Patents
Literature
775 results about "Micromachinery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Micromachines are mechanical objects that are fabricated in the same general manner as integrated circuits. They are generally considered to be between 100 nanometres to 100 micrometres in size, though that is debatable. The applications of micromachines include accelerometers that detect when a car has hit an object and trigger an airbag. Complex systems of gears and levers are another application.
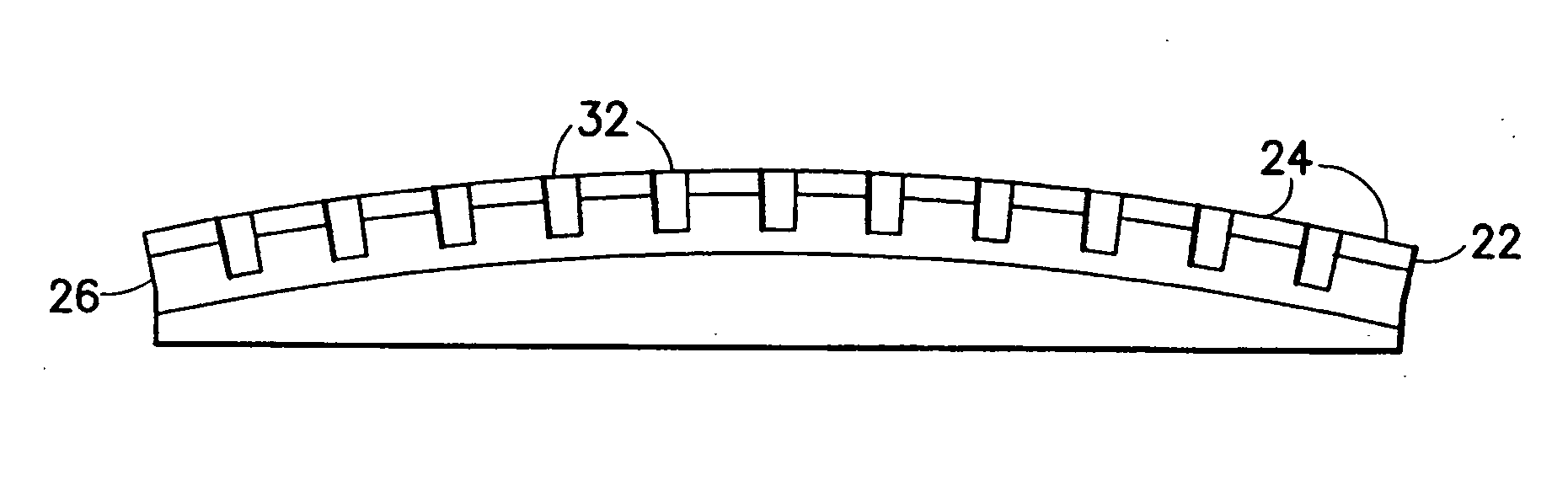
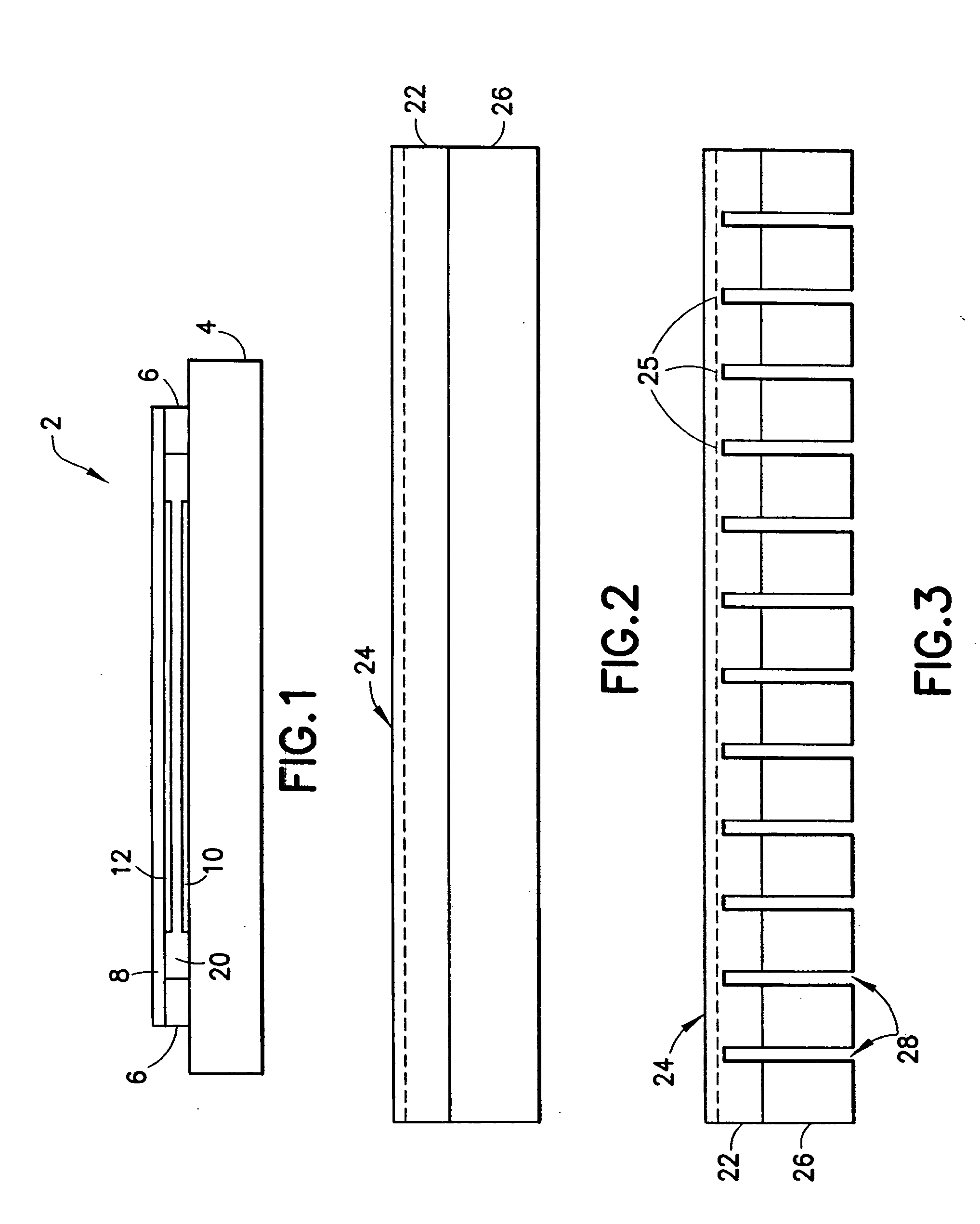
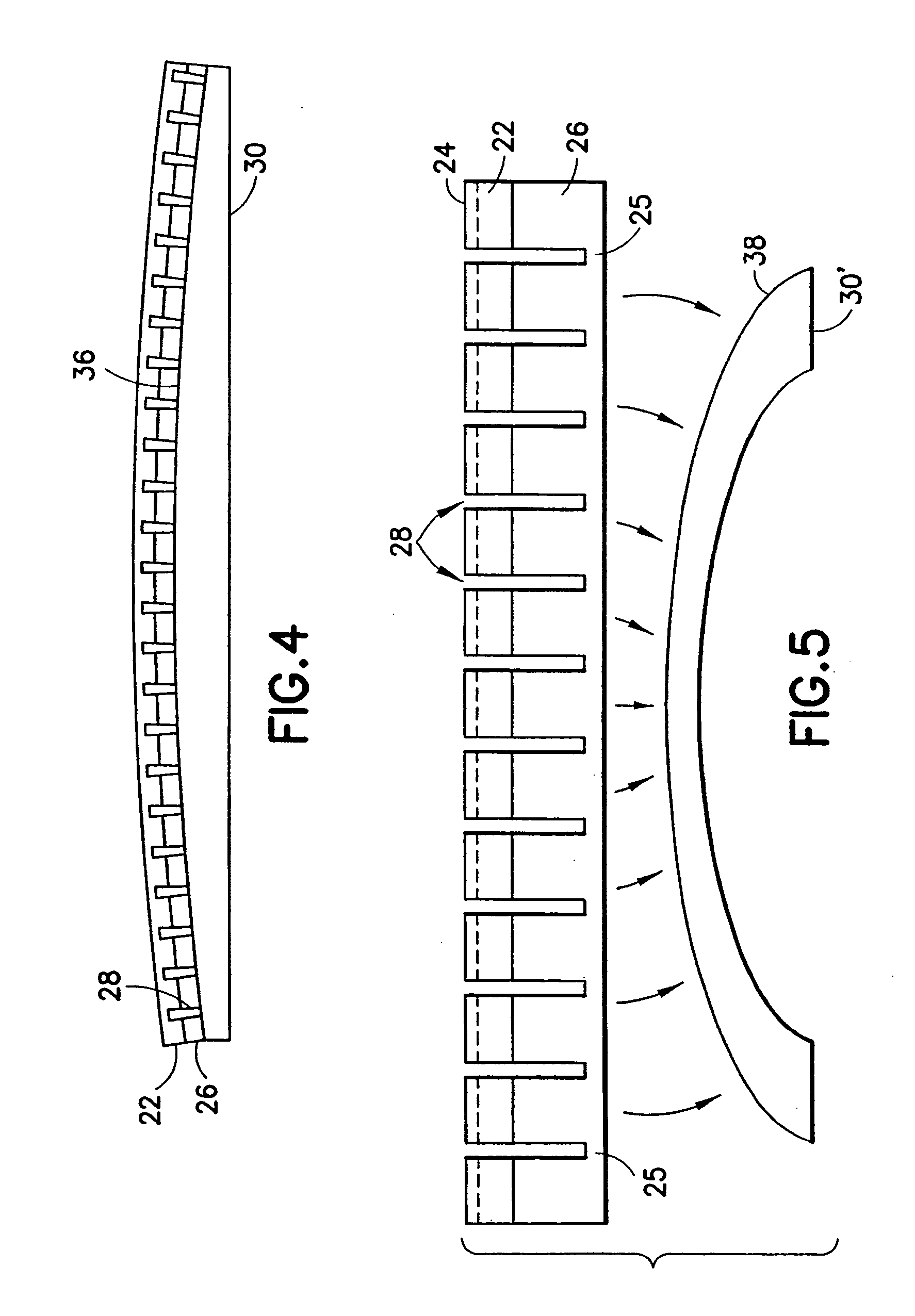
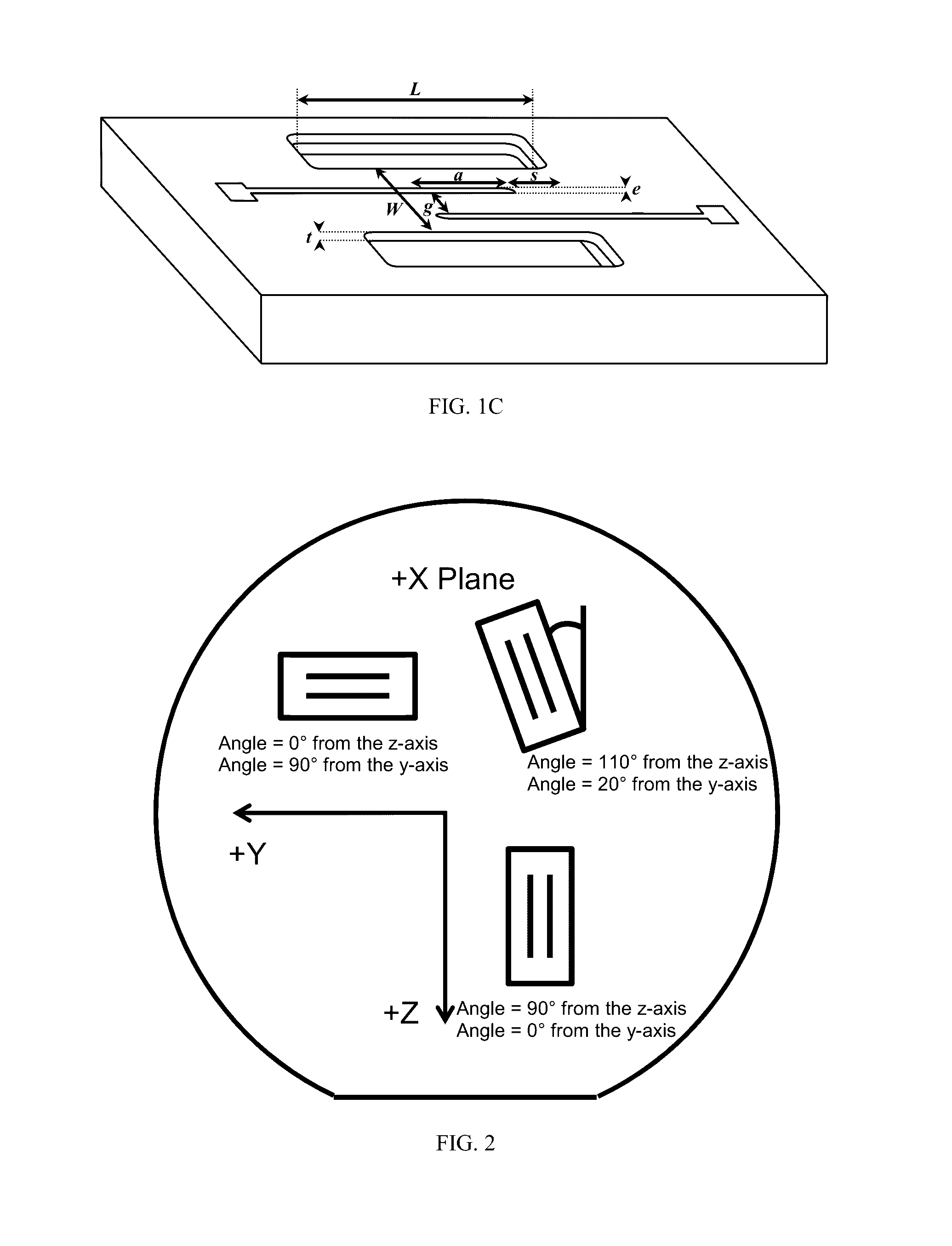
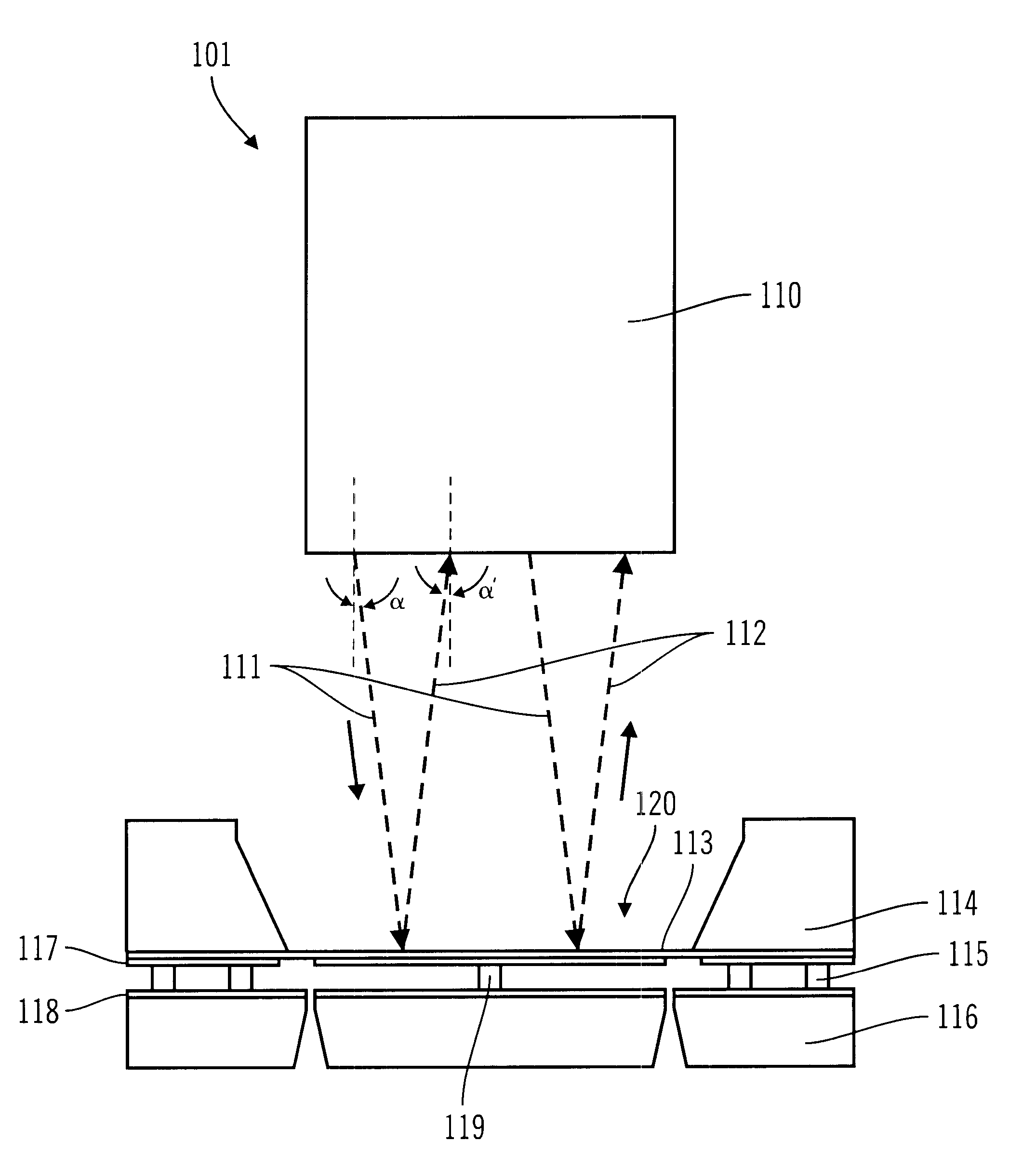
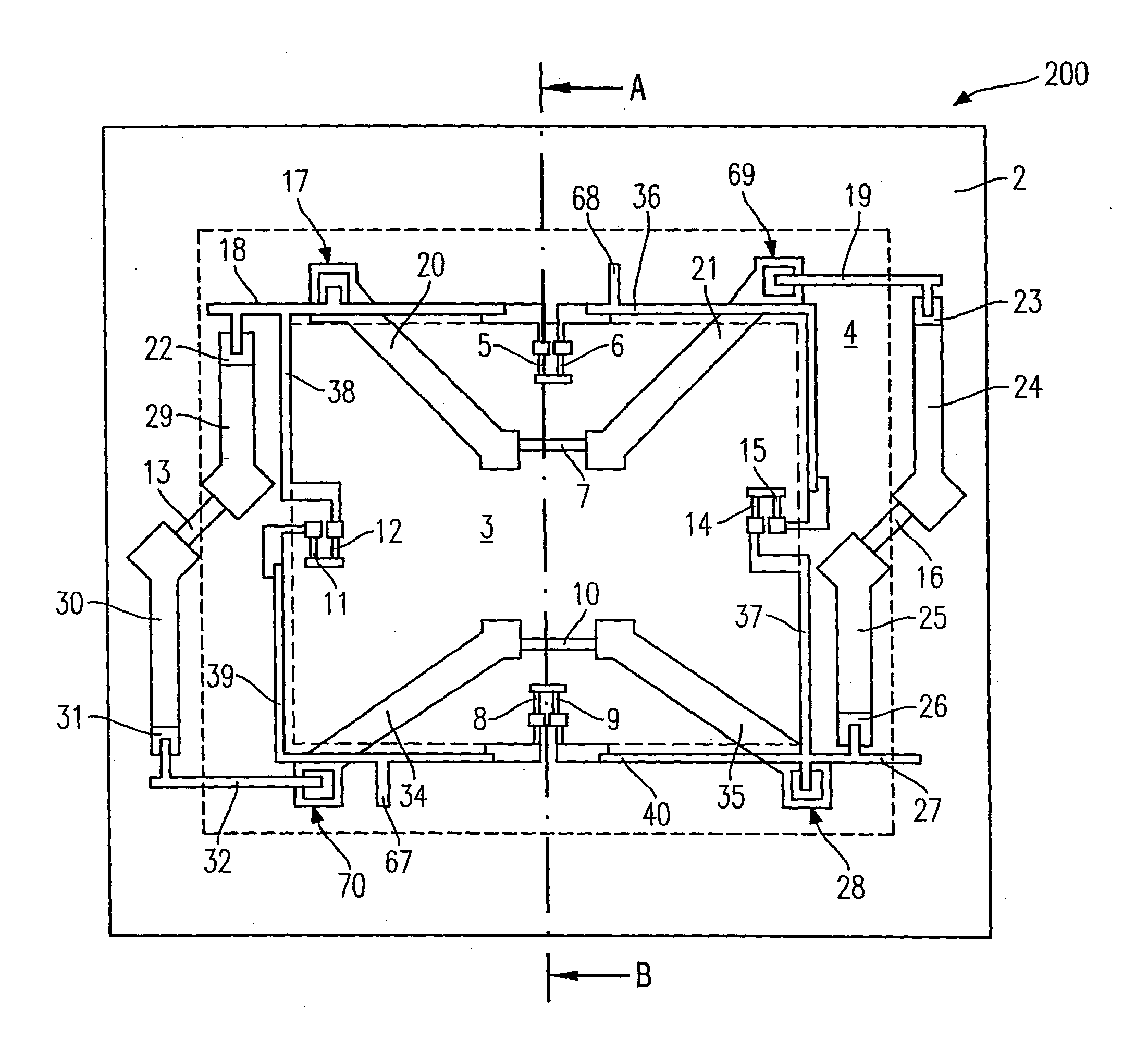
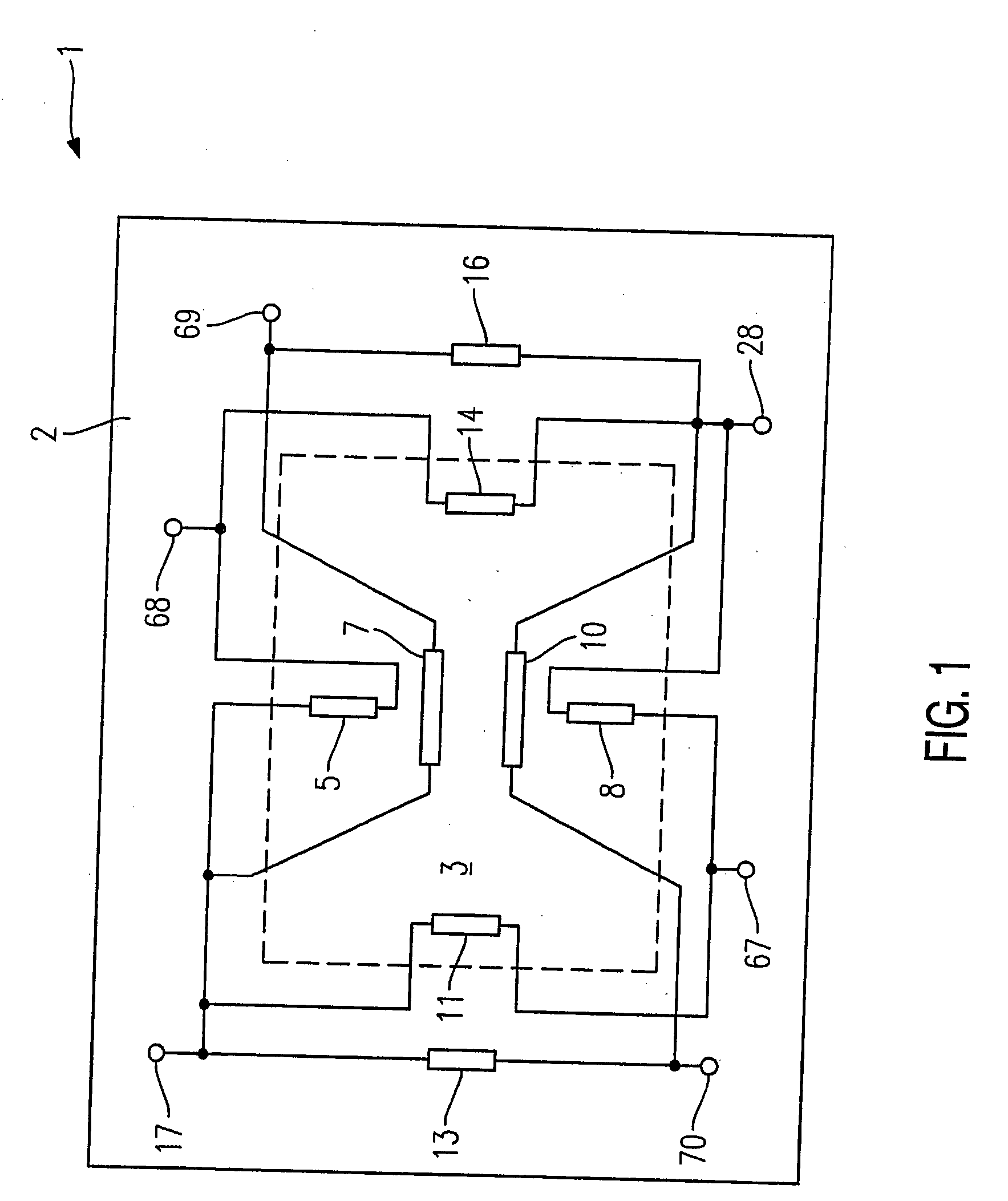
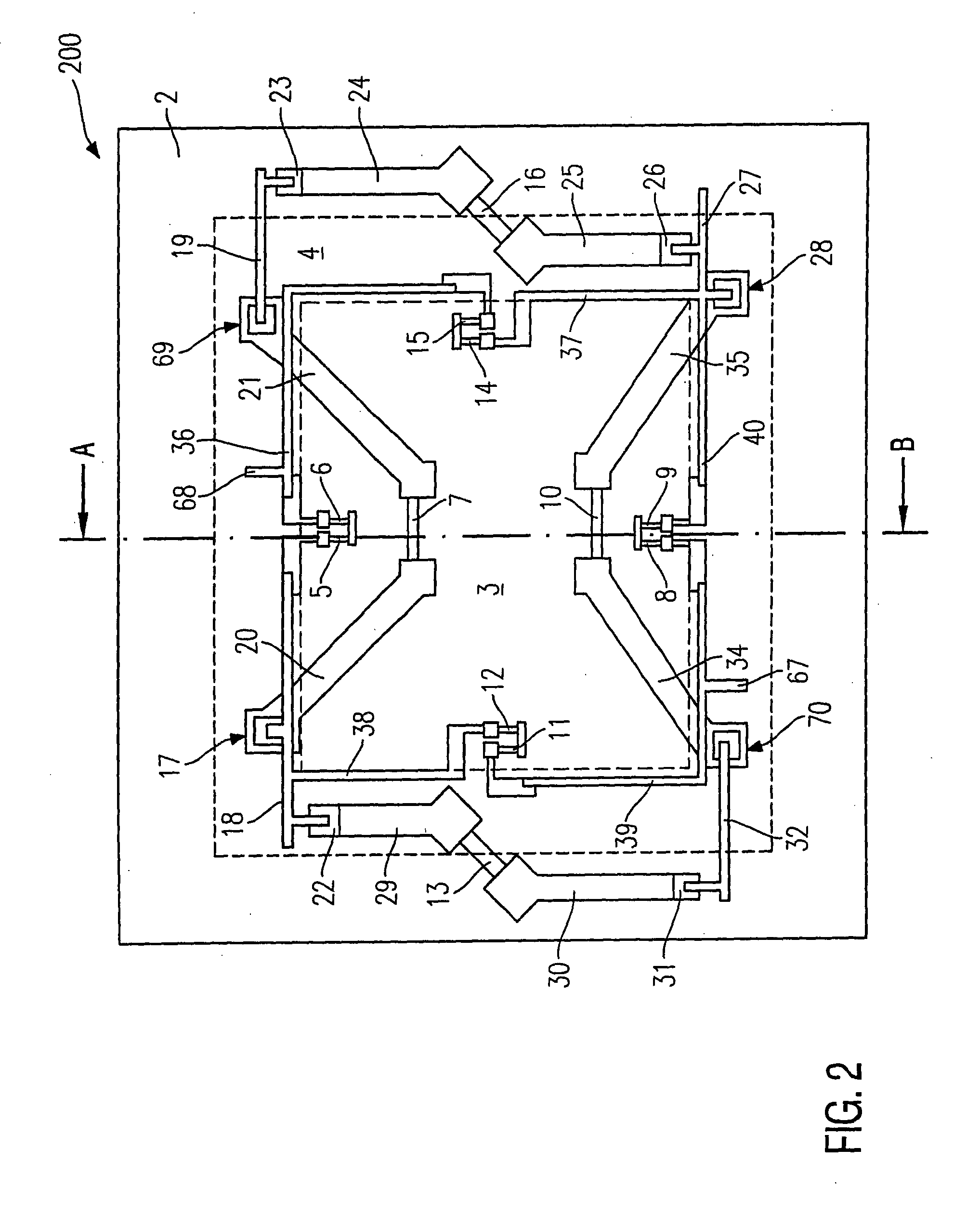
Curved micromachined ultrasonic transducer arrays and related methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20050146247A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFixed microstructural devicesPMUTEngineering
A curved sensor device, such as an ultrasonic transducer array, is fabricated from a flat micromachined sensor (such as cMUT or pMUT) array constructed using micromachined electromechanical systems (MEMS) techniques. The device comprises: a support structure comprising a spine having a profile that is generally curved and a multiplicity of teeth extending from one side of the curved spine; and a multiplicity of sensors built on the support structure. The spine can be bent forward or backward and attached to a curved front face of a support member, thereby causing the sensors to adopt a curved array.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
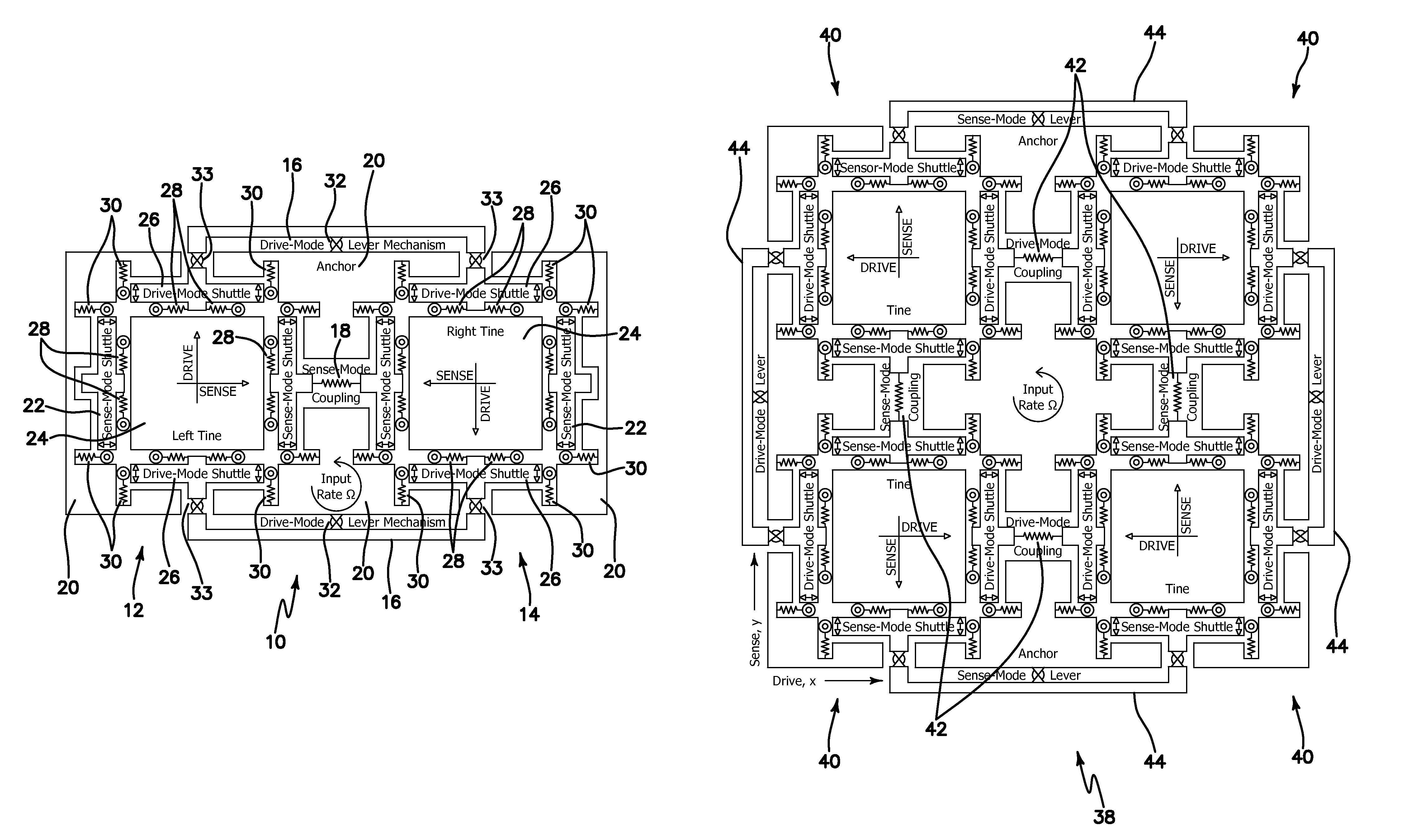
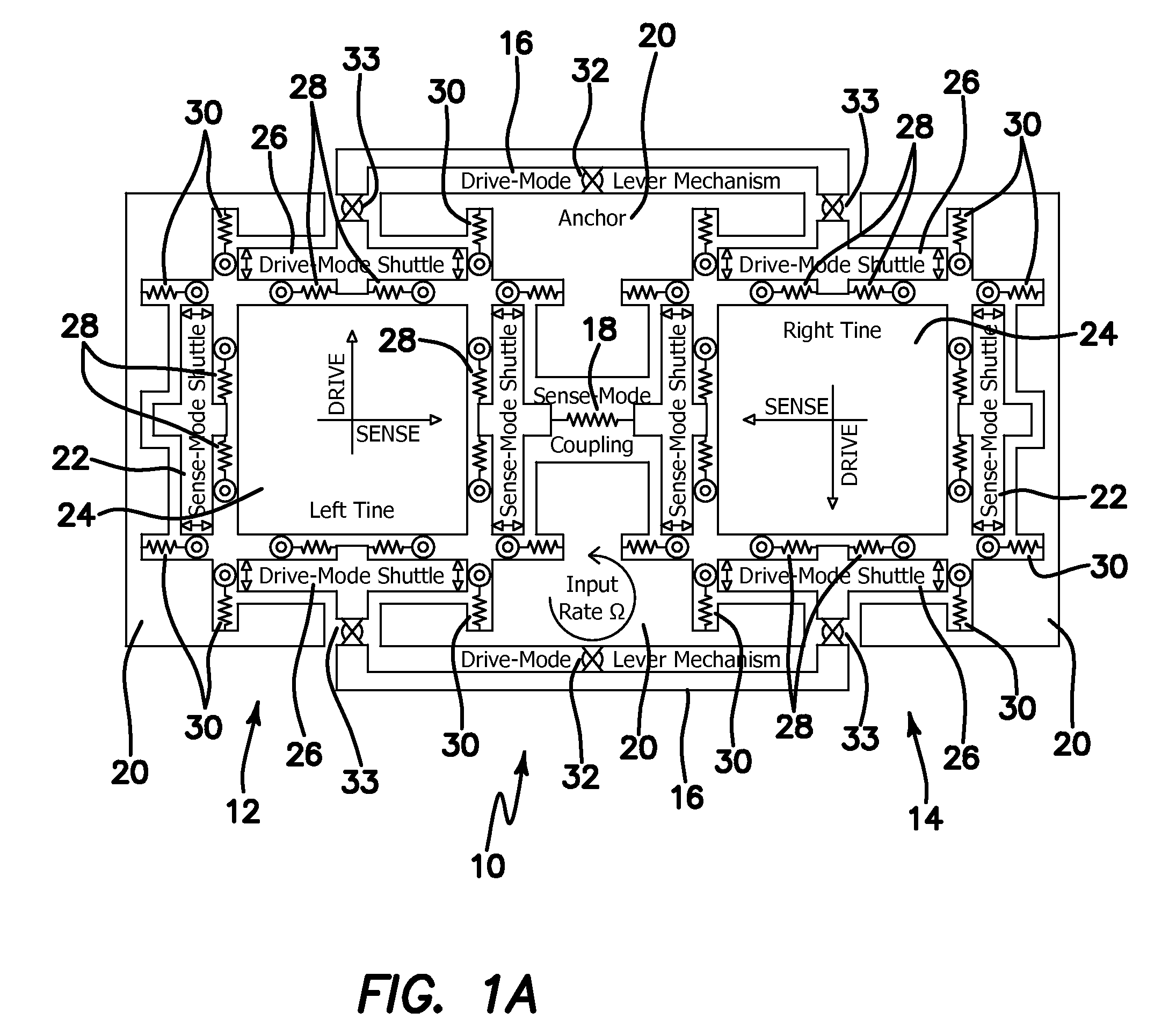
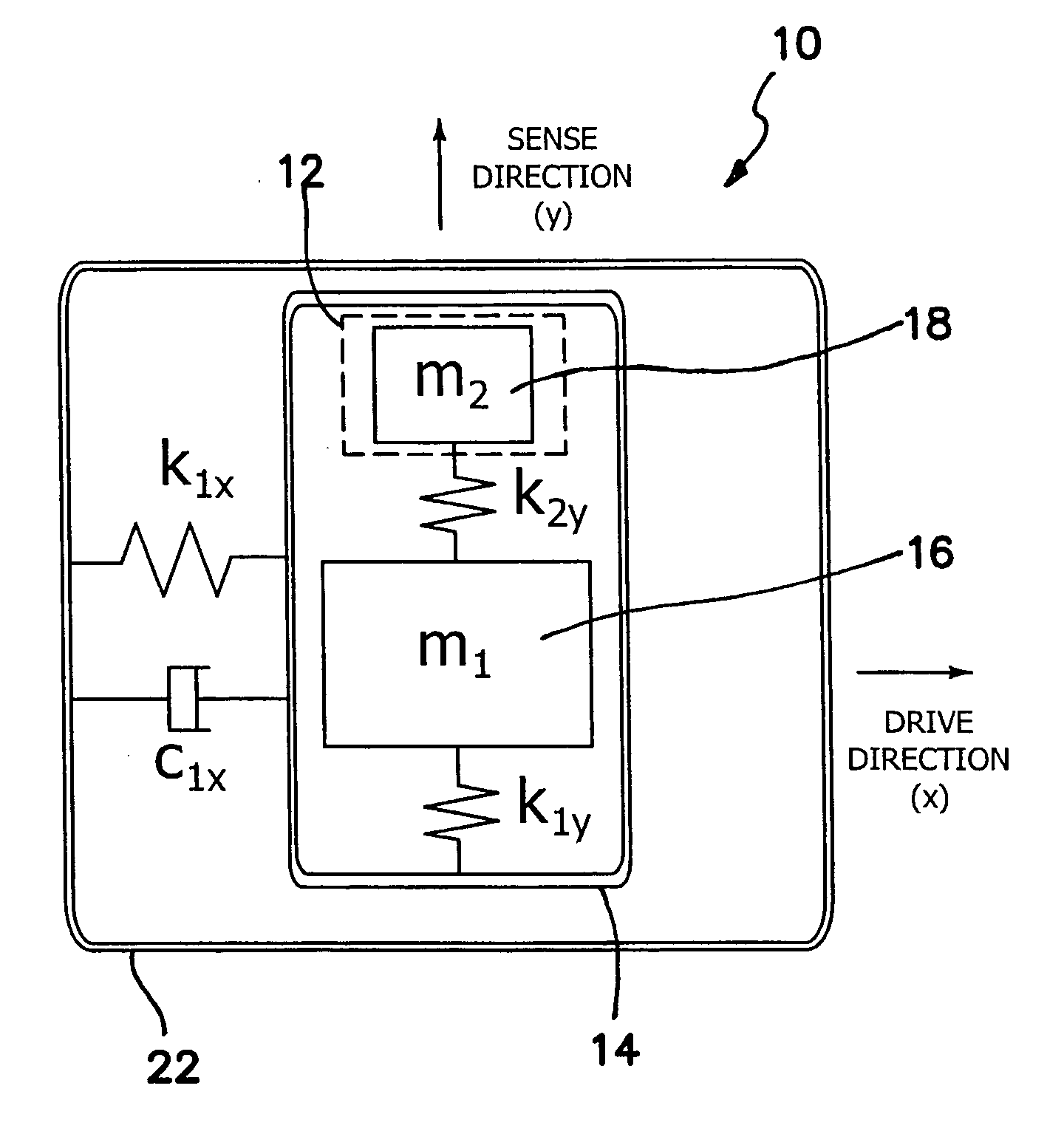
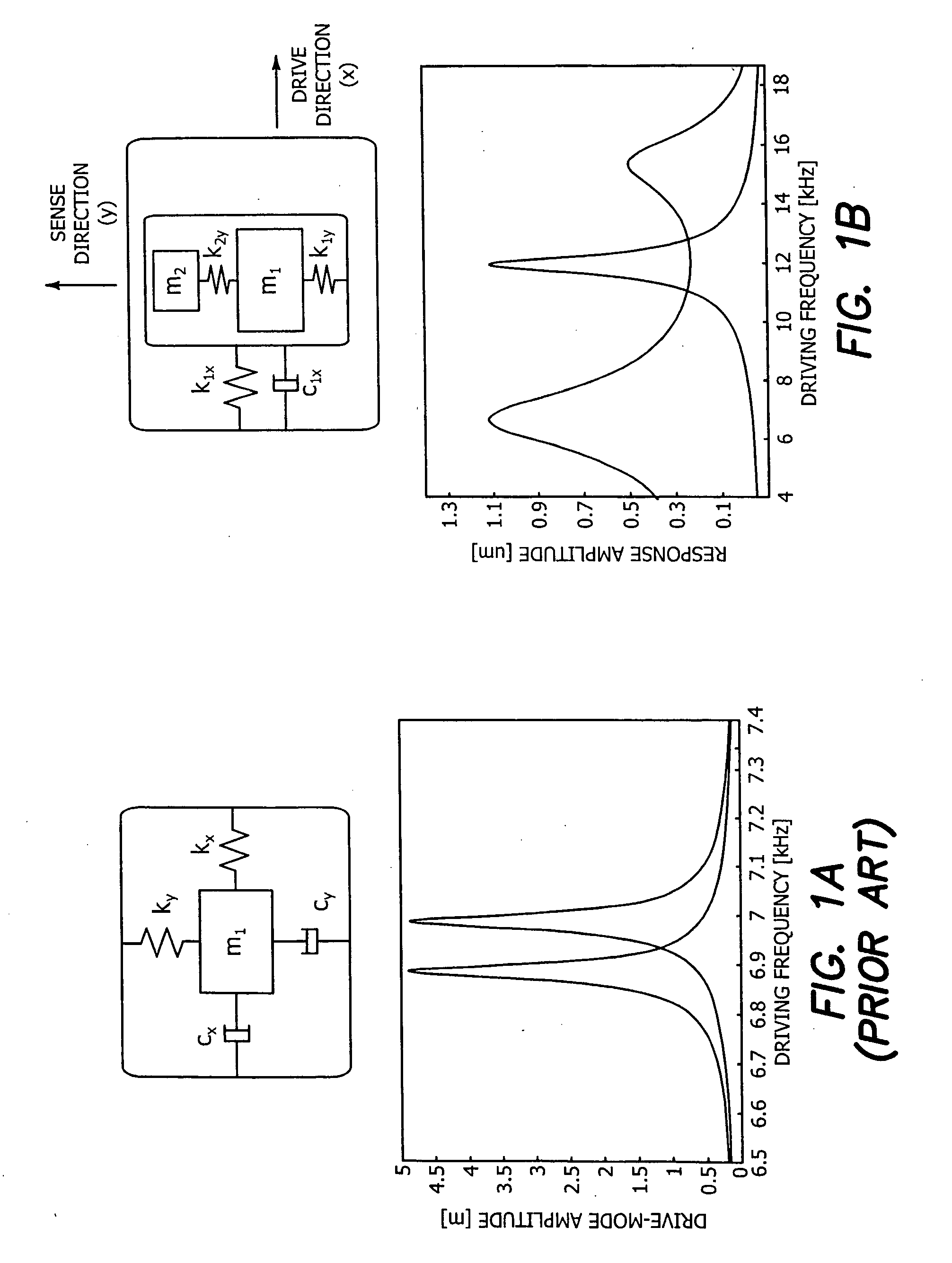
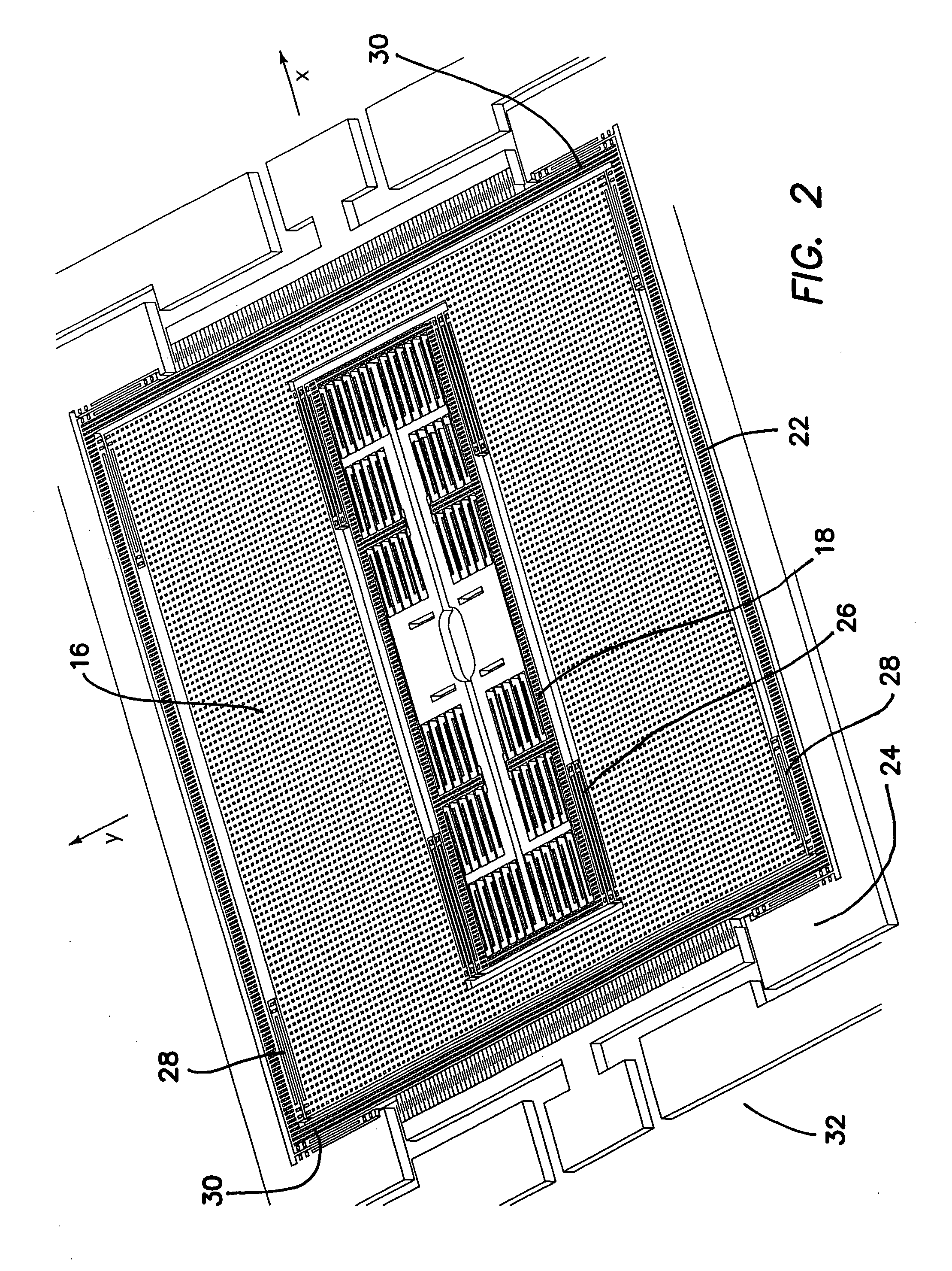
Micromachined tuning fork gyroscopes with ultra-high sensitivity and shock rejection
ActiveUS8322213B2Energy consumption is minimizedQuality improvementAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkDynamic balance
A vibratory rate z-axis gyroscope is characterized by drive-mode and sense-mode quality factors and rate sensitivity and is fabricated with at least two decoupled vibratory tines, a levered drive-mode mechanism coupled between the tines to structurally force anti-phase drive-mode motion of the tines at a predetermined drive frequency, to eliminate spurious frequency modes of the anti-phase drive-mode motion of the tines lower than the predetermined drive frequency and to provide synchronization of drive- and sense-mode motion of the tines, and a sense-mode mechanism coupled between the tines arranged and configured to provide a linearly coupled, dynamically balanced anti-phase sense-mode motion of the tines to minimize substrate energy dissipation and to enhance the sense-mode quality factor and rate sensitivity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
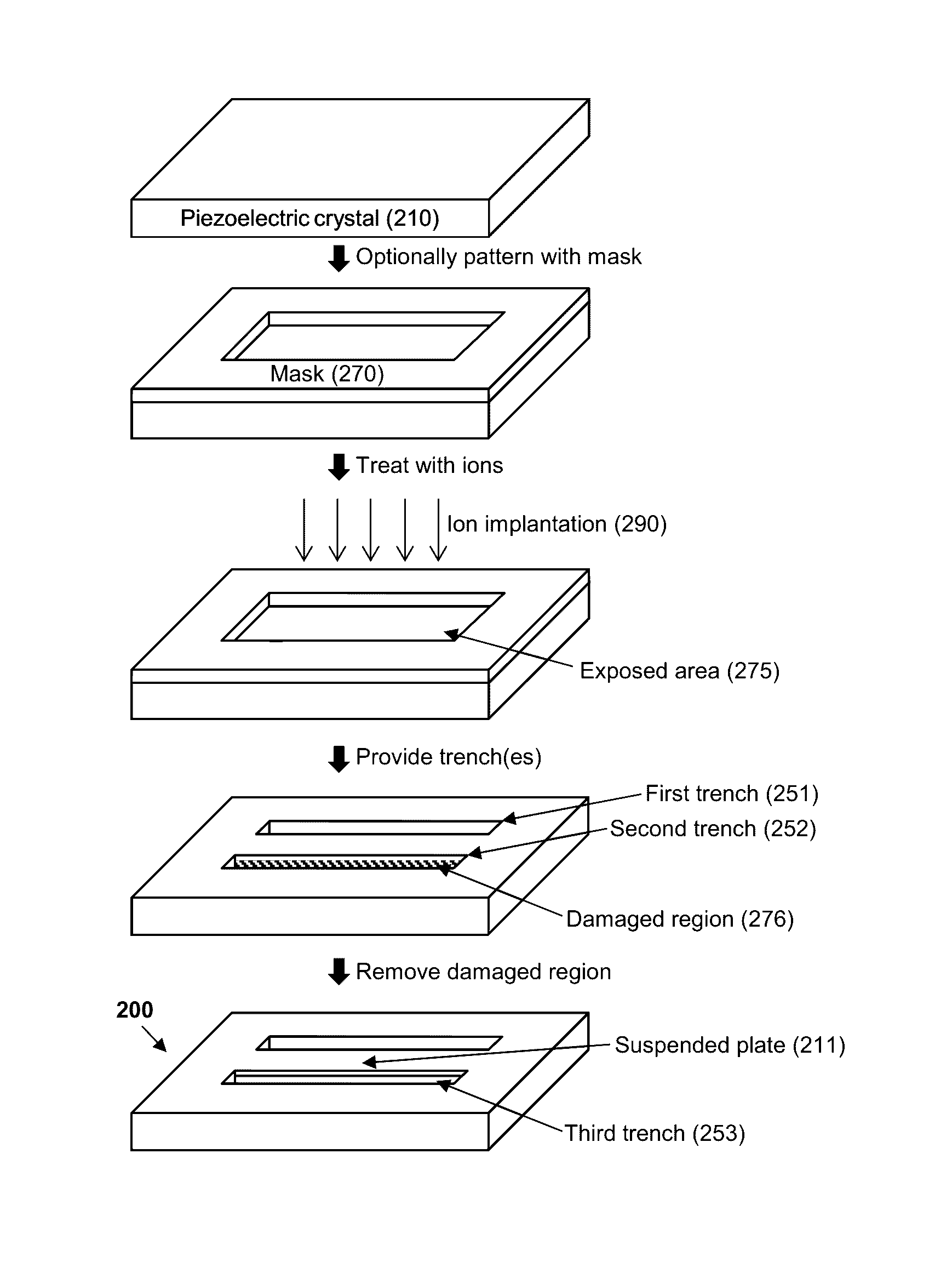
Single crystal micromechanical resonator and fabrication methods thereof
The present invention relates to a single crystal micromechanical resonator. In particular, the resonator includes a lithium niobate or lithium tantalate suspended plate. Also provided are improved microfabrication methods of making resonators, which does not rely on complicated wafer bonding, layer fracturing, and mechanical polishing steps. Rather, the methods allow the resonator and its components to be formed from a single crystal.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Micromachined bilayer unit for filtration of small molecules
InactiveUS7776021B2Enhanced convectionFacilitated DiffusionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationSmall molecule
Methods and materials for making an apparatus which duplicates the functionality of a physiological system id provided.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
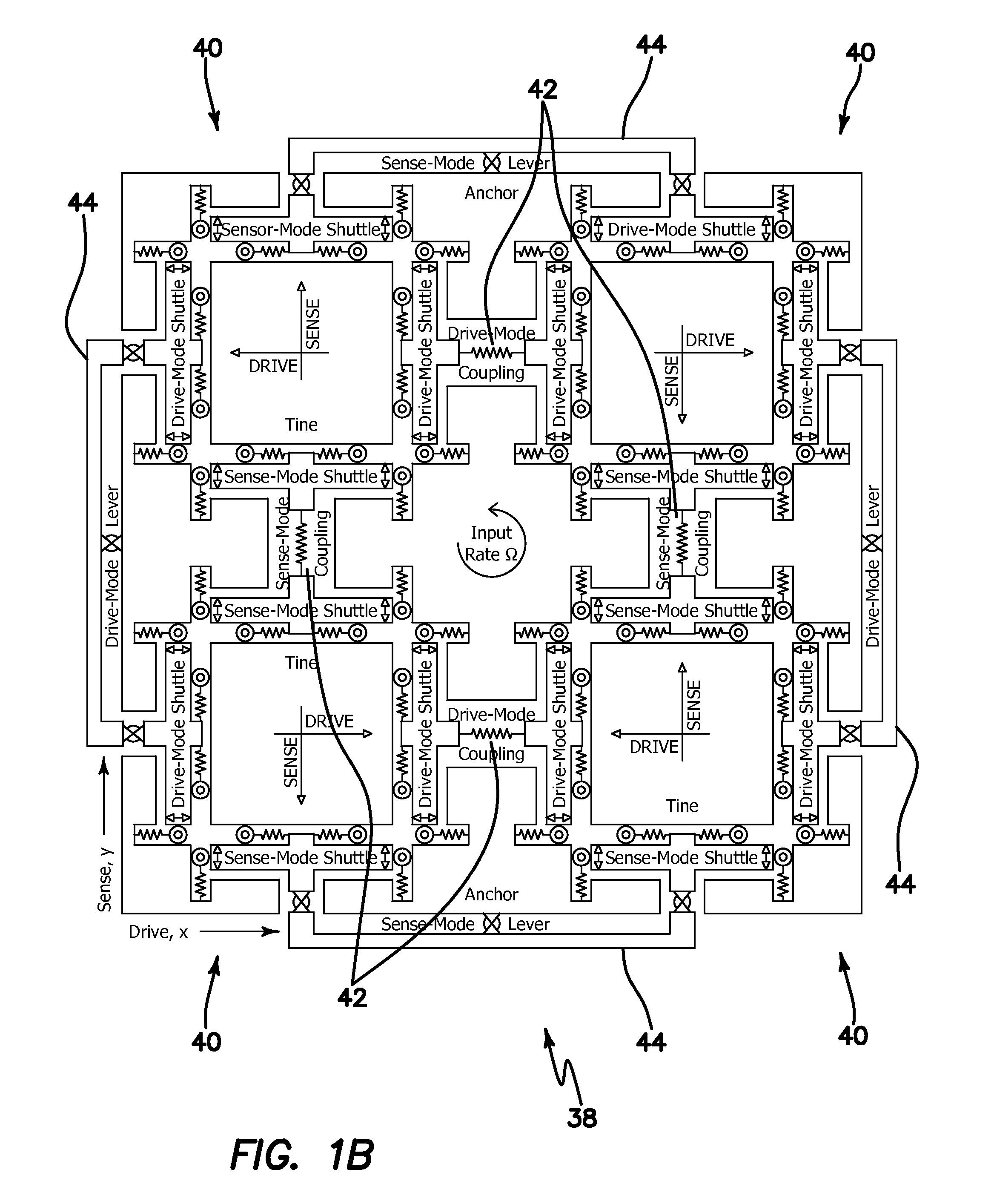
Robust micromachined gyroscopes with two degrees of freedom sense-mode oscillator
ActiveUS20070034005A1High bandwidthHigh sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopePlanar substrate
A three-degrees of freedom (DOF) MEMS inertial micromachined gyroscope with nonresonant actuation with a drive direction, sense direction and a direction perpendicular to the drive and sense directions comprises a planar substrate, a 2-DOF sense-mode oscillator coupled to the substrate operated at a flattened wide-bandwidth frequency region, and a 1-DOF drive mode oscillator coupled operated at resonance in the flattened wide-bandwidth frequency region to achieve large drive-mode amplitudes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Micromachined voltage controlled optical attenuator
InactiveUS6343178B1Improve seismic performanceReduce the starting voltageMirrorsCoupling light guidesUltrasound attenuationSemiconductor structure
This invention provides a very sensitive optical attenuator, which can be used to couple and attenuate optical signals between optical fibers with a wide range of attenuation level. Such an optical attenuator includes a flexible conductive membrane to be moved by an external force, such as electrostatic force, to achieve deformation of the conductive membrane. The conductive membrane can be formed, for example, by a vacuum deposited silicon nitride film. A thin metallic, conductive layer is then deposited on the flexible membrane to form a reflective mirror to receive and reflect incident optical signals. The semiconductor structure includes one or more spacing posts, with which the first structural member is to be joined and bonded. Electrodes are placed on the semiconductor structure in close proximity to the flexible membrane. At various areas of the semiconductor structure, additional spacing posts are added to cause deformation of the conductive membrane when a voltage is applied between the membrane and the electrodes on the semiconductor structure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Contour-mode piezoelectric micromechanical resonators
ActiveUS20060290449A1Reduce packaging costsLower resistanceImpedence networksEngineeringMicromachinery
A contour mode micromechanical piezoelectric resonator. The resonator has a bottom electrode; a top electrode; and a piezoelectric layer disposed between the bottom electrode and the top electrode. The piezoelectric resonator has a planar surface with a cantilevered periphery, dimensioned to undergo in-plane lateral displacement at the periphery. The resonator also includes means for applying an alternating electric field across the thickness of the piezoelectric resonator. The electric field is configured to cause the resonator to have a contour mode in-plane lateral displacement that is substantially in the plane of the planar surface of the resonator, wherein the fundamental frequency for the displacement of the piezoelectric resonator is set in part lithographically by the planar dimension of the bottom electrode, the top electrode or the piezoelectric layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
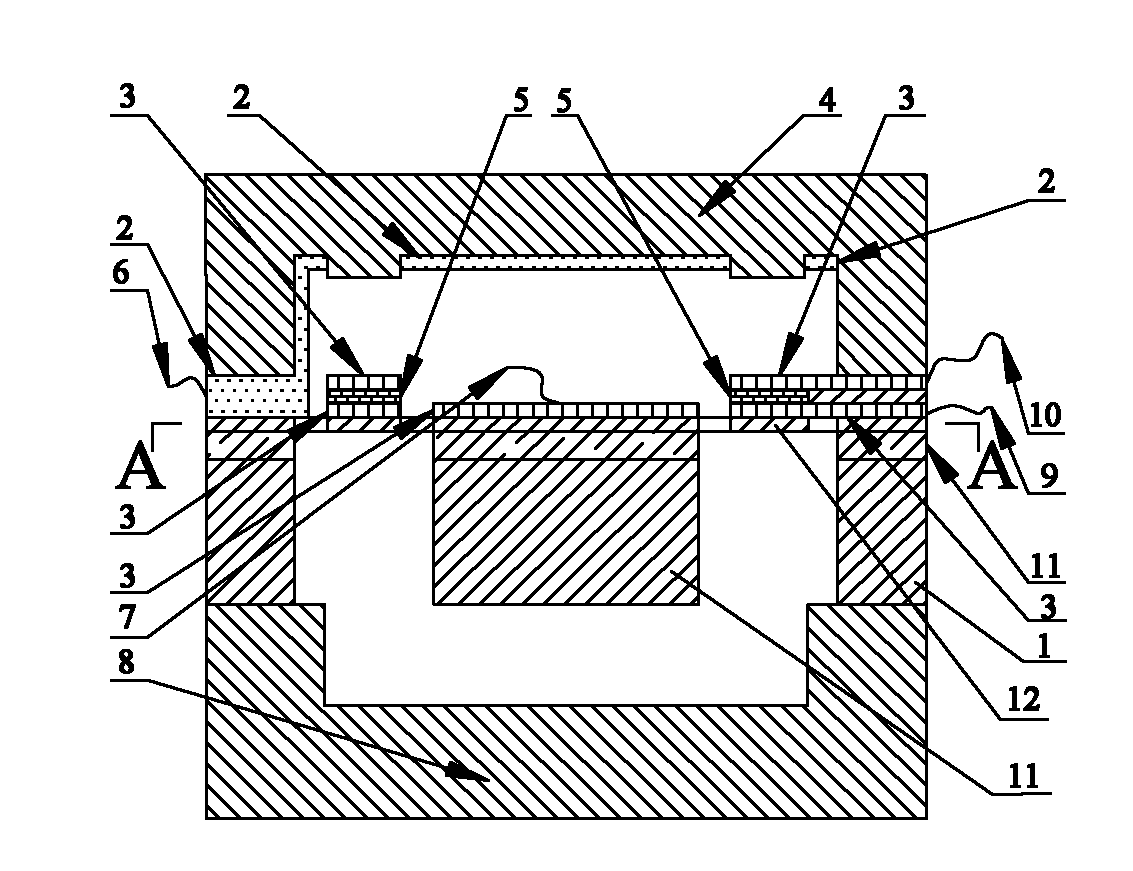
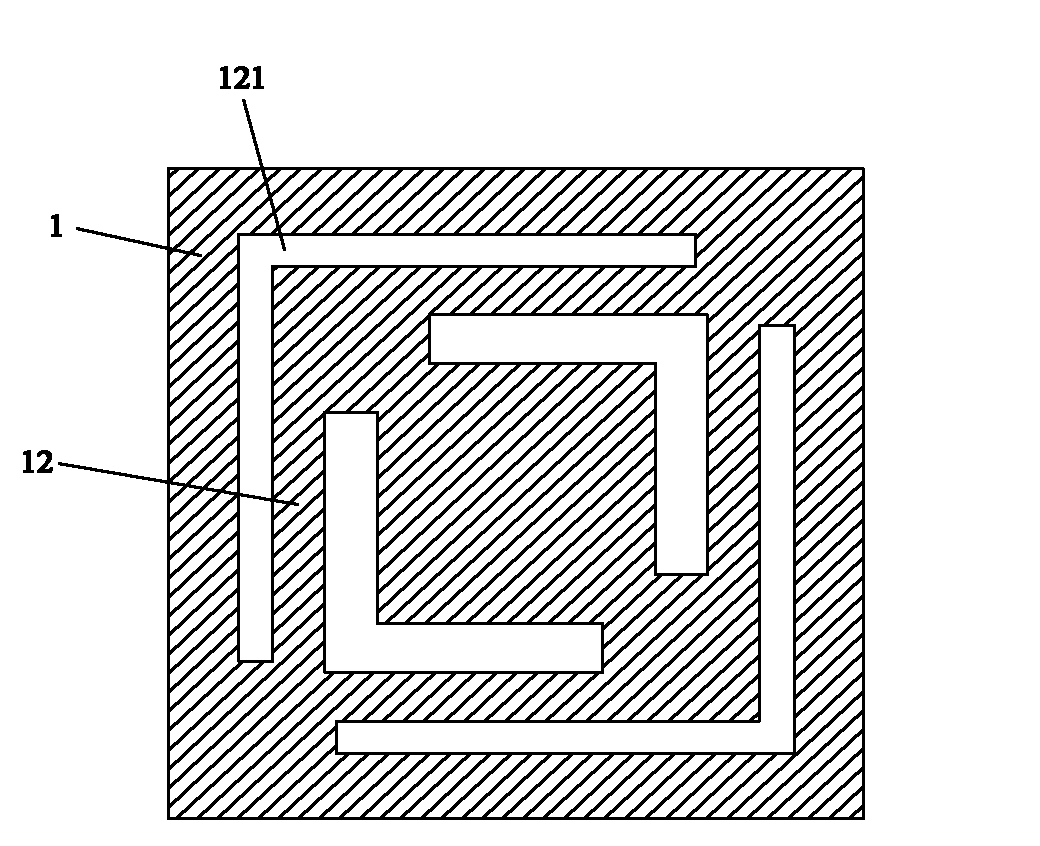
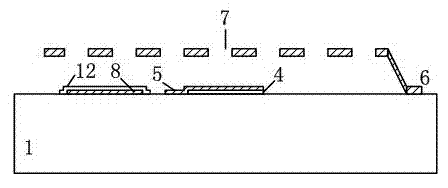
Micromechanical silicon-based clamped beam-based phase detector and detection method
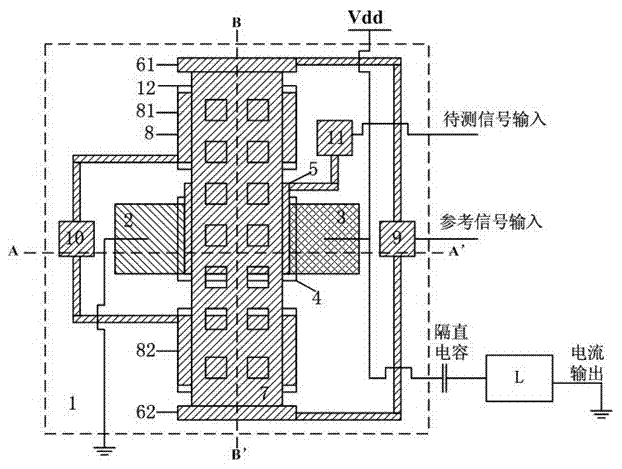
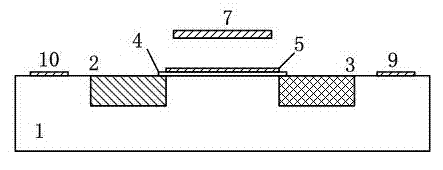
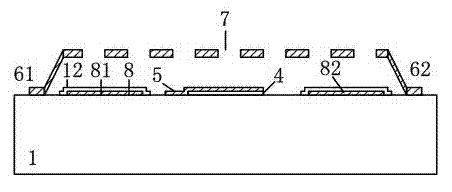
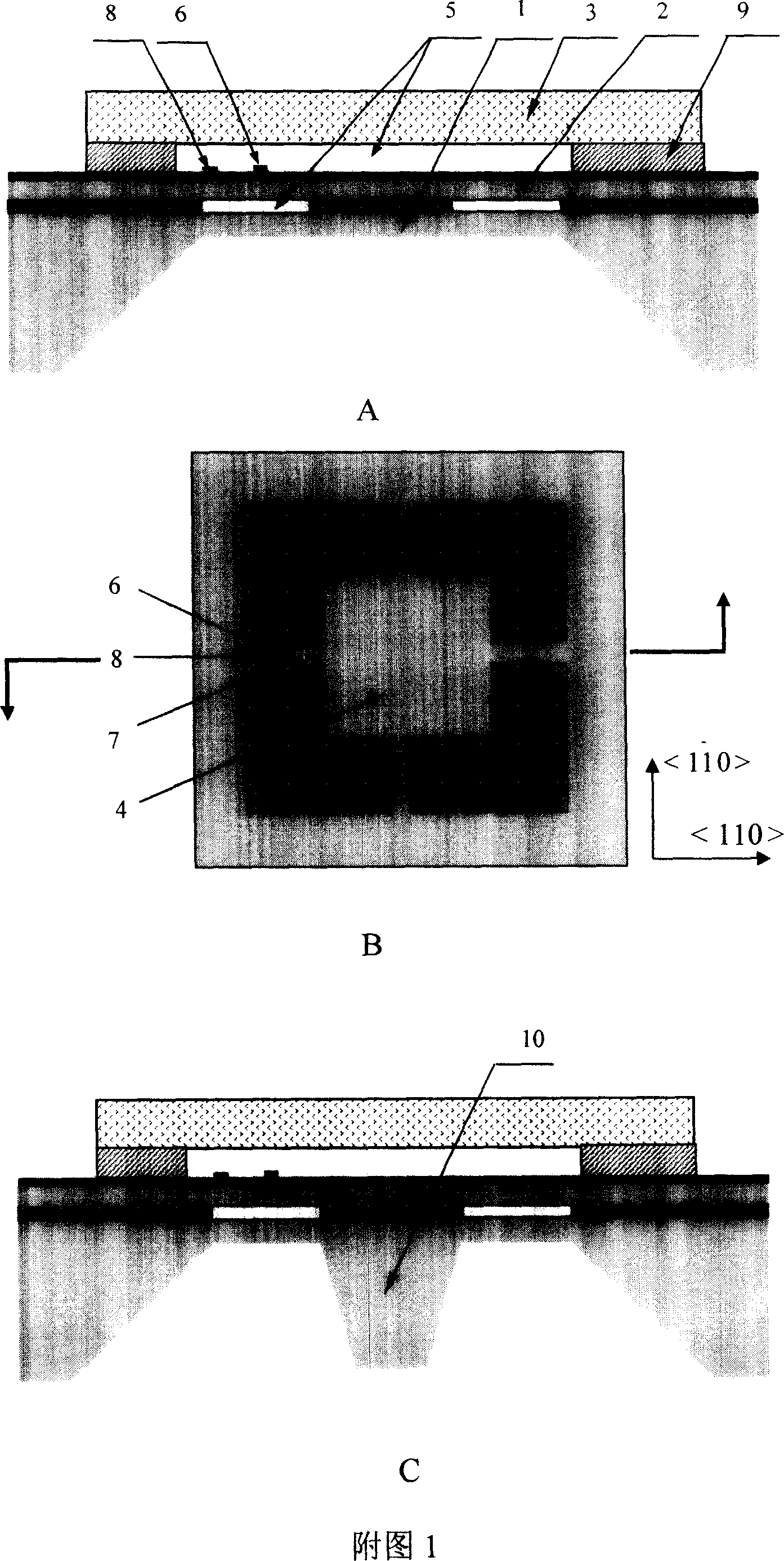
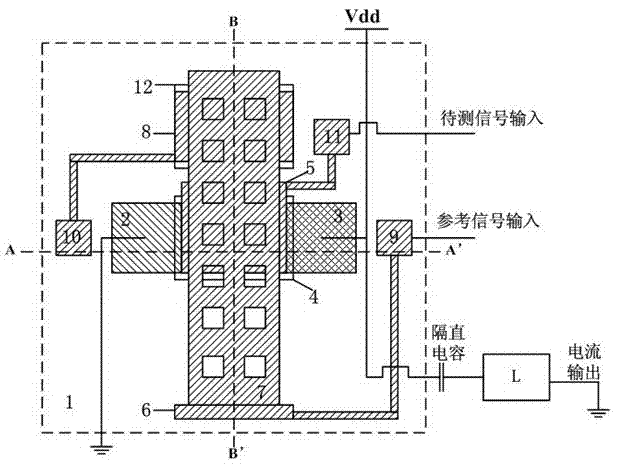
The invention discloses a micromechanical silicon-based clamped beam-based phase detector and a detection method. The phase detector comprises a silicon substrate (1), a source (2), a drain (3), a first clamped beam-anchoring area (61), a second clamped beam-anchoring area (62), a grid (5) and a clamped beam (7), wherein the source (2) and the drain (3) are grown on the surface of the silicon substrate (1) and used for outputting saturation current, the source (2) is arranged opposite from the drain (3), and the clamped beam (7) is arranged upon the grid (5) and is opposite to the grid (5). The detection method includes the following steps: when a direct-current offset is loaded on a first pull-down electrode (81) and a second pull-down electrode (82) and the clamped beam (7) is pulled down and is in contact with the grid (5), two microwave signals which have the same frequency and certain phase difference are simultaneously loaded on the grid (5); the saturation current of the drain (3) is processed, so that high-frequency signals are filtered, and therefore the current signal of phase difference information is obtained. The structure of the phase detector is simple, and measurement is easy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
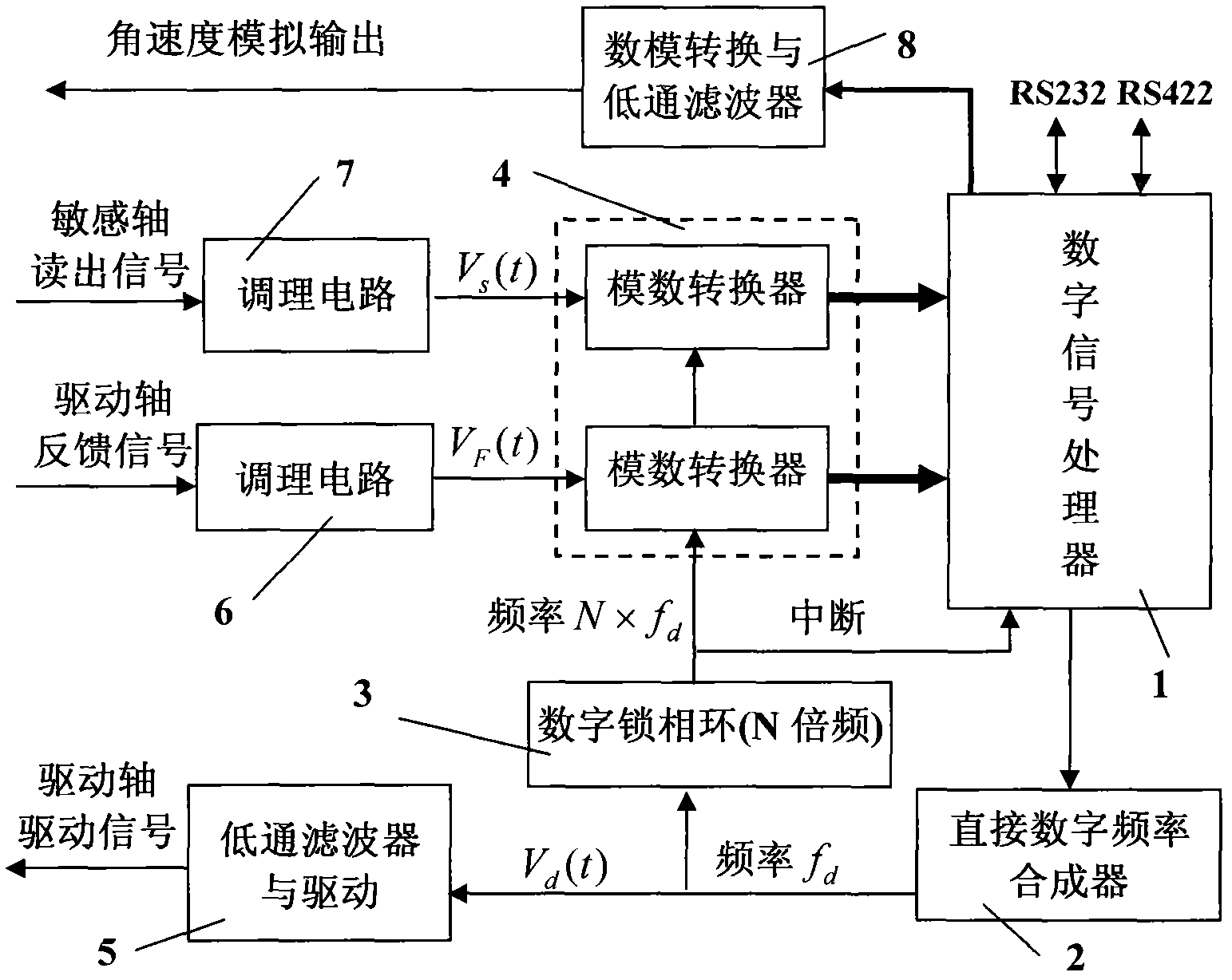
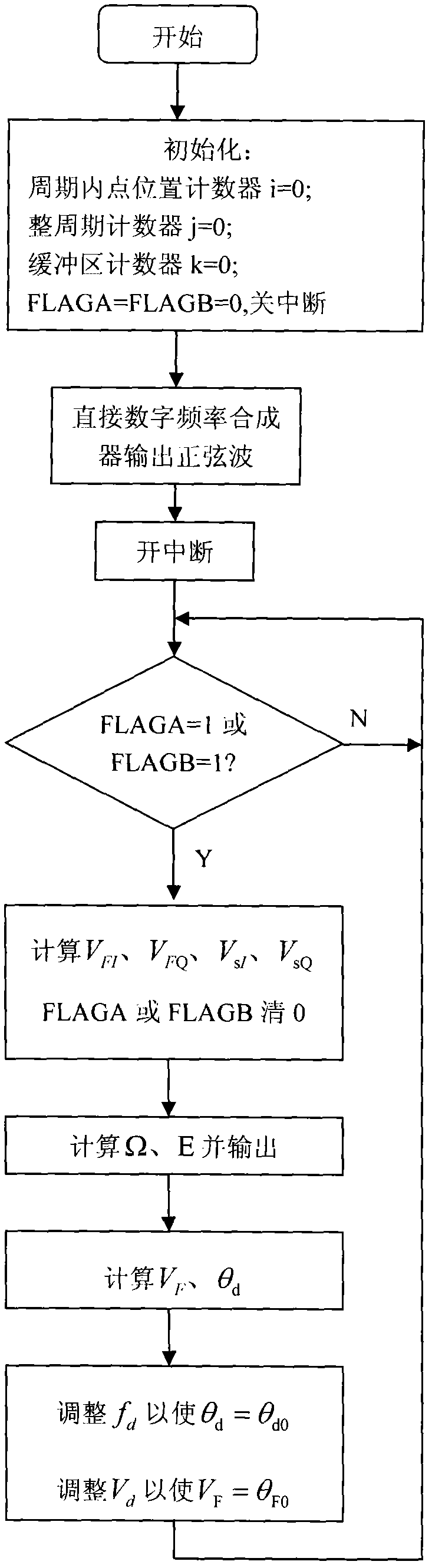
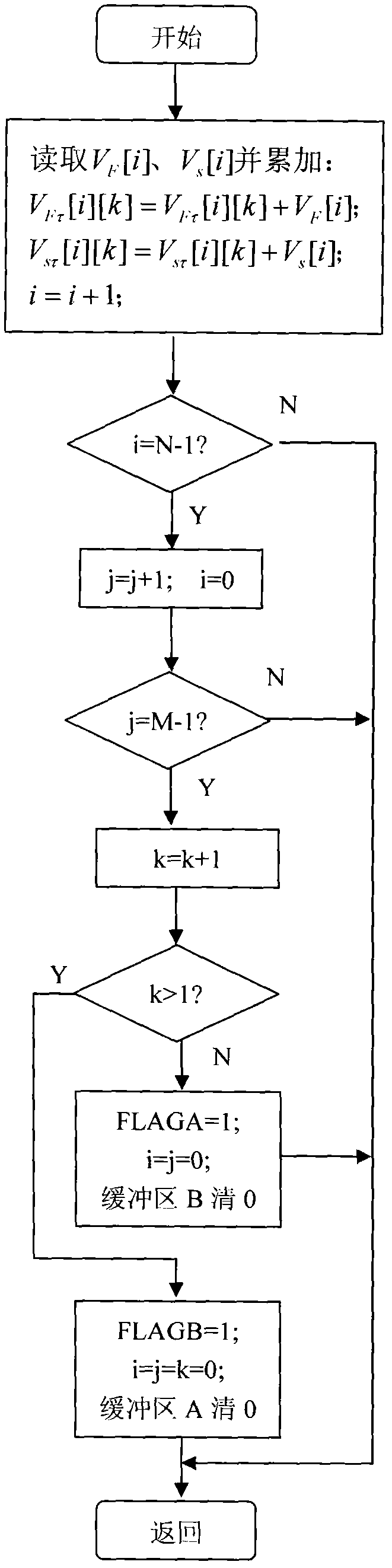
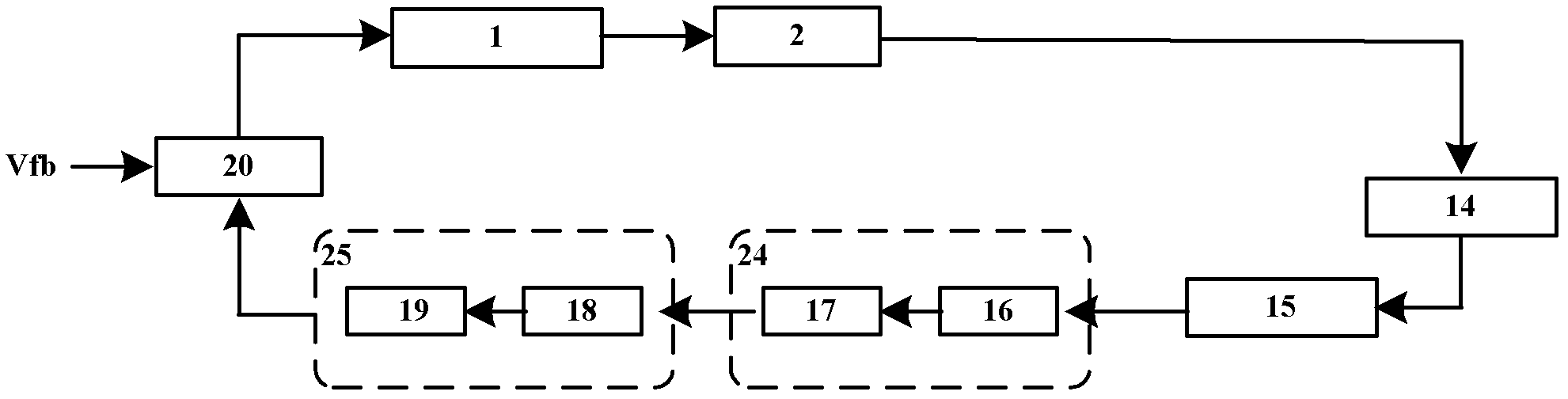
Digital signal processing method and device for micro-mechanical gyroscope
InactiveCN102109345ASpectrum pureHigh frequency resolutionSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTurn-sensitive devicesDigital signal processingVibration amplitude
The invention relates to a digital signal processing method and a device for a micro-mechanical gyroscope. The device mainly comprises a digital signal processor, a direct digital frequency synthesizer, a digital phase-locked loop and an analog-to-digital converter. The frequency synthesizer is used for outputting a sine drive signal with controllable frequency and amplitude. A drive feedback signal and an angular velocity readout signal are synchronously converted by the analog-to-digital converter; the converted frequency is an integral multiple of the frequency of the drive signal, and thesampling time length is an integral multiple of the period of the drive signal. With the adoption of the digital signal processor, the sampling data is multiplied by the fixed sine and cosine coefficients, and the input angular velocity and the orthotropic error as well as the phase and the amplitude of the drive feedback signal are resolved in an accumulative manner, and the phase parameters areutilized for adjusting the frequency of the drive signal, so that the frequency of the drive signal follows up the resonance frequency of the gyroscope. The amplitude parameters are utilized for adjusting the amplitude of the drive signal, so that the vibration amplitude is constant. The device realizes the drive of the micro-mechanical gyroscope and the digitization of the angular velocity demodulation, has simple structure and high computation precision, and is easy to produce and transplant in batch.
Owner:谢元平
Functional Capping
ActiveUS20120267773A1Eliminate risk of damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsEngineering
A wafer level method of making a micro-electronic and / or micro-mechanic device, having a capping with electrical wafer through connections (vias), comprising the steps of providing a first wafer of a semiconductor material having a first and a second side and a plurality of holes and / or recesses in the first side, and a barrier structure extending over the wafer on the second side, said barrier comprising an inner layer an insulating material, such as oxide, and an outer layer of another material. Then, metal is applied in said holes so as to cover the walls in the holes and the bottom of the holes. The barrier structure is removed and contacts are provided to the wafer through connections on the back-side of the wafer. Bonding structures are provided on either of said first side or the second side of the wafer. The wafer is bonded to another wafer carrying electronic and micro-electronic / mechanic components, such that the first wafer forms a capping structure covering the second wafer. Finally the wafer is singulated to individual devices.
Owner:SILEX MICROSYST
Polymeric piezoresistive sensors
InactiveUS20060071286A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSolid-state devicesOrganic semiconductorResonator
A MEMS system, such as a biosensor, includes a micromechanical resonator and a piezoresistive sensing element which includes an organic semiconductor, such as an organic thin film transistor.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
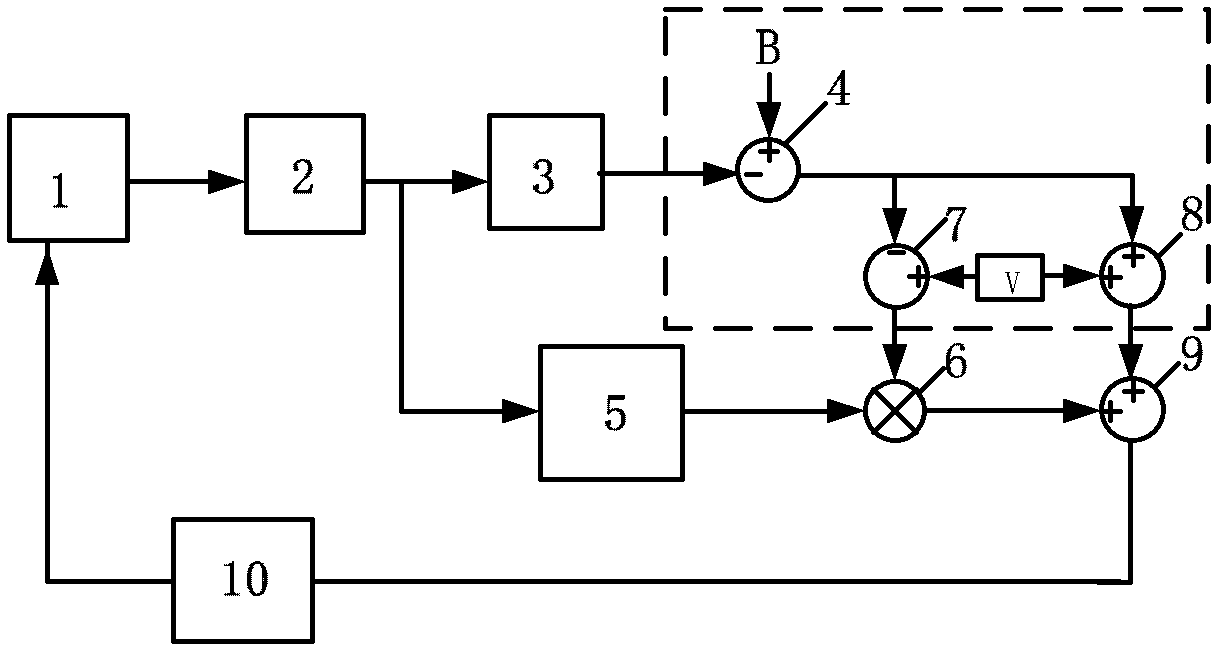
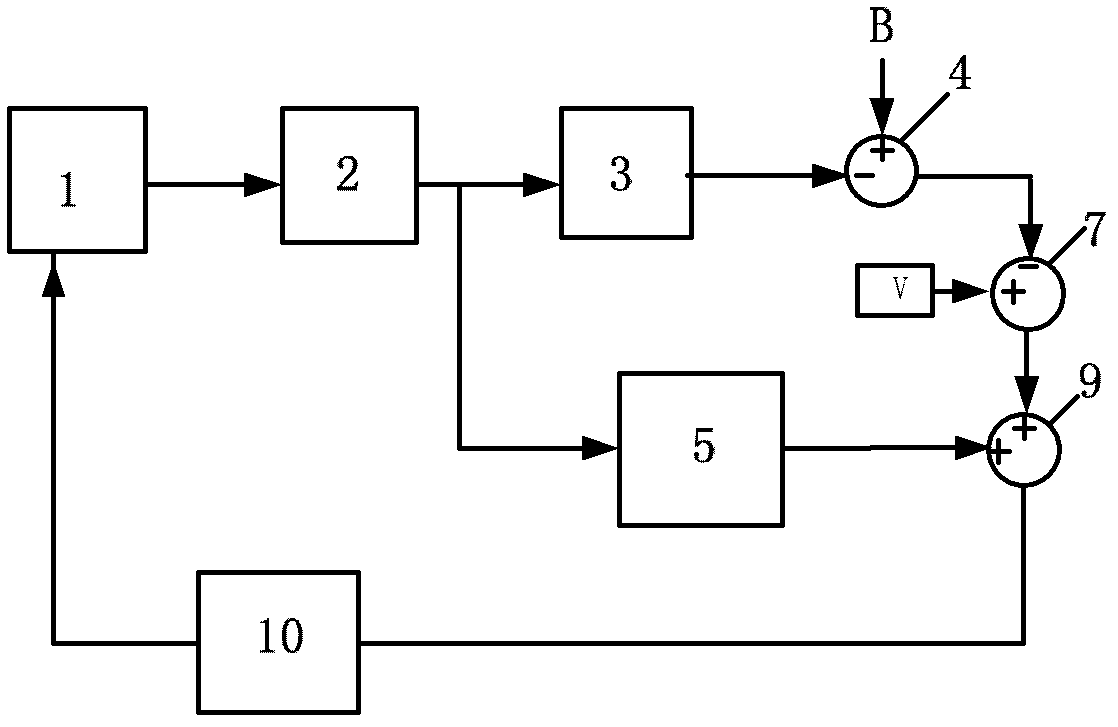
Double-closed-loop control circuit of micromechanical gyroscope
ActiveCN102620726AEasy to controlHigh precisionPulse automatic controlTurn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a double-closed-loop control circuit of a micromechanical gyroscope and belongs to the field of guide or control devices based on a Coriolis effect. The circuit is used for closed-loop control of driving and detection modes of the micromechanical gyroscope. A simplified self-oscillation closed-loop control circuit based on automatic gain control (AGC) is employed for the driving mode of the circuit, and the frequency stability and amplitude stability of the micromechanical gyroscope in the driving mode can be effectively improved; and a six-order continuous band-pass Sigma Delta M closed-loop control circuit for the detection mode has six-order noise reshaping capacity, and the signal to noise ratio (SNR), linearity and zero-bias stability of a system detection signal can be improved. The double-closed-loop control circuit of the micromechanical gyroscope is easy to control and simple, the accuracy of a system is improved, the SNR of the system is high, and the system is self-adaptively adjusted and high in stability.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Molded package for micromechanical devices and method of fabrication
InactiveUS7026710B2Low costIncrease productionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSpatial light modulatorMicromachinery
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
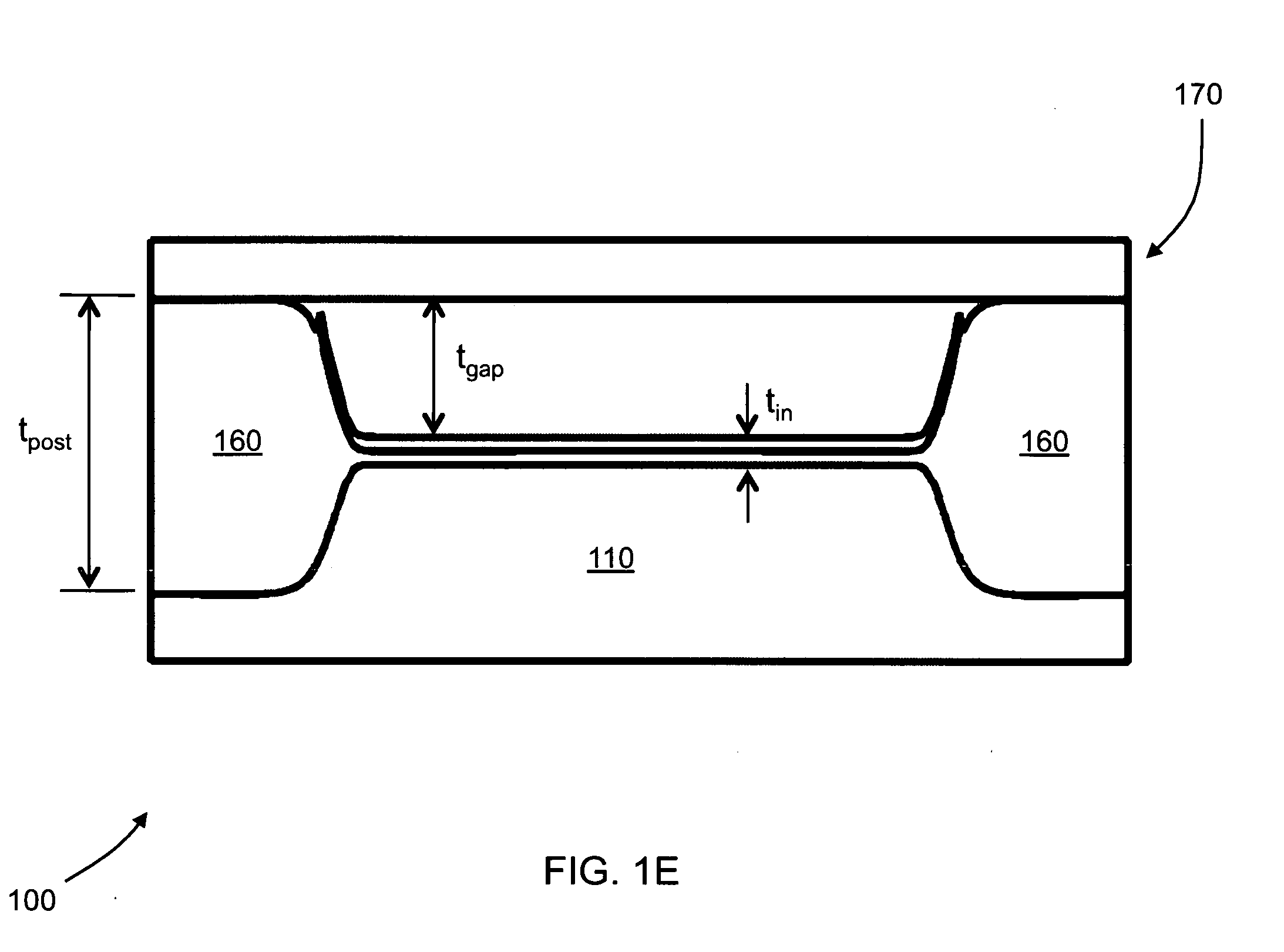
Fabrication of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers by local oxidation
ActiveUS20090142872A1Improve breakdown voltageReduce parasitic capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMechanical vibrations separationParasitic capacitorCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
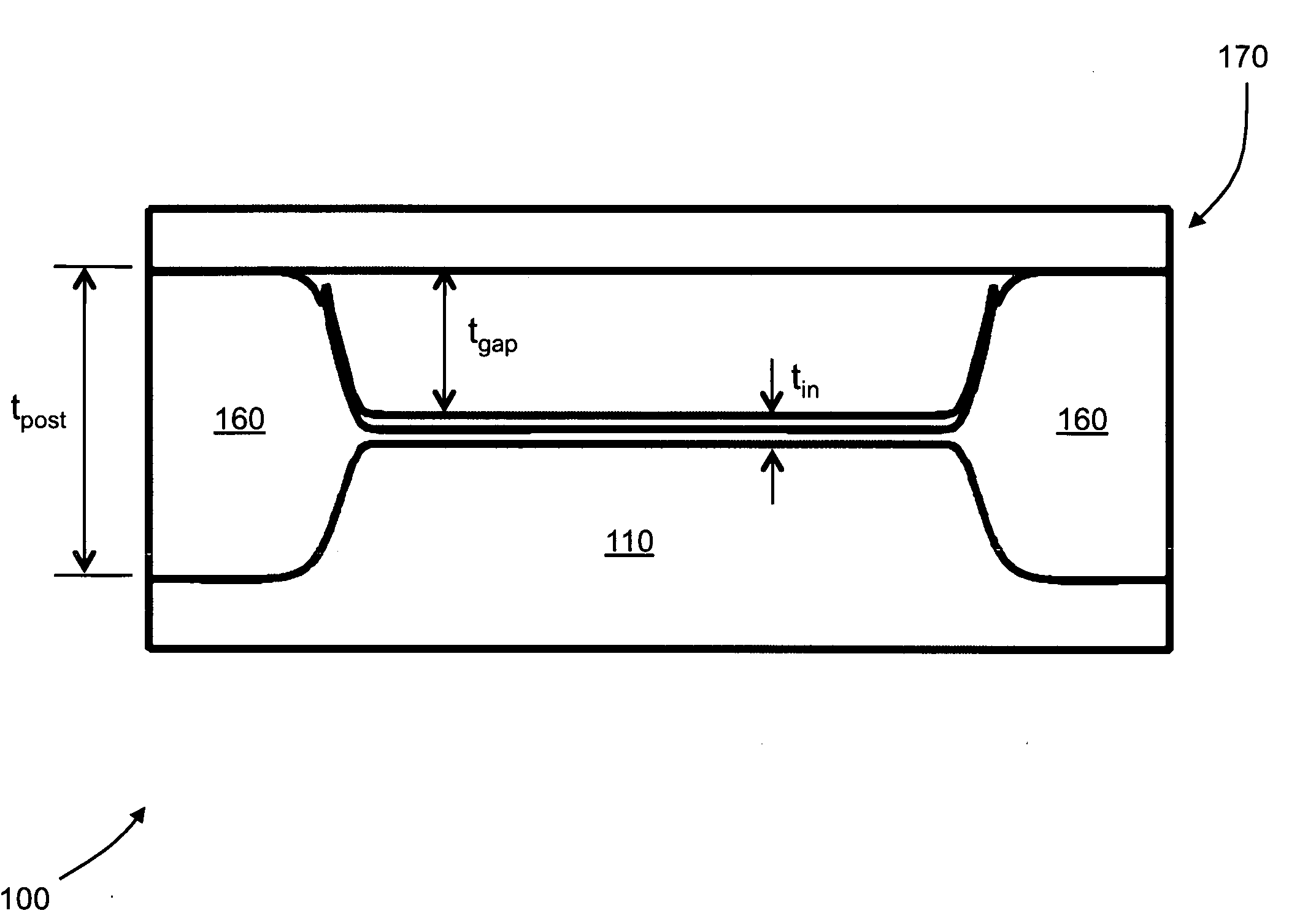
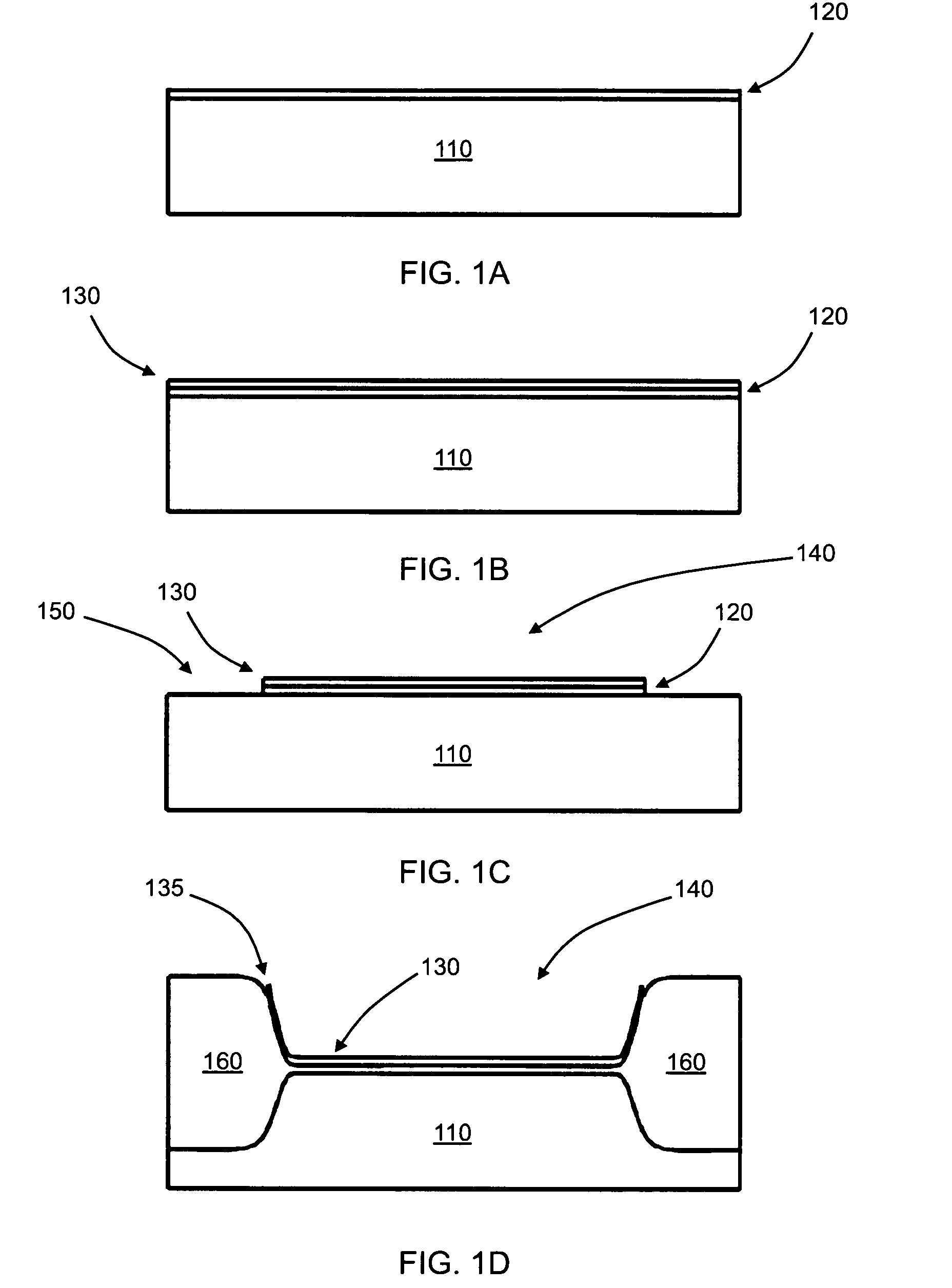
Fabrication methods for capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers (CMUTS) with independent and precise gap and post thickness control are provided. The fabrication methods are based on local oxidation or local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) to grow oxide posts. The process steps enable low surface roughness to be maintained to allow for direct wafer bonding of the membrane. In addition, methods for fabricating a step in a substrate are provided with reduced or minimal over-etch time by utilizing the nonlinearity of oxide growth. The fabrication methods of the present invention produce CMUTs with unmatched uniformity, low parasitic capacitance, and high breakdown voltage.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
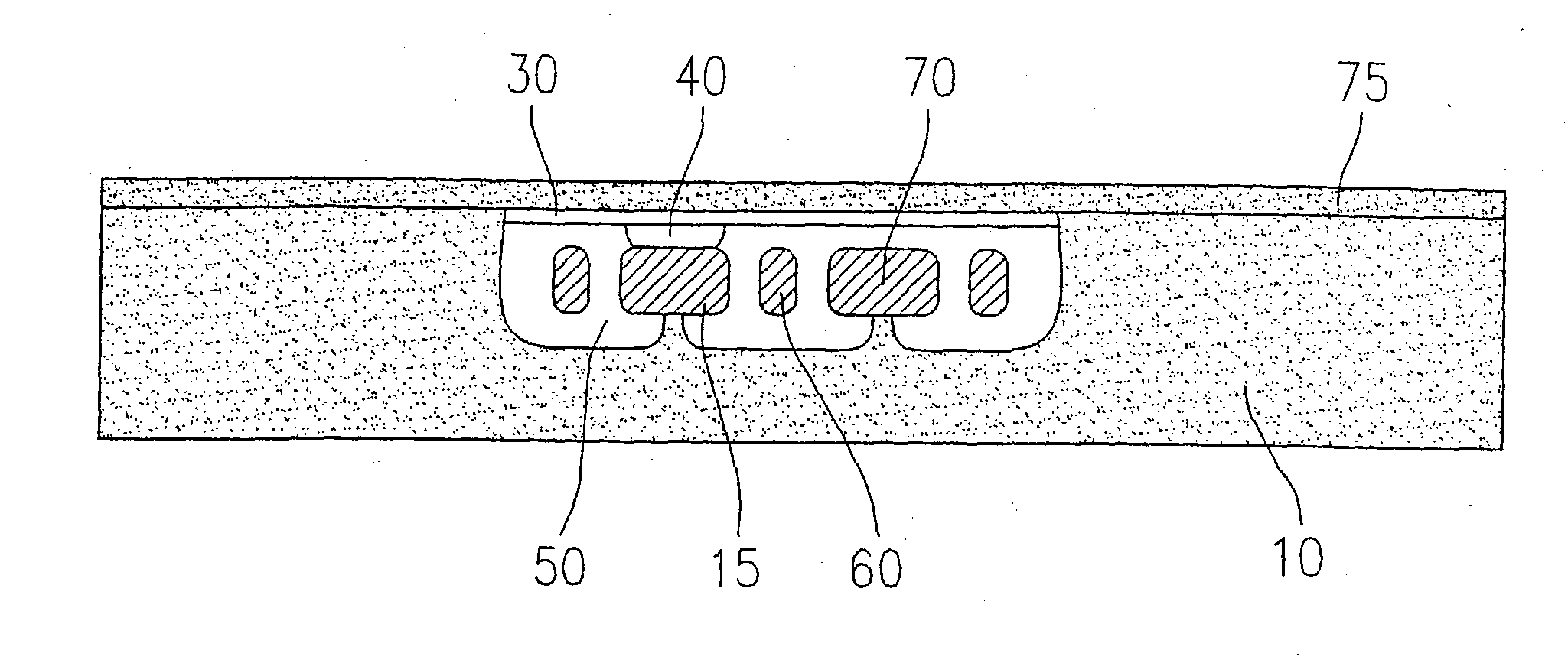
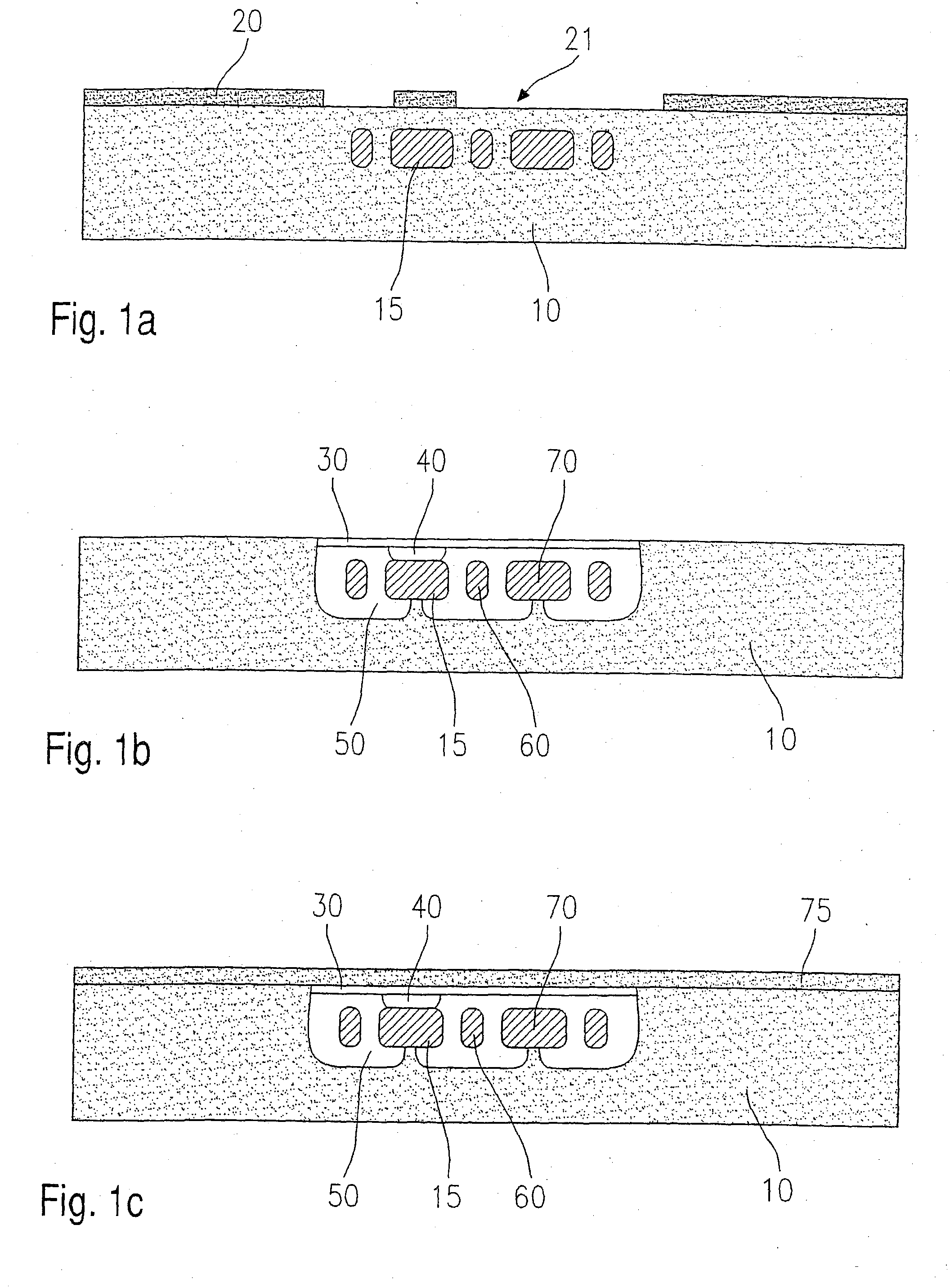
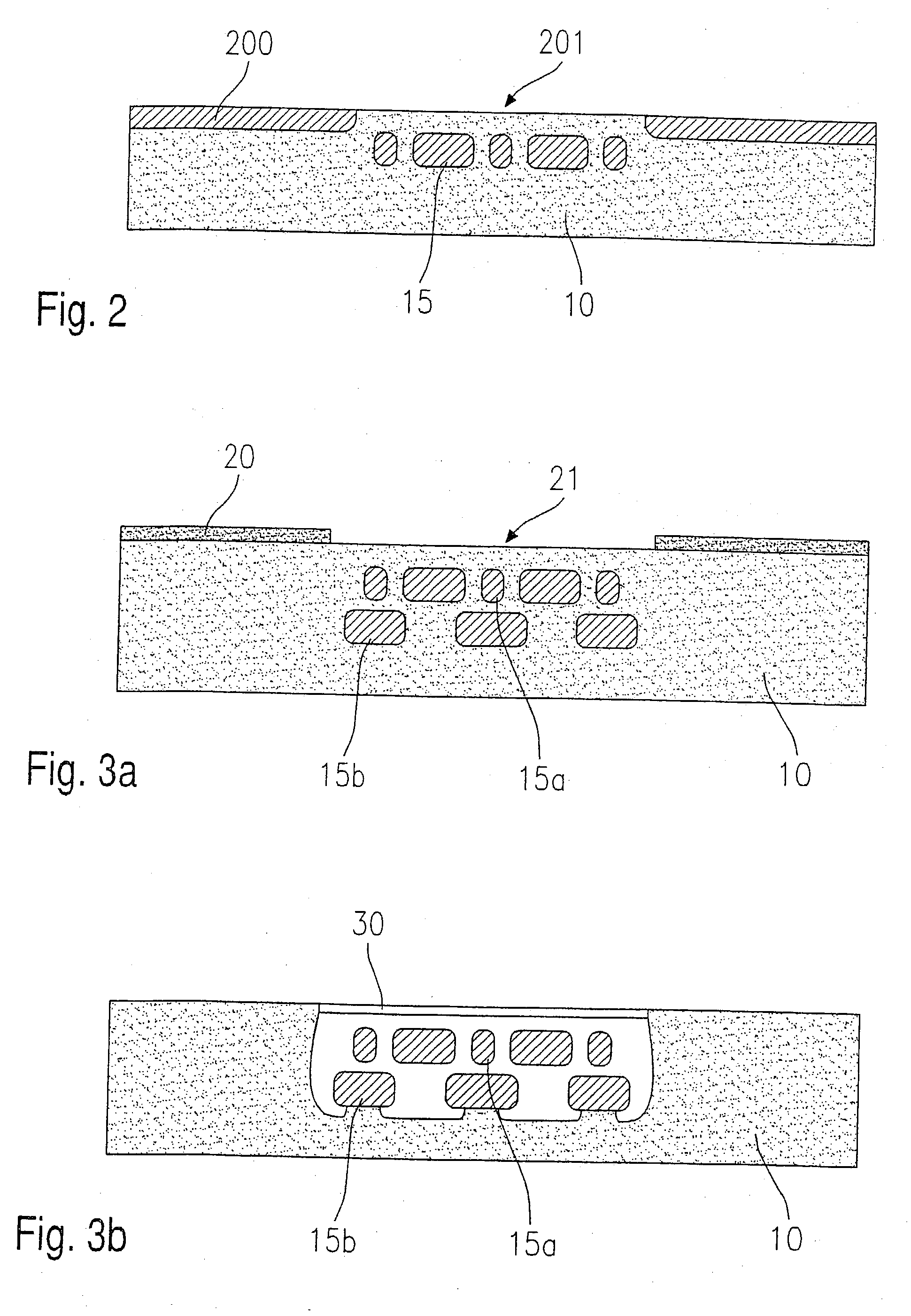
Micromechanical component and corresponing production method
A micromechanical component having a substrate (10) made from a substrate material having a first doping type (p), a micromechanical functional structure provided in the substrate (10) and a cover layer to at least partially cover the micromechanical functional structure. The micromechanical functional structure has zones (15; 15a; 15b; 15c; 730; 740; 830) made from the substrate material having a second doping type (n), the zones being at least partially surrounded by a cavity (50; 50e-f), and the cover layer has a porous layer (30) made from the substrate material.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Mode-Matching Apparatus and Method for Micromachined Inertial Sensors
ActiveUS20100294039A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAccelerometerMicromachinery
A mode matching servo for an inertial sensor having a resonator and an accelerometer provides a test signal at a frequency higher than a predetermined inertial sensor response frequency and lower than an accelerometer resonance mode frequency so as to induce acceleration signals from the accelerometer substantially at the test signal frequency when the modes are not matched. A feedback signal is provided in response to such induced signals to substantially nullify the signals.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Minute structure, micromachine, organic transistor, electric appliance, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20070001224A1High light transmittanceIncrease opening ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSilicon
A micromachine is generally formed using a semiconductor substrate such as a silicon wafer. One of the objects of the present invention is to realize further reduction in cost by integrating a minute structure and a semiconductor element controlling the minute structure over one insulating surface in one step. A minute structure has a structure in which a first layer formed into a frame-shape are provided over an insulating surface, a space is formed inside the frame, and a second layer is formed to cross over the first layer. Such a minute structure and a thin film transistor can be integrated over one insulating surface in one step.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Micromachined fluidic device and method for making same
InactiveUS7311503B2Reliably madeMinimizing dead volumeFunctional valve typesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsEngineeringSilicon
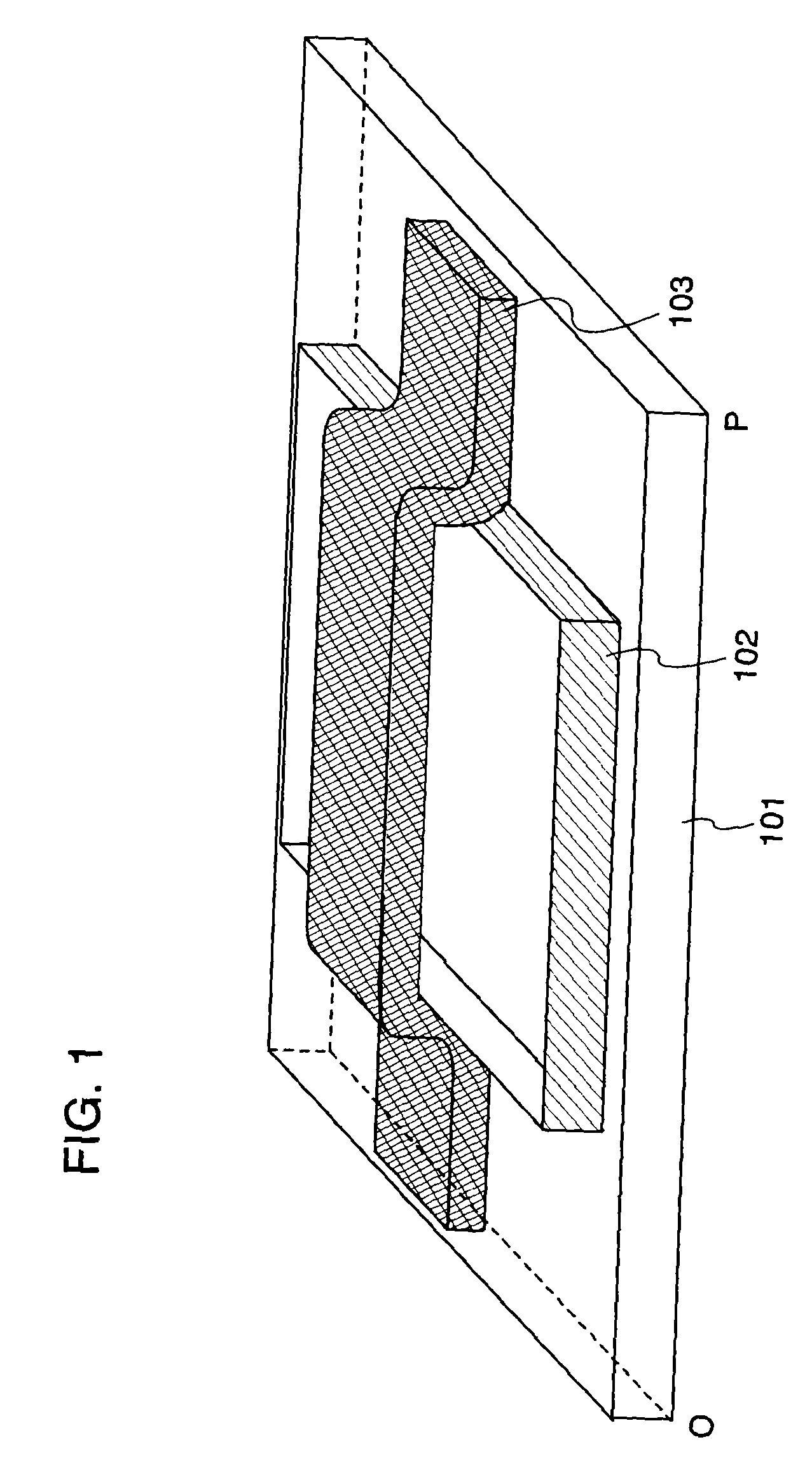
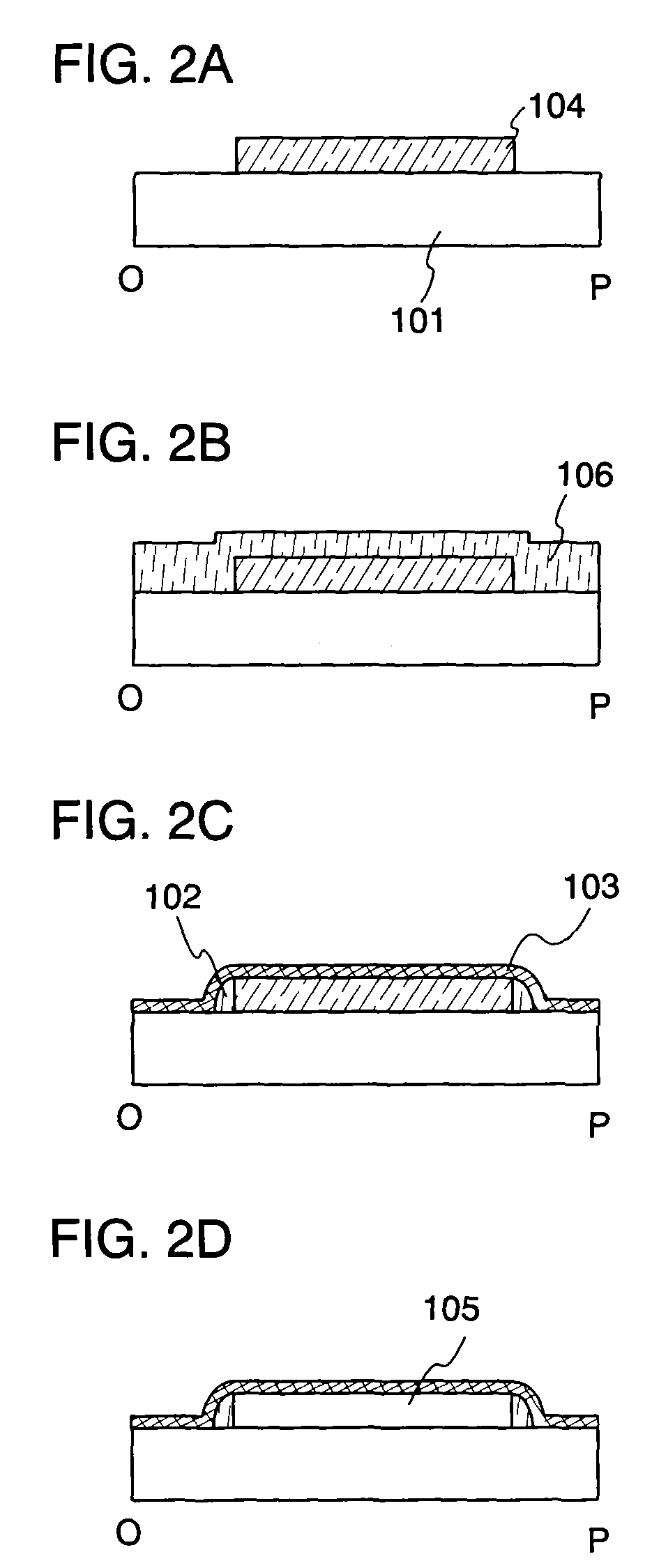
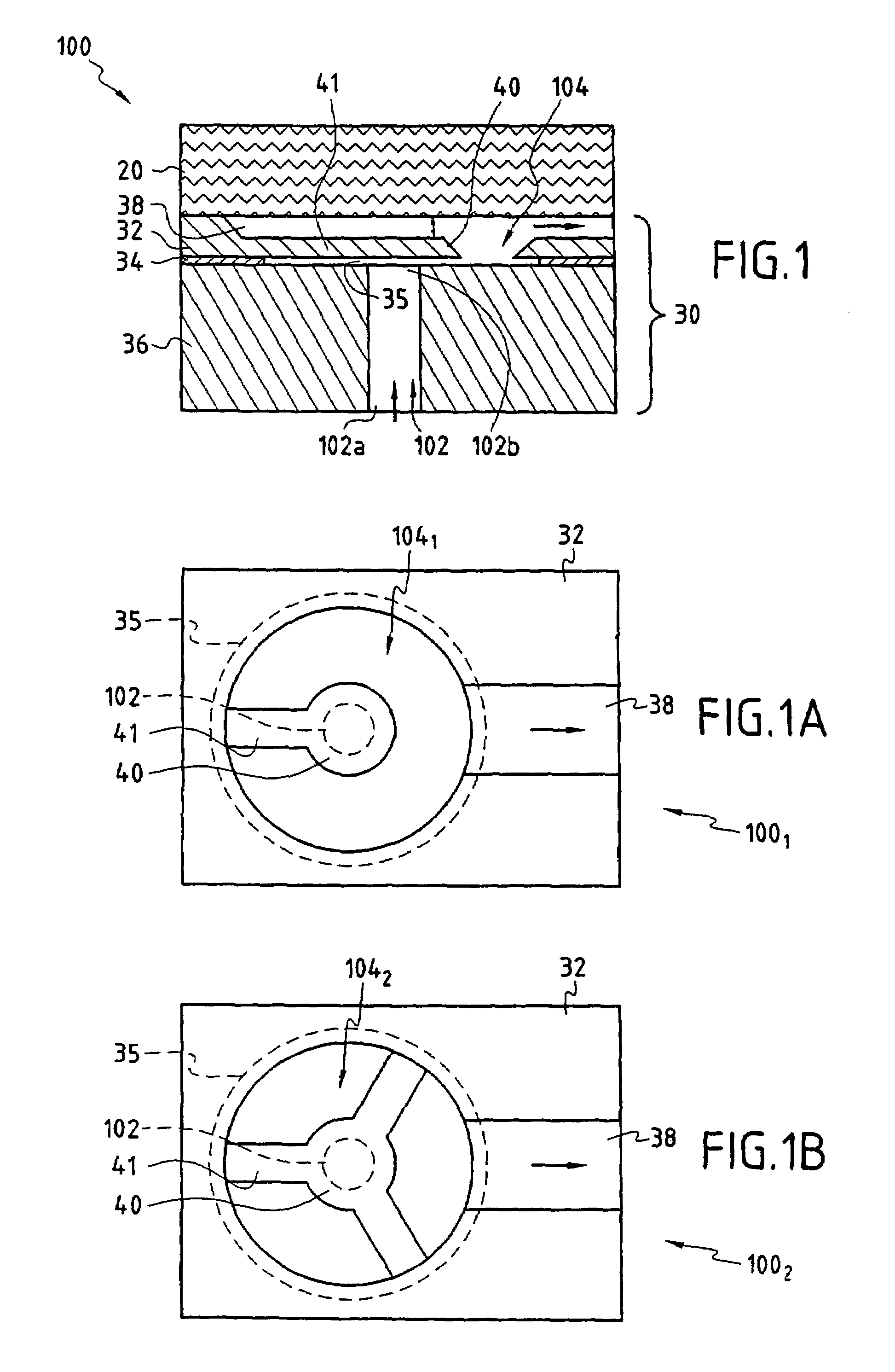
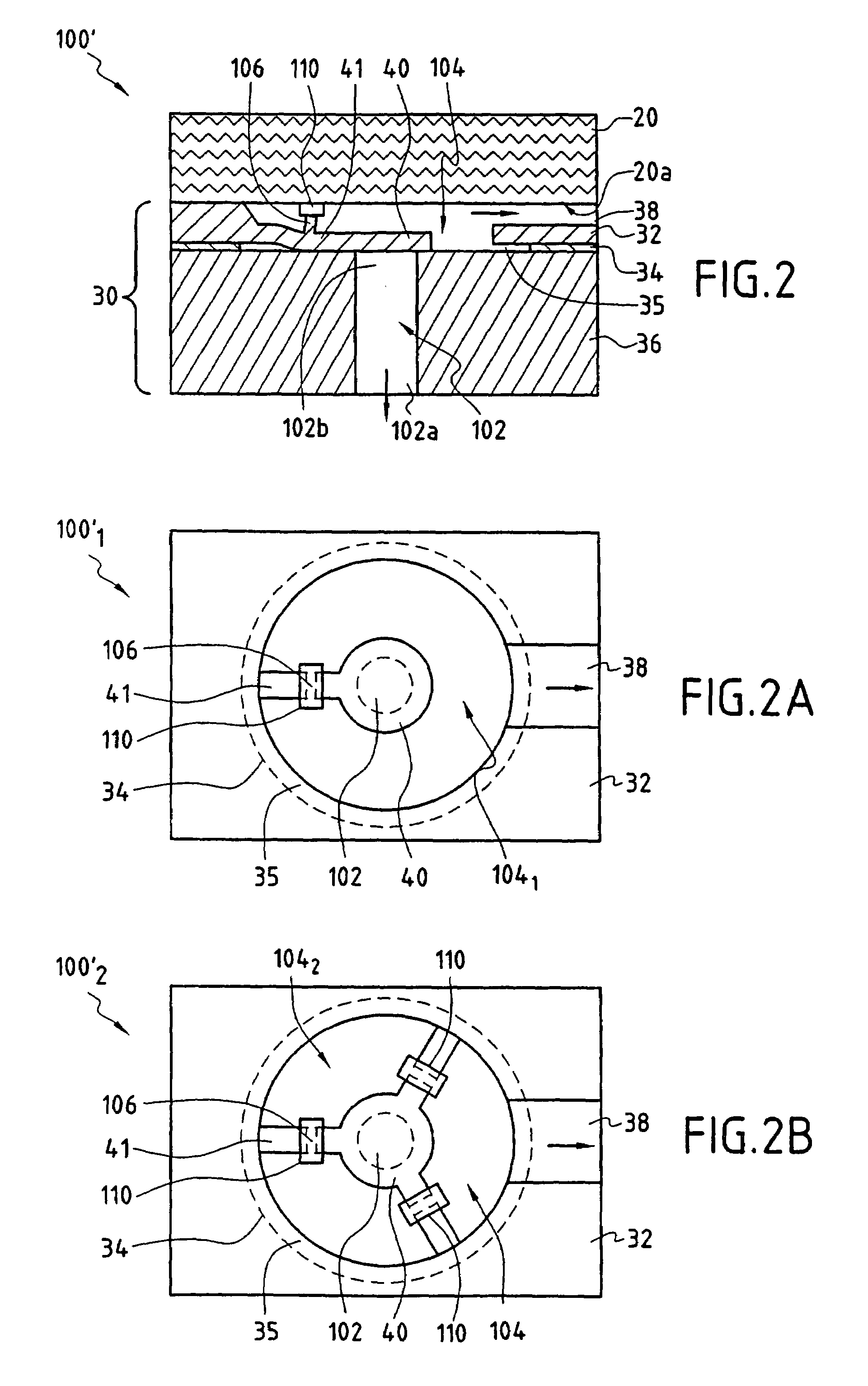
The fluid-flow device (100) of the invention comprises a stack (30) covered by a closure wafer (20), said stack (30) comprising a support wafer (36), a layer of insulating material (34), and a silicon layer (32). The closure wafer (20) and / or said silicon layer (32) are machined so as to define a cavity (38) between said closure wafer (20) and said silicon layer (32), said support wafer (36) has at least one duct (102) passing right through it, said layer of insulating material (34) presenting at least one zone (35) that is entirely free of material placed at least in line with said duct (102) so as to co-operate with said cavity (38) to define a moving member (40) in said silicon layer (32), the moving member being suitable under the pressure of liquid in said cavity (38) for reversibly moving towards said support wafer (36) until contact is made between said moving member (40) and said support wafer (36).
Owner:DEBIOTECH SA
Structure of silicon micromachine resonant micro-pressure sensor chip and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN101153825AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionForce measurement by measuring frquency variationsFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Rigid core
The invention discloses a structure of two resonant micro pressure sensor chips and a method of manufacturing the same. The structure of two resonant micro pressure sensor chips comprises a pressure inductive diaphragm with one or two rigid cores, a double-end clamped support beam and a cover plate 3. Under the function of fluid pressure, the diaphragm with rigid cores deforms to exert the double-end clamped support beams on the surface of the diaphragm to change resonant frequency upon the function of axial stress. Fluid pressure can be reflected by measuring the change in the resonant frequency of the double-end clamped support beam. The silicon resonant micro pressure sensor of the invention has higher signal-to-noise ratio, resolution, sensitivity and measurement precision and the output of the invention is the frequency signal.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Magnetic bead-based arrays
InactiveUS20080187472A1Easy to separateEasy to replaceSequential/parallel process reactionsFlow mixersFluorescenceMagnetic bead
The present invention relates to magnetic particle separators using micromachined magnetic arrays and more particularly, to magnetic particle separators or manipulators using controlled magnetization on micromachined magnetic arrays for the separation of cells and other biological materials. The present invention also pertains to using such devices for the separation and analysis of biological materials for immunoassays, DNA sequencing, protein analysis, and biochemical detection applications. The present invention can also be viewed as a novel method for fabricating fully integrated permanent magnet components within any microelectromechanical system (“MEMS”) structures. The present invention also provides a magnetic particle separation and manipulation system for rapid separation and accurate manipulation of magnetic particles in two-dimensional electromagnetic arrays, which utilize high throughput biological analyses. A disposable cartridge can be produced in low cost using a low cost substrate such as plastic or other polymer, glass, or metal. Magnetic flux is generated by conventional or micromachined electromagnets a platform system consisting of magnetic flux sources, magnetic flux guidance, and a microprocessor control interface. By controlling direction of electric currents into inductors on the platform system, arbitrary magnetic poles can be generated on Permalloy structures of the cartridge to separate and manipulate magnetic particles. The magnetic particle separator and manipulator in the present invention can be easily combined with automated detection systems such as a fluorescent monitoring system.
Owner:AHN CHONG H +2
Semiconductor micromachine and manufacturing method thereof
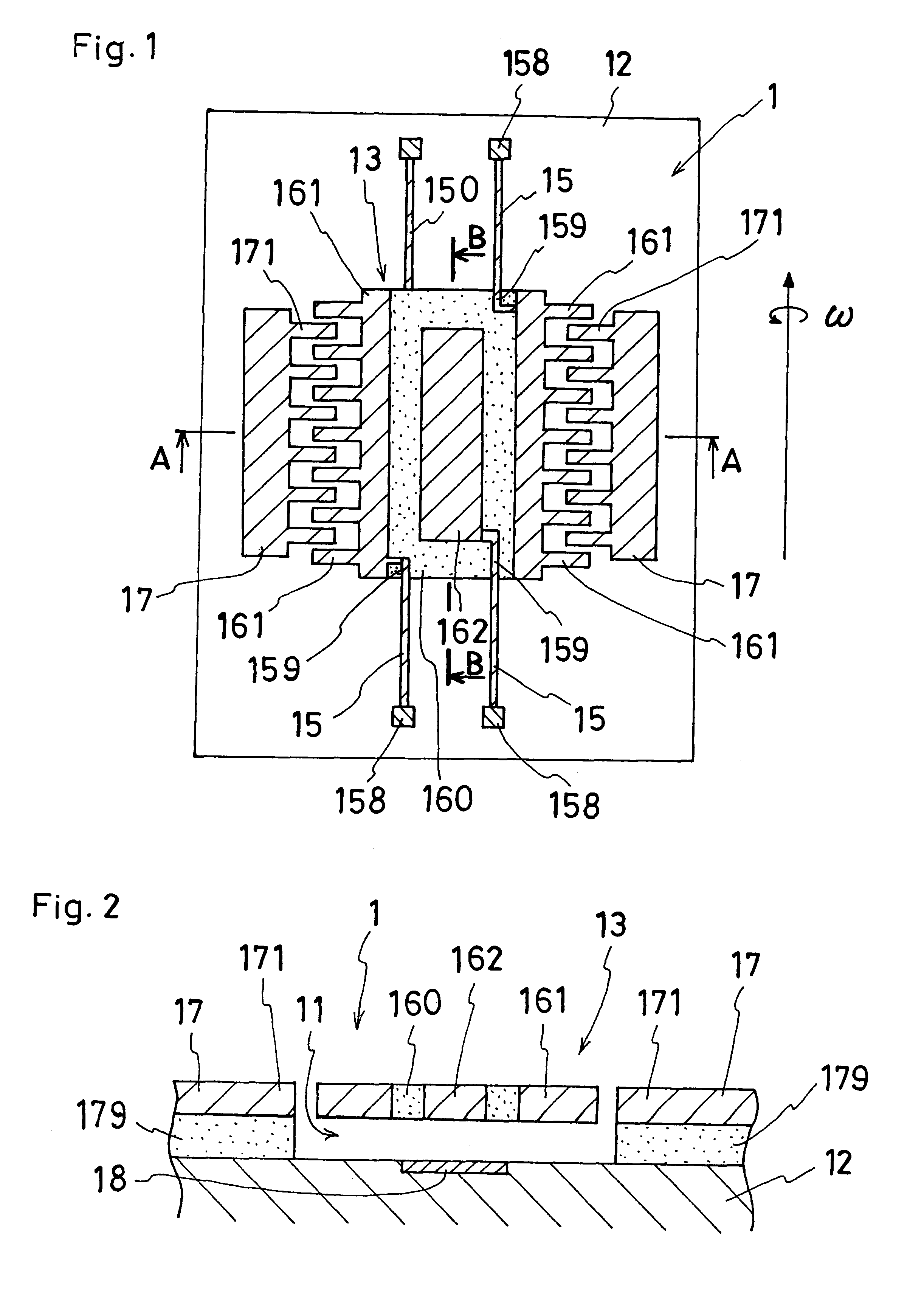
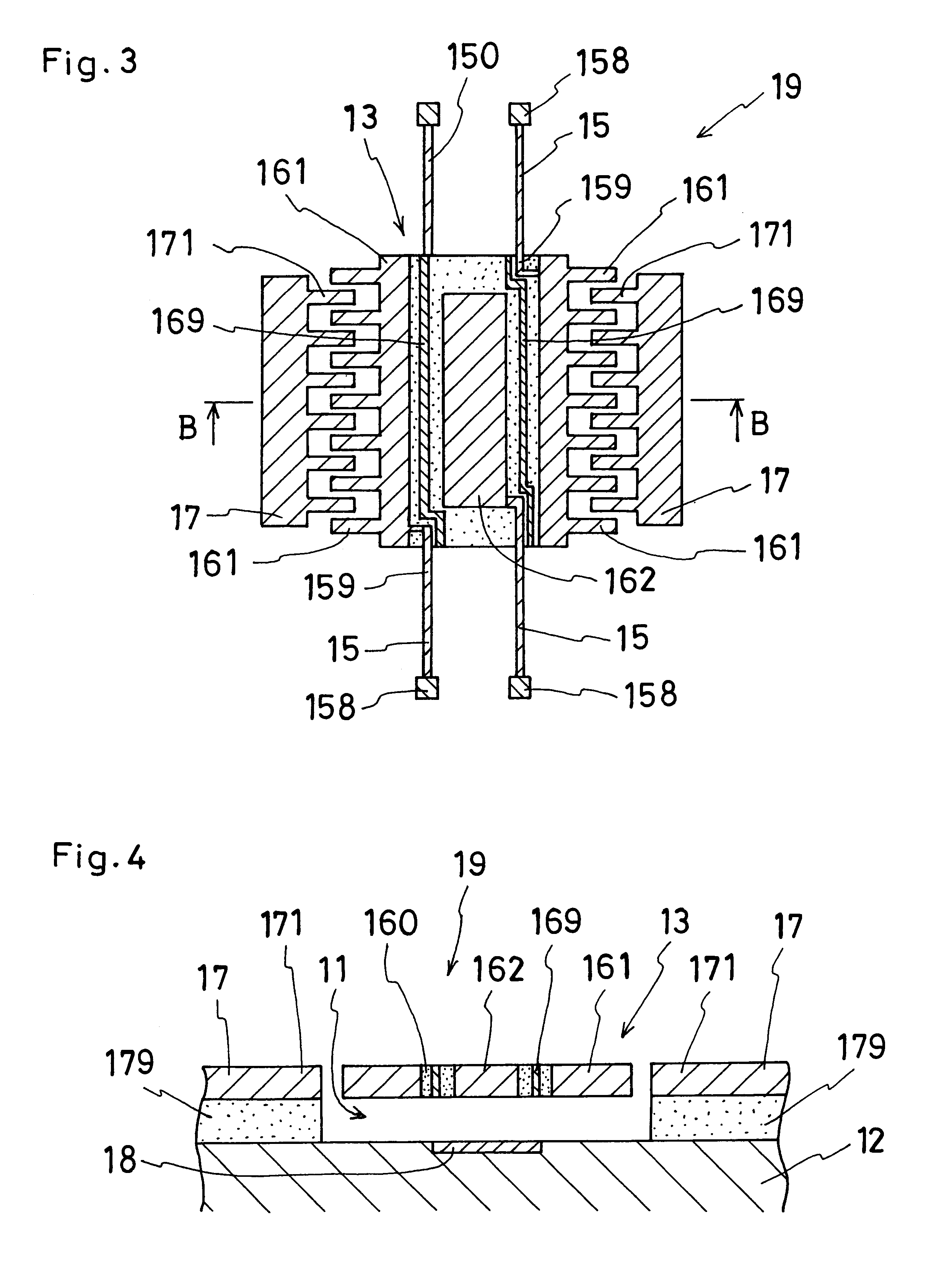
InactiveUS6190571B1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsThin membraneEngineering
A semiconductor micromachine and method of making the micromachine, wherein the micromachine includes a substrate and a movable portion made of a semiconductor thin film. The movable portion is arranged opposite the substrate with a gap interposed therebetween, and is supported by acicular bodies. This movable portion is provided with electrode sections, wires and an electrical insulation section interconnecting the electrode sections and the wires. The electrical insulation section prevents crosstalk of signals among the electrode sections and the wires to achieve a high S / N ratio as well as a high degree of design freedom. In order to achieve this purpose, the semiconductor micromachine of the present invention includes.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
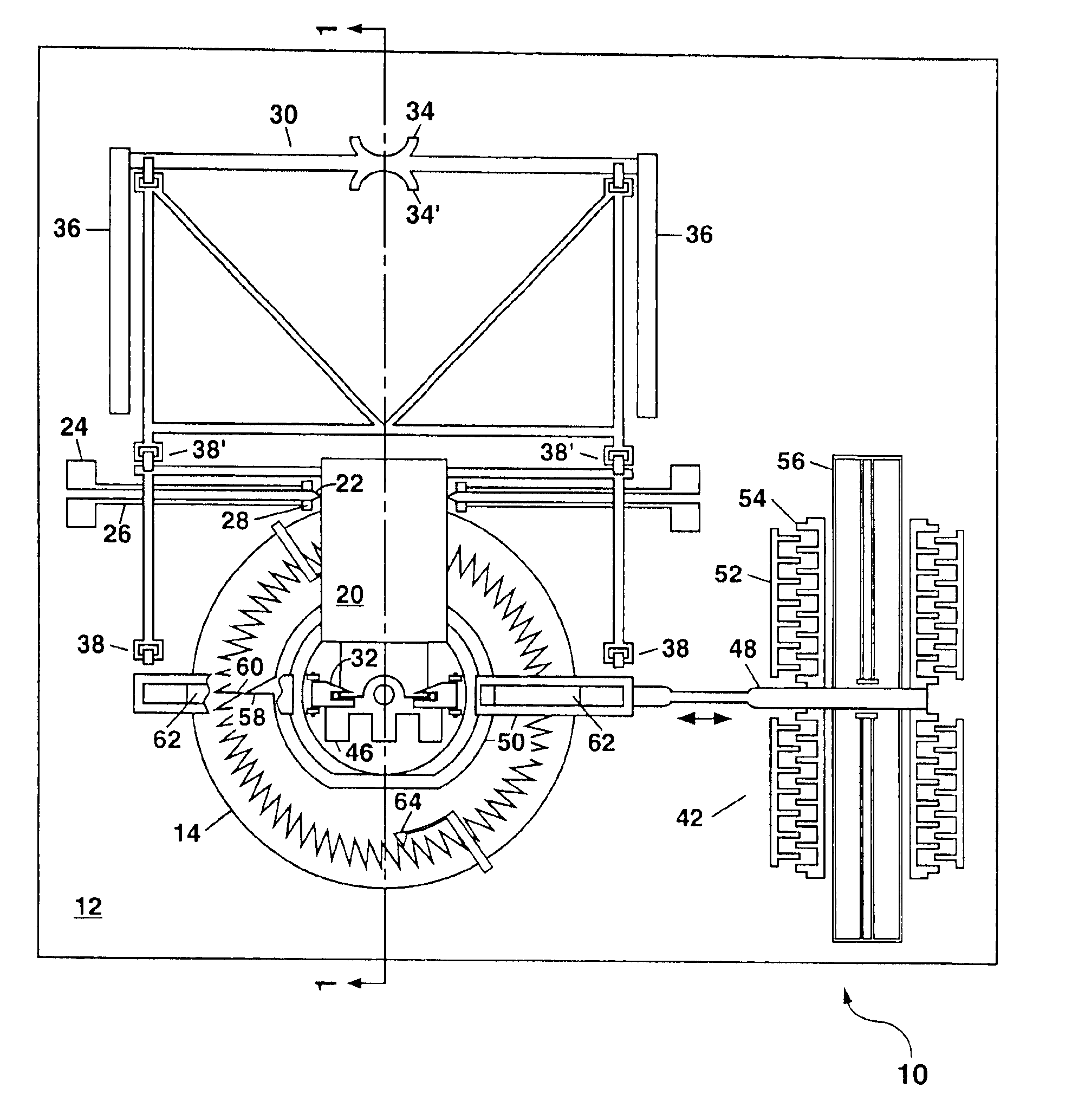
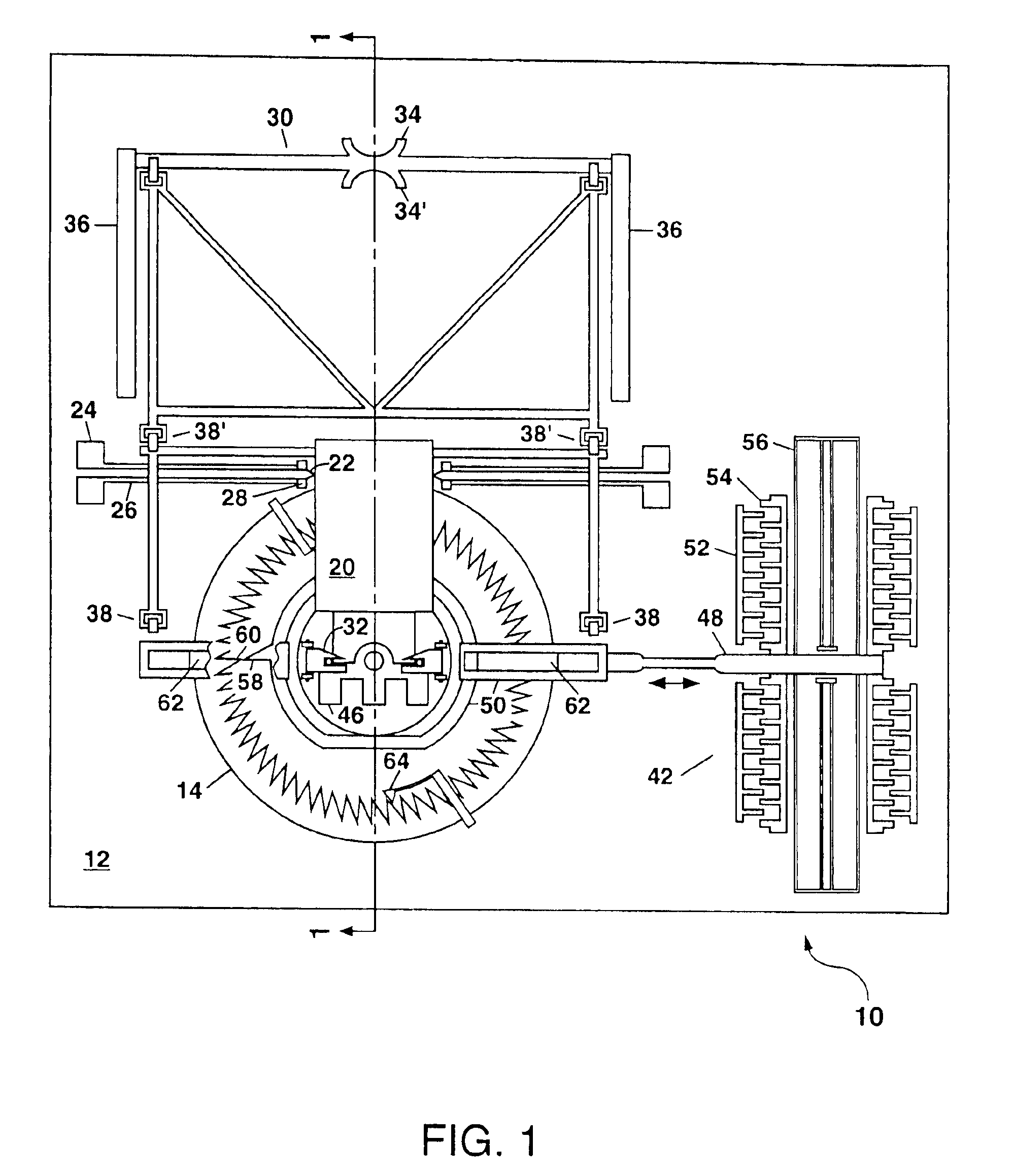
Erected mirror optical switch
A microelectromechanical (MEM) optical switching apparatus is disclosed that is based on an erectable mirror which is formed on a rotatable stage using surface micromachining. An electrostatic actuator is also formed on the substrate to rotate the stage and mirror with a high angular precision. The mirror can be erected manually after fabrication of the device and used to redirect an incident light beam at an arbitrary angel and to maintain this state in the absence of any applied electrical power. A 1×N optical switch can be formed using a single rotatable mirror. In some embodiments of the present invention, a plurality of rotatable mirrors can be configured so that the stages and mirrors rotate in unison when driven by a single micromotor thereby forming a 2×2 optical switch which can be used to switch a pair of incident light beams, or as a building block to form a higher-order optical switch.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method for manufacturing a hybrid integrated component
ActiveUS20130285165A1Easily and inexpensively permittingHigh degree of miniaturizationPrecision positioning equipmentSolid-state devicesWafer stackingMiniaturization
A manufacturing method for hybrid integrated components having a very high degree of miniaturization is provided, which hybrid integrated components each have at least two MEMS elements each having at least one assigned ASIC element. Two MEMS / ASIC wafer stacks are initially created independently of one another in that two ASIC substrates are processed independently of one another; a semiconductor substrate is mounted on the processed surface of each of the two ASIC substrates, and a micromechanical structure is subsequently created in each of the two semiconductor substrates. The two MEMS / ASIC wafer stacks are mounted on top of each other, MEMS on MEMS. Only subsequently are the components separated.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Micro inertial measuring unit
ActiveCN102778232AHigh measurement accuracyReduce measurement errorAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEngineeringInertia
The invention discloses a micro inertial measuring unit which comprises a shell, a top cover, a main circuit board, a micro inertial measurement combination, a first double-shaft micro-machined accelerometer and a second double-shaft micro-machined accelerometer, wherein the top cover is arranged on the top end of the shell, a cavity is limited by the top cover and the shell, the main circuit board is arranged in the cavity, the micro inertia measurement combination is arranged in the cavity and is connected with the main circuit board, the micro inertia measurement combination comprises a three-shaft micro-machined gyroscope, a three-shaft micro-machined accelerometer and a three-shaft magnetometer; and the first double-shaft micro-machined accelerometer and the second double-shaft micro-machined accelerometer are respectively arranged in the cavity and respectively connected with the main circuit board. The micro inertial measuring unit can be used for measuring motion parameters of a small aircraft under a high-dynamic and large-overload motion state, and calculating a motion attitude and a motion track of the small aircraft.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
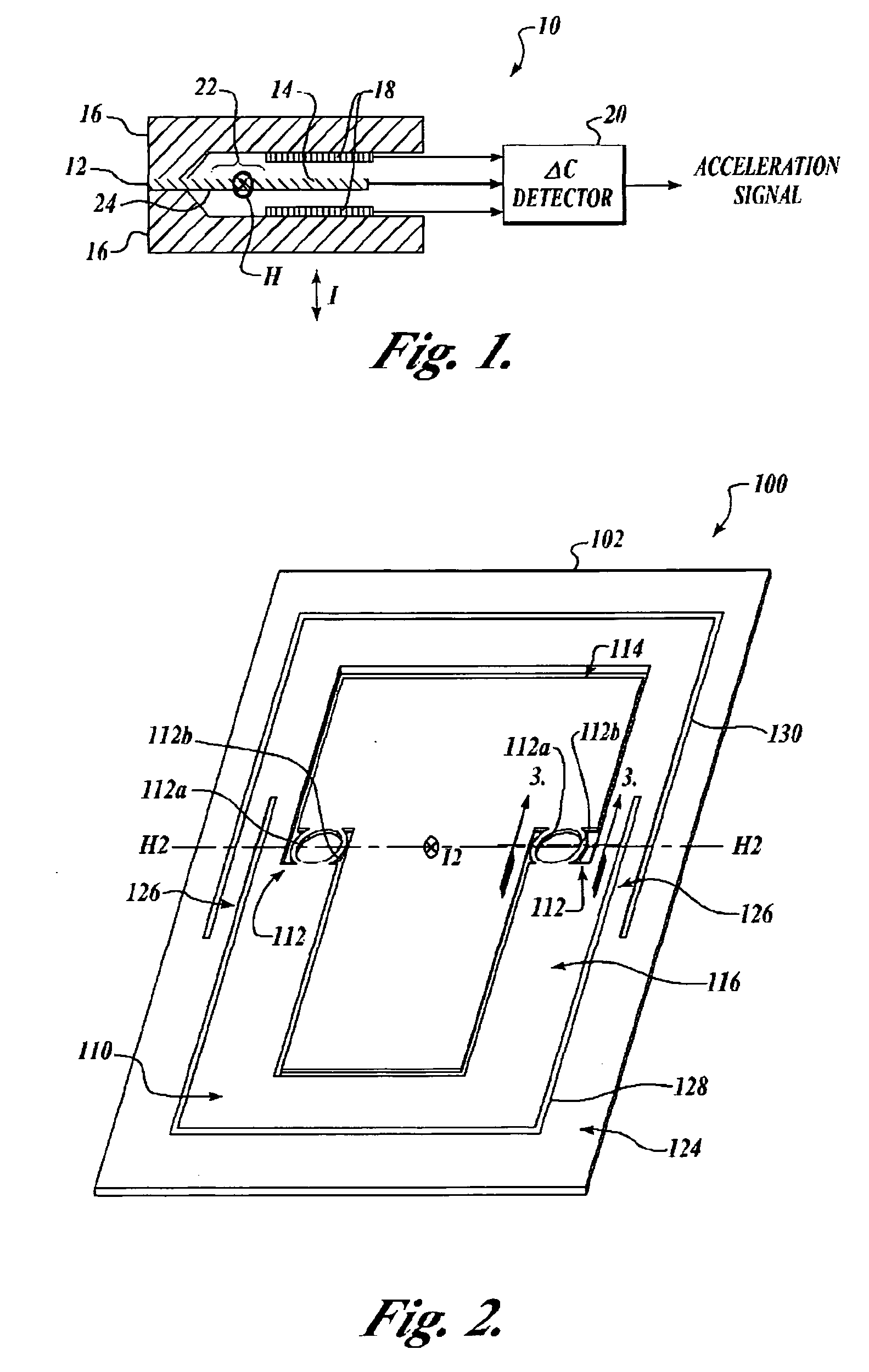
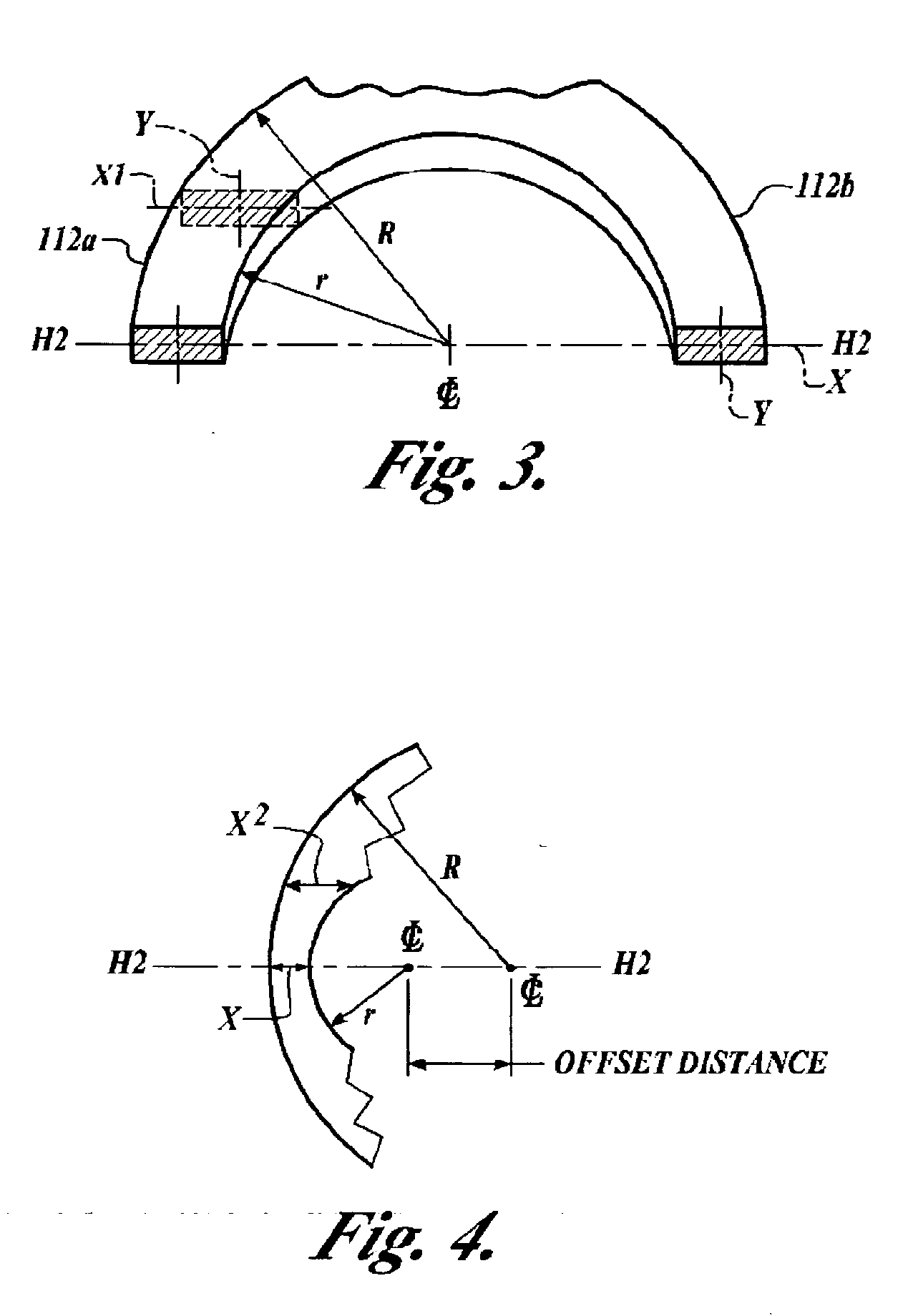
Micro-machined electromechanical system (MEMS) accelerometer device having arcuately shaped flexures
InactiveUS20050202585A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAccelerometerElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Piezoelectric-static compound micro machine vibration energy collector and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN102570902AAvoid instabilityAchieve self-supplyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceMachining vibrations
The invention relates to a piezoelectric-static composite micro machine vibration energy collector and a manufacture method of the collector, and relates to an energy collecting device. The piezoelectric-static composite micro machine vibration energy collector comprises a chip main body and a chip external circuit, wherein the chip main body is of a three-layer laminated structure, and the chip main body comprises an upper glass piece device, an SOI (Silicon On Insulator) piece device, a lower glass piece device, a piezoelectric ceramic wafer device, a piezoelectric ceramic wafer electrode and a variable capacitance plate electrode. The chip external circuit is provided with a rectification circuit, a filter capacitor, a first switch, a second switch and an energy storage capacitor, or is provided with a rectification circuit, a filter capacitor, a first switch, a second switch and an energy storage capacitor and a variable capacitance plate starting power supply. The manufacture method comprises the following steps of: manufacturing the lower glass piece device; manufacturing the SOI piece device; manufacturing the upper glass piece device; assembling; and connecting the chip external circuit. According to the collector and the manufacture method, the process is simple, the defects of poorer device stability and performance and the like caused by,manufacturing a PZT (Piezoelectric Transducer) by using the traditional sol gel can be overcome, and wide band and high efficiency collection of energy can be realized.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Induction microscanner
InactiveUS6285485B1Consumes less powerIncrease deflection angleDynamo-electric machinesOptical elementsControl electronicsPhysics
A micro-electromechanical scanner is disclosed for the efficient, controlled deflection of light beams. The device comprises a moving rotor, a suspension system, and a stator. The rotor comprises a closed-circuit coil and a mirror. The suspension system may be, for example, a set of torsion bars on which the rotor is mounted. The stator may be, for example, a rectangular frame holding the suspension system. When placed in a constant magnetic field and excited by an alternating magnet field, the rotor oscillates at the frequency of the alternating magnetic field, All else being equal, the highest deflection angles occur at the natural mechanical resonance frequency of the rotor-suspension combination. Compared to conventional devices, the novel device can be smaller, can be less expensive, can consume less power, and may exhibit higher deflection angles over a given time scale than other micromechanical devices operating on different actuation principles. The novel device may be used, for example, to replace the scanning devices currently used in laser printers, laser bar-code readers, and laser image projectors (e.g., large screen televisions). The control electronics may optionally be manufactured on the same device, eliminating the need for a separate controller and reducing costs.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Micromechanical pressure sensor device and corresponding measurement system
InactiveUS20040079159A1Fluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationPressure difference measurement between multiple valvesLinear componentSemiconductor materials
A micromechanical pressure sensor device, particularly for measuring low absolute pressures and / or small differential pressures. The device includes a frame that is formed at least partially by a semiconductor material, a membrane retained by the frame, at least one measuring resistor that is disposed at a first location in or on the membrane and whose resistance value is a function of pressure-induced mechanical stresses in the membrane, and at least one compensating resistor that is disposed at a second location in or on the membrane and whose resistance value is a function of pressure-induced mechanical stresses in the membrane. The resistance value changes at the first location with a first linear component and a first quadratic component as a function of the pressure, and the resistance value changes at the second location approximately without a linear component and with a second quadratic component, which is proportional to the first quadratic component, as a function of the pressure.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Detection of resonator motion using piezoresistive signal downmixing
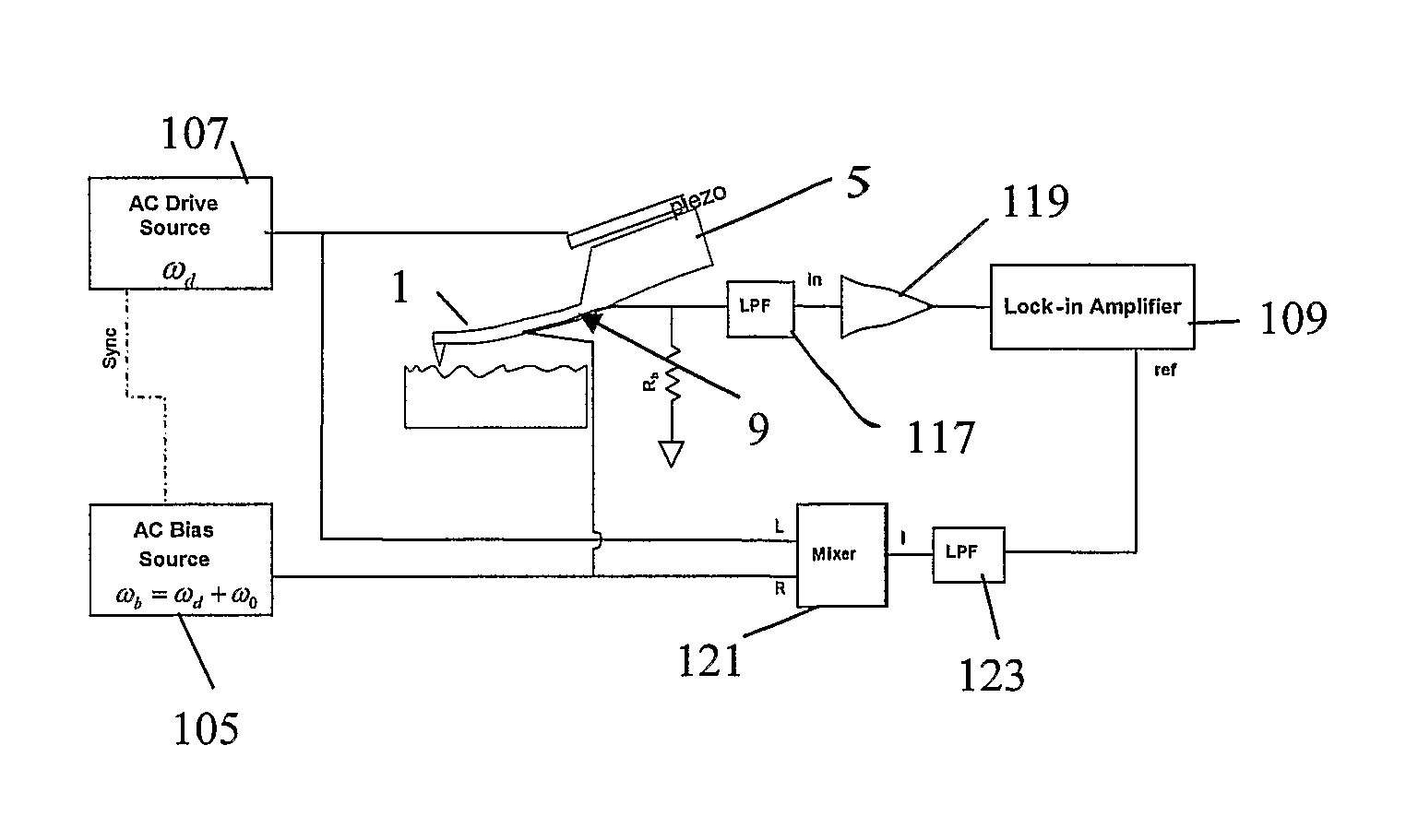
ActiveUS7552645B2Force measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMicromachinery
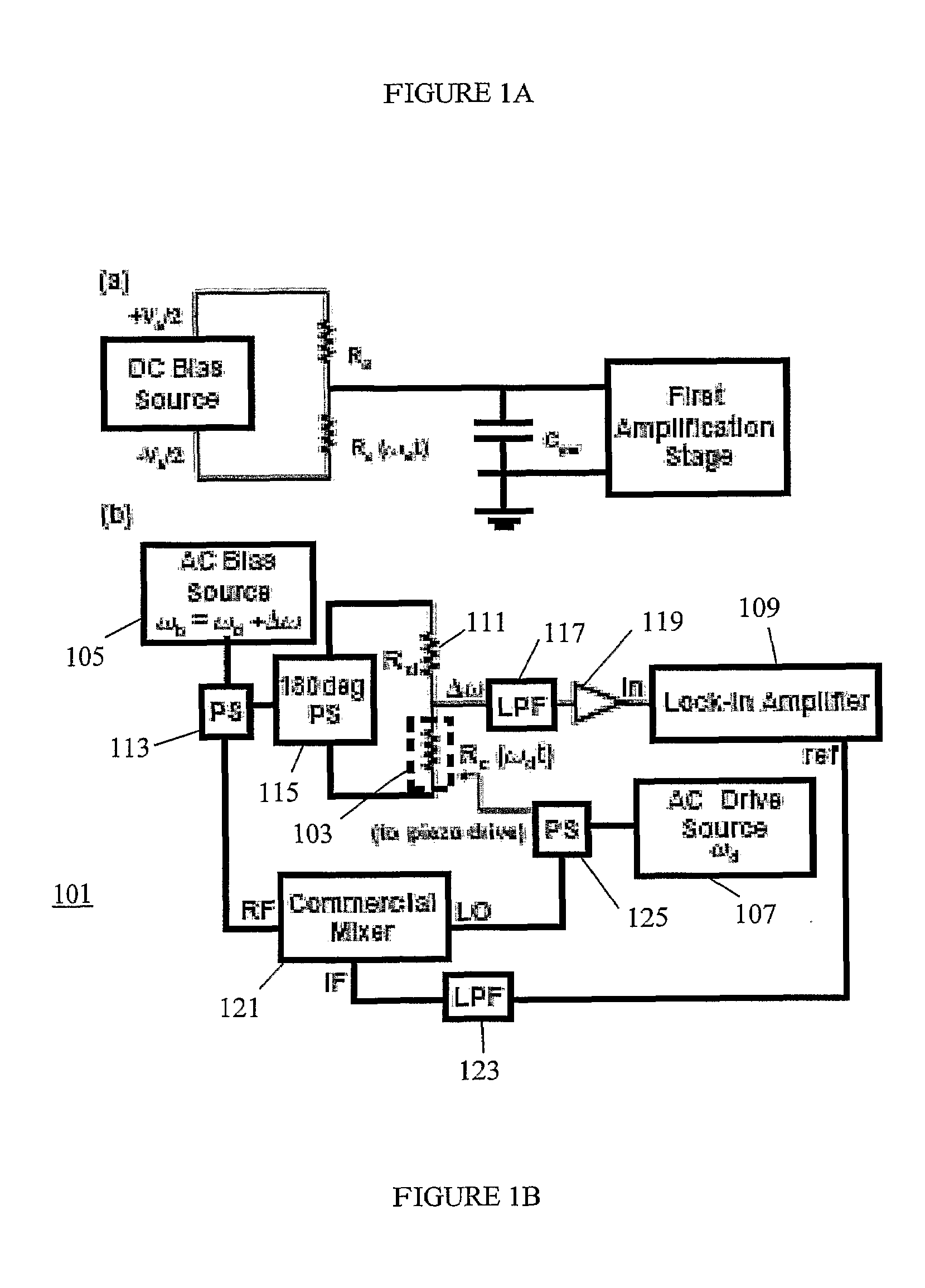
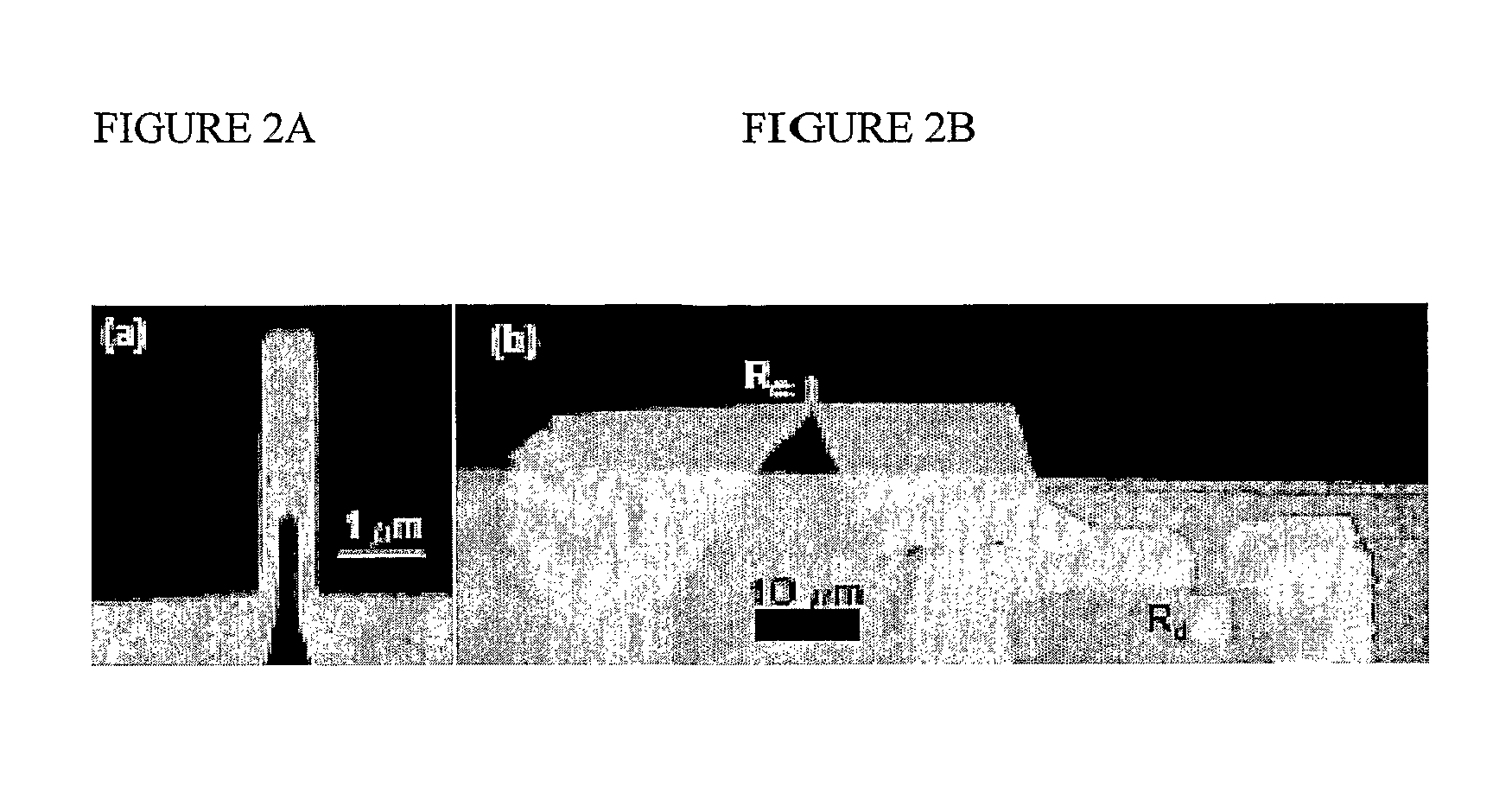
A system containing a micro-mechanical or nano-mechanical device and a method of operating the same is provided. The device includes a resonator and a piezoresistive element connected to the resonator. The method includes AC biasing the piezoresistive element at a first frequency, driving the resonator at a second frequency different from the first frequency, and detecting a mechanical response of the resonator at one or both of a difference frequency and a sum frequency of the first and second frequencies.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
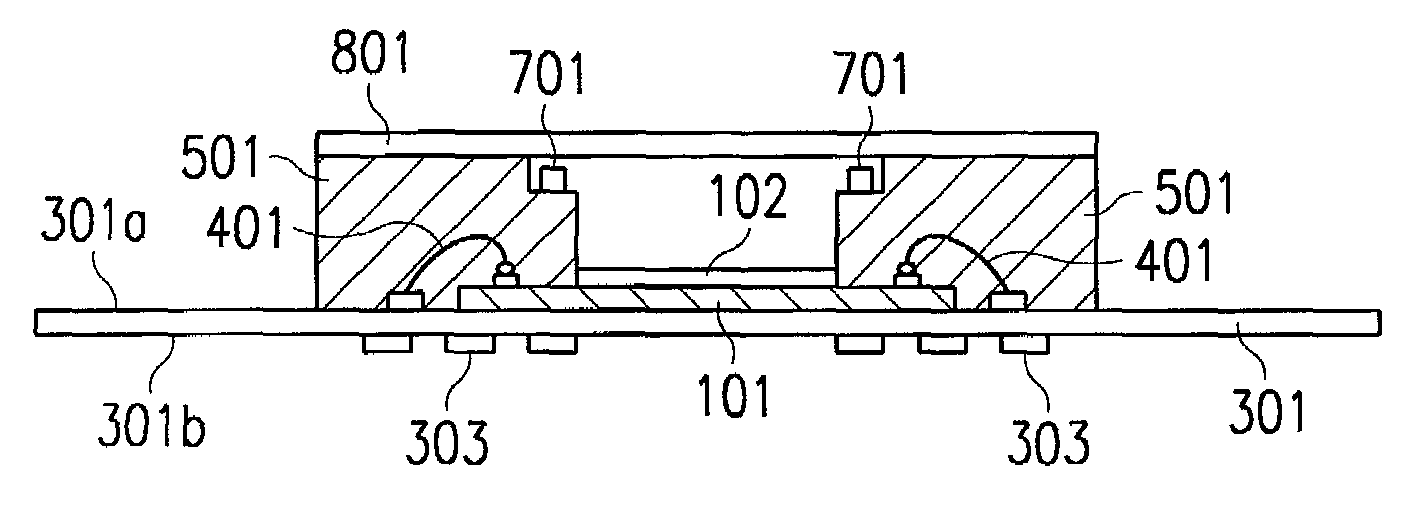
Phase detector based on micro-mechanical silicon-based cantilever beam and detection method
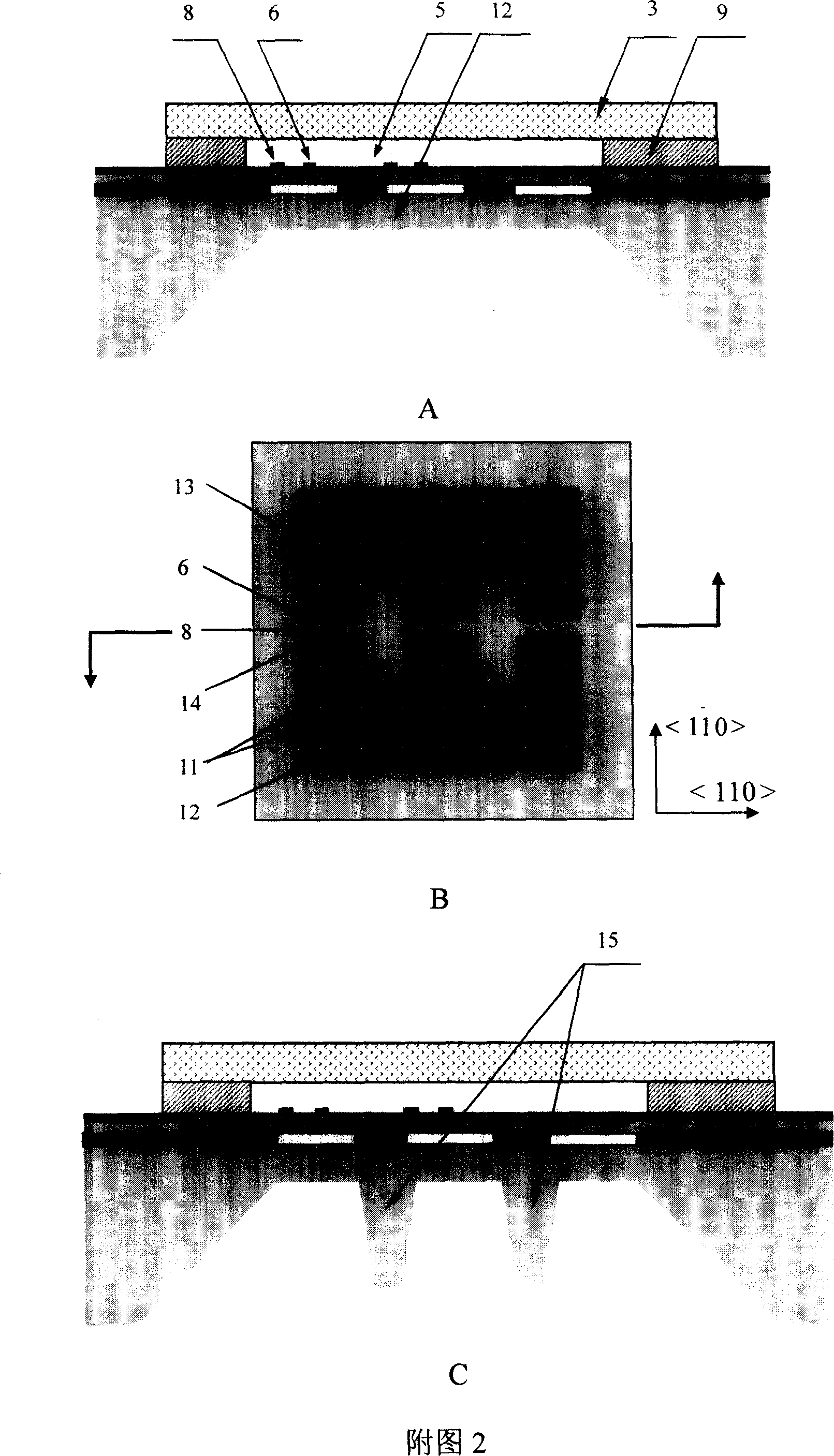
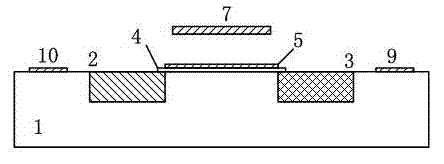
The invention discloses a phase detector based on a micro-mechanical silicon-based cantilever beam and a detection method. The phase detector comprises a silicon substrate (1), a source (2) and a drain (3), wherein the source (2) and the drain (3) grow on the surface of the silicon substrate (1) and are used for outputting saturation current; the source (2) is opposite to the drain (3); a cantilever beam anchor area (6) is arranged outside the source (2) or the drain (3); a gate oxide layer (4) is bridged between the source (2) and the drain (3); and a gate (5) is arranged on the surface of the gate oxide layer (4). The method comprises the following steps of: when direct current offset is loaded to a pull-down electrode (8) and a cantilever beam (7) is pulled down and contacted with the gate (5), simultaneously loading two microwave signals with the same frequency and certain phase difference to the gate (5); and filtering a high-frequency signal from the saturation current of the drain (3) through a blocking capacitor and a low-pass filter, and thus obtaining a current signal with phase difference information. The invention has the advantages of simple structure and convenience for measurement.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com