Patents
Literature
228 results about "LOCOS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
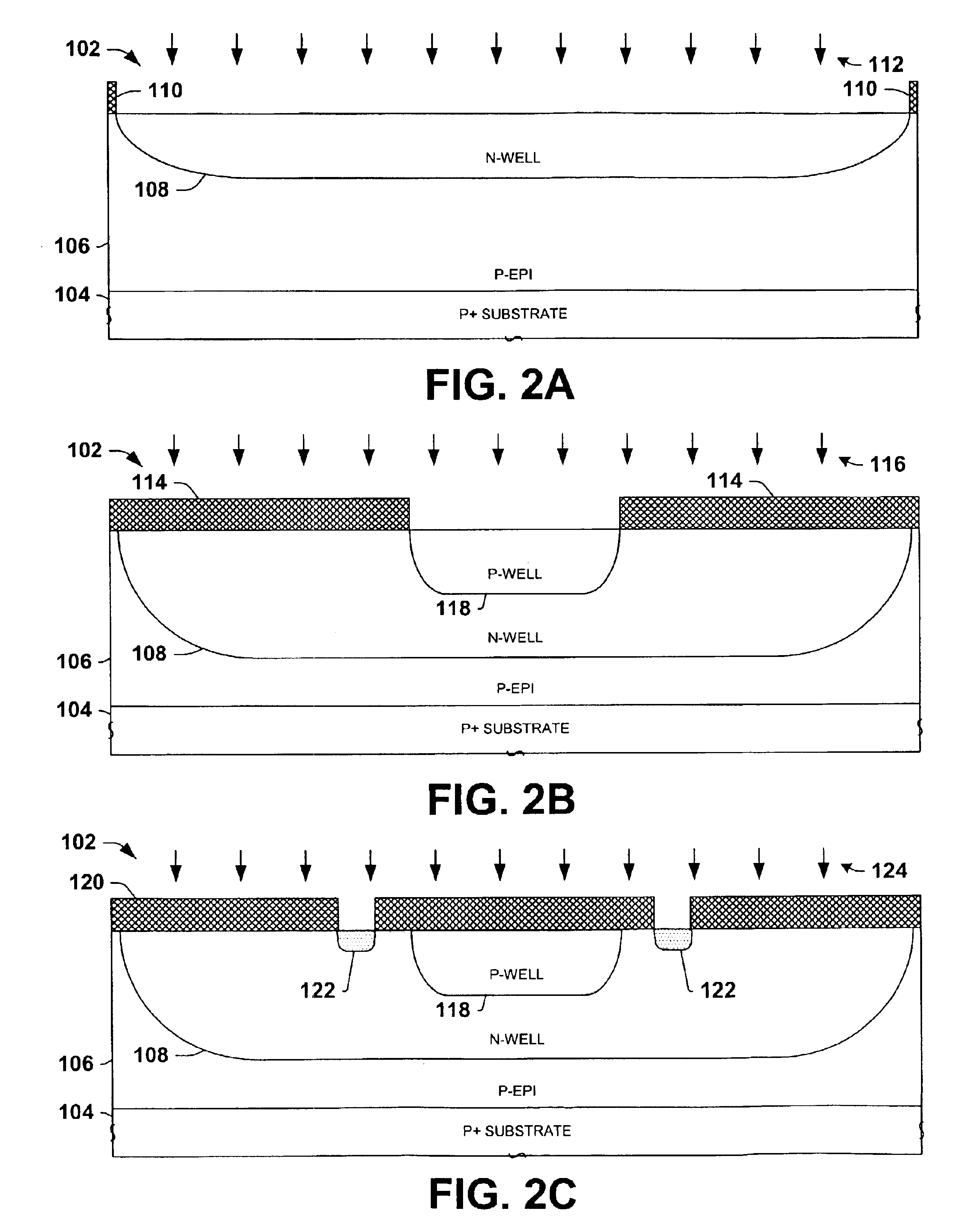
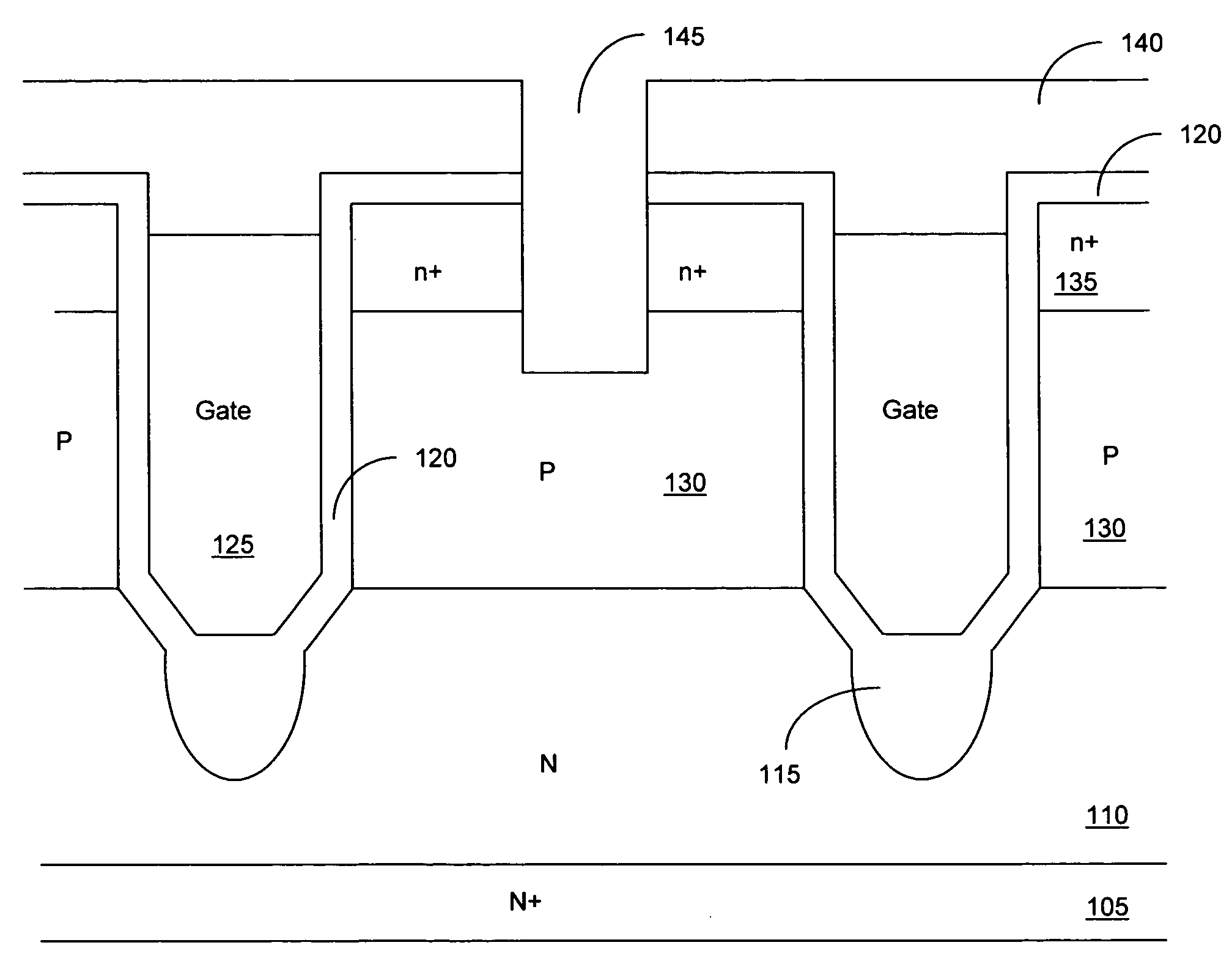
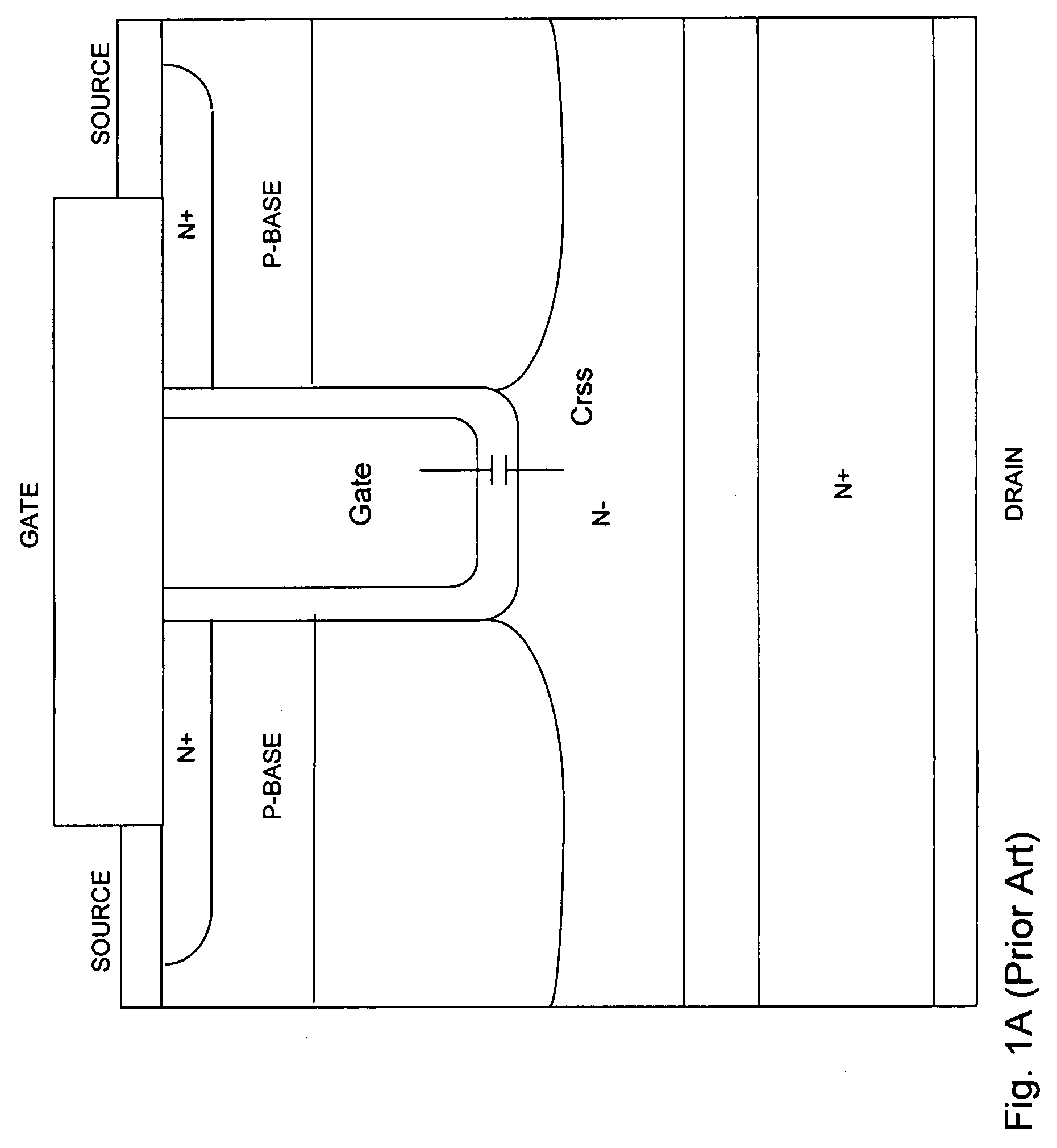
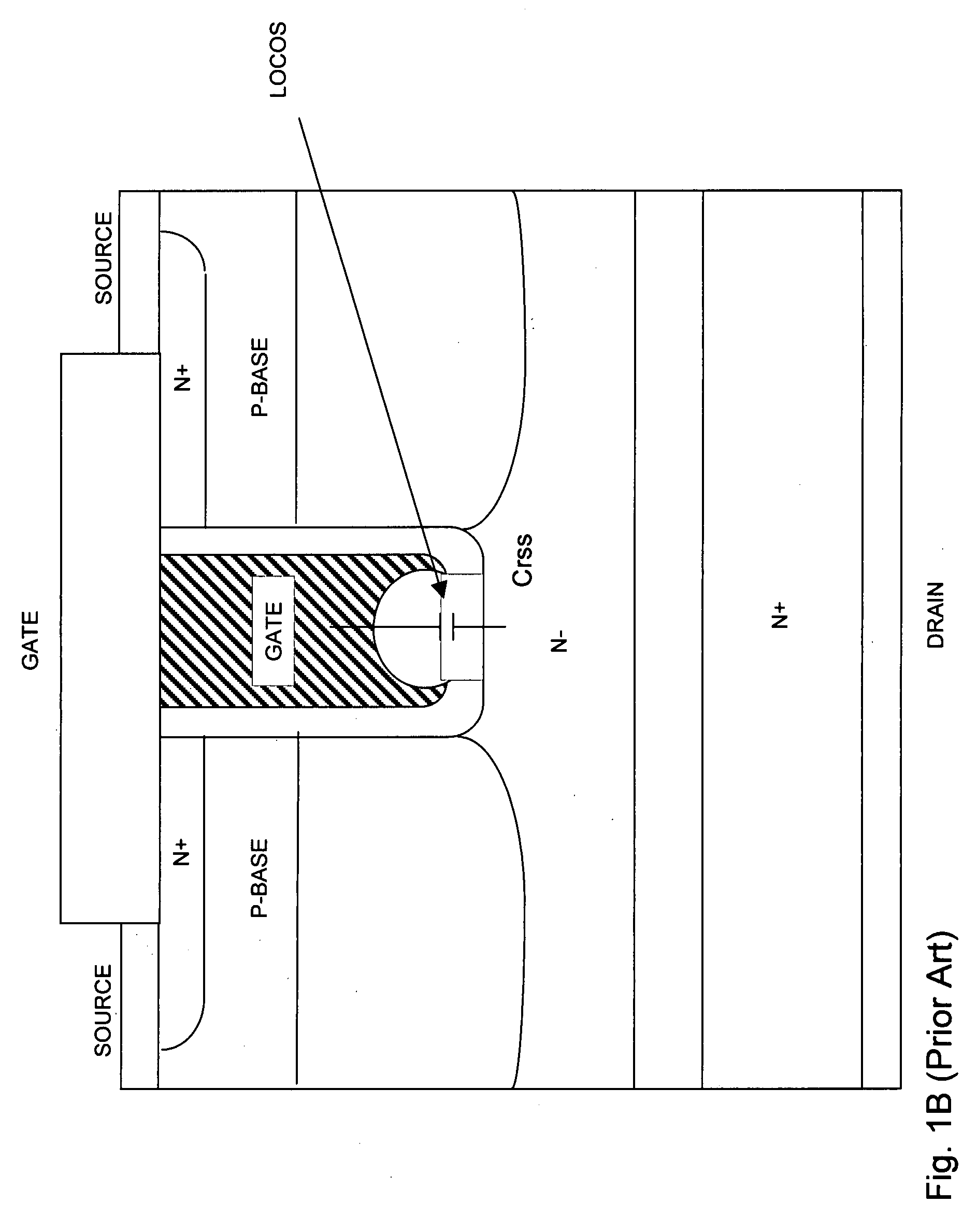
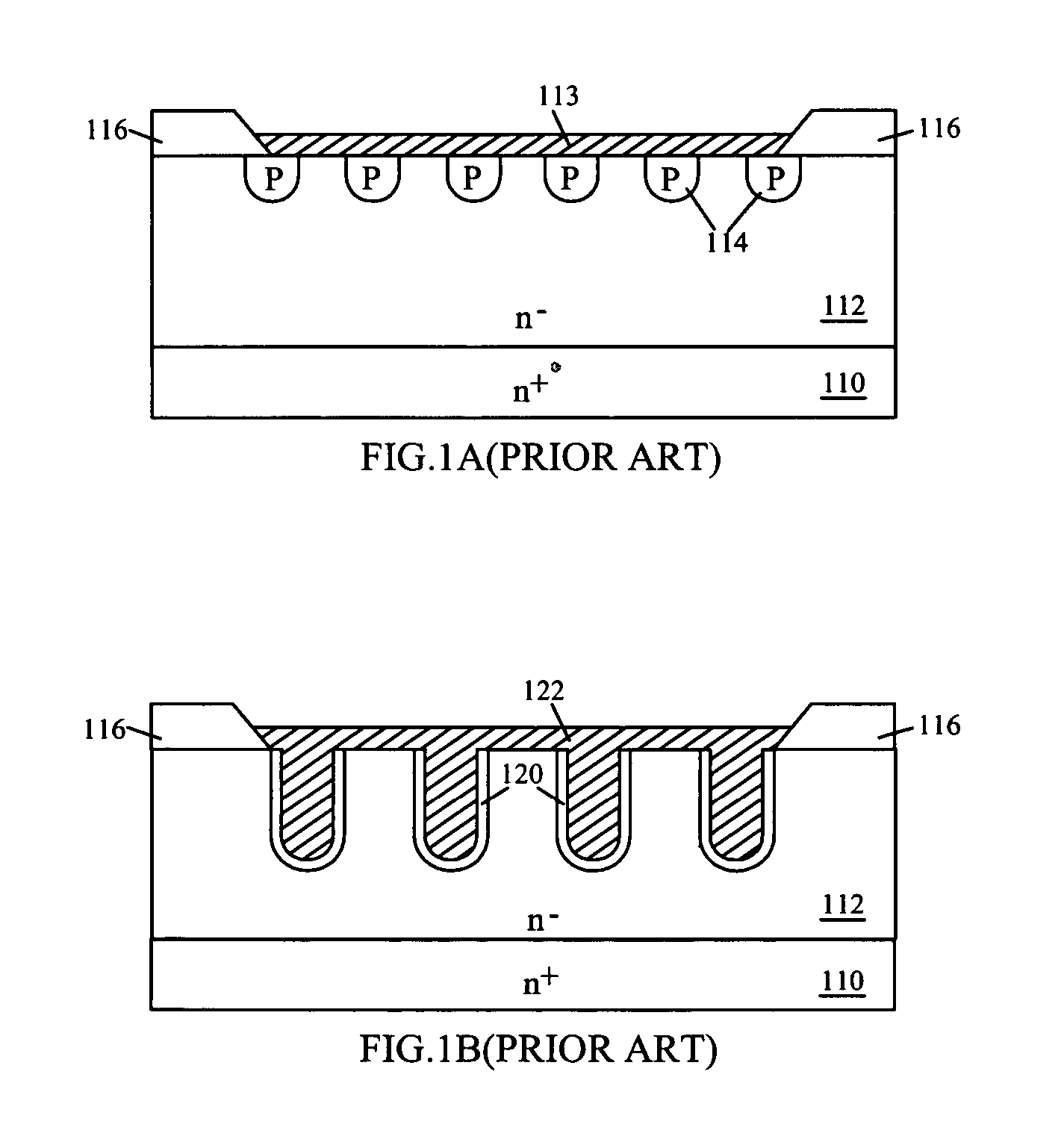
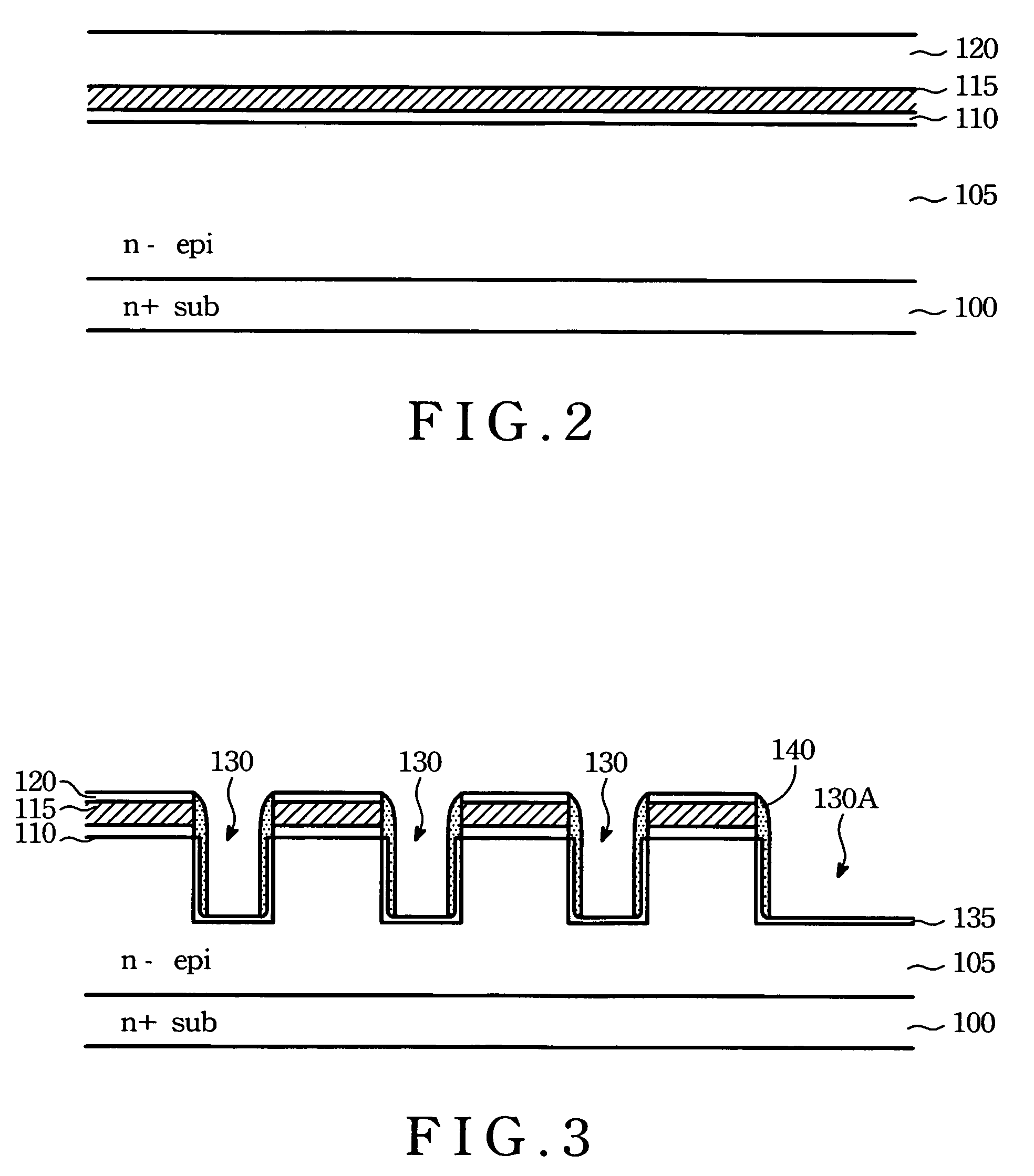
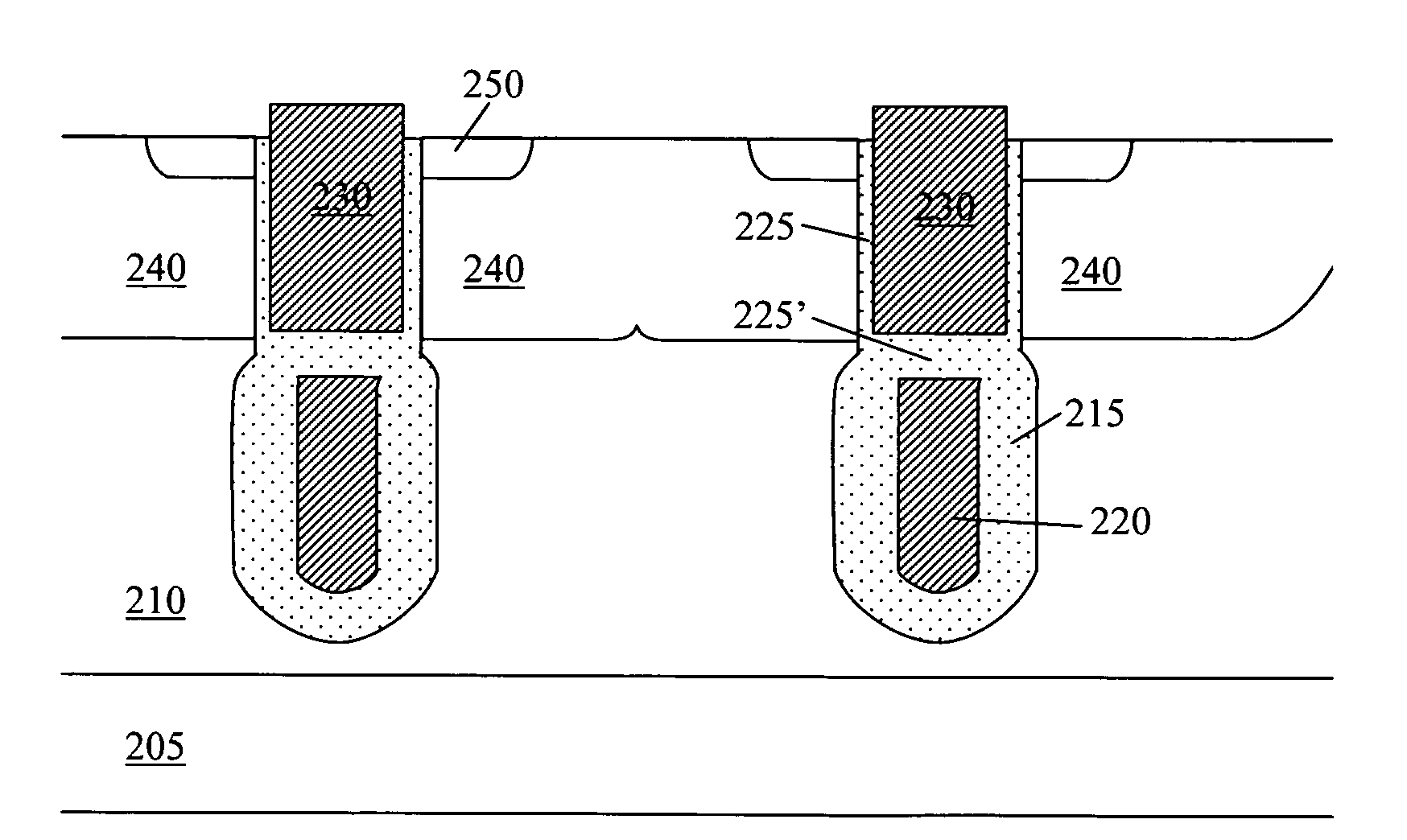
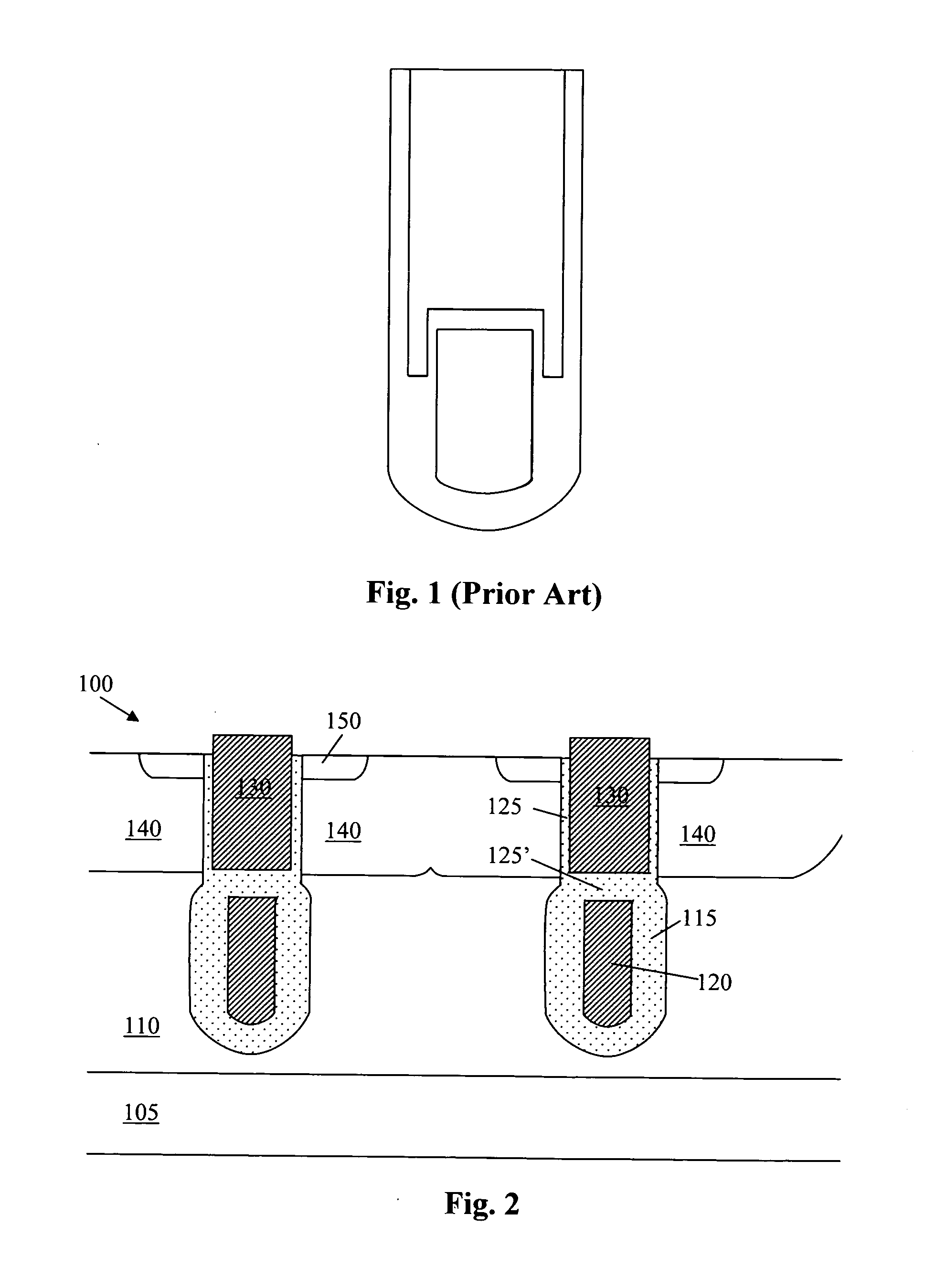
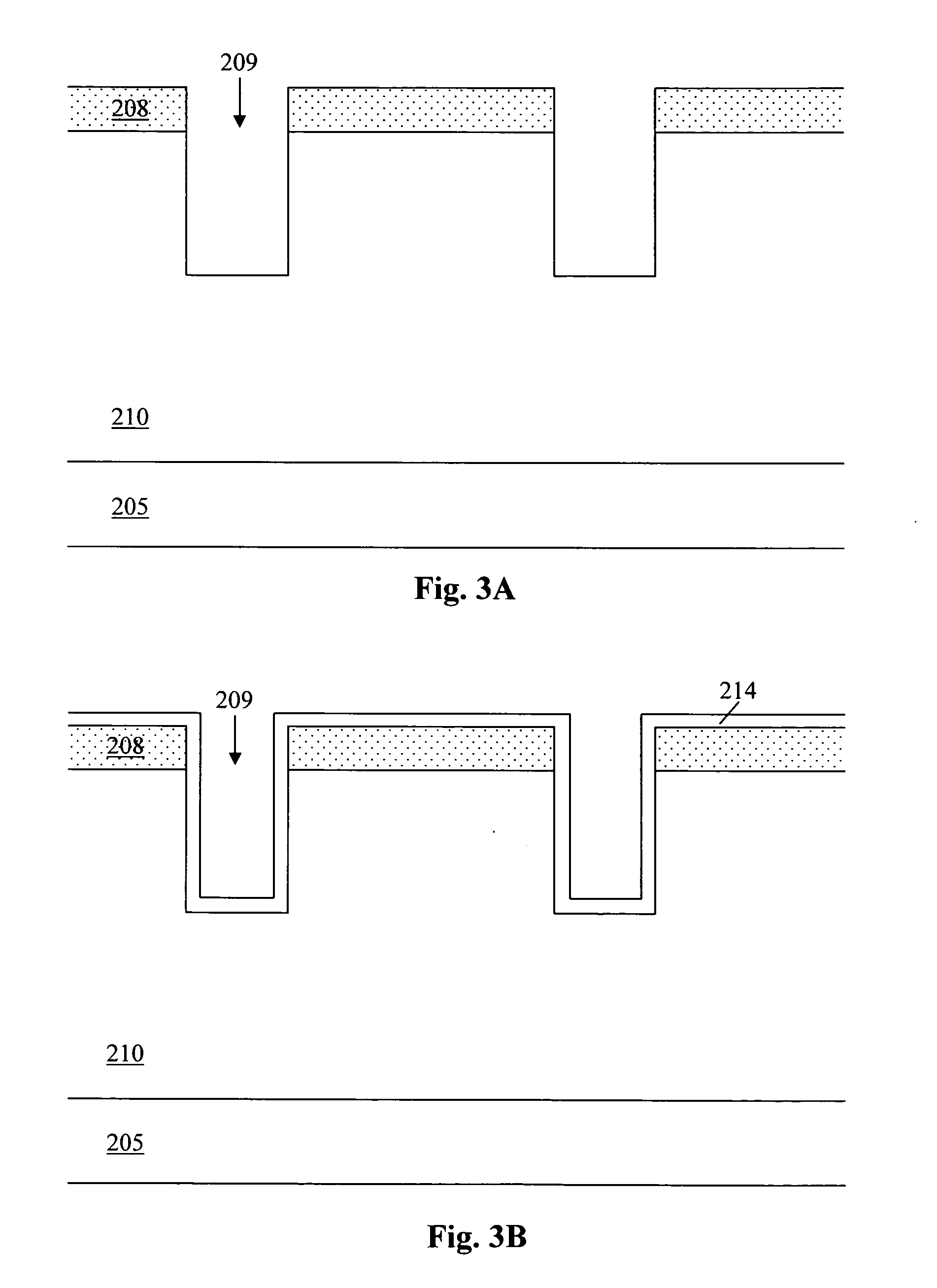
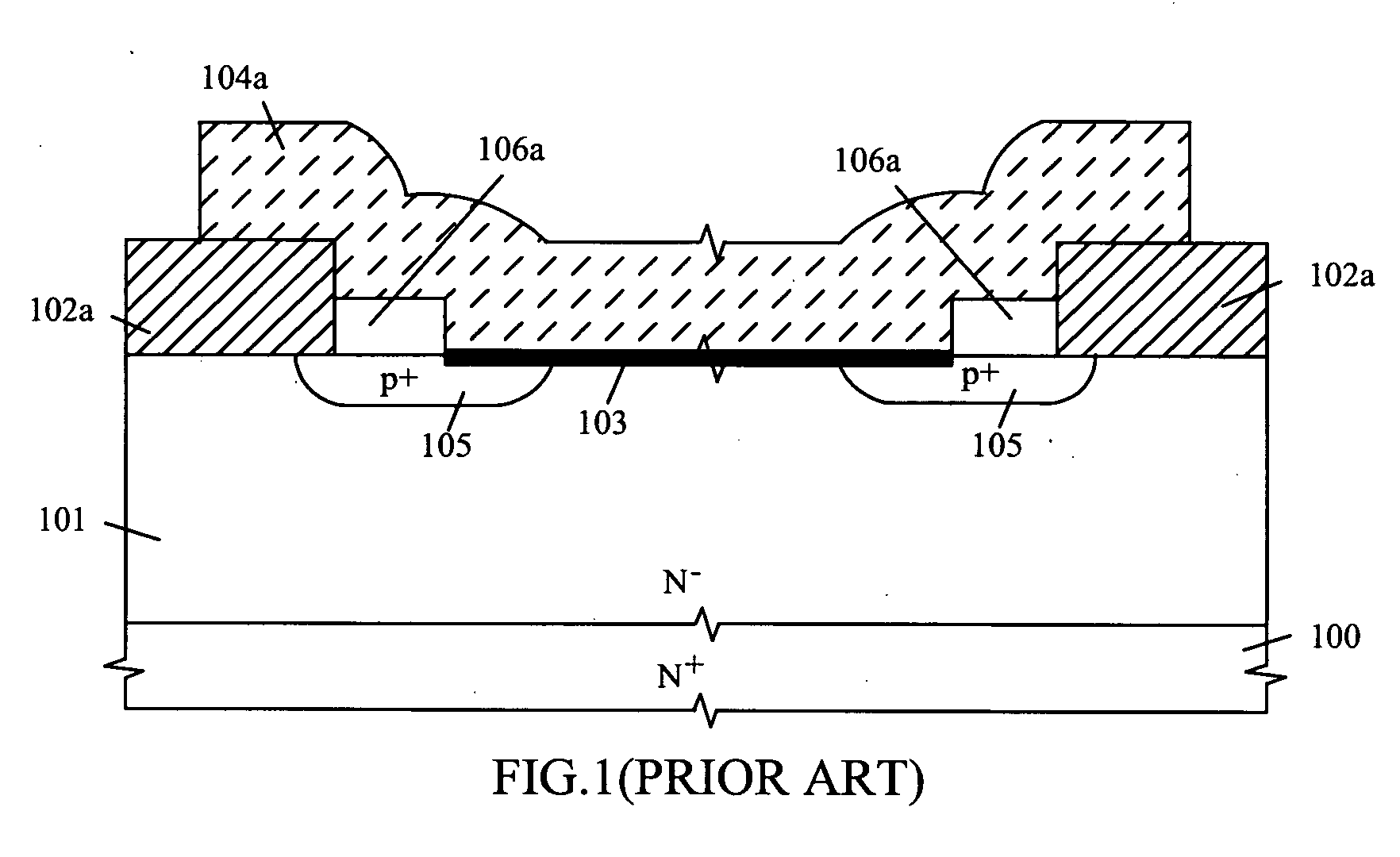
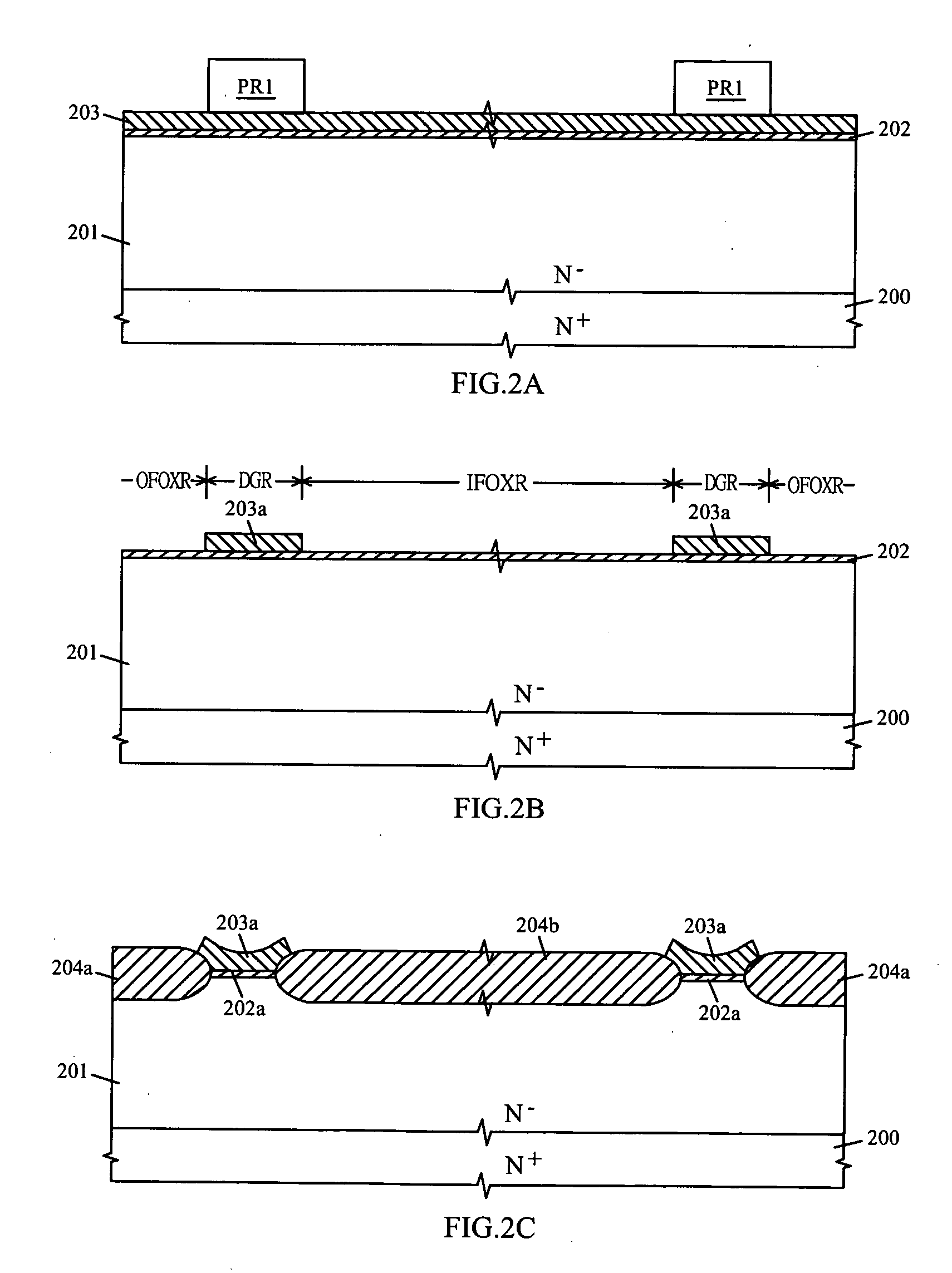
LOCOS, short for LOCal Oxidation of Silicon, is a microfabrication process where silicon dioxide is formed in selected areas on a silicon wafer having the Si-SiO₂ interface at a lower point than the rest of the silicon surface.
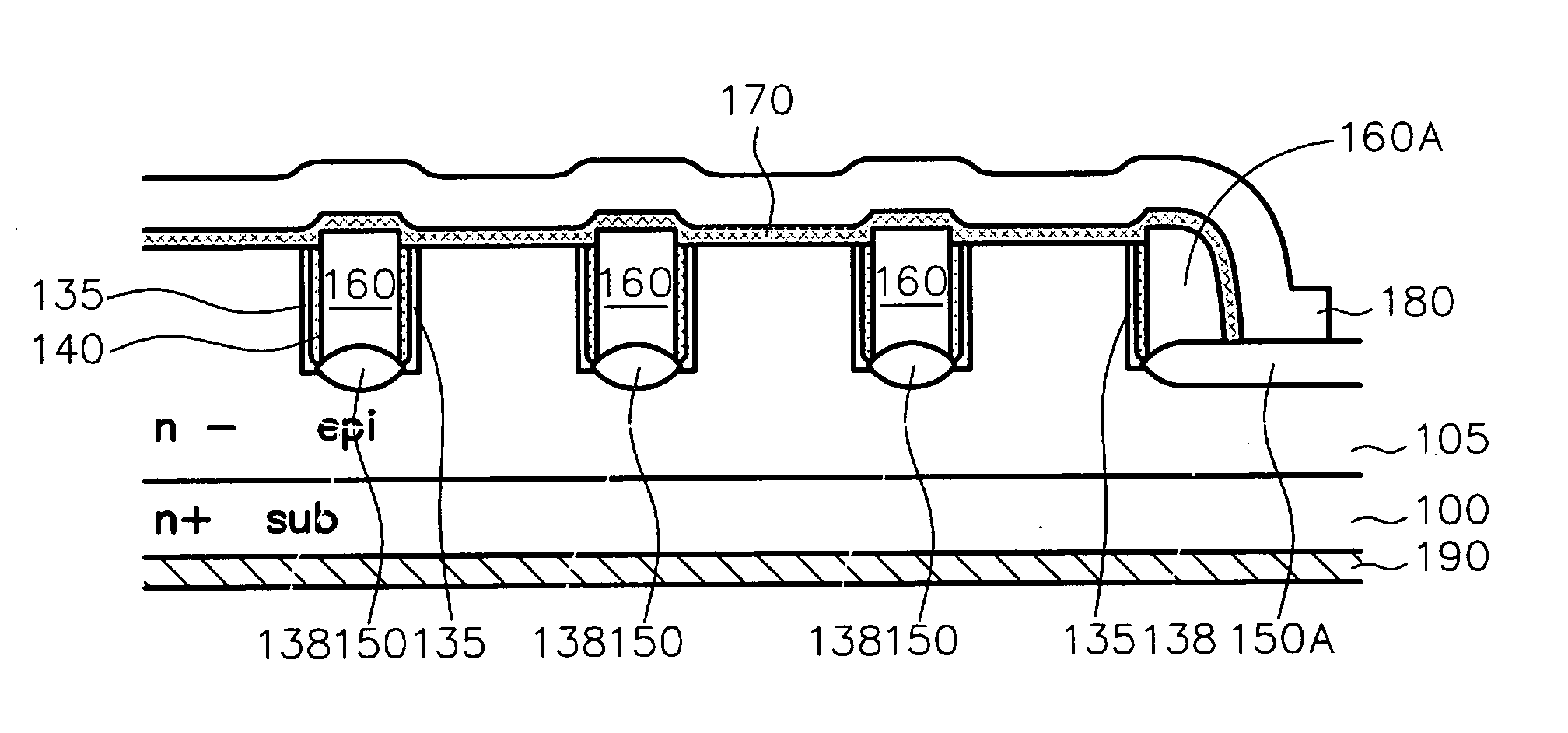
Semiconductor device and fabrication method for the same
InactiveUS7205204B2Secure performanceImprove reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLOCOSSingle crystal
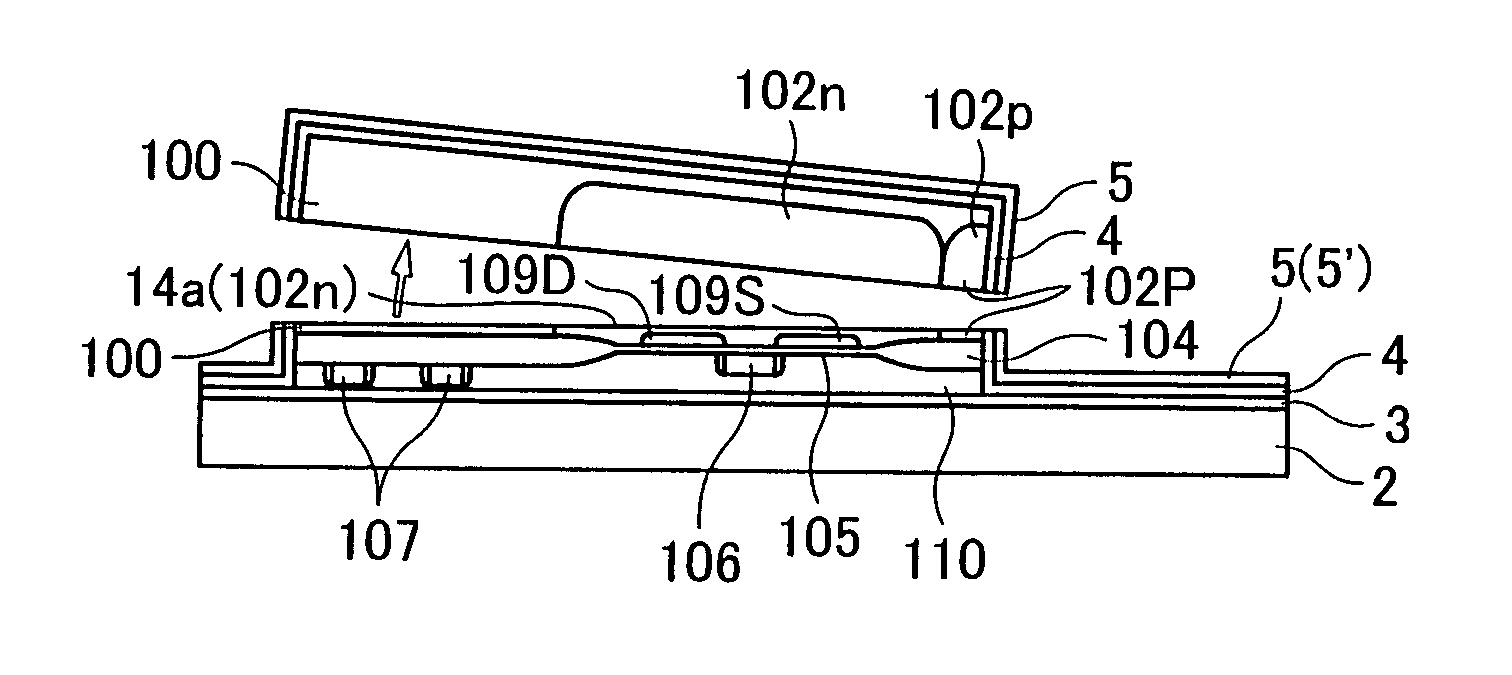
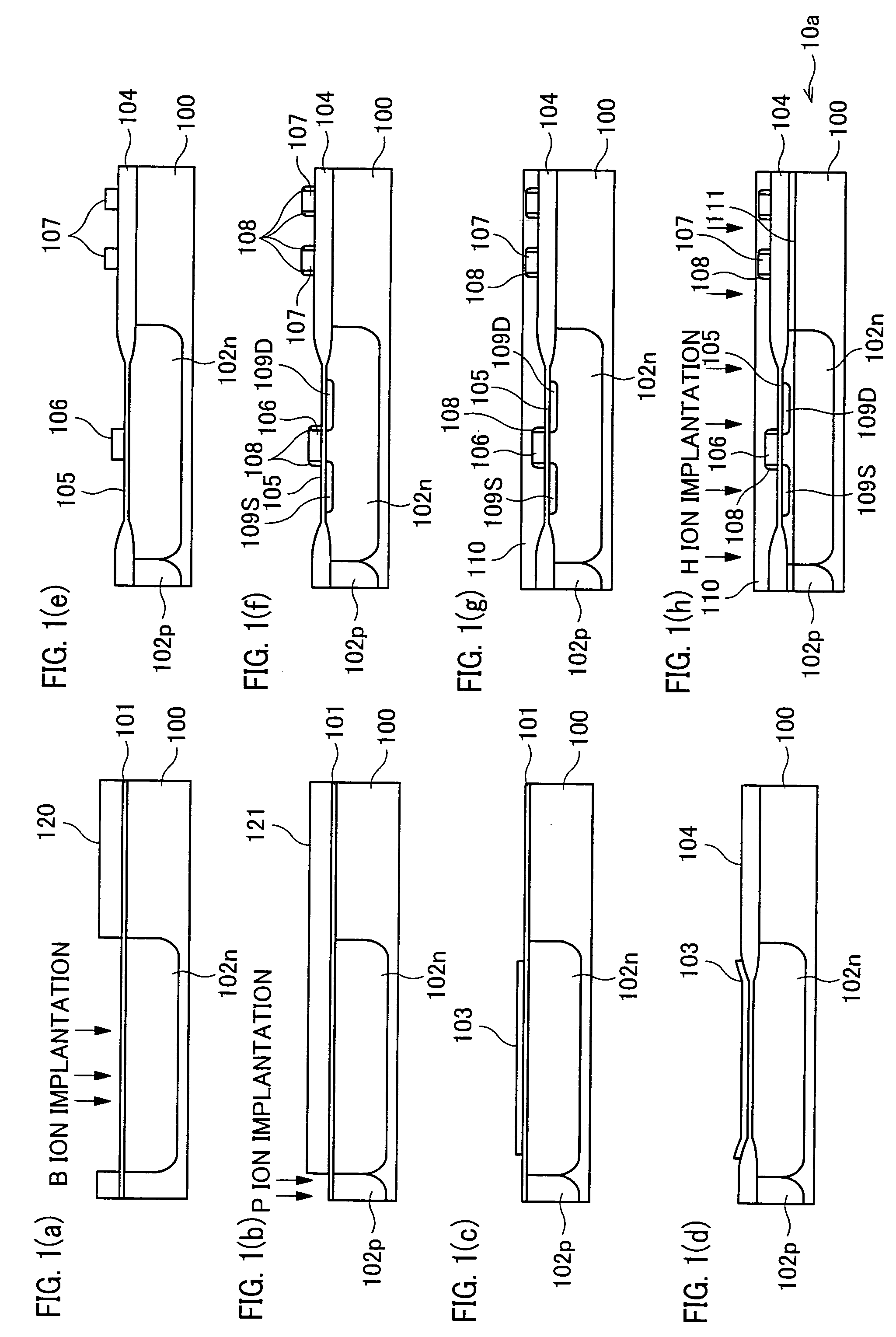
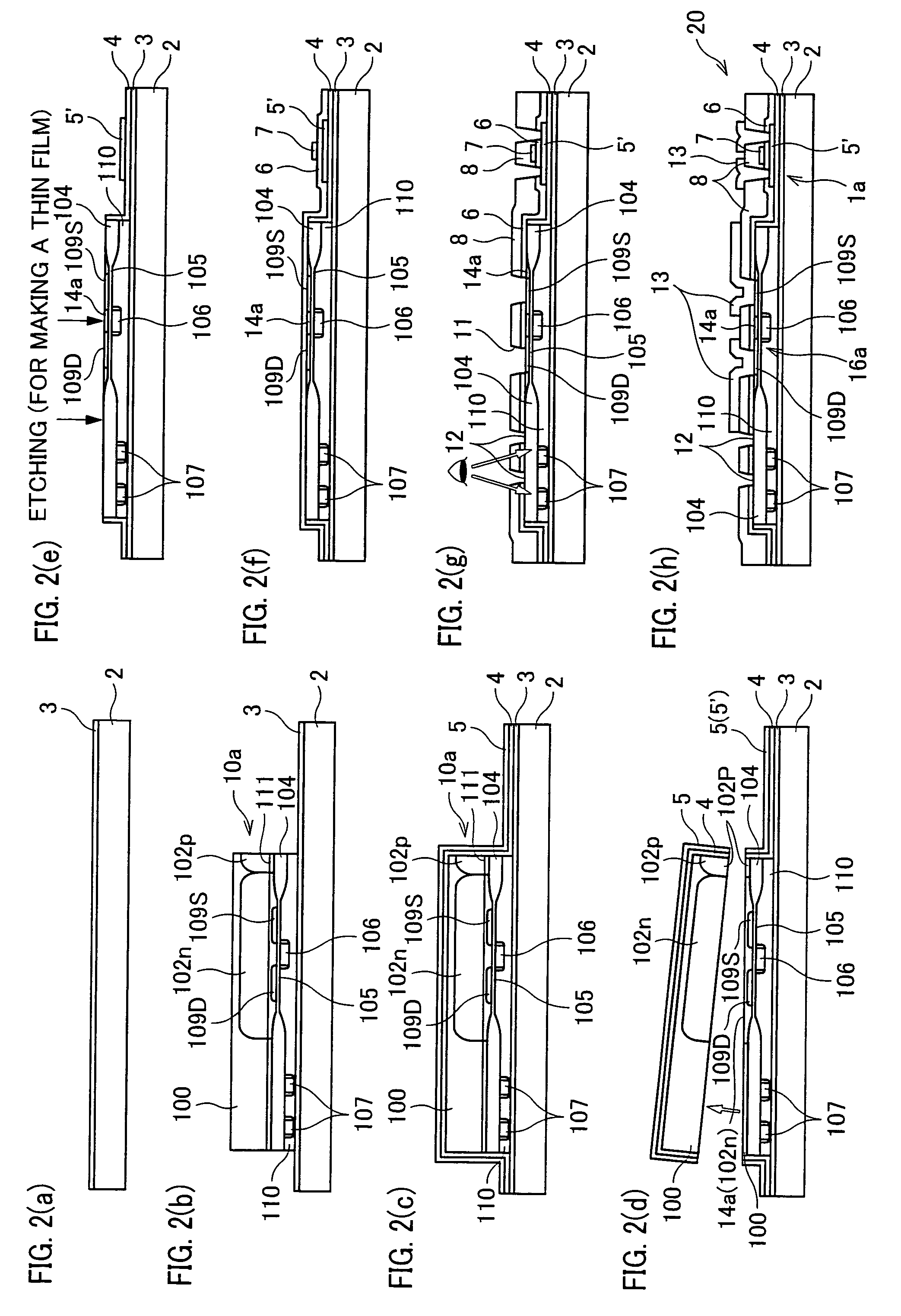
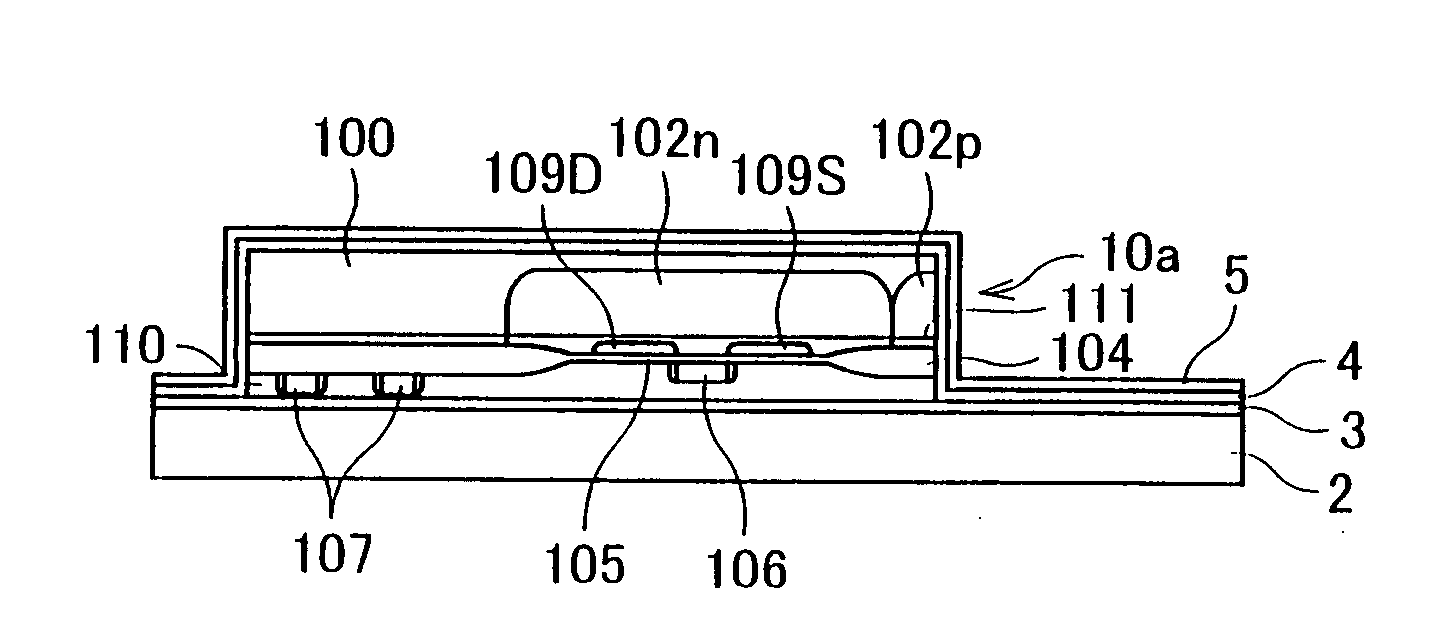
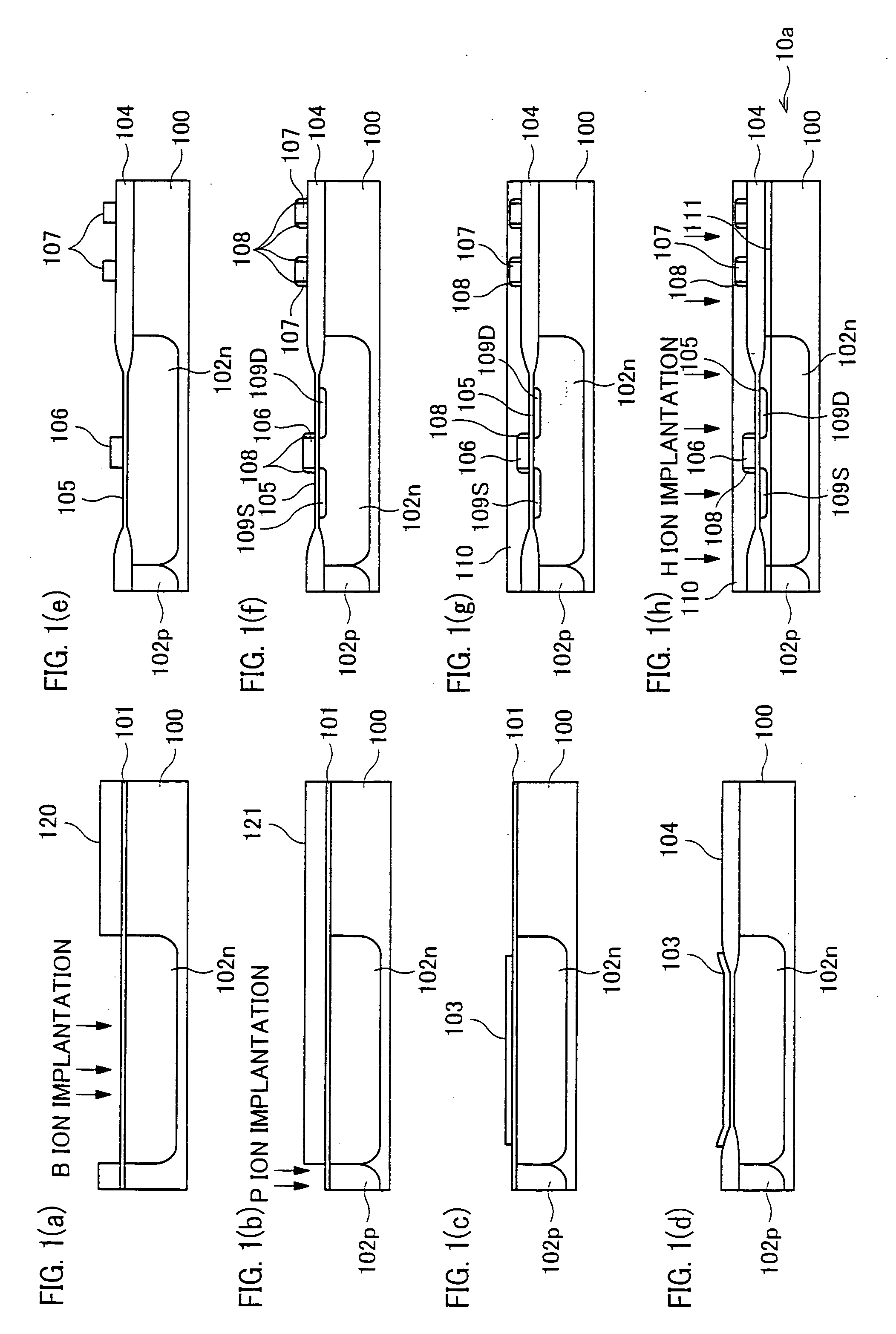
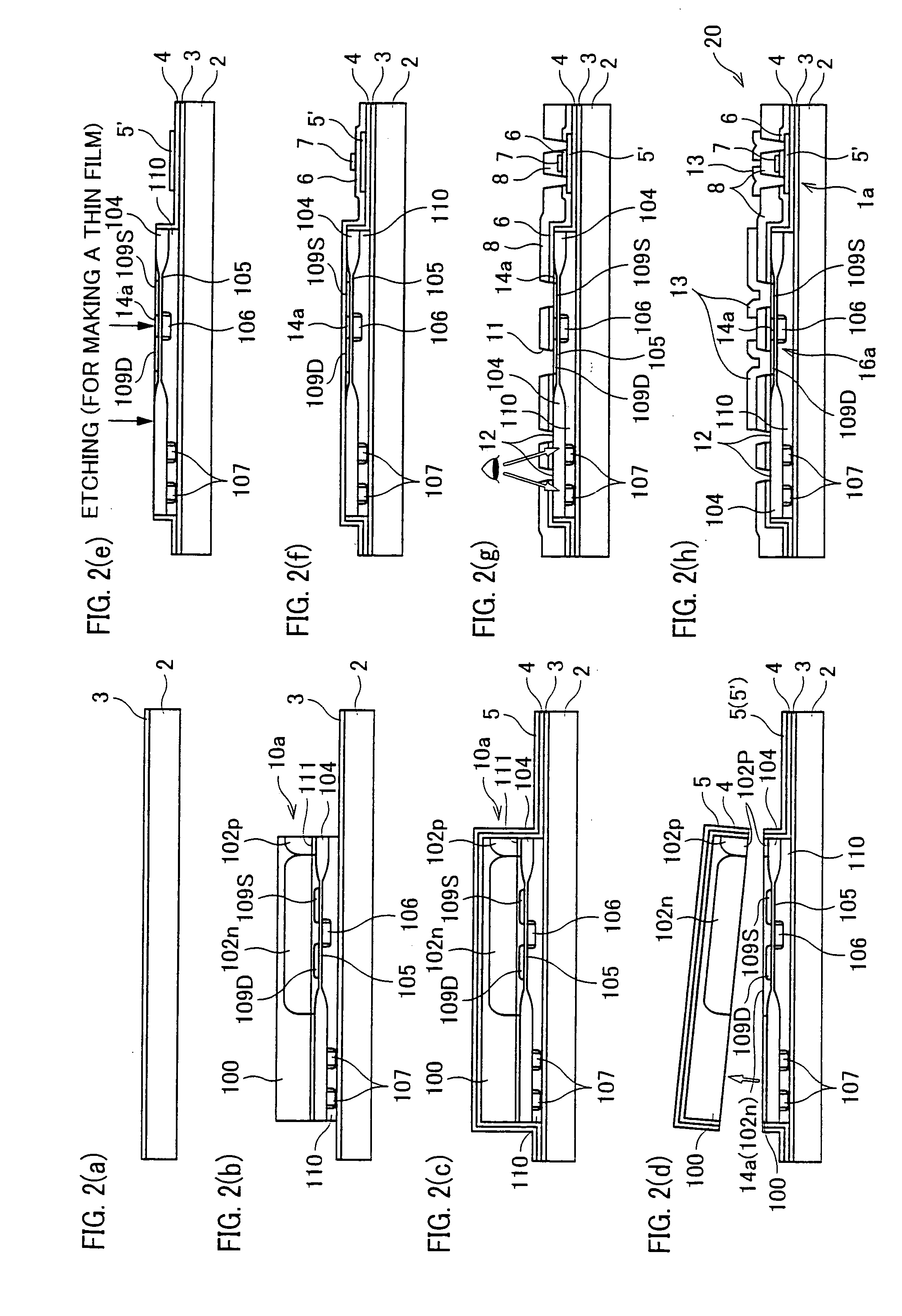
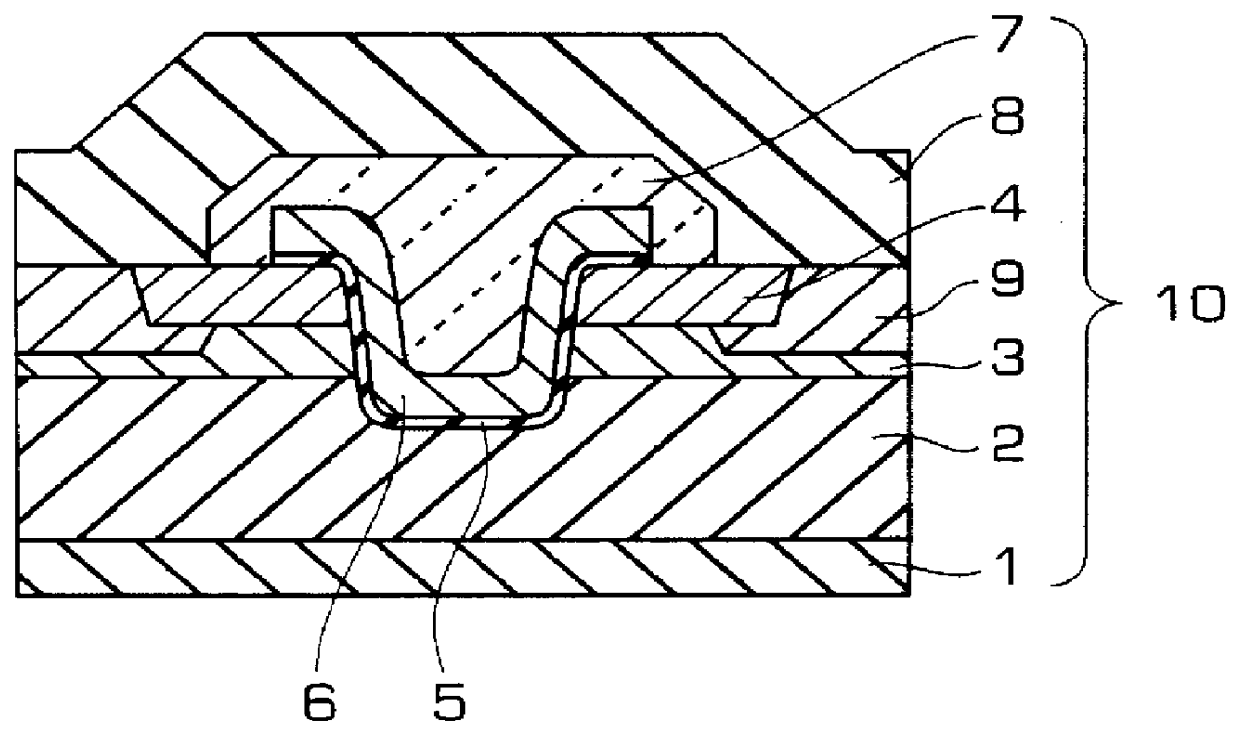
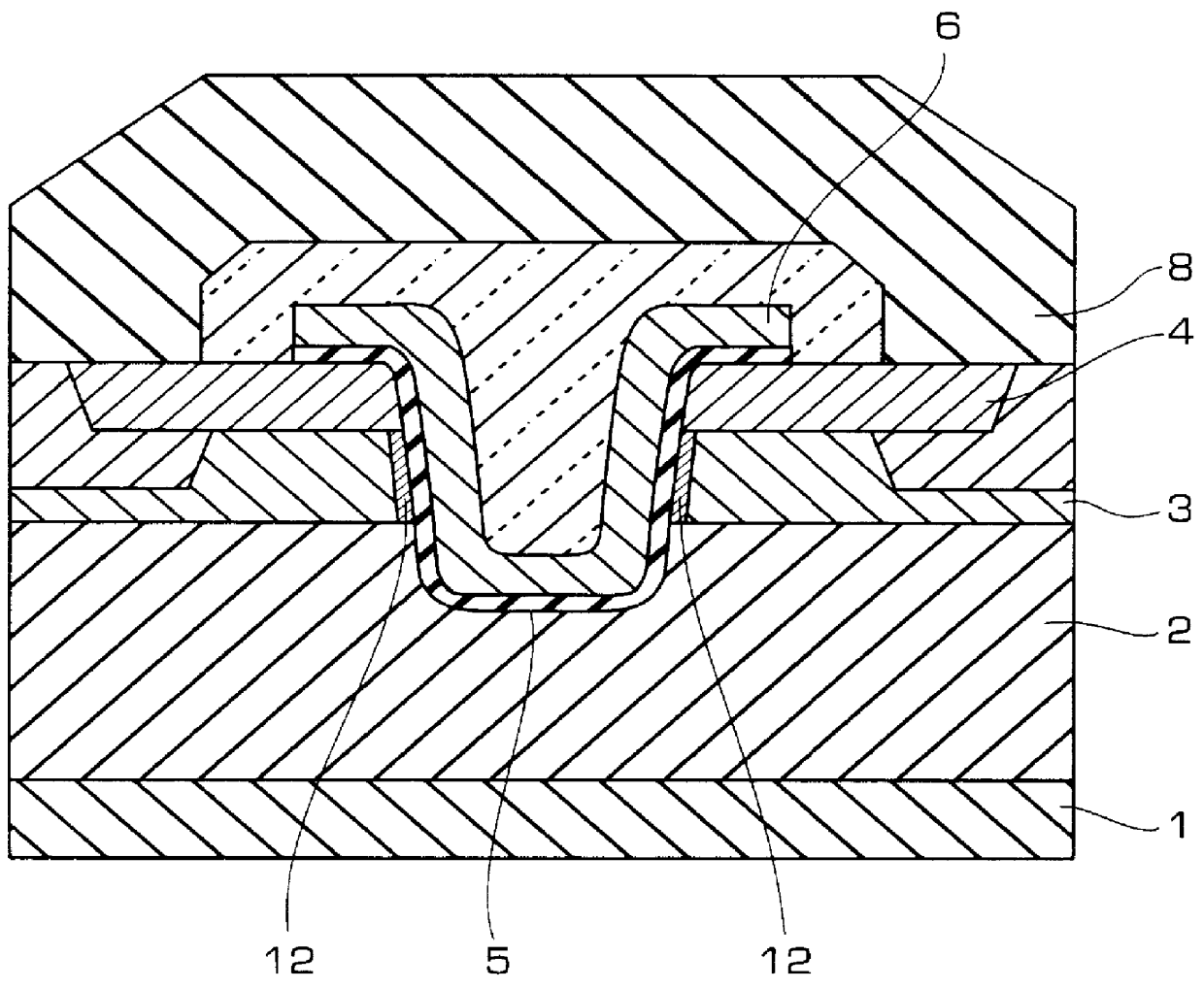
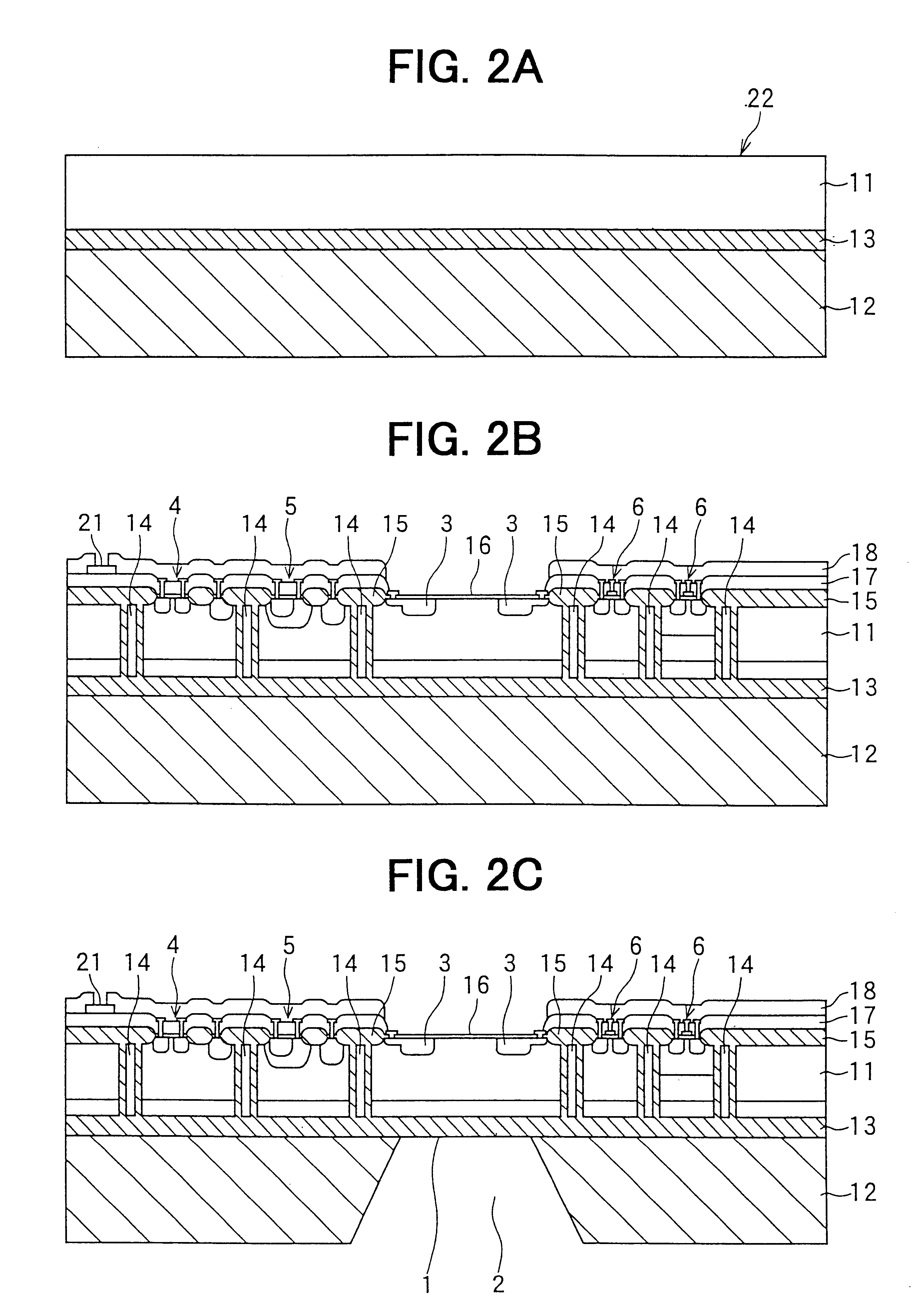
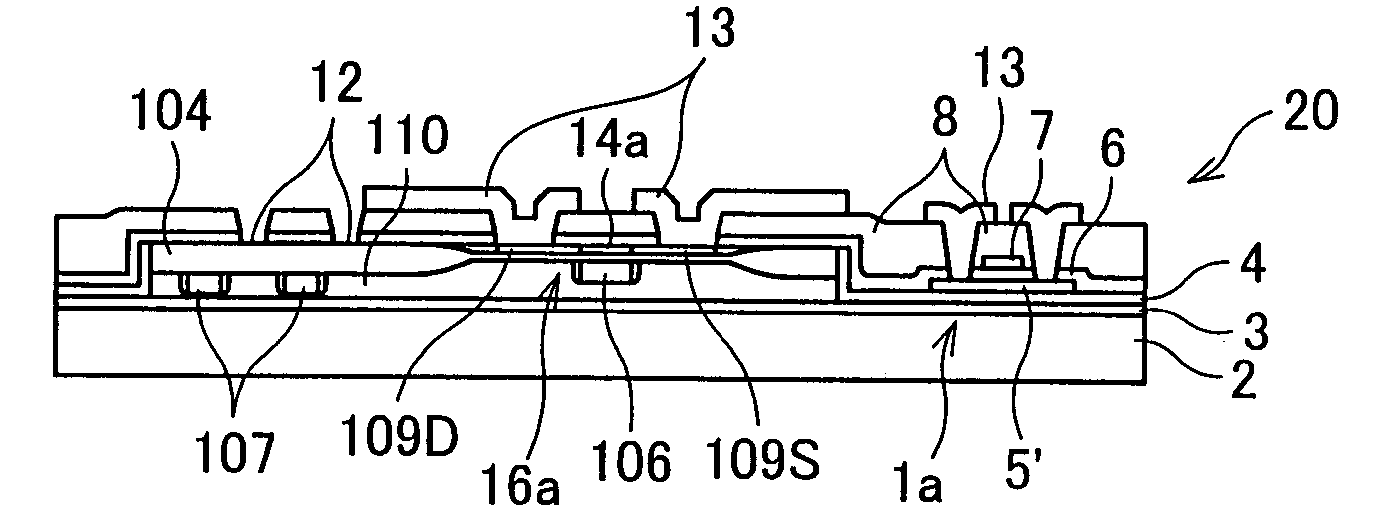
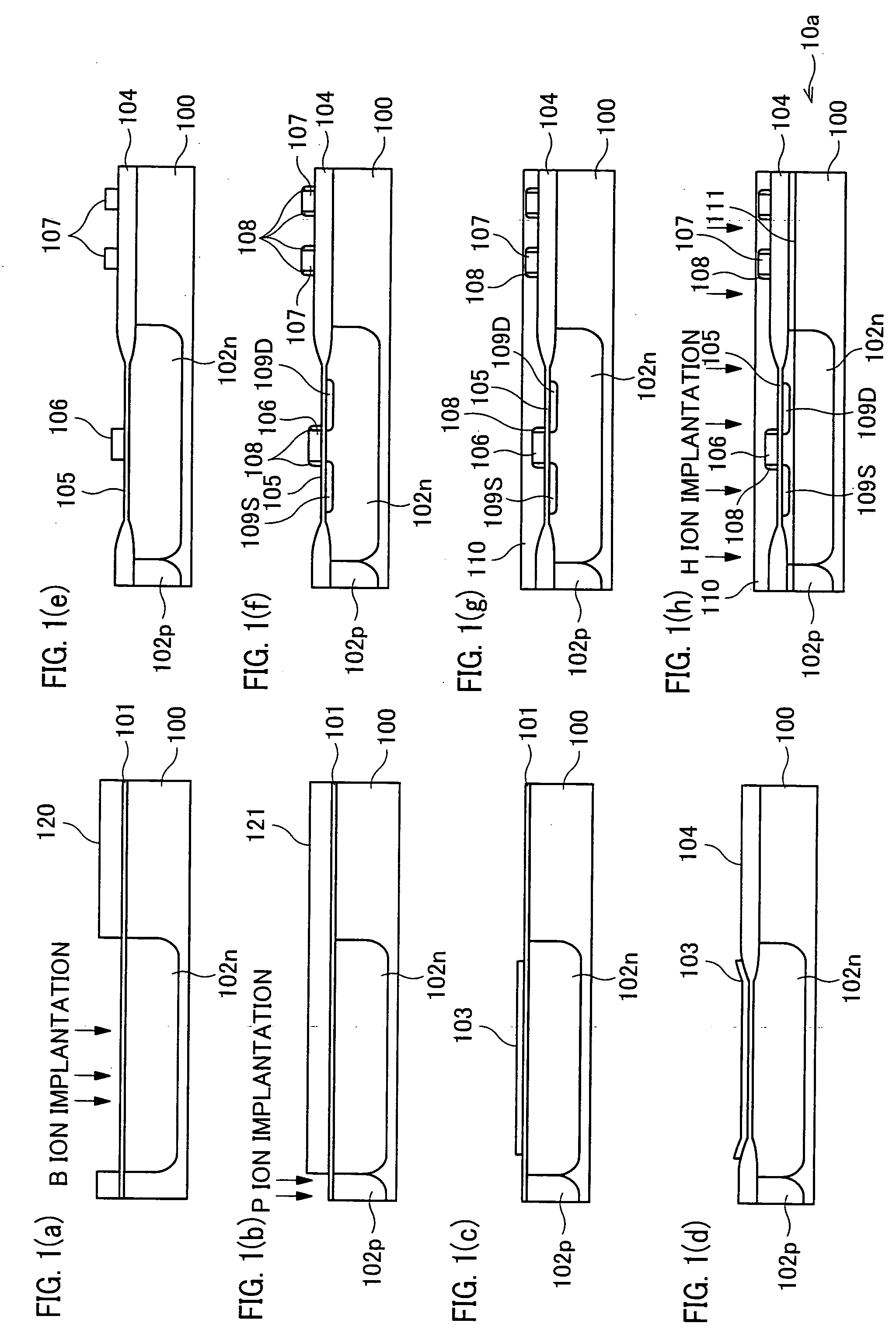
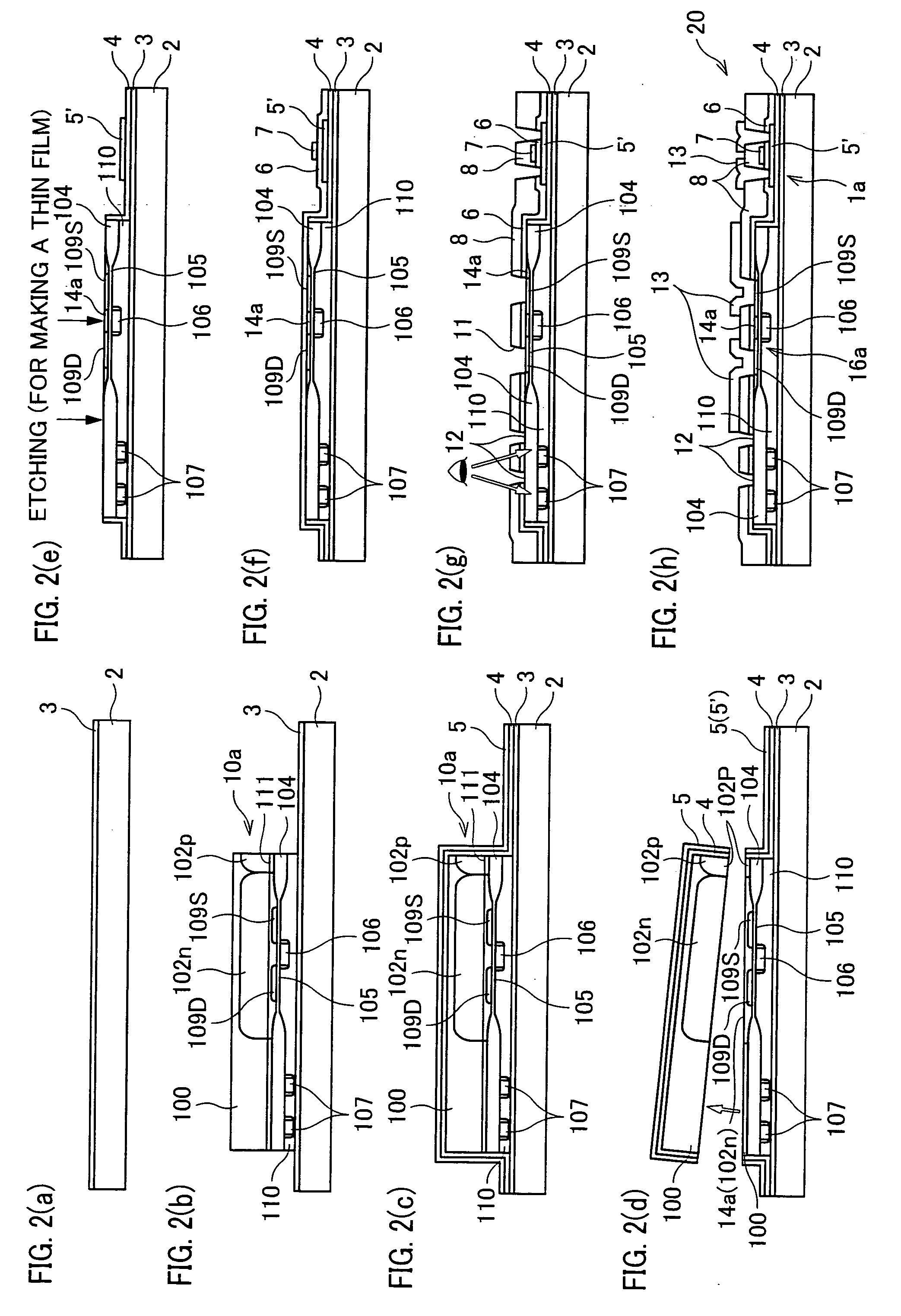
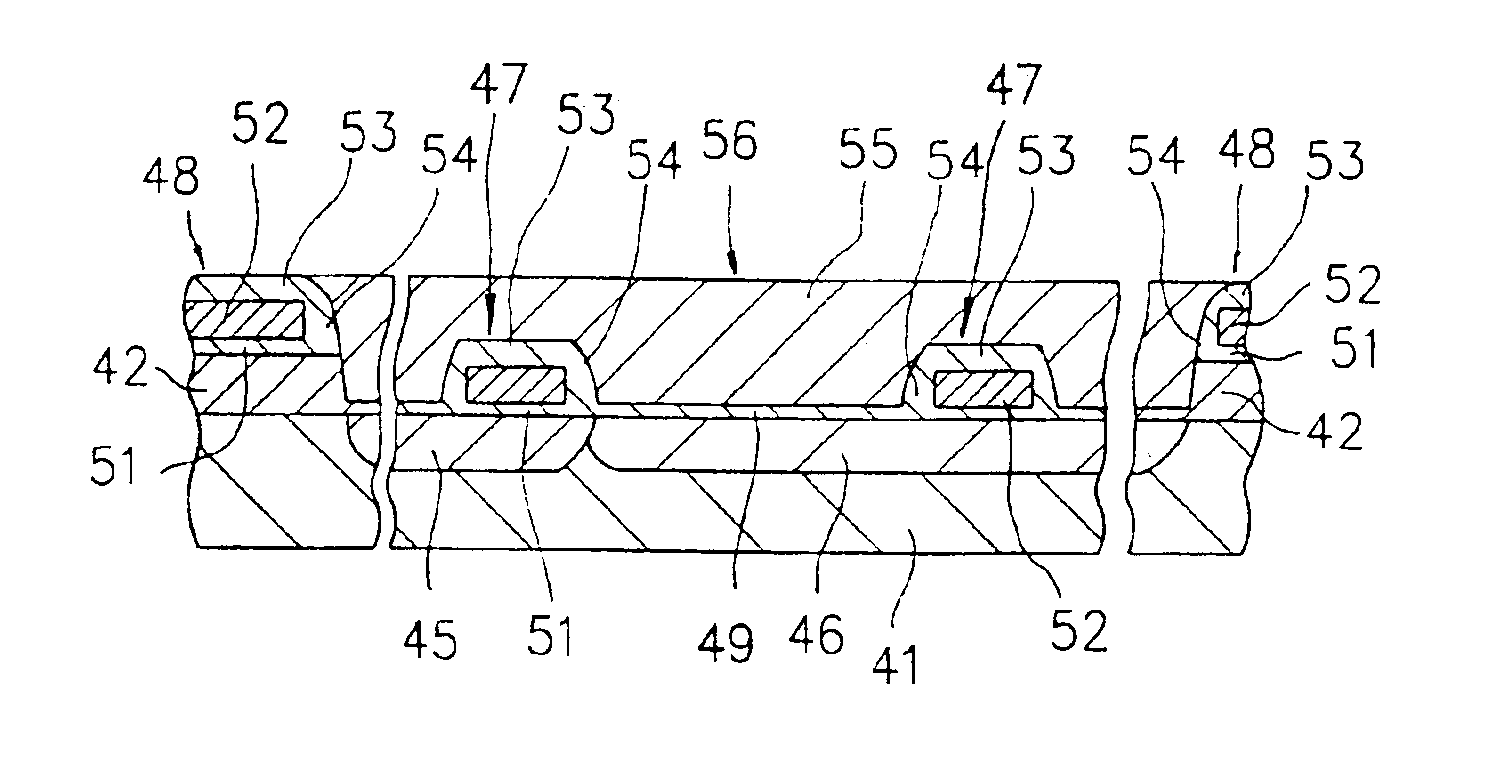
In a semiconductor device including a monocrystalline thin film transistor 16a that has been formed on a monocrystalline Si wafer 100 and then is transferred to a insulating substrate 2, LOCOS oxidization is performed with respect to the element-isolation region of the monocrystalline Si wafer 100 so as to create a field oxide film (SiO2 film) 104, and a marker 107 is formed on the field oxide film 104. With this structure, alignment of components may be performed based on a gate electrode 106 upon or after the transfer step.
Owner:SHARP KK
Semiconductor device and fabrication method for the same
InactiveUS20070108523A1Secure performanceImprove reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialLOCOS
In a semiconductor device including a monocrystalline thin film transistor 16a that has been formed on a monocrystalline Si wafer 100 and then is transferred to a insulating substrate 2, LOCOS oxidization is performed with respect to the element-isolation region of the monocrystalline Si wafer 100 so as to create a field oxide film (SiO2 film) 104, and a marker 107 is formed on the field oxide film 104. With this structure, alignment of components may be performed based on a gate electrode 106 upon or after the transfer step.
Owner:SHARP KK
LDMOS transistors and methods for making the same
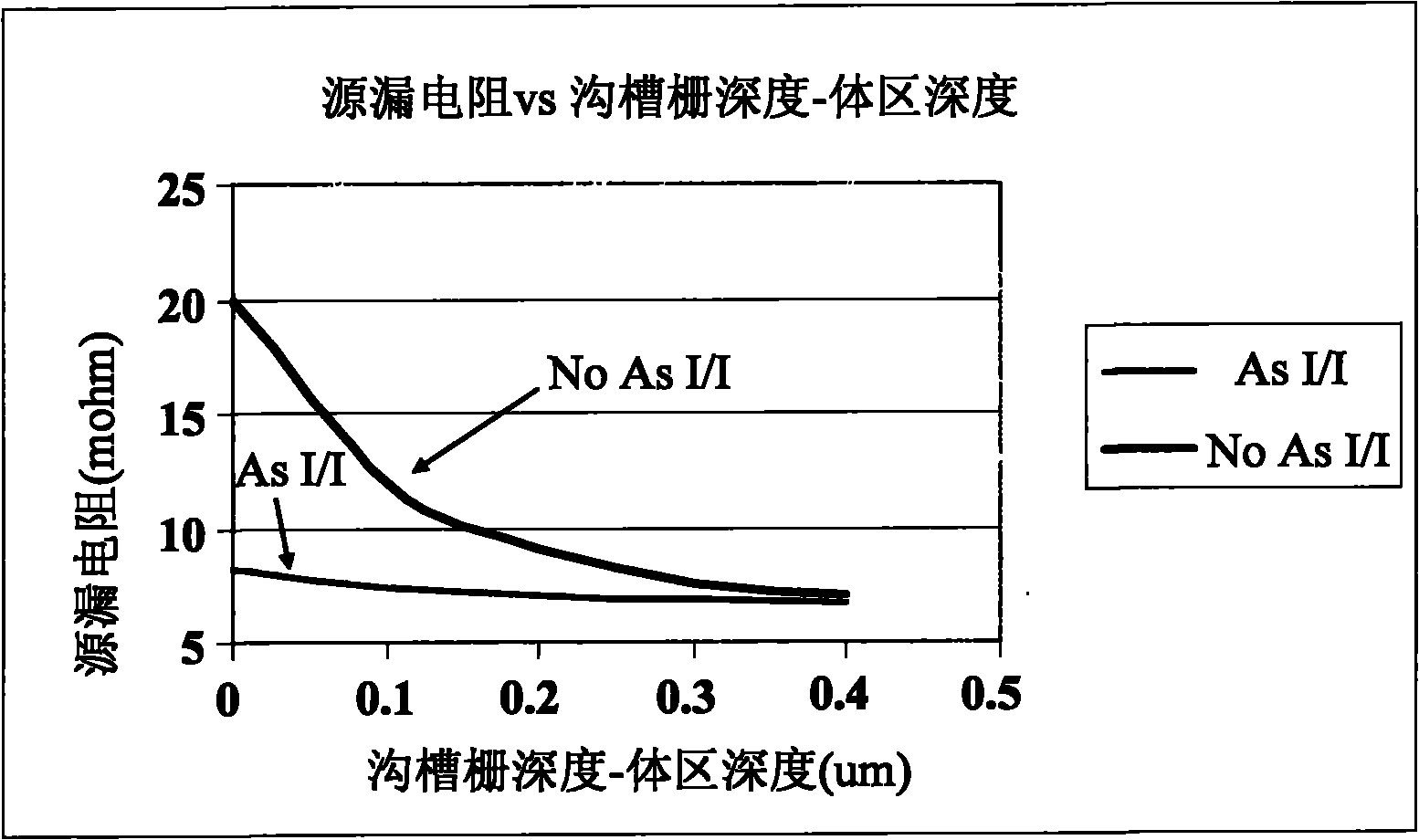
InactiveUS6900101B2Reduce or inhibit current flow constrictionLower on-state resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantDielectric
LDMOS transistor devices and fabrication methods are provided, in which additional dopants are provided to region of a substrate near a thick dielectric between the channel and the drain to reduce device resistance without significantly impacting breakdown voltage. The extra dopants are added by implantation prior to formation of the thick dielectric, such as before oxidizing silicon in a LOCOS process or following trench formation and before filling the trench in an STI process.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Structures and techniques for using mesh-structure diodes for electro-static discharge (ESD) protection
ActiveUS20130200488A1Improve immunityReduce input capacitanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLOCOSBlocking layer
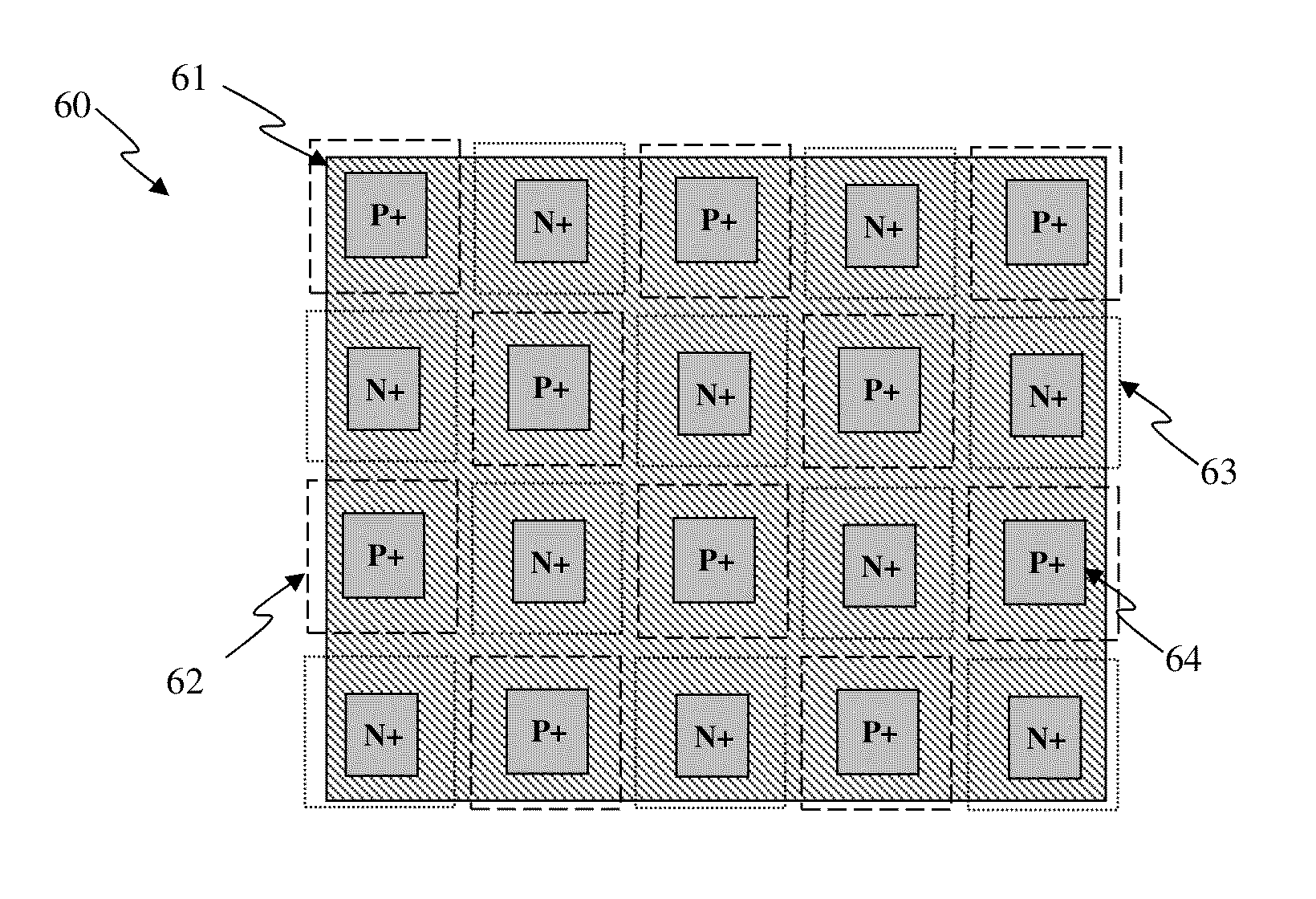
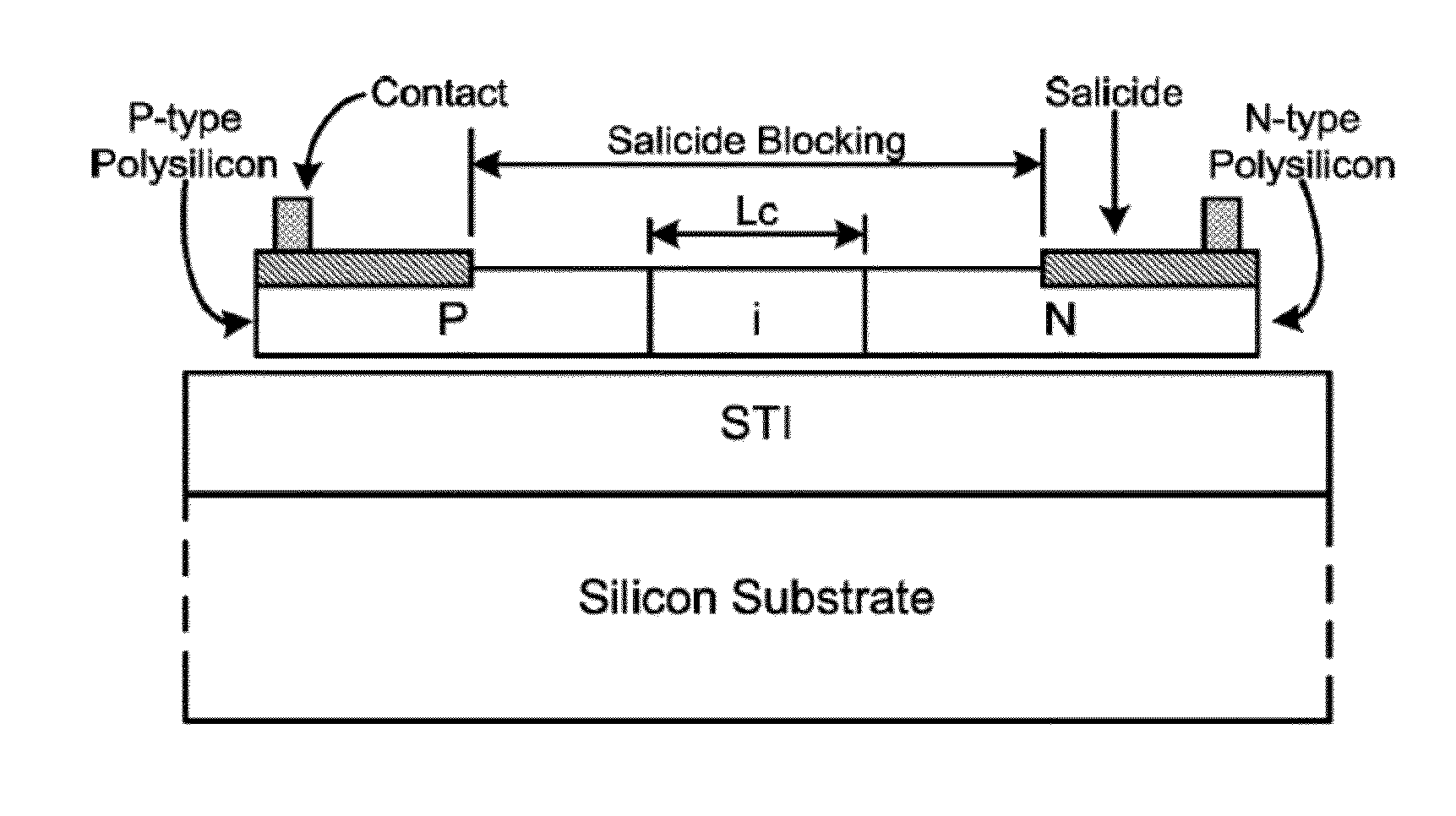
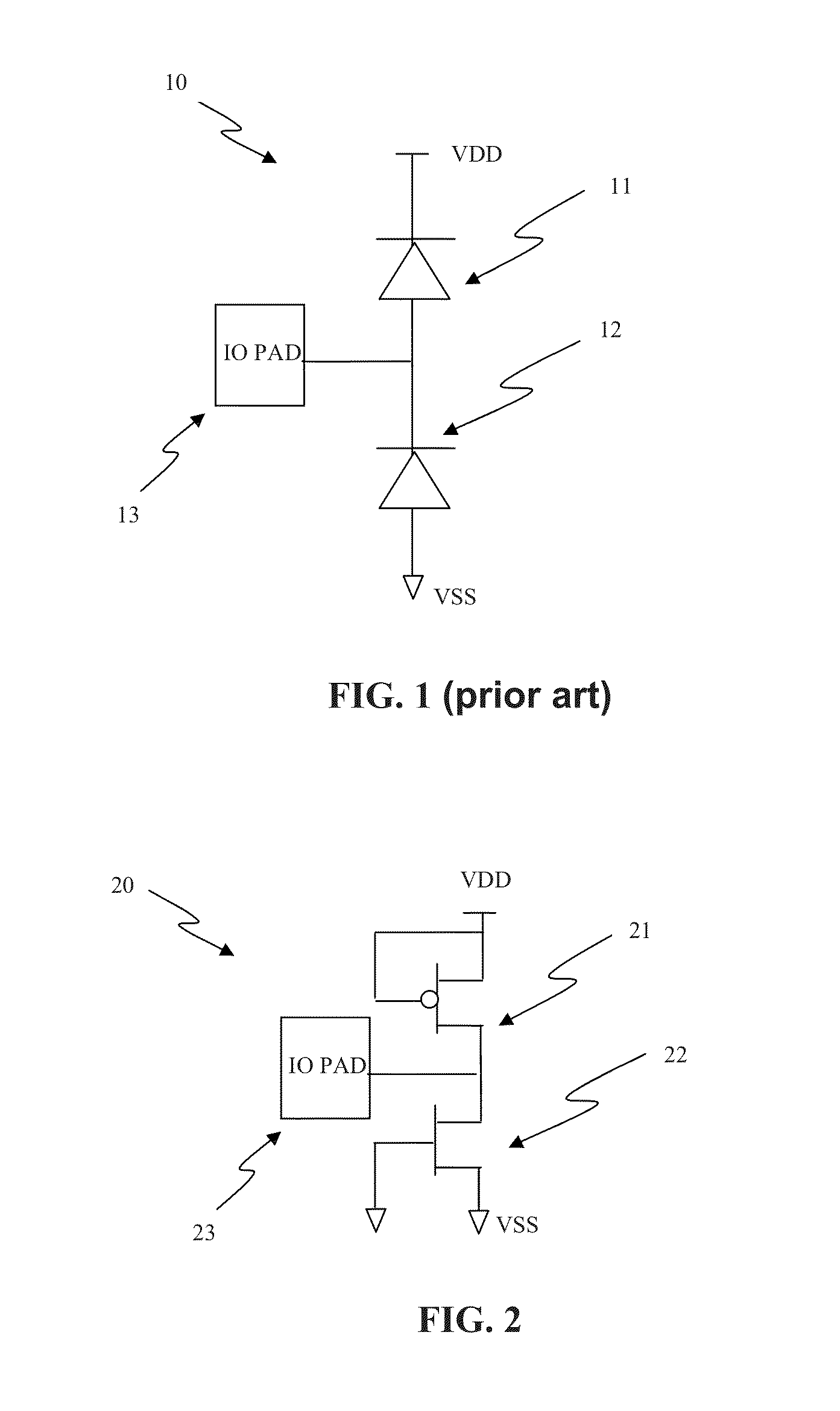
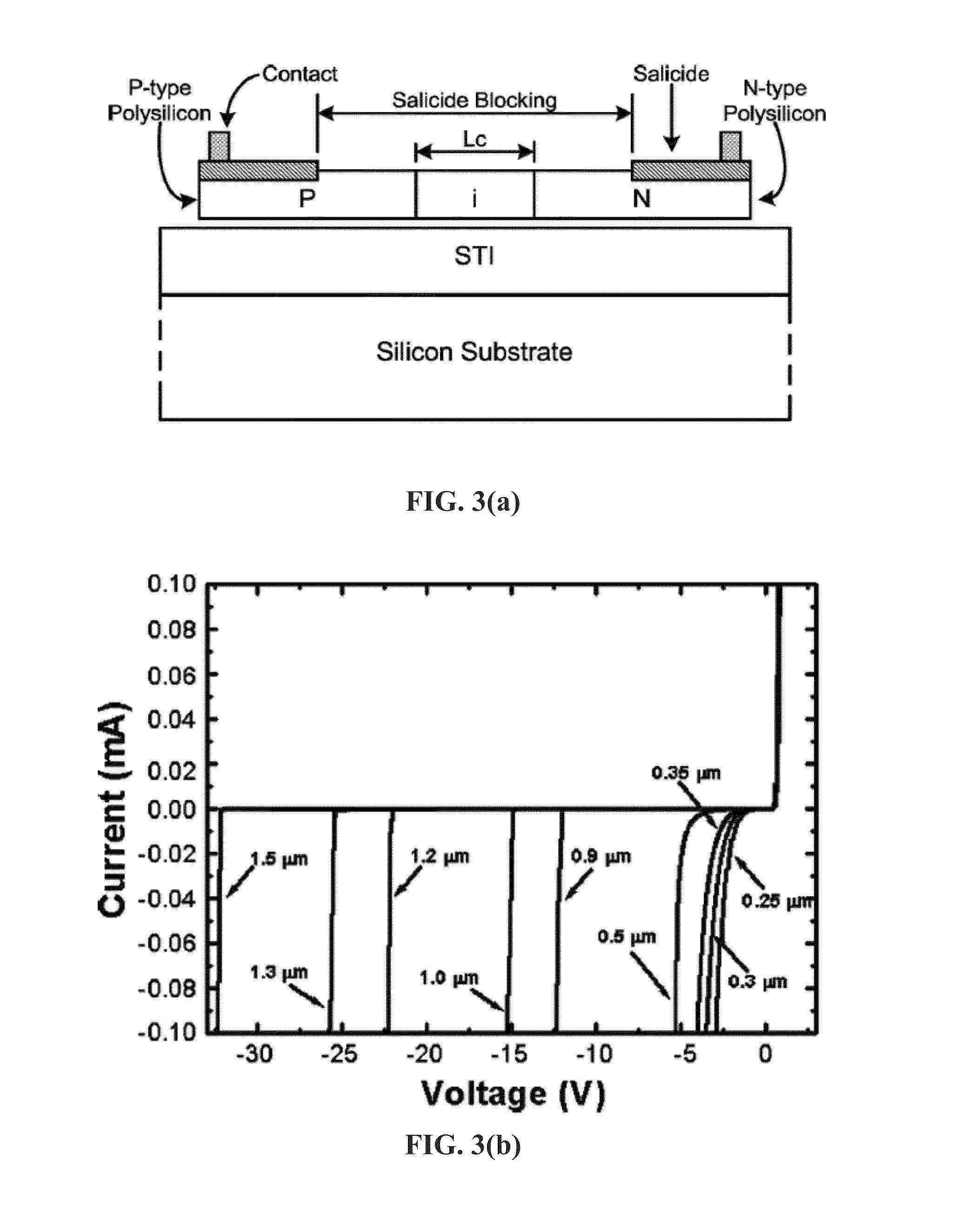
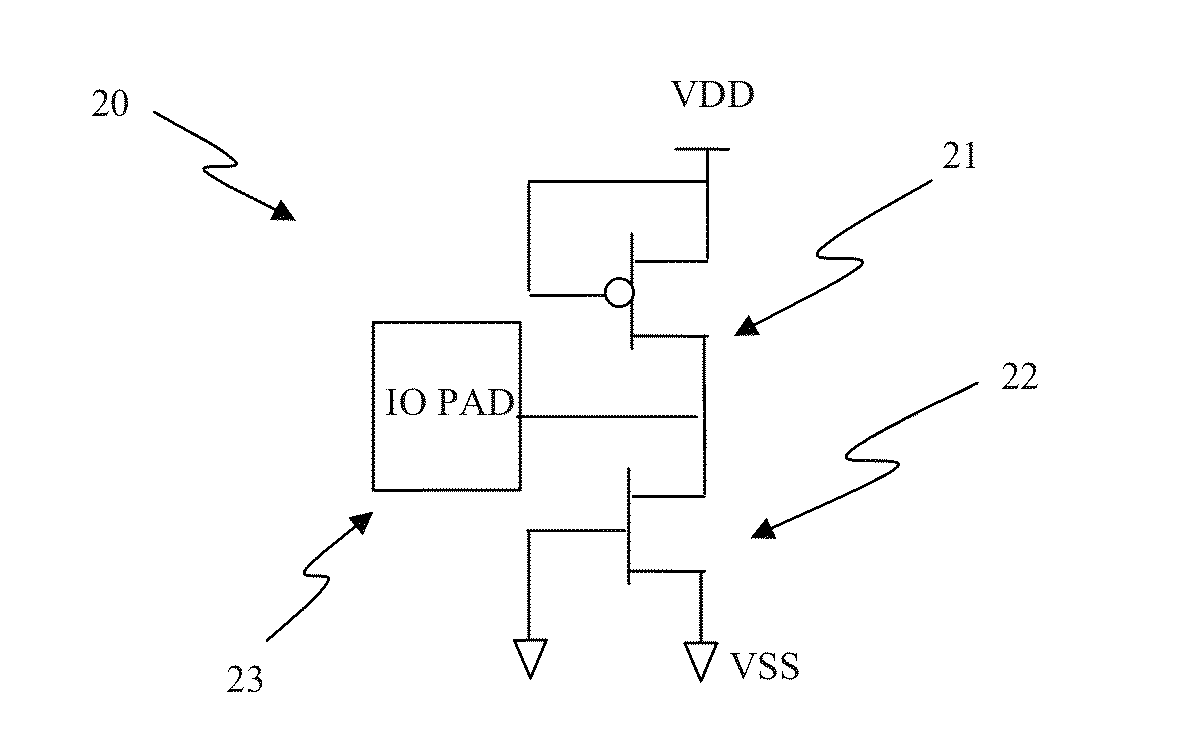
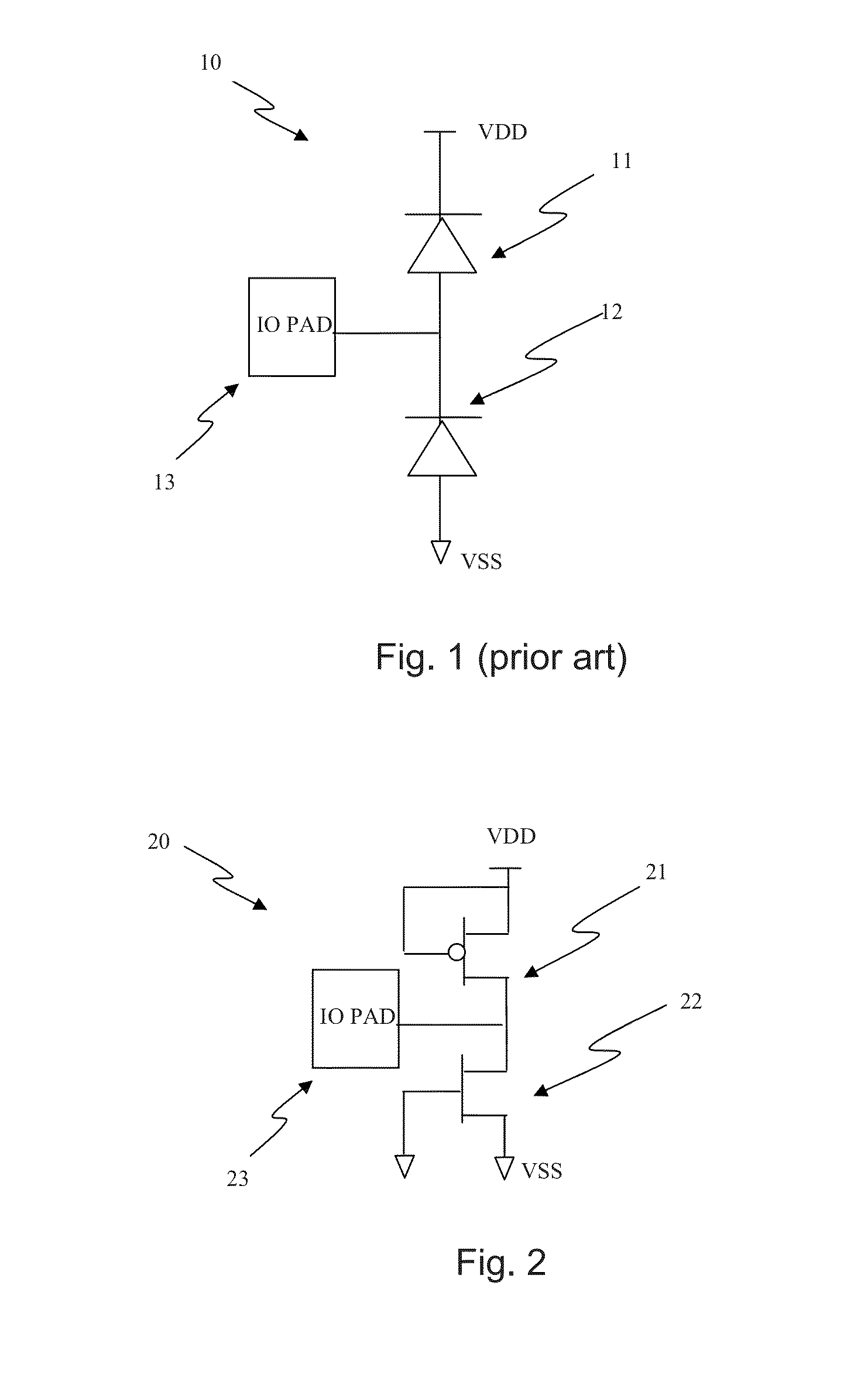
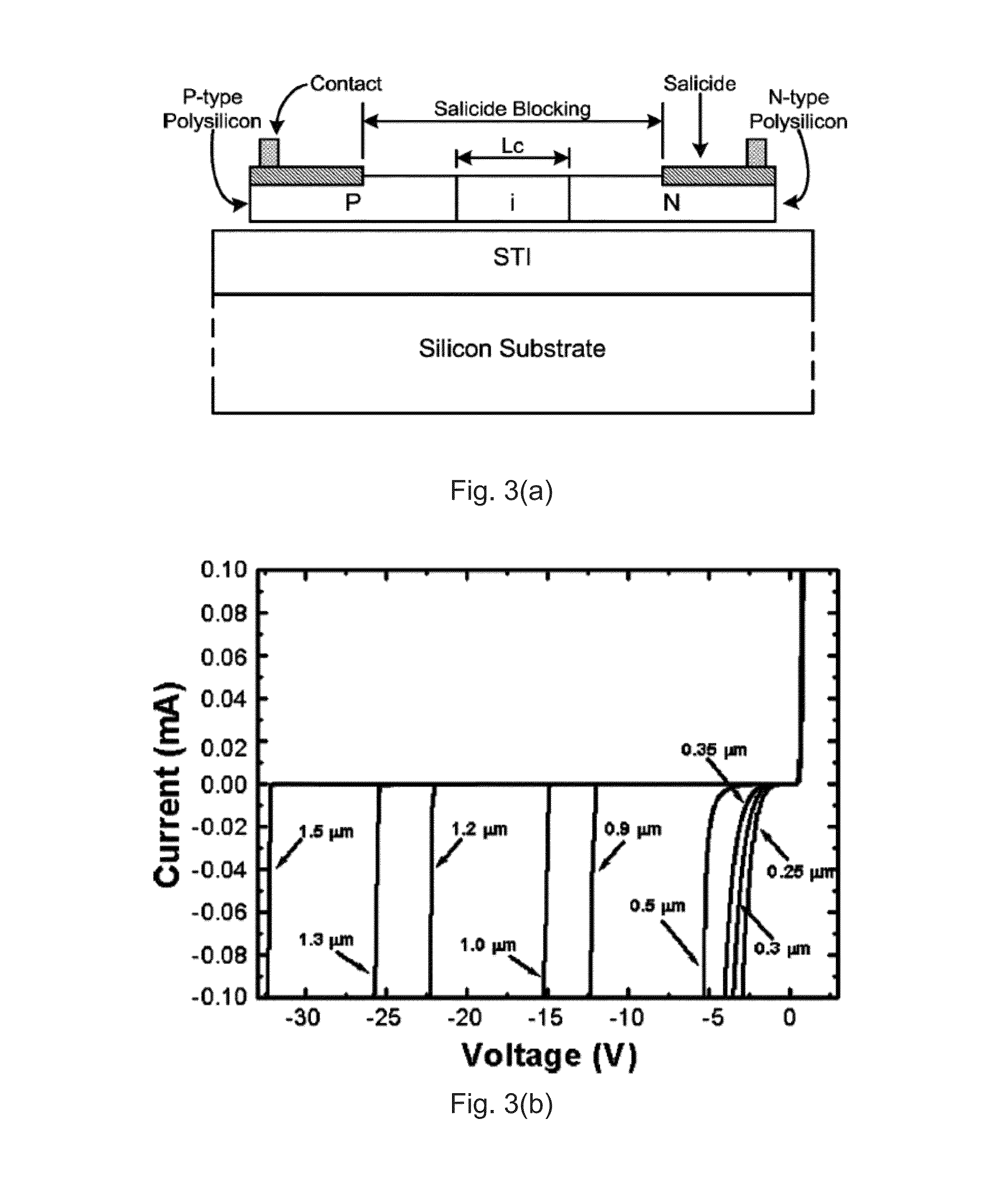
An Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) protection using at least one I / O pad with at least one mesh structure of diodes provided on a semiconductor body is disclosed. The mesh structure has a plurality of cells. At least one cell can have a first type of implant surrounded by at least one cell with a second type of implant in at least one side of the cell, and at least cell can have a second type of implant surrounded by at least one cell with a first type of implant in at least one side of the cell. The two types of implant regions can be separated with a gap. A silicide block layer (SBL) can cover the gap and overlap into the both implant regions to construct P / N junctions on the polysilicon or active-region body on an insulated substrate. Alternatively, the two types of implant regions can be isolated by LOCOS, STI, dummy gate, or SBL on silicon substrate. The regions with the first and the second type of implants can be coupled to serve as the first and second terminal of a diode, respectively. The mesh structure can have a first terminal coupled to the I / O pad and a first terminal coupled to a first supply voltage.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Structures and techniques for electro-static discharge (ESD) protection using ring structured diodes
InactiveUS20140131710A1High ESD immunityReduce input capacitanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLOCOSEngineering
Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) protection using at least one ring-shape diode is disclosed. The ring-shape diode can be constructed from polysilicon, active region body on insulated substrate, or junction diode on silicon substrate. The diodes can have a first type of implant in an outer ring and a second type of implant in an inner ring to serve as two terminals of a diode coupled through contacts, vias, or metals. The two types of implant ring regions are separated with an isolation structure. The isolation can be LOCOS, STI, dummy gate, or silicide block layer (SBL). The ESD structure has at least a ring-shape diode with a first terminal coupled to an I / O pad and the second terminal coupled to a first supply voltage. The contours of the ring-shape diode can be circles, polygons, or other shapes. The ring-shape ESD structures can be multiple and be constructed in concentric manner.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Structures and techniques for using mesh-structure diodes for electro-static discharge (ESD) protection
InactiveUS20140133056A1High ESD immunityReduce input capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLOCOSImplant
An Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) protection using at least one I / O pad with at least one mesh structure of diodes provided on a semiconductor body is disclosed. The mesh structure has a plurality of cells. At least one cell can have a first type of implant surrounded by at least one cell with a second type of implant in at least one side of the cell, and at least cell can have a second type of implant surrounded by at least one cell with a first type of implant in at least one side of the cell. The two types of implant regions can be separated with a gap. A silicide block layer (SBL) can cover the gap and overlap into the both implant regions to construct P / N junctions on the polysilicon or active-region body on an insulated substrate. Alternatively, the two types of implant regions can be isolated by LOCOS, STI, dummy gate, or SBL on silicon substrate. The regions with the first and the second type of implants can be coupled to serve as the first and second terminal of a diode, respectively. The mesh structure can have a first terminal coupled to the I / O pad and a first terminal coupled to a first supply voltage.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
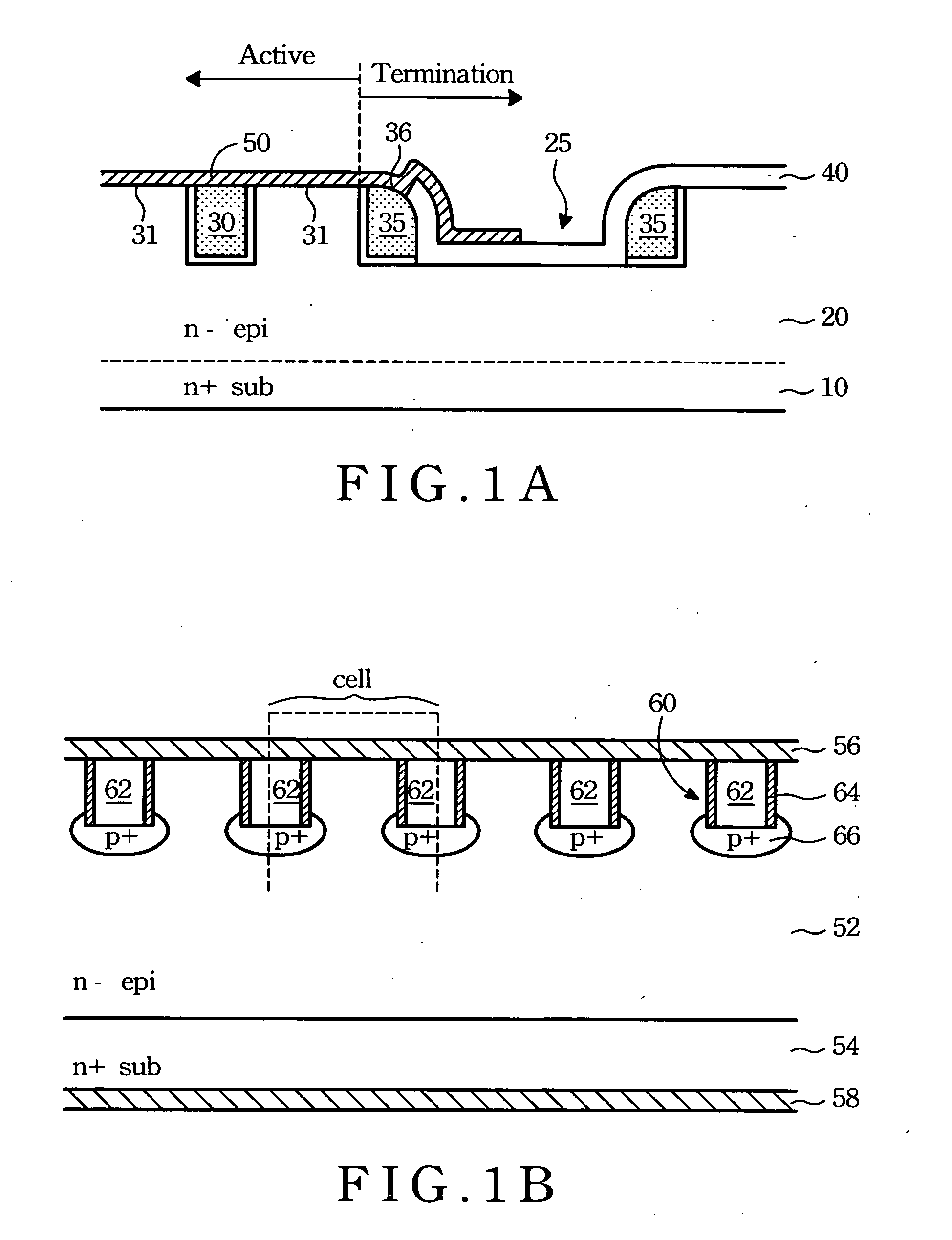
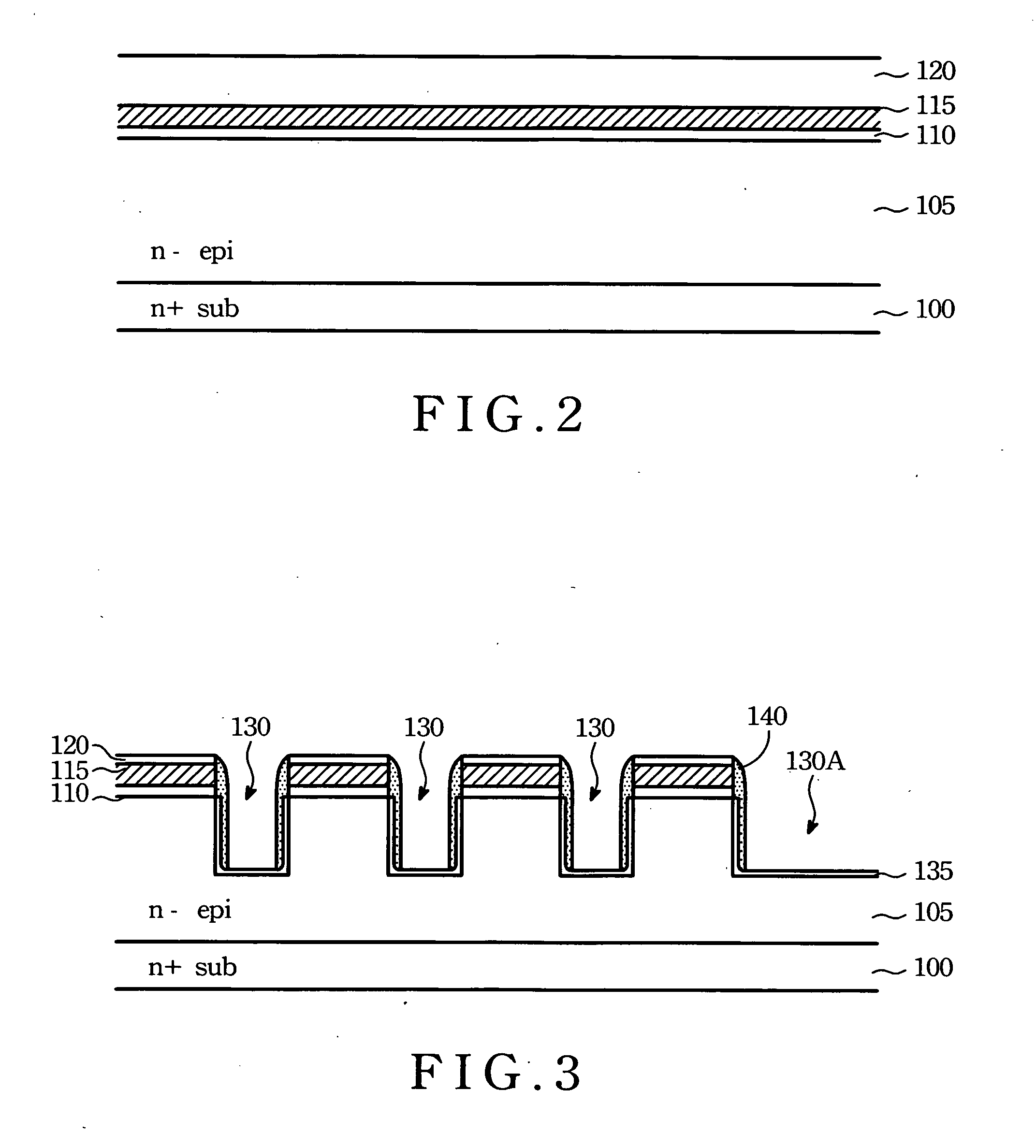
Production method of a vertical type MOSFET
InactiveUS6015737AMade smallSmall on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDouble diffusionLOCOS
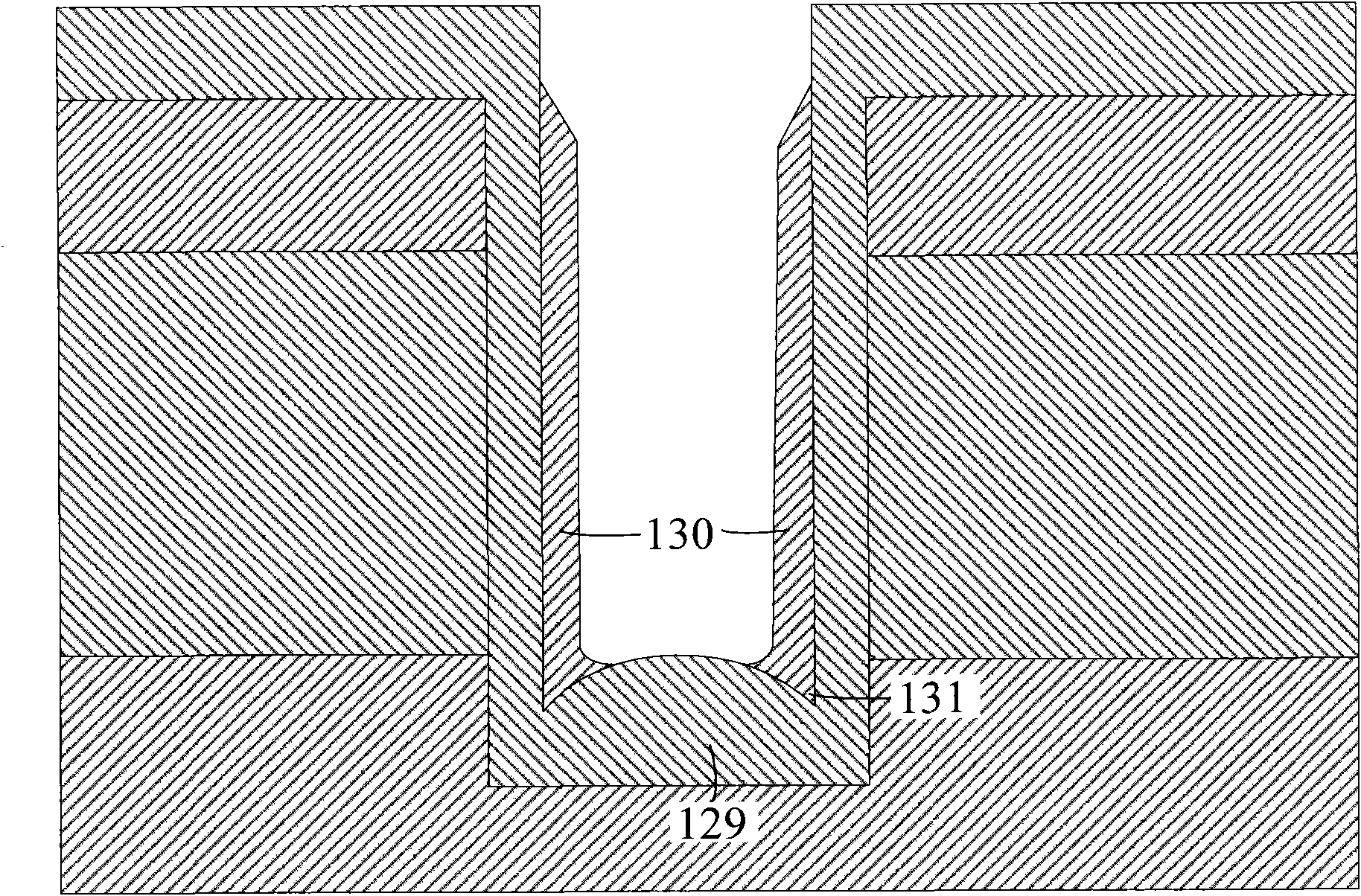
A vertical type power MOSFET remarkably reduces its ON-resistance per area. A substantial groove formation in which a gate structure is constituted is performed beforehand utilizing the LOCOS method before the formation of a p-type base layer and an n+-type source layer. The p-type base layer and the n+-type source layer are then formed by double diffusion in a manner of self-alignment with respect to a LOCOS oxide film, simultaneously with which channels are set at sidewall portions of the LOCOS oxide film. Thereafter the LOCOS oxide film is removed to provide a U-groove so as to constitute the gate structure. Namely, the channels are set by the double diffusion of the manner of self-alignment with respect to the LOCOS oxide film, so that the channels, which are set at the sidewall portions at both sides of the groove, provide a structure of exact bilateral symmetry, there is no positional deviation of the U-groove with respect to the base layer end, and the length of the bottom face of the U-groove can be made minimally short. Therefore, the unit cell size is greatly reduced, and the ON-resistance per area is greatly decreased.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Fabrication of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers by local oxidation
ActiveUS20090142872A1Improve breakdown voltageReduce parasitic capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMechanical vibrations separationParasitic capacitorCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
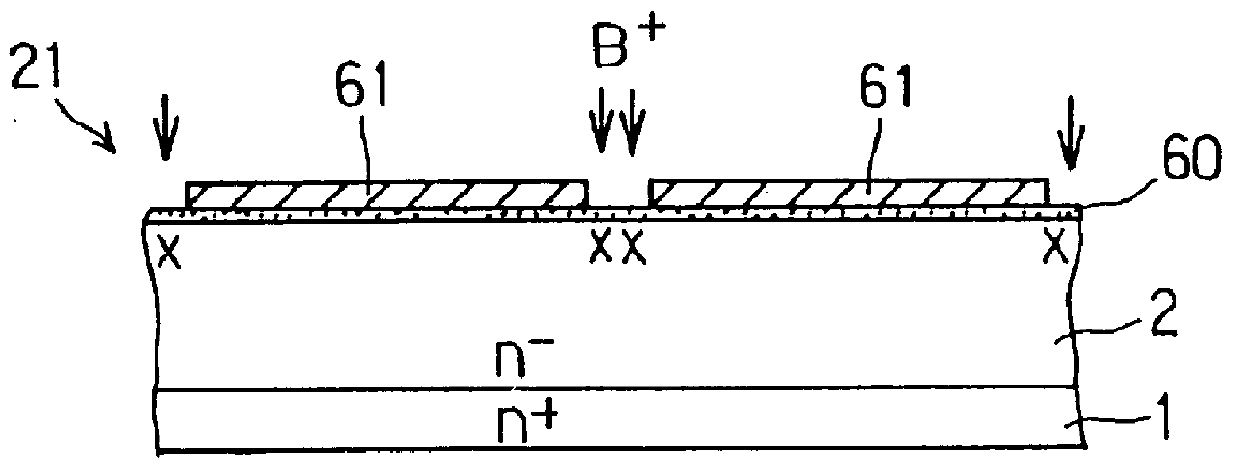
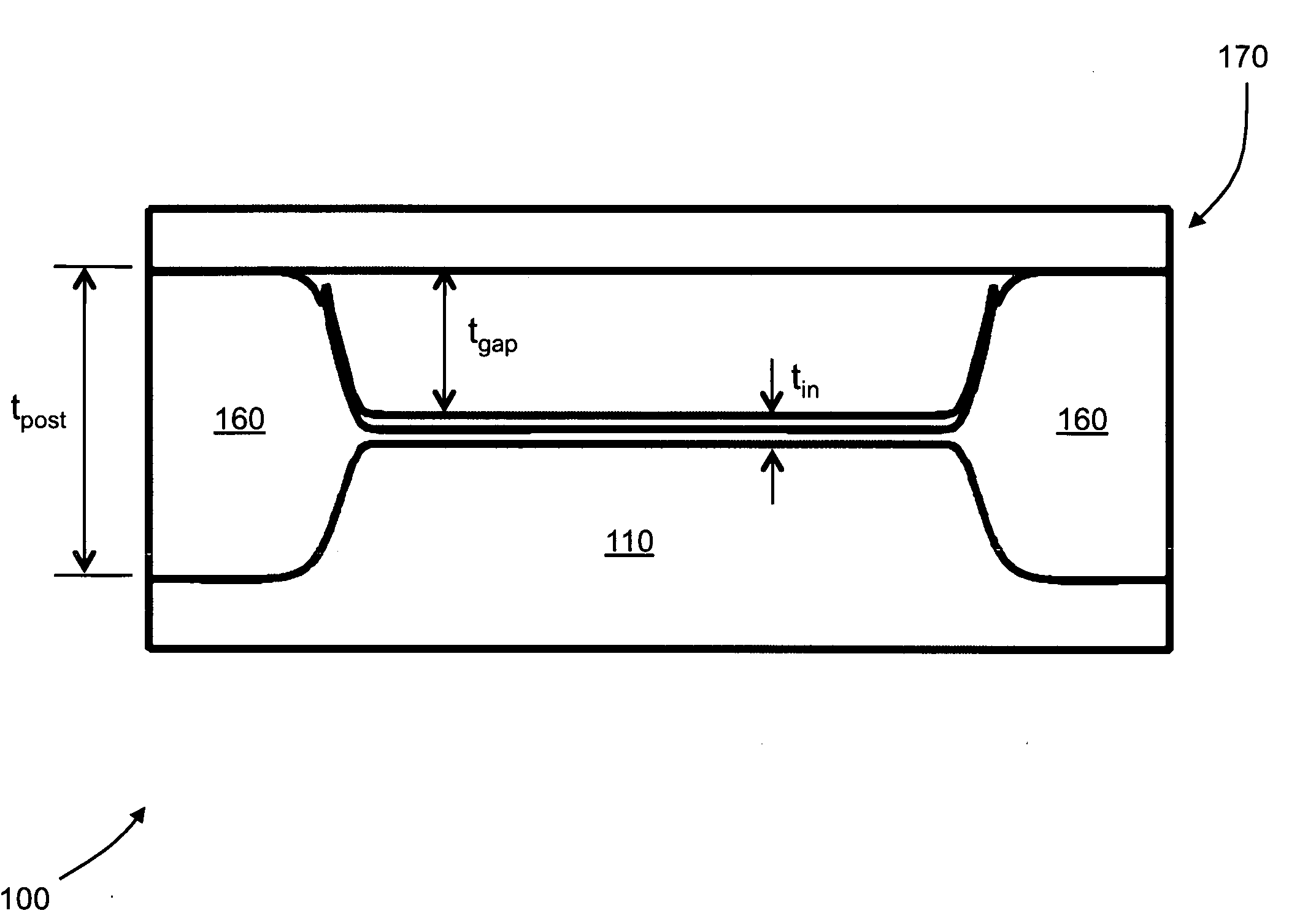
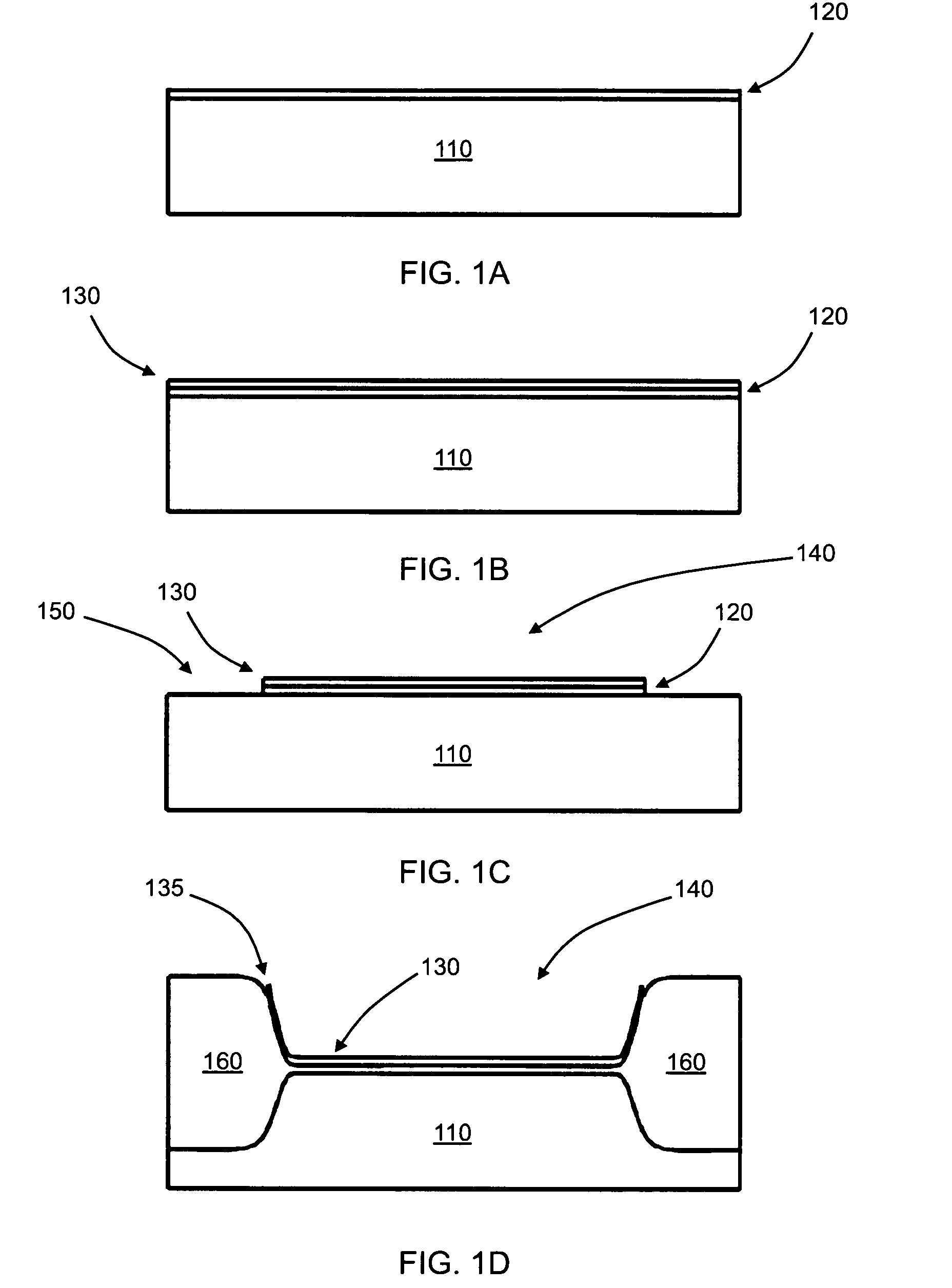
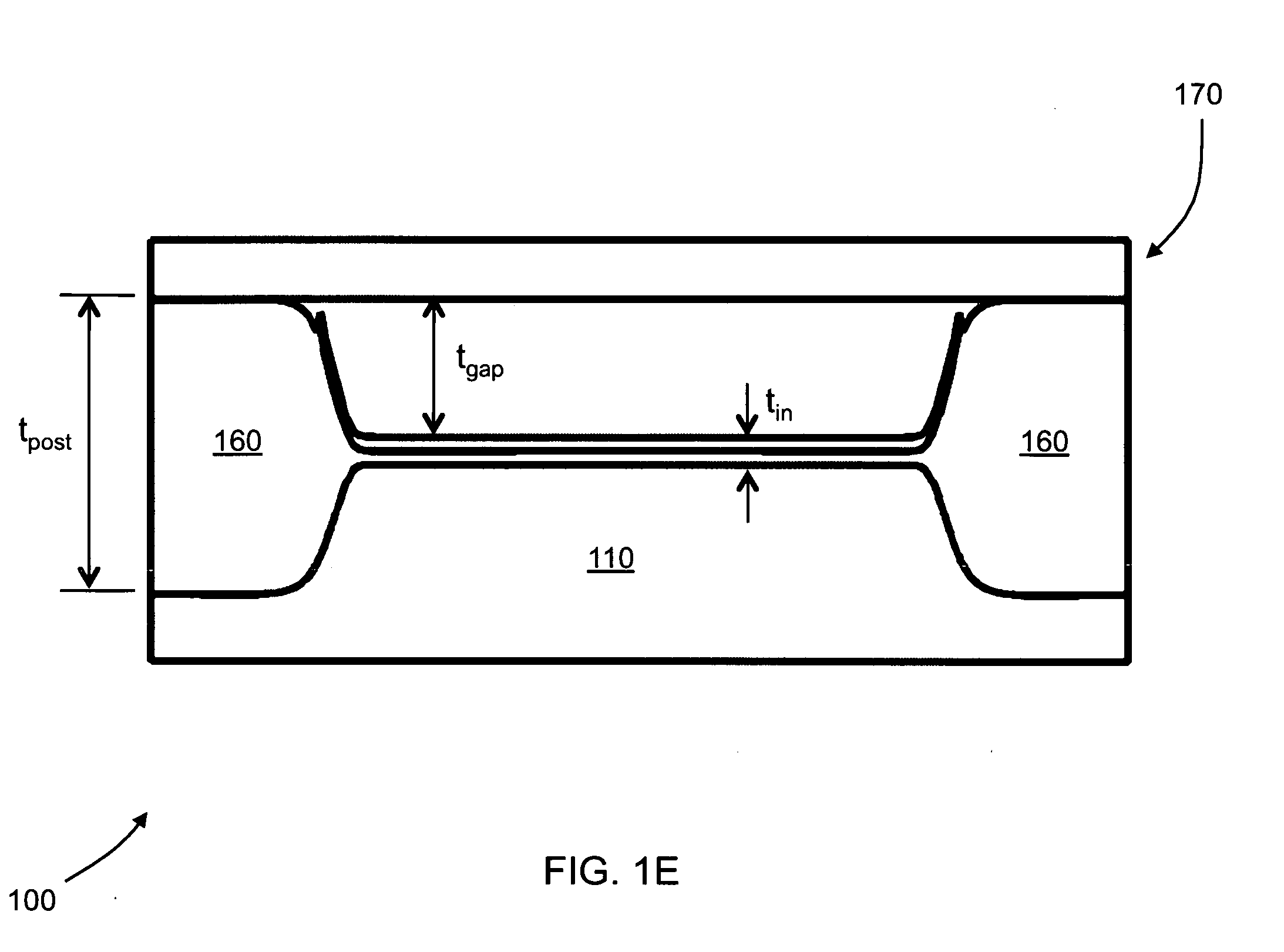
Fabrication methods for capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers (CMUTS) with independent and precise gap and post thickness control are provided. The fabrication methods are based on local oxidation or local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) to grow oxide posts. The process steps enable low surface roughness to be maintained to allow for direct wafer bonding of the membrane. In addition, methods for fabricating a step in a substrate are provided with reduced or minimal over-etch time by utilizing the nonlinearity of oxide growth. The fabrication methods of the present invention produce CMUTs with unmatched uniformity, low parasitic capacitance, and high breakdown voltage.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
High switching speed two mask schottky diode with high field breakdown
InactiveUS20070290234A1Minimize current leakageImprove reverse breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSchottky barrierLOCOS
A power Schottky rectifier device and method of making the same are disclosed. The Schottky rectifier device includes a LOCOS structure grown on the bottom of the trenches by using nitride spacer on the sidewall of the trenches as a thermal oxidation mask. A polycrystalline silicon layer is then filled the first trenches. Under LOCOS structure, a p doped region is optionally formed to minimize the current leakage when the device undergoes a reverse biased. A Schottky barrier silicide layer formed by sputtering and annealing steps is formed on the upper surfaces of the epi-layer and the polycrystalline silicon layer. A top metal layer served as anode is then formed on the Schottky barrier silicide layer and extended to cover a portion of field oxide region of the termination trench. A metal layer served as a cathode electrode is then formed on the backside surface of the substrate opposite to the top metal layer.
Owner:CHIP INTEGRATION TECH +1
Vertical MOSFET and method of manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS6133099AReduce parasitic capacitanceInhibit deteriorationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETOhmic contact
A vertical MOSFET of the present invention comprises a semiconductor wafer having a groove selectively etching in the semiconductor wafer to have substantially vertical side walls. The groove is oxidized using local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) at 1100.degree. C. or greater to form a LOCOS film on the semiconductor wafer in the groove so that a whole side surface of said semiconductor wafer exposed by the groove is substantially vertical and essentially flat. The LOCOS film in the groove is removed and a thermal insulating film on the semiconductor wafer in the groove. Then a gate electrode made of a conductive film is formed on the thermal insulating film. An interlayer insulating film is formed on the gate electrode and a source electrode is formed in ohmic contact with a source region and a base region. A drain electrode is connected to the opposite side of the semiconductor wafer. As a result, the vertical MOSFET of the present invention has improved on-state resistance, reduced parasitic capacitance and higher breakdown voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor physical-quantity sensor having a locos oxide film, for sensing a physical quantity such as acceleration, yaw rate, or the like
InactiveUS6137150AAcceleration measurement using interia forcesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsDiffusionElectricity
The present invention provides a semiconductor physical-quantity sensor which can perform measurement of high accuracy without occurrence of deformation or displacement of a fixed electrode for vibration use even if voltage applied to the fixed electrode for vibration use is changed, and which can increase a dielectric breakdown voltage between the fixed electrode for vibration use and a substrate without varying a thickness of an insulative sacrificial layer or causing sacrificial-layer etching time to be affected. A semiconductor physical-quantity sensor according to the present invention forms an electrode-anchor portion on a sufficiently thick insulation film and causes dielectric breakdown voltage with a semiconductor substrate to be increased. In particular, the sufficiently thick insulation film is given by a LOCOS oxide film formed during sensor detection-circuit fabrication or separation of a diffusion electrode.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Semiconductor substrate, semiconductor device, and manufacturing methods for them
InactiveUS20050245046A1Improve performanceLess varied in characteristicTransistorStatic indicating devicesLOCOSEngineering
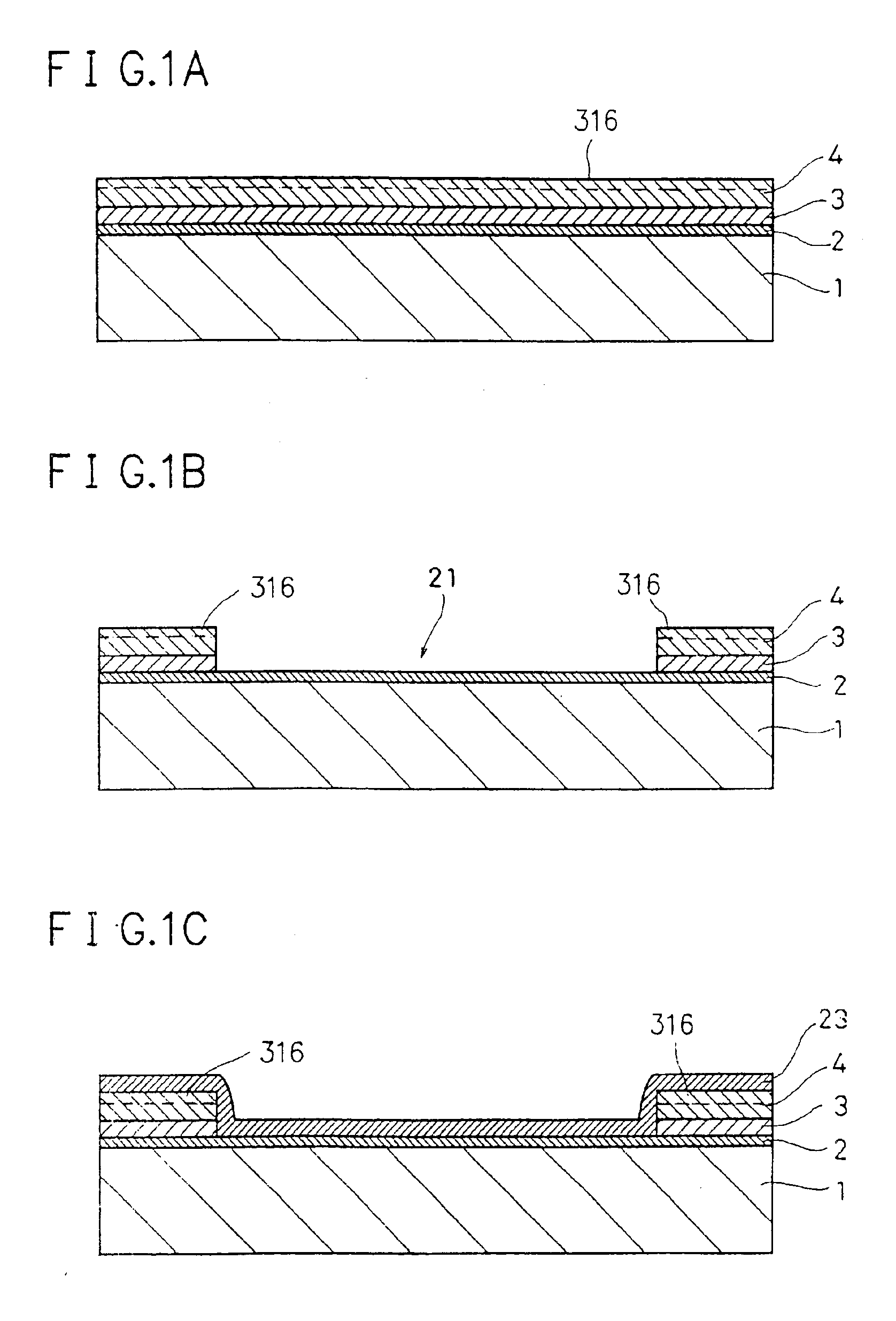
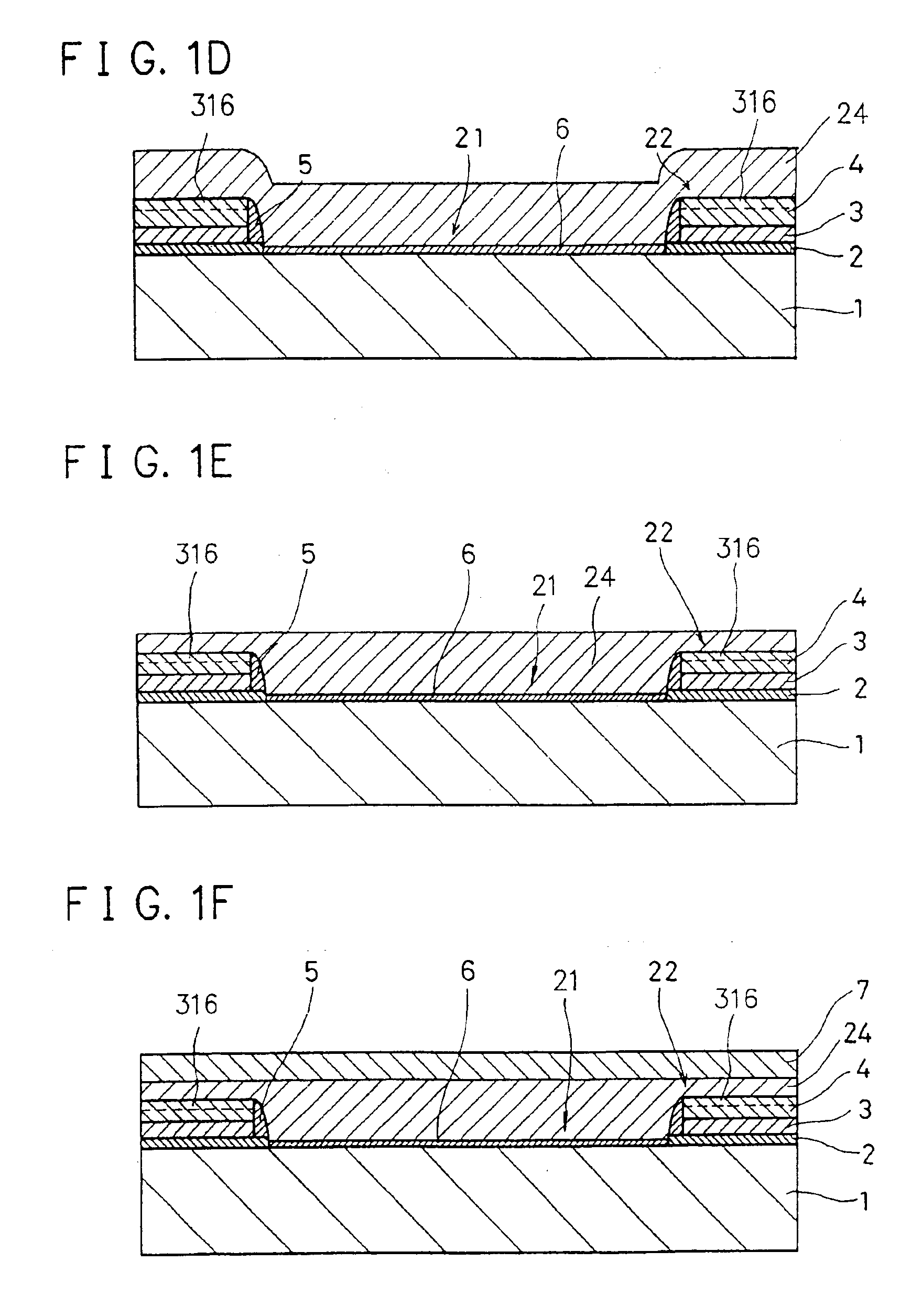
The present invention provides a semiconductor substrate, which comprises a singlecrystalline Si substrate which includes an active layer having a channel region, a source region, and a drain region, the singlecrystalline Si substrate including at least a part of a device structure not containing a well-structure or a channel stop region; a gate insulating film formed on the singlecrystalline Si substrate; a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film; a LOCOS oxide film whose thickness is more than a thickness of the gate insulating film, the LOCOS oxide film being formed on the singlecrystalline Si substrate by surrounding the active layer; and an insulating film formed over the gate electrode and the LOCOS oxide film. On this account, on fabricating the semiconductor device having a high-performance integration system by forming the non-singlecrystalline Si semiconductor element and the singlecrystalline Si semiconductor element on the large insulating substrate, the process for making the singlecrystalline Si is simplified. Further, the foregoing arrangement provides a semiconductor substrate and a fabrication method thereof, which ensures device isolation of the minute singlecrystalline Si semiconductor element without highly-accurate photolithography, when the singlecrystalline Si semiconductor element is transferred onto the large insulating substrate.
Owner:SHARP KK
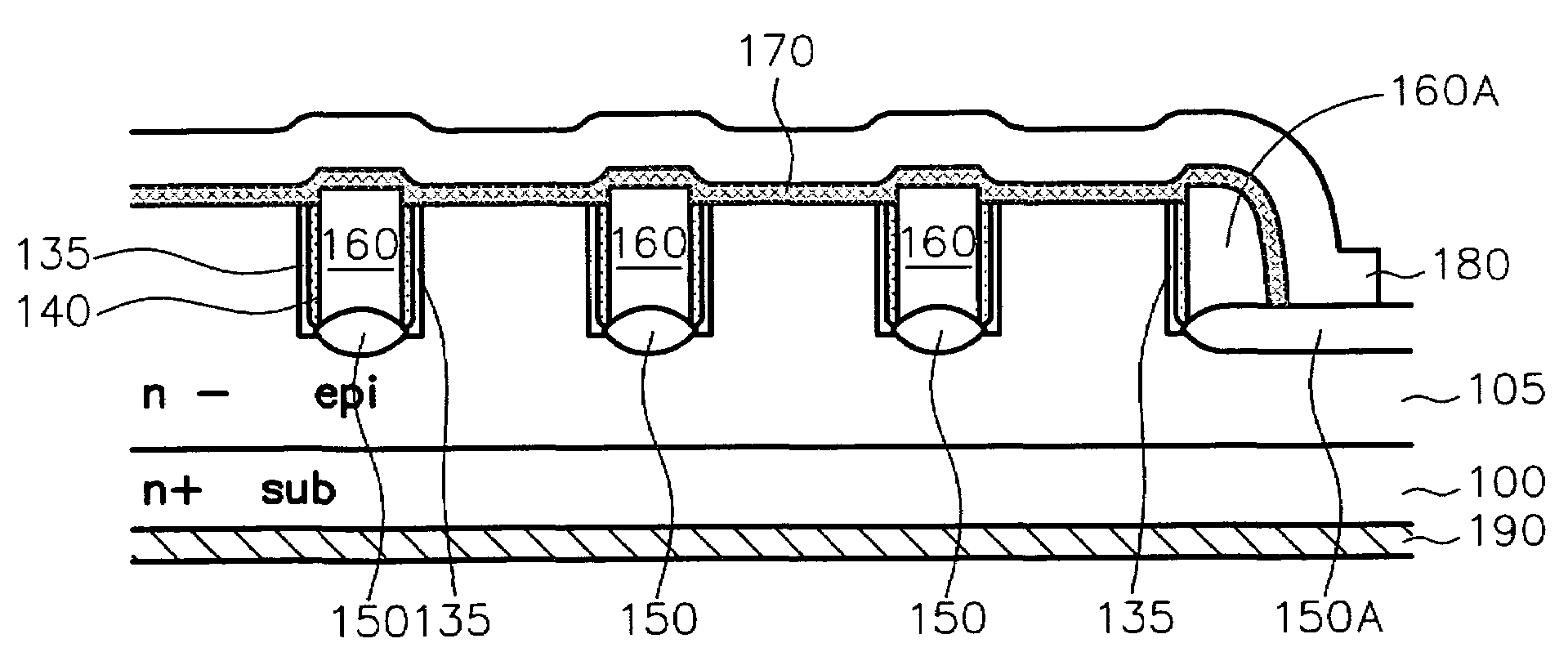
Trench MOSFET with thick bottom oxide tub
InactiveUS20090085107A1Reduce gate-to-drain capacitanceIncreasing the on-resistance of the MOSFET deviceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrench mosfetHigh density
A semiconductor power device includes a plurality of trenched gates. The trenched gates include a thin dielectric layer padded sidewalls of the trenched gate and a tub-shaped thick dielectric layer below a bottom of the trenched gates having a width narrower than the trenched gate. In an exemplary embodiment, the tub-shaped thick dielectric layer below a bottom of the trenched gates further includes a local deposition of silicon oxide (LOCOS) filling in a tub-shaped trench having a narrower width than the trenched gate. In another exemplary embodiment, the tub-shaped thick dielectric layer below a bottom of the trenched gates further comprising a high density plasma (HDP) chemical vapor deposition (CVD) silicon oxide filled in a tub-shaped trench having a narrower width than the trenched gate.
Owner:FORCE MOS TECH CO LTD
Method for manufacturing trench metal-oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET)
InactiveCN102097378AReduce RdsRds smallTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrench mosfetInsulation layer
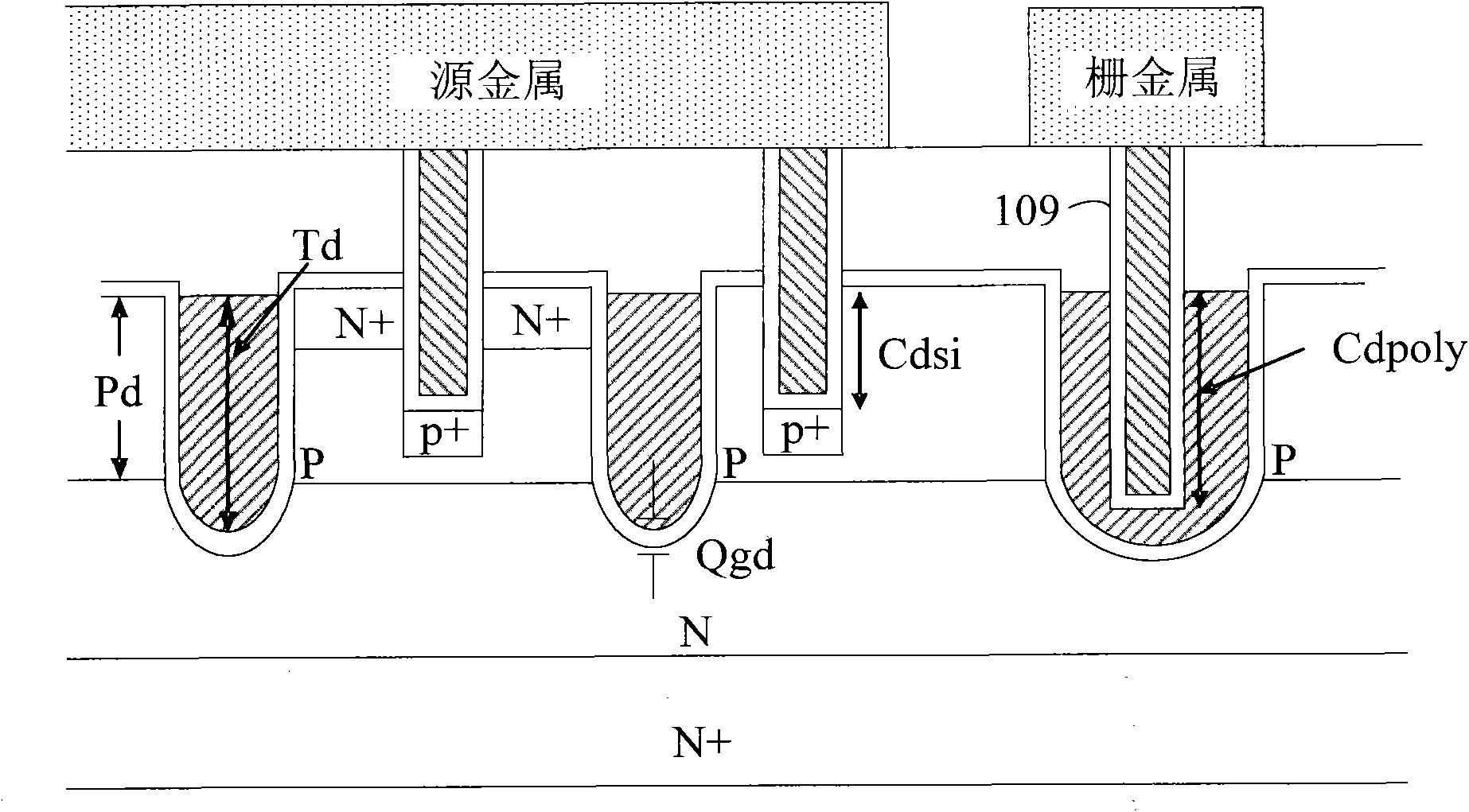
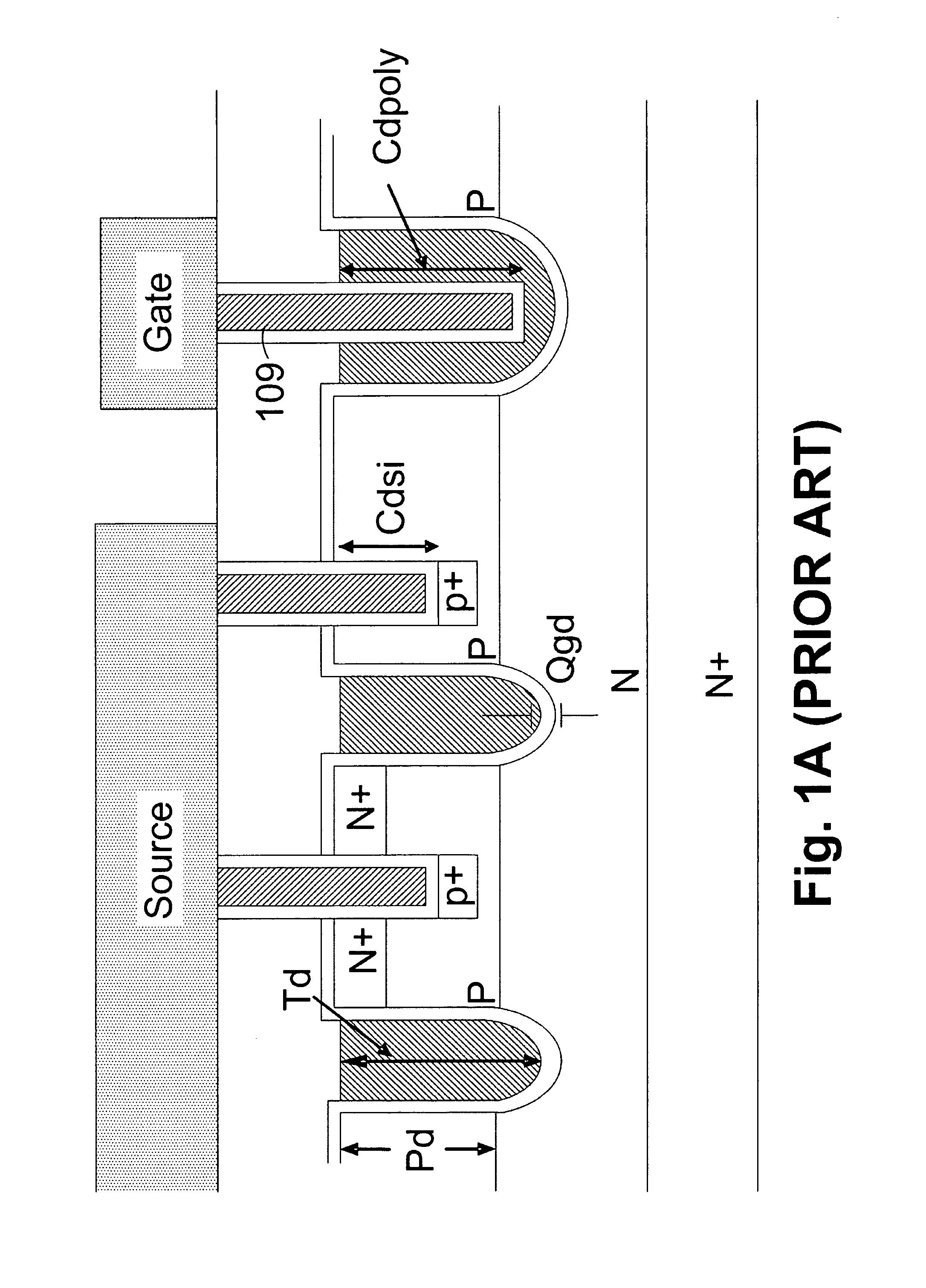
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a trench metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET). According to the trench MOSFET provided by the invention, the bottom of a trench grid in the epitaxial layer of the trench MOSFET has a thicker insulation layer compared with the side wall of the trench grid. The manufacture method provided by the invention avoids a bird beak effect generated by the thicker insulation layer at the bottom of the trench grid growing by utilizing a LOCOS (Local Oxidation Of Silicon) method in the prior art. Meanwhile, a shallow trench MOSFET based on the invention has lower Qgd (Grid Drain Charge) and lower Rds (Resource Drain Charge).
Owner:FORCE MOS TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor pressure sensor having strain gauge and circuit portion on semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS6653702B2Television system detailsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesLOCOSSoi substrate
A semiconductor pressure sensor includes a SOI substrate composed of first and second silicon substrates. A diaphragm portion is formed by the first silicon substrate as a bottom of a recess portion formed in the second silicon substrate. Strain gauges are formed on the diaphragm portion, and a circuit portion is formed on the first silicon substrate at a region other than the diaphragm portion. A LOCOS film for isolating the strain gauges from the circuit portion is formed on the first silicon substrate outside the outermost peripheral portion of the diaphragm portion.
Owner:DENSO CORP
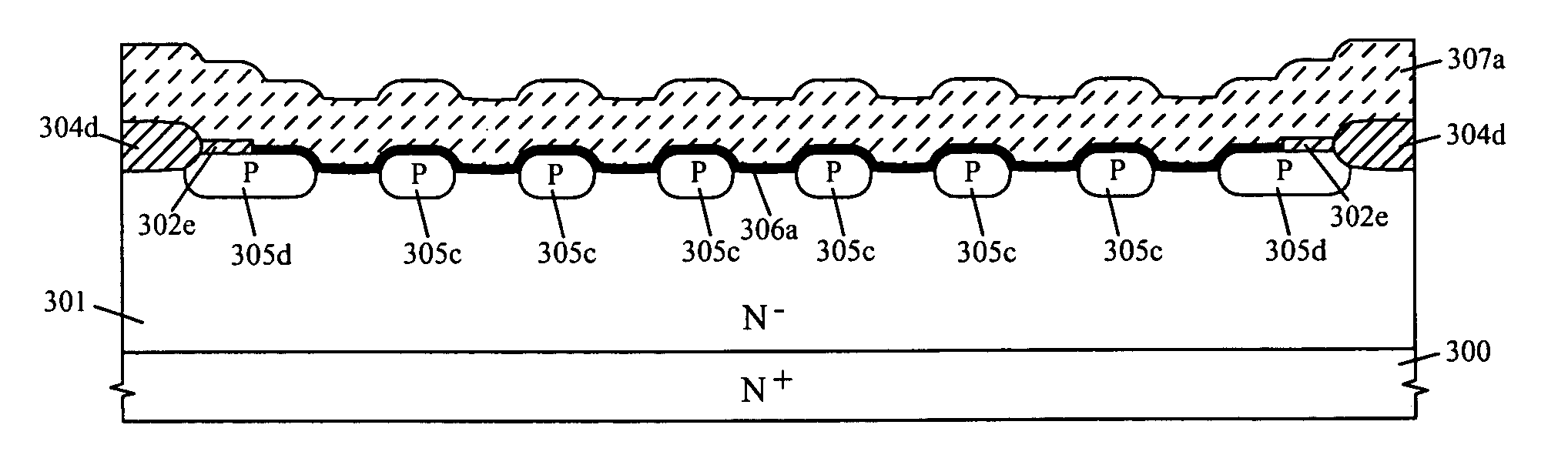
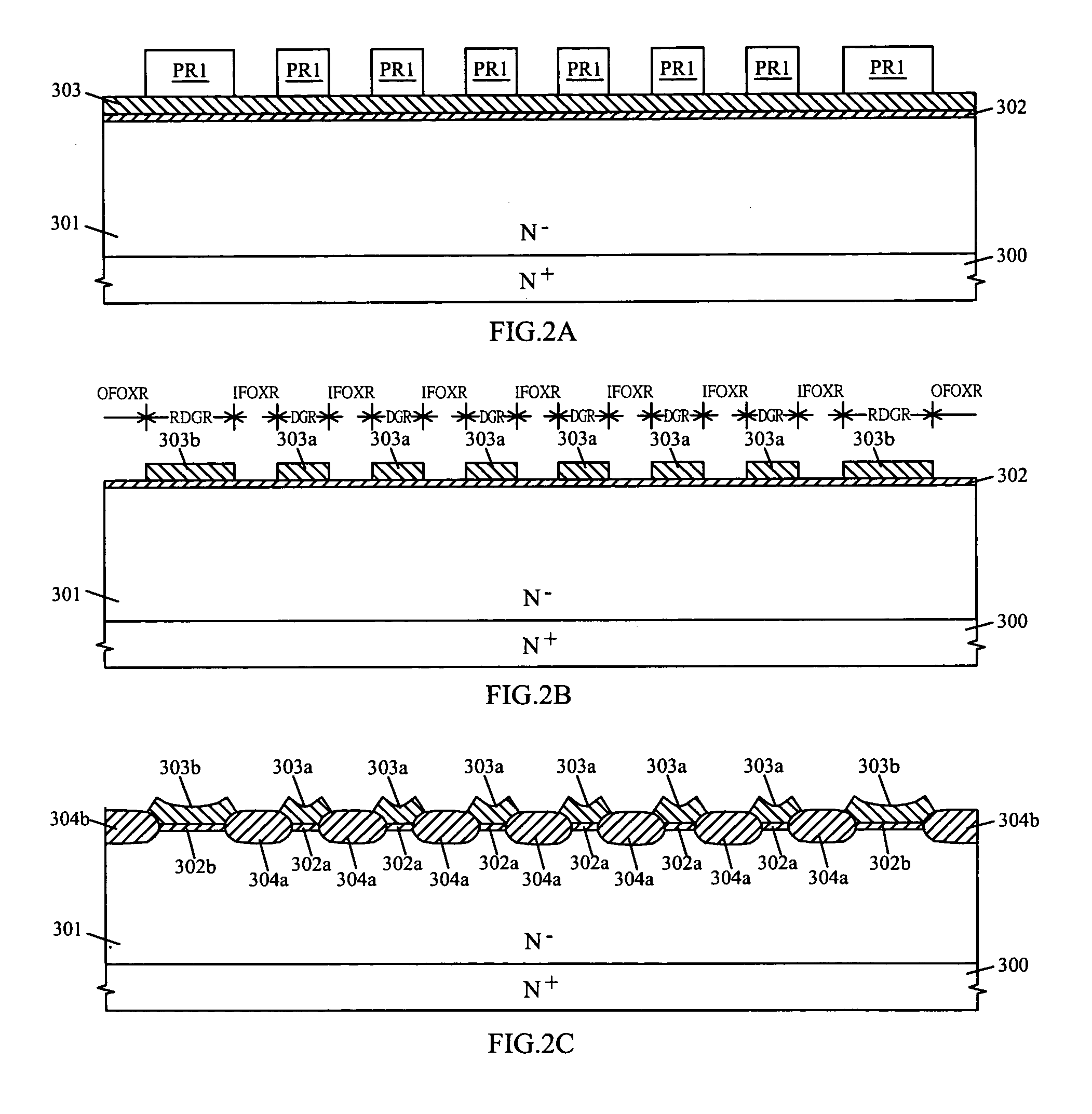
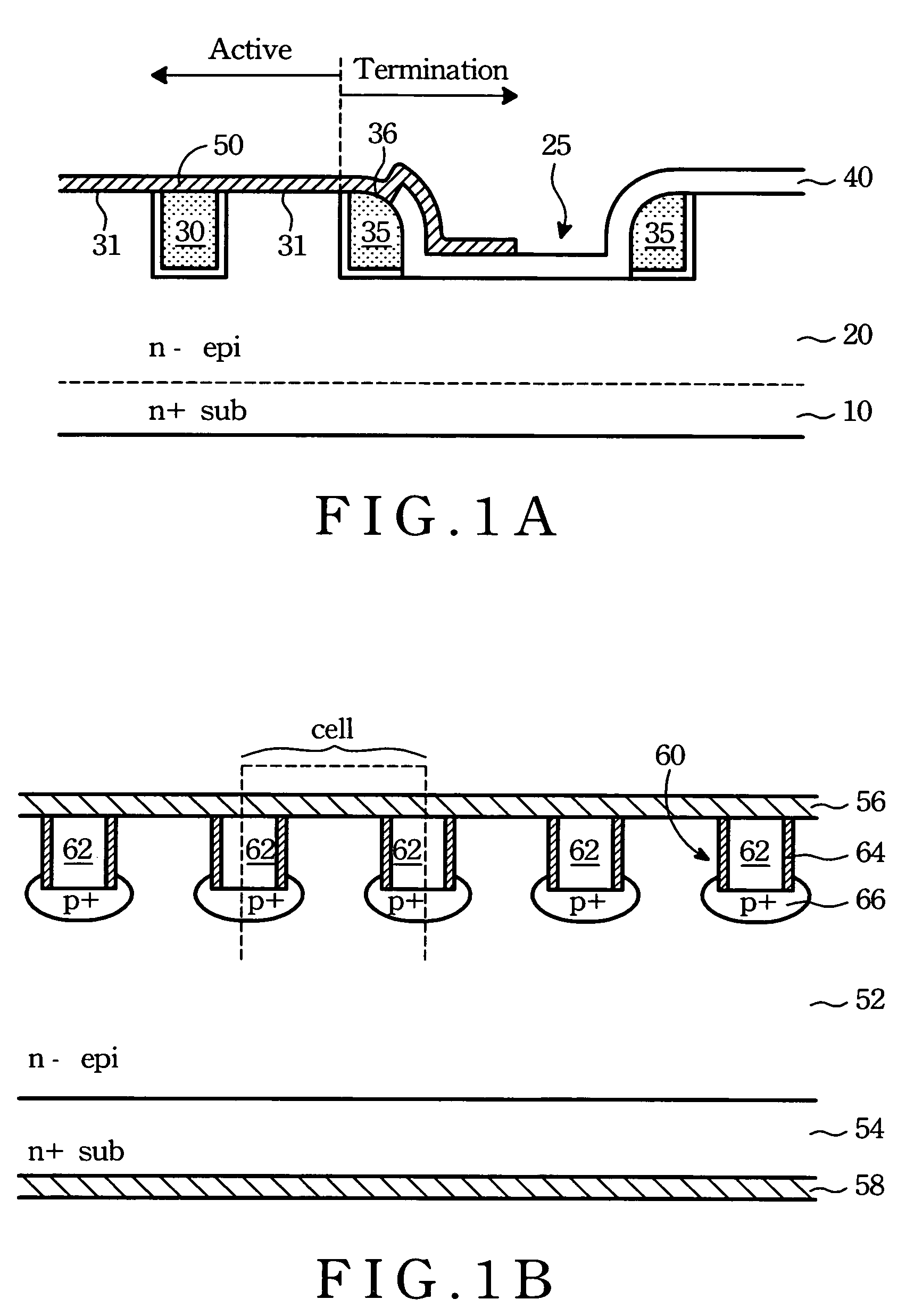
LOCOS-based junction-pinched schottky rectifier and its manufacturing methods
The LOCOS-based junction-pinched Schottky rectifier comprises a raised diffusion guard ring surrounded by an outer LOCOS field oxide layer, a raised diffusion grid or a plurality of raised diffusion rings or stripes surrounded by the raised diffusion guard ring, a plurality of recessed semiconductor surfaces formed on a lightly-doped epitaxial semiconductor layer surrounded by the raised diffusion guard ring and the raised diffusion grid or by the raised diffusion guard ring and the plurality of raised diffusion rings or stripes, and a metal silicide layer or a metal layer being at least formed over a portion of the raised diffusion guard ring, the plurality of recessed semiconductor surfaces and the raised diffusion grid or the plurality of raised diffusion rings or stripes. A plurality of compensated diffusion layers can be formed in surface portions of the lightly-doped epitaxial semiconductor layer under the plurality of recessed semiconductor surfaces.
Owner:SILICON BASED TECH
Semiconductor device and fabrication method for the same
InactiveUS20050087739A1Secure performanceSecurely preventedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialLOCOS
In a semiconductor device including a monocrystalline thin film transistor 16a that has been formed on a monocrystalline Si wafer 100 and then is transferred to a insulating substrate 2, LOCOS oxidization is performed with respect to the element-isolation region of the monocrystalline Si wafer 100 so as to create a field oxide film (SiO2 film) 104, and a marker 107 is formed on the field oxide film 104. With this structure, alignment of components may be performed based on a gate electrode 106 upon or after the transfer step.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for making trench MOSFET with shallow trench structures
InactiveUS20110070708A1Reduce QgdAvoid over-etching issueSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrench mosfetLOCOS
A method for making trench MOSFET with shallow trench structures with thick trench bottom is disclosed. The improved method resolves the problem of deterioration of breakdown voltage resulted by LOCOS having a bird's beak shape introduced in prior art, and at the same time, the inventive device has a lower Qgd and lower Rds.
Owner:MEMOIR SYST +1
High switching speed two mask schottky diode with high field breakdown
InactiveUS7491633B2Minimise currentImprove reverse breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky barrierLOCOS
A power Schottky rectifier device and method of making the same are disclosed. The Schottky rectifier device includes a LOCOS structure grown on the bottom of the trenches by using nitride spacer on the sidewall of the trenches as a thermal oxidation mask. A polycrystalline silicon layer is then filled the first trenches. Under LOCOS structure, a p doped region is optionally formed to minimize the current leakage when the device undergoes a reverse biased. A Schottky barrier silicide layer formed by sputtering and annealing steps is formed on the upper surfaces of the epi-layer and the polycrystalline silicon layer. A top metal layer served as anode is then formed on the Schottky barrier silicide layer and extended to cover a portion of field oxide region of the termination trench. A metal layer served as a cathode electrode is then formed on the backside surface of the substrate opposite to the top metal layer.
Owner:CHIP INTEGRATION TECH +1
Method for forming gate oxides of different thicknesses
InactiveUS6165918AWithout adversely affecting carrier mobilityCost effectiveSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPhysical chemistryLOCOS
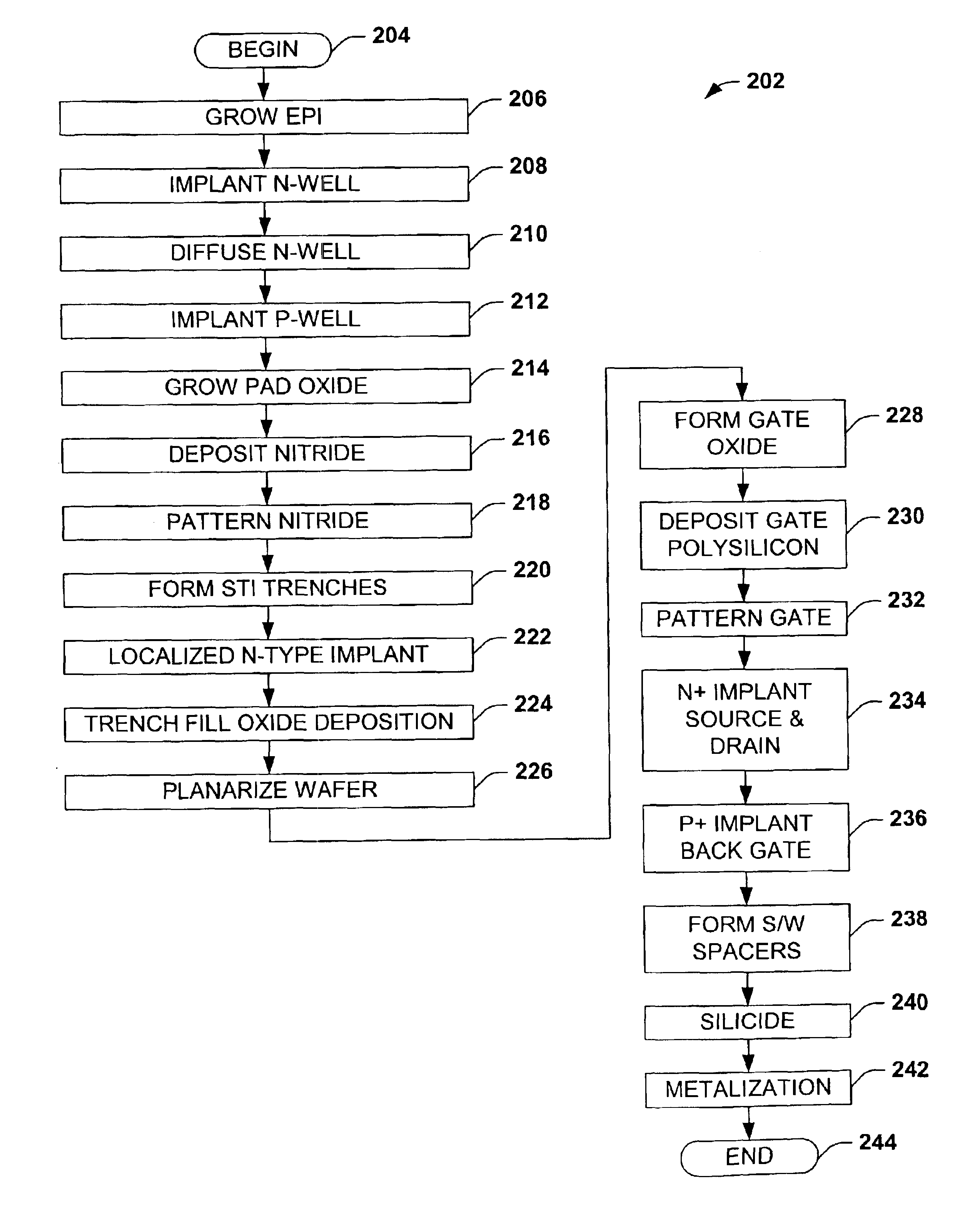
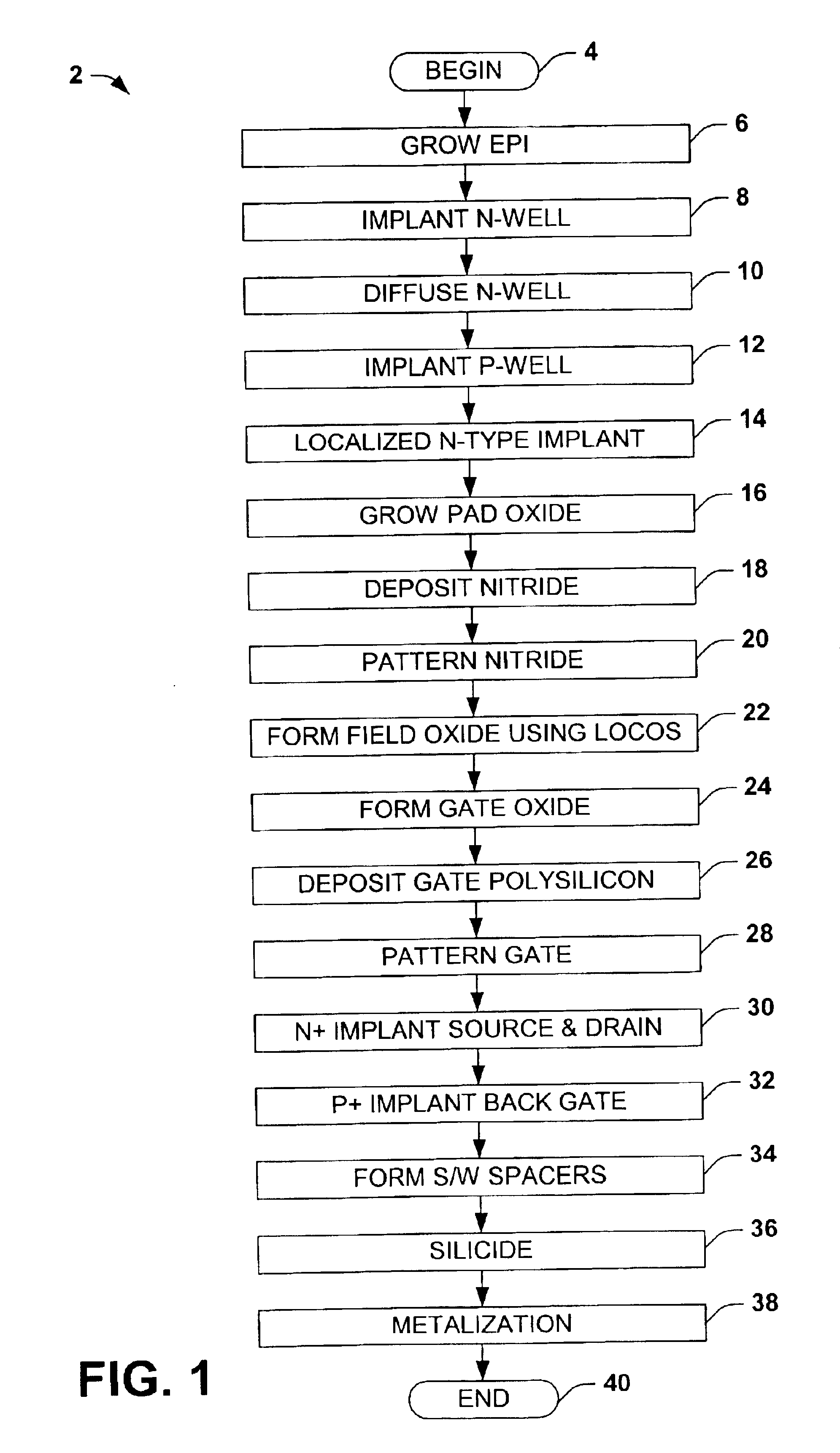
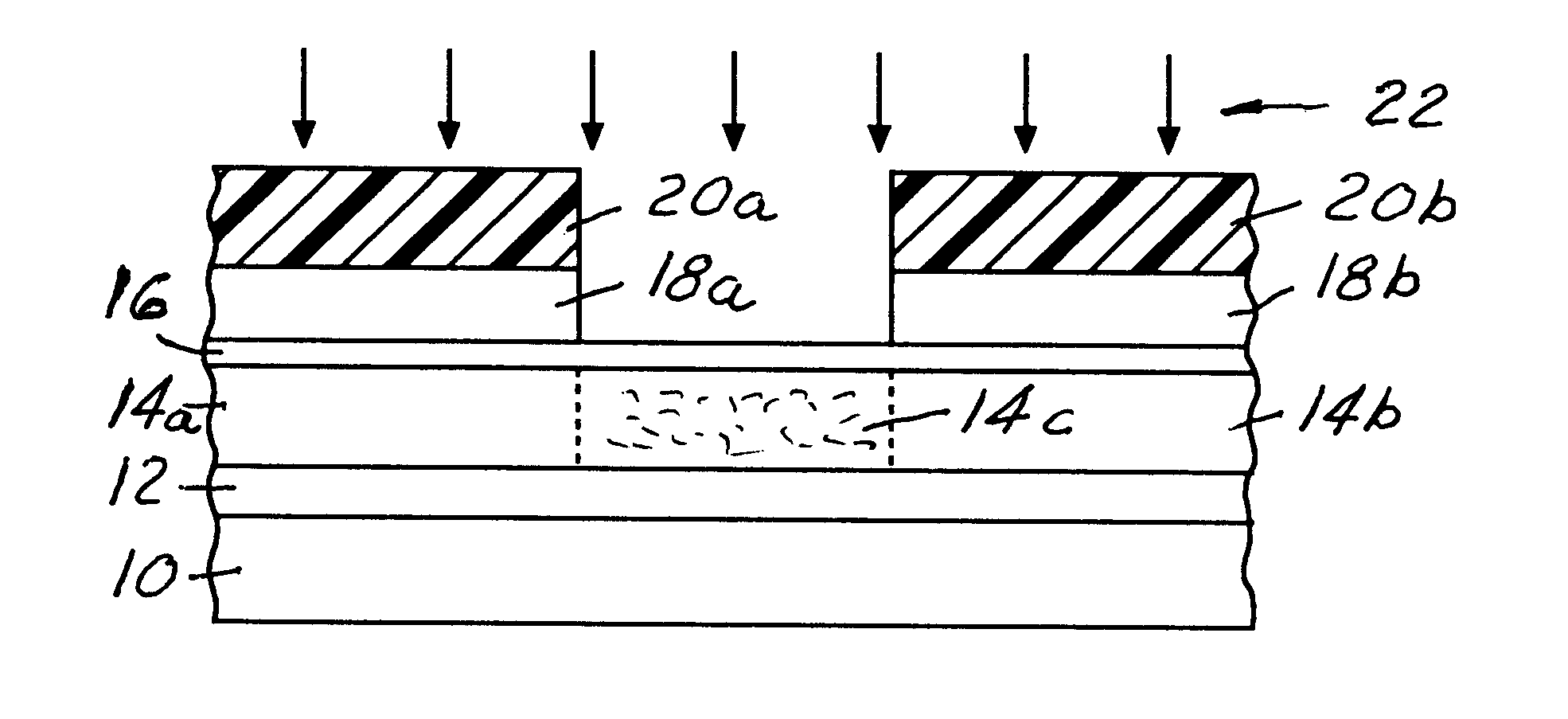
Systems and methods are described for fabricating semiconductor gate oxides of different thicknesses. Two methods for forming gate oxides of different thicknesses in conjunction with local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) are disclosed. Similarly, two methods for forming gate oxides of different thicknesses in conjunction with shallow trench isolation (STI) are disclosed. Techniques that use two poly-silicon sub-layers of substantially equal thickness and techniques that use two poly-silicon sub-layers of substantially unequal thickness are described for both LOCOS and STI. The systems and methods provide advantages because gate uniformity and quality are improved, the processes and resulting devices are cleaner, and there is less degradation of carrier mobility.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Semiconductor device, a method of manufacturing the semiconductor device and a method of deleting information from the semiconductor device
InactiveUS6917076B2Increase process marginEasy and proper formationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLOCOSEngineering
A semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same and method for deleting information in use of the semiconductor device, in which field shield isolation or a trench type isolation between elements is used with suppression of penetration of field oxide into element active region of the device, that is, a defect involved in conventional LOCOS type process, are disclosed. A non-LOCOS insulating device isolation block is formed in a semiconductor substrate. The non-LOCOS insulating device isolation block uses a field shield element isolation structure or trench type element isolation structure. After gate electrode wiring layers are formed in a field region and an active region to the same level, a pad polysilicon film formed on the entire surface to cover the patterns of these gate electrode wiring layers is polished by chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) using the cap insulating films of the gate electrode wiring layers as stoppers, thereby forming the gate electrode wiring layers into separated patterns. With this arrangement, even when the width of the gate electrode wiring layer is reduced to the exposure limit in photolithography, the pad polysilicon film can be separated and patterned.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
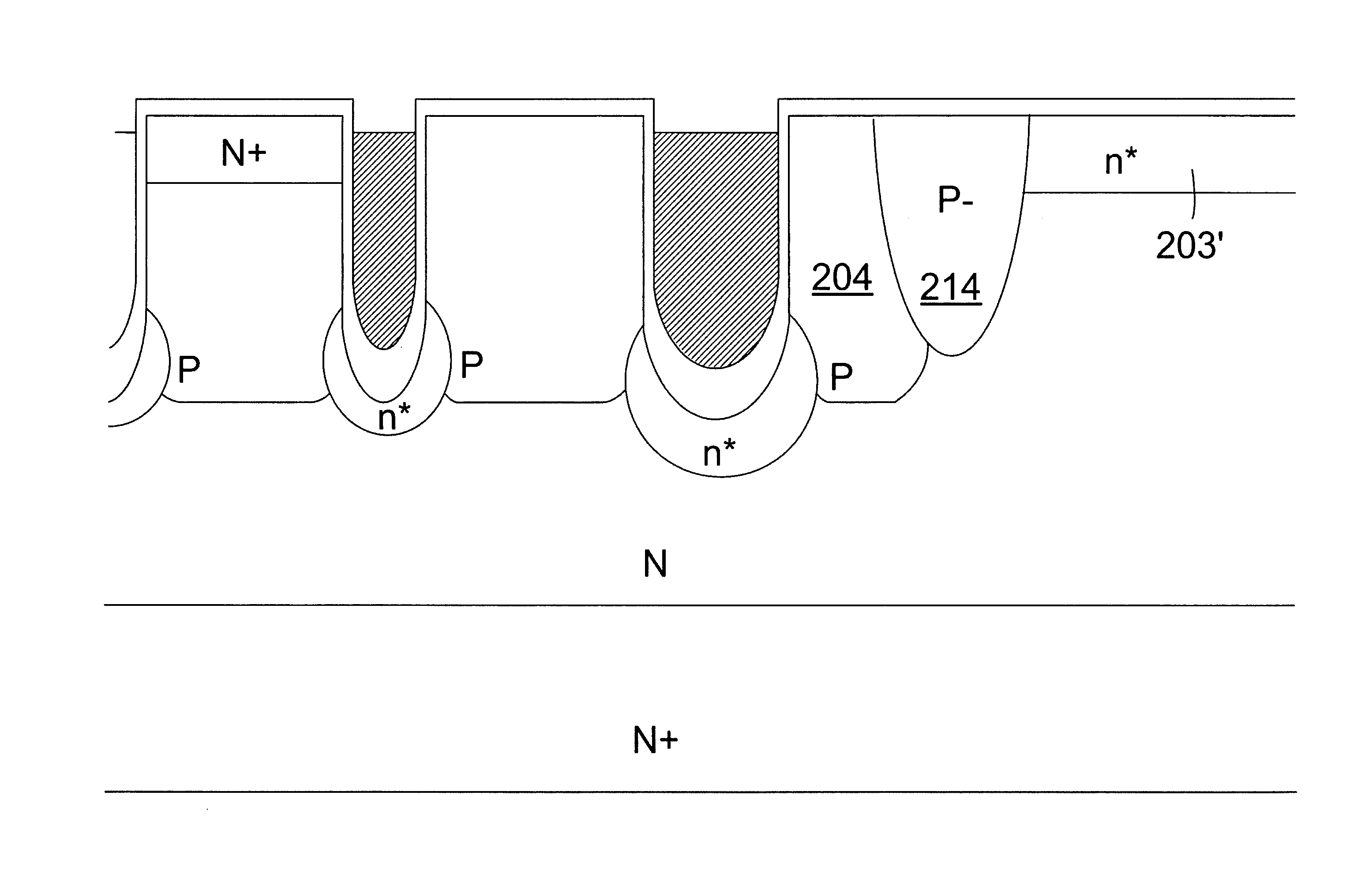
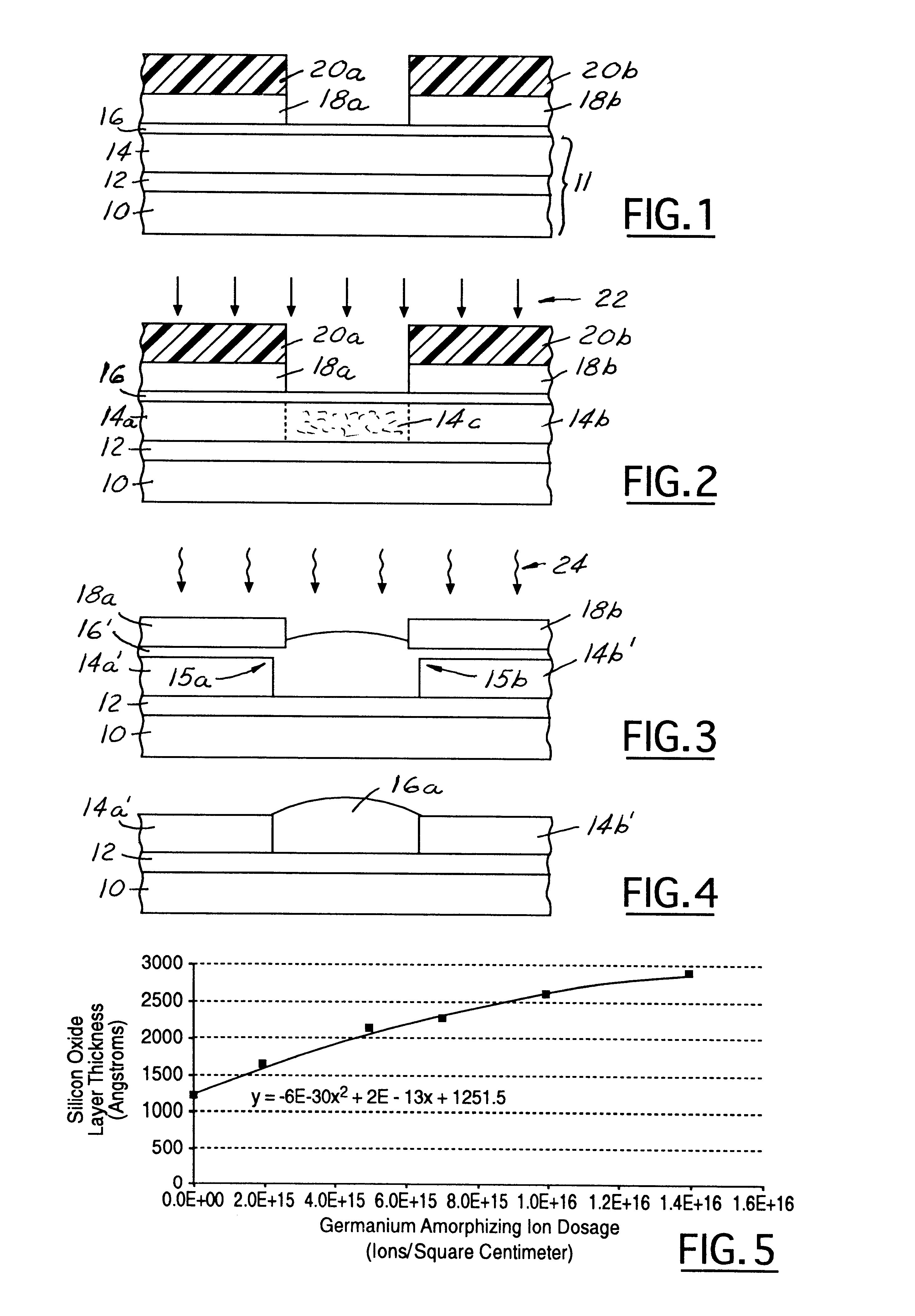
Amorphizing ion implant local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) method for forming an isolation region
InactiveUS6686255B2Readily commercially implementedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLOCOSSilicon oxide
Within a local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) method for forming a silicon oxide isolation region, there is first amorphized areally completely at least a surface sub-layer portion of a silicon layer within an isolation region location within the silicon layer defined by an oxidation mask layer formed over the silicon layer, to form an amorphized silicon region within the isolation region location. Thus, when thermally oxidizing the silicon layer having formed thereover the oxidation mask layer to form at least in part from the amorphized silicon region a silicon oxide isolation region, the silicon oxide isolation region is formed with an attenuated bird's beak extension.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device, a method of manufacturing the semiconductor device and a method of deleting information from the semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050242377A1Increase process marginEasy and proper formationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialLOCOS
A semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same and method for deleting information in use of the semiconductor device, in which field shield isolation or a trench type isolation between elements is used with suppression of penetration of field oxide into element active region of the device, that is, a defect involved in conventional LOGOS type process, are disclosed. A non-LOCOS insulating device isolation block is formed in a semiconductor substrate. The non-LOCOS insulating device isolation block uses a field shield element isolation structure or trench type element isolation structure. After gate electrode wiring layers are formed in a field region and an active region to the same level, a pad polysilicon film formed on the entire surface to cover the patterns of these gate electrode wiring layers is polished by chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) using the cap insulating films of the gate electrode wiring layers as stoppers, thereby forming the gate electrode wiring layers into separated patterns. With this arrangement, even when the width of the gate electrode wiring layer is reduced to the exposure limit in photolithography, the pad polysilicon film can be separated and patterned.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Double gate manufactured with locos techniques
InactiveUS20100015770A1Avoid overetchingEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLOCOSInterface point
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
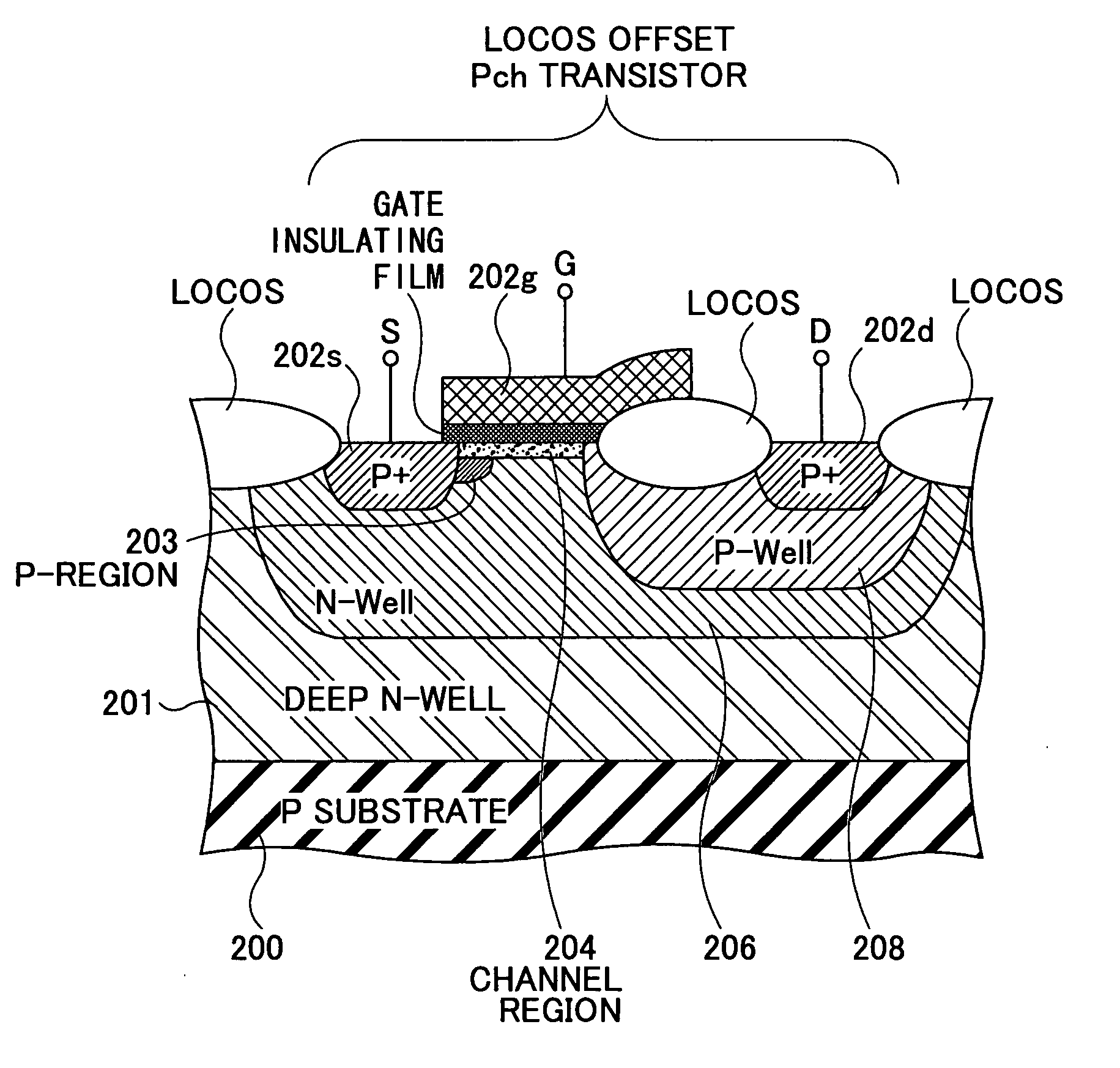
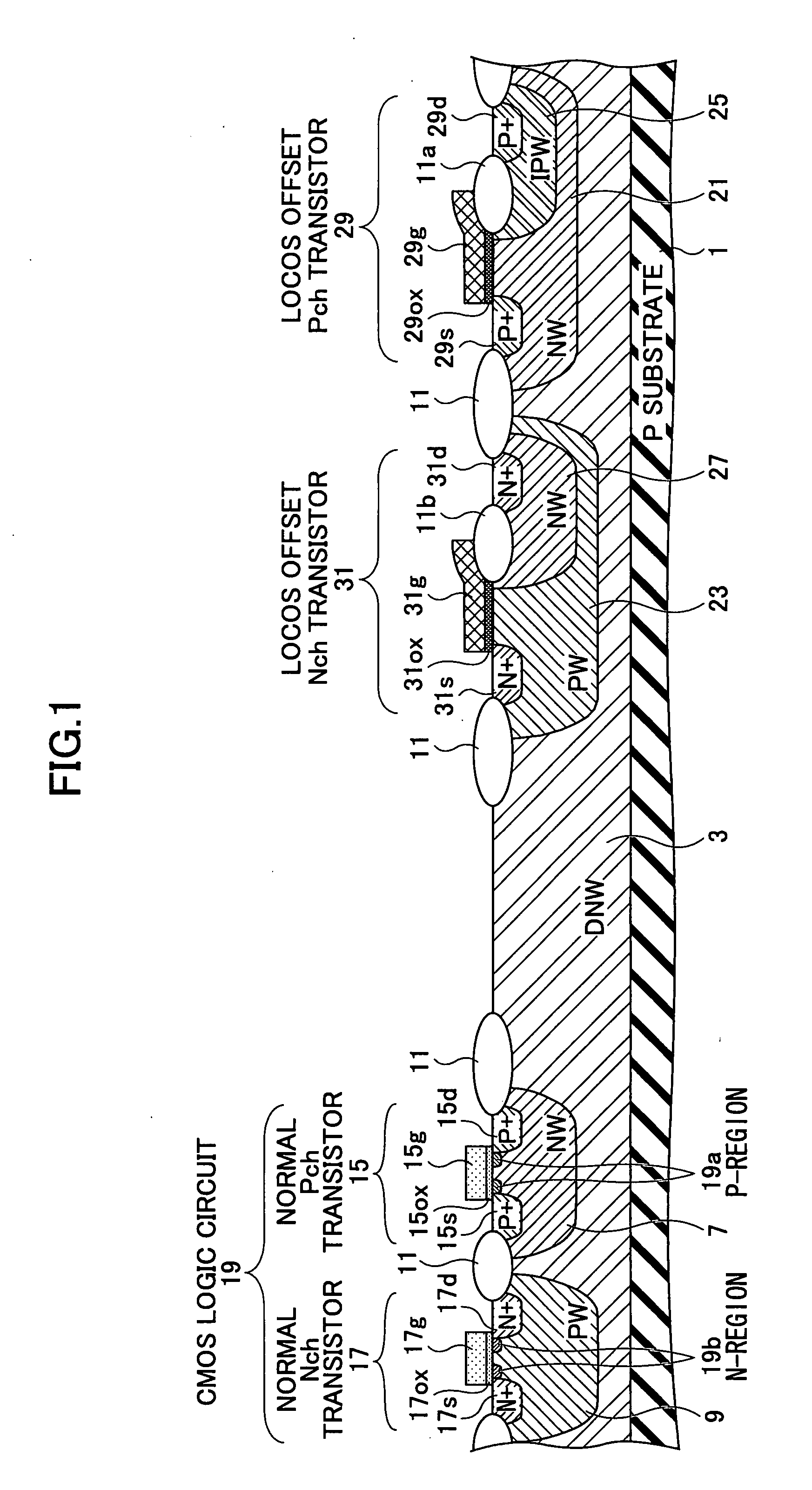
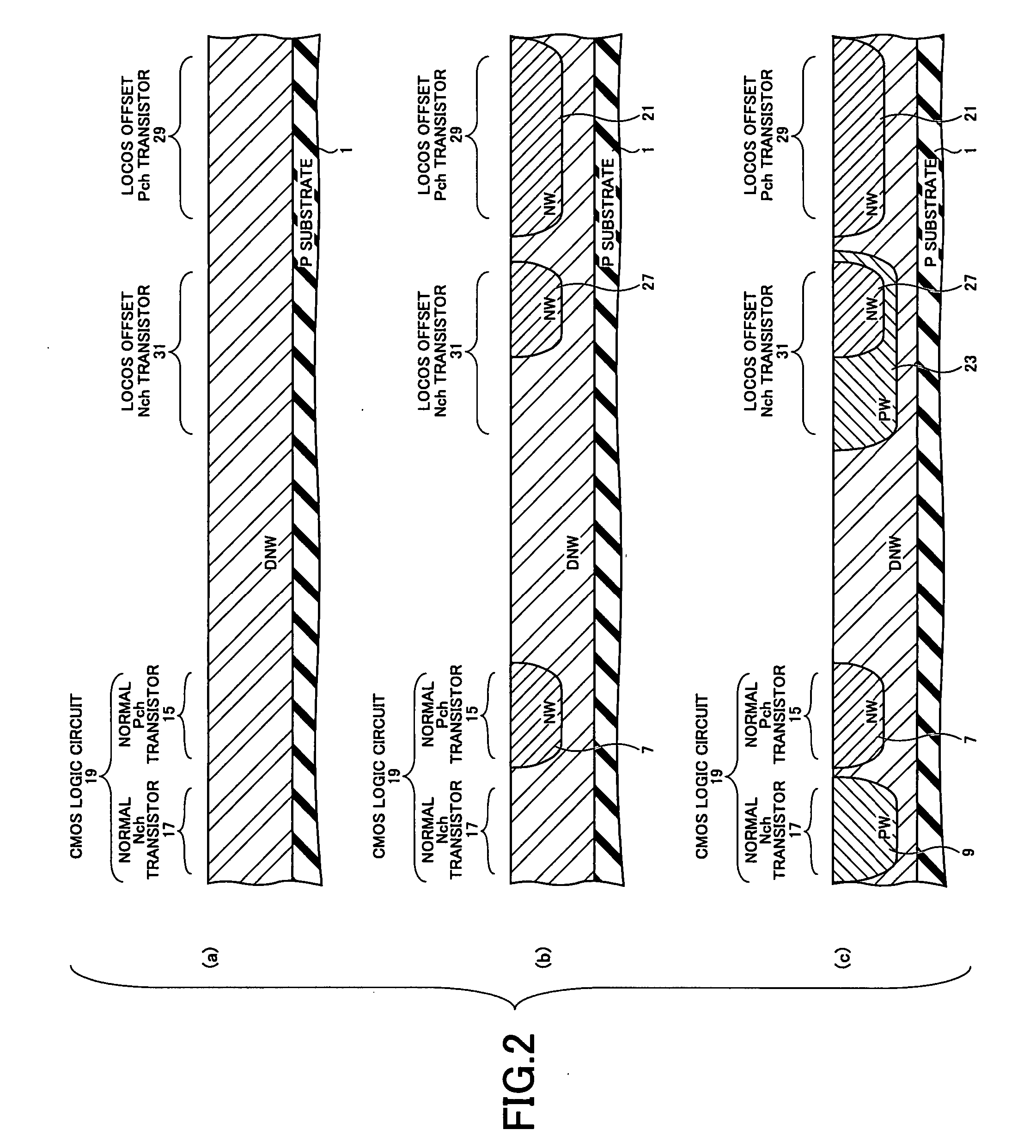
Semiconductor device including MOS transistor having LOCOS offset structure and manufacturing method thereof
A disclosed semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate; at least one normal transistor disposed on the semiconductor substrate; and at least one LOCOS offset transistor disposed on the semiconductor substrate. The normal transistor has an LDD region between a channel and a source and between the channel and a drain. And the LOCOS offset transistor has no LDD region between a channel and a source and between the channel and a drain.
Owner:RICOH KK
Flash memory process with high voltage LDMOS embedded
InactiveUS7282410B2Low production costImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLOCOSHigh pressure
A method of embedding the forming of peripheral devices such as HV-LDMOS into the forming of flash memory is presented. A layered structure is formed with a first insulating layer formed on a substrate, and a poly silicon formed on the first insulating layer in the flash memory region. A mask layer is formed. Openings are formed in the flash memory region in the peripheral region. A local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) is performed to form thick oxides on poly silicon, and a field oxide on silicon substrate respectively. The mask layer is removed. A control gate and a control gate oxide are formed on the thick oxide and the poly silicon. A gate electrode is formed with at least one end residing on a field oxide so that the resulting HV-LDMOS has a high breakdown voltage. Spacers and a source / drain of the flash cells and HV-LDMOSs are then formed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
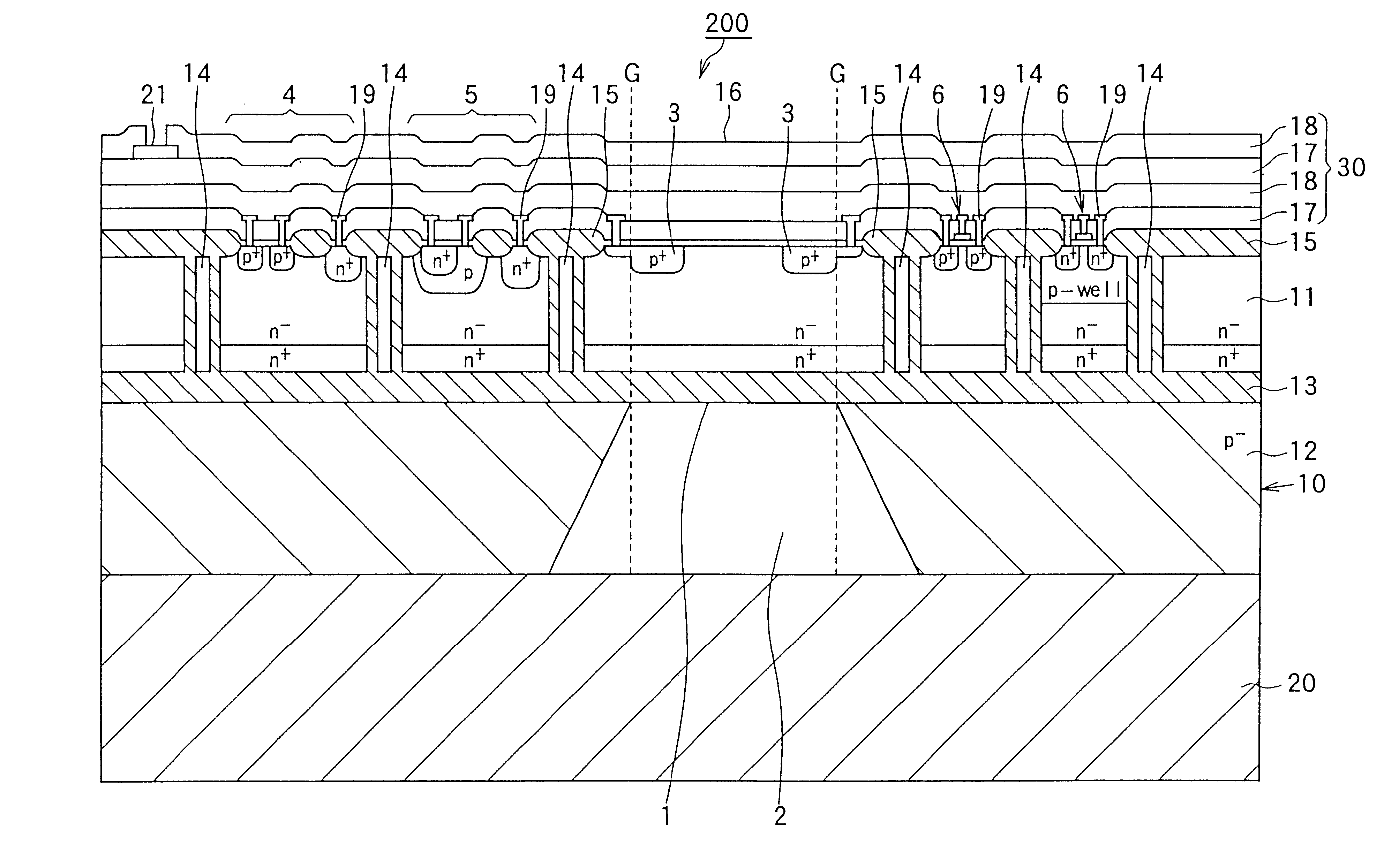
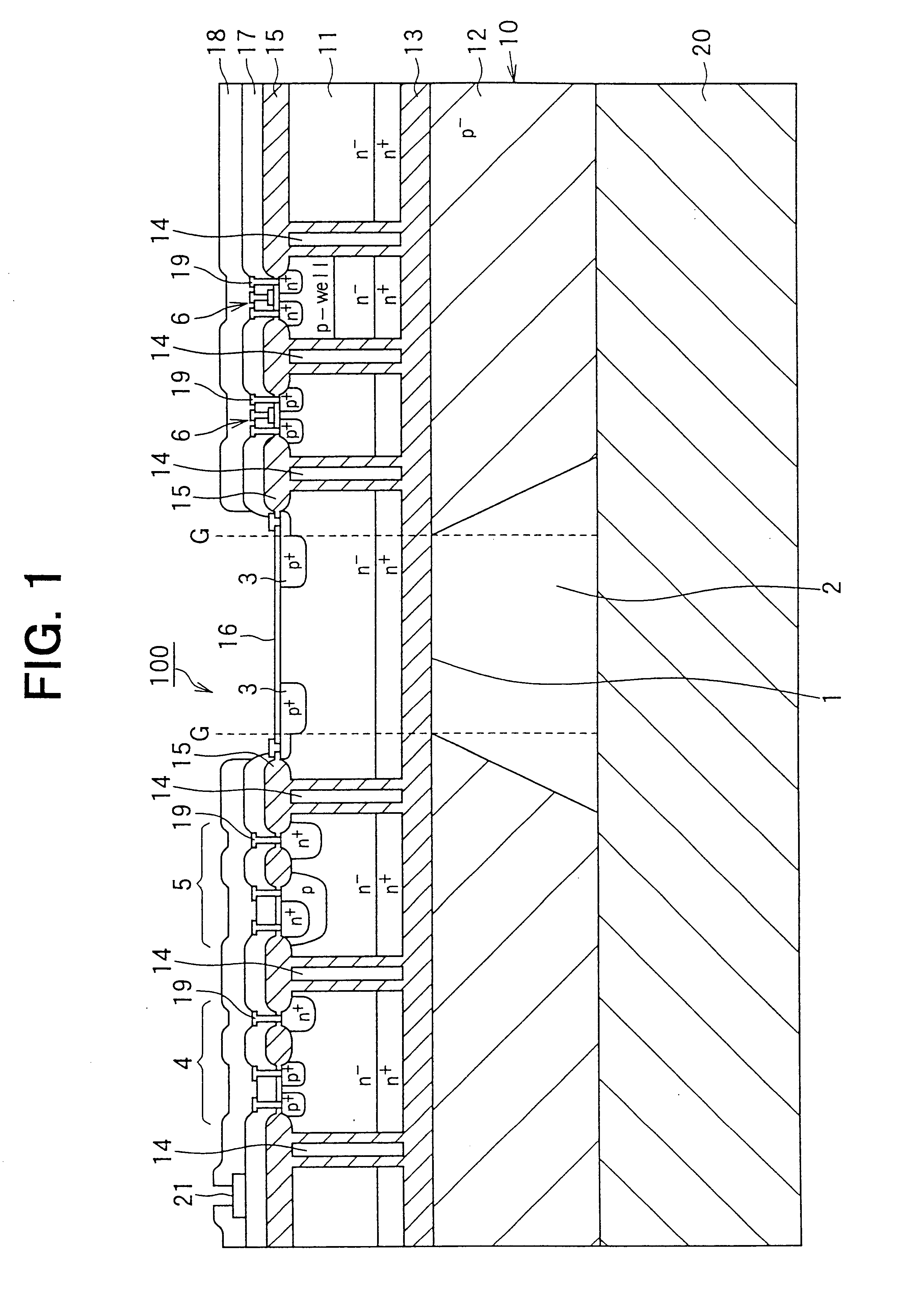
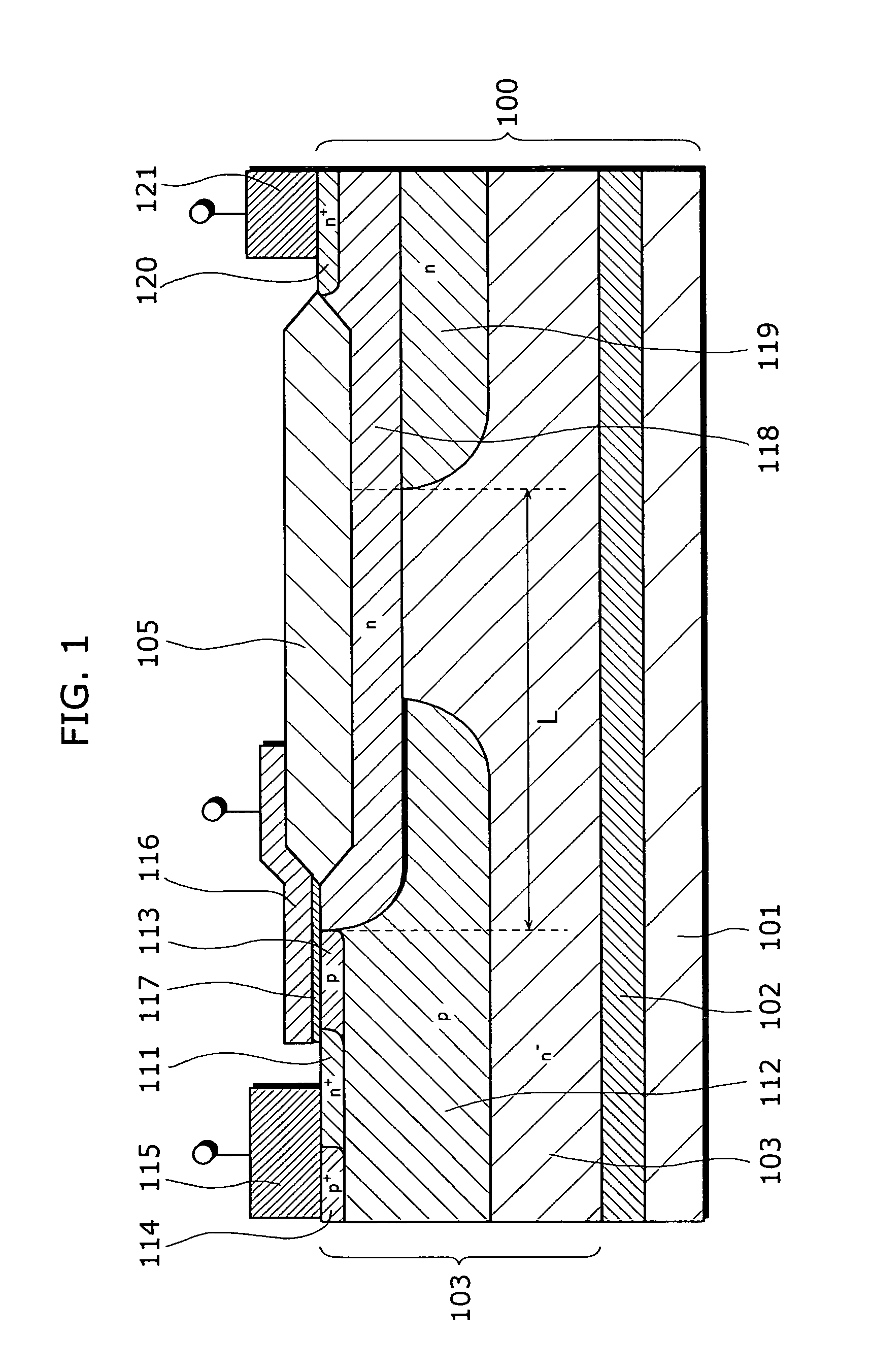
ActiveUS20060001122A1Increase drain-to-source breakdown voltageLower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLOCOSEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device that is able to realize a low on-resistance maintaining a high drain-to-source breakdown voltage, and a method for manufacturing thereof, the present invention including: a supporting substrate 1; a semiconductor layer 3 having a P− type active region 3a that is formed on the supporting substrate 1, interposing a buried oxide film 2 between the semiconductor layer 3 and the supporting substrate 1; and a gate electrode 16a that is formed on the semiconductor layer 103, interposing a gate oxide film 17 and a part of a LOCOS film 5a between the gate electrode 16a and the semiconductor layer 103, wherein the P− type active region 3a has: an N+ type source region 11; a P type body region 12; a P+ type back gate contact region 14; an N type drain offset region 19; an N+ type drain contact region 20; and an N type drain buffer region 18 that is formed in a limited region between the N type drain offset region 19 and the P type body region 12, and the N type drain buffer region 18 is in contact with a source side end of the LOCOS film 5a and is shallower than the N type drain offset region 19.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing high-voltage lateral dual-diffusion N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) based on standard complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor (CMOS) process
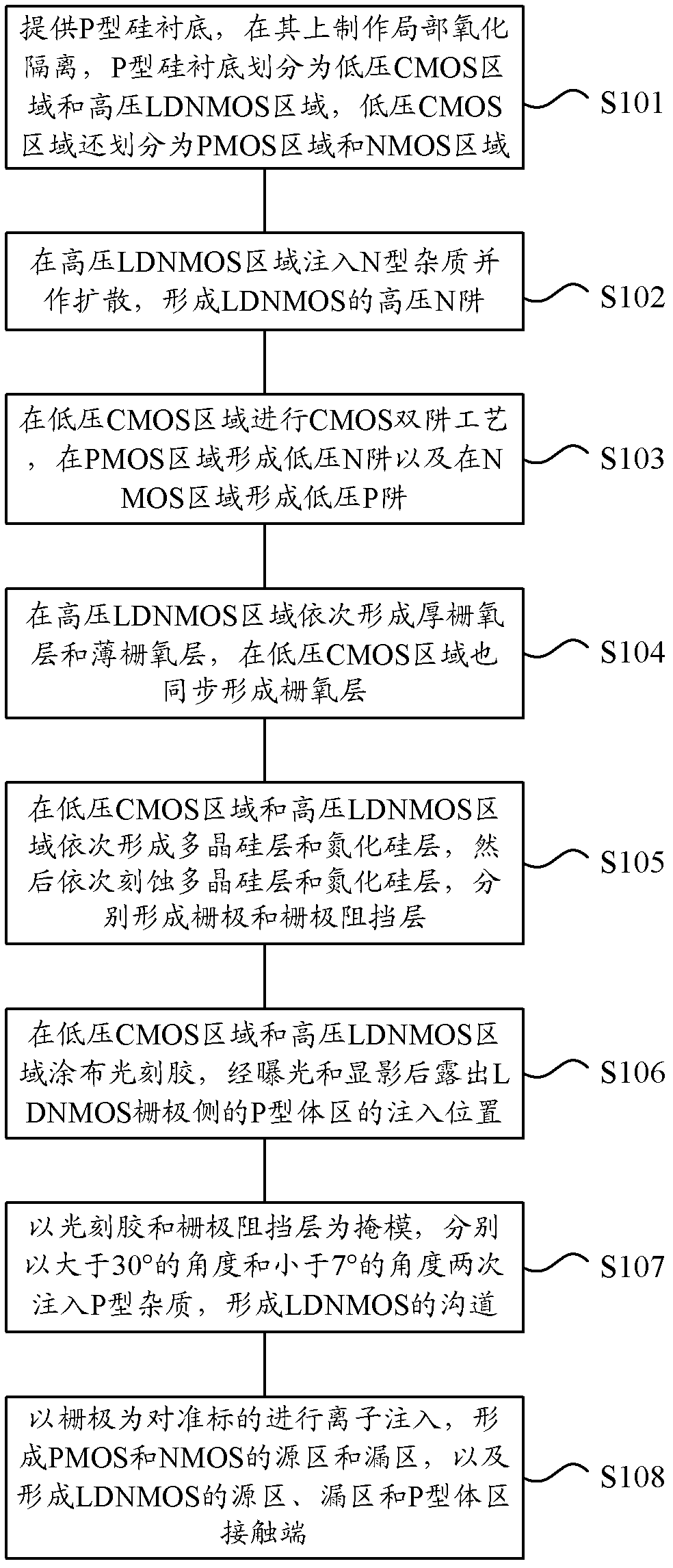
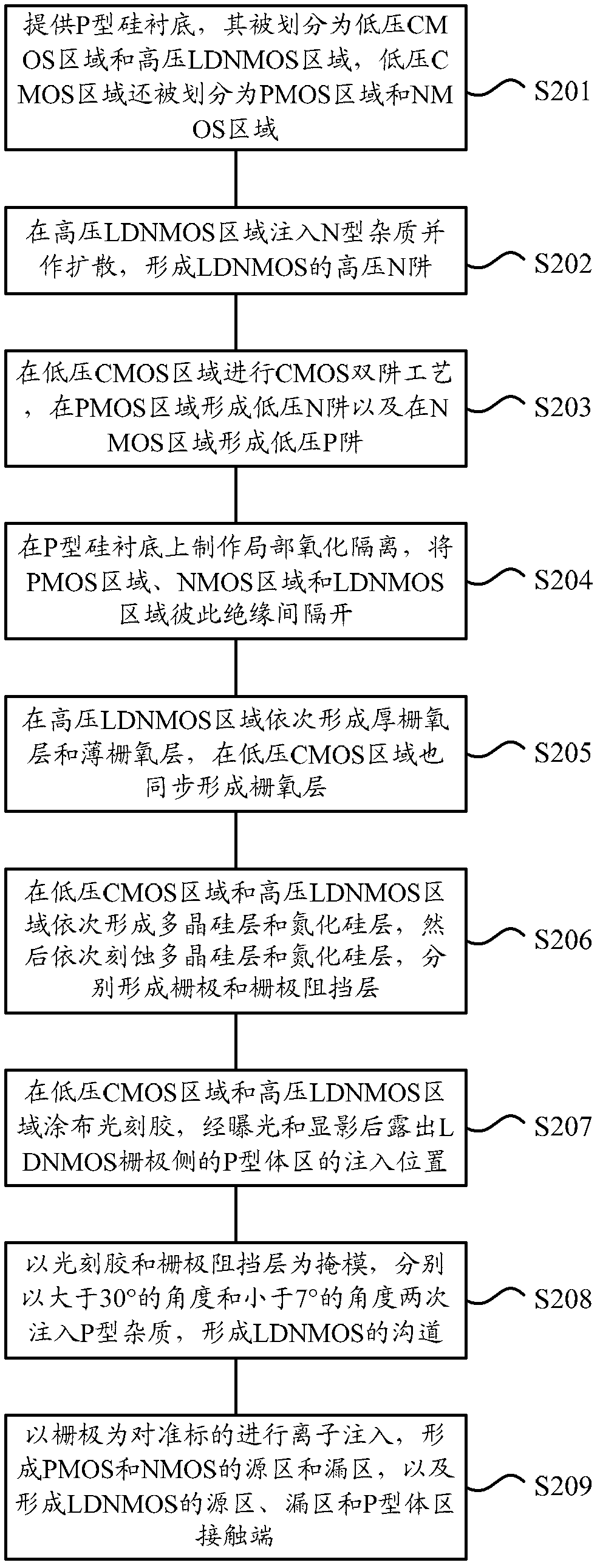
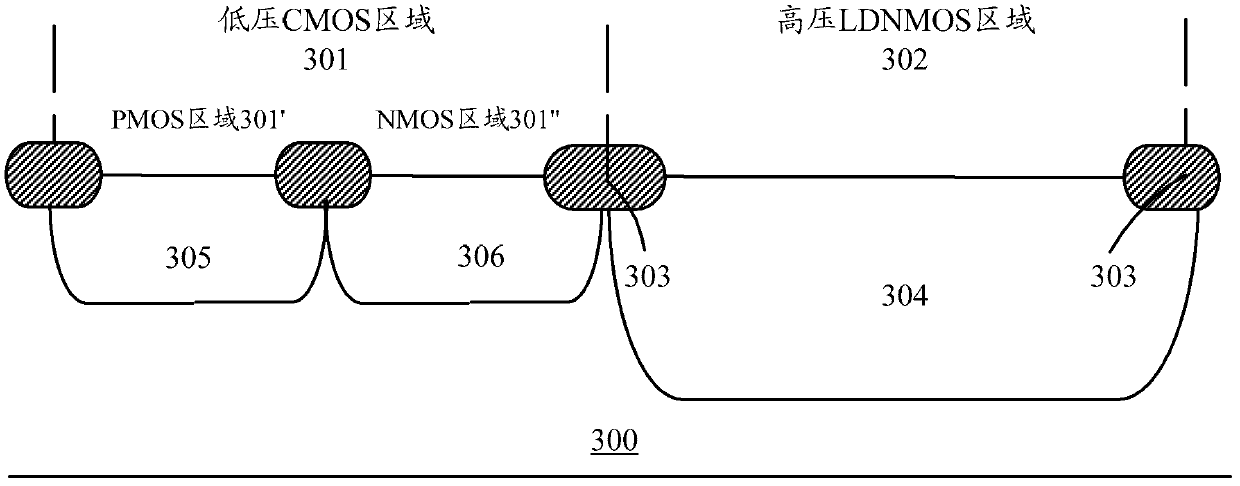
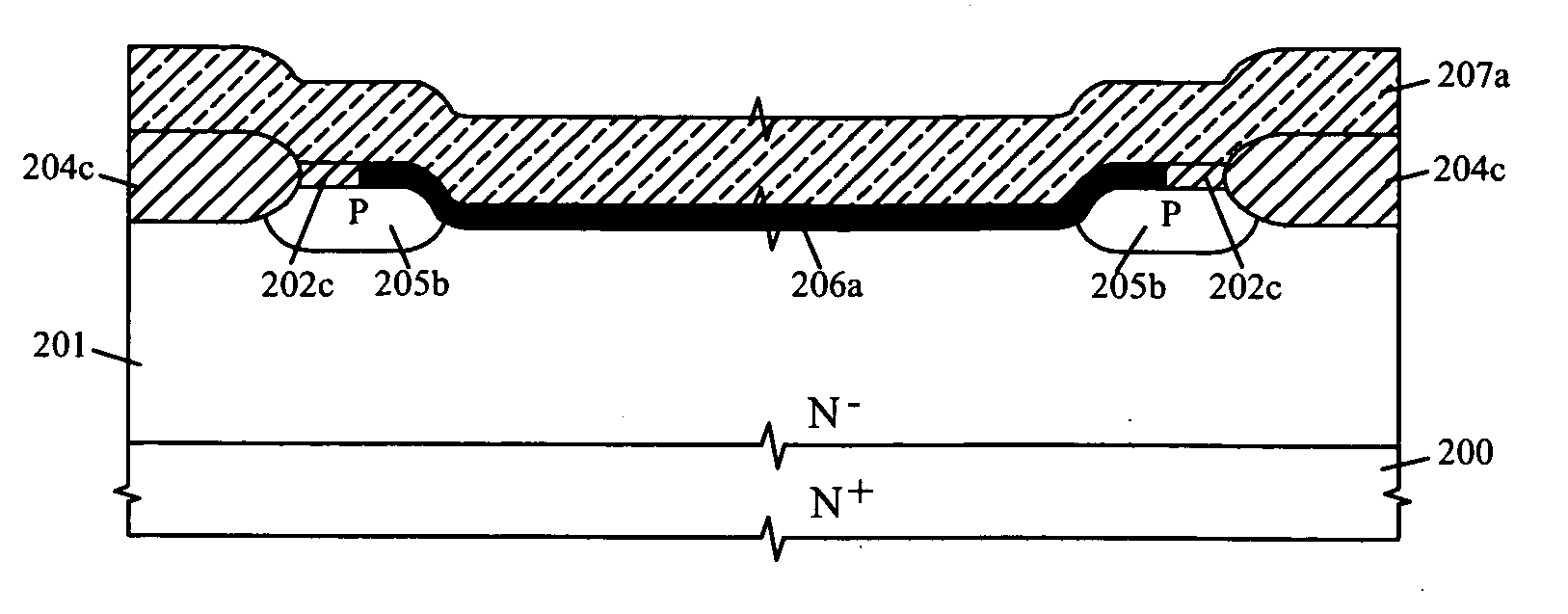
ActiveCN102184871ASimple processIdeal high drive currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLOCOSP type silicon
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a high-voltage lateral dual-diffusion N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) based on a standard complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor (CMOS) process. The method comprises the following steps of: providing a P type silicon substrate, manufacturing local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) on the P type silicon substrate, and dividing theLOCOS into a low-voltage CMOS area and a high-voltage lateral diffused N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (LDNMOS) area; injecting phosphor into the LDNMOS area and diffusing the phosphor to form a high-voltage N well; performing a two-well process in the CMOS area to form a low-voltage N well and a low-voltage P well; sequentially forming a thick gate oxide layer and a thin gate oxide layer in the LDNMOS area; sequentially forming a polysilicon layer and a silicon nitride layer and sequentially etching the polysilicon layer and the silicon nitride layer to form a grid electrode and a buffering layer respectively; coating a photoresist, and exposing the injection position of a P type area of the LDNMOS area after exposing and development; injecting P type ions for two times at the anglesof more than 30 degrees and less than 7 degrees respectively to form channels of an LDNMOS, wherein the photoresist and the buffering layer serve as masks; and forming source areas and drain areas ofa P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) and an NMOS, and contact ends of a source area, a drain area and a P type area of the LDNMOS by taking the grid electrode as an alignment mark. Because a large-angle injection process is used for forming the channels after the grid electrode is formed, a long-time high-temperature heating process is not required and the process is compatible.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON MFG CO LTD
LOCOS-based Schottky barrier diode and its manufacturing methods
InactiveUS20060113624A1Reduce junction curvature effectReduce parasitic series resistanceSemiconductor devicesLOCOSMetal silicide
The LOCOS-based Schottky barrier diode of the present invention comprises a raised diffusion guard ring surrounded by an outer LOCOS field oxide layer, a recessed semiconductor substrate with or without a compensated diffusion layer surrounded by the raised diffusion guard ring, a metal silicide layer formed over a portion of the raised diffusion guard ring and the recessed semiconductor substrate, and a patterned metal layer formed at least over the metal silicide layer, wherein the raised diffusion guard ring is formed between an inner LOCOS field oxide layer and the outer LOCOS field oxide layer and the recessed semiconductor substrate is formed by removing the inner LOCOS field oxide layer. The LOCOS-based Schottky barrier diode comprises the raised diffusion guard ring to reduce junction curvature effect on reverse breakdown voltage, the recessed semiconductor substrate to reduce forward voltage, and the compensated diffusion layer to reduce reverse leakage current.
Owner:SILICON BASED TECH
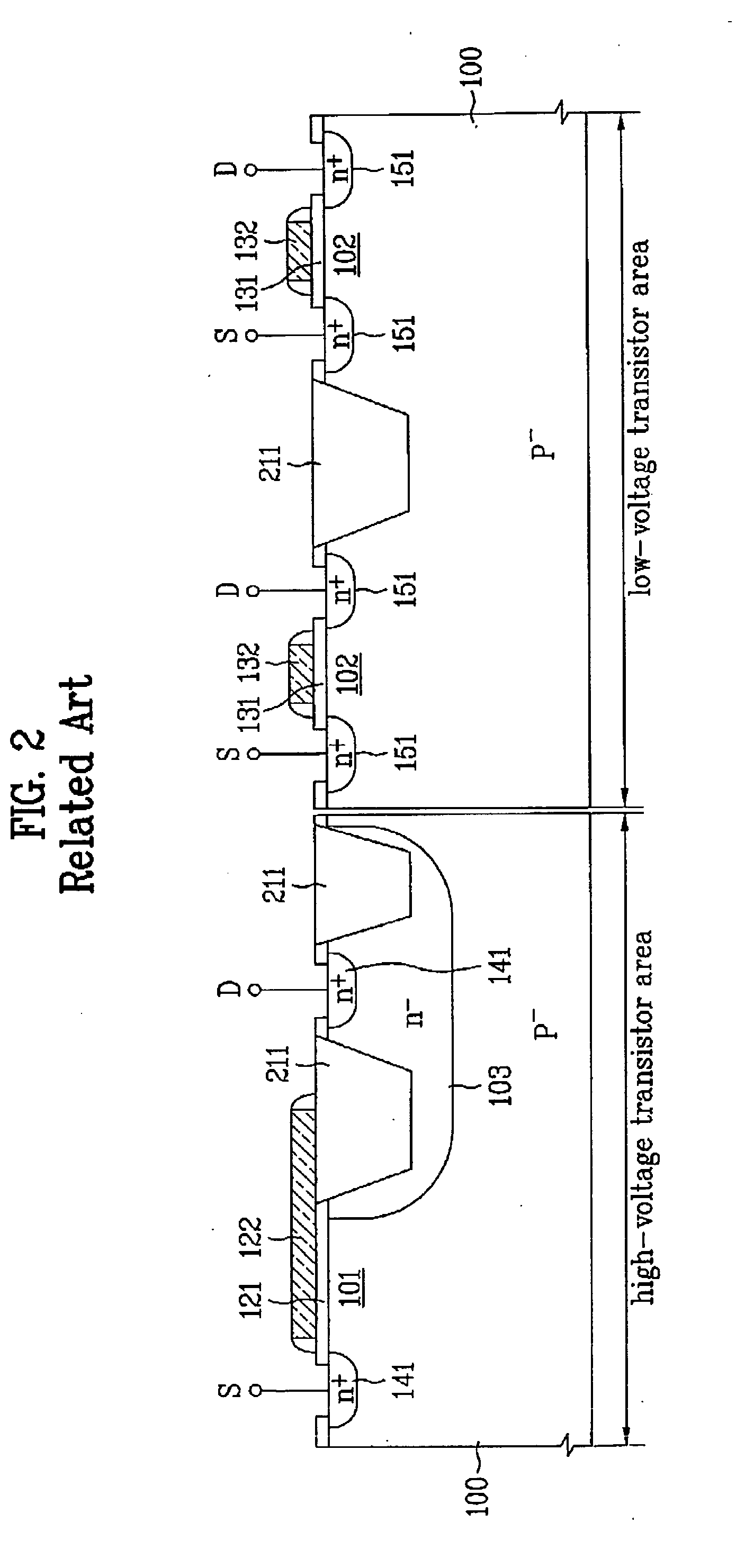
Semiconductor device
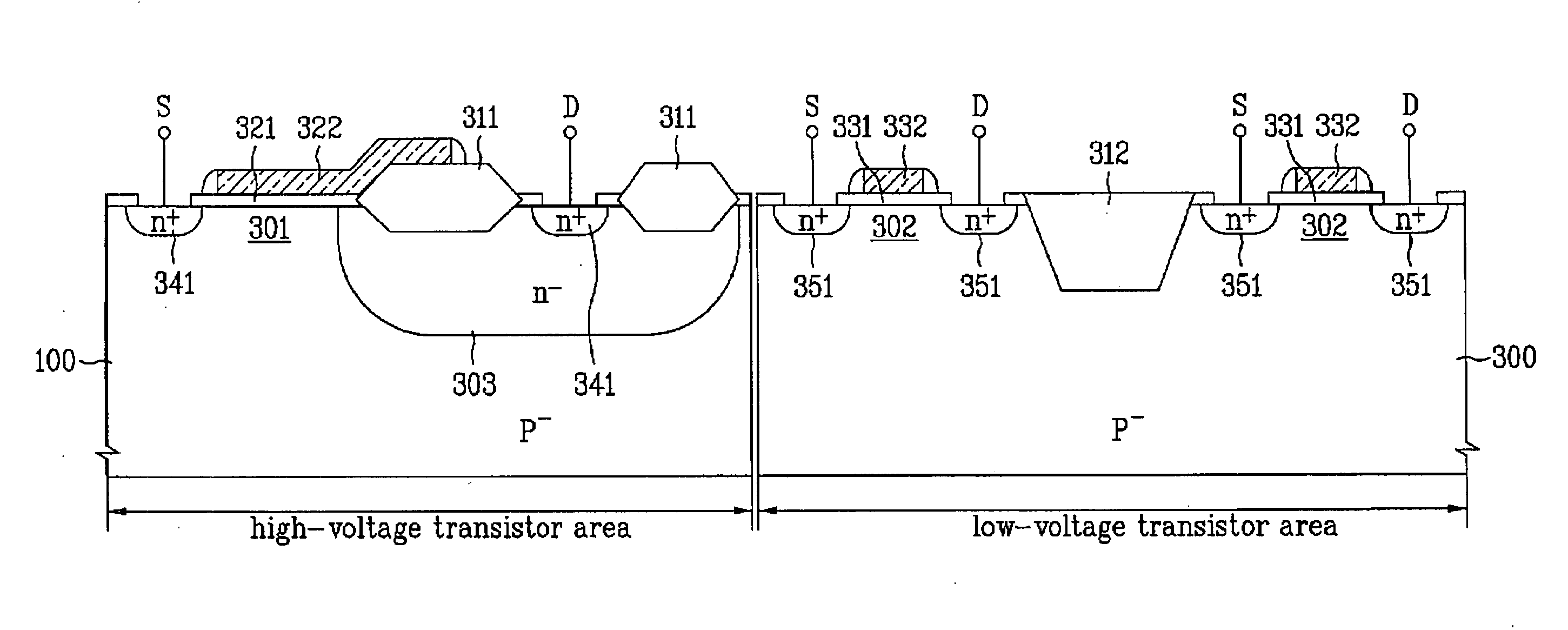
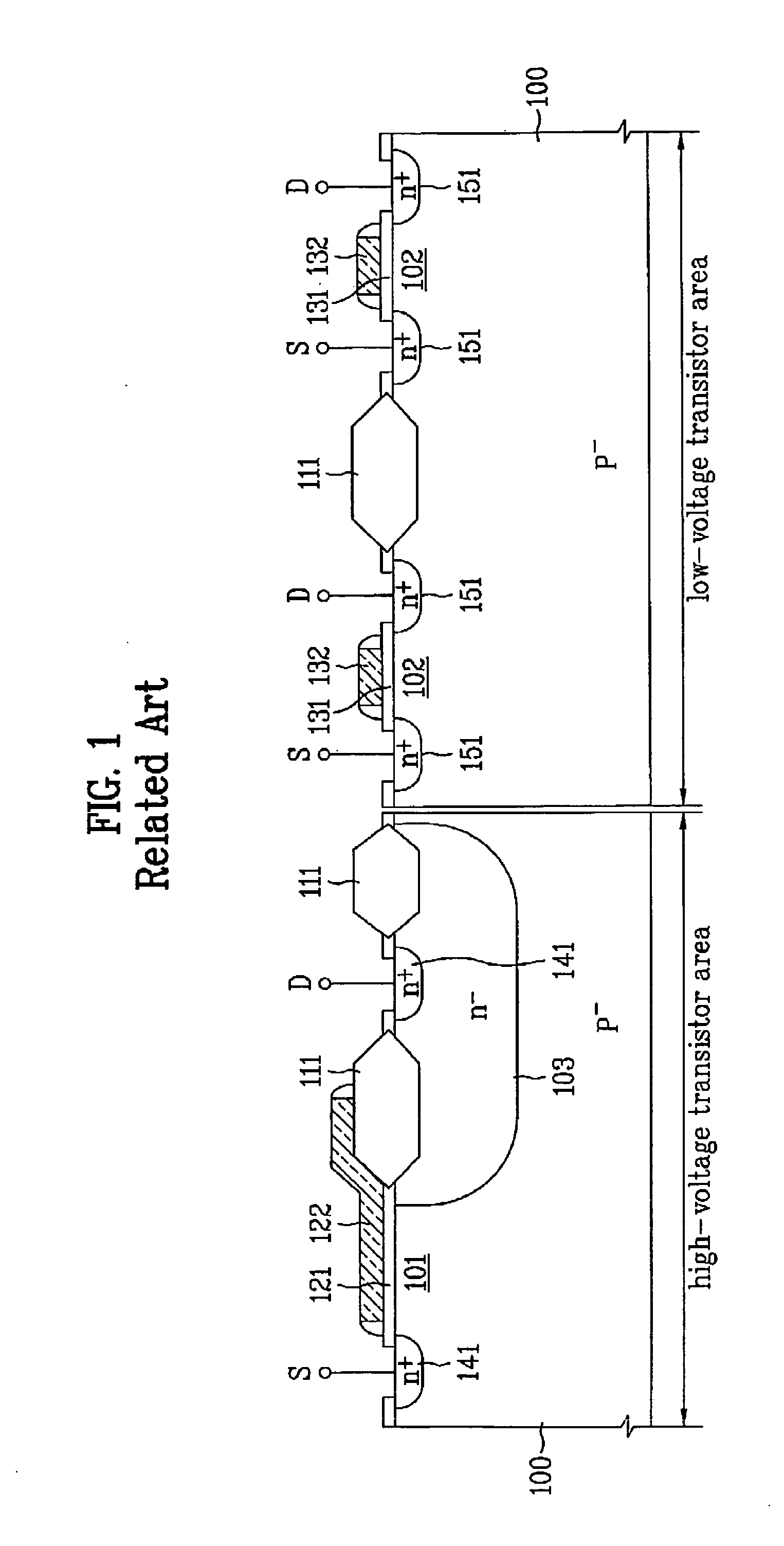
InactiveUS20060138584A1Sufficient level of breakdown voltageChip areaTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh voltage transistorsLOCOS
A semiconductor device includes a substrate including a high-voltage transistor area provided with a high-voltage transistor and a low-voltage transistor area provided with a low-voltage transistor; a LOCOS layer provided as a device isolation layer of the high-voltage transistor area; and a shallow-trench isolation layer provided as a device isolation layer of the low-voltage transistor area. Accordingly, a sufficient breakdown voltage level can be provided in a high-voltage transistor area, on-resistance and leakage current can be enhanced, and the chip area in a low-voltage transistor area can be reduced.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com