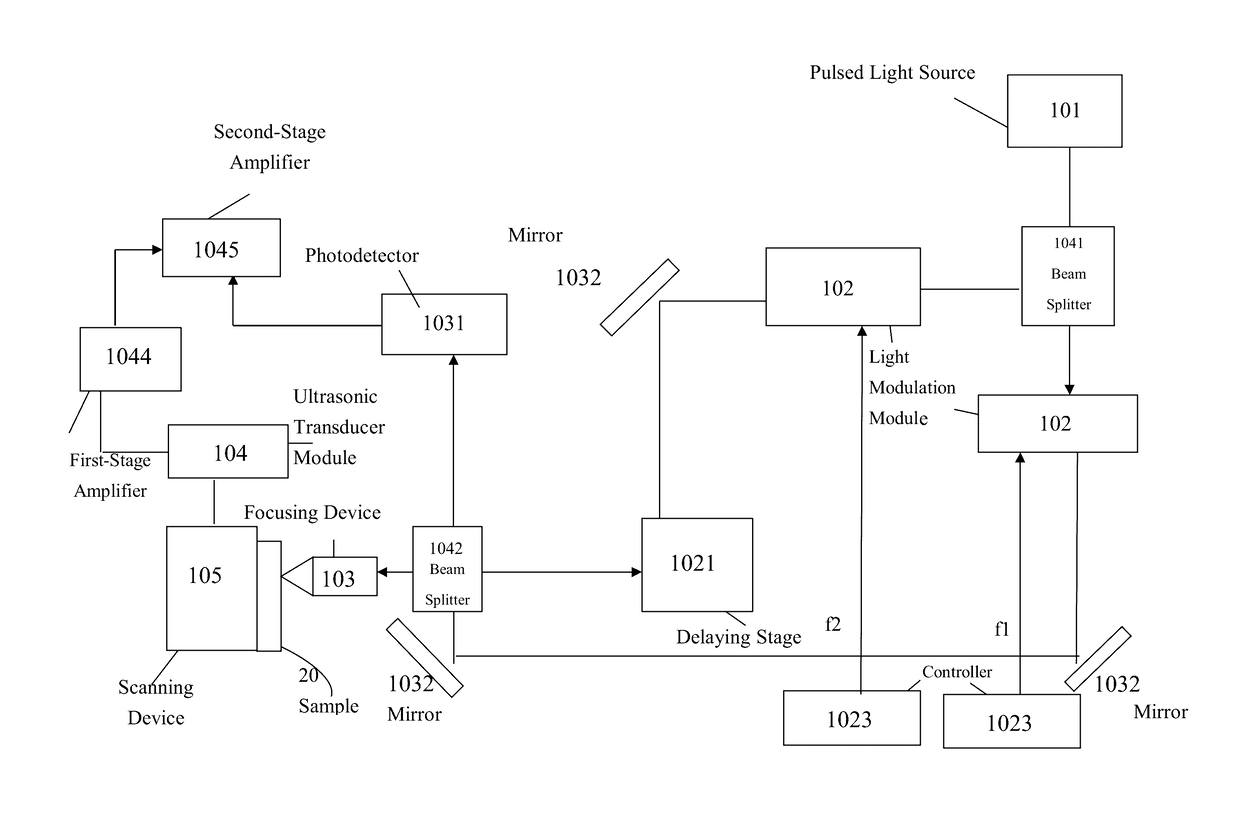
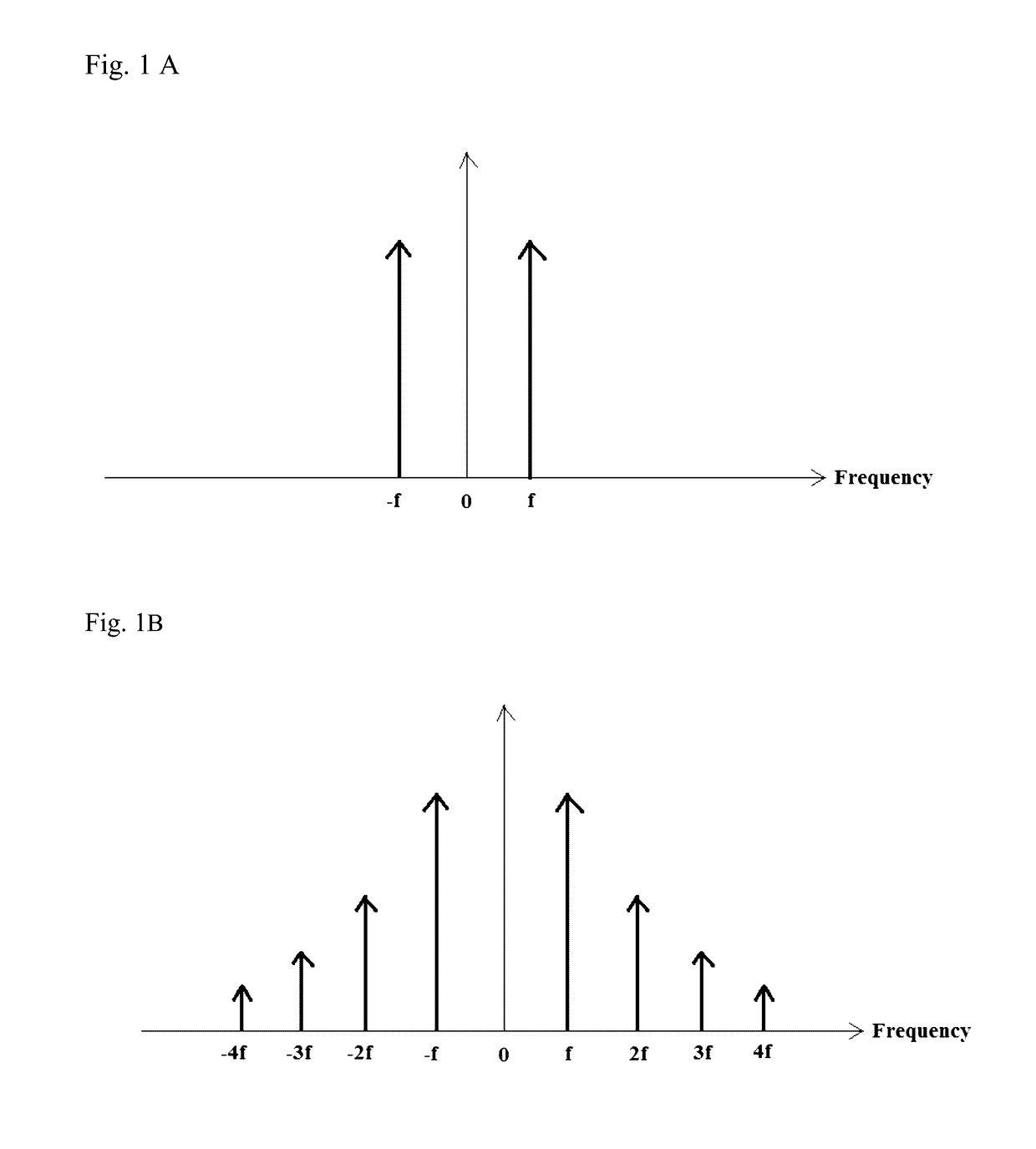
Patents
Literature
173 results about "Photoacoustic effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The photoacoustic effect or optoacoustic effect is the formation of sound waves following light absorption in a material sample. In order to obtain this effect the light intensity must vary, either periodically (modulated light) or as a single flash (pulsed light). The photoacoustic effect is quantified by measuring the formed sound (pressure changes) with appropriate detectors, such as microphones or piezoelectric sensors. The time variation of the electric output (current or voltage) from these detectors is the photoacoustic signal. These measurements are useful to determine certain properties of the studied sample. For example, in photoacoustic spectroscopy, the photoacoustic signal is used to obtain the actual absorption of light in either opaque or transparent objects. It is useful for substances in extremely low concentrations, because very strong pulses of light from a laser can be used to increase sensitivity and very narrow wavelengths can be used for specificity. Furthermore, photoacoustic measurements serve as a valuable research tool in the study of the heat evolved in photochemical reactions (see: photochemistry), particularly in the study of photosynthesis.
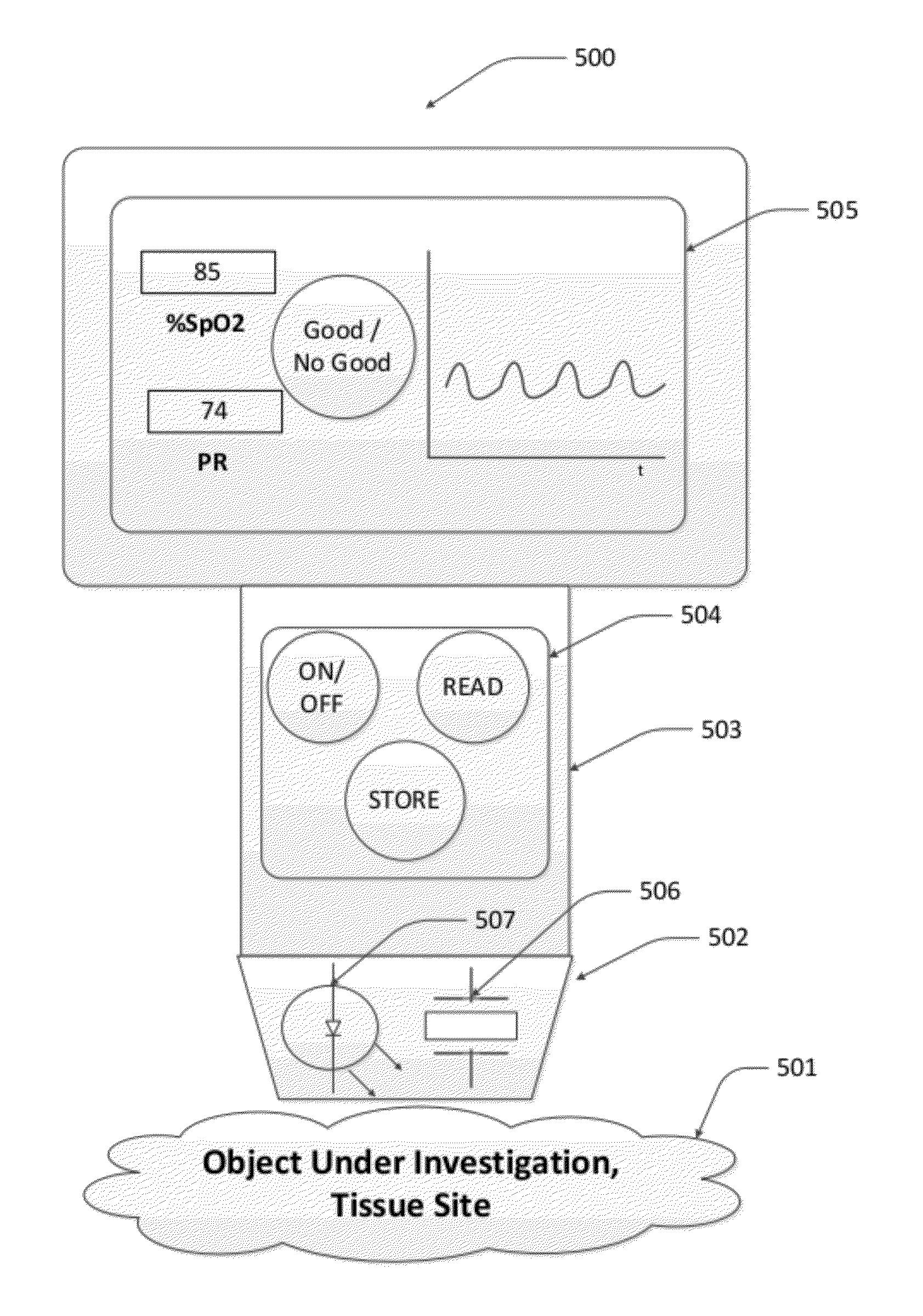
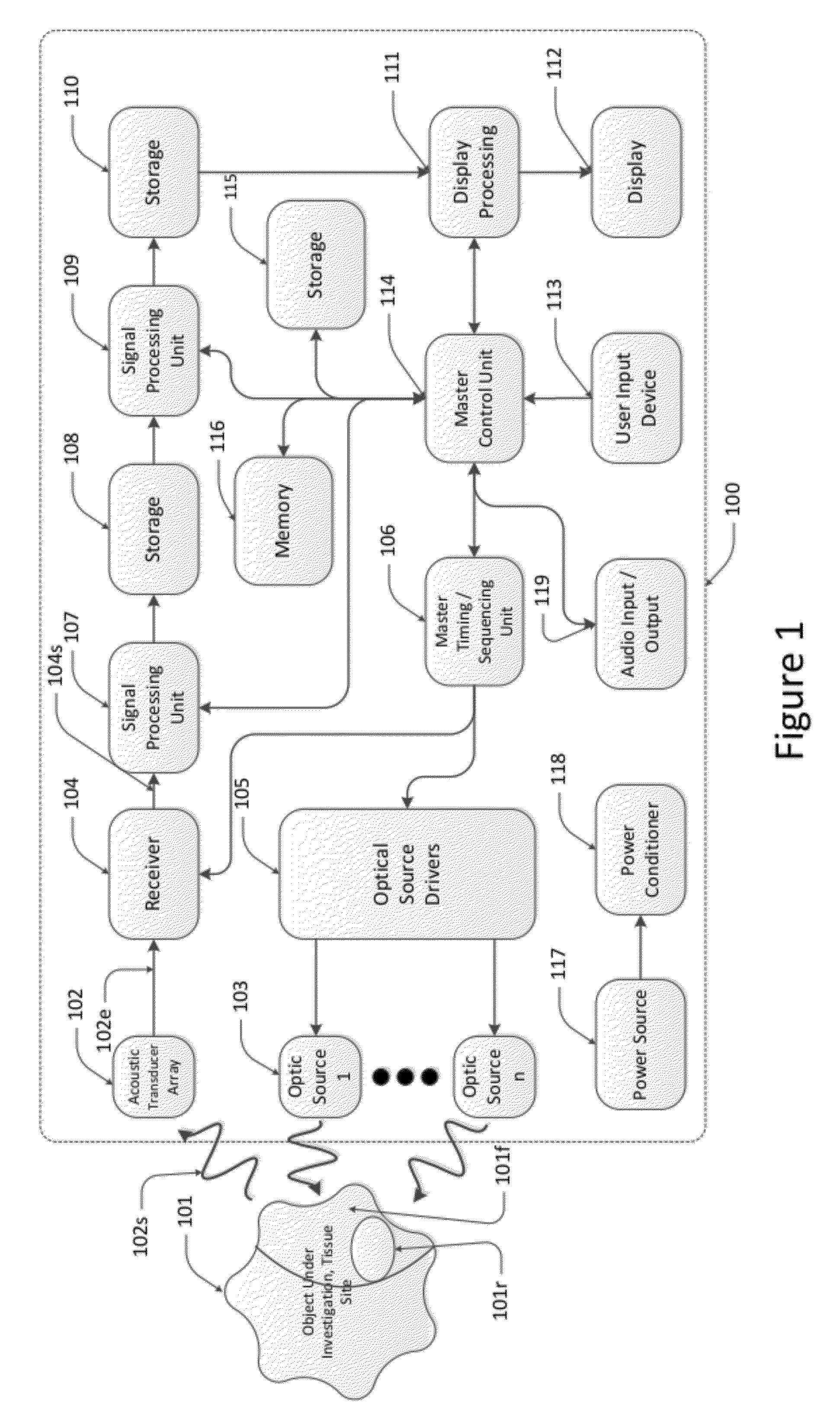
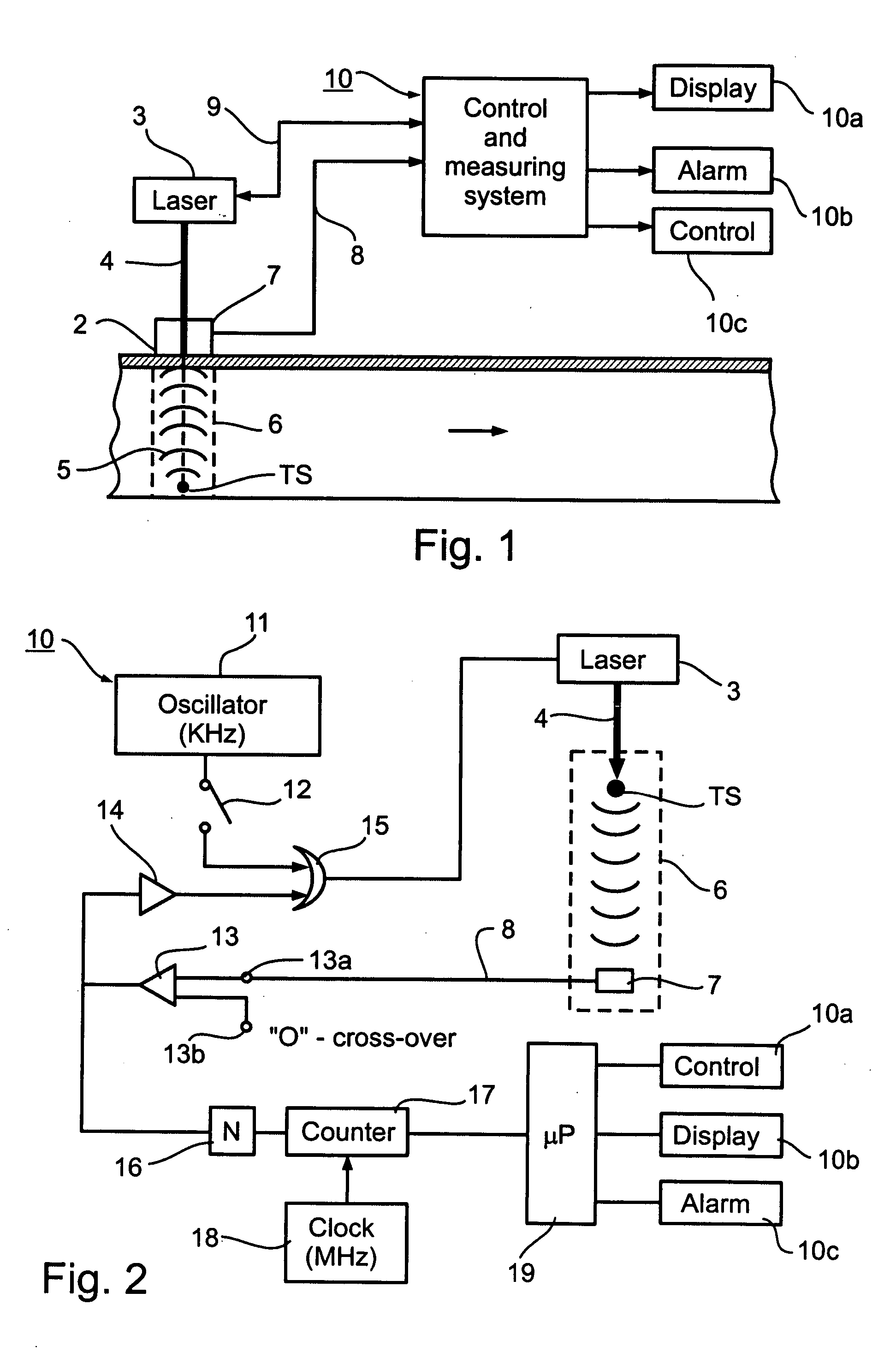
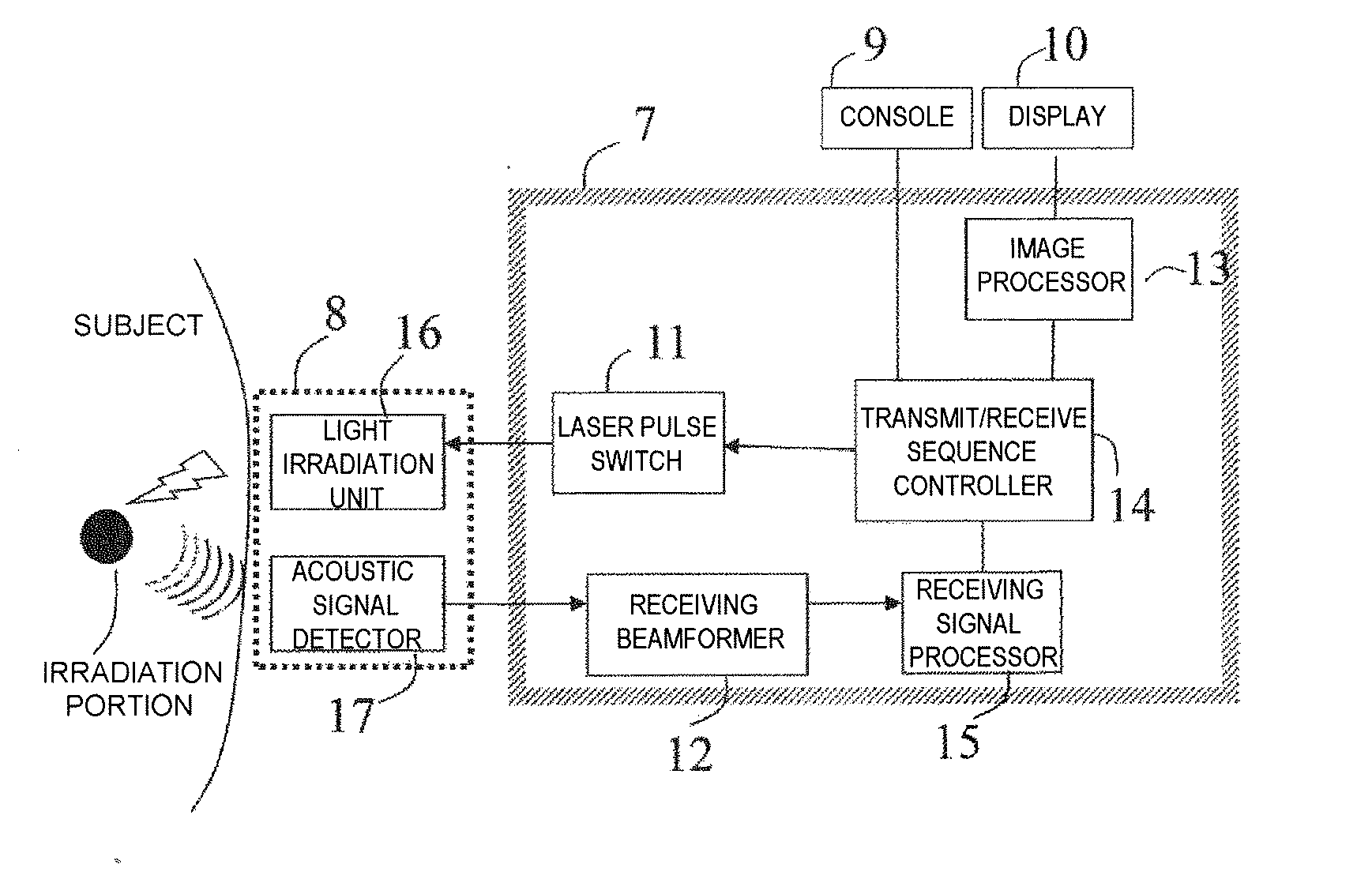
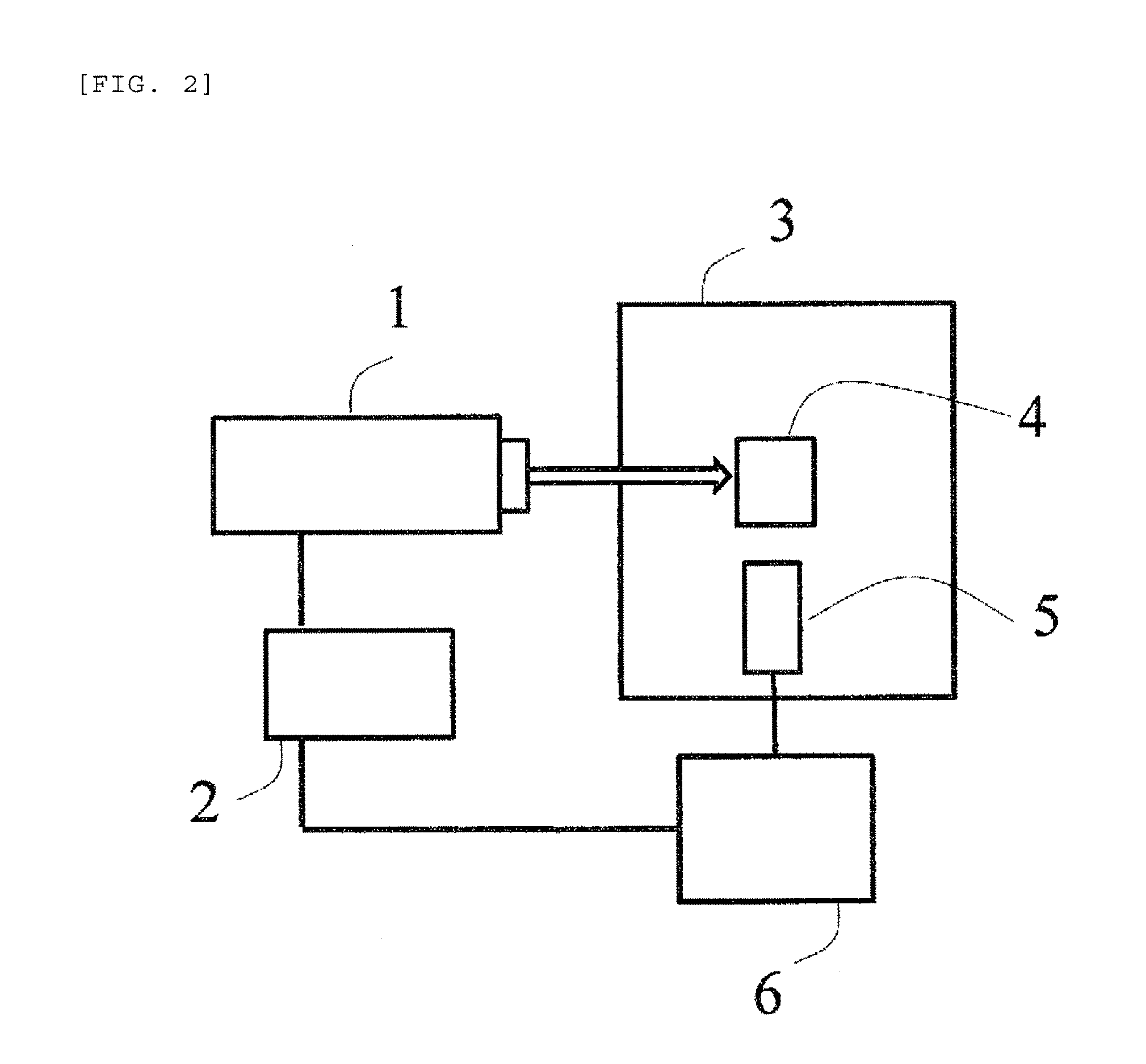
Photoacoustic analyzer of region of interest in a human body
InactiveUS7515948B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSafer light energyAuscultation instrumentsDiagnostic recording/measuringAuditory radiationHuman body
A method and apparatus are presented for non-invasively monitoring at least one characteristic of a region of interest in a body. The body is illuminated by pulsed light to induce a photoacoustic effect. Acoustic radiation is detected, and measured data indicative thereof is generated. The photoacoustic effect is controlled by carrying out at least one of the following: providing the pulsed light of at least two different wavelength, analyzing the measured data to determine time variations of at least one predetermined parameter of a time dependent acoustic signal for each of wavelength, and determining oxygen saturation level in the region of interest; and operating a plurality of acoustic elements configured for detection of the acoustic radiation, to thereby define a focal volume for acoustic radiation detection to match dimensions of the region of interest.
Owner:ORNIM
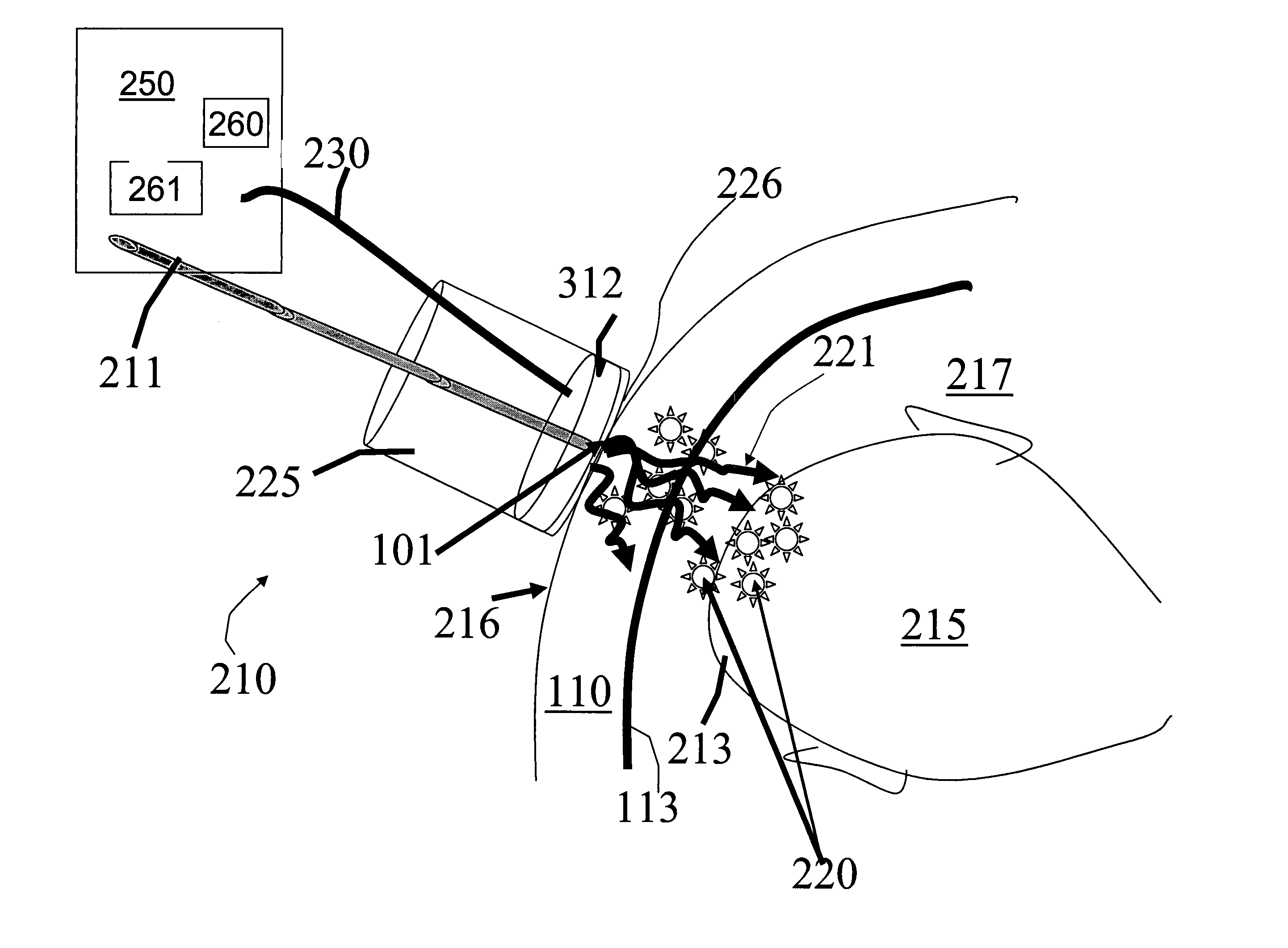
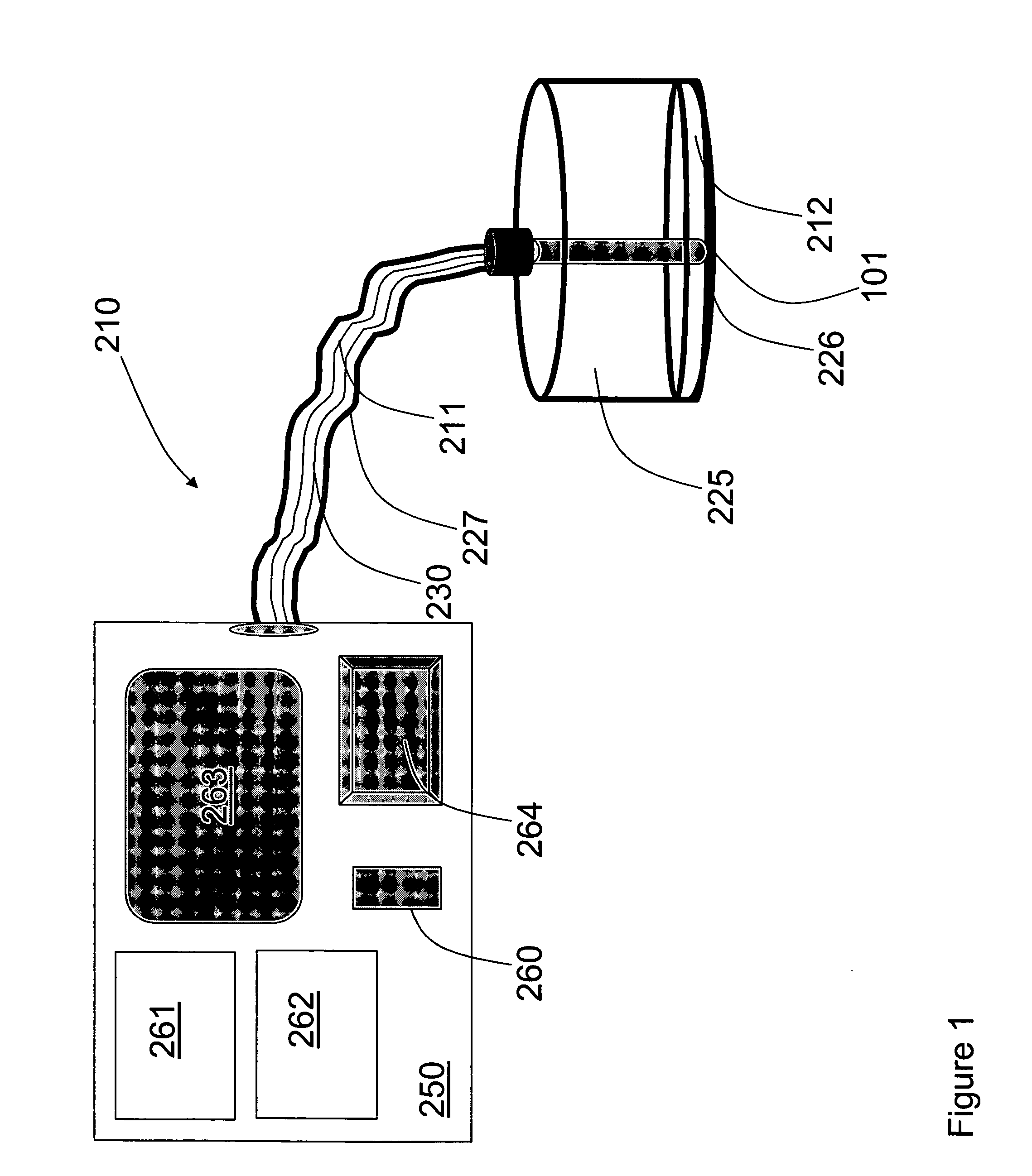
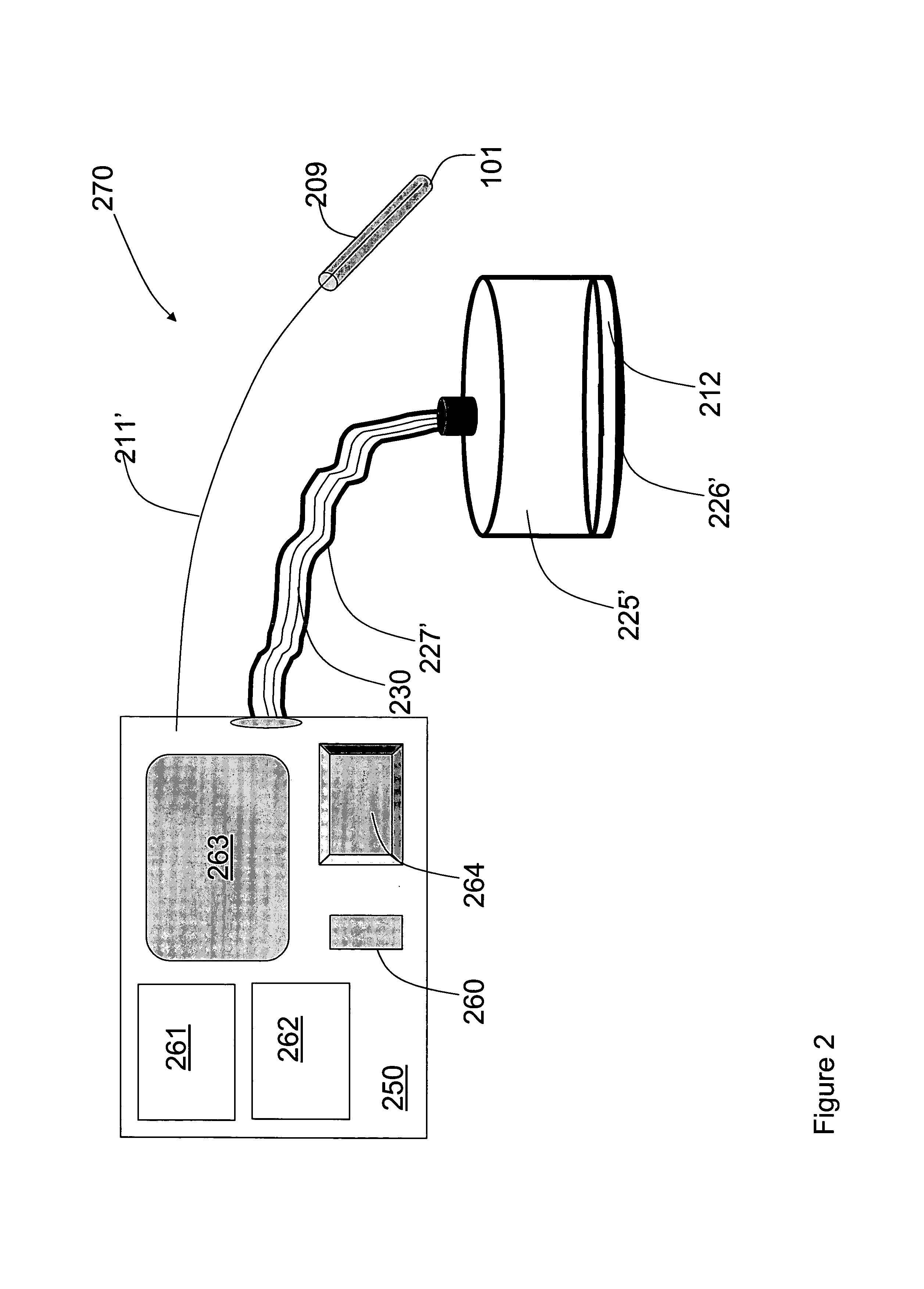
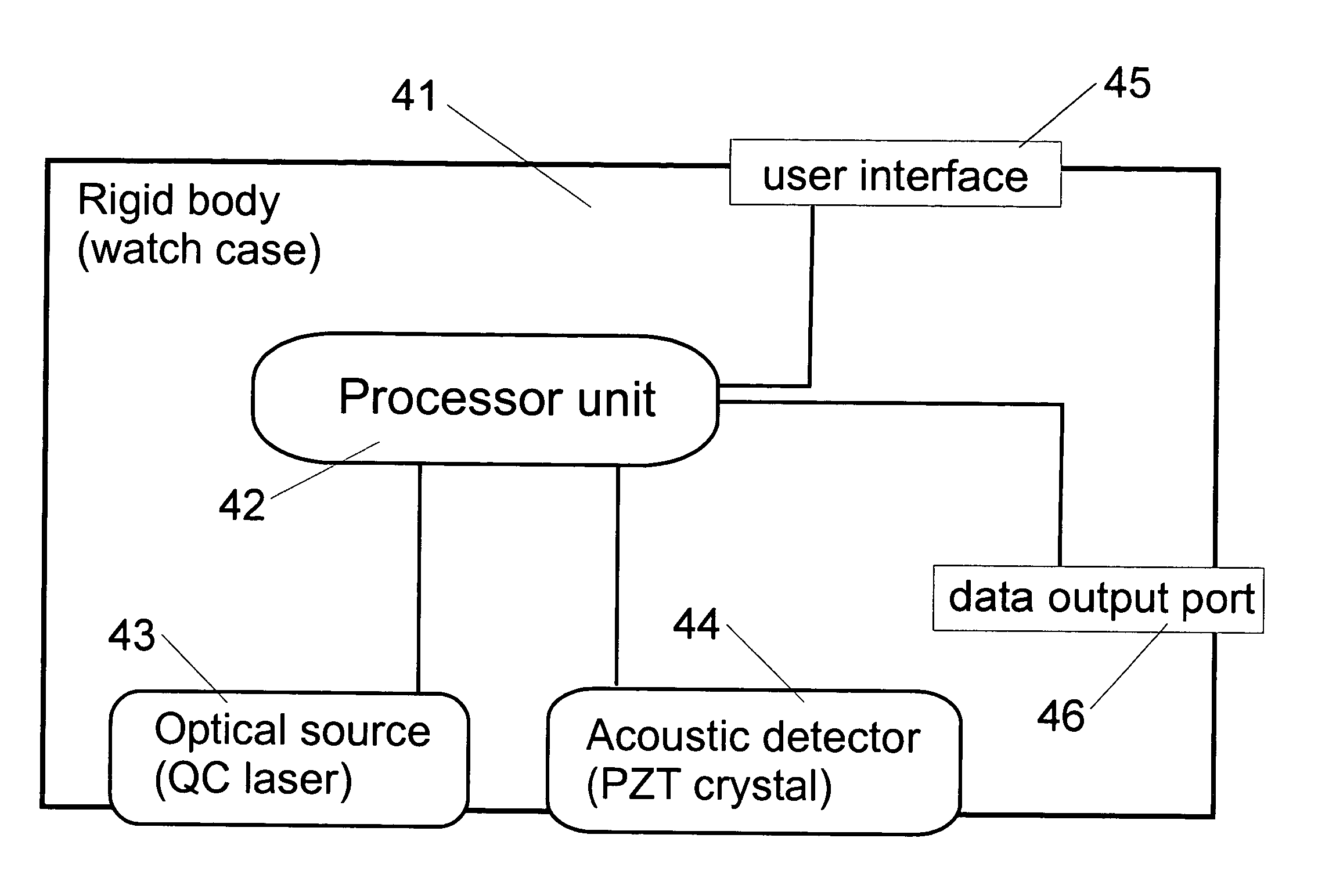
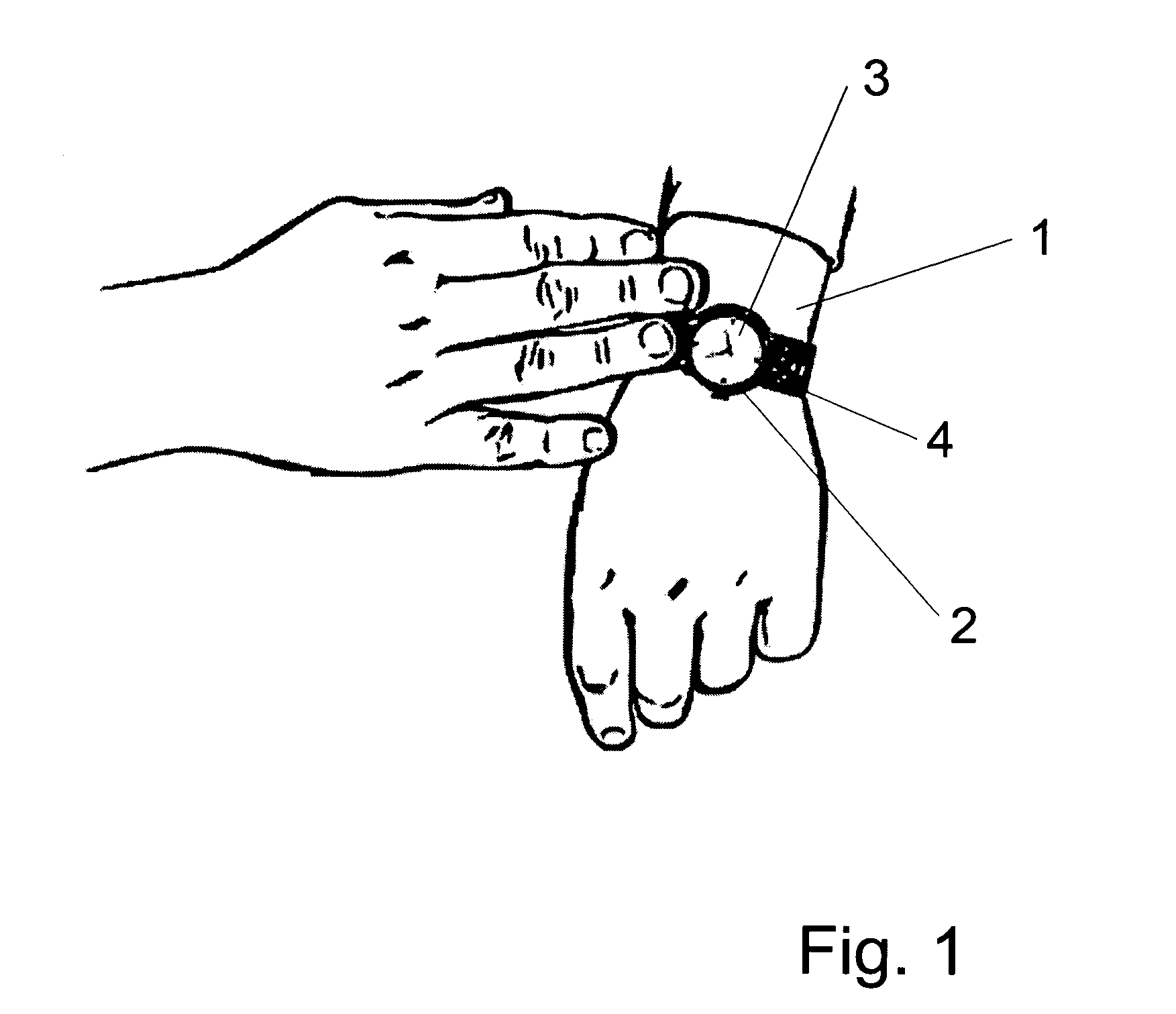
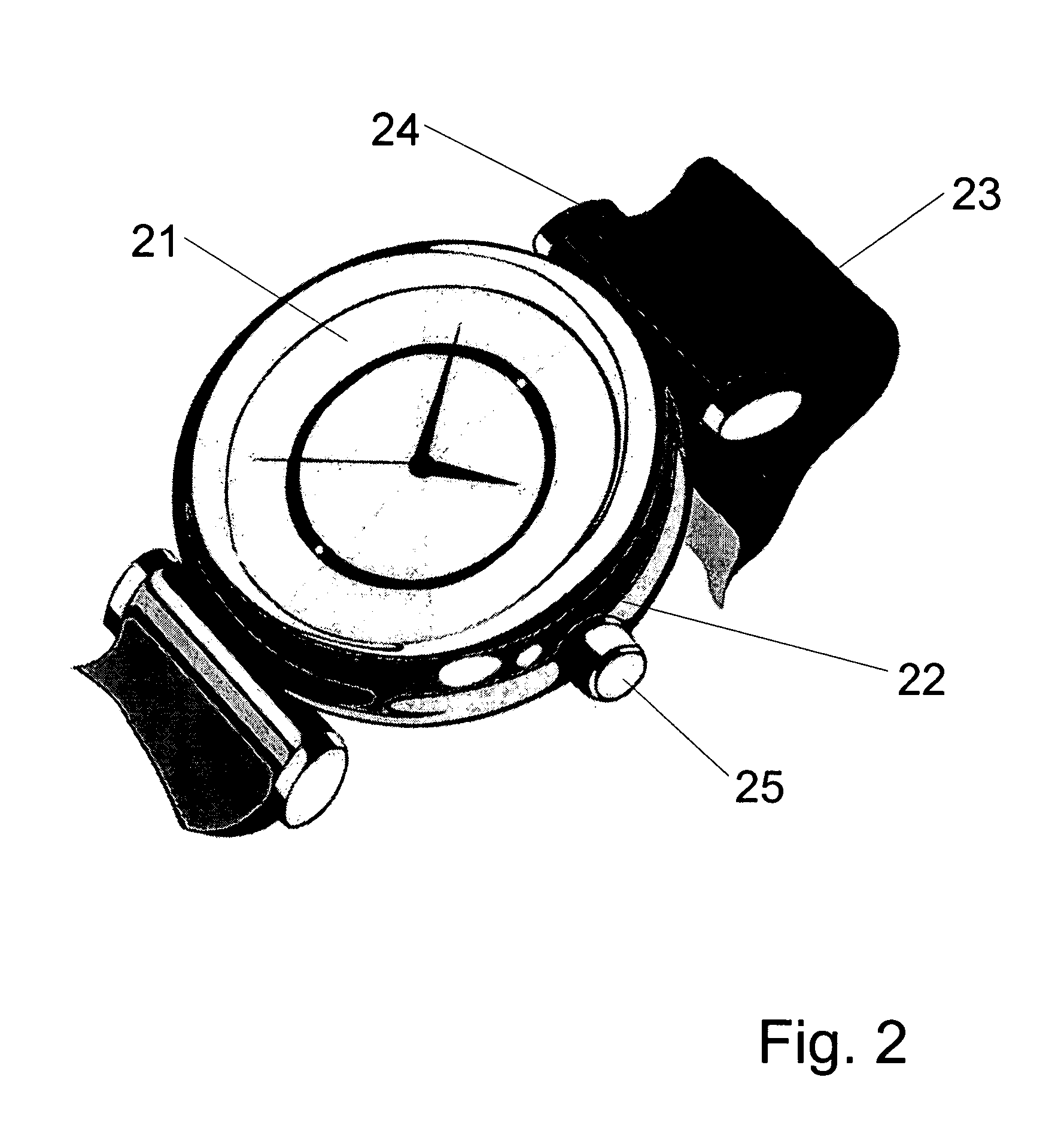
Highly portable and wearable blood analyte measurement system
InactiveUS20050054907A1Encourages better and more complete use of the instrumentDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsContinuous measurementNon invasive
Non-invasive wearable systems for continuous measurement of blood glucose concentrations help diabetics maintain best awareness and control. A wearable article such as a wristwatch includes elements integrated therewith to provide for biometric measurements. Specifically, both optical and acoustic transducers are arranged within an article such that they are coupled to tissue in a manner which permits blood analytes measurements to be made. In best versions, a quantum cascade laser is arranged with crystalline acoustic detectors in a photoacoustic effect measurement scheme. Laser pulses stimulate special vibrational states of glucose molecules to produce an acoustic return signal to be received at a piezoelectric detector. A wristwatch case may include a back member which supports arrangements and coupling between the back of the watch, elements contained therein, and tissue in contact with the device.
Owner:PAGE JOSEPH +1
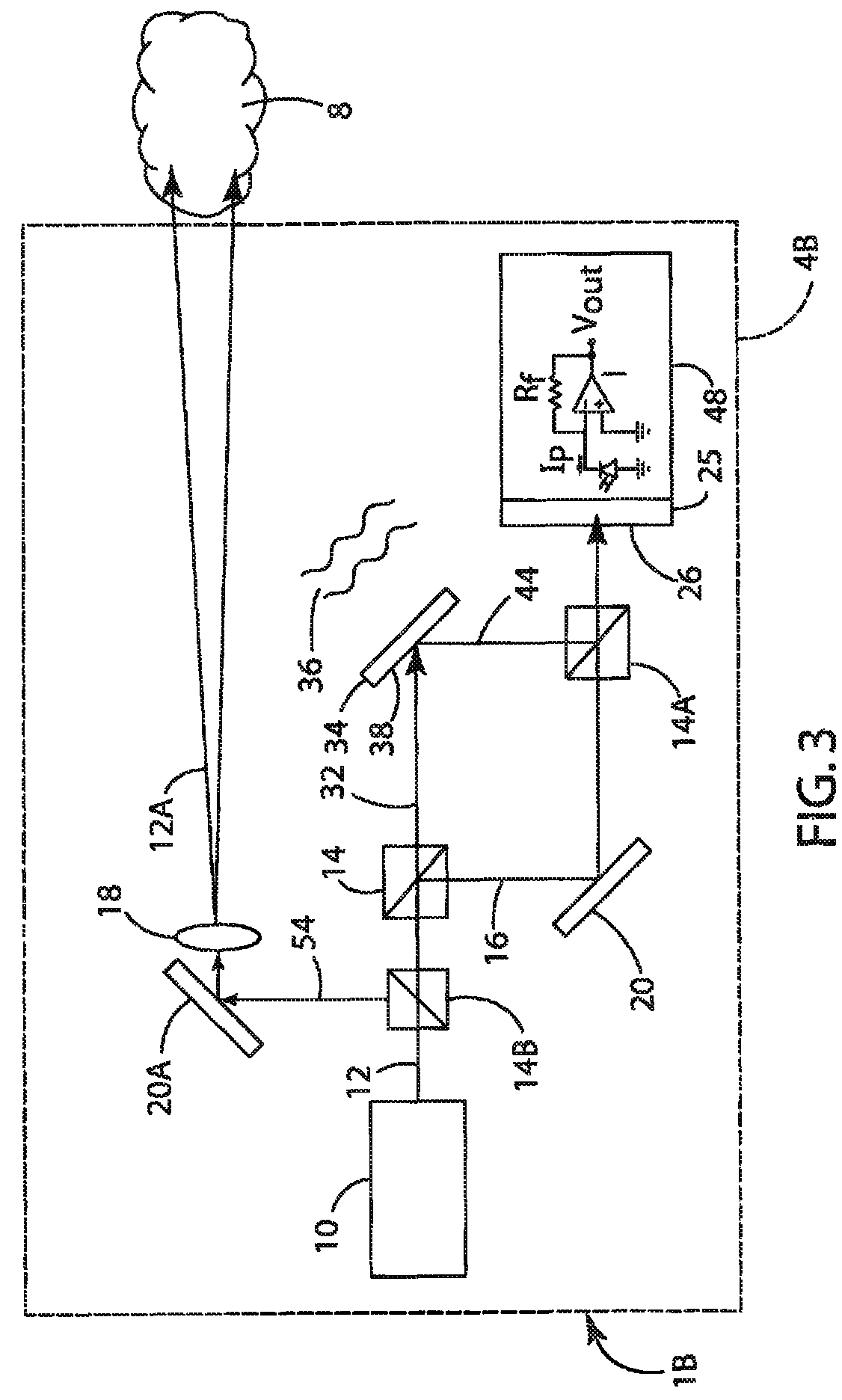
Photoacoustic transducer and imaging system
InactiveUS20130190591A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringEpoxyUltrasonic sensor
The invention disclosed herein features a photoacoustic scan head that includes laser fibers integrated into the housing of an arrayed ultrasound transducer using an optically transparent epoxy or other resin. The light-emitting ends of the fibers are positioned adjacent to the front surface of the transducer and direct laser light onto a subject being scanned by the transducer. The light beams generated by the fibers may be angled to intersect the acoustic field generated by the transducer so as to generate a photoacoustic effect in the region scanned by the transducer.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
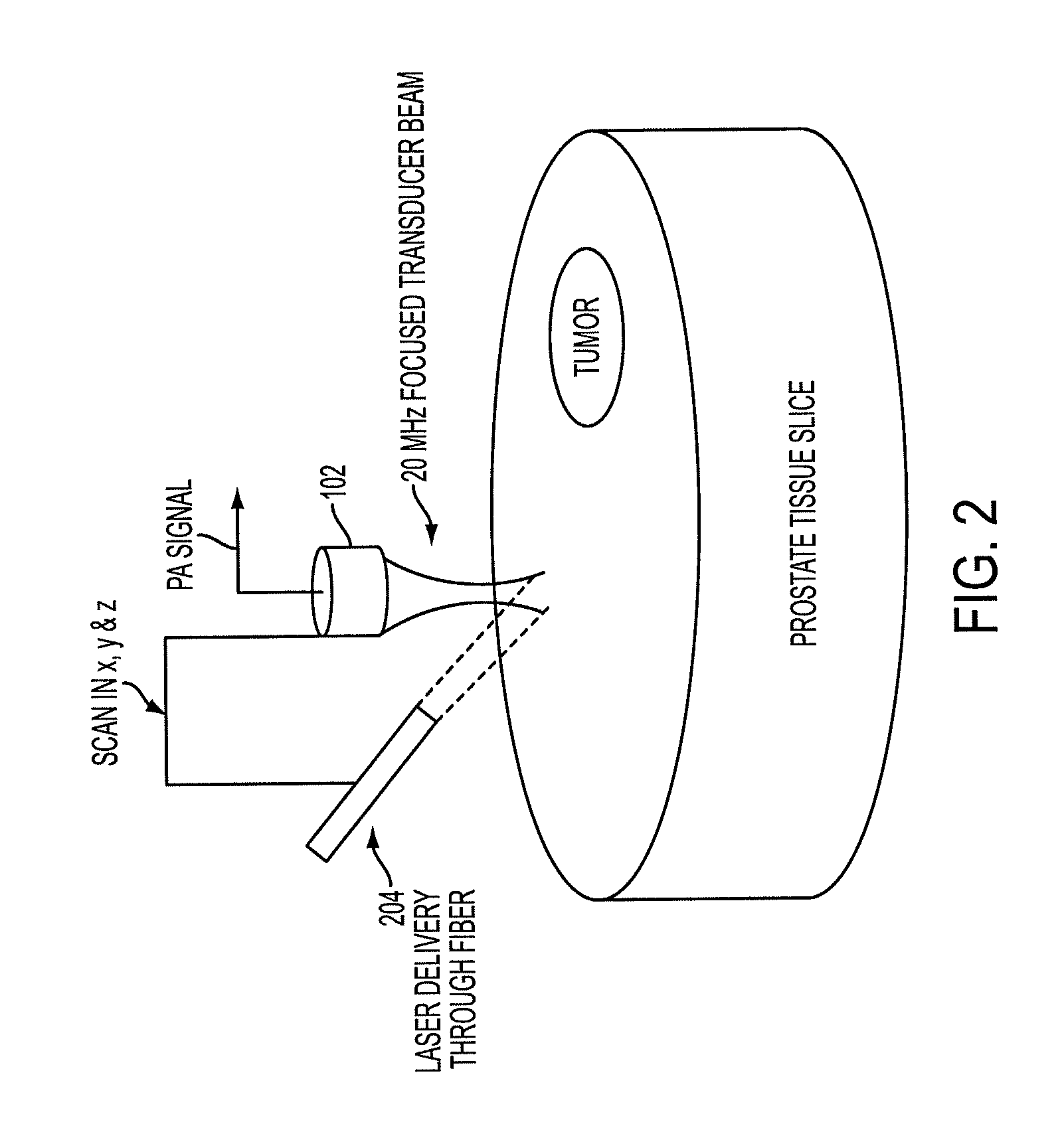
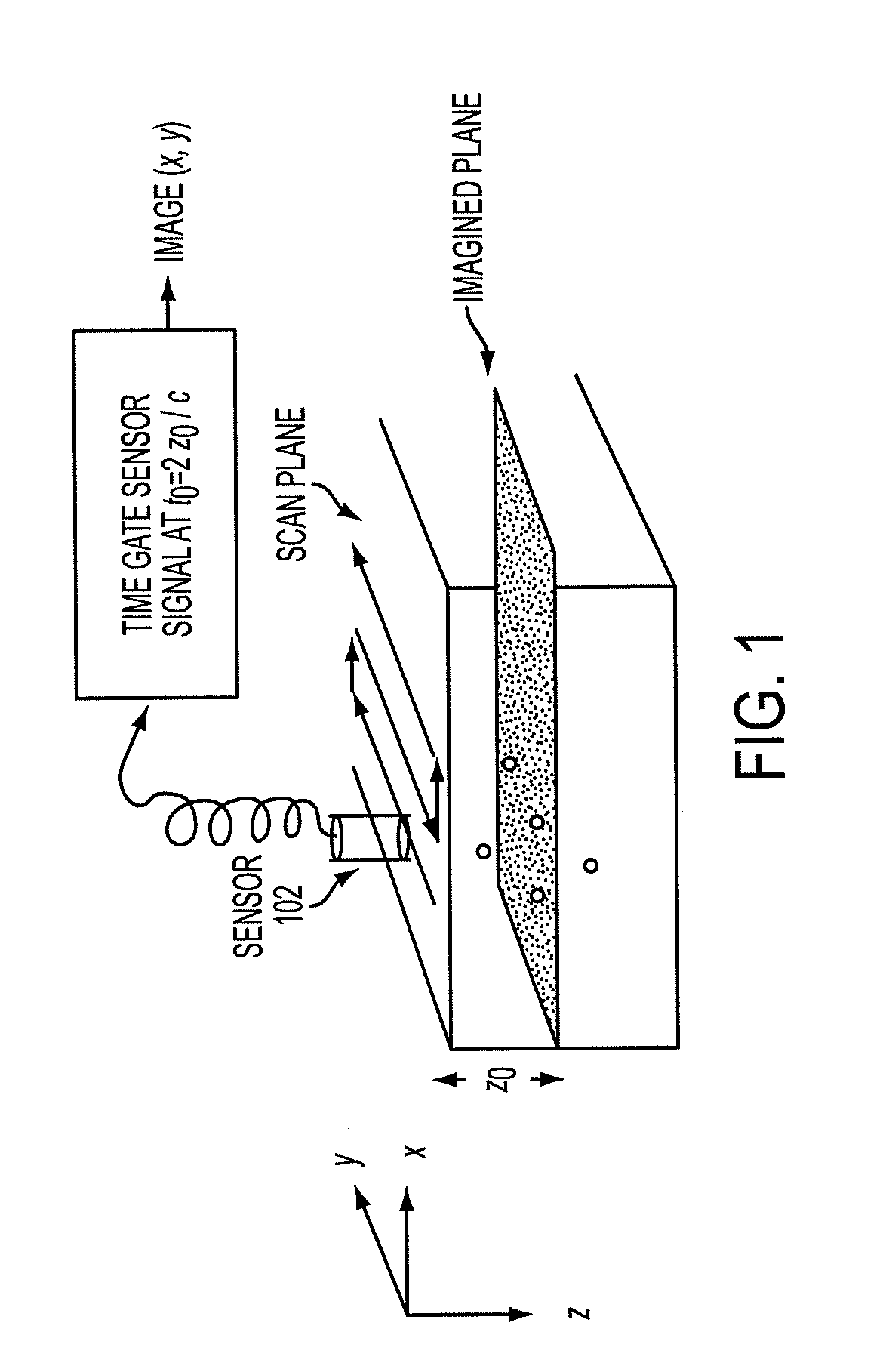
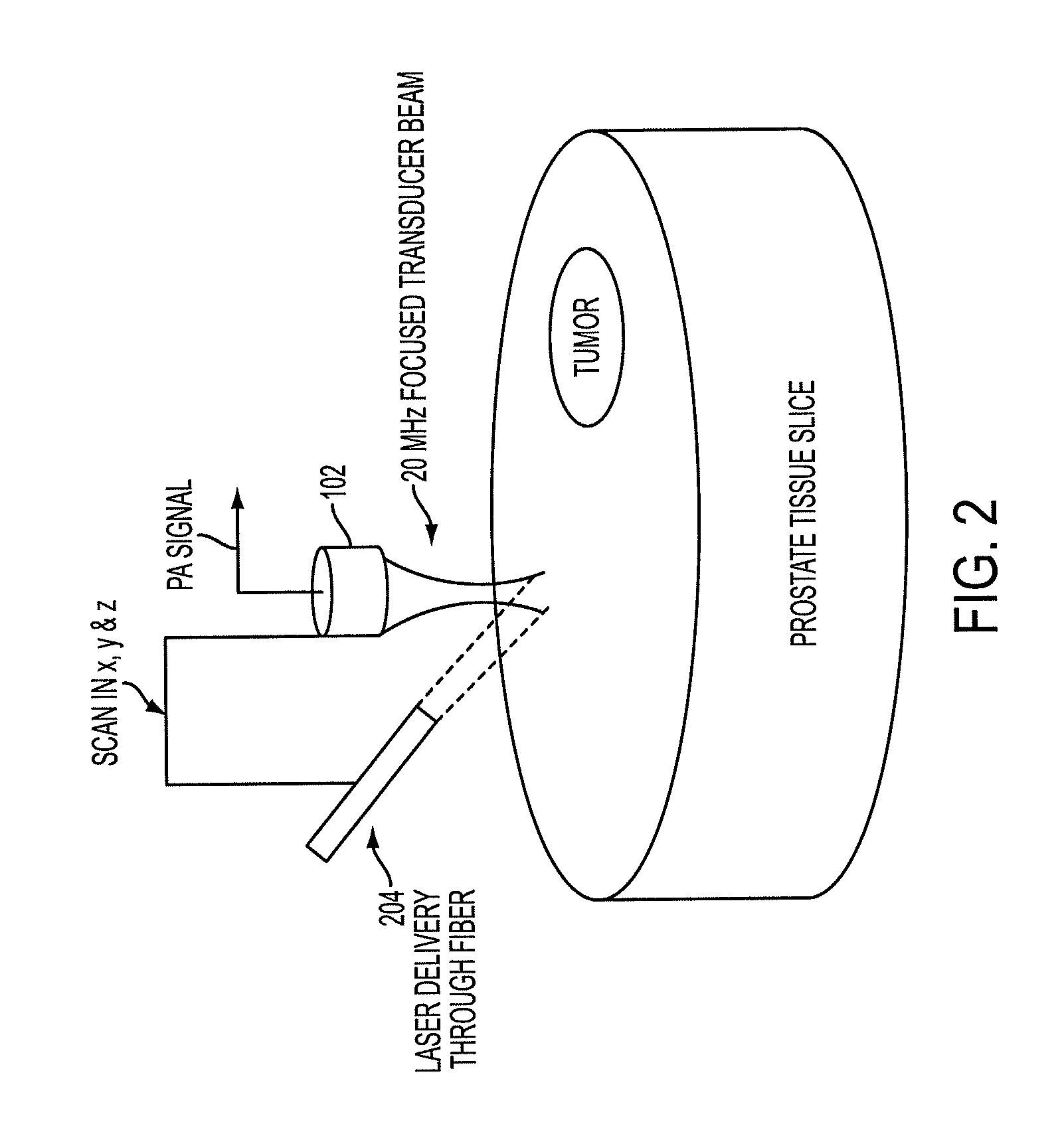
Low-cost device for c-scan photoacoustic imaging
ActiveUS20100016717A1Small sizeLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsSensor arraySonification
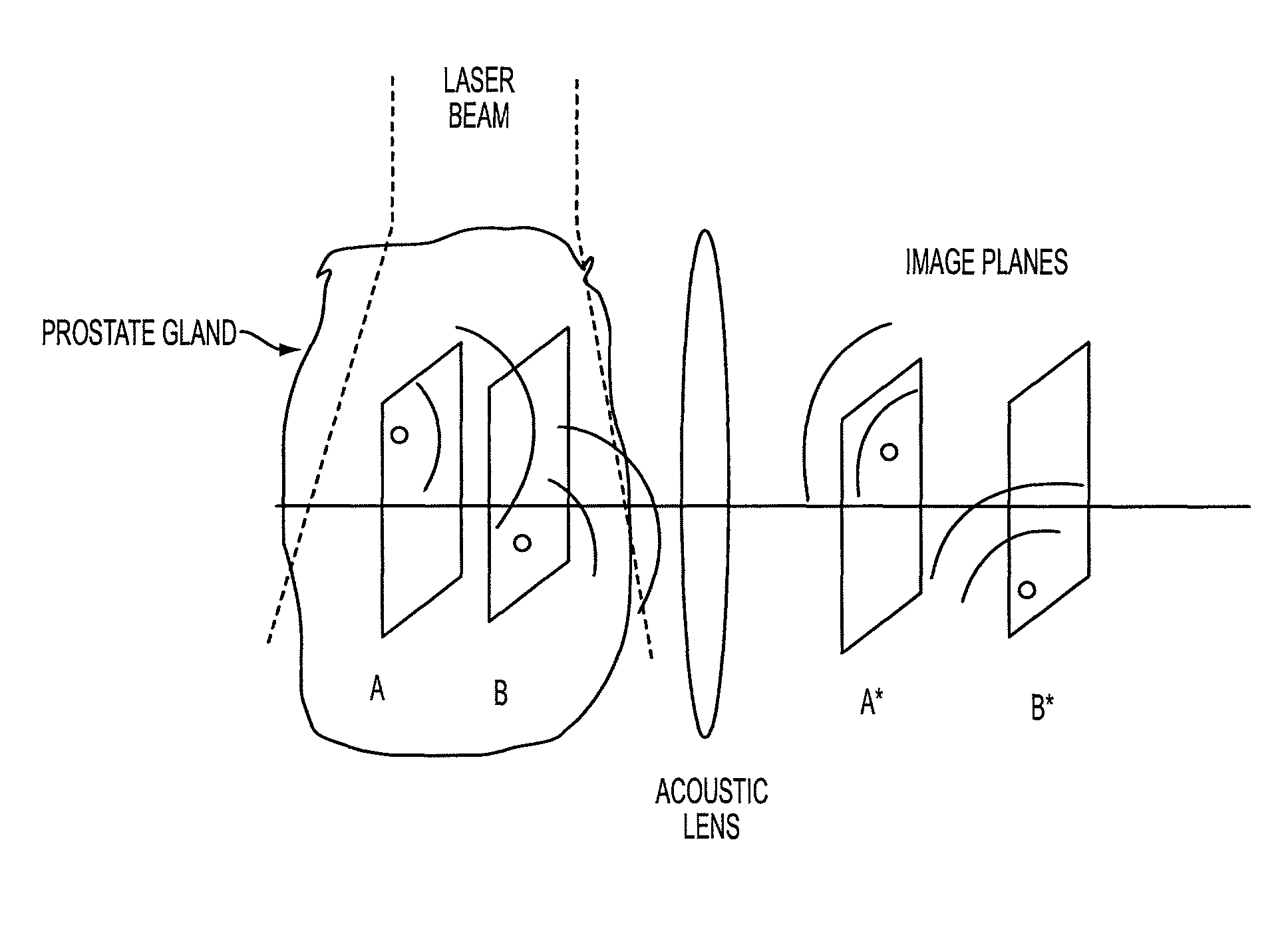
The prostate gland or other region of interest is stimulated with laser light, resulting in ultrasound waves (photoacoustic effect) which are focused by an acoustic lens and captured by a specific 1- or 2D sensor array and subsequently displayed as a C-scan on a computer screen. The amplitude of the ultrasound waves generated by laser stimulation is proportional to the optical absorption of the tissue element at that spatial location. Variability in tissue absorption results in C-scan image contrast. The photoacoustic imaging is combined with an ultrasound C-scan image produced with a plane ultrasound wave applied to the region of interest.
Owner:ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
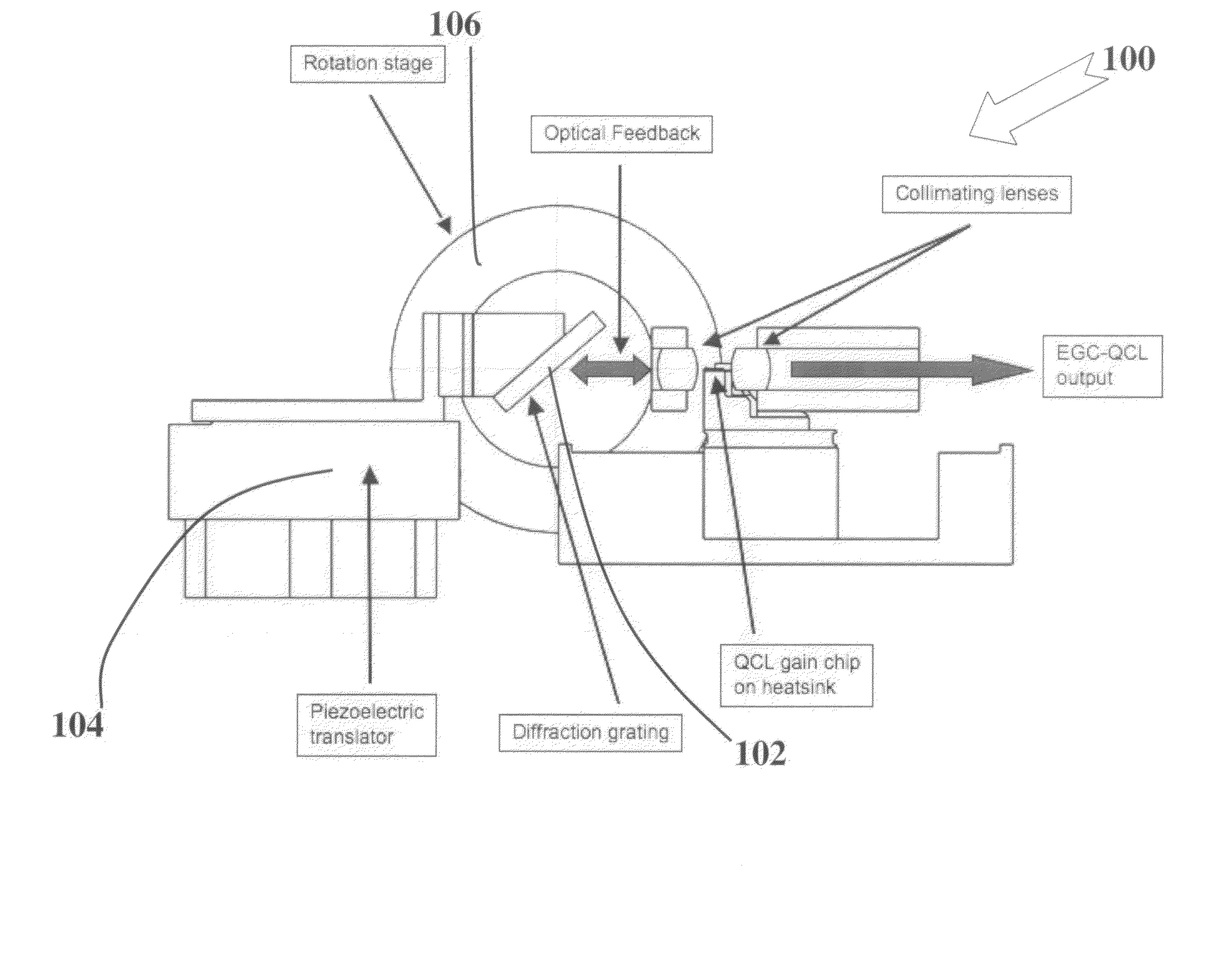
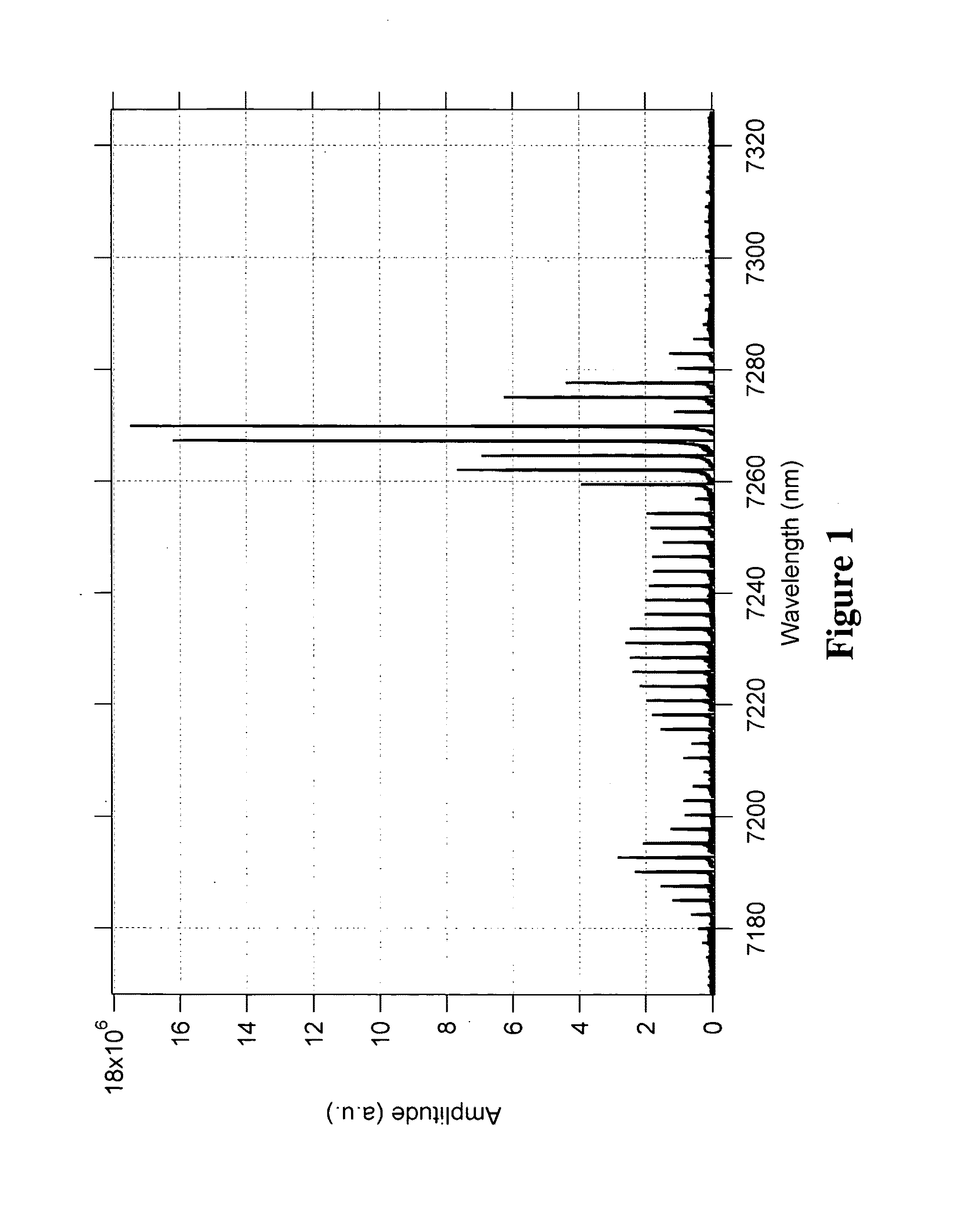
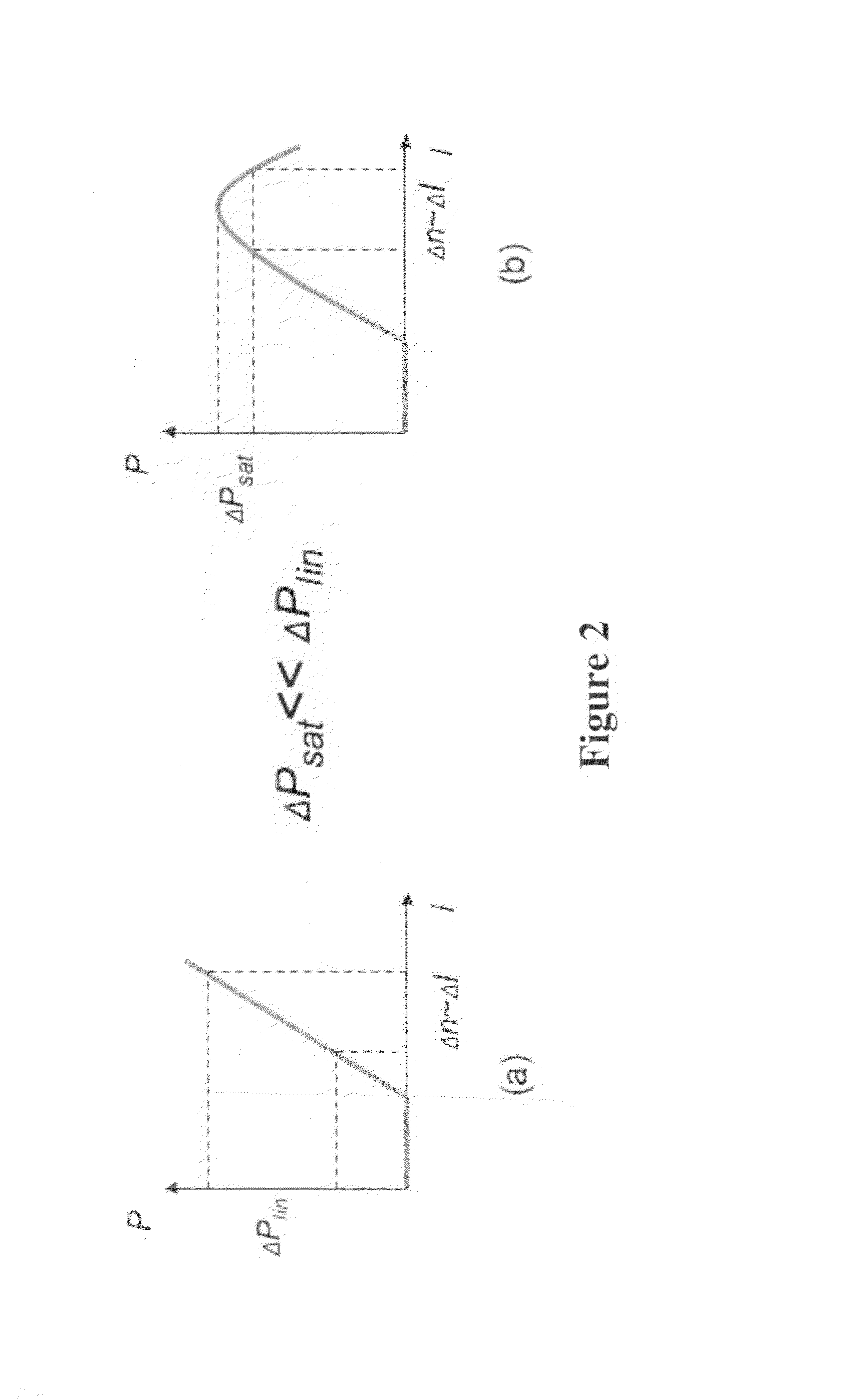
Tunable quantum cascade lasers and photoacoustic detection of trace gases, TNT, TATP and precursors acetone and hydrogen peroxide
ActiveUS7903704B2High rejectionShorten the timeMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical resonator shape and constructionQuantum cascade laserPeroxide
Methods and apparatus for broad tuning of single wavelength quantum cascade lasers and the use of light output from such lasers for highly sensitive detection of trace gases such as nitrogen dioxide, acetylene, and vapors of explosives such as trinitrotoluene (TNT) and triacetone triperoxide (TATP) and TATP's precursors including acetone and hydrogen peroxide. These methods and apparatus are also suitable for high sensitivity, high selectivity detection of other chemical compounds including chemical warfare agents and toxic industrial chemicals. A quantum cascade laser (QCL) system that better achieves single mode, continuous, mode-hop free tuning for use in L-PAS (laser photoacoustic spectroscopy) by independently coordinating gain chip current, diffraction grating angle and external cavity length is described. An all mechanical method that achieves similar performance is also described. Additionally, methods for improving the sensor performance by critical selection of wavelengths are presented.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Photoacoustic apparatus
InactiveUS20100058870A1Information obtainMultiple-port networksMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic waveAcoustic lens
A photoacoustic apparatus includes an acoustic lens configured to collect a acoustic wave, an acoustic detector configured to detect the acoustic wave collected by the acoustic lens, a driver configured to move at least one of the acoustic detector and the acoustic lens so as to measure the acoustic wave generated from an object to be measured due to a photoacoustic effect, and a controller configured to output a first measurement signal resulting from the acoustic wave that is generated from a first position in the object, and to eliminate a second measurement signal resulting from the acoustic wave that is generated from a second position different from the first position in the object.
Owner:CANON KK
Hybrid catheter apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20150359595A1Enhance separation debulkingImprove clinical efficacyEndoscopesCatheterOrgan wallLaser cutting
A hybrid catheter device for performing cutting action on a region of a tissue, using sequential laser and mechanical cutting processes, and incorporating an acoustic sensor on the end of the device, such that if a pulsed laser beam is used for the laser cutting, the absorption of that beam in the tissue being cut can provide information about the progress of the cut by means of the opto-acoustic effect. Other hybrid catheter devices incorporate blunt protrusions on the end of said device, but having sharp lateral edges, such that rotation of the catheter device generates mechanical cutting action in the tissue. The blunt protrusion ends prevents uncontrolled cutting in the forward motion. Other hybrid catheter devices enable controlled incisions into an organ wall, such as the duodenum, and held in place by means of an inflatable balloon. A dual-wavelength nail fungus treatment hybrid catheter is also shown.
Owner:EXIMO MEDICAL
Non-invasive method and device for rapidly detecting blood sugar
InactiveCN101467884AEliminate distractionsQuick checkDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUltrasonic sensorBiological activation
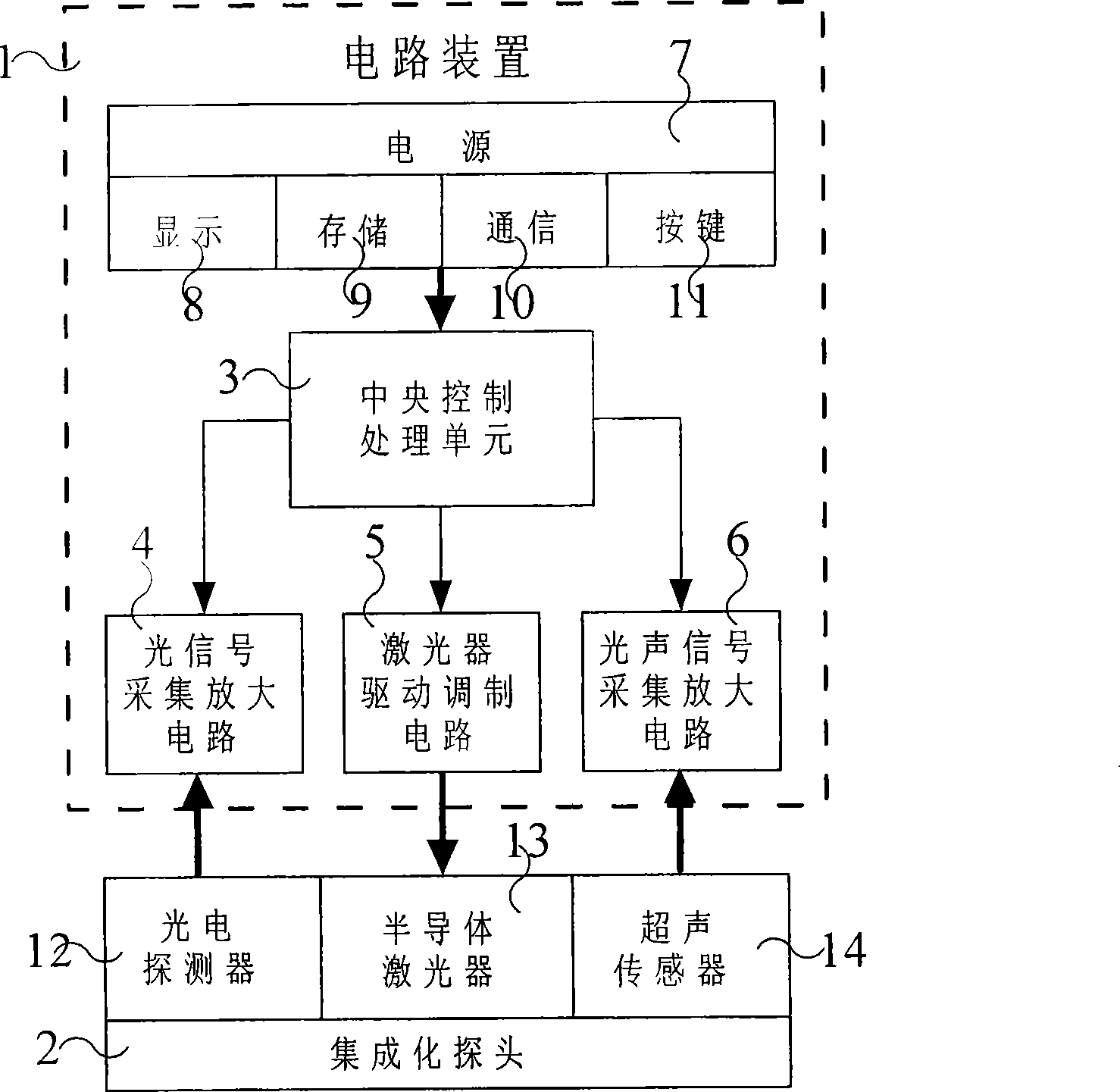
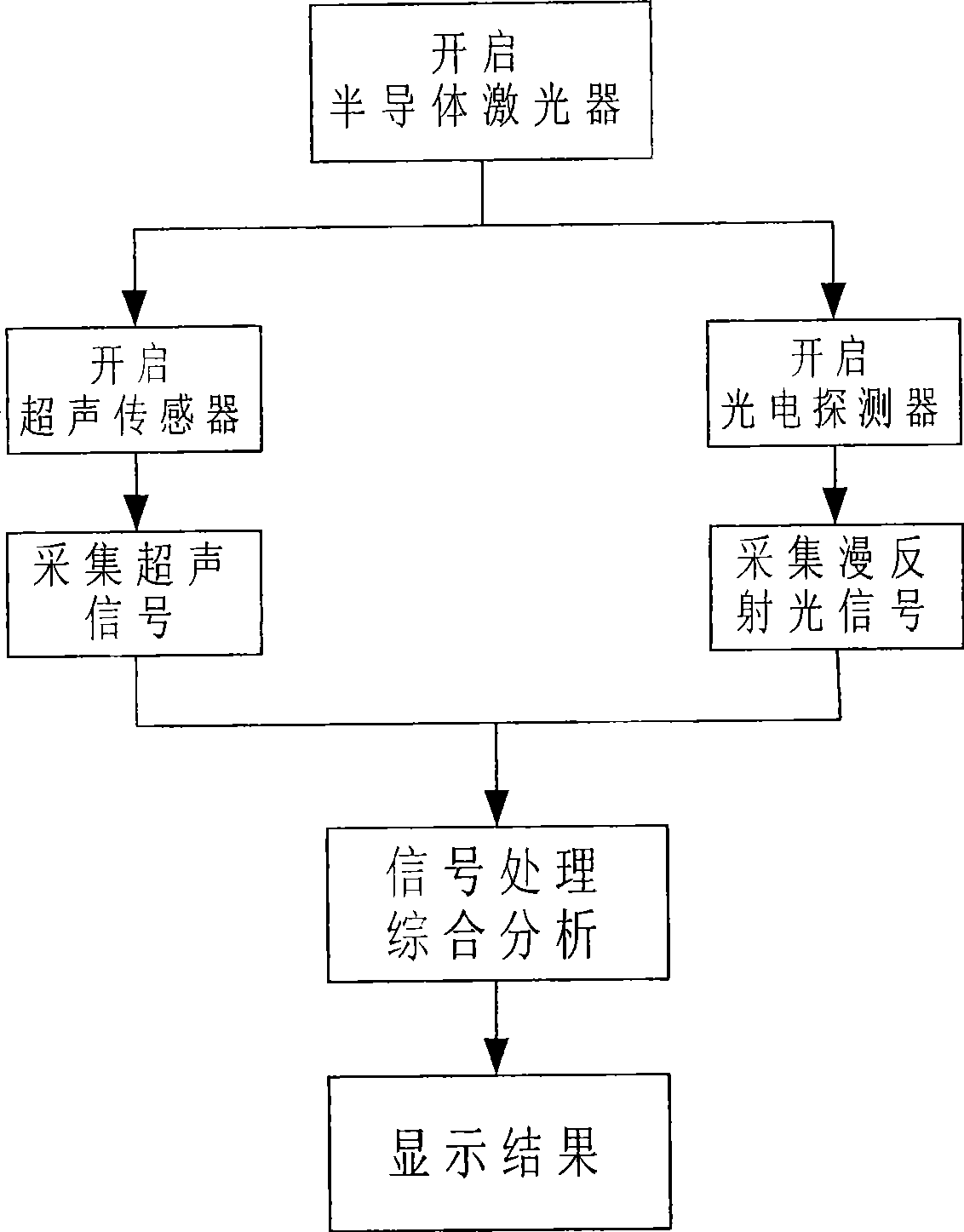
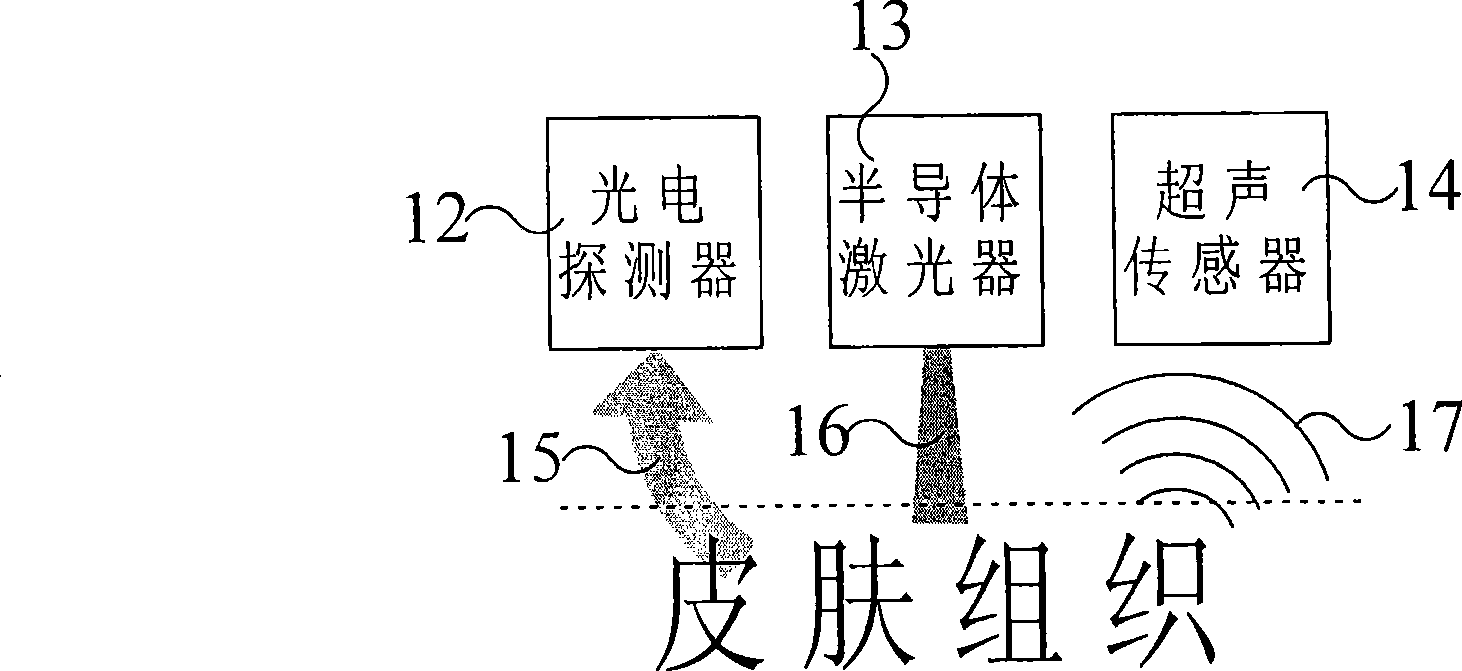
The invention relating to biomedicine detecting technique provides a non-invasive blood sugar fast detecting method and a device thereof. The method comprises steps of controlling a pulse laser to irradiate the skin tissue of a human body, using an ultrasonic transducer to detect the acoustic and light signals PA generated by the photoacoustic effect, using a photoelectric detector to detect scattered reflection photosignal A at the same time, and performing data analysis by using the acoustic and light signals PA and the reflection photosignal A to obtain a blood sugar concentration value to realize non-invasive blood sugar fast detecting. The device comprises a circuit part and an integrated probe, wherein, the circuit part comprises a central control processing unit and a photosignal collecting and amplifying circuit connected with the same, an acoustic and light signals collecting and amplifying circuit, a laser activation and modulation circuit, control function modules of displaying, storing, communicating, button-pressing and the like and an electric power. The integrated probe comprises a semiconductor pulsed laser, the ultrasonic transducer and the photoelectric detector.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for remote sensing of molecular species at nanoscale utilizing a reverse photoacoustic effect
InactiveUS7665364B2Increase temperatureAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic property measurementsChemical compositionLight irradiation
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Low-cost device for C-scan photoacoustic imaging
ActiveUS8353833B2Low costSmall sizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsImage contrastLaser light
The prostate gland or other region of interest is stimulated with laser light, resulting in ultrasound waves (photoacoustic effect) which are focused by an acoustic lens and captured by a specific 1- or 2D sensor array and subsequently displayed as a C-scan on a computer screen. The amplitude of the ultrasound waves generated by laser stimulation is proportional to the optical absorption of the tissue element at that spatial location. Variability in tissue absorption results in C-scan image contrast. The photoacoustic imaging is combined with an ultrasound C-scan image produced with a plane ultrasound wave applied to the region of interest.
Owner:ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Apparatus, system and methods for photoacoustic detection of deep vein thrombosis
InactiveUS20120203093A1Avoid flowNoise signalUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsThrombusWavelength
Embodiments of the invention provide apparatus, systems and methods for the detection of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) using photoacoustic measurement of hemoglobin in different states of oxgyenation within tissue. One embodiment of a system for DVT detection comprises at least a first and second light source that emit light at first and second wavelengths, an acoustic transducer, a data converter and a processor. The first and second light sources are directed on the patient's skin to produce a photoacoustic signal (PS) correlated to an amount of absorbance of the first and second wavelengths by a target region of tissue beneath the patient's skin. The acoustic transducer detects the PS and transduces it into an electrical signal which is correlated to the PS. The data converter converts the electrical signal into a digital signal which is analyzed by the processor to detect the presence of DVT within the target region.
Owner:INCUBE LABS
Method and apparatus for remote sensing utilizing a reverse photoacoustic effect
InactiveUS20070220979A1Reliable identificationIncrease temperatureAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNanosensorsChemical compositionSignal on
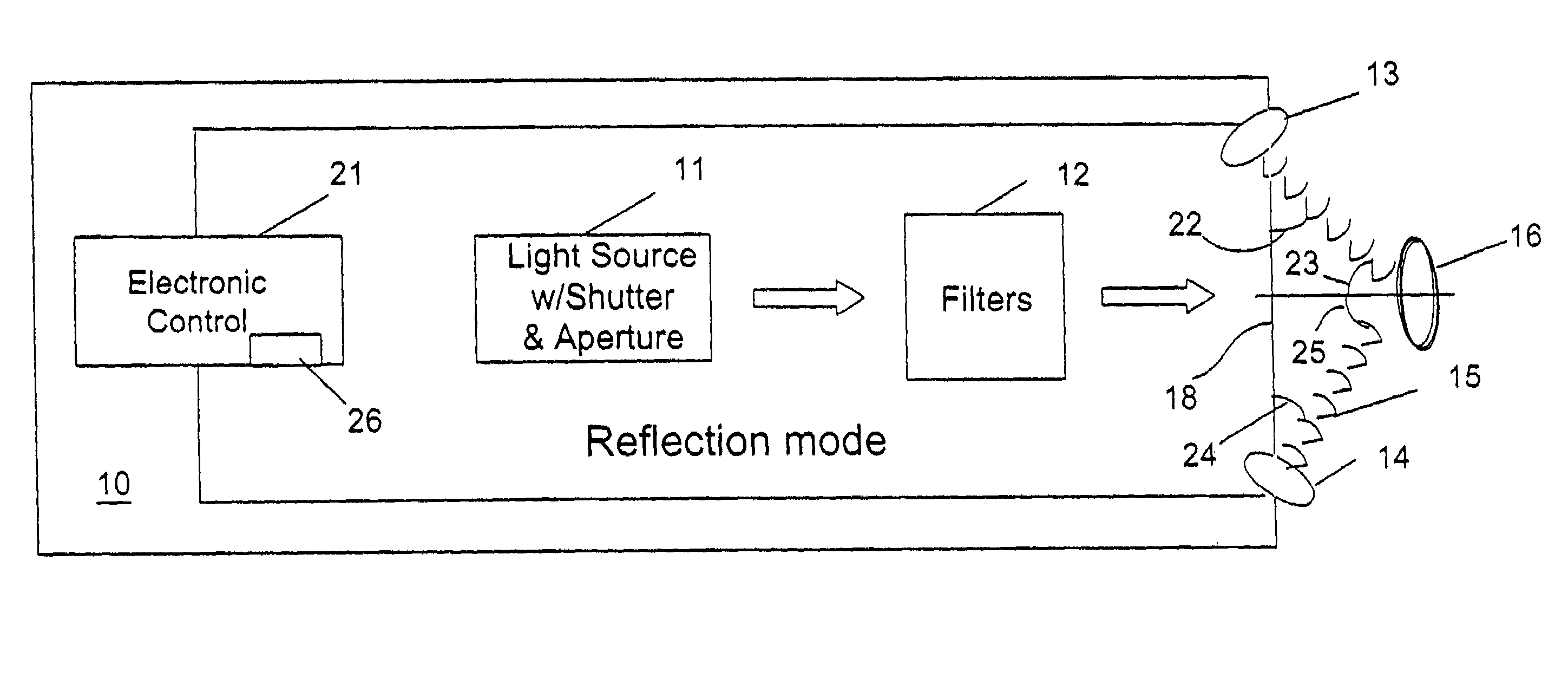
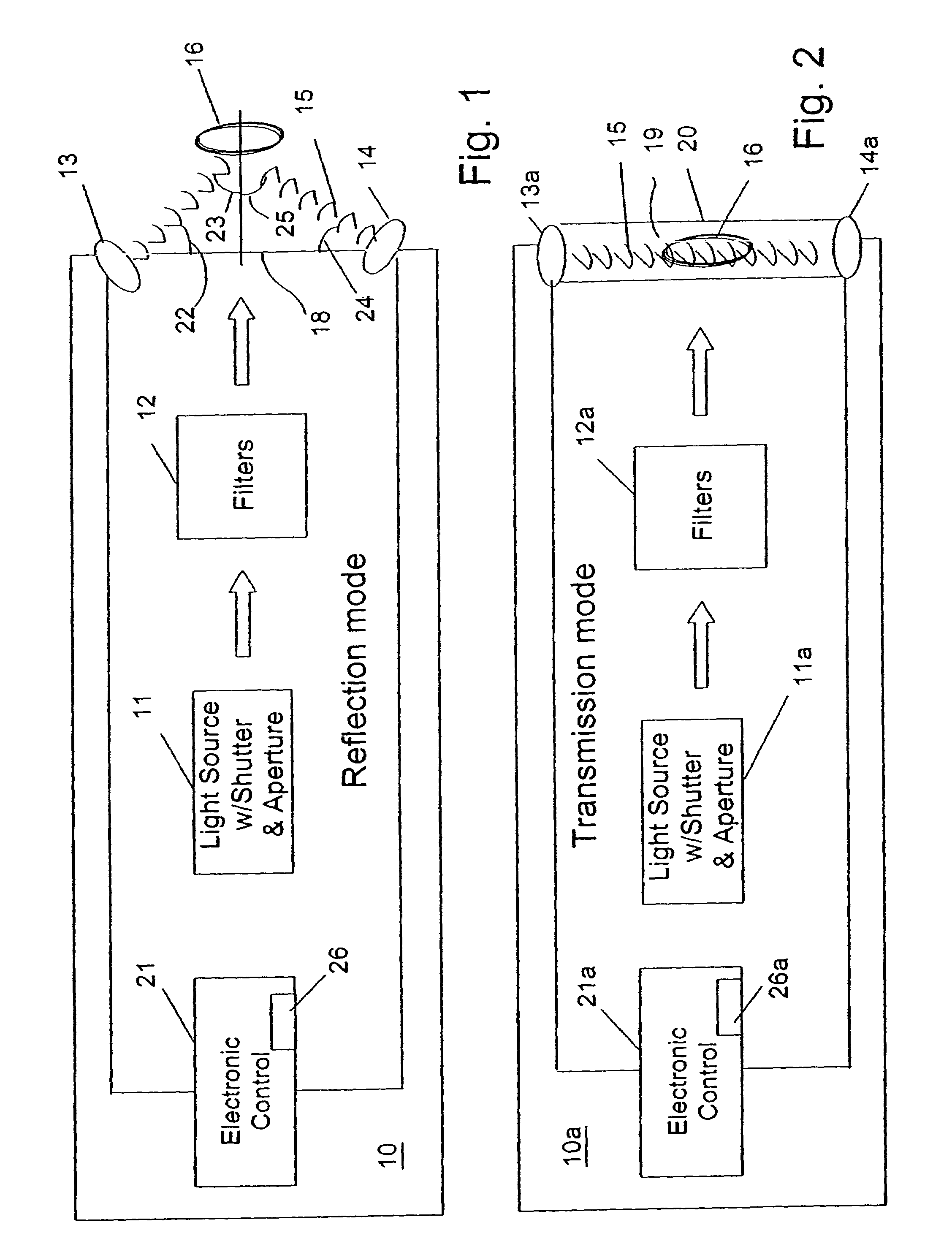
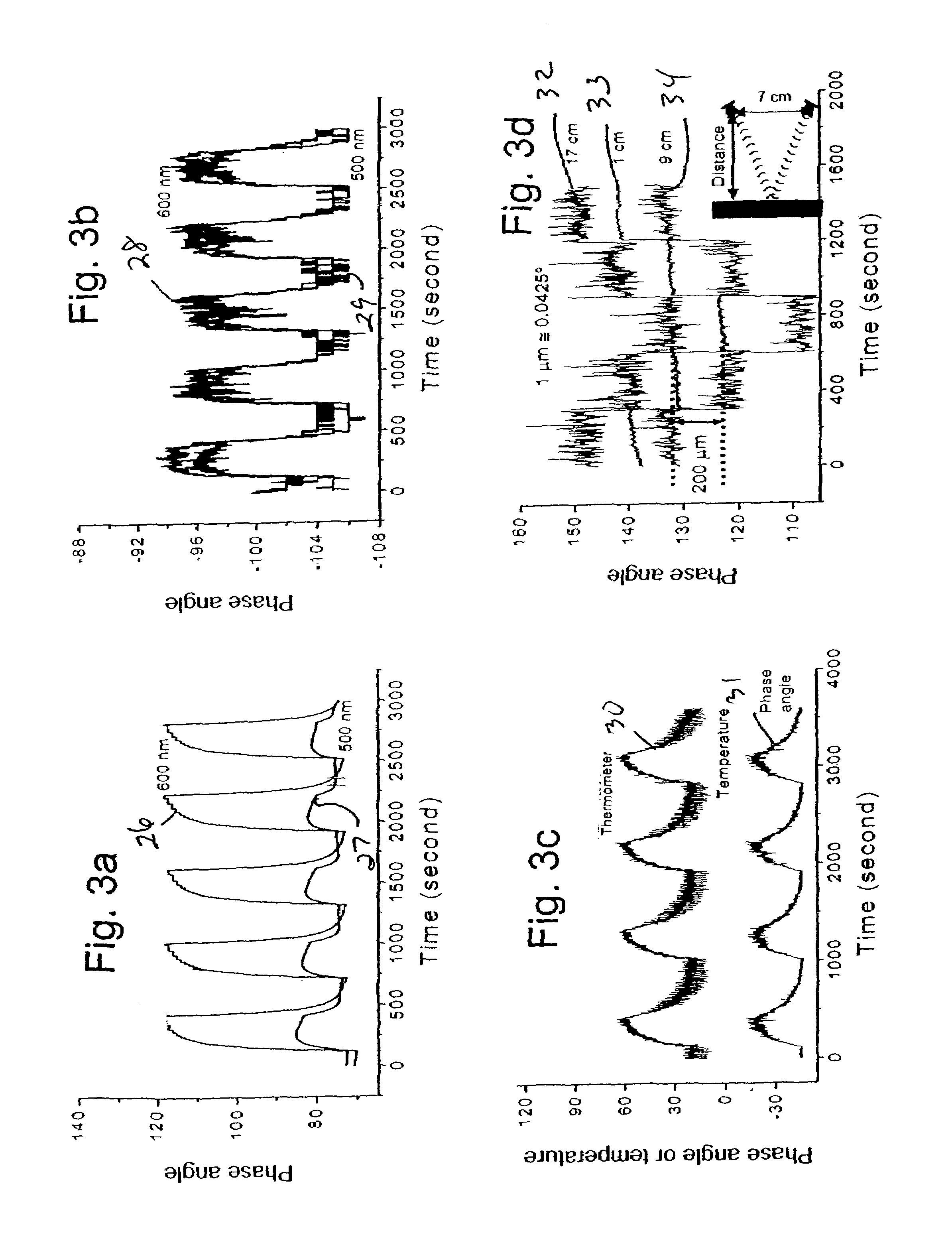
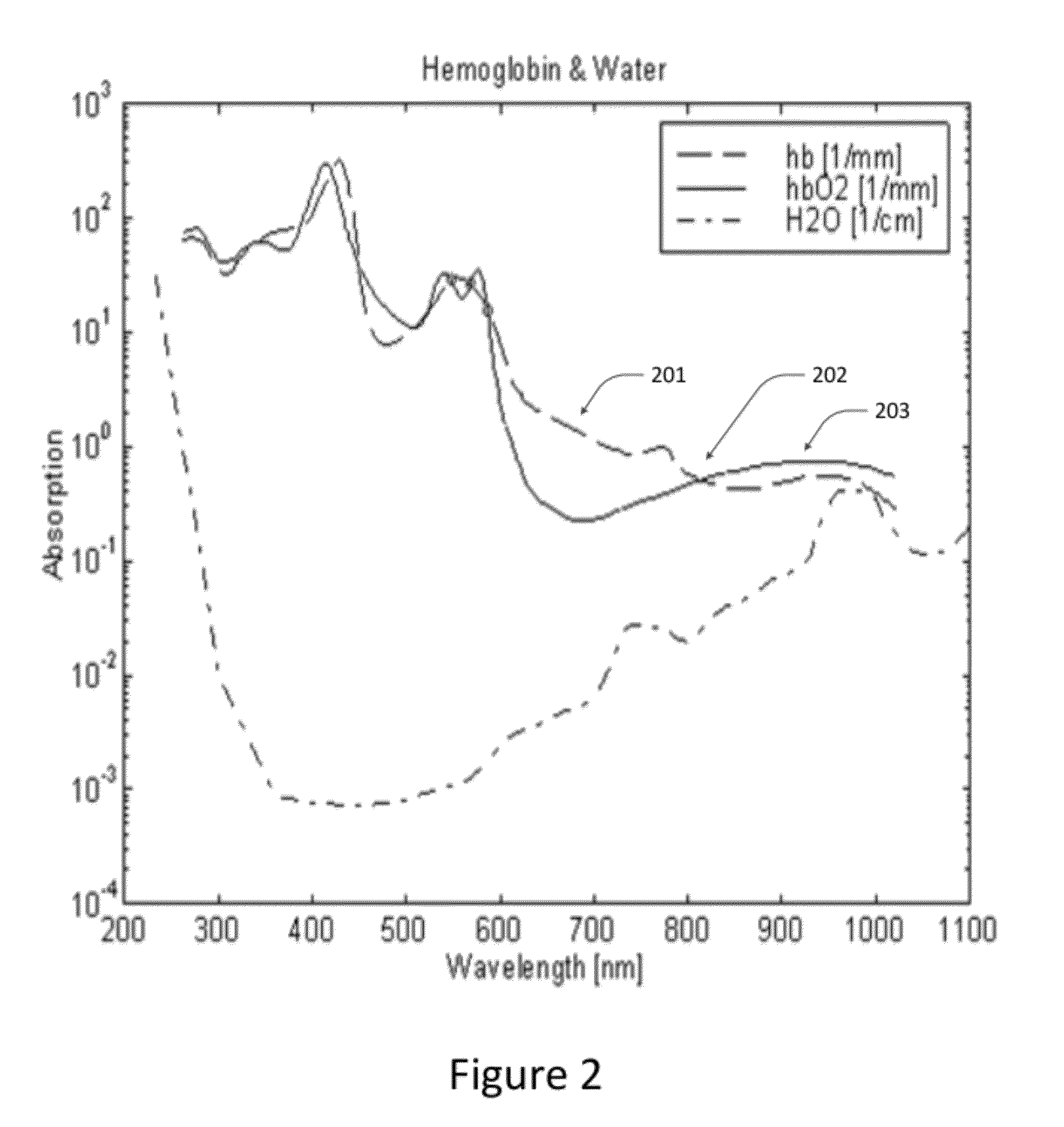
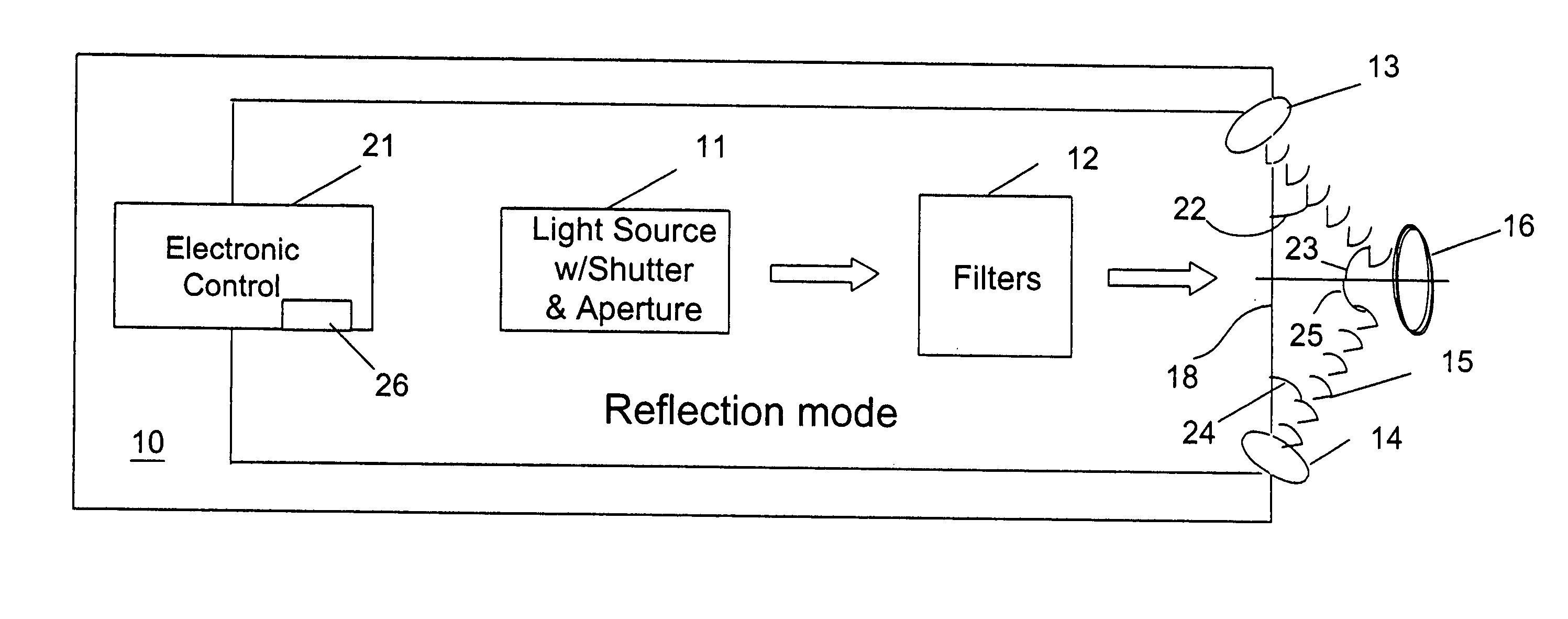
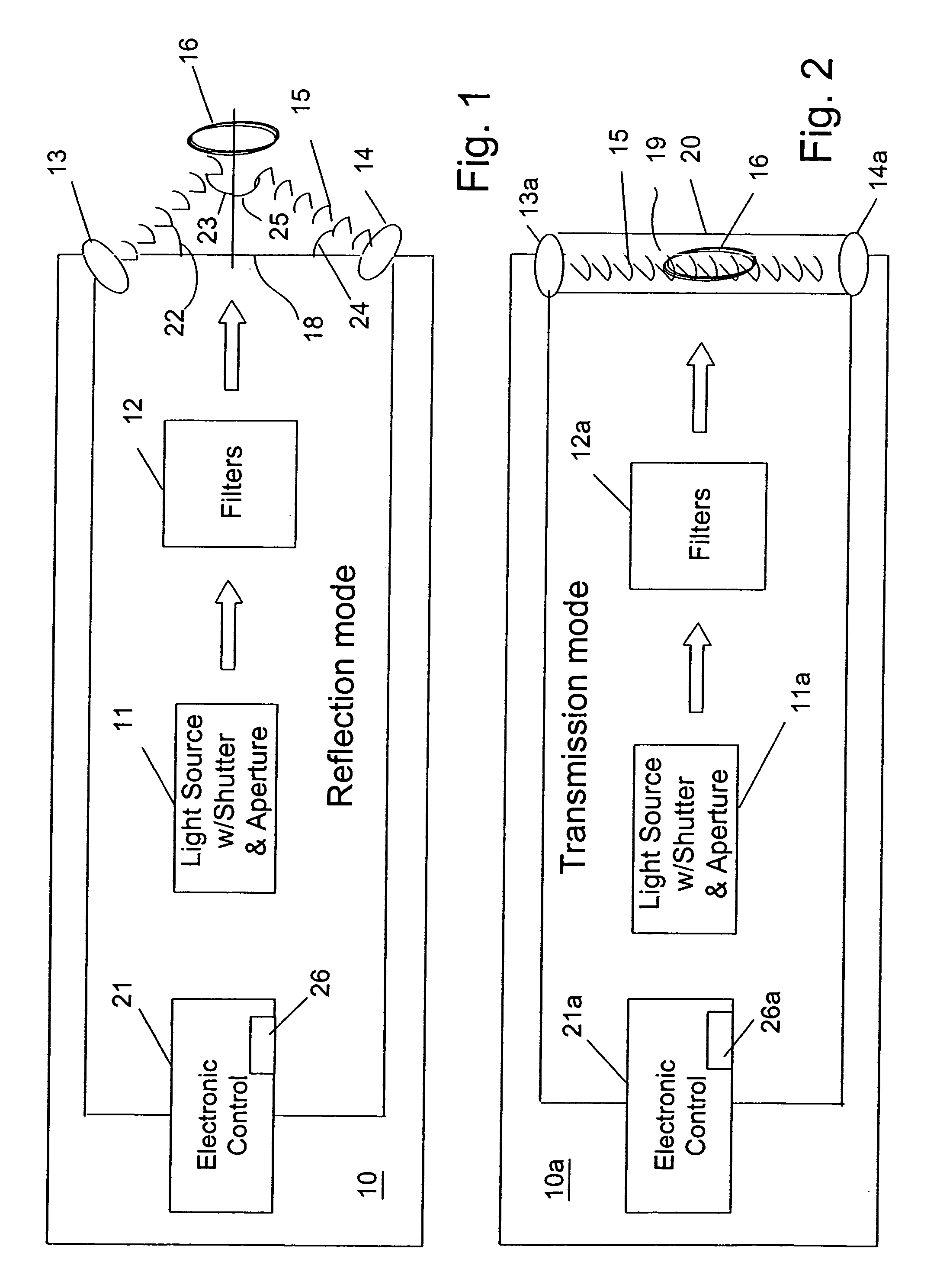
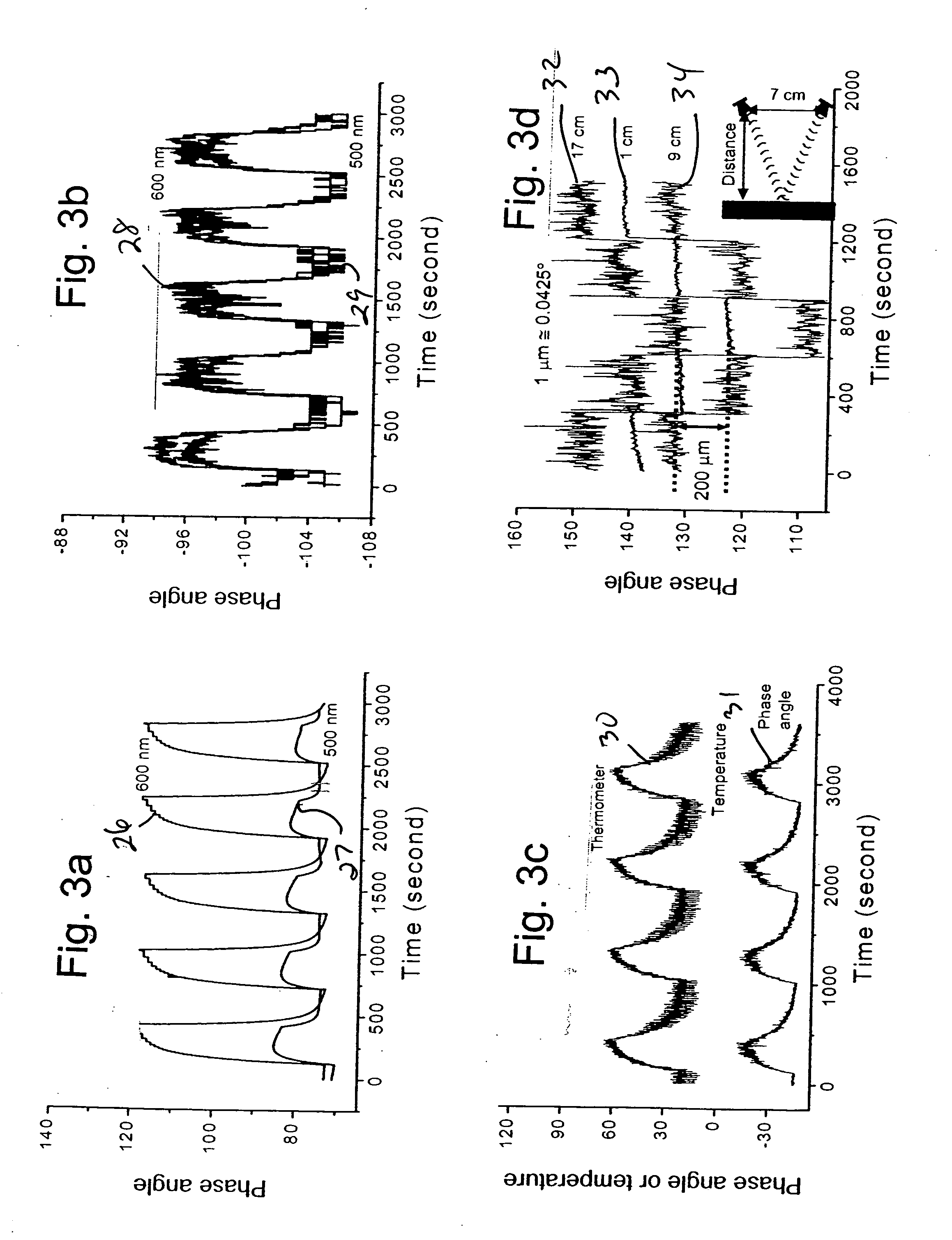
A method and apparatus for identifying a sample, involves illuminating the sample with light of varying wavelengths, transmitting an acoustic signal against the sample from one side and receiving a resulting acoustic signal on another side, detecting a change of phase in the acoustic signal corresponding to the light of varying wavelengths, and analyzing the change of phase in the acoustic signal for the varying wavelengths of illumination to identify the sample. The apparatus has a controlled source for illuminating the sample with light of varying wavelengths, a transmitter for transmitting an acoustic wave, a receiver for receiving the acoustic wave and converting the acoustic wave to an electronic signal, and an electronic circuit for detecting a change of phase in the acoustic wave corresponding to respective ones of the varying wavelengths and outputting the change of phase for the varying wavelengths to allow identification of the sample. The method and apparatus can be used to detect chemical composition or visual features. A transmission mode and a reflection mode of operation are disclosed.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Photoacoustic apparatus
InactiveUS8397573B2Multiple-port networksMaterial analysis by optical meansAcoustic waveAcoustic lens
A photoacoustic apparatus includes an acoustic lens configured to collect a acoustic wave, an acoustic detector configured to detect the acoustic wave collected by the acoustic lens, a driver configured to move at least one of the acoustic detector and the acoustic lens so as to measure the acoustic wave generated from an object to be measured due to a photoacoustic effect, and a controller configured to output a first measurement signal resulting from the acoustic wave that is generated from a first position in the object, and to eliminate a second measurement signal resulting from the acoustic wave that is generated from a second position different from the first position in the object.
Owner:CANON KK
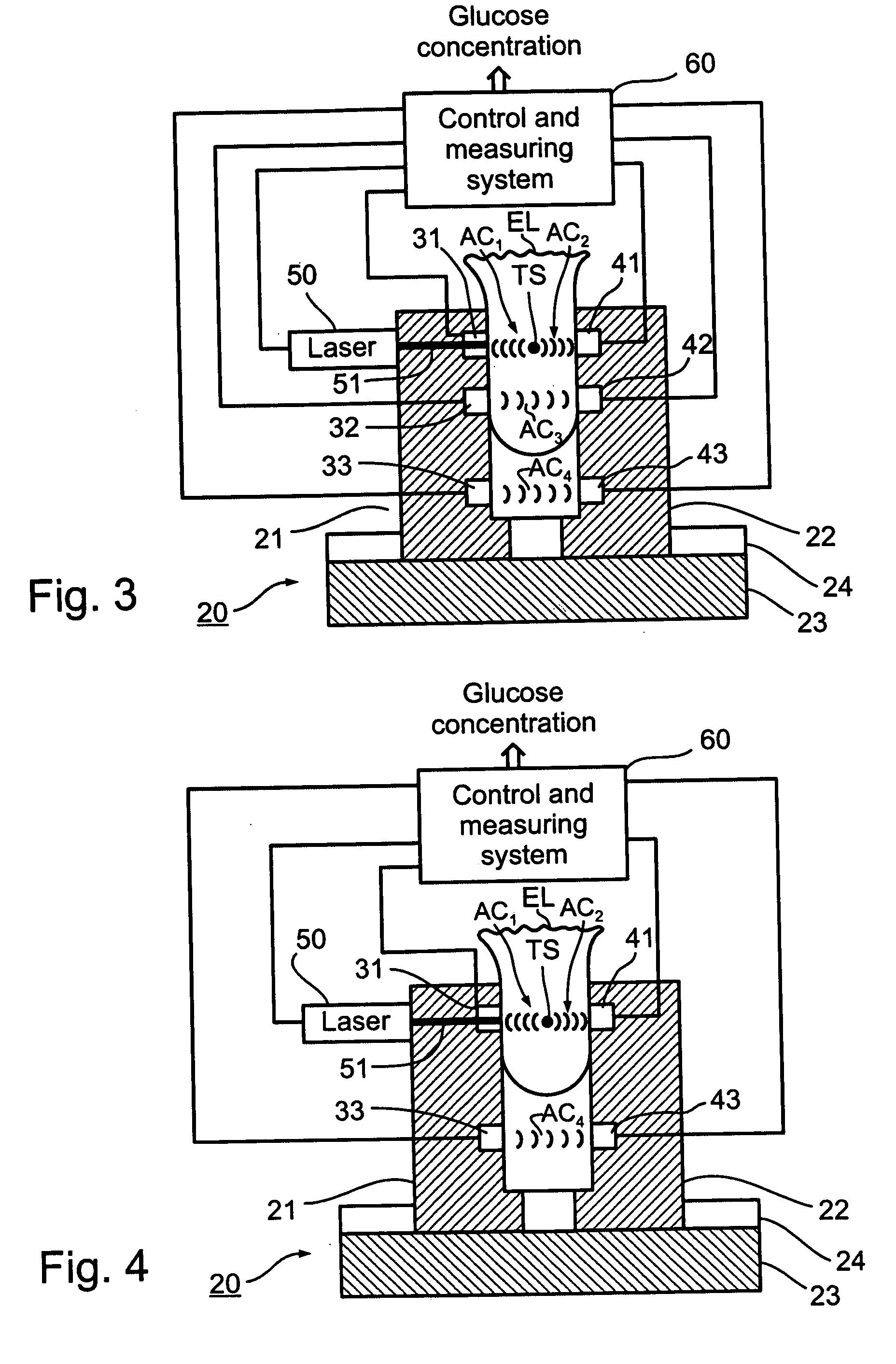
Method and apparatus for non-invasively monitoring concentrations of glucose or other target substances
InactiveUS20050272990A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMedicineAcoustic wave
A method and apparatus for non-invasively measuring concentration of a target substance such as glucose within a body by: activating a pulse source to apply to the body a series of pulses of energy highly absorbable by the target substance to generate, by the photoacoustic effect, a series of acoustic waves propagated through an acoustic channel in the body; detecting the acoustic waves to produce an electrical signal having a frequency corresponding to the frequency of the acoustic waves generated by the photoacoustic effect; controlling the pulse source to change the frequency at which the energy pulses are applied to the body such that the detector detects a whole integer number of wavelengths in the acoustic channel irrespective of variations in the target substance concentration within the body; and utilizing a measurement of the frequency, or change in frequency, of the pulses to produce a measurement of the concentration, or change in concentration, of the target substance.
Owner:NEXENSE
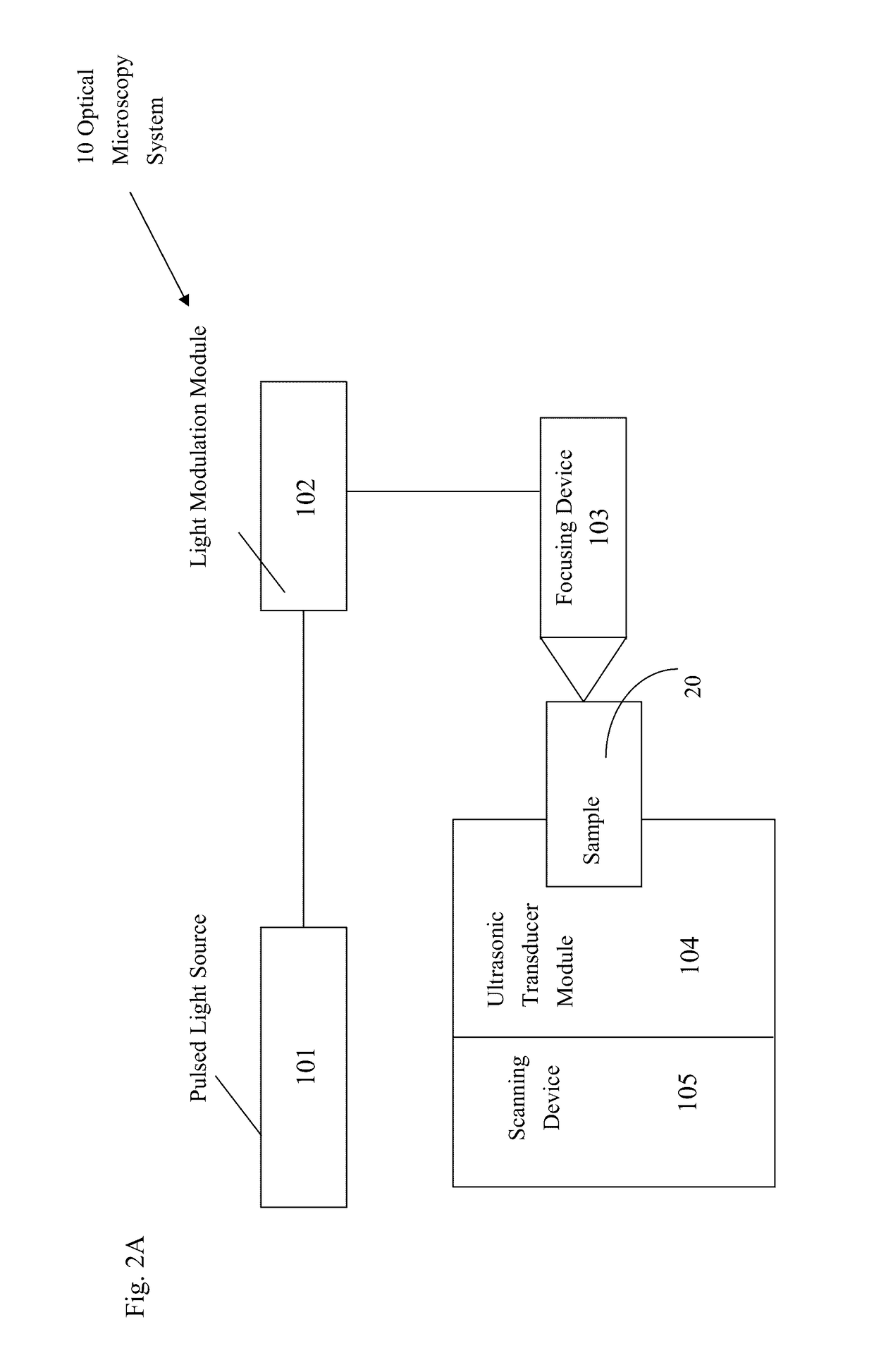
Optical microscopy systems based on photoacoustic imaging
ActiveUS9618445B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectricitySinusoidal modulation
The present application discloses optical microscopy systems and related method that use modulation techniques and contrast agents to enable the systems to detect nonlinear photoacoustic signals with high spectrum sensitivity and frequency selectivity for imaging. A laser beam is amplitude modulated for pure sinusoidal modulation using either the loss modulation technique or the single light amplitude modulation technique. The sample used in the invention is an endogenous contrast agent by itself or is treated by at least one exogenous contrast agent to produce or enhance photoacoustic effect induced by multi-photon absorption. The modulated laser beam is focused via a focusing device onto a sample which absorbs multiple photons simultaneously and generates ultrasonic (acoustic) waves via nonlinear photoacoustic effect. The ultrasonic waves are received and transformed into electrical signals and the frequency signals within the electrical signals are detected and recorded to create images.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
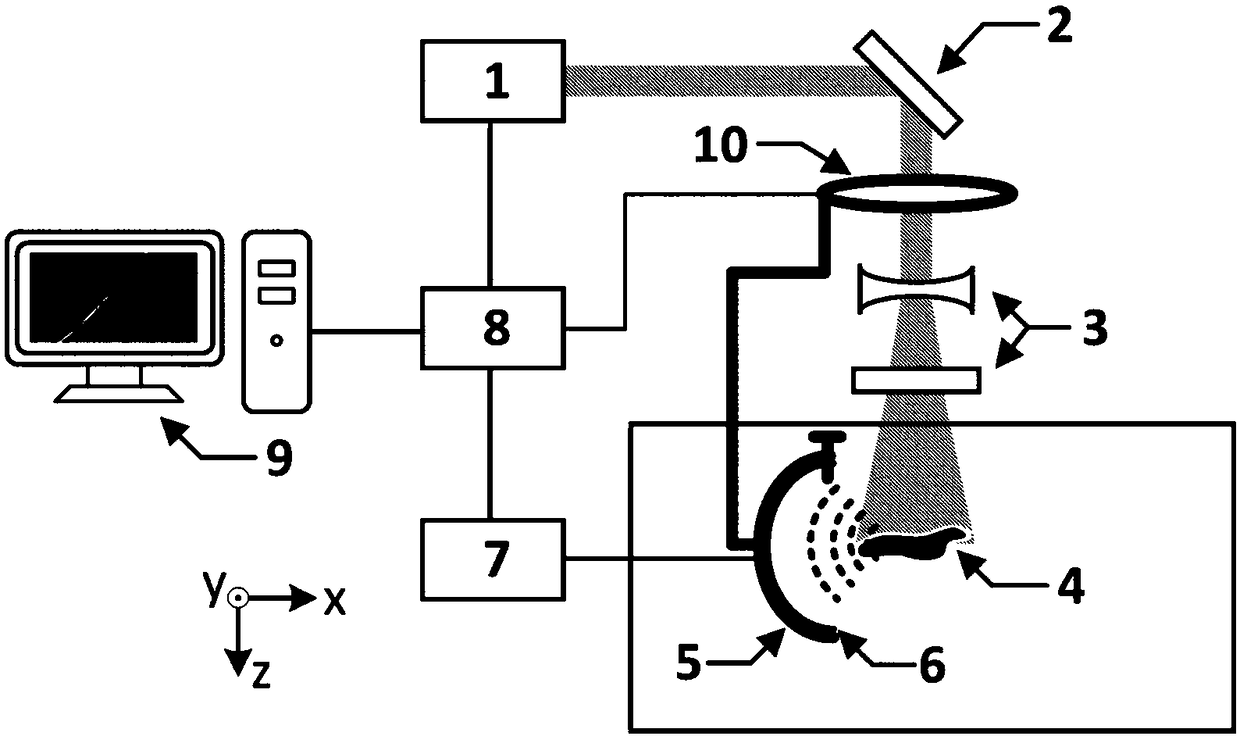
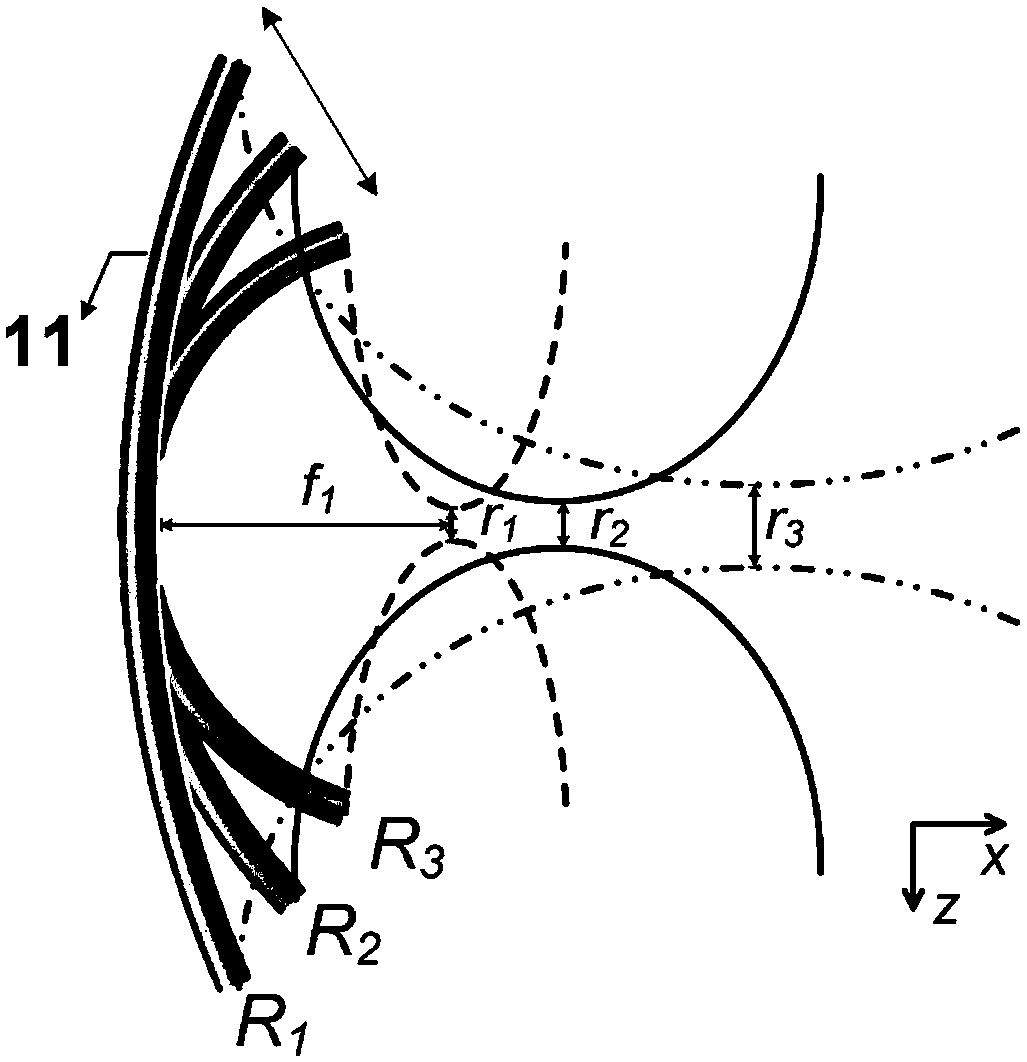
Photoacoustic computed tomography system based on adjustable focusing type optical fiber sensor
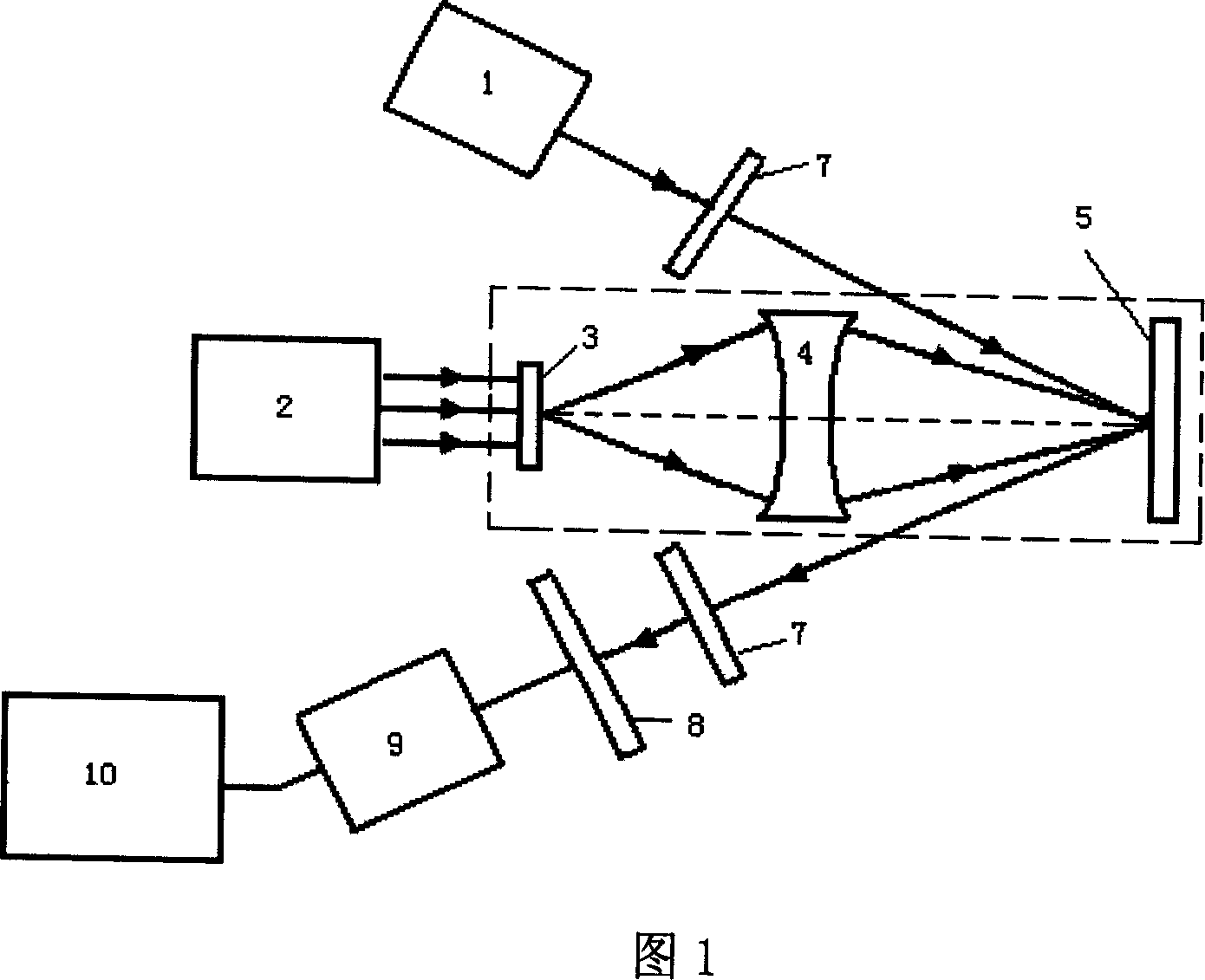
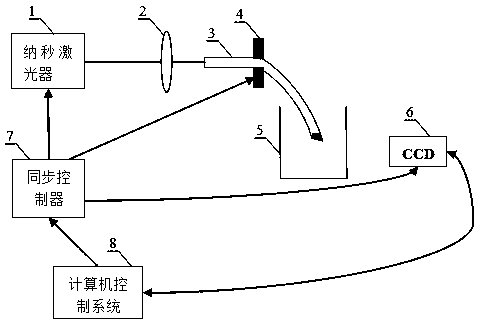
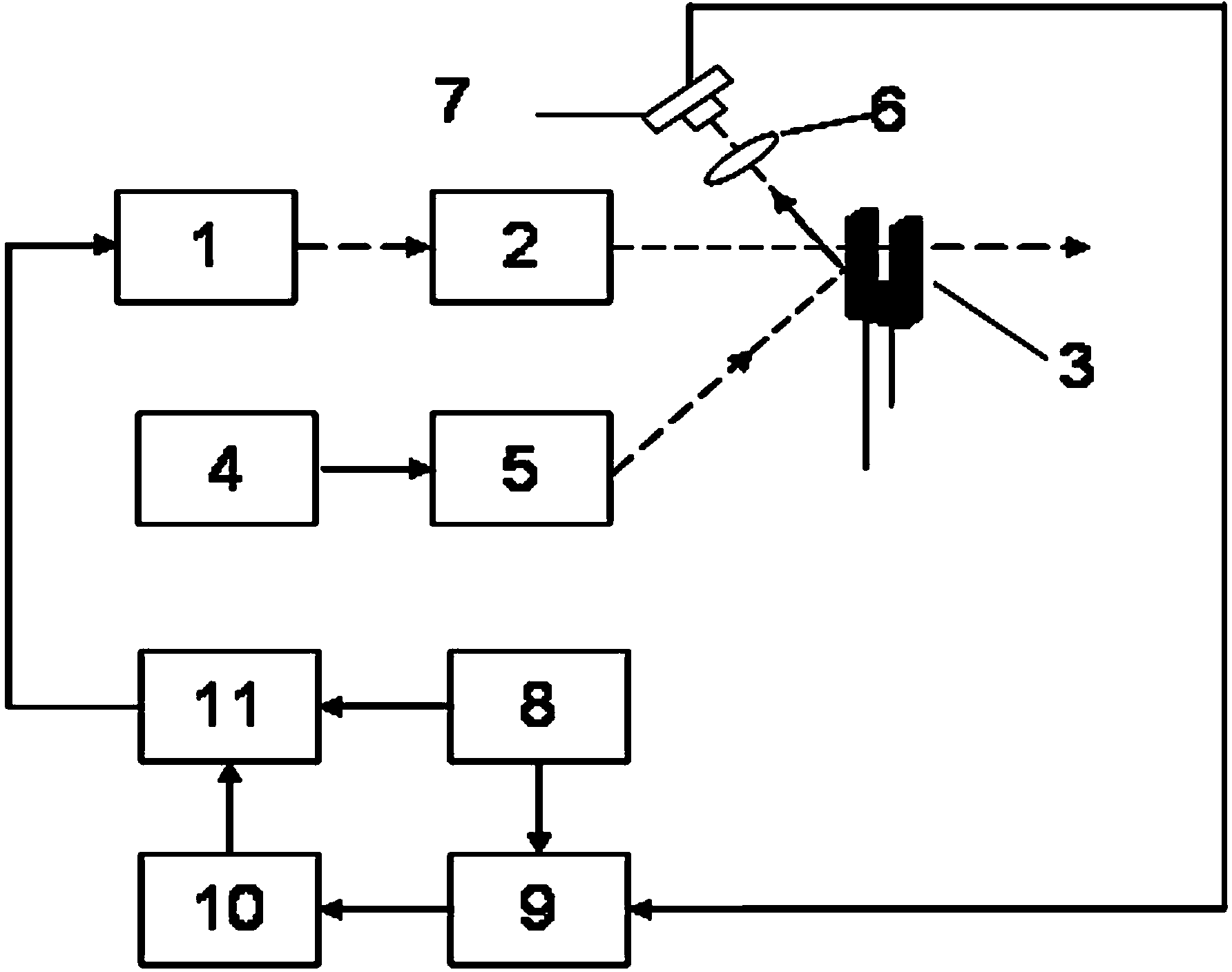
ActiveCN108606777ACompact structureEasy to adjustMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotoelectric effectPhotoacoustic effect
The invention discloses a photoacoustic computed tomography system based on an adjustable focusing type optical fiber sensor. The photoacoustic computed tomography system comprises a short-pulse laserdevice, a reflector, a beam expander, a water tank, a to-be-measured object, an optical fiber clamp, the adjustable focusing type optical fiber sensor, a rotary stepping motor, a photoelectric detector, a data collecting card and a computer and is characterized in that the short-pulse laser device emits short-pulse laser which irradiates the to-be-measured object, the to-be-measured object generates an ultrasonic wave due to a photoacoustic effect, the optical fiber sensor receives the ultrasonic wave and converts the same into an optical signal, the optical signal is processed by the photoelectric detector and the data collecting card and transmitted to the computer for reconstruction to obtain a two-dimensional tomography image, and a linear translation platform controls the to-be-measured object to move axially to obtain a three-dimensional tomography image. The adjustable focusing type optical fiber sensor is simple in structure, adjustable in curvature, high in sensitivity and suitable for being used in the photoacoustic computed tomography system.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Real-time acousto-optic imaging method based on acoustic lens and polarizing inspection
InactiveCN101028184AProtection from radiation damageImaging biological functionsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsAcousto-opticsAcoustic effect
A real-time optico-acoustic imaging method based on acoustic lens and polarization detection is disclosed. The acoustic lens is used to generate the acoustic pressure distribution of biologic tissue duto optico-acoustic effect and couple it to an imaging plane for directly imaging on it. A polarization analyzing method is used to convert said acoustic pressure distribution to light intensity distribution, which is recorded by CCD to obtain a clear image of a tissue layer. Its apparatus is composed of transparent flexible rubber layer, optical fiber, acoustic lens, laser, 1 / 4 wave plate, polarization analyzer, CCD, computer, and cylindrical cavity made of aluminum.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Laser-driven macroscopic liquid flow device and method based on optical fiber
ActiveCN108252891ASpeed up the flowEasy to control directionPumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesNanosecond laser pulseGold particles
The invention provides a laser-driven macroscopic liquid flow device and method based on optical fiber which is used for solving the problem that macroscopic liquid flow cannot be produced through simple combination of a photoacoustic effect and a sound wave driving fluid effect. According to the laser-driven macroscopic liquid flow device and method based on the optical fiber, nanometer gold particles are injected into one end face of the optical fiber by adopting an injection technology, and fixed and immersed in a driven solution, meanwhile, a nanosecond laser pulse is coupled into the optical fiber from the other end face of the optical fiber, and the laser pulse interacts with the nanometer gold particles injected into the optical fiber; the nanometer gold particles produce ultrasoundunder the effect of laser due to the photoacoustic effect, and meanwhile, a liquid is driven to flow due to the sound wave driving fluid effect; a fixed liquid-liquid interface and a liquid flow channel are needed, special requirements for the flowing liquid and the environment do not exist, the laser-driven macroscopic liquid flow device and method based on optical fiber is suitable for any liquids, tenability of the flow speed and direction of the driven liquid can be achieved, flowing of the driven liquid is monitored on line in real time by adopting a CCD, the control accuracy is improvedgreatly, and operation is convenient and easy.
Owner:深圳市比洋光通信科技股份有限公司
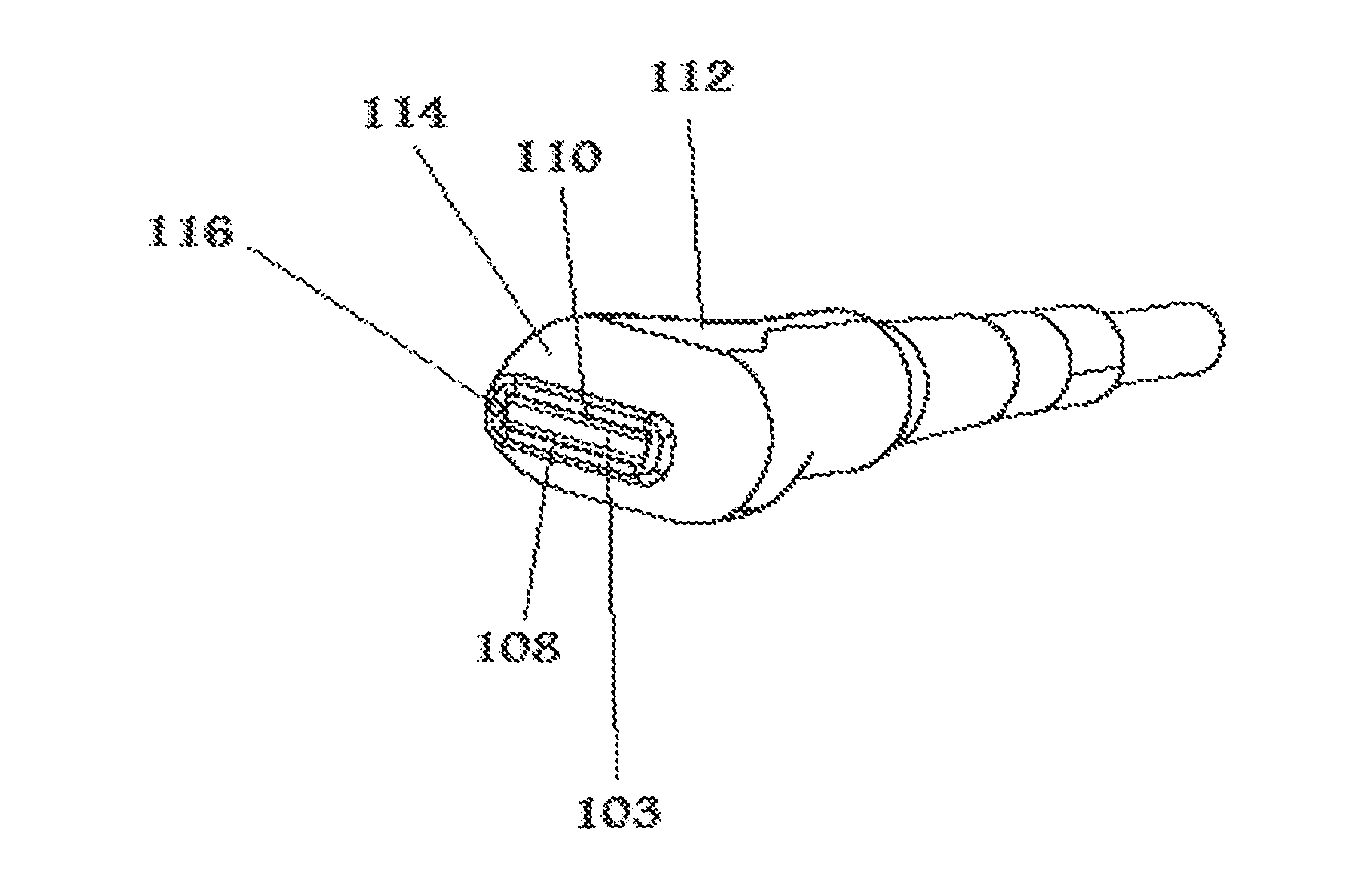
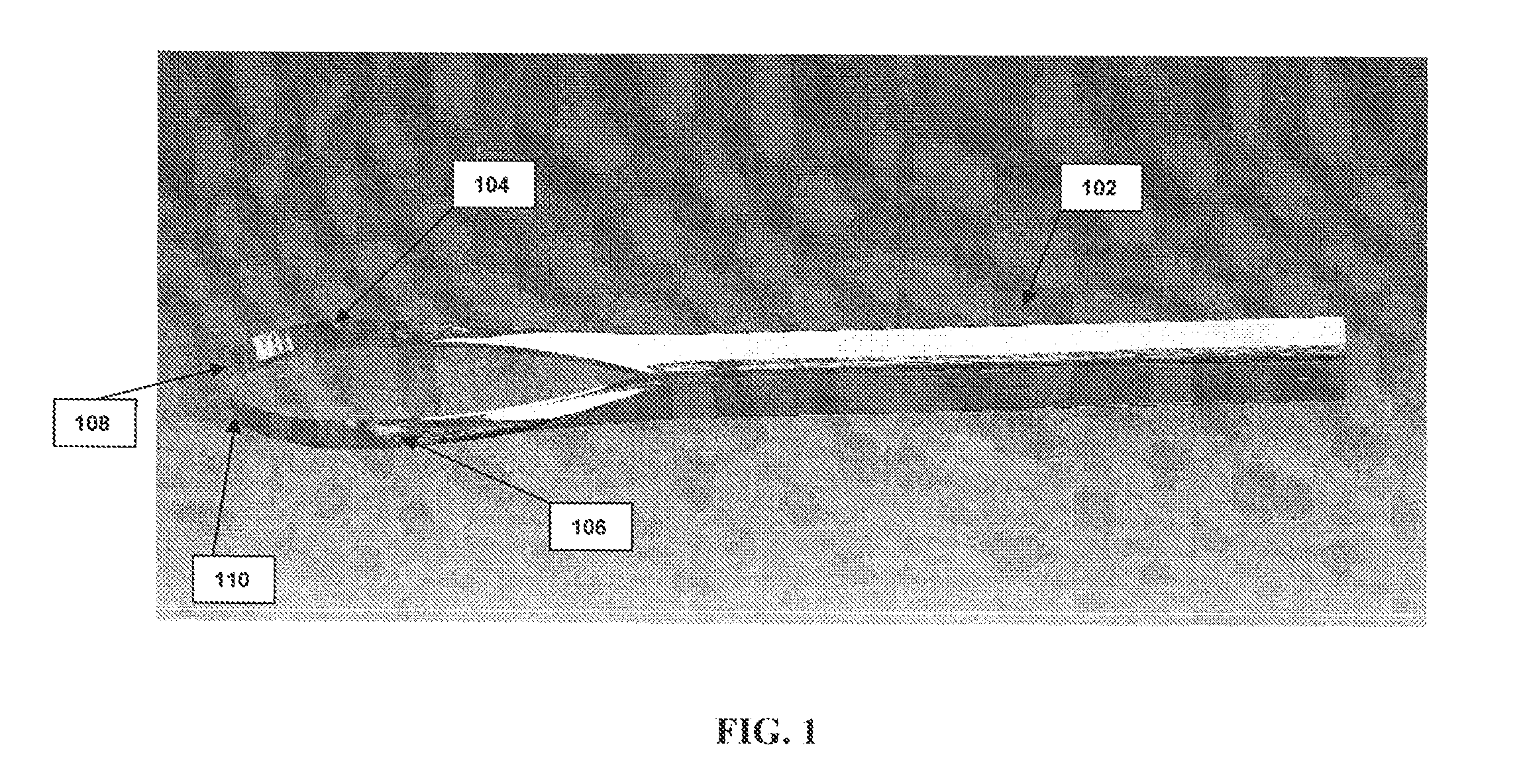
Background acoustic signal suppression in photoacoustic detector
InactiveCN101095042AReduce sensitivityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansAir quality improvementCell cavityLight beam
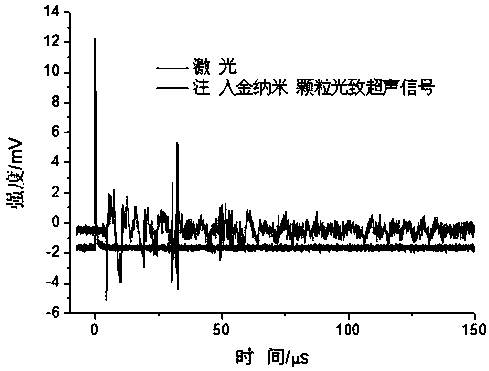
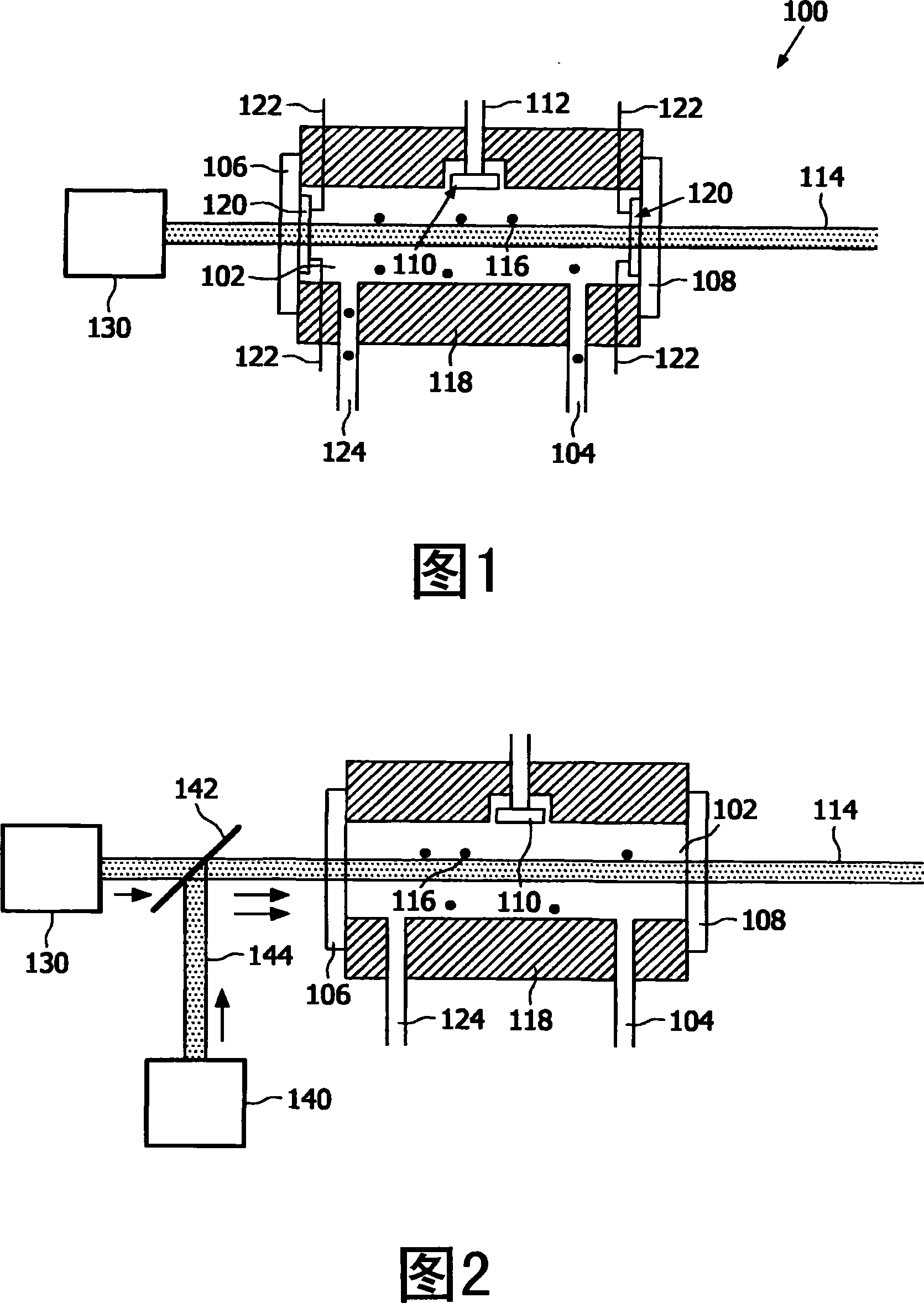
The present invention relates to a photo-acoustic device (100) for photo-acoustic analysis of a sample such as exhaled human breath.The device includes a sample cell cavity (102) for containing the sample (116), a first light source (130) outside the sample cell cavity for emitting a first modulated light beam (114) at a wavelength in an absorbing range of the searched component. The first light beam is led into the cavity through a transparent cavity wall (106). The searched gas component absorbs the first light beam and first acoustic waves are thus generated which are picked up by the microphone (110). The microphone also picks up background acoustic waves caused by the laser light beam going trough the cavity wall. The device is further equipped with a noise cancellation system (120, 122) that generates a second set of acoustic waves in anti-phase with the background acoustic waves.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Photoacoustic chemical detector
ActiveUS9995674B2Promote absorptionIncrease rangeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementProcessing detected response signalVibrating membraneLaser beams
A laser vibrometer for measurement of ambient chemical species includes a laser that produces a beam that is split into a reference readout beam and a signal readout beam. A probe laser beam is tuned to an absorption feature of a molecular transition, and generates acoustic signals when incident on a gaseous species via the photo acoustic effect. The scattered acoustic signals are incident on a thin membrane that vibrates. The readout laser beam reflected from the vibrating membrane is mixed with the reference beam at the surface of a photo-EMF detector. Interferrometric fringes are generated at the surface of the photo-EMF detector. Electric current is generated in the photo-EMF detector when the fringes are in motion due to undulations in the signal readout beam imparted by the vibrating membrane. A highly sensitive photo-EMF detector is capable of detecting picoJoules or less laser energy generated by vibrating processes.
Owner:NASA
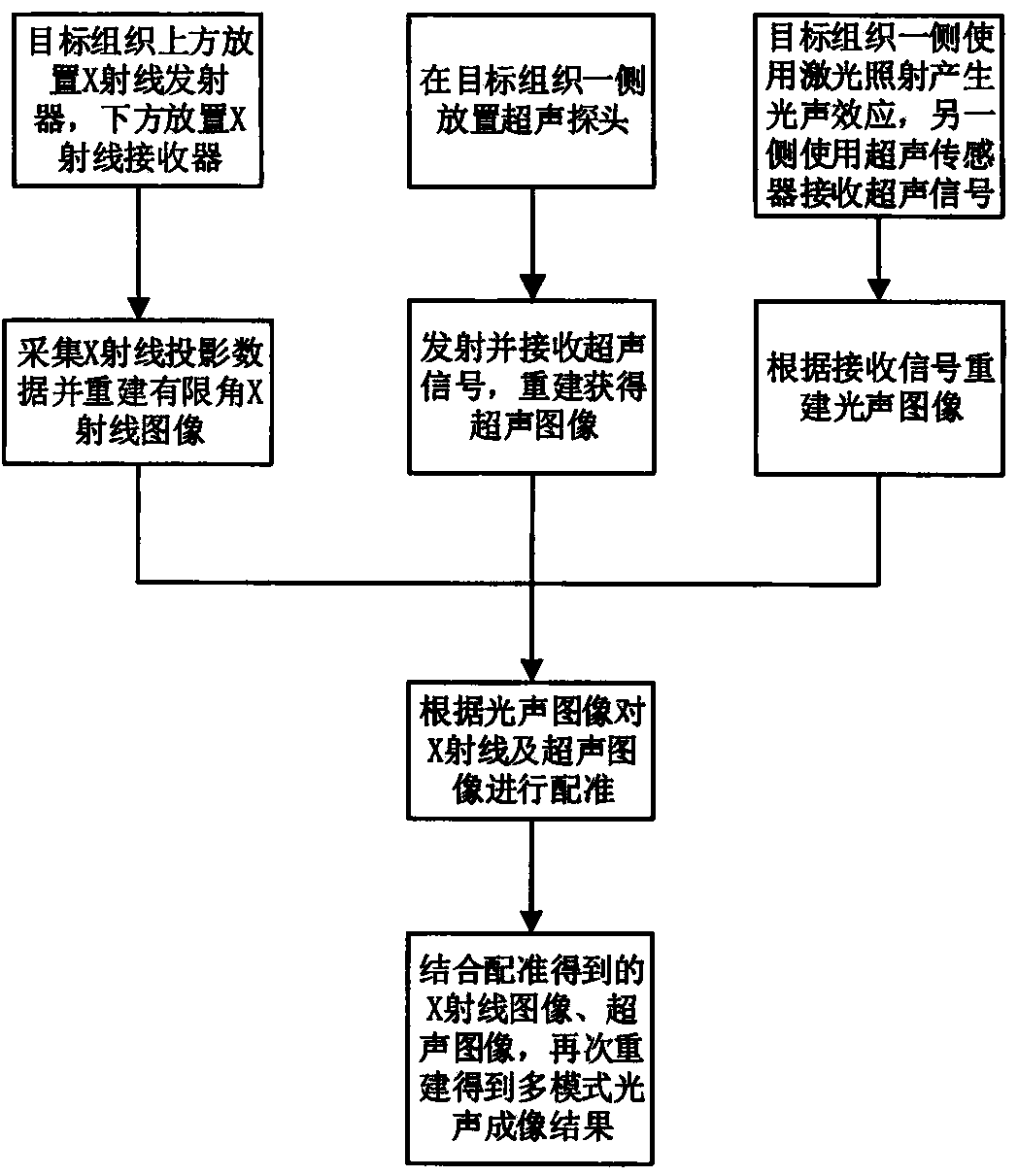
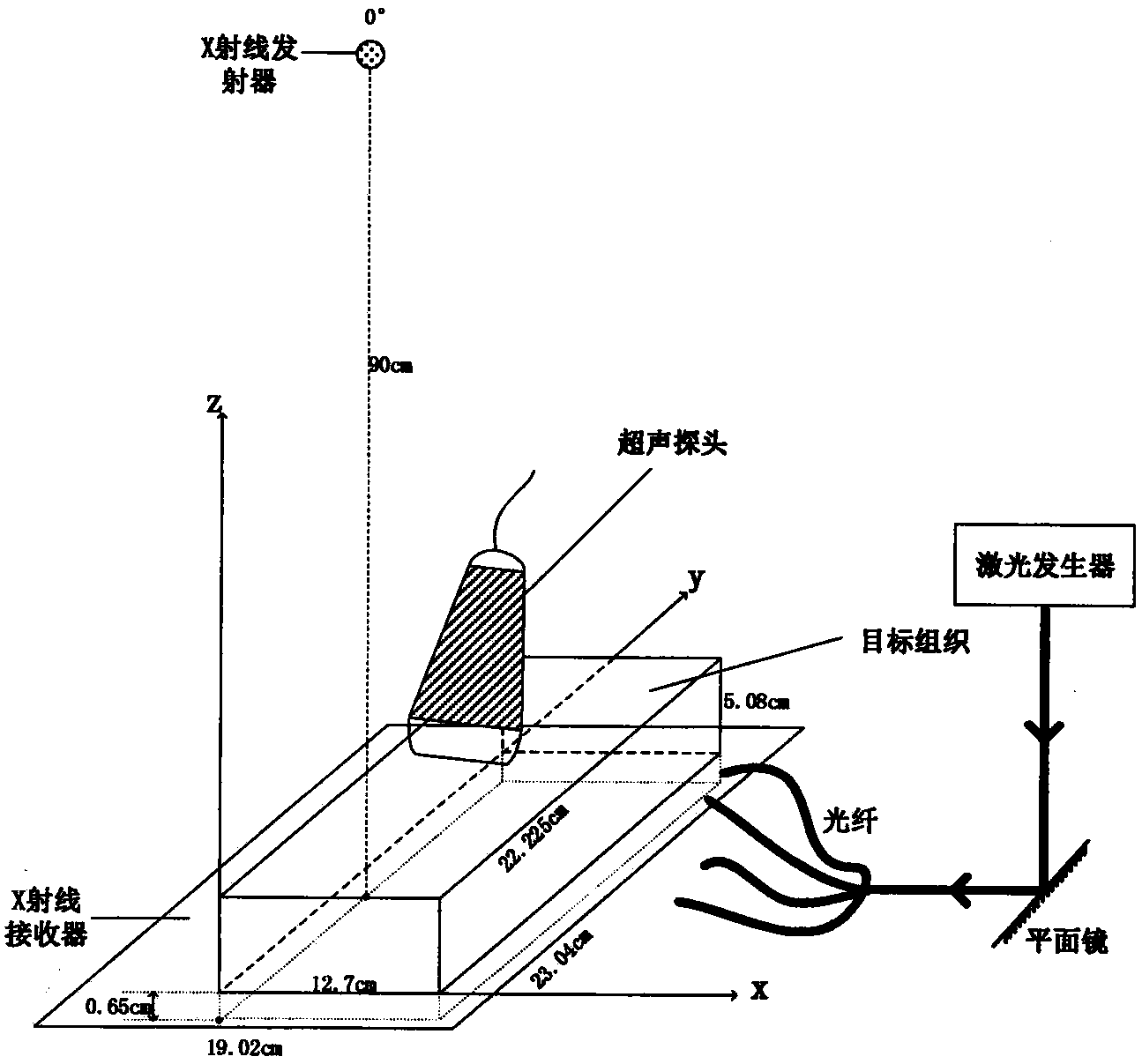
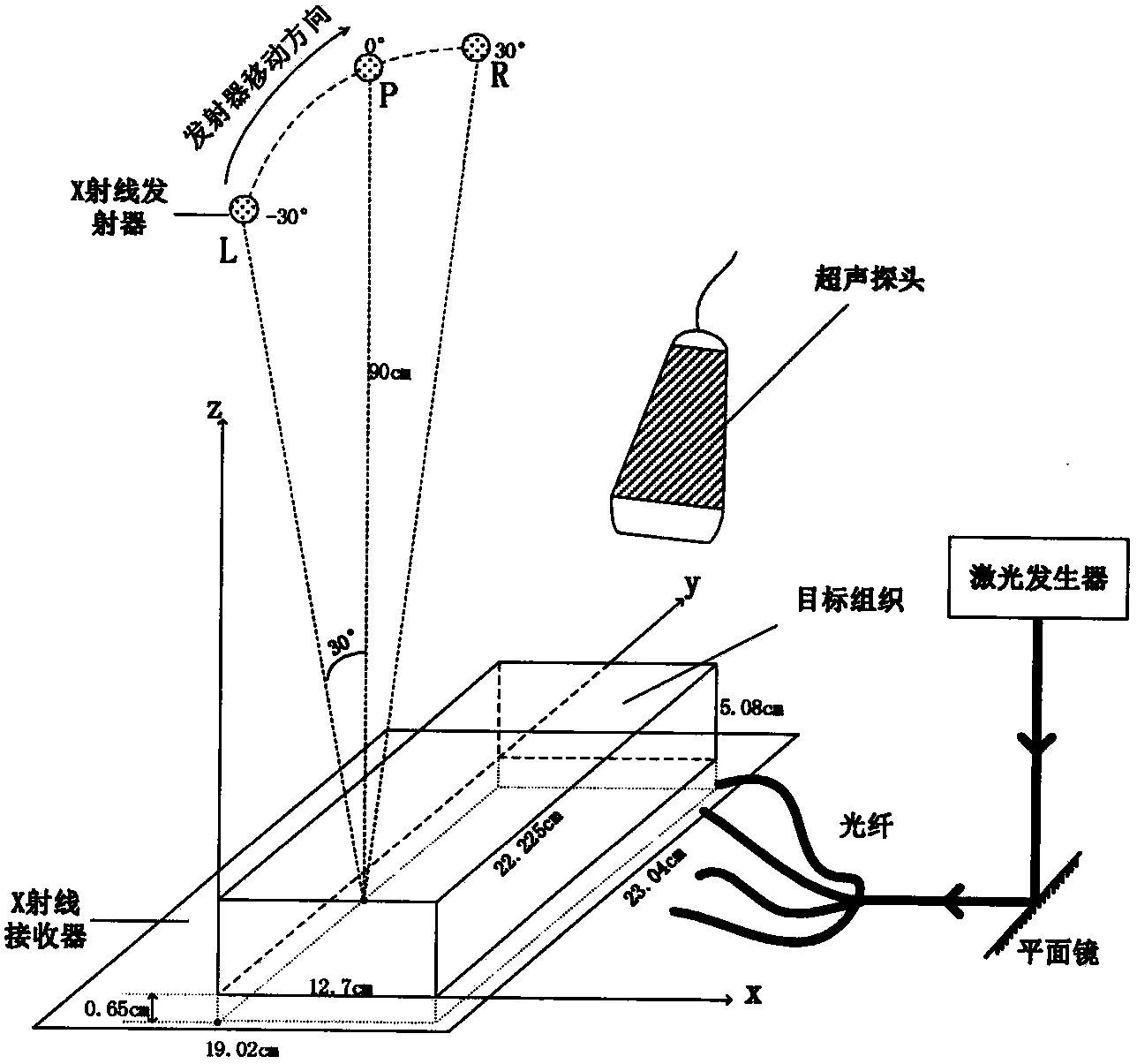
Multi-mode photoacoustic imaging method combined with limited angle X ray imaging and ultrasonic imaging
InactiveCN103829961AQuality improvementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSignal onImaging quality
The invention discloses a multi-mode photoacoustic imaging method combined with limited angle X ray imaging and ultrasonic imaging. The multi-mode photoacoustic imaging method includes the following steps that an X ray emitter and a receiver are arranged above and below a target organization respectively, X ray projection data are collected and a limited angle X ray image obtaining the organization is reconstructed; an ultrasonic probe is arranged on one side of the target organization and emits ultrasonic signals to the inside of the organization and reconstructs an ultrasonic image according to the received ultrasonic signals; laser irradiating is carried on one side of the organization to generate the optoacoustic effect, an ultrasonic sensor is used for receiving the signals on the other side of the organization and a photoacoustic image is reconstructed according to the received signals; according to the photoacoustic image, the X ray image and the ultrasonic image are rectified; a multi-mode photoacoustic imaging result is obtained through reconstruction by being combined with the rectified X ray image and the rectified ultrasonic imaging result. The features that X ray imaging and ultrasonic imaging are good in imaging quality and high in resolution in individual imaging planes are utilized in the multi-mode photoacoustic imaging method, the image quality of photoacoustic imaging is improved and innovativeness is obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
All-optical gas detection method and device based on quartz enhanced photoacoustic spectrum
ActiveCN103411898AImprove anti-electromagnetic interference performanceStrong technical applicabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsElectromagnetic environmentMeasurement site
The invention relates to photoacoustic spectrum measurement technologies, in particular to an all-optical gas detection method and a device based on a quartz enhanced photoacoustic spectrum, and solves the technical problems that detection signals are susceptible to electromagnetic environment interference and the device layout is easily influenced by the space size in existing photoacoustic spectrum technologies. The all-optical trace gas detection method based on the quartz enhanced photoacoustic spectrum includes: introducing a beam of probe light to the external side of arbitrary vibration arm of a tuning fork quartz crystal oscillator, gathering the information of intensity change caused by reflection direction change of reflected light received by one receiving plane fixed at a spatial position, and acquiring the concentration of a to-be-detected gas according to the intensity change information. The device only has optical components at a measurement site, thus having very strong anti-electromagnetic interference ability. The device and the method have very strong technical universality, and is completely applicable to remote nondestructive detection of environmental monitoring, food safety monitoring, industrial production control and other different fields.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Apparatus and method for measurement of trace gas with photoacoustic spectroscopy technology
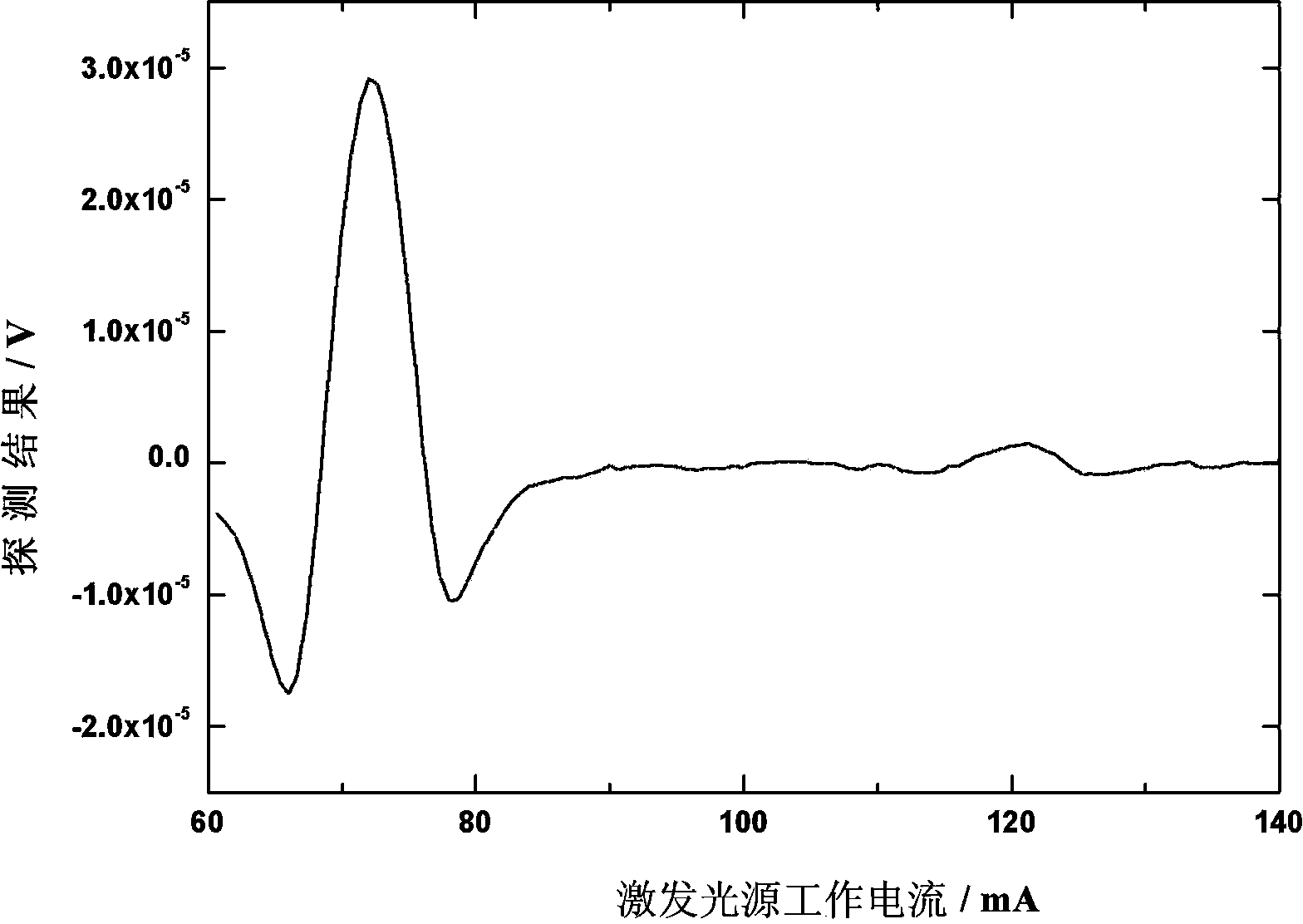
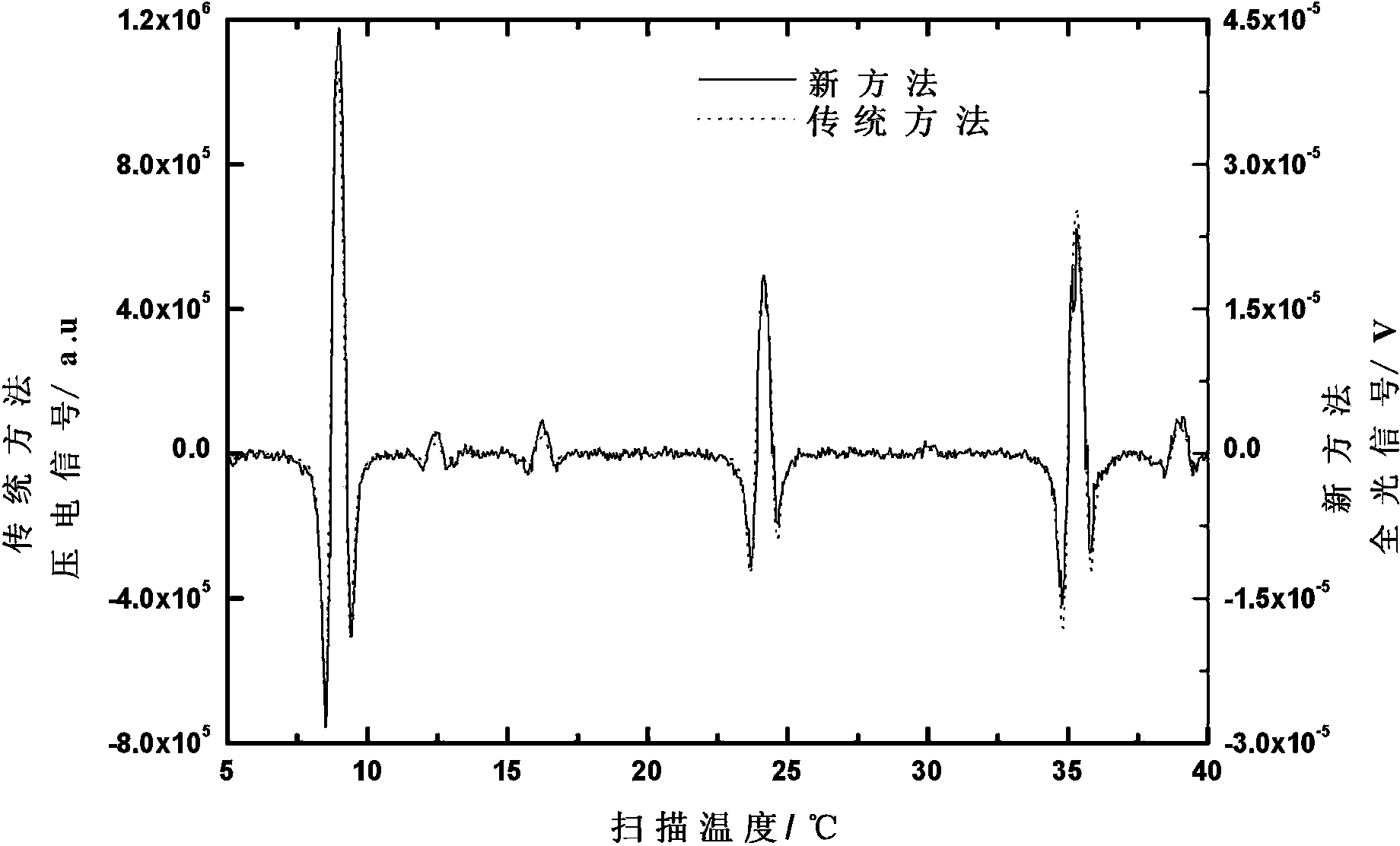
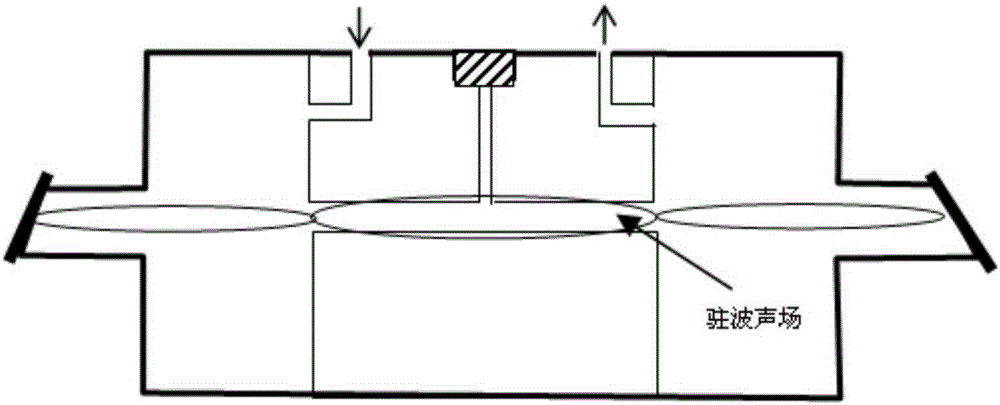
InactiveCN105241814AImprove detection signal-to-noise ratioImprove detection limitColor/spectral properties measurementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Resonance
The invention discloses an apparatus and method for measurement of trace gas with photoacoustic spectroscopy technology. On the basis of the first-order longitudinal resonance photoacoustic spectroscopy technology, a differential photoacoustic signal method is utilized to significantly weaken the influence of correlated noise caused by photoacoustic effect in solid and improve the detection signal-to-noise ratio of a photoacoustic signal. Compared with existing photoacoustic spectroscopy detection methods, the method provided by the invention further improves the detection limit of trace gas.
Owner:ANHUI WAYEE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Photoacoustic Measurement Device
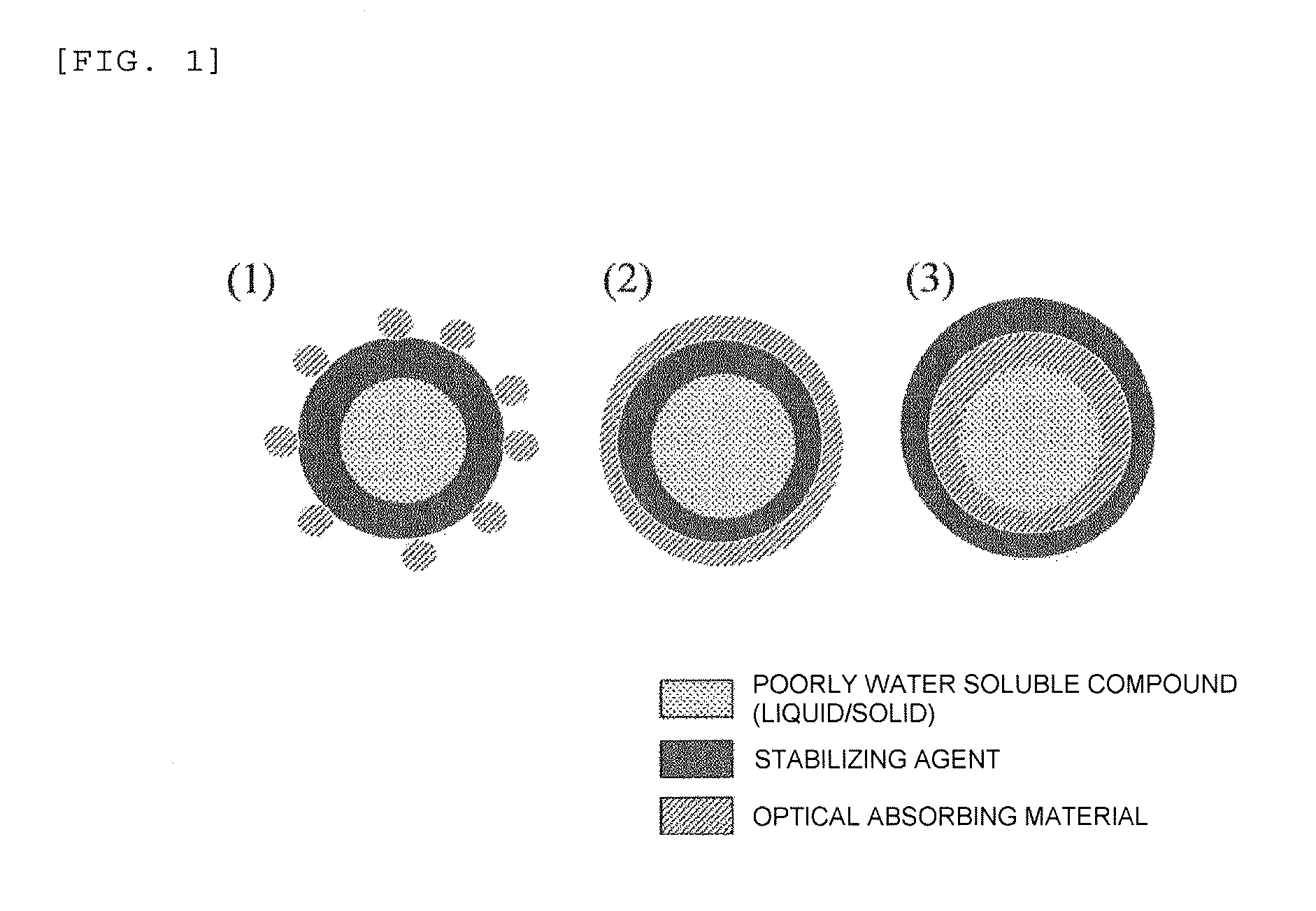
InactiveUS20140005537A1High sensitivityHigh resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansMeasurement deviceLight irradiation
A device and an agent for performing imaging in a deep part with high sensitivity and high resolution are to be provided. A photoacoustic measurement device (photoacoustic imaging device) performs light irradiation on an inspection area of a subject to which a photoacoustic agent generating an acoustic signal by causing phase change from a solid phase or a liquid phase to a gas phase by the light irradiation is administered, while the irradiated energy amount is increased, and detects the acoustic signal generated in the inspection area due to the light irradiation to form an imaged image of the inspection area based on the detected acoustic signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Photoacoustic spectrometry gas detection device based on pulse infrared light source
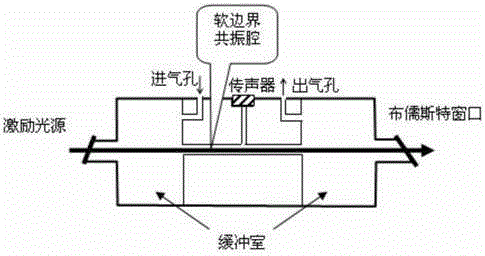
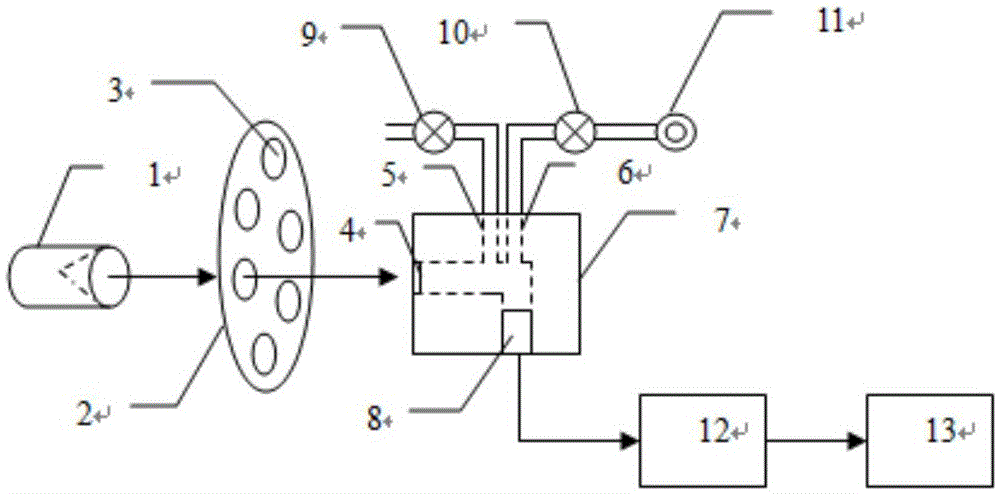
InactiveCN105548024ANo need to polluteDoes not need to be easily pollutedMaterial analysis by optical meansBandpass filteringData acquisition
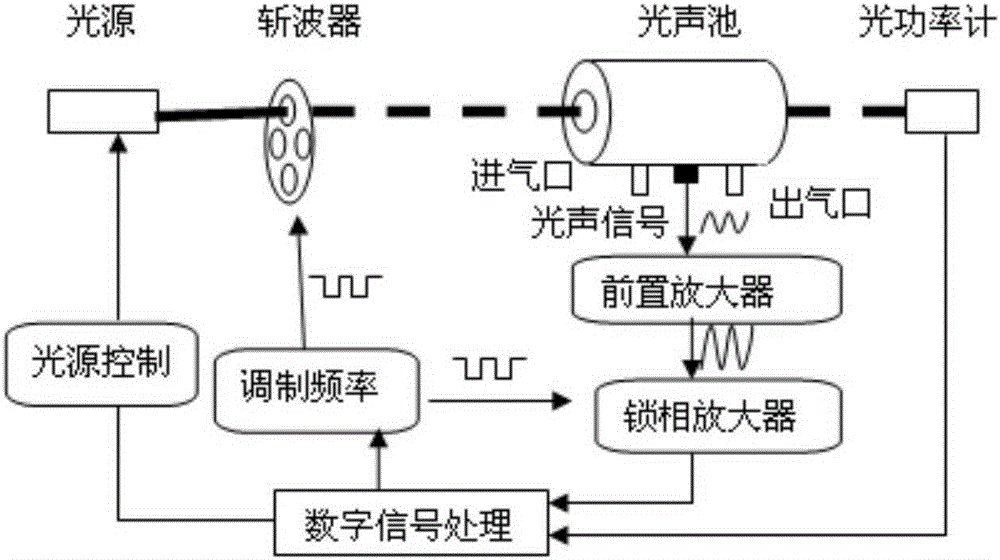
The invention discloses a photoacoustic spectrometry gas detection device based on a pulse infrared light source. The infrared light source is used as an emitting light source, pulse modulation is conducted on the light source, and concentration detection can be conducted on gas easy to absorb within the whole emission spectrum range of the infrared light source. The concentration of specific gas is detected through a filter wheel and light filters, wherein the six light filters can be installed on the filter wheel, the filter wheel is controlled by a serial port to rotate so that different light filters can be selected, and six types of gas can be detected at the same time at most. The photoacoustic effect generated after to-be-detected gas in an inner cavity of a photoacoustic pool absorbs an optical signal with the specific wavelength is converted into an electric signal through a microphone, a band-pass filter amplification circuit is input, analysis and calculation are conducted through a data collection and control module, and concentration of various types of gas is obtained. By means of the device, six types of gas including CO, CO2, CH4, C2H2, C2H4 and C2H6 can be quantitatively detected, and the device is suitable for on-site detection of gas in transformer oil.
Owner:HUBEI SUPERE ELECTRIC
Optical microscopy systems based on photoacoustic imaging
ActiveUS20150160120A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricitySinusoidal modulation
The present application discloses optical microscopy systems and related method that use modulation techniques and contrast agents to enable the systems to detect nonlinear photoacoustic signals with high spectrum sensitivity and frequency selectivity for imaging. A laser beam is amplitude modulated for pure sinusoidal modulation using either the loss modulation technique or the single light amplitude modulation technique. The sample used in the invention is an endogenous contrast agent by itself or is treated by at least one exogenous contrast agent to produce or enhance photoacoustic effect induced by multi-photon absorption. The modulated laser beam is focused via a focusing device onto a sample which absorbs multiple photons simultaneously and generates ultrasonic (acoustic) waves via nonlinear photoacoutic effect. The ultrasonic waves are received and transformed into electrical signals and the frequency signals within the electrical signals are detected and recorded to create images.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Cell opto-acoustic microscopic imaging method and device thereof
InactiveCN101782518AHigh resolutionImprove spatial resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationAnalysis by material excitationMicroscopic imageLaser scanning
The invention relates to a cell opto-acoustic microscopic imaging method, which comprises the following steps: placing a cell on the concave surface of microscopic glass, irradiating the cell with laser light permeating the microscopic glass, producing opto-acoustic effect after the cell absorbs the light, transferring acoustic pressure variation produced by the opto-acoustic effect to an opto-acoustic sensor, and detecting the opto-acoustic variation and outputting an opto-acoustic signal by using the opto-acoustic sensor to realize opto-acoustic detection of the single cell; and performing two-dimensional scanning on the cell by using light beam scanning and a micro objective with high resolution to realize the opto-acoustic microscopic imaging of the single cell. The invention also relates to a cell opto-acoustic microscopic imaging device, which comprises a laser light scanning imaging mechanism, the opto-acoustic sensor and a signal processor. In the method and the device, light beam scanning technology without mechanical noise is combined with the micro objective with the high resolution to generate the opto-acoustic signal with high spatial resolution and then the opto-acoustic sensor is adopted for the opto-acoustic detection to perform the opto-acoustic microscopic imaging on the cell, wherein the solution is less than 1 micron.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method of nondestructive elasticity measurement by photoacoustic eigen spectrum analysis
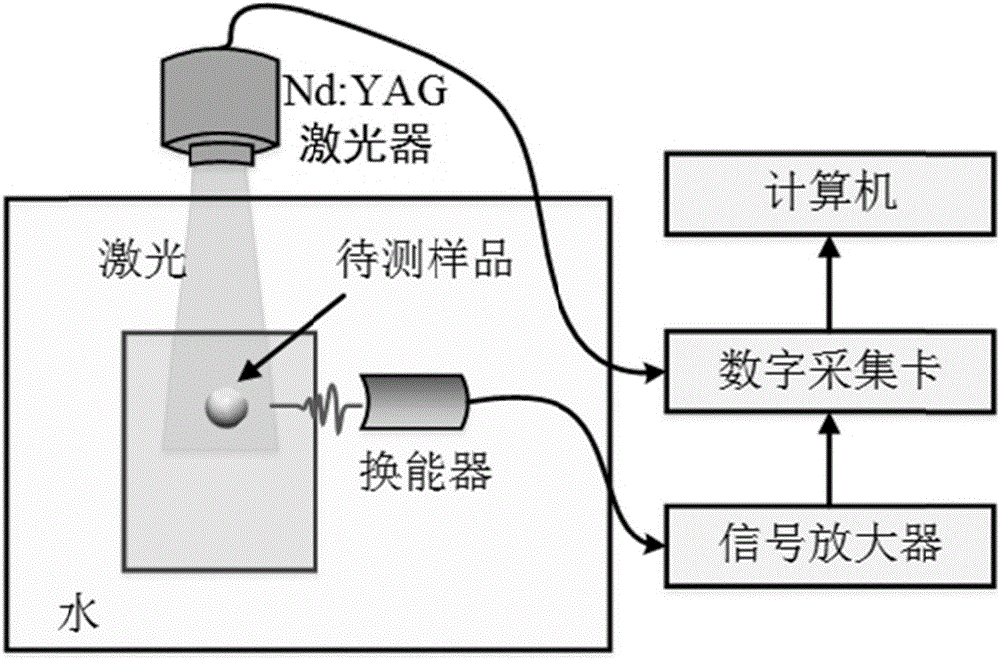
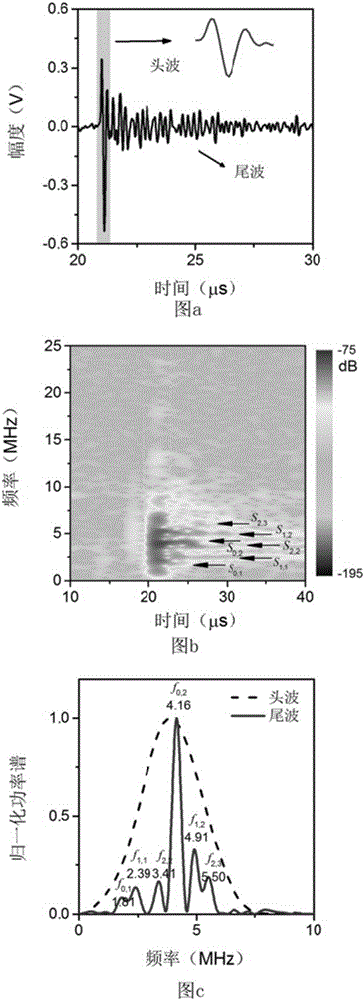
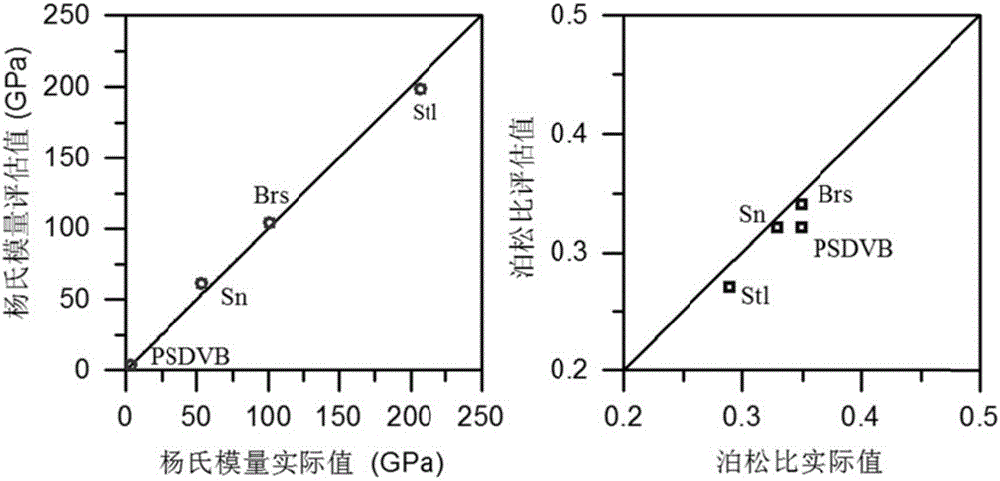
The invention discloses a method of nondestructive elasticity measurement by photoacoustic eigen spectrum analysis. The method provided by the invention utilizes laser pulse to irradiate an elastomer to make it radiate sound wave under the action of photoacoustic effect, and through analysis of the photoacoubtic signal radiated by the elastomer, a photoacoustic eigen spectrum of the elastomer can be obtained, the eigen frequency of the elastomer can be extracted from the photoacoustic eigen spectrum, on the basis of the eigen frequency, inversion algorithm is also utilized to evaluate the elastic properties of the elastomer. The method of nondestructive elasticity measurement by photoacoustic eigen spectrum analysis provided by the invention has no need for mutual contact of an acoustic transducer and the elastomer during measurement, and also has no need for any dissection treatment on the elastomer. The method can realize non-contact and nondestructive evaluation of elastic parameters, and has high safety and usability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
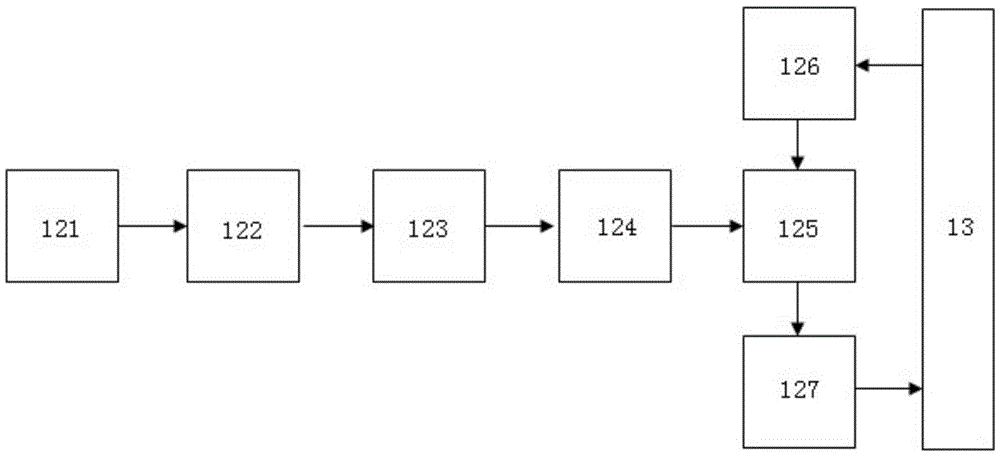
Wide-spectrum pulsed light detector based on photoacoustic effect and detection method
InactiveCN110686771AEasy to useAccurate measurementPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsFilm baseMaterials science
The invention relates to a wide-spectrum pulsed light detector based on a photoacoustic effect. The wide-spectrum pulsed light detector comprises a light-to-sound module, a sound coupling module, an ultrasonic detection module, a signal line and a shell; the light-to-sound module is used as a probe, and the light-to-sound module includes a focusing lens group and a photoacoustic thin film with a wide-spectrum light absorption characteristic; the ultrasonic detection module includes a piezoelectric thin film and a sound absorbing material; the focusing lens group, the photoacoustic thin film, the sound coupling module, the piezoelectric thin film, and the sound absorbing material are arranged in sequence; and the photoacoustic thin film, the sound coupling module, the piezoelectric thin film and the sound absorbing material are arranged in an inner cavity formed by the shell. The wide-spectrum pulsed light detector uses the photoacoustic thin film based on the photoacoustic effect, thephotoacoustic thin film generates ultrasound due to the photoacoustic effect, so that the problem of wavelength selectivity of a photoelectric effect light detector is solved.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
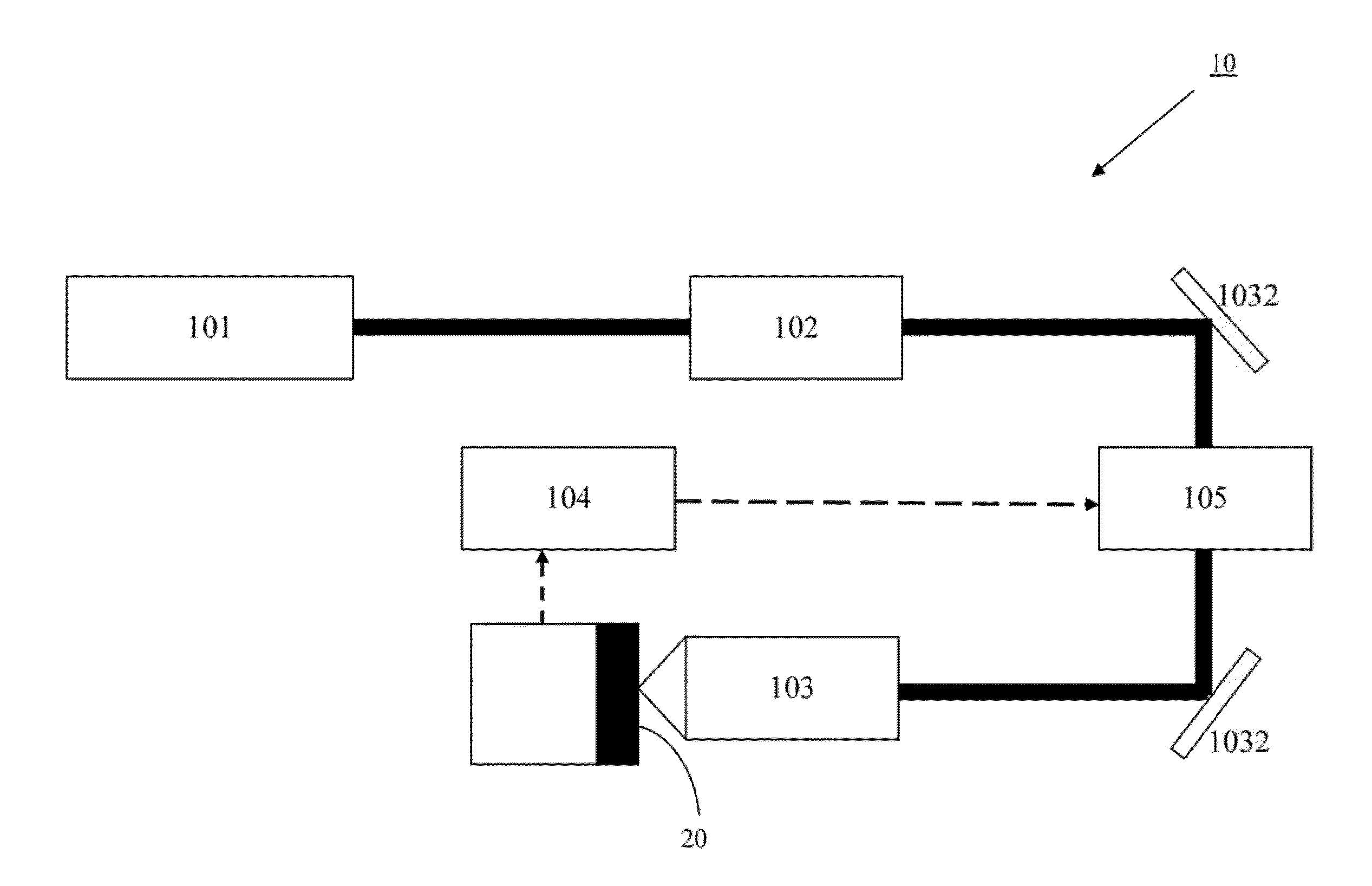
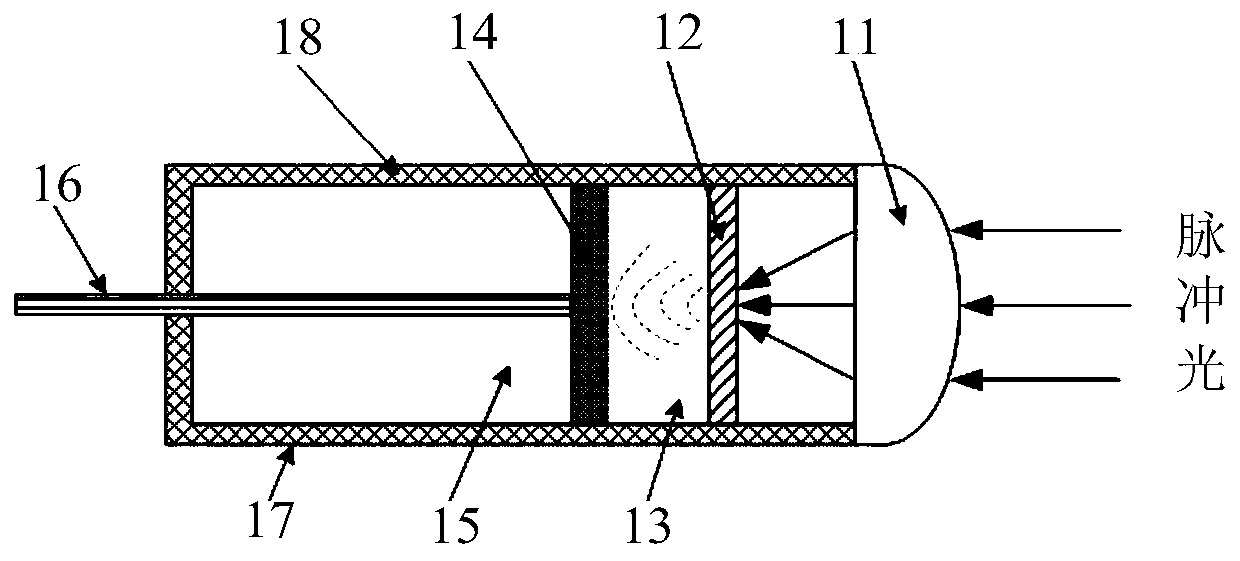
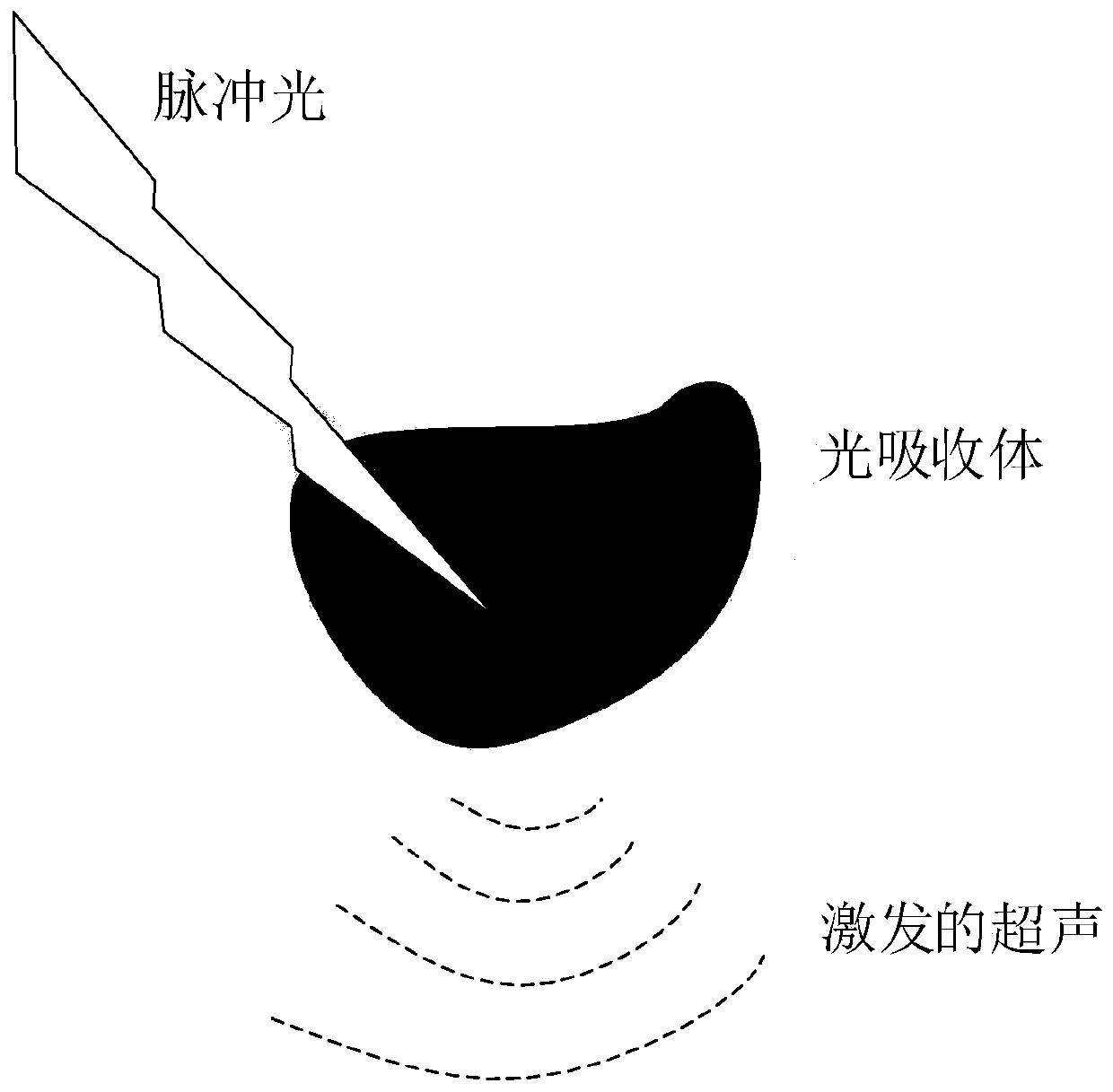
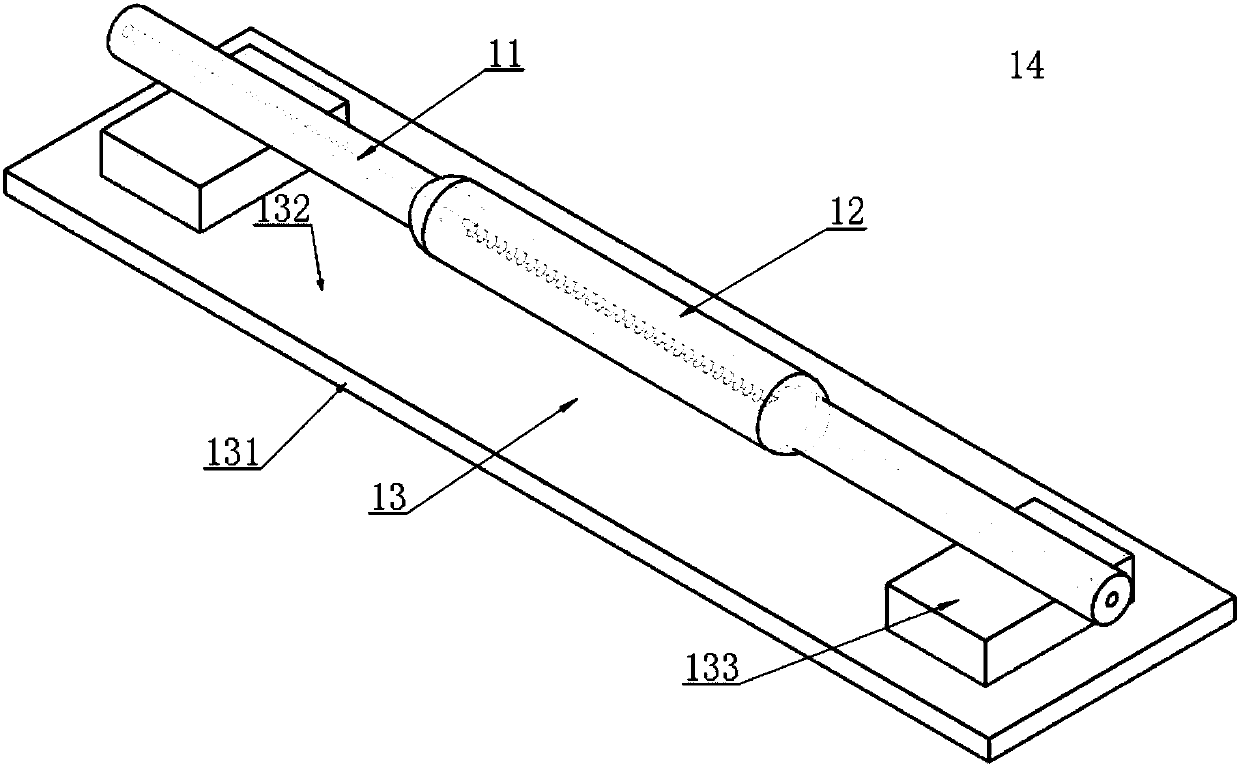
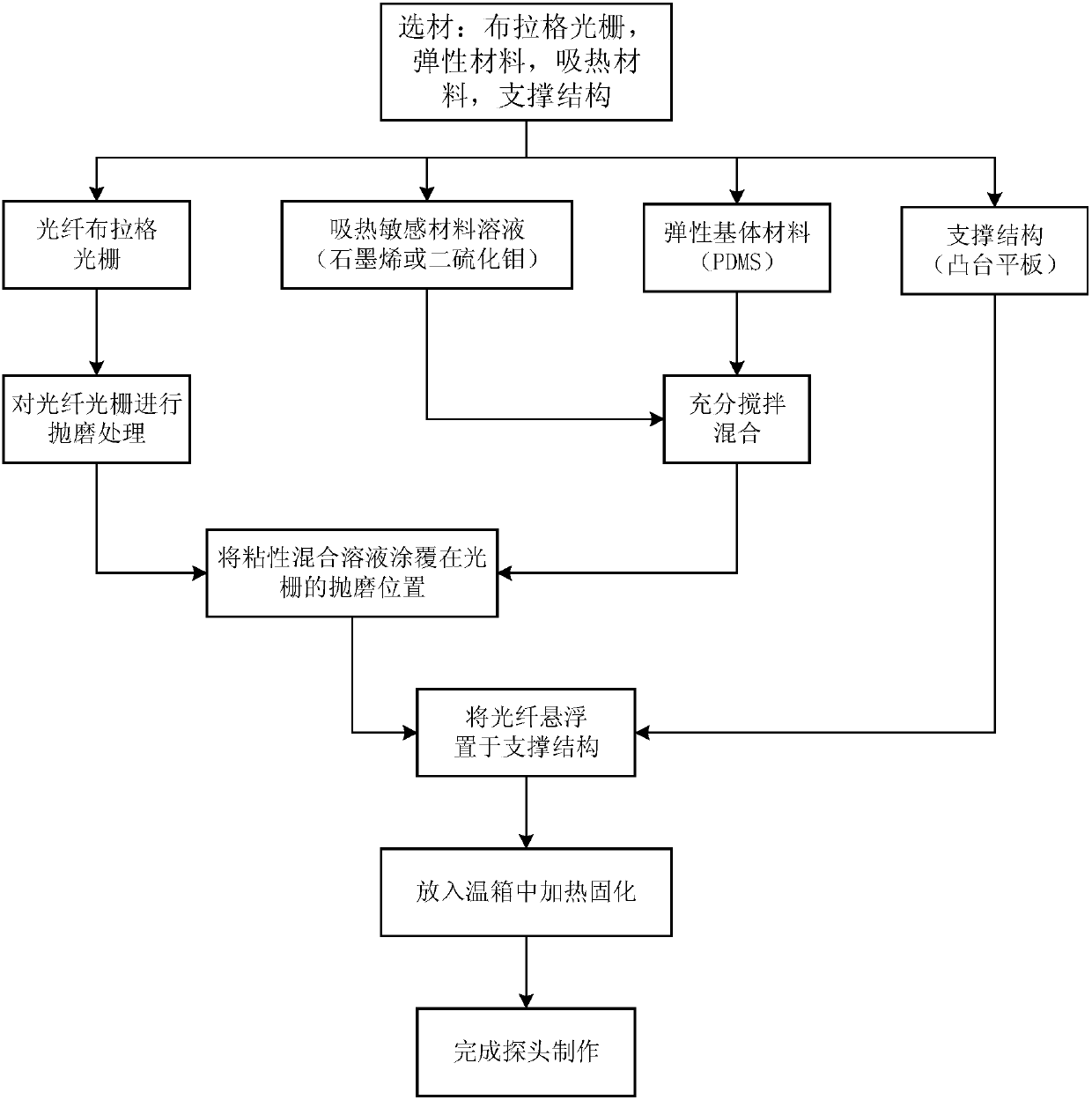
Optical acoustic excitation and detection integrated probe based on side edge polishing and grinding fiber grating and manufacturing method and test method of optical acoustic excitation and detection integrated probe
ActiveCN107907150AImprove light and heat coupling effectImprove energy conversion efficiencyConverting sensor output opticallyFiberProbe type
The invention discloses an optical acoustic excitation and detection integrated probe based on side edge polishing and grinding fiber grating and a manufacturing method and a test method of the optical acoustic excitation and detection integrated probe. A sensing unit of an optical acoustic signal excitation part is made of elastic base body materials and heat sensitive materials with high heat adsorption ability in a mixed manner and the surface of the side edge polishing and grinding fiber is coated with the sensing unit. Thus, by importing pulse laser into the sensitive materials, by use ofoptoacoustic effects, broadband acoustic signals can be excited. On the other hand, by fully using the sensitivity of the side edge polishing and grinding fiber grating to bending strain, detection of weak acoustic signals can be achieved. Thus, the probe is advantaged by simple manufacturing, small size, anti-electromagnetic interference ability, high photoacoustic energy conversion efficiency,big signal bandwidth and online distributed measurement; and meanwhile, through the small probe-type compact structure integrated with the optical acoustic excitation and detection, the probe has obvious application advantages in field of medical optoacoustic imaging, lossless detection, material science and the like.
Owner:JIAXING NAJIE MICROELECTRONICS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com