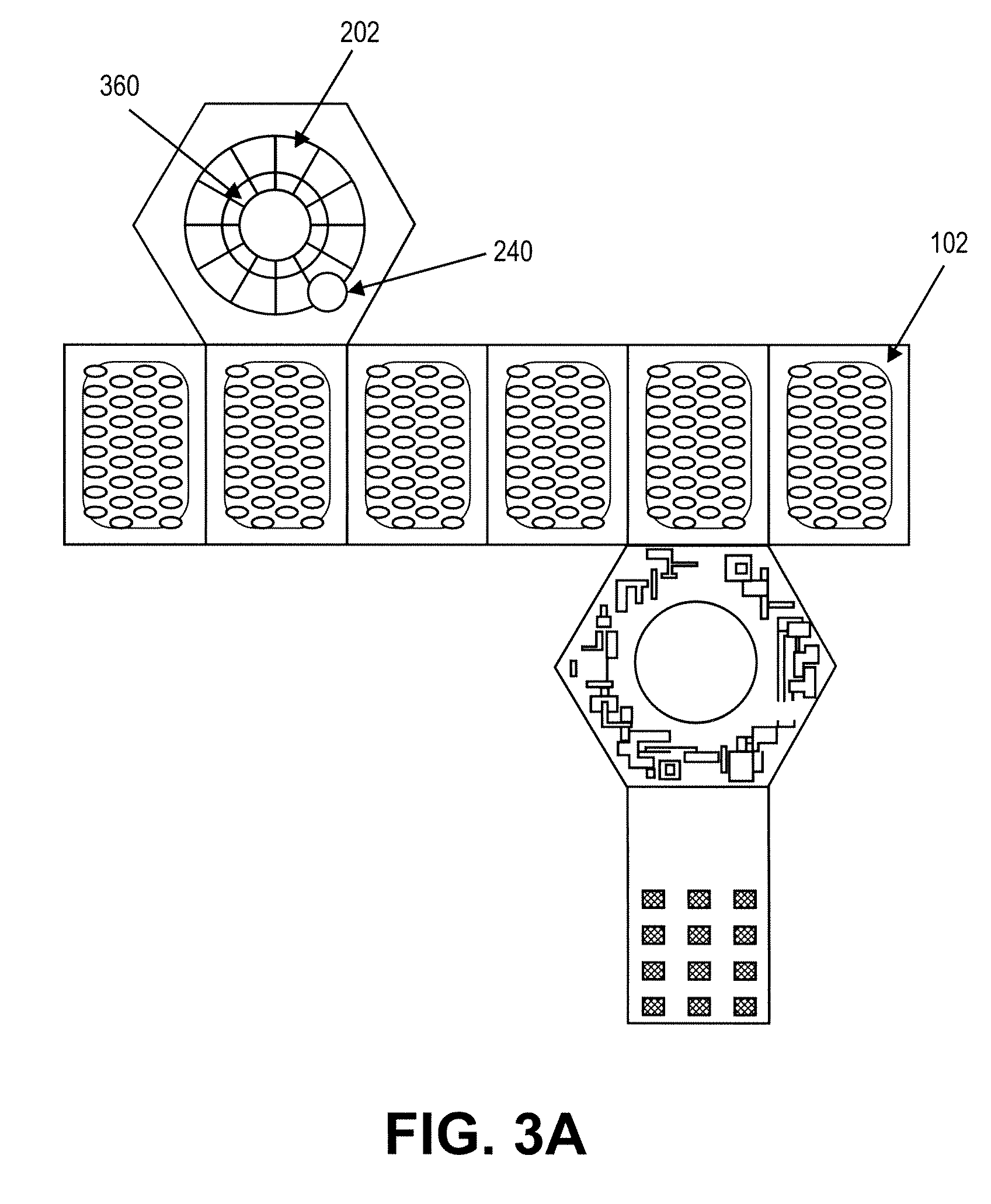
A photoacoustic medical imaging device may include a substrate, an array of ultrasonic transducers on the substrate, at least one groove etched on the substrate, at least one optical fiber, and at least one facet. Each optical fiber is disposed in one of the grooves. Each facet is etched in one of the grooves and coated with a layer of metal having high infrared reflectivity. Each optical fiber is configured to guide infrared light from a light source through the fiber and toward the respective facet. The facet is configured to reflect the infrared light toward a target.
Owner:STC UNM
Photoacoustic imaging devices and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20110190617A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansUltrasonic sensorTransducer
A photoacoustic imaging device includes an array of light sources configured and arranged to illuminate a target region and an array of ultrasonic transducers between the array of light sources and the target region. The array of transducers may be fixedly coupled to the array of light sources, and the array of ultrasonic transducers may be configured and arranged to receive ultrasound transmissions from the target region.
Owner:STC UNM
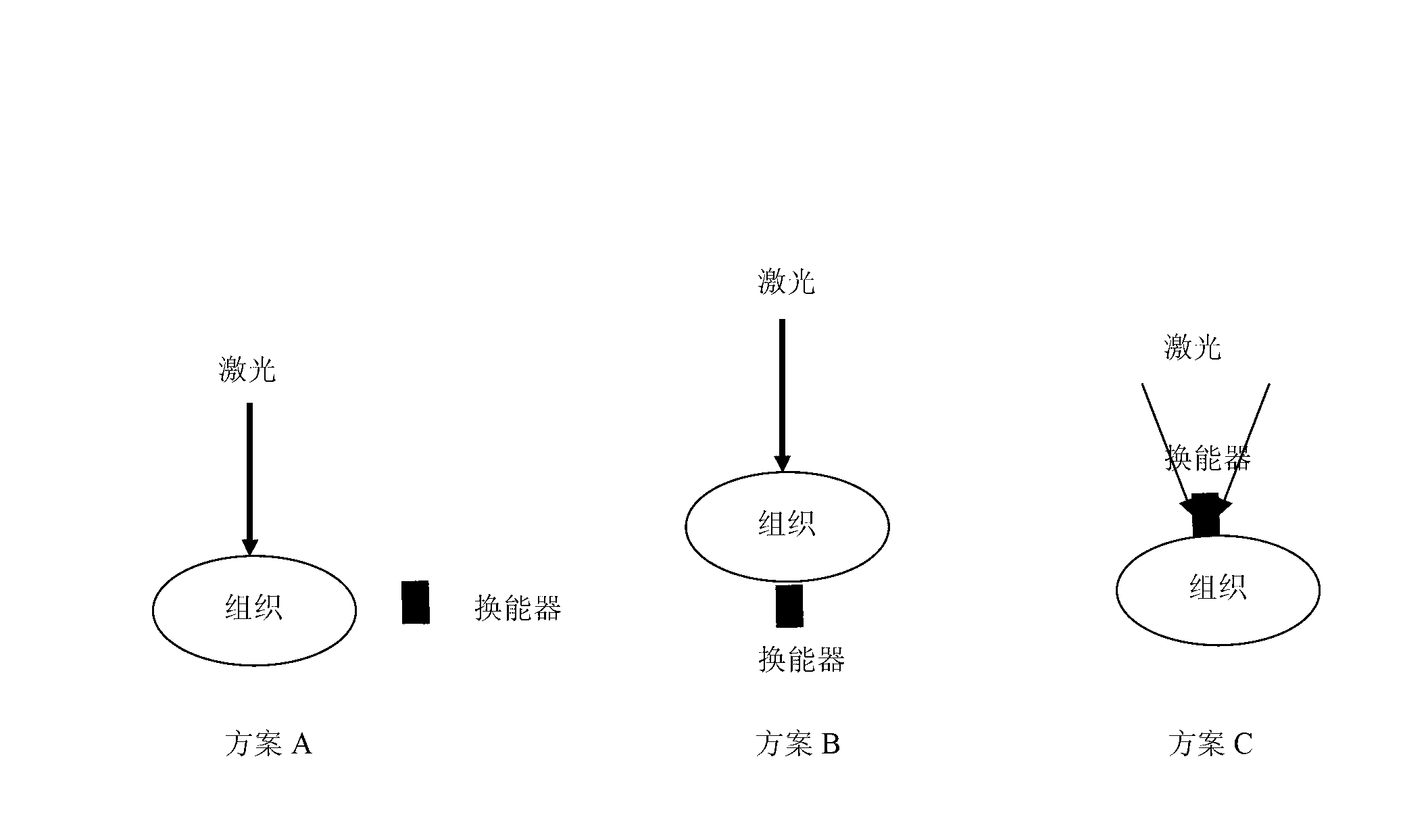
Acoustic imaging probe incorporating photoacoustic excitation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide for a photoacoustic imaging probe for use in a photoacoustic imaging system, whereby the probe is comprised of a cohesive composite, acoustic lens incorporating aspheric geometry and exhibiting low or practically no measurable dispersion of acoustic waves constructed of at least one material with a low acoustic impedance and attenuation and a relatively low acoustic velocity and at least one other material with a low acoustic impedance and attenuation and a relatively high acoustic velocity. The probe is housed in a conduit filled with a low acoustic velocity and low acoustic impedance fluid such as water or mineral oil. The lens may be designed as a telecentric lens, an acoustic zoom lens, a catadioptric lens, or a reflective lens. The lens focuses acoustic waves on an acoustic imager which detects the image. The acoustic imager may be designed as a 2 dimensional array of transducers. Research to date indicates that within the range of acoustic frequencies of interest, 1 MHz-50 MHz and preferable 2 MHz-10 MHz, there exists little velocity variation within the materials of interest, and the lens design approach may currently be considered to be essentially monochromatic. The acoustic waves can be generated when an emitting light source illuminates a test subject comprising materials that generate acoustic waves at differing intensities and / or frequencies when illuminated with light, for example tissue containing blood vessels, wherein the blood vessels excite and generate an acoustic pulse. The probe has an acoustic window made of a material with low acoustic impedance which allows the acoustic pulse to enter the probe without distortion and then may be reflected by a mirror onto the acoustic lens. The probe may include the emitting light source and an optical window to allow light emitting from said light source to illuminate the test subject.
Owner:ARNOLD STEPHEN C
System for photoacoustic imaging and related methods
InactiveUS20110054292A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAcoustic sensorsSonificationUltrasonic sensor
Photoacoustic imaging systems and methods that allow for the creation of three-dimensional (3D) images of a subject are described herein. The systems include one or more optical fibers attached to an ultrasound transducer. Ultrasonic waves are generated by laser light emitted from the optical fiber(s) and detected by the ultrasound transducer. 3D images are acquired by ultrasound signals from a series of adjacent scan planes or frames that are then stacked together to create 3D volume data.
Owner:VISUALSONICS
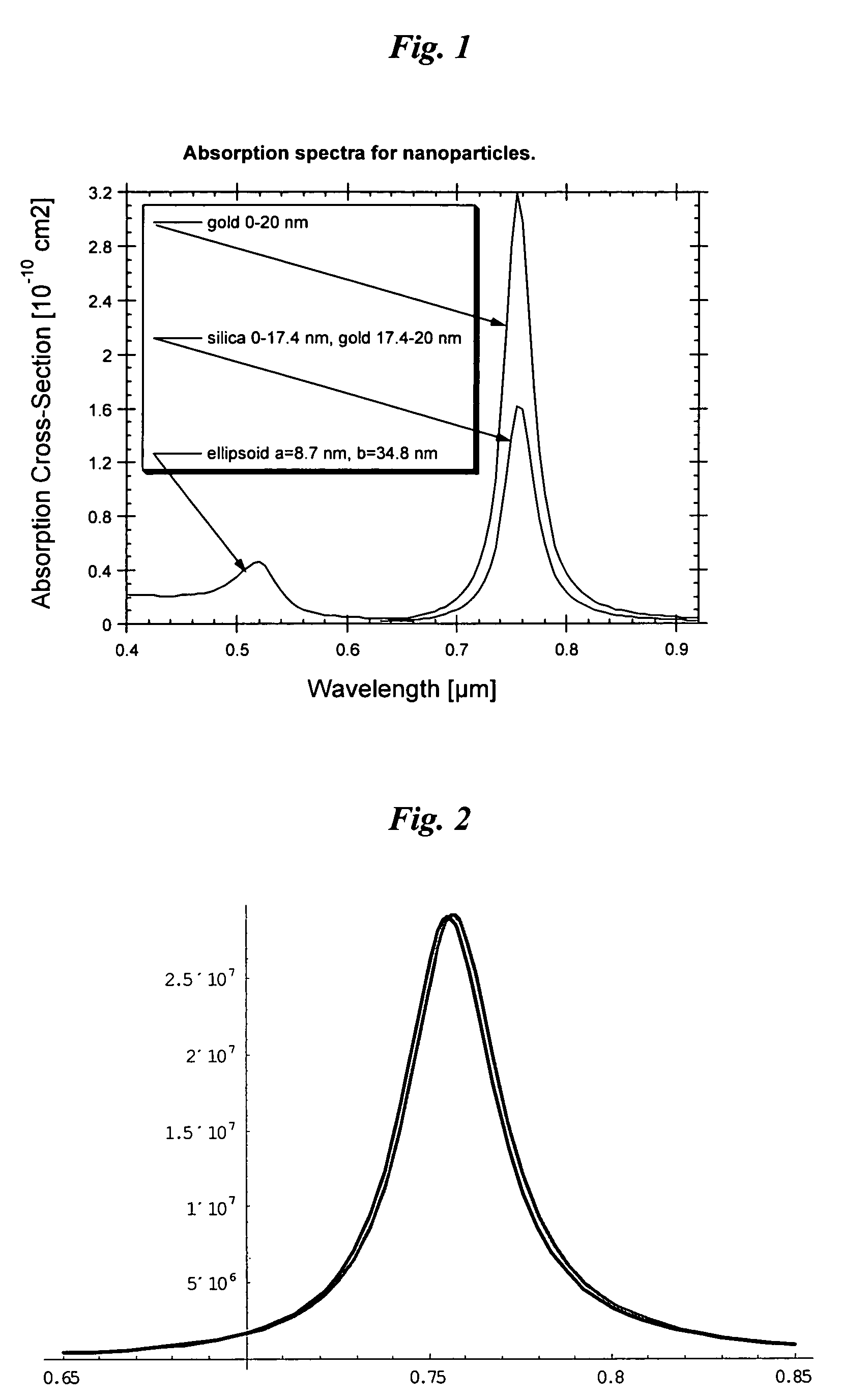
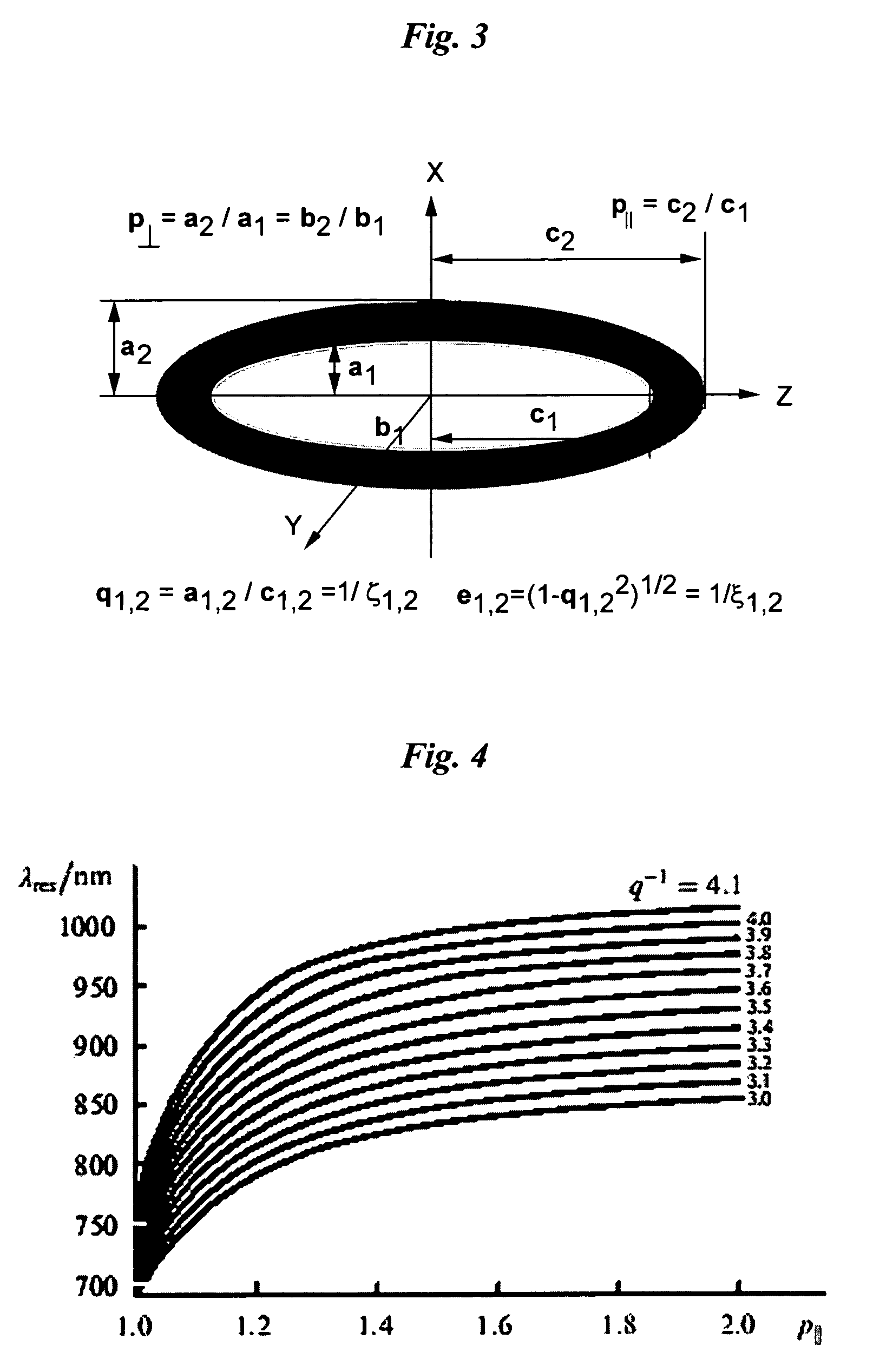
High contrast optoacoustic imaging using nanoparticles
InactiveUS7500953B2Maximize both the optical absorbanceIncrease the effective absorbanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryNanoparticleElectromagnetic radiation
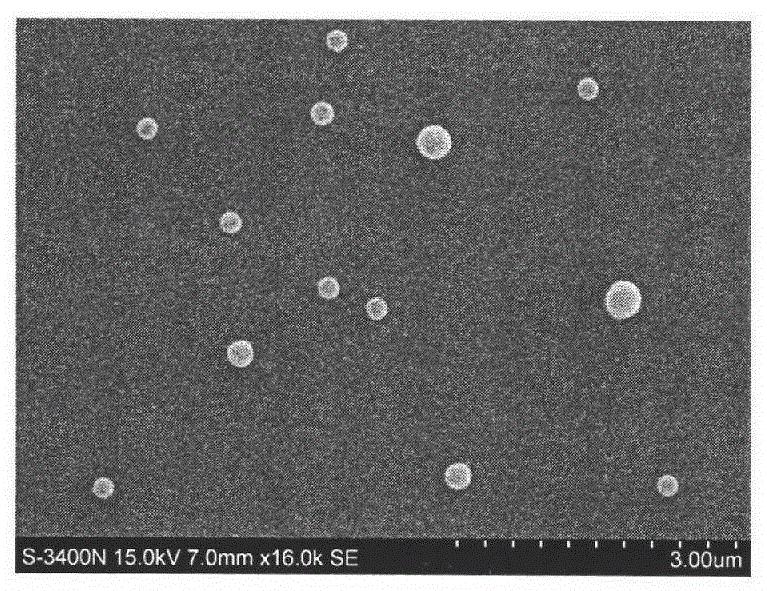
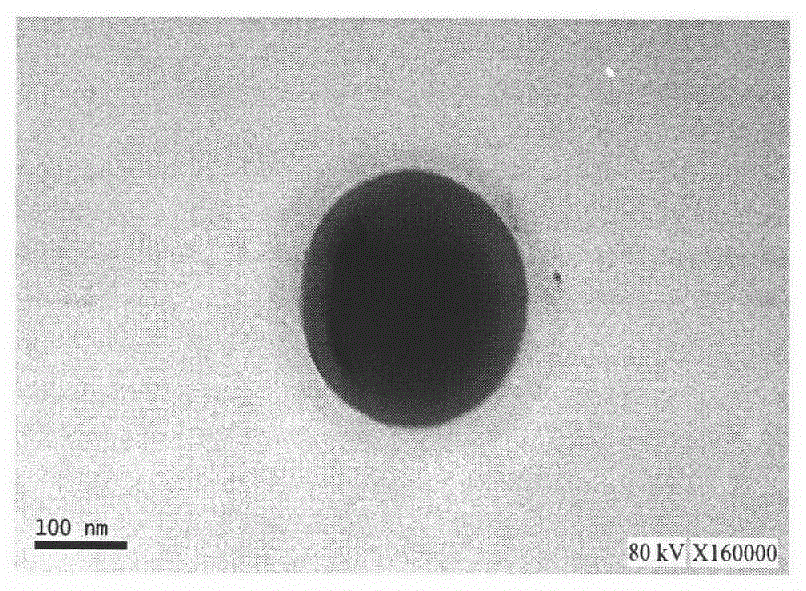
A method of enhancing detection for a specific object in a body. A nanoparticulate is administered to the body for location in an area to be explored for detection of the object, if present. The nanoparticulate is at least partially metallic, has a formed non-spherical shape having a minimal characteristic dimension in the range from about 1 to about 3000 nanometers, and has a formed composition capable of producing thermal pressure either in the nanoparticulate or in the object greater than the object could produce in the absence of the nanoparticulate. Electromagnetic radiation is directed into the body. The electromagnetic radiation has a specific wavelength or spectrum of wavelengths in the range from 300 nm to 300 mm selected so that the wavelength or wavelength spectrum is longer by a factor of at least 3 than the minimum characteristic dimension of the nanoparticulate. The nanoparticulate absorbs the electromagnetic radiation more than would one or more non-aggregated spherically shaped particles of the same total volume with a composition identical to the nanoparticulate. The nanoparticulate produces an enhanced optoacoustic signal resulting from the absorption that is received and converted into an electronic signal and presented for assessment of the at least one parameter by a human or a machine.
Owner:SENO MEDICAL INSTR
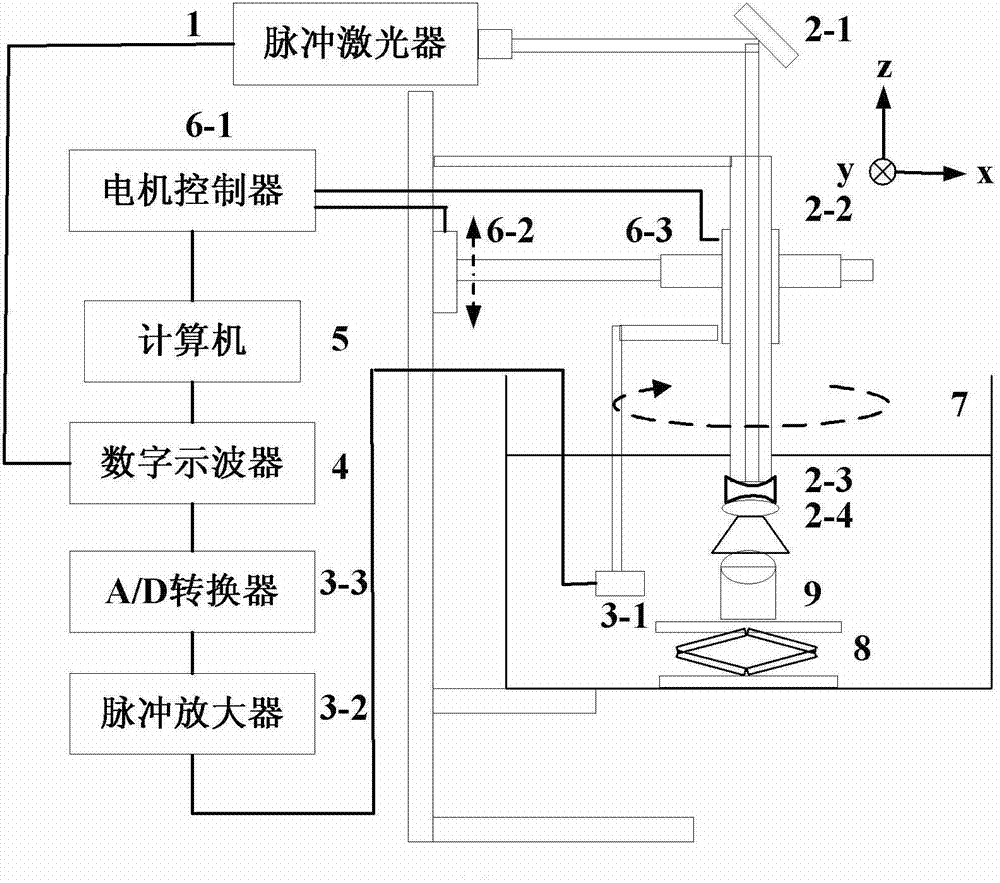
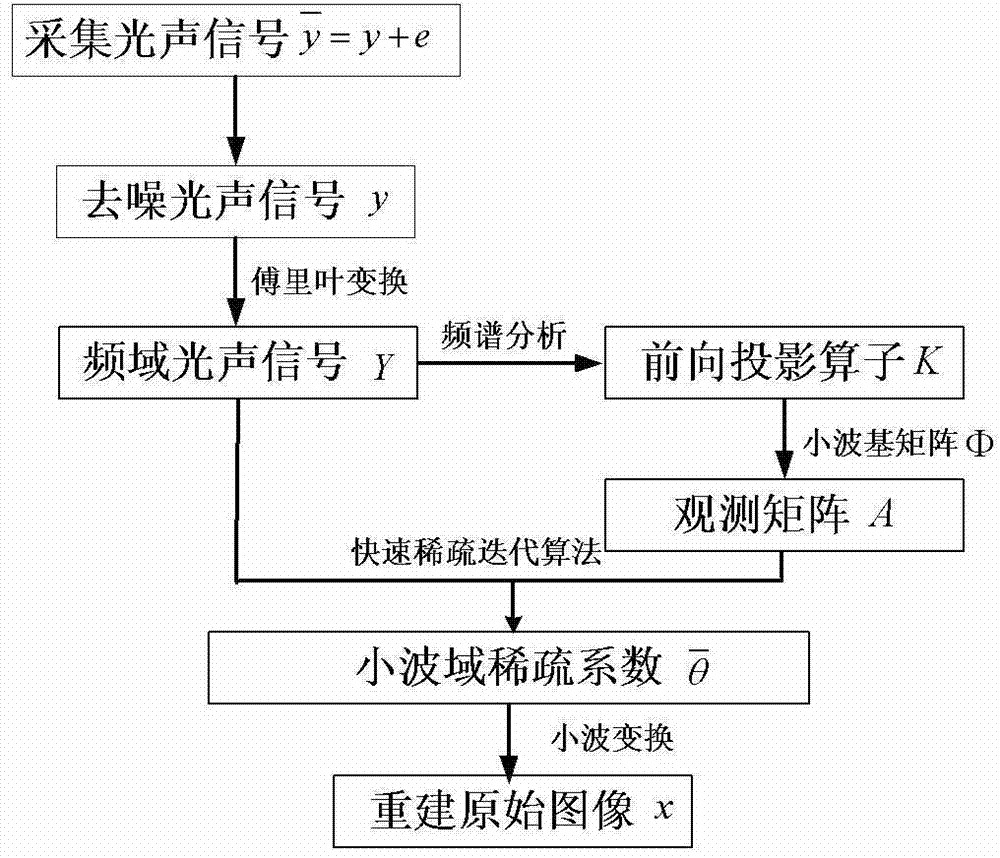
Photoacoustic tomography device and method based on limited-angle scanning
ActiveCN102727259AImprove reliabilityReduce hardware costsTomographyThinning algorithmDigital signal
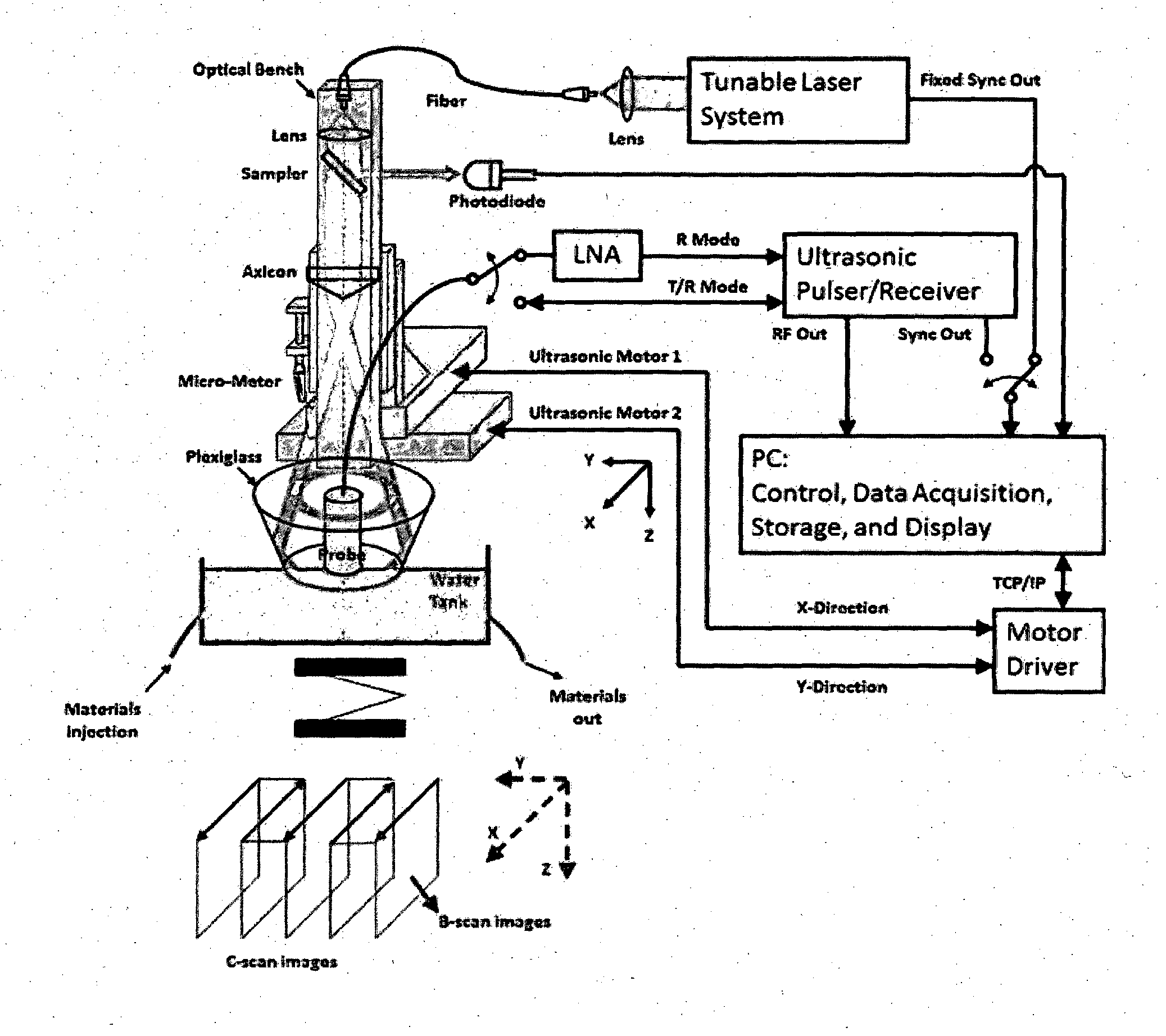
The invention relates to the technical field of photoacoustic imaging and discloses a rapid photoacoustic tomography device and a rapid photoacoustic tomography method based on limited-angle scanning. The method comprises the following steps of: transmitting pulse laser into an imaging sample to generate a photoacoustic signal, acquiring the photoacoustic signal at a limited position on an arc through an ultrasonic detector unit, amplifying the signal through a signal amplifier, converting the photoacoustic signal into an electric signal through an analog / digital (A / D) converter, and finally transmitting the electric signal to an oscilloscope to finish digital signal acquisition; inputting the photoacoustic signal of the imaging sample into a computer, performing filtering and Fourier transform processing on the photoacoustic signal through the computer, extracting the frequency domain information of the photoacoustic signal according to experiment conditions, establishing a forward projection operator and a measurement matrix, and performing reconstruction imaging on the signal based on a quick thinning algorithm through the computer. The method and the device have the advantages of short signal acquisition time, high reconstruction speed, convenience in operation, high adaptability, high expansibility and the like.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
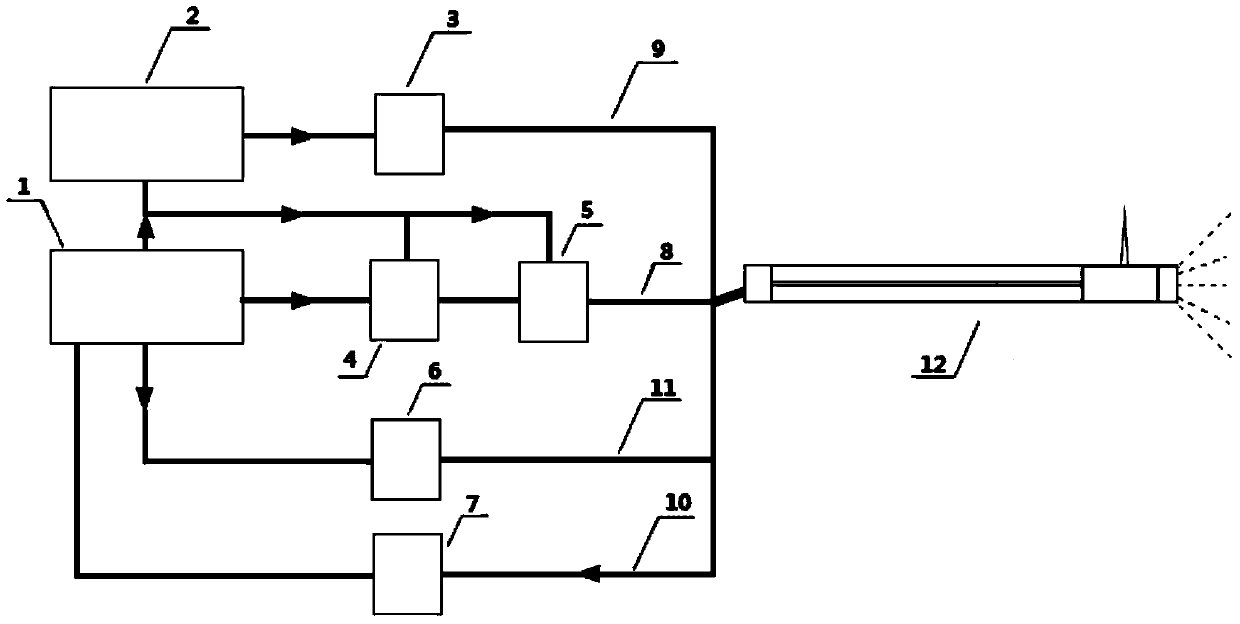
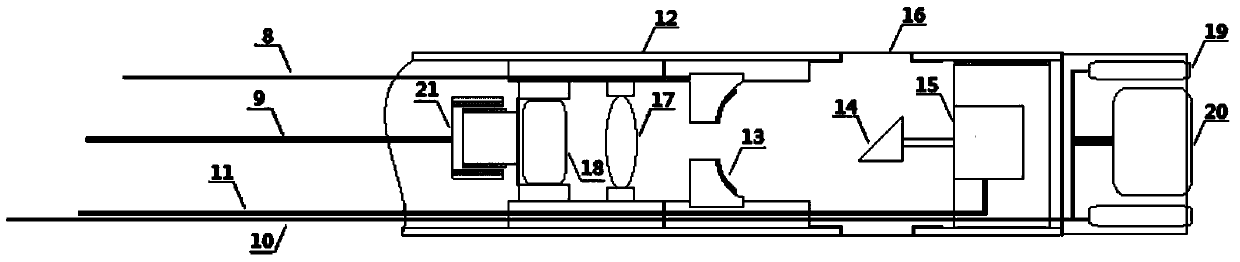
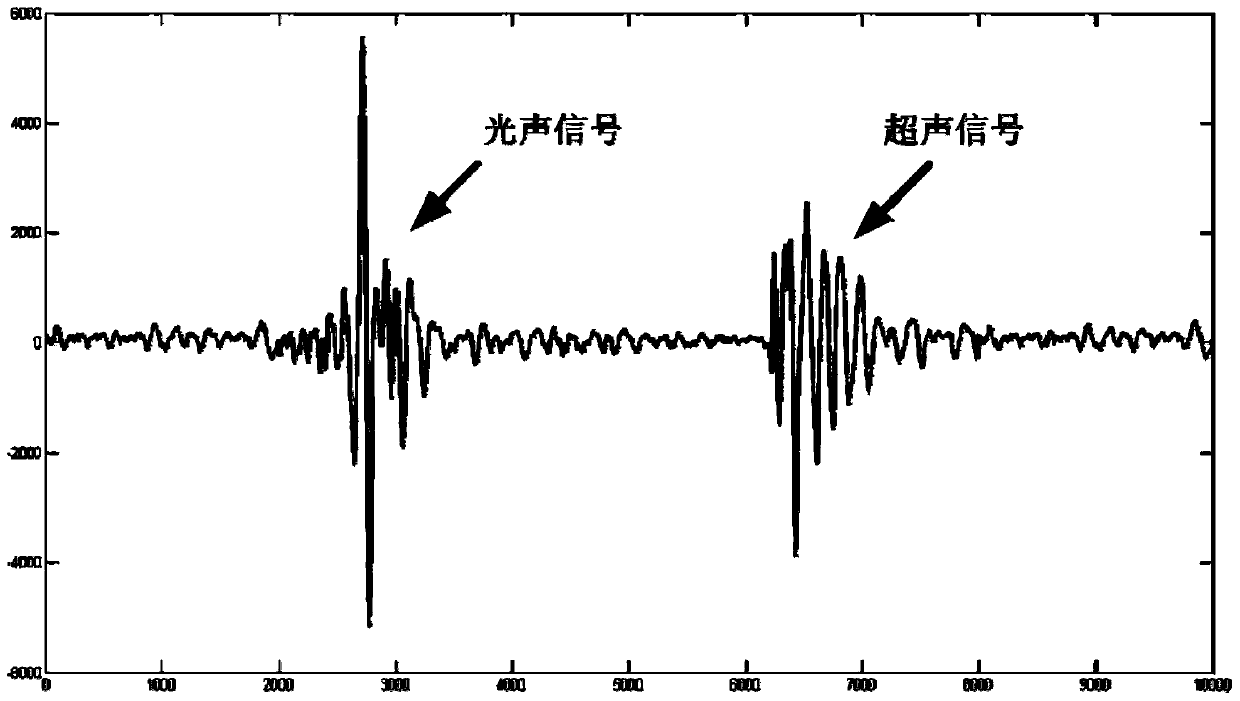
Internal rectal optical, optoacoustic and ultrasonic multimode imaging endoscope and imaging method thereof
ActiveCN103690141AEnable simultaneous acquisition of imagingSimplify testing proceduresEndoscopesUltrasound imagingPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
The invention discloses an internal rectal optical, optoacoustic and ultrasonic multimode imaging endoscope which comprises a sleeve, an optoacoustic signal activating component, an ultrasonic signal activating and collecting component, an optical imaging component and an image reconstructing and displaying component. A device comprises a compact internal rectal optical, optoacoustic and ultrasonic multimode imaging endoscope, three kinds of imaging can be performed simultaneously, multi-parameter physical information and multi-scale structural images in recta can be acquired. The invention further provides a configuration scheme of the whole device and a method for utilizing the device for imaging. Three imaging techniques are highly integrated into one set of instrument, each imaging technique is optimized, and combination of three rectal endoscopic imaging methods of optical imaging, optoacoustic imaging and ultrasonic imaging is realized. The integrated endoscope combines specific advantages of three imaging modes, rectal physical images with multi-parameter information and multi-scale structural characteristics can be acquired, and application requirements of a rectal endoscope on medicine can be met better.
Owner:广州佰奥廷电子科技有限公司
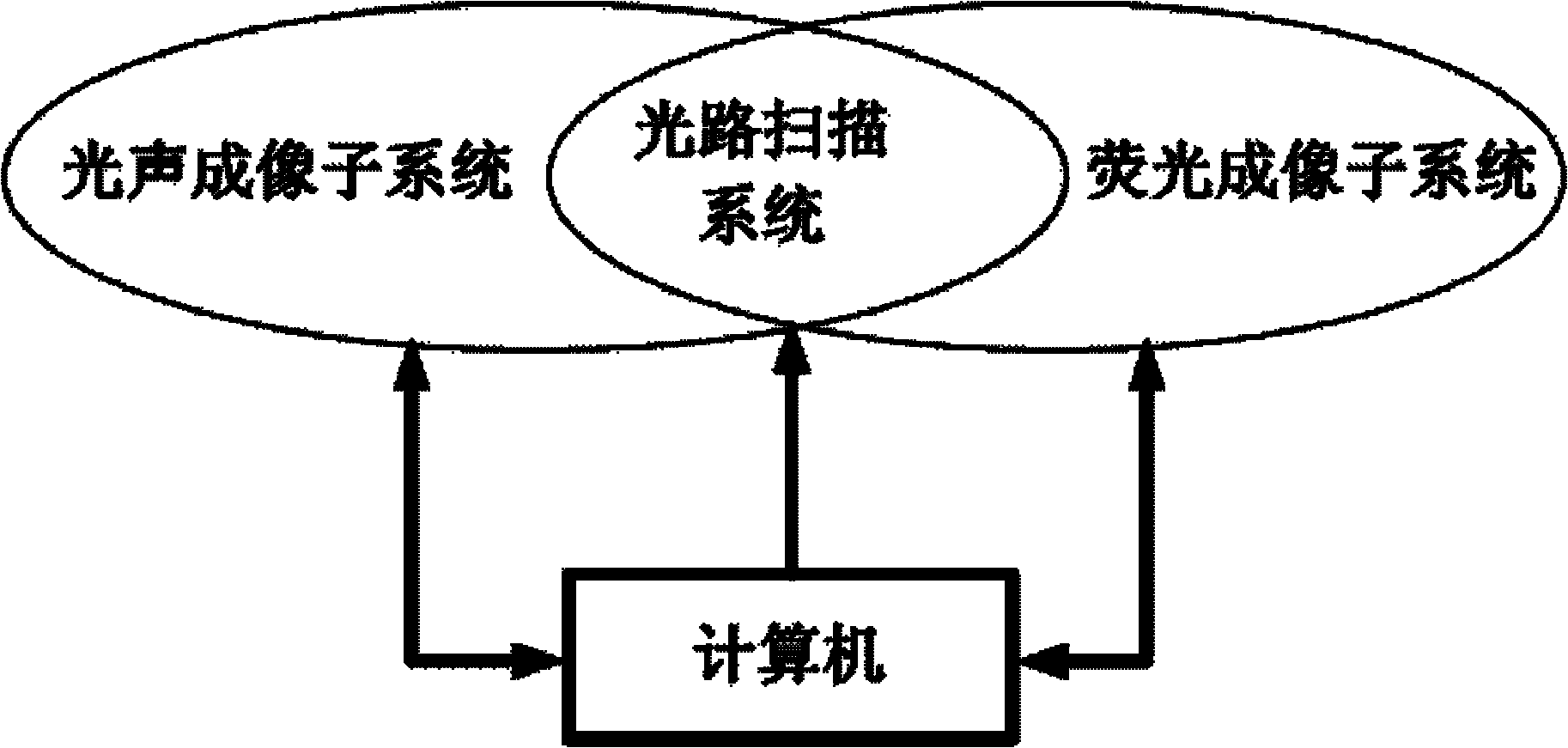
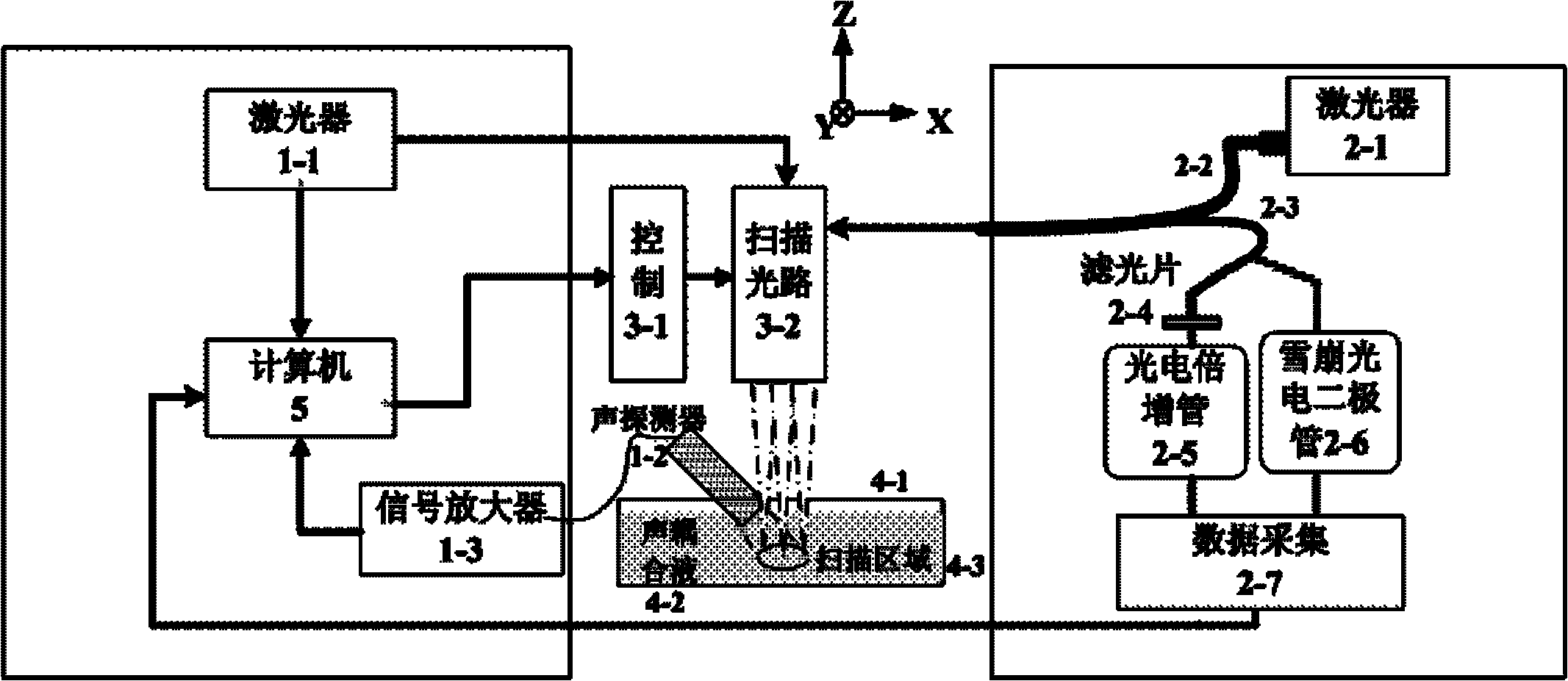
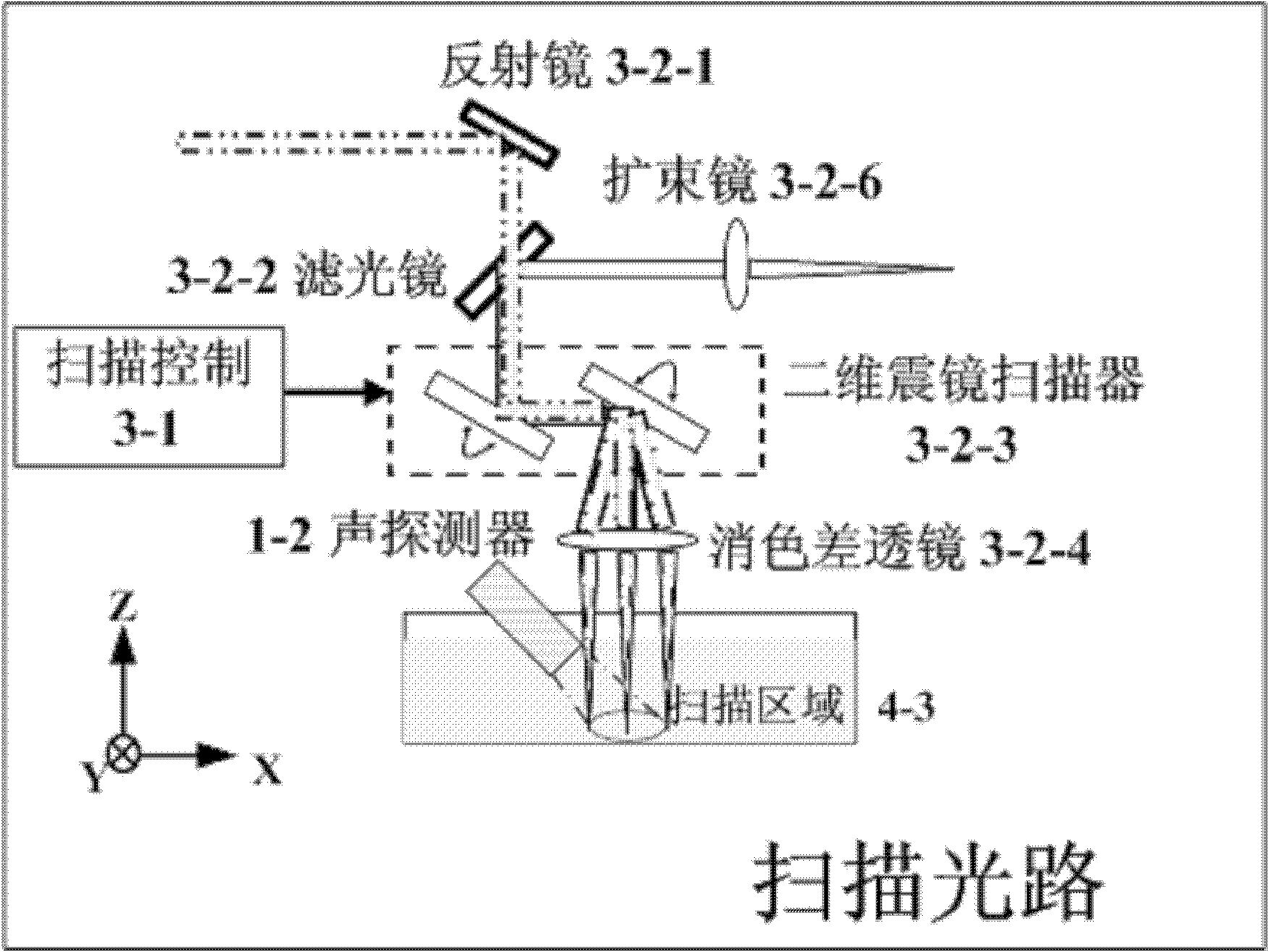
Bimodal system and method integrating photoacoustic imaging and fluorescence imaging
InactiveCN101785662ARealize Simultaneous ImagingHigh sensitivityAuscultation instrumentsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicineFluorescent imaging
The invention discloses a bimodal system and method integrating photoacoustic imaging and fluorescence imaging. In the invention, the complementarity between photoacoustic imaging and fluorescence imaging on the imaging theory is used, and through a common scanning light path system, photoacoustic imaging and fluorescence imaging are effectively integrated into a whole. The device for realizing the method of the invention comprises an photoacoustic imaging subsystem, a fluorescence imaging subsystem and a computer, wherein the photoacoustic imaging subsystem and the fluorescence imaging subsystem are integrated through the scanning light path system; the computer is respectively connected with the photoacoustic imaging subsystem, the fluorescence imaging subsystem and the scanning light path system; and the computer not only controls the scanning mode of the scanning light path system, but also processes the data of the photoacoustic imaging subsystem and the fluorescence imaging subsystem, combines the photoacoustic information and fluorescence information, and reconstructs photoacoustic and fluorescence bimodal images. The method of the invention has accurate positioning and high resolution, and the imaging system has lower cost and easy popularization.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Quantitative optoacoustic tomography with enhanced contrast
InactiveUS20070238958A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyOptoacoustic imaging
Provided herein is an optoacoustic imaging system configured to produce images of one or more objects in a body using at least a maximum angular amplitude probability algorithm to reconstruct the optoacoustic images of the body. In addition the optoacoustic imaging system may be configured to produce 3D maps from the reconstructed optoacoustic images of the body. Also, provided is a method for diagnosing a pathophysiological condition characterized by abnormal optical properties of tissues in a body from maps so produced.
Owner:SENO MEDICAL INSTR
Rapid three-dimensional photoacoustic imaging system based on ultrasonic plane array detector and method thereof
ActiveCN101813672AAchieve receptionQuick collectionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationSonificationInstability
The invention discloses a rapid three-dimensional photoacoustic imaging system based on an ultrasonic plane array detector which has the advantages of simple operation, low manufacturing cost and convenient detection and an imaging method thereof. The rapid three-dimensional photoacoustic imaging method based on the ultrasonic plane array detector mainly comprises the following steps: adopting a laser pulse to excite ultrasonic signals which can produce a light induced thermal elastic effect, collecting photoacoustic signals in parallel simultaneously with a plane array detector and multiple array elements, processing the signals in a three-dimensional phase-controlled algorithm, and reconstructing an optical absorption and distribution image for a sample to be detected. The three-dimensional photoacoustic imaging device comprises a photoacoustic excitation source device, a photoacoustic signal receiving and collecting device and a computer component. The invention overcomes the defects of the traditional technology such as low imaging speed, poor stability due to long-term system operation, complex device and the like, simultaneously combines the advantages of pure acoustics and pure optical imaging, and can provide images reflecting optical absorption and distribution of tissues. The device of the invention has the advantages of simple structure and easy promotion.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
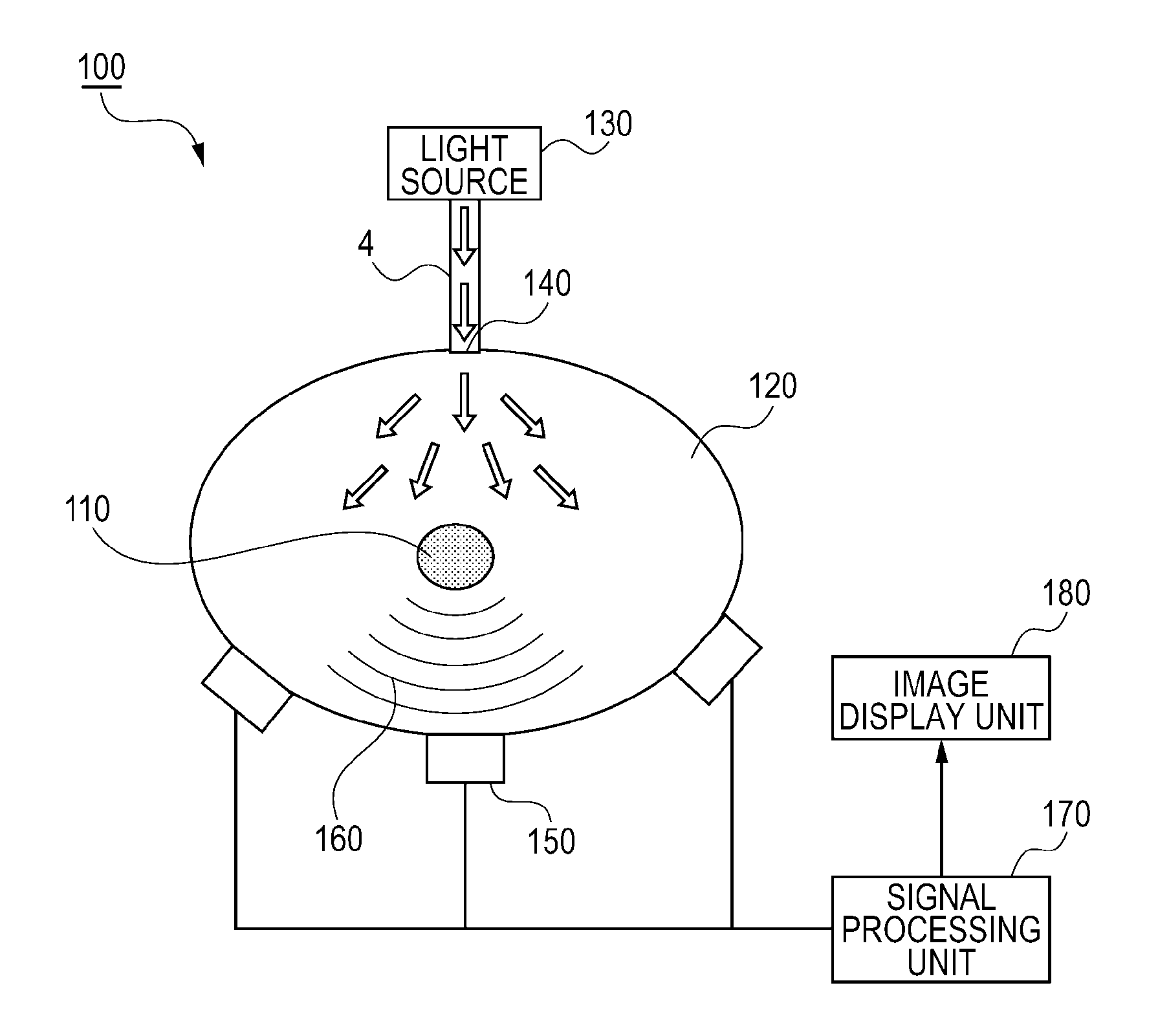
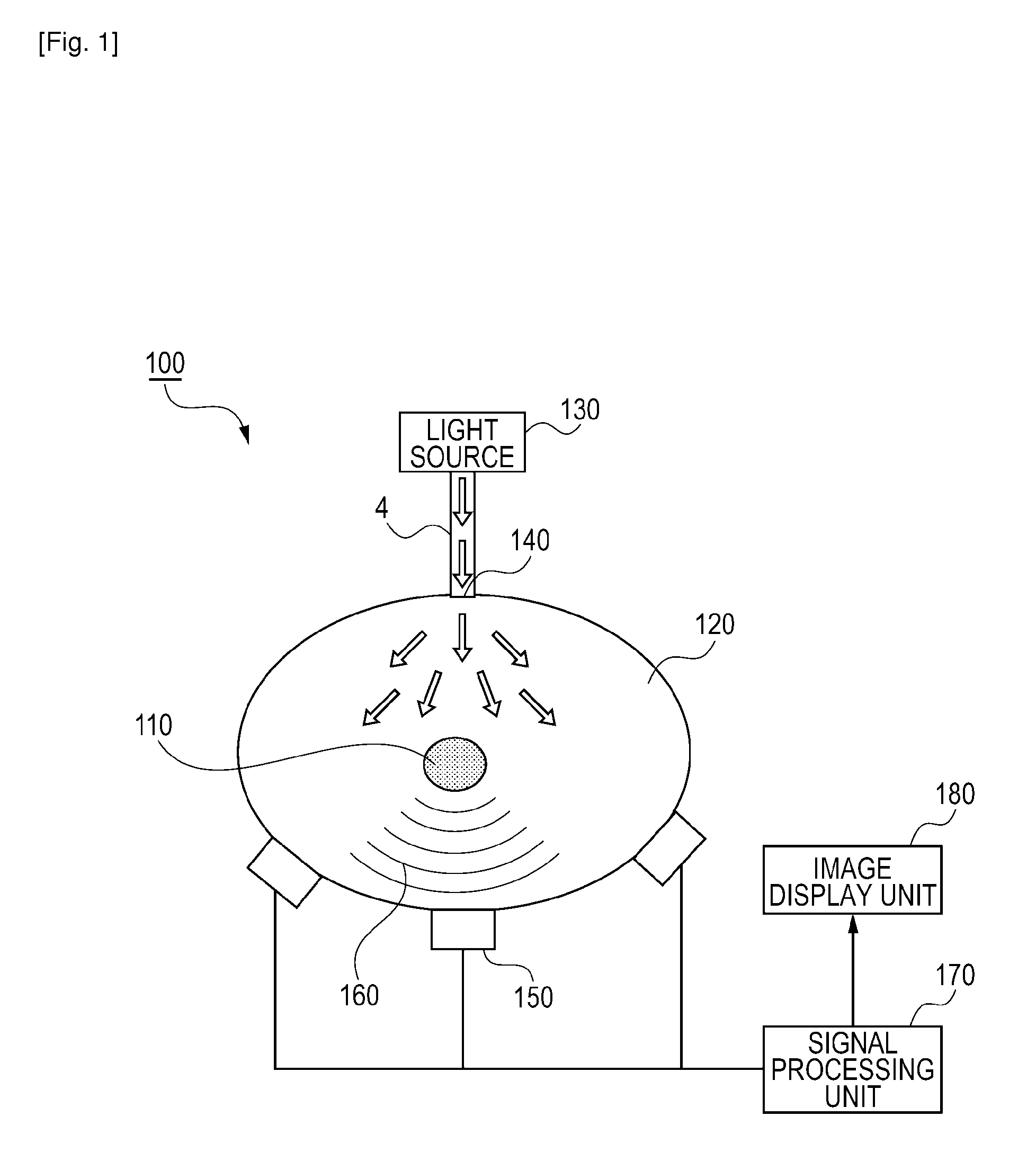
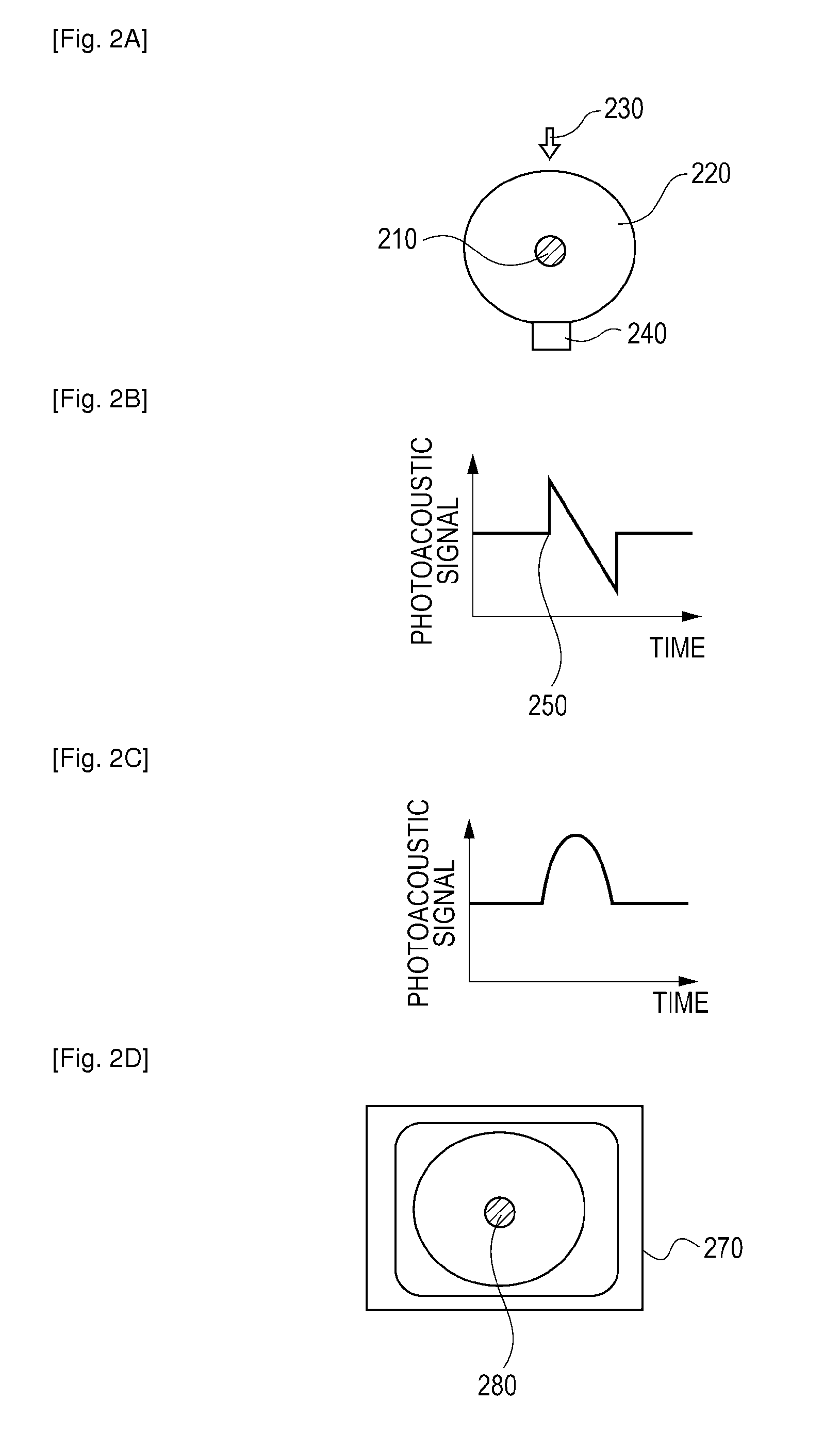
Photoacoustic imaging apparatus and photoacoustic imaging method
InactiveUS20110239766A1Imaging be performVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAbsorbed energyAcoustic wave
A photoacoustic imaging apparatus performs imaging of an optical absorber. The photoacoustic imaging apparatus includes a light source, a detector configured to detect an acoustic wave generated from the optical absorber that has absorbed energy of light emitted from the light source, and a signal processing unit configured to form an image of the optical absorber. The signal processing unit stores information indicating whether a rate of change in pressure of the acoustic wave detected by the detector is positive or negative before performing a waveform process on the acoustic wave.
Owner:CANON KK
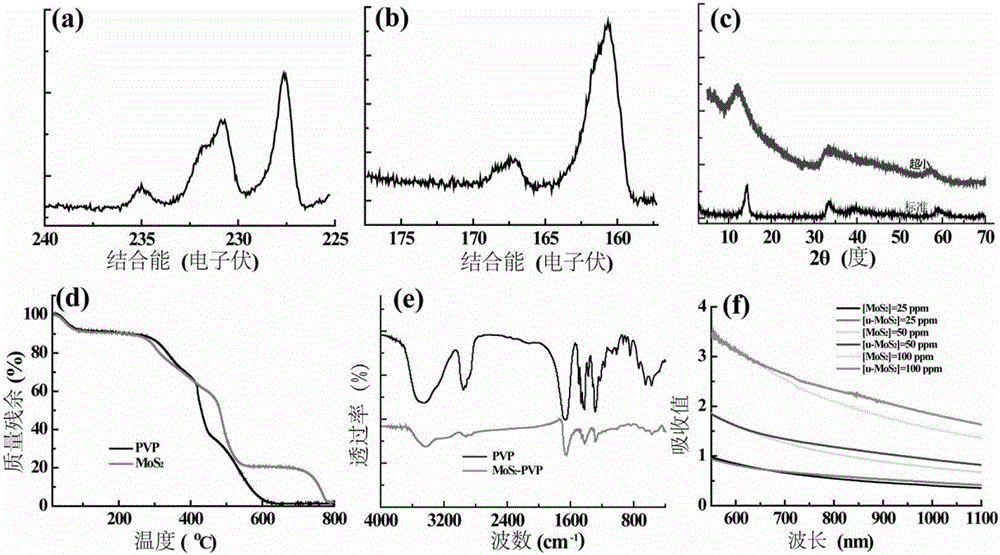
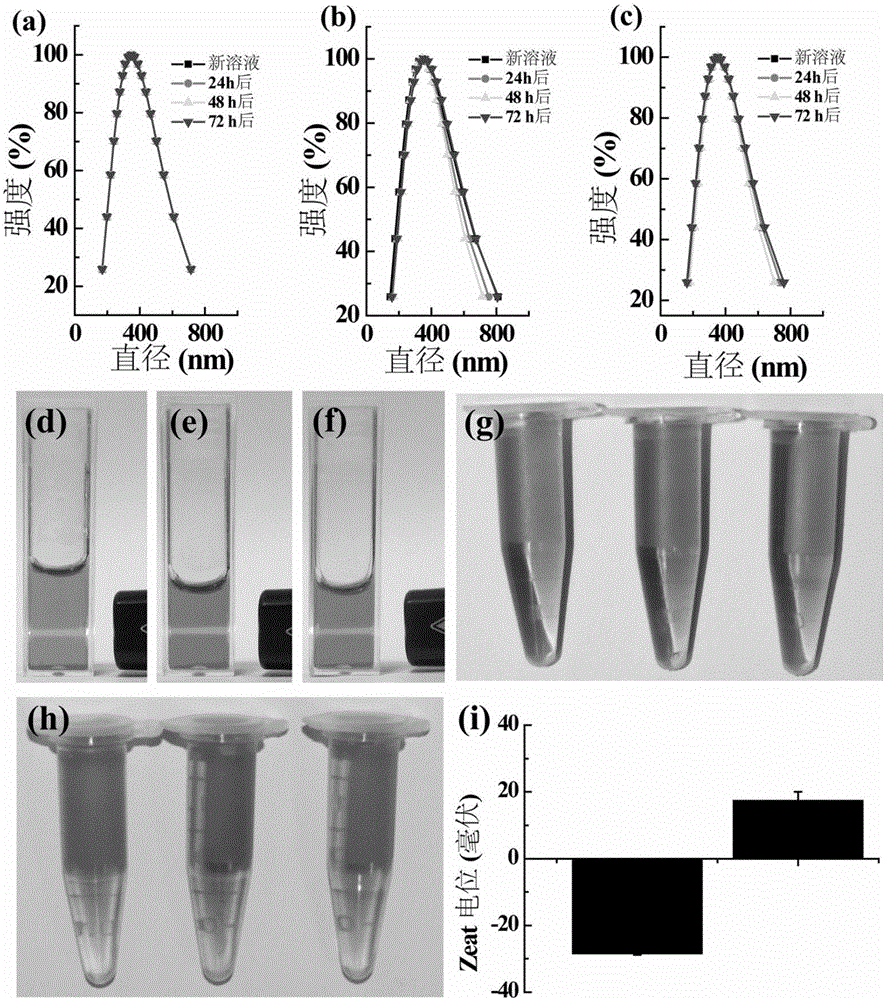
Ultra-small MoS2 nanosheet as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106075438AImprove colloidal stabilityGood biocompatibilityEnergy modified materialsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsSulfurDistilled water
The invention discloses an ultra-small MoS2 nanosheet. The surface of the MoS2 nanosheet is modified with polyvinylpyrrolidone, and the diameter of the modified MoS2 nanosheet ranges from 15 nm to 25 nm. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the ultra-small MoS2 nanosheet. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a sulfur source and a molybdenum source are dissolved in water and stirred until the resources are completely dissolved; polyvinylpyrrolidone is dissolved in the solution of the sulfur source and the molybdenum source; the solution is transferred into a stainless steel reaction kettle with a polyphenyl lining for closed reaction, a reaction product is washed with an ethanolamine water solution and distilled water, and the ultra-small MoS2 nanosheet with the surface modified with polyvinylpyrrolidone is obtained. The invention further provides an application of the ultra-small MoS2 nanosheet as a photo-thermal conversion material. The ultra-small MoS2 nanosheet has good colloid stability, photo-thermal conversion capacity and photo-acoustic imaging capacity and has broad application prospect in the fields of tumor treatment and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH +1
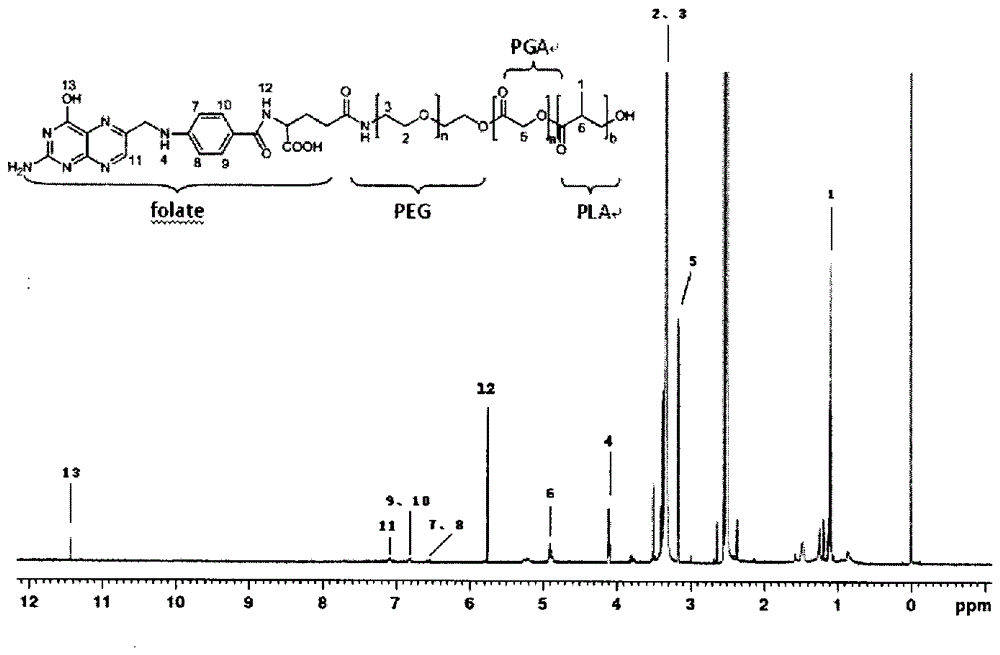
Multifunctional multimode tumor-specific targeting phase-change nano-microsphere photoacoustic contrast medium and application thereof
ActiveCN106267241AEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsX-ray constrast preparationsMicrosphereCell membrane
The invention discloses a multifunctional multimode tumor-specific targeting phase-change nano-microsphere photoacoustic contrast medium, structurally comprising, from outside to inside, a ligand that is positioned on the surface of nano-microspheres and specifically binds with a tumor cell membrane surface receptor; the ligand is connected with shell membrane material through linker molecules, and the shell membrane material wraps photo-absorbers and phase-change molecules to the core. A preparation method of the medium includes: linking the ligand to the shell membrane material through the linker molecules by a 'five-step process' to prepare a targeting shell; wrapping the photo-absorbers and phase-change molecules to the core of the nano-microspheres by a special double-emulsification process, while making sure the targeting ligand is positioned on the surface of the nano-microspheres. In-vivo and in-vitro experiments indicate that the photoacoustic contrast medium may specifically bind with tumor cells to experience phase change; there are strong photoacoustic, ultrasonic and X-ray signals, and the medium is applicable to photoacoustic imaging, ultrasonic imaging and computed tomography.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Low-cost device for C-scan photoacoustic imaging
ActiveUS8353833B2Low costSmall sizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsImage contrastLaser light
The prostate gland or other region of interest is stimulated with laser light, resulting in ultrasound waves (photoacoustic effect) which are focused by an acoustic lens and captured by a specific 1- or 2D sensor array and subsequently displayed as a C-scan on a computer screen. The amplitude of the ultrasound waves generated by laser stimulation is proportional to the optical absorption of the tissue element at that spatial location. Variability in tissue absorption results in C-scan image contrast. The photoacoustic imaging is combined with an ultrasound C-scan image produced with a plane ultrasound wave applied to the region of interest.
Owner:ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
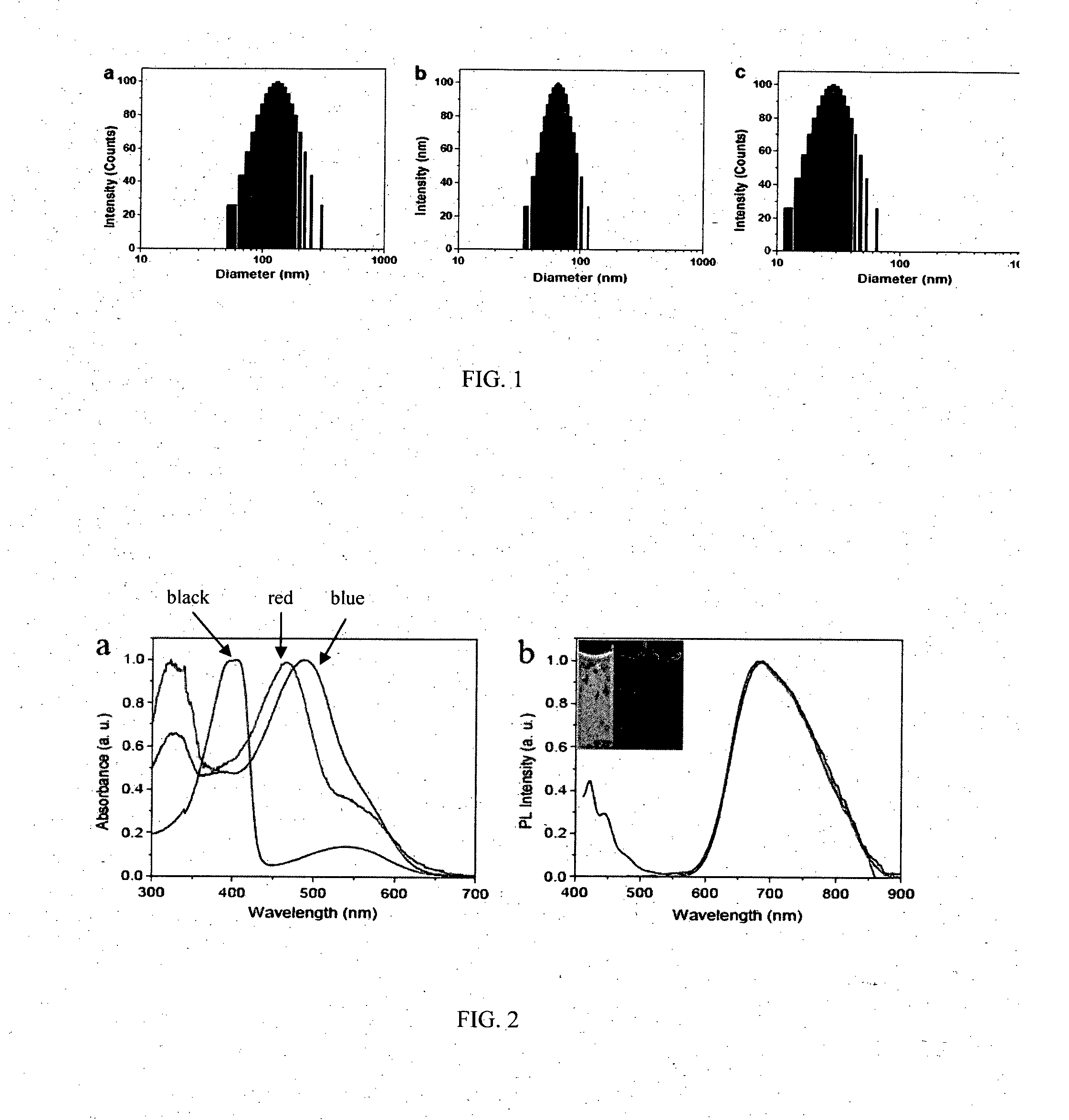
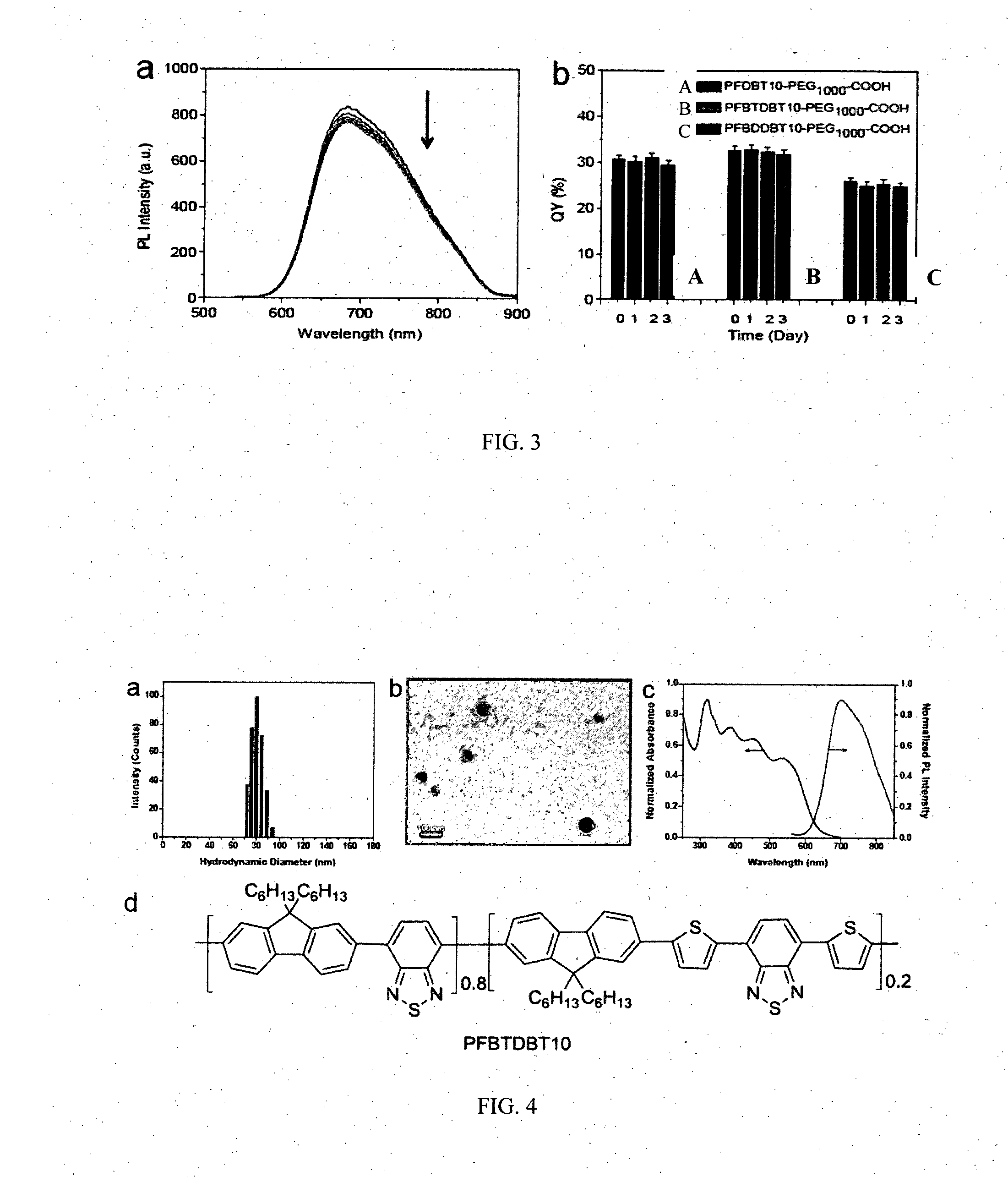
Highly Emissive Far-Red/Near-Infrared Fluorescent Conjugated Polymer-Based Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20150175747A1High quantum yieldImprove light resistancePowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyFar-redFluorescence
A series of conjugated polymer-based nanoparticles having far-red / near infrared emission ranges are disclosed. Cross coupling methods to prepare the conjugated polymers and methods of nanoparticle preparation are also discussed. The conjugated polymer nanoparticles are used as FR / NIR fluorescent probes in in vitro and in vivo biosensing and bioimaging applications, and are also used in photoacoustic imaging as contrast agents. Finally, use of the conjugated polymer nanoparticles in photothermal therapy is described.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
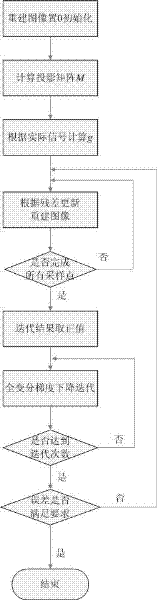
Image reconstruction method for photoacoustic imaging in random scanning mode
InactiveCN102306385AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnostics2D-image generationRadiologyPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
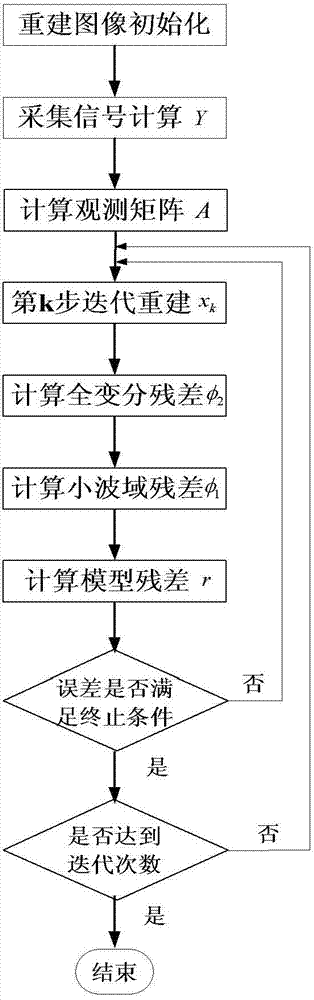
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoacoustic imaging, in particular to an image reconstruction method applicable for photoacoustic imaging in a random scanning mode. In the method, a reconstructed image is obtained by calculating a residual error between a projection signal and an actual signal of the reconstructed image, modifying and iterating the reconstructed image, comprehensively taking the characteristics of total variation sparsity in an iterating process into consideration, and combining a total variation gradient descent method. By the method, a photoacoustic image can be reconstructed precisely in the random scanning mode, so that the method has practical using significance.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Photoacoustic imaging apparatus and photoacoustic imaging method
InactiveUS20130338478A1Avoid spaceImprove securityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicineAcoustic wave
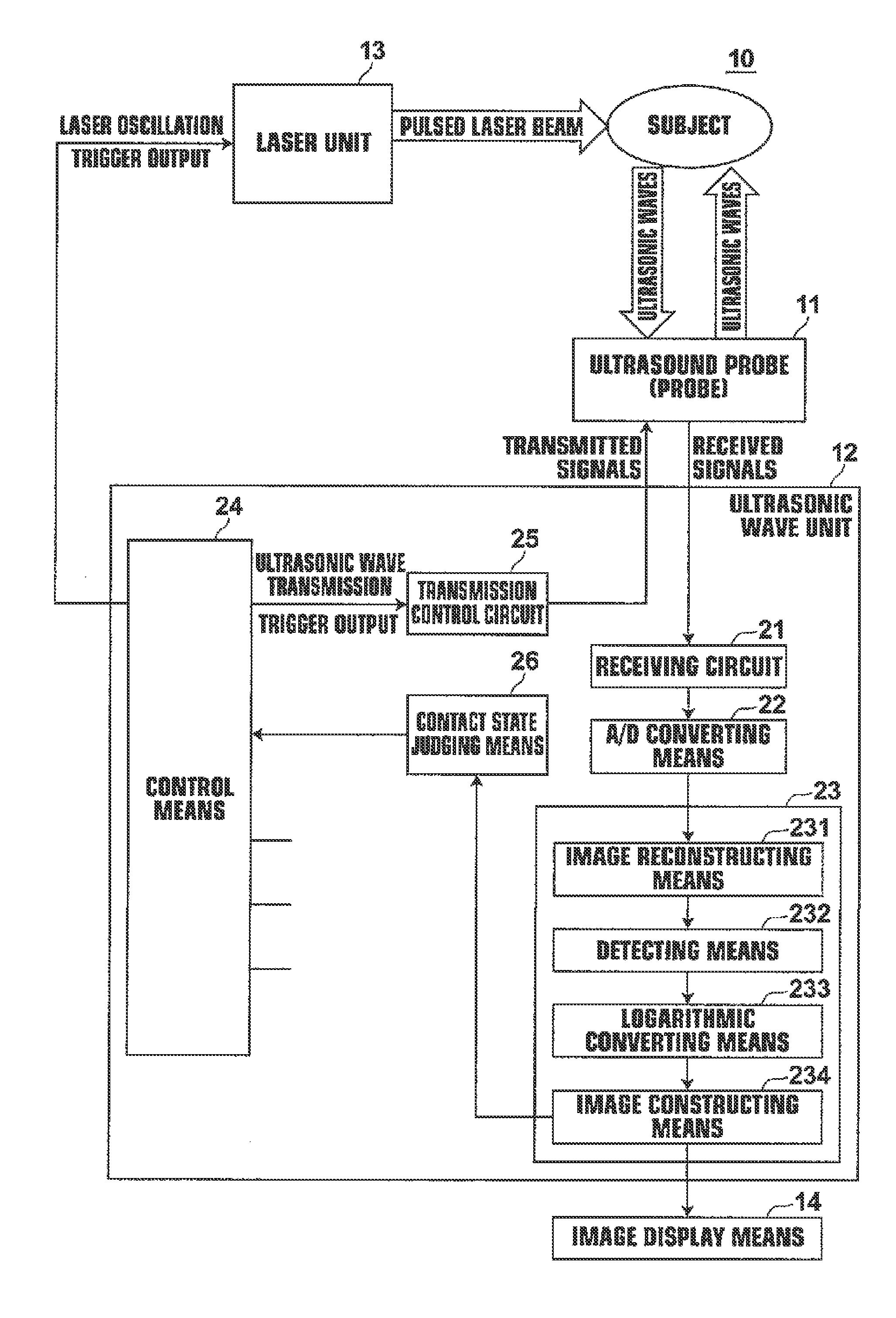
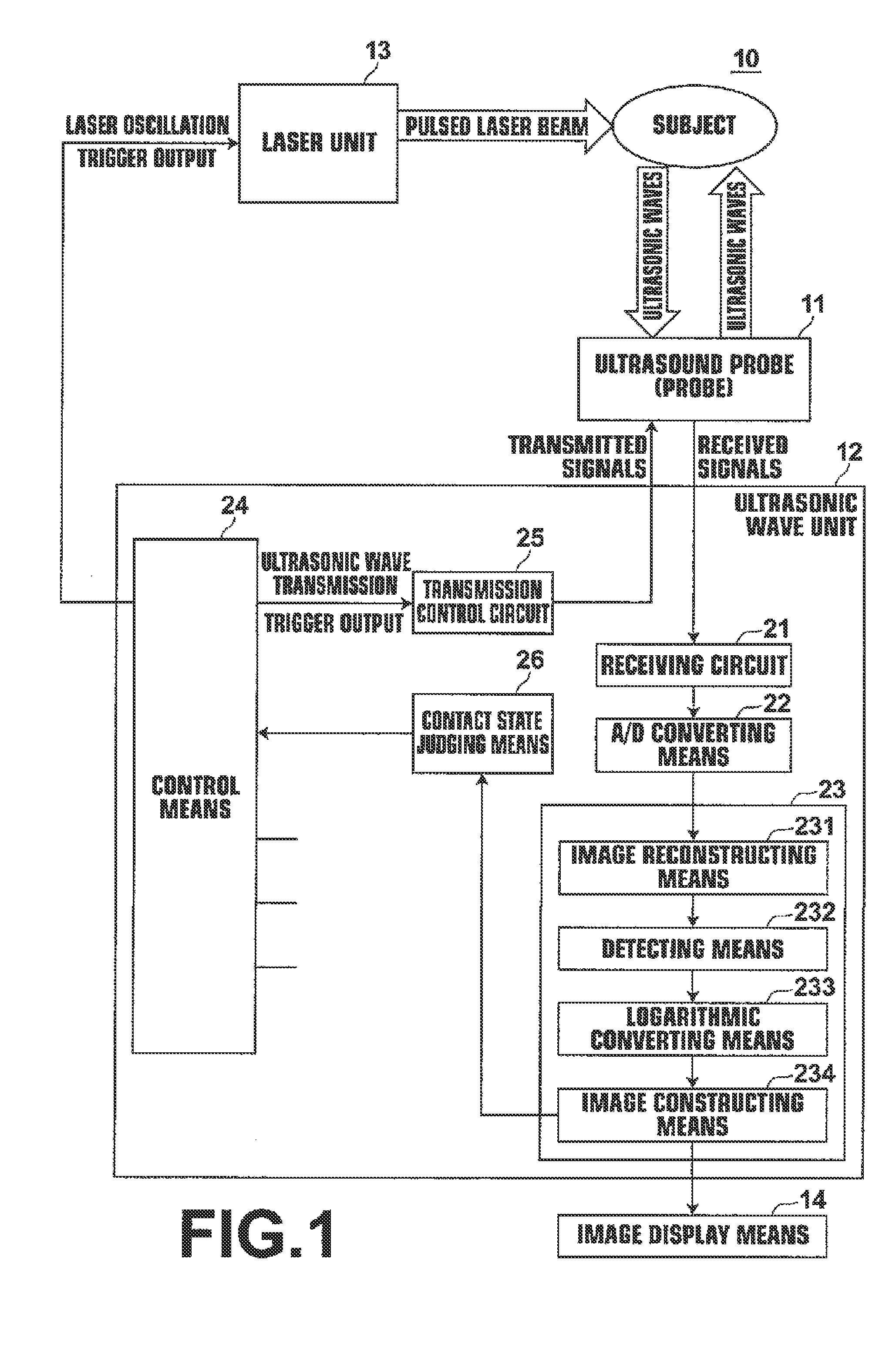
A probe transmits acoustic waves toward a subject. After transmission of the acoustic waves, the probe receives reflected acoustic waves of the transmitted acoustic waves. Whether the probe is in contact with a subject is judged based on the received reflected acoustic waves. The probe irradiates light toward the subject when it is judged that the probe is in contact with the subject. After the light is irradiated, acoustic waves generated within the subject due to the light being irradiated are received. A photoacoustic image is generated based on the received acoustic waves generated due to the light being irradiated.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Microcirculation in meridian skin tissue real-time monitoring method, system and probe head
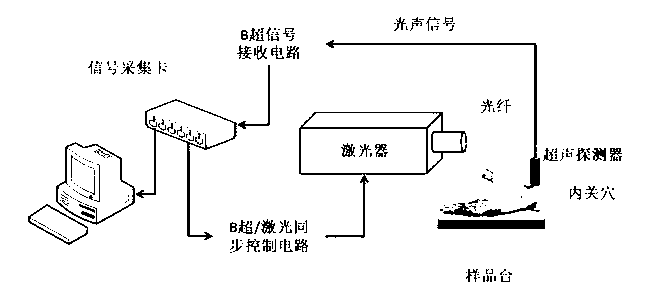
ActiveCN103054553AReal-time monitoring of microcirculationSolve real-time monitoring problemsOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseUltrasonic sensor
The utility model is applicable to the field of medical device and provides a microcirculation in meridian skin tissue real-time monitoring method, system and probe head. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, computer controls laser device to output laser according to certain frequency; secondly, the laser is conducted to probe head through optical fiber so as to irradiate tissue to be measured; thirdly, ultrasonic transducer inside the probe head receives ultrasonic signals generated by the tissue, and then transmits the ultrasonic signals back to computer; finally, the computer generates images according to the ultrasonic signals in the tissue. The embodiment can obtain microcirculation information in meridian skin tissue by utilizing photocoustic imaging technology, solve the problem of real-time monitoring of microcirculation in meridian skin tissue and provides basis or guidance for early diagnosis and treatment of related diseases. The microcirculation in meridian skin tissue real-time monitoring method, system and probe head is characterized in that photocoustic imaging is performed towards the meridian skin tissue in the process of acupuncture without moving the probe head and tissue so that real-time monition of microcirculation in meridian skin tissue is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
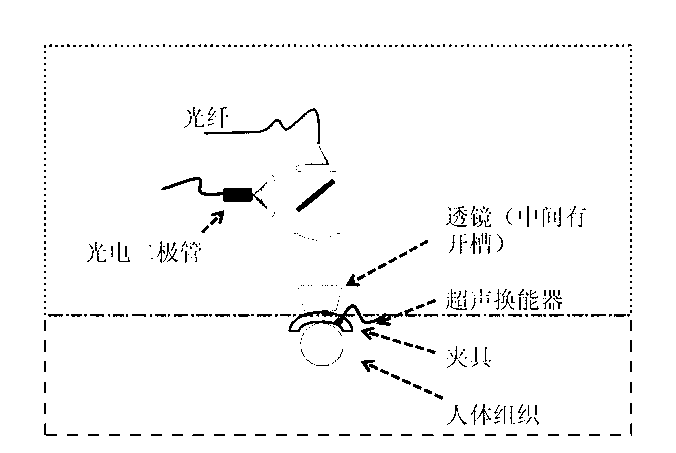
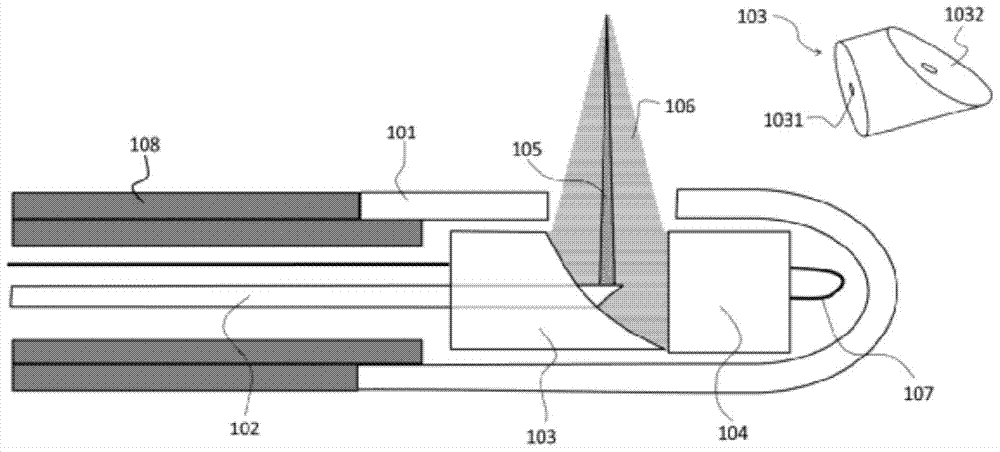
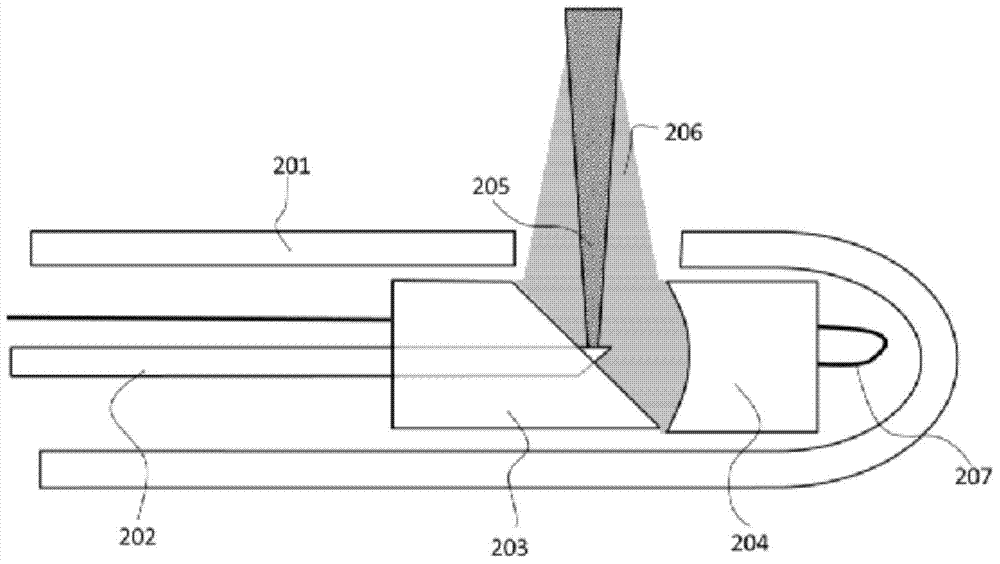
Endoscopic imaging probe and imaging method with same
ActiveCN104257342ASmall diameterEasy to processUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityOptical Module
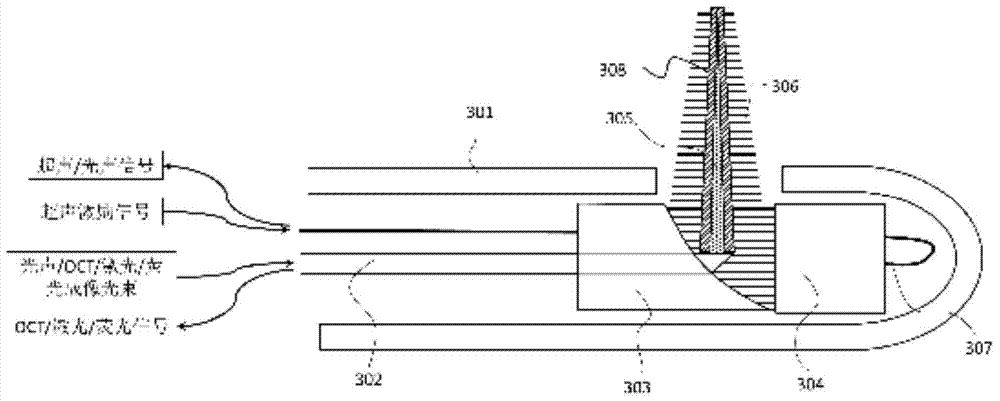
The invention provides an endoscopic imaging probe. The endoscopic imaging probe comprises an optical module, an ultrasonic module and a probe protective shell, wherein the ultrasonic module comprises an ultrasonic reflecting module and an ultrasonic detector; the protective shell is provided with an imaging window; the ultrasonic reflecting module comprises an ultrasonic reflecting surface corresponding to the imaging window in position and is arranged on the optical path of optical imaging light beams and / or optoacoustic exciting light beams, so that the optical imaging light beams and / or the optoacoustic exciting light beams can be emitted out in a direction coaxial to the ultrasonic wave beams reflected through the ultrasonic reflecting surface after penetrating the ultrasonic reflecting module. Besides, the invention also provides an endoscopic imaging method with the endoscopic imaging probe. Therefore, single-mode or multi-mode imaging of the same position point through optoacoustic imaging, optical imaging and ultrasonic imaging can be achieved, the imaging accuracy of every mode can be improved, the detecting efficiency of entire one-dimensional optoacoustic signals can be improved, and the diameter of the probe and the probe machining difficulty can be reduced as much as possible.
Owner:白晓苓
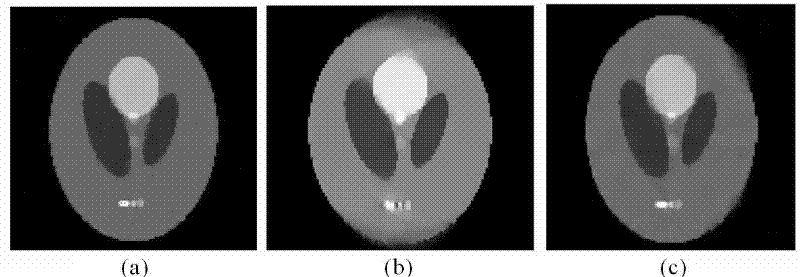
Method for rebuilding photoacoustic imaging image based on sparse coefficient p norm and total vibration parameter of image
InactiveCN103279966AImprove reconstruction qualityFast convergenceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnostics2D-image generationRadiologyPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoacoustic imaging, and particularly relates to a method for rebuilding a photoacoustic imaging image based on a sparse coefficient p norm and a total vibration parameter of the image. According to the method, the sparse representation coefficient p (0<p<1) norm and the total vibration parameter of the image are calculated to conduct iterative correction on the image, the sparse representation coefficient p (0<p<1) norm and the total vibration parameter are recalculated according to the iterated image, iteration is conducted repeatedly until an end condition is reached, and finally a rebuilt photoacoustic image is obtained. The method can improve the quality of the rebuilt photoacoustic image, is high in convergence speed, and has practical significance on the rebuilding of the photoacoustic imaging image.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Conjugated chain functional benzoindole hematocyanine dye and application
InactiveCN109370247AThe synthesis steps are simpleEasy to purifyMethine/polymethine dyesEnergy modified materialsFunctional activityIn vivo
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic chemistry and discloses a conjugated chain functional benzoindole hematocyanine dye and an application. The stability of the novel hematocyaninedye is obviously superior to that of an existing cyanine fluorescent probe, and the novel hematocyanine dye has the multiple functional activity such as near infrared fluorescence and tumor mitochondria targeted accumulation and photo-thermal and photo-power synergic treatment of killing tumor cells. Applied as the near infrared fluorescence probe in living cell imaging research and living body infrared optical molecular imaging, a precise and efficient photo-thermal and photo-power antitumor effect is achieved synchronously. The dye can be applied to near infrared in vivo optical imaging andphoto-sound imaging of tumors, is applied to optical assisted operation navigation, and has an efficient antitumor function. The dye not only can develop a target tissue in real time, but also kill tumor cells specifically. The preparation method of the benzoindole hematocyanine dye is mild in reaction condition, simple in step and easy to operate and low in raw material cost, and is easy to purify and relatively high in yield.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
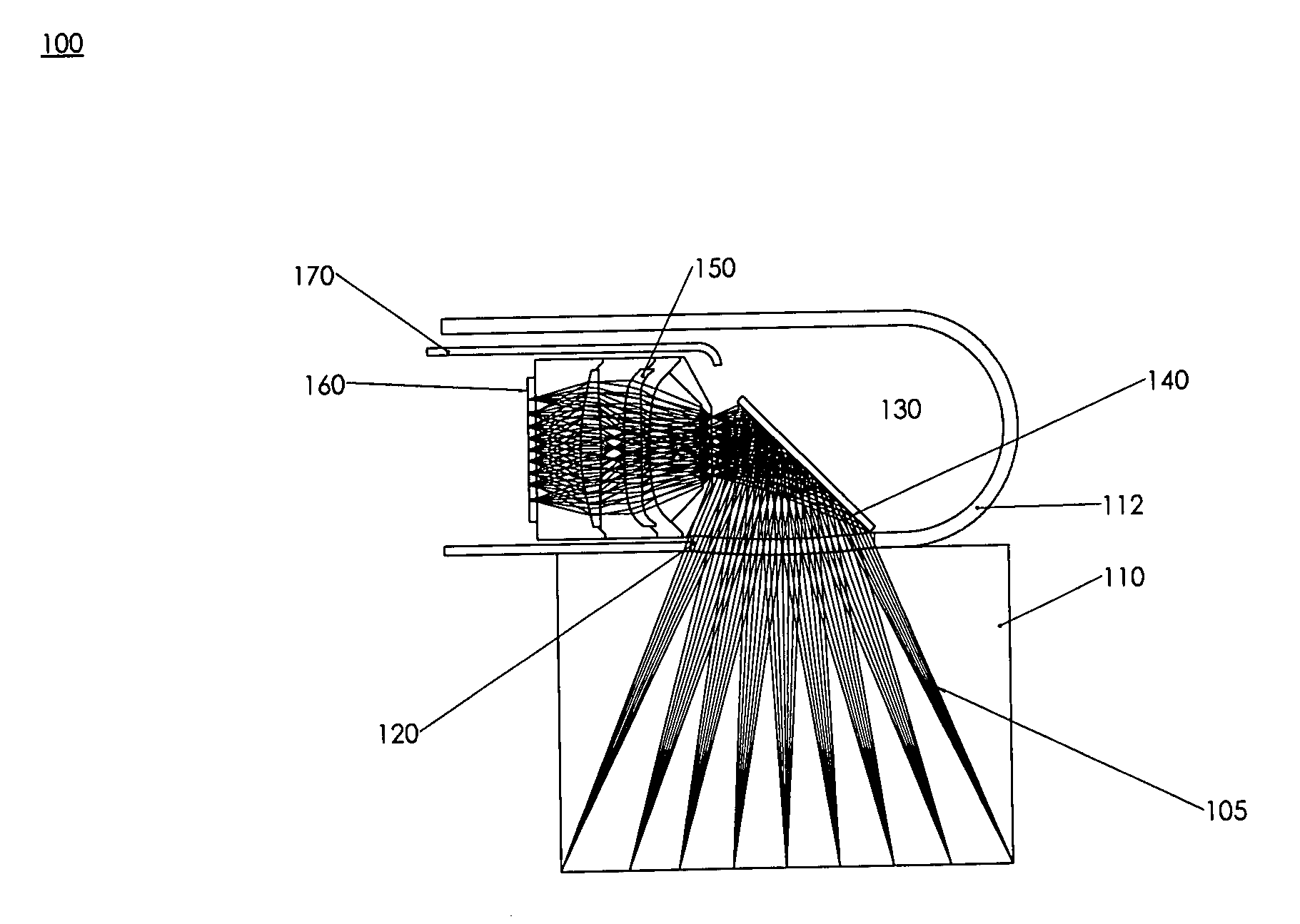
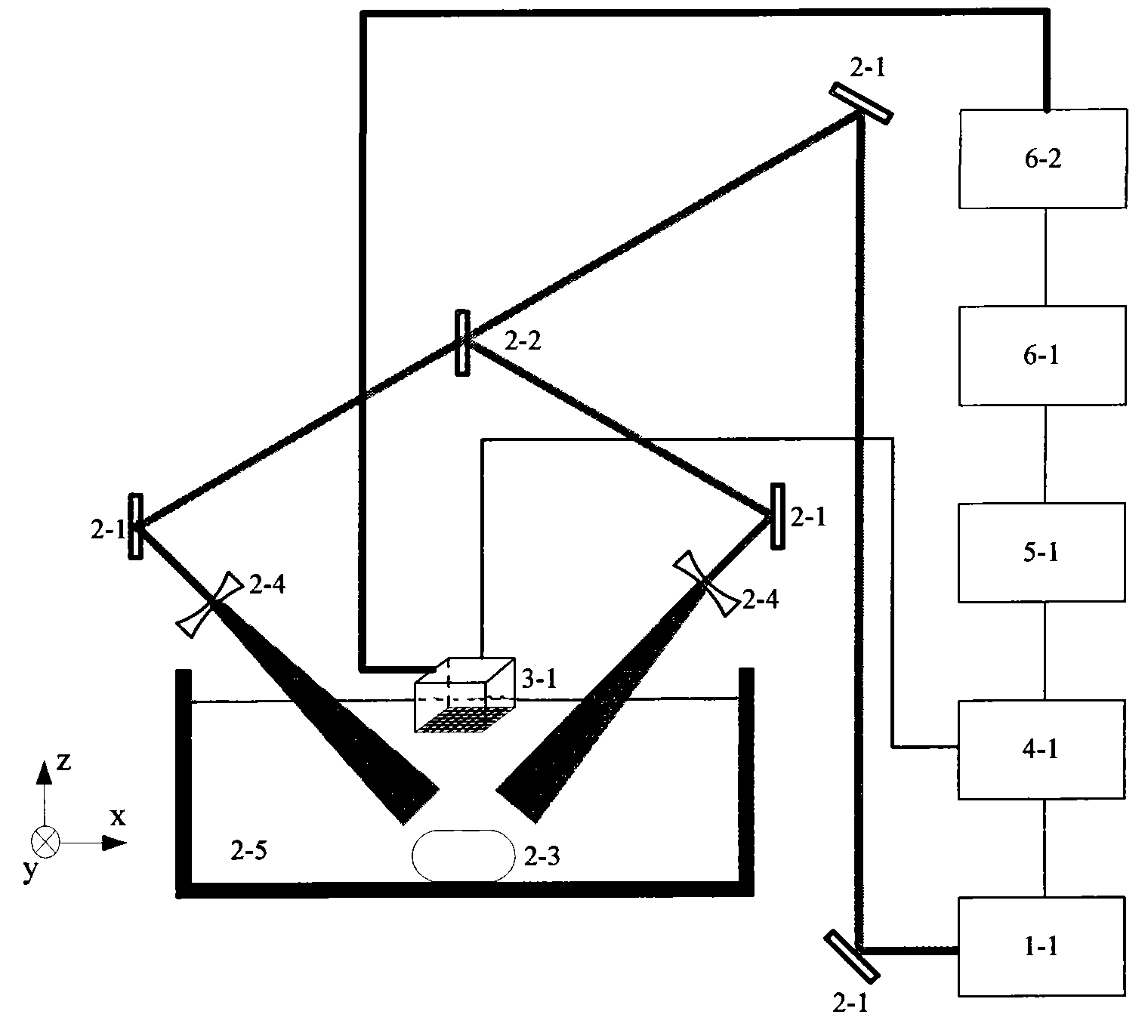
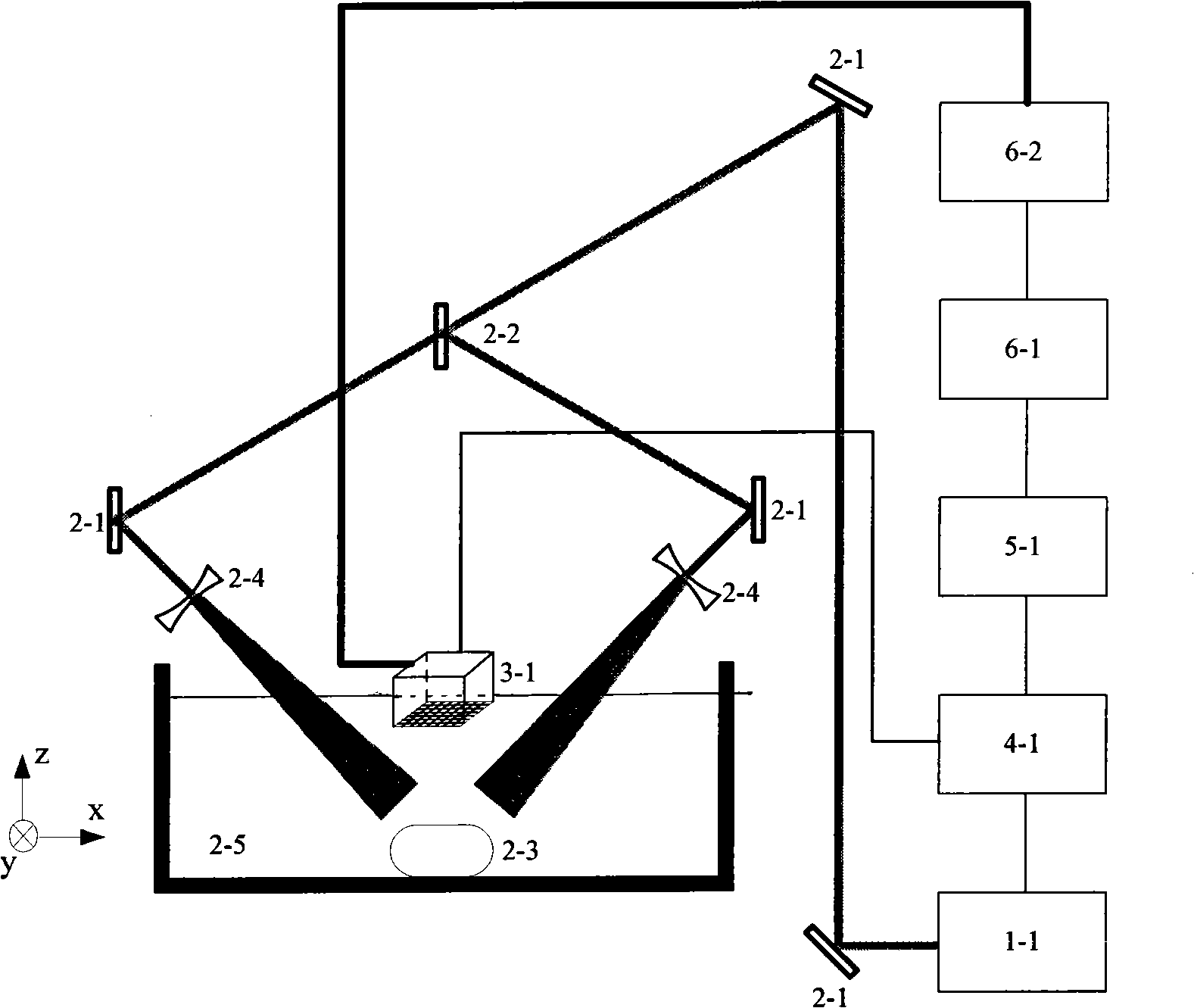
Probe for an Optoacoustic Imaging Device
InactiveUS20160061650A1Cost advantageVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicineOptoacoustic imaging
A probe for an optoacoustic imaging device has an irradiator and a detector. The irradiator includes a light-emitting semiconductor element light source that irradiates a tested object with light. The detector detects an optoacoustic wave generated in the tested object as a result. The irradiator is removably fitted to the detector.
Owner:PREXION
Preparation method and application of composite nanomaterial with aggregation-induced luminescent property and photothermal conversion property
ActiveCN109294557ACapable of light-to-heat conversionDifferent fluorescence intensityEnergy modified materialsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsDual modeNanoparticle
The invention relates to a composite nanomaterial with an aggregation-induced luminescent property and a photothermal conversion property. The composite nanomaterial comprises molecules with aggregation-induced luminescent property and with tetraphenylethylene as a main body and a semiconductor polymer with near-infrared photothermal conversion property and with a diketopyrrolopyrrole as a skeleton. The material is nano-particles with uniform particle size and good biological safety, and the problems of coexistence and adjustability of fluorescent property and photothermal conversion propertyare solved. The composite nanomaterial has dual-mode imaging properties of fluorescent imaging and photoacoustic imaging, has photothermal conversion ability, and can be used in cell fluorescent imaging, cell organ fluorescent imaging, tumor fluorescent-photoacoustic imaging and tumor photothermal treatment applications, and has potential applications in other biological imaging fields.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Multifunctional thermosensitive agarose hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105903015AAvoid damageHas temperature-responsive gel propertiesOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsTomographyPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
The invention provides multifunctional thermosensitive agarose hydrogel, which comprises an agarose solution, wherein a photo-thermal material and a chemotherapeutic medicine are loaded in the agarose solution; and the photo-thermal conversion material is any one of a two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheet, an MoS2 / Bi2S3-PEG nanosheet, graphene oxide or a palladium nanosheet. The invention further provides a preparation method of the hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving agarose into a solvent, and heating and stirring the agarose until the agarose is completely dissolved; dispersing the two-dimensional photo-thermal conversion material and the chemotherapeutic medicine into the agarose solution to obtain a mixed solution; cooling the mixed solution to obtain the multifunctional thermosensitive agarose hydrogel. The invention further provides an application of the hydrogel as a carrier for loading an anti-tumor medicine or the photo-thermal conversion material. The multifunctional thermosensitive agarose hydrogel has excellent photo-thermal conversion capability, computerized tomography imaging capability and photoacoustic imaging capability, and can be applied to the field of efficient coordination treatment of tumors; and release of the chemotherapeutic medicine can be effectively controlled.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Optical microscopy systems based on photoacoustic imaging
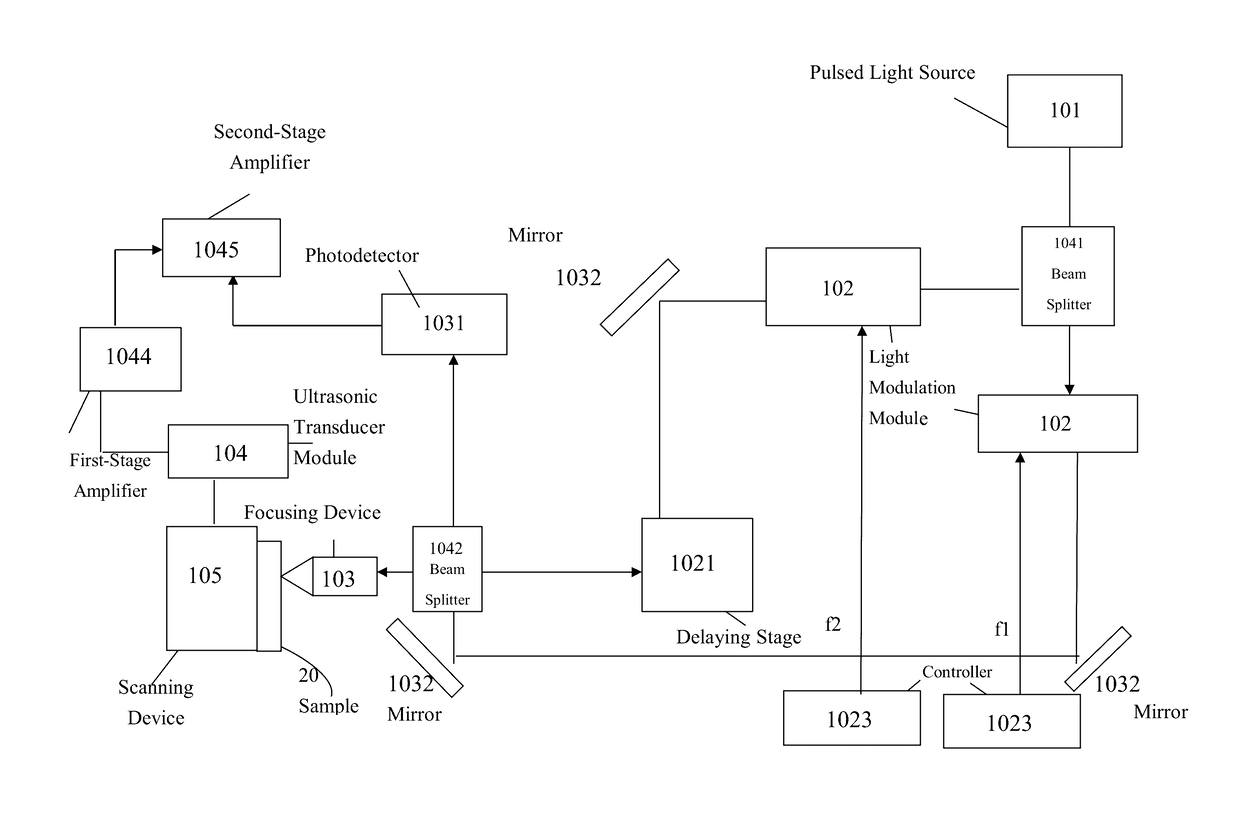
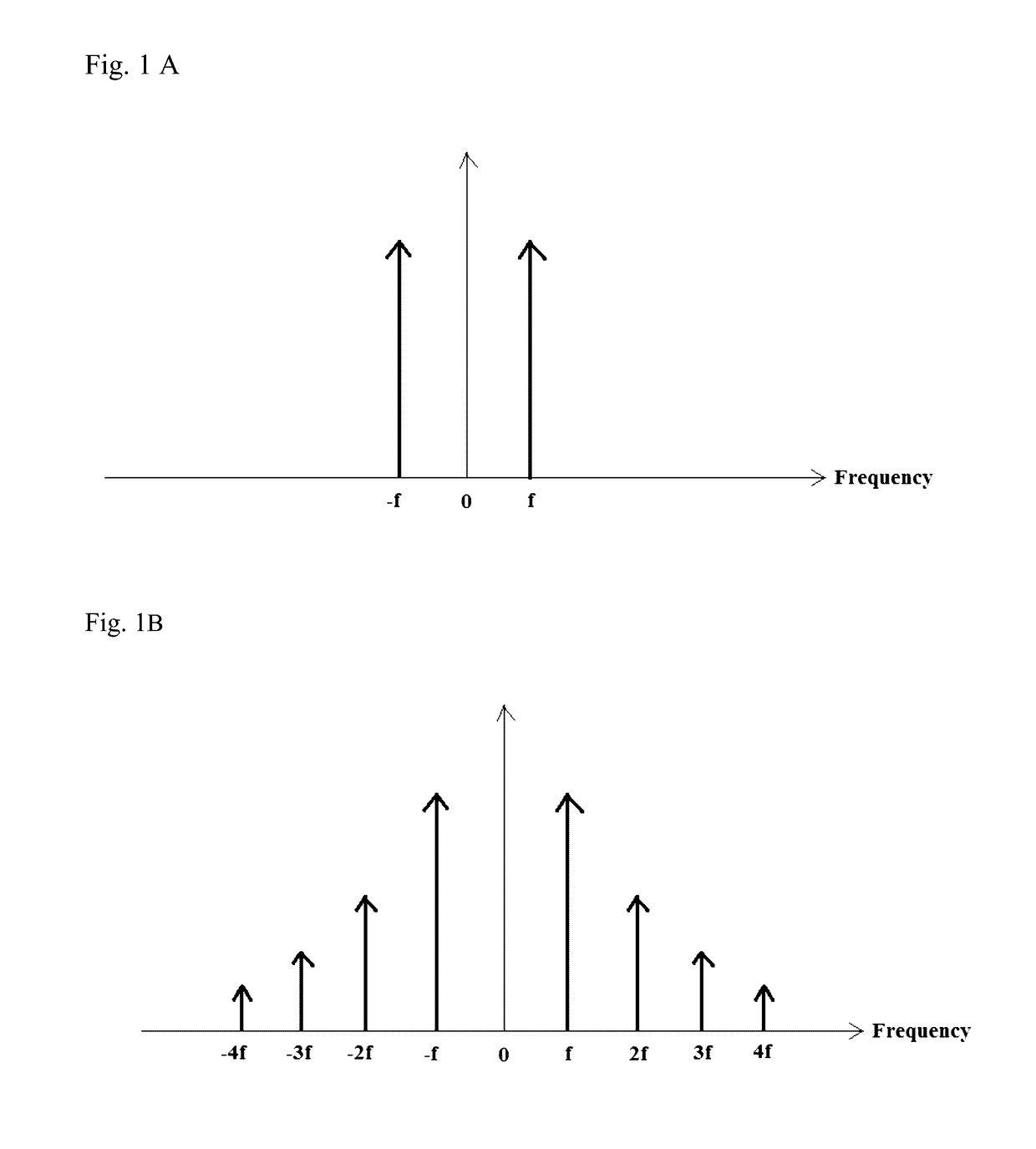
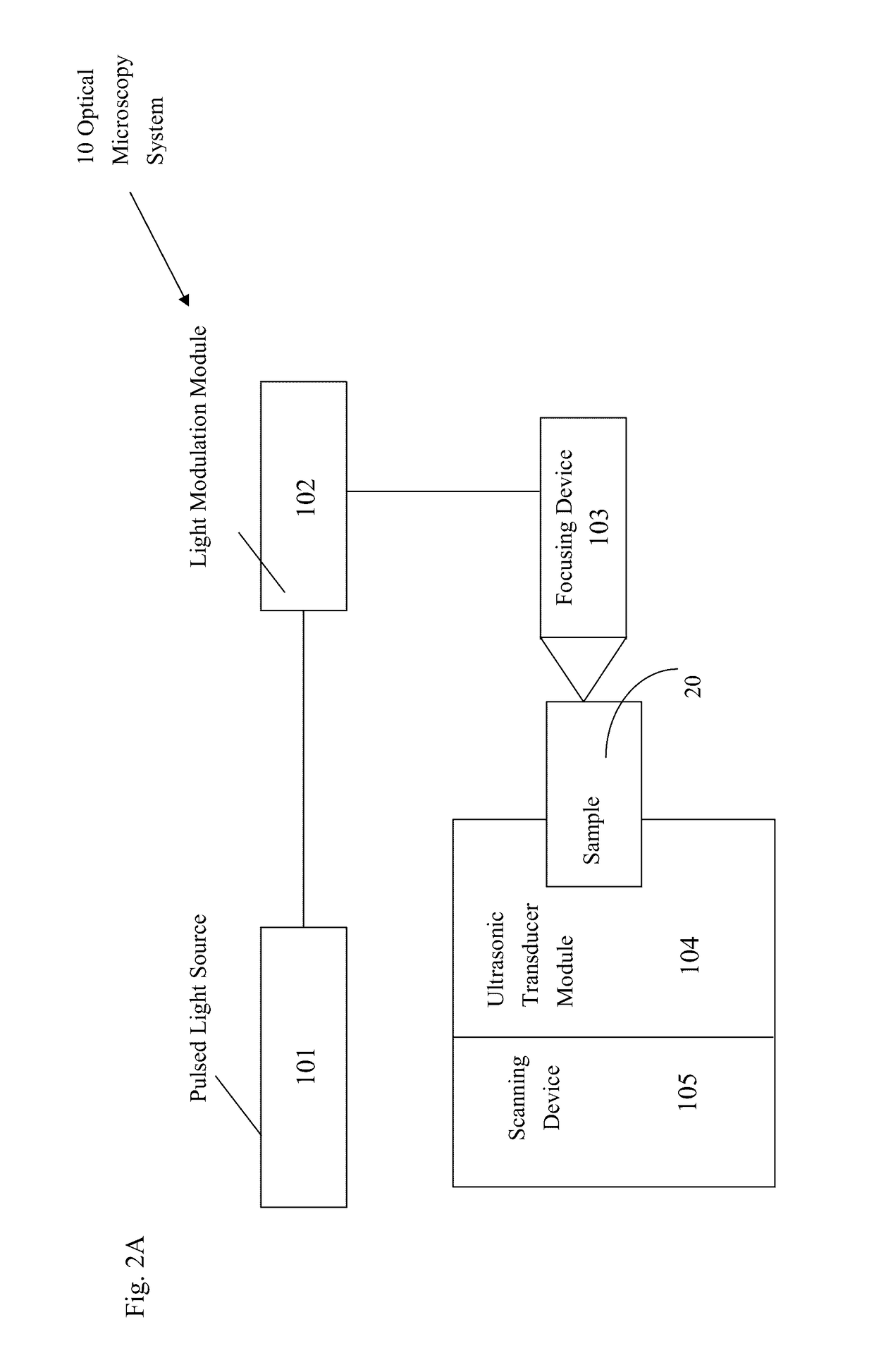
ActiveUS9618445B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectricitySinusoidal modulation
The present application discloses optical microscopy systems and related method that use modulation techniques and contrast agents to enable the systems to detect nonlinear photoacoustic signals with high spectrum sensitivity and frequency selectivity for imaging. A laser beam is amplitude modulated for pure sinusoidal modulation using either the loss modulation technique or the single light amplitude modulation technique. The sample used in the invention is an endogenous contrast agent by itself or is treated by at least one exogenous contrast agent to produce or enhance photoacoustic effect induced by multi-photon absorption. The modulated laser beam is focused via a focusing device onto a sample which absorbs multiple photons simultaneously and generates ultrasonic (acoustic) waves via nonlinear photoacoustic effect. The ultrasonic waves are received and transformed into electrical signals and the frequency signals within the electrical signals are detected and recorded to create images.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Preparation method and application of functional photoacoustic probe based on assembly of gold nanoparticles
InactiveCN106924764AReach UV absorptionEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsMicrocapsulesChemistryBiotin-streptavidin complex
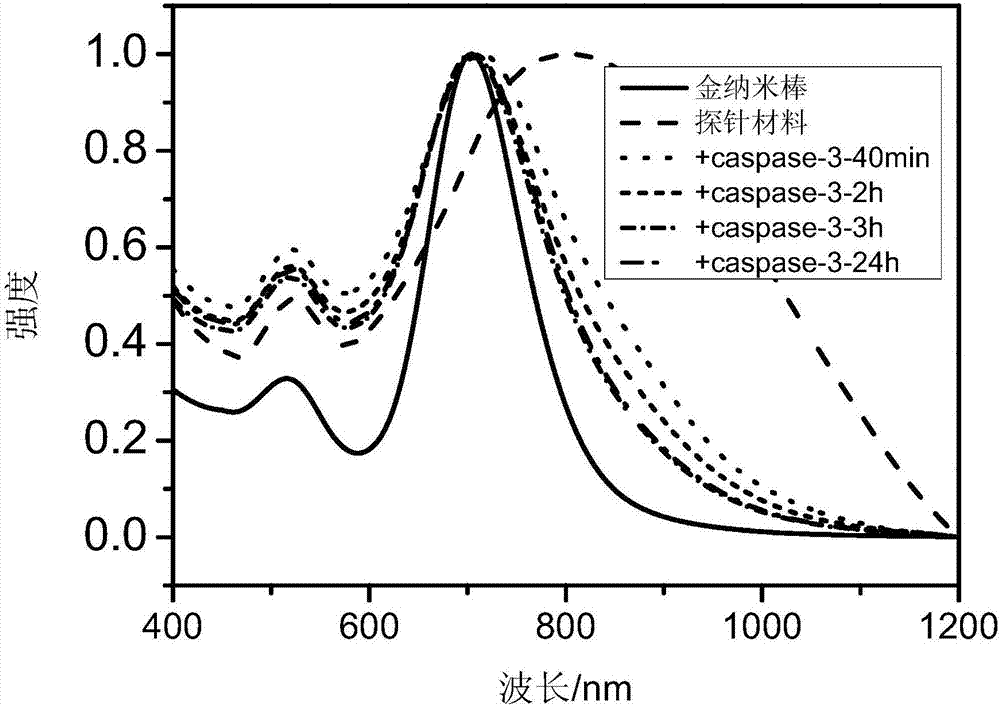
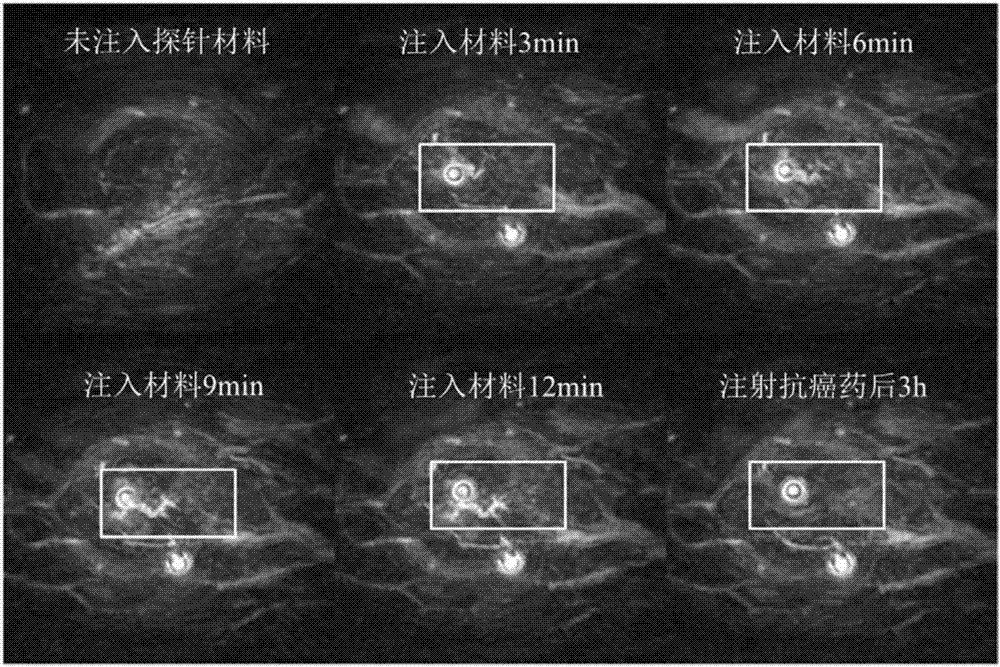
The invention relates to the field of nano materials, in particular to a preparation method and application of a functional photoacoustic probe based on assembly of gold nanoparticles. The preparation method of the functional photoacoustic probe includes the steps that peptide chains with one ends of -SH, the other ends of biotin and the middle parts of specific sequences DEVD are used for modification of the surfaces of the gold nanoparticles, meanwhile, functional micromolecules with one ends of -SH and the other ends of streptavidin are used for modification of the surfaces of gold nanorods, and the self-assembly process of the gold nanorods and the gold nanoparticles is completed by the specific biological coupling reaction of the streptavidin and the biotin. As an apoptosis enzyme caspase-3 can recognize and lyse the specific sequences DEVD of the peptide chains, the gold nanorods are separated from the gold nanoparticles, so that ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra and photoacoustic imaging signal strength begin to change; thus production of caspase-3 in tumor cells can be monitored with the method of photoacoustic imaging so as to judge the apoptosis process of the tumor cells after treatment, and the functional photoacoustic probe is also used for evaluating the effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy, which has great significance in clinical medicine and disease diagnosis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Green preparation method of sea urchin shaped nanogold and application of nanogold in tumor imaging and treatment
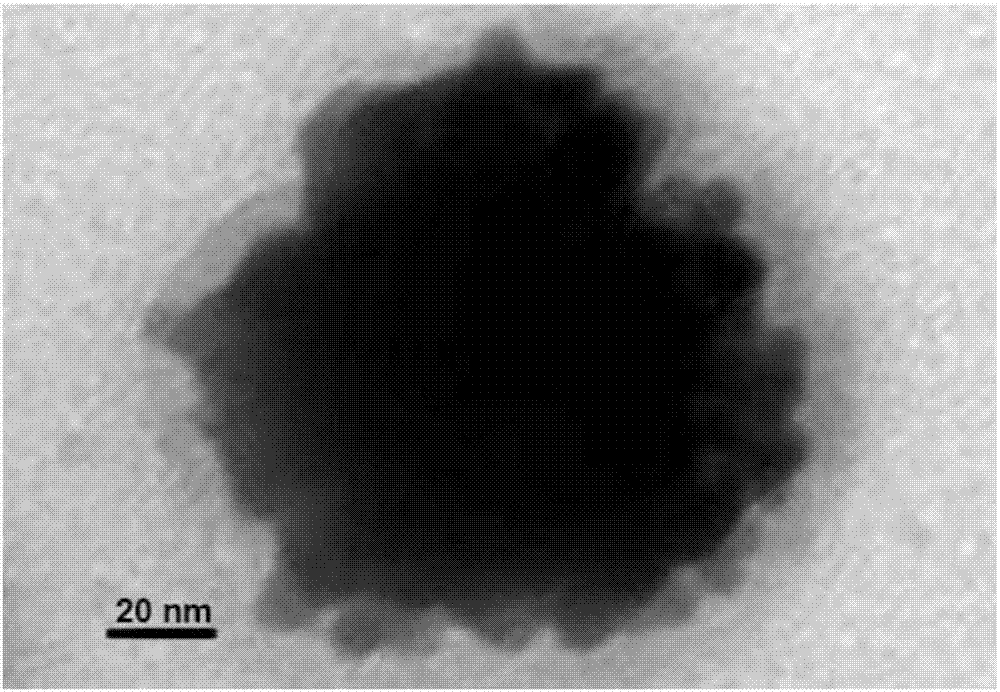
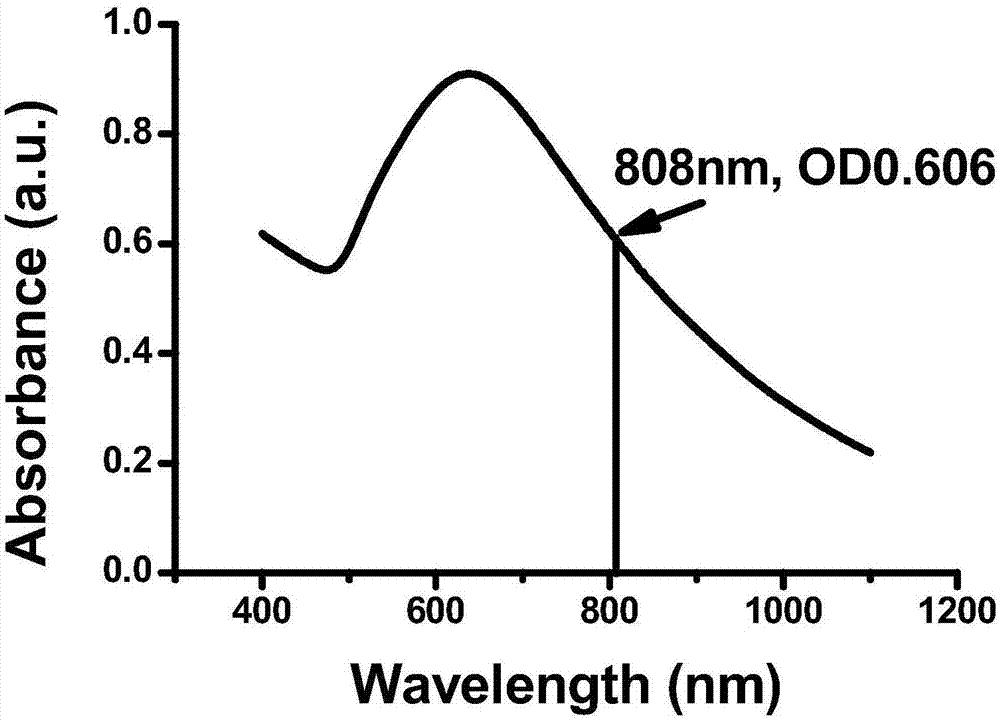
ActiveCN107308462APromote absorptionEnhance the effect of radiation therapyDispersion deliveryEnergy modified materialsGrowth retardantSide effect
The invention discloses a green preparation method of sea urchin shaped nanogold and application of the nanogold in tumor imaging and treatment. Chloroauric acid is mainly used as a gold source, a stabilizer, a reducing agent and a growth inhibitor are successively added, and the nanogold is prepared by adopting a one-step synthesis method. The method is simple, mild, green and friendly to the environment. The synthesized sea urchin shaped nanogold can serve as a contrast agent to be applied to multiple medical imaging modes such as opto-acoustic imaging (PA), positron emission computed tomography imaging (PET) and infrared thermal imaging (TI), patients can obtain multiple diagnostic effects only by needing to bear one contrast agent for dose, the dosage of contrast agent can be reduced, and the toxic and side effects are thus reduced. In addition, the material can achieve conversion of light and heat under near-infrared light irradiation of 808 nm, can absorb a large number of X rays, has higher light-heat conversion efficiency, and can be used for the preparation of a therapeutic agent for light and heat treatment (PTT), radiotherapy (RT), or combined therapy of PTT / RT of tumor cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com