Patents
Literature
716 results about "Tuning fork" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A tuning fork is an acoustic resonator in the form of a two-pronged fork with the prongs (tines) formed from a U-shaped bar of elastic metal (usually steel). It resonates at a specific constant pitch when set vibrating by striking it against a surface or with an object, and emits a pure musical tone once the high overtones fade out. A tuning fork's pitch depends on the length and mass of the two prongs. They are traditional sources of standard pitch for tuning musical instruments.
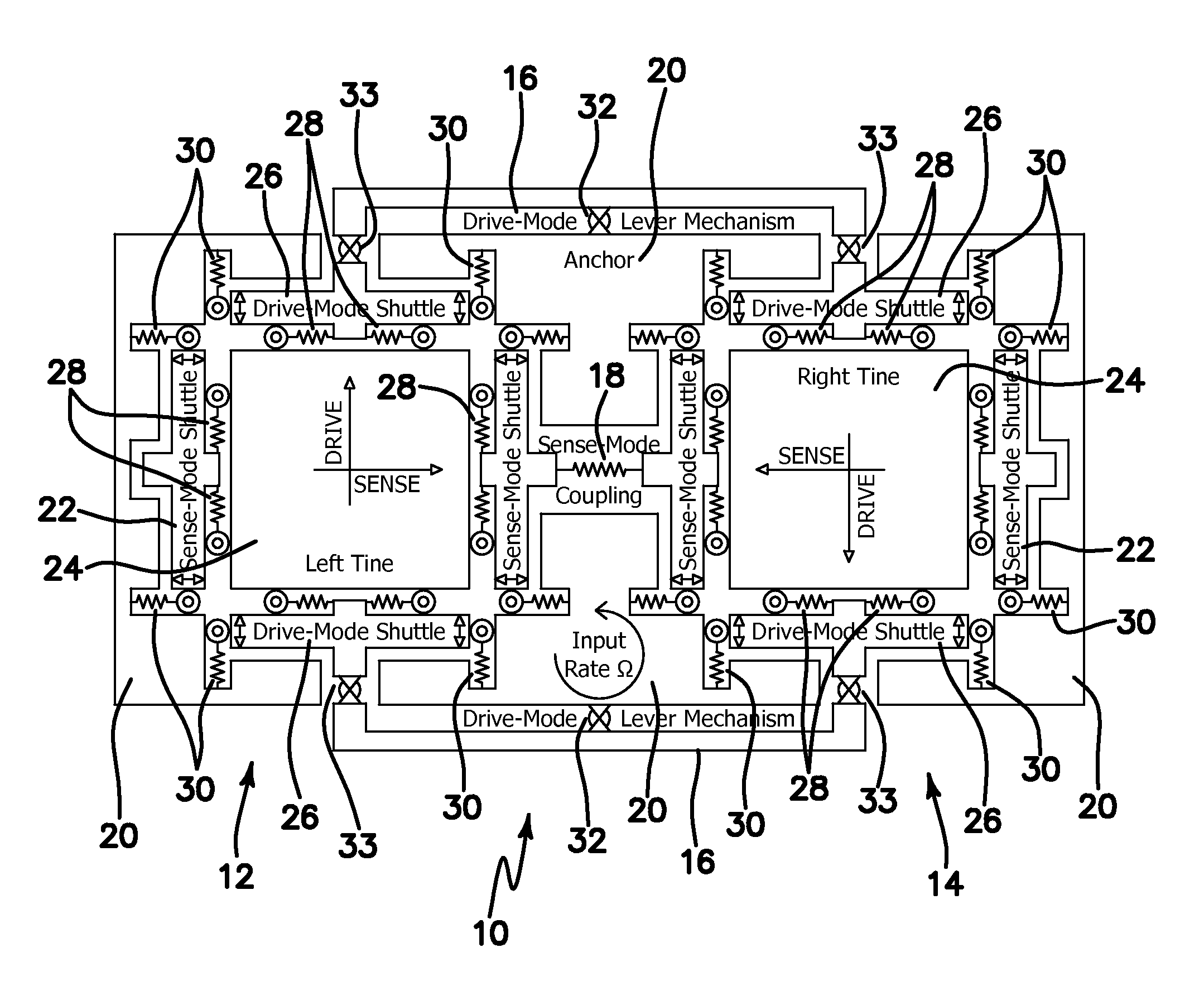
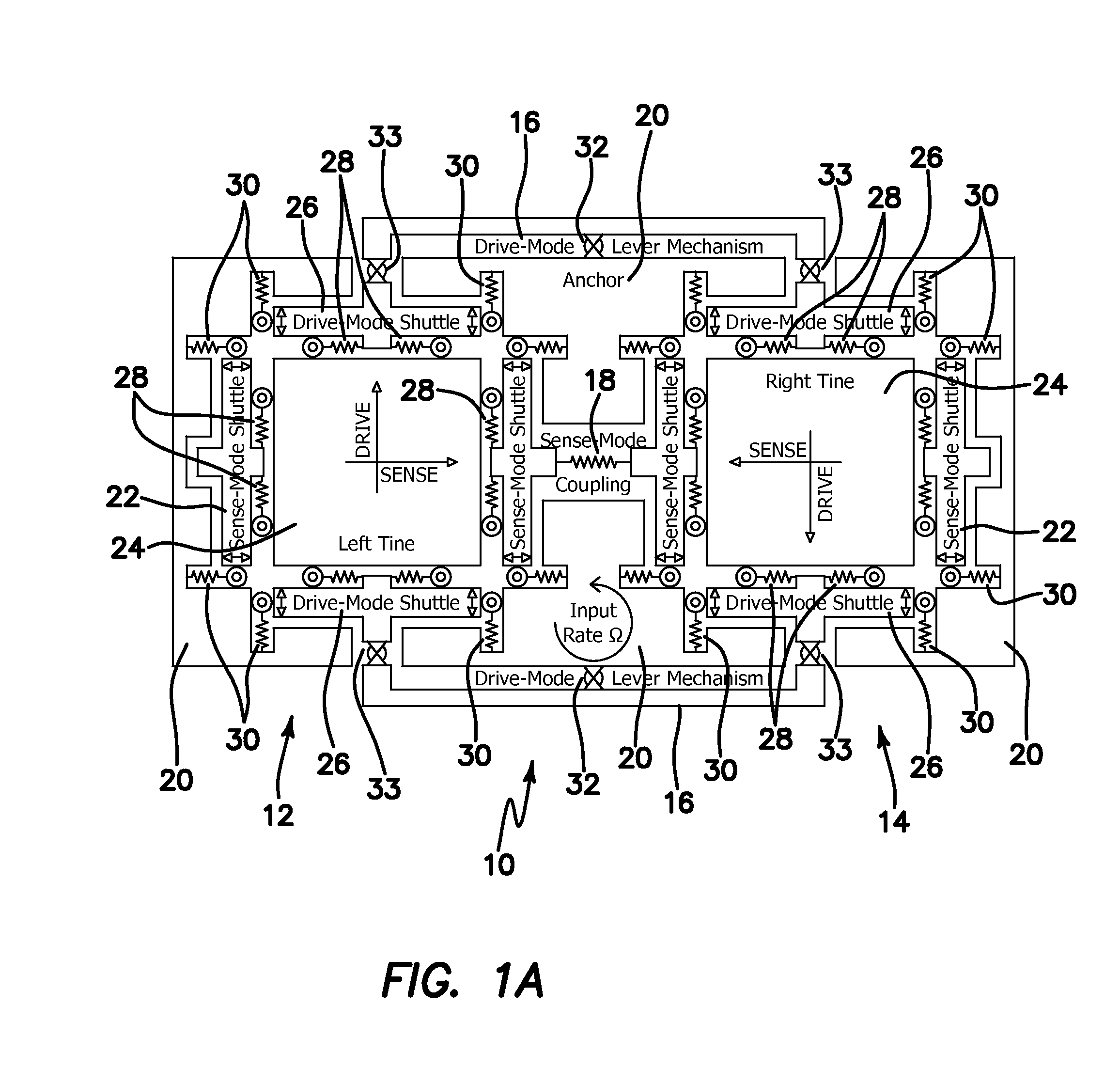
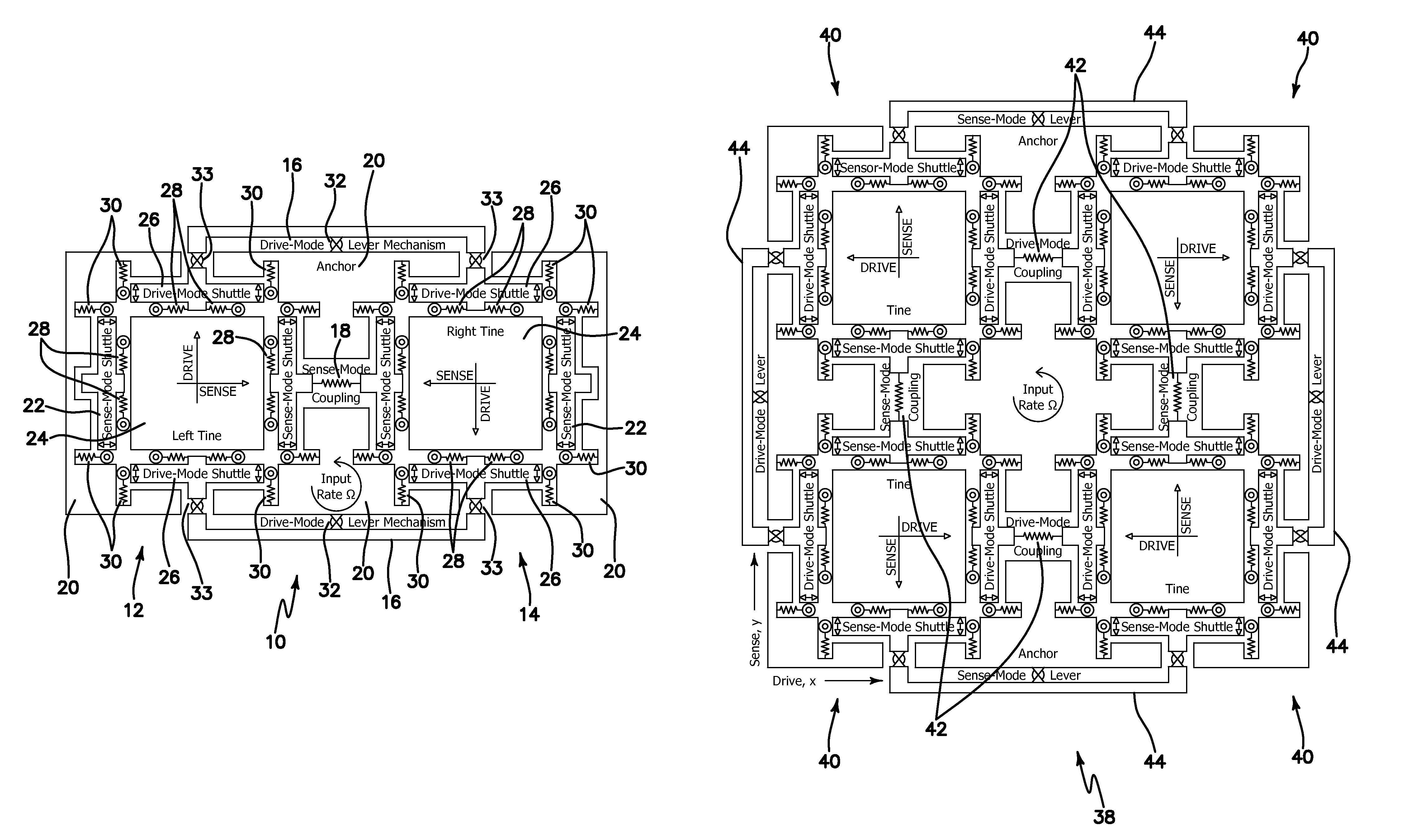
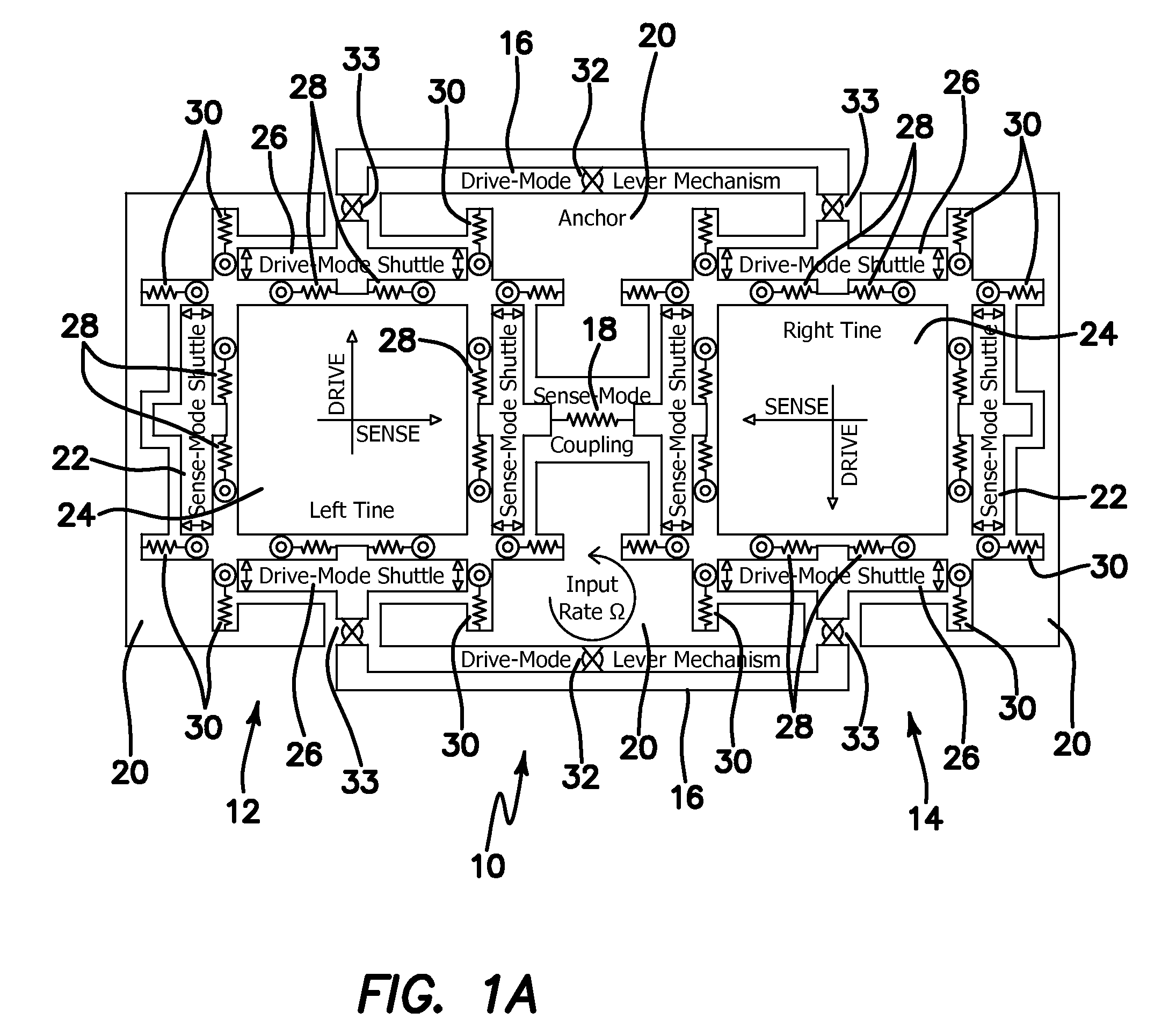
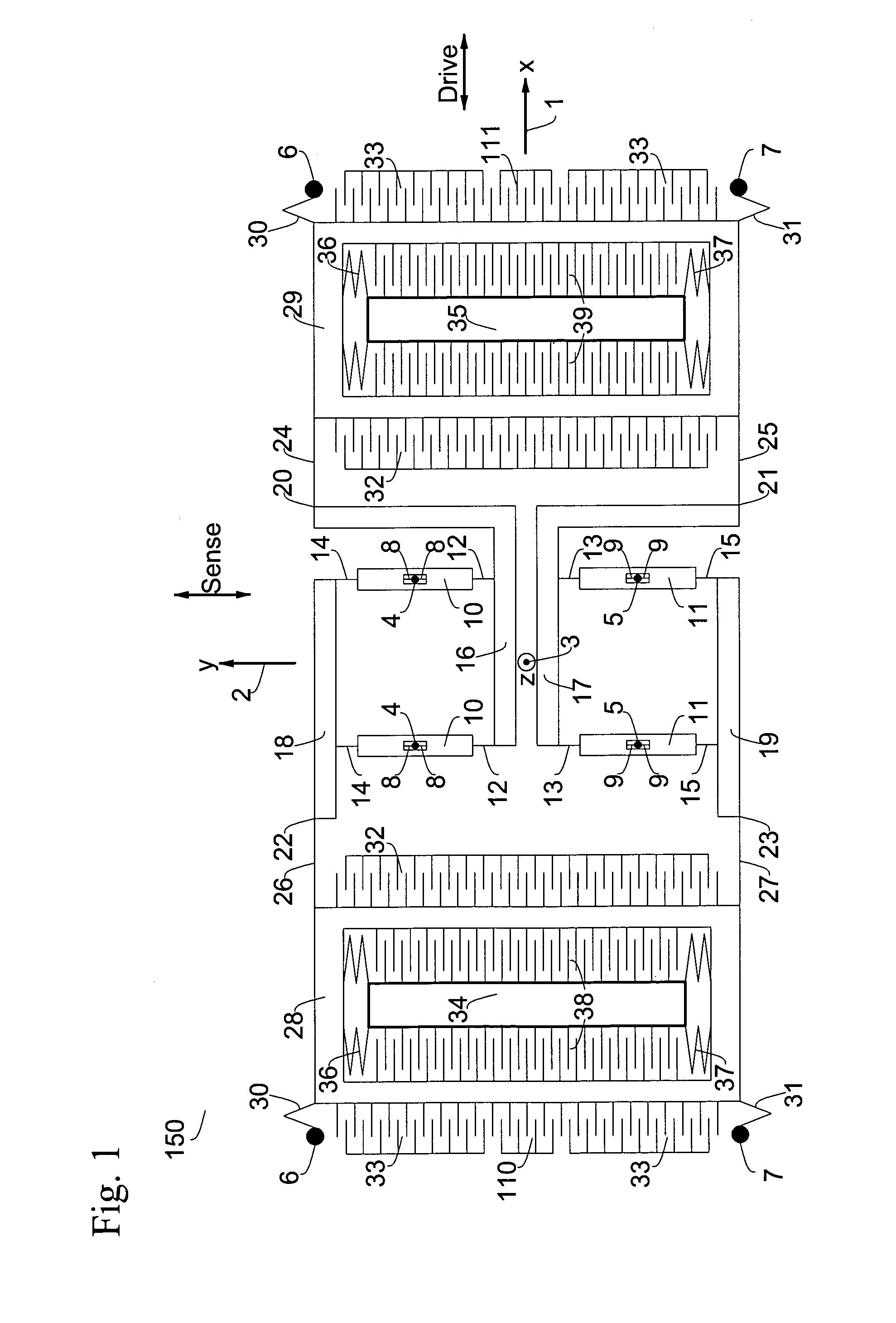
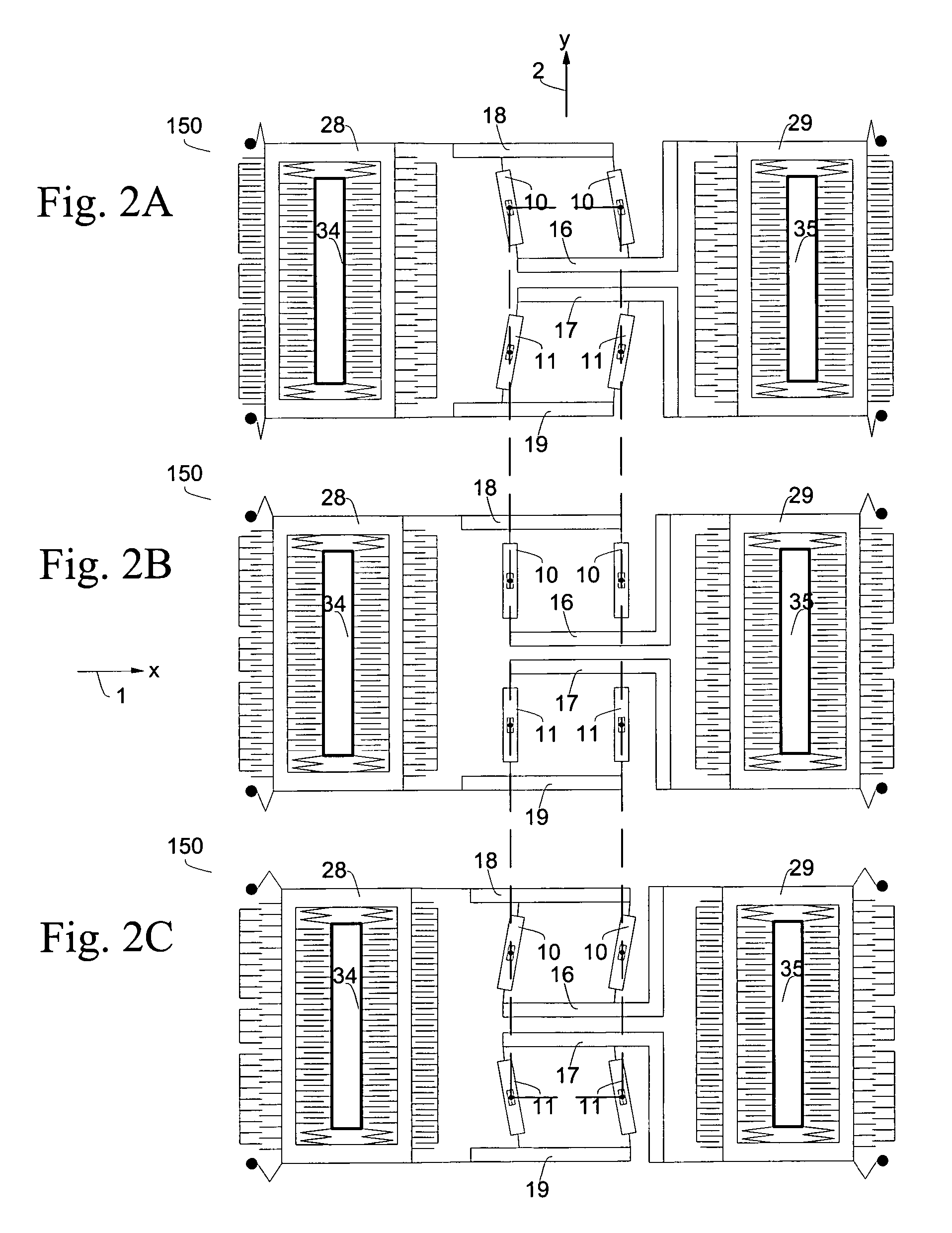
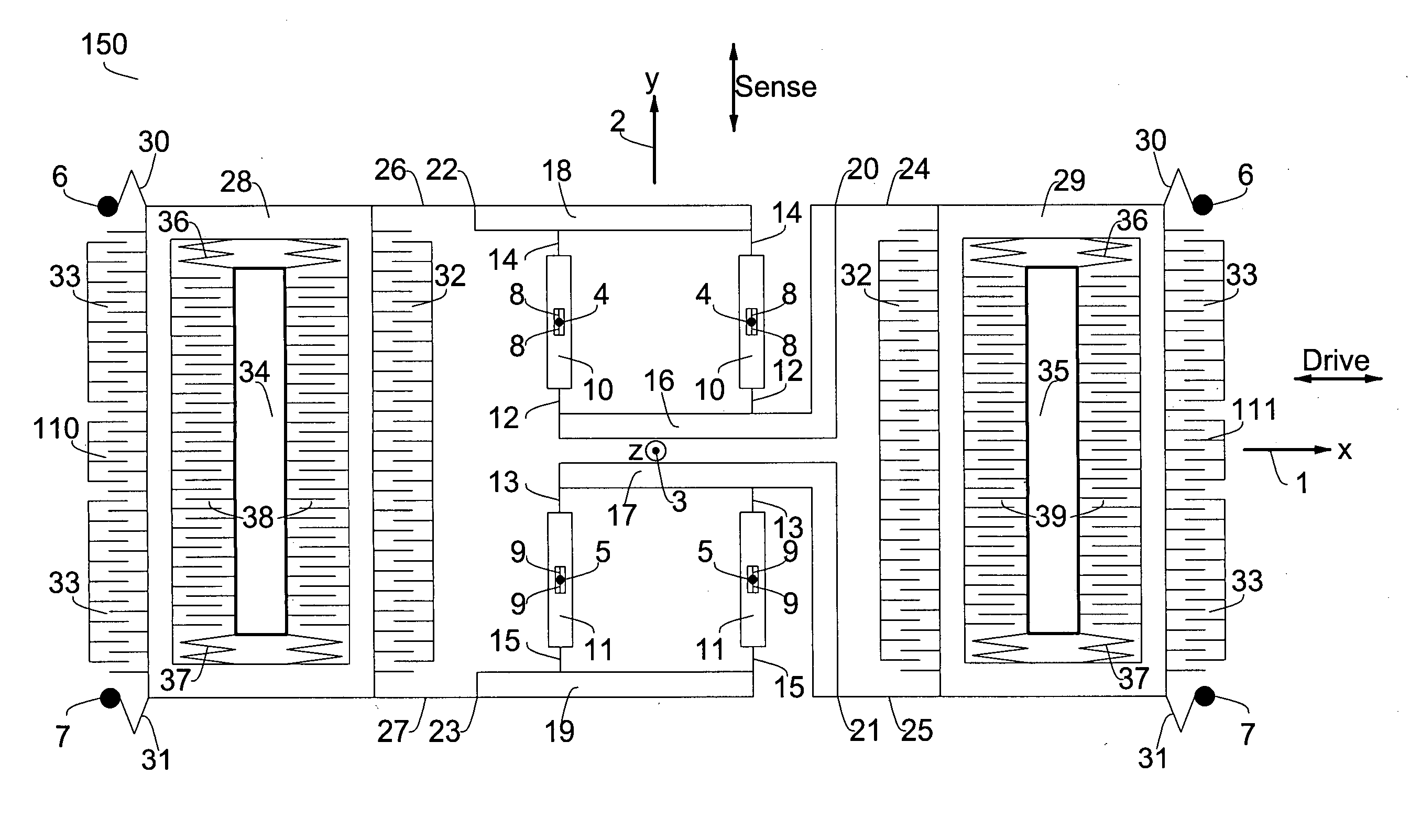
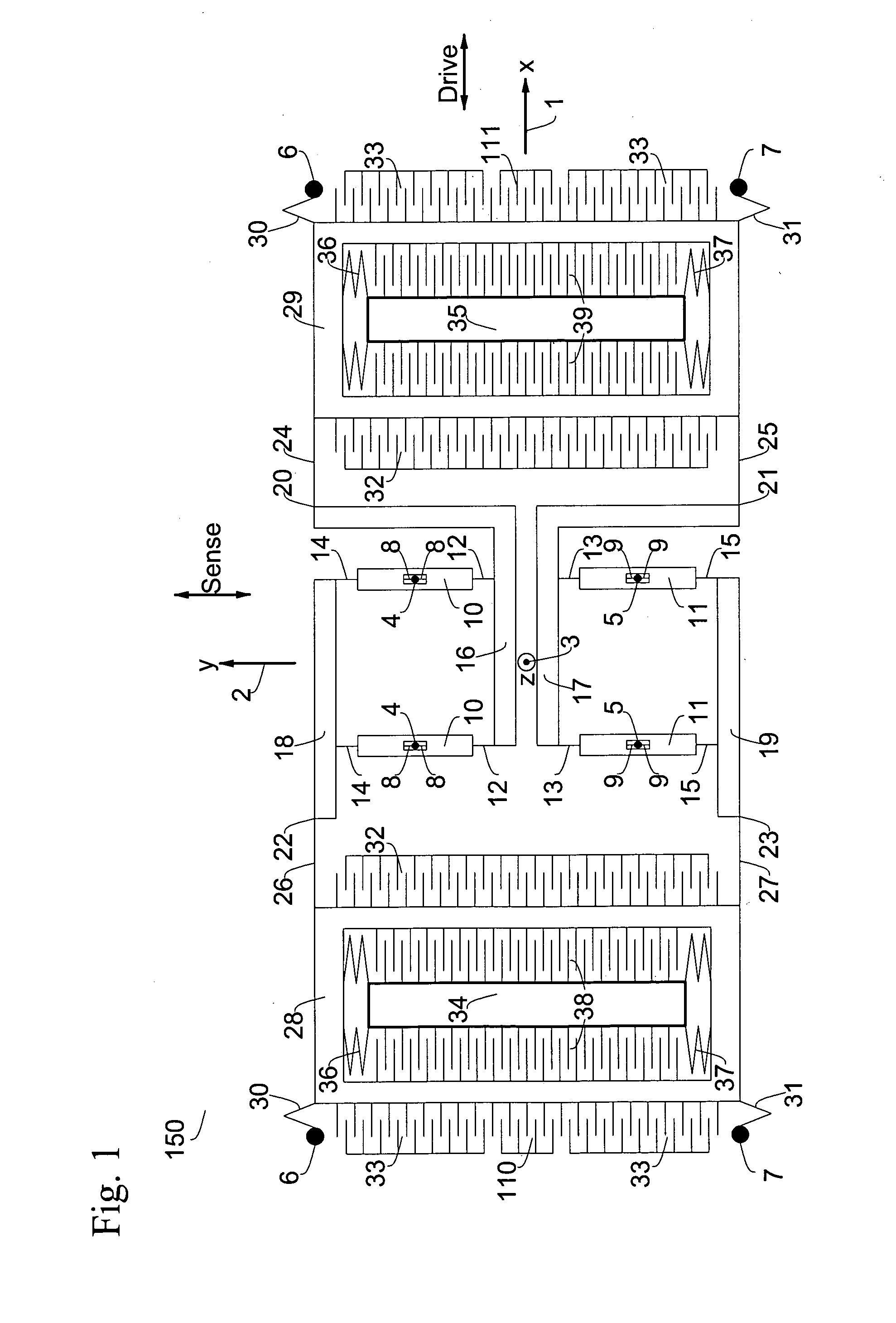
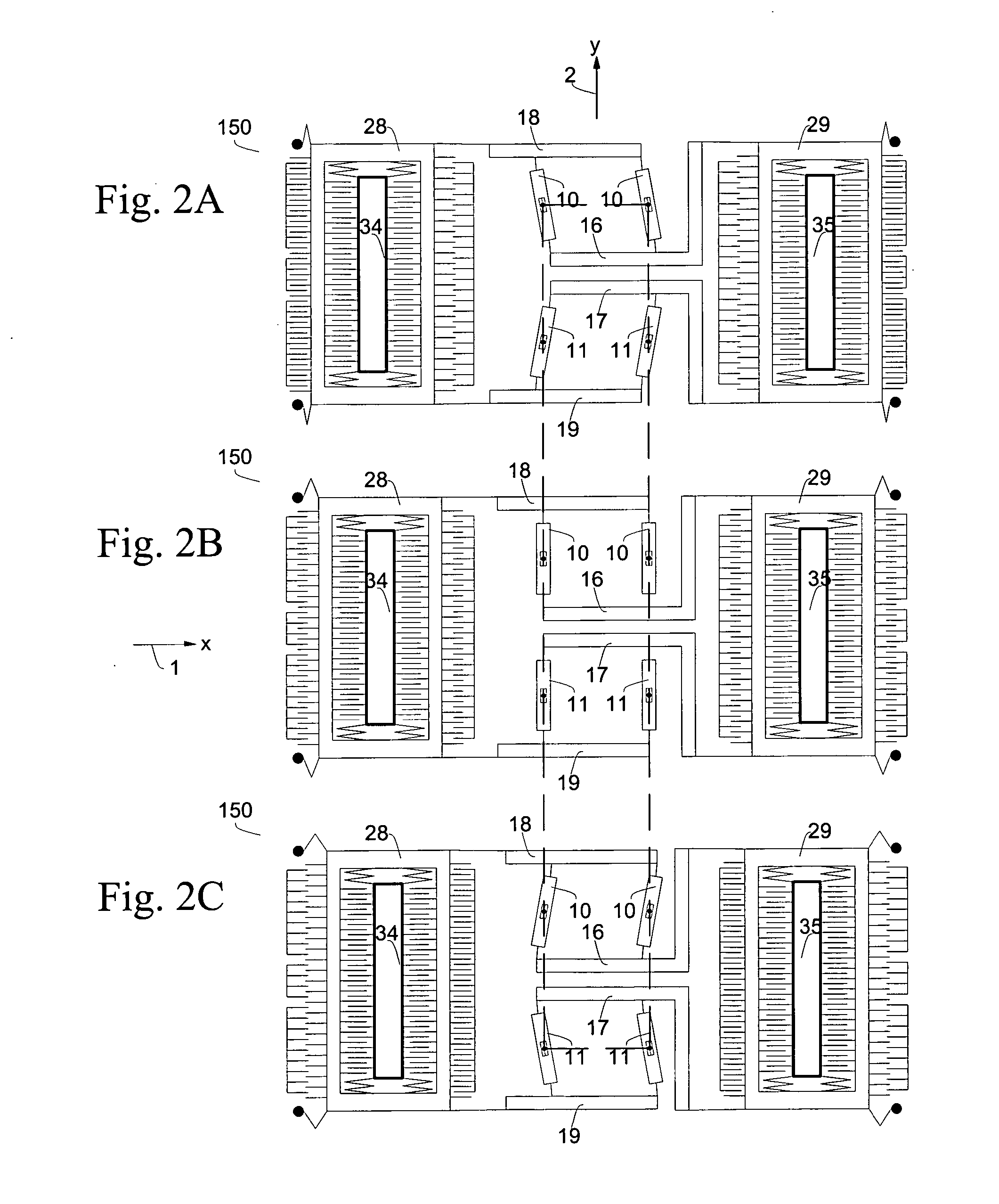
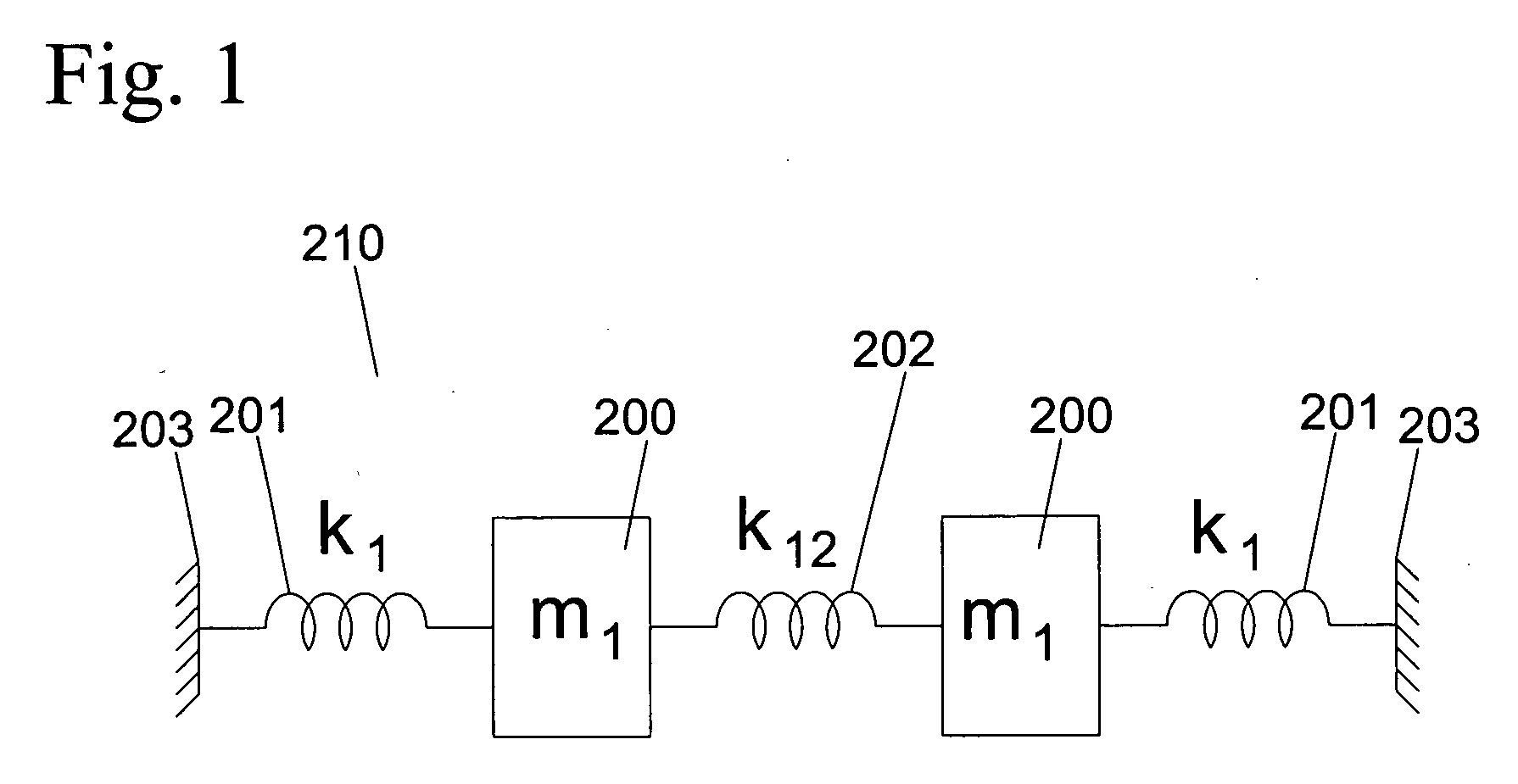
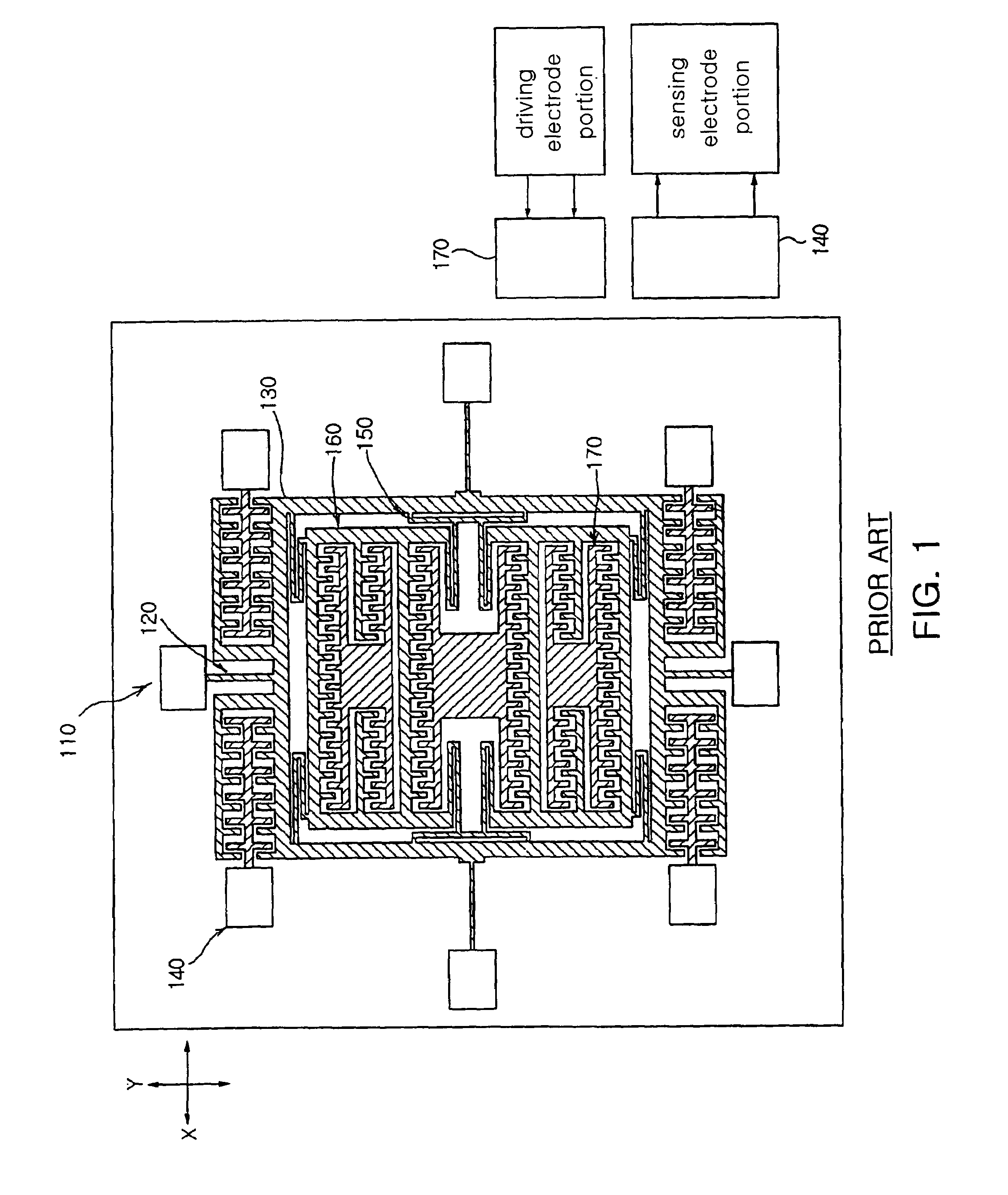
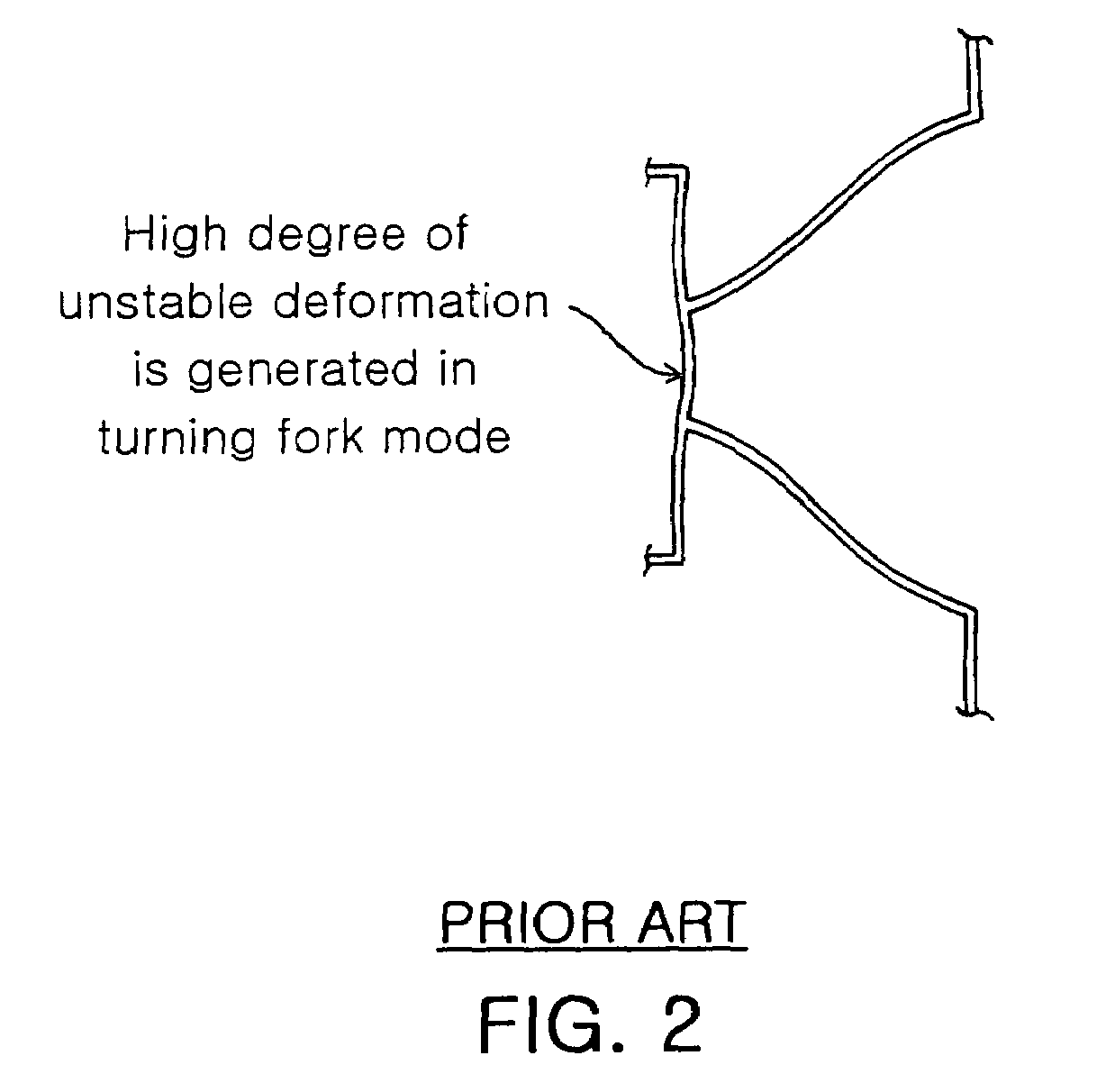
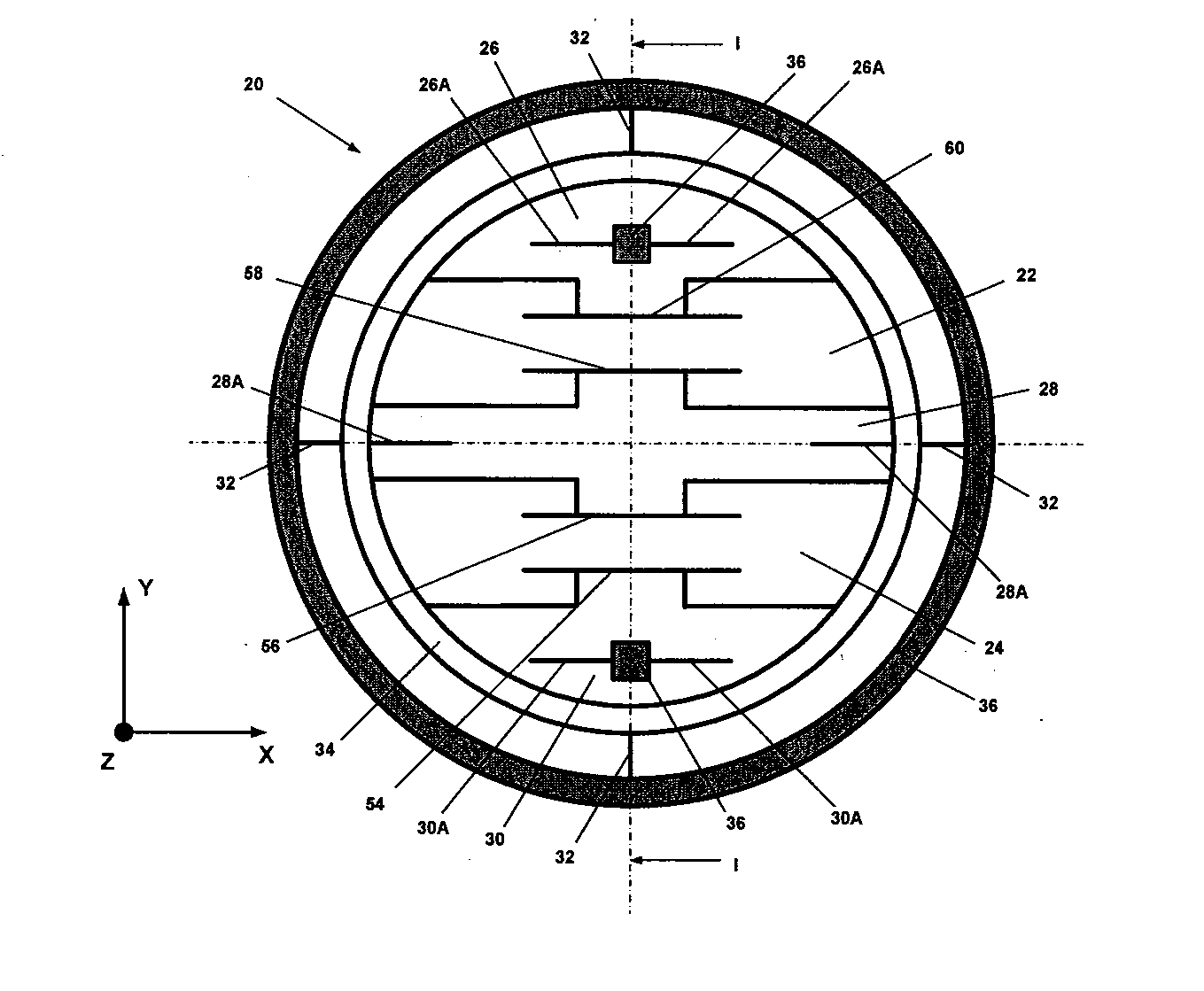
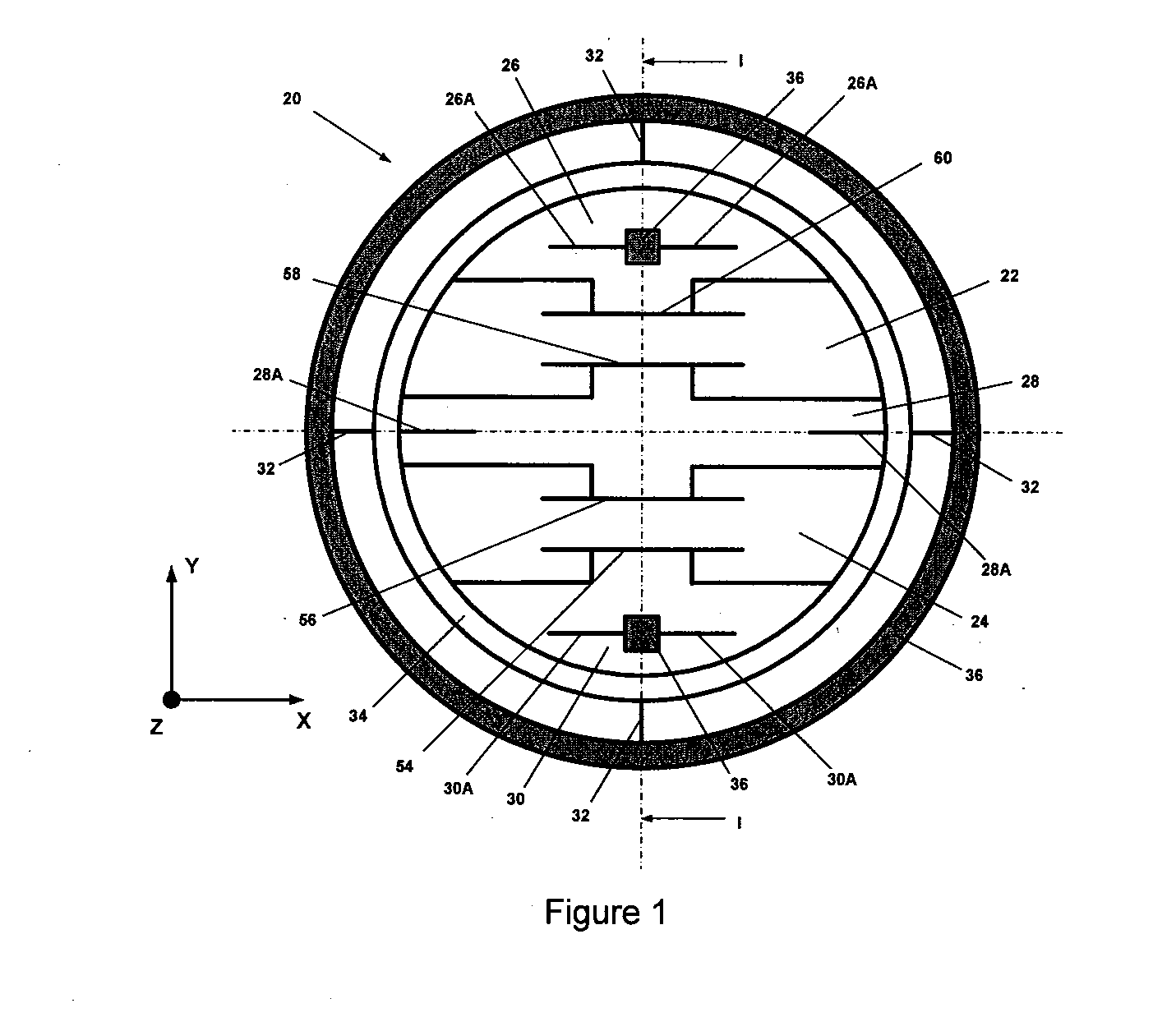
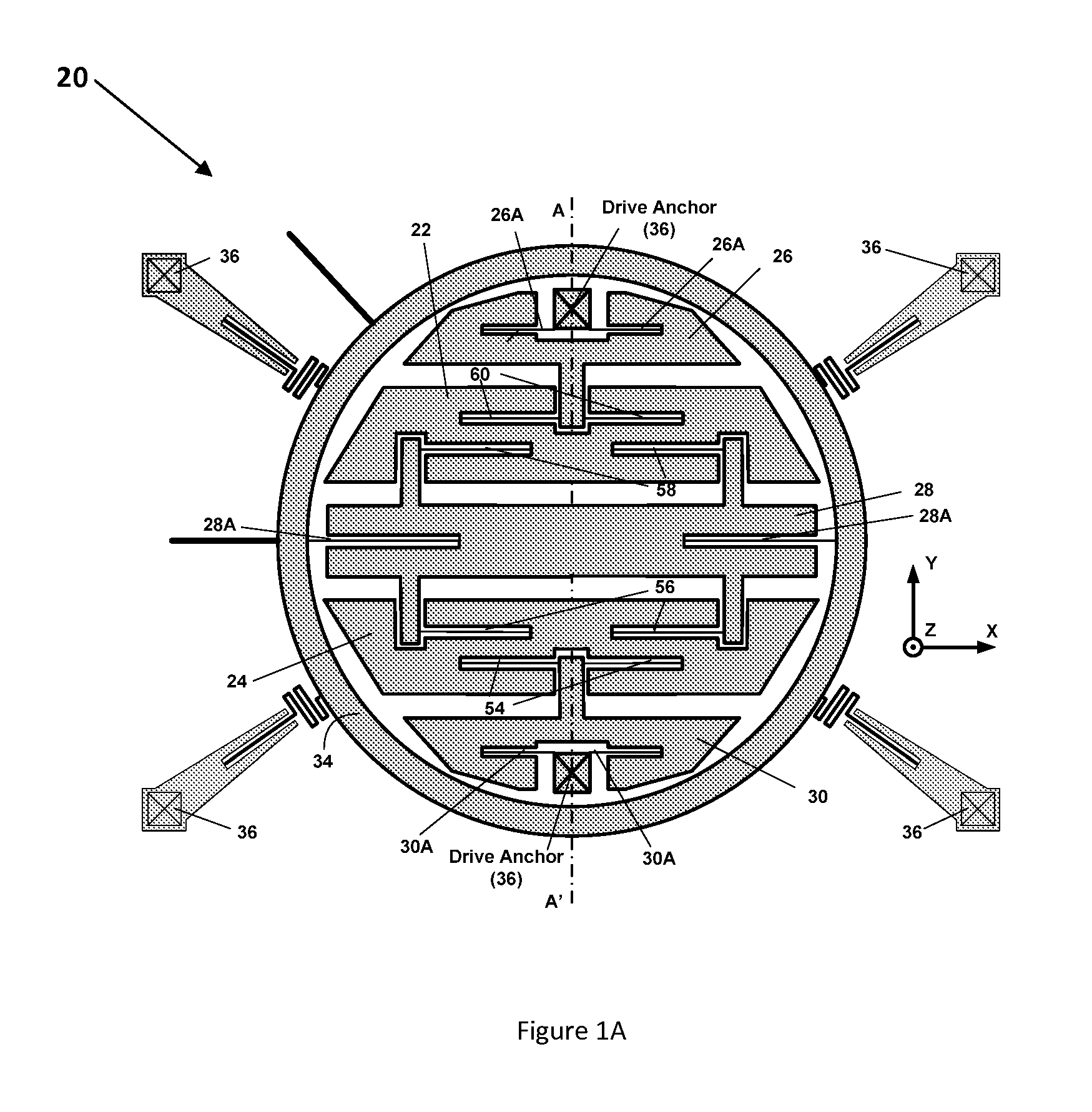
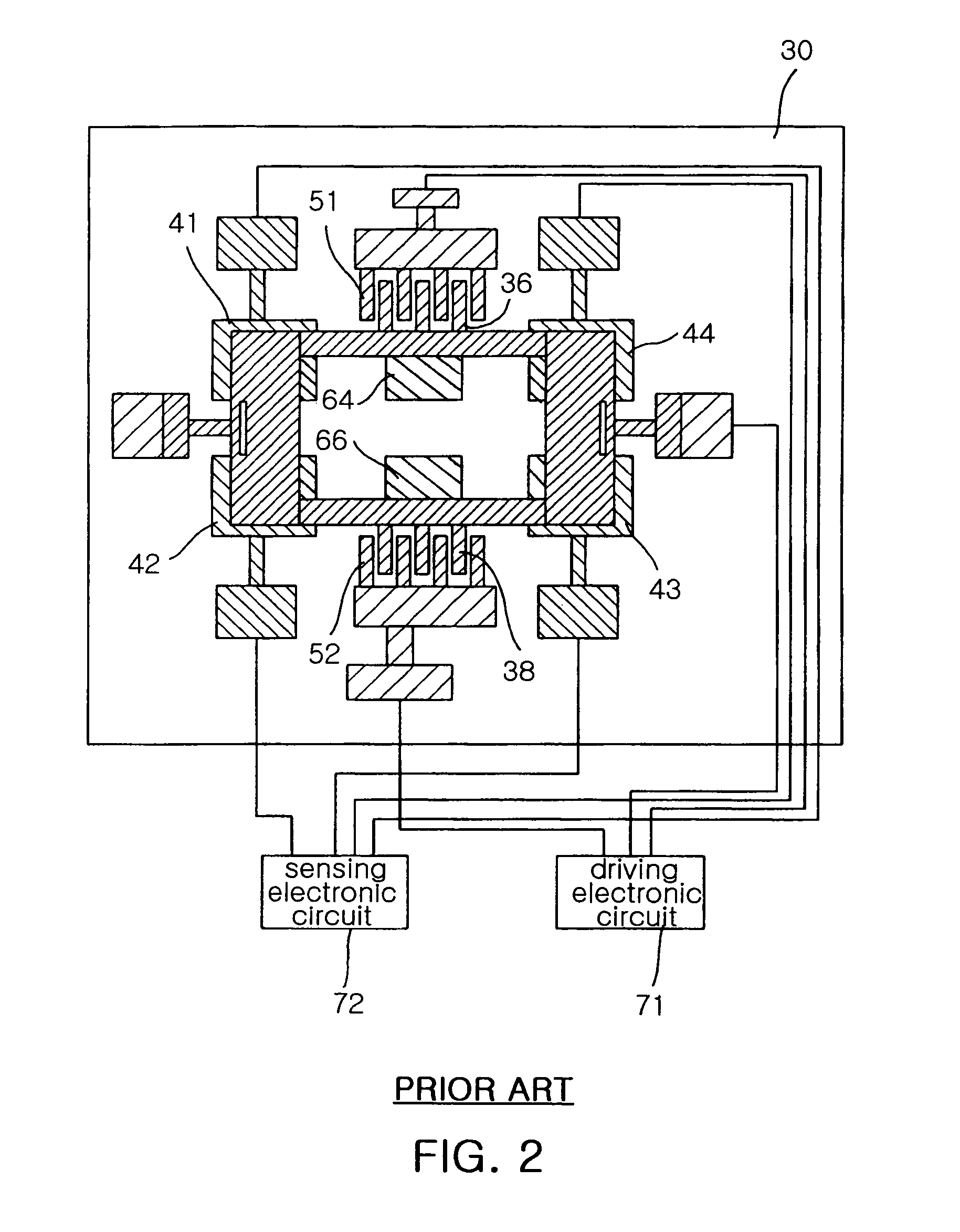
Micromachined tuning fork gyroscopes with ultra-high sensitivity and shock rejection
ActiveUS20100313657A1Eliminate spursEnergy consumption is minimizedAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkDynamic balance
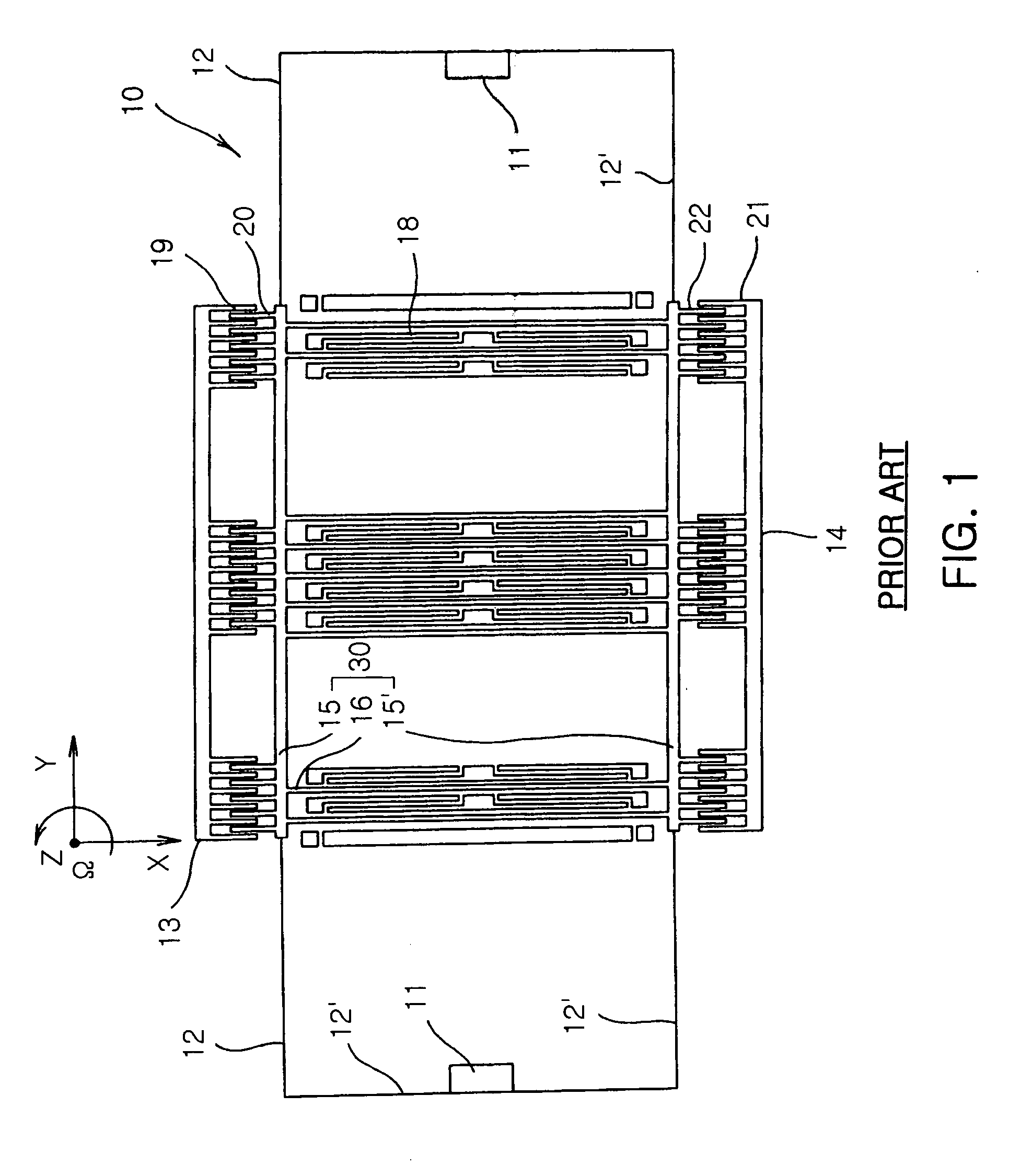
A vibratory rate z-axis gyroscope is characterized by drive-mode and sense-mode quality factors and rate sensitivity and is fabricated with at least two decoupled vibratory tines, a levered drive-mode mechanism coupled between the tines to structurally force anti-phase drive-mode motion of the tines at a predetermined drive frequency, to eliminate spurious frequency modes of the anti-phase drive-mode motion of the tines lower than the predetermined drive frequency and to provide synchronization of drive- and sense-mode motion of the tines, and a sense-mode mechanism coupled between the tines arranged and configured to provide a linearly coupled, dynamically balanced anti-phase sense-mode motion of the tines to minimize substrate energy dissipation and to enhance the sense-mode quality factor and rate sensitivity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Micromachined tuning fork gyroscopes with ultra-high sensitivity and shock rejection
ActiveUS8322213B2Energy consumption is minimizedQuality improvementAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkDynamic balance
A vibratory rate z-axis gyroscope is characterized by drive-mode and sense-mode quality factors and rate sensitivity and is fabricated with at least two decoupled vibratory tines, a levered drive-mode mechanism coupled between the tines to structurally force anti-phase drive-mode motion of the tines at a predetermined drive frequency, to eliminate spurious frequency modes of the anti-phase drive-mode motion of the tines lower than the predetermined drive frequency and to provide synchronization of drive- and sense-mode motion of the tines, and a sense-mode mechanism coupled between the tines arranged and configured to provide a linearly coupled, dynamically balanced anti-phase sense-mode motion of the tines to minimize substrate energy dissipation and to enhance the sense-mode quality factor and rate sensitivity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
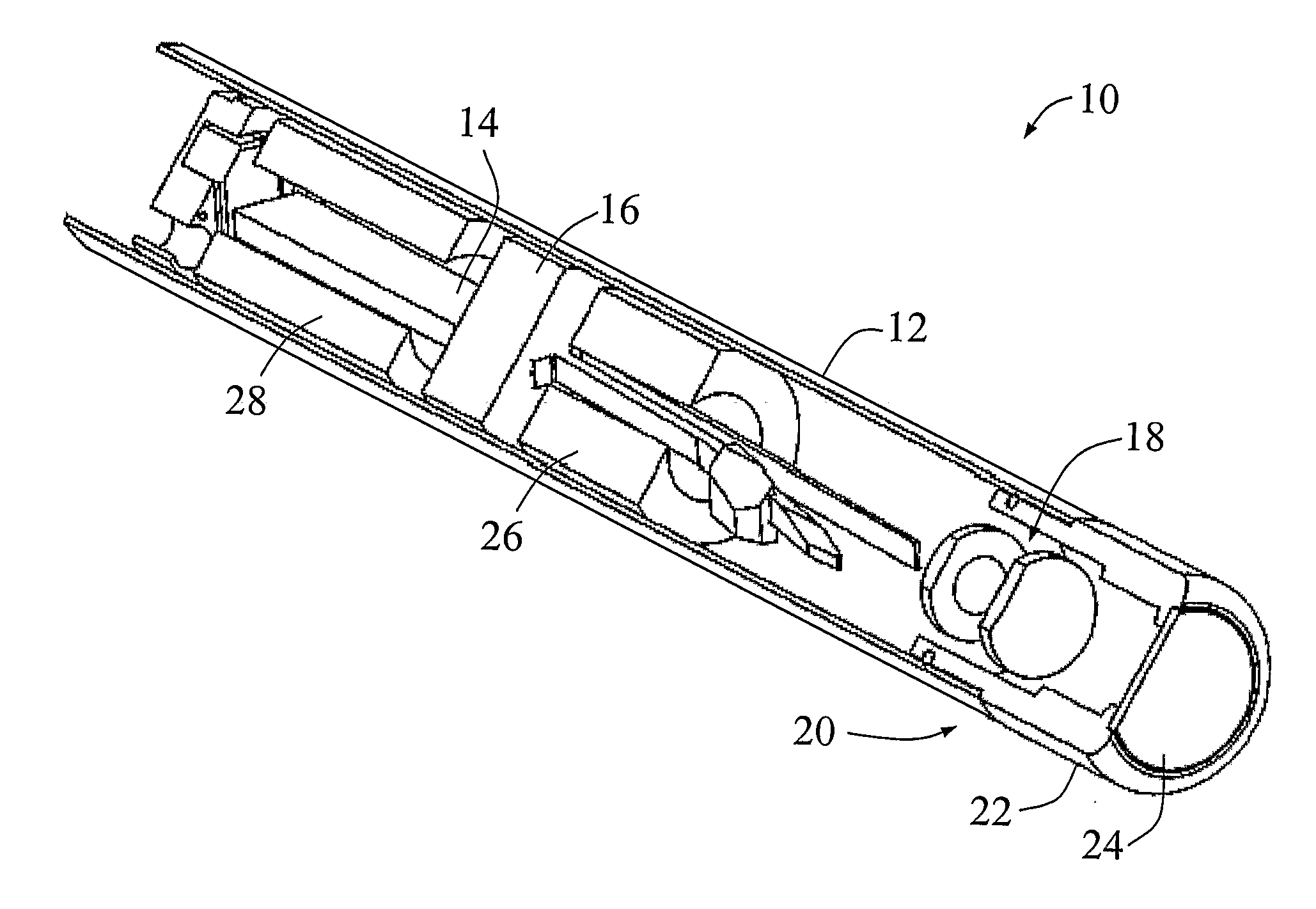
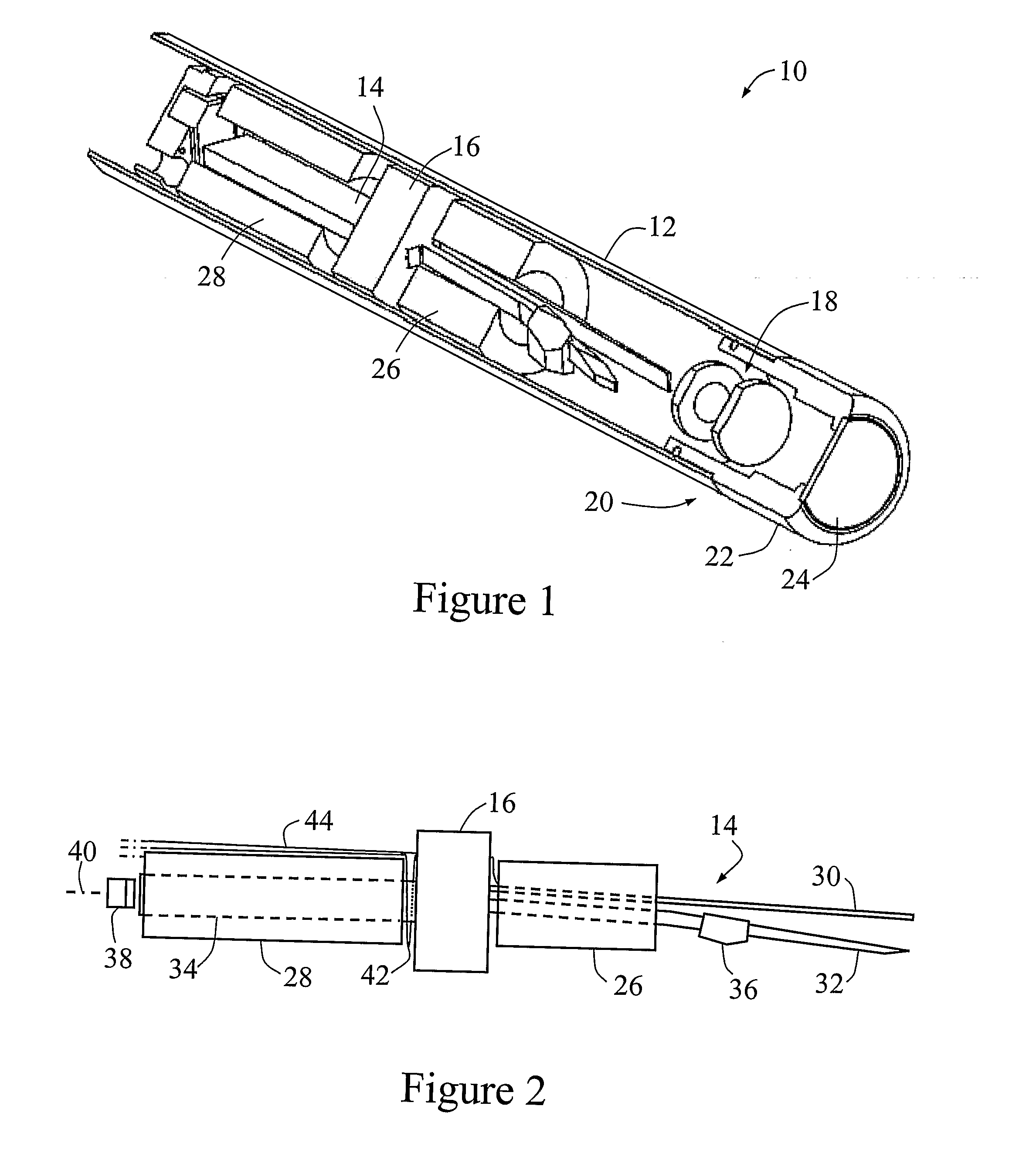
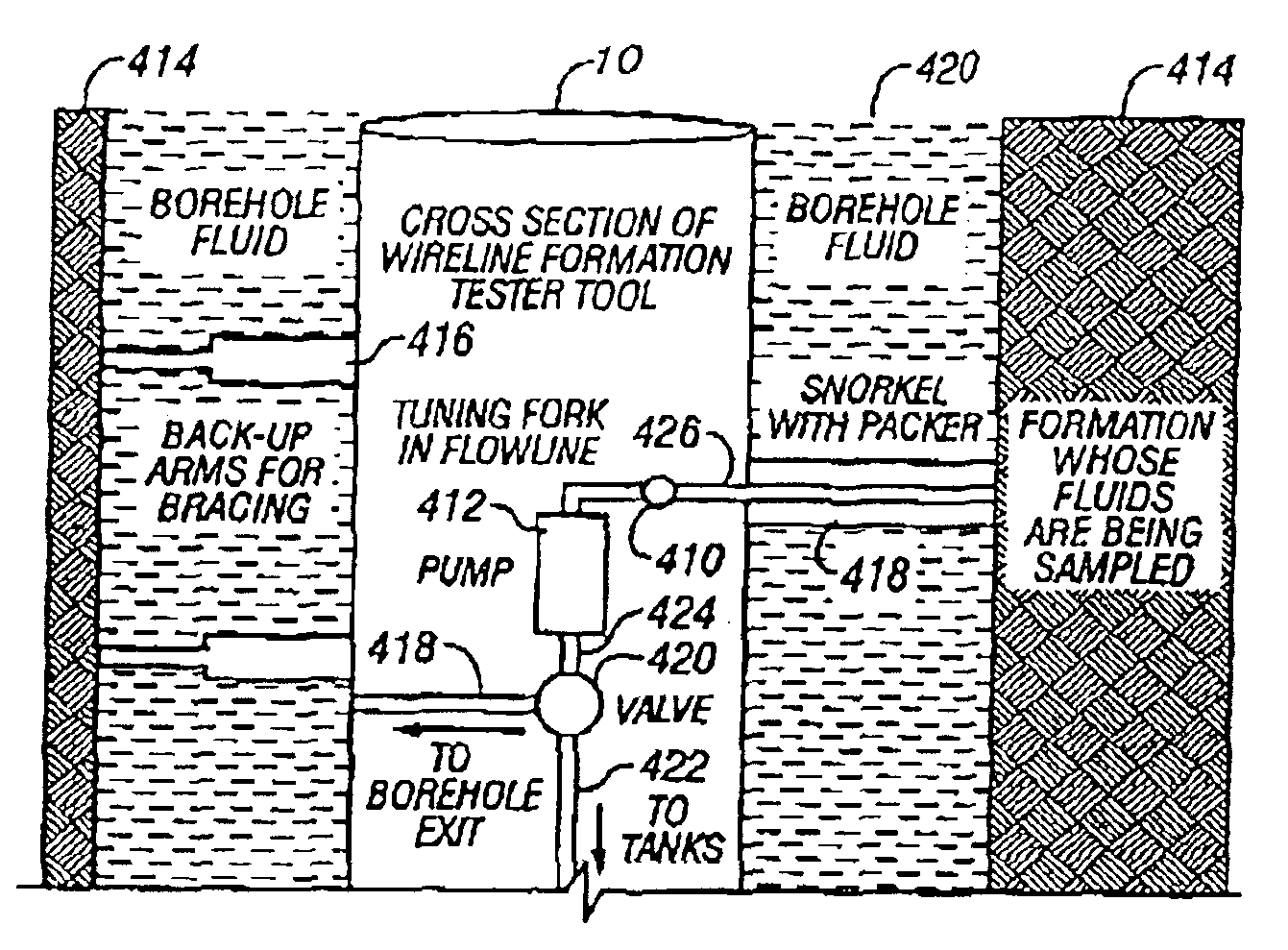
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid characterization using flexural mechanical resonators
InactiveUS20020178805A1Avoid contact corrosionProtection from damageElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkFormation fluid
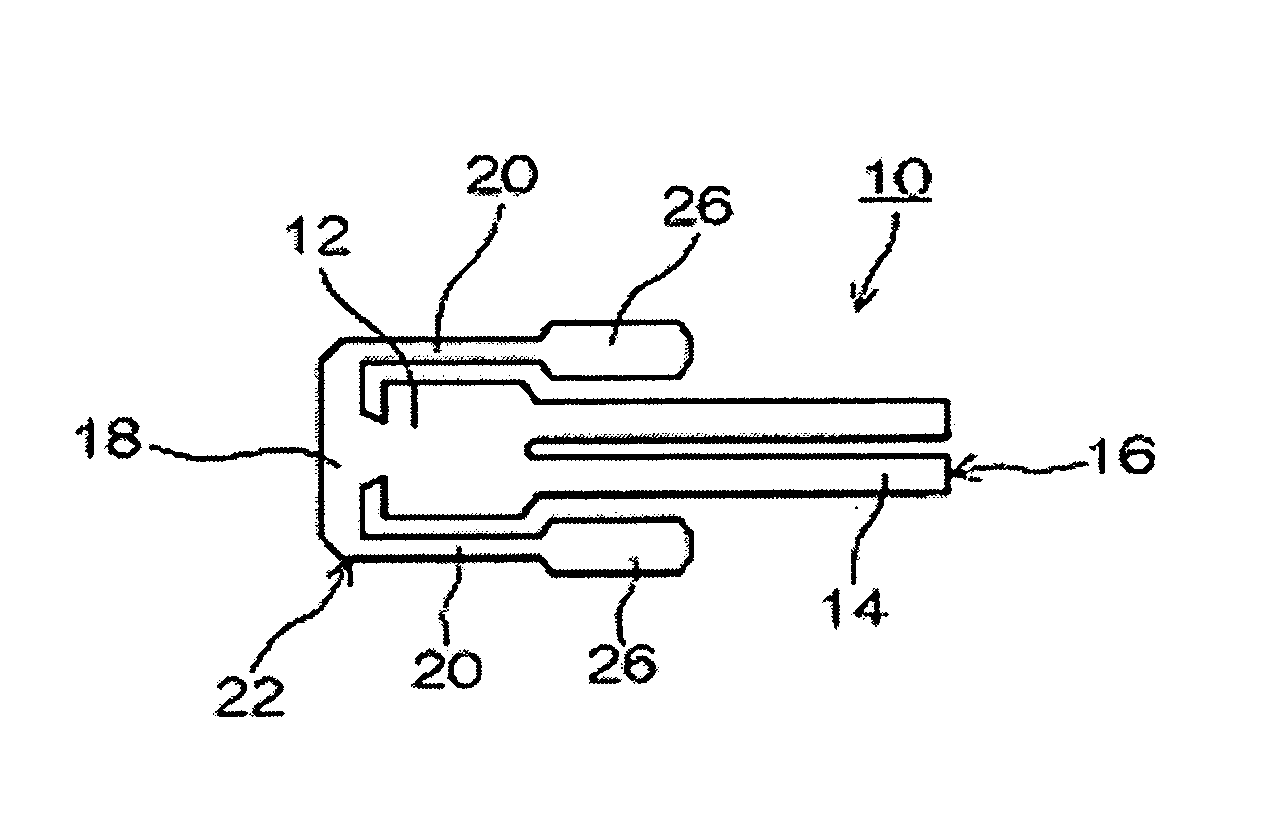
The present invention provides a downhole method and apparatus using a flexural mechanical resonator, for example, a tuning fork to provide real-time direct measurements and estimates of the viscosity, density and dielectric constant of formation fluid or filtrate in a hydrocarbon producing well. The present invention additionally provides a method and apparatus for monitoring cleanup from a leveling off of viscosity or density over time, measuring or estimating bubble point for formation fluid, measuring or estimating dew point for formation fluid, and determining the onset of asphaltene precipitation. The present invention also provides for intercalibration of plural pressure gauges used to determine a pressure differential downhole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
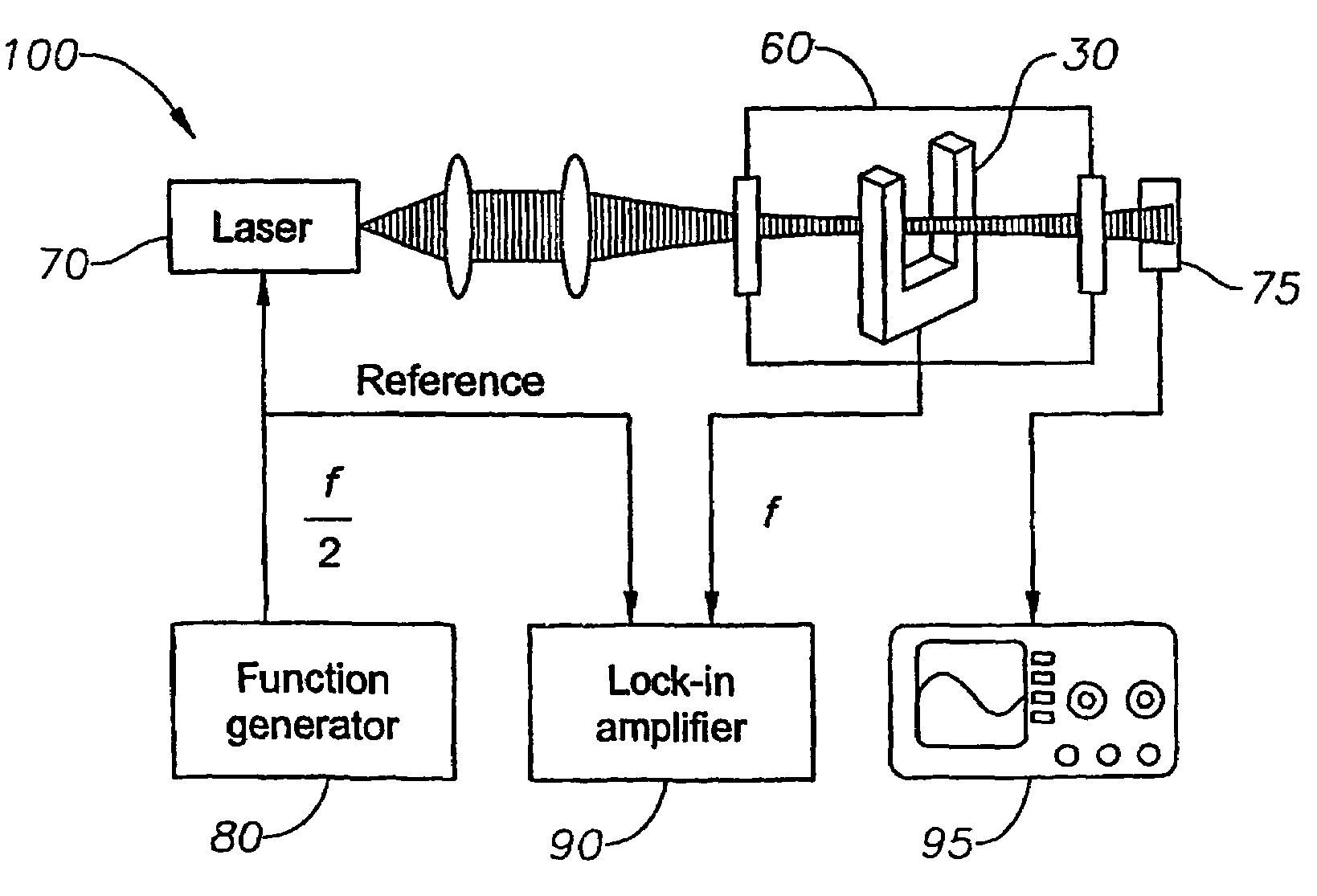
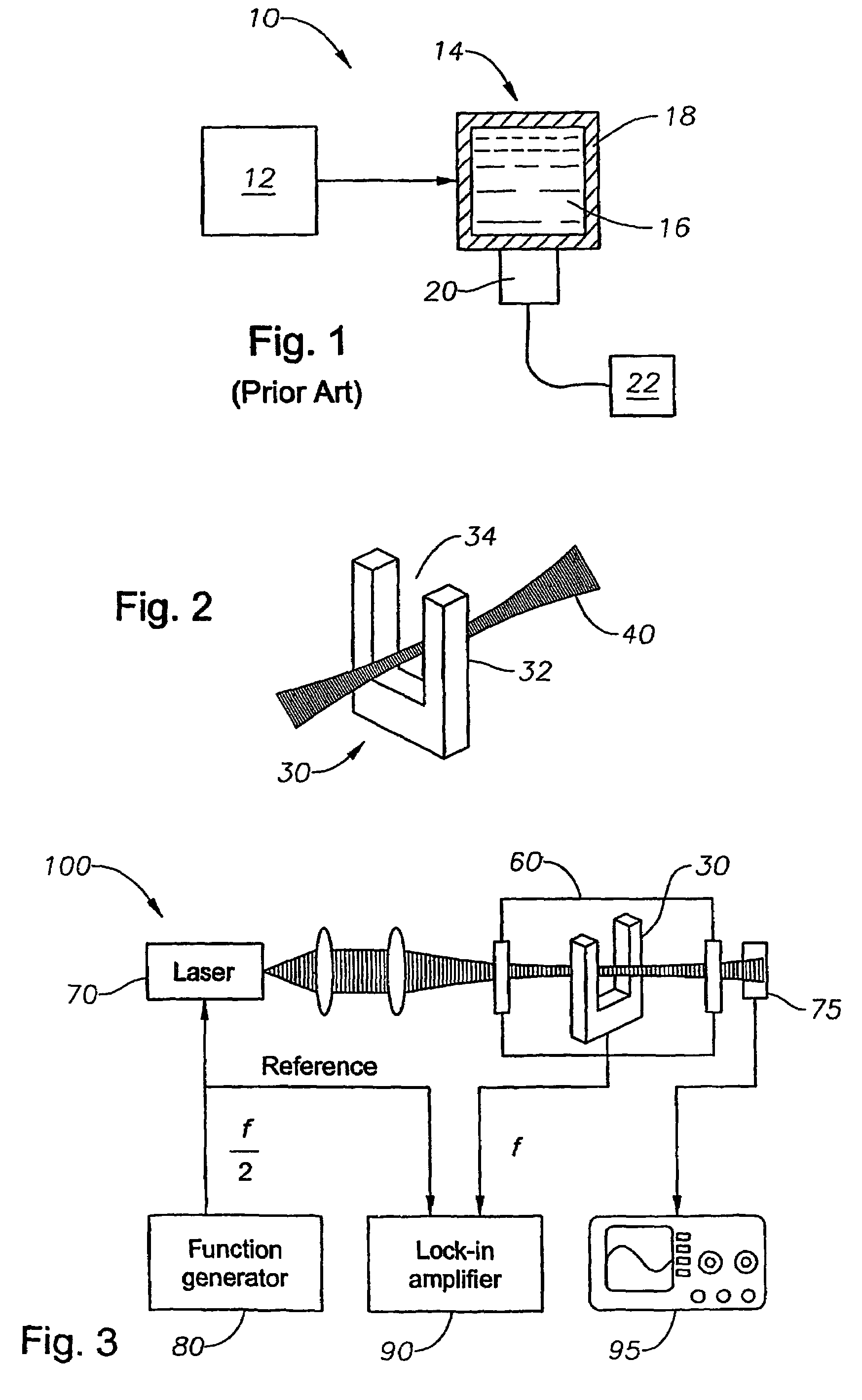
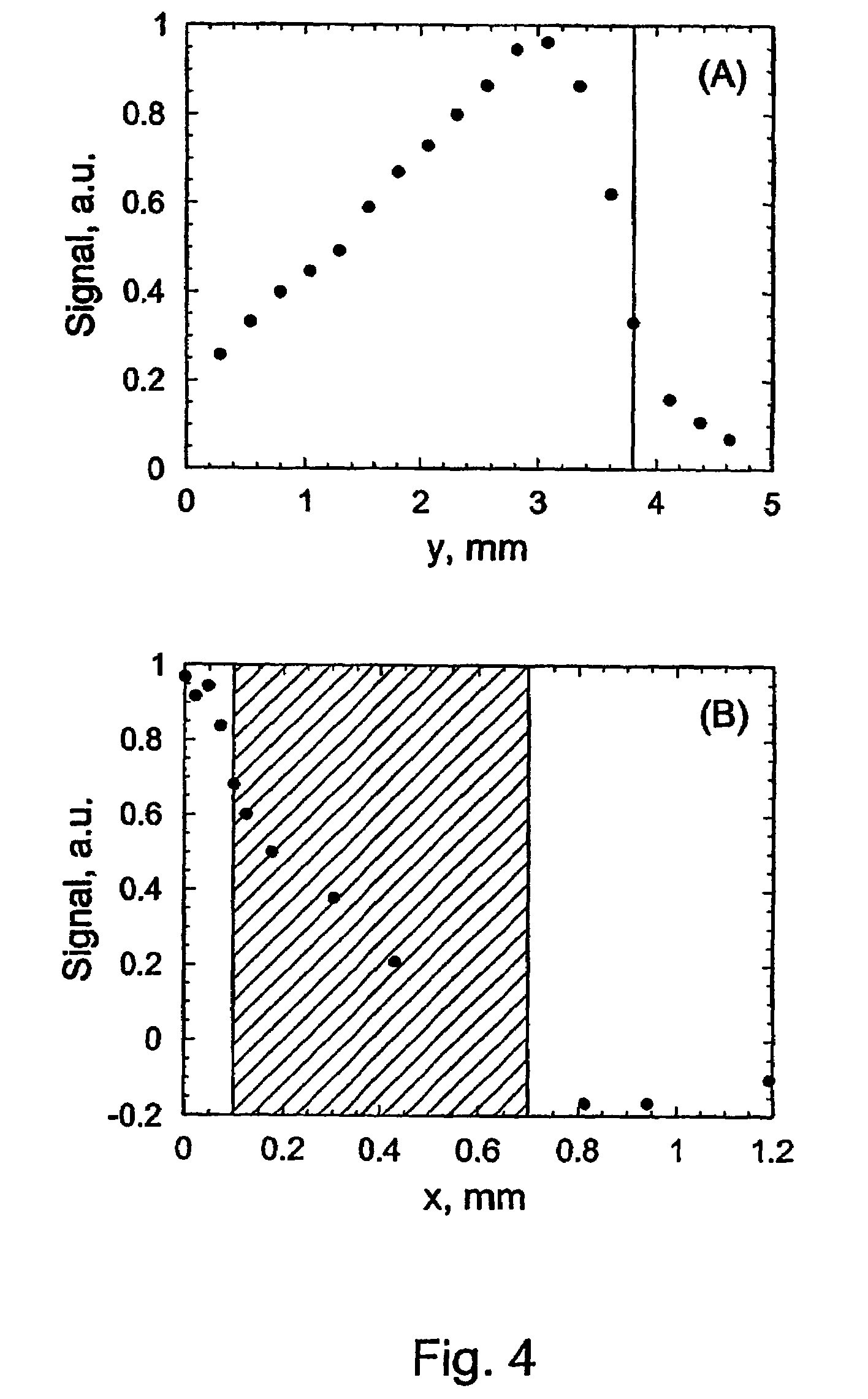
Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050117155A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkAbsorbed energy
Methods and apparatus for detecting photoacoustic signals in fluid media are described. The present invention differs from conventional photoacoustic spectroscopy in that rather than accumulating the absorbed energy in the fluid of a sample cell, the absorbed energy is accumulated in an acoustic detector or sensitive element. In a preferred embodiment, the acoustic detector comprises piezoelectric crystal quartz. The quartz is preferably in the shape of a tuning fork.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS7245380B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRadiation pyrometryPhotoacoustic microscopyTuning fork
Methods and apparatus for detecting photoacoustic signals in fluid media are described. The present invention differs from conventional photoacoustic spectroscopy in that rather than accumulating the absorbed energy in the fluid of a sample cell, the absorbed energy is accumulated in an acoustic detector or sensitive element. In a preferred embodiment, the acoustic detector comprises piezoelectric crystal quartz. The quartz is preferably in the shape of a tuning fork.
Owner:RICE UNIV
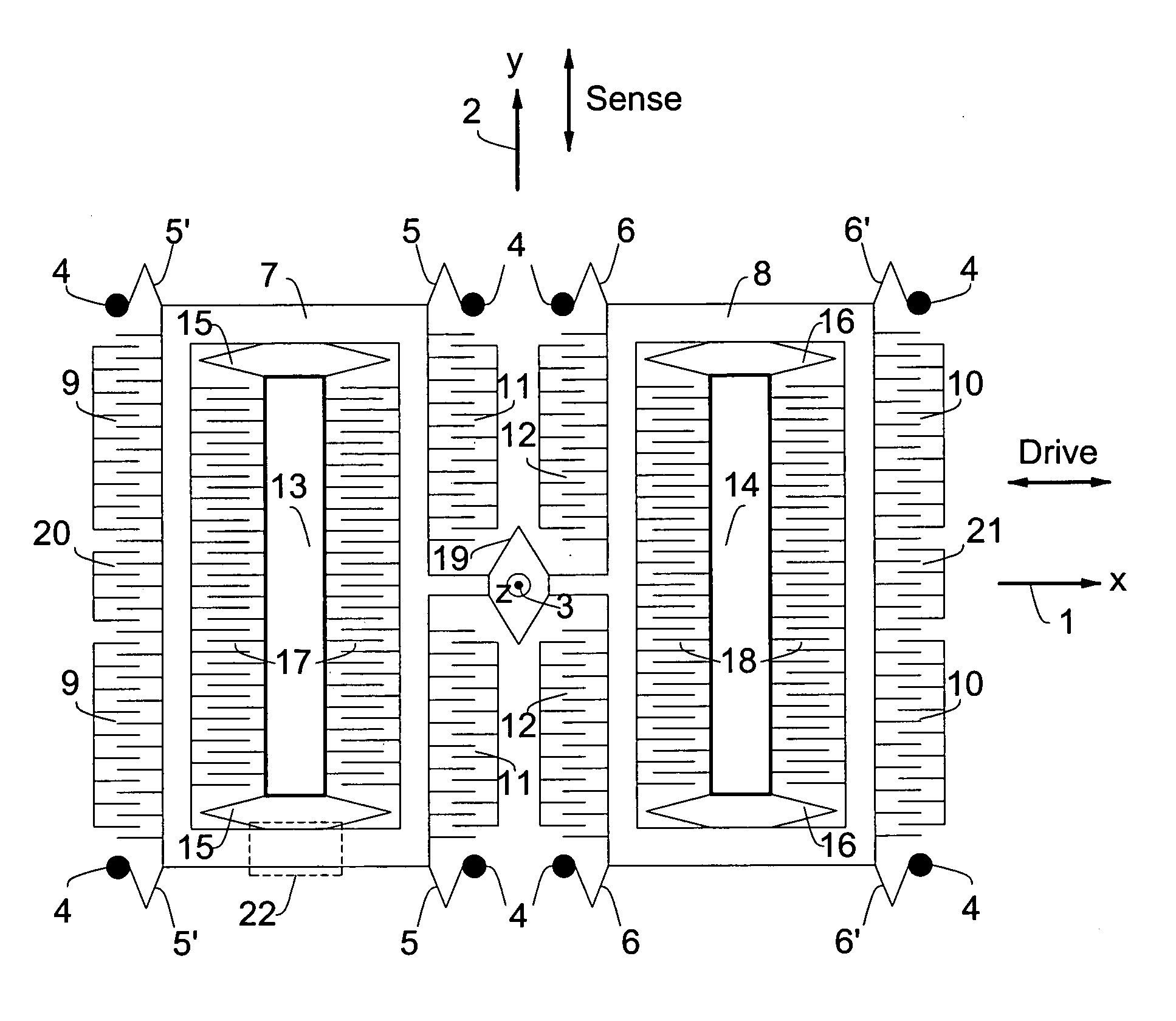
Z-axis angular rate sensor
ActiveUS7036372B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkAngular rate sensor
An oscillatory rate sensor is described for sensing rotation about the “z-axis”. It is tuning-fork in nature with structural linkages and dynamics such that fundamental anti-phase oscillation of two proof masses is accomplished by virtue of the mechanical linkages.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
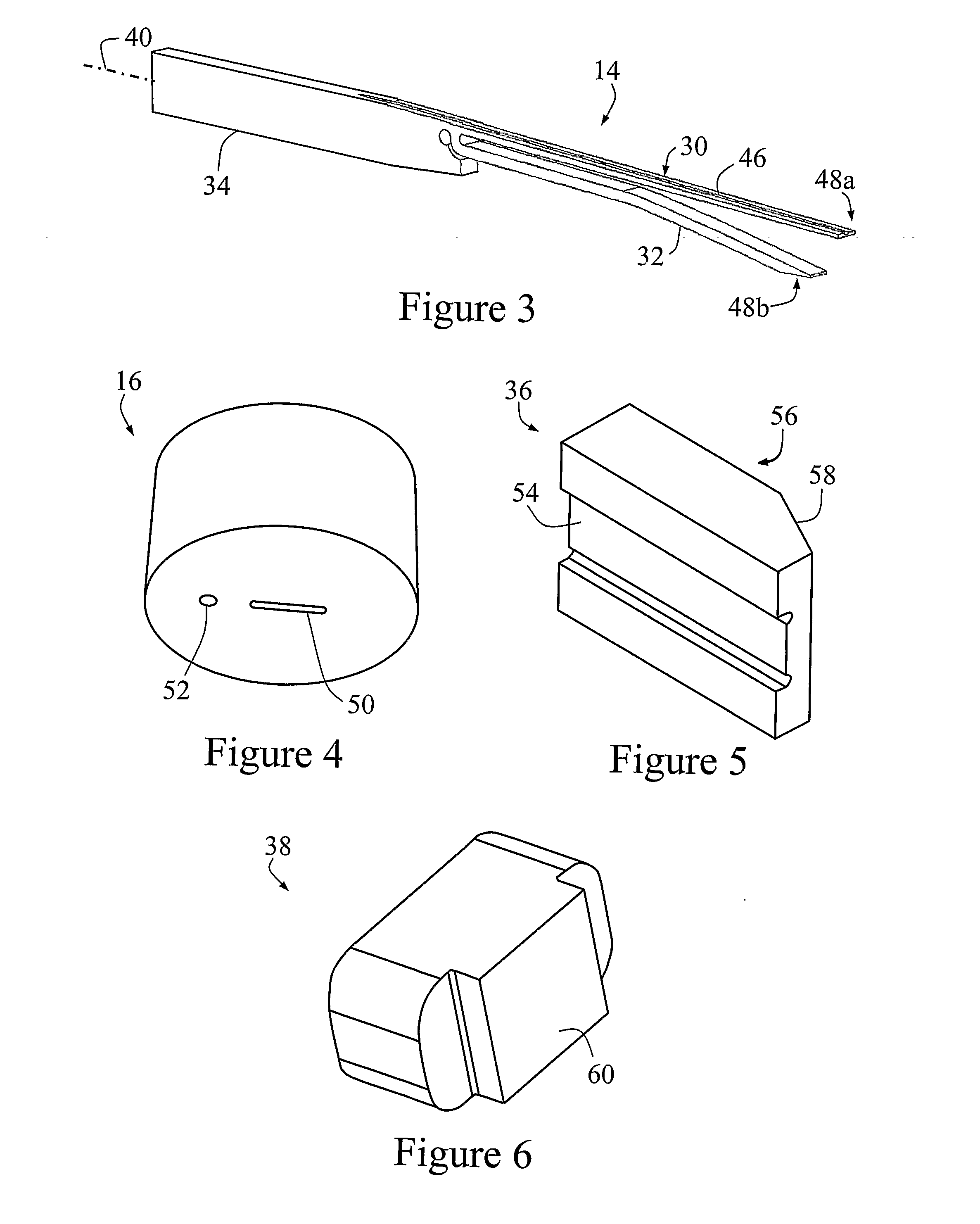
Tuning-Fork-Type Scanning Apparatus with a Counterweight
ActiveUS20070242330A1Compensation-greater lengthReduce the overall diameterBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsEndoscopesTuning forkEngineering
A scanning method and apparatus, the apparatus comprising a fork with first and second forwardly extending tines and a rearwardly extending counterweight member, a mount for supporting the fork at a point between the tines and the counterweight member, and a drive for effecting relative vibration between the tines to provide a fast scan and for driving the fork to provide a slow scan transverse to the fast scan.
Owner:OPTISCAN +1
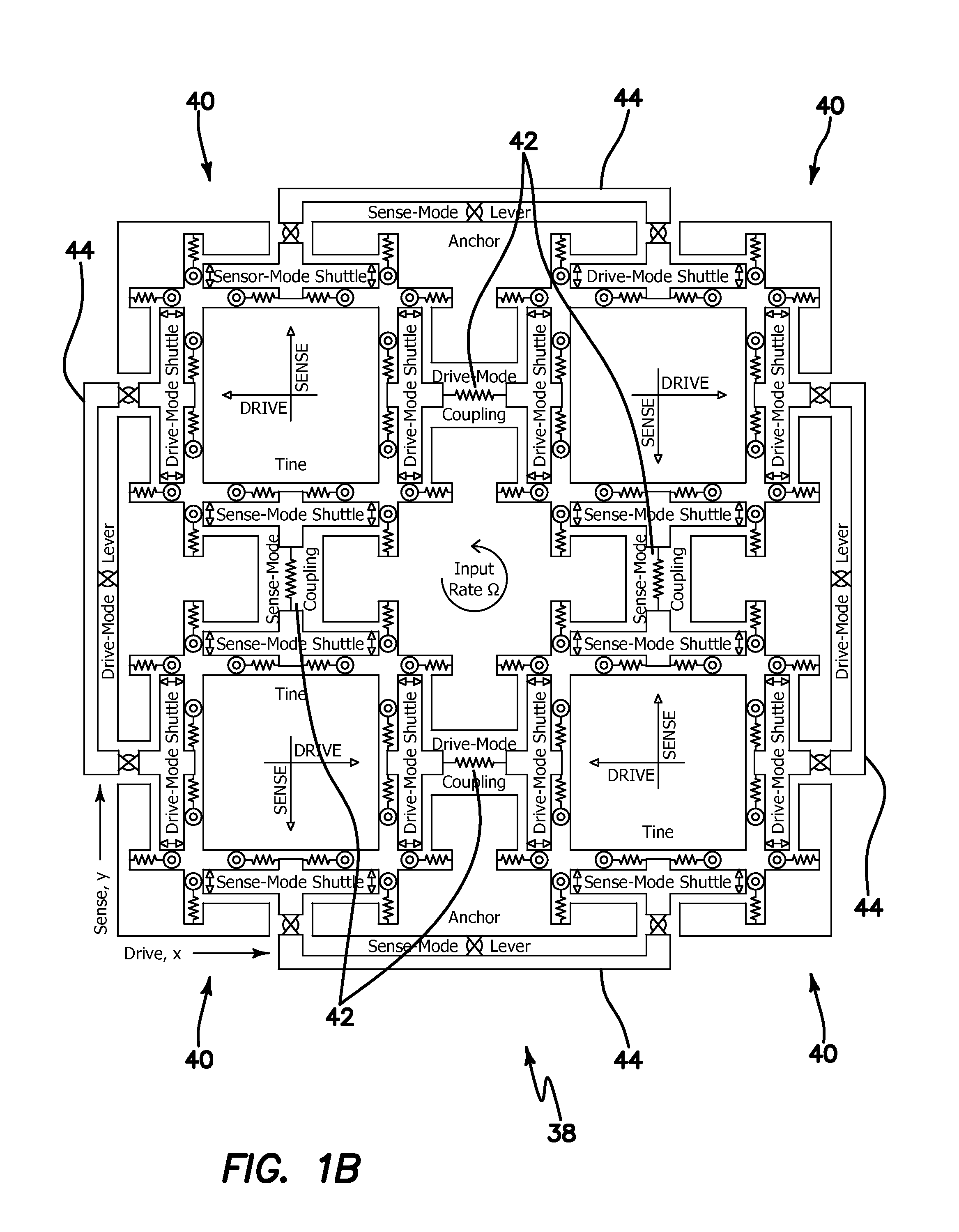
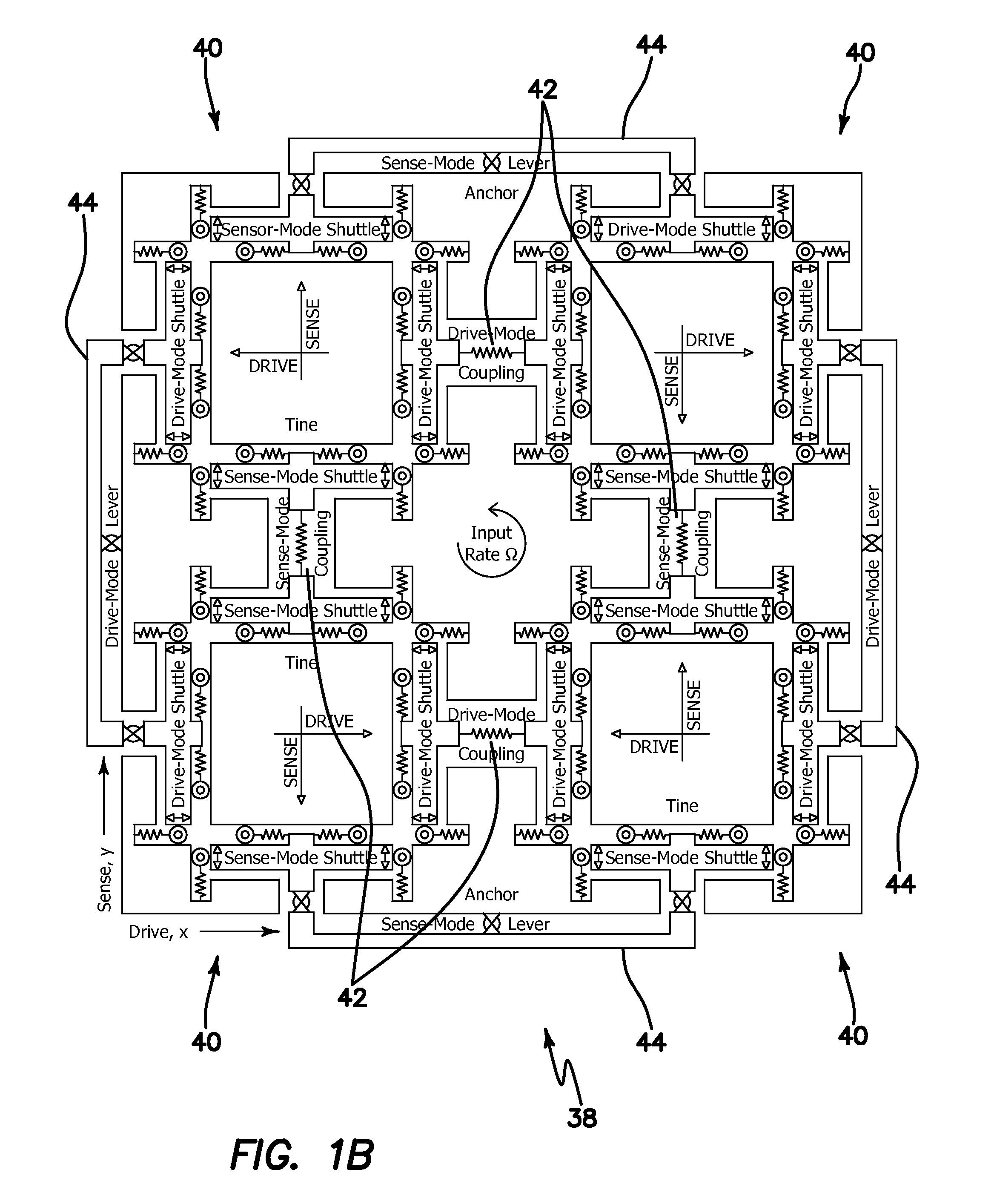
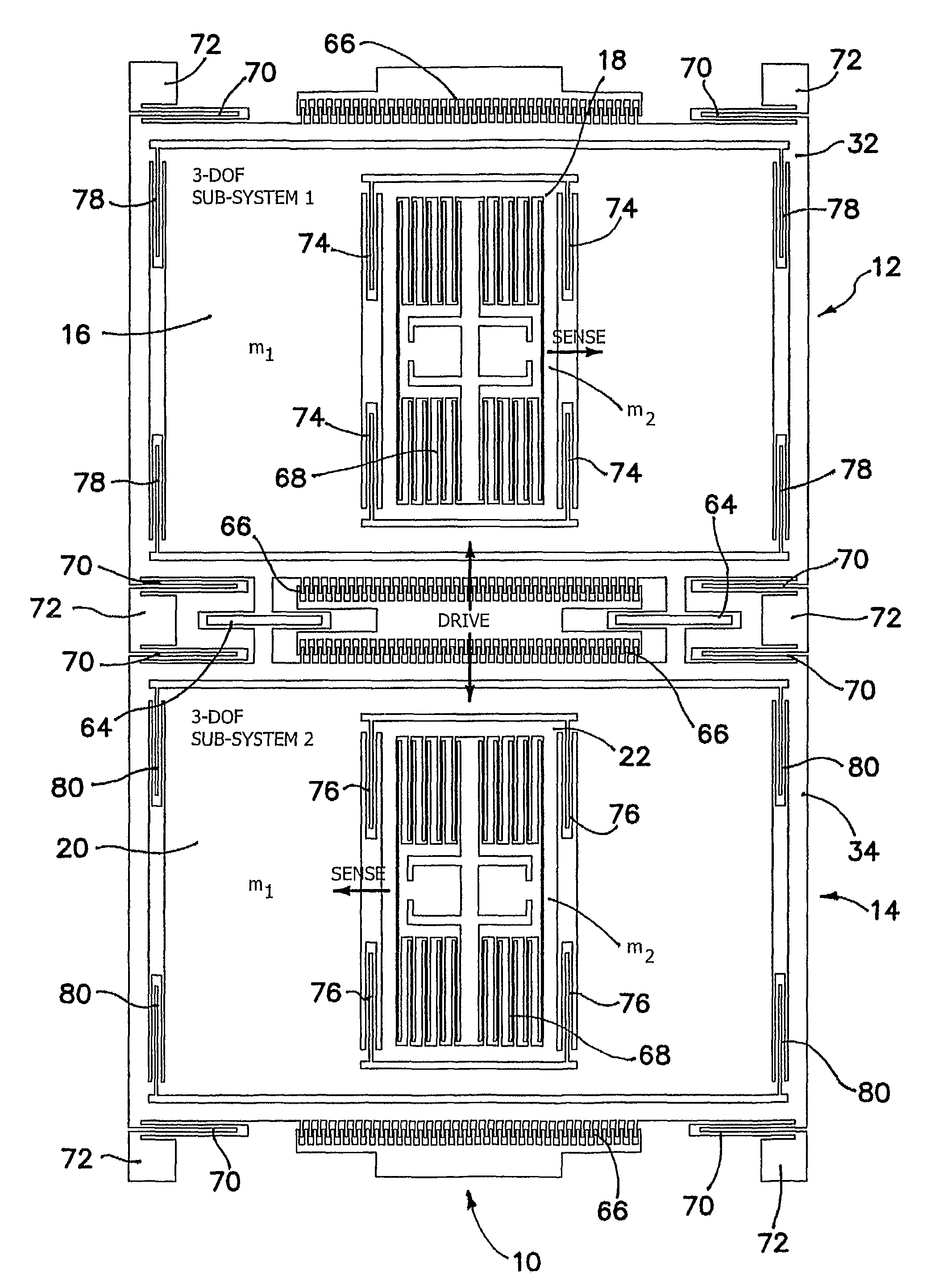
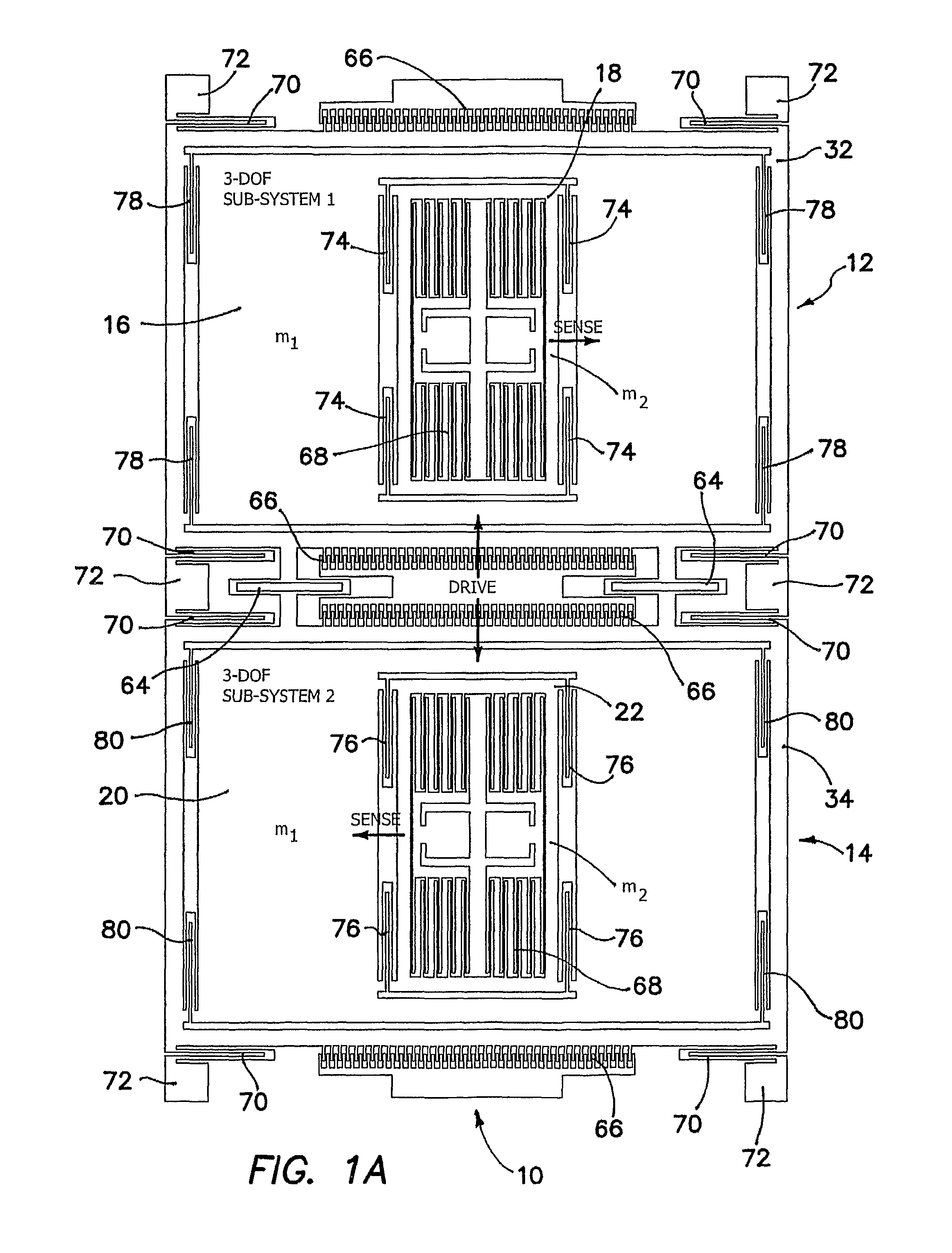
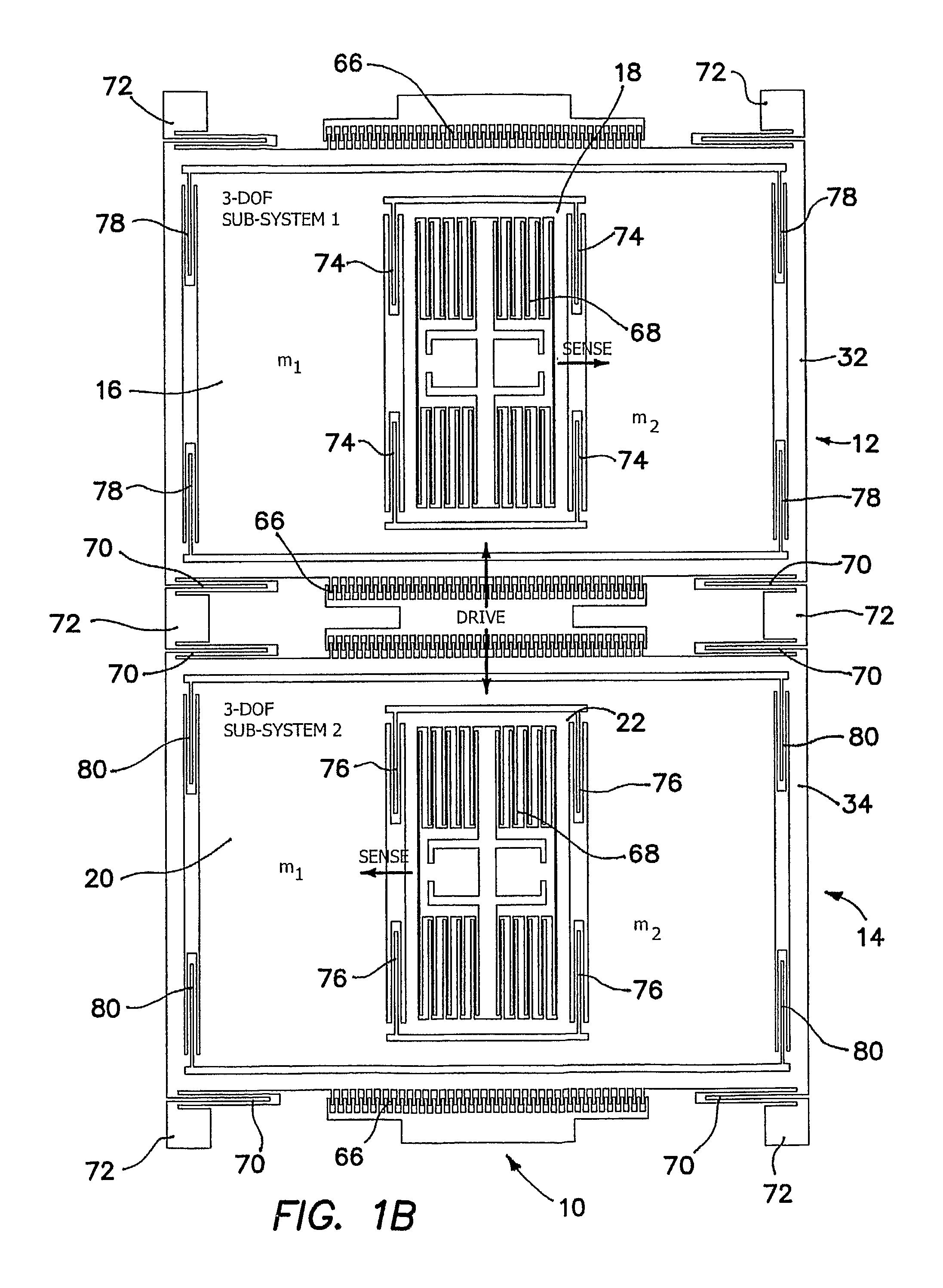
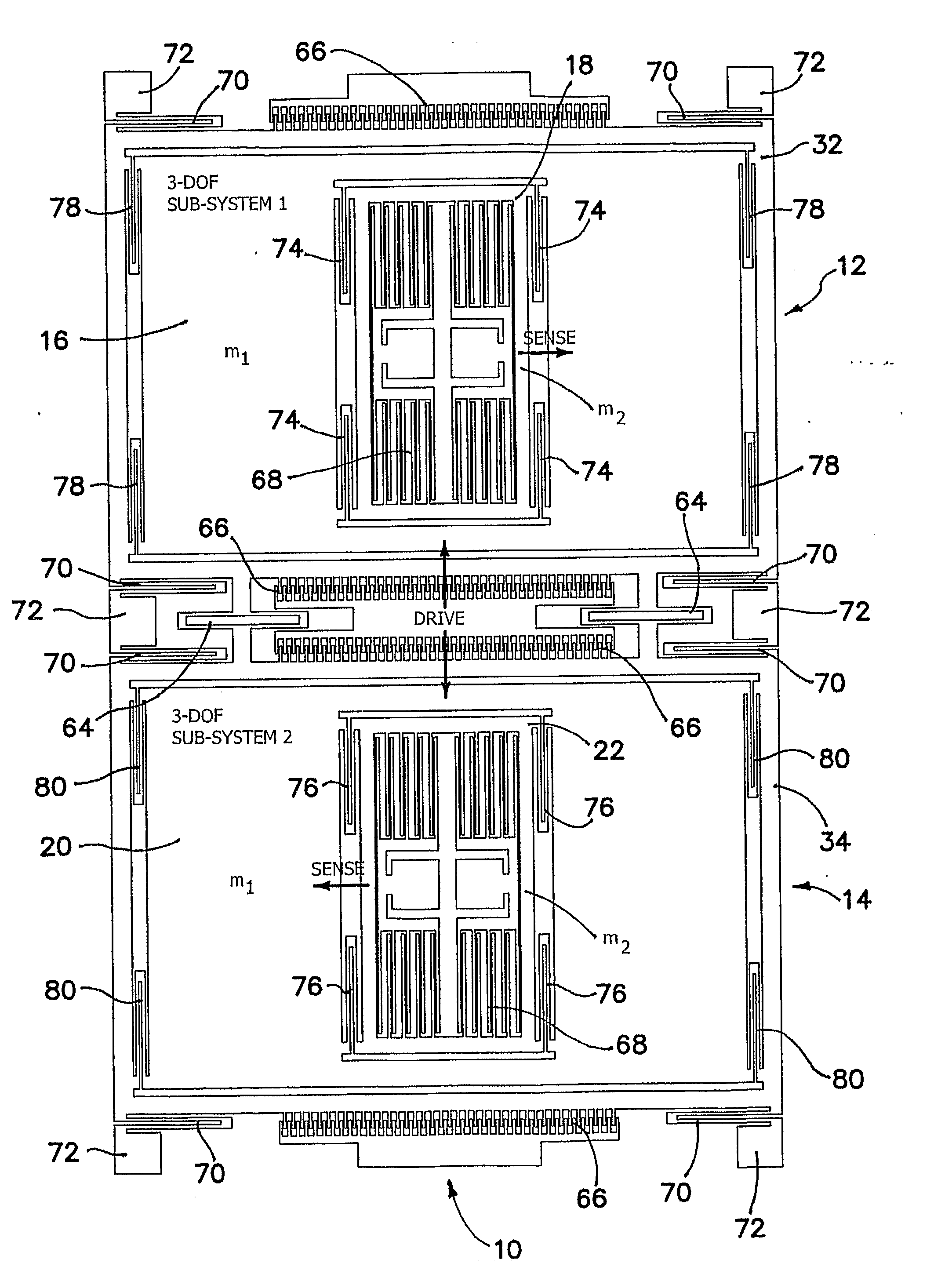
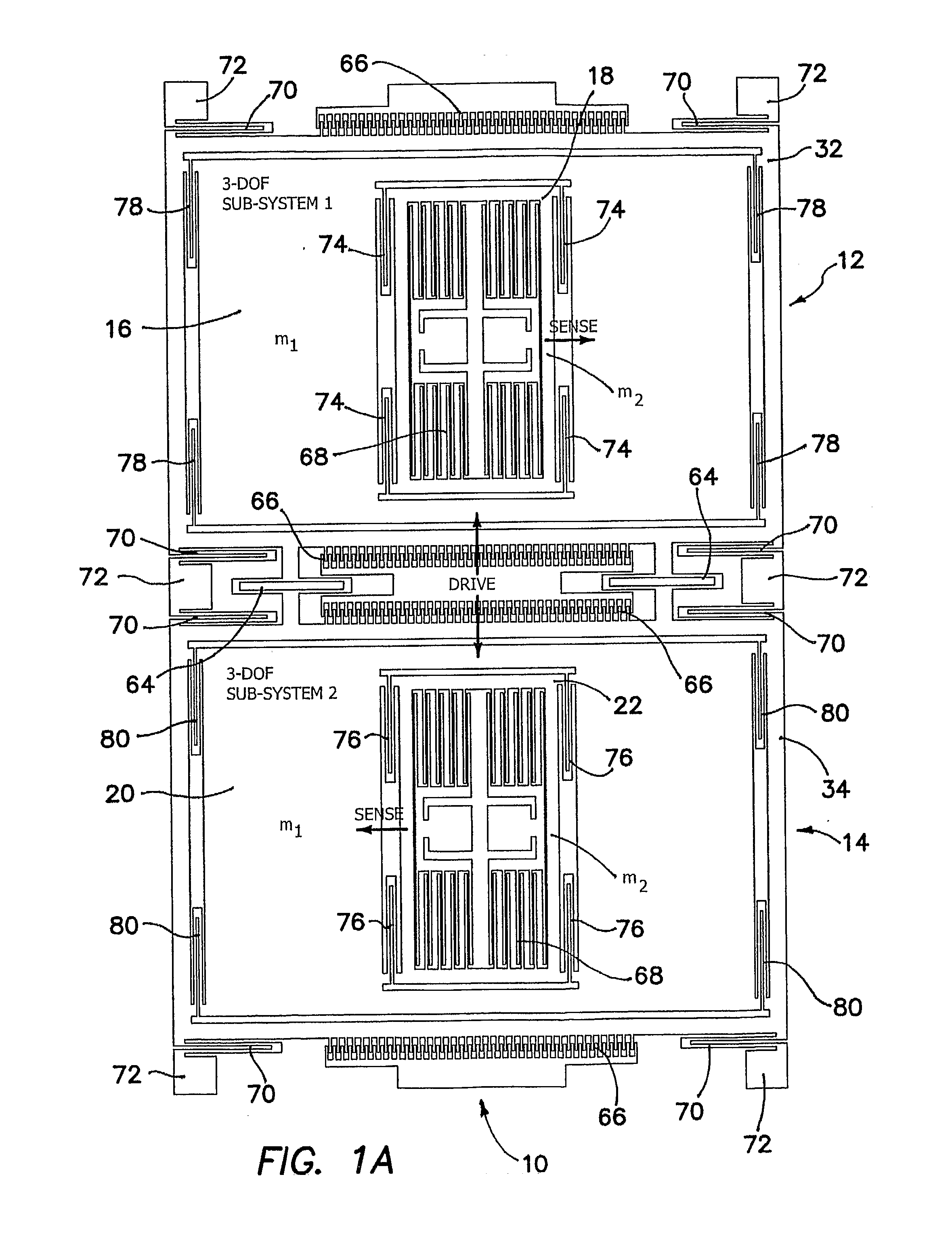
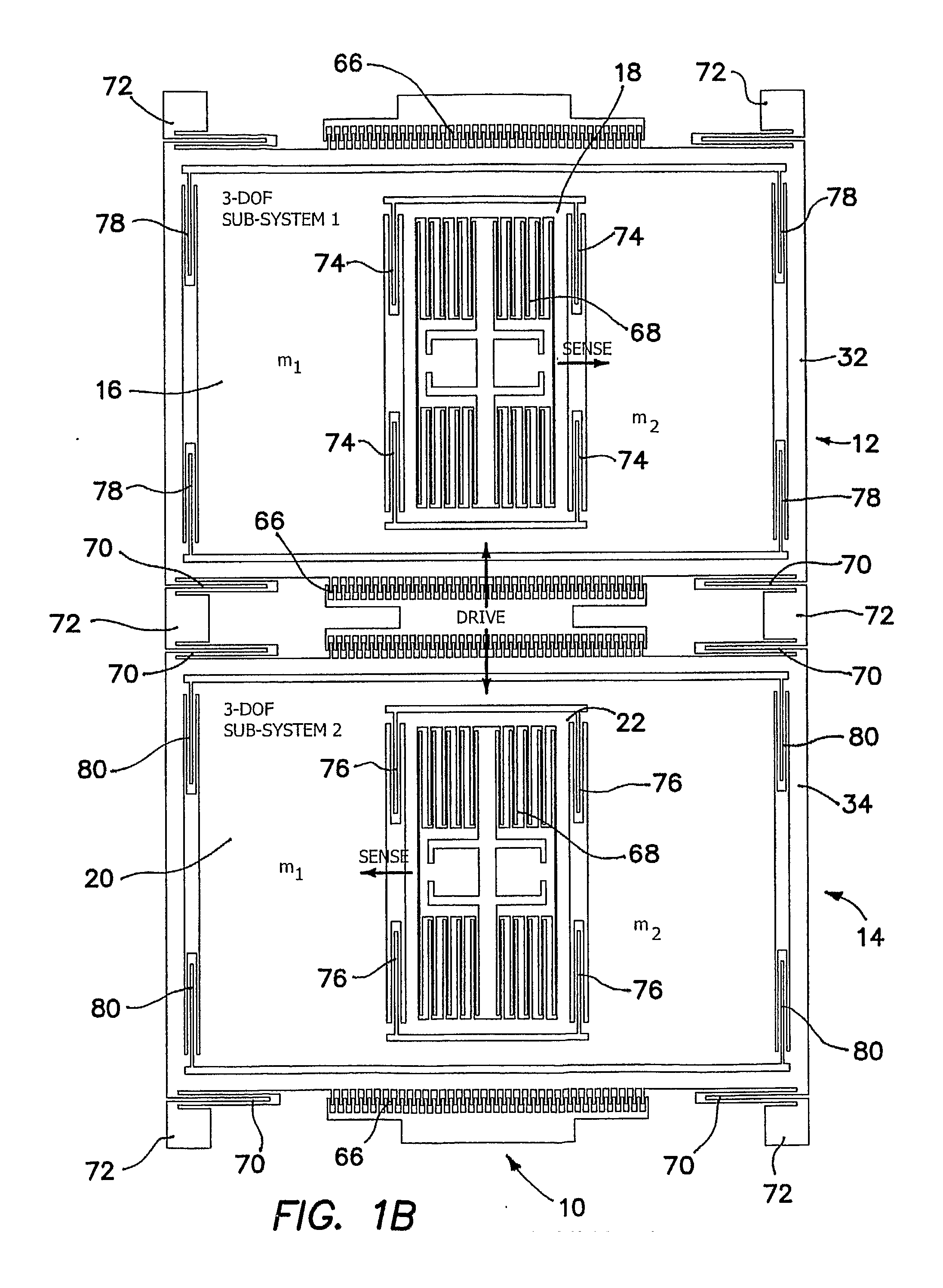
Robust six degree-of-freedom micromachined gyroscope with anti-phase drive scheme and method of operation of the same
ActiveUS8113050B2Effectively and substantially rejectEfficiently rejectedMechanical apparatusAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTuning forkGyroscope
A method of operating an anti-phase six degree-of-freedom tuning fork gyroscope system comprises the steps of driving a first three degree-of-freedom gyroscope subsystem, and driving a second three degree-of freedom gyroscope subsystem in an anti-phase mode with the first gyroscope subsystem at an anti-phase resonant frequency. Acceleration or an angular rate of motion is sensed by the first and second three degree-of-freedom gyroscope subsystems operating in a flat frequency response range where the anti-phase resonant frequency is designed. Response gain and phase are stable and environmental and fabrication perturbations are avoided by such operation. A anti-phase six degree-of-freedom tuning fork gyroscope system which operates as described is also characterized.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid characterization using flexural mechanical resonators
InactiveUS6938470B2Avoid contact corrosionInversely to viscosityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkFormation fluid
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
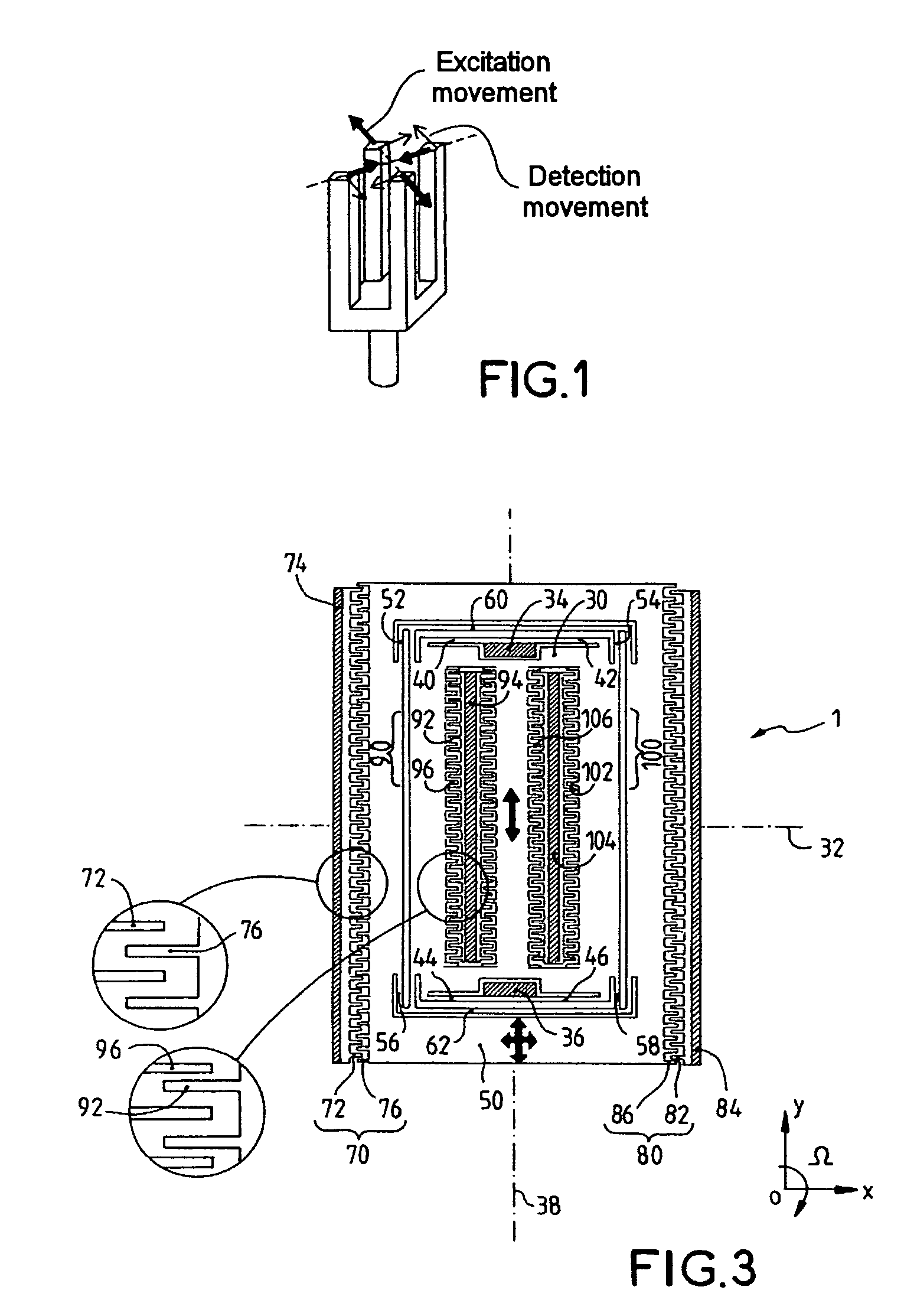
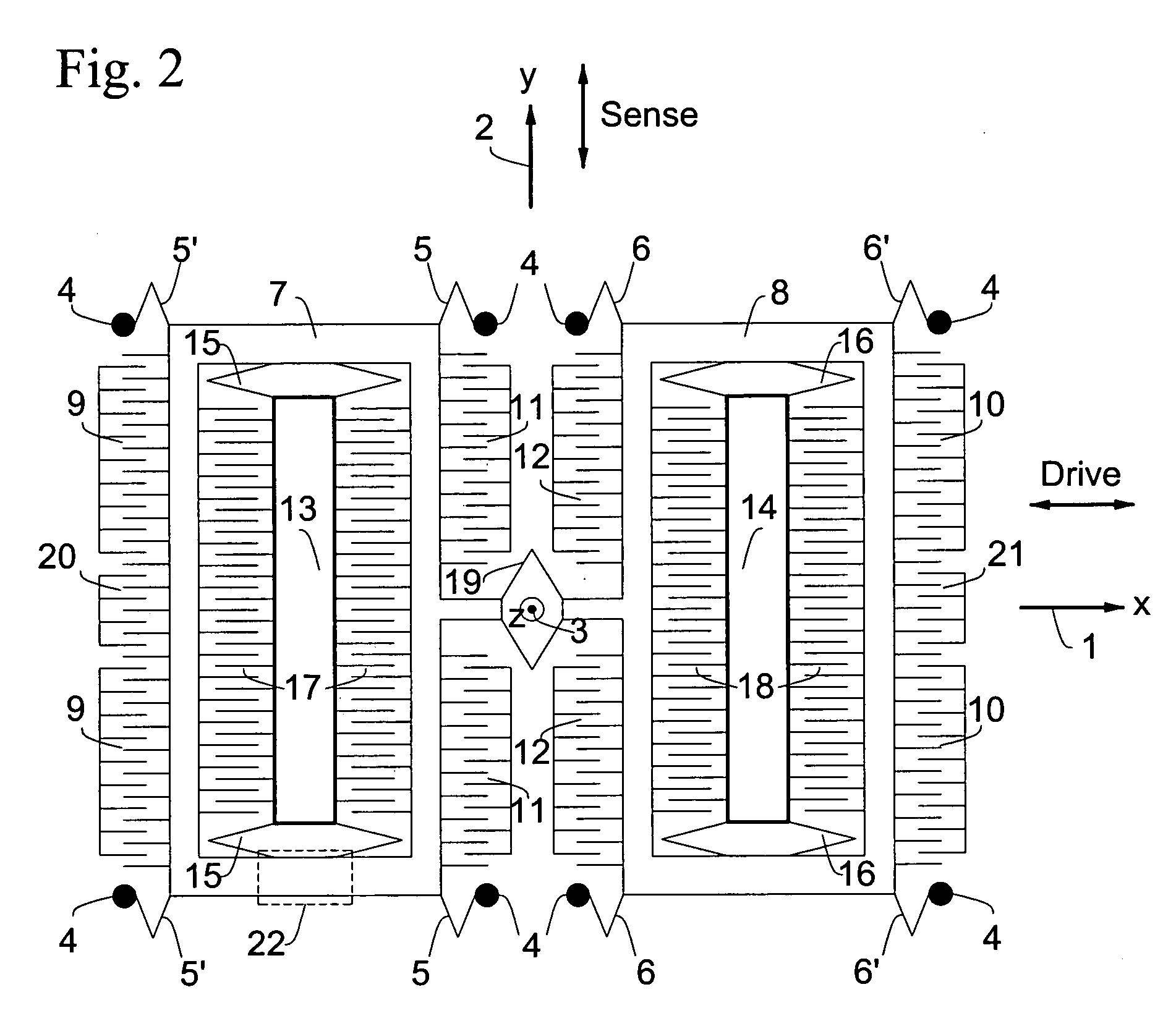
High-resolution in-plane tuning fork gyroscope and methods of fabrication
ActiveUS7043985B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesWave amplification devicesTuning forkSolid mass
A microstructure comprising an in-plane solid-mass electrically conductive tuning fork gyroscope and fabrication methods. The gyroscope is formed using substrate material having lower and upper layers sandwiching a sacrificial insulating layer. An exemplary gyroscope comprises a low-resistivity single-crystal silicon substrate having a lower support layer and an upper flexible support layer. Two opposed proof masses that are separated from the lower support layer lie in and are supported by the upper flexible support layer. Two drive electrodes are disposed adjacent to the proof masses and are insulatably supported by the lower support layer and are separated from the upper flexible support layer. Sense, balance and tuning electrodes are disposed adjacent to the proof masses and are insulatably supported by the lower support layer and are separated from the upper flexible support layer. The operational mode shapes are in-plane with the substrate surface and only measures angular motion that are orthogonal to the plane of the substrate. The microstructure flexural design enables the sense and the drive resonant frequencies to occur in close proximity of one another. This enables matched-mode operation of the device thereby ensuring maximum sensitivity.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Micromachined double tuning-fork gyrometer with detection in the plane of the machined wafer
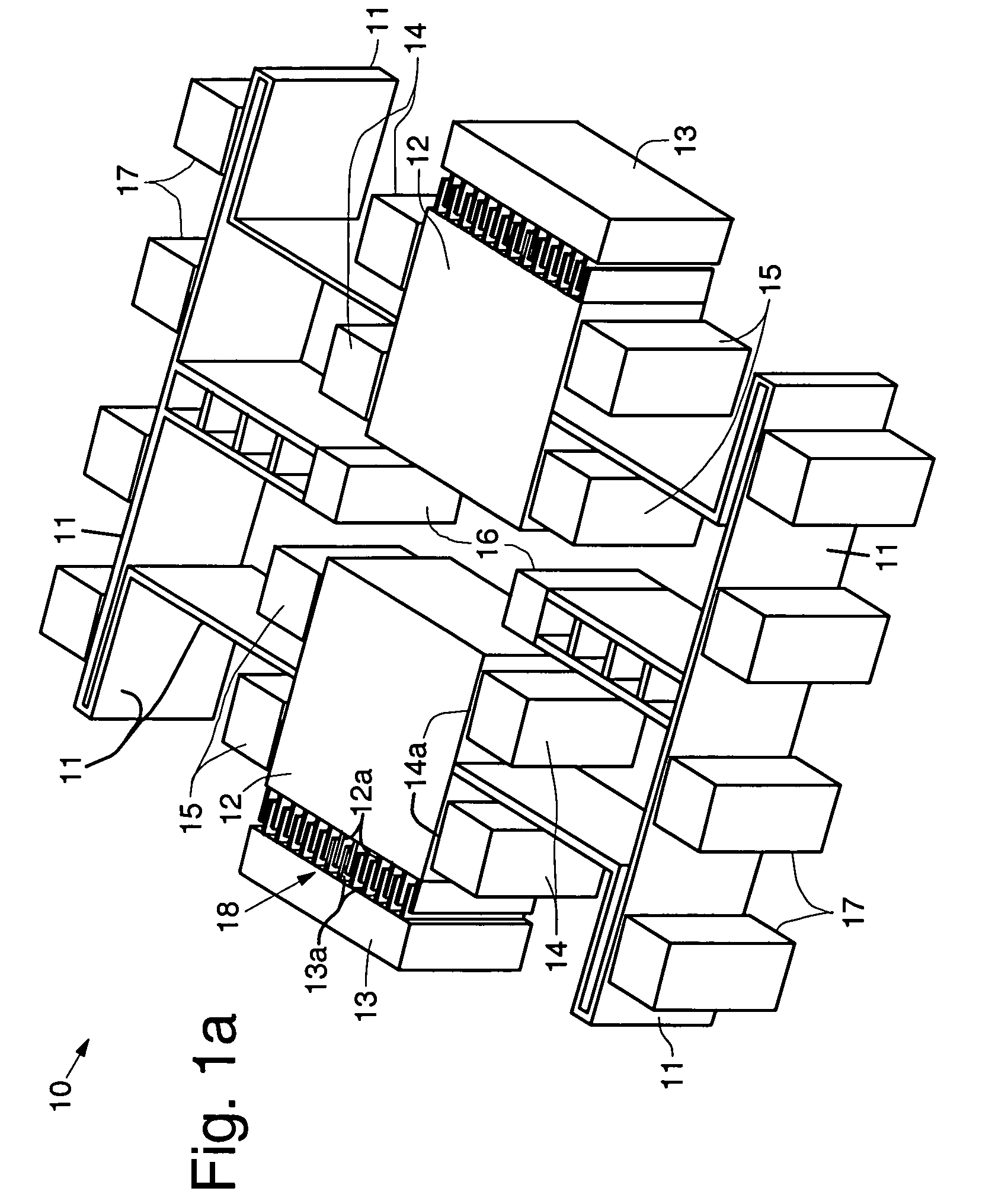
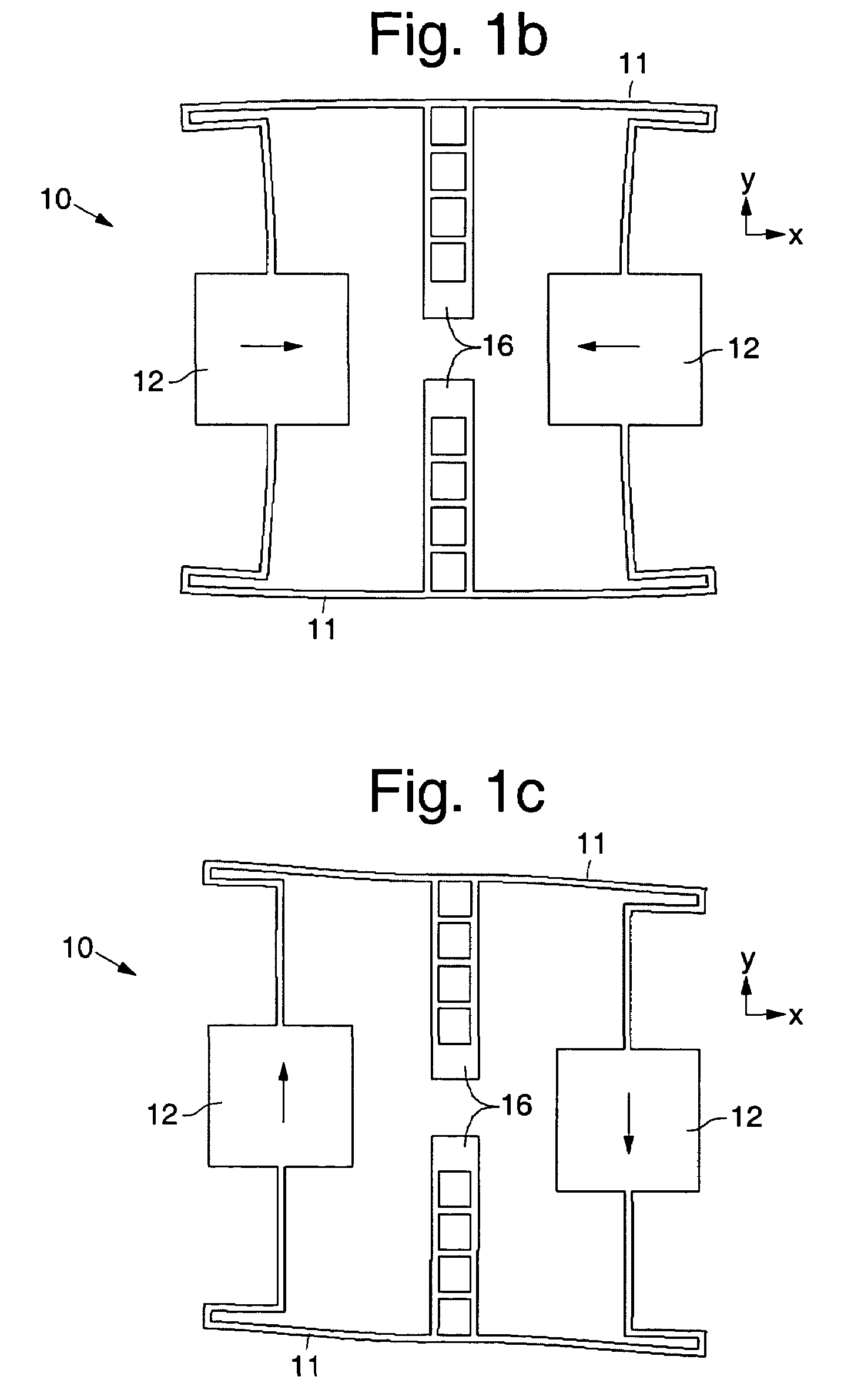
ActiveUS7284429B2Increase resistanceLow stiffnessAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkGyroscope
The invention relates to a gyrometer based on a vibrating structure, produced by micromachining in a thin planar wafer. It comprises four moving assemblies placed at the vertices of a virtual rectangle, each moving assembly being coupled to two moving assemblies located at neighboring vertices via a coupling structure and comprising an inertial first moving element connected to the coupling structure and intended to vibrate in two orthogonal directions in the plane of the wafer, namely an excitation direction and a detection direction, and a second moving element intended to vibrate in the detection direction and connected, on one side, to the first moving element and, on the other side, to anchoring zones via linking means.
Owner:THALES SA
Combined sensor and its fabrication method
InactiveUS20070062282A1Desired optimum vibration characteristicDetection sensitivity can be easilyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkAcoustics
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Z-axis angular rate sensor
ActiveUS20050072231A1Error is negligibleEnhanced signalAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkAngular rate sensor
An oscillatory rate sensor is described for sensing rotation about the “z-axis”. It is tuning-fork in nature with structural linkages and dynamics such that fundamental anti-phase oscillation of two proof masses is accomplished by virtue of the mechanical linkages.
Owner:KIONIX CORP
Z-axis angular rate micro electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) sensor
InactiveUS20050066728A1Avoid using forceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTurn-sensitive devicesTuning forkMems sensors
An oscillatory angular rate MEMS sensor is described for sensing rotation about the “Z-axis”. Embodiments are either coupled-mass tuning-fork or single oscillating-mass in nature. The sensor includes mechanical and electrical function integration, and is preferably manufactured by a unique MEMS fabrication process.
Owner:KIONIX CORP
Flow detectors having mechanical oscillators, and use thereof in flow characterization systems
ActiveUS20030000291A1Ability to useNormalize signalAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComponent separationTuning forkEngineering
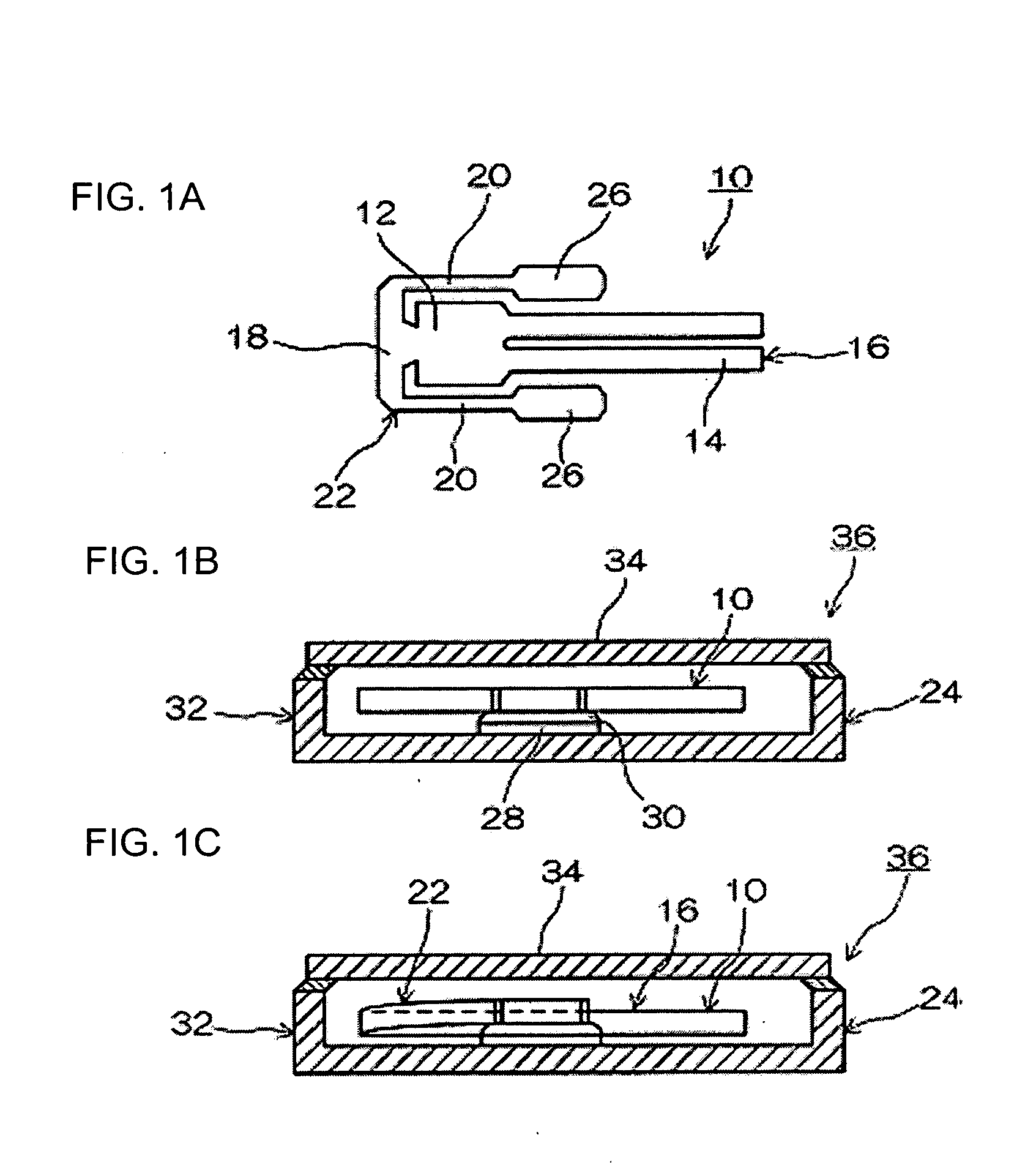
An improved system, device and method for characterizing a fluid sample that includes injecting a fluid sample into a mobile phase of a flow characterization system, and detecting a property of the fluid sample or of a component thereof with a flow detector comprising a mechanical resonator, preferably one that is operated at a frequency less than about 1 MHz, such as a tuning fork resonator.
Owner:MEAS FRANCE
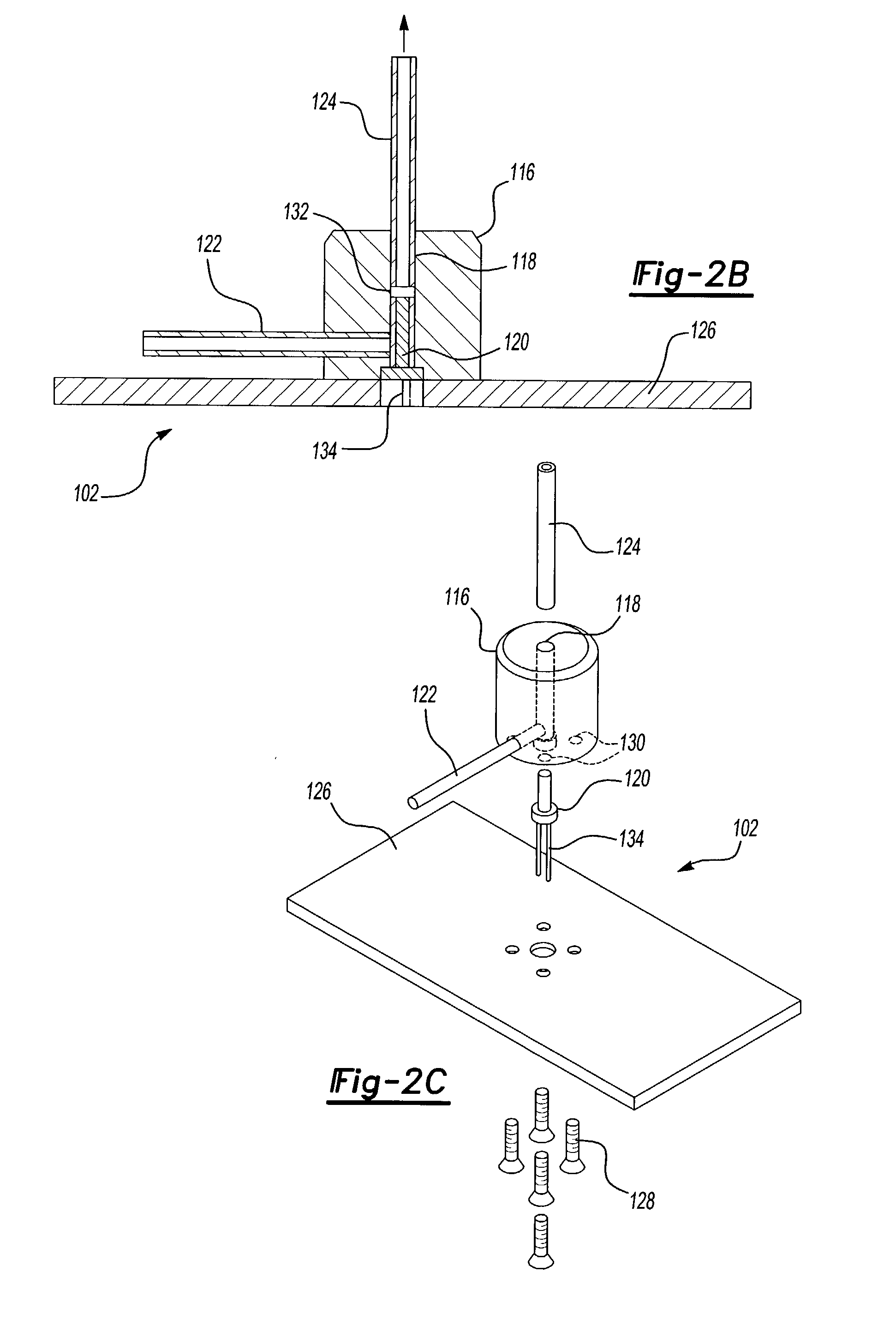
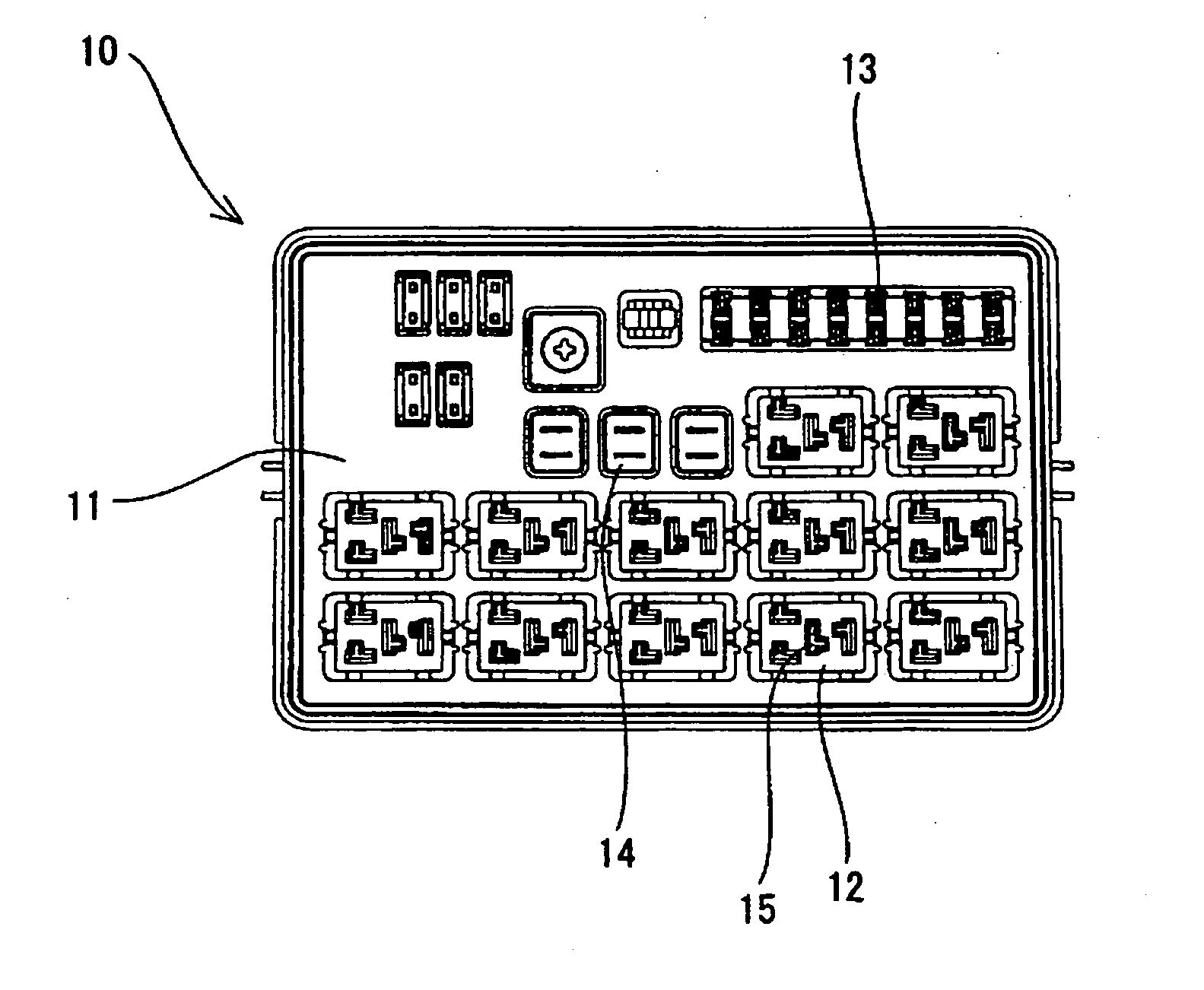
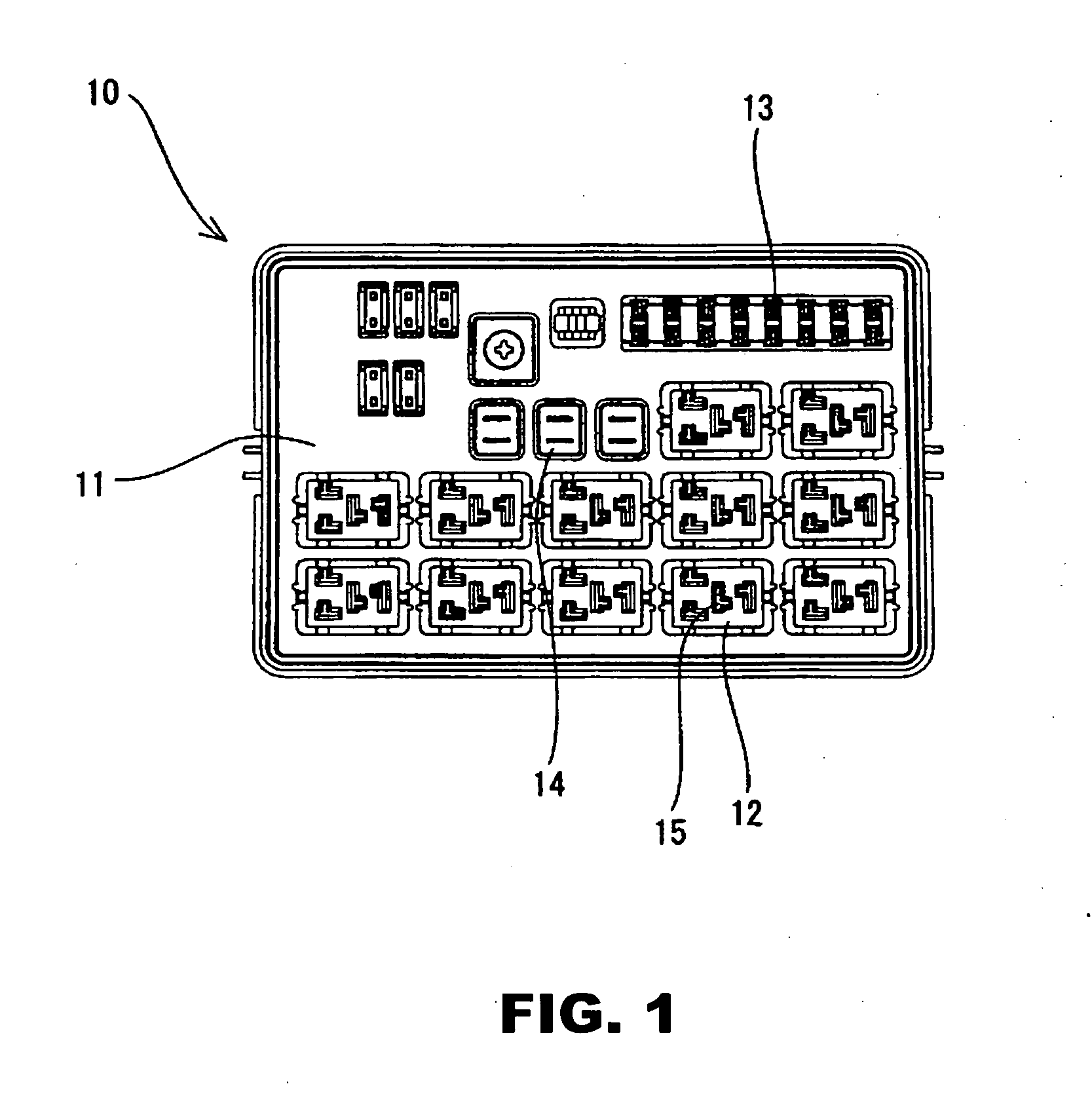
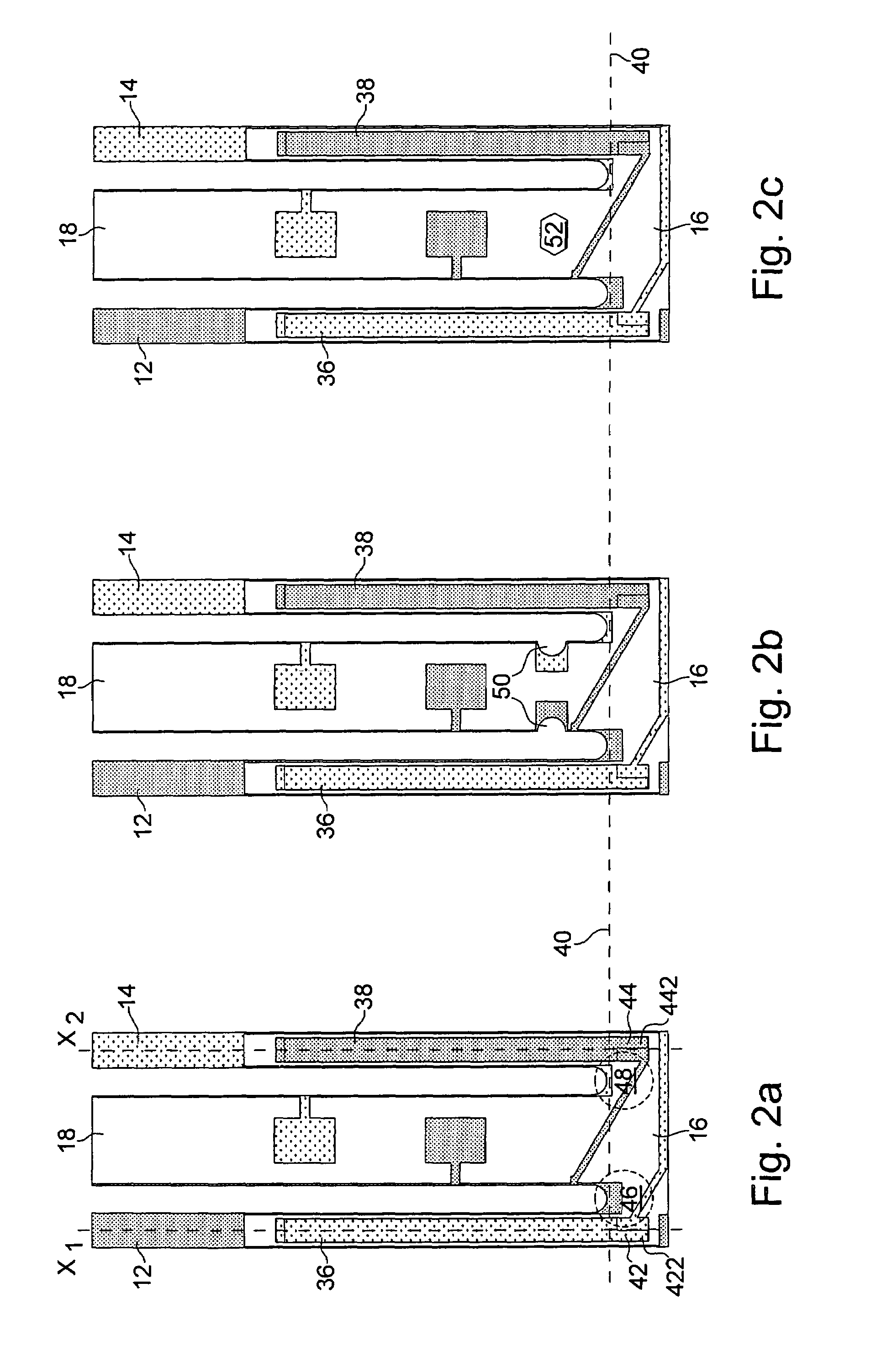
Electrical junction box having an inspection section of a slit width of a tuning fork-like terminal
InactiveUS20050032401A1Eliminate misjudgmentImprove electrical connection reliabilityLine/current collector detailsVehicle connectorsElectrical junctionTuning fork
A tuning fork-like terminal is accommodated in a terminal-containing section. The tuning fork-like terminal is provided on the central end with a slit adapted to receive a tab being connected. Clamping portions are projected from the opposed surfaces of the slit to pinch the tab between the clamping portions. A slit gage is inserted into a rectangular terminal hole formed in an end of the terminal-containing section to inspect a slit width between the clamping portions of the tuning fork-like terminal. A wide hole portion is formed in the rectangular terminal hole at the insertion position of the slit gage. The wide hole portion is formed by widening a length of a short side of the rectangular terminal hole. The central position of the slit in the tuning fork-like terminal and the central position of the slit gage coincide with each other, even if the tuning fork-like terminal is maximally shifted from the central position in the terminal-containing section, whereby the slit width can be precisely inspected to precisely inspect a slit width in a tuning fork-like terminal accommodated in a terminal-containing section of an electrical junction box.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Tuning-fork type piezo-oscillator piece and mounting method thereof
ActiveUS20050062368A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksTuning forkMechanical engineering
Aspects of the invention can provide a tuning-fork type piezo-oscillator piece, whose package, in which the tuning-fork type piezo-oscillator piece is mounted, is protected from colliding with oscillating arms even though a physical shock is given onto the tuning-fork type piezo-oscillator piece, and a mounting method thereof. The tuning-fork type piezo-oscillator piece can include a tuning-fork type piezo-oscillator piece main body equipped with a plurality of oscillating arms, a short side part formed along a direction perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the tuning-fork type piezo-oscillator piece main body and connected to the tuning-fork type piezo-oscillator piece main body, and a long side part formed along the longitudinal direction of the tuning-fork type piezo-oscillator piece main body, while starting from the short side part, and equipped with a shock-absorbing part.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Tuning fork vibratory MEMS gyroscope
ActiveUS7191653B2Guaranteed uptimeImprove efficiencyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkGyroscope
A tuning fork vibratory MEMS gyroscope for sensing angular velocity and angular acceleration generated due to the rotation of a movable body. The tuning fork vibratory MEMS gyroscope includes an external fixed support portion formed on a substrate; a plurality of external elastic members; first and second external frames respectively including driving combs; first and second driving electrodes respectively including comb drivers; first and second internal elastic members respectively including a plurality of spring members; first and second internal frames respectively including sensing combs; and first and second sensing electrodes respectively including comb sensors. The tuning fork vibratory MEMS gyroscope withstands a noise at a peripheral area, is driven at the external portions of internal frames, is sensed at the internal portions of the internal frames, and comprises the elastic members having a wine glass shape, thereby being more stably operated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
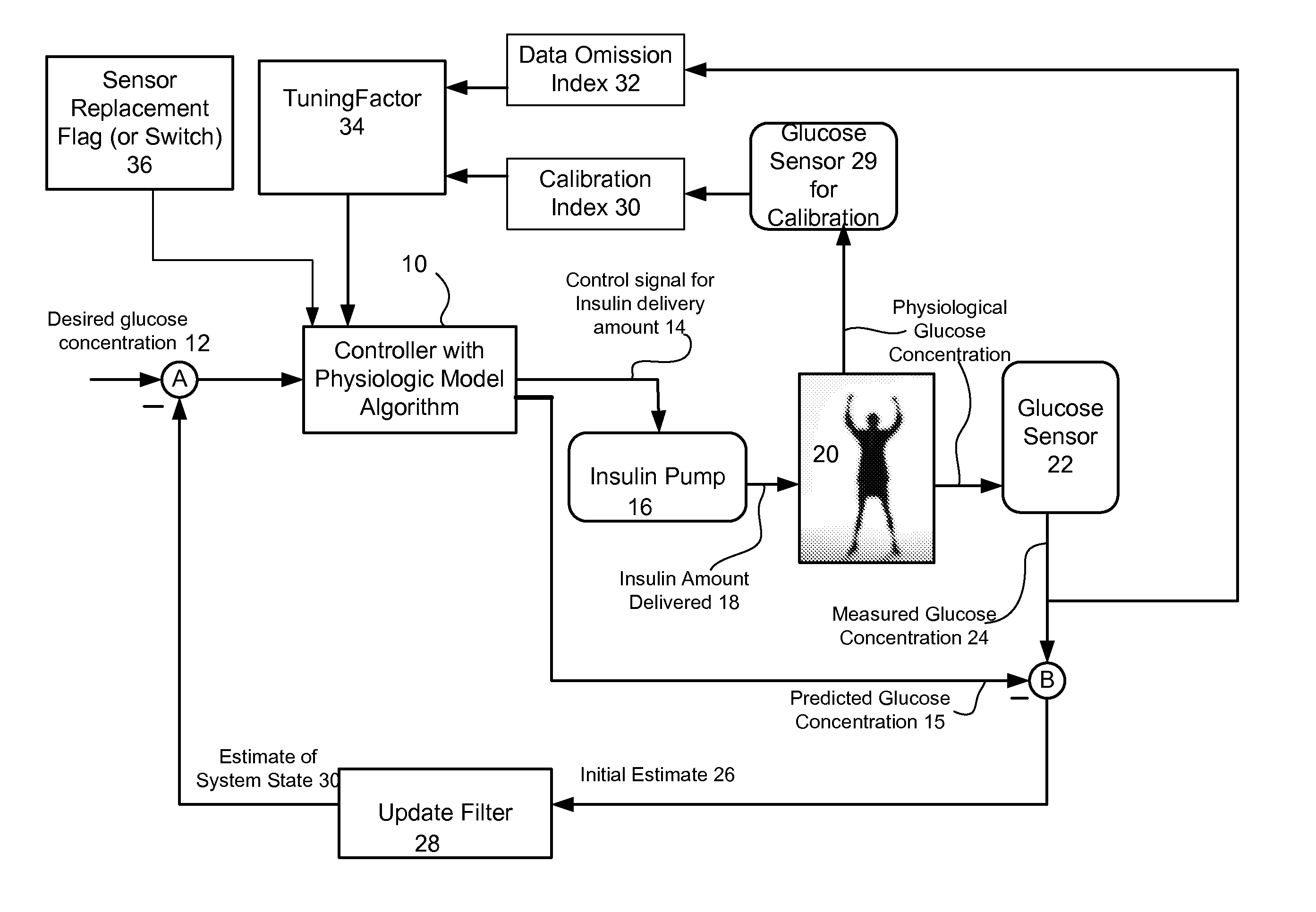
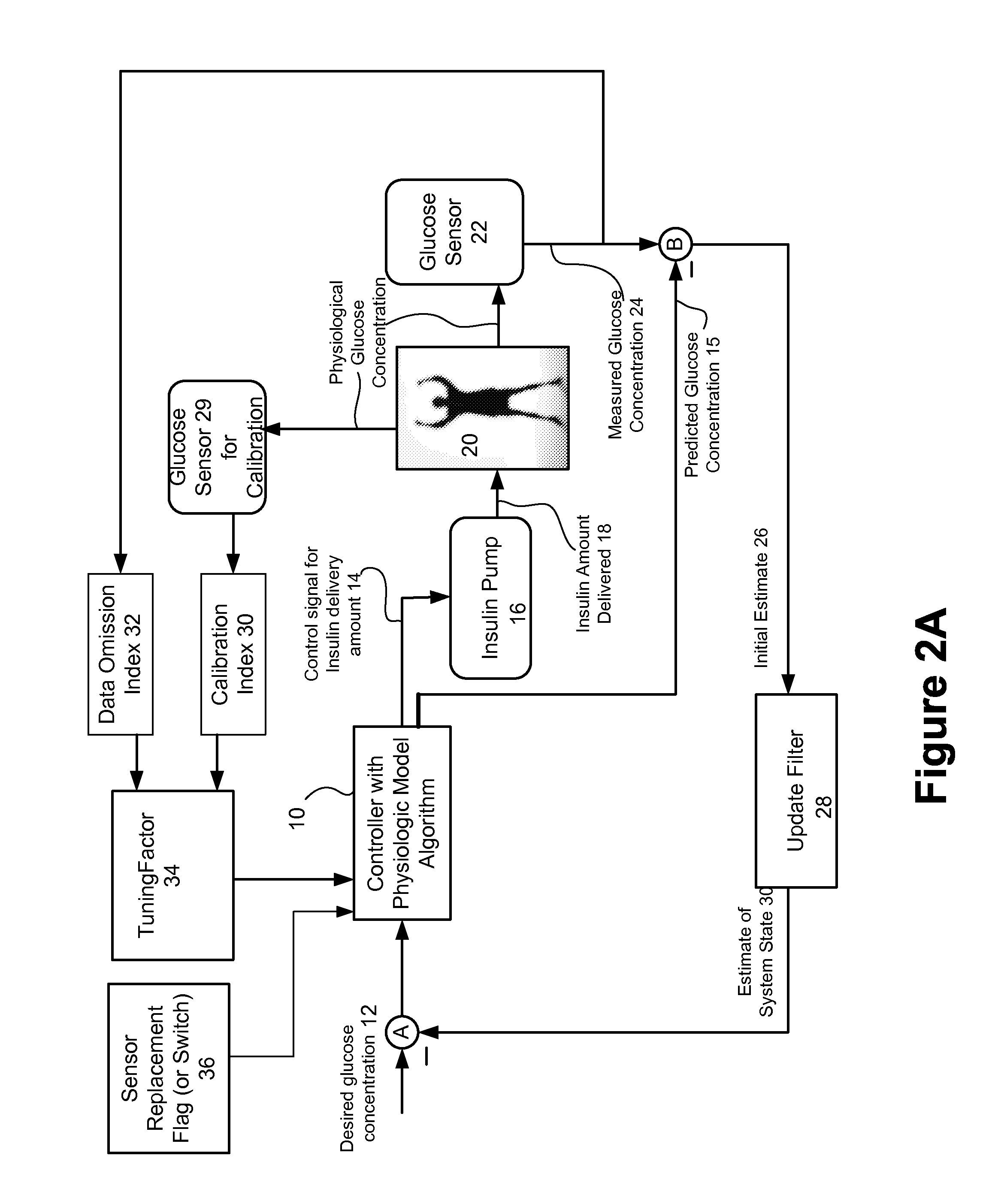
Method and system for controlling a tuning factor due to sensor replacement for closed-loop controller in an artificial pancreas
Described and illustrated is a system for management of diabetes that includes an infusion pump, glucose sensor and controller with a method programmed in the controller. The infusion pump is configured to deliver insulin. The glucose sensor senses glucose levels in the subject and provide output signals representative of the glucose levels in the subject. The controller is programmed receives signals from at least one of the glucose sensor and the pump and configured to issue signals to the pump to deliver an amount of insulin determined by a feedback controller that utilizes a model predictive control based on desired glucose levels, insulin amount delivered and measured glucose levels of the subject. The controller is also configured to deliver insulin using a tuning factor (R) for a model predictive controller in the microcontroller as a conservative setting otherwise the system maintains a current tuning factor (R) for the controller.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
X-Y axis dual-mass tuning fork gyroscope with vertically integrated electronics and wafer-scale hermetic packaging
InactiveUS7621183B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkWafering
An angular velocity sensor has two masses which are laterally disposed in an X-Y plane and indirectly connected to a frame. The two masses are linked together by a linkage such that they necessarily move in opposite directions along Z. Angular velocity of the sensor about the Y axis can be sensed by driving the two masses into Z-directed antiphase oscillation and measuring the angular oscillation amplitude thereby imparted to the frame. In a preferred embodiment, the angular velocity sensor is fabricated from a bulk MEMS gyroscope wafer, a cap wafer and a reference wafer. In a further preferred embodiment, this assembly of wafers provides a hermetic barrier between the masses and an ambient environment.
Owner:INVENSENSE
X-y axis dual-mass tuning fork gyroscope with vertically integrated electronics and wafer-scale hermetic packaging
ActiveUS20080115579A1High measurement accuracyGood Common Mode RejectionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkGyroscope
An angular velocity sensor has two masses which are laterally disposed in an X-Y plane and indirectly connected to a frame. The two masses are linked together by a linkage such that they necessarily move in opposite directions along Z. Angular velocity of the sensor about the Y axis can be sensed by driving the two masses into Z-directed antiphase oscillation and measuring the angular oscillation amplitude thereby imparted to the frame. In a preferred embodiment, the angular velocity sensor is fabricated from a bulk MEMS gyroscope wafer, a cap wafer and a reference wafer. In a further preferred embodiment, this assembly of wafers provides a hermetic barrier between the masses and an ambient environment.
Owner:INVENSENSE
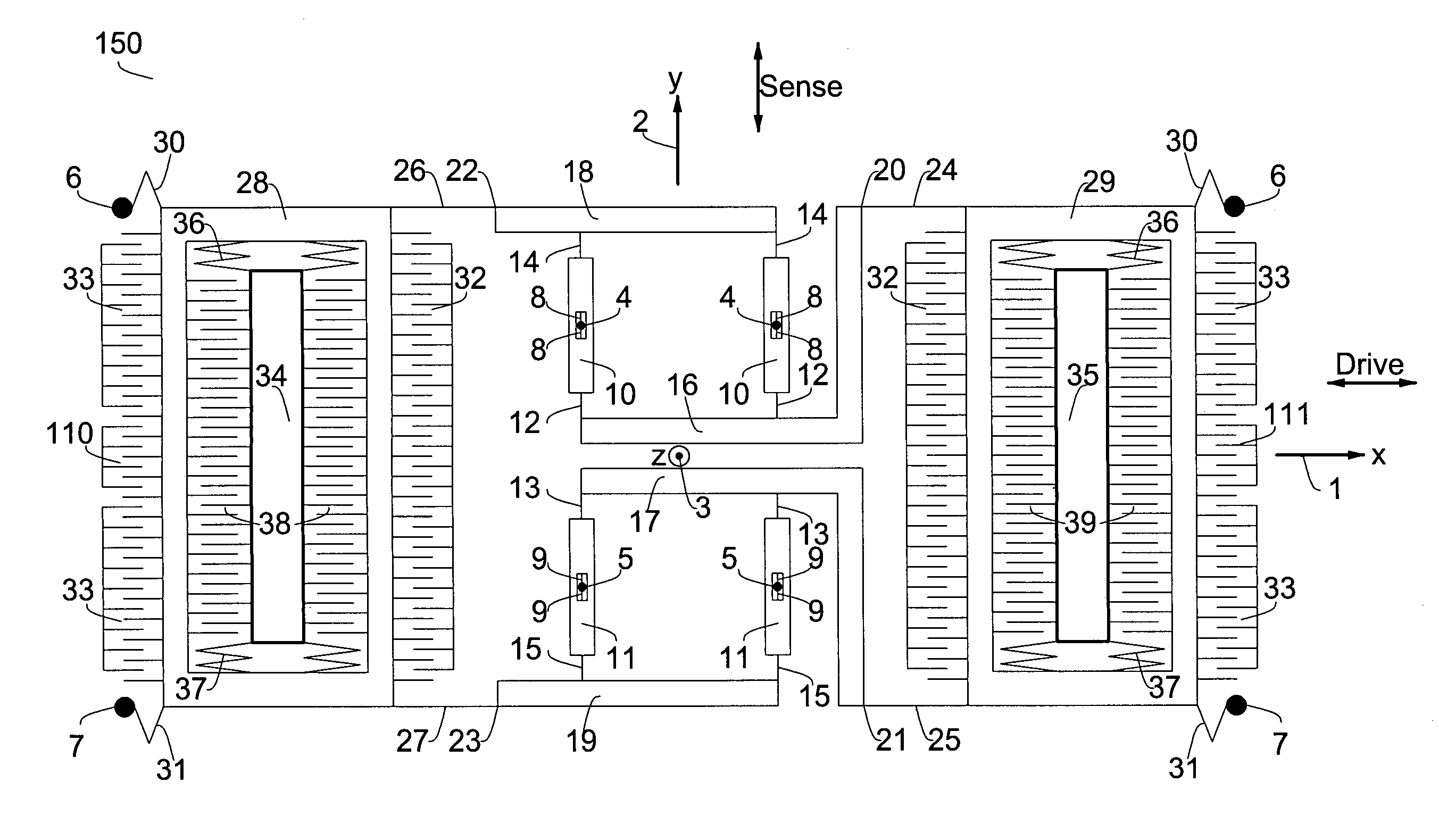
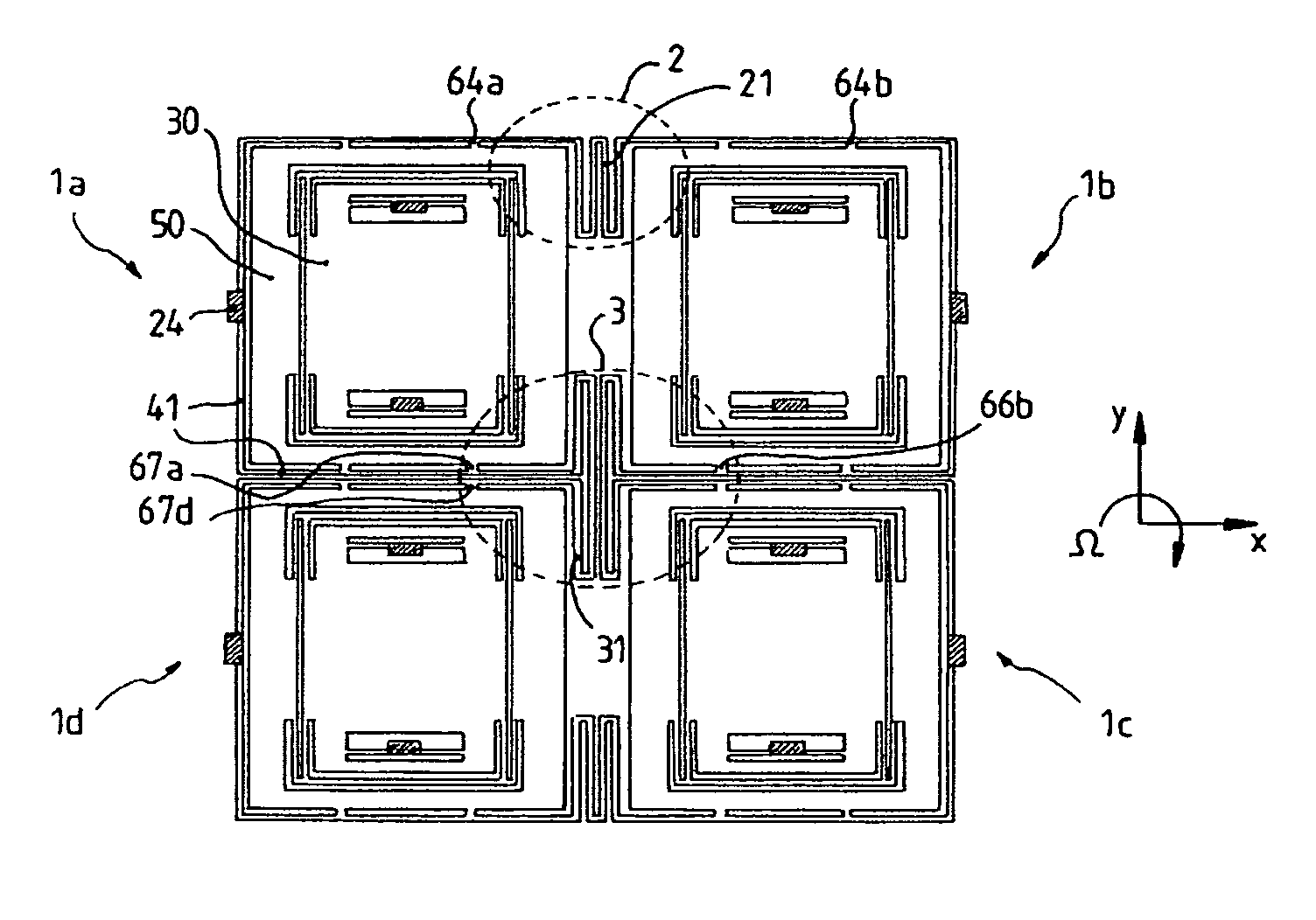
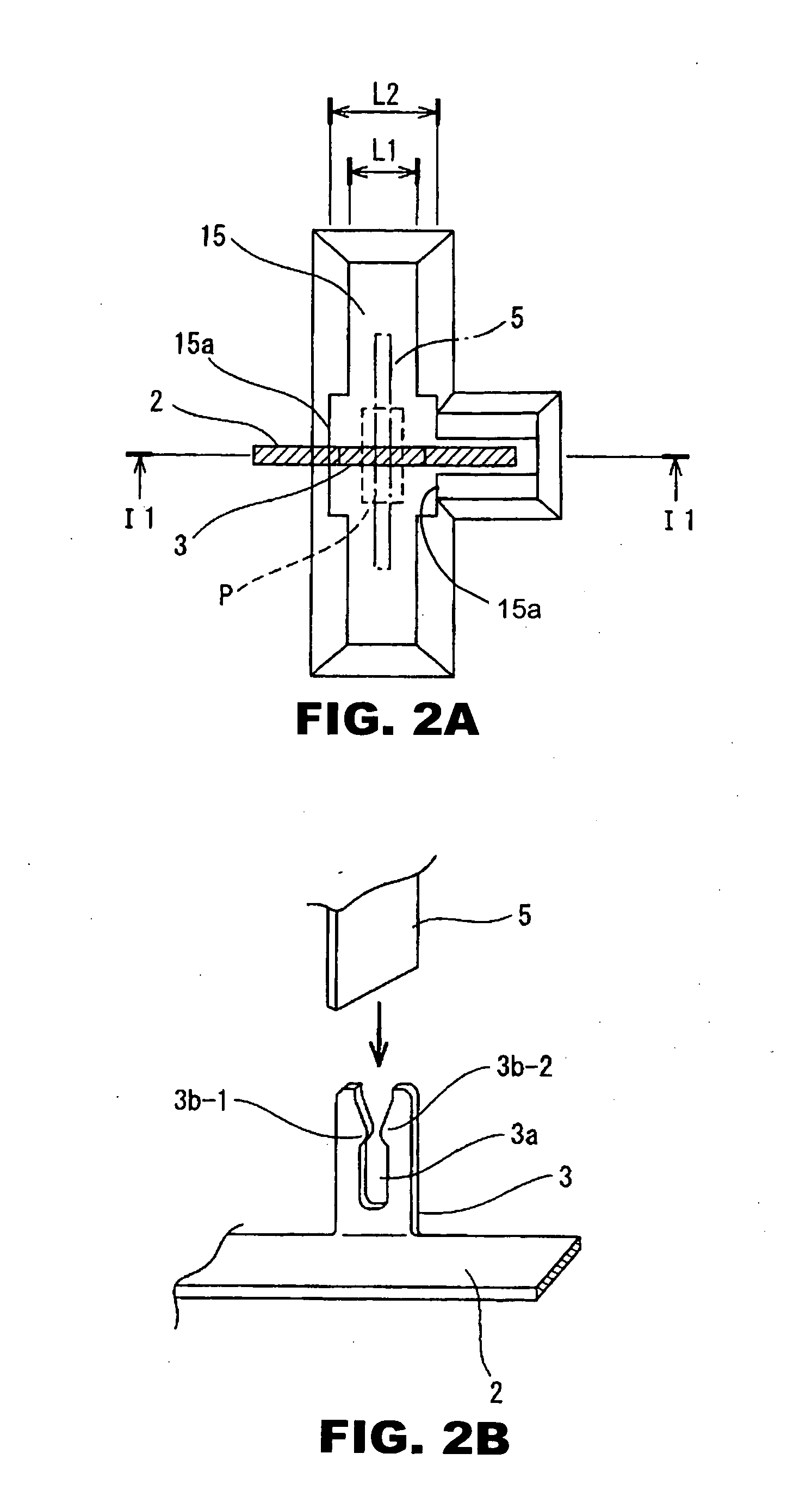
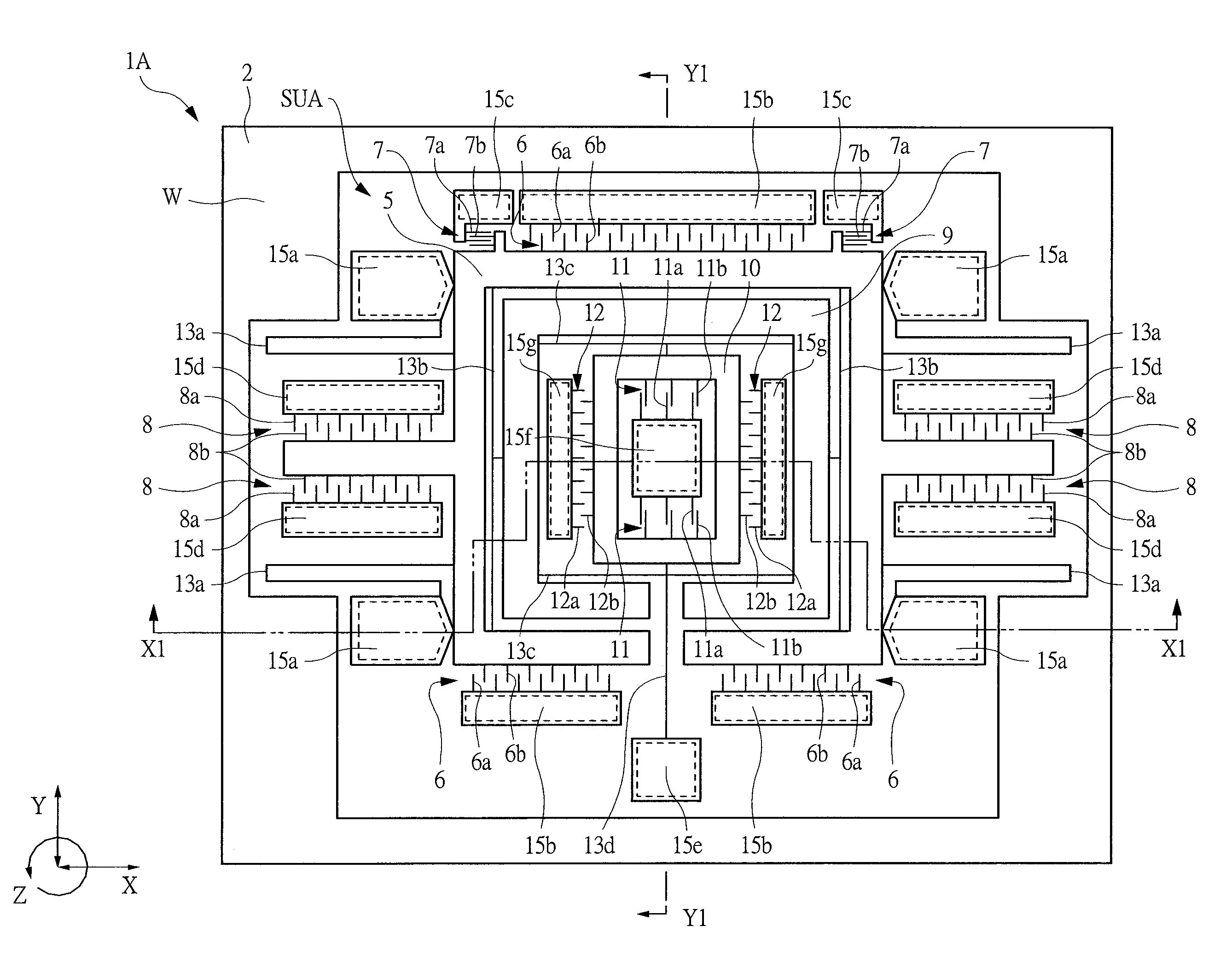
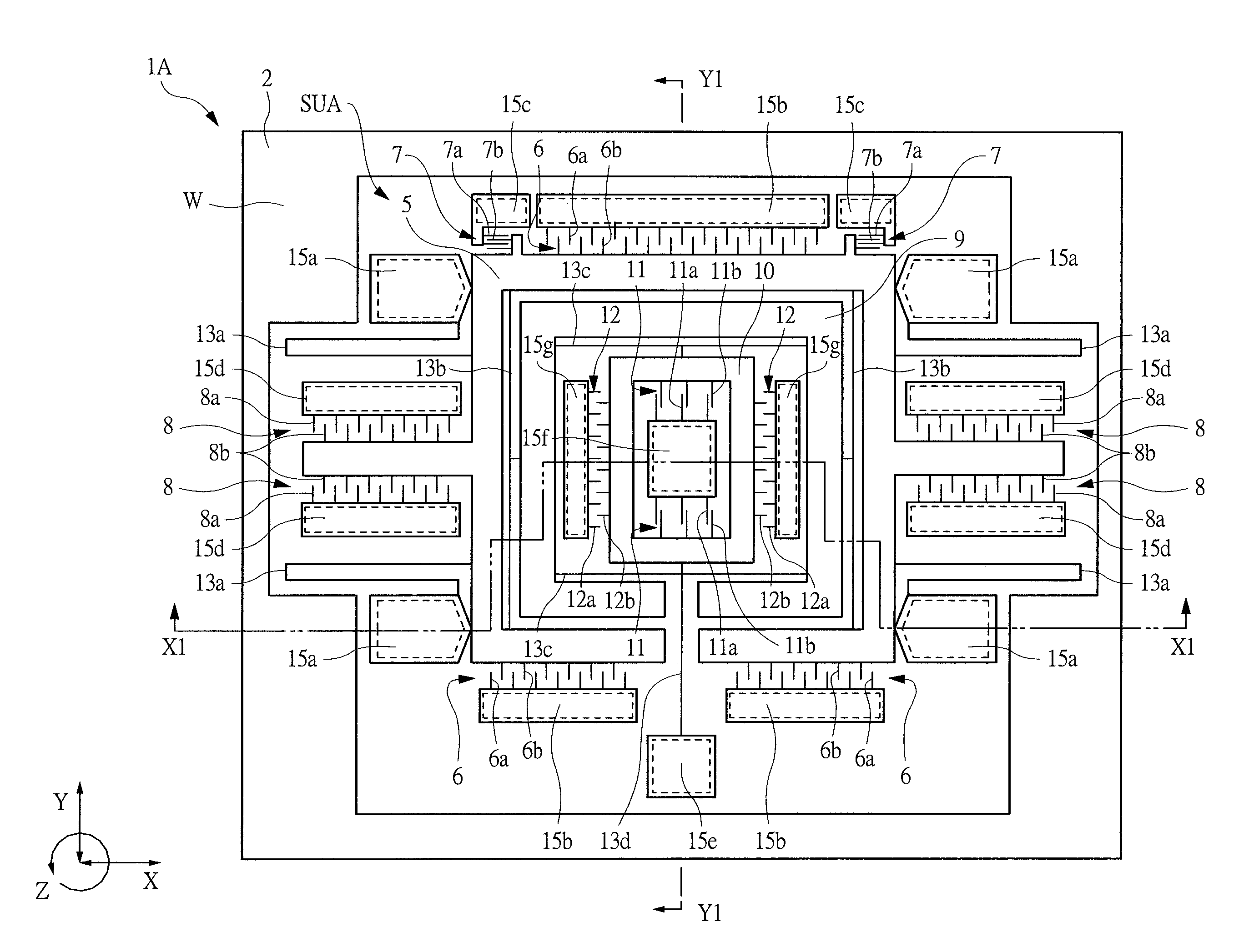
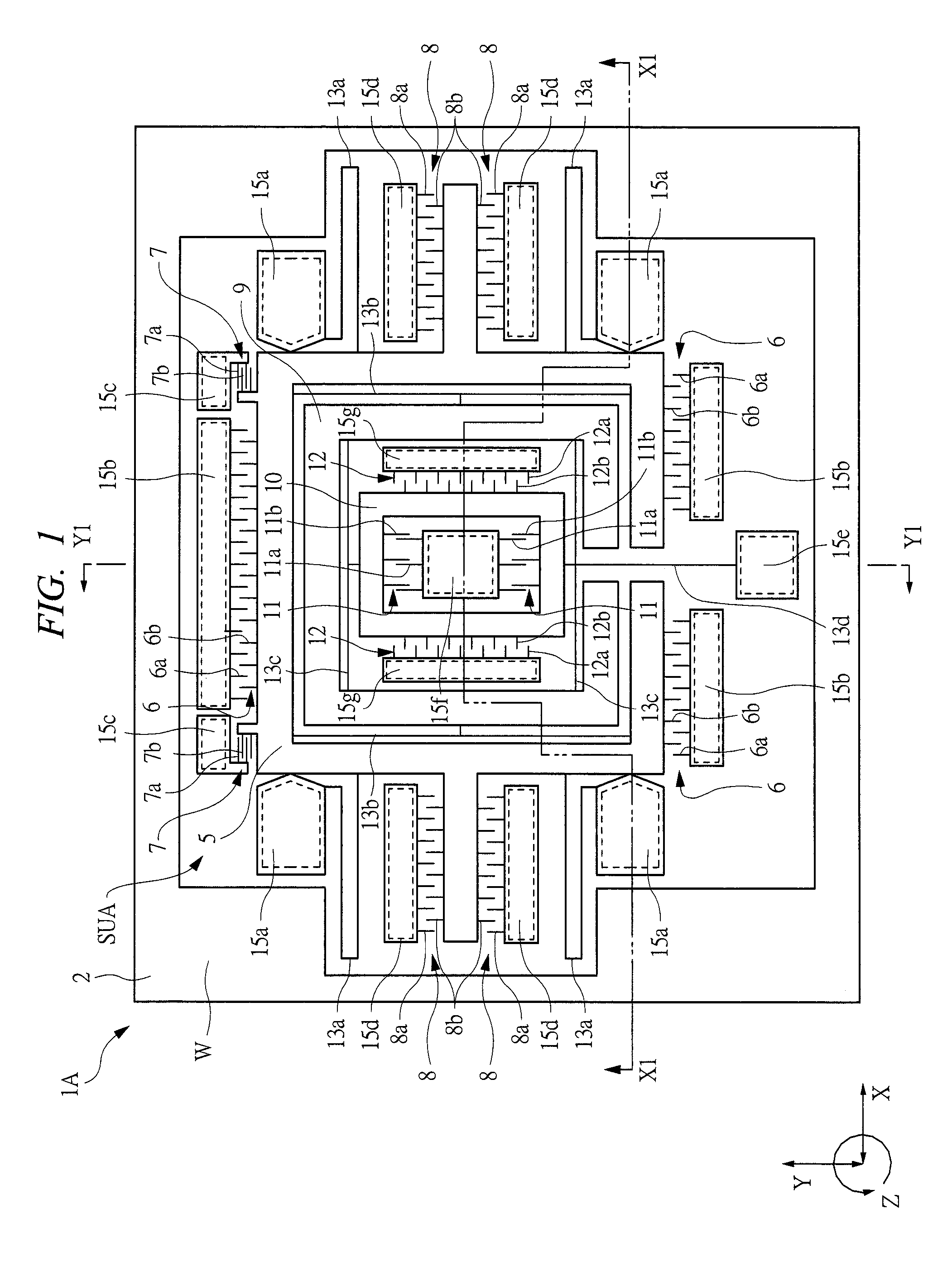
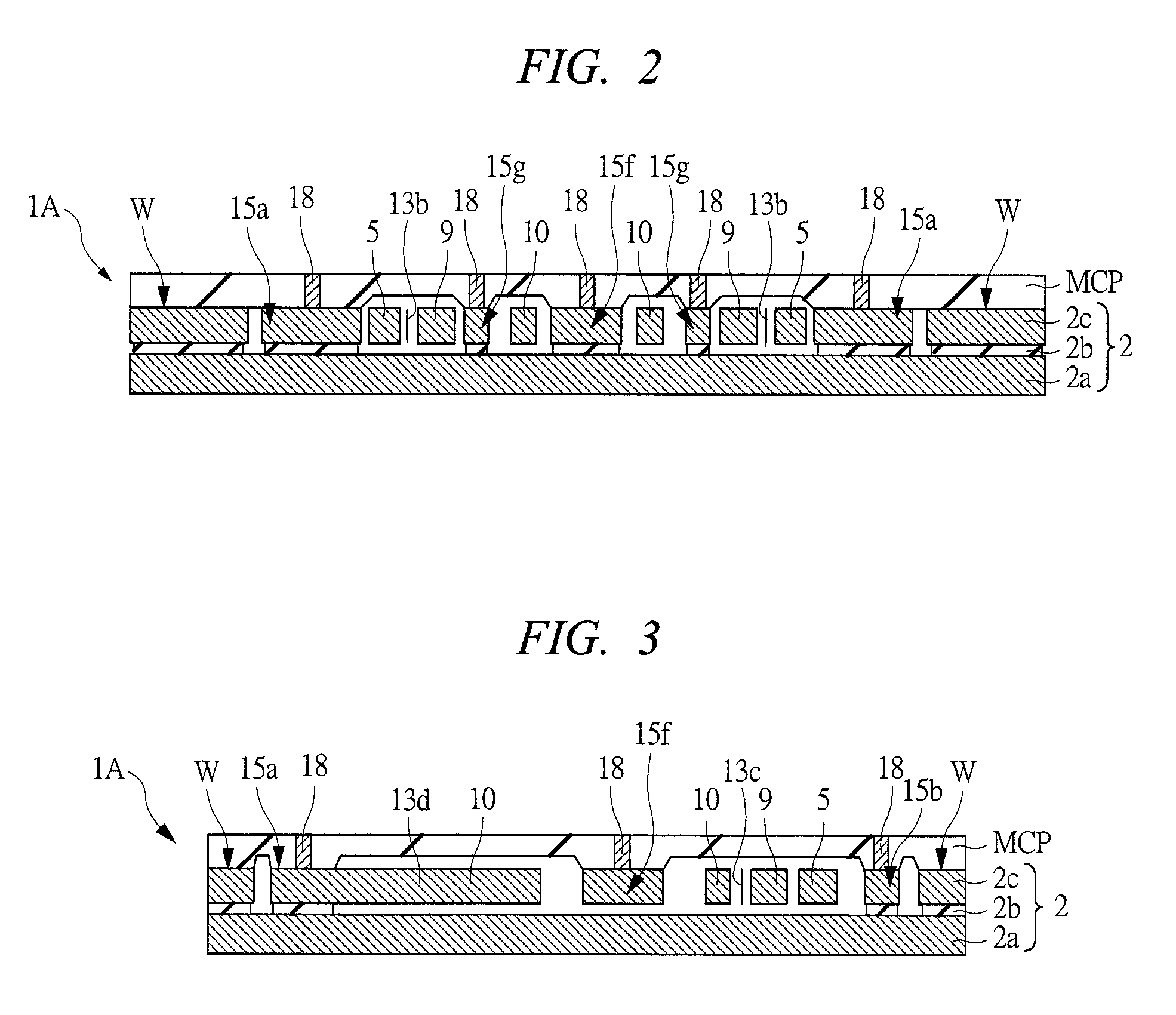
Inertial sensor
ActiveUS20070131030A1Reduce the amplitudeReduce vibrationAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkEngineering
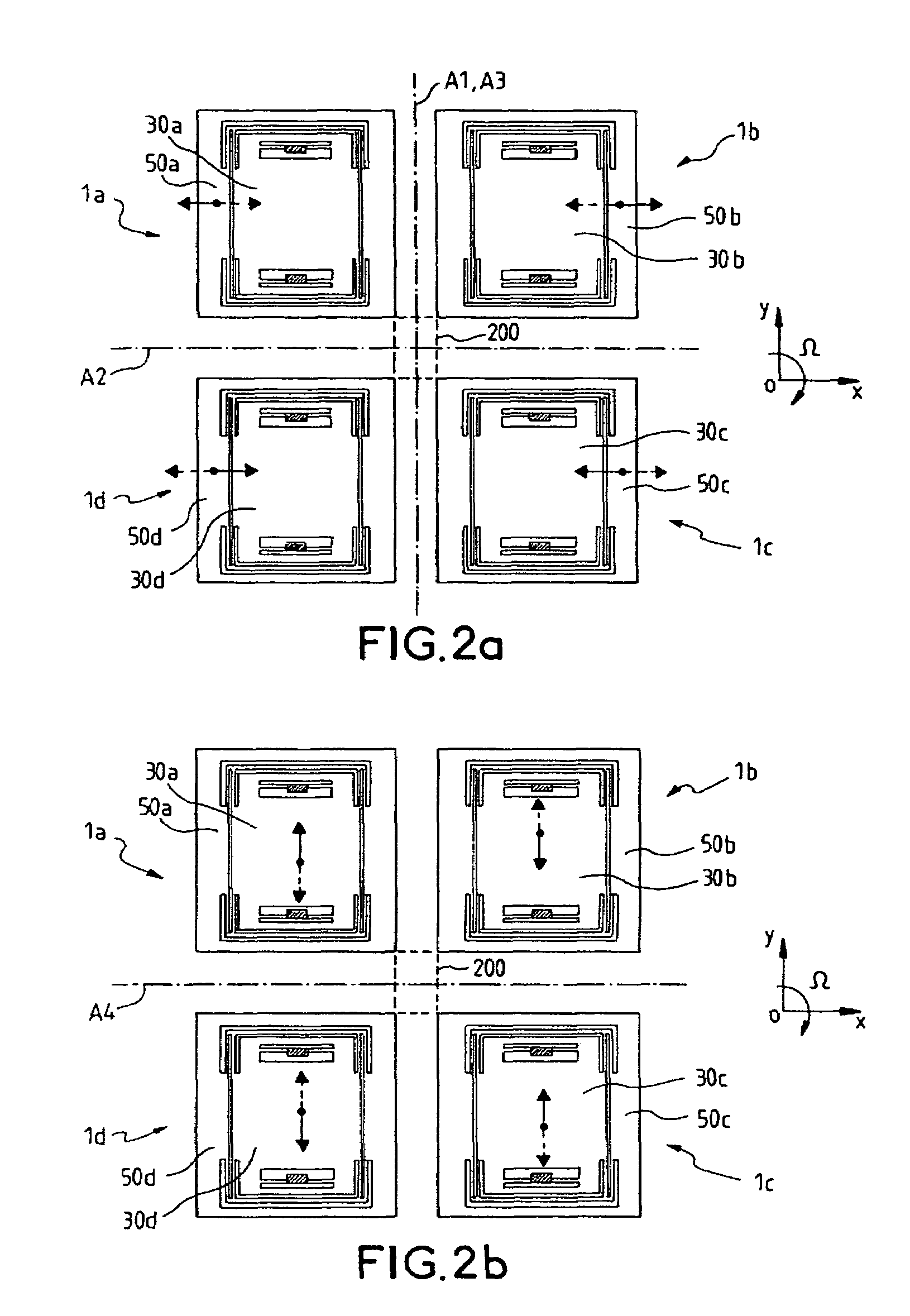
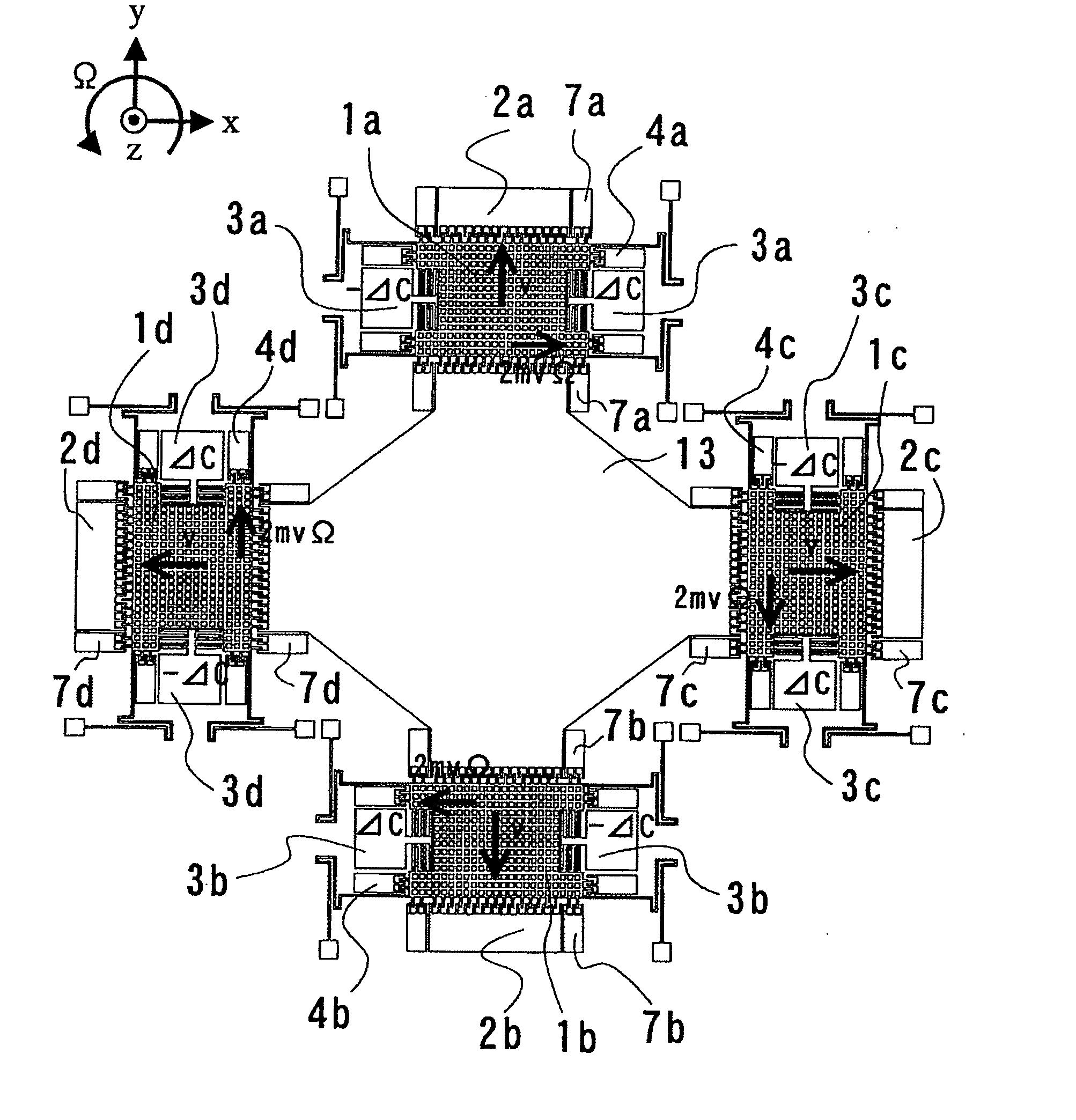
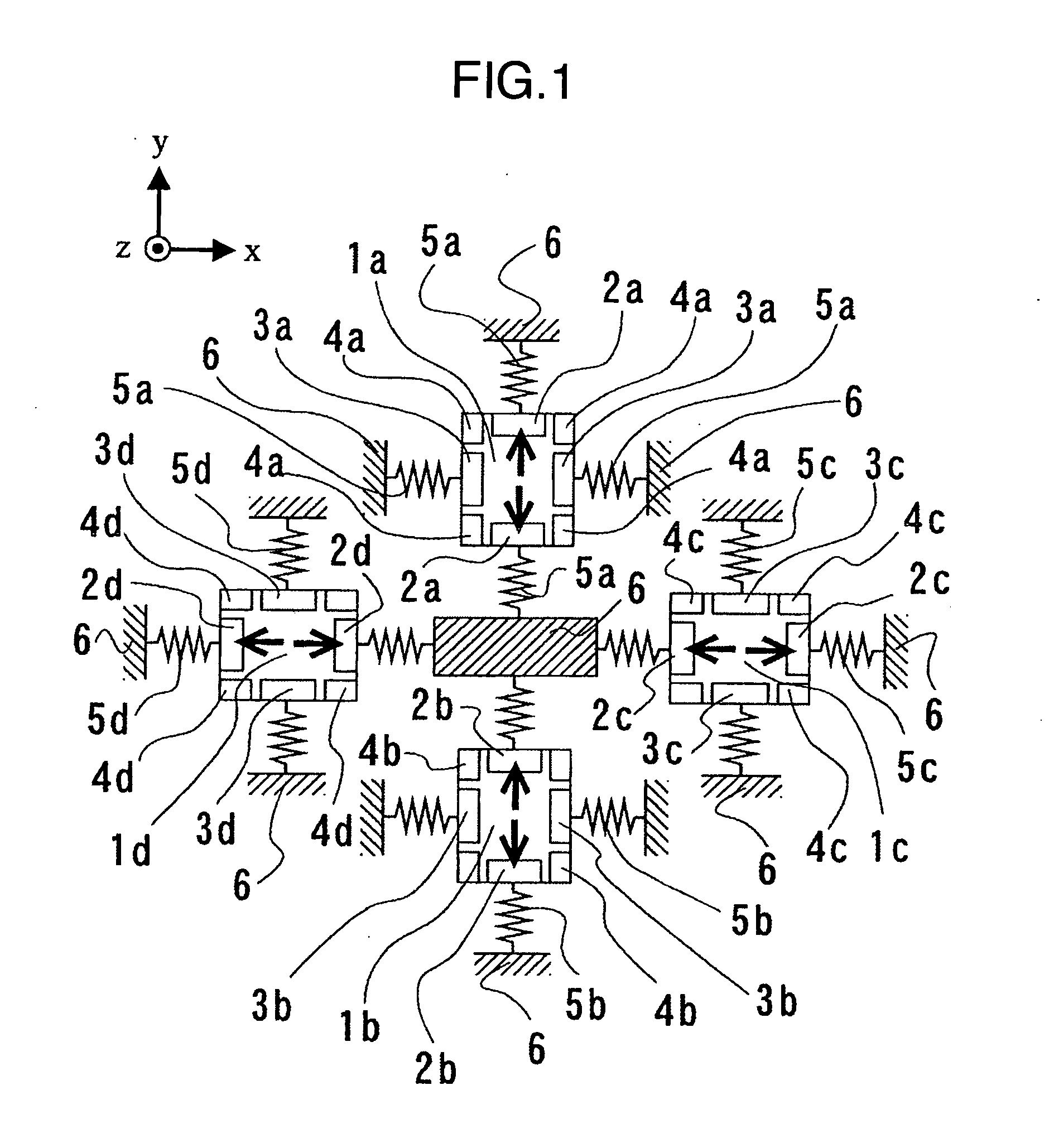
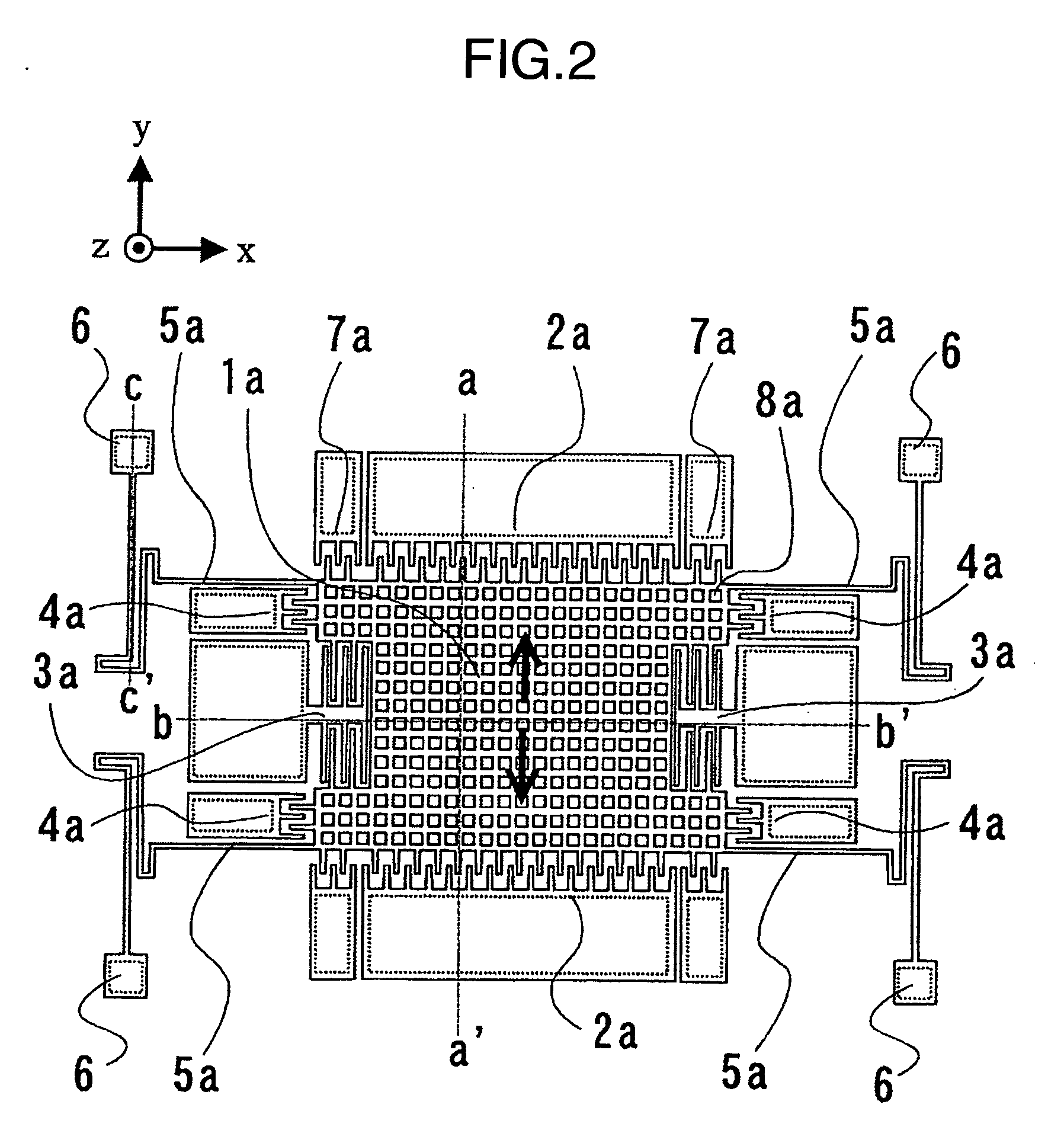
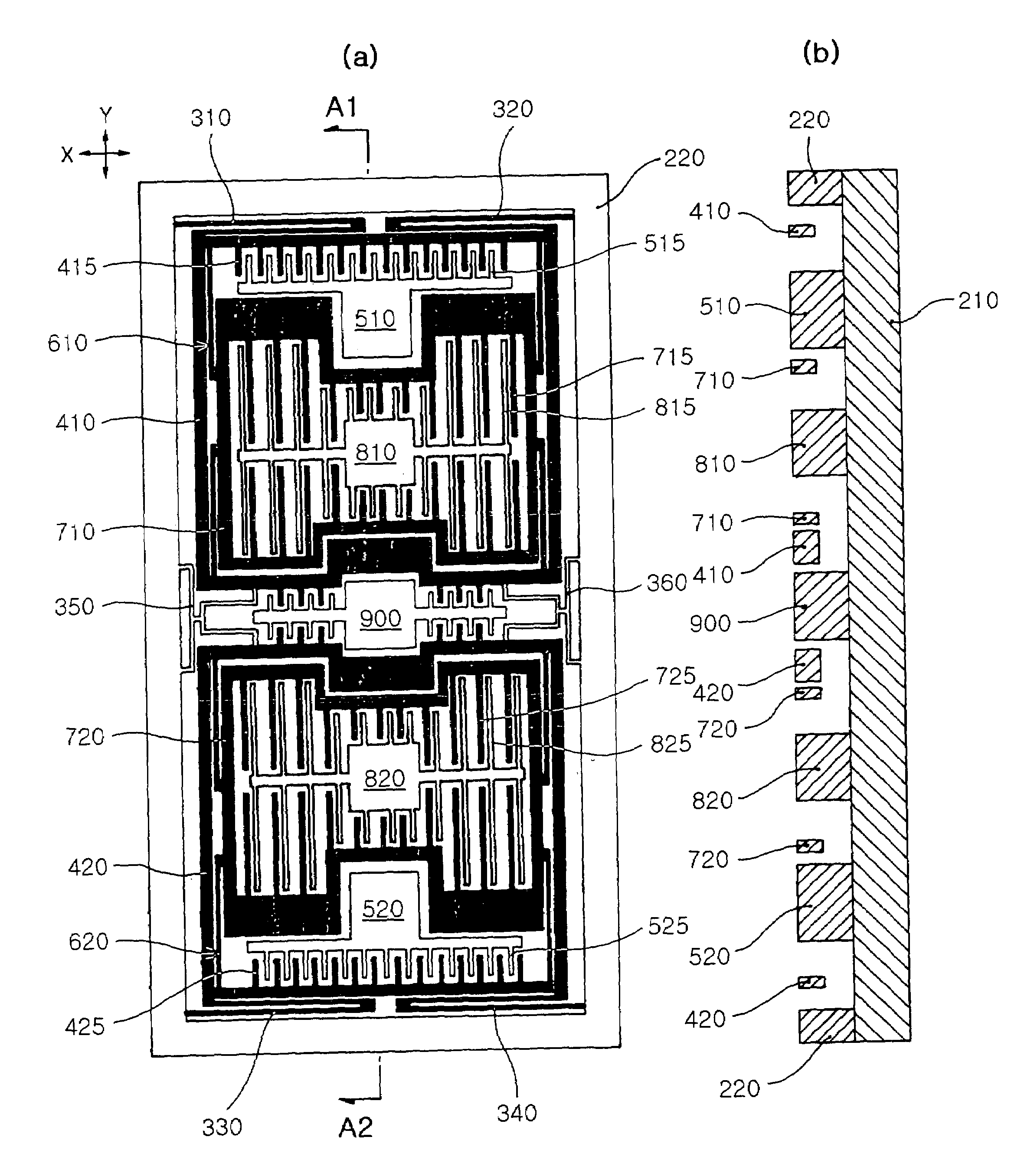
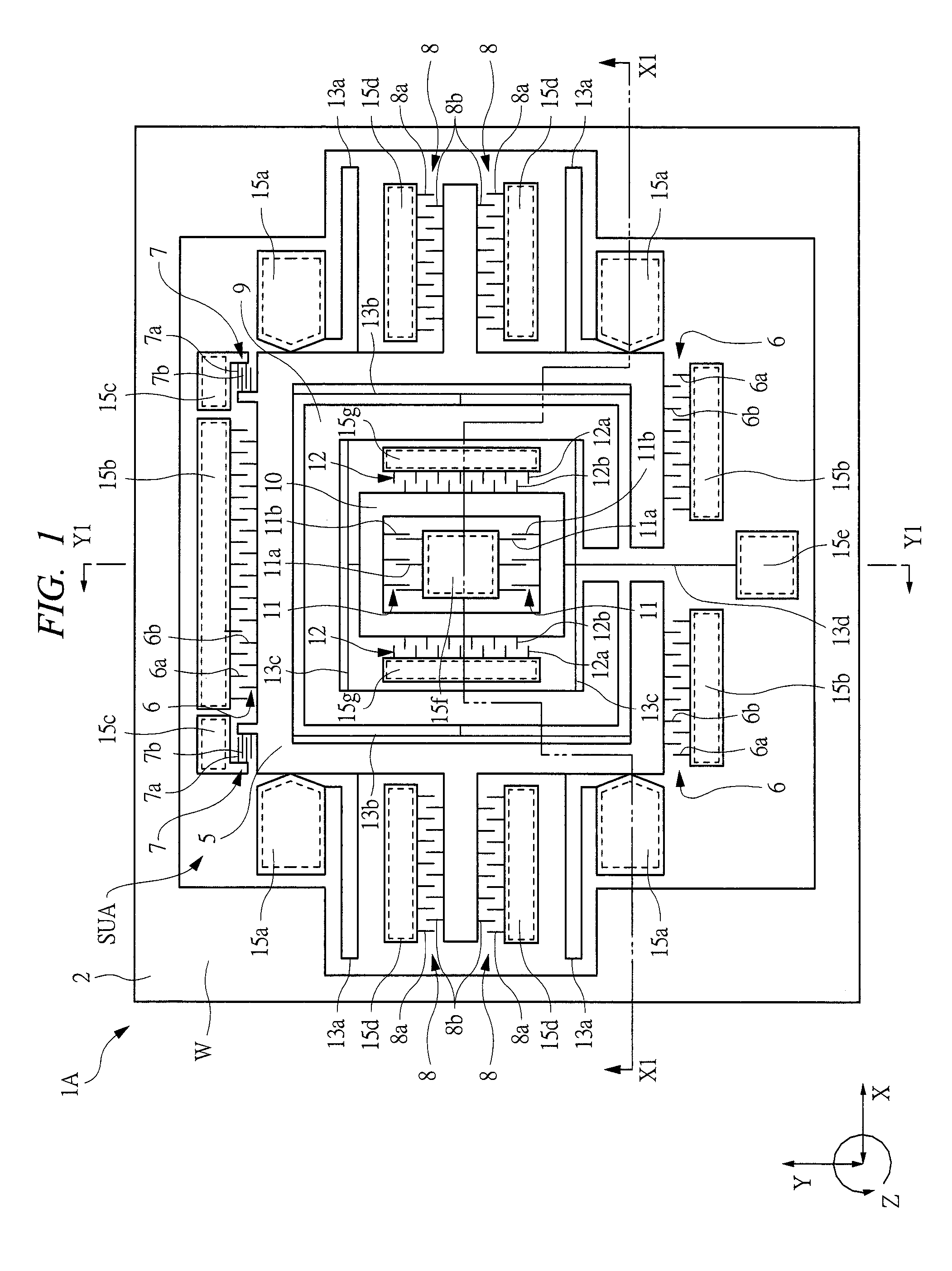
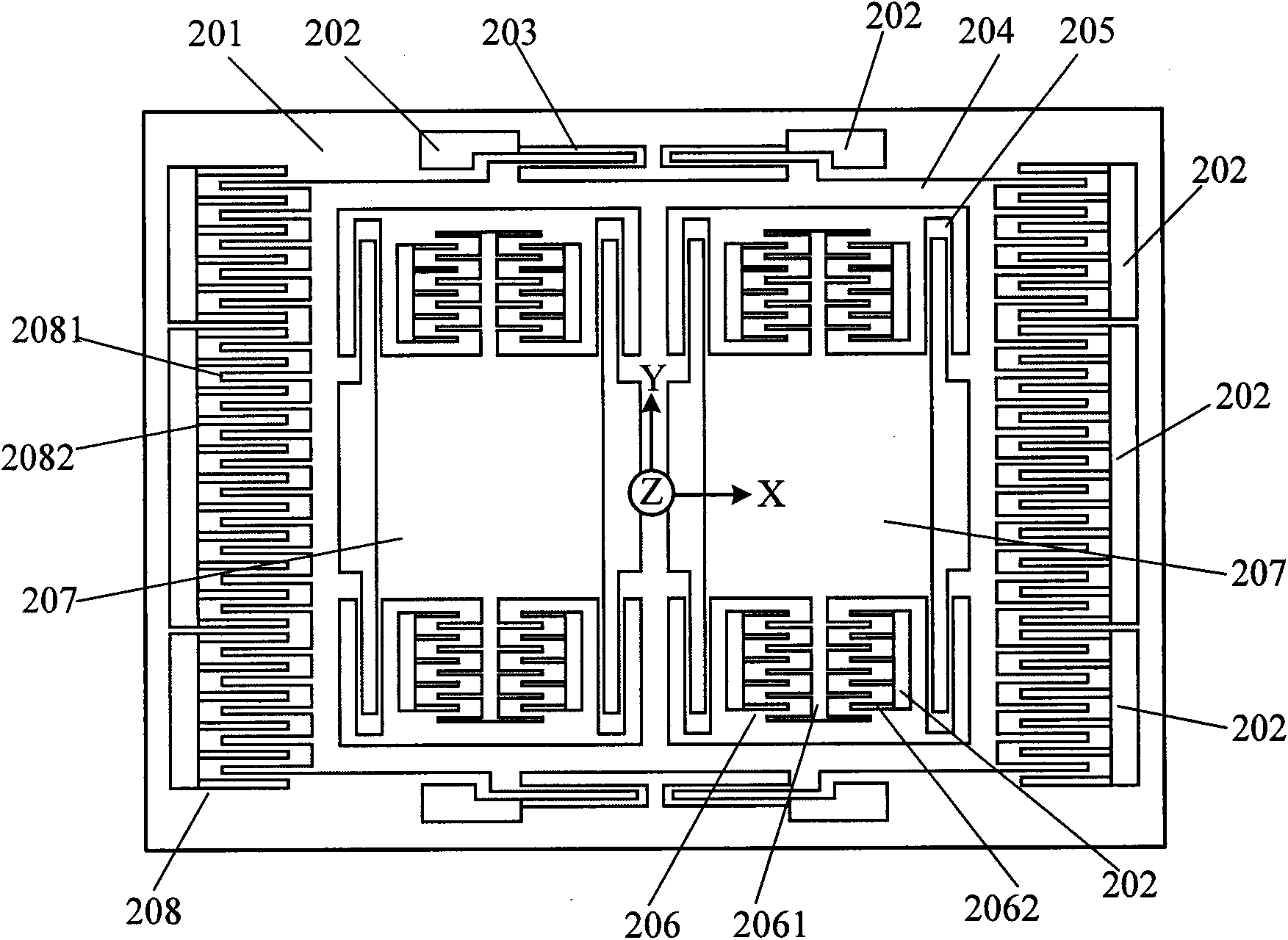
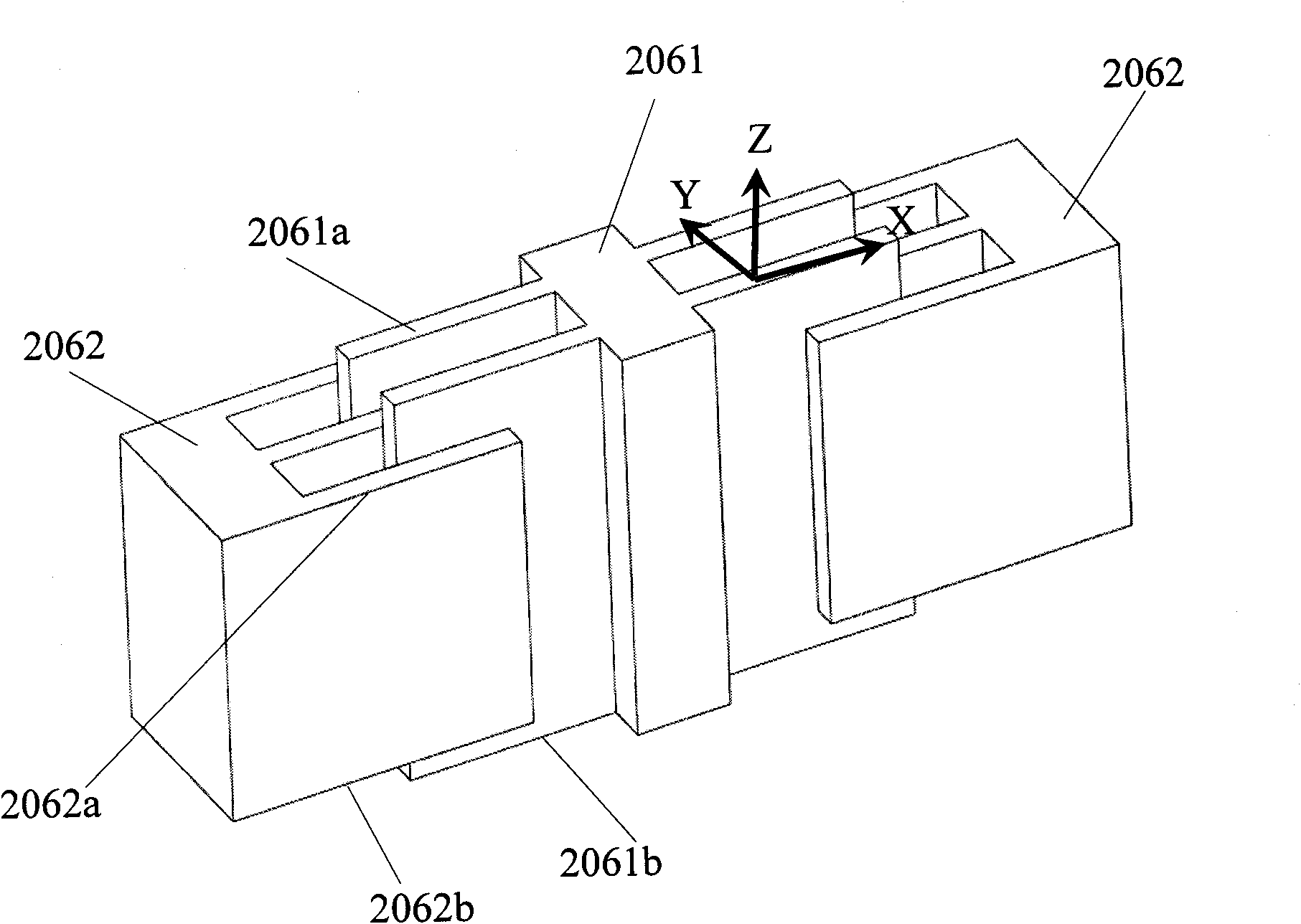
Four sensor units (SUA1 to SUA4) are disposed symmetrically about a point, on both top and bottom and left and right centering around one point of a support (15e). Furthermore, four sensor units (SUA1 to SUA4) are designed so that all the components are fully in tuning-fork structure. Drive frames (5, 5) of the sensor units (SUA1, SUA2) disposed adjacent to each other in a first direction (Y) are vibrated in mutually inverted phases, and drive frames of the other sensor units (SUA3, SUA4) disposed adjacent to each other in a second direction (X) are vibrated in mutually inverted phases as well. Moreover, the drive frames of the sensor units (SUA1, SUA2) and the drive frames of the other sensor units (SUA3, SUA4) are operated in synchronization in the state in which phases are shifted by 90 degrees. Whereby, it is possible to reduce or prevent vibration coupling in the driving direction and in the detection direction, and the leakage (loss) of excitation energy and Coriolis force. Thereby, performance of an inertial sensor is improved.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Small-sized piezoelectric resonator
ActiveUS7084556B1Reduce energy consumptionReduce vibrationImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTuning forkPiezoelectric resonators
The piezoelectric resonator according to the invention includes a tuning fork shaped part with two parallel vibrating arms, connected to each other by a linking part, from which protrude a central arm located between both vibrating arms of the tuning fork shaped part, wherein at least one groove is formed on at least one of a front side and a rear side of each vibrating arm.
Owner:ETA SA MFG HORLOGERE SUISSE
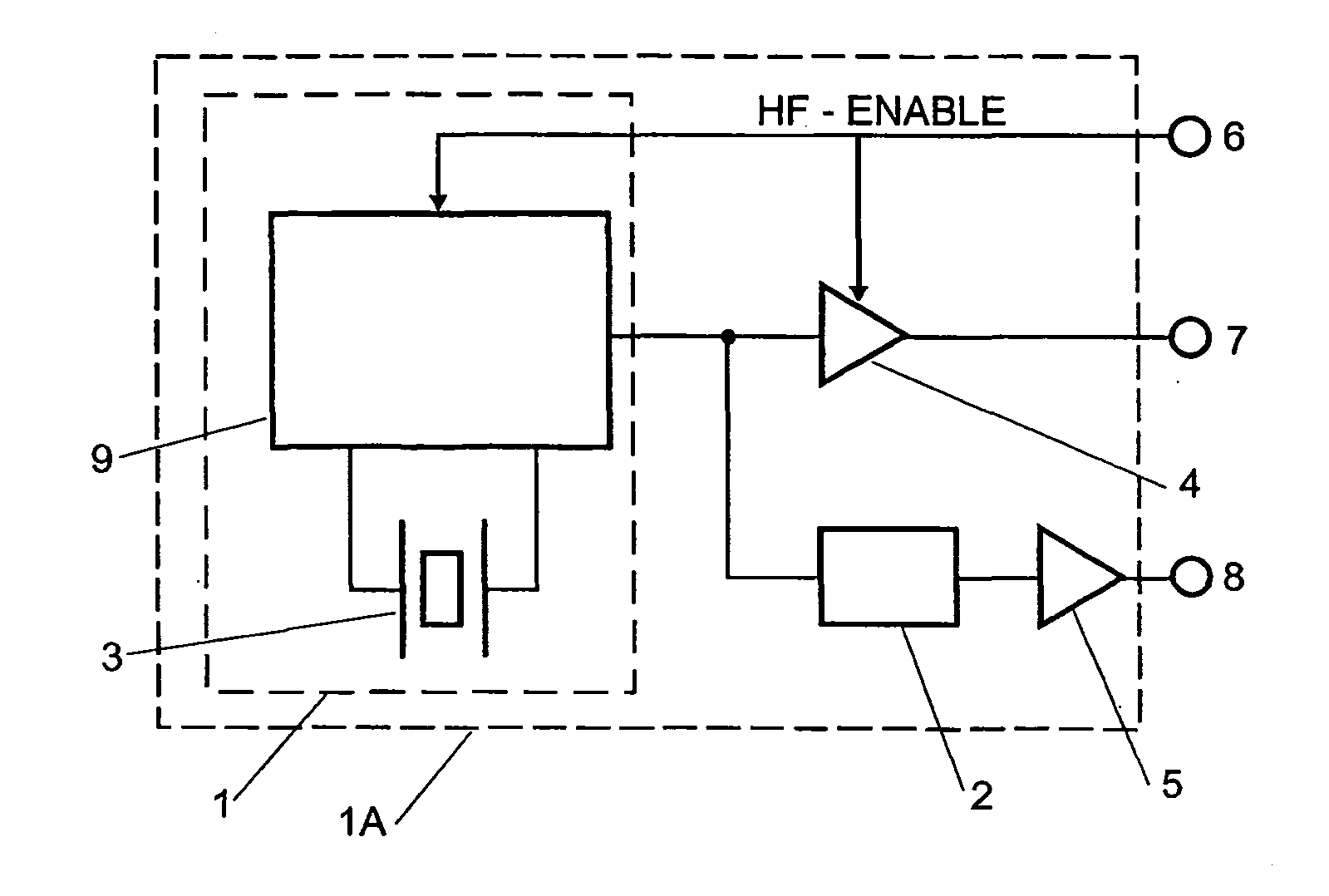
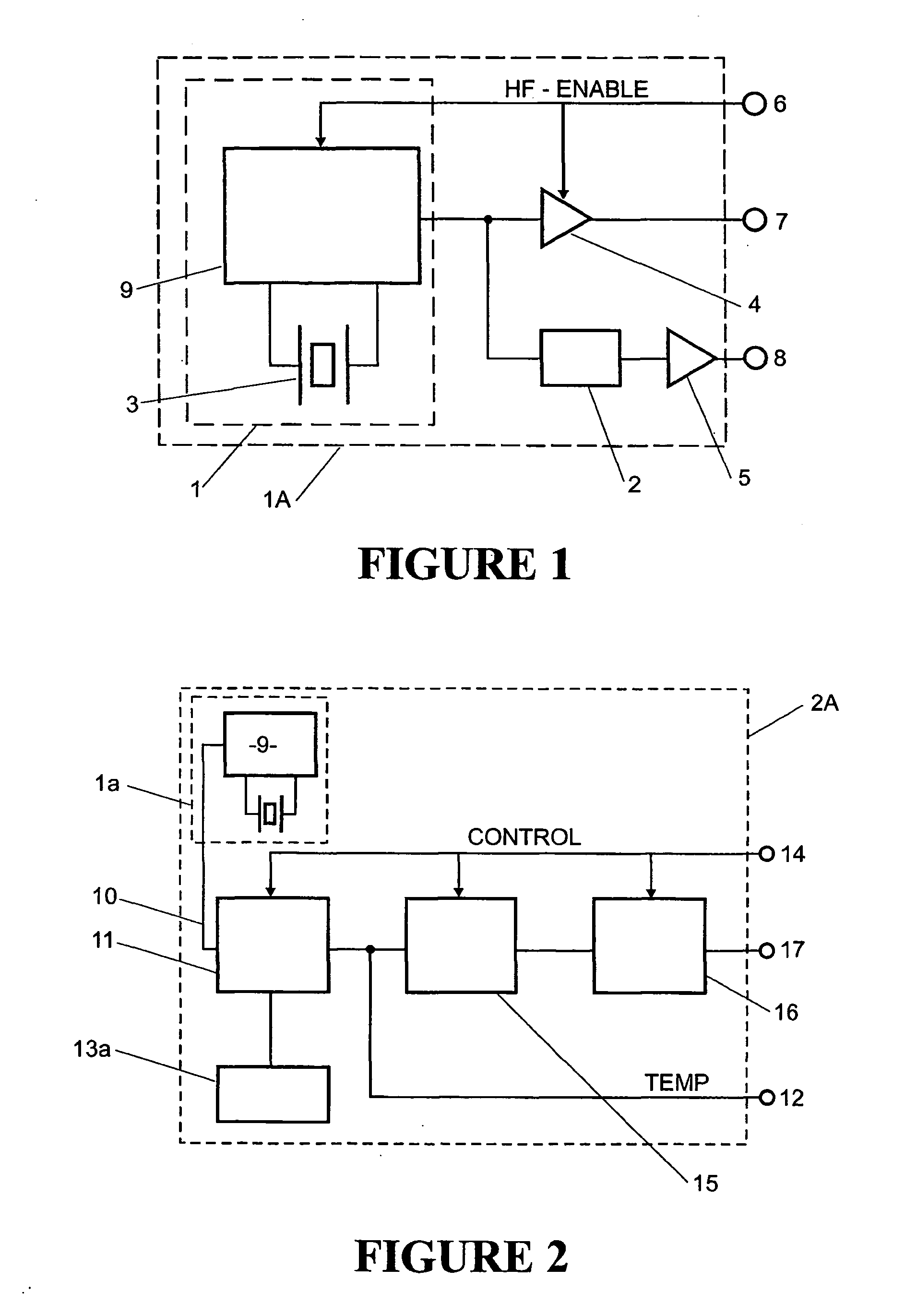
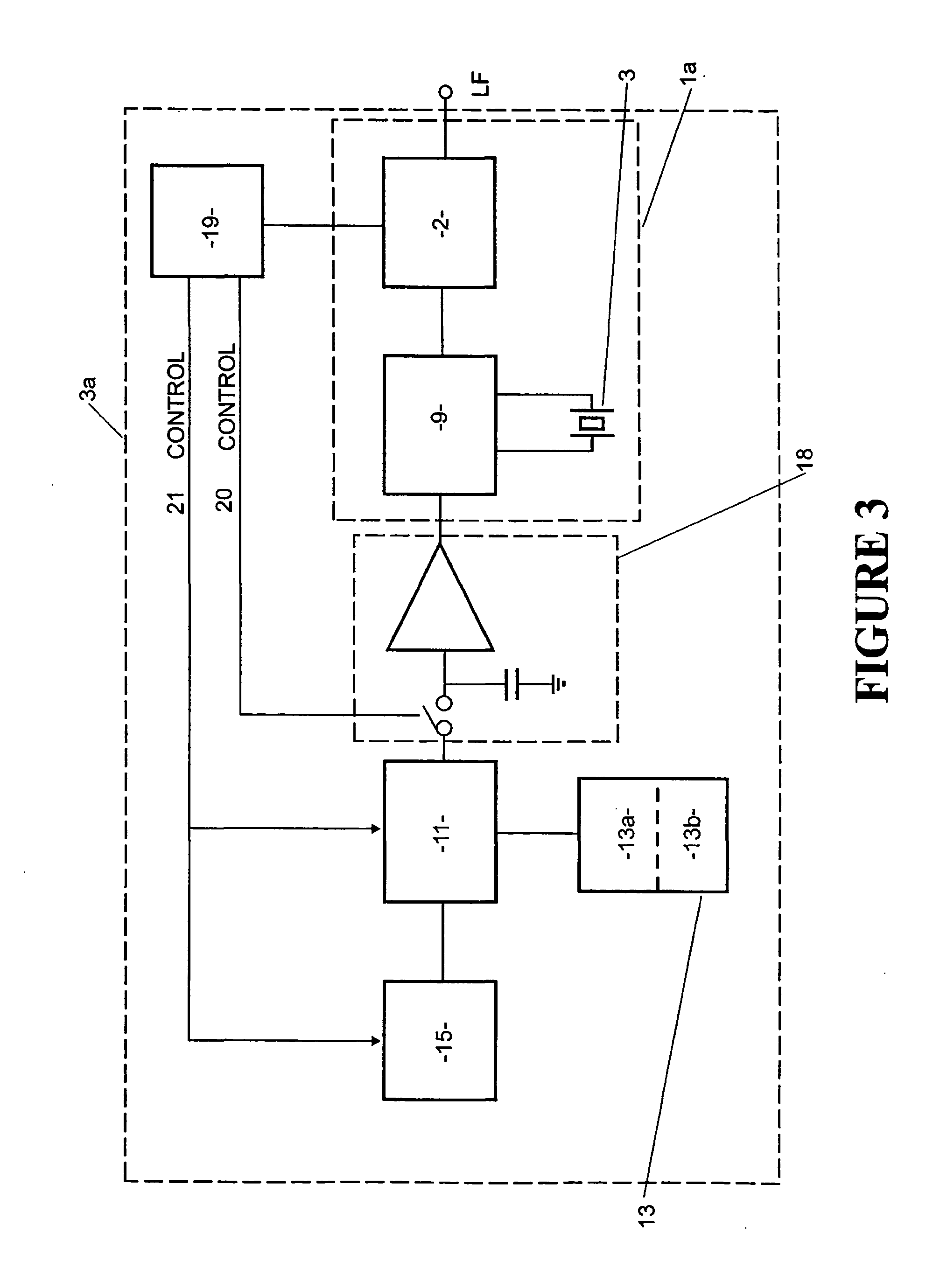
Low power crystal oscillator
InactiveUS20050007205A1Reduce frequencyReduce bias currentGenerator stabilizationOscillations generatorsPhase noiseEngineering
The present invention relates to a timing system including an integrated circuit having an oscillator that provides both high and low frequency clock signals from a single high frequency crystal without the necessity of a tuning fork crystal. The low frequency signal is available for time-keeping applications, with low power consumption during “idle” periods. The high performance high frequency signal is available on demand for clock and frequency reference use. The oscillator of the present invention provides improved time-keeping accuracy, whilst size, cost and component count is reduced. Furthermore, phase noise and other critical parameters of the high frequency oscillator are not compromised. Shock vulnerability, a known problem for tuning fork crystals, is reduced.
Owner:RAKON
Inertial sensor
ActiveUS7513155B2Reduce the amplitudeReduce vibrationAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkEngineering
Four sensor units (SUA1 to SUA4) are disposed symmetrically about a point, on both top and bottom and left and right centering around one point of a support (15e). Furthermore, four sensor units (SUA1 to SUA4) are designed so that all the components are fully in tuning-fork structure. Drive frames (5, 5) of the sensor units (SUA1, SUA2) disposed adjacent to each other in a first direction (Y) are vibrated in mutually inverted phases, and drive frames of the other sensor units (SUA3, SUA4) disposed adjacent to each other in a second direction (X) are vibrated in mutually inverted phases as well. Moreover, the drive frames of the sensor units (SUA1, SUA2) and the drive frames of the other sensor units (SUA3, SUA4) are operated in synchronization in the state in which phases are shifted by 90 degrees. Whereby, it is possible to reduce or prevent vibration coupling in the driving direction and in the detection direction, and the leakage (loss) of excitation energy and Coriolis force. Thereby, performance of an inertial sensor is improved.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
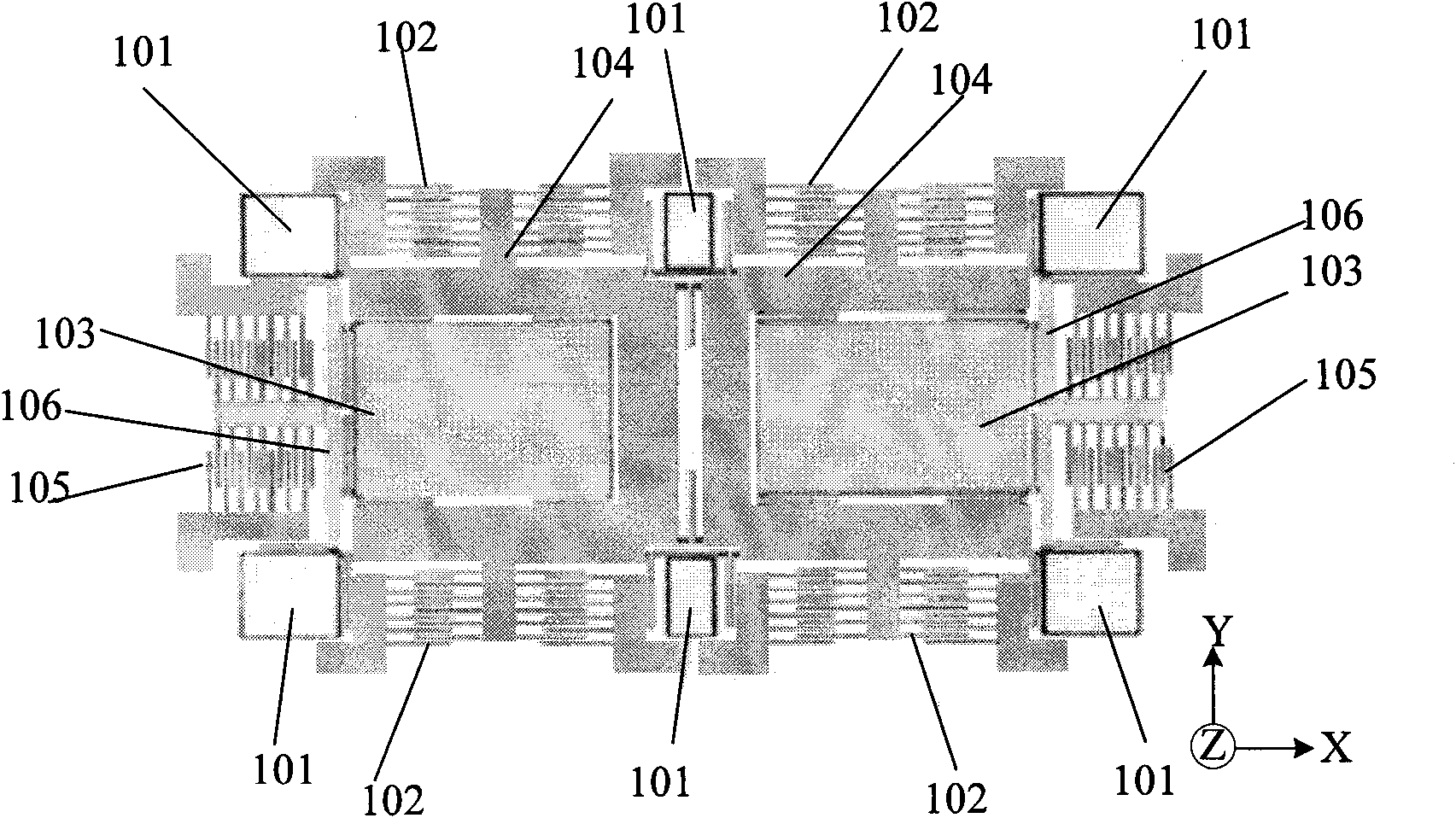
Capacitive micromachined tuning fork gyroscope
InactiveCN102062604ASuppress couplingNo changeTelevision system detailsImpedence networksCapacitanceTuning fork
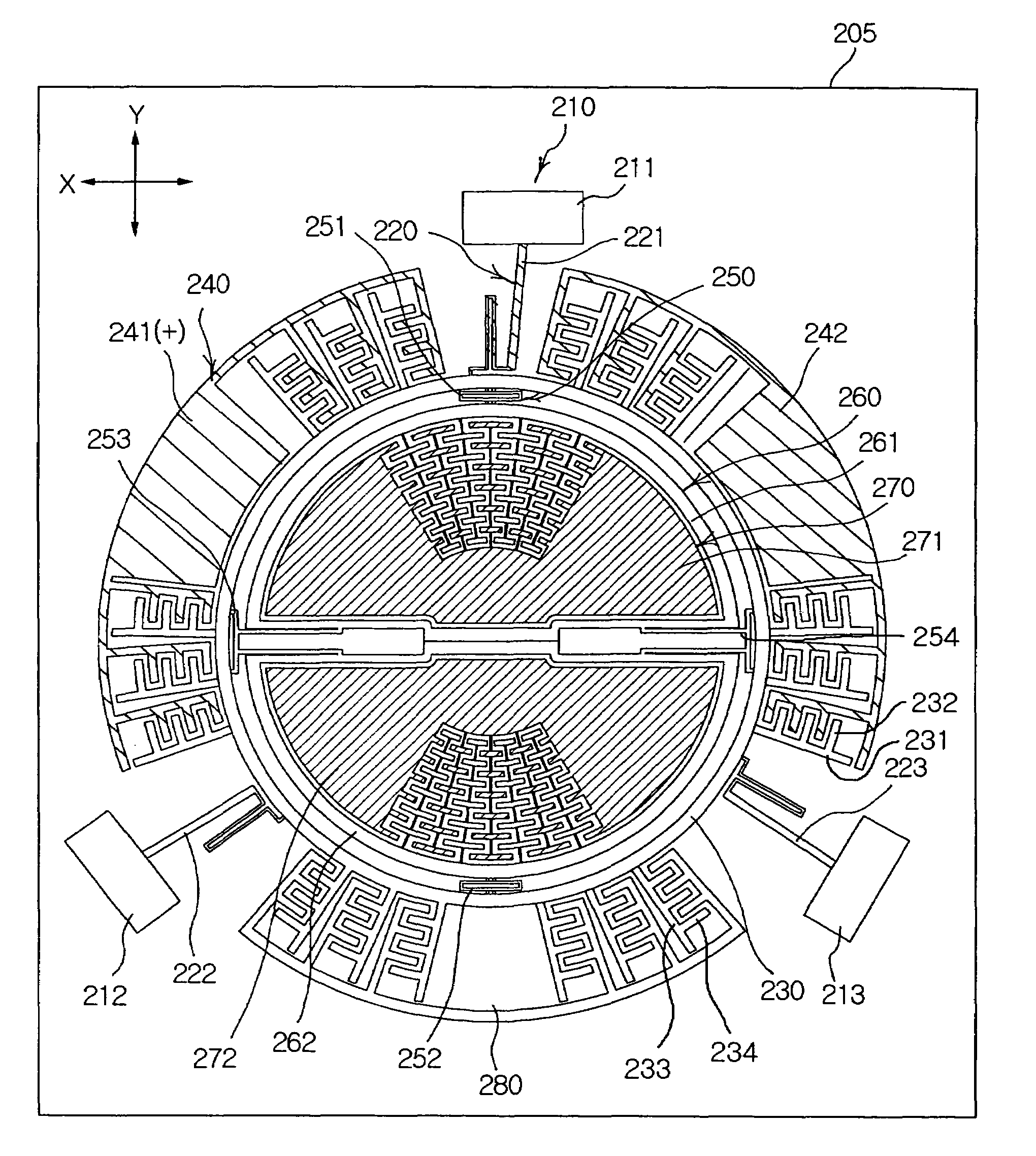
The invention provides a capacitive micromachined tuning fork gyroscope. The gyroscope is the symmetrical dual-mass structural gyroscope, comprising a substrate and a framework arranged in the centre of the substrate, wherein the middle of the framework is provided with a framework beam perpendicular to the framework; two detection mass blocks are symmetrically arranged in the framework with the framework beam as a symmetry axis, and four corners of each detection mass block are connected with the framework and the framework beam through at least four drive beams; decoupling drive comb capacitors are respectively arranged at both ends of each detection mass block in the direction of a vertical axis; detection comb capacitors are symmetrically arranged on both outer sides of the framework in the direction of a horizontal axis; at least four detection beams are arranged on both outer sides of the framework in the direction of the vertical axis; and the detection beams are distributed symmetrically relative to the vertical axis and the horizontal axis and are fixed on the substrate through corresponding anchor points. According to the capacitive horizontal-axis micromachined tuning fork gyroscope provided by the invention, the mechanical coupling between the detection mode and the driving mode of the micromachined tuning fork gyroscope can be solved easily and effectively.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Horizontal and tuning fork vibratory microgyroscope
InactiveUS6918298B2Minimize impactAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkResonance
A horizontal and tuning fork vibratory microgyroscope detects angular velocity and angular acceleration of an inertial object when the inertial object is rotated, wherein resonance directions of the microgyroscope are on the same horizontal plane in both sensing and driving modes. The microgyroscope includes a substrate, an anchored pad unit, an outer elastic element unit, an outer frame, a sensing electrode unit, an inner elastic element unit including a plurality of inner elastic elements connected to the inside of the outer frame, an inner weighted element unit including a pair of first and second inner weighted elements each having a driven comb, and a driven electrode unit including a comb drive forming a comb structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Robust Six Degree-of-Freedom Micromachined Gyroscope with Anti-Phase Drive Scheme and Mehtod of Operation of the Same
ActiveUS20090272189A1Effectively and substantially rejectEfficiently rejectedMechanical apparatusAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTuning forkGyroscope
A method of operating an anti-phase six degree-of-freedom tuning fork gyroscope system comprises the steps of driving a first three degree-of-freedom gyroscope subsystem, and driving a second three degree-of freedom gyroscope subsystem in an anti-phase mode with the first gyroscope subsystem at an anti-phase resonant frequency. Acceleration or an angular rate of motion is sensed by means of the first and second three degree-of-freedom gyroscope subsystems operating in a flat frequency response range where the anti-phase resonant frequency is designed. Response gain and phase are stable and environmental and fabrication perturbations are avoided by such operation. A anti-phase six degree-of-freedom tuning fork gyroscope system which operates as described is also characterized.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for manufacturing a quartz crystal unit
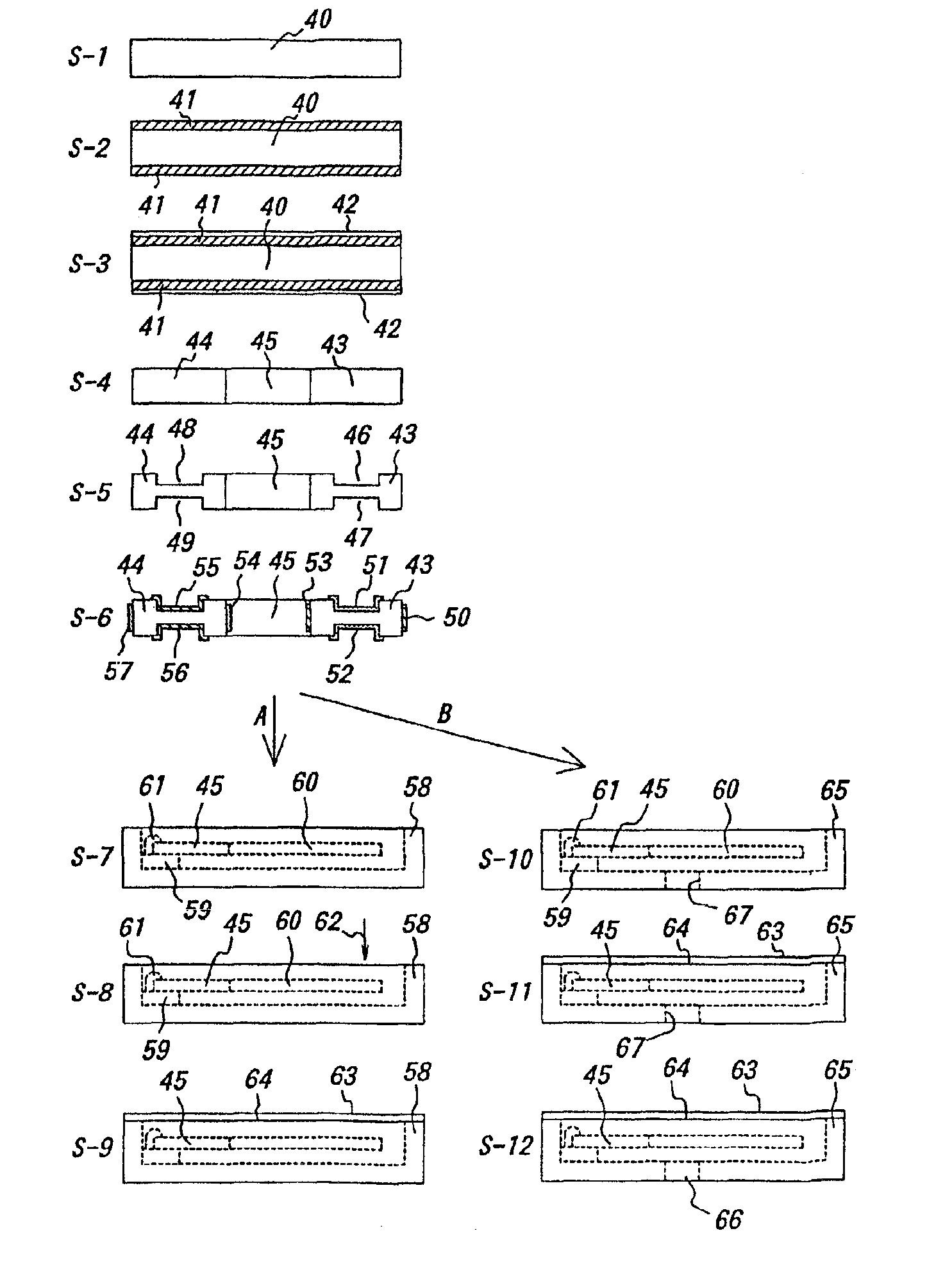
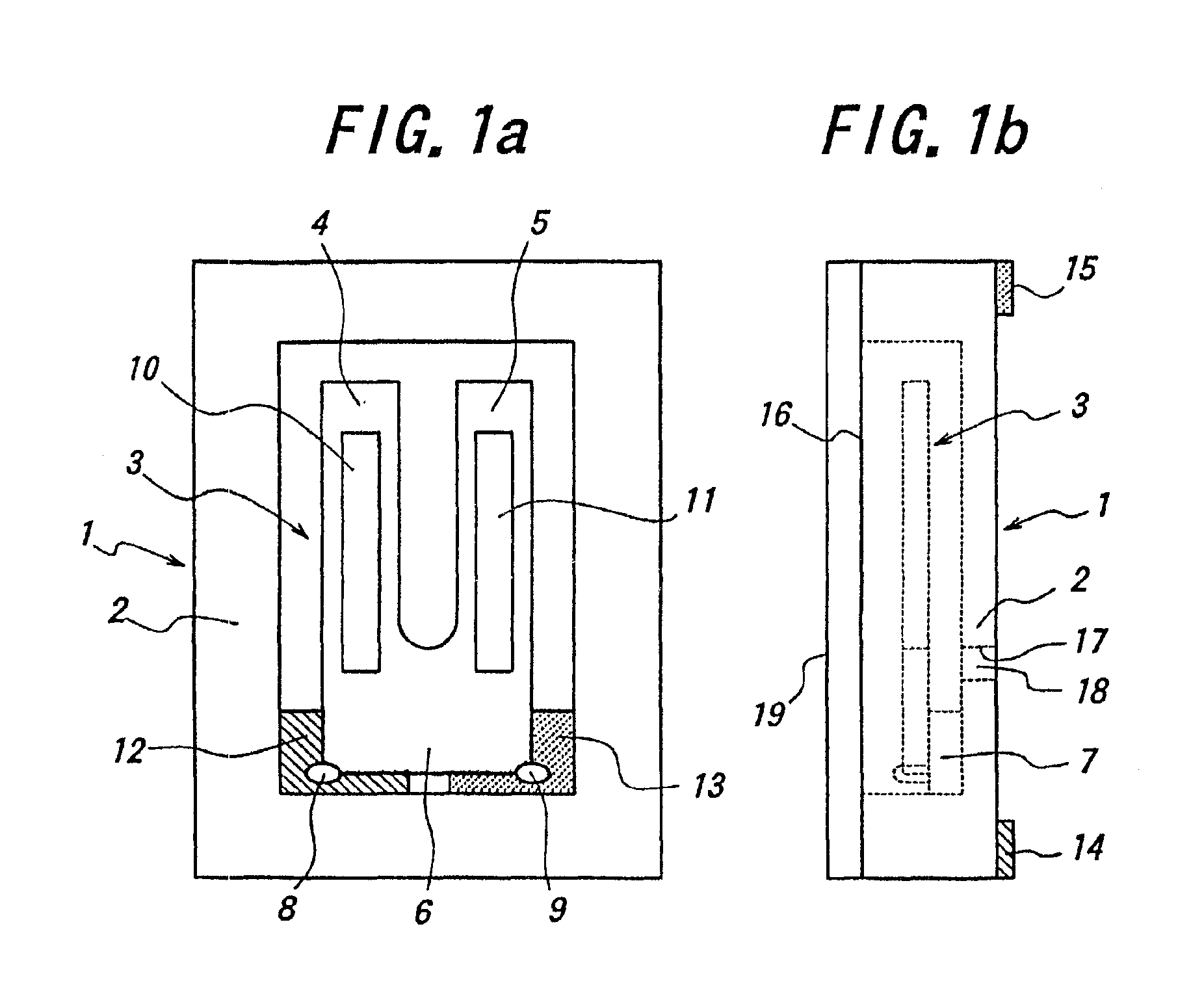
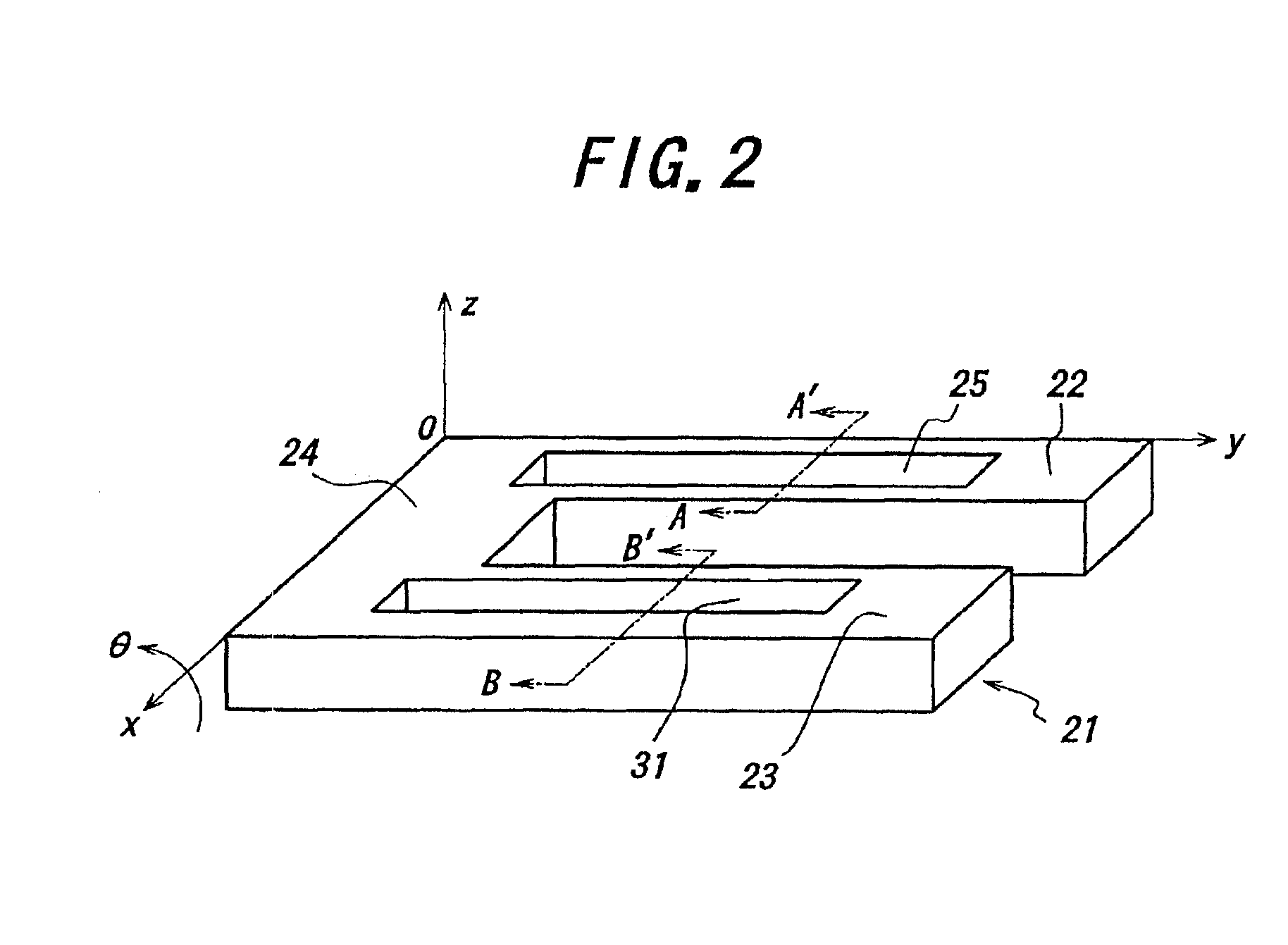
InactiveUS6898832B2Improve accuracyLow pricePrinted circuit assemblingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyResonatorTuning fork
In a method for manufacturing a quartz crystal unit, a quartz crystal tuning fork resonator is formed by etching a quartz crystal wafer to form a quartz crystal tuning fork base, quartz crystal tuning fork tines connected to the quartz crystal tuning fork base, and a groove having stepped portions in at least one of opposite main surfaces of each of the quartz crystal tuning fork tines. A first electrode is disposed on at least one of the stepped portions of each of the grooves and a second electrode is disposed on each of side surfaces of each of the quartz crystal tuning fork tines. A frequency of oscillation of the quartz crystal tuning fork resonator is adjusted at least twice and in different steps. The quartz crystal tuning fork resonator is then mounted in a case and an open end of the case is covered with a lid.
Owner:PIEDEK TECHN LAB
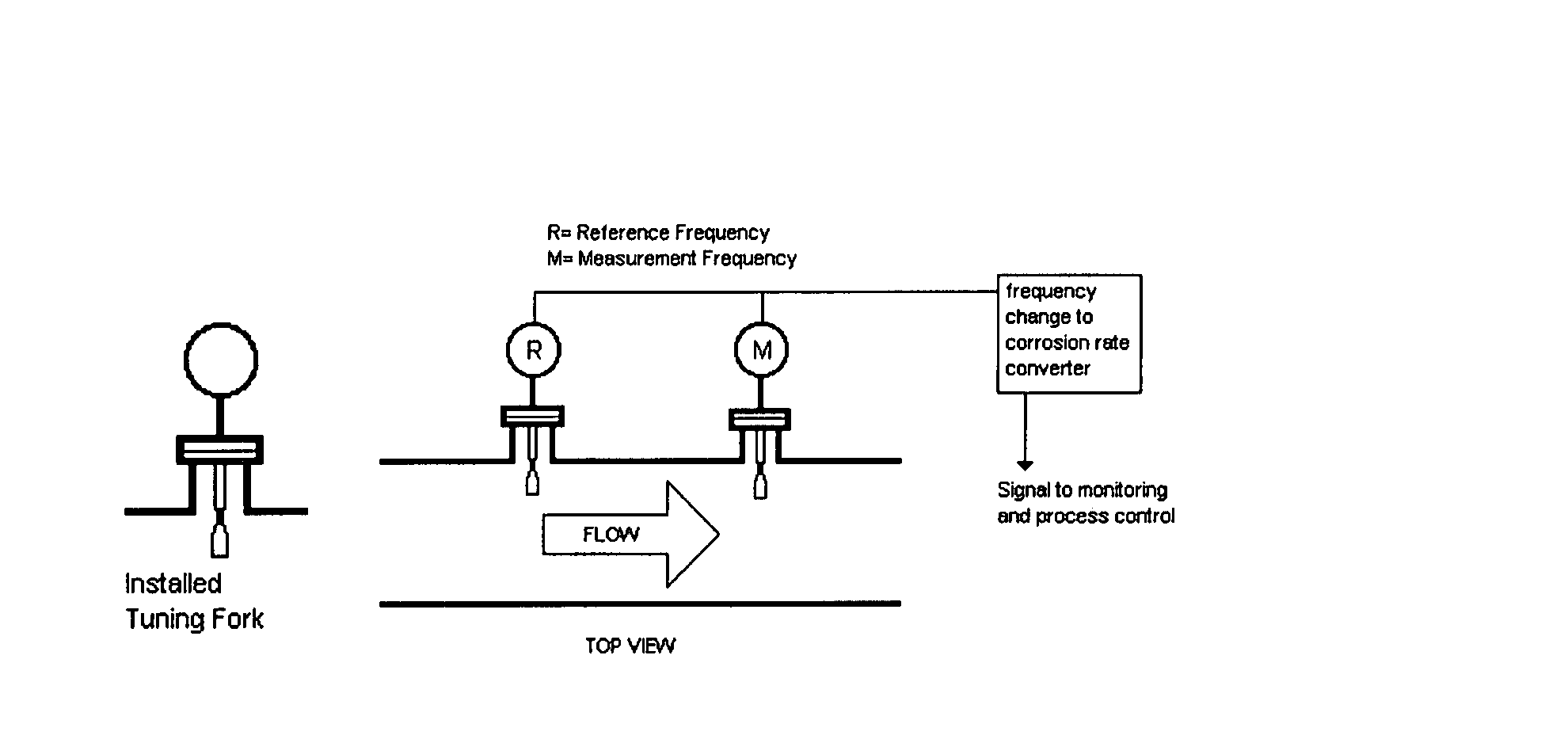
Metal loss rate sensor and measurement using a mechanical oscillator
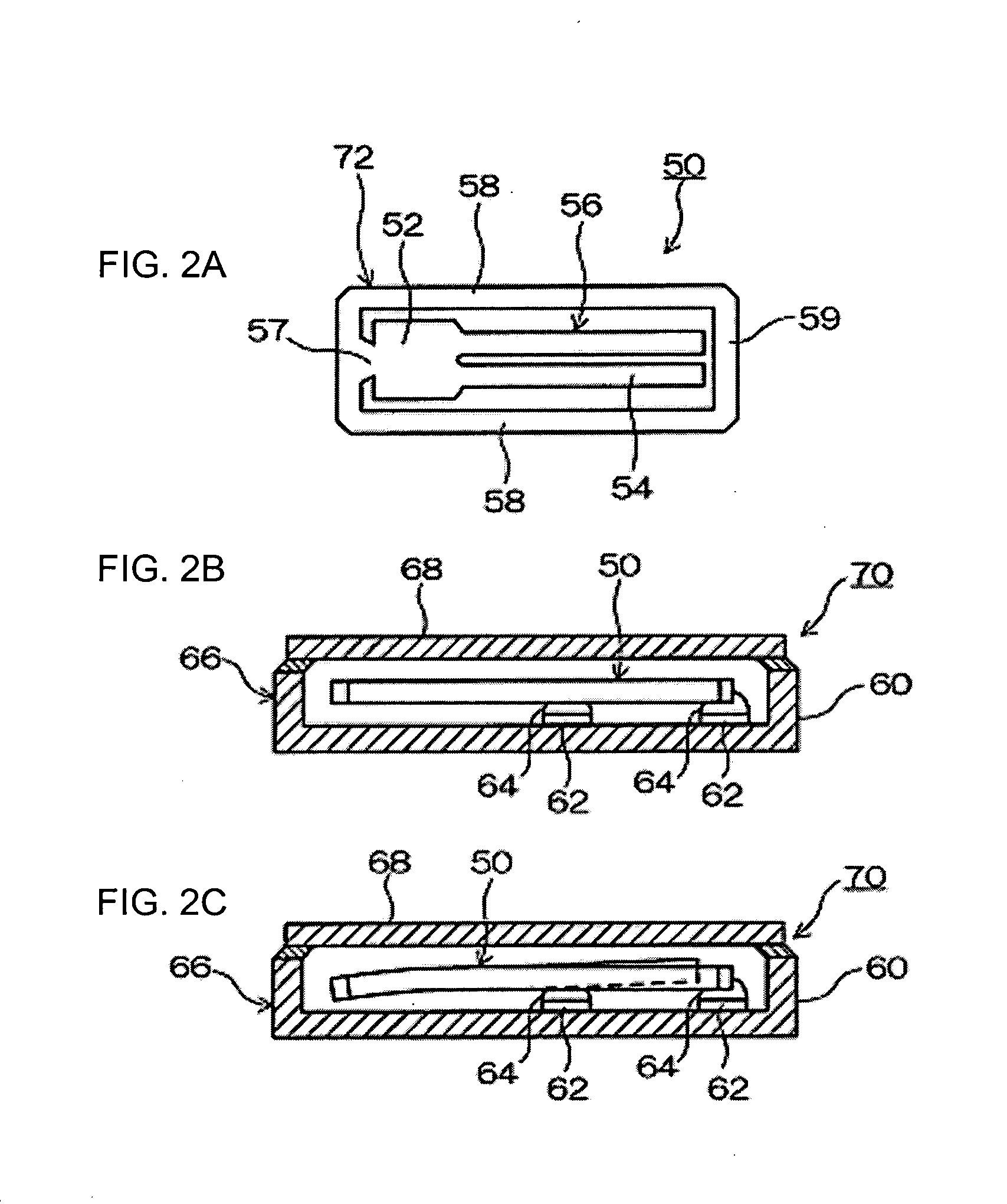
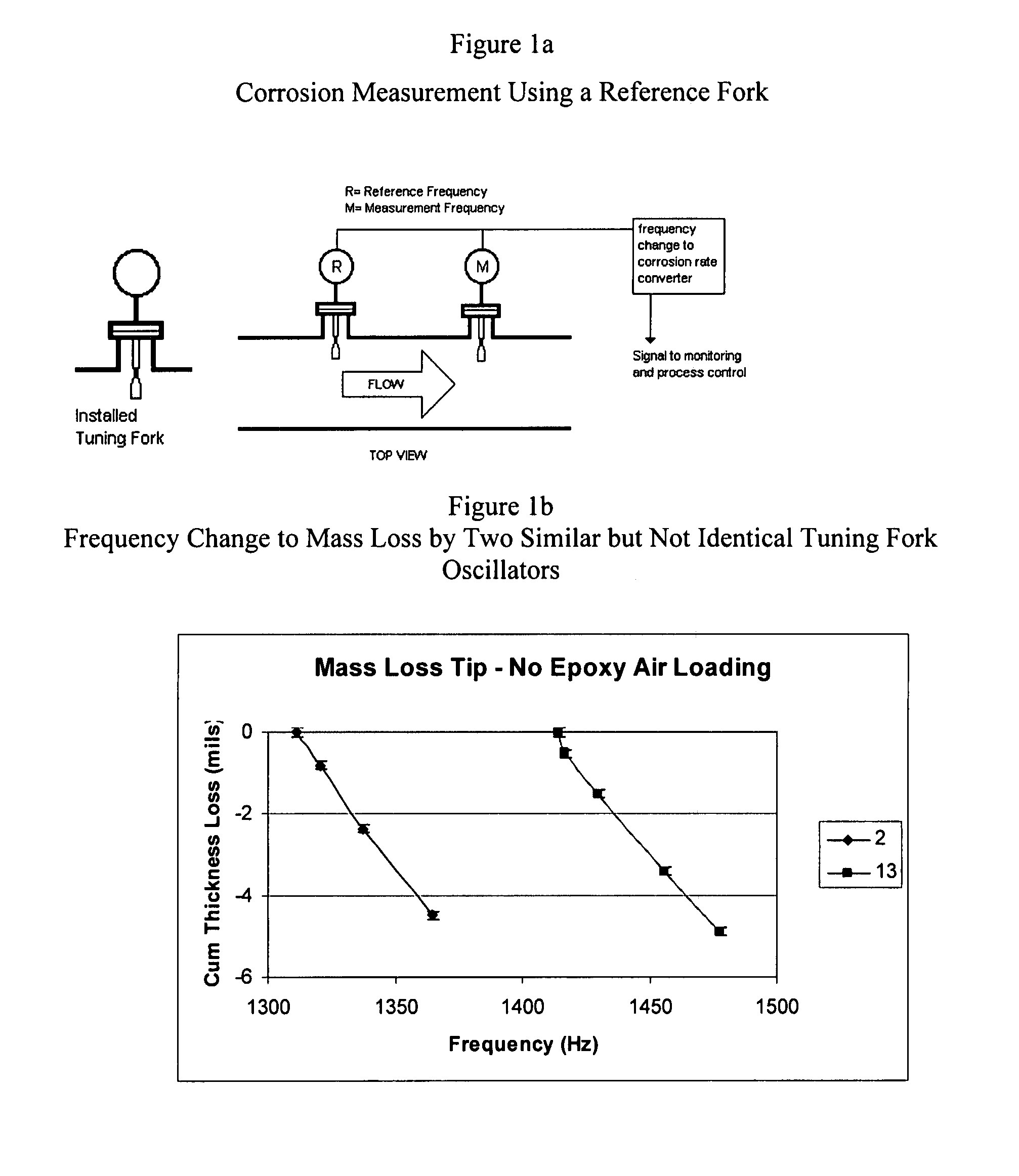
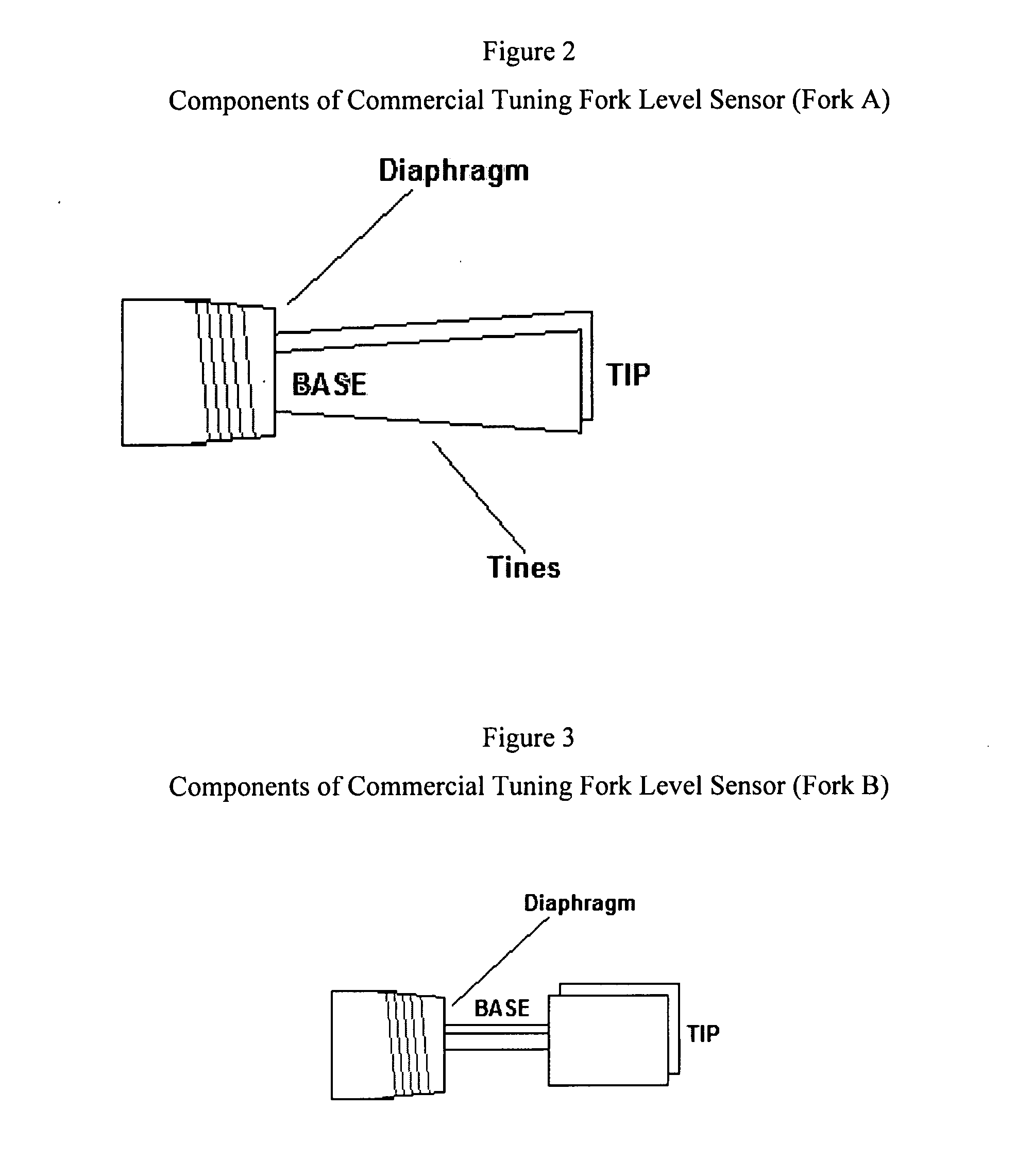
InactiveUS20070199379A1Interference minimizationVibration measurement in solidsWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersTuning forkLoss rate
The present invention is a mechanical oscillator metal loss sensor for use in a corrosive or erosive environment. The elements include a means for mechanical excitation, and a mechanical oscillator with two regions that corrode differently, where the regions are determined to affect specific influences on the resonance parameters, wherein said mechanical oscillator has a resonant frequency, f, and a quality factor, Q. In a preferred embodiment, the mechanical oscillator has the shape of a tuning fork.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com