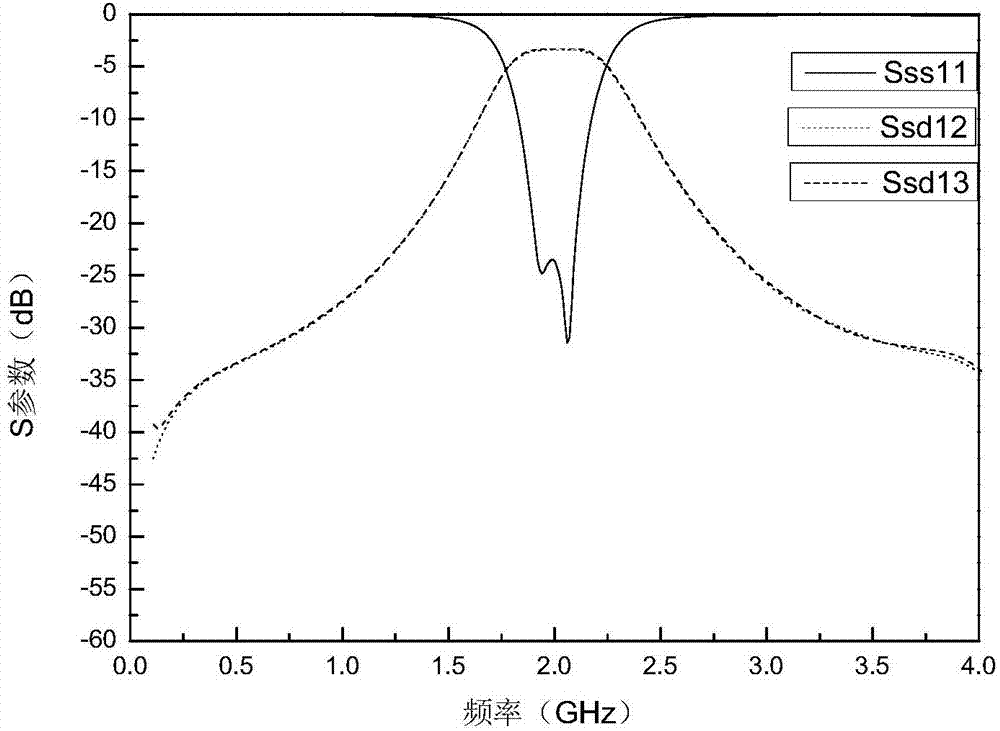
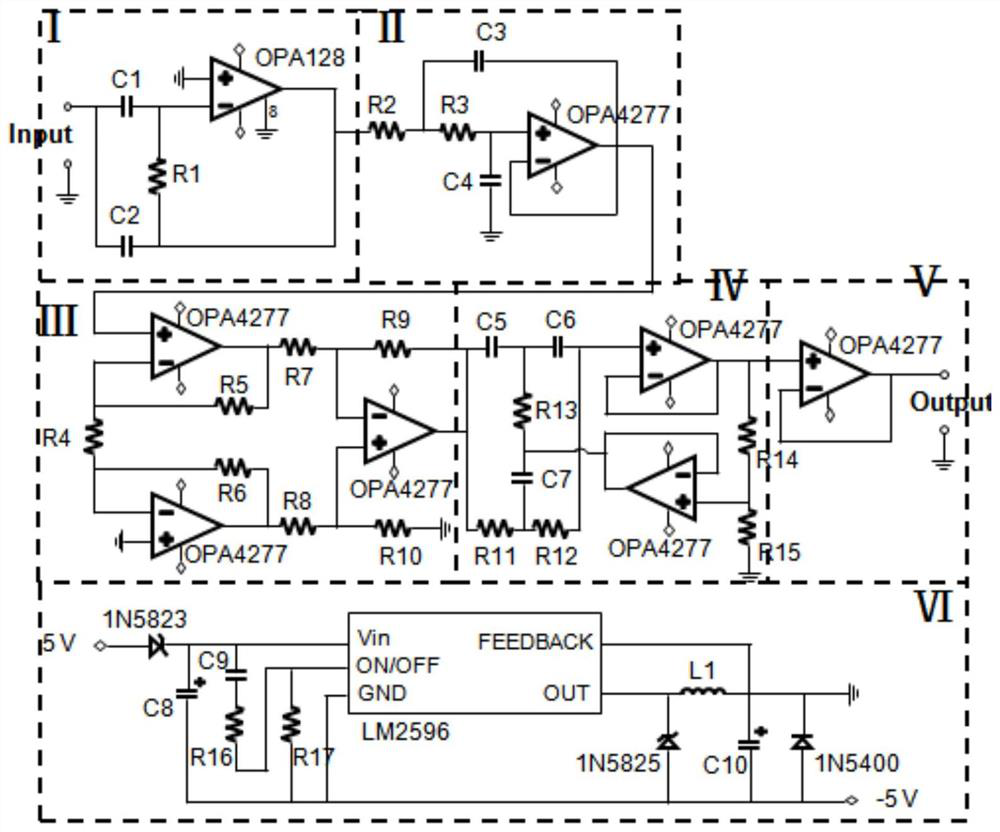
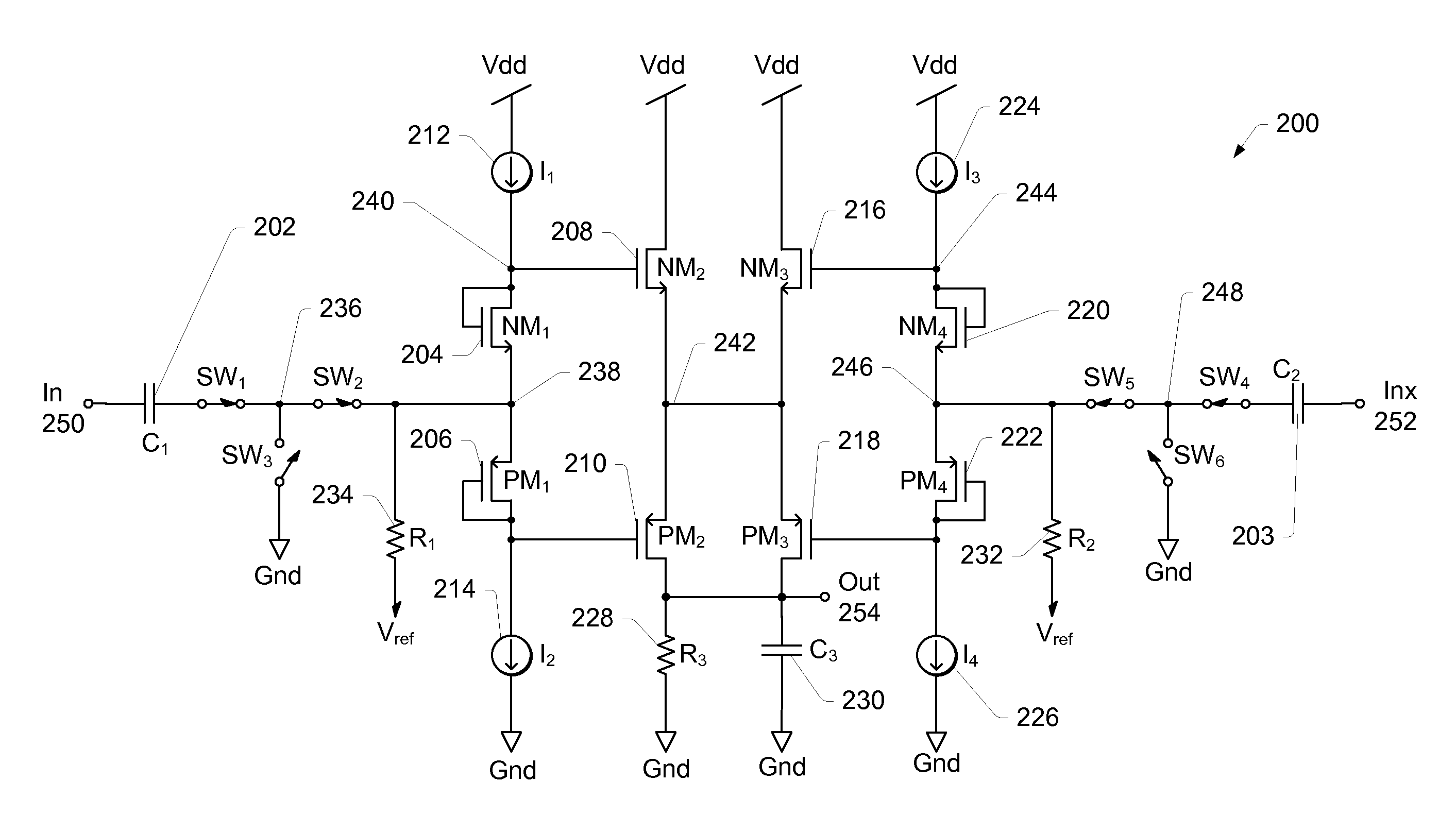
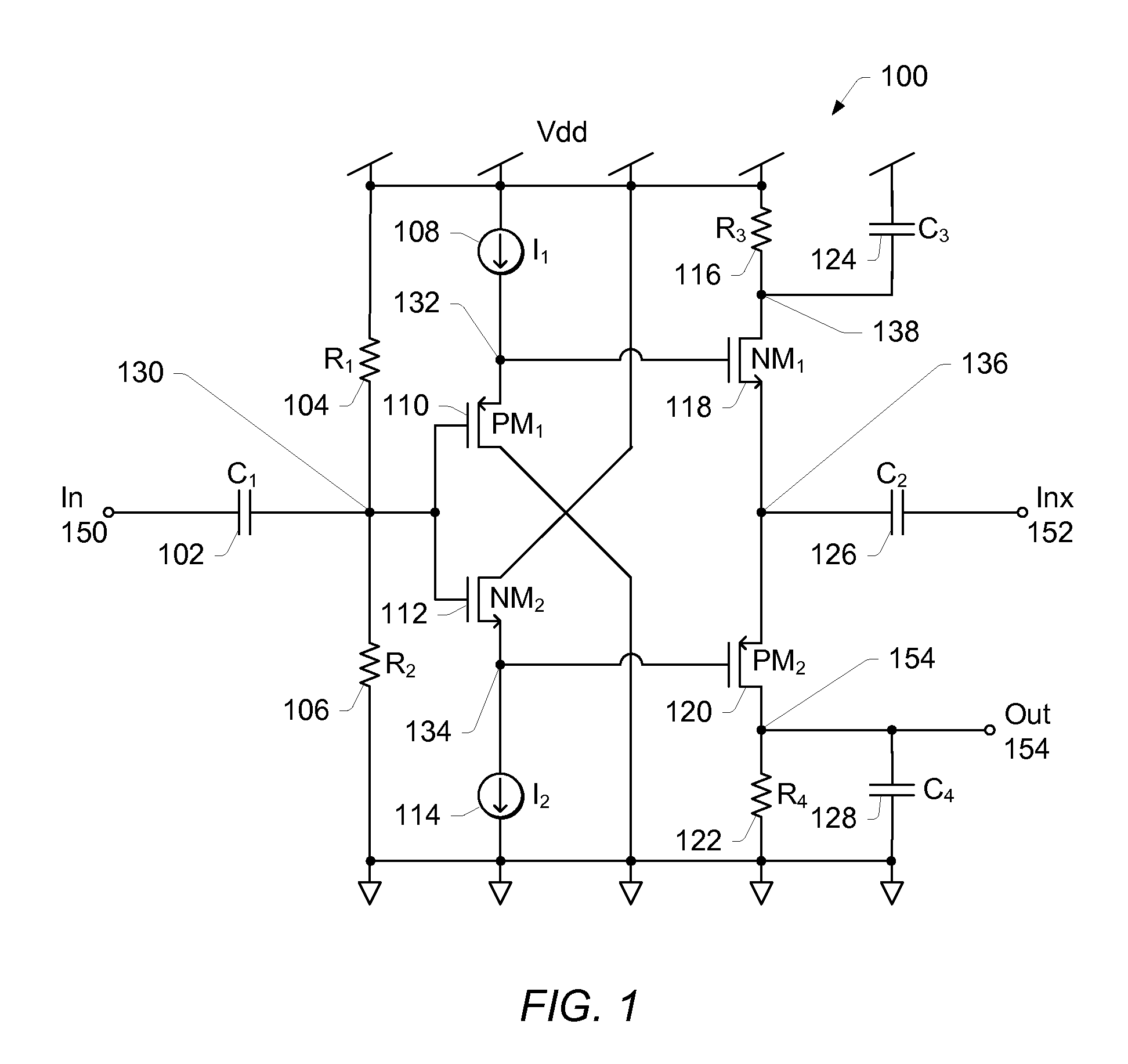
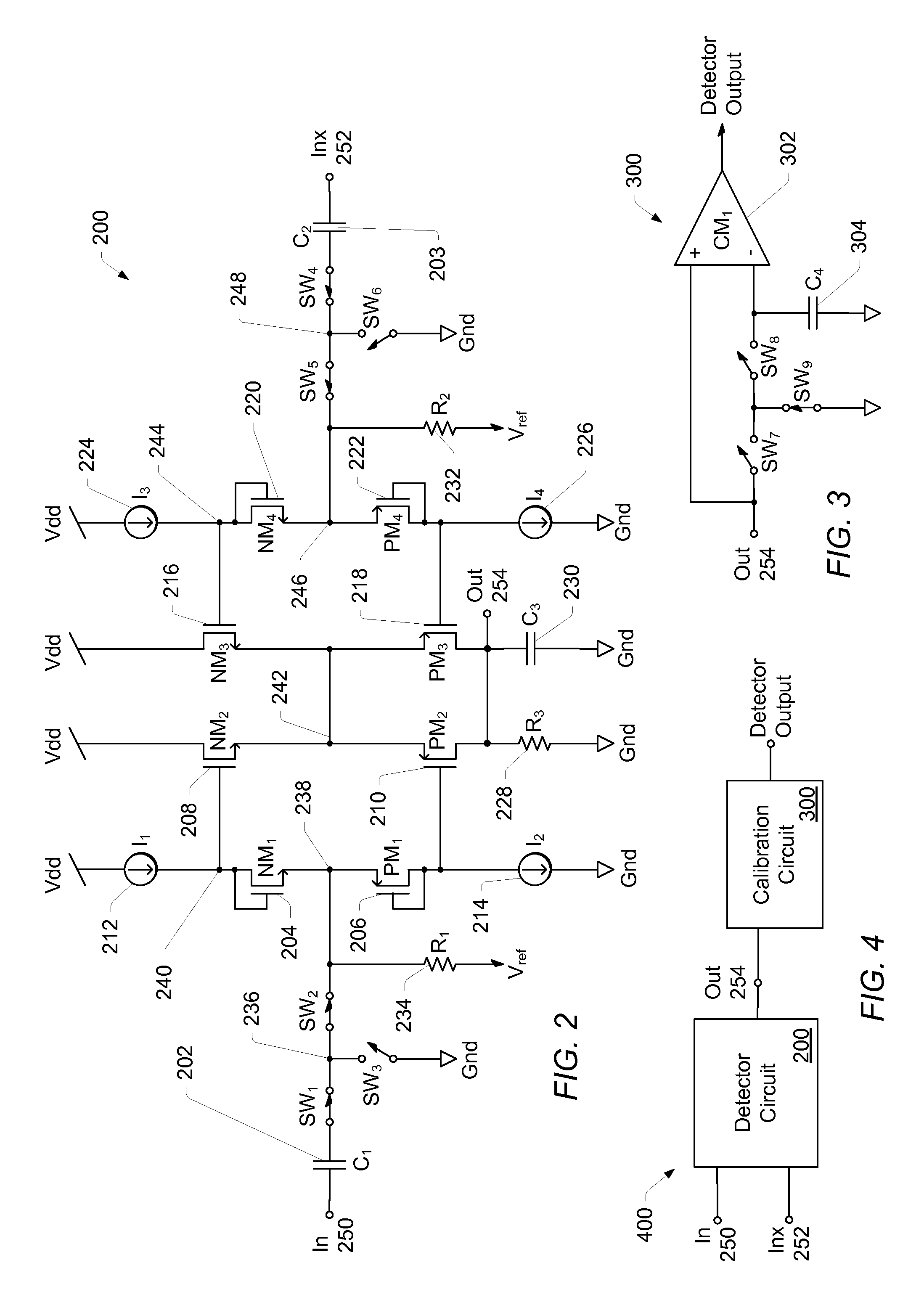
Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Good Common Mode Rejection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
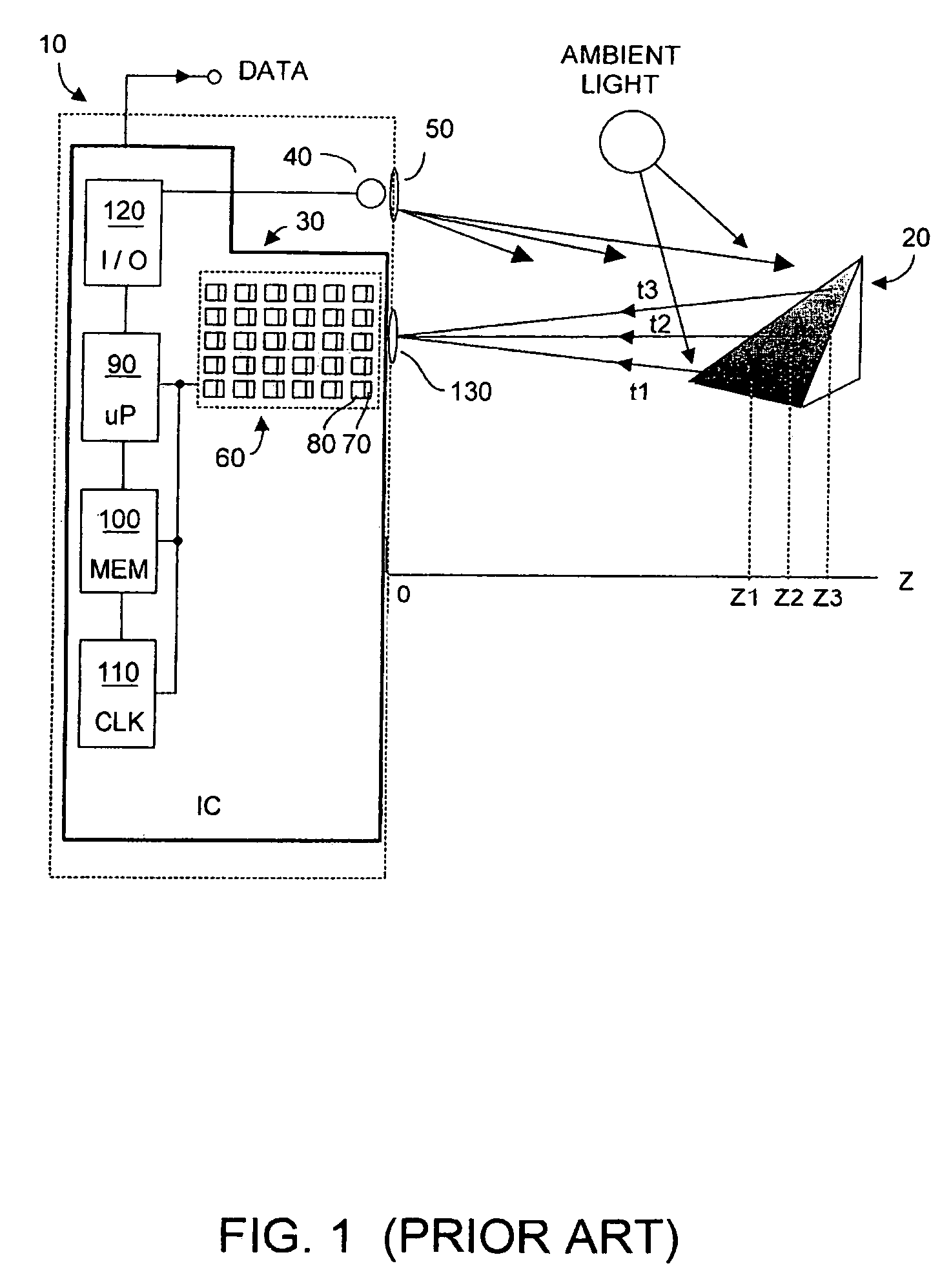
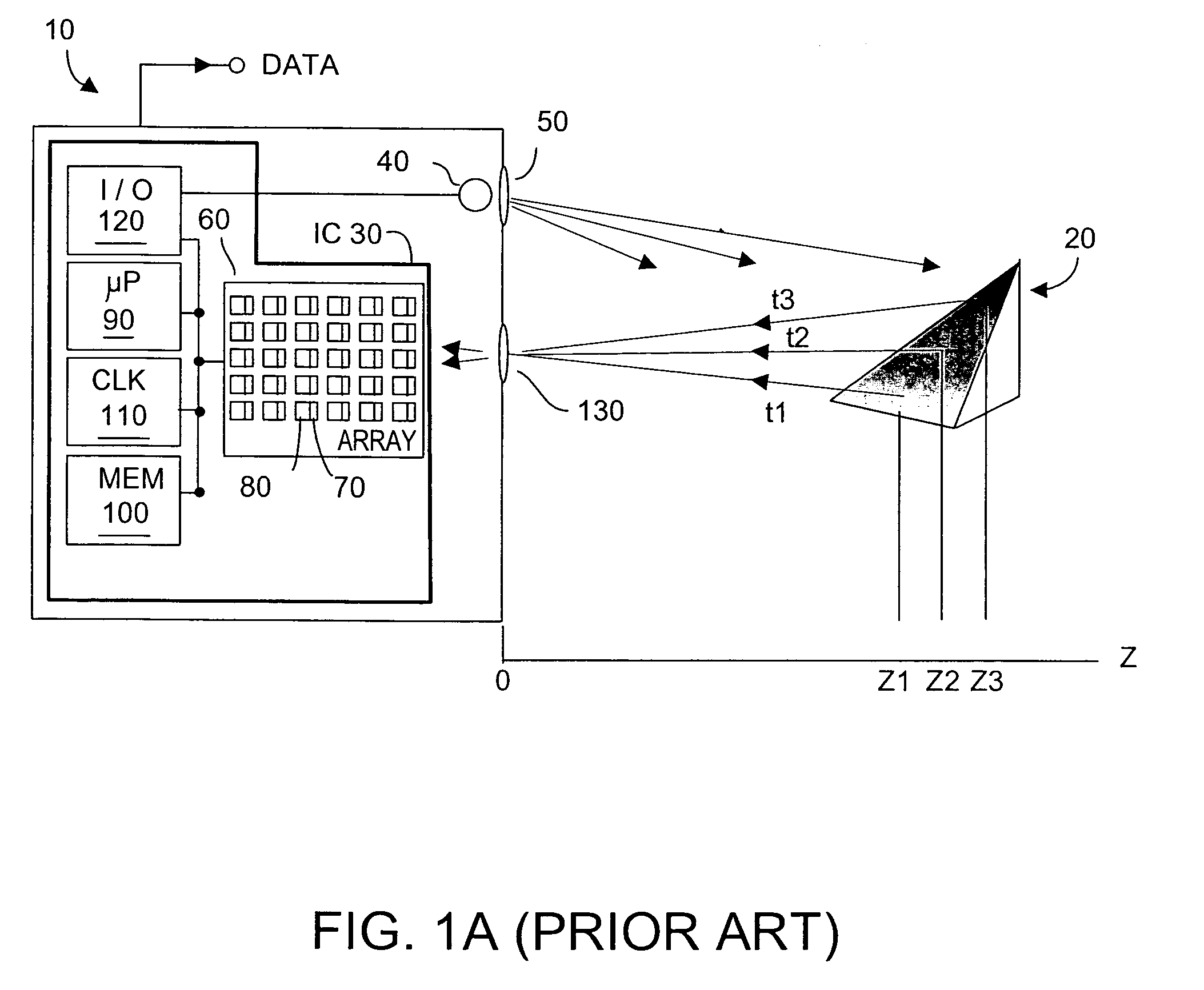
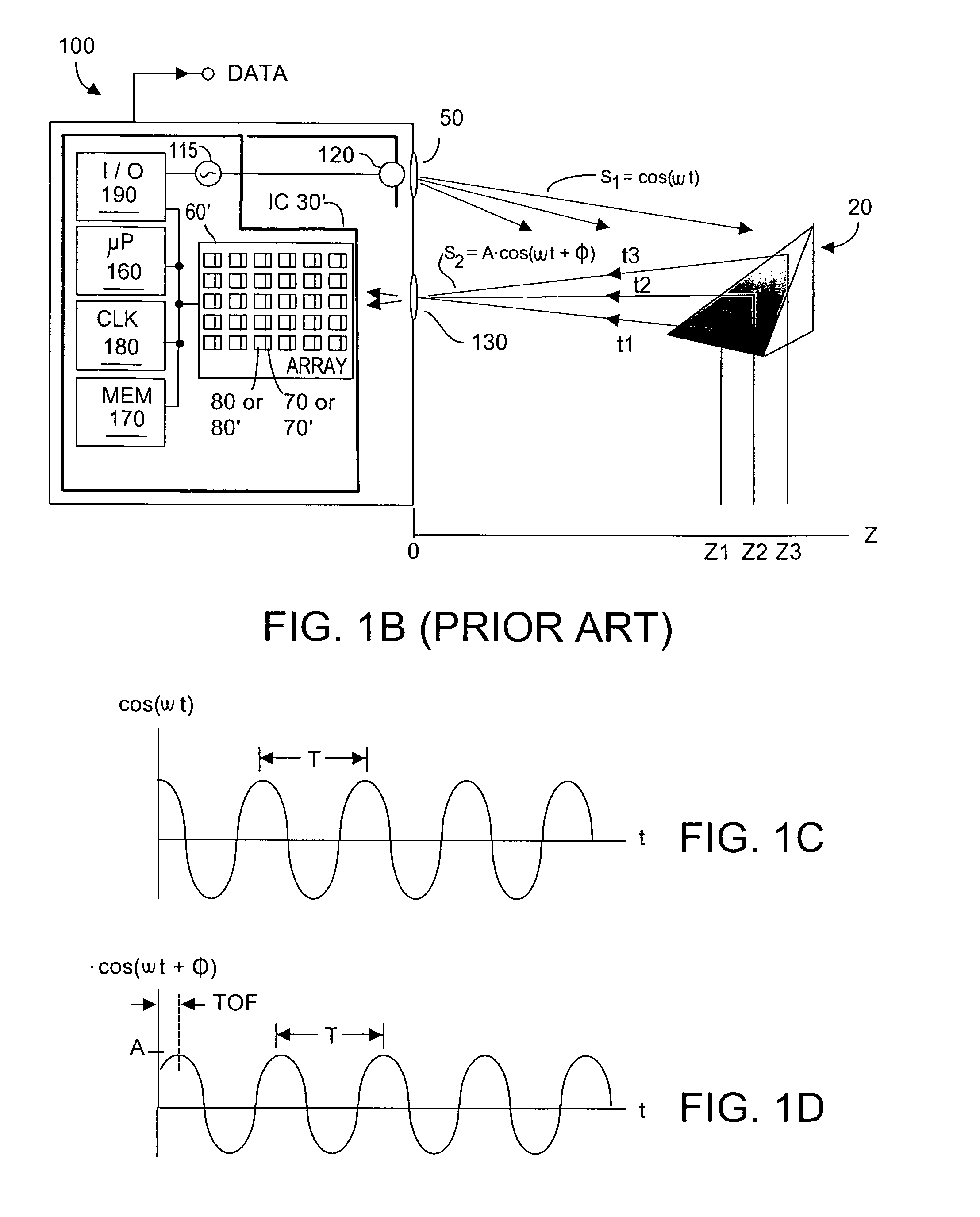
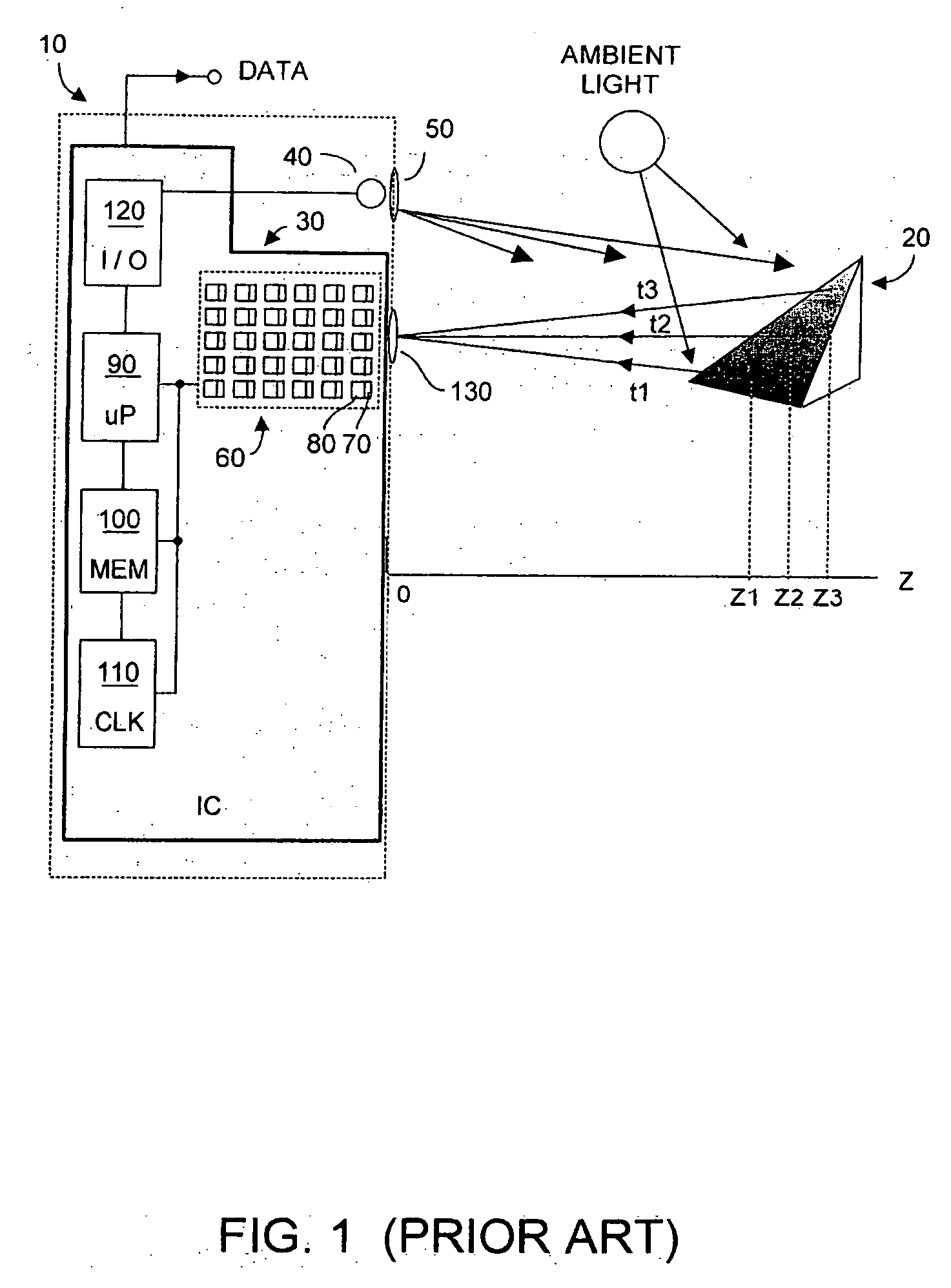
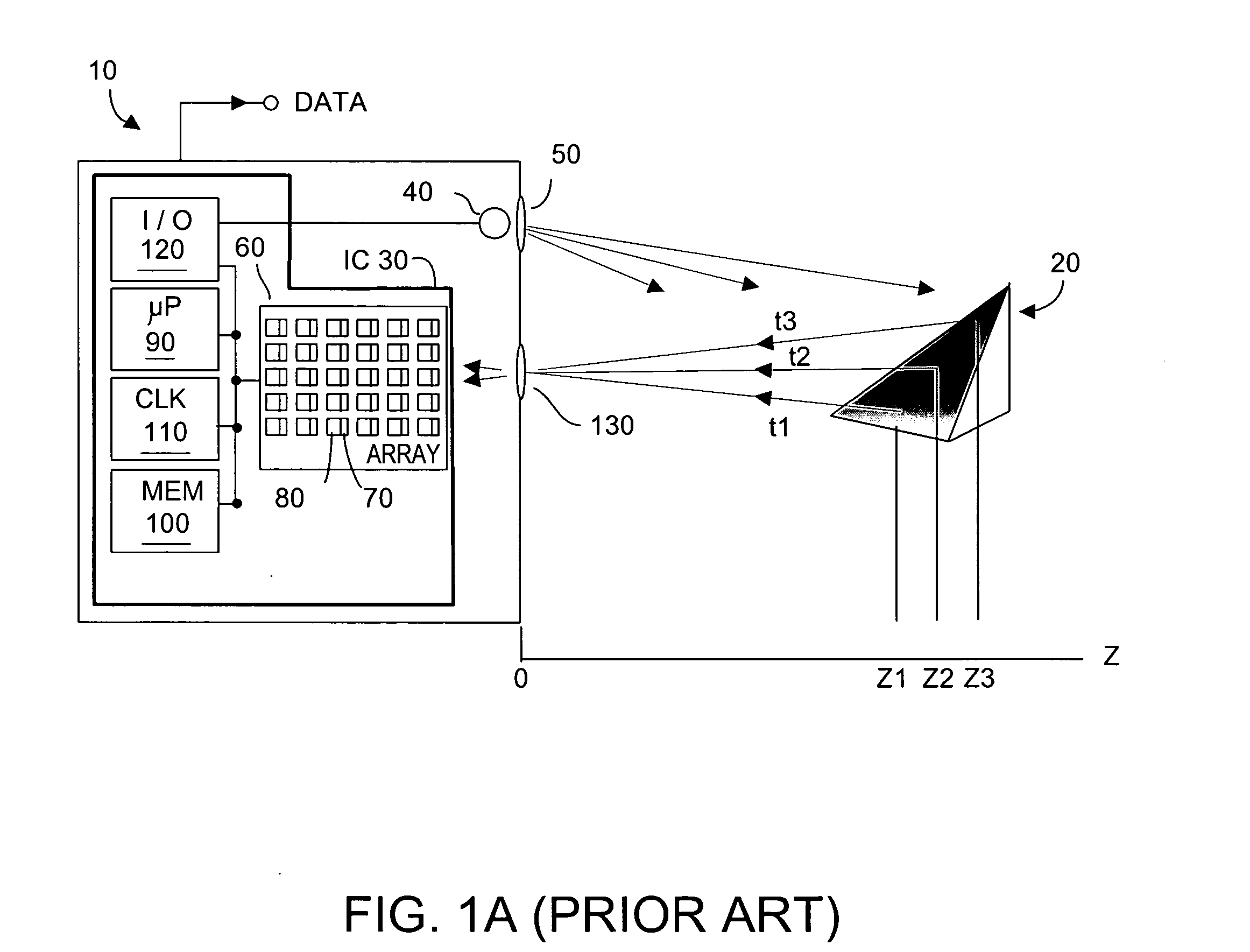
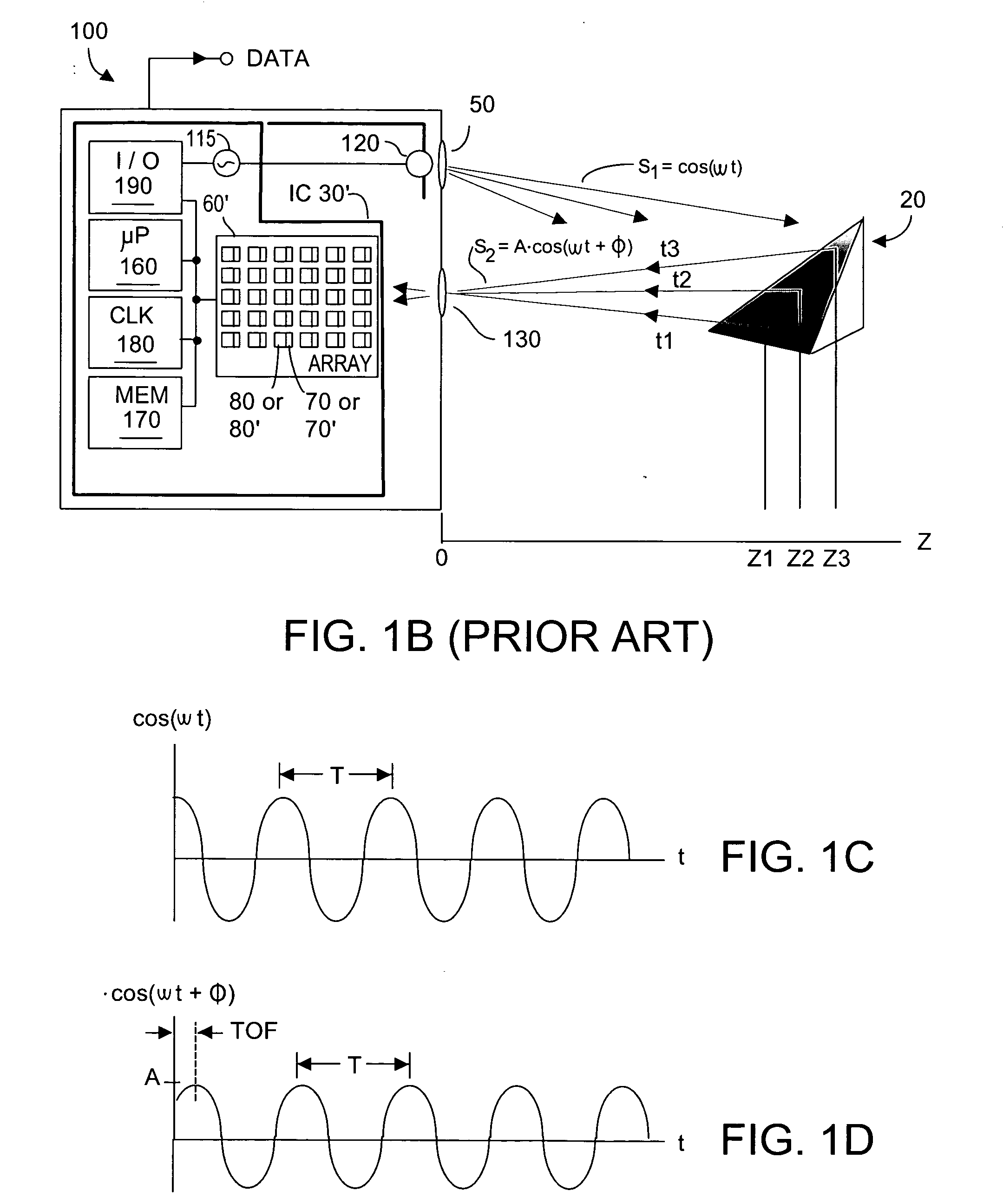
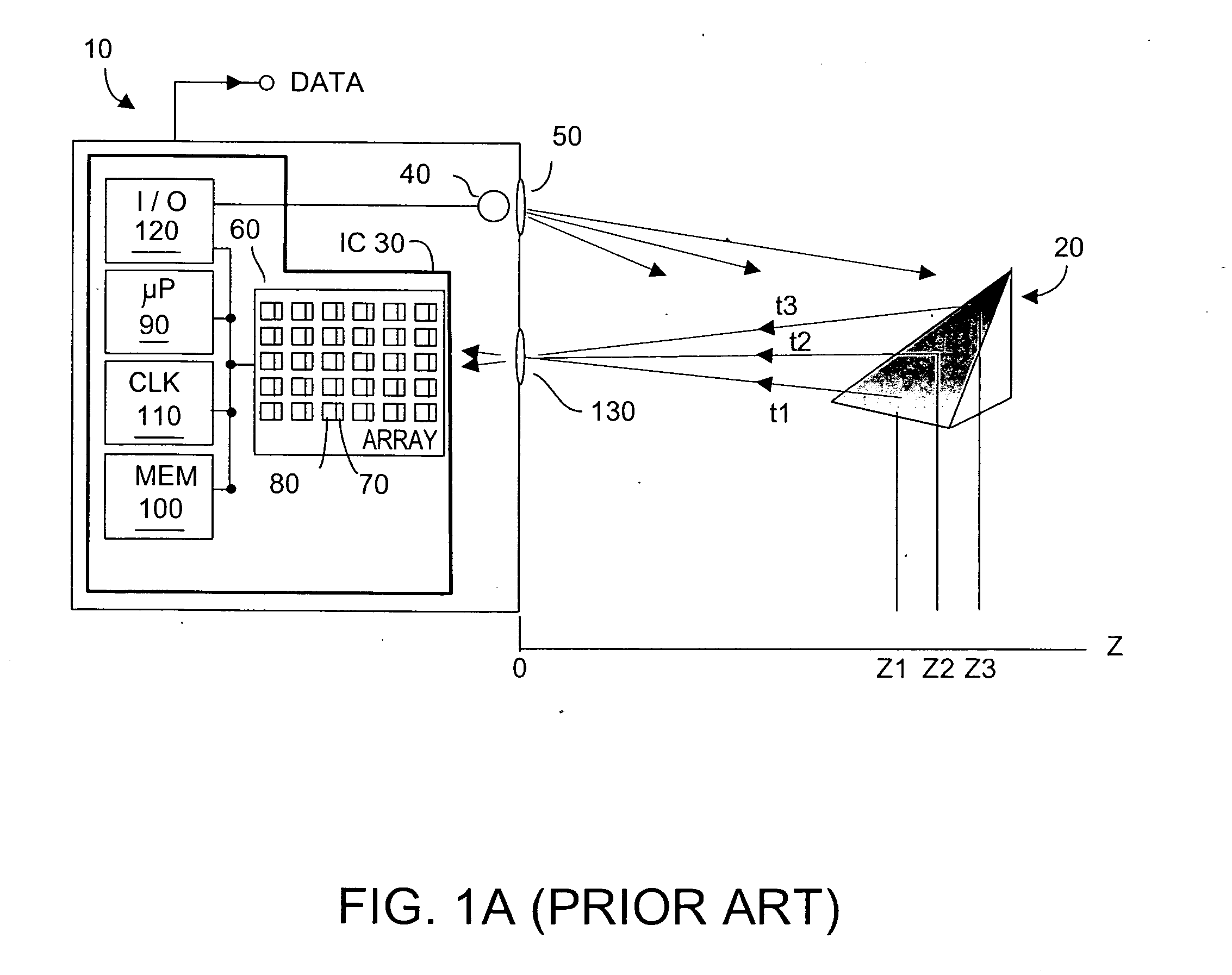
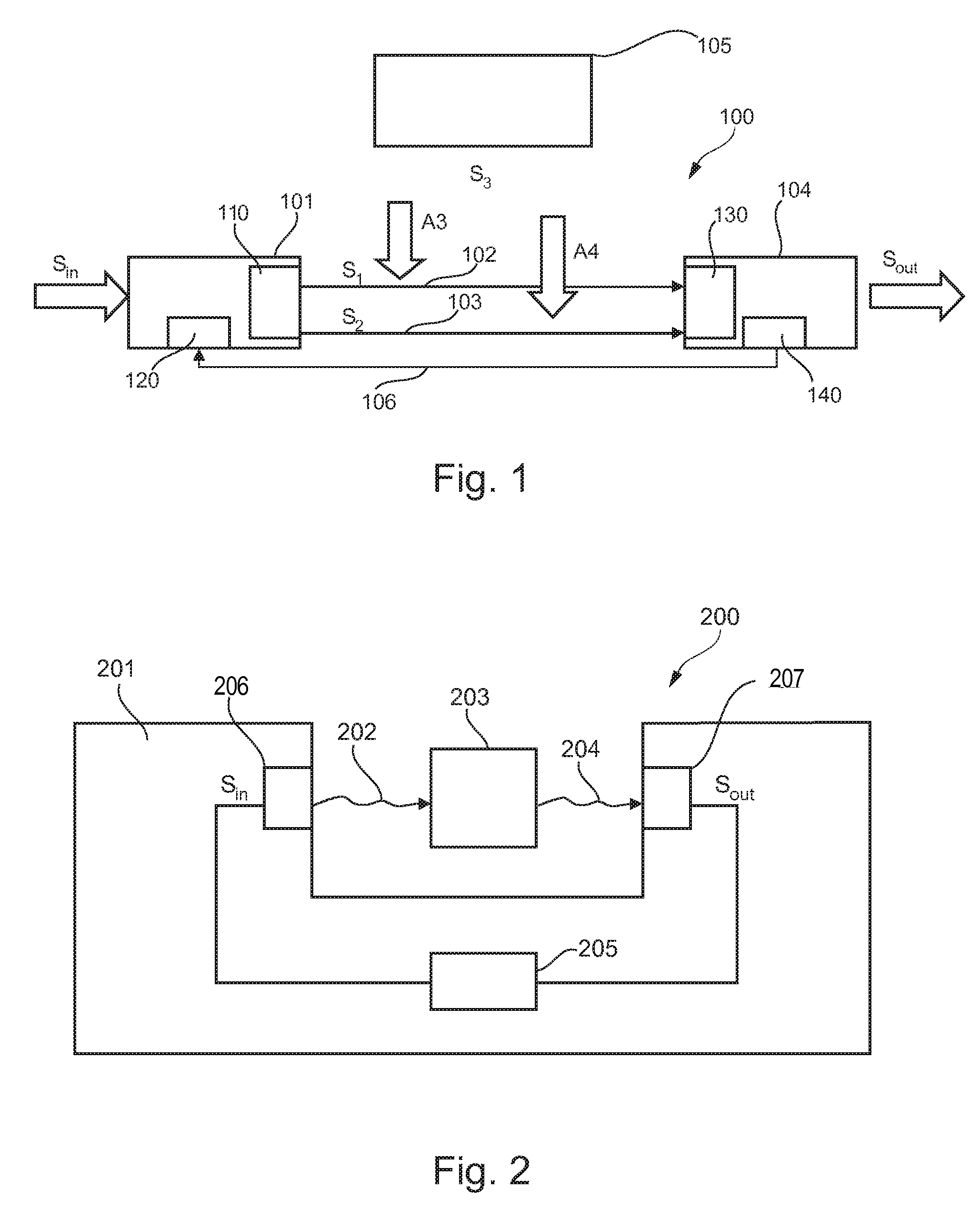
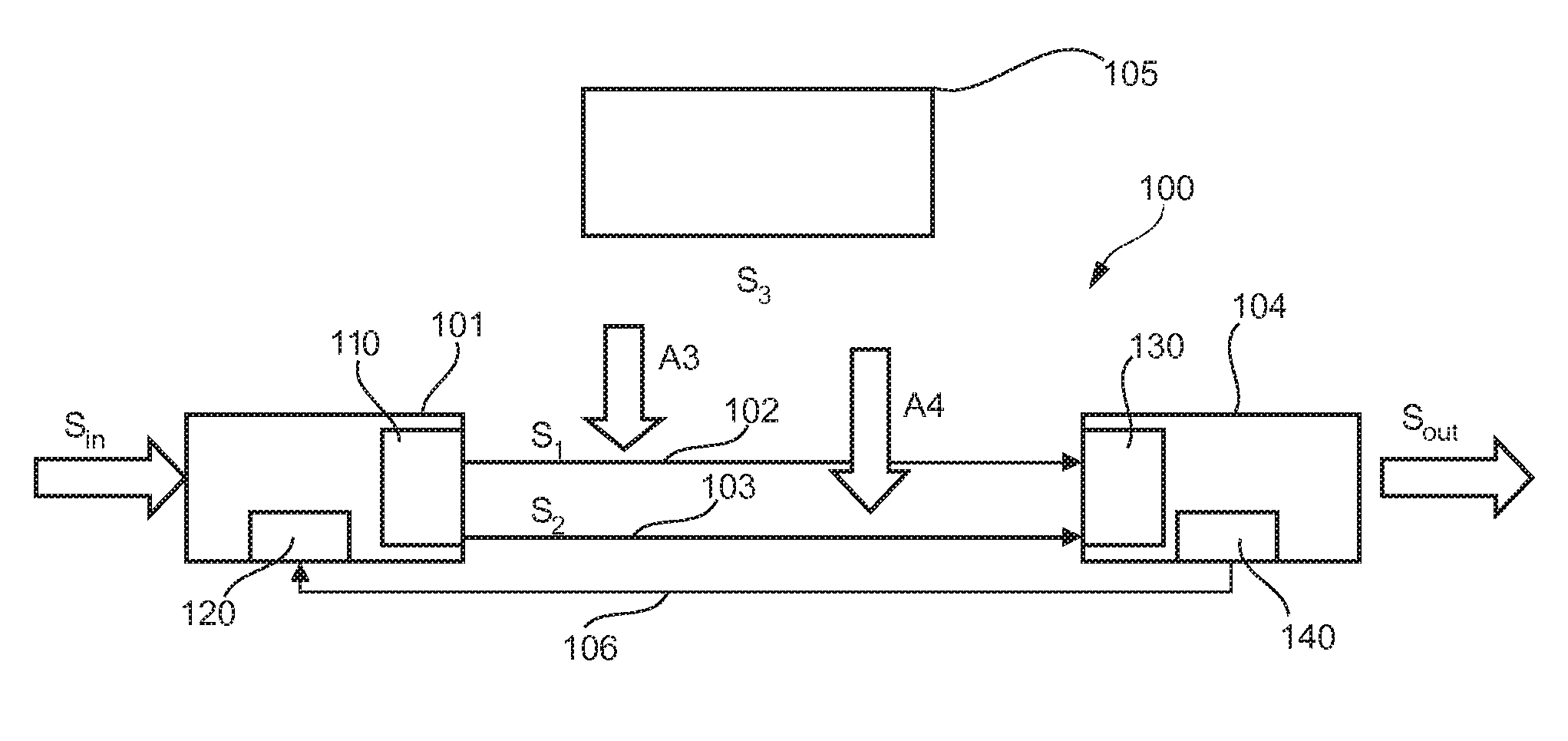
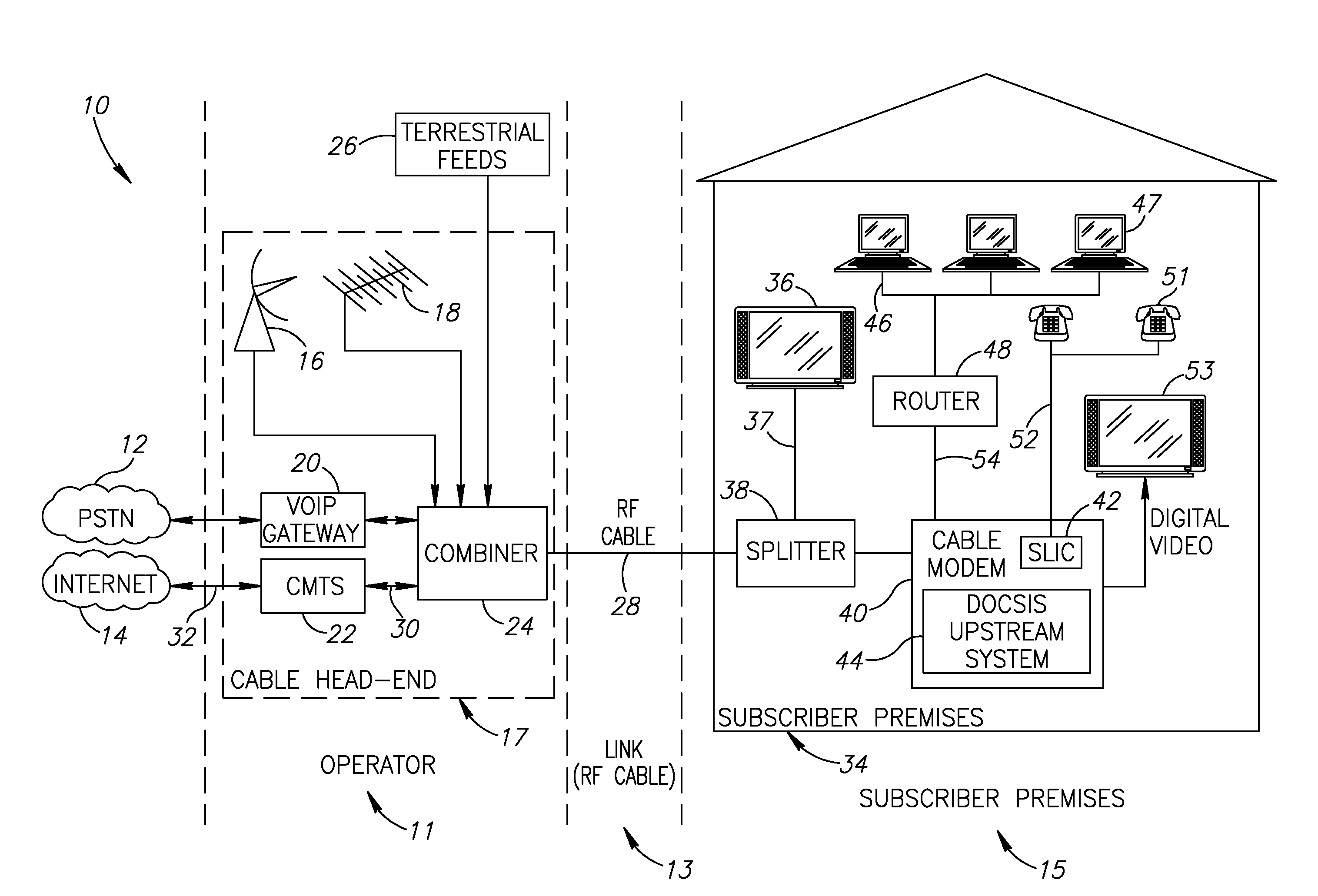
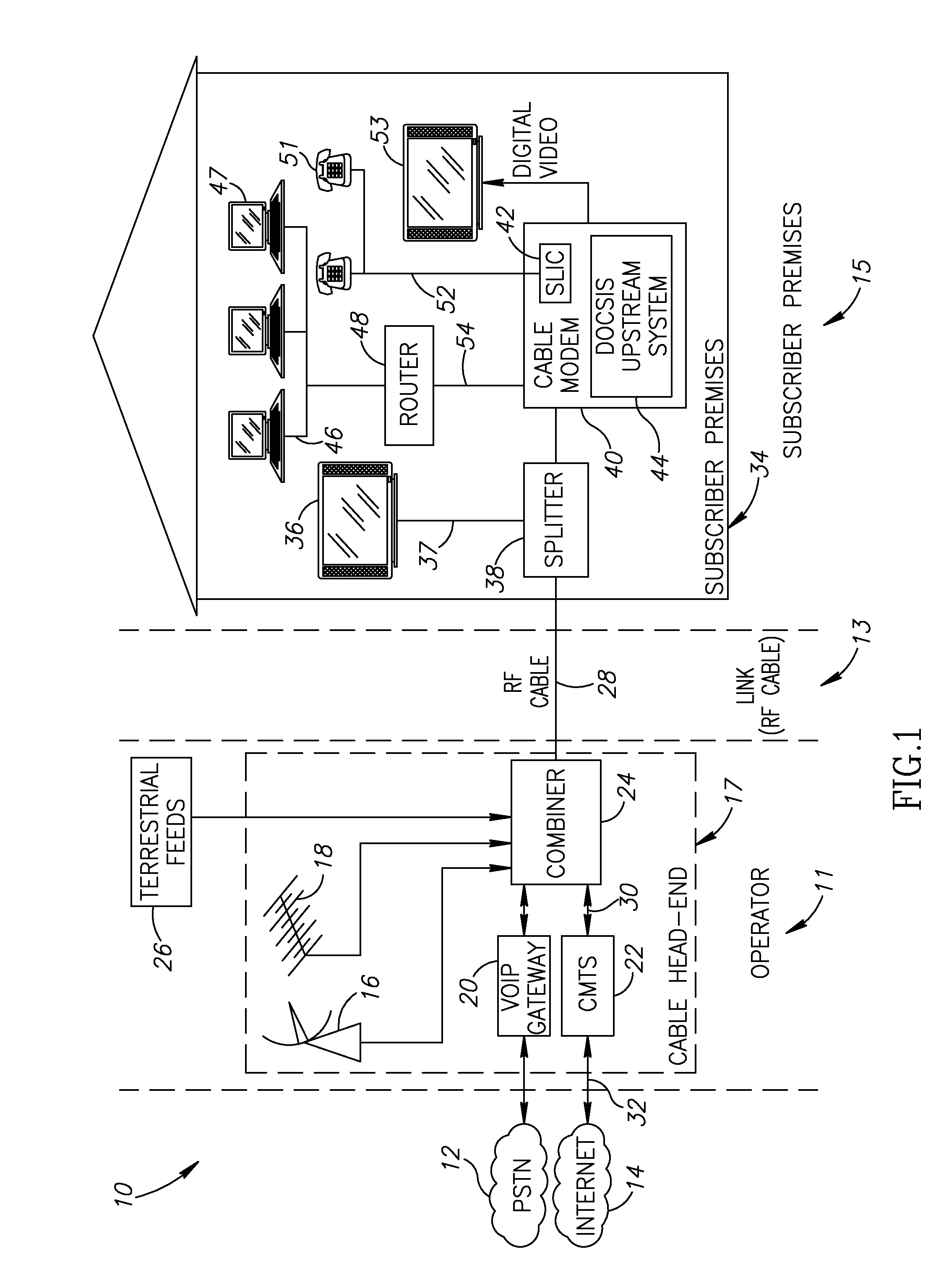
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
ActiveUS7157685B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSCapacitor voltage
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
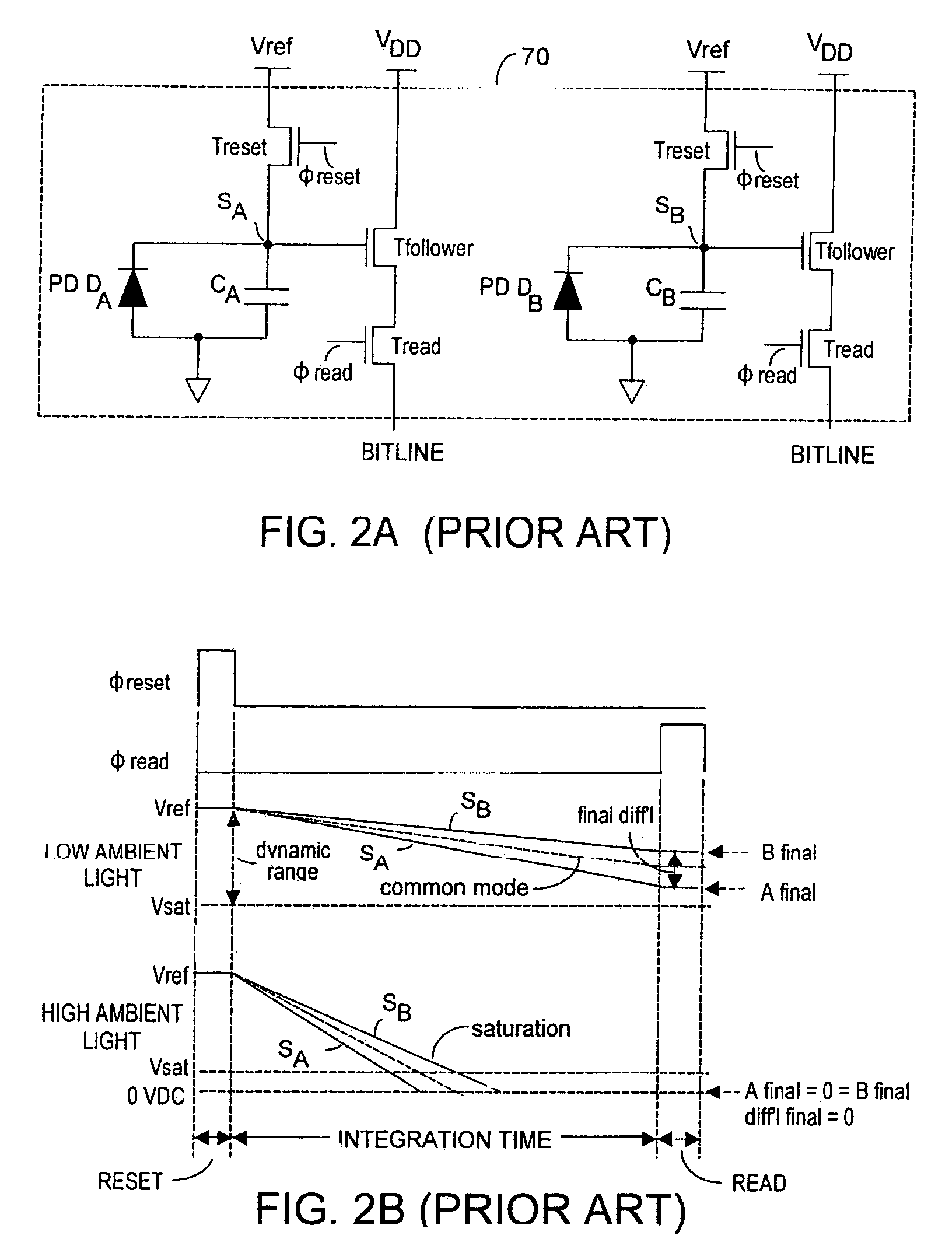
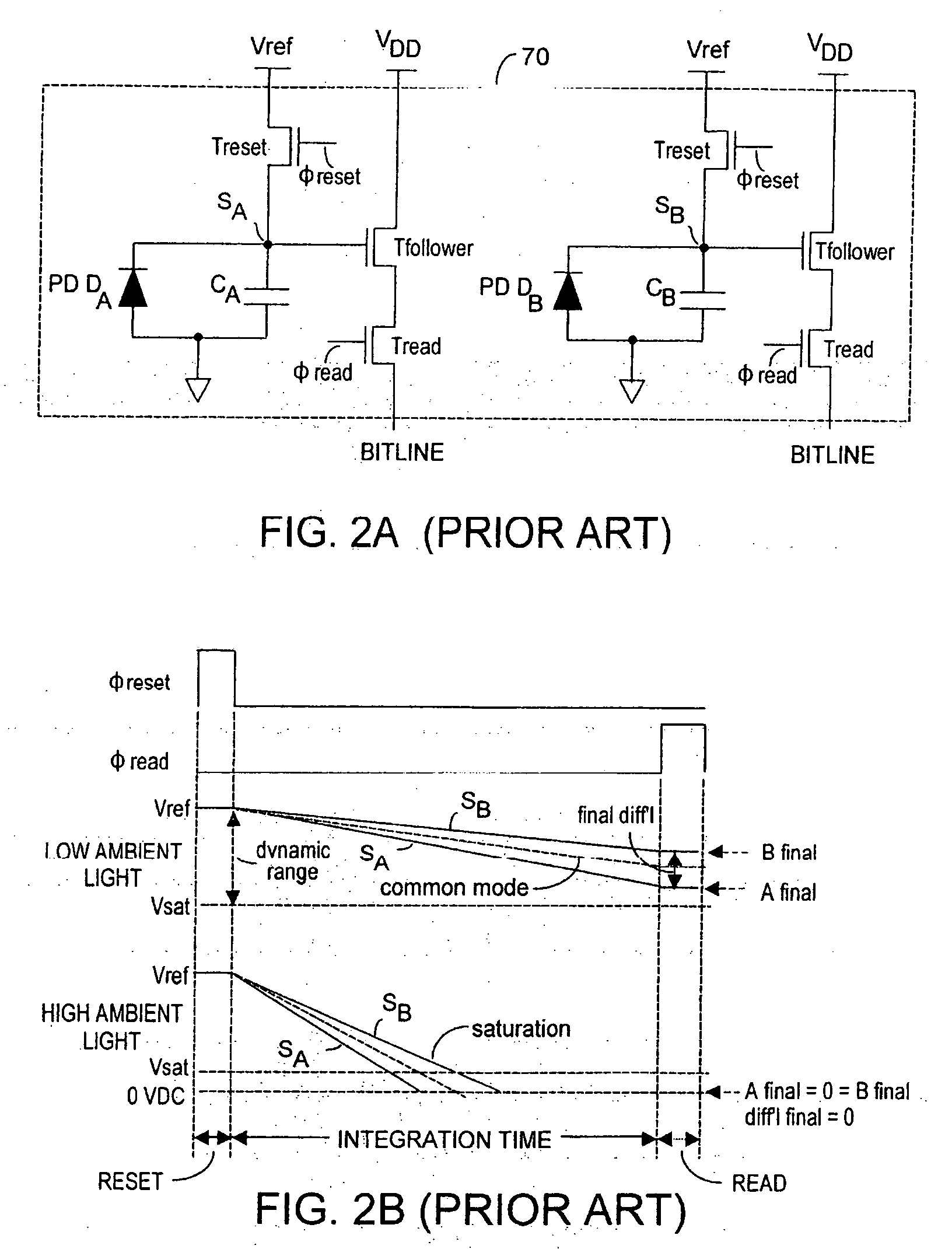
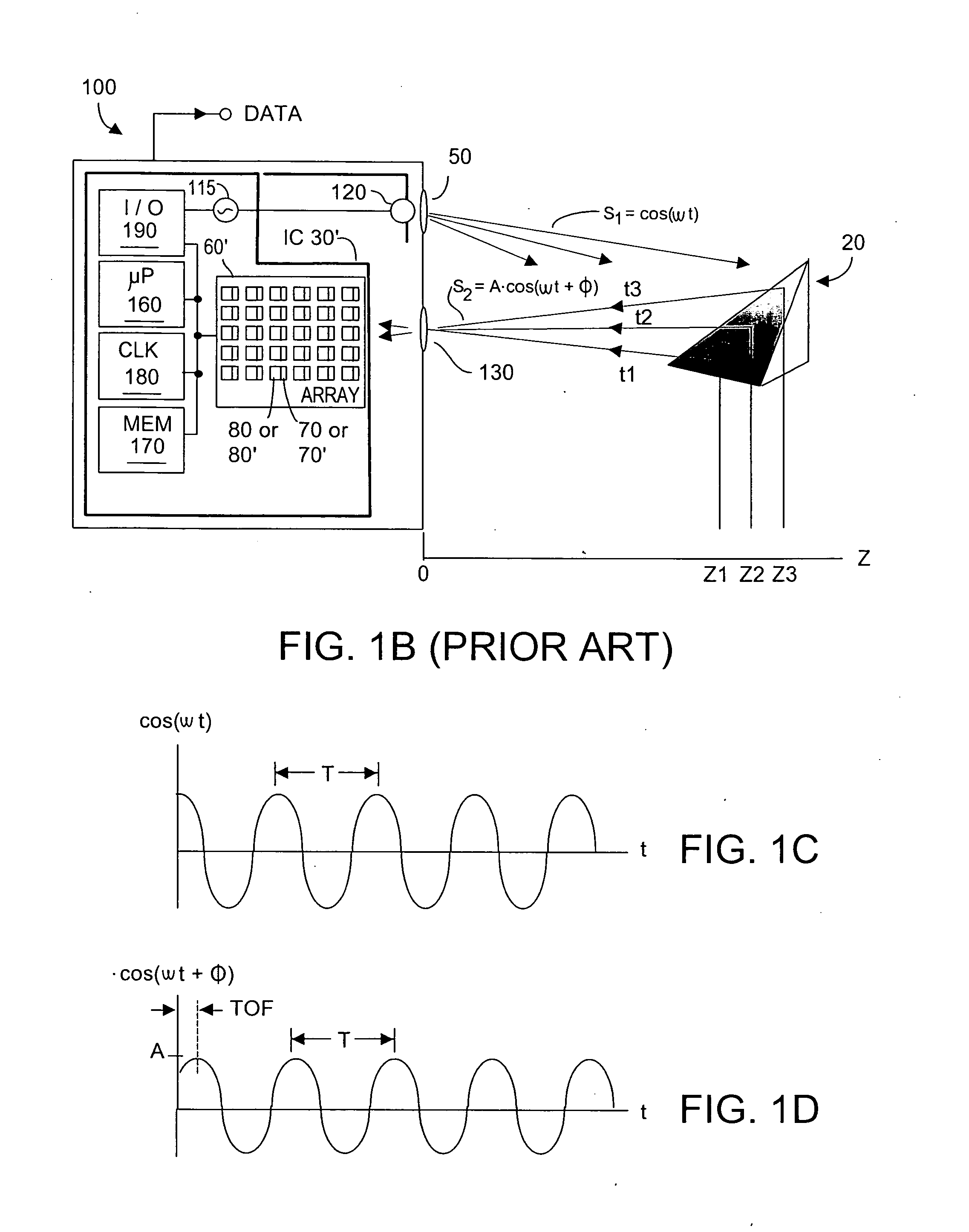
Method and system to differentially enhance sensor dynamic range using enhanced common mode reset
ActiveUS7176438B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierPhotodetector
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
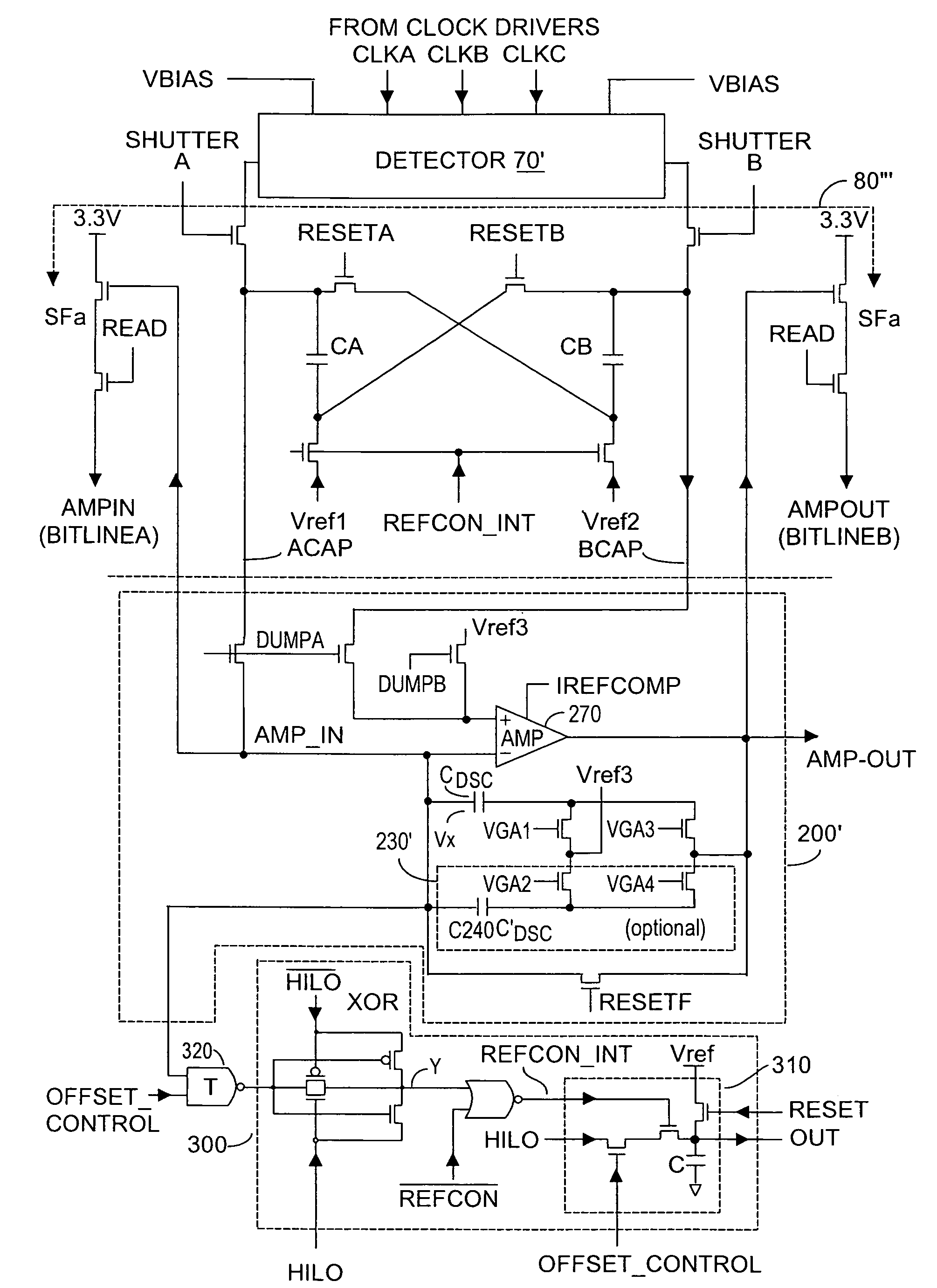
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
InactiveUS7321111B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSAudio power amplifier
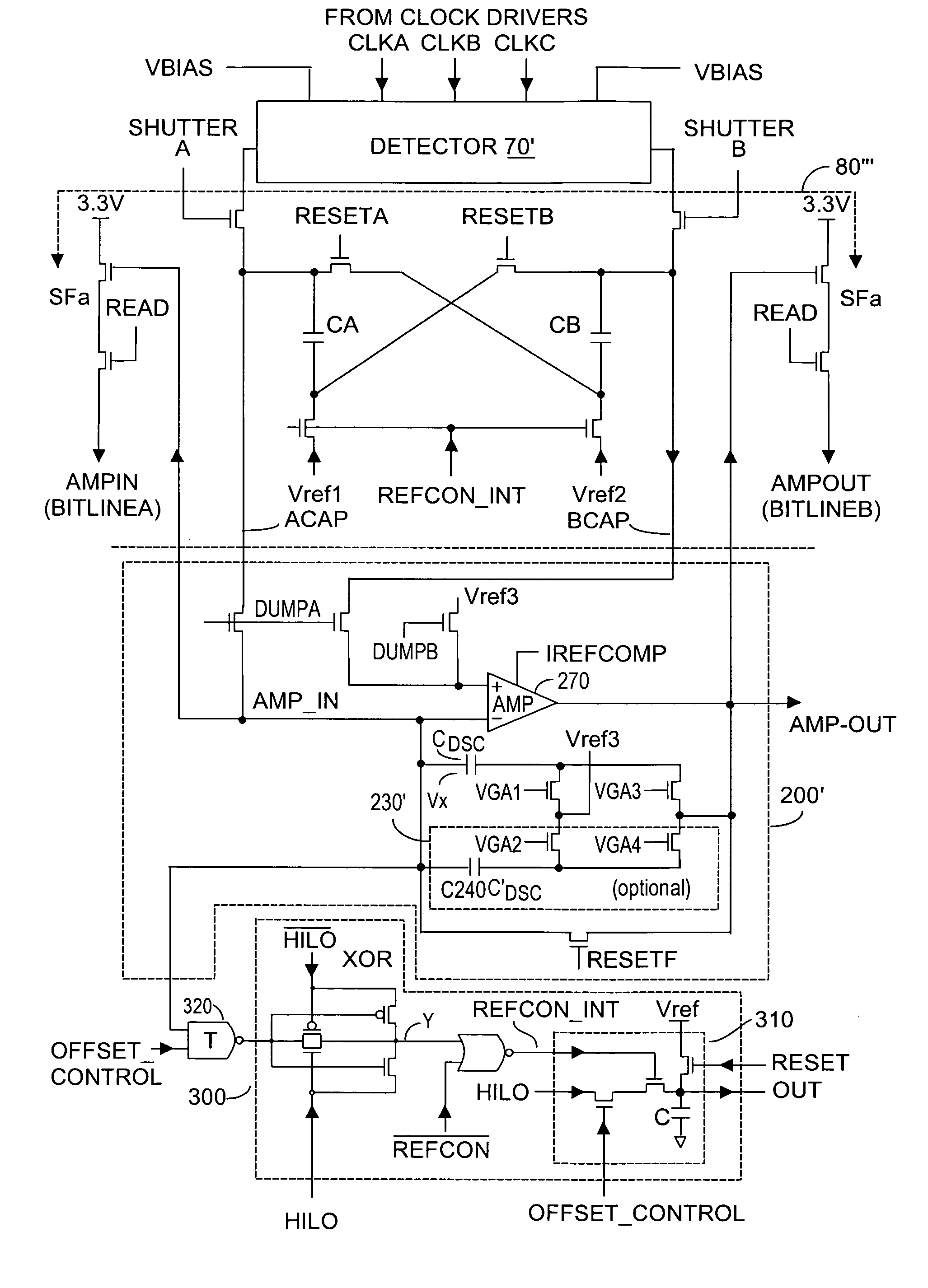
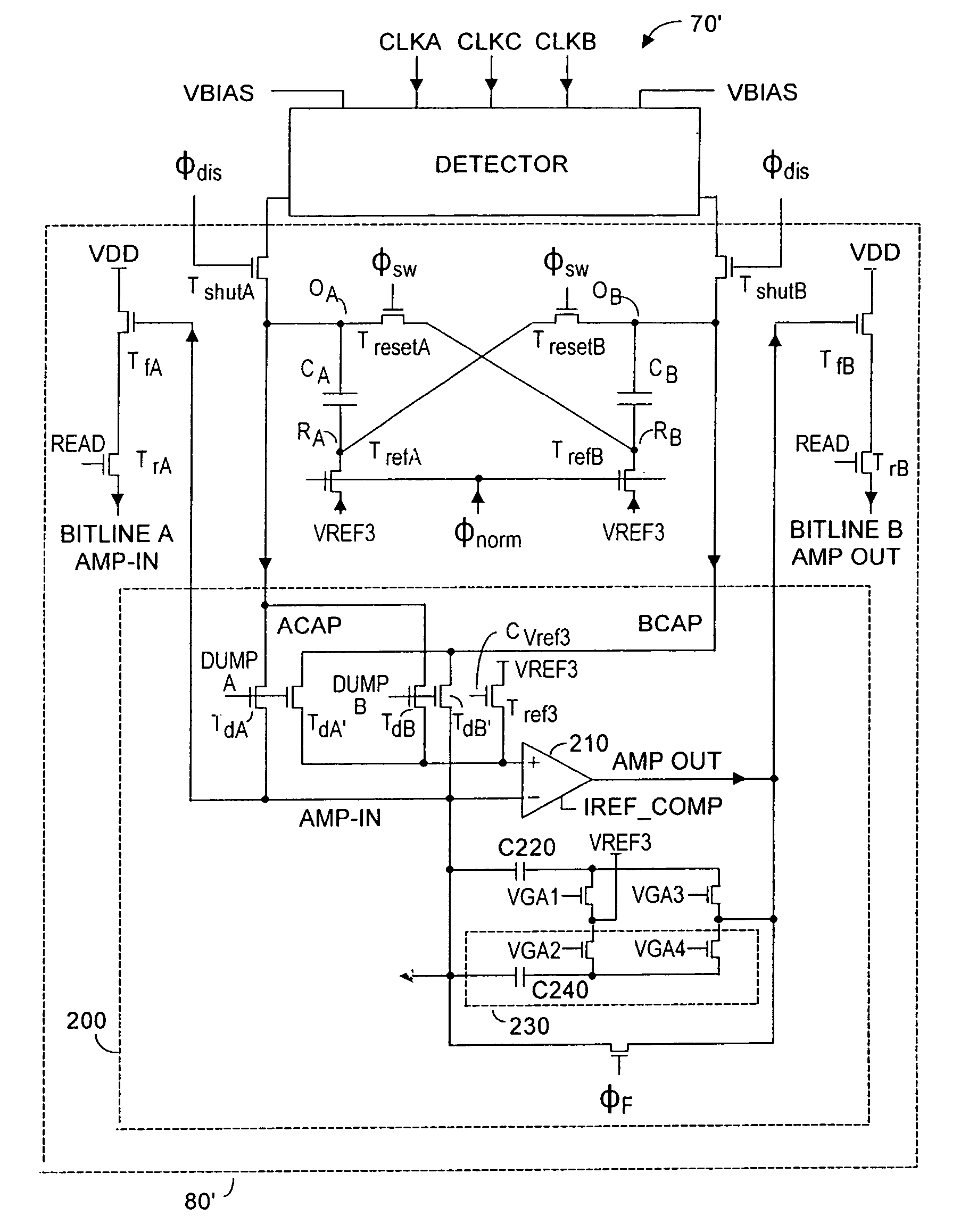
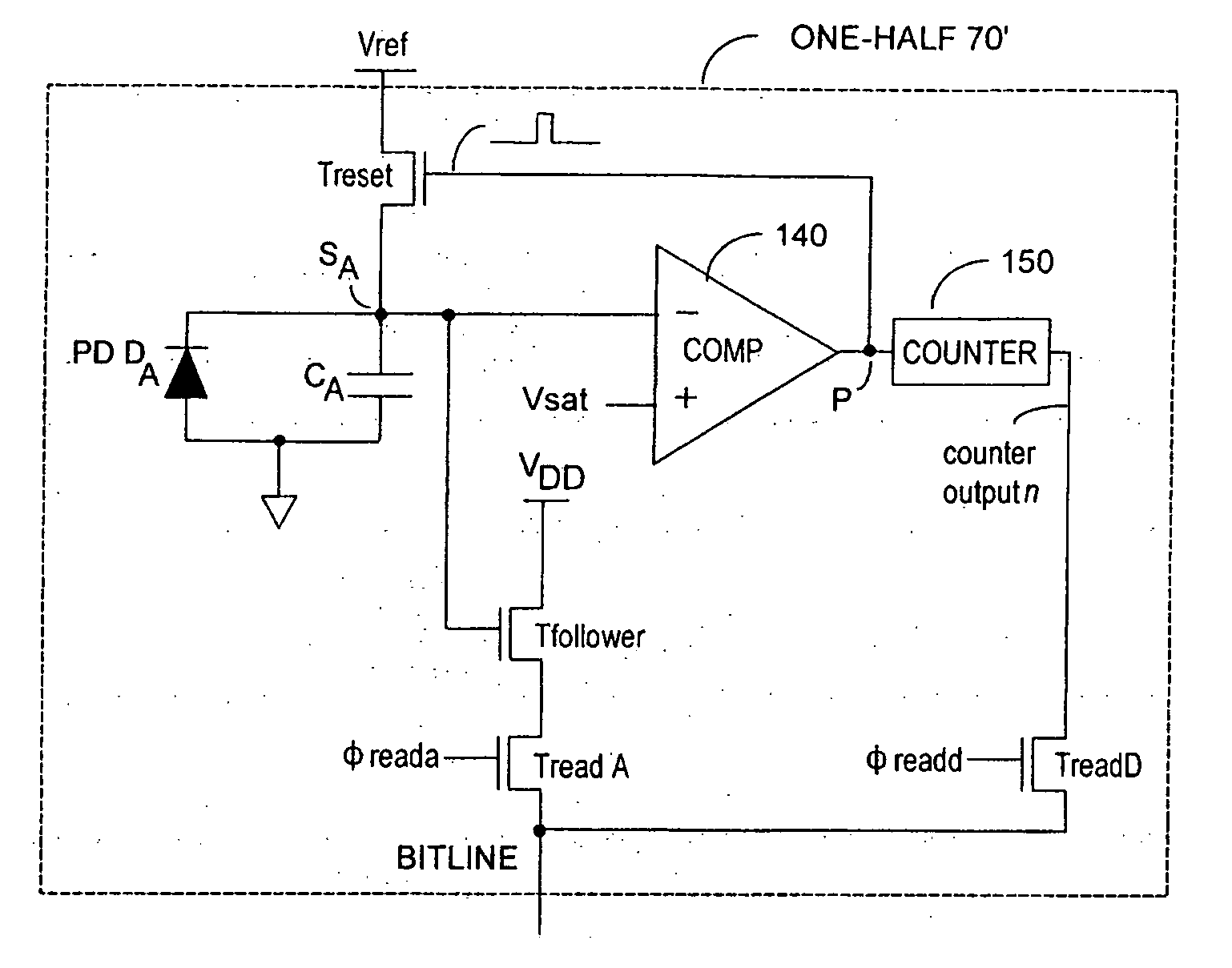
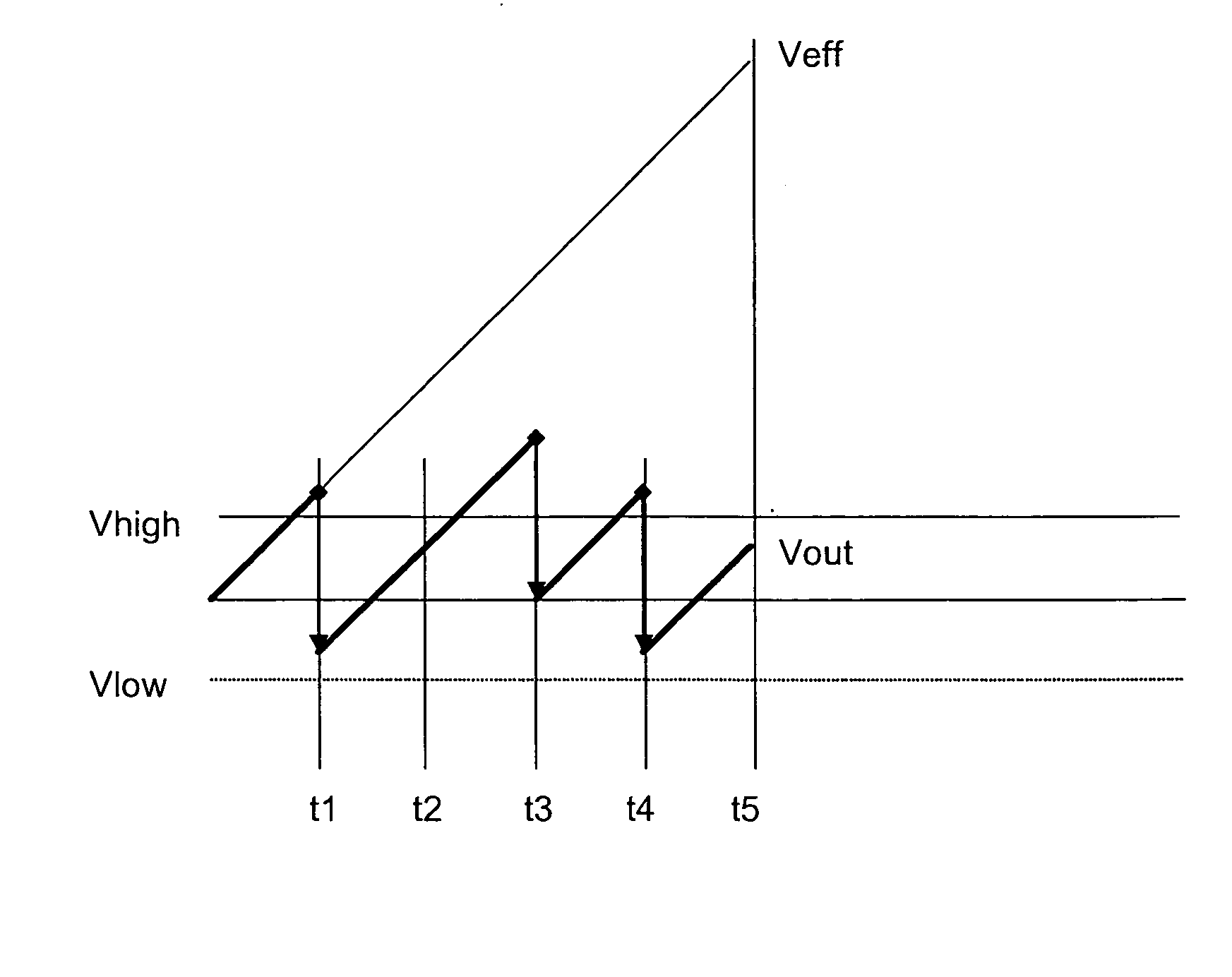
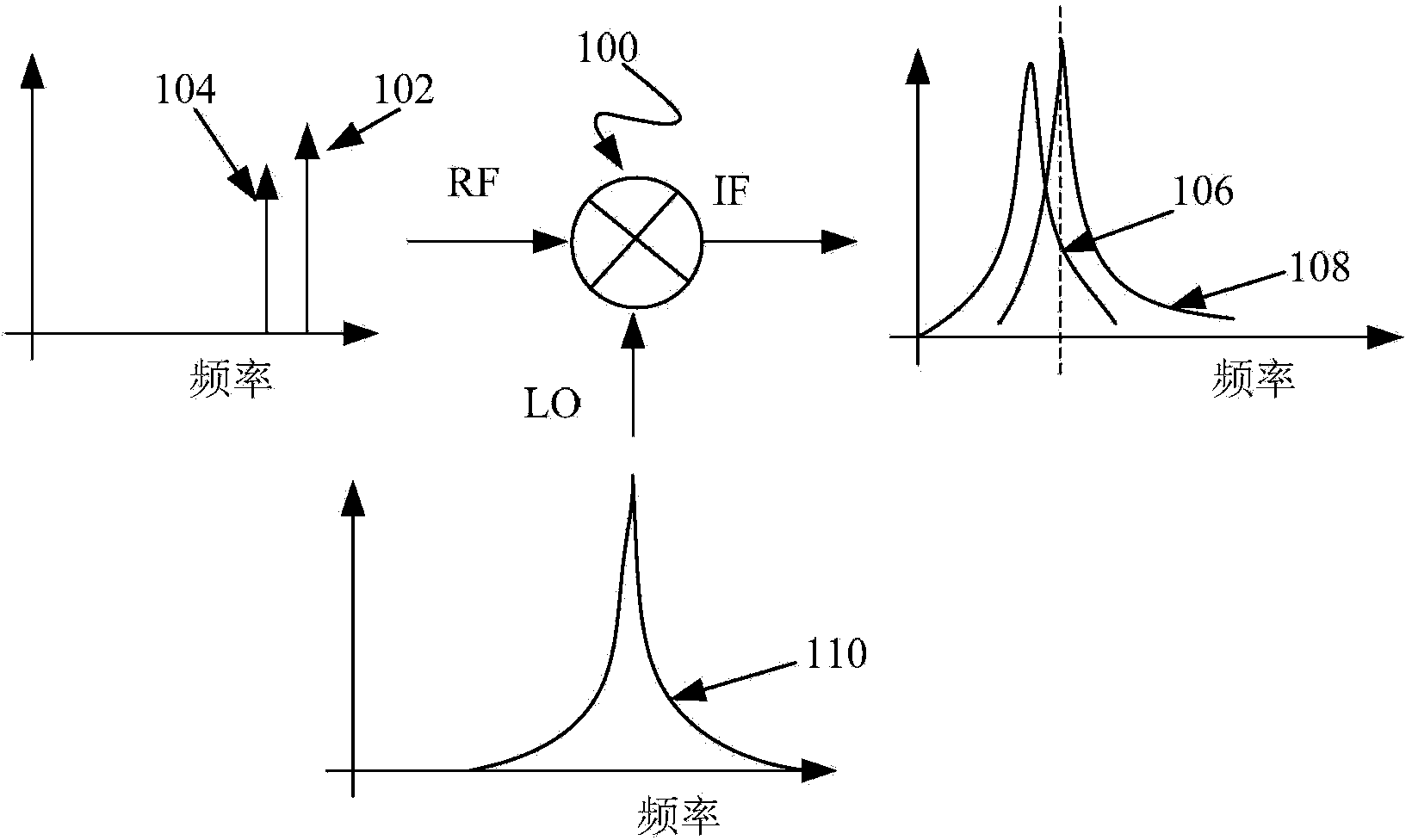
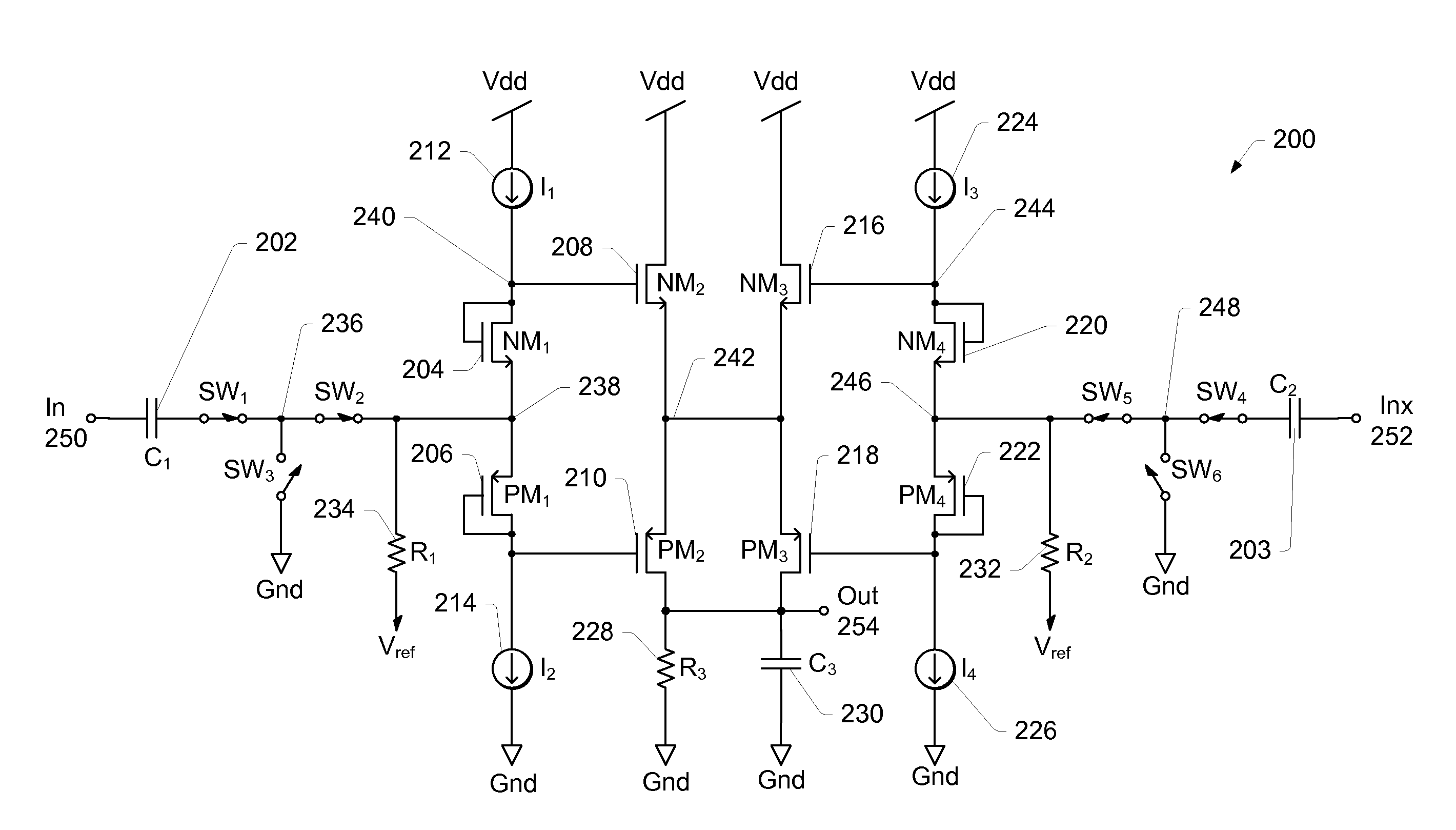
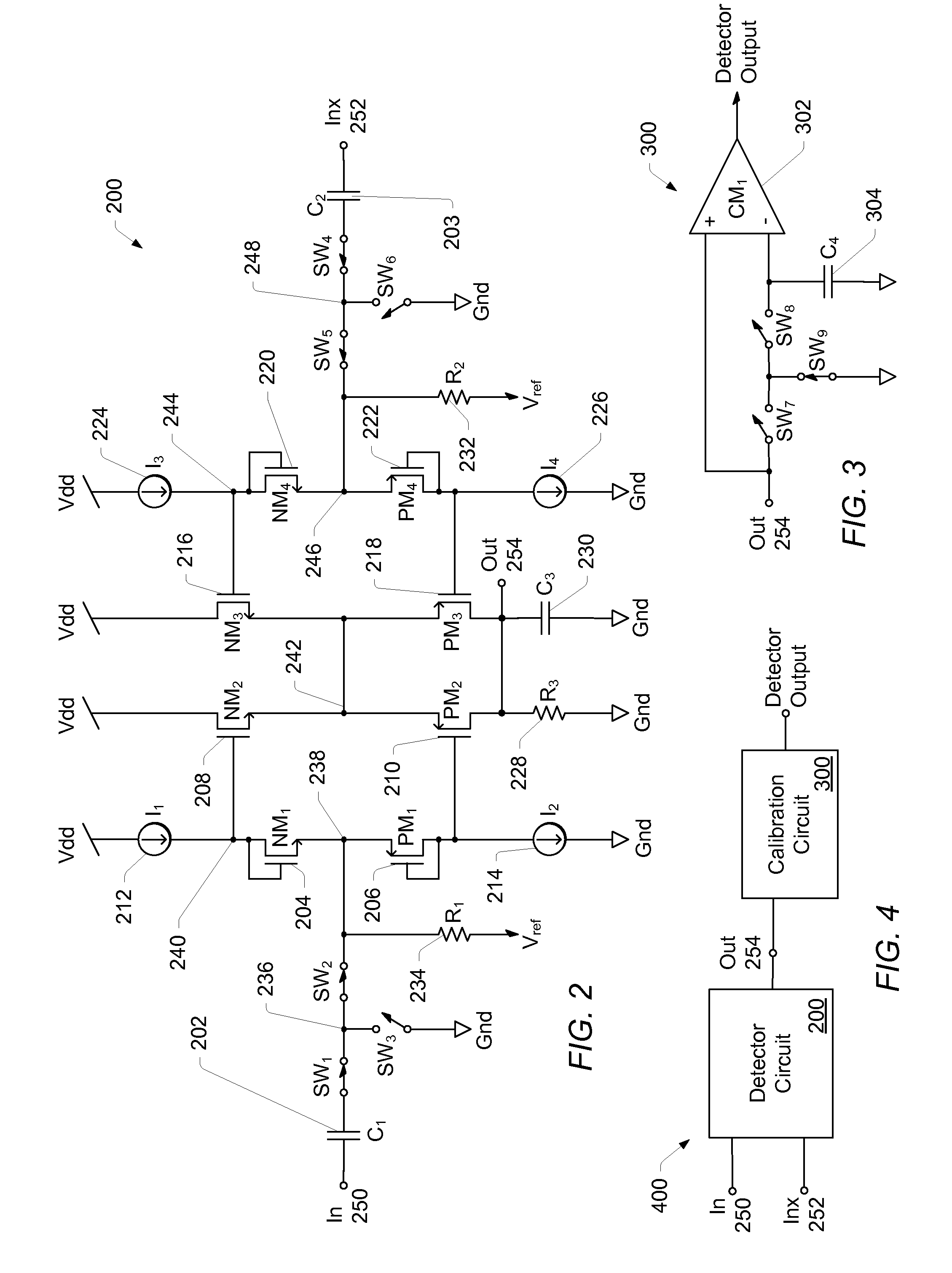
Dynamic range of a differential pixel is enhanced by injecting, synchronously or asynchronously, a compensating offset (ΔCOMP) into a differential signal capacitor whenever magnitude of the differential signal across the capacitor exceeds a predetermined value. Positive and negative magnitudes of ΔCOMP need not be equal. The number (N) of ΔCOMP offsets made is counted. Effective differential signal capacitor voltage V(t)=Vo±N·ΔCOMP, where Vo is capacitor voltage. In other embodiments magnitude of ΔCOMP in a sequence of compensations can differ, and the sum total of compensations in recorded. Differential pixel signal / noise ratio is increased by dynamically maximizing operational amplifier gain AG for each differential pixel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
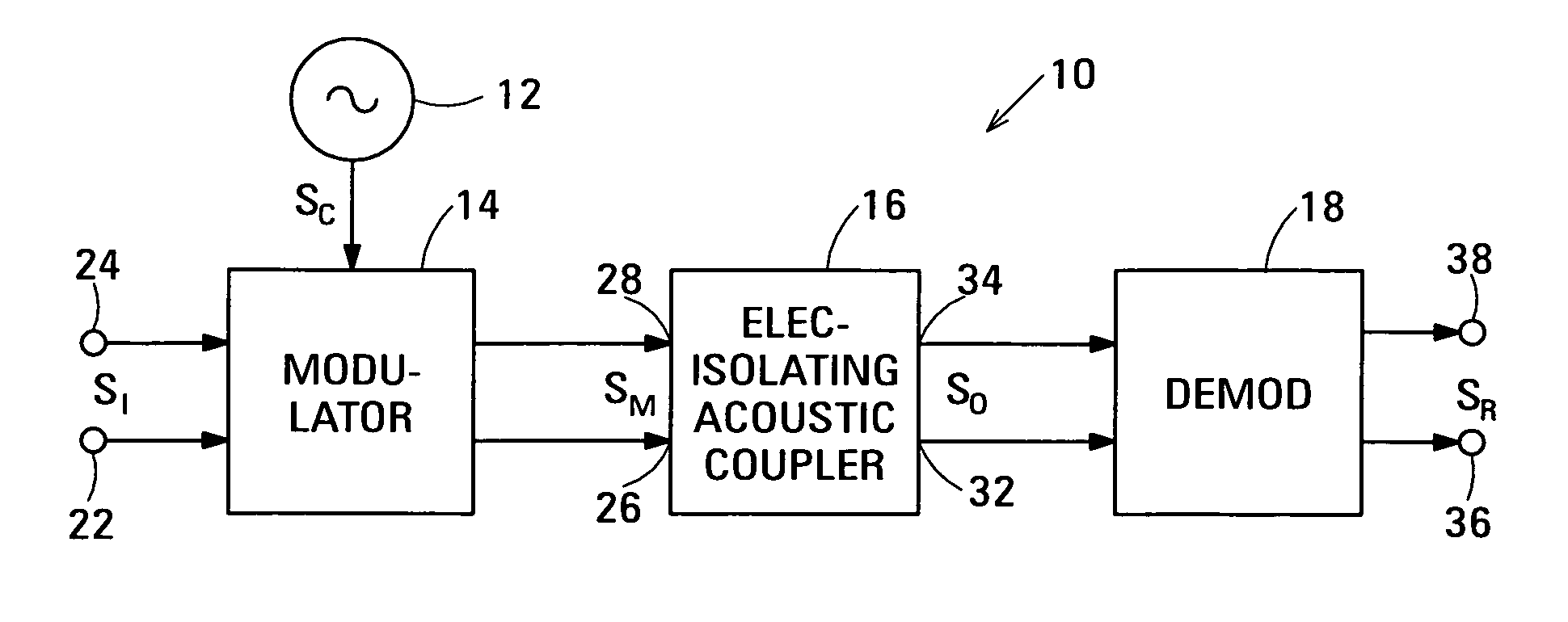
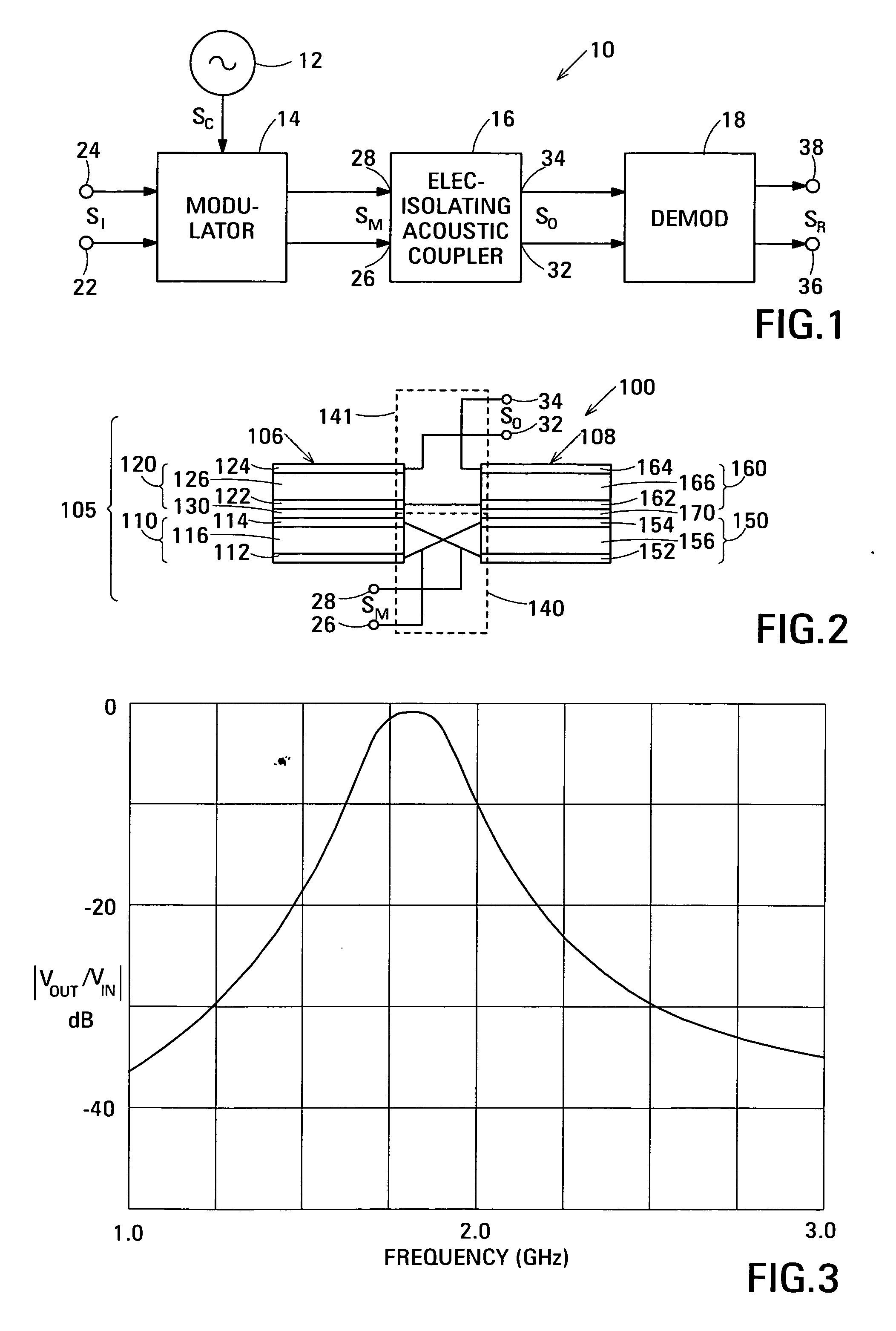
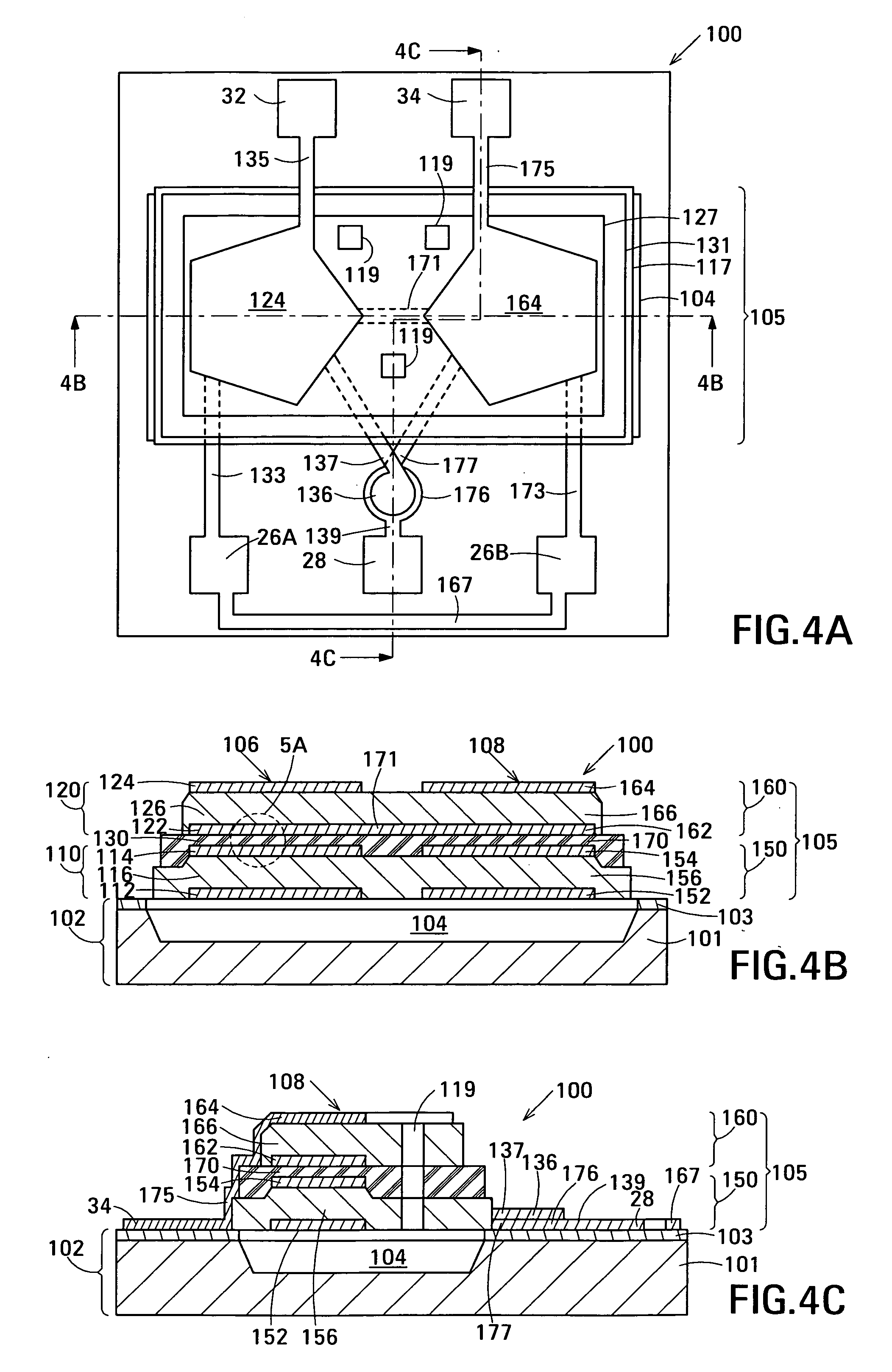
Acoustic galvanic isolator incorporating film acoustically-coupled transformer
ActiveUS20070085631A1Inexpensive to fabricateGood Common Mode RejectionImpedence networksCarrier signalEngineering
Embodiments of the acoustic galvanic isolator comprise a carrier signal source, a modulator connected to receive an information signal and the carrier signal, a demodulator, and, connected between the modulator and the demodulator, an electrically-isolating acoustic coupler comprising an electrically-isolating film acoustically-coupled transformer (FACT).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
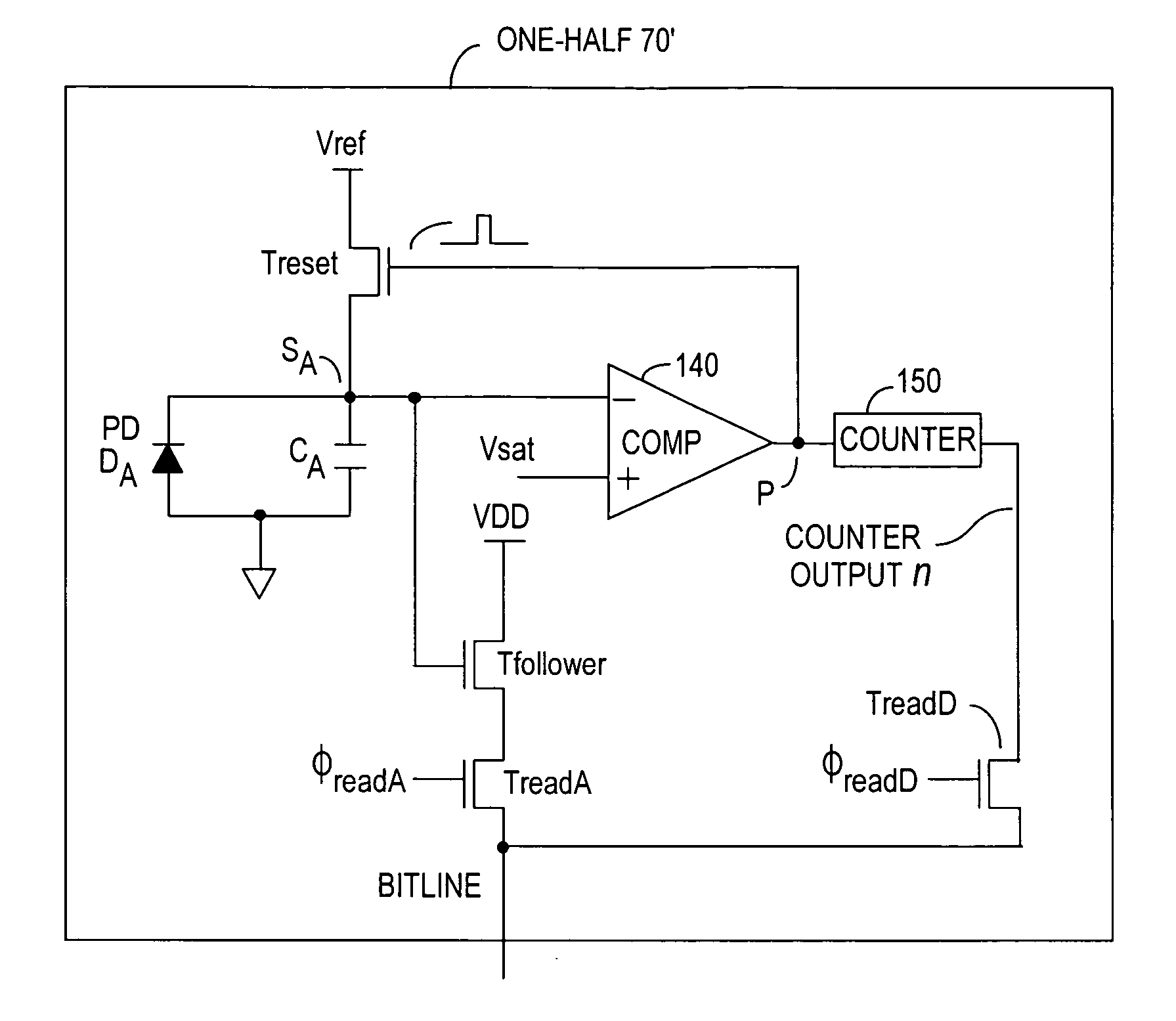
Method and system to differentially enhance sensor dynamic range using enhanced common mode reset
ActiveUS20060027730A1Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibition effectTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierPhotovoltaic detectors
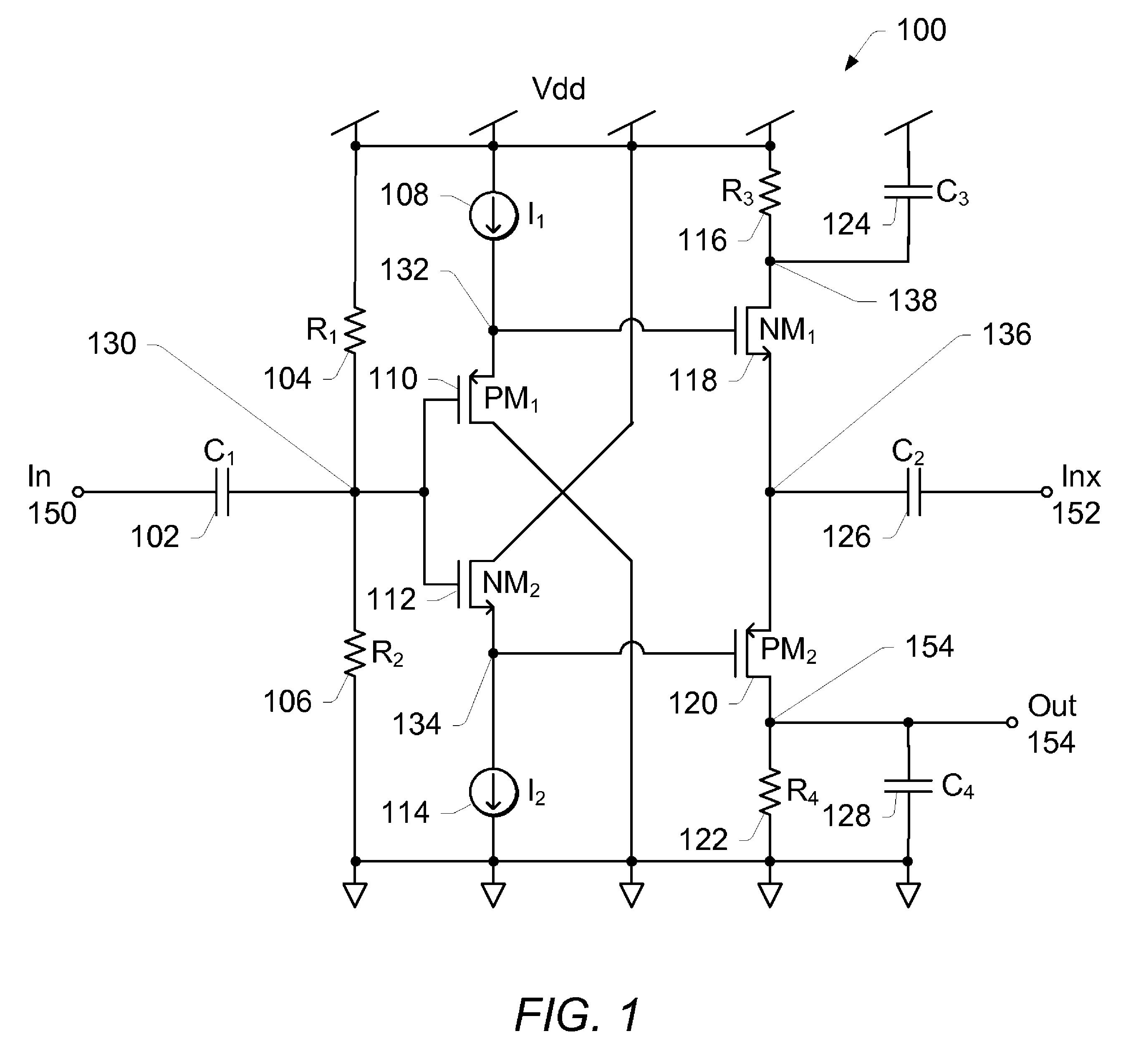
Effective differential dynamic range and common mode rejection in a differential pixel detector are enhanced by capturing and isolating differential detector charge output before using common mode reset to avoid detector saturation due to common mode components of optical energy to be detected. Differential charge is stored into an integration capacitor associated with an operational amplifier coupled to receive as input the differential detector outputs. Common mode reset is achieved by resetting storage capacitors coupled to the outputs of the differential detector at least once within an integration time T before storage potential exceeds a saturation voltage Vsat for the photodetector.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
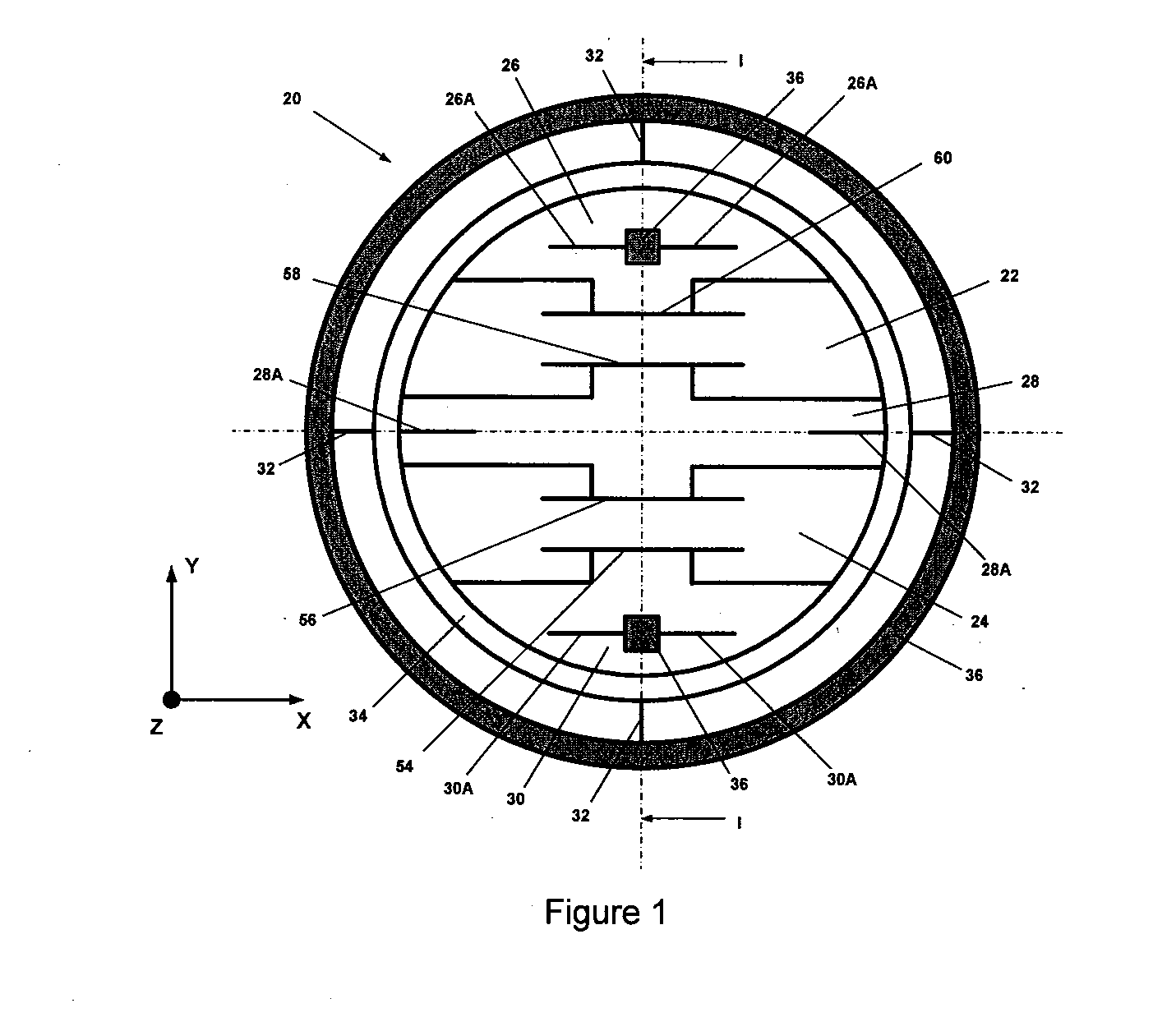
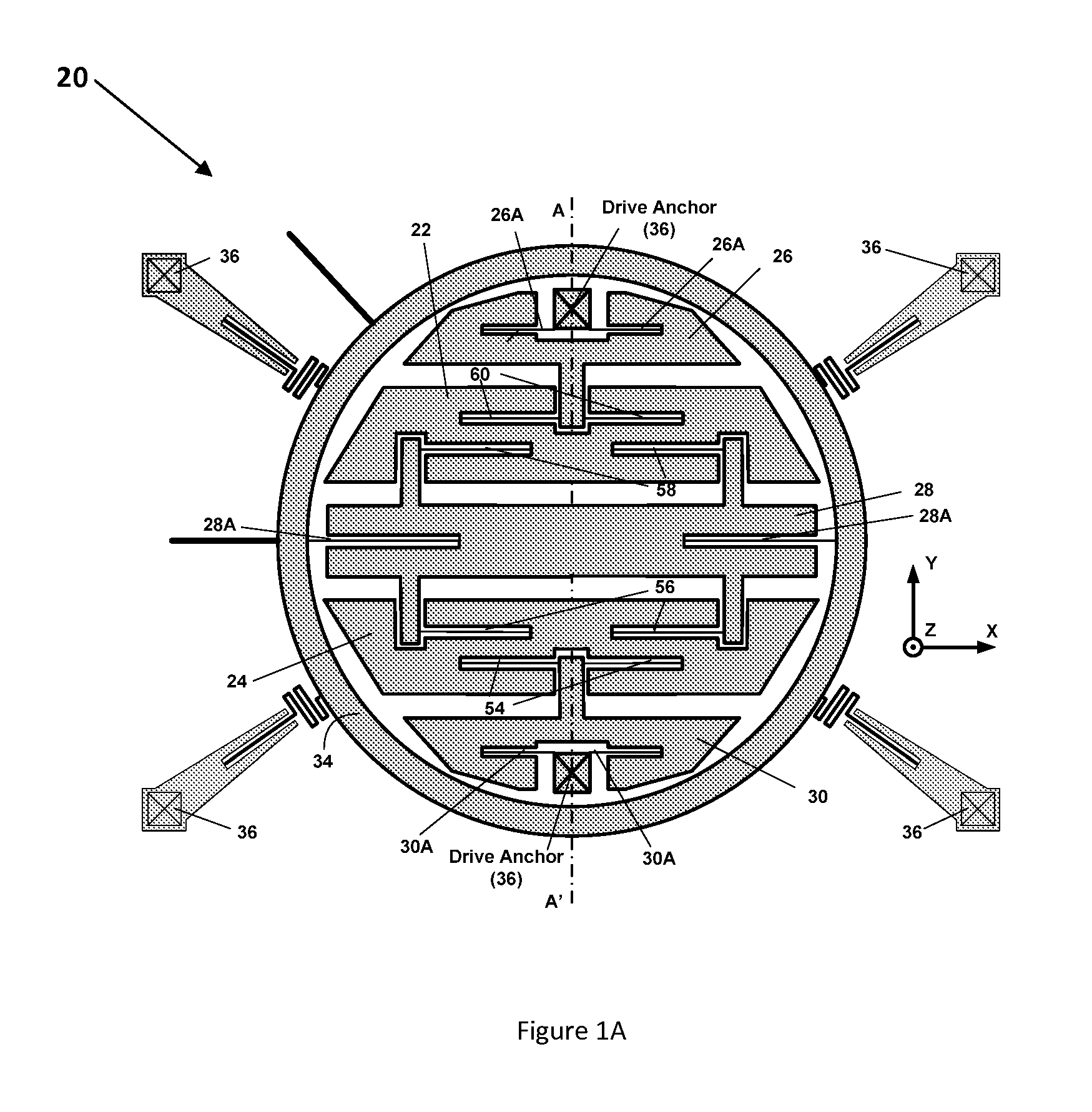
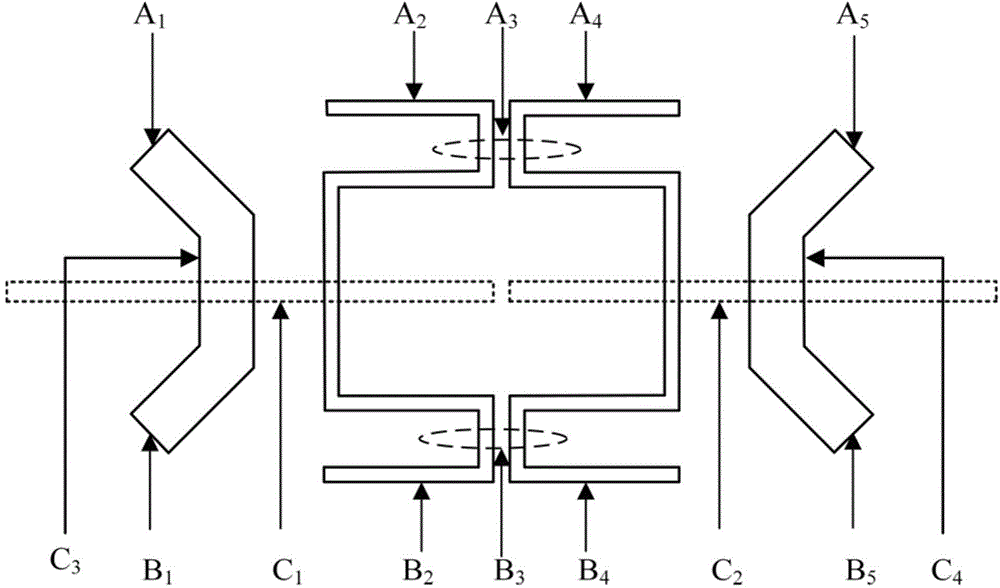
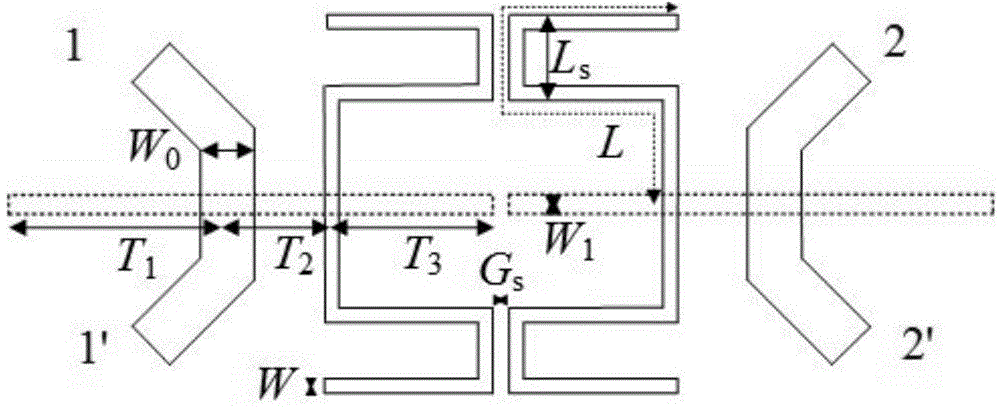
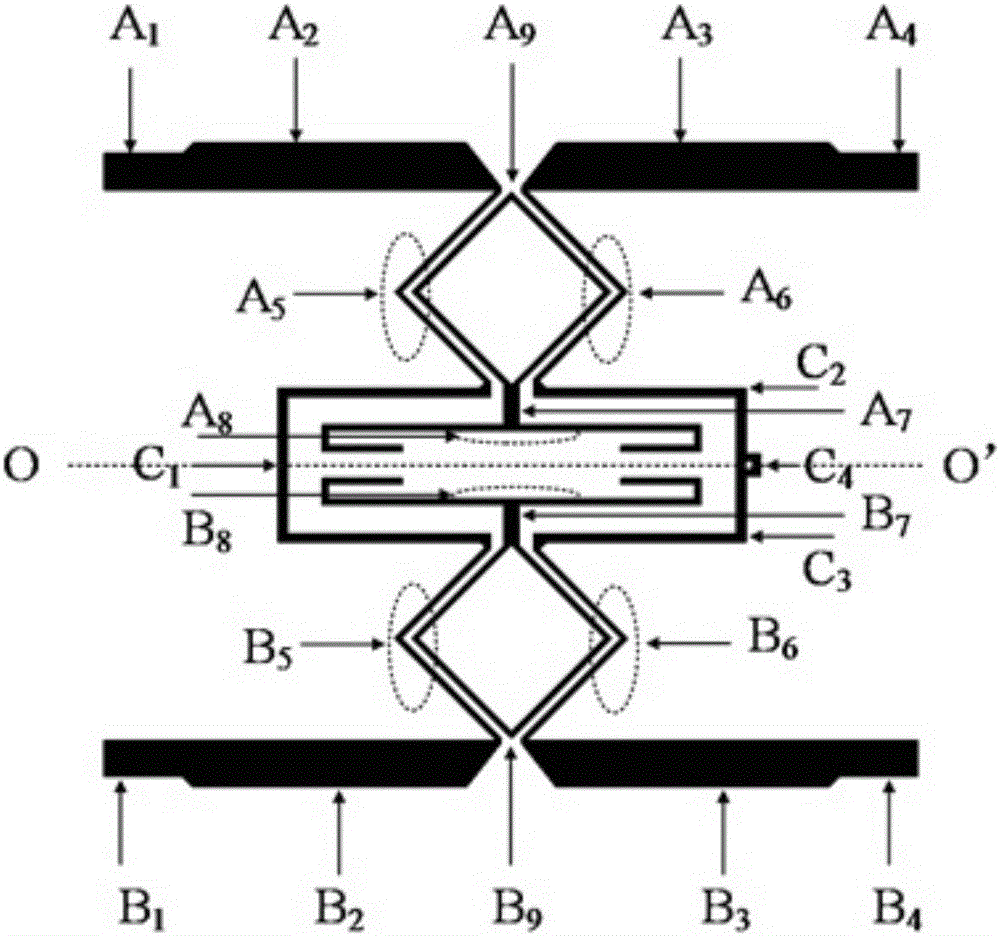
X-y axis dual-mass tuning fork gyroscope with vertically integrated electronics and wafer-scale hermetic packaging
ActiveUS20080115579A1High measurement accuracyGood Common Mode RejectionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTuning forkGyroscope
An angular velocity sensor has two masses which are laterally disposed in an X-Y plane and indirectly connected to a frame. The two masses are linked together by a linkage such that they necessarily move in opposite directions along Z. Angular velocity of the sensor about the Y axis can be sensed by driving the two masses into Z-directed antiphase oscillation and measuring the angular oscillation amplitude thereby imparted to the frame. In a preferred embodiment, the angular velocity sensor is fabricated from a bulk MEMS gyroscope wafer, a cap wafer and a reference wafer. In a further preferred embodiment, this assembly of wafers provides a hermetic barrier between the masses and an ambient environment.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
ActiveUS20060157643A1Increase elasticityFunction providedTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSAudio power amplifier
Dynamic range of a differential pixel is enhanced by injecting, synchronously or asynchronously, a fixed compensating offset (ΔV) into a differential signal capacitor whenever magnitude of the differential signal across the capacitor exceeds a predetermined value. The number (N) of ΔV offsets made is counted. Effective differential signal capacitor voltage V(t)=Vo+N·ΔV, where Vo is capacitor voltage. Differential pixel signal / noise ratio is increased by dynamically maximizing operational amplifier gain AG for each differential pixel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
InactiveUS20070158533A1Increase elasticityFunction providedTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSCapacitance
Dynamic range of a differential pixel is enhanced by injecting, synchronously or asynchronously, a compensating offset (ΔCOMP) into a differential signal capacitor whenever magnitude of the differential signal across the capacitor exceeds a predetermined value. Positive and negative magnitudes of ΔCOMP need not be equal. The number (N) of ΔCOMP offsets made is counted. Effective differential signal capacitor voltage V(t)=Vo±N·ΔCOMP, where Vo is capacitor voltage. In other embodiments magnitude of ΔCOMP in a sequence of compensations can differ, and the sum total of compensations in recorded. Differential pixel signal / noise ratio is increased by dynamically maximizing operational amplifier gain AG for each differential pixel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
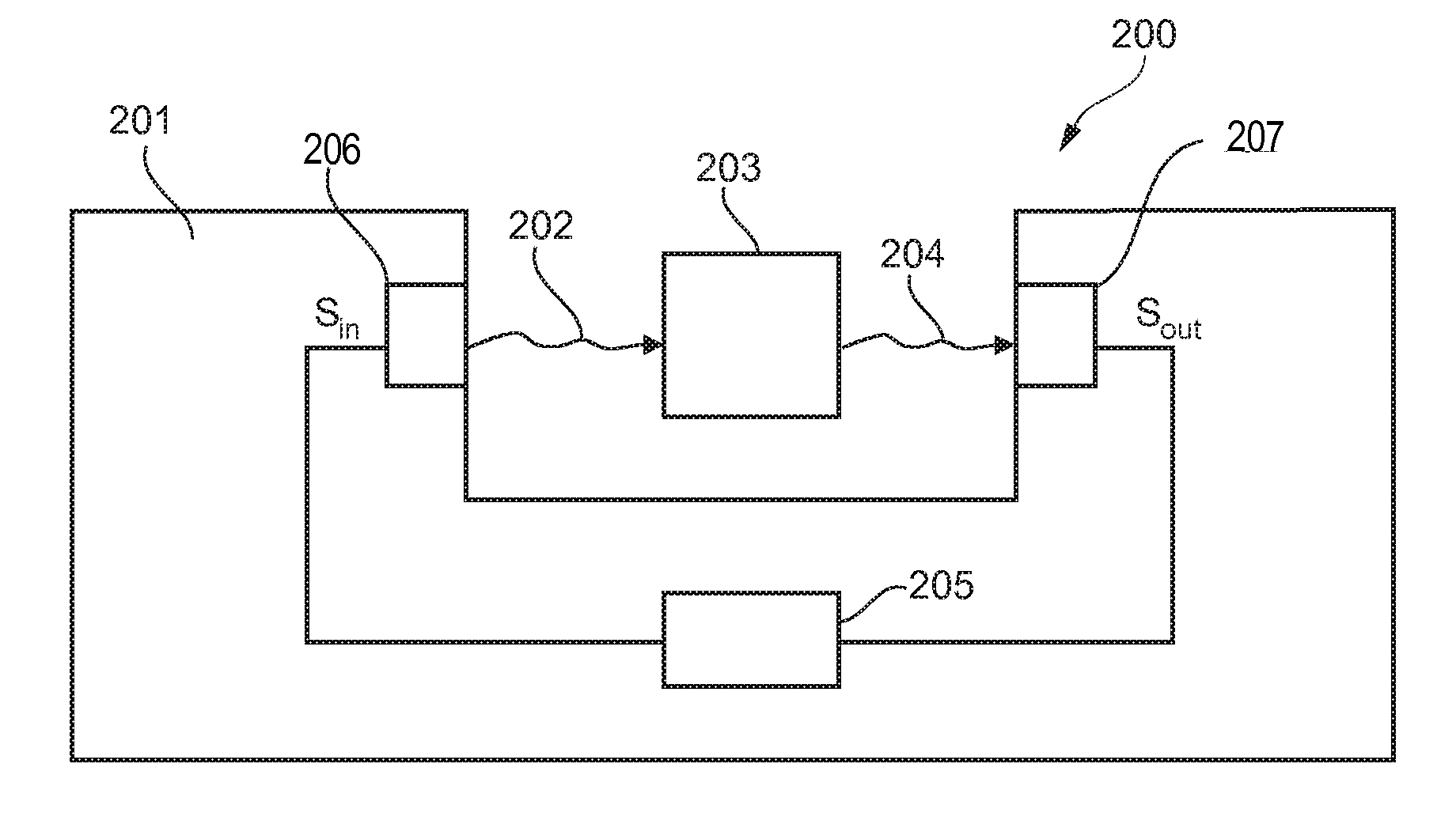
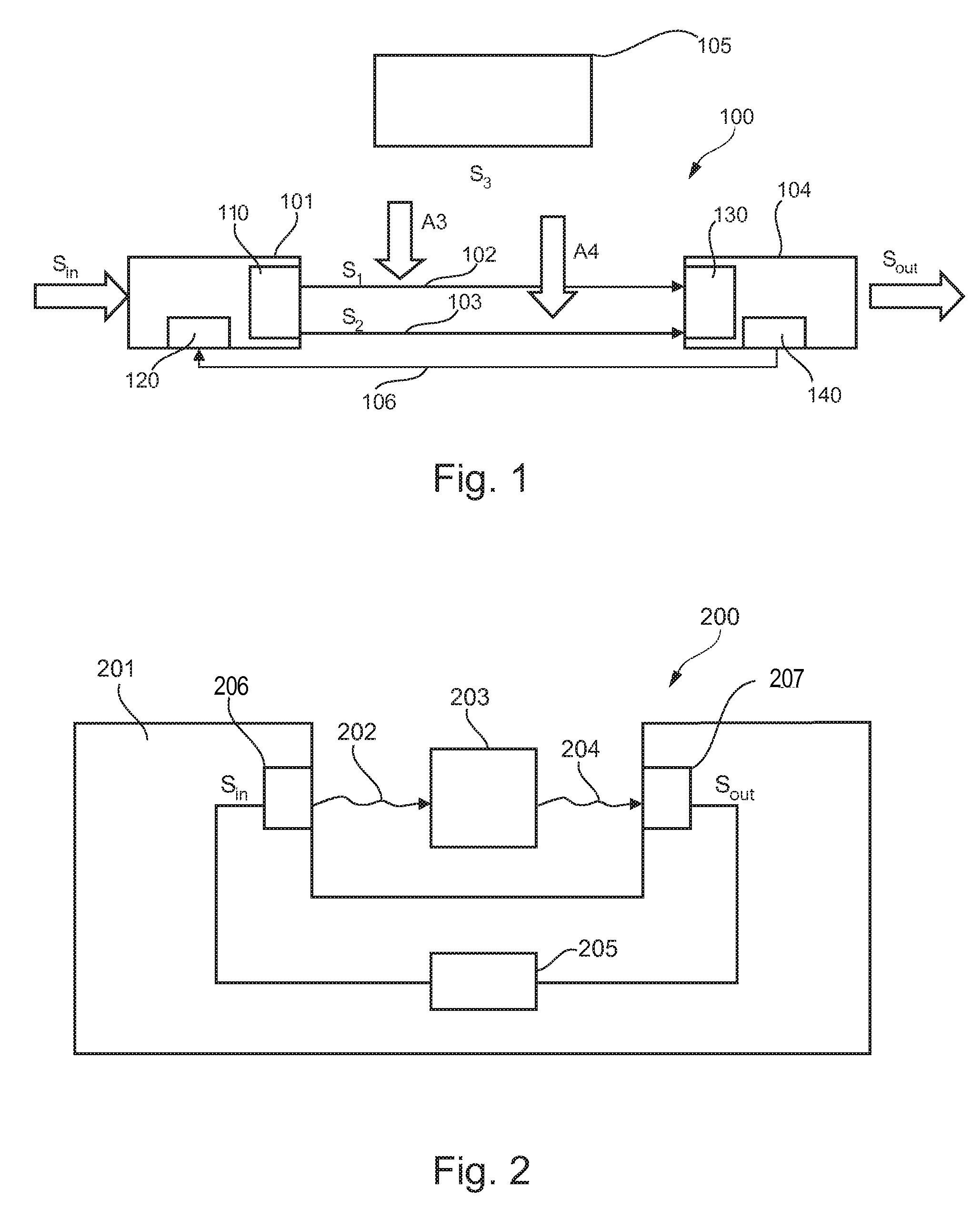
Signal transmission system
ActiveUS20100246707A1Inhibition is effectiveReduce output signalElectric signal transmission systemsElectric controllersEngineeringTransmitter
A method of operating a system (100, 200) for transmitting signals (si, S2, 202) from a transmitter (101, 206) to a receiver (104, 207), the method comprising the step of muting the transmitter (101, 206), adjusting a receiver transfer function of the receiver (104, 207) so that an output signal (sout) of the receiver (104, 207) is minimized, and setting a transmitter transfer function of the transmitter (101, 206) to be inverse to the adjusted receiver transfer function.
Owner:III HLDG 6
Signal transmission system
ActiveUS8509340B2Reduce output signalInhibition is effectiveElectric signal transmission systemsElectric controllersEngineeringTransmitter
Owner:III HLDG 6
Lc oscillator with tail current source and transformer-based tank circuit
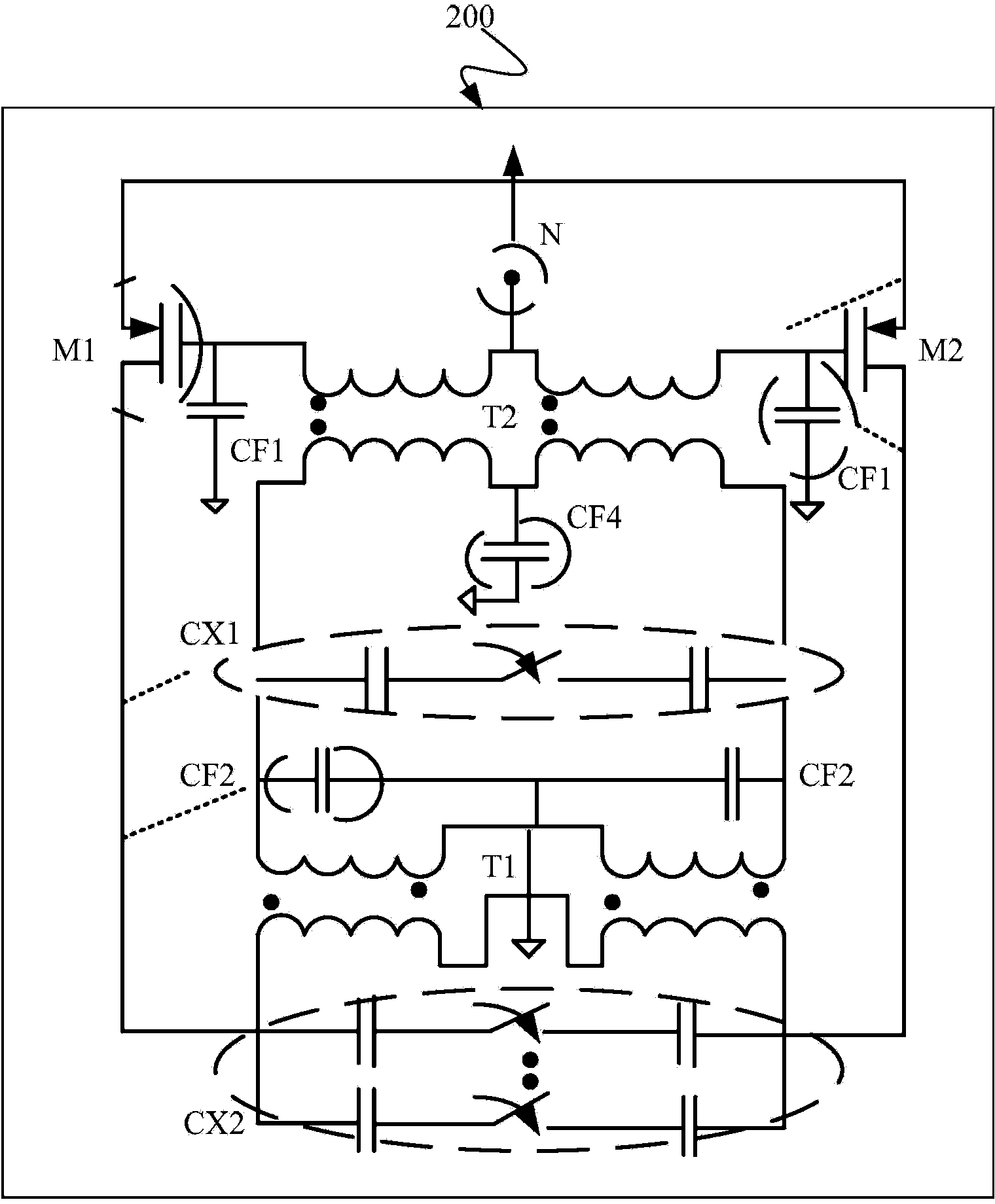
ActiveCN104272583ALower quality factorImprove reliabilityPulse automatic controlActive element networkTransformerInductance
An oscillator, comprising: a pair of transistors to which source terminals are interconnected and to which drain and gate terminals are coupled by a positive feedback loop comprising an oscillator tank, wherein the source terminals of the transistors are connected to a current source configured to control physical parameters of the oscillator.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Same-side differential feeding substrate integrated waveguide slot antenna
ActiveCN110061357AFacilitates direct integrationEnsure balanceRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationWaveguideSlot antenna
The invention discloses a same-side differential feeding substrate integrated waveguide slot antenna. The same-side differential feeding substrate integrated waveguide slot antenna comprises a substrate integrated waveguide cavity and a differential feeding transmission line, wherein the substrate integrated waveguide cavity comprises a metal through hole array, the differential feeding transmission line is used for connecting a differential circuit, two paths of transmission lines of the differential feeding transmission line are arranged at the same side of the substrate integrated waveguidecavity and are connected with the substrate integrated waveguide cavity by a transition structure, and a plurality of rectangular radiation gaps are formed in a top layer or a bottom layer of the substrate integrated waveguide cavity. On the basis that common-mode suppression of a traditional opposite-side differential feeding technology is inherited, the distance of an antenna differential pairis reduced to a great extent, the same-side differential feeding substrate integrated waveguide slot antenna is compact in integral structure and is suitable for direct integration with a differentialcircuit; and moreover, a higher-order mode is more easily simulated by the substrate integrated waveguide back cavity antenna, high-gain radiation characteristic is achieved, and the same-side differential feeding substrate integrated waveguide slot antenna has high application value in actual engineering application.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
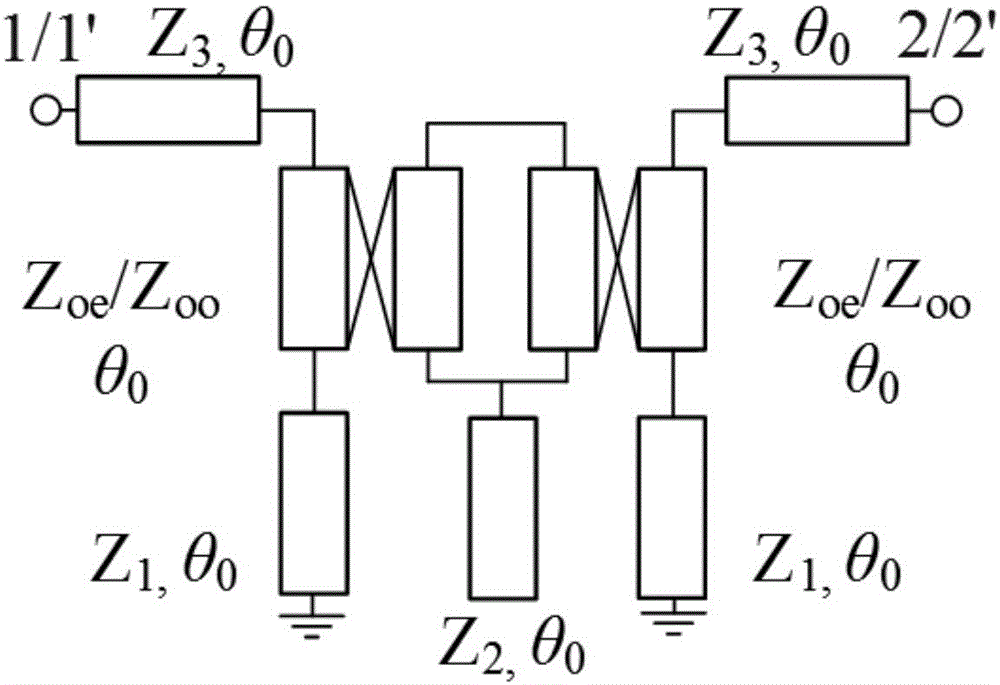
Balance-to-unbalance signal filtering power divider
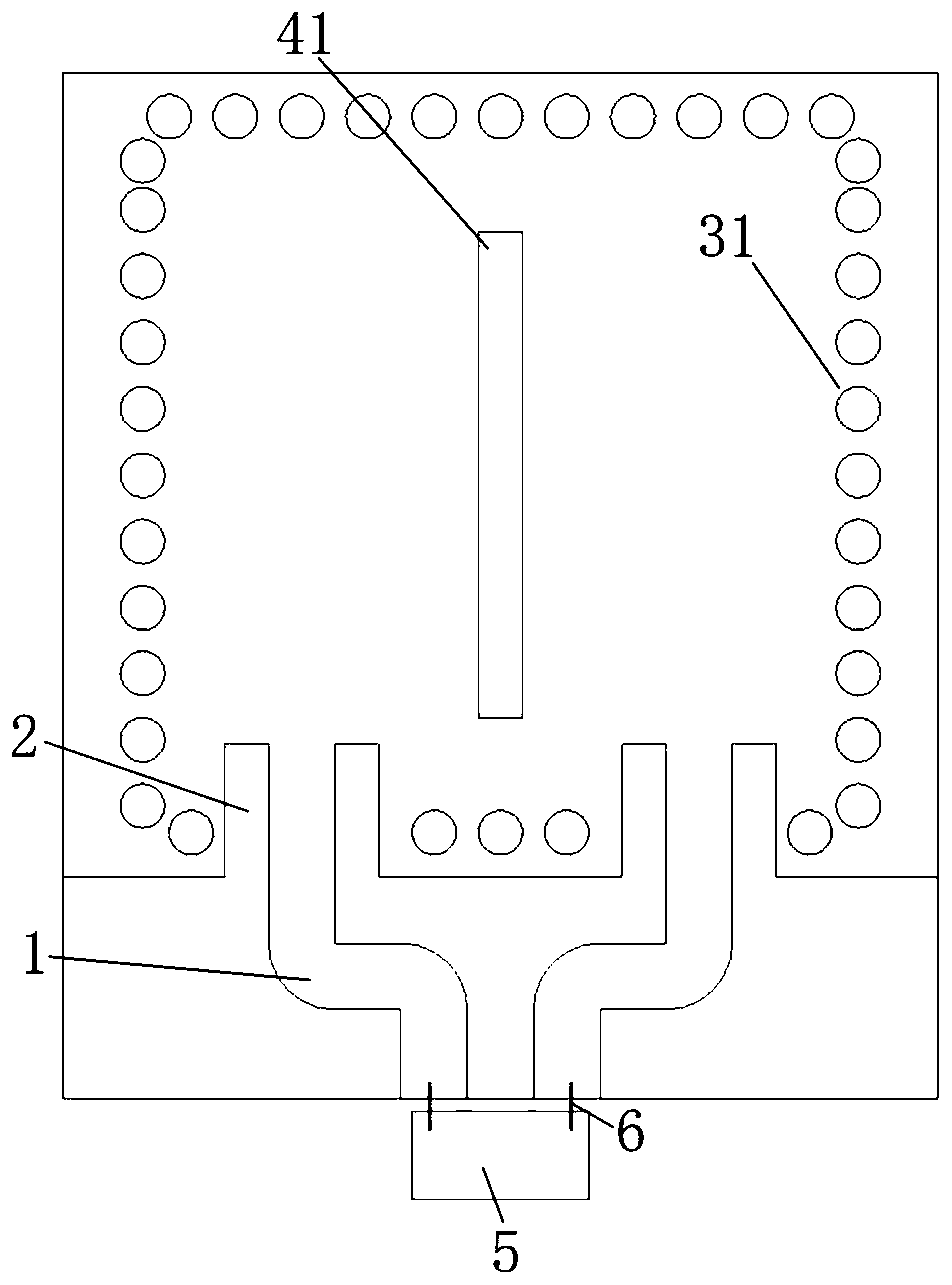
ActiveCN107464978AWith filter functionGood Common Mode RejectionCoupling devicesDielectric substrateResonator
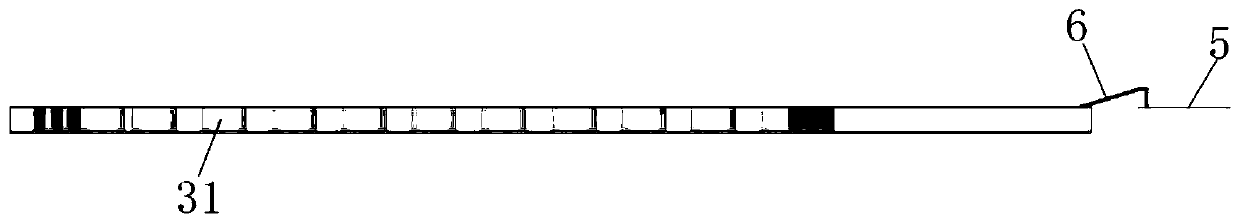
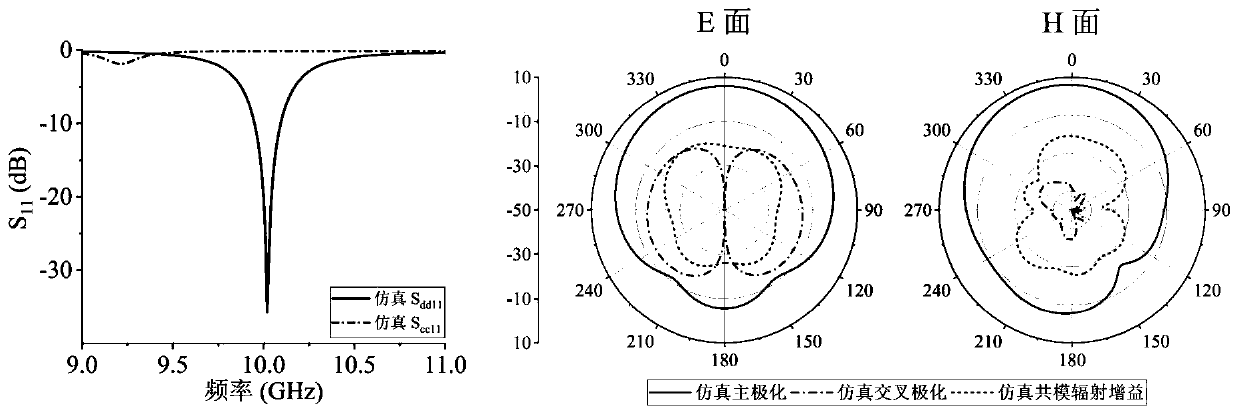
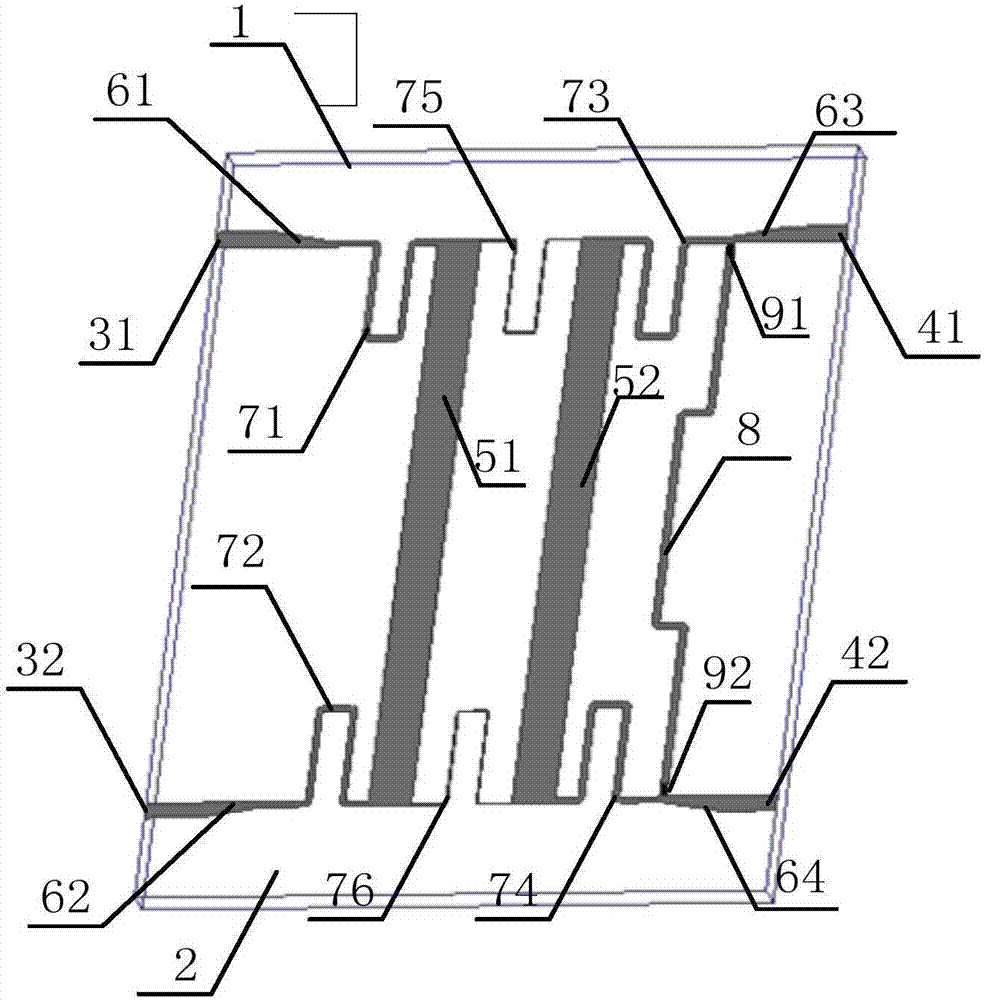
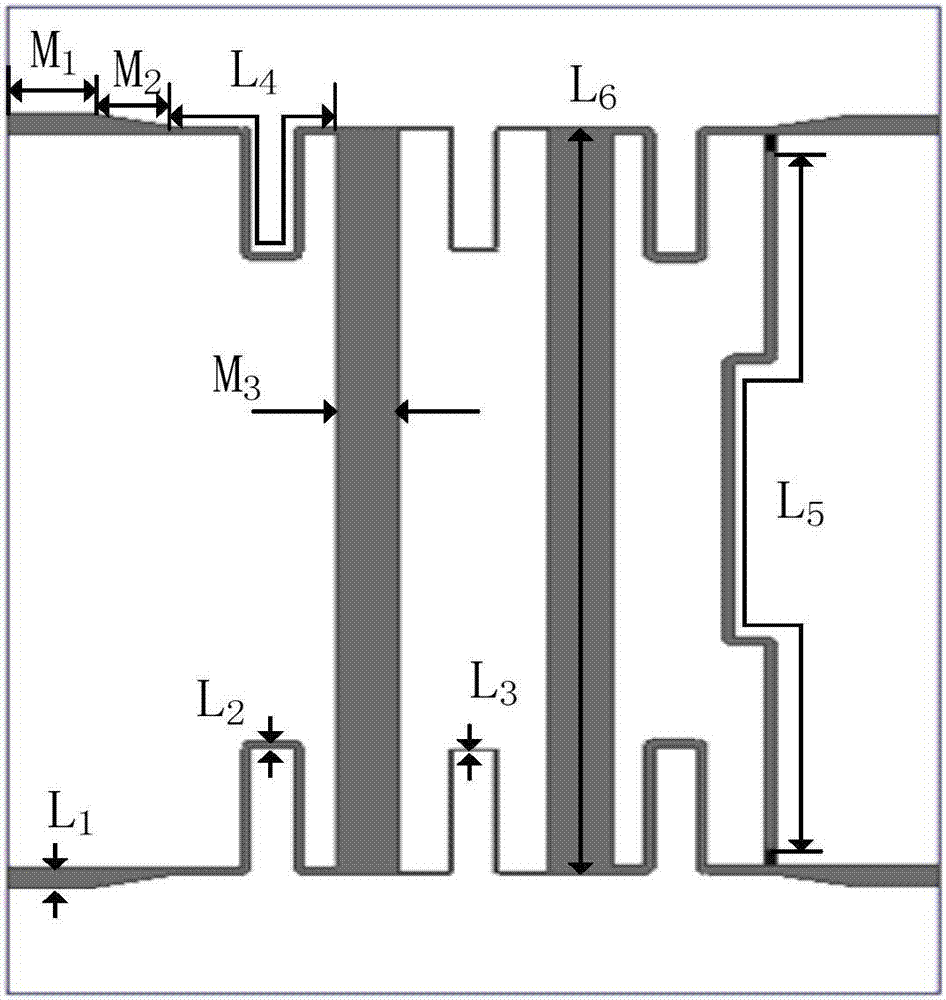
The invention discloses a balance-to-unbalance signal filtering power divider which comprises a metal grounding plate (2), first and second input port feeder lines (31 and 32) and first and second output port feeder lines (41 and 42), wherein the metal grounding plate (2) is fully covered on the lower surface of a rectangular dielectric substrate (1); the first and second input port feeder lines (31 and 32) and the first and second output port feeder lines (41 and 42) are laminated on the upper surface of the dielectric substrate (1); the upper surface of the dielectric substrate (1) comprises a first resonator and a second resonator (51, 52), first to fourth micro-strip impedance tapered lines (61, 62, 63 and 64), first to sixth coupling lines (71-76), a micro-strip line (8) and a first isolation resistor and a second isolation resistor (91 and 92). The balance-to-unbalance signal filtering power divider disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, small in size and excellent in common-mode rejection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electric connector
ActiveCN106299887AGood crosstalk shielding performanceGood Common Mode RejectionCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsElectricityElectromagnetic shielding
The invention relates to an electric connector, which comprises an insulating part, signal terminal groups, grounding terminals, a grounding lug and a shielding sheet, wherein the signal terminal groups, the grounding terminals, the grounding lug and the shielding sheet all are arranged in the insulating part; each grounding terminal is located between two adjacent signal terminal groups; the grounding lug is in contact with connection parts of the grounding terminals; and first connection holes are formed in the shielding sheet for penetrating of contact pins of the grounding lug, so that the grounding lug is connected with the shielding sheet. A first panel is inserted into a slot in the insulating part, the other side, opposite to the slot, of the insulating part is connected with a second panel, and the signal terminal groups are electrically connected with the first panel and the second panel respectively. Each grounding terminal is located between two signal terminal groups, crosstalk can be well isolated by a plurality of grounding terminals, and the grounding terminals, the grounding lug and the shielding sheet form electromagnetic shielding on the signal terminal groups, so that the electric connector has relatively good crosstalk shielding performance to achieve good common-mode rejection performance, and high-speed data communication of a high-speed differential signal from the first panel to the second panel is ensured.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHENTAI WEIXIANG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Passive circuit for improved differential amplifier common mode rejection
InactiveUS20090133083A1Good Common Mode RejectionLow costAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTwo-way working systemsAudio power amplifierInductor
A novel passive circuit for providing improved common mode rejection of a differential amplifier novel. The passive circuit functions to compensate for amplitude mismatches between the two outputs of a differential amplifier. To compensate for the amplitude mismatch between the output traces of the amplifier, a resistor is inserted in series with at either one or both of the differential outputs. The values of the resistors are set such that the mismatch is substantially eliminated. Inductors are connected in parallel with the resistors to create a zero ohm path for power. At high frequencies the inductor impedance is sufficiently high that the series resistor compensates for the imbalance caused by spurious products. The imbalance in the amplifier outputs is corrected with the resulting increase in the rejection of spurious frequency products by exploiting the differential common mode rejection (CMR) effect of the differential amplifier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
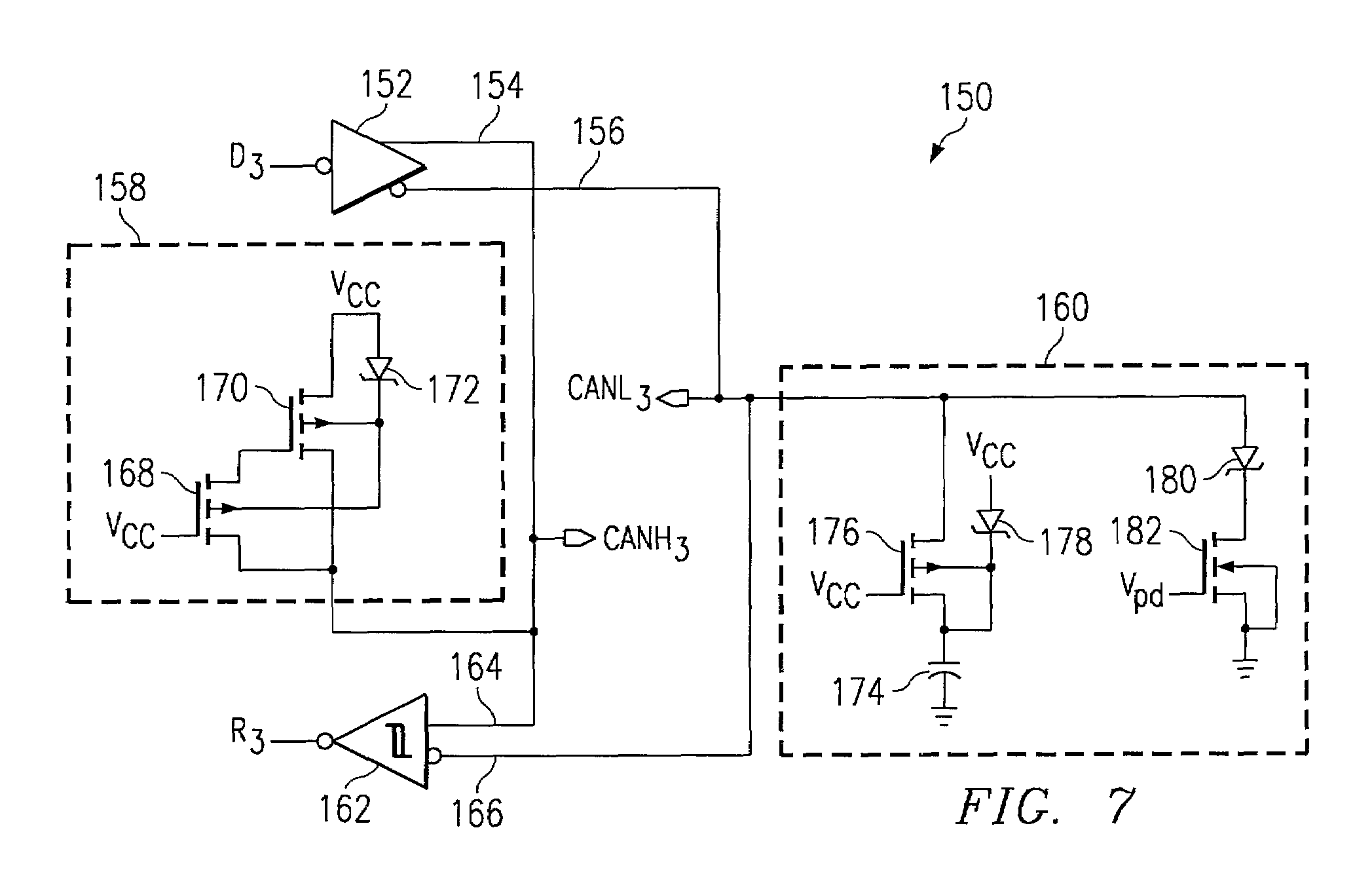
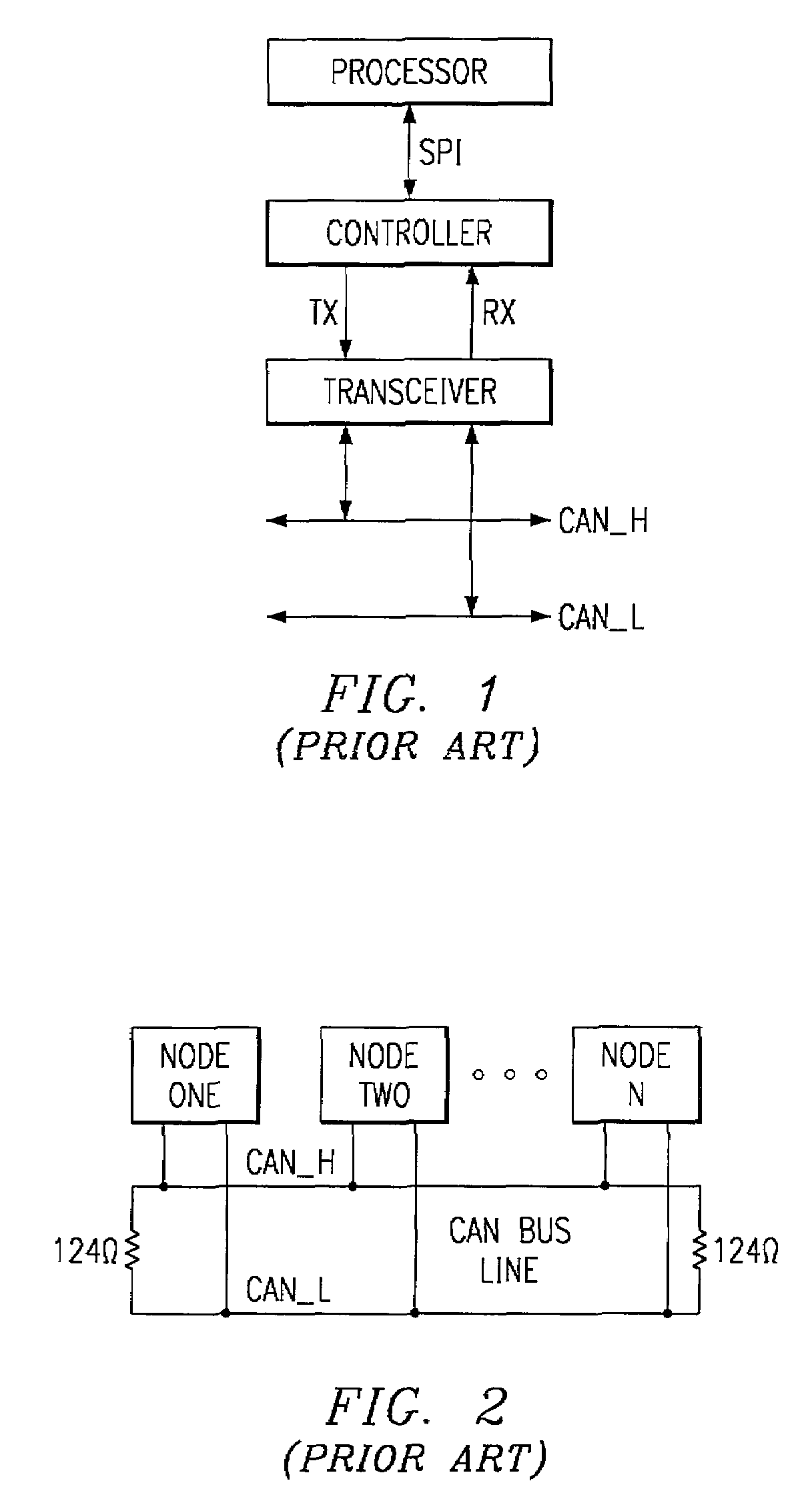
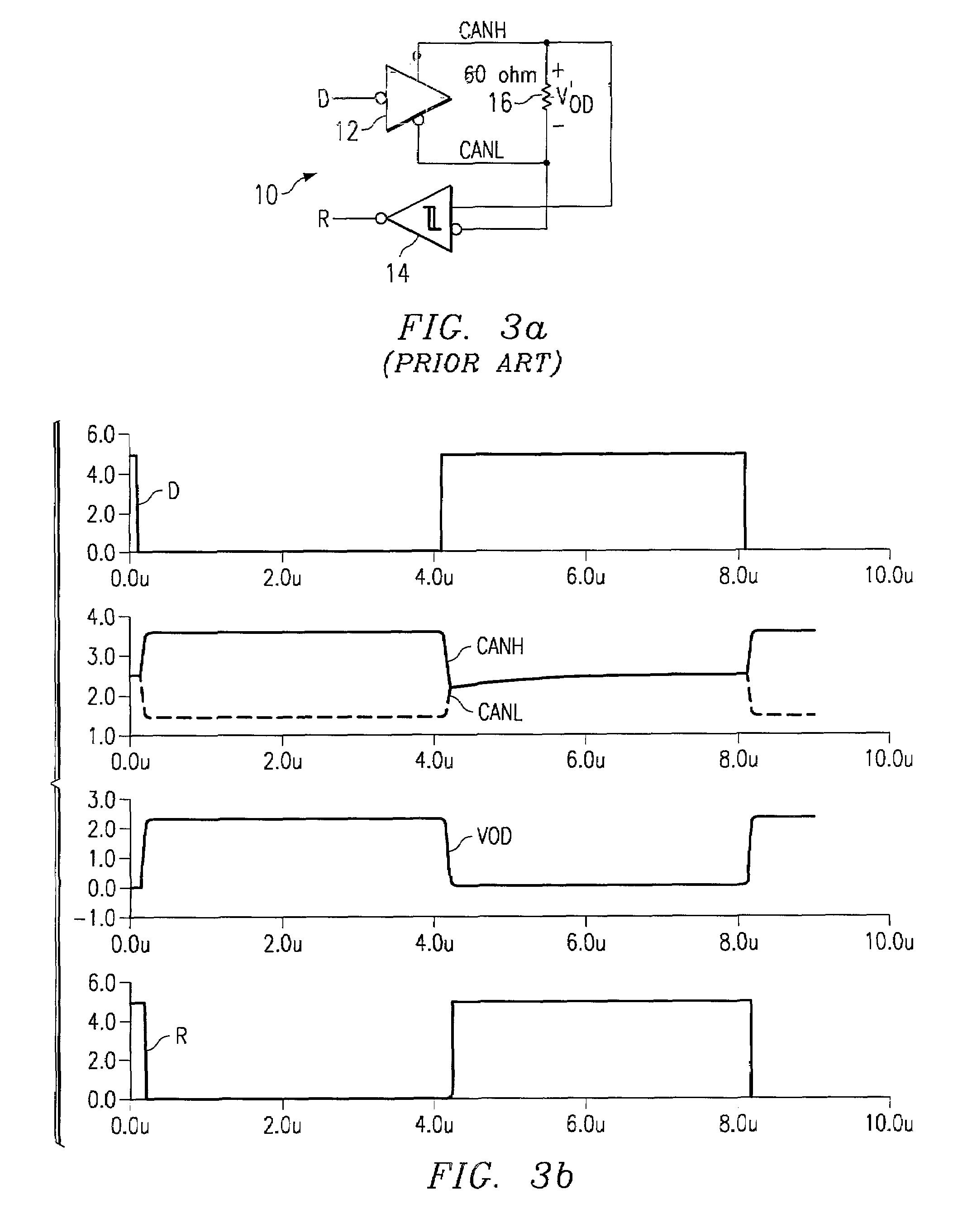
Controller area network transceiver having capacitive balancing circuit for improved receiver common-mode rejection
ActiveUS7113759B2Reduce capacityGood rejectionMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasCapacitanceTransceiver
A controller area network transceiver and a transmission method for a controller area network provides improved symmetry between its differential output signal CANH and CANL such that capacitive imbalance is minimized. The transceiver disclosed herein includes a driver including a non-inverted output that couples to the first output terminal CANH and a inverted output that couples to the second output terminal CANL. A receiver comparator includes a non-inverted input coupled to the first output terminal CANH and a inverted input coupled to the second output terminal CANL. A first and second impedance matching circuit portions capacitively balance the first and second output terminals such that efficient common-mode rejection is enabled by setting the RC time constants formed by each impedance matching circuit and external resistances to be substantially equivalent. This transceiver provides a high performance, simple, and cost effective design which eliminates capacitive imbalance while decreasing required die area.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
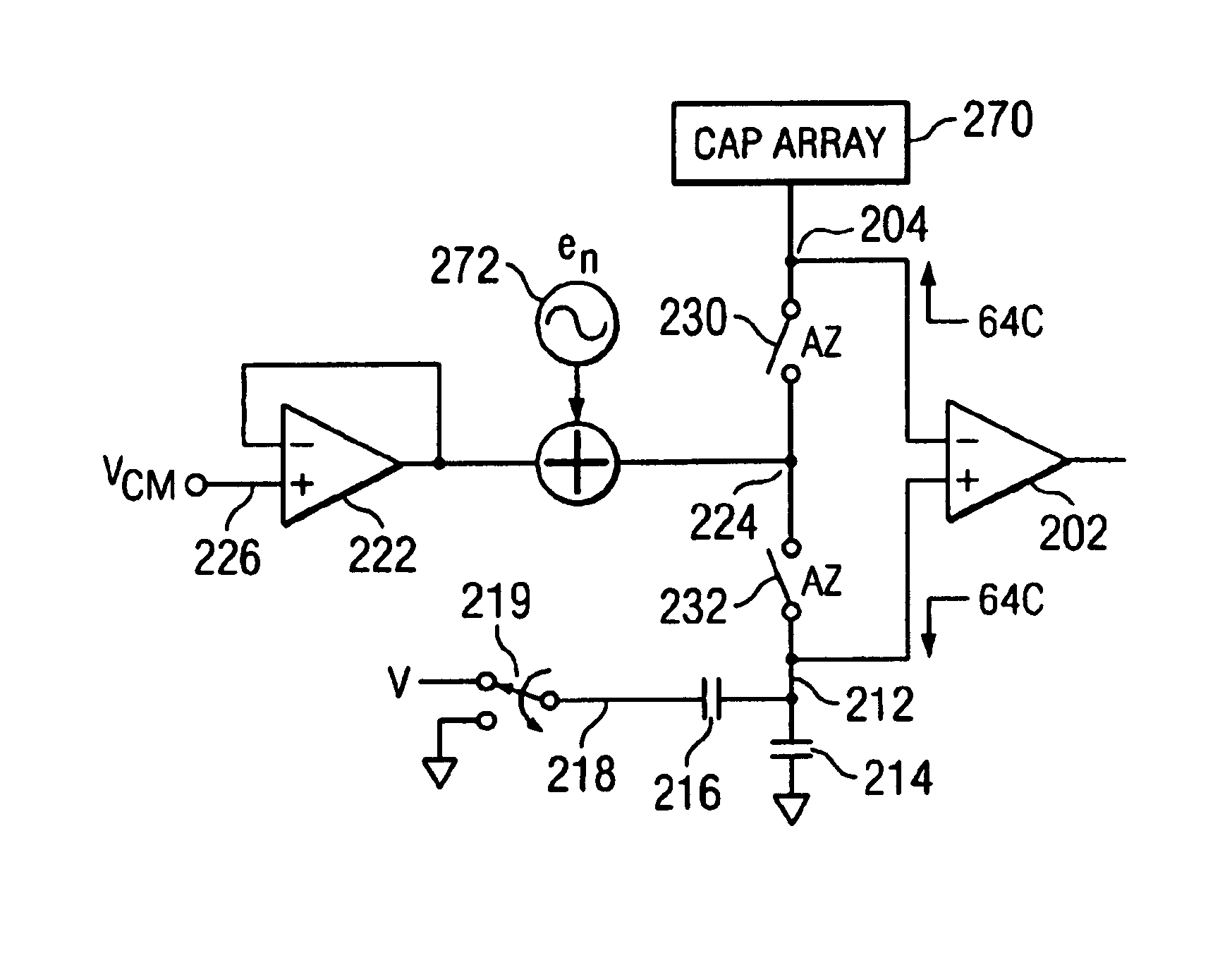
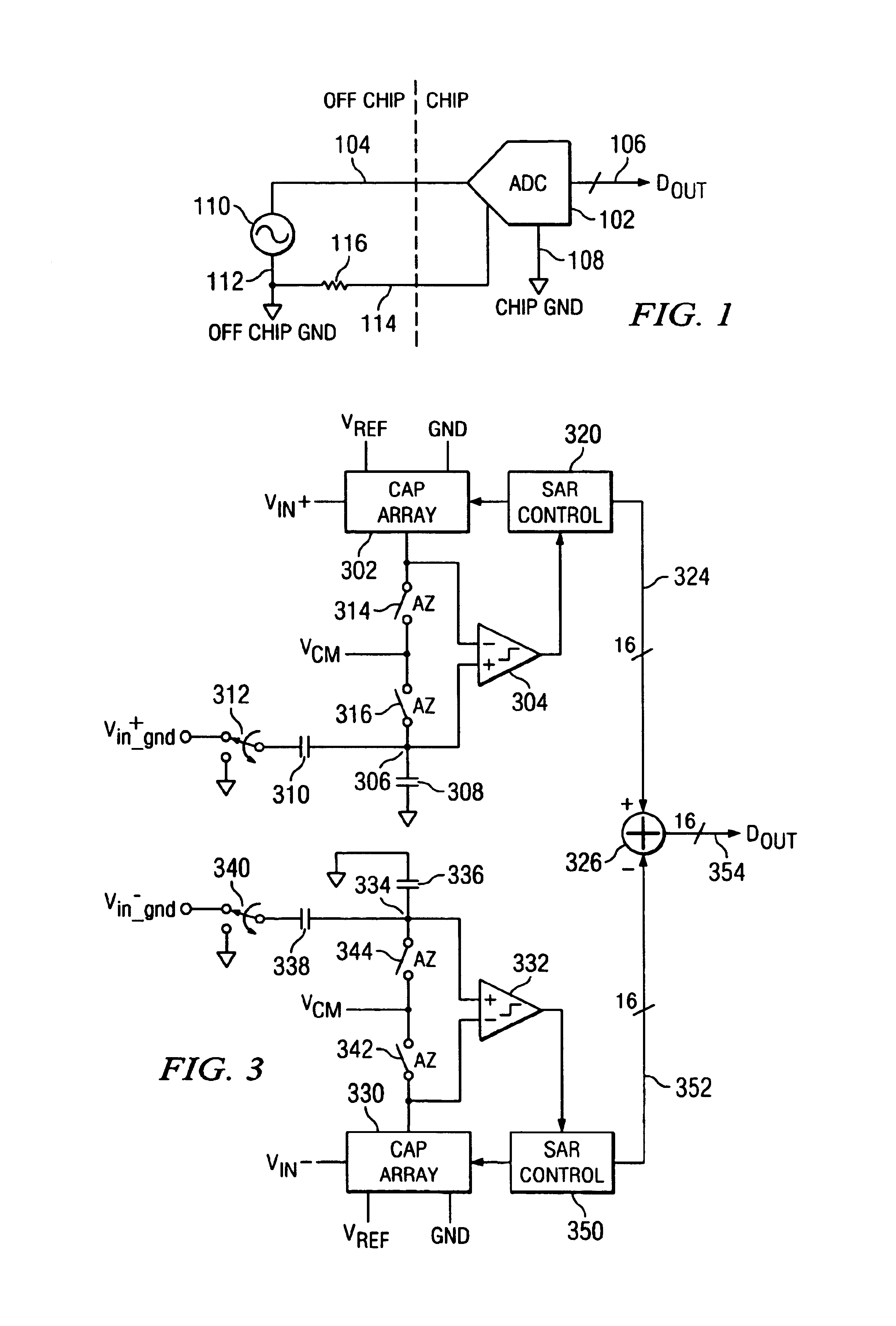
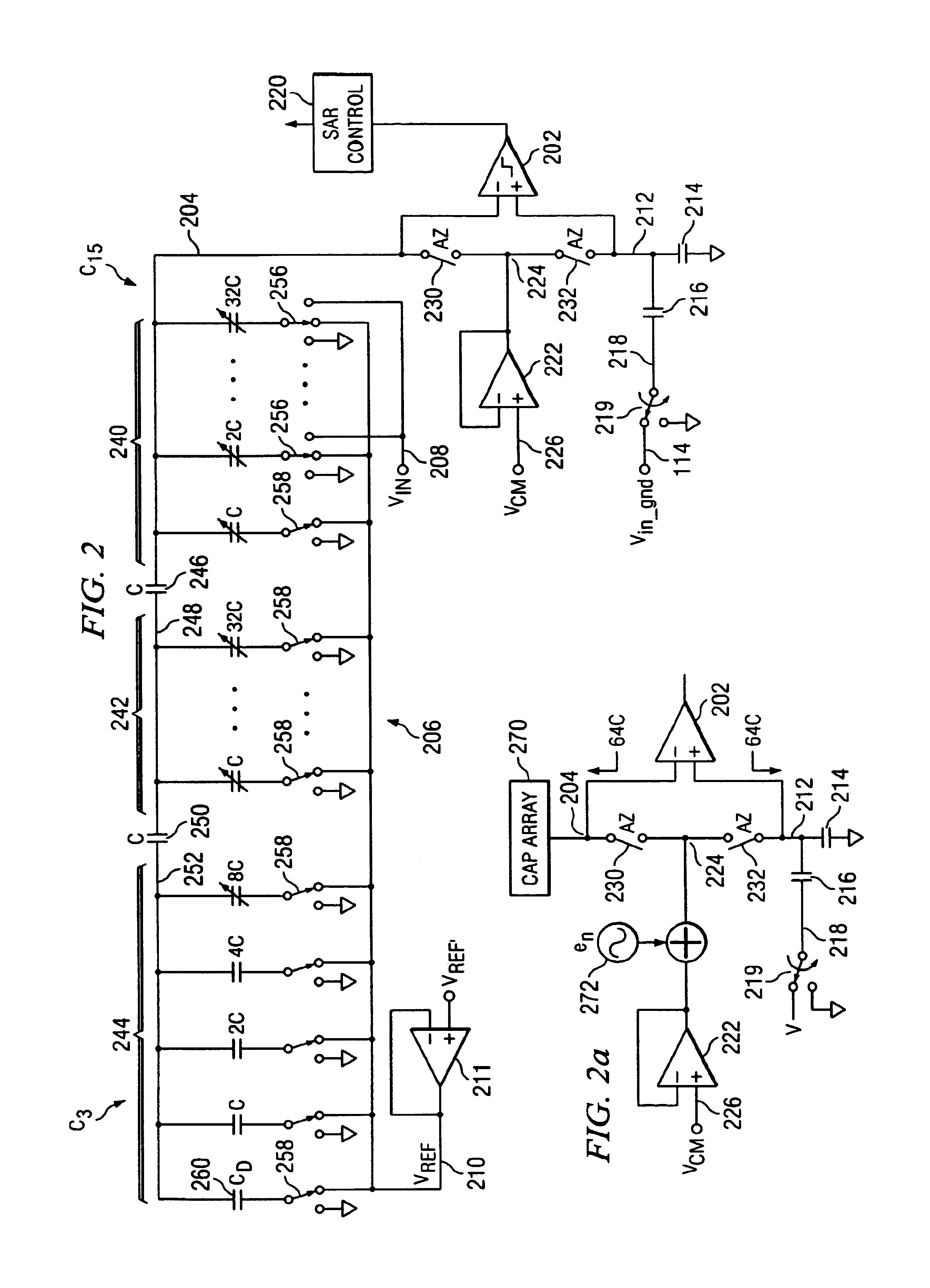
Noise cancellation in a single ended SAR converter
InactiveUS6950052B2Good Common Mode RejectionElectric signal transmission systemsResistors with plural resistive elementsCapacitanceSignal on
Noise cancellation in a single ended SAR converter. A single ended SAR converter front end is disclosed with common mode driver noise cancellation. The SAR converter front end includes a differential amplifier having positive and negative inputs and an output. A switched capacitor array is provided that is operable in a SAR data conversion operation to vary the voltage on one of the positive or negative inputs of the differential amplifier. A common mode driver drives a common mode node with a low impedance common mode voltage signal to a common mode node, and switching circuitry then switches the common mode voltage signal on the common mode node to the positive and negative inputs of the differential amplifier during a portion of a SAR data conversion cycle. A capacitor reference circuit is attached to the other of the positive or negative inputs of the differential, amplifier during at least the portion of the SAR data conversion cycle, the capacitor reference circuit and the capacitor array during at least the portion of the SAR data conversion cycle having relative capacitance values that increase the common mode rejection of any noise introduced to the common mode node at the input of the differential amplifier.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Grooved wire coupling and feeding bandpass unit for multi-frequency balance filter/diplexer
InactiveCN104900948ACommon mode is simpleCommon Mode ImprovementResonatorsCouplingMicrostrip resonators
The invention discloses a grooved wire coupling and feeding bandpass unit for a multi-frequency balance filter / diplexer. The grooved wire coupling and feeding bandpass unit comprises symmetric first and second differential input-output port pairs, symmetric first and second grooved wire resonators and symmetric first and second microstrip resonator pairs, wherein the first differential input-output port pair comprises first and second input-output ports for an object, the first grooved wire resonator and the first differential input-output port pair have a microstrip feed line coupling portion, the second differential input-output port pair comprises symmetric third and fourth input-output ports, and the second grooved wire resonator and the second differential input-output port pair have a microstrip feed line coupling portion. The first microstrip resonator is formed by a first microstrip resonator and a second microstrip resonator, and the second microstrip resonator is formed by a third microstrip resonator and a fourth microstrip resonator. The grooved wire coupling and feeding bandpass unit realizes multi-frequency balance filter and balance diplexer with high selectivity, high common mode inhibition, independent and controllable frequency and bandwidth.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Insulation resistance detecting control circuit and detecting method of electric vehicle
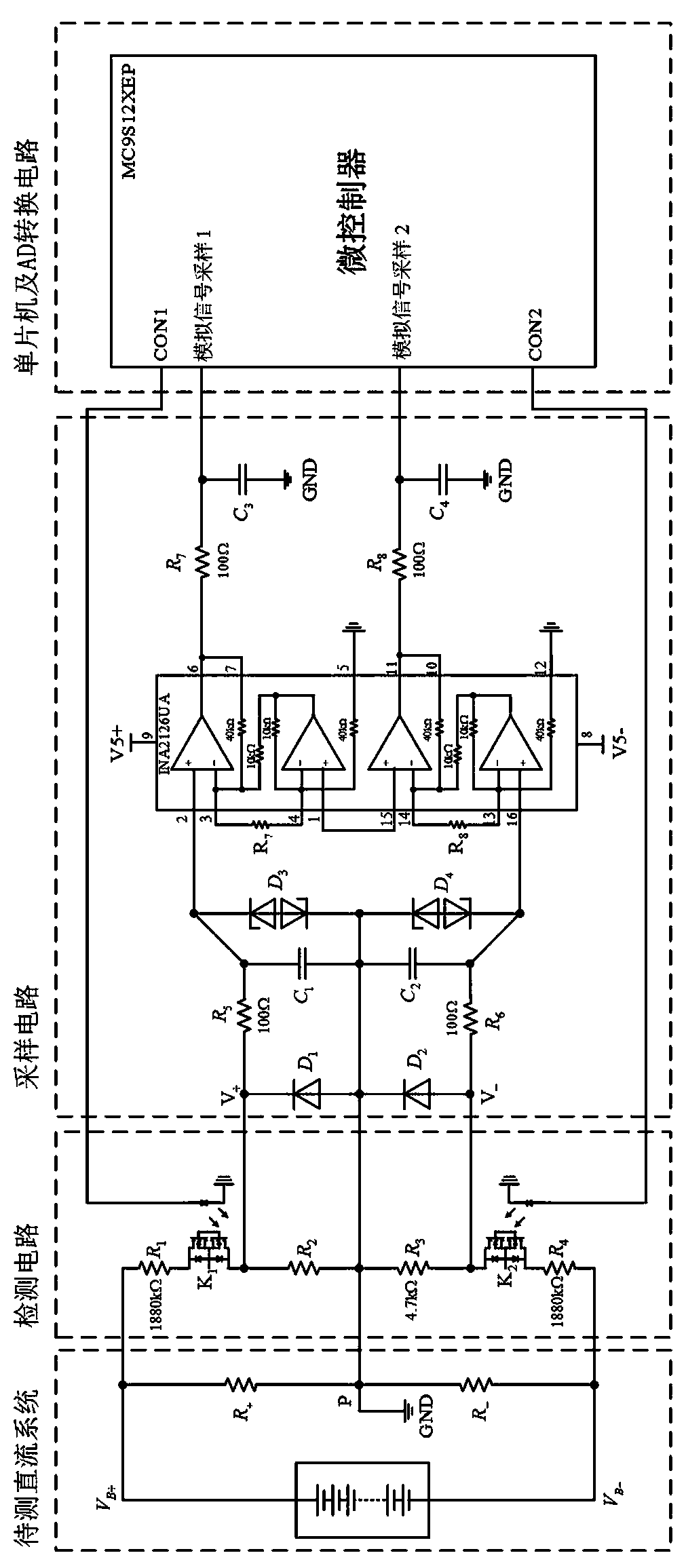
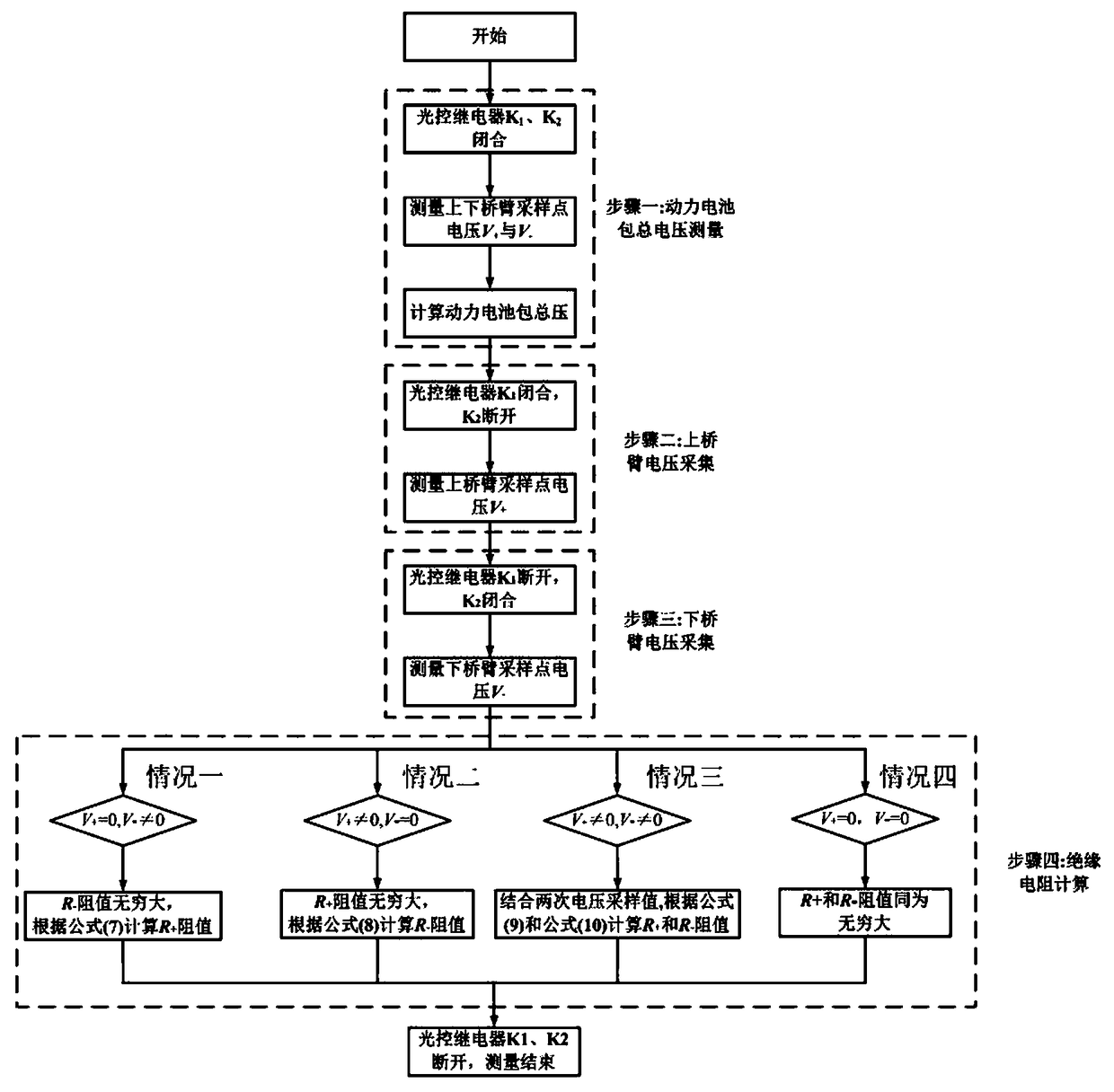
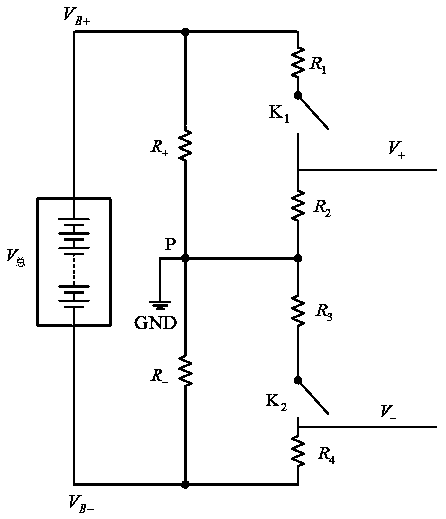
InactiveCN108614158AReduce the impactLower Offset VoltageResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductanceInstrumentation amplifier
The invention discloses an insulation resistance detecting control circuit and detecting method of an electric vehicle. The circuit is based on a balanced bridge; a light-control type relay is used for controlling opening or closing of corresponding bridge arms of the bridge; a high-precision instrumentation amplifier is used for amplifying a weak voltage signal and realizing voltage polarity conversion. On the basis of the basic characteristics of the above circuit, a four-step insulation resistance calculation method is designed. The insulation resistance detecting control circuit and the detecting method, the insulation resistance of the positive and negative terminals can be measured simultaneously; online detection is realized; and the precision and reliability are high.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
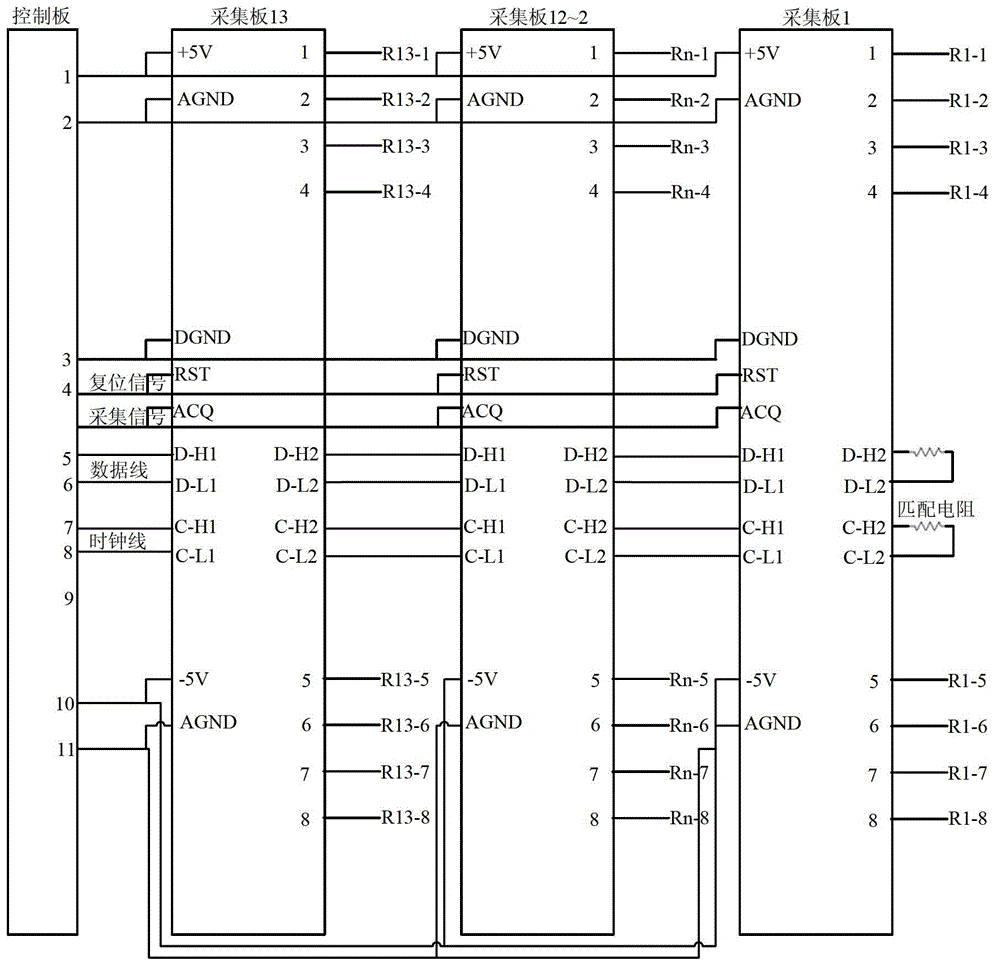
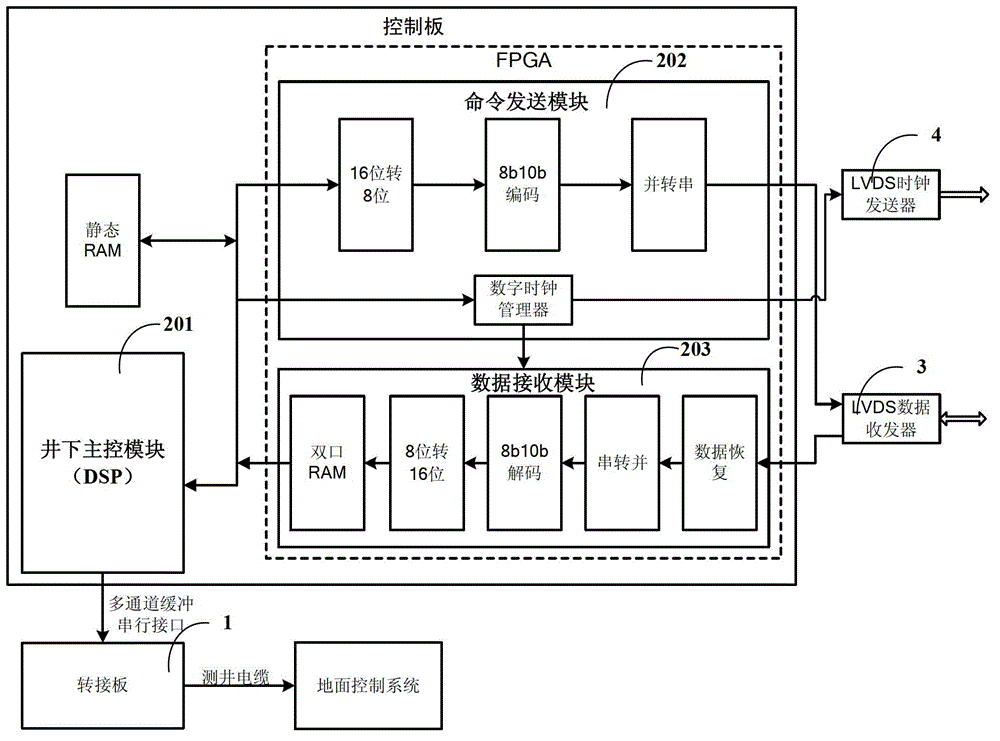
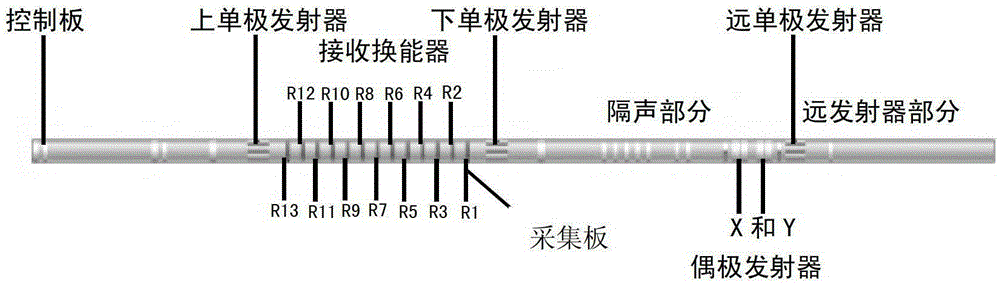
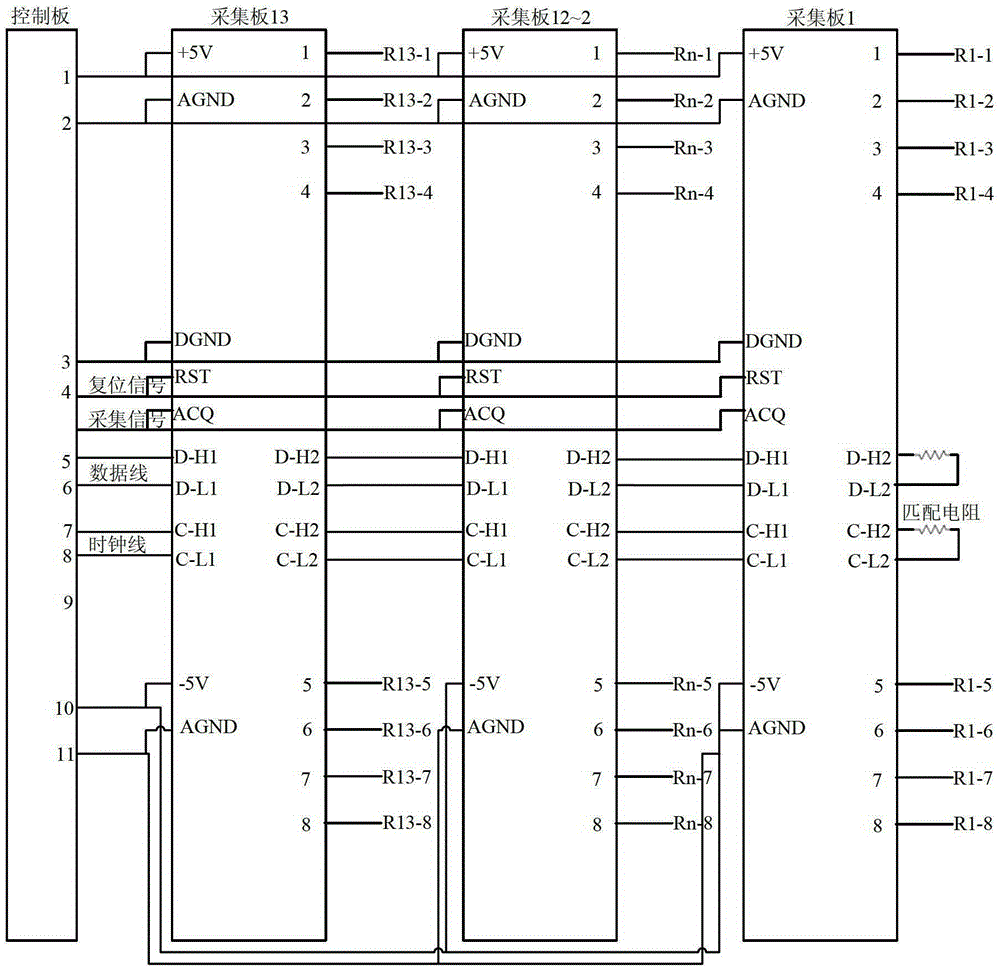
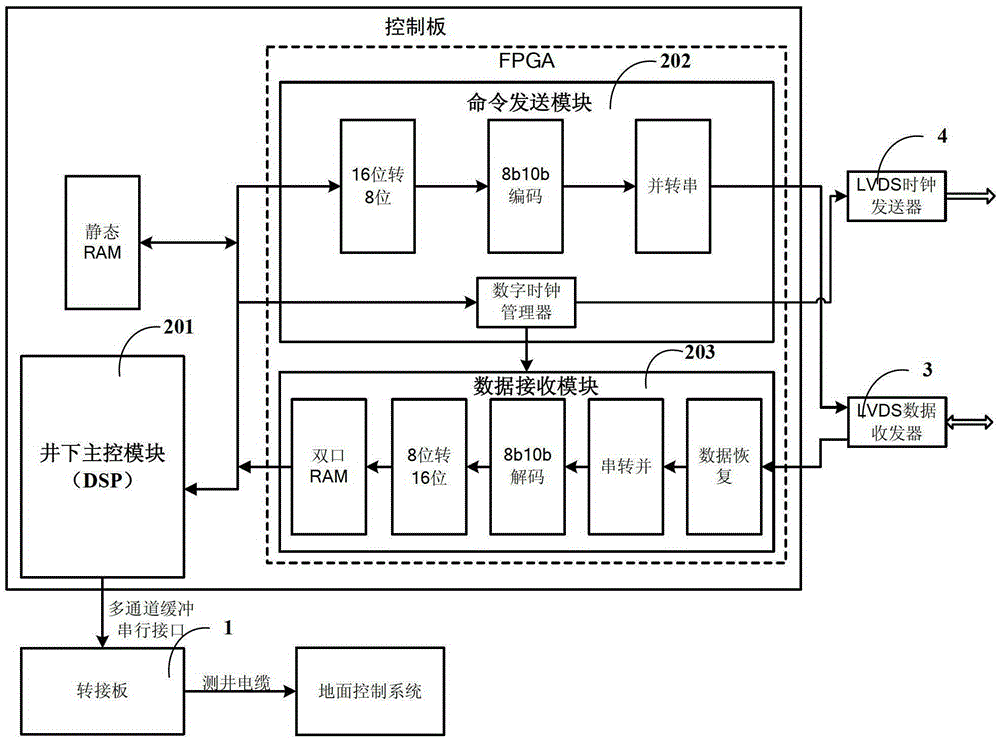
Three dimensional sonic logging data high-speed transmission device based on LVDS technology
The invention discloses a three dimensional sonic logging data high-speed transmission device based on an LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) technology. Firstly, a ground control system issues control commands, a pinboard receives commands through an LAN (local area network) port and downloads the commands to a control panel through an Mcbsp (Multichannel Buffercd Scrial Port) interface, and command control and high-speed serial transmission of three dimensional logging sound wave data can be achieved by using an LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) interface. The LVDS communication interface technology refers that data transmission is performed by using extremely low voltage swing in a high-speed differential manner, has the advantages of low noise, excellent common mode inhibiting capability and low power consumption, and can integrate a circuit into a systematical IC (integrated circuit), thereby overcoming problems of far distance sonic logging data transmission, complex circuit working environment and high possibility of external interferences to three dimensional sonic logging signal, and high-speed date transmission between the control panel and the collection board can be accurately achieved in a real time manner.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
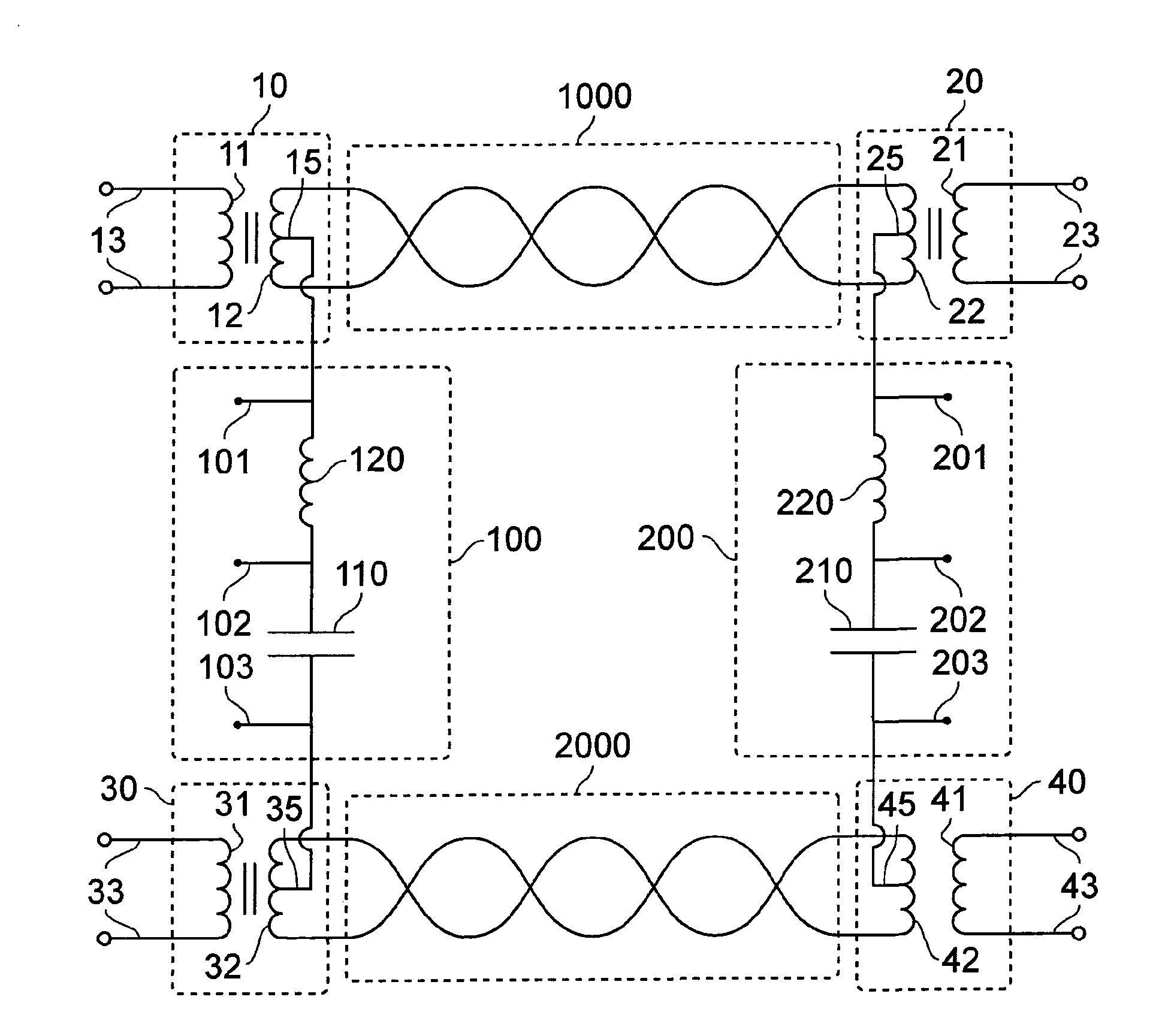
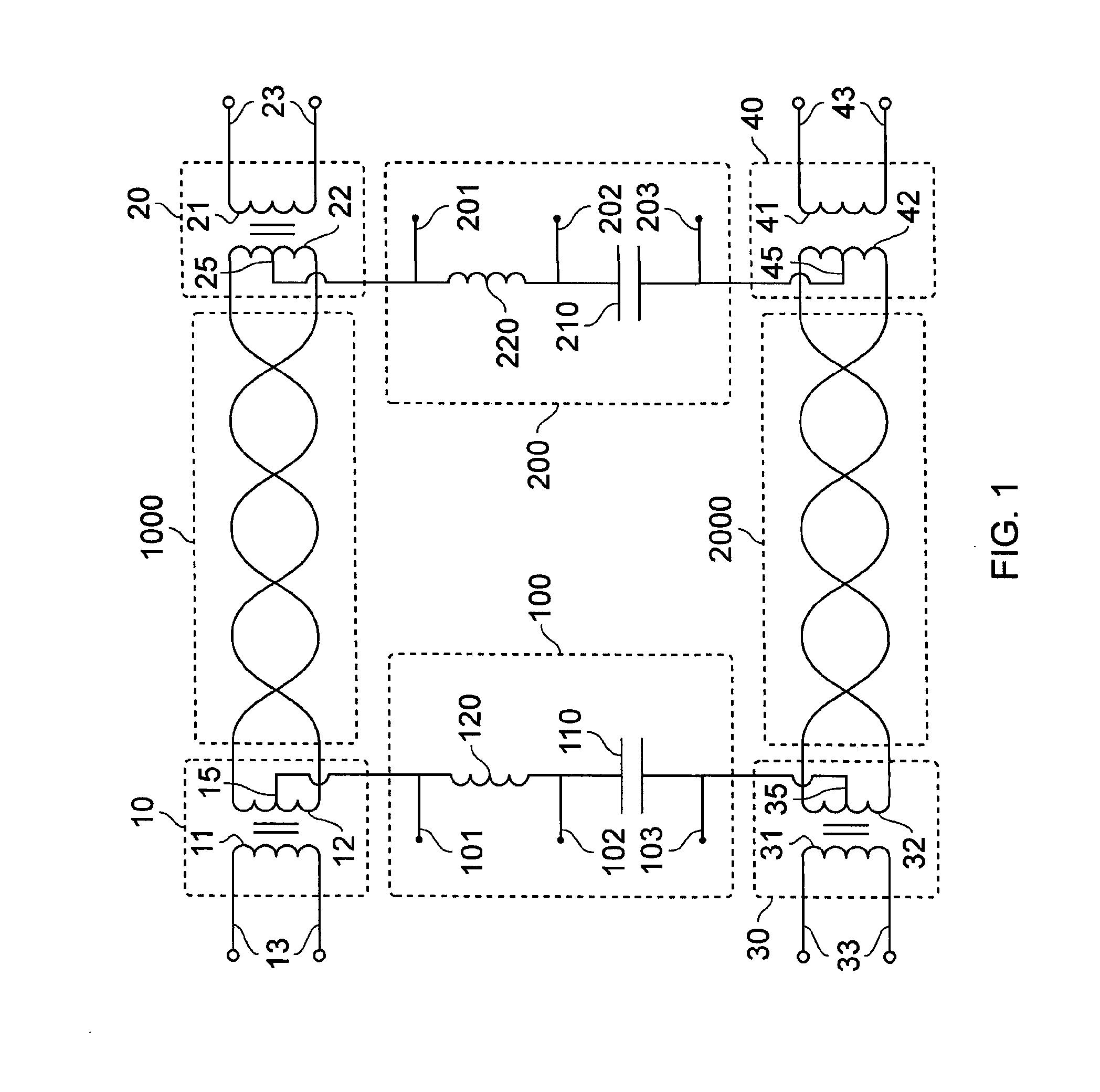
Electrical System Adapted to Transfer Data and Power Between Devices on a Network
ActiveUS20150130270A1Simpler and cheap to installFacilitate communicationPower distribution line transmissionLock network applicationsTransceiverEngineering
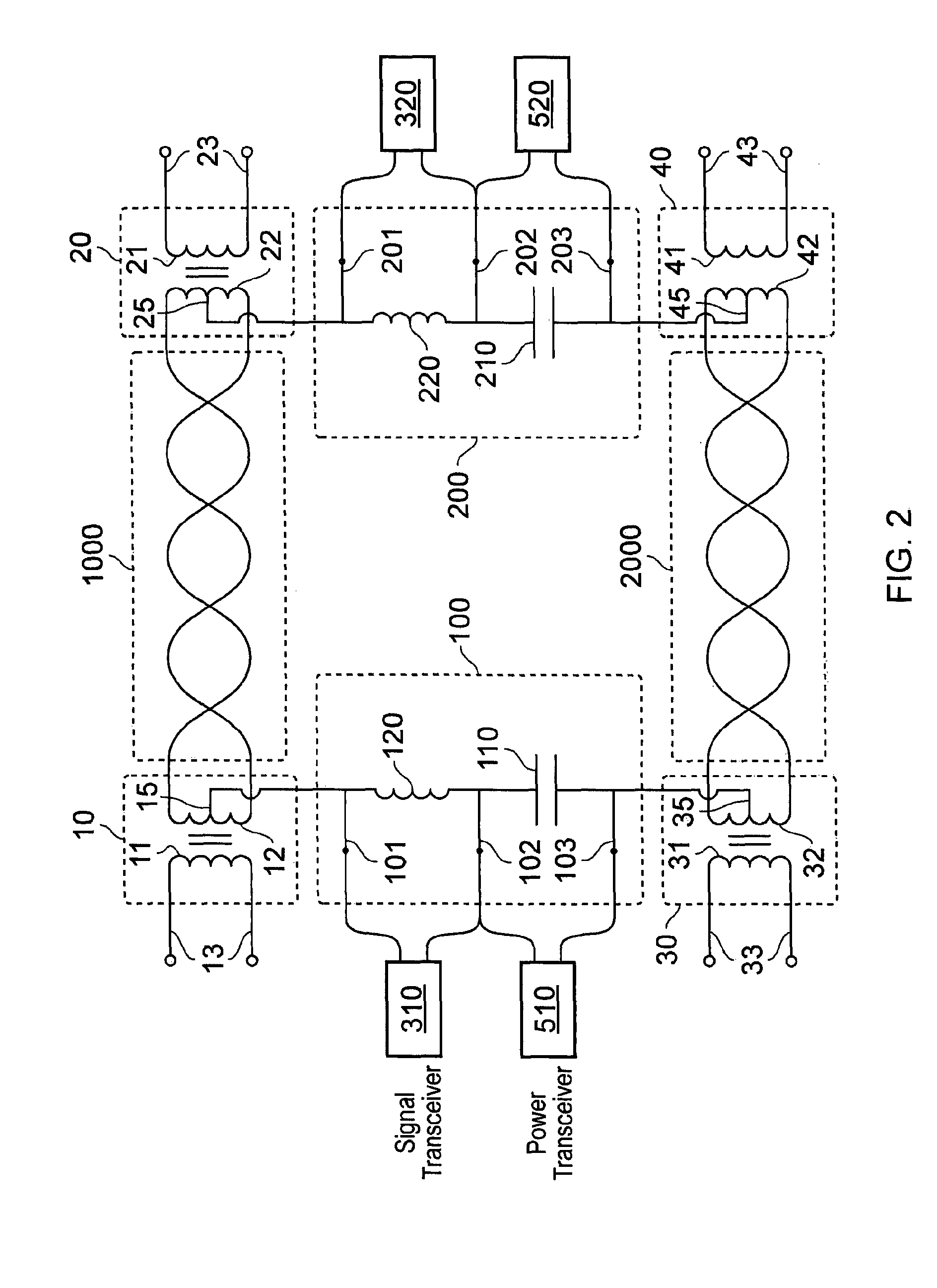
This invention relates to an electrical system which enables peripheral devices to communicate exclusively of other AC and power transceivers which provide to the electrical system and receive from the electrical system power and signals. The invention is an electrical system that comprises network channels (1000, 2000) connected by circuits (100, 200). Peripheral devices plugged into the network channels communicate with each other. AC and power transceivers connected to the circuits communicate with each other and distribute power through the network channels.
Owner:POWDAC
Balanced filter using improved coupling feed line
ActiveCN104882653AIndependent designImproved common mode rejectionWaveguide type devicesFeed lineTransmission line
The invention discloses a balanced filter using an improved coupling feed line. The balanced filter comprises input and output ports and two cascaded improved coupling feed lines. One improved coupling feed line comprises a first coupling transmission line, a second coupling transmission line and a first branch knot loaded between the first coupling transmission line and the second coupling transmission line, wherein the first coupling transmission line and the second coupling transmission line are symmetrically distributed. The other improved coupling feed line comprises a third coupling transmission line, a fourth coupling transmission line, a second branch knot, a third branch knot, a fourth branch knot and a fifth branch knot, wherein the third coupling transmission line and the fourth coupling transmission line are symmetrically distributed; the second branch knot, the third branch knot, the fourth branch knot and the fifth branch knot are loaded between the third coupling transmission line and the fourth coupling transmission line. The first coupling transmission line, the second coupling transmission line, the third coupling transmission line and the fourth coupling transmission line are connected to one input and output port respectively. Each input and output port is loaded with a coupling branch knot which is used for introducing a transmission zero point. By using the filter of the invention, because of common mode rejection of the filter itself, a differential mode and a common mode can be designed separately and the common mode rejection can be obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Electrical physical layer activity detector
ActiveUS7990182B2Good Common Mode RejectionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsCurrent/voltage measurementElectricityDetector circuits
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Balanced ultra-wideband band-pass filter based on multimode slot line resonator
ActiveCN113708030AAchieving Ultra-Wideband FeaturesImprove out-of-band rejection performanceHigh level techniquesWaveguide type devicesUltra-widebandDielectric substrate
The invention provides a balanced ultra-wideband band-pass filter based on a slot multi-mode resonator, and solves the problems of strong common-mode interference, narrow passband, low selectivity and large size. The filter comprises two U-shaped and rectangular microstrip lines printed on the upper surface of a dielectric substrate, and a first stepped impedance slot line, a second stepped impedance slot line and a multimode slot resonator are etched on a metal floor. The rectangular microstrip line coincides with the interpenetrating position of the first stepped impedance slot line and the second stepped impedance slot line on the metal bottom plate to form a three-line interdigital coupling structure. According to the invention, a U-shaped microstrip-to-rectangular slot line structure is used to separate a common mode from a differential mode, so that good common mode suppression is realized; the three-wire interdigital coupling structure strengthens coupling of input and output signals; and the notch characteristic of the filter is adjusted by using the multimode slot resonator. The filter has the characteristics of ultra-bandwidth, small size, high selectivity and good common-mode rejection, and is applied to the field of electromagnetic microwave and radio frequency circuits and systems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
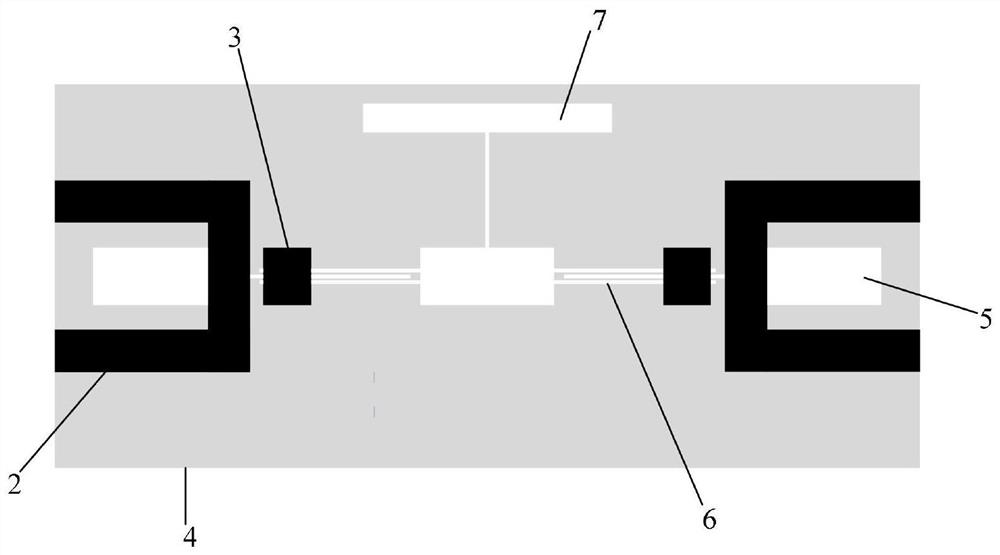
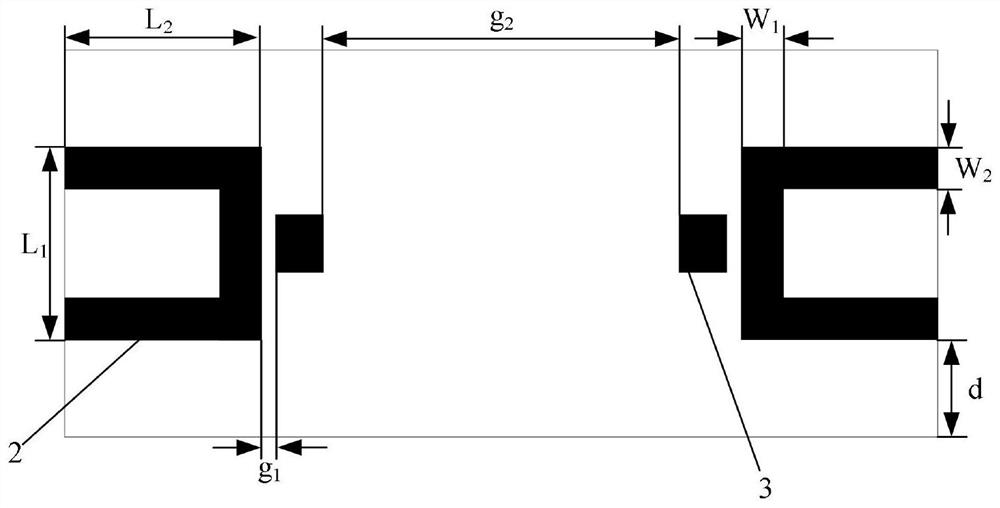
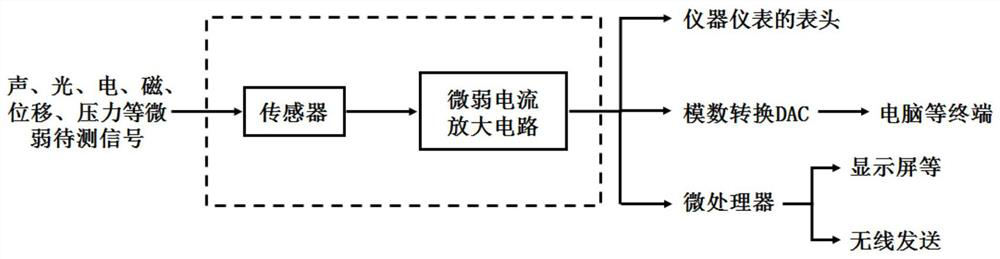
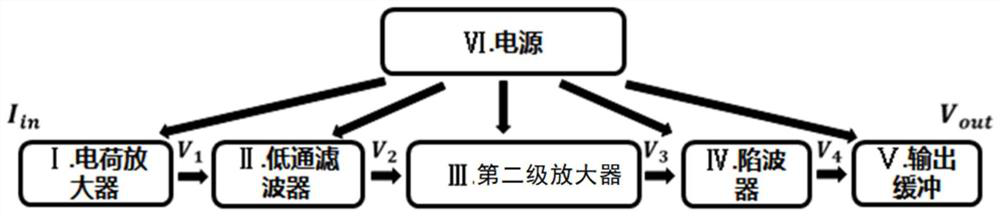
Weak current amplifying circuit and sensor system
ActiveCN112968682AImprove portabilityRaise the amplitude ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplifiers with multiple amplifying elementsTelecommunicationsHemt circuits
The invention relates to a weak current amplifying circuit and a sensor system. The weak current amplifying circuit is provided with a two-stage amplifying structure and a two-stage filtering structure which are arranged in a crossed mode; the weak current amplifying circuit comprises a charge amplifier, a first-stage filter, a second-stage amplifier and a band elimination filter which are connected, and the charge amplifier converts weak current into amplified voltage output; the first-stage filter performs at least one of low-pass filtering, band-pass filtering and high-pass filtering on the voltage output by the charge amplifier, the second-stage amplifier performs a second-stage amplification process, the second-stage amplifier is provided with two stages of differential amplifier circuits, wherein the preceding stage amplifies a differential-mode input signal in an in-phase differential input mode, and plays a role in following the common-mode input signal so as to improve the amplitude ratio of the differential-mode signal and the common-mode signal which are sent to the rear stage, and is used for filtering 50Hz power frequency noise interference. The weak current amplifying circuit overcomes the problems of strong noise, power frequency interference, output end impedance mismatching, operational amplifier output saturation and the like of the conventional amplifying circuit.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Symmetrical Electrical Physical Layer Activity Detector
ActiveUS20110267110A1Good Common Mode RejectionCurrent/voltage measurementInstant pulse delivery arrangementsDetector circuitsDifferential signaling
A low-current differential signal activity detector circuit may be configured to reject large common mode signals on differential input lines, while still detecting smaller differential signals applied to the same set of differential input lines. The detector circuit may comprise a translinear buffer that is driven at the buffer input and at the buffer output by the differential input signals. The differential signal thereby driving the inputs of the detector circuit may be half-wave rectified through the buffer output devices and may be filtered to provide the detected output. When applying a common mode signal, the buffer's input and output may track each other, and no current may be rectified in the output devices, thus providing common-mode signal rejection. The detector circuit may also be configured with two buffers having their outputs coupled to a common node, each buffer input driven by a respective one of the differential input signals. The differential signal thereby driving the inputs of the detector circuit may be fully rectified through the output devices of the two buffers, and may be filtered to provide the detected output. The two buffers may be configured in a symmetrical structure that allows for the rejection of common-mode signals when the outputs of the buffers are coupled to a common node.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Differential circularly polarized directional antenna
PendingCN107611586AGood Common Mode RejectionImprove performanceRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationPhase shiftedPhysics
The invention discloses a differential circularly polarized directional antenna, which comprises a dielectric substrate, a floor located at the lower part of the dielectric substrate, a first coaxialline and a second coaxial line, wherein the first coaxial line and the second coaxial line are parallel to each other; the dielectric substrate is provided with two 90-degree phase-shift patches and four radiation patches; the four radiation patches are sequentially arranged on the lower surface of the dielectric substrate around the center of the dielectric substrate and are in mirror symmetry; inner conductors at the upper ends of the first coaxial line and the second coaxial line are connected with the two 90-degree phase-shift patches separately and outer conductors are connected with tworadiation patches arranged at opposite angles separately; and the lower ends of the first coaxial line and the second coaxial line pass through the floor. The differential circularly polarized directional antenna is provided with two pairs of dipoles, has a circular polarization characteristic and a difference characteristic, has relatively large impedance bandwidth and axial ratio bandwidth and relatively large gain and can meet the requirements of an LTE mobile phone base station antenna applied to a broadband high-speed wireless communication system of 1.61-2.8GHz.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
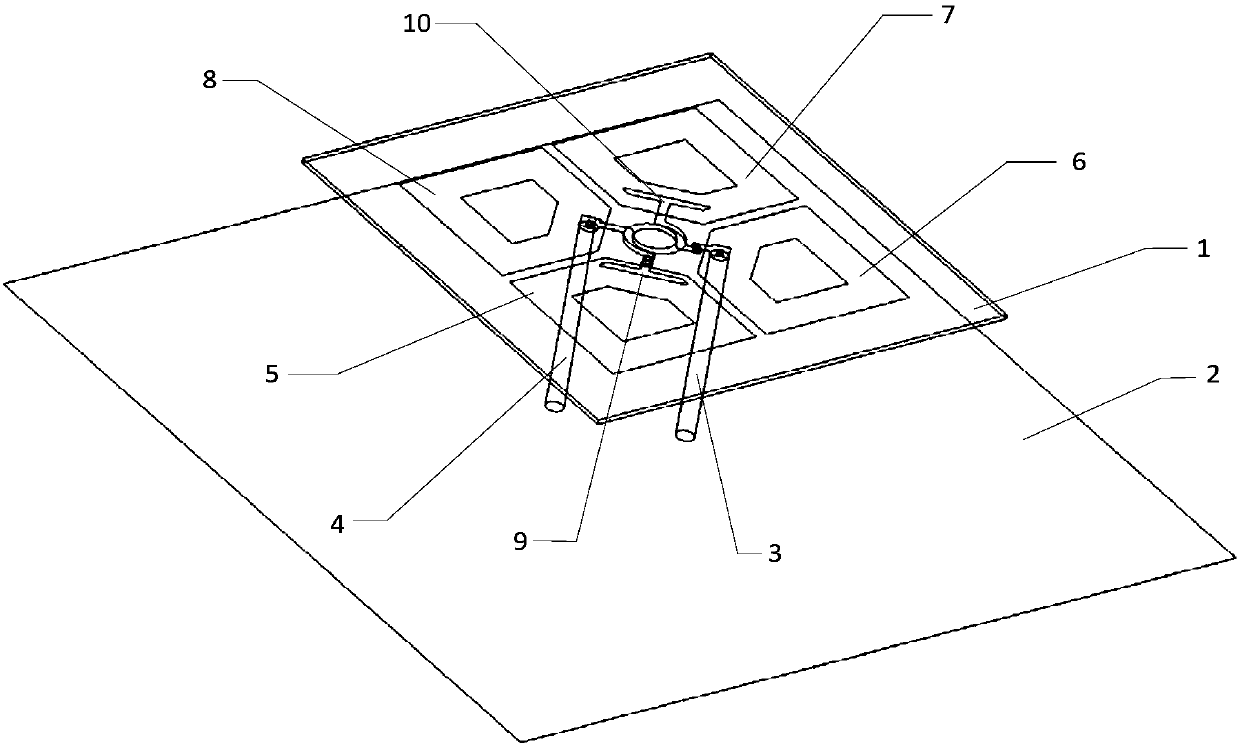
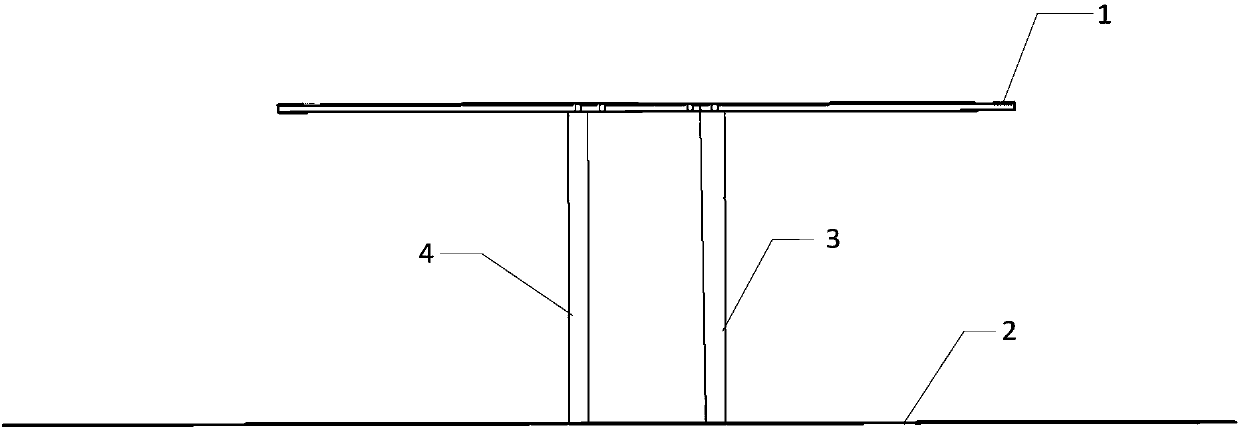
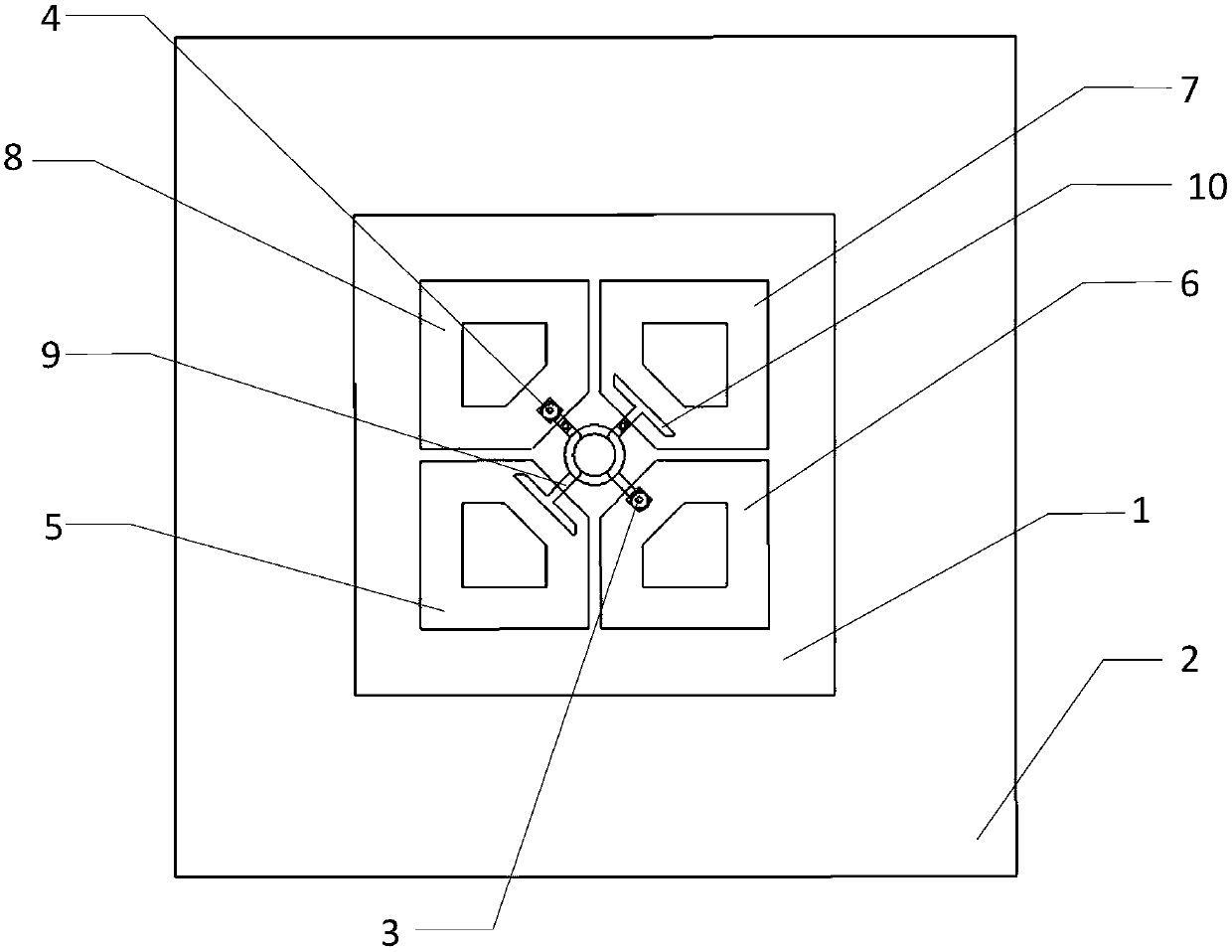
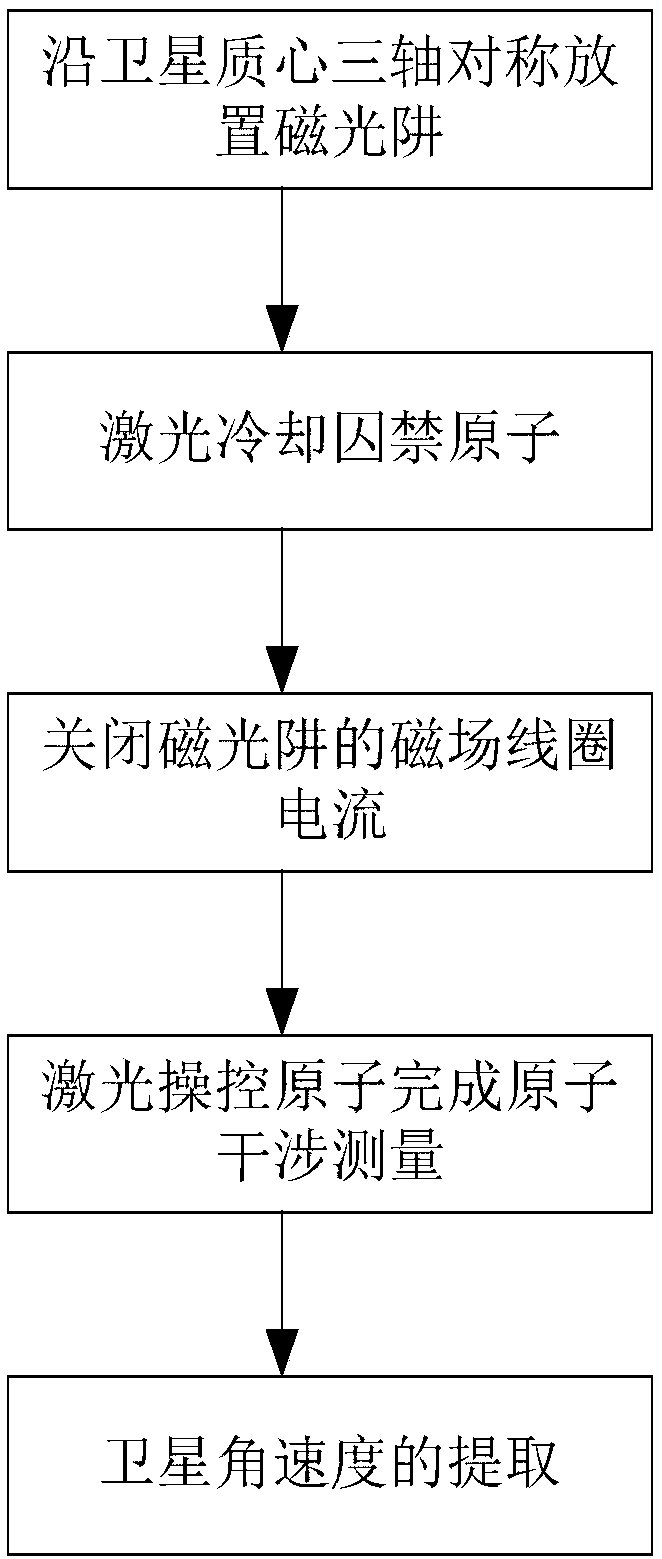
Atom interference gravity gradient measuring method under satellite borne microgravity environment
InactiveCN108051865ALarge intervening intervalHigh measurement accuracyGravitational wave measurementNatural satelliteMagneto-optical trap
The invention provides an atom interference gravity gradient measuring method under a satellite borne microgravity environment; the method comprises the following steps: 1, symmetrically placing magneto-optical traps with respect to satellite center of mass three-shaft; 2, laser-cooling capturing cold atoms; 3, closing the magnetic field coil current of the magneto-optical traps; 4, laser-controlling atoms to finish the atom interference measurement; 5, extracting the satellite angular velocity. The method utilizes the unique conditions that atoms freely float in a damping-free flight state under the space weight loss environment, directly enables laser and the free floating atoms in the space to mutually react, thus enabling the atoms to form the interference effect, and carrying out gravity gradient measurement. The method is simple, easy to operate, and can be easily applied in space.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Multi-transmission zero balancing filter using coupling feeder lines to perform loading
The invention discloses a multi-transmission zero balancing filter using coupling feeder lines to perform loading. The filter comprises symmetrical first and second differential input ports, symmetrical first and second differential output ports and symmetrical first and second branch loading ring resonators. The first and second differential input ports are respectively in cascade connection with first and second impedance conversion lines. The first and second differential output ports are respectively in cascade connection with third and fourth impedance conversion lines. The first impedance conversion line is loaded with a first feeder line. The third impedance conversion line is loaded with a second feeder line. The ring resonator part of the first branch loading ring resonator is coupled with the first and second feeder lines. The second impedance conversion line is loaded with a third feeder line. The fourth impedance conversion line is loaded with a fourth loader line. The ring resonator part of the second branch loading ring resonator is coupled with the third and fourth feeder lines. A first branch is loaded between the first and third feeder line. A second branch and a third branch are loaded between the second and fourth feeder lines. The filter is advantaged by high selectivity, high common-mode rejection and low loss.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A high-speed transmission device for 3D acoustic logging data based on LVDS technology
The invention discloses a three-dimensional acoustic logging data high-speed transmission device based on LVDS technology. Firstly, the ground control system issues a control command, the adapter board receives the command through the LAN port, and transmits the command through the Mcbsp interface, that is, the multi-channel buffer serial port. to the control board, and then use LVDS interface technology to realize high-speed serial transmission of control commands and 3D logging acoustic data. LVDS communication interface technology uses extremely low voltage swing to transmit data in a high-speed differential manner. It has low noise, good common-mode rejection capability, low power consumption and the circuit can be integrated into the system-level IC, thus overcoming the three-dimensional The transmission distance of acoustic logging data is long, the working environment of downhole circuits is complex, and the 3D acoustic logging signal is easily disturbed by the outside world. The high-speed data transmission between the control board and the acquisition board can be completed accurately in real time.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com